User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Which specialties get the biggest markups over Medicare rates?
Anesthesiologists charge private insurers more than 300% above Medicare rates, a markup that is higher than that of 16 other specialties, according to a study released by the Urban Institute.
The Washington-based nonprofit institute found that the lowest markups were in psychiatry, ophthalmology, ob.gyn., family medicine, gastroenterology, and internal medicine, at 110%-120% of Medicare rates. .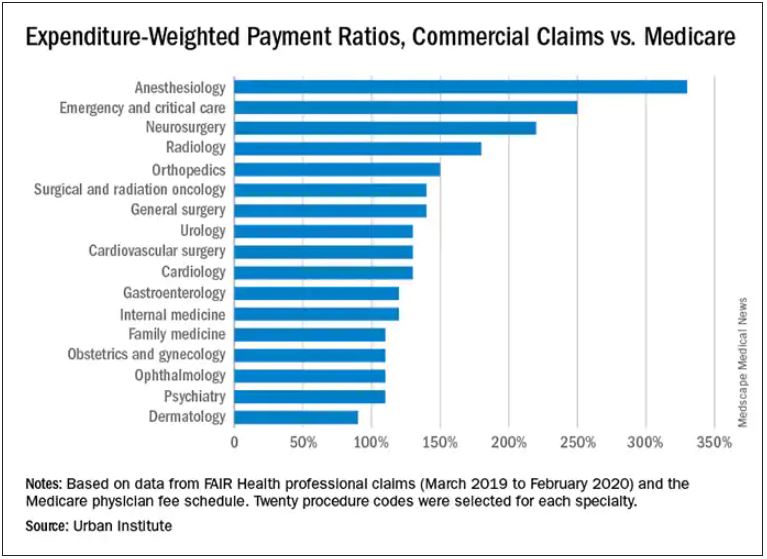
In the middle are cardiology and cardiovascular surgery (130%), urology (130%), general surgery, surgical and radiation oncology (all at 140%), and orthopedics (150%).
At the top end were radiology (180%), neurosurgery (220%), emergency and critical care (250%), and anesthesiology (330%).
The wide variation in payments could be cited in support of the idea of applying Medicare rates across all physician specialties, say the study authors. Although lowering practitioner payments might lead to savings, it “will also create more pushback from providers, especially if these rates are introduced in the employer market,” write researchers Stacey McMorrow, PhD, Robert A. Berenson, MD, and John Holahan, PhD.
It is not known whether lowering commercial payment rates might decrease patient access, they write.
The authors also note that specialties in which the potential for a fee reduction was greatest were also the specialties for which baseline compensation was highest – from $350,000 annually for emergency physicians to $800,000 a year for neurosurgeons. Annual compensation for ob.gyns., dermatologists, and opthalmologists is about $350,000 a year, which suggests that “these specialties are similarly well compensated by both Medicare and commercial insurers,” the authors write.
The investigators assessed the top 20 procedure codes by expenditure in each of 17 physician specialties. They estimated the commercial-to-Medicare payment ratio for each service and constructed weighted averages across services for each specialty at the national level and for 12 states for which data for all the specialties and services were available.
The researchers analyzed claims from the FAIR Health database between March 2019 and March 2020. That database represents 60 insurers covering 150 million people.
Pediatric and geriatric specialties, nonphysician practitioners, out-of-network clinicians, and ambulatory surgery center claims were excluded. Codes with modifiers, J codes, and clinical laboratory services were also not included.
The charges used in the study were not the actual contracted rates. The authors instead used “imputed allowed amounts” for each claim line. That method was used to protect the confidentiality of the negotiated rates.
With regard to all specialties, the lowest compensated services were procedures, evaluation and management, and tests, which received 140%-150% of the Medicare rate. Treatments and imaging were marked up 160%. Anesthesia was reimbursed at a rate 330% higher than the rate Medicare would pay.
The authors also assessed geographic variation for the 12 states for which they had data.
Similar to findings in other studies, the researchers found that the markup was lowest in Pennsylvania (120%) and highest in Wisconsin (260%). The U.S. average was 160%. California and Missouri were at 150%; Michigan was right at the average.
For physicians in Illinois, Louisiana, Colorado, Texas, and New York, markups were 170%-180% over the Medicare rate. Markups for clinicians in New Jersey (190%) and Arizona (200%) were closest to the Wisconsin rate.
The authors note some study limitations, including the fact that they excluded out-of-network practitioners, “and such payments may disproportionately affect certain specialties.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Anesthesiologists charge private insurers more than 300% above Medicare rates, a markup that is higher than that of 16 other specialties, according to a study released by the Urban Institute.
The Washington-based nonprofit institute found that the lowest markups were in psychiatry, ophthalmology, ob.gyn., family medicine, gastroenterology, and internal medicine, at 110%-120% of Medicare rates. .
In the middle are cardiology and cardiovascular surgery (130%), urology (130%), general surgery, surgical and radiation oncology (all at 140%), and orthopedics (150%).
At the top end were radiology (180%), neurosurgery (220%), emergency and critical care (250%), and anesthesiology (330%).
The wide variation in payments could be cited in support of the idea of applying Medicare rates across all physician specialties, say the study authors. Although lowering practitioner payments might lead to savings, it “will also create more pushback from providers, especially if these rates are introduced in the employer market,” write researchers Stacey McMorrow, PhD, Robert A. Berenson, MD, and John Holahan, PhD.
It is not known whether lowering commercial payment rates might decrease patient access, they write.
The authors also note that specialties in which the potential for a fee reduction was greatest were also the specialties for which baseline compensation was highest – from $350,000 annually for emergency physicians to $800,000 a year for neurosurgeons. Annual compensation for ob.gyns., dermatologists, and opthalmologists is about $350,000 a year, which suggests that “these specialties are similarly well compensated by both Medicare and commercial insurers,” the authors write.
The investigators assessed the top 20 procedure codes by expenditure in each of 17 physician specialties. They estimated the commercial-to-Medicare payment ratio for each service and constructed weighted averages across services for each specialty at the national level and for 12 states for which data for all the specialties and services were available.
The researchers analyzed claims from the FAIR Health database between March 2019 and March 2020. That database represents 60 insurers covering 150 million people.
Pediatric and geriatric specialties, nonphysician practitioners, out-of-network clinicians, and ambulatory surgery center claims were excluded. Codes with modifiers, J codes, and clinical laboratory services were also not included.
The charges used in the study were not the actual contracted rates. The authors instead used “imputed allowed amounts” for each claim line. That method was used to protect the confidentiality of the negotiated rates.
With regard to all specialties, the lowest compensated services were procedures, evaluation and management, and tests, which received 140%-150% of the Medicare rate. Treatments and imaging were marked up 160%. Anesthesia was reimbursed at a rate 330% higher than the rate Medicare would pay.
The authors also assessed geographic variation for the 12 states for which they had data.
Similar to findings in other studies, the researchers found that the markup was lowest in Pennsylvania (120%) and highest in Wisconsin (260%). The U.S. average was 160%. California and Missouri were at 150%; Michigan was right at the average.
For physicians in Illinois, Louisiana, Colorado, Texas, and New York, markups were 170%-180% over the Medicare rate. Markups for clinicians in New Jersey (190%) and Arizona (200%) were closest to the Wisconsin rate.
The authors note some study limitations, including the fact that they excluded out-of-network practitioners, “and such payments may disproportionately affect certain specialties.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Anesthesiologists charge private insurers more than 300% above Medicare rates, a markup that is higher than that of 16 other specialties, according to a study released by the Urban Institute.
The Washington-based nonprofit institute found that the lowest markups were in psychiatry, ophthalmology, ob.gyn., family medicine, gastroenterology, and internal medicine, at 110%-120% of Medicare rates. .
In the middle are cardiology and cardiovascular surgery (130%), urology (130%), general surgery, surgical and radiation oncology (all at 140%), and orthopedics (150%).
At the top end were radiology (180%), neurosurgery (220%), emergency and critical care (250%), and anesthesiology (330%).
The wide variation in payments could be cited in support of the idea of applying Medicare rates across all physician specialties, say the study authors. Although lowering practitioner payments might lead to savings, it “will also create more pushback from providers, especially if these rates are introduced in the employer market,” write researchers Stacey McMorrow, PhD, Robert A. Berenson, MD, and John Holahan, PhD.
It is not known whether lowering commercial payment rates might decrease patient access, they write.
The authors also note that specialties in which the potential for a fee reduction was greatest were also the specialties for which baseline compensation was highest – from $350,000 annually for emergency physicians to $800,000 a year for neurosurgeons. Annual compensation for ob.gyns., dermatologists, and opthalmologists is about $350,000 a year, which suggests that “these specialties are similarly well compensated by both Medicare and commercial insurers,” the authors write.
The investigators assessed the top 20 procedure codes by expenditure in each of 17 physician specialties. They estimated the commercial-to-Medicare payment ratio for each service and constructed weighted averages across services for each specialty at the national level and for 12 states for which data for all the specialties and services were available.
The researchers analyzed claims from the FAIR Health database between March 2019 and March 2020. That database represents 60 insurers covering 150 million people.
Pediatric and geriatric specialties, nonphysician practitioners, out-of-network clinicians, and ambulatory surgery center claims were excluded. Codes with modifiers, J codes, and clinical laboratory services were also not included.
The charges used in the study were not the actual contracted rates. The authors instead used “imputed allowed amounts” for each claim line. That method was used to protect the confidentiality of the negotiated rates.
With regard to all specialties, the lowest compensated services were procedures, evaluation and management, and tests, which received 140%-150% of the Medicare rate. Treatments and imaging were marked up 160%. Anesthesia was reimbursed at a rate 330% higher than the rate Medicare would pay.
The authors also assessed geographic variation for the 12 states for which they had data.
Similar to findings in other studies, the researchers found that the markup was lowest in Pennsylvania (120%) and highest in Wisconsin (260%). The U.S. average was 160%. California and Missouri were at 150%; Michigan was right at the average.
For physicians in Illinois, Louisiana, Colorado, Texas, and New York, markups were 170%-180% over the Medicare rate. Markups for clinicians in New Jersey (190%) and Arizona (200%) were closest to the Wisconsin rate.
The authors note some study limitations, including the fact that they excluded out-of-network practitioners, “and such payments may disproportionately affect certain specialties.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hot temperatures in outdoor lockboxes increase sample errors
, according to results from a recent study published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
“Our findings indicate that samples (centrifuged or not centrifuged) were impacted by extreme summer temperatures when stored for short periods of time inside commonly used steel lockboxes,” Joseph R. Wiencek, PhD, medical director of clinical chemistry, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Core Laboratory in Nashville, said in an interview.
Dr. Wiencek and colleagues picked two dates during the summer of 2019 in a mid-Atlantic state to place two courier lockboxes (LabLocker-KF300) outside in hot temperatures (32º C) starting at 11 a.m., with one lockbox containing two 24-oz cold packs (Nordic NI24) and the other containing no cold packs. The researchers monitored the temperatures of each lockbox over the course of 4 hours.
Overall, eight participants had seven samples in lithium heparin drawn for two studies evaluating centrifuged or not centrifuged samples. In the first study, four participants had seven samples drawn, with one centrifuged sample serving as a control for each patient. The other six samples were wrapped in paper towels, placed in resealable plastic bags, and distributed evenly in the warm and cold lockboxes. The samples did not directly touch the cold packs in the cold lockbox. At 1 hour, 2 hours, and 4 hours, a participant’s sample was removed from each lockbox and centrifuged.
In the second study, another four participants had seven samples drawn. As in the first study, all samples were centrifuged and placed in the lockboxes. For both studies, when samples were centrifuged, plasma from samples was left on the gel barrier when analyzed for concentrations of C-reactive protein, a comprehensive metabolic panel, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), a lipid panel, magnesium, and phosphorus (Abbott Architect c16000).
In the study of uncentrifuged samples, Dr. Wiencek and colleagues found that when the temperature outside ranged from 28.2º to 44.0º C (mean 40.4º C), the temperature of the cold lockbox was between 16.5º to 22.3º C (mean 22.3º C). The temperature ranged between 34.4º to 46.9º C (mean 42.6º C) in the warm lockbox. For centrifuged samples, the cold lockbox temperature was between 12.2º to 23.0º C (mean 18.0º C) and the warm lockbox was between 25. to 40.8º C (mean 35.2º C) when the outdoor temperature ranged from 27.2º to 46.3º C (mean 37.9º C).
The researchers also calculated the significant change limit (SCL) for each analyte in each sample, finding that aspartate aminotransferase, glucose, LDH, and potassium significantly exceeded the SCL in both the centrifuged and uncentrifuged samples, with the greatest changes seen at the 4-hour timepoint for samples in the warm lockbox (P < .05 for all).
Lockbox instructions are “consistently inconsistent”
In viewing instructions for lockboxes across institutions, Dr. Wiencek said the “outdoor courier lockbox instructions among private, academic and reference laboratories were consistently inconsistent.” For example, no laboratories cited time restrictions for samples in lockboxes, and their descriptions on the number of cold packs a laboratory should use and where the lockbox should be placed varied. The inconsistencies “highlighted the emergent need for standardization and guidance documents for institutions to implement,” Dr. Wiencek said.
One unanswered question is how widespread the problem is. It is unclear how many outdoor courier lockboxes are currently in use in the United States or globally; however, experts agreed it was a common occurrence, with some of the largest laboratory service providers offering outdoor courier lockboxes to their clients.
“Courier lockboxes are everywhere. All you need to do is walk around your clinics that are at your hospitals or clinics located around your grocery store to find them,” Dr. Wiencek said. “Some hang on doors, while others can be found on the ground in direct sunlight on a hot summer day.”
What’s more, institutions may not realize how leaving samples outdoors for extended periods can affect results. “Care teams are commonly unaware that samples placed in these poorly designed lockboxes can experience extreme summer or winter temperatures that may lead to incorrect results,” Dr. Wiencek said. “Healthcare providers need to understand the hidden dangers courier lockboxes have on the quality of their patient’s test results.”
Amy L. Pyle-Eilola, PhD, clinical chemistry director at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, said a major strength of the study by Dr. Wiencek and colleagues “is just that it was done at all.”
“I appreciate the real-world nature of this study and that it provides a snapshot of what conditions are really like in a lockbox in the summer,” she said in an interview.
In the clinical lab, receiving samples that had been sitting in a courier lockbox “is not uncommon,” Dr. Pyle-Eilola said.
“When I have encountered these situations, I have struggled to decide if it is still appropriate to run the tests. I always look to the medical literature for assistance with these situations, but there has been a paucity of information available on the impact of lockbox storage,” she explained.
The study by Dr. Wiencek and colleagues “provides some much-needed evidence for what is acceptable for lockbox storage conditions,” she said.
Areas of future research
Rodney E. Rohde, PhD, university distinguished chair and professor of the Clinical Laboratory Science (CLS) Program at Texas State University in San Marcos, said in an interview that the study “does a nice job of looking at multiple analytes and controlling for several variables,” but the sample size is small and the results may be difficult to generalize.
Dr. Pyle-Eilola highlighted another limitation — “a common shortcoming of these kinds of studies” — in the use of healthy donors for patient samples, which narrows the range of assay results.
“It is possible that more significant variation in results may be observed in additional analytes if the samples had higher concentrations of those analytes,” she said. “Moreover, this is clinically relevant as the samples stored in such lockboxes are not always from healthy individuals and have abnormal concentrations of analytes.”
Mario Plebani, MD, professor of clinical biochemistry and clinical molecular biology and chief of the department of laboratory medicine at University Hospital of Padova in Padova, Italy, agreed with that assessment.
“[T]he risks for errors and patient safety are higher for values near to the upper or lower reference value, and in general for samples collected in patients with particular diseases and clinical conditions,” he said in an interview.
“This paper deserves a commenting editorial to better highlight the urgent need for further studies on the same issue and in general on the risk in the pre-pre-analytical phase, including sample storage and transportation,” he noted.
Another area of future research is studying patient samples exposed to hotter or colder temperatures in outdoor courier lockboxes outside the mid-Atlantic area. “Here in Texas, temperatures can reach extreme heat levels,” Dr. Rohde said, who added that use of outdoor lockboxes is “very common in my region.”
Dr. Wiencek disclosed he has been a consultant on this research topic for Roche Diagnostics and received an honorarium for speaking on the subject from the American Association for Clinical Chemistry and American Society of Clinical Pathology. The other authors have no relevant conflict of interest. Dr. Pyle-Eilola, Dr. Rohde, and Dr. Plebani have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to results from a recent study published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
“Our findings indicate that samples (centrifuged or not centrifuged) were impacted by extreme summer temperatures when stored for short periods of time inside commonly used steel lockboxes,” Joseph R. Wiencek, PhD, medical director of clinical chemistry, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Core Laboratory in Nashville, said in an interview.
Dr. Wiencek and colleagues picked two dates during the summer of 2019 in a mid-Atlantic state to place two courier lockboxes (LabLocker-KF300) outside in hot temperatures (32º C) starting at 11 a.m., with one lockbox containing two 24-oz cold packs (Nordic NI24) and the other containing no cold packs. The researchers monitored the temperatures of each lockbox over the course of 4 hours.
Overall, eight participants had seven samples in lithium heparin drawn for two studies evaluating centrifuged or not centrifuged samples. In the first study, four participants had seven samples drawn, with one centrifuged sample serving as a control for each patient. The other six samples were wrapped in paper towels, placed in resealable plastic bags, and distributed evenly in the warm and cold lockboxes. The samples did not directly touch the cold packs in the cold lockbox. At 1 hour, 2 hours, and 4 hours, a participant’s sample was removed from each lockbox and centrifuged.
In the second study, another four participants had seven samples drawn. As in the first study, all samples were centrifuged and placed in the lockboxes. For both studies, when samples were centrifuged, plasma from samples was left on the gel barrier when analyzed for concentrations of C-reactive protein, a comprehensive metabolic panel, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), a lipid panel, magnesium, and phosphorus (Abbott Architect c16000).
In the study of uncentrifuged samples, Dr. Wiencek and colleagues found that when the temperature outside ranged from 28.2º to 44.0º C (mean 40.4º C), the temperature of the cold lockbox was between 16.5º to 22.3º C (mean 22.3º C). The temperature ranged between 34.4º to 46.9º C (mean 42.6º C) in the warm lockbox. For centrifuged samples, the cold lockbox temperature was between 12.2º to 23.0º C (mean 18.0º C) and the warm lockbox was between 25. to 40.8º C (mean 35.2º C) when the outdoor temperature ranged from 27.2º to 46.3º C (mean 37.9º C).
The researchers also calculated the significant change limit (SCL) for each analyte in each sample, finding that aspartate aminotransferase, glucose, LDH, and potassium significantly exceeded the SCL in both the centrifuged and uncentrifuged samples, with the greatest changes seen at the 4-hour timepoint for samples in the warm lockbox (P < .05 for all).
Lockbox instructions are “consistently inconsistent”
In viewing instructions for lockboxes across institutions, Dr. Wiencek said the “outdoor courier lockbox instructions among private, academic and reference laboratories were consistently inconsistent.” For example, no laboratories cited time restrictions for samples in lockboxes, and their descriptions on the number of cold packs a laboratory should use and where the lockbox should be placed varied. The inconsistencies “highlighted the emergent need for standardization and guidance documents for institutions to implement,” Dr. Wiencek said.
One unanswered question is how widespread the problem is. It is unclear how many outdoor courier lockboxes are currently in use in the United States or globally; however, experts agreed it was a common occurrence, with some of the largest laboratory service providers offering outdoor courier lockboxes to their clients.
“Courier lockboxes are everywhere. All you need to do is walk around your clinics that are at your hospitals or clinics located around your grocery store to find them,” Dr. Wiencek said. “Some hang on doors, while others can be found on the ground in direct sunlight on a hot summer day.”
What’s more, institutions may not realize how leaving samples outdoors for extended periods can affect results. “Care teams are commonly unaware that samples placed in these poorly designed lockboxes can experience extreme summer or winter temperatures that may lead to incorrect results,” Dr. Wiencek said. “Healthcare providers need to understand the hidden dangers courier lockboxes have on the quality of their patient’s test results.”
Amy L. Pyle-Eilola, PhD, clinical chemistry director at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, said a major strength of the study by Dr. Wiencek and colleagues “is just that it was done at all.”
“I appreciate the real-world nature of this study and that it provides a snapshot of what conditions are really like in a lockbox in the summer,” she said in an interview.
In the clinical lab, receiving samples that had been sitting in a courier lockbox “is not uncommon,” Dr. Pyle-Eilola said.
“When I have encountered these situations, I have struggled to decide if it is still appropriate to run the tests. I always look to the medical literature for assistance with these situations, but there has been a paucity of information available on the impact of lockbox storage,” she explained.
The study by Dr. Wiencek and colleagues “provides some much-needed evidence for what is acceptable for lockbox storage conditions,” she said.
Areas of future research
Rodney E. Rohde, PhD, university distinguished chair and professor of the Clinical Laboratory Science (CLS) Program at Texas State University in San Marcos, said in an interview that the study “does a nice job of looking at multiple analytes and controlling for several variables,” but the sample size is small and the results may be difficult to generalize.
Dr. Pyle-Eilola highlighted another limitation — “a common shortcoming of these kinds of studies” — in the use of healthy donors for patient samples, which narrows the range of assay results.
“It is possible that more significant variation in results may be observed in additional analytes if the samples had higher concentrations of those analytes,” she said. “Moreover, this is clinically relevant as the samples stored in such lockboxes are not always from healthy individuals and have abnormal concentrations of analytes.”
Mario Plebani, MD, professor of clinical biochemistry and clinical molecular biology and chief of the department of laboratory medicine at University Hospital of Padova in Padova, Italy, agreed with that assessment.
“[T]he risks for errors and patient safety are higher for values near to the upper or lower reference value, and in general for samples collected in patients with particular diseases and clinical conditions,” he said in an interview.
“This paper deserves a commenting editorial to better highlight the urgent need for further studies on the same issue and in general on the risk in the pre-pre-analytical phase, including sample storage and transportation,” he noted.
Another area of future research is studying patient samples exposed to hotter or colder temperatures in outdoor courier lockboxes outside the mid-Atlantic area. “Here in Texas, temperatures can reach extreme heat levels,” Dr. Rohde said, who added that use of outdoor lockboxes is “very common in my region.”
Dr. Wiencek disclosed he has been a consultant on this research topic for Roche Diagnostics and received an honorarium for speaking on the subject from the American Association for Clinical Chemistry and American Society of Clinical Pathology. The other authors have no relevant conflict of interest. Dr. Pyle-Eilola, Dr. Rohde, and Dr. Plebani have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to results from a recent study published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
“Our findings indicate that samples (centrifuged or not centrifuged) were impacted by extreme summer temperatures when stored for short periods of time inside commonly used steel lockboxes,” Joseph R. Wiencek, PhD, medical director of clinical chemistry, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Core Laboratory in Nashville, said in an interview.
Dr. Wiencek and colleagues picked two dates during the summer of 2019 in a mid-Atlantic state to place two courier lockboxes (LabLocker-KF300) outside in hot temperatures (32º C) starting at 11 a.m., with one lockbox containing two 24-oz cold packs (Nordic NI24) and the other containing no cold packs. The researchers monitored the temperatures of each lockbox over the course of 4 hours.
Overall, eight participants had seven samples in lithium heparin drawn for two studies evaluating centrifuged or not centrifuged samples. In the first study, four participants had seven samples drawn, with one centrifuged sample serving as a control for each patient. The other six samples were wrapped in paper towels, placed in resealable plastic bags, and distributed evenly in the warm and cold lockboxes. The samples did not directly touch the cold packs in the cold lockbox. At 1 hour, 2 hours, and 4 hours, a participant’s sample was removed from each lockbox and centrifuged.
In the second study, another four participants had seven samples drawn. As in the first study, all samples were centrifuged and placed in the lockboxes. For both studies, when samples were centrifuged, plasma from samples was left on the gel barrier when analyzed for concentrations of C-reactive protein, a comprehensive metabolic panel, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), a lipid panel, magnesium, and phosphorus (Abbott Architect c16000).
In the study of uncentrifuged samples, Dr. Wiencek and colleagues found that when the temperature outside ranged from 28.2º to 44.0º C (mean 40.4º C), the temperature of the cold lockbox was between 16.5º to 22.3º C (mean 22.3º C). The temperature ranged between 34.4º to 46.9º C (mean 42.6º C) in the warm lockbox. For centrifuged samples, the cold lockbox temperature was between 12.2º to 23.0º C (mean 18.0º C) and the warm lockbox was between 25. to 40.8º C (mean 35.2º C) when the outdoor temperature ranged from 27.2º to 46.3º C (mean 37.9º C).
The researchers also calculated the significant change limit (SCL) for each analyte in each sample, finding that aspartate aminotransferase, glucose, LDH, and potassium significantly exceeded the SCL in both the centrifuged and uncentrifuged samples, with the greatest changes seen at the 4-hour timepoint for samples in the warm lockbox (P < .05 for all).
Lockbox instructions are “consistently inconsistent”
In viewing instructions for lockboxes across institutions, Dr. Wiencek said the “outdoor courier lockbox instructions among private, academic and reference laboratories were consistently inconsistent.” For example, no laboratories cited time restrictions for samples in lockboxes, and their descriptions on the number of cold packs a laboratory should use and where the lockbox should be placed varied. The inconsistencies “highlighted the emergent need for standardization and guidance documents for institutions to implement,” Dr. Wiencek said.
One unanswered question is how widespread the problem is. It is unclear how many outdoor courier lockboxes are currently in use in the United States or globally; however, experts agreed it was a common occurrence, with some of the largest laboratory service providers offering outdoor courier lockboxes to their clients.
“Courier lockboxes are everywhere. All you need to do is walk around your clinics that are at your hospitals or clinics located around your grocery store to find them,” Dr. Wiencek said. “Some hang on doors, while others can be found on the ground in direct sunlight on a hot summer day.”
What’s more, institutions may not realize how leaving samples outdoors for extended periods can affect results. “Care teams are commonly unaware that samples placed in these poorly designed lockboxes can experience extreme summer or winter temperatures that may lead to incorrect results,” Dr. Wiencek said. “Healthcare providers need to understand the hidden dangers courier lockboxes have on the quality of their patient’s test results.”
Amy L. Pyle-Eilola, PhD, clinical chemistry director at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, said a major strength of the study by Dr. Wiencek and colleagues “is just that it was done at all.”
“I appreciate the real-world nature of this study and that it provides a snapshot of what conditions are really like in a lockbox in the summer,” she said in an interview.
In the clinical lab, receiving samples that had been sitting in a courier lockbox “is not uncommon,” Dr. Pyle-Eilola said.
“When I have encountered these situations, I have struggled to decide if it is still appropriate to run the tests. I always look to the medical literature for assistance with these situations, but there has been a paucity of information available on the impact of lockbox storage,” she explained.
The study by Dr. Wiencek and colleagues “provides some much-needed evidence for what is acceptable for lockbox storage conditions,” she said.
Areas of future research
Rodney E. Rohde, PhD, university distinguished chair and professor of the Clinical Laboratory Science (CLS) Program at Texas State University in San Marcos, said in an interview that the study “does a nice job of looking at multiple analytes and controlling for several variables,” but the sample size is small and the results may be difficult to generalize.
Dr. Pyle-Eilola highlighted another limitation — “a common shortcoming of these kinds of studies” — in the use of healthy donors for patient samples, which narrows the range of assay results.
“It is possible that more significant variation in results may be observed in additional analytes if the samples had higher concentrations of those analytes,” she said. “Moreover, this is clinically relevant as the samples stored in such lockboxes are not always from healthy individuals and have abnormal concentrations of analytes.”
Mario Plebani, MD, professor of clinical biochemistry and clinical molecular biology and chief of the department of laboratory medicine at University Hospital of Padova in Padova, Italy, agreed with that assessment.
“[T]he risks for errors and patient safety are higher for values near to the upper or lower reference value, and in general for samples collected in patients with particular diseases and clinical conditions,” he said in an interview.
“This paper deserves a commenting editorial to better highlight the urgent need for further studies on the same issue and in general on the risk in the pre-pre-analytical phase, including sample storage and transportation,” he noted.
Another area of future research is studying patient samples exposed to hotter or colder temperatures in outdoor courier lockboxes outside the mid-Atlantic area. “Here in Texas, temperatures can reach extreme heat levels,” Dr. Rohde said, who added that use of outdoor lockboxes is “very common in my region.”
Dr. Wiencek disclosed he has been a consultant on this research topic for Roche Diagnostics and received an honorarium for speaking on the subject from the American Association for Clinical Chemistry and American Society of Clinical Pathology. The other authors have no relevant conflict of interest. Dr. Pyle-Eilola, Dr. Rohde, and Dr. Plebani have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment with novel laser in acne studies targets sebaceous glands
at 12 months, a development that indicates the promise this has a treatment for acne in the future.
Currently, “there is no strong evidence that lasers are better than conventional treatments for acne,” Fernanda H. Sakamoto, MD, PhD, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. Some patients struggling with acne “search for so many different options and they end up spending a lot of money,” which, she said, includes an estimated $222 million for laser treatment alone in 2019.
Unlike other existing laser and light options for acne treatment, however, Accure is the first light-based platform to selectively target and injure sebaceous glands, the main source of sebum production and the key to a durable solution for acne. The laser, which uses a 1,726-nm wavelength, is being developed by researchers at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston and was granted the European CE mark, which allows marketing of the product in Europe, in May of 2020.
In 2012, Dr. Sakamoto, a dermatologist at the center, and her Wellman colleagues were the first to describe the use of selective photothermolysis to target sebaceous glands. “We found that the peak absorption of lipids in sebaceous glands occurs between 1,700 and 1,720 nm,” she said. “Compared to water, the contrast is not high, so for us to develop a laser that is selective for acne, we needed to develop a strong cooling system and we had to create different methods to make it more selective.” She said that it took about 10 years to develop this laser.
The latest Accure prototype features a smart laser handpiece for real time thermal monitoring and precise delivery of laser emissions. “We have developed a mathematical model which permits us to predict safe and effective treatment patterns,” Dr. Sakamoto said at the meeting, which was named “Laser & Aesthetic Skin Therapy: What’s the Truth?” and was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “It has a unique cooling system that can control and protect the skin.”
The clinical trial for Food and Drug Administration clearance, which was delayed because of the COVID-19 pandemic, is still underway, she said, and the hope is that the laser will cleared by the FDA by next year. She and her Wellman colleagues have been working with four veteran dermatologists to conduct clinical trials of the device: Emil Tanghetti, MD, in California; Roy Geronemus, MD, in New York; Joel Cohen, MD, in Colorado; and Daniel Friedmann, MD, in Texas. As of Oct. 2, 2021, more than 50 patients were enrolled in four IRB-approved studies and an additional 30 are enrolled in a pilot facial acne trial, Dr. Sakamoto said. In the trials, patients are followed at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment.
Among patients enrolled in the pilot facial acne trial, researchers have observed a 100% responder rate for patients with more than five acne lesions at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment. The average lesion reduction at week 12 was 82% and the mean Visual Analog Scale score immediately after treatment was 2.10 out of 10. Each patient received more than 12,000 trigger pulls of energy from the device with no adverse events.
“This laser is absorbed in the near-infrared spectrum, so there is no melanin absorption,” Dr. Sakamoto explained. “It’s pretty much a color-blind laser, so we can treat darker skin types safely, with no side effects.” In other findings, researchers observed a 45% reduction in acne lesions after one treatment session, which “keeps improving over time,” she said. “At 12 weeks, we have clearance of over 80% of the lesions.”
At 12 months, they observed a 90% inflammatory lesion count reduction from baseline and a rapid response to treatment: a 73% reduction achieved after the first two treatment sessions. Histological studies revealed selective sebaceous gland destruction with no damage to the epidermis, surrounding dermis, or other follicular structures.
Dr. Sakamoto disclosed that she has received portions of patent royalties from Massachusetts General Hospital. Accure was cofounded by R. Rox Anderson, MD, the director of the Wellman Center.
at 12 months, a development that indicates the promise this has a treatment for acne in the future.
Currently, “there is no strong evidence that lasers are better than conventional treatments for acne,” Fernanda H. Sakamoto, MD, PhD, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. Some patients struggling with acne “search for so many different options and they end up spending a lot of money,” which, she said, includes an estimated $222 million for laser treatment alone in 2019.
Unlike other existing laser and light options for acne treatment, however, Accure is the first light-based platform to selectively target and injure sebaceous glands, the main source of sebum production and the key to a durable solution for acne. The laser, which uses a 1,726-nm wavelength, is being developed by researchers at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston and was granted the European CE mark, which allows marketing of the product in Europe, in May of 2020.
In 2012, Dr. Sakamoto, a dermatologist at the center, and her Wellman colleagues were the first to describe the use of selective photothermolysis to target sebaceous glands. “We found that the peak absorption of lipids in sebaceous glands occurs between 1,700 and 1,720 nm,” she said. “Compared to water, the contrast is not high, so for us to develop a laser that is selective for acne, we needed to develop a strong cooling system and we had to create different methods to make it more selective.” She said that it took about 10 years to develop this laser.
The latest Accure prototype features a smart laser handpiece for real time thermal monitoring and precise delivery of laser emissions. “We have developed a mathematical model which permits us to predict safe and effective treatment patterns,” Dr. Sakamoto said at the meeting, which was named “Laser & Aesthetic Skin Therapy: What’s the Truth?” and was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “It has a unique cooling system that can control and protect the skin.”
The clinical trial for Food and Drug Administration clearance, which was delayed because of the COVID-19 pandemic, is still underway, she said, and the hope is that the laser will cleared by the FDA by next year. She and her Wellman colleagues have been working with four veteran dermatologists to conduct clinical trials of the device: Emil Tanghetti, MD, in California; Roy Geronemus, MD, in New York; Joel Cohen, MD, in Colorado; and Daniel Friedmann, MD, in Texas. As of Oct. 2, 2021, more than 50 patients were enrolled in four IRB-approved studies and an additional 30 are enrolled in a pilot facial acne trial, Dr. Sakamoto said. In the trials, patients are followed at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment.
Among patients enrolled in the pilot facial acne trial, researchers have observed a 100% responder rate for patients with more than five acne lesions at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment. The average lesion reduction at week 12 was 82% and the mean Visual Analog Scale score immediately after treatment was 2.10 out of 10. Each patient received more than 12,000 trigger pulls of energy from the device with no adverse events.
“This laser is absorbed in the near-infrared spectrum, so there is no melanin absorption,” Dr. Sakamoto explained. “It’s pretty much a color-blind laser, so we can treat darker skin types safely, with no side effects.” In other findings, researchers observed a 45% reduction in acne lesions after one treatment session, which “keeps improving over time,” she said. “At 12 weeks, we have clearance of over 80% of the lesions.”
At 12 months, they observed a 90% inflammatory lesion count reduction from baseline and a rapid response to treatment: a 73% reduction achieved after the first two treatment sessions. Histological studies revealed selective sebaceous gland destruction with no damage to the epidermis, surrounding dermis, or other follicular structures.
Dr. Sakamoto disclosed that she has received portions of patent royalties from Massachusetts General Hospital. Accure was cofounded by R. Rox Anderson, MD, the director of the Wellman Center.
at 12 months, a development that indicates the promise this has a treatment for acne in the future.
Currently, “there is no strong evidence that lasers are better than conventional treatments for acne,” Fernanda H. Sakamoto, MD, PhD, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. Some patients struggling with acne “search for so many different options and they end up spending a lot of money,” which, she said, includes an estimated $222 million for laser treatment alone in 2019.
Unlike other existing laser and light options for acne treatment, however, Accure is the first light-based platform to selectively target and injure sebaceous glands, the main source of sebum production and the key to a durable solution for acne. The laser, which uses a 1,726-nm wavelength, is being developed by researchers at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston and was granted the European CE mark, which allows marketing of the product in Europe, in May of 2020.
In 2012, Dr. Sakamoto, a dermatologist at the center, and her Wellman colleagues were the first to describe the use of selective photothermolysis to target sebaceous glands. “We found that the peak absorption of lipids in sebaceous glands occurs between 1,700 and 1,720 nm,” she said. “Compared to water, the contrast is not high, so for us to develop a laser that is selective for acne, we needed to develop a strong cooling system and we had to create different methods to make it more selective.” She said that it took about 10 years to develop this laser.
The latest Accure prototype features a smart laser handpiece for real time thermal monitoring and precise delivery of laser emissions. “We have developed a mathematical model which permits us to predict safe and effective treatment patterns,” Dr. Sakamoto said at the meeting, which was named “Laser & Aesthetic Skin Therapy: What’s the Truth?” and was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “It has a unique cooling system that can control and protect the skin.”
The clinical trial for Food and Drug Administration clearance, which was delayed because of the COVID-19 pandemic, is still underway, she said, and the hope is that the laser will cleared by the FDA by next year. She and her Wellman colleagues have been working with four veteran dermatologists to conduct clinical trials of the device: Emil Tanghetti, MD, in California; Roy Geronemus, MD, in New York; Joel Cohen, MD, in Colorado; and Daniel Friedmann, MD, in Texas. As of Oct. 2, 2021, more than 50 patients were enrolled in four IRB-approved studies and an additional 30 are enrolled in a pilot facial acne trial, Dr. Sakamoto said. In the trials, patients are followed at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment.
Among patients enrolled in the pilot facial acne trial, researchers have observed a 100% responder rate for patients with more than five acne lesions at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment. The average lesion reduction at week 12 was 82% and the mean Visual Analog Scale score immediately after treatment was 2.10 out of 10. Each patient received more than 12,000 trigger pulls of energy from the device with no adverse events.
“This laser is absorbed in the near-infrared spectrum, so there is no melanin absorption,” Dr. Sakamoto explained. “It’s pretty much a color-blind laser, so we can treat darker skin types safely, with no side effects.” In other findings, researchers observed a 45% reduction in acne lesions after one treatment session, which “keeps improving over time,” she said. “At 12 weeks, we have clearance of over 80% of the lesions.”
At 12 months, they observed a 90% inflammatory lesion count reduction from baseline and a rapid response to treatment: a 73% reduction achieved after the first two treatment sessions. Histological studies revealed selective sebaceous gland destruction with no damage to the epidermis, surrounding dermis, or other follicular structures.
Dr. Sakamoto disclosed that she has received portions of patent royalties from Massachusetts General Hospital. Accure was cofounded by R. Rox Anderson, MD, the director of the Wellman Center.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE
Selective cooling technology being used to remove age spots
, according to Arisa E. Ortiz, MD.
“What’s unique about this device is that I can see results without any downtime,” Dr. Ortiz, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “Most other devices are not like that. It was well tolerated; there was minimal pain. There was no postinflammatory hyperpigmentation; it really is customizable to the patients’ needs.”
First cleared by the Food and Drug Administration in 2016 to remove benign lesions of the skin, Glacial Rx received an expanded indication in 2020 to temporarily reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation. The device, which was developed by R2 Technologies, relies on cryomodulation, a concept developed at Massachusetts General Hospital and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, Boston, to improve skin appearance and freeze melanin at the source. “Cryomodulation pauses melanin production, but the melanocyte function is preserved, the epidermal barrier is not disrupted, and there is no persistent inflammatory response, which is key, because it decreases the risk of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, especially in darker skin types,” Dr. Ortiz said.
Here’s how it works: The handpiece of the device is placed on top of the skin and cooling is delivered to targeted solar lentigos and other benign lesions. Ice nucleation takes place within the dendrites. As cell turnover takes place, melanin-free cells migrate upward and appear as new skin. “Clinically, this appears as clearance of the lesion,” Dr. Ortiz said.
She discussed her clinical experience treating 15 patients with a beta version of the device. Since that time, Glacial Rx was redesigned to include a smaller-tipped handpiece, easier and faster prep time, and a proprietary water-based gel to facilitate ice crystal propagation, which is applied to the targeted lesions just prior to treatment.
For the trial at UCSD, the researchers performed 29 treatment sessions on 15 patients with Fitzpatrick skin types I-IV, to gain clinical experience and evaluate the effectiveness of the device. They found that the treatment was well tolerated, with minimal discomfort. The amount of heat extracted ranged from 107 to 166 kJ/cm2. No long-term dyschromia was observed, and some patients had lesion clearance after just one treatment.
“The settings are able to be titrated to where you have zero downtime, but you still get a lightening effect,” Dr. Ortiz said during the meeting, named “Laser & Aesthetic Skin Therapy: What’s the Truth?” sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “With other devices such as intense pulsed light, if you don’t see darkening than it probably didn’t work. With this device, you can titrate the length of the cooling and the temperature of the cooling.”
Posttreatment side effects commonly observed in the study were mild erythema, swelling, itching, and darkening. “There was minimal erythema in the higher settings, and some reports of itching and transient darkening in some of the higher settings,” she said.
Future indications for Glacial Rx may include psoriasis, acne, and rosacea. “We did try to use this for melasma,” she said. “It was effective, but I wouldn’t say it’s a cure for melasma. Melasma is very stubborn and requires a combination treatment, but it’s something we can use in our armamentarium.”
Dr. Ortiz reported having received consulting fees from R2 Technologies. She has been a paid consultant for and has received equipment from many device companies.
, according to Arisa E. Ortiz, MD.
“What’s unique about this device is that I can see results without any downtime,” Dr. Ortiz, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “Most other devices are not like that. It was well tolerated; there was minimal pain. There was no postinflammatory hyperpigmentation; it really is customizable to the patients’ needs.”
First cleared by the Food and Drug Administration in 2016 to remove benign lesions of the skin, Glacial Rx received an expanded indication in 2020 to temporarily reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation. The device, which was developed by R2 Technologies, relies on cryomodulation, a concept developed at Massachusetts General Hospital and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, Boston, to improve skin appearance and freeze melanin at the source. “Cryomodulation pauses melanin production, but the melanocyte function is preserved, the epidermal barrier is not disrupted, and there is no persistent inflammatory response, which is key, because it decreases the risk of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, especially in darker skin types,” Dr. Ortiz said.
Here’s how it works: The handpiece of the device is placed on top of the skin and cooling is delivered to targeted solar lentigos and other benign lesions. Ice nucleation takes place within the dendrites. As cell turnover takes place, melanin-free cells migrate upward and appear as new skin. “Clinically, this appears as clearance of the lesion,” Dr. Ortiz said.
She discussed her clinical experience treating 15 patients with a beta version of the device. Since that time, Glacial Rx was redesigned to include a smaller-tipped handpiece, easier and faster prep time, and a proprietary water-based gel to facilitate ice crystal propagation, which is applied to the targeted lesions just prior to treatment.
For the trial at UCSD, the researchers performed 29 treatment sessions on 15 patients with Fitzpatrick skin types I-IV, to gain clinical experience and evaluate the effectiveness of the device. They found that the treatment was well tolerated, with minimal discomfort. The amount of heat extracted ranged from 107 to 166 kJ/cm2. No long-term dyschromia was observed, and some patients had lesion clearance after just one treatment.
“The settings are able to be titrated to where you have zero downtime, but you still get a lightening effect,” Dr. Ortiz said during the meeting, named “Laser & Aesthetic Skin Therapy: What’s the Truth?” sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “With other devices such as intense pulsed light, if you don’t see darkening than it probably didn’t work. With this device, you can titrate the length of the cooling and the temperature of the cooling.”
Posttreatment side effects commonly observed in the study were mild erythema, swelling, itching, and darkening. “There was minimal erythema in the higher settings, and some reports of itching and transient darkening in some of the higher settings,” she said.
Future indications for Glacial Rx may include psoriasis, acne, and rosacea. “We did try to use this for melasma,” she said. “It was effective, but I wouldn’t say it’s a cure for melasma. Melasma is very stubborn and requires a combination treatment, but it’s something we can use in our armamentarium.”
Dr. Ortiz reported having received consulting fees from R2 Technologies. She has been a paid consultant for and has received equipment from many device companies.
, according to Arisa E. Ortiz, MD.
“What’s unique about this device is that I can see results without any downtime,” Dr. Ortiz, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “Most other devices are not like that. It was well tolerated; there was minimal pain. There was no postinflammatory hyperpigmentation; it really is customizable to the patients’ needs.”
First cleared by the Food and Drug Administration in 2016 to remove benign lesions of the skin, Glacial Rx received an expanded indication in 2020 to temporarily reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation. The device, which was developed by R2 Technologies, relies on cryomodulation, a concept developed at Massachusetts General Hospital and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, Boston, to improve skin appearance and freeze melanin at the source. “Cryomodulation pauses melanin production, but the melanocyte function is preserved, the epidermal barrier is not disrupted, and there is no persistent inflammatory response, which is key, because it decreases the risk of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, especially in darker skin types,” Dr. Ortiz said.
Here’s how it works: The handpiece of the device is placed on top of the skin and cooling is delivered to targeted solar lentigos and other benign lesions. Ice nucleation takes place within the dendrites. As cell turnover takes place, melanin-free cells migrate upward and appear as new skin. “Clinically, this appears as clearance of the lesion,” Dr. Ortiz said.
She discussed her clinical experience treating 15 patients with a beta version of the device. Since that time, Glacial Rx was redesigned to include a smaller-tipped handpiece, easier and faster prep time, and a proprietary water-based gel to facilitate ice crystal propagation, which is applied to the targeted lesions just prior to treatment.
For the trial at UCSD, the researchers performed 29 treatment sessions on 15 patients with Fitzpatrick skin types I-IV, to gain clinical experience and evaluate the effectiveness of the device. They found that the treatment was well tolerated, with minimal discomfort. The amount of heat extracted ranged from 107 to 166 kJ/cm2. No long-term dyschromia was observed, and some patients had lesion clearance after just one treatment.
“The settings are able to be titrated to where you have zero downtime, but you still get a lightening effect,” Dr. Ortiz said during the meeting, named “Laser & Aesthetic Skin Therapy: What’s the Truth?” sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “With other devices such as intense pulsed light, if you don’t see darkening than it probably didn’t work. With this device, you can titrate the length of the cooling and the temperature of the cooling.”
Posttreatment side effects commonly observed in the study were mild erythema, swelling, itching, and darkening. “There was minimal erythema in the higher settings, and some reports of itching and transient darkening in some of the higher settings,” she said.
Future indications for Glacial Rx may include psoriasis, acne, and rosacea. “We did try to use this for melasma,” she said. “It was effective, but I wouldn’t say it’s a cure for melasma. Melasma is very stubborn and requires a combination treatment, but it’s something we can use in our armamentarium.”
Dr. Ortiz reported having received consulting fees from R2 Technologies. She has been a paid consultant for and has received equipment from many device companies.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE
Disinclined to offer laser hair removal? An expert makes the case to think otherwise
Omar A. Ibrahimi, MD, PhD, hears some dermatology colleagues say they don’t bother to offer laser hair removal in their practices because they figure that the procedure is under the purview of medical spas, but he sees it differently.
“I offer laser hair removal in my practice as a way to protect my patients from being picked off by medical spas,” Dr. Ibrahimi, a dermatologist and medical director of the Connecticut Skin Institute, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “These patients are going to want to get laser hair removal. If they’re not going to have the opportunity to get it at your practice, they’re going to seek it elsewhere. When they go elsewhere, they’re going to be picked off for other procedures as well.”
First developed in 1995 by R. Rox Anderson, MD, and colleagues at The Wellman Center for Photomedicine, laser hair removal has become the gold standard for permanent hair destruction, and ranks as the most common energy-based procedure performed in the world, Dr. Ibrahimi said. “Results are very long lasting and durable beyond 2 years after treatment,” he said. “These patients tend to be highly satisfied and have permanence with these treatments.”
Treatment goal, patient selection
While the target chromophore for the procedure is melanin, the goal is to destroy the stem cells located in the hair bulge and the hair bulb. “This is technically called the extended theory of selective photothermolysis, but it’s the same concept except that our target chromophore and our desired target for destruction are slightly spatially separated,” he said.
Proper patient selection is key, so a focused medical history and physical exam are essential prior to the procedure. If unwanted hair is located on the face, jawline, or chest of a female, consider and ask about potential endocrine-related dysfunctions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). “Getting those addressed can often help the hypertrichosis as well,” he said. “Another condition is explosive hypertrichosis where hair growth starts very suddenly. It’s uncommon but it’s something to think about.”
Pregnancy is not an absolute contraindication for laser hair removal, Dr. Ibrahimi continued, but he elects not to perform the procedure on pregnant patients. He also asks patients about any history of photosensitivity, active infection at the intended treatment site, keloids, or hypertrophic scarring. Past methods of hair removal also matter. “What we’re targeting is the pigment in the hair shafts,” he said. “So, if your patient is waxing or plucking or epilating or removing the hair in some manner, they’re actually removing the target chromophore.”
Patients with darker Fitzpatrick skin types can be treated safely but tanned individuals face a risk of complications because of active melanocytes. “As we approach summer in New England, we slow down the amount of hair removal we do because it’s a riskier procedure,” he said. “I recommend that my patients not get any significant amount of sun exposure a month before or after treatment.”
The color and quality of hair also drive treatment success. Black and brown terminal hairs absorb the millisecond laser energy, but white, gray, red, and light blond hairs lack adequate melanin to make them suitable target chromophores.
Excessive and unwanted body hair ranges in severity and can usually be classified as either hypertrichosis or hirsutism.
The desired clinical endpoint is perifollicular edema and erythema. Treatment parameters that can be varied with Food and Drug Administration–cleared devices include wavelength, fluence, pulse duration, spot size, and skin cooling. The most popular devices are the Alexandrite 755 nm laser; the diode 800 nm laser; and the 1064 nm Nd:YAG laser, which is safe for all skin types. “Often you have to use higher relative fluences to treat patients with the 1064 nm Nd:YAG because on the absorption spectrum, the 1064-nm wavelength has a relatively lower absorption for melanin compared to the alexandrite. However, you can still get effective, long-term hair reduction with the Nd:YAG laser,” he said (Arch Dermatol. 2008 Oct;144[10]:1323-7).
More recently, Dr. Ibrahimi and colleagues found that a 1060-nm diode laser system with multiple handpieces for permanent hair reduction was safe for all skin types, in an open label prospective study.
Higher fluences have been correlated with greater rates of permanent hair removal, but they also are more likely to cause undesired side effects. Dr. Ibrahimi advises clinicians new to laser hair removal to conduct a few different test spots and look for the desired clinical endpoint of perifollicular erythema and edema. “The highest fluence that gives you that endpoint without any adverse reactions is going to the best fluence for treatment,” he said at the meeting, which was named “Laser & Aesthetic Skin Therapy: What’s the Truth” and was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “Do a few test spots, bring them back a week later and see which ones were tolerated well without any side effects and which weren’t. That gives you a good starting point for your treatment.”
Cooling down the epidermal melanin not only keeps the procedure safe, it’s a salve for pain. “There are a variety of methods of passive and active cooling,” said Dr. Ibrahimi, a member of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery board of directors. “You can use something as simple as cold gel, but the active methods are better because once the method of passive application of cold gel warms up, you lose that cooling effect. You can use forced chilled air. Many commercial devices come with a cold tip which cools down the epidermal melanin. Others use dynamic cooling, which emit cryogen spray from a separate part of the handpiece. It hits right where the laser pulse is going to go, is absorbed by the skin, and it cools down the epidermal melanin.”
Treatment complications
Complications that can occur from treatment include pigmentary changes such as hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation. “In lighter skinned individuals, sometimes excess fluence can lead to an erythematous appearance,” he said. “In darker-skinned individuals, this often manifests as hyperpigmentation and can be very long-lasting.” Dr. Ibrahimi ranks improper technique as a complication, “because ideally you want to lay your pulses down with 10%-15% overlap during treatment,” he explained. “If you don’t overlap, you’re going to have zones that don’t get any of the laser photons. If you do, then your patient is not going to be happy with you.”
Paradoxical hypertrichosis occurs in 1%-5% of patients, typically in women from Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, or South Asian ethnic backgrounds. This tends to develop on the lateral or jawline part of the face. “Often it occurs in the setting where they come in and want these vellus hairs treated,” he said. “Somehow the laser, instead of destroying the hair shaft, triggers it and stimulates it and can’t differentiate a vellus hair from a terminal hair. This is important to discuss during your informed consent, especially when you’re treating on the lateral jawline or the sideburn area. If this happens, you can treat through it.”
Transgender patients and future directions
Dr. Ibrahimi pointed out that increasing numbers of transgender patients are visiting dermatologists seeking laser hair removal. About 16 million Americans are estimated to have a gender identity that differs from the one assigned to them at birth, yet they face several barriers to care, “ranging from ignorance on our end to maybe our own biases being transposed onto these patients,” he said. “We really need to do a better job for them. We really have an obligation to provide good care for all of our patients.”
Transgender women typically seek hair removal on the face and neck as well as in the genital area to remove hairs in preparation for vaginoplasty. Transgender men typically seek hair reduction on the forearm or on the thigh, because those are graft sites in preparation for phalloplasty. As a resource for transgender care, he recommends the UCSF Transgender Care website.
As for future directions in the field, Dr. Ibrahimi predicted that hair removal devices for home use will continue to improve and become more widespread. “This raises a host of considerations, from the risk of eye damage to the risk for paradoxical hypertrichosis, and what happens when pigmented lesions get treated with these low-powered machines compared to the ones we have in our office,” he said. “I also think we’re going to see office-based devices with larger spot sizes, smarter devices that are capable of taking over more of the functions we do. I’m most excited about the potential for treating nonpigmented white hair or poorly pigmented blond or reddish hair in the future.”
Dr. Ibrahimi disclosed that he has received research funding and speaker honoraria from Lutronic, Lumenis, Cutera, and Syneron-Candela. He also holds stock in AVAVA Inc.
Omar A. Ibrahimi, MD, PhD, hears some dermatology colleagues say they don’t bother to offer laser hair removal in their practices because they figure that the procedure is under the purview of medical spas, but he sees it differently.
“I offer laser hair removal in my practice as a way to protect my patients from being picked off by medical spas,” Dr. Ibrahimi, a dermatologist and medical director of the Connecticut Skin Institute, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “These patients are going to want to get laser hair removal. If they’re not going to have the opportunity to get it at your practice, they’re going to seek it elsewhere. When they go elsewhere, they’re going to be picked off for other procedures as well.”
First developed in 1995 by R. Rox Anderson, MD, and colleagues at The Wellman Center for Photomedicine, laser hair removal has become the gold standard for permanent hair destruction, and ranks as the most common energy-based procedure performed in the world, Dr. Ibrahimi said. “Results are very long lasting and durable beyond 2 years after treatment,” he said. “These patients tend to be highly satisfied and have permanence with these treatments.”
Treatment goal, patient selection
While the target chromophore for the procedure is melanin, the goal is to destroy the stem cells located in the hair bulge and the hair bulb. “This is technically called the extended theory of selective photothermolysis, but it’s the same concept except that our target chromophore and our desired target for destruction are slightly spatially separated,” he said.
Proper patient selection is key, so a focused medical history and physical exam are essential prior to the procedure. If unwanted hair is located on the face, jawline, or chest of a female, consider and ask about potential endocrine-related dysfunctions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). “Getting those addressed can often help the hypertrichosis as well,” he said. “Another condition is explosive hypertrichosis where hair growth starts very suddenly. It’s uncommon but it’s something to think about.”
Pregnancy is not an absolute contraindication for laser hair removal, Dr. Ibrahimi continued, but he elects not to perform the procedure on pregnant patients. He also asks patients about any history of photosensitivity, active infection at the intended treatment site, keloids, or hypertrophic scarring. Past methods of hair removal also matter. “What we’re targeting is the pigment in the hair shafts,” he said. “So, if your patient is waxing or plucking or epilating or removing the hair in some manner, they’re actually removing the target chromophore.”
Patients with darker Fitzpatrick skin types can be treated safely but tanned individuals face a risk of complications because of active melanocytes. “As we approach summer in New England, we slow down the amount of hair removal we do because it’s a riskier procedure,” he said. “I recommend that my patients not get any significant amount of sun exposure a month before or after treatment.”
The color and quality of hair also drive treatment success. Black and brown terminal hairs absorb the millisecond laser energy, but white, gray, red, and light blond hairs lack adequate melanin to make them suitable target chromophores.
Excessive and unwanted body hair ranges in severity and can usually be classified as either hypertrichosis or hirsutism.
The desired clinical endpoint is perifollicular edema and erythema. Treatment parameters that can be varied with Food and Drug Administration–cleared devices include wavelength, fluence, pulse duration, spot size, and skin cooling. The most popular devices are the Alexandrite 755 nm laser; the diode 800 nm laser; and the 1064 nm Nd:YAG laser, which is safe for all skin types. “Often you have to use higher relative fluences to treat patients with the 1064 nm Nd:YAG because on the absorption spectrum, the 1064-nm wavelength has a relatively lower absorption for melanin compared to the alexandrite. However, you can still get effective, long-term hair reduction with the Nd:YAG laser,” he said (Arch Dermatol. 2008 Oct;144[10]:1323-7).
More recently, Dr. Ibrahimi and colleagues found that a 1060-nm diode laser system with multiple handpieces for permanent hair reduction was safe for all skin types, in an open label prospective study.
Higher fluences have been correlated with greater rates of permanent hair removal, but they also are more likely to cause undesired side effects. Dr. Ibrahimi advises clinicians new to laser hair removal to conduct a few different test spots and look for the desired clinical endpoint of perifollicular erythema and edema. “The highest fluence that gives you that endpoint without any adverse reactions is going to the best fluence for treatment,” he said at the meeting, which was named “Laser & Aesthetic Skin Therapy: What’s the Truth” and was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “Do a few test spots, bring them back a week later and see which ones were tolerated well without any side effects and which weren’t. That gives you a good starting point for your treatment.”
Cooling down the epidermal melanin not only keeps the procedure safe, it’s a salve for pain. “There are a variety of methods of passive and active cooling,” said Dr. Ibrahimi, a member of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery board of directors. “You can use something as simple as cold gel, but the active methods are better because once the method of passive application of cold gel warms up, you lose that cooling effect. You can use forced chilled air. Many commercial devices come with a cold tip which cools down the epidermal melanin. Others use dynamic cooling, which emit cryogen spray from a separate part of the handpiece. It hits right where the laser pulse is going to go, is absorbed by the skin, and it cools down the epidermal melanin.”
Treatment complications
Complications that can occur from treatment include pigmentary changes such as hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation. “In lighter skinned individuals, sometimes excess fluence can lead to an erythematous appearance,” he said. “In darker-skinned individuals, this often manifests as hyperpigmentation and can be very long-lasting.” Dr. Ibrahimi ranks improper technique as a complication, “because ideally you want to lay your pulses down with 10%-15% overlap during treatment,” he explained. “If you don’t overlap, you’re going to have zones that don’t get any of the laser photons. If you do, then your patient is not going to be happy with you.”
Paradoxical hypertrichosis occurs in 1%-5% of patients, typically in women from Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, or South Asian ethnic backgrounds. This tends to develop on the lateral or jawline part of the face. “Often it occurs in the setting where they come in and want these vellus hairs treated,” he said. “Somehow the laser, instead of destroying the hair shaft, triggers it and stimulates it and can’t differentiate a vellus hair from a terminal hair. This is important to discuss during your informed consent, especially when you’re treating on the lateral jawline or the sideburn area. If this happens, you can treat through it.”
Transgender patients and future directions
Dr. Ibrahimi pointed out that increasing numbers of transgender patients are visiting dermatologists seeking laser hair removal. About 16 million Americans are estimated to have a gender identity that differs from the one assigned to them at birth, yet they face several barriers to care, “ranging from ignorance on our end to maybe our own biases being transposed onto these patients,” he said. “We really need to do a better job for them. We really have an obligation to provide good care for all of our patients.”
Transgender women typically seek hair removal on the face and neck as well as in the genital area to remove hairs in preparation for vaginoplasty. Transgender men typically seek hair reduction on the forearm or on the thigh, because those are graft sites in preparation for phalloplasty. As a resource for transgender care, he recommends the UCSF Transgender Care website.
As for future directions in the field, Dr. Ibrahimi predicted that hair removal devices for home use will continue to improve and become more widespread. “This raises a host of considerations, from the risk of eye damage to the risk for paradoxical hypertrichosis, and what happens when pigmented lesions get treated with these low-powered machines compared to the ones we have in our office,” he said. “I also think we’re going to see office-based devices with larger spot sizes, smarter devices that are capable of taking over more of the functions we do. I’m most excited about the potential for treating nonpigmented white hair or poorly pigmented blond or reddish hair in the future.”
Dr. Ibrahimi disclosed that he has received research funding and speaker honoraria from Lutronic, Lumenis, Cutera, and Syneron-Candela. He also holds stock in AVAVA Inc.
Omar A. Ibrahimi, MD, PhD, hears some dermatology colleagues say they don’t bother to offer laser hair removal in their practices because they figure that the procedure is under the purview of medical spas, but he sees it differently.
“I offer laser hair removal in my practice as a way to protect my patients from being picked off by medical spas,” Dr. Ibrahimi, a dermatologist and medical director of the Connecticut Skin Institute, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “These patients are going to want to get laser hair removal. If they’re not going to have the opportunity to get it at your practice, they’re going to seek it elsewhere. When they go elsewhere, they’re going to be picked off for other procedures as well.”
First developed in 1995 by R. Rox Anderson, MD, and colleagues at The Wellman Center for Photomedicine, laser hair removal has become the gold standard for permanent hair destruction, and ranks as the most common energy-based procedure performed in the world, Dr. Ibrahimi said. “Results are very long lasting and durable beyond 2 years after treatment,” he said. “These patients tend to be highly satisfied and have permanence with these treatments.”
Treatment goal, patient selection
While the target chromophore for the procedure is melanin, the goal is to destroy the stem cells located in the hair bulge and the hair bulb. “This is technically called the extended theory of selective photothermolysis, but it’s the same concept except that our target chromophore and our desired target for destruction are slightly spatially separated,” he said.
Proper patient selection is key, so a focused medical history and physical exam are essential prior to the procedure. If unwanted hair is located on the face, jawline, or chest of a female, consider and ask about potential endocrine-related dysfunctions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). “Getting those addressed can often help the hypertrichosis as well,” he said. “Another condition is explosive hypertrichosis where hair growth starts very suddenly. It’s uncommon but it’s something to think about.”
Pregnancy is not an absolute contraindication for laser hair removal, Dr. Ibrahimi continued, but he elects not to perform the procedure on pregnant patients. He also asks patients about any history of photosensitivity, active infection at the intended treatment site, keloids, or hypertrophic scarring. Past methods of hair removal also matter. “What we’re targeting is the pigment in the hair shafts,” he said. “So, if your patient is waxing or plucking or epilating or removing the hair in some manner, they’re actually removing the target chromophore.”
Patients with darker Fitzpatrick skin types can be treated safely but tanned individuals face a risk of complications because of active melanocytes. “As we approach summer in New England, we slow down the amount of hair removal we do because it’s a riskier procedure,” he said. “I recommend that my patients not get any significant amount of sun exposure a month before or after treatment.”
The color and quality of hair also drive treatment success. Black and brown terminal hairs absorb the millisecond laser energy, but white, gray, red, and light blond hairs lack adequate melanin to make them suitable target chromophores.
Excessive and unwanted body hair ranges in severity and can usually be classified as either hypertrichosis or hirsutism.
The desired clinical endpoint is perifollicular edema and erythema. Treatment parameters that can be varied with Food and Drug Administration–cleared devices include wavelength, fluence, pulse duration, spot size, and skin cooling. The most popular devices are the Alexandrite 755 nm laser; the diode 800 nm laser; and the 1064 nm Nd:YAG laser, which is safe for all skin types. “Often you have to use higher relative fluences to treat patients with the 1064 nm Nd:YAG because on the absorption spectrum, the 1064-nm wavelength has a relatively lower absorption for melanin compared to the alexandrite. However, you can still get effective, long-term hair reduction with the Nd:YAG laser,” he said (Arch Dermatol. 2008 Oct;144[10]:1323-7).
More recently, Dr. Ibrahimi and colleagues found that a 1060-nm diode laser system with multiple handpieces for permanent hair reduction was safe for all skin types, in an open label prospective study.
Higher fluences have been correlated with greater rates of permanent hair removal, but they also are more likely to cause undesired side effects. Dr. Ibrahimi advises clinicians new to laser hair removal to conduct a few different test spots and look for the desired clinical endpoint of perifollicular erythema and edema. “The highest fluence that gives you that endpoint without any adverse reactions is going to the best fluence for treatment,” he said at the meeting, which was named “Laser & Aesthetic Skin Therapy: What’s the Truth” and was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “Do a few test spots, bring them back a week later and see which ones were tolerated well without any side effects and which weren’t. That gives you a good starting point for your treatment.”
Cooling down the epidermal melanin not only keeps the procedure safe, it’s a salve for pain. “There are a variety of methods of passive and active cooling,” said Dr. Ibrahimi, a member of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery board of directors. “You can use something as simple as cold gel, but the active methods are better because once the method of passive application of cold gel warms up, you lose that cooling effect. You can use forced chilled air. Many commercial devices come with a cold tip which cools down the epidermal melanin. Others use dynamic cooling, which emit cryogen spray from a separate part of the handpiece. It hits right where the laser pulse is going to go, is absorbed by the skin, and it cools down the epidermal melanin.”
Treatment complications
Complications that can occur from treatment include pigmentary changes such as hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation. “In lighter skinned individuals, sometimes excess fluence can lead to an erythematous appearance,” he said. “In darker-skinned individuals, this often manifests as hyperpigmentation and can be very long-lasting.” Dr. Ibrahimi ranks improper technique as a complication, “because ideally you want to lay your pulses down with 10%-15% overlap during treatment,” he explained. “If you don’t overlap, you’re going to have zones that don’t get any of the laser photons. If you do, then your patient is not going to be happy with you.”
Paradoxical hypertrichosis occurs in 1%-5% of patients, typically in women from Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, or South Asian ethnic backgrounds. This tends to develop on the lateral or jawline part of the face. “Often it occurs in the setting where they come in and want these vellus hairs treated,” he said. “Somehow the laser, instead of destroying the hair shaft, triggers it and stimulates it and can’t differentiate a vellus hair from a terminal hair. This is important to discuss during your informed consent, especially when you’re treating on the lateral jawline or the sideburn area. If this happens, you can treat through it.”
Transgender patients and future directions
Dr. Ibrahimi pointed out that increasing numbers of transgender patients are visiting dermatologists seeking laser hair removal. About 16 million Americans are estimated to have a gender identity that differs from the one assigned to them at birth, yet they face several barriers to care, “ranging from ignorance on our end to maybe our own biases being transposed onto these patients,” he said. “We really need to do a better job for them. We really have an obligation to provide good care for all of our patients.”
Transgender women typically seek hair removal on the face and neck as well as in the genital area to remove hairs in preparation for vaginoplasty. Transgender men typically seek hair reduction on the forearm or on the thigh, because those are graft sites in preparation for phalloplasty. As a resource for transgender care, he recommends the UCSF Transgender Care website.
As for future directions in the field, Dr. Ibrahimi predicted that hair removal devices for home use will continue to improve and become more widespread. “This raises a host of considerations, from the risk of eye damage to the risk for paradoxical hypertrichosis, and what happens when pigmented lesions get treated with these low-powered machines compared to the ones we have in our office,” he said. “I also think we’re going to see office-based devices with larger spot sizes, smarter devices that are capable of taking over more of the functions we do. I’m most excited about the potential for treating nonpigmented white hair or poorly pigmented blond or reddish hair in the future.”
Dr. Ibrahimi disclosed that he has received research funding and speaker honoraria from Lutronic, Lumenis, Cutera, and Syneron-Candela. He also holds stock in AVAVA Inc.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE
FDA panel votes to approve Pfizer’s vaccine for children
Seventeen of the 18 members of the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) on Oct. 26 voted to recommend the 10-microgram shot for kids, which is one-third the dose given to adults.
One member, Michael Kurilla, MD, director of the division of clinical innovation at the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., abstained from voting.
If the FDA follows the recommendation, as it typically does, and issues an Emergency Use Authorization for the vaccine, the shots could be available within days.
After the FDA’s final decision, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet to make specific recommendations for its use. The CDC committee must stick closely to the conditions for use spelled out in the EUA, so their recommendations are likely to be similar to those made by the FDA. Their next meeting is scheduled for Nov. 2 and 3.
In the end, some on the panel felt uneasy with their decision.
“I voted yes primarily because I wanted to make sure that children who really need this vaccine, the Black and brown children of our country, get the vaccine,” said James Hildreth, MD, PhD, president and CEO of Meharry Medical College in Nashville.
“But to be honest, the best way to protect the health of some children will be to do nothing because they will be just fine,” he said.
Others said they were surprised by how difficult the decision had been.
“This is a much tougher one than we had expected going into it,” said committee member Eric Rubin, MD, editor and chief of the New England Journal of Medicine, during the FDA advisory committee’s meeting.
Ahead of the vote, the committee heard presentations outlining the expected benefits of vaccinating children along with potential risks.
“Children have been greatly impacted by the pandemic,” said Fiona Havers, MD, a medical officer with the CDC in Atlanta who reviewed the epidemiology of COVID-19 in kids.
In the second year of the pandemic, as more seniors have been vaccinated against the virus, COVID cases have largely shifted from older to younger age groups.
So far, there have been more than 1.9 million COVID-19 cases in children ages 5 through 11 in the United States.. Cases in kids saw a big jump in July and August with summer travel, schools reopening, and the dominance of the Delta variant.
And those are just the cases reported to the CDC. Regular testing of anonymous blood samples collected at sites across the United States indicates that 6 times as many kids have had COVID than what is reflected in official counts.
Last winter, blood sample testing showed about 13% of children had antibodies against the virus, suggesting they’d been infected. By this summer, that number had risen to 42%.
That figure clearly made an impression on many members of the committee who asked the FDA’s vaccine reviewers if they had tried to account for immunity from past infections in their modeling. They had not.
Some felt that even with a highly effective vaccine — new data presented by Pfizer showed the children’s dose was 90% effective at preventing symptomatic infections in kids — caution was warranted as much is still unknown about myocarditis, a rare side effect of the mRNA vaccines.
Myocarditis has been more common in younger age groups. It usually goes away over time but requires hospital care. It’s not known if myocarditis could have lingering effects for those who experience it.
There were no cases of myocarditis seen in Pfizer’s studies of the vaccine in children, and no other serious events were seen. Vaccine side effects reported in the Pfizer studies were mostly mild and included fatigue, headache, and pain at the injection site.
“We think we have optimized the immune response and minimized our reactions,” said William Gruber, MD, senior vice president vaccine research and clinical development at Pfizer.
But the studies didn’t include enough participants to pick up rare, but serious adverse events like myocarditis.
“We’re worried about a side effect that we can’t measure yet, but it’s probably real, and we see a benefit that isn’t the same as it is in older age groups,” said Dr. Rubin.
Benefits vs. risks
FDA modeled the benefits and risks for children under a variety of scenarios. The benefits of the vaccines to children very much depend on the amount of transmission in the community.
When transmission is high, the benefits to children — in terms of infections, hospitalizations, ICU admissions — clearly outweigh its risks.
But when COVID-19 rates are low in the community, as they were in June, FDA analysts predicted the vaccines might send more children to the hospital for myocarditis than the virus would.
The FDA noted that kids who are hospitalized for myocarditis tend not to be as ill as children with COVID-19, however.
“If the trends continue the way they are going, the emergency for children is not what we might think it would be. That was my concern,” Dr. Hildreth said.
But others warned against complacency.
“Thinking that this is going to be the end of the wave permanently may be a little overly optimistic,” said committee chairman Arnold Monto, MD, a professor of public health and epidemiology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
The majority of COVID-19 cases in children are mild. Only about 1% of kids are hospitalized for their infections, according to CDC data. But the rates of hospitalizations in kids are about 3 times higher for people of color — including Blacks, Hispanics, and Native Americans, as compared to Whites and Asian Americans.
Since the start of the pandemic, 94 children ages 5 to 11 have died, making it the eighth leading cause of death for kids this age last year.
More than 5,200 children have developed a delayed complication from their infections called Multi-System Inflammatory Syndrome (MIS-C).
MIS-C can be severe and require hospital care and can lead to myocarditis. Children ages 5 to 11 are the age group at greatest risk for this complication.
Kids can also get long COVID. There’s not a lot of data on how often this happens, though it appears to be less frequent in children than in adults.
But a survey in the United Kingdom found that 7%-8% of kids have symptoms from their infections that last longer than 12 weeks, Dr. Havers said. Symptoms that can linger for kids include fatigue, cough, muscle and joint pain, headaches, and insomnia.
More than 1 million children have been impacted by school closures so far this year, and quarantines have had lasting impacts on learning, social development, and mental health.
Even though kids aren’t usually COVID superspreaders, they can still pass the infection on to others.
“What is clear is that secondary transmission from children, both to other children and to adults, does occur,” Dr. Havers said.
For that reason, they can continue the spread of the virus and give it opportunities to mutate and become more dangerous.
Safety monitoring to continue
Some committee members referenced thousands of letters they had received within the past few days urging them to vote against the vaccine.
Jay Portnoy, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Children’s Mercy Hospital in Kansas City, Mo., said he had personally received about 4,000 emails.
“But I feel like I need to also represent the consumers, the parents that I see every day in the clinic who are terrified of sending their children to school because they’re not protected against COVID,” he said, explaining his vote to recommend authorization.
“Our kids are going to be dealing with this virus for many years to come. It’s going to come repeatedly. Getting this vaccine is just the first step that they can take to protect themselves from having bad outcomes,” Dr. Portnoy said.
Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, reminded members of the committee that there were several government surveillance systems in place to catch any potential safety issues in near real time.
“I really appreciate very much the concern here. The safety monitoring of this vaccine will continue,” Dr. Marks said. “I do view this as one of our greatest responsibilities.”
“I really am so grateful that we had this discussion and voted to approve,” said Capt. Amanda Cohn, MD, chief medical officer at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
“I think the benefits in this age group really are super important even if they are lower than for other age groups.”
This article was updated 10/27/21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Seventeen of the 18 members of the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) on Oct. 26 voted to recommend the 10-microgram shot for kids, which is one-third the dose given to adults.
One member, Michael Kurilla, MD, director of the division of clinical innovation at the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., abstained from voting.
If the FDA follows the recommendation, as it typically does, and issues an Emergency Use Authorization for the vaccine, the shots could be available within days.
After the FDA’s final decision, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet to make specific recommendations for its use. The CDC committee must stick closely to the conditions for use spelled out in the EUA, so their recommendations are likely to be similar to those made by the FDA. Their next meeting is scheduled for Nov. 2 and 3.
In the end, some on the panel felt uneasy with their decision.
“I voted yes primarily because I wanted to make sure that children who really need this vaccine, the Black and brown children of our country, get the vaccine,” said James Hildreth, MD, PhD, president and CEO of Meharry Medical College in Nashville.
“But to be honest, the best way to protect the health of some children will be to do nothing because they will be just fine,” he said.
Others said they were surprised by how difficult the decision had been.
“This is a much tougher one than we had expected going into it,” said committee member Eric Rubin, MD, editor and chief of the New England Journal of Medicine, during the FDA advisory committee’s meeting.
Ahead of the vote, the committee heard presentations outlining the expected benefits of vaccinating children along with potential risks.
“Children have been greatly impacted by the pandemic,” said Fiona Havers, MD, a medical officer with the CDC in Atlanta who reviewed the epidemiology of COVID-19 in kids.
In the second year of the pandemic, as more seniors have been vaccinated against the virus, COVID cases have largely shifted from older to younger age groups.
So far, there have been more than 1.9 million COVID-19 cases in children ages 5 through 11 in the United States.. Cases in kids saw a big jump in July and August with summer travel, schools reopening, and the dominance of the Delta variant.
And those are just the cases reported to the CDC. Regular testing of anonymous blood samples collected at sites across the United States indicates that 6 times as many kids have had COVID than what is reflected in official counts.
Last winter, blood sample testing showed about 13% of children had antibodies against the virus, suggesting they’d been infected. By this summer, that number had risen to 42%.
That figure clearly made an impression on many members of the committee who asked the FDA’s vaccine reviewers if they had tried to account for immunity from past infections in their modeling. They had not.
Some felt that even with a highly effective vaccine — new data presented by Pfizer showed the children’s dose was 90% effective at preventing symptomatic infections in kids — caution was warranted as much is still unknown about myocarditis, a rare side effect of the mRNA vaccines.
Myocarditis has been more common in younger age groups. It usually goes away over time but requires hospital care. It’s not known if myocarditis could have lingering effects for those who experience it.
There were no cases of myocarditis seen in Pfizer’s studies of the vaccine in children, and no other serious events were seen. Vaccine side effects reported in the Pfizer studies were mostly mild and included fatigue, headache, and pain at the injection site.
“We think we have optimized the immune response and minimized our reactions,” said William Gruber, MD, senior vice president vaccine research and clinical development at Pfizer.
But the studies didn’t include enough participants to pick up rare, but serious adverse events like myocarditis.
“We’re worried about a side effect that we can’t measure yet, but it’s probably real, and we see a benefit that isn’t the same as it is in older age groups,” said Dr. Rubin.
Benefits vs. risks
FDA modeled the benefits and risks for children under a variety of scenarios. The benefits of the vaccines to children very much depend on the amount of transmission in the community.
When transmission is high, the benefits to children — in terms of infections, hospitalizations, ICU admissions — clearly outweigh its risks.
But when COVID-19 rates are low in the community, as they were in June, FDA analysts predicted the vaccines might send more children to the hospital for myocarditis than the virus would.
The FDA noted that kids who are hospitalized for myocarditis tend not to be as ill as children with COVID-19, however.
“If the trends continue the way they are going, the emergency for children is not what we might think it would be. That was my concern,” Dr. Hildreth said.
But others warned against complacency.
“Thinking that this is going to be the end of the wave permanently may be a little overly optimistic,” said committee chairman Arnold Monto, MD, a professor of public health and epidemiology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
The majority of COVID-19 cases in children are mild. Only about 1% of kids are hospitalized for their infections, according to CDC data. But the rates of hospitalizations in kids are about 3 times higher for people of color — including Blacks, Hispanics, and Native Americans, as compared to Whites and Asian Americans.
Since the start of the pandemic, 94 children ages 5 to 11 have died, making it the eighth leading cause of death for kids this age last year.
More than 5,200 children have developed a delayed complication from their infections called Multi-System Inflammatory Syndrome (MIS-C).
MIS-C can be severe and require hospital care and can lead to myocarditis. Children ages 5 to 11 are the age group at greatest risk for this complication.
Kids can also get long COVID. There’s not a lot of data on how often this happens, though it appears to be less frequent in children than in adults.
But a survey in the United Kingdom found that 7%-8% of kids have symptoms from their infections that last longer than 12 weeks, Dr. Havers said. Symptoms that can linger for kids include fatigue, cough, muscle and joint pain, headaches, and insomnia.
More than 1 million children have been impacted by school closures so far this year, and quarantines have had lasting impacts on learning, social development, and mental health.
Even though kids aren’t usually COVID superspreaders, they can still pass the infection on to others.
“What is clear is that secondary transmission from children, both to other children and to adults, does occur,” Dr. Havers said.
For that reason, they can continue the spread of the virus and give it opportunities to mutate and become more dangerous.
Safety monitoring to continue
Some committee members referenced thousands of letters they had received within the past few days urging them to vote against the vaccine.
Jay Portnoy, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Children’s Mercy Hospital in Kansas City, Mo., said he had personally received about 4,000 emails.
“But I feel like I need to also represent the consumers, the parents that I see every day in the clinic who are terrified of sending their children to school because they’re not protected against COVID,” he said, explaining his vote to recommend authorization.
“Our kids are going to be dealing with this virus for many years to come. It’s going to come repeatedly. Getting this vaccine is just the first step that they can take to protect themselves from having bad outcomes,” Dr. Portnoy said.
Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, reminded members of the committee that there were several government surveillance systems in place to catch any potential safety issues in near real time.
“I really appreciate very much the concern here. The safety monitoring of this vaccine will continue,” Dr. Marks said. “I do view this as one of our greatest responsibilities.”
“I really am so grateful that we had this discussion and voted to approve,” said Capt. Amanda Cohn, MD, chief medical officer at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
“I think the benefits in this age group really are super important even if they are lower than for other age groups.”
This article was updated 10/27/21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Seventeen of the 18 members of the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) on Oct. 26 voted to recommend the 10-microgram shot for kids, which is one-third the dose given to adults.
One member, Michael Kurilla, MD, director of the division of clinical innovation at the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., abstained from voting.
If the FDA follows the recommendation, as it typically does, and issues an Emergency Use Authorization for the vaccine, the shots could be available within days.
After the FDA’s final decision, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet to make specific recommendations for its use. The CDC committee must stick closely to the conditions for use spelled out in the EUA, so their recommendations are likely to be similar to those made by the FDA. Their next meeting is scheduled for Nov. 2 and 3.
In the end, some on the panel felt uneasy with their decision.
“I voted yes primarily because I wanted to make sure that children who really need this vaccine, the Black and brown children of our country, get the vaccine,” said James Hildreth, MD, PhD, president and CEO of Meharry Medical College in Nashville.
“But to be honest, the best way to protect the health of some children will be to do nothing because they will be just fine,” he said.
Others said they were surprised by how difficult the decision had been.
“This is a much tougher one than we had expected going into it,” said committee member Eric Rubin, MD, editor and chief of the New England Journal of Medicine, during the FDA advisory committee’s meeting.
Ahead of the vote, the committee heard presentations outlining the expected benefits of vaccinating children along with potential risks.
“Children have been greatly impacted by the pandemic,” said Fiona Havers, MD, a medical officer with the CDC in Atlanta who reviewed the epidemiology of COVID-19 in kids.
In the second year of the pandemic, as more seniors have been vaccinated against the virus, COVID cases have largely shifted from older to younger age groups.
So far, there have been more than 1.9 million COVID-19 cases in children ages 5 through 11 in the United States.. Cases in kids saw a big jump in July and August with summer travel, schools reopening, and the dominance of the Delta variant.
And those are just the cases reported to the CDC. Regular testing of anonymous blood samples collected at sites across the United States indicates that 6 times as many kids have had COVID than what is reflected in official counts.
Last winter, blood sample testing showed about 13% of children had antibodies against the virus, suggesting they’d been infected. By this summer, that number had risen to 42%.
That figure clearly made an impression on many members of the committee who asked the FDA’s vaccine reviewers if they had tried to account for immunity from past infections in their modeling. They had not.
Some felt that even with a highly effective vaccine — new data presented by Pfizer showed the children’s dose was 90% effective at preventing symptomatic infections in kids — caution was warranted as much is still unknown about myocarditis, a rare side effect of the mRNA vaccines.
Myocarditis has been more common in younger age groups. It usually goes away over time but requires hospital care. It’s not known if myocarditis could have lingering effects for those who experience it.
There were no cases of myocarditis seen in Pfizer’s studies of the vaccine in children, and no other serious events were seen. Vaccine side effects reported in the Pfizer studies were mostly mild and included fatigue, headache, and pain at the injection site.
“We think we have optimized the immune response and minimized our reactions,” said William Gruber, MD, senior vice president vaccine research and clinical development at Pfizer.
But the studies didn’t include enough participants to pick up rare, but serious adverse events like myocarditis.
“We’re worried about a side effect that we can’t measure yet, but it’s probably real, and we see a benefit that isn’t the same as it is in older age groups,” said Dr. Rubin.
Benefits vs. risks
FDA modeled the benefits and risks for children under a variety of scenarios. The benefits of the vaccines to children very much depend on the amount of transmission in the community.
When transmission is high, the benefits to children — in terms of infections, hospitalizations, ICU admissions — clearly outweigh its risks.
But when COVID-19 rates are low in the community, as they were in June, FDA analysts predicted the vaccines might send more children to the hospital for myocarditis than the virus would.
The FDA noted that kids who are hospitalized for myocarditis tend not to be as ill as children with COVID-19, however.
“If the trends continue the way they are going, the emergency for children is not what we might think it would be. That was my concern,” Dr. Hildreth said.
But others warned against complacency.
“Thinking that this is going to be the end of the wave permanently may be a little overly optimistic,” said committee chairman Arnold Monto, MD, a professor of public health and epidemiology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
The majority of COVID-19 cases in children are mild. Only about 1% of kids are hospitalized for their infections, according to CDC data. But the rates of hospitalizations in kids are about 3 times higher for people of color — including Blacks, Hispanics, and Native Americans, as compared to Whites and Asian Americans.
Since the start of the pandemic, 94 children ages 5 to 11 have died, making it the eighth leading cause of death for kids this age last year.
More than 5,200 children have developed a delayed complication from their infections called Multi-System Inflammatory Syndrome (MIS-C).
MIS-C can be severe and require hospital care and can lead to myocarditis. Children ages 5 to 11 are the age group at greatest risk for this complication.
Kids can also get long COVID. There’s not a lot of data on how often this happens, though it appears to be less frequent in children than in adults.
But a survey in the United Kingdom found that 7%-8% of kids have symptoms from their infections that last longer than 12 weeks, Dr. Havers said. Symptoms that can linger for kids include fatigue, cough, muscle and joint pain, headaches, and insomnia.
More than 1 million children have been impacted by school closures so far this year, and quarantines have had lasting impacts on learning, social development, and mental health.
Even though kids aren’t usually COVID superspreaders, they can still pass the infection on to others.
“What is clear is that secondary transmission from children, both to other children and to adults, does occur,” Dr. Havers said.
For that reason, they can continue the spread of the virus and give it opportunities to mutate and become more dangerous.
Safety monitoring to continue
Some committee members referenced thousands of letters they had received within the past few days urging them to vote against the vaccine.
Jay Portnoy, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Children’s Mercy Hospital in Kansas City, Mo., said he had personally received about 4,000 emails.
“But I feel like I need to also represent the consumers, the parents that I see every day in the clinic who are terrified of sending their children to school because they’re not protected against COVID,” he said, explaining his vote to recommend authorization.
“Our kids are going to be dealing with this virus for many years to come. It’s going to come repeatedly. Getting this vaccine is just the first step that they can take to protect themselves from having bad outcomes,” Dr. Portnoy said.
Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, reminded members of the committee that there were several government surveillance systems in place to catch any potential safety issues in near real time.
“I really appreciate very much the concern here. The safety monitoring of this vaccine will continue,” Dr. Marks said. “I do view this as one of our greatest responsibilities.”
“I really am so grateful that we had this discussion and voted to approve,” said Capt. Amanda Cohn, MD, chief medical officer at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
“I think the benefits in this age group really are super important even if they are lower than for other age groups.”
This article was updated 10/27/21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Major increase seen in cosmeceutical alternatives to topical hydroquinone
along with new strategies to improve their efficacy, according to a report at the Skin of Color Update 2021.
“Ten or 15 years ago, I was showing a slide with five [alternatives to hydroquinone]. Now there are dozens,” reported Heather Woolery-Lloyd, MD, director of the skin of color division in the department of dermatology at the University of Miami.
The growth in alternatives to hydroquinone is timely. After threats to do so for more than a decade, the Food and Drug Administration finally banned hydroquinone from OTC products in 2020. The ban was folded into the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act passed in March of 2020 and then implemented the following September.
Until the ban of hydroquinone, OTC products with this compound were widely sought by many individuals with darker skin tones to self-treat melasma and other forms of hyperpigmentation, according to Dr. Woolery-Lloyd. Hydroquinone is still available in prescription products, but she is often asked for OTC alternatives, and she says the list is long and getting longer.
Niacinamide
Detailing the products she has been recommending most frequently as substitutes, Dr. Woolery-Lloyd reported that several are supported by high quality studies. One example is niacinamide.
Of the several controlled studies she cited, one double-blind randomized trial found niacinamide to be equivalent to hydroquinone for melasma on the basis of colorimetric measures. The study compared 4% niacinamide cream applied on one side of the face with 4% hydroquinone cream applied on the other side in 27 patients with melasma. Although the proportion of responses rated good or excellent on a subjective basis was lower with niacinamide (44% vs. 55%), the difference was not statistically significant and niacinamide cream was clearly active, producing objective improvements in mast cell infiltrate and solar elastosis in melasma skin as well. Both were well tolerated.
In other studies, niacinamide has been shown to be effective in the treatment of melasma when combined with other active agents such as tranexamic acid, said Dr. Woolery-Lloyd, who added that OTC products containing niacinamide are now “among my favorites” when directing patients to cosmeceuticals for hyperpigmentation.
Topical vitamin C
Topical vitamin C or ascorbic acid is another. Like niacinamide, topical vitamin C has also been compared with hydroquinone in a double-blind, randomized trial. Although the niacinamide trial and this study were performed 10 or more years ago, these data have new relevance with the ban of OTC hydroquinone.
In the study, 5% ascorbic acid cream on one side of the face was compared with 4% hydroquinone cream, applied on the other side, in 16 women with melasma. Again, there were no statistical differences in colorimetric measures, but good to excellent results were reported for 93% of the sides of the face treated with hydroquinone versus 62.5% of the sides treated with vitamin C (P < .05). “Hydroquinone performed better, but the vitamin C was active and very well tolerated,” Dr. Woolery-Lloyd said.
However, the ascorbic acid cream was better tolerated, with a far lower rate of adverse events (6.2% vs. 68.7%), an advantage that makes it easy to recommend to patients, said Dr. Woolery-Lloyd, who now uses it frequently in her own practice.
Liquiritin, a licorice extract, is another lightening agent increasingly included in OTC products that she also recommends. In two older studies in medical journals published in Pakistan, both the 2% and 4% strengths of liquiritin cream outperformed hydroquinone on the basis of a Melasma Area and Severity Index (MASI) rating. The liquiritin cream was well tolerated in both studies.
Azelaic acid, tranexamic acid
OTC products containing azelaic acid are also effective for hyperpigmentation based on published trials in which they were compared with hydroquinone for treating melasma. In one study of 29 women with melasma cited by Dr. Woolery-Lloyd, 20% azelaic acid cream was more effective than hydroquinone 4% cream after 2 months of treatment on the basis of the mean MASI score (6.2 vs. 3.8).
The list also includes cysteamine, silymarin, and tranexamic acid.
In the case of tranexamic acid, Dr. Woolery-Lloyd cited a relatively recent study of 60 patients with melasma, comparing two strategies for applying tranexamic acid to treatment with hydroquinone over 12 weeks. Compared with 2% hydroquinone (applied nightly) or 1.8% liposomal tranexamic acid (applied twice a day), 5% tranexamic acid solution with microneedling (weekly) had a slightly greater rate of success defined as more than a 50% improvement in hyperpigmentation in an Asian population (30%, 27.8%, and 33.3%, respectively).
“Microneedling is a newer technology that appears to be effective at improving absorption,” said Dr. Woolery-Lloyd. She predicts that microneedling will be used with increasing frequency in combination with topical cosmeceuticals.
She also predicted that these topical agents will be increasingly employed in combinations as the field of cosmeceuticals becomes increasingly more sophisticated. “When it comes to skin quality, cosmeceuticals remain our first-line therapy, especially in skin of color,” she said.
The rapid growth and utility of OTC cosmeceuticals is an area that dermatologists need to be following, according to Darius Mehregan, MD, chair of the department of dermatology, Wayne State University, Detroit, who was senior author of an article published last year that reviewed the ingredients of popular OTC cosmeceuticals.
“Our patients have a great interest in cosmeceuticals and are looking to us for guidance. I think we have a responsibility to help them identify products supported by evidence and to warn them about potential side effects,” Dr. Mehregan, who was not at the meeting, said in an interview.
He agreed that the removal of hydroquinone from OTC products will create a specific need in the area of cosmeceuticals.
“Hydroquinone has for a long time been one of the most effective agents in OTC products for melasma, so patients are going to be looking for alternatives. Identifying which drugs have shown efficacy in controlled studies will be very helpful,” he said.
Dr. Woolery-Lloyd reports financial relationships with Ortho Dermatologics, L’Oréal, Galderma, Allergan, and Somabella Laboratories. Dr. Mehregan reports no potential conflicts of interest.
along with new strategies to improve their efficacy, according to a report at the Skin of Color Update 2021.
“Ten or 15 years ago, I was showing a slide with five [alternatives to hydroquinone]. Now there are dozens,” reported Heather Woolery-Lloyd, MD, director of the skin of color division in the department of dermatology at the University of Miami.
The growth in alternatives to hydroquinone is timely. After threats to do so for more than a decade, the Food and Drug Administration finally banned hydroquinone from OTC products in 2020. The ban was folded into the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act passed in March of 2020 and then implemented the following September.
Until the ban of hydroquinone, OTC products with this compound were widely sought by many individuals with darker skin tones to self-treat melasma and other forms of hyperpigmentation, according to Dr. Woolery-Lloyd. Hydroquinone is still available in prescription products, but she is often asked for OTC alternatives, and she says the list is long and getting longer.
Niacinamide
Detailing the products she has been recommending most frequently as substitutes, Dr. Woolery-Lloyd reported that several are supported by high quality studies. One example is niacinamide.
Of the several controlled studies she cited, one double-blind randomized trial found niacinamide to be equivalent to hydroquinone for melasma on the basis of colorimetric measures. The study compared 4% niacinamide cream applied on one side of the face with 4% hydroquinone cream applied on the other side in 27 patients with melasma. Although the proportion of responses rated good or excellent on a subjective basis was lower with niacinamide (44% vs. 55%), the difference was not statistically significant and niacinamide cream was clearly active, producing objective improvements in mast cell infiltrate and solar elastosis in melasma skin as well. Both were well tolerated.
In other studies, niacinamide has been shown to be effective in the treatment of melasma when combined with other active agents such as tranexamic acid, said Dr. Woolery-Lloyd, who added that OTC products containing niacinamide are now “among my favorites” when directing patients to cosmeceuticals for hyperpigmentation.
Topical vitamin C
Topical vitamin C or ascorbic acid is another. Like niacinamide, topical vitamin C has also been compared with hydroquinone in a double-blind, randomized trial. Although the niacinamide trial and this study were performed 10 or more years ago, these data have new relevance with the ban of OTC hydroquinone.
In the study, 5% ascorbic acid cream on one side of the face was compared with 4% hydroquinone cream, applied on the other side, in 16 women with melasma. Again, there were no statistical differences in colorimetric measures, but good to excellent results were reported for 93% of the sides of the face treated with hydroquinone versus 62.5% of the sides treated with vitamin C (P < .05). “Hydroquinone performed better, but the vitamin C was active and very well tolerated,” Dr. Woolery-Lloyd said.
However, the ascorbic acid cream was better tolerated, with a far lower rate of adverse events (6.2% vs. 68.7%), an advantage that makes it easy to recommend to patients, said Dr. Woolery-Lloyd, who now uses it frequently in her own practice.
Liquiritin, a licorice extract, is another lightening agent increasingly included in OTC products that she also recommends. In two older studies in medical journals published in Pakistan, both the 2% and 4% strengths of liquiritin cream outperformed hydroquinone on the basis of a Melasma Area and Severity Index (MASI) rating. The liquiritin cream was well tolerated in both studies.
Azelaic acid, tranexamic acid
OTC products containing azelaic acid are also effective for hyperpigmentation based on published trials in which they were compared with hydroquinone for treating melasma. In one study of 29 women with melasma cited by Dr. Woolery-Lloyd, 20% azelaic acid cream was more effective than hydroquinone 4% cream after 2 months of treatment on the basis of the mean MASI score (6.2 vs. 3.8).
The list also includes cysteamine, silymarin, and tranexamic acid.
In the case of tranexamic acid, Dr. Woolery-Lloyd cited a relatively recent study of 60 patients with melasma, comparing two strategies for applying tranexamic acid to treatment with hydroquinone over 12 weeks. Compared with 2% hydroquinone (applied nightly) or 1.8% liposomal tranexamic acid (applied twice a day), 5% tranexamic acid solution with microneedling (weekly) had a slightly greater rate of success defined as more than a 50% improvement in hyperpigmentation in an Asian population (30%, 27.8%, and 33.3%, respectively).
“Microneedling is a newer technology that appears to be effective at improving absorption,” said Dr. Woolery-Lloyd. She predicts that microneedling will be used with increasing frequency in combination with topical cosmeceuticals.
She also predicted that these topical agents will be increasingly employed in combinations as the field of cosmeceuticals becomes increasingly more sophisticated. “When it comes to skin quality, cosmeceuticals remain our first-line therapy, especially in skin of color,” she said.
The rapid growth and utility of OTC cosmeceuticals is an area that dermatologists need to be following, according to Darius Mehregan, MD, chair of the department of dermatology, Wayne State University, Detroit, who was senior author of an article published last year that reviewed the ingredients of popular OTC cosmeceuticals.
“Our patients have a great interest in cosmeceuticals and are looking to us for guidance. I think we have a responsibility to help them identify products supported by evidence and to warn them about potential side effects,” Dr. Mehregan, who was not at the meeting, said in an interview.
He agreed that the removal of hydroquinone from OTC products will create a specific need in the area of cosmeceuticals.
“Hydroquinone has for a long time been one of the most effective agents in OTC products for melasma, so patients are going to be looking for alternatives. Identifying which drugs have shown efficacy in controlled studies will be very helpful,” he said.
Dr. Woolery-Lloyd reports financial relationships with Ortho Dermatologics, L’Oréal, Galderma, Allergan, and Somabella Laboratories. Dr. Mehregan reports no potential conflicts of interest.
along with new strategies to improve their efficacy, according to a report at the Skin of Color Update 2021.
“Ten or 15 years ago, I was showing a slide with five [alternatives to hydroquinone]. Now there are dozens,” reported Heather Woolery-Lloyd, MD, director of the skin of color division in the department of dermatology at the University of Miami.
The growth in alternatives to hydroquinone is timely. After threats to do so for more than a decade, the Food and Drug Administration finally banned hydroquinone from OTC products in 2020. The ban was folded into the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act passed in March of 2020 and then implemented the following September.
Until the ban of hydroquinone, OTC products with this compound were widely sought by many individuals with darker skin tones to self-treat melasma and other forms of hyperpigmentation, according to Dr. Woolery-Lloyd. Hydroquinone is still available in prescription products, but she is often asked for OTC alternatives, and she says the list is long and getting longer.
Niacinamide
Detailing the products she has been recommending most frequently as substitutes, Dr. Woolery-Lloyd reported that several are supported by high quality studies. One example is niacinamide.
Of the several controlled studies she cited, one double-blind randomized trial found niacinamide to be equivalent to hydroquinone for melasma on the basis of colorimetric measures. The study compared 4% niacinamide cream applied on one side of the face with 4% hydroquinone cream applied on the other side in 27 patients with melasma. Although the proportion of responses rated good or excellent on a subjective basis was lower with niacinamide (44% vs. 55%), the difference was not statistically significant and niacinamide cream was clearly active, producing objective improvements in mast cell infiltrate and solar elastosis in melasma skin as well. Both were well tolerated.
In other studies, niacinamide has been shown to be effective in the treatment of melasma when combined with other active agents such as tranexamic acid, said Dr. Woolery-Lloyd, who added that OTC products containing niacinamide are now “among my favorites” when directing patients to cosmeceuticals for hyperpigmentation.
Topical vitamin C
Topical vitamin C or ascorbic acid is another. Like niacinamide, topical vitamin C has also been compared with hydroquinone in a double-blind, randomized trial. Although the niacinamide trial and this study were performed 10 or more years ago, these data have new relevance with the ban of OTC hydroquinone.
In the study, 5% ascorbic acid cream on one side of the face was compared with 4% hydroquinone cream, applied on the other side, in 16 women with melasma. Again, there were no statistical differences in colorimetric measures, but good to excellent results were reported for 93% of the sides of the face treated with hydroquinone versus 62.5% of the sides treated with vitamin C (P < .05). “Hydroquinone performed better, but the vitamin C was active and very well tolerated,” Dr. Woolery-Lloyd said.
However, the ascorbic acid cream was better tolerated, with a far lower rate of adverse events (6.2% vs. 68.7%), an advantage that makes it easy to recommend to patients, said Dr. Woolery-Lloyd, who now uses it frequently in her own practice.
Liquiritin, a licorice extract, is another lightening agent increasingly included in OTC products that she also recommends. In two older studies in medical journals published in Pakistan, both the 2% and 4% strengths of liquiritin cream outperformed hydroquinone on the basis of a Melasma Area and Severity Index (MASI) rating. The liquiritin cream was well tolerated in both studies.
Azelaic acid, tranexamic acid
OTC products containing azelaic acid are also effective for hyperpigmentation based on published trials in which they were compared with hydroquinone for treating melasma. In one study of 29 women with melasma cited by Dr. Woolery-Lloyd, 20% azelaic acid cream was more effective than hydroquinone 4% cream after 2 months of treatment on the basis of the mean MASI score (6.2 vs. 3.8).
The list also includes cysteamine, silymarin, and tranexamic acid.
In the case of tranexamic acid, Dr. Woolery-Lloyd cited a relatively recent study of 60 patients with melasma, comparing two strategies for applying tranexamic acid to treatment with hydroquinone over 12 weeks. Compared with 2% hydroquinone (applied nightly) or 1.8% liposomal tranexamic acid (applied twice a day), 5% tranexamic acid solution with microneedling (weekly) had a slightly greater rate of success defined as more than a 50% improvement in hyperpigmentation in an Asian population (30%, 27.8%, and 33.3%, respectively).
“Microneedling is a newer technology that appears to be effective at improving absorption,” said Dr. Woolery-Lloyd. She predicts that microneedling will be used with increasing frequency in combination with topical cosmeceuticals.
She also predicted that these topical agents will be increasingly employed in combinations as the field of cosmeceuticals becomes increasingly more sophisticated. “When it comes to skin quality, cosmeceuticals remain our first-line therapy, especially in skin of color,” she said.
The rapid growth and utility of OTC cosmeceuticals is an area that dermatologists need to be following, according to Darius Mehregan, MD, chair of the department of dermatology, Wayne State University, Detroit, who was senior author of an article published last year that reviewed the ingredients of popular OTC cosmeceuticals.
“Our patients have a great interest in cosmeceuticals and are looking to us for guidance. I think we have a responsibility to help them identify products supported by evidence and to warn them about potential side effects,” Dr. Mehregan, who was not at the meeting, said in an interview.
He agreed that the removal of hydroquinone from OTC products will create a specific need in the area of cosmeceuticals.
“Hydroquinone has for a long time been one of the most effective agents in OTC products for melasma, so patients are going to be looking for alternatives. Identifying which drugs have shown efficacy in controlled studies will be very helpful,” he said.
Dr. Woolery-Lloyd reports financial relationships with Ortho Dermatologics, L’Oréal, Galderma, Allergan, and Somabella Laboratories. Dr. Mehregan reports no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM SOC 2021
Unvaccinated people likely to catch COVID repeatedly
according to a recent study published in The Lancet Microbe.
Since COVID-19 hasn’t existed for long enough to perform a long-term study, researchers at Yale University and the University of North Carolina at Charlotte looked at reinfection data for six other human-infecting coronaviruses, including SARS and MERS.
“Reinfection can reasonably happen in three months or less,” Jeffrey Townsend, PhD, lead study author and a biostatistics professor at the Yale School of Public Health, said in a statement.
“Therefore, those who have been naturally infected should get vaccinated,” he said. “Previous infection alone can offer very little long-term protection against subsequent infections.”
The research team looked at post-infection data for six coronaviruses between 1984-2020 and found reinfection ranged from 128 days to 28 years. They calculated that reinfection with COVID-19 would likely occur between 3 months to 5 years after peak antibody response, with an average of 16 months. This is less than half the duration seen for other coronaviruses that circulate among humans.
The risk of COVID-19 reinfection is about 5% at three months, which jumps to 50% after 17 months, the research team found. Reinfection could become increasingly common as immunity wanes and new variants develop, they said.
“We tend to think about immunity as being immune or not immune. Our study cautions that we instead should be more focused on the risk of reinfection through time,” Alex Dornburg, PhD, senior study author and assistant professor of bioinformatics and genomics at UNC, said in the statement.
“As new variants arise, previous immune responses become less effective at combating the virus,” he said. “Those who were naturally infected early in the pandemic are increasingly likely to become reinfected in the near future.”
Study estimates are based on average times of declining immunity across different coronaviruses, the researchers told the Yale Daily News. At the individual level, people have different levels of immunity, which can provide shorter or longer duration of protection based on immune status, immunity within a community, age, underlying health conditions, environmental exposure, and other factors.
The research team said that preventive health measures and global distribution of vaccines will be “critical” in minimizing reinfection and COVID-19 deaths. In areas with low vaccination rates, for instance, unvaccinated people should continue safety practices such as social distancing, wearing masks, and proper indoor ventilation to avoid reinfection.
“We need to be very aware of the fact that this disease is likely to be circulating over the long term and that we don’t have this long-term immunity that many people seem to be hoping to rely on in order to protect them from disease,” Dr. Townsend told the newspaper.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according to a recent study published in The Lancet Microbe.
Since COVID-19 hasn’t existed for long enough to perform a long-term study, researchers at Yale University and the University of North Carolina at Charlotte looked at reinfection data for six other human-infecting coronaviruses, including SARS and MERS.
“Reinfection can reasonably happen in three months or less,” Jeffrey Townsend, PhD, lead study author and a biostatistics professor at the Yale School of Public Health, said in a statement.
“Therefore, those who have been naturally infected should get vaccinated,” he said. “Previous infection alone can offer very little long-term protection against subsequent infections.”
The research team looked at post-infection data for six coronaviruses between 1984-2020 and found reinfection ranged from 128 days to 28 years. They calculated that reinfection with COVID-19 would likely occur between 3 months to 5 years after peak antibody response, with an average of 16 months. This is less than half the duration seen for other coronaviruses that circulate among humans.
The risk of COVID-19 reinfection is about 5% at three months, which jumps to 50% after 17 months, the research team found. Reinfection could become increasingly common as immunity wanes and new variants develop, they said.
“We tend to think about immunity as being immune or not immune. Our study cautions that we instead should be more focused on the risk of reinfection through time,” Alex Dornburg, PhD, senior study author and assistant professor of bioinformatics and genomics at UNC, said in the statement.
“As new variants arise, previous immune responses become less effective at combating the virus,” he said. “Those who were naturally infected early in the pandemic are increasingly likely to become reinfected in the near future.”
Study estimates are based on average times of declining immunity across different coronaviruses, the researchers told the Yale Daily News. At the individual level, people have different levels of immunity, which can provide shorter or longer duration of protection based on immune status, immunity within a community, age, underlying health conditions, environmental exposure, and other factors.
The research team said that preventive health measures and global distribution of vaccines will be “critical” in minimizing reinfection and COVID-19 deaths. In areas with low vaccination rates, for instance, unvaccinated people should continue safety practices such as social distancing, wearing masks, and proper indoor ventilation to avoid reinfection.
“We need to be very aware of the fact that this disease is likely to be circulating over the long term and that we don’t have this long-term immunity that many people seem to be hoping to rely on in order to protect them from disease,” Dr. Townsend told the newspaper.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according to a recent study published in The Lancet Microbe.
Since COVID-19 hasn’t existed for long enough to perform a long-term study, researchers at Yale University and the University of North Carolina at Charlotte looked at reinfection data for six other human-infecting coronaviruses, including SARS and MERS.
“Reinfection can reasonably happen in three months or less,” Jeffrey Townsend, PhD, lead study author and a biostatistics professor at the Yale School of Public Health, said in a statement.
“Therefore, those who have been naturally infected should get vaccinated,” he said. “Previous infection alone can offer very little long-term protection against subsequent infections.”
The research team looked at post-infection data for six coronaviruses between 1984-2020 and found reinfection ranged from 128 days to 28 years. They calculated that reinfection with COVID-19 would likely occur between 3 months to 5 years after peak antibody response, with an average of 16 months. This is less than half the duration seen for other coronaviruses that circulate among humans.
The risk of COVID-19 reinfection is about 5% at three months, which jumps to 50% after 17 months, the research team found. Reinfection could become increasingly common as immunity wanes and new variants develop, they said.
“We tend to think about immunity as being immune or not immune. Our study cautions that we instead should be more focused on the risk of reinfection through time,” Alex Dornburg, PhD, senior study author and assistant professor of bioinformatics and genomics at UNC, said in the statement.
“As new variants arise, previous immune responses become less effective at combating the virus,” he said. “Those who were naturally infected early in the pandemic are increasingly likely to become reinfected in the near future.”
Study estimates are based on average times of declining immunity across different coronaviruses, the researchers told the Yale Daily News. At the individual level, people have different levels of immunity, which can provide shorter or longer duration of protection based on immune status, immunity within a community, age, underlying health conditions, environmental exposure, and other factors.
The research team said that preventive health measures and global distribution of vaccines will be “critical” in minimizing reinfection and COVID-19 deaths. In areas with low vaccination rates, for instance, unvaccinated people should continue safety practices such as social distancing, wearing masks, and proper indoor ventilation to avoid reinfection.
“We need to be very aware of the fact that this disease is likely to be circulating over the long term and that we don’t have this long-term immunity that many people seem to be hoping to rely on in order to protect them from disease,” Dr. Townsend told the newspaper.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Transgender use of dermatologic procedures has strong gender tilt
, according to the results of a recent survey.
Transfeminine persons – those assigned male at birth – were much more likely to report a previous dermatologic procedure, compared with transmasculine respondents, by a margin of 64.9%-7.5%, Laura Ragmanauskaite, MD, and associates reported.
“Hair removal was the most frequently reported procedure type, with electrolysis being more common than laser hair removal,” they said, noting that “previous research on hair removal treatments among gender minority persons did not detect differences in the use of electrolysis and laser hair removal.”
Just under one-third of all respondents (32.9%) said that they had undergone electrolysis and 4.6% reported previous laser hair removal. For electrolysis, that works out to 59.4% of transfeminine and 6.1% of transmasculine respondents, while 9.1% of all transfeminine and no transmasculine persons had received laser hair removal, Dr. Ragmanauskaite of the department of dermatology, Emory University, Atlanta, and her coauthors said.
Those who had undergone gender-affirming surgery were significantly more likely to report electrolysis (78.6%) than were persons who had received no gender-affirming surgery or hormone therapy alone (47.4%), a statistically significant difference (P < .01). All of the other, less common procedures included in the online survey – 696 responses were received from 350 transfeminine and 346 transmasculine persons participating in the Study of Transition, Outcomes, and Gender – were reported more often by the transfeminine respondents. The procedure with the closest gender distribution was body contouring, reported by nine transfeminine and six transmasculine persons, the researchers said.
Use of dermal fillers was even less common (2.8% among all respondents, all transfeminine persons), with just 11 reporting having received silicone and 8 reporting having received collagen, although the survey did not ask about how the injections were obtained. In a previous study, the prevalence of illicit filler injection in transgender women was 16.9%, they pointed out.
These types of noninvasive, gender-affirming procedures “may contribute to higher levels of self-confidence and [reduce] gender dysphoria. Future studies should examine motivations, barriers, and optimal timing” for such procedures in transgender persons, Dr. Ragmanauskaite and associates wrote.
The authors reported that they had no relevant disclosures.
, according to the results of a recent survey.
Transfeminine persons – those assigned male at birth – were much more likely to report a previous dermatologic procedure, compared with transmasculine respondents, by a margin of 64.9%-7.5%, Laura Ragmanauskaite, MD, and associates reported.
“Hair removal was the most frequently reported procedure type, with electrolysis being more common than laser hair removal,” they said, noting that “previous research on hair removal treatments among gender minority persons did not detect differences in the use of electrolysis and laser hair removal.”
Just under one-third of all respondents (32.9%) said that they had undergone electrolysis and 4.6% reported previous laser hair removal. For electrolysis, that works out to 59.4% of transfeminine and 6.1% of transmasculine respondents, while 9.1% of all transfeminine and no transmasculine persons had received laser hair removal, Dr. Ragmanauskaite of the department of dermatology, Emory University, Atlanta, and her coauthors said.
Those who had undergone gender-affirming surgery were significantly more likely to report electrolysis (78.6%) than were persons who had received no gender-affirming surgery or hormone therapy alone (47.4%), a statistically significant difference (P < .01). All of the other, less common procedures included in the online survey – 696 responses were received from 350 transfeminine and 346 transmasculine persons participating in the Study of Transition, Outcomes, and Gender – were reported more often by the transfeminine respondents. The procedure with the closest gender distribution was body contouring, reported by nine transfeminine and six transmasculine persons, the researchers said.
Use of dermal fillers was even less common (2.8% among all respondents, all transfeminine persons), with just 11 reporting having received silicone and 8 reporting having received collagen, although the survey did not ask about how the injections were obtained. In a previous study, the prevalence of illicit filler injection in transgender women was 16.9%, they pointed out.
These types of noninvasive, gender-affirming procedures “may contribute to higher levels of self-confidence and [reduce] gender dysphoria. Future studies should examine motivations, barriers, and optimal timing” for such procedures in transgender persons, Dr. Ragmanauskaite and associates wrote.
The authors reported that they had no relevant disclosures.
, according to the results of a recent survey.
Transfeminine persons – those assigned male at birth – were much more likely to report a previous dermatologic procedure, compared with transmasculine respondents, by a margin of 64.9%-7.5%, Laura Ragmanauskaite, MD, and associates reported.
“Hair removal was the most frequently reported procedure type, with electrolysis being more common than laser hair removal,” they said, noting that “previous research on hair removal treatments among gender minority persons did not detect differences in the use of electrolysis and laser hair removal.”
Just under one-third of all respondents (32.9%) said that they had undergone electrolysis and 4.6% reported previous laser hair removal. For electrolysis, that works out to 59.4% of transfeminine and 6.1% of transmasculine respondents, while 9.1% of all transfeminine and no transmasculine persons had received laser hair removal, Dr. Ragmanauskaite of the department of dermatology, Emory University, Atlanta, and her coauthors said.
Those who had undergone gender-affirming surgery were significantly more likely to report electrolysis (78.6%) than were persons who had received no gender-affirming surgery or hormone therapy alone (47.4%), a statistically significant difference (P < .01). All of the other, less common procedures included in the online survey – 696 responses were received from 350 transfeminine and 346 transmasculine persons participating in the Study of Transition, Outcomes, and Gender – were reported more often by the transfeminine respondents. The procedure with the closest gender distribution was body contouring, reported by nine transfeminine and six transmasculine persons, the researchers said.
Use of dermal fillers was even less common (2.8% among all respondents, all transfeminine persons), with just 11 reporting having received silicone and 8 reporting having received collagen, although the survey did not ask about how the injections were obtained. In a previous study, the prevalence of illicit filler injection in transgender women was 16.9%, they pointed out.
These types of noninvasive, gender-affirming procedures “may contribute to higher levels of self-confidence and [reduce] gender dysphoria. Future studies should examine motivations, barriers, and optimal timing” for such procedures in transgender persons, Dr. Ragmanauskaite and associates wrote.
The authors reported that they had no relevant disclosures.
FROM DERMATOLOGIC SURGERY
Molluscum Contagiosum Superimposed on Lymphangioma Circumscriptum
To the Editor:
Lymphangioma circumscriptum (LC) is a benign malformation of the lymphatic system.1 It is postulated to arise from abnormal lymphatic cisterns, and it grows separately from the normal lymphatic system. These cisterns are connected to malformed dermal lymphatic channels, and the contraction of smooth muscles lining cisterns will cause dilatation of connected lymphatic channels in the papillary dermis due to back pressure,1,2 which causes a classic LC manifestation characterized by multiple translucent, sometimes red-brown, small vesicles grouped together. Lymphangioma circumscriptum can be difficult to differentiate from molluscum contagiosum (MC) due to the similar morphology.1 We present a notable case of MC superimposed on LC.
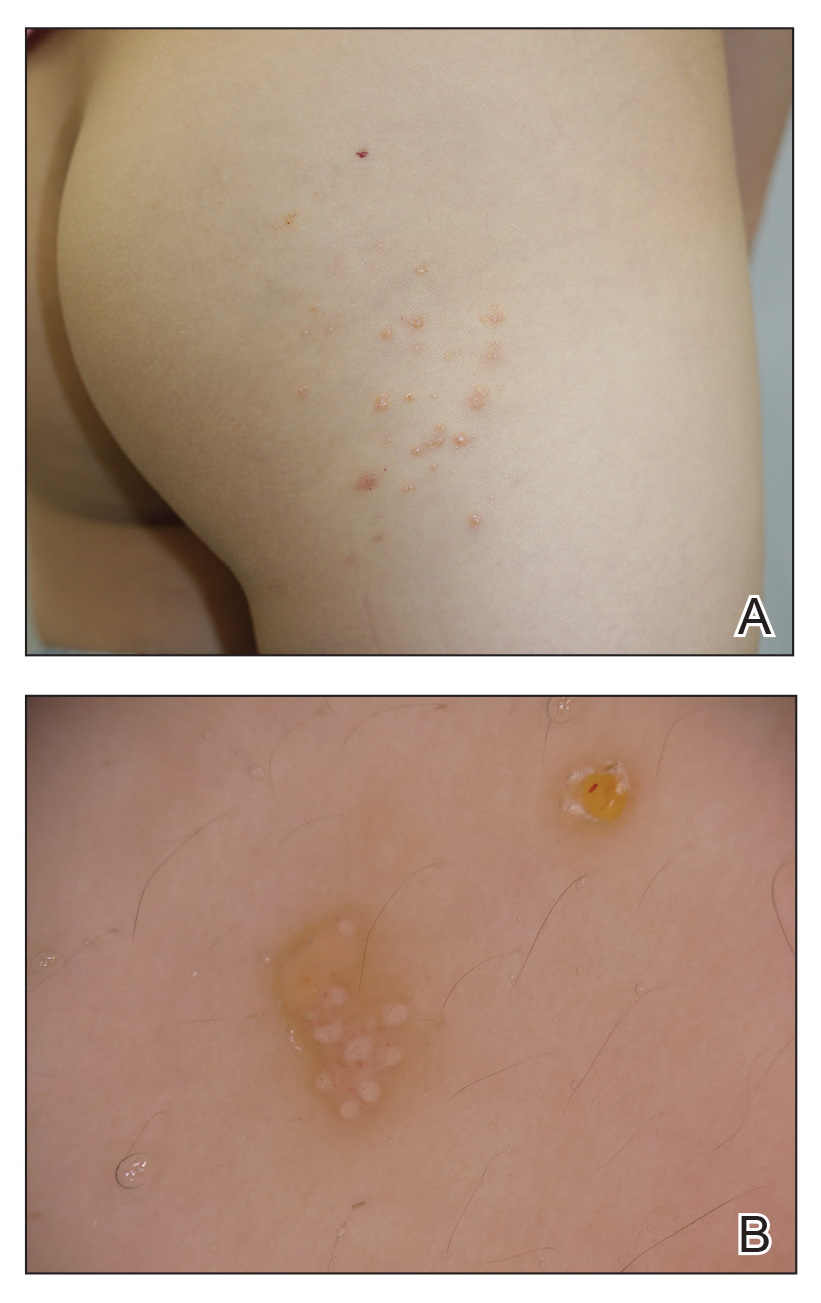
A 6-year-old girl presented with multiple grouped, clear, vesicular papules on the right buttock of 18 months’ duration. Some of the papules showed tiny whitish pearl-like particles on the top (Figure 1). Similar lesions were not present elsewhere on the body. She had no underlying disease and did not have a history of procedure, edema, or malformation of the lower extremities. Histopathology from one of the lesions showed dilated cystic lymphatic spaces in the papillary dermis lined with flattened endothelium and cup-shaped downward proliferation of the epidermis with presence of large intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies—features of both LC and MC (Figure 2). We waited 4 additional months for the MC lesions to self-resolve, but they persisted. The patient’s mother strongly requested for their removal, and the residual MC lesions were carefully removed by CO2 laser. To prevent unnecessary physical damage to underlying LC lesions and minimize scarring, we opted to use the CO2 laser and not simple curettage. She currently is under periodic observation with no signs of clinical recurrence of MC, but the LC lesions naturally persisted.
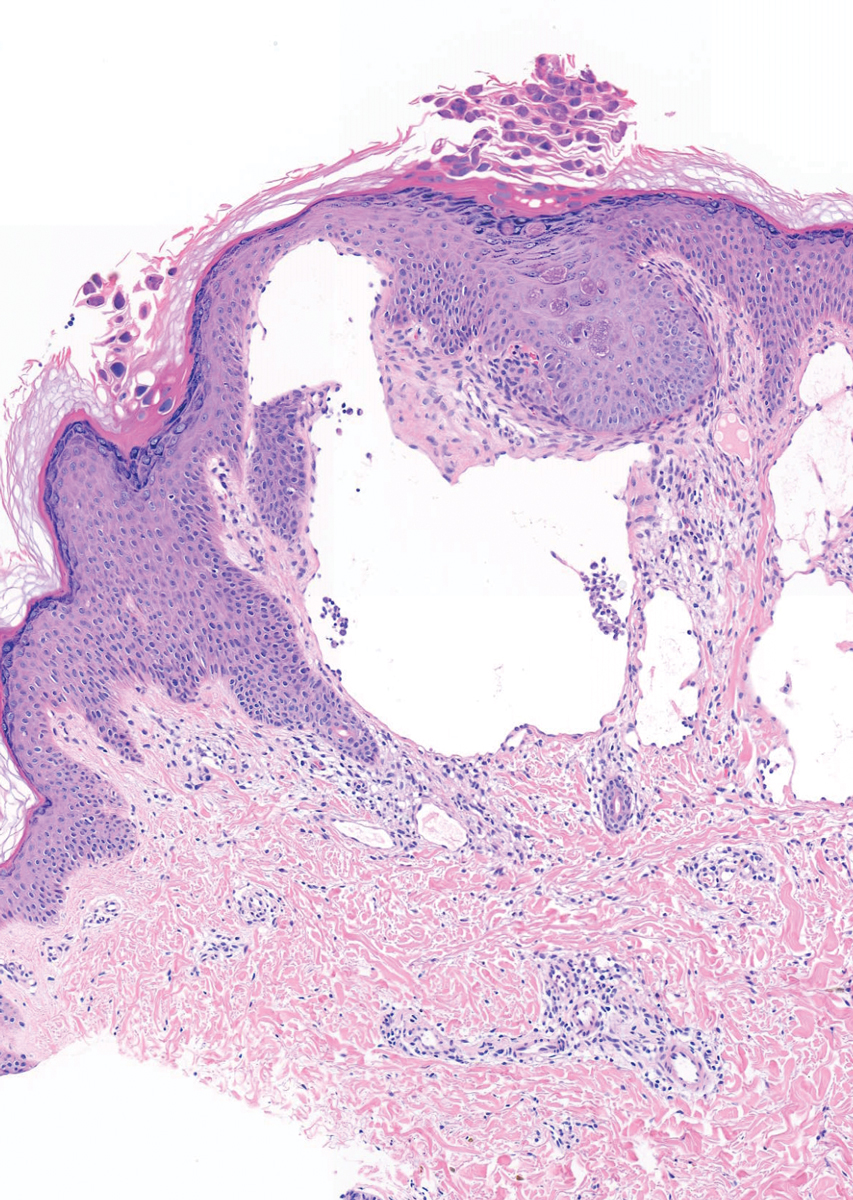
Due to its vesicular and sometimes warty appearance, LC can sometimes be hard to differentiate from MC. In one report, a vesicular plaquelike lesion on the trunk initially was misdiagnosed and treated as MC but was histologically confirmed as LC several years later.3 Our case demonstrates the coexistence of MC and LC. Although this phenomenon may be coincidental, we have not noticed any additional MC lesions on the body and MC only existed over the LC lesions, implying a possible pathophysiologic relationship. It is unlikely that MC might have preceded the development of LC. Although acquired LC exists, it has mostly been reported in the genital region of patients with conditions leading to lymphatic obstruction such as surgery, radiation therapy, malignancy, or serious infections.4 Because our patient developed lesions at an early age without any remarkable medical history, it is likely that she had congenital LC that was secondarily infected by the MC virus. Vesicular lesions in LC are known to rupture easily and may serve as a vulnerable entry site for pathogens. Subsequent secondary bacterial infections are common, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most prominent entity.1 However, secondary viral infection rarely is reported. It is possible that the abnormally dilated lymphatic channels of LC that lack communication with the normal lymphatic system have contributed to an LC site-specific vulnerability to MC virus. Further studies and subsequent reports are required to confirm this hypothesis.
- Patel GA, Schwartz RA. Cutaneous lymphangioma circumscriptum: frog spawn on the skin. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1290-1295. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04226.x
- Fatima S, Uddin N, Idrees R, et al. Lymphangioma circumscriptum: clinicopathological spectrum of 29 cases. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2015;25:658-661. doi:09.2015/JCPSP.658661
- Patel GA, Siperstein RD, Ragi G, Schwartz RA. Zosteriform lymphangioma circumscriptum. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2009;18:179-182.
- Chang MB, Newman CC, Davis MD, et al. Acquired lymphangiectasia (lymphangioma circumscriptum) of the vulva: clinicopathologic study of 11 patients from a single institution and 67 from the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:E482-E487. doi:10.1111/ijd.13264
To the Editor:
Lymphangioma circumscriptum (LC) is a benign malformation of the lymphatic system.1 It is postulated to arise from abnormal lymphatic cisterns, and it grows separately from the normal lymphatic system. These cisterns are connected to malformed dermal lymphatic channels, and the contraction of smooth muscles lining cisterns will cause dilatation of connected lymphatic channels in the papillary dermis due to back pressure,1,2 which causes a classic LC manifestation characterized by multiple translucent, sometimes red-brown, small vesicles grouped together. Lymphangioma circumscriptum can be difficult to differentiate from molluscum contagiosum (MC) due to the similar morphology.1 We present a notable case of MC superimposed on LC.

A 6-year-old girl presented with multiple grouped, clear, vesicular papules on the right buttock of 18 months’ duration. Some of the papules showed tiny whitish pearl-like particles on the top (Figure 1). Similar lesions were not present elsewhere on the body. She had no underlying disease and did not have a history of procedure, edema, or malformation of the lower extremities. Histopathology from one of the lesions showed dilated cystic lymphatic spaces in the papillary dermis lined with flattened endothelium and cup-shaped downward proliferation of the epidermis with presence of large intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies—features of both LC and MC (Figure 2). We waited 4 additional months for the MC lesions to self-resolve, but they persisted. The patient’s mother strongly requested for their removal, and the residual MC lesions were carefully removed by CO2 laser. To prevent unnecessary physical damage to underlying LC lesions and minimize scarring, we opted to use the CO2 laser and not simple curettage. She currently is under periodic observation with no signs of clinical recurrence of MC, but the LC lesions naturally persisted.

Due to its vesicular and sometimes warty appearance, LC can sometimes be hard to differentiate from MC. In one report, a vesicular plaquelike lesion on the trunk initially was misdiagnosed and treated as MC but was histologically confirmed as LC several years later.3 Our case demonstrates the coexistence of MC and LC. Although this phenomenon may be coincidental, we have not noticed any additional MC lesions on the body and MC only existed over the LC lesions, implying a possible pathophysiologic relationship. It is unlikely that MC might have preceded the development of LC. Although acquired LC exists, it has mostly been reported in the genital region of patients with conditions leading to lymphatic obstruction such as surgery, radiation therapy, malignancy, or serious infections.4 Because our patient developed lesions at an early age without any remarkable medical history, it is likely that she had congenital LC that was secondarily infected by the MC virus. Vesicular lesions in LC are known to rupture easily and may serve as a vulnerable entry site for pathogens. Subsequent secondary bacterial infections are common, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most prominent entity.1 However, secondary viral infection rarely is reported. It is possible that the abnormally dilated lymphatic channels of LC that lack communication with the normal lymphatic system have contributed to an LC site-specific vulnerability to MC virus. Further studies and subsequent reports are required to confirm this hypothesis.
To the Editor:
Lymphangioma circumscriptum (LC) is a benign malformation of the lymphatic system.1 It is postulated to arise from abnormal lymphatic cisterns, and it grows separately from the normal lymphatic system. These cisterns are connected to malformed dermal lymphatic channels, and the contraction of smooth muscles lining cisterns will cause dilatation of connected lymphatic channels in the papillary dermis due to back pressure,1,2 which causes a classic LC manifestation characterized by multiple translucent, sometimes red-brown, small vesicles grouped together. Lymphangioma circumscriptum can be difficult to differentiate from molluscum contagiosum (MC) due to the similar morphology.1 We present a notable case of MC superimposed on LC.

A 6-year-old girl presented with multiple grouped, clear, vesicular papules on the right buttock of 18 months’ duration. Some of the papules showed tiny whitish pearl-like particles on the top (Figure 1). Similar lesions were not present elsewhere on the body. She had no underlying disease and did not have a history of procedure, edema, or malformation of the lower extremities. Histopathology from one of the lesions showed dilated cystic lymphatic spaces in the papillary dermis lined with flattened endothelium and cup-shaped downward proliferation of the epidermis with presence of large intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies—features of both LC and MC (Figure 2). We waited 4 additional months for the MC lesions to self-resolve, but they persisted. The patient’s mother strongly requested for their removal, and the residual MC lesions were carefully removed by CO2 laser. To prevent unnecessary physical damage to underlying LC lesions and minimize scarring, we opted to use the CO2 laser and not simple curettage. She currently is under periodic observation with no signs of clinical recurrence of MC, but the LC lesions naturally persisted.

Due to its vesicular and sometimes warty appearance, LC can sometimes be hard to differentiate from MC. In one report, a vesicular plaquelike lesion on the trunk initially was misdiagnosed and treated as MC but was histologically confirmed as LC several years later.3 Our case demonstrates the coexistence of MC and LC. Although this phenomenon may be coincidental, we have not noticed any additional MC lesions on the body and MC only existed over the LC lesions, implying a possible pathophysiologic relationship. It is unlikely that MC might have preceded the development of LC. Although acquired LC exists, it has mostly been reported in the genital region of patients with conditions leading to lymphatic obstruction such as surgery, radiation therapy, malignancy, or serious infections.4 Because our patient developed lesions at an early age without any remarkable medical history, it is likely that she had congenital LC that was secondarily infected by the MC virus. Vesicular lesions in LC are known to rupture easily and may serve as a vulnerable entry site for pathogens. Subsequent secondary bacterial infections are common, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most prominent entity.1 However, secondary viral infection rarely is reported. It is possible that the abnormally dilated lymphatic channels of LC that lack communication with the normal lymphatic system have contributed to an LC site-specific vulnerability to MC virus. Further studies and subsequent reports are required to confirm this hypothesis.
- Patel GA, Schwartz RA. Cutaneous lymphangioma circumscriptum: frog spawn on the skin. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1290-1295. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04226.x
- Fatima S, Uddin N, Idrees R, et al. Lymphangioma circumscriptum: clinicopathological spectrum of 29 cases. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2015;25:658-661. doi:09.2015/JCPSP.658661
- Patel GA, Siperstein RD, Ragi G, Schwartz RA. Zosteriform lymphangioma circumscriptum. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2009;18:179-182.
- Chang MB, Newman CC, Davis MD, et al. Acquired lymphangiectasia (lymphangioma circumscriptum) of the vulva: clinicopathologic study of 11 patients from a single institution and 67 from the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:E482-E487. doi:10.1111/ijd.13264
- Patel GA, Schwartz RA. Cutaneous lymphangioma circumscriptum: frog spawn on the skin. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1290-1295. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04226.x
- Fatima S, Uddin N, Idrees R, et al. Lymphangioma circumscriptum: clinicopathological spectrum of 29 cases. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2015;25:658-661. doi:09.2015/JCPSP.658661
- Patel GA, Siperstein RD, Ragi G, Schwartz RA. Zosteriform lymphangioma circumscriptum. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2009;18:179-182.
- Chang MB, Newman CC, Davis MD, et al. Acquired lymphangiectasia (lymphangioma circumscriptum) of the vulva: clinicopathologic study of 11 patients from a single institution and 67 from the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:E482-E487. doi:10.1111/ijd.13264
Practice Points
- Lymphangioma circumscriptum (LC) is a benign malformation of the lymphatic system that can be misdiagnosed as molluscum contagiosum (MC).
- Secondary infection of LC is common, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most common entity, but MC virus also can be secondarily infected.