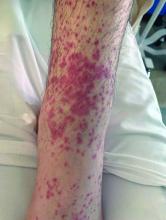
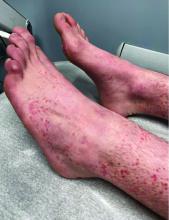
User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
Words from the wise
“When 900-years-old you reach, look as good you will not.” –Yoda
I’ve been on a roll lately: 100, 94, 90, 97, 94. These aren’t grades or even what I scratched on my scorecard for 18 holes (that’s more like 112), but rather patients I’ve seen.
Our oldest-old have been in COVID-19 protection for the last couple of years and only now feel safe to come out again. Many have skin cancers. Some of them have many. I’m grateful that for all their health problems, basal cell carcinomas at least I can cure. And
From a 94-year-old woman who was just discharged from the hospital for sepsis: First, sepsis can sneak up from behind and jump you when you’re 94. She was sitting in a waiting room for a routine exam when she passed out and woke up in the ICU. She made it home and is back on her feet, literally. When I asked her how she made it though, she was very matter of fact. Trust that the doctors know what’s right. Trust that someone will tell you what to do next. Trust that you know your own body and what you can and cannot do. Ask for help, then simply trust it will all work out. It usually does.
From a 97-year-old fighter pilot who fought in the Korean War: Let regrets drop away and live to fight another day. He’s had multiple marriages, built and lost companies, been fired and fired at, and made some doozy mistakes, some that caused considerable pain and collateral damage. But each day is new and requires your best. He has lived long enough to love dozens of grandkids and give away more than what most people ever make. His bottom line, if you worry and fret and regret, you’ll make even more mistakes ahead. Look ahead, the ground never comes up from behind you.
From a 94-year-old whose son was killed in a car accident nearly 60 years ago: You can be both happy and sad. When she retold the story of how the police knocked on her door with the news that her son was dead, she started to cry. Even 60 years isn’t long enough to blunt such pain. She still thinks of him often and to this day sometimes finds it difficult to believe he’s gone. Such pain never leaves you. But she is still a happy person with countless joys and is still having such fun. If you live long enough, both will likely be true.
From a 90-year old who still played tennis: “Just one and one.” That is, one beer and one shot, every day. No more. No less. I daren’t say I recommend this one; however, it might also be the social aspect of drinking that matters. He also advised to be free with friendships. You’ll have many people come in and out of your life; be open to new ones all the time. Also sometimes let your friends win.
From a 100-year-old, I asked how he managed to get through the Great Depression, WWII, civil unrest of the 1950s, and the Vietnam War. His reply? “To be honest, I’ve never seen anything quite like this before.”
When there’s time, consider asking for advice from those elders who happen to have an appointment with you. Bring you wisdom, they will.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
“When 900-years-old you reach, look as good you will not.” –Yoda
I’ve been on a roll lately: 100, 94, 90, 97, 94. These aren’t grades or even what I scratched on my scorecard for 18 holes (that’s more like 112), but rather patients I’ve seen.
Our oldest-old have been in COVID-19 protection for the last couple of years and only now feel safe to come out again. Many have skin cancers. Some of them have many. I’m grateful that for all their health problems, basal cell carcinomas at least I can cure. And
From a 94-year-old woman who was just discharged from the hospital for sepsis: First, sepsis can sneak up from behind and jump you when you’re 94. She was sitting in a waiting room for a routine exam when she passed out and woke up in the ICU. She made it home and is back on her feet, literally. When I asked her how she made it though, she was very matter of fact. Trust that the doctors know what’s right. Trust that someone will tell you what to do next. Trust that you know your own body and what you can and cannot do. Ask for help, then simply trust it will all work out. It usually does.
From a 97-year-old fighter pilot who fought in the Korean War: Let regrets drop away and live to fight another day. He’s had multiple marriages, built and lost companies, been fired and fired at, and made some doozy mistakes, some that caused considerable pain and collateral damage. But each day is new and requires your best. He has lived long enough to love dozens of grandkids and give away more than what most people ever make. His bottom line, if you worry and fret and regret, you’ll make even more mistakes ahead. Look ahead, the ground never comes up from behind you.
From a 94-year-old whose son was killed in a car accident nearly 60 years ago: You can be both happy and sad. When she retold the story of how the police knocked on her door with the news that her son was dead, she started to cry. Even 60 years isn’t long enough to blunt such pain. She still thinks of him often and to this day sometimes finds it difficult to believe he’s gone. Such pain never leaves you. But she is still a happy person with countless joys and is still having such fun. If you live long enough, both will likely be true.
From a 90-year old who still played tennis: “Just one and one.” That is, one beer and one shot, every day. No more. No less. I daren’t say I recommend this one; however, it might also be the social aspect of drinking that matters. He also advised to be free with friendships. You’ll have many people come in and out of your life; be open to new ones all the time. Also sometimes let your friends win.
From a 100-year-old, I asked how he managed to get through the Great Depression, WWII, civil unrest of the 1950s, and the Vietnam War. His reply? “To be honest, I’ve never seen anything quite like this before.”
When there’s time, consider asking for advice from those elders who happen to have an appointment with you. Bring you wisdom, they will.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
“When 900-years-old you reach, look as good you will not.” –Yoda
I’ve been on a roll lately: 100, 94, 90, 97, 94. These aren’t grades or even what I scratched on my scorecard for 18 holes (that’s more like 112), but rather patients I’ve seen.
Our oldest-old have been in COVID-19 protection for the last couple of years and only now feel safe to come out again. Many have skin cancers. Some of them have many. I’m grateful that for all their health problems, basal cell carcinomas at least I can cure. And
From a 94-year-old woman who was just discharged from the hospital for sepsis: First, sepsis can sneak up from behind and jump you when you’re 94. She was sitting in a waiting room for a routine exam when she passed out and woke up in the ICU. She made it home and is back on her feet, literally. When I asked her how she made it though, she was very matter of fact. Trust that the doctors know what’s right. Trust that someone will tell you what to do next. Trust that you know your own body and what you can and cannot do. Ask for help, then simply trust it will all work out. It usually does.
From a 97-year-old fighter pilot who fought in the Korean War: Let regrets drop away and live to fight another day. He’s had multiple marriages, built and lost companies, been fired and fired at, and made some doozy mistakes, some that caused considerable pain and collateral damage. But each day is new and requires your best. He has lived long enough to love dozens of grandkids and give away more than what most people ever make. His bottom line, if you worry and fret and regret, you’ll make even more mistakes ahead. Look ahead, the ground never comes up from behind you.
From a 94-year-old whose son was killed in a car accident nearly 60 years ago: You can be both happy and sad. When she retold the story of how the police knocked on her door with the news that her son was dead, she started to cry. Even 60 years isn’t long enough to blunt such pain. She still thinks of him often and to this day sometimes finds it difficult to believe he’s gone. Such pain never leaves you. But she is still a happy person with countless joys and is still having such fun. If you live long enough, both will likely be true.
From a 90-year old who still played tennis: “Just one and one.” That is, one beer and one shot, every day. No more. No less. I daren’t say I recommend this one; however, it might also be the social aspect of drinking that matters. He also advised to be free with friendships. You’ll have many people come in and out of your life; be open to new ones all the time. Also sometimes let your friends win.
From a 100-year-old, I asked how he managed to get through the Great Depression, WWII, civil unrest of the 1950s, and the Vietnam War. His reply? “To be honest, I’ve never seen anything quite like this before.”
When there’s time, consider asking for advice from those elders who happen to have an appointment with you. Bring you wisdom, they will.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
Adding rituximab to belimumab offers no help for lupus
Adding a single cycle of rituximab to belimumab (Benlysta) did not improve disease control for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in comparison with belimumab alone in a phase 3, randomized, controlled trial.
Among patients with SLE who were randomly assigned to receive belimumab with either rituximab, placebo, or standard care, there were no statistically significant differences between the rituximab and placebo arms for the primary endpoint of the proportion of patients with disease control at week 52 or in the secondary endpoints of clinical remission at week 64 or disease control at week 104, Cynthia Aranow, MD, reported in a late-breaking poster session presented during the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“Using a new, clinically meaningful endpoint underscores the efficacy of belimumab for disease control, with some patients maintaining disease control with considerable reductions in steroids, and no immunosuppressants,” said Dr. Aranow, a rheumatologist specializing in SLE and RA in New York and director of the Clinical Autoimmunity Center of Excellence at Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research, Manhasset, N.Y.
Use of the combination of belimumab and rituximab was, however, associated with significant improvement over belimumab and placebo in several secondary efficacy endpoints.
Investigators in the randomized, controlled trial, dubbed BLISS-BELIEVE, had previously published a rationale for sequential therapy with belimumab, a human monoclonal antibody that binds to soluble B-lymphocyte stimulator, and rituximab, a B-cell–depleting anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody.
“These biologics, which operate through complementary mechanisms, might result in an enhanced depletion of circulating and tissue-resident autoreactive B lymphocytes when administered together. Thus, belimumab and rituximab combination may be a highly effective treatment of SLE,” they wrote in an article published in 2019 in BMJ Open.
Three-arm trial
The investigators screened 396 patients, of whom 292 were randomly assigned in a 1:2:1 ratio to receive either subcutaneous belimumab 200 mg/wk plus intravenous placebo at weeks 4 and 6 (BEL/PBO, 72 patients), belimumab plus IV rituximab 1,000 mg at weeks 4 and 6 (BEL/RTX, 144 patients), or open-label belimumab plus standard therapy. Patients were allowed to continue taking antimalarial and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs throughout the study.
The primary disease-control endpoint was defined as a Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI-2K) score of 2 or less, achieved without other immunosuppression, equivalent to that achieved with prednisone 5 mg/day or less.
As noted before, there were no significant differences between the BEL/RTX and BEL/PBO arms in either disease control at week 52 or in the secondary endpoints of clinical remission at week 64 (SLEDAI-2K score, 0) or in the proportion of patients with disease control at week 104.
However, use of BEL/RTX was associated with a significantly longer duration of disease control through 52 weeks than was BEL/PBO (mean, 105.4 days vs. 60.1 days; P = .0188) and with a large SLEDAI-2K mean change from baseline at week 104 (–7.2 vs 5.1; P = .0033).
In addition, there was a trend toward a shift in proteinuria from baseline high (>0.5 g/24 h) to normal in the BEL/RTX group at week 52 and a significantly greater shift at week 104 (P = .0085).
The overall adverse event profiles were generally consistent with those of the individual agents, although serious infections and infestations occurred more frequently with BEL/RTX than BEL/PBO.
Further analyses planned to look for subgroups that benefit
In a poster discussion session, Akshat Khanna, PhD, of Newtown, Pa., a consultant with Effimed Life Sciences Research, asked Dr. Aranow about the rationale for giving rituximab and belimumab concurrently and noted that, in the BEAT-LUPUS and CALIBRATE trials, anti-CD20 agents were given first, followed by belimumab, to prevent activation of humoral immunity.
“The two B-cell agents were given sequentially. Belimumab was given first to maximize the effect of peripheral B-cell depletion and [was] then continued after rituximab to suppress the elevation [of B-lymphocyte stimulator] that occurs after rituximab monotherapy. We used this approach (instead of that used in CALIBRATE and BEAT LUPUS), as we thought this might be more efficacious,” she explained.
When asked whether there were subgroups of patients who might still benefit from the combination, compared with belimumab alone, Dr. Aranow replied: “There may be individual patients in which it might be considered. Further analyses of the data are ongoing/planned.”
The study was supported by GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Aranow has received grant/research support from GlaxoSmithKline and has consulted for Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Khanna has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adding a single cycle of rituximab to belimumab (Benlysta) did not improve disease control for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in comparison with belimumab alone in a phase 3, randomized, controlled trial.
Among patients with SLE who were randomly assigned to receive belimumab with either rituximab, placebo, or standard care, there were no statistically significant differences between the rituximab and placebo arms for the primary endpoint of the proportion of patients with disease control at week 52 or in the secondary endpoints of clinical remission at week 64 or disease control at week 104, Cynthia Aranow, MD, reported in a late-breaking poster session presented during the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“Using a new, clinically meaningful endpoint underscores the efficacy of belimumab for disease control, with some patients maintaining disease control with considerable reductions in steroids, and no immunosuppressants,” said Dr. Aranow, a rheumatologist specializing in SLE and RA in New York and director of the Clinical Autoimmunity Center of Excellence at Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research, Manhasset, N.Y.
Use of the combination of belimumab and rituximab was, however, associated with significant improvement over belimumab and placebo in several secondary efficacy endpoints.
Investigators in the randomized, controlled trial, dubbed BLISS-BELIEVE, had previously published a rationale for sequential therapy with belimumab, a human monoclonal antibody that binds to soluble B-lymphocyte stimulator, and rituximab, a B-cell–depleting anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody.
“These biologics, which operate through complementary mechanisms, might result in an enhanced depletion of circulating and tissue-resident autoreactive B lymphocytes when administered together. Thus, belimumab and rituximab combination may be a highly effective treatment of SLE,” they wrote in an article published in 2019 in BMJ Open.
Three-arm trial
The investigators screened 396 patients, of whom 292 were randomly assigned in a 1:2:1 ratio to receive either subcutaneous belimumab 200 mg/wk plus intravenous placebo at weeks 4 and 6 (BEL/PBO, 72 patients), belimumab plus IV rituximab 1,000 mg at weeks 4 and 6 (BEL/RTX, 144 patients), or open-label belimumab plus standard therapy. Patients were allowed to continue taking antimalarial and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs throughout the study.
The primary disease-control endpoint was defined as a Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI-2K) score of 2 or less, achieved without other immunosuppression, equivalent to that achieved with prednisone 5 mg/day or less.
As noted before, there were no significant differences between the BEL/RTX and BEL/PBO arms in either disease control at week 52 or in the secondary endpoints of clinical remission at week 64 (SLEDAI-2K score, 0) or in the proportion of patients with disease control at week 104.
However, use of BEL/RTX was associated with a significantly longer duration of disease control through 52 weeks than was BEL/PBO (mean, 105.4 days vs. 60.1 days; P = .0188) and with a large SLEDAI-2K mean change from baseline at week 104 (–7.2 vs 5.1; P = .0033).
In addition, there was a trend toward a shift in proteinuria from baseline high (>0.5 g/24 h) to normal in the BEL/RTX group at week 52 and a significantly greater shift at week 104 (P = .0085).
The overall adverse event profiles were generally consistent with those of the individual agents, although serious infections and infestations occurred more frequently with BEL/RTX than BEL/PBO.
Further analyses planned to look for subgroups that benefit
In a poster discussion session, Akshat Khanna, PhD, of Newtown, Pa., a consultant with Effimed Life Sciences Research, asked Dr. Aranow about the rationale for giving rituximab and belimumab concurrently and noted that, in the BEAT-LUPUS and CALIBRATE trials, anti-CD20 agents were given first, followed by belimumab, to prevent activation of humoral immunity.
“The two B-cell agents were given sequentially. Belimumab was given first to maximize the effect of peripheral B-cell depletion and [was] then continued after rituximab to suppress the elevation [of B-lymphocyte stimulator] that occurs after rituximab monotherapy. We used this approach (instead of that used in CALIBRATE and BEAT LUPUS), as we thought this might be more efficacious,” she explained.
When asked whether there were subgroups of patients who might still benefit from the combination, compared with belimumab alone, Dr. Aranow replied: “There may be individual patients in which it might be considered. Further analyses of the data are ongoing/planned.”
The study was supported by GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Aranow has received grant/research support from GlaxoSmithKline and has consulted for Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Khanna has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adding a single cycle of rituximab to belimumab (Benlysta) did not improve disease control for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in comparison with belimumab alone in a phase 3, randomized, controlled trial.
Among patients with SLE who were randomly assigned to receive belimumab with either rituximab, placebo, or standard care, there were no statistically significant differences between the rituximab and placebo arms for the primary endpoint of the proportion of patients with disease control at week 52 or in the secondary endpoints of clinical remission at week 64 or disease control at week 104, Cynthia Aranow, MD, reported in a late-breaking poster session presented during the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“Using a new, clinically meaningful endpoint underscores the efficacy of belimumab for disease control, with some patients maintaining disease control with considerable reductions in steroids, and no immunosuppressants,” said Dr. Aranow, a rheumatologist specializing in SLE and RA in New York and director of the Clinical Autoimmunity Center of Excellence at Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research, Manhasset, N.Y.
Use of the combination of belimumab and rituximab was, however, associated with significant improvement over belimumab and placebo in several secondary efficacy endpoints.
Investigators in the randomized, controlled trial, dubbed BLISS-BELIEVE, had previously published a rationale for sequential therapy with belimumab, a human monoclonal antibody that binds to soluble B-lymphocyte stimulator, and rituximab, a B-cell–depleting anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody.
“These biologics, which operate through complementary mechanisms, might result in an enhanced depletion of circulating and tissue-resident autoreactive B lymphocytes when administered together. Thus, belimumab and rituximab combination may be a highly effective treatment of SLE,” they wrote in an article published in 2019 in BMJ Open.
Three-arm trial
The investigators screened 396 patients, of whom 292 were randomly assigned in a 1:2:1 ratio to receive either subcutaneous belimumab 200 mg/wk plus intravenous placebo at weeks 4 and 6 (BEL/PBO, 72 patients), belimumab plus IV rituximab 1,000 mg at weeks 4 and 6 (BEL/RTX, 144 patients), or open-label belimumab plus standard therapy. Patients were allowed to continue taking antimalarial and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs throughout the study.
The primary disease-control endpoint was defined as a Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI-2K) score of 2 or less, achieved without other immunosuppression, equivalent to that achieved with prednisone 5 mg/day or less.
As noted before, there were no significant differences between the BEL/RTX and BEL/PBO arms in either disease control at week 52 or in the secondary endpoints of clinical remission at week 64 (SLEDAI-2K score, 0) or in the proportion of patients with disease control at week 104.
However, use of BEL/RTX was associated with a significantly longer duration of disease control through 52 weeks than was BEL/PBO (mean, 105.4 days vs. 60.1 days; P = .0188) and with a large SLEDAI-2K mean change from baseline at week 104 (–7.2 vs 5.1; P = .0033).
In addition, there was a trend toward a shift in proteinuria from baseline high (>0.5 g/24 h) to normal in the BEL/RTX group at week 52 and a significantly greater shift at week 104 (P = .0085).
The overall adverse event profiles were generally consistent with those of the individual agents, although serious infections and infestations occurred more frequently with BEL/RTX than BEL/PBO.
Further analyses planned to look for subgroups that benefit
In a poster discussion session, Akshat Khanna, PhD, of Newtown, Pa., a consultant with Effimed Life Sciences Research, asked Dr. Aranow about the rationale for giving rituximab and belimumab concurrently and noted that, in the BEAT-LUPUS and CALIBRATE trials, anti-CD20 agents were given first, followed by belimumab, to prevent activation of humoral immunity.
“The two B-cell agents were given sequentially. Belimumab was given first to maximize the effect of peripheral B-cell depletion and [was] then continued after rituximab to suppress the elevation [of B-lymphocyte stimulator] that occurs after rituximab monotherapy. We used this approach (instead of that used in CALIBRATE and BEAT LUPUS), as we thought this might be more efficacious,” she explained.
When asked whether there were subgroups of patients who might still benefit from the combination, compared with belimumab alone, Dr. Aranow replied: “There may be individual patients in which it might be considered. Further analyses of the data are ongoing/planned.”
The study was supported by GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Aranow has received grant/research support from GlaxoSmithKline and has consulted for Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Khanna has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2021
Tofacitinib postmarketing trial data shed light on JAK inhibitor risks
Additional analyses of a postmarketing trial that was required after the Food and Drug Administration’s approval of the Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz, Xeljanz XR) has identified characteristics of older patients with rheumatoid arthritis with at least one cardiovascular risk factor who may be at higher risk for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) when taking the drug.
Results from the phase 3b/4 ORAL Surveillance trial presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology show that people taking tofacitinib for RA with at least one cardiovascular (CV) risk factor had a nonsignificant higher risk for MACE than did people taking tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi), with the risk from tofacitinib more pronounced in current smokers, aspirin users, people older than 65 years, and men, compared with women.
“It is the first large, randomized safety study of active RA patients with increased CV risk comparing tofacitinib to TNF inhibition,” study author Christina Charles-Schoeman, MD, said in an interview. “These data emphasize the importance of assessing baseline CV risk when treating patients with RA.” Dr. Charles-Schoeman is chief of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles.
The results shed further light on the trial’s findings, which the FDA used in September 2021 to mandate boxed warnings about the risk of MI or stroke, cancer, venous thromboembolism, and death, as well as updated indications, for tofacitinib and other JAK inhibitors baricitinib (Olumiant) and upadacitinib (Rinvoq). The FDA limited all approved uses of these three medications to patients who have not responded well to TNFi to ensure their benefits outweigh their risks.
Tofacitinib is indicated for RA, psoriatic arthritis, ulcerative colitis, and polyarticular course juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Baricitinib and upadacitinib are approved only for RA.
While the overall results of the trial results show nonsignificant increased incidence rates for MACE in tofacitinib users versus TNFI users, Katherine Liao, MD, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, noted that more information is needed to determine who is at greatest risk. “Another thing to keep in mind is, while there was evidence of an elevated relative risk for MACE, compared to TNFi, the absolute risk, based on the numbers what we know so far, is small,” she said.
The trial compared two different doses of tofacitinib – 5 mg (1,455 patients) and 10 mg (n = 1,456) twice daily – and TNFi (n = 1,451) in people with moderate to severe RA over age 50. Patient characteristics were similar across all three treatment arms, Dr. Charles-Schoeman said. All patients had inadequate response to methotrexate, and about 57% in all three treatment groups were taking corticosteroids. The 10-mg tofacitinib patients switched to the 5-mg dose in February 2019 but represent the 10-mg group in the study analysis.
ORAL Surveillance demonstrated a 24% greater risk of MACE in the 5-mg tofacitinib patients and a 43% heightened risk the 10-mg group, compared with patients who received a TNFi.
The differentiating factor for MACE incidence was MI. The higher- and lower-dose tofacitinib groups had 69% and 80% greater risk for MI. While the risk for fatal MI were similar across all three treatment groups, the risk for nonfatal MI were more than doubled in the respective tofacitinib groups: hazard ratios of 2.32 and 2.08. The incidence of stroke was similar across all three arms, Dr. Charles-Schoeman said.
The study identified a number of baseline characteristics as independent overall risk factors for MACE across all treatment groups. Current smoking and aspirin use more than doubled the risk (HR, 2.18; P < .0001 and HR, 2.11; P = .004, respectively), while age greater than 65 years and male sex approached that level (HR, 1.81; P = .0011 and HR, 1.81; P = .0015) approached that level. Other factors that elevated the risk of MACE to a lesser extent were a history of diabetes, hypertension or coronary artery procedures, and a total cholesterol to HDL ratio greater than4.
Other ORAL Surveillance subanalyses and tofacitinib real-world data reported
This was one of several analyses presented at ACR 2021 that compared adverse event risks for tofacitinib versus TNFi drugs. A separate analysis of claims data from patients with RA in two U.S. insurance databases plus Medicare found a statistically nonsignificant increased risk of adverse CV outcomes (MI or stroke) with tofacitinib, compared with TNFi users, among patients who met the same inclusion and exclusion criteria of the ORAL Surveillance trial but not in a “real-world evidence” cohort of more than 102,000 patients with RA in routine care from the databases.
Two additional ORAL Surveillance analyses presented at ACR 2021 gave details about risk factors for higher rates of malignancies and venous thromboembolic events found in patients taking tofacitinib with at least one CV risk factor. As would be expected, older age (≥65 vs. 50-64 years) and current or past smoking (vs. never smoking) were independent risk factors for higher malignancy rates across all treatment arms. Pulmonary embolism events across treatment groups were independently associated with a history of venous thromboembolism, baseline use of oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy, baseline body mass index of at least 30 kg/m2, age 65 or older, and history of hypertension.
The ORAL Surveillance findings are worth considering when determining treatments for RA patients with CV risk factors, Dr. Charles-Schoeman said. “Tofacitinib remains an effective RA treatment,” she said. “The choice of specific RA treatment for any patient remains an individual decision between the patient and physician, which is decided based on a number of different factors. This new study provides additional information regarding both tofacitinib as well as traditional CV risk factors for discussion with the patient.”
The ORAL Surveillance results may give rheumatologists reason to rethink use of tofacitinib in some patients with CV risk, said Dr. Liao of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “Currently, we have limited data and are still awaiting a report of the full trial results,” she said in an interview. “Based on the data available, I can think of a few patients in my clinic where I would reconsider use of these drugs, i.e., history of heart attack with stable angina, especially if there are other options.” However, she noted that many patients on tofacitinib have already failed on older treatments.
These data emphasize the importance of addressing CV risk with patients, said Brittany N. Weber, MD, PhD, a cardio-rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital who works with Dr. Liao. “It is also an opportunity to discuss modification of risk factors and to discuss primary prevention therapies, such as statin therapy, where appropriate,” she added. “Based on the individual’s cardiovascular risk, there may be a role for further risk stratification to further understand an individual’s risk, which can also inform primary prevention cardiovascular therapies and help guide these discussions.” Risk stratification could include cardiac CT for calcium scoring or cardiac coronary CT angiography for determining atherosclerotic burden.
The study was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Charles-Schoeman disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, and Regeneron-Sanofi. Dr. Liao and Dr. Weber have no relevant disclosures.
Additional analyses of a postmarketing trial that was required after the Food and Drug Administration’s approval of the Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz, Xeljanz XR) has identified characteristics of older patients with rheumatoid arthritis with at least one cardiovascular risk factor who may be at higher risk for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) when taking the drug.
Results from the phase 3b/4 ORAL Surveillance trial presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology show that people taking tofacitinib for RA with at least one cardiovascular (CV) risk factor had a nonsignificant higher risk for MACE than did people taking tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi), with the risk from tofacitinib more pronounced in current smokers, aspirin users, people older than 65 years, and men, compared with women.
“It is the first large, randomized safety study of active RA patients with increased CV risk comparing tofacitinib to TNF inhibition,” study author Christina Charles-Schoeman, MD, said in an interview. “These data emphasize the importance of assessing baseline CV risk when treating patients with RA.” Dr. Charles-Schoeman is chief of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles.
The results shed further light on the trial’s findings, which the FDA used in September 2021 to mandate boxed warnings about the risk of MI or stroke, cancer, venous thromboembolism, and death, as well as updated indications, for tofacitinib and other JAK inhibitors baricitinib (Olumiant) and upadacitinib (Rinvoq). The FDA limited all approved uses of these three medications to patients who have not responded well to TNFi to ensure their benefits outweigh their risks.
Tofacitinib is indicated for RA, psoriatic arthritis, ulcerative colitis, and polyarticular course juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Baricitinib and upadacitinib are approved only for RA.
While the overall results of the trial results show nonsignificant increased incidence rates for MACE in tofacitinib users versus TNFI users, Katherine Liao, MD, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, noted that more information is needed to determine who is at greatest risk. “Another thing to keep in mind is, while there was evidence of an elevated relative risk for MACE, compared to TNFi, the absolute risk, based on the numbers what we know so far, is small,” she said.
The trial compared two different doses of tofacitinib – 5 mg (1,455 patients) and 10 mg (n = 1,456) twice daily – and TNFi (n = 1,451) in people with moderate to severe RA over age 50. Patient characteristics were similar across all three treatment arms, Dr. Charles-Schoeman said. All patients had inadequate response to methotrexate, and about 57% in all three treatment groups were taking corticosteroids. The 10-mg tofacitinib patients switched to the 5-mg dose in February 2019 but represent the 10-mg group in the study analysis.
ORAL Surveillance demonstrated a 24% greater risk of MACE in the 5-mg tofacitinib patients and a 43% heightened risk the 10-mg group, compared with patients who received a TNFi.
The differentiating factor for MACE incidence was MI. The higher- and lower-dose tofacitinib groups had 69% and 80% greater risk for MI. While the risk for fatal MI were similar across all three treatment groups, the risk for nonfatal MI were more than doubled in the respective tofacitinib groups: hazard ratios of 2.32 and 2.08. The incidence of stroke was similar across all three arms, Dr. Charles-Schoeman said.
The study identified a number of baseline characteristics as independent overall risk factors for MACE across all treatment groups. Current smoking and aspirin use more than doubled the risk (HR, 2.18; P < .0001 and HR, 2.11; P = .004, respectively), while age greater than 65 years and male sex approached that level (HR, 1.81; P = .0011 and HR, 1.81; P = .0015) approached that level. Other factors that elevated the risk of MACE to a lesser extent were a history of diabetes, hypertension or coronary artery procedures, and a total cholesterol to HDL ratio greater than4.
Other ORAL Surveillance subanalyses and tofacitinib real-world data reported
This was one of several analyses presented at ACR 2021 that compared adverse event risks for tofacitinib versus TNFi drugs. A separate analysis of claims data from patients with RA in two U.S. insurance databases plus Medicare found a statistically nonsignificant increased risk of adverse CV outcomes (MI or stroke) with tofacitinib, compared with TNFi users, among patients who met the same inclusion and exclusion criteria of the ORAL Surveillance trial but not in a “real-world evidence” cohort of more than 102,000 patients with RA in routine care from the databases.
Two additional ORAL Surveillance analyses presented at ACR 2021 gave details about risk factors for higher rates of malignancies and venous thromboembolic events found in patients taking tofacitinib with at least one CV risk factor. As would be expected, older age (≥65 vs. 50-64 years) and current or past smoking (vs. never smoking) were independent risk factors for higher malignancy rates across all treatment arms. Pulmonary embolism events across treatment groups were independently associated with a history of venous thromboembolism, baseline use of oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy, baseline body mass index of at least 30 kg/m2, age 65 or older, and history of hypertension.
The ORAL Surveillance findings are worth considering when determining treatments for RA patients with CV risk factors, Dr. Charles-Schoeman said. “Tofacitinib remains an effective RA treatment,” she said. “The choice of specific RA treatment for any patient remains an individual decision between the patient and physician, which is decided based on a number of different factors. This new study provides additional information regarding both tofacitinib as well as traditional CV risk factors for discussion with the patient.”
The ORAL Surveillance results may give rheumatologists reason to rethink use of tofacitinib in some patients with CV risk, said Dr. Liao of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “Currently, we have limited data and are still awaiting a report of the full trial results,” she said in an interview. “Based on the data available, I can think of a few patients in my clinic where I would reconsider use of these drugs, i.e., history of heart attack with stable angina, especially if there are other options.” However, she noted that many patients on tofacitinib have already failed on older treatments.
These data emphasize the importance of addressing CV risk with patients, said Brittany N. Weber, MD, PhD, a cardio-rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital who works with Dr. Liao. “It is also an opportunity to discuss modification of risk factors and to discuss primary prevention therapies, such as statin therapy, where appropriate,” she added. “Based on the individual’s cardiovascular risk, there may be a role for further risk stratification to further understand an individual’s risk, which can also inform primary prevention cardiovascular therapies and help guide these discussions.” Risk stratification could include cardiac CT for calcium scoring or cardiac coronary CT angiography for determining atherosclerotic burden.
The study was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Charles-Schoeman disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, and Regeneron-Sanofi. Dr. Liao and Dr. Weber have no relevant disclosures.
Additional analyses of a postmarketing trial that was required after the Food and Drug Administration’s approval of the Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz, Xeljanz XR) has identified characteristics of older patients with rheumatoid arthritis with at least one cardiovascular risk factor who may be at higher risk for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) when taking the drug.
Results from the phase 3b/4 ORAL Surveillance trial presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology show that people taking tofacitinib for RA with at least one cardiovascular (CV) risk factor had a nonsignificant higher risk for MACE than did people taking tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi), with the risk from tofacitinib more pronounced in current smokers, aspirin users, people older than 65 years, and men, compared with women.
“It is the first large, randomized safety study of active RA patients with increased CV risk comparing tofacitinib to TNF inhibition,” study author Christina Charles-Schoeman, MD, said in an interview. “These data emphasize the importance of assessing baseline CV risk when treating patients with RA.” Dr. Charles-Schoeman is chief of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles.
The results shed further light on the trial’s findings, which the FDA used in September 2021 to mandate boxed warnings about the risk of MI or stroke, cancer, venous thromboembolism, and death, as well as updated indications, for tofacitinib and other JAK inhibitors baricitinib (Olumiant) and upadacitinib (Rinvoq). The FDA limited all approved uses of these three medications to patients who have not responded well to TNFi to ensure their benefits outweigh their risks.
Tofacitinib is indicated for RA, psoriatic arthritis, ulcerative colitis, and polyarticular course juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Baricitinib and upadacitinib are approved only for RA.
While the overall results of the trial results show nonsignificant increased incidence rates for MACE in tofacitinib users versus TNFI users, Katherine Liao, MD, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, noted that more information is needed to determine who is at greatest risk. “Another thing to keep in mind is, while there was evidence of an elevated relative risk for MACE, compared to TNFi, the absolute risk, based on the numbers what we know so far, is small,” she said.
The trial compared two different doses of tofacitinib – 5 mg (1,455 patients) and 10 mg (n = 1,456) twice daily – and TNFi (n = 1,451) in people with moderate to severe RA over age 50. Patient characteristics were similar across all three treatment arms, Dr. Charles-Schoeman said. All patients had inadequate response to methotrexate, and about 57% in all three treatment groups were taking corticosteroids. The 10-mg tofacitinib patients switched to the 5-mg dose in February 2019 but represent the 10-mg group in the study analysis.
ORAL Surveillance demonstrated a 24% greater risk of MACE in the 5-mg tofacitinib patients and a 43% heightened risk the 10-mg group, compared with patients who received a TNFi.
The differentiating factor for MACE incidence was MI. The higher- and lower-dose tofacitinib groups had 69% and 80% greater risk for MI. While the risk for fatal MI were similar across all three treatment groups, the risk for nonfatal MI were more than doubled in the respective tofacitinib groups: hazard ratios of 2.32 and 2.08. The incidence of stroke was similar across all three arms, Dr. Charles-Schoeman said.
The study identified a number of baseline characteristics as independent overall risk factors for MACE across all treatment groups. Current smoking and aspirin use more than doubled the risk (HR, 2.18; P < .0001 and HR, 2.11; P = .004, respectively), while age greater than 65 years and male sex approached that level (HR, 1.81; P = .0011 and HR, 1.81; P = .0015) approached that level. Other factors that elevated the risk of MACE to a lesser extent were a history of diabetes, hypertension or coronary artery procedures, and a total cholesterol to HDL ratio greater than4.
Other ORAL Surveillance subanalyses and tofacitinib real-world data reported
This was one of several analyses presented at ACR 2021 that compared adverse event risks for tofacitinib versus TNFi drugs. A separate analysis of claims data from patients with RA in two U.S. insurance databases plus Medicare found a statistically nonsignificant increased risk of adverse CV outcomes (MI or stroke) with tofacitinib, compared with TNFi users, among patients who met the same inclusion and exclusion criteria of the ORAL Surveillance trial but not in a “real-world evidence” cohort of more than 102,000 patients with RA in routine care from the databases.
Two additional ORAL Surveillance analyses presented at ACR 2021 gave details about risk factors for higher rates of malignancies and venous thromboembolic events found in patients taking tofacitinib with at least one CV risk factor. As would be expected, older age (≥65 vs. 50-64 years) and current or past smoking (vs. never smoking) were independent risk factors for higher malignancy rates across all treatment arms. Pulmonary embolism events across treatment groups were independently associated with a history of venous thromboembolism, baseline use of oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy, baseline body mass index of at least 30 kg/m2, age 65 or older, and history of hypertension.
The ORAL Surveillance findings are worth considering when determining treatments for RA patients with CV risk factors, Dr. Charles-Schoeman said. “Tofacitinib remains an effective RA treatment,” she said. “The choice of specific RA treatment for any patient remains an individual decision between the patient and physician, which is decided based on a number of different factors. This new study provides additional information regarding both tofacitinib as well as traditional CV risk factors for discussion with the patient.”
The ORAL Surveillance results may give rheumatologists reason to rethink use of tofacitinib in some patients with CV risk, said Dr. Liao of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “Currently, we have limited data and are still awaiting a report of the full trial results,” she said in an interview. “Based on the data available, I can think of a few patients in my clinic where I would reconsider use of these drugs, i.e., history of heart attack with stable angina, especially if there are other options.” However, she noted that many patients on tofacitinib have already failed on older treatments.
These data emphasize the importance of addressing CV risk with patients, said Brittany N. Weber, MD, PhD, a cardio-rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital who works with Dr. Liao. “It is also an opportunity to discuss modification of risk factors and to discuss primary prevention therapies, such as statin therapy, where appropriate,” she added. “Based on the individual’s cardiovascular risk, there may be a role for further risk stratification to further understand an individual’s risk, which can also inform primary prevention cardiovascular therapies and help guide these discussions.” Risk stratification could include cardiac CT for calcium scoring or cardiac coronary CT angiography for determining atherosclerotic burden.
The study was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Charles-Schoeman disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, and Regeneron-Sanofi. Dr. Liao and Dr. Weber have no relevant disclosures.
FROM ACR 2021
Embezzlement: It can happen to you
In November, the office manager of a San Antonio dermatology practice was sentenced to 46 months in prison for defrauding the practice of nearly $350,000 from patient billings and employee profit sharing accounts.
Per the indictment, the practice conducted a nonprofit educational symposium in 2012. A bank account was established to collect contributions for that event, which was supposed to be closed at its conclusion; but the office manager kept it open, and deposited practice receipts into it. She then used the account as her slush fund for travel, property payments, meal purchases, and other personal expenses on credit cards she fraudulently opened in the practice’s name. This continued for several years.
Because this case has received national attention, I am republishing my column on embezzlement, which includes recommendations that could prevent such unfortunate situations from occurring.
Few crimes are more easily overlooked than theft from within. who think everything is fine. Most embezzlers are not skillful or discreet; but their transgressions may go undetected for years, simply because no one suspects it is happening.
Detecting fraud is an inexact science. There is no textbook approach that one can follow, but a few simple measures will prevent or expose the most common forms:
Make it more difficult. Theft and embezzlement are usually products of opportunity, so minimize those opportunities. No one person should be in charge of the entire bookkeeping process: the person who enters charges should be different from the one who enters payments. The one who writes checks or makes electronic fund transfers should not balance the books, and so on. Internal audits should be done on a regular basis, and all employees should know that. Your accountant can help.
Reconcile cash receipts daily. Embezzlement does not require sophisticated technology; the most common form is simply taking cash out of the till. In a typical scenario, a patient pays a copay of $15 in cash; the receptionist records the payment as $5, and pockets the rest. Make sure a receipt is generated for every cash transaction, and that someone other than the person accepting cash reconciles the charges, receipts, and cash totals daily.
Inventory your stock. Cash isn’t the only susceptible commodity. If you sell cosmetics or other products, inventory your stock frequently. And office personnel are not the only potential thieves: Over a year ago, a locum tenens physician down the street conspired with a receptionist to take cash transactions for cosmetic neurotoxins and fillers “off the books” and split the spoils. That office was being ripped off twice; first for the neurotoxin and filler materials themselves, and then for the cash proceeds.
Separate all accounting duties. Another popular ploy is false invoicing for imaginary supplies. A friend’s experience provides a good example (retold with his permission): His bookkeeper wrote sizable checks to herself, disguising them in the ledger as payments to vendors commonly used by his practice. Since the same employee also balanced the checkbook, she got away with it for years. “It wasn’t at all clever,” he told me, “and I’m embarrassed to admit that it happened to me.”
Once again, separation of duties is the key to prevention. One employee should enter invoices into the data system, another should issue the check or make the electronic transfer, and a third should match invoices to goods and services received.
Verify expense reports. False expense reporting is a subset of the fake invoice scam. When an employee asks for reimbursement of expenses, make sure those expenses are real.
Ask about computer safeguards. Computers facilitate a lot of financial chores, but they also consolidate financial data in one place, where it is potentially accessible to anybody, anywhere. Your computer vendor should be aware of this, and should have safeguards built into your system. Ask about them. If they aren’t there, ask why.
Hire honest employees. All applicants look great on paper, so check their references; and with their permission, you can run background checks for a few dollars on any of several public information websites. (See my previous columns on hiring at http://www.mdedge.com/dermatology/managing-your-practice.)
Look for “red flags.” Examples are employees who refuse to take vacations, because someone else will have do their work; or who insist on posting expenses that are a coworker’s responsibility, “just to be nice.” Anyone obviously living beyond his or her means merits suspicion as well.
Consider bonding your employees. Dishonesty bonds are relatively inexpensive, and you will be assured of some measure of recovery should your safeguards fail. In addition, the mere knowledge that your staff is bonded will frighten off most dishonest applicants. One effective screen is a question on your employment application: “Would you object to being bonded?”
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
In November, the office manager of a San Antonio dermatology practice was sentenced to 46 months in prison for defrauding the practice of nearly $350,000 from patient billings and employee profit sharing accounts.
Per the indictment, the practice conducted a nonprofit educational symposium in 2012. A bank account was established to collect contributions for that event, which was supposed to be closed at its conclusion; but the office manager kept it open, and deposited practice receipts into it. She then used the account as her slush fund for travel, property payments, meal purchases, and other personal expenses on credit cards she fraudulently opened in the practice’s name. This continued for several years.
Because this case has received national attention, I am republishing my column on embezzlement, which includes recommendations that could prevent such unfortunate situations from occurring.
Few crimes are more easily overlooked than theft from within. who think everything is fine. Most embezzlers are not skillful or discreet; but their transgressions may go undetected for years, simply because no one suspects it is happening.
Detecting fraud is an inexact science. There is no textbook approach that one can follow, but a few simple measures will prevent or expose the most common forms:
Make it more difficult. Theft and embezzlement are usually products of opportunity, so minimize those opportunities. No one person should be in charge of the entire bookkeeping process: the person who enters charges should be different from the one who enters payments. The one who writes checks or makes electronic fund transfers should not balance the books, and so on. Internal audits should be done on a regular basis, and all employees should know that. Your accountant can help.
Reconcile cash receipts daily. Embezzlement does not require sophisticated technology; the most common form is simply taking cash out of the till. In a typical scenario, a patient pays a copay of $15 in cash; the receptionist records the payment as $5, and pockets the rest. Make sure a receipt is generated for every cash transaction, and that someone other than the person accepting cash reconciles the charges, receipts, and cash totals daily.
Inventory your stock. Cash isn’t the only susceptible commodity. If you sell cosmetics or other products, inventory your stock frequently. And office personnel are not the only potential thieves: Over a year ago, a locum tenens physician down the street conspired with a receptionist to take cash transactions for cosmetic neurotoxins and fillers “off the books” and split the spoils. That office was being ripped off twice; first for the neurotoxin and filler materials themselves, and then for the cash proceeds.
Separate all accounting duties. Another popular ploy is false invoicing for imaginary supplies. A friend’s experience provides a good example (retold with his permission): His bookkeeper wrote sizable checks to herself, disguising them in the ledger as payments to vendors commonly used by his practice. Since the same employee also balanced the checkbook, she got away with it for years. “It wasn’t at all clever,” he told me, “and I’m embarrassed to admit that it happened to me.”
Once again, separation of duties is the key to prevention. One employee should enter invoices into the data system, another should issue the check or make the electronic transfer, and a third should match invoices to goods and services received.
Verify expense reports. False expense reporting is a subset of the fake invoice scam. When an employee asks for reimbursement of expenses, make sure those expenses are real.
Ask about computer safeguards. Computers facilitate a lot of financial chores, but they also consolidate financial data in one place, where it is potentially accessible to anybody, anywhere. Your computer vendor should be aware of this, and should have safeguards built into your system. Ask about them. If they aren’t there, ask why.
Hire honest employees. All applicants look great on paper, so check their references; and with their permission, you can run background checks for a few dollars on any of several public information websites. (See my previous columns on hiring at http://www.mdedge.com/dermatology/managing-your-practice.)
Look for “red flags.” Examples are employees who refuse to take vacations, because someone else will have do their work; or who insist on posting expenses that are a coworker’s responsibility, “just to be nice.” Anyone obviously living beyond his or her means merits suspicion as well.
Consider bonding your employees. Dishonesty bonds are relatively inexpensive, and you will be assured of some measure of recovery should your safeguards fail. In addition, the mere knowledge that your staff is bonded will frighten off most dishonest applicants. One effective screen is a question on your employment application: “Would you object to being bonded?”
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
In November, the office manager of a San Antonio dermatology practice was sentenced to 46 months in prison for defrauding the practice of nearly $350,000 from patient billings and employee profit sharing accounts.
Per the indictment, the practice conducted a nonprofit educational symposium in 2012. A bank account was established to collect contributions for that event, which was supposed to be closed at its conclusion; but the office manager kept it open, and deposited practice receipts into it. She then used the account as her slush fund for travel, property payments, meal purchases, and other personal expenses on credit cards she fraudulently opened in the practice’s name. This continued for several years.
Because this case has received national attention, I am republishing my column on embezzlement, which includes recommendations that could prevent such unfortunate situations from occurring.
Few crimes are more easily overlooked than theft from within. who think everything is fine. Most embezzlers are not skillful or discreet; but their transgressions may go undetected for years, simply because no one suspects it is happening.
Detecting fraud is an inexact science. There is no textbook approach that one can follow, but a few simple measures will prevent or expose the most common forms:
Make it more difficult. Theft and embezzlement are usually products of opportunity, so minimize those opportunities. No one person should be in charge of the entire bookkeeping process: the person who enters charges should be different from the one who enters payments. The one who writes checks or makes electronic fund transfers should not balance the books, and so on. Internal audits should be done on a regular basis, and all employees should know that. Your accountant can help.
Reconcile cash receipts daily. Embezzlement does not require sophisticated technology; the most common form is simply taking cash out of the till. In a typical scenario, a patient pays a copay of $15 in cash; the receptionist records the payment as $5, and pockets the rest. Make sure a receipt is generated for every cash transaction, and that someone other than the person accepting cash reconciles the charges, receipts, and cash totals daily.
Inventory your stock. Cash isn’t the only susceptible commodity. If you sell cosmetics or other products, inventory your stock frequently. And office personnel are not the only potential thieves: Over a year ago, a locum tenens physician down the street conspired with a receptionist to take cash transactions for cosmetic neurotoxins and fillers “off the books” and split the spoils. That office was being ripped off twice; first for the neurotoxin and filler materials themselves, and then for the cash proceeds.
Separate all accounting duties. Another popular ploy is false invoicing for imaginary supplies. A friend’s experience provides a good example (retold with his permission): His bookkeeper wrote sizable checks to herself, disguising them in the ledger as payments to vendors commonly used by his practice. Since the same employee also balanced the checkbook, she got away with it for years. “It wasn’t at all clever,” he told me, “and I’m embarrassed to admit that it happened to me.”
Once again, separation of duties is the key to prevention. One employee should enter invoices into the data system, another should issue the check or make the electronic transfer, and a third should match invoices to goods and services received.
Verify expense reports. False expense reporting is a subset of the fake invoice scam. When an employee asks for reimbursement of expenses, make sure those expenses are real.
Ask about computer safeguards. Computers facilitate a lot of financial chores, but they also consolidate financial data in one place, where it is potentially accessible to anybody, anywhere. Your computer vendor should be aware of this, and should have safeguards built into your system. Ask about them. If they aren’t there, ask why.
Hire honest employees. All applicants look great on paper, so check their references; and with their permission, you can run background checks for a few dollars on any of several public information websites. (See my previous columns on hiring at http://www.mdedge.com/dermatology/managing-your-practice.)
Look for “red flags.” Examples are employees who refuse to take vacations, because someone else will have do their work; or who insist on posting expenses that are a coworker’s responsibility, “just to be nice.” Anyone obviously living beyond his or her means merits suspicion as well.
Consider bonding your employees. Dishonesty bonds are relatively inexpensive, and you will be assured of some measure of recovery should your safeguards fail. In addition, the mere knowledge that your staff is bonded will frighten off most dishonest applicants. One effective screen is a question on your employment application: “Would you object to being bonded?”
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
AI: Skin of color underrepresented in datasets used to identify skin cancer
An in the databases, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
Out of 106,950 skin lesions documented in 21 open-access databases and 17 open-access atlases identified by David Wen, BMBCh, from the University of Oxford (England), and colleagues, 2,436 images contained information on Fitzpatrick skin type. Of these, “only 10 images were from individuals with Fitzpatrick skin type V, and only a single image was from an individual with Fitzpatrick skin type VI,” the researchers said. “The ethnicity of these individuals was either Brazilian or unknown.”
In two datasets containing 1,585 images with ethnicity data, “no images were from individuals with an African, Afro-Caribbean, or South Asian background,” Dr. Wen and colleagues noted. “Coupled with the geographical origins of datasets, there was massive under-representation of skin lesion images from darker-skinned populations.”
The results of their systematic review were presented at the National Cancer Research Institute Festival and published on Nov. 9, 2021, in The Lancet Digital Health. To the best of their knowledge, they wrote, this is “the first systematic review of publicly available skin lesion images comprising predominantly dermoscopic and macroscopic images available through open access datasets and atlases.”
Overall, 11 of 14 datasets (79%) were from North America, Europe, or Oceania among datasets with information on country of origin, the researchers said. Either dermoscopic images or macroscopic photographs were the only types of images available in 19 of 21 (91%) datasets. There was some variation in the clinical information available, with 81,662 images (76.4%) containing information on age, 82,848 images (77.5%) having information on gender, and 79,561 images having information about body site (74.4%).
The researchers explained that these datasets might be of limited use in a real-world setting where the images aren’t representative of the population. Artificial intelligence (AI) programs that train using images of patients with one skin type, for example, can potentially misdiagnose patients of another skin type, they said.
“AI programs hold a lot of potential for diagnosing skin cancer because it can look at pictures and quickly and cost-effectively evaluate any worrying spots on the skin,” Dr. Wen said in a press release from the NCRI Festival. “However, it’s important to know about the images and patients used to develop programs, as these influence which groups of people the programs will be most effective for in real-life settings. Research has shown that programs trained on images taken from people with lighter skin types only might not be as accurate for people with darker skin, and vice versa.”
There was also “limited information on who, how and why the images were taken,” Dr. Wen said in the release. “This has implications for the programs developed from these images, due to uncertainty around how they may perform in different groups of people, especially in those who aren’t well represented in datasets, such as those with darker skin. This can potentially lead to the exclusion or even harm of these groups from AI technologies.”
While there are no current guidelines for developing skin image datasets, quality standards are needed, according to the researchers.
“Ensuring equitable digital health includes building unbiased, representative datasets to ensure that the algorithms that are created benefit people of all backgrounds and skin types,” they concluded in the study.
Neil Steven, MBBS, MA, PhD, FRCP, an NCRI Skin Group member who was not involved with the research, stated in the press release that the results from the study by Dr. Wen and colleagues “raise concerns about the ability of AI to assist in skin cancer diagnosis, especially in a global context.”
“I hope this work will continue and help ensure that the progress we make in using AI in medicine will benefit all patients, recognizing that human skin color is highly diverse,” said Dr. Steven, honorary consultant in medical oncology at University Hospitals Birmingham (England) NHS Foundation Trust.
‘We need more images of everybody’
Dermatologist Adewole Adamson, MD, MPP, assistant professor in the department of internal medicine (division of dermatology) at the University of Texas at Austin, said in an interview that a “major potential downside” of algorithms not trained on diverse datasets is the potential for incorrect diagnoses.
“The harms of algorithms used for diagnostic purposes in the skin can be particularly significant because of the scalability of this technology. A lot of thought needs to be put into how these algorithms are developed and tested,” said Dr. Adamson, who reviewed the manuscript of The Lancet Digital Health study but was not involved with the research.
He referred to the results of a recently published study in JAMA Dermatology, which found that only 10% of studies used to develop or test deep-learning algorithms contained metadata on skin tone. “Furthermore, most datasets are from countries where darker skin types are not represented. [These] algorithms therefore likely underperform on people of darker skin types and thus, users should be wary,” Dr. Adamson said.
A consensus guideline should be developed for public AI algorithms, he said, which should have metadata containing information on sex, race/ethnicity, geographic location, skin type, and part of the body. “This distribution should also be reported in any publication of an algorithm so that users can see if the distribution of the population in the training data mirrors that of the population in which it is intended to be used,” he added.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was not involved with the research, said that, while this issue of underrepresentation has been known in dermatology for some time, the strength of the Lancet study is that it is a large study, with a message of “we need more images of everybody.”
“This is probably the broadest study looking at every possible accessible resource and taking an organized approach,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview. “But I think it also raises some important points about how we think about skin tones and how we refer to them as well with respect to misusing classification schemes that we currently have.”
While using ethnicity data and certain Fitzpatrick skin types as a proxy for darker skin is a limitation of the metadata the study authors had available, it also highlights “a broader problem with respect to lexicon regarding skin tone,” he explained.
“Skin does not have a race, it doesn’t have an ethnicity,” Dr. Friedman said.
A dataset that contains not only different skin tones but how different dermatologic conditions look across skin tones is important. “If you just look at one photo of one skin tone, you missed the fact that clinical presentations can be so polymorphic, especially because of different skin tones,” Dr. Friedman said.
“We need to keep pushing this message to ensure that images keep getting collected. We [need to] ensure that there’s quality control with these images and that we’re disseminating them in a way that everyone has access, both from self-learning, but also to teach others,” said Dr. Friedman, coeditor of a recently introduced dermatology atlas showing skin conditions in different skin tones.
Adamson reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Friedman is a coeditor of a dermatology atlas supported by Allergan Aesthetics and SkinBetter Science. This study was funded by NHSX and the Health Foundation. Three authors reported being paid employees of Databiology at the time of the study. The other authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An in the databases, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
Out of 106,950 skin lesions documented in 21 open-access databases and 17 open-access atlases identified by David Wen, BMBCh, from the University of Oxford (England), and colleagues, 2,436 images contained information on Fitzpatrick skin type. Of these, “only 10 images were from individuals with Fitzpatrick skin type V, and only a single image was from an individual with Fitzpatrick skin type VI,” the researchers said. “The ethnicity of these individuals was either Brazilian or unknown.”
In two datasets containing 1,585 images with ethnicity data, “no images were from individuals with an African, Afro-Caribbean, or South Asian background,” Dr. Wen and colleagues noted. “Coupled with the geographical origins of datasets, there was massive under-representation of skin lesion images from darker-skinned populations.”
The results of their systematic review were presented at the National Cancer Research Institute Festival and published on Nov. 9, 2021, in The Lancet Digital Health. To the best of their knowledge, they wrote, this is “the first systematic review of publicly available skin lesion images comprising predominantly dermoscopic and macroscopic images available through open access datasets and atlases.”
Overall, 11 of 14 datasets (79%) were from North America, Europe, or Oceania among datasets with information on country of origin, the researchers said. Either dermoscopic images or macroscopic photographs were the only types of images available in 19 of 21 (91%) datasets. There was some variation in the clinical information available, with 81,662 images (76.4%) containing information on age, 82,848 images (77.5%) having information on gender, and 79,561 images having information about body site (74.4%).
The researchers explained that these datasets might be of limited use in a real-world setting where the images aren’t representative of the population. Artificial intelligence (AI) programs that train using images of patients with one skin type, for example, can potentially misdiagnose patients of another skin type, they said.
“AI programs hold a lot of potential for diagnosing skin cancer because it can look at pictures and quickly and cost-effectively evaluate any worrying spots on the skin,” Dr. Wen said in a press release from the NCRI Festival. “However, it’s important to know about the images and patients used to develop programs, as these influence which groups of people the programs will be most effective for in real-life settings. Research has shown that programs trained on images taken from people with lighter skin types only might not be as accurate for people with darker skin, and vice versa.”
There was also “limited information on who, how and why the images were taken,” Dr. Wen said in the release. “This has implications for the programs developed from these images, due to uncertainty around how they may perform in different groups of people, especially in those who aren’t well represented in datasets, such as those with darker skin. This can potentially lead to the exclusion or even harm of these groups from AI technologies.”
While there are no current guidelines for developing skin image datasets, quality standards are needed, according to the researchers.
“Ensuring equitable digital health includes building unbiased, representative datasets to ensure that the algorithms that are created benefit people of all backgrounds and skin types,” they concluded in the study.
Neil Steven, MBBS, MA, PhD, FRCP, an NCRI Skin Group member who was not involved with the research, stated in the press release that the results from the study by Dr. Wen and colleagues “raise concerns about the ability of AI to assist in skin cancer diagnosis, especially in a global context.”
“I hope this work will continue and help ensure that the progress we make in using AI in medicine will benefit all patients, recognizing that human skin color is highly diverse,” said Dr. Steven, honorary consultant in medical oncology at University Hospitals Birmingham (England) NHS Foundation Trust.
‘We need more images of everybody’
Dermatologist Adewole Adamson, MD, MPP, assistant professor in the department of internal medicine (division of dermatology) at the University of Texas at Austin, said in an interview that a “major potential downside” of algorithms not trained on diverse datasets is the potential for incorrect diagnoses.
“The harms of algorithms used for diagnostic purposes in the skin can be particularly significant because of the scalability of this technology. A lot of thought needs to be put into how these algorithms are developed and tested,” said Dr. Adamson, who reviewed the manuscript of The Lancet Digital Health study but was not involved with the research.
He referred to the results of a recently published study in JAMA Dermatology, which found that only 10% of studies used to develop or test deep-learning algorithms contained metadata on skin tone. “Furthermore, most datasets are from countries where darker skin types are not represented. [These] algorithms therefore likely underperform on people of darker skin types and thus, users should be wary,” Dr. Adamson said.
A consensus guideline should be developed for public AI algorithms, he said, which should have metadata containing information on sex, race/ethnicity, geographic location, skin type, and part of the body. “This distribution should also be reported in any publication of an algorithm so that users can see if the distribution of the population in the training data mirrors that of the population in which it is intended to be used,” he added.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was not involved with the research, said that, while this issue of underrepresentation has been known in dermatology for some time, the strength of the Lancet study is that it is a large study, with a message of “we need more images of everybody.”
“This is probably the broadest study looking at every possible accessible resource and taking an organized approach,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview. “But I think it also raises some important points about how we think about skin tones and how we refer to them as well with respect to misusing classification schemes that we currently have.”
While using ethnicity data and certain Fitzpatrick skin types as a proxy for darker skin is a limitation of the metadata the study authors had available, it also highlights “a broader problem with respect to lexicon regarding skin tone,” he explained.
“Skin does not have a race, it doesn’t have an ethnicity,” Dr. Friedman said.
A dataset that contains not only different skin tones but how different dermatologic conditions look across skin tones is important. “If you just look at one photo of one skin tone, you missed the fact that clinical presentations can be so polymorphic, especially because of different skin tones,” Dr. Friedman said.
“We need to keep pushing this message to ensure that images keep getting collected. We [need to] ensure that there’s quality control with these images and that we’re disseminating them in a way that everyone has access, both from self-learning, but also to teach others,” said Dr. Friedman, coeditor of a recently introduced dermatology atlas showing skin conditions in different skin tones.
Adamson reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Friedman is a coeditor of a dermatology atlas supported by Allergan Aesthetics and SkinBetter Science. This study was funded by NHSX and the Health Foundation. Three authors reported being paid employees of Databiology at the time of the study. The other authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An in the databases, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
Out of 106,950 skin lesions documented in 21 open-access databases and 17 open-access atlases identified by David Wen, BMBCh, from the University of Oxford (England), and colleagues, 2,436 images contained information on Fitzpatrick skin type. Of these, “only 10 images were from individuals with Fitzpatrick skin type V, and only a single image was from an individual with Fitzpatrick skin type VI,” the researchers said. “The ethnicity of these individuals was either Brazilian or unknown.”
In two datasets containing 1,585 images with ethnicity data, “no images were from individuals with an African, Afro-Caribbean, or South Asian background,” Dr. Wen and colleagues noted. “Coupled with the geographical origins of datasets, there was massive under-representation of skin lesion images from darker-skinned populations.”
The results of their systematic review were presented at the National Cancer Research Institute Festival and published on Nov. 9, 2021, in The Lancet Digital Health. To the best of their knowledge, they wrote, this is “the first systematic review of publicly available skin lesion images comprising predominantly dermoscopic and macroscopic images available through open access datasets and atlases.”
Overall, 11 of 14 datasets (79%) were from North America, Europe, or Oceania among datasets with information on country of origin, the researchers said. Either dermoscopic images or macroscopic photographs were the only types of images available in 19 of 21 (91%) datasets. There was some variation in the clinical information available, with 81,662 images (76.4%) containing information on age, 82,848 images (77.5%) having information on gender, and 79,561 images having information about body site (74.4%).
The researchers explained that these datasets might be of limited use in a real-world setting where the images aren’t representative of the population. Artificial intelligence (AI) programs that train using images of patients with one skin type, for example, can potentially misdiagnose patients of another skin type, they said.
“AI programs hold a lot of potential for diagnosing skin cancer because it can look at pictures and quickly and cost-effectively evaluate any worrying spots on the skin,” Dr. Wen said in a press release from the NCRI Festival. “However, it’s important to know about the images and patients used to develop programs, as these influence which groups of people the programs will be most effective for in real-life settings. Research has shown that programs trained on images taken from people with lighter skin types only might not be as accurate for people with darker skin, and vice versa.”
There was also “limited information on who, how and why the images were taken,” Dr. Wen said in the release. “This has implications for the programs developed from these images, due to uncertainty around how they may perform in different groups of people, especially in those who aren’t well represented in datasets, such as those with darker skin. This can potentially lead to the exclusion or even harm of these groups from AI technologies.”
While there are no current guidelines for developing skin image datasets, quality standards are needed, according to the researchers.
“Ensuring equitable digital health includes building unbiased, representative datasets to ensure that the algorithms that are created benefit people of all backgrounds and skin types,” they concluded in the study.
Neil Steven, MBBS, MA, PhD, FRCP, an NCRI Skin Group member who was not involved with the research, stated in the press release that the results from the study by Dr. Wen and colleagues “raise concerns about the ability of AI to assist in skin cancer diagnosis, especially in a global context.”
“I hope this work will continue and help ensure that the progress we make in using AI in medicine will benefit all patients, recognizing that human skin color is highly diverse,” said Dr. Steven, honorary consultant in medical oncology at University Hospitals Birmingham (England) NHS Foundation Trust.
‘We need more images of everybody’
Dermatologist Adewole Adamson, MD, MPP, assistant professor in the department of internal medicine (division of dermatology) at the University of Texas at Austin, said in an interview that a “major potential downside” of algorithms not trained on diverse datasets is the potential for incorrect diagnoses.
“The harms of algorithms used for diagnostic purposes in the skin can be particularly significant because of the scalability of this technology. A lot of thought needs to be put into how these algorithms are developed and tested,” said Dr. Adamson, who reviewed the manuscript of The Lancet Digital Health study but was not involved with the research.
He referred to the results of a recently published study in JAMA Dermatology, which found that only 10% of studies used to develop or test deep-learning algorithms contained metadata on skin tone. “Furthermore, most datasets are from countries where darker skin types are not represented. [These] algorithms therefore likely underperform on people of darker skin types and thus, users should be wary,” Dr. Adamson said.
A consensus guideline should be developed for public AI algorithms, he said, which should have metadata containing information on sex, race/ethnicity, geographic location, skin type, and part of the body. “This distribution should also be reported in any publication of an algorithm so that users can see if the distribution of the population in the training data mirrors that of the population in which it is intended to be used,” he added.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was not involved with the research, said that, while this issue of underrepresentation has been known in dermatology for some time, the strength of the Lancet study is that it is a large study, with a message of “we need more images of everybody.”
“This is probably the broadest study looking at every possible accessible resource and taking an organized approach,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview. “But I think it also raises some important points about how we think about skin tones and how we refer to them as well with respect to misusing classification schemes that we currently have.”
While using ethnicity data and certain Fitzpatrick skin types as a proxy for darker skin is a limitation of the metadata the study authors had available, it also highlights “a broader problem with respect to lexicon regarding skin tone,” he explained.
“Skin does not have a race, it doesn’t have an ethnicity,” Dr. Friedman said.
A dataset that contains not only different skin tones but how different dermatologic conditions look across skin tones is important. “If you just look at one photo of one skin tone, you missed the fact that clinical presentations can be so polymorphic, especially because of different skin tones,” Dr. Friedman said.
“We need to keep pushing this message to ensure that images keep getting collected. We [need to] ensure that there’s quality control with these images and that we’re disseminating them in a way that everyone has access, both from self-learning, but also to teach others,” said Dr. Friedman, coeditor of a recently introduced dermatology atlas showing skin conditions in different skin tones.
Adamson reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Friedman is a coeditor of a dermatology atlas supported by Allergan Aesthetics and SkinBetter Science. This study was funded by NHSX and the Health Foundation. Three authors reported being paid employees of Databiology at the time of the study. The other authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sea buckthorn: What is it and what is it good for?
To avoid jumping on the bandwagon of another ingredient trend, we sought to examine the scientific background and properties of sea buckthorn oil and it’s utility for the skin.
Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) – also known as a Siberian pineapple tree, and as sandthorn, sallowthorn, or seaberry – is a thorny, dioecious shrub (or tree) in the oleaster family. It can grow up to 23 feet high and is found in coastal sea cliff areas and on mountain slopes of Western Europe, and in dry sandy areas of Asia Minor and Central Asia, Siberia, China, and Tibet. Common sea buckthorn flowers in late April and early May, producing a large number of small, green and brown flowers, turning into edible, usually yellow or orange round berries. The berries have a bitter, sour taste and have a mild aroma, resembling that of a pineapple. The fruit contains a small stone that covers an oily seed.
The berries are a source of antioxidant vitamins, flavonoids, and organic acids, and when pressed, produce a juice that separates into three layers: a thick cream (upper layer), a combination of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids (middle layer), and juice that is a source of fat (lower layer). The berries contain mainly vitamin C, but also vitamin A (alpha- and beta-carotene) and a mixture of other carotenoids, as well as varying concentrations of tocopherols (vitamin E), folic acid, and vitamin B complex–group vitamins.
In addition to flavonoids, the berries contain catechins and procyanidins, cyclitols, phospholipids, tannins, sugars (galactose, fructose, xylose), organic acids (maleic acid, oxalic acid, malic acid, tartaric acid), phenolic acids (such as ferulic acid), and fatty oil. The amount of vitamin C content varies with the variety of the plant and where it is found. The oil of sea buckthorn may be extracted from two parts of the plant, with mechanical cold pressing of seeds (up to 12.5% weight as oil content) and fruit pulp (8%-12% oil content).
Among vegetable oils, sea buckthorn fruit oil has the highest content of palmitoleic acid (omega-7).
Fruit and seed oils contain tocotrienols and plant sterols. Pulp sea buckthorn oil has a high carotenoid content, as opposed to seed oil, and in Mongolia, Russia, and China, is used as a topical therapy for skin burns.
Other significant fatty acids found in sea buckthorn oil are saturated fatty acids (palmitic acid and stearic acid) and polyunsaturated fatty acids, which include alpha-linolenic acid (omega-3), gamma-linolenic acid (omega-6), linolic acid (omega-6), oleic acid (omega-9), and eicosanoic acid (omega-9). Gamma-linoleic acid in particular is reduced in dry skin conditions, such as aging and atopic dermatitis. The human body can produce some gamma-linolenic acid, oleic acid, and palmitoleic acid, but not linolic acid and alpha-linolenic acid. The addition of these substances to diet or skin care has been found to be beneficial in improving dryness and the skin barrier.
In addition, linolic acid, a natural component of human sebum, has been noted to be decreased in the sebum of people with acne-prone skin. Preliminary evidence indicates that dietary supplements containing fatty acids such as docosahexaenoic acid, sea buckthorn oil, and hemp seed oil may decrease the severity of atopic dermatitis.
Besides use in topical skin care and cosmetic preparations, sea buckthorn has also been used successfully in the treatment of chronic gastric ulcer disease, inflammation of the vagina and cervix, and cervical erosion. The bark and leaves of sea buckthorn used to be applied to treat diarrhea and dermatologic conditions, while berry oil has been applied topically or taken orally to soften the skin.
In traditional Indian, Chinese, and Tibetan medicines, sea buckthorn berries are used for medicinal purposes, as their ingredients were thought to have a beneficial effect on the function of the alimentary, respiratory, and circulatory systems. Current studies and uses are now confirming their utility experienced over hundreds of years.
Harvesting sea buckthorn fruit is difficult because of dense thorn arrangement among the berries. Therefore, sometimes the only way to obtain fruit is to remove the entire branch of the shrub, which reduces future crops. For this reason berries can only be harvested once every 2 years.
Sea buckthorn has interesting properties and could be of benefit in topical skin care, as long as it is not overharvested or harvested in a way that has a detrimental impact on the environment.
Dr. Wesley and Lily Talakoub, MD, are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. This month’s column is by Dr. Wesley. Write to them at [email protected]. They had no relevant disclosures.
References
United States Department of Agriculture. PLANTS Profile for Hippophae rhamnoides (seaberry). 2007.
Zielińska A and Nowak I. Lipids Health Dis. 2017 May 19;16(1):95.
Reynolds KA et al. Int J Dermatol. 2019 Dec;58(12):1371-6.
To avoid jumping on the bandwagon of another ingredient trend, we sought to examine the scientific background and properties of sea buckthorn oil and it’s utility for the skin.
Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) – also known as a Siberian pineapple tree, and as sandthorn, sallowthorn, or seaberry – is a thorny, dioecious shrub (or tree) in the oleaster family. It can grow up to 23 feet high and is found in coastal sea cliff areas and on mountain slopes of Western Europe, and in dry sandy areas of Asia Minor and Central Asia, Siberia, China, and Tibet. Common sea buckthorn flowers in late April and early May, producing a large number of small, green and brown flowers, turning into edible, usually yellow or orange round berries. The berries have a bitter, sour taste and have a mild aroma, resembling that of a pineapple. The fruit contains a small stone that covers an oily seed.
The berries are a source of antioxidant vitamins, flavonoids, and organic acids, and when pressed, produce a juice that separates into three layers: a thick cream (upper layer), a combination of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids (middle layer), and juice that is a source of fat (lower layer). The berries contain mainly vitamin C, but also vitamin A (alpha- and beta-carotene) and a mixture of other carotenoids, as well as varying concentrations of tocopherols (vitamin E), folic acid, and vitamin B complex–group vitamins.
In addition to flavonoids, the berries contain catechins and procyanidins, cyclitols, phospholipids, tannins, sugars (galactose, fructose, xylose), organic acids (maleic acid, oxalic acid, malic acid, tartaric acid), phenolic acids (such as ferulic acid), and fatty oil. The amount of vitamin C content varies with the variety of the plant and where it is found. The oil of sea buckthorn may be extracted from two parts of the plant, with mechanical cold pressing of seeds (up to 12.5% weight as oil content) and fruit pulp (8%-12% oil content).
Among vegetable oils, sea buckthorn fruit oil has the highest content of palmitoleic acid (omega-7).
Fruit and seed oils contain tocotrienols and plant sterols. Pulp sea buckthorn oil has a high carotenoid content, as opposed to seed oil, and in Mongolia, Russia, and China, is used as a topical therapy for skin burns.
Other significant fatty acids found in sea buckthorn oil are saturated fatty acids (palmitic acid and stearic acid) and polyunsaturated fatty acids, which include alpha-linolenic acid (omega-3), gamma-linolenic acid (omega-6), linolic acid (omega-6), oleic acid (omega-9), and eicosanoic acid (omega-9). Gamma-linoleic acid in particular is reduced in dry skin conditions, such as aging and atopic dermatitis. The human body can produce some gamma-linolenic acid, oleic acid, and palmitoleic acid, but not linolic acid and alpha-linolenic acid. The addition of these substances to diet or skin care has been found to be beneficial in improving dryness and the skin barrier.
In addition, linolic acid, a natural component of human sebum, has been noted to be decreased in the sebum of people with acne-prone skin. Preliminary evidence indicates that dietary supplements containing fatty acids such as docosahexaenoic acid, sea buckthorn oil, and hemp seed oil may decrease the severity of atopic dermatitis.
Besides use in topical skin care and cosmetic preparations, sea buckthorn has also been used successfully in the treatment of chronic gastric ulcer disease, inflammation of the vagina and cervix, and cervical erosion. The bark and leaves of sea buckthorn used to be applied to treat diarrhea and dermatologic conditions, while berry oil has been applied topically or taken orally to soften the skin.
In traditional Indian, Chinese, and Tibetan medicines, sea buckthorn berries are used for medicinal purposes, as their ingredients were thought to have a beneficial effect on the function of the alimentary, respiratory, and circulatory systems. Current studies and uses are now confirming their utility experienced over hundreds of years.
Harvesting sea buckthorn fruit is difficult because of dense thorn arrangement among the berries. Therefore, sometimes the only way to obtain fruit is to remove the entire branch of the shrub, which reduces future crops. For this reason berries can only be harvested once every 2 years.
Sea buckthorn has interesting properties and could be of benefit in topical skin care, as long as it is not overharvested or harvested in a way that has a detrimental impact on the environment.
Dr. Wesley and Lily Talakoub, MD, are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. This month’s column is by Dr. Wesley. Write to them at [email protected]. They had no relevant disclosures.
References
United States Department of Agriculture. PLANTS Profile for Hippophae rhamnoides (seaberry). 2007.
Zielińska A and Nowak I. Lipids Health Dis. 2017 May 19;16(1):95.
Reynolds KA et al. Int J Dermatol. 2019 Dec;58(12):1371-6.
To avoid jumping on the bandwagon of another ingredient trend, we sought to examine the scientific background and properties of sea buckthorn oil and it’s utility for the skin.
Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) – also known as a Siberian pineapple tree, and as sandthorn, sallowthorn, or seaberry – is a thorny, dioecious shrub (or tree) in the oleaster family. It can grow up to 23 feet high and is found in coastal sea cliff areas and on mountain slopes of Western Europe, and in dry sandy areas of Asia Minor and Central Asia, Siberia, China, and Tibet. Common sea buckthorn flowers in late April and early May, producing a large number of small, green and brown flowers, turning into edible, usually yellow or orange round berries. The berries have a bitter, sour taste and have a mild aroma, resembling that of a pineapple. The fruit contains a small stone that covers an oily seed.
The berries are a source of antioxidant vitamins, flavonoids, and organic acids, and when pressed, produce a juice that separates into three layers: a thick cream (upper layer), a combination of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids (middle layer), and juice that is a source of fat (lower layer). The berries contain mainly vitamin C, but also vitamin A (alpha- and beta-carotene) and a mixture of other carotenoids, as well as varying concentrations of tocopherols (vitamin E), folic acid, and vitamin B complex–group vitamins.
In addition to flavonoids, the berries contain catechins and procyanidins, cyclitols, phospholipids, tannins, sugars (galactose, fructose, xylose), organic acids (maleic acid, oxalic acid, malic acid, tartaric acid), phenolic acids (such as ferulic acid), and fatty oil. The amount of vitamin C content varies with the variety of the plant and where it is found. The oil of sea buckthorn may be extracted from two parts of the plant, with mechanical cold pressing of seeds (up to 12.5% weight as oil content) and fruit pulp (8%-12% oil content).
Among vegetable oils, sea buckthorn fruit oil has the highest content of palmitoleic acid (omega-7).
Fruit and seed oils contain tocotrienols and plant sterols. Pulp sea buckthorn oil has a high carotenoid content, as opposed to seed oil, and in Mongolia, Russia, and China, is used as a topical therapy for skin burns.
Other significant fatty acids found in sea buckthorn oil are saturated fatty acids (palmitic acid and stearic acid) and polyunsaturated fatty acids, which include alpha-linolenic acid (omega-3), gamma-linolenic acid (omega-6), linolic acid (omega-6), oleic acid (omega-9), and eicosanoic acid (omega-9). Gamma-linoleic acid in particular is reduced in dry skin conditions, such as aging and atopic dermatitis. The human body can produce some gamma-linolenic acid, oleic acid, and palmitoleic acid, but not linolic acid and alpha-linolenic acid. The addition of these substances to diet or skin care has been found to be beneficial in improving dryness and the skin barrier.
In addition, linolic acid, a natural component of human sebum, has been noted to be decreased in the sebum of people with acne-prone skin. Preliminary evidence indicates that dietary supplements containing fatty acids such as docosahexaenoic acid, sea buckthorn oil, and hemp seed oil may decrease the severity of atopic dermatitis.
Besides use in topical skin care and cosmetic preparations, sea buckthorn has also been used successfully in the treatment of chronic gastric ulcer disease, inflammation of the vagina and cervix, and cervical erosion. The bark and leaves of sea buckthorn used to be applied to treat diarrhea and dermatologic conditions, while berry oil has been applied topically or taken orally to soften the skin.
In traditional Indian, Chinese, and Tibetan medicines, sea buckthorn berries are used for medicinal purposes, as their ingredients were thought to have a beneficial effect on the function of the alimentary, respiratory, and circulatory systems. Current studies and uses are now confirming their utility experienced over hundreds of years.
Harvesting sea buckthorn fruit is difficult because of dense thorn arrangement among the berries. Therefore, sometimes the only way to obtain fruit is to remove the entire branch of the shrub, which reduces future crops. For this reason berries can only be harvested once every 2 years.
Sea buckthorn has interesting properties and could be of benefit in topical skin care, as long as it is not overharvested or harvested in a way that has a detrimental impact on the environment.
Dr. Wesley and Lily Talakoub, MD, are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. This month’s column is by Dr. Wesley. Write to them at [email protected]. They had no relevant disclosures.
References
United States Department of Agriculture. PLANTS Profile for Hippophae rhamnoides (seaberry). 2007.
Zielińska A and Nowak I. Lipids Health Dis. 2017 May 19;16(1):95.
Reynolds KA et al. Int J Dermatol. 2019 Dec;58(12):1371-6.
Biden seeks to return Califf as FDA chief
On Nov. 12, president Joe Biden said he will nominate Robert Califf, MD, to be commissioner of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the top U.S. regulator of drugs and medical devices.
Dr. Califf, a cardiologist, served as FDA chief in the Obama administration, leading the agency from Feb. 2016 to Jan. 2017.
The coming nomination ends nearly 11 months of speculation over Mr. Biden’s pick to the lead the agency during the ongoing pandemic. Janet Woodcock, MD, an FDA veteran, has been serving as acting commissioner. The White House faced a Tuesday deadline to make a nomination or see Dr. Woodcock’s tenure as acting chief expire under federal law.
The initial reaction to the idea of Dr. Califf’s return to the FDA drew mixed reactions.
The nonprofit watchdog Public Citizen issued a statement about its opposition to the potential nomination of Dr. Califf. Michael Carome, MD, director of Public Citizen’s Health Research Group, said the United States “desperately needs an FDA leader who will reverse the decades-long trend in which the agency’s relationship with the pharmaceutical and medical-device industries has grown dangerously cozier – resulting in regulatory capture of the agency by industry.”
But the idea of Dr. Califf returning to the FDA pleased Harlan Krumholz, MD, a cardiologist who has been a leader in outcomes research.
Dr. Krumholz tweeted that the Biden administration likely was testing the reaction to a possible Dr. Califf nomination before making it official. “I realize that this is being floated and not officially announced ... but the nomination of [Califf] just makes so much sense,” Dr. Krumholz tweeted. Dr. Califf’s “expertise as a researcher, policymaker, clinician are unparalleled. In a time of partisanship, he should be a slam-dunk confirmation.”
Dr. Califf’s 2016 Senate confirmation process was marked by dissent from several Democrats who questioned his ties to industry. But the chamber voted 89-4 to confirm him.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On Nov. 12, president Joe Biden said he will nominate Robert Califf, MD, to be commissioner of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the top U.S. regulator of drugs and medical devices.
Dr. Califf, a cardiologist, served as FDA chief in the Obama administration, leading the agency from Feb. 2016 to Jan. 2017.
The coming nomination ends nearly 11 months of speculation over Mr. Biden’s pick to the lead the agency during the ongoing pandemic. Janet Woodcock, MD, an FDA veteran, has been serving as acting commissioner. The White House faced a Tuesday deadline to make a nomination or see Dr. Woodcock’s tenure as acting chief expire under federal law.
The initial reaction to the idea of Dr. Califf’s return to the FDA drew mixed reactions.
The nonprofit watchdog Public Citizen issued a statement about its opposition to the potential nomination of Dr. Califf. Michael Carome, MD, director of Public Citizen’s Health Research Group, said the United States “desperately needs an FDA leader who will reverse the decades-long trend in which the agency’s relationship with the pharmaceutical and medical-device industries has grown dangerously cozier – resulting in regulatory capture of the agency by industry.”
But the idea of Dr. Califf returning to the FDA pleased Harlan Krumholz, MD, a cardiologist who has been a leader in outcomes research.
Dr. Krumholz tweeted that the Biden administration likely was testing the reaction to a possible Dr. Califf nomination before making it official. “I realize that this is being floated and not officially announced ... but the nomination of [Califf] just makes so much sense,” Dr. Krumholz tweeted. Dr. Califf’s “expertise as a researcher, policymaker, clinician are unparalleled. In a time of partisanship, he should be a slam-dunk confirmation.”
Dr. Califf’s 2016 Senate confirmation process was marked by dissent from several Democrats who questioned his ties to industry. But the chamber voted 89-4 to confirm him.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On Nov. 12, president Joe Biden said he will nominate Robert Califf, MD, to be commissioner of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the top U.S. regulator of drugs and medical devices.
Dr. Califf, a cardiologist, served as FDA chief in the Obama administration, leading the agency from Feb. 2016 to Jan. 2017.
The coming nomination ends nearly 11 months of speculation over Mr. Biden’s pick to the lead the agency during the ongoing pandemic. Janet Woodcock, MD, an FDA veteran, has been serving as acting commissioner. The White House faced a Tuesday deadline to make a nomination or see Dr. Woodcock’s tenure as acting chief expire under federal law.
The initial reaction to the idea of Dr. Califf’s return to the FDA drew mixed reactions.
The nonprofit watchdog Public Citizen issued a statement about its opposition to the potential nomination of Dr. Califf. Michael Carome, MD, director of Public Citizen’s Health Research Group, said the United States “desperately needs an FDA leader who will reverse the decades-long trend in which the agency’s relationship with the pharmaceutical and medical-device industries has grown dangerously cozier – resulting in regulatory capture of the agency by industry.”
But the idea of Dr. Califf returning to the FDA pleased Harlan Krumholz, MD, a cardiologist who has been a leader in outcomes research.
Dr. Krumholz tweeted that the Biden administration likely was testing the reaction to a possible Dr. Califf nomination before making it official. “I realize that this is being floated and not officially announced ... but the nomination of [Califf] just makes so much sense,” Dr. Krumholz tweeted. Dr. Califf’s “expertise as a researcher, policymaker, clinician are unparalleled. In a time of partisanship, he should be a slam-dunk confirmation.”
Dr. Califf’s 2016 Senate confirmation process was marked by dissent from several Democrats who questioned his ties to industry. But the chamber voted 89-4 to confirm him.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
What is the diagnosis?
Numerous morphologies of skin rashes have been described in the setting of COVID-19, including pernio, livedoid rash, exanthem, and vasculitis. This classic constellation of symptoms (palpable purpura on buttocks/legs, abdominal pain, arthralgia, hematuria) is highly consistent with Henoch-Schonlein purpura (HSP). There are now multiple case reports of COVID-19–associated HSP.
HSP is the most common type of childhood systemic vasculitis. It is mediated by immunoglobulin A (IgA) immune complex deposition and has been associated with respiratory tract infections, streptococcal species, parainfluenza virus, and human parvovirus B19, medications, vaccinations, and malignancies. HSP is usually a self-limiting disease, with a course over 4-6 weeks, and can affect multiple organs, including the skin, gastrointestinal tract, joints, and the kidneys. The diagnostic criteria include palpable purpura in the presence of one or more of the following: diffuse abdominal pain, arthritis or arthralgia, any biopsy showing predominant IgA deposition, and renal involvement in the form of hematuria or proteinuria. Renal disease is variable and is the most significant indicator of long-term prognosis. This teenager was treated with oral corticosteroids because of the severe periarticular edema and responded rapidly. His subsequent urine analyses normalized.
What is on the differential?
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) is a rare, potentially fatal, complication of COVID-19 infection that causes inflammation of multiple organs, including the heart, lungs, kidneys, brain, skin, eyes, or the gastrointestinal tract. It commonly affects children around ages 8-9 years. Initial symptoms include fever, rash, red eyes, diarrhea, and vomiting that appear 2-6 weeks post COVID-19 infection. Like HSP, MIS-C can present with edema of the extremities, worsening hand/foot pain, and hematuria; however, the absence of both fever and the pattern of system involvement seen with MIS-C and classic findings in this patient are more consistent with HSP.
Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) was recently coined to encompass both infection-associated Stevens-Johnson eruptions including Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced rash and mucositis (MIRM) and mucocutaneous eruptions caused by nonmycoplasma pathogens (including Chlamydia pneumoniae, human parainfluenza virus 2, rhinovirus, adenovirus, enterovirus, human metapneumovirus, influenza B virus, and COVID-19). It is usually seen in male children and adolescents. Prodromal symptoms include cough, fever, and malaise and they precede the prominent feature of mucositis. Our patient’s lack of mucosal involvement is not consistent with RIME.
Perniosis (chilblains) is characterized by localized edematous patches of erythema or cyanosis on exposed extremities, that may be associated with cold exposure. Lesions are usually symmetric and self-limiting, and symptoms can include numbness, tingling, pruritus, burning, or pain. Pernio-like skin lesions have been seen during the COVID-19 pandemic, though many patients have negative testing for infection by PCR and serology. Pernio may also be seen with autoimmune diseases or malignancy.
Meningococcemia is a rare disease caused by infection with gram-negative diplococci bacteria Neisseria meningitidis and spreads through saliva or respiratory secretions. Its clinical presentation can vary widely, from transient fever to fulminant disease. It is characterized by upper respiratory tract infection, fever, and petechial lesions associated with thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Ms. Laborada is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield and Ms. Laborada have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
AlGhoozi DA, AlKhayyat HM. BMJ Case Reports CP 2021;14:e239910.
Jacobi M et al. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2021;40(2):e93-4.
Paller A, Mancini AJ. Hurwitz clinical pediatric dermatology: A textbook of skin disorders of childhood and adolescence. 4th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier Saunders; 2011.
Radia T et al. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2021;38:51-7.
Ramien ML. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021;46(3):420-9.
Numerous morphologies of skin rashes have been described in the setting of COVID-19, including pernio, livedoid rash, exanthem, and vasculitis. This classic constellation of symptoms (palpable purpura on buttocks/legs, abdominal pain, arthralgia, hematuria) is highly consistent with Henoch-Schonlein purpura (HSP). There are now multiple case reports of COVID-19–associated HSP.
HSP is the most common type of childhood systemic vasculitis. It is mediated by immunoglobulin A (IgA) immune complex deposition and has been associated with respiratory tract infections, streptococcal species, parainfluenza virus, and human parvovirus B19, medications, vaccinations, and malignancies. HSP is usually a self-limiting disease, with a course over 4-6 weeks, and can affect multiple organs, including the skin, gastrointestinal tract, joints, and the kidneys. The diagnostic criteria include palpable purpura in the presence of one or more of the following: diffuse abdominal pain, arthritis or arthralgia, any biopsy showing predominant IgA deposition, and renal involvement in the form of hematuria or proteinuria. Renal disease is variable and is the most significant indicator of long-term prognosis. This teenager was treated with oral corticosteroids because of the severe periarticular edema and responded rapidly. His subsequent urine analyses normalized.
What is on the differential?
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) is a rare, potentially fatal, complication of COVID-19 infection that causes inflammation of multiple organs, including the heart, lungs, kidneys, brain, skin, eyes, or the gastrointestinal tract. It commonly affects children around ages 8-9 years. Initial symptoms include fever, rash, red eyes, diarrhea, and vomiting that appear 2-6 weeks post COVID-19 infection. Like HSP, MIS-C can present with edema of the extremities, worsening hand/foot pain, and hematuria; however, the absence of both fever and the pattern of system involvement seen with MIS-C and classic findings in this patient are more consistent with HSP.
Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) was recently coined to encompass both infection-associated Stevens-Johnson eruptions including Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced rash and mucositis (MIRM) and mucocutaneous eruptions caused by nonmycoplasma pathogens (including Chlamydia pneumoniae, human parainfluenza virus 2, rhinovirus, adenovirus, enterovirus, human metapneumovirus, influenza B virus, and COVID-19). It is usually seen in male children and adolescents. Prodromal symptoms include cough, fever, and malaise and they precede the prominent feature of mucositis. Our patient’s lack of mucosal involvement is not consistent with RIME.
Perniosis (chilblains) is characterized by localized edematous patches of erythema or cyanosis on exposed extremities, that may be associated with cold exposure. Lesions are usually symmetric and self-limiting, and symptoms can include numbness, tingling, pruritus, burning, or pain. Pernio-like skin lesions have been seen during the COVID-19 pandemic, though many patients have negative testing for infection by PCR and serology. Pernio may also be seen with autoimmune diseases or malignancy.
Meningococcemia is a rare disease caused by infection with gram-negative diplococci bacteria Neisseria meningitidis and spreads through saliva or respiratory secretions. Its clinical presentation can vary widely, from transient fever to fulminant disease. It is characterized by upper respiratory tract infection, fever, and petechial lesions associated with thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Ms. Laborada is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield and Ms. Laborada have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
AlGhoozi DA, AlKhayyat HM. BMJ Case Reports CP 2021;14:e239910.
Jacobi M et al. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2021;40(2):e93-4.
Paller A, Mancini AJ. Hurwitz clinical pediatric dermatology: A textbook of skin disorders of childhood and adolescence. 4th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier Saunders; 2011.
Radia T et al. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2021;38:51-7.
Ramien ML. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021;46(3):420-9.
Numerous morphologies of skin rashes have been described in the setting of COVID-19, including pernio, livedoid rash, exanthem, and vasculitis. This classic constellation of symptoms (palpable purpura on buttocks/legs, abdominal pain, arthralgia, hematuria) is highly consistent with Henoch-Schonlein purpura (HSP). There are now multiple case reports of COVID-19–associated HSP.
HSP is the most common type of childhood systemic vasculitis. It is mediated by immunoglobulin A (IgA) immune complex deposition and has been associated with respiratory tract infections, streptococcal species, parainfluenza virus, and human parvovirus B19, medications, vaccinations, and malignancies. HSP is usually a self-limiting disease, with a course over 4-6 weeks, and can affect multiple organs, including the skin, gastrointestinal tract, joints, and the kidneys. The diagnostic criteria include palpable purpura in the presence of one or more of the following: diffuse abdominal pain, arthritis or arthralgia, any biopsy showing predominant IgA deposition, and renal involvement in the form of hematuria or proteinuria. Renal disease is variable and is the most significant indicator of long-term prognosis. This teenager was treated with oral corticosteroids because of the severe periarticular edema and responded rapidly. His subsequent urine analyses normalized.
What is on the differential?
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) is a rare, potentially fatal, complication of COVID-19 infection that causes inflammation of multiple organs, including the heart, lungs, kidneys, brain, skin, eyes, or the gastrointestinal tract. It commonly affects children around ages 8-9 years. Initial symptoms include fever, rash, red eyes, diarrhea, and vomiting that appear 2-6 weeks post COVID-19 infection. Like HSP, MIS-C can present with edema of the extremities, worsening hand/foot pain, and hematuria; however, the absence of both fever and the pattern of system involvement seen with MIS-C and classic findings in this patient are more consistent with HSP.
Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) was recently coined to encompass both infection-associated Stevens-Johnson eruptions including Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced rash and mucositis (MIRM) and mucocutaneous eruptions caused by nonmycoplasma pathogens (including Chlamydia pneumoniae, human parainfluenza virus 2, rhinovirus, adenovirus, enterovirus, human metapneumovirus, influenza B virus, and COVID-19). It is usually seen in male children and adolescents. Prodromal symptoms include cough, fever, and malaise and they precede the prominent feature of mucositis. Our patient’s lack of mucosal involvement is not consistent with RIME.
Perniosis (chilblains) is characterized by localized edematous patches of erythema or cyanosis on exposed extremities, that may be associated with cold exposure. Lesions are usually symmetric and self-limiting, and symptoms can include numbness, tingling, pruritus, burning, or pain. Pernio-like skin lesions have been seen during the COVID-19 pandemic, though many patients have negative testing for infection by PCR and serology. Pernio may also be seen with autoimmune diseases or malignancy.
Meningococcemia is a rare disease caused by infection with gram-negative diplococci bacteria Neisseria meningitidis and spreads through saliva or respiratory secretions. Its clinical presentation can vary widely, from transient fever to fulminant disease. It is characterized by upper respiratory tract infection, fever, and petechial lesions associated with thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Ms. Laborada is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield and Ms. Laborada have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
AlGhoozi DA, AlKhayyat HM. BMJ Case Reports CP 2021;14:e239910.
Jacobi M et al. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2021;40(2):e93-4.
Paller A, Mancini AJ. Hurwitz clinical pediatric dermatology: A textbook of skin disorders of childhood and adolescence. 4th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier Saunders; 2011.
Radia T et al. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2021;38:51-7.
Ramien ML. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021;46(3):420-9.
Striae gravidarum: More than a ‘nuisance,’ say researchers
In the study of healthy pregnant women, “we found that SG can be associated with a host of negative reactions reflecting increased psychological and emotional distress,” reported Kaveri Karhade, MD, from the Berman Skin Institute, Los Altos, Calif., and coauthors from the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Dr. Karhade was with the department of dermatology at the University of Michigan at the time the study was conducted.
“We suggest that health care providers should avoid thinking of SG as merely a cosmetic ‘nuisance,’ ” they wrote in an article published in the International Journal of Women’s Dermatology. “Instead, it would be reasonable for providers to approach SG like other dermatologic concerns, and to consider asking patients whether SG cause emotional distress and whether prevention or treatment strategies should be attempted, even if not completely effective and potentially costly.”
The investigators did not evaluate treatments, but Frank Wang, MD, senior author of the study and professor of clinical dermatology at the University of Michigan Medicine, said in an interview that, “while they aren’t completely effective, some treatments can still help.” In addition, “recommending something also shows that you are listening to patients’ concerns – taking their concerns and skin lesions seriously,” he said.
Patient survey
The authors conducted a cross-sectional survey of 116 healthy pregnant women with SG. Participants were asked about the emotional and psychological effects of the lesions and how SG affects quality of life. The survey was modeled on questions from the Dermatology Life Quality Index, which asks about the impact of skin disease on embarrassment/self-consciousness, clothing choice, leisure activities, and interpersonal problems. “Content of questions was also devised from direct discussion with pregnant women attending clinic appointments or participating in other research studies on SG at our institution, and discussion with expert colleagues in obstetrics and dermatology,” the authors explained.
The survey consisted of 35 questions concerning demographics, pregnancy characteristics, personal and family history of SG, specific physical concerns about SG, impact of SG on attitude toward pregnancy, willingness to prevent SG or seek treatment, severity of SG (self-evaluated), the impact of SG on specific life-quality facets, and the location of lesions.
About two-thirds of respondents were aged 25-36 years and were White; the remainder self-identified as Asian, Black, Native American, or “other.” Most women reported “average” weight gain during the current pregnancy. Almost half of participants (45%) reporting a history of SG from prior pregnancies, and 65% reported a family history of SG.
The abdomen was identified most frequently as the location of SG (75%), followed by the breasts (43%), hips (43%), thighs (36%), buttocks (19%), and other areas (6%).
For most women (75%), permanency of the lesions was their top concern. About half (51%) reported that they had attempted to prevent SG, mostly with topical creams or oils. Three-quarters (75%) expressed interest in seeking treatment for SG, but this percentage dropped significantly to 33% (P =.008) if that treatment would not be covered by insurance.
Regarding the psychological impact of SG, embarrassment/self-consciousness correlated most strongly with lesion severity, followed by general quality of life, impact on choice of attire, impact on self-image/self-esteem, feelings of anxiety/depression related to SG, alteration of social/leisure activities related to SG (all P < .0001), and creation of interpersonal problems related to SG (P = .02).
The investigators also found that an increase in the effect of SG on self-image/self-esteem was “moderately associated” with younger age (P < .001) and that increased embarrassment related to SG was “moderately associated” with weight gain during pregnancy (P < .001).
“For years, stretch marks have been a topic to avoid and something many women try to hide,” Timothy Johnson, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Michigan and coauthor of the study, said in a press release from the university. “Pregnant women talk about stretch marks with me every single week at clinic, and it’s time we break the stigma and start talking about them openly with all patients. ... By doing this study, we have an opportunity to normalize stretch marks in the context of all other dermatological conditions.”
Asked to comment on the findings, Tina Alster, MD, director of the Washington Institute of Dermatologic Laser Surgery and clinical professor of dermatology at Georgetown University, Washington, said her 3 decades of clinical experience support the authors’ findings. “Most patients who have striae are very self-conscious about them and report that their presence has negatively impacted their quality of life and self-confidence,” she said in an interview. “Of course, patients who come to my office are interested in having them treated, so my patient subset is skewed.”
She said treatment strategies that she discusses with patients include topical retinol/retinoids, which she said provide “low clinical response”; microneedling, which provides “marked” clinical response; and nonablative laser treatment, which provides “good” clinical response.
Considering particular patient characteristics, including budget, Dr. Alster said, “For those on a limited budget, I would propose daily use of a topical retinol, despite the low clinical effect. Many retinol-containing products are available over the counter. Prescription-strength retinoic acid tends to be pricey, often costing as much as in-office treatments.” Medical microneedling (not the cosmetic “roller” microneedling performed by aestheticians), she added, “gives the best results for the money and produces clinical results that mirror those achieved with lasers.”
Dr. Wang agreed that even recommending less expensive and less efficacious options such as over-the-counter creams can help alleviate patients’ concerns. “It shows that you are being holistic – not just caring for medical issues around pregnancy, but that you also take the emotional/psychological concerns of pregnant individuals and new parents seriously and that you recognize the impact of skin problems on quality of life. In the end, recommending something – in other words, providing some options, like creams or other therapies, for instance – is still, in my opinion, better than not recommending anything.”
Dr. Wang is involved with a study that is currently enrolling patients and that is evaluating the formation of early SG, which includes performing skin biopsies as soon as lesions appear.
The study had no funding. The study authors and Dr. Alster disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the study of healthy pregnant women, “we found that SG can be associated with a host of negative reactions reflecting increased psychological and emotional distress,” reported Kaveri Karhade, MD, from the Berman Skin Institute, Los Altos, Calif., and coauthors from the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Dr. Karhade was with the department of dermatology at the University of Michigan at the time the study was conducted.
“We suggest that health care providers should avoid thinking of SG as merely a cosmetic ‘nuisance,’ ” they wrote in an article published in the International Journal of Women’s Dermatology. “Instead, it would be reasonable for providers to approach SG like other dermatologic concerns, and to consider asking patients whether SG cause emotional distress and whether prevention or treatment strategies should be attempted, even if not completely effective and potentially costly.”
The investigators did not evaluate treatments, but Frank Wang, MD, senior author of the study and professor of clinical dermatology at the University of Michigan Medicine, said in an interview that, “while they aren’t completely effective, some treatments can still help.” In addition, “recommending something also shows that you are listening to patients’ concerns – taking their concerns and skin lesions seriously,” he said.
Patient survey
The authors conducted a cross-sectional survey of 116 healthy pregnant women with SG. Participants were asked about the emotional and psychological effects of the lesions and how SG affects quality of life. The survey was modeled on questions from the Dermatology Life Quality Index, which asks about the impact of skin disease on embarrassment/self-consciousness, clothing choice, leisure activities, and interpersonal problems. “Content of questions was also devised from direct discussion with pregnant women attending clinic appointments or participating in other research studies on SG at our institution, and discussion with expert colleagues in obstetrics and dermatology,” the authors explained.
The survey consisted of 35 questions concerning demographics, pregnancy characteristics, personal and family history of SG, specific physical concerns about SG, impact of SG on attitude toward pregnancy, willingness to prevent SG or seek treatment, severity of SG (self-evaluated), the impact of SG on specific life-quality facets, and the location of lesions.
About two-thirds of respondents were aged 25-36 years and were White; the remainder self-identified as Asian, Black, Native American, or “other.” Most women reported “average” weight gain during the current pregnancy. Almost half of participants (45%) reporting a history of SG from prior pregnancies, and 65% reported a family history of SG.
The abdomen was identified most frequently as the location of SG (75%), followed by the breasts (43%), hips (43%), thighs (36%), buttocks (19%), and other areas (6%).
For most women (75%), permanency of the lesions was their top concern. About half (51%) reported that they had attempted to prevent SG, mostly with topical creams or oils. Three-quarters (75%) expressed interest in seeking treatment for SG, but this percentage dropped significantly to 33% (P =.008) if that treatment would not be covered by insurance.
Regarding the psychological impact of SG, embarrassment/self-consciousness correlated most strongly with lesion severity, followed by general quality of life, impact on choice of attire, impact on self-image/self-esteem, feelings of anxiety/depression related to SG, alteration of social/leisure activities related to SG (all P < .0001), and creation of interpersonal problems related to SG (P = .02).
The investigators also found that an increase in the effect of SG on self-image/self-esteem was “moderately associated” with younger age (P < .001) and that increased embarrassment related to SG was “moderately associated” with weight gain during pregnancy (P < .001).
“For years, stretch marks have been a topic to avoid and something many women try to hide,” Timothy Johnson, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Michigan and coauthor of the study, said in a press release from the university. “Pregnant women talk about stretch marks with me every single week at clinic, and it’s time we break the stigma and start talking about them openly with all patients. ... By doing this study, we have an opportunity to normalize stretch marks in the context of all other dermatological conditions.”
Asked to comment on the findings, Tina Alster, MD, director of the Washington Institute of Dermatologic Laser Surgery and clinical professor of dermatology at Georgetown University, Washington, said her 3 decades of clinical experience support the authors’ findings. “Most patients who have striae are very self-conscious about them and report that their presence has negatively impacted their quality of life and self-confidence,” she said in an interview. “Of course, patients who come to my office are interested in having them treated, so my patient subset is skewed.”
She said treatment strategies that she discusses with patients include topical retinol/retinoids, which she said provide “low clinical response”; microneedling, which provides “marked” clinical response; and nonablative laser treatment, which provides “good” clinical response.
Considering particular patient characteristics, including budget, Dr. Alster said, “For those on a limited budget, I would propose daily use of a topical retinol, despite the low clinical effect. Many retinol-containing products are available over the counter. Prescription-strength retinoic acid tends to be pricey, often costing as much as in-office treatments.” Medical microneedling (not the cosmetic “roller” microneedling performed by aestheticians), she added, “gives the best results for the money and produces clinical results that mirror those achieved with lasers.”
Dr. Wang agreed that even recommending less expensive and less efficacious options such as over-the-counter creams can help alleviate patients’ concerns. “It shows that you are being holistic – not just caring for medical issues around pregnancy, but that you also take the emotional/psychological concerns of pregnant individuals and new parents seriously and that you recognize the impact of skin problems on quality of life. In the end, recommending something – in other words, providing some options, like creams or other therapies, for instance – is still, in my opinion, better than not recommending anything.”
Dr. Wang is involved with a study that is currently enrolling patients and that is evaluating the formation of early SG, which includes performing skin biopsies as soon as lesions appear.
The study had no funding. The study authors and Dr. Alster disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the study of healthy pregnant women, “we found that SG can be associated with a host of negative reactions reflecting increased psychological and emotional distress,” reported Kaveri Karhade, MD, from the Berman Skin Institute, Los Altos, Calif., and coauthors from the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Dr. Karhade was with the department of dermatology at the University of Michigan at the time the study was conducted.
“We suggest that health care providers should avoid thinking of SG as merely a cosmetic ‘nuisance,’ ” they wrote in an article published in the International Journal of Women’s Dermatology. “Instead, it would be reasonable for providers to approach SG like other dermatologic concerns, and to consider asking patients whether SG cause emotional distress and whether prevention or treatment strategies should be attempted, even if not completely effective and potentially costly.”
The investigators did not evaluate treatments, but Frank Wang, MD, senior author of the study and professor of clinical dermatology at the University of Michigan Medicine, said in an interview that, “while they aren’t completely effective, some treatments can still help.” In addition, “recommending something also shows that you are listening to patients’ concerns – taking their concerns and skin lesions seriously,” he said.
Patient survey
The authors conducted a cross-sectional survey of 116 healthy pregnant women with SG. Participants were asked about the emotional and psychological effects of the lesions and how SG affects quality of life. The survey was modeled on questions from the Dermatology Life Quality Index, which asks about the impact of skin disease on embarrassment/self-consciousness, clothing choice, leisure activities, and interpersonal problems. “Content of questions was also devised from direct discussion with pregnant women attending clinic appointments or participating in other research studies on SG at our institution, and discussion with expert colleagues in obstetrics and dermatology,” the authors explained.
The survey consisted of 35 questions concerning demographics, pregnancy characteristics, personal and family history of SG, specific physical concerns about SG, impact of SG on attitude toward pregnancy, willingness to prevent SG or seek treatment, severity of SG (self-evaluated), the impact of SG on specific life-quality facets, and the location of lesions.
About two-thirds of respondents were aged 25-36 years and were White; the remainder self-identified as Asian, Black, Native American, or “other.” Most women reported “average” weight gain during the current pregnancy. Almost half of participants (45%) reporting a history of SG from prior pregnancies, and 65% reported a family history of SG.
The abdomen was identified most frequently as the location of SG (75%), followed by the breasts (43%), hips (43%), thighs (36%), buttocks (19%), and other areas (6%).
For most women (75%), permanency of the lesions was their top concern. About half (51%) reported that they had attempted to prevent SG, mostly with topical creams or oils. Three-quarters (75%) expressed interest in seeking treatment for SG, but this percentage dropped significantly to 33% (P =.008) if that treatment would not be covered by insurance.
Regarding the psychological impact of SG, embarrassment/self-consciousness correlated most strongly with lesion severity, followed by general quality of life, impact on choice of attire, impact on self-image/self-esteem, feelings of anxiety/depression related to SG, alteration of social/leisure activities related to SG (all P < .0001), and creation of interpersonal problems related to SG (P = .02).
The investigators also found that an increase in the effect of SG on self-image/self-esteem was “moderately associated” with younger age (P < .001) and that increased embarrassment related to SG was “moderately associated” with weight gain during pregnancy (P < .001).
“For years, stretch marks have been a topic to avoid and something many women try to hide,” Timothy Johnson, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Michigan and coauthor of the study, said in a press release from the university. “Pregnant women talk about stretch marks with me every single week at clinic, and it’s time we break the stigma and start talking about them openly with all patients. ... By doing this study, we have an opportunity to normalize stretch marks in the context of all other dermatological conditions.”
Asked to comment on the findings, Tina Alster, MD, director of the Washington Institute of Dermatologic Laser Surgery and clinical professor of dermatology at Georgetown University, Washington, said her 3 decades of clinical experience support the authors’ findings. “Most patients who have striae are very self-conscious about them and report that their presence has negatively impacted their quality of life and self-confidence,” she said in an interview. “Of course, patients who come to my office are interested in having them treated, so my patient subset is skewed.”
She said treatment strategies that she discusses with patients include topical retinol/retinoids, which she said provide “low clinical response”; microneedling, which provides “marked” clinical response; and nonablative laser treatment, which provides “good” clinical response.
Considering particular patient characteristics, including budget, Dr. Alster said, “For those on a limited budget, I would propose daily use of a topical retinol, despite the low clinical effect. Many retinol-containing products are available over the counter. Prescription-strength retinoic acid tends to be pricey, often costing as much as in-office treatments.” Medical microneedling (not the cosmetic “roller” microneedling performed by aestheticians), she added, “gives the best results for the money and produces clinical results that mirror those achieved with lasers.”
Dr. Wang agreed that even recommending less expensive and less efficacious options such as over-the-counter creams can help alleviate patients’ concerns. “It shows that you are being holistic – not just caring for medical issues around pregnancy, but that you also take the emotional/psychological concerns of pregnant individuals and new parents seriously and that you recognize the impact of skin problems on quality of life. In the end, recommending something – in other words, providing some options, like creams or other therapies, for instance – is still, in my opinion, better than not recommending anything.”
Dr. Wang is involved with a study that is currently enrolling patients and that is evaluating the formation of early SG, which includes performing skin biopsies as soon as lesions appear.
The study had no funding. The study authors and Dr. Alster disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pandemic stresses harder on physician moms than physician dads: Study
COVID-19 has been difficult for parents trying to balance careers, home life, and keeping their loved ones safe. A new study indicates that, not only are physicians not immune to these stressors, but the long-term effects could be devastating for health care overall.
In a study published Nov. 11, 2021, in JAMA Network Open , researchers found that stresses to work/life balance and family life caused by the pandemic have differed among men and women physicians.
Physicians and other health care workers have been at the front lines of the COVID-19 pandemic, and their work lives have been the focus of a lot of attention in the media and by researchers. Their family lives, not so much. But physicians have families, and the pandemic has upended almost everything about their lives, particularly where work life and home life intersect. School and day care closures, working from home, working extra hours, or working less – all of these changes have consequences on family life and the mental health of parents who are also physicians.
Findings from a Medscape survey published in early 2021 indicate that more female physicians than male physicians were either “conflicted” or “very conflicted” as parents because of work demands (42% vs. 23%) nearly 6 months into the pandemic.
In the current study, researchers from the University of Michigan, Harvard University, and the Medical University of South Carolina teamed up to investigate gender differences in how work/family factors affected the mental health of early-career physician parents in the United States during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. The results suggest that the pandemic has increased gender disparity and added disproportionately to the burden of female physicians.
Managing the household falls mostly on moms
Participants were physicians enrolled in the Intern Health Study, a longitudinal study that regularly surveys medical interns in the United States to assess stress and mood. When researchers compared survey results from before the onset of the pandemic (2018) with later results (2020), they found a striking gender difference in how the pandemic has changed family and work duties for physicians.
The authors of the study pointed out that previous research had found that female physicians take on a greater share of household and childcare duties than male physicians. The current study found that their share had increased with the pandemic. Physician moms are now 30 times more likely to be in charge of these tasks than physician dads.
In families in which both parents were physicians, none of the men said they took the primary role in managing the extra demands caused by the pandemic. In addition, women were twice as likely as men to work primarily from home and to work reduced hours.
The extra stress seems to be taking a toll on women physicians. In the 2020 survey, physician mothers had higher scores for anxiety and depression symptoms, compared with men. Notably, the 2018 survey did not show a significant difference in depression scores between men and women. Nor were there significant differences in depression and anxiety scores between women and men who were not parents or in reports of work/family conflict before and after the pandemic.
In general, the results indicate that the pandemic has only widened the gender gap between women and men physicians when it comes to managing family life and dealing with the stresses of maintaining a suitable work-life balance.
‘Long-term repercussions’ for gender equity in medicine
Although these are serious problems for women physicians and their families, the effects go beyond the home and beyond individuals. Even before the pandemic, women in medicine struggled for parity in career advancement and opportunities as well as in pay, and this new setback could make those challenges even greater.
“Even short-term adjustments can have serious long-term repercussions as they may lead to lower earnings and negatively impact opportunities for promotion, further exacerbating gender inequalities in compensation and advancement,” the study’s authors wrote.
The potential damage extends to the entire profession and the health care system itself. The profession is already struggling to retain young female physicians, and this situation is likely to make that problem worse and have long-term consequences. Citing data showing that female physicians spend more time with patients and that their patients may have better outcomes, the authors wrote that the consequences of losing more early-career female physicians “could be devastating to the U.S. health care system, particularly in the context of a global pandemic and an impending physician shortage.”
The sample size was small (276 U.S. physicians), and the study relied on self-reported data. The findings suggest that more research on this topic is needed, especially research that includes other demographic factors, such as sexual orientation and ethnicity. The authors recommend that institutional and public policymakers take into account the effects of the pandemic on physician mothers to ensure that recent gains in gender equity for women physicians do not fall victim to COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 has been difficult for parents trying to balance careers, home life, and keeping their loved ones safe. A new study indicates that, not only are physicians not immune to these stressors, but the long-term effects could be devastating for health care overall.
In a study published Nov. 11, 2021, in JAMA Network Open , researchers found that stresses to work/life balance and family life caused by the pandemic have differed among men and women physicians.
Physicians and other health care workers have been at the front lines of the COVID-19 pandemic, and their work lives have been the focus of a lot of attention in the media and by researchers. Their family lives, not so much. But physicians have families, and the pandemic has upended almost everything about their lives, particularly where work life and home life intersect. School and day care closures, working from home, working extra hours, or working less – all of these changes have consequences on family life and the mental health of parents who are also physicians.
Findings from a Medscape survey published in early 2021 indicate that more female physicians than male physicians were either “conflicted” or “very conflicted” as parents because of work demands (42% vs. 23%) nearly 6 months into the pandemic.
In the current study, researchers from the University of Michigan, Harvard University, and the Medical University of South Carolina teamed up to investigate gender differences in how work/family factors affected the mental health of early-career physician parents in the United States during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. The results suggest that the pandemic has increased gender disparity and added disproportionately to the burden of female physicians.
Managing the household falls mostly on moms
Participants were physicians enrolled in the Intern Health Study, a longitudinal study that regularly surveys medical interns in the United States to assess stress and mood. When researchers compared survey results from before the onset of the pandemic (2018) with later results (2020), they found a striking gender difference in how the pandemic has changed family and work duties for physicians.
The authors of the study pointed out that previous research had found that female physicians take on a greater share of household and childcare duties than male physicians. The current study found that their share had increased with the pandemic. Physician moms are now 30 times more likely to be in charge of these tasks than physician dads.
In families in which both parents were physicians, none of the men said they took the primary role in managing the extra demands caused by the pandemic. In addition, women were twice as likely as men to work primarily from home and to work reduced hours.
The extra stress seems to be taking a toll on women physicians. In the 2020 survey, physician mothers had higher scores for anxiety and depression symptoms, compared with men. Notably, the 2018 survey did not show a significant difference in depression scores between men and women. Nor were there significant differences in depression and anxiety scores between women and men who were not parents or in reports of work/family conflict before and after the pandemic.
In general, the results indicate that the pandemic has only widened the gender gap between women and men physicians when it comes to managing family life and dealing with the stresses of maintaining a suitable work-life balance.
‘Long-term repercussions’ for gender equity in medicine
Although these are serious problems for women physicians and their families, the effects go beyond the home and beyond individuals. Even before the pandemic, women in medicine struggled for parity in career advancement and opportunities as well as in pay, and this new setback could make those challenges even greater.
“Even short-term adjustments can have serious long-term repercussions as they may lead to lower earnings and negatively impact opportunities for promotion, further exacerbating gender inequalities in compensation and advancement,” the study’s authors wrote.
The potential damage extends to the entire profession and the health care system itself. The profession is already struggling to retain young female physicians, and this situation is likely to make that problem worse and have long-term consequences. Citing data showing that female physicians spend more time with patients and that their patients may have better outcomes, the authors wrote that the consequences of losing more early-career female physicians “could be devastating to the U.S. health care system, particularly in the context of a global pandemic and an impending physician shortage.”
The sample size was small (276 U.S. physicians), and the study relied on self-reported data. The findings suggest that more research on this topic is needed, especially research that includes other demographic factors, such as sexual orientation and ethnicity. The authors recommend that institutional and public policymakers take into account the effects of the pandemic on physician mothers to ensure that recent gains in gender equity for women physicians do not fall victim to COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 has been difficult for parents trying to balance careers, home life, and keeping their loved ones safe. A new study indicates that, not only are physicians not immune to these stressors, but the long-term effects could be devastating for health care overall.
In a study published Nov. 11, 2021, in JAMA Network Open , researchers found that stresses to work/life balance and family life caused by the pandemic have differed among men and women physicians.
Physicians and other health care workers have been at the front lines of the COVID-19 pandemic, and their work lives have been the focus of a lot of attention in the media and by researchers. Their family lives, not so much. But physicians have families, and the pandemic has upended almost everything about their lives, particularly where work life and home life intersect. School and day care closures, working from home, working extra hours, or working less – all of these changes have consequences on family life and the mental health of parents who are also physicians.
Findings from a Medscape survey published in early 2021 indicate that more female physicians than male physicians were either “conflicted” or “very conflicted” as parents because of work demands (42% vs. 23%) nearly 6 months into the pandemic.
In the current study, researchers from the University of Michigan, Harvard University, and the Medical University of South Carolina teamed up to investigate gender differences in how work/family factors affected the mental health of early-career physician parents in the United States during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. The results suggest that the pandemic has increased gender disparity and added disproportionately to the burden of female physicians.
Managing the household falls mostly on moms
Participants were physicians enrolled in the Intern Health Study, a longitudinal study that regularly surveys medical interns in the United States to assess stress and mood. When researchers compared survey results from before the onset of the pandemic (2018) with later results (2020), they found a striking gender difference in how the pandemic has changed family and work duties for physicians.
The authors of the study pointed out that previous research had found that female physicians take on a greater share of household and childcare duties than male physicians. The current study found that their share had increased with the pandemic. Physician moms are now 30 times more likely to be in charge of these tasks than physician dads.
In families in which both parents were physicians, none of the men said they took the primary role in managing the extra demands caused by the pandemic. In addition, women were twice as likely as men to work primarily from home and to work reduced hours.
The extra stress seems to be taking a toll on women physicians. In the 2020 survey, physician mothers had higher scores for anxiety and depression symptoms, compared with men. Notably, the 2018 survey did not show a significant difference in depression scores between men and women. Nor were there significant differences in depression and anxiety scores between women and men who were not parents or in reports of work/family conflict before and after the pandemic.
In general, the results indicate that the pandemic has only widened the gender gap between women and men physicians when it comes to managing family life and dealing with the stresses of maintaining a suitable work-life balance.
‘Long-term repercussions’ for gender equity in medicine
Although these are serious problems for women physicians and their families, the effects go beyond the home and beyond individuals. Even before the pandemic, women in medicine struggled for parity in career advancement and opportunities as well as in pay, and this new setback could make those challenges even greater.
“Even short-term adjustments can have serious long-term repercussions as they may lead to lower earnings and negatively impact opportunities for promotion, further exacerbating gender inequalities in compensation and advancement,” the study’s authors wrote.
The potential damage extends to the entire profession and the health care system itself. The profession is already struggling to retain young female physicians, and this situation is likely to make that problem worse and have long-term consequences. Citing data showing that female physicians spend more time with patients and that their patients may have better outcomes, the authors wrote that the consequences of losing more early-career female physicians “could be devastating to the U.S. health care system, particularly in the context of a global pandemic and an impending physician shortage.”
The sample size was small (276 U.S. physicians), and the study relied on self-reported data. The findings suggest that more research on this topic is needed, especially research that includes other demographic factors, such as sexual orientation and ethnicity. The authors recommend that institutional and public policymakers take into account the effects of the pandemic on physician mothers to ensure that recent gains in gender equity for women physicians do not fall victim to COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.