User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
Most rheumatology drugs don’t increase COVID-19 hospitalization risk
The vast majority of patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases who contract COVID-19 recover from the virus, regardless of which medication they receive for their rheumatic condition, new international research suggests.
“These results provide, for the first time, information about the outcome of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases,” said study investigator Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, from University College London. “They should provide some reassurance to patients and healthcare providers.”
Machado and his colleagues looked at 600 COVID-19 patients from 40 countries, and found that those taking TNF inhibitors for their rheumatic disease were less likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19. However, treatment with more than 10 mg of prednisone daily — considered a moderate to high dose — was associated with a higher probability of hospitalization.
In addition, hospitalization was not associated with biologics; JAK inhibitors; conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), such as methotrexate; antimalarials, such as hydroxychloroquine; or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) — either alone or in combination with other biologics, such as TNF-alpha inhibitors.
The findings were presented at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress and were published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
“Initially, there was a huge concern that these drugs could affect the outcome of patients getting COVID-19, but what this is showing is that probably these drugs do not increase their risk of severe outcome,” Machado, who is chair of the EULAR standing committee on epidemiology and health services research, told Medscape Medical News.
As of June 1, 1061 patients from 28 participating countries had been entered into the EULAR COVID-19 database, which was launched as part of the international Global Rheumatology Alliance registry. Patient data are categorized by factors such as top rheumatology diagnosis, comorbidities, top-five COVID-19 symptoms, and DMARD therapy at the time of virus infection. Anonymized data will be shared with an international register based in the United States.
Machado’s team combined data from the EULAR and Global Rheumatology Alliance COVID-19 registries from March 24 to April 20. They looked at patient factors — such as age, sex, smoking status, rheumatic diagnosis, comorbidities, and rheumatic therapies — to examine the association of rheumatic therapies with hospitalization rates and COVID-19 disease course.
Of the 277 patients (46%) in the study cohort who required hospitalization, 55 (9%) died. But this finding shouldn’t be viewed as the true rate of hospitalization or death in patients with rheumatic disease and COVID-19, said Gerd Burmester, MD, from Charité–University Medicine Berlin.
“There’s tremendous bias in terms of more serious cases of COVID-19 being reported to the registries,” he explained, “because the mild cases won’t even show up at their rheumatologist’s office.”
“This can skew the idea that COVID-19 is much more dangerous to rheumatic patients than to the regular population,” Burmester told Medscape Medical News. “It scares the patients, obviously, but we believe this is not justified.”
It’s still unclear whether rituximab use raises the risk for severe COVID-19, he said. “It appears to be the only biologic for which the jury is still out,” he said.
“Anti-TNFs and anti-IL-6 drugs may even be beneficial, although we don’t have robust data,” he added.
The study can only highlight associations between rheumatic drugs and COVID-19 outcomes. “We cannot say there is a causal relationship between the findings,” Machado said.
Longer-term data, when available, should illuminate “more granular” aspects of COVID-19 outcomes in rheumatic patients, including their risks of requiring ventilation or developing a cytokine storm, he noted.
Burmester and Machado agree that research needs to continue as the pandemic rages on. But so far, “there are no data suggesting that, if you’re on a targeted, dedicated immunomodulator, your risk is higher to have a worse course of COVID-19 than the general population,” Burmester said.
“We simply didn’t know that when the pandemic started, and some patients even discontinued their drugs out of this fear,” he added. “It’s more reassuring than we originally thought.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The vast majority of patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases who contract COVID-19 recover from the virus, regardless of which medication they receive for their rheumatic condition, new international research suggests.
“These results provide, for the first time, information about the outcome of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases,” said study investigator Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, from University College London. “They should provide some reassurance to patients and healthcare providers.”
Machado and his colleagues looked at 600 COVID-19 patients from 40 countries, and found that those taking TNF inhibitors for their rheumatic disease were less likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19. However, treatment with more than 10 mg of prednisone daily — considered a moderate to high dose — was associated with a higher probability of hospitalization.
In addition, hospitalization was not associated with biologics; JAK inhibitors; conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), such as methotrexate; antimalarials, such as hydroxychloroquine; or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) — either alone or in combination with other biologics, such as TNF-alpha inhibitors.
The findings were presented at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress and were published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
“Initially, there was a huge concern that these drugs could affect the outcome of patients getting COVID-19, but what this is showing is that probably these drugs do not increase their risk of severe outcome,” Machado, who is chair of the EULAR standing committee on epidemiology and health services research, told Medscape Medical News.
As of June 1, 1061 patients from 28 participating countries had been entered into the EULAR COVID-19 database, which was launched as part of the international Global Rheumatology Alliance registry. Patient data are categorized by factors such as top rheumatology diagnosis, comorbidities, top-five COVID-19 symptoms, and DMARD therapy at the time of virus infection. Anonymized data will be shared with an international register based in the United States.
Machado’s team combined data from the EULAR and Global Rheumatology Alliance COVID-19 registries from March 24 to April 20. They looked at patient factors — such as age, sex, smoking status, rheumatic diagnosis, comorbidities, and rheumatic therapies — to examine the association of rheumatic therapies with hospitalization rates and COVID-19 disease course.
Of the 277 patients (46%) in the study cohort who required hospitalization, 55 (9%) died. But this finding shouldn’t be viewed as the true rate of hospitalization or death in patients with rheumatic disease and COVID-19, said Gerd Burmester, MD, from Charité–University Medicine Berlin.
“There’s tremendous bias in terms of more serious cases of COVID-19 being reported to the registries,” he explained, “because the mild cases won’t even show up at their rheumatologist’s office.”
“This can skew the idea that COVID-19 is much more dangerous to rheumatic patients than to the regular population,” Burmester told Medscape Medical News. “It scares the patients, obviously, but we believe this is not justified.”
It’s still unclear whether rituximab use raises the risk for severe COVID-19, he said. “It appears to be the only biologic for which the jury is still out,” he said.
“Anti-TNFs and anti-IL-6 drugs may even be beneficial, although we don’t have robust data,” he added.
The study can only highlight associations between rheumatic drugs and COVID-19 outcomes. “We cannot say there is a causal relationship between the findings,” Machado said.
Longer-term data, when available, should illuminate “more granular” aspects of COVID-19 outcomes in rheumatic patients, including their risks of requiring ventilation or developing a cytokine storm, he noted.
Burmester and Machado agree that research needs to continue as the pandemic rages on. But so far, “there are no data suggesting that, if you’re on a targeted, dedicated immunomodulator, your risk is higher to have a worse course of COVID-19 than the general population,” Burmester said.
“We simply didn’t know that when the pandemic started, and some patients even discontinued their drugs out of this fear,” he added. “It’s more reassuring than we originally thought.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The vast majority of patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases who contract COVID-19 recover from the virus, regardless of which medication they receive for their rheumatic condition, new international research suggests.
“These results provide, for the first time, information about the outcome of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases,” said study investigator Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, from University College London. “They should provide some reassurance to patients and healthcare providers.”
Machado and his colleagues looked at 600 COVID-19 patients from 40 countries, and found that those taking TNF inhibitors for their rheumatic disease were less likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19. However, treatment with more than 10 mg of prednisone daily — considered a moderate to high dose — was associated with a higher probability of hospitalization.
In addition, hospitalization was not associated with biologics; JAK inhibitors; conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), such as methotrexate; antimalarials, such as hydroxychloroquine; or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) — either alone or in combination with other biologics, such as TNF-alpha inhibitors.
The findings were presented at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress and were published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
“Initially, there was a huge concern that these drugs could affect the outcome of patients getting COVID-19, but what this is showing is that probably these drugs do not increase their risk of severe outcome,” Machado, who is chair of the EULAR standing committee on epidemiology and health services research, told Medscape Medical News.
As of June 1, 1061 patients from 28 participating countries had been entered into the EULAR COVID-19 database, which was launched as part of the international Global Rheumatology Alliance registry. Patient data are categorized by factors such as top rheumatology diagnosis, comorbidities, top-five COVID-19 symptoms, and DMARD therapy at the time of virus infection. Anonymized data will be shared with an international register based in the United States.
Machado’s team combined data from the EULAR and Global Rheumatology Alliance COVID-19 registries from March 24 to April 20. They looked at patient factors — such as age, sex, smoking status, rheumatic diagnosis, comorbidities, and rheumatic therapies — to examine the association of rheumatic therapies with hospitalization rates and COVID-19 disease course.
Of the 277 patients (46%) in the study cohort who required hospitalization, 55 (9%) died. But this finding shouldn’t be viewed as the true rate of hospitalization or death in patients with rheumatic disease and COVID-19, said Gerd Burmester, MD, from Charité–University Medicine Berlin.
“There’s tremendous bias in terms of more serious cases of COVID-19 being reported to the registries,” he explained, “because the mild cases won’t even show up at their rheumatologist’s office.”
“This can skew the idea that COVID-19 is much more dangerous to rheumatic patients than to the regular population,” Burmester told Medscape Medical News. “It scares the patients, obviously, but we believe this is not justified.”
It’s still unclear whether rituximab use raises the risk for severe COVID-19, he said. “It appears to be the only biologic for which the jury is still out,” he said.
“Anti-TNFs and anti-IL-6 drugs may even be beneficial, although we don’t have robust data,” he added.
The study can only highlight associations between rheumatic drugs and COVID-19 outcomes. “We cannot say there is a causal relationship between the findings,” Machado said.
Longer-term data, when available, should illuminate “more granular” aspects of COVID-19 outcomes in rheumatic patients, including their risks of requiring ventilation or developing a cytokine storm, he noted.
Burmester and Machado agree that research needs to continue as the pandemic rages on. But so far, “there are no data suggesting that, if you’re on a targeted, dedicated immunomodulator, your risk is higher to have a worse course of COVID-19 than the general population,” Burmester said.
“We simply didn’t know that when the pandemic started, and some patients even discontinued their drugs out of this fear,” he added. “It’s more reassuring than we originally thought.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Parenting special needs children: An unlikely model
COVID-19 can give physicians a window into lives of families
The last few months have tested the stamina of most families. Many people are struggling to keep some semblance of normalcy amid a radical transformation of everyday life. It seems as if everything changed overnight.
In a similar way, when a child with many needs is born into a family, adjustments also have to take place to receive the new baby. Families are, in most cases, not prepared for what is to come. Their expectations usually are not in sync with how their lives end up. They are crunched for time. They need to adjust, and at the same time, they mourn the loss of their previous less demanding lifestyle. More importantly, these parents learn that this might be an adjustment that they might need to make for a long time – in some instances, for a lifetime.
Stress load over time can correlate with a sense of burnout, and mental health professionals need to be prepared to address these issues in our patients.
Here is a list of some chronic struggles with which many special needs parents must contend. These strongly resemble the challenges parents in the general population have been facing with their families during this pandemic:
- Bypassing breaks to unwind and having to be always “on” while at home: These parents take care of children who need to be chronically tube fed, can’t sleep well at night because they are often sick, have recurrent seizures or maladaptive behaviors that affect the caretakers and the rest of the family. For parents of children who are on the autism spectrum, these challenges can be a constant struggle. Almost 60% of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) experience bodily difficulties, such as trouble breathing. However, nearly 100% of children with ASD experienced difficulties with their abilities and activities, such as self-care tasks like eating and dressing, and emotional or behavioral health, according to a 2016 report on child and adolescent health by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
- Taking on roles for which they are not trained: Parents may take on active roles supplementing their developmentally delayed children with educational experiences or therapeutic modalities in their own homes given that the needs might be too great to just rely on the school or therapy time. There are about 1.17 million children in the United States living with ASD and more than 12% of children with ASD have severe cases, the Hopkins report said. Parents frequently are forced to take on the role of “therapist” to meet the needs of their child.
- Staying home often: Some parents are unable to have a “regular sitter” to provide respite, because the needs of the child require a higher level of care, training, and consideration. Caring for a special child means parents often don’t have the option of leaving their older child alone. As a result, they may end up spending more time at home than their counterpart parents with children who are the same age.
- Struggling to meet everyone’s demands for attention while at home: The child might require full-time attention or prolonged hospitalizations, and the needs of other siblings are sometimes put on hold until time or energy are available for all.
- Not traveling unless absolutely necessary: Families have a hard time leaving home for vacations or for other reasons. They may have to travel with medical supplies and equipment. They need to make sure that their destination is ready to welcome their child with all needs taken into consideration (special diets, activities, and facilities). Will the vacation set them back because it might take more effort to go than to stay home?
- Avoiding unnecessary exposures: Trying to avoid infections (even the ones that may be innocuous to others) if their child is immunocompromised. These children may readily decompensate and end up hospitalized with a more serious medical complication.
- Being very aware of remaining physically distant from others: Parents must go to great lengths not to impinge on other people’s space if the child is being loud or moving in a disruptive way, or if other people negatively affect how the child responds. Some families are apprehensive because they have felt judged by others when they are in the community, restaurants, or other places of gathering.
- Feeling concerned about having the right food, medicines, and supplements in the house: Parents are constantly trying to fulfill special dietary requirements and have the reserve to make sure that all meals and treatments are accounted for in the near future. They might need oxygen or specialized formulas that are hard to find in local stores. Some treatments, when withdrawn or unavailable, can prove life threatening.
- Restricting social circles: Some families with children with severe autism may self-isolate when they feel it is hard to be around them and be friends with them, since they can’t readily participate in “usual family activities,” and the regular norms of socialization can’t apply to their family’s set of behaviors. Their child might seem to be disruptive, or loud, nonverbal, mute, or unable to easily relate to others.
- Experiencing a pervasive sense of uncertainty about the future: A child might continue to miss milestones, or might have a rare condition that hasn’t been diagnosed. When thinking of the future, parents can’t predict what level of care they need to plan and budget for.
- Being concerned about dying early and not being able to provide for their child: Parents worry about who would take care of their child for life. Who would take care of their aging adult “child” after parents are gone? They might have concerns about having a will in place early on.
- Facing financial stress secondary to losing a job or the cost of treatments: Absenteeism might be the end result of having to care for their child’s ongoing needs, appointments, and medical emergencies. Sometimes, they might depend on a caretaker who might be very difficult to replace. It might take extensive training once a candidate is found. Direct costs include medical care, hospitalizations, special education, special therapies (occupational, speech, and physical therapy), and paid caregivers. Indirect costs include lost productivity for family caregivers because of the inability to maintain employment while caring for affected individuals, as well as lost wages and benefits, the Hopkins report said.
- Struggling to coordinate daily schedules: Parents face this challenge not only with young children but with those who are chronically ill and might need ongoing 24/7 care. The schedule might include educational and therapeutic (physical, occupational, speech, language therapy, recreational) interventions regularly or daily. This schedule is to be superimposed on all the other necessary responsibilities parents already have to contend with. Forty-eight percent of school-aged children with ASD use three or more services. In addition, children with moderate or severe cases of ASD used three or more services at almost twice the rate of children with mild cases of ASD (60% vs. 35%).
- Longing for a cure or a medicine that will improve the outcome: Often, parents search for treatments so that their child could live a more comfortable or healthier life. For children who have a rare condition, there may not be sufficient research dedicated to their cause or diagnostic pursuits. Currently, it is estimated that 1 in 10 Americans has a rare disease – about 80% of which are genetically based. Of the nearly 7,000 rare diseases known to exist, less than 500 – roughly 5% – have a known treatment approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, reports the National Center for Advancing Translational Diseases and the Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center.
- Hoping for better times to come: It is difficult at times to appreciate the present when it happens to be so chronically challenging and exhausting for everyone.
Parents of children with significant special needs experience many hurdles that they learn to endure, overcome, and master. This pandemic can provide physicians with a window into the lives of these families.
Dr. Sotir is a psychiatrist in private practice in Wheaton, Ill. As a parent of three children, one with special needs, she has extensive experience helping parents challenged by having special needs children find balance, support, direction, and joy in all dimensions of individual and family life. This area is the focus of her practice and public speaking. In Part 2, she will explore how psychiatrists as a specialty can support these families. She has no disclosures.
COVID-19 can give physicians a window into lives of families
COVID-19 can give physicians a window into lives of families
The last few months have tested the stamina of most families. Many people are struggling to keep some semblance of normalcy amid a radical transformation of everyday life. It seems as if everything changed overnight.
In a similar way, when a child with many needs is born into a family, adjustments also have to take place to receive the new baby. Families are, in most cases, not prepared for what is to come. Their expectations usually are not in sync with how their lives end up. They are crunched for time. They need to adjust, and at the same time, they mourn the loss of their previous less demanding lifestyle. More importantly, these parents learn that this might be an adjustment that they might need to make for a long time – in some instances, for a lifetime.
Stress load over time can correlate with a sense of burnout, and mental health professionals need to be prepared to address these issues in our patients.
Here is a list of some chronic struggles with which many special needs parents must contend. These strongly resemble the challenges parents in the general population have been facing with their families during this pandemic:
- Bypassing breaks to unwind and having to be always “on” while at home: These parents take care of children who need to be chronically tube fed, can’t sleep well at night because they are often sick, have recurrent seizures or maladaptive behaviors that affect the caretakers and the rest of the family. For parents of children who are on the autism spectrum, these challenges can be a constant struggle. Almost 60% of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) experience bodily difficulties, such as trouble breathing. However, nearly 100% of children with ASD experienced difficulties with their abilities and activities, such as self-care tasks like eating and dressing, and emotional or behavioral health, according to a 2016 report on child and adolescent health by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
- Taking on roles for which they are not trained: Parents may take on active roles supplementing their developmentally delayed children with educational experiences or therapeutic modalities in their own homes given that the needs might be too great to just rely on the school or therapy time. There are about 1.17 million children in the United States living with ASD and more than 12% of children with ASD have severe cases, the Hopkins report said. Parents frequently are forced to take on the role of “therapist” to meet the needs of their child.
- Staying home often: Some parents are unable to have a “regular sitter” to provide respite, because the needs of the child require a higher level of care, training, and consideration. Caring for a special child means parents often don’t have the option of leaving their older child alone. As a result, they may end up spending more time at home than their counterpart parents with children who are the same age.
- Struggling to meet everyone’s demands for attention while at home: The child might require full-time attention or prolonged hospitalizations, and the needs of other siblings are sometimes put on hold until time or energy are available for all.
- Not traveling unless absolutely necessary: Families have a hard time leaving home for vacations or for other reasons. They may have to travel with medical supplies and equipment. They need to make sure that their destination is ready to welcome their child with all needs taken into consideration (special diets, activities, and facilities). Will the vacation set them back because it might take more effort to go than to stay home?
- Avoiding unnecessary exposures: Trying to avoid infections (even the ones that may be innocuous to others) if their child is immunocompromised. These children may readily decompensate and end up hospitalized with a more serious medical complication.
- Being very aware of remaining physically distant from others: Parents must go to great lengths not to impinge on other people’s space if the child is being loud or moving in a disruptive way, or if other people negatively affect how the child responds. Some families are apprehensive because they have felt judged by others when they are in the community, restaurants, or other places of gathering.
- Feeling concerned about having the right food, medicines, and supplements in the house: Parents are constantly trying to fulfill special dietary requirements and have the reserve to make sure that all meals and treatments are accounted for in the near future. They might need oxygen or specialized formulas that are hard to find in local stores. Some treatments, when withdrawn or unavailable, can prove life threatening.
- Restricting social circles: Some families with children with severe autism may self-isolate when they feel it is hard to be around them and be friends with them, since they can’t readily participate in “usual family activities,” and the regular norms of socialization can’t apply to their family’s set of behaviors. Their child might seem to be disruptive, or loud, nonverbal, mute, or unable to easily relate to others.
- Experiencing a pervasive sense of uncertainty about the future: A child might continue to miss milestones, or might have a rare condition that hasn’t been diagnosed. When thinking of the future, parents can’t predict what level of care they need to plan and budget for.
- Being concerned about dying early and not being able to provide for their child: Parents worry about who would take care of their child for life. Who would take care of their aging adult “child” after parents are gone? They might have concerns about having a will in place early on.
- Facing financial stress secondary to losing a job or the cost of treatments: Absenteeism might be the end result of having to care for their child’s ongoing needs, appointments, and medical emergencies. Sometimes, they might depend on a caretaker who might be very difficult to replace. It might take extensive training once a candidate is found. Direct costs include medical care, hospitalizations, special education, special therapies (occupational, speech, and physical therapy), and paid caregivers. Indirect costs include lost productivity for family caregivers because of the inability to maintain employment while caring for affected individuals, as well as lost wages and benefits, the Hopkins report said.
- Struggling to coordinate daily schedules: Parents face this challenge not only with young children but with those who are chronically ill and might need ongoing 24/7 care. The schedule might include educational and therapeutic (physical, occupational, speech, language therapy, recreational) interventions regularly or daily. This schedule is to be superimposed on all the other necessary responsibilities parents already have to contend with. Forty-eight percent of school-aged children with ASD use three or more services. In addition, children with moderate or severe cases of ASD used three or more services at almost twice the rate of children with mild cases of ASD (60% vs. 35%).
- Longing for a cure or a medicine that will improve the outcome: Often, parents search for treatments so that their child could live a more comfortable or healthier life. For children who have a rare condition, there may not be sufficient research dedicated to their cause or diagnostic pursuits. Currently, it is estimated that 1 in 10 Americans has a rare disease – about 80% of which are genetically based. Of the nearly 7,000 rare diseases known to exist, less than 500 – roughly 5% – have a known treatment approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, reports the National Center for Advancing Translational Diseases and the Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center.
- Hoping for better times to come: It is difficult at times to appreciate the present when it happens to be so chronically challenging and exhausting for everyone.
Parents of children with significant special needs experience many hurdles that they learn to endure, overcome, and master. This pandemic can provide physicians with a window into the lives of these families.
Dr. Sotir is a psychiatrist in private practice in Wheaton, Ill. As a parent of three children, one with special needs, she has extensive experience helping parents challenged by having special needs children find balance, support, direction, and joy in all dimensions of individual and family life. This area is the focus of her practice and public speaking. In Part 2, she will explore how psychiatrists as a specialty can support these families. She has no disclosures.
The last few months have tested the stamina of most families. Many people are struggling to keep some semblance of normalcy amid a radical transformation of everyday life. It seems as if everything changed overnight.
In a similar way, when a child with many needs is born into a family, adjustments also have to take place to receive the new baby. Families are, in most cases, not prepared for what is to come. Their expectations usually are not in sync with how their lives end up. They are crunched for time. They need to adjust, and at the same time, they mourn the loss of their previous less demanding lifestyle. More importantly, these parents learn that this might be an adjustment that they might need to make for a long time – in some instances, for a lifetime.
Stress load over time can correlate with a sense of burnout, and mental health professionals need to be prepared to address these issues in our patients.
Here is a list of some chronic struggles with which many special needs parents must contend. These strongly resemble the challenges parents in the general population have been facing with their families during this pandemic:
- Bypassing breaks to unwind and having to be always “on” while at home: These parents take care of children who need to be chronically tube fed, can’t sleep well at night because they are often sick, have recurrent seizures or maladaptive behaviors that affect the caretakers and the rest of the family. For parents of children who are on the autism spectrum, these challenges can be a constant struggle. Almost 60% of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) experience bodily difficulties, such as trouble breathing. However, nearly 100% of children with ASD experienced difficulties with their abilities and activities, such as self-care tasks like eating and dressing, and emotional or behavioral health, according to a 2016 report on child and adolescent health by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
- Taking on roles for which they are not trained: Parents may take on active roles supplementing their developmentally delayed children with educational experiences or therapeutic modalities in their own homes given that the needs might be too great to just rely on the school or therapy time. There are about 1.17 million children in the United States living with ASD and more than 12% of children with ASD have severe cases, the Hopkins report said. Parents frequently are forced to take on the role of “therapist” to meet the needs of their child.
- Staying home often: Some parents are unable to have a “regular sitter” to provide respite, because the needs of the child require a higher level of care, training, and consideration. Caring for a special child means parents often don’t have the option of leaving their older child alone. As a result, they may end up spending more time at home than their counterpart parents with children who are the same age.
- Struggling to meet everyone’s demands for attention while at home: The child might require full-time attention or prolonged hospitalizations, and the needs of other siblings are sometimes put on hold until time or energy are available for all.
- Not traveling unless absolutely necessary: Families have a hard time leaving home for vacations or for other reasons. They may have to travel with medical supplies and equipment. They need to make sure that their destination is ready to welcome their child with all needs taken into consideration (special diets, activities, and facilities). Will the vacation set them back because it might take more effort to go than to stay home?
- Avoiding unnecessary exposures: Trying to avoid infections (even the ones that may be innocuous to others) if their child is immunocompromised. These children may readily decompensate and end up hospitalized with a more serious medical complication.
- Being very aware of remaining physically distant from others: Parents must go to great lengths not to impinge on other people’s space if the child is being loud or moving in a disruptive way, or if other people negatively affect how the child responds. Some families are apprehensive because they have felt judged by others when they are in the community, restaurants, or other places of gathering.
- Feeling concerned about having the right food, medicines, and supplements in the house: Parents are constantly trying to fulfill special dietary requirements and have the reserve to make sure that all meals and treatments are accounted for in the near future. They might need oxygen or specialized formulas that are hard to find in local stores. Some treatments, when withdrawn or unavailable, can prove life threatening.
- Restricting social circles: Some families with children with severe autism may self-isolate when they feel it is hard to be around them and be friends with them, since they can’t readily participate in “usual family activities,” and the regular norms of socialization can’t apply to their family’s set of behaviors. Their child might seem to be disruptive, or loud, nonverbal, mute, or unable to easily relate to others.
- Experiencing a pervasive sense of uncertainty about the future: A child might continue to miss milestones, or might have a rare condition that hasn’t been diagnosed. When thinking of the future, parents can’t predict what level of care they need to plan and budget for.
- Being concerned about dying early and not being able to provide for their child: Parents worry about who would take care of their child for life. Who would take care of their aging adult “child” after parents are gone? They might have concerns about having a will in place early on.
- Facing financial stress secondary to losing a job or the cost of treatments: Absenteeism might be the end result of having to care for their child’s ongoing needs, appointments, and medical emergencies. Sometimes, they might depend on a caretaker who might be very difficult to replace. It might take extensive training once a candidate is found. Direct costs include medical care, hospitalizations, special education, special therapies (occupational, speech, and physical therapy), and paid caregivers. Indirect costs include lost productivity for family caregivers because of the inability to maintain employment while caring for affected individuals, as well as lost wages and benefits, the Hopkins report said.
- Struggling to coordinate daily schedules: Parents face this challenge not only with young children but with those who are chronically ill and might need ongoing 24/7 care. The schedule might include educational and therapeutic (physical, occupational, speech, language therapy, recreational) interventions regularly or daily. This schedule is to be superimposed on all the other necessary responsibilities parents already have to contend with. Forty-eight percent of school-aged children with ASD use three or more services. In addition, children with moderate or severe cases of ASD used three or more services at almost twice the rate of children with mild cases of ASD (60% vs. 35%).
- Longing for a cure or a medicine that will improve the outcome: Often, parents search for treatments so that their child could live a more comfortable or healthier life. For children who have a rare condition, there may not be sufficient research dedicated to their cause or diagnostic pursuits. Currently, it is estimated that 1 in 10 Americans has a rare disease – about 80% of which are genetically based. Of the nearly 7,000 rare diseases known to exist, less than 500 – roughly 5% – have a known treatment approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, reports the National Center for Advancing Translational Diseases and the Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center.
- Hoping for better times to come: It is difficult at times to appreciate the present when it happens to be so chronically challenging and exhausting for everyone.
Parents of children with significant special needs experience many hurdles that they learn to endure, overcome, and master. This pandemic can provide physicians with a window into the lives of these families.
Dr. Sotir is a psychiatrist in private practice in Wheaton, Ill. As a parent of three children, one with special needs, she has extensive experience helping parents challenged by having special needs children find balance, support, direction, and joy in all dimensions of individual and family life. This area is the focus of her practice and public speaking. In Part 2, she will explore how psychiatrists as a specialty can support these families. She has no disclosures.
More fatalities in heart transplant patients with COVID-19
COVID-19 infection is associated with a high risk for mortality in heart transplant (HT) recipients, a new case series suggests.
Investigators looked at data on 28 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 who received a HT between March 1, 2020, and April 24, 2020 and found a case-fatality rate of 25%.
“The high case fatality in our case series should alert physicians to the vulnerability of heart transplant recipients during the COVID-19 pandemic,” senior author Nir Uriel, MD, MSc, professor of medicine at Columbia University, New York, said in an interview.
“These patients require extra precautions to prevent the development of infection,” said Dr. Uriel, who is also a cardiologist at New York Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center.
The study was published online May 13 in JAMA Cardiology.
Similar presentation
HT recipients can have several comorbidities after the procedure, including hypertension, diabetes, cardiac allograft vasculopathy, and ongoing immunosuppression, all of which can place them at risk for infection and adverse outcomes with COVID-19 infection, the authors wrote.
The researchers therefore embarked on a case series looking at 28 HT recipients with COVID-19 infection (median age, 64.0 years; interquartile range, 53.5-70.5; 79% male) to “describe the outcomes of recipients of HT who are chronically immunosuppressed and develop COVID-19 and raise important questions about the role of the immune system in the process.”
The median time from HT to study period was 8.6 (IQR, 4.2-14.5) years. Most patients had numerous comorbidities.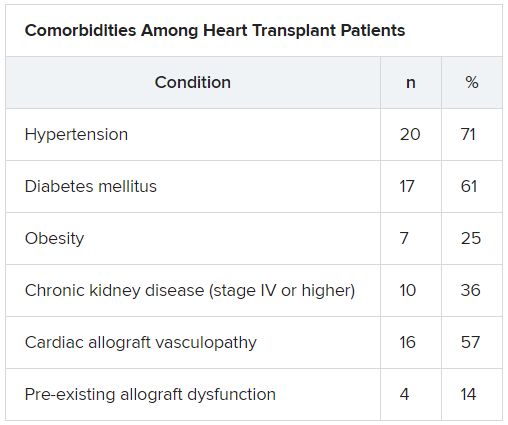
“The presentation of COVID-19 was similar to nontransplant patients with fever, dyspnea, cough, and GI symptoms,” Dr. Uriel reported.
No protective effect
Twenty-two patients (79%) required admission to the hospital, seven of whom (25%) required admission to the ICU and mechanical ventilation.
Despite the presence of immunosuppressive therapy, all patients had significant elevation of inflammatory biomarkers (median peak high-sensitivity C-reactive protein [hs-CRP], 11.83 mg/dL; IQR, 7.44-19.26; median peak interleukin [IL]-6, 105 pg/mL; IQR, 38-296).
Three-quarters had myocardial injury, with a median high-sensitivity troponin T of 0.055 (0.0205 - 0.1345) ng/mL.
Treatments of COVID-19 included hydroxychloroquine (18 patients; 78%), high-dose corticosteroids (eight patients; 47%), and IL-6 receptor antagonists (six patients; 26%).
Moreover, during hospitalization, mycophenolate mofetil was discontinued in most (70%) patients, and one-quarter had a reduction in their calcineurin inhibitor dose.
“Heart transplant recipients generally require more intense immunosuppressive therapy than most other solid organ transplant recipients, and this high baseline immunosuppression increases their propensity to develop infections and their likelihood of experiencing severe manifestations of infections,” Dr. Uriel commented.
“With COVID-19, in which the body’s inflammatory reaction appears to play a role in disease severity, there has been a question of whether immunosuppression may offer a protective effect,” he continued.
“This case series suggests that this is not the case, although this would need to be confirmed in larger studies,” he said.
Low threshold
Among the 22 patients who were admitted to the hospital, half were discharged home and four (18%) were still hospitalized at the end of the study.
Of the seven patients who died, two died at the study center, and five died in an outside institution.
“In the HT population, social distancing (or isolation), strict use of masks when in public, proper handwashing, and sanitization of surfaces are of paramount importance in the prevention of COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Uriel stated.
“In addition, we have restricted these patients’ contact with the hospital as much as possible during the pandemic,” he said.
However, “there should be a low threshold to hospitalize heart transplant patients who develop infection with COVID-19. Furthermore, in our series, outcomes were better for patients hospitalized at the transplant center; therefore, strong consideration should be given to transferring HT patients when hospitalized at another hospital,” he added.
The authors emphasized that COVID-19 patients “will require ongoing monitoring in the recovery phase, as an immunosuppression regimen is reintroduced and the consequences to the allograft itself become apparent.”
Vulnerable population
Commenting on the study, Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, MSc, William Harvey Distinguished Chair in Advanced Cardiovascular Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, suggested that “in epidemiological terms, [the findings] might not look as bad as the way they are reflected in the paper.”
Given that Columbia is “one of the larger heart transplant centers in the U.S., following probably 1,000 patients, having only 22 out of perhaps thousands whom they transplanted or are actively following would actually represent a low serious infection rate,” said Dr. Mehra, who is also the executive director of the Center for Advanced Heart Disease at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
“We must not forget to emphasize that, when assessing these case fatality rates, we must look at the entire population at risk, not only the handful that we were able to observe,” explained Dr. Mehra, who was not involved with the study.
Moreover, the patients were “older and had comorbidities, with poor underlying kidney function and other complications, and underlying coronary artery disease in the transplanted heart,” so “it would not surprise me that they had such a high fatality rate, since they had a high degree of vulnerability,” he said.
Dr. Mehra, who is also the editor-in-chief of the Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation, said that the journal has received manuscripts still in the review process that suggest different fatality rates than those found in the current case series.
However, he acknowledged that, because these are patients with serious vulnerability due to underlying heart disease, “you can’t be lackadaisical and need to do everything to decrease this vulnerability.”
The authors noted that, although their study did not show a protective effect from immunosuppression against COVID-19, further studies are needed to assess each individual immunosuppressive agent and provide a definitive answer.
The study was supported by a grant to one of the investigators from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Uriel reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the publication. Dr. Mehra reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 infection is associated with a high risk for mortality in heart transplant (HT) recipients, a new case series suggests.
Investigators looked at data on 28 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 who received a HT between March 1, 2020, and April 24, 2020 and found a case-fatality rate of 25%.
“The high case fatality in our case series should alert physicians to the vulnerability of heart transplant recipients during the COVID-19 pandemic,” senior author Nir Uriel, MD, MSc, professor of medicine at Columbia University, New York, said in an interview.
“These patients require extra precautions to prevent the development of infection,” said Dr. Uriel, who is also a cardiologist at New York Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center.
The study was published online May 13 in JAMA Cardiology.
Similar presentation
HT recipients can have several comorbidities after the procedure, including hypertension, diabetes, cardiac allograft vasculopathy, and ongoing immunosuppression, all of which can place them at risk for infection and adverse outcomes with COVID-19 infection, the authors wrote.
The researchers therefore embarked on a case series looking at 28 HT recipients with COVID-19 infection (median age, 64.0 years; interquartile range, 53.5-70.5; 79% male) to “describe the outcomes of recipients of HT who are chronically immunosuppressed and develop COVID-19 and raise important questions about the role of the immune system in the process.”
The median time from HT to study period was 8.6 (IQR, 4.2-14.5) years. Most patients had numerous comorbidities.
“The presentation of COVID-19 was similar to nontransplant patients with fever, dyspnea, cough, and GI symptoms,” Dr. Uriel reported.
No protective effect
Twenty-two patients (79%) required admission to the hospital, seven of whom (25%) required admission to the ICU and mechanical ventilation.
Despite the presence of immunosuppressive therapy, all patients had significant elevation of inflammatory biomarkers (median peak high-sensitivity C-reactive protein [hs-CRP], 11.83 mg/dL; IQR, 7.44-19.26; median peak interleukin [IL]-6, 105 pg/mL; IQR, 38-296).
Three-quarters had myocardial injury, with a median high-sensitivity troponin T of 0.055 (0.0205 - 0.1345) ng/mL.
Treatments of COVID-19 included hydroxychloroquine (18 patients; 78%), high-dose corticosteroids (eight patients; 47%), and IL-6 receptor antagonists (six patients; 26%).
Moreover, during hospitalization, mycophenolate mofetil was discontinued in most (70%) patients, and one-quarter had a reduction in their calcineurin inhibitor dose.
“Heart transplant recipients generally require more intense immunosuppressive therapy than most other solid organ transplant recipients, and this high baseline immunosuppression increases their propensity to develop infections and their likelihood of experiencing severe manifestations of infections,” Dr. Uriel commented.
“With COVID-19, in which the body’s inflammatory reaction appears to play a role in disease severity, there has been a question of whether immunosuppression may offer a protective effect,” he continued.
“This case series suggests that this is not the case, although this would need to be confirmed in larger studies,” he said.
Low threshold
Among the 22 patients who were admitted to the hospital, half were discharged home and four (18%) were still hospitalized at the end of the study.
Of the seven patients who died, two died at the study center, and five died in an outside institution.
“In the HT population, social distancing (or isolation), strict use of masks when in public, proper handwashing, and sanitization of surfaces are of paramount importance in the prevention of COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Uriel stated.
“In addition, we have restricted these patients’ contact with the hospital as much as possible during the pandemic,” he said.
However, “there should be a low threshold to hospitalize heart transplant patients who develop infection with COVID-19. Furthermore, in our series, outcomes were better for patients hospitalized at the transplant center; therefore, strong consideration should be given to transferring HT patients when hospitalized at another hospital,” he added.
The authors emphasized that COVID-19 patients “will require ongoing monitoring in the recovery phase, as an immunosuppression regimen is reintroduced and the consequences to the allograft itself become apparent.”
Vulnerable population
Commenting on the study, Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, MSc, William Harvey Distinguished Chair in Advanced Cardiovascular Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, suggested that “in epidemiological terms, [the findings] might not look as bad as the way they are reflected in the paper.”
Given that Columbia is “one of the larger heart transplant centers in the U.S., following probably 1,000 patients, having only 22 out of perhaps thousands whom they transplanted or are actively following would actually represent a low serious infection rate,” said Dr. Mehra, who is also the executive director of the Center for Advanced Heart Disease at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
“We must not forget to emphasize that, when assessing these case fatality rates, we must look at the entire population at risk, not only the handful that we were able to observe,” explained Dr. Mehra, who was not involved with the study.
Moreover, the patients were “older and had comorbidities, with poor underlying kidney function and other complications, and underlying coronary artery disease in the transplanted heart,” so “it would not surprise me that they had such a high fatality rate, since they had a high degree of vulnerability,” he said.
Dr. Mehra, who is also the editor-in-chief of the Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation, said that the journal has received manuscripts still in the review process that suggest different fatality rates than those found in the current case series.
However, he acknowledged that, because these are patients with serious vulnerability due to underlying heart disease, “you can’t be lackadaisical and need to do everything to decrease this vulnerability.”
The authors noted that, although their study did not show a protective effect from immunosuppression against COVID-19, further studies are needed to assess each individual immunosuppressive agent and provide a definitive answer.
The study was supported by a grant to one of the investigators from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Uriel reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the publication. Dr. Mehra reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 infection is associated with a high risk for mortality in heart transplant (HT) recipients, a new case series suggests.
Investigators looked at data on 28 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 who received a HT between March 1, 2020, and April 24, 2020 and found a case-fatality rate of 25%.
“The high case fatality in our case series should alert physicians to the vulnerability of heart transplant recipients during the COVID-19 pandemic,” senior author Nir Uriel, MD, MSc, professor of medicine at Columbia University, New York, said in an interview.
“These patients require extra precautions to prevent the development of infection,” said Dr. Uriel, who is also a cardiologist at New York Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center.
The study was published online May 13 in JAMA Cardiology.
Similar presentation
HT recipients can have several comorbidities after the procedure, including hypertension, diabetes, cardiac allograft vasculopathy, and ongoing immunosuppression, all of which can place them at risk for infection and adverse outcomes with COVID-19 infection, the authors wrote.
The researchers therefore embarked on a case series looking at 28 HT recipients with COVID-19 infection (median age, 64.0 years; interquartile range, 53.5-70.5; 79% male) to “describe the outcomes of recipients of HT who are chronically immunosuppressed and develop COVID-19 and raise important questions about the role of the immune system in the process.”
The median time from HT to study period was 8.6 (IQR, 4.2-14.5) years. Most patients had numerous comorbidities.
“The presentation of COVID-19 was similar to nontransplant patients with fever, dyspnea, cough, and GI symptoms,” Dr. Uriel reported.
No protective effect
Twenty-two patients (79%) required admission to the hospital, seven of whom (25%) required admission to the ICU and mechanical ventilation.
Despite the presence of immunosuppressive therapy, all patients had significant elevation of inflammatory biomarkers (median peak high-sensitivity C-reactive protein [hs-CRP], 11.83 mg/dL; IQR, 7.44-19.26; median peak interleukin [IL]-6, 105 pg/mL; IQR, 38-296).
Three-quarters had myocardial injury, with a median high-sensitivity troponin T of 0.055 (0.0205 - 0.1345) ng/mL.
Treatments of COVID-19 included hydroxychloroquine (18 patients; 78%), high-dose corticosteroids (eight patients; 47%), and IL-6 receptor antagonists (six patients; 26%).
Moreover, during hospitalization, mycophenolate mofetil was discontinued in most (70%) patients, and one-quarter had a reduction in their calcineurin inhibitor dose.
“Heart transplant recipients generally require more intense immunosuppressive therapy than most other solid organ transplant recipients, and this high baseline immunosuppression increases their propensity to develop infections and their likelihood of experiencing severe manifestations of infections,” Dr. Uriel commented.
“With COVID-19, in which the body’s inflammatory reaction appears to play a role in disease severity, there has been a question of whether immunosuppression may offer a protective effect,” he continued.
“This case series suggests that this is not the case, although this would need to be confirmed in larger studies,” he said.
Low threshold
Among the 22 patients who were admitted to the hospital, half were discharged home and four (18%) were still hospitalized at the end of the study.
Of the seven patients who died, two died at the study center, and five died in an outside institution.
“In the HT population, social distancing (or isolation), strict use of masks when in public, proper handwashing, and sanitization of surfaces are of paramount importance in the prevention of COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Uriel stated.
“In addition, we have restricted these patients’ contact with the hospital as much as possible during the pandemic,” he said.
However, “there should be a low threshold to hospitalize heart transplant patients who develop infection with COVID-19. Furthermore, in our series, outcomes were better for patients hospitalized at the transplant center; therefore, strong consideration should be given to transferring HT patients when hospitalized at another hospital,” he added.
The authors emphasized that COVID-19 patients “will require ongoing monitoring in the recovery phase, as an immunosuppression regimen is reintroduced and the consequences to the allograft itself become apparent.”
Vulnerable population
Commenting on the study, Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, MSc, William Harvey Distinguished Chair in Advanced Cardiovascular Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, suggested that “in epidemiological terms, [the findings] might not look as bad as the way they are reflected in the paper.”
Given that Columbia is “one of the larger heart transplant centers in the U.S., following probably 1,000 patients, having only 22 out of perhaps thousands whom they transplanted or are actively following would actually represent a low serious infection rate,” said Dr. Mehra, who is also the executive director of the Center for Advanced Heart Disease at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
“We must not forget to emphasize that, when assessing these case fatality rates, we must look at the entire population at risk, not only the handful that we were able to observe,” explained Dr. Mehra, who was not involved with the study.
Moreover, the patients were “older and had comorbidities, with poor underlying kidney function and other complications, and underlying coronary artery disease in the transplanted heart,” so “it would not surprise me that they had such a high fatality rate, since they had a high degree of vulnerability,” he said.
Dr. Mehra, who is also the editor-in-chief of the Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation, said that the journal has received manuscripts still in the review process that suggest different fatality rates than those found in the current case series.
However, he acknowledged that, because these are patients with serious vulnerability due to underlying heart disease, “you can’t be lackadaisical and need to do everything to decrease this vulnerability.”
The authors noted that, although their study did not show a protective effect from immunosuppression against COVID-19, further studies are needed to assess each individual immunosuppressive agent and provide a definitive answer.
The study was supported by a grant to one of the investigators from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Uriel reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the publication. Dr. Mehra reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Study tests a simpler low disease activity measure for lupus
An alternative disease activity index for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus called the SLE-DAS (Disease Activity Score) has shown similar results to the Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) in classifying low disease activity but may be easier to potentially apply in daily clinical practice in treat-to-target strategies, according to research presented at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year because of COVID-19.
A treat-to-target approach, in which therapies are adjusted and the patient monitored to achieve the desired endpoint, has been proposed for patients with SLE. Clinical remission is the ideal goal, followed by achieving low disease activity (LDA) when clinical remission is unattainable, the first author of the SLE-DAS study, Helena Assunção, MD, of the department of rheumatology at Centro Hospitalar e Universitário de Coimbra (Portugal), said in an interview prior to the presentation of the study at the e-congress.
But to conduct a treat-to-target approach in the clinical setting, clinicians must have reliable, user-friendly targets to assess a patient’s progress, she said. But that’s not available right now. Proposed definitions of LDA, such as the LLDAS, are based on the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI-2K). This index doesn’t address some important manifestations of SLE and it is scored dichotomously – for example, giving a similar score for thrombocytopenia when platelet count is reduced to 100,000 or to 10,000.
To compensate for these limitations, the current LLDAS definition also requires the Physician Global Assessment and other steps, including a review of medication and changes to treatment or clinical status since the previous visit.
“It is not easy to apply,” Dr. Assunção said.
The SLE-DAS is a continuous index involving 17 parameters (4 continuous: arthritis, proteinuria, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia), assigning higher scores when a manifestation is more severe, and has manifestation information that SLEDAI-2K lacks (cardiopulmonary involvement, lupus enteritis, and hemolytic anemia).
In contrast, the LLDAS is defined as:
- A SLEDAI-2k score of 4 or less with no major organ involvement
- No new disease activity
- A physician global assessment of the patient of 1 or less on a 0-3 scale
- Maintenance on a prednisolone dosage of 7.5 mg/day or less
- Maintenance on a standard immunosuppressive regimen
A previous study validated the SLE-DAS (Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Mar;78[3]:365-71), and another exploratory study identified a cutoff SLE-DAS value of 3.77 or lower for LDA with SLE-DAS (Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:411-2).
Her group compared LDA status as measured with LLDAS versus the SLE-DAS in a cross-sectional study of 292 consecutive patients at their hospital. LDA on the SLE-DAS was defined as a score 3.77 or lower and a prednisolone dose of 7.5 mg/day or less. A total of 85% of patients were in LDA with SLE-DAS and 83.9% with LLDAS, and the agreement between LLDAS and SLE-DAS LDA was very high (Cohen’s kappa coefficient test; kappa = 0.831; P < .01). Out of 292 patients, only 13 were classified differently by the two definitions, 8 of which were classified as LDA by SLE-DAS, and 5 by LLDAS. Overall, 87% of patients were women and had a mean age of nearly 49 years, with a mean disease duration of about 14 years.
Dr. Assunção feels that the SLE-DAS LDA should be sufficient to monitor disease activity without adding the Physician Global Assessment and other steps, which would make it easier to apply than LLDAS. The fact that it is based on a continuous index is also an important difference. “Especially for low disease activity, it’s very good to be able to define it with a continuous index, because you are not that bad, but not that good, you’re in the middle,” she said.
The study should be regarded as exploratory, she said, but the results were encouraging. “We got similar results, and it’s definitely easier to apply.” She can also personally attest that the new model is easier to use, since she personally collected data for LLDAS assignment. “I had to check this, and this, and this … [SLE-DAS] is easier.”
Future work from her group will aim at deriving and validating a more robust definition of LDA, which will again be compared with the current LLDAS definition.
Her colleagues have already developed and validated a definition for clinical remission using SLE-DAS, although those results have not yet been published. They hope to define activity states using SLE-DAS, including mild, moderate, and high disease activity.
The team has produced an online SLE-DAS calculator (http://sle-das.eu/) where clinicians can score the 17 parameters. “You just input the values and it gives a number reflecting disease activity. Using this definition of SLE-DAS LDA you only need that number and to verify that the prednisolone dose is equal to or inferior to 7.5 mg/day,” said Dr. Assunção.
The study received no funding. Dr. Assunção has no financial disclosures, but one coauthor reported receiving grant/research support from Pfizer and AbbVie and serving as a consultant to Pfizer, AbbVie, Roche, Lilly, and Novartis.
SOURCE: Assunção H et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79[suppl 1]:60, Abstract OP0092.
An alternative disease activity index for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus called the SLE-DAS (Disease Activity Score) has shown similar results to the Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) in classifying low disease activity but may be easier to potentially apply in daily clinical practice in treat-to-target strategies, according to research presented at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year because of COVID-19.
A treat-to-target approach, in which therapies are adjusted and the patient monitored to achieve the desired endpoint, has been proposed for patients with SLE. Clinical remission is the ideal goal, followed by achieving low disease activity (LDA) when clinical remission is unattainable, the first author of the SLE-DAS study, Helena Assunção, MD, of the department of rheumatology at Centro Hospitalar e Universitário de Coimbra (Portugal), said in an interview prior to the presentation of the study at the e-congress.
But to conduct a treat-to-target approach in the clinical setting, clinicians must have reliable, user-friendly targets to assess a patient’s progress, she said. But that’s not available right now. Proposed definitions of LDA, such as the LLDAS, are based on the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI-2K). This index doesn’t address some important manifestations of SLE and it is scored dichotomously – for example, giving a similar score for thrombocytopenia when platelet count is reduced to 100,000 or to 10,000.
To compensate for these limitations, the current LLDAS definition also requires the Physician Global Assessment and other steps, including a review of medication and changes to treatment or clinical status since the previous visit.
“It is not easy to apply,” Dr. Assunção said.
The SLE-DAS is a continuous index involving 17 parameters (4 continuous: arthritis, proteinuria, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia), assigning higher scores when a manifestation is more severe, and has manifestation information that SLEDAI-2K lacks (cardiopulmonary involvement, lupus enteritis, and hemolytic anemia).
In contrast, the LLDAS is defined as:
- A SLEDAI-2k score of 4 or less with no major organ involvement
- No new disease activity
- A physician global assessment of the patient of 1 or less on a 0-3 scale
- Maintenance on a prednisolone dosage of 7.5 mg/day or less
- Maintenance on a standard immunosuppressive regimen
A previous study validated the SLE-DAS (Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Mar;78[3]:365-71), and another exploratory study identified a cutoff SLE-DAS value of 3.77 or lower for LDA with SLE-DAS (Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:411-2).
Her group compared LDA status as measured with LLDAS versus the SLE-DAS in a cross-sectional study of 292 consecutive patients at their hospital. LDA on the SLE-DAS was defined as a score 3.77 or lower and a prednisolone dose of 7.5 mg/day or less. A total of 85% of patients were in LDA with SLE-DAS and 83.9% with LLDAS, and the agreement between LLDAS and SLE-DAS LDA was very high (Cohen’s kappa coefficient test; kappa = 0.831; P < .01). Out of 292 patients, only 13 were classified differently by the two definitions, 8 of which were classified as LDA by SLE-DAS, and 5 by LLDAS. Overall, 87% of patients were women and had a mean age of nearly 49 years, with a mean disease duration of about 14 years.
Dr. Assunção feels that the SLE-DAS LDA should be sufficient to monitor disease activity without adding the Physician Global Assessment and other steps, which would make it easier to apply than LLDAS. The fact that it is based on a continuous index is also an important difference. “Especially for low disease activity, it’s very good to be able to define it with a continuous index, because you are not that bad, but not that good, you’re in the middle,” she said.
The study should be regarded as exploratory, she said, but the results were encouraging. “We got similar results, and it’s definitely easier to apply.” She can also personally attest that the new model is easier to use, since she personally collected data for LLDAS assignment. “I had to check this, and this, and this … [SLE-DAS] is easier.”
Future work from her group will aim at deriving and validating a more robust definition of LDA, which will again be compared with the current LLDAS definition.
Her colleagues have already developed and validated a definition for clinical remission using SLE-DAS, although those results have not yet been published. They hope to define activity states using SLE-DAS, including mild, moderate, and high disease activity.
The team has produced an online SLE-DAS calculator (http://sle-das.eu/) where clinicians can score the 17 parameters. “You just input the values and it gives a number reflecting disease activity. Using this definition of SLE-DAS LDA you only need that number and to verify that the prednisolone dose is equal to or inferior to 7.5 mg/day,” said Dr. Assunção.
The study received no funding. Dr. Assunção has no financial disclosures, but one coauthor reported receiving grant/research support from Pfizer and AbbVie and serving as a consultant to Pfizer, AbbVie, Roche, Lilly, and Novartis.
SOURCE: Assunção H et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79[suppl 1]:60, Abstract OP0092.
An alternative disease activity index for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus called the SLE-DAS (Disease Activity Score) has shown similar results to the Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) in classifying low disease activity but may be easier to potentially apply in daily clinical practice in treat-to-target strategies, according to research presented at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year because of COVID-19.
A treat-to-target approach, in which therapies are adjusted and the patient monitored to achieve the desired endpoint, has been proposed for patients with SLE. Clinical remission is the ideal goal, followed by achieving low disease activity (LDA) when clinical remission is unattainable, the first author of the SLE-DAS study, Helena Assunção, MD, of the department of rheumatology at Centro Hospitalar e Universitário de Coimbra (Portugal), said in an interview prior to the presentation of the study at the e-congress.
But to conduct a treat-to-target approach in the clinical setting, clinicians must have reliable, user-friendly targets to assess a patient’s progress, she said. But that’s not available right now. Proposed definitions of LDA, such as the LLDAS, are based on the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI-2K). This index doesn’t address some important manifestations of SLE and it is scored dichotomously – for example, giving a similar score for thrombocytopenia when platelet count is reduced to 100,000 or to 10,000.
To compensate for these limitations, the current LLDAS definition also requires the Physician Global Assessment and other steps, including a review of medication and changes to treatment or clinical status since the previous visit.
“It is not easy to apply,” Dr. Assunção said.
The SLE-DAS is a continuous index involving 17 parameters (4 continuous: arthritis, proteinuria, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia), assigning higher scores when a manifestation is more severe, and has manifestation information that SLEDAI-2K lacks (cardiopulmonary involvement, lupus enteritis, and hemolytic anemia).
In contrast, the LLDAS is defined as:
- A SLEDAI-2k score of 4 or less with no major organ involvement
- No new disease activity
- A physician global assessment of the patient of 1 or less on a 0-3 scale
- Maintenance on a prednisolone dosage of 7.5 mg/day or less
- Maintenance on a standard immunosuppressive regimen
A previous study validated the SLE-DAS (Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Mar;78[3]:365-71), and another exploratory study identified a cutoff SLE-DAS value of 3.77 or lower for LDA with SLE-DAS (Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:411-2).
Her group compared LDA status as measured with LLDAS versus the SLE-DAS in a cross-sectional study of 292 consecutive patients at their hospital. LDA on the SLE-DAS was defined as a score 3.77 or lower and a prednisolone dose of 7.5 mg/day or less. A total of 85% of patients were in LDA with SLE-DAS and 83.9% with LLDAS, and the agreement between LLDAS and SLE-DAS LDA was very high (Cohen’s kappa coefficient test; kappa = 0.831; P < .01). Out of 292 patients, only 13 were classified differently by the two definitions, 8 of which were classified as LDA by SLE-DAS, and 5 by LLDAS. Overall, 87% of patients were women and had a mean age of nearly 49 years, with a mean disease duration of about 14 years.
Dr. Assunção feels that the SLE-DAS LDA should be sufficient to monitor disease activity without adding the Physician Global Assessment and other steps, which would make it easier to apply than LLDAS. The fact that it is based on a continuous index is also an important difference. “Especially for low disease activity, it’s very good to be able to define it with a continuous index, because you are not that bad, but not that good, you’re in the middle,” she said.
The study should be regarded as exploratory, she said, but the results were encouraging. “We got similar results, and it’s definitely easier to apply.” She can also personally attest that the new model is easier to use, since she personally collected data for LLDAS assignment. “I had to check this, and this, and this … [SLE-DAS] is easier.”
Future work from her group will aim at deriving and validating a more robust definition of LDA, which will again be compared with the current LLDAS definition.
Her colleagues have already developed and validated a definition for clinical remission using SLE-DAS, although those results have not yet been published. They hope to define activity states using SLE-DAS, including mild, moderate, and high disease activity.
The team has produced an online SLE-DAS calculator (http://sle-das.eu/) where clinicians can score the 17 parameters. “You just input the values and it gives a number reflecting disease activity. Using this definition of SLE-DAS LDA you only need that number and to verify that the prednisolone dose is equal to or inferior to 7.5 mg/day,” said Dr. Assunção.
The study received no funding. Dr. Assunção has no financial disclosures, but one coauthor reported receiving grant/research support from Pfizer and AbbVie and serving as a consultant to Pfizer, AbbVie, Roche, Lilly, and Novartis.
SOURCE: Assunção H et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79[suppl 1]:60, Abstract OP0092.
FROM EULAR 2020 E-CONGRESS
Today’s top news highlights: COVID-19 could worsen gambling problems, food allergies less common than thought
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Could COVID-19 worsen gambling problems?
Take isolation, add excess available time and anxiety about illness or finances and you get the potential to increase problem gambling behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic. A call to action, recently published in the Journal of Addiction Medicine, says it’s essential to gather data and supply guidance on this issue. “People are likely to be experiencing stress at levels they haven’t experienced previously,” said coauthor Marc N. Potenza, MD, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn. While multiple factors can contribute to addictive behaviors, “with respect to the pandemic, one concern is that so-called negative reinforcement motivations – engaging in an addictive behavior to escape from depressed or negative mood states – may be a driving motivation for a significant number of people during this time,” he said. Read more.
Food allergies in children are less frequent than expected
Food allergies appear to be less common than previously reported among 6- to 10-year-olds in Europe, according to a recent study. Prevalance ranged from a low of 1.4% to a high of 3.8%, both of which are “considerably lower” than the 16% rate based on parental reports of symptoms such as rash, itching, or diarrhea, Linus Grabenhenrich, MD, MPH, and colleagues reported in Allergy. The most commonly reported allergies were to peanuts and hazelnuts, with a prevalence of just over 5% for both. Previous research on pediatric food allergy prevalence has largely consisted of single-center studies with heterogeneous designs, the researchers noted. Read more.
The grocery store hug
William G. Wilkoff, MD, grew up in a family that didn’t embrace hugging, but as a small-town pediatrician he warmed up to the concept so much that he would frequently hug a passing acquaintance at the grocery store. That’s something he misses in the current environment and that he doesn’t expect will return. “[N]early every week I encounter one or two people with whom I have a long and sometimes emotionally charged relationship,” Dr. Wilkoff wrote in a column on MDedge. “Nurses with whom I sweated over difficult delivery room resuscitations. Parents for whom their anxiety was getting in the way of their ability to parent. Parents and caregivers of complex multiply disabled children who are now adults. Peers who have lost a spouse or a child. I’m sure you have your own list of people who send off that we-need-to-hug spark.” Read more.
Identifying structural lesions of axial spondyloarthritis
What constitutes a structural lesion of the sacroiliac joints on MRI that’s indicative of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) has long been a matter of conjecture, but the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) MRI Working Group has developed new definitions that show a high degree of specificity in identifying such lesions in the disease. “Previous studies have described structural lesions in different ways, precluding meaningful comparisons between studies,” Walter P. Maksymowych, MD, said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19. “The ASAS MRI group has generated updated consensus lesion definitions that describe each of the MRI lesions in the sacroiliac joint. These definitions have been validated by seven expert readers from the ASAS MRI group on MRI images from the ASAS classification cohort.” Read more.
Making the world’s skin crawl
Clinicians should be aware of the skin manifestations of COVID-19, especially when triaging patients. In a commentary published on MDedge, Kathleen M. Coerdt and Amor Khachemoune, MD, describe the dermatologic implications of COVID-19, including the clinical manifestations of the disease, risk reduction techniques for patients and providers, personal protective equipment-associated adverse reactions, and the financial impact on dermatologists. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Could COVID-19 worsen gambling problems?
Take isolation, add excess available time and anxiety about illness or finances and you get the potential to increase problem gambling behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic. A call to action, recently published in the Journal of Addiction Medicine, says it’s essential to gather data and supply guidance on this issue. “People are likely to be experiencing stress at levels they haven’t experienced previously,” said coauthor Marc N. Potenza, MD, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn. While multiple factors can contribute to addictive behaviors, “with respect to the pandemic, one concern is that so-called negative reinforcement motivations – engaging in an addictive behavior to escape from depressed or negative mood states – may be a driving motivation for a significant number of people during this time,” he said. Read more.
Food allergies in children are less frequent than expected
Food allergies appear to be less common than previously reported among 6- to 10-year-olds in Europe, according to a recent study. Prevalance ranged from a low of 1.4% to a high of 3.8%, both of which are “considerably lower” than the 16% rate based on parental reports of symptoms such as rash, itching, or diarrhea, Linus Grabenhenrich, MD, MPH, and colleagues reported in Allergy. The most commonly reported allergies were to peanuts and hazelnuts, with a prevalence of just over 5% for both. Previous research on pediatric food allergy prevalence has largely consisted of single-center studies with heterogeneous designs, the researchers noted. Read more.
The grocery store hug
William G. Wilkoff, MD, grew up in a family that didn’t embrace hugging, but as a small-town pediatrician he warmed up to the concept so much that he would frequently hug a passing acquaintance at the grocery store. That’s something he misses in the current environment and that he doesn’t expect will return. “[N]early every week I encounter one or two people with whom I have a long and sometimes emotionally charged relationship,” Dr. Wilkoff wrote in a column on MDedge. “Nurses with whom I sweated over difficult delivery room resuscitations. Parents for whom their anxiety was getting in the way of their ability to parent. Parents and caregivers of complex multiply disabled children who are now adults. Peers who have lost a spouse or a child. I’m sure you have your own list of people who send off that we-need-to-hug spark.” Read more.
Identifying structural lesions of axial spondyloarthritis
What constitutes a structural lesion of the sacroiliac joints on MRI that’s indicative of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) has long been a matter of conjecture, but the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) MRI Working Group has developed new definitions that show a high degree of specificity in identifying such lesions in the disease. “Previous studies have described structural lesions in different ways, precluding meaningful comparisons between studies,” Walter P. Maksymowych, MD, said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19. “The ASAS MRI group has generated updated consensus lesion definitions that describe each of the MRI lesions in the sacroiliac joint. These definitions have been validated by seven expert readers from the ASAS MRI group on MRI images from the ASAS classification cohort.” Read more.
Making the world’s skin crawl
Clinicians should be aware of the skin manifestations of COVID-19, especially when triaging patients. In a commentary published on MDedge, Kathleen M. Coerdt and Amor Khachemoune, MD, describe the dermatologic implications of COVID-19, including the clinical manifestations of the disease, risk reduction techniques for patients and providers, personal protective equipment-associated adverse reactions, and the financial impact on dermatologists. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Could COVID-19 worsen gambling problems?
Take isolation, add excess available time and anxiety about illness or finances and you get the potential to increase problem gambling behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic. A call to action, recently published in the Journal of Addiction Medicine, says it’s essential to gather data and supply guidance on this issue. “People are likely to be experiencing stress at levels they haven’t experienced previously,” said coauthor Marc N. Potenza, MD, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn. While multiple factors can contribute to addictive behaviors, “with respect to the pandemic, one concern is that so-called negative reinforcement motivations – engaging in an addictive behavior to escape from depressed or negative mood states – may be a driving motivation for a significant number of people during this time,” he said. Read more.
Food allergies in children are less frequent than expected
Food allergies appear to be less common than previously reported among 6- to 10-year-olds in Europe, according to a recent study. Prevalance ranged from a low of 1.4% to a high of 3.8%, both of which are “considerably lower” than the 16% rate based on parental reports of symptoms such as rash, itching, or diarrhea, Linus Grabenhenrich, MD, MPH, and colleagues reported in Allergy. The most commonly reported allergies were to peanuts and hazelnuts, with a prevalence of just over 5% for both. Previous research on pediatric food allergy prevalence has largely consisted of single-center studies with heterogeneous designs, the researchers noted. Read more.
The grocery store hug
William G. Wilkoff, MD, grew up in a family that didn’t embrace hugging, but as a small-town pediatrician he warmed up to the concept so much that he would frequently hug a passing acquaintance at the grocery store. That’s something he misses in the current environment and that he doesn’t expect will return. “[N]early every week I encounter one or two people with whom I have a long and sometimes emotionally charged relationship,” Dr. Wilkoff wrote in a column on MDedge. “Nurses with whom I sweated over difficult delivery room resuscitations. Parents for whom their anxiety was getting in the way of their ability to parent. Parents and caregivers of complex multiply disabled children who are now adults. Peers who have lost a spouse or a child. I’m sure you have your own list of people who send off that we-need-to-hug spark.” Read more.
Identifying structural lesions of axial spondyloarthritis
What constitutes a structural lesion of the sacroiliac joints on MRI that’s indicative of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) has long been a matter of conjecture, but the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) MRI Working Group has developed new definitions that show a high degree of specificity in identifying such lesions in the disease. “Previous studies have described structural lesions in different ways, precluding meaningful comparisons between studies,” Walter P. Maksymowych, MD, said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19. “The ASAS MRI group has generated updated consensus lesion definitions that describe each of the MRI lesions in the sacroiliac joint. These definitions have been validated by seven expert readers from the ASAS MRI group on MRI images from the ASAS classification cohort.” Read more.
Making the world’s skin crawl
Clinicians should be aware of the skin manifestations of COVID-19, especially when triaging patients. In a commentary published on MDedge, Kathleen M. Coerdt and Amor Khachemoune, MD, describe the dermatologic implications of COVID-19, including the clinical manifestations of the disease, risk reduction techniques for patients and providers, personal protective equipment-associated adverse reactions, and the financial impact on dermatologists. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Americans avoided emergency departments early in the pandemic
compared with the corresponding period in 2019, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“The striking decline in ED visits nationwide … suggests that the pandemic has altered the use of the ED by the public,” Kathleen P. Hartnett, PhD, and associates at the CDC said June 3 in the Mortality and Morbidity Weekly Report.
The weekly mean was just over 1.2 million ED visits for the 4 weeks from March 29 to April 25, 2020, compared with the nearly 2.2 million visits per week recorded from March 31 to April 27, 2019 – a drop of 42%, based on an analysis of data from the National Syndromic Surveillance Program.
Despite that drop, ED visits for infectious disease–related reasons, taken as a proportion of all 1.2 ED visits during the early pandemic period, were 3.8 times higher than the comparison period in 2019, the investigators reported.
ED visits also were higher in 2020 for specified and unspecified lower respiratory disease not including influenza, pneumonia, asthma, or bronchitis (prevalence ratio of 1.99, compared with 2019), cardiac arrest and ventricular fibrillation (PR, 1.98), and pneumonia not caused by tuberculosis (PR, 1.91), Dr. Hartnett and associates said.
Prevalence ratios for the early pandemic period were down for most other conditions, with some of the largest decreases seen for influenza (PR, 0.16), otitis media (PR, 0.35), and neoplasm-related encounters (PR, 0.40), they said.
Visits have increased each week since reaching their lowest point during April 12-18, but the number for the most recent full week, May 24-30, which was not included in the analysis, was still 26% lower than the corresponding week in 2019, the CDC team pointed out.
“Some persons could be delaying care for conditions that might result in additional mortality if left untreated,” the investigators noted, and those “who use the ED as a safety net because they lack access to primary care and telemedicine might be disproportionately affected if they avoid seeking care because of concerns about the infection risk in the ED.”
SOURCE: Hartnett KP et al. MMWR. 2020 Jun 3. 69:1-6.
compared with the corresponding period in 2019, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

“The striking decline in ED visits nationwide … suggests that the pandemic has altered the use of the ED by the public,” Kathleen P. Hartnett, PhD, and associates at the CDC said June 3 in the Mortality and Morbidity Weekly Report.
The weekly mean was just over 1.2 million ED visits for the 4 weeks from March 29 to April 25, 2020, compared with the nearly 2.2 million visits per week recorded from March 31 to April 27, 2019 – a drop of 42%, based on an analysis of data from the National Syndromic Surveillance Program.
Despite that drop, ED visits for infectious disease–related reasons, taken as a proportion of all 1.2 ED visits during the early pandemic period, were 3.8 times higher than the comparison period in 2019, the investigators reported.
ED visits also were higher in 2020 for specified and unspecified lower respiratory disease not including influenza, pneumonia, asthma, or bronchitis (prevalence ratio of 1.99, compared with 2019), cardiac arrest and ventricular fibrillation (PR, 1.98), and pneumonia not caused by tuberculosis (PR, 1.91), Dr. Hartnett and associates said.
Prevalence ratios for the early pandemic period were down for most other conditions, with some of the largest decreases seen for influenza (PR, 0.16), otitis media (PR, 0.35), and neoplasm-related encounters (PR, 0.40), they said.
Visits have increased each week since reaching their lowest point during April 12-18, but the number for the most recent full week, May 24-30, which was not included in the analysis, was still 26% lower than the corresponding week in 2019, the CDC team pointed out.
“Some persons could be delaying care for conditions that might result in additional mortality if left untreated,” the investigators noted, and those “who use the ED as a safety net because they lack access to primary care and telemedicine might be disproportionately affected if they avoid seeking care because of concerns about the infection risk in the ED.”
SOURCE: Hartnett KP et al. MMWR. 2020 Jun 3. 69:1-6.
compared with the corresponding period in 2019, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

“The striking decline in ED visits nationwide … suggests that the pandemic has altered the use of the ED by the public,” Kathleen P. Hartnett, PhD, and associates at the CDC said June 3 in the Mortality and Morbidity Weekly Report.
The weekly mean was just over 1.2 million ED visits for the 4 weeks from March 29 to April 25, 2020, compared with the nearly 2.2 million visits per week recorded from March 31 to April 27, 2019 – a drop of 42%, based on an analysis of data from the National Syndromic Surveillance Program.
Despite that drop, ED visits for infectious disease–related reasons, taken as a proportion of all 1.2 ED visits during the early pandemic period, were 3.8 times higher than the comparison period in 2019, the investigators reported.
ED visits also were higher in 2020 for specified and unspecified lower respiratory disease not including influenza, pneumonia, asthma, or bronchitis (prevalence ratio of 1.99, compared with 2019), cardiac arrest and ventricular fibrillation (PR, 1.98), and pneumonia not caused by tuberculosis (PR, 1.91), Dr. Hartnett and associates said.
Prevalence ratios for the early pandemic period were down for most other conditions, with some of the largest decreases seen for influenza (PR, 0.16), otitis media (PR, 0.35), and neoplasm-related encounters (PR, 0.40), they said.
Visits have increased each week since reaching their lowest point during April 12-18, but the number for the most recent full week, May 24-30, which was not included in the analysis, was still 26% lower than the corresponding week in 2019, the CDC team pointed out.
“Some persons could be delaying care for conditions that might result in additional mortality if left untreated,” the investigators noted, and those “who use the ED as a safety net because they lack access to primary care and telemedicine might be disproportionately affected if they avoid seeking care because of concerns about the infection risk in the ED.”
SOURCE: Hartnett KP et al. MMWR. 2020 Jun 3. 69:1-6.
FROM MMWR
Atopic dermatitis in adults, children linked to neuropsychiatric disorders
according to a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology, held virtually.
“The risk increase ranges from as low as 5% up to 59%, depending on the outcome, with generally greater effects observed among the adults,” Joy Wan, MD, a postdoctoral dermatology fellow at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in her presentation. The risk was independent of other atopic disease, gender, age, and socioeconomic status.
Dr. Wan and colleagues conducted a cohort study of patients with AD in the United Kingdom using data from the Health Improvement Network (THIN) electronic records database, matching AD patients in THIN with up to five patients without AD, similar in age and also registered to general practices. The researchers validated AD disease status using an algorithm that identified patients with a diagnostic code and two therapy codes related to AD. Outcomes of interest included anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, ADHD, schizophrenia, and autism. Patients entered into the cohort when they were diagnosed with AD, registered by a practice, or when data from a practice was reported to THIN. The researchers stopped following patients when they developed a neuropsychiatric outcome of interest, left a practice, died, or when the study ended.
“Previous studies have found associations between atopic dermatitis and anxiety, depression, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. However, many previous studies had been cross-sectional and they were unable to evaluate the directionality of association between atopic dermatitis and neuropsychiatric outcomes, while other previous studies have relied on the self-report of atopic dermatitis and outcomes as well,” Dr. Wan said. “Thus, longitudinal studies, using validated measures of atopic dermatitis, and those that include the entire age span, are really needed.”
Overall, 434,859 children and adolescents under aged 18 with AD in the THIN database were matched to 1,983,589 controls, and 644,802 adults with AD were matched to almost 2,900,000 adults without AD. In the pediatric group, demographics were mostly balanced between children with and without AD: the average age ranged between about 5 and almost 6 years. In pediatric patients with AD, there was a higher rate of allergic rhinitis (6.2% vs. 4%) and asthma (13.5% vs. 9.3%) than in the control group.
For adults, the average age was about 48 years in both groups. Compared with patients who did not have AD, adults with AD also had higher rates of allergic rhinitis (15.2% vs. 9.6%) and asthma (19.9% vs. 12.6%).
After adjusting for age, gender, socioeconomic status, asthma, and allergic rhinitis, Dr. Wan and colleagues found greater rates of bipolar disorder (hazard ratio, 1.34; 95% confidence interval, 1.09-1.65), obsessive-compulsive disorder (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.21-1.41), anxiety (HR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.07-1.11), and depression (HR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.04-1.08) among children and adolescents with AD, compared with controls.
In the adult cohort, a diagnosis of AD was associated with an increased risk of autism (HR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.30-1.80), obsessive-compulsive disorder (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.40-1.59), ADHD (HR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.13-1.53), anxiety (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.15-1.18), depression (HR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.14-1.16), and bipolar disorder (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.04-1.21), after adjusting for age, gender, socioeconomic status, asthma, and allergic rhinitis.
One reason for the increased associations among the adults, even for ADHD and autism, which are more characteristically diagnosed in childhood, Dr. Wan said, is that, since they looked at incident outcomes, “many children may already have had these prevalent comorbidities at the time of the entry in the cohort.”
She noted that the study may have observation bias or unknown confounders, but she hopes these results raise awareness of the association between AD and neuropsychiatric disorders, although more research is needed to determine how AD severity affects neuropsychiatric outcomes. “Additional work is needed to really understand the mechanisms that drive these associations, whether it’s mediated through symptoms of atopic dermatitis such as itch and poor sleep, or potentially the stigma of having a chronic skin disease, or perhaps shared pathophysiology between atopic dermatitis and these neuropsychiatric diseases,” she said.
The study was funded by a grant from Pfizer. Dr. Wan reports receiving research funding from Pfizer paid to the University of Pennsylvania.
according to a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology, held virtually.
“The risk increase ranges from as low as 5% up to 59%, depending on the outcome, with generally greater effects observed among the adults,” Joy Wan, MD, a postdoctoral dermatology fellow at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in her presentation. The risk was independent of other atopic disease, gender, age, and socioeconomic status.
Dr. Wan and colleagues conducted a cohort study of patients with AD in the United Kingdom using data from the Health Improvement Network (THIN) electronic records database, matching AD patients in THIN with up to five patients without AD, similar in age and also registered to general practices. The researchers validated AD disease status using an algorithm that identified patients with a diagnostic code and two therapy codes related to AD. Outcomes of interest included anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, ADHD, schizophrenia, and autism. Patients entered into the cohort when they were diagnosed with AD, registered by a practice, or when data from a practice was reported to THIN. The researchers stopped following patients when they developed a neuropsychiatric outcome of interest, left a practice, died, or when the study ended.
“Previous studies have found associations between atopic dermatitis and anxiety, depression, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. However, many previous studies had been cross-sectional and they were unable to evaluate the directionality of association between atopic dermatitis and neuropsychiatric outcomes, while other previous studies have relied on the self-report of atopic dermatitis and outcomes as well,” Dr. Wan said. “Thus, longitudinal studies, using validated measures of atopic dermatitis, and those that include the entire age span, are really needed.”
Overall, 434,859 children and adolescents under aged 18 with AD in the THIN database were matched to 1,983,589 controls, and 644,802 adults with AD were matched to almost 2,900,000 adults without AD. In the pediatric group, demographics were mostly balanced between children with and without AD: the average age ranged between about 5 and almost 6 years. In pediatric patients with AD, there was a higher rate of allergic rhinitis (6.2% vs. 4%) and asthma (13.5% vs. 9.3%) than in the control group.
For adults, the average age was about 48 years in both groups. Compared with patients who did not have AD, adults with AD also had higher rates of allergic rhinitis (15.2% vs. 9.6%) and asthma (19.9% vs. 12.6%).
After adjusting for age, gender, socioeconomic status, asthma, and allergic rhinitis, Dr. Wan and colleagues found greater rates of bipolar disorder (hazard ratio, 1.34; 95% confidence interval, 1.09-1.65), obsessive-compulsive disorder (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.21-1.41), anxiety (HR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.07-1.11), and depression (HR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.04-1.08) among children and adolescents with AD, compared with controls.
In the adult cohort, a diagnosis of AD was associated with an increased risk of autism (HR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.30-1.80), obsessive-compulsive disorder (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.40-1.59), ADHD (HR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.13-1.53), anxiety (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.15-1.18), depression (HR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.14-1.16), and bipolar disorder (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.04-1.21), after adjusting for age, gender, socioeconomic status, asthma, and allergic rhinitis.
One reason for the increased associations among the adults, even for ADHD and autism, which are more characteristically diagnosed in childhood, Dr. Wan said, is that, since they looked at incident outcomes, “many children may already have had these prevalent comorbidities at the time of the entry in the cohort.”
She noted that the study may have observation bias or unknown confounders, but she hopes these results raise awareness of the association between AD and neuropsychiatric disorders, although more research is needed to determine how AD severity affects neuropsychiatric outcomes. “Additional work is needed to really understand the mechanisms that drive these associations, whether it’s mediated through symptoms of atopic dermatitis such as itch and poor sleep, or potentially the stigma of having a chronic skin disease, or perhaps shared pathophysiology between atopic dermatitis and these neuropsychiatric diseases,” she said.
The study was funded by a grant from Pfizer. Dr. Wan reports receiving research funding from Pfizer paid to the University of Pennsylvania.
according to a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology, held virtually.
“The risk increase ranges from as low as 5% up to 59%, depending on the outcome, with generally greater effects observed among the adults,” Joy Wan, MD, a postdoctoral dermatology fellow at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in her presentation. The risk was independent of other atopic disease, gender, age, and socioeconomic status.
Dr. Wan and colleagues conducted a cohort study of patients with AD in the United Kingdom using data from the Health Improvement Network (THIN) electronic records database, matching AD patients in THIN with up to five patients without AD, similar in age and also registered to general practices. The researchers validated AD disease status using an algorithm that identified patients with a diagnostic code and two therapy codes related to AD. Outcomes of interest included anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, ADHD, schizophrenia, and autism. Patients entered into the cohort when they were diagnosed with AD, registered by a practice, or when data from a practice was reported to THIN. The researchers stopped following patients when they developed a neuropsychiatric outcome of interest, left a practice, died, or when the study ended.
“Previous studies have found associations between atopic dermatitis and anxiety, depression, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. However, many previous studies had been cross-sectional and they were unable to evaluate the directionality of association between atopic dermatitis and neuropsychiatric outcomes, while other previous studies have relied on the self-report of atopic dermatitis and outcomes as well,” Dr. Wan said. “Thus, longitudinal studies, using validated measures of atopic dermatitis, and those that include the entire age span, are really needed.”
Overall, 434,859 children and adolescents under aged 18 with AD in the THIN database were matched to 1,983,589 controls, and 644,802 adults with AD were matched to almost 2,900,000 adults without AD. In the pediatric group, demographics were mostly balanced between children with and without AD: the average age ranged between about 5 and almost 6 years. In pediatric patients with AD, there was a higher rate of allergic rhinitis (6.2% vs. 4%) and asthma (13.5% vs. 9.3%) than in the control group.
For adults, the average age was about 48 years in both groups. Compared with patients who did not have AD, adults with AD also had higher rates of allergic rhinitis (15.2% vs. 9.6%) and asthma (19.9% vs. 12.6%).
After adjusting for age, gender, socioeconomic status, asthma, and allergic rhinitis, Dr. Wan and colleagues found greater rates of bipolar disorder (hazard ratio, 1.34; 95% confidence interval, 1.09-1.65), obsessive-compulsive disorder (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.21-1.41), anxiety (HR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.07-1.11), and depression (HR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.04-1.08) among children and adolescents with AD, compared with controls.
In the adult cohort, a diagnosis of AD was associated with an increased risk of autism (HR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.30-1.80), obsessive-compulsive disorder (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.40-1.59), ADHD (HR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.13-1.53), anxiety (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.15-1.18), depression (HR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.14-1.16), and bipolar disorder (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.04-1.21), after adjusting for age, gender, socioeconomic status, asthma, and allergic rhinitis.
One reason for the increased associations among the adults, even for ADHD and autism, which are more characteristically diagnosed in childhood, Dr. Wan said, is that, since they looked at incident outcomes, “many children may already have had these prevalent comorbidities at the time of the entry in the cohort.”
She noted that the study may have observation bias or unknown confounders, but she hopes these results raise awareness of the association between AD and neuropsychiatric disorders, although more research is needed to determine how AD severity affects neuropsychiatric outcomes. “Additional work is needed to really understand the mechanisms that drive these associations, whether it’s mediated through symptoms of atopic dermatitis such as itch and poor sleep, or potentially the stigma of having a chronic skin disease, or perhaps shared pathophysiology between atopic dermatitis and these neuropsychiatric diseases,” she said.
The study was funded by a grant from Pfizer. Dr. Wan reports receiving research funding from Pfizer paid to the University of Pennsylvania.
FROM SID 2020
The grocery store hug
I grew up in a family that was pretty much devoid of physical demonstrations of affection. I certainly felt that my folks loved me, but there was no hugging. I don’t recall ever seeing my parents kiss or touch each other. My dad would occasionally physically tease my mother. For example, I can remember one incident at the dinner table when he was playfully and gently laying a hand on my mother’s arm just as she was raising her fork to her mouth. After about three of these gentle holds, she lifted her water glass and tossed its contents in his face. This was the full extent of physicality in our family.
It wasn’t just my parents. I can’t remember aunts or uncles or cousins ever hugging us when we met. Grandmothers of course would request a hug. I never knew either of my grandfathers, but I suspect they would not have been the hugging kind.
I never felt I was missing out on anything, because in the generally WASPish atmosphere of the community in which I grew up I saw very few public displays of affection. But somewhere over time, hugging crept into the American repertoire of expression. This incursion may have been a ripple effect from the flower power, free love hippiedom of the ‘60s and ‘70s. Or it may have been a symptom of globalization as Americans became more familiar with other cultures in which physical expression was more common.
Whatever the reason for the more widespread adoption of hugging in our social vocabulary with my somewhat physically impoverished upbringing, it took me longer than most folks to comfortably include it in my greeting options. Although I may have come to the dance late, I have fully adopted hugging as a way to greet people with whom I have more than a passing acquaintance.
In fact, the ability to comfortably hug former coworkers, old friends I haven’t seen in years, and parents with whom I had shared a particularly troublesome child is what I miss most about the restrictions that have come with the COVID-19 pandemic. Now when I meet folks in the grocery store with whom I share a special affection that magnetic spark still leaps between our eyes, just visible over our face masks, but mentally and physically we take a step back and say to ourselves that this hug shouldn’t happen and it isn’t going to happen. And that makes me sad.
One of the great perks of practicing pediatrics in a small town and then remaining there in retirement is that nearly every week I encounter one or two people with whom I have a long and sometimes emotionally charged relationship. Nurses with whom I sweated over difficult delivery room resuscitations. Parents for whom their anxiety was getting in the way of their ability to parent. Parents and caregivers of complex multiply disabled children who are now adults. Peers who have lost a spouse or a child.
I can envision a day sometime in the relatively near future that I will be able to hug my two grandchildren whom I haven’t hugged even though they live a short 10-minute walk away. But I have trouble imagining when I will again be able to enjoy and be enriched by those special grocery store hugs that I have grown to savor.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
I grew up in a family that was pretty much devoid of physical demonstrations of affection. I certainly felt that my folks loved me, but there was no hugging. I don’t recall ever seeing my parents kiss or touch each other. My dad would occasionally physically tease my mother. For example, I can remember one incident at the dinner table when he was playfully and gently laying a hand on my mother’s arm just as she was raising her fork to her mouth. After about three of these gentle holds, she lifted her water glass and tossed its contents in his face. This was the full extent of physicality in our family.
It wasn’t just my parents. I can’t remember aunts or uncles or cousins ever hugging us when we met. Grandmothers of course would request a hug. I never knew either of my grandfathers, but I suspect they would not have been the hugging kind.
I never felt I was missing out on anything, because in the generally WASPish atmosphere of the community in which I grew up I saw very few public displays of affection. But somewhere over time, hugging crept into the American repertoire of expression. This incursion may have been a ripple effect from the flower power, free love hippiedom of the ‘60s and ‘70s. Or it may have been a symptom of globalization as Americans became more familiar with other cultures in which physical expression was more common.
Whatever the reason for the more widespread adoption of hugging in our social vocabulary with my somewhat physically impoverished upbringing, it took me longer than most folks to comfortably include it in my greeting options. Although I may have come to the dance late, I have fully adopted hugging as a way to greet people with whom I have more than a passing acquaintance.
In fact, the ability to comfortably hug former coworkers, old friends I haven’t seen in years, and parents with whom I had shared a particularly troublesome child is what I miss most about the restrictions that have come with the COVID-19 pandemic. Now when I meet folks in the grocery store with whom I share a special affection that magnetic spark still leaps between our eyes, just visible over our face masks, but mentally and physically we take a step back and say to ourselves that this hug shouldn’t happen and it isn’t going to happen. And that makes me sad.
One of the great perks of practicing pediatrics in a small town and then remaining there in retirement is that nearly every week I encounter one or two people with whom I have a long and sometimes emotionally charged relationship. Nurses with whom I sweated over difficult delivery room resuscitations. Parents for whom their anxiety was getting in the way of their ability to parent. Parents and caregivers of complex multiply disabled children who are now adults. Peers who have lost a spouse or a child.
I can envision a day sometime in the relatively near future that I will be able to hug my two grandchildren whom I haven’t hugged even though they live a short 10-minute walk away. But I have trouble imagining when I will again be able to enjoy and be enriched by those special grocery store hugs that I have grown to savor.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
I grew up in a family that was pretty much devoid of physical demonstrations of affection. I certainly felt that my folks loved me, but there was no hugging. I don’t recall ever seeing my parents kiss or touch each other. My dad would occasionally physically tease my mother. For example, I can remember one incident at the dinner table when he was playfully and gently laying a hand on my mother’s arm just as she was raising her fork to her mouth. After about three of these gentle holds, she lifted her water glass and tossed its contents in his face. This was the full extent of physicality in our family.
It wasn’t just my parents. I can’t remember aunts or uncles or cousins ever hugging us when we met. Grandmothers of course would request a hug. I never knew either of my grandfathers, but I suspect they would not have been the hugging kind.
I never felt I was missing out on anything, because in the generally WASPish atmosphere of the community in which I grew up I saw very few public displays of affection. But somewhere over time, hugging crept into the American repertoire of expression. This incursion may have been a ripple effect from the flower power, free love hippiedom of the ‘60s and ‘70s. Or it may have been a symptom of globalization as Americans became more familiar with other cultures in which physical expression was more common.
Whatever the reason for the more widespread adoption of hugging in our social vocabulary with my somewhat physically impoverished upbringing, it took me longer than most folks to comfortably include it in my greeting options. Although I may have come to the dance late, I have fully adopted hugging as a way to greet people with whom I have more than a passing acquaintance.
In fact, the ability to comfortably hug former coworkers, old friends I haven’t seen in years, and parents with whom I had shared a particularly troublesome child is what I miss most about the restrictions that have come with the COVID-19 pandemic. Now when I meet folks in the grocery store with whom I share a special affection that magnetic spark still leaps between our eyes, just visible over our face masks, but mentally and physically we take a step back and say to ourselves that this hug shouldn’t happen and it isn’t going to happen. And that makes me sad.
One of the great perks of practicing pediatrics in a small town and then remaining there in retirement is that nearly every week I encounter one or two people with whom I have a long and sometimes emotionally charged relationship. Nurses with whom I sweated over difficult delivery room resuscitations. Parents for whom their anxiety was getting in the way of their ability to parent. Parents and caregivers of complex multiply disabled children who are now adults. Peers who have lost a spouse or a child.
I can envision a day sometime in the relatively near future that I will be able to hug my two grandchildren whom I haven’t hugged even though they live a short 10-minute walk away. But I have trouble imagining when I will again be able to enjoy and be enriched by those special grocery store hugs that I have grown to savor.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
Biologics yield low rates of skin clearance in real-world psoriasis study
The study was published in May in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
High efficacy rates, which include PASI 100 scores, have been reported in randomized trials of biologics that include anti–interleukin (IL)–17A therapies (secukinumab and ixekizumab), anti–IL-17A–receptor therapies (brodalumab), and anti–IL-23 therapies (guselkumab and risankizumab), but information on rates in real-world cohorts has been limited. “Real-world evidence provided by registries is only beginning to emerge, and efficacy data have mostly been derived from clinical trials,” senior author Kristian Reich, MD, PhD, professor for translational research in inflammatory skin diseases at the Institute for Health Services Research in Dermatology and Nursing, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (Germany), said in an interview.
He and his coinvestigators conducted the PSO-BIO-REAL (Plaque Psoriasis Treated With Biologics in a Real World Setting) prospective trial in five countries, to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis over a year’s time following administration of a biologic therapy. Patients were 18 years of age or older and had either started a biologic for the first time (biologic-naive) or were transitioning to another biologic (biologic-experienced).
Among 846 participants, 32% were in the United States, followed by France (28%), Italy (22%), the United Kingdom (11%), and Germany (8%). Investigators estimated the proportion of patients achieving a PASI 100 (complete skin clearance) 6 months after starting a biologic as a primary objective, and as secondary objectives, PASI 100 scores at 1 year and PASI 100 maintenance from 6 to 12 months.
Nearly 200 patients withdrew during the course of the study, and 108 switched treatments. Therapies varied among patients: 61% received an anti–tumor necrosis factor agent such as etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, or certolizumab pegol as an initial biologic treatment, 30% received an anti–IL-12/-23 agent (ustekinumab), and 9% received an anti-IL-17 agent (secukinumab). Additionally, 23% received a concomitant psoriasis medication.
PASI assessments were completed in 603 patients at 6 months, and 522 patients at 12 months. At 6 and 12 months respectively, 23% and 26% of the patients had achieved a PASI 100 score. Investigators noted that the rate of complete skin clearance declined as the number of baseline comorbidities and the number of prior biologics increased.
Biologic-experienced patients at study entry had lower PASI 100 response rates (about 20% at 6 and 12 months) than the biologic-naive patients (25% at 6 months, 30% at 12 months). Dr. Reich pointed out that many biologic-experienced patients often have active disease, despite previous use of biologics, and “they’re likely to represent a more difficult-to-treat population.” Factors such as convenience, safety, and the fact that more complicated patients – those with weight issues, more comorbidities and pretreatments, and lower compliance – are treated in real life than in clinical trials, are likely to influence lack of response in real-world data, Dr. Reich said.
The study’s enrollment period took place from 2014 to 2015, so it did not include patients on newer biologics such as brodalumab, guselkumab, ixekizumab, and tildrakizumab. “Some of these newer therapies have shown greater efficacy than drugs such as ustekinumab and etanercept in clinical trials, and patients are more likely to achieve complete skin clearance. Therefore, real-world rates of complete clearance may have improved since this study concluded,” the investigators pointed out.
Possible limitations of the study include selection bias and possible confounders, they noted.
The study was sponsored by Amgen/AstraZeneca; the manuscript was sponsored by LEO Pharma. One author was an AstraZeneca employee, two are LEO pharma employees, one author had no disclosures, and the remaining authors, including Dr. Reich, disclosed serving as an adviser, paid speaker, consultant, and/or investigator for multiple pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Seneschal J et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16568.
The study was published in May in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
High efficacy rates, which include PASI 100 scores, have been reported in randomized trials of biologics that include anti–interleukin (IL)–17A therapies (secukinumab and ixekizumab), anti–IL-17A–receptor therapies (brodalumab), and anti–IL-23 therapies (guselkumab and risankizumab), but information on rates in real-world cohorts has been limited. “Real-world evidence provided by registries is only beginning to emerge, and efficacy data have mostly been derived from clinical trials,” senior author Kristian Reich, MD, PhD, professor for translational research in inflammatory skin diseases at the Institute for Health Services Research in Dermatology and Nursing, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (Germany), said in an interview.
He and his coinvestigators conducted the PSO-BIO-REAL (Plaque Psoriasis Treated With Biologics in a Real World Setting) prospective trial in five countries, to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis over a year’s time following administration of a biologic therapy. Patients were 18 years of age or older and had either started a biologic for the first time (biologic-naive) or were transitioning to another biologic (biologic-experienced).
Among 846 participants, 32% were in the United States, followed by France (28%), Italy (22%), the United Kingdom (11%), and Germany (8%). Investigators estimated the proportion of patients achieving a PASI 100 (complete skin clearance) 6 months after starting a biologic as a primary objective, and as secondary objectives, PASI 100 scores at 1 year and PASI 100 maintenance from 6 to 12 months.
Nearly 200 patients withdrew during the course of the study, and 108 switched treatments. Therapies varied among patients: 61% received an anti–tumor necrosis factor agent such as etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, or certolizumab pegol as an initial biologic treatment, 30% received an anti–IL-12/-23 agent (ustekinumab), and 9% received an anti-IL-17 agent (secukinumab). Additionally, 23% received a concomitant psoriasis medication.
PASI assessments were completed in 603 patients at 6 months, and 522 patients at 12 months. At 6 and 12 months respectively, 23% and 26% of the patients had achieved a PASI 100 score. Investigators noted that the rate of complete skin clearance declined as the number of baseline comorbidities and the number of prior biologics increased.
Biologic-experienced patients at study entry had lower PASI 100 response rates (about 20% at 6 and 12 months) than the biologic-naive patients (25% at 6 months, 30% at 12 months). Dr. Reich pointed out that many biologic-experienced patients often have active disease, despite previous use of biologics, and “they’re likely to represent a more difficult-to-treat population.” Factors such as convenience, safety, and the fact that more complicated patients – those with weight issues, more comorbidities and pretreatments, and lower compliance – are treated in real life than in clinical trials, are likely to influence lack of response in real-world data, Dr. Reich said.
The study’s enrollment period took place from 2014 to 2015, so it did not include patients on newer biologics such as brodalumab, guselkumab, ixekizumab, and tildrakizumab. “Some of these newer therapies have shown greater efficacy than drugs such as ustekinumab and etanercept in clinical trials, and patients are more likely to achieve complete skin clearance. Therefore, real-world rates of complete clearance may have improved since this study concluded,” the investigators pointed out.
Possible limitations of the study include selection bias and possible confounders, they noted.
The study was sponsored by Amgen/AstraZeneca; the manuscript was sponsored by LEO Pharma. One author was an AstraZeneca employee, two are LEO pharma employees, one author had no disclosures, and the remaining authors, including Dr. Reich, disclosed serving as an adviser, paid speaker, consultant, and/or investigator for multiple pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Seneschal J et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16568.
The study was published in May in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
High efficacy rates, which include PASI 100 scores, have been reported in randomized trials of biologics that include anti–interleukin (IL)–17A therapies (secukinumab and ixekizumab), anti–IL-17A–receptor therapies (brodalumab), and anti–IL-23 therapies (guselkumab and risankizumab), but information on rates in real-world cohorts has been limited. “Real-world evidence provided by registries is only beginning to emerge, and efficacy data have mostly been derived from clinical trials,” senior author Kristian Reich, MD, PhD, professor for translational research in inflammatory skin diseases at the Institute for Health Services Research in Dermatology and Nursing, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (Germany), said in an interview.
He and his coinvestigators conducted the PSO-BIO-REAL (Plaque Psoriasis Treated With Biologics in a Real World Setting) prospective trial in five countries, to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis over a year’s time following administration of a biologic therapy. Patients were 18 years of age or older and had either started a biologic for the first time (biologic-naive) or were transitioning to another biologic (biologic-experienced).
Among 846 participants, 32% were in the United States, followed by France (28%), Italy (22%), the United Kingdom (11%), and Germany (8%). Investigators estimated the proportion of patients achieving a PASI 100 (complete skin clearance) 6 months after starting a biologic as a primary objective, and as secondary objectives, PASI 100 scores at 1 year and PASI 100 maintenance from 6 to 12 months.
Nearly 200 patients withdrew during the course of the study, and 108 switched treatments. Therapies varied among patients: 61% received an anti–tumor necrosis factor agent such as etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, or certolizumab pegol as an initial biologic treatment, 30% received an anti–IL-12/-23 agent (ustekinumab), and 9% received an anti-IL-17 agent (secukinumab). Additionally, 23% received a concomitant psoriasis medication.
PASI assessments were completed in 603 patients at 6 months, and 522 patients at 12 months. At 6 and 12 months respectively, 23% and 26% of the patients had achieved a PASI 100 score. Investigators noted that the rate of complete skin clearance declined as the number of baseline comorbidities and the number of prior biologics increased.
Biologic-experienced patients at study entry had lower PASI 100 response rates (about 20% at 6 and 12 months) than the biologic-naive patients (25% at 6 months, 30% at 12 months). Dr. Reich pointed out that many biologic-experienced patients often have active disease, despite previous use of biologics, and “they’re likely to represent a more difficult-to-treat population.” Factors such as convenience, safety, and the fact that more complicated patients – those with weight issues, more comorbidities and pretreatments, and lower compliance – are treated in real life than in clinical trials, are likely to influence lack of response in real-world data, Dr. Reich said.
The study’s enrollment period took place from 2014 to 2015, so it did not include patients on newer biologics such as brodalumab, guselkumab, ixekizumab, and tildrakizumab. “Some of these newer therapies have shown greater efficacy than drugs such as ustekinumab and etanercept in clinical trials, and patients are more likely to achieve complete skin clearance. Therefore, real-world rates of complete clearance may have improved since this study concluded,” the investigators pointed out.
Possible limitations of the study include selection bias and possible confounders, they noted.
The study was sponsored by Amgen/AstraZeneca; the manuscript was sponsored by LEO Pharma. One author was an AstraZeneca employee, two are LEO pharma employees, one author had no disclosures, and the remaining authors, including Dr. Reich, disclosed serving as an adviser, paid speaker, consultant, and/or investigator for multiple pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Seneschal J et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16568.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE EUROPEAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY AND VENEREOLOGY
COVID-19: Problematic gambling could worsen
The confluence of isolation, excess available time, and anxiety about illness or finances as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic have the potential to increase problem gambling behaviors during this public health emergency, so it’s essential to gather data and supply guidance on this issue, according to a call to action published May 18 in the Journal of Addiction Medicine.
“When facing an unforeseen situation with confinement, fear of disease, and financial uncertainty for the future, problem gambling may be an important health hazard to monitor and prevent during and following the COVID-19 crisis, especially given current online gambling availability,” wrote Anders Håkansson, PhD, of Lund University in Sweden and coauthors.
Both stress and trauma have been linked to gambling problems, and both are occurring during the pandemic, said coauthor Marc N. Potenza, MD, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., in an interview.
“People are likely to be experiencing stress at levels they haven’t experienced previously,” Dr. Potenza said. While multiple factors can contribute to addictive behaviors, “with respect to the pandemic, one concern is that so-called negative reinforcement motivations – engaging in an addictive behavior to escape from depressed or negative mood states – may be a driving motivation for a significant number of people during this time,” he said.
David Hodgins, PhD, CPsych, a professor of psychology at the University of Calgary in Alberta, who was not involved with the commentary, noted that gambling relapse is triggered by “negative emotional states, interpersonal stress, and financial stress” – all three of which the pandemic contributes to.
Financial stress can especially “inflame erroneous gambling-related cognitions,” he said in an interview, including “beliefs such as the idea that gambling can solve financial problems, even when this is statistically almost impossible as debt increases, and that debt has been caused by gambling.”
Increased social isolation also is particularly problematic, pointed out Shane W. Kraus, PhD, from the University of Nevada, Las Vegas. Dr. Kraus also was not involved with the paper.
“If someone is already struggling with already negative emotions, negative feelings, thoughts, and depression, and you’re now isolating them quite a bit, that’s not going to be a recipe for success,” Dr. Kraus said in an interview.
Dr. Potenza said.
“We should be mindful of ways in which people develop addictions in these settings,” he said. “One of the aspects of the pandemic is that many people are at home for longer periods of time, and they use digital technologies more frequently.”
The use of digital technologies can include interaction on social media platforms and on meeting applications such as Zoom, but such use also offers opportunities for problematic gambling, gaming, and pornography use. The World Health Organization recognizes addiction disorders for gambling and for gaming, and online gaming platforms and pornography sites have reported substantial increases in their traffic during the pandemic, Dr. Potenza said.
The increase in frequency is unsurprising and not necessarily a concern by itself, Dr. Kraus said.
“It’s all about loss of control or difficulty engaging or disengaging,” Dr. Kraus said. “When you can’t stop doing something even if you like it or love it, when it interferes with your day-to-day activities and relationships, that’s when it’s a problem.”
Gambling online: Easy, available
The authors note that past research has identified increased gambling problems during economic crises in other countries.
“While currently speculative, financial hardships may promote gambling as individuals may be motivated to gamble to try to win money,” the authors suggested. “Although presently limited, existing data suggest that COVID-19–related financial concerns may increase gambling-related harms, and this possibility merits systematic research.”
But trends and characteristics of the gambling market, including direct effects from the pandemic, can potentially influence behaviors, too. Most casinos have closed during the pandemic, and most of the sports that people bet on have been canceled or postponed.
“Fewer people are gambling on sports, but they turn then to other areas,” Dr. Potenza said. “If they can’t bet on major league type sports, they might gamble on more local sporting events, or they may bet on other activities going on in society during the pandemic.”
But online gambling poses greater risk.
“Properties of online gambling may constitute a particular health hazard when many people are confined to their homes and have had rapid changes in working conditions, psychosocial stress, anxiety, and depression, as has been described in China,” the paper’s authors wrote. “Online gambling may be particularly concerning due to its availability and velocity” and association with higher debt levels.
In addition to online gaming’s ease and availability, past research has found patients report boredom and escapism as reasons they turned to it.
Again, boredom on its own is not necessarily a problem, but for those who already struggle with addictive behaviors, it can be a trigger, Dr. Kraus said.
“Boredom is very tough for them because it’s often associated with negative emotions,” such as dwelling on things not going well in their lives, he said. “In a pandemic, people are by themselves quite a bit, socially isolated, so for those who are struggling already with some depression or anxiety, it’s only going to be increased.”
Online gaming trends may vary with demographics, however. Dr. Kraus noted that his former clinic at the Veterans Administration has been seeing lower gambling in patients with addictive disorders, but those patients are also older and primarily frequented casinos.
“It’s going to depend on age and familiarity with technology,” he said, but even if older problem gamblers are not going to the Internet now, “let’s wait and see what happens in the next 2 or 3 months.”
The authors noted results from a small survey of patients in treatment for gambling addiction at the Bellvitge University Hospital in Barcelona, Spain, where two of the coauthors work. They conducted telephone surveys with 26 patients about the first 4 weeks of sheltering in place because of the coronavirus. All but four of the patients were male, and their average age was 45 years.
“Most presented worries about increased uncertainties, such as the negative impact on their work, risk of COVID-19 infection of themselves or their loved ones and their treatment,” the authors reported.
Although 19% were completely abstinent, an additional 12% (n = 3) reported worsened gambling. In addition, almost half (46%) reported anxiety symptoms and more than a quarter (27%) had depressive symptoms.
Appropriate care
A particularly complicating factor of the pandemic is how it has disrupted traditional ways of seeking health care, particularly with how much mental health and other medical care has shifted to telehealth and online delivery, Dr. Potenza pointed out.
“This is a change for many people, and it’s important for both caretakers and people in treatment to be mindful of this and to try to ensure that appropriate services are maintained for people during this time,” he said.
For example, 12-step programs traditionally meet in person, which is largely impossible during the pandemic. Some have moved meetings online, and other programs have turned to apps, such as the Addiction Policy Forum’s app Connections, an empirically validated digital therapy platform that lets patients and clinicians remain connected with remote check-ins.
The move to more telehealth may actually increase access, suggested Dr. Hodgins.
“There is no evidence that this is less effective, and in fact, its convenience might be an advantage in reaching more people,” he said. “More challenging is offering group therapies remotely, but this is also feasible.”
The treatment with the strongest evidence remains cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), Dr. Hodgins said.
“This therapy, in part, helps people become aware of their erroneous cognitions and to challenge them, but also helps people restructure their activities to change their habits,” he said. He also noted the rise of online therapy, whether supported by a therapist or entirely self-directed, such as Gambling Self-help.
“These programs typically provide cognitive behavior content but also content that comes from studying how people recover from gambling problems,” he said. “The challenge of completely self-directed approaches is follow-through. Like most online content, people tend to flit around more than they might in therapy.” Still, he added, research has shown good outcomes from these programs.
Dr. Potenza also noted that several organizations, including the International Society of Addiction Medicine and Children and Screens, have been hosting webinars related to COVID-19 coping and/or addiction that clinicians and patients might find helpful.
Identification of problematic behaviors
One challenge in watching for problematic gambling behaviors during the pandemic is the set of unusual living circumstances for most people right now. At almost no other time in history have people been primarily confined to their homes, many unable to go to work or working from home, with extra leisure time and nowhere to go.
“With the COVID-19 pandemic, a lot of daily life has changed,” Dr. Potenza said. “It’s unclear whether certain behaviors that have become habitual during the pandemic, such as gaming or online gambling, will then interfere with daily life when the pandemic subsides.”
“The problem is, a small proportion of people who are very vulnerable will develop a disorder and might maintain it,” Dr. Kraus said. Those who already struggle with mental health and may be out of work have greater potential for problematic behaviors.
Dr. Potenza collaborated with other psychiatrists in drafting consensus guidelines on maintaining healthy use of the Internet specifically during the pandemic (Compr Psychiatry. 2020 Jul. doi: 10.10161/comppsych.2020.152180).
“It’s important to think about where one draws the line between normative everyday behaviors – behaviors that are not interfering with life functioning – and those that do interfere with life functioning,” Dr. Potenza said. “If someone is having difficulty making work or family or school obligations, these are important signs that the behavior may be problematic.”
He offered suggestions for things people can do to promote their health during the pandemic, such as having regular routines that include getting physical exercise and social interaction, dining with family if isolating together, and making time for self-care. He also recommended setting limits on the use of digital devices and aiming for a healthy balance in keeping up with the news. The idea is to stay aware of what’s happening without getting burned out or traumatized by news coverage.
Guidance for clinicians
An urgent need for research and guidelines related to gambling and the pandemic exists, the authors argued.
In the meantime, aside from various validated screeners available, Dr. Kraus offered some practical advice for clinicians checking in with their patients: “Ask your patients what they have been doing to cope with this difficult time.”
Some might mention their faith, family, or friends, and others might not have an answer or mention drinking, gaming, or engaging in other activities. “We all do things to cope. Sometimes you use healthy coping and sometimes you use unhealthy coping,” Dr. Kraus said. “I would have a dialogue with my patients around, ‘How are you getting through? What’s helping you? What are some things you’ve tried that are tripping you up?’ ”
If gambling in particular is a possible concern, he encouraged clinicians to ask their patients whether they have tried to quit or what would happen if they stopped gambling.
“What we’d expect is the problem gamblers will have more irritability, crankiness, difficulty with quitting,” he said.
Dr. Hodgins agreed that checking in on how patients’ lives and activities have changed, and their emotion reactions to those changes, is prudent.
“The change in activities might be healthy or might include increased addictive behaviors, including increased use of substances, gaming, pornography, food, and gambling,” he said.
In addition, the paper authors list several examples of guidelines that might be considered in drafting guidance for clinicians, including the following:
- Limiting the extent of gambling
- Not gambling to regulate negative emotions
- Not gambling in order to try to solve financial problems or financial concerns
- Not gambling under the influence of alcohol or drugs
- Carefully monitoring gambling-related time and financial expenditures
- Maintaining and establishing daily routines involving activities other than gambling
- Minding gambling-related attitudes and behaviors in the presence of minors
- Not starting to gamble because of stressors
The research did not receive external funding. Dr. Håkansson has received research funding from the Swedish Sport Foundation, the Swedish alcohol monopoly Systembolaget, and the Swedish state-owned gambling operator AB Svenska Spel. He is working with the company Kontigo Care on devices for gambling addiction follow-up care. Dr. Potenza has received consulting or advisory compensation from several entities, including the Addiction Policy Forum, AXA Gaming, Idorsia, Opiant, and RiverMend Health. Dr. Potenza has received research funding from Mohegan Sun casino and the National Center for Responsible Gaming. No other authors or outside sources had industry-related disclosures.
SOURCE: Håkansson A et al. J Addict Med. 2020 May 18. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000690.
The confluence of isolation, excess available time, and anxiety about illness or finances as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic have the potential to increase problem gambling behaviors during this public health emergency, so it’s essential to gather data and supply guidance on this issue, according to a call to action published May 18 in the Journal of Addiction Medicine.
“When facing an unforeseen situation with confinement, fear of disease, and financial uncertainty for the future, problem gambling may be an important health hazard to monitor and prevent during and following the COVID-19 crisis, especially given current online gambling availability,” wrote Anders Håkansson, PhD, of Lund University in Sweden and coauthors.
Both stress and trauma have been linked to gambling problems, and both are occurring during the pandemic, said coauthor Marc N. Potenza, MD, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., in an interview.
“People are likely to be experiencing stress at levels they haven’t experienced previously,” Dr. Potenza said. While multiple factors can contribute to addictive behaviors, “with respect to the pandemic, one concern is that so-called negative reinforcement motivations – engaging in an addictive behavior to escape from depressed or negative mood states – may be a driving motivation for a significant number of people during this time,” he said.
David Hodgins, PhD, CPsych, a professor of psychology at the University of Calgary in Alberta, who was not involved with the commentary, noted that gambling relapse is triggered by “negative emotional states, interpersonal stress, and financial stress” – all three of which the pandemic contributes to.
Financial stress can especially “inflame erroneous gambling-related cognitions,” he said in an interview, including “beliefs such as the idea that gambling can solve financial problems, even when this is statistically almost impossible as debt increases, and that debt has been caused by gambling.”
Increased social isolation also is particularly problematic, pointed out Shane W. Kraus, PhD, from the University of Nevada, Las Vegas. Dr. Kraus also was not involved with the paper.
“If someone is already struggling with already negative emotions, negative feelings, thoughts, and depression, and you’re now isolating them quite a bit, that’s not going to be a recipe for success,” Dr. Kraus said in an interview.
Dr. Potenza said.
“We should be mindful of ways in which people develop addictions in these settings,” he said. “One of the aspects of the pandemic is that many people are at home for longer periods of time, and they use digital technologies more frequently.”
The use of digital technologies can include interaction on social media platforms and on meeting applications such as Zoom, but such use also offers opportunities for problematic gambling, gaming, and pornography use. The World Health Organization recognizes addiction disorders for gambling and for gaming, and online gaming platforms and pornography sites have reported substantial increases in their traffic during the pandemic, Dr. Potenza said.
The increase in frequency is unsurprising and not necessarily a concern by itself, Dr. Kraus said.
“It’s all about loss of control or difficulty engaging or disengaging,” Dr. Kraus said. “When you can’t stop doing something even if you like it or love it, when it interferes with your day-to-day activities and relationships, that’s when it’s a problem.”
Gambling online: Easy, available
The authors note that past research has identified increased gambling problems during economic crises in other countries.
“While currently speculative, financial hardships may promote gambling as individuals may be motivated to gamble to try to win money,” the authors suggested. “Although presently limited, existing data suggest that COVID-19–related financial concerns may increase gambling-related harms, and this possibility merits systematic research.”
But trends and characteristics of the gambling market, including direct effects from the pandemic, can potentially influence behaviors, too. Most casinos have closed during the pandemic, and most of the sports that people bet on have been canceled or postponed.
“Fewer people are gambling on sports, but they turn then to other areas,” Dr. Potenza said. “If they can’t bet on major league type sports, they might gamble on more local sporting events, or they may bet on other activities going on in society during the pandemic.”
But online gambling poses greater risk.
“Properties of online gambling may constitute a particular health hazard when many people are confined to their homes and have had rapid changes in working conditions, psychosocial stress, anxiety, and depression, as has been described in China,” the paper’s authors wrote. “Online gambling may be particularly concerning due to its availability and velocity” and association with higher debt levels.
In addition to online gaming’s ease and availability, past research has found patients report boredom and escapism as reasons they turned to it.
Again, boredom on its own is not necessarily a problem, but for those who already struggle with addictive behaviors, it can be a trigger, Dr. Kraus said.
“Boredom is very tough for them because it’s often associated with negative emotions,” such as dwelling on things not going well in their lives, he said. “In a pandemic, people are by themselves quite a bit, socially isolated, so for those who are struggling already with some depression or anxiety, it’s only going to be increased.”
Online gaming trends may vary with demographics, however. Dr. Kraus noted that his former clinic at the Veterans Administration has been seeing lower gambling in patients with addictive disorders, but those patients are also older and primarily frequented casinos.
“It’s going to depend on age and familiarity with technology,” he said, but even if older problem gamblers are not going to the Internet now, “let’s wait and see what happens in the next 2 or 3 months.”
The authors noted results from a small survey of patients in treatment for gambling addiction at the Bellvitge University Hospital in Barcelona, Spain, where two of the coauthors work. They conducted telephone surveys with 26 patients about the first 4 weeks of sheltering in place because of the coronavirus. All but four of the patients were male, and their average age was 45 years.
“Most presented worries about increased uncertainties, such as the negative impact on their work, risk of COVID-19 infection of themselves or their loved ones and their treatment,” the authors reported.
Although 19% were completely abstinent, an additional 12% (n = 3) reported worsened gambling. In addition, almost half (46%) reported anxiety symptoms and more than a quarter (27%) had depressive symptoms.
Appropriate care
A particularly complicating factor of the pandemic is how it has disrupted traditional ways of seeking health care, particularly with how much mental health and other medical care has shifted to telehealth and online delivery, Dr. Potenza pointed out.
“This is a change for many people, and it’s important for both caretakers and people in treatment to be mindful of this and to try to ensure that appropriate services are maintained for people during this time,” he said.
For example, 12-step programs traditionally meet in person, which is largely impossible during the pandemic. Some have moved meetings online, and other programs have turned to apps, such as the Addiction Policy Forum’s app Connections, an empirically validated digital therapy platform that lets patients and clinicians remain connected with remote check-ins.
The move to more telehealth may actually increase access, suggested Dr. Hodgins.
“There is no evidence that this is less effective, and in fact, its convenience might be an advantage in reaching more people,” he said. “More challenging is offering group therapies remotely, but this is also feasible.”
The treatment with the strongest evidence remains cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), Dr. Hodgins said.
“This therapy, in part, helps people become aware of their erroneous cognitions and to challenge them, but also helps people restructure their activities to change their habits,” he said. He also noted the rise of online therapy, whether supported by a therapist or entirely self-directed, such as Gambling Self-help.
“These programs typically provide cognitive behavior content but also content that comes from studying how people recover from gambling problems,” he said. “The challenge of completely self-directed approaches is follow-through. Like most online content, people tend to flit around more than they might in therapy.” Still, he added, research has shown good outcomes from these programs.
Dr. Potenza also noted that several organizations, including the International Society of Addiction Medicine and Children and Screens, have been hosting webinars related to COVID-19 coping and/or addiction that clinicians and patients might find helpful.
Identification of problematic behaviors
One challenge in watching for problematic gambling behaviors during the pandemic is the set of unusual living circumstances for most people right now. At almost no other time in history have people been primarily confined to their homes, many unable to go to work or working from home, with extra leisure time and nowhere to go.
“With the COVID-19 pandemic, a lot of daily life has changed,” Dr. Potenza said. “It’s unclear whether certain behaviors that have become habitual during the pandemic, such as gaming or online gambling, will then interfere with daily life when the pandemic subsides.”
“The problem is, a small proportion of people who are very vulnerable will develop a disorder and might maintain it,” Dr. Kraus said. Those who already struggle with mental health and may be out of work have greater potential for problematic behaviors.
Dr. Potenza collaborated with other psychiatrists in drafting consensus guidelines on maintaining healthy use of the Internet specifically during the pandemic (Compr Psychiatry. 2020 Jul. doi: 10.10161/comppsych.2020.152180).
“It’s important to think about where one draws the line between normative everyday behaviors – behaviors that are not interfering with life functioning – and those that do interfere with life functioning,” Dr. Potenza said. “If someone is having difficulty making work or family or school obligations, these are important signs that the behavior may be problematic.”
He offered suggestions for things people can do to promote their health during the pandemic, such as having regular routines that include getting physical exercise and social interaction, dining with family if isolating together, and making time for self-care. He also recommended setting limits on the use of digital devices and aiming for a healthy balance in keeping up with the news. The idea is to stay aware of what’s happening without getting burned out or traumatized by news coverage.
Guidance for clinicians
An urgent need for research and guidelines related to gambling and the pandemic exists, the authors argued.
In the meantime, aside from various validated screeners available, Dr. Kraus offered some practical advice for clinicians checking in with their patients: “Ask your patients what they have been doing to cope with this difficult time.”
Some might mention their faith, family, or friends, and others might not have an answer or mention drinking, gaming, or engaging in other activities. “We all do things to cope. Sometimes you use healthy coping and sometimes you use unhealthy coping,” Dr. Kraus said. “I would have a dialogue with my patients around, ‘How are you getting through? What’s helping you? What are some things you’ve tried that are tripping you up?’ ”
If gambling in particular is a possible concern, he encouraged clinicians to ask their patients whether they have tried to quit or what would happen if they stopped gambling.
“What we’d expect is the problem gamblers will have more irritability, crankiness, difficulty with quitting,” he said.
Dr. Hodgins agreed that checking in on how patients’ lives and activities have changed, and their emotion reactions to those changes, is prudent.
“The change in activities might be healthy or might include increased addictive behaviors, including increased use of substances, gaming, pornography, food, and gambling,” he said.
In addition, the paper authors list several examples of guidelines that might be considered in drafting guidance for clinicians, including the following:
- Limiting the extent of gambling
- Not gambling to regulate negative emotions
- Not gambling in order to try to solve financial problems or financial concerns
- Not gambling under the influence of alcohol or drugs
- Carefully monitoring gambling-related time and financial expenditures
- Maintaining and establishing daily routines involving activities other than gambling
- Minding gambling-related attitudes and behaviors in the presence of minors
- Not starting to gamble because of stressors
The research did not receive external funding. Dr. Håkansson has received research funding from the Swedish Sport Foundation, the Swedish alcohol monopoly Systembolaget, and the Swedish state-owned gambling operator AB Svenska Spel. He is working with the company Kontigo Care on devices for gambling addiction follow-up care. Dr. Potenza has received consulting or advisory compensation from several entities, including the Addiction Policy Forum, AXA Gaming, Idorsia, Opiant, and RiverMend Health. Dr. Potenza has received research funding from Mohegan Sun casino and the National Center for Responsible Gaming. No other authors or outside sources had industry-related disclosures.
SOURCE: Håkansson A et al. J Addict Med. 2020 May 18. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000690.
The confluence of isolation, excess available time, and anxiety about illness or finances as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic have the potential to increase problem gambling behaviors during this public health emergency, so it’s essential to gather data and supply guidance on this issue, according to a call to action published May 18 in the Journal of Addiction Medicine.
“When facing an unforeseen situation with confinement, fear of disease, and financial uncertainty for the future, problem gambling may be an important health hazard to monitor and prevent during and following the COVID-19 crisis, especially given current online gambling availability,” wrote Anders Håkansson, PhD, of Lund University in Sweden and coauthors.
Both stress and trauma have been linked to gambling problems, and both are occurring during the pandemic, said coauthor Marc N. Potenza, MD, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., in an interview.
“People are likely to be experiencing stress at levels they haven’t experienced previously,” Dr. Potenza said. While multiple factors can contribute to addictive behaviors, “with respect to the pandemic, one concern is that so-called negative reinforcement motivations – engaging in an addictive behavior to escape from depressed or negative mood states – may be a driving motivation for a significant number of people during this time,” he said.
David Hodgins, PhD, CPsych, a professor of psychology at the University of Calgary in Alberta, who was not involved with the commentary, noted that gambling relapse is triggered by “negative emotional states, interpersonal stress, and financial stress” – all three of which the pandemic contributes to.
Financial stress can especially “inflame erroneous gambling-related cognitions,” he said in an interview, including “beliefs such as the idea that gambling can solve financial problems, even when this is statistically almost impossible as debt increases, and that debt has been caused by gambling.”
Increased social isolation also is particularly problematic, pointed out Shane W. Kraus, PhD, from the University of Nevada, Las Vegas. Dr. Kraus also was not involved with the paper.
“If someone is already struggling with already negative emotions, negative feelings, thoughts, and depression, and you’re now isolating them quite a bit, that’s not going to be a recipe for success,” Dr. Kraus said in an interview.
Dr. Potenza said.
“We should be mindful of ways in which people develop addictions in these settings,” he said. “One of the aspects of the pandemic is that many people are at home for longer periods of time, and they use digital technologies more frequently.”
The use of digital technologies can include interaction on social media platforms and on meeting applications such as Zoom, but such use also offers opportunities for problematic gambling, gaming, and pornography use. The World Health Organization recognizes addiction disorders for gambling and for gaming, and online gaming platforms and pornography sites have reported substantial increases in their traffic during the pandemic, Dr. Potenza said.
The increase in frequency is unsurprising and not necessarily a concern by itself, Dr. Kraus said.
“It’s all about loss of control or difficulty engaging or disengaging,” Dr. Kraus said. “When you can’t stop doing something even if you like it or love it, when it interferes with your day-to-day activities and relationships, that’s when it’s a problem.”
Gambling online: Easy, available
The authors note that past research has identified increased gambling problems during economic crises in other countries.
“While currently speculative, financial hardships may promote gambling as individuals may be motivated to gamble to try to win money,” the authors suggested. “Although presently limited, existing data suggest that COVID-19–related financial concerns may increase gambling-related harms, and this possibility merits systematic research.”
But trends and characteristics of the gambling market, including direct effects from the pandemic, can potentially influence behaviors, too. Most casinos have closed during the pandemic, and most of the sports that people bet on have been canceled or postponed.
“Fewer people are gambling on sports, but they turn then to other areas,” Dr. Potenza said. “If they can’t bet on major league type sports, they might gamble on more local sporting events, or they may bet on other activities going on in society during the pandemic.”
But online gambling poses greater risk.
“Properties of online gambling may constitute a particular health hazard when many people are confined to their homes and have had rapid changes in working conditions, psychosocial stress, anxiety, and depression, as has been described in China,” the paper’s authors wrote. “Online gambling may be particularly concerning due to its availability and velocity” and association with higher debt levels.
In addition to online gaming’s ease and availability, past research has found patients report boredom and escapism as reasons they turned to it.
Again, boredom on its own is not necessarily a problem, but for those who already struggle with addictive behaviors, it can be a trigger, Dr. Kraus said.
“Boredom is very tough for them because it’s often associated with negative emotions,” such as dwelling on things not going well in their lives, he said. “In a pandemic, people are by themselves quite a bit, socially isolated, so for those who are struggling already with some depression or anxiety, it’s only going to be increased.”
Online gaming trends may vary with demographics, however. Dr. Kraus noted that his former clinic at the Veterans Administration has been seeing lower gambling in patients with addictive disorders, but those patients are also older and primarily frequented casinos.
“It’s going to depend on age and familiarity with technology,” he said, but even if older problem gamblers are not going to the Internet now, “let’s wait and see what happens in the next 2 or 3 months.”
The authors noted results from a small survey of patients in treatment for gambling addiction at the Bellvitge University Hospital in Barcelona, Spain, where two of the coauthors work. They conducted telephone surveys with 26 patients about the first 4 weeks of sheltering in place because of the coronavirus. All but four of the patients were male, and their average age was 45 years.
“Most presented worries about increased uncertainties, such as the negative impact on their work, risk of COVID-19 infection of themselves or their loved ones and their treatment,” the authors reported.
Although 19% were completely abstinent, an additional 12% (n = 3) reported worsened gambling. In addition, almost half (46%) reported anxiety symptoms and more than a quarter (27%) had depressive symptoms.
Appropriate care
A particularly complicating factor of the pandemic is how it has disrupted traditional ways of seeking health care, particularly with how much mental health and other medical care has shifted to telehealth and online delivery, Dr. Potenza pointed out.
“This is a change for many people, and it’s important for both caretakers and people in treatment to be mindful of this and to try to ensure that appropriate services are maintained for people during this time,” he said.
For example, 12-step programs traditionally meet in person, which is largely impossible during the pandemic. Some have moved meetings online, and other programs have turned to apps, such as the Addiction Policy Forum’s app Connections, an empirically validated digital therapy platform that lets patients and clinicians remain connected with remote check-ins.
The move to more telehealth may actually increase access, suggested Dr. Hodgins.
“There is no evidence that this is less effective, and in fact, its convenience might be an advantage in reaching more people,” he said. “More challenging is offering group therapies remotely, but this is also feasible.”
The treatment with the strongest evidence remains cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), Dr. Hodgins said.
“This therapy, in part, helps people become aware of their erroneous cognitions and to challenge them, but also helps people restructure their activities to change their habits,” he said. He also noted the rise of online therapy, whether supported by a therapist or entirely self-directed, such as Gambling Self-help.
“These programs typically provide cognitive behavior content but also content that comes from studying how people recover from gambling problems,” he said. “The challenge of completely self-directed approaches is follow-through. Like most online content, people tend to flit around more than they might in therapy.” Still, he added, research has shown good outcomes from these programs.
Dr. Potenza also noted that several organizations, including the International Society of Addiction Medicine and Children and Screens, have been hosting webinars related to COVID-19 coping and/or addiction that clinicians and patients might find helpful.
Identification of problematic behaviors
One challenge in watching for problematic gambling behaviors during the pandemic is the set of unusual living circumstances for most people right now. At almost no other time in history have people been primarily confined to their homes, many unable to go to work or working from home, with extra leisure time and nowhere to go.
“With the COVID-19 pandemic, a lot of daily life has changed,” Dr. Potenza said. “It’s unclear whether certain behaviors that have become habitual during the pandemic, such as gaming or online gambling, will then interfere with daily life when the pandemic subsides.”
“The problem is, a small proportion of people who are very vulnerable will develop a disorder and might maintain it,” Dr. Kraus said. Those who already struggle with mental health and may be out of work have greater potential for problematic behaviors.
Dr. Potenza collaborated with other psychiatrists in drafting consensus guidelines on maintaining healthy use of the Internet specifically during the pandemic (Compr Psychiatry. 2020 Jul. doi: 10.10161/comppsych.2020.152180).
“It’s important to think about where one draws the line between normative everyday behaviors – behaviors that are not interfering with life functioning – and those that do interfere with life functioning,” Dr. Potenza said. “If someone is having difficulty making work or family or school obligations, these are important signs that the behavior may be problematic.”
He offered suggestions for things people can do to promote their health during the pandemic, such as having regular routines that include getting physical exercise and social interaction, dining with family if isolating together, and making time for self-care. He also recommended setting limits on the use of digital devices and aiming for a healthy balance in keeping up with the news. The idea is to stay aware of what’s happening without getting burned out or traumatized by news coverage.
Guidance for clinicians
An urgent need for research and guidelines related to gambling and the pandemic exists, the authors argued.
In the meantime, aside from various validated screeners available, Dr. Kraus offered some practical advice for clinicians checking in with their patients: “Ask your patients what they have been doing to cope with this difficult time.”
Some might mention their faith, family, or friends, and others might not have an answer or mention drinking, gaming, or engaging in other activities. “We all do things to cope. Sometimes you use healthy coping and sometimes you use unhealthy coping,” Dr. Kraus said. “I would have a dialogue with my patients around, ‘How are you getting through? What’s helping you? What are some things you’ve tried that are tripping you up?’ ”
If gambling in particular is a possible concern, he encouraged clinicians to ask their patients whether they have tried to quit or what would happen if they stopped gambling.
“What we’d expect is the problem gamblers will have more irritability, crankiness, difficulty with quitting,” he said.
Dr. Hodgins agreed that checking in on how patients’ lives and activities have changed, and their emotion reactions to those changes, is prudent.
“The change in activities might be healthy or might include increased addictive behaviors, including increased use of substances, gaming, pornography, food, and gambling,” he said.
In addition, the paper authors list several examples of guidelines that might be considered in drafting guidance for clinicians, including the following:
- Limiting the extent of gambling
- Not gambling to regulate negative emotions
- Not gambling in order to try to solve financial problems or financial concerns
- Not gambling under the influence of alcohol or drugs
- Carefully monitoring gambling-related time and financial expenditures
- Maintaining and establishing daily routines involving activities other than gambling
- Minding gambling-related attitudes and behaviors in the presence of minors
- Not starting to gamble because of stressors
The research did not receive external funding. Dr. Håkansson has received research funding from the Swedish Sport Foundation, the Swedish alcohol monopoly Systembolaget, and the Swedish state-owned gambling operator AB Svenska Spel. He is working with the company Kontigo Care on devices for gambling addiction follow-up care. Dr. Potenza has received consulting or advisory compensation from several entities, including the Addiction Policy Forum, AXA Gaming, Idorsia, Opiant, and RiverMend Health. Dr. Potenza has received research funding from Mohegan Sun casino and the National Center for Responsible Gaming. No other authors or outside sources had industry-related disclosures.
SOURCE: Håkansson A et al. J Addict Med. 2020 May 18. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000690.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ADDICTION MEDICINE












