User login
Commentary: Research on Potential Migraine Triggers, January 2023
January's theme is migraine triggers. We'll take a look at three recent studies that have tried to better determine the nature of specific triggers for headache.
One of the most common and reportedly consistent migraine triggers is exposure to alcohol, and the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-3) includes alcohol-induced headache as a secondary headache. Little is known regarding the association between migraine and alcohol. Vives-Mestres and colleagues investigated the alcohol intake of people using a digital health diary for headache. They specifically looked at the 48 hours preceding a migraine attack and whether alcohol was consumed, and also the number of beverages consumed. This was further adjusted for sex, age, and average weekly alcohol intake.
The N1-Headache Tracker is a digital headache diary that patients use to track their daily headache symptoms and inform them of potential migraine risk factors. Over a 90-day period, this study followed patients that did not meet the criteria for a diagnosis of chronic migraine. They also reported on their intake to the platform that they regularly consume alcohol. Of note, persons who never tracked alcohol consumption were excluded from this study. On intake to the platform, alcohol exposure was characterized both as whether daily consumption of alcohol was occurring and as the total daily number of alcoholic beverages.
The primary outcome of this study was migraine attack 1 day after alcohol consumption. Participants were specifically asked if their headaches were diagnosed as migraine by a physician. Migraine attack onset was considered binary, and a logistic model was used to estimate the probability of having a migraine attack on any given day with the association of alcohol intake for up to 48 hours prior to that day.
A total of 487 people with migraine were included in this trial and they collectively contributed over 43,000 diary days; almost 6000 were first days of a migraine attack. Overall alcohol consumption was not considered high and was noted to vary between groups; people with lower frequency migraine tended to have higher rates of alcohol intake. No significant correlation was observed between the presence of migraine attacks within 48 hours after alcohol consumption. This did not vary among different probability models; a population-level model showed that the probability of a migraine attack 2 days after alcohol intake was 25% lower than the probability of an attack with no alcohol consumption. This was also true after adjustment for age, sex, and average number of alcoholic beverages per week.
The association between migraine and alcohol is complicated, and the concept of migraine triggers in general is very complex. Although over 70% of people with migraine say that they have a consistent trigger, and alcohol is consistently at the top of the list of those reported triggers, there does not appear to be a direct correlation between migraine and alcohol exposure. The greatest caveat of this study is the fact that people with chronic migraine were excluded. Further research should specifically investigate triggers such as alcohol in this population.
The use of proton pump inhibitors (PPI) has been shown in previous studies over the past few years to be associated with a number of neurologic events and risks, including impaired hearing, vision, and memory, as well as migraine occurrence. The specifics of this association are not well known — specifically, whether the duration of use is the main factor, or whether it is acute exposure to a PPI medication that is a trigger. Kang and colleagues reviewed data in the Korean national database and developed a case-control model to study this association specifically.
The migraine and control groups were equally matched: They had the same demographics, smoking status, alcohol consumption, blood pressure range, fasting glucose, and total cholesterol. Past and current PPI use and comparisons of migraine occurrence were further differentiated among patients who were exposed to PPI medications for < 30 days, 30-365 days, and > 365 days.
The use of PPI treatments was noted to be linked to increased migraine regardless of duration, and regardless of the acute presence of the PPI. Even a history of prior PPI use was noted to increase the odds ratio of migraine development. This was significant among all subgroups, independent of age, sex, and other comorbidities. There was no difference in the presence of aura associated with migraine.
As we noted above, the concept of migraine triggers is overall poorly understood. This is even more the case when it comes to historical exposures. Although the use of PPI medications appears to be associated with the occurrence of migraine in this population, these medications are necessary in many instances, including in patients with severe gastritis and gastroesophageal reflux refractory to diet changes. It remains to be seen precisely how PPI medications would potentially lead to a higher incidence of migraine.
Among many of the triggers discussed, specific foods are commonly thought to be associated with migraine. Although there is scant evidence for a specific diet to improve migraine frequency, many patients are very interested in potential dietary changes that may help them. Prior studies and reviews have looked at gluten-free, dairy-free, low-carbohydrate, low-tyramine, and elimination diets — all of which were not associated with a significant improvement in migraine frequency or severity. Bakıran and colleagues sought to investigate an antioxidant-rich diet that included polyphenols and carotenoids — substances that may improve systemic inflammation, glucose metabolism, and oxidative stress.
Phytochemical-rich foods include fruits and vegetables (excluding potatoes) as well as nuts, whole grains, pulses, and olive oil. The phytochemical index is a tool used by dietitians and nutritionists to assess the phytochemical content in a diet.
A total of 90 patients who had a diagnosis of episodic migraine by a neurologist were enrolled. Individuals were excluded if they had a body mass index > 40 or < 18 or had other significant chronic comorbidities, such as hypertension, diabetes, hepatic or renal disease, or other neurologic conditions. Participants filled out a headache diary over 3 months; the Migraine Disability Assessment (MIDAS) questionnaire was also followed in order to assess migraine-related disability. Diet quality was cataloged as per patient records; patients also filled out a 3-day nonconsecutive food diary. This information was added to a food software program that calculated specific nutrients, including the phytochemical index.
Participants were divided into groups with good diet quality and poor diet quality based on their phytochemical index. No differences were seen in migraine frequency or disability between these groups, although mean attack duration was lower in those with poor diet quality. Severity was noted to be higher in those with poor diet quality; 75% of participants with poor diet quality experienced severe attacks.
Overall, the results of this study are very mixed. Participants on the recommended high phytochemical diet were seen to have lower severity of migraine but a prolonged duration of attack. There also was no correlation between this diet and either frequency or disability. This was a small study, and further research should focus on this among other diet changes that have the possibility to improve the quality of life of people with migraine.
January's theme is migraine triggers. We'll take a look at three recent studies that have tried to better determine the nature of specific triggers for headache.
One of the most common and reportedly consistent migraine triggers is exposure to alcohol, and the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-3) includes alcohol-induced headache as a secondary headache. Little is known regarding the association between migraine and alcohol. Vives-Mestres and colleagues investigated the alcohol intake of people using a digital health diary for headache. They specifically looked at the 48 hours preceding a migraine attack and whether alcohol was consumed, and also the number of beverages consumed. This was further adjusted for sex, age, and average weekly alcohol intake.
The N1-Headache Tracker is a digital headache diary that patients use to track their daily headache symptoms and inform them of potential migraine risk factors. Over a 90-day period, this study followed patients that did not meet the criteria for a diagnosis of chronic migraine. They also reported on their intake to the platform that they regularly consume alcohol. Of note, persons who never tracked alcohol consumption were excluded from this study. On intake to the platform, alcohol exposure was characterized both as whether daily consumption of alcohol was occurring and as the total daily number of alcoholic beverages.
The primary outcome of this study was migraine attack 1 day after alcohol consumption. Participants were specifically asked if their headaches were diagnosed as migraine by a physician. Migraine attack onset was considered binary, and a logistic model was used to estimate the probability of having a migraine attack on any given day with the association of alcohol intake for up to 48 hours prior to that day.
A total of 487 people with migraine were included in this trial and they collectively contributed over 43,000 diary days; almost 6000 were first days of a migraine attack. Overall alcohol consumption was not considered high and was noted to vary between groups; people with lower frequency migraine tended to have higher rates of alcohol intake. No significant correlation was observed between the presence of migraine attacks within 48 hours after alcohol consumption. This did not vary among different probability models; a population-level model showed that the probability of a migraine attack 2 days after alcohol intake was 25% lower than the probability of an attack with no alcohol consumption. This was also true after adjustment for age, sex, and average number of alcoholic beverages per week.
The association between migraine and alcohol is complicated, and the concept of migraine triggers in general is very complex. Although over 70% of people with migraine say that they have a consistent trigger, and alcohol is consistently at the top of the list of those reported triggers, there does not appear to be a direct correlation between migraine and alcohol exposure. The greatest caveat of this study is the fact that people with chronic migraine were excluded. Further research should specifically investigate triggers such as alcohol in this population.
The use of proton pump inhibitors (PPI) has been shown in previous studies over the past few years to be associated with a number of neurologic events and risks, including impaired hearing, vision, and memory, as well as migraine occurrence. The specifics of this association are not well known — specifically, whether the duration of use is the main factor, or whether it is acute exposure to a PPI medication that is a trigger. Kang and colleagues reviewed data in the Korean national database and developed a case-control model to study this association specifically.
The migraine and control groups were equally matched: They had the same demographics, smoking status, alcohol consumption, blood pressure range, fasting glucose, and total cholesterol. Past and current PPI use and comparisons of migraine occurrence were further differentiated among patients who were exposed to PPI medications for < 30 days, 30-365 days, and > 365 days.
The use of PPI treatments was noted to be linked to increased migraine regardless of duration, and regardless of the acute presence of the PPI. Even a history of prior PPI use was noted to increase the odds ratio of migraine development. This was significant among all subgroups, independent of age, sex, and other comorbidities. There was no difference in the presence of aura associated with migraine.
As we noted above, the concept of migraine triggers is overall poorly understood. This is even more the case when it comes to historical exposures. Although the use of PPI medications appears to be associated with the occurrence of migraine in this population, these medications are necessary in many instances, including in patients with severe gastritis and gastroesophageal reflux refractory to diet changes. It remains to be seen precisely how PPI medications would potentially lead to a higher incidence of migraine.
Among many of the triggers discussed, specific foods are commonly thought to be associated with migraine. Although there is scant evidence for a specific diet to improve migraine frequency, many patients are very interested in potential dietary changes that may help them. Prior studies and reviews have looked at gluten-free, dairy-free, low-carbohydrate, low-tyramine, and elimination diets — all of which were not associated with a significant improvement in migraine frequency or severity. Bakıran and colleagues sought to investigate an antioxidant-rich diet that included polyphenols and carotenoids — substances that may improve systemic inflammation, glucose metabolism, and oxidative stress.
Phytochemical-rich foods include fruits and vegetables (excluding potatoes) as well as nuts, whole grains, pulses, and olive oil. The phytochemical index is a tool used by dietitians and nutritionists to assess the phytochemical content in a diet.
A total of 90 patients who had a diagnosis of episodic migraine by a neurologist were enrolled. Individuals were excluded if they had a body mass index > 40 or < 18 or had other significant chronic comorbidities, such as hypertension, diabetes, hepatic or renal disease, or other neurologic conditions. Participants filled out a headache diary over 3 months; the Migraine Disability Assessment (MIDAS) questionnaire was also followed in order to assess migraine-related disability. Diet quality was cataloged as per patient records; patients also filled out a 3-day nonconsecutive food diary. This information was added to a food software program that calculated specific nutrients, including the phytochemical index.
Participants were divided into groups with good diet quality and poor diet quality based on their phytochemical index. No differences were seen in migraine frequency or disability between these groups, although mean attack duration was lower in those with poor diet quality. Severity was noted to be higher in those with poor diet quality; 75% of participants with poor diet quality experienced severe attacks.
Overall, the results of this study are very mixed. Participants on the recommended high phytochemical diet were seen to have lower severity of migraine but a prolonged duration of attack. There also was no correlation between this diet and either frequency or disability. This was a small study, and further research should focus on this among other diet changes that have the possibility to improve the quality of life of people with migraine.
January's theme is migraine triggers. We'll take a look at three recent studies that have tried to better determine the nature of specific triggers for headache.
One of the most common and reportedly consistent migraine triggers is exposure to alcohol, and the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-3) includes alcohol-induced headache as a secondary headache. Little is known regarding the association between migraine and alcohol. Vives-Mestres and colleagues investigated the alcohol intake of people using a digital health diary for headache. They specifically looked at the 48 hours preceding a migraine attack and whether alcohol was consumed, and also the number of beverages consumed. This was further adjusted for sex, age, and average weekly alcohol intake.
The N1-Headache Tracker is a digital headache diary that patients use to track their daily headache symptoms and inform them of potential migraine risk factors. Over a 90-day period, this study followed patients that did not meet the criteria for a diagnosis of chronic migraine. They also reported on their intake to the platform that they regularly consume alcohol. Of note, persons who never tracked alcohol consumption were excluded from this study. On intake to the platform, alcohol exposure was characterized both as whether daily consumption of alcohol was occurring and as the total daily number of alcoholic beverages.
The primary outcome of this study was migraine attack 1 day after alcohol consumption. Participants were specifically asked if their headaches were diagnosed as migraine by a physician. Migraine attack onset was considered binary, and a logistic model was used to estimate the probability of having a migraine attack on any given day with the association of alcohol intake for up to 48 hours prior to that day.
A total of 487 people with migraine were included in this trial and they collectively contributed over 43,000 diary days; almost 6000 were first days of a migraine attack. Overall alcohol consumption was not considered high and was noted to vary between groups; people with lower frequency migraine tended to have higher rates of alcohol intake. No significant correlation was observed between the presence of migraine attacks within 48 hours after alcohol consumption. This did not vary among different probability models; a population-level model showed that the probability of a migraine attack 2 days after alcohol intake was 25% lower than the probability of an attack with no alcohol consumption. This was also true after adjustment for age, sex, and average number of alcoholic beverages per week.
The association between migraine and alcohol is complicated, and the concept of migraine triggers in general is very complex. Although over 70% of people with migraine say that they have a consistent trigger, and alcohol is consistently at the top of the list of those reported triggers, there does not appear to be a direct correlation between migraine and alcohol exposure. The greatest caveat of this study is the fact that people with chronic migraine were excluded. Further research should specifically investigate triggers such as alcohol in this population.
The use of proton pump inhibitors (PPI) has been shown in previous studies over the past few years to be associated with a number of neurologic events and risks, including impaired hearing, vision, and memory, as well as migraine occurrence. The specifics of this association are not well known — specifically, whether the duration of use is the main factor, or whether it is acute exposure to a PPI medication that is a trigger. Kang and colleagues reviewed data in the Korean national database and developed a case-control model to study this association specifically.
The migraine and control groups were equally matched: They had the same demographics, smoking status, alcohol consumption, blood pressure range, fasting glucose, and total cholesterol. Past and current PPI use and comparisons of migraine occurrence were further differentiated among patients who were exposed to PPI medications for < 30 days, 30-365 days, and > 365 days.
The use of PPI treatments was noted to be linked to increased migraine regardless of duration, and regardless of the acute presence of the PPI. Even a history of prior PPI use was noted to increase the odds ratio of migraine development. This was significant among all subgroups, independent of age, sex, and other comorbidities. There was no difference in the presence of aura associated with migraine.
As we noted above, the concept of migraine triggers is overall poorly understood. This is even more the case when it comes to historical exposures. Although the use of PPI medications appears to be associated with the occurrence of migraine in this population, these medications are necessary in many instances, including in patients with severe gastritis and gastroesophageal reflux refractory to diet changes. It remains to be seen precisely how PPI medications would potentially lead to a higher incidence of migraine.
Among many of the triggers discussed, specific foods are commonly thought to be associated with migraine. Although there is scant evidence for a specific diet to improve migraine frequency, many patients are very interested in potential dietary changes that may help them. Prior studies and reviews have looked at gluten-free, dairy-free, low-carbohydrate, low-tyramine, and elimination diets — all of which were not associated with a significant improvement in migraine frequency or severity. Bakıran and colleagues sought to investigate an antioxidant-rich diet that included polyphenols and carotenoids — substances that may improve systemic inflammation, glucose metabolism, and oxidative stress.
Phytochemical-rich foods include fruits and vegetables (excluding potatoes) as well as nuts, whole grains, pulses, and olive oil. The phytochemical index is a tool used by dietitians and nutritionists to assess the phytochemical content in a diet.
A total of 90 patients who had a diagnosis of episodic migraine by a neurologist were enrolled. Individuals were excluded if they had a body mass index > 40 or < 18 or had other significant chronic comorbidities, such as hypertension, diabetes, hepatic or renal disease, or other neurologic conditions. Participants filled out a headache diary over 3 months; the Migraine Disability Assessment (MIDAS) questionnaire was also followed in order to assess migraine-related disability. Diet quality was cataloged as per patient records; patients also filled out a 3-day nonconsecutive food diary. This information was added to a food software program that calculated specific nutrients, including the phytochemical index.
Participants were divided into groups with good diet quality and poor diet quality based on their phytochemical index. No differences were seen in migraine frequency or disability between these groups, although mean attack duration was lower in those with poor diet quality. Severity was noted to be higher in those with poor diet quality; 75% of participants with poor diet quality experienced severe attacks.
Overall, the results of this study are very mixed. Participants on the recommended high phytochemical diet were seen to have lower severity of migraine but a prolonged duration of attack. There also was no correlation between this diet and either frequency or disability. This was a small study, and further research should focus on this among other diet changes that have the possibility to improve the quality of life of people with migraine.
Atypical Keratotic Nodule on the Knuckle
The Diagnosis: Atypical Mycobacterial Infection
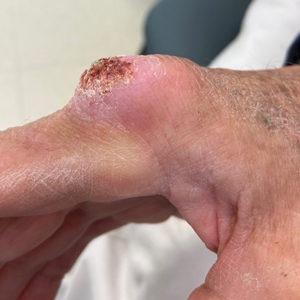
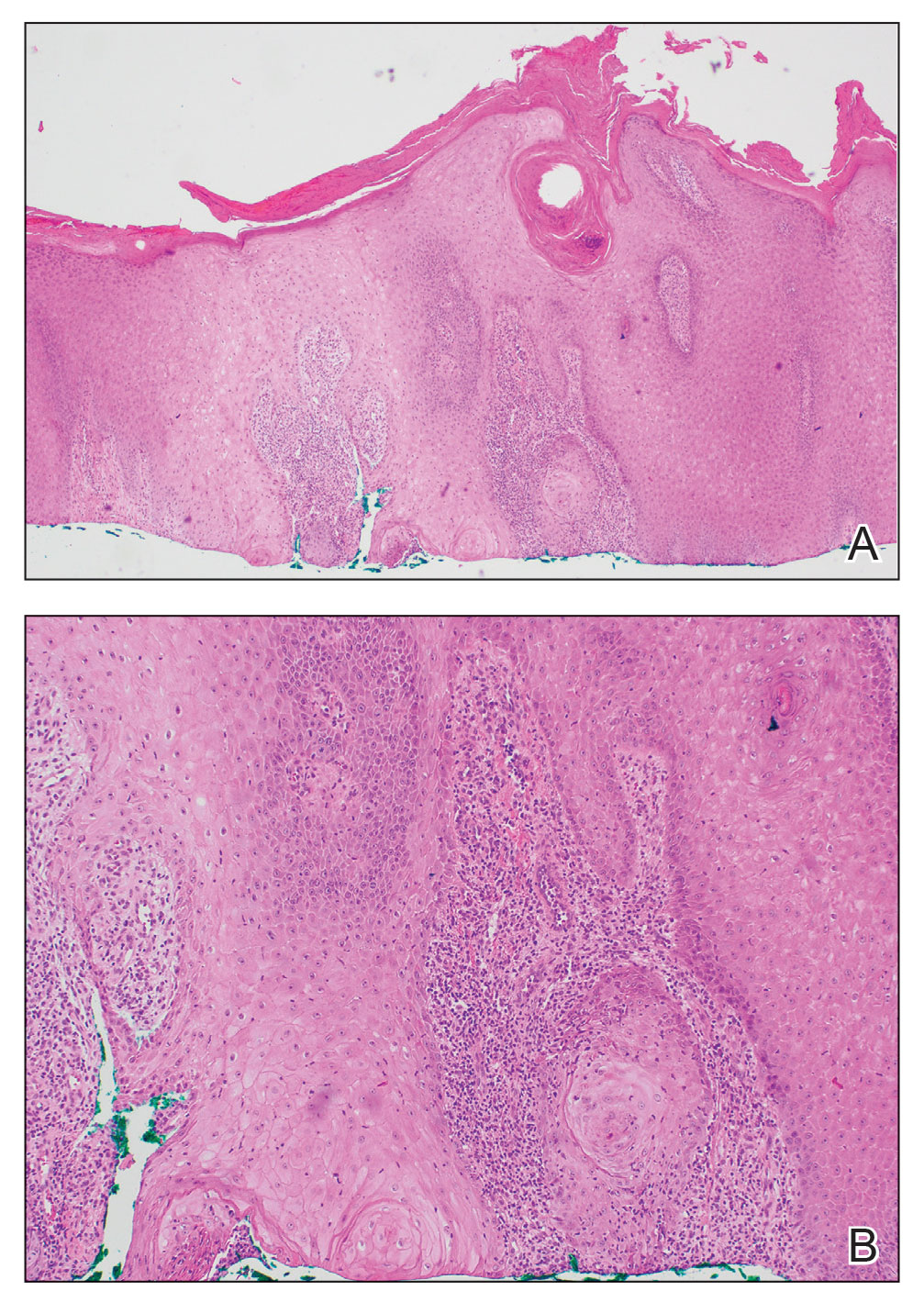
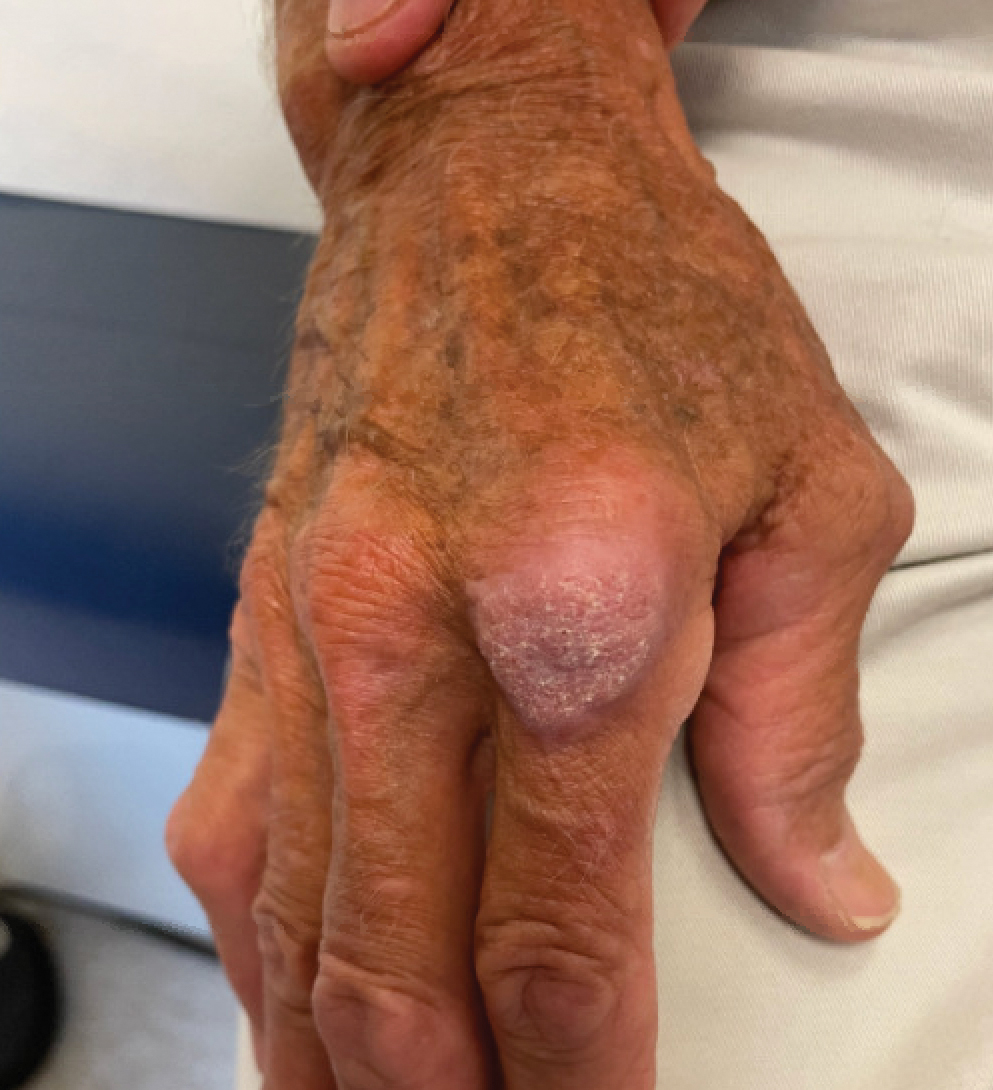
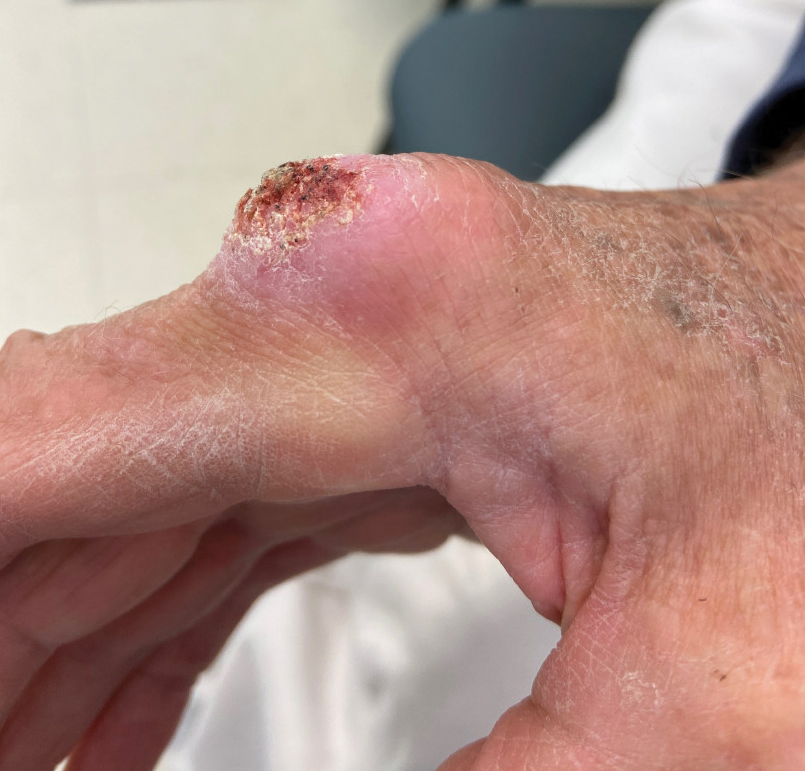
The history of rapid growth followed by shrinkage as well as the craterlike clinical appearance of our patient’s lesion were suspicious for the keratoacanthoma variant of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Periodic acid–Schiff green staining was negative for fungal or bacterial organisms, and the biopsy findings of keratinocyte atypia and irregular epidermal proliferation seemed to confirm our suspicion for well-differentiated SCC (Figure 1). Our patient subsequently was scheduled for Mohs micrographic surgery. Fortunately, a sample of tissue had been sent for panculture—bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial—to rule out infectious etiologies, given the history of possible traumatic inoculation, and returned positive for Mycobacterium marinum infection prior to the surgery. Mohs surgery was canceled, and he was referred to an infectious disease specialist who started antibiotic treatment with azithromycin, ethambutol, and rifabutin. After 1 month of treatment the lesion substantially improved (Figure 2), further supporting the diagnosis of M marinum infection over SCC.
The differential diagnosis also included sporotrichosis, leishmaniasis, and chromoblastomycosis. Sporotrichosis lesions typically develop as multiple nodules and ulcers along a path of lymphatic drainage and can exhibit asteroid bodies and cigar-shaped yeast forms on histology. Chromoblastomycosis may display pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia and granulomatous inflammation; however, pathognomonic pigmented Medlar bodies also likely would be present.1 Leishmaniasis has a wide variety of presentations; however, it typically occurs in patients with exposure to endemic areas outside of the United States. Although leishmaniasis may demonstrate pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, ulceration, and mixed inflammation on histology, it also likely would show amastigotes within dermal macrophages.2
Atypical mycobacterial infections initially may be misdiagnosed as SCC due to their tendency to induce irregular acanthosis in the form of pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia as well as mild keratinocyte atypia secondary to inflammation.3,4 Our case is unique because it occurred with M marinum infection specifically. The histopathologic findings of M marinum infections are variable and may additionally include granulomas, most commonly suppurative; intraepithelial abscesses; small vessel proliferation; dermal fibrosis; multinucleated giant cells; and transepidermal elimination.4,5 Periodic acid–Schiff, Ziehl-Neelsen (acid-fast bacilli), and Fite staining may be used to distinguish M marinum infection from SCC but have low sensitivities (approximately 30%). Culture remains the most reliable test, with a sensitivity of nearly 80%.5-7 In our patient, a Periodic acid–Schiff stain was obtained prior to receiving culture results, and acid-fast bacilli and Fite staining were added after the culture returned positive; however, all 3 stains failed to highlight any mycobacteria.
The primary risk factor for infection with M marinum is contact with aquatic environments or marine animals, and most cases involve the fingers or the hand.6 After we reached the diagnosis and further discussed the patient’s history, he recalled fishing for and cleaning raw shrimp around the time that he had a splinter. The Infectious Diseases Society of America recommends a treatment course extending 1 to 2 months after clinical symptoms resolve with ethambutol in addition to clarithromycin or azithromycin.8 If the infection is near a joint, rifampin should be empirically added to account for a potentially deeper infection. Imaging should be obtained to evaluate for joint space involvement, with magnetic resonance imaging being the preferred modality. If joint space involvement is confirmed, surgical debridement is indicated. Surgical debridement also is indicated for infections that fail to respond to antibiotic therapy.8
This case highlights M marinum infection as a potential mimicker of SCC, particularly if the biopsy is relatively superficial, as often occurs when obtained via the common shave technique. The distinction is critical, as M marinum infection is highly treatable and inappropriate surgery on the typical hand and finger locations may subject patients to substantial morbidity, such as the need for a skin graft, reduced mobility from scarring, or risk for serious wound infection.9 For superficial biopsies of an atypical squamous process, pathologists also may consider routinely recommending tissue culture, especially for hand and finger locations or when a history of local trauma is reported, instead of recommending complete excision or repeat biopsy alone.
- Elewski BE, Hughey LC, Hunt KM, et al. Fungal diseases. In: Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:1329-1363.
- Bravo FG. Protozoa and worms. In: Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:1470-1502.
- Zayour M, Lazova R. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia: a review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:112-122; quiz 123-126. doi:10.1097 /DAD.0b013e3181fcfb47
- Li JJ, Beresford R, Fyfe J, et al. Clinical and histopathological features of cutaneous nontuberculous mycobacterial infection: a review of 13 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:433-443. doi:10.1111/cup.12903
- Abbas O, Marrouch N, Kattar MM, et al. Cutaneous non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections: a clinical and histopathological study of 17 cases from Lebanon. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:33-42. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03684.x
- Johnson MG, Stout JE. Twenty-eight cases of Mycobacterium marinum infection: retrospective case series and literature review. Infection. 2015;43:655-662. doi:10.1007/s15010-015-0776-8
- Aubry A, Mougari F, Reibel F, et al. Mycobacterium marinum. Microbiol Spectr. 2017;5. doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.TNMI7-0038-2016
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367-416. doi:10.1164/rccm.200604-571ST
- Alam M, Ibrahim O, Nodzenski M, et al. Adverse events associated with Mohs micrographic surgery: multicenter prospective cohort study of 20,821 cases at 23 centers. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:1378-1385. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.6255
The Diagnosis: Atypical Mycobacterial Infection
The history of rapid growth followed by shrinkage as well as the craterlike clinical appearance of our patient’s lesion were suspicious for the keratoacanthoma variant of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Periodic acid–Schiff green staining was negative for fungal or bacterial organisms, and the biopsy findings of keratinocyte atypia and irregular epidermal proliferation seemed to confirm our suspicion for well-differentiated SCC (Figure 1). Our patient subsequently was scheduled for Mohs micrographic surgery. Fortunately, a sample of tissue had been sent for panculture—bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial—to rule out infectious etiologies, given the history of possible traumatic inoculation, and returned positive for Mycobacterium marinum infection prior to the surgery. Mohs surgery was canceled, and he was referred to an infectious disease specialist who started antibiotic treatment with azithromycin, ethambutol, and rifabutin. After 1 month of treatment the lesion substantially improved (Figure 2), further supporting the diagnosis of M marinum infection over SCC.

The differential diagnosis also included sporotrichosis, leishmaniasis, and chromoblastomycosis. Sporotrichosis lesions typically develop as multiple nodules and ulcers along a path of lymphatic drainage and can exhibit asteroid bodies and cigar-shaped yeast forms on histology. Chromoblastomycosis may display pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia and granulomatous inflammation; however, pathognomonic pigmented Medlar bodies also likely would be present.1 Leishmaniasis has a wide variety of presentations; however, it typically occurs in patients with exposure to endemic areas outside of the United States. Although leishmaniasis may demonstrate pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, ulceration, and mixed inflammation on histology, it also likely would show amastigotes within dermal macrophages.2

Atypical mycobacterial infections initially may be misdiagnosed as SCC due to their tendency to induce irregular acanthosis in the form of pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia as well as mild keratinocyte atypia secondary to inflammation.3,4 Our case is unique because it occurred with M marinum infection specifically. The histopathologic findings of M marinum infections are variable and may additionally include granulomas, most commonly suppurative; intraepithelial abscesses; small vessel proliferation; dermal fibrosis; multinucleated giant cells; and transepidermal elimination.4,5 Periodic acid–Schiff, Ziehl-Neelsen (acid-fast bacilli), and Fite staining may be used to distinguish M marinum infection from SCC but have low sensitivities (approximately 30%). Culture remains the most reliable test, with a sensitivity of nearly 80%.5-7 In our patient, a Periodic acid–Schiff stain was obtained prior to receiving culture results, and acid-fast bacilli and Fite staining were added after the culture returned positive; however, all 3 stains failed to highlight any mycobacteria.
The primary risk factor for infection with M marinum is contact with aquatic environments or marine animals, and most cases involve the fingers or the hand.6 After we reached the diagnosis and further discussed the patient’s history, he recalled fishing for and cleaning raw shrimp around the time that he had a splinter. The Infectious Diseases Society of America recommends a treatment course extending 1 to 2 months after clinical symptoms resolve with ethambutol in addition to clarithromycin or azithromycin.8 If the infection is near a joint, rifampin should be empirically added to account for a potentially deeper infection. Imaging should be obtained to evaluate for joint space involvement, with magnetic resonance imaging being the preferred modality. If joint space involvement is confirmed, surgical debridement is indicated. Surgical debridement also is indicated for infections that fail to respond to antibiotic therapy.8
This case highlights M marinum infection as a potential mimicker of SCC, particularly if the biopsy is relatively superficial, as often occurs when obtained via the common shave technique. The distinction is critical, as M marinum infection is highly treatable and inappropriate surgery on the typical hand and finger locations may subject patients to substantial morbidity, such as the need for a skin graft, reduced mobility from scarring, or risk for serious wound infection.9 For superficial biopsies of an atypical squamous process, pathologists also may consider routinely recommending tissue culture, especially for hand and finger locations or when a history of local trauma is reported, instead of recommending complete excision or repeat biopsy alone.
The Diagnosis: Atypical Mycobacterial Infection
The history of rapid growth followed by shrinkage as well as the craterlike clinical appearance of our patient’s lesion were suspicious for the keratoacanthoma variant of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Periodic acid–Schiff green staining was negative for fungal or bacterial organisms, and the biopsy findings of keratinocyte atypia and irregular epidermal proliferation seemed to confirm our suspicion for well-differentiated SCC (Figure 1). Our patient subsequently was scheduled for Mohs micrographic surgery. Fortunately, a sample of tissue had been sent for panculture—bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial—to rule out infectious etiologies, given the history of possible traumatic inoculation, and returned positive for Mycobacterium marinum infection prior to the surgery. Mohs surgery was canceled, and he was referred to an infectious disease specialist who started antibiotic treatment with azithromycin, ethambutol, and rifabutin. After 1 month of treatment the lesion substantially improved (Figure 2), further supporting the diagnosis of M marinum infection over SCC.

The differential diagnosis also included sporotrichosis, leishmaniasis, and chromoblastomycosis. Sporotrichosis lesions typically develop as multiple nodules and ulcers along a path of lymphatic drainage and can exhibit asteroid bodies and cigar-shaped yeast forms on histology. Chromoblastomycosis may display pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia and granulomatous inflammation; however, pathognomonic pigmented Medlar bodies also likely would be present.1 Leishmaniasis has a wide variety of presentations; however, it typically occurs in patients with exposure to endemic areas outside of the United States. Although leishmaniasis may demonstrate pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, ulceration, and mixed inflammation on histology, it also likely would show amastigotes within dermal macrophages.2

Atypical mycobacterial infections initially may be misdiagnosed as SCC due to their tendency to induce irregular acanthosis in the form of pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia as well as mild keratinocyte atypia secondary to inflammation.3,4 Our case is unique because it occurred with M marinum infection specifically. The histopathologic findings of M marinum infections are variable and may additionally include granulomas, most commonly suppurative; intraepithelial abscesses; small vessel proliferation; dermal fibrosis; multinucleated giant cells; and transepidermal elimination.4,5 Periodic acid–Schiff, Ziehl-Neelsen (acid-fast bacilli), and Fite staining may be used to distinguish M marinum infection from SCC but have low sensitivities (approximately 30%). Culture remains the most reliable test, with a sensitivity of nearly 80%.5-7 In our patient, a Periodic acid–Schiff stain was obtained prior to receiving culture results, and acid-fast bacilli and Fite staining were added after the culture returned positive; however, all 3 stains failed to highlight any mycobacteria.
The primary risk factor for infection with M marinum is contact with aquatic environments or marine animals, and most cases involve the fingers or the hand.6 After we reached the diagnosis and further discussed the patient’s history, he recalled fishing for and cleaning raw shrimp around the time that he had a splinter. The Infectious Diseases Society of America recommends a treatment course extending 1 to 2 months after clinical symptoms resolve with ethambutol in addition to clarithromycin or azithromycin.8 If the infection is near a joint, rifampin should be empirically added to account for a potentially deeper infection. Imaging should be obtained to evaluate for joint space involvement, with magnetic resonance imaging being the preferred modality. If joint space involvement is confirmed, surgical debridement is indicated. Surgical debridement also is indicated for infections that fail to respond to antibiotic therapy.8
This case highlights M marinum infection as a potential mimicker of SCC, particularly if the biopsy is relatively superficial, as often occurs when obtained via the common shave technique. The distinction is critical, as M marinum infection is highly treatable and inappropriate surgery on the typical hand and finger locations may subject patients to substantial morbidity, such as the need for a skin graft, reduced mobility from scarring, or risk for serious wound infection.9 For superficial biopsies of an atypical squamous process, pathologists also may consider routinely recommending tissue culture, especially for hand and finger locations or when a history of local trauma is reported, instead of recommending complete excision or repeat biopsy alone.
- Elewski BE, Hughey LC, Hunt KM, et al. Fungal diseases. In: Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:1329-1363.
- Bravo FG. Protozoa and worms. In: Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:1470-1502.
- Zayour M, Lazova R. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia: a review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:112-122; quiz 123-126. doi:10.1097 /DAD.0b013e3181fcfb47
- Li JJ, Beresford R, Fyfe J, et al. Clinical and histopathological features of cutaneous nontuberculous mycobacterial infection: a review of 13 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:433-443. doi:10.1111/cup.12903
- Abbas O, Marrouch N, Kattar MM, et al. Cutaneous non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections: a clinical and histopathological study of 17 cases from Lebanon. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:33-42. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03684.x
- Johnson MG, Stout JE. Twenty-eight cases of Mycobacterium marinum infection: retrospective case series and literature review. Infection. 2015;43:655-662. doi:10.1007/s15010-015-0776-8
- Aubry A, Mougari F, Reibel F, et al. Mycobacterium marinum. Microbiol Spectr. 2017;5. doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.TNMI7-0038-2016
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367-416. doi:10.1164/rccm.200604-571ST
- Alam M, Ibrahim O, Nodzenski M, et al. Adverse events associated with Mohs micrographic surgery: multicenter prospective cohort study of 20,821 cases at 23 centers. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:1378-1385. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.6255
- Elewski BE, Hughey LC, Hunt KM, et al. Fungal diseases. In: Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:1329-1363.
- Bravo FG. Protozoa and worms. In: Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:1470-1502.
- Zayour M, Lazova R. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia: a review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:112-122; quiz 123-126. doi:10.1097 /DAD.0b013e3181fcfb47
- Li JJ, Beresford R, Fyfe J, et al. Clinical and histopathological features of cutaneous nontuberculous mycobacterial infection: a review of 13 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:433-443. doi:10.1111/cup.12903
- Abbas O, Marrouch N, Kattar MM, et al. Cutaneous non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections: a clinical and histopathological study of 17 cases from Lebanon. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:33-42. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03684.x
- Johnson MG, Stout JE. Twenty-eight cases of Mycobacterium marinum infection: retrospective case series and literature review. Infection. 2015;43:655-662. doi:10.1007/s15010-015-0776-8
- Aubry A, Mougari F, Reibel F, et al. Mycobacterium marinum. Microbiol Spectr. 2017;5. doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.TNMI7-0038-2016
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367-416. doi:10.1164/rccm.200604-571ST
- Alam M, Ibrahim O, Nodzenski M, et al. Adverse events associated with Mohs micrographic surgery: multicenter prospective cohort study of 20,821 cases at 23 centers. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:1378-1385. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.6255
A 75-year-old man presented with a lesion on the knuckle of 5 months’ duration. He reported that the lesion initially grew very quickly before shrinking down to its current size. He denied any bleeding or pain but thought he may have had a splinter in the area around the time the lesion appeared. He reported spending a lot of time outdoors and noted several recent insect and tick bites. He also owned a boat and frequently went fishing. He previously had been treated for actinic keratoses but had no history of skin cancer and no family history of melanoma. Physical examination revealed a 2-cm erythematous nodule with central hyperkeratosis overlying the metacarpophalangeal joint of the right index finger. A shave biopsy was performed.
Feedback and Education in Dermatology Residency
A dermatology resident has more education and experience than a medical student or intern but less than a fellow or attending physician. Because of this position, residents have a unique opportunity to provide feedback and education to those with less knowledge and experience as a teacher and also to provide feedback to their more senior colleagues about their teaching effectiveness while simultaneously learning from them. The reciprocal exchange of information—from patients and colleagues in clinic, co-residents or attendings in lectures, or in other environments such as pathology at the microscope or skills during simulation training sessions—is the cornerstone of medical education. Being able to give effective feedback while also learning to accept it is one of the most vital skills a resident can learn to thrive in medical education.
The importance of feedback cannot be understated. The art of medicine involves the scientific knowledge needed to treat disease, as well as the social ability to educate, comfort, and heal those afflicted. Mastering this art takes a lifetime. The direct imparting of knowledge from those more experienced to those learning occurs via feedback. In addition, the desire to better oneself leads to more satisfaction with work and improved performance.1 The ability to give and receive feedback is vital for the field of dermatology and medicine in general.
Types and Implementation of Feedback
Feedback comes in many forms and can be classified via different characteristics such as formal vs informal, written vs spoken, real time vs delayed, and single observer vs pooled data. Each style of feedback has positive and negative aspects, and a feedback provider will need to weigh the pros and cons when deciding the most appropriate one. Although there is no one correct way to provide feedback, the literature shows that some forms of feedback may be more effective and better received than others. This can depend on the context of what is being evaluated.
Many dermatology residencies employ formal scheduled feedback as part of their curricula, ensuring that residents will receive feedback at preset time intervals and providing residency directors with information to assess improvement and areas where more growth is needed. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education provides a reference for programs on how to give this formal standardized feedback in The Milestones Guidebook.2 This feedback is a minimum required amount, with a survey of residents showing preference for frequent informal feedback sessions in addition to standardized formal feedback.3 Another study showed that residents want feedback that is confidential, in person, shortly after experiences, and specific to their actions.4 Medical students also voiced a need for frequent, transparent, and actionable feedback during protected, predetermined, and communicated times.5 Clearly, learners appreciate spoken intentional feedback as opposed to the traditional formal model of feedback.
Finally, a study was performed analyzing how prior generations of physician educators view millennial trainees.6 Because most current dermatology residents were born between 1981 and 1996, this study seemed to pinpoint thoughts toward teaching current residents. The study found that although negative judgments such as millennial entitlement (P<.001), impoliteness (P<.001), oversensitivity (P<.001), and inferior work ethic (P<.001) reached significance, millennial ideals of social justice (P<.001) and savviness with technology (P<.001) also were notable. Overall, millennials were thought to be good colleagues (P<.001), were equally competent to more experienced clinicians (P<.001), and would lead medicine to a good future (P=.039).6
Identifying and Maximizing the Impact of Feedback
In addition to how and when to provide feedback, there are discrepancies between attending and resident perception of what is considered feedback. This disconnect can be seen in a study of 122 respondents (67 residents and 55 attendings) that showed 31% of attendings reported giving feedback daily, as opposed to only 9% of residents who reported receiving daily feedback.4 When feedback is to be performed, it may be important to specifically announce the process so that it can be properly acknowledged.7
Beach8 provided a systematic breakdown of clinical teaching to those who may be unfamiliar with the process. This method is divided into preclinic, in-clinic, and postclinic strategies to maximize learning. The author recommended establishing the objectives of the rotation from the teacher’s perspective and inquiring about the objectives of the learner. Both perspectives should inform the lessons to be learned; for example, if a medical student expresses specific interest in psoriasis (a well-established part of a medical student curriculum), all efforts should be placed on arranging for that student to see those specific patients. Beach8 also recommended providing resources and creating a positive supportive learning environment to better utilize precious clinic time and create investment in all learning parties. The author recommended matching trainees during clinic to competence-specific challenges in clinical practice where appropriate technical skill is needed. Appropriate autonomy also is promoted, as it requires higher levels of learning and knowledge consolidation. Group discussions can be facilitated by asking questions of increasing levels of difficulty as experience increases. Finally, postclinic feedback should be timely and constructive.8
One technique discussed by Beach8 is the “1-minute preceptor plus” approach. In this approach, the teacher wants to establish 5 “micro-skills” by first getting a commitment, then checking for supportive evidence of this initial plan, teaching a general principle, reinforcing what was properly performed, and correcting errors. The “plus” comes from trying to take that lesson and apply it to a broader concept. Although this concept is meant to be used in a time-limited setting, it can be expanded to larger conversations. A common example could be made when residents teach rotating medical students through direct observation and supervision during clinic. In this hypothetical situation, the resident and medical student see a patient with erythematous silver-scaled plaques on the elbows and knees. During the patient encounter, the student then inquires about any personal history of cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. After leaving the examination room, the medical student asserts the diagnosis is plaque psoriasis because of the physical examination findings and distribution of lesions. A discussion about the relationship between psoriasis and metabolic syndrome commences, emphasizing the pathophysiology of type 1 helper T-cell–mediated and type 17 helper T-cell–mediated inflammation with vascular damage and growth from inflammatory cytokines.9 The student subsequently is praised on inquiring about relevant comorbidities, and a relevant journal article is retrieved for the student’s future studies. Teaching points regarding the Koebner phenomenon, such as that it is not an instantaneous process and comes with a differential diagnosis, are then provided.
Situation-Behavior-Impact is another teaching method developed by the Center for Creative Leadership. In this technique, one will identify what specifically happened, how the learner responded, and what occurred because of the response.10 This technique is exemplified in the following mock conversation between an attending and their resident following a challenging patient situation: “When you walked into the room and asked the patient coming in for a follow-up appointment ‘What brings you in today?,’ they immediately tensed up and responded that you should already know and check your electronic medical record. This tension could be ameliorated by reviewing the patient’s medical record and addressing what they initially presented for, followed by inquiring if there are other skin problems they want to discuss afterwards.” By identifying the cause-and-effect relationship, helpful and unhelpful responses can be identified and ways to mitigate or continue behaviors can be brainstormed.
The Learning Process
Brodell et all11 outlined techniques to augment the education process that are specific to dermatology. They recommended learning general applicable concepts instead of contextless memorization, mnemonic devices to assist memory for associations and lists, and repetition and practice of learned material. For teaching, they divided techniques into Aristotelian or Socratic; Aristotelian teaching is the formal lecture style, whereas Socratic is conversation based. Both have a place in teaching—as fundamental knowledge grows via Aristotelian teaching, critical thinking can be enhanced via the Socratic method. The authors then outlined tips to create the most conducive learning environment for students.11
Feedback is a reciprocal process with information being given and received by both the teacher and the learner. This is paramount because perfecting the art of teaching is a career-long process and can only be achieved via correction of oversights and mistakes. A questionnaire-based study found that when critiquing the teacher, a combination of self-assessment with assessment from learners was effective in stimulating the greatest level of change in the teacher.12 This finding likely is because the educator was able to see the juxtaposition of how they think they performed with how students interpreted the same situation. Another survey-based study showed that of 68 attending physicians, 28 attendings saw utility in specialized feedback training; an additional 11 attendings agreed with online modules to improve their feedback skills. A recommendation that trainees receive training on the acceptance feedback also was proposed.13 Specialized training to give and receive feedback could be initiated for both attending and resident physicians to fully create an environment emphasizing improvement and teamwork.
Final Thoughts
The art of giving and receiving feedback is a deliberate process that develops with experience and training. Because residents are early in their medical career, being familiar with techniques such as those outlined in this article can enhance teaching and the reception of feedback. Residents are in a unique position, as residency itself is a time of dramatic learning and teaching. Providing feedback gives us a way to advance medicine and better ourselves by solidifying good habits and knowledge.
Acknowledgment—I thank Warren R. Heymann, MD (Camden, New Jersey), for assisting in the creation of this topic and reviewing this article.
- Crommelinck M, Anseel F. Understanding and encouraging feedback-seeking behavior: a literature review. Med Educ. 2013;47:232-241.
- Edgar L, McLean S, Hogan SO, et al. The Milestones Guidebook. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education; 2020. Accessed December 12, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/milestonesguidebook.pdf
- Wang JV, O’Connor M, McGuinn K, et al. Feedback practices in dermatology residency programs: building a culture for millennials. Clin Dermatol. 2019;37:282-283.
- Hajar T, Wanat KA, Fett N. Survey of resident physician and attending physician feedback perceptions: there is still work to be done. Dermatol Online J. 2020;25:13030/qt2sg354p6.
- Yoon J, Said JT, Thompson LL, et al. Medical student perceptions of assessment systems, subjectivity, and variability on introductory dermatology clerkships. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:232-330.
- Marka A, LeBoeuf MR, Vidal NY. Perspectives of dermatology faculty toward millennial trainees and colleagues: a national survey. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2021;5:65-71.
- Bernard AW, Kman NE, Khandelwal S. Feedback in the emergency medicine clerkship. West J Emerg Med. 2011;12:537-542.
- Beach RA. Strategies to maximise teaching in your next ambulatory clinic. Clin Teach. 2017;14:85-89.
- Takeshita J, Grewal S, Langan SM, et al. Psoriasis and comorbid diseases part I. epidemiology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:377-390.
- Olbricht SM. What makes feedback productive? Cutis. 2016;98:222-223.
- Brodell RT, Wile MZ, Chren M, et al. Learning and teaching in dermatology: a practitioner’s guide. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:946-952.
- Stalmeijer RE, Dolmans DHJM, Wolfhagen IHAP, et al. Combined student ratings and self-assessment provide useful feedback for clinical teachers. Adv in Health Sci Educ. 2010;15:315-328.
- Chelliah P, Srivastava D, Nijhawan RI. What makes giving feedback challenging? a survey of the Association of Professors of Dermatology (APD)[published online July 19, 2022]. Arch Dermatol Res. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02370-y
A dermatology resident has more education and experience than a medical student or intern but less than a fellow or attending physician. Because of this position, residents have a unique opportunity to provide feedback and education to those with less knowledge and experience as a teacher and also to provide feedback to their more senior colleagues about their teaching effectiveness while simultaneously learning from them. The reciprocal exchange of information—from patients and colleagues in clinic, co-residents or attendings in lectures, or in other environments such as pathology at the microscope or skills during simulation training sessions—is the cornerstone of medical education. Being able to give effective feedback while also learning to accept it is one of the most vital skills a resident can learn to thrive in medical education.
The importance of feedback cannot be understated. The art of medicine involves the scientific knowledge needed to treat disease, as well as the social ability to educate, comfort, and heal those afflicted. Mastering this art takes a lifetime. The direct imparting of knowledge from those more experienced to those learning occurs via feedback. In addition, the desire to better oneself leads to more satisfaction with work and improved performance.1 The ability to give and receive feedback is vital for the field of dermatology and medicine in general.
Types and Implementation of Feedback
Feedback comes in many forms and can be classified via different characteristics such as formal vs informal, written vs spoken, real time vs delayed, and single observer vs pooled data. Each style of feedback has positive and negative aspects, and a feedback provider will need to weigh the pros and cons when deciding the most appropriate one. Although there is no one correct way to provide feedback, the literature shows that some forms of feedback may be more effective and better received than others. This can depend on the context of what is being evaluated.
Many dermatology residencies employ formal scheduled feedback as part of their curricula, ensuring that residents will receive feedback at preset time intervals and providing residency directors with information to assess improvement and areas where more growth is needed. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education provides a reference for programs on how to give this formal standardized feedback in The Milestones Guidebook.2 This feedback is a minimum required amount, with a survey of residents showing preference for frequent informal feedback sessions in addition to standardized formal feedback.3 Another study showed that residents want feedback that is confidential, in person, shortly after experiences, and specific to their actions.4 Medical students also voiced a need for frequent, transparent, and actionable feedback during protected, predetermined, and communicated times.5 Clearly, learners appreciate spoken intentional feedback as opposed to the traditional formal model of feedback.
Finally, a study was performed analyzing how prior generations of physician educators view millennial trainees.6 Because most current dermatology residents were born between 1981 and 1996, this study seemed to pinpoint thoughts toward teaching current residents. The study found that although negative judgments such as millennial entitlement (P<.001), impoliteness (P<.001), oversensitivity (P<.001), and inferior work ethic (P<.001) reached significance, millennial ideals of social justice (P<.001) and savviness with technology (P<.001) also were notable. Overall, millennials were thought to be good colleagues (P<.001), were equally competent to more experienced clinicians (P<.001), and would lead medicine to a good future (P=.039).6
Identifying and Maximizing the Impact of Feedback
In addition to how and when to provide feedback, there are discrepancies between attending and resident perception of what is considered feedback. This disconnect can be seen in a study of 122 respondents (67 residents and 55 attendings) that showed 31% of attendings reported giving feedback daily, as opposed to only 9% of residents who reported receiving daily feedback.4 When feedback is to be performed, it may be important to specifically announce the process so that it can be properly acknowledged.7
Beach8 provided a systematic breakdown of clinical teaching to those who may be unfamiliar with the process. This method is divided into preclinic, in-clinic, and postclinic strategies to maximize learning. The author recommended establishing the objectives of the rotation from the teacher’s perspective and inquiring about the objectives of the learner. Both perspectives should inform the lessons to be learned; for example, if a medical student expresses specific interest in psoriasis (a well-established part of a medical student curriculum), all efforts should be placed on arranging for that student to see those specific patients. Beach8 also recommended providing resources and creating a positive supportive learning environment to better utilize precious clinic time and create investment in all learning parties. The author recommended matching trainees during clinic to competence-specific challenges in clinical practice where appropriate technical skill is needed. Appropriate autonomy also is promoted, as it requires higher levels of learning and knowledge consolidation. Group discussions can be facilitated by asking questions of increasing levels of difficulty as experience increases. Finally, postclinic feedback should be timely and constructive.8
One technique discussed by Beach8 is the “1-minute preceptor plus” approach. In this approach, the teacher wants to establish 5 “micro-skills” by first getting a commitment, then checking for supportive evidence of this initial plan, teaching a general principle, reinforcing what was properly performed, and correcting errors. The “plus” comes from trying to take that lesson and apply it to a broader concept. Although this concept is meant to be used in a time-limited setting, it can be expanded to larger conversations. A common example could be made when residents teach rotating medical students through direct observation and supervision during clinic. In this hypothetical situation, the resident and medical student see a patient with erythematous silver-scaled plaques on the elbows and knees. During the patient encounter, the student then inquires about any personal history of cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. After leaving the examination room, the medical student asserts the diagnosis is plaque psoriasis because of the physical examination findings and distribution of lesions. A discussion about the relationship between psoriasis and metabolic syndrome commences, emphasizing the pathophysiology of type 1 helper T-cell–mediated and type 17 helper T-cell–mediated inflammation with vascular damage and growth from inflammatory cytokines.9 The student subsequently is praised on inquiring about relevant comorbidities, and a relevant journal article is retrieved for the student’s future studies. Teaching points regarding the Koebner phenomenon, such as that it is not an instantaneous process and comes with a differential diagnosis, are then provided.
Situation-Behavior-Impact is another teaching method developed by the Center for Creative Leadership. In this technique, one will identify what specifically happened, how the learner responded, and what occurred because of the response.10 This technique is exemplified in the following mock conversation between an attending and their resident following a challenging patient situation: “When you walked into the room and asked the patient coming in for a follow-up appointment ‘What brings you in today?,’ they immediately tensed up and responded that you should already know and check your electronic medical record. This tension could be ameliorated by reviewing the patient’s medical record and addressing what they initially presented for, followed by inquiring if there are other skin problems they want to discuss afterwards.” By identifying the cause-and-effect relationship, helpful and unhelpful responses can be identified and ways to mitigate or continue behaviors can be brainstormed.
The Learning Process
Brodell et all11 outlined techniques to augment the education process that are specific to dermatology. They recommended learning general applicable concepts instead of contextless memorization, mnemonic devices to assist memory for associations and lists, and repetition and practice of learned material. For teaching, they divided techniques into Aristotelian or Socratic; Aristotelian teaching is the formal lecture style, whereas Socratic is conversation based. Both have a place in teaching—as fundamental knowledge grows via Aristotelian teaching, critical thinking can be enhanced via the Socratic method. The authors then outlined tips to create the most conducive learning environment for students.11
Feedback is a reciprocal process with information being given and received by both the teacher and the learner. This is paramount because perfecting the art of teaching is a career-long process and can only be achieved via correction of oversights and mistakes. A questionnaire-based study found that when critiquing the teacher, a combination of self-assessment with assessment from learners was effective in stimulating the greatest level of change in the teacher.12 This finding likely is because the educator was able to see the juxtaposition of how they think they performed with how students interpreted the same situation. Another survey-based study showed that of 68 attending physicians, 28 attendings saw utility in specialized feedback training; an additional 11 attendings agreed with online modules to improve their feedback skills. A recommendation that trainees receive training on the acceptance feedback also was proposed.13 Specialized training to give and receive feedback could be initiated for both attending and resident physicians to fully create an environment emphasizing improvement and teamwork.
Final Thoughts
The art of giving and receiving feedback is a deliberate process that develops with experience and training. Because residents are early in their medical career, being familiar with techniques such as those outlined in this article can enhance teaching and the reception of feedback. Residents are in a unique position, as residency itself is a time of dramatic learning and teaching. Providing feedback gives us a way to advance medicine and better ourselves by solidifying good habits and knowledge.
Acknowledgment—I thank Warren R. Heymann, MD (Camden, New Jersey), for assisting in the creation of this topic and reviewing this article.
A dermatology resident has more education and experience than a medical student or intern but less than a fellow or attending physician. Because of this position, residents have a unique opportunity to provide feedback and education to those with less knowledge and experience as a teacher and also to provide feedback to their more senior colleagues about their teaching effectiveness while simultaneously learning from them. The reciprocal exchange of information—from patients and colleagues in clinic, co-residents or attendings in lectures, or in other environments such as pathology at the microscope or skills during simulation training sessions—is the cornerstone of medical education. Being able to give effective feedback while also learning to accept it is one of the most vital skills a resident can learn to thrive in medical education.
The importance of feedback cannot be understated. The art of medicine involves the scientific knowledge needed to treat disease, as well as the social ability to educate, comfort, and heal those afflicted. Mastering this art takes a lifetime. The direct imparting of knowledge from those more experienced to those learning occurs via feedback. In addition, the desire to better oneself leads to more satisfaction with work and improved performance.1 The ability to give and receive feedback is vital for the field of dermatology and medicine in general.
Types and Implementation of Feedback
Feedback comes in many forms and can be classified via different characteristics such as formal vs informal, written vs spoken, real time vs delayed, and single observer vs pooled data. Each style of feedback has positive and negative aspects, and a feedback provider will need to weigh the pros and cons when deciding the most appropriate one. Although there is no one correct way to provide feedback, the literature shows that some forms of feedback may be more effective and better received than others. This can depend on the context of what is being evaluated.
Many dermatology residencies employ formal scheduled feedback as part of their curricula, ensuring that residents will receive feedback at preset time intervals and providing residency directors with information to assess improvement and areas where more growth is needed. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education provides a reference for programs on how to give this formal standardized feedback in The Milestones Guidebook.2 This feedback is a minimum required amount, with a survey of residents showing preference for frequent informal feedback sessions in addition to standardized formal feedback.3 Another study showed that residents want feedback that is confidential, in person, shortly after experiences, and specific to their actions.4 Medical students also voiced a need for frequent, transparent, and actionable feedback during protected, predetermined, and communicated times.5 Clearly, learners appreciate spoken intentional feedback as opposed to the traditional formal model of feedback.
Finally, a study was performed analyzing how prior generations of physician educators view millennial trainees.6 Because most current dermatology residents were born between 1981 and 1996, this study seemed to pinpoint thoughts toward teaching current residents. The study found that although negative judgments such as millennial entitlement (P<.001), impoliteness (P<.001), oversensitivity (P<.001), and inferior work ethic (P<.001) reached significance, millennial ideals of social justice (P<.001) and savviness with technology (P<.001) also were notable. Overall, millennials were thought to be good colleagues (P<.001), were equally competent to more experienced clinicians (P<.001), and would lead medicine to a good future (P=.039).6
Identifying and Maximizing the Impact of Feedback
In addition to how and when to provide feedback, there are discrepancies between attending and resident perception of what is considered feedback. This disconnect can be seen in a study of 122 respondents (67 residents and 55 attendings) that showed 31% of attendings reported giving feedback daily, as opposed to only 9% of residents who reported receiving daily feedback.4 When feedback is to be performed, it may be important to specifically announce the process so that it can be properly acknowledged.7
Beach8 provided a systematic breakdown of clinical teaching to those who may be unfamiliar with the process. This method is divided into preclinic, in-clinic, and postclinic strategies to maximize learning. The author recommended establishing the objectives of the rotation from the teacher’s perspective and inquiring about the objectives of the learner. Both perspectives should inform the lessons to be learned; for example, if a medical student expresses specific interest in psoriasis (a well-established part of a medical student curriculum), all efforts should be placed on arranging for that student to see those specific patients. Beach8 also recommended providing resources and creating a positive supportive learning environment to better utilize precious clinic time and create investment in all learning parties. The author recommended matching trainees during clinic to competence-specific challenges in clinical practice where appropriate technical skill is needed. Appropriate autonomy also is promoted, as it requires higher levels of learning and knowledge consolidation. Group discussions can be facilitated by asking questions of increasing levels of difficulty as experience increases. Finally, postclinic feedback should be timely and constructive.8
One technique discussed by Beach8 is the “1-minute preceptor plus” approach. In this approach, the teacher wants to establish 5 “micro-skills” by first getting a commitment, then checking for supportive evidence of this initial plan, teaching a general principle, reinforcing what was properly performed, and correcting errors. The “plus” comes from trying to take that lesson and apply it to a broader concept. Although this concept is meant to be used in a time-limited setting, it can be expanded to larger conversations. A common example could be made when residents teach rotating medical students through direct observation and supervision during clinic. In this hypothetical situation, the resident and medical student see a patient with erythematous silver-scaled plaques on the elbows and knees. During the patient encounter, the student then inquires about any personal history of cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. After leaving the examination room, the medical student asserts the diagnosis is plaque psoriasis because of the physical examination findings and distribution of lesions. A discussion about the relationship between psoriasis and metabolic syndrome commences, emphasizing the pathophysiology of type 1 helper T-cell–mediated and type 17 helper T-cell–mediated inflammation with vascular damage and growth from inflammatory cytokines.9 The student subsequently is praised on inquiring about relevant comorbidities, and a relevant journal article is retrieved for the student’s future studies. Teaching points regarding the Koebner phenomenon, such as that it is not an instantaneous process and comes with a differential diagnosis, are then provided.
Situation-Behavior-Impact is another teaching method developed by the Center for Creative Leadership. In this technique, one will identify what specifically happened, how the learner responded, and what occurred because of the response.10 This technique is exemplified in the following mock conversation between an attending and their resident following a challenging patient situation: “When you walked into the room and asked the patient coming in for a follow-up appointment ‘What brings you in today?,’ they immediately tensed up and responded that you should already know and check your electronic medical record. This tension could be ameliorated by reviewing the patient’s medical record and addressing what they initially presented for, followed by inquiring if there are other skin problems they want to discuss afterwards.” By identifying the cause-and-effect relationship, helpful and unhelpful responses can be identified and ways to mitigate or continue behaviors can be brainstormed.
The Learning Process
Brodell et all11 outlined techniques to augment the education process that are specific to dermatology. They recommended learning general applicable concepts instead of contextless memorization, mnemonic devices to assist memory for associations and lists, and repetition and practice of learned material. For teaching, they divided techniques into Aristotelian or Socratic; Aristotelian teaching is the formal lecture style, whereas Socratic is conversation based. Both have a place in teaching—as fundamental knowledge grows via Aristotelian teaching, critical thinking can be enhanced via the Socratic method. The authors then outlined tips to create the most conducive learning environment for students.11
Feedback is a reciprocal process with information being given and received by both the teacher and the learner. This is paramount because perfecting the art of teaching is a career-long process and can only be achieved via correction of oversights and mistakes. A questionnaire-based study found that when critiquing the teacher, a combination of self-assessment with assessment from learners was effective in stimulating the greatest level of change in the teacher.12 This finding likely is because the educator was able to see the juxtaposition of how they think they performed with how students interpreted the same situation. Another survey-based study showed that of 68 attending physicians, 28 attendings saw utility in specialized feedback training; an additional 11 attendings agreed with online modules to improve their feedback skills. A recommendation that trainees receive training on the acceptance feedback also was proposed.13 Specialized training to give and receive feedback could be initiated for both attending and resident physicians to fully create an environment emphasizing improvement and teamwork.
Final Thoughts
The art of giving and receiving feedback is a deliberate process that develops with experience and training. Because residents are early in their medical career, being familiar with techniques such as those outlined in this article can enhance teaching and the reception of feedback. Residents are in a unique position, as residency itself is a time of dramatic learning and teaching. Providing feedback gives us a way to advance medicine and better ourselves by solidifying good habits and knowledge.
Acknowledgment—I thank Warren R. Heymann, MD (Camden, New Jersey), for assisting in the creation of this topic and reviewing this article.
- Crommelinck M, Anseel F. Understanding and encouraging feedback-seeking behavior: a literature review. Med Educ. 2013;47:232-241.
- Edgar L, McLean S, Hogan SO, et al. The Milestones Guidebook. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education; 2020. Accessed December 12, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/milestonesguidebook.pdf
- Wang JV, O’Connor M, McGuinn K, et al. Feedback practices in dermatology residency programs: building a culture for millennials. Clin Dermatol. 2019;37:282-283.
- Hajar T, Wanat KA, Fett N. Survey of resident physician and attending physician feedback perceptions: there is still work to be done. Dermatol Online J. 2020;25:13030/qt2sg354p6.
- Yoon J, Said JT, Thompson LL, et al. Medical student perceptions of assessment systems, subjectivity, and variability on introductory dermatology clerkships. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:232-330.
- Marka A, LeBoeuf MR, Vidal NY. Perspectives of dermatology faculty toward millennial trainees and colleagues: a national survey. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2021;5:65-71.
- Bernard AW, Kman NE, Khandelwal S. Feedback in the emergency medicine clerkship. West J Emerg Med. 2011;12:537-542.
- Beach RA. Strategies to maximise teaching in your next ambulatory clinic. Clin Teach. 2017;14:85-89.
- Takeshita J, Grewal S, Langan SM, et al. Psoriasis and comorbid diseases part I. epidemiology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:377-390.
- Olbricht SM. What makes feedback productive? Cutis. 2016;98:222-223.
- Brodell RT, Wile MZ, Chren M, et al. Learning and teaching in dermatology: a practitioner’s guide. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:946-952.
- Stalmeijer RE, Dolmans DHJM, Wolfhagen IHAP, et al. Combined student ratings and self-assessment provide useful feedback for clinical teachers. Adv in Health Sci Educ. 2010;15:315-328.
- Chelliah P, Srivastava D, Nijhawan RI. What makes giving feedback challenging? a survey of the Association of Professors of Dermatology (APD)[published online July 19, 2022]. Arch Dermatol Res. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02370-y
- Crommelinck M, Anseel F. Understanding and encouraging feedback-seeking behavior: a literature review. Med Educ. 2013;47:232-241.
- Edgar L, McLean S, Hogan SO, et al. The Milestones Guidebook. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education; 2020. Accessed December 12, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/milestonesguidebook.pdf
- Wang JV, O’Connor M, McGuinn K, et al. Feedback practices in dermatology residency programs: building a culture for millennials. Clin Dermatol. 2019;37:282-283.
- Hajar T, Wanat KA, Fett N. Survey of resident physician and attending physician feedback perceptions: there is still work to be done. Dermatol Online J. 2020;25:13030/qt2sg354p6.
- Yoon J, Said JT, Thompson LL, et al. Medical student perceptions of assessment systems, subjectivity, and variability on introductory dermatology clerkships. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:232-330.
- Marka A, LeBoeuf MR, Vidal NY. Perspectives of dermatology faculty toward millennial trainees and colleagues: a national survey. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2021;5:65-71.
- Bernard AW, Kman NE, Khandelwal S. Feedback in the emergency medicine clerkship. West J Emerg Med. 2011;12:537-542.
- Beach RA. Strategies to maximise teaching in your next ambulatory clinic. Clin Teach. 2017;14:85-89.
- Takeshita J, Grewal S, Langan SM, et al. Psoriasis and comorbid diseases part I. epidemiology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:377-390.
- Olbricht SM. What makes feedback productive? Cutis. 2016;98:222-223.
- Brodell RT, Wile MZ, Chren M, et al. Learning and teaching in dermatology: a practitioner’s guide. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:946-952.
- Stalmeijer RE, Dolmans DHJM, Wolfhagen IHAP, et al. Combined student ratings and self-assessment provide useful feedback for clinical teachers. Adv in Health Sci Educ. 2010;15:315-328.
- Chelliah P, Srivastava D, Nijhawan RI. What makes giving feedback challenging? a survey of the Association of Professors of Dermatology (APD)[published online July 19, 2022]. Arch Dermatol Res. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02370-y
RESIDENT PEARLS
- Feedback between dermatology trainees and their educators should be provided in a private and constructive way soon after the observation was performed.
- One method to improve education and feedback in a residency program is a specialty course to improve giving and receiving feedback by both residents and attending physicians.
Medicare pay cuts partly averted in massive budget bill
Congress averted bigger reductions in Medicare’s future payments for clinicians in its massive, year-end spending bill, but physicians will still see a 2% cut in a key payment variable in 2023.
The bill also authorizes new policies regarding accelerated drug approvals and substance use disorder treatment.
The House voted 225-201 to clear a wide-ranging legislative package, known as an omnibus, for President Joe Biden’s signature. The Senate voted 68-29 to approve the measure.
Clinicians had been facing as much as 8.5% in cuts to certain factors that set their Medicare payment. The American Medical Association credited an advocacy campaign it joined with more than 150 organizations with fending off the much-feared reimbursement cuts. The 2% trim for 2023 will decline to 1.25% for 2024.
These reductions will hit as many clinicians face the toll on rising costs for running their practices, as , the AMA said.
“Congress must immediately begin the work of long-overdue Medicare physician payment reform that will lead to the program stability that beneficiaries and physicians need,” AMA President Jack Resneck, MD, said in a statement.
While the omnibus bill blocks 6.5% of Medicare payment cuts originally slated to take effect in 2023, it still puts “untenable strain” on primary care clinicians, said Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, in a statement.
“However, we’re pleased to see several provisions that will improve access to care, including bolstering mental health services, extending telehealth, and expanding Medicaid and CHIP coverage,” Dr. Iroku-Malize added.
New health care policies in omnibus
Lawmakers adopted many health care policy changes in the omnibus package, which contained 12 overdue spending bills for fiscal year 2023. (Much of the federal government has been funded through stop-gap measures since this budget year began on Oct. 1.) The final measure runs to more than 4,100 pages in PDF form.
House Energy and Commerce Chairman Frank Pallone Jr. (D-NJ) said the health care provisions will:
- Expand patient access to opioid addiction treatment by making it easier for clinicians to dispense buprenorphine for opioid use disorder maintenance or detoxification treatment
- Require health care providers to complete a training requirement on identifying and treating patients with substance use disorders
- Guarantee 12 months of continuous Medicaid coverage for 40 million children
- Provide 2 years of additional Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) funding
- Permanently extend the option for states to offer 12 months of Medicaid coverage to new mothers
- Continue Medicare’s expanded access to telehealth by extending COVID-19 telehealth flexibilities through Dec. 31, 2024.
FDA’s accelerated approval
The omnibus also will shorten the period of uncertainty patients and clinicians face with medicines cleared under the accelerated approval pathway.
The Food and Drug Administration uses accelerated approvals to give conditional clearances to medicines for fatal and serious conditions based on limited evidence signaling a potential benefit. Companies are expected to continue research needed to prove whether promising signals, such as stemming tumor growth, benefits patients.
Concerns have mounted when companies delay confirmatory trials or try to maintain accelerated approvals for drugs that fail those trials.
Mr. Pallone said the omnibus contains provisions that:
- Require the FDA to specify conditions for required post-approval studies
- Authorize the FDA to require post-approval studies to be underway at the time of approval or within a specified time period following approval.
- Clarify and streamline current FDA authority to withdraw approvals when sponsors fail to conduct studies with due diligence.
Reshma Ramachandran, MD, MPP, MHS, who serves as the chair of the Doctors for America’s FDA Task Force, told this news organization that she was pleased to see these provisions pass. She had been disappointed they were not included earlier this year in the latest Prescription Drug User Fee Act reauthorization.
The provisions in the omnibus make “clear what steps the FDA can take to remove an unproven drug off the market should manufacturers fail to complete these studies or demonstrate meaningful clinical benefit,” Dr. Ramachandran wrote in an email.
Dr. Ramachandran said she hopes lawmakers build on these steps in the future. She suggested Congress add a mandate to require drug labels to clearly state when the FDA is still waiting for evidence needed to confirm benefits of medicines cleared by accelerated approval.
“Nevertheless, Congress in including and, hopefully, passing these reforms has made it clear that drug companies need to provide meaningful evidence that their accelerated approval drugs work in patients and FDA can take action to protect patients should this not occur,” Dr. Ramachandran wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Congress averted bigger reductions in Medicare’s future payments for clinicians in its massive, year-end spending bill, but physicians will still see a 2% cut in a key payment variable in 2023.
The bill also authorizes new policies regarding accelerated drug approvals and substance use disorder treatment.
The House voted 225-201 to clear a wide-ranging legislative package, known as an omnibus, for President Joe Biden’s signature. The Senate voted 68-29 to approve the measure.
Clinicians had been facing as much as 8.5% in cuts to certain factors that set their Medicare payment. The American Medical Association credited an advocacy campaign it joined with more than 150 organizations with fending off the much-feared reimbursement cuts. The 2% trim for 2023 will decline to 1.25% for 2024.
These reductions will hit as many clinicians face the toll on rising costs for running their practices, as , the AMA said.
“Congress must immediately begin the work of long-overdue Medicare physician payment reform that will lead to the program stability that beneficiaries and physicians need,” AMA President Jack Resneck, MD, said in a statement.
While the omnibus bill blocks 6.5% of Medicare payment cuts originally slated to take effect in 2023, it still puts “untenable strain” on primary care clinicians, said Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, in a statement.
“However, we’re pleased to see several provisions that will improve access to care, including bolstering mental health services, extending telehealth, and expanding Medicaid and CHIP coverage,” Dr. Iroku-Malize added.
New health care policies in omnibus
Lawmakers adopted many health care policy changes in the omnibus package, which contained 12 overdue spending bills for fiscal year 2023. (Much of the federal government has been funded through stop-gap measures since this budget year began on Oct. 1.) The final measure runs to more than 4,100 pages in PDF form.
House Energy and Commerce Chairman Frank Pallone Jr. (D-NJ) said the health care provisions will:
- Expand patient access to opioid addiction treatment by making it easier for clinicians to dispense buprenorphine for opioid use disorder maintenance or detoxification treatment
- Require health care providers to complete a training requirement on identifying and treating patients with substance use disorders
- Guarantee 12 months of continuous Medicaid coverage for 40 million children
- Provide 2 years of additional Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) funding
- Permanently extend the option for states to offer 12 months of Medicaid coverage to new mothers
- Continue Medicare’s expanded access to telehealth by extending COVID-19 telehealth flexibilities through Dec. 31, 2024.
FDA’s accelerated approval
The omnibus also will shorten the period of uncertainty patients and clinicians face with medicines cleared under the accelerated approval pathway.
The Food and Drug Administration uses accelerated approvals to give conditional clearances to medicines for fatal and serious conditions based on limited evidence signaling a potential benefit. Companies are expected to continue research needed to prove whether promising signals, such as stemming tumor growth, benefits patients.
Concerns have mounted when companies delay confirmatory trials or try to maintain accelerated approvals for drugs that fail those trials.
Mr. Pallone said the omnibus contains provisions that:
- Require the FDA to specify conditions for required post-approval studies
- Authorize the FDA to require post-approval studies to be underway at the time of approval or within a specified time period following approval.
- Clarify and streamline current FDA authority to withdraw approvals when sponsors fail to conduct studies with due diligence.
Reshma Ramachandran, MD, MPP, MHS, who serves as the chair of the Doctors for America’s FDA Task Force, told this news organization that she was pleased to see these provisions pass. She had been disappointed they were not included earlier this year in the latest Prescription Drug User Fee Act reauthorization.
The provisions in the omnibus make “clear what steps the FDA can take to remove an unproven drug off the market should manufacturers fail to complete these studies or demonstrate meaningful clinical benefit,” Dr. Ramachandran wrote in an email.
Dr. Ramachandran said she hopes lawmakers build on these steps in the future. She suggested Congress add a mandate to require drug labels to clearly state when the FDA is still waiting for evidence needed to confirm benefits of medicines cleared by accelerated approval.
“Nevertheless, Congress in including and, hopefully, passing these reforms has made it clear that drug companies need to provide meaningful evidence that their accelerated approval drugs work in patients and FDA can take action to protect patients should this not occur,” Dr. Ramachandran wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Congress averted bigger reductions in Medicare’s future payments for clinicians in its massive, year-end spending bill, but physicians will still see a 2% cut in a key payment variable in 2023.
The bill also authorizes new policies regarding accelerated drug approvals and substance use disorder treatment.
The House voted 225-201 to clear a wide-ranging legislative package, known as an omnibus, for President Joe Biden’s signature. The Senate voted 68-29 to approve the measure.
Clinicians had been facing as much as 8.5% in cuts to certain factors that set their Medicare payment. The American Medical Association credited an advocacy campaign it joined with more than 150 organizations with fending off the much-feared reimbursement cuts. The 2% trim for 2023 will decline to 1.25% for 2024.
These reductions will hit as many clinicians face the toll on rising costs for running their practices, as , the AMA said.
“Congress must immediately begin the work of long-overdue Medicare physician payment reform that will lead to the program stability that beneficiaries and physicians need,” AMA President Jack Resneck, MD, said in a statement.
While the omnibus bill blocks 6.5% of Medicare payment cuts originally slated to take effect in 2023, it still puts “untenable strain” on primary care clinicians, said Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, in a statement.
“However, we’re pleased to see several provisions that will improve access to care, including bolstering mental health services, extending telehealth, and expanding Medicaid and CHIP coverage,” Dr. Iroku-Malize added.
New health care policies in omnibus
Lawmakers adopted many health care policy changes in the omnibus package, which contained 12 overdue spending bills for fiscal year 2023. (Much of the federal government has been funded through stop-gap measures since this budget year began on Oct. 1.) The final measure runs to more than 4,100 pages in PDF form.
House Energy and Commerce Chairman Frank Pallone Jr. (D-NJ) said the health care provisions will:
- Expand patient access to opioid addiction treatment by making it easier for clinicians to dispense buprenorphine for opioid use disorder maintenance or detoxification treatment
- Require health care providers to complete a training requirement on identifying and treating patients with substance use disorders
- Guarantee 12 months of continuous Medicaid coverage for 40 million children
- Provide 2 years of additional Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) funding
- Permanently extend the option for states to offer 12 months of Medicaid coverage to new mothers
- Continue Medicare’s expanded access to telehealth by extending COVID-19 telehealth flexibilities through Dec. 31, 2024.
FDA’s accelerated approval
The omnibus also will shorten the period of uncertainty patients and clinicians face with medicines cleared under the accelerated approval pathway.
The Food and Drug Administration uses accelerated approvals to give conditional clearances to medicines for fatal and serious conditions based on limited evidence signaling a potential benefit. Companies are expected to continue research needed to prove whether promising signals, such as stemming tumor growth, benefits patients.
Concerns have mounted when companies delay confirmatory trials or try to maintain accelerated approvals for drugs that fail those trials.
Mr. Pallone said the omnibus contains provisions that:
- Require the FDA to specify conditions for required post-approval studies
- Authorize the FDA to require post-approval studies to be underway at the time of approval or within a specified time period following approval.
- Clarify and streamline current FDA authority to withdraw approvals when sponsors fail to conduct studies with due diligence.
Reshma Ramachandran, MD, MPP, MHS, who serves as the chair of the Doctors for America’s FDA Task Force, told this news organization that she was pleased to see these provisions pass. She had been disappointed they were not included earlier this year in the latest Prescription Drug User Fee Act reauthorization.
The provisions in the omnibus make “clear what steps the FDA can take to remove an unproven drug off the market should manufacturers fail to complete these studies or demonstrate meaningful clinical benefit,” Dr. Ramachandran wrote in an email.
Dr. Ramachandran said she hopes lawmakers build on these steps in the future. She suggested Congress add a mandate to require drug labels to clearly state when the FDA is still waiting for evidence needed to confirm benefits of medicines cleared by accelerated approval.
“Nevertheless, Congress in including and, hopefully, passing these reforms has made it clear that drug companies need to provide meaningful evidence that their accelerated approval drugs work in patients and FDA can take action to protect patients should this not occur,” Dr. Ramachandran wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Meningococcal B vaccine protects against gonorrhea
PARIS – All the way back in 1907, The Lancet published an article on a gonorrhea vaccine trial. Today, after continuous research throughout the intervening 110-plus years, scientists may finally have achieved success. Sébastien Fouéré, MD, discussed the details at a press conference that focused on the highlights of the Dermatology Days of Paris conference. Dr. Fouéré is the head of the genital dermatology and sexually transmitted infections unit at Saint-Louis Hospital, Paris.
Twin bacteria
Although the gonorrhea vaccine has long been the subject of research, Dr. Fouéré views 2017 as a turning point. This was when the results of a study led by Helen Petousis-Harris, PhD, were published.
“She tried to formalize the not completely indisputable results published by Cuba, where it seemed there were fewer gonococci in individuals vaccinated against meningococcal group B,” he noted.
Dr. Petousis-Harris, an immunologist, conducted a retrospective case-control study involving 11 clinics in New Zealand. The participants were aged 15-30 years, were eligible to receive the meningococcal B vaccine, and had been diagnosed with gonorrhea, chlamydia, or both. The researchers found that receiving the meningococcal B vaccine in childhood provides around 30% protection against Neisseria gonorrhoeae infections.
“It’s not perhaps a coincidence that a meningococcal B vaccine would be protective against gonorrhea,” Dr. Fouéré pointed out. He considers this protection logical, even expected, insofar as “meningococcus and gonococcus are almost twins.” There is 90% and 100% homology between membrane proteins of the two bacteria.
Vaccine is effective
Two retrospective case-control studies confirm that the vaccine is protective. One of the studies, carried out by an Australian team, found that the effectiveness was 32%, quite close to that reported by Petousis-Harris. In the other study, a U.S. team brought to light a dose-response relationship. while a complete vaccination series (two MenB-4C doses) was 40% effective.
Prospective studies are in progress, which will provide a higher level of evidence. The ANRS DOXYVAC trial has been underway since January 2021. The participants are men who have sex with men, who are highly exposed to the risk of sexually transmitted infections, and who presented with at least one STI in the year before their participation in the study. “The study is being conducted by Jean-Michel Molina of Saint-Louis Hospital. What they’re trying to do is protect our cohort of pre-exposure prophylaxis patients with meningococcal vaccine,” explained Dr. Fouéré.
Initial findings demonstrated the efficacy of a meningococcal B vaccine in reducing the risk of gonorrhea and the efficacy of doxycycline as preventive intervention for STIs when taken within 72 hours after sexual intercourse. In light of these results, a decision was made at the end of October to discontinue the trial and to recommend providing both interventions to all ANRS DOXYVAC participants. The follow-up of the participants will continue until the end of 2023. The results that led to stopping the study in its current form will be presented in early 2023.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PARIS – All the way back in 1907, The Lancet published an article on a gonorrhea vaccine trial. Today, after continuous research throughout the intervening 110-plus years, scientists may finally have achieved success. Sébastien Fouéré, MD, discussed the details at a press conference that focused on the highlights of the Dermatology Days of Paris conference. Dr. Fouéré is the head of the genital dermatology and sexually transmitted infections unit at Saint-Louis Hospital, Paris.
Twin bacteria
Although the gonorrhea vaccine has long been the subject of research, Dr. Fouéré views 2017 as a turning point. This was when the results of a study led by Helen Petousis-Harris, PhD, were published.
“She tried to formalize the not completely indisputable results published by Cuba, where it seemed there were fewer gonococci in individuals vaccinated against meningococcal group B,” he noted.
Dr. Petousis-Harris, an immunologist, conducted a retrospective case-control study involving 11 clinics in New Zealand. The participants were aged 15-30 years, were eligible to receive the meningococcal B vaccine, and had been diagnosed with gonorrhea, chlamydia, or both. The researchers found that receiving the meningococcal B vaccine in childhood provides around 30% protection against Neisseria gonorrhoeae infections.
“It’s not perhaps a coincidence that a meningococcal B vaccine would be protective against gonorrhea,” Dr. Fouéré pointed out. He considers this protection logical, even expected, insofar as “meningococcus and gonococcus are almost twins.” There is 90% and 100% homology between membrane proteins of the two bacteria.
Vaccine is effective
Two retrospective case-control studies confirm that the vaccine is protective. One of the studies, carried out by an Australian team, found that the effectiveness was 32%, quite close to that reported by Petousis-Harris. In the other study, a U.S. team brought to light a dose-response relationship. while a complete vaccination series (two MenB-4C doses) was 40% effective.
Prospective studies are in progress, which will provide a higher level of evidence. The ANRS DOXYVAC trial has been underway since January 2021. The participants are men who have sex with men, who are highly exposed to the risk of sexually transmitted infections, and who presented with at least one STI in the year before their participation in the study. “The study is being conducted by Jean-Michel Molina of Saint-Louis Hospital. What they’re trying to do is protect our cohort of pre-exposure prophylaxis patients with meningococcal vaccine,” explained Dr. Fouéré.
Initial findings demonstrated the efficacy of a meningococcal B vaccine in reducing the risk of gonorrhea and the efficacy of doxycycline as preventive intervention for STIs when taken within 72 hours after sexual intercourse. In light of these results, a decision was made at the end of October to discontinue the trial and to recommend providing both interventions to all ANRS DOXYVAC participants. The follow-up of the participants will continue until the end of 2023. The results that led to stopping the study in its current form will be presented in early 2023.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PARIS – All the way back in 1907, The Lancet published an article on a gonorrhea vaccine trial. Today, after continuous research throughout the intervening 110-plus years, scientists may finally have achieved success. Sébastien Fouéré, MD, discussed the details at a press conference that focused on the highlights of the Dermatology Days of Paris conference. Dr. Fouéré is the head of the genital dermatology and sexually transmitted infections unit at Saint-Louis Hospital, Paris.
Twin bacteria
Although the gonorrhea vaccine has long been the subject of research, Dr. Fouéré views 2017 as a turning point. This was when the results of a study led by Helen Petousis-Harris, PhD, were published.
“She tried to formalize the not completely indisputable results published by Cuba, where it seemed there were fewer gonococci in individuals vaccinated against meningococcal group B,” he noted.
Dr. Petousis-Harris, an immunologist, conducted a retrospective case-control study involving 11 clinics in New Zealand. The participants were aged 15-30 years, were eligible to receive the meningococcal B vaccine, and had been diagnosed with gonorrhea, chlamydia, or both. The researchers found that receiving the meningococcal B vaccine in childhood provides around 30% protection against Neisseria gonorrhoeae infections.
“It’s not perhaps a coincidence that a meningococcal B vaccine would be protective against gonorrhea,” Dr. Fouéré pointed out. He considers this protection logical, even expected, insofar as “meningococcus and gonococcus are almost twins.” There is 90% and 100% homology between membrane proteins of the two bacteria.
Vaccine is effective
Two retrospective case-control studies confirm that the vaccine is protective. One of the studies, carried out by an Australian team, found that the effectiveness was 32%, quite close to that reported by Petousis-Harris. In the other study, a U.S. team brought to light a dose-response relationship. while a complete vaccination series (two MenB-4C doses) was 40% effective.
Prospective studies are in progress, which will provide a higher level of evidence. The ANRS DOXYVAC trial has been underway since January 2021. The participants are men who have sex with men, who are highly exposed to the risk of sexually transmitted infections, and who presented with at least one STI in the year before their participation in the study. “The study is being conducted by Jean-Michel Molina of Saint-Louis Hospital. What they’re trying to do is protect our cohort of pre-exposure prophylaxis patients with meningococcal vaccine,” explained Dr. Fouéré.
Initial findings demonstrated the efficacy of a meningococcal B vaccine in reducing the risk of gonorrhea and the efficacy of doxycycline as preventive intervention for STIs when taken within 72 hours after sexual intercourse. In light of these results, a decision was made at the end of October to discontinue the trial and to recommend providing both interventions to all ANRS DOXYVAC participants. The follow-up of the participants will continue until the end of 2023. The results that led to stopping the study in its current form will be presented in early 2023.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Vegetarians suffer more depression than meat eaters
People who follow a vegetarian lifestyle have around twice as many depressive episodes as those who eat meat, according to the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health.
What to know
, including the vegetarian social experience; depression itself may increase the likelihood of becoming vegetarian, or both vegetarianism and depression may be associated with guilt through factors involving the meat industry.
Adopting a vegetarian diet might affect one’s relationship with others and involvement in social activities and may sometimes be associated with teasing or other forms of social ostracism.
It is possible that being depressed and dwelling on negative thoughts cause people to be more likely to become vegetarian rather than the other way around.
Videos depicting violence and cruelty in the meat industry may affect depressed people, causing them to dwell on the images, feel guilty for their part in creating the demand for meat, and become vegetarian.
Survey data were collected in Brazil, a country famous for its meat-heavy diet, and while there has been a sharp increase in vegetarianism, vegetarians still account for less than 0.5%.
This is a summary of the article, “Association Between Meatless Diet and Depressive Episodes: A Cross-sectional Analysis of Baseline Data From the Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil),” published in the Journal of Affective Disorders. The full article can be found at sciencedirect.com.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who follow a vegetarian lifestyle have around twice as many depressive episodes as those who eat meat, according to the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health.
What to know
, including the vegetarian social experience; depression itself may increase the likelihood of becoming vegetarian, or both vegetarianism and depression may be associated with guilt through factors involving the meat industry.
Adopting a vegetarian diet might affect one’s relationship with others and involvement in social activities and may sometimes be associated with teasing or other forms of social ostracism.
It is possible that being depressed and dwelling on negative thoughts cause people to be more likely to become vegetarian rather than the other way around.
Videos depicting violence and cruelty in the meat industry may affect depressed people, causing them to dwell on the images, feel guilty for their part in creating the demand for meat, and become vegetarian.
Survey data were collected in Brazil, a country famous for its meat-heavy diet, and while there has been a sharp increase in vegetarianism, vegetarians still account for less than 0.5%.
This is a summary of the article, “Association Between Meatless Diet and Depressive Episodes: A Cross-sectional Analysis of Baseline Data From the Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil),” published in the Journal of Affective Disorders. The full article can be found at sciencedirect.com.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who follow a vegetarian lifestyle have around twice as many depressive episodes as those who eat meat, according to the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health.
What to know
, including the vegetarian social experience; depression itself may increase the likelihood of becoming vegetarian, or both vegetarianism and depression may be associated with guilt through factors involving the meat industry.
Adopting a vegetarian diet might affect one’s relationship with others and involvement in social activities and may sometimes be associated with teasing or other forms of social ostracism.
It is possible that being depressed and dwelling on negative thoughts cause people to be more likely to become vegetarian rather than the other way around.
Videos depicting violence and cruelty in the meat industry may affect depressed people, causing them to dwell on the images, feel guilty for their part in creating the demand for meat, and become vegetarian.
Survey data were collected in Brazil, a country famous for its meat-heavy diet, and while there has been a sharp increase in vegetarianism, vegetarians still account for less than 0.5%.
This is a summary of the article, “Association Between Meatless Diet and Depressive Episodes: A Cross-sectional Analysis of Baseline Data From the Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil),” published in the Journal of Affective Disorders. The full article can be found at sciencedirect.com.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Focus on menopause
OBG Management caught up with Drs. Jan Shifren and Genevieve Neal-Perry while they were attending the annual meeting of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS), held October 12-15, 2022, in Atlanta, Georgia. Dr. Shifren presented on the “Ins and Outs of Hormone Therapy,” while Dr. Neal-Perry focused on “Menopause Physiology.”
Evaluating symptomatic patients for appropriate hormone therapy
OBG Management: In your presentation to the group at the NAMS meeting, you described a 51-year-old patient with the principal symptoms of frequent hot flashes and night sweats, sleep disruption, fatigue, irritability, vaginal dryness, and dyspareunia. As she reported already trying several lifestyle modification approaches, what are your questions for her to determine whether hormone therapy (HT), systemic or low-dose vaginal, is advisable?
Jan Shifren, MD: As with every patient, you need to begin with a thorough history and confirm her physical exam is up to date. If there are concerns related to genitourinary symptoms of menopause (GSM), then a pelvic exam is indicated. This patient is a healthy menopausal woman with bothersome hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. Sleep disruption from night sweats is likely the cause of her fatigue and irritability, and her dyspareunia due to atrophic vulvovaginal changes. The principal indication for systemic HT is bothersome vasomotor symptoms (VMS), and a healthy woman who is under age 60 or within 10 years of the onset of menopause is generally a very good candidate for hormones. For this healthy 51-year-old with bothersome VMS unresponsive to lifestyle modification, the benefits of HT should outweigh potential risks. As low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy is minimally absorbed and very safe, this would be recommended instead of systemic HT if her only menopause symptoms were vaginal dryness and dyspareunia.
HT types and formulations
OBG Management: For this patient, low-dose vaginal estrogen is appropriate. In general, how do you decide on recommendations for combination therapy or estrogen only, and what formulations and dosages do you recommend?
Dr. Shifren: Any woman with a uterus needs to take a progestogen together with estrogen to protect her uterus from estrogen-induced endometrial overgrowth. With low dose vaginal estrogen therapy, however, concurrent progestogen is not needed.
Continue to: Estrogen options...
Estrogen options. I ask my patients about their preferences, but I typically recommend transdermal or non-oral estradiol formulations for my menopausal patients. The most commonly prescribed non-oral menopausal estrogen is the patch—as they are convenient, come in a wide range of doses, and are generic and generally affordable. There are also US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved transdermal gels and creams, and a vaginal ring that provides systemic estrogen, but these options are typically more expensive than the patch. All non-oral estrogen formulations are composed of estradiol, which is especially nice for a patient preferring “bioidentical HT.”
Many of our patients like the idea that they are using “natural” HT. I inform them that bioidentical is a marketing term rather than a medical term, but if their goal is to take the same hormones that their ovaries made when they were younger, they should use FDA-approved formulations of estradiol and progesterone for their menopausal HT symptoms. I do not recommend compounded bioidentical HT due to concerns regarding product quality and safety. The combination of FDA-approved estradiol patches and oral micronized progesterone provides a high quality, carefully regulated bioidentical HT regimen. For women greatly preferring an oral estrogen, oral estradiol with micronized progesterone is an option.
In addition to patient preference for natural HT, the reasons that I encourage women to consider the estradiol transdermal patch for their menopausal HT include:
- no increased risk of venous thromboembolic events when physiologically dosed menopausal estradiol therapy is provided by a skin patch (observational data).1 With oral estrogens, even when dosed for menopause, VTE risk increases, as coagulation factors increase due to the first-pass hepatic effect. This does not occur with non-oral menopausal estrogens.
- no increased risk of gallbladder disease, which occurs with oral estrogen therapy (observational data)2
- possibly lower risk of stroke when low-dose menopausal HT is provided via skin patch (observational data)3
- convenience—the patches are changed once or twice weekly
- wide range of doses available, which optimizes identifying the lowest effective dose and decreasing the dose over time.
Progestogen options. Progestogens may be given daily or cyclically. Use of daily progestogen typically results in amenorrhea, which is preferred by most women. Cyclic use of a progestogen for 12-14 days each month results in a monthly withdrawal bleed, which is a good option for a woman experiencing bothersome breakthrough bleeding with daily progestogen. Use of a progestogen-releasing IUD is an off-label alternative for endometrial protection with menopausal HT. As discussed earlier, as many women prefer bioidentical HT, one of our preferred regimens is to provide transdermal estradiol with FDA-approved oral micronized progesterone. There are several patches that combine estradiol with a progestogen, but there is not a lot of dosing flexibility and product choice. There also is an approved product available that combines oral estradiol and micronized progesterone in one tablet.
Scheduling follow-up
OBG Management: Now that you have started the opening case patient on HT, how often are you going to monitor her for treatment?
Dr. Shifren: Women will not experience maximum efficacy for hot flash relief from their estrogen therapy for 3 months, so I typically see a patient back at 3 to 4 months to assess side effects and symptom control. I encourage women to reach out sooner if they are having a bothersome side effect. Once she is doing well on an HT regimen, we assess risks and benefits of ongoing treatment annually. The goal is to be certain she is on the lowest dose of estrogen that treats her symptoms, and we slowly decrease the estrogen dose over time.
Breast cancer risk
OBG Management: In your presentation, you mentioned that the risk of breast cancer does not increase appreciably with short-term use of HT. Is it possible to define short term?
Dr. Shifren: In the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI), a large double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of menopausal HT, there was a slight increase in breast cancer risk after approximately 4 to 5 years of use in women using estrogen with progestogen.4 I share with patients that this increased risk is about the same as that of obesity or drinking more than 1 alcoholic beverage daily. As an increased risk of breast cancer does not occur for several years, a woman may be able to take hormones for bothersome symptoms, feel well, and slowly come off without incurring significant breast cancer risk. In the WHI, there was no increase in breast cancer risk in women without a uterus randomized to estrogen alone.
Regarding cardiovascular risk, in the WHI, an increased risk of cardiovascular events generally was not seen in healthy women younger than age 60 and within 10 years of the onset of menopause.5 Benefits of HT may not outweigh risks for women with significant underlying cardiovascular risk factors, even if they are younger and close to menopause onset.
Continue to: The importance of shared decision making...
The importance of shared decision making
Dr. Shifren: As with any important health care decision, women should be involved in an individualized discussion of risks and benefits, with shared decision making about whether HT is the right choice. Women also should be involved in ongoing decisions regarding HT formulation, dose, and duration of use.
A nonhormonal option for hot flashes
OBG Management: How many women experience VMS around the time of menopause?
Dr. Genevieve Neal-Perry, MD, PhD: About 60% to 70% of individuals will experience hot flashes around the time of the menopause.6 Of those, about 40% are what we would call moderate to severe hot flashes—which are typically the most disruptive in terms of quality of life.7 The window of time in which they are likely to have them, at typically their most intense timeframe, is 2 years before the final menstrual period and the year after.7 In terms of the average duration, however, it’s about 7 years, which is a lot longer than what we previously thought.8 Moreover, there are disparities in that women of color, particularly African American women, can have them as long as 10 years.8
OBG Management: Can you explain why the VMS occur, and specifically around the time of menopause?
Dr. Neal-Perry: For many years we did not understand the basic biology of hot flashes. When you think about it, it’s completely amazing—when half of our population experiences hot flashes, and we don’t understand why, and we don’t have therapy that specifically targets hot flashes.
What we now know from work completed by Naomi Rance, in particular, is that a specific region of the brain, the hypothalamus, exhibited changes in number of neurons that seemed to be increased in size in menopausal people and smaller in size in people who were not menopausal.9 That started the journey to understanding the biology, and eventual mechanism, of hot flashes. It took about 10-15 years before we really began to understand why.
What we know now is that estrogen, a hormone that is made by the ovaries, activates and inactivates neurons located in the hypothalamus, a brain region that controls our thermoregulation—the way your body perceives temperature. The hypothalamus controls your response to temperature, either you experience chills or you dissipate heat by vasodilating (hot flush) and sweating.
The thermoregulatory region of the hypothalamus houses cells that receive messages from KNDy neurons, neurons also located in the hypothalamus that express kisspeptin, neurokinin, and dynorphin. Importantly, KNDy neurons express estrogen receptors. (The way that I like to think about estrogen and estrogen receptors is that estrogen is like the ball and the receptor is like the catcher’s mitt.) When estrogen interacts with this receptor, it keeps KNDy neurons quiet. But the increased variability and loss of estrogen that occurs around the time of menopause “disinhibits” KNDy neurons—meaning that they are no longer being reined in by estrogen. In response to decreased estrogen regulation, KNDy neurons become hypertrophied with neurotransmitters and more active. Specifically, KNDy neurons release neurokinin, a neuropeptide that self-stimulates KNDy neurons and activates neurons in the thermoregulatory zone of the brain—it’s a speed-forward feed-backward mechanism. The thermoregulatory neurons interpret this signal as “I feel hot,” and the body begins a series of functions to cool things down.
Continue to: Treatments that act on the thermoregulatory region
Treatments that act on the thermoregulatory region
Dr. Neal-Perry: I have described what happens in the brain around the time of menopause, and what triggers those hot flashes.
Estrogen. The reason that estrogen worked to treat the hot flashes is because estrogen inhibits and calms the neurons that become hyperactive during the menopause.
Fezolinetant. Fezolinetant is unique because it specifically targets the hormone receptor that triggers hot flashes, the neurokinin receptor. Fezolinetant is a nonhormone therapy that not only reduces the activity of KNDy neurons but also blocks the effects of neurons in the thermoregulatory zone, thereby reducing the sensation of the hot flashes. We are in such a special time in medical history for individuals who experience hot flashes because now we understand the basic biology of hot flashes, and we can generate targeted therapy to manage hot flashes—that is for both individuals who identify as women and individuals who identify as men, because both experience hot flashes.
OBG Management: Is there a particular threshold of hot flash symptoms that is considered important to treat, or is treatment based on essentially the bother to patients?
Dr. Neal-Perry: Treatment is solely based on if it bothers the patient. But we do know that people who have lots of bothersome hot flashes have a higher risk for heart disease and may have sleep disruption, reduced cognitive function, and poorer quality of life. Sleep dysfunction can impact the ability to think and function and can put those affected at increased risk for accidents.
For people who are having these symptoms that are disruptive to their life, you do want to treat them. You might say, “Well, we’ve had estrogen, why not use estrogen,” right? Well estrogen works very well, but there are lots of people who can’t use estrogen—individuals who have breast cancer, blood clotting disorders, significant heart disease, or diabetes. Then there are just some people who don’t feel comfortable using estrogen.
We have had a huge gap in care for individuals who experience hot flashes and who are ineligible for menopausal HT. While there are other nonhormonal options, they often have side effects like sexual dysfunction, hypersomnolence, or insomnia. Some people choose not to use these nonhormonal treatments because the side effects are worse for them than to trying to manage the hot flashes. The introduction to a nonhormonal therapy that is effective and does not have lots of side effects is exciting and will be welcomed by many who have not found relief.
OBG Management: Is fezolinetant available now for patients?
Dr. Neal-Perry: It is not available yet. Hopefully, it will be approved within the next year. Astellas recently completed a double blind randomized cross over design phase 3 study that found fezolinetant is highly effective for the management of hot flashes and that it has a low side effect profile.10 Fezolinetant’s most common side effect was COVID-19, a reflection of the fact that the trial was done during the COVID pandemic. The other most common side effect was headache. Everything else was minimal.
Other drugs in the same class as fezolinetant have been under development for the management of hot flashes; however, they encountered liver function challenges, and studies were stopped. Fezolinetant did not cause liver dysfunction.
Hot flash modifiers
OBG Management: Referring to that neuropathway, are there physiologic differences among women who do and do not experience hot flashes, and are there particular mechanisms that may protect patients against being bothered by hot flashes?
Dr. Neal-Perry: Well, there are some things that we can control, and there are things that we cannot control (like our genetic background). Some of the processes that are important for estrogen receptor function and estrogen metabolism, as well as some other receptor systems, can work differently. When estrogen metabolism is slightly different, it could result in reduced estrogen receptor activity and more hot flashes. Then there are some receptor polymorphisms that can increase or reduce the risk for hot flashes—the genetic piece.11
There are things that can modify your risk for hot flashes and the duration of hot flashes. Individuals who are obese or smoke may experience more hot flashes. Women of color, especially African American women, tend to have hot flashes occur earlier in their reproductive life and last for a longer duration; hot flashes may occur up to 2 years before menopause, last for more than 10 years, and be more disruptive. By contrast, Asian women tend to report fewer and less disruptive hot flashes.8
OBG Management: If fezolinetant were to be FDA approved, will there be particular patients that it will most appropriate for, since it is an estrogen alternative?
Dr. Neal-Perry: Yes, there may be different patients who might benefit from fezolinetant. This will depend on what the situation is—patients who have breast cancer, poorly controlled diabetes, or heart disease, and those patients who prefer not to use estrogen will benefit from fezolinetant, as we are going to look for other treatment options for those individuals. It will be important for medical providers to listen to their patients and understand the medical background of that individual to really define what is the best next step for the management of their hot flashes.
This is an exciting time for individuals affected by menopausal hot flashes; to understand the biology of hot flashes gives us real opportunities to bridge gaps around how to manage them. Individuals who experience hot flashes will know that they don’t have to suffer, that there are other options that are safe, that can help meet their needs and put them in a better place. ●
Excerpted from the presentation, “Do you see me? Culturally responsive care in menopause,” by Makeba Williams, MD, NCMP, at The North American Menopause Society meeting in Atlanta, Georgia, October 12-15, 2022.
Dr. Williams is Vice Chair of Professional Development and Wellness, Associate Professor, Washington University School of Medicine
The Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation (SWAN) challenged the notion that there is a universal menopausal experience.1 Up until that time, we had been using this universal experience that is based largely on the experiences of White women and applying that data to the experiences of women of color. Other research has shown that African American women have poorer quality of life and health status, and that they receive less treatment for a number of conditions.2,3
In a recent review of more than 20 years of literature, we found only 17 articles that met the inclusion criteria, reflecting the invisibility of African American women and other ethnic and racial minorities in the menopause literature and research. Key findings included that African American women1,4:
- experience an earlier age of onset of menopause
- have higher rates of premature menopause and early menopause, which is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease
- experience a longer time of the menopausal transition, with variability in the average age of menopause onset
- overall report lower rates of vaginal symptoms
- are less likely to report sleep disturbances than White women or Hispanic women, but more likely to report these symptoms than Asian women
- experience a higher prevalence, frequency, and severity of vasomotor symptoms (VMS), and were more bothered by those symptoms
− 48.4 years in the Healthy Women’s Study
− 50.9 years in the Penn Ovarian Aging Study
− 51.4 years in SWAN
- reported lower educational attainment, experiencing more socioeconomic disadvantage and exposure to more adverse life effects
- receive less treatment for VMS, hypertension, and depression, and are less likely to be prescribed statin drugs
- experience more discrimination
- use cigarettes and tobacco more, but are less likely to use alcohol and less likely to have physical activity.
Cultural influences on menopause
Im and colleagues have published many studies looking at cultural influences on African American, Hispanic, and Asian American women, and comparing them to White women.5 Notable differences were found regarding education level, family income, employment, number of children, and greater perceived health (which is associated with fewer menopausal symptoms). They identified 5 qualitative ideas:
- Positive acceptance. Minority women, or racial and ethnic women, perceived the transition to menopause more positively, and generally took on a posture of acceptance, reporting feeling liberated from many of the challenges associated with the reproductive period. In addition, many associated a greater sense of maturity and respect within their communities with the natural aging process.
- Optimism. Ethnic women tended to embrace menopause, using humor and laughter to express emotions during stressful life changes. This runs counter to many of the perspectives reported by White women, who often viewed the menopausal transition and aging negatively, as we equate aging with the loss of youthfulness in the United States.
- Unique, not universal. Most of the ethnic minority women thought that there was something unique about their menopausal experiences, and that they were influenced by immigration transition, financial situations, etc. Many White woman perceived that the menopausal experience was shared among all women.
- Closed, not open. There were differences in how we talk about symptoms, or whether or not we talk about them at all. Ethnic women tended to be silent about their symptoms. By contrast, White women tended to be more open and talkative and communicative about their symptoms.
- Minimizing, not controlling. No symptom management was the strategy of choice for most women. Minority women tended to manage their symptoms by tolerating and normalizing them. Only those women with the most serious symptoms sought out medication for temporary relief. Some expressed a tendency to downplay their symptoms because many of them had more important things that they were dealing with in their lives.
What is an individual social identity?
An individual social identity reflects the many groups to which one belongs. It is how one shows up, and yet it is much more than how they physically show up. When you pass your eye on patients, you are only seeing the tip of the iceberg. The full social identity of a patient resides below the surface. Social identity is complex, on a continuum, and can change depending on time and place. How we prioritize our social identities may change, depending on the context and the situation.
Our intersecting social identities give rise to our cultural identity, and it is through the prism of intersectionality that we can understand the ways in which our social identities converge to give rise to disparities in health care in midlife and menopausal women. Holding space for cultural identity, we can impact how our patients are perceiving their menopause, how they are moving through decision making about taking care of themselves in menopause. And we can provide more responsive care to their cultural identities, and hopefully at the end of the day we reduce some of these disparities that we are seeing in our menopausal patients and also are reducing our unconscious bias in our patient interactions.
Culturally responsive care
There are several components to home in on when we are trying to provide culturally responsive care to patients.
- A commitment to being culturally curious. We have to accept what the literature is sharing with us, that there is not a universal menopausal experience. We have for far too long applied this universal experience of menopause that has largely been based on White women to different racial and ethnic populations.
- Recognizing. I appreciate that my identity as a Black woman may be very different from other Black women in the room, or whatever their social identity. I am not expected to understand all of the others’ experiences, and I don’t expect that for you either.
- Acknowledge unconscious implicit biases. Acknowledge the groups to which you have a strong implicit bias, and allow it to drive you to reduce barriers to engaging with patients.
- Connecting with the individual patient. It is through a process of individuating that we learn from our patients’ unique characteristics, rather than relying on assumptions and stereotypes. We have a window of opportunity to see our patient and move beyond thinking of them in terms of racial and ethnic stereotypes or particular social groups. It is through this process of individualizing that we can seek answers to key questions.
The ultimate goal is to understand our individual patients’ perceptions, outlook on menopause, and contextual factors in their lives that influence the menopause journey.
CASE ENCOUNTER
I quickly look at the patient-filled form before I knock on the exam door, and I see that the patient has checked off that she has hot flashes, night sweats, and I make a mental note, she’s menopausal. I already have a preliminary plan to give this patient hormone therapy. I open the door, and I see that she’s Black. I know, based upon the data from SWAN and others, that her menopause means longer duration, more severe vasomotor symptoms. I have already teed up a prescription to go to the pharmacy.
The problem is, I have not even talked to her. She may actually nod her head, saying that she is going to go to the pharmacy, but she may never pick up that prescription. She likely leaves my office feeling unheard; her needs are unmet. I move onto the next patient. I feel good, but in actuality, I didn’t hear her. I have provided her bias and stereotyped care. I missed an opportunity to truly engage this patient and her care, and my good intentions of following the literature about her experience in menopause have contributed quite likely to her increased morbidity and mortality, her increased cardiovascular disease risk, all because I have not held space for her cultural identity.
References
- Harlow SD, Burnett-Bowie SM, Greendale GA, et al. Disparities in reproductive aging and midlife health between Black and White women: the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation (SWAN). Women’s Midlife Health. 2022;8:3. doi: 10.1186/s40695-022-00073-y.
- Chlebowski RT, Aragaki AK, Anderson GL, et al. Forty-year trends in menopausal hormone therapy use and breast cancer incidence among postmenopausal black and white women. Cancer. 2020;126:2956-2964. doi: 10.1002/ cncr.32846.
- Weng HH, McBride CM, Bosworth HB, et al. Racial differences in physician recommendation of hormone replacement therapy. Prev Med. 2001;33:668673. doi: 10.1006/pmed.2001.0943.
- Williams M, Richard-Davis G, Williams PL, et al. A review of African American women’s experiences in menopause. Menopause. 2022;29:1331-1337. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000002060.
- Im EO. Ethnic differences in symptoms experienced during the menopausal transition. Health Care Women Int. 2009;30:339-355. doi: 10.1080/07399330802695002.
- Canonico M, Oger E, Plu-Bureau G, et al; Estrogen and Thromboembolism Risk (ESTHER) Study Group. Hormone therapy and venous thromboembolism among postmenopausal women: impact of the route of estrogen administration and progestogens: the ESTHER study. Circulation. 2007;115:840-845. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.642280.
- Liu B, Beral V, Balkwill A, et al; Million Women Study Collaborators. Gallbladder disease and use of transdermal versus oral hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2008;337:a386. doi: 10.1136/bmj.a386.
- Renoux C, Dell’aniello S, Garbe E, et al. Transdermal and oral hormone replacement therapy and the risk of stroke: a nested case-control study. BMJ. 2010;340:c2519. doi: 10.1136/bmj. c2519.
- Chlebowski RT, Anderson GL, Aragaki AK, et al. Association of menopausal hormone therapy with breast cancer incidence and mortality during long-term follow-up of the Women’s Health Initiative randomized clinical trials. JAMA. 2020;324:369-380. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9482.
- Rossouw JE, Prentice RL, Manson JE, et al. Postmenopausal hormone therapy and risk of cardiovascular disease by age and years since menopause. JAMA. 2007;297:1465-1477. doi: 10.1001/jama.297.13.1465.
- Woods NF, Mitchell ES. Symptoms during the perimenopause: prevlance, severity, trajectory, and significance in women’s lives. Am J Med. 2005;118 suppl 12B:14-24. doi: 10.1016/j. amjmed.2005.09.031.
- Gold EB, Block G, Crawford S, et al. Lifestyle and demographic factors in relation to vasomotor symptoms: baseline results from the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation. Am J Epidemiol. 2004;159:1189-1199. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwh168.
- Avis NE, Crawford SL, Greendale G, et al. Duration of menopausal vasomotor symptoms over the menopause transition. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175:531-539. doi: 10.1001/ jamainternmed.2014.8093.
- Abel TW, Rance NE. Stereologic study of the hypothalamic infundibular nucleus in young and older women. J Comp Neurol. 2000;424:679-688. doi: 10.1002/1096-9861 (20000904)424:4<679::aid-cne9>3.0.co;2-l.
- Neal-Perry G. A phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study to investigate the long-term safety and tolerability of fezolinetant in women seeking treatment for vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause (SKYLIGHT 4) – Abstract S-11. Paper presented at ENDO 2022. June 11, 2022.
- Crandall CJ, Diamant AL, Maglione M, et al. Genetic variation and hot flashes: a systematic review. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105:e4907-e4957. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa536.
OBG Management caught up with Drs. Jan Shifren and Genevieve Neal-Perry while they were attending the annual meeting of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS), held October 12-15, 2022, in Atlanta, Georgia. Dr. Shifren presented on the “Ins and Outs of Hormone Therapy,” while Dr. Neal-Perry focused on “Menopause Physiology.”
Evaluating symptomatic patients for appropriate hormone therapy
OBG Management: In your presentation to the group at the NAMS meeting, you described a 51-year-old patient with the principal symptoms of frequent hot flashes and night sweats, sleep disruption, fatigue, irritability, vaginal dryness, and dyspareunia. As she reported already trying several lifestyle modification approaches, what are your questions for her to determine whether hormone therapy (HT), systemic or low-dose vaginal, is advisable?
Jan Shifren, MD: As with every patient, you need to begin with a thorough history and confirm her physical exam is up to date. If there are concerns related to genitourinary symptoms of menopause (GSM), then a pelvic exam is indicated. This patient is a healthy menopausal woman with bothersome hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. Sleep disruption from night sweats is likely the cause of her fatigue and irritability, and her dyspareunia due to atrophic vulvovaginal changes. The principal indication for systemic HT is bothersome vasomotor symptoms (VMS), and a healthy woman who is under age 60 or within 10 years of the onset of menopause is generally a very good candidate for hormones. For this healthy 51-year-old with bothersome VMS unresponsive to lifestyle modification, the benefits of HT should outweigh potential risks. As low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy is minimally absorbed and very safe, this would be recommended instead of systemic HT if her only menopause symptoms were vaginal dryness and dyspareunia.
HT types and formulations
OBG Management: For this patient, low-dose vaginal estrogen is appropriate. In general, how do you decide on recommendations for combination therapy or estrogen only, and what formulations and dosages do you recommend?
Dr. Shifren: Any woman with a uterus needs to take a progestogen together with estrogen to protect her uterus from estrogen-induced endometrial overgrowth. With low dose vaginal estrogen therapy, however, concurrent progestogen is not needed.
Continue to: Estrogen options...
Estrogen options. I ask my patients about their preferences, but I typically recommend transdermal or non-oral estradiol formulations for my menopausal patients. The most commonly prescribed non-oral menopausal estrogen is the patch—as they are convenient, come in a wide range of doses, and are generic and generally affordable. There are also US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved transdermal gels and creams, and a vaginal ring that provides systemic estrogen, but these options are typically more expensive than the patch. All non-oral estrogen formulations are composed of estradiol, which is especially nice for a patient preferring “bioidentical HT.”
Many of our patients like the idea that they are using “natural” HT. I inform them that bioidentical is a marketing term rather than a medical term, but if their goal is to take the same hormones that their ovaries made when they were younger, they should use FDA-approved formulations of estradiol and progesterone for their menopausal HT symptoms. I do not recommend compounded bioidentical HT due to concerns regarding product quality and safety. The combination of FDA-approved estradiol patches and oral micronized progesterone provides a high quality, carefully regulated bioidentical HT regimen. For women greatly preferring an oral estrogen, oral estradiol with micronized progesterone is an option.
In addition to patient preference for natural HT, the reasons that I encourage women to consider the estradiol transdermal patch for their menopausal HT include:
- no increased risk of venous thromboembolic events when physiologically dosed menopausal estradiol therapy is provided by a skin patch (observational data).1 With oral estrogens, even when dosed for menopause, VTE risk increases, as coagulation factors increase due to the first-pass hepatic effect. This does not occur with non-oral menopausal estrogens.
- no increased risk of gallbladder disease, which occurs with oral estrogen therapy (observational data)2
- possibly lower risk of stroke when low-dose menopausal HT is provided via skin patch (observational data)3
- convenience—the patches are changed once or twice weekly
- wide range of doses available, which optimizes identifying the lowest effective dose and decreasing the dose over time.
Progestogen options. Progestogens may be given daily or cyclically. Use of daily progestogen typically results in amenorrhea, which is preferred by most women. Cyclic use of a progestogen for 12-14 days each month results in a monthly withdrawal bleed, which is a good option for a woman experiencing bothersome breakthrough bleeding with daily progestogen. Use of a progestogen-releasing IUD is an off-label alternative for endometrial protection with menopausal HT. As discussed earlier, as many women prefer bioidentical HT, one of our preferred regimens is to provide transdermal estradiol with FDA-approved oral micronized progesterone. There are several patches that combine estradiol with a progestogen, but there is not a lot of dosing flexibility and product choice. There also is an approved product available that combines oral estradiol and micronized progesterone in one tablet.
Scheduling follow-up
OBG Management: Now that you have started the opening case patient on HT, how often are you going to monitor her for treatment?
Dr. Shifren: Women will not experience maximum efficacy for hot flash relief from their estrogen therapy for 3 months, so I typically see a patient back at 3 to 4 months to assess side effects and symptom control. I encourage women to reach out sooner if they are having a bothersome side effect. Once she is doing well on an HT regimen, we assess risks and benefits of ongoing treatment annually. The goal is to be certain she is on the lowest dose of estrogen that treats her symptoms, and we slowly decrease the estrogen dose over time.
Breast cancer risk
OBG Management: In your presentation, you mentioned that the risk of breast cancer does not increase appreciably with short-term use of HT. Is it possible to define short term?
Dr. Shifren: In the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI), a large double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of menopausal HT, there was a slight increase in breast cancer risk after approximately 4 to 5 years of use in women using estrogen with progestogen.4 I share with patients that this increased risk is about the same as that of obesity or drinking more than 1 alcoholic beverage daily. As an increased risk of breast cancer does not occur for several years, a woman may be able to take hormones for bothersome symptoms, feel well, and slowly come off without incurring significant breast cancer risk. In the WHI, there was no increase in breast cancer risk in women without a uterus randomized to estrogen alone.
Regarding cardiovascular risk, in the WHI, an increased risk of cardiovascular events generally was not seen in healthy women younger than age 60 and within 10 years of the onset of menopause.5 Benefits of HT may not outweigh risks for women with significant underlying cardiovascular risk factors, even if they are younger and close to menopause onset.
Continue to: The importance of shared decision making...
The importance of shared decision making
Dr. Shifren: As with any important health care decision, women should be involved in an individualized discussion of risks and benefits, with shared decision making about whether HT is the right choice. Women also should be involved in ongoing decisions regarding HT formulation, dose, and duration of use.
A nonhormonal option for hot flashes
OBG Management: How many women experience VMS around the time of menopause?
Dr. Genevieve Neal-Perry, MD, PhD: About 60% to 70% of individuals will experience hot flashes around the time of the menopause.6 Of those, about 40% are what we would call moderate to severe hot flashes—which are typically the most disruptive in terms of quality of life.7 The window of time in which they are likely to have them, at typically their most intense timeframe, is 2 years before the final menstrual period and the year after.7 In terms of the average duration, however, it’s about 7 years, which is a lot longer than what we previously thought.8 Moreover, there are disparities in that women of color, particularly African American women, can have them as long as 10 years.8
OBG Management: Can you explain why the VMS occur, and specifically around the time of menopause?
Dr. Neal-Perry: For many years we did not understand the basic biology of hot flashes. When you think about it, it’s completely amazing—when half of our population experiences hot flashes, and we don’t understand why, and we don’t have therapy that specifically targets hot flashes.
What we now know from work completed by Naomi Rance, in particular, is that a specific region of the brain, the hypothalamus, exhibited changes in number of neurons that seemed to be increased in size in menopausal people and smaller in size in people who were not menopausal.9 That started the journey to understanding the biology, and eventual mechanism, of hot flashes. It took about 10-15 years before we really began to understand why.
What we know now is that estrogen, a hormone that is made by the ovaries, activates and inactivates neurons located in the hypothalamus, a brain region that controls our thermoregulation—the way your body perceives temperature. The hypothalamus controls your response to temperature, either you experience chills or you dissipate heat by vasodilating (hot flush) and sweating.
The thermoregulatory region of the hypothalamus houses cells that receive messages from KNDy neurons, neurons also located in the hypothalamus that express kisspeptin, neurokinin, and dynorphin. Importantly, KNDy neurons express estrogen receptors. (The way that I like to think about estrogen and estrogen receptors is that estrogen is like the ball and the receptor is like the catcher’s mitt.) When estrogen interacts with this receptor, it keeps KNDy neurons quiet. But the increased variability and loss of estrogen that occurs around the time of menopause “disinhibits” KNDy neurons—meaning that they are no longer being reined in by estrogen. In response to decreased estrogen regulation, KNDy neurons become hypertrophied with neurotransmitters and more active. Specifically, KNDy neurons release neurokinin, a neuropeptide that self-stimulates KNDy neurons and activates neurons in the thermoregulatory zone of the brain—it’s a speed-forward feed-backward mechanism. The thermoregulatory neurons interpret this signal as “I feel hot,” and the body begins a series of functions to cool things down.
Continue to: Treatments that act on the thermoregulatory region
Treatments that act on the thermoregulatory region
Dr. Neal-Perry: I have described what happens in the brain around the time of menopause, and what triggers those hot flashes.
Estrogen. The reason that estrogen worked to treat the hot flashes is because estrogen inhibits and calms the neurons that become hyperactive during the menopause.
Fezolinetant. Fezolinetant is unique because it specifically targets the hormone receptor that triggers hot flashes, the neurokinin receptor. Fezolinetant is a nonhormone therapy that not only reduces the activity of KNDy neurons but also blocks the effects of neurons in the thermoregulatory zone, thereby reducing the sensation of the hot flashes. We are in such a special time in medical history for individuals who experience hot flashes because now we understand the basic biology of hot flashes, and we can generate targeted therapy to manage hot flashes—that is for both individuals who identify as women and individuals who identify as men, because both experience hot flashes.
OBG Management: Is there a particular threshold of hot flash symptoms that is considered important to treat, or is treatment based on essentially the bother to patients?
Dr. Neal-Perry: Treatment is solely based on if it bothers the patient. But we do know that people who have lots of bothersome hot flashes have a higher risk for heart disease and may have sleep disruption, reduced cognitive function, and poorer quality of life. Sleep dysfunction can impact the ability to think and function and can put those affected at increased risk for accidents.
For people who are having these symptoms that are disruptive to their life, you do want to treat them. You might say, “Well, we’ve had estrogen, why not use estrogen,” right? Well estrogen works very well, but there are lots of people who can’t use estrogen—individuals who have breast cancer, blood clotting disorders, significant heart disease, or diabetes. Then there are just some people who don’t feel comfortable using estrogen.
We have had a huge gap in care for individuals who experience hot flashes and who are ineligible for menopausal HT. While there are other nonhormonal options, they often have side effects like sexual dysfunction, hypersomnolence, or insomnia. Some people choose not to use these nonhormonal treatments because the side effects are worse for them than to trying to manage the hot flashes. The introduction to a nonhormonal therapy that is effective and does not have lots of side effects is exciting and will be welcomed by many who have not found relief.
OBG Management: Is fezolinetant available now for patients?
Dr. Neal-Perry: It is not available yet. Hopefully, it will be approved within the next year. Astellas recently completed a double blind randomized cross over design phase 3 study that found fezolinetant is highly effective for the management of hot flashes and that it has a low side effect profile.10 Fezolinetant’s most common side effect was COVID-19, a reflection of the fact that the trial was done during the COVID pandemic. The other most common side effect was headache. Everything else was minimal.
Other drugs in the same class as fezolinetant have been under development for the management of hot flashes; however, they encountered liver function challenges, and studies were stopped. Fezolinetant did not cause liver dysfunction.
Hot flash modifiers
OBG Management: Referring to that neuropathway, are there physiologic differences among women who do and do not experience hot flashes, and are there particular mechanisms that may protect patients against being bothered by hot flashes?
Dr. Neal-Perry: Well, there are some things that we can control, and there are things that we cannot control (like our genetic background). Some of the processes that are important for estrogen receptor function and estrogen metabolism, as well as some other receptor systems, can work differently. When estrogen metabolism is slightly different, it could result in reduced estrogen receptor activity and more hot flashes. Then there are some receptor polymorphisms that can increase or reduce the risk for hot flashes—the genetic piece.11
There are things that can modify your risk for hot flashes and the duration of hot flashes. Individuals who are obese or smoke may experience more hot flashes. Women of color, especially African American women, tend to have hot flashes occur earlier in their reproductive life and last for a longer duration; hot flashes may occur up to 2 years before menopause, last for more than 10 years, and be more disruptive. By contrast, Asian women tend to report fewer and less disruptive hot flashes.8
OBG Management: If fezolinetant were to be FDA approved, will there be particular patients that it will most appropriate for, since it is an estrogen alternative?
Dr. Neal-Perry: Yes, there may be different patients who might benefit from fezolinetant. This will depend on what the situation is—patients who have breast cancer, poorly controlled diabetes, or heart disease, and those patients who prefer not to use estrogen will benefit from fezolinetant, as we are going to look for other treatment options for those individuals. It will be important for medical providers to listen to their patients and understand the medical background of that individual to really define what is the best next step for the management of their hot flashes.
This is an exciting time for individuals affected by menopausal hot flashes; to understand the biology of hot flashes gives us real opportunities to bridge gaps around how to manage them. Individuals who experience hot flashes will know that they don’t have to suffer, that there are other options that are safe, that can help meet their needs and put them in a better place. ●
Excerpted from the presentation, “Do you see me? Culturally responsive care in menopause,” by Makeba Williams, MD, NCMP, at The North American Menopause Society meeting in Atlanta, Georgia, October 12-15, 2022.
Dr. Williams is Vice Chair of Professional Development and Wellness, Associate Professor, Washington University School of Medicine
The Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation (SWAN) challenged the notion that there is a universal menopausal experience.1 Up until that time, we had been using this universal experience that is based largely on the experiences of White women and applying that data to the experiences of women of color. Other research has shown that African American women have poorer quality of life and health status, and that they receive less treatment for a number of conditions.2,3
In a recent review of more than 20 years of literature, we found only 17 articles that met the inclusion criteria, reflecting the invisibility of African American women and other ethnic and racial minorities in the menopause literature and research. Key findings included that African American women1,4:
- experience an earlier age of onset of menopause
- have higher rates of premature menopause and early menopause, which is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease
- experience a longer time of the menopausal transition, with variability in the average age of menopause onset
- overall report lower rates of vaginal symptoms
- are less likely to report sleep disturbances than White women or Hispanic women, but more likely to report these symptoms than Asian women
- experience a higher prevalence, frequency, and severity of vasomotor symptoms (VMS), and were more bothered by those symptoms
− 48.4 years in the Healthy Women’s Study
− 50.9 years in the Penn Ovarian Aging Study
− 51.4 years in SWAN
- reported lower educational attainment, experiencing more socioeconomic disadvantage and exposure to more adverse life effects
- receive less treatment for VMS, hypertension, and depression, and are less likely to be prescribed statin drugs
- experience more discrimination
- use cigarettes and tobacco more, but are less likely to use alcohol and less likely to have physical activity.
Cultural influences on menopause
Im and colleagues have published many studies looking at cultural influences on African American, Hispanic, and Asian American women, and comparing them to White women.5 Notable differences were found regarding education level, family income, employment, number of children, and greater perceived health (which is associated with fewer menopausal symptoms). They identified 5 qualitative ideas:
- Positive acceptance. Minority women, or racial and ethnic women, perceived the transition to menopause more positively, and generally took on a posture of acceptance, reporting feeling liberated from many of the challenges associated with the reproductive period. In addition, many associated a greater sense of maturity and respect within their communities with the natural aging process.
- Optimism. Ethnic women tended to embrace menopause, using humor and laughter to express emotions during stressful life changes. This runs counter to many of the perspectives reported by White women, who often viewed the menopausal transition and aging negatively, as we equate aging with the loss of youthfulness in the United States.
- Unique, not universal. Most of the ethnic minority women thought that there was something unique about their menopausal experiences, and that they were influenced by immigration transition, financial situations, etc. Many White woman perceived that the menopausal experience was shared among all women.
- Closed, not open. There were differences in how we talk about symptoms, or whether or not we talk about them at all. Ethnic women tended to be silent about their symptoms. By contrast, White women tended to be more open and talkative and communicative about their symptoms.
- Minimizing, not controlling. No symptom management was the strategy of choice for most women. Minority women tended to manage their symptoms by tolerating and normalizing them. Only those women with the most serious symptoms sought out medication for temporary relief. Some expressed a tendency to downplay their symptoms because many of them had more important things that they were dealing with in their lives.
What is an individual social identity?
An individual social identity reflects the many groups to which one belongs. It is how one shows up, and yet it is much more than how they physically show up. When you pass your eye on patients, you are only seeing the tip of the iceberg. The full social identity of a patient resides below the surface. Social identity is complex, on a continuum, and can change depending on time and place. How we prioritize our social identities may change, depending on the context and the situation.
Our intersecting social identities give rise to our cultural identity, and it is through the prism of intersectionality that we can understand the ways in which our social identities converge to give rise to disparities in health care in midlife and menopausal women. Holding space for cultural identity, we can impact how our patients are perceiving their menopause, how they are moving through decision making about taking care of themselves in menopause. And we can provide more responsive care to their cultural identities, and hopefully at the end of the day we reduce some of these disparities that we are seeing in our menopausal patients and also are reducing our unconscious bias in our patient interactions.
Culturally responsive care
There are several components to home in on when we are trying to provide culturally responsive care to patients.
- A commitment to being culturally curious. We have to accept what the literature is sharing with us, that there is not a universal menopausal experience. We have for far too long applied this universal experience of menopause that has largely been based on White women to different racial and ethnic populations.
- Recognizing. I appreciate that my identity as a Black woman may be very different from other Black women in the room, or whatever their social identity. I am not expected to understand all of the others’ experiences, and I don’t expect that for you either.
- Acknowledge unconscious implicit biases. Acknowledge the groups to which you have a strong implicit bias, and allow it to drive you to reduce barriers to engaging with patients.
- Connecting with the individual patient. It is through a process of individuating that we learn from our patients’ unique characteristics, rather than relying on assumptions and stereotypes. We have a window of opportunity to see our patient and move beyond thinking of them in terms of racial and ethnic stereotypes or particular social groups. It is through this process of individualizing that we can seek answers to key questions.
The ultimate goal is to understand our individual patients’ perceptions, outlook on menopause, and contextual factors in their lives that influence the menopause journey.
CASE ENCOUNTER
I quickly look at the patient-filled form before I knock on the exam door, and I see that the patient has checked off that she has hot flashes, night sweats, and I make a mental note, she’s menopausal. I already have a preliminary plan to give this patient hormone therapy. I open the door, and I see that she’s Black. I know, based upon the data from SWAN and others, that her menopause means longer duration, more severe vasomotor symptoms. I have already teed up a prescription to go to the pharmacy.
The problem is, I have not even talked to her. She may actually nod her head, saying that she is going to go to the pharmacy, but she may never pick up that prescription. She likely leaves my office feeling unheard; her needs are unmet. I move onto the next patient. I feel good, but in actuality, I didn’t hear her. I have provided her bias and stereotyped care. I missed an opportunity to truly engage this patient and her care, and my good intentions of following the literature about her experience in menopause have contributed quite likely to her increased morbidity and mortality, her increased cardiovascular disease risk, all because I have not held space for her cultural identity.
References
- Harlow SD, Burnett-Bowie SM, Greendale GA, et al. Disparities in reproductive aging and midlife health between Black and White women: the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation (SWAN). Women’s Midlife Health. 2022;8:3. doi: 10.1186/s40695-022-00073-y.
- Chlebowski RT, Aragaki AK, Anderson GL, et al. Forty-year trends in menopausal hormone therapy use and breast cancer incidence among postmenopausal black and white women. Cancer. 2020;126:2956-2964. doi: 10.1002/ cncr.32846.
- Weng HH, McBride CM, Bosworth HB, et al. Racial differences in physician recommendation of hormone replacement therapy. Prev Med. 2001;33:668673. doi: 10.1006/pmed.2001.0943.
- Williams M, Richard-Davis G, Williams PL, et al. A review of African American women’s experiences in menopause. Menopause. 2022;29:1331-1337. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000002060.
- Im EO. Ethnic differences in symptoms experienced during the menopausal transition. Health Care Women Int. 2009;30:339-355. doi: 10.1080/07399330802695002.
OBG Management caught up with Drs. Jan Shifren and Genevieve Neal-Perry while they were attending the annual meeting of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS), held October 12-15, 2022, in Atlanta, Georgia. Dr. Shifren presented on the “Ins and Outs of Hormone Therapy,” while Dr. Neal-Perry focused on “Menopause Physiology.”
Evaluating symptomatic patients for appropriate hormone therapy
OBG Management: In your presentation to the group at the NAMS meeting, you described a 51-year-old patient with the principal symptoms of frequent hot flashes and night sweats, sleep disruption, fatigue, irritability, vaginal dryness, and dyspareunia. As she reported already trying several lifestyle modification approaches, what are your questions for her to determine whether hormone therapy (HT), systemic or low-dose vaginal, is advisable?
Jan Shifren, MD: As with every patient, you need to begin with a thorough history and confirm her physical exam is up to date. If there are concerns related to genitourinary symptoms of menopause (GSM), then a pelvic exam is indicated. This patient is a healthy menopausal woman with bothersome hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. Sleep disruption from night sweats is likely the cause of her fatigue and irritability, and her dyspareunia due to atrophic vulvovaginal changes. The principal indication for systemic HT is bothersome vasomotor symptoms (VMS), and a healthy woman who is under age 60 or within 10 years of the onset of menopause is generally a very good candidate for hormones. For this healthy 51-year-old with bothersome VMS unresponsive to lifestyle modification, the benefits of HT should outweigh potential risks. As low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy is minimally absorbed and very safe, this would be recommended instead of systemic HT if her only menopause symptoms were vaginal dryness and dyspareunia.
HT types and formulations
OBG Management: For this patient, low-dose vaginal estrogen is appropriate. In general, how do you decide on recommendations for combination therapy or estrogen only, and what formulations and dosages do you recommend?
Dr. Shifren: Any woman with a uterus needs to take a progestogen together with estrogen to protect her uterus from estrogen-induced endometrial overgrowth. With low dose vaginal estrogen therapy, however, concurrent progestogen is not needed.
Continue to: Estrogen options...
Estrogen options. I ask my patients about their preferences, but I typically recommend transdermal or non-oral estradiol formulations for my menopausal patients. The most commonly prescribed non-oral menopausal estrogen is the patch—as they are convenient, come in a wide range of doses, and are generic and generally affordable. There are also US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved transdermal gels and creams, and a vaginal ring that provides systemic estrogen, but these options are typically more expensive than the patch. All non-oral estrogen formulations are composed of estradiol, which is especially nice for a patient preferring “bioidentical HT.”
Many of our patients like the idea that they are using “natural” HT. I inform them that bioidentical is a marketing term rather than a medical term, but if their goal is to take the same hormones that their ovaries made when they were younger, they should use FDA-approved formulations of estradiol and progesterone for their menopausal HT symptoms. I do not recommend compounded bioidentical HT due to concerns regarding product quality and safety. The combination of FDA-approved estradiol patches and oral micronized progesterone provides a high quality, carefully regulated bioidentical HT regimen. For women greatly preferring an oral estrogen, oral estradiol with micronized progesterone is an option.
In addition to patient preference for natural HT, the reasons that I encourage women to consider the estradiol transdermal patch for their menopausal HT include:
- no increased risk of venous thromboembolic events when physiologically dosed menopausal estradiol therapy is provided by a skin patch (observational data).1 With oral estrogens, even when dosed for menopause, VTE risk increases, as coagulation factors increase due to the first-pass hepatic effect. This does not occur with non-oral menopausal estrogens.
- no increased risk of gallbladder disease, which occurs with oral estrogen therapy (observational data)2
- possibly lower risk of stroke when low-dose menopausal HT is provided via skin patch (observational data)3
- convenience—the patches are changed once or twice weekly
- wide range of doses available, which optimizes identifying the lowest effective dose and decreasing the dose over time.
Progestogen options. Progestogens may be given daily or cyclically. Use of daily progestogen typically results in amenorrhea, which is preferred by most women. Cyclic use of a progestogen for 12-14 days each month results in a monthly withdrawal bleed, which is a good option for a woman experiencing bothersome breakthrough bleeding with daily progestogen. Use of a progestogen-releasing IUD is an off-label alternative for endometrial protection with menopausal HT. As discussed earlier, as many women prefer bioidentical HT, one of our preferred regimens is to provide transdermal estradiol with FDA-approved oral micronized progesterone. There are several patches that combine estradiol with a progestogen, but there is not a lot of dosing flexibility and product choice. There also is an approved product available that combines oral estradiol and micronized progesterone in one tablet.
Scheduling follow-up
OBG Management: Now that you have started the opening case patient on HT, how often are you going to monitor her for treatment?
Dr. Shifren: Women will not experience maximum efficacy for hot flash relief from their estrogen therapy for 3 months, so I typically see a patient back at 3 to 4 months to assess side effects and symptom control. I encourage women to reach out sooner if they are having a bothersome side effect. Once she is doing well on an HT regimen, we assess risks and benefits of ongoing treatment annually. The goal is to be certain she is on the lowest dose of estrogen that treats her symptoms, and we slowly decrease the estrogen dose over time.
Breast cancer risk
OBG Management: In your presentation, you mentioned that the risk of breast cancer does not increase appreciably with short-term use of HT. Is it possible to define short term?
Dr. Shifren: In the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI), a large double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of menopausal HT, there was a slight increase in breast cancer risk after approximately 4 to 5 years of use in women using estrogen with progestogen.4 I share with patients that this increased risk is about the same as that of obesity or drinking more than 1 alcoholic beverage daily. As an increased risk of breast cancer does not occur for several years, a woman may be able to take hormones for bothersome symptoms, feel well, and slowly come off without incurring significant breast cancer risk. In the WHI, there was no increase in breast cancer risk in women without a uterus randomized to estrogen alone.
Regarding cardiovascular risk, in the WHI, an increased risk of cardiovascular events generally was not seen in healthy women younger than age 60 and within 10 years of the onset of menopause.5 Benefits of HT may not outweigh risks for women with significant underlying cardiovascular risk factors, even if they are younger and close to menopause onset.
Continue to: The importance of shared decision making...
The importance of shared decision making
Dr. Shifren: As with any important health care decision, women should be involved in an individualized discussion of risks and benefits, with shared decision making about whether HT is the right choice. Women also should be involved in ongoing decisions regarding HT formulation, dose, and duration of use.
A nonhormonal option for hot flashes
OBG Management: How many women experience VMS around the time of menopause?
Dr. Genevieve Neal-Perry, MD, PhD: About 60% to 70% of individuals will experience hot flashes around the time of the menopause.6 Of those, about 40% are what we would call moderate to severe hot flashes—which are typically the most disruptive in terms of quality of life.7 The window of time in which they are likely to have them, at typically their most intense timeframe, is 2 years before the final menstrual period and the year after.7 In terms of the average duration, however, it’s about 7 years, which is a lot longer than what we previously thought.8 Moreover, there are disparities in that women of color, particularly African American women, can have them as long as 10 years.8
OBG Management: Can you explain why the VMS occur, and specifically around the time of menopause?
Dr. Neal-Perry: For many years we did not understand the basic biology of hot flashes. When you think about it, it’s completely amazing—when half of our population experiences hot flashes, and we don’t understand why, and we don’t have therapy that specifically targets hot flashes.
What we now know from work completed by Naomi Rance, in particular, is that a specific region of the brain, the hypothalamus, exhibited changes in number of neurons that seemed to be increased in size in menopausal people and smaller in size in people who were not menopausal.9 That started the journey to understanding the biology, and eventual mechanism, of hot flashes. It took about 10-15 years before we really began to understand why.
What we know now is that estrogen, a hormone that is made by the ovaries, activates and inactivates neurons located in the hypothalamus, a brain region that controls our thermoregulation—the way your body perceives temperature. The hypothalamus controls your response to temperature, either you experience chills or you dissipate heat by vasodilating (hot flush) and sweating.
The thermoregulatory region of the hypothalamus houses cells that receive messages from KNDy neurons, neurons also located in the hypothalamus that express kisspeptin, neurokinin, and dynorphin. Importantly, KNDy neurons express estrogen receptors. (The way that I like to think about estrogen and estrogen receptors is that estrogen is like the ball and the receptor is like the catcher’s mitt.) When estrogen interacts with this receptor, it keeps KNDy neurons quiet. But the increased variability and loss of estrogen that occurs around the time of menopause “disinhibits” KNDy neurons—meaning that they are no longer being reined in by estrogen. In response to decreased estrogen regulation, KNDy neurons become hypertrophied with neurotransmitters and more active. Specifically, KNDy neurons release neurokinin, a neuropeptide that self-stimulates KNDy neurons and activates neurons in the thermoregulatory zone of the brain—it’s a speed-forward feed-backward mechanism. The thermoregulatory neurons interpret this signal as “I feel hot,” and the body begins a series of functions to cool things down.
Continue to: Treatments that act on the thermoregulatory region
Treatments that act on the thermoregulatory region
Dr. Neal-Perry: I have described what happens in the brain around the time of menopause, and what triggers those hot flashes.
Estrogen. The reason that estrogen worked to treat the hot flashes is because estrogen inhibits and calms the neurons that become hyperactive during the menopause.
Fezolinetant. Fezolinetant is unique because it specifically targets the hormone receptor that triggers hot flashes, the neurokinin receptor. Fezolinetant is a nonhormone therapy that not only reduces the activity of KNDy neurons but also blocks the effects of neurons in the thermoregulatory zone, thereby reducing the sensation of the hot flashes. We are in such a special time in medical history for individuals who experience hot flashes because now we understand the basic biology of hot flashes, and we can generate targeted therapy to manage hot flashes—that is for both individuals who identify as women and individuals who identify as men, because both experience hot flashes.
OBG Management: Is there a particular threshold of hot flash symptoms that is considered important to treat, or is treatment based on essentially the bother to patients?
Dr. Neal-Perry: Treatment is solely based on if it bothers the patient. But we do know that people who have lots of bothersome hot flashes have a higher risk for heart disease and may have sleep disruption, reduced cognitive function, and poorer quality of life. Sleep dysfunction can impact the ability to think and function and can put those affected at increased risk for accidents.
For people who are having these symptoms that are disruptive to their life, you do want to treat them. You might say, “Well, we’ve had estrogen, why not use estrogen,” right? Well estrogen works very well, but there are lots of people who can’t use estrogen—individuals who have breast cancer, blood clotting disorders, significant heart disease, or diabetes. Then there are just some people who don’t feel comfortable using estrogen.
We have had a huge gap in care for individuals who experience hot flashes and who are ineligible for menopausal HT. While there are other nonhormonal options, they often have side effects like sexual dysfunction, hypersomnolence, or insomnia. Some people choose not to use these nonhormonal treatments because the side effects are worse for them than to trying to manage the hot flashes. The introduction to a nonhormonal therapy that is effective and does not have lots of side effects is exciting and will be welcomed by many who have not found relief.
OBG Management: Is fezolinetant available now for patients?
Dr. Neal-Perry: It is not available yet. Hopefully, it will be approved within the next year. Astellas recently completed a double blind randomized cross over design phase 3 study that found fezolinetant is highly effective for the management of hot flashes and that it has a low side effect profile.10 Fezolinetant’s most common side effect was COVID-19, a reflection of the fact that the trial was done during the COVID pandemic. The other most common side effect was headache. Everything else was minimal.
Other drugs in the same class as fezolinetant have been under development for the management of hot flashes; however, they encountered liver function challenges, and studies were stopped. Fezolinetant did not cause liver dysfunction.
Hot flash modifiers
OBG Management: Referring to that neuropathway, are there physiologic differences among women who do and do not experience hot flashes, and are there particular mechanisms that may protect patients against being bothered by hot flashes?
Dr. Neal-Perry: Well, there are some things that we can control, and there are things that we cannot control (like our genetic background). Some of the processes that are important for estrogen receptor function and estrogen metabolism, as well as some other receptor systems, can work differently. When estrogen metabolism is slightly different, it could result in reduced estrogen receptor activity and more hot flashes. Then there are some receptor polymorphisms that can increase or reduce the risk for hot flashes—the genetic piece.11
There are things that can modify your risk for hot flashes and the duration of hot flashes. Individuals who are obese or smoke may experience more hot flashes. Women of color, especially African American women, tend to have hot flashes occur earlier in their reproductive life and last for a longer duration; hot flashes may occur up to 2 years before menopause, last for more than 10 years, and be more disruptive. By contrast, Asian women tend to report fewer and less disruptive hot flashes.8
OBG Management: If fezolinetant were to be FDA approved, will there be particular patients that it will most appropriate for, since it is an estrogen alternative?
Dr. Neal-Perry: Yes, there may be different patients who might benefit from fezolinetant. This will depend on what the situation is—patients who have breast cancer, poorly controlled diabetes, or heart disease, and those patients who prefer not to use estrogen will benefit from fezolinetant, as we are going to look for other treatment options for those individuals. It will be important for medical providers to listen to their patients and understand the medical background of that individual to really define what is the best next step for the management of their hot flashes.
This is an exciting time for individuals affected by menopausal hot flashes; to understand the biology of hot flashes gives us real opportunities to bridge gaps around how to manage them. Individuals who experience hot flashes will know that they don’t have to suffer, that there are other options that are safe, that can help meet their needs and put them in a better place. ●
Excerpted from the presentation, “Do you see me? Culturally responsive care in menopause,” by Makeba Williams, MD, NCMP, at The North American Menopause Society meeting in Atlanta, Georgia, October 12-15, 2022.
Dr. Williams is Vice Chair of Professional Development and Wellness, Associate Professor, Washington University School of Medicine
The Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation (SWAN) challenged the notion that there is a universal menopausal experience.1 Up until that time, we had been using this universal experience that is based largely on the experiences of White women and applying that data to the experiences of women of color. Other research has shown that African American women have poorer quality of life and health status, and that they receive less treatment for a number of conditions.2,3
In a recent review of more than 20 years of literature, we found only 17 articles that met the inclusion criteria, reflecting the invisibility of African American women and other ethnic and racial minorities in the menopause literature and research. Key findings included that African American women1,4:
- experience an earlier age of onset of menopause
- have higher rates of premature menopause and early menopause, which is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease
- experience a longer time of the menopausal transition, with variability in the average age of menopause onset
- overall report lower rates of vaginal symptoms
- are less likely to report sleep disturbances than White women or Hispanic women, but more likely to report these symptoms than Asian women
- experience a higher prevalence, frequency, and severity of vasomotor symptoms (VMS), and were more bothered by those symptoms
− 48.4 years in the Healthy Women’s Study
− 50.9 years in the Penn Ovarian Aging Study
− 51.4 years in SWAN
- reported lower educational attainment, experiencing more socioeconomic disadvantage and exposure to more adverse life effects
- receive less treatment for VMS, hypertension, and depression, and are less likely to be prescribed statin drugs
- experience more discrimination
- use cigarettes and tobacco more, but are less likely to use alcohol and less likely to have physical activity.
Cultural influences on menopause
Im and colleagues have published many studies looking at cultural influences on African American, Hispanic, and Asian American women, and comparing them to White women.5 Notable differences were found regarding education level, family income, employment, number of children, and greater perceived health (which is associated with fewer menopausal symptoms). They identified 5 qualitative ideas:
- Positive acceptance. Minority women, or racial and ethnic women, perceived the transition to menopause more positively, and generally took on a posture of acceptance, reporting feeling liberated from many of the challenges associated with the reproductive period. In addition, many associated a greater sense of maturity and respect within their communities with the natural aging process.
- Optimism. Ethnic women tended to embrace menopause, using humor and laughter to express emotions during stressful life changes. This runs counter to many of the perspectives reported by White women, who often viewed the menopausal transition and aging negatively, as we equate aging with the loss of youthfulness in the United States.
- Unique, not universal. Most of the ethnic minority women thought that there was something unique about their menopausal experiences, and that they were influenced by immigration transition, financial situations, etc. Many White woman perceived that the menopausal experience was shared among all women.
- Closed, not open. There were differences in how we talk about symptoms, or whether or not we talk about them at all. Ethnic women tended to be silent about their symptoms. By contrast, White women tended to be more open and talkative and communicative about their symptoms.
- Minimizing, not controlling. No symptom management was the strategy of choice for most women. Minority women tended to manage their symptoms by tolerating and normalizing them. Only those women with the most serious symptoms sought out medication for temporary relief. Some expressed a tendency to downplay their symptoms because many of them had more important things that they were dealing with in their lives.
What is an individual social identity?
An individual social identity reflects the many groups to which one belongs. It is how one shows up, and yet it is much more than how they physically show up. When you pass your eye on patients, you are only seeing the tip of the iceberg. The full social identity of a patient resides below the surface. Social identity is complex, on a continuum, and can change depending on time and place. How we prioritize our social identities may change, depending on the context and the situation.
Our intersecting social identities give rise to our cultural identity, and it is through the prism of intersectionality that we can understand the ways in which our social identities converge to give rise to disparities in health care in midlife and menopausal women. Holding space for cultural identity, we can impact how our patients are perceiving their menopause, how they are moving through decision making about taking care of themselves in menopause. And we can provide more responsive care to their cultural identities, and hopefully at the end of the day we reduce some of these disparities that we are seeing in our menopausal patients and also are reducing our unconscious bias in our patient interactions.
Culturally responsive care
There are several components to home in on when we are trying to provide culturally responsive care to patients.
- A commitment to being culturally curious. We have to accept what the literature is sharing with us, that there is not a universal menopausal experience. We have for far too long applied this universal experience of menopause that has largely been based on White women to different racial and ethnic populations.
- Recognizing. I appreciate that my identity as a Black woman may be very different from other Black women in the room, or whatever their social identity. I am not expected to understand all of the others’ experiences, and I don’t expect that for you either.
- Acknowledge unconscious implicit biases. Acknowledge the groups to which you have a strong implicit bias, and allow it to drive you to reduce barriers to engaging with patients.
- Connecting with the individual patient. It is through a process of individuating that we learn from our patients’ unique characteristics, rather than relying on assumptions and stereotypes. We have a window of opportunity to see our patient and move beyond thinking of them in terms of racial and ethnic stereotypes or particular social groups. It is through this process of individualizing that we can seek answers to key questions.
The ultimate goal is to understand our individual patients’ perceptions, outlook on menopause, and contextual factors in their lives that influence the menopause journey.
CASE ENCOUNTER
I quickly look at the patient-filled form before I knock on the exam door, and I see that the patient has checked off that she has hot flashes, night sweats, and I make a mental note, she’s menopausal. I already have a preliminary plan to give this patient hormone therapy. I open the door, and I see that she’s Black. I know, based upon the data from SWAN and others, that her menopause means longer duration, more severe vasomotor symptoms. I have already teed up a prescription to go to the pharmacy.
The problem is, I have not even talked to her. She may actually nod her head, saying that she is going to go to the pharmacy, but she may never pick up that prescription. She likely leaves my office feeling unheard; her needs are unmet. I move onto the next patient. I feel good, but in actuality, I didn’t hear her. I have provided her bias and stereotyped care. I missed an opportunity to truly engage this patient and her care, and my good intentions of following the literature about her experience in menopause have contributed quite likely to her increased morbidity and mortality, her increased cardiovascular disease risk, all because I have not held space for her cultural identity.
References
- Harlow SD, Burnett-Bowie SM, Greendale GA, et al. Disparities in reproductive aging and midlife health between Black and White women: the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation (SWAN). Women’s Midlife Health. 2022;8:3. doi: 10.1186/s40695-022-00073-y.
- Chlebowski RT, Aragaki AK, Anderson GL, et al. Forty-year trends in menopausal hormone therapy use and breast cancer incidence among postmenopausal black and white women. Cancer. 2020;126:2956-2964. doi: 10.1002/ cncr.32846.
- Weng HH, McBride CM, Bosworth HB, et al. Racial differences in physician recommendation of hormone replacement therapy. Prev Med. 2001;33:668673. doi: 10.1006/pmed.2001.0943.
- Williams M, Richard-Davis G, Williams PL, et al. A review of African American women’s experiences in menopause. Menopause. 2022;29:1331-1337. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000002060.
- Im EO. Ethnic differences in symptoms experienced during the menopausal transition. Health Care Women Int. 2009;30:339-355. doi: 10.1080/07399330802695002.
- Canonico M, Oger E, Plu-Bureau G, et al; Estrogen and Thromboembolism Risk (ESTHER) Study Group. Hormone therapy and venous thromboembolism among postmenopausal women: impact of the route of estrogen administration and progestogens: the ESTHER study. Circulation. 2007;115:840-845. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.642280.
- Liu B, Beral V, Balkwill A, et al; Million Women Study Collaborators. Gallbladder disease and use of transdermal versus oral hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2008;337:a386. doi: 10.1136/bmj.a386.
- Renoux C, Dell’aniello S, Garbe E, et al. Transdermal and oral hormone replacement therapy and the risk of stroke: a nested case-control study. BMJ. 2010;340:c2519. doi: 10.1136/bmj. c2519.
- Chlebowski RT, Anderson GL, Aragaki AK, et al. Association of menopausal hormone therapy with breast cancer incidence and mortality during long-term follow-up of the Women’s Health Initiative randomized clinical trials. JAMA. 2020;324:369-380. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9482.
- Rossouw JE, Prentice RL, Manson JE, et al. Postmenopausal hormone therapy and risk of cardiovascular disease by age and years since menopause. JAMA. 2007;297:1465-1477. doi: 10.1001/jama.297.13.1465.
- Woods NF, Mitchell ES. Symptoms during the perimenopause: prevlance, severity, trajectory, and significance in women’s lives. Am J Med. 2005;118 suppl 12B:14-24. doi: 10.1016/j. amjmed.2005.09.031.
- Gold EB, Block G, Crawford S, et al. Lifestyle and demographic factors in relation to vasomotor symptoms: baseline results from the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation. Am J Epidemiol. 2004;159:1189-1199. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwh168.
- Avis NE, Crawford SL, Greendale G, et al. Duration of menopausal vasomotor symptoms over the menopause transition. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175:531-539. doi: 10.1001/ jamainternmed.2014.8093.
- Abel TW, Rance NE. Stereologic study of the hypothalamic infundibular nucleus in young and older women. J Comp Neurol. 2000;424:679-688. doi: 10.1002/1096-9861 (20000904)424:4<679::aid-cne9>3.0.co;2-l.
- Neal-Perry G. A phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study to investigate the long-term safety and tolerability of fezolinetant in women seeking treatment for vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause (SKYLIGHT 4) – Abstract S-11. Paper presented at ENDO 2022. June 11, 2022.
- Crandall CJ, Diamant AL, Maglione M, et al. Genetic variation and hot flashes: a systematic review. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105:e4907-e4957. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa536.
- Canonico M, Oger E, Plu-Bureau G, et al; Estrogen and Thromboembolism Risk (ESTHER) Study Group. Hormone therapy and venous thromboembolism among postmenopausal women: impact of the route of estrogen administration and progestogens: the ESTHER study. Circulation. 2007;115:840-845. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.642280.
- Liu B, Beral V, Balkwill A, et al; Million Women Study Collaborators. Gallbladder disease and use of transdermal versus oral hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2008;337:a386. doi: 10.1136/bmj.a386.
- Renoux C, Dell’aniello S, Garbe E, et al. Transdermal and oral hormone replacement therapy and the risk of stroke: a nested case-control study. BMJ. 2010;340:c2519. doi: 10.1136/bmj. c2519.
- Chlebowski RT, Anderson GL, Aragaki AK, et al. Association of menopausal hormone therapy with breast cancer incidence and mortality during long-term follow-up of the Women’s Health Initiative randomized clinical trials. JAMA. 2020;324:369-380. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9482.
- Rossouw JE, Prentice RL, Manson JE, et al. Postmenopausal hormone therapy and risk of cardiovascular disease by age and years since menopause. JAMA. 2007;297:1465-1477. doi: 10.1001/jama.297.13.1465.
- Woods NF, Mitchell ES. Symptoms during the perimenopause: prevlance, severity, trajectory, and significance in women’s lives. Am J Med. 2005;118 suppl 12B:14-24. doi: 10.1016/j. amjmed.2005.09.031.
- Gold EB, Block G, Crawford S, et al. Lifestyle and demographic factors in relation to vasomotor symptoms: baseline results from the Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation. Am J Epidemiol. 2004;159:1189-1199. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwh168.
- Avis NE, Crawford SL, Greendale G, et al. Duration of menopausal vasomotor symptoms over the menopause transition. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175:531-539. doi: 10.1001/ jamainternmed.2014.8093.
- Abel TW, Rance NE. Stereologic study of the hypothalamic infundibular nucleus in young and older women. J Comp Neurol. 2000;424:679-688. doi: 10.1002/1096-9861 (20000904)424:4<679::aid-cne9>3.0.co;2-l.
- Neal-Perry G. A phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study to investigate the long-term safety and tolerability of fezolinetant in women seeking treatment for vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause (SKYLIGHT 4) – Abstract S-11. Paper presented at ENDO 2022. June 11, 2022.
- Crandall CJ, Diamant AL, Maglione M, et al. Genetic variation and hot flashes: a systematic review. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105:e4907-e4957. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa536.
Criminal liability: What are the risks for medical professionals?
Medical professionals are well aware that civil liability (malpractice) may incur when a patient is harmed because of carelessness (negligence). Recent criminal charges against physicians and a nurse, however, have called medical professionals’ attention to the fact that they also may face criminal charges for inappropriate practice.
We cite 2 cases in which criminal liability resulted from bad medical practice. In both instances, there was considerable concern among medical professionals that criminal charges for making a mistake would make it difficult to practice without fear of criminal charges. One concern is that criminal charges could drive good people out of the profession or make them too cautious.1
We look more closely at those 2 cases in which criminal liability was imposed. These cases are outliers. Relatively few criminal cases against medical professionals are based on the quality of care. (There are, however, more criminal charges related to fraudulent billing and other insurance fraud, kickbacks, Medicare and Medicaid abuse, and the like.2) At the same time, the criminal law does not stop at the front door of a clinic or hospital.3 When medical professionals engage in seriously inappropriate health care conduct that directly harms someone, criminal liability may result.4
Anatomy of a crime
Crimes generally require a specific mental state (mens rea) and an act (actus reus). The law specifies the mental state required for conviction. It can range from premeditation—once commonly called “malice aforethought”—to negligence. The mens rea requirement is an essential element of the crime—as we will see in the discussion of the prescription drug cases. A few offenses do not require even negligence, but overwhelmingly, crimes require something more than simple negligence.5
The act requirement is generally obvious, such as firing a gun, driving while intoxicated, or recklessly giving inappropriate medication to a patient. It may include “attempts,” crimes where an act was not completed. For example, attempted murder or conspiracy to commit do not require a completed offense, only intent plus overt acts toward carrying out the crime. Similarly, the wrongful act usually has to produce some harm, but again there are exceptions (attempts). To obtain a conviction, the prosecution must prove all of the elements of the crime, including the required mens rea, beyond a reasonable doubt.6
With this general background, we turn to the first case, in which the charge was a form of homicide. Please note that the following case description was derived from news descriptions of the case, because juries do not publish opinions concerning their conclusions and court documents are unavailable. The public reports therefore may contain factual gaps and errors.
CASE 1 Patient dies after nurse administers wrong drug
RaDonda Vaught, a 38-year-old experienced registered nurse employed at Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) in the intensive care unit (ICU), was providing care for a 76-year-old patient who was admitted to VUMC’s ICU in December 2017 in association with a brain injury. The brain injury involved a fall with resultant subdural hematoma. In preparation for a positron emission tomography (PET) scan to assess the patient’s injury, the physician team prescribed the sedative Versed (midazolam) because of the patient’s claustrophobia. During the course of treatment, Ms. Vaught inadvertently administered the wrong drug, a fatal dose of the muscle relaxant vecuronium, to the patient, which resulted in the patient being unable to breathe. Apparently, Ms. Vaught had been unable to find the midazolam and disengaged a safeguard, proceeding into override mode, and thus vecuronium was dispensed. By the time the error was noticed, the patient was already in cardiac arrest with resultant brain damage (partial brain death). The patient died soon thereafter.
How this medication error occurred
The medication error occurred when Ms. Vaught overrode a computer in the medical system when she could not find the “Versed” entry and typed in “VE,” which was the abbreviation for vecuronium. The prosecutors in the case stated that she failed to distinguish that vecuronium is dispensed as a powder and Versed as a liquid formula. The vecuronium has a red cap, which warns that it is a paralyzing agent. Ms. Vaught ignored these red flags, according to the prosecutors. Furthermore, the lawsuit filing documented her discussion that she was “distracted with something” at the time and admitted to overriding the medication warning.
Continue to: The charges in this case...
The charges in this case
The charges revolved around “criminally negligent homicide and gross neglect of an impaired adult,” the most notable charge being criminally negligent homicide. Potential consequences were up to an 8 years’ prison sentence.7
Furthermore, the Tennessee Board of Nursing revoked Ms. Vaught’s license in July 2021.8 The Board also reportedly fined her $3,000.9
The criminal proceedings were filed in Davidson County Criminal Court, with Judge Jennifer Smith presiding. Ms. Vaught repeatedly manifested remorse for the event. The patient’s family, including her son Michael and her daughters-in-law, provided tearful testimonies at the hearing. Ms. Vaught repeatedly cried during the testimonies. The nurse did not provide an apology, according to one daughter-in-law. The news media reported that the family did not want jail time for Ms. Vaught.7 Nurses across the country were “jolted,” as expressed by the news media.10
Why the controversy?
The entire issue of medical errors continues to be discussed among both the medical and the legal professions. To have a nursing personnel held to the level of criminal liability is unusual.
It was clear that Ms. Vaught took responsibility for her actions, and neither the prosecutors nor defendant attorneys sensed any evidence of malice on her part. On the other hand, there was enough evidence and concern for District Attorney Glenn Funk to proceed with prosecution-related action. Ms. Vaught was facing years in prison if convicted.
WHAT’S THE VERDICT?
In March 2022, the jury convicted Ms. Vaught of criminally negligent homicide—but not of reckless homicide, a more serious offense.
Judge Smith granted a judicial diversion, that is, the conviction would be expunged from the record if Ms. Vaught completed a 3-year probation. Judge Smith noted the “credible remorse expressed by Nurse Vaught” and went on to state, “this is a terrible, terrible, mistake and there have been consequences to the defendant.” In the courtroom, Ms. Vaught apologized to the patient’s family and conveyed that she will “forever be haunted by her role in the (patient’s) passing.”
Overall, this served as an opportunity for health care workers to address oftentimes poor working conditions, which have been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
The Davidson County District Attorney’s office conveyed that this was one case of a careless nurse and not a reflection of the nursing profession. The prosecutors were in accord with a probation verdict. The family felt that their mother, the patient, would not want to see the nurse serve a jail sentence: “Mom was a very forgiving person.”
The patient’s cause of death was listed as “intracerebral hemorrhage and cardiac arrest.” One year later, a new death certificate was issued and noted vecuronium intoxication as the cause of death.
Continue to: The health care institution’s involvement...
The health care institution’s involvement
Approximately 1 year after an apparent anonymous tip was made to health care officials, an unscheduled state and federal investigation, with the threat of possible sanctions, occurred at the VUMC. This was predicated on the criminal indictment related to Ms. Vaught. In the end, her nursing license was revoked, as noted earlier. The family earlier reached an out-of-court settlement with the hospital and there were a number of problems identified at the university medical center.11
Legal principles in the case
Most criminal cases are state cases. Crimes are defined in state statutes, and the trial takes place in state courts. Thus, crimes are defined a little differently from state to state. Ms. Vaught, for example, was tried in Tennessee under the laws of that state.
Homicide involves the killing of a human being. It may not be a crime. For example, there is “justifiable homicide,” such as self-defense. At the other extreme is first-degree murder, an intentional and planned killing. In this case, Ms. Vaught was charged with criminally negligent homicide, which is usually the least serious of criminal homicides but is still a felony. (Some states have misdemeanor manslaughter, which was not an issue in this case.) In some states, criminally negligent homicide is sometimes referred to as involuntary manslaughter. The mens rea for involuntary manslaughter is generally recklessness or “criminal negligence.” This crime goes by various names depending on the state, but involuntary manslaughter and criminally negligent homicide are common names.
Ordinary negligence versus criminal negligence. Criminal negligence is usually considered a more serious mistake than ordinary negligence. This is where there is a difference between civil malpractice negligence and criminal negligence. Criminal negligence is somewhat more careless than ordinary negligence. To use a driving example, if Dr. A was driving home from the hospital, missed seeing a red light, and killed Joe Pedestrian, it could be ordinary negligence. If, however, Dr. B was texting or drinking while driving, causing Dr. B to be distracted and miss seeing the red light, killing a pedestrian, it could be criminal negligence and result in the conviction for the homicide. Of course, in either case there could be civil liability for causing the death.
Applying these legal principles to the reported facts in Ms. Vaught’s case, it appears there was more than simple negligence. That is, the nurse was more than careless. Using “VE” for the wrong drug might have been negligent. In addition, however, she disengaged a safeguard meant to prevent wrongful use of the drug, failed to notice that the drug was a powder instead of a liquid, and ignored the red cap warning that the drug was a paralyzing agent. It becomes apparent why the jury could have found aggravated or criminal negligence.
It is worth emphasizing that in this case, the criminal charges were unusual. For years, studies have suggested that many deaths result from medical errors. The Institute of Medicine famously said that the number of deaths from medical errors was equivalent to that of a 747 airplane crashing every day.12,13 These events result in a relatively small number of malpractice actions but an infinitesimally small number of homicide charges. Among other things, prosecutors are reluctant to pursue such cases regarding acts carried out as part of clinical duties unless there is strong evidence, and grand juries may be reluctant to indict medical professionals.14
Nonetheless, medical professionals ultimately can be criminally responsible for deaths resulting from intentional, or criminally negligent, careless practice. Such liability should not dissuade nurses or others from medical practice any more than the much more common homicide charges that can occur from driving an automobile carelessly that results in someone’s death. A fundamental purpose of the criminal law is to disincentivize unnecessarily harmful (deadly) conduct, whether it is distracted driving or distracted nursing.
Continue to: The drug-prescribing crimes...
The drug-prescribing crimes
The US Supreme Court considered a much different kind of criminal medical practice in 2 (consolidated) cases in its 2021–2022 Term. Physicians in 2 states were each tried and convicted of federal charges of illegally dispensing or distributing (prescribing) controlled substances.15 A federal statute makes it a felony for a physician, or others, “except as authorized” to “knowingly or intentionally distribute, or dispense a controlled substance.”16 Federal regulations clarify the statute. The regulation provides that a prescription is authorized only if a doctor issues it “for a legitimate medical purpose . . . acting in the usual course of professional practice.”17
CASE 2 Physicians charged with overprescribing controlled substances
In these 2 drug-prescribing cases, the physicians had grossly overprescribed the opioids. One reportedly wrote prescriptions in 2 states in exchange for payments in cash or, infrequently, firearms, approximating the cost of the prescriptions to street drugs. The other had a clinic that, over about 4 years, issued 300,000 prescriptions for controlled substances and was a significant source for some kinds of fentanyl.18
WHAT’S THE VERDICT?
In each trial, the juries found the defendant guilty of improper distribution of controlled substances. Although the charges were not homicides, the sentencing judges were much more severe than the court had been in the nursing case discussed above. One physician received a prison term of 20 years, the other, a 25-year term. These undoubtedly reflect both the outrageous conduct and the likely great harm the defendants did.
The Supreme Court heard the cases
The Supreme Court reversed these physicians’ convictions. The Court held that the lower courts had not correctly described for the juries the mens rea required for a conviction under these charges. The Supreme Court held that to be convicted of these offenses, the government had to prove “beyond a reasonable doubt that the defendant [physician] knew that he or she was acting in an unauthorized manner.”19 Both can be retried and probably will be unless they reach a plea agreement with the federal government. Nonetheless, the Court established a very high standard. Carelessness is not enough, but rather “knowingly” acting in an unauthorized way is required. Although these physicians were prosecuted under federal law, other physicians have been prosecuted under state laws limiting the distribution of controlled substances.20
Some physicians have expressed concern that the Supreme Court, in these cases, made the practice of medicine more dangerous for physicians (the threat of criminal sanctions) and patients (making it more difficult to obtain pain control, for example).21,22 That view may be overly pessimistic for 2 reasons. First, the Court actually made it more difficult to convict physicians of writing excessive prescriptions. It did so by setting a higher mens rea standard than lower courts were using, that is, the physician had to “knowingly” act in an unauthorized way. Because “knowingly” can be implied by the circumstances, taking guns or cash would be evidence that the physician knowingly misprescribed.
More fundamentally, the actions of these physicians appear to be well outside even a generous legitimate level of controlled substance prescription. These convictions should not be misunderstood as a way of federal courts to crack down on pain medications. However, the original convictions are a warning to the small handful who grossly overprescribe controlled substances.
Lessons about criminal law and the practice of medicine
Medical professionals’ strong reaction to criminal charges is understandable. Criminal charges can result in jail time (the physicians involved in the controlled substance case were sentenced to 20 years or more) and hefty fines; bring social and professional disapprobation; may lead to license discipline; and are terribly disruptive even for those found not guilty. To make matters worse, malpractice insurance ordinarily does not cover criminal charges, so any fines and the cost of defense are likely out of pocket for those charged—and that can be very expensive. Therefore, the strong reaction to the cases we have described is understandable.
At the same time, the probability of criminal charges against medical personnel for their medical treatment is very low compared with, for example, fraudulent billing, their driving habits, or tax avoidance. Criminal charges are much more likely to arise from insurance fraud, Medicare or Medicaid dishonesty, kickbacks, false statements, and similar corruption crimes rather than inadequate practice. In the cases we examined here, there is an enhanced or aggravated negligence in one case and grossly inappropriate prescribing in the others (which the Supreme Court held must be “knowingly” wrong).
Finally, there is an irony. Medical professionals worried about practice-related criminal charges should be thankful for the malpractice system. Civil malpractice is, as a practical matter, an alternative for patients who believe they were mistreated or harmed by physicians or other providers. They have the option of finding a private attorney to file a civil complaint. In the absence of that system, they would be much more likely to take their grievance and complaint to the prosecutor to seek answers and retribution. Criminal law and civil liability are each a way of allowing someone harmed by another to seek redress. Both are intended to deter harmful conduct and provide some individual and social retribution for such behavior. The civil system, of course, also provides the potential for compensation to those injured. An injured patient without the possibility of a civil suit sometimes would turn to the criminal system for satisfaction. This way, the malpractice system is a better alternative to criminal charges. ●
- Kelman B. As a nurse faces prison for a deadly error, her colleagues worry: could I be next? NPR. March 22, 2022. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2022/03/22/1087903348/as-a-nurse-faces-prison-for-a-deadly-error-her-colleagues-worry-could-i-be-next
- US Department of Justice. National health care fraud enforcement action results in charges involving over $1.4 billion in alleged losses. September 17, 2021. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/national-health-care-fraud-enforcement-action-results-charges-involving-over-14-billion
- Steinman G. Stuff of nightmares: criminal prosecution for malpractice. OBG Manag. 2008;20(8):35-45.
- Maher V, Cwiek M. Criminal liability for nursing and medical harm. Hosp Top. 2022 July 13;1-8.
- Singer RG. The resurgence of mens rea: III—the rise and fall of strict criminal liability. Boston Coll Law Rev. 1989;30:337-408. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://lawdigitalcommons.bc.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=2431&context=bclr
- Sarch AF. Knowledge, recklessness and the connection requirement between actus reus and mens rea. Penn State Law Rev. 2015;120:1-51. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://ideas.dickinsonlaw.psu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=4120&context=dlra
- Timms M, Gluck F, Wegner R, et al. RaDonda Vaught sentenced to three years probation on a diverted sentence, could see record wiped. Tennessean. May 13, 2022. Accessed November 7, 2022. http://www.tennessean.com/story/news/crime/2022/05/13/radonda-vaught-sentened-vanderbilt-nurse/9717529002/
- Tennessee Board of Nursing. Disciplinary hearing: RaDonda Vaught, RN #205702, minutes. July 22-23, 2021. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://www.tn.gov/content/dam/tn/health/healthprofboards/nursing/meeting-minutes/Nursing%20Meeting%20Minutes%20July%2022-23,%202021.pdf
- Institute for Safe Medication Practices. TN Board of Nursing’s unjust decision to revoke nurse’s license: travesty on top of tragedy! August 12, 2021. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://www.ismp.org/resources/tn-board-nursings-unjust-decision-revoke-nurses-license-travesty-top-tragedy
- Medina E. Ex-nurse convicted in fatal medication error gets probation. New York Times. May 15, 2022. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://www.nytimes.com/2022/05/15/us/tennessee-nurse-sentencing.html
- Kelman B. In nurse’s trial, investigator says hospital bears ‘heavy’ responsibility for patient death. KHN. March 24, 2022. Accessed November 15, 2022. https://khn.org/news/article/radonda-vaught-fatal-drug-error-vanderbilt-hospital-responsibility/
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Quality of Health Care in America; Kohn LT, Corrigan JM, Donaldson MS, ed. To Err Is Human: Building a Safer Health System. National Academies Press; 2000.
- Bates DW, Singh H. Two decades since To Err Is Human: an assessment of progress and emerging priorities in patient safety. Health Affairs. 2018;37:1736-1743.
- Eisenberg RL, Berlin L. When does malpractice become manslaughter? Am J Roentgenol. 2002;179:331-335.
- Xiulu Ruan v United States, 20-1410, decided June 27, 2022. https://www.supremecourt.gov/opinions/21pdf/20 -1410_1an2.pdf
- 84 Stat. 1260, 21 U. S. C. §841(a).
- 21 CFR §1306.04(a) (2021).
- Liptak A. Supreme Court sides with doctors accused of running pill mills. The New York Times. June 27, 2022.
- Xiulu Ruan v United States, at 2 (slip opinion).
- Pedemonte S. State v. Christensen: criminalizing medical malpractice. Montana Law Rev. 2022;83(1):183-193. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://scholarworks.umt.edu/cgi/view content.cgi?article=2497&context=mlr
- Szalavitz M. A recent Supreme Court ruling will help people in pain. Scientific American. September 19, 2022. Accessed November 15, 2022. https://www.scientificamerican.com/ article/a-recent-supreme-court-ruling-will-help-people-in -pain/
- Lopez I. Opioid pill peddling case threatens future of pain treatment. Bloomberg Law. March 29, 2022. Accessed November 15, 2022. https://news.bloomberglaw.com/health -law-and-business/opioid-pill-peddling-case-threatens -future-of-pain-treatment
Medical professionals are well aware that civil liability (malpractice) may incur when a patient is harmed because of carelessness (negligence). Recent criminal charges against physicians and a nurse, however, have called medical professionals’ attention to the fact that they also may face criminal charges for inappropriate practice.
We cite 2 cases in which criminal liability resulted from bad medical practice. In both instances, there was considerable concern among medical professionals that criminal charges for making a mistake would make it difficult to practice without fear of criminal charges. One concern is that criminal charges could drive good people out of the profession or make them too cautious.1
We look more closely at those 2 cases in which criminal liability was imposed. These cases are outliers. Relatively few criminal cases against medical professionals are based on the quality of care. (There are, however, more criminal charges related to fraudulent billing and other insurance fraud, kickbacks, Medicare and Medicaid abuse, and the like.2) At the same time, the criminal law does not stop at the front door of a clinic or hospital.3 When medical professionals engage in seriously inappropriate health care conduct that directly harms someone, criminal liability may result.4
Anatomy of a crime
Crimes generally require a specific mental state (mens rea) and an act (actus reus). The law specifies the mental state required for conviction. It can range from premeditation—once commonly called “malice aforethought”—to negligence. The mens rea requirement is an essential element of the crime—as we will see in the discussion of the prescription drug cases. A few offenses do not require even negligence, but overwhelmingly, crimes require something more than simple negligence.5
The act requirement is generally obvious, such as firing a gun, driving while intoxicated, or recklessly giving inappropriate medication to a patient. It may include “attempts,” crimes where an act was not completed. For example, attempted murder or conspiracy to commit do not require a completed offense, only intent plus overt acts toward carrying out the crime. Similarly, the wrongful act usually has to produce some harm, but again there are exceptions (attempts). To obtain a conviction, the prosecution must prove all of the elements of the crime, including the required mens rea, beyond a reasonable doubt.6
With this general background, we turn to the first case, in which the charge was a form of homicide. Please note that the following case description was derived from news descriptions of the case, because juries do not publish opinions concerning their conclusions and court documents are unavailable. The public reports therefore may contain factual gaps and errors.
CASE 1 Patient dies after nurse administers wrong drug
RaDonda Vaught, a 38-year-old experienced registered nurse employed at Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) in the intensive care unit (ICU), was providing care for a 76-year-old patient who was admitted to VUMC’s ICU in December 2017 in association with a brain injury. The brain injury involved a fall with resultant subdural hematoma. In preparation for a positron emission tomography (PET) scan to assess the patient’s injury, the physician team prescribed the sedative Versed (midazolam) because of the patient’s claustrophobia. During the course of treatment, Ms. Vaught inadvertently administered the wrong drug, a fatal dose of the muscle relaxant vecuronium, to the patient, which resulted in the patient being unable to breathe. Apparently, Ms. Vaught had been unable to find the midazolam and disengaged a safeguard, proceeding into override mode, and thus vecuronium was dispensed. By the time the error was noticed, the patient was already in cardiac arrest with resultant brain damage (partial brain death). The patient died soon thereafter.
How this medication error occurred
The medication error occurred when Ms. Vaught overrode a computer in the medical system when she could not find the “Versed” entry and typed in “VE,” which was the abbreviation for vecuronium. The prosecutors in the case stated that she failed to distinguish that vecuronium is dispensed as a powder and Versed as a liquid formula. The vecuronium has a red cap, which warns that it is a paralyzing agent. Ms. Vaught ignored these red flags, according to the prosecutors. Furthermore, the lawsuit filing documented her discussion that she was “distracted with something” at the time and admitted to overriding the medication warning.
Continue to: The charges in this case...
The charges in this case
The charges revolved around “criminally negligent homicide and gross neglect of an impaired adult,” the most notable charge being criminally negligent homicide. Potential consequences were up to an 8 years’ prison sentence.7
Furthermore, the Tennessee Board of Nursing revoked Ms. Vaught’s license in July 2021.8 The Board also reportedly fined her $3,000.9
The criminal proceedings were filed in Davidson County Criminal Court, with Judge Jennifer Smith presiding. Ms. Vaught repeatedly manifested remorse for the event. The patient’s family, including her son Michael and her daughters-in-law, provided tearful testimonies at the hearing. Ms. Vaught repeatedly cried during the testimonies. The nurse did not provide an apology, according to one daughter-in-law. The news media reported that the family did not want jail time for Ms. Vaught.7 Nurses across the country were “jolted,” as expressed by the news media.10
Why the controversy?
The entire issue of medical errors continues to be discussed among both the medical and the legal professions. To have a nursing personnel held to the level of criminal liability is unusual.
It was clear that Ms. Vaught took responsibility for her actions, and neither the prosecutors nor defendant attorneys sensed any evidence of malice on her part. On the other hand, there was enough evidence and concern for District Attorney Glenn Funk to proceed with prosecution-related action. Ms. Vaught was facing years in prison if convicted.
WHAT’S THE VERDICT?
In March 2022, the jury convicted Ms. Vaught of criminally negligent homicide—but not of reckless homicide, a more serious offense.
Judge Smith granted a judicial diversion, that is, the conviction would be expunged from the record if Ms. Vaught completed a 3-year probation. Judge Smith noted the “credible remorse expressed by Nurse Vaught” and went on to state, “this is a terrible, terrible, mistake and there have been consequences to the defendant.” In the courtroom, Ms. Vaught apologized to the patient’s family and conveyed that she will “forever be haunted by her role in the (patient’s) passing.”
Overall, this served as an opportunity for health care workers to address oftentimes poor working conditions, which have been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
The Davidson County District Attorney’s office conveyed that this was one case of a careless nurse and not a reflection of the nursing profession. The prosecutors were in accord with a probation verdict. The family felt that their mother, the patient, would not want to see the nurse serve a jail sentence: “Mom was a very forgiving person.”
The patient’s cause of death was listed as “intracerebral hemorrhage and cardiac arrest.” One year later, a new death certificate was issued and noted vecuronium intoxication as the cause of death.
Continue to: The health care institution’s involvement...
The health care institution’s involvement
Approximately 1 year after an apparent anonymous tip was made to health care officials, an unscheduled state and federal investigation, with the threat of possible sanctions, occurred at the VUMC. This was predicated on the criminal indictment related to Ms. Vaught. In the end, her nursing license was revoked, as noted earlier. The family earlier reached an out-of-court settlement with the hospital and there were a number of problems identified at the university medical center.11
Legal principles in the case
Most criminal cases are state cases. Crimes are defined in state statutes, and the trial takes place in state courts. Thus, crimes are defined a little differently from state to state. Ms. Vaught, for example, was tried in Tennessee under the laws of that state.
Homicide involves the killing of a human being. It may not be a crime. For example, there is “justifiable homicide,” such as self-defense. At the other extreme is first-degree murder, an intentional and planned killing. In this case, Ms. Vaught was charged with criminally negligent homicide, which is usually the least serious of criminal homicides but is still a felony. (Some states have misdemeanor manslaughter, which was not an issue in this case.) In some states, criminally negligent homicide is sometimes referred to as involuntary manslaughter. The mens rea for involuntary manslaughter is generally recklessness or “criminal negligence.” This crime goes by various names depending on the state, but involuntary manslaughter and criminally negligent homicide are common names.
Ordinary negligence versus criminal negligence. Criminal negligence is usually considered a more serious mistake than ordinary negligence. This is where there is a difference between civil malpractice negligence and criminal negligence. Criminal negligence is somewhat more careless than ordinary negligence. To use a driving example, if Dr. A was driving home from the hospital, missed seeing a red light, and killed Joe Pedestrian, it could be ordinary negligence. If, however, Dr. B was texting or drinking while driving, causing Dr. B to be distracted and miss seeing the red light, killing a pedestrian, it could be criminal negligence and result in the conviction for the homicide. Of course, in either case there could be civil liability for causing the death.
Applying these legal principles to the reported facts in Ms. Vaught’s case, it appears there was more than simple negligence. That is, the nurse was more than careless. Using “VE” for the wrong drug might have been negligent. In addition, however, she disengaged a safeguard meant to prevent wrongful use of the drug, failed to notice that the drug was a powder instead of a liquid, and ignored the red cap warning that the drug was a paralyzing agent. It becomes apparent why the jury could have found aggravated or criminal negligence.
It is worth emphasizing that in this case, the criminal charges were unusual. For years, studies have suggested that many deaths result from medical errors. The Institute of Medicine famously said that the number of deaths from medical errors was equivalent to that of a 747 airplane crashing every day.12,13 These events result in a relatively small number of malpractice actions but an infinitesimally small number of homicide charges. Among other things, prosecutors are reluctant to pursue such cases regarding acts carried out as part of clinical duties unless there is strong evidence, and grand juries may be reluctant to indict medical professionals.14
Nonetheless, medical professionals ultimately can be criminally responsible for deaths resulting from intentional, or criminally negligent, careless practice. Such liability should not dissuade nurses or others from medical practice any more than the much more common homicide charges that can occur from driving an automobile carelessly that results in someone’s death. A fundamental purpose of the criminal law is to disincentivize unnecessarily harmful (deadly) conduct, whether it is distracted driving or distracted nursing.
Continue to: The drug-prescribing crimes...
The drug-prescribing crimes
The US Supreme Court considered a much different kind of criminal medical practice in 2 (consolidated) cases in its 2021–2022 Term. Physicians in 2 states were each tried and convicted of federal charges of illegally dispensing or distributing (prescribing) controlled substances.15 A federal statute makes it a felony for a physician, or others, “except as authorized” to “knowingly or intentionally distribute, or dispense a controlled substance.”16 Federal regulations clarify the statute. The regulation provides that a prescription is authorized only if a doctor issues it “for a legitimate medical purpose . . . acting in the usual course of professional practice.”17
CASE 2 Physicians charged with overprescribing controlled substances
In these 2 drug-prescribing cases, the physicians had grossly overprescribed the opioids. One reportedly wrote prescriptions in 2 states in exchange for payments in cash or, infrequently, firearms, approximating the cost of the prescriptions to street drugs. The other had a clinic that, over about 4 years, issued 300,000 prescriptions for controlled substances and was a significant source for some kinds of fentanyl.18
WHAT’S THE VERDICT?
In each trial, the juries found the defendant guilty of improper distribution of controlled substances. Although the charges were not homicides, the sentencing judges were much more severe than the court had been in the nursing case discussed above. One physician received a prison term of 20 years, the other, a 25-year term. These undoubtedly reflect both the outrageous conduct and the likely great harm the defendants did.
The Supreme Court heard the cases
The Supreme Court reversed these physicians’ convictions. The Court held that the lower courts had not correctly described for the juries the mens rea required for a conviction under these charges. The Supreme Court held that to be convicted of these offenses, the government had to prove “beyond a reasonable doubt that the defendant [physician] knew that he or she was acting in an unauthorized manner.”19 Both can be retried and probably will be unless they reach a plea agreement with the federal government. Nonetheless, the Court established a very high standard. Carelessness is not enough, but rather “knowingly” acting in an unauthorized way is required. Although these physicians were prosecuted under federal law, other physicians have been prosecuted under state laws limiting the distribution of controlled substances.20
Some physicians have expressed concern that the Supreme Court, in these cases, made the practice of medicine more dangerous for physicians (the threat of criminal sanctions) and patients (making it more difficult to obtain pain control, for example).21,22 That view may be overly pessimistic for 2 reasons. First, the Court actually made it more difficult to convict physicians of writing excessive prescriptions. It did so by setting a higher mens rea standard than lower courts were using, that is, the physician had to “knowingly” act in an unauthorized way. Because “knowingly” can be implied by the circumstances, taking guns or cash would be evidence that the physician knowingly misprescribed.
More fundamentally, the actions of these physicians appear to be well outside even a generous legitimate level of controlled substance prescription. These convictions should not be misunderstood as a way of federal courts to crack down on pain medications. However, the original convictions are a warning to the small handful who grossly overprescribe controlled substances.
Lessons about criminal law and the practice of medicine
Medical professionals’ strong reaction to criminal charges is understandable. Criminal charges can result in jail time (the physicians involved in the controlled substance case were sentenced to 20 years or more) and hefty fines; bring social and professional disapprobation; may lead to license discipline; and are terribly disruptive even for those found not guilty. To make matters worse, malpractice insurance ordinarily does not cover criminal charges, so any fines and the cost of defense are likely out of pocket for those charged—and that can be very expensive. Therefore, the strong reaction to the cases we have described is understandable.
At the same time, the probability of criminal charges against medical personnel for their medical treatment is very low compared with, for example, fraudulent billing, their driving habits, or tax avoidance. Criminal charges are much more likely to arise from insurance fraud, Medicare or Medicaid dishonesty, kickbacks, false statements, and similar corruption crimes rather than inadequate practice. In the cases we examined here, there is an enhanced or aggravated negligence in one case and grossly inappropriate prescribing in the others (which the Supreme Court held must be “knowingly” wrong).
Finally, there is an irony. Medical professionals worried about practice-related criminal charges should be thankful for the malpractice system. Civil malpractice is, as a practical matter, an alternative for patients who believe they were mistreated or harmed by physicians or other providers. They have the option of finding a private attorney to file a civil complaint. In the absence of that system, they would be much more likely to take their grievance and complaint to the prosecutor to seek answers and retribution. Criminal law and civil liability are each a way of allowing someone harmed by another to seek redress. Both are intended to deter harmful conduct and provide some individual and social retribution for such behavior. The civil system, of course, also provides the potential for compensation to those injured. An injured patient without the possibility of a civil suit sometimes would turn to the criminal system for satisfaction. This way, the malpractice system is a better alternative to criminal charges. ●
Medical professionals are well aware that civil liability (malpractice) may incur when a patient is harmed because of carelessness (negligence). Recent criminal charges against physicians and a nurse, however, have called medical professionals’ attention to the fact that they also may face criminal charges for inappropriate practice.
We cite 2 cases in which criminal liability resulted from bad medical practice. In both instances, there was considerable concern among medical professionals that criminal charges for making a mistake would make it difficult to practice without fear of criminal charges. One concern is that criminal charges could drive good people out of the profession or make them too cautious.1
We look more closely at those 2 cases in which criminal liability was imposed. These cases are outliers. Relatively few criminal cases against medical professionals are based on the quality of care. (There are, however, more criminal charges related to fraudulent billing and other insurance fraud, kickbacks, Medicare and Medicaid abuse, and the like.2) At the same time, the criminal law does not stop at the front door of a clinic or hospital.3 When medical professionals engage in seriously inappropriate health care conduct that directly harms someone, criminal liability may result.4
Anatomy of a crime
Crimes generally require a specific mental state (mens rea) and an act (actus reus). The law specifies the mental state required for conviction. It can range from premeditation—once commonly called “malice aforethought”—to negligence. The mens rea requirement is an essential element of the crime—as we will see in the discussion of the prescription drug cases. A few offenses do not require even negligence, but overwhelmingly, crimes require something more than simple negligence.5
The act requirement is generally obvious, such as firing a gun, driving while intoxicated, or recklessly giving inappropriate medication to a patient. It may include “attempts,” crimes where an act was not completed. For example, attempted murder or conspiracy to commit do not require a completed offense, only intent plus overt acts toward carrying out the crime. Similarly, the wrongful act usually has to produce some harm, but again there are exceptions (attempts). To obtain a conviction, the prosecution must prove all of the elements of the crime, including the required mens rea, beyond a reasonable doubt.6
With this general background, we turn to the first case, in which the charge was a form of homicide. Please note that the following case description was derived from news descriptions of the case, because juries do not publish opinions concerning their conclusions and court documents are unavailable. The public reports therefore may contain factual gaps and errors.
CASE 1 Patient dies after nurse administers wrong drug
RaDonda Vaught, a 38-year-old experienced registered nurse employed at Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) in the intensive care unit (ICU), was providing care for a 76-year-old patient who was admitted to VUMC’s ICU in December 2017 in association with a brain injury. The brain injury involved a fall with resultant subdural hematoma. In preparation for a positron emission tomography (PET) scan to assess the patient’s injury, the physician team prescribed the sedative Versed (midazolam) because of the patient’s claustrophobia. During the course of treatment, Ms. Vaught inadvertently administered the wrong drug, a fatal dose of the muscle relaxant vecuronium, to the patient, which resulted in the patient being unable to breathe. Apparently, Ms. Vaught had been unable to find the midazolam and disengaged a safeguard, proceeding into override mode, and thus vecuronium was dispensed. By the time the error was noticed, the patient was already in cardiac arrest with resultant brain damage (partial brain death). The patient died soon thereafter.
How this medication error occurred
The medication error occurred when Ms. Vaught overrode a computer in the medical system when she could not find the “Versed” entry and typed in “VE,” which was the abbreviation for vecuronium. The prosecutors in the case stated that she failed to distinguish that vecuronium is dispensed as a powder and Versed as a liquid formula. The vecuronium has a red cap, which warns that it is a paralyzing agent. Ms. Vaught ignored these red flags, according to the prosecutors. Furthermore, the lawsuit filing documented her discussion that she was “distracted with something” at the time and admitted to overriding the medication warning.
Continue to: The charges in this case...
The charges in this case
The charges revolved around “criminally negligent homicide and gross neglect of an impaired adult,” the most notable charge being criminally negligent homicide. Potential consequences were up to an 8 years’ prison sentence.7
Furthermore, the Tennessee Board of Nursing revoked Ms. Vaught’s license in July 2021.8 The Board also reportedly fined her $3,000.9
The criminal proceedings were filed in Davidson County Criminal Court, with Judge Jennifer Smith presiding. Ms. Vaught repeatedly manifested remorse for the event. The patient’s family, including her son Michael and her daughters-in-law, provided tearful testimonies at the hearing. Ms. Vaught repeatedly cried during the testimonies. The nurse did not provide an apology, according to one daughter-in-law. The news media reported that the family did not want jail time for Ms. Vaught.7 Nurses across the country were “jolted,” as expressed by the news media.10
Why the controversy?
The entire issue of medical errors continues to be discussed among both the medical and the legal professions. To have a nursing personnel held to the level of criminal liability is unusual.
It was clear that Ms. Vaught took responsibility for her actions, and neither the prosecutors nor defendant attorneys sensed any evidence of malice on her part. On the other hand, there was enough evidence and concern for District Attorney Glenn Funk to proceed with prosecution-related action. Ms. Vaught was facing years in prison if convicted.
WHAT’S THE VERDICT?
In March 2022, the jury convicted Ms. Vaught of criminally negligent homicide—but not of reckless homicide, a more serious offense.
Judge Smith granted a judicial diversion, that is, the conviction would be expunged from the record if Ms. Vaught completed a 3-year probation. Judge Smith noted the “credible remorse expressed by Nurse Vaught” and went on to state, “this is a terrible, terrible, mistake and there have been consequences to the defendant.” In the courtroom, Ms. Vaught apologized to the patient’s family and conveyed that she will “forever be haunted by her role in the (patient’s) passing.”
Overall, this served as an opportunity for health care workers to address oftentimes poor working conditions, which have been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
The Davidson County District Attorney’s office conveyed that this was one case of a careless nurse and not a reflection of the nursing profession. The prosecutors were in accord with a probation verdict. The family felt that their mother, the patient, would not want to see the nurse serve a jail sentence: “Mom was a very forgiving person.”
The patient’s cause of death was listed as “intracerebral hemorrhage and cardiac arrest.” One year later, a new death certificate was issued and noted vecuronium intoxication as the cause of death.
Continue to: The health care institution’s involvement...
The health care institution’s involvement
Approximately 1 year after an apparent anonymous tip was made to health care officials, an unscheduled state and federal investigation, with the threat of possible sanctions, occurred at the VUMC. This was predicated on the criminal indictment related to Ms. Vaught. In the end, her nursing license was revoked, as noted earlier. The family earlier reached an out-of-court settlement with the hospital and there were a number of problems identified at the university medical center.11
Legal principles in the case
Most criminal cases are state cases. Crimes are defined in state statutes, and the trial takes place in state courts. Thus, crimes are defined a little differently from state to state. Ms. Vaught, for example, was tried in Tennessee under the laws of that state.
Homicide involves the killing of a human being. It may not be a crime. For example, there is “justifiable homicide,” such as self-defense. At the other extreme is first-degree murder, an intentional and planned killing. In this case, Ms. Vaught was charged with criminally negligent homicide, which is usually the least serious of criminal homicides but is still a felony. (Some states have misdemeanor manslaughter, which was not an issue in this case.) In some states, criminally negligent homicide is sometimes referred to as involuntary manslaughter. The mens rea for involuntary manslaughter is generally recklessness or “criminal negligence.” This crime goes by various names depending on the state, but involuntary manslaughter and criminally negligent homicide are common names.
Ordinary negligence versus criminal negligence. Criminal negligence is usually considered a more serious mistake than ordinary negligence. This is where there is a difference between civil malpractice negligence and criminal negligence. Criminal negligence is somewhat more careless than ordinary negligence. To use a driving example, if Dr. A was driving home from the hospital, missed seeing a red light, and killed Joe Pedestrian, it could be ordinary negligence. If, however, Dr. B was texting or drinking while driving, causing Dr. B to be distracted and miss seeing the red light, killing a pedestrian, it could be criminal negligence and result in the conviction for the homicide. Of course, in either case there could be civil liability for causing the death.
Applying these legal principles to the reported facts in Ms. Vaught’s case, it appears there was more than simple negligence. That is, the nurse was more than careless. Using “VE” for the wrong drug might have been negligent. In addition, however, she disengaged a safeguard meant to prevent wrongful use of the drug, failed to notice that the drug was a powder instead of a liquid, and ignored the red cap warning that the drug was a paralyzing agent. It becomes apparent why the jury could have found aggravated or criminal negligence.
It is worth emphasizing that in this case, the criminal charges were unusual. For years, studies have suggested that many deaths result from medical errors. The Institute of Medicine famously said that the number of deaths from medical errors was equivalent to that of a 747 airplane crashing every day.12,13 These events result in a relatively small number of malpractice actions but an infinitesimally small number of homicide charges. Among other things, prosecutors are reluctant to pursue such cases regarding acts carried out as part of clinical duties unless there is strong evidence, and grand juries may be reluctant to indict medical professionals.14
Nonetheless, medical professionals ultimately can be criminally responsible for deaths resulting from intentional, or criminally negligent, careless practice. Such liability should not dissuade nurses or others from medical practice any more than the much more common homicide charges that can occur from driving an automobile carelessly that results in someone’s death. A fundamental purpose of the criminal law is to disincentivize unnecessarily harmful (deadly) conduct, whether it is distracted driving or distracted nursing.
Continue to: The drug-prescribing crimes...
The drug-prescribing crimes
The US Supreme Court considered a much different kind of criminal medical practice in 2 (consolidated) cases in its 2021–2022 Term. Physicians in 2 states were each tried and convicted of federal charges of illegally dispensing or distributing (prescribing) controlled substances.15 A federal statute makes it a felony for a physician, or others, “except as authorized” to “knowingly or intentionally distribute, or dispense a controlled substance.”16 Federal regulations clarify the statute. The regulation provides that a prescription is authorized only if a doctor issues it “for a legitimate medical purpose . . . acting in the usual course of professional practice.”17
CASE 2 Physicians charged with overprescribing controlled substances
In these 2 drug-prescribing cases, the physicians had grossly overprescribed the opioids. One reportedly wrote prescriptions in 2 states in exchange for payments in cash or, infrequently, firearms, approximating the cost of the prescriptions to street drugs. The other had a clinic that, over about 4 years, issued 300,000 prescriptions for controlled substances and was a significant source for some kinds of fentanyl.18
WHAT’S THE VERDICT?
In each trial, the juries found the defendant guilty of improper distribution of controlled substances. Although the charges were not homicides, the sentencing judges were much more severe than the court had been in the nursing case discussed above. One physician received a prison term of 20 years, the other, a 25-year term. These undoubtedly reflect both the outrageous conduct and the likely great harm the defendants did.
The Supreme Court heard the cases
The Supreme Court reversed these physicians’ convictions. The Court held that the lower courts had not correctly described for the juries the mens rea required for a conviction under these charges. The Supreme Court held that to be convicted of these offenses, the government had to prove “beyond a reasonable doubt that the defendant [physician] knew that he or she was acting in an unauthorized manner.”19 Both can be retried and probably will be unless they reach a plea agreement with the federal government. Nonetheless, the Court established a very high standard. Carelessness is not enough, but rather “knowingly” acting in an unauthorized way is required. Although these physicians were prosecuted under federal law, other physicians have been prosecuted under state laws limiting the distribution of controlled substances.20
Some physicians have expressed concern that the Supreme Court, in these cases, made the practice of medicine more dangerous for physicians (the threat of criminal sanctions) and patients (making it more difficult to obtain pain control, for example).21,22 That view may be overly pessimistic for 2 reasons. First, the Court actually made it more difficult to convict physicians of writing excessive prescriptions. It did so by setting a higher mens rea standard than lower courts were using, that is, the physician had to “knowingly” act in an unauthorized way. Because “knowingly” can be implied by the circumstances, taking guns or cash would be evidence that the physician knowingly misprescribed.
More fundamentally, the actions of these physicians appear to be well outside even a generous legitimate level of controlled substance prescription. These convictions should not be misunderstood as a way of federal courts to crack down on pain medications. However, the original convictions are a warning to the small handful who grossly overprescribe controlled substances.
Lessons about criminal law and the practice of medicine
Medical professionals’ strong reaction to criminal charges is understandable. Criminal charges can result in jail time (the physicians involved in the controlled substance case were sentenced to 20 years or more) and hefty fines; bring social and professional disapprobation; may lead to license discipline; and are terribly disruptive even for those found not guilty. To make matters worse, malpractice insurance ordinarily does not cover criminal charges, so any fines and the cost of defense are likely out of pocket for those charged—and that can be very expensive. Therefore, the strong reaction to the cases we have described is understandable.
At the same time, the probability of criminal charges against medical personnel for their medical treatment is very low compared with, for example, fraudulent billing, their driving habits, or tax avoidance. Criminal charges are much more likely to arise from insurance fraud, Medicare or Medicaid dishonesty, kickbacks, false statements, and similar corruption crimes rather than inadequate practice. In the cases we examined here, there is an enhanced or aggravated negligence in one case and grossly inappropriate prescribing in the others (which the Supreme Court held must be “knowingly” wrong).
Finally, there is an irony. Medical professionals worried about practice-related criminal charges should be thankful for the malpractice system. Civil malpractice is, as a practical matter, an alternative for patients who believe they were mistreated or harmed by physicians or other providers. They have the option of finding a private attorney to file a civil complaint. In the absence of that system, they would be much more likely to take their grievance and complaint to the prosecutor to seek answers and retribution. Criminal law and civil liability are each a way of allowing someone harmed by another to seek redress. Both are intended to deter harmful conduct and provide some individual and social retribution for such behavior. The civil system, of course, also provides the potential for compensation to those injured. An injured patient without the possibility of a civil suit sometimes would turn to the criminal system for satisfaction. This way, the malpractice system is a better alternative to criminal charges. ●
- Kelman B. As a nurse faces prison for a deadly error, her colleagues worry: could I be next? NPR. March 22, 2022. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2022/03/22/1087903348/as-a-nurse-faces-prison-for-a-deadly-error-her-colleagues-worry-could-i-be-next
- US Department of Justice. National health care fraud enforcement action results in charges involving over $1.4 billion in alleged losses. September 17, 2021. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/national-health-care-fraud-enforcement-action-results-charges-involving-over-14-billion
- Steinman G. Stuff of nightmares: criminal prosecution for malpractice. OBG Manag. 2008;20(8):35-45.
- Maher V, Cwiek M. Criminal liability for nursing and medical harm. Hosp Top. 2022 July 13;1-8.
- Singer RG. The resurgence of mens rea: III—the rise and fall of strict criminal liability. Boston Coll Law Rev. 1989;30:337-408. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://lawdigitalcommons.bc.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=2431&context=bclr
- Sarch AF. Knowledge, recklessness and the connection requirement between actus reus and mens rea. Penn State Law Rev. 2015;120:1-51. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://ideas.dickinsonlaw.psu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=4120&context=dlra
- Timms M, Gluck F, Wegner R, et al. RaDonda Vaught sentenced to three years probation on a diverted sentence, could see record wiped. Tennessean. May 13, 2022. Accessed November 7, 2022. http://www.tennessean.com/story/news/crime/2022/05/13/radonda-vaught-sentened-vanderbilt-nurse/9717529002/
- Tennessee Board of Nursing. Disciplinary hearing: RaDonda Vaught, RN #205702, minutes. July 22-23, 2021. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://www.tn.gov/content/dam/tn/health/healthprofboards/nursing/meeting-minutes/Nursing%20Meeting%20Minutes%20July%2022-23,%202021.pdf
- Institute for Safe Medication Practices. TN Board of Nursing’s unjust decision to revoke nurse’s license: travesty on top of tragedy! August 12, 2021. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://www.ismp.org/resources/tn-board-nursings-unjust-decision-revoke-nurses-license-travesty-top-tragedy
- Medina E. Ex-nurse convicted in fatal medication error gets probation. New York Times. May 15, 2022. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://www.nytimes.com/2022/05/15/us/tennessee-nurse-sentencing.html
- Kelman B. In nurse’s trial, investigator says hospital bears ‘heavy’ responsibility for patient death. KHN. March 24, 2022. Accessed November 15, 2022. https://khn.org/news/article/radonda-vaught-fatal-drug-error-vanderbilt-hospital-responsibility/
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Quality of Health Care in America; Kohn LT, Corrigan JM, Donaldson MS, ed. To Err Is Human: Building a Safer Health System. National Academies Press; 2000.
- Bates DW, Singh H. Two decades since To Err Is Human: an assessment of progress and emerging priorities in patient safety. Health Affairs. 2018;37:1736-1743.
- Eisenberg RL, Berlin L. When does malpractice become manslaughter? Am J Roentgenol. 2002;179:331-335.
- Xiulu Ruan v United States, 20-1410, decided June 27, 2022. https://www.supremecourt.gov/opinions/21pdf/20 -1410_1an2.pdf
- 84 Stat. 1260, 21 U. S. C. §841(a).
- 21 CFR §1306.04(a) (2021).
- Liptak A. Supreme Court sides with doctors accused of running pill mills. The New York Times. June 27, 2022.
- Xiulu Ruan v United States, at 2 (slip opinion).
- Pedemonte S. State v. Christensen: criminalizing medical malpractice. Montana Law Rev. 2022;83(1):183-193. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://scholarworks.umt.edu/cgi/view content.cgi?article=2497&context=mlr
- Szalavitz M. A recent Supreme Court ruling will help people in pain. Scientific American. September 19, 2022. Accessed November 15, 2022. https://www.scientificamerican.com/ article/a-recent-supreme-court-ruling-will-help-people-in -pain/
- Lopez I. Opioid pill peddling case threatens future of pain treatment. Bloomberg Law. March 29, 2022. Accessed November 15, 2022. https://news.bloomberglaw.com/health -law-and-business/opioid-pill-peddling-case-threatens -future-of-pain-treatment
- Kelman B. As a nurse faces prison for a deadly error, her colleagues worry: could I be next? NPR. March 22, 2022. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2022/03/22/1087903348/as-a-nurse-faces-prison-for-a-deadly-error-her-colleagues-worry-could-i-be-next
- US Department of Justice. National health care fraud enforcement action results in charges involving over $1.4 billion in alleged losses. September 17, 2021. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/national-health-care-fraud-enforcement-action-results-charges-involving-over-14-billion
- Steinman G. Stuff of nightmares: criminal prosecution for malpractice. OBG Manag. 2008;20(8):35-45.
- Maher V, Cwiek M. Criminal liability for nursing and medical harm. Hosp Top. 2022 July 13;1-8.
- Singer RG. The resurgence of mens rea: III—the rise and fall of strict criminal liability. Boston Coll Law Rev. 1989;30:337-408. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://lawdigitalcommons.bc.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=2431&context=bclr
- Sarch AF. Knowledge, recklessness and the connection requirement between actus reus and mens rea. Penn State Law Rev. 2015;120:1-51. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://ideas.dickinsonlaw.psu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=4120&context=dlra
- Timms M, Gluck F, Wegner R, et al. RaDonda Vaught sentenced to three years probation on a diverted sentence, could see record wiped. Tennessean. May 13, 2022. Accessed November 7, 2022. http://www.tennessean.com/story/news/crime/2022/05/13/radonda-vaught-sentened-vanderbilt-nurse/9717529002/
- Tennessee Board of Nursing. Disciplinary hearing: RaDonda Vaught, RN #205702, minutes. July 22-23, 2021. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://www.tn.gov/content/dam/tn/health/healthprofboards/nursing/meeting-minutes/Nursing%20Meeting%20Minutes%20July%2022-23,%202021.pdf
- Institute for Safe Medication Practices. TN Board of Nursing’s unjust decision to revoke nurse’s license: travesty on top of tragedy! August 12, 2021. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://www.ismp.org/resources/tn-board-nursings-unjust-decision-revoke-nurses-license-travesty-top-tragedy
- Medina E. Ex-nurse convicted in fatal medication error gets probation. New York Times. May 15, 2022. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://www.nytimes.com/2022/05/15/us/tennessee-nurse-sentencing.html
- Kelman B. In nurse’s trial, investigator says hospital bears ‘heavy’ responsibility for patient death. KHN. March 24, 2022. Accessed November 15, 2022. https://khn.org/news/article/radonda-vaught-fatal-drug-error-vanderbilt-hospital-responsibility/
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Quality of Health Care in America; Kohn LT, Corrigan JM, Donaldson MS, ed. To Err Is Human: Building a Safer Health System. National Academies Press; 2000.
- Bates DW, Singh H. Two decades since To Err Is Human: an assessment of progress and emerging priorities in patient safety. Health Affairs. 2018;37:1736-1743.
- Eisenberg RL, Berlin L. When does malpractice become manslaughter? Am J Roentgenol. 2002;179:331-335.
- Xiulu Ruan v United States, 20-1410, decided June 27, 2022. https://www.supremecourt.gov/opinions/21pdf/20 -1410_1an2.pdf
- 84 Stat. 1260, 21 U. S. C. §841(a).
- 21 CFR §1306.04(a) (2021).
- Liptak A. Supreme Court sides with doctors accused of running pill mills. The New York Times. June 27, 2022.
- Xiulu Ruan v United States, at 2 (slip opinion).
- Pedemonte S. State v. Christensen: criminalizing medical malpractice. Montana Law Rev. 2022;83(1):183-193. Accessed November 7, 2022. https://scholarworks.umt.edu/cgi/view content.cgi?article=2497&context=mlr
- Szalavitz M. A recent Supreme Court ruling will help people in pain. Scientific American. September 19, 2022. Accessed November 15, 2022. https://www.scientificamerican.com/ article/a-recent-supreme-court-ruling-will-help-people-in -pain/
- Lopez I. Opioid pill peddling case threatens future of pain treatment. Bloomberg Law. March 29, 2022. Accessed November 15, 2022. https://news.bloomberglaw.com/health -law-and-business/opioid-pill-peddling-case-threatens -future-of-pain-treatment
CDC reports uptick in invasive Strep A infections
Clinicians in the United States are reporting more cases of invasive group A streptococcal infection (iGAS) in children, according to an alert from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. These infections are rare but can be deadly, and they can affect adults as well as children.
including those with recent or co-occurring viral respiratory infections, the agency advised in a Dec. 22 alert.
In some cases, iGAS manifests as persistent or worsening symptoms after a patient with a known viral infection initially starts to show signs of improvement, according to the agency.
In November, the CDC was notified about a possible increase in cases of pediatric iGAS at a hospital in Colorado. Since then, two surveillance systems – the Infectious Diseases Society of America’s Emerging Infections Network and the CDC’s Active Bacterial Core Surveillance System – have detected potential increases in pediatric iGAS cases in other states.
The uptick has coincided with “increased circulation of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza viruses, SARS-CoV-2, and other respiratory viruses,” the advisory stated. “While the overall number of cases has remained relatively low and iGAS infections remain rare in children, [the] CDC is investigating these reports.”
Not just strep throat
Group A Streptococcus bacteria can cause strep throat and infections in skin and soft tissue. The pathogens also can lead to uncommon but severe diseases, such as sepsis, streptococcal toxic shock syndrome, and necrotizing fasciitis, according to the CDC. The severe illnesses “are associated with high mortality rates and require immediate treatment, including appropriate antibiotic therapy,” the agency said.
Groups at higher risk for iGAS include people aged 65 years or older, American Indian and Alaska Native populations, residents of long-term care facilities, those with wounds or skin disease, people who inject drugs, and people experiencing homelessness.
People with medical conditions such as diabetes, cancer, immunosuppression, and chronic kidney, heart, or respiratory disease also are at increased risk.
Invasive strep A infections initially decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic amid measures to reduce the spread of disease, such as masking and social distancing. But since September, monthly cases have exceeded those in 2020 and 2021. “It is too early to determine whether this rise is beyond what would be expected for pre-COVID” seasonal patterns, the CDC said.
Recommendations
Because iGAS can occur after the flu or chickenpox, health care providers should offer influenza and varicella vaccinations to all eligible people who are not up to date with their vaccines.
In addition, clinicians should educate patients about symptoms of iGAS that require urgent medical attention, including necrotizing fasciitis, cellulitis, and toxic shock syndrome.
They also should obtain cultures for suspected cases of iGAS as clinically indicated, follow guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of strep throat, and be aware of alternative ways to treat strep throat in children amid a shortage of amoxicillin suspension.
Researchers have reported more cases of iGAS in the United Kingdom this year, as well. According to the UK Health Security Agency, 74 deaths, including 16 children, in England have been attributed to iGAS since September.
“We know that this is concerning for parents, but I want to stress that while we are seeing an increase in cases in children, this remains very uncommon,” UKHSA Deputy Director Colin Brown said in a news release. “There are lots of winter bugs circulating that can make your child feel unwell that mostly aren’t cause for alarm. However, make sure you talk to a health professional if your child is getting worse after a bout of scarlet fever, a sore throat, or respiratory infection.”
A fever that doesn’t resolve, dehydration, extreme tiredness, and difficulty breathing are signs to watch out for, Dr. Brown said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinicians in the United States are reporting more cases of invasive group A streptococcal infection (iGAS) in children, according to an alert from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. These infections are rare but can be deadly, and they can affect adults as well as children.
including those with recent or co-occurring viral respiratory infections, the agency advised in a Dec. 22 alert.
In some cases, iGAS manifests as persistent or worsening symptoms after a patient with a known viral infection initially starts to show signs of improvement, according to the agency.
In November, the CDC was notified about a possible increase in cases of pediatric iGAS at a hospital in Colorado. Since then, two surveillance systems – the Infectious Diseases Society of America’s Emerging Infections Network and the CDC’s Active Bacterial Core Surveillance System – have detected potential increases in pediatric iGAS cases in other states.
The uptick has coincided with “increased circulation of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza viruses, SARS-CoV-2, and other respiratory viruses,” the advisory stated. “While the overall number of cases has remained relatively low and iGAS infections remain rare in children, [the] CDC is investigating these reports.”
Not just strep throat
Group A Streptococcus bacteria can cause strep throat and infections in skin and soft tissue. The pathogens also can lead to uncommon but severe diseases, such as sepsis, streptococcal toxic shock syndrome, and necrotizing fasciitis, according to the CDC. The severe illnesses “are associated with high mortality rates and require immediate treatment, including appropriate antibiotic therapy,” the agency said.
Groups at higher risk for iGAS include people aged 65 years or older, American Indian and Alaska Native populations, residents of long-term care facilities, those with wounds or skin disease, people who inject drugs, and people experiencing homelessness.
People with medical conditions such as diabetes, cancer, immunosuppression, and chronic kidney, heart, or respiratory disease also are at increased risk.
Invasive strep A infections initially decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic amid measures to reduce the spread of disease, such as masking and social distancing. But since September, monthly cases have exceeded those in 2020 and 2021. “It is too early to determine whether this rise is beyond what would be expected for pre-COVID” seasonal patterns, the CDC said.
Recommendations
Because iGAS can occur after the flu or chickenpox, health care providers should offer influenza and varicella vaccinations to all eligible people who are not up to date with their vaccines.
In addition, clinicians should educate patients about symptoms of iGAS that require urgent medical attention, including necrotizing fasciitis, cellulitis, and toxic shock syndrome.
They also should obtain cultures for suspected cases of iGAS as clinically indicated, follow guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of strep throat, and be aware of alternative ways to treat strep throat in children amid a shortage of amoxicillin suspension.
Researchers have reported more cases of iGAS in the United Kingdom this year, as well. According to the UK Health Security Agency, 74 deaths, including 16 children, in England have been attributed to iGAS since September.
“We know that this is concerning for parents, but I want to stress that while we are seeing an increase in cases in children, this remains very uncommon,” UKHSA Deputy Director Colin Brown said in a news release. “There are lots of winter bugs circulating that can make your child feel unwell that mostly aren’t cause for alarm. However, make sure you talk to a health professional if your child is getting worse after a bout of scarlet fever, a sore throat, or respiratory infection.”
A fever that doesn’t resolve, dehydration, extreme tiredness, and difficulty breathing are signs to watch out for, Dr. Brown said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinicians in the United States are reporting more cases of invasive group A streptococcal infection (iGAS) in children, according to an alert from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. These infections are rare but can be deadly, and they can affect adults as well as children.
including those with recent or co-occurring viral respiratory infections, the agency advised in a Dec. 22 alert.
In some cases, iGAS manifests as persistent or worsening symptoms after a patient with a known viral infection initially starts to show signs of improvement, according to the agency.
In November, the CDC was notified about a possible increase in cases of pediatric iGAS at a hospital in Colorado. Since then, two surveillance systems – the Infectious Diseases Society of America’s Emerging Infections Network and the CDC’s Active Bacterial Core Surveillance System – have detected potential increases in pediatric iGAS cases in other states.
The uptick has coincided with “increased circulation of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza viruses, SARS-CoV-2, and other respiratory viruses,” the advisory stated. “While the overall number of cases has remained relatively low and iGAS infections remain rare in children, [the] CDC is investigating these reports.”
Not just strep throat
Group A Streptococcus bacteria can cause strep throat and infections in skin and soft tissue. The pathogens also can lead to uncommon but severe diseases, such as sepsis, streptococcal toxic shock syndrome, and necrotizing fasciitis, according to the CDC. The severe illnesses “are associated with high mortality rates and require immediate treatment, including appropriate antibiotic therapy,” the agency said.
Groups at higher risk for iGAS include people aged 65 years or older, American Indian and Alaska Native populations, residents of long-term care facilities, those with wounds or skin disease, people who inject drugs, and people experiencing homelessness.
People with medical conditions such as diabetes, cancer, immunosuppression, and chronic kidney, heart, or respiratory disease also are at increased risk.
Invasive strep A infections initially decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic amid measures to reduce the spread of disease, such as masking and social distancing. But since September, monthly cases have exceeded those in 2020 and 2021. “It is too early to determine whether this rise is beyond what would be expected for pre-COVID” seasonal patterns, the CDC said.
Recommendations
Because iGAS can occur after the flu or chickenpox, health care providers should offer influenza and varicella vaccinations to all eligible people who are not up to date with their vaccines.
In addition, clinicians should educate patients about symptoms of iGAS that require urgent medical attention, including necrotizing fasciitis, cellulitis, and toxic shock syndrome.
They also should obtain cultures for suspected cases of iGAS as clinically indicated, follow guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of strep throat, and be aware of alternative ways to treat strep throat in children amid a shortage of amoxicillin suspension.
Researchers have reported more cases of iGAS in the United Kingdom this year, as well. According to the UK Health Security Agency, 74 deaths, including 16 children, in England have been attributed to iGAS since September.
“We know that this is concerning for parents, but I want to stress that while we are seeing an increase in cases in children, this remains very uncommon,” UKHSA Deputy Director Colin Brown said in a news release. “There are lots of winter bugs circulating that can make your child feel unwell that mostly aren’t cause for alarm. However, make sure you talk to a health professional if your child is getting worse after a bout of scarlet fever, a sore throat, or respiratory infection.”
A fever that doesn’t resolve, dehydration, extreme tiredness, and difficulty breathing are signs to watch out for, Dr. Brown said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study says food dye red 40 can trigger bowel problems
A common food dye found in candy, soft drinks, and some cereals, known as Allura Red, can lead to inflammatory bowel diseases, Crohn’s disease, and other health problems, new research shows.
Long-term ingestion of the dye disrupts gut function, causing a series of changes that lead to a higher risk of colitis, according to the research from McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont. The findings were published in Nature Communications.
The dye is also known as FD&C Red 40 and Food Red 17. It adds color and texture and is often used to attract children, according to a press release on Eurekalert.
These findings have important implications in the prevention and management of gut inflammation,” said senior author Waliul Khan, MBBS, PhD, a professor in the McMaster department of pathology and molecular medicine.
“What we have found is striking and alarming, as this common synthetic food dye is a possible dietary trigger for IBDs,” he said. “The literature suggests that the consumption of Allura Red also affects certain allergies, immune disorders, and behavioural problems in children, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.”
The human diet in Western cultures, with its reliance on processed fats, red and processed meat, and low fiber, contributes to IBDs as well, Dr. Khan said.
Food dyes such as Allura Red have been used more and more in recent years. Their effect on gut health hasn’t been studied much.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A common food dye found in candy, soft drinks, and some cereals, known as Allura Red, can lead to inflammatory bowel diseases, Crohn’s disease, and other health problems, new research shows.
Long-term ingestion of the dye disrupts gut function, causing a series of changes that lead to a higher risk of colitis, according to the research from McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont. The findings were published in Nature Communications.
The dye is also known as FD&C Red 40 and Food Red 17. It adds color and texture and is often used to attract children, according to a press release on Eurekalert.
These findings have important implications in the prevention and management of gut inflammation,” said senior author Waliul Khan, MBBS, PhD, a professor in the McMaster department of pathology and molecular medicine.
“What we have found is striking and alarming, as this common synthetic food dye is a possible dietary trigger for IBDs,” he said. “The literature suggests that the consumption of Allura Red also affects certain allergies, immune disorders, and behavioural problems in children, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.”
The human diet in Western cultures, with its reliance on processed fats, red and processed meat, and low fiber, contributes to IBDs as well, Dr. Khan said.
Food dyes such as Allura Red have been used more and more in recent years. Their effect on gut health hasn’t been studied much.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A common food dye found in candy, soft drinks, and some cereals, known as Allura Red, can lead to inflammatory bowel diseases, Crohn’s disease, and other health problems, new research shows.
Long-term ingestion of the dye disrupts gut function, causing a series of changes that lead to a higher risk of colitis, according to the research from McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont. The findings were published in Nature Communications.
The dye is also known as FD&C Red 40 and Food Red 17. It adds color and texture and is often used to attract children, according to a press release on Eurekalert.
These findings have important implications in the prevention and management of gut inflammation,” said senior author Waliul Khan, MBBS, PhD, a professor in the McMaster department of pathology and molecular medicine.
“What we have found is striking and alarming, as this common synthetic food dye is a possible dietary trigger for IBDs,” he said. “The literature suggests that the consumption of Allura Red also affects certain allergies, immune disorders, and behavioural problems in children, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.”
The human diet in Western cultures, with its reliance on processed fats, red and processed meat, and low fiber, contributes to IBDs as well, Dr. Khan said.
Food dyes such as Allura Red have been used more and more in recent years. Their effect on gut health hasn’t been studied much.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.