User login
‘Fragmented’ speech patterns may predict psychosis relapse
In the first study, an algorithm was created to analyze speech patterns and semantic content to create novel “speech networks.” Compared with their healthy peers, patients with FEP had smaller and more fragmented networks. At-risk individuals had fragmented values that were in between those of the FEP and healthy control groups.
“This suggests that semantic speech networks can enable deeper phenotyping of formal thought disorder and psychosis,” said lead author Caroline Nettekoven, PhD, department of psychiatry, University of Cambridge, England.
In the second study, Janna N. de Boer, MD, University of Groningen, the Netherlands, and colleagues examined patients with FEP who did and did not experience relapse after 24 months of follow-up.
An algorithm based on natural language processing (NLP) of speech recordings predicted the relapses with an accuracy of more than 80%.
NLP “is a powerful tool with high potential for clinical application and diagnosis and differentiation, given its ease in acquirement, low cost, and naturally low patient burden,” said de Boer.
The findings for both studies were presented at the annual congress of the Schizophrenia International Research Society.
Fragmented networks
Dr. Nettekoven noted that previous research has shown “mapping the speech of a psychosis patient as a network and analyzing the network using graph theory is useful for understanding formal thought disorder.”
However, these tools ignore the semantic content of speech, which is a “key feature” that is altered in psychotic language, she added.
The researchers therefore proposed a “novel type of network to map the content of speech.”
For example, if someone said, “I see a man,” a semantic speech network developed from this sentence would have the first and last words connected by “the edge” to the word “see,” Dr. Nettekoven explained.
To explore further, the investigators developed an algorithm known as “netts” that automatically creates semantic speech networks from transcribed speech.
They first applied the algorithm to transcribed speech from a general population sample of 436 individuals and then to a clinical sample (n = 53) comprising patients with FEP, those at clinical high risk for psychosis, and a healthy control group.
Comparing the general population sample with randomly generated semantic speech networks, the investigators found that networks from the general population had fewer but larger connected components, which “reflects the nonrandom nature of speech,” said Dr. Nettekoven.
In the clinical sample, networks from the FEP group had a significantly higher number of connected components compared with the healthy control group (P = .05) and a significantly smaller median connected-component size (P < .01).
“So patients’ mental speech networks are more fragmented than those from controls,” said Dr. Nettekoven. She added that the networks from clinically high-risk individuals “showed fragmentation values in between [those of] patients and controls.”
A further clustering analysis suggested the semantic speech networks “capture a novel signal that is not already described” by other NLP measures, Dr. Nettekoven said. In addition, the network features were related to negative symptom scores and scores on the Thought and Language Index.
However, Dr. Nettekoven noted that these relationships “did not survive correcting for multiple comparisons.”
Relapse predictor
During her presentation of the second study, Dr. de Boer said that “predicting relapse remains challenging” in FEP.
However, she noted that recent developments in NLP have proved to be effective in a “range of applications,” including early symptom recognition and differential diagnosis in psychosis.
To determine whether NLP could help predict relapse, the study included 104 patients aged 16-55 years with FEP whose conditions had been in remission for 3-6 months. Speech recordings were made at baseline and after 3 and 6 months and were analyzed via OpenSMILE software.
After a follow-up of 24 months, 24 of the patients remaining in the study had not experienced relapse, while 21 patients had experienced relapse. There were no significant age, education, or gender differences between those who did and those who did not experience relapse.
On the basis of speech analysis, the investigators identified a machine learning classifier, which showed an accuracy of 80.8% in predicting relapse 3 months in advance of the occurrence.
‘Valid and informative’
Commenting on the studies, Eric J. Tan, PhD, Centre for Mental Health, Swinburne University of Technology, Melbourne, said they are “but two of a variety of ways in which speech can be analyzed and are both equally valid and informative.”
The key takeaway “is that both studies are examples of the ways in which speech can be used clinically, such as for predicting relapse and for the potential proxy measure for the assessment of symptom severity,” said Dr. Tan, who was not involved with the research.
The studies also show that “speech is sensitive to different stages of the disorder, as well as its individual symptoms,” he added.
However, Dr. Tan noted that although “speech may be more of a sign of an underlying pathology or dysfunction, given that it waxes and wanes with illness severity, more analyses are needed before drawing definitive conclusions.” This is especially needed “given the relative infancy of quantitative speech analysis,” he said.
“It would also be useful to conduct these analyses across a variety of different languages to look for commonalities and differences that will help shed light on the variables most closely linked to the disorder,” Dr. Tan concluded.
The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tan has received an Early Career Research Fellowship from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the first study, an algorithm was created to analyze speech patterns and semantic content to create novel “speech networks.” Compared with their healthy peers, patients with FEP had smaller and more fragmented networks. At-risk individuals had fragmented values that were in between those of the FEP and healthy control groups.
“This suggests that semantic speech networks can enable deeper phenotyping of formal thought disorder and psychosis,” said lead author Caroline Nettekoven, PhD, department of psychiatry, University of Cambridge, England.
In the second study, Janna N. de Boer, MD, University of Groningen, the Netherlands, and colleagues examined patients with FEP who did and did not experience relapse after 24 months of follow-up.
An algorithm based on natural language processing (NLP) of speech recordings predicted the relapses with an accuracy of more than 80%.
NLP “is a powerful tool with high potential for clinical application and diagnosis and differentiation, given its ease in acquirement, low cost, and naturally low patient burden,” said de Boer.
The findings for both studies were presented at the annual congress of the Schizophrenia International Research Society.
Fragmented networks
Dr. Nettekoven noted that previous research has shown “mapping the speech of a psychosis patient as a network and analyzing the network using graph theory is useful for understanding formal thought disorder.”
However, these tools ignore the semantic content of speech, which is a “key feature” that is altered in psychotic language, she added.
The researchers therefore proposed a “novel type of network to map the content of speech.”
For example, if someone said, “I see a man,” a semantic speech network developed from this sentence would have the first and last words connected by “the edge” to the word “see,” Dr. Nettekoven explained.
To explore further, the investigators developed an algorithm known as “netts” that automatically creates semantic speech networks from transcribed speech.
They first applied the algorithm to transcribed speech from a general population sample of 436 individuals and then to a clinical sample (n = 53) comprising patients with FEP, those at clinical high risk for psychosis, and a healthy control group.
Comparing the general population sample with randomly generated semantic speech networks, the investigators found that networks from the general population had fewer but larger connected components, which “reflects the nonrandom nature of speech,” said Dr. Nettekoven.
In the clinical sample, networks from the FEP group had a significantly higher number of connected components compared with the healthy control group (P = .05) and a significantly smaller median connected-component size (P < .01).
“So patients’ mental speech networks are more fragmented than those from controls,” said Dr. Nettekoven. She added that the networks from clinically high-risk individuals “showed fragmentation values in between [those of] patients and controls.”
A further clustering analysis suggested the semantic speech networks “capture a novel signal that is not already described” by other NLP measures, Dr. Nettekoven said. In addition, the network features were related to negative symptom scores and scores on the Thought and Language Index.
However, Dr. Nettekoven noted that these relationships “did not survive correcting for multiple comparisons.”
Relapse predictor
During her presentation of the second study, Dr. de Boer said that “predicting relapse remains challenging” in FEP.
However, she noted that recent developments in NLP have proved to be effective in a “range of applications,” including early symptom recognition and differential diagnosis in psychosis.
To determine whether NLP could help predict relapse, the study included 104 patients aged 16-55 years with FEP whose conditions had been in remission for 3-6 months. Speech recordings were made at baseline and after 3 and 6 months and were analyzed via OpenSMILE software.
After a follow-up of 24 months, 24 of the patients remaining in the study had not experienced relapse, while 21 patients had experienced relapse. There were no significant age, education, or gender differences between those who did and those who did not experience relapse.
On the basis of speech analysis, the investigators identified a machine learning classifier, which showed an accuracy of 80.8% in predicting relapse 3 months in advance of the occurrence.
‘Valid and informative’
Commenting on the studies, Eric J. Tan, PhD, Centre for Mental Health, Swinburne University of Technology, Melbourne, said they are “but two of a variety of ways in which speech can be analyzed and are both equally valid and informative.”
The key takeaway “is that both studies are examples of the ways in which speech can be used clinically, such as for predicting relapse and for the potential proxy measure for the assessment of symptom severity,” said Dr. Tan, who was not involved with the research.
The studies also show that “speech is sensitive to different stages of the disorder, as well as its individual symptoms,” he added.
However, Dr. Tan noted that although “speech may be more of a sign of an underlying pathology or dysfunction, given that it waxes and wanes with illness severity, more analyses are needed before drawing definitive conclusions.” This is especially needed “given the relative infancy of quantitative speech analysis,” he said.
“It would also be useful to conduct these analyses across a variety of different languages to look for commonalities and differences that will help shed light on the variables most closely linked to the disorder,” Dr. Tan concluded.
The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tan has received an Early Career Research Fellowship from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the first study, an algorithm was created to analyze speech patterns and semantic content to create novel “speech networks.” Compared with their healthy peers, patients with FEP had smaller and more fragmented networks. At-risk individuals had fragmented values that were in between those of the FEP and healthy control groups.
“This suggests that semantic speech networks can enable deeper phenotyping of formal thought disorder and psychosis,” said lead author Caroline Nettekoven, PhD, department of psychiatry, University of Cambridge, England.
In the second study, Janna N. de Boer, MD, University of Groningen, the Netherlands, and colleagues examined patients with FEP who did and did not experience relapse after 24 months of follow-up.
An algorithm based on natural language processing (NLP) of speech recordings predicted the relapses with an accuracy of more than 80%.
NLP “is a powerful tool with high potential for clinical application and diagnosis and differentiation, given its ease in acquirement, low cost, and naturally low patient burden,” said de Boer.
The findings for both studies were presented at the annual congress of the Schizophrenia International Research Society.
Fragmented networks
Dr. Nettekoven noted that previous research has shown “mapping the speech of a psychosis patient as a network and analyzing the network using graph theory is useful for understanding formal thought disorder.”
However, these tools ignore the semantic content of speech, which is a “key feature” that is altered in psychotic language, she added.
The researchers therefore proposed a “novel type of network to map the content of speech.”
For example, if someone said, “I see a man,” a semantic speech network developed from this sentence would have the first and last words connected by “the edge” to the word “see,” Dr. Nettekoven explained.
To explore further, the investigators developed an algorithm known as “netts” that automatically creates semantic speech networks from transcribed speech.
They first applied the algorithm to transcribed speech from a general population sample of 436 individuals and then to a clinical sample (n = 53) comprising patients with FEP, those at clinical high risk for psychosis, and a healthy control group.
Comparing the general population sample with randomly generated semantic speech networks, the investigators found that networks from the general population had fewer but larger connected components, which “reflects the nonrandom nature of speech,” said Dr. Nettekoven.
In the clinical sample, networks from the FEP group had a significantly higher number of connected components compared with the healthy control group (P = .05) and a significantly smaller median connected-component size (P < .01).
“So patients’ mental speech networks are more fragmented than those from controls,” said Dr. Nettekoven. She added that the networks from clinically high-risk individuals “showed fragmentation values in between [those of] patients and controls.”
A further clustering analysis suggested the semantic speech networks “capture a novel signal that is not already described” by other NLP measures, Dr. Nettekoven said. In addition, the network features were related to negative symptom scores and scores on the Thought and Language Index.
However, Dr. Nettekoven noted that these relationships “did not survive correcting for multiple comparisons.”
Relapse predictor
During her presentation of the second study, Dr. de Boer said that “predicting relapse remains challenging” in FEP.
However, she noted that recent developments in NLP have proved to be effective in a “range of applications,” including early symptom recognition and differential diagnosis in psychosis.
To determine whether NLP could help predict relapse, the study included 104 patients aged 16-55 years with FEP whose conditions had been in remission for 3-6 months. Speech recordings were made at baseline and after 3 and 6 months and were analyzed via OpenSMILE software.
After a follow-up of 24 months, 24 of the patients remaining in the study had not experienced relapse, while 21 patients had experienced relapse. There were no significant age, education, or gender differences between those who did and those who did not experience relapse.
On the basis of speech analysis, the investigators identified a machine learning classifier, which showed an accuracy of 80.8% in predicting relapse 3 months in advance of the occurrence.
‘Valid and informative’
Commenting on the studies, Eric J. Tan, PhD, Centre for Mental Health, Swinburne University of Technology, Melbourne, said they are “but two of a variety of ways in which speech can be analyzed and are both equally valid and informative.”
The key takeaway “is that both studies are examples of the ways in which speech can be used clinically, such as for predicting relapse and for the potential proxy measure for the assessment of symptom severity,” said Dr. Tan, who was not involved with the research.
The studies also show that “speech is sensitive to different stages of the disorder, as well as its individual symptoms,” he added.
However, Dr. Tan noted that although “speech may be more of a sign of an underlying pathology or dysfunction, given that it waxes and wanes with illness severity, more analyses are needed before drawing definitive conclusions.” This is especially needed “given the relative infancy of quantitative speech analysis,” he said.
“It would also be useful to conduct these analyses across a variety of different languages to look for commonalities and differences that will help shed light on the variables most closely linked to the disorder,” Dr. Tan concluded.
The investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tan has received an Early Career Research Fellowship from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SIRS 2022
When CPI fails, HL patients should get timely allo-HCT
In fact, prior treatment with PD-1–directed therapies nivolumab (Opdivo) and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) appears to improve outcomes in allo-HCT patients, said Miguel-Angel Perales, MD, chief of the adult bone marrow transplant service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
“The use of allogeneic HCT is decreasing for Hodgkin even though it is a curative option, and we see patients referred after they have had multiple lines of therapy,” Dr. Perales said in an interview. “The lymphoma MDs have a perception that outcomes are poor, and therefore don’t refer.”
To illustrate his point, Dr. Perales shared data from the EBMT database. In 2014, the registry accrued approximately 450 allo-HCT cases; by 2021 this had fallen to fewer than 200 procedures.
Ironically, this declining enthusiasm for transplantation coincides with a steady improvement in transplant outcomes following PD-1 blockade, Dr. Perales noted. For example, an analysis, published in Nature, yielded an 82% overall survival (OS) at 3 years in patients who underwent allo-HCT after CPI treatment (n =209).
“Results of allo-HCT in patients with Hodgkin show a remarkable cure rate,” said Dr. Perales. “Part of that is probably driven by lower relapse due to enhanced graft-versus-lymphoma effect due to long CPI half-life.” (The half-lives of pembrolizumab and nivolumab are 22 and 25 days, respectively.)
At the EBMT meeting, Dr. Perales presented a new retrospective analysis that tested the hypothesis that CPIs might actually improve outcomes for allo-HCT patients. An international team of clinicians from EBMT and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) compared allo-HCT outcomes with (n = 347) and without (n = 1,382) prior treatment with a checkpoint inhibitor.
They found that prior CPI therapy was, indeed, associated with lower relapse (hazard ratio, 0.53; P = .00023) and longer progression-free survival (PFS) (HR, 0.75; P = .0171).
However, prior PD-1 drugs provided no survival advantage, Dr. Perales said. “The easiest explanation for a study showing a difference in PFS/relapse, not OS, is that we have good treatments that can treat patients who relapse and so their overall survival ends up being the same.”
The researchers also confirmed previous reports that patients who received PD-1 inhibitors prior to transplant had a higher incidence of GVHD. Prevalence of acute grades 2-4 GVHD was significantly higher (P = .027); however, acute grades 3-4 GVHD and chronic GVHD were not significantly different between the two groups.
Dr. Perales speculated that the use of posttransplant cyclophosphamide for GVHD prophylaxis would mitigate the risk of GVHD associated with PD-1 inhibitors, “we have not yet proven that formally ... [we] are still analyzing our data.”
Commenting on the results of the new analysis, Dr. Perales expressed concern that patients are being recruited to early-phase clinical trials after failing on a checkpoint inhibitor, instead of being offered allo-HCT – a potentially curative treatment – because treaters are misinformed about the safety of transplant after these drugs.
The NIH clinical-trials database backs up Dr. Perales’ worries. In the United States, for example, there are currently 19 trials recruiting for relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma patients prior to transplant. Of these, 15 studies permit enrollment of patients who have failed on CPIs, and 8 are phase 1 or 2 studies.
“The good news is that new drugs, including CPIs, have dramatically changed outcomes in this disease and that fewer patients now need an allo-HCT,” said Dr. Perales. And if a transplant is needed, “it is safe to perform allo-HCT in patients treated with prior CPI.”
However, time is of the essence. “Patients with Hodgkin lymphoma should be referred to allo-HCT if they are not responding or tolerating CPI, rather than go on a series of phase 1 trials,” Dr. Perales said. “Median age is 32, and we should be going for a cure, nothing less.”
Dr. Perales reported receiving honoraria from numerous pharmaceutical companies; serving on the data and safety monitoring boards of Cidara Therapeutics, Medigene, Sellas Life Sciences, and Servier; and serving on the scientific advisory board of NexImmune. He has ownership interests in NexImmune and Omeros, and has received institutional research support for clinical trials from Incyte, Kite/Gilead, Miltenyi Biotec, Nektar Therapeutics, and Novartis.
In fact, prior treatment with PD-1–directed therapies nivolumab (Opdivo) and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) appears to improve outcomes in allo-HCT patients, said Miguel-Angel Perales, MD, chief of the adult bone marrow transplant service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
“The use of allogeneic HCT is decreasing for Hodgkin even though it is a curative option, and we see patients referred after they have had multiple lines of therapy,” Dr. Perales said in an interview. “The lymphoma MDs have a perception that outcomes are poor, and therefore don’t refer.”
To illustrate his point, Dr. Perales shared data from the EBMT database. In 2014, the registry accrued approximately 450 allo-HCT cases; by 2021 this had fallen to fewer than 200 procedures.
Ironically, this declining enthusiasm for transplantation coincides with a steady improvement in transplant outcomes following PD-1 blockade, Dr. Perales noted. For example, an analysis, published in Nature, yielded an 82% overall survival (OS) at 3 years in patients who underwent allo-HCT after CPI treatment (n =209).
“Results of allo-HCT in patients with Hodgkin show a remarkable cure rate,” said Dr. Perales. “Part of that is probably driven by lower relapse due to enhanced graft-versus-lymphoma effect due to long CPI half-life.” (The half-lives of pembrolizumab and nivolumab are 22 and 25 days, respectively.)
At the EBMT meeting, Dr. Perales presented a new retrospective analysis that tested the hypothesis that CPIs might actually improve outcomes for allo-HCT patients. An international team of clinicians from EBMT and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) compared allo-HCT outcomes with (n = 347) and without (n = 1,382) prior treatment with a checkpoint inhibitor.
They found that prior CPI therapy was, indeed, associated with lower relapse (hazard ratio, 0.53; P = .00023) and longer progression-free survival (PFS) (HR, 0.75; P = .0171).
However, prior PD-1 drugs provided no survival advantage, Dr. Perales said. “The easiest explanation for a study showing a difference in PFS/relapse, not OS, is that we have good treatments that can treat patients who relapse and so their overall survival ends up being the same.”
The researchers also confirmed previous reports that patients who received PD-1 inhibitors prior to transplant had a higher incidence of GVHD. Prevalence of acute grades 2-4 GVHD was significantly higher (P = .027); however, acute grades 3-4 GVHD and chronic GVHD were not significantly different between the two groups.
Dr. Perales speculated that the use of posttransplant cyclophosphamide for GVHD prophylaxis would mitigate the risk of GVHD associated with PD-1 inhibitors, “we have not yet proven that formally ... [we] are still analyzing our data.”
Commenting on the results of the new analysis, Dr. Perales expressed concern that patients are being recruited to early-phase clinical trials after failing on a checkpoint inhibitor, instead of being offered allo-HCT – a potentially curative treatment – because treaters are misinformed about the safety of transplant after these drugs.
The NIH clinical-trials database backs up Dr. Perales’ worries. In the United States, for example, there are currently 19 trials recruiting for relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma patients prior to transplant. Of these, 15 studies permit enrollment of patients who have failed on CPIs, and 8 are phase 1 or 2 studies.
“The good news is that new drugs, including CPIs, have dramatically changed outcomes in this disease and that fewer patients now need an allo-HCT,” said Dr. Perales. And if a transplant is needed, “it is safe to perform allo-HCT in patients treated with prior CPI.”
However, time is of the essence. “Patients with Hodgkin lymphoma should be referred to allo-HCT if they are not responding or tolerating CPI, rather than go on a series of phase 1 trials,” Dr. Perales said. “Median age is 32, and we should be going for a cure, nothing less.”
Dr. Perales reported receiving honoraria from numerous pharmaceutical companies; serving on the data and safety monitoring boards of Cidara Therapeutics, Medigene, Sellas Life Sciences, and Servier; and serving on the scientific advisory board of NexImmune. He has ownership interests in NexImmune and Omeros, and has received institutional research support for clinical trials from Incyte, Kite/Gilead, Miltenyi Biotec, Nektar Therapeutics, and Novartis.
In fact, prior treatment with PD-1–directed therapies nivolumab (Opdivo) and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) appears to improve outcomes in allo-HCT patients, said Miguel-Angel Perales, MD, chief of the adult bone marrow transplant service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
“The use of allogeneic HCT is decreasing for Hodgkin even though it is a curative option, and we see patients referred after they have had multiple lines of therapy,” Dr. Perales said in an interview. “The lymphoma MDs have a perception that outcomes are poor, and therefore don’t refer.”
To illustrate his point, Dr. Perales shared data from the EBMT database. In 2014, the registry accrued approximately 450 allo-HCT cases; by 2021 this had fallen to fewer than 200 procedures.
Ironically, this declining enthusiasm for transplantation coincides with a steady improvement in transplant outcomes following PD-1 blockade, Dr. Perales noted. For example, an analysis, published in Nature, yielded an 82% overall survival (OS) at 3 years in patients who underwent allo-HCT after CPI treatment (n =209).
“Results of allo-HCT in patients with Hodgkin show a remarkable cure rate,” said Dr. Perales. “Part of that is probably driven by lower relapse due to enhanced graft-versus-lymphoma effect due to long CPI half-life.” (The half-lives of pembrolizumab and nivolumab are 22 and 25 days, respectively.)
At the EBMT meeting, Dr. Perales presented a new retrospective analysis that tested the hypothesis that CPIs might actually improve outcomes for allo-HCT patients. An international team of clinicians from EBMT and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) compared allo-HCT outcomes with (n = 347) and without (n = 1,382) prior treatment with a checkpoint inhibitor.
They found that prior CPI therapy was, indeed, associated with lower relapse (hazard ratio, 0.53; P = .00023) and longer progression-free survival (PFS) (HR, 0.75; P = .0171).
However, prior PD-1 drugs provided no survival advantage, Dr. Perales said. “The easiest explanation for a study showing a difference in PFS/relapse, not OS, is that we have good treatments that can treat patients who relapse and so their overall survival ends up being the same.”
The researchers also confirmed previous reports that patients who received PD-1 inhibitors prior to transplant had a higher incidence of GVHD. Prevalence of acute grades 2-4 GVHD was significantly higher (P = .027); however, acute grades 3-4 GVHD and chronic GVHD were not significantly different between the two groups.
Dr. Perales speculated that the use of posttransplant cyclophosphamide for GVHD prophylaxis would mitigate the risk of GVHD associated with PD-1 inhibitors, “we have not yet proven that formally ... [we] are still analyzing our data.”
Commenting on the results of the new analysis, Dr. Perales expressed concern that patients are being recruited to early-phase clinical trials after failing on a checkpoint inhibitor, instead of being offered allo-HCT – a potentially curative treatment – because treaters are misinformed about the safety of transplant after these drugs.
The NIH clinical-trials database backs up Dr. Perales’ worries. In the United States, for example, there are currently 19 trials recruiting for relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma patients prior to transplant. Of these, 15 studies permit enrollment of patients who have failed on CPIs, and 8 are phase 1 or 2 studies.
“The good news is that new drugs, including CPIs, have dramatically changed outcomes in this disease and that fewer patients now need an allo-HCT,” said Dr. Perales. And if a transplant is needed, “it is safe to perform allo-HCT in patients treated with prior CPI.”
However, time is of the essence. “Patients with Hodgkin lymphoma should be referred to allo-HCT if they are not responding or tolerating CPI, rather than go on a series of phase 1 trials,” Dr. Perales said. “Median age is 32, and we should be going for a cure, nothing less.”
Dr. Perales reported receiving honoraria from numerous pharmaceutical companies; serving on the data and safety monitoring boards of Cidara Therapeutics, Medigene, Sellas Life Sciences, and Servier; and serving on the scientific advisory board of NexImmune. He has ownership interests in NexImmune and Omeros, and has received institutional research support for clinical trials from Incyte, Kite/Gilead, Miltenyi Biotec, Nektar Therapeutics, and Novartis.
A 14-year-old male presents to clinic with a new-onset rash of the hands
Photosensitivity due to doxycycline
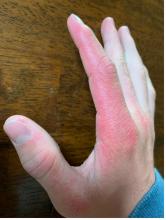
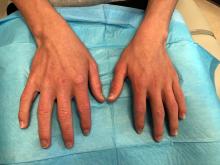
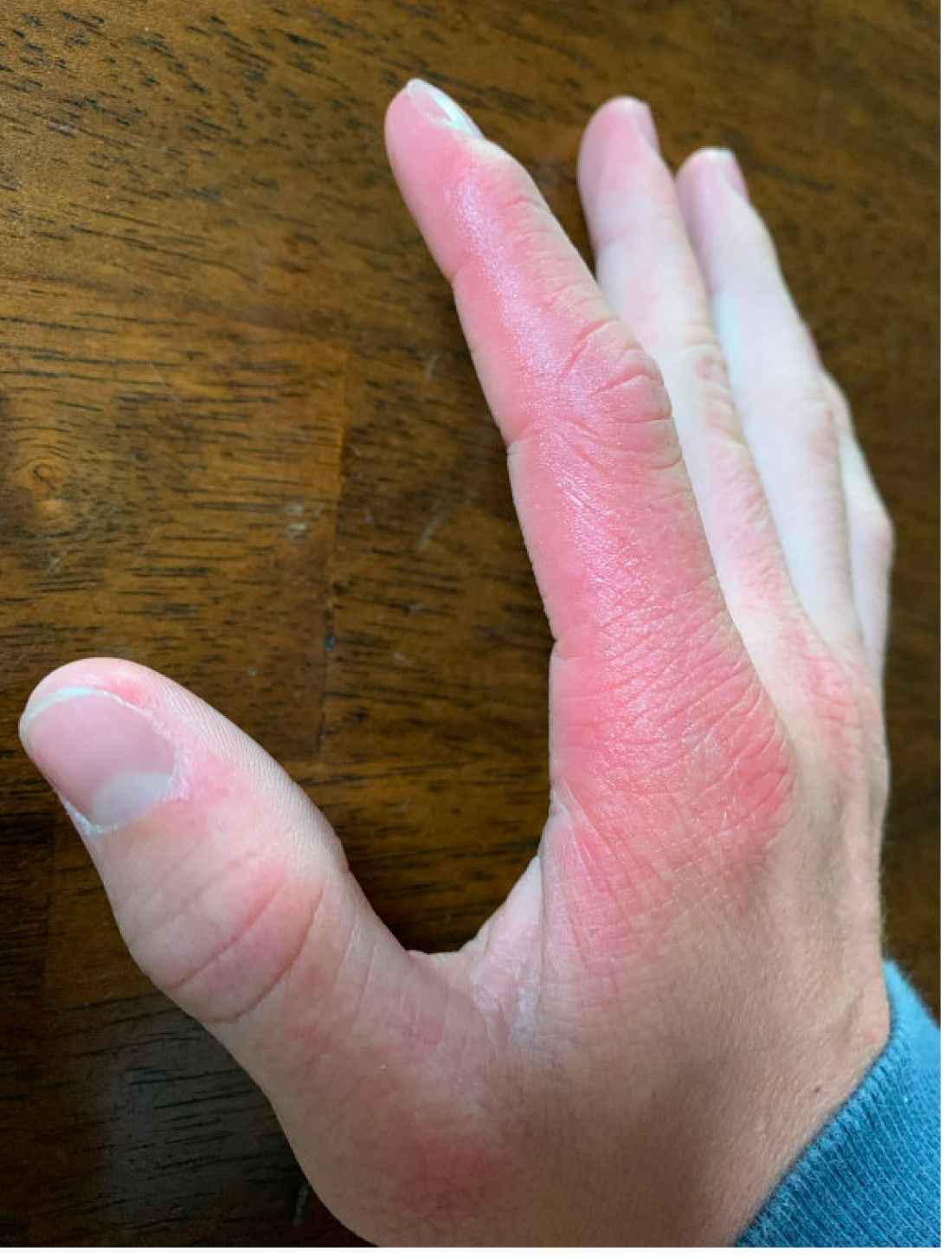
As the patient’s rash presented in sun-exposed areas with both skin and nail changes, our patient was diagnosed with a phototoxic reaction to doxycycline, the oral antibiotic used to treat his acne.
Photosensitive cutaneous drug eruptions are reactions that occur after exposure to a medication and subsequent exposure to UV radiation or visible light. Reactions can be classified into two ways based on their mechanism of action: phototoxic or photoallergic.1 Phototoxic reactions are more common and are a result of direct keratinocyte damage and cellular necrosis. Many classes of medications may cause this adverse effect, but the tetracycline class of antibiotics is a common culprit.2 Photoallergic reactions are less common and are a result of a type IV immune reaction to the offending agent.1
Phototoxic reactions generally present shortly after sun or UV exposure with a photo-distributed eruption pattern.3 Commonly involved areas include the face, the neck, and the extensor surfaces of extremities, with sparing of relatively protected skin such as the upper eyelids and the skin folds.2 Erythema may initially develop in the exposed skin areas, followed by appearance of edema, vesicles, or bullae.1-3 The eruption may be painful and itchy, with some patients reporting severe pain.3
Doxycycline phototoxicity may also cause onycholysis of the nails.2 The reaction is dose dependent, with higher doses of medication leading to a higher likelihood of symptoms.1,2 It is also more prevalent in patients with Fitzpatrick skin type I and II. The usual UVA wavelength required to induce this reaction appears to be in the 320-400 nm range of the UV spectrum.4 By contrast, photoallergic reactions are dose independent, and require a sensitization period prior to the eruption.1 An eczematous eruption is most commonly seen with photoallergic reactions.3
Treatment of drug-induced photosensitivity reactions requires proper identification of the diagnosis and the offending agent, followed by cessation of the medication. If cessation is not possible, then lowering the dose can help to minimize worsening of the condition. However, for photoallergic reactions, the reaction is dose independent so switching to another tolerated agent is likely required. For persistent symptoms following medication withdrawal, topical or systemic steroids and oral antihistamine can help with symptom management.1 For patients with photo-onycholysis, treatment involves stopping the medication and waiting for the intact nail plate to grow.
Prevention is key in the management of photosensitivity reactions. Patients should be counseled about the increased risk of photosensitivity while on tetracycline medications and encouraged to engage in enhanced sun protection measures such as wearing sun protective hats and clothing, increasing use of sunscreen that provides mainly UVA but also UVB protection, and avoiding the sun during the midday when the UV index is highest.1-3
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune condition that presents with skin lesions as well as systemic findings such as myositis. The cutaneous findings are variable, but pathognomonic findings include Gottron papules of the hands, Gottron’s sign on the elbows, knees, and ankles, and the heliotrope rash of the face. Eighty percent of patients have myopathy presenting as muscle weakness, and commonly have elevated creatine kinase, aspartate transaminase, and alanine transaminase values.5 Diagnosis may be confirmed through skin or muscle biopsy, though antibody studies can also play a helpful role in diagnosis. Treatment is generally with oral corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants as well as sun protection.6 The rash seen in our patient could have been seen in patients with dermatomyositis, though it was not in the typical location on the knuckles (Gottron papules) as it also affected the lateral sides of the fingers.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune condition characterized by systemic and cutaneous manifestations. Systemic symptoms may include weight loss, fever, fatigue, arthralgia, or arthritis; patients are at risk of renal, cardiovascular, pulmonary, and neurologic complications of SLE.7 The most common cutaneous finding is malar rash, though there are myriad dermatologic manifestations that can occur associated with photosensitivity. Diagnosis is made based on history, physical, and laboratory testing. Treatment options include NSAIDs, oral glucocorticoids, antimalarial drugs, and immunosuppressants.7 Though our patient exhibited photosensitivity, he had none of the systemic findings associated with SLE, making this diagnosis unlikely.
Allergic contact dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, and may present as acute, subacute, or chronic dermatitis. The clinical findings vary based on chronicity. Acute ACD presents as pruritic erythematous papules and vesicles or bullae, similar to how it occurred in our patient, though our patient’s lesions were more tender than pruritic. Chronic ACD presents with erythematous lesions with pruritis, lichenification, scaling, and/or fissuring. Observing shapes or sharp demarcation of lesions may help with diagnosis. Patch testing is also useful in the diagnosis of ACD.
Treatment generally involves avoiding the offending agent with topical corticosteroids for symptom management.8
Polymorphous light eruption
Polymorphous light eruption (PLE) is a delayed, type IV hypersensitivity reaction to UV-induced antigens, though these antigens are unknown. PLE presents hours to days following solar or UV exposure and presents only in sun-exposed areas. Itching and burning are always present, but lesion morphology varies from erythema and papules to vesico-papules and blisters. Notably, PLE must be distinguished from drug photosensitivity through history. Treatment generally involves symptom management with topical steroids and sun protective measures for prevention.9 While PLE may present similarly to drug photosensitivity reactions, our patient’s use of a known phototoxic agent makes PLE a less likely diagnosis.
Ms. Appiah is a pediatric dermatology research associate and medical student at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Neither Dr. Matiz nor Ms. Appiah has any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Montgomery S et al. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40(1):57-63.
2. Blakely KM et al. Drug Saf. 2019;42(7):827-47.
3. Goetze S et al. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;30(2):76-80.
4. Odorici G et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34(4):e14978.
5. DeWane ME et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):267-81.
6. Waldman R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):283-96.
7. Kiriakidou M et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(11):ITC81-ITC96.
8. Nassau S et al. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(1):61-76.
9. Guarrera M. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;996:61-70.
Photosensitivity due to doxycycline
As the patient’s rash presented in sun-exposed areas with both skin and nail changes, our patient was diagnosed with a phototoxic reaction to doxycycline, the oral antibiotic used to treat his acne.
Photosensitive cutaneous drug eruptions are reactions that occur after exposure to a medication and subsequent exposure to UV radiation or visible light. Reactions can be classified into two ways based on their mechanism of action: phototoxic or photoallergic.1 Phototoxic reactions are more common and are a result of direct keratinocyte damage and cellular necrosis. Many classes of medications may cause this adverse effect, but the tetracycline class of antibiotics is a common culprit.2 Photoallergic reactions are less common and are a result of a type IV immune reaction to the offending agent.1
Phototoxic reactions generally present shortly after sun or UV exposure with a photo-distributed eruption pattern.3 Commonly involved areas include the face, the neck, and the extensor surfaces of extremities, with sparing of relatively protected skin such as the upper eyelids and the skin folds.2 Erythema may initially develop in the exposed skin areas, followed by appearance of edema, vesicles, or bullae.1-3 The eruption may be painful and itchy, with some patients reporting severe pain.3
Doxycycline phototoxicity may also cause onycholysis of the nails.2 The reaction is dose dependent, with higher doses of medication leading to a higher likelihood of symptoms.1,2 It is also more prevalent in patients with Fitzpatrick skin type I and II. The usual UVA wavelength required to induce this reaction appears to be in the 320-400 nm range of the UV spectrum.4 By contrast, photoallergic reactions are dose independent, and require a sensitization period prior to the eruption.1 An eczematous eruption is most commonly seen with photoallergic reactions.3
Treatment of drug-induced photosensitivity reactions requires proper identification of the diagnosis and the offending agent, followed by cessation of the medication. If cessation is not possible, then lowering the dose can help to minimize worsening of the condition. However, for photoallergic reactions, the reaction is dose independent so switching to another tolerated agent is likely required. For persistent symptoms following medication withdrawal, topical or systemic steroids and oral antihistamine can help with symptom management.1 For patients with photo-onycholysis, treatment involves stopping the medication and waiting for the intact nail plate to grow.
Prevention is key in the management of photosensitivity reactions. Patients should be counseled about the increased risk of photosensitivity while on tetracycline medications and encouraged to engage in enhanced sun protection measures such as wearing sun protective hats and clothing, increasing use of sunscreen that provides mainly UVA but also UVB protection, and avoiding the sun during the midday when the UV index is highest.1-3
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune condition that presents with skin lesions as well as systemic findings such as myositis. The cutaneous findings are variable, but pathognomonic findings include Gottron papules of the hands, Gottron’s sign on the elbows, knees, and ankles, and the heliotrope rash of the face. Eighty percent of patients have myopathy presenting as muscle weakness, and commonly have elevated creatine kinase, aspartate transaminase, and alanine transaminase values.5 Diagnosis may be confirmed through skin or muscle biopsy, though antibody studies can also play a helpful role in diagnosis. Treatment is generally with oral corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants as well as sun protection.6 The rash seen in our patient could have been seen in patients with dermatomyositis, though it was not in the typical location on the knuckles (Gottron papules) as it also affected the lateral sides of the fingers.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune condition characterized by systemic and cutaneous manifestations. Systemic symptoms may include weight loss, fever, fatigue, arthralgia, or arthritis; patients are at risk of renal, cardiovascular, pulmonary, and neurologic complications of SLE.7 The most common cutaneous finding is malar rash, though there are myriad dermatologic manifestations that can occur associated with photosensitivity. Diagnosis is made based on history, physical, and laboratory testing. Treatment options include NSAIDs, oral glucocorticoids, antimalarial drugs, and immunosuppressants.7 Though our patient exhibited photosensitivity, he had none of the systemic findings associated with SLE, making this diagnosis unlikely.
Allergic contact dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, and may present as acute, subacute, or chronic dermatitis. The clinical findings vary based on chronicity. Acute ACD presents as pruritic erythematous papules and vesicles or bullae, similar to how it occurred in our patient, though our patient’s lesions were more tender than pruritic. Chronic ACD presents with erythematous lesions with pruritis, lichenification, scaling, and/or fissuring. Observing shapes or sharp demarcation of lesions may help with diagnosis. Patch testing is also useful in the diagnosis of ACD.
Treatment generally involves avoiding the offending agent with topical corticosteroids for symptom management.8
Polymorphous light eruption
Polymorphous light eruption (PLE) is a delayed, type IV hypersensitivity reaction to UV-induced antigens, though these antigens are unknown. PLE presents hours to days following solar or UV exposure and presents only in sun-exposed areas. Itching and burning are always present, but lesion morphology varies from erythema and papules to vesico-papules and blisters. Notably, PLE must be distinguished from drug photosensitivity through history. Treatment generally involves symptom management with topical steroids and sun protective measures for prevention.9 While PLE may present similarly to drug photosensitivity reactions, our patient’s use of a known phototoxic agent makes PLE a less likely diagnosis.
Ms. Appiah is a pediatric dermatology research associate and medical student at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Neither Dr. Matiz nor Ms. Appiah has any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Montgomery S et al. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40(1):57-63.
2. Blakely KM et al. Drug Saf. 2019;42(7):827-47.
3. Goetze S et al. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;30(2):76-80.
4. Odorici G et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34(4):e14978.
5. DeWane ME et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):267-81.
6. Waldman R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):283-96.
7. Kiriakidou M et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(11):ITC81-ITC96.
8. Nassau S et al. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(1):61-76.
9. Guarrera M. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;996:61-70.
Photosensitivity due to doxycycline
As the patient’s rash presented in sun-exposed areas with both skin and nail changes, our patient was diagnosed with a phototoxic reaction to doxycycline, the oral antibiotic used to treat his acne.
Photosensitive cutaneous drug eruptions are reactions that occur after exposure to a medication and subsequent exposure to UV radiation or visible light. Reactions can be classified into two ways based on their mechanism of action: phototoxic or photoallergic.1 Phototoxic reactions are more common and are a result of direct keratinocyte damage and cellular necrosis. Many classes of medications may cause this adverse effect, but the tetracycline class of antibiotics is a common culprit.2 Photoallergic reactions are less common and are a result of a type IV immune reaction to the offending agent.1
Phototoxic reactions generally present shortly after sun or UV exposure with a photo-distributed eruption pattern.3 Commonly involved areas include the face, the neck, and the extensor surfaces of extremities, with sparing of relatively protected skin such as the upper eyelids and the skin folds.2 Erythema may initially develop in the exposed skin areas, followed by appearance of edema, vesicles, or bullae.1-3 The eruption may be painful and itchy, with some patients reporting severe pain.3
Doxycycline phototoxicity may also cause onycholysis of the nails.2 The reaction is dose dependent, with higher doses of medication leading to a higher likelihood of symptoms.1,2 It is also more prevalent in patients with Fitzpatrick skin type I and II. The usual UVA wavelength required to induce this reaction appears to be in the 320-400 nm range of the UV spectrum.4 By contrast, photoallergic reactions are dose independent, and require a sensitization period prior to the eruption.1 An eczematous eruption is most commonly seen with photoallergic reactions.3
Treatment of drug-induced photosensitivity reactions requires proper identification of the diagnosis and the offending agent, followed by cessation of the medication. If cessation is not possible, then lowering the dose can help to minimize worsening of the condition. However, for photoallergic reactions, the reaction is dose independent so switching to another tolerated agent is likely required. For persistent symptoms following medication withdrawal, topical or systemic steroids and oral antihistamine can help with symptom management.1 For patients with photo-onycholysis, treatment involves stopping the medication and waiting for the intact nail plate to grow.
Prevention is key in the management of photosensitivity reactions. Patients should be counseled about the increased risk of photosensitivity while on tetracycline medications and encouraged to engage in enhanced sun protection measures such as wearing sun protective hats and clothing, increasing use of sunscreen that provides mainly UVA but also UVB protection, and avoiding the sun during the midday when the UV index is highest.1-3
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune condition that presents with skin lesions as well as systemic findings such as myositis. The cutaneous findings are variable, but pathognomonic findings include Gottron papules of the hands, Gottron’s sign on the elbows, knees, and ankles, and the heliotrope rash of the face. Eighty percent of patients have myopathy presenting as muscle weakness, and commonly have elevated creatine kinase, aspartate transaminase, and alanine transaminase values.5 Diagnosis may be confirmed through skin or muscle biopsy, though antibody studies can also play a helpful role in diagnosis. Treatment is generally with oral corticosteroids or other immunosuppressants as well as sun protection.6 The rash seen in our patient could have been seen in patients with dermatomyositis, though it was not in the typical location on the knuckles (Gottron papules) as it also affected the lateral sides of the fingers.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune condition characterized by systemic and cutaneous manifestations. Systemic symptoms may include weight loss, fever, fatigue, arthralgia, or arthritis; patients are at risk of renal, cardiovascular, pulmonary, and neurologic complications of SLE.7 The most common cutaneous finding is malar rash, though there are myriad dermatologic manifestations that can occur associated with photosensitivity. Diagnosis is made based on history, physical, and laboratory testing. Treatment options include NSAIDs, oral glucocorticoids, antimalarial drugs, and immunosuppressants.7 Though our patient exhibited photosensitivity, he had none of the systemic findings associated with SLE, making this diagnosis unlikely.
Allergic contact dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, and may present as acute, subacute, or chronic dermatitis. The clinical findings vary based on chronicity. Acute ACD presents as pruritic erythematous papules and vesicles or bullae, similar to how it occurred in our patient, though our patient’s lesions were more tender than pruritic. Chronic ACD presents with erythematous lesions with pruritis, lichenification, scaling, and/or fissuring. Observing shapes or sharp demarcation of lesions may help with diagnosis. Patch testing is also useful in the diagnosis of ACD.
Treatment generally involves avoiding the offending agent with topical corticosteroids for symptom management.8
Polymorphous light eruption
Polymorphous light eruption (PLE) is a delayed, type IV hypersensitivity reaction to UV-induced antigens, though these antigens are unknown. PLE presents hours to days following solar or UV exposure and presents only in sun-exposed areas. Itching and burning are always present, but lesion morphology varies from erythema and papules to vesico-papules and blisters. Notably, PLE must be distinguished from drug photosensitivity through history. Treatment generally involves symptom management with topical steroids and sun protective measures for prevention.9 While PLE may present similarly to drug photosensitivity reactions, our patient’s use of a known phototoxic agent makes PLE a less likely diagnosis.
Ms. Appiah is a pediatric dermatology research associate and medical student at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Neither Dr. Matiz nor Ms. Appiah has any relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Montgomery S et al. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40(1):57-63.
2. Blakely KM et al. Drug Saf. 2019;42(7):827-47.
3. Goetze S et al. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;30(2):76-80.
4. Odorici G et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34(4):e14978.
5. DeWane ME et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):267-81.
6. Waldman R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):283-96.
7. Kiriakidou M et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(11):ITC81-ITC96.
8. Nassau S et al. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(1):61-76.
9. Guarrera M. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;996:61-70.
He reported no hiking or gardening, no new topical products such as new sunscreens or lotions, and no new medications. The patient had a history of acne, for which he used over-the-counter benzoyl peroxide wash, adapalene gel, and an oral antibiotic for 3 months. His review of systems was negative for fevers, chills, muscle weakness, mouth sores, or joint pain and no prior rashes following sun exposure.
On physical exam he presented with pink plaques with thin vesicles on the dorsum of the hands that were more noticeable on the lateral aspect of both the first and second fingers (Figures 1 and 2). His nails also had a yellow discoloration.
MammoRisk: A novel tool for assessing breast cancer risk
, according to a recent study. The assessment is based on a patient’s clinical data and breast density, with or without a polygenic risk score (PRS). Adding the latter criterion to the model led to four out of 10 women being assigned a different risk category. Of note, three out of 10 women were changed to a higher risk category.
A multifaceted assessment
In France, biennial mammographic screening is recommended for women aged 50-74 years. A personalized risk assessment approach based not only on age, but also on various risk factors, is a promising strategy that is currently being studied for several types of cancer. These personalized screening approaches seek to contribute to early diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer at an early and curable stage, as well as to decrease overall health costs for society.
Women aged 40 years or older, with no more than one first-degree relative with breast cancer diagnosed after the age of 40 years, were eligible for risk assessment using MammoRisk. Women previously identified as high risk were, therefore, not enrolled. MammoRisk is a machine learning–based tool that evaluates a patient’s risk with or without considering PRS. A PRS reflects the individual’s genetic risk of developing breast cancer. To calculate this risk, DNA was extracted from saliva samples for genotyping of 76 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Patients underwent a complete breast cancer assessment, including a questionnaire, mammogram with evaluation of breast density, collection of saliva sample, and consultations with a radiologist and a breast cancer specialist, the investigators said.
PRS influenced risk
Out of the 290 women who underwent breast cancer assessment between January 2019 and May 2021, 68% were eligible for risk assessment using MammoRisk (median age, 52 years). The others were not eligible because they were younger than 40 years of age, had a history of atypical hyperplasia, were directed to oncogenetic consultation, had a non-White origin, or were considered for Tyrer–Cuzick risk assessment.
Following risk assessment using MammoRisk without PRS, 16% of patients were classified as moderate risk, 53% as intermediate risk, 31% as high risk, and 0% as very high risk. The median risk score (estimated risk at 5 years) was 1.5.
When PRS was added to MammoRisk, 25% were classified as moderate risk, 33% as intermediate risk, 42% as high risk, and 0% as very high risk. Again, the median risk score was 1.5.
A total of 40% of patients were assigned a different risk category when PRS was added to MammoRisk. Importantly, 28% of patients changed from intermediate risk to moderate or high risk.
One author has received speaker honorarium from Predilife, the company commercializing MammoRisk. The others report no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a recent study. The assessment is based on a patient’s clinical data and breast density, with or without a polygenic risk score (PRS). Adding the latter criterion to the model led to four out of 10 women being assigned a different risk category. Of note, three out of 10 women were changed to a higher risk category.
A multifaceted assessment
In France, biennial mammographic screening is recommended for women aged 50-74 years. A personalized risk assessment approach based not only on age, but also on various risk factors, is a promising strategy that is currently being studied for several types of cancer. These personalized screening approaches seek to contribute to early diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer at an early and curable stage, as well as to decrease overall health costs for society.
Women aged 40 years or older, with no more than one first-degree relative with breast cancer diagnosed after the age of 40 years, were eligible for risk assessment using MammoRisk. Women previously identified as high risk were, therefore, not enrolled. MammoRisk is a machine learning–based tool that evaluates a patient’s risk with or without considering PRS. A PRS reflects the individual’s genetic risk of developing breast cancer. To calculate this risk, DNA was extracted from saliva samples for genotyping of 76 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Patients underwent a complete breast cancer assessment, including a questionnaire, mammogram with evaluation of breast density, collection of saliva sample, and consultations with a radiologist and a breast cancer specialist, the investigators said.
PRS influenced risk
Out of the 290 women who underwent breast cancer assessment between January 2019 and May 2021, 68% were eligible for risk assessment using MammoRisk (median age, 52 years). The others were not eligible because they were younger than 40 years of age, had a history of atypical hyperplasia, were directed to oncogenetic consultation, had a non-White origin, or were considered for Tyrer–Cuzick risk assessment.
Following risk assessment using MammoRisk without PRS, 16% of patients were classified as moderate risk, 53% as intermediate risk, 31% as high risk, and 0% as very high risk. The median risk score (estimated risk at 5 years) was 1.5.
When PRS was added to MammoRisk, 25% were classified as moderate risk, 33% as intermediate risk, 42% as high risk, and 0% as very high risk. Again, the median risk score was 1.5.
A total of 40% of patients were assigned a different risk category when PRS was added to MammoRisk. Importantly, 28% of patients changed from intermediate risk to moderate or high risk.
One author has received speaker honorarium from Predilife, the company commercializing MammoRisk. The others report no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a recent study. The assessment is based on a patient’s clinical data and breast density, with or without a polygenic risk score (PRS). Adding the latter criterion to the model led to four out of 10 women being assigned a different risk category. Of note, three out of 10 women were changed to a higher risk category.
A multifaceted assessment
In France, biennial mammographic screening is recommended for women aged 50-74 years. A personalized risk assessment approach based not only on age, but also on various risk factors, is a promising strategy that is currently being studied for several types of cancer. These personalized screening approaches seek to contribute to early diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer at an early and curable stage, as well as to decrease overall health costs for society.
Women aged 40 years or older, with no more than one first-degree relative with breast cancer diagnosed after the age of 40 years, were eligible for risk assessment using MammoRisk. Women previously identified as high risk were, therefore, not enrolled. MammoRisk is a machine learning–based tool that evaluates a patient’s risk with or without considering PRS. A PRS reflects the individual’s genetic risk of developing breast cancer. To calculate this risk, DNA was extracted from saliva samples for genotyping of 76 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Patients underwent a complete breast cancer assessment, including a questionnaire, mammogram with evaluation of breast density, collection of saliva sample, and consultations with a radiologist and a breast cancer specialist, the investigators said.
PRS influenced risk
Out of the 290 women who underwent breast cancer assessment between January 2019 and May 2021, 68% were eligible for risk assessment using MammoRisk (median age, 52 years). The others were not eligible because they were younger than 40 years of age, had a history of atypical hyperplasia, were directed to oncogenetic consultation, had a non-White origin, or were considered for Tyrer–Cuzick risk assessment.
Following risk assessment using MammoRisk without PRS, 16% of patients were classified as moderate risk, 53% as intermediate risk, 31% as high risk, and 0% as very high risk. The median risk score (estimated risk at 5 years) was 1.5.
When PRS was added to MammoRisk, 25% were classified as moderate risk, 33% as intermediate risk, 42% as high risk, and 0% as very high risk. Again, the median risk score was 1.5.
A total of 40% of patients were assigned a different risk category when PRS was added to MammoRisk. Importantly, 28% of patients changed from intermediate risk to moderate or high risk.
One author has received speaker honorarium from Predilife, the company commercializing MammoRisk. The others report no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BREAST CANCER RESEARCH AND TREATMENT
The best statins to lower non-HDL cholesterol in diabetes?
A network meta-analysis of 42 clinical trials concludes that rosuvastatin, simvastatin, and atorvastatin are the statins most effective at lowering non-high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) in people with diabetes and at risk for cardiovascular disease.
The analysis focused on the efficacy of statin treatment on reducing non-HDL-C, as opposed to reducing low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), which has traditionally been used as a surrogate to determine cardiovascular disease risk from hypercholesterolemia.
“The National Cholesterol Education Program in the United States recommends that LDL-C values should be used to estimate the risk of cardiovascular disease related to lipoproteins,” lead author Alexander Hodkinson, MD, senior National Institute for Health Research fellow, University of Manchester, England, told this news organization.
“But we believe that non-high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol is more strongly associated with the risk of cardiovascular disease, because non-HDL-C combines all the bad types of cholesterol, which LDL-C misses, so it could be a better tool than LDL-C for assessing CVD risk and effects of treatment. We already knew which of the statins reduce LDL-C, but we wanted to know which ones reduced non-HDL-C; hence the reason for our study,” Dr. Hodkinson said.
The findings were published online in BMJ.
In April 2021, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in the United Kingdom updated guidelines for adults with diabetes to recommend that non-HDL-C should replace LDL-C as the primary target for reducing the risk for cardiovascular disease with lipid-lowering treatment.
Currently, NICE is alone in its recommendation. Other international guidelines do not have a non-HDL-C target and use LDL-C reduction instead. These include guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), and the National Lipid Association.
Non–HDL-C is simple to calculate and can easily be done by clinicians by subtracting HDL-C from the total cholesterol level, he added.
This analysis compared the effectiveness of different statins at different intensities in reducing levels of non-HDL-C in 42 randomized controlled trials that included 20,193 adults with diabetes.
Compared with placebo, rosuvastatin, given at moderate- and high-intensity doses, and simvastatin and atorvastatin at high-intensity doses, were the best at lowering levels of non-HDL-C over an average treatment period of 12 weeks.
High-intensity rosuvastatin led to a 2.31 mmol/L reduction in non-HDL-C (95% credible interval, –3.39 to –1.21). Moderate-intensity rosuvastatin led to a 2.27 mmol/L reduction in non-HDL-C (95% credible interval, –3.00 to –1.49).
High-intensity simvastatin led to a 2.26 mmol/L reduction in non-HDL-C (95% credible interval, –2.99 to –1.51).
High-intensity atorvastatin led to a 2.20 mmol/L reduction in non-HDL-C (95% credible interval, –2.69 to –1.70).
Atorvastatin and simvastatin at any intensity and pravastatin at low intensity were also effective in reducing levels of non-HDL-C, the researchers noted.
In 4,670 patients who were at great risk for a major cardiovascular event, atorvastatin at high intensity showed the largest reduction in levels of non-HDL-C (1.98 mmol/L; 95% credible interval, –4.16 to 0.26).
In addition, high-intensity simvastatin and rosuvastatin were the most effective in reducing LDL-C.
High-intensity simvastatin led to a 1.93 mmol/L reduction in LDL-C (95% credible interval, –2.63 to –1.21), and high-intensity rosuvastatin led to a 1.76 mmol/L reduction in LDL-C (95% credible interval, –2.37 to –1.15).
In four studies, significant reductions in nonfatal myocardial infarction were shown for atorvastatin at moderate intensity, compared with placebo (relative risk, 0.57; 95% confidence interval, 0.43-.76). No significant differences were seen for discontinuations, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular death.
“We hope our findings will help guide clinicians on statin selection itself, and what types of doses they should be giving patients. These results support using NICE’s new policy guidelines on cholesterol monitoring, using this non-HDL-C measure, which contains all the bad types of cholesterol for patients with diabetes,” Dr. Hodkinson said.
“This study further emphasizes what we have known about the benefit of statin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes,” Prakash Deedwania, MD, professor of medicine, University of California, San Francisco, told this news organization.
Dr. Deedwania and others have published data on patients with diabetes that showed that treatment with high-intensity atorvastatin was associated with significant reductions in major adverse cardiovascular events.
“Here they use non-HDL cholesterol as a target. The NICE guidelines are the only guidelines looking at non-HDL cholesterol; however, all guidelines suggest an LDL to be less than 70 in all people with diabetes, and for those with recent acute coronary syndromes, the latest evidence suggests the LDL should actually be less than 50,” said Dr. Deedwania, spokesperson for the AHA and ACC.
As far as which measure to use, he believes both are useful. “It’s six of one and half a dozen of the other, in my opinion. The societies have not recommended non-HDL cholesterol and it’s easier to stay with what is readily available for clinicians, and using LDL cholesterol is still okay. The results of this analysis are confirmatory, in that looking at non-HDL cholesterol gives results very similar to what these statins have shown for their effect on LDL cholesterol,” he said.
Non-HDL cholesterol a better marker?
For Robert Rosenson, MD, director of metabolism and lipids at Mount Sinai Health System and professor of medicine and cardiology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, non-HDL cholesterol is becoming an important marker of risk for several reasons.
“The focus on LDL cholesterol has been due to the causal relationship of LDL with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, but in the last few decades, non-HDL has emerged because more people are overweight, have insulin resistance, and have diabetes,” Dr. Rosenson told this news organization. “In those situations, the LDL cholesterol underrepresents the risk of the LDL particles. With insulin resistance, the particles become more triglycerides and less cholesterol, so on a per-particle basis, you need to get more LDL particles to get to a certain LDL cholesterol concentration.”
Non-HDL cholesterol testing does not require fasting, another advantage of using it to monitor cholesterol, he added.
What is often forgotten is that moderate- to high-intensity statins have very good triglyceride-lowering effects, Dr. Rosenson said.
“This article highlights that, by using higher doses, you get more triglyceride-lowering. Hopefully, this will get practitioners to recognize that non-HDL cholesterol is a better predictor of risk in people with diabetes,” he said.
The study was funded by the National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Hodkinson, Dr. Rosenson, and Dr. Deedwania report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A network meta-analysis of 42 clinical trials concludes that rosuvastatin, simvastatin, and atorvastatin are the statins most effective at lowering non-high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) in people with diabetes and at risk for cardiovascular disease.
The analysis focused on the efficacy of statin treatment on reducing non-HDL-C, as opposed to reducing low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), which has traditionally been used as a surrogate to determine cardiovascular disease risk from hypercholesterolemia.
“The National Cholesterol Education Program in the United States recommends that LDL-C values should be used to estimate the risk of cardiovascular disease related to lipoproteins,” lead author Alexander Hodkinson, MD, senior National Institute for Health Research fellow, University of Manchester, England, told this news organization.
“But we believe that non-high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol is more strongly associated with the risk of cardiovascular disease, because non-HDL-C combines all the bad types of cholesterol, which LDL-C misses, so it could be a better tool than LDL-C for assessing CVD risk and effects of treatment. We already knew which of the statins reduce LDL-C, but we wanted to know which ones reduced non-HDL-C; hence the reason for our study,” Dr. Hodkinson said.
The findings were published online in BMJ.
In April 2021, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in the United Kingdom updated guidelines for adults with diabetes to recommend that non-HDL-C should replace LDL-C as the primary target for reducing the risk for cardiovascular disease with lipid-lowering treatment.
Currently, NICE is alone in its recommendation. Other international guidelines do not have a non-HDL-C target and use LDL-C reduction instead. These include guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), and the National Lipid Association.
Non–HDL-C is simple to calculate and can easily be done by clinicians by subtracting HDL-C from the total cholesterol level, he added.
This analysis compared the effectiveness of different statins at different intensities in reducing levels of non-HDL-C in 42 randomized controlled trials that included 20,193 adults with diabetes.
Compared with placebo, rosuvastatin, given at moderate- and high-intensity doses, and simvastatin and atorvastatin at high-intensity doses, were the best at lowering levels of non-HDL-C over an average treatment period of 12 weeks.
High-intensity rosuvastatin led to a 2.31 mmol/L reduction in non-HDL-C (95% credible interval, –3.39 to –1.21). Moderate-intensity rosuvastatin led to a 2.27 mmol/L reduction in non-HDL-C (95% credible interval, –3.00 to –1.49).
High-intensity simvastatin led to a 2.26 mmol/L reduction in non-HDL-C (95% credible interval, –2.99 to –1.51).
High-intensity atorvastatin led to a 2.20 mmol/L reduction in non-HDL-C (95% credible interval, –2.69 to –1.70).
Atorvastatin and simvastatin at any intensity and pravastatin at low intensity were also effective in reducing levels of non-HDL-C, the researchers noted.
In 4,670 patients who were at great risk for a major cardiovascular event, atorvastatin at high intensity showed the largest reduction in levels of non-HDL-C (1.98 mmol/L; 95% credible interval, –4.16 to 0.26).
In addition, high-intensity simvastatin and rosuvastatin were the most effective in reducing LDL-C.
High-intensity simvastatin led to a 1.93 mmol/L reduction in LDL-C (95% credible interval, –2.63 to –1.21), and high-intensity rosuvastatin led to a 1.76 mmol/L reduction in LDL-C (95% credible interval, –2.37 to –1.15).
In four studies, significant reductions in nonfatal myocardial infarction were shown for atorvastatin at moderate intensity, compared with placebo (relative risk, 0.57; 95% confidence interval, 0.43-.76). No significant differences were seen for discontinuations, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular death.
“We hope our findings will help guide clinicians on statin selection itself, and what types of doses they should be giving patients. These results support using NICE’s new policy guidelines on cholesterol monitoring, using this non-HDL-C measure, which contains all the bad types of cholesterol for patients with diabetes,” Dr. Hodkinson said.
“This study further emphasizes what we have known about the benefit of statin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes,” Prakash Deedwania, MD, professor of medicine, University of California, San Francisco, told this news organization.
Dr. Deedwania and others have published data on patients with diabetes that showed that treatment with high-intensity atorvastatin was associated with significant reductions in major adverse cardiovascular events.
“Here they use non-HDL cholesterol as a target. The NICE guidelines are the only guidelines looking at non-HDL cholesterol; however, all guidelines suggest an LDL to be less than 70 in all people with diabetes, and for those with recent acute coronary syndromes, the latest evidence suggests the LDL should actually be less than 50,” said Dr. Deedwania, spokesperson for the AHA and ACC.
As far as which measure to use, he believes both are useful. “It’s six of one and half a dozen of the other, in my opinion. The societies have not recommended non-HDL cholesterol and it’s easier to stay with what is readily available for clinicians, and using LDL cholesterol is still okay. The results of this analysis are confirmatory, in that looking at non-HDL cholesterol gives results very similar to what these statins have shown for their effect on LDL cholesterol,” he said.
Non-HDL cholesterol a better marker?
For Robert Rosenson, MD, director of metabolism and lipids at Mount Sinai Health System and professor of medicine and cardiology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, non-HDL cholesterol is becoming an important marker of risk for several reasons.
“The focus on LDL cholesterol has been due to the causal relationship of LDL with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, but in the last few decades, non-HDL has emerged because more people are overweight, have insulin resistance, and have diabetes,” Dr. Rosenson told this news organization. “In those situations, the LDL cholesterol underrepresents the risk of the LDL particles. With insulin resistance, the particles become more triglycerides and less cholesterol, so on a per-particle basis, you need to get more LDL particles to get to a certain LDL cholesterol concentration.”
Non-HDL cholesterol testing does not require fasting, another advantage of using it to monitor cholesterol, he added.
What is often forgotten is that moderate- to high-intensity statins have very good triglyceride-lowering effects, Dr. Rosenson said.
“This article highlights that, by using higher doses, you get more triglyceride-lowering. Hopefully, this will get practitioners to recognize that non-HDL cholesterol is a better predictor of risk in people with diabetes,” he said.
The study was funded by the National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Hodkinson, Dr. Rosenson, and Dr. Deedwania report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A network meta-analysis of 42 clinical trials concludes that rosuvastatin, simvastatin, and atorvastatin are the statins most effective at lowering non-high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) in people with diabetes and at risk for cardiovascular disease.
The analysis focused on the efficacy of statin treatment on reducing non-HDL-C, as opposed to reducing low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), which has traditionally been used as a surrogate to determine cardiovascular disease risk from hypercholesterolemia.
“The National Cholesterol Education Program in the United States recommends that LDL-C values should be used to estimate the risk of cardiovascular disease related to lipoproteins,” lead author Alexander Hodkinson, MD, senior National Institute for Health Research fellow, University of Manchester, England, told this news organization.
“But we believe that non-high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol is more strongly associated with the risk of cardiovascular disease, because non-HDL-C combines all the bad types of cholesterol, which LDL-C misses, so it could be a better tool than LDL-C for assessing CVD risk and effects of treatment. We already knew which of the statins reduce LDL-C, but we wanted to know which ones reduced non-HDL-C; hence the reason for our study,” Dr. Hodkinson said.
The findings were published online in BMJ.
In April 2021, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in the United Kingdom updated guidelines for adults with diabetes to recommend that non-HDL-C should replace LDL-C as the primary target for reducing the risk for cardiovascular disease with lipid-lowering treatment.
Currently, NICE is alone in its recommendation. Other international guidelines do not have a non-HDL-C target and use LDL-C reduction instead. These include guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), and the National Lipid Association.
Non–HDL-C is simple to calculate and can easily be done by clinicians by subtracting HDL-C from the total cholesterol level, he added.
This analysis compared the effectiveness of different statins at different intensities in reducing levels of non-HDL-C in 42 randomized controlled trials that included 20,193 adults with diabetes.
Compared with placebo, rosuvastatin, given at moderate- and high-intensity doses, and simvastatin and atorvastatin at high-intensity doses, were the best at lowering levels of non-HDL-C over an average treatment period of 12 weeks.
High-intensity rosuvastatin led to a 2.31 mmol/L reduction in non-HDL-C (95% credible interval, –3.39 to –1.21). Moderate-intensity rosuvastatin led to a 2.27 mmol/L reduction in non-HDL-C (95% credible interval, –3.00 to –1.49).
High-intensity simvastatin led to a 2.26 mmol/L reduction in non-HDL-C (95% credible interval, –2.99 to –1.51).
High-intensity atorvastatin led to a 2.20 mmol/L reduction in non-HDL-C (95% credible interval, –2.69 to –1.70).
Atorvastatin and simvastatin at any intensity and pravastatin at low intensity were also effective in reducing levels of non-HDL-C, the researchers noted.
In 4,670 patients who were at great risk for a major cardiovascular event, atorvastatin at high intensity showed the largest reduction in levels of non-HDL-C (1.98 mmol/L; 95% credible interval, –4.16 to 0.26).
In addition, high-intensity simvastatin and rosuvastatin were the most effective in reducing LDL-C.
High-intensity simvastatin led to a 1.93 mmol/L reduction in LDL-C (95% credible interval, –2.63 to –1.21), and high-intensity rosuvastatin led to a 1.76 mmol/L reduction in LDL-C (95% credible interval, –2.37 to –1.15).
In four studies, significant reductions in nonfatal myocardial infarction were shown for atorvastatin at moderate intensity, compared with placebo (relative risk, 0.57; 95% confidence interval, 0.43-.76). No significant differences were seen for discontinuations, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular death.
“We hope our findings will help guide clinicians on statin selection itself, and what types of doses they should be giving patients. These results support using NICE’s new policy guidelines on cholesterol monitoring, using this non-HDL-C measure, which contains all the bad types of cholesterol for patients with diabetes,” Dr. Hodkinson said.
“This study further emphasizes what we have known about the benefit of statin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes,” Prakash Deedwania, MD, professor of medicine, University of California, San Francisco, told this news organization.
Dr. Deedwania and others have published data on patients with diabetes that showed that treatment with high-intensity atorvastatin was associated with significant reductions in major adverse cardiovascular events.
“Here they use non-HDL cholesterol as a target. The NICE guidelines are the only guidelines looking at non-HDL cholesterol; however, all guidelines suggest an LDL to be less than 70 in all people with diabetes, and for those with recent acute coronary syndromes, the latest evidence suggests the LDL should actually be less than 50,” said Dr. Deedwania, spokesperson for the AHA and ACC.
As far as which measure to use, he believes both are useful. “It’s six of one and half a dozen of the other, in my opinion. The societies have not recommended non-HDL cholesterol and it’s easier to stay with what is readily available for clinicians, and using LDL cholesterol is still okay. The results of this analysis are confirmatory, in that looking at non-HDL cholesterol gives results very similar to what these statins have shown for their effect on LDL cholesterol,” he said.
Non-HDL cholesterol a better marker?
For Robert Rosenson, MD, director of metabolism and lipids at Mount Sinai Health System and professor of medicine and cardiology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, non-HDL cholesterol is becoming an important marker of risk for several reasons.
“The focus on LDL cholesterol has been due to the causal relationship of LDL with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, but in the last few decades, non-HDL has emerged because more people are overweight, have insulin resistance, and have diabetes,” Dr. Rosenson told this news organization. “In those situations, the LDL cholesterol underrepresents the risk of the LDL particles. With insulin resistance, the particles become more triglycerides and less cholesterol, so on a per-particle basis, you need to get more LDL particles to get to a certain LDL cholesterol concentration.”
Non-HDL cholesterol testing does not require fasting, another advantage of using it to monitor cholesterol, he added.
What is often forgotten is that moderate- to high-intensity statins have very good triglyceride-lowering effects, Dr. Rosenson said.
“This article highlights that, by using higher doses, you get more triglyceride-lowering. Hopefully, this will get practitioners to recognize that non-HDL cholesterol is a better predictor of risk in people with diabetes,” he said.
The study was funded by the National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Hodkinson, Dr. Rosenson, and Dr. Deedwania report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Melanoma screening study stokes overdiagnosis debate
new research shows.
Without a corresponding decrease in melanoma mortality, an increase in the detection of those thin melanomas “raises the concern that early detection efforts, such as visual skin screening, may result in overdiagnosis,” the study authors wrote. “The value of a cancer screening program should most rigorously be measured not by the number of new, early cancers detected, but by its impact on the development of late-stage disease and its associated morbidity, cost, and mortality.”
The research, published in JAMA Dermatology, has reignited the controversy over the benefits and harms of primary care skin cancer screening, garnering two editorials that reflect different sides of the debate.
In one, Robert A. Swerlick, MD, pointed out that, “despite public messaging to the contrary, to my knowledge there is no evidence that routine skin examinations have any effect on melanoma mortality.
“The stage shift to smaller tumors should not be viewed as success and is very strong evidence of overdiagnosis,” wrote Dr. Swerlick, of the department of dermatology, Emory University, Atlanta.
The other editorial, however, argued that routine screening saves lives. “Most melanoma deaths are because of stage I disease, with an estimated 3%-15% of thin melanomas (≤ 1 mm) being lethal,” wrote a trio of editorialists from Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
When considering the high mutation rate associated with melanoma and the current limits of treatment options, early diagnosis becomes “particularly important and counterbalances the risk of overdiagnosis,” the editorialists asserted.
Primary care screening study
The new findings come from an observational study of a quality improvement initiative conducted at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center system between 2014 and 2018, in which primary care clinicians were offered training in melanoma identification through skin examination and were encouraged to offer annual skin cancer screening to patients aged 35 years and older.
Of 595,799 eligible patients, 144,851 (24.3%) were screened at least once during the study period. Those who received screening were more likely than unscreened patients to be older (median age, 59 vs. 55 years), women, and non-Hispanic White persons.
During a follow-up of 5 years, the researchers found that patients who received screening were significantly more likely than unscreened patients to be diagnosed with in situ melanoma (incidence, 30.4 vs. 14.4; hazard ratio, 2.6; P < .001) or thin invasive melanoma (incidence, 24.5 vs. 16.1; HR, 1.8; P < .001), after adjusting for factors that included age, sex, and race.
The screened patients were also more likely than unscreened patients to be diagnosed with in situ interval melanomas, defined as melanomas occurring at least 60 days after initial screening (incidence, 26.7 vs. 12.9; HR, 2.1; P < .001), as well as thin invasive interval melanomas (incidence, 18.5 vs. 14.4; HR, 1.3; P = .03).
The 60-day interval was included to account for the possible time to referral to a specialist for definitive diagnosis, the authors explained.
The incidence of the detection of melanomas thicker than 4 mm was lower in screened versus unscreened patients, but the difference was not statistically significant for all melanomas (2.7 vs. 3.3; HR, 0.8; P = .38) or interval melanomas (1.5 vs. 2.7; HR, 0.6; P = .15).
Experts weigh in
Although the follow-up period was of 5 years, not all patients were followed that long after undergoing screening. For instance, for some patients, follow-up occurred only 1 year after they had been screened.
The study’s senior author, Laura K. Ferris, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, University of Pittsburgh, noted that a longer follow-up could shift the results.
“When you look at the curves in our figures, you do start to see them separate more and more over time for the thicker melanomas,” Dr. Ferris said in an interview. “I do suspect that, if we followed patients longer, we might start to see a more significant difference.”
The findings nevertheless add to evidence that although routine screening substantially increases the detection of melanomas overall, these melanomas are often not the ones doctors are most worried about or that increase a person’s risk of mortality, Dr. Ferris noted.
When it comes to melanoma screening, balancing the risks and benefits is key. One major downside, Dr. Ferris said, is in regard to the burden such screening could place on the health care system, with potentially unproductive screenings causing delays in care for patients with more urgent needs.
“We are undersupplied in the dermatology workforce, and there is often a long wait to see dermatologists, so we really want to make sure, as trained professionals, that patients have access to us,” she said. “If we’re doing something that doesn’t have proven benefit and is increasing the wait time, that will come at the expense of other patients’ access.”
Costs involved in skin biopsies and excisions of borderline lesions as well as the potential to increase patients’ anxiety represent other important considerations, Dr. Ferris noted.
However, Sancy A. Leachman, MD, PhD, a coauthor of the editorial in favor of screening, said in an interview that “at the individual level, there are an almost infinite number of individual circumstances that could lead a person to decide that the potential benefits outweigh the harms.”
According to Dr. Leachman, who is chair of the department of dermatology, Oregon Health & Science University, these individual priorities may not align with those of the various decision-makers or with guidelines, such as those from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, which gives visual skin cancer screening of asymptomatic patients an “I” rating, indicating “insufficient evidence.”
“Many federal agencies and payer groups focus on minimizing costs and optimizing outcomes,” Dr. Leachman and coauthors wrote. As the only professional advocates for individual patients, physicians “have a responsibility to assure that the best interests of patients are served.”
The study was funded by the University of Pittsburgh Melanoma and Skin Cancer Program. Dr. Ferris and Dr. Swerlick disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Leachman is the principal investigator for War on Melanoma, an early-detection program in Oregon.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research shows.
Without a corresponding decrease in melanoma mortality, an increase in the detection of those thin melanomas “raises the concern that early detection efforts, such as visual skin screening, may result in overdiagnosis,” the study authors wrote. “The value of a cancer screening program should most rigorously be measured not by the number of new, early cancers detected, but by its impact on the development of late-stage disease and its associated morbidity, cost, and mortality.”
The research, published in JAMA Dermatology, has reignited the controversy over the benefits and harms of primary care skin cancer screening, garnering two editorials that reflect different sides of the debate.
In one, Robert A. Swerlick, MD, pointed out that, “despite public messaging to the contrary, to my knowledge there is no evidence that routine skin examinations have any effect on melanoma mortality.
“The stage shift to smaller tumors should not be viewed as success and is very strong evidence of overdiagnosis,” wrote Dr. Swerlick, of the department of dermatology, Emory University, Atlanta.
The other editorial, however, argued that routine screening saves lives. “Most melanoma deaths are because of stage I disease, with an estimated 3%-15% of thin melanomas (≤ 1 mm) being lethal,” wrote a trio of editorialists from Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
When considering the high mutation rate associated with melanoma and the current limits of treatment options, early diagnosis becomes “particularly important and counterbalances the risk of overdiagnosis,” the editorialists asserted.
Primary care screening study
The new findings come from an observational study of a quality improvement initiative conducted at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center system between 2014 and 2018, in which primary care clinicians were offered training in melanoma identification through skin examination and were encouraged to offer annual skin cancer screening to patients aged 35 years and older.
Of 595,799 eligible patients, 144,851 (24.3%) were screened at least once during the study period. Those who received screening were more likely than unscreened patients to be older (median age, 59 vs. 55 years), women, and non-Hispanic White persons.
During a follow-up of 5 years, the researchers found that patients who received screening were significantly more likely than unscreened patients to be diagnosed with in situ melanoma (incidence, 30.4 vs. 14.4; hazard ratio, 2.6; P < .001) or thin invasive melanoma (incidence, 24.5 vs. 16.1; HR, 1.8; P < .001), after adjusting for factors that included age, sex, and race.
The screened patients were also more likely than unscreened patients to be diagnosed with in situ interval melanomas, defined as melanomas occurring at least 60 days after initial screening (incidence, 26.7 vs. 12.9; HR, 2.1; P < .001), as well as thin invasive interval melanomas (incidence, 18.5 vs. 14.4; HR, 1.3; P = .03).
The 60-day interval was included to account for the possible time to referral to a specialist for definitive diagnosis, the authors explained.
The incidence of the detection of melanomas thicker than 4 mm was lower in screened versus unscreened patients, but the difference was not statistically significant for all melanomas (2.7 vs. 3.3; HR, 0.8; P = .38) or interval melanomas (1.5 vs. 2.7; HR, 0.6; P = .15).
Experts weigh in
Although the follow-up period was of 5 years, not all patients were followed that long after undergoing screening. For instance, for some patients, follow-up occurred only 1 year after they had been screened.
The study’s senior author, Laura K. Ferris, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, University of Pittsburgh, noted that a longer follow-up could shift the results.
“When you look at the curves in our figures, you do start to see them separate more and more over time for the thicker melanomas,” Dr. Ferris said in an interview. “I do suspect that, if we followed patients longer, we might start to see a more significant difference.”
The findings nevertheless add to evidence that although routine screening substantially increases the detection of melanomas overall, these melanomas are often not the ones doctors are most worried about or that increase a person’s risk of mortality, Dr. Ferris noted.
When it comes to melanoma screening, balancing the risks and benefits is key. One major downside, Dr. Ferris said, is in regard to the burden such screening could place on the health care system, with potentially unproductive screenings causing delays in care for patients with more urgent needs.
“We are undersupplied in the dermatology workforce, and there is often a long wait to see dermatologists, so we really want to make sure, as trained professionals, that patients have access to us,” she said. “If we’re doing something that doesn’t have proven benefit and is increasing the wait time, that will come at the expense of other patients’ access.”
Costs involved in skin biopsies and excisions of borderline lesions as well as the potential to increase patients’ anxiety represent other important considerations, Dr. Ferris noted.
However, Sancy A. Leachman, MD, PhD, a coauthor of the editorial in favor of screening, said in an interview that “at the individual level, there are an almost infinite number of individual circumstances that could lead a person to decide that the potential benefits outweigh the harms.”
According to Dr. Leachman, who is chair of the department of dermatology, Oregon Health & Science University, these individual priorities may not align with those of the various decision-makers or with guidelines, such as those from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, which gives visual skin cancer screening of asymptomatic patients an “I” rating, indicating “insufficient evidence.”
“Many federal agencies and payer groups focus on minimizing costs and optimizing outcomes,” Dr. Leachman and coauthors wrote. As the only professional advocates for individual patients, physicians “have a responsibility to assure that the best interests of patients are served.”
The study was funded by the University of Pittsburgh Melanoma and Skin Cancer Program. Dr. Ferris and Dr. Swerlick disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Leachman is the principal investigator for War on Melanoma, an early-detection program in Oregon.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research shows.
Without a corresponding decrease in melanoma mortality, an increase in the detection of those thin melanomas “raises the concern that early detection efforts, such as visual skin screening, may result in overdiagnosis,” the study authors wrote. “The value of a cancer screening program should most rigorously be measured not by the number of new, early cancers detected, but by its impact on the development of late-stage disease and its associated morbidity, cost, and mortality.”
The research, published in JAMA Dermatology, has reignited the controversy over the benefits and harms of primary care skin cancer screening, garnering two editorials that reflect different sides of the debate.
In one, Robert A. Swerlick, MD, pointed out that, “despite public messaging to the contrary, to my knowledge there is no evidence that routine skin examinations have any effect on melanoma mortality.
“The stage shift to smaller tumors should not be viewed as success and is very strong evidence of overdiagnosis,” wrote Dr. Swerlick, of the department of dermatology, Emory University, Atlanta.
The other editorial, however, argued that routine screening saves lives. “Most melanoma deaths are because of stage I disease, with an estimated 3%-15% of thin melanomas (≤ 1 mm) being lethal,” wrote a trio of editorialists from Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
When considering the high mutation rate associated with melanoma and the current limits of treatment options, early diagnosis becomes “particularly important and counterbalances the risk of overdiagnosis,” the editorialists asserted.
Primary care screening study
The new findings come from an observational study of a quality improvement initiative conducted at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center system between 2014 and 2018, in which primary care clinicians were offered training in melanoma identification through skin examination and were encouraged to offer annual skin cancer screening to patients aged 35 years and older.
Of 595,799 eligible patients, 144,851 (24.3%) were screened at least once during the study period. Those who received screening were more likely than unscreened patients to be older (median age, 59 vs. 55 years), women, and non-Hispanic White persons.
During a follow-up of 5 years, the researchers found that patients who received screening were significantly more likely than unscreened patients to be diagnosed with in situ melanoma (incidence, 30.4 vs. 14.4; hazard ratio, 2.6; P < .001) or thin invasive melanoma (incidence, 24.5 vs. 16.1; HR, 1.8; P < .001), after adjusting for factors that included age, sex, and race.
The screened patients were also more likely than unscreened patients to be diagnosed with in situ interval melanomas, defined as melanomas occurring at least 60 days after initial screening (incidence, 26.7 vs. 12.9; HR, 2.1; P < .001), as well as thin invasive interval melanomas (incidence, 18.5 vs. 14.4; HR, 1.3; P = .03).
The 60-day interval was included to account for the possible time to referral to a specialist for definitive diagnosis, the authors explained.
The incidence of the detection of melanomas thicker than 4 mm was lower in screened versus unscreened patients, but the difference was not statistically significant for all melanomas (2.7 vs. 3.3; HR, 0.8; P = .38) or interval melanomas (1.5 vs. 2.7; HR, 0.6; P = .15).
Experts weigh in
Although the follow-up period was of 5 years, not all patients were followed that long after undergoing screening. For instance, for some patients, follow-up occurred only 1 year after they had been screened.
The study’s senior author, Laura K. Ferris, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, University of Pittsburgh, noted that a longer follow-up could shift the results.
“When you look at the curves in our figures, you do start to see them separate more and more over time for the thicker melanomas,” Dr. Ferris said in an interview. “I do suspect that, if we followed patients longer, we might start to see a more significant difference.”
The findings nevertheless add to evidence that although routine screening substantially increases the detection of melanomas overall, these melanomas are often not the ones doctors are most worried about or that increase a person’s risk of mortality, Dr. Ferris noted.
When it comes to melanoma screening, balancing the risks and benefits is key. One major downside, Dr. Ferris said, is in regard to the burden such screening could place on the health care system, with potentially unproductive screenings causing delays in care for patients with more urgent needs.
“We are undersupplied in the dermatology workforce, and there is often a long wait to see dermatologists, so we really want to make sure, as trained professionals, that patients have access to us,” she said. “If we’re doing something that doesn’t have proven benefit and is increasing the wait time, that will come at the expense of other patients’ access.”
Costs involved in skin biopsies and excisions of borderline lesions as well as the potential to increase patients’ anxiety represent other important considerations, Dr. Ferris noted.
However, Sancy A. Leachman, MD, PhD, a coauthor of the editorial in favor of screening, said in an interview that “at the individual level, there are an almost infinite number of individual circumstances that could lead a person to decide that the potential benefits outweigh the harms.”
According to Dr. Leachman, who is chair of the department of dermatology, Oregon Health & Science University, these individual priorities may not align with those of the various decision-makers or with guidelines, such as those from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, which gives visual skin cancer screening of asymptomatic patients an “I” rating, indicating “insufficient evidence.”
“Many federal agencies and payer groups focus on minimizing costs and optimizing outcomes,” Dr. Leachman and coauthors wrote. As the only professional advocates for individual patients, physicians “have a responsibility to assure that the best interests of patients are served.”
The study was funded by the University of Pittsburgh Melanoma and Skin Cancer Program. Dr. Ferris and Dr. Swerlick disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Leachman is the principal investigator for War on Melanoma, an early-detection program in Oregon.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Ukraine and PTSD: How psychiatry can help
The war in Ukraine is resulting in a devastating loss of life, catastrophic injuries, and physical destruction. But the war also will take an enormous mental health toll on millions of people, resulting in what I think will lead to an epidemic of posttraumatic stress disorder.
Think about the horrors that Ukrainians are experiencing. Millions of Ukrainians have been displaced to locations inside and outside of the country. People are being forced to leave behind family members, neighbors, and their pets and homes. In one recent news report, a Ukrainian woman who left Kyiv for Belgium reported having dreams in which she heard explosions. Smells, sounds, and even colors can trigger intrusive memories and a host of other problems. The mind can barely comprehend the scope of this human crisis.
Ukrainian soldiers are witnessing horrors that are unspeakable. Doctors, emergency service workers, and other medical professionals in Ukraine are being exposed to the catastrophe on a large scale. Children and youth are among the most affected victims, and it is difficult to predict the impact all of this upheaval is having on them.
The most important question for those of us who treat mental illness is “how will we help devastated people suffering from extreme trauma tied to death, dying, severe injuries, and torture by the invading soldiers?”
I have been treating patients with PTSD for many years. In my lifetime, the devastation in Ukraine will translate into what I expect will be the first overwhelming mass epidemic of PTSD – at least that I can recall. Yes, surely PTSD occurred during and after the Holocaust in the World War II era, but at that time, the mental health profession was not equipped to recognize it – even though the disorder most certainly existed. Even in ancient times, an Assyrian text from Mesopotamia (currently Iraq) described what we would define as PTSD symptoms in soldiers, such as sleep disturbances, flashbacks, and “low mood,” according to a 2014 article in the journal Early Science and Medicine.
The DSM-5 describes numerous criteria for PTSD mainly centering on trauma exposing a person to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or a variety of assaults, including direct exposure or witnessing the event. However, in my clinical experience, I’ve seen lesser events leading to PTSD. Much depends on how each individual processes what is occurring or has occurred.
What appears to be clear is that some key aspects of PTSD according to the DSM-5 – such as trauma-related thoughts or feelings, or trauma-related reminders, as well as nightmares and flashbacks – are likely occurring among Ukrainians. In addition, hypervigilance and exaggerated startle response seem to be key components of PTSD whether or not the cause is a major event or what one would perceive as less traumatic or dramatic.
I’ve certainly seen PTSD secondary to a hospitalization, especially in care involving ICUs or cardiac care units. In addition, I’ve had the occasion to note PTSD signs and symptoms after financial loss or divorce, situations in which some clinicians would never believe PTSD would occur, and would often diagnose as anxiety or depression. For me, again from a clinical point of view, it’s always been critical to assess how individuals process the event or events around them.
We know that there is already a shortage of mental health clinicians across the globe. This means that, in light of the hundreds of thousands – possibly millions – of Ukrainians affected by PTSD, a one-to-one approach will not do. For those Ukrainians who are able to find safe havens, I believe that PTSD symptoms can be debilitating, and the mental health community needs to begin putting supports in place now to address this trauma.
Specifically, proven cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and guided imagery should be used to begin helping some of these people recover from the unbelievable trauma of war. For some, medication management might be helpful in those experiencing nightmares combined with anxiety and depression. But the main approach and first line of care should be CBT and guided imagery.
PTSD symptoms can make people feel like they are losing control, and prevent them from rebuilding their lives. We must do all we can in the mental health community to destigmatize care and develop support services to get ahead of this crisis. Only through medical, psychiatric, and health care organizations banding together using modern technology can the large number of people psychologically affected by this ongoing crisis be helped and saved.
Dr. London is a practicing psychiatrist who has been a newspaper columnist for 35 years, specializing in writing about short-term therapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy and guided imagery. He is author of “Find Freedom Fast” (New York: Kettlehole Publishing, 2019). He has no conflicts of interest.
The war in Ukraine is resulting in a devastating loss of life, catastrophic injuries, and physical destruction. But the war also will take an enormous mental health toll on millions of people, resulting in what I think will lead to an epidemic of posttraumatic stress disorder.
Think about the horrors that Ukrainians are experiencing. Millions of Ukrainians have been displaced to locations inside and outside of the country. People are being forced to leave behind family members, neighbors, and their pets and homes. In one recent news report, a Ukrainian woman who left Kyiv for Belgium reported having dreams in which she heard explosions. Smells, sounds, and even colors can trigger intrusive memories and a host of other problems. The mind can barely comprehend the scope of this human crisis.
Ukrainian soldiers are witnessing horrors that are unspeakable. Doctors, emergency service workers, and other medical professionals in Ukraine are being exposed to the catastrophe on a large scale. Children and youth are among the most affected victims, and it is difficult to predict the impact all of this upheaval is having on them.
The most important question for those of us who treat mental illness is “how will we help devastated people suffering from extreme trauma tied to death, dying, severe injuries, and torture by the invading soldiers?”
I have been treating patients with PTSD for many years. In my lifetime, the devastation in Ukraine will translate into what I expect will be the first overwhelming mass epidemic of PTSD – at least that I can recall. Yes, surely PTSD occurred during and after the Holocaust in the World War II era, but at that time, the mental health profession was not equipped to recognize it – even though the disorder most certainly existed. Even in ancient times, an Assyrian text from Mesopotamia (currently Iraq) described what we would define as PTSD symptoms in soldiers, such as sleep disturbances, flashbacks, and “low mood,” according to a 2014 article in the journal Early Science and Medicine.
The DSM-5 describes numerous criteria for PTSD mainly centering on trauma exposing a person to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or a variety of assaults, including direct exposure or witnessing the event. However, in my clinical experience, I’ve seen lesser events leading to PTSD. Much depends on how each individual processes what is occurring or has occurred.
What appears to be clear is that some key aspects of PTSD according to the DSM-5 – such as trauma-related thoughts or feelings, or trauma-related reminders, as well as nightmares and flashbacks – are likely occurring among Ukrainians. In addition, hypervigilance and exaggerated startle response seem to be key components of PTSD whether or not the cause is a major event or what one would perceive as less traumatic or dramatic.
I’ve certainly seen PTSD secondary to a hospitalization, especially in care involving ICUs or cardiac care units. In addition, I’ve had the occasion to note PTSD signs and symptoms after financial loss or divorce, situations in which some clinicians would never believe PTSD would occur, and would often diagnose as anxiety or depression. For me, again from a clinical point of view, it’s always been critical to assess how individuals process the event or events around them.
We know that there is already a shortage of mental health clinicians across the globe. This means that, in light of the hundreds of thousands – possibly millions – of Ukrainians affected by PTSD, a one-to-one approach will not do. For those Ukrainians who are able to find safe havens, I believe that PTSD symptoms can be debilitating, and the mental health community needs to begin putting supports in place now to address this trauma.
Specifically, proven cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and guided imagery should be used to begin helping some of these people recover from the unbelievable trauma of war. For some, medication management might be helpful in those experiencing nightmares combined with anxiety and depression. But the main approach and first line of care should be CBT and guided imagery.
PTSD symptoms can make people feel like they are losing control, and prevent them from rebuilding their lives. We must do all we can in the mental health community to destigmatize care and develop support services to get ahead of this crisis. Only through medical, psychiatric, and health care organizations banding together using modern technology can the large number of people psychologically affected by this ongoing crisis be helped and saved.
Dr. London is a practicing psychiatrist who has been a newspaper columnist for 35 years, specializing in writing about short-term therapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy and guided imagery. He is author of “Find Freedom Fast” (New York: Kettlehole Publishing, 2019). He has no conflicts of interest.
The war in Ukraine is resulting in a devastating loss of life, catastrophic injuries, and physical destruction. But the war also will take an enormous mental health toll on millions of people, resulting in what I think will lead to an epidemic of posttraumatic stress disorder.
Think about the horrors that Ukrainians are experiencing. Millions of Ukrainians have been displaced to locations inside and outside of the country. People are being forced to leave behind family members, neighbors, and their pets and homes. In one recent news report, a Ukrainian woman who left Kyiv for Belgium reported having dreams in which she heard explosions. Smells, sounds, and even colors can trigger intrusive memories and a host of other problems. The mind can barely comprehend the scope of this human crisis.
Ukrainian soldiers are witnessing horrors that are unspeakable. Doctors, emergency service workers, and other medical professionals in Ukraine are being exposed to the catastrophe on a large scale. Children and youth are among the most affected victims, and it is difficult to predict the impact all of this upheaval is having on them.
The most important question for those of us who treat mental illness is “how will we help devastated people suffering from extreme trauma tied to death, dying, severe injuries, and torture by the invading soldiers?”
I have been treating patients with PTSD for many years. In my lifetime, the devastation in Ukraine will translate into what I expect will be the first overwhelming mass epidemic of PTSD – at least that I can recall. Yes, surely PTSD occurred during and after the Holocaust in the World War II era, but at that time, the mental health profession was not equipped to recognize it – even though the disorder most certainly existed. Even in ancient times, an Assyrian text from Mesopotamia (currently Iraq) described what we would define as PTSD symptoms in soldiers, such as sleep disturbances, flashbacks, and “low mood,” according to a 2014 article in the journal Early Science and Medicine.
The DSM-5 describes numerous criteria for PTSD mainly centering on trauma exposing a person to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or a variety of assaults, including direct exposure or witnessing the event. However, in my clinical experience, I’ve seen lesser events leading to PTSD. Much depends on how each individual processes what is occurring or has occurred.
What appears to be clear is that some key aspects of PTSD according to the DSM-5 – such as trauma-related thoughts or feelings, or trauma-related reminders, as well as nightmares and flashbacks – are likely occurring among Ukrainians. In addition, hypervigilance and exaggerated startle response seem to be key components of PTSD whether or not the cause is a major event or what one would perceive as less traumatic or dramatic.
I’ve certainly seen PTSD secondary to a hospitalization, especially in care involving ICUs or cardiac care units. In addition, I’ve had the occasion to note PTSD signs and symptoms after financial loss or divorce, situations in which some clinicians would never believe PTSD would occur, and would often diagnose as anxiety or depression. For me, again from a clinical point of view, it’s always been critical to assess how individuals process the event or events around them.
We know that there is already a shortage of mental health clinicians across the globe. This means that, in light of the hundreds of thousands – possibly millions – of Ukrainians affected by PTSD, a one-to-one approach will not do. For those Ukrainians who are able to find safe havens, I believe that PTSD symptoms can be debilitating, and the mental health community needs to begin putting supports in place now to address this trauma.
Specifically, proven cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and guided imagery should be used to begin helping some of these people recover from the unbelievable trauma of war. For some, medication management might be helpful in those experiencing nightmares combined with anxiety and depression. But the main approach and first line of care should be CBT and guided imagery.
PTSD symptoms can make people feel like they are losing control, and prevent them from rebuilding their lives. We must do all we can in the mental health community to destigmatize care and develop support services to get ahead of this crisis. Only through medical, psychiatric, and health care organizations banding together using modern technology can the large number of people psychologically affected by this ongoing crisis be helped and saved.
Dr. London is a practicing psychiatrist who has been a newspaper columnist for 35 years, specializing in writing about short-term therapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy and guided imagery. He is author of “Find Freedom Fast” (New York: Kettlehole Publishing, 2019). He has no conflicts of interest.
Long-term cannabis use linked to dementia risk factors
A large prospective, longitudinal study showed long-term cannabis users had an intelligence quotient (IQ) decline from age 18 to midlife (mean, 5.5 IQ points), poorer learning and processing speed, compared with childhood, and self-reported memory and attention problems. Long-term cannabis users also showed hippocampal atrophy at midlife (age 45), which combined with mild midlife cognitive deficits, all known risk factors for dementia.
“Long-term cannabis users – people who have used cannabis from 18 or 19 years old and continued using through midlife – showed cognitive deficits, compared with nonusers. They also showed more severe cognitive deficits, compared with long-term alcohol users and long-term tobacco users. But people who used infrequently or recreationally in midlife did not show as severe cognitive deficits. Cognitive deficits were confined to cannabis users,” lead investigator Madeline Meier, PhD, associate professor of psychology, Arizona State University, Tempe, said in an interview.
“Long-term cannabis users had smaller hippocampal volume, but we also found that smaller hippocampal volume did not explain the cognitive deficits among the long-term cannabis users,” she added.
The study was recently published online in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Growing use in Boomers
Long-term cannabis use has been associated with memory problems. Studies examining the impact of cannabis use on the brain have shown conflicting results. Some suggest regular use in adolescence is associated with altered connectivity and reduced volume of brain regions involved in executive functions such as memory, learning, and impulse control compared with those who do not use cannabis.
Others found no significant structural differences between the brains of cannabis users and nonusers.
An earlier, large longitudinal study in New Zealand found that persistent cannabis use (with frequent use starting in adolescence) was associated with a loss of an average of six (or up to eight) IQ points measured in mid-adulthood.
Cannabis use is increasing among Baby Boomers – a group born between 1946 and 1964 – who used cannabis at historically high rates as young adults, and who now use it at historically high rates in midlife and as older adults.
To date, case-control studies, which are predominantly in adolescents and young adults, have found that cannabis users show subtle cognitive deficits and structural brain differences, but it is unclear whether these differences in young cannabis users might be larger in midlife and in older adults who have longer histories of use.
The study included a representative cohort of 1,037 individuals in Dunedin, New Zealand, born between April 1972 and March 1973, and followed from age 3 to 45.
Cannabis use and dependence were assessed at ages 18, 21, 26, 32, 38, and 45. IQ was assessed at ages 7, 9, 11, and 45. Specific neuropsychological functions and hippocampal volume were assessed at age 45.
“Most of the previous research has focused on adolescent and young-adult cannabis users. What we’re looking at here is long-term cannabis users in midlife, and we’re finding that long-term users show cognitive deficits. But we’re not just looking at a snapshot of people in midlife, we’re also doing a longitudinal comparison – comparing them to themselves in childhood. We saw that long-term cannabis users showed a decline in IQ from childhood to adulthood,” said Dr. Meier.
Participants in the study are members of the Dunedin Longitudinal Study, a representative birth cohort (n = 1,037; 91% of eligible births; 52% male) born between April 1972 and March 1973 in Dunedin, New Zealand, who participated in the first assessment at age 3.
This cohort matched socioeconomic status (SES), key health indicators, and demographics. Assessments were carried out at birth and ages 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 18, 21, 26, 32, 38, and 45. IQ was assessed at ages 7, 9, 11, and 45. Specific neuropsychological functions and hippocampal volume were assessed at age 45.
Shrinking hippocampal volume
Cannabis use, cognitive function, and hippocampal volume were assessed comparing long-term cannabis users (n = 84) against five distinct groups:
- Lifelong cannabis nonusers (n = 196) – to replicate the control group most often reported in the case-control literature
- Midlife recreational cannabis users (n = 65) – to determine if cognitive deficits and structural brain differences are apparent in nonproblem users – the majority of cannabis users
- Long-term tobacco users (n = 75)
- Long-term alcohol users (n = 57) – benchmark comparisons for any cannabis findings and to disentangle potential cannabis effects from tobacco and alcohol effects
- Cannabis quitters (n = 58) – to determine whether differences are apparent after cessation
Tests were conducted on dose-response associations using continuously measured persistence of cannabis use, rigorously adjusting for numerous confounders derived from multiple longitudinal waves and data sources.
The investigators also tested whether associations between continuously measured persistence of cannabis use and cognitive deficits were mediated by hippocampal volume differences.
The hippocampus was the area of focus because it has a high density of cannabinoid receptors and is also instrumental for learning and memory, which is one of the most consistently impaired cognitive domains in cannabis users, and has been the brain region that most consistently emerges as smaller in cannabis users relative to controls. Structural MRI was done at age 45 for 875 participants (93% of age 45 participants).
Of 997 cohort members still alive at age 45, 938 (94.1%) were assessed at age 45. Age 45 participants did not differ significantly from other participants on childhood SES, childhood self-control, or childhood IQ. Cognitive functioning among midlife recreational cannabis users was similar to representative cohort norms, suggesting that infrequent recreational cannabis use in midlife is unlikely to compromise cognitive functioning.
However, long-term cannabis users did not perform significantly worse on any test than cannabis quitters. Cannabis quitters showed subtle cognitive deficits that may explain inconsistent findings on the benefits of cessation.
Smaller hippocampal volume is thought to be a possible mediator of cannabis-related cognitive deficits because the hippocampus is rich in CB1 receptors and is involved in learning and memory.
Long-term cannabis users had smaller bilateral volume in total hippocampus and 5 of 12 structurally and functionally distinct subregions (tail, hippocampal amygdala transition area, CA1, molecular layer, and dentate gyrus), and significantly smaller volumes than midlife recreational cannabis users in the left and right hippocampus, and 3 of 12 subfields (tail, CA1, and molecular layer), compared with non-users, consistent with case-control studies.
More potent
“If you’ve been using cannabis very long term and now are in midlife, you might want to consider quitting. Quitting is associated with slightly better cognitive performance in midlife. We also need to watch for risk of dementia. We know that people who show cognitive deficits at midlife are at elevated risk for later life dementia. And the deficits we saw among long-term cannabis users (although fairly mild), they were in the range in terms of effect size of what we see among people in other studies who have gone on to develop dementia in later life,” said Dr. Meier.
The study findings conflict with those of other studies, including one by the same research group, which compared the cognitive functioning of twins who were discordant for cannabis use and found little evidence of cannabis-related cognitive deficits. Because long-term cannabis users also use tobacco, alcohol, and other illicit drugs, disentangling cannabis effects from other substances is challenging.
“Long-term cannabis users tend to be long-term polysubstance users, so it’s hard to isolate,” said Dr. Meier.
Additionally, some group sizes were small, raising concerns about low statistical power.
“Group sizes were small but we didn’t rely only on those group comparisons; however, we did find statistical differences. We also tested highly statistically powered dose-response associations between persistence of cannabis use over ages 18-45 and each of our outcomes (IQ, learning, and processing speed in midlife) while adjusting possible alternate explanations such as low childhood IQ, other substance use, [and] socioeconomic backgrounds.
“These dose-response associations used large sample sizes, were highly powered, and took into account a number of alternative explanations. These two different approaches showed very similar findings and one bolstered the other,” said Dr. Meier.
The study’s results were based on individuals who began using cannabis in the 1980s or ‘90s, but the concentration of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) has risen in recent years.
“When the study began, THC concentration was approximately 4%. Over the last decade we have seen it go up to 12% or even higher. A recent study surveying U.S. dispensaries found 20% THC. If THC accounts for impairment, then the effects can be larger [with higher concentrations]. One of the challenges in the U.S. is that there are laws prohibiting researchers from testing cannabis, so we have to rely on product labels, which we know are unreliable,” said Dr. Meier.
A separate report is forthcoming with results of exploratory analyses of associations between long-term cannabis use and comprehensive MRI measures of global and regional gray and white matter.
The data will also be used to answer a number of different questions about cognitive deficits, brain structure, aging preparedness, social preparedness (strength of social networks), financial and health preparedness, and biological aging (the pace of aging relative to chronological age) in long-term cannabis users, Dr. Meier noted.
‘Fantastic’ research
Commenting on the research for this news organization , Andrew J. Saxon, MD, professor, department of psychiatry & behavioral sciences at University of Washington, Seattle, and a member of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Addiction Psychiatry, said the study “provides more evidence that heavy and regular cannabis use is not benign behavior.”
“It’s a fantastic piece of research in which they enrolled participants at birth and have followed them up to age 45. In most of the other research that has been done, we have no idea what their baseline was. What’s so remarkable here is that they can clearly demonstrate the loss of IQ points from childhood to age 45,” said Dr. Saxon.
“It is clear that, in people using cannabis long term, cognition is impaired. It would be good to have a better handle on how much cognitive function can be regained if you quit, because that could be a motivator for quitting in people where cannabis is having an adverse effect on their lives,” he added.
On the issue of THC potency, Dr. Saxon said that, while it’s true the potency of cannabis is increasing in terms of THC concentrations, the question is: “Do people who use cannabis use a set amount or do they imbibe until they achieve the state of altered consciousness that they’re seeking? Although there has been some research in the area of self-regulation and cannabis potency, we do not yet have the answers to determine if there is any causation,” said Dr. Saxon.
Dr. Meier and Dr. Saxon reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A large prospective, longitudinal study showed long-term cannabis users had an intelligence quotient (IQ) decline from age 18 to midlife (mean, 5.5 IQ points), poorer learning and processing speed, compared with childhood, and self-reported memory and attention problems. Long-term cannabis users also showed hippocampal atrophy at midlife (age 45), which combined with mild midlife cognitive deficits, all known risk factors for dementia.
“Long-term cannabis users – people who have used cannabis from 18 or 19 years old and continued using through midlife – showed cognitive deficits, compared with nonusers. They also showed more severe cognitive deficits, compared with long-term alcohol users and long-term tobacco users. But people who used infrequently or recreationally in midlife did not show as severe cognitive deficits. Cognitive deficits were confined to cannabis users,” lead investigator Madeline Meier, PhD, associate professor of psychology, Arizona State University, Tempe, said in an interview.
“Long-term cannabis users had smaller hippocampal volume, but we also found that smaller hippocampal volume did not explain the cognitive deficits among the long-term cannabis users,” she added.
The study was recently published online in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Growing use in Boomers
Long-term cannabis use has been associated with memory problems. Studies examining the impact of cannabis use on the brain have shown conflicting results. Some suggest regular use in adolescence is associated with altered connectivity and reduced volume of brain regions involved in executive functions such as memory, learning, and impulse control compared with those who do not use cannabis.
Others found no significant structural differences between the brains of cannabis users and nonusers.
An earlier, large longitudinal study in New Zealand found that persistent cannabis use (with frequent use starting in adolescence) was associated with a loss of an average of six (or up to eight) IQ points measured in mid-adulthood.
Cannabis use is increasing among Baby Boomers – a group born between 1946 and 1964 – who used cannabis at historically high rates as young adults, and who now use it at historically high rates in midlife and as older adults.
To date, case-control studies, which are predominantly in adolescents and young adults, have found that cannabis users show subtle cognitive deficits and structural brain differences, but it is unclear whether these differences in young cannabis users might be larger in midlife and in older adults who have longer histories of use.
The study included a representative cohort of 1,037 individuals in Dunedin, New Zealand, born between April 1972 and March 1973, and followed from age 3 to 45.
Cannabis use and dependence were assessed at ages 18, 21, 26, 32, 38, and 45. IQ was assessed at ages 7, 9, 11, and 45. Specific neuropsychological functions and hippocampal volume were assessed at age 45.
“Most of the previous research has focused on adolescent and young-adult cannabis users. What we’re looking at here is long-term cannabis users in midlife, and we’re finding that long-term users show cognitive deficits. But we’re not just looking at a snapshot of people in midlife, we’re also doing a longitudinal comparison – comparing them to themselves in childhood. We saw that long-term cannabis users showed a decline in IQ from childhood to adulthood,” said Dr. Meier.
Participants in the study are members of the Dunedin Longitudinal Study, a representative birth cohort (n = 1,037; 91% of eligible births; 52% male) born between April 1972 and March 1973 in Dunedin, New Zealand, who participated in the first assessment at age 3.
This cohort matched socioeconomic status (SES), key health indicators, and demographics. Assessments were carried out at birth and ages 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 18, 21, 26, 32, 38, and 45. IQ was assessed at ages 7, 9, 11, and 45. Specific neuropsychological functions and hippocampal volume were assessed at age 45.
Shrinking hippocampal volume
Cannabis use, cognitive function, and hippocampal volume were assessed comparing long-term cannabis users (n = 84) against five distinct groups:
- Lifelong cannabis nonusers (n = 196) – to replicate the control group most often reported in the case-control literature
- Midlife recreational cannabis users (n = 65) – to determine if cognitive deficits and structural brain differences are apparent in nonproblem users – the majority of cannabis users
- Long-term tobacco users (n = 75)
- Long-term alcohol users (n = 57) – benchmark comparisons for any cannabis findings and to disentangle potential cannabis effects from tobacco and alcohol effects
- Cannabis quitters (n = 58) – to determine whether differences are apparent after cessation
Tests were conducted on dose-response associations using continuously measured persistence of cannabis use, rigorously adjusting for numerous confounders derived from multiple longitudinal waves and data sources.
The investigators also tested whether associations between continuously measured persistence of cannabis use and cognitive deficits were mediated by hippocampal volume differences.
The hippocampus was the area of focus because it has a high density of cannabinoid receptors and is also instrumental for learning and memory, which is one of the most consistently impaired cognitive domains in cannabis users, and has been the brain region that most consistently emerges as smaller in cannabis users relative to controls. Structural MRI was done at age 45 for 875 participants (93% of age 45 participants).
Of 997 cohort members still alive at age 45, 938 (94.1%) were assessed at age 45. Age 45 participants did not differ significantly from other participants on childhood SES, childhood self-control, or childhood IQ. Cognitive functioning among midlife recreational cannabis users was similar to representative cohort norms, suggesting that infrequent recreational cannabis use in midlife is unlikely to compromise cognitive functioning.
However, long-term cannabis users did not perform significantly worse on any test than cannabis quitters. Cannabis quitters showed subtle cognitive deficits that may explain inconsistent findings on the benefits of cessation.
Smaller hippocampal volume is thought to be a possible mediator of cannabis-related cognitive deficits because the hippocampus is rich in CB1 receptors and is involved in learning and memory.
Long-term cannabis users had smaller bilateral volume in total hippocampus and 5 of 12 structurally and functionally distinct subregions (tail, hippocampal amygdala transition area, CA1, molecular layer, and dentate gyrus), and significantly smaller volumes than midlife recreational cannabis users in the left and right hippocampus, and 3 of 12 subfields (tail, CA1, and molecular layer), compared with non-users, consistent with case-control studies.
More potent
“If you’ve been using cannabis very long term and now are in midlife, you might want to consider quitting. Quitting is associated with slightly better cognitive performance in midlife. We also need to watch for risk of dementia. We know that people who show cognitive deficits at midlife are at elevated risk for later life dementia. And the deficits we saw among long-term cannabis users (although fairly mild), they were in the range in terms of effect size of what we see among people in other studies who have gone on to develop dementia in later life,” said Dr. Meier.
The study findings conflict with those of other studies, including one by the same research group, which compared the cognitive functioning of twins who were discordant for cannabis use and found little evidence of cannabis-related cognitive deficits. Because long-term cannabis users also use tobacco, alcohol, and other illicit drugs, disentangling cannabis effects from other substances is challenging.
“Long-term cannabis users tend to be long-term polysubstance users, so it’s hard to isolate,” said Dr. Meier.
Additionally, some group sizes were small, raising concerns about low statistical power.
“Group sizes were small but we didn’t rely only on those group comparisons; however, we did find statistical differences. We also tested highly statistically powered dose-response associations between persistence of cannabis use over ages 18-45 and each of our outcomes (IQ, learning, and processing speed in midlife) while adjusting possible alternate explanations such as low childhood IQ, other substance use, [and] socioeconomic backgrounds.
“These dose-response associations used large sample sizes, were highly powered, and took into account a number of alternative explanations. These two different approaches showed very similar findings and one bolstered the other,” said Dr. Meier.
The study’s results were based on individuals who began using cannabis in the 1980s or ‘90s, but the concentration of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) has risen in recent years.
“When the study began, THC concentration was approximately 4%. Over the last decade we have seen it go up to 12% or even higher. A recent study surveying U.S. dispensaries found 20% THC. If THC accounts for impairment, then the effects can be larger [with higher concentrations]. One of the challenges in the U.S. is that there are laws prohibiting researchers from testing cannabis, so we have to rely on product labels, which we know are unreliable,” said Dr. Meier.
A separate report is forthcoming with results of exploratory analyses of associations between long-term cannabis use and comprehensive MRI measures of global and regional gray and white matter.
The data will also be used to answer a number of different questions about cognitive deficits, brain structure, aging preparedness, social preparedness (strength of social networks), financial and health preparedness, and biological aging (the pace of aging relative to chronological age) in long-term cannabis users, Dr. Meier noted.
‘Fantastic’ research
Commenting on the research for this news organization , Andrew J. Saxon, MD, professor, department of psychiatry & behavioral sciences at University of Washington, Seattle, and a member of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Addiction Psychiatry, said the study “provides more evidence that heavy and regular cannabis use is not benign behavior.”
“It’s a fantastic piece of research in which they enrolled participants at birth and have followed them up to age 45. In most of the other research that has been done, we have no idea what their baseline was. What’s so remarkable here is that they can clearly demonstrate the loss of IQ points from childhood to age 45,” said Dr. Saxon.
“It is clear that, in people using cannabis long term, cognition is impaired. It would be good to have a better handle on how much cognitive function can be regained if you quit, because that could be a motivator for quitting in people where cannabis is having an adverse effect on their lives,” he added.
On the issue of THC potency, Dr. Saxon said that, while it’s true the potency of cannabis is increasing in terms of THC concentrations, the question is: “Do people who use cannabis use a set amount or do they imbibe until they achieve the state of altered consciousness that they’re seeking? Although there has been some research in the area of self-regulation and cannabis potency, we do not yet have the answers to determine if there is any causation,” said Dr. Saxon.
Dr. Meier and Dr. Saxon reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A large prospective, longitudinal study showed long-term cannabis users had an intelligence quotient (IQ) decline from age 18 to midlife (mean, 5.5 IQ points), poorer learning and processing speed, compared with childhood, and self-reported memory and attention problems. Long-term cannabis users also showed hippocampal atrophy at midlife (age 45), which combined with mild midlife cognitive deficits, all known risk factors for dementia.
“Long-term cannabis users – people who have used cannabis from 18 or 19 years old and continued using through midlife – showed cognitive deficits, compared with nonusers. They also showed more severe cognitive deficits, compared with long-term alcohol users and long-term tobacco users. But people who used infrequently or recreationally in midlife did not show as severe cognitive deficits. Cognitive deficits were confined to cannabis users,” lead investigator Madeline Meier, PhD, associate professor of psychology, Arizona State University, Tempe, said in an interview.
“Long-term cannabis users had smaller hippocampal volume, but we also found that smaller hippocampal volume did not explain the cognitive deficits among the long-term cannabis users,” she added.
The study was recently published online in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Growing use in Boomers
Long-term cannabis use has been associated with memory problems. Studies examining the impact of cannabis use on the brain have shown conflicting results. Some suggest regular use in adolescence is associated with altered connectivity and reduced volume of brain regions involved in executive functions such as memory, learning, and impulse control compared with those who do not use cannabis.
Others found no significant structural differences between the brains of cannabis users and nonusers.
An earlier, large longitudinal study in New Zealand found that persistent cannabis use (with frequent use starting in adolescence) was associated with a loss of an average of six (or up to eight) IQ points measured in mid-adulthood.
Cannabis use is increasing among Baby Boomers – a group born between 1946 and 1964 – who used cannabis at historically high rates as young adults, and who now use it at historically high rates in midlife and as older adults.
To date, case-control studies, which are predominantly in adolescents and young adults, have found that cannabis users show subtle cognitive deficits and structural brain differences, but it is unclear whether these differences in young cannabis users might be larger in midlife and in older adults who have longer histories of use.
The study included a representative cohort of 1,037 individuals in Dunedin, New Zealand, born between April 1972 and March 1973, and followed from age 3 to 45.
Cannabis use and dependence were assessed at ages 18, 21, 26, 32, 38, and 45. IQ was assessed at ages 7, 9, 11, and 45. Specific neuropsychological functions and hippocampal volume were assessed at age 45.
“Most of the previous research has focused on adolescent and young-adult cannabis users. What we’re looking at here is long-term cannabis users in midlife, and we’re finding that long-term users show cognitive deficits. But we’re not just looking at a snapshot of people in midlife, we’re also doing a longitudinal comparison – comparing them to themselves in childhood. We saw that long-term cannabis users showed a decline in IQ from childhood to adulthood,” said Dr. Meier.
Participants in the study are members of the Dunedin Longitudinal Study, a representative birth cohort (n = 1,037; 91% of eligible births; 52% male) born between April 1972 and March 1973 in Dunedin, New Zealand, who participated in the first assessment at age 3.
This cohort matched socioeconomic status (SES), key health indicators, and demographics. Assessments were carried out at birth and ages 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 18, 21, 26, 32, 38, and 45. IQ was assessed at ages 7, 9, 11, and 45. Specific neuropsychological functions and hippocampal volume were assessed at age 45.
Shrinking hippocampal volume
Cannabis use, cognitive function, and hippocampal volume were assessed comparing long-term cannabis users (n = 84) against five distinct groups:
- Lifelong cannabis nonusers (n = 196) – to replicate the control group most often reported in the case-control literature
- Midlife recreational cannabis users (n = 65) – to determine if cognitive deficits and structural brain differences are apparent in nonproblem users – the majority of cannabis users
- Long-term tobacco users (n = 75)
- Long-term alcohol users (n = 57) – benchmark comparisons for any cannabis findings and to disentangle potential cannabis effects from tobacco and alcohol effects
- Cannabis quitters (n = 58) – to determine whether differences are apparent after cessation
Tests were conducted on dose-response associations using continuously measured persistence of cannabis use, rigorously adjusting for numerous confounders derived from multiple longitudinal waves and data sources.
The investigators also tested whether associations between continuously measured persistence of cannabis use and cognitive deficits were mediated by hippocampal volume differences.
The hippocampus was the area of focus because it has a high density of cannabinoid receptors and is also instrumental for learning and memory, which is one of the most consistently impaired cognitive domains in cannabis users, and has been the brain region that most consistently emerges as smaller in cannabis users relative to controls. Structural MRI was done at age 45 for 875 participants (93% of age 45 participants).
Of 997 cohort members still alive at age 45, 938 (94.1%) were assessed at age 45. Age 45 participants did not differ significantly from other participants on childhood SES, childhood self-control, or childhood IQ. Cognitive functioning among midlife recreational cannabis users was similar to representative cohort norms, suggesting that infrequent recreational cannabis use in midlife is unlikely to compromise cognitive functioning.
However, long-term cannabis users did not perform significantly worse on any test than cannabis quitters. Cannabis quitters showed subtle cognitive deficits that may explain inconsistent findings on the benefits of cessation.
Smaller hippocampal volume is thought to be a possible mediator of cannabis-related cognitive deficits because the hippocampus is rich in CB1 receptors and is involved in learning and memory.
Long-term cannabis users had smaller bilateral volume in total hippocampus and 5 of 12 structurally and functionally distinct subregions (tail, hippocampal amygdala transition area, CA1, molecular layer, and dentate gyrus), and significantly smaller volumes than midlife recreational cannabis users in the left and right hippocampus, and 3 of 12 subfields (tail, CA1, and molecular layer), compared with non-users, consistent with case-control studies.
More potent
“If you’ve been using cannabis very long term and now are in midlife, you might want to consider quitting. Quitting is associated with slightly better cognitive performance in midlife. We also need to watch for risk of dementia. We know that people who show cognitive deficits at midlife are at elevated risk for later life dementia. And the deficits we saw among long-term cannabis users (although fairly mild), they were in the range in terms of effect size of what we see among people in other studies who have gone on to develop dementia in later life,” said Dr. Meier.
The study findings conflict with those of other studies, including one by the same research group, which compared the cognitive functioning of twins who were discordant for cannabis use and found little evidence of cannabis-related cognitive deficits. Because long-term cannabis users also use tobacco, alcohol, and other illicit drugs, disentangling cannabis effects from other substances is challenging.
“Long-term cannabis users tend to be long-term polysubstance users, so it’s hard to isolate,” said Dr. Meier.
Additionally, some group sizes were small, raising concerns about low statistical power.
“Group sizes were small but we didn’t rely only on those group comparisons; however, we did find statistical differences. We also tested highly statistically powered dose-response associations between persistence of cannabis use over ages 18-45 and each of our outcomes (IQ, learning, and processing speed in midlife) while adjusting possible alternate explanations such as low childhood IQ, other substance use, [and] socioeconomic backgrounds.
“These dose-response associations used large sample sizes, were highly powered, and took into account a number of alternative explanations. These two different approaches showed very similar findings and one bolstered the other,” said Dr. Meier.
The study’s results were based on individuals who began using cannabis in the 1980s or ‘90s, but the concentration of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) has risen in recent years.
“When the study began, THC concentration was approximately 4%. Over the last decade we have seen it go up to 12% or even higher. A recent study surveying U.S. dispensaries found 20% THC. If THC accounts for impairment, then the effects can be larger [with higher concentrations]. One of the challenges in the U.S. is that there are laws prohibiting researchers from testing cannabis, so we have to rely on product labels, which we know are unreliable,” said Dr. Meier.
A separate report is forthcoming with results of exploratory analyses of associations between long-term cannabis use and comprehensive MRI measures of global and regional gray and white matter.
The data will also be used to answer a number of different questions about cognitive deficits, brain structure, aging preparedness, social preparedness (strength of social networks), financial and health preparedness, and biological aging (the pace of aging relative to chronological age) in long-term cannabis users, Dr. Meier noted.
‘Fantastic’ research
Commenting on the research for this news organization , Andrew J. Saxon, MD, professor, department of psychiatry & behavioral sciences at University of Washington, Seattle, and a member of the American Psychiatric Association’s Council on Addiction Psychiatry, said the study “provides more evidence that heavy and regular cannabis use is not benign behavior.”
“It’s a fantastic piece of research in which they enrolled participants at birth and have followed them up to age 45. In most of the other research that has been done, we have no idea what their baseline was. What’s so remarkable here is that they can clearly demonstrate the loss of IQ points from childhood to age 45,” said Dr. Saxon.
“It is clear that, in people using cannabis long term, cognition is impaired. It would be good to have a better handle on how much cognitive function can be regained if you quit, because that could be a motivator for quitting in people where cannabis is having an adverse effect on their lives,” he added.
On the issue of THC potency, Dr. Saxon said that, while it’s true the potency of cannabis is increasing in terms of THC concentrations, the question is: “Do people who use cannabis use a set amount or do they imbibe until they achieve the state of altered consciousness that they’re seeking? Although there has been some research in the area of self-regulation and cannabis potency, we do not yet have the answers to determine if there is any causation,” said Dr. Saxon.
Dr. Meier and Dr. Saxon reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHIATRY
New injectable gel can deliver immune cells directly to cancer tumors
A simple, two-ingredient gel may boost the fighting power of a groundbreaking cancer treatment, say Stanford University engineers.
The gel – made from water and a plant-based polymer – delivers targeted T cells adjacent to a cancer growth, taking aim at solid tumors.
It’s the latest development in CAR T-cell therapy, a type of immunotherapy that involves collecting the patient’s T cells, reengineering them to be stronger, and returning them to the patient’s body.
Results have been promising in blood cancers, such as leukemia and lymphoma, but less so in solid tumors, such as brain, breast, or kidney cancer, according to the National Cancer Institute.
The gel “is a really exciting step forward,” says Abigail Grosskopf, a PhD candidate at Stanford (Calif.) University, who is the lead study author, “because it can change the delivery of these cells and expand this kind of treatment to other cancers.”
CAR T-cell therapy: Limits in solid tumors
Currently available CAR T-cell therapies are administered by intravenous infusion. But that doesn’t do much against tumors in specific locations because the cells enter the bloodstream and flow throughout the body. The cancer-fighting effort exhausts the T cells, weakening their ability to infiltrate dense tumors.
CAR T cells need cytokines to tell them when to attack, Ms. Grosskopf explains. If delivered through an IV drip, the number of cytokines required to destroy a solid tumor would be toxic to other, healthy parts of the body.
So
In their study, which was published in Science Advances, the injections wiped out mouse tumors in 12 days. The gel degraded harmlessly a few weeks later.
A “leaky pen” that fights cancer
The reason a gel works better than a liquid is because of its staying power, says Ms. Grosskopf, who compares the method to a leaky pen.
The gel acts as the “pen,” releasing activated CAR T cells at regular intervals to attack the cancerous growth. Whereas liquid dissipates quickly, the gel’s structure is strong enough to stay in place for weeks, Ms. Grosskopf says. Plus, it’s biocompatible and harmless within the body, she adds.
More preclinical studies are needed before human clinical trials can occur, Ms. Grosskopf says.
“Not only could this be a way to deliver T cells and cytokines,” Ms. Grosskopf says, “but it may be used for other targeted therapy cancer drugs that are in development. So we see this as running parallel to those efforts.”
Taking an even broader view, the gel could have applications across medical specialties, such as slow-release delivery of vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A simple, two-ingredient gel may boost the fighting power of a groundbreaking cancer treatment, say Stanford University engineers.
The gel – made from water and a plant-based polymer – delivers targeted T cells adjacent to a cancer growth, taking aim at solid tumors.
It’s the latest development in CAR T-cell therapy, a type of immunotherapy that involves collecting the patient’s T cells, reengineering them to be stronger, and returning them to the patient’s body.
Results have been promising in blood cancers, such as leukemia and lymphoma, but less so in solid tumors, such as brain, breast, or kidney cancer, according to the National Cancer Institute.
The gel “is a really exciting step forward,” says Abigail Grosskopf, a PhD candidate at Stanford (Calif.) University, who is the lead study author, “because it can change the delivery of these cells and expand this kind of treatment to other cancers.”
CAR T-cell therapy: Limits in solid tumors
Currently available CAR T-cell therapies are administered by intravenous infusion. But that doesn’t do much against tumors in specific locations because the cells enter the bloodstream and flow throughout the body. The cancer-fighting effort exhausts the T cells, weakening their ability to infiltrate dense tumors.
CAR T cells need cytokines to tell them when to attack, Ms. Grosskopf explains. If delivered through an IV drip, the number of cytokines required to destroy a solid tumor would be toxic to other, healthy parts of the body.
So
In their study, which was published in Science Advances, the injections wiped out mouse tumors in 12 days. The gel degraded harmlessly a few weeks later.
A “leaky pen” that fights cancer
The reason a gel works better than a liquid is because of its staying power, says Ms. Grosskopf, who compares the method to a leaky pen.
The gel acts as the “pen,” releasing activated CAR T cells at regular intervals to attack the cancerous growth. Whereas liquid dissipates quickly, the gel’s structure is strong enough to stay in place for weeks, Ms. Grosskopf says. Plus, it’s biocompatible and harmless within the body, she adds.
More preclinical studies are needed before human clinical trials can occur, Ms. Grosskopf says.
“Not only could this be a way to deliver T cells and cytokines,” Ms. Grosskopf says, “but it may be used for other targeted therapy cancer drugs that are in development. So we see this as running parallel to those efforts.”
Taking an even broader view, the gel could have applications across medical specialties, such as slow-release delivery of vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A simple, two-ingredient gel may boost the fighting power of a groundbreaking cancer treatment, say Stanford University engineers.
The gel – made from water and a plant-based polymer – delivers targeted T cells adjacent to a cancer growth, taking aim at solid tumors.
It’s the latest development in CAR T-cell therapy, a type of immunotherapy that involves collecting the patient’s T cells, reengineering them to be stronger, and returning them to the patient’s body.
Results have been promising in blood cancers, such as leukemia and lymphoma, but less so in solid tumors, such as brain, breast, or kidney cancer, according to the National Cancer Institute.
The gel “is a really exciting step forward,” says Abigail Grosskopf, a PhD candidate at Stanford (Calif.) University, who is the lead study author, “because it can change the delivery of these cells and expand this kind of treatment to other cancers.”
CAR T-cell therapy: Limits in solid tumors
Currently available CAR T-cell therapies are administered by intravenous infusion. But that doesn’t do much against tumors in specific locations because the cells enter the bloodstream and flow throughout the body. The cancer-fighting effort exhausts the T cells, weakening their ability to infiltrate dense tumors.
CAR T cells need cytokines to tell them when to attack, Ms. Grosskopf explains. If delivered through an IV drip, the number of cytokines required to destroy a solid tumor would be toxic to other, healthy parts of the body.
So
In their study, which was published in Science Advances, the injections wiped out mouse tumors in 12 days. The gel degraded harmlessly a few weeks later.
A “leaky pen” that fights cancer
The reason a gel works better than a liquid is because of its staying power, says Ms. Grosskopf, who compares the method to a leaky pen.
The gel acts as the “pen,” releasing activated CAR T cells at regular intervals to attack the cancerous growth. Whereas liquid dissipates quickly, the gel’s structure is strong enough to stay in place for weeks, Ms. Grosskopf says. Plus, it’s biocompatible and harmless within the body, she adds.
More preclinical studies are needed before human clinical trials can occur, Ms. Grosskopf says.
“Not only could this be a way to deliver T cells and cytokines,” Ms. Grosskopf says, “but it may be used for other targeted therapy cancer drugs that are in development. So we see this as running parallel to those efforts.”
Taking an even broader view, the gel could have applications across medical specialties, such as slow-release delivery of vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SCIENCE ADVANCES
U.S. life expectancy dropped by 2 years in 2020: Study
according to a new study.
The study, published in medRxiv, said U.S. life expectancy went from 78.86 years in 2019 to 76.99 years in 2020, during the thick of the global COVID-19 pandemic. Though vaccines were widely available in 2021, the U.S. life expectancy was expected to keep going down, to 76.60 years.
In “peer countries” – Austria, Belgium, Denmark, England and Wales, Finland, France, Germany, Israel, Italy, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Northern Ireland, Norway, Portugal, Scotland, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, and Switzerland – life expectancy went down only 0.57 years from 2019 to 2020 and increased by 0.28 years in 2021, the study said. The peer countries now have a life expectancy that’s 5 years longer than in the United States.
“The fact the U.S. lost so many more lives than other high-income countries speaks not only to how we managed the pandemic, but also to more deeply rooted problems that predated the pandemic,” said Steven H. Woolf, MD, one of the study authors and a professor of family medicine and population health at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, according to Reuters.
“U.S. life expectancy has been falling behind other countries since the 1980s, and the gap has widened over time, especially in the last decade.”
Lack of universal health care, income and educational inequality, and less-healthy physical and social environments helped lead to the decline in American life expectancy, according to Dr. Woolf.
The life expectancy drop from 2019 to 2020 hit Black and Hispanic people hardest, according to the study. But the drop from 2020 to 2021 affected White people the most, with average life expectancy among them going down about a third of a year.
Researchers looked at death data from the National Center for Health Statistics, the Human Mortality Database, and overseas statistical agencies. Life expectancy for 2021 was estimated “using a previously validated modeling method,” the study said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according to a new study.
The study, published in medRxiv, said U.S. life expectancy went from 78.86 years in 2019 to 76.99 years in 2020, during the thick of the global COVID-19 pandemic. Though vaccines were widely available in 2021, the U.S. life expectancy was expected to keep going down, to 76.60 years.
In “peer countries” – Austria, Belgium, Denmark, England and Wales, Finland, France, Germany, Israel, Italy, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Northern Ireland, Norway, Portugal, Scotland, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, and Switzerland – life expectancy went down only 0.57 years from 2019 to 2020 and increased by 0.28 years in 2021, the study said. The peer countries now have a life expectancy that’s 5 years longer than in the United States.
“The fact the U.S. lost so many more lives than other high-income countries speaks not only to how we managed the pandemic, but also to more deeply rooted problems that predated the pandemic,” said Steven H. Woolf, MD, one of the study authors and a professor of family medicine and population health at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, according to Reuters.
“U.S. life expectancy has been falling behind other countries since the 1980s, and the gap has widened over time, especially in the last decade.”
Lack of universal health care, income and educational inequality, and less-healthy physical and social environments helped lead to the decline in American life expectancy, according to Dr. Woolf.
The life expectancy drop from 2019 to 2020 hit Black and Hispanic people hardest, according to the study. But the drop from 2020 to 2021 affected White people the most, with average life expectancy among them going down about a third of a year.
Researchers looked at death data from the National Center for Health Statistics, the Human Mortality Database, and overseas statistical agencies. Life expectancy for 2021 was estimated “using a previously validated modeling method,” the study said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according to a new study.
The study, published in medRxiv, said U.S. life expectancy went from 78.86 years in 2019 to 76.99 years in 2020, during the thick of the global COVID-19 pandemic. Though vaccines were widely available in 2021, the U.S. life expectancy was expected to keep going down, to 76.60 years.
In “peer countries” – Austria, Belgium, Denmark, England and Wales, Finland, France, Germany, Israel, Italy, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Northern Ireland, Norway, Portugal, Scotland, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, and Switzerland – life expectancy went down only 0.57 years from 2019 to 2020 and increased by 0.28 years in 2021, the study said. The peer countries now have a life expectancy that’s 5 years longer than in the United States.
“The fact the U.S. lost so many more lives than other high-income countries speaks not only to how we managed the pandemic, but also to more deeply rooted problems that predated the pandemic,” said Steven H. Woolf, MD, one of the study authors and a professor of family medicine and population health at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, according to Reuters.
“U.S. life expectancy has been falling behind other countries since the 1980s, and the gap has widened over time, especially in the last decade.”
Lack of universal health care, income and educational inequality, and less-healthy physical and social environments helped lead to the decline in American life expectancy, according to Dr. Woolf.
The life expectancy drop from 2019 to 2020 hit Black and Hispanic people hardest, according to the study. But the drop from 2020 to 2021 affected White people the most, with average life expectancy among them going down about a third of a year.
Researchers looked at death data from the National Center for Health Statistics, the Human Mortality Database, and overseas statistical agencies. Life expectancy for 2021 was estimated “using a previously validated modeling method,” the study said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM MEDRXIV