User login
Metastatic breast cancer: Survival has improved over time
Key clinical point: The survival among patients with metastatic breast cancer has improved over past 3 decades.
Major finding: During 1988-2015, 1-year overall survival (OS) rate increased from 62.3% to 72.4% and 1-year cancer-specific survival (CSS) rate increased from 64.7% to 74.1%. Similarly, 5-year OS rate increased from 19.4% to 24.3% and 5-year CSS rate increased from 23.4% to 28.0% during 1998-2011.
Study details: A retrospective cohort study of 47,034 patients with de novo metastatic breast cancer in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database from 1988 to 2016.
Disclosures: This study is in part supported by Duke Cancer Institute. Dr. OM Fayanju is supported by the National Institutes of Health. Some of the authors received research funding and consulting/advisory fees from various sources. Dr. JK Plichta and Dr. ES Hwang have served on various Cancer Committees. The other authors reported no competing interests.
Source: Taskindoust M. Ann Surg Oncol. 2021 May 28. doi: 10.1245/s10434-021-10227-3.
Key clinical point: The survival among patients with metastatic breast cancer has improved over past 3 decades.
Major finding: During 1988-2015, 1-year overall survival (OS) rate increased from 62.3% to 72.4% and 1-year cancer-specific survival (CSS) rate increased from 64.7% to 74.1%. Similarly, 5-year OS rate increased from 19.4% to 24.3% and 5-year CSS rate increased from 23.4% to 28.0% during 1998-2011.
Study details: A retrospective cohort study of 47,034 patients with de novo metastatic breast cancer in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database from 1988 to 2016.
Disclosures: This study is in part supported by Duke Cancer Institute. Dr. OM Fayanju is supported by the National Institutes of Health. Some of the authors received research funding and consulting/advisory fees from various sources. Dr. JK Plichta and Dr. ES Hwang have served on various Cancer Committees. The other authors reported no competing interests.
Source: Taskindoust M. Ann Surg Oncol. 2021 May 28. doi: 10.1245/s10434-021-10227-3.
Key clinical point: The survival among patients with metastatic breast cancer has improved over past 3 decades.
Major finding: During 1988-2015, 1-year overall survival (OS) rate increased from 62.3% to 72.4% and 1-year cancer-specific survival (CSS) rate increased from 64.7% to 74.1%. Similarly, 5-year OS rate increased from 19.4% to 24.3% and 5-year CSS rate increased from 23.4% to 28.0% during 1998-2011.
Study details: A retrospective cohort study of 47,034 patients with de novo metastatic breast cancer in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database from 1988 to 2016.
Disclosures: This study is in part supported by Duke Cancer Institute. Dr. OM Fayanju is supported by the National Institutes of Health. Some of the authors received research funding and consulting/advisory fees from various sources. Dr. JK Plichta and Dr. ES Hwang have served on various Cancer Committees. The other authors reported no competing interests.
Source: Taskindoust M. Ann Surg Oncol. 2021 May 28. doi: 10.1245/s10434-021-10227-3.
TNBC: Lower recurrence risk with breast-conserving surgery compared with mastectomy
Key clinical point: In patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), the risk for locoregional recurrence and distant metastasis is lower when treated with breast-conserving surgery (BCS) vs. mastectomy.
Major finding: BCS vs. mastectomy was associated with lower risk for locoregional recurrence (unadjusted pooled odds ratio, 0.64; P = .002). The risk for distant metastasis was also significantly lower with BCS vs. mastectomy (unadjusted pooled odds ratio, 0.70; P = .02).
Study details: A meta-analysis of 14 studies including 19,819 patients with TNBC who underwent either BCS or mastectomy.
Disclosures: This meta-analysis was supported by investigator grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council and the National Breast Cancer Foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Fancellu A. Br J Surg. 2021 May 31. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znab145.
Key clinical point: In patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), the risk for locoregional recurrence and distant metastasis is lower when treated with breast-conserving surgery (BCS) vs. mastectomy.
Major finding: BCS vs. mastectomy was associated with lower risk for locoregional recurrence (unadjusted pooled odds ratio, 0.64; P = .002). The risk for distant metastasis was also significantly lower with BCS vs. mastectomy (unadjusted pooled odds ratio, 0.70; P = .02).
Study details: A meta-analysis of 14 studies including 19,819 patients with TNBC who underwent either BCS or mastectomy.
Disclosures: This meta-analysis was supported by investigator grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council and the National Breast Cancer Foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Fancellu A. Br J Surg. 2021 May 31. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znab145.
Key clinical point: In patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), the risk for locoregional recurrence and distant metastasis is lower when treated with breast-conserving surgery (BCS) vs. mastectomy.
Major finding: BCS vs. mastectomy was associated with lower risk for locoregional recurrence (unadjusted pooled odds ratio, 0.64; P = .002). The risk for distant metastasis was also significantly lower with BCS vs. mastectomy (unadjusted pooled odds ratio, 0.70; P = .02).
Study details: A meta-analysis of 14 studies including 19,819 patients with TNBC who underwent either BCS or mastectomy.
Disclosures: This meta-analysis was supported by investigator grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council and the National Breast Cancer Foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Fancellu A. Br J Surg. 2021 May 31. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znab145.
HR-positive breast cancer: Aromatase inhibitors-based treatment yields survival benefit
Key clinical point: Patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive breast cancer derive survival benefit from treatment with predominantly aromatase inhibitors after chemotherapy.
Major finding: The recurrence-free survival significantly improved in patients who received aromatase inhibitor for greater than 75% of their endocrine treatment duration (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.63; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.46-0.86) and overall survival (aHR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.34-0.74) vs. those who received aromatase inhibitors for less than 25% of their endocrine treatment duration.
Study details: A population-based cohort study of patients with stage I-III, HR-positive invasive breast cancer diagnosed between 2004 and 2007 and received adjuvant chemotherapy and endocrine treatment.
Disclosures: This work was funded by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, A Sisters Hope, and De Vrienden van UMC Utrecht. Some authors reported research support, grants, advisory fees, and nonfinancial support from various sources outside this work.
Source: Dackus GM et al. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2021 Jun 8. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djab091.
Key clinical point: Patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive breast cancer derive survival benefit from treatment with predominantly aromatase inhibitors after chemotherapy.
Major finding: The recurrence-free survival significantly improved in patients who received aromatase inhibitor for greater than 75% of their endocrine treatment duration (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.63; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.46-0.86) and overall survival (aHR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.34-0.74) vs. those who received aromatase inhibitors for less than 25% of their endocrine treatment duration.
Study details: A population-based cohort study of patients with stage I-III, HR-positive invasive breast cancer diagnosed between 2004 and 2007 and received adjuvant chemotherapy and endocrine treatment.
Disclosures: This work was funded by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, A Sisters Hope, and De Vrienden van UMC Utrecht. Some authors reported research support, grants, advisory fees, and nonfinancial support from various sources outside this work.
Source: Dackus GM et al. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2021 Jun 8. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djab091.
Key clinical point: Patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive breast cancer derive survival benefit from treatment with predominantly aromatase inhibitors after chemotherapy.
Major finding: The recurrence-free survival significantly improved in patients who received aromatase inhibitor for greater than 75% of their endocrine treatment duration (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.63; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.46-0.86) and overall survival (aHR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.34-0.74) vs. those who received aromatase inhibitors for less than 25% of their endocrine treatment duration.
Study details: A population-based cohort study of patients with stage I-III, HR-positive invasive breast cancer diagnosed between 2004 and 2007 and received adjuvant chemotherapy and endocrine treatment.
Disclosures: This work was funded by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, A Sisters Hope, and De Vrienden van UMC Utrecht. Some authors reported research support, grants, advisory fees, and nonfinancial support from various sources outside this work.
Source: Dackus GM et al. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2021 Jun 8. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djab091.
Adding ribociclib extends survival in HR-positive, HER-negative breast cancer
Key clinical point: In patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth receptor (HER)-negative advanced breast cancer, the addition of ribociclib to fulvestrant extends median overall survival by 12 months.
Major finding: The median overall survival was 53.7 months with ribociclib and 41.5 months with placebo (hazard ratio, 0.73; 95% confidence interval, 0.59-0.90 months) at a median follow-up of 56.3 months. Neutropenia was the most common grade 3-4 adverse event.
Study details: A phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled MONALEESA-3 trial including 726 chemotherapy-naïve patients (men and postmenopausal women) with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer randomly assigned 2:1 to receive fulvestrant with either ribociclib or placebo.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. The authors reported advisory/consulting fees, stock ownership, research funding, grants, personal fees, honoraria, travel expenses, and nonfinancial support from various sources outside this work.
Source: Slamon DJ et al. Ann Oncol. 2021 Jun 5. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.05.353.
Key clinical point: In patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth receptor (HER)-negative advanced breast cancer, the addition of ribociclib to fulvestrant extends median overall survival by 12 months.
Major finding: The median overall survival was 53.7 months with ribociclib and 41.5 months with placebo (hazard ratio, 0.73; 95% confidence interval, 0.59-0.90 months) at a median follow-up of 56.3 months. Neutropenia was the most common grade 3-4 adverse event.
Study details: A phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled MONALEESA-3 trial including 726 chemotherapy-naïve patients (men and postmenopausal women) with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer randomly assigned 2:1 to receive fulvestrant with either ribociclib or placebo.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. The authors reported advisory/consulting fees, stock ownership, research funding, grants, personal fees, honoraria, travel expenses, and nonfinancial support from various sources outside this work.
Source: Slamon DJ et al. Ann Oncol. 2021 Jun 5. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.05.353.
Key clinical point: In patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth receptor (HER)-negative advanced breast cancer, the addition of ribociclib to fulvestrant extends median overall survival by 12 months.
Major finding: The median overall survival was 53.7 months with ribociclib and 41.5 months with placebo (hazard ratio, 0.73; 95% confidence interval, 0.59-0.90 months) at a median follow-up of 56.3 months. Neutropenia was the most common grade 3-4 adverse event.
Study details: A phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled MONALEESA-3 trial including 726 chemotherapy-naïve patients (men and postmenopausal women) with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer randomly assigned 2:1 to receive fulvestrant with either ribociclib or placebo.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. The authors reported advisory/consulting fees, stock ownership, research funding, grants, personal fees, honoraria, travel expenses, and nonfinancial support from various sources outside this work.
Source: Slamon DJ et al. Ann Oncol. 2021 Jun 5. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.05.353.
Residual TNBC: Platinum therapy does not improve outcomes
Key clinical point: Platinum agents do not improve outcomes in patients with basal subtype triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and residual invasive disease post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) and are associated with higher toxicity rate vs. capecitabine.
Major finding: The invasive disease-free survival was not significantly different between platinum and capecitabine groups (hazard ratio, 1.06; 95% confidence interval, 0.62-1.81) after a median follow-up of 20 months. Grade 3 and 4 toxicities were more frequent in the platinum vs. capecitabine group (26% vs. 15%).
Study details: A phase 3, randomized controlled EA1131 trial involving 415 patients with stage II-III TNBC post-NAC, randomly assigned to receive platinum-based chemotherapy or capecitabine.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. The authors received consulting/advisory fees, research funding, honoraria, travel/accommodation/expenses, and reported stock and other ownership interests in various companies. Some authors also reported patents, royalties, and other intellectual property.
Source: Mayer IA et al. J Clin Oncol. 2021 Jun 6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.00976.
Key clinical point: Platinum agents do not improve outcomes in patients with basal subtype triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and residual invasive disease post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) and are associated with higher toxicity rate vs. capecitabine.
Major finding: The invasive disease-free survival was not significantly different between platinum and capecitabine groups (hazard ratio, 1.06; 95% confidence interval, 0.62-1.81) after a median follow-up of 20 months. Grade 3 and 4 toxicities were more frequent in the platinum vs. capecitabine group (26% vs. 15%).
Study details: A phase 3, randomized controlled EA1131 trial involving 415 patients with stage II-III TNBC post-NAC, randomly assigned to receive platinum-based chemotherapy or capecitabine.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. The authors received consulting/advisory fees, research funding, honoraria, travel/accommodation/expenses, and reported stock and other ownership interests in various companies. Some authors also reported patents, royalties, and other intellectual property.
Source: Mayer IA et al. J Clin Oncol. 2021 Jun 6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.00976.
Key clinical point: Platinum agents do not improve outcomes in patients with basal subtype triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and residual invasive disease post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) and are associated with higher toxicity rate vs. capecitabine.
Major finding: The invasive disease-free survival was not significantly different between platinum and capecitabine groups (hazard ratio, 1.06; 95% confidence interval, 0.62-1.81) after a median follow-up of 20 months. Grade 3 and 4 toxicities were more frequent in the platinum vs. capecitabine group (26% vs. 15%).
Study details: A phase 3, randomized controlled EA1131 trial involving 415 patients with stage II-III TNBC post-NAC, randomly assigned to receive platinum-based chemotherapy or capecitabine.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. The authors received consulting/advisory fees, research funding, honoraria, travel/accommodation/expenses, and reported stock and other ownership interests in various companies. Some authors also reported patents, royalties, and other intellectual property.
Source: Mayer IA et al. J Clin Oncol. 2021 Jun 6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.00976.
Adjuvant olaparib yields survival benefit in HER2-negative BRCA1/2 breast cancer
Key clinical point: Adjuvant olaparib prolongs invasive disease-free survival and distant disease-free survival in patients with high-risk BRCA1/2-mutated human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2)-negative early breast cancer who received local treatment and adjuvant/neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Major finding: Adjuvant olaparib significantly improved invasive disease-free survival (hazard ratio, 0.58; P less than .001) and distant disease-free survival (hazard ratio, 0.57; P less than .001). The serious adverse event rate was 8.7% in the olaparib group and 8.4% in the placebo group.
Study details: A phase 3 double-blind, randomized OlympiA trial evaluated 1,836 patients with high-risk BRCA1/2-mutated HER2-negative early breast cancer who received local treatment and adjuvant/neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Patients were randomly assigned to olaparib or placebo.
Disclosures: The study received funding from the National Cancer Institute and AstraZeneca. The authors reported receiving grants, honoraria, advisory/speaker/consulting fees, financial/nonfinancial support, and travel expense from various sources and/or owning stocks in pharmaceutical companies. Dr. SJ Hollingsworth, Dr. A Fielding, and Dr. N Baker were employees at AstraZeneca.
Source: Tutt ANJ et al. New Eng J Med. 2021 Jun 3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2105215.
Key clinical point: Adjuvant olaparib prolongs invasive disease-free survival and distant disease-free survival in patients with high-risk BRCA1/2-mutated human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2)-negative early breast cancer who received local treatment and adjuvant/neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Major finding: Adjuvant olaparib significantly improved invasive disease-free survival (hazard ratio, 0.58; P less than .001) and distant disease-free survival (hazard ratio, 0.57; P less than .001). The serious adverse event rate was 8.7% in the olaparib group and 8.4% in the placebo group.
Study details: A phase 3 double-blind, randomized OlympiA trial evaluated 1,836 patients with high-risk BRCA1/2-mutated HER2-negative early breast cancer who received local treatment and adjuvant/neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Patients were randomly assigned to olaparib or placebo.
Disclosures: The study received funding from the National Cancer Institute and AstraZeneca. The authors reported receiving grants, honoraria, advisory/speaker/consulting fees, financial/nonfinancial support, and travel expense from various sources and/or owning stocks in pharmaceutical companies. Dr. SJ Hollingsworth, Dr. A Fielding, and Dr. N Baker were employees at AstraZeneca.
Source: Tutt ANJ et al. New Eng J Med. 2021 Jun 3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2105215.
Key clinical point: Adjuvant olaparib prolongs invasive disease-free survival and distant disease-free survival in patients with high-risk BRCA1/2-mutated human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2)-negative early breast cancer who received local treatment and adjuvant/neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Major finding: Adjuvant olaparib significantly improved invasive disease-free survival (hazard ratio, 0.58; P less than .001) and distant disease-free survival (hazard ratio, 0.57; P less than .001). The serious adverse event rate was 8.7% in the olaparib group and 8.4% in the placebo group.
Study details: A phase 3 double-blind, randomized OlympiA trial evaluated 1,836 patients with high-risk BRCA1/2-mutated HER2-negative early breast cancer who received local treatment and adjuvant/neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Patients were randomly assigned to olaparib or placebo.
Disclosures: The study received funding from the National Cancer Institute and AstraZeneca. The authors reported receiving grants, honoraria, advisory/speaker/consulting fees, financial/nonfinancial support, and travel expense from various sources and/or owning stocks in pharmaceutical companies. Dr. SJ Hollingsworth, Dr. A Fielding, and Dr. N Baker were employees at AstraZeneca.
Source: Tutt ANJ et al. New Eng J Med. 2021 Jun 3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2105215.
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: Breast Cancer July 2021
The role of adjuvant olaparib was investigated in the phase 3 OlympiA trial, which included 1,836 patients with high-risk HER2-negative gBRCAm early breast cancer who received local treatment and adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy. One year of adjuvant olaparib was associated with a significant improvement in invasive disease-free survival (hazard ratio [HR] 0.58, P < .001) and distant disease-free survival (HR 0.57, P < .001). The 3-year invasive disease-free survival (iDFS) was 85.9% in the olaparib group and 77.1% in the placebo group (absolute benefit of 8.8%), and 3-year distant disease-free survival (dDFS) was 87.5% and 80.4%, respectively (difference of 7.1%). These results are considered practice changing and lead to questions regarding the expansion of germline testing in early stage breast cancer. Furthermore, PARP inhibitors have shown exciting results in the neoadjuvant setting. Among 61 patients with gBRCAm HER2-negative early breast cancer, neoadjuvant talazoparib produced a pathologic complete response (pCR) in 49.2%, and there may be a subgroup of patients for whom this approach is relevant.
The presence of residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy has prognostic implications and can help tailor adjuvant treatment recommendations. The CREATE-X trial has established the role of adjuvant capecitabine for patients with triple-negative breast cancer with residual disease after pre-operative chemotherapy. The phase 3 EA1131 trial randomized 415 patients with stage II-III triple-negative breast cancer and residual disease post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy to platinum agent or capecitabine. There was no significant difference in 3-year iDFS (42% for platinum vs 49% for capecitabine; HR 1.06, 95% CI 0.62-1.81), and higher hematologic toxicity and dose reductions in the platinum arm. These data support the continued use of capecitabine in this population, and the high event rate highlights the need for more effective therapies in this setting.
The majority of patients with HR+/HER2- MBC will receive a CDK 4/6 inhibitor at some point during their treatment course. In an updated analysis of the phase 3 MONALEESA-3 trial which included postmenopausal patients with HR+HER2- MBC, with median follow-up of 56.3 months, ribociclib plus fulvestrant continued to show an overall survival (OS) benefit of greater than 1 year compared with fulvestrant alone (median OS 53.7 months vs 41.5 months in the ribociclib vs placebo arm, respectively; HR 0.726, 95% CI 0.59-0.90). Additionally, extended follow-up of the PALOMA-3 trial demonstrated OS benefit with palbociclib plus fulvestrant compared to fulvestrant alone in patients with HR+/HER2- MBC; at median follow-up of 73.3 months, median OS was 34.8 months in the palbociclib arm vs 28.0 months in the placebo arm (HR 0.81, P = .0221). Sequencing of other targeted therapies (such as PI3K inhibitors), predictors of CDK 4/6 inhibitor response in different intrinsic subtypes, and the role of CDK 4/6 inhibitor use beyond progression are areas where further research is warranted.
References:
Robson M, Im SA, Senkus E, et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Breast Cancer in Patients with a Germline BRCA Mutation. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(6):523-533.
Litton JK, Beck JT, Jones JM, et al. Neoadjuvant talazoparib in patients with germline BRCA1/2 (gBRCA1/2) mutation-positive, early HER2-negative breast cancer (BC): Results of a phase 2 study. J Clin Oncol 39, 2021 (suppl 15; abstr 505).
Symmans WF, Wei C, Gould R, et al. Long-Term Prognostic Risk After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Associated With Residual Cancer Burden and Breast Cancer Subtype. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:1049-1060.
Masuda N, Lee SJ, Ohtani S, et al. Adjuvant Capecitabine for Breast Cancer after Preoperative Chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:2147-2159.
Cristofanilli M, Rugo H, Im SA, et al. Overall survival (OS) with palbociclib (PAL) + fulvestrant (FUL) in women with hormone receptor–positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative (HER2–) advanced breast cancer (ABC): Updated analyses from PALOMA-3. J Clin Oncol. 2021; 39:15_suppl, 1000-1000.
The role of adjuvant olaparib was investigated in the phase 3 OlympiA trial, which included 1,836 patients with high-risk HER2-negative gBRCAm early breast cancer who received local treatment and adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy. One year of adjuvant olaparib was associated with a significant improvement in invasive disease-free survival (hazard ratio [HR] 0.58, P < .001) and distant disease-free survival (HR 0.57, P < .001). The 3-year invasive disease-free survival (iDFS) was 85.9% in the olaparib group and 77.1% in the placebo group (absolute benefit of 8.8%), and 3-year distant disease-free survival (dDFS) was 87.5% and 80.4%, respectively (difference of 7.1%). These results are considered practice changing and lead to questions regarding the expansion of germline testing in early stage breast cancer. Furthermore, PARP inhibitors have shown exciting results in the neoadjuvant setting. Among 61 patients with gBRCAm HER2-negative early breast cancer, neoadjuvant talazoparib produced a pathologic complete response (pCR) in 49.2%, and there may be a subgroup of patients for whom this approach is relevant.
The presence of residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy has prognostic implications and can help tailor adjuvant treatment recommendations. The CREATE-X trial has established the role of adjuvant capecitabine for patients with triple-negative breast cancer with residual disease after pre-operative chemotherapy. The phase 3 EA1131 trial randomized 415 patients with stage II-III triple-negative breast cancer and residual disease post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy to platinum agent or capecitabine. There was no significant difference in 3-year iDFS (42% for platinum vs 49% for capecitabine; HR 1.06, 95% CI 0.62-1.81), and higher hematologic toxicity and dose reductions in the platinum arm. These data support the continued use of capecitabine in this population, and the high event rate highlights the need for more effective therapies in this setting.
The majority of patients with HR+/HER2- MBC will receive a CDK 4/6 inhibitor at some point during their treatment course. In an updated analysis of the phase 3 MONALEESA-3 trial which included postmenopausal patients with HR+HER2- MBC, with median follow-up of 56.3 months, ribociclib plus fulvestrant continued to show an overall survival (OS) benefit of greater than 1 year compared with fulvestrant alone (median OS 53.7 months vs 41.5 months in the ribociclib vs placebo arm, respectively; HR 0.726, 95% CI 0.59-0.90). Additionally, extended follow-up of the PALOMA-3 trial demonstrated OS benefit with palbociclib plus fulvestrant compared to fulvestrant alone in patients with HR+/HER2- MBC; at median follow-up of 73.3 months, median OS was 34.8 months in the palbociclib arm vs 28.0 months in the placebo arm (HR 0.81, P = .0221). Sequencing of other targeted therapies (such as PI3K inhibitors), predictors of CDK 4/6 inhibitor response in different intrinsic subtypes, and the role of CDK 4/6 inhibitor use beyond progression are areas where further research is warranted.
References:
Robson M, Im SA, Senkus E, et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Breast Cancer in Patients with a Germline BRCA Mutation. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(6):523-533.
Litton JK, Beck JT, Jones JM, et al. Neoadjuvant talazoparib in patients with germline BRCA1/2 (gBRCA1/2) mutation-positive, early HER2-negative breast cancer (BC): Results of a phase 2 study. J Clin Oncol 39, 2021 (suppl 15; abstr 505).
Symmans WF, Wei C, Gould R, et al. Long-Term Prognostic Risk After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Associated With Residual Cancer Burden and Breast Cancer Subtype. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:1049-1060.
Masuda N, Lee SJ, Ohtani S, et al. Adjuvant Capecitabine for Breast Cancer after Preoperative Chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:2147-2159.
Cristofanilli M, Rugo H, Im SA, et al. Overall survival (OS) with palbociclib (PAL) + fulvestrant (FUL) in women with hormone receptor–positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative (HER2–) advanced breast cancer (ABC): Updated analyses from PALOMA-3. J Clin Oncol. 2021; 39:15_suppl, 1000-1000.
The role of adjuvant olaparib was investigated in the phase 3 OlympiA trial, which included 1,836 patients with high-risk HER2-negative gBRCAm early breast cancer who received local treatment and adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy. One year of adjuvant olaparib was associated with a significant improvement in invasive disease-free survival (hazard ratio [HR] 0.58, P < .001) and distant disease-free survival (HR 0.57, P < .001). The 3-year invasive disease-free survival (iDFS) was 85.9% in the olaparib group and 77.1% in the placebo group (absolute benefit of 8.8%), and 3-year distant disease-free survival (dDFS) was 87.5% and 80.4%, respectively (difference of 7.1%). These results are considered practice changing and lead to questions regarding the expansion of germline testing in early stage breast cancer. Furthermore, PARP inhibitors have shown exciting results in the neoadjuvant setting. Among 61 patients with gBRCAm HER2-negative early breast cancer, neoadjuvant talazoparib produced a pathologic complete response (pCR) in 49.2%, and there may be a subgroup of patients for whom this approach is relevant.
The presence of residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy has prognostic implications and can help tailor adjuvant treatment recommendations. The CREATE-X trial has established the role of adjuvant capecitabine for patients with triple-negative breast cancer with residual disease after pre-operative chemotherapy. The phase 3 EA1131 trial randomized 415 patients with stage II-III triple-negative breast cancer and residual disease post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy to platinum agent or capecitabine. There was no significant difference in 3-year iDFS (42% for platinum vs 49% for capecitabine; HR 1.06, 95% CI 0.62-1.81), and higher hematologic toxicity and dose reductions in the platinum arm. These data support the continued use of capecitabine in this population, and the high event rate highlights the need for more effective therapies in this setting.
The majority of patients with HR+/HER2- MBC will receive a CDK 4/6 inhibitor at some point during their treatment course. In an updated analysis of the phase 3 MONALEESA-3 trial which included postmenopausal patients with HR+HER2- MBC, with median follow-up of 56.3 months, ribociclib plus fulvestrant continued to show an overall survival (OS) benefit of greater than 1 year compared with fulvestrant alone (median OS 53.7 months vs 41.5 months in the ribociclib vs placebo arm, respectively; HR 0.726, 95% CI 0.59-0.90). Additionally, extended follow-up of the PALOMA-3 trial demonstrated OS benefit with palbociclib plus fulvestrant compared to fulvestrant alone in patients with HR+/HER2- MBC; at median follow-up of 73.3 months, median OS was 34.8 months in the palbociclib arm vs 28.0 months in the placebo arm (HR 0.81, P = .0221). Sequencing of other targeted therapies (such as PI3K inhibitors), predictors of CDK 4/6 inhibitor response in different intrinsic subtypes, and the role of CDK 4/6 inhibitor use beyond progression are areas where further research is warranted.
References:
Robson M, Im SA, Senkus E, et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Breast Cancer in Patients with a Germline BRCA Mutation. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(6):523-533.
Litton JK, Beck JT, Jones JM, et al. Neoadjuvant talazoparib in patients with germline BRCA1/2 (gBRCA1/2) mutation-positive, early HER2-negative breast cancer (BC): Results of a phase 2 study. J Clin Oncol 39, 2021 (suppl 15; abstr 505).
Symmans WF, Wei C, Gould R, et al. Long-Term Prognostic Risk After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Associated With Residual Cancer Burden and Breast Cancer Subtype. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:1049-1060.
Masuda N, Lee SJ, Ohtani S, et al. Adjuvant Capecitabine for Breast Cancer after Preoperative Chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:2147-2159.
Cristofanilli M, Rugo H, Im SA, et al. Overall survival (OS) with palbociclib (PAL) + fulvestrant (FUL) in women with hormone receptor–positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative (HER2–) advanced breast cancer (ABC): Updated analyses from PALOMA-3. J Clin Oncol. 2021; 39:15_suppl, 1000-1000.
5-year-old boy • calf pain • fever • cough & rhinitis • Dx?
THE CASE
A 5-year-old previously healthy white boy presented to clinic with bilateral calf pain and refusal to bear weight since awakening that morning. Associated symptoms included a 3-day history of generalized fatigue, subjective fevers, cough, congestion, and rhinitis. The night prior to presentation, he showed no symptoms of gait abnormalities, muscle pain, or weakness. There was no history of similar symptoms, trauma, overexertion, foreign travel, or family history of musculoskeletal disease. He was fully immunized, except for the annual influenza vaccine. He was not taking any medications. This case occurred before the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Objective findings included fever of 101 °F, refusal to bear weight, and symmetrical bilateral tenderness to palpation of the gastrocnemius-soleus complex. Pain was elicited with passive dorsiflexion. There was no erythema, edema, or sensory deficits, and the distal leg compartments were soft. There was normal range of motion of the hips, knees, and ankles. Dorsalis pedis pulses were 2+, and patella reflexes were 2/4 bilaterally.
Lab results included a white blood cell count of 2500/μL (normal range, 4500 to 11,000/μL);absolute neutrophil count, 900/μL (1500 to 8000/μL); platelet count, 131,000/μL (150,000 to 450,000/μL); creatine kinase level, 869 IU/L (22 to 198 U/L); and aspartate aminotransferase level, 116 U/L (8 to 33 U/L). A rapid influenza swab was positive for influenza B. Plain films of the bilateral hips and lower extremities were unremarkable. C-reactive protein (CRP) level, urinalysis, and renal function tests were within normal limits. Creatine kinase (CK) level peaked (1935 U/L; normal range, 22 to 198 U/L) within the first 24 hours of presentation and then trended down.
The Diagnosis
The patient’s sudden onset of symmetrical bilateral calf pain in the setting of an upper respiratory tract infection was extremely suspicious for benign acute childhood myositis (BACM). Lab work and radiologic evaluation were performed to rule out more ominous causes of refusal to bear weight. The suspicion of BACM was further validated by influenza B serology, an elevated CK, and a normal CRP.
Discussion
BACM was first described by Lundberg in 1957.1 The overall incidence and prevalence are unclear.2 A viral prodrome involving rhinorrhea, low-grade fever, sore throat, cough, and malaise typically precedes bilateral calf pain by 3 days.2-4 Myositis symptoms typically last for 4 days.3 While several infectious etiologies have been linked to this condition, influenza B has the greatest association.5,6
❚ Patient population. BACM occurs predominately in school-aged children (6-8 years old) and has a male-to-female ratio of 2:1.3,5,6 In a retrospective study of 219 children, BACM was strongly associated with male gender and ages 6 to 9 years.3 In another retrospective study of 54 children,80% of patients were male, and the mean age was 7.3 years.5
❚ Key symptoms and differential. The distinguishing feature of BACM is bilateral symmetric gastrocnemius-soleus tenderness.2,4 Additionally, the lack of neurologic symptoms is an important differentiator, as long as refusal to bear weight is not mistaken for weakness.6 These features help to distinguish BACM from other items in the differential, including trauma, Guillain-Barre syndrome, osteomyelitis, malignancy, deep vein thrombosis, and inherited musculoskeletal disorders.2
Continue to: Labratory evaluation...
❚ Laboratory evaluation will often show mild neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and mild elevation in CK.7,8 CRP is typically normal.4,7,9 In a retrospective study of 28 admissions for BACM from 2001 to 2012, common findings included leukopenia (35%), neutropenia (25%), and thrombocytopenia (21%). The median CK value was 4181 U/L.4 In another analysis of BACM cases, mean CK was 1872 U/L.5
❚ Biopsy is unnecessary; however, calf muscle samples from 11 of 12 children with suspected BACM due to influenza B infection were consistent with patchy necrosis without significant myositis.10
❚ Complications. Rhabdomyolysis, although rare, has been reported with BACM. In 1 analysis, 10 of 316 patients with influenza-associated myositis developed rhabdomyolysis; 8 experienced renal failure. Rhabdomyolysis was 4 times more likely to occur in girls, and 86% of cases were associated with influenza A.6 Common manifestations of rhabdomyolysis associated with influenza include diffuse myopathy, gross hematuria, and myoglobinuria.6
❚ Treatment is mainly supportive.4,8,9 Antivirals typically are not indicated, as the bilateral calf pain manifests during the recovery phase of the illness.4,9,11 BACM is self-limited and should resolve within 3 days of myositis manifestation.2 Patients should follow up in 2 to 3 weeks to verify symptom resolution.2
If muscle pain, swelling, and tenderness worsen, further work-up is indicated. In more severe cases, including those involving renal failure, intensive care management and even dialysis may be necessary.4,6
❚ Our patient was hospitalized due to fever in the setting of neutropenia. Ultimately, he was treated with acetaminophen and intravenous fluids for mild dehydration and elevated CK levels. He was discharged home after 3 days, at which time he had complete resolution of pain and was able to resume normal activities.
The Takeaway
Benign acute childhood myositis is a self-limited disorder with an excellent prognosis. It has a typical presentation and therefore should be a clinical diagnosis; however, investigative studies may be warranted to rule out more ominous causes. Reassurance to family that the condition should self-resolve in a few days is important. Close follow-up should be scheduled to ensure resolution of symptoms.
CORRESPONDENCE
Nicholas A. Rathjen, DO, William Beaumont Army Medical Center, Department of Soldier and Family Care, 11335 SSG Sims Street, Fort Bliss, TX 79918; nicholas.a.rathjen@gmail. com
- Lundberg A. Myalgia cruris epidemica. Acta Paediatr. 1957;46:18-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1957.tb08627.x
- Magee H, Goldman RD. Viral myositis in children. Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:365-368.
- Mall S, Buchholz U, Tibussek D, et al. A large outbreak of influenza B-associated benign acute childhood myositis in Germany, 2007/2008. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011;30:e142-e146. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e318217e356
- Santos JA, Albuquerque C, Lito D, et al. Benign acute childhood myositis: an alarming condition with an excellent prognosis! Am J Emerg Med. 2014;32:1418-1419. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2014.08.022
- Rosenberg T, Heitner S, Scolnik D, et al. Outcome of benign acute childhood myositis: the experience of 2 large tertiary care pediatric hospitals. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2018;34:400-402. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0000000000000830
- Agyeman P, Duppenthaler A, Heininger U, et al. Influenza-associated myositis in children. Infection. 2004;32:199-203. doi: 10.1007/s15010-004-4003-2
- Mackay MT, Kornberg AJ, Shield LK, et al. Benign acute childhood myositis: laboratory and clinical features. Neurology. 1999;53:2127-2131. doi: 10.1212/wnl.53.9.2127
- Neocleous C, Spanou C, Mpampalis E, et al. Unnecessary diagnostic investigations in benign acute childhood myositis: a case series report. Scott Med J. 2012;57:182. doi: 10.1258/smj.2012.012023
- Felipe Cavagnaro SM, Alejandra Aird G, Ingrid Harwardt R, et al. Benign acute childhood myositis: clinical series and literature review. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2017;88:268-274. doi: 10.1016/j.rchipe.2016.07.002
- Bove KE, Hilton PK, Partin J, et al. Morphology of acute myopathy associated with influenza B infection. Pediatric Pathology. 1983;1:51-66. https://doi.org/10.3109/15513818309048284
- Koliou M, Hadjiloizou S, Ourani S, et al. A case of benign acute childhood myositis associated with influenza A (HINI) virus infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010;16:193-195. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.03064.x
THE CASE
A 5-year-old previously healthy white boy presented to clinic with bilateral calf pain and refusal to bear weight since awakening that morning. Associated symptoms included a 3-day history of generalized fatigue, subjective fevers, cough, congestion, and rhinitis. The night prior to presentation, he showed no symptoms of gait abnormalities, muscle pain, or weakness. There was no history of similar symptoms, trauma, overexertion, foreign travel, or family history of musculoskeletal disease. He was fully immunized, except for the annual influenza vaccine. He was not taking any medications. This case occurred before the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Objective findings included fever of 101 °F, refusal to bear weight, and symmetrical bilateral tenderness to palpation of the gastrocnemius-soleus complex. Pain was elicited with passive dorsiflexion. There was no erythema, edema, or sensory deficits, and the distal leg compartments were soft. There was normal range of motion of the hips, knees, and ankles. Dorsalis pedis pulses were 2+, and patella reflexes were 2/4 bilaterally.
Lab results included a white blood cell count of 2500/μL (normal range, 4500 to 11,000/μL);absolute neutrophil count, 900/μL (1500 to 8000/μL); platelet count, 131,000/μL (150,000 to 450,000/μL); creatine kinase level, 869 IU/L (22 to 198 U/L); and aspartate aminotransferase level, 116 U/L (8 to 33 U/L). A rapid influenza swab was positive for influenza B. Plain films of the bilateral hips and lower extremities were unremarkable. C-reactive protein (CRP) level, urinalysis, and renal function tests were within normal limits. Creatine kinase (CK) level peaked (1935 U/L; normal range, 22 to 198 U/L) within the first 24 hours of presentation and then trended down.
The Diagnosis
The patient’s sudden onset of symmetrical bilateral calf pain in the setting of an upper respiratory tract infection was extremely suspicious for benign acute childhood myositis (BACM). Lab work and radiologic evaluation were performed to rule out more ominous causes of refusal to bear weight. The suspicion of BACM was further validated by influenza B serology, an elevated CK, and a normal CRP.
Discussion
BACM was first described by Lundberg in 1957.1 The overall incidence and prevalence are unclear.2 A viral prodrome involving rhinorrhea, low-grade fever, sore throat, cough, and malaise typically precedes bilateral calf pain by 3 days.2-4 Myositis symptoms typically last for 4 days.3 While several infectious etiologies have been linked to this condition, influenza B has the greatest association.5,6
❚ Patient population. BACM occurs predominately in school-aged children (6-8 years old) and has a male-to-female ratio of 2:1.3,5,6 In a retrospective study of 219 children, BACM was strongly associated with male gender and ages 6 to 9 years.3 In another retrospective study of 54 children,80% of patients were male, and the mean age was 7.3 years.5
❚ Key symptoms and differential. The distinguishing feature of BACM is bilateral symmetric gastrocnemius-soleus tenderness.2,4 Additionally, the lack of neurologic symptoms is an important differentiator, as long as refusal to bear weight is not mistaken for weakness.6 These features help to distinguish BACM from other items in the differential, including trauma, Guillain-Barre syndrome, osteomyelitis, malignancy, deep vein thrombosis, and inherited musculoskeletal disorders.2
Continue to: Labratory evaluation...
❚ Laboratory evaluation will often show mild neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and mild elevation in CK.7,8 CRP is typically normal.4,7,9 In a retrospective study of 28 admissions for BACM from 2001 to 2012, common findings included leukopenia (35%), neutropenia (25%), and thrombocytopenia (21%). The median CK value was 4181 U/L.4 In another analysis of BACM cases, mean CK was 1872 U/L.5
❚ Biopsy is unnecessary; however, calf muscle samples from 11 of 12 children with suspected BACM due to influenza B infection were consistent with patchy necrosis without significant myositis.10
❚ Complications. Rhabdomyolysis, although rare, has been reported with BACM. In 1 analysis, 10 of 316 patients with influenza-associated myositis developed rhabdomyolysis; 8 experienced renal failure. Rhabdomyolysis was 4 times more likely to occur in girls, and 86% of cases were associated with influenza A.6 Common manifestations of rhabdomyolysis associated with influenza include diffuse myopathy, gross hematuria, and myoglobinuria.6
❚ Treatment is mainly supportive.4,8,9 Antivirals typically are not indicated, as the bilateral calf pain manifests during the recovery phase of the illness.4,9,11 BACM is self-limited and should resolve within 3 days of myositis manifestation.2 Patients should follow up in 2 to 3 weeks to verify symptom resolution.2
If muscle pain, swelling, and tenderness worsen, further work-up is indicated. In more severe cases, including those involving renal failure, intensive care management and even dialysis may be necessary.4,6
❚ Our patient was hospitalized due to fever in the setting of neutropenia. Ultimately, he was treated with acetaminophen and intravenous fluids for mild dehydration and elevated CK levels. He was discharged home after 3 days, at which time he had complete resolution of pain and was able to resume normal activities.
The Takeaway
Benign acute childhood myositis is a self-limited disorder with an excellent prognosis. It has a typical presentation and therefore should be a clinical diagnosis; however, investigative studies may be warranted to rule out more ominous causes. Reassurance to family that the condition should self-resolve in a few days is important. Close follow-up should be scheduled to ensure resolution of symptoms.
CORRESPONDENCE
Nicholas A. Rathjen, DO, William Beaumont Army Medical Center, Department of Soldier and Family Care, 11335 SSG Sims Street, Fort Bliss, TX 79918; nicholas.a.rathjen@gmail. com
THE CASE
A 5-year-old previously healthy white boy presented to clinic with bilateral calf pain and refusal to bear weight since awakening that morning. Associated symptoms included a 3-day history of generalized fatigue, subjective fevers, cough, congestion, and rhinitis. The night prior to presentation, he showed no symptoms of gait abnormalities, muscle pain, or weakness. There was no history of similar symptoms, trauma, overexertion, foreign travel, or family history of musculoskeletal disease. He was fully immunized, except for the annual influenza vaccine. He was not taking any medications. This case occurred before the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Objective findings included fever of 101 °F, refusal to bear weight, and symmetrical bilateral tenderness to palpation of the gastrocnemius-soleus complex. Pain was elicited with passive dorsiflexion. There was no erythema, edema, or sensory deficits, and the distal leg compartments were soft. There was normal range of motion of the hips, knees, and ankles. Dorsalis pedis pulses were 2+, and patella reflexes were 2/4 bilaterally.
Lab results included a white blood cell count of 2500/μL (normal range, 4500 to 11,000/μL);absolute neutrophil count, 900/μL (1500 to 8000/μL); platelet count, 131,000/μL (150,000 to 450,000/μL); creatine kinase level, 869 IU/L (22 to 198 U/L); and aspartate aminotransferase level, 116 U/L (8 to 33 U/L). A rapid influenza swab was positive for influenza B. Plain films of the bilateral hips and lower extremities were unremarkable. C-reactive protein (CRP) level, urinalysis, and renal function tests were within normal limits. Creatine kinase (CK) level peaked (1935 U/L; normal range, 22 to 198 U/L) within the first 24 hours of presentation and then trended down.
The Diagnosis
The patient’s sudden onset of symmetrical bilateral calf pain in the setting of an upper respiratory tract infection was extremely suspicious for benign acute childhood myositis (BACM). Lab work and radiologic evaluation were performed to rule out more ominous causes of refusal to bear weight. The suspicion of BACM was further validated by influenza B serology, an elevated CK, and a normal CRP.
Discussion
BACM was first described by Lundberg in 1957.1 The overall incidence and prevalence are unclear.2 A viral prodrome involving rhinorrhea, low-grade fever, sore throat, cough, and malaise typically precedes bilateral calf pain by 3 days.2-4 Myositis symptoms typically last for 4 days.3 While several infectious etiologies have been linked to this condition, influenza B has the greatest association.5,6
❚ Patient population. BACM occurs predominately in school-aged children (6-8 years old) and has a male-to-female ratio of 2:1.3,5,6 In a retrospective study of 219 children, BACM was strongly associated with male gender and ages 6 to 9 years.3 In another retrospective study of 54 children,80% of patients were male, and the mean age was 7.3 years.5
❚ Key symptoms and differential. The distinguishing feature of BACM is bilateral symmetric gastrocnemius-soleus tenderness.2,4 Additionally, the lack of neurologic symptoms is an important differentiator, as long as refusal to bear weight is not mistaken for weakness.6 These features help to distinguish BACM from other items in the differential, including trauma, Guillain-Barre syndrome, osteomyelitis, malignancy, deep vein thrombosis, and inherited musculoskeletal disorders.2
Continue to: Labratory evaluation...
❚ Laboratory evaluation will often show mild neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and mild elevation in CK.7,8 CRP is typically normal.4,7,9 In a retrospective study of 28 admissions for BACM from 2001 to 2012, common findings included leukopenia (35%), neutropenia (25%), and thrombocytopenia (21%). The median CK value was 4181 U/L.4 In another analysis of BACM cases, mean CK was 1872 U/L.5
❚ Biopsy is unnecessary; however, calf muscle samples from 11 of 12 children with suspected BACM due to influenza B infection were consistent with patchy necrosis without significant myositis.10
❚ Complications. Rhabdomyolysis, although rare, has been reported with BACM. In 1 analysis, 10 of 316 patients with influenza-associated myositis developed rhabdomyolysis; 8 experienced renal failure. Rhabdomyolysis was 4 times more likely to occur in girls, and 86% of cases were associated with influenza A.6 Common manifestations of rhabdomyolysis associated with influenza include diffuse myopathy, gross hematuria, and myoglobinuria.6
❚ Treatment is mainly supportive.4,8,9 Antivirals typically are not indicated, as the bilateral calf pain manifests during the recovery phase of the illness.4,9,11 BACM is self-limited and should resolve within 3 days of myositis manifestation.2 Patients should follow up in 2 to 3 weeks to verify symptom resolution.2
If muscle pain, swelling, and tenderness worsen, further work-up is indicated. In more severe cases, including those involving renal failure, intensive care management and even dialysis may be necessary.4,6
❚ Our patient was hospitalized due to fever in the setting of neutropenia. Ultimately, he was treated with acetaminophen and intravenous fluids for mild dehydration and elevated CK levels. He was discharged home after 3 days, at which time he had complete resolution of pain and was able to resume normal activities.
The Takeaway
Benign acute childhood myositis is a self-limited disorder with an excellent prognosis. It has a typical presentation and therefore should be a clinical diagnosis; however, investigative studies may be warranted to rule out more ominous causes. Reassurance to family that the condition should self-resolve in a few days is important. Close follow-up should be scheduled to ensure resolution of symptoms.
CORRESPONDENCE
Nicholas A. Rathjen, DO, William Beaumont Army Medical Center, Department of Soldier and Family Care, 11335 SSG Sims Street, Fort Bliss, TX 79918; nicholas.a.rathjen@gmail. com
- Lundberg A. Myalgia cruris epidemica. Acta Paediatr. 1957;46:18-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1957.tb08627.x
- Magee H, Goldman RD. Viral myositis in children. Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:365-368.
- Mall S, Buchholz U, Tibussek D, et al. A large outbreak of influenza B-associated benign acute childhood myositis in Germany, 2007/2008. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011;30:e142-e146. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e318217e356
- Santos JA, Albuquerque C, Lito D, et al. Benign acute childhood myositis: an alarming condition with an excellent prognosis! Am J Emerg Med. 2014;32:1418-1419. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2014.08.022
- Rosenberg T, Heitner S, Scolnik D, et al. Outcome of benign acute childhood myositis: the experience of 2 large tertiary care pediatric hospitals. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2018;34:400-402. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0000000000000830
- Agyeman P, Duppenthaler A, Heininger U, et al. Influenza-associated myositis in children. Infection. 2004;32:199-203. doi: 10.1007/s15010-004-4003-2
- Mackay MT, Kornberg AJ, Shield LK, et al. Benign acute childhood myositis: laboratory and clinical features. Neurology. 1999;53:2127-2131. doi: 10.1212/wnl.53.9.2127
- Neocleous C, Spanou C, Mpampalis E, et al. Unnecessary diagnostic investigations in benign acute childhood myositis: a case series report. Scott Med J. 2012;57:182. doi: 10.1258/smj.2012.012023
- Felipe Cavagnaro SM, Alejandra Aird G, Ingrid Harwardt R, et al. Benign acute childhood myositis: clinical series and literature review. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2017;88:268-274. doi: 10.1016/j.rchipe.2016.07.002
- Bove KE, Hilton PK, Partin J, et al. Morphology of acute myopathy associated with influenza B infection. Pediatric Pathology. 1983;1:51-66. https://doi.org/10.3109/15513818309048284
- Koliou M, Hadjiloizou S, Ourani S, et al. A case of benign acute childhood myositis associated with influenza A (HINI) virus infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010;16:193-195. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.03064.x
- Lundberg A. Myalgia cruris epidemica. Acta Paediatr. 1957;46:18-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1957.tb08627.x
- Magee H, Goldman RD. Viral myositis in children. Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:365-368.
- Mall S, Buchholz U, Tibussek D, et al. A large outbreak of influenza B-associated benign acute childhood myositis in Germany, 2007/2008. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011;30:e142-e146. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e318217e356
- Santos JA, Albuquerque C, Lito D, et al. Benign acute childhood myositis: an alarming condition with an excellent prognosis! Am J Emerg Med. 2014;32:1418-1419. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2014.08.022
- Rosenberg T, Heitner S, Scolnik D, et al. Outcome of benign acute childhood myositis: the experience of 2 large tertiary care pediatric hospitals. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2018;34:400-402. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0000000000000830
- Agyeman P, Duppenthaler A, Heininger U, et al. Influenza-associated myositis in children. Infection. 2004;32:199-203. doi: 10.1007/s15010-004-4003-2
- Mackay MT, Kornberg AJ, Shield LK, et al. Benign acute childhood myositis: laboratory and clinical features. Neurology. 1999;53:2127-2131. doi: 10.1212/wnl.53.9.2127
- Neocleous C, Spanou C, Mpampalis E, et al. Unnecessary diagnostic investigations in benign acute childhood myositis: a case series report. Scott Med J. 2012;57:182. doi: 10.1258/smj.2012.012023
- Felipe Cavagnaro SM, Alejandra Aird G, Ingrid Harwardt R, et al. Benign acute childhood myositis: clinical series and literature review. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2017;88:268-274. doi: 10.1016/j.rchipe.2016.07.002
- Bove KE, Hilton PK, Partin J, et al. Morphology of acute myopathy associated with influenza B infection. Pediatric Pathology. 1983;1:51-66. https://doi.org/10.3109/15513818309048284
- Koliou M, Hadjiloizou S, Ourani S, et al. A case of benign acute childhood myositis associated with influenza A (HINI) virus infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010;16:193-195. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.03064.x
Difficult patient, or something else? A review of personality disorders
Specific behaviors or expressed thoughts may signal a need for screening. Take into account an individual’s strengths and limitations when designing a Tx approach.
THE CASES
Winston S* is a 23-year-old man referred by a psychiatrist colleague for primary care. He works delivering papers in the early morning hours and spends his day alone in his apartment mainly eating frozen pizza. He has worked solitary jobs his entire life and says he prefers it that way. His answers to questions lack emotion. He doesn’t seem to have any friends or regular contact with family. He follows the medical advice he receives but can’t seem to get out of the house to exercise or socialize. His psychiatrist was treating him with a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor for depression when he was referred.
Denise L* is a 37-year-old woman who transferred to your practice because she says the previous practice’s office manager was disrespectful and the doctor did not listen to her. She has been “very appreciative” of you and your “well-run office.” You have addressed her fibromyalgia and she has shared several personal details about her life. In the following weeks, you receive several phone calls and messages from her. At a follow-up visit, she asks questions about your family and seems agitated when you hesitate to answer. She questions whether you remember details of her history. She pushes, “Did you remember that, doctor?” She also mentions that your front desk staff seems rude to her.
Ruth B* is an 82-year-old woman whose blood pressure measured in your office is 176/94 mm Hg. When you recommend starting a medication and getting blood tests, she responds with a litany of fearful questions. She seems immobilized by worries about treatment and equally so about the risks of nontreatment. You can’t seem to get past the anxiety to decide on a satisfactory plan. She has to write everything down on a notepad and worries if she does not get every detail.
●
* This patient’s name has been changed to protect his identity. The other 2 patients are an amalgam of patients for whom the authors have provided care.
According to a survey of practicing primary care physicians, as many as 15% of patient encounters can be difficult.1 Demanding, intrusive, or angry patients who reject health care interventions are often-cited sources of these difficulties.2,3 While it is true that patient, physician, and environmental factors may contribute to challenging interactions, some patients who are “difficult” may actually have a personality disorder that requires a distinctive approach to care. Recognizing these patients can help empower physicians to provide compassionate and effective care, reduce team angst, and minimize burnout.
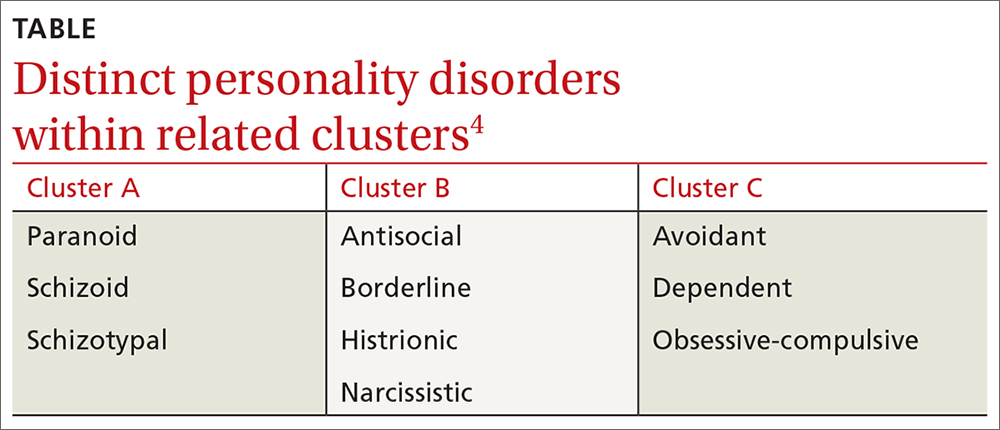
❚ What qualifies as a personality disorder? A personality disorder is an enduring pattern of inner experience and behavior that deviates markedly from the expectations of the individual’s culture, is pervasive and inflexible, has an onset in adolescence or early adulthood, is unchanging over time, and leads to distress or impairment in social or occupational functioning.4 The prevalence of any personality disorder seems to have increased over the past decade from 9.1%4 to 12.16%.5 The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) classifies personality disorders in 3 clusters—A, B, and C (TABLE4)—with prevalence rates at 7.23%, 5.53%, and 6.7%, respectively.5 The review below will focus on the distinct personality disorders exhibited by the patients described in the opening cases.
Continue to: A closer look at the clusters...
A closer look at the clusters
Cluster A disorders
Paranoid, schizoid, and schizotypal disorders are part of this cluster. These patients exhibit odd or eccentric thinking and behavior. Individuals with schizoid personality disorder, for instance, usually lack relationships and lack the desire to acquire and maintain relationships.4 They often organize their lives to remain isolated and will choose occupations that require little social interaction. They sometimes view themselves as observers rather than participants in their own lives.6
Cluster B disorders
Dramatic, overly emotional, or unpredictable thinking and behavior are characteristic of individuals who have antisocial, borderline, histrionic, or narcissistic disorders. Patients with borderline personality disorder (BPD), for example, demonstrate a longstanding pattern of instability in affect, self-image, and relationships.4 Patients with BPD often display extreme interpersonal hypersensitivity and make frantic efforts to avoid real or imagined abandonment. Identity disturbance, feelings of emptiness, and efforts to avoid abandonment have all been associated with increased suicide risk.7
In a primary care setting, such a patient may display extremely strong reactions to minor disappointments. When the physician is unavailable for a last-minute appointment or to authorize an unscheduled medication refill or to receive an after-hours phone call, the patient may become irate. The physician, who previously was idealized by the patient as “the only person who understands me,” is now devalued as “the worst doctor I’ve ever had.”8
Cluster C disorders
With these individuals, anxious or fearful thinking and behavior predominate. Avoidant, dependent, and obsessive-compulsive disorders are included in this cluster.
Dependent personality disorder (DPD) is characterized by a pervasive and extreme need to be taken care of. Submissive and clingy behavior and fear of separation are excessive. This patient may have difficulty making everyday decisions, being assertive, or expressing disagreement with others.4
Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder falls in this cluster and is typified by a pervasive preoccupation with orderliness, perfectionism, and control, at the price of flexibility and efficiency. This individual may be reluctant to get rid of sentimental objects, have rigid moral beliefs, and have significant difficulty working with others who do not follow their rules.4
Continue to: These clues may suggest...
These clues may suggest a personality disorder
If you find that encounters with a particular patient are growing increasingly difficult, consider whether the following behaviors, attitudes, and patterns of thinking are coming into play. If they are, you may want to consider using a screening tool, which we’ll discuss in a moment.
❚ Clues to cluster A disorders
- The patient has no peer relationships outside immediate family.
- The patient almost always chooses solitary activities for work and personal enjoyment.
❚ Cluster B clues
- Hypersensitivity to treatment disagreements or cancelled appointments are common (and likely experienced as rejection).
- Mood changes occur very quickly, even during a single visit.
- There is a history of many failed relationships with providers and others.
- The patient will describe an individual as both “wonderful” and “terrible” (ie, splitting) and may do so during the course of one visit.
- The patient may also split groups (eg, medical staff) by affective extremes (eg, adoration and hatred).
- The patient may hint at suicide or acts of self-harm.7
❚ Cluster C clues
- There is an excessive dependency on family, friends, or providers.
- Significant anxiety is experienced when the patient has to make an independent decision.
- There is a fear of relationship loss and resultant vulnerability to exploitation or abuse.
- Pervasive perfectionism makes treatment planning or course changes difficult.
- Anxiety and fear are unrelieved despite support and ample information.
Consider these screening tools
Several screening tools for personality disorders can be used to follow up on your initial clinical impressions. We also highly recommend you consider concurrent screening for substance abuse, as addiction is a common comorbidity with personality disorders.
❚
❚ A sampling of screening tools. The Standardised Assessment of Personality Abbreviated Scale (SAPAS)9 is an 8-item measure that correlates well with disorders in clusters A and C.
BPD (cluster B) has many brief scale options, including the McLean Screening Instrument for Borderline Personality Disorder (MSI-BPD).10 This 10-item questionnaire demonstrates sensitivity and specificity for BPD.
The International Personality Disorder Examination (IPDE) includes a 15-minute screening tool to help identify patients who may have any personality disorder, regardless of cluster.11
Improve patient encounters with these Tx pearls
In the family medicine clinic, a collaborative primary care and behavioral health team can be extremely helpful in the diagnosis and management of patients with personality disorders.12 First-line treatment of these disorders is psychotherapy, whereas medications are mainly used for symptom management. See Black and colleagues’ work for a thorough discussion on psychopharmacology considerations with personality disorders. 13
The following tips can help you to improve your interactions with patients who have personality disorders.
❚ Cluster A approaches
- Recommend treatment that respects the patient’s need for relative isolation.14
- Don’t be personally offended by your patient’s flat or disinterested affect or concrete thinking; don’t let it diminish the emotional support you provide.6
- Consult with a health psychologist (who has expertise in physical health conditions, brief treatments, and the medical system) to connect the patient with a long-term therapist. It is better to focus on fundamental changes, rather than employing brief behavioral techniques, for symptom relief. Patients with personality disorders tend to have better outcomes with long-term psychological care.15
❚ Cluster B approaches
- Set boundaries—eg, specific time limits for visits—and keep them.8
- Schedule brief, more frequent, appointments to reduce perceived feelings of abandonment.
- Coordinate plans with the entire clinic team to avoid splitting and blaming.16
- Avoid providing patients with personal information, as it may provide fodder for splitting behavior. 8
- Do not take things personally. Let patients “own” their own distress. These patients often take an emotional toll on the provider.16
- Engage the help of a health psychologist to reduce burnout and for more long-term continuity of care. A health psychologist who specializes in dialectical behavioral therapy to work on emotion regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness would be ideal.17
Continue to: Cluster C approaches...
❚
❚ Cluster C approaches
- Engage the help of family and other trusted individuals in supporting treatment plans.18,19
- Try to provide just 2 treatment choices to the patient and reinforce his or her responsibility to help make the decision collaboratively. This step is important since it is difficult to enhance autonomy in these patients.20
- Engage the help of a cognitive behavioral therapist who can work on assertiveness and problem-solving skills.19
- Be empathetic with the patient and patiently build a trusting relationship, rather than “arguing” with the patient about each specific worry.20
- Make only one change at a time. Give small assignments to the patient, such as monitoring symptoms or reading up on their condition. These can help the patient feel more in control.21
- Present information in brief, clear terms. Avoid “grey areas” to reduce anxiety.21
- Engage a behavioral health provider to reduce rigid expectations and ideally increase feelings of self-esteem; this has been shown to predict better treatment outcomes.22
CASES
Mr. S displays cluster-A characteristics of schizoid personality disorder in addition to the depression he is being treated for. His physician was not put off by his flat affect and respected his limitations with social activities. Use of a stationary bike was recommended for exercise rather than walks outdoors. He also preferred phone calls to in-person encounters, so his follow-up visits were conducted by phone.
Ms. L exhibits cluster-B characteristics of BPD. You begin the tricky dance of setting limits, keeping communication clear, and not blaming yourself or others on your team for Ms. L’s feelings. You schedule regular visits with explicit time limits and discuss with your entire team how to avoid splitting. You involve a psychologist, familiar with treating BPD, who helps the patient learn positive interpersonal coping skills.
Ms. B displays cluster-C characteristics of dependent and obsessive-compulsive personality disorders. At her follow-up visit, you provide a great deal of empathy and try not to argue her out of each worry that she brings up. You make one change at a time and enlist the help of her daughter in giving her pills at home and offering reassurance. You collaborate with a cognitive behavioral therapist who works on exposing her to moderately anxiety-provoking situations/decisions.
1. Hull SK, Broquet K. How to manage difficult patient encounters. Fam Pract Manag. 2007;14:30-34.
2. Groves JE. Taking care of the hateful patient. N Engl J Med.1978;298: 883-887.
3. O’Dowd TC. Five years of heartsink patients in primary care. BMJ. 1988;297:528-530.
4. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th edition (DSM-5). American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
5. Volkert J, Gablonski TC, Rabung S. Prevalence of personality disorders in the general adult population in Western countries: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry. 2018;213:709-715.
6. Esterberg ML, Goulding SM, Walker EF. Cluster A personality disorders: schizotypal, schizoid and paranoid personality disorders in childhood and adolescence. J Psychopathol Behav Assess. 2010;32:515-528.
7. Yen S, Peters JR, Nishar S, et al. Association of borderline personality disorder criteria with suicide attempts: findings from the collaborative longitudinal study of personality disorders over 10 years of follow-up. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78:187-194.
8. Dubovsky AN, Kiefer MM. Borderline personality disorder in the primary care setting. Med Clin North Am. 2014;98:1049-1064.
9. Hesse M, Moran P. (2010). Screening for personality disorder with the Standardised Assessment of Personality: Abbreviated Scale (SAPAS): further evidence of concurrent validity. BMC Psychiatry. 2010;10:10.
10. Zanarini MC, Vujanovic AA, Parachini EA, et al. A screening measure for BPD: the McLean screening instrument for borderline personality disorder (MSI-BPD). J Pers Disord. 2003;17:568-573.
11. Loranger AW, Sartorius N, Andreoli A, et al. The International Personality Disorder Examination. The World Health Organization/Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration international pilot study of personality disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994;51:215-224.12. Nelson KJ, Skodol A, Friedman M. Pharmacotherapy for personality disorders. UpToDate. Accessed April 22, 2021. www.uptodate.com/contents/pharmacotherapy-for-personality-disorders
13. Black D, Paris J, Schulz C. Evidence-based integrated biopsychosocial treatment of borderline personality disorder. In: Muse M (ed). Cognitive Behavioral Psychopharmacology: the Clinical Practice of Evidence-Based Biopsychosocial Integration. Wiley; 2017:137-166.
14. Beck AT, Davis DD, Freeman A. Cognitive Therapy of Personality Disorders. 3rd ed. The Guilford Press; 2015.
15. Thylstrup B, Hesse M. “I am not complaining”–ambivalence construct in schizoid personality disorder. Am J Psychother. 2009;63:147-167.
16. Ricke AK, Lee MJ, Chambers JE. The difficult patient: borderline personality disorder in the obstetrical and gynecological patient. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2012;67:495-502.
17. Seow LLY, Page AC, Hooke GR. Severity of borderline personality disorder symptoms as a moderator of the association between the use of dialectical behaviour therapy skills and treatment outcomes. Psychother Res. 2020;30:920-933.
18. Nichols WC. Integrative marital and family treatment of dependent personality disorders. In: MacFarlane MM (Ed.) Family Treatment of Personality Disorders: Advances in Clinical Practice. Haworth Clinical Practice Press; 2004:173-204.
19. Disney KL. Dependent personality disorder: a critical review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2013;33:1184-1196.
20. Bender DS. The therapeutic alliance in the treatment of personality disorders. J Psychiatr Pract. 2005;11:73-87.
21. Ward RK. Assessment and management of personality disorders. Am Fam Physician. 2004;70:1505-1512.
22. Cummings JA, Hayes AM, Cardaciotto L, et al. The dynamics of self-esteem in cognitive therapy for avoidant and obsessive-compulsive personality disorders: an adaptive role of self-esteem variability? Cognit Ther Res. 2012;36:272-281.
Specific behaviors or expressed thoughts may signal a need for screening. Take into account an individual’s strengths and limitations when designing a Tx approach.
Specific behaviors or expressed thoughts may signal a need for screening. Take into account an individual’s strengths and limitations when designing a Tx approach.
THE CASES
Winston S* is a 23-year-old man referred by a psychiatrist colleague for primary care. He works delivering papers in the early morning hours and spends his day alone in his apartment mainly eating frozen pizza. He has worked solitary jobs his entire life and says he prefers it that way. His answers to questions lack emotion. He doesn’t seem to have any friends or regular contact with family. He follows the medical advice he receives but can’t seem to get out of the house to exercise or socialize. His psychiatrist was treating him with a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor for depression when he was referred.
Denise L* is a 37-year-old woman who transferred to your practice because she says the previous practice’s office manager was disrespectful and the doctor did not listen to her. She has been “very appreciative” of you and your “well-run office.” You have addressed her fibromyalgia and she has shared several personal details about her life. In the following weeks, you receive several phone calls and messages from her. At a follow-up visit, she asks questions about your family and seems agitated when you hesitate to answer. She questions whether you remember details of her history. She pushes, “Did you remember that, doctor?” She also mentions that your front desk staff seems rude to her.
Ruth B* is an 82-year-old woman whose blood pressure measured in your office is 176/94 mm Hg. When you recommend starting a medication and getting blood tests, she responds with a litany of fearful questions. She seems immobilized by worries about treatment and equally so about the risks of nontreatment. You can’t seem to get past the anxiety to decide on a satisfactory plan. She has to write everything down on a notepad and worries if she does not get every detail.
●
* This patient’s name has been changed to protect his identity. The other 2 patients are an amalgam of patients for whom the authors have provided care.
According to a survey of practicing primary care physicians, as many as 15% of patient encounters can be difficult.1 Demanding, intrusive, or angry patients who reject health care interventions are often-cited sources of these difficulties.2,3 While it is true that patient, physician, and environmental factors may contribute to challenging interactions, some patients who are “difficult” may actually have a personality disorder that requires a distinctive approach to care. Recognizing these patients can help empower physicians to provide compassionate and effective care, reduce team angst, and minimize burnout.
❚ What qualifies as a personality disorder? A personality disorder is an enduring pattern of inner experience and behavior that deviates markedly from the expectations of the individual’s culture, is pervasive and inflexible, has an onset in adolescence or early adulthood, is unchanging over time, and leads to distress or impairment in social or occupational functioning.4 The prevalence of any personality disorder seems to have increased over the past decade from 9.1%4 to 12.16%.5 The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) classifies personality disorders in 3 clusters—A, B, and C (TABLE4)—with prevalence rates at 7.23%, 5.53%, and 6.7%, respectively.5 The review below will focus on the distinct personality disorders exhibited by the patients described in the opening cases.

Continue to: A closer look at the clusters...
A closer look at the clusters
Cluster A disorders
Paranoid, schizoid, and schizotypal disorders are part of this cluster. These patients exhibit odd or eccentric thinking and behavior. Individuals with schizoid personality disorder, for instance, usually lack relationships and lack the desire to acquire and maintain relationships.4 They often organize their lives to remain isolated and will choose occupations that require little social interaction. They sometimes view themselves as observers rather than participants in their own lives.6
Cluster B disorders
Dramatic, overly emotional, or unpredictable thinking and behavior are characteristic of individuals who have antisocial, borderline, histrionic, or narcissistic disorders. Patients with borderline personality disorder (BPD), for example, demonstrate a longstanding pattern of instability in affect, self-image, and relationships.4 Patients with BPD often display extreme interpersonal hypersensitivity and make frantic efforts to avoid real or imagined abandonment. Identity disturbance, feelings of emptiness, and efforts to avoid abandonment have all been associated with increased suicide risk.7
In a primary care setting, such a patient may display extremely strong reactions to minor disappointments. When the physician is unavailable for a last-minute appointment or to authorize an unscheduled medication refill or to receive an after-hours phone call, the patient may become irate. The physician, who previously was idealized by the patient as “the only person who understands me,” is now devalued as “the worst doctor I’ve ever had.”8
Cluster C disorders
With these individuals, anxious or fearful thinking and behavior predominate. Avoidant, dependent, and obsessive-compulsive disorders are included in this cluster.
Dependent personality disorder (DPD) is characterized by a pervasive and extreme need to be taken care of. Submissive and clingy behavior and fear of separation are excessive. This patient may have difficulty making everyday decisions, being assertive, or expressing disagreement with others.4
Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder falls in this cluster and is typified by a pervasive preoccupation with orderliness, perfectionism, and control, at the price of flexibility and efficiency. This individual may be reluctant to get rid of sentimental objects, have rigid moral beliefs, and have significant difficulty working with others who do not follow their rules.4
Continue to: These clues may suggest...
These clues may suggest a personality disorder
If you find that encounters with a particular patient are growing increasingly difficult, consider whether the following behaviors, attitudes, and patterns of thinking are coming into play. If they are, you may want to consider using a screening tool, which we’ll discuss in a moment.
❚ Clues to cluster A disorders
- The patient has no peer relationships outside immediate family.
- The patient almost always chooses solitary activities for work and personal enjoyment.
❚ Cluster B clues
- Hypersensitivity to treatment disagreements or cancelled appointments are common (and likely experienced as rejection).
- Mood changes occur very quickly, even during a single visit.
- There is a history of many failed relationships with providers and others.
- The patient will describe an individual as both “wonderful” and “terrible” (ie, splitting) and may do so during the course of one visit.
- The patient may also split groups (eg, medical staff) by affective extremes (eg, adoration and hatred).
- The patient may hint at suicide or acts of self-harm.7
❚ Cluster C clues
- There is an excessive dependency on family, friends, or providers.
- Significant anxiety is experienced when the patient has to make an independent decision.
- There is a fear of relationship loss and resultant vulnerability to exploitation or abuse.
- Pervasive perfectionism makes treatment planning or course changes difficult.
- Anxiety and fear are unrelieved despite support and ample information.
Consider these screening tools
Several screening tools for personality disorders can be used to follow up on your initial clinical impressions. We also highly recommend you consider concurrent screening for substance abuse, as addiction is a common comorbidity with personality disorders.
❚
❚ A sampling of screening tools. The Standardised Assessment of Personality Abbreviated Scale (SAPAS)9 is an 8-item measure that correlates well with disorders in clusters A and C.
BPD (cluster B) has many brief scale options, including the McLean Screening Instrument for Borderline Personality Disorder (MSI-BPD).10 This 10-item questionnaire demonstrates sensitivity and specificity for BPD.
The International Personality Disorder Examination (IPDE) includes a 15-minute screening tool to help identify patients who may have any personality disorder, regardless of cluster.11
Improve patient encounters with these Tx pearls
In the family medicine clinic, a collaborative primary care and behavioral health team can be extremely helpful in the diagnosis and management of patients with personality disorders.12 First-line treatment of these disorders is psychotherapy, whereas medications are mainly used for symptom management. See Black and colleagues’ work for a thorough discussion on psychopharmacology considerations with personality disorders. 13
The following tips can help you to improve your interactions with patients who have personality disorders.
❚ Cluster A approaches
- Recommend treatment that respects the patient’s need for relative isolation.14
- Don’t be personally offended by your patient’s flat or disinterested affect or concrete thinking; don’t let it diminish the emotional support you provide.6
- Consult with a health psychologist (who has expertise in physical health conditions, brief treatments, and the medical system) to connect the patient with a long-term therapist. It is better to focus on fundamental changes, rather than employing brief behavioral techniques, for symptom relief. Patients with personality disorders tend to have better outcomes with long-term psychological care.15
❚ Cluster B approaches
- Set boundaries—eg, specific time limits for visits—and keep them.8
- Schedule brief, more frequent, appointments to reduce perceived feelings of abandonment.
- Coordinate plans with the entire clinic team to avoid splitting and blaming.16
- Avoid providing patients with personal information, as it may provide fodder for splitting behavior. 8
- Do not take things personally. Let patients “own” their own distress. These patients often take an emotional toll on the provider.16
- Engage the help of a health psychologist to reduce burnout and for more long-term continuity of care. A health psychologist who specializes in dialectical behavioral therapy to work on emotion regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness would be ideal.17
Continue to: Cluster C approaches...
❚
❚ Cluster C approaches
- Engage the help of family and other trusted individuals in supporting treatment plans.18,19
- Try to provide just 2 treatment choices to the patient and reinforce his or her responsibility to help make the decision collaboratively. This step is important since it is difficult to enhance autonomy in these patients.20
- Engage the help of a cognitive behavioral therapist who can work on assertiveness and problem-solving skills.19
- Be empathetic with the patient and patiently build a trusting relationship, rather than “arguing” with the patient about each specific worry.20
- Make only one change at a time. Give small assignments to the patient, such as monitoring symptoms or reading up on their condition. These can help the patient feel more in control.21
- Present information in brief, clear terms. Avoid “grey areas” to reduce anxiety.21
- Engage a behavioral health provider to reduce rigid expectations and ideally increase feelings of self-esteem; this has been shown to predict better treatment outcomes.22
CASES
Mr. S displays cluster-A characteristics of schizoid personality disorder in addition to the depression he is being treated for. His physician was not put off by his flat affect and respected his limitations with social activities. Use of a stationary bike was recommended for exercise rather than walks outdoors. He also preferred phone calls to in-person encounters, so his follow-up visits were conducted by phone.
Ms. L exhibits cluster-B characteristics of BPD. You begin the tricky dance of setting limits, keeping communication clear, and not blaming yourself or others on your team for Ms. L’s feelings. You schedule regular visits with explicit time limits and discuss with your entire team how to avoid splitting. You involve a psychologist, familiar with treating BPD, who helps the patient learn positive interpersonal coping skills.
Ms. B displays cluster-C characteristics of dependent and obsessive-compulsive personality disorders. At her follow-up visit, you provide a great deal of empathy and try not to argue her out of each worry that she brings up. You make one change at a time and enlist the help of her daughter in giving her pills at home and offering reassurance. You collaborate with a cognitive behavioral therapist who works on exposing her to moderately anxiety-provoking situations/decisions.
THE CASES
Winston S* is a 23-year-old man referred by a psychiatrist colleague for primary care. He works delivering papers in the early morning hours and spends his day alone in his apartment mainly eating frozen pizza. He has worked solitary jobs his entire life and says he prefers it that way. His answers to questions lack emotion. He doesn’t seem to have any friends or regular contact with family. He follows the medical advice he receives but can’t seem to get out of the house to exercise or socialize. His psychiatrist was treating him with a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor for depression when he was referred.
Denise L* is a 37-year-old woman who transferred to your practice because she says the previous practice’s office manager was disrespectful and the doctor did not listen to her. She has been “very appreciative” of you and your “well-run office.” You have addressed her fibromyalgia and she has shared several personal details about her life. In the following weeks, you receive several phone calls and messages from her. At a follow-up visit, she asks questions about your family and seems agitated when you hesitate to answer. She questions whether you remember details of her history. She pushes, “Did you remember that, doctor?” She also mentions that your front desk staff seems rude to her.
Ruth B* is an 82-year-old woman whose blood pressure measured in your office is 176/94 mm Hg. When you recommend starting a medication and getting blood tests, she responds with a litany of fearful questions. She seems immobilized by worries about treatment and equally so about the risks of nontreatment. You can’t seem to get past the anxiety to decide on a satisfactory plan. She has to write everything down on a notepad and worries if she does not get every detail.
●
* This patient’s name has been changed to protect his identity. The other 2 patients are an amalgam of patients for whom the authors have provided care.
According to a survey of practicing primary care physicians, as many as 15% of patient encounters can be difficult.1 Demanding, intrusive, or angry patients who reject health care interventions are often-cited sources of these difficulties.2,3 While it is true that patient, physician, and environmental factors may contribute to challenging interactions, some patients who are “difficult” may actually have a personality disorder that requires a distinctive approach to care. Recognizing these patients can help empower physicians to provide compassionate and effective care, reduce team angst, and minimize burnout.
❚ What qualifies as a personality disorder? A personality disorder is an enduring pattern of inner experience and behavior that deviates markedly from the expectations of the individual’s culture, is pervasive and inflexible, has an onset in adolescence or early adulthood, is unchanging over time, and leads to distress or impairment in social or occupational functioning.4 The prevalence of any personality disorder seems to have increased over the past decade from 9.1%4 to 12.16%.5 The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) classifies personality disorders in 3 clusters—A, B, and C (TABLE4)—with prevalence rates at 7.23%, 5.53%, and 6.7%, respectively.5 The review below will focus on the distinct personality disorders exhibited by the patients described in the opening cases.

Continue to: A closer look at the clusters...
A closer look at the clusters
Cluster A disorders
Paranoid, schizoid, and schizotypal disorders are part of this cluster. These patients exhibit odd or eccentric thinking and behavior. Individuals with schizoid personality disorder, for instance, usually lack relationships and lack the desire to acquire and maintain relationships.4 They often organize their lives to remain isolated and will choose occupations that require little social interaction. They sometimes view themselves as observers rather than participants in their own lives.6
Cluster B disorders
Dramatic, overly emotional, or unpredictable thinking and behavior are characteristic of individuals who have antisocial, borderline, histrionic, or narcissistic disorders. Patients with borderline personality disorder (BPD), for example, demonstrate a longstanding pattern of instability in affect, self-image, and relationships.4 Patients with BPD often display extreme interpersonal hypersensitivity and make frantic efforts to avoid real or imagined abandonment. Identity disturbance, feelings of emptiness, and efforts to avoid abandonment have all been associated with increased suicide risk.7
In a primary care setting, such a patient may display extremely strong reactions to minor disappointments. When the physician is unavailable for a last-minute appointment or to authorize an unscheduled medication refill or to receive an after-hours phone call, the patient may become irate. The physician, who previously was idealized by the patient as “the only person who understands me,” is now devalued as “the worst doctor I’ve ever had.”8
Cluster C disorders
With these individuals, anxious or fearful thinking and behavior predominate. Avoidant, dependent, and obsessive-compulsive disorders are included in this cluster.
Dependent personality disorder (DPD) is characterized by a pervasive and extreme need to be taken care of. Submissive and clingy behavior and fear of separation are excessive. This patient may have difficulty making everyday decisions, being assertive, or expressing disagreement with others.4
Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder falls in this cluster and is typified by a pervasive preoccupation with orderliness, perfectionism, and control, at the price of flexibility and efficiency. This individual may be reluctant to get rid of sentimental objects, have rigid moral beliefs, and have significant difficulty working with others who do not follow their rules.4
Continue to: These clues may suggest...
These clues may suggest a personality disorder
If you find that encounters with a particular patient are growing increasingly difficult, consider whether the following behaviors, attitudes, and patterns of thinking are coming into play. If they are, you may want to consider using a screening tool, which we’ll discuss in a moment.
❚ Clues to cluster A disorders
- The patient has no peer relationships outside immediate family.
- The patient almost always chooses solitary activities for work and personal enjoyment.
❚ Cluster B clues
- Hypersensitivity to treatment disagreements or cancelled appointments are common (and likely experienced as rejection).
- Mood changes occur very quickly, even during a single visit.
- There is a history of many failed relationships with providers and others.
- The patient will describe an individual as both “wonderful” and “terrible” (ie, splitting) and may do so during the course of one visit.
- The patient may also split groups (eg, medical staff) by affective extremes (eg, adoration and hatred).
- The patient may hint at suicide or acts of self-harm.7
❚ Cluster C clues
- There is an excessive dependency on family, friends, or providers.
- Significant anxiety is experienced when the patient has to make an independent decision.
- There is a fear of relationship loss and resultant vulnerability to exploitation or abuse.
- Pervasive perfectionism makes treatment planning or course changes difficult.
- Anxiety and fear are unrelieved despite support and ample information.
Consider these screening tools
Several screening tools for personality disorders can be used to follow up on your initial clinical impressions. We also highly recommend you consider concurrent screening for substance abuse, as addiction is a common comorbidity with personality disorders.
❚
❚ A sampling of screening tools. The Standardised Assessment of Personality Abbreviated Scale (SAPAS)9 is an 8-item measure that correlates well with disorders in clusters A and C.
BPD (cluster B) has many brief scale options, including the McLean Screening Instrument for Borderline Personality Disorder (MSI-BPD).10 This 10-item questionnaire demonstrates sensitivity and specificity for BPD.
The International Personality Disorder Examination (IPDE) includes a 15-minute screening tool to help identify patients who may have any personality disorder, regardless of cluster.11
Improve patient encounters with these Tx pearls
In the family medicine clinic, a collaborative primary care and behavioral health team can be extremely helpful in the diagnosis and management of patients with personality disorders.12 First-line treatment of these disorders is psychotherapy, whereas medications are mainly used for symptom management. See Black and colleagues’ work for a thorough discussion on psychopharmacology considerations with personality disorders. 13
The following tips can help you to improve your interactions with patients who have personality disorders.
❚ Cluster A approaches
- Recommend treatment that respects the patient’s need for relative isolation.14
- Don’t be personally offended by your patient’s flat or disinterested affect or concrete thinking; don’t let it diminish the emotional support you provide.6
- Consult with a health psychologist (who has expertise in physical health conditions, brief treatments, and the medical system) to connect the patient with a long-term therapist. It is better to focus on fundamental changes, rather than employing brief behavioral techniques, for symptom relief. Patients with personality disorders tend to have better outcomes with long-term psychological care.15
❚ Cluster B approaches
- Set boundaries—eg, specific time limits for visits—and keep them.8
- Schedule brief, more frequent, appointments to reduce perceived feelings of abandonment.
- Coordinate plans with the entire clinic team to avoid splitting and blaming.16
- Avoid providing patients with personal information, as it may provide fodder for splitting behavior. 8
- Do not take things personally. Let patients “own” their own distress. These patients often take an emotional toll on the provider.16
- Engage the help of a health psychologist to reduce burnout and for more long-term continuity of care. A health psychologist who specializes in dialectical behavioral therapy to work on emotion regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness would be ideal.17
Continue to: Cluster C approaches...
❚
❚ Cluster C approaches
- Engage the help of family and other trusted individuals in supporting treatment plans.18,19
- Try to provide just 2 treatment choices to the patient and reinforce his or her responsibility to help make the decision collaboratively. This step is important since it is difficult to enhance autonomy in these patients.20
- Engage the help of a cognitive behavioral therapist who can work on assertiveness and problem-solving skills.19
- Be empathetic with the patient and patiently build a trusting relationship, rather than “arguing” with the patient about each specific worry.20
- Make only one change at a time. Give small assignments to the patient, such as monitoring symptoms or reading up on their condition. These can help the patient feel more in control.21
- Present information in brief, clear terms. Avoid “grey areas” to reduce anxiety.21
- Engage a behavioral health provider to reduce rigid expectations and ideally increase feelings of self-esteem; this has been shown to predict better treatment outcomes.22
CASES
Mr. S displays cluster-A characteristics of schizoid personality disorder in addition to the depression he is being treated for. His physician was not put off by his flat affect and respected his limitations with social activities. Use of a stationary bike was recommended for exercise rather than walks outdoors. He also preferred phone calls to in-person encounters, so his follow-up visits were conducted by phone.
Ms. L exhibits cluster-B characteristics of BPD. You begin the tricky dance of setting limits, keeping communication clear, and not blaming yourself or others on your team for Ms. L’s feelings. You schedule regular visits with explicit time limits and discuss with your entire team how to avoid splitting. You involve a psychologist, familiar with treating BPD, who helps the patient learn positive interpersonal coping skills.
Ms. B displays cluster-C characteristics of dependent and obsessive-compulsive personality disorders. At her follow-up visit, you provide a great deal of empathy and try not to argue her out of each worry that she brings up. You make one change at a time and enlist the help of her daughter in giving her pills at home and offering reassurance. You collaborate with a cognitive behavioral therapist who works on exposing her to moderately anxiety-provoking situations/decisions.
1. Hull SK, Broquet K. How to manage difficult patient encounters. Fam Pract Manag. 2007;14:30-34.
2. Groves JE. Taking care of the hateful patient. N Engl J Med.1978;298: 883-887.
3. O’Dowd TC. Five years of heartsink patients in primary care. BMJ. 1988;297:528-530.
4. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th edition (DSM-5). American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
5. Volkert J, Gablonski TC, Rabung S. Prevalence of personality disorders in the general adult population in Western countries: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry. 2018;213:709-715.
6. Esterberg ML, Goulding SM, Walker EF. Cluster A personality disorders: schizotypal, schizoid and paranoid personality disorders in childhood and adolescence. J Psychopathol Behav Assess. 2010;32:515-528.
7. Yen S, Peters JR, Nishar S, et al. Association of borderline personality disorder criteria with suicide attempts: findings from the collaborative longitudinal study of personality disorders over 10 years of follow-up. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78:187-194.
8. Dubovsky AN, Kiefer MM. Borderline personality disorder in the primary care setting. Med Clin North Am. 2014;98:1049-1064.
9. Hesse M, Moran P. (2010). Screening for personality disorder with the Standardised Assessment of Personality: Abbreviated Scale (SAPAS): further evidence of concurrent validity. BMC Psychiatry. 2010;10:10.
10. Zanarini MC, Vujanovic AA, Parachini EA, et al. A screening measure for BPD: the McLean screening instrument for borderline personality disorder (MSI-BPD). J Pers Disord. 2003;17:568-573.
11. Loranger AW, Sartorius N, Andreoli A, et al. The International Personality Disorder Examination. The World Health Organization/Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration international pilot study of personality disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994;51:215-224.12. Nelson KJ, Skodol A, Friedman M. Pharmacotherapy for personality disorders. UpToDate. Accessed April 22, 2021. www.uptodate.com/contents/pharmacotherapy-for-personality-disorders
13. Black D, Paris J, Schulz C. Evidence-based integrated biopsychosocial treatment of borderline personality disorder. In: Muse M (ed). Cognitive Behavioral Psychopharmacology: the Clinical Practice of Evidence-Based Biopsychosocial Integration. Wiley; 2017:137-166.
14. Beck AT, Davis DD, Freeman A. Cognitive Therapy of Personality Disorders. 3rd ed. The Guilford Press; 2015.
15. Thylstrup B, Hesse M. “I am not complaining”–ambivalence construct in schizoid personality disorder. Am J Psychother. 2009;63:147-167.
16. Ricke AK, Lee MJ, Chambers JE. The difficult patient: borderline personality disorder in the obstetrical and gynecological patient. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2012;67:495-502.
17. Seow LLY, Page AC, Hooke GR. Severity of borderline personality disorder symptoms as a moderator of the association between the use of dialectical behaviour therapy skills and treatment outcomes. Psychother Res. 2020;30:920-933.
18. Nichols WC. Integrative marital and family treatment of dependent personality disorders. In: MacFarlane MM (Ed.) Family Treatment of Personality Disorders: Advances in Clinical Practice. Haworth Clinical Practice Press; 2004:173-204.
19. Disney KL. Dependent personality disorder: a critical review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2013;33:1184-1196.
20. Bender DS. The therapeutic alliance in the treatment of personality disorders. J Psychiatr Pract. 2005;11:73-87.
21. Ward RK. Assessment and management of personality disorders. Am Fam Physician. 2004;70:1505-1512.
22. Cummings JA, Hayes AM, Cardaciotto L, et al. The dynamics of self-esteem in cognitive therapy for avoidant and obsessive-compulsive personality disorders: an adaptive role of self-esteem variability? Cognit Ther Res. 2012;36:272-281.
1. Hull SK, Broquet K. How to manage difficult patient encounters. Fam Pract Manag. 2007;14:30-34.
2. Groves JE. Taking care of the hateful patient. N Engl J Med.1978;298: 883-887.
3. O’Dowd TC. Five years of heartsink patients in primary care. BMJ. 1988;297:528-530.
4. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th edition (DSM-5). American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
5. Volkert J, Gablonski TC, Rabung S. Prevalence of personality disorders in the general adult population in Western countries: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry. 2018;213:709-715.
6. Esterberg ML, Goulding SM, Walker EF. Cluster A personality disorders: schizotypal, schizoid and paranoid personality disorders in childhood and adolescence. J Psychopathol Behav Assess. 2010;32:515-528.
7. Yen S, Peters JR, Nishar S, et al. Association of borderline personality disorder criteria with suicide attempts: findings from the collaborative longitudinal study of personality disorders over 10 years of follow-up. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78:187-194.
8. Dubovsky AN, Kiefer MM. Borderline personality disorder in the primary care setting. Med Clin North Am. 2014;98:1049-1064.
9. Hesse M, Moran P. (2010). Screening for personality disorder with the Standardised Assessment of Personality: Abbreviated Scale (SAPAS): further evidence of concurrent validity. BMC Psychiatry. 2010;10:10.
10. Zanarini MC, Vujanovic AA, Parachini EA, et al. A screening measure for BPD: the McLean screening instrument for borderline personality disorder (MSI-BPD). J Pers Disord. 2003;17:568-573.
11. Loranger AW, Sartorius N, Andreoli A, et al. The International Personality Disorder Examination. The World Health Organization/Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration international pilot study of personality disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994;51:215-224.12. Nelson KJ, Skodol A, Friedman M. Pharmacotherapy for personality disorders. UpToDate. Accessed April 22, 2021. www.uptodate.com/contents/pharmacotherapy-for-personality-disorders
13. Black D, Paris J, Schulz C. Evidence-based integrated biopsychosocial treatment of borderline personality disorder. In: Muse M (ed). Cognitive Behavioral Psychopharmacology: the Clinical Practice of Evidence-Based Biopsychosocial Integration. Wiley; 2017:137-166.
14. Beck AT, Davis DD, Freeman A. Cognitive Therapy of Personality Disorders. 3rd ed. The Guilford Press; 2015.
15. Thylstrup B, Hesse M. “I am not complaining”–ambivalence construct in schizoid personality disorder. Am J Psychother. 2009;63:147-167.
16. Ricke AK, Lee MJ, Chambers JE. The difficult patient: borderline personality disorder in the obstetrical and gynecological patient. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2012;67:495-502.
17. Seow LLY, Page AC, Hooke GR. Severity of borderline personality disorder symptoms as a moderator of the association between the use of dialectical behaviour therapy skills and treatment outcomes. Psychother Res. 2020;30:920-933.
18. Nichols WC. Integrative marital and family treatment of dependent personality disorders. In: MacFarlane MM (Ed.) Family Treatment of Personality Disorders: Advances in Clinical Practice. Haworth Clinical Practice Press; 2004:173-204.
19. Disney KL. Dependent personality disorder: a critical review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2013;33:1184-1196.
20. Bender DS. The therapeutic alliance in the treatment of personality disorders. J Psychiatr Pract. 2005;11:73-87.
21. Ward RK. Assessment and management of personality disorders. Am Fam Physician. 2004;70:1505-1512.
22. Cummings JA, Hayes AM, Cardaciotto L, et al. The dynamics of self-esteem in cognitive therapy for avoidant and obsessive-compulsive personality disorders: an adaptive role of self-esteem variability? Cognit Ther Res. 2012;36:272-281.
An overlooked cause of palpitations
Your article, “Is an underlying cardiac condition causing your patient’s palpitations?” (J Fam Pract. 2021;70:60-68), listed a number of causes of palpitations in the table on page 62. However, 1 cause was noticeably missing: underlying genetic disorders, such as amyloidosis. Genetic disorders can affect the cardiac muscle and lead to increased rates of both cardiac arrhythmias and palpitations.
I recently treated a 43-year-old man who presented with shortness of breath and presyncopal episodes; his medical history included anxiety and gastritis. He previously had undergone a cervical spine fusion and was postoperatively given a diagnosis of bigeminy and frequent premature ventricular contractions (PVCs). An echocardiogram was ordered and came back negative, while a Holter monitor showed PVCs > 30%. Genetic testing was performed only after the family history offered some clues. The diagnosis was hereditary transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis. Now, he is awaiting cardiac magnetic resonance imaging to determine whether muscle or pericardium has been affected.
When I discussed the findings with the patient, he wisely stated, “Perhaps it is more common than studies show if patients are not normally tested until elderly or hospitalized.” This resonated with me when I considered that routine lab work done in an office would miss amyloidosis. This definitely reinforced my philosophy to always listen to the patient and take symptoms seriously, as sometimes we just haven’t figured out the true diagnosis yet.
Your article, “Is an underlying cardiac condition causing your patient’s palpitations?” (J Fam Pract. 2021;70:60-68), listed a number of causes of palpitations in the table on page 62. However, 1 cause was noticeably missing: underlying genetic disorders, such as amyloidosis. Genetic disorders can affect the cardiac muscle and lead to increased rates of both cardiac arrhythmias and palpitations.
I recently treated a 43-year-old man who presented with shortness of breath and presyncopal episodes; his medical history included anxiety and gastritis. He previously had undergone a cervical spine fusion and was postoperatively given a diagnosis of bigeminy and frequent premature ventricular contractions (PVCs). An echocardiogram was ordered and came back negative, while a Holter monitor showed PVCs > 30%. Genetic testing was performed only after the family history offered some clues. The diagnosis was hereditary transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis. Now, he is awaiting cardiac magnetic resonance imaging to determine whether muscle or pericardium has been affected.
When I discussed the findings with the patient, he wisely stated, “Perhaps it is more common than studies show if patients are not normally tested until elderly or hospitalized.” This resonated with me when I considered that routine lab work done in an office would miss amyloidosis. This definitely reinforced my philosophy to always listen to the patient and take symptoms seriously, as sometimes we just haven’t figured out the true diagnosis yet.
Your article, “Is an underlying cardiac condition causing your patient’s palpitations?” (J Fam Pract. 2021;70:60-68), listed a number of causes of palpitations in the table on page 62. However, 1 cause was noticeably missing: underlying genetic disorders, such as amyloidosis. Genetic disorders can affect the cardiac muscle and lead to increased rates of both cardiac arrhythmias and palpitations.
I recently treated a 43-year-old man who presented with shortness of breath and presyncopal episodes; his medical history included anxiety and gastritis. He previously had undergone a cervical spine fusion and was postoperatively given a diagnosis of bigeminy and frequent premature ventricular contractions (PVCs). An echocardiogram was ordered and came back negative, while a Holter monitor showed PVCs > 30%. Genetic testing was performed only after the family history offered some clues. The diagnosis was hereditary transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis. Now, he is awaiting cardiac magnetic resonance imaging to determine whether muscle or pericardium has been affected.
When I discussed the findings with the patient, he wisely stated, “Perhaps it is more common than studies show if patients are not normally tested until elderly or hospitalized.” This resonated with me when I considered that routine lab work done in an office would miss amyloidosis. This definitely reinforced my philosophy to always listen to the patient and take symptoms seriously, as sometimes we just haven’t figured out the true diagnosis yet.