User login
Be among the first to commit to AGA Giving Day
Our patients face racial health disparities daily, leading to inequalities in care and poorer health outcomes.
At this important moment in history, the AGA Research Foundation is uniquely qualified to push forward innovative research in health disparities in gastroenterology. With donations from AGA members to our new initiative called AGA Giving Day, we can provide researchers with a secure source of funding that helps understand the causes of known health disparities, understand why the disparity exists, and develop interventions to reduce and eliminate health disparities.
The AGA Research Foundation invites you to support AGA Giving Day today through Dec. 3. Contributors will be recognized as supporters of our fight to achieve equity and eradicate disparities in digestive diseases.
Learn more at gastro.org/agagivingday.
[email protected]
Our patients face racial health disparities daily, leading to inequalities in care and poorer health outcomes.
At this important moment in history, the AGA Research Foundation is uniquely qualified to push forward innovative research in health disparities in gastroenterology. With donations from AGA members to our new initiative called AGA Giving Day, we can provide researchers with a secure source of funding that helps understand the causes of known health disparities, understand why the disparity exists, and develop interventions to reduce and eliminate health disparities.
The AGA Research Foundation invites you to support AGA Giving Day today through Dec. 3. Contributors will be recognized as supporters of our fight to achieve equity and eradicate disparities in digestive diseases.
Learn more at gastro.org/agagivingday.
[email protected]
Our patients face racial health disparities daily, leading to inequalities in care and poorer health outcomes.
At this important moment in history, the AGA Research Foundation is uniquely qualified to push forward innovative research in health disparities in gastroenterology. With donations from AGA members to our new initiative called AGA Giving Day, we can provide researchers with a secure source of funding that helps understand the causes of known health disparities, understand why the disparity exists, and develop interventions to reduce and eliminate health disparities.
The AGA Research Foundation invites you to support AGA Giving Day today through Dec. 3. Contributors will be recognized as supporters of our fight to achieve equity and eradicate disparities in digestive diseases.
Learn more at gastro.org/agagivingday.
[email protected]
AGA releases largest real-world report on safety and effectiveness of fecal microbiota transplantation
Ninety percent of patients tracked in the AGA FMT National Registry were cured of Clostridioides difficile infection with few serious side effects.
AGA has released the first results from the NIH-funded AGA Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT) National Registry, the largest real-world study on the safety and effectiveness of FMT. Few serious side effects were reported.
“While the value of fecal microbiota transplantation for treating recurrent C. difficile infection is clear from research studies, the potential long-term consequences of altering a patient’s gut microbiota are not fully known,” says Colleen R. Kelly, MD, AGAF, associate professor of medicine at Brown University in Providence, R.I. and co-principal investigator of the AGA FMT National Registry. “Releasing the initial results of the AGA FMT National Registry is an important step toward understanding the true risks and benefits of microbiota therapeutics in a real-world setting.”
This new report details effectiveness and safety outcomes from the first 259 patients enrolled in the registry between December 2017 and September 2019. Almost all participants received FMT using an unknown donor from stool banks. The most common method of FMT delivery was colonoscopy followed by upper endoscopy. Of the 222 participants who returned for the one-month follow-up, 200 participants (90%) had their C. difficile infection cured with 197 of those requiring only a single FMT. Infections were reported in 11 participants, but only 2 were thought to be possibly related to the procedure. FMT response was deemed durable, with recurrence of C. difficile infection in the 6 months after successful FMT occurring in only 4% of participants. This data includes patients with comorbidities, such as inflammatory bowel disease and immunocompromised status, who are typically excluded from FMT clinical trials.
“These initial results show a high success rate of FMT in the real-world setting. We’ll continue to track these patients for 10 years to assess long-term safety, which will be critical to determining the full safety profile of FMT,” added Dr. Kelly.
Ninety percent of patients tracked in the AGA FMT National Registry were cured of Clostridioides difficile infection with few serious side effects.
AGA has released the first results from the NIH-funded AGA Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT) National Registry, the largest real-world study on the safety and effectiveness of FMT. Few serious side effects were reported.
“While the value of fecal microbiota transplantation for treating recurrent C. difficile infection is clear from research studies, the potential long-term consequences of altering a patient’s gut microbiota are not fully known,” says Colleen R. Kelly, MD, AGAF, associate professor of medicine at Brown University in Providence, R.I. and co-principal investigator of the AGA FMT National Registry. “Releasing the initial results of the AGA FMT National Registry is an important step toward understanding the true risks and benefits of microbiota therapeutics in a real-world setting.”
This new report details effectiveness and safety outcomes from the first 259 patients enrolled in the registry between December 2017 and September 2019. Almost all participants received FMT using an unknown donor from stool banks. The most common method of FMT delivery was colonoscopy followed by upper endoscopy. Of the 222 participants who returned for the one-month follow-up, 200 participants (90%) had their C. difficile infection cured with 197 of those requiring only a single FMT. Infections were reported in 11 participants, but only 2 were thought to be possibly related to the procedure. FMT response was deemed durable, with recurrence of C. difficile infection in the 6 months after successful FMT occurring in only 4% of participants. This data includes patients with comorbidities, such as inflammatory bowel disease and immunocompromised status, who are typically excluded from FMT clinical trials.
“These initial results show a high success rate of FMT in the real-world setting. We’ll continue to track these patients for 10 years to assess long-term safety, which will be critical to determining the full safety profile of FMT,” added Dr. Kelly.
Ninety percent of patients tracked in the AGA FMT National Registry were cured of Clostridioides difficile infection with few serious side effects.
AGA has released the first results from the NIH-funded AGA Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT) National Registry, the largest real-world study on the safety and effectiveness of FMT. Few serious side effects were reported.
“While the value of fecal microbiota transplantation for treating recurrent C. difficile infection is clear from research studies, the potential long-term consequences of altering a patient’s gut microbiota are not fully known,” says Colleen R. Kelly, MD, AGAF, associate professor of medicine at Brown University in Providence, R.I. and co-principal investigator of the AGA FMT National Registry. “Releasing the initial results of the AGA FMT National Registry is an important step toward understanding the true risks and benefits of microbiota therapeutics in a real-world setting.”
This new report details effectiveness and safety outcomes from the first 259 patients enrolled in the registry between December 2017 and September 2019. Almost all participants received FMT using an unknown donor from stool banks. The most common method of FMT delivery was colonoscopy followed by upper endoscopy. Of the 222 participants who returned for the one-month follow-up, 200 participants (90%) had their C. difficile infection cured with 197 of those requiring only a single FMT. Infections were reported in 11 participants, but only 2 were thought to be possibly related to the procedure. FMT response was deemed durable, with recurrence of C. difficile infection in the 6 months after successful FMT occurring in only 4% of participants. This data includes patients with comorbidities, such as inflammatory bowel disease and immunocompromised status, who are typically excluded from FMT clinical trials.
“These initial results show a high success rate of FMT in the real-world setting. We’ll continue to track these patients for 10 years to assess long-term safety, which will be critical to determining the full safety profile of FMT,” added Dr. Kelly.
Engage rather than react: A call for hepatologists
In a new practice management commentary, Dr. Meena B. Bansal challenges hepatologists to champion value-based care.
In the September issue of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Meena B. Bansal, MD, FAASLD, from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, provides clinicians with practical guidance on their essential role in value-based health care. Read the article, which appears in CGH’s Practice Management: The Road Ahead column: How Hepatologists Can Contribute to Value-Based Care.
Since hepatologists care for some of the sickest patients in the system, their role in documenting and managing chronic conditions is paramount to a system’s success in value-based care. Hepatologists can expand their reach by:
- Advocating for improvement of coding specificity.
- Participating in quality improvement work.
- Supporting efforts to create a shift in the cost curve for their high-risk patients.
By highlighting how they can shift the cost curve while improving outcomes, they can advocate for the additional resources needed to care for this high-risk population and can have the opportunity to show the return on investment. With this outlook, hepatologists who “engage” rather than “react” can make a real impact on system leadership and play a key role in this dynamic health care landscape.
Read the full article in the September issue of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
In a new practice management commentary, Dr. Meena B. Bansal challenges hepatologists to champion value-based care.
In the September issue of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Meena B. Bansal, MD, FAASLD, from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, provides clinicians with practical guidance on their essential role in value-based health care. Read the article, which appears in CGH’s Practice Management: The Road Ahead column: How Hepatologists Can Contribute to Value-Based Care.
Since hepatologists care for some of the sickest patients in the system, their role in documenting and managing chronic conditions is paramount to a system’s success in value-based care. Hepatologists can expand their reach by:
- Advocating for improvement of coding specificity.
- Participating in quality improvement work.
- Supporting efforts to create a shift in the cost curve for their high-risk patients.
By highlighting how they can shift the cost curve while improving outcomes, they can advocate for the additional resources needed to care for this high-risk population and can have the opportunity to show the return on investment. With this outlook, hepatologists who “engage” rather than “react” can make a real impact on system leadership and play a key role in this dynamic health care landscape.
Read the full article in the September issue of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
In a new practice management commentary, Dr. Meena B. Bansal challenges hepatologists to champion value-based care.
In the September issue of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Meena B. Bansal, MD, FAASLD, from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, provides clinicians with practical guidance on their essential role in value-based health care. Read the article, which appears in CGH’s Practice Management: The Road Ahead column: How Hepatologists Can Contribute to Value-Based Care.
Since hepatologists care for some of the sickest patients in the system, their role in documenting and managing chronic conditions is paramount to a system’s success in value-based care. Hepatologists can expand their reach by:
- Advocating for improvement of coding specificity.
- Participating in quality improvement work.
- Supporting efforts to create a shift in the cost curve for their high-risk patients.
By highlighting how they can shift the cost curve while improving outcomes, they can advocate for the additional resources needed to care for this high-risk population and can have the opportunity to show the return on investment. With this outlook, hepatologists who “engage” rather than “react” can make a real impact on system leadership and play a key role in this dynamic health care landscape.
Read the full article in the September issue of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
IBD can be treated with diet alone
Dear colleagues and friends,
Thank you for your continued interest and support of the Perspectives debates. In this edition, Dr. Ashwin Ananthakrishnan and Dr. Laura Raffals explore the controversial topic of diet-based therapy in inflammatory bowel disease, highlights of the rationales for and against, and the current state of the evidence. All gastroenterologists frequently face questions pertaining to diet and its purported effects on digestive health. I found the discussion relevant to my own general practice, and I hope you will enjoy reading it as much as I did. As always, I welcome your comments and suggestions for future topics at [email protected].
Charles Kahi, MD, MS, AGAF, professor of medicine, Indiana University, Indianapolis. He is also an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
IBD can be treated with diet alone
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), comprising Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, have emerged as global diseases. The past 3 decades have seen a rising incidence of these diseases not just in the Western hemisphere, where their prevalence has been well recognized, but also in regions of the world such as Asia and South America where they were previously rare. Whereas several possible factors have been proposed to explain this rising incidence and globalization of disease with varying degrees of supportive evidence, one of the most likely factors is a changing diet. Over the same period that the disease incidence and prevalence have risen, diets worldwide have converged with several common trends observed across countries and continents. These include reductions in dietary fiber, fruits, and vegetables, and increased intake of processed food, animal protein, fats, and sugary drinks, all of which have been linked epidemiologically to Crohn’s disease.
Treatment of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis over the past 2 decades has focused on the immunologic dysfunction observed in these patients. Successful treatment has relied on suppressing immune responses either broadly or through targeted suppression of specific immunologic pathways. By and large, whereas these approaches have enabled us to make significant progress in reducing disease-related morbidity, success has been moderate at best, with fewer than half of patients in any clinical trial achieving remission at the end of a year. Thus, this approach alone may not be sufficient for most patients with IBD.
Treatment of IBD with diet was long considered out of the mainstream and confined to the realm of anecdotes and message boards. Despite most patients believing that diet played a role in development of IBD and onset of flares and that dietary modification was helpful in relieving symptoms, physicians – who for the most part were not trained in these approaches – were not believers, and probably rightly so in the absence of any supporting data.1 However, the parallel emergence of three bodies of literature has now brought diet back into the mainstream of IBD care (such that not a single IBD conference goes by without at least a session or two on diet). First, large prospective cohorts from Europe and North America provided robust evidence linking long-term adult dietary patterns to disease incidence in adult-onset IBD, which supports many important case-control observations made over the past 2 decades.2 Second, and perhaps most important, we began understanding the role of the microbiome in the development of these diseases and recognizing its centrality to bowel inflammation. One of the key determinants of the microbiome is diet, exerting both short-term and long-term influences on the microbial structure. While microbial changes are by no means the only mechanism through which diet can influence intestinal inflammation, they are among the most important, with broad effects across many dietary components. These findings provided a robust scientific basis for investigating the role of diet. Third, while still far from the high-quality (and expensive) set-up of investigational trials of pharmacologic therapies, dietary therapy studies have also evolved to randomized controlled trial designs and investigation of mechanism-driven dietary combinations. Together, I think these three recent advances, in addition to the wealth of existing literature and anecdotal experience, have been important in moving diet (back) into the IBD mainstream.
So what evidence is there that diet is effective in the treatment of IBD? Randomized controlled trials published more than a decade ago demonstrated that exclusive enteral nutrition, wherein all table foods are eliminated from a diet and the patient relies on an elemental diet alone for nutrition, was effective in not just inducing clinical remission but also improving inflammatory biomarkers.3 With results replicated in several trials, exclusive enteral nutrition is, in many parts of the world, one of the first-line treatments for pediatric Crohn’s disease. That this has not been translated to longer-term maintenance therapy is not necessarily an indicator of lack of durable efficacy, but reflects the challenges of maintaining such a restrictive diet long term while living an active, normal life. However, more recent rigorous studies have demonstrated that the effects of exclusive enteral nutrition can be mimicked either by a selected, less-restrictive diet (such as CD-TREAT4), which is more sustainable, or by combining partial enteral nutrition with an elimination diet that is quite diverse (such as CDED5). The latter two are considerably more promising as longer-term dietary treatments for Crohn’s disease with durable efficacy in open-label studies and randomized trials.
What are my final arguments for diet being used as a treatment for IBD? With the exception of very restrictive ones, diets are generally safe. Of course, patients on restricted diets need monitoring for nutritional deficiencies, but this monitoring is likely less intense than that needed for many of our immunosuppressive therapies. Dietary therapies are not associated with an increase in risk of infections or malignancy (unlike our traditional immunosuppressive therapies), and consequently are much more likely to be accepted by our patients than what we are currently offering. In addition, the existing treatments are expensive and consequently difficult to sustain globally with the increasing burden of these diseases. On the other hand, as eating and dietary choices are a routine part of day-to-day life, dietary therapies are not likely to be associated with any excess costs.
Therefore, treating IBD with diet alone is supported by epidemiologic, mechanistic, and clinical evidence and is a safe, effective, and inexpensive alternative for our patients.
References
1. Zallot C et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013 Jan;19(1):66-72.
2. Sasson AN et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Dec 5;S1542-3565(19)31394-1.
3. Wall CL et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:7652-60.
4. Svolos V et al. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:1354-67.e6.
5. Levine A et al. Gastroenterology. 2019;157:440-50.e8.
Dr. Ananthakrishnan is a gastroenterologist in the division of gastroenterology, Crohn’s and Colitis Center, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston. He is supported by funding from the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation and the Chleck Family Foundation.
IBD can be treated with diet alone – No, it cannot!
The cause of IBD is not completely understood, but we believe something in our environment triggers a dysregulated immune response in individuals with a genetic predisposition to IBD. Among the environmental triggers commonly recognized, diet is considered an important trigger through its ability to affect the composition and health of the gut microbiome and host barrier function. Epidemiologic data support this assumption. Westernization of diet has been associated with the increasing incidence of IBD across the globe and in immigrants who move from developing countries to an industrialized country. Observational studies have shown diets higher in meat and polyunsaturated fatty acids and omega-6 fatty acids are associated with a higher risk for IBD, whereas diets high in fruits, vegetables, and other sources of dietary fiber have a lower risk of IBD.
A growing body of evidence supports the impact food can have on gut health, specifically in mouse IBD models, but it is challenging to translate findings from animal studies into dietary interventions for IBD patients. Mouse studies help us understand the mechanistic basis of how diet may affect IBD, but randomized clinical trials establishing their role in IBD are lacking. This is not surprising as dietary studies are challenging, particularly if done in a robust manner, given the difficulties of ensuring and measuring dietary compliance.
Exclusive enteral nutrition (EEN) has been studied the most rigorously of all diets in IBD and has demonstrated the greatest benefit, compared with other diet studies in IBD. EEN requires the intake of elemental, semi-elemental, or polymeric formulas to meet all nutritional requirements without additional intake of food for 6-8 weeks. Studies have been performed mostly in pediatric populations and have shown effectiveness in induction of remission with reduction in inflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and fecal calprotectin, and even mucosal healing. EEN has not worked out as well for adult populations, because of the poor tolerability of exclusive intake of enteral formulas. Because of this limitation, studies of partial enteral nutrition have been performed that generally allow some food intake in addition to the enteral nutrition. When compared with EEN or anti–tumor necrosis factor–alpha therapy, partial enteral nutrition is a less-effective treatment of Crohn’s disease; however, partial enteral nutrition does appear to improve clinical symptoms.
Beyond EEN, there are many diets that have been considered for the treatment of IBD, including the specific carbohydrate diet (SCD), Crohn’s disease exclusion diet, autoimmune diet, low FODMAP (fermentable oligo-, di-, mono-saccharides and polyols), Paleolithic diet, Mediterranean diet, and the semi-vegetarian diet, to name a few. Of these, only the SCD and Crohn’s disease exclusion diets have shown improvement in clinical remission and reduction in inflammatory markers.
The SCD diet is based on the theory that malabsorption of disaccharide and polysaccharide carbohydrates leads to bacterial overgrowth and host barrier dysfunction. This diet eliminates grains, dairy, processed meats, and certain vegetables such as potatoes, yams, and legumes. Small uncontrolled studies have shown improvement in symptoms and endoscopy findings. However, this restrictive diet is nearly impossible to follow long term. The Crohn’s disease exclusion diet is a whole foods diet avoiding all processed foods, animal fats, dairy, and gluten. Small studies of this diet have also shown improvement in clinical symptoms and inflammatory markers.
The plethora of studies and reports of the therapeutic effect of diet on IBD provide some promise of the benefit dietary modifications can bring to our IBD patients. However, most dietary studies are underpowered, lack a control arm, and do not include endoscopic endpoints. The current body of evidence remains insufficient to support the use of diet alone for the treatment of IBD. We need randomized clinical controlled trials that are held to the same rigor as those of our approved medical treatments for IBD. Although such trials are challenging, we’ve seen groups rise to the task to carry out more robust dietary studies in the IBD population, and we await the results of several ongoing trials.
IBD is a challenging disease to live with and often leaves our patients feeling out of control. Dietary choices provide an avenue for patients to have some control of their health. However, current evidence does not support the prescription of dietary interventions alone to treat IBD, particularly when we have known, effective therapies. While I am not ready to prescribe diet as a stand-alone treatment for IBD, I make a point to discuss the role diet may play in helping our patients achieve optimal health. As health care providers, it is our responsibility to provide holistic care to our patients, which includes promotion of a healthy diet, absent processed foods and added sugars. Healthy lifestyle choices combined with effective medical and surgical treatments offer our patients the best shot at sustained disease control.
References
1. Hou JK et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106(4):563-73.
2. Zachos M et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007(1):CD000542.
3. Lee D et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015;21(8):1786-93.
4. Obih C et al. Nutrition. 2016;32(4):418-25.
5. Sigall Boneh R et al. J Crohns Colitis. 2017;11(10):1205-12.
Dr. Raffals is a gastroenterologist in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. She has no financial conflicts of interest relevant to this paper.
Dear colleagues and friends,
Thank you for your continued interest and support of the Perspectives debates. In this edition, Dr. Ashwin Ananthakrishnan and Dr. Laura Raffals explore the controversial topic of diet-based therapy in inflammatory bowel disease, highlights of the rationales for and against, and the current state of the evidence. All gastroenterologists frequently face questions pertaining to diet and its purported effects on digestive health. I found the discussion relevant to my own general practice, and I hope you will enjoy reading it as much as I did. As always, I welcome your comments and suggestions for future topics at [email protected].
Charles Kahi, MD, MS, AGAF, professor of medicine, Indiana University, Indianapolis. He is also an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
IBD can be treated with diet alone
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), comprising Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, have emerged as global diseases. The past 3 decades have seen a rising incidence of these diseases not just in the Western hemisphere, where their prevalence has been well recognized, but also in regions of the world such as Asia and South America where they were previously rare. Whereas several possible factors have been proposed to explain this rising incidence and globalization of disease with varying degrees of supportive evidence, one of the most likely factors is a changing diet. Over the same period that the disease incidence and prevalence have risen, diets worldwide have converged with several common trends observed across countries and continents. These include reductions in dietary fiber, fruits, and vegetables, and increased intake of processed food, animal protein, fats, and sugary drinks, all of which have been linked epidemiologically to Crohn’s disease.
Treatment of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis over the past 2 decades has focused on the immunologic dysfunction observed in these patients. Successful treatment has relied on suppressing immune responses either broadly or through targeted suppression of specific immunologic pathways. By and large, whereas these approaches have enabled us to make significant progress in reducing disease-related morbidity, success has been moderate at best, with fewer than half of patients in any clinical trial achieving remission at the end of a year. Thus, this approach alone may not be sufficient for most patients with IBD.
Treatment of IBD with diet was long considered out of the mainstream and confined to the realm of anecdotes and message boards. Despite most patients believing that diet played a role in development of IBD and onset of flares and that dietary modification was helpful in relieving symptoms, physicians – who for the most part were not trained in these approaches – were not believers, and probably rightly so in the absence of any supporting data.1 However, the parallel emergence of three bodies of literature has now brought diet back into the mainstream of IBD care (such that not a single IBD conference goes by without at least a session or two on diet). First, large prospective cohorts from Europe and North America provided robust evidence linking long-term adult dietary patterns to disease incidence in adult-onset IBD, which supports many important case-control observations made over the past 2 decades.2 Second, and perhaps most important, we began understanding the role of the microbiome in the development of these diseases and recognizing its centrality to bowel inflammation. One of the key determinants of the microbiome is diet, exerting both short-term and long-term influences on the microbial structure. While microbial changes are by no means the only mechanism through which diet can influence intestinal inflammation, they are among the most important, with broad effects across many dietary components. These findings provided a robust scientific basis for investigating the role of diet. Third, while still far from the high-quality (and expensive) set-up of investigational trials of pharmacologic therapies, dietary therapy studies have also evolved to randomized controlled trial designs and investigation of mechanism-driven dietary combinations. Together, I think these three recent advances, in addition to the wealth of existing literature and anecdotal experience, have been important in moving diet (back) into the IBD mainstream.
So what evidence is there that diet is effective in the treatment of IBD? Randomized controlled trials published more than a decade ago demonstrated that exclusive enteral nutrition, wherein all table foods are eliminated from a diet and the patient relies on an elemental diet alone for nutrition, was effective in not just inducing clinical remission but also improving inflammatory biomarkers.3 With results replicated in several trials, exclusive enteral nutrition is, in many parts of the world, one of the first-line treatments for pediatric Crohn’s disease. That this has not been translated to longer-term maintenance therapy is not necessarily an indicator of lack of durable efficacy, but reflects the challenges of maintaining such a restrictive diet long term while living an active, normal life. However, more recent rigorous studies have demonstrated that the effects of exclusive enteral nutrition can be mimicked either by a selected, less-restrictive diet (such as CD-TREAT4), which is more sustainable, or by combining partial enteral nutrition with an elimination diet that is quite diverse (such as CDED5). The latter two are considerably more promising as longer-term dietary treatments for Crohn’s disease with durable efficacy in open-label studies and randomized trials.
What are my final arguments for diet being used as a treatment for IBD? With the exception of very restrictive ones, diets are generally safe. Of course, patients on restricted diets need monitoring for nutritional deficiencies, but this monitoring is likely less intense than that needed for many of our immunosuppressive therapies. Dietary therapies are not associated with an increase in risk of infections or malignancy (unlike our traditional immunosuppressive therapies), and consequently are much more likely to be accepted by our patients than what we are currently offering. In addition, the existing treatments are expensive and consequently difficult to sustain globally with the increasing burden of these diseases. On the other hand, as eating and dietary choices are a routine part of day-to-day life, dietary therapies are not likely to be associated with any excess costs.
Therefore, treating IBD with diet alone is supported by epidemiologic, mechanistic, and clinical evidence and is a safe, effective, and inexpensive alternative for our patients.
References
1. Zallot C et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013 Jan;19(1):66-72.
2. Sasson AN et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Dec 5;S1542-3565(19)31394-1.
3. Wall CL et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:7652-60.
4. Svolos V et al. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:1354-67.e6.
5. Levine A et al. Gastroenterology. 2019;157:440-50.e8.
Dr. Ananthakrishnan is a gastroenterologist in the division of gastroenterology, Crohn’s and Colitis Center, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston. He is supported by funding from the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation and the Chleck Family Foundation.
IBD can be treated with diet alone – No, it cannot!
The cause of IBD is not completely understood, but we believe something in our environment triggers a dysregulated immune response in individuals with a genetic predisposition to IBD. Among the environmental triggers commonly recognized, diet is considered an important trigger through its ability to affect the composition and health of the gut microbiome and host barrier function. Epidemiologic data support this assumption. Westernization of diet has been associated with the increasing incidence of IBD across the globe and in immigrants who move from developing countries to an industrialized country. Observational studies have shown diets higher in meat and polyunsaturated fatty acids and omega-6 fatty acids are associated with a higher risk for IBD, whereas diets high in fruits, vegetables, and other sources of dietary fiber have a lower risk of IBD.
A growing body of evidence supports the impact food can have on gut health, specifically in mouse IBD models, but it is challenging to translate findings from animal studies into dietary interventions for IBD patients. Mouse studies help us understand the mechanistic basis of how diet may affect IBD, but randomized clinical trials establishing their role in IBD are lacking. This is not surprising as dietary studies are challenging, particularly if done in a robust manner, given the difficulties of ensuring and measuring dietary compliance.
Exclusive enteral nutrition (EEN) has been studied the most rigorously of all diets in IBD and has demonstrated the greatest benefit, compared with other diet studies in IBD. EEN requires the intake of elemental, semi-elemental, or polymeric formulas to meet all nutritional requirements without additional intake of food for 6-8 weeks. Studies have been performed mostly in pediatric populations and have shown effectiveness in induction of remission with reduction in inflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and fecal calprotectin, and even mucosal healing. EEN has not worked out as well for adult populations, because of the poor tolerability of exclusive intake of enteral formulas. Because of this limitation, studies of partial enteral nutrition have been performed that generally allow some food intake in addition to the enteral nutrition. When compared with EEN or anti–tumor necrosis factor–alpha therapy, partial enteral nutrition is a less-effective treatment of Crohn’s disease; however, partial enteral nutrition does appear to improve clinical symptoms.
Beyond EEN, there are many diets that have been considered for the treatment of IBD, including the specific carbohydrate diet (SCD), Crohn’s disease exclusion diet, autoimmune diet, low FODMAP (fermentable oligo-, di-, mono-saccharides and polyols), Paleolithic diet, Mediterranean diet, and the semi-vegetarian diet, to name a few. Of these, only the SCD and Crohn’s disease exclusion diets have shown improvement in clinical remission and reduction in inflammatory markers.
The SCD diet is based on the theory that malabsorption of disaccharide and polysaccharide carbohydrates leads to bacterial overgrowth and host barrier dysfunction. This diet eliminates grains, dairy, processed meats, and certain vegetables such as potatoes, yams, and legumes. Small uncontrolled studies have shown improvement in symptoms and endoscopy findings. However, this restrictive diet is nearly impossible to follow long term. The Crohn’s disease exclusion diet is a whole foods diet avoiding all processed foods, animal fats, dairy, and gluten. Small studies of this diet have also shown improvement in clinical symptoms and inflammatory markers.
The plethora of studies and reports of the therapeutic effect of diet on IBD provide some promise of the benefit dietary modifications can bring to our IBD patients. However, most dietary studies are underpowered, lack a control arm, and do not include endoscopic endpoints. The current body of evidence remains insufficient to support the use of diet alone for the treatment of IBD. We need randomized clinical controlled trials that are held to the same rigor as those of our approved medical treatments for IBD. Although such trials are challenging, we’ve seen groups rise to the task to carry out more robust dietary studies in the IBD population, and we await the results of several ongoing trials.
IBD is a challenging disease to live with and often leaves our patients feeling out of control. Dietary choices provide an avenue for patients to have some control of their health. However, current evidence does not support the prescription of dietary interventions alone to treat IBD, particularly when we have known, effective therapies. While I am not ready to prescribe diet as a stand-alone treatment for IBD, I make a point to discuss the role diet may play in helping our patients achieve optimal health. As health care providers, it is our responsibility to provide holistic care to our patients, which includes promotion of a healthy diet, absent processed foods and added sugars. Healthy lifestyle choices combined with effective medical and surgical treatments offer our patients the best shot at sustained disease control.
References
1. Hou JK et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106(4):563-73.
2. Zachos M et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007(1):CD000542.
3. Lee D et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015;21(8):1786-93.
4. Obih C et al. Nutrition. 2016;32(4):418-25.
5. Sigall Boneh R et al. J Crohns Colitis. 2017;11(10):1205-12.
Dr. Raffals is a gastroenterologist in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. She has no financial conflicts of interest relevant to this paper.
Dear colleagues and friends,
Thank you for your continued interest and support of the Perspectives debates. In this edition, Dr. Ashwin Ananthakrishnan and Dr. Laura Raffals explore the controversial topic of diet-based therapy in inflammatory bowel disease, highlights of the rationales for and against, and the current state of the evidence. All gastroenterologists frequently face questions pertaining to diet and its purported effects on digestive health. I found the discussion relevant to my own general practice, and I hope you will enjoy reading it as much as I did. As always, I welcome your comments and suggestions for future topics at [email protected].
Charles Kahi, MD, MS, AGAF, professor of medicine, Indiana University, Indianapolis. He is also an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
IBD can be treated with diet alone
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), comprising Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, have emerged as global diseases. The past 3 decades have seen a rising incidence of these diseases not just in the Western hemisphere, where their prevalence has been well recognized, but also in regions of the world such as Asia and South America where they were previously rare. Whereas several possible factors have been proposed to explain this rising incidence and globalization of disease with varying degrees of supportive evidence, one of the most likely factors is a changing diet. Over the same period that the disease incidence and prevalence have risen, diets worldwide have converged with several common trends observed across countries and continents. These include reductions in dietary fiber, fruits, and vegetables, and increased intake of processed food, animal protein, fats, and sugary drinks, all of which have been linked epidemiologically to Crohn’s disease.
Treatment of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis over the past 2 decades has focused on the immunologic dysfunction observed in these patients. Successful treatment has relied on suppressing immune responses either broadly or through targeted suppression of specific immunologic pathways. By and large, whereas these approaches have enabled us to make significant progress in reducing disease-related morbidity, success has been moderate at best, with fewer than half of patients in any clinical trial achieving remission at the end of a year. Thus, this approach alone may not be sufficient for most patients with IBD.
Treatment of IBD with diet was long considered out of the mainstream and confined to the realm of anecdotes and message boards. Despite most patients believing that diet played a role in development of IBD and onset of flares and that dietary modification was helpful in relieving symptoms, physicians – who for the most part were not trained in these approaches – were not believers, and probably rightly so in the absence of any supporting data.1 However, the parallel emergence of three bodies of literature has now brought diet back into the mainstream of IBD care (such that not a single IBD conference goes by without at least a session or two on diet). First, large prospective cohorts from Europe and North America provided robust evidence linking long-term adult dietary patterns to disease incidence in adult-onset IBD, which supports many important case-control observations made over the past 2 decades.2 Second, and perhaps most important, we began understanding the role of the microbiome in the development of these diseases and recognizing its centrality to bowel inflammation. One of the key determinants of the microbiome is diet, exerting both short-term and long-term influences on the microbial structure. While microbial changes are by no means the only mechanism through which diet can influence intestinal inflammation, they are among the most important, with broad effects across many dietary components. These findings provided a robust scientific basis for investigating the role of diet. Third, while still far from the high-quality (and expensive) set-up of investigational trials of pharmacologic therapies, dietary therapy studies have also evolved to randomized controlled trial designs and investigation of mechanism-driven dietary combinations. Together, I think these three recent advances, in addition to the wealth of existing literature and anecdotal experience, have been important in moving diet (back) into the IBD mainstream.
So what evidence is there that diet is effective in the treatment of IBD? Randomized controlled trials published more than a decade ago demonstrated that exclusive enteral nutrition, wherein all table foods are eliminated from a diet and the patient relies on an elemental diet alone for nutrition, was effective in not just inducing clinical remission but also improving inflammatory biomarkers.3 With results replicated in several trials, exclusive enteral nutrition is, in many parts of the world, one of the first-line treatments for pediatric Crohn’s disease. That this has not been translated to longer-term maintenance therapy is not necessarily an indicator of lack of durable efficacy, but reflects the challenges of maintaining such a restrictive diet long term while living an active, normal life. However, more recent rigorous studies have demonstrated that the effects of exclusive enteral nutrition can be mimicked either by a selected, less-restrictive diet (such as CD-TREAT4), which is more sustainable, or by combining partial enteral nutrition with an elimination diet that is quite diverse (such as CDED5). The latter two are considerably more promising as longer-term dietary treatments for Crohn’s disease with durable efficacy in open-label studies and randomized trials.
What are my final arguments for diet being used as a treatment for IBD? With the exception of very restrictive ones, diets are generally safe. Of course, patients on restricted diets need monitoring for nutritional deficiencies, but this monitoring is likely less intense than that needed for many of our immunosuppressive therapies. Dietary therapies are not associated with an increase in risk of infections or malignancy (unlike our traditional immunosuppressive therapies), and consequently are much more likely to be accepted by our patients than what we are currently offering. In addition, the existing treatments are expensive and consequently difficult to sustain globally with the increasing burden of these diseases. On the other hand, as eating and dietary choices are a routine part of day-to-day life, dietary therapies are not likely to be associated with any excess costs.
Therefore, treating IBD with diet alone is supported by epidemiologic, mechanistic, and clinical evidence and is a safe, effective, and inexpensive alternative for our patients.
References
1. Zallot C et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013 Jan;19(1):66-72.
2. Sasson AN et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Dec 5;S1542-3565(19)31394-1.
3. Wall CL et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:7652-60.
4. Svolos V et al. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:1354-67.e6.
5. Levine A et al. Gastroenterology. 2019;157:440-50.e8.
Dr. Ananthakrishnan is a gastroenterologist in the division of gastroenterology, Crohn’s and Colitis Center, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston. He is supported by funding from the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation and the Chleck Family Foundation.
IBD can be treated with diet alone – No, it cannot!
The cause of IBD is not completely understood, but we believe something in our environment triggers a dysregulated immune response in individuals with a genetic predisposition to IBD. Among the environmental triggers commonly recognized, diet is considered an important trigger through its ability to affect the composition and health of the gut microbiome and host barrier function. Epidemiologic data support this assumption. Westernization of diet has been associated with the increasing incidence of IBD across the globe and in immigrants who move from developing countries to an industrialized country. Observational studies have shown diets higher in meat and polyunsaturated fatty acids and omega-6 fatty acids are associated with a higher risk for IBD, whereas diets high in fruits, vegetables, and other sources of dietary fiber have a lower risk of IBD.
A growing body of evidence supports the impact food can have on gut health, specifically in mouse IBD models, but it is challenging to translate findings from animal studies into dietary interventions for IBD patients. Mouse studies help us understand the mechanistic basis of how diet may affect IBD, but randomized clinical trials establishing their role in IBD are lacking. This is not surprising as dietary studies are challenging, particularly if done in a robust manner, given the difficulties of ensuring and measuring dietary compliance.
Exclusive enteral nutrition (EEN) has been studied the most rigorously of all diets in IBD and has demonstrated the greatest benefit, compared with other diet studies in IBD. EEN requires the intake of elemental, semi-elemental, or polymeric formulas to meet all nutritional requirements without additional intake of food for 6-8 weeks. Studies have been performed mostly in pediatric populations and have shown effectiveness in induction of remission with reduction in inflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and fecal calprotectin, and even mucosal healing. EEN has not worked out as well for adult populations, because of the poor tolerability of exclusive intake of enteral formulas. Because of this limitation, studies of partial enteral nutrition have been performed that generally allow some food intake in addition to the enteral nutrition. When compared with EEN or anti–tumor necrosis factor–alpha therapy, partial enteral nutrition is a less-effective treatment of Crohn’s disease; however, partial enteral nutrition does appear to improve clinical symptoms.
Beyond EEN, there are many diets that have been considered for the treatment of IBD, including the specific carbohydrate diet (SCD), Crohn’s disease exclusion diet, autoimmune diet, low FODMAP (fermentable oligo-, di-, mono-saccharides and polyols), Paleolithic diet, Mediterranean diet, and the semi-vegetarian diet, to name a few. Of these, only the SCD and Crohn’s disease exclusion diets have shown improvement in clinical remission and reduction in inflammatory markers.
The SCD diet is based on the theory that malabsorption of disaccharide and polysaccharide carbohydrates leads to bacterial overgrowth and host barrier dysfunction. This diet eliminates grains, dairy, processed meats, and certain vegetables such as potatoes, yams, and legumes. Small uncontrolled studies have shown improvement in symptoms and endoscopy findings. However, this restrictive diet is nearly impossible to follow long term. The Crohn’s disease exclusion diet is a whole foods diet avoiding all processed foods, animal fats, dairy, and gluten. Small studies of this diet have also shown improvement in clinical symptoms and inflammatory markers.
The plethora of studies and reports of the therapeutic effect of diet on IBD provide some promise of the benefit dietary modifications can bring to our IBD patients. However, most dietary studies are underpowered, lack a control arm, and do not include endoscopic endpoints. The current body of evidence remains insufficient to support the use of diet alone for the treatment of IBD. We need randomized clinical controlled trials that are held to the same rigor as those of our approved medical treatments for IBD. Although such trials are challenging, we’ve seen groups rise to the task to carry out more robust dietary studies in the IBD population, and we await the results of several ongoing trials.
IBD is a challenging disease to live with and often leaves our patients feeling out of control. Dietary choices provide an avenue for patients to have some control of their health. However, current evidence does not support the prescription of dietary interventions alone to treat IBD, particularly when we have known, effective therapies. While I am not ready to prescribe diet as a stand-alone treatment for IBD, I make a point to discuss the role diet may play in helping our patients achieve optimal health. As health care providers, it is our responsibility to provide holistic care to our patients, which includes promotion of a healthy diet, absent processed foods and added sugars. Healthy lifestyle choices combined with effective medical and surgical treatments offer our patients the best shot at sustained disease control.
References
1. Hou JK et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106(4):563-73.
2. Zachos M et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007(1):CD000542.
3. Lee D et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015;21(8):1786-93.
4. Obih C et al. Nutrition. 2016;32(4):418-25.
5. Sigall Boneh R et al. J Crohns Colitis. 2017;11(10):1205-12.
Dr. Raffals is a gastroenterologist in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. She has no financial conflicts of interest relevant to this paper.
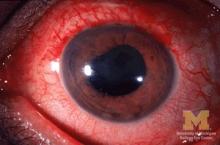
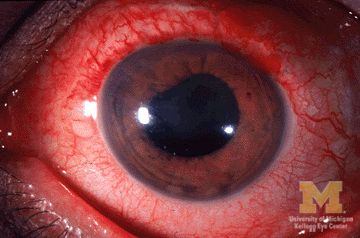
JIA arthritis and uveitis flares ‘often run parallel’
Children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis–associated uveitis (JIA-U) are significantly more likely to experience a flare in their eye disease if their arthritis is also worsening, a team of U.S.-based researchers has found.
In a longitudinal cohort study, children with active arthritis at the time of a routine rheumatology assessment had an almost 2.5-fold increased risk of also having active uveitis 45 days before or after the assessment than did children whose arthritis was not flaring at the rheumatology assessment.
“We demonstrate that the two diseases often run parallel courses,” corresponding author Emily J. Liebling, MD, of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and associates state in Arthritis Care & Research, noting that the magnitude of the association is striking.
“Although there are known risk factors associated with uveitis development in children with JIA, less data are available about factors associated with uveitis flare or activity,” said Sheila T. Angeles-Han, MD, MSc, of the departments of pediatrics and ophthalmology at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center who commented on the study in an interview.
“If proven, this knowledge has the potential to impact practice patterns and current guidelines wherein a pediatric rheumatologist who evaluates a child with JIA-associated uveitis and finds active arthritis would request an expedited ophthalmic examination,” Dr. Angeles-Han suggested.
Dr. Angeles-Han led the development of the first American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation Guideline for the Screening, Monitoring, and Treatment of JIA-Associated Uveitis, which recommends regular screening for uveitis in all children with JIA. Children found to have uveitis should then be screened at least every 3 months, and more frequently if they are taking glucocorticoids and treatment is being tapered.
JIA-associated uveitis accounts for around 20%-40% of all cases of noninfectious childhood eye inflammation, and it can run an insidious and chronic course.
“Children with acute anterior uveitis are symptomatic and tend to have a painful red eye, thus prompting an ophthalmic evaluation,” Dr. Angeles-Han explained. “This is different from children with chronic anterior uveitis who tend not to have any symptoms, thus a screening examination is critical to detect ocular inflammation.”
While the ACR/AF guideline distinguishes between acute and chronic uveitis, Dr. Liebling and colleagues explain that they did not because their experience shows that “even patients with chronic anterior uveitis, typically thought to have silent disease, may exhibit symptoms of eye pain, redness, vision changes, and photophobia.”
Conversely, they say “the JIA subtypes usually associated with acute anterior uveitis may instead manifest as asymptomatic eye disease.”
For their study, Dr. Liebling and coinvestigators examined the records of children seen at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia over a 6.5-year period. For inclusion, children had to have a physician diagnosis of JIA of any subtype and a history of uveitis.
A total of 98 children were included in the retrospective evaluation; the median age at diagnosis of JIA was 3.3 years, and the median age at first uveitis diagnosis was 5.1 years. The majority (82%) were female, 69% were antinuclear antibody (ANA) positive, and 60% had oligoarthritis – all of which have been associated with having a higher risk for developing uveitis.
However, independent of these and several other factors, the probability of having active uveitis within 45 days of a rheumatology assessment was 65% in those with active arthritis versus 42% for those with no active joints.
Their data are based on 1,229 rheumatology visits that occurred between 2013 and 2019, with a median of 13 visits per patient. Overall, arthritis was defined as being active in 17% of visits, and active uveitis was observed in 18% of rheumatology visits.
Concordance between arthritis and uveitis activity was observed 73% of the time, the researchers reported. A sensitivity analysis that excluded children with the enthesitis-related arthritis subtype of JIA, who may not undergo frequent eye exams, did not change their findings.
Decreased odds of active uveitis at any time point were seen with the use of combination biologic and nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Years from uveitis diagnosis was also associated with lower odds of active uveitis over time.
Other factors associated with lower odds of uveitis were female sex, HLA-B27 positivity, and having any subtype of JIA other than the oligoarticular subtype.
Dr. Liebling and coinvestigators concluded that, contrary to the historical dogma, arthritis and uveitis do not run distinct and unrelated courses: “In patients with JIA-U, there is a significant temporal association between arthritis and uveitis disease activity.”
The study was sponsored by the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Rheumatology Research Fund. The investigators for the study had no financial support from commercial sources or any other potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Angeles-Han had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Liebling EJ et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2020 Oct 12. doi: 10.1002/acr.24483.
Children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis–associated uveitis (JIA-U) are significantly more likely to experience a flare in their eye disease if their arthritis is also worsening, a team of U.S.-based researchers has found.
In a longitudinal cohort study, children with active arthritis at the time of a routine rheumatology assessment had an almost 2.5-fold increased risk of also having active uveitis 45 days before or after the assessment than did children whose arthritis was not flaring at the rheumatology assessment.
“We demonstrate that the two diseases often run parallel courses,” corresponding author Emily J. Liebling, MD, of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and associates state in Arthritis Care & Research, noting that the magnitude of the association is striking.
“Although there are known risk factors associated with uveitis development in children with JIA, less data are available about factors associated with uveitis flare or activity,” said Sheila T. Angeles-Han, MD, MSc, of the departments of pediatrics and ophthalmology at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center who commented on the study in an interview.
“If proven, this knowledge has the potential to impact practice patterns and current guidelines wherein a pediatric rheumatologist who evaluates a child with JIA-associated uveitis and finds active arthritis would request an expedited ophthalmic examination,” Dr. Angeles-Han suggested.
Dr. Angeles-Han led the development of the first American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation Guideline for the Screening, Monitoring, and Treatment of JIA-Associated Uveitis, which recommends regular screening for uveitis in all children with JIA. Children found to have uveitis should then be screened at least every 3 months, and more frequently if they are taking glucocorticoids and treatment is being tapered.
JIA-associated uveitis accounts for around 20%-40% of all cases of noninfectious childhood eye inflammation, and it can run an insidious and chronic course.
“Children with acute anterior uveitis are symptomatic and tend to have a painful red eye, thus prompting an ophthalmic evaluation,” Dr. Angeles-Han explained. “This is different from children with chronic anterior uveitis who tend not to have any symptoms, thus a screening examination is critical to detect ocular inflammation.”
While the ACR/AF guideline distinguishes between acute and chronic uveitis, Dr. Liebling and colleagues explain that they did not because their experience shows that “even patients with chronic anterior uveitis, typically thought to have silent disease, may exhibit symptoms of eye pain, redness, vision changes, and photophobia.”
Conversely, they say “the JIA subtypes usually associated with acute anterior uveitis may instead manifest as asymptomatic eye disease.”
For their study, Dr. Liebling and coinvestigators examined the records of children seen at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia over a 6.5-year period. For inclusion, children had to have a physician diagnosis of JIA of any subtype and a history of uveitis.
A total of 98 children were included in the retrospective evaluation; the median age at diagnosis of JIA was 3.3 years, and the median age at first uveitis diagnosis was 5.1 years. The majority (82%) were female, 69% were antinuclear antibody (ANA) positive, and 60% had oligoarthritis – all of which have been associated with having a higher risk for developing uveitis.
However, independent of these and several other factors, the probability of having active uveitis within 45 days of a rheumatology assessment was 65% in those with active arthritis versus 42% for those with no active joints.
Their data are based on 1,229 rheumatology visits that occurred between 2013 and 2019, with a median of 13 visits per patient. Overall, arthritis was defined as being active in 17% of visits, and active uveitis was observed in 18% of rheumatology visits.
Concordance between arthritis and uveitis activity was observed 73% of the time, the researchers reported. A sensitivity analysis that excluded children with the enthesitis-related arthritis subtype of JIA, who may not undergo frequent eye exams, did not change their findings.
Decreased odds of active uveitis at any time point were seen with the use of combination biologic and nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Years from uveitis diagnosis was also associated with lower odds of active uveitis over time.
Other factors associated with lower odds of uveitis were female sex, HLA-B27 positivity, and having any subtype of JIA other than the oligoarticular subtype.
Dr. Liebling and coinvestigators concluded that, contrary to the historical dogma, arthritis and uveitis do not run distinct and unrelated courses: “In patients with JIA-U, there is a significant temporal association between arthritis and uveitis disease activity.”
The study was sponsored by the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Rheumatology Research Fund. The investigators for the study had no financial support from commercial sources or any other potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Angeles-Han had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Liebling EJ et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2020 Oct 12. doi: 10.1002/acr.24483.
Children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis–associated uveitis (JIA-U) are significantly more likely to experience a flare in their eye disease if their arthritis is also worsening, a team of U.S.-based researchers has found.
In a longitudinal cohort study, children with active arthritis at the time of a routine rheumatology assessment had an almost 2.5-fold increased risk of also having active uveitis 45 days before or after the assessment than did children whose arthritis was not flaring at the rheumatology assessment.
“We demonstrate that the two diseases often run parallel courses,” corresponding author Emily J. Liebling, MD, of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and associates state in Arthritis Care & Research, noting that the magnitude of the association is striking.
“Although there are known risk factors associated with uveitis development in children with JIA, less data are available about factors associated with uveitis flare or activity,” said Sheila T. Angeles-Han, MD, MSc, of the departments of pediatrics and ophthalmology at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center who commented on the study in an interview.
“If proven, this knowledge has the potential to impact practice patterns and current guidelines wherein a pediatric rheumatologist who evaluates a child with JIA-associated uveitis and finds active arthritis would request an expedited ophthalmic examination,” Dr. Angeles-Han suggested.
Dr. Angeles-Han led the development of the first American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation Guideline for the Screening, Monitoring, and Treatment of JIA-Associated Uveitis, which recommends regular screening for uveitis in all children with JIA. Children found to have uveitis should then be screened at least every 3 months, and more frequently if they are taking glucocorticoids and treatment is being tapered.
JIA-associated uveitis accounts for around 20%-40% of all cases of noninfectious childhood eye inflammation, and it can run an insidious and chronic course.
“Children with acute anterior uveitis are symptomatic and tend to have a painful red eye, thus prompting an ophthalmic evaluation,” Dr. Angeles-Han explained. “This is different from children with chronic anterior uveitis who tend not to have any symptoms, thus a screening examination is critical to detect ocular inflammation.”
While the ACR/AF guideline distinguishes between acute and chronic uveitis, Dr. Liebling and colleagues explain that they did not because their experience shows that “even patients with chronic anterior uveitis, typically thought to have silent disease, may exhibit symptoms of eye pain, redness, vision changes, and photophobia.”
Conversely, they say “the JIA subtypes usually associated with acute anterior uveitis may instead manifest as asymptomatic eye disease.”
For their study, Dr. Liebling and coinvestigators examined the records of children seen at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia over a 6.5-year period. For inclusion, children had to have a physician diagnosis of JIA of any subtype and a history of uveitis.
A total of 98 children were included in the retrospective evaluation; the median age at diagnosis of JIA was 3.3 years, and the median age at first uveitis diagnosis was 5.1 years. The majority (82%) were female, 69% were antinuclear antibody (ANA) positive, and 60% had oligoarthritis – all of which have been associated with having a higher risk for developing uveitis.
However, independent of these and several other factors, the probability of having active uveitis within 45 days of a rheumatology assessment was 65% in those with active arthritis versus 42% for those with no active joints.
Their data are based on 1,229 rheumatology visits that occurred between 2013 and 2019, with a median of 13 visits per patient. Overall, arthritis was defined as being active in 17% of visits, and active uveitis was observed in 18% of rheumatology visits.
Concordance between arthritis and uveitis activity was observed 73% of the time, the researchers reported. A sensitivity analysis that excluded children with the enthesitis-related arthritis subtype of JIA, who may not undergo frequent eye exams, did not change their findings.
Decreased odds of active uveitis at any time point were seen with the use of combination biologic and nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Years from uveitis diagnosis was also associated with lower odds of active uveitis over time.
Other factors associated with lower odds of uveitis were female sex, HLA-B27 positivity, and having any subtype of JIA other than the oligoarticular subtype.
Dr. Liebling and coinvestigators concluded that, contrary to the historical dogma, arthritis and uveitis do not run distinct and unrelated courses: “In patients with JIA-U, there is a significant temporal association between arthritis and uveitis disease activity.”
The study was sponsored by the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Rheumatology Research Fund. The investigators for the study had no financial support from commercial sources or any other potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Angeles-Han had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Liebling EJ et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2020 Oct 12. doi: 10.1002/acr.24483.
FROM ARTHRITIS CARE & RESEARCH
Sleep-disordered breathing in neuromuscular disease
Sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) is a common sleep disturbance in neuromuscular disease (NMD) affecting 36% to 53% of diagnosed adults (Arens R, et al. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2010;11[1]:24). Disturbances in sleep may serve as the earliest sign of muscle weakness in these patients, at times being detected before their underlying neuromuscular disease is diagnosed. This is of paramount importance to sleep medicine and pulmonary physicians who may be among the first specialists to evaluate these patients and can play a vital role in the recognition and diagnosis of neuromuscular disease. Herein, we will provide a guide to aid the reader in recognizing the early signs and symptoms of NMD as it pertains to sleep, as earlier diagnosis may lead to improved quality of life or possibly even survival, in some cases.
Pathophysiology
To begin, it is important to understand the pathophysiology of NMD and how it is altered during the sleep state. Sleep-related physiologic changes in healthy humans include reduction in upper airway muscle tone, blunting of chemoreceptors associated with pharyngeal dilator augmentation, and sleep stage-specific changes in skeletal muscle tone. In patients with NMD, these changes may not be adequately compensated for, leading to sleep-disordered breathing that can present as sleep apnea, hypoventilation, or hypoxia (Govindarajan R, et al. Sleep Issues in Neuromuscular Disorders: A Clinical Guide. Springer International Publishing AG, Springer Nature 2018).
Central respiratory control
The respiratory centers in the pons and medulla are generally spared from the primary effects of most NMD; however, over time, they may be affected secondarily. Similar to obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS), untreated chronic sleep-related hypoventilation from NMD can impair the sensitivity of respiratory chemoreceptors leading to worsening hypoventilation.
Upper airway resistance
Pharyngeal muscle tone is key to maintaining a patent airway during sleep. In some NMD, bulbar muscle weakness with pharyngeal dilator muscle hypotonia leads to increased upper airway resistance, especially during REM sleep, which can result in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). In addition to weakness affecting the upper airway musculature, anatomical changes may also contribute to sleep-disordered breathing. In Pompe disease, for example, macroglossia and fibro-fatty replacement of tongue muscles may occur, leading to the development of OSA.
Diaphragm weakness
In NMD that affects the diaphragm, there is an increased reliance on the skeletal muscles of respiration to maintain adequate ventilation as the underlying disease progresses. Generally, weakness of the diaphragm will cause disturbances in REM sleep first as, during REM, ventilation predominately depends on the diaphragm and patients lose the assistance of their skeletal muscles. However, over time, the progressive weakening of the diaphragm will progress to involve NREM sleep as well, clinically manifesting with frank sleep apnea, hypoventilation, and, ultimately, chronic hypercapnic respiratory failure.
Inspiratory muscle weakness
As noted above, there are many other muscles used in inspiration in addition to the diaphragm. Other primary muscles include the intercostal and scalene muscles, and accessory muscles include the sternocleidomastoid, pectoralis, latissimus dorsi, erector spinae, and trapezius muscles. While sleep and breathing problems may begin early in the course of a neuromuscular disease, the complex restrictive lung disease pattern that we see in these patients may not develop until the respiratory muscles of the chest wall are involved. This restriction, which corresponds to lower lung volumes, leads to a fall in the caudal traction force of the airways which can lead to reduction in the pharyngeal airway cross section. Because these issues are worsened in the supine position, their pathophysiologic effects on respiration are most notable during sleep, putting patients at higher risk of OSA.
Cardiac abnormalities
Lastly, it should be noted that diseases such as the muscular dystrophies, myotonic dystrophy, mitochondriopathies, and nemaline myopathy can be associated with a cardiomyopathy ,which can lead to central sleep apnea in the form of Cheyne-Stokes breathing.
Sleep-disordered breathing in specific NMDs
In amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), up to 75% of patients may have SDB, the majority of which is central sleep apnea (CSA) and hypoventilation although they still have a higher prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) than the general population. Whether the diaphragm or the pharyngeal muscles are predominantly affected may have something to do with the type of apnea a patient experiences; however, studies have shown that even in bulbar ALS, CSA is most common. It should be noted, that this is not Cheyne-Stokes CSA, but rather lack of chest wall and abdominal movement due to weakness. (David WS, et al. J Neurol Sci. 1997;152[suppl 1]:S29-35).
In myasthenia gravis (MG), about 40% to 60% of patients have SDB, and about 30% develop overt respiratory weakness, generally late in the course of their disease. Many of these patients report excessive daytime sleepiness, often attributed to myasthenic fatigue requiring treatment with corticosteroids. It is important to evaluate for sleep apnea, given that if diagnosed and treated, their generalized fatigue may improve and the need for steroids may be reduced or eliminated altogether. It is also important to note that the respiratory and sleep issues MG patients face may not correlate with the severity of their overall disease, such that patients well-controlled on medications from a generalized weakness standpoint may still require home noninvasive ventilation (NIV) for chronic respiratory failure due to weakness of the respiratory system muscles.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), an X-linked disease associated with dysfunction of dystrophin synthesis, is often diagnosed in early childhood and gradually progresses over years. Their initial sleep and respiratory symptoms can be subtle and may start with increased nighttime awakenings and daytime somnolence. Generally, these patients will develop OSA in the first decade of life and progress to hypoventilation in their second decade and beyond. These patients are especially important to recognize, as studies have shown appropriate NIV therapy may significantly prolong their life (Finder JD, et al; American Thoracic Society. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004(Aug 15);170[4]:456-465).
In addition to the well-known motor neuron and neuromuscular diseases mentioned above, neuropathic diseases can lead to sleep disturbances, as well. In Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT), pharyngeal and laryngeal neuropathy, as well as hypoglossal nerve dysfunction, lead to OSA. Similar to ALS and MG, there is a significant amount of CSA and hypoventilation, likely related to phrenic neuropathy. In contrast to MG, in CMT, the severity of neuropathic disease does correlate to the severity of sleep apnea.
Testing
Testing can range from overnight oximetry to polysomnogram (PSG) with CO2 monitoring. Generally, all patients with a rapidly progressive neuromuscular disease should get pulmonary function testing (PFT) (upright and supine) to evaluate forced vital capacity (FVC) every 3 to 6 months to monitor for respiratory failure. Laboratory studies that can be helpful in assessing for SDB are the PaCO2 (> 45 mm Hg) measured on an arterial blood gas and serum bicarbonate levels (>27 mmol/L or a base excess >4 mmol/L). Patients can qualify for NIV with an overnight SaO2 less than or equal to 88% for greater than or equal to 5 minutes in a 2-hour recording period, PaCO2 greater than or equal to 45 mm Hg, forced vital capacity (FVC) < 50% of predicted, or maximal inspiratory pressure (MIP) <60 cm H2O. For ALS specifically, sniff nasal pressure < 40 cm H2O and orthopnea are additional criteria that can be used. It is worth noting that a PSG is not required for NIV qualification in neuromuscular respiratory insufficiency. However, PSG is beneficial in patients with preserved PFTs but suspected of having early nocturnal respiratory impairment.
Therapy
NIV is the mainstay of therapy for SDB in patients with NMD and has been associated with a slower decline in FVC and improved survival in some cases, as demonstrated in studies of patients with DMD or ALS. Generally, a bi-level PAP mode is preferred; the expiratory positive airway pressure prevents micro-atelectasis and improves V/Q matching and the inspiratory positive airway pressure reduces inspiratory muscle load and optimizes ventilation. As weakness progresses, patients may have difficulty creating enough negative force to initiate a spontaneous breath, thus a mode with a set respiratory rate is preferred that can be implemented in bi-level PAP or more advanced modes such as volume-assured pressure support (VAPS) modality. For patients who are unable to tolerate NIV, particularly those with severe bulbar disease and difficult to manage respiratory secretions, tracheostomy with mechanical ventilation may ultimately be needed. This decision should be made as part of a multidisciplinary shared decision-making conversation with the patient, their family, and their team of providers.
Summary
Sleep is a particularly vulnerable state for patients with NMD, and in many patients, disturbances in sleep may be the first clue to their ultimate diagnosis. It is important that sleep medicine and pulmonary specialists understand the pathophysiology and management of NMD as they can play a vital role in the interdisciplinary care of these patients.
Dr. Greer is a Sleep Medicine Fellow, Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine; Dr. Collop is Professor of Medicine and Neurology, Director, Emory Sleep Center; Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia.
Sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) is a common sleep disturbance in neuromuscular disease (NMD) affecting 36% to 53% of diagnosed adults (Arens R, et al. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2010;11[1]:24). Disturbances in sleep may serve as the earliest sign of muscle weakness in these patients, at times being detected before their underlying neuromuscular disease is diagnosed. This is of paramount importance to sleep medicine and pulmonary physicians who may be among the first specialists to evaluate these patients and can play a vital role in the recognition and diagnosis of neuromuscular disease. Herein, we will provide a guide to aid the reader in recognizing the early signs and symptoms of NMD as it pertains to sleep, as earlier diagnosis may lead to improved quality of life or possibly even survival, in some cases.
Pathophysiology
To begin, it is important to understand the pathophysiology of NMD and how it is altered during the sleep state. Sleep-related physiologic changes in healthy humans include reduction in upper airway muscle tone, blunting of chemoreceptors associated with pharyngeal dilator augmentation, and sleep stage-specific changes in skeletal muscle tone. In patients with NMD, these changes may not be adequately compensated for, leading to sleep-disordered breathing that can present as sleep apnea, hypoventilation, or hypoxia (Govindarajan R, et al. Sleep Issues in Neuromuscular Disorders: A Clinical Guide. Springer International Publishing AG, Springer Nature 2018).
Central respiratory control
The respiratory centers in the pons and medulla are generally spared from the primary effects of most NMD; however, over time, they may be affected secondarily. Similar to obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS), untreated chronic sleep-related hypoventilation from NMD can impair the sensitivity of respiratory chemoreceptors leading to worsening hypoventilation.
Upper airway resistance
Pharyngeal muscle tone is key to maintaining a patent airway during sleep. In some NMD, bulbar muscle weakness with pharyngeal dilator muscle hypotonia leads to increased upper airway resistance, especially during REM sleep, which can result in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). In addition to weakness affecting the upper airway musculature, anatomical changes may also contribute to sleep-disordered breathing. In Pompe disease, for example, macroglossia and fibro-fatty replacement of tongue muscles may occur, leading to the development of OSA.
Diaphragm weakness
In NMD that affects the diaphragm, there is an increased reliance on the skeletal muscles of respiration to maintain adequate ventilation as the underlying disease progresses. Generally, weakness of the diaphragm will cause disturbances in REM sleep first as, during REM, ventilation predominately depends on the diaphragm and patients lose the assistance of their skeletal muscles. However, over time, the progressive weakening of the diaphragm will progress to involve NREM sleep as well, clinically manifesting with frank sleep apnea, hypoventilation, and, ultimately, chronic hypercapnic respiratory failure.
Inspiratory muscle weakness
As noted above, there are many other muscles used in inspiration in addition to the diaphragm. Other primary muscles include the intercostal and scalene muscles, and accessory muscles include the sternocleidomastoid, pectoralis, latissimus dorsi, erector spinae, and trapezius muscles. While sleep and breathing problems may begin early in the course of a neuromuscular disease, the complex restrictive lung disease pattern that we see in these patients may not develop until the respiratory muscles of the chest wall are involved. This restriction, which corresponds to lower lung volumes, leads to a fall in the caudal traction force of the airways which can lead to reduction in the pharyngeal airway cross section. Because these issues are worsened in the supine position, their pathophysiologic effects on respiration are most notable during sleep, putting patients at higher risk of OSA.
Cardiac abnormalities
Lastly, it should be noted that diseases such as the muscular dystrophies, myotonic dystrophy, mitochondriopathies, and nemaline myopathy can be associated with a cardiomyopathy ,which can lead to central sleep apnea in the form of Cheyne-Stokes breathing.
Sleep-disordered breathing in specific NMDs
In amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), up to 75% of patients may have SDB, the majority of which is central sleep apnea (CSA) and hypoventilation although they still have a higher prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) than the general population. Whether the diaphragm or the pharyngeal muscles are predominantly affected may have something to do with the type of apnea a patient experiences; however, studies have shown that even in bulbar ALS, CSA is most common. It should be noted, that this is not Cheyne-Stokes CSA, but rather lack of chest wall and abdominal movement due to weakness. (David WS, et al. J Neurol Sci. 1997;152[suppl 1]:S29-35).
In myasthenia gravis (MG), about 40% to 60% of patients have SDB, and about 30% develop overt respiratory weakness, generally late in the course of their disease. Many of these patients report excessive daytime sleepiness, often attributed to myasthenic fatigue requiring treatment with corticosteroids. It is important to evaluate for sleep apnea, given that if diagnosed and treated, their generalized fatigue may improve and the need for steroids may be reduced or eliminated altogether. It is also important to note that the respiratory and sleep issues MG patients face may not correlate with the severity of their overall disease, such that patients well-controlled on medications from a generalized weakness standpoint may still require home noninvasive ventilation (NIV) for chronic respiratory failure due to weakness of the respiratory system muscles.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), an X-linked disease associated with dysfunction of dystrophin synthesis, is often diagnosed in early childhood and gradually progresses over years. Their initial sleep and respiratory symptoms can be subtle and may start with increased nighttime awakenings and daytime somnolence. Generally, these patients will develop OSA in the first decade of life and progress to hypoventilation in their second decade and beyond. These patients are especially important to recognize, as studies have shown appropriate NIV therapy may significantly prolong their life (Finder JD, et al; American Thoracic Society. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004(Aug 15);170[4]:456-465).
In addition to the well-known motor neuron and neuromuscular diseases mentioned above, neuropathic diseases can lead to sleep disturbances, as well. In Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT), pharyngeal and laryngeal neuropathy, as well as hypoglossal nerve dysfunction, lead to OSA. Similar to ALS and MG, there is a significant amount of CSA and hypoventilation, likely related to phrenic neuropathy. In contrast to MG, in CMT, the severity of neuropathic disease does correlate to the severity of sleep apnea.
Testing
Testing can range from overnight oximetry to polysomnogram (PSG) with CO2 monitoring. Generally, all patients with a rapidly progressive neuromuscular disease should get pulmonary function testing (PFT) (upright and supine) to evaluate forced vital capacity (FVC) every 3 to 6 months to monitor for respiratory failure. Laboratory studies that can be helpful in assessing for SDB are the PaCO2 (> 45 mm Hg) measured on an arterial blood gas and serum bicarbonate levels (>27 mmol/L or a base excess >4 mmol/L). Patients can qualify for NIV with an overnight SaO2 less than or equal to 88% for greater than or equal to 5 minutes in a 2-hour recording period, PaCO2 greater than or equal to 45 mm Hg, forced vital capacity (FVC) < 50% of predicted, or maximal inspiratory pressure (MIP) <60 cm H2O. For ALS specifically, sniff nasal pressure < 40 cm H2O and orthopnea are additional criteria that can be used. It is worth noting that a PSG is not required for NIV qualification in neuromuscular respiratory insufficiency. However, PSG is beneficial in patients with preserved PFTs but suspected of having early nocturnal respiratory impairment.
Therapy
NIV is the mainstay of therapy for SDB in patients with NMD and has been associated with a slower decline in FVC and improved survival in some cases, as demonstrated in studies of patients with DMD or ALS. Generally, a bi-level PAP mode is preferred; the expiratory positive airway pressure prevents micro-atelectasis and improves V/Q matching and the inspiratory positive airway pressure reduces inspiratory muscle load and optimizes ventilation. As weakness progresses, patients may have difficulty creating enough negative force to initiate a spontaneous breath, thus a mode with a set respiratory rate is preferred that can be implemented in bi-level PAP or more advanced modes such as volume-assured pressure support (VAPS) modality. For patients who are unable to tolerate NIV, particularly those with severe bulbar disease and difficult to manage respiratory secretions, tracheostomy with mechanical ventilation may ultimately be needed. This decision should be made as part of a multidisciplinary shared decision-making conversation with the patient, their family, and their team of providers.
Summary
Sleep is a particularly vulnerable state for patients with NMD, and in many patients, disturbances in sleep may be the first clue to their ultimate diagnosis. It is important that sleep medicine and pulmonary specialists understand the pathophysiology and management of NMD as they can play a vital role in the interdisciplinary care of these patients.
Dr. Greer is a Sleep Medicine Fellow, Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine; Dr. Collop is Professor of Medicine and Neurology, Director, Emory Sleep Center; Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia.
Sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) is a common sleep disturbance in neuromuscular disease (NMD) affecting 36% to 53% of diagnosed adults (Arens R, et al. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2010;11[1]:24). Disturbances in sleep may serve as the earliest sign of muscle weakness in these patients, at times being detected before their underlying neuromuscular disease is diagnosed. This is of paramount importance to sleep medicine and pulmonary physicians who may be among the first specialists to evaluate these patients and can play a vital role in the recognition and diagnosis of neuromuscular disease. Herein, we will provide a guide to aid the reader in recognizing the early signs and symptoms of NMD as it pertains to sleep, as earlier diagnosis may lead to improved quality of life or possibly even survival, in some cases.
Pathophysiology
To begin, it is important to understand the pathophysiology of NMD and how it is altered during the sleep state. Sleep-related physiologic changes in healthy humans include reduction in upper airway muscle tone, blunting of chemoreceptors associated with pharyngeal dilator augmentation, and sleep stage-specific changes in skeletal muscle tone. In patients with NMD, these changes may not be adequately compensated for, leading to sleep-disordered breathing that can present as sleep apnea, hypoventilation, or hypoxia (Govindarajan R, et al. Sleep Issues in Neuromuscular Disorders: A Clinical Guide. Springer International Publishing AG, Springer Nature 2018).
Central respiratory control
The respiratory centers in the pons and medulla are generally spared from the primary effects of most NMD; however, over time, they may be affected secondarily. Similar to obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS), untreated chronic sleep-related hypoventilation from NMD can impair the sensitivity of respiratory chemoreceptors leading to worsening hypoventilation.
Upper airway resistance
Pharyngeal muscle tone is key to maintaining a patent airway during sleep. In some NMD, bulbar muscle weakness with pharyngeal dilator muscle hypotonia leads to increased upper airway resistance, especially during REM sleep, which can result in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). In addition to weakness affecting the upper airway musculature, anatomical changes may also contribute to sleep-disordered breathing. In Pompe disease, for example, macroglossia and fibro-fatty replacement of tongue muscles may occur, leading to the development of OSA.
Diaphragm weakness
In NMD that affects the diaphragm, there is an increased reliance on the skeletal muscles of respiration to maintain adequate ventilation as the underlying disease progresses. Generally, weakness of the diaphragm will cause disturbances in REM sleep first as, during REM, ventilation predominately depends on the diaphragm and patients lose the assistance of their skeletal muscles. However, over time, the progressive weakening of the diaphragm will progress to involve NREM sleep as well, clinically manifesting with frank sleep apnea, hypoventilation, and, ultimately, chronic hypercapnic respiratory failure.
Inspiratory muscle weakness
As noted above, there are many other muscles used in inspiration in addition to the diaphragm. Other primary muscles include the intercostal and scalene muscles, and accessory muscles include the sternocleidomastoid, pectoralis, latissimus dorsi, erector spinae, and trapezius muscles. While sleep and breathing problems may begin early in the course of a neuromuscular disease, the complex restrictive lung disease pattern that we see in these patients may not develop until the respiratory muscles of the chest wall are involved. This restriction, which corresponds to lower lung volumes, leads to a fall in the caudal traction force of the airways which can lead to reduction in the pharyngeal airway cross section. Because these issues are worsened in the supine position, their pathophysiologic effects on respiration are most notable during sleep, putting patients at higher risk of OSA.
Cardiac abnormalities
Lastly, it should be noted that diseases such as the muscular dystrophies, myotonic dystrophy, mitochondriopathies, and nemaline myopathy can be associated with a cardiomyopathy ,which can lead to central sleep apnea in the form of Cheyne-Stokes breathing.
Sleep-disordered breathing in specific NMDs
In amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), up to 75% of patients may have SDB, the majority of which is central sleep apnea (CSA) and hypoventilation although they still have a higher prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) than the general population. Whether the diaphragm or the pharyngeal muscles are predominantly affected may have something to do with the type of apnea a patient experiences; however, studies have shown that even in bulbar ALS, CSA is most common. It should be noted, that this is not Cheyne-Stokes CSA, but rather lack of chest wall and abdominal movement due to weakness. (David WS, et al. J Neurol Sci. 1997;152[suppl 1]:S29-35).
In myasthenia gravis (MG), about 40% to 60% of patients have SDB, and about 30% develop overt respiratory weakness, generally late in the course of their disease. Many of these patients report excessive daytime sleepiness, often attributed to myasthenic fatigue requiring treatment with corticosteroids. It is important to evaluate for sleep apnea, given that if diagnosed and treated, their generalized fatigue may improve and the need for steroids may be reduced or eliminated altogether. It is also important to note that the respiratory and sleep issues MG patients face may not correlate with the severity of their overall disease, such that patients well-controlled on medications from a generalized weakness standpoint may still require home noninvasive ventilation (NIV) for chronic respiratory failure due to weakness of the respiratory system muscles.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), an X-linked disease associated with dysfunction of dystrophin synthesis, is often diagnosed in early childhood and gradually progresses over years. Their initial sleep and respiratory symptoms can be subtle and may start with increased nighttime awakenings and daytime somnolence. Generally, these patients will develop OSA in the first decade of life and progress to hypoventilation in their second decade and beyond. These patients are especially important to recognize, as studies have shown appropriate NIV therapy may significantly prolong their life (Finder JD, et al; American Thoracic Society. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004(Aug 15);170[4]:456-465).
In addition to the well-known motor neuron and neuromuscular diseases mentioned above, neuropathic diseases can lead to sleep disturbances, as well. In Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT), pharyngeal and laryngeal neuropathy, as well as hypoglossal nerve dysfunction, lead to OSA. Similar to ALS and MG, there is a significant amount of CSA and hypoventilation, likely related to phrenic neuropathy. In contrast to MG, in CMT, the severity of neuropathic disease does correlate to the severity of sleep apnea.
Testing
Testing can range from overnight oximetry to polysomnogram (PSG) with CO2 monitoring. Generally, all patients with a rapidly progressive neuromuscular disease should get pulmonary function testing (PFT) (upright and supine) to evaluate forced vital capacity (FVC) every 3 to 6 months to monitor for respiratory failure. Laboratory studies that can be helpful in assessing for SDB are the PaCO2 (> 45 mm Hg) measured on an arterial blood gas and serum bicarbonate levels (>27 mmol/L or a base excess >4 mmol/L). Patients can qualify for NIV with an overnight SaO2 less than or equal to 88% for greater than or equal to 5 minutes in a 2-hour recording period, PaCO2 greater than or equal to 45 mm Hg, forced vital capacity (FVC) < 50% of predicted, or maximal inspiratory pressure (MIP) <60 cm H2O. For ALS specifically, sniff nasal pressure < 40 cm H2O and orthopnea are additional criteria that can be used. It is worth noting that a PSG is not required for NIV qualification in neuromuscular respiratory insufficiency. However, PSG is beneficial in patients with preserved PFTs but suspected of having early nocturnal respiratory impairment.
Therapy
NIV is the mainstay of therapy for SDB in patients with NMD and has been associated with a slower decline in FVC and improved survival in some cases, as demonstrated in studies of patients with DMD or ALS. Generally, a bi-level PAP mode is preferred; the expiratory positive airway pressure prevents micro-atelectasis and improves V/Q matching and the inspiratory positive airway pressure reduces inspiratory muscle load and optimizes ventilation. As weakness progresses, patients may have difficulty creating enough negative force to initiate a spontaneous breath, thus a mode with a set respiratory rate is preferred that can be implemented in bi-level PAP or more advanced modes such as volume-assured pressure support (VAPS) modality. For patients who are unable to tolerate NIV, particularly those with severe bulbar disease and difficult to manage respiratory secretions, tracheostomy with mechanical ventilation may ultimately be needed. This decision should be made as part of a multidisciplinary shared decision-making conversation with the patient, their family, and their team of providers.
Summary
Sleep is a particularly vulnerable state for patients with NMD, and in many patients, disturbances in sleep may be the first clue to their ultimate diagnosis. It is important that sleep medicine and pulmonary specialists understand the pathophysiology and management of NMD as they can play a vital role in the interdisciplinary care of these patients.
Dr. Greer is a Sleep Medicine Fellow, Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine; Dr. Collop is Professor of Medicine and Neurology, Director, Emory Sleep Center; Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia.
Red, Swollen, Tender Ear
The Diagnosis: Relapsing Polychondritis
Due to suspicion of relapsing polychondritis (RP), we also performed an audiometric evaluation, which demonstrated bilateral sensorineural hearing loss. Echocardiography highlighted mild to moderate mitralic and tricuspidal insufficiency without hemodynamic impairment (ejection fraction, 50%). Corticosteroid therapy was started (prednisone 0.5 mg/kg/d). After 7 days of treatment, inflammation was remarkably reduced, and the patient no longer reported pain.
Relapsing polychondritis is a rare noninfective condition characterized by focal inflammatory destruction of ear cartilage, followed by fibroblastic regeneration. It often is associated with ocular inflammation, including conjunctivitis, scleritis, and episcleritis; cochlear or vestibular lesions; and seronegative nonerosive inflammatory arthritis.1 Clinical examination of the affected area shows swelling, redness, and tenderness of the ear, which could lead to a misdiagnosis of cellulitis. A typical and useful differentiating sign is the sparing of the noncartilaginous parts of the ear lobule. If not promptly diagnosed and treated, the destructive process can cause thinning of the cartilage, leading to deformities of the external ear.
The differential diagnosis includes erysipelas, which presents as a rapidly appearing inflammatory patch with sharply defined borders, accompanied by regional lymphadenopathy or skin streaking as well as fever. Sweet syndrome usually presents with tender erythematous or violaceous skin papules, plaques, or nodules, frequently with a pseudovesicular appearance; patients generally present with a classic fever and peripheral neutrophilia.2 The localized cutaneous form of leishmaniasis usually appears with a papule that generally develops into an ulcerative nodular lesion. Our patient did not have a history of exposure to topical substances that could point to photocontact dermatitis.
Dion et al3 proposed 3 distinct clinical phenotypes of RP: (1) patients with concomitant myelodysplastic syndrome or other hematologic malignancy (<10% of patients), mostly older men with a poor prognosis; (2) patients with tracheobronchial involvement (approximately 25% of patients); and (3) patients who do not have hematologic or tracheobronchial involvement (approximately 65% of patients) with a good prognosis.
Two sets of diagnostic criteria have been proposed. The criteria from McAdam et al4 required the presence of 3 or more of the following clinical features: bilateral auricular chondritis, nonerosive seronegative inflammatory polyarthritis, nasal chondritis, ocular inflammation (eg, conjunctivitis, keratitis, scleritis/episcleritis, uveitis), respiratory tract chondritis (laryngeal and/or tracheal cartilages), and cochlear and/or vestibular dysfunction (eg, neurosensory hearing loss, tinnitus, vertigo). These criteria were modified by Damiani and Levine.5 According to the latter, all patients were required to have one of the following: at least 4 of the McAdam et al4 diagnostic criteria; 1 or more of the clinical findings included in the McAdam et al4 criteria with histologic features suggestive for RP; or chondritis at 2 or more separate anatomic locations with a response to glucocorticoids and/or dapsone.
No laboratory findings are specific for RP, and nonspecific indicators of inflammation--elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein--often are present.
The cause of RP is unknown. Familial clustering has not been observed. Terao et al6 found that HLA-DRB1*1602, -DQB1*0502, and -B*6701, in linkage disequilibrium with each other, are associated with susceptibility to RP.
There is no universal consensus about treatment, but a course of steroids leads to the resolution of the acute phase. Maintenance treatment can include dapsone, azathioprine, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, and cyclosporine.7,8 Some studies have described the successful use of anti-tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors and rituximab.9,10
- Borgia F, Giuffrida R, Guarneri F, et al. Relapsing polychondritis: an updated review. Biomedicines. 2018;6:84.
- Rednic S, Damian L, Talarico R, et al. Relapsing polychondritis: state of the art on clinical practice guidelines. RMD Open. 2018:4(suppl 1)e000788.
- Dion J, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Sène D, et al. Relapsing polychondritis can be characterized by three different clinical phenotypes: analysis of a recent series of 142 patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68:2992-3001.
- McAdam LP, O'Hanlan MA, Bluestone R, et al. Relapsing polychondritis: prospective study of 23 patients and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1976;55:193.
- Damiani JM, Levine HL. Relapsing polychondritis--report of ten cases. Laryngoscope. 1979;89:929-946.
- Terao C, Yoshifuji H, Yamano Y, et al. Genotyping of relapsing polychondritis identified novel susceptibility HLA alleles and distinct genetic characteristics from other rheumatic diseases. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016;55:1686.016-82
- Goldenberg G, Sangueza OP, Jorizzo JL. Successful treatment of relapsing polychondritis with mycophenolate mofetil. J Dermatolog Treat. 2006;17:158-159.
- Handler RP. Leflunomide for relapsing polychondritis: successful longterm treatment. J Rheumatol. 2006;33:1916; author reply 1916-1917.
- Carter JD. Treatment of relapsing polychondritis with a TNF antagonist. J Rheumatol. 2005;32:1413.
- Leroux G, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Brihaye B, et al. Treatment of relapsing polychondritis with rituximab: a retrospective study of nine patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61:577-582.
The Diagnosis: Relapsing Polychondritis
Due to suspicion of relapsing polychondritis (RP), we also performed an audiometric evaluation, which demonstrated bilateral sensorineural hearing loss. Echocardiography highlighted mild to moderate mitralic and tricuspidal insufficiency without hemodynamic impairment (ejection fraction, 50%). Corticosteroid therapy was started (prednisone 0.5 mg/kg/d). After 7 days of treatment, inflammation was remarkably reduced, and the patient no longer reported pain.
Relapsing polychondritis is a rare noninfective condition characterized by focal inflammatory destruction of ear cartilage, followed by fibroblastic regeneration. It often is associated with ocular inflammation, including conjunctivitis, scleritis, and episcleritis; cochlear or vestibular lesions; and seronegative nonerosive inflammatory arthritis.1 Clinical examination of the affected area shows swelling, redness, and tenderness of the ear, which could lead to a misdiagnosis of cellulitis. A typical and useful differentiating sign is the sparing of the noncartilaginous parts of the ear lobule. If not promptly diagnosed and treated, the destructive process can cause thinning of the cartilage, leading to deformities of the external ear.
The differential diagnosis includes erysipelas, which presents as a rapidly appearing inflammatory patch with sharply defined borders, accompanied by regional lymphadenopathy or skin streaking as well as fever. Sweet syndrome usually presents with tender erythematous or violaceous skin papules, plaques, or nodules, frequently with a pseudovesicular appearance; patients generally present with a classic fever and peripheral neutrophilia.2 The localized cutaneous form of leishmaniasis usually appears with a papule that generally develops into an ulcerative nodular lesion. Our patient did not have a history of exposure to topical substances that could point to photocontact dermatitis.
Dion et al3 proposed 3 distinct clinical phenotypes of RP: (1) patients with concomitant myelodysplastic syndrome or other hematologic malignancy (<10% of patients), mostly older men with a poor prognosis; (2) patients with tracheobronchial involvement (approximately 25% of patients); and (3) patients who do not have hematologic or tracheobronchial involvement (approximately 65% of patients) with a good prognosis.
Two sets of diagnostic criteria have been proposed. The criteria from McAdam et al4 required the presence of 3 or more of the following clinical features: bilateral auricular chondritis, nonerosive seronegative inflammatory polyarthritis, nasal chondritis, ocular inflammation (eg, conjunctivitis, keratitis, scleritis/episcleritis, uveitis), respiratory tract chondritis (laryngeal and/or tracheal cartilages), and cochlear and/or vestibular dysfunction (eg, neurosensory hearing loss, tinnitus, vertigo). These criteria were modified by Damiani and Levine.5 According to the latter, all patients were required to have one of the following: at least 4 of the McAdam et al4 diagnostic criteria; 1 or more of the clinical findings included in the McAdam et al4 criteria with histologic features suggestive for RP; or chondritis at 2 or more separate anatomic locations with a response to glucocorticoids and/or dapsone.
No laboratory findings are specific for RP, and nonspecific indicators of inflammation--elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein--often are present.
The cause of RP is unknown. Familial clustering has not been observed. Terao et al6 found that HLA-DRB1*1602, -DQB1*0502, and -B*6701, in linkage disequilibrium with each other, are associated with susceptibility to RP.
There is no universal consensus about treatment, but a course of steroids leads to the resolution of the acute phase. Maintenance treatment can include dapsone, azathioprine, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, and cyclosporine.7,8 Some studies have described the successful use of anti-tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors and rituximab.9,10
The Diagnosis: Relapsing Polychondritis
Due to suspicion of relapsing polychondritis (RP), we also performed an audiometric evaluation, which demonstrated bilateral sensorineural hearing loss. Echocardiography highlighted mild to moderate mitralic and tricuspidal insufficiency without hemodynamic impairment (ejection fraction, 50%). Corticosteroid therapy was started (prednisone 0.5 mg/kg/d). After 7 days of treatment, inflammation was remarkably reduced, and the patient no longer reported pain.
Relapsing polychondritis is a rare noninfective condition characterized by focal inflammatory destruction of ear cartilage, followed by fibroblastic regeneration. It often is associated with ocular inflammation, including conjunctivitis, scleritis, and episcleritis; cochlear or vestibular lesions; and seronegative nonerosive inflammatory arthritis.1 Clinical examination of the affected area shows swelling, redness, and tenderness of the ear, which could lead to a misdiagnosis of cellulitis. A typical and useful differentiating sign is the sparing of the noncartilaginous parts of the ear lobule. If not promptly diagnosed and treated, the destructive process can cause thinning of the cartilage, leading to deformities of the external ear.
The differential diagnosis includes erysipelas, which presents as a rapidly appearing inflammatory patch with sharply defined borders, accompanied by regional lymphadenopathy or skin streaking as well as fever. Sweet syndrome usually presents with tender erythematous or violaceous skin papules, plaques, or nodules, frequently with a pseudovesicular appearance; patients generally present with a classic fever and peripheral neutrophilia.2 The localized cutaneous form of leishmaniasis usually appears with a papule that generally develops into an ulcerative nodular lesion. Our patient did not have a history of exposure to topical substances that could point to photocontact dermatitis.
Dion et al3 proposed 3 distinct clinical phenotypes of RP: (1) patients with concomitant myelodysplastic syndrome or other hematologic malignancy (<10% of patients), mostly older men with a poor prognosis; (2) patients with tracheobronchial involvement (approximately 25% of patients); and (3) patients who do not have hematologic or tracheobronchial involvement (approximately 65% of patients) with a good prognosis.
Two sets of diagnostic criteria have been proposed. The criteria from McAdam et al4 required the presence of 3 or more of the following clinical features: bilateral auricular chondritis, nonerosive seronegative inflammatory polyarthritis, nasal chondritis, ocular inflammation (eg, conjunctivitis, keratitis, scleritis/episcleritis, uveitis), respiratory tract chondritis (laryngeal and/or tracheal cartilages), and cochlear and/or vestibular dysfunction (eg, neurosensory hearing loss, tinnitus, vertigo). These criteria were modified by Damiani and Levine.5 According to the latter, all patients were required to have one of the following: at least 4 of the McAdam et al4 diagnostic criteria; 1 or more of the clinical findings included in the McAdam et al4 criteria with histologic features suggestive for RP; or chondritis at 2 or more separate anatomic locations with a response to glucocorticoids and/or dapsone.
No laboratory findings are specific for RP, and nonspecific indicators of inflammation--elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein--often are present.
The cause of RP is unknown. Familial clustering has not been observed. Terao et al6 found that HLA-DRB1*1602, -DQB1*0502, and -B*6701, in linkage disequilibrium with each other, are associated with susceptibility to RP.
There is no universal consensus about treatment, but a course of steroids leads to the resolution of the acute phase. Maintenance treatment can include dapsone, azathioprine, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, and cyclosporine.7,8 Some studies have described the successful use of anti-tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors and rituximab.9,10
- Borgia F, Giuffrida R, Guarneri F, et al. Relapsing polychondritis: an updated review. Biomedicines. 2018;6:84.
- Rednic S, Damian L, Talarico R, et al. Relapsing polychondritis: state of the art on clinical practice guidelines. RMD Open. 2018:4(suppl 1)e000788.
- Dion J, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Sène D, et al. Relapsing polychondritis can be characterized by three different clinical phenotypes: analysis of a recent series of 142 patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68:2992-3001.
- McAdam LP, O'Hanlan MA, Bluestone R, et al. Relapsing polychondritis: prospective study of 23 patients and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1976;55:193.
- Damiani JM, Levine HL. Relapsing polychondritis--report of ten cases. Laryngoscope. 1979;89:929-946.
- Terao C, Yoshifuji H, Yamano Y, et al. Genotyping of relapsing polychondritis identified novel susceptibility HLA alleles and distinct genetic characteristics from other rheumatic diseases. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016;55:1686.016-82
- Goldenberg G, Sangueza OP, Jorizzo JL. Successful treatment of relapsing polychondritis with mycophenolate mofetil. J Dermatolog Treat. 2006;17:158-159.
- Handler RP. Leflunomide for relapsing polychondritis: successful longterm treatment. J Rheumatol. 2006;33:1916; author reply 1916-1917.
- Carter JD. Treatment of relapsing polychondritis with a TNF antagonist. J Rheumatol. 2005;32:1413.
- Leroux G, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Brihaye B, et al. Treatment of relapsing polychondritis with rituximab: a retrospective study of nine patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61:577-582.
- Borgia F, Giuffrida R, Guarneri F, et al. Relapsing polychondritis: an updated review. Biomedicines. 2018;6:84.
- Rednic S, Damian L, Talarico R, et al. Relapsing polychondritis: state of the art on clinical practice guidelines. RMD Open. 2018:4(suppl 1)e000788.
- Dion J, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Sène D, et al. Relapsing polychondritis can be characterized by three different clinical phenotypes: analysis of a recent series of 142 patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68:2992-3001.
- McAdam LP, O'Hanlan MA, Bluestone R, et al. Relapsing polychondritis: prospective study of 23 patients and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1976;55:193.
- Damiani JM, Levine HL. Relapsing polychondritis--report of ten cases. Laryngoscope. 1979;89:929-946.
- Terao C, Yoshifuji H, Yamano Y, et al. Genotyping of relapsing polychondritis identified novel susceptibility HLA alleles and distinct genetic characteristics from other rheumatic diseases. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016;55:1686.016-82
- Goldenberg G, Sangueza OP, Jorizzo JL. Successful treatment of relapsing polychondritis with mycophenolate mofetil. J Dermatolog Treat. 2006;17:158-159.
- Handler RP. Leflunomide for relapsing polychondritis: successful longterm treatment. J Rheumatol. 2006;33:1916; author reply 1916-1917.
- Carter JD. Treatment of relapsing polychondritis with a TNF antagonist. J Rheumatol. 2005;32:1413.
- Leroux G, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Brihaye B, et al. Treatment of relapsing polychondritis with rituximab: a retrospective study of nine patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61:577-582.
A 67-year-old woman presented with severe pain of the left external ear. She explained that similar episodes had occurred 2 years prior and affected the right ear and the nose. Her general practitioner prescribed topical and systemic antibiotic treatment, but there was no improvement. The patient also reported diffuse small joint pain without any radiologic sign of erosive arthritis. Physical examination revealed a red swollen external ear that was tender to the touch from the helix to the antitragus; conversely, the earlobe did not present any sign of inflammation. Redness of the left eye also was noticed, and a slit-lamp examination confirmed our suspect of scleritis. Results from routine blood tests, including an autoimmune panel, were within reference range, except for a nonspecific increase of inflammatory markers (erythrocyte sedimentation rate, 43 mm/h [reference range, 0–20 mm/h]; C-reactive protein, 5.65 mg/L [reference range, 0.08–3.1 mg/L]).
President’s final report
As I am writing my final presidential report, my presidential year is coming to a close. It was certainly not what I could have anticipated, but an incredible opportunity for my personal and professional growth, and a year in which CHEST adapted and grew, as well. We accomplished a great deal during this unprecedented year, and I will take this opportunity for a year-in-review!
In the winter, As COVID-19 appeared across the globe, we established a COVID-19 Task Force led by then incoming President, Dr. Steve Simpson, with the goal of keeping our members updated on the latest research and clinical management of COVID-19 illness, as well as distilling and delivering the latest COVID-19 related information quickly to those on the front lines. We have held weekly COVID-19 webinars, disseminated infographics, and developed an interactive COVID-19 quiz. CHEST also published several COVID-19-related guideline statements and expert panel reports on bronchoscopy, tracheostomy, lung nodule management, and venous thromboembolism in the setting of COVID-19.
Knowing the stress that our health-care workers were under, we also established a CHEST Wellness Center. This longitudinal, webinar-based curriculum, led by Dr. Alex Niven, had its impetus with COVID-19 but will continue and be extended to general wellness topics.
In March, we joined forces with NAMDRC, under the CHEST umbrella and a combination of our board members and their former board members now make up our Health Policy and Advocacy Committee (HPAC), led by Drs. Neil Freedman and Jim Lamberti, with CHEST Past-President, Dr. John Studdard, also actively involved. Our HPAC is already focusing on home ventilation and competitive bidding, oxygen prescribing, education and access, pulmonary rehabilitation, and tobacco and vaping. The monthly Washington Watchline online publication features the latest on advocacy-related issues of interest to our membership. Last month, the HPAC held a multiorganizational technical expert panel meeting on nocturnal noninvasive ventilation, with plans to submit a manuscript on outcomes from the meeting to the journal CHEST®. These activities are an answer to our member’s requests and needs in the areas of advocacy.
With the onset of the pandemic, we pivoted the delivery of our signature education to virtual platforms beginning with a successful global congress in Bologna in June with 3,500 registered attendees. This was a wonderful way to provide education to our global audience. I want to thank co-chairs Dr. Bill Kelly and Dr. Girolamo Pelaia, and Dr. Francesco de Blasio from our Italian Delegation for their innovative leadership. In August, we held our first virtual Board Review Courses in Pulmonary Medicine, Critical Care Medicine, and Pediatric Pulmonary Medicine, attended by 775 registered attendees complete with didactic sessions, audience response sessions, SEEK sessions and live Q&A with the faculty. The on-demand versions of these courses are also available.
The CHEST® journal, in its second year with Dr. Peter Mazzone at the helm, continues to be a leading source of clinically relevant research and patient management guidance for pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine clinicians worldwide. The year 2020 has been a year like no other -- submission rates have doubled since the start of the pandemic, with nearly 5,000 manuscript submissions so far, this year. The journal has rapidly built a robust and growing COVID-19 topic collection, with relevant original research, guidelines, commentaries, and more, published online, within days of acceptance. The journal will continue to seek innovative ways to meet the needs of its readers and contributors during this time when our members and their patients urgently need current and high-quality information.
This year, CHEST hit a publishing milestone, with the publication of SEEK Critical Care 30, and the SEEK program is celebrating 30 years! Those who registered for CHEST 2020 by October 15 received the announcement regarding the commemorative “30 years of SEEK” collection.
Our Guidelines Oversight Committee has continued to publish evidence-based guidelines in the areas of cough and cryobiopsy, with a guideline on hypersensitivity pneumonitis and updated guidelines in our core topics of lung cancer and venous thromboembolism in the works.
Under the leadership of Dr. Aneesa Das, the NetWorks Task Force started work to accomplish the goal of increasing member engagement and reach by developing pilot projects focusing on infographics interviews with key opinion leaders and social media communications. Additionally, the Digital Strategy Task Force launched a redesigned website for the Foundation, which you can see at chestfoundation.org, and look for exciting changes coming to the CHEST website in the very near future.
We have continued our collaborative partnerships with our sister societies. We established the volunteer clinician matching program with the American Thoracic Society (ATS) to send clinicians to areas of need during the pandemic, and partnered on other COVID-19 related activities. We held a virtual fellow’s graduation with ATS and the Association of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Program Directors. CHEST leadership attended the Asian Pacific Respiratory Society in Vietnam in November, the Society of Critical Care Medicine, and Forum of International Respiratory Societies in February and the recent virtual meetings of ATS, European Respiratory Society, and the Brazilian Thoracic Society.
The CHEST Foundation has continued on their mission to champion lung health and make a difference through their successful fundraising. This was highlighted with a tremendous foundation gala in San Antonio in December, The Golden Era of Erin Popovich, attended by more than 500 people. Since COVID-19, the Foundation held several creative virtual fundraising events ranging from wine tastings to poker night to bingo night to a recent trivia night, as well as actively participating in COVID-19-related campaigns, such as the partnership with ATS for COVID-19 public service announcements directed to those affected by COVID-19, and other fundraising campaigns, such as the Buy-a-Mask Give-a-Mask campaign. In addition, the Foundation has continued with their support for clinical research grants, community service grants, and patient education resources and toolkits. For example, they have developed an oxygen tool kit to provide access and empowerment to patients in need.
Thank you to all our donors for continuing to support these CHEST Foundation initiatives. The Foundation couldn’t continue to do this amazing work to create an impact and raise awareness for lung health without you.
As the movement to combat racism and racial disparity swept across our nation, we issued a statement of equity in early June. In September, the CHEST Foundation launched the first of a series of Listening Tours to hear from community needs in the areas of trust, access, and equity. Information from these tours will be used to launch a designated fund to have the power to transform these needs into action. CHEST is now actively developing a strategic plan focusing on how CHEST can make an impactful difference in this arena. We want to ensure we take this essential time to listen, reflect, and make appropriate plans for ways we can truly make a difference. Expect more to come on this in the coming year.
The year concluded with CHEST 2020. CHEST 2020 had the highest number of case reports and abstracts ever submitted to a CHEST Annual meeting, and a total registration of more than 4,000. At CHEST 2020, you had an opportunity to see a reimagined virtual annual meeting with combinations of interactive live and prerecorded didactic sessions, audience response sessions, live Q&A with the faculty, educational games at the CHEST Gaming Hub, CHEST Challenge Championship, networking opportunities, narrated abstracts, case reports, original research presentations, COVID-19 update sessions, industry-sponsored programs, a virtual exhibit hall, and surprises, to deliver the in–person CHEST experience virtually. In addition, this came with the greatest number of CME/MOC credits we have ever offered! And, CHEST 2020 education will continue throughout the year with ongoing postgraduate courses creating the ultimate longitudinal educational experience. While nothing can replace the opportunity to connect with our community in person, I hope you found that this year’s meeting provided a wealth of learning, connection, and fun.
My sincere thanks to the CHEST 2020 Program Chair, Dr. Victor Test, to the entire Scientific Program Committee, and to our incredible CHEST staff, for the immense amount of hard work over the past year to reimagine CHEST 2020 and make it a reality. Little did Victor know that he would be planning three meetings, a live meeting, a hybrid meeting, and, ultimately, a virtual meeting. Thank you for all you did to make CHEST 2020 a meeting to remember. We plan to continue our efforts to maintain and grow educational innovation year-round through more e-learning, virtual learning, and, hopefully soon, live learning, both locally, nationally, and internationally.
As my year closes, you are in excellent hands with Dr. Steven Simpson, your 83rd President, who will lead the organization forward. You will hear more from him, but you are in the hands of a thoughtful and dedicated leader with a long history of CHEST experience, strong expertise in critical care, and a thought leader in the COVID-19 pandemic, including serving on the NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel.
There are so many people to thank! I want to thank my family, my husband and children, and my work family, the faculty and fellows of my division, for their unwavering support. I also want to thank my Co-President lineage group for their counsel and wisdom, several Past Presidents who I have called on over this past year for advice, Drs. John Studdard, Gerard Silvestri, and Darcy Marciniuk among others, the Board (who I only saw face-to-face once!), our CHEST leadership and educators, and the incredible CHEST staff, the Executive Leadership Team, and our superb, hard-working CEO/EVP Bob Musacchio. Last, and most importantly, I would like to thank our members for being in the trenches this year as we all dealt with COVID-19. You are the heroes! At the beginning of my term last year, I told you that my goal was to be “the welcoming home” for interprofessional health-care team members seeking to obtain the best possible educational experiences and patient outcomes. I had no idea how absolutely needed this would be for our chest medicine family this year. CHEST has always been your connection to relevant clinical information and late-breaking updates in our field – but this year, our CHEST community has been even more than that. Through this year of crisis and change, you all have shown resilience; a resilience molded by being flexible. Not only have you embodied flexibility at your home institutions, you’ve embodied flexibility in your learning, teaching, and connecting. You’ve joined us as we’ve reimagined what learning at CHEST is all about – I sincerely thank you for that!
As I am writing my final presidential report, my presidential year is coming to a close. It was certainly not what I could have anticipated, but an incredible opportunity for my personal and professional growth, and a year in which CHEST adapted and grew, as well. We accomplished a great deal during this unprecedented year, and I will take this opportunity for a year-in-review!
In the winter, As COVID-19 appeared across the globe, we established a COVID-19 Task Force led by then incoming President, Dr. Steve Simpson, with the goal of keeping our members updated on the latest research and clinical management of COVID-19 illness, as well as distilling and delivering the latest COVID-19 related information quickly to those on the front lines. We have held weekly COVID-19 webinars, disseminated infographics, and developed an interactive COVID-19 quiz. CHEST also published several COVID-19-related guideline statements and expert panel reports on bronchoscopy, tracheostomy, lung nodule management, and venous thromboembolism in the setting of COVID-19.
Knowing the stress that our health-care workers were under, we also established a CHEST Wellness Center. This longitudinal, webinar-based curriculum, led by Dr. Alex Niven, had its impetus with COVID-19 but will continue and be extended to general wellness topics.
In March, we joined forces with NAMDRC, under the CHEST umbrella and a combination of our board members and their former board members now make up our Health Policy and Advocacy Committee (HPAC), led by Drs. Neil Freedman and Jim Lamberti, with CHEST Past-President, Dr. John Studdard, also actively involved. Our HPAC is already focusing on home ventilation and competitive bidding, oxygen prescribing, education and access, pulmonary rehabilitation, and tobacco and vaping. The monthly Washington Watchline online publication features the latest on advocacy-related issues of interest to our membership. Last month, the HPAC held a multiorganizational technical expert panel meeting on nocturnal noninvasive ventilation, with plans to submit a manuscript on outcomes from the meeting to the journal CHEST®. These activities are an answer to our member’s requests and needs in the areas of advocacy.
With the onset of the pandemic, we pivoted the delivery of our signature education to virtual platforms beginning with a successful global congress in Bologna in June with 3,500 registered attendees. This was a wonderful way to provide education to our global audience. I want to thank co-chairs Dr. Bill Kelly and Dr. Girolamo Pelaia, and Dr. Francesco de Blasio from our Italian Delegation for their innovative leadership. In August, we held our first virtual Board Review Courses in Pulmonary Medicine, Critical Care Medicine, and Pediatric Pulmonary Medicine, attended by 775 registered attendees complete with didactic sessions, audience response sessions, SEEK sessions and live Q&A with the faculty. The on-demand versions of these courses are also available.
The CHEST® journal, in its second year with Dr. Peter Mazzone at the helm, continues to be a leading source of clinically relevant research and patient management guidance for pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine clinicians worldwide. The year 2020 has been a year like no other -- submission rates have doubled since the start of the pandemic, with nearly 5,000 manuscript submissions so far, this year. The journal has rapidly built a robust and growing COVID-19 topic collection, with relevant original research, guidelines, commentaries, and more, published online, within days of acceptance. The journal will continue to seek innovative ways to meet the needs of its readers and contributors during this time when our members and their patients urgently need current and high-quality information.
This year, CHEST hit a publishing milestone, with the publication of SEEK Critical Care 30, and the SEEK program is celebrating 30 years! Those who registered for CHEST 2020 by October 15 received the announcement regarding the commemorative “30 years of SEEK” collection.
Our Guidelines Oversight Committee has continued to publish evidence-based guidelines in the areas of cough and cryobiopsy, with a guideline on hypersensitivity pneumonitis and updated guidelines in our core topics of lung cancer and venous thromboembolism in the works.
Under the leadership of Dr. Aneesa Das, the NetWorks Task Force started work to accomplish the goal of increasing member engagement and reach by developing pilot projects focusing on infographics interviews with key opinion leaders and social media communications. Additionally, the Digital Strategy Task Force launched a redesigned website for the Foundation, which you can see at chestfoundation.org, and look for exciting changes coming to the CHEST website in the very near future.
We have continued our collaborative partnerships with our sister societies. We established the volunteer clinician matching program with the American Thoracic Society (ATS) to send clinicians to areas of need during the pandemic, and partnered on other COVID-19 related activities. We held a virtual fellow’s graduation with ATS and the Association of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Program Directors. CHEST leadership attended the Asian Pacific Respiratory Society in Vietnam in November, the Society of Critical Care Medicine, and Forum of International Respiratory Societies in February and the recent virtual meetings of ATS, European Respiratory Society, and the Brazilian Thoracic Society.
The CHEST Foundation has continued on their mission to champion lung health and make a difference through their successful fundraising. This was highlighted with a tremendous foundation gala in San Antonio in December, The Golden Era of Erin Popovich, attended by more than 500 people. Since COVID-19, the Foundation held several creative virtual fundraising events ranging from wine tastings to poker night to bingo night to a recent trivia night, as well as actively participating in COVID-19-related campaigns, such as the partnership with ATS for COVID-19 public service announcements directed to those affected by COVID-19, and other fundraising campaigns, such as the Buy-a-Mask Give-a-Mask campaign. In addition, the Foundation has continued with their support for clinical research grants, community service grants, and patient education resources and toolkits. For example, they have developed an oxygen tool kit to provide access and empowerment to patients in need.
Thank you to all our donors for continuing to support these CHEST Foundation initiatives. The Foundation couldn’t continue to do this amazing work to create an impact and raise awareness for lung health without you.
As the movement to combat racism and racial disparity swept across our nation, we issued a statement of equity in early June. In September, the CHEST Foundation launched the first of a series of Listening Tours to hear from community needs in the areas of trust, access, and equity. Information from these tours will be used to launch a designated fund to have the power to transform these needs into action. CHEST is now actively developing a strategic plan focusing on how CHEST can make an impactful difference in this arena. We want to ensure we take this essential time to listen, reflect, and make appropriate plans for ways we can truly make a difference. Expect more to come on this in the coming year.
The year concluded with CHEST 2020. CHEST 2020 had the highest number of case reports and abstracts ever submitted to a CHEST Annual meeting, and a total registration of more than 4,000. At CHEST 2020, you had an opportunity to see a reimagined virtual annual meeting with combinations of interactive live and prerecorded didactic sessions, audience response sessions, live Q&A with the faculty, educational games at the CHEST Gaming Hub, CHEST Challenge Championship, networking opportunities, narrated abstracts, case reports, original research presentations, COVID-19 update sessions, industry-sponsored programs, a virtual exhibit hall, and surprises, to deliver the in–person CHEST experience virtually. In addition, this came with the greatest number of CME/MOC credits we have ever offered! And, CHEST 2020 education will continue throughout the year with ongoing postgraduate courses creating the ultimate longitudinal educational experience. While nothing can replace the opportunity to connect with our community in person, I hope you found that this year’s meeting provided a wealth of learning, connection, and fun.
My sincere thanks to the CHEST 2020 Program Chair, Dr. Victor Test, to the entire Scientific Program Committee, and to our incredible CHEST staff, for the immense amount of hard work over the past year to reimagine CHEST 2020 and make it a reality. Little did Victor know that he would be planning three meetings, a live meeting, a hybrid meeting, and, ultimately, a virtual meeting. Thank you for all you did to make CHEST 2020 a meeting to remember. We plan to continue our efforts to maintain and grow educational innovation year-round through more e-learning, virtual learning, and, hopefully soon, live learning, both locally, nationally, and internationally.
As my year closes, you are in excellent hands with Dr. Steven Simpson, your 83rd President, who will lead the organization forward. You will hear more from him, but you are in the hands of a thoughtful and dedicated leader with a long history of CHEST experience, strong expertise in critical care, and a thought leader in the COVID-19 pandemic, including serving on the NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel.
There are so many people to thank! I want to thank my family, my husband and children, and my work family, the faculty and fellows of my division, for their unwavering support. I also want to thank my Co-President lineage group for their counsel and wisdom, several Past Presidents who I have called on over this past year for advice, Drs. John Studdard, Gerard Silvestri, and Darcy Marciniuk among others, the Board (who I only saw face-to-face once!), our CHEST leadership and educators, and the incredible CHEST staff, the Executive Leadership Team, and our superb, hard-working CEO/EVP Bob Musacchio. Last, and most importantly, I would like to thank our members for being in the trenches this year as we all dealt with COVID-19. You are the heroes! At the beginning of my term last year, I told you that my goal was to be “the welcoming home” for interprofessional health-care team members seeking to obtain the best possible educational experiences and patient outcomes. I had no idea how absolutely needed this would be for our chest medicine family this year. CHEST has always been your connection to relevant clinical information and late-breaking updates in our field – but this year, our CHEST community has been even more than that. Through this year of crisis and change, you all have shown resilience; a resilience molded by being flexible. Not only have you embodied flexibility at your home institutions, you’ve embodied flexibility in your learning, teaching, and connecting. You’ve joined us as we’ve reimagined what learning at CHEST is all about – I sincerely thank you for that!
As I am writing my final presidential report, my presidential year is coming to a close. It was certainly not what I could have anticipated, but an incredible opportunity for my personal and professional growth, and a year in which CHEST adapted and grew, as well. We accomplished a great deal during this unprecedented year, and I will take this opportunity for a year-in-review!
In the winter, As COVID-19 appeared across the globe, we established a COVID-19 Task Force led by then incoming President, Dr. Steve Simpson, with the goal of keeping our members updated on the latest research and clinical management of COVID-19 illness, as well as distilling and delivering the latest COVID-19 related information quickly to those on the front lines. We have held weekly COVID-19 webinars, disseminated infographics, and developed an interactive COVID-19 quiz. CHEST also published several COVID-19-related guideline statements and expert panel reports on bronchoscopy, tracheostomy, lung nodule management, and venous thromboembolism in the setting of COVID-19.
Knowing the stress that our health-care workers were under, we also established a CHEST Wellness Center. This longitudinal, webinar-based curriculum, led by Dr. Alex Niven, had its impetus with COVID-19 but will continue and be extended to general wellness topics.
In March, we joined forces with NAMDRC, under the CHEST umbrella and a combination of our board members and their former board members now make up our Health Policy and Advocacy Committee (HPAC), led by Drs. Neil Freedman and Jim Lamberti, with CHEST Past-President, Dr. John Studdard, also actively involved. Our HPAC is already focusing on home ventilation and competitive bidding, oxygen prescribing, education and access, pulmonary rehabilitation, and tobacco and vaping. The monthly Washington Watchline online publication features the latest on advocacy-related issues of interest to our membership. Last month, the HPAC held a multiorganizational technical expert panel meeting on nocturnal noninvasive ventilation, with plans to submit a manuscript on outcomes from the meeting to the journal CHEST®. These activities are an answer to our member’s requests and needs in the areas of advocacy.
With the onset of the pandemic, we pivoted the delivery of our signature education to virtual platforms beginning with a successful global congress in Bologna in June with 3,500 registered attendees. This was a wonderful way to provide education to our global audience. I want to thank co-chairs Dr. Bill Kelly and Dr. Girolamo Pelaia, and Dr. Francesco de Blasio from our Italian Delegation for their innovative leadership. In August, we held our first virtual Board Review Courses in Pulmonary Medicine, Critical Care Medicine, and Pediatric Pulmonary Medicine, attended by 775 registered attendees complete with didactic sessions, audience response sessions, SEEK sessions and live Q&A with the faculty. The on-demand versions of these courses are also available.
The CHEST® journal, in its second year with Dr. Peter Mazzone at the helm, continues to be a leading source of clinically relevant research and patient management guidance for pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine clinicians worldwide. The year 2020 has been a year like no other -- submission rates have doubled since the start of the pandemic, with nearly 5,000 manuscript submissions so far, this year. The journal has rapidly built a robust and growing COVID-19 topic collection, with relevant original research, guidelines, commentaries, and more, published online, within days of acceptance. The journal will continue to seek innovative ways to meet the needs of its readers and contributors during this time when our members and their patients urgently need current and high-quality information.
This year, CHEST hit a publishing milestone, with the publication of SEEK Critical Care 30, and the SEEK program is celebrating 30 years! Those who registered for CHEST 2020 by October 15 received the announcement regarding the commemorative “30 years of SEEK” collection.
Our Guidelines Oversight Committee has continued to publish evidence-based guidelines in the areas of cough and cryobiopsy, with a guideline on hypersensitivity pneumonitis and updated guidelines in our core topics of lung cancer and venous thromboembolism in the works.
Under the leadership of Dr. Aneesa Das, the NetWorks Task Force started work to accomplish the goal of increasing member engagement and reach by developing pilot projects focusing on infographics interviews with key opinion leaders and social media communications. Additionally, the Digital Strategy Task Force launched a redesigned website for the Foundation, which you can see at chestfoundation.org, and look for exciting changes coming to the CHEST website in the very near future.
We have continued our collaborative partnerships with our sister societies. We established the volunteer clinician matching program with the American Thoracic Society (ATS) to send clinicians to areas of need during the pandemic, and partnered on other COVID-19 related activities. We held a virtual fellow’s graduation with ATS and the Association of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Program Directors. CHEST leadership attended the Asian Pacific Respiratory Society in Vietnam in November, the Society of Critical Care Medicine, and Forum of International Respiratory Societies in February and the recent virtual meetings of ATS, European Respiratory Society, and the Brazilian Thoracic Society.
The CHEST Foundation has continued on their mission to champion lung health and make a difference through their successful fundraising. This was highlighted with a tremendous foundation gala in San Antonio in December, The Golden Era of Erin Popovich, attended by more than 500 people. Since COVID-19, the Foundation held several creative virtual fundraising events ranging from wine tastings to poker night to bingo night to a recent trivia night, as well as actively participating in COVID-19-related campaigns, such as the partnership with ATS for COVID-19 public service announcements directed to those affected by COVID-19, and other fundraising campaigns, such as the Buy-a-Mask Give-a-Mask campaign. In addition, the Foundation has continued with their support for clinical research grants, community service grants, and patient education resources and toolkits. For example, they have developed an oxygen tool kit to provide access and empowerment to patients in need.
Thank you to all our donors for continuing to support these CHEST Foundation initiatives. The Foundation couldn’t continue to do this amazing work to create an impact and raise awareness for lung health without you.
As the movement to combat racism and racial disparity swept across our nation, we issued a statement of equity in early June. In September, the CHEST Foundation launched the first of a series of Listening Tours to hear from community needs in the areas of trust, access, and equity. Information from these tours will be used to launch a designated fund to have the power to transform these needs into action. CHEST is now actively developing a strategic plan focusing on how CHEST can make an impactful difference in this arena. We want to ensure we take this essential time to listen, reflect, and make appropriate plans for ways we can truly make a difference. Expect more to come on this in the coming year.
The year concluded with CHEST 2020. CHEST 2020 had the highest number of case reports and abstracts ever submitted to a CHEST Annual meeting, and a total registration of more than 4,000. At CHEST 2020, you had an opportunity to see a reimagined virtual annual meeting with combinations of interactive live and prerecorded didactic sessions, audience response sessions, live Q&A with the faculty, educational games at the CHEST Gaming Hub, CHEST Challenge Championship, networking opportunities, narrated abstracts, case reports, original research presentations, COVID-19 update sessions, industry-sponsored programs, a virtual exhibit hall, and surprises, to deliver the in–person CHEST experience virtually. In addition, this came with the greatest number of CME/MOC credits we have ever offered! And, CHEST 2020 education will continue throughout the year with ongoing postgraduate courses creating the ultimate longitudinal educational experience. While nothing can replace the opportunity to connect with our community in person, I hope you found that this year’s meeting provided a wealth of learning, connection, and fun.
My sincere thanks to the CHEST 2020 Program Chair, Dr. Victor Test, to the entire Scientific Program Committee, and to our incredible CHEST staff, for the immense amount of hard work over the past year to reimagine CHEST 2020 and make it a reality. Little did Victor know that he would be planning three meetings, a live meeting, a hybrid meeting, and, ultimately, a virtual meeting. Thank you for all you did to make CHEST 2020 a meeting to remember. We plan to continue our efforts to maintain and grow educational innovation year-round through more e-learning, virtual learning, and, hopefully soon, live learning, both locally, nationally, and internationally.
As my year closes, you are in excellent hands with Dr. Steven Simpson, your 83rd President, who will lead the organization forward. You will hear more from him, but you are in the hands of a thoughtful and dedicated leader with a long history of CHEST experience, strong expertise in critical care, and a thought leader in the COVID-19 pandemic, including serving on the NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel.
There are so many people to thank! I want to thank my family, my husband and children, and my work family, the faculty and fellows of my division, for their unwavering support. I also want to thank my Co-President lineage group for their counsel and wisdom, several Past Presidents who I have called on over this past year for advice, Drs. John Studdard, Gerard Silvestri, and Darcy Marciniuk among others, the Board (who I only saw face-to-face once!), our CHEST leadership and educators, and the incredible CHEST staff, the Executive Leadership Team, and our superb, hard-working CEO/EVP Bob Musacchio. Last, and most importantly, I would like to thank our members for being in the trenches this year as we all dealt with COVID-19. You are the heroes! At the beginning of my term last year, I told you that my goal was to be “the welcoming home” for interprofessional health-care team members seeking to obtain the best possible educational experiences and patient outcomes. I had no idea how absolutely needed this would be for our chest medicine family this year. CHEST has always been your connection to relevant clinical information and late-breaking updates in our field – but this year, our CHEST community has been even more than that. Through this year of crisis and change, you all have shown resilience; a resilience molded by being flexible. Not only have you embodied flexibility at your home institutions, you’ve embodied flexibility in your learning, teaching, and connecting. You’ve joined us as we’ve reimagined what learning at CHEST is all about – I sincerely thank you for that!
PICC lines often used inappropriately in advanced CKD patients
Background: PICC insertion is associated with risk for venous thrombosis and stenosis. National guidelines recommend avoiding PICC lines in patients with CKD stage 3b (glomerular filtration rate less than 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2) in order to preserve venous integrity for future creation of arteriovenous fistula, which is the ideal vascular access for hemodialysis.
Study design: Prospective cohort.
Setting: 52 hospitals in Michigan.
Synopsis: Data obtained from inpatients within the Michigan Hospital Medicine Safety Consortium between 2013 and 2016 showed that, of 20,545 total PICCs placed, 23% were placed in patients with a glomerular filtration rate less than 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and 3.2% were placed in those receiving dialysis. PICC placement in advanced CKD was more common in the ICU than in the ward setting, and placement more frequently utilized multilumen instead of single-lumen catheters. PICC-related complications were not more common in advanced CKD but were more often seen in the ICU and with multilumen PICCs. About one-quarter of PICCs were used for durations of less than 5 days.
The study is limited by lack of data in a subset of patients who had no documented GFR (2.7%) or missing covariate data (2.7%). The inability to ascertain other clinical information, such as nephrology approval of PICC, functional AV fistula or other hemodialysis access, or PICC complications after discharge further limit the findings.
Hospitalists should first decide if a PICC line is truly indicated, and if so, carefully weigh the risks and benefits of PICC placement in patients with advanced CKD.
Bottom line: PICC placement is common and often inappropriate in hospitalized patients with advanced CKD.
Citation: Paje D et al. Use of peripherally inserted central catheters in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease A prospective cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Jun 4;171:10-8.
Dr. Hageman is a hospitalist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn.
Background: PICC insertion is associated with risk for venous thrombosis and stenosis. National guidelines recommend avoiding PICC lines in patients with CKD stage 3b (glomerular filtration rate less than 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2) in order to preserve venous integrity for future creation of arteriovenous fistula, which is the ideal vascular access for hemodialysis.
Study design: Prospective cohort.
Setting: 52 hospitals in Michigan.
Synopsis: Data obtained from inpatients within the Michigan Hospital Medicine Safety Consortium between 2013 and 2016 showed that, of 20,545 total PICCs placed, 23% were placed in patients with a glomerular filtration rate less than 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and 3.2% were placed in those receiving dialysis. PICC placement in advanced CKD was more common in the ICU than in the ward setting, and placement more frequently utilized multilumen instead of single-lumen catheters. PICC-related complications were not more common in advanced CKD but were more often seen in the ICU and with multilumen PICCs. About one-quarter of PICCs were used for durations of less than 5 days.
The study is limited by lack of data in a subset of patients who had no documented GFR (2.7%) or missing covariate data (2.7%). The inability to ascertain other clinical information, such as nephrology approval of PICC, functional AV fistula or other hemodialysis access, or PICC complications after discharge further limit the findings.
Hospitalists should first decide if a PICC line is truly indicated, and if so, carefully weigh the risks and benefits of PICC placement in patients with advanced CKD.
Bottom line: PICC placement is common and often inappropriate in hospitalized patients with advanced CKD.
Citation: Paje D et al. Use of peripherally inserted central catheters in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease A prospective cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Jun 4;171:10-8.
Dr. Hageman is a hospitalist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn.
Background: PICC insertion is associated with risk for venous thrombosis and stenosis. National guidelines recommend avoiding PICC lines in patients with CKD stage 3b (glomerular filtration rate less than 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2) in order to preserve venous integrity for future creation of arteriovenous fistula, which is the ideal vascular access for hemodialysis.
Study design: Prospective cohort.
Setting: 52 hospitals in Michigan.
Synopsis: Data obtained from inpatients within the Michigan Hospital Medicine Safety Consortium between 2013 and 2016 showed that, of 20,545 total PICCs placed, 23% were placed in patients with a glomerular filtration rate less than 45 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and 3.2% were placed in those receiving dialysis. PICC placement in advanced CKD was more common in the ICU than in the ward setting, and placement more frequently utilized multilumen instead of single-lumen catheters. PICC-related complications were not more common in advanced CKD but were more often seen in the ICU and with multilumen PICCs. About one-quarter of PICCs were used for durations of less than 5 days.
The study is limited by lack of data in a subset of patients who had no documented GFR (2.7%) or missing covariate data (2.7%). The inability to ascertain other clinical information, such as nephrology approval of PICC, functional AV fistula or other hemodialysis access, or PICC complications after discharge further limit the findings.
Hospitalists should first decide if a PICC line is truly indicated, and if so, carefully weigh the risks and benefits of PICC placement in patients with advanced CKD.
Bottom line: PICC placement is common and often inappropriate in hospitalized patients with advanced CKD.
Citation: Paje D et al. Use of peripherally inserted central catheters in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease A prospective cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Jun 4;171:10-8.
Dr. Hageman is a hospitalist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn.
Lower BP and better tumor control with drug combo?
It’s not ready for the clinic, but new research suggests that angiotensin receptor II blockers (ARBs) widely used to treat hypertension may improve responses to cancer immunotherapy agents targeted against the programmed death-1/ligand-1 (PD-1/PD-L1) pathway.
That conclusion comes from an observational study of 597 patients with more than 3 dozen different cancer types treated in clinical trials at the US National Institutes of Health. Investigators found that both objective response rates and 3-year overall survival (OS) rates were significantly higher for patients treated with a PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor who were on ARBs, compared with patients who weren’t taking the antihypertensive agents.
An association was also seen between higher ORR and OS rates for patients taking ACE inhibitors, but it was not statistically significant, reported Julius Strauss, MD, from the Center for Cancer Research at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md.
All study patients received PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, and the ORR for patients treated with ARBs was 33.8%, compared with 19.5% for those treated with ACE inhibitors, and 17% for those who took neither drug. The respective complete response (CR) rates were 11.3%, 3.7%, and 3.1%.
Strauss discussed the data during an online briefing prior to his presentation of the findings during the 32nd EORTC-NCI-AACR Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics, which is taking place virtually.
Several early studies have suggested that angiotensin II, in addition to its effect on blood pressure, can also affect cancer growth by leading to downstream production of two proteins: vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor–beta (TGF-beta), he explained.
“Both of these [proteins] have been linked to cancer growth and cancer resistance to immune system attack,” Strauss observed.
He also discussed the mechanics of possible effects. Angiotensin II increases VEGF and TGF-beta through binding to the AT1 receptor, but has the opposite effect when it binds to the AT2 receptor, resulting in a decrease in both of the growth factors, he added.
ACE inhibitors prevent the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, with the result being that the drugs indirectly block both the AT1 and AT2 receptors.
In contrast, ARBs block only the AT1 receptor and leave the AT2 counter-regulatory receptor alone, said Strauss.
More data, including on overall survival
Strauss and colleagues examined whether ACE inhibitors and/or ARBs could have an effect on the response to PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors delivered with or without other immunotherapies, such as anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) checkpoint inhibitors, or targeted agents such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
They pooled data on 597 patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in clinical trials for various cancers, including 71 receiving concomitant ARBs, 82 receiving an ACE inhibitor, and 444 who were not receiving either class of antihypertensives.
The above-mentioned improvement in ORR with ARBs compared with patients not receiving the drug was statistically significant (P = .001), as was the improvement in CR rates (P = .002). In contrast, neither ORR nor CR were significantly better with patients on ACE inhibitors compared with patients not taking these drugs.
In multiple regression analysis controlling for age, gender, body mass index (BMI), tumor type, and additional therapies given, the superior ORR and CR rates with ARBs remained (P = .039 and .002, respectively), while there continued to be no significant additional benefit with ACE inhibitors.
The median overall survival was 35.2 months for patients on ARBs, 26.2 months for those on ACE inhibitors, and 18.8 months for patients on neither drug. The respective 3-year OS rates were 48.1%, 37.2%, and 31.5%, with the difference between the ARB and no-drug groups being significant (P = .0078).
In regression analysis controlling for the factors mentioned before, the OS advantage with ARBs but not ACE inhibitors remained significant (P = .006 for ARBs, and .078 for ACE inhibitors).
Strauss emphasized that further study is needed to determine if AT1 blockade can improve outcomes when combined anti-PD-1/PD-L1-based therapy.
It might be reasonable for patients who are taking ACE inhibitors to control blood pressure and are also receiving immunotherapy with a PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor to be switched to an ARB if it is deemed safe and if further research bears it out, said Strauss in response to a question from Medscape Medical News.
Hypothesis-generating study
Meeting cochair Emiliano Calvo, MD, PhD, from Hospital de Madrid Norte Sanchinarro in Madrid, who attended the media briefing but was not involved in the study, commented that hypothesis-generating research using drugs already on the market for other indications adds important value to cancer therapy.
James Gulley, MD, PhD, from the Center for Cancer Research at the NCI, also a meeting cochair, agreed with Calvo.
“Thinking about utilizing the data that already exists to really get hypothesis-generating questions, it also opens up the possibility for real-world data, real-world evidence from these big datasets from [electronic medical records] that we could really interrogate and understand what we might see and get these hypothesis-generating findings that we could then prospectively evaluate,” Gulley said.
The research was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Strauss and Gulley are National Cancer Institute employees. Calvo disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s not ready for the clinic, but new research suggests that angiotensin receptor II blockers (ARBs) widely used to treat hypertension may improve responses to cancer immunotherapy agents targeted against the programmed death-1/ligand-1 (PD-1/PD-L1) pathway.
That conclusion comes from an observational study of 597 patients with more than 3 dozen different cancer types treated in clinical trials at the US National Institutes of Health. Investigators found that both objective response rates and 3-year overall survival (OS) rates were significantly higher for patients treated with a PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor who were on ARBs, compared with patients who weren’t taking the antihypertensive agents.
An association was also seen between higher ORR and OS rates for patients taking ACE inhibitors, but it was not statistically significant, reported Julius Strauss, MD, from the Center for Cancer Research at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md.
All study patients received PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, and the ORR for patients treated with ARBs was 33.8%, compared with 19.5% for those treated with ACE inhibitors, and 17% for those who took neither drug. The respective complete response (CR) rates were 11.3%, 3.7%, and 3.1%.
Strauss discussed the data during an online briefing prior to his presentation of the findings during the 32nd EORTC-NCI-AACR Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics, which is taking place virtually.
Several early studies have suggested that angiotensin II, in addition to its effect on blood pressure, can also affect cancer growth by leading to downstream production of two proteins: vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor–beta (TGF-beta), he explained.
“Both of these [proteins] have been linked to cancer growth and cancer resistance to immune system attack,” Strauss observed.
He also discussed the mechanics of possible effects. Angiotensin II increases VEGF and TGF-beta through binding to the AT1 receptor, but has the opposite effect when it binds to the AT2 receptor, resulting in a decrease in both of the growth factors, he added.
ACE inhibitors prevent the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, with the result being that the drugs indirectly block both the AT1 and AT2 receptors.
In contrast, ARBs block only the AT1 receptor and leave the AT2 counter-regulatory receptor alone, said Strauss.
More data, including on overall survival
Strauss and colleagues examined whether ACE inhibitors and/or ARBs could have an effect on the response to PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors delivered with or without other immunotherapies, such as anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) checkpoint inhibitors, or targeted agents such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
They pooled data on 597 patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in clinical trials for various cancers, including 71 receiving concomitant ARBs, 82 receiving an ACE inhibitor, and 444 who were not receiving either class of antihypertensives.
The above-mentioned improvement in ORR with ARBs compared with patients not receiving the drug was statistically significant (P = .001), as was the improvement in CR rates (P = .002). In contrast, neither ORR nor CR were significantly better with patients on ACE inhibitors compared with patients not taking these drugs.
In multiple regression analysis controlling for age, gender, body mass index (BMI), tumor type, and additional therapies given, the superior ORR and CR rates with ARBs remained (P = .039 and .002, respectively), while there continued to be no significant additional benefit with ACE inhibitors.
The median overall survival was 35.2 months for patients on ARBs, 26.2 months for those on ACE inhibitors, and 18.8 months for patients on neither drug. The respective 3-year OS rates were 48.1%, 37.2%, and 31.5%, with the difference between the ARB and no-drug groups being significant (P = .0078).
In regression analysis controlling for the factors mentioned before, the OS advantage with ARBs but not ACE inhibitors remained significant (P = .006 for ARBs, and .078 for ACE inhibitors).
Strauss emphasized that further study is needed to determine if AT1 blockade can improve outcomes when combined anti-PD-1/PD-L1-based therapy.
It might be reasonable for patients who are taking ACE inhibitors to control blood pressure and are also receiving immunotherapy with a PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor to be switched to an ARB if it is deemed safe and if further research bears it out, said Strauss in response to a question from Medscape Medical News.
Hypothesis-generating study
Meeting cochair Emiliano Calvo, MD, PhD, from Hospital de Madrid Norte Sanchinarro in Madrid, who attended the media briefing but was not involved in the study, commented that hypothesis-generating research using drugs already on the market for other indications adds important value to cancer therapy.
James Gulley, MD, PhD, from the Center for Cancer Research at the NCI, also a meeting cochair, agreed with Calvo.
“Thinking about utilizing the data that already exists to really get hypothesis-generating questions, it also opens up the possibility for real-world data, real-world evidence from these big datasets from [electronic medical records] that we could really interrogate and understand what we might see and get these hypothesis-generating findings that we could then prospectively evaluate,” Gulley said.
The research was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Strauss and Gulley are National Cancer Institute employees. Calvo disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s not ready for the clinic, but new research suggests that angiotensin receptor II blockers (ARBs) widely used to treat hypertension may improve responses to cancer immunotherapy agents targeted against the programmed death-1/ligand-1 (PD-1/PD-L1) pathway.
That conclusion comes from an observational study of 597 patients with more than 3 dozen different cancer types treated in clinical trials at the US National Institutes of Health. Investigators found that both objective response rates and 3-year overall survival (OS) rates were significantly higher for patients treated with a PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor who were on ARBs, compared with patients who weren’t taking the antihypertensive agents.
An association was also seen between higher ORR and OS rates for patients taking ACE inhibitors, but it was not statistically significant, reported Julius Strauss, MD, from the Center for Cancer Research at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md.
All study patients received PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, and the ORR for patients treated with ARBs was 33.8%, compared with 19.5% for those treated with ACE inhibitors, and 17% for those who took neither drug. The respective complete response (CR) rates were 11.3%, 3.7%, and 3.1%.
Strauss discussed the data during an online briefing prior to his presentation of the findings during the 32nd EORTC-NCI-AACR Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics, which is taking place virtually.
Several early studies have suggested that angiotensin II, in addition to its effect on blood pressure, can also affect cancer growth by leading to downstream production of two proteins: vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor–beta (TGF-beta), he explained.
“Both of these [proteins] have been linked to cancer growth and cancer resistance to immune system attack,” Strauss observed.
He also discussed the mechanics of possible effects. Angiotensin II increases VEGF and TGF-beta through binding to the AT1 receptor, but has the opposite effect when it binds to the AT2 receptor, resulting in a decrease in both of the growth factors, he added.
ACE inhibitors prevent the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, with the result being that the drugs indirectly block both the AT1 and AT2 receptors.
In contrast, ARBs block only the AT1 receptor and leave the AT2 counter-regulatory receptor alone, said Strauss.
More data, including on overall survival
Strauss and colleagues examined whether ACE inhibitors and/or ARBs could have an effect on the response to PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors delivered with or without other immunotherapies, such as anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) checkpoint inhibitors, or targeted agents such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
They pooled data on 597 patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in clinical trials for various cancers, including 71 receiving concomitant ARBs, 82 receiving an ACE inhibitor, and 444 who were not receiving either class of antihypertensives.
The above-mentioned improvement in ORR with ARBs compared with patients not receiving the drug was statistically significant (P = .001), as was the improvement in CR rates (P = .002). In contrast, neither ORR nor CR were significantly better with patients on ACE inhibitors compared with patients not taking these drugs.
In multiple regression analysis controlling for age, gender, body mass index (BMI), tumor type, and additional therapies given, the superior ORR and CR rates with ARBs remained (P = .039 and .002, respectively), while there continued to be no significant additional benefit with ACE inhibitors.
The median overall survival was 35.2 months for patients on ARBs, 26.2 months for those on ACE inhibitors, and 18.8 months for patients on neither drug. The respective 3-year OS rates were 48.1%, 37.2%, and 31.5%, with the difference between the ARB and no-drug groups being significant (P = .0078).
In regression analysis controlling for the factors mentioned before, the OS advantage with ARBs but not ACE inhibitors remained significant (P = .006 for ARBs, and .078 for ACE inhibitors).
Strauss emphasized that further study is needed to determine if AT1 blockade can improve outcomes when combined anti-PD-1/PD-L1-based therapy.
It might be reasonable for patients who are taking ACE inhibitors to control blood pressure and are also receiving immunotherapy with a PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor to be switched to an ARB if it is deemed safe and if further research bears it out, said Strauss in response to a question from Medscape Medical News.
Hypothesis-generating study
Meeting cochair Emiliano Calvo, MD, PhD, from Hospital de Madrid Norte Sanchinarro in Madrid, who attended the media briefing but was not involved in the study, commented that hypothesis-generating research using drugs already on the market for other indications adds important value to cancer therapy.
James Gulley, MD, PhD, from the Center for Cancer Research at the NCI, also a meeting cochair, agreed with Calvo.
“Thinking about utilizing the data that already exists to really get hypothesis-generating questions, it also opens up the possibility for real-world data, real-world evidence from these big datasets from [electronic medical records] that we could really interrogate and understand what we might see and get these hypothesis-generating findings that we could then prospectively evaluate,” Gulley said.
The research was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Strauss and Gulley are National Cancer Institute employees. Calvo disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.