User login
Long-lasting COVID-19 symptoms: Patients want answers
Q&A with Dr. Sachin Gupta
For some patients, a bout of COVID-19 may not be over after hospital discharge, acute symptoms subside, or a couple of tests for SARS-CoV-2 come back negative. Those who have reached these milestones of conquering the disease may find that their recovery journey has only begun. Debilitating symptoms such as fatigue, headache, and dyspnea may linger for weeks or longer. Patients with persistent symptoms, often referred to as “long haulers” in reference to the duration of their recovery, are looking for answers about their condition and when their COVID-19 illness will finally resolve.
Long-haul patients organize
What started as an accumulation of anecdotal evidence in social media, blogs, and the mainstream press about slow recovery and long-lasting symptoms of COVID-19 is now the focus of clinical trials in the population of recovering patients. Projects such as the COVID Symptom Study, initiated by the Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston; the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston; King’s College London; and Stanford (Calif.) University, are collecting data on symptoms from millions of patients and will eventually contribute to a better understanding of prolonged recovery.
Patients looking for answers have created groups on social media such as Facebook to exchange information about their experiences (e.g., Survivor Corps, COVID-19 Support Group, COVID-19 Recovered Survivors). Recovering patients have created patient-led research organizations (Body Politic COVID-19 Support Group) to explore persistent symptoms and begin to create data for research.
Some data on lingering symptoms
A small study of 143 previously hospitalized, recovering patients in Italy found that 87.4% of the cohort had at least one persistent symptom 2 months or longer after initial onset and at more than a month after discharge. In this sample, only 5% had been intubated. (JAMA 2020 Jul 9. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12603).
One study found that even patients who have had relatively mild symptoms and were not hospitalized can have persistent symptoms. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention conducted a survey of adults who tested positive for the positive reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction test for SARS-CoV-2 and found that, among the 292 respondents, 35% were still feeling the impact of the disease 2-3 weeks after testing. Fatigue (71%), cough (61%), and headache (61%) were the most commonly reported symptoms. The survey found that delayed recovery was evident in nearly a quarter of 18- to 34-year-olds and in a third of 35- to 49-year-olds who were not sick enough to require hospitalization (MMWR. 2020 Jul 24. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6930e1).
Sachin Gupta, MD, FCCP, ATSF, a pulmonologist and member of the CHEST Physician editorial advisory board, has treated patients with COVID-19 and shared some of his thoughts on the problem of prolonged symptoms of COVID-19.
Q: Should clinicians expect to see COVID-19 patients who have symptoms persisting weeks after they are diagnosed?
Dr. Gupta: I think clinicians, especially in primary care, are already seeing many patients with lingering symptoms, both respiratory and nonrespiratory related, and debility. A few patients here in the San Francisco Bay Area that I have spoken with 4-6 weeks out from their acute illness have complained of persisting, though improving, fatigue and cough. Early studies are confirming this as a topical issue. There may be other long-lasting sequelae of COVID-19 beyond the common mild lingering symptoms. It will also be important to consider (and get more data on) to what degree asymptomatic patients develop some degree of mild inflammatory and subsequent fibrotic changes in organs like the lungs and heart
Q: How does the recovery phase of COVID-19 compare with recovery from severe influenza or ARDS?
Dr. Gupta: Most prior influenza and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) studies have provided initial follow-up at 3 months and beyond, so technically speaking, it is a little difficult to compare the symptomatology patterns in the JAMA study of 2 months on follow-up. Nevertheless, the key takeaway is that, even though few patients in the study had ARDS requiring intubation (severe disease), many patients with milder disease had significant lingering symptoms (55% with three or more symptoms) at 2 months.
This fits logically with the premise, which we have some limited data on with ARDS (N Engl J Med. 2003;348:683-93. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022450) and severe influenza infection survivors (Nature Sci Rep. 2017;7:17275. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17497-6) that varying degrees of the inflammation cascade triggered by certain viruses can lead to changes in important patient-reported outcomes, and objective measures such as pulmonary function over the long term.
Q: What can you do for patients with lingering symptoms of COVID-19 or what can you tell them about their symptoms?
Dr. Gupta: For many patients, there is fear, given the novel nature of the virus/pandemic, that their symptoms may persist long term. Acknowledgment of their symptoms is validating and important for us to recognize as we learn more about the virus. As we are finding, many patients are going online to find answers, after sometimes feeling rushed or dismissed initially in the clinical setting.
In my experience, the bar is fairly high for most patients to reach out to their physicians with complaints of lingering symptoms after acute infection. For the ones who do reach out, they tend to have either a greater constellation of symptoms or higher severity of one or two key symptoms. After assessing and, when appropriate, ruling out secondary infections or newly developed conditions, I shift toward symptom management. I encourage such patients to build up slowly. I suggest they work first on their activities of daily living (bathing, grooming), then their instrumental activities of daily living (cooking, cleaning, checking the mail), and then to engage, based on their tolerance of symptoms, to light purposeful exercise. There are many online resources for at-home exercise activities that I recommend to patients who are more debilitated; some larger centers are beginning to offer some forms of telepulmonary rehab.
Based on what we know about other causes of viral pneumonitis and ARDS, I ask such symptomatic patients to expect a slow, gradual, and in most cases a complete recovery, and depending on the individual case, I recommend pulmonary function tests and imaging that may be helpful to track that progress.
I remind myself, and patients, that our understanding may change as we learn more over time. Checking in at set intervals, even if not in person but through a phone call, can go a long way in a setting where we do not have a specific therapy, other than gradual exercise training, to help these patients recover faster. Reassurance and encouragement are vital for patients who are struggling with the lingering burden of disease and who may find it difficult to return to work or function as usual at home. The final point is to be mindful of our patient’s mental health and, where our reassurance is not enough, to consider appropriate mental health referrals.
Q: Can you handle this kind of problem with telemedicine or which patients with lingering symptoms need to come into the office – or failing that, the ED?
Dr. Gupta: Telemedicine in the outpatient setting provides a helpful tool to assess and manage patients, in my experience, with limited and straightforward complaints. Its scope is limited diagnostically (assessing symptoms and signs) as is its reach (ability to connect with elderly, disabled, or patients without/limited telemedicine access). In many instances, telemedicine limits our ability to connect with patients emotionally and build trust. Many patients who have gone through the acute illness that we see in pulmonary clinic on follow-up are older in age, and for many, video visits are not a practical solution. Telemedicine visits can sometimes present challenges for me as well in terms of thoroughly conveying lifestyle and symptom management strategies. Health literacy is typically easier to gauge and address in person.
For patients with any degree of enduring dyspnea, more so in the acute phase, I recommend home pulse oximetry for monitoring their oxygen saturation if it is financially and technically feasible for them to obtain one. Sending a patient to the ED is an option of last resort, but one that is necessary in some cases. I expect patients with lingering symptoms to tell me that symptoms may be persisting, hopefully gradually improving, and not getting worse. If post–COVID-19 symptoms such as fever, dyspnea, fatigue, or lightheadedness are new or worsening, particularly rapidly, the safest and best option I advise patients is to go to the ED for further assessment and testing. Postviral bacterial pneumonia is something we should consider, and there is some potential for aspergillosis as well.
Q: Do you have any concerns about patients with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or other pulmonary issues having lingering symptoms that may mask exacerbations or may cause exacerbation of their disease?
Dr. Gupta: So far, patients with chronic lung conditions do not appear to have not been disproportionately affected by the pandemic in terms of absolute numbers or percentage wise compared to the general public. I think that sheltering in place has been readily followed by many of these patients, and in addition, I assume better adherence to their maintenance therapies has likely helped. The very few cases of patients with underlying chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and interstitial lung disease that I have seen have fared very poorly when they were diagnosed with COVID-19 in the hospital. There are emerging data about short-term outcomes from severe COVID-19 infection in patients with interstitial lung disease in Europe (medRxiv. 2020 Jul 17. doi: 10.1101/2020.07.15.20152967), and from physicians treating pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020 Jul 29. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202005-521OC). But so far, little has been published on the outcomes of mild disease in these patients with chronic lung disease.
Q: It’s still early days to know the significance of lingering symptoms. But at what point do you begin to consider the possibility of some kind of relapse? And what is your next move if the symptoms get worse?
Dr. Gupta: COVID-19 recurrence, whether because of reinfection or relapse, is a potential concern but not one that is very commonly seen so far in my purview. Generally, symptoms of post–COVID-19 infection that are lingering trend toward getting better, even if slowly. If post–COVID-19 infection symptoms are progressing (particularly if rapidly), that would be a strong indication to evaluate that patient in the ED (less likely in clinic), reswab them for SARS-CoV-2, and obtain further testing such as blood work and imaging. A significant challenge from a research perspective will be determining if coinfection with another virus is playing a role as we move closer to the fall season.
Q&A with Dr. Sachin Gupta
Q&A with Dr. Sachin Gupta
For some patients, a bout of COVID-19 may not be over after hospital discharge, acute symptoms subside, or a couple of tests for SARS-CoV-2 come back negative. Those who have reached these milestones of conquering the disease may find that their recovery journey has only begun. Debilitating symptoms such as fatigue, headache, and dyspnea may linger for weeks or longer. Patients with persistent symptoms, often referred to as “long haulers” in reference to the duration of their recovery, are looking for answers about their condition and when their COVID-19 illness will finally resolve.
Long-haul patients organize
What started as an accumulation of anecdotal evidence in social media, blogs, and the mainstream press about slow recovery and long-lasting symptoms of COVID-19 is now the focus of clinical trials in the population of recovering patients. Projects such as the COVID Symptom Study, initiated by the Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston; the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston; King’s College London; and Stanford (Calif.) University, are collecting data on symptoms from millions of patients and will eventually contribute to a better understanding of prolonged recovery.
Patients looking for answers have created groups on social media such as Facebook to exchange information about their experiences (e.g., Survivor Corps, COVID-19 Support Group, COVID-19 Recovered Survivors). Recovering patients have created patient-led research organizations (Body Politic COVID-19 Support Group) to explore persistent symptoms and begin to create data for research.
Some data on lingering symptoms
A small study of 143 previously hospitalized, recovering patients in Italy found that 87.4% of the cohort had at least one persistent symptom 2 months or longer after initial onset and at more than a month after discharge. In this sample, only 5% had been intubated. (JAMA 2020 Jul 9. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12603).
One study found that even patients who have had relatively mild symptoms and were not hospitalized can have persistent symptoms. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention conducted a survey of adults who tested positive for the positive reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction test for SARS-CoV-2 and found that, among the 292 respondents, 35% were still feeling the impact of the disease 2-3 weeks after testing. Fatigue (71%), cough (61%), and headache (61%) were the most commonly reported symptoms. The survey found that delayed recovery was evident in nearly a quarter of 18- to 34-year-olds and in a third of 35- to 49-year-olds who were not sick enough to require hospitalization (MMWR. 2020 Jul 24. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6930e1).
Sachin Gupta, MD, FCCP, ATSF, a pulmonologist and member of the CHEST Physician editorial advisory board, has treated patients with COVID-19 and shared some of his thoughts on the problem of prolonged symptoms of COVID-19.
Q: Should clinicians expect to see COVID-19 patients who have symptoms persisting weeks after they are diagnosed?
Dr. Gupta: I think clinicians, especially in primary care, are already seeing many patients with lingering symptoms, both respiratory and nonrespiratory related, and debility. A few patients here in the San Francisco Bay Area that I have spoken with 4-6 weeks out from their acute illness have complained of persisting, though improving, fatigue and cough. Early studies are confirming this as a topical issue. There may be other long-lasting sequelae of COVID-19 beyond the common mild lingering symptoms. It will also be important to consider (and get more data on) to what degree asymptomatic patients develop some degree of mild inflammatory and subsequent fibrotic changes in organs like the lungs and heart
Q: How does the recovery phase of COVID-19 compare with recovery from severe influenza or ARDS?
Dr. Gupta: Most prior influenza and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) studies have provided initial follow-up at 3 months and beyond, so technically speaking, it is a little difficult to compare the symptomatology patterns in the JAMA study of 2 months on follow-up. Nevertheless, the key takeaway is that, even though few patients in the study had ARDS requiring intubation (severe disease), many patients with milder disease had significant lingering symptoms (55% with three or more symptoms) at 2 months.
This fits logically with the premise, which we have some limited data on with ARDS (N Engl J Med. 2003;348:683-93. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022450) and severe influenza infection survivors (Nature Sci Rep. 2017;7:17275. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17497-6) that varying degrees of the inflammation cascade triggered by certain viruses can lead to changes in important patient-reported outcomes, and objective measures such as pulmonary function over the long term.
Q: What can you do for patients with lingering symptoms of COVID-19 or what can you tell them about their symptoms?
Dr. Gupta: For many patients, there is fear, given the novel nature of the virus/pandemic, that their symptoms may persist long term. Acknowledgment of their symptoms is validating and important for us to recognize as we learn more about the virus. As we are finding, many patients are going online to find answers, after sometimes feeling rushed or dismissed initially in the clinical setting.
In my experience, the bar is fairly high for most patients to reach out to their physicians with complaints of lingering symptoms after acute infection. For the ones who do reach out, they tend to have either a greater constellation of symptoms or higher severity of one or two key symptoms. After assessing and, when appropriate, ruling out secondary infections or newly developed conditions, I shift toward symptom management. I encourage such patients to build up slowly. I suggest they work first on their activities of daily living (bathing, grooming), then their instrumental activities of daily living (cooking, cleaning, checking the mail), and then to engage, based on their tolerance of symptoms, to light purposeful exercise. There are many online resources for at-home exercise activities that I recommend to patients who are more debilitated; some larger centers are beginning to offer some forms of telepulmonary rehab.
Based on what we know about other causes of viral pneumonitis and ARDS, I ask such symptomatic patients to expect a slow, gradual, and in most cases a complete recovery, and depending on the individual case, I recommend pulmonary function tests and imaging that may be helpful to track that progress.
I remind myself, and patients, that our understanding may change as we learn more over time. Checking in at set intervals, even if not in person but through a phone call, can go a long way in a setting where we do not have a specific therapy, other than gradual exercise training, to help these patients recover faster. Reassurance and encouragement are vital for patients who are struggling with the lingering burden of disease and who may find it difficult to return to work or function as usual at home. The final point is to be mindful of our patient’s mental health and, where our reassurance is not enough, to consider appropriate mental health referrals.
Q: Can you handle this kind of problem with telemedicine or which patients with lingering symptoms need to come into the office – or failing that, the ED?
Dr. Gupta: Telemedicine in the outpatient setting provides a helpful tool to assess and manage patients, in my experience, with limited and straightforward complaints. Its scope is limited diagnostically (assessing symptoms and signs) as is its reach (ability to connect with elderly, disabled, or patients without/limited telemedicine access). In many instances, telemedicine limits our ability to connect with patients emotionally and build trust. Many patients who have gone through the acute illness that we see in pulmonary clinic on follow-up are older in age, and for many, video visits are not a practical solution. Telemedicine visits can sometimes present challenges for me as well in terms of thoroughly conveying lifestyle and symptom management strategies. Health literacy is typically easier to gauge and address in person.
For patients with any degree of enduring dyspnea, more so in the acute phase, I recommend home pulse oximetry for monitoring their oxygen saturation if it is financially and technically feasible for them to obtain one. Sending a patient to the ED is an option of last resort, but one that is necessary in some cases. I expect patients with lingering symptoms to tell me that symptoms may be persisting, hopefully gradually improving, and not getting worse. If post–COVID-19 symptoms such as fever, dyspnea, fatigue, or lightheadedness are new or worsening, particularly rapidly, the safest and best option I advise patients is to go to the ED for further assessment and testing. Postviral bacterial pneumonia is something we should consider, and there is some potential for aspergillosis as well.
Q: Do you have any concerns about patients with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or other pulmonary issues having lingering symptoms that may mask exacerbations or may cause exacerbation of their disease?
Dr. Gupta: So far, patients with chronic lung conditions do not appear to have not been disproportionately affected by the pandemic in terms of absolute numbers or percentage wise compared to the general public. I think that sheltering in place has been readily followed by many of these patients, and in addition, I assume better adherence to their maintenance therapies has likely helped. The very few cases of patients with underlying chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and interstitial lung disease that I have seen have fared very poorly when they were diagnosed with COVID-19 in the hospital. There are emerging data about short-term outcomes from severe COVID-19 infection in patients with interstitial lung disease in Europe (medRxiv. 2020 Jul 17. doi: 10.1101/2020.07.15.20152967), and from physicians treating pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020 Jul 29. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202005-521OC). But so far, little has been published on the outcomes of mild disease in these patients with chronic lung disease.
Q: It’s still early days to know the significance of lingering symptoms. But at what point do you begin to consider the possibility of some kind of relapse? And what is your next move if the symptoms get worse?
Dr. Gupta: COVID-19 recurrence, whether because of reinfection or relapse, is a potential concern but not one that is very commonly seen so far in my purview. Generally, symptoms of post–COVID-19 infection that are lingering trend toward getting better, even if slowly. If post–COVID-19 infection symptoms are progressing (particularly if rapidly), that would be a strong indication to evaluate that patient in the ED (less likely in clinic), reswab them for SARS-CoV-2, and obtain further testing such as blood work and imaging. A significant challenge from a research perspective will be determining if coinfection with another virus is playing a role as we move closer to the fall season.
For some patients, a bout of COVID-19 may not be over after hospital discharge, acute symptoms subside, or a couple of tests for SARS-CoV-2 come back negative. Those who have reached these milestones of conquering the disease may find that their recovery journey has only begun. Debilitating symptoms such as fatigue, headache, and dyspnea may linger for weeks or longer. Patients with persistent symptoms, often referred to as “long haulers” in reference to the duration of their recovery, are looking for answers about their condition and when their COVID-19 illness will finally resolve.
Long-haul patients organize
What started as an accumulation of anecdotal evidence in social media, blogs, and the mainstream press about slow recovery and long-lasting symptoms of COVID-19 is now the focus of clinical trials in the population of recovering patients. Projects such as the COVID Symptom Study, initiated by the Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston; the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston; King’s College London; and Stanford (Calif.) University, are collecting data on symptoms from millions of patients and will eventually contribute to a better understanding of prolonged recovery.
Patients looking for answers have created groups on social media such as Facebook to exchange information about their experiences (e.g., Survivor Corps, COVID-19 Support Group, COVID-19 Recovered Survivors). Recovering patients have created patient-led research organizations (Body Politic COVID-19 Support Group) to explore persistent symptoms and begin to create data for research.
Some data on lingering symptoms
A small study of 143 previously hospitalized, recovering patients in Italy found that 87.4% of the cohort had at least one persistent symptom 2 months or longer after initial onset and at more than a month after discharge. In this sample, only 5% had been intubated. (JAMA 2020 Jul 9. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12603).
One study found that even patients who have had relatively mild symptoms and were not hospitalized can have persistent symptoms. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention conducted a survey of adults who tested positive for the positive reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction test for SARS-CoV-2 and found that, among the 292 respondents, 35% were still feeling the impact of the disease 2-3 weeks after testing. Fatigue (71%), cough (61%), and headache (61%) were the most commonly reported symptoms. The survey found that delayed recovery was evident in nearly a quarter of 18- to 34-year-olds and in a third of 35- to 49-year-olds who were not sick enough to require hospitalization (MMWR. 2020 Jul 24. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6930e1).
Sachin Gupta, MD, FCCP, ATSF, a pulmonologist and member of the CHEST Physician editorial advisory board, has treated patients with COVID-19 and shared some of his thoughts on the problem of prolonged symptoms of COVID-19.
Q: Should clinicians expect to see COVID-19 patients who have symptoms persisting weeks after they are diagnosed?
Dr. Gupta: I think clinicians, especially in primary care, are already seeing many patients with lingering symptoms, both respiratory and nonrespiratory related, and debility. A few patients here in the San Francisco Bay Area that I have spoken with 4-6 weeks out from their acute illness have complained of persisting, though improving, fatigue and cough. Early studies are confirming this as a topical issue. There may be other long-lasting sequelae of COVID-19 beyond the common mild lingering symptoms. It will also be important to consider (and get more data on) to what degree asymptomatic patients develop some degree of mild inflammatory and subsequent fibrotic changes in organs like the lungs and heart
Q: How does the recovery phase of COVID-19 compare with recovery from severe influenza or ARDS?
Dr. Gupta: Most prior influenza and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) studies have provided initial follow-up at 3 months and beyond, so technically speaking, it is a little difficult to compare the symptomatology patterns in the JAMA study of 2 months on follow-up. Nevertheless, the key takeaway is that, even though few patients in the study had ARDS requiring intubation (severe disease), many patients with milder disease had significant lingering symptoms (55% with three or more symptoms) at 2 months.
This fits logically with the premise, which we have some limited data on with ARDS (N Engl J Med. 2003;348:683-93. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022450) and severe influenza infection survivors (Nature Sci Rep. 2017;7:17275. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17497-6) that varying degrees of the inflammation cascade triggered by certain viruses can lead to changes in important patient-reported outcomes, and objective measures such as pulmonary function over the long term.
Q: What can you do for patients with lingering symptoms of COVID-19 or what can you tell them about their symptoms?
Dr. Gupta: For many patients, there is fear, given the novel nature of the virus/pandemic, that their symptoms may persist long term. Acknowledgment of their symptoms is validating and important for us to recognize as we learn more about the virus. As we are finding, many patients are going online to find answers, after sometimes feeling rushed or dismissed initially in the clinical setting.
In my experience, the bar is fairly high for most patients to reach out to their physicians with complaints of lingering symptoms after acute infection. For the ones who do reach out, they tend to have either a greater constellation of symptoms or higher severity of one or two key symptoms. After assessing and, when appropriate, ruling out secondary infections or newly developed conditions, I shift toward symptom management. I encourage such patients to build up slowly. I suggest they work first on their activities of daily living (bathing, grooming), then their instrumental activities of daily living (cooking, cleaning, checking the mail), and then to engage, based on their tolerance of symptoms, to light purposeful exercise. There are many online resources for at-home exercise activities that I recommend to patients who are more debilitated; some larger centers are beginning to offer some forms of telepulmonary rehab.
Based on what we know about other causes of viral pneumonitis and ARDS, I ask such symptomatic patients to expect a slow, gradual, and in most cases a complete recovery, and depending on the individual case, I recommend pulmonary function tests and imaging that may be helpful to track that progress.
I remind myself, and patients, that our understanding may change as we learn more over time. Checking in at set intervals, even if not in person but through a phone call, can go a long way in a setting where we do not have a specific therapy, other than gradual exercise training, to help these patients recover faster. Reassurance and encouragement are vital for patients who are struggling with the lingering burden of disease and who may find it difficult to return to work or function as usual at home. The final point is to be mindful of our patient’s mental health and, where our reassurance is not enough, to consider appropriate mental health referrals.
Q: Can you handle this kind of problem with telemedicine or which patients with lingering symptoms need to come into the office – or failing that, the ED?
Dr. Gupta: Telemedicine in the outpatient setting provides a helpful tool to assess and manage patients, in my experience, with limited and straightforward complaints. Its scope is limited diagnostically (assessing symptoms and signs) as is its reach (ability to connect with elderly, disabled, or patients without/limited telemedicine access). In many instances, telemedicine limits our ability to connect with patients emotionally and build trust. Many patients who have gone through the acute illness that we see in pulmonary clinic on follow-up are older in age, and for many, video visits are not a practical solution. Telemedicine visits can sometimes present challenges for me as well in terms of thoroughly conveying lifestyle and symptom management strategies. Health literacy is typically easier to gauge and address in person.
For patients with any degree of enduring dyspnea, more so in the acute phase, I recommend home pulse oximetry for monitoring their oxygen saturation if it is financially and technically feasible for them to obtain one. Sending a patient to the ED is an option of last resort, but one that is necessary in some cases. I expect patients with lingering symptoms to tell me that symptoms may be persisting, hopefully gradually improving, and not getting worse. If post–COVID-19 symptoms such as fever, dyspnea, fatigue, or lightheadedness are new or worsening, particularly rapidly, the safest and best option I advise patients is to go to the ED for further assessment and testing. Postviral bacterial pneumonia is something we should consider, and there is some potential for aspergillosis as well.
Q: Do you have any concerns about patients with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or other pulmonary issues having lingering symptoms that may mask exacerbations or may cause exacerbation of their disease?
Dr. Gupta: So far, patients with chronic lung conditions do not appear to have not been disproportionately affected by the pandemic in terms of absolute numbers or percentage wise compared to the general public. I think that sheltering in place has been readily followed by many of these patients, and in addition, I assume better adherence to their maintenance therapies has likely helped. The very few cases of patients with underlying chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and interstitial lung disease that I have seen have fared very poorly when they were diagnosed with COVID-19 in the hospital. There are emerging data about short-term outcomes from severe COVID-19 infection in patients with interstitial lung disease in Europe (medRxiv. 2020 Jul 17. doi: 10.1101/2020.07.15.20152967), and from physicians treating pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020 Jul 29. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202005-521OC). But so far, little has been published on the outcomes of mild disease in these patients with chronic lung disease.
Q: It’s still early days to know the significance of lingering symptoms. But at what point do you begin to consider the possibility of some kind of relapse? And what is your next move if the symptoms get worse?
Dr. Gupta: COVID-19 recurrence, whether because of reinfection or relapse, is a potential concern but not one that is very commonly seen so far in my purview. Generally, symptoms of post–COVID-19 infection that are lingering trend toward getting better, even if slowly. If post–COVID-19 infection symptoms are progressing (particularly if rapidly), that would be a strong indication to evaluate that patient in the ED (less likely in clinic), reswab them for SARS-CoV-2, and obtain further testing such as blood work and imaging. A significant challenge from a research perspective will be determining if coinfection with another virus is playing a role as we move closer to the fall season.
FDA approves first oral treatment for spinal muscular atrophy
This marks the first approval of an oral therapy for the rare and devastating condition.
Risdiplam, marketed by Roche and PTC Therapeutics, provides “an important treatment option for patients with SMA, following the approval of the first treatment for this devastating disease less than 4 years ago,” Billy Dunn, MD, director of the Office of Neuroscience in the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research at the FDA, said in a release from the agency.
The approval was based on the results from two trials. In the open-label FIREFISH study of infantile-onset SMA, 7 (41%) of the 17 participants (mean baseline age, 6.7 months) were able to sit independently for more than 5 seconds after 12 months of treatment with risdiplam. This was a “meaningful difference from the natural progression of the disease because all untreated infants with infantile-onset SMA cannot sit independently,” the FDA noted. In addition, 81% of the participants were alive after 23 or more months of treatment – and without need of permanent ventilation.
The second study was the randomized controlled trial known as SUNFISH and included 180 patients with SMA between the ages of 2 and 25 years. Those who received the study drug had an average 1.36 increase from baseline on a motor function measure versus a 0.19 decrease in function for those who received placebo.
The FDA noted that the most common treatment-related adverse events (AEs) include fever, diarrhea, rash, ulcers of the mouth, arthralgia, and urinary tract infections. Additional AEs reported in some patients with infantile-onset SMA included upper respiratory tract infection, pneumonia, constipation, and vomiting.
The drug received fast track designation and priority review from the FDA, as well as orphan drug designation.
‘Eagerly awaited’
“Today marks an incredibly important moment for the broader SMA patient community that had been in dire need of safe and effective treatment options,” Stuart W. Peltz, PhD, chief executive officer of PTC Therapeutics, said in a company statement.
“Given [that] the majority of people with SMA in the U.S. remain untreated, we believe Evrysdi, with its favorable clinical profile and oral administration, may offer meaningful benefits for many living with this rare neurological disease,” Levi Garraway, MD, PhD, chief medical officer and head of global product development for Genentech, added in the company’s press release. Genentech is a member of the Roche Group.
The drug is continuing to be studied in more than 450 individuals as part of a “large and robust clinical trial program in SMA,” the company reports. These participants are between the ages of 2 months and 60 years.
“The approval of Evrysdi is an eagerly awaited milestone for our community. We appreciate Genentech’s commitment to … developing a treatment that can be administered at home,” Kenneth Hobby, president of the nonprofit Cure SMA, said in the same release.
In May 2019, the FDA approved the first gene therapy for SMA – the infusion drug onasemnogene abeparvovec-xioi (Zolgensma, AveXis Inc).
Genentech announced that the new oral drug will be available in the United States within 2 weeks “for direct delivery to patients’ homes.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This marks the first approval of an oral therapy for the rare and devastating condition.
Risdiplam, marketed by Roche and PTC Therapeutics, provides “an important treatment option for patients with SMA, following the approval of the first treatment for this devastating disease less than 4 years ago,” Billy Dunn, MD, director of the Office of Neuroscience in the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research at the FDA, said in a release from the agency.
The approval was based on the results from two trials. In the open-label FIREFISH study of infantile-onset SMA, 7 (41%) of the 17 participants (mean baseline age, 6.7 months) were able to sit independently for more than 5 seconds after 12 months of treatment with risdiplam. This was a “meaningful difference from the natural progression of the disease because all untreated infants with infantile-onset SMA cannot sit independently,” the FDA noted. In addition, 81% of the participants were alive after 23 or more months of treatment – and without need of permanent ventilation.
The second study was the randomized controlled trial known as SUNFISH and included 180 patients with SMA between the ages of 2 and 25 years. Those who received the study drug had an average 1.36 increase from baseline on a motor function measure versus a 0.19 decrease in function for those who received placebo.
The FDA noted that the most common treatment-related adverse events (AEs) include fever, diarrhea, rash, ulcers of the mouth, arthralgia, and urinary tract infections. Additional AEs reported in some patients with infantile-onset SMA included upper respiratory tract infection, pneumonia, constipation, and vomiting.
The drug received fast track designation and priority review from the FDA, as well as orphan drug designation.
‘Eagerly awaited’
“Today marks an incredibly important moment for the broader SMA patient community that had been in dire need of safe and effective treatment options,” Stuart W. Peltz, PhD, chief executive officer of PTC Therapeutics, said in a company statement.
“Given [that] the majority of people with SMA in the U.S. remain untreated, we believe Evrysdi, with its favorable clinical profile and oral administration, may offer meaningful benefits for many living with this rare neurological disease,” Levi Garraway, MD, PhD, chief medical officer and head of global product development for Genentech, added in the company’s press release. Genentech is a member of the Roche Group.
The drug is continuing to be studied in more than 450 individuals as part of a “large and robust clinical trial program in SMA,” the company reports. These participants are between the ages of 2 months and 60 years.
“The approval of Evrysdi is an eagerly awaited milestone for our community. We appreciate Genentech’s commitment to … developing a treatment that can be administered at home,” Kenneth Hobby, president of the nonprofit Cure SMA, said in the same release.
In May 2019, the FDA approved the first gene therapy for SMA – the infusion drug onasemnogene abeparvovec-xioi (Zolgensma, AveXis Inc).
Genentech announced that the new oral drug will be available in the United States within 2 weeks “for direct delivery to patients’ homes.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This marks the first approval of an oral therapy for the rare and devastating condition.
Risdiplam, marketed by Roche and PTC Therapeutics, provides “an important treatment option for patients with SMA, following the approval of the first treatment for this devastating disease less than 4 years ago,” Billy Dunn, MD, director of the Office of Neuroscience in the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research at the FDA, said in a release from the agency.
The approval was based on the results from two trials. In the open-label FIREFISH study of infantile-onset SMA, 7 (41%) of the 17 participants (mean baseline age, 6.7 months) were able to sit independently for more than 5 seconds after 12 months of treatment with risdiplam. This was a “meaningful difference from the natural progression of the disease because all untreated infants with infantile-onset SMA cannot sit independently,” the FDA noted. In addition, 81% of the participants were alive after 23 or more months of treatment – and without need of permanent ventilation.
The second study was the randomized controlled trial known as SUNFISH and included 180 patients with SMA between the ages of 2 and 25 years. Those who received the study drug had an average 1.36 increase from baseline on a motor function measure versus a 0.19 decrease in function for those who received placebo.
The FDA noted that the most common treatment-related adverse events (AEs) include fever, diarrhea, rash, ulcers of the mouth, arthralgia, and urinary tract infections. Additional AEs reported in some patients with infantile-onset SMA included upper respiratory tract infection, pneumonia, constipation, and vomiting.
The drug received fast track designation and priority review from the FDA, as well as orphan drug designation.
‘Eagerly awaited’
“Today marks an incredibly important moment for the broader SMA patient community that had been in dire need of safe and effective treatment options,” Stuart W. Peltz, PhD, chief executive officer of PTC Therapeutics, said in a company statement.
“Given [that] the majority of people with SMA in the U.S. remain untreated, we believe Evrysdi, with its favorable clinical profile and oral administration, may offer meaningful benefits for many living with this rare neurological disease,” Levi Garraway, MD, PhD, chief medical officer and head of global product development for Genentech, added in the company’s press release. Genentech is a member of the Roche Group.
The drug is continuing to be studied in more than 450 individuals as part of a “large and robust clinical trial program in SMA,” the company reports. These participants are between the ages of 2 months and 60 years.
“The approval of Evrysdi is an eagerly awaited milestone for our community. We appreciate Genentech’s commitment to … developing a treatment that can be administered at home,” Kenneth Hobby, president of the nonprofit Cure SMA, said in the same release.
In May 2019, the FDA approved the first gene therapy for SMA – the infusion drug onasemnogene abeparvovec-xioi (Zolgensma, AveXis Inc).
Genentech announced that the new oral drug will be available in the United States within 2 weeks “for direct delivery to patients’ homes.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Sleep problems in young children linked to lower QOL in later years
Sleep problems in children from birth to middle childhood may lead to decreased emotional well-being and quality of life by the time a child is 10-11 years old, a recent longitudinal study has found.
The effects of these impairments increased over time and included internalizing and externalizing concerns, self-control, and quality of life, but did not appear to significantly affect cognitive or academic skills, according to Ariel A. Williamson, PhD, DBSM, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and colleagues. While children with consistent sleep problems experienced the worse outcomes, mild sleep problems also were associated with impairment, the researchers said.
“The range of impairments across academic and psychosocial domains in middle childhood indicate that it is important to screen for sleep problems consistently over the course of a child’s development, especially to target children who experience persistent sleep problems over time,” said Dr. Williamson in a press release.
The researchers examined data from 5,107 children in the Longitudinal Study of Australian Children – Birth Cohort, where sleep problems and well-being outcomes were measured at multiple time points. Behaviors such as difficulty getting off to sleep at night, not happy to sleep alone, and waking during the night were defined as sleep problems. The investigators found five main domains of sleep issues: children who had persistent sleep problems through middle childhood (7.7%), limited sleep problems as an infant or during preschool (9.0%), mild sleep problems over time (14.4%), increased sleep problems during middle childhood (17.0%), and a group that did not experience sleep problems (51.9%).
Caregivers reported sleep issues in the cohort, while well-being outcomes were reported by caregivers and teachers, and tasks were completed by the children at 10-11 years of age. Dr. Williamson and colleagues examined well-being in terms of emotional and behavioral functioning, health-related quality of life, cognitive skills, and academic achievement.
Different reports from teacher and caregivers
Teacher and caregivers reported different effects in children with persistent sleep problems. Teachers reported moderate internalizing (effect size, –0.65; 95% confidence interval [CI],–0.87 to –0.43; P < .001) and externalizing concerns (ES, –0.40; 95% CI, –0.58 to –0.21; P less than .001), compared with children who did not have sleep problems, whereas caregivers reported large internalizing (ES, –0.75; 95% CI, –0.92 to –0.57; P less than .001) and externalizing concerns (ES, –0.70; 95% CI, –0.86 to –0.53; P < .001). Children with persistent sleep problems had moderate impairment of self-control as reported by caregivers, compared with children with no sleep problems (ES, –0.37; 95% CI, –0.52 to –0.21; P < .001). Psychosocial and health-related quality of life reported by caregivers were worse in children with persistent sleep problems, compared with children who did not have sleep problems (ES range, –0.78 to –0.90; 95% CI, –1.06 to –0.56; P < .001).
For children who exhibited increased sleep problems in middle childhood, caregivers (ES for both, –0.61; 95% CI, –0.76 to –0.46; P < .001) and teachers (ES range, –0.29 to –0.39; 95% CI, –0.53 to –0.15; P < .001) reported greater rates of internalizing and externalizing symptoms, compared with children who had no sleep issues.
Small impairments in internalizing internal or externalizing symptoms were seen in children who had limited sleep problems as an infant or in preschool (ES, –0.12; 95% CI, –0.23 to –0.01; P < .05) as reported by teachers, and in children with mild sleep problems over time (ES, –0.19; 95% CI, –0.30 to –0.08; P < .001) as reported by caregivers. There were no significant impairments in self-control for children in either the infant or preschool impairment group or in the group of children with mild sleep problems.
Across all groups, sleep problems did not significantly impair nonverbal reasoning, and most areas of academic competencies were not significantly impaired among groups except in language and literacy, and mathematical thinking for children with persistent sleep problems (ES, –0.41 for both; 95% CI, –0.60 to –0.23; P < .001). Children with increased sleep problems during middle childhood “had few academic and cognitive impairments,” and academic impairments among children with mild sleep problems were not significant.
Expert opinion
Brandon M. Seay MD, FAAP, pediatric pulmonologist and sleep specialist at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, said in an interview that the study is one of the first to offer longitudinal data for impairment in children with sleep problems. He said the paper emphasizes the need for recognizing when children are demonstrating sleep problems. “It just shows that problems that aren’t dealt with earlier on definitely have bigger impacts on sleep as you go through life,” he said.
Although primary care physicians and pediatricians should be already asking questions about sleep through anticipatory guidance, he said, intervening earlier for sleep problems is important. He noted children who exhibit sleep problems over time are more likely to have issues in handling their emotions and eventually may develop cognitive issues. “[W]e know that if these problems continue to go through, this paper’s showing us that they have worse effects down the road,” he said.
Impact of the COVID-19 crisis
These problems may also be worsened by the COVID-19 pandemic. Dr. Seay noted that with many parents working from home, sleep schedules can be affected and parents may also be co-sleeping with their children, which can cause chronic insomnia and early waking. To help address sleep issues, especially ones that may have arisen during COVID-19, parents should make sure their children show up for primary care visits to report problems, and clinicians should make a sleep routine a focus of conversations around sleep problems.
Prior to the pandemic, “we already were hitting upon that in sleep clinic, making sure [they] get the same schedule every day,” said Dr. Seay. For parents with children who have “issues with insomnia or waking up during the night, having that routine in place does help to mitigate that a little bit, so if that routine is not there, it can actually exacerbate the issues.”
This study was funded by the Australian federal government. The authors report no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Seay reports no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Williamson AA et al. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2020 Jul 26. doi:10.1111/jcpp.13303.
Sleep problems in children from birth to middle childhood may lead to decreased emotional well-being and quality of life by the time a child is 10-11 years old, a recent longitudinal study has found.
The effects of these impairments increased over time and included internalizing and externalizing concerns, self-control, and quality of life, but did not appear to significantly affect cognitive or academic skills, according to Ariel A. Williamson, PhD, DBSM, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and colleagues. While children with consistent sleep problems experienced the worse outcomes, mild sleep problems also were associated with impairment, the researchers said.
“The range of impairments across academic and psychosocial domains in middle childhood indicate that it is important to screen for sleep problems consistently over the course of a child’s development, especially to target children who experience persistent sleep problems over time,” said Dr. Williamson in a press release.
The researchers examined data from 5,107 children in the Longitudinal Study of Australian Children – Birth Cohort, where sleep problems and well-being outcomes were measured at multiple time points. Behaviors such as difficulty getting off to sleep at night, not happy to sleep alone, and waking during the night were defined as sleep problems. The investigators found five main domains of sleep issues: children who had persistent sleep problems through middle childhood (7.7%), limited sleep problems as an infant or during preschool (9.0%), mild sleep problems over time (14.4%), increased sleep problems during middle childhood (17.0%), and a group that did not experience sleep problems (51.9%).
Caregivers reported sleep issues in the cohort, while well-being outcomes were reported by caregivers and teachers, and tasks were completed by the children at 10-11 years of age. Dr. Williamson and colleagues examined well-being in terms of emotional and behavioral functioning, health-related quality of life, cognitive skills, and academic achievement.
Different reports from teacher and caregivers
Teacher and caregivers reported different effects in children with persistent sleep problems. Teachers reported moderate internalizing (effect size, –0.65; 95% confidence interval [CI],–0.87 to –0.43; P < .001) and externalizing concerns (ES, –0.40; 95% CI, –0.58 to –0.21; P less than .001), compared with children who did not have sleep problems, whereas caregivers reported large internalizing (ES, –0.75; 95% CI, –0.92 to –0.57; P less than .001) and externalizing concerns (ES, –0.70; 95% CI, –0.86 to –0.53; P < .001). Children with persistent sleep problems had moderate impairment of self-control as reported by caregivers, compared with children with no sleep problems (ES, –0.37; 95% CI, –0.52 to –0.21; P < .001). Psychosocial and health-related quality of life reported by caregivers were worse in children with persistent sleep problems, compared with children who did not have sleep problems (ES range, –0.78 to –0.90; 95% CI, –1.06 to –0.56; P < .001).
For children who exhibited increased sleep problems in middle childhood, caregivers (ES for both, –0.61; 95% CI, –0.76 to –0.46; P < .001) and teachers (ES range, –0.29 to –0.39; 95% CI, –0.53 to –0.15; P < .001) reported greater rates of internalizing and externalizing symptoms, compared with children who had no sleep issues.
Small impairments in internalizing internal or externalizing symptoms were seen in children who had limited sleep problems as an infant or in preschool (ES, –0.12; 95% CI, –0.23 to –0.01; P < .05) as reported by teachers, and in children with mild sleep problems over time (ES, –0.19; 95% CI, –0.30 to –0.08; P < .001) as reported by caregivers. There were no significant impairments in self-control for children in either the infant or preschool impairment group or in the group of children with mild sleep problems.
Across all groups, sleep problems did not significantly impair nonverbal reasoning, and most areas of academic competencies were not significantly impaired among groups except in language and literacy, and mathematical thinking for children with persistent sleep problems (ES, –0.41 for both; 95% CI, –0.60 to –0.23; P < .001). Children with increased sleep problems during middle childhood “had few academic and cognitive impairments,” and academic impairments among children with mild sleep problems were not significant.
Expert opinion
Brandon M. Seay MD, FAAP, pediatric pulmonologist and sleep specialist at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, said in an interview that the study is one of the first to offer longitudinal data for impairment in children with sleep problems. He said the paper emphasizes the need for recognizing when children are demonstrating sleep problems. “It just shows that problems that aren’t dealt with earlier on definitely have bigger impacts on sleep as you go through life,” he said.
Although primary care physicians and pediatricians should be already asking questions about sleep through anticipatory guidance, he said, intervening earlier for sleep problems is important. He noted children who exhibit sleep problems over time are more likely to have issues in handling their emotions and eventually may develop cognitive issues. “[W]e know that if these problems continue to go through, this paper’s showing us that they have worse effects down the road,” he said.
Impact of the COVID-19 crisis
These problems may also be worsened by the COVID-19 pandemic. Dr. Seay noted that with many parents working from home, sleep schedules can be affected and parents may also be co-sleeping with their children, which can cause chronic insomnia and early waking. To help address sleep issues, especially ones that may have arisen during COVID-19, parents should make sure their children show up for primary care visits to report problems, and clinicians should make a sleep routine a focus of conversations around sleep problems.
Prior to the pandemic, “we already were hitting upon that in sleep clinic, making sure [they] get the same schedule every day,” said Dr. Seay. For parents with children who have “issues with insomnia or waking up during the night, having that routine in place does help to mitigate that a little bit, so if that routine is not there, it can actually exacerbate the issues.”
This study was funded by the Australian federal government. The authors report no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Seay reports no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Williamson AA et al. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2020 Jul 26. doi:10.1111/jcpp.13303.
Sleep problems in children from birth to middle childhood may lead to decreased emotional well-being and quality of life by the time a child is 10-11 years old, a recent longitudinal study has found.
The effects of these impairments increased over time and included internalizing and externalizing concerns, self-control, and quality of life, but did not appear to significantly affect cognitive or academic skills, according to Ariel A. Williamson, PhD, DBSM, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and colleagues. While children with consistent sleep problems experienced the worse outcomes, mild sleep problems also were associated with impairment, the researchers said.
“The range of impairments across academic and psychosocial domains in middle childhood indicate that it is important to screen for sleep problems consistently over the course of a child’s development, especially to target children who experience persistent sleep problems over time,” said Dr. Williamson in a press release.
The researchers examined data from 5,107 children in the Longitudinal Study of Australian Children – Birth Cohort, where sleep problems and well-being outcomes were measured at multiple time points. Behaviors such as difficulty getting off to sleep at night, not happy to sleep alone, and waking during the night were defined as sleep problems. The investigators found five main domains of sleep issues: children who had persistent sleep problems through middle childhood (7.7%), limited sleep problems as an infant or during preschool (9.0%), mild sleep problems over time (14.4%), increased sleep problems during middle childhood (17.0%), and a group that did not experience sleep problems (51.9%).
Caregivers reported sleep issues in the cohort, while well-being outcomes were reported by caregivers and teachers, and tasks were completed by the children at 10-11 years of age. Dr. Williamson and colleagues examined well-being in terms of emotional and behavioral functioning, health-related quality of life, cognitive skills, and academic achievement.
Different reports from teacher and caregivers
Teacher and caregivers reported different effects in children with persistent sleep problems. Teachers reported moderate internalizing (effect size, –0.65; 95% confidence interval [CI],–0.87 to –0.43; P < .001) and externalizing concerns (ES, –0.40; 95% CI, –0.58 to –0.21; P less than .001), compared with children who did not have sleep problems, whereas caregivers reported large internalizing (ES, –0.75; 95% CI, –0.92 to –0.57; P less than .001) and externalizing concerns (ES, –0.70; 95% CI, –0.86 to –0.53; P < .001). Children with persistent sleep problems had moderate impairment of self-control as reported by caregivers, compared with children with no sleep problems (ES, –0.37; 95% CI, –0.52 to –0.21; P < .001). Psychosocial and health-related quality of life reported by caregivers were worse in children with persistent sleep problems, compared with children who did not have sleep problems (ES range, –0.78 to –0.90; 95% CI, –1.06 to –0.56; P < .001).
For children who exhibited increased sleep problems in middle childhood, caregivers (ES for both, –0.61; 95% CI, –0.76 to –0.46; P < .001) and teachers (ES range, –0.29 to –0.39; 95% CI, –0.53 to –0.15; P < .001) reported greater rates of internalizing and externalizing symptoms, compared with children who had no sleep issues.
Small impairments in internalizing internal or externalizing symptoms were seen in children who had limited sleep problems as an infant or in preschool (ES, –0.12; 95% CI, –0.23 to –0.01; P < .05) as reported by teachers, and in children with mild sleep problems over time (ES, –0.19; 95% CI, –0.30 to –0.08; P < .001) as reported by caregivers. There were no significant impairments in self-control for children in either the infant or preschool impairment group or in the group of children with mild sleep problems.
Across all groups, sleep problems did not significantly impair nonverbal reasoning, and most areas of academic competencies were not significantly impaired among groups except in language and literacy, and mathematical thinking for children with persistent sleep problems (ES, –0.41 for both; 95% CI, –0.60 to –0.23; P < .001). Children with increased sleep problems during middle childhood “had few academic and cognitive impairments,” and academic impairments among children with mild sleep problems were not significant.
Expert opinion
Brandon M. Seay MD, FAAP, pediatric pulmonologist and sleep specialist at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, said in an interview that the study is one of the first to offer longitudinal data for impairment in children with sleep problems. He said the paper emphasizes the need for recognizing when children are demonstrating sleep problems. “It just shows that problems that aren’t dealt with earlier on definitely have bigger impacts on sleep as you go through life,” he said.
Although primary care physicians and pediatricians should be already asking questions about sleep through anticipatory guidance, he said, intervening earlier for sleep problems is important. He noted children who exhibit sleep problems over time are more likely to have issues in handling their emotions and eventually may develop cognitive issues. “[W]e know that if these problems continue to go through, this paper’s showing us that they have worse effects down the road,” he said.
Impact of the COVID-19 crisis
These problems may also be worsened by the COVID-19 pandemic. Dr. Seay noted that with many parents working from home, sleep schedules can be affected and parents may also be co-sleeping with their children, which can cause chronic insomnia and early waking. To help address sleep issues, especially ones that may have arisen during COVID-19, parents should make sure their children show up for primary care visits to report problems, and clinicians should make a sleep routine a focus of conversations around sleep problems.
Prior to the pandemic, “we already were hitting upon that in sleep clinic, making sure [they] get the same schedule every day,” said Dr. Seay. For parents with children who have “issues with insomnia or waking up during the night, having that routine in place does help to mitigate that a little bit, so if that routine is not there, it can actually exacerbate the issues.”
This study was funded by the Australian federal government. The authors report no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Seay reports no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Williamson AA et al. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2020 Jul 26. doi:10.1111/jcpp.13303.
FROM JOURNAL OF CHILD PSYCHOLOGY AND PSYCHIATRY
AHA statement recommends dietary screening at routine checkups
A new scientific statement from the American Heart Association recommends incorporating a rapid diet-screening tool into routine primary care visits to inform dietary counseling and integrating the tool into patients’ electronic health record platforms across all healthcare settings.
The statement authors evaluated 15 existing screening tools and, although they did not recommend a specific tool, they did present advantages and disadvantages of some of the tools and encouraged “critical conversations” among clinicians and other specialists to arrive at a tool that would be most appropriate for use in a particular health care setting.
“The key takeaway is for clinicians to incorporate discussion of dietary patterns into routine preventive care appointments because a suboptimal diet is the No. 1 risk factor for cardiovascular disease,” Maya Vadiveloo, PhD, RD, chair of the statement group, said in an interview.
“We also wanted to touch on the fact the screening tool could be incorporated into the EHR and then used for clinical support and for tracking and monitoring the patient’s dietary patterns over time,” said Dr. Vadiveloo, assistant professor of nutrition and food sciences in the College of Health Science, University of Rhode Island, Kingston.
The statement was published online Aug. 7 in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
Competing demands
Poor dietary quality has “surpassed all other mortality risk factors, accounting for 11 million deaths and about 50% of cardiovascular disease (CVD) deaths globally,” the authors wrote.
Diets deficient in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains and high in red and processed meat, added sugars, sodium, and total energy are the “leading determinants” of the risks for CVD and other conditions, so “strategies that promote holistically healthier dietary patterns to reduce chronic disease risk are of contemporary importance.”
Most clinicians and other members of health care teams “do not currently assess or counsel patients about their food and beverage intake during routine clinical care,” the authors observed.
Reasons for this may include lack of training and knowledge, insufficient time, insufficient integration of nutrition services into health care settings, insufficient reimbursement, and “competing demands during the visit,” they noted.
Dr. Vadiveloo said that an evidence-based rapid screening tool can go a long way toward helping to overcome these barriers.
“Research shows that when primary care practitioners discuss diet with patients, the patients are receptive, but we also know that clinical workloads are already very compressed, and adding another thing to a routine preventive care appointment is challenging,” she said. “So we wanted to look and see if there were already screening tools that showed promise as valid, reliable, reflective of the best science, and easy to incorporate into various types of practice settings.”
Top picks
The authors established “theoretical and practice-based criteria” for an optimal diet screening tool for use in the adult population (aged 20 to 75 years). The tool had to:
- Be developed or used within clinical practice in the past 10 years.
- Be evidence-based, reliable, and valid.
- Assess total dietary pattern rather than focusing on a single food or nutrient.
- Be able to be completed and scored at administration without special knowledge or software.
- Give actionable next steps and support to patients.
- Be able track and monitor dietary change over time.
- Be brief.
- Be useful for chronic disease management.
Of the 15 tools reviewed, the three that met the most theoretical and practice-based validity criteria were the Mediterranean Diet Adherence Screener (MEDAS) and its variations; the modified, shortened Rapid Eating Assessment for Participants (REAP), and the modified version of the Starting the Conversation Tool. However, the authors noted that the Powell and Greenberg Screening Tool was the “least time-intensive.”
One size does not fit all
No single tool will be appropriate for all practice settings, so “we would like clinicians to discuss what will work in their particular setting,” Dr. Vadiveloo emphasized.
For example, should the screening tool be completed by the clinician, a member of the health care team, or the patient? Advantages of a tool completed by clinicians or team members include collection of the information in real time, where it can be used in shared decision-making during the encounter and increased reliability because the screen has been completed by a clinician. On the other hand, the clinician might not be able to prioritize administering the screening tool during a short clinical encounter.
Advantages of a tool completed by the patient via an EHR portal is that the patient may feel less risk of judgment by the clinician or health care professional and patients can complete the screen at their convenience. Disadvantages are limited reach into underserved populations and, potentially, less reliability than clinician-administered tools.
“It is advantageous to have tools that can be administered by multiple members of health care teams to ease the demand on clinicians, if such staff is available, but in other settings, self-administration might be better, so we tried to leave it open-ended,” Dr. Vadiveloo explained.
‘Ideal platform’
“The EHR is the ideal platform to prompt clinicians and other members of the health care team to capture dietary data and deliver dietary advice to patients,” the authors observed.
EHRs allow secure storage of data and also enable access to these data when needed at the point of care. They are also important for documentation purposes.
The authors noted that the use of “myriad EHR platforms and versions of platforms” have created “technical challenges.” They recommended “standardized approaches” for transmitting health data that will “more seamlessly allow rapid diet screeners to be implemented in the EHR.”
They also recommended that the prototypes of rapid diet screeners be tested by end users prior to implementation within particular clinics. “Gathering these data ahead of time can improve the uptake of the application in the real world,” they stated.
Dr. Vadiveloo added that dietary counseling can be conducted by several members of a health care team, such as a dietitian, not just by the physician. Or the patient may need to be referred to a dietitian for counseling and follow-up.
The authors concluded by characterizing the AHA statement as “a call to action ... designed to accelerate efforts to make diet quality assessment an integral part of office-based care delivery by encouraging critical conversations among clinicians, individuals with diet/lifestyle expertise, and specialists in information technology.”
Dr. Vadiveloo has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original paper.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A new scientific statement from the American Heart Association recommends incorporating a rapid diet-screening tool into routine primary care visits to inform dietary counseling and integrating the tool into patients’ electronic health record platforms across all healthcare settings.
The statement authors evaluated 15 existing screening tools and, although they did not recommend a specific tool, they did present advantages and disadvantages of some of the tools and encouraged “critical conversations” among clinicians and other specialists to arrive at a tool that would be most appropriate for use in a particular health care setting.
“The key takeaway is for clinicians to incorporate discussion of dietary patterns into routine preventive care appointments because a suboptimal diet is the No. 1 risk factor for cardiovascular disease,” Maya Vadiveloo, PhD, RD, chair of the statement group, said in an interview.
“We also wanted to touch on the fact the screening tool could be incorporated into the EHR and then used for clinical support and for tracking and monitoring the patient’s dietary patterns over time,” said Dr. Vadiveloo, assistant professor of nutrition and food sciences in the College of Health Science, University of Rhode Island, Kingston.
The statement was published online Aug. 7 in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
Competing demands
Poor dietary quality has “surpassed all other mortality risk factors, accounting for 11 million deaths and about 50% of cardiovascular disease (CVD) deaths globally,” the authors wrote.
Diets deficient in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains and high in red and processed meat, added sugars, sodium, and total energy are the “leading determinants” of the risks for CVD and other conditions, so “strategies that promote holistically healthier dietary patterns to reduce chronic disease risk are of contemporary importance.”
Most clinicians and other members of health care teams “do not currently assess or counsel patients about their food and beverage intake during routine clinical care,” the authors observed.
Reasons for this may include lack of training and knowledge, insufficient time, insufficient integration of nutrition services into health care settings, insufficient reimbursement, and “competing demands during the visit,” they noted.
Dr. Vadiveloo said that an evidence-based rapid screening tool can go a long way toward helping to overcome these barriers.
“Research shows that when primary care practitioners discuss diet with patients, the patients are receptive, but we also know that clinical workloads are already very compressed, and adding another thing to a routine preventive care appointment is challenging,” she said. “So we wanted to look and see if there were already screening tools that showed promise as valid, reliable, reflective of the best science, and easy to incorporate into various types of practice settings.”
Top picks
The authors established “theoretical and practice-based criteria” for an optimal diet screening tool for use in the adult population (aged 20 to 75 years). The tool had to:
- Be developed or used within clinical practice in the past 10 years.
- Be evidence-based, reliable, and valid.
- Assess total dietary pattern rather than focusing on a single food or nutrient.
- Be able to be completed and scored at administration without special knowledge or software.
- Give actionable next steps and support to patients.
- Be able track and monitor dietary change over time.
- Be brief.
- Be useful for chronic disease management.
Of the 15 tools reviewed, the three that met the most theoretical and practice-based validity criteria were the Mediterranean Diet Adherence Screener (MEDAS) and its variations; the modified, shortened Rapid Eating Assessment for Participants (REAP), and the modified version of the Starting the Conversation Tool. However, the authors noted that the Powell and Greenberg Screening Tool was the “least time-intensive.”
One size does not fit all
No single tool will be appropriate for all practice settings, so “we would like clinicians to discuss what will work in their particular setting,” Dr. Vadiveloo emphasized.
For example, should the screening tool be completed by the clinician, a member of the health care team, or the patient? Advantages of a tool completed by clinicians or team members include collection of the information in real time, where it can be used in shared decision-making during the encounter and increased reliability because the screen has been completed by a clinician. On the other hand, the clinician might not be able to prioritize administering the screening tool during a short clinical encounter.
Advantages of a tool completed by the patient via an EHR portal is that the patient may feel less risk of judgment by the clinician or health care professional and patients can complete the screen at their convenience. Disadvantages are limited reach into underserved populations and, potentially, less reliability than clinician-administered tools.
“It is advantageous to have tools that can be administered by multiple members of health care teams to ease the demand on clinicians, if such staff is available, but in other settings, self-administration might be better, so we tried to leave it open-ended,” Dr. Vadiveloo explained.
‘Ideal platform’
“The EHR is the ideal platform to prompt clinicians and other members of the health care team to capture dietary data and deliver dietary advice to patients,” the authors observed.
EHRs allow secure storage of data and also enable access to these data when needed at the point of care. They are also important for documentation purposes.
The authors noted that the use of “myriad EHR platforms and versions of platforms” have created “technical challenges.” They recommended “standardized approaches” for transmitting health data that will “more seamlessly allow rapid diet screeners to be implemented in the EHR.”
They also recommended that the prototypes of rapid diet screeners be tested by end users prior to implementation within particular clinics. “Gathering these data ahead of time can improve the uptake of the application in the real world,” they stated.
Dr. Vadiveloo added that dietary counseling can be conducted by several members of a health care team, such as a dietitian, not just by the physician. Or the patient may need to be referred to a dietitian for counseling and follow-up.
The authors concluded by characterizing the AHA statement as “a call to action ... designed to accelerate efforts to make diet quality assessment an integral part of office-based care delivery by encouraging critical conversations among clinicians, individuals with diet/lifestyle expertise, and specialists in information technology.”
Dr. Vadiveloo has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original paper.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A new scientific statement from the American Heart Association recommends incorporating a rapid diet-screening tool into routine primary care visits to inform dietary counseling and integrating the tool into patients’ electronic health record platforms across all healthcare settings.
The statement authors evaluated 15 existing screening tools and, although they did not recommend a specific tool, they did present advantages and disadvantages of some of the tools and encouraged “critical conversations” among clinicians and other specialists to arrive at a tool that would be most appropriate for use in a particular health care setting.
“The key takeaway is for clinicians to incorporate discussion of dietary patterns into routine preventive care appointments because a suboptimal diet is the No. 1 risk factor for cardiovascular disease,” Maya Vadiveloo, PhD, RD, chair of the statement group, said in an interview.
“We also wanted to touch on the fact the screening tool could be incorporated into the EHR and then used for clinical support and for tracking and monitoring the patient’s dietary patterns over time,” said Dr. Vadiveloo, assistant professor of nutrition and food sciences in the College of Health Science, University of Rhode Island, Kingston.
The statement was published online Aug. 7 in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
Competing demands
Poor dietary quality has “surpassed all other mortality risk factors, accounting for 11 million deaths and about 50% of cardiovascular disease (CVD) deaths globally,” the authors wrote.
Diets deficient in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains and high in red and processed meat, added sugars, sodium, and total energy are the “leading determinants” of the risks for CVD and other conditions, so “strategies that promote holistically healthier dietary patterns to reduce chronic disease risk are of contemporary importance.”
Most clinicians and other members of health care teams “do not currently assess or counsel patients about their food and beverage intake during routine clinical care,” the authors observed.
Reasons for this may include lack of training and knowledge, insufficient time, insufficient integration of nutrition services into health care settings, insufficient reimbursement, and “competing demands during the visit,” they noted.
Dr. Vadiveloo said that an evidence-based rapid screening tool can go a long way toward helping to overcome these barriers.
“Research shows that when primary care practitioners discuss diet with patients, the patients are receptive, but we also know that clinical workloads are already very compressed, and adding another thing to a routine preventive care appointment is challenging,” she said. “So we wanted to look and see if there were already screening tools that showed promise as valid, reliable, reflective of the best science, and easy to incorporate into various types of practice settings.”
Top picks
The authors established “theoretical and practice-based criteria” for an optimal diet screening tool for use in the adult population (aged 20 to 75 years). The tool had to:
- Be developed or used within clinical practice in the past 10 years.
- Be evidence-based, reliable, and valid.
- Assess total dietary pattern rather than focusing on a single food or nutrient.
- Be able to be completed and scored at administration without special knowledge or software.
- Give actionable next steps and support to patients.
- Be able track and monitor dietary change over time.
- Be brief.
- Be useful for chronic disease management.
Of the 15 tools reviewed, the three that met the most theoretical and practice-based validity criteria were the Mediterranean Diet Adherence Screener (MEDAS) and its variations; the modified, shortened Rapid Eating Assessment for Participants (REAP), and the modified version of the Starting the Conversation Tool. However, the authors noted that the Powell and Greenberg Screening Tool was the “least time-intensive.”
One size does not fit all
No single tool will be appropriate for all practice settings, so “we would like clinicians to discuss what will work in their particular setting,” Dr. Vadiveloo emphasized.
For example, should the screening tool be completed by the clinician, a member of the health care team, or the patient? Advantages of a tool completed by clinicians or team members include collection of the information in real time, where it can be used in shared decision-making during the encounter and increased reliability because the screen has been completed by a clinician. On the other hand, the clinician might not be able to prioritize administering the screening tool during a short clinical encounter.
Advantages of a tool completed by the patient via an EHR portal is that the patient may feel less risk of judgment by the clinician or health care professional and patients can complete the screen at their convenience. Disadvantages are limited reach into underserved populations and, potentially, less reliability than clinician-administered tools.
“It is advantageous to have tools that can be administered by multiple members of health care teams to ease the demand on clinicians, if such staff is available, but in other settings, self-administration might be better, so we tried to leave it open-ended,” Dr. Vadiveloo explained.
‘Ideal platform’
“The EHR is the ideal platform to prompt clinicians and other members of the health care team to capture dietary data and deliver dietary advice to patients,” the authors observed.
EHRs allow secure storage of data and also enable access to these data when needed at the point of care. They are also important for documentation purposes.
The authors noted that the use of “myriad EHR platforms and versions of platforms” have created “technical challenges.” They recommended “standardized approaches” for transmitting health data that will “more seamlessly allow rapid diet screeners to be implemented in the EHR.”
They also recommended that the prototypes of rapid diet screeners be tested by end users prior to implementation within particular clinics. “Gathering these data ahead of time can improve the uptake of the application in the real world,” they stated.
Dr. Vadiveloo added that dietary counseling can be conducted by several members of a health care team, such as a dietitian, not just by the physician. Or the patient may need to be referred to a dietitian for counseling and follow-up.
The authors concluded by characterizing the AHA statement as “a call to action ... designed to accelerate efforts to make diet quality assessment an integral part of office-based care delivery by encouraging critical conversations among clinicians, individuals with diet/lifestyle expertise, and specialists in information technology.”
Dr. Vadiveloo has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original paper.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 cases in children nearly doubled in just 4 weeks
The cumulative number of new COVID-19 cases among children in the United States jumped by 90% during a recent 4-week period, according to a report that confirms children are not immune to the coronavirus.
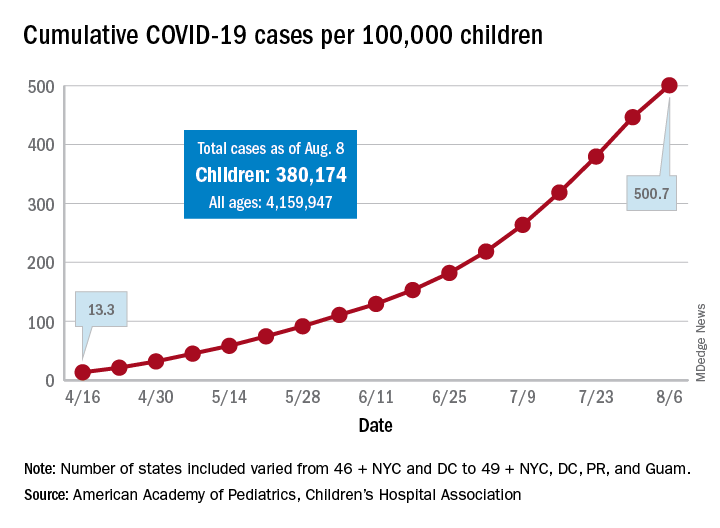
“In areas with rapid community spread, it’s likely that more children will also be infected, and these data show that,” Sally Goza, MD, president of the American Academy of Pediatrics, said in a written statement. “I urge people to wear cloth face coverings and be diligent in social distancing and hand-washing. It is up to us to make the difference, community by community.”
The joint report from the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association draws on data from state and local health departments in 49 states, New York City, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children as of Aug. 6, 2020, was 380,174, and that number is 90% higher – an increase of 179,990 cases – than the total on July 9, just 4 weeks earlier, the two organizations said in the report.
and 27 states out of 47 with available data now report that over 10% of their cases were children, with Wyoming the highest at 16.5% and New Jersey the lowest at 2.9%, the report data show.
Alabama has a higher percentage of 22.5%, but the state has been reporting cases in individuals aged 0-24 years as child cases since May 7. The report’s findings are somewhat limited by differences in reporting among the states and by “gaps in the data they are reporting [that affect] how the data can be interpreted,” the AAP said in its statement.
The cumulative number of cases per 100,000 children has risen from 13.3 in mid-April, when the total number was 9,259 cases, to 500.7 per 100,000 as of Aug. 6, and there are now 21 states, along with the District of Columbia, reporting a rate of over 500 cases per 100,000 children. Arizona has the highest rate at 1,206.4, followed by South Carolina (1,074.4) and Tennessee (1,050.8), the AAP and the CHA said.
In New York City, the early epicenter of the pandemic, the 390.5 cases per 100,000 children have been reported, and in New Jersey, which joined New York in the initial surge of cases, the number is 269.5. As of Aug. 6, Hawaii had the fewest cases of any state at 91.2 per 100,000, according to the report.
Children continue to represent a very low proportion of COVID-19 deaths, “but as case counts rise across the board, that is likely to impact more children with severe illness as well,” Sean O’Leary, MD, MPH, vice chair of the AAP’s committee on infectious diseases, said in the AAP statement.
It is possible that “some of the increase in numbers of cases in children could be due to more testing. Early in the pandemic, testing only occurred for the sickest individuals. Now that there is more testing capacity … the numbers reflect a broader slice of the population, including children who may have mild or few symptoms,” the AAP suggested.
This article was updated on 8/17/2020.
The cumulative number of new COVID-19 cases among children in the United States jumped by 90% during a recent 4-week period, according to a report that confirms children are not immune to the coronavirus.

“In areas with rapid community spread, it’s likely that more children will also be infected, and these data show that,” Sally Goza, MD, president of the American Academy of Pediatrics, said in a written statement. “I urge people to wear cloth face coverings and be diligent in social distancing and hand-washing. It is up to us to make the difference, community by community.”
The joint report from the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association draws on data from state and local health departments in 49 states, New York City, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children as of Aug. 6, 2020, was 380,174, and that number is 90% higher – an increase of 179,990 cases – than the total on July 9, just 4 weeks earlier, the two organizations said in the report.
and 27 states out of 47 with available data now report that over 10% of their cases were children, with Wyoming the highest at 16.5% and New Jersey the lowest at 2.9%, the report data show.
Alabama has a higher percentage of 22.5%, but the state has been reporting cases in individuals aged 0-24 years as child cases since May 7. The report’s findings are somewhat limited by differences in reporting among the states and by “gaps in the data they are reporting [that affect] how the data can be interpreted,” the AAP said in its statement.
The cumulative number of cases per 100,000 children has risen from 13.3 in mid-April, when the total number was 9,259 cases, to 500.7 per 100,000 as of Aug. 6, and there are now 21 states, along with the District of Columbia, reporting a rate of over 500 cases per 100,000 children. Arizona has the highest rate at 1,206.4, followed by South Carolina (1,074.4) and Tennessee (1,050.8), the AAP and the CHA said.
In New York City, the early epicenter of the pandemic, the 390.5 cases per 100,000 children have been reported, and in New Jersey, which joined New York in the initial surge of cases, the number is 269.5. As of Aug. 6, Hawaii had the fewest cases of any state at 91.2 per 100,000, according to the report.
Children continue to represent a very low proportion of COVID-19 deaths, “but as case counts rise across the board, that is likely to impact more children with severe illness as well,” Sean O’Leary, MD, MPH, vice chair of the AAP’s committee on infectious diseases, said in the AAP statement.
It is possible that “some of the increase in numbers of cases in children could be due to more testing. Early in the pandemic, testing only occurred for the sickest individuals. Now that there is more testing capacity … the numbers reflect a broader slice of the population, including children who may have mild or few symptoms,” the AAP suggested.
This article was updated on 8/17/2020.
The cumulative number of new COVID-19 cases among children in the United States jumped by 90% during a recent 4-week period, according to a report that confirms children are not immune to the coronavirus.

“In areas with rapid community spread, it’s likely that more children will also be infected, and these data show that,” Sally Goza, MD, president of the American Academy of Pediatrics, said in a written statement. “I urge people to wear cloth face coverings and be diligent in social distancing and hand-washing. It is up to us to make the difference, community by community.”
The joint report from the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association draws on data from state and local health departments in 49 states, New York City, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children as of Aug. 6, 2020, was 380,174, and that number is 90% higher – an increase of 179,990 cases – than the total on July 9, just 4 weeks earlier, the two organizations said in the report.
and 27 states out of 47 with available data now report that over 10% of their cases were children, with Wyoming the highest at 16.5% and New Jersey the lowest at 2.9%, the report data show.
Alabama has a higher percentage of 22.5%, but the state has been reporting cases in individuals aged 0-24 years as child cases since May 7. The report’s findings are somewhat limited by differences in reporting among the states and by “gaps in the data they are reporting [that affect] how the data can be interpreted,” the AAP said in its statement.
The cumulative number of cases per 100,000 children has risen from 13.3 in mid-April, when the total number was 9,259 cases, to 500.7 per 100,000 as of Aug. 6, and there are now 21 states, along with the District of Columbia, reporting a rate of over 500 cases per 100,000 children. Arizona has the highest rate at 1,206.4, followed by South Carolina (1,074.4) and Tennessee (1,050.8), the AAP and the CHA said.
In New York City, the early epicenter of the pandemic, the 390.5 cases per 100,000 children have been reported, and in New Jersey, which joined New York in the initial surge of cases, the number is 269.5. As of Aug. 6, Hawaii had the fewest cases of any state at 91.2 per 100,000, according to the report.
Children continue to represent a very low proportion of COVID-19 deaths, “but as case counts rise across the board, that is likely to impact more children with severe illness as well,” Sean O’Leary, MD, MPH, vice chair of the AAP’s committee on infectious diseases, said in the AAP statement.
It is possible that “some of the increase in numbers of cases in children could be due to more testing. Early in the pandemic, testing only occurred for the sickest individuals. Now that there is more testing capacity … the numbers reflect a broader slice of the population, including children who may have mild or few symptoms,” the AAP suggested.
This article was updated on 8/17/2020.
Successful bowel preps linked with modifiable risk factors
Background: IBP is very common and associated with increased length of stay and cost of care. Many nonmodifiable risk factors have been identified such as socioeconomic status, male gender, and increased age, but no studies have been done to look at modifiable risk factors such as medication use, timing of colonoscopy, and diet before colonoscopy. Furthermore, no studies have been done to assess the effects of these modifiable factors on IBP.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study using multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Setting: Cleveland Clinic Hospitals in Ohio and Florida.
Synopsis: Records of 8,819 patients (aged greater than 18 years) undergoing colonoscopy at Cleveland Clinic between January 2011 and June 2017 were reviewed. They found that 51% had IBP. Modifiable risk factors, including opiate use within 3 days of colonoscopy, colonoscopy performed before noon, and solid diet the day before colonoscopy, were associated with IBP. After adjustment for these variables, they found the rates of IBP were reduced by 5.6%. They also found that patients who had IBP had increased length of stay by 1 day (6 days vs. 5 days; P less than .001). This translates into 494 unnecessary hospital days or approximately $1 million dollars in unnecessary costs based on the number of patients (almost 9,000).
This study was performed in a single institution so it may be difficult to extrapolate to other institutions. Further studies need to be performed using multicenter institutions to assess accuracy of data.
Bottom line: Liquid diet or nothing by mouth (NPO) 1 day prior to colonoscopy, performing colonoscopy before noon, and avoiding opioids 3 days prior to colonoscopy are modifiable risk factors that may decrease the rate of inadequate bowel preparations in hospitalized patients.
Citation: Garber A et al. Modifiable factors associated with quality of bowel preparation among hospitalized patients undergoing colonoscopy. J Hosp Med. 2019;5:278-83.
Dr. Newsom is a hospitalist at Ochsner Health System, New Orleans.
Background: IBP is very common and associated with increased length of stay and cost of care. Many nonmodifiable risk factors have been identified such as socioeconomic status, male gender, and increased age, but no studies have been done to look at modifiable risk factors such as medication use, timing of colonoscopy, and diet before colonoscopy. Furthermore, no studies have been done to assess the effects of these modifiable factors on IBP.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study using multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Setting: Cleveland Clinic Hospitals in Ohio and Florida.
Synopsis: Records of 8,819 patients (aged greater than 18 years) undergoing colonoscopy at Cleveland Clinic between January 2011 and June 2017 were reviewed. They found that 51% had IBP. Modifiable risk factors, including opiate use within 3 days of colonoscopy, colonoscopy performed before noon, and solid diet the day before colonoscopy, were associated with IBP. After adjustment for these variables, they found the rates of IBP were reduced by 5.6%. They also found that patients who had IBP had increased length of stay by 1 day (6 days vs. 5 days; P less than .001). This translates into 494 unnecessary hospital days or approximately $1 million dollars in unnecessary costs based on the number of patients (almost 9,000).
This study was performed in a single institution so it may be difficult to extrapolate to other institutions. Further studies need to be performed using multicenter institutions to assess accuracy of data.
Bottom line: Liquid diet or nothing by mouth (NPO) 1 day prior to colonoscopy, performing colonoscopy before noon, and avoiding opioids 3 days prior to colonoscopy are modifiable risk factors that may decrease the rate of inadequate bowel preparations in hospitalized patients.
Citation: Garber A et al. Modifiable factors associated with quality of bowel preparation among hospitalized patients undergoing colonoscopy. J Hosp Med. 2019;5:278-83.
Dr. Newsom is a hospitalist at Ochsner Health System, New Orleans.
Background: IBP is very common and associated with increased length of stay and cost of care. Many nonmodifiable risk factors have been identified such as socioeconomic status, male gender, and increased age, but no studies have been done to look at modifiable risk factors such as medication use, timing of colonoscopy, and diet before colonoscopy. Furthermore, no studies have been done to assess the effects of these modifiable factors on IBP.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study using multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Setting: Cleveland Clinic Hospitals in Ohio and Florida.
Synopsis: Records of 8,819 patients (aged greater than 18 years) undergoing colonoscopy at Cleveland Clinic between January 2011 and June 2017 were reviewed. They found that 51% had IBP. Modifiable risk factors, including opiate use within 3 days of colonoscopy, colonoscopy performed before noon, and solid diet the day before colonoscopy, were associated with IBP. After adjustment for these variables, they found the rates of IBP were reduced by 5.6%. They also found that patients who had IBP had increased length of stay by 1 day (6 days vs. 5 days; P less than .001). This translates into 494 unnecessary hospital days or approximately $1 million dollars in unnecessary costs based on the number of patients (almost 9,000).
This study was performed in a single institution so it may be difficult to extrapolate to other institutions. Further studies need to be performed using multicenter institutions to assess accuracy of data.
Bottom line: Liquid diet or nothing by mouth (NPO) 1 day prior to colonoscopy, performing colonoscopy before noon, and avoiding opioids 3 days prior to colonoscopy are modifiable risk factors that may decrease the rate of inadequate bowel preparations in hospitalized patients.
Citation: Garber A et al. Modifiable factors associated with quality of bowel preparation among hospitalized patients undergoing colonoscopy. J Hosp Med. 2019;5:278-83.
Dr. Newsom is a hospitalist at Ochsner Health System, New Orleans.
iResident: Virtual care on hospital medicine teaching services during a pandemic
At the start of each shift on his clinical service with rotating internal medicine residents, Benji Mathews, MD, SFHM, now adds a few components to his usual preparation. First, visiting the Minnesota Department of Health and various organizational websites to review the latest COVID-19 updates and guidelines. Next comes checking to see where he needs to pick up the surgical mask and eye protection that he will need to wear through the day. Last, he evaluates which of his patients are in telemedicine-equipped rooms; this last change has fast become a crucial part of working with his resident learners during a pandemic.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, residents and residency programs find themselves in a unique situation. Balancing the educational needs of a training program with the safety of trainees is a challenging task, specifically when taking care of patients who are COVID-19 positive or patients under investigation (PUI). One increasingly available tool that can help protect trainees while continuing to prioritize patient care and medical education is the use of telemedicine for virtual rounding. For our internal medicine residents through the University of Minnesota Internal Medicine Residency program rotating at Regions Hospital in Saint Paul, Minn., we have used video visits to continue our mandate as both health care and education professionals.
Virtual care decision tree
Virtual care can mitigate exposure risk, minimize use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and improve communications with patients and their families. To guide our teaching teams on the optimal situations for telemedicine, we needed to select those patients who would be most appropriate for a virtual visit.
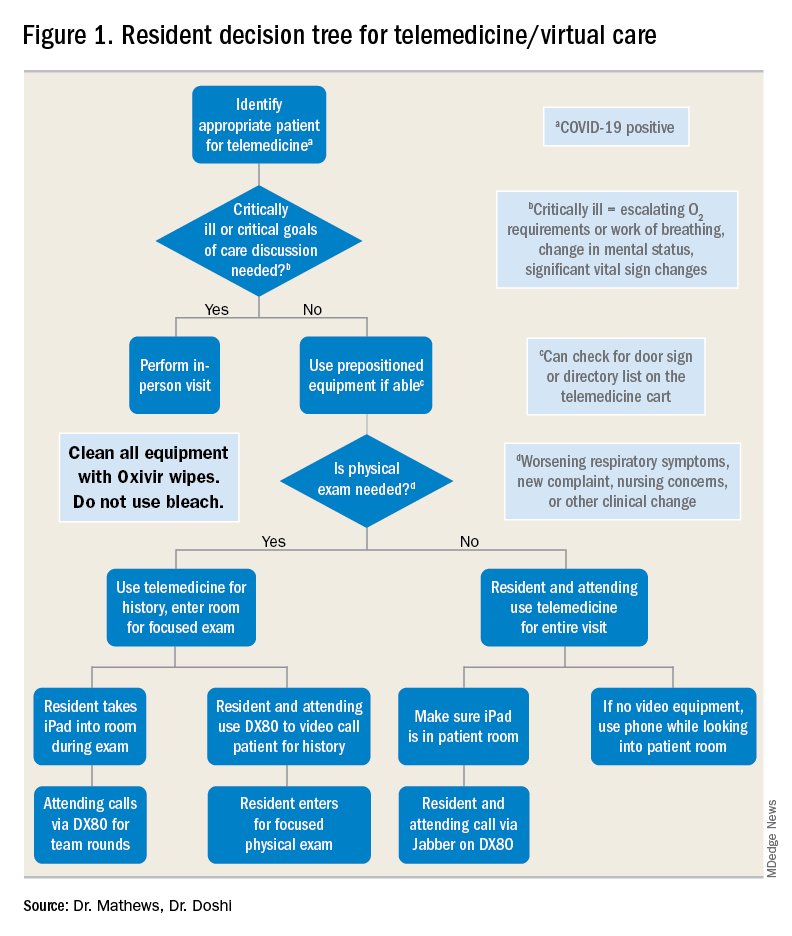
For example, patients with advanced dementia, or intubated in the intensive care unit, would have less utility from a real-time video encounter. Further, we implemented a simple decision tree (Figure 1). First, the team needs to decide whether the patient needs an immediate in-person assessment; for instance, for critically ill patients or those who need end-of-life care discussions, telemedicine would not be an appropriate modality. Next, the decision is made on whether a patient requires an in-person exam at that time. The idea of forgoing the in-person physical exam may run counterintuitive to the core training medical providers undergo, but in certain circumstances telemedicine can still provide the appropriate level of care a patient requires.
Virtual rounding with residents: Pros and cons
Through the course of this pandemic, there have many questions raised regarding how to handle inpatient teaching services: Should resident teams be assigned COVID-19 positives or PUIs? How do you optimize assessing and learning from patients’ conditions that require human touch? Should all members of the teaching team be donning PPE and entering the patient room?
Internal medicine residents in our hospital have been assigned COVID-19 positive and PUI patients. With proper PPE, and donning and doffing practices, residents may continue to learn from this important training opportunity while also optimizing care for patients supplemented by telemedicine. This pandemic has flattened the hierarchy; often residents are teaching their attendings much of the latest literature and best practices around COVID-19. Residents also benefit by joining the organization’s daily virtual interprofessional COVID-19 huddle where they partner with infectious disease, critical care, pharmacy, and other experts to collaborate in the care of these patients.
There have been counterarguments made for residents joining the front lines with COVID-19 patients. Some have conditions that limit them from seeing this subgroup of patients, such as their immune status or other issues. For these residents, we do not assign COVID-19–positive patients. However, they may continue to support in virtually updating COVID-19 patients and their families. A second argument has been the use of PPE. We have implemented telemedicine to limit the total number of exposures and have a protocol for the fewest number of providers possible to see any at-risk or confirmed COVID-19 patient. For example, a resident who sees a COVID-19 patient in person may also be simultaneously virtually supervised by the attending.
Webside manner
The physical exam is only one of several operational considerations when delivering virtual care, whether with a teaching or nonteaching service. One important aspect is the “webside manner” of the provider, the virtual analogue to bedside manner.
Inherent parts of in-person encounters, such as eye contact and allowing for patients to finish their sentences, have added nuances with virtual care. For instance, providers must adjust to looking into the web camera to make eye contact, even though the patient’s face may be on the screen below. Additionally, for patients who are hard of hearing or unfamiliar with video calling, providers must be cognizant of projecting well over an Internet connection and timing responses to avoid overlapping conversation.
Similarly, there are nuances to the virtual physical exam, some specific to care in the COVID-19 era. In our previous virtual care practice, a bedside facilitator assisted in using tools such a digital stethoscope. In contrast, our current practice aims to refine the observational skills of our learners in conjunction with chart review, vital signs, and actively incorporating the patient in the physical exam. This does not mean asking them to auscultate themselves, but is more toward allowing patients to participate in focused evaluations, such as assessing abdominal tenderness or working through range of motion. Remote guidance for virtual exams also extends itself to teaching teams; for example, in our practice, we have been able to conduct bedside ultrasound teaching with in-person team members and a virtual facilitator.
Maskless connections: ‘Face-to-face’ visits with patients
As many hospitalists have witnessed, COVID-19 is so isolating for patients and their families. Patients have limited visitors, and their care team members are aiming to minimize exposures. Those who are entering the rooms wear masks and face shields that limit connecting with patients in a truly “face-to-face” manner. Telemedicine provides a face-to-face encounter that arguably improves upon portions of the traditional in-person encounter during this pandemic, with providers wearing PPE. For medical learners, gaining the interpersonal skills essential for health care professionals has been skewed with pandemic-related limitations; telemedicine can provide a tool to adapt to this unique era and augment this important educational piece.
Limitations, equity, and technological considerations
Realistically, the virtual exam during COVID-19 does have its limitations. An important part of virtual care and teaching services is instilling the appropriate times for use of telemedicine. If a patient has a clinical change (such as increase in FiO2 requirements) or other clinical need, there should be no hesitation for learners to conduct in-person assessments with appropriate PPE.
Nonexam indications are just as important – for example, if a patient requires extensive goals of care counseling, we recommend this not be done virtually. Other indications may vary between organizations; in our practice, we suggest at least one in-person assessment on the initial and discharge hospital days. Regardless of the specific indications, a successful virtual inpatient teaching service must be predicated on outlining the appropriate uses of telemedicine.
In the United States, there are already health care disparities for people of color and non–English speakers. If there is not a careful consideration for these marginalized groups, their health disparities could be further exacerbated – not just around COVID-19, but also for other inpatient conditions where telemedicine is being used. Groups whose equity must be thoughtfully managed include those who do not speak English and those who do not have access to smartphones or the Internet. Our HealthPartners organization has implemented the integration of interpreters for virtual three-way connections with patients and their clinicians to help mitigate this for non–English speakers. Additionally, utilizing easy-to-use tablets and telemedicine-capable carts has helped patients overcome technology barriers.
Last, the members of the teaching team must know the essential technical aspects of the technology they are using. Robust information technology (IT) support is also needed, but no matter how simple the equipment may be, staff and trainees must know how to both operate it and handle basic troubleshooting (such as audio or video disconnections). This also dovetails with the important element of on-boarding other members of the care team. In our practice, nursing staff, chaplains, interpreters, and dietitians also use virtual care as part of their workflow. However, even if it is used only by the teaching team, orienting other care team members will limit technical problems such as equipment being turned off or moved out of position.
Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine adoption was limited because of lack of awareness, barriers in training, understanding, and narrow beliefs regarding the innovation. The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in a remarkable increase in the provision of telemedicine services in the inpatient hospital medicine services. Importantly, it is, and should be, a developing part of the education and training for health care learners. This pandemic has underscored the need for providing telemedicine services that will likely long outlast this crisis, and to support our health care learners in being effective “iResidents” on our care teams.
Takeaways
- The future of graduate medical education involves virtual care.
The COVID-19 pandemic response has demonstrated that virtual care plays an instrumental part in patient care, and its effects will not dissipate when the pandemic is done. The curriculum for health care trainees should incorporate telemedicine competencies so that they may more effectively leverage this technology for improving care delivery.
- Selection of telemedicine patients must be stratified.
In order to obtain the highest utility for medical learners on telemedicine, there needs to be a clear decision process for which patients can be seen virtually. This involves both clinical criteria, such as avoiding virtual care for end-of-life discussions, and patient criteria, such as those who are hard of hearing.
- Virtual communication requires new communication skills.
Seeing patients via telemedicine mandates a different skill set than in-person communication. Learners must improve their “webside manner” in order to build the patient-provider relationship. Instilling these tools can pay dividends in settings where telemedicine has high yield, such as maskless communication during a pandemic.
- Health disparities could be further exacerbated by telemedicine and should not be overlooked.
Equity in access to health care applies to telemedicine as it does to many other elements. There are multiple groups that can suffer from disparities, such as patients who need interpreters, or those who have lower technological literacy and access to digital devices. Creating awareness of these pitfalls in virtual care can help medical learners recognize and support in creative solutions for these factors.
Dr. Mathews is chief, hospital medicine, at Regions Hospital, HealthPartners, St. Paul, Minn. Dr. Doshi is telemedicine director, hospital medicine, HealthPartners.
At the start of each shift on his clinical service with rotating internal medicine residents, Benji Mathews, MD, SFHM, now adds a few components to his usual preparation. First, visiting the Minnesota Department of Health and various organizational websites to review the latest COVID-19 updates and guidelines. Next comes checking to see where he needs to pick up the surgical mask and eye protection that he will need to wear through the day. Last, he evaluates which of his patients are in telemedicine-equipped rooms; this last change has fast become a crucial part of working with his resident learners during a pandemic.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, residents and residency programs find themselves in a unique situation. Balancing the educational needs of a training program with the safety of trainees is a challenging task, specifically when taking care of patients who are COVID-19 positive or patients under investigation (PUI). One increasingly available tool that can help protect trainees while continuing to prioritize patient care and medical education is the use of telemedicine for virtual rounding. For our internal medicine residents through the University of Minnesota Internal Medicine Residency program rotating at Regions Hospital in Saint Paul, Minn., we have used video visits to continue our mandate as both health care and education professionals.
Virtual care decision tree
Virtual care can mitigate exposure risk, minimize use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and improve communications with patients and their families. To guide our teaching teams on the optimal situations for telemedicine, we needed to select those patients who would be most appropriate for a virtual visit.

For example, patients with advanced dementia, or intubated in the intensive care unit, would have less utility from a real-time video encounter. Further, we implemented a simple decision tree (Figure 1). First, the team needs to decide whether the patient needs an immediate in-person assessment; for instance, for critically ill patients or those who need end-of-life care discussions, telemedicine would not be an appropriate modality. Next, the decision is made on whether a patient requires an in-person exam at that time. The idea of forgoing the in-person physical exam may run counterintuitive to the core training medical providers undergo, but in certain circumstances telemedicine can still provide the appropriate level of care a patient requires.
Virtual rounding with residents: Pros and cons
Through the course of this pandemic, there have many questions raised regarding how to handle inpatient teaching services: Should resident teams be assigned COVID-19 positives or PUIs? How do you optimize assessing and learning from patients’ conditions that require human touch? Should all members of the teaching team be donning PPE and entering the patient room?
Internal medicine residents in our hospital have been assigned COVID-19 positive and PUI patients. With proper PPE, and donning and doffing practices, residents may continue to learn from this important training opportunity while also optimizing care for patients supplemented by telemedicine. This pandemic has flattened the hierarchy; often residents are teaching their attendings much of the latest literature and best practices around COVID-19. Residents also benefit by joining the organization’s daily virtual interprofessional COVID-19 huddle where they partner with infectious disease, critical care, pharmacy, and other experts to collaborate in the care of these patients.
There have been counterarguments made for residents joining the front lines with COVID-19 patients. Some have conditions that limit them from seeing this subgroup of patients, such as their immune status or other issues. For these residents, we do not assign COVID-19–positive patients. However, they may continue to support in virtually updating COVID-19 patients and their families. A second argument has been the use of PPE. We have implemented telemedicine to limit the total number of exposures and have a protocol for the fewest number of providers possible to see any at-risk or confirmed COVID-19 patient. For example, a resident who sees a COVID-19 patient in person may also be simultaneously virtually supervised by the attending.
Webside manner
The physical exam is only one of several operational considerations when delivering virtual care, whether with a teaching or nonteaching service. One important aspect is the “webside manner” of the provider, the virtual analogue to bedside manner.
Inherent parts of in-person encounters, such as eye contact and allowing for patients to finish their sentences, have added nuances with virtual care. For instance, providers must adjust to looking into the web camera to make eye contact, even though the patient’s face may be on the screen below. Additionally, for patients who are hard of hearing or unfamiliar with video calling, providers must be cognizant of projecting well over an Internet connection and timing responses to avoid overlapping conversation.
Similarly, there are nuances to the virtual physical exam, some specific to care in the COVID-19 era. In our previous virtual care practice, a bedside facilitator assisted in using tools such a digital stethoscope. In contrast, our current practice aims to refine the observational skills of our learners in conjunction with chart review, vital signs, and actively incorporating the patient in the physical exam. This does not mean asking them to auscultate themselves, but is more toward allowing patients to participate in focused evaluations, such as assessing abdominal tenderness or working through range of motion. Remote guidance for virtual exams also extends itself to teaching teams; for example, in our practice, we have been able to conduct bedside ultrasound teaching with in-person team members and a virtual facilitator.
Maskless connections: ‘Face-to-face’ visits with patients
As many hospitalists have witnessed, COVID-19 is so isolating for patients and their families. Patients have limited visitors, and their care team members are aiming to minimize exposures. Those who are entering the rooms wear masks and face shields that limit connecting with patients in a truly “face-to-face” manner. Telemedicine provides a face-to-face encounter that arguably improves upon portions of the traditional in-person encounter during this pandemic, with providers wearing PPE. For medical learners, gaining the interpersonal skills essential for health care professionals has been skewed with pandemic-related limitations; telemedicine can provide a tool to adapt to this unique era and augment this important educational piece.
Limitations, equity, and technological considerations
Realistically, the virtual exam during COVID-19 does have its limitations. An important part of virtual care and teaching services is instilling the appropriate times for use of telemedicine. If a patient has a clinical change (such as increase in FiO2 requirements) or other clinical need, there should be no hesitation for learners to conduct in-person assessments with appropriate PPE.
Nonexam indications are just as important – for example, if a patient requires extensive goals of care counseling, we recommend this not be done virtually. Other indications may vary between organizations; in our practice, we suggest at least one in-person assessment on the initial and discharge hospital days. Regardless of the specific indications, a successful virtual inpatient teaching service must be predicated on outlining the appropriate uses of telemedicine.
In the United States, there are already health care disparities for people of color and non–English speakers. If there is not a careful consideration for these marginalized groups, their health disparities could be further exacerbated – not just around COVID-19, but also for other inpatient conditions where telemedicine is being used. Groups whose equity must be thoughtfully managed include those who do not speak English and those who do not have access to smartphones or the Internet. Our HealthPartners organization has implemented the integration of interpreters for virtual three-way connections with patients and their clinicians to help mitigate this for non–English speakers. Additionally, utilizing easy-to-use tablets and telemedicine-capable carts has helped patients overcome technology barriers.
Last, the members of the teaching team must know the essential technical aspects of the technology they are using. Robust information technology (IT) support is also needed, but no matter how simple the equipment may be, staff and trainees must know how to both operate it and handle basic troubleshooting (such as audio or video disconnections). This also dovetails with the important element of on-boarding other members of the care team. In our practice, nursing staff, chaplains, interpreters, and dietitians also use virtual care as part of their workflow. However, even if it is used only by the teaching team, orienting other care team members will limit technical problems such as equipment being turned off or moved out of position.
Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine adoption was limited because of lack of awareness, barriers in training, understanding, and narrow beliefs regarding the innovation. The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in a remarkable increase in the provision of telemedicine services in the inpatient hospital medicine services. Importantly, it is, and should be, a developing part of the education and training for health care learners. This pandemic has underscored the need for providing telemedicine services that will likely long outlast this crisis, and to support our health care learners in being effective “iResidents” on our care teams.
Takeaways
- The future of graduate medical education involves virtual care.
The COVID-19 pandemic response has demonstrated that virtual care plays an instrumental part in patient care, and its effects will not dissipate when the pandemic is done. The curriculum for health care trainees should incorporate telemedicine competencies so that they may more effectively leverage this technology for improving care delivery.
- Selection of telemedicine patients must be stratified.
In order to obtain the highest utility for medical learners on telemedicine, there needs to be a clear decision process for which patients can be seen virtually. This involves both clinical criteria, such as avoiding virtual care for end-of-life discussions, and patient criteria, such as those who are hard of hearing.
- Virtual communication requires new communication skills.
Seeing patients via telemedicine mandates a different skill set than in-person communication. Learners must improve their “webside manner” in order to build the patient-provider relationship. Instilling these tools can pay dividends in settings where telemedicine has high yield, such as maskless communication during a pandemic.
- Health disparities could be further exacerbated by telemedicine and should not be overlooked.
Equity in access to health care applies to telemedicine as it does to many other elements. There are multiple groups that can suffer from disparities, such as patients who need interpreters, or those who have lower technological literacy and access to digital devices. Creating awareness of these pitfalls in virtual care can help medical learners recognize and support in creative solutions for these factors.
Dr. Mathews is chief, hospital medicine, at Regions Hospital, HealthPartners, St. Paul, Minn. Dr. Doshi is telemedicine director, hospital medicine, HealthPartners.
At the start of each shift on his clinical service with rotating internal medicine residents, Benji Mathews, MD, SFHM, now adds a few components to his usual preparation. First, visiting the Minnesota Department of Health and various organizational websites to review the latest COVID-19 updates and guidelines. Next comes checking to see where he needs to pick up the surgical mask and eye protection that he will need to wear through the day. Last, he evaluates which of his patients are in telemedicine-equipped rooms; this last change has fast become a crucial part of working with his resident learners during a pandemic.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, residents and residency programs find themselves in a unique situation. Balancing the educational needs of a training program with the safety of trainees is a challenging task, specifically when taking care of patients who are COVID-19 positive or patients under investigation (PUI). One increasingly available tool that can help protect trainees while continuing to prioritize patient care and medical education is the use of telemedicine for virtual rounding. For our internal medicine residents through the University of Minnesota Internal Medicine Residency program rotating at Regions Hospital in Saint Paul, Minn., we have used video visits to continue our mandate as both health care and education professionals.
Virtual care decision tree
Virtual care can mitigate exposure risk, minimize use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and improve communications with patients and their families. To guide our teaching teams on the optimal situations for telemedicine, we needed to select those patients who would be most appropriate for a virtual visit.

For example, patients with advanced dementia, or intubated in the intensive care unit, would have less utility from a real-time video encounter. Further, we implemented a simple decision tree (Figure 1). First, the team needs to decide whether the patient needs an immediate in-person assessment; for instance, for critically ill patients or those who need end-of-life care discussions, telemedicine would not be an appropriate modality. Next, the decision is made on whether a patient requires an in-person exam at that time. The idea of forgoing the in-person physical exam may run counterintuitive to the core training medical providers undergo, but in certain circumstances telemedicine can still provide the appropriate level of care a patient requires.
Virtual rounding with residents: Pros and cons
Through the course of this pandemic, there have many questions raised regarding how to handle inpatient teaching services: Should resident teams be assigned COVID-19 positives or PUIs? How do you optimize assessing and learning from patients’ conditions that require human touch? Should all members of the teaching team be donning PPE and entering the patient room?
Internal medicine residents in our hospital have been assigned COVID-19 positive and PUI patients. With proper PPE, and donning and doffing practices, residents may continue to learn from this important training opportunity while also optimizing care for patients supplemented by telemedicine. This pandemic has flattened the hierarchy; often residents are teaching their attendings much of the latest literature and best practices around COVID-19. Residents also benefit by joining the organization’s daily virtual interprofessional COVID-19 huddle where they partner with infectious disease, critical care, pharmacy, and other experts to collaborate in the care of these patients.
There have been counterarguments made for residents joining the front lines with COVID-19 patients. Some have conditions that limit them from seeing this subgroup of patients, such as their immune status or other issues. For these residents, we do not assign COVID-19–positive patients. However, they may continue to support in virtually updating COVID-19 patients and their families. A second argument has been the use of PPE. We have implemented telemedicine to limit the total number of exposures and have a protocol for the fewest number of providers possible to see any at-risk or confirmed COVID-19 patient. For example, a resident who sees a COVID-19 patient in person may also be simultaneously virtually supervised by the attending.
Webside manner
The physical exam is only one of several operational considerations when delivering virtual care, whether with a teaching or nonteaching service. One important aspect is the “webside manner” of the provider, the virtual analogue to bedside manner.
Inherent parts of in-person encounters, such as eye contact and allowing for patients to finish their sentences, have added nuances with virtual care. For instance, providers must adjust to looking into the web camera to make eye contact, even though the patient’s face may be on the screen below. Additionally, for patients who are hard of hearing or unfamiliar with video calling, providers must be cognizant of projecting well over an Internet connection and timing responses to avoid overlapping conversation.
Similarly, there are nuances to the virtual physical exam, some specific to care in the COVID-19 era. In our previous virtual care practice, a bedside facilitator assisted in using tools such a digital stethoscope. In contrast, our current practice aims to refine the observational skills of our learners in conjunction with chart review, vital signs, and actively incorporating the patient in the physical exam. This does not mean asking them to auscultate themselves, but is more toward allowing patients to participate in focused evaluations, such as assessing abdominal tenderness or working through range of motion. Remote guidance for virtual exams also extends itself to teaching teams; for example, in our practice, we have been able to conduct bedside ultrasound teaching with in-person team members and a virtual facilitator.
Maskless connections: ‘Face-to-face’ visits with patients
As many hospitalists have witnessed, COVID-19 is so isolating for patients and their families. Patients have limited visitors, and their care team members are aiming to minimize exposures. Those who are entering the rooms wear masks and face shields that limit connecting with patients in a truly “face-to-face” manner. Telemedicine provides a face-to-face encounter that arguably improves upon portions of the traditional in-person encounter during this pandemic, with providers wearing PPE. For medical learners, gaining the interpersonal skills essential for health care professionals has been skewed with pandemic-related limitations; telemedicine can provide a tool to adapt to this unique era and augment this important educational piece.
Limitations, equity, and technological considerations
Realistically, the virtual exam during COVID-19 does have its limitations. An important part of virtual care and teaching services is instilling the appropriate times for use of telemedicine. If a patient has a clinical change (such as increase in FiO2 requirements) or other clinical need, there should be no hesitation for learners to conduct in-person assessments with appropriate PPE.
Nonexam indications are just as important – for example, if a patient requires extensive goals of care counseling, we recommend this not be done virtually. Other indications may vary between organizations; in our practice, we suggest at least one in-person assessment on the initial and discharge hospital days. Regardless of the specific indications, a successful virtual inpatient teaching service must be predicated on outlining the appropriate uses of telemedicine.
In the United States, there are already health care disparities for people of color and non–English speakers. If there is not a careful consideration for these marginalized groups, their health disparities could be further exacerbated – not just around COVID-19, but also for other inpatient conditions where telemedicine is being used. Groups whose equity must be thoughtfully managed include those who do not speak English and those who do not have access to smartphones or the Internet. Our HealthPartners organization has implemented the integration of interpreters for virtual three-way connections with patients and their clinicians to help mitigate this for non–English speakers. Additionally, utilizing easy-to-use tablets and telemedicine-capable carts has helped patients overcome technology barriers.
Last, the members of the teaching team must know the essential technical aspects of the technology they are using. Robust information technology (IT) support is also needed, but no matter how simple the equipment may be, staff and trainees must know how to both operate it and handle basic troubleshooting (such as audio or video disconnections). This also dovetails with the important element of on-boarding other members of the care team. In our practice, nursing staff, chaplains, interpreters, and dietitians also use virtual care as part of their workflow. However, even if it is used only by the teaching team, orienting other care team members will limit technical problems such as equipment being turned off or moved out of position.
Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine adoption was limited because of lack of awareness, barriers in training, understanding, and narrow beliefs regarding the innovation. The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in a remarkable increase in the provision of telemedicine services in the inpatient hospital medicine services. Importantly, it is, and should be, a developing part of the education and training for health care learners. This pandemic has underscored the need for providing telemedicine services that will likely long outlast this crisis, and to support our health care learners in being effective “iResidents” on our care teams.
Takeaways
- The future of graduate medical education involves virtual care.
The COVID-19 pandemic response has demonstrated that virtual care plays an instrumental part in patient care, and its effects will not dissipate when the pandemic is done. The curriculum for health care trainees should incorporate telemedicine competencies so that they may more effectively leverage this technology for improving care delivery.
- Selection of telemedicine patients must be stratified.
In order to obtain the highest utility for medical learners on telemedicine, there needs to be a clear decision process for which patients can be seen virtually. This involves both clinical criteria, such as avoiding virtual care for end-of-life discussions, and patient criteria, such as those who are hard of hearing.
- Virtual communication requires new communication skills.
Seeing patients via telemedicine mandates a different skill set than in-person communication. Learners must improve their “webside manner” in order to build the patient-provider relationship. Instilling these tools can pay dividends in settings where telemedicine has high yield, such as maskless communication during a pandemic.
- Health disparities could be further exacerbated by telemedicine and should not be overlooked.
Equity in access to health care applies to telemedicine as it does to many other elements. There are multiple groups that can suffer from disparities, such as patients who need interpreters, or those who have lower technological literacy and access to digital devices. Creating awareness of these pitfalls in virtual care can help medical learners recognize and support in creative solutions for these factors.
Dr. Mathews is chief, hospital medicine, at Regions Hospital, HealthPartners, St. Paul, Minn. Dr. Doshi is telemedicine director, hospital medicine, HealthPartners.
Apremilast and Systemic Retinoid Combination Treatment for Moderate to Severe Palmoplantar Psoriasis
To the Editor:
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory papulosquamous skin disease affecting 2% to 3% of the population.1 Its pathogenesis is multifactorial, consisting of a disrupted skin barrier and dysregulated immune activation.2
A wide armamentarium of topical and systemic treatments targeting different aspects of the disease pathogenesis have been developed over the years.3,4 Psoriasis was once considered a skin disease exclusively, but accumulating evidence suggests that it is accompanied by a multitude of systemic inflammatory comorbidities.5 This insight supports the concept of systemic treatment for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. As a chronic disease, psoriasis requires continuous therapy. The treatment approach should focus on achieving efficacy and minimizing side effects. These goals can be achieved by combination, rotational, and sequential treatment approaches.6 Many therapeutic combinations have proven effective, using beneficially different mechanisms of action (MOAs) and toxicity profiles.7 We present a patient with moderate to severe recalcitrant palmoplantar psoriasis who demonstrated improvement with combination therapy.
A 50-year-old man presented with palmoplantar psoriasis of 7 years’ duration. His medical history included mild hyperlipidemia treated with atorvastatin. Prior topical treatments including calcipotriene, betamethasone dipropionate, and tacrolimus ointment did not result in improvement. Persistent acral involvement required further intervention, and the excimer laser was added to the therapeutic regimen with a minor additive therapeutic value. Acitretin (25 mg/d) was initiated; however, the disease flared up soon after. Acitretin was discontinued, and the patient was treated with apremilast (30 mg twice daily) for 9 months with a slight improvement. Physical examination revealed erythematous, fissured, scaly plaques involving both the palms and soles. Acitretin (25 mg/d) was reintroduced to the therapeutic regimen, and the acitretin-apremilast combination was used for 2 months. With this regimen, the patient experienced 90% improvement (Figures 1 and 2).

Palmoplantar psoriasis is a debilitating dermatosis that is extremely challenging to treat and is unresponsive to many modalities.8 Increased understanding of psoriasis mechanisms paved the path for the development of highly targeted biologic therapies9 with fewer side effects than drugs such as cyclosporine that indiscriminately neutralize multiple components of the immune system. Although highly specific, these targeted approaches are not without side effects10 and lead to diverse therapeutic outcomes, particularly when prescribed for palmoplantar psoriasis.11,12
The small-molecule inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4—apremilast—was approved for plaque psoriasis treatment in late 2014. Although not fully elucidated, its MOA involves interfering with intracellular signaling, leading to increased intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels in inflammatory cells and keratinocytes.13 Proximal interruption of the pathologic cascade leads to the reduction of multiple proinflammatory cytokines with a simultaneous increase in anti-inflammatory mediators.13 Its efficacy and safety in the treatment of psoriasis have been shown in phase 2 and 3 clinical trials.14,15 In contrast to traditional oral therapies for psoriasis (ie, methotrexate, cyclosporine, acitretin), no laboratory test monitoring is needed and the safety profile is notably better.16
Acitretin, the active metabolite of etretinate, modulates epidermal differentiation and has immunomodulating activities.17 It commonly is used for treating palmoplantar psoriasis.8 Until recently, it was the only nonimmunosuppressive systemic treatment for psoriasis, and its combination with other systemic treatments, particularly biologics, has been advocated.18 Prior reports showed remarkable disease improvement when combining acitretin with alefacept, etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, and ustekinumab.19 The optimal combination should include modalities with different MOAs without overlapping toxicities.19 Apremilast and acitretin have different MOAs and side-effect profiles, but another theoretical advantage is that they both interfere with intracellular signaling on the transcription level rather than affecting extracellular targets.13
Our patient with moderate to severe recalcitrant palmoplantar psoriasis demonstrated approximately 90% improvement following apremilast and acitretin combination therapy. This treatment regimen should be considered in cases of persistent acral disease resistant to other therapeutic efforts.
- Rachakonda TD, Schupp CW, Armstrong AW. Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:512-516.
- Nograles KE, Davidovici B, Krueger JG. New insights in the immunologic basis of psoriasis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2010;29:3-9.
- Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 4. guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with traditional systemic agents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:451-485.
- Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 3. guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:643-659.
- Ryan C, Kirby B. Psoriasis is a systemic disease with multiple cardiovascular and metabolic comorbidities. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:41-44.
- Lebwohl M, Menter A, Koo J, et al. Combination therapy to treat moderate to severe psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:416-430.
- Cather JC, Menter A. Combining traditional agents and biologics for the treatment of psoriasis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2005;24:37-45.
- Janagond AB, Kanwar AJ, Handa S. Efficacy and safety of systemic methotrexate vs. acitretin in psoriasis patients with significant palmoplantar involvement: a prospective, randomized study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:E384-E389.
- Campa M, Mansouri B, Warren R, et al. A review of biologic therapies targeting IL-23 and IL-17 for use in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis [published online December 29, 2015]. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2015;6:1-12.
- Menter A, Gottlieb A, Feldman SR, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 1. overview of psoriasis and guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:826-850.
- Jacobi A, Schuler G, Hertl M. Differential clinical response to alefacept in combination with methotrexate in two patients with refractory palmar psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:178-180.
- Meyer V, Goerge T, Luger TA, et al. Successful treatment of palmoplantar hyperkeratotic psoriasis with a combination of etanercept and alitretinoin. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:45-46.
- Schafer P. Apremilast mechanism of action and application to psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;83:1583-1590.
- Papp K, Reich K, Leonardi CL, et al. Apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: results of a phase III, randomized, controlled trial (Efficacy and Safety Trial Evaluating the Effects of Apremilast in Psoriasis [ESTEEM] 1). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:37-49.
- Paul C, Cather J, Gooderham M, et al. Efficacy and safety of apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis over 52 weeks: a phase III, randomized controlled trial (ESTEEM 2). Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1387-1399.
- Zerilli T, Ocheretyaner E. Apremilast (Otezla): a new oral treatment for adults with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. P T. 2015;40:495-500.
- Pilkington T, Brogden RN. Acitretin—a review of its pharmacology and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1992;43:597-627.
- Lebwohl M. Combining the new biologic agents with our current psoriasis armamentarium. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:S118-S124.
- Heinecke GM, Luber AJ, Levitt JO, et al. Combination use of ustekinumab with other systemic therapies: a retrospective study in a tertiary referral center. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12:1098-1102.
To the Editor:
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory papulosquamous skin disease affecting 2% to 3% of the population.1 Its pathogenesis is multifactorial, consisting of a disrupted skin barrier and dysregulated immune activation.2
A wide armamentarium of topical and systemic treatments targeting different aspects of the disease pathogenesis have been developed over the years.3,4 Psoriasis was once considered a skin disease exclusively, but accumulating evidence suggests that it is accompanied by a multitude of systemic inflammatory comorbidities.5 This insight supports the concept of systemic treatment for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. As a chronic disease, psoriasis requires continuous therapy. The treatment approach should focus on achieving efficacy and minimizing side effects. These goals can be achieved by combination, rotational, and sequential treatment approaches.6 Many therapeutic combinations have proven effective, using beneficially different mechanisms of action (MOAs) and toxicity profiles.7 We present a patient with moderate to severe recalcitrant palmoplantar psoriasis who demonstrated improvement with combination therapy.
A 50-year-old man presented with palmoplantar psoriasis of 7 years’ duration. His medical history included mild hyperlipidemia treated with atorvastatin. Prior topical treatments including calcipotriene, betamethasone dipropionate, and tacrolimus ointment did not result in improvement. Persistent acral involvement required further intervention, and the excimer laser was added to the therapeutic regimen with a minor additive therapeutic value. Acitretin (25 mg/d) was initiated; however, the disease flared up soon after. Acitretin was discontinued, and the patient was treated with apremilast (30 mg twice daily) for 9 months with a slight improvement. Physical examination revealed erythematous, fissured, scaly plaques involving both the palms and soles. Acitretin (25 mg/d) was reintroduced to the therapeutic regimen, and the acitretin-apremilast combination was used for 2 months. With this regimen, the patient experienced 90% improvement (Figures 1 and 2).


Palmoplantar psoriasis is a debilitating dermatosis that is extremely challenging to treat and is unresponsive to many modalities.8 Increased understanding of psoriasis mechanisms paved the path for the development of highly targeted biologic therapies9 with fewer side effects than drugs such as cyclosporine that indiscriminately neutralize multiple components of the immune system. Although highly specific, these targeted approaches are not without side effects10 and lead to diverse therapeutic outcomes, particularly when prescribed for palmoplantar psoriasis.11,12
The small-molecule inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4—apremilast—was approved for plaque psoriasis treatment in late 2014. Although not fully elucidated, its MOA involves interfering with intracellular signaling, leading to increased intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels in inflammatory cells and keratinocytes.13 Proximal interruption of the pathologic cascade leads to the reduction of multiple proinflammatory cytokines with a simultaneous increase in anti-inflammatory mediators.13 Its efficacy and safety in the treatment of psoriasis have been shown in phase 2 and 3 clinical trials.14,15 In contrast to traditional oral therapies for psoriasis (ie, methotrexate, cyclosporine, acitretin), no laboratory test monitoring is needed and the safety profile is notably better.16
Acitretin, the active metabolite of etretinate, modulates epidermal differentiation and has immunomodulating activities.17 It commonly is used for treating palmoplantar psoriasis.8 Until recently, it was the only nonimmunosuppressive systemic treatment for psoriasis, and its combination with other systemic treatments, particularly biologics, has been advocated.18 Prior reports showed remarkable disease improvement when combining acitretin with alefacept, etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, and ustekinumab.19 The optimal combination should include modalities with different MOAs without overlapping toxicities.19 Apremilast and acitretin have different MOAs and side-effect profiles, but another theoretical advantage is that they both interfere with intracellular signaling on the transcription level rather than affecting extracellular targets.13
Our patient with moderate to severe recalcitrant palmoplantar psoriasis demonstrated approximately 90% improvement following apremilast and acitretin combination therapy. This treatment regimen should be considered in cases of persistent acral disease resistant to other therapeutic efforts.
To the Editor:
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory papulosquamous skin disease affecting 2% to 3% of the population.1 Its pathogenesis is multifactorial, consisting of a disrupted skin barrier and dysregulated immune activation.2
A wide armamentarium of topical and systemic treatments targeting different aspects of the disease pathogenesis have been developed over the years.3,4 Psoriasis was once considered a skin disease exclusively, but accumulating evidence suggests that it is accompanied by a multitude of systemic inflammatory comorbidities.5 This insight supports the concept of systemic treatment for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. As a chronic disease, psoriasis requires continuous therapy. The treatment approach should focus on achieving efficacy and minimizing side effects. These goals can be achieved by combination, rotational, and sequential treatment approaches.6 Many therapeutic combinations have proven effective, using beneficially different mechanisms of action (MOAs) and toxicity profiles.7 We present a patient with moderate to severe recalcitrant palmoplantar psoriasis who demonstrated improvement with combination therapy.
A 50-year-old man presented with palmoplantar psoriasis of 7 years’ duration. His medical history included mild hyperlipidemia treated with atorvastatin. Prior topical treatments including calcipotriene, betamethasone dipropionate, and tacrolimus ointment did not result in improvement. Persistent acral involvement required further intervention, and the excimer laser was added to the therapeutic regimen with a minor additive therapeutic value. Acitretin (25 mg/d) was initiated; however, the disease flared up soon after. Acitretin was discontinued, and the patient was treated with apremilast (30 mg twice daily) for 9 months with a slight improvement. Physical examination revealed erythematous, fissured, scaly plaques involving both the palms and soles. Acitretin (25 mg/d) was reintroduced to the therapeutic regimen, and the acitretin-apremilast combination was used for 2 months. With this regimen, the patient experienced 90% improvement (Figures 1 and 2).


Palmoplantar psoriasis is a debilitating dermatosis that is extremely challenging to treat and is unresponsive to many modalities.8 Increased understanding of psoriasis mechanisms paved the path for the development of highly targeted biologic therapies9 with fewer side effects than drugs such as cyclosporine that indiscriminately neutralize multiple components of the immune system. Although highly specific, these targeted approaches are not without side effects10 and lead to diverse therapeutic outcomes, particularly when prescribed for palmoplantar psoriasis.11,12
The small-molecule inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4—apremilast—was approved for plaque psoriasis treatment in late 2014. Although not fully elucidated, its MOA involves interfering with intracellular signaling, leading to increased intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels in inflammatory cells and keratinocytes.13 Proximal interruption of the pathologic cascade leads to the reduction of multiple proinflammatory cytokines with a simultaneous increase in anti-inflammatory mediators.13 Its efficacy and safety in the treatment of psoriasis have been shown in phase 2 and 3 clinical trials.14,15 In contrast to traditional oral therapies for psoriasis (ie, methotrexate, cyclosporine, acitretin), no laboratory test monitoring is needed and the safety profile is notably better.16
Acitretin, the active metabolite of etretinate, modulates epidermal differentiation and has immunomodulating activities.17 It commonly is used for treating palmoplantar psoriasis.8 Until recently, it was the only nonimmunosuppressive systemic treatment for psoriasis, and its combination with other systemic treatments, particularly biologics, has been advocated.18 Prior reports showed remarkable disease improvement when combining acitretin with alefacept, etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, and ustekinumab.19 The optimal combination should include modalities with different MOAs without overlapping toxicities.19 Apremilast and acitretin have different MOAs and side-effect profiles, but another theoretical advantage is that they both interfere with intracellular signaling on the transcription level rather than affecting extracellular targets.13
Our patient with moderate to severe recalcitrant palmoplantar psoriasis demonstrated approximately 90% improvement following apremilast and acitretin combination therapy. This treatment regimen should be considered in cases of persistent acral disease resistant to other therapeutic efforts.
- Rachakonda TD, Schupp CW, Armstrong AW. Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:512-516.
- Nograles KE, Davidovici B, Krueger JG. New insights in the immunologic basis of psoriasis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2010;29:3-9.
- Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 4. guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with traditional systemic agents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:451-485.
- Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 3. guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:643-659.
- Ryan C, Kirby B. Psoriasis is a systemic disease with multiple cardiovascular and metabolic comorbidities. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:41-44.
- Lebwohl M, Menter A, Koo J, et al. Combination therapy to treat moderate to severe psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:416-430.
- Cather JC, Menter A. Combining traditional agents and biologics for the treatment of psoriasis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2005;24:37-45.
- Janagond AB, Kanwar AJ, Handa S. Efficacy and safety of systemic methotrexate vs. acitretin in psoriasis patients with significant palmoplantar involvement: a prospective, randomized study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:E384-E389.
- Campa M, Mansouri B, Warren R, et al. A review of biologic therapies targeting IL-23 and IL-17 for use in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis [published online December 29, 2015]. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2015;6:1-12.
- Menter A, Gottlieb A, Feldman SR, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 1. overview of psoriasis and guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:826-850.
- Jacobi A, Schuler G, Hertl M. Differential clinical response to alefacept in combination with methotrexate in two patients with refractory palmar psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:178-180.
- Meyer V, Goerge T, Luger TA, et al. Successful treatment of palmoplantar hyperkeratotic psoriasis with a combination of etanercept and alitretinoin. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:45-46.
- Schafer P. Apremilast mechanism of action and application to psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;83:1583-1590.
- Papp K, Reich K, Leonardi CL, et al. Apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: results of a phase III, randomized, controlled trial (Efficacy and Safety Trial Evaluating the Effects of Apremilast in Psoriasis [ESTEEM] 1). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:37-49.
- Paul C, Cather J, Gooderham M, et al. Efficacy and safety of apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis over 52 weeks: a phase III, randomized controlled trial (ESTEEM 2). Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1387-1399.
- Zerilli T, Ocheretyaner E. Apremilast (Otezla): a new oral treatment for adults with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. P T. 2015;40:495-500.
- Pilkington T, Brogden RN. Acitretin—a review of its pharmacology and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1992;43:597-627.
- Lebwohl M. Combining the new biologic agents with our current psoriasis armamentarium. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:S118-S124.
- Heinecke GM, Luber AJ, Levitt JO, et al. Combination use of ustekinumab with other systemic therapies: a retrospective study in a tertiary referral center. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12:1098-1102.
- Rachakonda TD, Schupp CW, Armstrong AW. Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:512-516.
- Nograles KE, Davidovici B, Krueger JG. New insights in the immunologic basis of psoriasis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2010;29:3-9.
- Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 4. guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with traditional systemic agents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:451-485.
- Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 3. guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:643-659.
- Ryan C, Kirby B. Psoriasis is a systemic disease with multiple cardiovascular and metabolic comorbidities. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:41-44.
- Lebwohl M, Menter A, Koo J, et al. Combination therapy to treat moderate to severe psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:416-430.
- Cather JC, Menter A. Combining traditional agents and biologics for the treatment of psoriasis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2005;24:37-45.
- Janagond AB, Kanwar AJ, Handa S. Efficacy and safety of systemic methotrexate vs. acitretin in psoriasis patients with significant palmoplantar involvement: a prospective, randomized study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:E384-E389.
- Campa M, Mansouri B, Warren R, et al. A review of biologic therapies targeting IL-23 and IL-17 for use in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis [published online December 29, 2015]. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2015;6:1-12.
- Menter A, Gottlieb A, Feldman SR, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 1. overview of psoriasis and guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:826-850.
- Jacobi A, Schuler G, Hertl M. Differential clinical response to alefacept in combination with methotrexate in two patients with refractory palmar psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:178-180.
- Meyer V, Goerge T, Luger TA, et al. Successful treatment of palmoplantar hyperkeratotic psoriasis with a combination of etanercept and alitretinoin. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:45-46.
- Schafer P. Apremilast mechanism of action and application to psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;83:1583-1590.
- Papp K, Reich K, Leonardi CL, et al. Apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: results of a phase III, randomized, controlled trial (Efficacy and Safety Trial Evaluating the Effects of Apremilast in Psoriasis [ESTEEM] 1). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:37-49.
- Paul C, Cather J, Gooderham M, et al. Efficacy and safety of apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis over 52 weeks: a phase III, randomized controlled trial (ESTEEM 2). Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1387-1399.
- Zerilli T, Ocheretyaner E. Apremilast (Otezla): a new oral treatment for adults with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. P T. 2015;40:495-500.
- Pilkington T, Brogden RN. Acitretin—a review of its pharmacology and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1992;43:597-627.
- Lebwohl M. Combining the new biologic agents with our current psoriasis armamentarium. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:S118-S124.
- Heinecke GM, Luber AJ, Levitt JO, et al. Combination use of ustekinumab with other systemic therapies: a retrospective study in a tertiary referral center. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12:1098-1102.
Practice Points
- Palmoplantar psoriasis is challenging to treat and is unresponsive to many modalities.
- Combination, rotational, and sequential treatment approaches may minimize side effects and loss of efficacy as well as enhance treatment responses.
- Apremilast and acitretin combination therapy led to 90% skin improvement in a case of severe recalcitrant palmoplantar psoriasis.
Sintilimab scintillates in first-line nonsquamous NSCLC
The investigational anti-PD-1 antibody sintilimab (Tyvyt, Innovent Biologics and Eli Lilly) has shown that it improves the efficacy of platinum-based chemotherapy in the first-line treatment of patients with advanced nonsquamous non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in a phase 3 trial dubbed ORIENT-11.
The study was presented at the World Congress on Lung Cancer 2020 Virtual Presidential Symposium, held virtually due to the COVID-19 pandemic, on August 8. It was also published simultaneously in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology.
Sintilimab is a fully human IgG4 monoclonal antibody that blocks the binding of programmed death (PD)-1 to PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1) or PD-L2 with high affinity, and has received market authorization in China for the treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma.
For ORIENT-11, almost 400 patients with advanced nonsquamous NSCLC were randomly assigned to sintilimab or placebo plus pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy in a 2:1 ratio.
“The addition of sintilimab to pemetrexed and platinum significantly improved PFS [progression-free survival], compared to placebo,” reducing progression rates by 52%, noted lead investigator Li Zhang, MD, professor of medical oncology, Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China.
Crucially, this benefit “was seen across key clinical subgroups,” he added.
He noted that the overall response rate “was also improved, with a durable response,” while the results, which are not yet mature, suggest the experimental arm was associated with an overall survival (OS) benefit.
Study discussant Misako Nagasaka, MD, a thoracic oncologist and clinical investigator at Karmanos Cancer Institute, Detroit, said that the PFS benefit seen in the study is “certainly encouraging.”
Adding a note of caution, she continued: “But we have seen studies with PFS improvement which did not translate into OS improvement.
“Longer follow-up would allow events to mature and we will ultimately see if there would be a significant OS benefit,” she said.
Dr. Nagasaka also pointed out that the greater benefit with sintilimab seen in patients with high PD-L1 begs the question as to what would be the preferred regimen in those with higher or lower expression.
And, she said, this is not just about what regimen to choose but “more importantly, why?”
“Perhaps you’d like to use something with the best response rate, perhaps you’re sticking to a single agent immunotherapy because the toxicity profile is more favorable, or perhaps you [are] convinced with a certain regimen because of the robust PFS and OS data,” she said.
“Whatever you chose, there was a reason for your choice,” she said, adding that the sintilimab combination would have to “fulfill those reasons for you to consider choosing this regimen.”
Study details
Dr. Zhang began his presentation by noting that previous phase 1b studies have shown that sintilimab plus pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy has a “tolerable safety profile and promising efficacy” in previously untreated non-squamous NSCLC.
They therefore conducted ORIENT-11, a randomized, double-blind, phase 3 study involving 397 patients with untreated stage IIIB/C or IV nonsquamous NSCLC who had neither EGFR nor ALK gene alterations.
The patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 fashion to sintilimab plus pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy (n = 266) or placebo plus pemetrexed and chemo (n = 131) for four cycles, followed by sintilimab or placebo plus pemetrexed for up to 24 months.
Thirty-five patients in the placebo arm crossed over to sintilimab monotherapy, representing 31.3% of the intention-to-treat population.
At the data cutoff of Nov. 15, 2019, 198 events had occurred, at a median follow-up of 8.9 months.
The team found that median PFS was significantly higher with sintilimab than placebo combination therapy, at 8.9 months vs. 5.0 months, or a hazard ratio of 0.482 (P < .00001).
Dr. Zhang noted that the benefit with sintilimab plus pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy was seen across all subgroups.
However, it was notable that the impact of adding sintilimab on PFS was greater in patients with a tumor proportion score (TPS) ≥50%.
The HR for progression vs. the placebo treatment arm was 0.310, with median PFS not reached, which decreased to 0.503 in patients with a TPS of 1%-49% and 0.664 among those with a TPS <1%.
The results also showed that there was a “nominally significant improvement” in overall survival with sintilimab versus placebo, at a HR of 0.609 (P = 0.01921).
The ORR was markedly different between the sintilimab and placebo groups, at 51.9% vs. 29.8%, with the duration of response not reached in the sintilimab arm compared with 5.5 months in the placebo arm.
The sintilimab arm included three (1.1%) complete responses, which was not observed with pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy alone.
Finally, Dr. Zhang observed that the safety profiles of the sintilimab and placebo arms were similar, with comparable rates of any, grade 3-5, and serious adverse events largely driven by high rates of chemotherapy-related events.
While there were fewer adverse events that led to death with sintilimab, at 2.3% vs. 6.9% with placebo, there were, as expected, more immune-related adverse events, at 43.2% vs. 36.6%, respectively.
Comparison with pembrolizumab
In her discussion, Dr. Nagasaka said that the first question that came to mind when she saw the results was: “How does the ORIENT-11 data compare with KEYNOTE-189?”
For that study, pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck) was added to pemetrexed plus carboplatin chemotherapy and compared with standard of care alone in patients with untreated metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC.
As reported by Medscape Medical News, pembrolizumab was associated with a 48% reduced risk of disease progression, as well as improved overall survival.
Dr. Nagasaka said that ORIENT-11 “had patients that tended to be younger, there were more males, more with performance status 1, and those who had never smoked” than those in KEYNOTE-189.
“But most importantly, KEYNOTE-189 had a very small number of patients from East Asia, only 1% in the pembro arm and 2.9% in the placebo arm.”
In contrast, all the patients included in ORIENT-11 were from East Asia, making the study of “high importance.”
She added that, “while across-trial comparisons must be taken with caution, the medium PFS of ORIENT-11 ... appears comparable to those of KEYNOTE-189,” while the HR “appears identical.”
This is despite median follow-up time in ORIENT-11 of “only” 8.9 months vs. a median of 23.1 months in the updated KEYNOTE-189 data.
There are plans to register the sintilimab combination therapy in China for the treatment of nonsquamous NSCLC, where it will go up against pembrolizumab as well as, potentially, tislelizumab (BeiGene).
The study was sponsored by Innovent Biologics and Eli Lilly. Dr. Zhang disclosed research grants from Eli Lilly and Pfizer. Dr. Nagasaka disclosed serving on the advisory boards of AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Takeda, Novartis, and EMD Serono; as a consultant for Caris Life Sciences; and receiving travel support from An Hearts Therapeutics.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The investigational anti-PD-1 antibody sintilimab (Tyvyt, Innovent Biologics and Eli Lilly) has shown that it improves the efficacy of platinum-based chemotherapy in the first-line treatment of patients with advanced nonsquamous non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in a phase 3 trial dubbed ORIENT-11.
The study was presented at the World Congress on Lung Cancer 2020 Virtual Presidential Symposium, held virtually due to the COVID-19 pandemic, on August 8. It was also published simultaneously in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology.
Sintilimab is a fully human IgG4 monoclonal antibody that blocks the binding of programmed death (PD)-1 to PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1) or PD-L2 with high affinity, and has received market authorization in China for the treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma.
For ORIENT-11, almost 400 patients with advanced nonsquamous NSCLC were randomly assigned to sintilimab or placebo plus pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy in a 2:1 ratio.
“The addition of sintilimab to pemetrexed and platinum significantly improved PFS [progression-free survival], compared to placebo,” reducing progression rates by 52%, noted lead investigator Li Zhang, MD, professor of medical oncology, Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China.
Crucially, this benefit “was seen across key clinical subgroups,” he added.
He noted that the overall response rate “was also improved, with a durable response,” while the results, which are not yet mature, suggest the experimental arm was associated with an overall survival (OS) benefit.
Study discussant Misako Nagasaka, MD, a thoracic oncologist and clinical investigator at Karmanos Cancer Institute, Detroit, said that the PFS benefit seen in the study is “certainly encouraging.”
Adding a note of caution, she continued: “But we have seen studies with PFS improvement which did not translate into OS improvement.
“Longer follow-up would allow events to mature and we will ultimately see if there would be a significant OS benefit,” she said.
Dr. Nagasaka also pointed out that the greater benefit with sintilimab seen in patients with high PD-L1 begs the question as to what would be the preferred regimen in those with higher or lower expression.
And, she said, this is not just about what regimen to choose but “more importantly, why?”
“Perhaps you’d like to use something with the best response rate, perhaps you’re sticking to a single agent immunotherapy because the toxicity profile is more favorable, or perhaps you [are] convinced with a certain regimen because of the robust PFS and OS data,” she said.
“Whatever you chose, there was a reason for your choice,” she said, adding that the sintilimab combination would have to “fulfill those reasons for you to consider choosing this regimen.”
Study details
Dr. Zhang began his presentation by noting that previous phase 1b studies have shown that sintilimab plus pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy has a “tolerable safety profile and promising efficacy” in previously untreated non-squamous NSCLC.
They therefore conducted ORIENT-11, a randomized, double-blind, phase 3 study involving 397 patients with untreated stage IIIB/C or IV nonsquamous NSCLC who had neither EGFR nor ALK gene alterations.
The patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 fashion to sintilimab plus pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy (n = 266) or placebo plus pemetrexed and chemo (n = 131) for four cycles, followed by sintilimab or placebo plus pemetrexed for up to 24 months.
Thirty-five patients in the placebo arm crossed over to sintilimab monotherapy, representing 31.3% of the intention-to-treat population.
At the data cutoff of Nov. 15, 2019, 198 events had occurred, at a median follow-up of 8.9 months.
The team found that median PFS was significantly higher with sintilimab than placebo combination therapy, at 8.9 months vs. 5.0 months, or a hazard ratio of 0.482 (P < .00001).
Dr. Zhang noted that the benefit with sintilimab plus pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy was seen across all subgroups.
However, it was notable that the impact of adding sintilimab on PFS was greater in patients with a tumor proportion score (TPS) ≥50%.
The HR for progression vs. the placebo treatment arm was 0.310, with median PFS not reached, which decreased to 0.503 in patients with a TPS of 1%-49% and 0.664 among those with a TPS <1%.
The results also showed that there was a “nominally significant improvement” in overall survival with sintilimab versus placebo, at a HR of 0.609 (P = 0.01921).
The ORR was markedly different between the sintilimab and placebo groups, at 51.9% vs. 29.8%, with the duration of response not reached in the sintilimab arm compared with 5.5 months in the placebo arm.
The sintilimab arm included three (1.1%) complete responses, which was not observed with pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy alone.
Finally, Dr. Zhang observed that the safety profiles of the sintilimab and placebo arms were similar, with comparable rates of any, grade 3-5, and serious adverse events largely driven by high rates of chemotherapy-related events.
While there were fewer adverse events that led to death with sintilimab, at 2.3% vs. 6.9% with placebo, there were, as expected, more immune-related adverse events, at 43.2% vs. 36.6%, respectively.
Comparison with pembrolizumab
In her discussion, Dr. Nagasaka said that the first question that came to mind when she saw the results was: “How does the ORIENT-11 data compare with KEYNOTE-189?”
For that study, pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck) was added to pemetrexed plus carboplatin chemotherapy and compared with standard of care alone in patients with untreated metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC.
As reported by Medscape Medical News, pembrolizumab was associated with a 48% reduced risk of disease progression, as well as improved overall survival.
Dr. Nagasaka said that ORIENT-11 “had patients that tended to be younger, there were more males, more with performance status 1, and those who had never smoked” than those in KEYNOTE-189.
“But most importantly, KEYNOTE-189 had a very small number of patients from East Asia, only 1% in the pembro arm and 2.9% in the placebo arm.”
In contrast, all the patients included in ORIENT-11 were from East Asia, making the study of “high importance.”
She added that, “while across-trial comparisons must be taken with caution, the medium PFS of ORIENT-11 ... appears comparable to those of KEYNOTE-189,” while the HR “appears identical.”
This is despite median follow-up time in ORIENT-11 of “only” 8.9 months vs. a median of 23.1 months in the updated KEYNOTE-189 data.
There are plans to register the sintilimab combination therapy in China for the treatment of nonsquamous NSCLC, where it will go up against pembrolizumab as well as, potentially, tislelizumab (BeiGene).
The study was sponsored by Innovent Biologics and Eli Lilly. Dr. Zhang disclosed research grants from Eli Lilly and Pfizer. Dr. Nagasaka disclosed serving on the advisory boards of AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Takeda, Novartis, and EMD Serono; as a consultant for Caris Life Sciences; and receiving travel support from An Hearts Therapeutics.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The investigational anti-PD-1 antibody sintilimab (Tyvyt, Innovent Biologics and Eli Lilly) has shown that it improves the efficacy of platinum-based chemotherapy in the first-line treatment of patients with advanced nonsquamous non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in a phase 3 trial dubbed ORIENT-11.
The study was presented at the World Congress on Lung Cancer 2020 Virtual Presidential Symposium, held virtually due to the COVID-19 pandemic, on August 8. It was also published simultaneously in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology.
Sintilimab is a fully human IgG4 monoclonal antibody that blocks the binding of programmed death (PD)-1 to PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1) or PD-L2 with high affinity, and has received market authorization in China for the treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma.
For ORIENT-11, almost 400 patients with advanced nonsquamous NSCLC were randomly assigned to sintilimab or placebo plus pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy in a 2:1 ratio.
“The addition of sintilimab to pemetrexed and platinum significantly improved PFS [progression-free survival], compared to placebo,” reducing progression rates by 52%, noted lead investigator Li Zhang, MD, professor of medical oncology, Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China.
Crucially, this benefit “was seen across key clinical subgroups,” he added.
He noted that the overall response rate “was also improved, with a durable response,” while the results, which are not yet mature, suggest the experimental arm was associated with an overall survival (OS) benefit.
Study discussant Misako Nagasaka, MD, a thoracic oncologist and clinical investigator at Karmanos Cancer Institute, Detroit, said that the PFS benefit seen in the study is “certainly encouraging.”
Adding a note of caution, she continued: “But we have seen studies with PFS improvement which did not translate into OS improvement.
“Longer follow-up would allow events to mature and we will ultimately see if there would be a significant OS benefit,” she said.
Dr. Nagasaka also pointed out that the greater benefit with sintilimab seen in patients with high PD-L1 begs the question as to what would be the preferred regimen in those with higher or lower expression.
And, she said, this is not just about what regimen to choose but “more importantly, why?”
“Perhaps you’d like to use something with the best response rate, perhaps you’re sticking to a single agent immunotherapy because the toxicity profile is more favorable, or perhaps you [are] convinced with a certain regimen because of the robust PFS and OS data,” she said.
“Whatever you chose, there was a reason for your choice,” she said, adding that the sintilimab combination would have to “fulfill those reasons for you to consider choosing this regimen.”
Study details
Dr. Zhang began his presentation by noting that previous phase 1b studies have shown that sintilimab plus pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy has a “tolerable safety profile and promising efficacy” in previously untreated non-squamous NSCLC.
They therefore conducted ORIENT-11, a randomized, double-blind, phase 3 study involving 397 patients with untreated stage IIIB/C or IV nonsquamous NSCLC who had neither EGFR nor ALK gene alterations.
The patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 fashion to sintilimab plus pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy (n = 266) or placebo plus pemetrexed and chemo (n = 131) for four cycles, followed by sintilimab or placebo plus pemetrexed for up to 24 months.
Thirty-five patients in the placebo arm crossed over to sintilimab monotherapy, representing 31.3% of the intention-to-treat population.
At the data cutoff of Nov. 15, 2019, 198 events had occurred, at a median follow-up of 8.9 months.
The team found that median PFS was significantly higher with sintilimab than placebo combination therapy, at 8.9 months vs. 5.0 months, or a hazard ratio of 0.482 (P < .00001).
Dr. Zhang noted that the benefit with sintilimab plus pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy was seen across all subgroups.
However, it was notable that the impact of adding sintilimab on PFS was greater in patients with a tumor proportion score (TPS) ≥50%.
The HR for progression vs. the placebo treatment arm was 0.310, with median PFS not reached, which decreased to 0.503 in patients with a TPS of 1%-49% and 0.664 among those with a TPS <1%.
The results also showed that there was a “nominally significant improvement” in overall survival with sintilimab versus placebo, at a HR of 0.609 (P = 0.01921).
The ORR was markedly different between the sintilimab and placebo groups, at 51.9% vs. 29.8%, with the duration of response not reached in the sintilimab arm compared with 5.5 months in the placebo arm.
The sintilimab arm included three (1.1%) complete responses, which was not observed with pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy alone.
Finally, Dr. Zhang observed that the safety profiles of the sintilimab and placebo arms were similar, with comparable rates of any, grade 3-5, and serious adverse events largely driven by high rates of chemotherapy-related events.
While there were fewer adverse events that led to death with sintilimab, at 2.3% vs. 6.9% with placebo, there were, as expected, more immune-related adverse events, at 43.2% vs. 36.6%, respectively.
Comparison with pembrolizumab
In her discussion, Dr. Nagasaka said that the first question that came to mind when she saw the results was: “How does the ORIENT-11 data compare with KEYNOTE-189?”
For that study, pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck) was added to pemetrexed plus carboplatin chemotherapy and compared with standard of care alone in patients with untreated metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC.
As reported by Medscape Medical News, pembrolizumab was associated with a 48% reduced risk of disease progression, as well as improved overall survival.
Dr. Nagasaka said that ORIENT-11 “had patients that tended to be younger, there were more males, more with performance status 1, and those who had never smoked” than those in KEYNOTE-189.
“But most importantly, KEYNOTE-189 had a very small number of patients from East Asia, only 1% in the pembro arm and 2.9% in the placebo arm.”
In contrast, all the patients included in ORIENT-11 were from East Asia, making the study of “high importance.”
She added that, “while across-trial comparisons must be taken with caution, the medium PFS of ORIENT-11 ... appears comparable to those of KEYNOTE-189,” while the HR “appears identical.”
This is despite median follow-up time in ORIENT-11 of “only” 8.9 months vs. a median of 23.1 months in the updated KEYNOTE-189 data.
There are plans to register the sintilimab combination therapy in China for the treatment of nonsquamous NSCLC, where it will go up against pembrolizumab as well as, potentially, tislelizumab (BeiGene).
The study was sponsored by Innovent Biologics and Eli Lilly. Dr. Zhang disclosed research grants from Eli Lilly and Pfizer. Dr. Nagasaka disclosed serving on the advisory boards of AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Takeda, Novartis, and EMD Serono; as a consultant for Caris Life Sciences; and receiving travel support from An Hearts Therapeutics.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chemo-free management of mesothelioma on horizon
Patients with untreated mesothelioma may be able to avoid chemotherapy, say researchers reporting new survival data with the immunotherapy combination of nivolumab (Opdivo) and ipilimumab (Yervoy).
The two approaches were compared in more than 600 patients with treatment-naive mesothelioma in the phase 3 CheckMate 743 trial, which was supported by the manufacturer of both immunotherapies, Bristol-Myers Squibb.
The trial “met its primary endpoint of statistically improving overall survival for the experimental arm vs chemotherapy in a prespecified interim analysis,” reported Paul Baas, MD, PhD, Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, The Netherlands,
The combined nivo+ipi immunotherapy regimen was associated with a 26% improvement in overall survival. At 2 years, 41% of patients in the immunotherapy arm were still alive, vs 27% in the chemotherapy group.
“This is the first positive randomized trial of dual immunotherapy in the first-line treatment of patients with mesothelioma,” he said. He suggested that it should therefore “be considered as a new standard of care.”
The data were presented on August 8 in the presidential symposium of the World Congress on Lung Cancer 2020, which was held online because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A key analysis for the study was by histologic subgroup. It is known that standard-of-care chemotherapy performs better in patients with epithelioid as opposed to nonepithelioid tumor subtypes.
Bass highlighted that the performance of nivo+ipi was “almost the same” in patients with epithelioid and nonepithelioid tumors, at a median overall survival of 18.7 months and 18.1 months, respectively.
In contrast, overall survival in the chemotherapy arm was markedly lower in patients with nonepithelioid tumors, at 8.8 months vs 16.5 months among those with epithelioid tumors.
This was reflected in the hazard ratios for overall survival vs nivo+ipi, at 0.46 and 0.86, respectively, the latter nonsignificantly different from combination immunotherapy.
For study discussant Dean A. Fennell, MD, PhD, professor and consultant in thoracic medical oncology, University of Leicester, United Kingdom, the epithet of a “new standard of care” for nivo+ipi should be reserved for nonepithelioid disease.
In this setting, he described the overall survival improvement as “transformative,” considering the “marked chemo resistance” of nonepithelioid tumors, which is “almost certainly” associated with epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
In the future, he suggested, combinations of chemotherapy and immunotherapy involving all histologies or selective targeting of nonepithelioid mesothelioma “could further extend the benefit for patients.”
Improving survival in mesothelioma
“We have been trying to improve the overall survival of patients with mesothelioma now for many decades,” Bass commented. Platinum-based chemotherapy plus pemetrexed is a standard of care, although the 5-year survival rate «is still below 10%,” he noted.
Randomized trials of single-agent immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in the second-line treatment of patients with mesothelioma have not shown any significant benefits.
However, nivolumab and ipilimumab have a “complementary mechanism of action,” and two previous reports have indicated that together, they have clinical activity in the second-line setting.
The team conducted CheckMate 743 to determine the efficacy of the combination in the first-line setting.
The study involved 605 patients with pleural mesothelioma who had received no prior systemic therapy and had good performance status.
They were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive nivo+ipi for up to 2 years or six cycles of pemetrexed plus cisplatin or carboplatin until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurred.
“Patients could have a subsequent therapy,” Bass noted; 44.0% of patients in the experimental arm received subsequent therapy, vs 44.1% of those in the chemotherapy arm.
Of the latter, 20% received an immune checkpoint inhibitor as subsequent therapy.
The minimum follow-up for overall survival was 22.1 months; the median follow-up was 29.7 months.
Nivo+ipi was associated with a significant improvement in overall survival vs standard-of-care chemotherapy, at a median overall survival of 18.1 months vs 14.1 months, with a hazard ratio of 0.74 (P = .0020).
The results indicated that overall survival was similar across key subgroups, which suggests that “no subgroup was harmed” by nivo+ipi, Bass said.
Stratification by PD-LI expression
Stratifying the patients by the absence or presence of programmed cell death–ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression, the team found that the performance of nivo+ipi was “the same” as that of chemotherapy, Bass said.
“But in cases where there is any expression of PD-L1, the experimental arm performs better,” at an overall survival 18.0 months vs 13.3 months for chemotherapy and a hazard ratio of 0.69, he said.
There was no difference between the two treatment arms in progression-free survival. Chemotherapy performed better in the first 6 months of treatment, after which the nivo+ipi arm had lower event rates.
Nivo+ipi was also associated with a greater duration of response, at a median of 11.0 months vs 6.7 months for standard-of-care chemotherapy.
Moreover, at 24 months, 32% of nivo+ipi patients were still experiencing a response, whereas 8% of those in the chemotherapy arm were.
Treatment-related adverse events rates were almost identical between the two treatment groups, although treatment with nivo+ipi was associated with more grade 3/4 serious treatment-related adverse events, at 15 vs six for chemotherapy.
Choosing immunotherapy vs. chemotherapy
In his discussion of the new study, Fennell compared the current results with those from two studies, INITIATE and MAPS2. “What’s very clear is the response rate is slightly higher,” as is the disease control rate, he said.
This, he explained, “is perhaps not surprising, given that these two previous trials were in the relapse setting.”
He pointed out, however, that the progression-free survival data from those previous trials were “not a million miles away” from results seen in CheckMate 743, “suggesting that this immunotherapy does have significant activity in the relapse setting.”
For Fennell, the “pivotal data” are in patients with nonepithelioid tumors, particularly inasmuch as chemotherapy performed “poorly” in this setting, whereas it performs “as expected” in epithelioid mesothelioma.
He believes that the driver for this is the poor prognosis associated with sarcomatoid biphasic disease, a subtype characterized by increased expression of vimentin and ZEB1, proteins both associated with EMT.
“What does this mean?” Fennell asked.
“If you have have enrichment of EMT, what you see is increased drug resistance, increased invasiveness, something we know well with sarcomatoid mesotheliomas in particular, and this drug-resistance phenotype may account for the drug resistance that we see in CheckMate 743 with chemotherapy.
“This does not appear, however, to impact in any way the efficacy of the immunotherapy,” he noted.
Fennell believes that, with regard to both efficacy and safety, the balance is “very much in favor” of nivo+ipi in epithelioid mesothelioma, although there is less to choose between immunotherapy and chemotherapy in the nonepithelioid setting.
Indeed, the choice is “possible tilting slightly towards chemotherapy” in patients with the nonepithelioid tumors, owing to the lower rates of grade 3/4 serious treatment-related adverse events in comparison with combination immunotherapy.
The study was supported by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Bass has served on the advisory boards of MSD, AstraZeneca, and Takeda. Fennell has received research support from AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Clovis Oncology, Eli Lilly, MSD, and Roche; research funding from Astex Therapeutics, Bayer, and Boehringer Ingelheim; has served on the speaker bureau of AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Roche; has acted as a consultant for Bayer and Lab 21; and has served on the advisory board of Atara Biotherapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Inventiva.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with untreated mesothelioma may be able to avoid chemotherapy, say researchers reporting new survival data with the immunotherapy combination of nivolumab (Opdivo) and ipilimumab (Yervoy).
The two approaches were compared in more than 600 patients with treatment-naive mesothelioma in the phase 3 CheckMate 743 trial, which was supported by the manufacturer of both immunotherapies, Bristol-Myers Squibb.
The trial “met its primary endpoint of statistically improving overall survival for the experimental arm vs chemotherapy in a prespecified interim analysis,” reported Paul Baas, MD, PhD, Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, The Netherlands,
The combined nivo+ipi immunotherapy regimen was associated with a 26% improvement in overall survival. At 2 years, 41% of patients in the immunotherapy arm were still alive, vs 27% in the chemotherapy group.
“This is the first positive randomized trial of dual immunotherapy in the first-line treatment of patients with mesothelioma,” he said. He suggested that it should therefore “be considered as a new standard of care.”
The data were presented on August 8 in the presidential symposium of the World Congress on Lung Cancer 2020, which was held online because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A key analysis for the study was by histologic subgroup. It is known that standard-of-care chemotherapy performs better in patients with epithelioid as opposed to nonepithelioid tumor subtypes.
Bass highlighted that the performance of nivo+ipi was “almost the same” in patients with epithelioid and nonepithelioid tumors, at a median overall survival of 18.7 months and 18.1 months, respectively.
In contrast, overall survival in the chemotherapy arm was markedly lower in patients with nonepithelioid tumors, at 8.8 months vs 16.5 months among those with epithelioid tumors.
This was reflected in the hazard ratios for overall survival vs nivo+ipi, at 0.46 and 0.86, respectively, the latter nonsignificantly different from combination immunotherapy.
For study discussant Dean A. Fennell, MD, PhD, professor and consultant in thoracic medical oncology, University of Leicester, United Kingdom, the epithet of a “new standard of care” for nivo+ipi should be reserved for nonepithelioid disease.
In this setting, he described the overall survival improvement as “transformative,” considering the “marked chemo resistance” of nonepithelioid tumors, which is “almost certainly” associated with epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
In the future, he suggested, combinations of chemotherapy and immunotherapy involving all histologies or selective targeting of nonepithelioid mesothelioma “could further extend the benefit for patients.”
Improving survival in mesothelioma
“We have been trying to improve the overall survival of patients with mesothelioma now for many decades,” Bass commented. Platinum-based chemotherapy plus pemetrexed is a standard of care, although the 5-year survival rate «is still below 10%,” he noted.
Randomized trials of single-agent immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in the second-line treatment of patients with mesothelioma have not shown any significant benefits.
However, nivolumab and ipilimumab have a “complementary mechanism of action,” and two previous reports have indicated that together, they have clinical activity in the second-line setting.
The team conducted CheckMate 743 to determine the efficacy of the combination in the first-line setting.
The study involved 605 patients with pleural mesothelioma who had received no prior systemic therapy and had good performance status.
They were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive nivo+ipi for up to 2 years or six cycles of pemetrexed plus cisplatin or carboplatin until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurred.
“Patients could have a subsequent therapy,” Bass noted; 44.0% of patients in the experimental arm received subsequent therapy, vs 44.1% of those in the chemotherapy arm.
Of the latter, 20% received an immune checkpoint inhibitor as subsequent therapy.
The minimum follow-up for overall survival was 22.1 months; the median follow-up was 29.7 months.
Nivo+ipi was associated with a significant improvement in overall survival vs standard-of-care chemotherapy, at a median overall survival of 18.1 months vs 14.1 months, with a hazard ratio of 0.74 (P = .0020).
The results indicated that overall survival was similar across key subgroups, which suggests that “no subgroup was harmed” by nivo+ipi, Bass said.
Stratification by PD-LI expression
Stratifying the patients by the absence or presence of programmed cell death–ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression, the team found that the performance of nivo+ipi was “the same” as that of chemotherapy, Bass said.
“But in cases where there is any expression of PD-L1, the experimental arm performs better,” at an overall survival 18.0 months vs 13.3 months for chemotherapy and a hazard ratio of 0.69, he said.
There was no difference between the two treatment arms in progression-free survival. Chemotherapy performed better in the first 6 months of treatment, after which the nivo+ipi arm had lower event rates.
Nivo+ipi was also associated with a greater duration of response, at a median of 11.0 months vs 6.7 months for standard-of-care chemotherapy.
Moreover, at 24 months, 32% of nivo+ipi patients were still experiencing a response, whereas 8% of those in the chemotherapy arm were.
Treatment-related adverse events rates were almost identical between the two treatment groups, although treatment with nivo+ipi was associated with more grade 3/4 serious treatment-related adverse events, at 15 vs six for chemotherapy.
Choosing immunotherapy vs. chemotherapy
In his discussion of the new study, Fennell compared the current results with those from two studies, INITIATE and MAPS2. “What’s very clear is the response rate is slightly higher,” as is the disease control rate, he said.
This, he explained, “is perhaps not surprising, given that these two previous trials were in the relapse setting.”
He pointed out, however, that the progression-free survival data from those previous trials were “not a million miles away” from results seen in CheckMate 743, “suggesting that this immunotherapy does have significant activity in the relapse setting.”
For Fennell, the “pivotal data” are in patients with nonepithelioid tumors, particularly inasmuch as chemotherapy performed “poorly” in this setting, whereas it performs “as expected” in epithelioid mesothelioma.
He believes that the driver for this is the poor prognosis associated with sarcomatoid biphasic disease, a subtype characterized by increased expression of vimentin and ZEB1, proteins both associated with EMT.
“What does this mean?” Fennell asked.
“If you have have enrichment of EMT, what you see is increased drug resistance, increased invasiveness, something we know well with sarcomatoid mesotheliomas in particular, and this drug-resistance phenotype may account for the drug resistance that we see in CheckMate 743 with chemotherapy.
“This does not appear, however, to impact in any way the efficacy of the immunotherapy,” he noted.
Fennell believes that, with regard to both efficacy and safety, the balance is “very much in favor” of nivo+ipi in epithelioid mesothelioma, although there is less to choose between immunotherapy and chemotherapy in the nonepithelioid setting.
Indeed, the choice is “possible tilting slightly towards chemotherapy” in patients with the nonepithelioid tumors, owing to the lower rates of grade 3/4 serious treatment-related adverse events in comparison with combination immunotherapy.
The study was supported by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Bass has served on the advisory boards of MSD, AstraZeneca, and Takeda. Fennell has received research support from AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Clovis Oncology, Eli Lilly, MSD, and Roche; research funding from Astex Therapeutics, Bayer, and Boehringer Ingelheim; has served on the speaker bureau of AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Roche; has acted as a consultant for Bayer and Lab 21; and has served on the advisory board of Atara Biotherapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Inventiva.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with untreated mesothelioma may be able to avoid chemotherapy, say researchers reporting new survival data with the immunotherapy combination of nivolumab (Opdivo) and ipilimumab (Yervoy).
The two approaches were compared in more than 600 patients with treatment-naive mesothelioma in the phase 3 CheckMate 743 trial, which was supported by the manufacturer of both immunotherapies, Bristol-Myers Squibb.
The trial “met its primary endpoint of statistically improving overall survival for the experimental arm vs chemotherapy in a prespecified interim analysis,” reported Paul Baas, MD, PhD, Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, The Netherlands,
The combined nivo+ipi immunotherapy regimen was associated with a 26% improvement in overall survival. At 2 years, 41% of patients in the immunotherapy arm were still alive, vs 27% in the chemotherapy group.
“This is the first positive randomized trial of dual immunotherapy in the first-line treatment of patients with mesothelioma,” he said. He suggested that it should therefore “be considered as a new standard of care.”
The data were presented on August 8 in the presidential symposium of the World Congress on Lung Cancer 2020, which was held online because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A key analysis for the study was by histologic subgroup. It is known that standard-of-care chemotherapy performs better in patients with epithelioid as opposed to nonepithelioid tumor subtypes.
Bass highlighted that the performance of nivo+ipi was “almost the same” in patients with epithelioid and nonepithelioid tumors, at a median overall survival of 18.7 months and 18.1 months, respectively.
In contrast, overall survival in the chemotherapy arm was markedly lower in patients with nonepithelioid tumors, at 8.8 months vs 16.5 months among those with epithelioid tumors.
This was reflected in the hazard ratios for overall survival vs nivo+ipi, at 0.46 and 0.86, respectively, the latter nonsignificantly different from combination immunotherapy.
For study discussant Dean A. Fennell, MD, PhD, professor and consultant in thoracic medical oncology, University of Leicester, United Kingdom, the epithet of a “new standard of care” for nivo+ipi should be reserved for nonepithelioid disease.
In this setting, he described the overall survival improvement as “transformative,” considering the “marked chemo resistance” of nonepithelioid tumors, which is “almost certainly” associated with epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
In the future, he suggested, combinations of chemotherapy and immunotherapy involving all histologies or selective targeting of nonepithelioid mesothelioma “could further extend the benefit for patients.”
Improving survival in mesothelioma
“We have been trying to improve the overall survival of patients with mesothelioma now for many decades,” Bass commented. Platinum-based chemotherapy plus pemetrexed is a standard of care, although the 5-year survival rate «is still below 10%,” he noted.
Randomized trials of single-agent immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in the second-line treatment of patients with mesothelioma have not shown any significant benefits.
However, nivolumab and ipilimumab have a “complementary mechanism of action,” and two previous reports have indicated that together, they have clinical activity in the second-line setting.
The team conducted CheckMate 743 to determine the efficacy of the combination in the first-line setting.
The study involved 605 patients with pleural mesothelioma who had received no prior systemic therapy and had good performance status.
They were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive nivo+ipi for up to 2 years or six cycles of pemetrexed plus cisplatin or carboplatin until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurred.
“Patients could have a subsequent therapy,” Bass noted; 44.0% of patients in the experimental arm received subsequent therapy, vs 44.1% of those in the chemotherapy arm.
Of the latter, 20% received an immune checkpoint inhibitor as subsequent therapy.
The minimum follow-up for overall survival was 22.1 months; the median follow-up was 29.7 months.
Nivo+ipi was associated with a significant improvement in overall survival vs standard-of-care chemotherapy, at a median overall survival of 18.1 months vs 14.1 months, with a hazard ratio of 0.74 (P = .0020).
The results indicated that overall survival was similar across key subgroups, which suggests that “no subgroup was harmed” by nivo+ipi, Bass said.
Stratification by PD-LI expression
Stratifying the patients by the absence or presence of programmed cell death–ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression, the team found that the performance of nivo+ipi was “the same” as that of chemotherapy, Bass said.
“But in cases where there is any expression of PD-L1, the experimental arm performs better,” at an overall survival 18.0 months vs 13.3 months for chemotherapy and a hazard ratio of 0.69, he said.
There was no difference between the two treatment arms in progression-free survival. Chemotherapy performed better in the first 6 months of treatment, after which the nivo+ipi arm had lower event rates.
Nivo+ipi was also associated with a greater duration of response, at a median of 11.0 months vs 6.7 months for standard-of-care chemotherapy.
Moreover, at 24 months, 32% of nivo+ipi patients were still experiencing a response, whereas 8% of those in the chemotherapy arm were.
Treatment-related adverse events rates were almost identical between the two treatment groups, although treatment with nivo+ipi was associated with more grade 3/4 serious treatment-related adverse events, at 15 vs six for chemotherapy.
Choosing immunotherapy vs. chemotherapy
In his discussion of the new study, Fennell compared the current results with those from two studies, INITIATE and MAPS2. “What’s very clear is the response rate is slightly higher,” as is the disease control rate, he said.
This, he explained, “is perhaps not surprising, given that these two previous trials were in the relapse setting.”
He pointed out, however, that the progression-free survival data from those previous trials were “not a million miles away” from results seen in CheckMate 743, “suggesting that this immunotherapy does have significant activity in the relapse setting.”
For Fennell, the “pivotal data” are in patients with nonepithelioid tumors, particularly inasmuch as chemotherapy performed “poorly” in this setting, whereas it performs “as expected” in epithelioid mesothelioma.
He believes that the driver for this is the poor prognosis associated with sarcomatoid biphasic disease, a subtype characterized by increased expression of vimentin and ZEB1, proteins both associated with EMT.
“What does this mean?” Fennell asked.
“If you have have enrichment of EMT, what you see is increased drug resistance, increased invasiveness, something we know well with sarcomatoid mesotheliomas in particular, and this drug-resistance phenotype may account for the drug resistance that we see in CheckMate 743 with chemotherapy.
“This does not appear, however, to impact in any way the efficacy of the immunotherapy,” he noted.
Fennell believes that, with regard to both efficacy and safety, the balance is “very much in favor” of nivo+ipi in epithelioid mesothelioma, although there is less to choose between immunotherapy and chemotherapy in the nonepithelioid setting.
Indeed, the choice is “possible tilting slightly towards chemotherapy” in patients with the nonepithelioid tumors, owing to the lower rates of grade 3/4 serious treatment-related adverse events in comparison with combination immunotherapy.
The study was supported by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Bass has served on the advisory boards of MSD, AstraZeneca, and Takeda. Fennell has received research support from AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Clovis Oncology, Eli Lilly, MSD, and Roche; research funding from Astex Therapeutics, Bayer, and Boehringer Ingelheim; has served on the speaker bureau of AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Roche; has acted as a consultant for Bayer and Lab 21; and has served on the advisory board of Atara Biotherapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Inventiva.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.