User login
Colorectal Cancer Risk Increasing Across Successive Birth Cohorts
Colorectal cancer (CRC) epidemiology is changing due to a birth cohort effect, also called birth cohort CRC — the observed phenomena of the rising risk for CRC across successive generations of people born in 1960 and later — according to a new narrative review.
Birth cohort CRC is associated with increasing rectal cancer (greater than colon cancer) diagnosis and distant-stage (greater than local-stage) CRC diagnosis, and a rising incidence of early-onset CRC (EOCRC), defined as occurring before age 50.
Recognizing this birth cohort effect could improve the understanding of CRC risk factors, etiology, mechanisms, as well as the public health consequences of rising rates.
“The changing epidemiology means that we need to redouble our efforts at optimizing early detection and prevention of colorectal cancer,” Samir Gupta, MD, the review’s lead author and professor of gastroenterology at the University of California, San Diego, California, told this news organization. Dr. Gupta serves as the co-lead for the cancer control program at Moores Cancer Center at UC San Diego Health.
This requires “being alert for potential red flag signs and symptoms of colorectal cancer, such as iron deficiency anemia and rectal bleeding, that are otherwise unexplained, including for those under age 45,” he said.
We also should make “sure that all people eligible for screening — at age 45 and older — have every opportunity to get screened for colorectal cancer,” Dr. Gupta added.
The review was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Tracking Birth Cohort Trends
CRC rates have increased in the United States among people born since the early 1960s, the authors wrote.
Generation X (individuals born in 1965-1980) experienced an increase in EOCRC, and rates subsequently increased in this generation after age 50. Rates are 1.22-fold higher among people born in 1965-1969 and 1.58-fold higher among those born 1975-1979 than among people born in 1950-1954.
Now rates are also increasing across younger generations, particularly among Millennials (individuals born in 1981-1996) as they enter mid-adulthood. Incidence rates are 1.89-fold higher among people born in 1980-1984 and 2.98-fold higher among those born in 1990-1994 than among individuals born in 1950-1954.
These birth cohort effects are evident globally, despite differences in population age structures, screening programs, and diagnostic strategies around the world. Due to this ongoing trend, physicians anticipate that CRC rates will likely continue to increase as higher-risk birth cohorts become older, the authors wrote.
Notably, four important shifts in CRC incidence are apparent, they noted. First, rates are steadily increasing up to age 50 and plateauing after age 60. Rectal cancers are now predominant through ages 50-59. Rates of distant-stage disease have increased most rapidly among ages 30-49 and more slowly decreased among ages 60-79 compared with those of local-stage disease. In addition, the increasing rates of EOCRC have been observed across all racial and ethnic groups since the early 1990s.
These shifts led to major changes in the types of patients diagnosed with CRC now vs 30 years ago, with a higher proportion being patients younger than 60, as well as Black, Asian or Pacific Islander, American Indian/Alaska Native, and Hispanic patients.
The combination of age-related increases in CRC and birth cohort–related trends will likely lead to substantial increases in the number of people diagnosed with CRC in coming years, especially as Generation X patients move into their 50s and 60s, the authors wrote.
Research and Clinical Implications
Birth cohort CRC, including increasing EOCRC incidence, likely is driven by a range of influences, including demographic, lifestyle, early life, environmental, genetic, and somatic factors, as well as interactions among them, the authors noted. Examples within these broad categories include male sex, food insecurity, income inequality, diabetes, alcohol use, less healthy dietary patterns, in utero exposure to certain medications, and microbiome concerns such as early life antibiotic exposure or dysbiosis.
“From a research perspective, this means that we need to think about risk factors and mechanisms that are associated with birth cohorts, not just age at diagnosis,” Dr. Gupta said. “To date, most studies of changing epidemiology have not taken into account birth cohort, such as whether someone is Generation X or later versus pre-Baby Boomer.”
Although additional research is needed, the epidemiology changes have several immediate clinical implications, Dr. Gupta said. For those younger than 45, it is critical to raise awareness about the signs and symptoms of CRC, such as hematochezia, iron deficiency anemia, and unintentional weight loss, as well as family history.
For ages 45 and older, a major focus should be placed on increasing screening participation and follow-up after abnormal results, addressing disparities in screening participation, and optimizing screening quality.
In addition, as CRC incidence continues to increase, health systems and policymakers should ensure every patient has access to guideline-appropriate care and innovative clinical trials, the authors wrote. This access may be particularly important to address the increasing burden of rectal cancer, as treatment approaches rapidly evolve toward more effective therapies, such as neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radiation prior to surgery, and with less-morbid treatments on the horizon, they added.
‘An Interesting Concept’
“Birth cohort CRC is an interesting concept that allows people to think of their CRC risk according to their birth cohort in addition to age,” Shuji Ogino, MD, PhD, chief of the Molecular Pathological Epidemiology program at Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, told this news organization.
Dr. Ogino, who wasn’t involved with this study, serves as a member of the cancer immunology and cancer epidemiology programs at the Dana-Farber Harvard Cancer Center. In studies of EOCRC, he and colleagues have found various biogeographical and pathogenic trends across age groups.
“More research is needed to disentangle the complex etiologies of birth cohort CRC and early-onset CRC,” Dr. Ogino said. “Tumor cells and tissues have certain past and ongoing pathological marks, which we can detect to better understand birth cohort CRC and early-onset CRC.”
The study was funded by several National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute grants. Dr. Gupta disclosed consulting for Geneoscopy, Guardant Health, Universal Diagnostics, InterVenn Bio, and CellMax. Another author reported consulting for Freenome, Exact Sciences, Medtronic, and Geneoscopy. Dr. Ogino reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Colorectal cancer (CRC) epidemiology is changing due to a birth cohort effect, also called birth cohort CRC — the observed phenomena of the rising risk for CRC across successive generations of people born in 1960 and later — according to a new narrative review.
Birth cohort CRC is associated with increasing rectal cancer (greater than colon cancer) diagnosis and distant-stage (greater than local-stage) CRC diagnosis, and a rising incidence of early-onset CRC (EOCRC), defined as occurring before age 50.
Recognizing this birth cohort effect could improve the understanding of CRC risk factors, etiology, mechanisms, as well as the public health consequences of rising rates.
“The changing epidemiology means that we need to redouble our efforts at optimizing early detection and prevention of colorectal cancer,” Samir Gupta, MD, the review’s lead author and professor of gastroenterology at the University of California, San Diego, California, told this news organization. Dr. Gupta serves as the co-lead for the cancer control program at Moores Cancer Center at UC San Diego Health.
This requires “being alert for potential red flag signs and symptoms of colorectal cancer, such as iron deficiency anemia and rectal bleeding, that are otherwise unexplained, including for those under age 45,” he said.
We also should make “sure that all people eligible for screening — at age 45 and older — have every opportunity to get screened for colorectal cancer,” Dr. Gupta added.
The review was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Tracking Birth Cohort Trends
CRC rates have increased in the United States among people born since the early 1960s, the authors wrote.
Generation X (individuals born in 1965-1980) experienced an increase in EOCRC, and rates subsequently increased in this generation after age 50. Rates are 1.22-fold higher among people born in 1965-1969 and 1.58-fold higher among those born 1975-1979 than among people born in 1950-1954.
Now rates are also increasing across younger generations, particularly among Millennials (individuals born in 1981-1996) as they enter mid-adulthood. Incidence rates are 1.89-fold higher among people born in 1980-1984 and 2.98-fold higher among those born in 1990-1994 than among individuals born in 1950-1954.
These birth cohort effects are evident globally, despite differences in population age structures, screening programs, and diagnostic strategies around the world. Due to this ongoing trend, physicians anticipate that CRC rates will likely continue to increase as higher-risk birth cohorts become older, the authors wrote.
Notably, four important shifts in CRC incidence are apparent, they noted. First, rates are steadily increasing up to age 50 and plateauing after age 60. Rectal cancers are now predominant through ages 50-59. Rates of distant-stage disease have increased most rapidly among ages 30-49 and more slowly decreased among ages 60-79 compared with those of local-stage disease. In addition, the increasing rates of EOCRC have been observed across all racial and ethnic groups since the early 1990s.
These shifts led to major changes in the types of patients diagnosed with CRC now vs 30 years ago, with a higher proportion being patients younger than 60, as well as Black, Asian or Pacific Islander, American Indian/Alaska Native, and Hispanic patients.
The combination of age-related increases in CRC and birth cohort–related trends will likely lead to substantial increases in the number of people diagnosed with CRC in coming years, especially as Generation X patients move into their 50s and 60s, the authors wrote.
Research and Clinical Implications
Birth cohort CRC, including increasing EOCRC incidence, likely is driven by a range of influences, including demographic, lifestyle, early life, environmental, genetic, and somatic factors, as well as interactions among them, the authors noted. Examples within these broad categories include male sex, food insecurity, income inequality, diabetes, alcohol use, less healthy dietary patterns, in utero exposure to certain medications, and microbiome concerns such as early life antibiotic exposure or dysbiosis.
“From a research perspective, this means that we need to think about risk factors and mechanisms that are associated with birth cohorts, not just age at diagnosis,” Dr. Gupta said. “To date, most studies of changing epidemiology have not taken into account birth cohort, such as whether someone is Generation X or later versus pre-Baby Boomer.”
Although additional research is needed, the epidemiology changes have several immediate clinical implications, Dr. Gupta said. For those younger than 45, it is critical to raise awareness about the signs and symptoms of CRC, such as hematochezia, iron deficiency anemia, and unintentional weight loss, as well as family history.
For ages 45 and older, a major focus should be placed on increasing screening participation and follow-up after abnormal results, addressing disparities in screening participation, and optimizing screening quality.
In addition, as CRC incidence continues to increase, health systems and policymakers should ensure every patient has access to guideline-appropriate care and innovative clinical trials, the authors wrote. This access may be particularly important to address the increasing burden of rectal cancer, as treatment approaches rapidly evolve toward more effective therapies, such as neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radiation prior to surgery, and with less-morbid treatments on the horizon, they added.
‘An Interesting Concept’
“Birth cohort CRC is an interesting concept that allows people to think of their CRC risk according to their birth cohort in addition to age,” Shuji Ogino, MD, PhD, chief of the Molecular Pathological Epidemiology program at Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, told this news organization.
Dr. Ogino, who wasn’t involved with this study, serves as a member of the cancer immunology and cancer epidemiology programs at the Dana-Farber Harvard Cancer Center. In studies of EOCRC, he and colleagues have found various biogeographical and pathogenic trends across age groups.
“More research is needed to disentangle the complex etiologies of birth cohort CRC and early-onset CRC,” Dr. Ogino said. “Tumor cells and tissues have certain past and ongoing pathological marks, which we can detect to better understand birth cohort CRC and early-onset CRC.”
The study was funded by several National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute grants. Dr. Gupta disclosed consulting for Geneoscopy, Guardant Health, Universal Diagnostics, InterVenn Bio, and CellMax. Another author reported consulting for Freenome, Exact Sciences, Medtronic, and Geneoscopy. Dr. Ogino reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Colorectal cancer (CRC) epidemiology is changing due to a birth cohort effect, also called birth cohort CRC — the observed phenomena of the rising risk for CRC across successive generations of people born in 1960 and later — according to a new narrative review.
Birth cohort CRC is associated with increasing rectal cancer (greater than colon cancer) diagnosis and distant-stage (greater than local-stage) CRC diagnosis, and a rising incidence of early-onset CRC (EOCRC), defined as occurring before age 50.
Recognizing this birth cohort effect could improve the understanding of CRC risk factors, etiology, mechanisms, as well as the public health consequences of rising rates.
“The changing epidemiology means that we need to redouble our efforts at optimizing early detection and prevention of colorectal cancer,” Samir Gupta, MD, the review’s lead author and professor of gastroenterology at the University of California, San Diego, California, told this news organization. Dr. Gupta serves as the co-lead for the cancer control program at Moores Cancer Center at UC San Diego Health.
This requires “being alert for potential red flag signs and symptoms of colorectal cancer, such as iron deficiency anemia and rectal bleeding, that are otherwise unexplained, including for those under age 45,” he said.
We also should make “sure that all people eligible for screening — at age 45 and older — have every opportunity to get screened for colorectal cancer,” Dr. Gupta added.
The review was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Tracking Birth Cohort Trends
CRC rates have increased in the United States among people born since the early 1960s, the authors wrote.
Generation X (individuals born in 1965-1980) experienced an increase in EOCRC, and rates subsequently increased in this generation after age 50. Rates are 1.22-fold higher among people born in 1965-1969 and 1.58-fold higher among those born 1975-1979 than among people born in 1950-1954.
Now rates are also increasing across younger generations, particularly among Millennials (individuals born in 1981-1996) as they enter mid-adulthood. Incidence rates are 1.89-fold higher among people born in 1980-1984 and 2.98-fold higher among those born in 1990-1994 than among individuals born in 1950-1954.
These birth cohort effects are evident globally, despite differences in population age structures, screening programs, and diagnostic strategies around the world. Due to this ongoing trend, physicians anticipate that CRC rates will likely continue to increase as higher-risk birth cohorts become older, the authors wrote.
Notably, four important shifts in CRC incidence are apparent, they noted. First, rates are steadily increasing up to age 50 and plateauing after age 60. Rectal cancers are now predominant through ages 50-59. Rates of distant-stage disease have increased most rapidly among ages 30-49 and more slowly decreased among ages 60-79 compared with those of local-stage disease. In addition, the increasing rates of EOCRC have been observed across all racial and ethnic groups since the early 1990s.
These shifts led to major changes in the types of patients diagnosed with CRC now vs 30 years ago, with a higher proportion being patients younger than 60, as well as Black, Asian or Pacific Islander, American Indian/Alaska Native, and Hispanic patients.
The combination of age-related increases in CRC and birth cohort–related trends will likely lead to substantial increases in the number of people diagnosed with CRC in coming years, especially as Generation X patients move into their 50s and 60s, the authors wrote.
Research and Clinical Implications
Birth cohort CRC, including increasing EOCRC incidence, likely is driven by a range of influences, including demographic, lifestyle, early life, environmental, genetic, and somatic factors, as well as interactions among them, the authors noted. Examples within these broad categories include male sex, food insecurity, income inequality, diabetes, alcohol use, less healthy dietary patterns, in utero exposure to certain medications, and microbiome concerns such as early life antibiotic exposure or dysbiosis.
“From a research perspective, this means that we need to think about risk factors and mechanisms that are associated with birth cohorts, not just age at diagnosis,” Dr. Gupta said. “To date, most studies of changing epidemiology have not taken into account birth cohort, such as whether someone is Generation X or later versus pre-Baby Boomer.”
Although additional research is needed, the epidemiology changes have several immediate clinical implications, Dr. Gupta said. For those younger than 45, it is critical to raise awareness about the signs and symptoms of CRC, such as hematochezia, iron deficiency anemia, and unintentional weight loss, as well as family history.
For ages 45 and older, a major focus should be placed on increasing screening participation and follow-up after abnormal results, addressing disparities in screening participation, and optimizing screening quality.
In addition, as CRC incidence continues to increase, health systems and policymakers should ensure every patient has access to guideline-appropriate care and innovative clinical trials, the authors wrote. This access may be particularly important to address the increasing burden of rectal cancer, as treatment approaches rapidly evolve toward more effective therapies, such as neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radiation prior to surgery, and with less-morbid treatments on the horizon, they added.
‘An Interesting Concept’
“Birth cohort CRC is an interesting concept that allows people to think of their CRC risk according to their birth cohort in addition to age,” Shuji Ogino, MD, PhD, chief of the Molecular Pathological Epidemiology program at Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, told this news organization.
Dr. Ogino, who wasn’t involved with this study, serves as a member of the cancer immunology and cancer epidemiology programs at the Dana-Farber Harvard Cancer Center. In studies of EOCRC, he and colleagues have found various biogeographical and pathogenic trends across age groups.
“More research is needed to disentangle the complex etiologies of birth cohort CRC and early-onset CRC,” Dr. Ogino said. “Tumor cells and tissues have certain past and ongoing pathological marks, which we can detect to better understand birth cohort CRC and early-onset CRC.”
The study was funded by several National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute grants. Dr. Gupta disclosed consulting for Geneoscopy, Guardant Health, Universal Diagnostics, InterVenn Bio, and CellMax. Another author reported consulting for Freenome, Exact Sciences, Medtronic, and Geneoscopy. Dr. Ogino reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
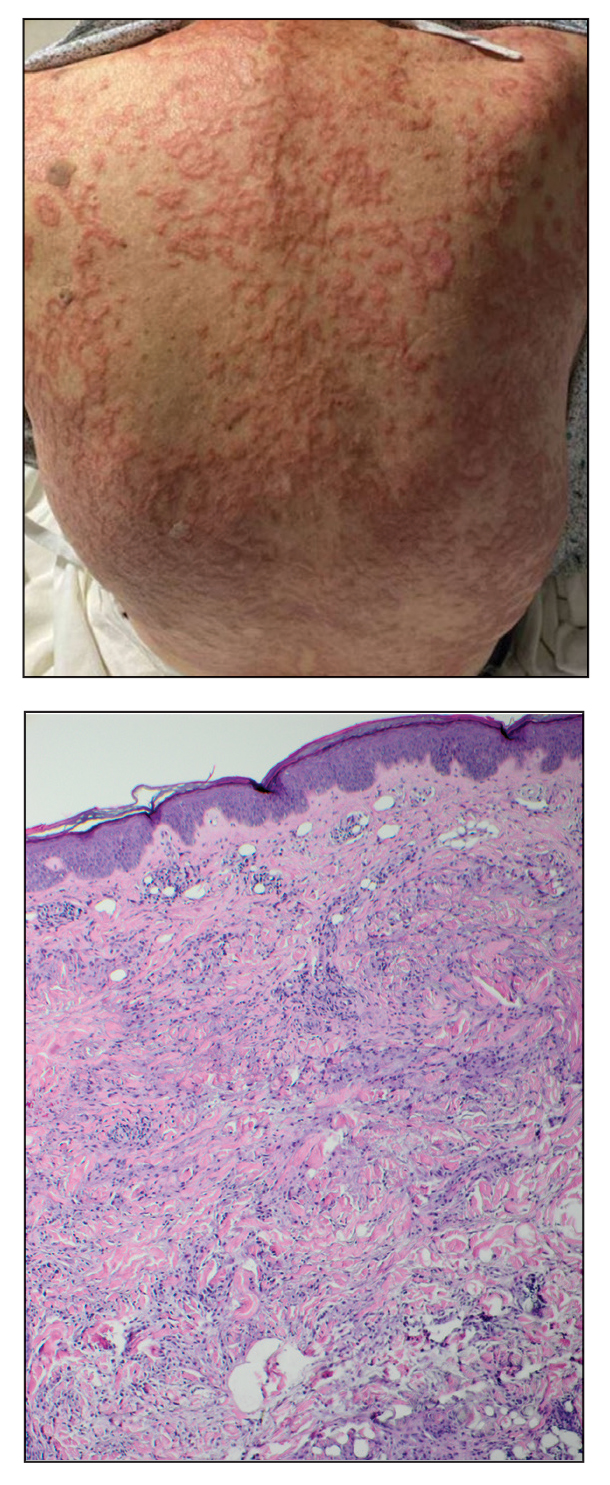
Annular Erythematous Plaques on the Back
The Diagnosis: Granuloma Annulare
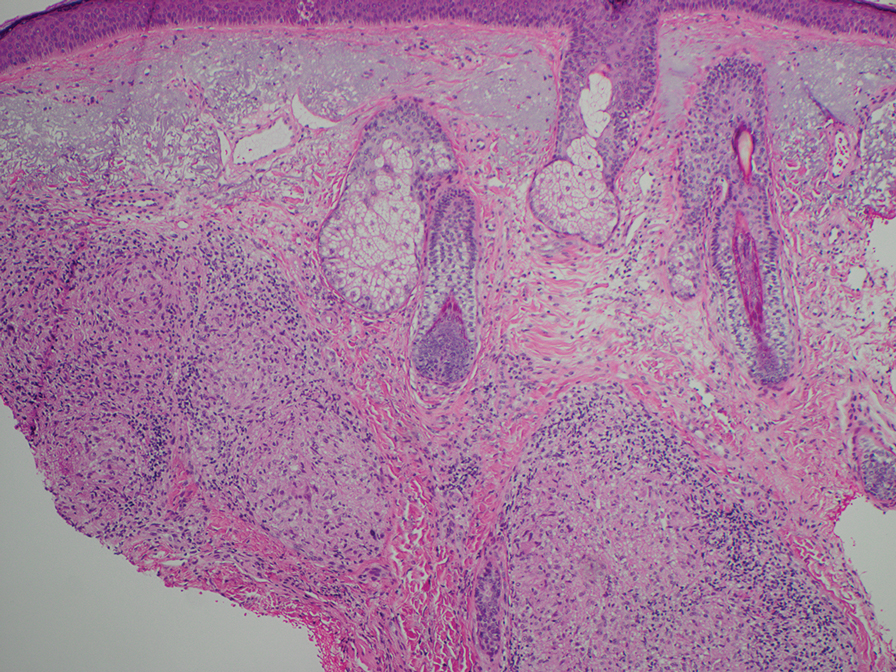
The biopsies revealed palisading granulomatous dermatitis consistent with granuloma annulare (GA). This diagnosis was supported by the clinical presentation and histopathologic findings. Although the pathogenesis of GA is unclear, it is a benign, self-limiting condition. Primarily affected sites include the trunk and forearms. Generalized GA (or GA with ≥10 lesions) may warrant workup for malignancy, as it may represent a paraneoplastic process.1 Histopathology reveals granulomas comprising a dermal lymphohistiocytic infiltrate as well as central mucin and nuclear debris. There are a few histologic subtypes of GA, including palisading and interstitial, which refer to the distribution of the histiocytic infiltrate.2,3 This case—with palisading histiocytes lining the collection of necrobiosis and mucin (bottom quiz image)—features palisading GA. Notably, GA exhibits central rather than diffuse mucin.4
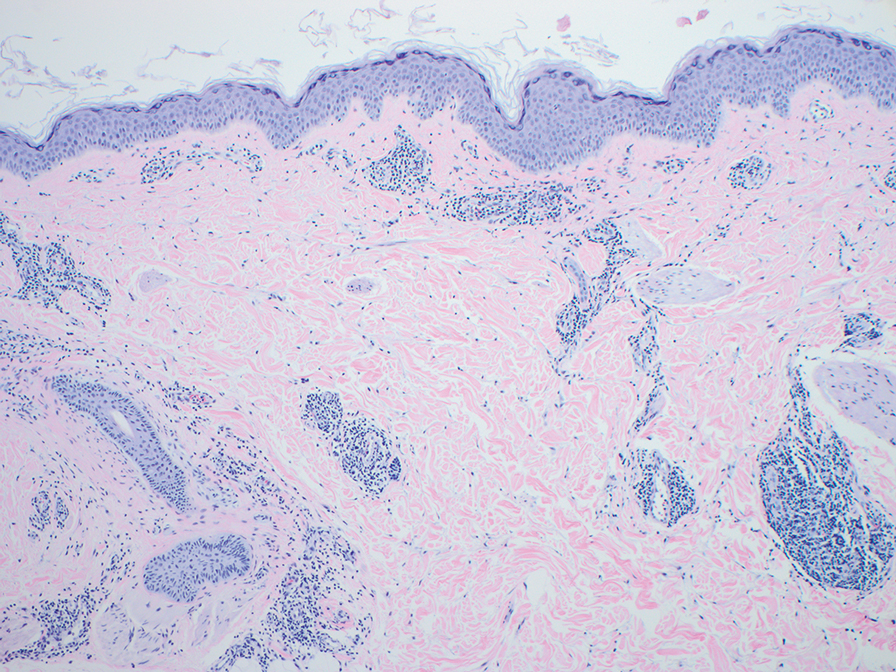
Erythema gyratum repens is a paraneoplastic arcuate erythema that manifests as erythematous figurate, gyrate, or annular plaques exhibiting a trailing scale. Clinically, erythema gyratum repens spreads rapidly—as quickly as 1 cm/d—and can be extensive (as in this case). Histopathology ruled out this diagnosis in our patient. Nonspecific findings of acanthosis, parakeratosis, and superficial spongiosis can be found in erythema gyratum repens. A superficial and deep perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate may be seen in figurate erythemas (Figure 1).5 Unlike GA, this infiltrate does not form granulomas, is more superficial, and does not contain mucin.
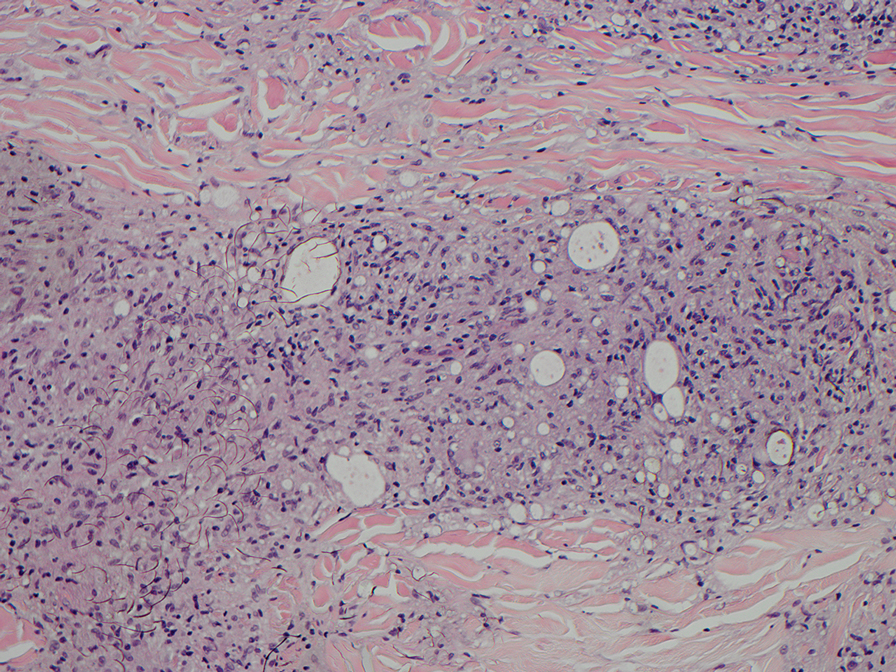
Histopathology also can help establish the diagnosis of leprosy and its specific subtype, as leprosy exists on a spectrum from tuberculoid to lepromatous, with a great deal of overlap in between.6 Lepromatous leprosy has many cutaneous clinical presentations but typically manifests as erythematous papules or nodules. It is multibacillary, and these mycobacteria form clumps known as globi that can be seen on Fite stain.7 In lepromatous leprosy, there is a characteristic dense lymphohistiocytic infiltrate (Figure 2) above which a Grenz zone can be seen.4,8 There are no well-formed granulomas in lepromatous leprosy, unlike in tuberculoid leprosy, which is paucibacillary and creates a granulomatous response surrounding nerves and adnexal structures.6
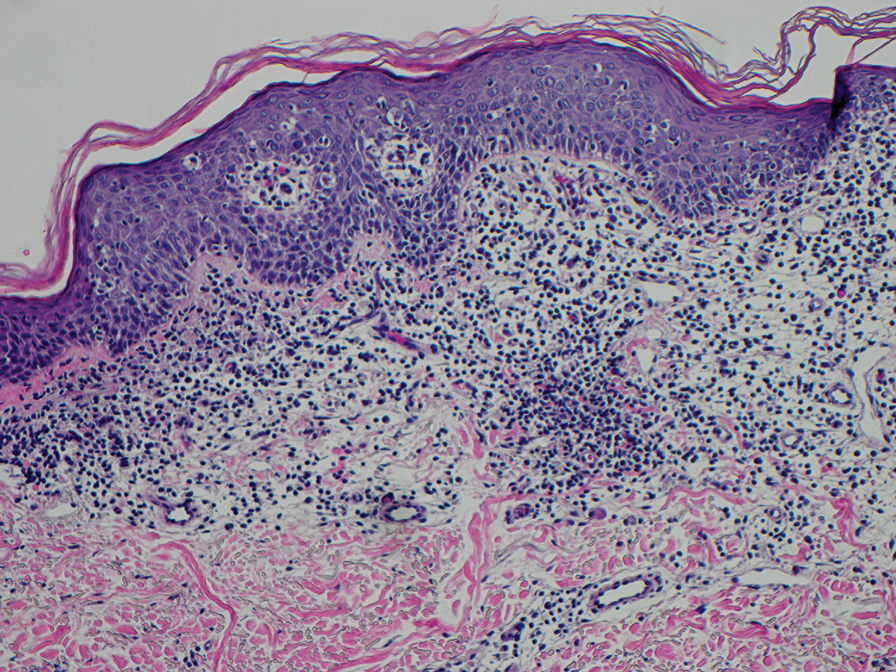
Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common cutaneous lymphoma. There are patch, plaque, and tumor stages of MF, each of which exhibits various histopathologic findings.9 In early patch-stage MF, lymphocytes have perinuclear clearing, and the degree of lymphocytic infiltrate is out of proportion to the spongiosis present. Epidermotropism and Pautrier microabscesses often are present in the epidermis (Figure 3). In the plaque stage, there is a denser lymphoid infiltrate in a lichenoid pattern with epidermotropism and Pautrier microabscesses. The tumor stage shows a dense dermal lymphoid infiltrate with more atypia and typically a lack of epidermotropism. Rarely, MF can exhibit a granulomatous variant in which epithelioid histiocytes collect to form granulomas along with atypical lymphocytes.10
The diagnosis of cutaneous sarcoidosis requires clinicopathologic corroboration. Histopathology demonstrates epithelioid histiocytes forming noncaseating granulomas with little to no lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure 4). There typically is no necrosis or necrobiosis as there is in GA. The diagnosis of sarcoidosis can be challenging histopathologically, and stains should be used to rule out infectious processes.4 Asteroid bodies— star-shaped eosinophilic inclusions within giant cells—may be present but are nonspecific for sarcoidosis.11 Schaumann bodies—inclusions of calcifications within giant cells—also may be present and can aid in diagnosis.12
- Kovich O, Burgin S. Generalized granuloma annulare [published online December 30, 2005]. Dermatol Online J. 2005;11:23.
- Al Ameer MA, Al-Natour SH, Alsahaf HAA, et al. Eruptive granuloma annulare in an elderly man with diabetes [published online January 14, 2022]. Cureus. 2022;14:E21242. doi:10.7759/cureus.21242
- Howard A, White CR Jr. Non-infectious granulomas. In: Bolognia JL, et al, eds. Dermatology. Mosby; 2003:1455.
- Elston DM, Ferringer T, Ko CJ, et al. Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2018.
- Gore M, Winters ME. Erythema gyratum repens: a rare paraneoplastic rash. West J Emerg Med. 2011;12:556-558. doi:10.5811/westjem.2010.11.2090
- Maymone MBC, Laughter M, Venkatesh S, et al. Leprosy: clinical aspects and diagnostic techniques. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1-14. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.12.080
- Pedley JC, Harman DJ, Waudby H, et al. Leprosy in peripheral nerves: histopathological findings in 119 untreated patients in Nepal. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980;43:198-204. doi:10.1136/jnnp.43.3.198
- Booth AV, Kovich OI. Lepromatous leprosy [published online January 27, 2007]. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13:9.
- Robson A. The pathology of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Oncology (Williston Park). 2007;21(2 suppl 1):9-12.
- Kempf W, Ostheeren-Michaelis S, Paulli M, et al. Granulomatous mycosis fungoides and granulomatous slack skin: a multicenter study of the Cutaneous Lymphoma Histopathology Task Force Group of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1609-1617. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2008.46
- Azar HA, Lunardelli C. Collagen nature of asteroid bodies of giant cells in sarcoidosis. Am J Pathol. 1969;57:81-92.
- Sreeja C, Priyadarshini A, Premika, et al. Sarcoidosis—a review article. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2022;26:242-253. doi:10.4103 /jomfp.jomfp_373_21
The Diagnosis: Granuloma Annulare
The biopsies revealed palisading granulomatous dermatitis consistent with granuloma annulare (GA). This diagnosis was supported by the clinical presentation and histopathologic findings. Although the pathogenesis of GA is unclear, it is a benign, self-limiting condition. Primarily affected sites include the trunk and forearms. Generalized GA (or GA with ≥10 lesions) may warrant workup for malignancy, as it may represent a paraneoplastic process.1 Histopathology reveals granulomas comprising a dermal lymphohistiocytic infiltrate as well as central mucin and nuclear debris. There are a few histologic subtypes of GA, including palisading and interstitial, which refer to the distribution of the histiocytic infiltrate.2,3 This case—with palisading histiocytes lining the collection of necrobiosis and mucin (bottom quiz image)—features palisading GA. Notably, GA exhibits central rather than diffuse mucin.4
Erythema gyratum repens is a paraneoplastic arcuate erythema that manifests as erythematous figurate, gyrate, or annular plaques exhibiting a trailing scale. Clinically, erythema gyratum repens spreads rapidly—as quickly as 1 cm/d—and can be extensive (as in this case). Histopathology ruled out this diagnosis in our patient. Nonspecific findings of acanthosis, parakeratosis, and superficial spongiosis can be found in erythema gyratum repens. A superficial and deep perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate may be seen in figurate erythemas (Figure 1).5 Unlike GA, this infiltrate does not form granulomas, is more superficial, and does not contain mucin.

Histopathology also can help establish the diagnosis of leprosy and its specific subtype, as leprosy exists on a spectrum from tuberculoid to lepromatous, with a great deal of overlap in between.6 Lepromatous leprosy has many cutaneous clinical presentations but typically manifests as erythematous papules or nodules. It is multibacillary, and these mycobacteria form clumps known as globi that can be seen on Fite stain.7 In lepromatous leprosy, there is a characteristic dense lymphohistiocytic infiltrate (Figure 2) above which a Grenz zone can be seen.4,8 There are no well-formed granulomas in lepromatous leprosy, unlike in tuberculoid leprosy, which is paucibacillary and creates a granulomatous response surrounding nerves and adnexal structures.6

Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common cutaneous lymphoma. There are patch, plaque, and tumor stages of MF, each of which exhibits various histopathologic findings.9 In early patch-stage MF, lymphocytes have perinuclear clearing, and the degree of lymphocytic infiltrate is out of proportion to the spongiosis present. Epidermotropism and Pautrier microabscesses often are present in the epidermis (Figure 3). In the plaque stage, there is a denser lymphoid infiltrate in a lichenoid pattern with epidermotropism and Pautrier microabscesses. The tumor stage shows a dense dermal lymphoid infiltrate with more atypia and typically a lack of epidermotropism. Rarely, MF can exhibit a granulomatous variant in which epithelioid histiocytes collect to form granulomas along with atypical lymphocytes.10

The diagnosis of cutaneous sarcoidosis requires clinicopathologic corroboration. Histopathology demonstrates epithelioid histiocytes forming noncaseating granulomas with little to no lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure 4). There typically is no necrosis or necrobiosis as there is in GA. The diagnosis of sarcoidosis can be challenging histopathologically, and stains should be used to rule out infectious processes.4 Asteroid bodies— star-shaped eosinophilic inclusions within giant cells—may be present but are nonspecific for sarcoidosis.11 Schaumann bodies—inclusions of calcifications within giant cells—also may be present and can aid in diagnosis.12

The Diagnosis: Granuloma Annulare
The biopsies revealed palisading granulomatous dermatitis consistent with granuloma annulare (GA). This diagnosis was supported by the clinical presentation and histopathologic findings. Although the pathogenesis of GA is unclear, it is a benign, self-limiting condition. Primarily affected sites include the trunk and forearms. Generalized GA (or GA with ≥10 lesions) may warrant workup for malignancy, as it may represent a paraneoplastic process.1 Histopathology reveals granulomas comprising a dermal lymphohistiocytic infiltrate as well as central mucin and nuclear debris. There are a few histologic subtypes of GA, including palisading and interstitial, which refer to the distribution of the histiocytic infiltrate.2,3 This case—with palisading histiocytes lining the collection of necrobiosis and mucin (bottom quiz image)—features palisading GA. Notably, GA exhibits central rather than diffuse mucin.4
Erythema gyratum repens is a paraneoplastic arcuate erythema that manifests as erythematous figurate, gyrate, or annular plaques exhibiting a trailing scale. Clinically, erythema gyratum repens spreads rapidly—as quickly as 1 cm/d—and can be extensive (as in this case). Histopathology ruled out this diagnosis in our patient. Nonspecific findings of acanthosis, parakeratosis, and superficial spongiosis can be found in erythema gyratum repens. A superficial and deep perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate may be seen in figurate erythemas (Figure 1).5 Unlike GA, this infiltrate does not form granulomas, is more superficial, and does not contain mucin.

Histopathology also can help establish the diagnosis of leprosy and its specific subtype, as leprosy exists on a spectrum from tuberculoid to lepromatous, with a great deal of overlap in between.6 Lepromatous leprosy has many cutaneous clinical presentations but typically manifests as erythematous papules or nodules. It is multibacillary, and these mycobacteria form clumps known as globi that can be seen on Fite stain.7 In lepromatous leprosy, there is a characteristic dense lymphohistiocytic infiltrate (Figure 2) above which a Grenz zone can be seen.4,8 There are no well-formed granulomas in lepromatous leprosy, unlike in tuberculoid leprosy, which is paucibacillary and creates a granulomatous response surrounding nerves and adnexal structures.6

Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common cutaneous lymphoma. There are patch, plaque, and tumor stages of MF, each of which exhibits various histopathologic findings.9 In early patch-stage MF, lymphocytes have perinuclear clearing, and the degree of lymphocytic infiltrate is out of proportion to the spongiosis present. Epidermotropism and Pautrier microabscesses often are present in the epidermis (Figure 3). In the plaque stage, there is a denser lymphoid infiltrate in a lichenoid pattern with epidermotropism and Pautrier microabscesses. The tumor stage shows a dense dermal lymphoid infiltrate with more atypia and typically a lack of epidermotropism. Rarely, MF can exhibit a granulomatous variant in which epithelioid histiocytes collect to form granulomas along with atypical lymphocytes.10

The diagnosis of cutaneous sarcoidosis requires clinicopathologic corroboration. Histopathology demonstrates epithelioid histiocytes forming noncaseating granulomas with little to no lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure 4). There typically is no necrosis or necrobiosis as there is in GA. The diagnosis of sarcoidosis can be challenging histopathologically, and stains should be used to rule out infectious processes.4 Asteroid bodies— star-shaped eosinophilic inclusions within giant cells—may be present but are nonspecific for sarcoidosis.11 Schaumann bodies—inclusions of calcifications within giant cells—also may be present and can aid in diagnosis.12

- Kovich O, Burgin S. Generalized granuloma annulare [published online December 30, 2005]. Dermatol Online J. 2005;11:23.
- Al Ameer MA, Al-Natour SH, Alsahaf HAA, et al. Eruptive granuloma annulare in an elderly man with diabetes [published online January 14, 2022]. Cureus. 2022;14:E21242. doi:10.7759/cureus.21242
- Howard A, White CR Jr. Non-infectious granulomas. In: Bolognia JL, et al, eds. Dermatology. Mosby; 2003:1455.
- Elston DM, Ferringer T, Ko CJ, et al. Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2018.
- Gore M, Winters ME. Erythema gyratum repens: a rare paraneoplastic rash. West J Emerg Med. 2011;12:556-558. doi:10.5811/westjem.2010.11.2090
- Maymone MBC, Laughter M, Venkatesh S, et al. Leprosy: clinical aspects and diagnostic techniques. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1-14. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.12.080
- Pedley JC, Harman DJ, Waudby H, et al. Leprosy in peripheral nerves: histopathological findings in 119 untreated patients in Nepal. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980;43:198-204. doi:10.1136/jnnp.43.3.198
- Booth AV, Kovich OI. Lepromatous leprosy [published online January 27, 2007]. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13:9.
- Robson A. The pathology of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Oncology (Williston Park). 2007;21(2 suppl 1):9-12.
- Kempf W, Ostheeren-Michaelis S, Paulli M, et al. Granulomatous mycosis fungoides and granulomatous slack skin: a multicenter study of the Cutaneous Lymphoma Histopathology Task Force Group of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1609-1617. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2008.46
- Azar HA, Lunardelli C. Collagen nature of asteroid bodies of giant cells in sarcoidosis. Am J Pathol. 1969;57:81-92.
- Sreeja C, Priyadarshini A, Premika, et al. Sarcoidosis—a review article. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2022;26:242-253. doi:10.4103 /jomfp.jomfp_373_21
- Kovich O, Burgin S. Generalized granuloma annulare [published online December 30, 2005]. Dermatol Online J. 2005;11:23.
- Al Ameer MA, Al-Natour SH, Alsahaf HAA, et al. Eruptive granuloma annulare in an elderly man with diabetes [published online January 14, 2022]. Cureus. 2022;14:E21242. doi:10.7759/cureus.21242
- Howard A, White CR Jr. Non-infectious granulomas. In: Bolognia JL, et al, eds. Dermatology. Mosby; 2003:1455.
- Elston DM, Ferringer T, Ko CJ, et al. Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2018.
- Gore M, Winters ME. Erythema gyratum repens: a rare paraneoplastic rash. West J Emerg Med. 2011;12:556-558. doi:10.5811/westjem.2010.11.2090
- Maymone MBC, Laughter M, Venkatesh S, et al. Leprosy: clinical aspects and diagnostic techniques. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1-14. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.12.080
- Pedley JC, Harman DJ, Waudby H, et al. Leprosy in peripheral nerves: histopathological findings in 119 untreated patients in Nepal. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980;43:198-204. doi:10.1136/jnnp.43.3.198
- Booth AV, Kovich OI. Lepromatous leprosy [published online January 27, 2007]. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13:9.
- Robson A. The pathology of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Oncology (Williston Park). 2007;21(2 suppl 1):9-12.
- Kempf W, Ostheeren-Michaelis S, Paulli M, et al. Granulomatous mycosis fungoides and granulomatous slack skin: a multicenter study of the Cutaneous Lymphoma Histopathology Task Force Group of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1609-1617. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2008.46
- Azar HA, Lunardelli C. Collagen nature of asteroid bodies of giant cells in sarcoidosis. Am J Pathol. 1969;57:81-92.
- Sreeja C, Priyadarshini A, Premika, et al. Sarcoidosis—a review article. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2022;26:242-253. doi:10.4103 /jomfp.jomfp_373_21
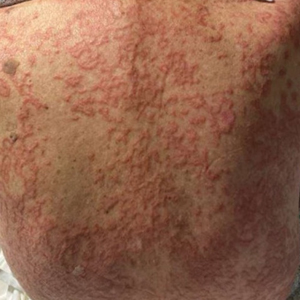
An 84-year-old man presented to the clinic for evaluation of a pruritic rash on the back of 6 months’ duration that spread to the neck and chest over the past 2 months and then to the abdomen and thighs more recently. His primary care provider prescribed a 1-week course of oral steroids and steroid cream. The oral medication did not help, but the cream alleviated the pruritus. He had a medical history of coronary artery disease, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. He also had a rash on the forearms that had waxed and waned for many years but was not associated with pruritus. He had not sought medical care for the rash and had never treated it. Physical examination revealed pink to violaceous annular plaques with central clearing and raised borders that coalesced into larger plaques on the trunk (top). Dusky, scaly, pink plaques were present on the dorsal forearms. Three punch biopsies—2 from the upper back (bottom) and 1 from the left forearm—all demonstrated consistent findings.
New Guidelines: Start PSA Screening Earlier in Black Men
Lowering the recommended age for baseline prostate-specific antigen (PSA) would reduce prostate cancer deaths by about 30% in Black men without significantly increasing the rate of overdiagnosis, according to new screening guidelines from the Prostate Cancer Foundation.
Specifically, baseline PSA testing in Black men should begin at age 40-45, sooner than current guidelines recommend, and should be followed by regular screening intervals, preferably annually, at least until age 70, a multidisciplinary panel of experts and patient advocates determined based on a comprehensive literature review.
The panel’s findings were presented in a poster at the ASCO Genitourinary Symposium.
“Black men in the United States are considered a high-risk population for being diagnosed with and dying from prostate cancer,” lead author Isla Garraway, MD, PhD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and colleagues wrote. Specifically, Black men are about two times more likely to be diagnosed with and die from prostate cancer than White men. But, the authors continued, “few guidelines have outlined specific recommendations for PSA-based prostate cancer screening among Black men.”
The US Preventive Services Taskforce recommendations, which are currently being updated, set the PSA screening start age at 55. The task force recommendations, which dictate insurance coverage in the United States, acknowledged “a potential mortality benefit for African American men when beginning screening before age 55 years” but did not explicitly recommend screening earlier.
Current guidelines from the American Cancer Society call for discussions about screening in average-risk men to begin at age 50-55. The recommendations do specify lowering the age to 45 for those at a high risk for prostate cancer, which includes Black men as well as those with a first-degree relative diagnosed with prostate cancer before age 65. In some cases, screening can begin at age 40 in the highest risk men — those with more than one first-degree relative who had prostate cancer at a young age.
The Prostate Cancer Foundation “wanted to address the confusion around different guideline statements and the lack of clarity around screening recommendations for Black men,” said William K. Oh, MD, of The Tisch Cancer Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, who chaired the panel for the new guidelines. “We thus convened a distinguished panel of experts from diverse backgrounds and expertise to create six guidelines statements to help Black men, their families, and their healthcare providers to consider options for prostate cancer screening based on the best available evidence.”
After reviewing 287, the expert panel developed six new guideline statements, reaching at least 80% consensus among panel members, addressing screening for Black men:
Because Black men are at a high risk for prostate cancer, the benefits of screening generally outweigh the risks.
PSA testing should be considered first line for prostate cancer screening, although some providers may recommend an optional digital rectal exam in addition to the PSA test.
Black men should engage in shared decision-making with their healthcare providers and other trusted sources of information to learn about the pros and cons of screening.
For Black men who elect screening, a baseline PSA test should be done between ages 40 and 45, and annual PSA screening should be strongly considered based on the PSA value and the individual’s health status.
Black men over age 70 who have been undergoing prostate cancer screening should talk with their healthcare provider about whether to continue PSA testing and make an informed decision based on their age, life expectancy, health status, family history, and prior PSA levels.
Black men who are at even higher risk due to a strong family history and/or known carriers of high-risk genetic variants should consider initiating annual PSA screening as early as age 40.
These statements are based on “the best available evidence, which overwhelmingly supports the conclusion that Black men in the US could benefit from a risk-adapted PSA screening,” the investigators concluded, noting that the latest evidence “warrants revisiting current recommendations for early [prostate cancer] detection in Black men from other national guideline groups.”
“We believe that the outcome of these more directed guidelines will be to give clarity to these men,” Dr. Oh added.
This research was funded by the Prostate Cancer Foundation, National Cancer Institute, Veterans Affairs, Jean Perkins Foundation, and Department of Defense. Dr. Garraway reported having no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lowering the recommended age for baseline prostate-specific antigen (PSA) would reduce prostate cancer deaths by about 30% in Black men without significantly increasing the rate of overdiagnosis, according to new screening guidelines from the Prostate Cancer Foundation.
Specifically, baseline PSA testing in Black men should begin at age 40-45, sooner than current guidelines recommend, and should be followed by regular screening intervals, preferably annually, at least until age 70, a multidisciplinary panel of experts and patient advocates determined based on a comprehensive literature review.
The panel’s findings were presented in a poster at the ASCO Genitourinary Symposium.
“Black men in the United States are considered a high-risk population for being diagnosed with and dying from prostate cancer,” lead author Isla Garraway, MD, PhD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and colleagues wrote. Specifically, Black men are about two times more likely to be diagnosed with and die from prostate cancer than White men. But, the authors continued, “few guidelines have outlined specific recommendations for PSA-based prostate cancer screening among Black men.”
The US Preventive Services Taskforce recommendations, which are currently being updated, set the PSA screening start age at 55. The task force recommendations, which dictate insurance coverage in the United States, acknowledged “a potential mortality benefit for African American men when beginning screening before age 55 years” but did not explicitly recommend screening earlier.
Current guidelines from the American Cancer Society call for discussions about screening in average-risk men to begin at age 50-55. The recommendations do specify lowering the age to 45 for those at a high risk for prostate cancer, which includes Black men as well as those with a first-degree relative diagnosed with prostate cancer before age 65. In some cases, screening can begin at age 40 in the highest risk men — those with more than one first-degree relative who had prostate cancer at a young age.
The Prostate Cancer Foundation “wanted to address the confusion around different guideline statements and the lack of clarity around screening recommendations for Black men,” said William K. Oh, MD, of The Tisch Cancer Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, who chaired the panel for the new guidelines. “We thus convened a distinguished panel of experts from diverse backgrounds and expertise to create six guidelines statements to help Black men, their families, and their healthcare providers to consider options for prostate cancer screening based on the best available evidence.”
After reviewing 287, the expert panel developed six new guideline statements, reaching at least 80% consensus among panel members, addressing screening for Black men:
Because Black men are at a high risk for prostate cancer, the benefits of screening generally outweigh the risks.
PSA testing should be considered first line for prostate cancer screening, although some providers may recommend an optional digital rectal exam in addition to the PSA test.
Black men should engage in shared decision-making with their healthcare providers and other trusted sources of information to learn about the pros and cons of screening.
For Black men who elect screening, a baseline PSA test should be done between ages 40 and 45, and annual PSA screening should be strongly considered based on the PSA value and the individual’s health status.
Black men over age 70 who have been undergoing prostate cancer screening should talk with their healthcare provider about whether to continue PSA testing and make an informed decision based on their age, life expectancy, health status, family history, and prior PSA levels.
Black men who are at even higher risk due to a strong family history and/or known carriers of high-risk genetic variants should consider initiating annual PSA screening as early as age 40.
These statements are based on “the best available evidence, which overwhelmingly supports the conclusion that Black men in the US could benefit from a risk-adapted PSA screening,” the investigators concluded, noting that the latest evidence “warrants revisiting current recommendations for early [prostate cancer] detection in Black men from other national guideline groups.”
“We believe that the outcome of these more directed guidelines will be to give clarity to these men,” Dr. Oh added.
This research was funded by the Prostate Cancer Foundation, National Cancer Institute, Veterans Affairs, Jean Perkins Foundation, and Department of Defense. Dr. Garraway reported having no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lowering the recommended age for baseline prostate-specific antigen (PSA) would reduce prostate cancer deaths by about 30% in Black men without significantly increasing the rate of overdiagnosis, according to new screening guidelines from the Prostate Cancer Foundation.
Specifically, baseline PSA testing in Black men should begin at age 40-45, sooner than current guidelines recommend, and should be followed by regular screening intervals, preferably annually, at least until age 70, a multidisciplinary panel of experts and patient advocates determined based on a comprehensive literature review.
The panel’s findings were presented in a poster at the ASCO Genitourinary Symposium.
“Black men in the United States are considered a high-risk population for being diagnosed with and dying from prostate cancer,” lead author Isla Garraway, MD, PhD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and colleagues wrote. Specifically, Black men are about two times more likely to be diagnosed with and die from prostate cancer than White men. But, the authors continued, “few guidelines have outlined specific recommendations for PSA-based prostate cancer screening among Black men.”
The US Preventive Services Taskforce recommendations, which are currently being updated, set the PSA screening start age at 55. The task force recommendations, which dictate insurance coverage in the United States, acknowledged “a potential mortality benefit for African American men when beginning screening before age 55 years” but did not explicitly recommend screening earlier.
Current guidelines from the American Cancer Society call for discussions about screening in average-risk men to begin at age 50-55. The recommendations do specify lowering the age to 45 for those at a high risk for prostate cancer, which includes Black men as well as those with a first-degree relative diagnosed with prostate cancer before age 65. In some cases, screening can begin at age 40 in the highest risk men — those with more than one first-degree relative who had prostate cancer at a young age.
The Prostate Cancer Foundation “wanted to address the confusion around different guideline statements and the lack of clarity around screening recommendations for Black men,” said William K. Oh, MD, of The Tisch Cancer Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, who chaired the panel for the new guidelines. “We thus convened a distinguished panel of experts from diverse backgrounds and expertise to create six guidelines statements to help Black men, their families, and their healthcare providers to consider options for prostate cancer screening based on the best available evidence.”
After reviewing 287, the expert panel developed six new guideline statements, reaching at least 80% consensus among panel members, addressing screening for Black men:
Because Black men are at a high risk for prostate cancer, the benefits of screening generally outweigh the risks.
PSA testing should be considered first line for prostate cancer screening, although some providers may recommend an optional digital rectal exam in addition to the PSA test.
Black men should engage in shared decision-making with their healthcare providers and other trusted sources of information to learn about the pros and cons of screening.
For Black men who elect screening, a baseline PSA test should be done between ages 40 and 45, and annual PSA screening should be strongly considered based on the PSA value and the individual’s health status.
Black men over age 70 who have been undergoing prostate cancer screening should talk with their healthcare provider about whether to continue PSA testing and make an informed decision based on their age, life expectancy, health status, family history, and prior PSA levels.
Black men who are at even higher risk due to a strong family history and/or known carriers of high-risk genetic variants should consider initiating annual PSA screening as early as age 40.
These statements are based on “the best available evidence, which overwhelmingly supports the conclusion that Black men in the US could benefit from a risk-adapted PSA screening,” the investigators concluded, noting that the latest evidence “warrants revisiting current recommendations for early [prostate cancer] detection in Black men from other national guideline groups.”
“We believe that the outcome of these more directed guidelines will be to give clarity to these men,” Dr. Oh added.
This research was funded by the Prostate Cancer Foundation, National Cancer Institute, Veterans Affairs, Jean Perkins Foundation, and Department of Defense. Dr. Garraway reported having no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ASCO GU 2024
CT Poses Risk for Malignant Hematopathies Among Children
More than a million European children undergo a CT scan each year. Ionizing radiation at moderate (> 100 mGy) to high (> 1 Gy) doses is a recognized risk factor for malignant hematopathies. The risk associated with exposure to low doses (< 100 mGy), typically delivered during a CT scan in children or adolescents, is unknown.
Previous studies assessed the risk for malignant hematopathies related to ionizing radiation from CT scans in young patients. Some showed an increased risk for leukemia with repeated scans, but confounding factors resulted in a lack of statistical power or biases in some cases. The EPI-CT study, coordinated by the International Agency for Research on Cancer, aimed to evaluate the cancer risk among children and adolescents after exposure to low doses of ionizing radiation during CT scans.
A European Cohort
A recent article presents an assessment of observed malignant hematopathies following CT scan. The authors followed a multinational European cohort of 948,174 patients who had a CT scan before age 22 years. Ionizing radiation doses to the bone marrow were evaluated based on the scanned body region, patient characteristics, scan year, and the technical parameters of the machine. The analysis involved 876,771 patients who underwent 1,331,896 scans (an average of 1.52 per patient) and were followed for at least 2 years after the first scan.
In total, 790 malignant hematopathies were diagnosed, including 578 lymphoid hematopathies and 203 myeloid hematopathies and acute leukemias. The average follow-up period was 7.8 years. At the time of diagnosis, 51% of patients were under the age of 20 years, and 88.5% were under the age of 30 years. There was an association between cumulative dose and the observed malignant hematopathy, with an observed rate of 1.96 per 100 mGy (790 cases).
This rate corresponds to a 16% increased rate per scan (for a dose observed per scan of 8 mGy). A higher rate for any type of malignant hematopathy was observed for doses > 10 mGy, with an observed rate of 2.66 for doses > 50 mGy, compared with doses < 5 mGy.
The rate of malignant hematopathy increased with older age at the time of radiation exposure, particularly for lymphoid observations. The rate in the 5- to 9-year age group and the > 10-year age group was, respectively, two times and three to four times higher than that in the < 5-year age group. The rate decreased over time, with the highest observed rate between 2 and 5 years after ionizing radiation exposure and the lowest after 10 years.
CT Scans Must Be Warranted
This study, which involved nearly a million patients, has higher statistical power than previous studies, despite missing or approximate data (including that related to actually delivered doses). An association was shown between cumulative dose to the bone marrow and the risk of developing malignant hematopathy, both lymphoid and myeloid, with an increased risk even at low doses (10-15 mGy).
The results suggest that for every 10,000 children examined today (with a dose per scan of 8 mGy), 1-2 could develop a radiation-related malignant hematopathy in the next 12 years (1.4 cases). This study confirms the higher risk for cancer at low radiation doses and emphasizes the importance of justifying each pediatric CT scan and optimizing delivered doses. It is important to recall that an MRI or ultrasound can sometimes be an adequate substitute for a CT scan.
This article was translated from JIM , which is part of the Medscape Professional Network. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
More than a million European children undergo a CT scan each year. Ionizing radiation at moderate (> 100 mGy) to high (> 1 Gy) doses is a recognized risk factor for malignant hematopathies. The risk associated with exposure to low doses (< 100 mGy), typically delivered during a CT scan in children or adolescents, is unknown.
Previous studies assessed the risk for malignant hematopathies related to ionizing radiation from CT scans in young patients. Some showed an increased risk for leukemia with repeated scans, but confounding factors resulted in a lack of statistical power or biases in some cases. The EPI-CT study, coordinated by the International Agency for Research on Cancer, aimed to evaluate the cancer risk among children and adolescents after exposure to low doses of ionizing radiation during CT scans.
A European Cohort
A recent article presents an assessment of observed malignant hematopathies following CT scan. The authors followed a multinational European cohort of 948,174 patients who had a CT scan before age 22 years. Ionizing radiation doses to the bone marrow were evaluated based on the scanned body region, patient characteristics, scan year, and the technical parameters of the machine. The analysis involved 876,771 patients who underwent 1,331,896 scans (an average of 1.52 per patient) and were followed for at least 2 years after the first scan.
In total, 790 malignant hematopathies were diagnosed, including 578 lymphoid hematopathies and 203 myeloid hematopathies and acute leukemias. The average follow-up period was 7.8 years. At the time of diagnosis, 51% of patients were under the age of 20 years, and 88.5% were under the age of 30 years. There was an association between cumulative dose and the observed malignant hematopathy, with an observed rate of 1.96 per 100 mGy (790 cases).
This rate corresponds to a 16% increased rate per scan (for a dose observed per scan of 8 mGy). A higher rate for any type of malignant hematopathy was observed for doses > 10 mGy, with an observed rate of 2.66 for doses > 50 mGy, compared with doses < 5 mGy.
The rate of malignant hematopathy increased with older age at the time of radiation exposure, particularly for lymphoid observations. The rate in the 5- to 9-year age group and the > 10-year age group was, respectively, two times and three to four times higher than that in the < 5-year age group. The rate decreased over time, with the highest observed rate between 2 and 5 years after ionizing radiation exposure and the lowest after 10 years.
CT Scans Must Be Warranted
This study, which involved nearly a million patients, has higher statistical power than previous studies, despite missing or approximate data (including that related to actually delivered doses). An association was shown between cumulative dose to the bone marrow and the risk of developing malignant hematopathy, both lymphoid and myeloid, with an increased risk even at low doses (10-15 mGy).
The results suggest that for every 10,000 children examined today (with a dose per scan of 8 mGy), 1-2 could develop a radiation-related malignant hematopathy in the next 12 years (1.4 cases). This study confirms the higher risk for cancer at low radiation doses and emphasizes the importance of justifying each pediatric CT scan and optimizing delivered doses. It is important to recall that an MRI or ultrasound can sometimes be an adequate substitute for a CT scan.
This article was translated from JIM , which is part of the Medscape Professional Network. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
More than a million European children undergo a CT scan each year. Ionizing radiation at moderate (> 100 mGy) to high (> 1 Gy) doses is a recognized risk factor for malignant hematopathies. The risk associated with exposure to low doses (< 100 mGy), typically delivered during a CT scan in children or adolescents, is unknown.
Previous studies assessed the risk for malignant hematopathies related to ionizing radiation from CT scans in young patients. Some showed an increased risk for leukemia with repeated scans, but confounding factors resulted in a lack of statistical power or biases in some cases. The EPI-CT study, coordinated by the International Agency for Research on Cancer, aimed to evaluate the cancer risk among children and adolescents after exposure to low doses of ionizing radiation during CT scans.
A European Cohort
A recent article presents an assessment of observed malignant hematopathies following CT scan. The authors followed a multinational European cohort of 948,174 patients who had a CT scan before age 22 years. Ionizing radiation doses to the bone marrow were evaluated based on the scanned body region, patient characteristics, scan year, and the technical parameters of the machine. The analysis involved 876,771 patients who underwent 1,331,896 scans (an average of 1.52 per patient) and were followed for at least 2 years after the first scan.
In total, 790 malignant hematopathies were diagnosed, including 578 lymphoid hematopathies and 203 myeloid hematopathies and acute leukemias. The average follow-up period was 7.8 years. At the time of diagnosis, 51% of patients were under the age of 20 years, and 88.5% were under the age of 30 years. There was an association between cumulative dose and the observed malignant hematopathy, with an observed rate of 1.96 per 100 mGy (790 cases).
This rate corresponds to a 16% increased rate per scan (for a dose observed per scan of 8 mGy). A higher rate for any type of malignant hematopathy was observed for doses > 10 mGy, with an observed rate of 2.66 for doses > 50 mGy, compared with doses < 5 mGy.
The rate of malignant hematopathy increased with older age at the time of radiation exposure, particularly for lymphoid observations. The rate in the 5- to 9-year age group and the > 10-year age group was, respectively, two times and three to four times higher than that in the < 5-year age group. The rate decreased over time, with the highest observed rate between 2 and 5 years after ionizing radiation exposure and the lowest after 10 years.
CT Scans Must Be Warranted
This study, which involved nearly a million patients, has higher statistical power than previous studies, despite missing or approximate data (including that related to actually delivered doses). An association was shown between cumulative dose to the bone marrow and the risk of developing malignant hematopathy, both lymphoid and myeloid, with an increased risk even at low doses (10-15 mGy).
The results suggest that for every 10,000 children examined today (with a dose per scan of 8 mGy), 1-2 could develop a radiation-related malignant hematopathy in the next 12 years (1.4 cases). This study confirms the higher risk for cancer at low radiation doses and emphasizes the importance of justifying each pediatric CT scan and optimizing delivered doses. It is important to recall that an MRI or ultrasound can sometimes be an adequate substitute for a CT scan.
This article was translated from JIM , which is part of the Medscape Professional Network. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Doctors With Limited Vacation Have Increased Burnout Risk
A recent study sheds light on the heightened risk for burnout among physicians who take infrequent vacations and engage in patient-related work during their time off.
Conducted by the American Medical Association (AMA), the study focuses on the United States, where labor regulations regarding vacation days and compensation differ from German norms. Despite this distinction, it provides valuable insights into the vacation behavior of doctors and its potential impact on burnout risk.
Christine A. Sinsky, MD, study author and senior physician advisor for physician satisfaction at the AMA, and her colleagues invited more than 90,000 physicians to participate in a survey that used postal and computer-based methods. In all, 3024 physicians, mainly those contacted by mail, filled out the questionnaire.
Limited Vacation Days
A significant proportion (59.6%) of respondents reported having taken fewer than 15 vacation days in the previous year, with nearly 20% taking fewer than 5 days off. Even when officially on vacation, most (70.4%) found themselves dealing with patient-related tasks. For one-third, these tasks consumed at least 30 minutes on a typical vacation day, often longer. This phenomenon was noted especially among female physicians.
Doctors who took less vacation and worked during their time off displayed higher emotional exhaustion and reported feeling less fulfilled in their profession.
Administrative Tasks
Administrative tasks, though no longer confined to paper, significantly influenced physicians’ vacation behavior. In the United States, handling messages from patients through the electronic health records (EHR) inbox demands a considerable amount of time.
Courses and tutorials on EHR inbox management are on the rise. A 2023 review linked electronic health records management to an increased burnout risk in the US medical community.
Lack of Coverage
Many physicians lack coverage for their EHR inbox during their absence. Less than half (49.1%) stated that someone else manages their inbox while they are on vacation.
Difficulty in finding coverage, whether for the EHR inbox or patient care, is a leading reason why many physicians seldom take more than 3 weeks of vacation per year. Financial considerations also contribute to this decision, as revealed in the survey.
Vacation Lowers Risk
Further analysis showed that doctors who took more than 3 weeks of vacation per year, which is not common, had a lower risk of developing burnout. Having coverage for vacation was also associated with reduced burnout risk and increased professional fulfillment.
However, these benefits applied only when physicians truly took a break during their vacation. Respondents who spent 30 minutes or more per day on patient-related work had a higher burnout risk. The risk was 1.58 times greater for 30-60 minutes, 1.97 times greater for 60-90 minutes, and 1.92 times greater for more than 90 minutes.
System-Level Interventions
The vacation behavior observed in this study likely exacerbates the effects of chronic workplace overload that are associated with long working hours, thus increasing the risk for burnout, according to the researchers.
“System-level measures must be implemented to ensure physicians take an appropriate number of vacation days,” wrote the researchers. “This includes having coverage available to handle clinical activities and administrative tasks, such as managing the EHR inbox. This could potentially reduce the burnout rate among physicians.”
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent study sheds light on the heightened risk for burnout among physicians who take infrequent vacations and engage in patient-related work during their time off.
Conducted by the American Medical Association (AMA), the study focuses on the United States, where labor regulations regarding vacation days and compensation differ from German norms. Despite this distinction, it provides valuable insights into the vacation behavior of doctors and its potential impact on burnout risk.
Christine A. Sinsky, MD, study author and senior physician advisor for physician satisfaction at the AMA, and her colleagues invited more than 90,000 physicians to participate in a survey that used postal and computer-based methods. In all, 3024 physicians, mainly those contacted by mail, filled out the questionnaire.
Limited Vacation Days
A significant proportion (59.6%) of respondents reported having taken fewer than 15 vacation days in the previous year, with nearly 20% taking fewer than 5 days off. Even when officially on vacation, most (70.4%) found themselves dealing with patient-related tasks. For one-third, these tasks consumed at least 30 minutes on a typical vacation day, often longer. This phenomenon was noted especially among female physicians.
Doctors who took less vacation and worked during their time off displayed higher emotional exhaustion and reported feeling less fulfilled in their profession.
Administrative Tasks
Administrative tasks, though no longer confined to paper, significantly influenced physicians’ vacation behavior. In the United States, handling messages from patients through the electronic health records (EHR) inbox demands a considerable amount of time.
Courses and tutorials on EHR inbox management are on the rise. A 2023 review linked electronic health records management to an increased burnout risk in the US medical community.
Lack of Coverage
Many physicians lack coverage for their EHR inbox during their absence. Less than half (49.1%) stated that someone else manages their inbox while they are on vacation.
Difficulty in finding coverage, whether for the EHR inbox or patient care, is a leading reason why many physicians seldom take more than 3 weeks of vacation per year. Financial considerations also contribute to this decision, as revealed in the survey.
Vacation Lowers Risk
Further analysis showed that doctors who took more than 3 weeks of vacation per year, which is not common, had a lower risk of developing burnout. Having coverage for vacation was also associated with reduced burnout risk and increased professional fulfillment.
However, these benefits applied only when physicians truly took a break during their vacation. Respondents who spent 30 minutes or more per day on patient-related work had a higher burnout risk. The risk was 1.58 times greater for 30-60 minutes, 1.97 times greater for 60-90 minutes, and 1.92 times greater for more than 90 minutes.
System-Level Interventions
The vacation behavior observed in this study likely exacerbates the effects of chronic workplace overload that are associated with long working hours, thus increasing the risk for burnout, according to the researchers.
“System-level measures must be implemented to ensure physicians take an appropriate number of vacation days,” wrote the researchers. “This includes having coverage available to handle clinical activities and administrative tasks, such as managing the EHR inbox. This could potentially reduce the burnout rate among physicians.”
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent study sheds light on the heightened risk for burnout among physicians who take infrequent vacations and engage in patient-related work during their time off.
Conducted by the American Medical Association (AMA), the study focuses on the United States, where labor regulations regarding vacation days and compensation differ from German norms. Despite this distinction, it provides valuable insights into the vacation behavior of doctors and its potential impact on burnout risk.
Christine A. Sinsky, MD, study author and senior physician advisor for physician satisfaction at the AMA, and her colleagues invited more than 90,000 physicians to participate in a survey that used postal and computer-based methods. In all, 3024 physicians, mainly those contacted by mail, filled out the questionnaire.
Limited Vacation Days
A significant proportion (59.6%) of respondents reported having taken fewer than 15 vacation days in the previous year, with nearly 20% taking fewer than 5 days off. Even when officially on vacation, most (70.4%) found themselves dealing with patient-related tasks. For one-third, these tasks consumed at least 30 minutes on a typical vacation day, often longer. This phenomenon was noted especially among female physicians.
Doctors who took less vacation and worked during their time off displayed higher emotional exhaustion and reported feeling less fulfilled in their profession.
Administrative Tasks
Administrative tasks, though no longer confined to paper, significantly influenced physicians’ vacation behavior. In the United States, handling messages from patients through the electronic health records (EHR) inbox demands a considerable amount of time.
Courses and tutorials on EHR inbox management are on the rise. A 2023 review linked electronic health records management to an increased burnout risk in the US medical community.
Lack of Coverage
Many physicians lack coverage for their EHR inbox during their absence. Less than half (49.1%) stated that someone else manages their inbox while they are on vacation.
Difficulty in finding coverage, whether for the EHR inbox or patient care, is a leading reason why many physicians seldom take more than 3 weeks of vacation per year. Financial considerations also contribute to this decision, as revealed in the survey.
Vacation Lowers Risk
Further analysis showed that doctors who took more than 3 weeks of vacation per year, which is not common, had a lower risk of developing burnout. Having coverage for vacation was also associated with reduced burnout risk and increased professional fulfillment.
However, these benefits applied only when physicians truly took a break during their vacation. Respondents who spent 30 minutes or more per day on patient-related work had a higher burnout risk. The risk was 1.58 times greater for 30-60 minutes, 1.97 times greater for 60-90 minutes, and 1.92 times greater for more than 90 minutes.
System-Level Interventions
The vacation behavior observed in this study likely exacerbates the effects of chronic workplace overload that are associated with long working hours, thus increasing the risk for burnout, according to the researchers.
“System-level measures must be implemented to ensure physicians take an appropriate number of vacation days,” wrote the researchers. “This includes having coverage available to handle clinical activities and administrative tasks, such as managing the EHR inbox. This could potentially reduce the burnout rate among physicians.”
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Mental Health Screening May Benefit Youth With Obesity
TOPLINE:
Mental health comorbidities are prevalent among youth with overweight or obesity, with the strongest risk factors being male sex, older age, and extreme obesity.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers compared clinical characteristics and outcomes among children, adolescents, and young adults with overweight or obesity with or without a comorbid mental disorder who participated in a lifestyle intervention program.
- Overall, data from 114,248 individuals (age, 6-30 years; 53% females) from 226 centers in Germany and Austria participating in the Adiposity Patient Registry were evaluated.
- Individuals were excluded if they had bariatric surgery or used weight-modifying drugs (metformin, orlistat, or glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues).
- Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as a standard deviation score (SDS) from a German youth population reference and was used to define overweight (90th to < 97th percentile), obesity (97th percentile), and severe obesity (≥ 99.5th percentile), which at age 18 correspond to adult cutoffs for overweight and obesity (25 kg/m2 and 30 kg/m2, respectively).
- Regression analysis identified the factors associated with mental disorders in those with overweight or obesity.
TAKEAWAY:
- A comorbid mental disorder was reported in 3969 individuals, with attention-deficit disorder (ADHD, 42.5%), anxiety (31.3%), depression (24.3%), and eating disorders (12.9%) being the most common.
- The factors most strongly associated with mental health comorbidity were male sex (odds ratio [OR], 1.39; 95% CI, 1.27-1.52), older age (OR, 1.42; 95% CI, 1.25-1.62), and severe obesity (OR, 1.45; 95% CI, 1.30-1.63).
- Mean BMI-SDS was higher in individuals with depression and eating disorders and lower in individuals with ADHD (both P < .001) than in those without mental disorders.
- Individuals with and without mental disorders benefited from similar BMI changes from lifestyle intervention programs.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors wrote, “Healthcare professionals caring for youth with overweight or obesity should be aware of comorbid mental disorders, and regular mental health screening should be considered.”
SOURCE:
This study, led by Angela Galler from the Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Germany, was published online on January 9, 2024, in the International Journal of Obesity.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s findings are based on data from a group of children, adolescents, and young adults with overweight or obesity treated in specialized obesity centers and may not be generalizable to all youth with obesity. Moreover, the study could not establish any conclusions regarding the cause or effect between obesity and mental disorders. Individuals were not tested psychologically for mental disorders and might have been underreported.
DISCLOSURES:
The manuscript is part of the Stratification of Obesity Phenotypes to Optimize Future Obesity Therapy project, which was funded by the Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Mental health comorbidities are prevalent among youth with overweight or obesity, with the strongest risk factors being male sex, older age, and extreme obesity.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers compared clinical characteristics and outcomes among children, adolescents, and young adults with overweight or obesity with or without a comorbid mental disorder who participated in a lifestyle intervention program.
- Overall, data from 114,248 individuals (age, 6-30 years; 53% females) from 226 centers in Germany and Austria participating in the Adiposity Patient Registry were evaluated.
- Individuals were excluded if they had bariatric surgery or used weight-modifying drugs (metformin, orlistat, or glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues).
- Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as a standard deviation score (SDS) from a German youth population reference and was used to define overweight (90th to < 97th percentile), obesity (97th percentile), and severe obesity (≥ 99.5th percentile), which at age 18 correspond to adult cutoffs for overweight and obesity (25 kg/m2 and 30 kg/m2, respectively).
- Regression analysis identified the factors associated with mental disorders in those with overweight or obesity.
TAKEAWAY:
- A comorbid mental disorder was reported in 3969 individuals, with attention-deficit disorder (ADHD, 42.5%), anxiety (31.3%), depression (24.3%), and eating disorders (12.9%) being the most common.
- The factors most strongly associated with mental health comorbidity were male sex (odds ratio [OR], 1.39; 95% CI, 1.27-1.52), older age (OR, 1.42; 95% CI, 1.25-1.62), and severe obesity (OR, 1.45; 95% CI, 1.30-1.63).
- Mean BMI-SDS was higher in individuals with depression and eating disorders and lower in individuals with ADHD (both P < .001) than in those without mental disorders.
- Individuals with and without mental disorders benefited from similar BMI changes from lifestyle intervention programs.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors wrote, “Healthcare professionals caring for youth with overweight or obesity should be aware of comorbid mental disorders, and regular mental health screening should be considered.”
SOURCE:
This study, led by Angela Galler from the Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Germany, was published online on January 9, 2024, in the International Journal of Obesity.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s findings are based on data from a group of children, adolescents, and young adults with overweight or obesity treated in specialized obesity centers and may not be generalizable to all youth with obesity. Moreover, the study could not establish any conclusions regarding the cause or effect between obesity and mental disorders. Individuals were not tested psychologically for mental disorders and might have been underreported.
DISCLOSURES:
The manuscript is part of the Stratification of Obesity Phenotypes to Optimize Future Obesity Therapy project, which was funded by the Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Mental health comorbidities are prevalent among youth with overweight or obesity, with the strongest risk factors being male sex, older age, and extreme obesity.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers compared clinical characteristics and outcomes among children, adolescents, and young adults with overweight or obesity with or without a comorbid mental disorder who participated in a lifestyle intervention program.
- Overall, data from 114,248 individuals (age, 6-30 years; 53% females) from 226 centers in Germany and Austria participating in the Adiposity Patient Registry were evaluated.
- Individuals were excluded if they had bariatric surgery or used weight-modifying drugs (metformin, orlistat, or glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues).
- Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as a standard deviation score (SDS) from a German youth population reference and was used to define overweight (90th to < 97th percentile), obesity (97th percentile), and severe obesity (≥ 99.5th percentile), which at age 18 correspond to adult cutoffs for overweight and obesity (25 kg/m2 and 30 kg/m2, respectively).
- Regression analysis identified the factors associated with mental disorders in those with overweight or obesity.
TAKEAWAY:
- A comorbid mental disorder was reported in 3969 individuals, with attention-deficit disorder (ADHD, 42.5%), anxiety (31.3%), depression (24.3%), and eating disorders (12.9%) being the most common.
- The factors most strongly associated with mental health comorbidity were male sex (odds ratio [OR], 1.39; 95% CI, 1.27-1.52), older age (OR, 1.42; 95% CI, 1.25-1.62), and severe obesity (OR, 1.45; 95% CI, 1.30-1.63).
- Mean BMI-SDS was higher in individuals with depression and eating disorders and lower in individuals with ADHD (both P < .001) than in those without mental disorders.
- Individuals with and without mental disorders benefited from similar BMI changes from lifestyle intervention programs.
IN PRACTICE:
The authors wrote, “Healthcare professionals caring for youth with overweight or obesity should be aware of comorbid mental disorders, and regular mental health screening should be considered.”
SOURCE:
This study, led by Angela Galler from the Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Germany, was published online on January 9, 2024, in the International Journal of Obesity.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s findings are based on data from a group of children, adolescents, and young adults with overweight or obesity treated in specialized obesity centers and may not be generalizable to all youth with obesity. Moreover, the study could not establish any conclusions regarding the cause or effect between obesity and mental disorders. Individuals were not tested psychologically for mental disorders and might have been underreported.
DISCLOSURES:
The manuscript is part of the Stratification of Obesity Phenotypes to Optimize Future Obesity Therapy project, which was funded by the Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Study Concludes Most Melanoma Overdiagnoses Are In Situ
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The increase in melanoma diagnoses in the United States, while mortality has remained flat, has raised concerns about overdiagnosis of melanoma, cases that may not result in harm if left untreated. How much of the overdiagnoses can be attributed to melanoma in situ vs invasive melanoma is unknown.
- To address this question, researchers collected data from the SEER 9 registries database.
- They used DevCan software to calculate the cumulative lifetime risk of White American men and women being diagnosed with melanoma between 1975 and 2018, adjusting for changes in longevity and risk factors over the study period.
- The primary outcome was excess lifetime risk for melanoma diagnosis between 1976 and 2018, adjusted for year 2018 competing mortality and changes in risk factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers found that between 1975 and 2018, the adjusted lifetime risk of being diagnosed with melanoma in situ increased from 0.17% to 2.7% in White men and 0.08% to 2% in White women.
- An estimated 49.7% and 64.6% of melanomas diagnosed in White men and White women, respectively, were overdiagnosed in 2018.
- Among individuals diagnosed with melanoma in situ, 89.4% of White men and 85.4% of White women were likely overdiagnosed in 2018.
IN PRACTICE:
“A large proportion of overdiagnosed melanomas are in situ cancers, pointing to a potential area to focus for an intervention de-escalation of the intensity of treatment and survivorship care,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Adewole S. Adamson, MD, of the Division of Dermatology at The University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School, led the research. The study was published in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine on January 19, 2024.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis only involved White individuals. Other limitations include a high risk for selection bias and that the researchers assumed no melanoma diagnosis in 1975, which may not be the case.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Adamson disclosed that he is supported by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation through The Harold Amos Medical Faculty Development Program. Coauthor Katy J.L. Bell, MBchB, PhD, of the University of Sydney, is supported by an Australian Government National Health and Medical Research Council Investigator Grant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The increase in melanoma diagnoses in the United States, while mortality has remained flat, has raised concerns about overdiagnosis of melanoma, cases that may not result in harm if left untreated. How much of the overdiagnoses can be attributed to melanoma in situ vs invasive melanoma is unknown.
- To address this question, researchers collected data from the SEER 9 registries database.
- They used DevCan software to calculate the cumulative lifetime risk of White American men and women being diagnosed with melanoma between 1975 and 2018, adjusting for changes in longevity and risk factors over the study period.
- The primary outcome was excess lifetime risk for melanoma diagnosis between 1976 and 2018, adjusted for year 2018 competing mortality and changes in risk factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers found that between 1975 and 2018, the adjusted lifetime risk of being diagnosed with melanoma in situ increased from 0.17% to 2.7% in White men and 0.08% to 2% in White women.
- An estimated 49.7% and 64.6% of melanomas diagnosed in White men and White women, respectively, were overdiagnosed in 2018.
- Among individuals diagnosed with melanoma in situ, 89.4% of White men and 85.4% of White women were likely overdiagnosed in 2018.
IN PRACTICE:
“A large proportion of overdiagnosed melanomas are in situ cancers, pointing to a potential area to focus for an intervention de-escalation of the intensity of treatment and survivorship care,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Adewole S. Adamson, MD, of the Division of Dermatology at The University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School, led the research. The study was published in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine on January 19, 2024.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis only involved White individuals. Other limitations include a high risk for selection bias and that the researchers assumed no melanoma diagnosis in 1975, which may not be the case.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Adamson disclosed that he is supported by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation through The Harold Amos Medical Faculty Development Program. Coauthor Katy J.L. Bell, MBchB, PhD, of the University of Sydney, is supported by an Australian Government National Health and Medical Research Council Investigator Grant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The increase in melanoma diagnoses in the United States, while mortality has remained flat, has raised concerns about overdiagnosis of melanoma, cases that may not result in harm if left untreated. How much of the overdiagnoses can be attributed to melanoma in situ vs invasive melanoma is unknown.
- To address this question, researchers collected data from the SEER 9 registries database.
- They used DevCan software to calculate the cumulative lifetime risk of White American men and women being diagnosed with melanoma between 1975 and 2018, adjusting for changes in longevity and risk factors over the study period.
- The primary outcome was excess lifetime risk for melanoma diagnosis between 1976 and 2018, adjusted for year 2018 competing mortality and changes in risk factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers found that between 1975 and 2018, the adjusted lifetime risk of being diagnosed with melanoma in situ increased from 0.17% to 2.7% in White men and 0.08% to 2% in White women.
- An estimated 49.7% and 64.6% of melanomas diagnosed in White men and White women, respectively, were overdiagnosed in 2018.
- Among individuals diagnosed with melanoma in situ, 89.4% of White men and 85.4% of White women were likely overdiagnosed in 2018.
IN PRACTICE:
“A large proportion of overdiagnosed melanomas are in situ cancers, pointing to a potential area to focus for an intervention de-escalation of the intensity of treatment and survivorship care,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Adewole S. Adamson, MD, of the Division of Dermatology at The University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School, led the research. The study was published in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine on January 19, 2024.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis only involved White individuals. Other limitations include a high risk for selection bias and that the researchers assumed no melanoma diagnosis in 1975, which may not be the case.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Adamson disclosed that he is supported by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation through The Harold Amos Medical Faculty Development Program. Coauthor Katy J.L. Bell, MBchB, PhD, of the University of Sydney, is supported by an Australian Government National Health and Medical Research Council Investigator Grant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rituximab Results in Sustained Remission for Pemphigus, Study Found
TOPLINE:
, an analysis showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- The short-term efficacy and safety of first-line treatment with rituximab for pemphigus were demonstrated in the Ritux 3 trial, but the rates of long-term remission are unknown.
- French investigators from 25 dermatology departments evaluated 83 patients from the Ritux 3 trial between January 1, 2010, and December 31, 2015.
- They used Kaplan-Meir curves to determine the 5- and 7-year rates of disease-free survival (DFS) without corticosteroids.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 83 patients, 44 were in the rituximab-plus-prednisone group and 39 were in the prednisone-only group, with a median follow-up of 87.3 months (7.3 years).
- Among patients in the rituximab plus prednisone group, 43 (93.5%) achieved complete remission without corticosteroids at any time during follow-up, compared with 17 patients (39%) in the prednisone-only group.
- DFS (without corticosteroid therapy) statistically favored patients in the rituximab plus prednisone group compared with patients in the prednisone-only group at follow-up times of 5 years (76.7% vs 35.3%, respectively) and 7 years (72.1% vs 35.3%; P < .001 for both associations).
- In another finding, 31 patients in the rituximab plus prednisone group reported fewer serious adverse events (SAEs) than 58 patients in the prednisone-only group, which corresponds to 0.67 and 1.32 SAEs per patient, respectively (P = .003).
IN PRACTICE:
The study findings demonstrated “the superiority of rituximab over a standard corticosteroids regimen, both in the short term and the long term,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Billal Tedbirt, MD, of the Department of Dermatology at CHU Rouen in France, led the study, which was published online on January 24, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Nearly 8% of patients did not attend the end of follow-up visit. Also, serum samples used to predict relapse were drawn at month 36, but the researchers said that a window of every 4-6 months might provide higher accuracy of relapses.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Tedbirt reported having no disclosures. Four of the study authors reported being investigators for and/or receiving personal fees from several pharmaceutical companies. The study was supported by a grant from the French Society of Dermatology.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, an analysis showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- The short-term efficacy and safety of first-line treatment with rituximab for pemphigus were demonstrated in the Ritux 3 trial, but the rates of long-term remission are unknown.
- French investigators from 25 dermatology departments evaluated 83 patients from the Ritux 3 trial between January 1, 2010, and December 31, 2015.
- They used Kaplan-Meir curves to determine the 5- and 7-year rates of disease-free survival (DFS) without corticosteroids.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 83 patients, 44 were in the rituximab-plus-prednisone group and 39 were in the prednisone-only group, with a median follow-up of 87.3 months (7.3 years).
- Among patients in the rituximab plus prednisone group, 43 (93.5%) achieved complete remission without corticosteroids at any time during follow-up, compared with 17 patients (39%) in the prednisone-only group.
- DFS (without corticosteroid therapy) statistically favored patients in the rituximab plus prednisone group compared with patients in the prednisone-only group at follow-up times of 5 years (76.7% vs 35.3%, respectively) and 7 years (72.1% vs 35.3%; P < .001 for both associations).
- In another finding, 31 patients in the rituximab plus prednisone group reported fewer serious adverse events (SAEs) than 58 patients in the prednisone-only group, which corresponds to 0.67 and 1.32 SAEs per patient, respectively (P = .003).
IN PRACTICE:
The study findings demonstrated “the superiority of rituximab over a standard corticosteroids regimen, both in the short term and the long term,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Billal Tedbirt, MD, of the Department of Dermatology at CHU Rouen in France, led the study, which was published online on January 24, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Nearly 8% of patients did not attend the end of follow-up visit. Also, serum samples used to predict relapse were drawn at month 36, but the researchers said that a window of every 4-6 months might provide higher accuracy of relapses.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Tedbirt reported having no disclosures. Four of the study authors reported being investigators for and/or receiving personal fees from several pharmaceutical companies. The study was supported by a grant from the French Society of Dermatology.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, an analysis showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- The short-term efficacy and safety of first-line treatment with rituximab for pemphigus were demonstrated in the Ritux 3 trial, but the rates of long-term remission are unknown.
- French investigators from 25 dermatology departments evaluated 83 patients from the Ritux 3 trial between January 1, 2010, and December 31, 2015.
- They used Kaplan-Meir curves to determine the 5- and 7-year rates of disease-free survival (DFS) without corticosteroids.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 83 patients, 44 were in the rituximab-plus-prednisone group and 39 were in the prednisone-only group, with a median follow-up of 87.3 months (7.3 years).
- Among patients in the rituximab plus prednisone group, 43 (93.5%) achieved complete remission without corticosteroids at any time during follow-up, compared with 17 patients (39%) in the prednisone-only group.
- DFS (without corticosteroid therapy) statistically favored patients in the rituximab plus prednisone group compared with patients in the prednisone-only group at follow-up times of 5 years (76.7% vs 35.3%, respectively) and 7 years (72.1% vs 35.3%; P < .001 for both associations).
- In another finding, 31 patients in the rituximab plus prednisone group reported fewer serious adverse events (SAEs) than 58 patients in the prednisone-only group, which corresponds to 0.67 and 1.32 SAEs per patient, respectively (P = .003).
IN PRACTICE:
The study findings demonstrated “the superiority of rituximab over a standard corticosteroids regimen, both in the short term and the long term,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Billal Tedbirt, MD, of the Department of Dermatology at CHU Rouen in France, led the study, which was published online on January 24, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Nearly 8% of patients did not attend the end of follow-up visit. Also, serum samples used to predict relapse were drawn at month 36, but the researchers said that a window of every 4-6 months might provide higher accuracy of relapses.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Tedbirt reported having no disclosures. Four of the study authors reported being investigators for and/or receiving personal fees from several pharmaceutical companies. The study was supported by a grant from the French Society of Dermatology.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Microbiome Impacts Vaccine Responses
When infants are born, they have nearly a clean slate with regard to their immune systems. Virtually all their immune cells are naive. They have no immunity memory. Vaccines at birth, and in the first 2 years of life, elicit variable antibody levels and cellular immune responses. Sometimes, this leaves fully vaccinated children unprotected against vaccine-preventable infectious diseases.
Newborns are bombarded at birth with microbes and other antigenic stimuli from the environment; food in the form of breast milk, formula, water; and vaccines, such as hepatitis B and, in other countries, with BCG. At birth, to avoid immunologically-induced injury, immune responses favor immunologic tolerance. However, adaptation must be rapid to avoid life-threatening infections. To navigate the gauntlet of microbe and environmental exposures and vaccines, the neonatal immune system moves through a gradual maturation process toward immune responsivity. The maturation occurs at different rates in different children.
Reassessing Vaccine Responsiveness
Vaccine responsiveness is usually assessed by measuring antibody levels in blood. Until recently, it was thought to be “bad luck” when a child failed to develop protective immunity following vaccination. The bad luck was suggested to involve illness at the time of vaccination, especially illness occurring with fever, and especially common viral infections. But studies proved that notion incorrect. About 10 years ago I became more interested in variability in vaccine responses in the first 2 years of life. In 2016, my laboratory described a specific population of children with specific cellular immune deficiencies that we classified as low vaccine responders (LVRs).1 To preclude the suggestion that low vaccine responses were to be considered normal biological variation, we chose an a priori definition of LVR as those with sub-protective IgG antibody levels to four (≥ 66 %) of six tested vaccines in DTaP-Hib (diphtheria toxoid, tetanus toxoid, pertussis toxoid, pertactin, and filamentous hemagglutinin [DTaP] and Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide capsule [Hib]). Antibody levels were measured at 1 year of age following primary vaccinations at child age 2, 4, and 6 months old. The remaining 89% of children we termed normal vaccine responders (NVRs). We additionally tested antibody responses to viral protein and pneumococcal polysaccharide conjugated antigens (polio serotypes 1, 2, and 3, hepatitis B, and Streptococcus pneumoniae capsular polysaccharides serotypes 6B, 14, and 23F). Responses to these vaccine antigens were similar to the six vaccines (DTaP/Hib) used to define LVR. We and other groups have used alternative definitions of low vaccine responses that rely on statistics.
I recently reviewed the topic of the determinants of vaccine responses in early life, with a focus on the infant microbiome and metabolome: a.) cesarean section versus vaginal delivery, b.) breast versus formula feeding and c.) antibiotic exposure, that impact the immune response2 (Figure). In the review I also discussed how microbiome may serve as natural adjuvants for vaccine responses, how microbiota-derived metabolites influence vaccine responses, and how low vaccine responses in early life may be linked to increased infection susceptibility (Figure).
Cesarean section births occur in nearly 30% of newborns. Cesarean section birth has been associated with adverse effects on immune development, including predisposing to infections, allergies, and inflammatory disorders. The association of these adverse outcomes has been linked to lower total microbiome diversity. Fecal microbiome seeding from mother to infant in vaginal-delivered infants results in a more favorable and stable microbiome compared with cesarean-delivered infants. Nasopharyngeal microbiome may also be adversely affected by cesarean delivery. In turn, those microbiome differences can be linked to variation in vaccine responsiveness in infants.
Multiple studies strongly support the notion that breastfeeding has a favorable impact on immune development in early life associated with better vaccine responses, mediated by the microbiome. The mechanism of favorable immune responses to vaccines largely relates to the presence of a specific bacteria species, Bifidobacterium infantis. Breast milk contains human milk oligosaccharides that are not digestible by newborns. B. infantis is a strain of bacteria that utilizes these non-digestible oligosaccharides. Thereby, infants fed breast milk provides B. infantis the essential source of nutrition for its growth and predominance in the newborn gut. Studies have shown that Bifidobacterium spp. abundance in early life is correlated with better immune responses to multiple vaccines. Bifidobacterium spp. abundance has been positively correlated with antibody responses measured after 2 years, linking the microbiome composition to the durability of vaccine-induced immune responses.
Antibiotic exposure in early life may disproportionately damage the newborn and infant microbiome compared with later childhood. The average child receives about three antibiotic courses by the age of 2 years. My lab was among the first to describe the adverse effects of antibiotics on vaccine responses in early life.3 We found that broader spectrum antibiotics had a greater adverse effect on vaccine-induced antibody levels than narrower spectrum antibiotics. Ten-day versus five-day treatment courses had a greater negative effect. Multiple antibiotic courses over time (cumulative antibiotic exposure) was negatively associated with vaccine-induced antibody levels.
Over 11 % of live births worldwide occur preterm. Because bacterial infections are frequent complications of preterm birth, 79 % of very low birthweight and 87 % of extremely low birthweight infants in US NICUs receive antibiotics within 3 days of birth. Recently, my group studied full-term infants at birth and found that exposure to parenteral antibiotics at birth or during the first days of life had an adverse effect on vaccine responses.4
Microbiome Impacts Immunity
How does the microbiome affect immunity, and specifically vaccine responses? Microbial-derived metabolites affect host immunity. Gut bacteria produce short chain fatty acids (SCFAs: acetate, propionate, butyrate) [115]. SCFAs positively influence immunity cells. Vitamin D metabolites are generated by intestinal bacteria and those metabolites positively influence immunity. Secondary bile acids produced by Clostridium spp. are involved in favorable immune responses. Increased levels of phenylpyruvic acid produced by gut and/or nasopharyngeal microbiota correlate with reduced vaccine responses and upregulated metabolome genes that encode for oxidative phosphorylation correlate with increased vaccine responses.
In summary, immune development commences at birth. Impairment in responses to vaccination in children have been linked to disturbance in the microbiome. Cesarean section and absence of breastfeeding are associated with adverse microbiota composition. Antibiotics perturb healthy microbiota development. The microbiota affect immunity in several ways, among them are effects by metabolites generated by the commensals that inhabit the child host. A child who responds poorly to vaccines and has specific immune cell dysfunction caused by problems with the microbiome also displays increased infection proneness. But that is a story for another column, later.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute, at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Pichichero ME et al. J Infect Dis. 2016 Jun 15;213(12):2014-2019. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw053.
2. Pichichero ME. Cell Immunol. 2023 Nov-Dec:393-394:104777. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2023.104777.
3. Chapman TJ et al. Pediatrics. 2022 May 1;149(5):e2021052061. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052061.
4. Shaffer M et al. mSystems. 2023 Oct 26;8(5):e0066123. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00661-23.
When infants are born, they have nearly a clean slate with regard to their immune systems. Virtually all their immune cells are naive. They have no immunity memory. Vaccines at birth, and in the first 2 years of life, elicit variable antibody levels and cellular immune responses. Sometimes, this leaves fully vaccinated children unprotected against vaccine-preventable infectious diseases.
Newborns are bombarded at birth with microbes and other antigenic stimuli from the environment; food in the form of breast milk, formula, water; and vaccines, such as hepatitis B and, in other countries, with BCG. At birth, to avoid immunologically-induced injury, immune responses favor immunologic tolerance. However, adaptation must be rapid to avoid life-threatening infections. To navigate the gauntlet of microbe and environmental exposures and vaccines, the neonatal immune system moves through a gradual maturation process toward immune responsivity. The maturation occurs at different rates in different children.
Reassessing Vaccine Responsiveness
Vaccine responsiveness is usually assessed by measuring antibody levels in blood. Until recently, it was thought to be “bad luck” when a child failed to develop protective immunity following vaccination. The bad luck was suggested to involve illness at the time of vaccination, especially illness occurring with fever, and especially common viral infections. But studies proved that notion incorrect. About 10 years ago I became more interested in variability in vaccine responses in the first 2 years of life. In 2016, my laboratory described a specific population of children with specific cellular immune deficiencies that we classified as low vaccine responders (LVRs).1 To preclude the suggestion that low vaccine responses were to be considered normal biological variation, we chose an a priori definition of LVR as those with sub-protective IgG antibody levels to four (≥ 66 %) of six tested vaccines in DTaP-Hib (diphtheria toxoid, tetanus toxoid, pertussis toxoid, pertactin, and filamentous hemagglutinin [DTaP] and Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide capsule [Hib]). Antibody levels were measured at 1 year of age following primary vaccinations at child age 2, 4, and 6 months old. The remaining 89% of children we termed normal vaccine responders (NVRs). We additionally tested antibody responses to viral protein and pneumococcal polysaccharide conjugated antigens (polio serotypes 1, 2, and 3, hepatitis B, and Streptococcus pneumoniae capsular polysaccharides serotypes 6B, 14, and 23F). Responses to these vaccine antigens were similar to the six vaccines (DTaP/Hib) used to define LVR. We and other groups have used alternative definitions of low vaccine responses that rely on statistics.
I recently reviewed the topic of the determinants of vaccine responses in early life, with a focus on the infant microbiome and metabolome: a.) cesarean section versus vaginal delivery, b.) breast versus formula feeding and c.) antibiotic exposure, that impact the immune response2 (Figure). In the review I also discussed how microbiome may serve as natural adjuvants for vaccine responses, how microbiota-derived metabolites influence vaccine responses, and how low vaccine responses in early life may be linked to increased infection susceptibility (Figure).
Cesarean section births occur in nearly 30% of newborns. Cesarean section birth has been associated with adverse effects on immune development, including predisposing to infections, allergies, and inflammatory disorders. The association of these adverse outcomes has been linked to lower total microbiome diversity. Fecal microbiome seeding from mother to infant in vaginal-delivered infants results in a more favorable and stable microbiome compared with cesarean-delivered infants. Nasopharyngeal microbiome may also be adversely affected by cesarean delivery. In turn, those microbiome differences can be linked to variation in vaccine responsiveness in infants.
Multiple studies strongly support the notion that breastfeeding has a favorable impact on immune development in early life associated with better vaccine responses, mediated by the microbiome. The mechanism of favorable immune responses to vaccines largely relates to the presence of a specific bacteria species, Bifidobacterium infantis. Breast milk contains human milk oligosaccharides that are not digestible by newborns. B. infantis is a strain of bacteria that utilizes these non-digestible oligosaccharides. Thereby, infants fed breast milk provides B. infantis the essential source of nutrition for its growth and predominance in the newborn gut. Studies have shown that Bifidobacterium spp. abundance in early life is correlated with better immune responses to multiple vaccines. Bifidobacterium spp. abundance has been positively correlated with antibody responses measured after 2 years, linking the microbiome composition to the durability of vaccine-induced immune responses.
Antibiotic exposure in early life may disproportionately damage the newborn and infant microbiome compared with later childhood. The average child receives about three antibiotic courses by the age of 2 years. My lab was among the first to describe the adverse effects of antibiotics on vaccine responses in early life.3 We found that broader spectrum antibiotics had a greater adverse effect on vaccine-induced antibody levels than narrower spectrum antibiotics. Ten-day versus five-day treatment courses had a greater negative effect. Multiple antibiotic courses over time (cumulative antibiotic exposure) was negatively associated with vaccine-induced antibody levels.
Over 11 % of live births worldwide occur preterm. Because bacterial infections are frequent complications of preterm birth, 79 % of very low birthweight and 87 % of extremely low birthweight infants in US NICUs receive antibiotics within 3 days of birth. Recently, my group studied full-term infants at birth and found that exposure to parenteral antibiotics at birth or during the first days of life had an adverse effect on vaccine responses.4
Microbiome Impacts Immunity
How does the microbiome affect immunity, and specifically vaccine responses? Microbial-derived metabolites affect host immunity. Gut bacteria produce short chain fatty acids (SCFAs: acetate, propionate, butyrate) [115]. SCFAs positively influence immunity cells. Vitamin D metabolites are generated by intestinal bacteria and those metabolites positively influence immunity. Secondary bile acids produced by Clostridium spp. are involved in favorable immune responses. Increased levels of phenylpyruvic acid produced by gut and/or nasopharyngeal microbiota correlate with reduced vaccine responses and upregulated metabolome genes that encode for oxidative phosphorylation correlate with increased vaccine responses.
In summary, immune development commences at birth. Impairment in responses to vaccination in children have been linked to disturbance in the microbiome. Cesarean section and absence of breastfeeding are associated with adverse microbiota composition. Antibiotics perturb healthy microbiota development. The microbiota affect immunity in several ways, among them are effects by metabolites generated by the commensals that inhabit the child host. A child who responds poorly to vaccines and has specific immune cell dysfunction caused by problems with the microbiome also displays increased infection proneness. But that is a story for another column, later.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute, at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Pichichero ME et al. J Infect Dis. 2016 Jun 15;213(12):2014-2019. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw053.
2. Pichichero ME. Cell Immunol. 2023 Nov-Dec:393-394:104777. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2023.104777.
3. Chapman TJ et al. Pediatrics. 2022 May 1;149(5):e2021052061. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052061.
4. Shaffer M et al. mSystems. 2023 Oct 26;8(5):e0066123. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00661-23.
When infants are born, they have nearly a clean slate with regard to their immune systems. Virtually all their immune cells are naive. They have no immunity memory. Vaccines at birth, and in the first 2 years of life, elicit variable antibody levels and cellular immune responses. Sometimes, this leaves fully vaccinated children unprotected against vaccine-preventable infectious diseases.
Newborns are bombarded at birth with microbes and other antigenic stimuli from the environment; food in the form of breast milk, formula, water; and vaccines, such as hepatitis B and, in other countries, with BCG. At birth, to avoid immunologically-induced injury, immune responses favor immunologic tolerance. However, adaptation must be rapid to avoid life-threatening infections. To navigate the gauntlet of microbe and environmental exposures and vaccines, the neonatal immune system moves through a gradual maturation process toward immune responsivity. The maturation occurs at different rates in different children.
Reassessing Vaccine Responsiveness
Vaccine responsiveness is usually assessed by measuring antibody levels in blood. Until recently, it was thought to be “bad luck” when a child failed to develop protective immunity following vaccination. The bad luck was suggested to involve illness at the time of vaccination, especially illness occurring with fever, and especially common viral infections. But studies proved that notion incorrect. About 10 years ago I became more interested in variability in vaccine responses in the first 2 years of life. In 2016, my laboratory described a specific population of children with specific cellular immune deficiencies that we classified as low vaccine responders (LVRs).1 To preclude the suggestion that low vaccine responses were to be considered normal biological variation, we chose an a priori definition of LVR as those with sub-protective IgG antibody levels to four (≥ 66 %) of six tested vaccines in DTaP-Hib (diphtheria toxoid, tetanus toxoid, pertussis toxoid, pertactin, and filamentous hemagglutinin [DTaP] and Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide capsule [Hib]). Antibody levels were measured at 1 year of age following primary vaccinations at child age 2, 4, and 6 months old. The remaining 89% of children we termed normal vaccine responders (NVRs). We additionally tested antibody responses to viral protein and pneumococcal polysaccharide conjugated antigens (polio serotypes 1, 2, and 3, hepatitis B, and Streptococcus pneumoniae capsular polysaccharides serotypes 6B, 14, and 23F). Responses to these vaccine antigens were similar to the six vaccines (DTaP/Hib) used to define LVR. We and other groups have used alternative definitions of low vaccine responses that rely on statistics.
I recently reviewed the topic of the determinants of vaccine responses in early life, with a focus on the infant microbiome and metabolome: a.) cesarean section versus vaginal delivery, b.) breast versus formula feeding and c.) antibiotic exposure, that impact the immune response2 (Figure). In the review I also discussed how microbiome may serve as natural adjuvants for vaccine responses, how microbiota-derived metabolites influence vaccine responses, and how low vaccine responses in early life may be linked to increased infection susceptibility (Figure).
Cesarean section births occur in nearly 30% of newborns. Cesarean section birth has been associated with adverse effects on immune development, including predisposing to infections, allergies, and inflammatory disorders. The association of these adverse outcomes has been linked to lower total microbiome diversity. Fecal microbiome seeding from mother to infant in vaginal-delivered infants results in a more favorable and stable microbiome compared with cesarean-delivered infants. Nasopharyngeal microbiome may also be adversely affected by cesarean delivery. In turn, those microbiome differences can be linked to variation in vaccine responsiveness in infants.
Multiple studies strongly support the notion that breastfeeding has a favorable impact on immune development in early life associated with better vaccine responses, mediated by the microbiome. The mechanism of favorable immune responses to vaccines largely relates to the presence of a specific bacteria species, Bifidobacterium infantis. Breast milk contains human milk oligosaccharides that are not digestible by newborns. B. infantis is a strain of bacteria that utilizes these non-digestible oligosaccharides. Thereby, infants fed breast milk provides B. infantis the essential source of nutrition for its growth and predominance in the newborn gut. Studies have shown that Bifidobacterium spp. abundance in early life is correlated with better immune responses to multiple vaccines. Bifidobacterium spp. abundance has been positively correlated with antibody responses measured after 2 years, linking the microbiome composition to the durability of vaccine-induced immune responses.
Antibiotic exposure in early life may disproportionately damage the newborn and infant microbiome compared with later childhood. The average child receives about three antibiotic courses by the age of 2 years. My lab was among the first to describe the adverse effects of antibiotics on vaccine responses in early life.3 We found that broader spectrum antibiotics had a greater adverse effect on vaccine-induced antibody levels than narrower spectrum antibiotics. Ten-day versus five-day treatment courses had a greater negative effect. Multiple antibiotic courses over time (cumulative antibiotic exposure) was negatively associated with vaccine-induced antibody levels.
Over 11 % of live births worldwide occur preterm. Because bacterial infections are frequent complications of preterm birth, 79 % of very low birthweight and 87 % of extremely low birthweight infants in US NICUs receive antibiotics within 3 days of birth. Recently, my group studied full-term infants at birth and found that exposure to parenteral antibiotics at birth or during the first days of life had an adverse effect on vaccine responses.4
Microbiome Impacts Immunity
How does the microbiome affect immunity, and specifically vaccine responses? Microbial-derived metabolites affect host immunity. Gut bacteria produce short chain fatty acids (SCFAs: acetate, propionate, butyrate) [115]. SCFAs positively influence immunity cells. Vitamin D metabolites are generated by intestinal bacteria and those metabolites positively influence immunity. Secondary bile acids produced by Clostridium spp. are involved in favorable immune responses. Increased levels of phenylpyruvic acid produced by gut and/or nasopharyngeal microbiota correlate with reduced vaccine responses and upregulated metabolome genes that encode for oxidative phosphorylation correlate with increased vaccine responses.
In summary, immune development commences at birth. Impairment in responses to vaccination in children have been linked to disturbance in the microbiome. Cesarean section and absence of breastfeeding are associated with adverse microbiota composition. Antibiotics perturb healthy microbiota development. The microbiota affect immunity in several ways, among them are effects by metabolites generated by the commensals that inhabit the child host. A child who responds poorly to vaccines and has specific immune cell dysfunction caused by problems with the microbiome also displays increased infection proneness. But that is a story for another column, later.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute, at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Pichichero ME et al. J Infect Dis. 2016 Jun 15;213(12):2014-2019. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw053.
2. Pichichero ME. Cell Immunol. 2023 Nov-Dec:393-394:104777. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2023.104777.
3. Chapman TJ et al. Pediatrics. 2022 May 1;149(5):e2021052061. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052061.
4. Shaffer M et al. mSystems. 2023 Oct 26;8(5):e0066123. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00661-23.
Ibuprofen Fails for Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm Infants
The study population included infants born between 23 weeks 0 days’ and 28 weeks 6 days’ gestation. The researchers randomized 326 extremely preterm infants with patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) at 72 hours or less after birth to ibuprofen at a loading dose of 10 mg/kg followed by two doses of 5 mg/kg at least 24 hours apart, and 327 to placebo.
The PDAs in the infants had a diameter of at least 1.5 mm with pulsatile flow.
Severe dysplasia outcome
The study’s primary outcome was a composite of death or moderate to severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia at 36 weeks’ postmenstrual age. Overall, a primary outcome occurred in 69.2% of infants who received ibuprofen and 63.5% of those who received a placebo.
Risk of death or bronchopulmonary dysplasia at 36 weeks’ postmenstrual age was not reduced by early ibuprofen vs. placebo for preterm infants, the researchers concluded. Moderate or severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia occurred in 64.2% of the infants in the ibuprofen group and 59.3% of the placebo group who survived to 36 weeks’ postmenstrual age.
‘Unforeseeable’ serious adverse events
Forty-four deaths occurred in the ibuprofen group and 33 in the placebo group (adjusted risk ratio 1.09). Two “unforeseeable” serious adverse events occurred during the study that were potentially related to ibuprofen.
The lead author was Samir Gupta, MD, of Sidra Medicine, Doha, Qatar. The study was published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Study limitations include incomplete data for some patients.
The study was supported by the National Institute for Health Research Health Technology Assessment Programme. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The study population included infants born between 23 weeks 0 days’ and 28 weeks 6 days’ gestation. The researchers randomized 326 extremely preterm infants with patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) at 72 hours or less after birth to ibuprofen at a loading dose of 10 mg/kg followed by two doses of 5 mg/kg at least 24 hours apart, and 327 to placebo.
The PDAs in the infants had a diameter of at least 1.5 mm with pulsatile flow.
Severe dysplasia outcome
The study’s primary outcome was a composite of death or moderate to severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia at 36 weeks’ postmenstrual age. Overall, a primary outcome occurred in 69.2% of infants who received ibuprofen and 63.5% of those who received a placebo.
Risk of death or bronchopulmonary dysplasia at 36 weeks’ postmenstrual age was not reduced by early ibuprofen vs. placebo for preterm infants, the researchers concluded. Moderate or severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia occurred in 64.2% of the infants in the ibuprofen group and 59.3% of the placebo group who survived to 36 weeks’ postmenstrual age.
‘Unforeseeable’ serious adverse events
Forty-four deaths occurred in the ibuprofen group and 33 in the placebo group (adjusted risk ratio 1.09). Two “unforeseeable” serious adverse events occurred during the study that were potentially related to ibuprofen.
The lead author was Samir Gupta, MD, of Sidra Medicine, Doha, Qatar. The study was published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Study limitations include incomplete data for some patients.
The study was supported by the National Institute for Health Research Health Technology Assessment Programme. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The study population included infants born between 23 weeks 0 days’ and 28 weeks 6 days’ gestation. The researchers randomized 326 extremely preterm infants with patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) at 72 hours or less after birth to ibuprofen at a loading dose of 10 mg/kg followed by two doses of 5 mg/kg at least 24 hours apart, and 327 to placebo.
The PDAs in the infants had a diameter of at least 1.5 mm with pulsatile flow.
Severe dysplasia outcome
The study’s primary outcome was a composite of death or moderate to severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia at 36 weeks’ postmenstrual age. Overall, a primary outcome occurred in 69.2% of infants who received ibuprofen and 63.5% of those who received a placebo.
Risk of death or bronchopulmonary dysplasia at 36 weeks’ postmenstrual age was not reduced by early ibuprofen vs. placebo for preterm infants, the researchers concluded. Moderate or severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia occurred in 64.2% of the infants in the ibuprofen group and 59.3% of the placebo group who survived to 36 weeks’ postmenstrual age.
‘Unforeseeable’ serious adverse events
Forty-four deaths occurred in the ibuprofen group and 33 in the placebo group (adjusted risk ratio 1.09). Two “unforeseeable” serious adverse events occurred during the study that were potentially related to ibuprofen.
The lead author was Samir Gupta, MD, of Sidra Medicine, Doha, Qatar. The study was published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Study limitations include incomplete data for some patients.
The study was supported by the National Institute for Health Research Health Technology Assessment Programme. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.