User login
In COPD, tai chi confers long-term benefit
and seems to confer better long-term improvement, suggests a study published online in the journal CHEST®.
Following 12 weeks of participation in tai chi or pulmonary rehabilitation, patients improved in most of the measurements taken, although no significant between-group differences were observed at that time. However, further improvements were observed in the tai chi group 12 weeks after the intervention had ended. These improvements manifested as a statistically significant 4.5 between-group difference in St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire points in favor of tai chi (P less than .001)
“This observation, supported also by improvements in dyspnea and exercise performance, suggests that tai chi could be substituted for PR [pulmonary rehabilitation] in the treatment of COPD with greater convenience for patients,” the researchers concluded.
SOURCE: Polkey MI et al. CHEST. 2018 May;153[5]:1116-24.
and seems to confer better long-term improvement, suggests a study published online in the journal CHEST®.
Following 12 weeks of participation in tai chi or pulmonary rehabilitation, patients improved in most of the measurements taken, although no significant between-group differences were observed at that time. However, further improvements were observed in the tai chi group 12 weeks after the intervention had ended. These improvements manifested as a statistically significant 4.5 between-group difference in St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire points in favor of tai chi (P less than .001)
“This observation, supported also by improvements in dyspnea and exercise performance, suggests that tai chi could be substituted for PR [pulmonary rehabilitation] in the treatment of COPD with greater convenience for patients,” the researchers concluded.
SOURCE: Polkey MI et al. CHEST. 2018 May;153[5]:1116-24.
and seems to confer better long-term improvement, suggests a study published online in the journal CHEST®.
Following 12 weeks of participation in tai chi or pulmonary rehabilitation, patients improved in most of the measurements taken, although no significant between-group differences were observed at that time. However, further improvements were observed in the tai chi group 12 weeks after the intervention had ended. These improvements manifested as a statistically significant 4.5 between-group difference in St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire points in favor of tai chi (P less than .001)
“This observation, supported also by improvements in dyspnea and exercise performance, suggests that tai chi could be substituted for PR [pulmonary rehabilitation] in the treatment of COPD with greater convenience for patients,” the researchers concluded.
SOURCE: Polkey MI et al. CHEST. 2018 May;153[5]:1116-24.
FROM THE JOURNAL CHEST®
Rapid-Response Teams Can Decrease Admission Times for Patients With Stroke
LOS ANGELES—Adding a rapid-response team member into the emergency department process to coordinate care for patients eligible for IV t-PA significantly reduces door-to-admission times, according to research presented at the International Stroke Conference 2018. This improvement may be attributed to faster placement and prioritized processing of admission orders.
In this study, the rapid-response team “acted as a control center, relaying vital information to the admission office and the acute stroke unit charge nurse,” said Tarun Girotra, MD, a neurologist at the Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit, and colleagues. “The emergency department registered nurse (RN) was relieved of some of the administrative responsibilities and was able to focus solely on patient care, which resulted in decreased misses in the vital sign documentations.”
The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends a door-to-admission time of less than three hours for patients eligible for IV t-PA. In large tertiary hospitals, administrative complexity and the coordination required often cause delays in admissions, said the researchers. Few studies have examined methods for streamlining the process of admitting patients for treatment with IV t-PA and for increasing compliance with the AHA Get With the Guidelines initiative’s quality measures.
Examining a Policy’s Effect on Time to Admission
Dr. Girotra and colleagues conducted a study to assess whether having a dedicated rapid-response team RN available to respond to the emergency department to coordinate care of patients receiving IV t-PA reduces door-to-admission times. A rapid-response team comprises nurses trained for intensive care units who coordinate care within hospitals and actively participate in inpatient emergencies that require resuscitation.
For this study, the emergency department at the authors’ hospital implemented a policy of notifying the rapid-response team RN of all patients eligible for IV t-PA. The role of the rapid-response team was defined as facilitating admissions through the coordination of care between neurology residents, emergency department physicians, the emergency department RN, the stroke unit charge RN, and the admissions office.
The study’s primary end point was door-to-admission times, which were collected prospectively for three months before and after the intervention (ie, the new policy). Secondary end points included the number of missed neurologic checks and vital sign checks, which AHA guidelines recommend recording. Researchers used the Wilcoxon two-sample test to analyze time variables and compliance rates.
Policy Did Not Affect Neurologic Checks
In all, 13 patients were admitted to receive IV t-PA before the intervention, and 16 were admitted after the intervention. Thirty-eight percent of patients in the preintervention group were female, and 56% of patients in the postintervention group were female. The mean age of participants in the preintervention group was 62.7, and the mean age of participants in the postintervention group was 67. The study lasted six months,
Overall, the intervention decreased the mean door-to-admission time from 242.7 minutes to 167.9 minutes. In addition, significantly fewer patients had more than one miss in their documented vital signs after the intervention, compared with before the intervention. No significant difference was observed in the documented neurologic checks per the AHA protocol. There was a higher-than-expected number of misses in neurologic exams by the emergency department RN, however, said the authors. Other centers could use similar interventions to help decrease door-to-admission times, the investigators concluded.
—Erica Tricarico
LOS ANGELES—Adding a rapid-response team member into the emergency department process to coordinate care for patients eligible for IV t-PA significantly reduces door-to-admission times, according to research presented at the International Stroke Conference 2018. This improvement may be attributed to faster placement and prioritized processing of admission orders.
In this study, the rapid-response team “acted as a control center, relaying vital information to the admission office and the acute stroke unit charge nurse,” said Tarun Girotra, MD, a neurologist at the Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit, and colleagues. “The emergency department registered nurse (RN) was relieved of some of the administrative responsibilities and was able to focus solely on patient care, which resulted in decreased misses in the vital sign documentations.”
The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends a door-to-admission time of less than three hours for patients eligible for IV t-PA. In large tertiary hospitals, administrative complexity and the coordination required often cause delays in admissions, said the researchers. Few studies have examined methods for streamlining the process of admitting patients for treatment with IV t-PA and for increasing compliance with the AHA Get With the Guidelines initiative’s quality measures.
Examining a Policy’s Effect on Time to Admission
Dr. Girotra and colleagues conducted a study to assess whether having a dedicated rapid-response team RN available to respond to the emergency department to coordinate care of patients receiving IV t-PA reduces door-to-admission times. A rapid-response team comprises nurses trained for intensive care units who coordinate care within hospitals and actively participate in inpatient emergencies that require resuscitation.
For this study, the emergency department at the authors’ hospital implemented a policy of notifying the rapid-response team RN of all patients eligible for IV t-PA. The role of the rapid-response team was defined as facilitating admissions through the coordination of care between neurology residents, emergency department physicians, the emergency department RN, the stroke unit charge RN, and the admissions office.
The study’s primary end point was door-to-admission times, which were collected prospectively for three months before and after the intervention (ie, the new policy). Secondary end points included the number of missed neurologic checks and vital sign checks, which AHA guidelines recommend recording. Researchers used the Wilcoxon two-sample test to analyze time variables and compliance rates.
Policy Did Not Affect Neurologic Checks
In all, 13 patients were admitted to receive IV t-PA before the intervention, and 16 were admitted after the intervention. Thirty-eight percent of patients in the preintervention group were female, and 56% of patients in the postintervention group were female. The mean age of participants in the preintervention group was 62.7, and the mean age of participants in the postintervention group was 67. The study lasted six months,
Overall, the intervention decreased the mean door-to-admission time from 242.7 minutes to 167.9 minutes. In addition, significantly fewer patients had more than one miss in their documented vital signs after the intervention, compared with before the intervention. No significant difference was observed in the documented neurologic checks per the AHA protocol. There was a higher-than-expected number of misses in neurologic exams by the emergency department RN, however, said the authors. Other centers could use similar interventions to help decrease door-to-admission times, the investigators concluded.
—Erica Tricarico
LOS ANGELES—Adding a rapid-response team member into the emergency department process to coordinate care for patients eligible for IV t-PA significantly reduces door-to-admission times, according to research presented at the International Stroke Conference 2018. This improvement may be attributed to faster placement and prioritized processing of admission orders.
In this study, the rapid-response team “acted as a control center, relaying vital information to the admission office and the acute stroke unit charge nurse,” said Tarun Girotra, MD, a neurologist at the Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit, and colleagues. “The emergency department registered nurse (RN) was relieved of some of the administrative responsibilities and was able to focus solely on patient care, which resulted in decreased misses in the vital sign documentations.”
The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends a door-to-admission time of less than three hours for patients eligible for IV t-PA. In large tertiary hospitals, administrative complexity and the coordination required often cause delays in admissions, said the researchers. Few studies have examined methods for streamlining the process of admitting patients for treatment with IV t-PA and for increasing compliance with the AHA Get With the Guidelines initiative’s quality measures.
Examining a Policy’s Effect on Time to Admission
Dr. Girotra and colleagues conducted a study to assess whether having a dedicated rapid-response team RN available to respond to the emergency department to coordinate care of patients receiving IV t-PA reduces door-to-admission times. A rapid-response team comprises nurses trained for intensive care units who coordinate care within hospitals and actively participate in inpatient emergencies that require resuscitation.
For this study, the emergency department at the authors’ hospital implemented a policy of notifying the rapid-response team RN of all patients eligible for IV t-PA. The role of the rapid-response team was defined as facilitating admissions through the coordination of care between neurology residents, emergency department physicians, the emergency department RN, the stroke unit charge RN, and the admissions office.
The study’s primary end point was door-to-admission times, which were collected prospectively for three months before and after the intervention (ie, the new policy). Secondary end points included the number of missed neurologic checks and vital sign checks, which AHA guidelines recommend recording. Researchers used the Wilcoxon two-sample test to analyze time variables and compliance rates.
Policy Did Not Affect Neurologic Checks
In all, 13 patients were admitted to receive IV t-PA before the intervention, and 16 were admitted after the intervention. Thirty-eight percent of patients in the preintervention group were female, and 56% of patients in the postintervention group were female. The mean age of participants in the preintervention group was 62.7, and the mean age of participants in the postintervention group was 67. The study lasted six months,
Overall, the intervention decreased the mean door-to-admission time from 242.7 minutes to 167.9 minutes. In addition, significantly fewer patients had more than one miss in their documented vital signs after the intervention, compared with before the intervention. No significant difference was observed in the documented neurologic checks per the AHA protocol. There was a higher-than-expected number of misses in neurologic exams by the emergency department RN, however, said the authors. Other centers could use similar interventions to help decrease door-to-admission times, the investigators concluded.
—Erica Tricarico
VIDEO: Few transgender patients desire care in a transgender-only clinic
AUSTIN, TEX. – Transgender patients face many barriers to care, including a lack of necessary expertise among providers, but a large majority of those surveyed in a study in which they were asked whether they would want to go to a transgender-only clinic said they would not.
Lauren Abern, MD, of Atrius Health, Cambridge, Mass., discussed the aims and results of her survey at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
The anonymous online survey consisted of 120 individuals, aged 18-64 years: 100 transgender men and 20 transgender women. Of these, 83 reported experiencing barriers to care. The most common problem cited was cost (68, 82%), and other barriers were access to care (47, 57%), stigma (33, 40%), and discrimination (23, 26%). Cost was a factor even though a large majority of the respondents had health insurance; a majority of respondents had an income of less than $24,000 per year.
The most common way respondents found transgender-competent health care was through word of mouth (79, 77%).
When asked whether they would want to go to a transgender-only clinic, a majority of both transgender women and transgender men respondents either answered, “no,” or that they were unsure (86, 77%). Some respondents cited a desire not to out themselves as transgender, and others considered the separate clinic medically unnecessary. One wrote: “You wouldn’t need a broken foot–only clinic.”
“Basic preventative services can be provided without specific expertise in transgender health. If providers are uncomfortable, they should refer [transgender patients] elsewhere.” said Dr. Abern.
The survey project was conducted in collaboration with the University of Miami and the YES Institute in Miami.
Dr. Abern also spoke about wider transgender health considerations for the ob.gyn. in a separate presentation at the meeting and in a video interview.
For example, transgender men on testosterone may have persistent bleeding and may be uncomfortable with pelvic exams.
Making more inclusive intake forms and fostering a respectful office environment (for example, having a nondiscrimination policy displayed in the waiting area) are measures beneficial to all patients, she said.
“My dream or goal would be that transgender people can be seen and accepted at any office and feel comfortable and not avoid seeking health care.”
AUSTIN, TEX. – Transgender patients face many barriers to care, including a lack of necessary expertise among providers, but a large majority of those surveyed in a study in which they were asked whether they would want to go to a transgender-only clinic said they would not.
Lauren Abern, MD, of Atrius Health, Cambridge, Mass., discussed the aims and results of her survey at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
The anonymous online survey consisted of 120 individuals, aged 18-64 years: 100 transgender men and 20 transgender women. Of these, 83 reported experiencing barriers to care. The most common problem cited was cost (68, 82%), and other barriers were access to care (47, 57%), stigma (33, 40%), and discrimination (23, 26%). Cost was a factor even though a large majority of the respondents had health insurance; a majority of respondents had an income of less than $24,000 per year.
The most common way respondents found transgender-competent health care was through word of mouth (79, 77%).
When asked whether they would want to go to a transgender-only clinic, a majority of both transgender women and transgender men respondents either answered, “no,” or that they were unsure (86, 77%). Some respondents cited a desire not to out themselves as transgender, and others considered the separate clinic medically unnecessary. One wrote: “You wouldn’t need a broken foot–only clinic.”
“Basic preventative services can be provided without specific expertise in transgender health. If providers are uncomfortable, they should refer [transgender patients] elsewhere.” said Dr. Abern.
The survey project was conducted in collaboration with the University of Miami and the YES Institute in Miami.
Dr. Abern also spoke about wider transgender health considerations for the ob.gyn. in a separate presentation at the meeting and in a video interview.
For example, transgender men on testosterone may have persistent bleeding and may be uncomfortable with pelvic exams.
Making more inclusive intake forms and fostering a respectful office environment (for example, having a nondiscrimination policy displayed in the waiting area) are measures beneficial to all patients, she said.
“My dream or goal would be that transgender people can be seen and accepted at any office and feel comfortable and not avoid seeking health care.”
AUSTIN, TEX. – Transgender patients face many barriers to care, including a lack of necessary expertise among providers, but a large majority of those surveyed in a study in which they were asked whether they would want to go to a transgender-only clinic said they would not.
Lauren Abern, MD, of Atrius Health, Cambridge, Mass., discussed the aims and results of her survey at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
The anonymous online survey consisted of 120 individuals, aged 18-64 years: 100 transgender men and 20 transgender women. Of these, 83 reported experiencing barriers to care. The most common problem cited was cost (68, 82%), and other barriers were access to care (47, 57%), stigma (33, 40%), and discrimination (23, 26%). Cost was a factor even though a large majority of the respondents had health insurance; a majority of respondents had an income of less than $24,000 per year.
The most common way respondents found transgender-competent health care was through word of mouth (79, 77%).
When asked whether they would want to go to a transgender-only clinic, a majority of both transgender women and transgender men respondents either answered, “no,” or that they were unsure (86, 77%). Some respondents cited a desire not to out themselves as transgender, and others considered the separate clinic medically unnecessary. One wrote: “You wouldn’t need a broken foot–only clinic.”
“Basic preventative services can be provided without specific expertise in transgender health. If providers are uncomfortable, they should refer [transgender patients] elsewhere.” said Dr. Abern.
The survey project was conducted in collaboration with the University of Miami and the YES Institute in Miami.
Dr. Abern also spoke about wider transgender health considerations for the ob.gyn. in a separate presentation at the meeting and in a video interview.
For example, transgender men on testosterone may have persistent bleeding and may be uncomfortable with pelvic exams.
Making more inclusive intake forms and fostering a respectful office environment (for example, having a nondiscrimination policy displayed in the waiting area) are measures beneficial to all patients, she said.
“My dream or goal would be that transgender people can be seen and accepted at any office and feel comfortable and not avoid seeking health care.”
REPORTING FROM ACOG 2018
Energy-Based Devices for Actinic Keratosis Field Therapy
In cutaneous field cancerization, focal treatments such as cryotherapy are impractical, thus necessitating the use of field-directed therapies over the lesion and the surrounding skin field. Although evidence-based guidelines do not exist, field-directed therapy has been proposed in cases of 3 or more actinic keratoses (AKs) in a 25-cm2 area or larger.1 It can be further speculated that patients who are vulnerable to aggressive phenotypes of cutaneous malignancies, such as those with a genodermatosis or who are immunocompromised, necessitate a higher index of suspicion for field effect with even 1 or 2 AKs.
Current field-directed therapies include topical agents (imiquimod, fluorouracil, ingenol mebutate, and diclo-fenac), photodynamic therapy (PDT), and resurfacing procedures (lasers, chemical peels, dermabrasion). Although topical agents and PDT currently are gold standards in field treatment, the use of energy-based devices (ie, ablative and nonablative lasers) are attractive options as monotherapy or as part of a combination therapy. These devices are attractive options for field-directed therapy because they offer defined, customizable control of settings, allowing for optimal cosmesis and precision of therapy.
Principally, lasers function by damaging skin tissue to induce resurfacing, neocollagenesis, and vascular restructuring. Fractional versions of ablative and nonablative systems are available to target a fraction of the treatment area in evenly spaced microthermal zones and to minimize overall thermal damage.2
Given recent advances in laser systems and numerous investigations reported in the literature, a review of ablative and nonablative lasers that have been studied as treatment options for cutaneous field cancerization is provided, with a focus on treatment efficacy.
Ablative Lasers
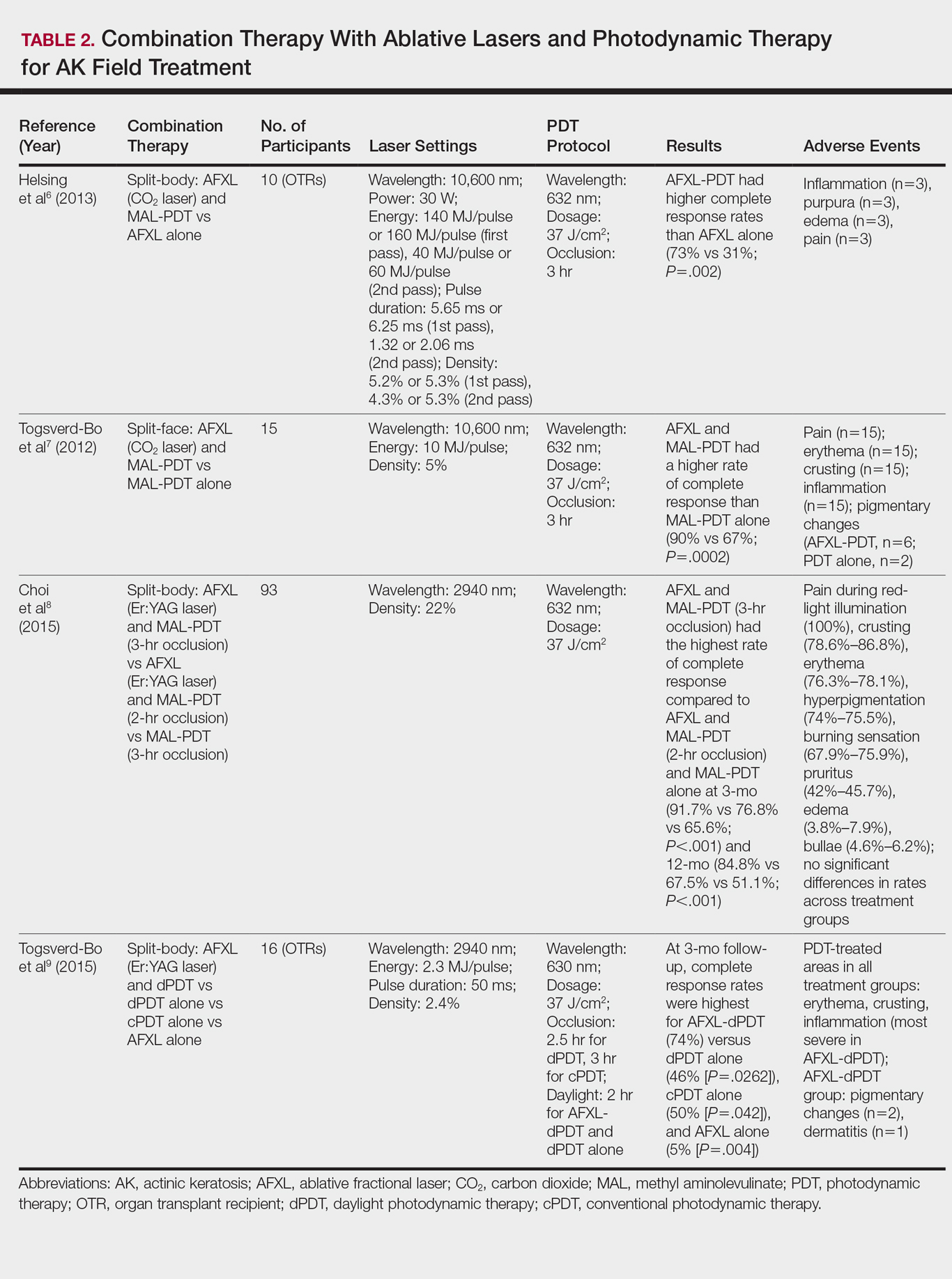
Ablative lasers operate at higher wavelengths than nonablative lasers to destroy epidermal and dermal tissue. The 10,600-nm carbon dioxide (CO2) and 2940-nm Er:YAG lasers have been heavily investigated for field therapy for multiple AKs, both as monotherapies (Table 1) and in combination with PDT (Table 2).
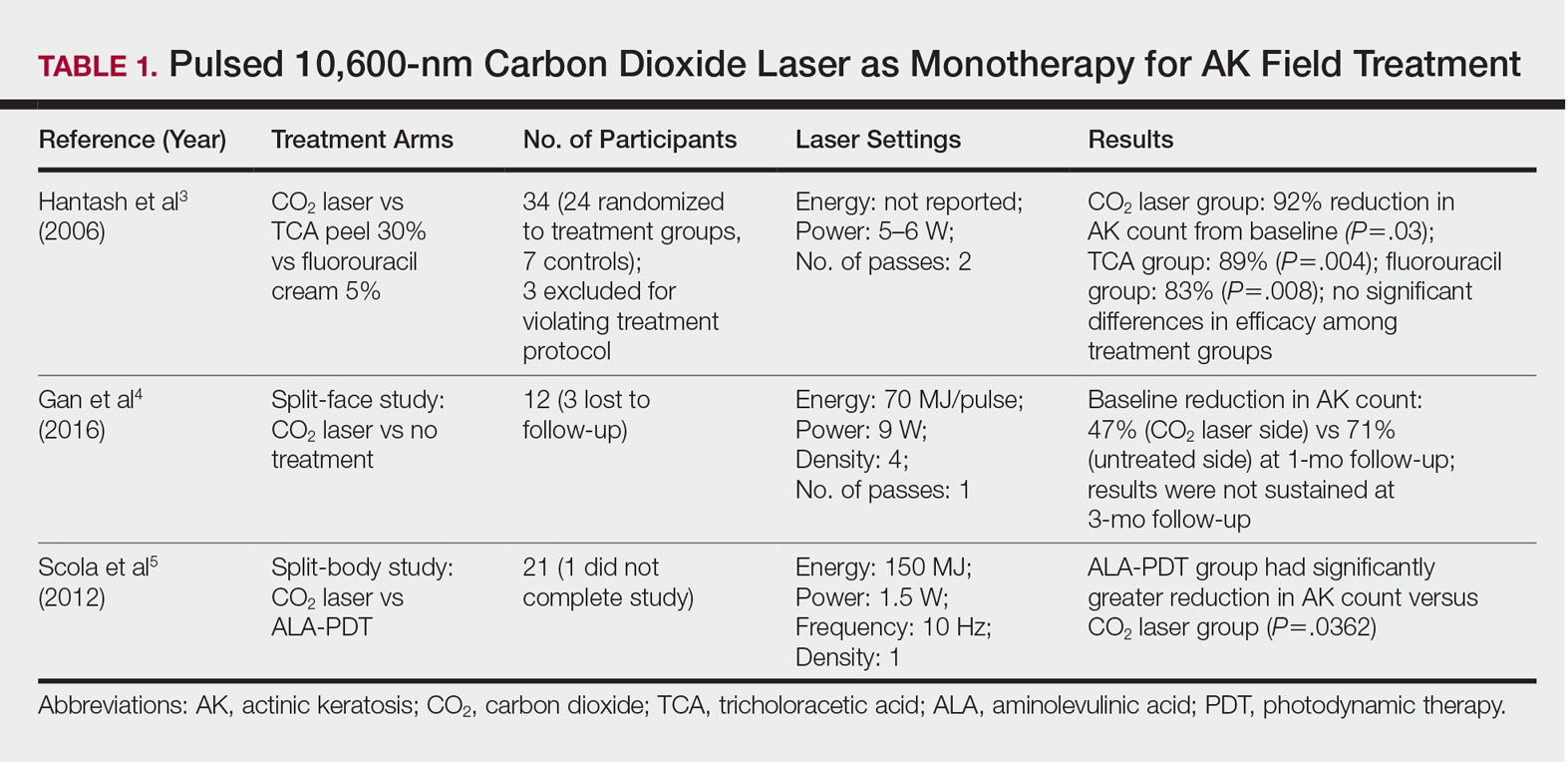
Monotherapy
One randomized trial with 5-year follow-up compared the efficacy of full-face pulsed CO2 laser therapy, full-face trichloroacetic acid (TCA) peel 30%, and fluorouracil cream 5% (twice daily for 3 weeks) on AKs on the face and head.3 Thirty-one participants were randomized to the 3 treatment arms and a negative control arm. The mean AK counts at baseline for the CO2, TCA, and fluorouracil treatment groups were 78.0, 83.7, and 61.8, respectively. At 3-month follow-up, all treatment groups had significant reductions in the mean AK count from baseline (CO2 group, 92% [P=.03]; TCA group, 89% [P=.004]; fluorouracil group, 83% [P=.008]). No significant differences in efficacy among the treatment groups were noted. All 3 treatment groups had a demonstrably lower incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer over 5-year follow-up compared to the control group (P<.001).3
In contrast to these promising results, the pulsed CO2 laser showed only short-term efficacy in a split-face study of 12 participants with at least 5 facial or scalp AKs on each of 2 symmetric facial sides who were randomized to 1 treatment side.4 At 1-month follow-up, the treatment side exhibited significantly fewer AKs compared to the control side (47% vs 71% at baseline; P=.01), but the improvement was not sustained at 3-month follow-up (49% vs 57%; P=.47).4
In another study, the CO2 laser was found to be inferior to 5-aminolevulinic acid PDT.5 Twenty-one participants who had at least 4 AKs in each symmetric half of a body region (head, hands, forearms) were randomized to PDT on 1 side and CO2 laser therapy on the other. Median baseline AK counts for the PDT and CO2 laser groups were 6 and 8, respectively. Both treatment groups exhibited significant median AK reduction from baseline 4 weeks posttreatment (PDT group, 82.1% [P<.05], CO2 laser group, 100% [P<.05]); however. at 3 months posttreatment the PDT group had significantly higher absolute (P=.0155) and relative (P=.0362) reductions in AK count compared to the CO2 laser group. One participant received a topical antibiotic for superficial infection on the PDT treatment side.5
Many questions remain regarding the practical application of laser ablation monotherapy for multiple AKs. More studies are needed to determine the practicality and long-term clinical efficacy of these devices.
PDT Combination Therapy
Laser ablation may be combined with PDT to increase efficacy and prolong remission rates. In fact, laser ablation may be thought of as a physical drug-delivery system to boost uptake of topical agents—in this case, aminolevulinic acid and methyl aminolevulinate (MAL)—given that it disrupts the skin barrier.
In a comparative study of ablative fractional laser (AFXL)–assisted PDT and AFXL alone in 10 organ transplant recipients on immunosuppression with at least 5 AKs on each dorsal hand, participants were randomized to AFXL-PDT on one treatment side and PDT on the other side.6 Participants received AFXL in an initial lesion-directed pass and then a second field-directed pass of a fractional CO2 laser. After AFXL exposure, methyl aminolevulinate was applied to the AFXL-PDT treatment side, with 3-hour occlusion. A total of 680 AKs were treated (335 in the AFXL-PDT group, 345 in the PDT group); results were stratified by the clinical grade of the lesion (1, slightly palpable; 2, moderately thick; 3, very thick or obvious). At 4-month follow-up, the AFXL-PDT group had a significantly higher median complete response rate of 73% compared to 31% in the AFXL group (P=.002). Interestingly, AFXL-PDT was also significantly more efficacious compared to AFXL for grades 1 (80% vs 37%; P=.02) and 2 (53% vs 7%, P=.009) AKs but not grade 3 AKs (4% vs 0%, P=.17).6
The combination of fractional CO2 laser and PDT also demonstrated superiority to PDT.7 In a split-face investigation, 15 participants with bilateral symmetric areas of 2 to 10 AKs on the face or scalp were randomized to receive fractional CO2 laser and MAL-PDT combination therapy on 1 treatment side and conventional MAL-PDT on the other side.7 The AFXL-PDT treatment side received laser ablation with immediate subsequent application of MAL to both treatment sides under 3-hour occlusion. At baseline, 103 AKs were treated by AFXL-PDT and 109 AKs were treated with conventional PDT. At 3-month follow-up, the AFXL-PDT treatment group exhibited a significantly higher rate of complete response (90%) compared to the conventional PDT group (67%)(P=.0002).7
Like the CO2 laser, the Er:YAG laser has demonstrated superior results when used in combination with PDT to treat field cancerization compared to either treatment alone. In a comparison study, 93 patients with 2 to 10 AK lesions on the face or scalp were randomized to treatment with AFXL (Er:YAG laser) and MAL-PDT with 3-hour occlusion, AFXL (Er:YAG laser) and MAL-PDT with 2-hour occlusion, and MAL-PDT with 3-hour occlusion.8 A total of 440 baseline AK lesions on the face or scalp were treated. At 3-month follow-up, the AFXL-PDT (3-hour occlusion) group had the highest rate of complete response (91.7%), compared to 76.8% (P=.001) in the AFXL-PDT (2-hour occlusion) and 65.6% (P=.001) in the PDT groups, regardless of the grade of AK lesion. The AFXL-PDT (2-hour occlusion) treatment was also superior to PDT alone (P=.038). These findings were sustained at 12-month follow-up (84.8% in the AFXL-PDT [3-hour occlusion] group [P<.001, compared to others]; 67.5% in the AFXL-PDT [2-hour occlusion] group [P<.001, compared to 3-hour PDT]; 51.1% in the PDT group). Importantly, the AK lesion recurrence rate was also lowest in the AFL-PDT (3-hour occlusion) group (7.5% vs 12.1% and 22.1% in the AFXL-PDT [2-hour occlusion] and PDT groups, respectively; P=.007).8
Combination therapy with AFXL and daylight PDT (dPDT) may improve the tolerability of PDT and the efficacy rate of field therapy in organ transplant recipients. One study demonstrated the superiority of this combination therapy in a population of 16 organ transplant recipients on immunosuppressants with at least 2 moderate to severely thick AKs in each of 4 comparable areas in the same anatomic region.9 The 4 areas were randomized to a single session of AFXL-dPDT, dPDT alone, conventional PDT, or AFXL alone. Ablation was performed with a fractional Er:YAG laser. The AFXL-dPDT and dPDT alone groups received MAL for 2.5 hours without occlusion, and the conventional PDT group received MAL for 3 hours with occlusion. Daylight exposure in dPDT groups was initiated 30 minutes after MAL application for 2 hours total. A baseline total of 542 AKs were treated. At 3-month follow-up, the complete response rate was highest for the AFXL-dPDT group (74%) compared to dPDT alone (46%; P=.0262), conventional PDT (50%; P=.042), and AFXL alone (5%; P=.004). Pain scores for AFXL–dPDT and dPDT alone were significantly lower than for conventional PDT and AFXL alone (P<.001).9
Nonablative Lasers
By heating the dermis to induce neogenesis without destruction, nonablative lasers offer superior healing times compared to their ablative counterparts. Multiple treatments with nonablative lasers may be necessary for maximal effect. Four nonablative laser devices have demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of multiple AKs10-14: (1) the Q-switched 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser, with or without a 532-nm potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) laser; (2) the 1540-nm fractional erbium glass laser; (3) the 1550-nm fractional erbium-doped fiber laser; and (4) the 1927-nm fractional thulium laser (Table 3).
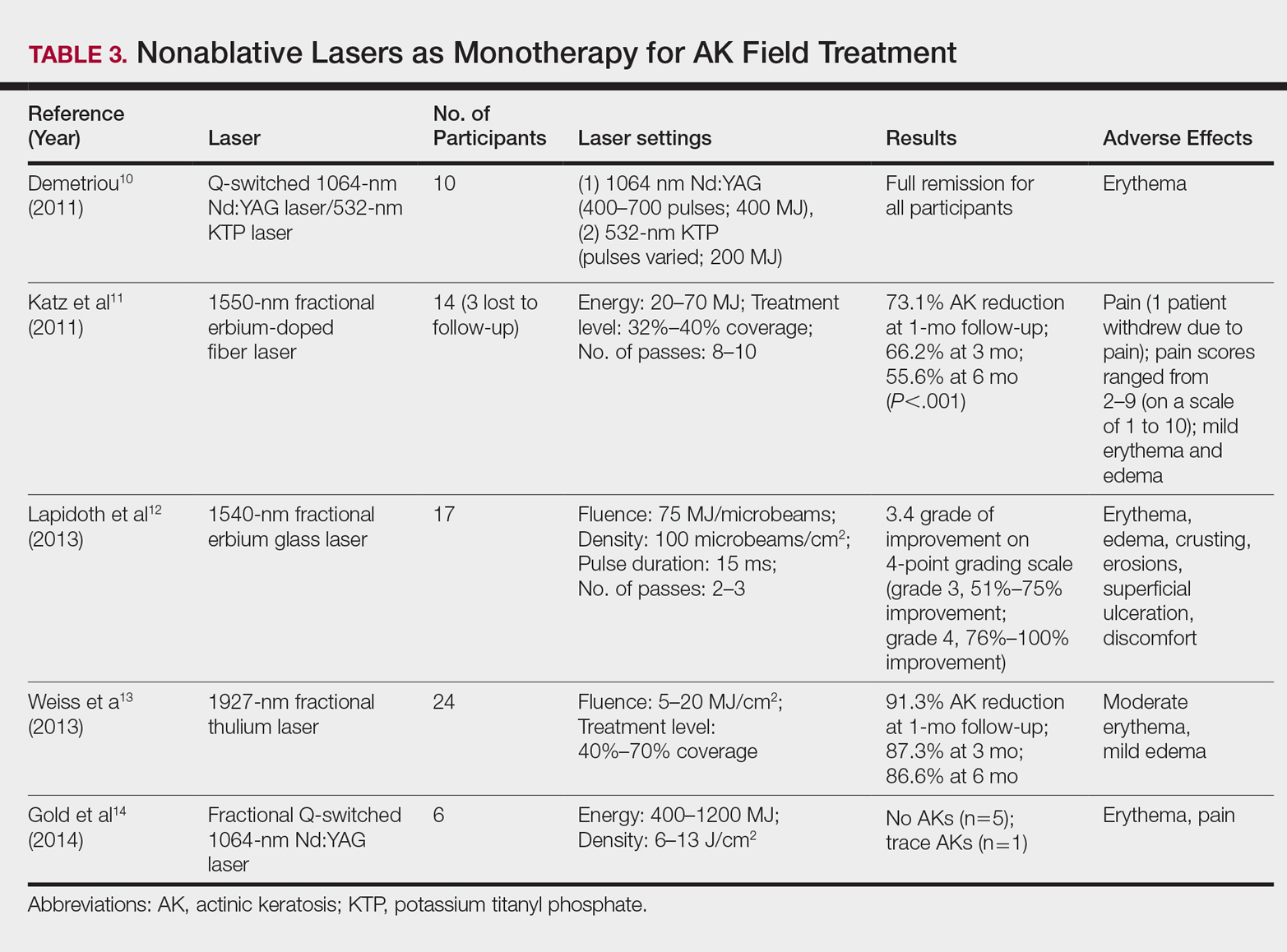
In a proof-of-concept study of the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser with the 532-nm KTP laser, 1 treatment session induced full remission of AKs in 10 patients at follow-up day 20, although the investigator did not grade improvement on a numerical scale.10 In a study of the fractional Q-switched 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser alone, 6 patients with trace or mild AKs received 4 treatment sessions at approximately 2-week intervals.14 All but 1 patient (who had trace AKs) had no AKs at 3-month follow-up.
The efficacy of the 1540-nm fractional erbium glass laser was examined in 17 participants with investigator-rated moderate-to-severe AK involvement of the scalp and face.12 Participants were given 2 or 3 treatment sessions at 3- to 4-week intervals and were graded by blinded dermatologists on a quartile scale of 0 (no improvement), 1 (1%–25% improvement), 2 (26%–50% improvement), 3 (51%–75% improvement), or 4 (76%–100% improvement). At 3 months posttreatment, the average grade of improvement was 3.4.12
The 1550-nm fractional erbium-doped fiber laser was tested in 14 men with multiple facial AKs (range, 9–44 AKs [mean, 22.1 AKs]).11 Participants received 5 treatment sessions at 2- to 4-week intervals, with majority energies used at 70 MJ and treatment level 11. The mean AK count was reduced significantly by 73.1%, 66.2%, and 55.6% at 1-, 3-, and 6-month follow-up, respectively (P<.001).11
The 1927-nm fractional thulium laser showed promising results in 24 participants with facial AKs.13 Participants received up to 4 treatment sessions at intervals from 2 to 6 weeks at the investigators’ discretion. At baseline, patients had an average of 14.04 facial AKs. At 1-, 3-, and 6-month follow-up, participants exhibited 91.3%, 87.3%, and 86.6% reduction in AK counts, respectively. The mean AK count at 3-month follow-up was 1.88.13
Due to limited sample sizes and/or lack of quantifiable results and controls in these studies, more studies are needed to fully elucidate the role of nonablative lasers in the treatment of AK.
Future Directions
Iontophoresis involves the noninvasive induction of an electrical current to facilitate ion movement through the skin and may be a novel method to boost the efficacy of current field therapies. In the first known study of its kisnd, iontophoresis-assisted AFXL-PDT was found to be noninferior to conventional AFXL-PDT15; however, additional studies demonstrating its superiority are needed before more widespread clinical use is considered.
Pretreatment with AFXL prior to topical field-directed therapies also has been proposed.16 In a case series of 13 patients, combination therapy with AFXL and ingenol mebutate was shown to be superior to ingenol mebutate alone (AK clearance rate, 89.2% vs 72.1%, respectively; P<.001).16 Randomized studies with longer follow-up time are needed.
Conclusion
Ablative and nonablative laser systems have yielded limited data about their potential as monotherapies for treatment of multiple AKs and are unlikely to replace topical agents and PDT as a first-line modality in field-directed treatment at this time. More studies with a larger number of participants and long-term follow-up are needed for further clarification of efficacy, safety, and clinical feasibility. Nevertheless, fractional ablative lasers in combination with PDT have shown robust efficacy and a favorable safety profile for treatment of multiple AKs.6-9 Further, this combination therapy exhibited a superior clearance rate and lower lesion recurrence in organ transplant recipients—a demographic that classically is difficult to treat.6-9
With continued rapid evolution of laser systems and more widespread use in dermatology, monotherapy and combination therapy may offer a dynamic new option in field cancerization that can decrease disease burden and treatment frequency.
- Peris K, Calzavara-Pinton PG, Neri L, et al. Italian expert consensus for the management of actinic keratosis in immunocompetent patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:1077-1084.
- Alexiades-Armenakas MR, Dover JS, Arndt KA. The spectrum of laser skin resurfacing: nonablative, fractional, and ablative laser resurfacing. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:719-737; quiz 738-740.
- Hantash BM, Stewart DB, Cooper ZA, et al. Facial resurfacing for nonmelanoma skin cancer prophylaxis. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:976-982.
- Gan SD, Hsu SH, Chuang G, et al. Ablative fractional laser therapy for the treatment of actinic keratosis: a split-face study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:387-389.
- Scola N, Terras S, Georgas D, et al. A randomized, half-side comparative study of aminolaevulinate photodynamic therapy vs. CO(2) laser ablation in immunocompetent patients with multiple actinic keratoses. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1366-1373.
- Helsing P, Togsverd-Bo K, Veierod MB, et al. Intensified fractional CO2 laser-assisted photodynamic therapy vs. laser alone for organ transplant recipients with multiple actinic keratoses and wart-like lesions: a randomized half-side comparative trial on dorsal hands. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:1087-1092.
- Togsverd-Bo K, Haak CS, Thaysen-Petersen D, et al. Intensified photodynamic therapy of actinic keratoses with fractional CO2 laser: a randomized clinical trial. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1262-1269.
- Choi SH, Kim KH, Song KH. Efficacy of ablative fractional laser-assisted photodynamic therapy with short-incubation time for the treatment of facial and scalp actinic keratosis: 12-month follow-up results of a randomized, prospective, comparative trial. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1598-1605.
- Togsverd-Bo K, Lei U, Erlendsson AM, et al. Combination of ablative fractional laser and daylight-mediated photodynamic therapy for actinic keratosis in organ transplant recipients—a randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2015;172:467-474.
- Demetriou C. Reversing precancerous actinic damage by mixing wavelengths (1064 nm, 532 nm). J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2011;13:113-119.
- Katz TM, Goldberg LH, Marquez D, et al. Nonablative fractional photothermolysis for facial actinic keratoses: 6-month follow-up with histologic evaluation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:349-356.
- Lapidoth M, Adatto M, Halachmi S. Treatment of actinic keratoses and photodamage with non-contact fractional 1540-nm laser quasi-ablation: an ex vivo and clinical evaluation. Lasers Med Sci. 2013;28:537-542.
- Weiss ET, Brauer JA, Anolik R, et al. 1927-nm fractional resurfacing of facial actinic keratoses: a promising new therapeutic option. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:98-102.
- Gold MH, Sensing W, Biron J. Fractional Q-switched 1,064-nm laser for the treatment of photoaged-photodamaged skin. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2014;16:69-76.
- Choi SH, Kim TH, Song KH. Efficacy of iontophoresis-assisted ablative fractional laser photodynamic therapy with short incubation time for the treatment of actinic keratosis: 12-month follow-up results of a prospective, randomised, comparative trial. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2017;18:105-110.
- Nisticò S, Sannino M, Del Duca E, et al. Ablative fractional laser improves treatment of actinic keratoses with ingenol mebutate. Eur J Inflamm. 2016;14:200-205.
In cutaneous field cancerization, focal treatments such as cryotherapy are impractical, thus necessitating the use of field-directed therapies over the lesion and the surrounding skin field. Although evidence-based guidelines do not exist, field-directed therapy has been proposed in cases of 3 or more actinic keratoses (AKs) in a 25-cm2 area or larger.1 It can be further speculated that patients who are vulnerable to aggressive phenotypes of cutaneous malignancies, such as those with a genodermatosis or who are immunocompromised, necessitate a higher index of suspicion for field effect with even 1 or 2 AKs.
Current field-directed therapies include topical agents (imiquimod, fluorouracil, ingenol mebutate, and diclo-fenac), photodynamic therapy (PDT), and resurfacing procedures (lasers, chemical peels, dermabrasion). Although topical agents and PDT currently are gold standards in field treatment, the use of energy-based devices (ie, ablative and nonablative lasers) are attractive options as monotherapy or as part of a combination therapy. These devices are attractive options for field-directed therapy because they offer defined, customizable control of settings, allowing for optimal cosmesis and precision of therapy.
Principally, lasers function by damaging skin tissue to induce resurfacing, neocollagenesis, and vascular restructuring. Fractional versions of ablative and nonablative systems are available to target a fraction of the treatment area in evenly spaced microthermal zones and to minimize overall thermal damage.2
Given recent advances in laser systems and numerous investigations reported in the literature, a review of ablative and nonablative lasers that have been studied as treatment options for cutaneous field cancerization is provided, with a focus on treatment efficacy.
Ablative Lasers
Ablative lasers operate at higher wavelengths than nonablative lasers to destroy epidermal and dermal tissue. The 10,600-nm carbon dioxide (CO2) and 2940-nm Er:YAG lasers have been heavily investigated for field therapy for multiple AKs, both as monotherapies (Table 1) and in combination with PDT (Table 2).


Monotherapy
One randomized trial with 5-year follow-up compared the efficacy of full-face pulsed CO2 laser therapy, full-face trichloroacetic acid (TCA) peel 30%, and fluorouracil cream 5% (twice daily for 3 weeks) on AKs on the face and head.3 Thirty-one participants were randomized to the 3 treatment arms and a negative control arm. The mean AK counts at baseline for the CO2, TCA, and fluorouracil treatment groups were 78.0, 83.7, and 61.8, respectively. At 3-month follow-up, all treatment groups had significant reductions in the mean AK count from baseline (CO2 group, 92% [P=.03]; TCA group, 89% [P=.004]; fluorouracil group, 83% [P=.008]). No significant differences in efficacy among the treatment groups were noted. All 3 treatment groups had a demonstrably lower incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer over 5-year follow-up compared to the control group (P<.001).3
In contrast to these promising results, the pulsed CO2 laser showed only short-term efficacy in a split-face study of 12 participants with at least 5 facial or scalp AKs on each of 2 symmetric facial sides who were randomized to 1 treatment side.4 At 1-month follow-up, the treatment side exhibited significantly fewer AKs compared to the control side (47% vs 71% at baseline; P=.01), but the improvement was not sustained at 3-month follow-up (49% vs 57%; P=.47).4
In another study, the CO2 laser was found to be inferior to 5-aminolevulinic acid PDT.5 Twenty-one participants who had at least 4 AKs in each symmetric half of a body region (head, hands, forearms) were randomized to PDT on 1 side and CO2 laser therapy on the other. Median baseline AK counts for the PDT and CO2 laser groups were 6 and 8, respectively. Both treatment groups exhibited significant median AK reduction from baseline 4 weeks posttreatment (PDT group, 82.1% [P<.05], CO2 laser group, 100% [P<.05]); however. at 3 months posttreatment the PDT group had significantly higher absolute (P=.0155) and relative (P=.0362) reductions in AK count compared to the CO2 laser group. One participant received a topical antibiotic for superficial infection on the PDT treatment side.5
Many questions remain regarding the practical application of laser ablation monotherapy for multiple AKs. More studies are needed to determine the practicality and long-term clinical efficacy of these devices.
PDT Combination Therapy
Laser ablation may be combined with PDT to increase efficacy and prolong remission rates. In fact, laser ablation may be thought of as a physical drug-delivery system to boost uptake of topical agents—in this case, aminolevulinic acid and methyl aminolevulinate (MAL)—given that it disrupts the skin barrier.
In a comparative study of ablative fractional laser (AFXL)–assisted PDT and AFXL alone in 10 organ transplant recipients on immunosuppression with at least 5 AKs on each dorsal hand, participants were randomized to AFXL-PDT on one treatment side and PDT on the other side.6 Participants received AFXL in an initial lesion-directed pass and then a second field-directed pass of a fractional CO2 laser. After AFXL exposure, methyl aminolevulinate was applied to the AFXL-PDT treatment side, with 3-hour occlusion. A total of 680 AKs were treated (335 in the AFXL-PDT group, 345 in the PDT group); results were stratified by the clinical grade of the lesion (1, slightly palpable; 2, moderately thick; 3, very thick or obvious). At 4-month follow-up, the AFXL-PDT group had a significantly higher median complete response rate of 73% compared to 31% in the AFXL group (P=.002). Interestingly, AFXL-PDT was also significantly more efficacious compared to AFXL for grades 1 (80% vs 37%; P=.02) and 2 (53% vs 7%, P=.009) AKs but not grade 3 AKs (4% vs 0%, P=.17).6
The combination of fractional CO2 laser and PDT also demonstrated superiority to PDT.7 In a split-face investigation, 15 participants with bilateral symmetric areas of 2 to 10 AKs on the face or scalp were randomized to receive fractional CO2 laser and MAL-PDT combination therapy on 1 treatment side and conventional MAL-PDT on the other side.7 The AFXL-PDT treatment side received laser ablation with immediate subsequent application of MAL to both treatment sides under 3-hour occlusion. At baseline, 103 AKs were treated by AFXL-PDT and 109 AKs were treated with conventional PDT. At 3-month follow-up, the AFXL-PDT treatment group exhibited a significantly higher rate of complete response (90%) compared to the conventional PDT group (67%)(P=.0002).7
Like the CO2 laser, the Er:YAG laser has demonstrated superior results when used in combination with PDT to treat field cancerization compared to either treatment alone. In a comparison study, 93 patients with 2 to 10 AK lesions on the face or scalp were randomized to treatment with AFXL (Er:YAG laser) and MAL-PDT with 3-hour occlusion, AFXL (Er:YAG laser) and MAL-PDT with 2-hour occlusion, and MAL-PDT with 3-hour occlusion.8 A total of 440 baseline AK lesions on the face or scalp were treated. At 3-month follow-up, the AFXL-PDT (3-hour occlusion) group had the highest rate of complete response (91.7%), compared to 76.8% (P=.001) in the AFXL-PDT (2-hour occlusion) and 65.6% (P=.001) in the PDT groups, regardless of the grade of AK lesion. The AFXL-PDT (2-hour occlusion) treatment was also superior to PDT alone (P=.038). These findings were sustained at 12-month follow-up (84.8% in the AFXL-PDT [3-hour occlusion] group [P<.001, compared to others]; 67.5% in the AFXL-PDT [2-hour occlusion] group [P<.001, compared to 3-hour PDT]; 51.1% in the PDT group). Importantly, the AK lesion recurrence rate was also lowest in the AFL-PDT (3-hour occlusion) group (7.5% vs 12.1% and 22.1% in the AFXL-PDT [2-hour occlusion] and PDT groups, respectively; P=.007).8
Combination therapy with AFXL and daylight PDT (dPDT) may improve the tolerability of PDT and the efficacy rate of field therapy in organ transplant recipients. One study demonstrated the superiority of this combination therapy in a population of 16 organ transplant recipients on immunosuppressants with at least 2 moderate to severely thick AKs in each of 4 comparable areas in the same anatomic region.9 The 4 areas were randomized to a single session of AFXL-dPDT, dPDT alone, conventional PDT, or AFXL alone. Ablation was performed with a fractional Er:YAG laser. The AFXL-dPDT and dPDT alone groups received MAL for 2.5 hours without occlusion, and the conventional PDT group received MAL for 3 hours with occlusion. Daylight exposure in dPDT groups was initiated 30 minutes after MAL application for 2 hours total. A baseline total of 542 AKs were treated. At 3-month follow-up, the complete response rate was highest for the AFXL-dPDT group (74%) compared to dPDT alone (46%; P=.0262), conventional PDT (50%; P=.042), and AFXL alone (5%; P=.004). Pain scores for AFXL–dPDT and dPDT alone were significantly lower than for conventional PDT and AFXL alone (P<.001).9
Nonablative Lasers
By heating the dermis to induce neogenesis without destruction, nonablative lasers offer superior healing times compared to their ablative counterparts. Multiple treatments with nonablative lasers may be necessary for maximal effect. Four nonablative laser devices have demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of multiple AKs10-14: (1) the Q-switched 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser, with or without a 532-nm potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) laser; (2) the 1540-nm fractional erbium glass laser; (3) the 1550-nm fractional erbium-doped fiber laser; and (4) the 1927-nm fractional thulium laser (Table 3).

In a proof-of-concept study of the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser with the 532-nm KTP laser, 1 treatment session induced full remission of AKs in 10 patients at follow-up day 20, although the investigator did not grade improvement on a numerical scale.10 In a study of the fractional Q-switched 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser alone, 6 patients with trace or mild AKs received 4 treatment sessions at approximately 2-week intervals.14 All but 1 patient (who had trace AKs) had no AKs at 3-month follow-up.
The efficacy of the 1540-nm fractional erbium glass laser was examined in 17 participants with investigator-rated moderate-to-severe AK involvement of the scalp and face.12 Participants were given 2 or 3 treatment sessions at 3- to 4-week intervals and were graded by blinded dermatologists on a quartile scale of 0 (no improvement), 1 (1%–25% improvement), 2 (26%–50% improvement), 3 (51%–75% improvement), or 4 (76%–100% improvement). At 3 months posttreatment, the average grade of improvement was 3.4.12
The 1550-nm fractional erbium-doped fiber laser was tested in 14 men with multiple facial AKs (range, 9–44 AKs [mean, 22.1 AKs]).11 Participants received 5 treatment sessions at 2- to 4-week intervals, with majority energies used at 70 MJ and treatment level 11. The mean AK count was reduced significantly by 73.1%, 66.2%, and 55.6% at 1-, 3-, and 6-month follow-up, respectively (P<.001).11
The 1927-nm fractional thulium laser showed promising results in 24 participants with facial AKs.13 Participants received up to 4 treatment sessions at intervals from 2 to 6 weeks at the investigators’ discretion. At baseline, patients had an average of 14.04 facial AKs. At 1-, 3-, and 6-month follow-up, participants exhibited 91.3%, 87.3%, and 86.6% reduction in AK counts, respectively. The mean AK count at 3-month follow-up was 1.88.13
Due to limited sample sizes and/or lack of quantifiable results and controls in these studies, more studies are needed to fully elucidate the role of nonablative lasers in the treatment of AK.
Future Directions
Iontophoresis involves the noninvasive induction of an electrical current to facilitate ion movement through the skin and may be a novel method to boost the efficacy of current field therapies. In the first known study of its kisnd, iontophoresis-assisted AFXL-PDT was found to be noninferior to conventional AFXL-PDT15; however, additional studies demonstrating its superiority are needed before more widespread clinical use is considered.
Pretreatment with AFXL prior to topical field-directed therapies also has been proposed.16 In a case series of 13 patients, combination therapy with AFXL and ingenol mebutate was shown to be superior to ingenol mebutate alone (AK clearance rate, 89.2% vs 72.1%, respectively; P<.001).16 Randomized studies with longer follow-up time are needed.
Conclusion
Ablative and nonablative laser systems have yielded limited data about their potential as monotherapies for treatment of multiple AKs and are unlikely to replace topical agents and PDT as a first-line modality in field-directed treatment at this time. More studies with a larger number of participants and long-term follow-up are needed for further clarification of efficacy, safety, and clinical feasibility. Nevertheless, fractional ablative lasers in combination with PDT have shown robust efficacy and a favorable safety profile for treatment of multiple AKs.6-9 Further, this combination therapy exhibited a superior clearance rate and lower lesion recurrence in organ transplant recipients—a demographic that classically is difficult to treat.6-9
With continued rapid evolution of laser systems and more widespread use in dermatology, monotherapy and combination therapy may offer a dynamic new option in field cancerization that can decrease disease burden and treatment frequency.
In cutaneous field cancerization, focal treatments such as cryotherapy are impractical, thus necessitating the use of field-directed therapies over the lesion and the surrounding skin field. Although evidence-based guidelines do not exist, field-directed therapy has been proposed in cases of 3 or more actinic keratoses (AKs) in a 25-cm2 area or larger.1 It can be further speculated that patients who are vulnerable to aggressive phenotypes of cutaneous malignancies, such as those with a genodermatosis or who are immunocompromised, necessitate a higher index of suspicion for field effect with even 1 or 2 AKs.
Current field-directed therapies include topical agents (imiquimod, fluorouracil, ingenol mebutate, and diclo-fenac), photodynamic therapy (PDT), and resurfacing procedures (lasers, chemical peels, dermabrasion). Although topical agents and PDT currently are gold standards in field treatment, the use of energy-based devices (ie, ablative and nonablative lasers) are attractive options as monotherapy or as part of a combination therapy. These devices are attractive options for field-directed therapy because they offer defined, customizable control of settings, allowing for optimal cosmesis and precision of therapy.
Principally, lasers function by damaging skin tissue to induce resurfacing, neocollagenesis, and vascular restructuring. Fractional versions of ablative and nonablative systems are available to target a fraction of the treatment area in evenly spaced microthermal zones and to minimize overall thermal damage.2
Given recent advances in laser systems and numerous investigations reported in the literature, a review of ablative and nonablative lasers that have been studied as treatment options for cutaneous field cancerization is provided, with a focus on treatment efficacy.
Ablative Lasers
Ablative lasers operate at higher wavelengths than nonablative lasers to destroy epidermal and dermal tissue. The 10,600-nm carbon dioxide (CO2) and 2940-nm Er:YAG lasers have been heavily investigated for field therapy for multiple AKs, both as monotherapies (Table 1) and in combination with PDT (Table 2).


Monotherapy
One randomized trial with 5-year follow-up compared the efficacy of full-face pulsed CO2 laser therapy, full-face trichloroacetic acid (TCA) peel 30%, and fluorouracil cream 5% (twice daily for 3 weeks) on AKs on the face and head.3 Thirty-one participants were randomized to the 3 treatment arms and a negative control arm. The mean AK counts at baseline for the CO2, TCA, and fluorouracil treatment groups were 78.0, 83.7, and 61.8, respectively. At 3-month follow-up, all treatment groups had significant reductions in the mean AK count from baseline (CO2 group, 92% [P=.03]; TCA group, 89% [P=.004]; fluorouracil group, 83% [P=.008]). No significant differences in efficacy among the treatment groups were noted. All 3 treatment groups had a demonstrably lower incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer over 5-year follow-up compared to the control group (P<.001).3
In contrast to these promising results, the pulsed CO2 laser showed only short-term efficacy in a split-face study of 12 participants with at least 5 facial or scalp AKs on each of 2 symmetric facial sides who were randomized to 1 treatment side.4 At 1-month follow-up, the treatment side exhibited significantly fewer AKs compared to the control side (47% vs 71% at baseline; P=.01), but the improvement was not sustained at 3-month follow-up (49% vs 57%; P=.47).4
In another study, the CO2 laser was found to be inferior to 5-aminolevulinic acid PDT.5 Twenty-one participants who had at least 4 AKs in each symmetric half of a body region (head, hands, forearms) were randomized to PDT on 1 side and CO2 laser therapy on the other. Median baseline AK counts for the PDT and CO2 laser groups were 6 and 8, respectively. Both treatment groups exhibited significant median AK reduction from baseline 4 weeks posttreatment (PDT group, 82.1% [P<.05], CO2 laser group, 100% [P<.05]); however. at 3 months posttreatment the PDT group had significantly higher absolute (P=.0155) and relative (P=.0362) reductions in AK count compared to the CO2 laser group. One participant received a topical antibiotic for superficial infection on the PDT treatment side.5
Many questions remain regarding the practical application of laser ablation monotherapy for multiple AKs. More studies are needed to determine the practicality and long-term clinical efficacy of these devices.
PDT Combination Therapy
Laser ablation may be combined with PDT to increase efficacy and prolong remission rates. In fact, laser ablation may be thought of as a physical drug-delivery system to boost uptake of topical agents—in this case, aminolevulinic acid and methyl aminolevulinate (MAL)—given that it disrupts the skin barrier.
In a comparative study of ablative fractional laser (AFXL)–assisted PDT and AFXL alone in 10 organ transplant recipients on immunosuppression with at least 5 AKs on each dorsal hand, participants were randomized to AFXL-PDT on one treatment side and PDT on the other side.6 Participants received AFXL in an initial lesion-directed pass and then a second field-directed pass of a fractional CO2 laser. After AFXL exposure, methyl aminolevulinate was applied to the AFXL-PDT treatment side, with 3-hour occlusion. A total of 680 AKs were treated (335 in the AFXL-PDT group, 345 in the PDT group); results were stratified by the clinical grade of the lesion (1, slightly palpable; 2, moderately thick; 3, very thick or obvious). At 4-month follow-up, the AFXL-PDT group had a significantly higher median complete response rate of 73% compared to 31% in the AFXL group (P=.002). Interestingly, AFXL-PDT was also significantly more efficacious compared to AFXL for grades 1 (80% vs 37%; P=.02) and 2 (53% vs 7%, P=.009) AKs but not grade 3 AKs (4% vs 0%, P=.17).6
The combination of fractional CO2 laser and PDT also demonstrated superiority to PDT.7 In a split-face investigation, 15 participants with bilateral symmetric areas of 2 to 10 AKs on the face or scalp were randomized to receive fractional CO2 laser and MAL-PDT combination therapy on 1 treatment side and conventional MAL-PDT on the other side.7 The AFXL-PDT treatment side received laser ablation with immediate subsequent application of MAL to both treatment sides under 3-hour occlusion. At baseline, 103 AKs were treated by AFXL-PDT and 109 AKs were treated with conventional PDT. At 3-month follow-up, the AFXL-PDT treatment group exhibited a significantly higher rate of complete response (90%) compared to the conventional PDT group (67%)(P=.0002).7
Like the CO2 laser, the Er:YAG laser has demonstrated superior results when used in combination with PDT to treat field cancerization compared to either treatment alone. In a comparison study, 93 patients with 2 to 10 AK lesions on the face or scalp were randomized to treatment with AFXL (Er:YAG laser) and MAL-PDT with 3-hour occlusion, AFXL (Er:YAG laser) and MAL-PDT with 2-hour occlusion, and MAL-PDT with 3-hour occlusion.8 A total of 440 baseline AK lesions on the face or scalp were treated. At 3-month follow-up, the AFXL-PDT (3-hour occlusion) group had the highest rate of complete response (91.7%), compared to 76.8% (P=.001) in the AFXL-PDT (2-hour occlusion) and 65.6% (P=.001) in the PDT groups, regardless of the grade of AK lesion. The AFXL-PDT (2-hour occlusion) treatment was also superior to PDT alone (P=.038). These findings were sustained at 12-month follow-up (84.8% in the AFXL-PDT [3-hour occlusion] group [P<.001, compared to others]; 67.5% in the AFXL-PDT [2-hour occlusion] group [P<.001, compared to 3-hour PDT]; 51.1% in the PDT group). Importantly, the AK lesion recurrence rate was also lowest in the AFL-PDT (3-hour occlusion) group (7.5% vs 12.1% and 22.1% in the AFXL-PDT [2-hour occlusion] and PDT groups, respectively; P=.007).8
Combination therapy with AFXL and daylight PDT (dPDT) may improve the tolerability of PDT and the efficacy rate of field therapy in organ transplant recipients. One study demonstrated the superiority of this combination therapy in a population of 16 organ transplant recipients on immunosuppressants with at least 2 moderate to severely thick AKs in each of 4 comparable areas in the same anatomic region.9 The 4 areas were randomized to a single session of AFXL-dPDT, dPDT alone, conventional PDT, or AFXL alone. Ablation was performed with a fractional Er:YAG laser. The AFXL-dPDT and dPDT alone groups received MAL for 2.5 hours without occlusion, and the conventional PDT group received MAL for 3 hours with occlusion. Daylight exposure in dPDT groups was initiated 30 minutes after MAL application for 2 hours total. A baseline total of 542 AKs were treated. At 3-month follow-up, the complete response rate was highest for the AFXL-dPDT group (74%) compared to dPDT alone (46%; P=.0262), conventional PDT (50%; P=.042), and AFXL alone (5%; P=.004). Pain scores for AFXL–dPDT and dPDT alone were significantly lower than for conventional PDT and AFXL alone (P<.001).9
Nonablative Lasers
By heating the dermis to induce neogenesis without destruction, nonablative lasers offer superior healing times compared to their ablative counterparts. Multiple treatments with nonablative lasers may be necessary for maximal effect. Four nonablative laser devices have demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of multiple AKs10-14: (1) the Q-switched 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser, with or without a 532-nm potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) laser; (2) the 1540-nm fractional erbium glass laser; (3) the 1550-nm fractional erbium-doped fiber laser; and (4) the 1927-nm fractional thulium laser (Table 3).

In a proof-of-concept study of the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser with the 532-nm KTP laser, 1 treatment session induced full remission of AKs in 10 patients at follow-up day 20, although the investigator did not grade improvement on a numerical scale.10 In a study of the fractional Q-switched 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser alone, 6 patients with trace or mild AKs received 4 treatment sessions at approximately 2-week intervals.14 All but 1 patient (who had trace AKs) had no AKs at 3-month follow-up.
The efficacy of the 1540-nm fractional erbium glass laser was examined in 17 participants with investigator-rated moderate-to-severe AK involvement of the scalp and face.12 Participants were given 2 or 3 treatment sessions at 3- to 4-week intervals and were graded by blinded dermatologists on a quartile scale of 0 (no improvement), 1 (1%–25% improvement), 2 (26%–50% improvement), 3 (51%–75% improvement), or 4 (76%–100% improvement). At 3 months posttreatment, the average grade of improvement was 3.4.12
The 1550-nm fractional erbium-doped fiber laser was tested in 14 men with multiple facial AKs (range, 9–44 AKs [mean, 22.1 AKs]).11 Participants received 5 treatment sessions at 2- to 4-week intervals, with majority energies used at 70 MJ and treatment level 11. The mean AK count was reduced significantly by 73.1%, 66.2%, and 55.6% at 1-, 3-, and 6-month follow-up, respectively (P<.001).11
The 1927-nm fractional thulium laser showed promising results in 24 participants with facial AKs.13 Participants received up to 4 treatment sessions at intervals from 2 to 6 weeks at the investigators’ discretion. At baseline, patients had an average of 14.04 facial AKs. At 1-, 3-, and 6-month follow-up, participants exhibited 91.3%, 87.3%, and 86.6% reduction in AK counts, respectively. The mean AK count at 3-month follow-up was 1.88.13
Due to limited sample sizes and/or lack of quantifiable results and controls in these studies, more studies are needed to fully elucidate the role of nonablative lasers in the treatment of AK.
Future Directions
Iontophoresis involves the noninvasive induction of an electrical current to facilitate ion movement through the skin and may be a novel method to boost the efficacy of current field therapies. In the first known study of its kisnd, iontophoresis-assisted AFXL-PDT was found to be noninferior to conventional AFXL-PDT15; however, additional studies demonstrating its superiority are needed before more widespread clinical use is considered.
Pretreatment with AFXL prior to topical field-directed therapies also has been proposed.16 In a case series of 13 patients, combination therapy with AFXL and ingenol mebutate was shown to be superior to ingenol mebutate alone (AK clearance rate, 89.2% vs 72.1%, respectively; P<.001).16 Randomized studies with longer follow-up time are needed.
Conclusion
Ablative and nonablative laser systems have yielded limited data about their potential as monotherapies for treatment of multiple AKs and are unlikely to replace topical agents and PDT as a first-line modality in field-directed treatment at this time. More studies with a larger number of participants and long-term follow-up are needed for further clarification of efficacy, safety, and clinical feasibility. Nevertheless, fractional ablative lasers in combination with PDT have shown robust efficacy and a favorable safety profile for treatment of multiple AKs.6-9 Further, this combination therapy exhibited a superior clearance rate and lower lesion recurrence in organ transplant recipients—a demographic that classically is difficult to treat.6-9
With continued rapid evolution of laser systems and more widespread use in dermatology, monotherapy and combination therapy may offer a dynamic new option in field cancerization that can decrease disease burden and treatment frequency.
- Peris K, Calzavara-Pinton PG, Neri L, et al. Italian expert consensus for the management of actinic keratosis in immunocompetent patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:1077-1084.
- Alexiades-Armenakas MR, Dover JS, Arndt KA. The spectrum of laser skin resurfacing: nonablative, fractional, and ablative laser resurfacing. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:719-737; quiz 738-740.
- Hantash BM, Stewart DB, Cooper ZA, et al. Facial resurfacing for nonmelanoma skin cancer prophylaxis. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:976-982.
- Gan SD, Hsu SH, Chuang G, et al. Ablative fractional laser therapy for the treatment of actinic keratosis: a split-face study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:387-389.
- Scola N, Terras S, Georgas D, et al. A randomized, half-side comparative study of aminolaevulinate photodynamic therapy vs. CO(2) laser ablation in immunocompetent patients with multiple actinic keratoses. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1366-1373.
- Helsing P, Togsverd-Bo K, Veierod MB, et al. Intensified fractional CO2 laser-assisted photodynamic therapy vs. laser alone for organ transplant recipients with multiple actinic keratoses and wart-like lesions: a randomized half-side comparative trial on dorsal hands. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:1087-1092.
- Togsverd-Bo K, Haak CS, Thaysen-Petersen D, et al. Intensified photodynamic therapy of actinic keratoses with fractional CO2 laser: a randomized clinical trial. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1262-1269.
- Choi SH, Kim KH, Song KH. Efficacy of ablative fractional laser-assisted photodynamic therapy with short-incubation time for the treatment of facial and scalp actinic keratosis: 12-month follow-up results of a randomized, prospective, comparative trial. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1598-1605.
- Togsverd-Bo K, Lei U, Erlendsson AM, et al. Combination of ablative fractional laser and daylight-mediated photodynamic therapy for actinic keratosis in organ transplant recipients—a randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2015;172:467-474.
- Demetriou C. Reversing precancerous actinic damage by mixing wavelengths (1064 nm, 532 nm). J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2011;13:113-119.
- Katz TM, Goldberg LH, Marquez D, et al. Nonablative fractional photothermolysis for facial actinic keratoses: 6-month follow-up with histologic evaluation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:349-356.
- Lapidoth M, Adatto M, Halachmi S. Treatment of actinic keratoses and photodamage with non-contact fractional 1540-nm laser quasi-ablation: an ex vivo and clinical evaluation. Lasers Med Sci. 2013;28:537-542.
- Weiss ET, Brauer JA, Anolik R, et al. 1927-nm fractional resurfacing of facial actinic keratoses: a promising new therapeutic option. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:98-102.
- Gold MH, Sensing W, Biron J. Fractional Q-switched 1,064-nm laser for the treatment of photoaged-photodamaged skin. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2014;16:69-76.
- Choi SH, Kim TH, Song KH. Efficacy of iontophoresis-assisted ablative fractional laser photodynamic therapy with short incubation time for the treatment of actinic keratosis: 12-month follow-up results of a prospective, randomised, comparative trial. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2017;18:105-110.
- Nisticò S, Sannino M, Del Duca E, et al. Ablative fractional laser improves treatment of actinic keratoses with ingenol mebutate. Eur J Inflamm. 2016;14:200-205.
- Peris K, Calzavara-Pinton PG, Neri L, et al. Italian expert consensus for the management of actinic keratosis in immunocompetent patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:1077-1084.
- Alexiades-Armenakas MR, Dover JS, Arndt KA. The spectrum of laser skin resurfacing: nonablative, fractional, and ablative laser resurfacing. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:719-737; quiz 738-740.
- Hantash BM, Stewart DB, Cooper ZA, et al. Facial resurfacing for nonmelanoma skin cancer prophylaxis. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:976-982.
- Gan SD, Hsu SH, Chuang G, et al. Ablative fractional laser therapy for the treatment of actinic keratosis: a split-face study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:387-389.
- Scola N, Terras S, Georgas D, et al. A randomized, half-side comparative study of aminolaevulinate photodynamic therapy vs. CO(2) laser ablation in immunocompetent patients with multiple actinic keratoses. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1366-1373.
- Helsing P, Togsverd-Bo K, Veierod MB, et al. Intensified fractional CO2 laser-assisted photodynamic therapy vs. laser alone for organ transplant recipients with multiple actinic keratoses and wart-like lesions: a randomized half-side comparative trial on dorsal hands. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:1087-1092.
- Togsverd-Bo K, Haak CS, Thaysen-Petersen D, et al. Intensified photodynamic therapy of actinic keratoses with fractional CO2 laser: a randomized clinical trial. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1262-1269.
- Choi SH, Kim KH, Song KH. Efficacy of ablative fractional laser-assisted photodynamic therapy with short-incubation time for the treatment of facial and scalp actinic keratosis: 12-month follow-up results of a randomized, prospective, comparative trial. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1598-1605.
- Togsverd-Bo K, Lei U, Erlendsson AM, et al. Combination of ablative fractional laser and daylight-mediated photodynamic therapy for actinic keratosis in organ transplant recipients—a randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2015;172:467-474.
- Demetriou C. Reversing precancerous actinic damage by mixing wavelengths (1064 nm, 532 nm). J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2011;13:113-119.
- Katz TM, Goldberg LH, Marquez D, et al. Nonablative fractional photothermolysis for facial actinic keratoses: 6-month follow-up with histologic evaluation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:349-356.
- Lapidoth M, Adatto M, Halachmi S. Treatment of actinic keratoses and photodamage with non-contact fractional 1540-nm laser quasi-ablation: an ex vivo and clinical evaluation. Lasers Med Sci. 2013;28:537-542.
- Weiss ET, Brauer JA, Anolik R, et al. 1927-nm fractional resurfacing of facial actinic keratoses: a promising new therapeutic option. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:98-102.
- Gold MH, Sensing W, Biron J. Fractional Q-switched 1,064-nm laser for the treatment of photoaged-photodamaged skin. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2014;16:69-76.
- Choi SH, Kim TH, Song KH. Efficacy of iontophoresis-assisted ablative fractional laser photodynamic therapy with short incubation time for the treatment of actinic keratosis: 12-month follow-up results of a prospective, randomised, comparative trial. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2017;18:105-110.
- Nisticò S, Sannino M, Del Duca E, et al. Ablative fractional laser improves treatment of actinic keratoses with ingenol mebutate. Eur J Inflamm. 2016;14:200-205.
Practice Points
- Ablative fractional laser therapy in combination with photodynamic therapy has demonstrated increased efficacy in treating field actinic keratoses (AKs) for up to 12 months of follow-up over either modality alone.
- Ablative and nonablative lasers as monotherapy in treating field AKs require further studies with larger sample sizes to determine efficacy and safety.
Treatment of basal cell carcinoma with 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser promising
DALLAS – One year after patients underwent treatment of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) with the 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser, no recurrences have occurred, according to early results from a study being conducted at two centers.
“ Arisa E. Ortiz, MD, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “Clearance rates are comparable to or better than other topical modalities such as electrodesiccation and curettage and topical imiquimod. It’s a reasonable alternative for treatment patients with multiple tumors or those who are poor surgical candidates.”
In an ongoing study, she and Mathew M. Avram, MD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser & Cosmetic Center, Boston, have treated 19 superficial, nodular, and pigmented BCC tumors in 11 patients 31-85 years of age. Tumor sizes ranged from 3 mm x 3 mm to 21 mm x 11 mm. Indications for laser treatment have included being a poor surgical candidate (one patient had a history of bleeding complications), having multiple tumors (one patient had Curry-Jones syndrome) – or simply wishing to not undergo surgery. “They didn’t want a surgical scar, or they didn’t want to limit their activity after surgery,” Dr. Ortiz said.
Patients underwent one 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser treatment. The anesthesia was 0.5% lidocaine with no epinephrine. Treatment settings were a 5-mm spot size delivered at a fluence of 140 J/cm2 in a pulse duration of 7-8 milliseconds. The number of pulses ranged from 14 to 36. The immediate endpoint was slight graying and slight contraction. “When you’re using the 1064-nm Nd:YAG for cosmetic purposes, you don’t want to see these endpoints, but we are treating skin cancer, so you do want to see some contraction and graying,” she said. The procedure was covered under insurance and billed as malignant destruction (CPT codes 17260-17266 and 17280-17283).
Dr. Ortiz reported that there have been no recurrences in the 11 patients at 1-year follow-up as determined by clinical observation. “There are many advantages to laser treatment of basal cell carcinoma,” she concluded. “There’s only one treatment visit, so you don’t have to come back for suture removal, and it’s a very quick treatment. There’s no significant downtime or limitation on activities, and there’s minimal wound care – just ointment and a Band-Aid – and relatively decreased risk for complications such as infection or bleeding, and minimal to no scar.”
“Laser surgery also provides precision that ordinary surgical techniques cannot match. Despite the obvious obstacles, there is no reason such surgical techniques cannot be expanded someday to other internal cutaneous tumors, including GI tumors. To some extent this is happening already. Vascular lasers are being used to treat a bleeding disorder of the colon known as angiodysplasia. Cautious exploration of laser- and light-based treatments should be further explored as a means of sparing tissue and surgical morbidity.”
Dr. Ortiz disclosed that she has received grant funding from Sienna and Revance, as well as equipment from BTL, Invasix, and Sciton. She has received consulting fees from Alastin, Merz, and Sciton; honoraria from Alastin, Cutera, Invasix, and Sciton; and she holds ownership interest with Allergan. She also has served on the advisory boards for Alastin, Allergan, Invasix, Rodan + Fields, Sciton, Sienna, and Merz.
Dr. Avram disclosed that he serves on the medical advisory board of Sciton and on the scientific advisory boards of Sienna Biopharmaceuticals, Cytrellis, and Allergan. He is also a consultant for Merz Aesthetics, Allergan, Soliton, Invasix, and Revance and has intellectual property with Cytrellis. He also holds stock options with Cytrellis, Invasix, and Zalea.
DALLAS – One year after patients underwent treatment of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) with the 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser, no recurrences have occurred, according to early results from a study being conducted at two centers.
“ Arisa E. Ortiz, MD, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “Clearance rates are comparable to or better than other topical modalities such as electrodesiccation and curettage and topical imiquimod. It’s a reasonable alternative for treatment patients with multiple tumors or those who are poor surgical candidates.”
In an ongoing study, she and Mathew M. Avram, MD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser & Cosmetic Center, Boston, have treated 19 superficial, nodular, and pigmented BCC tumors in 11 patients 31-85 years of age. Tumor sizes ranged from 3 mm x 3 mm to 21 mm x 11 mm. Indications for laser treatment have included being a poor surgical candidate (one patient had a history of bleeding complications), having multiple tumors (one patient had Curry-Jones syndrome) – or simply wishing to not undergo surgery. “They didn’t want a surgical scar, or they didn’t want to limit their activity after surgery,” Dr. Ortiz said.
Patients underwent one 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser treatment. The anesthesia was 0.5% lidocaine with no epinephrine. Treatment settings were a 5-mm spot size delivered at a fluence of 140 J/cm2 in a pulse duration of 7-8 milliseconds. The number of pulses ranged from 14 to 36. The immediate endpoint was slight graying and slight contraction. “When you’re using the 1064-nm Nd:YAG for cosmetic purposes, you don’t want to see these endpoints, but we are treating skin cancer, so you do want to see some contraction and graying,” she said. The procedure was covered under insurance and billed as malignant destruction (CPT codes 17260-17266 and 17280-17283).
Dr. Ortiz reported that there have been no recurrences in the 11 patients at 1-year follow-up as determined by clinical observation. “There are many advantages to laser treatment of basal cell carcinoma,” she concluded. “There’s only one treatment visit, so you don’t have to come back for suture removal, and it’s a very quick treatment. There’s no significant downtime or limitation on activities, and there’s minimal wound care – just ointment and a Band-Aid – and relatively decreased risk for complications such as infection or bleeding, and minimal to no scar.”
“Laser surgery also provides precision that ordinary surgical techniques cannot match. Despite the obvious obstacles, there is no reason such surgical techniques cannot be expanded someday to other internal cutaneous tumors, including GI tumors. To some extent this is happening already. Vascular lasers are being used to treat a bleeding disorder of the colon known as angiodysplasia. Cautious exploration of laser- and light-based treatments should be further explored as a means of sparing tissue and surgical morbidity.”
Dr. Ortiz disclosed that she has received grant funding from Sienna and Revance, as well as equipment from BTL, Invasix, and Sciton. She has received consulting fees from Alastin, Merz, and Sciton; honoraria from Alastin, Cutera, Invasix, and Sciton; and she holds ownership interest with Allergan. She also has served on the advisory boards for Alastin, Allergan, Invasix, Rodan + Fields, Sciton, Sienna, and Merz.
Dr. Avram disclosed that he serves on the medical advisory board of Sciton and on the scientific advisory boards of Sienna Biopharmaceuticals, Cytrellis, and Allergan. He is also a consultant for Merz Aesthetics, Allergan, Soliton, Invasix, and Revance and has intellectual property with Cytrellis. He also holds stock options with Cytrellis, Invasix, and Zalea.
DALLAS – One year after patients underwent treatment of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) with the 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser, no recurrences have occurred, according to early results from a study being conducted at two centers.
“ Arisa E. Ortiz, MD, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “Clearance rates are comparable to or better than other topical modalities such as electrodesiccation and curettage and topical imiquimod. It’s a reasonable alternative for treatment patients with multiple tumors or those who are poor surgical candidates.”
In an ongoing study, she and Mathew M. Avram, MD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser & Cosmetic Center, Boston, have treated 19 superficial, nodular, and pigmented BCC tumors in 11 patients 31-85 years of age. Tumor sizes ranged from 3 mm x 3 mm to 21 mm x 11 mm. Indications for laser treatment have included being a poor surgical candidate (one patient had a history of bleeding complications), having multiple tumors (one patient had Curry-Jones syndrome) – or simply wishing to not undergo surgery. “They didn’t want a surgical scar, or they didn’t want to limit their activity after surgery,” Dr. Ortiz said.
Patients underwent one 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser treatment. The anesthesia was 0.5% lidocaine with no epinephrine. Treatment settings were a 5-mm spot size delivered at a fluence of 140 J/cm2 in a pulse duration of 7-8 milliseconds. The number of pulses ranged from 14 to 36. The immediate endpoint was slight graying and slight contraction. “When you’re using the 1064-nm Nd:YAG for cosmetic purposes, you don’t want to see these endpoints, but we are treating skin cancer, so you do want to see some contraction and graying,” she said. The procedure was covered under insurance and billed as malignant destruction (CPT codes 17260-17266 and 17280-17283).
Dr. Ortiz reported that there have been no recurrences in the 11 patients at 1-year follow-up as determined by clinical observation. “There are many advantages to laser treatment of basal cell carcinoma,” she concluded. “There’s only one treatment visit, so you don’t have to come back for suture removal, and it’s a very quick treatment. There’s no significant downtime or limitation on activities, and there’s minimal wound care – just ointment and a Band-Aid – and relatively decreased risk for complications such as infection or bleeding, and minimal to no scar.”
“Laser surgery also provides precision that ordinary surgical techniques cannot match. Despite the obvious obstacles, there is no reason such surgical techniques cannot be expanded someday to other internal cutaneous tumors, including GI tumors. To some extent this is happening already. Vascular lasers are being used to treat a bleeding disorder of the colon known as angiodysplasia. Cautious exploration of laser- and light-based treatments should be further explored as a means of sparing tissue and surgical morbidity.”
Dr. Ortiz disclosed that she has received grant funding from Sienna and Revance, as well as equipment from BTL, Invasix, and Sciton. She has received consulting fees from Alastin, Merz, and Sciton; honoraria from Alastin, Cutera, Invasix, and Sciton; and she holds ownership interest with Allergan. She also has served on the advisory boards for Alastin, Allergan, Invasix, Rodan + Fields, Sciton, Sienna, and Merz.
Dr. Avram disclosed that he serves on the medical advisory board of Sciton and on the scientific advisory boards of Sienna Biopharmaceuticals, Cytrellis, and Allergan. He is also a consultant for Merz Aesthetics, Allergan, Soliton, Invasix, and Revance and has intellectual property with Cytrellis. He also holds stock options with Cytrellis, Invasix, and Zalea.
REPORTING FROM ASLMS 2018
Key clinical point: Clinicians can noninvasively treat certain basal cell carcinoma tumor subtypes with the 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser.
Major finding: After 1 year of follow-up, no recurrences of basal cell carcinoma have occurred.
Study details: A 1-year follow-up study of 19 BCC tumors in 11 patients 31 to 85 years of age who were treated with the 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser.
Disclosures: Dr. Ortiz disclosed that she has received grant funding from Sienna and Revance, as well as equipment from BTL, Invasix, and Sciton. She has received consulting fees from Alastin, Merz, and Sciton; honoraria from Alastin, Cutera, Invasix, and Sciton; and she holds ownership interest with Allergan. She also has served on the advisory boards for Alastin, Allergan, Invasix, Rodan + Fields, Sciton, Sienna, and Merz.
Dr. Avram disclosed that he serves on the medical advisory board of Sciton and on the scientific advisory boards of Sienna Biopharmaceuticals, Cytrellis, and Allergan. He is also a consultant for Merz Aesthetics, Allergan, Soliton, Invasix, and Revance and has intellectual property with Cytrellis. He also holds stock options with Cytrellis, Invasix, and Zalea.
Hepatic adenoma assessment: Wait longer to avoid overtreatment?
LAS VEGAS – For women with larger hepatic adenomas, current guidelines suggest reassessment at 6 months after oral contraceptive withdrawal to determine whether resection is warranted.
However, emerging data show reassessing at that time point may lead to overtreatment, according to Laura M. Kulik, MD, professor of medicine (gastroenterology and hepatology), radiology and surgery (organ transplantation), Northwestern University, Chicago.
“There’s been some controversy that 6 months may be too short,” Dr. Kulik said at the inaugural Perspectives in Digestive Diseases meeting held by Global Academy for Medical Education.
Unlike other benign liver lesions, hepatic adenomas can hemorrhage and transform to hepatocellular carcinoma. Current guidelines from the European Association for the Study of the Liver state that larger lesions (i.e., 5 cm or greater on baseline imaging) are associated with a higher risk of complications. According to one systematic review cited in the document, almost all cases of hemorrhage or spontaneous rupture occur in lesions 5 cm or larger.
Oral contraceptive use has been associated with a 30- to 40-fold increase in hepatic adenoma incidence, according to the guidelines.
All men with hepatic adenomas should undergo resection or curative treatment, the guidelines say, since they have a significantly higher risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.
By contrast, women with hepatic adenomas larger than 5 cm should discontinue oral contraceptives – which may lead to tumor regression in some cases – and should be reassessed 6 months later with contrast-enhanced MRI; if the lesion is still greater than 5 cm at that time, they should be considered for resection or curative treatment, the guidelines say.
However, authors of a retrospective cohort study have challenged that advice, suggesting that a 6-month follow-up may not always be long enough to see adequate tumor regression (HPB 2017 Apr;19[Suppl 1]:S3).
In the study, researchers from Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, reviewed records for patients who were diagnosed with a hepatic adenoma of at least 5 cm and followed for at least 6 months after oral contraceptives were stopped.
Of that group, 104 underwent surgical treatment for a lesion larger than 5 cm, while the remaining 86 were conservatively treated.
The researchers found that in the conservatively treated group, 61 lesions (71%) regressed below the 5-cm cutoff after a median of 85 weeks (95% confidence interval, 52-110 weeks), with larger lesions taking significantly longer to regress.
Based on those findings, the investigators said the 6-month cutoff may lead to overtreatment, and that for some patients with particularly large tumors, it may be justified to wait up to 24 months.
“The study does suggest that, potentially, 6 months may be too short,” Dr. Kulik told attendees at the meeting. “They do caution that beta-catenin mutated adenomas should probably be removed without waiting longer because of the risk of developing cancer.”
Dr. Kulik reported disclosures related to Bayer, BMS, BTG, and Eisai. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – For women with larger hepatic adenomas, current guidelines suggest reassessment at 6 months after oral contraceptive withdrawal to determine whether resection is warranted.
However, emerging data show reassessing at that time point may lead to overtreatment, according to Laura M. Kulik, MD, professor of medicine (gastroenterology and hepatology), radiology and surgery (organ transplantation), Northwestern University, Chicago.
“There’s been some controversy that 6 months may be too short,” Dr. Kulik said at the inaugural Perspectives in Digestive Diseases meeting held by Global Academy for Medical Education.
Unlike other benign liver lesions, hepatic adenomas can hemorrhage and transform to hepatocellular carcinoma. Current guidelines from the European Association for the Study of the Liver state that larger lesions (i.e., 5 cm or greater on baseline imaging) are associated with a higher risk of complications. According to one systematic review cited in the document, almost all cases of hemorrhage or spontaneous rupture occur in lesions 5 cm or larger.
Oral contraceptive use has been associated with a 30- to 40-fold increase in hepatic adenoma incidence, according to the guidelines.
All men with hepatic adenomas should undergo resection or curative treatment, the guidelines say, since they have a significantly higher risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.
By contrast, women with hepatic adenomas larger than 5 cm should discontinue oral contraceptives – which may lead to tumor regression in some cases – and should be reassessed 6 months later with contrast-enhanced MRI; if the lesion is still greater than 5 cm at that time, they should be considered for resection or curative treatment, the guidelines say.
However, authors of a retrospective cohort study have challenged that advice, suggesting that a 6-month follow-up may not always be long enough to see adequate tumor regression (HPB 2017 Apr;19[Suppl 1]:S3).
In the study, researchers from Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, reviewed records for patients who were diagnosed with a hepatic adenoma of at least 5 cm and followed for at least 6 months after oral contraceptives were stopped.
Of that group, 104 underwent surgical treatment for a lesion larger than 5 cm, while the remaining 86 were conservatively treated.
The researchers found that in the conservatively treated group, 61 lesions (71%) regressed below the 5-cm cutoff after a median of 85 weeks (95% confidence interval, 52-110 weeks), with larger lesions taking significantly longer to regress.
Based on those findings, the investigators said the 6-month cutoff may lead to overtreatment, and that for some patients with particularly large tumors, it may be justified to wait up to 24 months.
“The study does suggest that, potentially, 6 months may be too short,” Dr. Kulik told attendees at the meeting. “They do caution that beta-catenin mutated adenomas should probably be removed without waiting longer because of the risk of developing cancer.”
Dr. Kulik reported disclosures related to Bayer, BMS, BTG, and Eisai. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – For women with larger hepatic adenomas, current guidelines suggest reassessment at 6 months after oral contraceptive withdrawal to determine whether resection is warranted.
However, emerging data show reassessing at that time point may lead to overtreatment, according to Laura M. Kulik, MD, professor of medicine (gastroenterology and hepatology), radiology and surgery (organ transplantation), Northwestern University, Chicago.
“There’s been some controversy that 6 months may be too short,” Dr. Kulik said at the inaugural Perspectives in Digestive Diseases meeting held by Global Academy for Medical Education.
Unlike other benign liver lesions, hepatic adenomas can hemorrhage and transform to hepatocellular carcinoma. Current guidelines from the European Association for the Study of the Liver state that larger lesions (i.e., 5 cm or greater on baseline imaging) are associated with a higher risk of complications. According to one systematic review cited in the document, almost all cases of hemorrhage or spontaneous rupture occur in lesions 5 cm or larger.
Oral contraceptive use has been associated with a 30- to 40-fold increase in hepatic adenoma incidence, according to the guidelines.
All men with hepatic adenomas should undergo resection or curative treatment, the guidelines say, since they have a significantly higher risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.
By contrast, women with hepatic adenomas larger than 5 cm should discontinue oral contraceptives – which may lead to tumor regression in some cases – and should be reassessed 6 months later with contrast-enhanced MRI; if the lesion is still greater than 5 cm at that time, they should be considered for resection or curative treatment, the guidelines say.
However, authors of a retrospective cohort study have challenged that advice, suggesting that a 6-month follow-up may not always be long enough to see adequate tumor regression (HPB 2017 Apr;19[Suppl 1]:S3).
In the study, researchers from Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, reviewed records for patients who were diagnosed with a hepatic adenoma of at least 5 cm and followed for at least 6 months after oral contraceptives were stopped.
Of that group, 104 underwent surgical treatment for a lesion larger than 5 cm, while the remaining 86 were conservatively treated.
The researchers found that in the conservatively treated group, 61 lesions (71%) regressed below the 5-cm cutoff after a median of 85 weeks (95% confidence interval, 52-110 weeks), with larger lesions taking significantly longer to regress.
Based on those findings, the investigators said the 6-month cutoff may lead to overtreatment, and that for some patients with particularly large tumors, it may be justified to wait up to 24 months.
“The study does suggest that, potentially, 6 months may be too short,” Dr. Kulik told attendees at the meeting. “They do caution that beta-catenin mutated adenomas should probably be removed without waiting longer because of the risk of developing cancer.”
Dr. Kulik reported disclosures related to Bayer, BMS, BTG, and Eisai. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM PERSPECTIVES IN DIGESTIVE DISEASES
Enhanced Melanoma Diagnosis With Multispectral Digital Skin Lesion Analysis
Early detection of melanoma, which is known to improve survival rates, remains a challenge for dermatologists. Suspicious pigmented lesions typically are evaluated via clinical examination and dermoscopy; however, new technologies are being developed to provide additional objective information for clinicians to incorporate into their biopsy decisions.
Multispectral digital skin lesion analysis (MSDSLA) uses 10 bands of visible and near-infrared light (430–950 nm) to image and analyze pigmented skin lesions (PSLs) down to 2.5 mm below the skin surface and measures the distribution of melanin using 75 unique algorithms to determine the degree of the morphologic disorder. Using a logical regression model previously validated on a set of 1632 PSLs, the probability of melanoma and probability of being a melanoma/PSL of high-risk malignant potential are then provided to the clinician.1
In this study, we analyzed aggregate data from 7 prior studies2-8 to better determine how MSDSLA impacts the biopsy decisions of dermatologists and nondermatologists following clinical examination and dermoscopic evaluation of PSLs.
Methods
Results
Overall sensitivity for the detection of melanoma or other high-grade PSLs improved from 70% on clinical and dermoscopic evaluation to 88% after MSDSLA information was provided (P<.0001), and specificity increased from 52% to 58% (P<.001). Diagnostic accuracy also improved from 59% on clinical evaluation to 69% after review of MSDSLA findings (P<.0001). The positive predictive value of biopsy decisions was 47% following clinical evaluation, which improved to 56% after evaluation of MSDSLA findings (P<.001), and the negative predictive value increased from 74% to 89% (P<.0001). The overall percentage of lesions selected for biopsy did not significantly change following MSDSLA data integration (57% vs 60%)(Figure). Given that similar numbers of lesions were biopsied with improved sensitivity and specificity, the integration of MSDSLA data into the biopsy decision led to an improved biopsy ratio (ratio of melanomas biopsied to total biopsies) and fewer unnecessary biopsies.
Comment
Our broad analysis further supported the findings of prior studies that decisions to biopsy clinically suspicious PSLs are more sensitive, specific, and accurate when practitioners are provided MSDSLA information following clinical examination.2-8
Given the evolution in health care economics, it is clear that greater emphasis will continue to be placed on superior, evidence-based, effective care. The reported diagnostic sensitivities and specificities of clinical evaluation and dermoscopy for melanoma detection vary widely throughout the literature, with sensitivities ranging from 58% to over 90% and specificities ranging from 77% to 99%.9-11
Our study had several limitations. For this analysis to be more representative of lesion biopsy selection in the clinical setting, biopsy sensitivity (correctly identifying lesions appropriate for biopsy) vs melanoma sensitivity (identifying a lesion as melanoma) was used.13 The overall sensitivity found was within the range of prior studies,2-8 but this approach may have potentially led to a lower specificity due to an increased number of lesions biopsied. Additionally, the melanomas selected for these studies were early (malignant melanoma in situ or mean thickness of invasive malignant melanoma of 0.3 mm), and the nonmelanomas (including low-grade dysplastic nevi) were not necessarily diagnostically straightforward. This may have led to the clinical and dermoscopic sensitivity and specificity noted being lower than in some prior studies.9-11
The risk of missing a melanoma with MSDSLA devices has led manufacturers to strive for a high sensitivity for their devices, leading to lower specificity as a consequence. For this reason and other ambiguous practical considerations (eg, device and patient costs, difficulty with insurance reimbursement), the adoption of this technology into routine clinical practice has remained relatively static; however, using enhanced diagnostic technologies such as MSDSLA may help with more accurate identification of high-risk PSLs, thereby leading to earlier detection and overall less expensive, more cost-effective treatment of melanoma.
- Monheit G, Cognetta AB, Ferris L, et al. The performance of MelaFind: a prospective multicenter study. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:188-194.
- Rigel DS, Roy M, Yoo J, et al. Impact of guidance from a computer-aided multispectral digital skin lesion analysis device on decision to biopsy lesions clinically suggestive of melanoma. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:541-543.
- Yoo J, Rigel DS, Roy M, et al. Impact of guidance from a multispectral digital skin lesion analysis device on dermatology residents decisions to biopsy lesions clinically suggestive of melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:AB152.
- Winkelmann RR, Yoo J, Tucker N, et al. Impact of guidance provided by a multispectral digital skin lesion analysis device following dermoscopy on decisions to biopsy atypical melanocytic lesions. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2015;8:21-24.
- Winkelmann RR, Hauschild A, Tucker N, et al. The impact of multispectral digital skin lesion analysis on German dermatologist decisions to biopsy atypical pigmented lesions with clinical characteristics of melanoma. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2015;8:27-29.
- Winkelmann RR, Tucker N, White R, et al. Pigmented skin lesion biopsies after computer-aided multispectral digital skin lesion analysis. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2015;115:666-669.
- Winkelmann RR, Farberg AS, Tucker N, et al. Enhancement of international dermatologists’ pigmented skin lesion biopsy decisions following dermoscopy with subsequent integration of multispectral digital skin lesion analysis [published online July 1, 2016]. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2016;9:53-55.
- Farberg AS, Winkelmann RR, Tucker N, et al. The impact of quantitative data provided by a multi-spectral digital skin lesion analysis device on dermatologists’ decisions to biopsy pigmented lesions [published online September 1, 2017]. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2017;10:24-26.
- Wolf IH, Smolle J, Soyer HP, et al. Sensitivity in the clinical diagnosis of malignant melanoma. Melanoma Res. 1998;8:425-429.
- Kittler H, Pehamberger H, Wolff K, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy. Lancet Oncol. 2002;3:159-165.
- Ascierto PA, Palmieri G, Celentano E, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of epiluminescence microscopy: evaluation on a sample of 2731 excised cutaneous pigmented lesions: the Melanoma Cooperative Study. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:893-898.
- Carli P, Nardini P, Crocetti E, et al. Frequency and characteristics of melanomas missed at a pigmented lesion clinic: a registry-based study. Melanoma Res. 2004;14:403-407.
- Friedman RJ, Gutkowicz-Krusin D, Farber MJ, et al. The diagnostic performance of expert dermoscopists vs a computer-vision system on small-diameter melanomas. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:476-482.
Early detection of melanoma, which is known to improve survival rates, remains a challenge for dermatologists. Suspicious pigmented lesions typically are evaluated via clinical examination and dermoscopy; however, new technologies are being developed to provide additional objective information for clinicians to incorporate into their biopsy decisions.
Multispectral digital skin lesion analysis (MSDSLA) uses 10 bands of visible and near-infrared light (430–950 nm) to image and analyze pigmented skin lesions (PSLs) down to 2.5 mm below the skin surface and measures the distribution of melanin using 75 unique algorithms to determine the degree of the morphologic disorder. Using a logical regression model previously validated on a set of 1632 PSLs, the probability of melanoma and probability of being a melanoma/PSL of high-risk malignant potential are then provided to the clinician.1
In this study, we analyzed aggregate data from 7 prior studies2-8 to better determine how MSDSLA impacts the biopsy decisions of dermatologists and nondermatologists following clinical examination and dermoscopic evaluation of PSLs.
Methods

Results
Overall sensitivity for the detection of melanoma or other high-grade PSLs improved from 70% on clinical and dermoscopic evaluation to 88% after MSDSLA information was provided (P<.0001), and specificity increased from 52% to 58% (P<.001). Diagnostic accuracy also improved from 59% on clinical evaluation to 69% after review of MSDSLA findings (P<.0001). The positive predictive value of biopsy decisions was 47% following clinical evaluation, which improved to 56% after evaluation of MSDSLA findings (P<.001), and the negative predictive value increased from 74% to 89% (P<.0001). The overall percentage of lesions selected for biopsy did not significantly change following MSDSLA data integration (57% vs 60%)(Figure). Given that similar numbers of lesions were biopsied with improved sensitivity and specificity, the integration of MSDSLA data into the biopsy decision led to an improved biopsy ratio (ratio of melanomas biopsied to total biopsies) and fewer unnecessary biopsies.

Comment
Our broad analysis further supported the findings of prior studies that decisions to biopsy clinically suspicious PSLs are more sensitive, specific, and accurate when practitioners are provided MSDSLA information following clinical examination.2-8
Given the evolution in health care economics, it is clear that greater emphasis will continue to be placed on superior, evidence-based, effective care. The reported diagnostic sensitivities and specificities of clinical evaluation and dermoscopy for melanoma detection vary widely throughout the literature, with sensitivities ranging from 58% to over 90% and specificities ranging from 77% to 99%.9-11
Our study had several limitations. For this analysis to be more representative of lesion biopsy selection in the clinical setting, biopsy sensitivity (correctly identifying lesions appropriate for biopsy) vs melanoma sensitivity (identifying a lesion as melanoma) was used.13 The overall sensitivity found was within the range of prior studies,2-8 but this approach may have potentially led to a lower specificity due to an increased number of lesions biopsied. Additionally, the melanomas selected for these studies were early (malignant melanoma in situ or mean thickness of invasive malignant melanoma of 0.3 mm), and the nonmelanomas (including low-grade dysplastic nevi) were not necessarily diagnostically straightforward. This may have led to the clinical and dermoscopic sensitivity and specificity noted being lower than in some prior studies.9-11
The risk of missing a melanoma with MSDSLA devices has led manufacturers to strive for a high sensitivity for their devices, leading to lower specificity as a consequence. For this reason and other ambiguous practical considerations (eg, device and patient costs, difficulty with insurance reimbursement), the adoption of this technology into routine clinical practice has remained relatively static; however, using enhanced diagnostic technologies such as MSDSLA may help with more accurate identification of high-risk PSLs, thereby leading to earlier detection and overall less expensive, more cost-effective treatment of melanoma.
Early detection of melanoma, which is known to improve survival rates, remains a challenge for dermatologists. Suspicious pigmented lesions typically are evaluated via clinical examination and dermoscopy; however, new technologies are being developed to provide additional objective information for clinicians to incorporate into their biopsy decisions.
Multispectral digital skin lesion analysis (MSDSLA) uses 10 bands of visible and near-infrared light (430–950 nm) to image and analyze pigmented skin lesions (PSLs) down to 2.5 mm below the skin surface and measures the distribution of melanin using 75 unique algorithms to determine the degree of the morphologic disorder. Using a logical regression model previously validated on a set of 1632 PSLs, the probability of melanoma and probability of being a melanoma/PSL of high-risk malignant potential are then provided to the clinician.1
In this study, we analyzed aggregate data from 7 prior studies2-8 to better determine how MSDSLA impacts the biopsy decisions of dermatologists and nondermatologists following clinical examination and dermoscopic evaluation of PSLs.
Methods

Results
Overall sensitivity for the detection of melanoma or other high-grade PSLs improved from 70% on clinical and dermoscopic evaluation to 88% after MSDSLA information was provided (P<.0001), and specificity increased from 52% to 58% (P<.001). Diagnostic accuracy also improved from 59% on clinical evaluation to 69% after review of MSDSLA findings (P<.0001). The positive predictive value of biopsy decisions was 47% following clinical evaluation, which improved to 56% after evaluation of MSDSLA findings (P<.001), and the negative predictive value increased from 74% to 89% (P<.0001). The overall percentage of lesions selected for biopsy did not significantly change following MSDSLA data integration (57% vs 60%)(Figure). Given that similar numbers of lesions were biopsied with improved sensitivity and specificity, the integration of MSDSLA data into the biopsy decision led to an improved biopsy ratio (ratio of melanomas biopsied to total biopsies) and fewer unnecessary biopsies.

Comment
Our broad analysis further supported the findings of prior studies that decisions to biopsy clinically suspicious PSLs are more sensitive, specific, and accurate when practitioners are provided MSDSLA information following clinical examination.2-8
Given the evolution in health care economics, it is clear that greater emphasis will continue to be placed on superior, evidence-based, effective care. The reported diagnostic sensitivities and specificities of clinical evaluation and dermoscopy for melanoma detection vary widely throughout the literature, with sensitivities ranging from 58% to over 90% and specificities ranging from 77% to 99%.9-11
Our study had several limitations. For this analysis to be more representative of lesion biopsy selection in the clinical setting, biopsy sensitivity (correctly identifying lesions appropriate for biopsy) vs melanoma sensitivity (identifying a lesion as melanoma) was used.13 The overall sensitivity found was within the range of prior studies,2-8 but this approach may have potentially led to a lower specificity due to an increased number of lesions biopsied. Additionally, the melanomas selected for these studies were early (malignant melanoma in situ or mean thickness of invasive malignant melanoma of 0.3 mm), and the nonmelanomas (including low-grade dysplastic nevi) were not necessarily diagnostically straightforward. This may have led to the clinical and dermoscopic sensitivity and specificity noted being lower than in some prior studies.9-11
The risk of missing a melanoma with MSDSLA devices has led manufacturers to strive for a high sensitivity for their devices, leading to lower specificity as a consequence. For this reason and other ambiguous practical considerations (eg, device and patient costs, difficulty with insurance reimbursement), the adoption of this technology into routine clinical practice has remained relatively static; however, using enhanced diagnostic technologies such as MSDSLA may help with more accurate identification of high-risk PSLs, thereby leading to earlier detection and overall less expensive, more cost-effective treatment of melanoma.
- Monheit G, Cognetta AB, Ferris L, et al. The performance of MelaFind: a prospective multicenter study. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:188-194.
- Rigel DS, Roy M, Yoo J, et al. Impact of guidance from a computer-aided multispectral digital skin lesion analysis device on decision to biopsy lesions clinically suggestive of melanoma. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:541-543.
- Yoo J, Rigel DS, Roy M, et al. Impact of guidance from a multispectral digital skin lesion analysis device on dermatology residents decisions to biopsy lesions clinically suggestive of melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:AB152.
- Winkelmann RR, Yoo J, Tucker N, et al. Impact of guidance provided by a multispectral digital skin lesion analysis device following dermoscopy on decisions to biopsy atypical melanocytic lesions. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2015;8:21-24.
- Winkelmann RR, Hauschild A, Tucker N, et al. The impact of multispectral digital skin lesion analysis on German dermatologist decisions to biopsy atypical pigmented lesions with clinical characteristics of melanoma. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2015;8:27-29.
- Winkelmann RR, Tucker N, White R, et al. Pigmented skin lesion biopsies after computer-aided multispectral digital skin lesion analysis. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2015;115:666-669.
- Winkelmann RR, Farberg AS, Tucker N, et al. Enhancement of international dermatologists’ pigmented skin lesion biopsy decisions following dermoscopy with subsequent integration of multispectral digital skin lesion analysis [published online July 1, 2016]. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2016;9:53-55.
- Farberg AS, Winkelmann RR, Tucker N, et al. The impact of quantitative data provided by a multi-spectral digital skin lesion analysis device on dermatologists’ decisions to biopsy pigmented lesions [published online September 1, 2017]. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2017;10:24-26.
- Wolf IH, Smolle J, Soyer HP, et al. Sensitivity in the clinical diagnosis of malignant melanoma. Melanoma Res. 1998;8:425-429.
- Kittler H, Pehamberger H, Wolff K, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy. Lancet Oncol. 2002;3:159-165.
- Ascierto PA, Palmieri G, Celentano E, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of epiluminescence microscopy: evaluation on a sample of 2731 excised cutaneous pigmented lesions: the Melanoma Cooperative Study. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:893-898.
- Carli P, Nardini P, Crocetti E, et al. Frequency and characteristics of melanomas missed at a pigmented lesion clinic: a registry-based study. Melanoma Res. 2004;14:403-407.
- Friedman RJ, Gutkowicz-Krusin D, Farber MJ, et al. The diagnostic performance of expert dermoscopists vs a computer-vision system on small-diameter melanomas. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:476-482.
- Monheit G, Cognetta AB, Ferris L, et al. The performance of MelaFind: a prospective multicenter study. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:188-194.
- Rigel DS, Roy M, Yoo J, et al. Impact of guidance from a computer-aided multispectral digital skin lesion analysis device on decision to biopsy lesions clinically suggestive of melanoma. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:541-543.
- Yoo J, Rigel DS, Roy M, et al. Impact of guidance from a multispectral digital skin lesion analysis device on dermatology residents decisions to biopsy lesions clinically suggestive of melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:AB152.
- Winkelmann RR, Yoo J, Tucker N, et al. Impact of guidance provided by a multispectral digital skin lesion analysis device following dermoscopy on decisions to biopsy atypical melanocytic lesions. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2015;8:21-24.
- Winkelmann RR, Hauschild A, Tucker N, et al. The impact of multispectral digital skin lesion analysis on German dermatologist decisions to biopsy atypical pigmented lesions with clinical characteristics of melanoma. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2015;8:27-29.
- Winkelmann RR, Tucker N, White R, et al. Pigmented skin lesion biopsies after computer-aided multispectral digital skin lesion analysis. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2015;115:666-669.
- Winkelmann RR, Farberg AS, Tucker N, et al. Enhancement of international dermatologists’ pigmented skin lesion biopsy decisions following dermoscopy with subsequent integration of multispectral digital skin lesion analysis [published online July 1, 2016]. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2016;9:53-55.
- Farberg AS, Winkelmann RR, Tucker N, et al. The impact of quantitative data provided by a multi-spectral digital skin lesion analysis device on dermatologists’ decisions to biopsy pigmented lesions [published online September 1, 2017]. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2017;10:24-26.
- Wolf IH, Smolle J, Soyer HP, et al. Sensitivity in the clinical diagnosis of malignant melanoma. Melanoma Res. 1998;8:425-429.
- Kittler H, Pehamberger H, Wolff K, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy. Lancet Oncol. 2002;3:159-165.
- Ascierto PA, Palmieri G, Celentano E, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of epiluminescence microscopy: evaluation on a sample of 2731 excised cutaneous pigmented lesions: the Melanoma Cooperative Study. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:893-898.
- Carli P, Nardini P, Crocetti E, et al. Frequency and characteristics of melanomas missed at a pigmented lesion clinic: a registry-based study. Melanoma Res. 2004;14:403-407.
- Friedman RJ, Gutkowicz-Krusin D, Farber MJ, et al. The diagnostic performance of expert dermoscopists vs a computer-vision system on small-diameter melanomas. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:476-482.
Practice Points
- Multispectral digital skin lesion analysis (MSDSLA) can be a valuable tool in the evaluation of pigmented skin lesions (PSLs).
- MSDSLA may help to better identify high-risk PSLs and improve cost of care.
Teledermatology in the US Military: A Historic Foundation for Current and Future Applications
Telemedicine arose from the need to provide critical and timely advice directly to health care providers and patients in remote or resource-scarce settings. Whether by radio, telephone, or other means of telecommunication technology, the US military has long utilized telemedicine. What started as a way to expedite the delivery of emergency consultations and medical expertise to remote populations in need has since evolved into a billion-dollar innovation industry that is poised to improve health care efficiency and access to specialist care as well as to lower health care costs for all patients.
Teledermatology in the Military
A primary mission of military medicine is to keep service members anywhere in the world in good health on the job during training, combat, and humanitarian operations.1 Telemedicine greatly supports this mission by bringing the expertise of medical specialists to service members in the field without the cost or risks of travel for physicians. Telemedicine also is effective in promoting timely triage of patients and administration of the most appropriate levels of care. With the advent and globalization of high-speed wireless networks, advancements in telemedicine continue to develop and are becoming increasingly useful in military medicine.
As a specialty, dermatology is heavily reliant on visual information and therefore is particularly amenable to telemedicine applications. The rising popularity of such services has led to the development of the term teledermatology. While early teledermatology services were provided using radio, telephone, fax, and videoconferencing,2 three distinct visual methods typically are used today, including (1) store-and-forward (S&F), (2) live-interactive, and (3) a hybrid of the two.3 Military dermatology predominantly utilizes an S&F system, as still photographs of lesions generally are preferred over video for more focused visualization.
In 2004, the US Army Medical Department established a centralized telemedicine program using Army Knowledge Online,1 an S&F system that allows providers in remote locations to store and forward information about a patient’s clinical history along with digital photographs of the patient’s condition to a military dermatologist to review and make a diagnosis or suggest a treatment from a different location at a later time. Using this platform to provide asynchronous teledermatology services avoids the logistics required to schedule appointments and promotes convenience and more efficient use of physicians’ time and resources.
Given the ease of use of S&F systems among military practitioners, dermatology became one of the most heavily utilized teleconsultation specialties within the Army Knowledge Online system, accounting for 40% of the 10,817 consultations initiated from April 2004 to December 2012.5 It also is important to note that skin conditions historically account for 15% to 75% of outpatient visits during wartime; therefore, there is a need for dermatologic consultations, as primary care providers typically are responsible for providing dermatologic care to these patients.6 Because of the high demand for and low volume of US military dermatologists, the use of teledermatology (ie, Amy Knowledge Online) in the US military became a helpful educational tool and specialist extender for many primary care providers in the military.
Teledermatology in the military has evolved to not only provide timely and efficient care but also to reduce health care costs.
Advances in Teledermatology
While the military continues to use S&F teleconsultations—a model in which a deployed referring clinician sends information to a military dermatologist for diagnosis and/or management recommendations—a number of teledermatology programs have been developed for civilians that provide additional advantages over standard face-to-face dermatology care. The advantages of S&F teledermatology applications are many, including faster communication with dermatology providers, diagnostic concordance comparable to face-to-face appointments, cost-effective care for patients, the ability to educate providers remotely,8 and similar outcomes to in-person care.9 However, as to be expected, in-person care remains the gold standard, especially when diagnostic accuracy depends on biopsy findings.
The development of the smartphone along with advances in digital photography and consumer-friendly mobile applications has allowed for the emergence of direct-to-consumer (DTC) teledermatology applications. Regardless of the user’s ability, the quality of photographs taken with smartphones has improved, as standard features such as high-resolution cameras with image stabilization, automatic focus, and lighting have become commonplace. The popularity of smartphone technology also has increased, with nearly 75% of all adults and more than 90% of adults younger than 35 years of age owning a smartphone according to a 2016 survey.11
In 2015, there were at least 29 DTC teledermatology applications available on various mobile platforms,12 accounting for an estimated 1.25 million teleconsultations with providers.13 Teledermatology platforms such as DermatologistOnCall and Spruce Health have made accessing dermatologic care convenient, timely, and affordable for patients via patient-friendly mobile applications.
Regular access to dermatologic care is especially important for patients who have chronic skin conditions. Several unique practice models have emerged as innovative solutions to providing more convenient and timely care. For example, Curology (https://curology.com) is an online teledermatology practice specializing in acne treatment.
Although DTC teledermatology practices are convenient for many patients and providers, some have been criticized for providing poor quality of care12 or facilitating fragmented care by not integrating with established electronic health record (EHR) systems.15 As a result, recommended practice guidelines for DTC teledermatology have been developed by the American Academy of Dermatology and some state medical boards.16 Moreover, several EHR systems, such as Epic (www.epic.com) and Modernizing Medicine’s EMA (www.modmed.com), have developed fully integrated S&F teledermatology platforms to be incorporated with established brick-and-mortar care.17
The Future of Teledermatology in the Military
The Army Knowledge Online telemedicine platform used by the US military has continued to be useful, particularly when treating patients in remote locations, and shows promise for improving routine domestic dermatology care. It has reduced the number of medical evacuations and improved care for those who do not have access to a dermatologist.4 Furthermore, one study noted that most consultations submitted via teledermatology applications from a combat zone received a diagnosis and treatment recommendation from a military dermatologist faster than they would have stateside, where the wait often is 4 to 8 weeks. On average, a teledermatology consultation from Afghanistan was answered in less than 6 hours.4 Although this response time might not be realistic for all dermatology practices, there clearly is potential in certain situations and utilizing certain models of care to diagnose and treat more patients more efficiently utilizing teledermatology applications than in an in-person office visit. A review of 658 teledermatology consultations in the US military from January 2011 to December 2012 revealed that the leading diagnoses were eczematous dermatitis (14%), contact dermatitis (9%), nonmelanoma skin cancer (5%), psoriasis (4%), and urticaria (4%).4 Increased use of teledermatology evaluation of these conditions in routine US-based military practice could help expedite care, decrease patient travel time, and utilize in-clinic dermatologist time more efficiently. Teledermatology visits for postoperative concerns also have demonstrated utility and convenience for triage and management of patients in the civilian setting and may be an additional novel use of teledermatology in the military setting.18 With the use of an integrated S&F teledermatology platform within an existing EHR system that is paired with a secure patient mobile application that allows easy upload of photos, medical history, and messaging, it can be argued that quality of life could greatly be enhanced for both military patients and providers.
Limitations of Teledermatology
Certainly, there are and will always be limitations to teledermatology. Even as digital photography improves, the quality and context of clinical images are user dependent, and key associated skin findings in other locations of the body can be missed. The ability to palpate the skin also is lacking in virtual encounters. Therefore, teledermatology might be considered most appropriate for specific diseases and conditions (eg, acne, psoriasis, eczema). Embracing teledermatology does not mean replacing in-person care; rather, it should be seen as an adjunct used to manage the high demand for dermatology expertise in military and civilian practice. For the US military, the promise and potential to embrace innovation in providing dermatologic care is there, as long as there are leaders to continue to champion it. In the current state of health care, many of the perceived barriers of teledermatology applications have already been overcome, including lack of training, lack of reimbursement, and perceived medicolegal risks.19
The US Federal Government is a large entity, and it will undoubtedly take time and effort to implement new and innovative programs such as the ones described here in the military. The first step in implementation is awareness that the possibilities exist; then, with the cooperation of dermatologists and support from the chain of command, it will be possible to incorporate advances in teledermatology and cultivate new ones.
Final Thoughts
The S&F teledermatology method used in the military setting has become commonplace in both military and civilian settings alike. Newer innovations in telemedicine, particularly in teledermatology, will continue to shape the future of military and civilian medicine for years to come.
- Vidmar DA. The history of teledermatology in the Department of Defense. Dermatol Clin. 1999;17:113-124.
- McManus J, Salinas J, Morton M, et al. Teleconsultation program for deployed soldiers and healthcare professionals in remote and austere environments. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2008;23:210-216.
- Tensen E, Van Der Heijden JP, Jaspers MW, et al. Two decades of teledermatology: current status and integration in national healthcare systems. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2016;5:96-104.
- Hwang JS, Lappan CM, Sperling LC, et al. Utilization of telemedicine in the U.S. military in a deployed setting. Mil Med. 2014;179:1347-1353.
- McGraw TA, Norton SA. Military aeromedical evacuations from central and southwest Asia for ill-defined dermatologic diseases. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:165-170.
- Shissel DJ, Wilde J. Operational dermatology. Mil Med. 2004;169:444-447.
- Henning JS, Wohltmann W, Hivnor C. Teledermatology from a combat zone. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:676-677.
- Whited JD, Hall RP, Simel DL, et al. Reliability and accuracy of dermatologists’ clinic-based and digital image consultations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:693-702.
- Pak H, Triplett CA, Lindquist JH, et al. Store-and-forward teledermatology results in similar clinical outcomes to conventional clinic-based care. J Telemed Telecare. 2007;13:26-30.
- Finnane A, Dallest K, Janda M, et al. Teledermatology for the diagnosis and management of skin cancer: a systematic review. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:319-327.
- Poushter J. Smartphone ownership and internet usage continues to climb in emerging economies. Washington, DC: Pew Research Center. www.pewglobal.org/2016/02/22/smartphone-ownership-and-internet-usage-continues-to-climbin-emerging-economies/. Published February 22, 2016. Accessed February 2, 2018.
- Peart JM, Kovarik C. Direct-to-patient teledermatology practices. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:907-909.
- Huff C. Medical diagnosis by webcam? Washington, DC: American Association of Retired Persons. www.aarp.org/health/conditions-treatments/info-2015/telemedicine-health-symptoms-diagnosis.html. Published December 2015. Accessed February 2, 2018.
- Mehrotra A. The convenience revolution for the treatment of low-acuity conditions. JAMA. 2013;310:35-36.
- Resneck JS Jr, Abrouk M, Steuer M, et al. Choice, transparency, coordination, and quality among direct-to-consumer telemedicine websites and apps treating skin disease. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:768-775.
- Teledermatology toolkit. American Academy of Dermatology website. https://www.aad.org/practicecenter/managing-a-practice/teledermatology. Accessed April 24, 2018.
- Carter ZA, Goldman S, Anderson K, et al. Creation of an internalteledermatology store-and-forward system in an existing electronic health record: a pilot study in a safety-net public health and hospital system. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:644-650.
- Jeyamohan SR, Moye MS, Srivastava D, et al. Patient-acquired photographs for the management of postoperative concerns. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:226-227.
- Edison KE, Dyer JA, Whited JD, et al. Practice gaps. the barriers and the promise of teledermatology. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:650-651.
Telemedicine arose from the need to provide critical and timely advice directly to health care providers and patients in remote or resource-scarce settings. Whether by radio, telephone, or other means of telecommunication technology, the US military has long utilized telemedicine. What started as a way to expedite the delivery of emergency consultations and medical expertise to remote populations in need has since evolved into a billion-dollar innovation industry that is poised to improve health care efficiency and access to specialist care as well as to lower health care costs for all patients.
Teledermatology in the Military
A primary mission of military medicine is to keep service members anywhere in the world in good health on the job during training, combat, and humanitarian operations.1 Telemedicine greatly supports this mission by bringing the expertise of medical specialists to service members in the field without the cost or risks of travel for physicians. Telemedicine also is effective in promoting timely triage of patients and administration of the most appropriate levels of care. With the advent and globalization of high-speed wireless networks, advancements in telemedicine continue to develop and are becoming increasingly useful in military medicine.
As a specialty, dermatology is heavily reliant on visual information and therefore is particularly amenable to telemedicine applications. The rising popularity of such services has led to the development of the term teledermatology. While early teledermatology services were provided using radio, telephone, fax, and videoconferencing,2 three distinct visual methods typically are used today, including (1) store-and-forward (S&F), (2) live-interactive, and (3) a hybrid of the two.3 Military dermatology predominantly utilizes an S&F system, as still photographs of lesions generally are preferred over video for more focused visualization.
In 2004, the US Army Medical Department established a centralized telemedicine program using Army Knowledge Online,1 an S&F system that allows providers in remote locations to store and forward information about a patient’s clinical history along with digital photographs of the patient’s condition to a military dermatologist to review and make a diagnosis or suggest a treatment from a different location at a later time. Using this platform to provide asynchronous teledermatology services avoids the logistics required to schedule appointments and promotes convenience and more efficient use of physicians’ time and resources.
Given the ease of use of S&F systems among military practitioners, dermatology became one of the most heavily utilized teleconsultation specialties within the Army Knowledge Online system, accounting for 40% of the 10,817 consultations initiated from April 2004 to December 2012.5 It also is important to note that skin conditions historically account for 15% to 75% of outpatient visits during wartime; therefore, there is a need for dermatologic consultations, as primary care providers typically are responsible for providing dermatologic care to these patients.6 Because of the high demand for and low volume of US military dermatologists, the use of teledermatology (ie, Amy Knowledge Online) in the US military became a helpful educational tool and specialist extender for many primary care providers in the military.
Teledermatology in the military has evolved to not only provide timely and efficient care but also to reduce health care costs.
Advances in Teledermatology
While the military continues to use S&F teleconsultations—a model in which a deployed referring clinician sends information to a military dermatologist for diagnosis and/or management recommendations—a number of teledermatology programs have been developed for civilians that provide additional advantages over standard face-to-face dermatology care. The advantages of S&F teledermatology applications are many, including faster communication with dermatology providers, diagnostic concordance comparable to face-to-face appointments, cost-effective care for patients, the ability to educate providers remotely,8 and similar outcomes to in-person care.9 However, as to be expected, in-person care remains the gold standard, especially when diagnostic accuracy depends on biopsy findings.
The development of the smartphone along with advances in digital photography and consumer-friendly mobile applications has allowed for the emergence of direct-to-consumer (DTC) teledermatology applications. Regardless of the user’s ability, the quality of photographs taken with smartphones has improved, as standard features such as high-resolution cameras with image stabilization, automatic focus, and lighting have become commonplace. The popularity of smartphone technology also has increased, with nearly 75% of all adults and more than 90% of adults younger than 35 years of age owning a smartphone according to a 2016 survey.11
In 2015, there were at least 29 DTC teledermatology applications available on various mobile platforms,12 accounting for an estimated 1.25 million teleconsultations with providers.13 Teledermatology platforms such as DermatologistOnCall and Spruce Health have made accessing dermatologic care convenient, timely, and affordable for patients via patient-friendly mobile applications.
Regular access to dermatologic care is especially important for patients who have chronic skin conditions. Several unique practice models have emerged as innovative solutions to providing more convenient and timely care. For example, Curology (https://curology.com) is an online teledermatology practice specializing in acne treatment.
Although DTC teledermatology practices are convenient for many patients and providers, some have been criticized for providing poor quality of care12 or facilitating fragmented care by not integrating with established electronic health record (EHR) systems.15 As a result, recommended practice guidelines for DTC teledermatology have been developed by the American Academy of Dermatology and some state medical boards.16 Moreover, several EHR systems, such as Epic (www.epic.com) and Modernizing Medicine’s EMA (www.modmed.com), have developed fully integrated S&F teledermatology platforms to be incorporated with established brick-and-mortar care.17
The Future of Teledermatology in the Military
The Army Knowledge Online telemedicine platform used by the US military has continued to be useful, particularly when treating patients in remote locations, and shows promise for improving routine domestic dermatology care. It has reduced the number of medical evacuations and improved care for those who do not have access to a dermatologist.4 Furthermore, one study noted that most consultations submitted via teledermatology applications from a combat zone received a diagnosis and treatment recommendation from a military dermatologist faster than they would have stateside, where the wait often is 4 to 8 weeks. On average, a teledermatology consultation from Afghanistan was answered in less than 6 hours.4 Although this response time might not be realistic for all dermatology practices, there clearly is potential in certain situations and utilizing certain models of care to diagnose and treat more patients more efficiently utilizing teledermatology applications than in an in-person office visit. A review of 658 teledermatology consultations in the US military from January 2011 to December 2012 revealed that the leading diagnoses were eczematous dermatitis (14%), contact dermatitis (9%), nonmelanoma skin cancer (5%), psoriasis (4%), and urticaria (4%).4 Increased use of teledermatology evaluation of these conditions in routine US-based military practice could help expedite care, decrease patient travel time, and utilize in-clinic dermatologist time more efficiently. Teledermatology visits for postoperative concerns also have demonstrated utility and convenience for triage and management of patients in the civilian setting and may be an additional novel use of teledermatology in the military setting.18 With the use of an integrated S&F teledermatology platform within an existing EHR system that is paired with a secure patient mobile application that allows easy upload of photos, medical history, and messaging, it can be argued that quality of life could greatly be enhanced for both military patients and providers.
Limitations of Teledermatology
Certainly, there are and will always be limitations to teledermatology. Even as digital photography improves, the quality and context of clinical images are user dependent, and key associated skin findings in other locations of the body can be missed. The ability to palpate the skin also is lacking in virtual encounters. Therefore, teledermatology might be considered most appropriate for specific diseases and conditions (eg, acne, psoriasis, eczema). Embracing teledermatology does not mean replacing in-person care; rather, it should be seen as an adjunct used to manage the high demand for dermatology expertise in military and civilian practice. For the US military, the promise and potential to embrace innovation in providing dermatologic care is there, as long as there are leaders to continue to champion it. In the current state of health care, many of the perceived barriers of teledermatology applications have already been overcome, including lack of training, lack of reimbursement, and perceived medicolegal risks.19
The US Federal Government is a large entity, and it will undoubtedly take time and effort to implement new and innovative programs such as the ones described here in the military. The first step in implementation is awareness that the possibilities exist; then, with the cooperation of dermatologists and support from the chain of command, it will be possible to incorporate advances in teledermatology and cultivate new ones.
Final Thoughts
The S&F teledermatology method used in the military setting has become commonplace in both military and civilian settings alike. Newer innovations in telemedicine, particularly in teledermatology, will continue to shape the future of military and civilian medicine for years to come.
Telemedicine arose from the need to provide critical and timely advice directly to health care providers and patients in remote or resource-scarce settings. Whether by radio, telephone, or other means of telecommunication technology, the US military has long utilized telemedicine. What started as a way to expedite the delivery of emergency consultations and medical expertise to remote populations in need has since evolved into a billion-dollar innovation industry that is poised to improve health care efficiency and access to specialist care as well as to lower health care costs for all patients.
Teledermatology in the Military
A primary mission of military medicine is to keep service members anywhere in the world in good health on the job during training, combat, and humanitarian operations.1 Telemedicine greatly supports this mission by bringing the expertise of medical specialists to service members in the field without the cost or risks of travel for physicians. Telemedicine also is effective in promoting timely triage of patients and administration of the most appropriate levels of care. With the advent and globalization of high-speed wireless networks, advancements in telemedicine continue to develop and are becoming increasingly useful in military medicine.
As a specialty, dermatology is heavily reliant on visual information and therefore is particularly amenable to telemedicine applications. The rising popularity of such services has led to the development of the term teledermatology. While early teledermatology services were provided using radio, telephone, fax, and videoconferencing,2 three distinct visual methods typically are used today, including (1) store-and-forward (S&F), (2) live-interactive, and (3) a hybrid of the two.3 Military dermatology predominantly utilizes an S&F system, as still photographs of lesions generally are preferred over video for more focused visualization.
In 2004, the US Army Medical Department established a centralized telemedicine program using Army Knowledge Online,1 an S&F system that allows providers in remote locations to store and forward information about a patient’s clinical history along with digital photographs of the patient’s condition to a military dermatologist to review and make a diagnosis or suggest a treatment from a different location at a later time. Using this platform to provide asynchronous teledermatology services avoids the logistics required to schedule appointments and promotes convenience and more efficient use of physicians’ time and resources.
Given the ease of use of S&F systems among military practitioners, dermatology became one of the most heavily utilized teleconsultation specialties within the Army Knowledge Online system, accounting for 40% of the 10,817 consultations initiated from April 2004 to December 2012.5 It also is important to note that skin conditions historically account for 15% to 75% of outpatient visits during wartime; therefore, there is a need for dermatologic consultations, as primary care providers typically are responsible for providing dermatologic care to these patients.6 Because of the high demand for and low volume of US military dermatologists, the use of teledermatology (ie, Amy Knowledge Online) in the US military became a helpful educational tool and specialist extender for many primary care providers in the military.
Teledermatology in the military has evolved to not only provide timely and efficient care but also to reduce health care costs.
Advances in Teledermatology
While the military continues to use S&F teleconsultations—a model in which a deployed referring clinician sends information to a military dermatologist for diagnosis and/or management recommendations—a number of teledermatology programs have been developed for civilians that provide additional advantages over standard face-to-face dermatology care. The advantages of S&F teledermatology applications are many, including faster communication with dermatology providers, diagnostic concordance comparable to face-to-face appointments, cost-effective care for patients, the ability to educate providers remotely,8 and similar outcomes to in-person care.9 However, as to be expected, in-person care remains the gold standard, especially when diagnostic accuracy depends on biopsy findings.
The development of the smartphone along with advances in digital photography and consumer-friendly mobile applications has allowed for the emergence of direct-to-consumer (DTC) teledermatology applications. Regardless of the user’s ability, the quality of photographs taken with smartphones has improved, as standard features such as high-resolution cameras with image stabilization, automatic focus, and lighting have become commonplace. The popularity of smartphone technology also has increased, with nearly 75% of all adults and more than 90% of adults younger than 35 years of age owning a smartphone according to a 2016 survey.11
In 2015, there were at least 29 DTC teledermatology applications available on various mobile platforms,12 accounting for an estimated 1.25 million teleconsultations with providers.13 Teledermatology platforms such as DermatologistOnCall and Spruce Health have made accessing dermatologic care convenient, timely, and affordable for patients via patient-friendly mobile applications.
Regular access to dermatologic care is especially important for patients who have chronic skin conditions. Several unique practice models have emerged as innovative solutions to providing more convenient and timely care. For example, Curology (https://curology.com) is an online teledermatology practice specializing in acne treatment.
Although DTC teledermatology practices are convenient for many patients and providers, some have been criticized for providing poor quality of care12 or facilitating fragmented care by not integrating with established electronic health record (EHR) systems.15 As a result, recommended practice guidelines for DTC teledermatology have been developed by the American Academy of Dermatology and some state medical boards.16 Moreover, several EHR systems, such as Epic (www.epic.com) and Modernizing Medicine’s EMA (www.modmed.com), have developed fully integrated S&F teledermatology platforms to be incorporated with established brick-and-mortar care.17
The Future of Teledermatology in the Military
The Army Knowledge Online telemedicine platform used by the US military has continued to be useful, particularly when treating patients in remote locations, and shows promise for improving routine domestic dermatology care. It has reduced the number of medical evacuations and improved care for those who do not have access to a dermatologist.4 Furthermore, one study noted that most consultations submitted via teledermatology applications from a combat zone received a diagnosis and treatment recommendation from a military dermatologist faster than they would have stateside, where the wait often is 4 to 8 weeks. On average, a teledermatology consultation from Afghanistan was answered in less than 6 hours.4 Although this response time might not be realistic for all dermatology practices, there clearly is potential in certain situations and utilizing certain models of care to diagnose and treat more patients more efficiently utilizing teledermatology applications than in an in-person office visit. A review of 658 teledermatology consultations in the US military from January 2011 to December 2012 revealed that the leading diagnoses were eczematous dermatitis (14%), contact dermatitis (9%), nonmelanoma skin cancer (5%), psoriasis (4%), and urticaria (4%).4 Increased use of teledermatology evaluation of these conditions in routine US-based military practice could help expedite care, decrease patient travel time, and utilize in-clinic dermatologist time more efficiently. Teledermatology visits for postoperative concerns also have demonstrated utility and convenience for triage and management of patients in the civilian setting and may be an additional novel use of teledermatology in the military setting.18 With the use of an integrated S&F teledermatology platform within an existing EHR system that is paired with a secure patient mobile application that allows easy upload of photos, medical history, and messaging, it can be argued that quality of life could greatly be enhanced for both military patients and providers.
Limitations of Teledermatology
Certainly, there are and will always be limitations to teledermatology. Even as digital photography improves, the quality and context of clinical images are user dependent, and key associated skin findings in other locations of the body can be missed. The ability to palpate the skin also is lacking in virtual encounters. Therefore, teledermatology might be considered most appropriate for specific diseases and conditions (eg, acne, psoriasis, eczema). Embracing teledermatology does not mean replacing in-person care; rather, it should be seen as an adjunct used to manage the high demand for dermatology expertise in military and civilian practice. For the US military, the promise and potential to embrace innovation in providing dermatologic care is there, as long as there are leaders to continue to champion it. In the current state of health care, many of the perceived barriers of teledermatology applications have already been overcome, including lack of training, lack of reimbursement, and perceived medicolegal risks.19
The US Federal Government is a large entity, and it will undoubtedly take time and effort to implement new and innovative programs such as the ones described here in the military. The first step in implementation is awareness that the possibilities exist; then, with the cooperation of dermatologists and support from the chain of command, it will be possible to incorporate advances in teledermatology and cultivate new ones.
Final Thoughts
The S&F teledermatology method used in the military setting has become commonplace in both military and civilian settings alike. Newer innovations in telemedicine, particularly in teledermatology, will continue to shape the future of military and civilian medicine for years to come.
- Vidmar DA. The history of teledermatology in the Department of Defense. Dermatol Clin. 1999;17:113-124.
- McManus J, Salinas J, Morton M, et al. Teleconsultation program for deployed soldiers and healthcare professionals in remote and austere environments. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2008;23:210-216.
- Tensen E, Van Der Heijden JP, Jaspers MW, et al. Two decades of teledermatology: current status and integration in national healthcare systems. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2016;5:96-104.
- Hwang JS, Lappan CM, Sperling LC, et al. Utilization of telemedicine in the U.S. military in a deployed setting. Mil Med. 2014;179:1347-1353.
- McGraw TA, Norton SA. Military aeromedical evacuations from central and southwest Asia for ill-defined dermatologic diseases. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:165-170.
- Shissel DJ, Wilde J. Operational dermatology. Mil Med. 2004;169:444-447.
- Henning JS, Wohltmann W, Hivnor C. Teledermatology from a combat zone. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:676-677.
- Whited JD, Hall RP, Simel DL, et al. Reliability and accuracy of dermatologists’ clinic-based and digital image consultations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:693-702.
- Pak H, Triplett CA, Lindquist JH, et al. Store-and-forward teledermatology results in similar clinical outcomes to conventional clinic-based care. J Telemed Telecare. 2007;13:26-30.
- Finnane A, Dallest K, Janda M, et al. Teledermatology for the diagnosis and management of skin cancer: a systematic review. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:319-327.
- Poushter J. Smartphone ownership and internet usage continues to climb in emerging economies. Washington, DC: Pew Research Center. www.pewglobal.org/2016/02/22/smartphone-ownership-and-internet-usage-continues-to-climbin-emerging-economies/. Published February 22, 2016. Accessed February 2, 2018.
- Peart JM, Kovarik C. Direct-to-patient teledermatology practices. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:907-909.
- Huff C. Medical diagnosis by webcam? Washington, DC: American Association of Retired Persons. www.aarp.org/health/conditions-treatments/info-2015/telemedicine-health-symptoms-diagnosis.html. Published December 2015. Accessed February 2, 2018.
- Mehrotra A. The convenience revolution for the treatment of low-acuity conditions. JAMA. 2013;310:35-36.
- Resneck JS Jr, Abrouk M, Steuer M, et al. Choice, transparency, coordination, and quality among direct-to-consumer telemedicine websites and apps treating skin disease. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:768-775.
- Teledermatology toolkit. American Academy of Dermatology website. https://www.aad.org/practicecenter/managing-a-practice/teledermatology. Accessed April 24, 2018.
- Carter ZA, Goldman S, Anderson K, et al. Creation of an internalteledermatology store-and-forward system in an existing electronic health record: a pilot study in a safety-net public health and hospital system. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:644-650.
- Jeyamohan SR, Moye MS, Srivastava D, et al. Patient-acquired photographs for the management of postoperative concerns. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:226-227.
- Edison KE, Dyer JA, Whited JD, et al. Practice gaps. the barriers and the promise of teledermatology. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:650-651.
- Vidmar DA. The history of teledermatology in the Department of Defense. Dermatol Clin. 1999;17:113-124.
- McManus J, Salinas J, Morton M, et al. Teleconsultation program for deployed soldiers and healthcare professionals in remote and austere environments. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2008;23:210-216.
- Tensen E, Van Der Heijden JP, Jaspers MW, et al. Two decades of teledermatology: current status and integration in national healthcare systems. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2016;5:96-104.
- Hwang JS, Lappan CM, Sperling LC, et al. Utilization of telemedicine in the U.S. military in a deployed setting. Mil Med. 2014;179:1347-1353.
- McGraw TA, Norton SA. Military aeromedical evacuations from central and southwest Asia for ill-defined dermatologic diseases. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:165-170.
- Shissel DJ, Wilde J. Operational dermatology. Mil Med. 2004;169:444-447.
- Henning JS, Wohltmann W, Hivnor C. Teledermatology from a combat zone. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:676-677.
- Whited JD, Hall RP, Simel DL, et al. Reliability and accuracy of dermatologists’ clinic-based and digital image consultations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:693-702.
- Pak H, Triplett CA, Lindquist JH, et al. Store-and-forward teledermatology results in similar clinical outcomes to conventional clinic-based care. J Telemed Telecare. 2007;13:26-30.
- Finnane A, Dallest K, Janda M, et al. Teledermatology for the diagnosis and management of skin cancer: a systematic review. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:319-327.
- Poushter J. Smartphone ownership and internet usage continues to climb in emerging economies. Washington, DC: Pew Research Center. www.pewglobal.org/2016/02/22/smartphone-ownership-and-internet-usage-continues-to-climbin-emerging-economies/. Published February 22, 2016. Accessed February 2, 2018.
- Peart JM, Kovarik C. Direct-to-patient teledermatology practices. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:907-909.
- Huff C. Medical diagnosis by webcam? Washington, DC: American Association of Retired Persons. www.aarp.org/health/conditions-treatments/info-2015/telemedicine-health-symptoms-diagnosis.html. Published December 2015. Accessed February 2, 2018.
- Mehrotra A. The convenience revolution for the treatment of low-acuity conditions. JAMA. 2013;310:35-36.
- Resneck JS Jr, Abrouk M, Steuer M, et al. Choice, transparency, coordination, and quality among direct-to-consumer telemedicine websites and apps treating skin disease. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:768-775.
- Teledermatology toolkit. American Academy of Dermatology website. https://www.aad.org/practicecenter/managing-a-practice/teledermatology. Accessed April 24, 2018.
- Carter ZA, Goldman S, Anderson K, et al. Creation of an internalteledermatology store-and-forward system in an existing electronic health record: a pilot study in a safety-net public health and hospital system. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:644-650.
- Jeyamohan SR, Moye MS, Srivastava D, et al. Patient-acquired photographs for the management of postoperative concerns. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:226-227.
- Edison KE, Dyer JA, Whited JD, et al. Practice gaps. the barriers and the promise of teledermatology. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:650-651.
Practice Points
- Teledermatology is increasing in its use and applications in both military and civilian medicine.
- The increased availability of high-quality digital photography as a result of smartphone technology lends itself well to store-and-forward (S&F) teledermatology applications.
- In the civilian community, new methods and platforms for teledermatology have been created based largely on those used by the military to maximize access to and efficiency of health care, including secure direct-to-consumer (DTC) mobile applications, live interactive methods, and integrated S&F platforms within electronic health record (EHR) systems.
Early results favor combo IL-15/anti-CD20 in indolent NHL
CHICAGO – A combination of an immunostimulatory IL-15-based agent, ALT-803, with a therapeutic monoclonal antibody (mAb) against CD20, was well tolerated and had clinical activity in patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL), according to preliminary findings from a phase 1 study.
“The cancer immunotherapy breakthrough that happened several years ago continues year after year, with a plethora of different modalities of immunotherapy at our disposal,” Todd A. Fehniger, MD, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Immunotherapy with anti-CD20 mAbs, alone or in combination with chemotherapy, is a standard therapy for iNHL patients. Since iNHL cells express CD20, targeting it with mAbs triggers antitumor responses via cell surface receptors resulting in a potent antibody-dependent cellular toxicity. However, response in patients is highly heterogeneous, with relapse within a few months in a subset of patients. In addition, chemotherapeutic combinations can be toxic and result in serious and long-term complications.
“Relapsed or refractory iNHL is not curable and treatment strategies without long-term complications are needed,” said Dr. Fehniger, associate professor of medicine at Washington University, St. Louis.
In an attempt to address this, Dr. Fehniger and his colleagues combined rituximab, an anti-CD20 antibody, with a relatively new IL-15 agonist immunostimulatory agent called ALT-803.
In the phase 1 trial, the researchers enrolled patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma who had relapsed after at least 1 prior to CD20 antibody containing therapy. The study was a standard 3+3 dose escalation design with rituximab administered by intravenous infusion, 375 mg/m2 in four weekly doses, followed by a rest and four consolidation doses every 8 weeks for four cycles.
ALT-803 was administered concurrently at dose levels of 1 mcg/kg, 3 mcg/kg, and 6 mcg/kg IV followed by 6 mcg/kg, 10 mcg/kg, 15 mcg/kg, and 20 mcg/kg subcutaneously.
In total, 21 patients were treated: 16 patients had follicular lymphoma, four patients had marginal zone lymphoma, and one patient had small lymphocytic lymphoma. The median prior therapies received was two (range: 1-18) and five patients were treated who were refractory to prior anti-CD20 MAb therapy.
ALT-803 was well tolerated with no dose limiting toxicities or grade 4 or 5 adverse events. No patients discontinued ALT-803 and the recommended phase 2 dose was 20 mcg/kg subcutaneously. Grade 3 adverse events, regardless of attribution to ALT-803, included transient hypertension (14%), anemia (5%), nausea (5%), chills (5%), fever (5%), neutropenia (5%), and hyperglycemia (5%).
“Patients who received [subcutaneous] ALT-803 developed a unique injection site rash reaction that peaked 7-10 days later but resolved typically within 14 days. It was self-limited and resolved on its own,” Dr. Fehniger said.
At the time of the presentation, the best overall response rate was achieved in 11 of 21 patients (52%), with 9 complete responders (43%), and 2 partial responders (10%).
Of the 12 patients treated with ALT-803 subcutaneously, 11 patients had either stable disease, or partial or complete responses. All 11 patients remained on study and were in consolidation or follow-up and have not relapsed, Dr. Fehniger reported.
Among the five rituximab-refractory patients, the researchers observed one complete response, two patients with stable disease (45% and 36% tumor volume decrease), and two patients with partial disease. The durability of the responses can only be understood with longer follow-up, Dr. Fehniger said.
The peripheral blood of the patients was analyzed via flow cytometry and mass cytometry. Over the duration of four weekly doses, there was an increase in percentage (sixfold, P less than .001) and absolute number (10-fold, P less than .001) of natural killer cells at the 15-mcg/kg and 20-mcg/kg subcutaneous dose levels of ALT-803.
These results suggest that further studies of ALT-803 with other therapeutic targeting mAbs, or other immunotherapy modalities, are warranted, the researchers concluded.
Dr. Fehniger reported research funding from Altor BioScience.
SOURCE: Fehniger TA et al. AACR Annual Meeting, Abstract CT146.
CHICAGO – A combination of an immunostimulatory IL-15-based agent, ALT-803, with a therapeutic monoclonal antibody (mAb) against CD20, was well tolerated and had clinical activity in patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL), according to preliminary findings from a phase 1 study.
“The cancer immunotherapy breakthrough that happened several years ago continues year after year, with a plethora of different modalities of immunotherapy at our disposal,” Todd A. Fehniger, MD, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Immunotherapy with anti-CD20 mAbs, alone or in combination with chemotherapy, is a standard therapy for iNHL patients. Since iNHL cells express CD20, targeting it with mAbs triggers antitumor responses via cell surface receptors resulting in a potent antibody-dependent cellular toxicity. However, response in patients is highly heterogeneous, with relapse within a few months in a subset of patients. In addition, chemotherapeutic combinations can be toxic and result in serious and long-term complications.
“Relapsed or refractory iNHL is not curable and treatment strategies without long-term complications are needed,” said Dr. Fehniger, associate professor of medicine at Washington University, St. Louis.
In an attempt to address this, Dr. Fehniger and his colleagues combined rituximab, an anti-CD20 antibody, with a relatively new IL-15 agonist immunostimulatory agent called ALT-803.
In the phase 1 trial, the researchers enrolled patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma who had relapsed after at least 1 prior to CD20 antibody containing therapy. The study was a standard 3+3 dose escalation design with rituximab administered by intravenous infusion, 375 mg/m2 in four weekly doses, followed by a rest and four consolidation doses every 8 weeks for four cycles.
ALT-803 was administered concurrently at dose levels of 1 mcg/kg, 3 mcg/kg, and 6 mcg/kg IV followed by 6 mcg/kg, 10 mcg/kg, 15 mcg/kg, and 20 mcg/kg subcutaneously.
In total, 21 patients were treated: 16 patients had follicular lymphoma, four patients had marginal zone lymphoma, and one patient had small lymphocytic lymphoma. The median prior therapies received was two (range: 1-18) and five patients were treated who were refractory to prior anti-CD20 MAb therapy.
ALT-803 was well tolerated with no dose limiting toxicities or grade 4 or 5 adverse events. No patients discontinued ALT-803 and the recommended phase 2 dose was 20 mcg/kg subcutaneously. Grade 3 adverse events, regardless of attribution to ALT-803, included transient hypertension (14%), anemia (5%), nausea (5%), chills (5%), fever (5%), neutropenia (5%), and hyperglycemia (5%).
“Patients who received [subcutaneous] ALT-803 developed a unique injection site rash reaction that peaked 7-10 days later but resolved typically within 14 days. It was self-limited and resolved on its own,” Dr. Fehniger said.
At the time of the presentation, the best overall response rate was achieved in 11 of 21 patients (52%), with 9 complete responders (43%), and 2 partial responders (10%).
Of the 12 patients treated with ALT-803 subcutaneously, 11 patients had either stable disease, or partial or complete responses. All 11 patients remained on study and were in consolidation or follow-up and have not relapsed, Dr. Fehniger reported.
Among the five rituximab-refractory patients, the researchers observed one complete response, two patients with stable disease (45% and 36% tumor volume decrease), and two patients with partial disease. The durability of the responses can only be understood with longer follow-up, Dr. Fehniger said.
The peripheral blood of the patients was analyzed via flow cytometry and mass cytometry. Over the duration of four weekly doses, there was an increase in percentage (sixfold, P less than .001) and absolute number (10-fold, P less than .001) of natural killer cells at the 15-mcg/kg and 20-mcg/kg subcutaneous dose levels of ALT-803.
These results suggest that further studies of ALT-803 with other therapeutic targeting mAbs, or other immunotherapy modalities, are warranted, the researchers concluded.
Dr. Fehniger reported research funding from Altor BioScience.
SOURCE: Fehniger TA et al. AACR Annual Meeting, Abstract CT146.
CHICAGO – A combination of an immunostimulatory IL-15-based agent, ALT-803, with a therapeutic monoclonal antibody (mAb) against CD20, was well tolerated and had clinical activity in patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL), according to preliminary findings from a phase 1 study.
“The cancer immunotherapy breakthrough that happened several years ago continues year after year, with a plethora of different modalities of immunotherapy at our disposal,” Todd A. Fehniger, MD, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Immunotherapy with anti-CD20 mAbs, alone or in combination with chemotherapy, is a standard therapy for iNHL patients. Since iNHL cells express CD20, targeting it with mAbs triggers antitumor responses via cell surface receptors resulting in a potent antibody-dependent cellular toxicity. However, response in patients is highly heterogeneous, with relapse within a few months in a subset of patients. In addition, chemotherapeutic combinations can be toxic and result in serious and long-term complications.
“Relapsed or refractory iNHL is not curable and treatment strategies without long-term complications are needed,” said Dr. Fehniger, associate professor of medicine at Washington University, St. Louis.
In an attempt to address this, Dr. Fehniger and his colleagues combined rituximab, an anti-CD20 antibody, with a relatively new IL-15 agonist immunostimulatory agent called ALT-803.
In the phase 1 trial, the researchers enrolled patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma who had relapsed after at least 1 prior to CD20 antibody containing therapy. The study was a standard 3+3 dose escalation design with rituximab administered by intravenous infusion, 375 mg/m2 in four weekly doses, followed by a rest and four consolidation doses every 8 weeks for four cycles.
ALT-803 was administered concurrently at dose levels of 1 mcg/kg, 3 mcg/kg, and 6 mcg/kg IV followed by 6 mcg/kg, 10 mcg/kg, 15 mcg/kg, and 20 mcg/kg subcutaneously.
In total, 21 patients were treated: 16 patients had follicular lymphoma, four patients had marginal zone lymphoma, and one patient had small lymphocytic lymphoma. The median prior therapies received was two (range: 1-18) and five patients were treated who were refractory to prior anti-CD20 MAb therapy.
ALT-803 was well tolerated with no dose limiting toxicities or grade 4 or 5 adverse events. No patients discontinued ALT-803 and the recommended phase 2 dose was 20 mcg/kg subcutaneously. Grade 3 adverse events, regardless of attribution to ALT-803, included transient hypertension (14%), anemia (5%), nausea (5%), chills (5%), fever (5%), neutropenia (5%), and hyperglycemia (5%).
“Patients who received [subcutaneous] ALT-803 developed a unique injection site rash reaction that peaked 7-10 days later but resolved typically within 14 days. It was self-limited and resolved on its own,” Dr. Fehniger said.
At the time of the presentation, the best overall response rate was achieved in 11 of 21 patients (52%), with 9 complete responders (43%), and 2 partial responders (10%).
Of the 12 patients treated with ALT-803 subcutaneously, 11 patients had either stable disease, or partial or complete responses. All 11 patients remained on study and were in consolidation or follow-up and have not relapsed, Dr. Fehniger reported.
Among the five rituximab-refractory patients, the researchers observed one complete response, two patients with stable disease (45% and 36% tumor volume decrease), and two patients with partial disease. The durability of the responses can only be understood with longer follow-up, Dr. Fehniger said.
The peripheral blood of the patients was analyzed via flow cytometry and mass cytometry. Over the duration of four weekly doses, there was an increase in percentage (sixfold, P less than .001) and absolute number (10-fold, P less than .001) of natural killer cells at the 15-mcg/kg and 20-mcg/kg subcutaneous dose levels of ALT-803.
These results suggest that further studies of ALT-803 with other therapeutic targeting mAbs, or other immunotherapy modalities, are warranted, the researchers concluded.
Dr. Fehniger reported research funding from Altor BioScience.
SOURCE: Fehniger TA et al. AACR Annual Meeting, Abstract CT146.
REPORTING FROM THE AACR ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The ALT-803 plus rituximab combination achieved an overall response rate in 52% of patients, a complete response in 43%, and partial response in 10%.
Study details: A phase 1 study of 21 patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Disclosures: Dr. Fehniger reported research funding from Altor BioScience LLC.
Source: Fehniger TA et al. AACR Annual Meeting, Abstract CT146.
Mohs Micrographic Surgery for Digital Melanoma and Nonmelanoma Skin Cancers
Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) is a specialized surgical technique for the treatment of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSCs).1-3 The procedure involves surgical excision, histopathologic examination, precise mapping of malignant tissue, and wound management. Indications for MMS in skin cancer patients include recurring lesions, lesions in high-risk anatomic locations, aggressive histologic subtypes (ie, morpheaform, micronodular, infiltrative, high-grade, poorly differentiated), perineural invasion, large lesion size (>2 cm in diameter), poorly defined lateral or vertical clinical borders, rapid growth of the lesion, immunocompromised status, and sites of positive margins on prior excision. The therapeutic advantages of MMS include tissue conservation and optimal margin control in cosmetically or functionally sensitive areas, such as acral sites (eg, hands, feet, digits).1,3
The intricacies of the nail apparatus complicate diagnostic biopsy and precise delineation of peripheral margins in digital skin cancers; thus, early diagnosis and intraoperative histologic examination of the margins are essential. Traditionally, the surgical approach to subungual cutaneous tumors such as melanoma has included digital amputation4; however, a study of the treatment of subungual melanoma revealed no difference in survival based on the level of amputation, therefore advocating for less radical treatment.4
Interestingly, MMS for cutaneous tumors localized to the digits is not frequently reviewed in the dermatologic literature. We present a retrospective case series evaluating the clinical outcomes of digital melanoma and NMSCs treated with MMS.
Methods
A retrospective chart review was performed at a private dermatology practice to identify patients who underwent MMS for melanoma or NMSC localized to the digits from January 2009 to December 2014. All patients were treated in the office by 1 Mohs surgeon (A.H.) and were evaluated before and after MMS. Data were collected from the electronic medical record of the practice, including patient demographics, histopathologic diagnosis, tumor status (primary or recurrent lesion), anatomic site of the tumor, preoperative and postoperative size of the lesion, number of MMS stages, surgical repair technique, postoperative complications, and follow-up period.
Results
Twenty-seven patients (13 male, 14 female) with a total of 28 lesions (malignant melanoma or NMSC) localized to the digits were identified (Table). The mean age at the time of MMS was 64.07 years.
Surgical techniques used for repair following MMS included xenograft (10/28 [35.71%]); split-thickness skin graft (7/28 [25.0%]); secondary intention (4/28 [14.29%]); flap (4/28 [14.29%]); full-thickness skin graft (2/28 [7.14%]); and complex closure (1/28 [3.57%]). Clinical preoperative, operative, and postoperative photos from Patient 21 in this series are shown here (Figure). Two patients required bony phalanx resection due to invasion of the tumor into the periosteum: 1 had a malignant melanoma (Breslow depth, 2.52 mm); the other had an SCC. In addition, following removal of a severely dysplastic nevus, debulked tissue revealed melanoma in 1 patient.
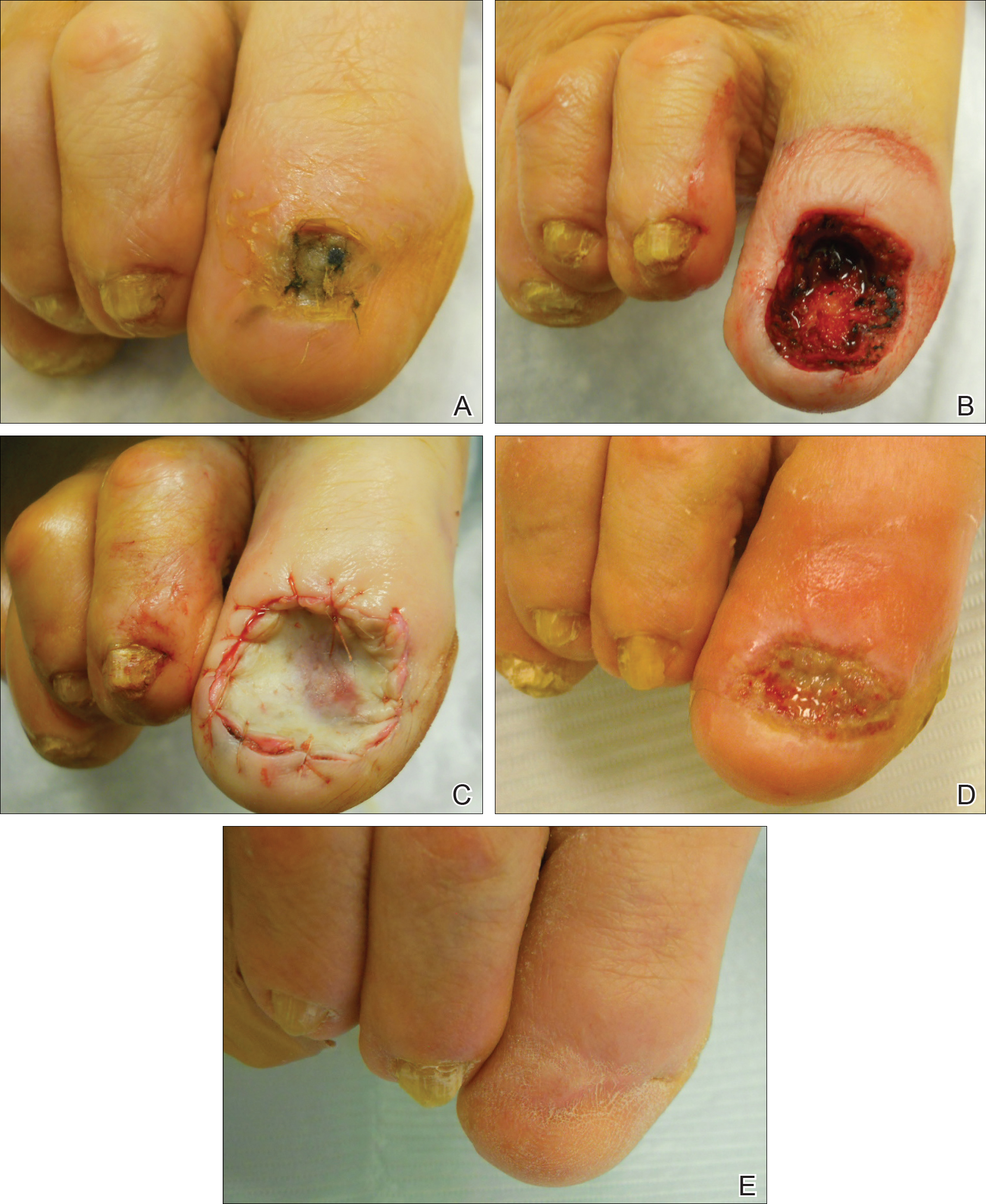
Postoperative complications were noted in 4 (14.29%) of 28 MMS procedures, including bacterial wound infection (3.57%), excess granulation tissue that required wound debridement (7.14%), and delay in wound healing (3.57%). Follow-up data were available for 25 of the 28 MMS procedures (mean follow-up, 35.4 months), during which no recurrences were observed.
Comment
Mohs micrographic surgery is a specialized technique used in the treatment of cutaneous tumors, including basal cell carcinoma, SCC, melanoma in situ, atypical fibroxanthoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, sebaceous carcinoma, microcystic adnexal carcinoma, and Merkel cell carcinoma, among other cutaneous tumors.1-3 Mohs micrographic surgery provides the advantage of tissue conservation as well as optimal margin control in cosmetically or functionally sensitive areas while providing a higher cure rate than surgical excision. During the procedure, the surgical margin is examined histologically, thus ensuring definitive removal of the tumor but minimal loss of surrounding normal tissue.1-3 Mohs micrographic surgery is particularly useful for treating lesions on acral sites (eg, hands, feet, and digits).3-5
The treatment of digital skin cancers has evolved over the past 50 years with advancements resulting in more precise, tissue-sparing methods, in contrast to previous treatments such as amputation and wide local excision.6 More specifically, traditional digital amputation for the treatment of subungual melanoma has been reevaluated in multiple studies, which did not demonstrate a statistically significant difference in survival based on the level of amputation, thereby favoring less radical treatment.4,6 Moehrle et al7 found no statistical difference in recurrence rate when comparing patients with digital melanomas treated with partial amputation and those treated with digit-sparing surgery with limited excision and histologic evaluation of margins. Additionally, in a study conducted by Lazar et al,8 no recurrence of 13 subungual malignancies treated with MMS that utilized a full-thickness graft was reported at 4-year follow-up. In a large retrospective series of digital melanomas treated with MMS, Terushkin et al5 reported that 96.5% (55/57) of patients with primary melanomas that were treated with MMS avoided amputation, and the 5- and 10-year melanoma-specific survival rates for all patients treated with MMS were 95.0% and 82.6%, respectively.
In our study, cutaneous malignancies were located most often on the fingers, and the most common skin cancer identified was SCC in situ. The literature has shown that SCC in situ and SCC are the most common cutaneous neoplasms of the digits and nail unit.9 The most common specific anatomic site of cutaneous malignancy in our study was the great toe, followed by the fourth finger. A study conducted by Tan et al9 revealed that the great toe was the most common location of melanoma of the nail bed and subungual region, followed by the thumb. In contrast, primary subungual SCCs occur most frequently on the finger, with rare cases involving the toes.10
The etiology of digital SCC may involve extensive sun exposure, chronic trauma and wounds, and viral infection.9,11 More specifically, the dermatologic literature provides evidence of human papillomavirus (HPV) type 16 involvement in the pathogenesis of digital and periungual SCC. A genital-digital mechanism of spread has been implicated.11,12 An increased recurrence rate of HPV-associated digital SCCs has been reported following MMS, likely secondary to residual postsurgical HPV infection.11,12
Maintaining function and cosmesis of the hands, feet, and digits following MMS can be challenging, sometimes requiring skin grafts and flaps to close the defect. In the 28 MMS procedures evaluated in our study, 19 (67.9%) surgical defects were repaired with a graft (ie, split-thickness skin graft, full-thickness skin graft, xenograft), 4 (14.3%) with a flap (advancement and rotation), 4 (14.3%) by secondary intention, and 1 (3.6%) with primary complex closure.
Surgical grafts can be categorized based on the origin of the graft.2,13 Autografts, derived from the patient’s skin, are the most frequently used dermatologic graft and can be further categorized as full-thickness skin grafts, which include the epidermis and the entire dermis, thus preserving adnexal structures, and split-thickness skin grafts, which include the epidermis and partial dermis.2,13
A cross-sectional survey of fellowship-trained Mohs surgeons revealed that more than two-thirds of repairs for cutaneous acral cancers were performed using a primary closure technique, and one-fourth of closures were performed using secondary intention.15 Of the less frequently utilized skin-graft repairs, more were for acral lesions on the legs than on the arms.14 The type of procedure and graft used is dependent on multiple variables, including the anatomic location of the lesion and final size of the defect following MMS.2 Similarly, the use of specific types of sutures depends on the anatomic location of the lesion, relative thickness of the skin, degree of tension, and desired cosmetic result.15 The expertise of a hand surgeon may be required, particularly in cases in which the extensor tendon of the distal interphalangeal joint is compromised, manifested by a droopy fingertip when the hand is held horizontally. Additionally, special attention should be paid to removing the entire nail matrix before skin grafting for subungual tumors to avoid nail growth under the skin graft.
Evaluation of debulked tissue from digital skin cancers proved to be important in our study. In Patient 21, debulked tissue revealed melanoma following removal of a severely dysplastic nevus. This finding emphasizes the importance of complete excision of such lesions, as remaining underlying portions of the lesion can reveal residual tumor of the same or different histopathology.
In a prospective study, MMS was shown to have a low rate (0.91%; 95% confidence interval, 0.38%-1.45%) of surgical site infection in the absence of prophylactic antibiotics.16 The highest rates of surgical site infection were closely associated with flap closure. In our study, most patients had an uncomplicated and successful postoperative recovery. Only 1 (3.57%) of the 28 MMS procedures (Patient 22) was complicated by a bacterial wound infection postoperatively. The lesion removed in this case was a severely dysplastic melanocytic nevus on the toe. Infection resolved after a course of oral antibiotics, but the underlying cause of the wound infection in the patient was unclear. Other postoperative complications in our study included delayed wound healing and excess granulation tissue requiring wound debridement.
There are limited data in the dermatologic literature regarding outcomes following MMS for the treatment of cutaneous malignancies localized to the digits.
Additional limitations of this case review include its single-center and retrospective design, the small sample size, and 1 Mohs surgeon having performed all surgeries.
Conclusion
This study provides further evidence of the benefit of MMS for the treatment of malignant melanoma and NMSCs of the digits. This procedure provides margin-controlled excision of these malignant neoplasms while preserving maximal normal tissue, thereby providing patients with improved postoperative function and cosmesis. Long-term follow-up data demonstrating a lack of tumor recurrence underscores the assertion that MMS is safe and effective for the treatment of skin cancer of the digits.
- Dim-Jamora KC, Perone JB. Management of cutaneous tumors with mohs micrographic surgery. Semin Plast Surg. 2008;22:247-256.
- McLeod MP, Choudhary S, Alqubaisy YA, et al. Indications for Mohs micrographic surgery. In: Nouri K, ed. Mohs Micrographic Surgery. New York, NY: Springer; 2012:5-13.
- Loosemore MP, Morales-Burgos A, Goldberg LH. Acral lentiginous melanoma of the toe treated using Mohs surgery with sparing of the digit and subsequent reconstruction using split-thickness skin graft. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:136-138.
- Rayatt SS, Dancey AL, Davison PM. Thumb subungual melanoma: is amputation necessary? J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2007;60:635-638.
- Terushkin V, Brodland DG, Sharon DJ, et al. Digit-sparing Mohs surgery for melanoma. Dermatol Surg. 2016;42:83-93.
- Viola KV, Jhaveri MB, Soulos PR, et al. Mohs micrographic surgery and surgical excision for nonmelanoma skin cancer treatment in the Medicare population. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:473-477.
- Moehrle M, Metzger S, Schippert W. “Functional” surgery in subungual melanoma. Dermatol Surg. 2003;29:366-374.
- Lazar A, Abimelec P, Dumontier C, et al. Full thickness skin graft from nail unit reconstruction. J Hand Surg Br. 2005;30:194-198.
- Tan KB, Moncrieff M, Thompson JF, et al. Subungual melanoma: a study of 124 cases highlighting features of early lesions, potential for histologic reports. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:1902-1912.
- Nasca MR, Innocenzi D, Micali G. Subungual squamous cell carcinoma of the toe: report on three cases. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30:345-348.
- Dika E, Piraccini BM, Balestri RR, et al. Mohs surgery for squamous cell carcinoma of the nail: report of 15 cases. our experience and a long-term follow-up. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1310-1314.
- Alam M, Caldwell JB, Eliezri YD. Human papillomavirus-associated digital squamous cell carcinoma: literature review and report of 21 new cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:385-393.
- Filho L, Anselmo J, Dadalti P, et al. Skin grafts in cutaneous oncology. Braz Ann Dermatol. 2006;81:465-472.
- Raimer DW, Group AR, Petitt MS, et al. Porcine xenograft biosynthetic wound dressings for the management of postoperative Mohs wounds. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:1.
- Alam M, Helenowksi IB, Cohen JL, et al. Association between type of reconstruction after Mohs micrographic surgery and surgeon-, patient-, and tumor-specific features: a cross-sectional study. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:51-55.
- Rogers HD, Desciak EB, Marcus RP, et al. Prospective study of wound infections in Mohs micrographic surgery using clean surgical technique in the absence of prophylactic antibiotics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:842-851.
Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) is a specialized surgical technique for the treatment of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSCs).1-3 The procedure involves surgical excision, histopathologic examination, precise mapping of malignant tissue, and wound management. Indications for MMS in skin cancer patients include recurring lesions, lesions in high-risk anatomic locations, aggressive histologic subtypes (ie, morpheaform, micronodular, infiltrative, high-grade, poorly differentiated), perineural invasion, large lesion size (>2 cm in diameter), poorly defined lateral or vertical clinical borders, rapid growth of the lesion, immunocompromised status, and sites of positive margins on prior excision. The therapeutic advantages of MMS include tissue conservation and optimal margin control in cosmetically or functionally sensitive areas, such as acral sites (eg, hands, feet, digits).1,3
The intricacies of the nail apparatus complicate diagnostic biopsy and precise delineation of peripheral margins in digital skin cancers; thus, early diagnosis and intraoperative histologic examination of the margins are essential. Traditionally, the surgical approach to subungual cutaneous tumors such as melanoma has included digital amputation4; however, a study of the treatment of subungual melanoma revealed no difference in survival based on the level of amputation, therefore advocating for less radical treatment.4
Interestingly, MMS for cutaneous tumors localized to the digits is not frequently reviewed in the dermatologic literature. We present a retrospective case series evaluating the clinical outcomes of digital melanoma and NMSCs treated with MMS.
Methods
A retrospective chart review was performed at a private dermatology practice to identify patients who underwent MMS for melanoma or NMSC localized to the digits from January 2009 to December 2014. All patients were treated in the office by 1 Mohs surgeon (A.H.) and were evaluated before and after MMS. Data were collected from the electronic medical record of the practice, including patient demographics, histopathologic diagnosis, tumor status (primary or recurrent lesion), anatomic site of the tumor, preoperative and postoperative size of the lesion, number of MMS stages, surgical repair technique, postoperative complications, and follow-up period.
Results
Twenty-seven patients (13 male, 14 female) with a total of 28 lesions (malignant melanoma or NMSC) localized to the digits were identified (Table). The mean age at the time of MMS was 64.07 years.

Surgical techniques used for repair following MMS included xenograft (10/28 [35.71%]); split-thickness skin graft (7/28 [25.0%]); secondary intention (4/28 [14.29%]); flap (4/28 [14.29%]); full-thickness skin graft (2/28 [7.14%]); and complex closure (1/28 [3.57%]). Clinical preoperative, operative, and postoperative photos from Patient 21 in this series are shown here (Figure). Two patients required bony phalanx resection due to invasion of the tumor into the periosteum: 1 had a malignant melanoma (Breslow depth, 2.52 mm); the other had an SCC. In addition, following removal of a severely dysplastic nevus, debulked tissue revealed melanoma in 1 patient.

Postoperative complications were noted in 4 (14.29%) of 28 MMS procedures, including bacterial wound infection (3.57%), excess granulation tissue that required wound debridement (7.14%), and delay in wound healing (3.57%). Follow-up data were available for 25 of the 28 MMS procedures (mean follow-up, 35.4 months), during which no recurrences were observed.
Comment
Mohs micrographic surgery is a specialized technique used in the treatment of cutaneous tumors, including basal cell carcinoma, SCC, melanoma in situ, atypical fibroxanthoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, sebaceous carcinoma, microcystic adnexal carcinoma, and Merkel cell carcinoma, among other cutaneous tumors.1-3 Mohs micrographic surgery provides the advantage of tissue conservation as well as optimal margin control in cosmetically or functionally sensitive areas while providing a higher cure rate than surgical excision. During the procedure, the surgical margin is examined histologically, thus ensuring definitive removal of the tumor but minimal loss of surrounding normal tissue.1-3 Mohs micrographic surgery is particularly useful for treating lesions on acral sites (eg, hands, feet, and digits).3-5
The treatment of digital skin cancers has evolved over the past 50 years with advancements resulting in more precise, tissue-sparing methods, in contrast to previous treatments such as amputation and wide local excision.6 More specifically, traditional digital amputation for the treatment of subungual melanoma has been reevaluated in multiple studies, which did not demonstrate a statistically significant difference in survival based on the level of amputation, thereby favoring less radical treatment.4,6 Moehrle et al7 found no statistical difference in recurrence rate when comparing patients with digital melanomas treated with partial amputation and those treated with digit-sparing surgery with limited excision and histologic evaluation of margins. Additionally, in a study conducted by Lazar et al,8 no recurrence of 13 subungual malignancies treated with MMS that utilized a full-thickness graft was reported at 4-year follow-up. In a large retrospective series of digital melanomas treated with MMS, Terushkin et al5 reported that 96.5% (55/57) of patients with primary melanomas that were treated with MMS avoided amputation, and the 5- and 10-year melanoma-specific survival rates for all patients treated with MMS were 95.0% and 82.6%, respectively.
In our study, cutaneous malignancies were located most often on the fingers, and the most common skin cancer identified was SCC in situ. The literature has shown that SCC in situ and SCC are the most common cutaneous neoplasms of the digits and nail unit.9 The most common specific anatomic site of cutaneous malignancy in our study was the great toe, followed by the fourth finger. A study conducted by Tan et al9 revealed that the great toe was the most common location of melanoma of the nail bed and subungual region, followed by the thumb. In contrast, primary subungual SCCs occur most frequently on the finger, with rare cases involving the toes.10
The etiology of digital SCC may involve extensive sun exposure, chronic trauma and wounds, and viral infection.9,11 More specifically, the dermatologic literature provides evidence of human papillomavirus (HPV) type 16 involvement in the pathogenesis of digital and periungual SCC. A genital-digital mechanism of spread has been implicated.11,12 An increased recurrence rate of HPV-associated digital SCCs has been reported following MMS, likely secondary to residual postsurgical HPV infection.11,12
Maintaining function and cosmesis of the hands, feet, and digits following MMS can be challenging, sometimes requiring skin grafts and flaps to close the defect. In the 28 MMS procedures evaluated in our study, 19 (67.9%) surgical defects were repaired with a graft (ie, split-thickness skin graft, full-thickness skin graft, xenograft), 4 (14.3%) with a flap (advancement and rotation), 4 (14.3%) by secondary intention, and 1 (3.6%) with primary complex closure.
Surgical grafts can be categorized based on the origin of the graft.2,13 Autografts, derived from the patient’s skin, are the most frequently used dermatologic graft and can be further categorized as full-thickness skin grafts, which include the epidermis and the entire dermis, thus preserving adnexal structures, and split-thickness skin grafts, which include the epidermis and partial dermis.2,13
A cross-sectional survey of fellowship-trained Mohs surgeons revealed that more than two-thirds of repairs for cutaneous acral cancers were performed using a primary closure technique, and one-fourth of closures were performed using secondary intention.15 Of the less frequently utilized skin-graft repairs, more were for acral lesions on the legs than on the arms.14 The type of procedure and graft used is dependent on multiple variables, including the anatomic location of the lesion and final size of the defect following MMS.2 Similarly, the use of specific types of sutures depends on the anatomic location of the lesion, relative thickness of the skin, degree of tension, and desired cosmetic result.15 The expertise of a hand surgeon may be required, particularly in cases in which the extensor tendon of the distal interphalangeal joint is compromised, manifested by a droopy fingertip when the hand is held horizontally. Additionally, special attention should be paid to removing the entire nail matrix before skin grafting for subungual tumors to avoid nail growth under the skin graft.
Evaluation of debulked tissue from digital skin cancers proved to be important in our study. In Patient 21, debulked tissue revealed melanoma following removal of a severely dysplastic nevus. This finding emphasizes the importance of complete excision of such lesions, as remaining underlying portions of the lesion can reveal residual tumor of the same or different histopathology.
In a prospective study, MMS was shown to have a low rate (0.91%; 95% confidence interval, 0.38%-1.45%) of surgical site infection in the absence of prophylactic antibiotics.16 The highest rates of surgical site infection were closely associated with flap closure. In our study, most patients had an uncomplicated and successful postoperative recovery. Only 1 (3.57%) of the 28 MMS procedures (Patient 22) was complicated by a bacterial wound infection postoperatively. The lesion removed in this case was a severely dysplastic melanocytic nevus on the toe. Infection resolved after a course of oral antibiotics, but the underlying cause of the wound infection in the patient was unclear. Other postoperative complications in our study included delayed wound healing and excess granulation tissue requiring wound debridement.
There are limited data in the dermatologic literature regarding outcomes following MMS for the treatment of cutaneous malignancies localized to the digits.
Additional limitations of this case review include its single-center and retrospective design, the small sample size, and 1 Mohs surgeon having performed all surgeries.
Conclusion
This study provides further evidence of the benefit of MMS for the treatment of malignant melanoma and NMSCs of the digits. This procedure provides margin-controlled excision of these malignant neoplasms while preserving maximal normal tissue, thereby providing patients with improved postoperative function and cosmesis. Long-term follow-up data demonstrating a lack of tumor recurrence underscores the assertion that MMS is safe and effective for the treatment of skin cancer of the digits.
Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) is a specialized surgical technique for the treatment of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSCs).1-3 The procedure involves surgical excision, histopathologic examination, precise mapping of malignant tissue, and wound management. Indications for MMS in skin cancer patients include recurring lesions, lesions in high-risk anatomic locations, aggressive histologic subtypes (ie, morpheaform, micronodular, infiltrative, high-grade, poorly differentiated), perineural invasion, large lesion size (>2 cm in diameter), poorly defined lateral or vertical clinical borders, rapid growth of the lesion, immunocompromised status, and sites of positive margins on prior excision. The therapeutic advantages of MMS include tissue conservation and optimal margin control in cosmetically or functionally sensitive areas, such as acral sites (eg, hands, feet, digits).1,3
The intricacies of the nail apparatus complicate diagnostic biopsy and precise delineation of peripheral margins in digital skin cancers; thus, early diagnosis and intraoperative histologic examination of the margins are essential. Traditionally, the surgical approach to subungual cutaneous tumors such as melanoma has included digital amputation4; however, a study of the treatment of subungual melanoma revealed no difference in survival based on the level of amputation, therefore advocating for less radical treatment.4
Interestingly, MMS for cutaneous tumors localized to the digits is not frequently reviewed in the dermatologic literature. We present a retrospective case series evaluating the clinical outcomes of digital melanoma and NMSCs treated with MMS.
Methods
A retrospective chart review was performed at a private dermatology practice to identify patients who underwent MMS for melanoma or NMSC localized to the digits from January 2009 to December 2014. All patients were treated in the office by 1 Mohs surgeon (A.H.) and were evaluated before and after MMS. Data were collected from the electronic medical record of the practice, including patient demographics, histopathologic diagnosis, tumor status (primary or recurrent lesion), anatomic site of the tumor, preoperative and postoperative size of the lesion, number of MMS stages, surgical repair technique, postoperative complications, and follow-up period.
Results
Twenty-seven patients (13 male, 14 female) with a total of 28 lesions (malignant melanoma or NMSC) localized to the digits were identified (Table). The mean age at the time of MMS was 64.07 years.

Surgical techniques used for repair following MMS included xenograft (10/28 [35.71%]); split-thickness skin graft (7/28 [25.0%]); secondary intention (4/28 [14.29%]); flap (4/28 [14.29%]); full-thickness skin graft (2/28 [7.14%]); and complex closure (1/28 [3.57%]). Clinical preoperative, operative, and postoperative photos from Patient 21 in this series are shown here (Figure). Two patients required bony phalanx resection due to invasion of the tumor into the periosteum: 1 had a malignant melanoma (Breslow depth, 2.52 mm); the other had an SCC. In addition, following removal of a severely dysplastic nevus, debulked tissue revealed melanoma in 1 patient.

Postoperative complications were noted in 4 (14.29%) of 28 MMS procedures, including bacterial wound infection (3.57%), excess granulation tissue that required wound debridement (7.14%), and delay in wound healing (3.57%). Follow-up data were available for 25 of the 28 MMS procedures (mean follow-up, 35.4 months), during which no recurrences were observed.
Comment
Mohs micrographic surgery is a specialized technique used in the treatment of cutaneous tumors, including basal cell carcinoma, SCC, melanoma in situ, atypical fibroxanthoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, sebaceous carcinoma, microcystic adnexal carcinoma, and Merkel cell carcinoma, among other cutaneous tumors.1-3 Mohs micrographic surgery provides the advantage of tissue conservation as well as optimal margin control in cosmetically or functionally sensitive areas while providing a higher cure rate than surgical excision. During the procedure, the surgical margin is examined histologically, thus ensuring definitive removal of the tumor but minimal loss of surrounding normal tissue.1-3 Mohs micrographic surgery is particularly useful for treating lesions on acral sites (eg, hands, feet, and digits).3-5
The treatment of digital skin cancers has evolved over the past 50 years with advancements resulting in more precise, tissue-sparing methods, in contrast to previous treatments such as amputation and wide local excision.6 More specifically, traditional digital amputation for the treatment of subungual melanoma has been reevaluated in multiple studies, which did not demonstrate a statistically significant difference in survival based on the level of amputation, thereby favoring less radical treatment.4,6 Moehrle et al7 found no statistical difference in recurrence rate when comparing patients with digital melanomas treated with partial amputation and those treated with digit-sparing surgery with limited excision and histologic evaluation of margins. Additionally, in a study conducted by Lazar et al,8 no recurrence of 13 subungual malignancies treated with MMS that utilized a full-thickness graft was reported at 4-year follow-up. In a large retrospective series of digital melanomas treated with MMS, Terushkin et al5 reported that 96.5% (55/57) of patients with primary melanomas that were treated with MMS avoided amputation, and the 5- and 10-year melanoma-specific survival rates for all patients treated with MMS were 95.0% and 82.6%, respectively.
In our study, cutaneous malignancies were located most often on the fingers, and the most common skin cancer identified was SCC in situ. The literature has shown that SCC in situ and SCC are the most common cutaneous neoplasms of the digits and nail unit.9 The most common specific anatomic site of cutaneous malignancy in our study was the great toe, followed by the fourth finger. A study conducted by Tan et al9 revealed that the great toe was the most common location of melanoma of the nail bed and subungual region, followed by the thumb. In contrast, primary subungual SCCs occur most frequently on the finger, with rare cases involving the toes.10
The etiology of digital SCC may involve extensive sun exposure, chronic trauma and wounds, and viral infection.9,11 More specifically, the dermatologic literature provides evidence of human papillomavirus (HPV) type 16 involvement in the pathogenesis of digital and periungual SCC. A genital-digital mechanism of spread has been implicated.11,12 An increased recurrence rate of HPV-associated digital SCCs has been reported following MMS, likely secondary to residual postsurgical HPV infection.11,12
Maintaining function and cosmesis of the hands, feet, and digits following MMS can be challenging, sometimes requiring skin grafts and flaps to close the defect. In the 28 MMS procedures evaluated in our study, 19 (67.9%) surgical defects were repaired with a graft (ie, split-thickness skin graft, full-thickness skin graft, xenograft), 4 (14.3%) with a flap (advancement and rotation), 4 (14.3%) by secondary intention, and 1 (3.6%) with primary complex closure.
Surgical grafts can be categorized based on the origin of the graft.2,13 Autografts, derived from the patient’s skin, are the most frequently used dermatologic graft and can be further categorized as full-thickness skin grafts, which include the epidermis and the entire dermis, thus preserving adnexal structures, and split-thickness skin grafts, which include the epidermis and partial dermis.2,13
A cross-sectional survey of fellowship-trained Mohs surgeons revealed that more than two-thirds of repairs for cutaneous acral cancers were performed using a primary closure technique, and one-fourth of closures were performed using secondary intention.15 Of the less frequently utilized skin-graft repairs, more were for acral lesions on the legs than on the arms.14 The type of procedure and graft used is dependent on multiple variables, including the anatomic location of the lesion and final size of the defect following MMS.2 Similarly, the use of specific types of sutures depends on the anatomic location of the lesion, relative thickness of the skin, degree of tension, and desired cosmetic result.15 The expertise of a hand surgeon may be required, particularly in cases in which the extensor tendon of the distal interphalangeal joint is compromised, manifested by a droopy fingertip when the hand is held horizontally. Additionally, special attention should be paid to removing the entire nail matrix before skin grafting for subungual tumors to avoid nail growth under the skin graft.
Evaluation of debulked tissue from digital skin cancers proved to be important in our study. In Patient 21, debulked tissue revealed melanoma following removal of a severely dysplastic nevus. This finding emphasizes the importance of complete excision of such lesions, as remaining underlying portions of the lesion can reveal residual tumor of the same or different histopathology.
In a prospective study, MMS was shown to have a low rate (0.91%; 95% confidence interval, 0.38%-1.45%) of surgical site infection in the absence of prophylactic antibiotics.16 The highest rates of surgical site infection were closely associated with flap closure. In our study, most patients had an uncomplicated and successful postoperative recovery. Only 1 (3.57%) of the 28 MMS procedures (Patient 22) was complicated by a bacterial wound infection postoperatively. The lesion removed in this case was a severely dysplastic melanocytic nevus on the toe. Infection resolved after a course of oral antibiotics, but the underlying cause of the wound infection in the patient was unclear. Other postoperative complications in our study included delayed wound healing and excess granulation tissue requiring wound debridement.
There are limited data in the dermatologic literature regarding outcomes following MMS for the treatment of cutaneous malignancies localized to the digits.
Additional limitations of this case review include its single-center and retrospective design, the small sample size, and 1 Mohs surgeon having performed all surgeries.
Conclusion
This study provides further evidence of the benefit of MMS for the treatment of malignant melanoma and NMSCs of the digits. This procedure provides margin-controlled excision of these malignant neoplasms while preserving maximal normal tissue, thereby providing patients with improved postoperative function and cosmesis. Long-term follow-up data demonstrating a lack of tumor recurrence underscores the assertion that MMS is safe and effective for the treatment of skin cancer of the digits.
- Dim-Jamora KC, Perone JB. Management of cutaneous tumors with mohs micrographic surgery. Semin Plast Surg. 2008;22:247-256.
- McLeod MP, Choudhary S, Alqubaisy YA, et al. Indications for Mohs micrographic surgery. In: Nouri K, ed. Mohs Micrographic Surgery. New York, NY: Springer; 2012:5-13.
- Loosemore MP, Morales-Burgos A, Goldberg LH. Acral lentiginous melanoma of the toe treated using Mohs surgery with sparing of the digit and subsequent reconstruction using split-thickness skin graft. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:136-138.
- Rayatt SS, Dancey AL, Davison PM. Thumb subungual melanoma: is amputation necessary? J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2007;60:635-638.
- Terushkin V, Brodland DG, Sharon DJ, et al. Digit-sparing Mohs surgery for melanoma. Dermatol Surg. 2016;42:83-93.
- Viola KV, Jhaveri MB, Soulos PR, et al. Mohs micrographic surgery and surgical excision for nonmelanoma skin cancer treatment in the Medicare population. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:473-477.
- Moehrle M, Metzger S, Schippert W. “Functional” surgery in subungual melanoma. Dermatol Surg. 2003;29:366-374.
- Lazar A, Abimelec P, Dumontier C, et al. Full thickness skin graft from nail unit reconstruction. J Hand Surg Br. 2005;30:194-198.
- Tan KB, Moncrieff M, Thompson JF, et al. Subungual melanoma: a study of 124 cases highlighting features of early lesions, potential for histologic reports. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:1902-1912.
- Nasca MR, Innocenzi D, Micali G. Subungual squamous cell carcinoma of the toe: report on three cases. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30:345-348.
- Dika E, Piraccini BM, Balestri RR, et al. Mohs surgery for squamous cell carcinoma of the nail: report of 15 cases. our experience and a long-term follow-up. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1310-1314.
- Alam M, Caldwell JB, Eliezri YD. Human papillomavirus-associated digital squamous cell carcinoma: literature review and report of 21 new cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:385-393.
- Filho L, Anselmo J, Dadalti P, et al. Skin grafts in cutaneous oncology. Braz Ann Dermatol. 2006;81:465-472.
- Raimer DW, Group AR, Petitt MS, et al. Porcine xenograft biosynthetic wound dressings for the management of postoperative Mohs wounds. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:1.
- Alam M, Helenowksi IB, Cohen JL, et al. Association between type of reconstruction after Mohs micrographic surgery and surgeon-, patient-, and tumor-specific features: a cross-sectional study. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:51-55.
- Rogers HD, Desciak EB, Marcus RP, et al. Prospective study of wound infections in Mohs micrographic surgery using clean surgical technique in the absence of prophylactic antibiotics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:842-851.
- Dim-Jamora KC, Perone JB. Management of cutaneous tumors with mohs micrographic surgery. Semin Plast Surg. 2008;22:247-256.
- McLeod MP, Choudhary S, Alqubaisy YA, et al. Indications for Mohs micrographic surgery. In: Nouri K, ed. Mohs Micrographic Surgery. New York, NY: Springer; 2012:5-13.
- Loosemore MP, Morales-Burgos A, Goldberg LH. Acral lentiginous melanoma of the toe treated using Mohs surgery with sparing of the digit and subsequent reconstruction using split-thickness skin graft. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:136-138.
- Rayatt SS, Dancey AL, Davison PM. Thumb subungual melanoma: is amputation necessary? J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2007;60:635-638.
- Terushkin V, Brodland DG, Sharon DJ, et al. Digit-sparing Mohs surgery for melanoma. Dermatol Surg. 2016;42:83-93.
- Viola KV, Jhaveri MB, Soulos PR, et al. Mohs micrographic surgery and surgical excision for nonmelanoma skin cancer treatment in the Medicare population. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:473-477.
- Moehrle M, Metzger S, Schippert W. “Functional” surgery in subungual melanoma. Dermatol Surg. 2003;29:366-374.
- Lazar A, Abimelec P, Dumontier C, et al. Full thickness skin graft from nail unit reconstruction. J Hand Surg Br. 2005;30:194-198.
- Tan KB, Moncrieff M, Thompson JF, et al. Subungual melanoma: a study of 124 cases highlighting features of early lesions, potential for histologic reports. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:1902-1912.
- Nasca MR, Innocenzi D, Micali G. Subungual squamous cell carcinoma of the toe: report on three cases. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30:345-348.
- Dika E, Piraccini BM, Balestri RR, et al. Mohs surgery for squamous cell carcinoma of the nail: report of 15 cases. our experience and a long-term follow-up. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1310-1314.
- Alam M, Caldwell JB, Eliezri YD. Human papillomavirus-associated digital squamous cell carcinoma: literature review and report of 21 new cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:385-393.
- Filho L, Anselmo J, Dadalti P, et al. Skin grafts in cutaneous oncology. Braz Ann Dermatol. 2006;81:465-472.
- Raimer DW, Group AR, Petitt MS, et al. Porcine xenograft biosynthetic wound dressings for the management of postoperative Mohs wounds. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:1.
- Alam M, Helenowksi IB, Cohen JL, et al. Association between type of reconstruction after Mohs micrographic surgery and surgeon-, patient-, and tumor-specific features: a cross-sectional study. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:51-55.
- Rogers HD, Desciak EB, Marcus RP, et al. Prospective study of wound infections in Mohs micrographic surgery using clean surgical technique in the absence of prophylactic antibiotics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:842-851.
Practice Points
- Melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancers of the digits traditionally have been treated with wide local surgical excision and even amputation.
- Conservative tissue sparing techniques such as Mohs micrographic surgery can be used to treat digital skin cancers with high cure rates and improved functional and cosmetic results.