User login
Data Trends 2023: Infertility
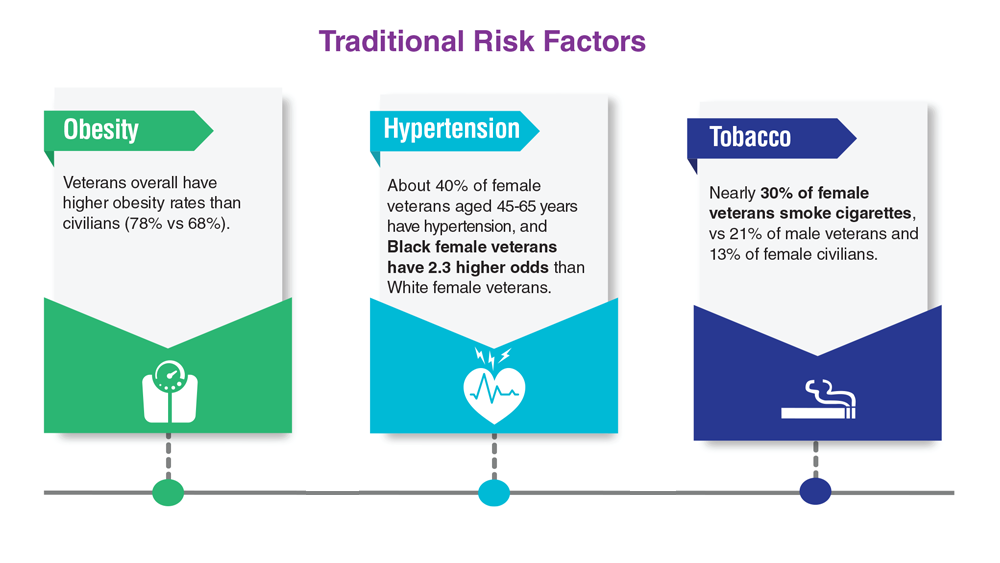
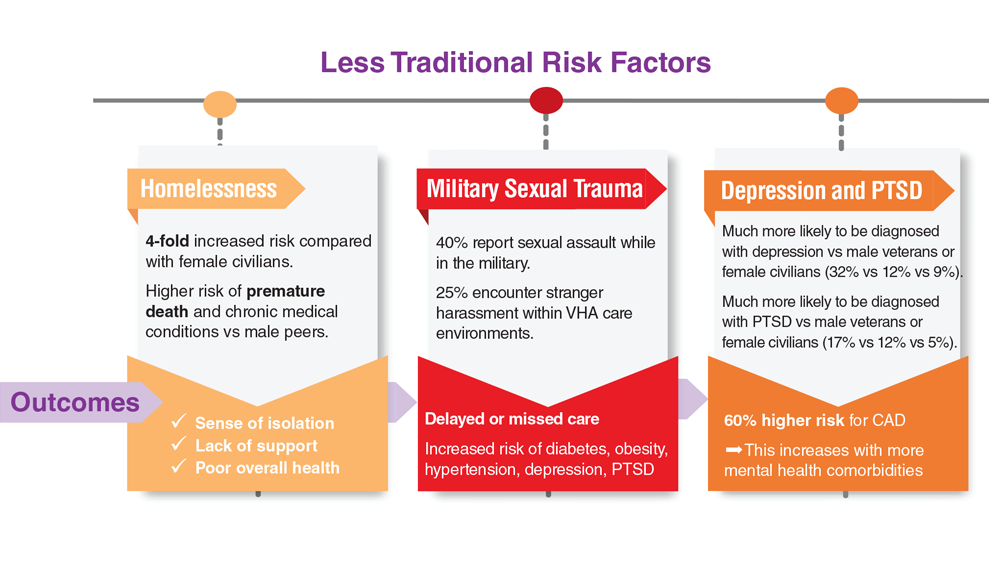
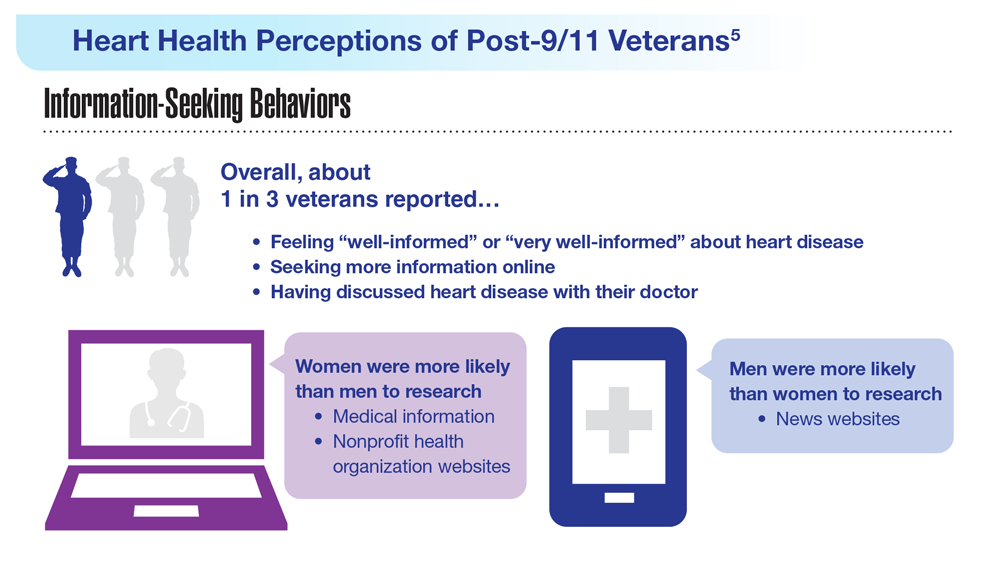
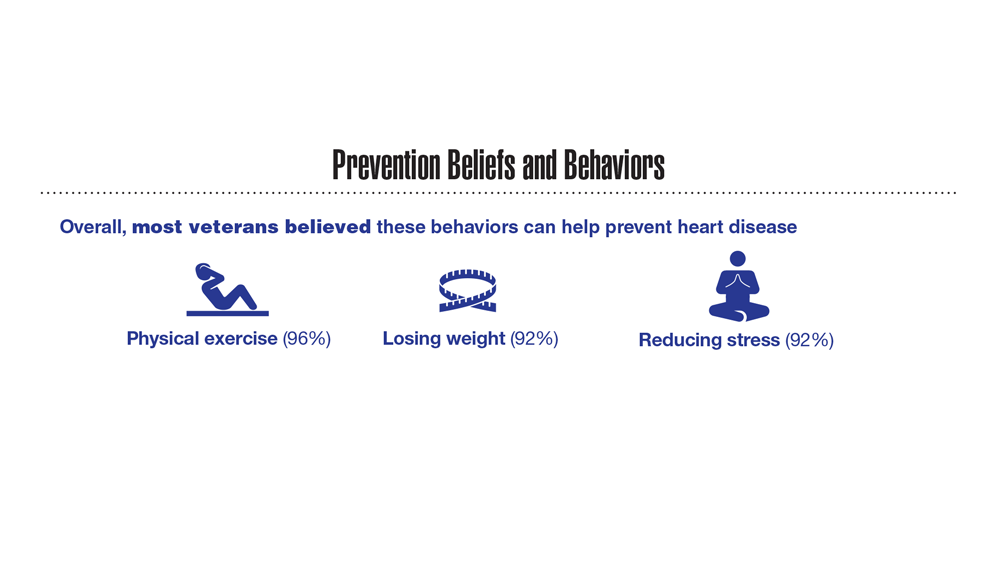
- US Department of Veteran Affairs. Facts and statistics: women veterans in focus. Updated January 31, 2023. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://www.womenshealth.va.gov/materials-and-resources/facts-and-statistics.asp
- US Department of Defense. Department of Defense Releases Annual Demographics Report — Upward Trend in Number of Women Serving Continues. Published December 14, 2022. Accessed June 12, 2023. https://www.defense.gov/News/Releases/Release/Article/3246268/department-of-defense-releases-annual-demographics-report-upwardtrend-in-numbe/
- Meadows SO, Collins RL, Schuler MS, Beckman RL, Cefalu M. The Women’s Reproductive Health Survey (WRHS) of active-duty service members. RAND Corporation. Published 2022. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_reports/RRA1031-1.html
- Congressional Research Service Report. Infertility in the military. Updated May 26, 2021. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/IF/IF11504
- Mancuso AC et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022;227(5):744.e1-744.e12. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2022.07.002
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Infertility FAQs. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/infertility/
- Kroll-Desrosiers A et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;1-7. Online ahead of print. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08080-z
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Infertility and IVF. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://www.womenshealth.va.gov/topics/infertility-and-ivf.asp
- US Department of Veteran Affairs. Facts and statistics: women veterans in focus. Updated January 31, 2023. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://www.womenshealth.va.gov/materials-and-resources/facts-and-statistics.asp
- US Department of Defense. Department of Defense Releases Annual Demographics Report — Upward Trend in Number of Women Serving Continues. Published December 14, 2022. Accessed June 12, 2023. https://www.defense.gov/News/Releases/Release/Article/3246268/department-of-defense-releases-annual-demographics-report-upwardtrend-in-numbe/
- Meadows SO, Collins RL, Schuler MS, Beckman RL, Cefalu M. The Women’s Reproductive Health Survey (WRHS) of active-duty service members. RAND Corporation. Published 2022. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_reports/RRA1031-1.html
- Congressional Research Service Report. Infertility in the military. Updated May 26, 2021. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/IF/IF11504
- Mancuso AC et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022;227(5):744.e1-744.e12. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2022.07.002
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Infertility FAQs. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/infertility/
- Kroll-Desrosiers A et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;1-7. Online ahead of print. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08080-z
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Infertility and IVF. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://www.womenshealth.va.gov/topics/infertility-and-ivf.asp
- US Department of Veteran Affairs. Facts and statistics: women veterans in focus. Updated January 31, 2023. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://www.womenshealth.va.gov/materials-and-resources/facts-and-statistics.asp
- US Department of Defense. Department of Defense Releases Annual Demographics Report — Upward Trend in Number of Women Serving Continues. Published December 14, 2022. Accessed June 12, 2023. https://www.defense.gov/News/Releases/Release/Article/3246268/department-of-defense-releases-annual-demographics-report-upwardtrend-in-numbe/
- Meadows SO, Collins RL, Schuler MS, Beckman RL, Cefalu M. The Women’s Reproductive Health Survey (WRHS) of active-duty service members. RAND Corporation. Published 2022. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_reports/RRA1031-1.html
- Congressional Research Service Report. Infertility in the military. Updated May 26, 2021. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/IF/IF11504
- Mancuso AC et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022;227(5):744.e1-744.e12. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2022.07.002
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Infertility FAQs. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/infertility/
- Kroll-Desrosiers A et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;1-7. Online ahead of print. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08080-z
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Infertility and IVF. Accessed May 5, 2023. https://www.womenshealth.va.gov/topics/infertility-and-ivf.asp
Multivitamins and dementia: Untangling the COSMOS study web
I have written before about the COSMOS study and its finding that multivitamins (and chocolate) did not improve brain or cardiovascular health. So I was surprised to read that a “new” study found that vitamins can forestall dementia and age-related cognitive decline.
Upon closer look, the new data are neither new nor convincing, at least to me.
Chocolate and multivitamins for CVD and cancer prevention
The large randomized COSMOS trial was supposed to be the definitive study on chocolate that would establish its heart-health benefits without a doubt. Or, rather, the benefits of a cocoa bean extract in pill form given to healthy, older volunteers. The COSMOS study was negative. Chocolate, or the cocoa bean extract they used, did not reduce cardiovascular events.
And yet for all the prepublication importance attached to COSMOS, it is scarcely mentioned. Had it been positive, rest assured that Mars, the candy bar company that cofunded the research, and other interested parties would have been shouting it from the rooftops. As it is, they’re already spinning it.
Which brings us to the multivitamin component. COSMOS actually had a 2 × 2 design. In other words, there were four groups in this study: chocolate plus multivitamin, chocolate plus placebo, placebo plus multivitamin, and placebo plus placebo. This type of study design allows you to study two different interventions simultaneously, provided that they are independent and do not interact with each other. In addition to the primary cardiovascular endpoint, they also studied a cancer endpoint.
The multivitamin supplement didn’t reduce cardiovascular events either. Nor did it affect cancer outcomes. The main COSMOS study was negative and reinforced what countless other studies have proven: Taking a daily multivitamin does not reduce your risk of having a heart attack or developing cancer.
But wait, there’s more: COSMOS-Mind
But no researcher worth his salt studies just one or two endpoints in a study. The participants also underwent neurologic and memory testing. These results were reported separately in the COSMOS-Mind study.
COSMOS-Mind is often described as a separate (or “new”) study. In reality, it included the same participants from the original COSMOS trial and measured yet another primary outcome of cognitive performance on a series of tests administered by telephone. Although there is nothing inherently wrong with studying multiple outcomes in your patient population (after all, that salami isn’t going to slice itself), they cannot all be primary outcomes. Some, by necessity, must be secondary hypothesis–generating outcomes. If you test enough endpoints, multiple hypothesis testing dictates that eventually you will get a positive result simply by chance.
There was a time when the neurocognitive outcomes of COSMOS would have been reported in the same paper as the cardiovascular outcomes, but that time seems to have passed us by. Researchers live or die by the number of their publications, and there is an inherent advantage to squeezing as many publications as possible from the same dataset. Though, to be fair, the journal would probably have asked them to split up the paper as well.
In brief, the cocoa extract again fell short in COSMOS-Mind, but the multivitamin arm did better on the composite cognitive outcome. It was a fairly small difference – a 0.07-point improvement on the z-score at the 3-year mark (the z-score is the mean divided by the standard deviation). Much was also made of the fact that the improvement seemed to vary by prior history of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Those with a history of CVD had a 0.11-point improvement, whereas those without had a 0.06-point improvement. The authors couldn’t offer a definitive explanation for these findings. Any argument that multivitamins improve cardiovascular health and therefore prevent vascular dementia has to contend with the fact that the main COSMOS study didn’t show a cardiovascular benefit for vitamins. Speculation that you are treating nutritional deficiencies is exactly that: speculation.
A more salient question is: What does a 0.07-point improvement on the z-score mean clinically? This study didn’t assess whether a multivitamin supplement prevented dementia or allowed people to live independently for longer. In fairness, that would have been exceptionally difficult to do and would have required a much longer study.
Their one attempt to quantify the cognitive benefit clinically was a calculation about normal age-related decline. Test scores were 0.045 points lower for every 1-year increase in age among participants (their mean age was 73 years). So the authors contend that a 0.07-point increase, or the 0.083-point increase that they found at year 3, corresponds to 1.8 years of age-related decline forestalled. Whether this is an appropriate assumption, I leave for the reader to decide.
COSMOS-Web and replication
The results of COSMOS-Mind were seemingly bolstered by the recent publication of COSMOS-Web. Although I’ve seen this study described as having replicated the results of COSMOS-Mind, that description is a bit misleading. This was yet another ancillary COSMOS study; more than half of the 2,262 participants in COSMOS-Mind were also included in COSMOS-Web. Replicating results in the same people isn’t true replication.
The main difference between COSMOS-Mind and COSMOS-Web is that the former used a telephone interview to administer the cognitive tests and the latter used the Internet. They also had different endpoints, with COSMOS-Web looking at immediate recall rather than a global test composite.
COSMOS-Web was a positive study in that patients getting the multivitamin supplement did better on the test for immediate memory recall (remembering a list of 20 words), though they didn’t improve on tests of memory retention, executive function, or novel object recognition (basically a test where subjects have to identify matching geometric patterns and then recall them later). They were able to remember an additional 0.71 word on average, compared with 0.44 word in the placebo group. (For the record, it found no benefit for the cocoa extract).
Everybody does better on memory tests the second time around because practice makes perfect, hence the improvement in the placebo group. This benefit at 1 year did not survive to the end of follow-up at 3 years, in contrast to COSMOS-Mind, where the benefit was not apparent at 1 year and seen only at year 3. A history of cardiovascular disease didn’t seem to affect the results in COSMOS-Web as it did in COSMOS-Mind. As far as replications go, COSMOS-Web has some very non-negligible differences, compared with COSMOS-Mind. This incongruity, especially given the overlap in the patient populations is hard to reconcile. If COSMOS-Web was supposed to assuage any doubts that persisted after COSMOS-Mind, it hasn’t for me.
One of these studies is not like the others
Finally, although the COSMOS trial and all its ancillary study analyses suggest a neurocognitive benefit to multivitamin supplementation, it’s not the first study to test the matter. The Age-Related Eye Disease Study looked at vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, zinc, and copper. There was no benefit on any of the six cognitive tests administered to patients. The Women’s Health Study, the Women’s Antioxidant Cardiovascular Study and PREADViSE have all failed to show any benefit to the various vitamins and minerals they studied. A meta-analysis of 11 trials found no benefit to B vitamins in slowing cognitive aging.
The claim that COSMOS is the “first” study to test the hypothesis hinges on some careful wordplay. Prior studies tested specific vitamins, not a multivitamin. In the discussion of the paper, these other studies are critiqued for being short term. But the Physicians’ Health Study II did in fact study a multivitamin and assessed cognitive performance on average 2.5 years after randomization. It found no benefit. The authors of COSMOS-Web critiqued the 2.5-year wait to perform cognitive testing, saying it would have missed any short-term benefits. Although, given that they simultaneously praised their 3 years of follow-up, the criticism is hard to fully accept or even understand.
Whether follow-up is short or long, uses individual vitamins or a multivitamin, the results excluding COSMOS are uniformly negative.
Do enough tests in the same population, and something will rise above the noise just by chance. When you get a positive result in your research, it’s always exciting. But when a slew of studies that came before you are negative, you aren’t groundbreaking. You’re an outlier.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
I have written before about the COSMOS study and its finding that multivitamins (and chocolate) did not improve brain or cardiovascular health. So I was surprised to read that a “new” study found that vitamins can forestall dementia and age-related cognitive decline.
Upon closer look, the new data are neither new nor convincing, at least to me.
Chocolate and multivitamins for CVD and cancer prevention
The large randomized COSMOS trial was supposed to be the definitive study on chocolate that would establish its heart-health benefits without a doubt. Or, rather, the benefits of a cocoa bean extract in pill form given to healthy, older volunteers. The COSMOS study was negative. Chocolate, or the cocoa bean extract they used, did not reduce cardiovascular events.
And yet for all the prepublication importance attached to COSMOS, it is scarcely mentioned. Had it been positive, rest assured that Mars, the candy bar company that cofunded the research, and other interested parties would have been shouting it from the rooftops. As it is, they’re already spinning it.
Which brings us to the multivitamin component. COSMOS actually had a 2 × 2 design. In other words, there were four groups in this study: chocolate plus multivitamin, chocolate plus placebo, placebo plus multivitamin, and placebo plus placebo. This type of study design allows you to study two different interventions simultaneously, provided that they are independent and do not interact with each other. In addition to the primary cardiovascular endpoint, they also studied a cancer endpoint.
The multivitamin supplement didn’t reduce cardiovascular events either. Nor did it affect cancer outcomes. The main COSMOS study was negative and reinforced what countless other studies have proven: Taking a daily multivitamin does not reduce your risk of having a heart attack or developing cancer.
But wait, there’s more: COSMOS-Mind
But no researcher worth his salt studies just one or two endpoints in a study. The participants also underwent neurologic and memory testing. These results were reported separately in the COSMOS-Mind study.
COSMOS-Mind is often described as a separate (or “new”) study. In reality, it included the same participants from the original COSMOS trial and measured yet another primary outcome of cognitive performance on a series of tests administered by telephone. Although there is nothing inherently wrong with studying multiple outcomes in your patient population (after all, that salami isn’t going to slice itself), they cannot all be primary outcomes. Some, by necessity, must be secondary hypothesis–generating outcomes. If you test enough endpoints, multiple hypothesis testing dictates that eventually you will get a positive result simply by chance.
There was a time when the neurocognitive outcomes of COSMOS would have been reported in the same paper as the cardiovascular outcomes, but that time seems to have passed us by. Researchers live or die by the number of their publications, and there is an inherent advantage to squeezing as many publications as possible from the same dataset. Though, to be fair, the journal would probably have asked them to split up the paper as well.
In brief, the cocoa extract again fell short in COSMOS-Mind, but the multivitamin arm did better on the composite cognitive outcome. It was a fairly small difference – a 0.07-point improvement on the z-score at the 3-year mark (the z-score is the mean divided by the standard deviation). Much was also made of the fact that the improvement seemed to vary by prior history of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Those with a history of CVD had a 0.11-point improvement, whereas those without had a 0.06-point improvement. The authors couldn’t offer a definitive explanation for these findings. Any argument that multivitamins improve cardiovascular health and therefore prevent vascular dementia has to contend with the fact that the main COSMOS study didn’t show a cardiovascular benefit for vitamins. Speculation that you are treating nutritional deficiencies is exactly that: speculation.
A more salient question is: What does a 0.07-point improvement on the z-score mean clinically? This study didn’t assess whether a multivitamin supplement prevented dementia or allowed people to live independently for longer. In fairness, that would have been exceptionally difficult to do and would have required a much longer study.
Their one attempt to quantify the cognitive benefit clinically was a calculation about normal age-related decline. Test scores were 0.045 points lower for every 1-year increase in age among participants (their mean age was 73 years). So the authors contend that a 0.07-point increase, or the 0.083-point increase that they found at year 3, corresponds to 1.8 years of age-related decline forestalled. Whether this is an appropriate assumption, I leave for the reader to decide.
COSMOS-Web and replication
The results of COSMOS-Mind were seemingly bolstered by the recent publication of COSMOS-Web. Although I’ve seen this study described as having replicated the results of COSMOS-Mind, that description is a bit misleading. This was yet another ancillary COSMOS study; more than half of the 2,262 participants in COSMOS-Mind were also included in COSMOS-Web. Replicating results in the same people isn’t true replication.
The main difference between COSMOS-Mind and COSMOS-Web is that the former used a telephone interview to administer the cognitive tests and the latter used the Internet. They also had different endpoints, with COSMOS-Web looking at immediate recall rather than a global test composite.
COSMOS-Web was a positive study in that patients getting the multivitamin supplement did better on the test for immediate memory recall (remembering a list of 20 words), though they didn’t improve on tests of memory retention, executive function, or novel object recognition (basically a test where subjects have to identify matching geometric patterns and then recall them later). They were able to remember an additional 0.71 word on average, compared with 0.44 word in the placebo group. (For the record, it found no benefit for the cocoa extract).
Everybody does better on memory tests the second time around because practice makes perfect, hence the improvement in the placebo group. This benefit at 1 year did not survive to the end of follow-up at 3 years, in contrast to COSMOS-Mind, where the benefit was not apparent at 1 year and seen only at year 3. A history of cardiovascular disease didn’t seem to affect the results in COSMOS-Web as it did in COSMOS-Mind. As far as replications go, COSMOS-Web has some very non-negligible differences, compared with COSMOS-Mind. This incongruity, especially given the overlap in the patient populations is hard to reconcile. If COSMOS-Web was supposed to assuage any doubts that persisted after COSMOS-Mind, it hasn’t for me.
One of these studies is not like the others
Finally, although the COSMOS trial and all its ancillary study analyses suggest a neurocognitive benefit to multivitamin supplementation, it’s not the first study to test the matter. The Age-Related Eye Disease Study looked at vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, zinc, and copper. There was no benefit on any of the six cognitive tests administered to patients. The Women’s Health Study, the Women’s Antioxidant Cardiovascular Study and PREADViSE have all failed to show any benefit to the various vitamins and minerals they studied. A meta-analysis of 11 trials found no benefit to B vitamins in slowing cognitive aging.
The claim that COSMOS is the “first” study to test the hypothesis hinges on some careful wordplay. Prior studies tested specific vitamins, not a multivitamin. In the discussion of the paper, these other studies are critiqued for being short term. But the Physicians’ Health Study II did in fact study a multivitamin and assessed cognitive performance on average 2.5 years after randomization. It found no benefit. The authors of COSMOS-Web critiqued the 2.5-year wait to perform cognitive testing, saying it would have missed any short-term benefits. Although, given that they simultaneously praised their 3 years of follow-up, the criticism is hard to fully accept or even understand.
Whether follow-up is short or long, uses individual vitamins or a multivitamin, the results excluding COSMOS are uniformly negative.
Do enough tests in the same population, and something will rise above the noise just by chance. When you get a positive result in your research, it’s always exciting. But when a slew of studies that came before you are negative, you aren’t groundbreaking. You’re an outlier.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
I have written before about the COSMOS study and its finding that multivitamins (and chocolate) did not improve brain or cardiovascular health. So I was surprised to read that a “new” study found that vitamins can forestall dementia and age-related cognitive decline.
Upon closer look, the new data are neither new nor convincing, at least to me.
Chocolate and multivitamins for CVD and cancer prevention
The large randomized COSMOS trial was supposed to be the definitive study on chocolate that would establish its heart-health benefits without a doubt. Or, rather, the benefits of a cocoa bean extract in pill form given to healthy, older volunteers. The COSMOS study was negative. Chocolate, or the cocoa bean extract they used, did not reduce cardiovascular events.
And yet for all the prepublication importance attached to COSMOS, it is scarcely mentioned. Had it been positive, rest assured that Mars, the candy bar company that cofunded the research, and other interested parties would have been shouting it from the rooftops. As it is, they’re already spinning it.
Which brings us to the multivitamin component. COSMOS actually had a 2 × 2 design. In other words, there were four groups in this study: chocolate plus multivitamin, chocolate plus placebo, placebo plus multivitamin, and placebo plus placebo. This type of study design allows you to study two different interventions simultaneously, provided that they are independent and do not interact with each other. In addition to the primary cardiovascular endpoint, they also studied a cancer endpoint.
The multivitamin supplement didn’t reduce cardiovascular events either. Nor did it affect cancer outcomes. The main COSMOS study was negative and reinforced what countless other studies have proven: Taking a daily multivitamin does not reduce your risk of having a heart attack or developing cancer.
But wait, there’s more: COSMOS-Mind
But no researcher worth his salt studies just one or two endpoints in a study. The participants also underwent neurologic and memory testing. These results were reported separately in the COSMOS-Mind study.
COSMOS-Mind is often described as a separate (or “new”) study. In reality, it included the same participants from the original COSMOS trial and measured yet another primary outcome of cognitive performance on a series of tests administered by telephone. Although there is nothing inherently wrong with studying multiple outcomes in your patient population (after all, that salami isn’t going to slice itself), they cannot all be primary outcomes. Some, by necessity, must be secondary hypothesis–generating outcomes. If you test enough endpoints, multiple hypothesis testing dictates that eventually you will get a positive result simply by chance.
There was a time when the neurocognitive outcomes of COSMOS would have been reported in the same paper as the cardiovascular outcomes, but that time seems to have passed us by. Researchers live or die by the number of their publications, and there is an inherent advantage to squeezing as many publications as possible from the same dataset. Though, to be fair, the journal would probably have asked them to split up the paper as well.
In brief, the cocoa extract again fell short in COSMOS-Mind, but the multivitamin arm did better on the composite cognitive outcome. It was a fairly small difference – a 0.07-point improvement on the z-score at the 3-year mark (the z-score is the mean divided by the standard deviation). Much was also made of the fact that the improvement seemed to vary by prior history of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Those with a history of CVD had a 0.11-point improvement, whereas those without had a 0.06-point improvement. The authors couldn’t offer a definitive explanation for these findings. Any argument that multivitamins improve cardiovascular health and therefore prevent vascular dementia has to contend with the fact that the main COSMOS study didn’t show a cardiovascular benefit for vitamins. Speculation that you are treating nutritional deficiencies is exactly that: speculation.
A more salient question is: What does a 0.07-point improvement on the z-score mean clinically? This study didn’t assess whether a multivitamin supplement prevented dementia or allowed people to live independently for longer. In fairness, that would have been exceptionally difficult to do and would have required a much longer study.
Their one attempt to quantify the cognitive benefit clinically was a calculation about normal age-related decline. Test scores were 0.045 points lower for every 1-year increase in age among participants (their mean age was 73 years). So the authors contend that a 0.07-point increase, or the 0.083-point increase that they found at year 3, corresponds to 1.8 years of age-related decline forestalled. Whether this is an appropriate assumption, I leave for the reader to decide.
COSMOS-Web and replication
The results of COSMOS-Mind were seemingly bolstered by the recent publication of COSMOS-Web. Although I’ve seen this study described as having replicated the results of COSMOS-Mind, that description is a bit misleading. This was yet another ancillary COSMOS study; more than half of the 2,262 participants in COSMOS-Mind were also included in COSMOS-Web. Replicating results in the same people isn’t true replication.
The main difference between COSMOS-Mind and COSMOS-Web is that the former used a telephone interview to administer the cognitive tests and the latter used the Internet. They also had different endpoints, with COSMOS-Web looking at immediate recall rather than a global test composite.
COSMOS-Web was a positive study in that patients getting the multivitamin supplement did better on the test for immediate memory recall (remembering a list of 20 words), though they didn’t improve on tests of memory retention, executive function, or novel object recognition (basically a test where subjects have to identify matching geometric patterns and then recall them later). They were able to remember an additional 0.71 word on average, compared with 0.44 word in the placebo group. (For the record, it found no benefit for the cocoa extract).
Everybody does better on memory tests the second time around because practice makes perfect, hence the improvement in the placebo group. This benefit at 1 year did not survive to the end of follow-up at 3 years, in contrast to COSMOS-Mind, where the benefit was not apparent at 1 year and seen only at year 3. A history of cardiovascular disease didn’t seem to affect the results in COSMOS-Web as it did in COSMOS-Mind. As far as replications go, COSMOS-Web has some very non-negligible differences, compared with COSMOS-Mind. This incongruity, especially given the overlap in the patient populations is hard to reconcile. If COSMOS-Web was supposed to assuage any doubts that persisted after COSMOS-Mind, it hasn’t for me.
One of these studies is not like the others
Finally, although the COSMOS trial and all its ancillary study analyses suggest a neurocognitive benefit to multivitamin supplementation, it’s not the first study to test the matter. The Age-Related Eye Disease Study looked at vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, zinc, and copper. There was no benefit on any of the six cognitive tests administered to patients. The Women’s Health Study, the Women’s Antioxidant Cardiovascular Study and PREADViSE have all failed to show any benefit to the various vitamins and minerals they studied. A meta-analysis of 11 trials found no benefit to B vitamins in slowing cognitive aging.
The claim that COSMOS is the “first” study to test the hypothesis hinges on some careful wordplay. Prior studies tested specific vitamins, not a multivitamin. In the discussion of the paper, these other studies are critiqued for being short term. But the Physicians’ Health Study II did in fact study a multivitamin and assessed cognitive performance on average 2.5 years after randomization. It found no benefit. The authors of COSMOS-Web critiqued the 2.5-year wait to perform cognitive testing, saying it would have missed any short-term benefits. Although, given that they simultaneously praised their 3 years of follow-up, the criticism is hard to fully accept or even understand.
Whether follow-up is short or long, uses individual vitamins or a multivitamin, the results excluding COSMOS are uniformly negative.
Do enough tests in the same population, and something will rise above the noise just by chance. When you get a positive result in your research, it’s always exciting. But when a slew of studies that came before you are negative, you aren’t groundbreaking. You’re an outlier.
Dr. Labos is a cardiologist at Hôpital Notre-Dame, Montreal. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AHA updates CPR guidelines on cardiac arrest after poisoning
The update reflects treatment advances and new knowledge, including the use of venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) for patients whose condition is refractory to poison antidotes and other therapies.
The new guidelines are designed primarily for North American health care professionals who treat adults and children who are critically ill because of poisoning, including intentional and unintentional drug overdose, chemical exposure, and drug-drug interactions, the authors note.
Published online in Circulation, the update was endorsed by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
‘Nearly miraculous’
“It’s been 13 years since the poisoning treatment guidelines had a comprehensive update,” lead author Eric J. Lavonas, MD, professor of emergency medicine at Denver Health and the Rocky Mountain Poison and Drug Center, Colo., told this news organization. “In that time, we’ve learned a lot about how to best use antidotes and other treatments to save the most critically poisoned patients.”
Highlighting a few key points from the update, he said, “For those rare situations when antidotes aren’t enough, the new guidelines include the use of heart-lung machines (VA-ECMO) for patients with beta-blocker, calcium channel blocker, or sodium channel blocker poisoning causing cardiogenic shock.”
Furthermore, he said, “High-dose insulin treatment for patients with beta-blocker and calcium channel blocker poisoning [also recommended in the update] has really become mainstream. The doses are up to 10 times higher than the amount used to treat diabetic emergencies.
“Some excellent science has shown that giving IV lipid emulsion can save the life of someone with an accidental overdose of local anesthetic medications, particularly bupivacaine,” he added. “The result is sometimes nearly miraculous.
“But when this treatment is extended to poisoning from other medications, it often doesn’t work as well, and in some situations may make things worse,” he said. “The issue may be that giving lipids increases absorption of drug from the stomach and intestines, which can be dangerous when the patient took an overdose of pills.”
Low level of evidence
The guidelines were compiled by the Critical Poisoning Writing Group, which includes experts from emergency medicine, pediatrics, medical toxicology, pharmacology, critical care, emergency medical services, education, research, and nursing. Group members were appointed by the AHA Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science Subcommittee and were approved by the AHA Manuscript Oversight Committee.
First and foremost, the group recommends timely consultation with a medical toxicologist, a clinical toxicologist, or a regional poison center to facilitate rapid, effective therapy, because treatment of cardiac arrest and toxicity from poisoning often requires treatments that most clinicians don’t use frequently.
Other key points include the following:
- Naloxone administration may reverse respiratory arrest due to opioid overdose, preventing progression to cardiac arrest.
- Give high-dose insulin therapy early in the treatment of patients with beta-blocker and calcium channel blocker poisoning, Dr. Lavonas noted.
- Standard advanced life support plus sodium bicarbonate is appropriate for life-threatening dysrhythmias caused by cocaine or other sodium channel blockers.
- If cyanide poisoning is suspected, clinicians should not wait for confirmatory testing; treatment should begin immediately with hydroxocobalamin (preferred) or sodium nitrite plus sodium thiosulfate.
- Digoxin-specific immune antibody fragments can reverse life-threatening dysrhythmias from digoxin poisoning.
- Use of 20% intravenous lipid emulsion can be efficacious in the resuscitation of life-threatening local anesthetic toxicity, especially from bupivacaine, Dr. Lavonas indicated.
- Sedation is recommended for patients with severe agitation from sympathomimetic poisoning to manage hyperthermia and acidosis, prevent rhabdomyolysis and injury, and allow evaluation for other life-threatening conditions.
- Although flumazenil reverses central nervous system and respiratory depression from benzodiazepine poisoning, risks and contraindications, provided in the guidelines, limit its use.
- VA-ECMO can be lifesaving for patients with cardiogenic shock or dysrhythmias that are refractory to other treatments.
“Unfortunately, despite improvements in the design and funding support for resuscitation research, the overall certainty of the evidence base for resuscitation science and management of critical poisoning is low,” the group acknowledges.
Of the 73 guideline recommendations, only 2 are supported by level A evidence; 3 are supported by level B-randomized evidence, 12 by level B-nonrandomized evidence, and the rest by level C evidence.
“Accordingly, the strength of recommendations is weaker than optimal,” they write. “Clinical trials in resuscitation and the management of critical poisoning are sorely needed.”
‘Don’t go it alone!’
“Most critical poisonings are pretty uncommon, and each patient is different,” Dr. Lavonas said. “Even in the emergency department or ICU, most physicians will treat a patient who is critically ill with any given poison less than once a year. The antidotes and medication doses needed to effectively treat these patients are often very different than everyday medical practice.
“Don’t try to go it alone!” he urges. “Poisoning cases are complex, and the treatments work best when they are implemented quickly and assertively. A toxicologist can help sort through complex situations and get effective treatment started without delay.”
Every certified poison center has a medical toxicologist or clinical toxicologist on call 24/7 to give advice to physicians and hospitals about patients who are critically ill after being poisoned, he added. “Everyone in the U.S. has access to a poison center by calling one number: 1-800-222-1222.”
Dr. Lavonas has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The update reflects treatment advances and new knowledge, including the use of venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) for patients whose condition is refractory to poison antidotes and other therapies.
The new guidelines are designed primarily for North American health care professionals who treat adults and children who are critically ill because of poisoning, including intentional and unintentional drug overdose, chemical exposure, and drug-drug interactions, the authors note.
Published online in Circulation, the update was endorsed by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
‘Nearly miraculous’
“It’s been 13 years since the poisoning treatment guidelines had a comprehensive update,” lead author Eric J. Lavonas, MD, professor of emergency medicine at Denver Health and the Rocky Mountain Poison and Drug Center, Colo., told this news organization. “In that time, we’ve learned a lot about how to best use antidotes and other treatments to save the most critically poisoned patients.”
Highlighting a few key points from the update, he said, “For those rare situations when antidotes aren’t enough, the new guidelines include the use of heart-lung machines (VA-ECMO) for patients with beta-blocker, calcium channel blocker, or sodium channel blocker poisoning causing cardiogenic shock.”
Furthermore, he said, “High-dose insulin treatment for patients with beta-blocker and calcium channel blocker poisoning [also recommended in the update] has really become mainstream. The doses are up to 10 times higher than the amount used to treat diabetic emergencies.
“Some excellent science has shown that giving IV lipid emulsion can save the life of someone with an accidental overdose of local anesthetic medications, particularly bupivacaine,” he added. “The result is sometimes nearly miraculous.
“But when this treatment is extended to poisoning from other medications, it often doesn’t work as well, and in some situations may make things worse,” he said. “The issue may be that giving lipids increases absorption of drug from the stomach and intestines, which can be dangerous when the patient took an overdose of pills.”
Low level of evidence
The guidelines were compiled by the Critical Poisoning Writing Group, which includes experts from emergency medicine, pediatrics, medical toxicology, pharmacology, critical care, emergency medical services, education, research, and nursing. Group members were appointed by the AHA Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science Subcommittee and were approved by the AHA Manuscript Oversight Committee.
First and foremost, the group recommends timely consultation with a medical toxicologist, a clinical toxicologist, or a regional poison center to facilitate rapid, effective therapy, because treatment of cardiac arrest and toxicity from poisoning often requires treatments that most clinicians don’t use frequently.
Other key points include the following:
- Naloxone administration may reverse respiratory arrest due to opioid overdose, preventing progression to cardiac arrest.
- Give high-dose insulin therapy early in the treatment of patients with beta-blocker and calcium channel blocker poisoning, Dr. Lavonas noted.
- Standard advanced life support plus sodium bicarbonate is appropriate for life-threatening dysrhythmias caused by cocaine or other sodium channel blockers.
- If cyanide poisoning is suspected, clinicians should not wait for confirmatory testing; treatment should begin immediately with hydroxocobalamin (preferred) or sodium nitrite plus sodium thiosulfate.
- Digoxin-specific immune antibody fragments can reverse life-threatening dysrhythmias from digoxin poisoning.
- Use of 20% intravenous lipid emulsion can be efficacious in the resuscitation of life-threatening local anesthetic toxicity, especially from bupivacaine, Dr. Lavonas indicated.
- Sedation is recommended for patients with severe agitation from sympathomimetic poisoning to manage hyperthermia and acidosis, prevent rhabdomyolysis and injury, and allow evaluation for other life-threatening conditions.
- Although flumazenil reverses central nervous system and respiratory depression from benzodiazepine poisoning, risks and contraindications, provided in the guidelines, limit its use.
- VA-ECMO can be lifesaving for patients with cardiogenic shock or dysrhythmias that are refractory to other treatments.
“Unfortunately, despite improvements in the design and funding support for resuscitation research, the overall certainty of the evidence base for resuscitation science and management of critical poisoning is low,” the group acknowledges.
Of the 73 guideline recommendations, only 2 are supported by level A evidence; 3 are supported by level B-randomized evidence, 12 by level B-nonrandomized evidence, and the rest by level C evidence.
“Accordingly, the strength of recommendations is weaker than optimal,” they write. “Clinical trials in resuscitation and the management of critical poisoning are sorely needed.”
‘Don’t go it alone!’
“Most critical poisonings are pretty uncommon, and each patient is different,” Dr. Lavonas said. “Even in the emergency department or ICU, most physicians will treat a patient who is critically ill with any given poison less than once a year. The antidotes and medication doses needed to effectively treat these patients are often very different than everyday medical practice.
“Don’t try to go it alone!” he urges. “Poisoning cases are complex, and the treatments work best when they are implemented quickly and assertively. A toxicologist can help sort through complex situations and get effective treatment started without delay.”
Every certified poison center has a medical toxicologist or clinical toxicologist on call 24/7 to give advice to physicians and hospitals about patients who are critically ill after being poisoned, he added. “Everyone in the U.S. has access to a poison center by calling one number: 1-800-222-1222.”
Dr. Lavonas has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The update reflects treatment advances and new knowledge, including the use of venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) for patients whose condition is refractory to poison antidotes and other therapies.
The new guidelines are designed primarily for North American health care professionals who treat adults and children who are critically ill because of poisoning, including intentional and unintentional drug overdose, chemical exposure, and drug-drug interactions, the authors note.
Published online in Circulation, the update was endorsed by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
‘Nearly miraculous’
“It’s been 13 years since the poisoning treatment guidelines had a comprehensive update,” lead author Eric J. Lavonas, MD, professor of emergency medicine at Denver Health and the Rocky Mountain Poison and Drug Center, Colo., told this news organization. “In that time, we’ve learned a lot about how to best use antidotes and other treatments to save the most critically poisoned patients.”
Highlighting a few key points from the update, he said, “For those rare situations when antidotes aren’t enough, the new guidelines include the use of heart-lung machines (VA-ECMO) for patients with beta-blocker, calcium channel blocker, or sodium channel blocker poisoning causing cardiogenic shock.”
Furthermore, he said, “High-dose insulin treatment for patients with beta-blocker and calcium channel blocker poisoning [also recommended in the update] has really become mainstream. The doses are up to 10 times higher than the amount used to treat diabetic emergencies.
“Some excellent science has shown that giving IV lipid emulsion can save the life of someone with an accidental overdose of local anesthetic medications, particularly bupivacaine,” he added. “The result is sometimes nearly miraculous.
“But when this treatment is extended to poisoning from other medications, it often doesn’t work as well, and in some situations may make things worse,” he said. “The issue may be that giving lipids increases absorption of drug from the stomach and intestines, which can be dangerous when the patient took an overdose of pills.”
Low level of evidence
The guidelines were compiled by the Critical Poisoning Writing Group, which includes experts from emergency medicine, pediatrics, medical toxicology, pharmacology, critical care, emergency medical services, education, research, and nursing. Group members were appointed by the AHA Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science Subcommittee and were approved by the AHA Manuscript Oversight Committee.
First and foremost, the group recommends timely consultation with a medical toxicologist, a clinical toxicologist, or a regional poison center to facilitate rapid, effective therapy, because treatment of cardiac arrest and toxicity from poisoning often requires treatments that most clinicians don’t use frequently.
Other key points include the following:
- Naloxone administration may reverse respiratory arrest due to opioid overdose, preventing progression to cardiac arrest.
- Give high-dose insulin therapy early in the treatment of patients with beta-blocker and calcium channel blocker poisoning, Dr. Lavonas noted.
- Standard advanced life support plus sodium bicarbonate is appropriate for life-threatening dysrhythmias caused by cocaine or other sodium channel blockers.
- If cyanide poisoning is suspected, clinicians should not wait for confirmatory testing; treatment should begin immediately with hydroxocobalamin (preferred) or sodium nitrite plus sodium thiosulfate.
- Digoxin-specific immune antibody fragments can reverse life-threatening dysrhythmias from digoxin poisoning.
- Use of 20% intravenous lipid emulsion can be efficacious in the resuscitation of life-threatening local anesthetic toxicity, especially from bupivacaine, Dr. Lavonas indicated.
- Sedation is recommended for patients with severe agitation from sympathomimetic poisoning to manage hyperthermia and acidosis, prevent rhabdomyolysis and injury, and allow evaluation for other life-threatening conditions.
- Although flumazenil reverses central nervous system and respiratory depression from benzodiazepine poisoning, risks and contraindications, provided in the guidelines, limit its use.
- VA-ECMO can be lifesaving for patients with cardiogenic shock or dysrhythmias that are refractory to other treatments.
“Unfortunately, despite improvements in the design and funding support for resuscitation research, the overall certainty of the evidence base for resuscitation science and management of critical poisoning is low,” the group acknowledges.
Of the 73 guideline recommendations, only 2 are supported by level A evidence; 3 are supported by level B-randomized evidence, 12 by level B-nonrandomized evidence, and the rest by level C evidence.
“Accordingly, the strength of recommendations is weaker than optimal,” they write. “Clinical trials in resuscitation and the management of critical poisoning are sorely needed.”
‘Don’t go it alone!’
“Most critical poisonings are pretty uncommon, and each patient is different,” Dr. Lavonas said. “Even in the emergency department or ICU, most physicians will treat a patient who is critically ill with any given poison less than once a year. The antidotes and medication doses needed to effectively treat these patients are often very different than everyday medical practice.
“Don’t try to go it alone!” he urges. “Poisoning cases are complex, and the treatments work best when they are implemented quickly and assertively. A toxicologist can help sort through complex situations and get effective treatment started without delay.”
Every certified poison center has a medical toxicologist or clinical toxicologist on call 24/7 to give advice to physicians and hospitals about patients who are critically ill after being poisoned, he added. “Everyone in the U.S. has access to a poison center by calling one number: 1-800-222-1222.”
Dr. Lavonas has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Data Trends 2023: Cardiology
- Dhruva SS et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(suppl 3):806-815. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07595-1
- Han JK et al. Circulation. 2019;139(8):1102-1109. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037748
- Hinojosa R. Chronic Illn. 2020;16(1):55-68. doi:10.1177/1742395318785237
- Lee MT et al. JAMA Cardiol. 2021;6(7):782-790. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.0683
- Gaffey AE et al. Health Psychol. 2021;40(11):737-746. doi:10.1037/hea0001110
- Dhruva SS et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(suppl 3):806-815. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07595-1
- Han JK et al. Circulation. 2019;139(8):1102-1109. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037748
- Hinojosa R. Chronic Illn. 2020;16(1):55-68. doi:10.1177/1742395318785237
- Lee MT et al. JAMA Cardiol. 2021;6(7):782-790. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.0683
- Gaffey AE et al. Health Psychol. 2021;40(11):737-746. doi:10.1037/hea0001110
- Dhruva SS et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(suppl 3):806-815. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07595-1
- Han JK et al. Circulation. 2019;139(8):1102-1109. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037748
- Hinojosa R. Chronic Illn. 2020;16(1):55-68. doi:10.1177/1742395318785237
- Lee MT et al. JAMA Cardiol. 2021;6(7):782-790. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.0683
- Gaffey AE et al. Health Psychol. 2021;40(11):737-746. doi:10.1037/hea0001110
Video-Based Coaching for Dermatology Resident Surgical Education
To the Editor:
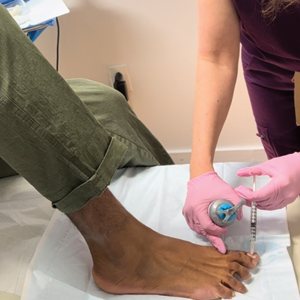
Video-based coaching (VBC) involves a surgeon recording a surgery and then reviewing the video with a surgical coach; it is a form of education that is gaining popularity among surgical specialties.1 Video-based education is underutilized in dermatology residency training.2 We conducted a pilot study at our dermatology residency program to evaluate the efficacy and feasibility of VBC.
The University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School institutional review board approved this study. All 4 first-year dermatology residents were recruited to participate in this study. Participants filled out a prestudy survey assessing their surgical experience, confidence in performing surgery, and attitudes on VBC. Participants used a head-mounted point-of-view camera to record themselves performing a wide local excision on the trunk or extremities of a live human patient. Participants then reviewed the recording on their own and scored themselves using the Objective Structured Assessment of Technical Skills (OSATS) scoring table (scored from 1 to 5, with 5 being the highest possible score for each element), which is a validated tool for assessing surgical skills (eTable 1).3 Given that there were no assistants participating in the surgery, this element of the OSATS scoring table was excluded, making a maximum possible score of 30 and a minimum possible score of 6. After scoring themselves, participants then had a 1-on-1 coaching session with a fellowship-trained dermatologic surgeon (M.F. or T.H.) via online teleconferencing.
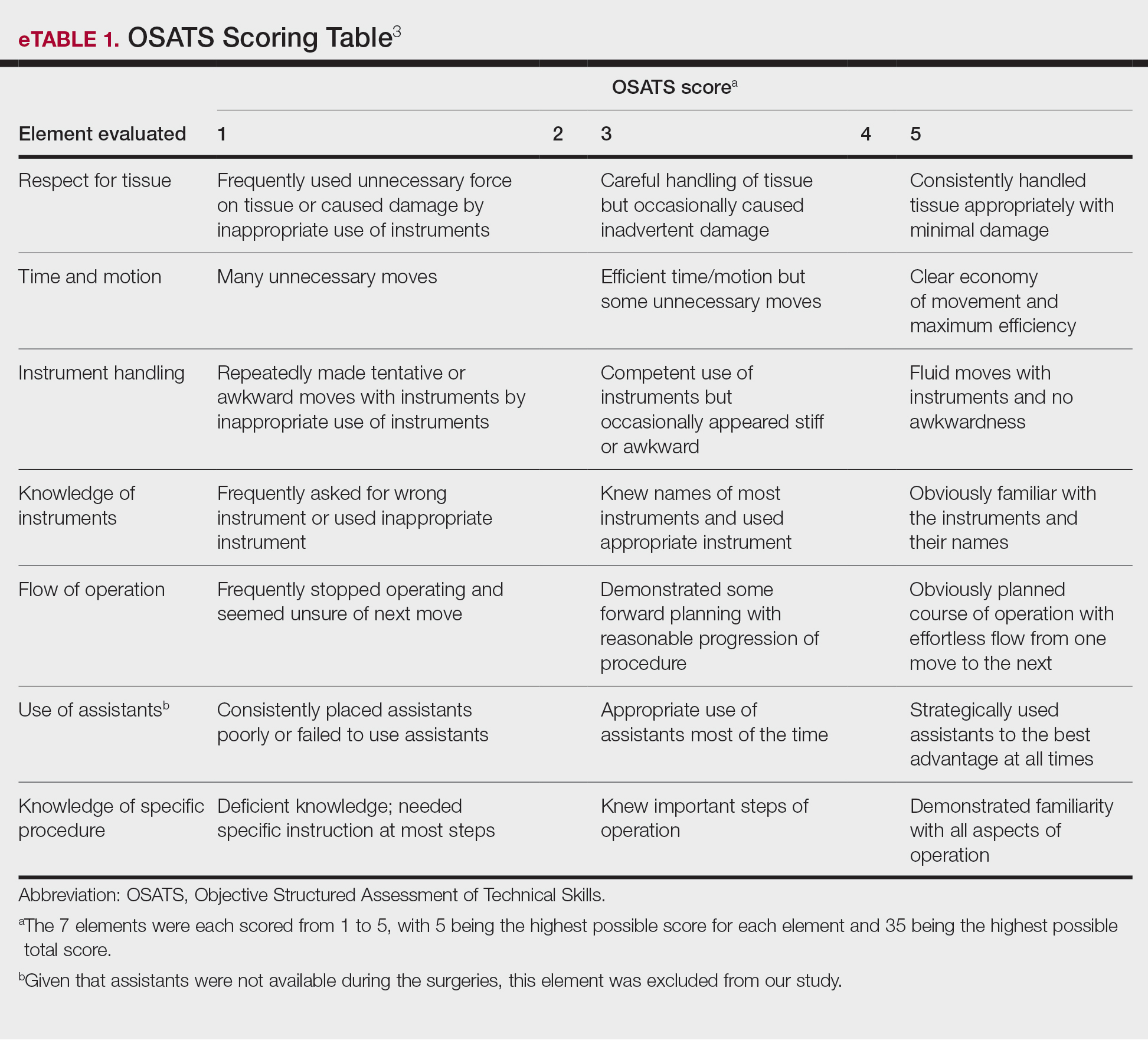
During the coaching session, participants and coaches reviewed the video. The surgical coaches also scored the residents using the OSATS, then residents and coaches discussed how the resident could improve using the OSATS scores as a guide. The residents then completed a poststudy survey assessing their surgical experience, confidence in performing surgery, and attitudes on VBC. Descriptive statistics were reported.
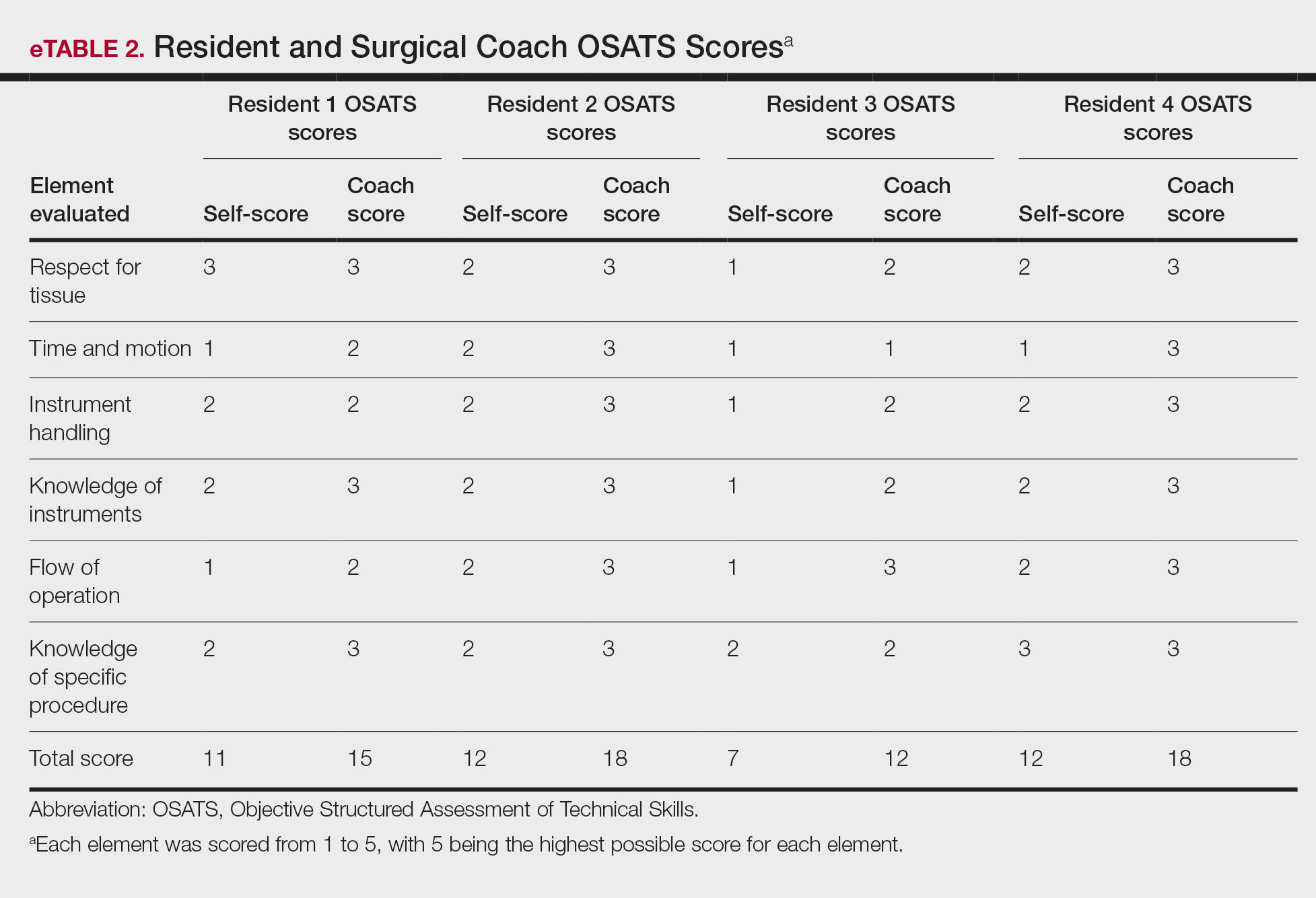
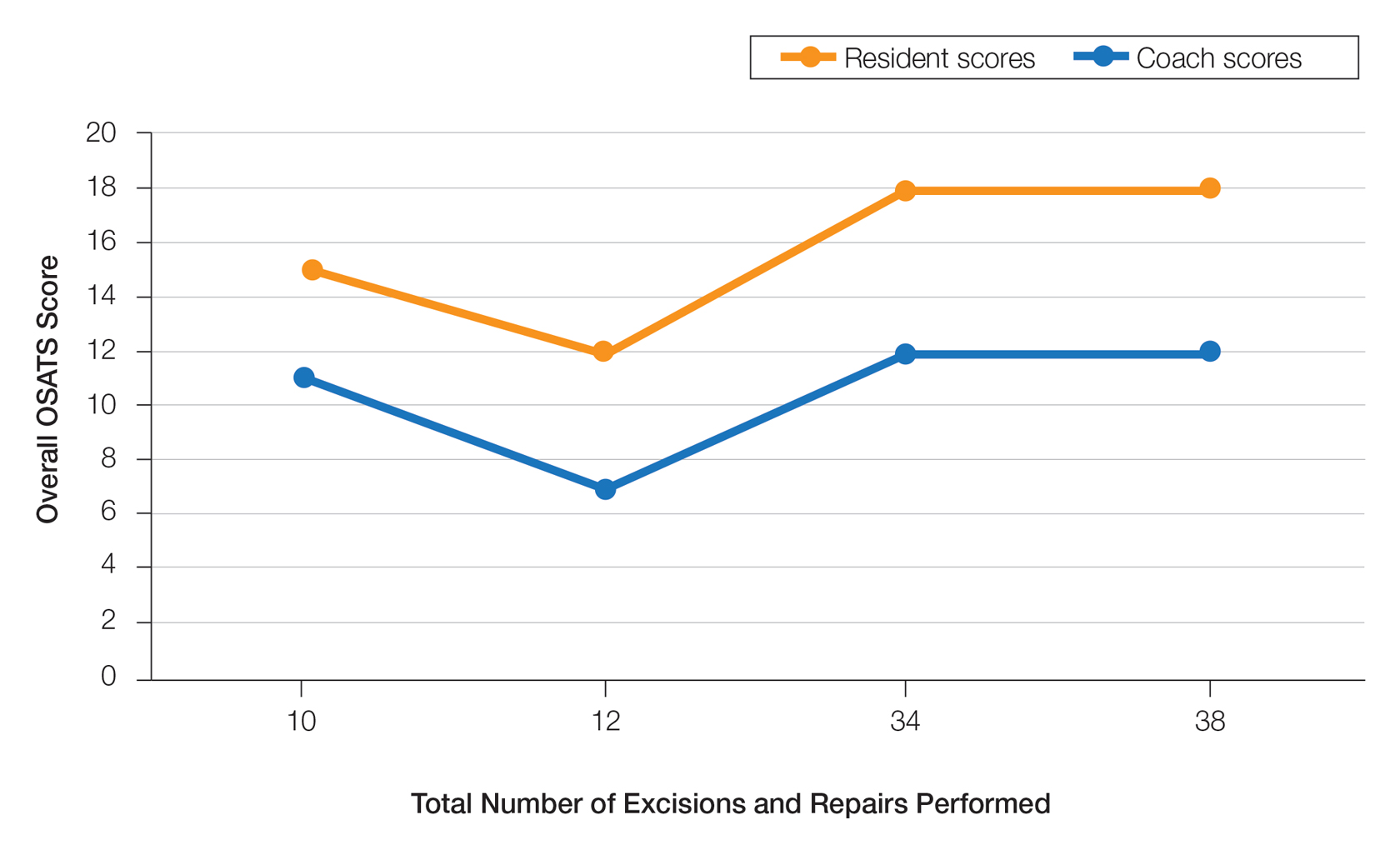
On average, residents spent 31.3 minutes reviewing their own surgeries and scoring themselves. The average time for a coaching session, which included time spent scoring, was 13.8 minutes. Residents scored themselves lower than the surgical coaches did by an average of 5.25 points (eTable 2). Residents gave themselves an average total score of 10.5, while their respective surgical coaches gave the residents an average score of 15.75. There was a trend of residents with greater surgical experience having higher OSATS scores (Figure). After the coaching session, 3 of 4 residents reported that they felt more confident in their surgical skills. All residents felt more confident in assessing their surgical skills and felt that VBC was an effective teaching measure. All residents agreed that VBC should be continued as part of their residency training.
Video-based coaching has the potential to provide several benefits for dermatology trainees. Because receiving feedback intraoperatively often can be distracting and incomplete, video review can instead allow the surgeon to focus on performing the surgery and then later focus on learning while reviewing the video.1,4 Feedback also can be more comprehensive and delivered without concern for time constraints or disturbing clinic flow as well as without the additional concern of the patient overhearing comments and feedback.3 Although independent video review in the absence of coaching can lead to improvement in surgical skills, the addition of VBC provides even greater potential educational benefit.4 During the COVID-19 pandemic, VBC allowed coaches to provide feedback without additional exposures. We utilized dermatologic surgery faculty as coaches, but this format of training also would apply to general dermatology faculty.
Another goal of VBC is to enhance a trainee’s ability to perform self-directed learning, which requires accurate self-assessment.4 Accurately assessing one’s own strengths empowers a trainee to act with appropriate confidence, while understanding one’s own weaknesses allows a trainee to effectively balance confidence and caution in daily practice.5 Interestingly, in our study all residents scored themselves lower than surgical coaches, but with 1 coaching session, the residents subsequently reported greater surgical confidence.
Time constraints can be a potential barrier to surgical coaching.4 Our study demonstrates that VBC requires minimal time investment. Increasing the speed of video playback allowed for efficient evaluation of resident surgeries without compromising the coach’s ability to provide comprehensive feedback. Our feedback sessions were performed virtually, which allowed for ease of scheduling between trainees and coaches.
Our pilot study demonstrated that VBC is relatively easy to implement in a dermatology residency training setting, leveraging relatively low-cost technologies and allowing for a means of learning that residents felt was effective. Video-based coaching requires minimal time investment from both trainees and coaches and has the potential to enhance surgical confidence. Our current study is limited by its small sample size. Future studies should include follow-up recordings and assess the efficacy of VBC in enhancing surgical skills.
- Greenberg CC, Dombrowski J, Dimick JB. Video-based surgical coaching: an emerging approach to performance improvement. JAMA Surg. 2016;151:282-283.
- Dai J, Bordeaux JS, Miller CJ, et al. Assessing surgical training and deliberate practice methods in dermatology residency: a survey of dermatology program directors. Dermatol Surg. 2016;42:977-984.
- Chitgopeker P, Sidey K, Aronson A, et al. Surgical skills video-based assessment tool for dermatology residents: a prospective pilot study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:614-616.
- Bull NB, Silverman CD, Bonrath EM. Targeted surgical coaching can improve operative self-assessment ability: a single-blinded nonrandomized trial. Surgery. 2020;167:308-313.
- Eva KW, Regehr G. Self-assessment in the health professions: a reformulation and research agenda. Acad Med. 2005;80(10 suppl):S46-S54.
To the Editor:
Video-based coaching (VBC) involves a surgeon recording a surgery and then reviewing the video with a surgical coach; it is a form of education that is gaining popularity among surgical specialties.1 Video-based education is underutilized in dermatology residency training.2 We conducted a pilot study at our dermatology residency program to evaluate the efficacy and feasibility of VBC.
The University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School institutional review board approved this study. All 4 first-year dermatology residents were recruited to participate in this study. Participants filled out a prestudy survey assessing their surgical experience, confidence in performing surgery, and attitudes on VBC. Participants used a head-mounted point-of-view camera to record themselves performing a wide local excision on the trunk or extremities of a live human patient. Participants then reviewed the recording on their own and scored themselves using the Objective Structured Assessment of Technical Skills (OSATS) scoring table (scored from 1 to 5, with 5 being the highest possible score for each element), which is a validated tool for assessing surgical skills (eTable 1).3 Given that there were no assistants participating in the surgery, this element of the OSATS scoring table was excluded, making a maximum possible score of 30 and a minimum possible score of 6. After scoring themselves, participants then had a 1-on-1 coaching session with a fellowship-trained dermatologic surgeon (M.F. or T.H.) via online teleconferencing.

During the coaching session, participants and coaches reviewed the video. The surgical coaches also scored the residents using the OSATS, then residents and coaches discussed how the resident could improve using the OSATS scores as a guide. The residents then completed a poststudy survey assessing their surgical experience, confidence in performing surgery, and attitudes on VBC. Descriptive statistics were reported.

On average, residents spent 31.3 minutes reviewing their own surgeries and scoring themselves. The average time for a coaching session, which included time spent scoring, was 13.8 minutes. Residents scored themselves lower than the surgical coaches did by an average of 5.25 points (eTable 2). Residents gave themselves an average total score of 10.5, while their respective surgical coaches gave the residents an average score of 15.75. There was a trend of residents with greater surgical experience having higher OSATS scores (Figure). After the coaching session, 3 of 4 residents reported that they felt more confident in their surgical skills. All residents felt more confident in assessing their surgical skills and felt that VBC was an effective teaching measure. All residents agreed that VBC should be continued as part of their residency training.

Video-based coaching has the potential to provide several benefits for dermatology trainees. Because receiving feedback intraoperatively often can be distracting and incomplete, video review can instead allow the surgeon to focus on performing the surgery and then later focus on learning while reviewing the video.1,4 Feedback also can be more comprehensive and delivered without concern for time constraints or disturbing clinic flow as well as without the additional concern of the patient overhearing comments and feedback.3 Although independent video review in the absence of coaching can lead to improvement in surgical skills, the addition of VBC provides even greater potential educational benefit.4 During the COVID-19 pandemic, VBC allowed coaches to provide feedback without additional exposures. We utilized dermatologic surgery faculty as coaches, but this format of training also would apply to general dermatology faculty.
Another goal of VBC is to enhance a trainee’s ability to perform self-directed learning, which requires accurate self-assessment.4 Accurately assessing one’s own strengths empowers a trainee to act with appropriate confidence, while understanding one’s own weaknesses allows a trainee to effectively balance confidence and caution in daily practice.5 Interestingly, in our study all residents scored themselves lower than surgical coaches, but with 1 coaching session, the residents subsequently reported greater surgical confidence.
Time constraints can be a potential barrier to surgical coaching.4 Our study demonstrates that VBC requires minimal time investment. Increasing the speed of video playback allowed for efficient evaluation of resident surgeries without compromising the coach’s ability to provide comprehensive feedback. Our feedback sessions were performed virtually, which allowed for ease of scheduling between trainees and coaches.
Our pilot study demonstrated that VBC is relatively easy to implement in a dermatology residency training setting, leveraging relatively low-cost technologies and allowing for a means of learning that residents felt was effective. Video-based coaching requires minimal time investment from both trainees and coaches and has the potential to enhance surgical confidence. Our current study is limited by its small sample size. Future studies should include follow-up recordings and assess the efficacy of VBC in enhancing surgical skills.
To the Editor:
Video-based coaching (VBC) involves a surgeon recording a surgery and then reviewing the video with a surgical coach; it is a form of education that is gaining popularity among surgical specialties.1 Video-based education is underutilized in dermatology residency training.2 We conducted a pilot study at our dermatology residency program to evaluate the efficacy and feasibility of VBC.
The University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School institutional review board approved this study. All 4 first-year dermatology residents were recruited to participate in this study. Participants filled out a prestudy survey assessing their surgical experience, confidence in performing surgery, and attitudes on VBC. Participants used a head-mounted point-of-view camera to record themselves performing a wide local excision on the trunk or extremities of a live human patient. Participants then reviewed the recording on their own and scored themselves using the Objective Structured Assessment of Technical Skills (OSATS) scoring table (scored from 1 to 5, with 5 being the highest possible score for each element), which is a validated tool for assessing surgical skills (eTable 1).3 Given that there were no assistants participating in the surgery, this element of the OSATS scoring table was excluded, making a maximum possible score of 30 and a minimum possible score of 6. After scoring themselves, participants then had a 1-on-1 coaching session with a fellowship-trained dermatologic surgeon (M.F. or T.H.) via online teleconferencing.

During the coaching session, participants and coaches reviewed the video. The surgical coaches also scored the residents using the OSATS, then residents and coaches discussed how the resident could improve using the OSATS scores as a guide. The residents then completed a poststudy survey assessing their surgical experience, confidence in performing surgery, and attitudes on VBC. Descriptive statistics were reported.

On average, residents spent 31.3 minutes reviewing their own surgeries and scoring themselves. The average time for a coaching session, which included time spent scoring, was 13.8 minutes. Residents scored themselves lower than the surgical coaches did by an average of 5.25 points (eTable 2). Residents gave themselves an average total score of 10.5, while their respective surgical coaches gave the residents an average score of 15.75. There was a trend of residents with greater surgical experience having higher OSATS scores (Figure). After the coaching session, 3 of 4 residents reported that they felt more confident in their surgical skills. All residents felt more confident in assessing their surgical skills and felt that VBC was an effective teaching measure. All residents agreed that VBC should be continued as part of their residency training.

Video-based coaching has the potential to provide several benefits for dermatology trainees. Because receiving feedback intraoperatively often can be distracting and incomplete, video review can instead allow the surgeon to focus on performing the surgery and then later focus on learning while reviewing the video.1,4 Feedback also can be more comprehensive and delivered without concern for time constraints or disturbing clinic flow as well as without the additional concern of the patient overhearing comments and feedback.3 Although independent video review in the absence of coaching can lead to improvement in surgical skills, the addition of VBC provides even greater potential educational benefit.4 During the COVID-19 pandemic, VBC allowed coaches to provide feedback without additional exposures. We utilized dermatologic surgery faculty as coaches, but this format of training also would apply to general dermatology faculty.
Another goal of VBC is to enhance a trainee’s ability to perform self-directed learning, which requires accurate self-assessment.4 Accurately assessing one’s own strengths empowers a trainee to act with appropriate confidence, while understanding one’s own weaknesses allows a trainee to effectively balance confidence and caution in daily practice.5 Interestingly, in our study all residents scored themselves lower than surgical coaches, but with 1 coaching session, the residents subsequently reported greater surgical confidence.
Time constraints can be a potential barrier to surgical coaching.4 Our study demonstrates that VBC requires minimal time investment. Increasing the speed of video playback allowed for efficient evaluation of resident surgeries without compromising the coach’s ability to provide comprehensive feedback. Our feedback sessions were performed virtually, which allowed for ease of scheduling between trainees and coaches.
Our pilot study demonstrated that VBC is relatively easy to implement in a dermatology residency training setting, leveraging relatively low-cost technologies and allowing for a means of learning that residents felt was effective. Video-based coaching requires minimal time investment from both trainees and coaches and has the potential to enhance surgical confidence. Our current study is limited by its small sample size. Future studies should include follow-up recordings and assess the efficacy of VBC in enhancing surgical skills.
- Greenberg CC, Dombrowski J, Dimick JB. Video-based surgical coaching: an emerging approach to performance improvement. JAMA Surg. 2016;151:282-283.
- Dai J, Bordeaux JS, Miller CJ, et al. Assessing surgical training and deliberate practice methods in dermatology residency: a survey of dermatology program directors. Dermatol Surg. 2016;42:977-984.
- Chitgopeker P, Sidey K, Aronson A, et al. Surgical skills video-based assessment tool for dermatology residents: a prospective pilot study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:614-616.
- Bull NB, Silverman CD, Bonrath EM. Targeted surgical coaching can improve operative self-assessment ability: a single-blinded nonrandomized trial. Surgery. 2020;167:308-313.
- Eva KW, Regehr G. Self-assessment in the health professions: a reformulation and research agenda. Acad Med. 2005;80(10 suppl):S46-S54.
- Greenberg CC, Dombrowski J, Dimick JB. Video-based surgical coaching: an emerging approach to performance improvement. JAMA Surg. 2016;151:282-283.
- Dai J, Bordeaux JS, Miller CJ, et al. Assessing surgical training and deliberate practice methods in dermatology residency: a survey of dermatology program directors. Dermatol Surg. 2016;42:977-984.
- Chitgopeker P, Sidey K, Aronson A, et al. Surgical skills video-based assessment tool for dermatology residents: a prospective pilot study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:614-616.
- Bull NB, Silverman CD, Bonrath EM. Targeted surgical coaching can improve operative self-assessment ability: a single-blinded nonrandomized trial. Surgery. 2020;167:308-313.
- Eva KW, Regehr G. Self-assessment in the health professions: a reformulation and research agenda. Acad Med. 2005;80(10 suppl):S46-S54.
PRACTICE POINTS
- Video-based coaching (VBC) for surgical procedures is an up-and-coming form of medical education that allows a “coach” to provide thoughtful and in-depth feedback while reviewing a recording with the surgeon in a private setting. This format has potential utility in teaching dermatology resident surgeons being coached by a dermatology faculty member.
- We performed a pilot study demonstrating that VBC can be performed easily with a minimal time investment for both the surgeon and the coach. Dermatology residents not only felt that VBC was an effective teaching method but also should become a formal part of their education.
Update on Dermatology Reimbursement in 2024
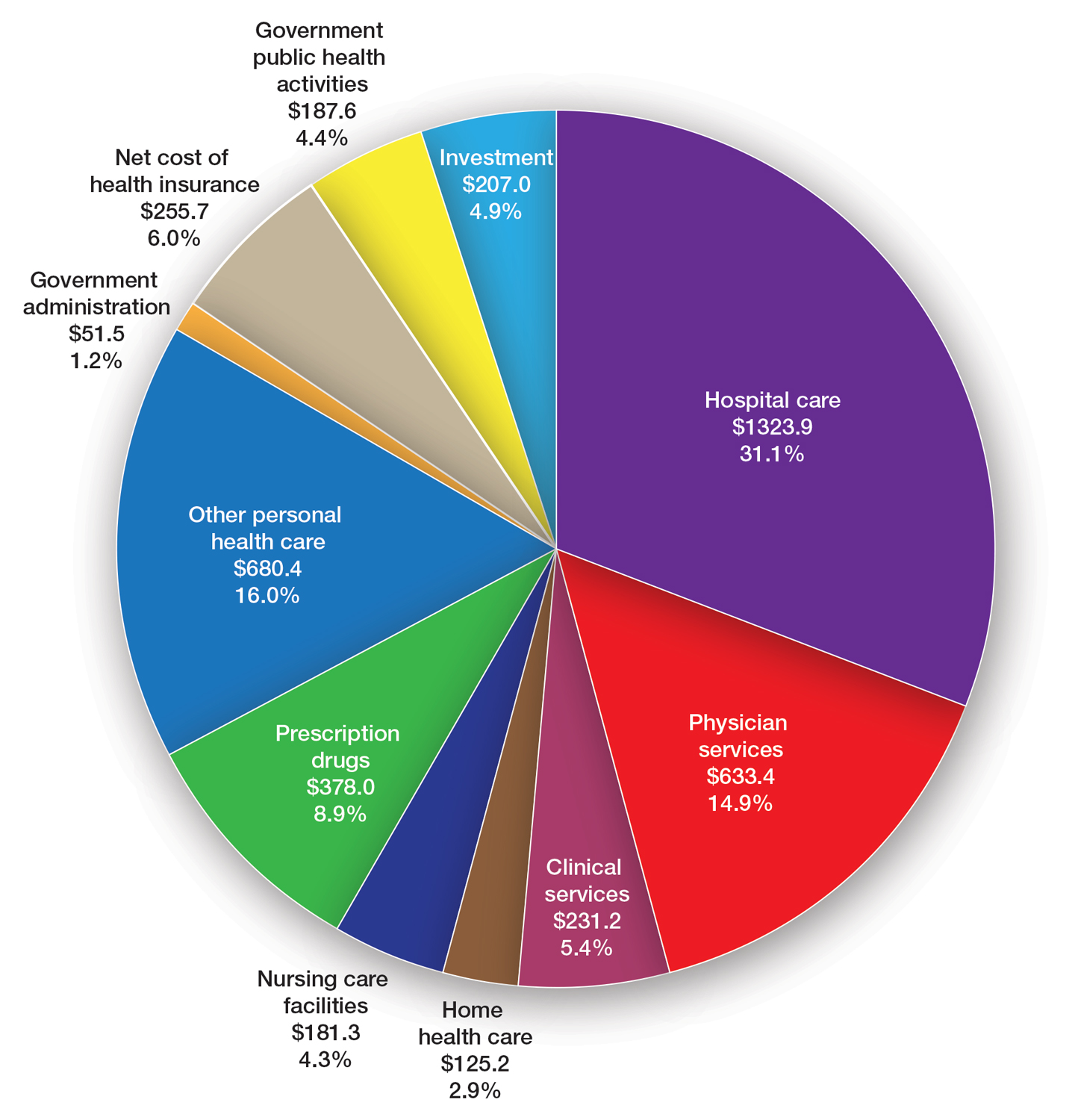
Health care spending in the United States remained relatively flat from 2019 to 2021 and only increased 2.7% in 2021, reaching $4.3 billion or $12,914 per person. Physician services account for 15% of health care spending (Figure). Relative value units (RVUs) signify the time it took a physician to complete a task multiplied by a conversion factor (CF). When RVUs initially were created in 1992 by what is now the Centers for Medicare &Medicaid Services (CMS), the CF was $32.00. Thirty-one years later, the CF is $33.89 in 2023; however, it would be $66.00 if the CF had increased with inflation.1 If the proposed 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule (MPFS) is adopted, the payment formula would decrease by 3.4% ($32.75) relative to the 2023 fee schedule ($33.89), which would be a 9% decrease relative to 2019 ($36.04).2,3 This reduction is due to the budget neutrality adjustment required by changes in RVUs, implementation of the evaluation and management (E/M) add-on code G2211, and proposed increases in primary are services.2,3 Since 2001, Medicare physician payment has declined by 26%.4 Adjustments to the CF typically are made based on 3 factors: (1) the Medicare Economic Index (MEI); (2) an expenditure target performance adjustment; and (3) miscellaneous adjustments, including those for budget neutrality required by law. Despite continued substantial increases in practice expenses, physicians’ reimbursement has remained flat while other service providers, such as those in skilled nursing facilities and hospitals, have received favorable payment increases compared to practice cost inflation and the Consumer Price Index.4
The CMS will not incorporate 2017 MEI cost weights for the RVUs in the MPFS rate setting for 2024 because all key measures of practice expenses in the MEI accelerated in 2022. Instead, the CMS is updating data on practice expense per hour to calculate payment for physician services with a survey for physician practices that launched on July 31, 2023.5 The American Medical Association contracted with Mathematica, an independent research company, to conduct a physician practice information survey that will be used to determine indirect practice expenses. Physicians should be on the lookout for emails regarding completion of these surveys and the appropriate financial expert in their practice should be contacted so the responses are accurate, as these data are key to future updates in the Medicare pay formula used to reimburse physicians.
Impact of Medicare Cuts
The recent congressional debt limit deal set spending caps for the next 2 fiscal years. Dermatology is facing an overall payment reduction of 1.87% (range, 1%–4%).2,3 The impact will depend on the services offered in an individual practice; for example, payment for a punch biopsy (Current Procedural Terminology [CPT] code 11104) would decrease by 3.9%. Payment for benign destruction (CPT code 17110) would decrease by 2.8%, and payment for even simple E/M of an established patient (CPT code 99213) would decrease by 1.6%. Overall, there would be a reduction of 2.75% for dermatopathology services, with a decrease of 2% for CPT code 88305 global and decreases for the technical component of 1% and professional component of 3%.2,3
Medicare cuts have reached a critical level, and physicians cannot continue to absorb the costs to own and operate their practices.4 This has led to health market consolidation, which in turn limits competition and patient access while driving up health care costs and driving down the quality of care. Small independent rural practices as well as those caring for historically marginalized patients will be disproportionately affected.
Proposed Addition of E/M Code G2211
In the calendar year (CY) 2021 final rule, the CMS tried to adopt a new add-on code—G2211—patients with a serious or complex condition that typically require referral and coordination of multispecialty care. Per the CMS, the primary policy goal of G2211 is to increase payments to primary care physicians and to reimburse them more appropriately for the care provided to patients with a serious or complex condition.2,3 It can be reported in conjunction with all office and outpatient E/M visits to better account for additional resources associated with primary care, or similarly ongoing medical care related to a patient’s single, serious condition, or complex condition.3 Typically, G2211 would not be used by dermatologists, as this add-on code requires visit complexity inherent to E/M associated with medical care services that serve as the continuing focal point for all needed health care services and/or with medical care services that are part of ongoing care related to a patient’s single serious condition or a complex condition.2,3
Initially, the CMS assumed that G2211 would be reported with 90% of all office and outpatient E/M visit claims, which would account for a considerable portion of total MPFS schedule spending; however, the House of Medicine disagreed and believed it would be 75%.2,3 Given the extremely high utilization estimate, G2211 would have had a substantial effect on budget neutrality, accounting for an estimated increase of $3.3 billion and a corresponding 3.0% cut to the CY 2021 MPFS. Because of the potential payment reductions to physicians and a successful advocacy effort by organized medicine, including the American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA), Congress delayed implementation of G2211 until CY 2024. Modifier -25 cannot be reported with G2211. The CMS revised its utilization assumptions from 90% of all E/M services to an initial utilization of 38% and then 54% when fully adopted. The proposed 2024 payment for G2211 is an additional $16.05.2,3
Advancing Health Equity With Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System G Codes
The CMS is proposing coding and payment for several new services to help underserved populations, including addressing unmet health-related social needs that can potentially interfere with the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions, which includes paying for certain caregiver training services as well as payment for community health integration services.2,3 These are the first MPFS services designed to include care involving community health workers, who link underserved communities with critical health care and social services in the community. Additionally, the rule also proposes coding and payment for evaluating the risks related to social factors that affect a patient’s health, such as access to affordable quality health care, that can take place during an annual wellness visit or in combination with an E/M visit.2,3 As dermatologists, we should be familiar with this set of G codes, as we will likely use them in practice for patients with transportation needs.
Advocacy Efforts on Medicare Payment Reform
Medicare physician payment reform needs to happen at a national level. Advocacy efforts by the AADA and other groups have been underway to mitigate the proposed 2024 cuts. The Strengthening Medicare for Patients and Providers Act (HR 2474) is a bill that was introduced by a bipartisan coalition of physicians to provide an inflation-based increase in Medicare payments in 2024 and beyond.6
Other Legislative Updates Affecting Dermatology
Modifier -25—Cigna’s policy requiring dermatologists to submit documentation to use modifier -25 when billing with E/M CPT codes 99212 through 99215 has been delayed indefinitely.7 If a payer denies a dermatologist payment, contact the AADA Patient Access and Payer Relations committee ([email protected]) for assistance.
Telehealth and Digital Pathology—Recent legislation authorized extension of many of the Medicare telehealth and digital pathology flexibilities that were put in place during the COVID-19 public health emergency through December 31, 2024.8,9 Seventeen newly approved CPT telemedicine codes for new and established patient audio-visual and audio-only visits recently were surveyed.2,3 The data from the survey will be used as a key element in assigning a specific RVU to the CMS and will be included in the MPFS.
Thirty additional new digital pathology add-on CPT category III codes for 2024 were added to the ones from 2023.2,3 These codes can be used to report additional clinical staff work and service requirements associated with digitizing glass microscope slides for primary diagnosis. They cannot be used for archival or educational purposes, clinical conferences, training, or validating artificial intelligence algorithms. Category III codes used for emerging technologies have no assigned RVUs or reimbursement.2,3
The Cures Act—The Cures Act aims to ensure that patients have timely access to their health information.10 It requires all physicians to make their office notes, laboratory results, and other diagnostic reports available to patients as soon as the office receives them. The rules went into effect on April 5, 2021, with a limited definition of electronic health information; on October 6, 2022, the Cures Act rule expanded to include all electronic health information. The AADA has urged the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology to collaborate with stakeholder organizations to re-evaluate federal policies concerning the immediate release of electronic health information and information blocking, particularly in cases with life-altering diagnoses.10 They stressed the importance of prioritizing the well-being and emotional stability of patients and enhancing care by providing patients adequate time and support to process, comprehend, and discuss findings with their physician.
Proposed 2024 Medicare Quality Payment Program Requirements
The CMS proposed to increase the performance threshold in the quality payment program from 75 to 82 points for the 2024 Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) performance period, impacting the 2026 payment year.2,3,11 As a result of this increase, there could be more MIPS-eligible clinicians receiving penalties, which could be a reduction of up to 9%. The AADA will firmly oppose any increase in the threshold and strongly urge CMS to maintain the 75-point threshold. The performance category weights for the 2024 performance year will remain unchanged from the 2023 performance year.2,3,11
2024 Proposed Quality MIPS Measures Set—The CMS proposed to remove the topped-out MIPS measure 138 (coordination of care for melanoma).2,3,11 Additionally, it proposed to remove MIPS measure 402 (tobacco use and help with quitting among adolescents) as a quality measure from MIPS because the agency believes it is duplicative of measure 226 (preventive care and screening: tobacco use: screening and cessation intervention).2,3,11
MIPS Value Pathways—The CMS consolidated 2 previously established MIPS value pathways (MVPs): the Promoting Wellness MVP and the Optimizing Chronic Disease Management MVP.2,3,11 Proposed new MVPs for 2024 include Focusing on Women’s Health; Quality Care for the Treatment of Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorders; Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Disorders Including Hepatitis C and HIV; Quality Care in Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders; and Rehabilitative Support for Musculoskeletal Care. Dermatology is not impacted; however, the CMS plans to sunset traditional MIPS and replace it with MVPs—the future of MIPS.2,3,11 The AADA maintains that traditional MIPS should continue to be an option because MVPs have a limited number of measures for dermatologists.
Update on Reporting Suture Removal
There are 2 new CPT add-on codes—15853 and 15854—for the removal of sutures or staples not requiring anesthesia to be listed separately in addition to an appropriate E/M service. These add-on codes went into effect on January 1, 2023.12 These codes were created with the intent to capture and ensure remuneration for practice expenses that are not included in a stand-alone E/M encounter that occur after a 0-day procedure (eg, services reported with CPT codes 11102–11107 and 11300–11313) for wound check and suture removal where appropriate. These new add-on codes do not have physician work RVUs assigned to them because they are only for practice expenses (eg, clinical staff time, disposable supplies, use of equipment); CPT code 15853 is reported for the removal of sutures or staples, and CPT code 15854 is reported when both sutures and staples are removed. These codes can only be reported if an E/M service also is reported for the patient encounter.12
Final Thoughts
The AADA is working with the House of Medicine and the medical specialty community to develop specific proposals to reform the Medicare payment system.4 The proposed 2024 MPFS was released on July 13, 2023, and final regulations are expected in the late fall of 2023. The AADA will continue to engage with the CMS, but it is important for physicians to learn about and support advocacy priorities and efforts as well as join forces to protect their practices. As health care professionals, we have unique insights into the challenges and needs of our patients and the health care system. Advocacy can take various forms, such as supporting or opposing specific legislations, participating in grassroots campaigns, engaging with policymakers, and/or joining professional organizations that advocate for health care–related issues. Get involved, stay informed, and stay engaged through dermatology medical societies; together we can make a difference.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. NHE fact sheet. Updated September 6, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems/Statistics-Trends-and-Reports/NationalHealthExpendData/NHE-Fact-Sheet
- Medicare and Medicaid Programs; CY 2024 payment policies under the physician fee schedule and other changes to part B payment and coverage policies; Medicare shared savings program requirements; Medicare advantage; Medicare and Medicaid provider and supplier enrollment policies; and basic health program. Fed Regist. 2023;88:52262-53197. To be codified at 42 CFR §405, §410, §411, §414, §415, §418, §422, §423, §424, §425, §455, §489, §491, §495, §498, and §600. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2023/08/07/2023-14624/medicare-and-medicaid-programs-cy-2024-payment-policies-under-the-physician-fee-schedule-and-other
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Calendar year (CY) 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule proposed rule. Published July 13, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/newsroom/fact-sheets/calendar-year-cy-2024-medicare-physician-fee-schedule-proposed-rule
- American Medical Association. Payment reform. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/health-care-advocacypayment-reform
- American Medical Association. Physician answers on this survey will shape future Medicare pay. Published July 31, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/medicare-medicaid/physician-answers-survey-will-shape-future -medicare-pay
- Strengthening Medicare for Patients and Providers Act, HR 2474, 118 Congress (2023-2024). https://www.congress.gov/bill/118th-congress/house-bill/2474
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. Academy advocacy priorities. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.aad.org/member/advocacy/priorities
- College of American Pathologists. Remote sign-out of cases with digital pathology FAQs. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cap.org/covid-19/remote-sign-out-faqs
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Telehealth. Updated September 6, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/medicare/coverage/telehealth
- The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology. ONC’s Cures Act final rule. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.healthit.gov/topic/oncs-cures-act-final-rule
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Calendar Year (CY) 2024 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (PFS) Notice of Proposed Rule Making Quality Payment Program Policy Overview: Proposals and Requests for Information. Accessed September 12, 2023. https://email.aadresources.org/e3t/Ctc/I6+113/cVKqx04/VVWzj43dDbctW8c23GW1ZLnJHW1xTZ7Q50Y DYN89Qzy5nCVhV3Zsc37CgFV9W5Ck4-D42qs9BW38PtXn4LSlNLW1QKpPL4xT8BMW6Mcwww3FdwCHN3vfGTMXbtF-W2-Zzfy5WHDg6W88tx1F1KgsgxW7zDzT46C2sFXW800vQJ3lLsS_W5D6f1d30-f3cN1njgZ_dX7xkW447ldH2-kgc5VCs7Xg1GY6dsN87pLVJqJG5XW8VWwD-7VxVkJN777f5fJL7jBW8RxkQM1lcSDjVV746T3C-stpN52V_S5xj7q6W3_vldf3p1Yk2Vbd4ZD3cPrHqW5Pwv9m567fkzW1vfDm51H-T7rW1jVrxl8gstXyW5RVTn8863CVFW8g6LgK2YdhpkW34HC4z3_pGYgW8V_qWH3g-tTlW4S3RD-1dKry7W4_rW8d1ssZ1fVwXQjQ9krVMW8Y0bTt8Nr5CNW6vbG0h3wyx59W8WCrNW50p5n6W1r-VBC2rKh93N4W2RyYr7vvm3kxG1
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Chapter III surgery: integumentary system CPT codes 10000-19999 for Medicare national correct coding initiative policy manual. Updated January 1, 2023. Accessed September 26, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/medicare-ncci-policy-manual-2023-chapter-3.pdf
Health care spending in the United States remained relatively flat from 2019 to 2021 and only increased 2.7% in 2021, reaching $4.3 billion or $12,914 per person. Physician services account for 15% of health care spending (Figure). Relative value units (RVUs) signify the time it took a physician to complete a task multiplied by a conversion factor (CF). When RVUs initially were created in 1992 by what is now the Centers for Medicare &Medicaid Services (CMS), the CF was $32.00. Thirty-one years later, the CF is $33.89 in 2023; however, it would be $66.00 if the CF had increased with inflation.1 If the proposed 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule (MPFS) is adopted, the payment formula would decrease by 3.4% ($32.75) relative to the 2023 fee schedule ($33.89), which would be a 9% decrease relative to 2019 ($36.04).2,3 This reduction is due to the budget neutrality adjustment required by changes in RVUs, implementation of the evaluation and management (E/M) add-on code G2211, and proposed increases in primary are services.2,3 Since 2001, Medicare physician payment has declined by 26%.4 Adjustments to the CF typically are made based on 3 factors: (1) the Medicare Economic Index (MEI); (2) an expenditure target performance adjustment; and (3) miscellaneous adjustments, including those for budget neutrality required by law. Despite continued substantial increases in practice expenses, physicians’ reimbursement has remained flat while other service providers, such as those in skilled nursing facilities and hospitals, have received favorable payment increases compared to practice cost inflation and the Consumer Price Index.4

The CMS will not incorporate 2017 MEI cost weights for the RVUs in the MPFS rate setting for 2024 because all key measures of practice expenses in the MEI accelerated in 2022. Instead, the CMS is updating data on practice expense per hour to calculate payment for physician services with a survey for physician practices that launched on July 31, 2023.5 The American Medical Association contracted with Mathematica, an independent research company, to conduct a physician practice information survey that will be used to determine indirect practice expenses. Physicians should be on the lookout for emails regarding completion of these surveys and the appropriate financial expert in their practice should be contacted so the responses are accurate, as these data are key to future updates in the Medicare pay formula used to reimburse physicians.
Impact of Medicare Cuts
The recent congressional debt limit deal set spending caps for the next 2 fiscal years. Dermatology is facing an overall payment reduction of 1.87% (range, 1%–4%).2,3 The impact will depend on the services offered in an individual practice; for example, payment for a punch biopsy (Current Procedural Terminology [CPT] code 11104) would decrease by 3.9%. Payment for benign destruction (CPT code 17110) would decrease by 2.8%, and payment for even simple E/M of an established patient (CPT code 99213) would decrease by 1.6%. Overall, there would be a reduction of 2.75% for dermatopathology services, with a decrease of 2% for CPT code 88305 global and decreases for the technical component of 1% and professional component of 3%.2,3
Medicare cuts have reached a critical level, and physicians cannot continue to absorb the costs to own and operate their practices.4 This has led to health market consolidation, which in turn limits competition and patient access while driving up health care costs and driving down the quality of care. Small independent rural practices as well as those caring for historically marginalized patients will be disproportionately affected.
Proposed Addition of E/M Code G2211
In the calendar year (CY) 2021 final rule, the CMS tried to adopt a new add-on code—G2211—patients with a serious or complex condition that typically require referral and coordination of multispecialty care. Per the CMS, the primary policy goal of G2211 is to increase payments to primary care physicians and to reimburse them more appropriately for the care provided to patients with a serious or complex condition.2,3 It can be reported in conjunction with all office and outpatient E/M visits to better account for additional resources associated with primary care, or similarly ongoing medical care related to a patient’s single, serious condition, or complex condition.3 Typically, G2211 would not be used by dermatologists, as this add-on code requires visit complexity inherent to E/M associated with medical care services that serve as the continuing focal point for all needed health care services and/or with medical care services that are part of ongoing care related to a patient’s single serious condition or a complex condition.2,3
Initially, the CMS assumed that G2211 would be reported with 90% of all office and outpatient E/M visit claims, which would account for a considerable portion of total MPFS schedule spending; however, the House of Medicine disagreed and believed it would be 75%.2,3 Given the extremely high utilization estimate, G2211 would have had a substantial effect on budget neutrality, accounting for an estimated increase of $3.3 billion and a corresponding 3.0% cut to the CY 2021 MPFS. Because of the potential payment reductions to physicians and a successful advocacy effort by organized medicine, including the American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA), Congress delayed implementation of G2211 until CY 2024. Modifier -25 cannot be reported with G2211. The CMS revised its utilization assumptions from 90% of all E/M services to an initial utilization of 38% and then 54% when fully adopted. The proposed 2024 payment for G2211 is an additional $16.05.2,3
Advancing Health Equity With Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System G Codes
The CMS is proposing coding and payment for several new services to help underserved populations, including addressing unmet health-related social needs that can potentially interfere with the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions, which includes paying for certain caregiver training services as well as payment for community health integration services.2,3 These are the first MPFS services designed to include care involving community health workers, who link underserved communities with critical health care and social services in the community. Additionally, the rule also proposes coding and payment for evaluating the risks related to social factors that affect a patient’s health, such as access to affordable quality health care, that can take place during an annual wellness visit or in combination with an E/M visit.2,3 As dermatologists, we should be familiar with this set of G codes, as we will likely use them in practice for patients with transportation needs.
Advocacy Efforts on Medicare Payment Reform
Medicare physician payment reform needs to happen at a national level. Advocacy efforts by the AADA and other groups have been underway to mitigate the proposed 2024 cuts. The Strengthening Medicare for Patients and Providers Act (HR 2474) is a bill that was introduced by a bipartisan coalition of physicians to provide an inflation-based increase in Medicare payments in 2024 and beyond.6
Other Legislative Updates Affecting Dermatology
Modifier -25—Cigna’s policy requiring dermatologists to submit documentation to use modifier -25 when billing with E/M CPT codes 99212 through 99215 has been delayed indefinitely.7 If a payer denies a dermatologist payment, contact the AADA Patient Access and Payer Relations committee ([email protected]) for assistance.
Telehealth and Digital Pathology—Recent legislation authorized extension of many of the Medicare telehealth and digital pathology flexibilities that were put in place during the COVID-19 public health emergency through December 31, 2024.8,9 Seventeen newly approved CPT telemedicine codes for new and established patient audio-visual and audio-only visits recently were surveyed.2,3 The data from the survey will be used as a key element in assigning a specific RVU to the CMS and will be included in the MPFS.
Thirty additional new digital pathology add-on CPT category III codes for 2024 were added to the ones from 2023.2,3 These codes can be used to report additional clinical staff work and service requirements associated with digitizing glass microscope slides for primary diagnosis. They cannot be used for archival or educational purposes, clinical conferences, training, or validating artificial intelligence algorithms. Category III codes used for emerging technologies have no assigned RVUs or reimbursement.2,3
The Cures Act—The Cures Act aims to ensure that patients have timely access to their health information.10 It requires all physicians to make their office notes, laboratory results, and other diagnostic reports available to patients as soon as the office receives them. The rules went into effect on April 5, 2021, with a limited definition of electronic health information; on October 6, 2022, the Cures Act rule expanded to include all electronic health information. The AADA has urged the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology to collaborate with stakeholder organizations to re-evaluate federal policies concerning the immediate release of electronic health information and information blocking, particularly in cases with life-altering diagnoses.10 They stressed the importance of prioritizing the well-being and emotional stability of patients and enhancing care by providing patients adequate time and support to process, comprehend, and discuss findings with their physician.
Proposed 2024 Medicare Quality Payment Program Requirements
The CMS proposed to increase the performance threshold in the quality payment program from 75 to 82 points for the 2024 Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) performance period, impacting the 2026 payment year.2,3,11 As a result of this increase, there could be more MIPS-eligible clinicians receiving penalties, which could be a reduction of up to 9%. The AADA will firmly oppose any increase in the threshold and strongly urge CMS to maintain the 75-point threshold. The performance category weights for the 2024 performance year will remain unchanged from the 2023 performance year.2,3,11
2024 Proposed Quality MIPS Measures Set—The CMS proposed to remove the topped-out MIPS measure 138 (coordination of care for melanoma).2,3,11 Additionally, it proposed to remove MIPS measure 402 (tobacco use and help with quitting among adolescents) as a quality measure from MIPS because the agency believes it is duplicative of measure 226 (preventive care and screening: tobacco use: screening and cessation intervention).2,3,11
MIPS Value Pathways—The CMS consolidated 2 previously established MIPS value pathways (MVPs): the Promoting Wellness MVP and the Optimizing Chronic Disease Management MVP.2,3,11 Proposed new MVPs for 2024 include Focusing on Women’s Health; Quality Care for the Treatment of Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorders; Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Disorders Including Hepatitis C and HIV; Quality Care in Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders; and Rehabilitative Support for Musculoskeletal Care. Dermatology is not impacted; however, the CMS plans to sunset traditional MIPS and replace it with MVPs—the future of MIPS.2,3,11 The AADA maintains that traditional MIPS should continue to be an option because MVPs have a limited number of measures for dermatologists.
Update on Reporting Suture Removal
There are 2 new CPT add-on codes—15853 and 15854—for the removal of sutures or staples not requiring anesthesia to be listed separately in addition to an appropriate E/M service. These add-on codes went into effect on January 1, 2023.12 These codes were created with the intent to capture and ensure remuneration for practice expenses that are not included in a stand-alone E/M encounter that occur after a 0-day procedure (eg, services reported with CPT codes 11102–11107 and 11300–11313) for wound check and suture removal where appropriate. These new add-on codes do not have physician work RVUs assigned to them because they are only for practice expenses (eg, clinical staff time, disposable supplies, use of equipment); CPT code 15853 is reported for the removal of sutures or staples, and CPT code 15854 is reported when both sutures and staples are removed. These codes can only be reported if an E/M service also is reported for the patient encounter.12
Final Thoughts
The AADA is working with the House of Medicine and the medical specialty community to develop specific proposals to reform the Medicare payment system.4 The proposed 2024 MPFS was released on July 13, 2023, and final regulations are expected in the late fall of 2023. The AADA will continue to engage with the CMS, but it is important for physicians to learn about and support advocacy priorities and efforts as well as join forces to protect their practices. As health care professionals, we have unique insights into the challenges and needs of our patients and the health care system. Advocacy can take various forms, such as supporting or opposing specific legislations, participating in grassroots campaigns, engaging with policymakers, and/or joining professional organizations that advocate for health care–related issues. Get involved, stay informed, and stay engaged through dermatology medical societies; together we can make a difference.
Health care spending in the United States remained relatively flat from 2019 to 2021 and only increased 2.7% in 2021, reaching $4.3 billion or $12,914 per person. Physician services account for 15% of health care spending (Figure). Relative value units (RVUs) signify the time it took a physician to complete a task multiplied by a conversion factor (CF). When RVUs initially were created in 1992 by what is now the Centers for Medicare &Medicaid Services (CMS), the CF was $32.00. Thirty-one years later, the CF is $33.89 in 2023; however, it would be $66.00 if the CF had increased with inflation.1 If the proposed 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule (MPFS) is adopted, the payment formula would decrease by 3.4% ($32.75) relative to the 2023 fee schedule ($33.89), which would be a 9% decrease relative to 2019 ($36.04).2,3 This reduction is due to the budget neutrality adjustment required by changes in RVUs, implementation of the evaluation and management (E/M) add-on code G2211, and proposed increases in primary are services.2,3 Since 2001, Medicare physician payment has declined by 26%.4 Adjustments to the CF typically are made based on 3 factors: (1) the Medicare Economic Index (MEI); (2) an expenditure target performance adjustment; and (3) miscellaneous adjustments, including those for budget neutrality required by law. Despite continued substantial increases in practice expenses, physicians’ reimbursement has remained flat while other service providers, such as those in skilled nursing facilities and hospitals, have received favorable payment increases compared to practice cost inflation and the Consumer Price Index.4

The CMS will not incorporate 2017 MEI cost weights for the RVUs in the MPFS rate setting for 2024 because all key measures of practice expenses in the MEI accelerated in 2022. Instead, the CMS is updating data on practice expense per hour to calculate payment for physician services with a survey for physician practices that launched on July 31, 2023.5 The American Medical Association contracted with Mathematica, an independent research company, to conduct a physician practice information survey that will be used to determine indirect practice expenses. Physicians should be on the lookout for emails regarding completion of these surveys and the appropriate financial expert in their practice should be contacted so the responses are accurate, as these data are key to future updates in the Medicare pay formula used to reimburse physicians.
Impact of Medicare Cuts
The recent congressional debt limit deal set spending caps for the next 2 fiscal years. Dermatology is facing an overall payment reduction of 1.87% (range, 1%–4%).2,3 The impact will depend on the services offered in an individual practice; for example, payment for a punch biopsy (Current Procedural Terminology [CPT] code 11104) would decrease by 3.9%. Payment for benign destruction (CPT code 17110) would decrease by 2.8%, and payment for even simple E/M of an established patient (CPT code 99213) would decrease by 1.6%. Overall, there would be a reduction of 2.75% for dermatopathology services, with a decrease of 2% for CPT code 88305 global and decreases for the technical component of 1% and professional component of 3%.2,3
Medicare cuts have reached a critical level, and physicians cannot continue to absorb the costs to own and operate their practices.4 This has led to health market consolidation, which in turn limits competition and patient access while driving up health care costs and driving down the quality of care. Small independent rural practices as well as those caring for historically marginalized patients will be disproportionately affected.
Proposed Addition of E/M Code G2211
In the calendar year (CY) 2021 final rule, the CMS tried to adopt a new add-on code—G2211—patients with a serious or complex condition that typically require referral and coordination of multispecialty care. Per the CMS, the primary policy goal of G2211 is to increase payments to primary care physicians and to reimburse them more appropriately for the care provided to patients with a serious or complex condition.2,3 It can be reported in conjunction with all office and outpatient E/M visits to better account for additional resources associated with primary care, or similarly ongoing medical care related to a patient’s single, serious condition, or complex condition.3 Typically, G2211 would not be used by dermatologists, as this add-on code requires visit complexity inherent to E/M associated with medical care services that serve as the continuing focal point for all needed health care services and/or with medical care services that are part of ongoing care related to a patient’s single serious condition or a complex condition.2,3
Initially, the CMS assumed that G2211 would be reported with 90% of all office and outpatient E/M visit claims, which would account for a considerable portion of total MPFS schedule spending; however, the House of Medicine disagreed and believed it would be 75%.2,3 Given the extremely high utilization estimate, G2211 would have had a substantial effect on budget neutrality, accounting for an estimated increase of $3.3 billion and a corresponding 3.0% cut to the CY 2021 MPFS. Because of the potential payment reductions to physicians and a successful advocacy effort by organized medicine, including the American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA), Congress delayed implementation of G2211 until CY 2024. Modifier -25 cannot be reported with G2211. The CMS revised its utilization assumptions from 90% of all E/M services to an initial utilization of 38% and then 54% when fully adopted. The proposed 2024 payment for G2211 is an additional $16.05.2,3
Advancing Health Equity With Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System G Codes
The CMS is proposing coding and payment for several new services to help underserved populations, including addressing unmet health-related social needs that can potentially interfere with the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions, which includes paying for certain caregiver training services as well as payment for community health integration services.2,3 These are the first MPFS services designed to include care involving community health workers, who link underserved communities with critical health care and social services in the community. Additionally, the rule also proposes coding and payment for evaluating the risks related to social factors that affect a patient’s health, such as access to affordable quality health care, that can take place during an annual wellness visit or in combination with an E/M visit.2,3 As dermatologists, we should be familiar with this set of G codes, as we will likely use them in practice for patients with transportation needs.
Advocacy Efforts on Medicare Payment Reform
Medicare physician payment reform needs to happen at a national level. Advocacy efforts by the AADA and other groups have been underway to mitigate the proposed 2024 cuts. The Strengthening Medicare for Patients and Providers Act (HR 2474) is a bill that was introduced by a bipartisan coalition of physicians to provide an inflation-based increase in Medicare payments in 2024 and beyond.6
Other Legislative Updates Affecting Dermatology
Modifier -25—Cigna’s policy requiring dermatologists to submit documentation to use modifier -25 when billing with E/M CPT codes 99212 through 99215 has been delayed indefinitely.7 If a payer denies a dermatologist payment, contact the AADA Patient Access and Payer Relations committee ([email protected]) for assistance.
Telehealth and Digital Pathology—Recent legislation authorized extension of many of the Medicare telehealth and digital pathology flexibilities that were put in place during the COVID-19 public health emergency through December 31, 2024.8,9 Seventeen newly approved CPT telemedicine codes for new and established patient audio-visual and audio-only visits recently were surveyed.2,3 The data from the survey will be used as a key element in assigning a specific RVU to the CMS and will be included in the MPFS.
Thirty additional new digital pathology add-on CPT category III codes for 2024 were added to the ones from 2023.2,3 These codes can be used to report additional clinical staff work and service requirements associated with digitizing glass microscope slides for primary diagnosis. They cannot be used for archival or educational purposes, clinical conferences, training, or validating artificial intelligence algorithms. Category III codes used for emerging technologies have no assigned RVUs or reimbursement.2,3
The Cures Act—The Cures Act aims to ensure that patients have timely access to their health information.10 It requires all physicians to make their office notes, laboratory results, and other diagnostic reports available to patients as soon as the office receives them. The rules went into effect on April 5, 2021, with a limited definition of electronic health information; on October 6, 2022, the Cures Act rule expanded to include all electronic health information. The AADA has urged the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology to collaborate with stakeholder organizations to re-evaluate federal policies concerning the immediate release of electronic health information and information blocking, particularly in cases with life-altering diagnoses.10 They stressed the importance of prioritizing the well-being and emotional stability of patients and enhancing care by providing patients adequate time and support to process, comprehend, and discuss findings with their physician.
Proposed 2024 Medicare Quality Payment Program Requirements
The CMS proposed to increase the performance threshold in the quality payment program from 75 to 82 points for the 2024 Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) performance period, impacting the 2026 payment year.2,3,11 As a result of this increase, there could be more MIPS-eligible clinicians receiving penalties, which could be a reduction of up to 9%. The AADA will firmly oppose any increase in the threshold and strongly urge CMS to maintain the 75-point threshold. The performance category weights for the 2024 performance year will remain unchanged from the 2023 performance year.2,3,11
2024 Proposed Quality MIPS Measures Set—The CMS proposed to remove the topped-out MIPS measure 138 (coordination of care for melanoma).2,3,11 Additionally, it proposed to remove MIPS measure 402 (tobacco use and help with quitting among adolescents) as a quality measure from MIPS because the agency believes it is duplicative of measure 226 (preventive care and screening: tobacco use: screening and cessation intervention).2,3,11
MIPS Value Pathways—The CMS consolidated 2 previously established MIPS value pathways (MVPs): the Promoting Wellness MVP and the Optimizing Chronic Disease Management MVP.2,3,11 Proposed new MVPs for 2024 include Focusing on Women’s Health; Quality Care for the Treatment of Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorders; Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Disorders Including Hepatitis C and HIV; Quality Care in Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders; and Rehabilitative Support for Musculoskeletal Care. Dermatology is not impacted; however, the CMS plans to sunset traditional MIPS and replace it with MVPs—the future of MIPS.2,3,11 The AADA maintains that traditional MIPS should continue to be an option because MVPs have a limited number of measures for dermatologists.
Update on Reporting Suture Removal
There are 2 new CPT add-on codes—15853 and 15854—for the removal of sutures or staples not requiring anesthesia to be listed separately in addition to an appropriate E/M service. These add-on codes went into effect on January 1, 2023.12 These codes were created with the intent to capture and ensure remuneration for practice expenses that are not included in a stand-alone E/M encounter that occur after a 0-day procedure (eg, services reported with CPT codes 11102–11107 and 11300–11313) for wound check and suture removal where appropriate. These new add-on codes do not have physician work RVUs assigned to them because they are only for practice expenses (eg, clinical staff time, disposable supplies, use of equipment); CPT code 15853 is reported for the removal of sutures or staples, and CPT code 15854 is reported when both sutures and staples are removed. These codes can only be reported if an E/M service also is reported for the patient encounter.12
Final Thoughts
The AADA is working with the House of Medicine and the medical specialty community to develop specific proposals to reform the Medicare payment system.4 The proposed 2024 MPFS was released on July 13, 2023, and final regulations are expected in the late fall of 2023. The AADA will continue to engage with the CMS, but it is important for physicians to learn about and support advocacy priorities and efforts as well as join forces to protect their practices. As health care professionals, we have unique insights into the challenges and needs of our patients and the health care system. Advocacy can take various forms, such as supporting or opposing specific legislations, participating in grassroots campaigns, engaging with policymakers, and/or joining professional organizations that advocate for health care–related issues. Get involved, stay informed, and stay engaged through dermatology medical societies; together we can make a difference.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. NHE fact sheet. Updated September 6, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems/Statistics-Trends-and-Reports/NationalHealthExpendData/NHE-Fact-Sheet
- Medicare and Medicaid Programs; CY 2024 payment policies under the physician fee schedule and other changes to part B payment and coverage policies; Medicare shared savings program requirements; Medicare advantage; Medicare and Medicaid provider and supplier enrollment policies; and basic health program. Fed Regist. 2023;88:52262-53197. To be codified at 42 CFR §405, §410, §411, §414, §415, §418, §422, §423, §424, §425, §455, §489, §491, §495, §498, and §600. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2023/08/07/2023-14624/medicare-and-medicaid-programs-cy-2024-payment-policies-under-the-physician-fee-schedule-and-other
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Calendar year (CY) 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule proposed rule. Published July 13, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/newsroom/fact-sheets/calendar-year-cy-2024-medicare-physician-fee-schedule-proposed-rule
- American Medical Association. Payment reform. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/health-care-advocacypayment-reform
- American Medical Association. Physician answers on this survey will shape future Medicare pay. Published July 31, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/medicare-medicaid/physician-answers-survey-will-shape-future -medicare-pay
- Strengthening Medicare for Patients and Providers Act, HR 2474, 118 Congress (2023-2024). https://www.congress.gov/bill/118th-congress/house-bill/2474
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. Academy advocacy priorities. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.aad.org/member/advocacy/priorities
- College of American Pathologists. Remote sign-out of cases with digital pathology FAQs. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cap.org/covid-19/remote-sign-out-faqs
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Telehealth. Updated September 6, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/medicare/coverage/telehealth
- The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology. ONC’s Cures Act final rule. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.healthit.gov/topic/oncs-cures-act-final-rule
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Calendar Year (CY) 2024 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (PFS) Notice of Proposed Rule Making Quality Payment Program Policy Overview: Proposals and Requests for Information. Accessed September 12, 2023. https://email.aadresources.org/e3t/Ctc/I6+113/cVKqx04/VVWzj43dDbctW8c23GW1ZLnJHW1xTZ7Q50Y DYN89Qzy5nCVhV3Zsc37CgFV9W5Ck4-D42qs9BW38PtXn4LSlNLW1QKpPL4xT8BMW6Mcwww3FdwCHN3vfGTMXbtF-W2-Zzfy5WHDg6W88tx1F1KgsgxW7zDzT46C2sFXW800vQJ3lLsS_W5D6f1d30-f3cN1njgZ_dX7xkW447ldH2-kgc5VCs7Xg1GY6dsN87pLVJqJG5XW8VWwD-7VxVkJN777f5fJL7jBW8RxkQM1lcSDjVV746T3C-stpN52V_S5xj7q6W3_vldf3p1Yk2Vbd4ZD3cPrHqW5Pwv9m567fkzW1vfDm51H-T7rW1jVrxl8gstXyW5RVTn8863CVFW8g6LgK2YdhpkW34HC4z3_pGYgW8V_qWH3g-tTlW4S3RD-1dKry7W4_rW8d1ssZ1fVwXQjQ9krVMW8Y0bTt8Nr5CNW6vbG0h3wyx59W8WCrNW50p5n6W1r-VBC2rKh93N4W2RyYr7vvm3kxG1
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Chapter III surgery: integumentary system CPT codes 10000-19999 for Medicare national correct coding initiative policy manual. Updated January 1, 2023. Accessed September 26, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/medicare-ncci-policy-manual-2023-chapter-3.pdf
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. NHE fact sheet. Updated September 6, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems/Statistics-Trends-and-Reports/NationalHealthExpendData/NHE-Fact-Sheet
- Medicare and Medicaid Programs; CY 2024 payment policies under the physician fee schedule and other changes to part B payment and coverage policies; Medicare shared savings program requirements; Medicare advantage; Medicare and Medicaid provider and supplier enrollment policies; and basic health program. Fed Regist. 2023;88:52262-53197. To be codified at 42 CFR §405, §410, §411, §414, §415, §418, §422, §423, §424, §425, §455, §489, §491, §495, §498, and §600. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2023/08/07/2023-14624/medicare-and-medicaid-programs-cy-2024-payment-policies-under-the-physician-fee-schedule-and-other
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Calendar year (CY) 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule proposed rule. Published July 13, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/newsroom/fact-sheets/calendar-year-cy-2024-medicare-physician-fee-schedule-proposed-rule
- American Medical Association. Payment reform. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/health-care-advocacypayment-reform
- American Medical Association. Physician answers on this survey will shape future Medicare pay. Published July 31, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/medicare-medicaid/physician-answers-survey-will-shape-future -medicare-pay
- Strengthening Medicare for Patients and Providers Act, HR 2474, 118 Congress (2023-2024). https://www.congress.gov/bill/118th-congress/house-bill/2474
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. Academy advocacy priorities. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.aad.org/member/advocacy/priorities
- College of American Pathologists. Remote sign-out of cases with digital pathology FAQs. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cap.org/covid-19/remote-sign-out-faqs
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Telehealth. Updated September 6, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/medicare/coverage/telehealth
- The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology. ONC’s Cures Act final rule. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.healthit.gov/topic/oncs-cures-act-final-rule
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Calendar Year (CY) 2024 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (PFS) Notice of Proposed Rule Making Quality Payment Program Policy Overview: Proposals and Requests for Information. Accessed September 12, 2023. https://email.aadresources.org/e3t/Ctc/I6+113/cVKqx04/VVWzj43dDbctW8c23GW1ZLnJHW1xTZ7Q50Y DYN89Qzy5nCVhV3Zsc37CgFV9W5Ck4-D42qs9BW38PtXn4LSlNLW1QKpPL4xT8BMW6Mcwww3FdwCHN3vfGTMXbtF-W2-Zzfy5WHDg6W88tx1F1KgsgxW7zDzT46C2sFXW800vQJ3lLsS_W5D6f1d30-f3cN1njgZ_dX7xkW447ldH2-kgc5VCs7Xg1GY6dsN87pLVJqJG5XW8VWwD-7VxVkJN777f5fJL7jBW8RxkQM1lcSDjVV746T3C-stpN52V_S5xj7q6W3_vldf3p1Yk2Vbd4ZD3cPrHqW5Pwv9m567fkzW1vfDm51H-T7rW1jVrxl8gstXyW5RVTn8863CVFW8g6LgK2YdhpkW34HC4z3_pGYgW8V_qWH3g-tTlW4S3RD-1dKry7W4_rW8d1ssZ1fVwXQjQ9krVMW8Y0bTt8Nr5CNW6vbG0h3wyx59W8WCrNW50p5n6W1r-VBC2rKh93N4W2RyYr7vvm3kxG1
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Chapter III surgery: integumentary system CPT codes 10000-19999 for Medicare national correct coding initiative policy manual. Updated January 1, 2023. Accessed September 26, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/medicare-ncci-policy-manual-2023-chapter-3.pdf
PRACTICE POINTS
- The proposed 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule published by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services in July 2023 will negatively impact dermatology practices.
- The final regulations are expected in November 2023.
What’s Eating You? Noble False Widow Spider (Steatoda nobilis)
Incidence and Characteristics
The noble false widow spider (Steatoda nobilis) is one of the world’s most invasive spider species, having spread across the globe from Madeira and the Canary Islands into the North Atlantic.1,2 Steatoda comprise multiple species of false widow spiders, named for their resemblance to black widow spiders (Latrodectus). The noble false widow spider is the dominant species in buildings in southern Ireland and Great Britain, with a population surge in 2018 that caused multiple temporary school closures in London, England, for fumigation.3 The noble false widow spider was first documented in the United States in Ventura County, California, in 2011, with numerous specimens found in urban areas (eg, in parks, underneath garbage cans) closer to the coastline as well as farther inland. The species may have been introduced to this area by way of Port Hueneme, a city in California with a US naval base with routes to various other military bases in Western Europe.4 Given its already rapid expansion outside of the United States with a concurrent rise in bite reports, dermatologists should be familiar with these invasive and potentially dangerous arachnids.
The spread of noble false widow spiders is assisted by their wide range of temperature tolerance and ability to survive for months with little food and no water. They can live for several years, with one report of a noble false widow spider living up to 7 years.5 These spiders are found inside homes and buildings year-round, and they prefer to build their webs in an elevated position such as the top corner of a room. Steatoda weave tangle webs with crisscrossing threads that often have a denser middle section.5
Noble false widow spiders are sexually dimorphic, with males typically no larger than 1-cm long and females up to 1.4-cm long. They have a dark brown to black thorax and brown abdomen with red-brown legs. Males have brighter cream-colored abdominal markings than females, who lack markings altogether on their distinctive globular abdomen (Figure). The abdominal markings are known to resemble a skull or house.

Although noble false widow spiders are not exclusively synanthropic, they can be found in any crevice in homes or other structures where there are humans such as office buildings.5-7 Up until the last 20 years, reports of bites from noble false widow spiders worldwide were few and far between. In Great Britain, the spiders were first considered to be common in the 1980s, with recent evidence of an urban population boom in the last 5 to 10 years that has coincided with an increase in bite reports.5,8,9
Clinical Significance
Most bites occur in a defensive manner, such as when humans perform activities that disturb the hiding space, cause vibrations in the web, or compress the body of the arachnid. Most envenomations in Great Britain occur while the individual is in bed, though they also may occur during other activities that disturb the spider, such as moving boxes or putting on a pair of pants.5 Occupational exposure to noble false widow spiders may soon be a concern for those involved in construction, carpentry, cleaning, and decorating given their recent invasive spread into the United States.
The venom from these spiders is neurotoxic and cytotoxic, causing moderate to intense pain that may resemble a wasp sting. The incidence of steatodism—which can include symptoms of pain in addition to fever, hypotension, headache, lethargy, nausea, localized diaphoresis, abdominal pain, paresthesias, and malaise—is unknown but reportedly rare.5,10 There are considerable similarities between Steatoda and true black widow spider venom, which explains the symptom overlap with latrodectism. There are reports of severe debilitation lasting weeks due to pain and decreased affected limb movement after bites from noble false widow spiders.10-12
Nearly all noble false widow spider bite reports describe immediate pain upon bite/envenomation, which is unlike the delayed pain from a black widow spider bite (after 10 minutes or more).6,13,14 Erythema and swelling occur around a pale raised site of envenomation lasting up to 72 hours. The bite site may be highly tender and blister or ulcerate, with reports of cellulitis and local skin necrosis.7,15 Pruritus during this period can be intense, and excoriation increases the risk for complications such as infection. Reports of anaphylaxis following a noble false widow spider bite are rare.5,16 The incidence of bites may be underreported due to the lack of proper identification of the responsible arachnid for those who do not seek care or require hospitalization, though this is not unique to Steatoda.
There are reports of secondary infection after bites and even cases of limb amputation, septicemia, and death.14,17 However, it is unknown if noble false widow spiders are vectors for bacteria transmitted during envenomation, and infection likely is secondary to scratching or inadequate wound care.18,19 Potentially pathogenic bacteria have been isolated from the body surfaces of the noble false widow spider, including Pseudomonas putida, Staphylococcus capitis, and Staphylococcus epidermidis.20 Fortunately, most captured cases (ie, events in which the biting arachnid was properly identified) report symptoms ranging from mild to moderate in severity without the need for hospitalization. A series of 24 reports revealed that all individuals experienced sharp pain upon the initial bite followed by erythema, and 18 of them experienced considerable swelling of the area soon thereafter. One individual experienced temporary paralysis of the affected limb, and 3 individuals experienced hypotension or hypertension in addition to fever, skin necrosis, or cellulitis.14
Treatment
The envenomation site should be washed with antibacterial soap and warm water and should be kept clean to prevent infection. There is no evidence that tight pressure bandaging of these bite sites will restrict venom flow; because it may worsen pain in the area, pressure bandaging is not recommended. When possible, the arachnid should be collected for identification. Supportive care is warranted for symptoms of pain, erythema, and swelling, with the use of cool compresses, oral pain relievers (eg, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acetaminophen), topical anesthetic (eg, lidocaine), or antihistamines as needed.
Urgent care is warranted for patients who experience severe symptoms of steatodism such as hypertension, lymphadenopathy, paresthesia, or limb paralysis. Limited reports show onset of this distress typically within an hour of envenomation. Treatments analogous to those for latrodectism including muscle relaxers and pain medications have demonstrated rapid attenuation of symptoms upon intramuscular administration of antivenom made from Latrodectus species.21-23
Signs of infection warrant bacterial culture with antibiotic susceptibilities to ensure adequate treatment.20 Infections from spider bites can present a few days to a week following envenomation. Symptoms may include spreading redness or an enlarging wound site, pus formation, worsening or unrelenting pain after 24 hours, fevers, flulike symptoms, and muscle cramps.
Final Thoughts
- Kulczycki A, Legittimo C, Simeon E, et al. New records of Steatoda nobilis (Thorell, 1875) (Araneae, Theridiidae), an introduced species on the Italian mainland and in Sardinia. Bull Br Arachnological Soc. 2012;15:269-272.
- Bauer T, Feldmeier S, Krehenwinkel H, et al. Steatoda nobilis, a false widow on the rise: a synthesis of past and current distribution trends. NeoBiota. 2019; 42:19. doi:10.3897/neobiota.42.31582
- Murphy A. Web of cries: false widow spider infestation fears forceeleventh school in London to close as outbreak spreads. The Sun.October 19, 2018. Accessed September 21, 2023. https://www.thesun.co.uk/news/7534016/false-widow-spider-infestation-fears-force-eleventh-londonschool-closing
- Vetter R, Rust M. A large European combfoot spider, Steatoda nobilis (Thorell 1875)(Araneae: Theridiidae), newly established in Ventura County, California. The Pan-Pacific Entomologist. 2012;88:92-97.
- Hambler C. The ‘noble false widow’ spider Steatoda nobilis is an emerging public health and ecological threat. OSF Preprints. Preprint posted online October 15, 2019. doi:10.31219/osf.io/axbd4
- Dunbar J, Schulte J, Lyons K, et al. New Irish record for Steatoda triangulosa (Walckenaer, 1802), and new county records for Steatoda nobilis (Thorell, 1875), Steatoda bipunctata (Linnaeus, 1758) and Steatoda grossa (C.L. Koch, 1838). Ir Naturalists J. 2018;36:39-43.
- Duon M, Dunbar J, Afoullouss S, et al. Occurrence, reproductive rate and identification of the non-native noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis (Thorell, 1875) in Ireland. Biol Environment: Proc Royal Ir Acad. 2017;117B:77-89. doi:10.3318/bioe.2017.11
- Burrows T. Great bitten: Britain’s spider bite capital revealed as Essex with 450 attacks—find out where your town ranks. The Sun. Published April 3, 2019. Accessed September 14, 2023. https://www.thesun.co.uk/news/8782355/britains-spider-bite-capital-revealed-as-essex-with-450- attacks-find-out-where-your-town-ranks/
- Wathen T. Essex is the UK capital for spider bites—and the amount is terrifying. Essex News. April 4, 2019. Accessed September 21, 2023. https://www.essexlive.news/news/essex-news/essex-uk-capital-spider-bites- 2720935
- Dunbar J, Afoullouss S, Sulpice R, et al. Envenomation by the noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis (Thorell, 1875)—five new cases of steatodism from Ireland and Great Britain. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2018;56:433-435. doi:10.1080/15563650.2017.1393084
- Dunbar J, Fort A, Redureau D, et al. Venomics approach reveals a high proportion of Latrodectus-like toxins in the venom of the noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis. Toxins. 2020;12:402.
- Warrell D, Shaheen J, Hillyard P, et al. Neurotoxic envenoming by an immigrant spider (Steatoda nobilis) in southern England. Toxicon. 1991;29:1263-1265.
- Zhou H, Xu K, Zheng PY, et. al. Clinical characteristics of patients with black widow spider bites: a report of 59 patients and single-center experience. World J Emerg Med. 2021;12:317-320. doi:10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2021.04.011
- Dunbar J, Vitkauskaite A, O’Keeffe D, et. al. Bites by the noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis can induce Latrodectus-like symptoms and vector-borne bacterial infections with implications for public health: a case series. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2022;60:59-70. doi:10.1080/15563650.2021.1928165
- Dunbar J, Sulpice R, Dugon M. The kiss of (cell) death: can venom-induced immune response contribute to dermal necrosis following arthropod envenomations? Clin Toxicol. 2019;57:677-685. doi:10.1080/15563650.2019.1578367
- Magee J. Bite ‘nightmare’: close encounter with a false widow. The Bournemouth Echo. September 7, 2009. Accessed September 21, 2023. http://www.bournemouthecho.co.uk/news/4582887.Bite____nightmare_____close_encounter_with_a_false_widow_spider/
- Marsh H. Woman nearly loses hand after bite from false widow. Daily Echo. April 17, 2012. Accessed September 21, 2023. https://www.bournemouthecho.co.uk/news/9652335.woman-nearly-loses-hand-after-bite-from-false-widow-spider/
- Stuber N, Nentwig W. How informative are case studies of spider bites in the medical literature? Toxicon. 2016;114:40-44. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.02.023
- Vetter R, Swanson D, Weinstein S, et. al. Do spiders vector bacteria during bites? the evidence indicates otherwise. Toxicon. 2015;93:171-174. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2014.11.229
- Dunbar J, Khan N, Abberton C, et al. Synanthropic spiders, including the global invasive noble false widow Steatoda nobilis, are reservoirs for medically important and antibiotic resistant bacteria. Sci Rep. 2020;10:20916. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-77839-9
- Atakuziev BU, Wright CE, Graudins A, et al. Efficacy of Australian red-back spider (Latrodectus hasselti) antivenom in the treatment of clinical envenomation by the cupboard spider Steatoda capensis (Theridiidae). Toxicon. 2014;86:68-78. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2014.04.011
- Graudins A, Gunja N, Broady KW, et al. Clinical and in vitro evidence for the efficacy of Australian red-back spider (Latrodectus hasselti) antivenom in the treatment of envenomation by a cupboard spider (Steatoda grossa). Toxicon. 2002;40:767-775. doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(01)00280-X.
- South M, Wirth P, Winkel KD. Redback spider antivenom used to treat envenomation by a juvenile Steatoda spider. Med J Aust. 1998;169:642-642. doi:10.5694/j.1326-5377.1998.tb123445.x
Incidence and Characteristics
The noble false widow spider (Steatoda nobilis) is one of the world’s most invasive spider species, having spread across the globe from Madeira and the Canary Islands into the North Atlantic.1,2 Steatoda comprise multiple species of false widow spiders, named for their resemblance to black widow spiders (Latrodectus). The noble false widow spider is the dominant species in buildings in southern Ireland and Great Britain, with a population surge in 2018 that caused multiple temporary school closures in London, England, for fumigation.3 The noble false widow spider was first documented in the United States in Ventura County, California, in 2011, with numerous specimens found in urban areas (eg, in parks, underneath garbage cans) closer to the coastline as well as farther inland. The species may have been introduced to this area by way of Port Hueneme, a city in California with a US naval base with routes to various other military bases in Western Europe.4 Given its already rapid expansion outside of the United States with a concurrent rise in bite reports, dermatologists should be familiar with these invasive and potentially dangerous arachnids.
The spread of noble false widow spiders is assisted by their wide range of temperature tolerance and ability to survive for months with little food and no water. They can live for several years, with one report of a noble false widow spider living up to 7 years.5 These spiders are found inside homes and buildings year-round, and they prefer to build their webs in an elevated position such as the top corner of a room. Steatoda weave tangle webs with crisscrossing threads that often have a denser middle section.5
Noble false widow spiders are sexually dimorphic, with males typically no larger than 1-cm long and females up to 1.4-cm long. They have a dark brown to black thorax and brown abdomen with red-brown legs. Males have brighter cream-colored abdominal markings than females, who lack markings altogether on their distinctive globular abdomen (Figure). The abdominal markings are known to resemble a skull or house.

Although noble false widow spiders are not exclusively synanthropic, they can be found in any crevice in homes or other structures where there are humans such as office buildings.5-7 Up until the last 20 years, reports of bites from noble false widow spiders worldwide were few and far between. In Great Britain, the spiders were first considered to be common in the 1980s, with recent evidence of an urban population boom in the last 5 to 10 years that has coincided with an increase in bite reports.5,8,9
Clinical Significance
Most bites occur in a defensive manner, such as when humans perform activities that disturb the hiding space, cause vibrations in the web, or compress the body of the arachnid. Most envenomations in Great Britain occur while the individual is in bed, though they also may occur during other activities that disturb the spider, such as moving boxes or putting on a pair of pants.5 Occupational exposure to noble false widow spiders may soon be a concern for those involved in construction, carpentry, cleaning, and decorating given their recent invasive spread into the United States.
The venom from these spiders is neurotoxic and cytotoxic, causing moderate to intense pain that may resemble a wasp sting. The incidence of steatodism—which can include symptoms of pain in addition to fever, hypotension, headache, lethargy, nausea, localized diaphoresis, abdominal pain, paresthesias, and malaise—is unknown but reportedly rare.5,10 There are considerable similarities between Steatoda and true black widow spider venom, which explains the symptom overlap with latrodectism. There are reports of severe debilitation lasting weeks due to pain and decreased affected limb movement after bites from noble false widow spiders.10-12
Nearly all noble false widow spider bite reports describe immediate pain upon bite/envenomation, which is unlike the delayed pain from a black widow spider bite (after 10 minutes or more).6,13,14 Erythema and swelling occur around a pale raised site of envenomation lasting up to 72 hours. The bite site may be highly tender and blister or ulcerate, with reports of cellulitis and local skin necrosis.7,15 Pruritus during this period can be intense, and excoriation increases the risk for complications such as infection. Reports of anaphylaxis following a noble false widow spider bite are rare.5,16 The incidence of bites may be underreported due to the lack of proper identification of the responsible arachnid for those who do not seek care or require hospitalization, though this is not unique to Steatoda.
There are reports of secondary infection after bites and even cases of limb amputation, septicemia, and death.14,17 However, it is unknown if noble false widow spiders are vectors for bacteria transmitted during envenomation, and infection likely is secondary to scratching or inadequate wound care.18,19 Potentially pathogenic bacteria have been isolated from the body surfaces of the noble false widow spider, including Pseudomonas putida, Staphylococcus capitis, and Staphylococcus epidermidis.20 Fortunately, most captured cases (ie, events in which the biting arachnid was properly identified) report symptoms ranging from mild to moderate in severity without the need for hospitalization. A series of 24 reports revealed that all individuals experienced sharp pain upon the initial bite followed by erythema, and 18 of them experienced considerable swelling of the area soon thereafter. One individual experienced temporary paralysis of the affected limb, and 3 individuals experienced hypotension or hypertension in addition to fever, skin necrosis, or cellulitis.14
Treatment
The envenomation site should be washed with antibacterial soap and warm water and should be kept clean to prevent infection. There is no evidence that tight pressure bandaging of these bite sites will restrict venom flow; because it may worsen pain in the area, pressure bandaging is not recommended. When possible, the arachnid should be collected for identification. Supportive care is warranted for symptoms of pain, erythema, and swelling, with the use of cool compresses, oral pain relievers (eg, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acetaminophen), topical anesthetic (eg, lidocaine), or antihistamines as needed.
Urgent care is warranted for patients who experience severe symptoms of steatodism such as hypertension, lymphadenopathy, paresthesia, or limb paralysis. Limited reports show onset of this distress typically within an hour of envenomation. Treatments analogous to those for latrodectism including muscle relaxers and pain medications have demonstrated rapid attenuation of symptoms upon intramuscular administration of antivenom made from Latrodectus species.21-23
Signs of infection warrant bacterial culture with antibiotic susceptibilities to ensure adequate treatment.20 Infections from spider bites can present a few days to a week following envenomation. Symptoms may include spreading redness or an enlarging wound site, pus formation, worsening or unrelenting pain after 24 hours, fevers, flulike symptoms, and muscle cramps.
Final Thoughts
Incidence and Characteristics
The noble false widow spider (Steatoda nobilis) is one of the world’s most invasive spider species, having spread across the globe from Madeira and the Canary Islands into the North Atlantic.1,2 Steatoda comprise multiple species of false widow spiders, named for their resemblance to black widow spiders (Latrodectus). The noble false widow spider is the dominant species in buildings in southern Ireland and Great Britain, with a population surge in 2018 that caused multiple temporary school closures in London, England, for fumigation.3 The noble false widow spider was first documented in the United States in Ventura County, California, in 2011, with numerous specimens found in urban areas (eg, in parks, underneath garbage cans) closer to the coastline as well as farther inland. The species may have been introduced to this area by way of Port Hueneme, a city in California with a US naval base with routes to various other military bases in Western Europe.4 Given its already rapid expansion outside of the United States with a concurrent rise in bite reports, dermatologists should be familiar with these invasive and potentially dangerous arachnids.
The spread of noble false widow spiders is assisted by their wide range of temperature tolerance and ability to survive for months with little food and no water. They can live for several years, with one report of a noble false widow spider living up to 7 years.5 These spiders are found inside homes and buildings year-round, and they prefer to build their webs in an elevated position such as the top corner of a room. Steatoda weave tangle webs with crisscrossing threads that often have a denser middle section.5
Noble false widow spiders are sexually dimorphic, with males typically no larger than 1-cm long and females up to 1.4-cm long. They have a dark brown to black thorax and brown abdomen with red-brown legs. Males have brighter cream-colored abdominal markings than females, who lack markings altogether on their distinctive globular abdomen (Figure). The abdominal markings are known to resemble a skull or house.

Although noble false widow spiders are not exclusively synanthropic, they can be found in any crevice in homes or other structures where there are humans such as office buildings.5-7 Up until the last 20 years, reports of bites from noble false widow spiders worldwide were few and far between. In Great Britain, the spiders were first considered to be common in the 1980s, with recent evidence of an urban population boom in the last 5 to 10 years that has coincided with an increase in bite reports.5,8,9
Clinical Significance
Most bites occur in a defensive manner, such as when humans perform activities that disturb the hiding space, cause vibrations in the web, or compress the body of the arachnid. Most envenomations in Great Britain occur while the individual is in bed, though they also may occur during other activities that disturb the spider, such as moving boxes or putting on a pair of pants.5 Occupational exposure to noble false widow spiders may soon be a concern for those involved in construction, carpentry, cleaning, and decorating given their recent invasive spread into the United States.
The venom from these spiders is neurotoxic and cytotoxic, causing moderate to intense pain that may resemble a wasp sting. The incidence of steatodism—which can include symptoms of pain in addition to fever, hypotension, headache, lethargy, nausea, localized diaphoresis, abdominal pain, paresthesias, and malaise—is unknown but reportedly rare.5,10 There are considerable similarities between Steatoda and true black widow spider venom, which explains the symptom overlap with latrodectism. There are reports of severe debilitation lasting weeks due to pain and decreased affected limb movement after bites from noble false widow spiders.10-12
Nearly all noble false widow spider bite reports describe immediate pain upon bite/envenomation, which is unlike the delayed pain from a black widow spider bite (after 10 minutes or more).6,13,14 Erythema and swelling occur around a pale raised site of envenomation lasting up to 72 hours. The bite site may be highly tender and blister or ulcerate, with reports of cellulitis and local skin necrosis.7,15 Pruritus during this period can be intense, and excoriation increases the risk for complications such as infection. Reports of anaphylaxis following a noble false widow spider bite are rare.5,16 The incidence of bites may be underreported due to the lack of proper identification of the responsible arachnid for those who do not seek care or require hospitalization, though this is not unique to Steatoda.
There are reports of secondary infection after bites and even cases of limb amputation, septicemia, and death.14,17 However, it is unknown if noble false widow spiders are vectors for bacteria transmitted during envenomation, and infection likely is secondary to scratching or inadequate wound care.18,19 Potentially pathogenic bacteria have been isolated from the body surfaces of the noble false widow spider, including Pseudomonas putida, Staphylococcus capitis, and Staphylococcus epidermidis.20 Fortunately, most captured cases (ie, events in which the biting arachnid was properly identified) report symptoms ranging from mild to moderate in severity without the need for hospitalization. A series of 24 reports revealed that all individuals experienced sharp pain upon the initial bite followed by erythema, and 18 of them experienced considerable swelling of the area soon thereafter. One individual experienced temporary paralysis of the affected limb, and 3 individuals experienced hypotension or hypertension in addition to fever, skin necrosis, or cellulitis.14
Treatment
The envenomation site should be washed with antibacterial soap and warm water and should be kept clean to prevent infection. There is no evidence that tight pressure bandaging of these bite sites will restrict venom flow; because it may worsen pain in the area, pressure bandaging is not recommended. When possible, the arachnid should be collected for identification. Supportive care is warranted for symptoms of pain, erythema, and swelling, with the use of cool compresses, oral pain relievers (eg, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acetaminophen), topical anesthetic (eg, lidocaine), or antihistamines as needed.
Urgent care is warranted for patients who experience severe symptoms of steatodism such as hypertension, lymphadenopathy, paresthesia, or limb paralysis. Limited reports show onset of this distress typically within an hour of envenomation. Treatments analogous to those for latrodectism including muscle relaxers and pain medications have demonstrated rapid attenuation of symptoms upon intramuscular administration of antivenom made from Latrodectus species.21-23
Signs of infection warrant bacterial culture with antibiotic susceptibilities to ensure adequate treatment.20 Infections from spider bites can present a few days to a week following envenomation. Symptoms may include spreading redness or an enlarging wound site, pus formation, worsening or unrelenting pain after 24 hours, fevers, flulike symptoms, and muscle cramps.
Final Thoughts
- Kulczycki A, Legittimo C, Simeon E, et al. New records of Steatoda nobilis (Thorell, 1875) (Araneae, Theridiidae), an introduced species on the Italian mainland and in Sardinia. Bull Br Arachnological Soc. 2012;15:269-272.
- Bauer T, Feldmeier S, Krehenwinkel H, et al. Steatoda nobilis, a false widow on the rise: a synthesis of past and current distribution trends. NeoBiota. 2019; 42:19. doi:10.3897/neobiota.42.31582
- Murphy A. Web of cries: false widow spider infestation fears forceeleventh school in London to close as outbreak spreads. The Sun.October 19, 2018. Accessed September 21, 2023. https://www.thesun.co.uk/news/7534016/false-widow-spider-infestation-fears-force-eleventh-londonschool-closing
- Vetter R, Rust M. A large European combfoot spider, Steatoda nobilis (Thorell 1875)(Araneae: Theridiidae), newly established in Ventura County, California. The Pan-Pacific Entomologist. 2012;88:92-97.
- Hambler C. The ‘noble false widow’ spider Steatoda nobilis is an emerging public health and ecological threat. OSF Preprints. Preprint posted online October 15, 2019. doi:10.31219/osf.io/axbd4
- Dunbar J, Schulte J, Lyons K, et al. New Irish record for Steatoda triangulosa (Walckenaer, 1802), and new county records for Steatoda nobilis (Thorell, 1875), Steatoda bipunctata (Linnaeus, 1758) and Steatoda grossa (C.L. Koch, 1838). Ir Naturalists J. 2018;36:39-43.
- Duon M, Dunbar J, Afoullouss S, et al. Occurrence, reproductive rate and identification of the non-native noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis (Thorell, 1875) in Ireland. Biol Environment: Proc Royal Ir Acad. 2017;117B:77-89. doi:10.3318/bioe.2017.11
- Burrows T. Great bitten: Britain’s spider bite capital revealed as Essex with 450 attacks—find out where your town ranks. The Sun. Published April 3, 2019. Accessed September 14, 2023. https://www.thesun.co.uk/news/8782355/britains-spider-bite-capital-revealed-as-essex-with-450- attacks-find-out-where-your-town-ranks/
- Wathen T. Essex is the UK capital for spider bites—and the amount is terrifying. Essex News. April 4, 2019. Accessed September 21, 2023. https://www.essexlive.news/news/essex-news/essex-uk-capital-spider-bites- 2720935
- Dunbar J, Afoullouss S, Sulpice R, et al. Envenomation by the noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis (Thorell, 1875)—five new cases of steatodism from Ireland and Great Britain. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2018;56:433-435. doi:10.1080/15563650.2017.1393084
- Dunbar J, Fort A, Redureau D, et al. Venomics approach reveals a high proportion of Latrodectus-like toxins in the venom of the noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis. Toxins. 2020;12:402.
- Warrell D, Shaheen J, Hillyard P, et al. Neurotoxic envenoming by an immigrant spider (Steatoda nobilis) in southern England. Toxicon. 1991;29:1263-1265.
- Zhou H, Xu K, Zheng PY, et. al. Clinical characteristics of patients with black widow spider bites: a report of 59 patients and single-center experience. World J Emerg Med. 2021;12:317-320. doi:10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2021.04.011
- Dunbar J, Vitkauskaite A, O’Keeffe D, et. al. Bites by the noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis can induce Latrodectus-like symptoms and vector-borne bacterial infections with implications for public health: a case series. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2022;60:59-70. doi:10.1080/15563650.2021.1928165
- Dunbar J, Sulpice R, Dugon M. The kiss of (cell) death: can venom-induced immune response contribute to dermal necrosis following arthropod envenomations? Clin Toxicol. 2019;57:677-685. doi:10.1080/15563650.2019.1578367
- Magee J. Bite ‘nightmare’: close encounter with a false widow. The Bournemouth Echo. September 7, 2009. Accessed September 21, 2023. http://www.bournemouthecho.co.uk/news/4582887.Bite____nightmare_____close_encounter_with_a_false_widow_spider/
- Marsh H. Woman nearly loses hand after bite from false widow. Daily Echo. April 17, 2012. Accessed September 21, 2023. https://www.bournemouthecho.co.uk/news/9652335.woman-nearly-loses-hand-after-bite-from-false-widow-spider/
- Stuber N, Nentwig W. How informative are case studies of spider bites in the medical literature? Toxicon. 2016;114:40-44. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.02.023
- Vetter R, Swanson D, Weinstein S, et. al. Do spiders vector bacteria during bites? the evidence indicates otherwise. Toxicon. 2015;93:171-174. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2014.11.229
- Dunbar J, Khan N, Abberton C, et al. Synanthropic spiders, including the global invasive noble false widow Steatoda nobilis, are reservoirs for medically important and antibiotic resistant bacteria. Sci Rep. 2020;10:20916. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-77839-9
- Atakuziev BU, Wright CE, Graudins A, et al. Efficacy of Australian red-back spider (Latrodectus hasselti) antivenom in the treatment of clinical envenomation by the cupboard spider Steatoda capensis (Theridiidae). Toxicon. 2014;86:68-78. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2014.04.011
- Graudins A, Gunja N, Broady KW, et al. Clinical and in vitro evidence for the efficacy of Australian red-back spider (Latrodectus hasselti) antivenom in the treatment of envenomation by a cupboard spider (Steatoda grossa). Toxicon. 2002;40:767-775. doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(01)00280-X.
- South M, Wirth P, Winkel KD. Redback spider antivenom used to treat envenomation by a juvenile Steatoda spider. Med J Aust. 1998;169:642-642. doi:10.5694/j.1326-5377.1998.tb123445.x
- Kulczycki A, Legittimo C, Simeon E, et al. New records of Steatoda nobilis (Thorell, 1875) (Araneae, Theridiidae), an introduced species on the Italian mainland and in Sardinia. Bull Br Arachnological Soc. 2012;15:269-272.
- Bauer T, Feldmeier S, Krehenwinkel H, et al. Steatoda nobilis, a false widow on the rise: a synthesis of past and current distribution trends. NeoBiota. 2019; 42:19. doi:10.3897/neobiota.42.31582
- Murphy A. Web of cries: false widow spider infestation fears forceeleventh school in London to close as outbreak spreads. The Sun.October 19, 2018. Accessed September 21, 2023. https://www.thesun.co.uk/news/7534016/false-widow-spider-infestation-fears-force-eleventh-londonschool-closing
- Vetter R, Rust M. A large European combfoot spider, Steatoda nobilis (Thorell 1875)(Araneae: Theridiidae), newly established in Ventura County, California. The Pan-Pacific Entomologist. 2012;88:92-97.
- Hambler C. The ‘noble false widow’ spider Steatoda nobilis is an emerging public health and ecological threat. OSF Preprints. Preprint posted online October 15, 2019. doi:10.31219/osf.io/axbd4
- Dunbar J, Schulte J, Lyons K, et al. New Irish record for Steatoda triangulosa (Walckenaer, 1802), and new county records for Steatoda nobilis (Thorell, 1875), Steatoda bipunctata (Linnaeus, 1758) and Steatoda grossa (C.L. Koch, 1838). Ir Naturalists J. 2018;36:39-43.
- Duon M, Dunbar J, Afoullouss S, et al. Occurrence, reproductive rate and identification of the non-native noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis (Thorell, 1875) in Ireland. Biol Environment: Proc Royal Ir Acad. 2017;117B:77-89. doi:10.3318/bioe.2017.11
- Burrows T. Great bitten: Britain’s spider bite capital revealed as Essex with 450 attacks—find out where your town ranks. The Sun. Published April 3, 2019. Accessed September 14, 2023. https://www.thesun.co.uk/news/8782355/britains-spider-bite-capital-revealed-as-essex-with-450- attacks-find-out-where-your-town-ranks/
- Wathen T. Essex is the UK capital for spider bites—and the amount is terrifying. Essex News. April 4, 2019. Accessed September 21, 2023. https://www.essexlive.news/news/essex-news/essex-uk-capital-spider-bites- 2720935
- Dunbar J, Afoullouss S, Sulpice R, et al. Envenomation by the noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis (Thorell, 1875)—five new cases of steatodism from Ireland and Great Britain. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2018;56:433-435. doi:10.1080/15563650.2017.1393084
- Dunbar J, Fort A, Redureau D, et al. Venomics approach reveals a high proportion of Latrodectus-like toxins in the venom of the noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis. Toxins. 2020;12:402.
- Warrell D, Shaheen J, Hillyard P, et al. Neurotoxic envenoming by an immigrant spider (Steatoda nobilis) in southern England. Toxicon. 1991;29:1263-1265.
- Zhou H, Xu K, Zheng PY, et. al. Clinical characteristics of patients with black widow spider bites: a report of 59 patients and single-center experience. World J Emerg Med. 2021;12:317-320. doi:10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2021.04.011
- Dunbar J, Vitkauskaite A, O’Keeffe D, et. al. Bites by the noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis can induce Latrodectus-like symptoms and vector-borne bacterial infections with implications for public health: a case series. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2022;60:59-70. doi:10.1080/15563650.2021.1928165
- Dunbar J, Sulpice R, Dugon M. The kiss of (cell) death: can venom-induced immune response contribute to dermal necrosis following arthropod envenomations? Clin Toxicol. 2019;57:677-685. doi:10.1080/15563650.2019.1578367
- Magee J. Bite ‘nightmare’: close encounter with a false widow. The Bournemouth Echo. September 7, 2009. Accessed September 21, 2023. http://www.bournemouthecho.co.uk/news/4582887.Bite____nightmare_____close_encounter_with_a_false_widow_spider/
- Marsh H. Woman nearly loses hand after bite from false widow. Daily Echo. April 17, 2012. Accessed September 21, 2023. https://www.bournemouthecho.co.uk/news/9652335.woman-nearly-loses-hand-after-bite-from-false-widow-spider/
- Stuber N, Nentwig W. How informative are case studies of spider bites in the medical literature? Toxicon. 2016;114:40-44. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.02.023
- Vetter R, Swanson D, Weinstein S, et. al. Do spiders vector bacteria during bites? the evidence indicates otherwise. Toxicon. 2015;93:171-174. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2014.11.229
- Dunbar J, Khan N, Abberton C, et al. Synanthropic spiders, including the global invasive noble false widow Steatoda nobilis, are reservoirs for medically important and antibiotic resistant bacteria. Sci Rep. 2020;10:20916. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-77839-9
- Atakuziev BU, Wright CE, Graudins A, et al. Efficacy of Australian red-back spider (Latrodectus hasselti) antivenom in the treatment of clinical envenomation by the cupboard spider Steatoda capensis (Theridiidae). Toxicon. 2014;86:68-78. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2014.04.011
- Graudins A, Gunja N, Broady KW, et al. Clinical and in vitro evidence for the efficacy of Australian red-back spider (Latrodectus hasselti) antivenom in the treatment of envenomation by a cupboard spider (Steatoda grossa). Toxicon. 2002;40:767-775. doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(01)00280-X.
- South M, Wirth P, Winkel KD. Redback spider antivenom used to treat envenomation by a juvenile Steatoda spider. Med J Aust. 1998;169:642-642. doi:10.5694/j.1326-5377.1998.tb123445.x
PRACTICE POINTS
- With evidence of a recent population boom of noble false widow spiders in Europe and spread to California, dermatologists should be aware of these spiders and their bites.
- Symptoms of Steatoda bites (steatodism) include immediate pain followed by intense pruritus, swelling, erythema, and possibly systemic symptoms such as fever. Secondary infections such as cellulitis and septicemia are risks.
- The envenomation site should be kept clean to prevent secondary infection, and medical care should be sought when there is evidence of ulceration or cellulitis.
Youth Exposure to Spironolactone in TikTok Videos
The short-form video hosting service TikTok has become a mainstream platform for individuals to share their ideas and educate the public regarding dermatologic diseases such as atopic dermatitis, alopecia, and acne. Users can create and post videos, leave comments, and indicate their interest in or approval of certain content by “liking” videos. In 2022, according to a Pew Research Center survey, approximately 67% of American teenagers aged 13 to 17 years reported using TikTok at least once.1 This population, along with the rest of its users, are increasing their use of TikTok to share information on dermatologic topics such as acne and isotretinoin.2,3 Spironolactone is an effective medication for acne but is not as widely known to the public as other acne medications such as retinoids, salicylic acid, and benzoyl peroxide. Being aware of youth exposure to media related to acne and spironolactone can help dermatologists understand gaps in education and refine their interactions with this patient population.
To gain insight into youth exposure to spironolactone, we conducted a search of TikTok on July 26, 2022, using the term #spironolactone to retrieve the top 50 videos identified by TikTok under the “Top” tab on spironolactone. Search results and the top 10 comments for each video were reviewed. The total number of views and likes for the top 50 videos were 6,735,992 and 851,856, respectively.
Videos were subdivided into educational information related to spironolactone and/or skin care (32% [16/50]), discussion of side effects of spironolactone (26% [13/50]), those with noticeable improvement of acne following treatment with spironolactone (20% [10/50]), recommendations to see a physician or dermatologist to treat acne (10% [5/50]), and other (12% [6/50]). Other takeaways from the top 50 videos included the following:
- Common side effects: irregular periods (10% [5/50]), frequent urination (8% [4/50]), dizziness/lightheadedness (8% [4/50]), and breast tenderness (6% [3/50])
- Longest reported use of spironolactone: 4 years, with complete acne resolution
- Average treatment length prior to noticeable results: 4 to 6 months, with the shortest being 1 month
- Reported dosages of spironolactone: ranged from 50 to 200 mg/d. The most common dosage was 100 mg/d (10% [5/50]). The lowest reported dosage was 50 mg/d (4% [2/50]), while the highest reported dosage was 200 mg/d (2% [1/50])
- Self-reported concurrent use of spironolactone with a combined oral contraceptive: drospirenoneTimes New Roman–ethinyl estradiol (4% [2/50]), norethindrone acetateTimes New Roman–ethinyl estradiol/ferrous fumarate (2% [1/50]), and norgestimateTimes New Roman–ethinyl estradiol (2% [1/50])
- Negative experiences with side effects and lack of acne improvement that led to treatment cessation: 8% (4/50).
Even though spironolactone is not as well-known as other treatments for acne, we found many TikTok users posting about, commenting on, and highlighting the relevance of this therapeutic option. There was no suggestion in any of the videos that spironolactone could be obtained without physician care and/or prescription. A prior report discussing youth sentiment of isotretinoin use on TikTok found that popular videos and videos with the most likes focused on the drug’s positive impact on acne improvement, while comments displayed heightened desires to learn more about isotretinoin and its side effects.3 Our analysis showed a similar response to spironolactone. In all videos showcasing the skin before and after treatment, there were noticeable improvements in the poster’s acne. Most of the video comments displayed a desire to learn more about spironolactone and its side effects. There also were many questions about time to noticeable results. In contrast to the study on isotretinoin,3 the most-liked spironolactone videos contained educational information about spironolactone and/or skin care rather than focusing solely on the impact of the drug on acne. Additionally, the study on isotretinoin found no videos mentioning the importance of seeing a dermatologist or other health care professional,3 while our search found multiple videos (10% [5/50]) on spironolactone that advised seeking physician help. In fact, several popular videos (8% [4/50]) were created by board-certified dermatologists who mainly focused on providing educational information. This difference in educational content may be attributed to spironolactone’s lesser-known function in treating acne. Furthermore, the comments suggested a growing interest in learning more about spironolactone as a treatment option for acne, specifically its mechanism of action and side effects.
With nearly 2 billion monthly active users globally and 94.1 million monthly active users in the United States (as of March 2023),4 TikTok is a popular social media platform that allows dermatologists to better understand youth sentiment on acne treatments such as spironolactone and isotretinoin and also provides an opportunity for medical education to reach a larger audience. This increased youth insight from TikTok can be utilized by dermatologists to make more informed decisions in developing patient-centered care that appeals to the adolescent population.
- Vogels EA, Gelles-Watnick R, Massarat N. Teens, social media and technology 2022. Published August 10, 2022. Accessed September 16, 2023. https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2022/08/10/teens-social-media-and-technology-2022/
- Szeto MD, Mamo A, Afrin A, et al. Social media in dermatology and an overview of popular social media platforms. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2021;10:97-104. doi:10.1007/s13671-021-00343-4
- Galamgam J, Jia JL. “Accutane check”: insights into youth sentiment toward isotretinoin from a TikTok trend. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38:980-981. doi:10.1111/pde.14660
- Aslam S. TikTok by the numbers: stats, demographics & fun facts. Omnicore website. February 27, 2023. Accessed September 14, 2023. https://www.omnicoreagency.com/tiktok-statistics/
The short-form video hosting service TikTok has become a mainstream platform for individuals to share their ideas and educate the public regarding dermatologic diseases such as atopic dermatitis, alopecia, and acne. Users can create and post videos, leave comments, and indicate their interest in or approval of certain content by “liking” videos. In 2022, according to a Pew Research Center survey, approximately 67% of American teenagers aged 13 to 17 years reported using TikTok at least once.1 This population, along with the rest of its users, are increasing their use of TikTok to share information on dermatologic topics such as acne and isotretinoin.2,3 Spironolactone is an effective medication for acne but is not as widely known to the public as other acne medications such as retinoids, salicylic acid, and benzoyl peroxide. Being aware of youth exposure to media related to acne and spironolactone can help dermatologists understand gaps in education and refine their interactions with this patient population.
To gain insight into youth exposure to spironolactone, we conducted a search of TikTok on July 26, 2022, using the term #spironolactone to retrieve the top 50 videos identified by TikTok under the “Top” tab on spironolactone. Search results and the top 10 comments for each video were reviewed. The total number of views and likes for the top 50 videos were 6,735,992 and 851,856, respectively.
Videos were subdivided into educational information related to spironolactone and/or skin care (32% [16/50]), discussion of side effects of spironolactone (26% [13/50]), those with noticeable improvement of acne following treatment with spironolactone (20% [10/50]), recommendations to see a physician or dermatologist to treat acne (10% [5/50]), and other (12% [6/50]). Other takeaways from the top 50 videos included the following:
- Common side effects: irregular periods (10% [5/50]), frequent urination (8% [4/50]), dizziness/lightheadedness (8% [4/50]), and breast tenderness (6% [3/50])
- Longest reported use of spironolactone: 4 years, with complete acne resolution
- Average treatment length prior to noticeable results: 4 to 6 months, with the shortest being 1 month
- Reported dosages of spironolactone: ranged from 50 to 200 mg/d. The most common dosage was 100 mg/d (10% [5/50]). The lowest reported dosage was 50 mg/d (4% [2/50]), while the highest reported dosage was 200 mg/d (2% [1/50])
- Self-reported concurrent use of spironolactone with a combined oral contraceptive: drospirenoneTimes New Roman–ethinyl estradiol (4% [2/50]), norethindrone acetateTimes New Roman–ethinyl estradiol/ferrous fumarate (2% [1/50]), and norgestimateTimes New Roman–ethinyl estradiol (2% [1/50])
- Negative experiences with side effects and lack of acne improvement that led to treatment cessation: 8% (4/50).
Even though spironolactone is not as well-known as other treatments for acne, we found many TikTok users posting about, commenting on, and highlighting the relevance of this therapeutic option. There was no suggestion in any of the videos that spironolactone could be obtained without physician care and/or prescription. A prior report discussing youth sentiment of isotretinoin use on TikTok found that popular videos and videos with the most likes focused on the drug’s positive impact on acne improvement, while comments displayed heightened desires to learn more about isotretinoin and its side effects.3 Our analysis showed a similar response to spironolactone. In all videos showcasing the skin before and after treatment, there were noticeable improvements in the poster’s acne. Most of the video comments displayed a desire to learn more about spironolactone and its side effects. There also were many questions about time to noticeable results. In contrast to the study on isotretinoin,3 the most-liked spironolactone videos contained educational information about spironolactone and/or skin care rather than focusing solely on the impact of the drug on acne. Additionally, the study on isotretinoin found no videos mentioning the importance of seeing a dermatologist or other health care professional,3 while our search found multiple videos (10% [5/50]) on spironolactone that advised seeking physician help. In fact, several popular videos (8% [4/50]) were created by board-certified dermatologists who mainly focused on providing educational information. This difference in educational content may be attributed to spironolactone’s lesser-known function in treating acne. Furthermore, the comments suggested a growing interest in learning more about spironolactone as a treatment option for acne, specifically its mechanism of action and side effects.
With nearly 2 billion monthly active users globally and 94.1 million monthly active users in the United States (as of March 2023),4 TikTok is a popular social media platform that allows dermatologists to better understand youth sentiment on acne treatments such as spironolactone and isotretinoin and also provides an opportunity for medical education to reach a larger audience. This increased youth insight from TikTok can be utilized by dermatologists to make more informed decisions in developing patient-centered care that appeals to the adolescent population.
The short-form video hosting service TikTok has become a mainstream platform for individuals to share their ideas and educate the public regarding dermatologic diseases such as atopic dermatitis, alopecia, and acne. Users can create and post videos, leave comments, and indicate their interest in or approval of certain content by “liking” videos. In 2022, according to a Pew Research Center survey, approximately 67% of American teenagers aged 13 to 17 years reported using TikTok at least once.1 This population, along with the rest of its users, are increasing their use of TikTok to share information on dermatologic topics such as acne and isotretinoin.2,3 Spironolactone is an effective medication for acne but is not as widely known to the public as other acne medications such as retinoids, salicylic acid, and benzoyl peroxide. Being aware of youth exposure to media related to acne and spironolactone can help dermatologists understand gaps in education and refine their interactions with this patient population.
To gain insight into youth exposure to spironolactone, we conducted a search of TikTok on July 26, 2022, using the term #spironolactone to retrieve the top 50 videos identified by TikTok under the “Top” tab on spironolactone. Search results and the top 10 comments for each video were reviewed. The total number of views and likes for the top 50 videos were 6,735,992 and 851,856, respectively.
Videos were subdivided into educational information related to spironolactone and/or skin care (32% [16/50]), discussion of side effects of spironolactone (26% [13/50]), those with noticeable improvement of acne following treatment with spironolactone (20% [10/50]), recommendations to see a physician or dermatologist to treat acne (10% [5/50]), and other (12% [6/50]). Other takeaways from the top 50 videos included the following:
- Common side effects: irregular periods (10% [5/50]), frequent urination (8% [4/50]), dizziness/lightheadedness (8% [4/50]), and breast tenderness (6% [3/50])
- Longest reported use of spironolactone: 4 years, with complete acne resolution
- Average treatment length prior to noticeable results: 4 to 6 months, with the shortest being 1 month
- Reported dosages of spironolactone: ranged from 50 to 200 mg/d. The most common dosage was 100 mg/d (10% [5/50]). The lowest reported dosage was 50 mg/d (4% [2/50]), while the highest reported dosage was 200 mg/d (2% [1/50])
- Self-reported concurrent use of spironolactone with a combined oral contraceptive: drospirenoneTimes New Roman–ethinyl estradiol (4% [2/50]), norethindrone acetateTimes New Roman–ethinyl estradiol/ferrous fumarate (2% [1/50]), and norgestimateTimes New Roman–ethinyl estradiol (2% [1/50])
- Negative experiences with side effects and lack of acne improvement that led to treatment cessation: 8% (4/50).
Even though spironolactone is not as well-known as other treatments for acne, we found many TikTok users posting about, commenting on, and highlighting the relevance of this therapeutic option. There was no suggestion in any of the videos that spironolactone could be obtained without physician care and/or prescription. A prior report discussing youth sentiment of isotretinoin use on TikTok found that popular videos and videos with the most likes focused on the drug’s positive impact on acne improvement, while comments displayed heightened desires to learn more about isotretinoin and its side effects.3 Our analysis showed a similar response to spironolactone. In all videos showcasing the skin before and after treatment, there were noticeable improvements in the poster’s acne. Most of the video comments displayed a desire to learn more about spironolactone and its side effects. There also were many questions about time to noticeable results. In contrast to the study on isotretinoin,3 the most-liked spironolactone videos contained educational information about spironolactone and/or skin care rather than focusing solely on the impact of the drug on acne. Additionally, the study on isotretinoin found no videos mentioning the importance of seeing a dermatologist or other health care professional,3 while our search found multiple videos (10% [5/50]) on spironolactone that advised seeking physician help. In fact, several popular videos (8% [4/50]) were created by board-certified dermatologists who mainly focused on providing educational information. This difference in educational content may be attributed to spironolactone’s lesser-known function in treating acne. Furthermore, the comments suggested a growing interest in learning more about spironolactone as a treatment option for acne, specifically its mechanism of action and side effects.
With nearly 2 billion monthly active users globally and 94.1 million monthly active users in the United States (as of March 2023),4 TikTok is a popular social media platform that allows dermatologists to better understand youth sentiment on acne treatments such as spironolactone and isotretinoin and also provides an opportunity for medical education to reach a larger audience. This increased youth insight from TikTok can be utilized by dermatologists to make more informed decisions in developing patient-centered care that appeals to the adolescent population.
- Vogels EA, Gelles-Watnick R, Massarat N. Teens, social media and technology 2022. Published August 10, 2022. Accessed September 16, 2023. https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2022/08/10/teens-social-media-and-technology-2022/
- Szeto MD, Mamo A, Afrin A, et al. Social media in dermatology and an overview of popular social media platforms. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2021;10:97-104. doi:10.1007/s13671-021-00343-4
- Galamgam J, Jia JL. “Accutane check”: insights into youth sentiment toward isotretinoin from a TikTok trend. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38:980-981. doi:10.1111/pde.14660
- Aslam S. TikTok by the numbers: stats, demographics & fun facts. Omnicore website. February 27, 2023. Accessed September 14, 2023. https://www.omnicoreagency.com/tiktok-statistics/
- Vogels EA, Gelles-Watnick R, Massarat N. Teens, social media and technology 2022. Published August 10, 2022. Accessed September 16, 2023. https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2022/08/10/teens-social-media-and-technology-2022/
- Szeto MD, Mamo A, Afrin A, et al. Social media in dermatology and an overview of popular social media platforms. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2021;10:97-104. doi:10.1007/s13671-021-00343-4
- Galamgam J, Jia JL. “Accutane check”: insights into youth sentiment toward isotretinoin from a TikTok trend. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38:980-981. doi:10.1111/pde.14660
- Aslam S. TikTok by the numbers: stats, demographics & fun facts. Omnicore website. February 27, 2023. Accessed September 14, 2023. https://www.omnicoreagency.com/tiktok-statistics/
Knead a Hand? Use of a Portable Massager to Reduce Patient Pain and Anxiety During Nail Surgery
Practice Gap
Pain and anxiety are common in fully conscious patients undergoing dermatologic surgery with local anesthesia. Particularly during nail surgery, pain from anesthetic injection—caused by both needle insertion and fluid infiltration—occurs because the nail unit is highly vascularized and innervated.1 Current methods to improve patient comfort during infiltration include use of a buffered anesthetic solution, warming the anesthetic, slower technique, and direct cold application.2
Perioperative anxiety correlates with increased postoperative pain, analgesic use, and delayed recovery. Furthermore, increased perioperative anxiety reduces the pain threshold and elevates estimates of pain intensity.3 Therefore, reducing procedure-related anxiety and pain may improve quality of care and ease patient discomfort.
Distraction is a common and practical nonpharmacotherapeutic technique for reducing pain and anxiety during medical procedures. The refocusing method of distraction aims to divert attention away from pain to more pleasant stimuli to reduce pain perception.3 Several methods of distraction—using stress balls, engaging in conversation, hand-holding, applying virtual reality, and playing videos—can decrease perioperative anxiety and pain.3-6
Procedural pain and distraction techniques have been evaluated in the pediatric population more than in adults.4 Nail surgery–associated pain and distraction techniques for nail surgery have been inadequately studied.7
We offer a distraction technique utilizing a portable massager to ensure that patients are as comfortable as possible when the local anesthetic is injected prior to the first incision.
The Technique
A portable shiatsu massager that uses heat and deep-tissue kneading is placed on the upper thigh for toenail cases or lower arm for fingernail cases during injection of anesthetic to divert the patient’s attention from the surgical site (Figure). Kneading from the massage helps distract the patient from pain by introducing a competing, more pleasant, vibrating sensation that overrides pain signals; the relaxation component helps to diminish patient anxiety during injection.
Practice Implications
Use of a portable massager may reduce pain through both distraction and vibration. In a randomized clinical trial of 115 patients undergoing hand or facial surgery, patients who viewed a distraction video during the procedure reported a lower pain score compared to the control group (mean [SD] visual analog scale of pain score, 3.4 [2.6] vs 4.5 [2.6][P=.01]).4 In another randomized clinical trial of 25 patients undergoing lip augmentation, 92% of patients (23/25) in the vibration-assisted arm endorsed less pain during procedures compared to the arm without vibration (mean [SD] pain score, 3.82 [1.73] vs 5.6 [1.76][P<.001]).8
Utilization of a portable massager is a safe means of improving the patient experience; the distracting and relaxing effects and intense pulsations simultaneously reduce anxiety and pain during nail surgery. Controlled clinical trials are needed to evaluate its efficacy in diminishing both anxiety and pain during nail procedures compared to other analgesic methods.
- Lipner SR. Pain-minimizing strategies for nail surgery. Cutis. 2018;101:76-77.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Air cooling for improved analgesia during local anesthetic infiltration for nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:E231-E232. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.11.032
- Hudson BF, Ogden J, Whiteley MS. Randomized controlled trial to compare the effect of simple distraction interventions on pain and anxiety experienced during conscious surgery. Eur J Pain. 2015;19:1447-1455. doi:10.1002/ejp.675
- Molleman J, Tielemans JF, Braam MJI, et al. Distraction as a simple and effective method to reduce pain during local anesthesia: a randomized controlled trial. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2019;72:1979-1985. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2019.07.023
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilization of a stress ball to diminish anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2020;105:294.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilizing a sleep mask to reduce patient anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2021;108:36. doi:10.12788/cutis.0285
- Ricardo JW, Qiu Y, Lipner SR. Longitudinal perioperative pain assessment in nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:874-876. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.11.042
- Guney K, Sezgin B, Yavuzer R. The efficacy of vibration anesthesia on reducing pain levels during lip augmentation: worth the buzz? Aesthet Surg J. 2017;37:1044-1048. doi:10.1093/asj/sjx073
Practice Gap
Pain and anxiety are common in fully conscious patients undergoing dermatologic surgery with local anesthesia. Particularly during nail surgery, pain from anesthetic injection—caused by both needle insertion and fluid infiltration—occurs because the nail unit is highly vascularized and innervated.1 Current methods to improve patient comfort during infiltration include use of a buffered anesthetic solution, warming the anesthetic, slower technique, and direct cold application.2
Perioperative anxiety correlates with increased postoperative pain, analgesic use, and delayed recovery. Furthermore, increased perioperative anxiety reduces the pain threshold and elevates estimates of pain intensity.3 Therefore, reducing procedure-related anxiety and pain may improve quality of care and ease patient discomfort.
Distraction is a common and practical nonpharmacotherapeutic technique for reducing pain and anxiety during medical procedures. The refocusing method of distraction aims to divert attention away from pain to more pleasant stimuli to reduce pain perception.3 Several methods of distraction—using stress balls, engaging in conversation, hand-holding, applying virtual reality, and playing videos—can decrease perioperative anxiety and pain.3-6
Procedural pain and distraction techniques have been evaluated in the pediatric population more than in adults.4 Nail surgery–associated pain and distraction techniques for nail surgery have been inadequately studied.7
We offer a distraction technique utilizing a portable massager to ensure that patients are as comfortable as possible when the local anesthetic is injected prior to the first incision.
The Technique
A portable shiatsu massager that uses heat and deep-tissue kneading is placed on the upper thigh for toenail cases or lower arm for fingernail cases during injection of anesthetic to divert the patient’s attention from the surgical site (Figure). Kneading from the massage helps distract the patient from pain by introducing a competing, more pleasant, vibrating sensation that overrides pain signals; the relaxation component helps to diminish patient anxiety during injection.

Practice Implications
Use of a portable massager may reduce pain through both distraction and vibration. In a randomized clinical trial of 115 patients undergoing hand or facial surgery, patients who viewed a distraction video during the procedure reported a lower pain score compared to the control group (mean [SD] visual analog scale of pain score, 3.4 [2.6] vs 4.5 [2.6][P=.01]).4 In another randomized clinical trial of 25 patients undergoing lip augmentation, 92% of patients (23/25) in the vibration-assisted arm endorsed less pain during procedures compared to the arm without vibration (mean [SD] pain score, 3.82 [1.73] vs 5.6 [1.76][P<.001]).8
Utilization of a portable massager is a safe means of improving the patient experience; the distracting and relaxing effects and intense pulsations simultaneously reduce anxiety and pain during nail surgery. Controlled clinical trials are needed to evaluate its efficacy in diminishing both anxiety and pain during nail procedures compared to other analgesic methods.
Practice Gap
Pain and anxiety are common in fully conscious patients undergoing dermatologic surgery with local anesthesia. Particularly during nail surgery, pain from anesthetic injection—caused by both needle insertion and fluid infiltration—occurs because the nail unit is highly vascularized and innervated.1 Current methods to improve patient comfort during infiltration include use of a buffered anesthetic solution, warming the anesthetic, slower technique, and direct cold application.2
Perioperative anxiety correlates with increased postoperative pain, analgesic use, and delayed recovery. Furthermore, increased perioperative anxiety reduces the pain threshold and elevates estimates of pain intensity.3 Therefore, reducing procedure-related anxiety and pain may improve quality of care and ease patient discomfort.
Distraction is a common and practical nonpharmacotherapeutic technique for reducing pain and anxiety during medical procedures. The refocusing method of distraction aims to divert attention away from pain to more pleasant stimuli to reduce pain perception.3 Several methods of distraction—using stress balls, engaging in conversation, hand-holding, applying virtual reality, and playing videos—can decrease perioperative anxiety and pain.3-6
Procedural pain and distraction techniques have been evaluated in the pediatric population more than in adults.4 Nail surgery–associated pain and distraction techniques for nail surgery have been inadequately studied.7
We offer a distraction technique utilizing a portable massager to ensure that patients are as comfortable as possible when the local anesthetic is injected prior to the first incision.
The Technique
A portable shiatsu massager that uses heat and deep-tissue kneading is placed on the upper thigh for toenail cases or lower arm for fingernail cases during injection of anesthetic to divert the patient’s attention from the surgical site (Figure). Kneading from the massage helps distract the patient from pain by introducing a competing, more pleasant, vibrating sensation that overrides pain signals; the relaxation component helps to diminish patient anxiety during injection.

Practice Implications
Use of a portable massager may reduce pain through both distraction and vibration. In a randomized clinical trial of 115 patients undergoing hand or facial surgery, patients who viewed a distraction video during the procedure reported a lower pain score compared to the control group (mean [SD] visual analog scale of pain score, 3.4 [2.6] vs 4.5 [2.6][P=.01]).4 In another randomized clinical trial of 25 patients undergoing lip augmentation, 92% of patients (23/25) in the vibration-assisted arm endorsed less pain during procedures compared to the arm without vibration (mean [SD] pain score, 3.82 [1.73] vs 5.6 [1.76][P<.001]).8
Utilization of a portable massager is a safe means of improving the patient experience; the distracting and relaxing effects and intense pulsations simultaneously reduce anxiety and pain during nail surgery. Controlled clinical trials are needed to evaluate its efficacy in diminishing both anxiety and pain during nail procedures compared to other analgesic methods.
- Lipner SR. Pain-minimizing strategies for nail surgery. Cutis. 2018;101:76-77.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Air cooling for improved analgesia during local anesthetic infiltration for nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:E231-E232. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.11.032
- Hudson BF, Ogden J, Whiteley MS. Randomized controlled trial to compare the effect of simple distraction interventions on pain and anxiety experienced during conscious surgery. Eur J Pain. 2015;19:1447-1455. doi:10.1002/ejp.675
- Molleman J, Tielemans JF, Braam MJI, et al. Distraction as a simple and effective method to reduce pain during local anesthesia: a randomized controlled trial. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2019;72:1979-1985. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2019.07.023
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilization of a stress ball to diminish anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2020;105:294.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilizing a sleep mask to reduce patient anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2021;108:36. doi:10.12788/cutis.0285
- Ricardo JW, Qiu Y, Lipner SR. Longitudinal perioperative pain assessment in nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:874-876. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.11.042
- Guney K, Sezgin B, Yavuzer R. The efficacy of vibration anesthesia on reducing pain levels during lip augmentation: worth the buzz? Aesthet Surg J. 2017;37:1044-1048. doi:10.1093/asj/sjx073
- Lipner SR. Pain-minimizing strategies for nail surgery. Cutis. 2018;101:76-77.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Air cooling for improved analgesia during local anesthetic infiltration for nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:E231-E232. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.11.032
- Hudson BF, Ogden J, Whiteley MS. Randomized controlled trial to compare the effect of simple distraction interventions on pain and anxiety experienced during conscious surgery. Eur J Pain. 2015;19:1447-1455. doi:10.1002/ejp.675
- Molleman J, Tielemans JF, Braam MJI, et al. Distraction as a simple and effective method to reduce pain during local anesthesia: a randomized controlled trial. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2019;72:1979-1985. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2019.07.023
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilization of a stress ball to diminish anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2020;105:294.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilizing a sleep mask to reduce patient anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2021;108:36. doi:10.12788/cutis.0285
- Ricardo JW, Qiu Y, Lipner SR. Longitudinal perioperative pain assessment in nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:874-876. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.11.042
- Guney K, Sezgin B, Yavuzer R. The efficacy of vibration anesthesia on reducing pain levels during lip augmentation: worth the buzz? Aesthet Surg J. 2017;37:1044-1048. doi:10.1093/asj/sjx073
FLOTCH Syndrome: A Case of Leukonychia Totalis and Multiple Pilar Cysts
FLOTCH (leukonychia totalis-trichilemmal cysts-ciliary dystrophy syndrome) syndrome is a rare genetic cutaneous disorder primarily characterized by multiple recurrent trichilemmal pilar cysts and leukonychia. It may be associated with ciliary dystrophy, koilonychia, and/or less frequently renal calculi and pancreatitis. This disorder often presents in an autosomal-dominant pattern of inheritance. Leukonychia and associated pilar cysts originally were termed Bauer syndrome in 1920 and later described in 1986 as FLOTCH syndrome secondary to the association with ciliary dystrophy. 1,2 The term FLOTCH was coined by Friedel et al 1 to describe a combination of diagnoses experienced by a family in which several members had multiple pilar cysts, leukonychia, and ciliary dystrophy. We present a 25-year-old Black woman with suspected FLOTCH syndrome who was seen in our clinic for enlarging cysts.
Case Report
A 25-year-old Black woman with no notable medical history presented to the clinic for a surgical evaluation of cysts of several years’ duration that were enlarging and tender. Physical examination revealed multiple firm, fixed, tender nodules on the left superior parietal scalp, left inferior frontal scalp (Figure 1A), right inferior parietal scalp, right central postauricular skin, and right inferior occipital scalp. Similar-appearing cysts measuring 1.5 to 2 cm were seen on the left rib cage (Figure 1B) and left lateral forearm. Upon further examination, there was homogeneous, nonblanchable, white discoloration of all 10 fingernails consistent with true leukonychia (Figure 1C). When questioned about the nails, the patient stated they had been this color her whole life. Moreover, the patient confirmed that her brother’s nails had a similar appearance.
The patient subsequently underwent elliptical excision of the cysts located on the left medial forehead and left rib cage, and histopathology revealed trichilemmal pilar cysts with dystrophic calcification, dermal fibrosis, and mild chronic inflammation (Figure 2). The pathology report also noted that the anatomic site was somewhat unusual; however, the features were otherwise typical and diagnostic. Given the presentation of multiple pilar cysts throughout the body, leukonychia totalis, and positive family history, the patient was diagnosed with FLOTCH syndrome. Unfortunately, the patient was lost to follow-up following the excision, and no further management could be provided.
Comment
Leukonychia is an abnormality of the nail that results in a visible distribution of white color across the nail plate. It can be classified as totalis when covering the entire nail or partialis when covering localized areas of the nail. The disease also is categorized as acquired or inherited. Acquired leukonychia may appear after damage to a particular area of the nail or secondary to an underlying systemic disease, clinically appearing as white puncta or transverse striae. Hereditary leukonychia is rare, primarily covering the entire nail (totalis), and often is inherited in an autosomal-dominant pattern.3,4 The appearance of this disease can be an isolated occurrence or may be a component of a condition such as FLOTCH syndrome, as proposed in this case.
Pilar cysts (also known as trichilemmal cysts) are benign, slowly growing, firm, subcutaneous nodules that are similar to epidermoid cysts but arise from the root sheaths of hair follicles. Pilar cysts are inherited in an autosomal-dominant pattern and are caused by a mutation involving a 2-hit mechanism of variants of the phospholipase C delta 1 gene, PLCD1. Patients typically present with multiple cysts,5 as in our case.
This association of leukonychia and multiple pilar cysts previously has been reported in 7 family lines.1-3,6-9 The molecular basis of FLOTCH syndrome is unknown, and these combined diagnoses may be of syndromic nature. Histologic observations of leukonychia and the mechanism of the creation of pilar cysts suggest derivation from similar abnormal keratinization in the nail beds and hair follicles, respectively.6
The first familial association between leukonychia totalis and sebaceous cysts was described by Bauer2 in 1920. In 1975, Bushkell and Gorlin7 reported a similar inherited association with the addition of a history of renal calculi. In 1986, Friedel et al1 coined the term FLOTCH syndrome when reporting a case of an affected family presenting with leukonychia, recurrent cysts, and ciliary dystrophy. Slee et al8 reported 2 cases of pancreatitis experienced by patients presenting with these cysts and leukonychia. The etiology of the pancreatitis was unknown, leading researchers to believe it may be a complication associated with the spectrum of diseases.8 In 2008, Morin et al6 proposed that those with linked leukonychia and trichilemmal cysts may be at risk for neuromas or spinal tumors and suggested systematic screening after observing a family member with an ependymoma and bilateral multiple acoustic tumors. Rodríguez-Lojo et al3 described a 5-generation family with leukonychia totalis and numerous pilar cysts. Mutoh et al9 reported another 5-generation family with associated leukonychia and multiple pilar cysts as well as koilonychia. One family member had a reported history of renal calculus.9
In our case, FLOTCH syndrome was suspected given the patient’s concurrent pilar and follicular infundibular cysts. No specific treatment was indicated; however, as seen in prior cases and in ours, many patients prefer to have the cysts excised. A more comprehensive investigation could have revealed other associations, such as ciliary dystrophy, renal calculi, or pancreatitis. It is possible that in conjunction with the syndrome, patients could develop other such clinical manifestations. Pilar cysts most frequently are found on the scalp, yet in patients with concurrent leukonychia, the cysts have been shown to also develop in other regions of the body, as seen in our patient and in the case reported by Mutoh et al.9 Given the autosomal-dominant nature of this disease and the keratinizing structures affected, we confer with the hypotheses that a general keratin dysfunction is suspected. Further investigation is needed to determine the exact altered genetic mechanism or deficiency that may be causing this abnormal keratinization as well as a more extensive examination of patients to confirm if other described symptoms may be related.
- Friedel J, Heid E, Grosshans E. The FLOTCH syndrome. familial occurrence of total leukonychia, trichilemmal cysts and ciliary dystrophy with dominant autosomal heredity [in French]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1986;113:549-553.
- Bauer AW. Beiträge zur klinischen Konstitutionspathologie, V. heredofamiliäre leukonychie und multiple atherombilderung der kopfhaut. Z Menschl Vererb. Konstitutitionslehre. 1920;5:47-48.
- Rodríguez-Lojo R, Del Pozo J, Sacristán F, et al. Leukonychia totalis associated with multiple pilar cysts: report of a five-generation family: FLOTCH syndrome? Eur J Dermatol. 2011;21:484-486.
- Claudel CD, Zic JA, Boyd AS. Idiopathic leukonychia totalis and partialis in a 12-year-old patient. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:379-380.
- Hörer S, Marrakchi S, Radner FPW, et al. A monoallelic two-hit mechanism in PLCD1 explains the genetic pathogenesis of hereditary trichilemmal cyst formation. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:2154-2163.e5.
- Morin G, Desenclos C, Jeanpetit C, et al. Additional familial case of subtotal leukonychia and sebaceous cysts (Bauer syndrome): belong the nervous tumours to the phenotype? Eur J Med Genet. 2008;51:436-443.
- Bushkell LL, Gorlin RJ. Leukonychia totalis, multiple sebaceous cysts, and renal calculi. Arch Dermatol. 1975;111:899-901.
- Slee JJ, Wallman IS, Goldblatt J. A syndrome or leukonychia totalis and multiple sebaceous cysts. Clin Dysmorphol. 1997;6:229-233.
- Mutoh M, Niiyama S, Nishikawa S, et al. A syndrome of leukonychia, koilonychia and multiple pilar cysts. Acta Derm Venereol. 2015;95:249-250. doi:10.2340/00015555-1893
FLOTCH (leukonychia totalis-trichilemmal cysts-ciliary dystrophy syndrome) syndrome is a rare genetic cutaneous disorder primarily characterized by multiple recurrent trichilemmal pilar cysts and leukonychia. It may be associated with ciliary dystrophy, koilonychia, and/or less frequently renal calculi and pancreatitis. This disorder often presents in an autosomal-dominant pattern of inheritance. Leukonychia and associated pilar cysts originally were termed Bauer syndrome in 1920 and later described in 1986 as FLOTCH syndrome secondary to the association with ciliary dystrophy. 1,2 The term FLOTCH was coined by Friedel et al 1 to describe a combination of diagnoses experienced by a family in which several members had multiple pilar cysts, leukonychia, and ciliary dystrophy. We present a 25-year-old Black woman with suspected FLOTCH syndrome who was seen in our clinic for enlarging cysts.
Case Report
A 25-year-old Black woman with no notable medical history presented to the clinic for a surgical evaluation of cysts of several years’ duration that were enlarging and tender. Physical examination revealed multiple firm, fixed, tender nodules on the left superior parietal scalp, left inferior frontal scalp (Figure 1A), right inferior parietal scalp, right central postauricular skin, and right inferior occipital scalp. Similar-appearing cysts measuring 1.5 to 2 cm were seen on the left rib cage (Figure 1B) and left lateral forearm. Upon further examination, there was homogeneous, nonblanchable, white discoloration of all 10 fingernails consistent with true leukonychia (Figure 1C). When questioned about the nails, the patient stated they had been this color her whole life. Moreover, the patient confirmed that her brother’s nails had a similar appearance.

The patient subsequently underwent elliptical excision of the cysts located on the left medial forehead and left rib cage, and histopathology revealed trichilemmal pilar cysts with dystrophic calcification, dermal fibrosis, and mild chronic inflammation (Figure 2). The pathology report also noted that the anatomic site was somewhat unusual; however, the features were otherwise typical and diagnostic. Given the presentation of multiple pilar cysts throughout the body, leukonychia totalis, and positive family history, the patient was diagnosed with FLOTCH syndrome. Unfortunately, the patient was lost to follow-up following the excision, and no further management could be provided.

Comment
Leukonychia is an abnormality of the nail that results in a visible distribution of white color across the nail plate. It can be classified as totalis when covering the entire nail or partialis when covering localized areas of the nail. The disease also is categorized as acquired or inherited. Acquired leukonychia may appear after damage to a particular area of the nail or secondary to an underlying systemic disease, clinically appearing as white puncta or transverse striae. Hereditary leukonychia is rare, primarily covering the entire nail (totalis), and often is inherited in an autosomal-dominant pattern.3,4 The appearance of this disease can be an isolated occurrence or may be a component of a condition such as FLOTCH syndrome, as proposed in this case.
Pilar cysts (also known as trichilemmal cysts) are benign, slowly growing, firm, subcutaneous nodules that are similar to epidermoid cysts but arise from the root sheaths of hair follicles. Pilar cysts are inherited in an autosomal-dominant pattern and are caused by a mutation involving a 2-hit mechanism of variants of the phospholipase C delta 1 gene, PLCD1. Patients typically present with multiple cysts,5 as in our case.
This association of leukonychia and multiple pilar cysts previously has been reported in 7 family lines.1-3,6-9 The molecular basis of FLOTCH syndrome is unknown, and these combined diagnoses may be of syndromic nature. Histologic observations of leukonychia and the mechanism of the creation of pilar cysts suggest derivation from similar abnormal keratinization in the nail beds and hair follicles, respectively.6
The first familial association between leukonychia totalis and sebaceous cysts was described by Bauer2 in 1920. In 1975, Bushkell and Gorlin7 reported a similar inherited association with the addition of a history of renal calculi. In 1986, Friedel et al1 coined the term FLOTCH syndrome when reporting a case of an affected family presenting with leukonychia, recurrent cysts, and ciliary dystrophy. Slee et al8 reported 2 cases of pancreatitis experienced by patients presenting with these cysts and leukonychia. The etiology of the pancreatitis was unknown, leading researchers to believe it may be a complication associated with the spectrum of diseases.8 In 2008, Morin et al6 proposed that those with linked leukonychia and trichilemmal cysts may be at risk for neuromas or spinal tumors and suggested systematic screening after observing a family member with an ependymoma and bilateral multiple acoustic tumors. Rodríguez-Lojo et al3 described a 5-generation family with leukonychia totalis and numerous pilar cysts. Mutoh et al9 reported another 5-generation family with associated leukonychia and multiple pilar cysts as well as koilonychia. One family member had a reported history of renal calculus.9
In our case, FLOTCH syndrome was suspected given the patient’s concurrent pilar and follicular infundibular cysts. No specific treatment was indicated; however, as seen in prior cases and in ours, many patients prefer to have the cysts excised. A more comprehensive investigation could have revealed other associations, such as ciliary dystrophy, renal calculi, or pancreatitis. It is possible that in conjunction with the syndrome, patients could develop other such clinical manifestations. Pilar cysts most frequently are found on the scalp, yet in patients with concurrent leukonychia, the cysts have been shown to also develop in other regions of the body, as seen in our patient and in the case reported by Mutoh et al.9 Given the autosomal-dominant nature of this disease and the keratinizing structures affected, we confer with the hypotheses that a general keratin dysfunction is suspected. Further investigation is needed to determine the exact altered genetic mechanism or deficiency that may be causing this abnormal keratinization as well as a more extensive examination of patients to confirm if other described symptoms may be related.
FLOTCH (leukonychia totalis-trichilemmal cysts-ciliary dystrophy syndrome) syndrome is a rare genetic cutaneous disorder primarily characterized by multiple recurrent trichilemmal pilar cysts and leukonychia. It may be associated with ciliary dystrophy, koilonychia, and/or less frequently renal calculi and pancreatitis. This disorder often presents in an autosomal-dominant pattern of inheritance. Leukonychia and associated pilar cysts originally were termed Bauer syndrome in 1920 and later described in 1986 as FLOTCH syndrome secondary to the association with ciliary dystrophy. 1,2 The term FLOTCH was coined by Friedel et al 1 to describe a combination of diagnoses experienced by a family in which several members had multiple pilar cysts, leukonychia, and ciliary dystrophy. We present a 25-year-old Black woman with suspected FLOTCH syndrome who was seen in our clinic for enlarging cysts.
Case Report
A 25-year-old Black woman with no notable medical history presented to the clinic for a surgical evaluation of cysts of several years’ duration that were enlarging and tender. Physical examination revealed multiple firm, fixed, tender nodules on the left superior parietal scalp, left inferior frontal scalp (Figure 1A), right inferior parietal scalp, right central postauricular skin, and right inferior occipital scalp. Similar-appearing cysts measuring 1.5 to 2 cm were seen on the left rib cage (Figure 1B) and left lateral forearm. Upon further examination, there was homogeneous, nonblanchable, white discoloration of all 10 fingernails consistent with true leukonychia (Figure 1C). When questioned about the nails, the patient stated they had been this color her whole life. Moreover, the patient confirmed that her brother’s nails had a similar appearance.

The patient subsequently underwent elliptical excision of the cysts located on the left medial forehead and left rib cage, and histopathology revealed trichilemmal pilar cysts with dystrophic calcification, dermal fibrosis, and mild chronic inflammation (Figure 2). The pathology report also noted that the anatomic site was somewhat unusual; however, the features were otherwise typical and diagnostic. Given the presentation of multiple pilar cysts throughout the body, leukonychia totalis, and positive family history, the patient was diagnosed with FLOTCH syndrome. Unfortunately, the patient was lost to follow-up following the excision, and no further management could be provided.

Comment
Leukonychia is an abnormality of the nail that results in a visible distribution of white color across the nail plate. It can be classified as totalis when covering the entire nail or partialis when covering localized areas of the nail. The disease also is categorized as acquired or inherited. Acquired leukonychia may appear after damage to a particular area of the nail or secondary to an underlying systemic disease, clinically appearing as white puncta or transverse striae. Hereditary leukonychia is rare, primarily covering the entire nail (totalis), and often is inherited in an autosomal-dominant pattern.3,4 The appearance of this disease can be an isolated occurrence or may be a component of a condition such as FLOTCH syndrome, as proposed in this case.
Pilar cysts (also known as trichilemmal cysts) are benign, slowly growing, firm, subcutaneous nodules that are similar to epidermoid cysts but arise from the root sheaths of hair follicles. Pilar cysts are inherited in an autosomal-dominant pattern and are caused by a mutation involving a 2-hit mechanism of variants of the phospholipase C delta 1 gene, PLCD1. Patients typically present with multiple cysts,5 as in our case.
This association of leukonychia and multiple pilar cysts previously has been reported in 7 family lines.1-3,6-9 The molecular basis of FLOTCH syndrome is unknown, and these combined diagnoses may be of syndromic nature. Histologic observations of leukonychia and the mechanism of the creation of pilar cysts suggest derivation from similar abnormal keratinization in the nail beds and hair follicles, respectively.6
The first familial association between leukonychia totalis and sebaceous cysts was described by Bauer2 in 1920. In 1975, Bushkell and Gorlin7 reported a similar inherited association with the addition of a history of renal calculi. In 1986, Friedel et al1 coined the term FLOTCH syndrome when reporting a case of an affected family presenting with leukonychia, recurrent cysts, and ciliary dystrophy. Slee et al8 reported 2 cases of pancreatitis experienced by patients presenting with these cysts and leukonychia. The etiology of the pancreatitis was unknown, leading researchers to believe it may be a complication associated with the spectrum of diseases.8 In 2008, Morin et al6 proposed that those with linked leukonychia and trichilemmal cysts may be at risk for neuromas or spinal tumors and suggested systematic screening after observing a family member with an ependymoma and bilateral multiple acoustic tumors. Rodríguez-Lojo et al3 described a 5-generation family with leukonychia totalis and numerous pilar cysts. Mutoh et al9 reported another 5-generation family with associated leukonychia and multiple pilar cysts as well as koilonychia. One family member had a reported history of renal calculus.9
In our case, FLOTCH syndrome was suspected given the patient’s concurrent pilar and follicular infundibular cysts. No specific treatment was indicated; however, as seen in prior cases and in ours, many patients prefer to have the cysts excised. A more comprehensive investigation could have revealed other associations, such as ciliary dystrophy, renal calculi, or pancreatitis. It is possible that in conjunction with the syndrome, patients could develop other such clinical manifestations. Pilar cysts most frequently are found on the scalp, yet in patients with concurrent leukonychia, the cysts have been shown to also develop in other regions of the body, as seen in our patient and in the case reported by Mutoh et al.9 Given the autosomal-dominant nature of this disease and the keratinizing structures affected, we confer with the hypotheses that a general keratin dysfunction is suspected. Further investigation is needed to determine the exact altered genetic mechanism or deficiency that may be causing this abnormal keratinization as well as a more extensive examination of patients to confirm if other described symptoms may be related.
- Friedel J, Heid E, Grosshans E. The FLOTCH syndrome. familial occurrence of total leukonychia, trichilemmal cysts and ciliary dystrophy with dominant autosomal heredity [in French]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1986;113:549-553.
- Bauer AW. Beiträge zur klinischen Konstitutionspathologie, V. heredofamiliäre leukonychie und multiple atherombilderung der kopfhaut. Z Menschl Vererb. Konstitutitionslehre. 1920;5:47-48.
- Rodríguez-Lojo R, Del Pozo J, Sacristán F, et al. Leukonychia totalis associated with multiple pilar cysts: report of a five-generation family: FLOTCH syndrome? Eur J Dermatol. 2011;21:484-486.
- Claudel CD, Zic JA, Boyd AS. Idiopathic leukonychia totalis and partialis in a 12-year-old patient. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:379-380.
- Hörer S, Marrakchi S, Radner FPW, et al. A monoallelic two-hit mechanism in PLCD1 explains the genetic pathogenesis of hereditary trichilemmal cyst formation. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:2154-2163.e5.
- Morin G, Desenclos C, Jeanpetit C, et al. Additional familial case of subtotal leukonychia and sebaceous cysts (Bauer syndrome): belong the nervous tumours to the phenotype? Eur J Med Genet. 2008;51:436-443.
- Bushkell LL, Gorlin RJ. Leukonychia totalis, multiple sebaceous cysts, and renal calculi. Arch Dermatol. 1975;111:899-901.
- Slee JJ, Wallman IS, Goldblatt J. A syndrome or leukonychia totalis and multiple sebaceous cysts. Clin Dysmorphol. 1997;6:229-233.
- Mutoh M, Niiyama S, Nishikawa S, et al. A syndrome of leukonychia, koilonychia and multiple pilar cysts. Acta Derm Venereol. 2015;95:249-250. doi:10.2340/00015555-1893
- Friedel J, Heid E, Grosshans E. The FLOTCH syndrome. familial occurrence of total leukonychia, trichilemmal cysts and ciliary dystrophy with dominant autosomal heredity [in French]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1986;113:549-553.
- Bauer AW. Beiträge zur klinischen Konstitutionspathologie, V. heredofamiliäre leukonychie und multiple atherombilderung der kopfhaut. Z Menschl Vererb. Konstitutitionslehre. 1920;5:47-48.
- Rodríguez-Lojo R, Del Pozo J, Sacristán F, et al. Leukonychia totalis associated with multiple pilar cysts: report of a five-generation family: FLOTCH syndrome? Eur J Dermatol. 2011;21:484-486.
- Claudel CD, Zic JA, Boyd AS. Idiopathic leukonychia totalis and partialis in a 12-year-old patient. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:379-380.
- Hörer S, Marrakchi S, Radner FPW, et al. A monoallelic two-hit mechanism in PLCD1 explains the genetic pathogenesis of hereditary trichilemmal cyst formation. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:2154-2163.e5.
- Morin G, Desenclos C, Jeanpetit C, et al. Additional familial case of subtotal leukonychia and sebaceous cysts (Bauer syndrome): belong the nervous tumours to the phenotype? Eur J Med Genet. 2008;51:436-443.
- Bushkell LL, Gorlin RJ. Leukonychia totalis, multiple sebaceous cysts, and renal calculi. Arch Dermatol. 1975;111:899-901.
- Slee JJ, Wallman IS, Goldblatt J. A syndrome or leukonychia totalis and multiple sebaceous cysts. Clin Dysmorphol. 1997;6:229-233.
- Mutoh M, Niiyama S, Nishikawa S, et al. A syndrome of leukonychia, koilonychia and multiple pilar cysts. Acta Derm Venereol. 2015;95:249-250. doi:10.2340/00015555-1893
PRACTICE POINTS
- FLOTCH (leukonychia totalis-trichilemmal cysts-ciliary dystrophy syndrome) syndrome is an extremely rare condition that presents with multiple pilar cysts and leukonychia totalis. Pilar cysts in unusual locations along with distinct nail changes should prompt clinicians to consider further investigation for conditions such as FLOTCH syndrome.
- Although FLOTCH syndrome has been associated with other conditions such as ciliary dystrophy, renal calculi, pancreatitis, and central nervous system tumors, this does not preclude an extensive workup. Rather, careful family history may be the best predictor of clinical manifestations along the spectrum of this disease.