User login
Obesity drug with swallowable balloon boosts weight loss
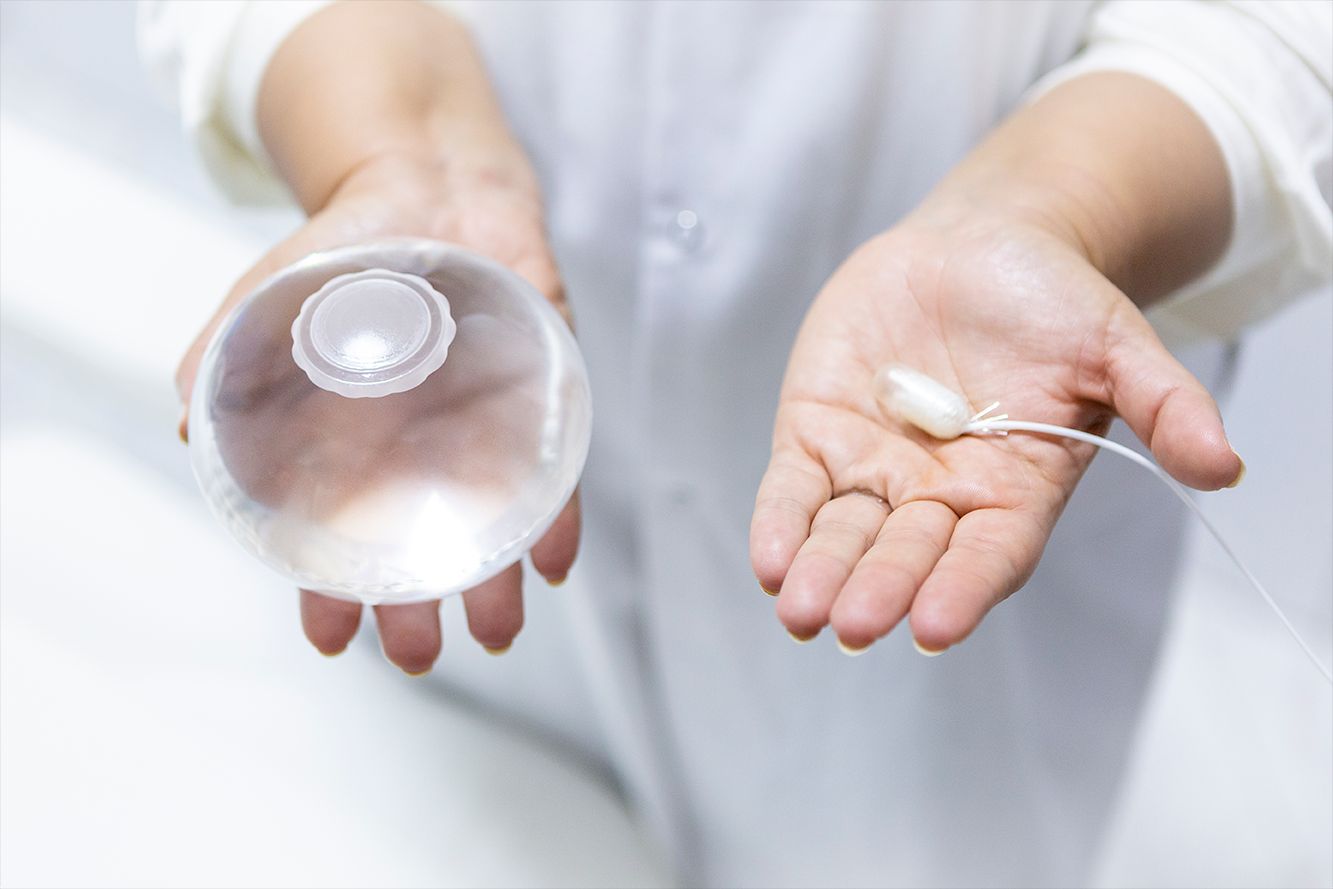
DUBLIN – A swallowable gastric balloon (Allurion Balloon, formerly known as Elipse) combined with daily subcutaneous injections of the glucagonlike peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonist liraglutide (Saxenda, Novo Nordisk), leads to a significant average total body weight loss of 19% (18 kg or 40 lb) after around 4 months in people with obesity.
said Roberta Ienca, MD, from the Clinica Nuova Villa Claudia, Rome, who presented the findings at this year’s European Congress on Obesity.
“Despite both the balloon and liraglutide working on the early satiety feeling, the introduction of liraglutide around 1 month after [swallowing the balloon] or more frequently after 3-4 months, could sustain these feelings for a longer period of time,” she said in an interview.
“The addition of the GLP-1 agonist therapy (liraglutide) to patients treated with the Allurion program [gastric balloon] is feasible, safe, and effective in those who need additional weight loss,” she emphasized.
The balloon stayed inside participants’ stomachs for an average of 16 weeks and liraglutide was continued for an average of 4 months, resulting in a mean reduction in body mass index (BMI) of 6.4 kg/m2.
The Allurion is the world’s first and only swallowable gastric balloon placed without surgery, endoscopy, or anesthesia, and is excreted naturally after around 16 weeks.
The Allurion program delivered “excellent weight loss in individuals with overweight and obesity without going under the knife, and liraglutide has the potential to further safely enhance weight loss in cases of suboptimal adherence with the program,” Dr. Ienca said. “These two treatment approaches appear to have complementary mechanisms of action in a geographically and demographically diverse population.”
Adelardo Caballero, MD, director of the Institute of Obesity, Madrid, said that he had over 6 years of experience with the Allurion balloon in around 2,500 cases. “Over the last 3 years, we have been using Allurion balloons in combination with GLP-1 agonists. In Europe, use of the swallowable gastric balloon is common, the results are good, and it is a safe tool.”
“Using liraglutide daily in subcutaneous form is authorized in Europe and is useful in overweight and mild obesity, while use in the combination [with the balloon] is also very popular,” he explained. “In the future, the combined use of semaglutide once-weekly GLP-1 agonist or the use of dual GLP-1/gastric inhibitory polypeptide agonists [such as tirzepatide] with the swallowable intragastric balloon Allurion program or endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty will improve results,” he added.
Average 40-lb weight loss with balloon and liraglutide
For the current study, data from three international multidisciplinary obesity centers (in Italy, Spain, and Egypt) were retrospectively analyzed. All 181 patients received the combination of the Allurion balloon and liraglutide, with the latter added 4-16 weeks after swallowing the balloon.
During a 20-minute outpatient visit, participants swallowed the balloon, which was filled with liquid after reaching the stomach, and placement was confirmed by x-ray. The balloon remained inserted for around 15-17 weeks (mean 16 weeks) before natural excretion. All patients received liraglutide once daily for 1-6 months (mean 4 months). After excreting the balloon, patients started the Mediterranean diet for weight maintenance and were followed for at least 6 months.
Patients were monitored for weight loss, percentage total body weight loss, percentage excess weight loss, and BMI reduction. The timing of combining drug therapy with the Allurion program, metabolic results, and adverse event data were collected. However, Dr. Ienca explained that “the study was preliminary and aimed to evaluate feasibility and results of a combined treatment, so we didn’t collect long-term data.”
Liraglutide was mostly added in cases of unsatisfactory weight loss to boost weight reduction in patients with high BMIs, to sustain weight maintenance, and to aid diabetes control in patients with satisfactory weight loss. There were no criteria for time of onset of drug therapy in terms of a time point or percentage weight loss.
Before treatment, mean weight was 94.8 ± 21 kg and mean BMI was 33.7 ± 6.2 kg/m2. After 4 months of balloon treatment, weight loss, percentage total body weight loss, percentage excess weight loss, and decrease in BMI were 13.1 ± 7 kg, 13.9% ± 7.7%, 74.3% ± 57.1%, and 4.5 ±1.4 kg/m2 respectively.
After a mean duration of 4 months of liraglutide treatment (in addition to the gastric balloon), participants lost on average 18.1 ± 12.1 kg overall and 18.7% ± 12% of their initial total body weight. They shed 99.4% ± 84.9% of excess weight and reduced BMI by 6.4 ± 5.9 kg/m2.
Dr. Ienca explained that the study did not explore the separate contributions of the balloon or drug therapy to weight loss. “However, existing literature shows that the Allurion program leads to a weight loss of approximately 14% of total body weight after 4 months, while liraglutide studies report 12% of total body weight loss at 1 year,” he noted.
When describing the mechanism of action, Dr. Ienca said the Allurion balloon induces satiety and delays gastric emptying but the feeling of satiety starts to decrease after the first month. “For a few patients, this feeling of satiety decreases more rapidly or they have more difficulty putting in place new alimentary habits. In these patients, the addition of liraglutide gives an additional boost to support this behavioral change.”
Liraglutide-related adverse events included nausea (16.5%), diarrhea (3.3%), constipation (2.2%), and headache (1.7%), as well as drug discontinuation due to tachycardia/chest pain (1.1%) and gastrointestinal symptoms (1.1%).
Balloon removal because of intolerance occurred in 1.1% of patients, gastric dilation in 0.5%, and early balloon deflation in 0.5%. Other expected balloon-related adverse events included nausea, vomiting, and abdominal cramps.
The researchers note that the Allurion program offers a more acceptable option to balloon placement by endoscopy.
“The ease of use, low rate of adverse events, and potentially lower cost of the Allurion Program could enable much wider application of this critical intervention, and ultimately, help the millions who struggle with obesity and its associated health complications.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
DUBLIN – A swallowable gastric balloon (Allurion Balloon, formerly known as Elipse) combined with daily subcutaneous injections of the glucagonlike peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonist liraglutide (Saxenda, Novo Nordisk), leads to a significant average total body weight loss of 19% (18 kg or 40 lb) after around 4 months in people with obesity.
said Roberta Ienca, MD, from the Clinica Nuova Villa Claudia, Rome, who presented the findings at this year’s European Congress on Obesity.
“Despite both the balloon and liraglutide working on the early satiety feeling, the introduction of liraglutide around 1 month after [swallowing the balloon] or more frequently after 3-4 months, could sustain these feelings for a longer period of time,” she said in an interview.
“The addition of the GLP-1 agonist therapy (liraglutide) to patients treated with the Allurion program [gastric balloon] is feasible, safe, and effective in those who need additional weight loss,” she emphasized.
The balloon stayed inside participants’ stomachs for an average of 16 weeks and liraglutide was continued for an average of 4 months, resulting in a mean reduction in body mass index (BMI) of 6.4 kg/m2.
The Allurion is the world’s first and only swallowable gastric balloon placed without surgery, endoscopy, or anesthesia, and is excreted naturally after around 16 weeks.
The Allurion program delivered “excellent weight loss in individuals with overweight and obesity without going under the knife, and liraglutide has the potential to further safely enhance weight loss in cases of suboptimal adherence with the program,” Dr. Ienca said. “These two treatment approaches appear to have complementary mechanisms of action in a geographically and demographically diverse population.”
Adelardo Caballero, MD, director of the Institute of Obesity, Madrid, said that he had over 6 years of experience with the Allurion balloon in around 2,500 cases. “Over the last 3 years, we have been using Allurion balloons in combination with GLP-1 agonists. In Europe, use of the swallowable gastric balloon is common, the results are good, and it is a safe tool.”
“Using liraglutide daily in subcutaneous form is authorized in Europe and is useful in overweight and mild obesity, while use in the combination [with the balloon] is also very popular,” he explained. “In the future, the combined use of semaglutide once-weekly GLP-1 agonist or the use of dual GLP-1/gastric inhibitory polypeptide agonists [such as tirzepatide] with the swallowable intragastric balloon Allurion program or endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty will improve results,” he added.
Average 40-lb weight loss with balloon and liraglutide
For the current study, data from three international multidisciplinary obesity centers (in Italy, Spain, and Egypt) were retrospectively analyzed. All 181 patients received the combination of the Allurion balloon and liraglutide, with the latter added 4-16 weeks after swallowing the balloon.
During a 20-minute outpatient visit, participants swallowed the balloon, which was filled with liquid after reaching the stomach, and placement was confirmed by x-ray. The balloon remained inserted for around 15-17 weeks (mean 16 weeks) before natural excretion. All patients received liraglutide once daily for 1-6 months (mean 4 months). After excreting the balloon, patients started the Mediterranean diet for weight maintenance and were followed for at least 6 months.
Patients were monitored for weight loss, percentage total body weight loss, percentage excess weight loss, and BMI reduction. The timing of combining drug therapy with the Allurion program, metabolic results, and adverse event data were collected. However, Dr. Ienca explained that “the study was preliminary and aimed to evaluate feasibility and results of a combined treatment, so we didn’t collect long-term data.”
Liraglutide was mostly added in cases of unsatisfactory weight loss to boost weight reduction in patients with high BMIs, to sustain weight maintenance, and to aid diabetes control in patients with satisfactory weight loss. There were no criteria for time of onset of drug therapy in terms of a time point or percentage weight loss.
Before treatment, mean weight was 94.8 ± 21 kg and mean BMI was 33.7 ± 6.2 kg/m2. After 4 months of balloon treatment, weight loss, percentage total body weight loss, percentage excess weight loss, and decrease in BMI were 13.1 ± 7 kg, 13.9% ± 7.7%, 74.3% ± 57.1%, and 4.5 ±1.4 kg/m2 respectively.
After a mean duration of 4 months of liraglutide treatment (in addition to the gastric balloon), participants lost on average 18.1 ± 12.1 kg overall and 18.7% ± 12% of their initial total body weight. They shed 99.4% ± 84.9% of excess weight and reduced BMI by 6.4 ± 5.9 kg/m2.
Dr. Ienca explained that the study did not explore the separate contributions of the balloon or drug therapy to weight loss. “However, existing literature shows that the Allurion program leads to a weight loss of approximately 14% of total body weight after 4 months, while liraglutide studies report 12% of total body weight loss at 1 year,” he noted.
When describing the mechanism of action, Dr. Ienca said the Allurion balloon induces satiety and delays gastric emptying but the feeling of satiety starts to decrease after the first month. “For a few patients, this feeling of satiety decreases more rapidly or they have more difficulty putting in place new alimentary habits. In these patients, the addition of liraglutide gives an additional boost to support this behavioral change.”
Liraglutide-related adverse events included nausea (16.5%), diarrhea (3.3%), constipation (2.2%), and headache (1.7%), as well as drug discontinuation due to tachycardia/chest pain (1.1%) and gastrointestinal symptoms (1.1%).
Balloon removal because of intolerance occurred in 1.1% of patients, gastric dilation in 0.5%, and early balloon deflation in 0.5%. Other expected balloon-related adverse events included nausea, vomiting, and abdominal cramps.
The researchers note that the Allurion program offers a more acceptable option to balloon placement by endoscopy.
“The ease of use, low rate of adverse events, and potentially lower cost of the Allurion Program could enable much wider application of this critical intervention, and ultimately, help the millions who struggle with obesity and its associated health complications.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
DUBLIN – A swallowable gastric balloon (Allurion Balloon, formerly known as Elipse) combined with daily subcutaneous injections of the glucagonlike peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonist liraglutide (Saxenda, Novo Nordisk), leads to a significant average total body weight loss of 19% (18 kg or 40 lb) after around 4 months in people with obesity.
said Roberta Ienca, MD, from the Clinica Nuova Villa Claudia, Rome, who presented the findings at this year’s European Congress on Obesity.
“Despite both the balloon and liraglutide working on the early satiety feeling, the introduction of liraglutide around 1 month after [swallowing the balloon] or more frequently after 3-4 months, could sustain these feelings for a longer period of time,” she said in an interview.
“The addition of the GLP-1 agonist therapy (liraglutide) to patients treated with the Allurion program [gastric balloon] is feasible, safe, and effective in those who need additional weight loss,” she emphasized.
The balloon stayed inside participants’ stomachs for an average of 16 weeks and liraglutide was continued for an average of 4 months, resulting in a mean reduction in body mass index (BMI) of 6.4 kg/m2.
The Allurion is the world’s first and only swallowable gastric balloon placed without surgery, endoscopy, or anesthesia, and is excreted naturally after around 16 weeks.
The Allurion program delivered “excellent weight loss in individuals with overweight and obesity without going under the knife, and liraglutide has the potential to further safely enhance weight loss in cases of suboptimal adherence with the program,” Dr. Ienca said. “These two treatment approaches appear to have complementary mechanisms of action in a geographically and demographically diverse population.”
Adelardo Caballero, MD, director of the Institute of Obesity, Madrid, said that he had over 6 years of experience with the Allurion balloon in around 2,500 cases. “Over the last 3 years, we have been using Allurion balloons in combination with GLP-1 agonists. In Europe, use of the swallowable gastric balloon is common, the results are good, and it is a safe tool.”
“Using liraglutide daily in subcutaneous form is authorized in Europe and is useful in overweight and mild obesity, while use in the combination [with the balloon] is also very popular,” he explained. “In the future, the combined use of semaglutide once-weekly GLP-1 agonist or the use of dual GLP-1/gastric inhibitory polypeptide agonists [such as tirzepatide] with the swallowable intragastric balloon Allurion program or endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty will improve results,” he added.
Average 40-lb weight loss with balloon and liraglutide
For the current study, data from three international multidisciplinary obesity centers (in Italy, Spain, and Egypt) were retrospectively analyzed. All 181 patients received the combination of the Allurion balloon and liraglutide, with the latter added 4-16 weeks after swallowing the balloon.
During a 20-minute outpatient visit, participants swallowed the balloon, which was filled with liquid after reaching the stomach, and placement was confirmed by x-ray. The balloon remained inserted for around 15-17 weeks (mean 16 weeks) before natural excretion. All patients received liraglutide once daily for 1-6 months (mean 4 months). After excreting the balloon, patients started the Mediterranean diet for weight maintenance and were followed for at least 6 months.
Patients were monitored for weight loss, percentage total body weight loss, percentage excess weight loss, and BMI reduction. The timing of combining drug therapy with the Allurion program, metabolic results, and adverse event data were collected. However, Dr. Ienca explained that “the study was preliminary and aimed to evaluate feasibility and results of a combined treatment, so we didn’t collect long-term data.”
Liraglutide was mostly added in cases of unsatisfactory weight loss to boost weight reduction in patients with high BMIs, to sustain weight maintenance, and to aid diabetes control in patients with satisfactory weight loss. There were no criteria for time of onset of drug therapy in terms of a time point or percentage weight loss.
Before treatment, mean weight was 94.8 ± 21 kg and mean BMI was 33.7 ± 6.2 kg/m2. After 4 months of balloon treatment, weight loss, percentage total body weight loss, percentage excess weight loss, and decrease in BMI were 13.1 ± 7 kg, 13.9% ± 7.7%, 74.3% ± 57.1%, and 4.5 ±1.4 kg/m2 respectively.
After a mean duration of 4 months of liraglutide treatment (in addition to the gastric balloon), participants lost on average 18.1 ± 12.1 kg overall and 18.7% ± 12% of their initial total body weight. They shed 99.4% ± 84.9% of excess weight and reduced BMI by 6.4 ± 5.9 kg/m2.
Dr. Ienca explained that the study did not explore the separate contributions of the balloon or drug therapy to weight loss. “However, existing literature shows that the Allurion program leads to a weight loss of approximately 14% of total body weight after 4 months, while liraglutide studies report 12% of total body weight loss at 1 year,” he noted.
When describing the mechanism of action, Dr. Ienca said the Allurion balloon induces satiety and delays gastric emptying but the feeling of satiety starts to decrease after the first month. “For a few patients, this feeling of satiety decreases more rapidly or they have more difficulty putting in place new alimentary habits. In these patients, the addition of liraglutide gives an additional boost to support this behavioral change.”
Liraglutide-related adverse events included nausea (16.5%), diarrhea (3.3%), constipation (2.2%), and headache (1.7%), as well as drug discontinuation due to tachycardia/chest pain (1.1%) and gastrointestinal symptoms (1.1%).
Balloon removal because of intolerance occurred in 1.1% of patients, gastric dilation in 0.5%, and early balloon deflation in 0.5%. Other expected balloon-related adverse events included nausea, vomiting, and abdominal cramps.
The researchers note that the Allurion program offers a more acceptable option to balloon placement by endoscopy.
“The ease of use, low rate of adverse events, and potentially lower cost of the Allurion Program could enable much wider application of this critical intervention, and ultimately, help the millions who struggle with obesity and its associated health complications.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ECO 2023
Skin changes and pain
The history and findings in this case are suggestive of inflammatory breast cancer.
Breast cancer is the leading life-threatening cancer diagnosed and the second-leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women worldwide. In the United States, estimates suggest that 287,850 new cases of invasive breast cancer were diagnosed in 2022 and 43,250 women died of the disease. Globally, approximately 2.3 million new diagnoses and 685,000 breast cancer–related deaths were reported in 2020.
Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare and highly aggressive subtype of locally advanced breast cancer. In the United States, inflammatory breast cancer accounts for approximately 2%-4% of breast cancer cases. Although its incidence is rare, 7% of breast cancer caused mortality is attributed to inflammatory breast cancer. Cases of inflammatory breast cancer tend to be diagnosed at a younger age compared with noninflammatory breast cancer cases. Risk factors include African-American race and obesity.
The symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer can vary broadly, ranging from subtle skin erythema to diffuse breast involvement with skin dimpling and nipple inversion. Diagnostic criteria include erythema occupying at least one third of the breast, edema, peau d'orange, and/or warmth, with or without an underlying mass; rapid onset (< 3 months); and pathologic confirmation of invasive breast carcinoma. Histologic findings include florid tumor emboli that obstruct dermal lymphatics, which results in swelling and inflammation of the affected breast.
Inflammatory breast cancer has been associated with a poor prognosis. However, treatment advances are helping to improve outcomes. Currently, 5-year survival rates are reported to be 40%-70%, with a median survival of 2-4 years. According to 2023 guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), the first-line treatment of inflammatory breast cancer involves neoadjuvant chemotherapy, modified radical mastectomy, and adjuvant radiation to the chest wall and regional nodes. Endocrine treatment should also be given to patients who are ER-positive and/or PR-positive (sequential chemotherapy followed by endocrine therapy). For patients who are HER2-positive, up to 1 year of HER2-targeted therapy should be given. HER2-targeted therapies can be administered concurrently with radiation and with endocrine therapy if indicated.
Delayed reconstruction after mastectomy remains the clinical standard for inflammatory breast cancer. This is because the need to resect involved skin negates the benefit of skin-sparing mastectomy for immediate reconstruction. Moreover, high rates of local and distant recurrence warrant comprehensive regional node irradiation in a timely fashion, which may be more challenging or subject to delay after immediate reconstruction. Rarely, the extent of skin excision at the time of mastectomy prohibits primary or local closure. In such cases, reconstruction of the chest wall defect with autologous tissue is required, and concomitant immediate reconstruction may be undertaken.
Detailed guidance on the treatment of inflammatory breast cancer, in the first line and beyond, are available from the NCCN.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, Assistant Member, Department of Breast Oncology, Moffitt Cancer Center, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The history and findings in this case are suggestive of inflammatory breast cancer.
Breast cancer is the leading life-threatening cancer diagnosed and the second-leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women worldwide. In the United States, estimates suggest that 287,850 new cases of invasive breast cancer were diagnosed in 2022 and 43,250 women died of the disease. Globally, approximately 2.3 million new diagnoses and 685,000 breast cancer–related deaths were reported in 2020.
Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare and highly aggressive subtype of locally advanced breast cancer. In the United States, inflammatory breast cancer accounts for approximately 2%-4% of breast cancer cases. Although its incidence is rare, 7% of breast cancer caused mortality is attributed to inflammatory breast cancer. Cases of inflammatory breast cancer tend to be diagnosed at a younger age compared with noninflammatory breast cancer cases. Risk factors include African-American race and obesity.
The symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer can vary broadly, ranging from subtle skin erythema to diffuse breast involvement with skin dimpling and nipple inversion. Diagnostic criteria include erythema occupying at least one third of the breast, edema, peau d'orange, and/or warmth, with or without an underlying mass; rapid onset (< 3 months); and pathologic confirmation of invasive breast carcinoma. Histologic findings include florid tumor emboli that obstruct dermal lymphatics, which results in swelling and inflammation of the affected breast.
Inflammatory breast cancer has been associated with a poor prognosis. However, treatment advances are helping to improve outcomes. Currently, 5-year survival rates are reported to be 40%-70%, with a median survival of 2-4 years. According to 2023 guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), the first-line treatment of inflammatory breast cancer involves neoadjuvant chemotherapy, modified radical mastectomy, and adjuvant radiation to the chest wall and regional nodes. Endocrine treatment should also be given to patients who are ER-positive and/or PR-positive (sequential chemotherapy followed by endocrine therapy). For patients who are HER2-positive, up to 1 year of HER2-targeted therapy should be given. HER2-targeted therapies can be administered concurrently with radiation and with endocrine therapy if indicated.
Delayed reconstruction after mastectomy remains the clinical standard for inflammatory breast cancer. This is because the need to resect involved skin negates the benefit of skin-sparing mastectomy for immediate reconstruction. Moreover, high rates of local and distant recurrence warrant comprehensive regional node irradiation in a timely fashion, which may be more challenging or subject to delay after immediate reconstruction. Rarely, the extent of skin excision at the time of mastectomy prohibits primary or local closure. In such cases, reconstruction of the chest wall defect with autologous tissue is required, and concomitant immediate reconstruction may be undertaken.
Detailed guidance on the treatment of inflammatory breast cancer, in the first line and beyond, are available from the NCCN.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, Assistant Member, Department of Breast Oncology, Moffitt Cancer Center, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The history and findings in this case are suggestive of inflammatory breast cancer.
Breast cancer is the leading life-threatening cancer diagnosed and the second-leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women worldwide. In the United States, estimates suggest that 287,850 new cases of invasive breast cancer were diagnosed in 2022 and 43,250 women died of the disease. Globally, approximately 2.3 million new diagnoses and 685,000 breast cancer–related deaths were reported in 2020.
Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare and highly aggressive subtype of locally advanced breast cancer. In the United States, inflammatory breast cancer accounts for approximately 2%-4% of breast cancer cases. Although its incidence is rare, 7% of breast cancer caused mortality is attributed to inflammatory breast cancer. Cases of inflammatory breast cancer tend to be diagnosed at a younger age compared with noninflammatory breast cancer cases. Risk factors include African-American race and obesity.
The symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer can vary broadly, ranging from subtle skin erythema to diffuse breast involvement with skin dimpling and nipple inversion. Diagnostic criteria include erythema occupying at least one third of the breast, edema, peau d'orange, and/or warmth, with or without an underlying mass; rapid onset (< 3 months); and pathologic confirmation of invasive breast carcinoma. Histologic findings include florid tumor emboli that obstruct dermal lymphatics, which results in swelling and inflammation of the affected breast.
Inflammatory breast cancer has been associated with a poor prognosis. However, treatment advances are helping to improve outcomes. Currently, 5-year survival rates are reported to be 40%-70%, with a median survival of 2-4 years. According to 2023 guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), the first-line treatment of inflammatory breast cancer involves neoadjuvant chemotherapy, modified radical mastectomy, and adjuvant radiation to the chest wall and regional nodes. Endocrine treatment should also be given to patients who are ER-positive and/or PR-positive (sequential chemotherapy followed by endocrine therapy). For patients who are HER2-positive, up to 1 year of HER2-targeted therapy should be given. HER2-targeted therapies can be administered concurrently with radiation and with endocrine therapy if indicated.
Delayed reconstruction after mastectomy remains the clinical standard for inflammatory breast cancer. This is because the need to resect involved skin negates the benefit of skin-sparing mastectomy for immediate reconstruction. Moreover, high rates of local and distant recurrence warrant comprehensive regional node irradiation in a timely fashion, which may be more challenging or subject to delay after immediate reconstruction. Rarely, the extent of skin excision at the time of mastectomy prohibits primary or local closure. In such cases, reconstruction of the chest wall defect with autologous tissue is required, and concomitant immediate reconstruction may be undertaken.
Detailed guidance on the treatment of inflammatory breast cancer, in the first line and beyond, are available from the NCCN.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, Assistant Member, Department of Breast Oncology, Moffitt Cancer Center, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 51-year-old nonsmoking Black woman presents with a lump in her left breast, as well as associated skin changes and pain of approximately 3 months' duration. The patient last underwent routine screening breast imaging 2 years earlier. The patient is 5 ft 7 in and weighs 200 lb (BMI 31.3). Previous medical history is unremarkable. There is a family history of breast cancer (maternal aunt) and lung cancer (maternal uncle). Physical examination reveals a palpable abnormality in the left breast with edema, skin thickening, and peau d'orange. More than one third of the breast is erythematous. A bilateral mammography reveals an irregular mass and calcifications in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast as well as numerous additional masses and focal asymmetries involving the upper outer and lower outer quadrant of the left breast that extend into the inner left breast. A 1.6-cm mass in the upper left breast is noted, with total abnormality spanning 12.7 cm. Left axillary lymphadenopathy is also observed. Skin punch biopsy of the affected breast reveals dermal lymphatic invasion by tumor cells and tumor emboli. Left axial fine-needle aspiration biopsy reveals malignant cells.
Internet use a modifiable dementia risk factor in older adults?
Investigators followed more than 18,000 older individuals and found that regular Internet use was associated with about a 50% reduction in dementia risk, compared with their counterparts who did not use the Internet regularly.
They also found that longer duration of regular Internet use was associated with a reduced risk of dementia, although excessive daily Internet usage appeared to adversely affect dementia risk.
“Online engagement can develop and maintain cognitive reserve – resiliency against physiological damage to the brain – and increased cognitive reserve can, in turn, compensate for brain aging and reduce the risk of dementia,” study investigator Gawon Cho, a doctoral candidate at New York University School of Global Public Health, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
Unexamined benefits
Prior research has shown that older adult Internet users have “better overall cognitive performance, verbal reasoning, and memory,” compared with nonusers, the authors note.
However, because this body of research consists of cross-sectional analyses and longitudinal studies with brief follow-up periods, the long-term cognitive benefits of Internet usage remain “unexamined.”
In addition, despite “extensive evidence of a disproportionately high burden of dementia in people of color, individuals without higher education, and adults who experienced other socioeconomic hardships, little is known about whether the Internet has exacerbated population-level disparities in cognitive health,” the investigators add.
Another question concerns whether excessive Internet usage may actually be detrimental to neurocognitive outcomes. However, “existing evidence on the adverse effects of Internet usage is concentrated in younger populations whose brains are still undergoing maturation.”
Ms. Cho said the motivation for the study was the lack of longitudinal studies on this topic, especially those with sufficient follow-up periods. In addition, she said, there is insufficient evidence about how changes in Internet usage in older age are associated with prospective dementia risk.
For the study, investigators turned to participants in the Health and Retirement Study, an ongoing longitudinal survey of a nationally representative sample of U.S.-based older adults (aged ≥ 50 years).
All participants (n = 18,154; 47.36% male; median age, 55.17 years) were dementia-free, community-dwelling older adults who completed a 2002 baseline cognitive assessment and were asked about Internet usage every 2 years thereafter.
Participants were followed from 2002 to 2018 for a maximum of 17.1 years (median, 7.9 years), which is the longest follow-up period to date. Of the total sample, 64.76% were regular Internet users.
The study’s primary outcome was incident dementia, based on performance on the Modified Telephone Interview for Cognitive Status (TICS-M), which was administered every 2 years.
The exposure examined in the study was cumulative Internet usage in late adulthood, defined as “the number of biennial waves where participants used the Internet regularly during the first three waves.”
In addition, participants were asked how many hours they spent using the Internet during the past week for activities other than viewing television shows or movies.
The researchers also investigated whether the link between Internet usage and dementia risk varied by educational attainment, race-ethnicity, sex, and generational cohort.
Covariates included baseline TICS-M score, health, age, household income, marital status, and region of residence.
U-shaped curve
More than half of the sample (52.96%) showed no changes in Internet use from baseline during the study period, while one-fifth (20.54%) did show changes in use.
Investigators found a robust link between Internet usage and lower dementia risk (cause-specific hazard ratio, 0.57 [95% CI, 0.46-0.71]) – a finding that remained even after adjusting for self-selection into baseline usage (csHR, 0.54 [0.41-0.72]) and signs of cognitive decline at baseline (csHR, 0.62 [0.46-0.85]).
Each additional wave of regular Internet usage was associated with a 21% decrease in the risk of dementia (95% CI, 13%-29%), wherein additional regular periods were associated with reduced dementia risk (csHR, 0.80 [95% CI, 0.68-0.95]).
“The difference in risk between regular and nonregular users did not vary by educational attainment, race-ethnicity, sex, and generation,” the investigators note.
A U-shaped association was found between daily hours of online engagement, wherein the lowest risk was observed in those with 0.1-2 hours of usage (compared with 0 hours of usage). The risk increased in a “monotonic fashion” after 2 hours, with 6.1-8 hours of usage showing the highest risk.
This finding was not considered statistically significant, but the “consistent U-shaped trend offers a preliminary suggestion that excessive online engagement may have adverse cognitive effects on older adults,” the investigators note.
“Among older adults, regular Internet users may experience a lower risk of dementia compared to nonregular users, and longer periods of regular Internet usage in late adulthood may help reduce the risks of subsequent dementia incidence,” said Ms. Cho. “Nonetheless, using the Internet excessively daily may negatively affect the risk of dementia in older adults.”
Bidirectional relationship?
Commenting for this article, Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association senior director of scientific programs and outreach, noted that some risk factors for Alzheimer’s or other dementias can’t be changed, while others are modifiable, “either at a personal or a population level.”
She called the current research “important” because it “identifies a potentially modifiable factor that may influence dementia risk.”
However, cautioned Dr. Sexton, who was not involved with the study, the findings cannot establish cause and effect. In fact, the relationship may be bidirectional.
“It may be that regular Internet usage is associated with increased cognitive stimulation, and in turn reduced risk of dementia; or it may be that individuals with lower risk of dementia are more likely to engage in regular Internet usage,” she said. Thus, “interventional studies are able to shed more light on causation.”
The Health and Retirement Study is sponsored by the National Institute on Aging and is conducted by the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Ms. Cho, her coauthors, and Dr. Sexton have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators followed more than 18,000 older individuals and found that regular Internet use was associated with about a 50% reduction in dementia risk, compared with their counterparts who did not use the Internet regularly.
They also found that longer duration of regular Internet use was associated with a reduced risk of dementia, although excessive daily Internet usage appeared to adversely affect dementia risk.
“Online engagement can develop and maintain cognitive reserve – resiliency against physiological damage to the brain – and increased cognitive reserve can, in turn, compensate for brain aging and reduce the risk of dementia,” study investigator Gawon Cho, a doctoral candidate at New York University School of Global Public Health, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
Unexamined benefits
Prior research has shown that older adult Internet users have “better overall cognitive performance, verbal reasoning, and memory,” compared with nonusers, the authors note.
However, because this body of research consists of cross-sectional analyses and longitudinal studies with brief follow-up periods, the long-term cognitive benefits of Internet usage remain “unexamined.”
In addition, despite “extensive evidence of a disproportionately high burden of dementia in people of color, individuals without higher education, and adults who experienced other socioeconomic hardships, little is known about whether the Internet has exacerbated population-level disparities in cognitive health,” the investigators add.
Another question concerns whether excessive Internet usage may actually be detrimental to neurocognitive outcomes. However, “existing evidence on the adverse effects of Internet usage is concentrated in younger populations whose brains are still undergoing maturation.”
Ms. Cho said the motivation for the study was the lack of longitudinal studies on this topic, especially those with sufficient follow-up periods. In addition, she said, there is insufficient evidence about how changes in Internet usage in older age are associated with prospective dementia risk.
For the study, investigators turned to participants in the Health and Retirement Study, an ongoing longitudinal survey of a nationally representative sample of U.S.-based older adults (aged ≥ 50 years).
All participants (n = 18,154; 47.36% male; median age, 55.17 years) were dementia-free, community-dwelling older adults who completed a 2002 baseline cognitive assessment and were asked about Internet usage every 2 years thereafter.
Participants were followed from 2002 to 2018 for a maximum of 17.1 years (median, 7.9 years), which is the longest follow-up period to date. Of the total sample, 64.76% were regular Internet users.
The study’s primary outcome was incident dementia, based on performance on the Modified Telephone Interview for Cognitive Status (TICS-M), which was administered every 2 years.
The exposure examined in the study was cumulative Internet usage in late adulthood, defined as “the number of biennial waves where participants used the Internet regularly during the first three waves.”
In addition, participants were asked how many hours they spent using the Internet during the past week for activities other than viewing television shows or movies.
The researchers also investigated whether the link between Internet usage and dementia risk varied by educational attainment, race-ethnicity, sex, and generational cohort.
Covariates included baseline TICS-M score, health, age, household income, marital status, and region of residence.
U-shaped curve
More than half of the sample (52.96%) showed no changes in Internet use from baseline during the study period, while one-fifth (20.54%) did show changes in use.
Investigators found a robust link between Internet usage and lower dementia risk (cause-specific hazard ratio, 0.57 [95% CI, 0.46-0.71]) – a finding that remained even after adjusting for self-selection into baseline usage (csHR, 0.54 [0.41-0.72]) and signs of cognitive decline at baseline (csHR, 0.62 [0.46-0.85]).
Each additional wave of regular Internet usage was associated with a 21% decrease in the risk of dementia (95% CI, 13%-29%), wherein additional regular periods were associated with reduced dementia risk (csHR, 0.80 [95% CI, 0.68-0.95]).
“The difference in risk between regular and nonregular users did not vary by educational attainment, race-ethnicity, sex, and generation,” the investigators note.
A U-shaped association was found between daily hours of online engagement, wherein the lowest risk was observed in those with 0.1-2 hours of usage (compared with 0 hours of usage). The risk increased in a “monotonic fashion” after 2 hours, with 6.1-8 hours of usage showing the highest risk.
This finding was not considered statistically significant, but the “consistent U-shaped trend offers a preliminary suggestion that excessive online engagement may have adverse cognitive effects on older adults,” the investigators note.
“Among older adults, regular Internet users may experience a lower risk of dementia compared to nonregular users, and longer periods of regular Internet usage in late adulthood may help reduce the risks of subsequent dementia incidence,” said Ms. Cho. “Nonetheless, using the Internet excessively daily may negatively affect the risk of dementia in older adults.”
Bidirectional relationship?
Commenting for this article, Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association senior director of scientific programs and outreach, noted that some risk factors for Alzheimer’s or other dementias can’t be changed, while others are modifiable, “either at a personal or a population level.”
She called the current research “important” because it “identifies a potentially modifiable factor that may influence dementia risk.”
However, cautioned Dr. Sexton, who was not involved with the study, the findings cannot establish cause and effect. In fact, the relationship may be bidirectional.
“It may be that regular Internet usage is associated with increased cognitive stimulation, and in turn reduced risk of dementia; or it may be that individuals with lower risk of dementia are more likely to engage in regular Internet usage,” she said. Thus, “interventional studies are able to shed more light on causation.”
The Health and Retirement Study is sponsored by the National Institute on Aging and is conducted by the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Ms. Cho, her coauthors, and Dr. Sexton have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators followed more than 18,000 older individuals and found that regular Internet use was associated with about a 50% reduction in dementia risk, compared with their counterparts who did not use the Internet regularly.
They also found that longer duration of regular Internet use was associated with a reduced risk of dementia, although excessive daily Internet usage appeared to adversely affect dementia risk.
“Online engagement can develop and maintain cognitive reserve – resiliency against physiological damage to the brain – and increased cognitive reserve can, in turn, compensate for brain aging and reduce the risk of dementia,” study investigator Gawon Cho, a doctoral candidate at New York University School of Global Public Health, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
Unexamined benefits
Prior research has shown that older adult Internet users have “better overall cognitive performance, verbal reasoning, and memory,” compared with nonusers, the authors note.
However, because this body of research consists of cross-sectional analyses and longitudinal studies with brief follow-up periods, the long-term cognitive benefits of Internet usage remain “unexamined.”
In addition, despite “extensive evidence of a disproportionately high burden of dementia in people of color, individuals without higher education, and adults who experienced other socioeconomic hardships, little is known about whether the Internet has exacerbated population-level disparities in cognitive health,” the investigators add.
Another question concerns whether excessive Internet usage may actually be detrimental to neurocognitive outcomes. However, “existing evidence on the adverse effects of Internet usage is concentrated in younger populations whose brains are still undergoing maturation.”
Ms. Cho said the motivation for the study was the lack of longitudinal studies on this topic, especially those with sufficient follow-up periods. In addition, she said, there is insufficient evidence about how changes in Internet usage in older age are associated with prospective dementia risk.
For the study, investigators turned to participants in the Health and Retirement Study, an ongoing longitudinal survey of a nationally representative sample of U.S.-based older adults (aged ≥ 50 years).
All participants (n = 18,154; 47.36% male; median age, 55.17 years) were dementia-free, community-dwelling older adults who completed a 2002 baseline cognitive assessment and were asked about Internet usage every 2 years thereafter.
Participants were followed from 2002 to 2018 for a maximum of 17.1 years (median, 7.9 years), which is the longest follow-up period to date. Of the total sample, 64.76% were regular Internet users.
The study’s primary outcome was incident dementia, based on performance on the Modified Telephone Interview for Cognitive Status (TICS-M), which was administered every 2 years.
The exposure examined in the study was cumulative Internet usage in late adulthood, defined as “the number of biennial waves where participants used the Internet regularly during the first three waves.”
In addition, participants were asked how many hours they spent using the Internet during the past week for activities other than viewing television shows or movies.
The researchers also investigated whether the link between Internet usage and dementia risk varied by educational attainment, race-ethnicity, sex, and generational cohort.
Covariates included baseline TICS-M score, health, age, household income, marital status, and region of residence.
U-shaped curve
More than half of the sample (52.96%) showed no changes in Internet use from baseline during the study period, while one-fifth (20.54%) did show changes in use.
Investigators found a robust link between Internet usage and lower dementia risk (cause-specific hazard ratio, 0.57 [95% CI, 0.46-0.71]) – a finding that remained even after adjusting for self-selection into baseline usage (csHR, 0.54 [0.41-0.72]) and signs of cognitive decline at baseline (csHR, 0.62 [0.46-0.85]).
Each additional wave of regular Internet usage was associated with a 21% decrease in the risk of dementia (95% CI, 13%-29%), wherein additional regular periods were associated with reduced dementia risk (csHR, 0.80 [95% CI, 0.68-0.95]).
“The difference in risk between regular and nonregular users did not vary by educational attainment, race-ethnicity, sex, and generation,” the investigators note.
A U-shaped association was found between daily hours of online engagement, wherein the lowest risk was observed in those with 0.1-2 hours of usage (compared with 0 hours of usage). The risk increased in a “monotonic fashion” after 2 hours, with 6.1-8 hours of usage showing the highest risk.
This finding was not considered statistically significant, but the “consistent U-shaped trend offers a preliminary suggestion that excessive online engagement may have adverse cognitive effects on older adults,” the investigators note.
“Among older adults, regular Internet users may experience a lower risk of dementia compared to nonregular users, and longer periods of regular Internet usage in late adulthood may help reduce the risks of subsequent dementia incidence,” said Ms. Cho. “Nonetheless, using the Internet excessively daily may negatively affect the risk of dementia in older adults.”
Bidirectional relationship?
Commenting for this article, Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association senior director of scientific programs and outreach, noted that some risk factors for Alzheimer’s or other dementias can’t be changed, while others are modifiable, “either at a personal or a population level.”
She called the current research “important” because it “identifies a potentially modifiable factor that may influence dementia risk.”
However, cautioned Dr. Sexton, who was not involved with the study, the findings cannot establish cause and effect. In fact, the relationship may be bidirectional.
“It may be that regular Internet usage is associated with increased cognitive stimulation, and in turn reduced risk of dementia; or it may be that individuals with lower risk of dementia are more likely to engage in regular Internet usage,” she said. Thus, “interventional studies are able to shed more light on causation.”
The Health and Retirement Study is sponsored by the National Institute on Aging and is conducted by the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Ms. Cho, her coauthors, and Dr. Sexton have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN GERIATRICS SOCIETY
Guidelines for children with obesity: Family and treatment are key
Douglas Lunsford’s son Samuel has struggled with obesity all his life.
Just before turning 14, Samuel, now 25, took part in a program at Ohio-based Nationwide Children’s Hospital’s Center for Healthy Weight and Nutrition. The program consisted of twice-weekly meetings with a nutritionist, including lessons in food portion size, what food does within the body, what foods can be used to supplement other foods, and similar topics, as well as physical exercise.
Although the program was designed for youngsters with weight problems, Mr. Lunsford also took part.
“They would exercise us and work us out,” he said.
Father and son did the program together for 2 years. Since then, Mr. Lunsford has advocated for youngsters with obesity.
“Samuel’s struggle spurred us into action,” he said.
Eventually, Mr. Lunsford helped create the American Academy of Pediatrics’ recently released Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Treatment of Children and Adolescents With Obesity.
Helping create change
According to Sandra Hassink, MD, coauthor of the guideline and vice chair of the Clinical Practice Guideline Subcommittee on Obesity, the goal was to “help patients make changes in lifestyle, behaviors, or environment in a sustainable way and also to involve families in decision-making at every step of the way.”
Ideally, a child would receive intense behavioral and lifestyle treatment, although this approach isn’t always available and might be challenging to deliver. The most effective treatments include at least 26 hours of face-to-face, family-based treatments, consisting of many different components and lasting 3-12 months.
The guideline suggests that doctors offer adolescents 12 and older medication to assist in weight loss, along with health, behavior, and lifestyle treatment, and that teens who have severe obesity should consider metabolic and bariatric surgery as they continue intense health behavior and lifestyle treatment.
“We’re living at a time where we’ve watched obesity affect our children and adult population for 4 decades and, along with the risk of obesity, we’ve watched a rise in obesity; we’re seeing increases in illness that go along with obesity, such as type 2 diabetes, lipid diseases like high cholesterol, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,” Dr. Hassink said.
She explained that, as people gain weight, the cells in adipose (fatty) tissues start to malfunction and produce inflammatory chemicals that cause these illnesses.
“So having extra adipose tissue is a risk,” she said. “As pediatricians, we measure body mass index [BMI] – which is calculated based on height and weight – as a way of seeing whether the child could be at risk for developing these dysfunctioning cells. If so, we screen them for prediabetes, lipid disease, or liver disease and other obesity-related comorbidities.”
In addition, “we’re concerned about the mental health of children with obesity because of the weight bias in our culture,” said Dr. Hassink. “A child gets stigmatized, and this takes the form of bullying and teasing, and leads to low self-esteem, depression, and anxiety. So we know we have a host of physical problems we need to look out for, as well as the emotional and psychological effects of how our culture views things.”
Are parents ready for the new approach?
A new report from Harmony Healthcare IT, a data management firm that works with health data, looked at how parents regard their children’s obesity. The company surveyed more than 1,000 parents and found that one-tenth of respondents had children who were overweight or obese and over a quarter (26%) worried about their child’s weight.
Nearly 40% of parents would consider weight loss medication for their child if the child became obese at age 12, and about 16% would consider weight loss surgery. But most parents would not consider this surgery until their child was an average age of 15 rather than the AAP’s recommended age of 13.
Mr. Lunsford said that his son considered surgery and medication but was “never comfortable” with these approaches.
This isn’t unusual, Dr. Hassink said. “Not every parent will think the same way, and their view will be based on their experience and what’s going on with their child.”
The guideline wasn’t designed to encourage every child to try medication or have surgery, she said.
“But parents now know that there are potentially helpful choices here that we didn’t have years ago, and those can be discussed with the child’s pediatrician.”
Challenges to keeping healthy
It’s tough to stay healthy and not develop obesity in our modern environment, Dr. Hassink said.
“There’s a lot of processed food, a lot of sugar in our foods, a lot of sedentary behavior, and a decrease in physical activity. In many communities, it’s hard for people to get healthy foods.”
Mr. Lunsford said that when his son was in his late teens and would go out with friends, they typically went to fast-food restaurants.
“Sam would say ‘yes’ to these foods, although he knew they weren’t good for him, because he wanted to be like everyone else,” he said.
But parents now know that there are potentially helpful choices here that we didn’t have years ago, and those can be discussed with the child’s pediatrician, he said.
Harmony Health IT’s survey found that many parents say it is a struggle to get kids to eat healthy foods and get enough sleep. Although almost all respondents (83%) said they try to prepare healthy, home-cooked meals, 39% eat fast food at least once a week, mostly because parents are too tired to cook.
Dr. Hassink said the COVID-19 pandemic also played a role.
“We knew that COVID would be hard for kids with obesity, and there might be weight gain because of the extra sedentary time and fewer sporting activities, and there was a high cost of food to families who are already economically strapped,” she said.
In general, family support is essential, Dr. Hassink said. “Obesity treatment requires that the family be involved. The family is living in the same nutritional and activity environment as their child. Everyone has to be on board.”
Talking to kids about food and weight
The survey found that many parents struggle to talk about food and weight with their children. The AAP guideline notes that involving a health care professional can help.
“If a parent or caregiver is concerned about a child’s weight, he or she can take the child to their pediatrician,” Dr. Hassink said. “The first thing the pediatrician will do is ask about the child’s overall health, review the family history – because obesity tends to run in families – and see if other conditions, like diabetes, also run in the family.”
The pediatrician will do a physical examination that includes BMI and, if it’s high, other tests looking at blood sugar, lipids, and liver function may be performed.
Ideally, the child will be prescribed intense lifestyle and behavioral treatment that will take the child’s and family’s nutrition into account, as well as physical activity and the amount of sleep the child is getting, which is sometimes tied to weight gain. If the child has disordered eating, such as binge eating disorder, they can be evaluated and treated for that.
Each child is seen as an individual with a particular set of needs. “One size doesn’t fit all,” Dr. Hassink said.
Providing emotional support for children with obesity
Pediatricians can assess the child’s mental, emotional, and social well-being. “Children who are bullied or teased may need help working through that. Children experiencing depression may need treatment,” Dr. Hassink said.
Mr. Lunsford said Samuel was fortunate in that he rarely got taunted.
“Part of the reason is that, although weight was an issue, he never allowed his weight to define him,” he said. “He was always an extroverted kind of kid, athletic, very outgoing and friendly, and being overweight was never part of his identity.”
Mr. Lunsford encourages parents whose children are teased or bullied to create a “no-judgment” zone at home.
“Let your kids know that their parents love them for who they are,” he said. “Emphasize that weight is a ‘number’ and health is a ‘lifestyle.’ Try to highlight the good things in their lives and encourage them to be as active as they can in the things that interest them.”
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
Douglas Lunsford’s son Samuel has struggled with obesity all his life.
Just before turning 14, Samuel, now 25, took part in a program at Ohio-based Nationwide Children’s Hospital’s Center for Healthy Weight and Nutrition. The program consisted of twice-weekly meetings with a nutritionist, including lessons in food portion size, what food does within the body, what foods can be used to supplement other foods, and similar topics, as well as physical exercise.
Although the program was designed for youngsters with weight problems, Mr. Lunsford also took part.
“They would exercise us and work us out,” he said.
Father and son did the program together for 2 years. Since then, Mr. Lunsford has advocated for youngsters with obesity.
“Samuel’s struggle spurred us into action,” he said.
Eventually, Mr. Lunsford helped create the American Academy of Pediatrics’ recently released Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Treatment of Children and Adolescents With Obesity.
Helping create change
According to Sandra Hassink, MD, coauthor of the guideline and vice chair of the Clinical Practice Guideline Subcommittee on Obesity, the goal was to “help patients make changes in lifestyle, behaviors, or environment in a sustainable way and also to involve families in decision-making at every step of the way.”
Ideally, a child would receive intense behavioral and lifestyle treatment, although this approach isn’t always available and might be challenging to deliver. The most effective treatments include at least 26 hours of face-to-face, family-based treatments, consisting of many different components and lasting 3-12 months.
The guideline suggests that doctors offer adolescents 12 and older medication to assist in weight loss, along with health, behavior, and lifestyle treatment, and that teens who have severe obesity should consider metabolic and bariatric surgery as they continue intense health behavior and lifestyle treatment.
“We’re living at a time where we’ve watched obesity affect our children and adult population for 4 decades and, along with the risk of obesity, we’ve watched a rise in obesity; we’re seeing increases in illness that go along with obesity, such as type 2 diabetes, lipid diseases like high cholesterol, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,” Dr. Hassink said.
She explained that, as people gain weight, the cells in adipose (fatty) tissues start to malfunction and produce inflammatory chemicals that cause these illnesses.
“So having extra adipose tissue is a risk,” she said. “As pediatricians, we measure body mass index [BMI] – which is calculated based on height and weight – as a way of seeing whether the child could be at risk for developing these dysfunctioning cells. If so, we screen them for prediabetes, lipid disease, or liver disease and other obesity-related comorbidities.”
In addition, “we’re concerned about the mental health of children with obesity because of the weight bias in our culture,” said Dr. Hassink. “A child gets stigmatized, and this takes the form of bullying and teasing, and leads to low self-esteem, depression, and anxiety. So we know we have a host of physical problems we need to look out for, as well as the emotional and psychological effects of how our culture views things.”
Are parents ready for the new approach?
A new report from Harmony Healthcare IT, a data management firm that works with health data, looked at how parents regard their children’s obesity. The company surveyed more than 1,000 parents and found that one-tenth of respondents had children who were overweight or obese and over a quarter (26%) worried about their child’s weight.
Nearly 40% of parents would consider weight loss medication for their child if the child became obese at age 12, and about 16% would consider weight loss surgery. But most parents would not consider this surgery until their child was an average age of 15 rather than the AAP’s recommended age of 13.
Mr. Lunsford said that his son considered surgery and medication but was “never comfortable” with these approaches.
This isn’t unusual, Dr. Hassink said. “Not every parent will think the same way, and their view will be based on their experience and what’s going on with their child.”
The guideline wasn’t designed to encourage every child to try medication or have surgery, she said.
“But parents now know that there are potentially helpful choices here that we didn’t have years ago, and those can be discussed with the child’s pediatrician.”
Challenges to keeping healthy
It’s tough to stay healthy and not develop obesity in our modern environment, Dr. Hassink said.
“There’s a lot of processed food, a lot of sugar in our foods, a lot of sedentary behavior, and a decrease in physical activity. In many communities, it’s hard for people to get healthy foods.”
Mr. Lunsford said that when his son was in his late teens and would go out with friends, they typically went to fast-food restaurants.
“Sam would say ‘yes’ to these foods, although he knew they weren’t good for him, because he wanted to be like everyone else,” he said.
But parents now know that there are potentially helpful choices here that we didn’t have years ago, and those can be discussed with the child’s pediatrician, he said.
Harmony Health IT’s survey found that many parents say it is a struggle to get kids to eat healthy foods and get enough sleep. Although almost all respondents (83%) said they try to prepare healthy, home-cooked meals, 39% eat fast food at least once a week, mostly because parents are too tired to cook.
Dr. Hassink said the COVID-19 pandemic also played a role.
“We knew that COVID would be hard for kids with obesity, and there might be weight gain because of the extra sedentary time and fewer sporting activities, and there was a high cost of food to families who are already economically strapped,” she said.
In general, family support is essential, Dr. Hassink said. “Obesity treatment requires that the family be involved. The family is living in the same nutritional and activity environment as their child. Everyone has to be on board.”
Talking to kids about food and weight
The survey found that many parents struggle to talk about food and weight with their children. The AAP guideline notes that involving a health care professional can help.
“If a parent or caregiver is concerned about a child’s weight, he or she can take the child to their pediatrician,” Dr. Hassink said. “The first thing the pediatrician will do is ask about the child’s overall health, review the family history – because obesity tends to run in families – and see if other conditions, like diabetes, also run in the family.”
The pediatrician will do a physical examination that includes BMI and, if it’s high, other tests looking at blood sugar, lipids, and liver function may be performed.
Ideally, the child will be prescribed intense lifestyle and behavioral treatment that will take the child’s and family’s nutrition into account, as well as physical activity and the amount of sleep the child is getting, which is sometimes tied to weight gain. If the child has disordered eating, such as binge eating disorder, they can be evaluated and treated for that.
Each child is seen as an individual with a particular set of needs. “One size doesn’t fit all,” Dr. Hassink said.
Providing emotional support for children with obesity
Pediatricians can assess the child’s mental, emotional, and social well-being. “Children who are bullied or teased may need help working through that. Children experiencing depression may need treatment,” Dr. Hassink said.
Mr. Lunsford said Samuel was fortunate in that he rarely got taunted.
“Part of the reason is that, although weight was an issue, he never allowed his weight to define him,” he said. “He was always an extroverted kind of kid, athletic, very outgoing and friendly, and being overweight was never part of his identity.”
Mr. Lunsford encourages parents whose children are teased or bullied to create a “no-judgment” zone at home.
“Let your kids know that their parents love them for who they are,” he said. “Emphasize that weight is a ‘number’ and health is a ‘lifestyle.’ Try to highlight the good things in their lives and encourage them to be as active as they can in the things that interest them.”
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
Douglas Lunsford’s son Samuel has struggled with obesity all his life.
Just before turning 14, Samuel, now 25, took part in a program at Ohio-based Nationwide Children’s Hospital’s Center for Healthy Weight and Nutrition. The program consisted of twice-weekly meetings with a nutritionist, including lessons in food portion size, what food does within the body, what foods can be used to supplement other foods, and similar topics, as well as physical exercise.
Although the program was designed for youngsters with weight problems, Mr. Lunsford also took part.
“They would exercise us and work us out,” he said.
Father and son did the program together for 2 years. Since then, Mr. Lunsford has advocated for youngsters with obesity.
“Samuel’s struggle spurred us into action,” he said.
Eventually, Mr. Lunsford helped create the American Academy of Pediatrics’ recently released Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Treatment of Children and Adolescents With Obesity.
Helping create change
According to Sandra Hassink, MD, coauthor of the guideline and vice chair of the Clinical Practice Guideline Subcommittee on Obesity, the goal was to “help patients make changes in lifestyle, behaviors, or environment in a sustainable way and also to involve families in decision-making at every step of the way.”
Ideally, a child would receive intense behavioral and lifestyle treatment, although this approach isn’t always available and might be challenging to deliver. The most effective treatments include at least 26 hours of face-to-face, family-based treatments, consisting of many different components and lasting 3-12 months.
The guideline suggests that doctors offer adolescents 12 and older medication to assist in weight loss, along with health, behavior, and lifestyle treatment, and that teens who have severe obesity should consider metabolic and bariatric surgery as they continue intense health behavior and lifestyle treatment.
“We’re living at a time where we’ve watched obesity affect our children and adult population for 4 decades and, along with the risk of obesity, we’ve watched a rise in obesity; we’re seeing increases in illness that go along with obesity, such as type 2 diabetes, lipid diseases like high cholesterol, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,” Dr. Hassink said.
She explained that, as people gain weight, the cells in adipose (fatty) tissues start to malfunction and produce inflammatory chemicals that cause these illnesses.
“So having extra adipose tissue is a risk,” she said. “As pediatricians, we measure body mass index [BMI] – which is calculated based on height and weight – as a way of seeing whether the child could be at risk for developing these dysfunctioning cells. If so, we screen them for prediabetes, lipid disease, or liver disease and other obesity-related comorbidities.”
In addition, “we’re concerned about the mental health of children with obesity because of the weight bias in our culture,” said Dr. Hassink. “A child gets stigmatized, and this takes the form of bullying and teasing, and leads to low self-esteem, depression, and anxiety. So we know we have a host of physical problems we need to look out for, as well as the emotional and psychological effects of how our culture views things.”
Are parents ready for the new approach?
A new report from Harmony Healthcare IT, a data management firm that works with health data, looked at how parents regard their children’s obesity. The company surveyed more than 1,000 parents and found that one-tenth of respondents had children who were overweight or obese and over a quarter (26%) worried about their child’s weight.
Nearly 40% of parents would consider weight loss medication for their child if the child became obese at age 12, and about 16% would consider weight loss surgery. But most parents would not consider this surgery until their child was an average age of 15 rather than the AAP’s recommended age of 13.
Mr. Lunsford said that his son considered surgery and medication but was “never comfortable” with these approaches.
This isn’t unusual, Dr. Hassink said. “Not every parent will think the same way, and their view will be based on their experience and what’s going on with their child.”
The guideline wasn’t designed to encourage every child to try medication or have surgery, she said.
“But parents now know that there are potentially helpful choices here that we didn’t have years ago, and those can be discussed with the child’s pediatrician.”
Challenges to keeping healthy
It’s tough to stay healthy and not develop obesity in our modern environment, Dr. Hassink said.
“There’s a lot of processed food, a lot of sugar in our foods, a lot of sedentary behavior, and a decrease in physical activity. In many communities, it’s hard for people to get healthy foods.”
Mr. Lunsford said that when his son was in his late teens and would go out with friends, they typically went to fast-food restaurants.
“Sam would say ‘yes’ to these foods, although he knew they weren’t good for him, because he wanted to be like everyone else,” he said.
But parents now know that there are potentially helpful choices here that we didn’t have years ago, and those can be discussed with the child’s pediatrician, he said.
Harmony Health IT’s survey found that many parents say it is a struggle to get kids to eat healthy foods and get enough sleep. Although almost all respondents (83%) said they try to prepare healthy, home-cooked meals, 39% eat fast food at least once a week, mostly because parents are too tired to cook.
Dr. Hassink said the COVID-19 pandemic also played a role.
“We knew that COVID would be hard for kids with obesity, and there might be weight gain because of the extra sedentary time and fewer sporting activities, and there was a high cost of food to families who are already economically strapped,” she said.
In general, family support is essential, Dr. Hassink said. “Obesity treatment requires that the family be involved. The family is living in the same nutritional and activity environment as their child. Everyone has to be on board.”
Talking to kids about food and weight
The survey found that many parents struggle to talk about food and weight with their children. The AAP guideline notes that involving a health care professional can help.
“If a parent or caregiver is concerned about a child’s weight, he or she can take the child to their pediatrician,” Dr. Hassink said. “The first thing the pediatrician will do is ask about the child’s overall health, review the family history – because obesity tends to run in families – and see if other conditions, like diabetes, also run in the family.”
The pediatrician will do a physical examination that includes BMI and, if it’s high, other tests looking at blood sugar, lipids, and liver function may be performed.
Ideally, the child will be prescribed intense lifestyle and behavioral treatment that will take the child’s and family’s nutrition into account, as well as physical activity and the amount of sleep the child is getting, which is sometimes tied to weight gain. If the child has disordered eating, such as binge eating disorder, they can be evaluated and treated for that.
Each child is seen as an individual with a particular set of needs. “One size doesn’t fit all,” Dr. Hassink said.
Providing emotional support for children with obesity
Pediatricians can assess the child’s mental, emotional, and social well-being. “Children who are bullied or teased may need help working through that. Children experiencing depression may need treatment,” Dr. Hassink said.
Mr. Lunsford said Samuel was fortunate in that he rarely got taunted.
“Part of the reason is that, although weight was an issue, he never allowed his weight to define him,” he said. “He was always an extroverted kind of kid, athletic, very outgoing and friendly, and being overweight was never part of his identity.”
Mr. Lunsford encourages parents whose children are teased or bullied to create a “no-judgment” zone at home.
“Let your kids know that their parents love them for who they are,” he said. “Emphasize that weight is a ‘number’ and health is a ‘lifestyle.’ Try to highlight the good things in their lives and encourage them to be as active as they can in the things that interest them.”
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
What to expect in the new concussion guidelines
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Andrew N. Wilner, MD: I’m your host, Dr. Andrew Wilner, reporting virtually from the 2023 American Academy of Neurology meeting in Boston. It’s my pleasure today to speak with Dr. Shae Datta, codirector of the NYU Langone Concussion Center.
She’s also a clinical assistant professor of neurology at NYU School of Medicine. Dr. Datta is chair of the AAN Sports Neurology Section, and she’s leading a panel on concussion at this year’s meeting. She’s going to give us an update. Welcome, Dr. Datta.
Shae Datta, MD: Thank you so much, Andrew. I really love the fact that I’m here speaking to you about all of the new, exciting developments in the field.
Dr. Wilner: Before we get too deep, tell us how you got interested in this topic.
Dr. Datta: I initially thought, when I was in training as a resident, that I wanted to do something like neurocritical care or EEG. It also puzzled me why these seemingly smaller head injuries that didn’t end up in the hospital or ICU were bounced from neurology headache clinic to neuro-ophthalmology headache clinic to neurovestibular headache clinic, and nobody seemed to be able to put together the dots about why they’re having so many different issues — but at the same time, nobody could help them.
At that time, this field was very new. I was on a plane to Paris to a neurocritical care conference as a resident, and I saw the movie Concussion with Will Smith.
It featured one of my current mentors who taught at the fellowship that I graduated from, and it was a fascinating field. I just started looking deeply into it, and I saw that there was a new training fellowship for sports neurology and concussion management, and this is basically why we’re here today.
New concussion consensus guidelines coming
Dr. Wilner: I think this field has really exploded. It used to be that you banged your head, you did a CT scan – remember, I trained about 45 years ago – and if there was nothing on the CT scan, you were done. If you had headaches, you took Tylenol until they went away.
Now, we do MRI, and we realized that it’s really a syndrome. I understand that there are going to be some formal guidelines that have been put together. Is that correct?
Dr. Datta: That’s correct. The 6th International Consensus Conference on Concussion in Sport, in Amsterdam, where I attended and presented a poster, was really a meeting of all the best minds – clinicians and researchers in brain injury – to form a consensus on the newest guidelines that are going to direct our treatment going forward.
Dr. Wilner: I’m going to ask you a trick question because the last time I looked it up I did not get a satisfying answer. What is a concussion?
Dr. Datta: That’s a very good question, and everyone always asks. A concussion is an external force that is emitted upon the head or the neck, or the body, in general, that may cause temporary loss of function. It’s a functional problem.
We don’t see much on CT. We can do MRI. We can do SPECT or we can do these very fancy images, sometimes, of high-velocity head injuries and see small microhemorrhages.
Often, we don’t see anything, but still the patient is loopy. They can’t see straight. They are double-visioned. They have vertigo. Why is that happening? On the cellular level, we have an energy deficit in the sodium-potassium-ATPase pump of the neurons themselves.
Dr. Wilner: Suppose you do see diffuse axonal injury; does that take it out of concussion, or can you have a concussion with visible injury?
Dr. Datta: I think you can have overlap in the symptoms. The diffuse axonal injury would put it into a higher grade of head injury as opposed to a mild traumatic brain injury. Definitely, we would need to work together with our trauma doctors to ensure that patients are not on blood thinners or anything until they heal well enough. Obviously, I would pick them up as an outpatient and follow them until we resolve or rehab them as best as possible.
Concussion assessment tools
Dr. Wilner: There are many sports out there where concussions are fairly frequent, like American football and hockey, for example. Are there any statements in the new guidelines?
Dr. Datta: There are no statements for or against a particular sport because that would really make too much of a bold statement about cause and effect. There is a cause and effect in long-term, repetitive exposure, I would say, in terms of someone being able to play or sustain injury.
Right now, at least at the concussion conference I went to and in the upcoming consensus statement, they will not comment on a specific sport. Obviously, we know that the higher-impact sports are a little more dangerous.
Let’s be honest. At the high school, middle school, or even younger level, some kids are not necessarily the most athletic, right? They play because their friends are playing. If they’re repeatedly getting injured, it’s time for an astute clinician, or a coach, and a whole team to assess them to see if maybe this person is just going to continue to get hurt if they’re not taken out of the game and perhaps they should go to a lower-impact sport.
Dr. Wilner: In schools, often there’s a big size and weight difference. There are 14-year-olds who are 6 fett 2 inches and 200 pounds, and there are 14-year-olds who are 5 feet 2 inches and 110 pounds. Obviously, they’re mismatched on the football field.
You mentioned coaches. Is there anything in the guidelines about training coaches?
Dr. Datta: Specifically, there was nothing in the guidelines about that. There’s a tool for coaches at every level to use, which is called the Sports Concussion Assessment Tool, or SCAT, which is going to be updated to the SCAT6. At the NCAA level, they must receive annual training on concussion management and be given an NCAA concussion handout for coaches.
Obviously, there are more rigorous protocols for national-level coaching. As it stands now, it is not mandatory, but they are given tools to assess someone once they’ve gotten a hit to take them out of the game.
Dr. Wilner: I’ve been following the concussion research through the years. They did some neuropsychological testing on athletes who’ve had this many concussions or that many concussions, and they would find deficits here or subtle deficits there, but they had no baseline.
Then, there was a movement to start testing athletes before the season starts so that they could do a repeat test after concussion and see if there is any difference. Is that something we’re recommending?
Dr. Datta: Most of the time, NCAA-level – certainly where I trained – and national-level sports do testing, but it’s not everywhere. Prior guidelines have indicated that preseason testing is not required. That is largely because there has been no standardized neuropsychological testing established.
There are computerized testing options where the validity and reliability are questionable. Also, let’s say it’s a college student; they didn’t sleep all night and then they took this computer test. They would probably do worse than they would if they had received a head hit.
Just to be on the safe side, most places that have collegiate-level sports that are at a high level do preseason testing. If I were to speak personally, aside from the guidelines, I would say that it’s been helpful for me to look at the before and after, in general, overall, to make a decision about my treatment protocol.
Dr. Wilner: Let’s talk about the patient. You have a 20-year-old guy. He’s playing football. There’s a big play. Bonk, he gets hit on the head. He’s on the ground. He’s dazed, staggers a little bit, gets up, and you ask how he is feeling. He says he’s fine and then he wobbles off to the sideline. What do you do with that kid?
Dr. Datta: Obviously, the first thing is to remove him from the play environment to a quiet space. Second, either an athletic trainer or a coach would administer basic screening neurologic tests, such as “where are you, what’s today’s date, what is your name?” and other orientation questions.
They’ll also go through the SCAT – that’ll be SCAT6 starting in July – the SCAT5 symptom questionnaire to see what symptoms they have. Often, they’re using sideline testing software.
There are two things that can be used on a card to test eye movements, to see if they’re slower. They come out of NYU, coincidentally – the Memory Image Completion (MIC) and the Mobile Universal Lexicon Evaluation System (MULES) – and are used to determine whether eye movements are slower. That way, you can tell whether someone is, compared with before they got their head hit, slower than before.
Based on this composite information, usually the teammates and the head people on the team will know if a player looks different.
They need to be taken out, obviously, if there is nausea or vomiting, any neurologic signs and symptoms, or a neck injury that needs to be stabilized. ABCs first, right? If there’s any vomiting or seizures, they should be taken to the ER right away.
The first thing is to take them out, then do a sideline assessment. Third, see if they need to immediately go to the ED versus follow-up outpatient with me within a day or two.
Dr. Wilner: I think it’s the subtle injuries that are the tough ones. Back to our 20-year-old. He says: “Oh, I’m fine. I want to go back in the game.” Everybody can tell he’s not quite right, even though he passed all the tests. What do you do then?
Dr. Datta: You have to make a judgment call for the safety of the player. They always want to go back, right? This is also an issue when they’re competing for college scholarships and things of that nature. Sometimes they’re sandbagging, where they memorize the answers.
Everything’s on the Internet nowadays, right? We have to make a judgment call as members of the healthcare community and the sports community to keep that player safe.
Just keep them out. Don’t bring them back in the game. Keep them out for a reasonable amount of time. There’s a test called the Buffalo Concussion Treadmill Test; Dr. John Leddy from University of Buffalo has developed a way for us to put athletes through a screening protocol.
This can be part of their vestibular and ocular rehabilitation, where if they don’t have symptoms when we bring their heart rate to certain levels, then we can slowly clear them for return to play as long as they’re nonsymptomatic.
Dr. Wilner: I spoke with your colleague, Dr. Riggins, who is also on your panel, and we were talking about when they can go back. She said they can go back when they don’t have any symptoms. No more headache, no more dizziness, no more lightheadedness, no more trouble concentrating or with memory – all those things have gone away.
Sometimes these symptoms are stubborn. If you have, say, 100 patients like our 20-year-old who got bonked on the head, has some headaches, and doesn’t feel quite right, what usually happens? How many are back to play the next day, the next week, or the next month? How many are out for the season? How does that play out?
Dr. Datta: It depends on a couple of different factors. One, have they had previous head injuries? Two, do they have preexisting symptoms or signs, or diagnoses like migraines, which are likely to get worse after a head injury? Anything that’s preexisting, like a mood disorder, anxiety, depression, or trouble sleeping, is going to get worse.
If they were compensating for untreated ADD or borderline personality or bipolar, I’ve seen many people who’ve developed them. These are not the norm, but I’m saying that you have to be very careful.
Getting back to the question, you treat them. Reasonably, if they’re healthy and they don’t have preexisting signs and symptoms, I would say more than half are back in about 2 weeks.. I would say 60%-70%. It all depends. If they have preexisting issues, then it’s going to take much longer.
From SCAT to SCOAT
Dr. Wilner: This has been very informative. Before we wrap up, tell us what to expect from these guidelines in July. How are they really going to help?
Dr. Datta: We’ve been using the SCAT, which was meant for more sideline assessment because that’s all we had, and it’s worked perfectly well.
This will be better because we often see them within 24-48 hours, when the symptoms are sometimes a little bit better.
We also will see the sport and concussion group come up with added athlete perspectives, ethics discussion, power-sport athlete considerations, and development of this new SCOAT.
Dr. Wilner: Dr. Datta, this is very exciting. I look forward to reading these guidelines in July. I want to thank you for your hard work. I also look forward to talking to you at next year’s meeting. Thank you very much for giving us this update.
Dr. Datta: No problem. It’s my pleasure.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Andrew N. Wilner, MD: I’m your host, Dr. Andrew Wilner, reporting virtually from the 2023 American Academy of Neurology meeting in Boston. It’s my pleasure today to speak with Dr. Shae Datta, codirector of the NYU Langone Concussion Center.
She’s also a clinical assistant professor of neurology at NYU School of Medicine. Dr. Datta is chair of the AAN Sports Neurology Section, and she’s leading a panel on concussion at this year’s meeting. She’s going to give us an update. Welcome, Dr. Datta.
Shae Datta, MD: Thank you so much, Andrew. I really love the fact that I’m here speaking to you about all of the new, exciting developments in the field.
Dr. Wilner: Before we get too deep, tell us how you got interested in this topic.
Dr. Datta: I initially thought, when I was in training as a resident, that I wanted to do something like neurocritical care or EEG. It also puzzled me why these seemingly smaller head injuries that didn’t end up in the hospital or ICU were bounced from neurology headache clinic to neuro-ophthalmology headache clinic to neurovestibular headache clinic, and nobody seemed to be able to put together the dots about why they’re having so many different issues — but at the same time, nobody could help them.
At that time, this field was very new. I was on a plane to Paris to a neurocritical care conference as a resident, and I saw the movie Concussion with Will Smith.
It featured one of my current mentors who taught at the fellowship that I graduated from, and it was a fascinating field. I just started looking deeply into it, and I saw that there was a new training fellowship for sports neurology and concussion management, and this is basically why we’re here today.
New concussion consensus guidelines coming
Dr. Wilner: I think this field has really exploded. It used to be that you banged your head, you did a CT scan – remember, I trained about 45 years ago – and if there was nothing on the CT scan, you were done. If you had headaches, you took Tylenol until they went away.
Now, we do MRI, and we realized that it’s really a syndrome. I understand that there are going to be some formal guidelines that have been put together. Is that correct?
Dr. Datta: That’s correct. The 6th International Consensus Conference on Concussion in Sport, in Amsterdam, where I attended and presented a poster, was really a meeting of all the best minds – clinicians and researchers in brain injury – to form a consensus on the newest guidelines that are going to direct our treatment going forward.
Dr. Wilner: I’m going to ask you a trick question because the last time I looked it up I did not get a satisfying answer. What is a concussion?
Dr. Datta: That’s a very good question, and everyone always asks. A concussion is an external force that is emitted upon the head or the neck, or the body, in general, that may cause temporary loss of function. It’s a functional problem.
We don’t see much on CT. We can do MRI. We can do SPECT or we can do these very fancy images, sometimes, of high-velocity head injuries and see small microhemorrhages.
Often, we don’t see anything, but still the patient is loopy. They can’t see straight. They are double-visioned. They have vertigo. Why is that happening? On the cellular level, we have an energy deficit in the sodium-potassium-ATPase pump of the neurons themselves.
Dr. Wilner: Suppose you do see diffuse axonal injury; does that take it out of concussion, or can you have a concussion with visible injury?
Dr. Datta: I think you can have overlap in the symptoms. The diffuse axonal injury would put it into a higher grade of head injury as opposed to a mild traumatic brain injury. Definitely, we would need to work together with our trauma doctors to ensure that patients are not on blood thinners or anything until they heal well enough. Obviously, I would pick them up as an outpatient and follow them until we resolve or rehab them as best as possible.
Concussion assessment tools
Dr. Wilner: There are many sports out there where concussions are fairly frequent, like American football and hockey, for example. Are there any statements in the new guidelines?
Dr. Datta: There are no statements for or against a particular sport because that would really make too much of a bold statement about cause and effect. There is a cause and effect in long-term, repetitive exposure, I would say, in terms of someone being able to play or sustain injury.
Right now, at least at the concussion conference I went to and in the upcoming consensus statement, they will not comment on a specific sport. Obviously, we know that the higher-impact sports are a little more dangerous.
Let’s be honest. At the high school, middle school, or even younger level, some kids are not necessarily the most athletic, right? They play because their friends are playing. If they’re repeatedly getting injured, it’s time for an astute clinician, or a coach, and a whole team to assess them to see if maybe this person is just going to continue to get hurt if they’re not taken out of the game and perhaps they should go to a lower-impact sport.
Dr. Wilner: In schools, often there’s a big size and weight difference. There are 14-year-olds who are 6 fett 2 inches and 200 pounds, and there are 14-year-olds who are 5 feet 2 inches and 110 pounds. Obviously, they’re mismatched on the football field.
You mentioned coaches. Is there anything in the guidelines about training coaches?
Dr. Datta: Specifically, there was nothing in the guidelines about that. There’s a tool for coaches at every level to use, which is called the Sports Concussion Assessment Tool, or SCAT, which is going to be updated to the SCAT6. At the NCAA level, they must receive annual training on concussion management and be given an NCAA concussion handout for coaches.
Obviously, there are more rigorous protocols for national-level coaching. As it stands now, it is not mandatory, but they are given tools to assess someone once they’ve gotten a hit to take them out of the game.
Dr. Wilner: I’ve been following the concussion research through the years. They did some neuropsychological testing on athletes who’ve had this many concussions or that many concussions, and they would find deficits here or subtle deficits there, but they had no baseline.
Then, there was a movement to start testing athletes before the season starts so that they could do a repeat test after concussion and see if there is any difference. Is that something we’re recommending?
Dr. Datta: Most of the time, NCAA-level – certainly where I trained – and national-level sports do testing, but it’s not everywhere. Prior guidelines have indicated that preseason testing is not required. That is largely because there has been no standardized neuropsychological testing established.
There are computerized testing options where the validity and reliability are questionable. Also, let’s say it’s a college student; they didn’t sleep all night and then they took this computer test. They would probably do worse than they would if they had received a head hit.
Just to be on the safe side, most places that have collegiate-level sports that are at a high level do preseason testing. If I were to speak personally, aside from the guidelines, I would say that it’s been helpful for me to look at the before and after, in general, overall, to make a decision about my treatment protocol.
Dr. Wilner: Let’s talk about the patient. You have a 20-year-old guy. He’s playing football. There’s a big play. Bonk, he gets hit on the head. He’s on the ground. He’s dazed, staggers a little bit, gets up, and you ask how he is feeling. He says he’s fine and then he wobbles off to the sideline. What do you do with that kid?
Dr. Datta: Obviously, the first thing is to remove him from the play environment to a quiet space. Second, either an athletic trainer or a coach would administer basic screening neurologic tests, such as “where are you, what’s today’s date, what is your name?” and other orientation questions.
They’ll also go through the SCAT – that’ll be SCAT6 starting in July – the SCAT5 symptom questionnaire to see what symptoms they have. Often, they’re using sideline testing software.
There are two things that can be used on a card to test eye movements, to see if they’re slower. They come out of NYU, coincidentally – the Memory Image Completion (MIC) and the Mobile Universal Lexicon Evaluation System (MULES) – and are used to determine whether eye movements are slower. That way, you can tell whether someone is, compared with before they got their head hit, slower than before.
Based on this composite information, usually the teammates and the head people on the team will know if a player looks different.
They need to be taken out, obviously, if there is nausea or vomiting, any neurologic signs and symptoms, or a neck injury that needs to be stabilized. ABCs first, right? If there’s any vomiting or seizures, they should be taken to the ER right away.
The first thing is to take them out, then do a sideline assessment. Third, see if they need to immediately go to the ED versus follow-up outpatient with me within a day or two.
Dr. Wilner: I think it’s the subtle injuries that are the tough ones. Back to our 20-year-old. He says: “Oh, I’m fine. I want to go back in the game.” Everybody can tell he’s not quite right, even though he passed all the tests. What do you do then?
Dr. Datta: You have to make a judgment call for the safety of the player. They always want to go back, right? This is also an issue when they’re competing for college scholarships and things of that nature. Sometimes they’re sandbagging, where they memorize the answers.
Everything’s on the Internet nowadays, right? We have to make a judgment call as members of the healthcare community and the sports community to keep that player safe.
Just keep them out. Don’t bring them back in the game. Keep them out for a reasonable amount of time. There’s a test called the Buffalo Concussion Treadmill Test; Dr. John Leddy from University of Buffalo has developed a way for us to put athletes through a screening protocol.
This can be part of their vestibular and ocular rehabilitation, where if they don’t have symptoms when we bring their heart rate to certain levels, then we can slowly clear them for return to play as long as they’re nonsymptomatic.
Dr. Wilner: I spoke with your colleague, Dr. Riggins, who is also on your panel, and we were talking about when they can go back. She said they can go back when they don’t have any symptoms. No more headache, no more dizziness, no more lightheadedness, no more trouble concentrating or with memory – all those things have gone away.
Sometimes these symptoms are stubborn. If you have, say, 100 patients like our 20-year-old who got bonked on the head, has some headaches, and doesn’t feel quite right, what usually happens? How many are back to play the next day, the next week, or the next month? How many are out for the season? How does that play out?
Dr. Datta: It depends on a couple of different factors. One, have they had previous head injuries? Two, do they have preexisting symptoms or signs, or diagnoses like migraines, which are likely to get worse after a head injury? Anything that’s preexisting, like a mood disorder, anxiety, depression, or trouble sleeping, is going to get worse.
If they were compensating for untreated ADD or borderline personality or bipolar, I’ve seen many people who’ve developed them. These are not the norm, but I’m saying that you have to be very careful.
Getting back to the question, you treat them. Reasonably, if they’re healthy and they don’t have preexisting signs and symptoms, I would say more than half are back in about 2 weeks.. I would say 60%-70%. It all depends. If they have preexisting issues, then it’s going to take much longer.
From SCAT to SCOAT
Dr. Wilner: This has been very informative. Before we wrap up, tell us what to expect from these guidelines in July. How are they really going to help?
Dr. Datta: We’ve been using the SCAT, which was meant for more sideline assessment because that’s all we had, and it’s worked perfectly well.
This will be better because we often see them within 24-48 hours, when the symptoms are sometimes a little bit better.
We also will see the sport and concussion group come up with added athlete perspectives, ethics discussion, power-sport athlete considerations, and development of this new SCOAT.
Dr. Wilner: Dr. Datta, this is very exciting. I look forward to reading these guidelines in July. I want to thank you for your hard work. I also look forward to talking to you at next year’s meeting. Thank you very much for giving us this update.
Dr. Datta: No problem. It’s my pleasure.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Andrew N. Wilner, MD: I’m your host, Dr. Andrew Wilner, reporting virtually from the 2023 American Academy of Neurology meeting in Boston. It’s my pleasure today to speak with Dr. Shae Datta, codirector of the NYU Langone Concussion Center.
She’s also a clinical assistant professor of neurology at NYU School of Medicine. Dr. Datta is chair of the AAN Sports Neurology Section, and she’s leading a panel on concussion at this year’s meeting. She’s going to give us an update. Welcome, Dr. Datta.
Shae Datta, MD: Thank you so much, Andrew. I really love the fact that I’m here speaking to you about all of the new, exciting developments in the field.
Dr. Wilner: Before we get too deep, tell us how you got interested in this topic.
Dr. Datta: I initially thought, when I was in training as a resident, that I wanted to do something like neurocritical care or EEG. It also puzzled me why these seemingly smaller head injuries that didn’t end up in the hospital or ICU were bounced from neurology headache clinic to neuro-ophthalmology headache clinic to neurovestibular headache clinic, and nobody seemed to be able to put together the dots about why they’re having so many different issues — but at the same time, nobody could help them.
At that time, this field was very new. I was on a plane to Paris to a neurocritical care conference as a resident, and I saw the movie Concussion with Will Smith.
It featured one of my current mentors who taught at the fellowship that I graduated from, and it was a fascinating field. I just started looking deeply into it, and I saw that there was a new training fellowship for sports neurology and concussion management, and this is basically why we’re here today.
New concussion consensus guidelines coming
Dr. Wilner: I think this field has really exploded. It used to be that you banged your head, you did a CT scan – remember, I trained about 45 years ago – and if there was nothing on the CT scan, you were done. If you had headaches, you took Tylenol until they went away.
Now, we do MRI, and we realized that it’s really a syndrome. I understand that there are going to be some formal guidelines that have been put together. Is that correct?
Dr. Datta: That’s correct. The 6th International Consensus Conference on Concussion in Sport, in Amsterdam, where I attended and presented a poster, was really a meeting of all the best minds – clinicians and researchers in brain injury – to form a consensus on the newest guidelines that are going to direct our treatment going forward.
Dr. Wilner: I’m going to ask you a trick question because the last time I looked it up I did not get a satisfying answer. What is a concussion?
Dr. Datta: That’s a very good question, and everyone always asks. A concussion is an external force that is emitted upon the head or the neck, or the body, in general, that may cause temporary loss of function. It’s a functional problem.
We don’t see much on CT. We can do MRI. We can do SPECT or we can do these very fancy images, sometimes, of high-velocity head injuries and see small microhemorrhages.
Often, we don’t see anything, but still the patient is loopy. They can’t see straight. They are double-visioned. They have vertigo. Why is that happening? On the cellular level, we have an energy deficit in the sodium-potassium-ATPase pump of the neurons themselves.
Dr. Wilner: Suppose you do see diffuse axonal injury; does that take it out of concussion, or can you have a concussion with visible injury?
Dr. Datta: I think you can have overlap in the symptoms. The diffuse axonal injury would put it into a higher grade of head injury as opposed to a mild traumatic brain injury. Definitely, we would need to work together with our trauma doctors to ensure that patients are not on blood thinners or anything until they heal well enough. Obviously, I would pick them up as an outpatient and follow them until we resolve or rehab them as best as possible.
Concussion assessment tools
Dr. Wilner: There are many sports out there where concussions are fairly frequent, like American football and hockey, for example. Are there any statements in the new guidelines?
Dr. Datta: There are no statements for or against a particular sport because that would really make too much of a bold statement about cause and effect. There is a cause and effect in long-term, repetitive exposure, I would say, in terms of someone being able to play or sustain injury.
Right now, at least at the concussion conference I went to and in the upcoming consensus statement, they will not comment on a specific sport. Obviously, we know that the higher-impact sports are a little more dangerous.
Let’s be honest. At the high school, middle school, or even younger level, some kids are not necessarily the most athletic, right? They play because their friends are playing. If they’re repeatedly getting injured, it’s time for an astute clinician, or a coach, and a whole team to assess them to see if maybe this person is just going to continue to get hurt if they’re not taken out of the game and perhaps they should go to a lower-impact sport.
Dr. Wilner: In schools, often there’s a big size and weight difference. There are 14-year-olds who are 6 fett 2 inches and 200 pounds, and there are 14-year-olds who are 5 feet 2 inches and 110 pounds. Obviously, they’re mismatched on the football field.
You mentioned coaches. Is there anything in the guidelines about training coaches?
Dr. Datta: Specifically, there was nothing in the guidelines about that. There’s a tool for coaches at every level to use, which is called the Sports Concussion Assessment Tool, or SCAT, which is going to be updated to the SCAT6. At the NCAA level, they must receive annual training on concussion management and be given an NCAA concussion handout for coaches.
Obviously, there are more rigorous protocols for national-level coaching. As it stands now, it is not mandatory, but they are given tools to assess someone once they’ve gotten a hit to take them out of the game.
Dr. Wilner: I’ve been following the concussion research through the years. They did some neuropsychological testing on athletes who’ve had this many concussions or that many concussions, and they would find deficits here or subtle deficits there, but they had no baseline.
Then, there was a movement to start testing athletes before the season starts so that they could do a repeat test after concussion and see if there is any difference. Is that something we’re recommending?
Dr. Datta: Most of the time, NCAA-level – certainly where I trained – and national-level sports do testing, but it’s not everywhere. Prior guidelines have indicated that preseason testing is not required. That is largely because there has been no standardized neuropsychological testing established.
There are computerized testing options where the validity and reliability are questionable. Also, let’s say it’s a college student; they didn’t sleep all night and then they took this computer test. They would probably do worse than they would if they had received a head hit.
Just to be on the safe side, most places that have collegiate-level sports that are at a high level do preseason testing. If I were to speak personally, aside from the guidelines, I would say that it’s been helpful for me to look at the before and after, in general, overall, to make a decision about my treatment protocol.
Dr. Wilner: Let’s talk about the patient. You have a 20-year-old guy. He’s playing football. There’s a big play. Bonk, he gets hit on the head. He’s on the ground. He’s dazed, staggers a little bit, gets up, and you ask how he is feeling. He says he’s fine and then he wobbles off to the sideline. What do you do with that kid?
Dr. Datta: Obviously, the first thing is to remove him from the play environment to a quiet space. Second, either an athletic trainer or a coach would administer basic screening neurologic tests, such as “where are you, what’s today’s date, what is your name?” and other orientation questions.
They’ll also go through the SCAT – that’ll be SCAT6 starting in July – the SCAT5 symptom questionnaire to see what symptoms they have. Often, they’re using sideline testing software.
There are two things that can be used on a card to test eye movements, to see if they’re slower. They come out of NYU, coincidentally – the Memory Image Completion (MIC) and the Mobile Universal Lexicon Evaluation System (MULES) – and are used to determine whether eye movements are slower. That way, you can tell whether someone is, compared with before they got their head hit, slower than before.
Based on this composite information, usually the teammates and the head people on the team will know if a player looks different.
They need to be taken out, obviously, if there is nausea or vomiting, any neurologic signs and symptoms, or a neck injury that needs to be stabilized. ABCs first, right? If there’s any vomiting or seizures, they should be taken to the ER right away.
The first thing is to take them out, then do a sideline assessment. Third, see if they need to immediately go to the ED versus follow-up outpatient with me within a day or two.
Dr. Wilner: I think it’s the subtle injuries that are the tough ones. Back to our 20-year-old. He says: “Oh, I’m fine. I want to go back in the game.” Everybody can tell he’s not quite right, even though he passed all the tests. What do you do then?
Dr. Datta: You have to make a judgment call for the safety of the player. They always want to go back, right? This is also an issue when they’re competing for college scholarships and things of that nature. Sometimes they’re sandbagging, where they memorize the answers.
Everything’s on the Internet nowadays, right? We have to make a judgment call as members of the healthcare community and the sports community to keep that player safe.
Just keep them out. Don’t bring them back in the game. Keep them out for a reasonable amount of time. There’s a test called the Buffalo Concussion Treadmill Test; Dr. John Leddy from University of Buffalo has developed a way for us to put athletes through a screening protocol.
This can be part of their vestibular and ocular rehabilitation, where if they don’t have symptoms when we bring their heart rate to certain levels, then we can slowly clear them for return to play as long as they’re nonsymptomatic.
Dr. Wilner: I spoke with your colleague, Dr. Riggins, who is also on your panel, and we were talking about when they can go back. She said they can go back when they don’t have any symptoms. No more headache, no more dizziness, no more lightheadedness, no more trouble concentrating or with memory – all those things have gone away.
Sometimes these symptoms are stubborn. If you have, say, 100 patients like our 20-year-old who got bonked on the head, has some headaches, and doesn’t feel quite right, what usually happens? How many are back to play the next day, the next week, or the next month? How many are out for the season? How does that play out?
Dr. Datta: It depends on a couple of different factors. One, have they had previous head injuries? Two, do they have preexisting symptoms or signs, or diagnoses like migraines, which are likely to get worse after a head injury? Anything that’s preexisting, like a mood disorder, anxiety, depression, or trouble sleeping, is going to get worse.
If they were compensating for untreated ADD or borderline personality or bipolar, I’ve seen many people who’ve developed them. These are not the norm, but I’m saying that you have to be very careful.
Getting back to the question, you treat them. Reasonably, if they’re healthy and they don’t have preexisting signs and symptoms, I would say more than half are back in about 2 weeks.. I would say 60%-70%. It all depends. If they have preexisting issues, then it’s going to take much longer.
From SCAT to SCOAT
Dr. Wilner: This has been very informative. Before we wrap up, tell us what to expect from these guidelines in July. How are they really going to help?
Dr. Datta: We’ve been using the SCAT, which was meant for more sideline assessment because that’s all we had, and it’s worked perfectly well.
This will be better because we often see them within 24-48 hours, when the symptoms are sometimes a little bit better.
We also will see the sport and concussion group come up with added athlete perspectives, ethics discussion, power-sport athlete considerations, and development of this new SCOAT.
Dr. Wilner: Dr. Datta, this is very exciting. I look forward to reading these guidelines in July. I want to thank you for your hard work. I also look forward to talking to you at next year’s meeting. Thank you very much for giving us this update.
Dr. Datta: No problem. It’s my pleasure.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Morning PT
Tuesdays and Fridays are tough. Not so much because of clinic, but rather because of the 32 minutes before clinic that I’m on the Peloton bike. They are the mornings I dedicate to training VO2max.
Training VO2max, or maximal oxygen consumption, is simple. Spin for a leisurely, easy-breathing, 4 minutes, then for 4 minutes push yourself until you see the light of heaven and wish for death to come. Then relax for 4 minutes again. Repeat this cycle four to six times. Done justly, you will dread Tuesdays and Fridays too. The punishing cycle of a 4-minute push, then 4-minute recovery is, however, an excellent way to improve cardiovascular fitness. And no, I’m not training for the Boston Marathon, so why am I working so hard? Because I’m training for marathon clinic days for the next 20 years.
Now more than ever, I feel we have to be physically fit to deal with a physicians’ day’s work. It’s exhausting. The root cause is too much work, yes, but I believe being physically fit could help.
I was talking to an 86-year-old patient about this very topic recently. He was short, with a well-manicured goatee and shiny head. He stuck his arm out to shake my hand. “Glad we’re back to handshakes again, doc.” His grip was that of a 30-year-old. “Buff” you’d likely describe him: He is noticeably muscular, not a skinny old man. He’s an old Navy Master Chief who started a business in wholesale flowers, which distributes all over the United States. And he’s still working full time. Impressed, I asked his secret for such vigor. PT, he replied.
PT, or physical training, is a foundational element of the Navy. Every sailor starts his or her day with morning PT before carrying out their duties. Some 30 years later, this guy is still getting after it. He does push-ups, sit-ups, and pull-ups nearly every morning. Morning PT is what he attributes to his success not only in health, but also business. As he sees it, he has the business savvy and experience of an old guy and the energy and stamina of a college kid. A good combination for a successful life.
I’ve always been pretty fit. Lately, I’ve been trying to take it to the next level, to not just be “physically active,” but rather “high-performance fit.” There are plenty of sources for instruction; how to stay young and healthy isn’t a new idea after all. I mean, Herodotus wrote of finding the Fountain of Youth in the 5th century BCE. A couple thousand years later, it’s still on trend. One of my favorite sages giving health span advice is Peter Attia, MD. I’ve been a fan since I met him at TEDMED in 2013 and I marvel at the astounding body of work he has created since. A Johns Hopkins–trained surgeon, he has spent his career reviewing the scientific literature about longevity and sharing it as actionable content. His book, “Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity” (New York: Penguin Random House, 2023) is a nice summary of his work. I recommend it.
Right now I’m switching between type 2 muscle fiber work (lots of jumping like my 2-year-old) and cardiovascular training including the aforementioned VO2max work. I cannot say that my patient inbox is any cleaner, or that I’m faster in the office, but I’m not flagging by the end of the day anymore. Master Chief challenged me to match his 10 pull-ups before he returns for his follow up visit. I’ll gladly give up Peloton sprints to work on that.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
Tuesdays and Fridays are tough. Not so much because of clinic, but rather because of the 32 minutes before clinic that I’m on the Peloton bike. They are the mornings I dedicate to training VO2max.
Training VO2max, or maximal oxygen consumption, is simple. Spin for a leisurely, easy-breathing, 4 minutes, then for 4 minutes push yourself until you see the light of heaven and wish for death to come. Then relax for 4 minutes again. Repeat this cycle four to six times. Done justly, you will dread Tuesdays and Fridays too. The punishing cycle of a 4-minute push, then 4-minute recovery is, however, an excellent way to improve cardiovascular fitness. And no, I’m not training for the Boston Marathon, so why am I working so hard? Because I’m training for marathon clinic days for the next 20 years.
Now more than ever, I feel we have to be physically fit to deal with a physicians’ day’s work. It’s exhausting. The root cause is too much work, yes, but I believe being physically fit could help.
I was talking to an 86-year-old patient about this very topic recently. He was short, with a well-manicured goatee and shiny head. He stuck his arm out to shake my hand. “Glad we’re back to handshakes again, doc.” His grip was that of a 30-year-old. “Buff” you’d likely describe him: He is noticeably muscular, not a skinny old man. He’s an old Navy Master Chief who started a business in wholesale flowers, which distributes all over the United States. And he’s still working full time. Impressed, I asked his secret for such vigor. PT, he replied.
PT, or physical training, is a foundational element of the Navy. Every sailor starts his or her day with morning PT before carrying out their duties. Some 30 years later, this guy is still getting after it. He does push-ups, sit-ups, and pull-ups nearly every morning. Morning PT is what he attributes to his success not only in health, but also business. As he sees it, he has the business savvy and experience of an old guy and the energy and stamina of a college kid. A good combination for a successful life.
I’ve always been pretty fit. Lately, I’ve been trying to take it to the next level, to not just be “physically active,” but rather “high-performance fit.” There are plenty of sources for instruction; how to stay young and healthy isn’t a new idea after all. I mean, Herodotus wrote of finding the Fountain of Youth in the 5th century BCE. A couple thousand years later, it’s still on trend. One of my favorite sages giving health span advice is Peter Attia, MD. I’ve been a fan since I met him at TEDMED in 2013 and I marvel at the astounding body of work he has created since. A Johns Hopkins–trained surgeon, he has spent his career reviewing the scientific literature about longevity and sharing it as actionable content. His book, “Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity” (New York: Penguin Random House, 2023) is a nice summary of his work. I recommend it.
Right now I’m switching between type 2 muscle fiber work (lots of jumping like my 2-year-old) and cardiovascular training including the aforementioned VO2max work. I cannot say that my patient inbox is any cleaner, or that I’m faster in the office, but I’m not flagging by the end of the day anymore. Master Chief challenged me to match his 10 pull-ups before he returns for his follow up visit. I’ll gladly give up Peloton sprints to work on that.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
Tuesdays and Fridays are tough. Not so much because of clinic, but rather because of the 32 minutes before clinic that I’m on the Peloton bike. They are the mornings I dedicate to training VO2max.
Training VO2max, or maximal oxygen consumption, is simple. Spin for a leisurely, easy-breathing, 4 minutes, then for 4 minutes push yourself until you see the light of heaven and wish for death to come. Then relax for 4 minutes again. Repeat this cycle four to six times. Done justly, you will dread Tuesdays and Fridays too. The punishing cycle of a 4-minute push, then 4-minute recovery is, however, an excellent way to improve cardiovascular fitness. And no, I’m not training for the Boston Marathon, so why am I working so hard? Because I’m training for marathon clinic days for the next 20 years.
Now more than ever, I feel we have to be physically fit to deal with a physicians’ day’s work. It’s exhausting. The root cause is too much work, yes, but I believe being physically fit could help.
I was talking to an 86-year-old patient about this very topic recently. He was short, with a well-manicured goatee and shiny head. He stuck his arm out to shake my hand. “Glad we’re back to handshakes again, doc.” His grip was that of a 30-year-old. “Buff” you’d likely describe him: He is noticeably muscular, not a skinny old man. He’s an old Navy Master Chief who started a business in wholesale flowers, which distributes all over the United States. And he’s still working full time. Impressed, I asked his secret for such vigor. PT, he replied.
PT, or physical training, is a foundational element of the Navy. Every sailor starts his or her day with morning PT before carrying out their duties. Some 30 years later, this guy is still getting after it. He does push-ups, sit-ups, and pull-ups nearly every morning. Morning PT is what he attributes to his success not only in health, but also business. As he sees it, he has the business savvy and experience of an old guy and the energy and stamina of a college kid. A good combination for a successful life.
I’ve always been pretty fit. Lately, I’ve been trying to take it to the next level, to not just be “physically active,” but rather “high-performance fit.” There are plenty of sources for instruction; how to stay young and healthy isn’t a new idea after all. I mean, Herodotus wrote of finding the Fountain of Youth in the 5th century BCE. A couple thousand years later, it’s still on trend. One of my favorite sages giving health span advice is Peter Attia, MD. I’ve been a fan since I met him at TEDMED in 2013 and I marvel at the astounding body of work he has created since. A Johns Hopkins–trained surgeon, he has spent his career reviewing the scientific literature about longevity and sharing it as actionable content. His book, “Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity” (New York: Penguin Random House, 2023) is a nice summary of his work. I recommend it.
Right now I’m switching between type 2 muscle fiber work (lots of jumping like my 2-year-old) and cardiovascular training including the aforementioned VO2max work. I cannot say that my patient inbox is any cleaner, or that I’m faster in the office, but I’m not flagging by the end of the day anymore. Master Chief challenged me to match his 10 pull-ups before he returns for his follow up visit. I’ll gladly give up Peloton sprints to work on that.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
Review supports continued mask-wearing in health care visits
A new study urges people to continue wearing protective masks in medical settings, even though the U.S. public health emergency declaration around COVID-19 has expired.
Masks continue to lower the risk of catching the virus during medical visits, according to the study, published in Annals of Internal Medicine. And there was not much difference between wearing surgical masks and N95 respirators in health care settings.
The researchers reviewed 3 randomized trials and 21 observational studies to compare the effectiveness of those and cloth masks in reducing COVID-19 transmission.
Tara N. Palmore, MD, of George Washington University, Washington, and David K. Henderson, MD, of the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., wrote in an opinion article accompanying the study.
“In our enthusiasm to return to the appearance and feeling of normalcy, and as institutions decide which mitigation strategies to discontinue, we strongly advocate not discarding this important lesson learned for the sake of our patients’ safety,” Dr. Palmore and Dr. Henderson wrote.
Surgical masks limit the spread of aerosols and droplets from people who have the flu, coronaviruses or other respiratory viruses, CNN reported. And while masks are not 100% effective, they substantially lower the amount of virus put into the air via coughing and talking.
The study said one reason people should wear masks to medical settings is because “health care personnel are notorious for coming to work while ill.” Transmission from patient to staff and staff to patient is still possible, but rare, when both are masked.
The review authors reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Palmore has received grants from the NIH, Rigel, Gilead, and AbbVie, and Dr. Henderson is a past president of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A new study urges people to continue wearing protective masks in medical settings, even though the U.S. public health emergency declaration around COVID-19 has expired.
Masks continue to lower the risk of catching the virus during medical visits, according to the study, published in Annals of Internal Medicine. And there was not much difference between wearing surgical masks and N95 respirators in health care settings.
The researchers reviewed 3 randomized trials and 21 observational studies to compare the effectiveness of those and cloth masks in reducing COVID-19 transmission.
Tara N. Palmore, MD, of George Washington University, Washington, and David K. Henderson, MD, of the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., wrote in an opinion article accompanying the study.
“In our enthusiasm to return to the appearance and feeling of normalcy, and as institutions decide which mitigation strategies to discontinue, we strongly advocate not discarding this important lesson learned for the sake of our patients’ safety,” Dr. Palmore and Dr. Henderson wrote.
Surgical masks limit the spread of aerosols and droplets from people who have the flu, coronaviruses or other respiratory viruses, CNN reported. And while masks are not 100% effective, they substantially lower the amount of virus put into the air via coughing and talking.
The study said one reason people should wear masks to medical settings is because “health care personnel are notorious for coming to work while ill.” Transmission from patient to staff and staff to patient is still possible, but rare, when both are masked.
The review authors reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Palmore has received grants from the NIH, Rigel, Gilead, and AbbVie, and Dr. Henderson is a past president of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A new study urges people to continue wearing protective masks in medical settings, even though the U.S. public health emergency declaration around COVID-19 has expired.
Masks continue to lower the risk of catching the virus during medical visits, according to the study, published in Annals of Internal Medicine. And there was not much difference between wearing surgical masks and N95 respirators in health care settings.
The researchers reviewed 3 randomized trials and 21 observational studies to compare the effectiveness of those and cloth masks in reducing COVID-19 transmission.
Tara N. Palmore, MD, of George Washington University, Washington, and David K. Henderson, MD, of the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., wrote in an opinion article accompanying the study.
“In our enthusiasm to return to the appearance and feeling of normalcy, and as institutions decide which mitigation strategies to discontinue, we strongly advocate not discarding this important lesson learned for the sake of our patients’ safety,” Dr. Palmore and Dr. Henderson wrote.
Surgical masks limit the spread of aerosols and droplets from people who have the flu, coronaviruses or other respiratory viruses, CNN reported. And while masks are not 100% effective, they substantially lower the amount of virus put into the air via coughing and talking.
The study said one reason people should wear masks to medical settings is because “health care personnel are notorious for coming to work while ill.” Transmission from patient to staff and staff to patient is still possible, but rare, when both are masked.
The review authors reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Palmore has received grants from the NIH, Rigel, Gilead, and AbbVie, and Dr. Henderson is a past president of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
COVID emergency over, but hundreds are still dying weekly
Traci Sikes’s older sister Debbie had survived several health setbacks in life – a heart attack, a cancer diagnosis, and a couple of botched surgeries for a bad back. But by early 2023, the 68-year-old from Brownwood, Tex., was in remission from lymphoma, feeling stronger, and celebrating a birthday for one of her 11 beloved grandchildren.
Then Debbie caught COVID-19. Less than 2 months later, in March, she died of severe lung damage caused by the coronavirus.
Traci was able to make the trip from her home in Washington state to Texas to be with Debbie before she died. She was grateful that she arrived while her sister was still lucid and to hear her sister’s last word – “love” – spoken to one of her grandchildren before she took her final breath.
“My sister was wonderful,” Sikes said. “And she shouldn’t be gone.”
Just 6 months after President Joe Biden declared last fall that “the pandemic is over,” Just as both the World Health Organization and U.S. government recently ended the 3-year-old coronavirus public health emergency, COVID is still killing more than 100 people every day in the U.S., according to the CDC, and amid widespread efforts to move on and drop protective measures, the country’s most vulnerable people are still at significant risk.
The prevailing attitude that we need to learn to live with the current level of risk feels like a “slap in the face,” for COVID grievers who have already paid the price,” said Sabila Khan, who cofounded a Facebook group for COVID loss support, which now has more than 14,000 members.
It also minimizes the continuing loss of life and that so many people are still dying traumatic and unnecessary deaths, she said.
“It feels like it’s been brushed aside,” she said. “Like, ‘It’s business as usual. It’s over. Take off your mask.’ My family and I are still masked, and we’re probably the only ones masked in any given room.”
The abandoning of protective measures also fails to recognize the ongoing and catastrophic risks of long COVID and the experiences of an estimated 26 million people in the U.S. living with long COVID.
“It’s been drummed into us that death is the only serious outcome [of the virus] and we still haven’t made enough space for the idea that long COVID is a very serious outcome,” said David Putrino, PhD, director of rehabilitation innovation for the Mount Sinai Health System in New York, who has helped care for thousands of patients with long COVID.
Historic drop in life expectancy
More than 1.1 million Americans have died from COVID over the past 3 years, and experts say the official numbers are likely underestimated because of errors in death certificate reporting. Although deaths have waned from earlier in the pandemic, the disease has become the fourth leading cause of death in the United States after heart disease, cancer, and “unintentional injury” such as drug overdoses.
What makes these deaths all the more tragic is that COVID is a preventable disease, said Carla Sevin, MD, a critical care doctor and director of the Pulmonary Patient Care Center at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn. Masking, available vaccines, and social distancing have all been shown to significantly lower the risk of spreading and catching the virus. New drugs have also made it possible for infected people to survive COVID.
“It’s possible to not spread COVID,” she said. “It’s possible to protect yourself against COVID. It’s possible to treat COVID. And we’re doing all of those things imperfectly.”
By the end of 2021, Americans overall were dying 3 years sooner, on average, than they were before the pandemic, with life expectancy dropping from 79 years to 76 years, the largest decline in a century.
Globally, the COVID death toll is nearing 7 million. Across all ages, on average, each person who died passed away 10 years younger than they otherwise would have. That’s tens of millions of years wiped away.
As U.S. surgeon and health researcher Atul Gawande, MD, put it in a New York Times essay about the pandemic response: “Human development has been pushed into reverse.”
What is an acceptable threshold of death?
In the United States, more than 80% of deaths from the disease have been in people age 65 and older. Underlying medical conditions and disabilities also raise the risk of severe illness and dying from COVID.
The virus is also disproportionately killing Black, Hispanic, and Indigenous people and those with less access to health care. Racialized groups are dying from COVID at younger ages. COVID advocates and Americans who’ve lost loved ones to the disease say our willingness to accept these facts and the current mortality rate amounts to health-based discrimination.
“Would politicians be approaching this differently had it mostly affected rich white people?” Ms. Khan said.
Ms. Khan’s dad, Shafqat, was an advocate and community organizer for Pakistani immigrants. After contracting COVID, he was rushed to a hospital near his daughter’s Jersey City, N.J., home from a rehab facility where he was being treated for an aggressive form of Parkinson’s disease. For the 8 days her father was in the hospital, she and other family members couldn’t visit him, and he wasn’t even well enough to talk on the phone. He died from COVID in April 2020.
“My father was an extraordinary person who did so much good and he died alone, terrified in a hospital,” she said. “I can’t even wrap my head around that and how he deserved more. No one deserves that.”
At Vanderbilt University Medical Center, where she works as a critical care doctor, COVID deaths are now different from those in the early days of the pandemic, Dr. Sevin said. Most patients now in the intensive care unit are older and immunocompromised – and they tend to blend in more with others in the intensive care unit. That makes the impact of COVID even more hidden and easily ignored.
“It’s easy not to value somebody who’s an invisible number you don’t know,” she said. “You don’t see them writing their will and talking to their best friend. You don’t see the tears rolling down their face because they know what’s going to happen to them and they’re going to asphyxiate to death.”
One COVID patient who died recently in Dr. Sevin’s ICU ward was an older woman who had no living relatives. “She was very, very lonely, and we would always stand outside the door on rounds, and she would motion for us to come in, but we had to then all gown up,” Dr. Sevin said. “It just breaks your heart that people are still having to go through it.”
Dr. Sevin finds it frustrating that so many of the measures that public health officials fought so hard for over the last 3 years – including masking guidelines, government-funded vaccine clinics, and access to potentially life-saving antiviral medications – are now going away because of the lifting of the pandemic emergency declaration.
What makes matters worse, she said, is that public consciousness about taking precautions to protect others is starting to disappear in favor of an “all or nothing attitude” about the continued risks.
“Like either I’m going to stay home and be a hermit, or I’m going to just throw caution to the wind and go to bars and let people yell in my face,” she said. “We learned some hard lessons, and I wish we could hold onto those.”
Americans like Traci Sikes who’ve lost loved ones and health care workers on the front lines say it is particularly frustrating that so many people are framing the current response to the risks of COVID as “personal choice” over responsibility to others, as well as a sense of fatalism and lack of urgent care.
“Why does nobody seem to be angry about this?” Ms. Sikes said. “People talk about COVID like it’s just another thing to die from. But my sister didn’t have to die from it at all.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Traci Sikes’s older sister Debbie had survived several health setbacks in life – a heart attack, a cancer diagnosis, and a couple of botched surgeries for a bad back. But by early 2023, the 68-year-old from Brownwood, Tex., was in remission from lymphoma, feeling stronger, and celebrating a birthday for one of her 11 beloved grandchildren.
Then Debbie caught COVID-19. Less than 2 months later, in March, she died of severe lung damage caused by the coronavirus.
Traci was able to make the trip from her home in Washington state to Texas to be with Debbie before she died. She was grateful that she arrived while her sister was still lucid and to hear her sister’s last word – “love” – spoken to one of her grandchildren before she took her final breath.
“My sister was wonderful,” Sikes said. “And she shouldn’t be gone.”
Just 6 months after President Joe Biden declared last fall that “the pandemic is over,” Just as both the World Health Organization and U.S. government recently ended the 3-year-old coronavirus public health emergency, COVID is still killing more than 100 people every day in the U.S., according to the CDC, and amid widespread efforts to move on and drop protective measures, the country’s most vulnerable people are still at significant risk.
The prevailing attitude that we need to learn to live with the current level of risk feels like a “slap in the face,” for COVID grievers who have already paid the price,” said Sabila Khan, who cofounded a Facebook group for COVID loss support, which now has more than 14,000 members.
It also minimizes the continuing loss of life and that so many people are still dying traumatic and unnecessary deaths, she said.
“It feels like it’s been brushed aside,” she said. “Like, ‘It’s business as usual. It’s over. Take off your mask.’ My family and I are still masked, and we’re probably the only ones masked in any given room.”
The abandoning of protective measures also fails to recognize the ongoing and catastrophic risks of long COVID and the experiences of an estimated 26 million people in the U.S. living with long COVID.
“It’s been drummed into us that death is the only serious outcome [of the virus] and we still haven’t made enough space for the idea that long COVID is a very serious outcome,” said David Putrino, PhD, director of rehabilitation innovation for the Mount Sinai Health System in New York, who has helped care for thousands of patients with long COVID.
Historic drop in life expectancy
More than 1.1 million Americans have died from COVID over the past 3 years, and experts say the official numbers are likely underestimated because of errors in death certificate reporting. Although deaths have waned from earlier in the pandemic, the disease has become the fourth leading cause of death in the United States after heart disease, cancer, and “unintentional injury” such as drug overdoses.
What makes these deaths all the more tragic is that COVID is a preventable disease, said Carla Sevin, MD, a critical care doctor and director of the Pulmonary Patient Care Center at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn. Masking, available vaccines, and social distancing have all been shown to significantly lower the risk of spreading and catching the virus. New drugs have also made it possible for infected people to survive COVID.
“It’s possible to not spread COVID,” she said. “It’s possible to protect yourself against COVID. It’s possible to treat COVID. And we’re doing all of those things imperfectly.”
By the end of 2021, Americans overall were dying 3 years sooner, on average, than they were before the pandemic, with life expectancy dropping from 79 years to 76 years, the largest decline in a century.
Globally, the COVID death toll is nearing 7 million. Across all ages, on average, each person who died passed away 10 years younger than they otherwise would have. That’s tens of millions of years wiped away.
As U.S. surgeon and health researcher Atul Gawande, MD, put it in a New York Times essay about the pandemic response: “Human development has been pushed into reverse.”
What is an acceptable threshold of death?
In the United States, more than 80% of deaths from the disease have been in people age 65 and older. Underlying medical conditions and disabilities also raise the risk of severe illness and dying from COVID.
The virus is also disproportionately killing Black, Hispanic, and Indigenous people and those with less access to health care. Racialized groups are dying from COVID at younger ages. COVID advocates and Americans who’ve lost loved ones to the disease say our willingness to accept these facts and the current mortality rate amounts to health-based discrimination.
“Would politicians be approaching this differently had it mostly affected rich white people?” Ms. Khan said.
Ms. Khan’s dad, Shafqat, was an advocate and community organizer for Pakistani immigrants. After contracting COVID, he was rushed to a hospital near his daughter’s Jersey City, N.J., home from a rehab facility where he was being treated for an aggressive form of Parkinson’s disease. For the 8 days her father was in the hospital, she and other family members couldn’t visit him, and he wasn’t even well enough to talk on the phone. He died from COVID in April 2020.
“My father was an extraordinary person who did so much good and he died alone, terrified in a hospital,” she said. “I can’t even wrap my head around that and how he deserved more. No one deserves that.”
At Vanderbilt University Medical Center, where she works as a critical care doctor, COVID deaths are now different from those in the early days of the pandemic, Dr. Sevin said. Most patients now in the intensive care unit are older and immunocompromised – and they tend to blend in more with others in the intensive care unit. That makes the impact of COVID even more hidden and easily ignored.
“It’s easy not to value somebody who’s an invisible number you don’t know,” she said. “You don’t see them writing their will and talking to their best friend. You don’t see the tears rolling down their face because they know what’s going to happen to them and they’re going to asphyxiate to death.”
One COVID patient who died recently in Dr. Sevin’s ICU ward was an older woman who had no living relatives. “She was very, very lonely, and we would always stand outside the door on rounds, and she would motion for us to come in, but we had to then all gown up,” Dr. Sevin said. “It just breaks your heart that people are still having to go through it.”
Dr. Sevin finds it frustrating that so many of the measures that public health officials fought so hard for over the last 3 years – including masking guidelines, government-funded vaccine clinics, and access to potentially life-saving antiviral medications – are now going away because of the lifting of the pandemic emergency declaration.
What makes matters worse, she said, is that public consciousness about taking precautions to protect others is starting to disappear in favor of an “all or nothing attitude” about the continued risks.
“Like either I’m going to stay home and be a hermit, or I’m going to just throw caution to the wind and go to bars and let people yell in my face,” she said. “We learned some hard lessons, and I wish we could hold onto those.”
Americans like Traci Sikes who’ve lost loved ones and health care workers on the front lines say it is particularly frustrating that so many people are framing the current response to the risks of COVID as “personal choice” over responsibility to others, as well as a sense of fatalism and lack of urgent care.
“Why does nobody seem to be angry about this?” Ms. Sikes said. “People talk about COVID like it’s just another thing to die from. But my sister didn’t have to die from it at all.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Traci Sikes’s older sister Debbie had survived several health setbacks in life – a heart attack, a cancer diagnosis, and a couple of botched surgeries for a bad back. But by early 2023, the 68-year-old from Brownwood, Tex., was in remission from lymphoma, feeling stronger, and celebrating a birthday for one of her 11 beloved grandchildren.
Then Debbie caught COVID-19. Less than 2 months later, in March, she died of severe lung damage caused by the coronavirus.
Traci was able to make the trip from her home in Washington state to Texas to be with Debbie before she died. She was grateful that she arrived while her sister was still lucid and to hear her sister’s last word – “love” – spoken to one of her grandchildren before she took her final breath.
“My sister was wonderful,” Sikes said. “And she shouldn’t be gone.”
Just 6 months after President Joe Biden declared last fall that “the pandemic is over,” Just as both the World Health Organization and U.S. government recently ended the 3-year-old coronavirus public health emergency, COVID is still killing more than 100 people every day in the U.S., according to the CDC, and amid widespread efforts to move on and drop protective measures, the country’s most vulnerable people are still at significant risk.
The prevailing attitude that we need to learn to live with the current level of risk feels like a “slap in the face,” for COVID grievers who have already paid the price,” said Sabila Khan, who cofounded a Facebook group for COVID loss support, which now has more than 14,000 members.
It also minimizes the continuing loss of life and that so many people are still dying traumatic and unnecessary deaths, she said.
“It feels like it’s been brushed aside,” she said. “Like, ‘It’s business as usual. It’s over. Take off your mask.’ My family and I are still masked, and we’re probably the only ones masked in any given room.”
The abandoning of protective measures also fails to recognize the ongoing and catastrophic risks of long COVID and the experiences of an estimated 26 million people in the U.S. living with long COVID.
“It’s been drummed into us that death is the only serious outcome [of the virus] and we still haven’t made enough space for the idea that long COVID is a very serious outcome,” said David Putrino, PhD, director of rehabilitation innovation for the Mount Sinai Health System in New York, who has helped care for thousands of patients with long COVID.
Historic drop in life expectancy
More than 1.1 million Americans have died from COVID over the past 3 years, and experts say the official numbers are likely underestimated because of errors in death certificate reporting. Although deaths have waned from earlier in the pandemic, the disease has become the fourth leading cause of death in the United States after heart disease, cancer, and “unintentional injury” such as drug overdoses.
What makes these deaths all the more tragic is that COVID is a preventable disease, said Carla Sevin, MD, a critical care doctor and director of the Pulmonary Patient Care Center at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn. Masking, available vaccines, and social distancing have all been shown to significantly lower the risk of spreading and catching the virus. New drugs have also made it possible for infected people to survive COVID.
“It’s possible to not spread COVID,” she said. “It’s possible to protect yourself against COVID. It’s possible to treat COVID. And we’re doing all of those things imperfectly.”
By the end of 2021, Americans overall were dying 3 years sooner, on average, than they were before the pandemic, with life expectancy dropping from 79 years to 76 years, the largest decline in a century.
Globally, the COVID death toll is nearing 7 million. Across all ages, on average, each person who died passed away 10 years younger than they otherwise would have. That’s tens of millions of years wiped away.
As U.S. surgeon and health researcher Atul Gawande, MD, put it in a New York Times essay about the pandemic response: “Human development has been pushed into reverse.”
What is an acceptable threshold of death?
In the United States, more than 80% of deaths from the disease have been in people age 65 and older. Underlying medical conditions and disabilities also raise the risk of severe illness and dying from COVID.
The virus is also disproportionately killing Black, Hispanic, and Indigenous people and those with less access to health care. Racialized groups are dying from COVID at younger ages. COVID advocates and Americans who’ve lost loved ones to the disease say our willingness to accept these facts and the current mortality rate amounts to health-based discrimination.
“Would politicians be approaching this differently had it mostly affected rich white people?” Ms. Khan said.
Ms. Khan’s dad, Shafqat, was an advocate and community organizer for Pakistani immigrants. After contracting COVID, he was rushed to a hospital near his daughter’s Jersey City, N.J., home from a rehab facility where he was being treated for an aggressive form of Parkinson’s disease. For the 8 days her father was in the hospital, she and other family members couldn’t visit him, and he wasn’t even well enough to talk on the phone. He died from COVID in April 2020.
“My father was an extraordinary person who did so much good and he died alone, terrified in a hospital,” she said. “I can’t even wrap my head around that and how he deserved more. No one deserves that.”
At Vanderbilt University Medical Center, where she works as a critical care doctor, COVID deaths are now different from those in the early days of the pandemic, Dr. Sevin said. Most patients now in the intensive care unit are older and immunocompromised – and they tend to blend in more with others in the intensive care unit. That makes the impact of COVID even more hidden and easily ignored.
“It’s easy not to value somebody who’s an invisible number you don’t know,” she said. “You don’t see them writing their will and talking to their best friend. You don’t see the tears rolling down their face because they know what’s going to happen to them and they’re going to asphyxiate to death.”
One COVID patient who died recently in Dr. Sevin’s ICU ward was an older woman who had no living relatives. “She was very, very lonely, and we would always stand outside the door on rounds, and she would motion for us to come in, but we had to then all gown up,” Dr. Sevin said. “It just breaks your heart that people are still having to go through it.”
Dr. Sevin finds it frustrating that so many of the measures that public health officials fought so hard for over the last 3 years – including masking guidelines, government-funded vaccine clinics, and access to potentially life-saving antiviral medications – are now going away because of the lifting of the pandemic emergency declaration.
What makes matters worse, she said, is that public consciousness about taking precautions to protect others is starting to disappear in favor of an “all or nothing attitude” about the continued risks.
“Like either I’m going to stay home and be a hermit, or I’m going to just throw caution to the wind and go to bars and let people yell in my face,” she said. “We learned some hard lessons, and I wish we could hold onto those.”
Americans like Traci Sikes who’ve lost loved ones and health care workers on the front lines say it is particularly frustrating that so many people are framing the current response to the risks of COVID as “personal choice” over responsibility to others, as well as a sense of fatalism and lack of urgent care.
“Why does nobody seem to be angry about this?” Ms. Sikes said. “People talk about COVID like it’s just another thing to die from. But my sister didn’t have to die from it at all.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Evidence of TAVR benefit extends to cardiogenic shock
Early risks outweighed at 1 year
For patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), adverse outcomes are more common in those who are in cardiogenic shock than those who are not, but the greater risks appear to be completely concentrated in the early period of recovery, suggests a propensity-matched study.
reported Abhijeet Dhoble, MD, associate professor and an interventional cardiologist at McGovern Medical School, University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston.
Their results were presented at the annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
The study, which drew data from the Society of Thoracic Surgeons/American College of Cardiology Transcatheter Valve Replacement (STS/ACC TVR) Registry, looked only at patients who underwent TAVR with the Sapien3 or Sapience3 Ultra device. Patients with CS were propensity matched to Sapien device-treated patients in the registry without CS.
Taken from a pool of 9,348 patients with CS and 299,600 patients without, the matching included a large array of clinically relevant covariates, including age, gender, prior cardiovascular events, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), and New York Heart Association (NYHA) class.
After matching, there were 4,952 patients in each arm. The baseline Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) risk score was approximately 10.0 in both arms. About half had atrial fibrillation and 90% were in NYHA class III or IV. The median LVEF in both groups was 39.9%.
Mortality more than twofold higher in CS patients
At 30 days, outcomes were worse in patients with CS, including the proportion who died (12.9% vs. 4.9%; P < .0001) and the proportion with stroke (3.3% vs. 1.9%; P < .0001).
The only major study endpoint not significantly different, although higher in the CS group, was the rate of readmission (12.0% vs. 11.0%; P = .25).
At 1 year, the differences in the rates of mortality (29.7% vs. 22.6%; P < .0001) and stroke (4.3% vs. 3.1%; P = .0004) had narrowed modestly but remained highly significant. A closer analysis indicated that almost all of the difference in the rate of events occurred prior to hospital discharge.
In fact, mortality (9.9% vs. 2.7%; P < .0001), stroke (2.9% vs. 1.5%; P < .0001), major vascular complications (2.3% vs. 1.9%; P = .0002), life-threatening bleeding (2.5% vs. 0.7%; P < .0001), new dialysis (3.5% vs. 1.1%; P < .0001) and new onset atrial fibrillation (3.8% vs. 1.6%; P < .0001) were all significantly higher in the CS group in this very early time period. By hazard ratio (HR), the risk of a major event prior to leaving the hospital was nearly threefold higher (HR 2.3; P < .0001) in the CS group.
Yet, there was no significant difference in the accumulation of adverse events after discharge. When compared for major events in the landmark analysis, the event curves were essentially superimposable from 30 days to 1 year. During this period, event rates were 19.3% versus 18.5% for CS and non-CS patients (HR 1.07; P = .2640).
The higher rate of events was unrelated to procedural complications, which were very low in both groups and did not differ significantly. Transition to open surgery, annular disruption, aortic dissection, coronary occlusion, and device embolization occurred in < 1% of patients in both groups.
Predictors of a poor outcome identified
On multivariate analysis, the predictors of events in the CS patients were comorbidities. Despite propensity matching, being on dialysis, having a permanent pacemaker, or having a mechanical assist device were all independent predictors of mortality risk specific to the CS group.
Age and baseline Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) score were not predictors.
These risk factors deserve consideration when evaluating CS candidates for TAVR, but Dr. Dhoble said that none are absolute contraindications. Rather, he advised that they should be considered in the context of the entire clinical picture, including the expected benefit from TAVR. Indeed, the benefit-to-risk ratio generally favors TAVR in CS patients, particularly those with obstructive CS caused by aortic stenosis, according to Dr. Dhoble.
“Efforts should be made not only to avoid delaying TAVR in such patients but also to prevent CS by early definitive treatment of patients with aortic stenosis,” he said.
These data are useful and important, said Jonathan Schwartz, MD, medical director, interventional cardiology, Atrium Health, Charlotte, N.C.
CS candidates for TAVR “are some of the sickest patients we treat. It is nice to finally have some data for this group,” he said. He agreed that CS patients can derive major benefit from TAVR if appropriately selected.
While many CS patients are already considered for TAVR, one source of hesitation has been the exclusion of CS patients from major TAVR trials, said Dr. Dhoble. He hopes these data will provide a framework for clinical decisions.
Ironically, the first TAVR patient and half of the initial series of 38 TAVR patients had CS, noted Alain G. Cribier, MD, director of cardiology, Charles Nicolle Hospital, University of Rouen, France. As the primary investigator of that initial TAVR study, conducted more than 20 years ago, he said he was not surprised by the favorable results of the propensity analysis.
“There is an almost miraculous clinical improvement to be achieved when you succeed with the procedure,” said Dr. Cribier, recounting his own experience. Improvements in LVEF of up to 30% can be achieved “within a day or two or even the first day,” he said.
Dr. Dhoble reports financial relationships with Abbott Vascular and Edwards Lifesciences. Dr. Schwartz reports that he has financial relationships with Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, Cordis, Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic. Dr. Cribier reports a financial relationship with Edwards Lifesciences.
Early risks outweighed at 1 year
Early risks outweighed at 1 year
For patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), adverse outcomes are more common in those who are in cardiogenic shock than those who are not, but the greater risks appear to be completely concentrated in the early period of recovery, suggests a propensity-matched study.
reported Abhijeet Dhoble, MD, associate professor and an interventional cardiologist at McGovern Medical School, University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston.
Their results were presented at the annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
The study, which drew data from the Society of Thoracic Surgeons/American College of Cardiology Transcatheter Valve Replacement (STS/ACC TVR) Registry, looked only at patients who underwent TAVR with the Sapien3 or Sapience3 Ultra device. Patients with CS were propensity matched to Sapien device-treated patients in the registry without CS.
Taken from a pool of 9,348 patients with CS and 299,600 patients without, the matching included a large array of clinically relevant covariates, including age, gender, prior cardiovascular events, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), and New York Heart Association (NYHA) class.
After matching, there were 4,952 patients in each arm. The baseline Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) risk score was approximately 10.0 in both arms. About half had atrial fibrillation and 90% were in NYHA class III or IV. The median LVEF in both groups was 39.9%.
Mortality more than twofold higher in CS patients
At 30 days, outcomes were worse in patients with CS, including the proportion who died (12.9% vs. 4.9%; P < .0001) and the proportion with stroke (3.3% vs. 1.9%; P < .0001).
The only major study endpoint not significantly different, although higher in the CS group, was the rate of readmission (12.0% vs. 11.0%; P = .25).
At 1 year, the differences in the rates of mortality (29.7% vs. 22.6%; P < .0001) and stroke (4.3% vs. 3.1%; P = .0004) had narrowed modestly but remained highly significant. A closer analysis indicated that almost all of the difference in the rate of events occurred prior to hospital discharge.
In fact, mortality (9.9% vs. 2.7%; P < .0001), stroke (2.9% vs. 1.5%; P < .0001), major vascular complications (2.3% vs. 1.9%; P = .0002), life-threatening bleeding (2.5% vs. 0.7%; P < .0001), new dialysis (3.5% vs. 1.1%; P < .0001) and new onset atrial fibrillation (3.8% vs. 1.6%; P < .0001) were all significantly higher in the CS group in this very early time period. By hazard ratio (HR), the risk of a major event prior to leaving the hospital was nearly threefold higher (HR 2.3; P < .0001) in the CS group.
Yet, there was no significant difference in the accumulation of adverse events after discharge. When compared for major events in the landmark analysis, the event curves were essentially superimposable from 30 days to 1 year. During this period, event rates were 19.3% versus 18.5% for CS and non-CS patients (HR 1.07; P = .2640).
The higher rate of events was unrelated to procedural complications, which were very low in both groups and did not differ significantly. Transition to open surgery, annular disruption, aortic dissection, coronary occlusion, and device embolization occurred in < 1% of patients in both groups.
Predictors of a poor outcome identified
On multivariate analysis, the predictors of events in the CS patients were comorbidities. Despite propensity matching, being on dialysis, having a permanent pacemaker, or having a mechanical assist device were all independent predictors of mortality risk specific to the CS group.
Age and baseline Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) score were not predictors.
These risk factors deserve consideration when evaluating CS candidates for TAVR, but Dr. Dhoble said that none are absolute contraindications. Rather, he advised that they should be considered in the context of the entire clinical picture, including the expected benefit from TAVR. Indeed, the benefit-to-risk ratio generally favors TAVR in CS patients, particularly those with obstructive CS caused by aortic stenosis, according to Dr. Dhoble.
“Efforts should be made not only to avoid delaying TAVR in such patients but also to prevent CS by early definitive treatment of patients with aortic stenosis,” he said.
These data are useful and important, said Jonathan Schwartz, MD, medical director, interventional cardiology, Atrium Health, Charlotte, N.C.
CS candidates for TAVR “are some of the sickest patients we treat. It is nice to finally have some data for this group,” he said. He agreed that CS patients can derive major benefit from TAVR if appropriately selected.
While many CS patients are already considered for TAVR, one source of hesitation has been the exclusion of CS patients from major TAVR trials, said Dr. Dhoble. He hopes these data will provide a framework for clinical decisions.
Ironically, the first TAVR patient and half of the initial series of 38 TAVR patients had CS, noted Alain G. Cribier, MD, director of cardiology, Charles Nicolle Hospital, University of Rouen, France. As the primary investigator of that initial TAVR study, conducted more than 20 years ago, he said he was not surprised by the favorable results of the propensity analysis.
“There is an almost miraculous clinical improvement to be achieved when you succeed with the procedure,” said Dr. Cribier, recounting his own experience. Improvements in LVEF of up to 30% can be achieved “within a day or two or even the first day,” he said.
Dr. Dhoble reports financial relationships with Abbott Vascular and Edwards Lifesciences. Dr. Schwartz reports that he has financial relationships with Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, Cordis, Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic. Dr. Cribier reports a financial relationship with Edwards Lifesciences.
For patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), adverse outcomes are more common in those who are in cardiogenic shock than those who are not, but the greater risks appear to be completely concentrated in the early period of recovery, suggests a propensity-matched study.
reported Abhijeet Dhoble, MD, associate professor and an interventional cardiologist at McGovern Medical School, University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston.
Their results were presented at the annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
The study, which drew data from the Society of Thoracic Surgeons/American College of Cardiology Transcatheter Valve Replacement (STS/ACC TVR) Registry, looked only at patients who underwent TAVR with the Sapien3 or Sapience3 Ultra device. Patients with CS were propensity matched to Sapien device-treated patients in the registry without CS.
Taken from a pool of 9,348 patients with CS and 299,600 patients without, the matching included a large array of clinically relevant covariates, including age, gender, prior cardiovascular events, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), and New York Heart Association (NYHA) class.
After matching, there were 4,952 patients in each arm. The baseline Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) risk score was approximately 10.0 in both arms. About half had atrial fibrillation and 90% were in NYHA class III or IV. The median LVEF in both groups was 39.9%.
Mortality more than twofold higher in CS patients
At 30 days, outcomes were worse in patients with CS, including the proportion who died (12.9% vs. 4.9%; P < .0001) and the proportion with stroke (3.3% vs. 1.9%; P < .0001).
The only major study endpoint not significantly different, although higher in the CS group, was the rate of readmission (12.0% vs. 11.0%; P = .25).
At 1 year, the differences in the rates of mortality (29.7% vs. 22.6%; P < .0001) and stroke (4.3% vs. 3.1%; P = .0004) had narrowed modestly but remained highly significant. A closer analysis indicated that almost all of the difference in the rate of events occurred prior to hospital discharge.
In fact, mortality (9.9% vs. 2.7%; P < .0001), stroke (2.9% vs. 1.5%; P < .0001), major vascular complications (2.3% vs. 1.9%; P = .0002), life-threatening bleeding (2.5% vs. 0.7%; P < .0001), new dialysis (3.5% vs. 1.1%; P < .0001) and new onset atrial fibrillation (3.8% vs. 1.6%; P < .0001) were all significantly higher in the CS group in this very early time period. By hazard ratio (HR), the risk of a major event prior to leaving the hospital was nearly threefold higher (HR 2.3; P < .0001) in the CS group.
Yet, there was no significant difference in the accumulation of adverse events after discharge. When compared for major events in the landmark analysis, the event curves were essentially superimposable from 30 days to 1 year. During this period, event rates were 19.3% versus 18.5% for CS and non-CS patients (HR 1.07; P = .2640).
The higher rate of events was unrelated to procedural complications, which were very low in both groups and did not differ significantly. Transition to open surgery, annular disruption, aortic dissection, coronary occlusion, and device embolization occurred in < 1% of patients in both groups.
Predictors of a poor outcome identified
On multivariate analysis, the predictors of events in the CS patients were comorbidities. Despite propensity matching, being on dialysis, having a permanent pacemaker, or having a mechanical assist device were all independent predictors of mortality risk specific to the CS group.
Age and baseline Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) score were not predictors.
These risk factors deserve consideration when evaluating CS candidates for TAVR, but Dr. Dhoble said that none are absolute contraindications. Rather, he advised that they should be considered in the context of the entire clinical picture, including the expected benefit from TAVR. Indeed, the benefit-to-risk ratio generally favors TAVR in CS patients, particularly those with obstructive CS caused by aortic stenosis, according to Dr. Dhoble.
“Efforts should be made not only to avoid delaying TAVR in such patients but also to prevent CS by early definitive treatment of patients with aortic stenosis,” he said.
These data are useful and important, said Jonathan Schwartz, MD, medical director, interventional cardiology, Atrium Health, Charlotte, N.C.
CS candidates for TAVR “are some of the sickest patients we treat. It is nice to finally have some data for this group,” he said. He agreed that CS patients can derive major benefit from TAVR if appropriately selected.
While many CS patients are already considered for TAVR, one source of hesitation has been the exclusion of CS patients from major TAVR trials, said Dr. Dhoble. He hopes these data will provide a framework for clinical decisions.
Ironically, the first TAVR patient and half of the initial series of 38 TAVR patients had CS, noted Alain G. Cribier, MD, director of cardiology, Charles Nicolle Hospital, University of Rouen, France. As the primary investigator of that initial TAVR study, conducted more than 20 years ago, he said he was not surprised by the favorable results of the propensity analysis.
“There is an almost miraculous clinical improvement to be achieved when you succeed with the procedure,” said Dr. Cribier, recounting his own experience. Improvements in LVEF of up to 30% can be achieved “within a day or two or even the first day,” he said.
Dr. Dhoble reports financial relationships with Abbott Vascular and Edwards Lifesciences. Dr. Schwartz reports that he has financial relationships with Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, Cordis, Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic. Dr. Cribier reports a financial relationship with Edwards Lifesciences.
FROM EUROPCR 2023
CDC warns of Mpox resurgence in summer of 2023
A resurgence of mpox this summer could be larger than last year’s caseload, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said in a warning to public health officials this week.
“The outbreak is not over,” the CDC alert stated, noting that springtime and summertime gatherings and festivals could lead to renewed virus spread. A new cluster of 13 cases is being investigated in Chicago, all among men, and four among people who recently traveled to New York City, New Orleans, or Mexico.
Mpox, formerly called monkeypox, is a virus that causes a rash and sometimes flulike symptoms. It is most often transmitted through sexual contact, but it can also be spread in nonsexual ways that involve contact with skin lesions or with saliva or upper respiratory secretions like snot or mucus, the CDC says. Most cases in the United States have been among gay or bisexual men, men who have sex with men, and transgender people.
Last year, the U.S. government declared mpox a public health emergency as cases peaked at 460 per day in August, infecting more than 30,000 people and killing 42 people. Public health officials worked to quickly distribute vaccinations to people at high risk for contracting the virus. The CDC says 23% of people most at risk of getting mpox have been vaccinated.
Vaccination does not necessarily prevent infection but can lessen the severity of symptoms. Nine of the men who were recently infected in Chicago were fully vaccinated.
“It’s important to remember that vaccines, while incredibly helpful, are not our only way to reduce the risk of contracting mpox,” Richard Silvera, MD, MPH, of the department of infectious diseases at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, told ABC News.
Other ways to reduce risk are “things like avoiding social and sexual contact if you have new skin lesions and asking your intimate contacts if they are experiencing symptoms or new skin changes,” Dr. Silvera said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A resurgence of mpox this summer could be larger than last year’s caseload, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said in a warning to public health officials this week.
“The outbreak is not over,” the CDC alert stated, noting that springtime and summertime gatherings and festivals could lead to renewed virus spread. A new cluster of 13 cases is being investigated in Chicago, all among men, and four among people who recently traveled to New York City, New Orleans, or Mexico.
Mpox, formerly called monkeypox, is a virus that causes a rash and sometimes flulike symptoms. It is most often transmitted through sexual contact, but it can also be spread in nonsexual ways that involve contact with skin lesions or with saliva or upper respiratory secretions like snot or mucus, the CDC says. Most cases in the United States have been among gay or bisexual men, men who have sex with men, and transgender people.
Last year, the U.S. government declared mpox a public health emergency as cases peaked at 460 per day in August, infecting more than 30,000 people and killing 42 people. Public health officials worked to quickly distribute vaccinations to people at high risk for contracting the virus. The CDC says 23% of people most at risk of getting mpox have been vaccinated.
Vaccination does not necessarily prevent infection but can lessen the severity of symptoms. Nine of the men who were recently infected in Chicago were fully vaccinated.
“It’s important to remember that vaccines, while incredibly helpful, are not our only way to reduce the risk of contracting mpox,” Richard Silvera, MD, MPH, of the department of infectious diseases at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, told ABC News.
Other ways to reduce risk are “things like avoiding social and sexual contact if you have new skin lesions and asking your intimate contacts if they are experiencing symptoms or new skin changes,” Dr. Silvera said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A resurgence of mpox this summer could be larger than last year’s caseload, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said in a warning to public health officials this week.
“The outbreak is not over,” the CDC alert stated, noting that springtime and summertime gatherings and festivals could lead to renewed virus spread. A new cluster of 13 cases is being investigated in Chicago, all among men, and four among people who recently traveled to New York City, New Orleans, or Mexico.
Mpox, formerly called monkeypox, is a virus that causes a rash and sometimes flulike symptoms. It is most often transmitted through sexual contact, but it can also be spread in nonsexual ways that involve contact with skin lesions or with saliva or upper respiratory secretions like snot or mucus, the CDC says. Most cases in the United States have been among gay or bisexual men, men who have sex with men, and transgender people.
Last year, the U.S. government declared mpox a public health emergency as cases peaked at 460 per day in August, infecting more than 30,000 people and killing 42 people. Public health officials worked to quickly distribute vaccinations to people at high risk for contracting the virus. The CDC says 23% of people most at risk of getting mpox have been vaccinated.
Vaccination does not necessarily prevent infection but can lessen the severity of symptoms. Nine of the men who were recently infected in Chicago were fully vaccinated.
“It’s important to remember that vaccines, while incredibly helpful, are not our only way to reduce the risk of contracting mpox,” Richard Silvera, MD, MPH, of the department of infectious diseases at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, told ABC News.
Other ways to reduce risk are “things like avoiding social and sexual contact if you have new skin lesions and asking your intimate contacts if they are experiencing symptoms or new skin changes,” Dr. Silvera said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.