User login
New guidelines say pediatricians should screen for anxiety: Now what?
Recently the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force issued a formal recommendation that adolescents and children as young as 8 should be screened for anxiety.1 The advice was based on a review of the research that concluded that anxiety disorders were common in youth (prevalence around 8%), screening was not overly burdensome or dangerous, and treatments were available and effective.
While pediatricians fully appreciate how common clinically significant anxiety is and its impact on the lives of youth, the reception for the recommendations have been mixed. Some are concerned that it could lead to the overprescribing of medications. Arguably, the biggest pushback, however, relates to the question of what to do when a child screens positive in a time when finding an available child and adolescent psychiatrist or other type of pediatric mental health professional can feel next to impossible. The hope of this article is to fill in some of those gaps.
Screening for anxiety disorders
The recommendations suggest using a rating scale as part of the screen but doesn’t dictate which one. A common instrument that has been employed is the Screen for Child Anxiety and Related Disorders, which is a freely available 41-item instrument that has versions for youth self-report and parent-report. A shorter 7-item rating scale, the General Anxiety Disorder–7, and the even shorter GAD-2 (the first two questions of the GAD-7), are also popular but focus, as the name applies, on general anxiety disorder and not related conditions such as social or separation anxiety that can have some different symptoms. These instruments can be given to patients and families in the waiting room or administered with the help of a nurse, physician, or embedded mental health professional. The recommendations do not include specific guidance on how often the screening should be done but repeated screenings are likely important at some interval.
Confirming the diagnosis
Of course, a screening isn’t a formal diagnosis. The American Academy of Pediatrics has expressed the view that the initial diagnosis and treatment for anxiety disorders is well within a pediatrician’s scope of practice, which means further steps are likely required beyond a referral. Fortunately, going from a positive screen to an initial diagnosis does not have to overly laborious and can focus on reviewing the DSM-5 criteria for key anxiety disorders while also ensuring that there isn’t a nonpsychiatric cause driving the symptoms, such as the often cited but rarely seen pheochromocytoma. More common rule-outs include medication-induced anxiety or substance use, excessive caffeine intake, and cardiac arrhythmias. Assessing for current and past trauma or specific causes of the anxiety such as bullying are also important.
It is important to note that it is the rule rather than the exception that youth with clinical levels of anxiety will frequently endorse a number of criteria that span multiple diagnoses including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and separation anxiety disorder.2 Spending a lot of effort to narrow things down to a single anxiety diagnosis often is unnecessary, as both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic treatments don’t change all that much between individual diagnoses.
Explaining the diagnosis
In general, I’m a strong proponent of trying to explain any behavioral diagnoses that you make to kids in a way that is accurate but nonstigmatizing. When it comes to anxiety, one parallel I often draw is to our immune system, which most youth understand at least in basic terms. Both our immune system and our anxiety networks are natural and important; as a species, we wouldn’t have lasted long without them. Both are built to assess and respond to threats. Problems can arise, however, if the response is too strong relative to the threat or the response is activated when it doesn’t need to be. Treatment is directed not at ridding ourselves of anxiety but at helping regulate it so it works for us and not against us. Spending a few minutes going through a discussion like this can be very helpful, and perhaps more so than some dry summary of DSM-5 criteria.
Starting treatment
It is important to note that best practice recommendations when it comes to the treatment of anxiety disorder in youth do not suggest medications as the only type of treatment and often urge clinicians to try nonpharmacological interventions first.3 A specific type of psychotherapy called cognitive-behavioral therapy has the strongest scientific support as an effective treatment for anxiety but other modalities, including parenting guidance, can be helpful as well. Consequently, a referral to a good psychotherapist is paramount. For many kids, the key to overcoming anxiety is exposure: which means confronting anxiety slowly, with support, and with specific skills.
If there is a traumatic source of the anxiety, addressing that as much as possible is obviously critical and could involve working with the family or school. For some kids, this may involve frightening things they are seeing online or through other media. Finally, some health promotion activities such as exercise or mindfulness can also be quite useful.
Despite the fact that SSRIs are referred to as antidepressants, there is increasing appreciation that these medications are useful for anxiety, perhaps even more so than for mood. While only one medication, duloxetine, has Food and Drug Administration approval to treat anxiety in children as young as 7, there is good evidence to support the use of many of the most common SSRIs in treating clinical anxiety. Buspirone, beta-blockers, and antihistamine medications like hydroxyzine also can have their place in treatment, while benzodiazepines and antipsychotic medications are generally best avoided for anxious youth, especially in the primary care setting. A short but helpful medication guide with regard to pediatric anxiety has been published by the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.4
Conclusions
Clinical levels of anxiety in children and adolescents are both common and quite treatable, which has prompted new recommendations that primary care clinicians screen for them starting at age 8. While this recommendation may at first seem like yet one more task to fit in, following the guidance can be accomplished with the help of short screening tools and a managed multimodal approach to treatment.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist with Lane County Behavioral Health in Eugene, Ore., and Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. You can follow him on Twitter and Facebook @PediPsych.
References
1. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2022;328(14):1438-44.
2. Strawn JR. Curr Psychiatry. 2012;11(9):16-21.
3. Walter HJ et al. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2020;59(10):1107-24.
4. Anxiety Disorders: Parents’ Medication Guide Workgroup. “Anxiety disorders: Parents’ medication guide.” Washington D.C.: American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 2020.
Recently the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force issued a formal recommendation that adolescents and children as young as 8 should be screened for anxiety.1 The advice was based on a review of the research that concluded that anxiety disorders were common in youth (prevalence around 8%), screening was not overly burdensome or dangerous, and treatments were available and effective.
While pediatricians fully appreciate how common clinically significant anxiety is and its impact on the lives of youth, the reception for the recommendations have been mixed. Some are concerned that it could lead to the overprescribing of medications. Arguably, the biggest pushback, however, relates to the question of what to do when a child screens positive in a time when finding an available child and adolescent psychiatrist or other type of pediatric mental health professional can feel next to impossible. The hope of this article is to fill in some of those gaps.
Screening for anxiety disorders
The recommendations suggest using a rating scale as part of the screen but doesn’t dictate which one. A common instrument that has been employed is the Screen for Child Anxiety and Related Disorders, which is a freely available 41-item instrument that has versions for youth self-report and parent-report. A shorter 7-item rating scale, the General Anxiety Disorder–7, and the even shorter GAD-2 (the first two questions of the GAD-7), are also popular but focus, as the name applies, on general anxiety disorder and not related conditions such as social or separation anxiety that can have some different symptoms. These instruments can be given to patients and families in the waiting room or administered with the help of a nurse, physician, or embedded mental health professional. The recommendations do not include specific guidance on how often the screening should be done but repeated screenings are likely important at some interval.
Confirming the diagnosis
Of course, a screening isn’t a formal diagnosis. The American Academy of Pediatrics has expressed the view that the initial diagnosis and treatment for anxiety disorders is well within a pediatrician’s scope of practice, which means further steps are likely required beyond a referral. Fortunately, going from a positive screen to an initial diagnosis does not have to overly laborious and can focus on reviewing the DSM-5 criteria for key anxiety disorders while also ensuring that there isn’t a nonpsychiatric cause driving the symptoms, such as the often cited but rarely seen pheochromocytoma. More common rule-outs include medication-induced anxiety or substance use, excessive caffeine intake, and cardiac arrhythmias. Assessing for current and past trauma or specific causes of the anxiety such as bullying are also important.
It is important to note that it is the rule rather than the exception that youth with clinical levels of anxiety will frequently endorse a number of criteria that span multiple diagnoses including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and separation anxiety disorder.2 Spending a lot of effort to narrow things down to a single anxiety diagnosis often is unnecessary, as both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic treatments don’t change all that much between individual diagnoses.
Explaining the diagnosis
In general, I’m a strong proponent of trying to explain any behavioral diagnoses that you make to kids in a way that is accurate but nonstigmatizing. When it comes to anxiety, one parallel I often draw is to our immune system, which most youth understand at least in basic terms. Both our immune system and our anxiety networks are natural and important; as a species, we wouldn’t have lasted long without them. Both are built to assess and respond to threats. Problems can arise, however, if the response is too strong relative to the threat or the response is activated when it doesn’t need to be. Treatment is directed not at ridding ourselves of anxiety but at helping regulate it so it works for us and not against us. Spending a few minutes going through a discussion like this can be very helpful, and perhaps more so than some dry summary of DSM-5 criteria.
Starting treatment
It is important to note that best practice recommendations when it comes to the treatment of anxiety disorder in youth do not suggest medications as the only type of treatment and often urge clinicians to try nonpharmacological interventions first.3 A specific type of psychotherapy called cognitive-behavioral therapy has the strongest scientific support as an effective treatment for anxiety but other modalities, including parenting guidance, can be helpful as well. Consequently, a referral to a good psychotherapist is paramount. For many kids, the key to overcoming anxiety is exposure: which means confronting anxiety slowly, with support, and with specific skills.
If there is a traumatic source of the anxiety, addressing that as much as possible is obviously critical and could involve working with the family or school. For some kids, this may involve frightening things they are seeing online or through other media. Finally, some health promotion activities such as exercise or mindfulness can also be quite useful.
Despite the fact that SSRIs are referred to as antidepressants, there is increasing appreciation that these medications are useful for anxiety, perhaps even more so than for mood. While only one medication, duloxetine, has Food and Drug Administration approval to treat anxiety in children as young as 7, there is good evidence to support the use of many of the most common SSRIs in treating clinical anxiety. Buspirone, beta-blockers, and antihistamine medications like hydroxyzine also can have their place in treatment, while benzodiazepines and antipsychotic medications are generally best avoided for anxious youth, especially in the primary care setting. A short but helpful medication guide with regard to pediatric anxiety has been published by the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.4
Conclusions
Clinical levels of anxiety in children and adolescents are both common and quite treatable, which has prompted new recommendations that primary care clinicians screen for them starting at age 8. While this recommendation may at first seem like yet one more task to fit in, following the guidance can be accomplished with the help of short screening tools and a managed multimodal approach to treatment.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist with Lane County Behavioral Health in Eugene, Ore., and Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. You can follow him on Twitter and Facebook @PediPsych.
References
1. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2022;328(14):1438-44.
2. Strawn JR. Curr Psychiatry. 2012;11(9):16-21.
3. Walter HJ et al. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2020;59(10):1107-24.
4. Anxiety Disorders: Parents’ Medication Guide Workgroup. “Anxiety disorders: Parents’ medication guide.” Washington D.C.: American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 2020.
Recently the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force issued a formal recommendation that adolescents and children as young as 8 should be screened for anxiety.1 The advice was based on a review of the research that concluded that anxiety disorders were common in youth (prevalence around 8%), screening was not overly burdensome or dangerous, and treatments were available and effective.
While pediatricians fully appreciate how common clinically significant anxiety is and its impact on the lives of youth, the reception for the recommendations have been mixed. Some are concerned that it could lead to the overprescribing of medications. Arguably, the biggest pushback, however, relates to the question of what to do when a child screens positive in a time when finding an available child and adolescent psychiatrist or other type of pediatric mental health professional can feel next to impossible. The hope of this article is to fill in some of those gaps.
Screening for anxiety disorders
The recommendations suggest using a rating scale as part of the screen but doesn’t dictate which one. A common instrument that has been employed is the Screen for Child Anxiety and Related Disorders, which is a freely available 41-item instrument that has versions for youth self-report and parent-report. A shorter 7-item rating scale, the General Anxiety Disorder–7, and the even shorter GAD-2 (the first two questions of the GAD-7), are also popular but focus, as the name applies, on general anxiety disorder and not related conditions such as social or separation anxiety that can have some different symptoms. These instruments can be given to patients and families in the waiting room or administered with the help of a nurse, physician, or embedded mental health professional. The recommendations do not include specific guidance on how often the screening should be done but repeated screenings are likely important at some interval.
Confirming the diagnosis
Of course, a screening isn’t a formal diagnosis. The American Academy of Pediatrics has expressed the view that the initial diagnosis and treatment for anxiety disorders is well within a pediatrician’s scope of practice, which means further steps are likely required beyond a referral. Fortunately, going from a positive screen to an initial diagnosis does not have to overly laborious and can focus on reviewing the DSM-5 criteria for key anxiety disorders while also ensuring that there isn’t a nonpsychiatric cause driving the symptoms, such as the often cited but rarely seen pheochromocytoma. More common rule-outs include medication-induced anxiety or substance use, excessive caffeine intake, and cardiac arrhythmias. Assessing for current and past trauma or specific causes of the anxiety such as bullying are also important.
It is important to note that it is the rule rather than the exception that youth with clinical levels of anxiety will frequently endorse a number of criteria that span multiple diagnoses including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and separation anxiety disorder.2 Spending a lot of effort to narrow things down to a single anxiety diagnosis often is unnecessary, as both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic treatments don’t change all that much between individual diagnoses.
Explaining the diagnosis
In general, I’m a strong proponent of trying to explain any behavioral diagnoses that you make to kids in a way that is accurate but nonstigmatizing. When it comes to anxiety, one parallel I often draw is to our immune system, which most youth understand at least in basic terms. Both our immune system and our anxiety networks are natural and important; as a species, we wouldn’t have lasted long without them. Both are built to assess and respond to threats. Problems can arise, however, if the response is too strong relative to the threat or the response is activated when it doesn’t need to be. Treatment is directed not at ridding ourselves of anxiety but at helping regulate it so it works for us and not against us. Spending a few minutes going through a discussion like this can be very helpful, and perhaps more so than some dry summary of DSM-5 criteria.
Starting treatment
It is important to note that best practice recommendations when it comes to the treatment of anxiety disorder in youth do not suggest medications as the only type of treatment and often urge clinicians to try nonpharmacological interventions first.3 A specific type of psychotherapy called cognitive-behavioral therapy has the strongest scientific support as an effective treatment for anxiety but other modalities, including parenting guidance, can be helpful as well. Consequently, a referral to a good psychotherapist is paramount. For many kids, the key to overcoming anxiety is exposure: which means confronting anxiety slowly, with support, and with specific skills.
If there is a traumatic source of the anxiety, addressing that as much as possible is obviously critical and could involve working with the family or school. For some kids, this may involve frightening things they are seeing online or through other media. Finally, some health promotion activities such as exercise or mindfulness can also be quite useful.
Despite the fact that SSRIs are referred to as antidepressants, there is increasing appreciation that these medications are useful for anxiety, perhaps even more so than for mood. While only one medication, duloxetine, has Food and Drug Administration approval to treat anxiety in children as young as 7, there is good evidence to support the use of many of the most common SSRIs in treating clinical anxiety. Buspirone, beta-blockers, and antihistamine medications like hydroxyzine also can have their place in treatment, while benzodiazepines and antipsychotic medications are generally best avoided for anxious youth, especially in the primary care setting. A short but helpful medication guide with regard to pediatric anxiety has been published by the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.4
Conclusions
Clinical levels of anxiety in children and adolescents are both common and quite treatable, which has prompted new recommendations that primary care clinicians screen for them starting at age 8. While this recommendation may at first seem like yet one more task to fit in, following the guidance can be accomplished with the help of short screening tools and a managed multimodal approach to treatment.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist with Lane County Behavioral Health in Eugene, Ore., and Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. You can follow him on Twitter and Facebook @PediPsych.
References
1. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2022;328(14):1438-44.
2. Strawn JR. Curr Psychiatry. 2012;11(9):16-21.
3. Walter HJ et al. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2020;59(10):1107-24.
4. Anxiety Disorders: Parents’ Medication Guide Workgroup. “Anxiety disorders: Parents’ medication guide.” Washington D.C.: American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 2020.
Optimal psychiatric treatment: Target the brain and avoid the body
Pharmacotherapy for psychiatric disorders is a mixed blessing. The advent of psychotropic medications since the 1950s (antipsychotics, antidepressants, anxiolytics, mood stabilizers) has revolutionized the treatment of serious psychiatric brain disorders, allowing certain patients to be discharged to the community after a lifetime of institutionalization.
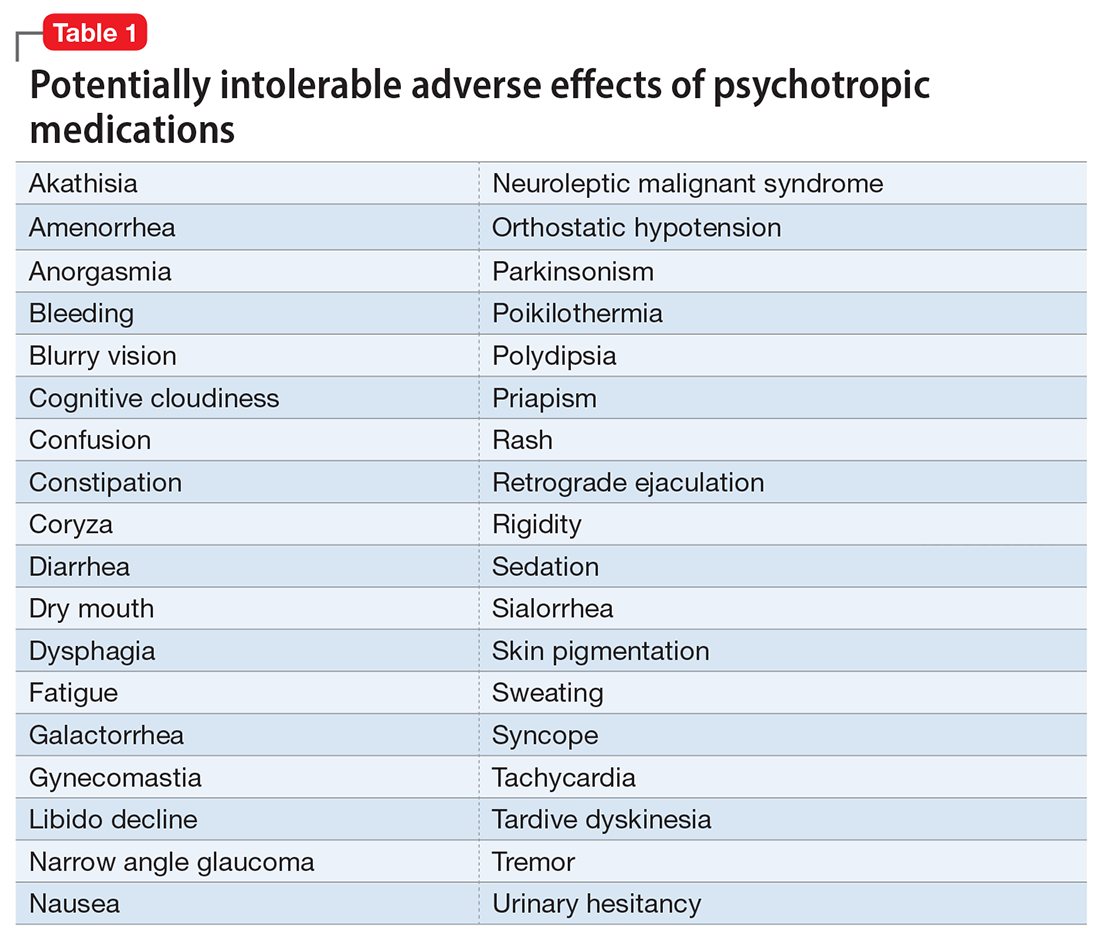
However, like all medications, psychotropic agents are often associated with various potentially intolerable symptoms (Table 1) or safety complications (Table 2) because they interact with every organ in the body besides their intended target, the brain, and its neurochemical circuitry.
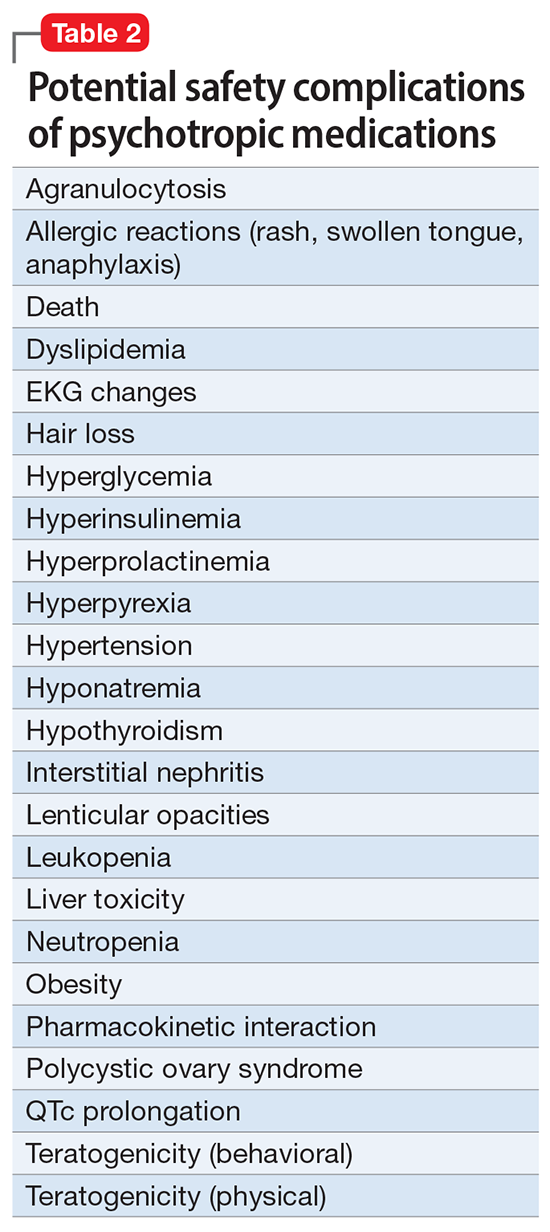
Imagine if we could treat our psychiatric patients while bypassing the body and achieve response, remission, and ultimately recovery without any systemic adverse effects. Adherence would dramatically improve, our patients’ quality of life would be enhanced, and the overall effectiveness (defined as the complex package of efficacy, safety, and tolerability) would be superior to current pharmacotherapies. This is important because most psychiatric medications must be taken daily for years, even a lifetime, to avoid a relapse of the illness. Psychiatrists frequently must manage adverse effects or switch the patient to a different medication if a tolerability or safety issue emerges, which is very common in psychiatric practice. A significant part of psychopharmacologic management includes ordering various laboratory tests to monitor adverse reactions in major organs, especially the liver, kidney, and heart. Additionally, psychiatric physicians must be constantly cognizant of medications prescribed by other clinicians for comorbid medical conditions to successfully navigate the turbulent seas of pharmacokinetic interactions.
I am sure you have noticed that whenever you watch a direct-to-consumer commercial for any medication, 90% of the advertisement is a background voice listing the various tolerability and safety complications of the medication as required by the FDA. Interestingly, these ads frequently contain colorful scenery and joyful clips, which I suspect are cleverly designed to distract the audience from focusing on the list of adverse effects.
Benefits of nonpharmacologic treatments
No wonder I am a fan of psychotherapy, a well-established psychiatric treatment modality that completely avoids body tissues. It directly targets the brain without needlessly interacting with any other organ. Psychotherapy’s many benefits (improving insight, enhancing adherence, improving self-esteem, reducing risky behaviors, guiding stress management and coping skills, modifying unhealthy beliefs, and ultimately relieving symptoms such as anxiety and depression) are achieved without any somatic adverse effects! Psychotherapy has also been shown to induce neuroplasticity and reduce inflammatory biomarkers.1 Unlike FDA-approved medications, psychotherapy does not include a “package insert,” 10 to 20 pages (in small print) that mostly focus on warnings, precautions, and sundry physical adverse effects. Even the dosing of psychotherapy is left entirely up to the treating clinician!
Although I have had many gratifying results with pharmacotherapy in my practice, especially in combination with psychotherapy,2 I also have observed excellent outcomes with nonpharmacologic approaches, especially neuromodulation therapies. The best antidepressant I have ever used since my residency training days is electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). My experience is consistent with a large meta-analysis3showing a huge effect size (Cohen d = .91) in contrast to the usual effect size of .3 to .5 for standard antidepressants (except IV ketamine). A recent study showed ECT is even better than the vaunted rapid-acting ketamine,4 which is further evidence of its remarkable efficacy in depression. Neuroimaging studies report that ECT rapidly increases the volume of the hippocampus,5,6 which shrinks in size in patients with unipolar or bipolar depression.
Neuromodulation may very well be the future of psychiatric therapeutics. It targets the brain and avoids the body, thus achieving efficacy with minimal systemic tolerability (ie, patient complaints) (Table 1) or safety (abnormal laboratory test results) issues (Table 2). This sounds ideal, and it is arguably an optimal approach to repairing the brain and healing the mind.
Continue to: ECT is the oldest...
ECT is the oldest neuromodulation technique (developed almost 100 years ago and significantly refined since then). Newer FDA-approved neuromodulation therapies include repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), which was approved for depression in 2013, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in 2018, smoking cessation in 2020, and anxious depression in 2021.7 Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is used for drug-resistant epilepsy and was later approved for treatment-resistant depression,8,9 but some studies report it can be helpful for fear and anxiety in autism spectrum disorder10 and primary insomnia.11
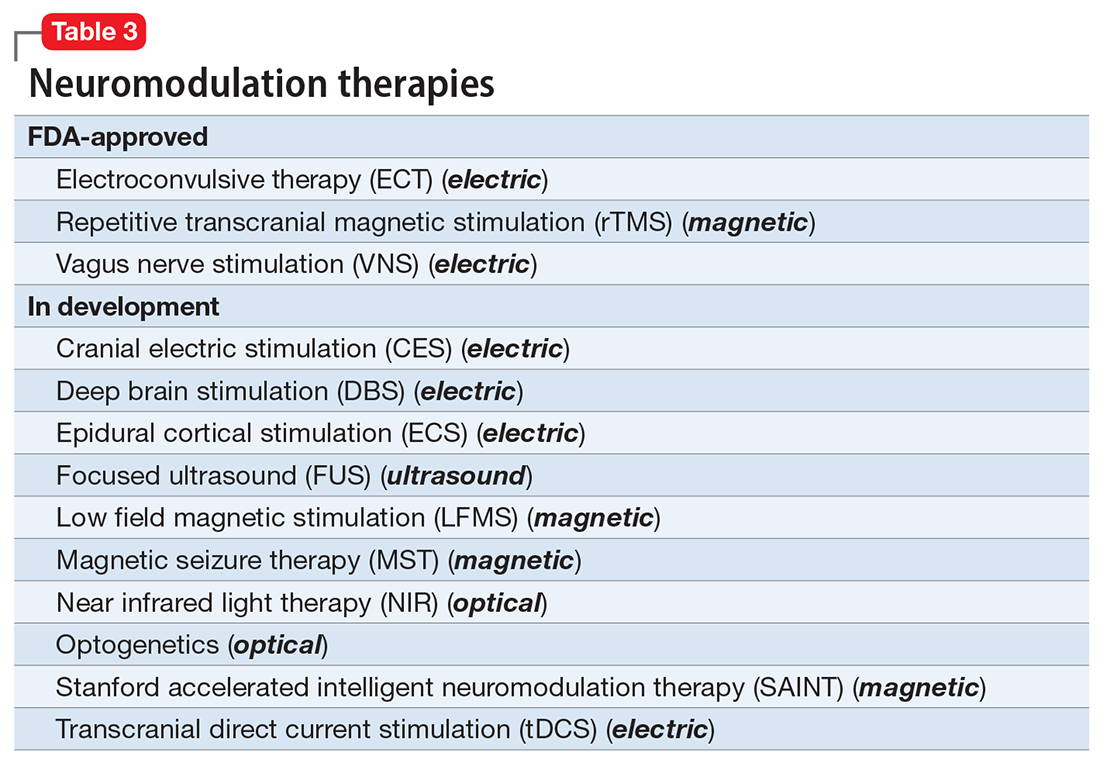
There are many other neuromodulation therapies in development12 that have not yet been FDA approved (Table 3). The most prominent of these is deep brain stimulation (DBS), which is approved for Parkinson disease and has been reported in many studies to improve treatment-resistant depression13,14 and OCD.15 Another promising neuromodulation therapy is transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), which has promising results in schizophrenia16 similar to ECT’s effects in treatment-resistant schizophrenia.17
A particularly exciting neuromodulation approach published by Stanford University researchers is Stanford accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy (SAINT),18 which uses intermittent theta-burst stimulation (iTBS) daily for 5 days, targeted at the subgenual anterior cingulate gyrus (Brodman area 25). Remarkably, efficacy was rapid, with a very high remission rate (absence of symptoms) in approximately 90% of patients with severe depression.18
The future is bright for neuromodulation therapies, and for a good reason. Why send a chemical agent to every cell and organ in the body when the brain can be targeted directly? As psychiatric neuroscience advances to a point where we can localize the abnormal neurologic circuit in a specific brain region for each psychiatric disorder, it will be possible to treat almost all psychiatric disorders without burdening patients with the intolerable symptoms or safety adverse effects of medications. Psychiatrists should modulate their perspective about the future of psychiatric treatments. And finally, I propose that psychotherapy should be reclassified as a “verbal neuromodulation” technique.
1. Nasrallah HA. Repositioning psychotherapy as a neurobiological intervention. Current Psychiatry. 2013;12(12):18-19.
2. Nasrallah HA. Bipolar disorder: clinical questions beg for answers. Current Psychiatry. 2006;5(12):11-12.
3. UK ECT Review Group. Efficacy and safety of electroconvulsive therapy in depressive disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2003;361(9360):799-808.
4. Rhee TG, Shim SR, Forester BP, et al. Efficacy and safety of ketamine vs electroconvulsive therapy among patients with major depressive episode: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2022:e223352. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2022.3352
5. Nuninga JO, Mandl RCW, Boks MP, et al. Volume increase in the dentate gyrus after electroconvulsive therapy in depressed patients as measured with 7T. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(7):1559-1568.
6. Joshi SH, Espinoza RT, Pirnia T, et al. Structural plasticity of the hippocampus and amygdala induced by electroconvulsive therapy in major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2016;79(4):282-292.
7. Rhee TG, Olfson M, Nierenberg AA, et al. 20-year trends in the pharmacologic treatment of bipolar disorder by psychiatrists in outpatient care settings. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(8):706-715.
8. Hilz MJ. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation - a brief introduction and overview. Auton Neurosci. 2022;243:103038. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2022.103038
9. Pigato G, Rosson S, Bresolin N, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation in treatment-resistant depression: a case series of long-term follow-up. J ECT. 2022. doi:10.1097/YCT.0000000000000869
10. Shivaswamy T, Souza RR, Engineer CT, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation as a treatment for fear and anxiety in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. J Psychiatr Brain Sci. 2022;7(4):e220007. doi:10.20900/jpbs.20220007
11. Wu Y, Song L, Wang X, et al. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation could improve the effective rate on the quality of sleep in the treatment of primary insomnia: a randomized control trial. Brain Sci. 2022;12(10):1296. doi:10.3390/brainsci12101296
12. Rosa MA, Lisanby SH. Somatic treatments for mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37(1):102-116.
13. Mayberg HS, Lozano AM, Voon V, et al. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron. 2005;45(5):651-660.
14. Choi KS, Mayberg H. Connectomic DBS in major depression. In: Horn A, ed. Connectomic Deep Brain Stimulation. Academic Press; 2022:433-447.
15. Cruz S, Gutiérrez-Rojas L, González-Domenech P, et al. Deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder: results from meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2022;317:114869. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2022.114869
16. Lisoni J, Baldacci G, Nibbio G, et al. Effects of bilateral, bipolar-nonbalanced, frontal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) on negative symptoms and neurocognition in a sample of patients living with schizophrenia: results of a randomized double-blind sham-controlled trial. J Psychiatr Res. 2022;155:430-442.
17. Sinclair DJ, Zhao S, Qi F, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy for treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;3(3):CD011847. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011847.pub2
18. Cole EJ, Stimpson KH, Bentzley BS, et al. Stanford accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy for treatment-resistant depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(8):716-726.
Pharmacotherapy for psychiatric disorders is a mixed blessing. The advent of psychotropic medications since the 1950s (antipsychotics, antidepressants, anxiolytics, mood stabilizers) has revolutionized the treatment of serious psychiatric brain disorders, allowing certain patients to be discharged to the community after a lifetime of institutionalization.

However, like all medications, psychotropic agents are often associated with various potentially intolerable symptoms (Table 1) or safety complications (Table 2) because they interact with every organ in the body besides their intended target, the brain, and its neurochemical circuitry.

Imagine if we could treat our psychiatric patients while bypassing the body and achieve response, remission, and ultimately recovery without any systemic adverse effects. Adherence would dramatically improve, our patients’ quality of life would be enhanced, and the overall effectiveness (defined as the complex package of efficacy, safety, and tolerability) would be superior to current pharmacotherapies. This is important because most psychiatric medications must be taken daily for years, even a lifetime, to avoid a relapse of the illness. Psychiatrists frequently must manage adverse effects or switch the patient to a different medication if a tolerability or safety issue emerges, which is very common in psychiatric practice. A significant part of psychopharmacologic management includes ordering various laboratory tests to monitor adverse reactions in major organs, especially the liver, kidney, and heart. Additionally, psychiatric physicians must be constantly cognizant of medications prescribed by other clinicians for comorbid medical conditions to successfully navigate the turbulent seas of pharmacokinetic interactions.
I am sure you have noticed that whenever you watch a direct-to-consumer commercial for any medication, 90% of the advertisement is a background voice listing the various tolerability and safety complications of the medication as required by the FDA. Interestingly, these ads frequently contain colorful scenery and joyful clips, which I suspect are cleverly designed to distract the audience from focusing on the list of adverse effects.
Benefits of nonpharmacologic treatments
No wonder I am a fan of psychotherapy, a well-established psychiatric treatment modality that completely avoids body tissues. It directly targets the brain without needlessly interacting with any other organ. Psychotherapy’s many benefits (improving insight, enhancing adherence, improving self-esteem, reducing risky behaviors, guiding stress management and coping skills, modifying unhealthy beliefs, and ultimately relieving symptoms such as anxiety and depression) are achieved without any somatic adverse effects! Psychotherapy has also been shown to induce neuroplasticity and reduce inflammatory biomarkers.1 Unlike FDA-approved medications, psychotherapy does not include a “package insert,” 10 to 20 pages (in small print) that mostly focus on warnings, precautions, and sundry physical adverse effects. Even the dosing of psychotherapy is left entirely up to the treating clinician!
Although I have had many gratifying results with pharmacotherapy in my practice, especially in combination with psychotherapy,2 I also have observed excellent outcomes with nonpharmacologic approaches, especially neuromodulation therapies. The best antidepressant I have ever used since my residency training days is electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). My experience is consistent with a large meta-analysis3showing a huge effect size (Cohen d = .91) in contrast to the usual effect size of .3 to .5 for standard antidepressants (except IV ketamine). A recent study showed ECT is even better than the vaunted rapid-acting ketamine,4 which is further evidence of its remarkable efficacy in depression. Neuroimaging studies report that ECT rapidly increases the volume of the hippocampus,5,6 which shrinks in size in patients with unipolar or bipolar depression.
Neuromodulation may very well be the future of psychiatric therapeutics. It targets the brain and avoids the body, thus achieving efficacy with minimal systemic tolerability (ie, patient complaints) (Table 1) or safety (abnormal laboratory test results) issues (Table 2). This sounds ideal, and it is arguably an optimal approach to repairing the brain and healing the mind.
Continue to: ECT is the oldest...
ECT is the oldest neuromodulation technique (developed almost 100 years ago and significantly refined since then). Newer FDA-approved neuromodulation therapies include repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), which was approved for depression in 2013, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in 2018, smoking cessation in 2020, and anxious depression in 2021.7 Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is used for drug-resistant epilepsy and was later approved for treatment-resistant depression,8,9 but some studies report it can be helpful for fear and anxiety in autism spectrum disorder10 and primary insomnia.11
There are many other neuromodulation therapies in development12 that have not yet been FDA approved (Table 3). The most prominent of these is deep brain stimulation (DBS), which is approved for Parkinson disease and has been reported in many studies to improve treatment-resistant depression13,14 and OCD.15 Another promising neuromodulation therapy is transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), which has promising results in schizophrenia16 similar to ECT’s effects in treatment-resistant schizophrenia.17

A particularly exciting neuromodulation approach published by Stanford University researchers is Stanford accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy (SAINT),18 which uses intermittent theta-burst stimulation (iTBS) daily for 5 days, targeted at the subgenual anterior cingulate gyrus (Brodman area 25). Remarkably, efficacy was rapid, with a very high remission rate (absence of symptoms) in approximately 90% of patients with severe depression.18
The future is bright for neuromodulation therapies, and for a good reason. Why send a chemical agent to every cell and organ in the body when the brain can be targeted directly? As psychiatric neuroscience advances to a point where we can localize the abnormal neurologic circuit in a specific brain region for each psychiatric disorder, it will be possible to treat almost all psychiatric disorders without burdening patients with the intolerable symptoms or safety adverse effects of medications. Psychiatrists should modulate their perspective about the future of psychiatric treatments. And finally, I propose that psychotherapy should be reclassified as a “verbal neuromodulation” technique.
Pharmacotherapy for psychiatric disorders is a mixed blessing. The advent of psychotropic medications since the 1950s (antipsychotics, antidepressants, anxiolytics, mood stabilizers) has revolutionized the treatment of serious psychiatric brain disorders, allowing certain patients to be discharged to the community after a lifetime of institutionalization.

However, like all medications, psychotropic agents are often associated with various potentially intolerable symptoms (Table 1) or safety complications (Table 2) because they interact with every organ in the body besides their intended target, the brain, and its neurochemical circuitry.

Imagine if we could treat our psychiatric patients while bypassing the body and achieve response, remission, and ultimately recovery without any systemic adverse effects. Adherence would dramatically improve, our patients’ quality of life would be enhanced, and the overall effectiveness (defined as the complex package of efficacy, safety, and tolerability) would be superior to current pharmacotherapies. This is important because most psychiatric medications must be taken daily for years, even a lifetime, to avoid a relapse of the illness. Psychiatrists frequently must manage adverse effects or switch the patient to a different medication if a tolerability or safety issue emerges, which is very common in psychiatric practice. A significant part of psychopharmacologic management includes ordering various laboratory tests to monitor adverse reactions in major organs, especially the liver, kidney, and heart. Additionally, psychiatric physicians must be constantly cognizant of medications prescribed by other clinicians for comorbid medical conditions to successfully navigate the turbulent seas of pharmacokinetic interactions.
I am sure you have noticed that whenever you watch a direct-to-consumer commercial for any medication, 90% of the advertisement is a background voice listing the various tolerability and safety complications of the medication as required by the FDA. Interestingly, these ads frequently contain colorful scenery and joyful clips, which I suspect are cleverly designed to distract the audience from focusing on the list of adverse effects.
Benefits of nonpharmacologic treatments
No wonder I am a fan of psychotherapy, a well-established psychiatric treatment modality that completely avoids body tissues. It directly targets the brain without needlessly interacting with any other organ. Psychotherapy’s many benefits (improving insight, enhancing adherence, improving self-esteem, reducing risky behaviors, guiding stress management and coping skills, modifying unhealthy beliefs, and ultimately relieving symptoms such as anxiety and depression) are achieved without any somatic adverse effects! Psychotherapy has also been shown to induce neuroplasticity and reduce inflammatory biomarkers.1 Unlike FDA-approved medications, psychotherapy does not include a “package insert,” 10 to 20 pages (in small print) that mostly focus on warnings, precautions, and sundry physical adverse effects. Even the dosing of psychotherapy is left entirely up to the treating clinician!
Although I have had many gratifying results with pharmacotherapy in my practice, especially in combination with psychotherapy,2 I also have observed excellent outcomes with nonpharmacologic approaches, especially neuromodulation therapies. The best antidepressant I have ever used since my residency training days is electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). My experience is consistent with a large meta-analysis3showing a huge effect size (Cohen d = .91) in contrast to the usual effect size of .3 to .5 for standard antidepressants (except IV ketamine). A recent study showed ECT is even better than the vaunted rapid-acting ketamine,4 which is further evidence of its remarkable efficacy in depression. Neuroimaging studies report that ECT rapidly increases the volume of the hippocampus,5,6 which shrinks in size in patients with unipolar or bipolar depression.
Neuromodulation may very well be the future of psychiatric therapeutics. It targets the brain and avoids the body, thus achieving efficacy with minimal systemic tolerability (ie, patient complaints) (Table 1) or safety (abnormal laboratory test results) issues (Table 2). This sounds ideal, and it is arguably an optimal approach to repairing the brain and healing the mind.
Continue to: ECT is the oldest...
ECT is the oldest neuromodulation technique (developed almost 100 years ago and significantly refined since then). Newer FDA-approved neuromodulation therapies include repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), which was approved for depression in 2013, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in 2018, smoking cessation in 2020, and anxious depression in 2021.7 Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is used for drug-resistant epilepsy and was later approved for treatment-resistant depression,8,9 but some studies report it can be helpful for fear and anxiety in autism spectrum disorder10 and primary insomnia.11
There are many other neuromodulation therapies in development12 that have not yet been FDA approved (Table 3). The most prominent of these is deep brain stimulation (DBS), which is approved for Parkinson disease and has been reported in many studies to improve treatment-resistant depression13,14 and OCD.15 Another promising neuromodulation therapy is transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), which has promising results in schizophrenia16 similar to ECT’s effects in treatment-resistant schizophrenia.17

A particularly exciting neuromodulation approach published by Stanford University researchers is Stanford accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy (SAINT),18 which uses intermittent theta-burst stimulation (iTBS) daily for 5 days, targeted at the subgenual anterior cingulate gyrus (Brodman area 25). Remarkably, efficacy was rapid, with a very high remission rate (absence of symptoms) in approximately 90% of patients with severe depression.18
The future is bright for neuromodulation therapies, and for a good reason. Why send a chemical agent to every cell and organ in the body when the brain can be targeted directly? As psychiatric neuroscience advances to a point where we can localize the abnormal neurologic circuit in a specific brain region for each psychiatric disorder, it will be possible to treat almost all psychiatric disorders without burdening patients with the intolerable symptoms or safety adverse effects of medications. Psychiatrists should modulate their perspective about the future of psychiatric treatments. And finally, I propose that psychotherapy should be reclassified as a “verbal neuromodulation” technique.
1. Nasrallah HA. Repositioning psychotherapy as a neurobiological intervention. Current Psychiatry. 2013;12(12):18-19.
2. Nasrallah HA. Bipolar disorder: clinical questions beg for answers. Current Psychiatry. 2006;5(12):11-12.
3. UK ECT Review Group. Efficacy and safety of electroconvulsive therapy in depressive disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2003;361(9360):799-808.
4. Rhee TG, Shim SR, Forester BP, et al. Efficacy and safety of ketamine vs electroconvulsive therapy among patients with major depressive episode: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2022:e223352. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2022.3352
5. Nuninga JO, Mandl RCW, Boks MP, et al. Volume increase in the dentate gyrus after electroconvulsive therapy in depressed patients as measured with 7T. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(7):1559-1568.
6. Joshi SH, Espinoza RT, Pirnia T, et al. Structural plasticity of the hippocampus and amygdala induced by electroconvulsive therapy in major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2016;79(4):282-292.
7. Rhee TG, Olfson M, Nierenberg AA, et al. 20-year trends in the pharmacologic treatment of bipolar disorder by psychiatrists in outpatient care settings. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(8):706-715.
8. Hilz MJ. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation - a brief introduction and overview. Auton Neurosci. 2022;243:103038. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2022.103038
9. Pigato G, Rosson S, Bresolin N, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation in treatment-resistant depression: a case series of long-term follow-up. J ECT. 2022. doi:10.1097/YCT.0000000000000869
10. Shivaswamy T, Souza RR, Engineer CT, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation as a treatment for fear and anxiety in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. J Psychiatr Brain Sci. 2022;7(4):e220007. doi:10.20900/jpbs.20220007
11. Wu Y, Song L, Wang X, et al. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation could improve the effective rate on the quality of sleep in the treatment of primary insomnia: a randomized control trial. Brain Sci. 2022;12(10):1296. doi:10.3390/brainsci12101296
12. Rosa MA, Lisanby SH. Somatic treatments for mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37(1):102-116.
13. Mayberg HS, Lozano AM, Voon V, et al. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron. 2005;45(5):651-660.
14. Choi KS, Mayberg H. Connectomic DBS in major depression. In: Horn A, ed. Connectomic Deep Brain Stimulation. Academic Press; 2022:433-447.
15. Cruz S, Gutiérrez-Rojas L, González-Domenech P, et al. Deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder: results from meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2022;317:114869. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2022.114869
16. Lisoni J, Baldacci G, Nibbio G, et al. Effects of bilateral, bipolar-nonbalanced, frontal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) on negative symptoms and neurocognition in a sample of patients living with schizophrenia: results of a randomized double-blind sham-controlled trial. J Psychiatr Res. 2022;155:430-442.
17. Sinclair DJ, Zhao S, Qi F, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy for treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;3(3):CD011847. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011847.pub2
18. Cole EJ, Stimpson KH, Bentzley BS, et al. Stanford accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy for treatment-resistant depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(8):716-726.
1. Nasrallah HA. Repositioning psychotherapy as a neurobiological intervention. Current Psychiatry. 2013;12(12):18-19.
2. Nasrallah HA. Bipolar disorder: clinical questions beg for answers. Current Psychiatry. 2006;5(12):11-12.
3. UK ECT Review Group. Efficacy and safety of electroconvulsive therapy in depressive disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2003;361(9360):799-808.
4. Rhee TG, Shim SR, Forester BP, et al. Efficacy and safety of ketamine vs electroconvulsive therapy among patients with major depressive episode: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2022:e223352. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2022.3352
5. Nuninga JO, Mandl RCW, Boks MP, et al. Volume increase in the dentate gyrus after electroconvulsive therapy in depressed patients as measured with 7T. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(7):1559-1568.
6. Joshi SH, Espinoza RT, Pirnia T, et al. Structural plasticity of the hippocampus and amygdala induced by electroconvulsive therapy in major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2016;79(4):282-292.
7. Rhee TG, Olfson M, Nierenberg AA, et al. 20-year trends in the pharmacologic treatment of bipolar disorder by psychiatrists in outpatient care settings. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(8):706-715.
8. Hilz MJ. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation - a brief introduction and overview. Auton Neurosci. 2022;243:103038. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2022.103038
9. Pigato G, Rosson S, Bresolin N, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation in treatment-resistant depression: a case series of long-term follow-up. J ECT. 2022. doi:10.1097/YCT.0000000000000869
10. Shivaswamy T, Souza RR, Engineer CT, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation as a treatment for fear and anxiety in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. J Psychiatr Brain Sci. 2022;7(4):e220007. doi:10.20900/jpbs.20220007
11. Wu Y, Song L, Wang X, et al. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation could improve the effective rate on the quality of sleep in the treatment of primary insomnia: a randomized control trial. Brain Sci. 2022;12(10):1296. doi:10.3390/brainsci12101296
12. Rosa MA, Lisanby SH. Somatic treatments for mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37(1):102-116.
13. Mayberg HS, Lozano AM, Voon V, et al. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron. 2005;45(5):651-660.
14. Choi KS, Mayberg H. Connectomic DBS in major depression. In: Horn A, ed. Connectomic Deep Brain Stimulation. Academic Press; 2022:433-447.
15. Cruz S, Gutiérrez-Rojas L, González-Domenech P, et al. Deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder: results from meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2022;317:114869. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2022.114869
16. Lisoni J, Baldacci G, Nibbio G, et al. Effects of bilateral, bipolar-nonbalanced, frontal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) on negative symptoms and neurocognition in a sample of patients living with schizophrenia: results of a randomized double-blind sham-controlled trial. J Psychiatr Res. 2022;155:430-442.
17. Sinclair DJ, Zhao S, Qi F, et al. Electroconvulsive therapy for treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;3(3):CD011847. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011847.pub2
18. Cole EJ, Stimpson KH, Bentzley BS, et al. Stanford accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy for treatment-resistant depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(8):716-726.
More on social entropy
As leaders of the American Psychiatric Association, we received dozens of communications from members who were shocked by the discriminatory and transphobic commentary in the recent editorial “The accelerating societal entropy undermines mental health” (
Specifically, citing “lack of certainty about gender identity in children and adults” as an indicator of societal turmoil that undermines mental health is contrary to the scientific understanding of gender identity. Physicians have professional obligations to advance patients’ well-being and do no harm.
The medical profession, including psychiatry, is at a critical juncture in coming to terms with and dismantling its longstanding history of systemic racism and discrimination. Authors and editors must be aware that harmful and divisive language negatively affects mental health, especially for people who have been subject to discrimination individually and/or as members of historically excluded and/or minoritized groups.
In publishing this editorial,
Rebecca W. Brendel, MD, JD, DFAPA
President
American Psychiatric Association
Saul Levin, MD, MPA, FRCP-E, FRCPsych
CEO and Medical Director
American Psychiatric Association
Disclosures
The authors report no financial relationships with any companies whose products are mentioned in this letter, or with manufacturers of competing products.
Dr. Nasrallah responds
I regret that the sentence about gender identity in my October editorial was regarded as transphobic and harmful. While the phrasing reflected my patients’ comments to me, I realize my unfortunate choice of words deeply offended individuals who are transgender, who have been subjected to ongoing discrimination and prejudice.
I apologize to our readers; to my American Psychiatric Association LGBTQAI+ friends, colleagues, and relatives; and to the LGBTQAI+ community at large. The sentence has been deleted from the online version of my editorial. This has been a teachable moment for me.
Henry A. Nasrallah, MD
Editor-In-Chief
Continue to: More on psychiatric documentation
More on psychiatric documentation
Dr. Joshi’s helpful discussion of clinical documentation strategies (“Medical record documentation: What to do, and what to avoid,”
The mental health record may not always be as confidential as psychiatrists think (or hope) it is. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Privacy Rule, for example, generally does not distinguish between medical and mental health information, nor does it provide special rules for the latter (although certain state laws may do so). HIPAA provides added protections for “psychotherapy notes,” but this category explicitly excludes progress notes that discuss treatment modalities, diagnosis, and clinical milestones. To retain their protected status, psychotherapists’ private, “desk-drawer memory joggers” must never be comingled with the patient chart.1 For mental health professionals, this distinction underscores the importance of keeping personal details broad in the progress note; scandalous or embarrassing narratives recounted in the medical record itself are routinely accessible to the patient and may be lawfully disclosed to others under specified circumstances.
In addition to avoiding speculation and including patient quotes when appropriate, documenting objectively and nonjudgmentally means annotating facts and observations that helped the clinician arrive at their conclusion. For example, “patient appears intoxicated” is less helpful than noting the patient’s slurred speech, impaired gait and/or coordination, and alcohol odor.
Clinical care and its associated documentation are so intertwined that they can become virtually indistinguishable. In a medical malpractice case, the burden is on the plaintiff to prove their injury resulted from substandard care. Some courts, however, have held that missing or incomplete records can effectively shift the burden from the recipient to the provider of care to show that the treatment at issue was rendered non-negligently.2 Statutes of limitations restricting the amount of time in which a patient can sue after an adverse event are sometimes triggered by the date on which they knew or should have known of the alleged malpractice.3 One of the best ways of ascertaining this date, and starting the statute of limitations clock, can be a clear annotation in the medical record that the patient was apprised of an unanticipated outcome or iatrogenic harm. In this way, a timely and thorough note can be critical not just to defending the physician’s quality of care, but potentially to precluding a cognizable lawsuit altogether.
Charles G. Kels, JD
Defense Health Agency
San Antonio, Texas
Disclosures
The views expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of any government agency, nor do they constitute individualized legal advice. The author reports no financial relationships with any companies whose products are mentioned in this letter, or with manufacturers of competing products.
References
1. 45 CFR Parts 160 and 164, Subparts A and E.
2. Valcin v Public Health Trust, 473 So. 2d 1297 (1984).
3. US v Kubrick, 444 US 111 (1979).
As leaders of the American Psychiatric Association, we received dozens of communications from members who were shocked by the discriminatory and transphobic commentary in the recent editorial “The accelerating societal entropy undermines mental health” (
Specifically, citing “lack of certainty about gender identity in children and adults” as an indicator of societal turmoil that undermines mental health is contrary to the scientific understanding of gender identity. Physicians have professional obligations to advance patients’ well-being and do no harm.
The medical profession, including psychiatry, is at a critical juncture in coming to terms with and dismantling its longstanding history of systemic racism and discrimination. Authors and editors must be aware that harmful and divisive language negatively affects mental health, especially for people who have been subject to discrimination individually and/or as members of historically excluded and/or minoritized groups.
In publishing this editorial,
Rebecca W. Brendel, MD, JD, DFAPA
President
American Psychiatric Association
Saul Levin, MD, MPA, FRCP-E, FRCPsych
CEO and Medical Director
American Psychiatric Association
Disclosures
The authors report no financial relationships with any companies whose products are mentioned in this letter, or with manufacturers of competing products.
Dr. Nasrallah responds
I regret that the sentence about gender identity in my October editorial was regarded as transphobic and harmful. While the phrasing reflected my patients’ comments to me, I realize my unfortunate choice of words deeply offended individuals who are transgender, who have been subjected to ongoing discrimination and prejudice.
I apologize to our readers; to my American Psychiatric Association LGBTQAI+ friends, colleagues, and relatives; and to the LGBTQAI+ community at large. The sentence has been deleted from the online version of my editorial. This has been a teachable moment for me.
Henry A. Nasrallah, MD
Editor-In-Chief
Continue to: More on psychiatric documentation
More on psychiatric documentation
Dr. Joshi’s helpful discussion of clinical documentation strategies (“Medical record documentation: What to do, and what to avoid,”
The mental health record may not always be as confidential as psychiatrists think (or hope) it is. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Privacy Rule, for example, generally does not distinguish between medical and mental health information, nor does it provide special rules for the latter (although certain state laws may do so). HIPAA provides added protections for “psychotherapy notes,” but this category explicitly excludes progress notes that discuss treatment modalities, diagnosis, and clinical milestones. To retain their protected status, psychotherapists’ private, “desk-drawer memory joggers” must never be comingled with the patient chart.1 For mental health professionals, this distinction underscores the importance of keeping personal details broad in the progress note; scandalous or embarrassing narratives recounted in the medical record itself are routinely accessible to the patient and may be lawfully disclosed to others under specified circumstances.
In addition to avoiding speculation and including patient quotes when appropriate, documenting objectively and nonjudgmentally means annotating facts and observations that helped the clinician arrive at their conclusion. For example, “patient appears intoxicated” is less helpful than noting the patient’s slurred speech, impaired gait and/or coordination, and alcohol odor.
Clinical care and its associated documentation are so intertwined that they can become virtually indistinguishable. In a medical malpractice case, the burden is on the plaintiff to prove their injury resulted from substandard care. Some courts, however, have held that missing or incomplete records can effectively shift the burden from the recipient to the provider of care to show that the treatment at issue was rendered non-negligently.2 Statutes of limitations restricting the amount of time in which a patient can sue after an adverse event are sometimes triggered by the date on which they knew or should have known of the alleged malpractice.3 One of the best ways of ascertaining this date, and starting the statute of limitations clock, can be a clear annotation in the medical record that the patient was apprised of an unanticipated outcome or iatrogenic harm. In this way, a timely and thorough note can be critical not just to defending the physician’s quality of care, but potentially to precluding a cognizable lawsuit altogether.
Charles G. Kels, JD
Defense Health Agency
San Antonio, Texas
Disclosures
The views expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of any government agency, nor do they constitute individualized legal advice. The author reports no financial relationships with any companies whose products are mentioned in this letter, or with manufacturers of competing products.
References
1. 45 CFR Parts 160 and 164, Subparts A and E.
2. Valcin v Public Health Trust, 473 So. 2d 1297 (1984).
3. US v Kubrick, 444 US 111 (1979).
As leaders of the American Psychiatric Association, we received dozens of communications from members who were shocked by the discriminatory and transphobic commentary in the recent editorial “The accelerating societal entropy undermines mental health” (
Specifically, citing “lack of certainty about gender identity in children and adults” as an indicator of societal turmoil that undermines mental health is contrary to the scientific understanding of gender identity. Physicians have professional obligations to advance patients’ well-being and do no harm.
The medical profession, including psychiatry, is at a critical juncture in coming to terms with and dismantling its longstanding history of systemic racism and discrimination. Authors and editors must be aware that harmful and divisive language negatively affects mental health, especially for people who have been subject to discrimination individually and/or as members of historically excluded and/or minoritized groups.
In publishing this editorial,
Rebecca W. Brendel, MD, JD, DFAPA
President
American Psychiatric Association
Saul Levin, MD, MPA, FRCP-E, FRCPsych
CEO and Medical Director
American Psychiatric Association
Disclosures
The authors report no financial relationships with any companies whose products are mentioned in this letter, or with manufacturers of competing products.
Dr. Nasrallah responds
I regret that the sentence about gender identity in my October editorial was regarded as transphobic and harmful. While the phrasing reflected my patients’ comments to me, I realize my unfortunate choice of words deeply offended individuals who are transgender, who have been subjected to ongoing discrimination and prejudice.
I apologize to our readers; to my American Psychiatric Association LGBTQAI+ friends, colleagues, and relatives; and to the LGBTQAI+ community at large. The sentence has been deleted from the online version of my editorial. This has been a teachable moment for me.
Henry A. Nasrallah, MD
Editor-In-Chief
Continue to: More on psychiatric documentation
More on psychiatric documentation
Dr. Joshi’s helpful discussion of clinical documentation strategies (“Medical record documentation: What to do, and what to avoid,”
The mental health record may not always be as confidential as psychiatrists think (or hope) it is. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Privacy Rule, for example, generally does not distinguish between medical and mental health information, nor does it provide special rules for the latter (although certain state laws may do so). HIPAA provides added protections for “psychotherapy notes,” but this category explicitly excludes progress notes that discuss treatment modalities, diagnosis, and clinical milestones. To retain their protected status, psychotherapists’ private, “desk-drawer memory joggers” must never be comingled with the patient chart.1 For mental health professionals, this distinction underscores the importance of keeping personal details broad in the progress note; scandalous or embarrassing narratives recounted in the medical record itself are routinely accessible to the patient and may be lawfully disclosed to others under specified circumstances.
In addition to avoiding speculation and including patient quotes when appropriate, documenting objectively and nonjudgmentally means annotating facts and observations that helped the clinician arrive at their conclusion. For example, “patient appears intoxicated” is less helpful than noting the patient’s slurred speech, impaired gait and/or coordination, and alcohol odor.
Clinical care and its associated documentation are so intertwined that they can become virtually indistinguishable. In a medical malpractice case, the burden is on the plaintiff to prove their injury resulted from substandard care. Some courts, however, have held that missing or incomplete records can effectively shift the burden from the recipient to the provider of care to show that the treatment at issue was rendered non-negligently.2 Statutes of limitations restricting the amount of time in which a patient can sue after an adverse event are sometimes triggered by the date on which they knew or should have known of the alleged malpractice.3 One of the best ways of ascertaining this date, and starting the statute of limitations clock, can be a clear annotation in the medical record that the patient was apprised of an unanticipated outcome or iatrogenic harm. In this way, a timely and thorough note can be critical not just to defending the physician’s quality of care, but potentially to precluding a cognizable lawsuit altogether.
Charles G. Kels, JD
Defense Health Agency
San Antonio, Texas
Disclosures
The views expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of any government agency, nor do they constitute individualized legal advice. The author reports no financial relationships with any companies whose products are mentioned in this letter, or with manufacturers of competing products.
References
1. 45 CFR Parts 160 and 164, Subparts A and E.
2. Valcin v Public Health Trust, 473 So. 2d 1297 (1984).
3. US v Kubrick, 444 US 111 (1979).
Should residents be taught how to prescribe monoamine oxidase inhibitors?
What else can I offer this patient?
This thought passed through my mind as the patient’s desperation grew palpable. He had experienced intractable major depressive disorder (MDD) for years and had exhausted multiple classes of antidepressants, trying various combinations without any relief.
The previous resident had arranged for intranasal ketamine treatment, but the patient was unable to receive it due to lack of transportation. As I combed through the list of the dozens of medications the patient previously had been prescribed, I noticed the absence of a certain class of agents: monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
My knowledge of MAOIs stemmed from medical school, where the dietary restrictions, potential for hypertensive crisis, and capricious drug-drug interactions were heavily emphasized while their value was minimized. I did not have any practical experience with these medications, and even the attending physician disclosed he had not prescribed an MAOI in more than 30 years. Nonetheless, both the attending physician and patient agreed that the patient would try one.
Following a washout period, the patient began tranylcypromine. After taking tranylcypromine 40 mg/d for 3 months, he reported he felt like a weight had been lifted off his chest. He felt less irritable and depressed, more energetic, and more hopeful for the future. He also felt that his symptoms were improving for the first time in many years.
An older but still potentially helpful class of medications
MDD is one of the leading causes of disability in the United States, affecting millions of people. Its economic burden is estimated to be more than $200 billion, with a large contingent consisting of direct medical cost and suicide-related costs.1 MDD is often recurrent—60% of patients experience another episode within 5 years.2 Most of these patients are classified as having treatment-resistant depression (TRD), which typically is defined as the failure to respond to 2 different medications given at adequate doses for a sufficient duration.3 The Sequenced Treatment Alternatives to Relieve Depression trial suggested that after each medication failure, depression becomes increasingly difficult to treat, with many patients developing TRD.4 For some patients with TRD, MAOIs may be a powerful and beneficial option.5,6 Studies have shown that MAOIs (at adequate doses) can be effective in approximately one-half of patients with TRD. Patients with anxious, endogenous, or atypical depression may also respond to MAOIs.7
MAOIs were among the earliest antidepressants on the market, starting in the late 1950s with isocarboxazid, phenelzine, tranylcypromine, and selegiline. The use of MAOIs as a treatment for depression was serendipitously discovered when iproniazid, a tuberculosis drug, was observed to have mood-elevating adverse effects that were explained by its monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitory properties.8 This sparked the hypothesis that a deficiency in serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine played a central role in depressive disorders. MAOs encompass a class of enzymes that metabolize catecholamines, which include the previously mentioned neurotransmitters and the trace amine tyramine. The MAO isoenzymes also inhabit many tissues, including the central and peripheral nervous system, liver, and intestines.
There are 2 subtypes of MAOs: MAO-A and MAO-B. MAO-A inhibits tyramine, serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. MAO-B is mainly responsible for the degradation of dopamine, which makes MAO-B inhibitors (ie, rasagiline) useful in treating Parkinson disease.9
Continue to: For most psychiatrists...
For most psychiatrists, MAOIs have fallen out of favor due to their discomfort with their potential adverse effects and drug-drug interactions, the dietary restrictions patients must face, and the perception that newer medications have fewer adverse effects.10 Prescribing an MAOI requires the clinician to remain vigilant of any new medication the patient is taking that may potentiate intrasynaptic serotonin, which may include certain antibiotics or analgesics, causing serotonin syndrome. Close monitoring of the patient’s diet also is necessary so the patient avoids foods rich in tyramine that may trigger a hypertensive crisis. This is because excess tyramine can precipitate an increase in catecholamine release, causing a dangerous increase in blood pressure. However, many foods have safe levels of tyramine (<6 mg/serving), although the perception of tyramine levels in modern foods remains overestimated.5
Residents need to know how to use MAOIs
Psychiatrists should weigh the risks and benefits prior to prescribing any new medication, and MAOIs should be no exception. A patient’s enduring pain is often overshadowed by the potential for adverse effects, which occasionally is overemphasized. Other treatments for severe psychiatric illnesses (such as lithium and clozapine) are also declining due to these agents’ requirement for cumbersome monitoring and potential for adverse effects despite evidence of their superior efficacy and antisuicidal properties.11,12
Fortunately, there are many novel therapies available that can be effective for patients with TRD, including transcranial magnetic stimulation, ketamine, and vagal nerve stimulation. However, as psychiatrists, especially during training, our armamentarium should be equipped with all modalities of psychopharmacology. Training and teaching residents to prescribe MAOIs safely and effectively may add a glimmer of hope for an otherwise hopeless patient.
1. Greenberg PE, Fournier AA, Sisitsky T, et al. The economic burden of adults with major depressive disorder in the United States (2010 and 2018). Pharmacoeconomics. 2021;39(6):653-665.
2. Hardeveld F, Spijker J, De Graaf R, et al. Prevalence and predictors of recurrence of major depressive disorder in the adult population. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2010;122(3):184-191.
3. Gaynes BN, Lux L, Gartlehner G, et al. Defining treatment-resistant depression. Depress Anxiety. 2020;37(2):134-145.
4. Trivedi MH, Rush AJ, Wisniewski SR, et al. Evaluation of outcomes with citalopram for depression using measurement-based care in STAR*D: implications for clinical practice. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(1):28-40.
5. Fiedorowicz JG, Swartz KL. The role of monoamine oxidase inhibitors in current psychiatric practice. J Psychiatr Pract. 2004;10(4):239-248.
6. Amsterdam JD, Shults J. MAOI efficacy and safety in advanced stage treatment-resistant depression--a retrospective study. J Affect Disord. 2005;89(1-3):183-188.
7. Amsterdam JD, Hornig-Rohan M. Treatment algorithms in treatment-resistant depression. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 1996;19(2):371-386.
8. Ramachandraih CT, Subramanyam N, Bar KJ, et al. Antidepressants: from MAOIs to SSRIs and more. Indian J Psychiatry. 2011;53(2):180-182.
9. Tipton KF. 90 years of monoamine oxidase: some progress and some confusion. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018;125(11):1519-1551.
10. Gillman PK, Feinberg SS, Fochtmann LJ. Revitalizing monoamine oxidase inhibitors: a call for action. CNS Spectr. 2020;25(4):452-454.
11. Kelly DL, Wehring HJ, Vyas G. Current status of clozapine in the United States. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. 2012;24(2):110-113.
12. Tibrewal P, Ng T, Bastiampillai T, et al. Why is lithium use declining? Asian J Psychiatr. 2019;43:219-220.
What else can I offer this patient?
This thought passed through my mind as the patient’s desperation grew palpable. He had experienced intractable major depressive disorder (MDD) for years and had exhausted multiple classes of antidepressants, trying various combinations without any relief.
The previous resident had arranged for intranasal ketamine treatment, but the patient was unable to receive it due to lack of transportation. As I combed through the list of the dozens of medications the patient previously had been prescribed, I noticed the absence of a certain class of agents: monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
My knowledge of MAOIs stemmed from medical school, where the dietary restrictions, potential for hypertensive crisis, and capricious drug-drug interactions were heavily emphasized while their value was minimized. I did not have any practical experience with these medications, and even the attending physician disclosed he had not prescribed an MAOI in more than 30 years. Nonetheless, both the attending physician and patient agreed that the patient would try one.
Following a washout period, the patient began tranylcypromine. After taking tranylcypromine 40 mg/d for 3 months, he reported he felt like a weight had been lifted off his chest. He felt less irritable and depressed, more energetic, and more hopeful for the future. He also felt that his symptoms were improving for the first time in many years.
An older but still potentially helpful class of medications
MDD is one of the leading causes of disability in the United States, affecting millions of people. Its economic burden is estimated to be more than $200 billion, with a large contingent consisting of direct medical cost and suicide-related costs.1 MDD is often recurrent—60% of patients experience another episode within 5 years.2 Most of these patients are classified as having treatment-resistant depression (TRD), which typically is defined as the failure to respond to 2 different medications given at adequate doses for a sufficient duration.3 The Sequenced Treatment Alternatives to Relieve Depression trial suggested that after each medication failure, depression becomes increasingly difficult to treat, with many patients developing TRD.4 For some patients with TRD, MAOIs may be a powerful and beneficial option.5,6 Studies have shown that MAOIs (at adequate doses) can be effective in approximately one-half of patients with TRD. Patients with anxious, endogenous, or atypical depression may also respond to MAOIs.7
MAOIs were among the earliest antidepressants on the market, starting in the late 1950s with isocarboxazid, phenelzine, tranylcypromine, and selegiline. The use of MAOIs as a treatment for depression was serendipitously discovered when iproniazid, a tuberculosis drug, was observed to have mood-elevating adverse effects that were explained by its monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitory properties.8 This sparked the hypothesis that a deficiency in serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine played a central role in depressive disorders. MAOs encompass a class of enzymes that metabolize catecholamines, which include the previously mentioned neurotransmitters and the trace amine tyramine. The MAO isoenzymes also inhabit many tissues, including the central and peripheral nervous system, liver, and intestines.
There are 2 subtypes of MAOs: MAO-A and MAO-B. MAO-A inhibits tyramine, serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. MAO-B is mainly responsible for the degradation of dopamine, which makes MAO-B inhibitors (ie, rasagiline) useful in treating Parkinson disease.9
Continue to: For most psychiatrists...
For most psychiatrists, MAOIs have fallen out of favor due to their discomfort with their potential adverse effects and drug-drug interactions, the dietary restrictions patients must face, and the perception that newer medications have fewer adverse effects.10 Prescribing an MAOI requires the clinician to remain vigilant of any new medication the patient is taking that may potentiate intrasynaptic serotonin, which may include certain antibiotics or analgesics, causing serotonin syndrome. Close monitoring of the patient’s diet also is necessary so the patient avoids foods rich in tyramine that may trigger a hypertensive crisis. This is because excess tyramine can precipitate an increase in catecholamine release, causing a dangerous increase in blood pressure. However, many foods have safe levels of tyramine (<6 mg/serving), although the perception of tyramine levels in modern foods remains overestimated.5
Residents need to know how to use MAOIs
Psychiatrists should weigh the risks and benefits prior to prescribing any new medication, and MAOIs should be no exception. A patient’s enduring pain is often overshadowed by the potential for adverse effects, which occasionally is overemphasized. Other treatments for severe psychiatric illnesses (such as lithium and clozapine) are also declining due to these agents’ requirement for cumbersome monitoring and potential for adverse effects despite evidence of their superior efficacy and antisuicidal properties.11,12
Fortunately, there are many novel therapies available that can be effective for patients with TRD, including transcranial magnetic stimulation, ketamine, and vagal nerve stimulation. However, as psychiatrists, especially during training, our armamentarium should be equipped with all modalities of psychopharmacology. Training and teaching residents to prescribe MAOIs safely and effectively may add a glimmer of hope for an otherwise hopeless patient.
What else can I offer this patient?
This thought passed through my mind as the patient’s desperation grew palpable. He had experienced intractable major depressive disorder (MDD) for years and had exhausted multiple classes of antidepressants, trying various combinations without any relief.
The previous resident had arranged for intranasal ketamine treatment, but the patient was unable to receive it due to lack of transportation. As I combed through the list of the dozens of medications the patient previously had been prescribed, I noticed the absence of a certain class of agents: monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
My knowledge of MAOIs stemmed from medical school, where the dietary restrictions, potential for hypertensive crisis, and capricious drug-drug interactions were heavily emphasized while their value was minimized. I did not have any practical experience with these medications, and even the attending physician disclosed he had not prescribed an MAOI in more than 30 years. Nonetheless, both the attending physician and patient agreed that the patient would try one.
Following a washout period, the patient began tranylcypromine. After taking tranylcypromine 40 mg/d for 3 months, he reported he felt like a weight had been lifted off his chest. He felt less irritable and depressed, more energetic, and more hopeful for the future. He also felt that his symptoms were improving for the first time in many years.
An older but still potentially helpful class of medications
MDD is one of the leading causes of disability in the United States, affecting millions of people. Its economic burden is estimated to be more than $200 billion, with a large contingent consisting of direct medical cost and suicide-related costs.1 MDD is often recurrent—60% of patients experience another episode within 5 years.2 Most of these patients are classified as having treatment-resistant depression (TRD), which typically is defined as the failure to respond to 2 different medications given at adequate doses for a sufficient duration.3 The Sequenced Treatment Alternatives to Relieve Depression trial suggested that after each medication failure, depression becomes increasingly difficult to treat, with many patients developing TRD.4 For some patients with TRD, MAOIs may be a powerful and beneficial option.5,6 Studies have shown that MAOIs (at adequate doses) can be effective in approximately one-half of patients with TRD. Patients with anxious, endogenous, or atypical depression may also respond to MAOIs.7
MAOIs were among the earliest antidepressants on the market, starting in the late 1950s with isocarboxazid, phenelzine, tranylcypromine, and selegiline. The use of MAOIs as a treatment for depression was serendipitously discovered when iproniazid, a tuberculosis drug, was observed to have mood-elevating adverse effects that were explained by its monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitory properties.8 This sparked the hypothesis that a deficiency in serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine played a central role in depressive disorders. MAOs encompass a class of enzymes that metabolize catecholamines, which include the previously mentioned neurotransmitters and the trace amine tyramine. The MAO isoenzymes also inhabit many tissues, including the central and peripheral nervous system, liver, and intestines.
There are 2 subtypes of MAOs: MAO-A and MAO-B. MAO-A inhibits tyramine, serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. MAO-B is mainly responsible for the degradation of dopamine, which makes MAO-B inhibitors (ie, rasagiline) useful in treating Parkinson disease.9
Continue to: For most psychiatrists...
For most psychiatrists, MAOIs have fallen out of favor due to their discomfort with their potential adverse effects and drug-drug interactions, the dietary restrictions patients must face, and the perception that newer medications have fewer adverse effects.10 Prescribing an MAOI requires the clinician to remain vigilant of any new medication the patient is taking that may potentiate intrasynaptic serotonin, which may include certain antibiotics or analgesics, causing serotonin syndrome. Close monitoring of the patient’s diet also is necessary so the patient avoids foods rich in tyramine that may trigger a hypertensive crisis. This is because excess tyramine can precipitate an increase in catecholamine release, causing a dangerous increase in blood pressure. However, many foods have safe levels of tyramine (<6 mg/serving), although the perception of tyramine levels in modern foods remains overestimated.5
Residents need to know how to use MAOIs
Psychiatrists should weigh the risks and benefits prior to prescribing any new medication, and MAOIs should be no exception. A patient’s enduring pain is often overshadowed by the potential for adverse effects, which occasionally is overemphasized. Other treatments for severe psychiatric illnesses (such as lithium and clozapine) are also declining due to these agents’ requirement for cumbersome monitoring and potential for adverse effects despite evidence of their superior efficacy and antisuicidal properties.11,12
Fortunately, there are many novel therapies available that can be effective for patients with TRD, including transcranial magnetic stimulation, ketamine, and vagal nerve stimulation. However, as psychiatrists, especially during training, our armamentarium should be equipped with all modalities of psychopharmacology. Training and teaching residents to prescribe MAOIs safely and effectively may add a glimmer of hope for an otherwise hopeless patient.
1. Greenberg PE, Fournier AA, Sisitsky T, et al. The economic burden of adults with major depressive disorder in the United States (2010 and 2018). Pharmacoeconomics. 2021;39(6):653-665.
2. Hardeveld F, Spijker J, De Graaf R, et al. Prevalence and predictors of recurrence of major depressive disorder in the adult population. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2010;122(3):184-191.
3. Gaynes BN, Lux L, Gartlehner G, et al. Defining treatment-resistant depression. Depress Anxiety. 2020;37(2):134-145.
4. Trivedi MH, Rush AJ, Wisniewski SR, et al. Evaluation of outcomes with citalopram for depression using measurement-based care in STAR*D: implications for clinical practice. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(1):28-40.
5. Fiedorowicz JG, Swartz KL. The role of monoamine oxidase inhibitors in current psychiatric practice. J Psychiatr Pract. 2004;10(4):239-248.
6. Amsterdam JD, Shults J. MAOI efficacy and safety in advanced stage treatment-resistant depression--a retrospective study. J Affect Disord. 2005;89(1-3):183-188.
7. Amsterdam JD, Hornig-Rohan M. Treatment algorithms in treatment-resistant depression. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 1996;19(2):371-386.
8. Ramachandraih CT, Subramanyam N, Bar KJ, et al. Antidepressants: from MAOIs to SSRIs and more. Indian J Psychiatry. 2011;53(2):180-182.
9. Tipton KF. 90 years of monoamine oxidase: some progress and some confusion. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018;125(11):1519-1551.
10. Gillman PK, Feinberg SS, Fochtmann LJ. Revitalizing monoamine oxidase inhibitors: a call for action. CNS Spectr. 2020;25(4):452-454.
11. Kelly DL, Wehring HJ, Vyas G. Current status of clozapine in the United States. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. 2012;24(2):110-113.
12. Tibrewal P, Ng T, Bastiampillai T, et al. Why is lithium use declining? Asian J Psychiatr. 2019;43:219-220.
1. Greenberg PE, Fournier AA, Sisitsky T, et al. The economic burden of adults with major depressive disorder in the United States (2010 and 2018). Pharmacoeconomics. 2021;39(6):653-665.
2. Hardeveld F, Spijker J, De Graaf R, et al. Prevalence and predictors of recurrence of major depressive disorder in the adult population. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2010;122(3):184-191.
3. Gaynes BN, Lux L, Gartlehner G, et al. Defining treatment-resistant depression. Depress Anxiety. 2020;37(2):134-145.
4. Trivedi MH, Rush AJ, Wisniewski SR, et al. Evaluation of outcomes with citalopram for depression using measurement-based care in STAR*D: implications for clinical practice. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(1):28-40.
5. Fiedorowicz JG, Swartz KL. The role of monoamine oxidase inhibitors in current psychiatric practice. J Psychiatr Pract. 2004;10(4):239-248.
6. Amsterdam JD, Shults J. MAOI efficacy and safety in advanced stage treatment-resistant depression--a retrospective study. J Affect Disord. 2005;89(1-3):183-188.
7. Amsterdam JD, Hornig-Rohan M. Treatment algorithms in treatment-resistant depression. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 1996;19(2):371-386.
8. Ramachandraih CT, Subramanyam N, Bar KJ, et al. Antidepressants: from MAOIs to SSRIs and more. Indian J Psychiatry. 2011;53(2):180-182.
9. Tipton KF. 90 years of monoamine oxidase: some progress and some confusion. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018;125(11):1519-1551.
10. Gillman PK, Feinberg SS, Fochtmann LJ. Revitalizing monoamine oxidase inhibitors: a call for action. CNS Spectr. 2020;25(4):452-454.
11. Kelly DL, Wehring HJ, Vyas G. Current status of clozapine in the United States. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. 2012;24(2):110-113.
12. Tibrewal P, Ng T, Bastiampillai T, et al. Why is lithium use declining? Asian J Psychiatr. 2019;43:219-220.
What my Grandma’s schizophrenia taught me
Editor’s note: Readers’ Forum is a department for correspondence from readers that is not in response to articles published in
Grandma was sitting in her chair in the corner of the living room, and her eyes were wide, filled with fear and suspicion as she glanced between me, Mom, and Papa. “They are out to get me,” she said, slightly frantic. She glanced down at her right hand, fixated on a spot on the dorsum. Gingerly lifting her arm, she angled her hand toward my mom’s face. “You see that? They have been conducting experiments on me. I AM THE QUEEN,” she sobbed, “and you are planning together” she said, directing her attention to Papa and me. In that moment, Grandma was convinced Papa and I were conspiring to assassinate her. It hurt to see my grandmother look at me with genuine fear in her eyes. It was overwhelming to watch her deteriorate from the person I had been accustomed to for most of my life to the paranoid individual shaking in front of me.
This was the first time I had really observed my grandmother experiencing acute psychosis. My mom explained to me at a young age that my grandmother had an illness in her mind. I noticed that compared to other people in my life, my grandmother seemed to express less emotion and changed topics in conversations frequently, but by having an understanding provided by my mother, my brother and I didn’t think much of it; that was just Grandma. She would occasionally talk about her experiences with hearing voices or people on the television talking about her. For the most part, though, she was stable; she was able to carry out cleaning, cooking, and watching her favorite shows.
That was until she turned 65 and started on Medicare for insurance. The government required her to trial a less expensive medication and wanted her family practitioner to adjust the medications she had been on for years. This decision was made by people unfamiliar with my grandmother and her story. As a result, my family struggled alongside Grandma for over a month as she battled hallucinations and labile emotions. Living in rural Ohio, she had no access to a psychiatrist or other mental health professional during this period. The adjustments to her medications, changes in her insurance coverage, and lack of consistent psychiatric care led to a deterioration of her stability. This was the only time in my life that I saw Grandma at a place where she would have needed to be hospitalized if the symptoms lasted much longer. I spent evenings sitting with her in that dark and scary place, listening, sympathizing, and challenging her distortions of reality. This experience laid the foundation for my growing passion for providing care and advocating for people experiencing mental illness. I observed firsthand how the absence of consistent, compassionate, and informed care could lead to psychiatric hospitalization.
In the past, my grandfather hid my grandmother’s diagnosis from those around them. This approach prevented my uncle from disclosing the same information to my cousins. I observed how they would look at her with confusion and sometimes fear, which was rooted in a lack of understanding. This desire to hide Grandma’s schizophrenia stemmed from the marginalization society imposed upon her. There were sneers, comments regarding lack of religious faith, and expressions that she was not trying hard enough. My grandparents decided together to inform their church of my grandmother’s illness. The results were astounding. People looked at my grandmother not with confusion but with sympathy and would go out of their way to check on her. Knowledge is power, and awareness can break down stigma. Seeing the difference knowledge could have on a church community further solidified my desire to educate not only patients and their family members but also communities.
Access is another huge barrier my grandmother has faced. There is a lack of referring and awareness as well as large geographic disparities of psychiatrists around my hometown. My grandmother has also had struggles with being able to pay for services, medication, and therapy. This shows the desperate need for more mental health professionals who are competent and knowledgeable in how social determinants of health impact outcomes. These factors contributed to my decision to pursue a Master of Public Health degree. I aspire to use this background to prevent what happened to my Grandma from happening to other patients and to be an advocate for enhanced access to services, improving community mental health and awareness, and promoting continuity of care to increase treatment compliance. That is what my Grandma has fostered in me as a future psychiatrist.
Editor’s note: Readers’ Forum is a department for correspondence from readers that is not in response to articles published in
Grandma was sitting in her chair in the corner of the living room, and her eyes were wide, filled with fear and suspicion as she glanced between me, Mom, and Papa. “They are out to get me,” she said, slightly frantic. She glanced down at her right hand, fixated on a spot on the dorsum. Gingerly lifting her arm, she angled her hand toward my mom’s face. “You see that? They have been conducting experiments on me. I AM THE QUEEN,” she sobbed, “and you are planning together” she said, directing her attention to Papa and me. In that moment, Grandma was convinced Papa and I were conspiring to assassinate her. It hurt to see my grandmother look at me with genuine fear in her eyes. It was overwhelming to watch her deteriorate from the person I had been accustomed to for most of my life to the paranoid individual shaking in front of me.
This was the first time I had really observed my grandmother experiencing acute psychosis. My mom explained to me at a young age that my grandmother had an illness in her mind. I noticed that compared to other people in my life, my grandmother seemed to express less emotion and changed topics in conversations frequently, but by having an understanding provided by my mother, my brother and I didn’t think much of it; that was just Grandma. She would occasionally talk about her experiences with hearing voices or people on the television talking about her. For the most part, though, she was stable; she was able to carry out cleaning, cooking, and watching her favorite shows.
That was until she turned 65 and started on Medicare for insurance. The government required her to trial a less expensive medication and wanted her family practitioner to adjust the medications she had been on for years. This decision was made by people unfamiliar with my grandmother and her story. As a result, my family struggled alongside Grandma for over a month as she battled hallucinations and labile emotions. Living in rural Ohio, she had no access to a psychiatrist or other mental health professional during this period. The adjustments to her medications, changes in her insurance coverage, and lack of consistent psychiatric care led to a deterioration of her stability. This was the only time in my life that I saw Grandma at a place where she would have needed to be hospitalized if the symptoms lasted much longer. I spent evenings sitting with her in that dark and scary place, listening, sympathizing, and challenging her distortions of reality. This experience laid the foundation for my growing passion for providing care and advocating for people experiencing mental illness. I observed firsthand how the absence of consistent, compassionate, and informed care could lead to psychiatric hospitalization.
In the past, my grandfather hid my grandmother’s diagnosis from those around them. This approach prevented my uncle from disclosing the same information to my cousins. I observed how they would look at her with confusion and sometimes fear, which was rooted in a lack of understanding. This desire to hide Grandma’s schizophrenia stemmed from the marginalization society imposed upon her. There were sneers, comments regarding lack of religious faith, and expressions that she was not trying hard enough. My grandparents decided together to inform their church of my grandmother’s illness. The results were astounding. People looked at my grandmother not with confusion but with sympathy and would go out of their way to check on her. Knowledge is power, and awareness can break down stigma. Seeing the difference knowledge could have on a church community further solidified my desire to educate not only patients and their family members but also communities.
Access is another huge barrier my grandmother has faced. There is a lack of referring and awareness as well as large geographic disparities of psychiatrists around my hometown. My grandmother has also had struggles with being able to pay for services, medication, and therapy. This shows the desperate need for more mental health professionals who are competent and knowledgeable in how social determinants of health impact outcomes. These factors contributed to my decision to pursue a Master of Public Health degree. I aspire to use this background to prevent what happened to my Grandma from happening to other patients and to be an advocate for enhanced access to services, improving community mental health and awareness, and promoting continuity of care to increase treatment compliance. That is what my Grandma has fostered in me as a future psychiatrist.
Editor’s note: Readers’ Forum is a department for correspondence from readers that is not in response to articles published in
Grandma was sitting in her chair in the corner of the living room, and her eyes were wide, filled with fear and suspicion as she glanced between me, Mom, and Papa. “They are out to get me,” she said, slightly frantic. She glanced down at her right hand, fixated on a spot on the dorsum. Gingerly lifting her arm, she angled her hand toward my mom’s face. “You see that? They have been conducting experiments on me. I AM THE QUEEN,” she sobbed, “and you are planning together” she said, directing her attention to Papa and me. In that moment, Grandma was convinced Papa and I were conspiring to assassinate her. It hurt to see my grandmother look at me with genuine fear in her eyes. It was overwhelming to watch her deteriorate from the person I had been accustomed to for most of my life to the paranoid individual shaking in front of me.
This was the first time I had really observed my grandmother experiencing acute psychosis. My mom explained to me at a young age that my grandmother had an illness in her mind. I noticed that compared to other people in my life, my grandmother seemed to express less emotion and changed topics in conversations frequently, but by having an understanding provided by my mother, my brother and I didn’t think much of it; that was just Grandma. She would occasionally talk about her experiences with hearing voices or people on the television talking about her. For the most part, though, she was stable; she was able to carry out cleaning, cooking, and watching her favorite shows.
That was until she turned 65 and started on Medicare for insurance. The government required her to trial a less expensive medication and wanted her family practitioner to adjust the medications she had been on for years. This decision was made by people unfamiliar with my grandmother and her story. As a result, my family struggled alongside Grandma for over a month as she battled hallucinations and labile emotions. Living in rural Ohio, she had no access to a psychiatrist or other mental health professional during this period. The adjustments to her medications, changes in her insurance coverage, and lack of consistent psychiatric care led to a deterioration of her stability. This was the only time in my life that I saw Grandma at a place where she would have needed to be hospitalized if the symptoms lasted much longer. I spent evenings sitting with her in that dark and scary place, listening, sympathizing, and challenging her distortions of reality. This experience laid the foundation for my growing passion for providing care and advocating for people experiencing mental illness. I observed firsthand how the absence of consistent, compassionate, and informed care could lead to psychiatric hospitalization.
In the past, my grandfather hid my grandmother’s diagnosis from those around them. This approach prevented my uncle from disclosing the same information to my cousins. I observed how they would look at her with confusion and sometimes fear, which was rooted in a lack of understanding. This desire to hide Grandma’s schizophrenia stemmed from the marginalization society imposed upon her. There were sneers, comments regarding lack of religious faith, and expressions that she was not trying hard enough. My grandparents decided together to inform their church of my grandmother’s illness. The results were astounding. People looked at my grandmother not with confusion but with sympathy and would go out of their way to check on her. Knowledge is power, and awareness can break down stigma. Seeing the difference knowledge could have on a church community further solidified my desire to educate not only patients and their family members but also communities.
Access is another huge barrier my grandmother has faced. There is a lack of referring and awareness as well as large geographic disparities of psychiatrists around my hometown. My grandmother has also had struggles with being able to pay for services, medication, and therapy. This shows the desperate need for more mental health professionals who are competent and knowledgeable in how social determinants of health impact outcomes. These factors contributed to my decision to pursue a Master of Public Health degree. I aspire to use this background to prevent what happened to my Grandma from happening to other patients and to be an advocate for enhanced access to services, improving community mental health and awareness, and promoting continuity of care to increase treatment compliance. That is what my Grandma has fostered in me as a future psychiatrist.
GIHN’s Crystal Anniversary: Reflecting on the future of GI
Our December 2022 issue marks the conclusion of GIHN’s 15th Anniversary Series. We hope you have enjoyed these special articles intended to celebrate the success of AGA’s official newspaper since its launch in 2007, mirroring equally rapid advances in our field. Over the past year, GIHN’s esteemed Associate Editors and former Editors-in-Chief have helped us “look back” on how the fields of gastroenterology and hepatology have changed since the newspaper’s inception, including advances in our understanding of the microbiome, innovations in endoscopic practice, changes in the demographics of the GI workforce, and breakthroughs in the treatment of hepatitis C. Now, as we conclude our 15th-anniversary year, it is only fitting that we “look forward” and consider the type of innovative coverage that will grace GIHN’s pages in the future. To that end, we asked a distinguished group of AGA thought leaders, representing various backgrounds and practice settings, to share their perspectives on what are likely to be the biggest change(s) in the field of GI over the next 15 years. We hope you find their answers inspiring as you consider your own reflections on this question.
As we close out 2022, we also wish to extend a big “thank you” to all the individuals who have provided thoughtful commentary to our coverage, helping us to understand the implications of innovative research findings on clinical practice and how changes in health policy impact our practices and our patients. I would also like to acknowledge our hardworking AGA and Frontline Medical Communications editorial teams, without whom this publication would not be possible. We wish you all a restful holiday season with your family and friends and look forward to reconnecting in 2023 – stay tuned for the launch of an exciting new GIHN initiative as part of our January issue!
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor-in-Chief
Our December 2022 issue marks the conclusion of GIHN’s 15th Anniversary Series. We hope you have enjoyed these special articles intended to celebrate the success of AGA’s official newspaper since its launch in 2007, mirroring equally rapid advances in our field. Over the past year, GIHN’s esteemed Associate Editors and former Editors-in-Chief have helped us “look back” on how the fields of gastroenterology and hepatology have changed since the newspaper’s inception, including advances in our understanding of the microbiome, innovations in endoscopic practice, changes in the demographics of the GI workforce, and breakthroughs in the treatment of hepatitis C. Now, as we conclude our 15th-anniversary year, it is only fitting that we “look forward” and consider the type of innovative coverage that will grace GIHN’s pages in the future. To that end, we asked a distinguished group of AGA thought leaders, representing various backgrounds and practice settings, to share their perspectives on what are likely to be the biggest change(s) in the field of GI over the next 15 years. We hope you find their answers inspiring as you consider your own reflections on this question.
As we close out 2022, we also wish to extend a big “thank you” to all the individuals who have provided thoughtful commentary to our coverage, helping us to understand the implications of innovative research findings on clinical practice and how changes in health policy impact our practices and our patients. I would also like to acknowledge our hardworking AGA and Frontline Medical Communications editorial teams, without whom this publication would not be possible. We wish you all a restful holiday season with your family and friends and look forward to reconnecting in 2023 – stay tuned for the launch of an exciting new GIHN initiative as part of our January issue!
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor-in-Chief
Our December 2022 issue marks the conclusion of GIHN’s 15th Anniversary Series. We hope you have enjoyed these special articles intended to celebrate the success of AGA’s official newspaper since its launch in 2007, mirroring equally rapid advances in our field. Over the past year, GIHN’s esteemed Associate Editors and former Editors-in-Chief have helped us “look back” on how the fields of gastroenterology and hepatology have changed since the newspaper’s inception, including advances in our understanding of the microbiome, innovations in endoscopic practice, changes in the demographics of the GI workforce, and breakthroughs in the treatment of hepatitis C. Now, as we conclude our 15th-anniversary year, it is only fitting that we “look forward” and consider the type of innovative coverage that will grace GIHN’s pages in the future. To that end, we asked a distinguished group of AGA thought leaders, representing various backgrounds and practice settings, to share their perspectives on what are likely to be the biggest change(s) in the field of GI over the next 15 years. We hope you find their answers inspiring as you consider your own reflections on this question.
As we close out 2022, we also wish to extend a big “thank you” to all the individuals who have provided thoughtful commentary to our coverage, helping us to understand the implications of innovative research findings on clinical practice and how changes in health policy impact our practices and our patients. I would also like to acknowledge our hardworking AGA and Frontline Medical Communications editorial teams, without whom this publication would not be possible. We wish you all a restful holiday season with your family and friends and look forward to reconnecting in 2023 – stay tuned for the launch of an exciting new GIHN initiative as part of our January issue!
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor-in-Chief
The surprising failure of vitamin D in deficient kids
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
My basic gripe is that you’ve got all these observational studies linking lower levels of vitamin D to everything from dementia to falls to cancer to COVID infection, and then you do a big randomized trial of supplementation and don’t see an effect.
And the explanation is that vitamin D is not necessarily the thing causing these bad outcomes; it’s a bystander – a canary in the coal mine. Your vitamin D level is a marker of your lifestyle; it’s higher in people who eat healthier foods, who exercise, and who spend more time out in the sun.
And yet ... if you were to ask me whether supplementing vitamin D in children with vitamin D deficiency would help them grow better and be healthier, I probably would have been on board for the idea.
And, it looks like, I would have been wrong.
Yes, it’s another negative randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation to add to the seemingly ever-growing body of literature suggesting that your money is better spent on a day at the park rather than buying D3 from your local GNC.
We are talking about this study, appearing in JAMA Pediatrics.
Briefly, 8,851 children from around Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, were randomized to receive 14,000 international units of vitamin D3 or placebo every week for 3 years.
Before we get into the results of the study, I need to point out that this part of Mongolia has a high rate of vitamin D deficiency. Beyond that, a prior observational study by these authors had shown that lower vitamin D levels were linked to the risk of acquiring latent tuberculosis infection in this area. Other studies have linked vitamin D deficiency with poorer growth metrics in children. Given the global scourge that is TB (around 2 million deaths a year) and childhood malnutrition (around 10% of children around the world), vitamin D supplementation is incredibly attractive as a public health intervention. It is relatively low on side effects and, importantly, it is cheap – and thus scalable.
Back to the study. These kids had pretty poor vitamin D levels at baseline; 95% of them were deficient, based on the accepted standard of levels less than 20 ng/mL. Over 30% were severely deficient, with levels less than 10 ng/mL.
The initial purpose of this study was to see if supplementation would prevent TB, but that analysis, which was published a few months ago, was negative. Vitamin D levels went up dramatically in the intervention group – they were taking their pills – but there was no difference in the rate of latent TB infection, active TB, other respiratory infections, or even serum interferon gamma levels.
Nothing.
But to be fair, the TB seroconversion rate was lower than expected, potentially leading to an underpowered study.
Which brings us to the just-published analysis which moves away from infectious disease to something where vitamin D should have some stronger footing: growth.
Would the kids who were randomized to vitamin D, those same kids who got their vitamin D levels into the normal range over 3 years of supplementation, grow more or grow better than the kids who didn’t?
And, unfortunately, the answer is still no.
At the end of follow-up, height z scores were not different between the groups. BMI z scores were not different between the groups. Pubertal development was not different between the groups. This was true not only overall, but across various subgroups, including analyses of those kids who had vitamin D levels less than 10 ng/mL to start with.
So, what’s going on? There are two very broad possibilities we can endorse. First, there’s the idea that vitamin D supplementation simply doesn’t do much for health. This is supported, now, by a long string of large clinical trials that show no effect across a variety of disease states and predisease states. In other words, the observational data linking low vitamin D to bad outcomes is correlation, not causation.
Or we can take the tack of some vitamin D apologists and decide that this trial just got it wrong. Perhaps the dose wasn’t given correctly, or 3 years isn’t long enough to see a real difference, or the growth metrics were wrong, or vitamin D needs to be given alongside something else to really work and so on. This is fine; no study is perfect and there is always something to criticize, believe me. But we need to be careful not to fall into the baby-and-bathwater fallacy. Just because we think a study could have done something better, or differently, doesn’t mean we can ignore all the results. And as each new randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation comes out, it’s getting harder and harder to believe that these trialists keep getting their methods wrong. Maybe they are just testing something that doesn’t work.
What to do? Well, it should be obvious. If low vitamin D levels are linked to TB rates and poor growth but supplementation doesn’t fix the problem, then we have to fix what is upstream of the problem. We need to boost vitamin D levels not through supplements, but through nutrition, exercise, activity, and getting outside. That’s a randomized trial you can sign me up for any day.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor, department of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this video transcript first appeared on Medscape.com.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
My basic gripe is that you’ve got all these observational studies linking lower levels of vitamin D to everything from dementia to falls to cancer to COVID infection, and then you do a big randomized trial of supplementation and don’t see an effect.
And the explanation is that vitamin D is not necessarily the thing causing these bad outcomes; it’s a bystander – a canary in the coal mine. Your vitamin D level is a marker of your lifestyle; it’s higher in people who eat healthier foods, who exercise, and who spend more time out in the sun.
And yet ... if you were to ask me whether supplementing vitamin D in children with vitamin D deficiency would help them grow better and be healthier, I probably would have been on board for the idea.
And, it looks like, I would have been wrong.
Yes, it’s another negative randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation to add to the seemingly ever-growing body of literature suggesting that your money is better spent on a day at the park rather than buying D3 from your local GNC.
We are talking about this study, appearing in JAMA Pediatrics.
Briefly, 8,851 children from around Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, were randomized to receive 14,000 international units of vitamin D3 or placebo every week for 3 years.
Before we get into the results of the study, I need to point out that this part of Mongolia has a high rate of vitamin D deficiency. Beyond that, a prior observational study by these authors had shown that lower vitamin D levels were linked to the risk of acquiring latent tuberculosis infection in this area. Other studies have linked vitamin D deficiency with poorer growth metrics in children. Given the global scourge that is TB (around 2 million deaths a year) and childhood malnutrition (around 10% of children around the world), vitamin D supplementation is incredibly attractive as a public health intervention. It is relatively low on side effects and, importantly, it is cheap – and thus scalable.
Back to the study. These kids had pretty poor vitamin D levels at baseline; 95% of them were deficient, based on the accepted standard of levels less than 20 ng/mL. Over 30% were severely deficient, with levels less than 10 ng/mL.
The initial purpose of this study was to see if supplementation would prevent TB, but that analysis, which was published a few months ago, was negative. Vitamin D levels went up dramatically in the intervention group – they were taking their pills – but there was no difference in the rate of latent TB infection, active TB, other respiratory infections, or even serum interferon gamma levels.
Nothing.
But to be fair, the TB seroconversion rate was lower than expected, potentially leading to an underpowered study.
Which brings us to the just-published analysis which moves away from infectious disease to something where vitamin D should have some stronger footing: growth.
Would the kids who were randomized to vitamin D, those same kids who got their vitamin D levels into the normal range over 3 years of supplementation, grow more or grow better than the kids who didn’t?
And, unfortunately, the answer is still no.
At the end of follow-up, height z scores were not different between the groups. BMI z scores were not different between the groups. Pubertal development was not different between the groups. This was true not only overall, but across various subgroups, including analyses of those kids who had vitamin D levels less than 10 ng/mL to start with.
So, what’s going on? There are two very broad possibilities we can endorse. First, there’s the idea that vitamin D supplementation simply doesn’t do much for health. This is supported, now, by a long string of large clinical trials that show no effect across a variety of disease states and predisease states. In other words, the observational data linking low vitamin D to bad outcomes is correlation, not causation.
Or we can take the tack of some vitamin D apologists and decide that this trial just got it wrong. Perhaps the dose wasn’t given correctly, or 3 years isn’t long enough to see a real difference, or the growth metrics were wrong, or vitamin D needs to be given alongside something else to really work and so on. This is fine; no study is perfect and there is always something to criticize, believe me. But we need to be careful not to fall into the baby-and-bathwater fallacy. Just because we think a study could have done something better, or differently, doesn’t mean we can ignore all the results. And as each new randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation comes out, it’s getting harder and harder to believe that these trialists keep getting their methods wrong. Maybe they are just testing something that doesn’t work.
What to do? Well, it should be obvious. If low vitamin D levels are linked to TB rates and poor growth but supplementation doesn’t fix the problem, then we have to fix what is upstream of the problem. We need to boost vitamin D levels not through supplements, but through nutrition, exercise, activity, and getting outside. That’s a randomized trial you can sign me up for any day.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor, department of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this video transcript first appeared on Medscape.com.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
My basic gripe is that you’ve got all these observational studies linking lower levels of vitamin D to everything from dementia to falls to cancer to COVID infection, and then you do a big randomized trial of supplementation and don’t see an effect.
And the explanation is that vitamin D is not necessarily the thing causing these bad outcomes; it’s a bystander – a canary in the coal mine. Your vitamin D level is a marker of your lifestyle; it’s higher in people who eat healthier foods, who exercise, and who spend more time out in the sun.
And yet ... if you were to ask me whether supplementing vitamin D in children with vitamin D deficiency would help them grow better and be healthier, I probably would have been on board for the idea.
And, it looks like, I would have been wrong.
Yes, it’s another negative randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation to add to the seemingly ever-growing body of literature suggesting that your money is better spent on a day at the park rather than buying D3 from your local GNC.
We are talking about this study, appearing in JAMA Pediatrics.
Briefly, 8,851 children from around Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, were randomized to receive 14,000 international units of vitamin D3 or placebo every week for 3 years.
Before we get into the results of the study, I need to point out that this part of Mongolia has a high rate of vitamin D deficiency. Beyond that, a prior observational study by these authors had shown that lower vitamin D levels were linked to the risk of acquiring latent tuberculosis infection in this area. Other studies have linked vitamin D deficiency with poorer growth metrics in children. Given the global scourge that is TB (around 2 million deaths a year) and childhood malnutrition (around 10% of children around the world), vitamin D supplementation is incredibly attractive as a public health intervention. It is relatively low on side effects and, importantly, it is cheap – and thus scalable.
Back to the study. These kids had pretty poor vitamin D levels at baseline; 95% of them were deficient, based on the accepted standard of levels less than 20 ng/mL. Over 30% were severely deficient, with levels less than 10 ng/mL.
The initial purpose of this study was to see if supplementation would prevent TB, but that analysis, which was published a few months ago, was negative. Vitamin D levels went up dramatically in the intervention group – they were taking their pills – but there was no difference in the rate of latent TB infection, active TB, other respiratory infections, or even serum interferon gamma levels.
Nothing.
But to be fair, the TB seroconversion rate was lower than expected, potentially leading to an underpowered study.
Which brings us to the just-published analysis which moves away from infectious disease to something where vitamin D should have some stronger footing: growth.
Would the kids who were randomized to vitamin D, those same kids who got their vitamin D levels into the normal range over 3 years of supplementation, grow more or grow better than the kids who didn’t?
And, unfortunately, the answer is still no.
At the end of follow-up, height z scores were not different between the groups. BMI z scores were not different between the groups. Pubertal development was not different between the groups. This was true not only overall, but across various subgroups, including analyses of those kids who had vitamin D levels less than 10 ng/mL to start with.
So, what’s going on? There are two very broad possibilities we can endorse. First, there’s the idea that vitamin D supplementation simply doesn’t do much for health. This is supported, now, by a long string of large clinical trials that show no effect across a variety of disease states and predisease states. In other words, the observational data linking low vitamin D to bad outcomes is correlation, not causation.
Or we can take the tack of some vitamin D apologists and decide that this trial just got it wrong. Perhaps the dose wasn’t given correctly, or 3 years isn’t long enough to see a real difference, or the growth metrics were wrong, or vitamin D needs to be given alongside something else to really work and so on. This is fine; no study is perfect and there is always something to criticize, believe me. But we need to be careful not to fall into the baby-and-bathwater fallacy. Just because we think a study could have done something better, or differently, doesn’t mean we can ignore all the results. And as each new randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation comes out, it’s getting harder and harder to believe that these trialists keep getting their methods wrong. Maybe they are just testing something that doesn’t work.
What to do? Well, it should be obvious. If low vitamin D levels are linked to TB rates and poor growth but supplementation doesn’t fix the problem, then we have to fix what is upstream of the problem. We need to boost vitamin D levels not through supplements, but through nutrition, exercise, activity, and getting outside. That’s a randomized trial you can sign me up for any day.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor, department of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this video transcript first appeared on Medscape.com.
New studies change beliefs about cardiovascular disease
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m going to review a few of these.
The first is the TIME study. The TIME study looked at whether it matters if you give antihypertensive agents in the morning or the evening. This was a prospective, pragmatic, parallel-group study that was performed in the U.K. and published in The Lancet.
Their question was whether evening dosing of antihypertensives has benefit in cardiovascular outcomes in adults. They enrolled over 21,000 people with hypertension who were taking at least one antihypertensive medication. Patients were randomized to morning or evening dosing.
The primary outcome was death or hospitalization due to myocardial infarction or stroke. There was no difference. It doesn’t matter if you take your antihypertensive agent in the morning or the evening. I think this is important because, clinically, the simpler the regimen for the patient, the greater the adherence, leading to better outcomes.
I know I can safely ask a patient when they would rather take their medicine. For many people, that may be the morning because they’re brushing their teeth and they remember. If they want to take it in the evening, that’s fine, too. We’re no longer slave to telling a patient to take their antihypertensive medications in the evening.
At the meeting of the American Society of Nephrology, results from a study on the use of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors in advanced CKD was presented, called the STOP ACEi trial. Again, another interesting trial asking a simple question. This was a randomized controlled trial (RCT) in patients who had an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) less than 30, and they were randomized to stop or continue therapy with their RAS inhibitors.
The primary outcome was the eGFR at 3 years. They enrolled 411 patients with a median baseline eGFR of 18. At 3 years, there was no difference in the eGFR between the groups. In the discontinuation group, the eGFR was 12.6 versus 13.3 in the continuation group. There were no differences in complications or anything else. Their conclusion was that among patients with advanced and progressive CKD, the discontinuation of a RAS inhibitor was not associated with a significant difference in the long-term rate of decrease in eGFR.
I think this is important because it changes our paradigm a bit. You can stop the RAS inhibitor; reduce the need for excessive medication in these patients; and, hopefully, focus on some newer medications that have been shown to prevent the decline in eGFR that are now available.
Next is from a letter published in JAMA, which asks the following question: Is diabetes itself an equivalent cardiovascular risk factor to those who have had a prior cardiovascular event?
We used to put having diabetes in that same high-risk category as people who’d already had a cardiovascular disease event. Well, have we made that any different? These authors are from Canada, and they did a retrospective population-based study looking at administrative health claims from Ontario, Canada, to assess the association of diabetes and prior cardiovascular disease with cardiovascular events from 1994 to 2014.
What I think is kind of cool, because I’m a diabetologist, is that over time the magnitude of the association between diabetes and cardiovascular event rates decreased. In somebody with diabetes, they don’t have the same high risk that a person who’s already had a cardiovascular event rate does. Diabetes is less of a risk factor for cardiovascular disease than having established cardiovascular disease, which means we’re treating diabetes better and reducing the risk for cardiovascular disease.
If you look at people with diabetes and a prior cardiovascular event, that’s still the very highest risk. The risk of people having another event who have established cardiovascular disease is pretty flat. Those people didn’t get better and the people with preexisting diabetes and cardiovascular events at baseline didn’t get much better, but those who had diabetes alone did improve in terms of looking at cardiovascular event rates.
I think this is good news because diabetes itself isn’t as high a cardiovascular risk factor as we once thought. It doesn’t mean that it isn’t a cardiovascular risk factor, but I think we’ve done better at mitigating the risk.
Finally, there is a relatively small study that was presented at the American Heart Association and published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, which asks whether supplements that are often used to lower LDL cholesterol are equivalent to a statin.
They compared six supplements with a placebo and with rosuvastatin, and looked to see what happened. This is not an outcome study, but a very short study, at 28 days, that used a placebo. They included 190 people with no history of cardiovascular disease but an increased 10-year risk for sclerotic cardiovascular disease.
The agents studied were rosuvastatin, placebo, fish oil, cinnamon, garlic, turmeric, plant sterols, and red yeast rice. Well, not surprisingly, rosuvastatin worked. It showed a 35% reduction in LDL cholesterol, and there was no significant impact on cholesterol levels with any of the other agents. The supplements yielded a similar response, as did the placebo. Side effects were similar, but they were most common with plant sterols and red yeast rice.
Clearly, a statin is better if you want to lower cholesterol levels. My approach, when patients want to take supplements, is to tell them what I know factually, which basically is that they don’t really cause much in the way of LDL cholesterol lowering. If I think the supplement isn’t going to hurt someone, I don’t tell them not to use it. I certainly tell them that they need to use agents that we know can actually reduce cardiovascular risk.
I think these studies really go through the gamut of asking questions. When can we stop an agent? What time of day do we need to give an agent? What, really, is the risk for type 2 diabetes with regard to cardiovascular events? What’s the value of supplements?
I think this is interesting, because I really encourage researchers to ask and answer these kinds of questions because it helps us clinically decide what’s best for treating our patients.
Thank you.
Dr. Peters is a professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She reported conflicts of interest with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m going to review a few of these.
The first is the TIME study. The TIME study looked at whether it matters if you give antihypertensive agents in the morning or the evening. This was a prospective, pragmatic, parallel-group study that was performed in the U.K. and published in The Lancet.
Their question was whether evening dosing of antihypertensives has benefit in cardiovascular outcomes in adults. They enrolled over 21,000 people with hypertension who were taking at least one antihypertensive medication. Patients were randomized to morning or evening dosing.
The primary outcome was death or hospitalization due to myocardial infarction or stroke. There was no difference. It doesn’t matter if you take your antihypertensive agent in the morning or the evening. I think this is important because, clinically, the simpler the regimen for the patient, the greater the adherence, leading to better outcomes.
I know I can safely ask a patient when they would rather take their medicine. For many people, that may be the morning because they’re brushing their teeth and they remember. If they want to take it in the evening, that’s fine, too. We’re no longer slave to telling a patient to take their antihypertensive medications in the evening.
At the meeting of the American Society of Nephrology, results from a study on the use of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors in advanced CKD was presented, called the STOP ACEi trial. Again, another interesting trial asking a simple question. This was a randomized controlled trial (RCT) in patients who had an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) less than 30, and they were randomized to stop or continue therapy with their RAS inhibitors.
The primary outcome was the eGFR at 3 years. They enrolled 411 patients with a median baseline eGFR of 18. At 3 years, there was no difference in the eGFR between the groups. In the discontinuation group, the eGFR was 12.6 versus 13.3 in the continuation group. There were no differences in complications or anything else. Their conclusion was that among patients with advanced and progressive CKD, the discontinuation of a RAS inhibitor was not associated with a significant difference in the long-term rate of decrease in eGFR.
I think this is important because it changes our paradigm a bit. You can stop the RAS inhibitor; reduce the need for excessive medication in these patients; and, hopefully, focus on some newer medications that have been shown to prevent the decline in eGFR that are now available.
Next is from a letter published in JAMA, which asks the following question: Is diabetes itself an equivalent cardiovascular risk factor to those who have had a prior cardiovascular event?
We used to put having diabetes in that same high-risk category as people who’d already had a cardiovascular disease event. Well, have we made that any different? These authors are from Canada, and they did a retrospective population-based study looking at administrative health claims from Ontario, Canada, to assess the association of diabetes and prior cardiovascular disease with cardiovascular events from 1994 to 2014.
What I think is kind of cool, because I’m a diabetologist, is that over time the magnitude of the association between diabetes and cardiovascular event rates decreased. In somebody with diabetes, they don’t have the same high risk that a person who’s already had a cardiovascular event rate does. Diabetes is less of a risk factor for cardiovascular disease than having established cardiovascular disease, which means we’re treating diabetes better and reducing the risk for cardiovascular disease.
If you look at people with diabetes and a prior cardiovascular event, that’s still the very highest risk. The risk of people having another event who have established cardiovascular disease is pretty flat. Those people didn’t get better and the people with preexisting diabetes and cardiovascular events at baseline didn’t get much better, but those who had diabetes alone did improve in terms of looking at cardiovascular event rates.
I think this is good news because diabetes itself isn’t as high a cardiovascular risk factor as we once thought. It doesn’t mean that it isn’t a cardiovascular risk factor, but I think we’ve done better at mitigating the risk.
Finally, there is a relatively small study that was presented at the American Heart Association and published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, which asks whether supplements that are often used to lower LDL cholesterol are equivalent to a statin.
They compared six supplements with a placebo and with rosuvastatin, and looked to see what happened. This is not an outcome study, but a very short study, at 28 days, that used a placebo. They included 190 people with no history of cardiovascular disease but an increased 10-year risk for sclerotic cardiovascular disease.
The agents studied were rosuvastatin, placebo, fish oil, cinnamon, garlic, turmeric, plant sterols, and red yeast rice. Well, not surprisingly, rosuvastatin worked. It showed a 35% reduction in LDL cholesterol, and there was no significant impact on cholesterol levels with any of the other agents. The supplements yielded a similar response, as did the placebo. Side effects were similar, but they were most common with plant sterols and red yeast rice.
Clearly, a statin is better if you want to lower cholesterol levels. My approach, when patients want to take supplements, is to tell them what I know factually, which basically is that they don’t really cause much in the way of LDL cholesterol lowering. If I think the supplement isn’t going to hurt someone, I don’t tell them not to use it. I certainly tell them that they need to use agents that we know can actually reduce cardiovascular risk.
I think these studies really go through the gamut of asking questions. When can we stop an agent? What time of day do we need to give an agent? What, really, is the risk for type 2 diabetes with regard to cardiovascular events? What’s the value of supplements?
I think this is interesting, because I really encourage researchers to ask and answer these kinds of questions because it helps us clinically decide what’s best for treating our patients.
Thank you.
Dr. Peters is a professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She reported conflicts of interest with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m going to review a few of these.
The first is the TIME study. The TIME study looked at whether it matters if you give antihypertensive agents in the morning or the evening. This was a prospective, pragmatic, parallel-group study that was performed in the U.K. and published in The Lancet.
Their question was whether evening dosing of antihypertensives has benefit in cardiovascular outcomes in adults. They enrolled over 21,000 people with hypertension who were taking at least one antihypertensive medication. Patients were randomized to morning or evening dosing.
The primary outcome was death or hospitalization due to myocardial infarction or stroke. There was no difference. It doesn’t matter if you take your antihypertensive agent in the morning or the evening. I think this is important because, clinically, the simpler the regimen for the patient, the greater the adherence, leading to better outcomes.
I know I can safely ask a patient when they would rather take their medicine. For many people, that may be the morning because they’re brushing their teeth and they remember. If they want to take it in the evening, that’s fine, too. We’re no longer slave to telling a patient to take their antihypertensive medications in the evening.
At the meeting of the American Society of Nephrology, results from a study on the use of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors in advanced CKD was presented, called the STOP ACEi trial. Again, another interesting trial asking a simple question. This was a randomized controlled trial (RCT) in patients who had an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) less than 30, and they were randomized to stop or continue therapy with their RAS inhibitors.
The primary outcome was the eGFR at 3 years. They enrolled 411 patients with a median baseline eGFR of 18. At 3 years, there was no difference in the eGFR between the groups. In the discontinuation group, the eGFR was 12.6 versus 13.3 in the continuation group. There were no differences in complications or anything else. Their conclusion was that among patients with advanced and progressive CKD, the discontinuation of a RAS inhibitor was not associated with a significant difference in the long-term rate of decrease in eGFR.
I think this is important because it changes our paradigm a bit. You can stop the RAS inhibitor; reduce the need for excessive medication in these patients; and, hopefully, focus on some newer medications that have been shown to prevent the decline in eGFR that are now available.
Next is from a letter published in JAMA, which asks the following question: Is diabetes itself an equivalent cardiovascular risk factor to those who have had a prior cardiovascular event?
We used to put having diabetes in that same high-risk category as people who’d already had a cardiovascular disease event. Well, have we made that any different? These authors are from Canada, and they did a retrospective population-based study looking at administrative health claims from Ontario, Canada, to assess the association of diabetes and prior cardiovascular disease with cardiovascular events from 1994 to 2014.
What I think is kind of cool, because I’m a diabetologist, is that over time the magnitude of the association between diabetes and cardiovascular event rates decreased. In somebody with diabetes, they don’t have the same high risk that a person who’s already had a cardiovascular event rate does. Diabetes is less of a risk factor for cardiovascular disease than having established cardiovascular disease, which means we’re treating diabetes better and reducing the risk for cardiovascular disease.
If you look at people with diabetes and a prior cardiovascular event, that’s still the very highest risk. The risk of people having another event who have established cardiovascular disease is pretty flat. Those people didn’t get better and the people with preexisting diabetes and cardiovascular events at baseline didn’t get much better, but those who had diabetes alone did improve in terms of looking at cardiovascular event rates.
I think this is good news because diabetes itself isn’t as high a cardiovascular risk factor as we once thought. It doesn’t mean that it isn’t a cardiovascular risk factor, but I think we’ve done better at mitigating the risk.
Finally, there is a relatively small study that was presented at the American Heart Association and published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, which asks whether supplements that are often used to lower LDL cholesterol are equivalent to a statin.
They compared six supplements with a placebo and with rosuvastatin, and looked to see what happened. This is not an outcome study, but a very short study, at 28 days, that used a placebo. They included 190 people with no history of cardiovascular disease but an increased 10-year risk for sclerotic cardiovascular disease.
The agents studied were rosuvastatin, placebo, fish oil, cinnamon, garlic, turmeric, plant sterols, and red yeast rice. Well, not surprisingly, rosuvastatin worked. It showed a 35% reduction in LDL cholesterol, and there was no significant impact on cholesterol levels with any of the other agents. The supplements yielded a similar response, as did the placebo. Side effects were similar, but they were most common with plant sterols and red yeast rice.
Clearly, a statin is better if you want to lower cholesterol levels. My approach, when patients want to take supplements, is to tell them what I know factually, which basically is that they don’t really cause much in the way of LDL cholesterol lowering. If I think the supplement isn’t going to hurt someone, I don’t tell them not to use it. I certainly tell them that they need to use agents that we know can actually reduce cardiovascular risk.
I think these studies really go through the gamut of asking questions. When can we stop an agent? What time of day do we need to give an agent? What, really, is the risk for type 2 diabetes with regard to cardiovascular events? What’s the value of supplements?
I think this is interesting, because I really encourage researchers to ask and answer these kinds of questions because it helps us clinically decide what’s best for treating our patients.
Thank you.
Dr. Peters is a professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She reported conflicts of interest with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Discontinuing immunotherapy: Is the infusion bag half empty or half full?
It’s a “champagne problem” many of us have encountered over the past few years in the clinic.
A patient with advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is fortunate enough to continue to do well for 2 years on ongoing pembrolizumab or perhaps pemetrexed and pembrolizumab as maintenance therapy. The latest CT shows a residual but far smaller primary tumor than what she started with.
In this instance, you may be considering stopping treatment but are concerned about doing so with evidence of disease still present.
Clinical trials of immunotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy have generally terminated treatment in nonprogressing patients after 2 years. We also know that some patients in early trials of immunotherapy stopped treatment after a fixed period of 1 or 2 years and continued to show no evidence of progression many years later.
The reason some patients experience this kind of success: Unlike the mechanism of action of conventional chemotherapy or targeted therapies, where ongoing treatment would be important to continue to exert an inhibitory effect, the active substrate of immunotherapy is the patient’s immune system, which can potentially have a self-sustaining efficacy beyond the stimulatory effect of the checkpoint inhibitor.
One trial directly addressed this question of stopping vs. continuing treatment in patients on immunotherapy. The CheckMate 153 trial, published in 2020, randomly assigned 252 previously treated patients who hadn’t demonstrated progression after 1 year on nivolumab to either discontinue nivolumab or continue nivolumab on an ongoing basis. The results were strongly in favor of ongoing therapy. Both progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were significantly longer in patients who continued therapy: PFS of 24.7 months vs. 9.4 months and OS not reached vs. 32.5 months.
This finding is important, but there’s an important caveat. The study population included many heavily pretreated patients, but, in practice, immunotherapy has generally moved into the first-line setting, where we see dramatic responses in a significant subset of patients.
Even more recent data are emerging that may help us evaluate who will do well off therapy and who should continue treatment.
We now have a growing collection of long-term data on patients who are more likely to have good outcomes with immunotherapy, specifically those with high tumor programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression (≥ 50%), from the KEYNOTE-024 trial. In this study, 39 of 151 (25.8%) patients assigned to pembrolizumab completed the planned maximum of 2 years of treatment, among whom 82.1% achieved an objective response; but, only 10% (4 patients) achieved a complete response. The proportion of patients without progression and remaining off therapy wasn’t reported, but the OS rate 3 years after completing treatment was 81.4%.
In addition, restarting immunotherapy after discontinuing appears to be a moderately effective strategy. In the KEYNOTE-024 trial, 12 patients received a second course of pembrolizumab because of disease progression a median of 15.2 months after discontinuing pembrolizumab. In this small cohort, eight of these patients (66.7%) were alive at the data cutoff, and six (50%) achieved stable disease.
Recently, we received additional insight in the follow-up from two chemoimmunotherapy trials that have most shaped my practice for patients with advanced NSCLC and any level of PD-L1 expression. These are the KEYNOTE-189 trial of platinum-pemetrexed with pembrolizumab vs. placebo in those with nonsquamous NSCLC, and the KEYNOTE-407 trial of carboplatin-taxane with pembrolizumab vs. placebo in patients with advanced squamous NSCLC. The National Comprehensive Cancer Network has designated each as a “preferred regimen” for patients with advanced NSCLC.
Both regimens have demonstrated sustained efficacy benefits with prolonged follow-up, including significantly superior objective response rate, PFS, and OS with the addition of pembrolizumab. These findings merely cemented the role of these regimens in our practice, but the trials also reported on the cohort of patients who completed 35 cycles of treatment over 2 years then discontinued therapy. In both, the majority of patients showed an objective response (86% in KEYNOTE-189 and 90% in KEYNOTE-407), with most patients alive at 3 years after 2 years of treatment (71.9% in KEYNOTE-189 and 69.5% in KEYNOTE-407). In addition, the proportion of patients alive without disease progression or subsequent therapy was notable – 40.4% in KEYNOTE-189 and 43.6% KEYNOTE-407.
How should we interpret these data for the patient who is in the exam room with us?
The short answer is that we don’t know. I see this as a half-empty, half-full conundrum.
I’m disappointed that more patients who responded for 2 years will experience disease progression in the 1-3 years that follow. This signals that their immune systems have not perpetuated their initial response over the long-term. But these patients may have demonstrated disease progression even if they had continued therapy.
We also know that some patients can be rechallenged and will respond again. Some of these patients will show stable disease, whereas others will progress with repeat treatment. I would love to be able to better predict which patients are destined to do well without treatment vs. those who benefit from treatment beyond 2 years.
Might the level of PD-L1 expression tell us? Can PET imaging discriminate those with residual hypermetabolism who may need continued treatment from those with no residual uptake who could be spared it? Would serial measurement of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in responding patients identify when they have achieved a point of diminishing returns, potentially indicating that some can safely discontinue treatment after 2 years, whereas others need to continue to suppress on prolonged maintenance therapy?
These questions have yet to be studied systematically. In the meantime, I take an individualized approach with my patients facing this decision. Some have experienced escalating arthralgias and myalgias, cost concerns, or other issues related to immunotherapy that may dissuade us from continuing treatment. But several others have been grateful to continue with their treatment, hesitant to do anything that could change the path of their disease.
In my patients who tolerate therapy well, I’m more worried about potential undertreatment than overtreatment. I tend to favor having my patients continue therapy in the absence of problematic toxicity or practical challenges. There is certainly room for debate here while we await data to better guide these decisions. How do you approach these patients?
Dr. West is Clinical Associate Professor, Department of Medical Oncology, City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Care, Duarte, Calif. He reported conflicts of interest with Ariad/Takeda, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Spectrum, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Genentech/Roche, Pfizer, Merck, and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s a “champagne problem” many of us have encountered over the past few years in the clinic.
A patient with advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is fortunate enough to continue to do well for 2 years on ongoing pembrolizumab or perhaps pemetrexed and pembrolizumab as maintenance therapy. The latest CT shows a residual but far smaller primary tumor than what she started with.
In this instance, you may be considering stopping treatment but are concerned about doing so with evidence of disease still present.
Clinical trials of immunotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy have generally terminated treatment in nonprogressing patients after 2 years. We also know that some patients in early trials of immunotherapy stopped treatment after a fixed period of 1 or 2 years and continued to show no evidence of progression many years later.
The reason some patients experience this kind of success: Unlike the mechanism of action of conventional chemotherapy or targeted therapies, where ongoing treatment would be important to continue to exert an inhibitory effect, the active substrate of immunotherapy is the patient’s immune system, which can potentially have a self-sustaining efficacy beyond the stimulatory effect of the checkpoint inhibitor.
One trial directly addressed this question of stopping vs. continuing treatment in patients on immunotherapy. The CheckMate 153 trial, published in 2020, randomly assigned 252 previously treated patients who hadn’t demonstrated progression after 1 year on nivolumab to either discontinue nivolumab or continue nivolumab on an ongoing basis. The results were strongly in favor of ongoing therapy. Both progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were significantly longer in patients who continued therapy: PFS of 24.7 months vs. 9.4 months and OS not reached vs. 32.5 months.
This finding is important, but there’s an important caveat. The study population included many heavily pretreated patients, but, in practice, immunotherapy has generally moved into the first-line setting, where we see dramatic responses in a significant subset of patients.
Even more recent data are emerging that may help us evaluate who will do well off therapy and who should continue treatment.
We now have a growing collection of long-term data on patients who are more likely to have good outcomes with immunotherapy, specifically those with high tumor programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression (≥ 50%), from the KEYNOTE-024 trial. In this study, 39 of 151 (25.8%) patients assigned to pembrolizumab completed the planned maximum of 2 years of treatment, among whom 82.1% achieved an objective response; but, only 10% (4 patients) achieved a complete response. The proportion of patients without progression and remaining off therapy wasn’t reported, but the OS rate 3 years after completing treatment was 81.4%.
In addition, restarting immunotherapy after discontinuing appears to be a moderately effective strategy. In the KEYNOTE-024 trial, 12 patients received a second course of pembrolizumab because of disease progression a median of 15.2 months after discontinuing pembrolizumab. In this small cohort, eight of these patients (66.7%) were alive at the data cutoff, and six (50%) achieved stable disease.
Recently, we received additional insight in the follow-up from two chemoimmunotherapy trials that have most shaped my practice for patients with advanced NSCLC and any level of PD-L1 expression. These are the KEYNOTE-189 trial of platinum-pemetrexed with pembrolizumab vs. placebo in those with nonsquamous NSCLC, and the KEYNOTE-407 trial of carboplatin-taxane with pembrolizumab vs. placebo in patients with advanced squamous NSCLC. The National Comprehensive Cancer Network has designated each as a “preferred regimen” for patients with advanced NSCLC.
Both regimens have demonstrated sustained efficacy benefits with prolonged follow-up, including significantly superior objective response rate, PFS, and OS with the addition of pembrolizumab. These findings merely cemented the role of these regimens in our practice, but the trials also reported on the cohort of patients who completed 35 cycles of treatment over 2 years then discontinued therapy. In both, the majority of patients showed an objective response (86% in KEYNOTE-189 and 90% in KEYNOTE-407), with most patients alive at 3 years after 2 years of treatment (71.9% in KEYNOTE-189 and 69.5% in KEYNOTE-407). In addition, the proportion of patients alive without disease progression or subsequent therapy was notable – 40.4% in KEYNOTE-189 and 43.6% KEYNOTE-407.
How should we interpret these data for the patient who is in the exam room with us?
The short answer is that we don’t know. I see this as a half-empty, half-full conundrum.
I’m disappointed that more patients who responded for 2 years will experience disease progression in the 1-3 years that follow. This signals that their immune systems have not perpetuated their initial response over the long-term. But these patients may have demonstrated disease progression even if they had continued therapy.
We also know that some patients can be rechallenged and will respond again. Some of these patients will show stable disease, whereas others will progress with repeat treatment. I would love to be able to better predict which patients are destined to do well without treatment vs. those who benefit from treatment beyond 2 years.
Might the level of PD-L1 expression tell us? Can PET imaging discriminate those with residual hypermetabolism who may need continued treatment from those with no residual uptake who could be spared it? Would serial measurement of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in responding patients identify when they have achieved a point of diminishing returns, potentially indicating that some can safely discontinue treatment after 2 years, whereas others need to continue to suppress on prolonged maintenance therapy?
These questions have yet to be studied systematically. In the meantime, I take an individualized approach with my patients facing this decision. Some have experienced escalating arthralgias and myalgias, cost concerns, or other issues related to immunotherapy that may dissuade us from continuing treatment. But several others have been grateful to continue with their treatment, hesitant to do anything that could change the path of their disease.
In my patients who tolerate therapy well, I’m more worried about potential undertreatment than overtreatment. I tend to favor having my patients continue therapy in the absence of problematic toxicity or practical challenges. There is certainly room for debate here while we await data to better guide these decisions. How do you approach these patients?
Dr. West is Clinical Associate Professor, Department of Medical Oncology, City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Care, Duarte, Calif. He reported conflicts of interest with Ariad/Takeda, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Spectrum, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Genentech/Roche, Pfizer, Merck, and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s a “champagne problem” many of us have encountered over the past few years in the clinic.
A patient with advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is fortunate enough to continue to do well for 2 years on ongoing pembrolizumab or perhaps pemetrexed and pembrolizumab as maintenance therapy. The latest CT shows a residual but far smaller primary tumor than what she started with.
In this instance, you may be considering stopping treatment but are concerned about doing so with evidence of disease still present.
Clinical trials of immunotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy have generally terminated treatment in nonprogressing patients after 2 years. We also know that some patients in early trials of immunotherapy stopped treatment after a fixed period of 1 or 2 years and continued to show no evidence of progression many years later.
The reason some patients experience this kind of success: Unlike the mechanism of action of conventional chemotherapy or targeted therapies, where ongoing treatment would be important to continue to exert an inhibitory effect, the active substrate of immunotherapy is the patient’s immune system, which can potentially have a self-sustaining efficacy beyond the stimulatory effect of the checkpoint inhibitor.
One trial directly addressed this question of stopping vs. continuing treatment in patients on immunotherapy. The CheckMate 153 trial, published in 2020, randomly assigned 252 previously treated patients who hadn’t demonstrated progression after 1 year on nivolumab to either discontinue nivolumab or continue nivolumab on an ongoing basis. The results were strongly in favor of ongoing therapy. Both progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were significantly longer in patients who continued therapy: PFS of 24.7 months vs. 9.4 months and OS not reached vs. 32.5 months.
This finding is important, but there’s an important caveat. The study population included many heavily pretreated patients, but, in practice, immunotherapy has generally moved into the first-line setting, where we see dramatic responses in a significant subset of patients.
Even more recent data are emerging that may help us evaluate who will do well off therapy and who should continue treatment.
We now have a growing collection of long-term data on patients who are more likely to have good outcomes with immunotherapy, specifically those with high tumor programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression (≥ 50%), from the KEYNOTE-024 trial. In this study, 39 of 151 (25.8%) patients assigned to pembrolizumab completed the planned maximum of 2 years of treatment, among whom 82.1% achieved an objective response; but, only 10% (4 patients) achieved a complete response. The proportion of patients without progression and remaining off therapy wasn’t reported, but the OS rate 3 years after completing treatment was 81.4%.
In addition, restarting immunotherapy after discontinuing appears to be a moderately effective strategy. In the KEYNOTE-024 trial, 12 patients received a second course of pembrolizumab because of disease progression a median of 15.2 months after discontinuing pembrolizumab. In this small cohort, eight of these patients (66.7%) were alive at the data cutoff, and six (50%) achieved stable disease.
Recently, we received additional insight in the follow-up from two chemoimmunotherapy trials that have most shaped my practice for patients with advanced NSCLC and any level of PD-L1 expression. These are the KEYNOTE-189 trial of platinum-pemetrexed with pembrolizumab vs. placebo in those with nonsquamous NSCLC, and the KEYNOTE-407 trial of carboplatin-taxane with pembrolizumab vs. placebo in patients with advanced squamous NSCLC. The National Comprehensive Cancer Network has designated each as a “preferred regimen” for patients with advanced NSCLC.
Both regimens have demonstrated sustained efficacy benefits with prolonged follow-up, including significantly superior objective response rate, PFS, and OS with the addition of pembrolizumab. These findings merely cemented the role of these regimens in our practice, but the trials also reported on the cohort of patients who completed 35 cycles of treatment over 2 years then discontinued therapy. In both, the majority of patients showed an objective response (86% in KEYNOTE-189 and 90% in KEYNOTE-407), with most patients alive at 3 years after 2 years of treatment (71.9% in KEYNOTE-189 and 69.5% in KEYNOTE-407). In addition, the proportion of patients alive without disease progression or subsequent therapy was notable – 40.4% in KEYNOTE-189 and 43.6% KEYNOTE-407.
How should we interpret these data for the patient who is in the exam room with us?
The short answer is that we don’t know. I see this as a half-empty, half-full conundrum.
I’m disappointed that more patients who responded for 2 years will experience disease progression in the 1-3 years that follow. This signals that their immune systems have not perpetuated their initial response over the long-term. But these patients may have demonstrated disease progression even if they had continued therapy.
We also know that some patients can be rechallenged and will respond again. Some of these patients will show stable disease, whereas others will progress with repeat treatment. I would love to be able to better predict which patients are destined to do well without treatment vs. those who benefit from treatment beyond 2 years.
Might the level of PD-L1 expression tell us? Can PET imaging discriminate those with residual hypermetabolism who may need continued treatment from those with no residual uptake who could be spared it? Would serial measurement of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in responding patients identify when they have achieved a point of diminishing returns, potentially indicating that some can safely discontinue treatment after 2 years, whereas others need to continue to suppress on prolonged maintenance therapy?
These questions have yet to be studied systematically. In the meantime, I take an individualized approach with my patients facing this decision. Some have experienced escalating arthralgias and myalgias, cost concerns, or other issues related to immunotherapy that may dissuade us from continuing treatment. But several others have been grateful to continue with their treatment, hesitant to do anything that could change the path of their disease.
In my patients who tolerate therapy well, I’m more worried about potential undertreatment than overtreatment. I tend to favor having my patients continue therapy in the absence of problematic toxicity or practical challenges. There is certainly room for debate here while we await data to better guide these decisions. How do you approach these patients?
Dr. West is Clinical Associate Professor, Department of Medical Oncology, City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Care, Duarte, Calif. He reported conflicts of interest with Ariad/Takeda, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Spectrum, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Genentech/Roche, Pfizer, Merck, and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hormonal management of gender-diverse patients: SOC8 updates
In September, the World Professional Association for Transgender Health released its much-anticipated standards of care (SOC8). While this update has unfortunately received intense scrutiny for its guidance about gender-diverse adolescents and youth, the SOC8 is their most evidence-based version to date. Recommendations were developed based on data from independent systematic literature reviews, background reviews, and expert opinions.1 These guidelines also recognize knowledge deficits and are intended to be flexible to meet the individual needs of transgender patients. While the scope of this column will not delve into all 258 pages of these new standards, it will highlight pertinent information on hormonal management.
Ever since the original publication of the standards of care in 1979, gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) has been considered medically necessary. The approach to GAHT depends on the patient’s goals and the age at which the patient is seeking to medically transition. Given the complexity of GAHT for transgender youth and adolescents, this article will focus primarily on adult patients.
There are a few pertinent differences in the management and monitoring of GAHT in adults. For patients assigned female at birth, testosterone is the primary modality by which patients can achieve masculinizing features. GAHT for patients assigned male at birth often consists of estrogen and an androgen-lowering medication. Like its predecessor, SOC8 recommends against prescribing ethinyl estradiol because of its marked association with thromboembolic events.
While the formulations of estrogen (oral, injectable, and patches) and hormone blockers (finasteride, spironolactone, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, and bicalutamide) are discussed in prior standards of care, SOC8 further delineates their utilization. It suggests that transdermal estrogen should be considered in transgender women over the age of 45 who are at high risk for developing a venous thromboembolism or have a previous history of thromboembolism. Furthermore, SOC8 establishes spironolactone as the mainstay for androgen blockage and discourages routine usage of bicalutamide and finasteride because of a lack of safety data and questionable efficacy.1 Even though some patients anecdotally report increased breast growth with progesterone supplementation, there is insufficient evidence to regularly prescribe progesterone for breast development.1
Both WPATH and the Endocrine Society recommend checking serum levels of sex hormones every 3 months during the first year until stable levels are achieved, then once or twice a year thereafter.1 Hormone levels should be maintained at physiologic concentrations of the targeted gender. Some patients on feminizing GAHT often request evaluation of estrone/estradiol ratios as there was an assumption that higher ratios were associated with antagonistic effects on breast development. However, recent published evidence refutes this claim and estrone/estradiol ratios need not be measured.1
In addition to monitoring sex hormone levels, providers should check the metabolic effects that can be associated with GAHT. Both testosterone and estrogen can influence lipid panels: Testosterone can increase the red blood cell count, and spironolactone may cause hyperkalemia. While the SOC7 previously encouraged assessment of these laboratory values every 3 months, the new guidelines are more flexible in the frequency of testing of asymptomatic individuals as there is no strong evidence from published studies that supports these 3-month intervals.1
Providers are responsible for informing patients about the possible effects of GAHT on fertility. Estrogen often will cause a reduction in spermatogenesis, which may be irreversible. Patients who plan on taking estrogen should be counseled regarding sperm cryopreservation prior to starting GAHT. Even though testosterone inhibits ovulation and induces menstrual suppression, patients often regain their fertility after cessation of testosterone therapy. However, given the significant knowledge deficit about long-term fertility in transmasculine patients, providers should still offer oocyte or embryo cryopreservation.
Health care providers should collaborate with surgeons regarding preoperative and postoperative GAHT. To mitigate the risk of thromboembolism, many surgeons would stop hormones 1-4 weeks before and after gender-affirming surgery. Recent evidence does not support this practice, as studies indicate no increased risk for venous thromboembolism in individuals on GAHT undergoing surgery. These studies are consistent with other well-established guidelines on preoperative management of cisgender women taking estrogen or progestins. As exogenous sex steroids are necessary for bone health in patients who undergo gonadectomy, surgeons and other health care providers should educate patients on the importance of continuing GAHT.
There are many procedures available for gender-affirming surgery. Many of these surgeries involve three regions: the face, chest/breast, and/or genitalia (both internal and external). Prior to making a surgical referral, providers should be familiar with the surgeon’s scope of practice, performance measures, and surgical outcomes.1 For the first time, the SOC8 also addresses the surgical training of the providers who offer these procedures. While gender-affirming surgery can be performed by a variety of different specialists, training and documented supervision (often by an existing expert in gender-affirming surgery) is essential. Maintaining an active practice in these procedures, tracking surgical outcomes, and continuing education within the field of gender-affirming surgery are additional requirements for surgeons performing these complex operations.1
As their name implies, the SOC8 attempts to create a standardized guide to assist practitioners caring for gender-diverse patients. It’s important for providers to be familiar with updates while also recognizing the evolving nature of this rapidly growing field.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
Reference
1. World Professional Association for Transgender Health. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, Version 8. Int J Transgend Health. 2022 Sep 15. doi: 10.1080/26895269.2022.2100644.
In September, the World Professional Association for Transgender Health released its much-anticipated standards of care (SOC8). While this update has unfortunately received intense scrutiny for its guidance about gender-diverse adolescents and youth, the SOC8 is their most evidence-based version to date. Recommendations were developed based on data from independent systematic literature reviews, background reviews, and expert opinions.1 These guidelines also recognize knowledge deficits and are intended to be flexible to meet the individual needs of transgender patients. While the scope of this column will not delve into all 258 pages of these new standards, it will highlight pertinent information on hormonal management.
Ever since the original publication of the standards of care in 1979, gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) has been considered medically necessary. The approach to GAHT depends on the patient’s goals and the age at which the patient is seeking to medically transition. Given the complexity of GAHT for transgender youth and adolescents, this article will focus primarily on adult patients.
There are a few pertinent differences in the management and monitoring of GAHT in adults. For patients assigned female at birth, testosterone is the primary modality by which patients can achieve masculinizing features. GAHT for patients assigned male at birth often consists of estrogen and an androgen-lowering medication. Like its predecessor, SOC8 recommends against prescribing ethinyl estradiol because of its marked association with thromboembolic events.
While the formulations of estrogen (oral, injectable, and patches) and hormone blockers (finasteride, spironolactone, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, and bicalutamide) are discussed in prior standards of care, SOC8 further delineates their utilization. It suggests that transdermal estrogen should be considered in transgender women over the age of 45 who are at high risk for developing a venous thromboembolism or have a previous history of thromboembolism. Furthermore, SOC8 establishes spironolactone as the mainstay for androgen blockage and discourages routine usage of bicalutamide and finasteride because of a lack of safety data and questionable efficacy.1 Even though some patients anecdotally report increased breast growth with progesterone supplementation, there is insufficient evidence to regularly prescribe progesterone for breast development.1
Both WPATH and the Endocrine Society recommend checking serum levels of sex hormones every 3 months during the first year until stable levels are achieved, then once or twice a year thereafter.1 Hormone levels should be maintained at physiologic concentrations of the targeted gender. Some patients on feminizing GAHT often request evaluation of estrone/estradiol ratios as there was an assumption that higher ratios were associated with antagonistic effects on breast development. However, recent published evidence refutes this claim and estrone/estradiol ratios need not be measured.1
In addition to monitoring sex hormone levels, providers should check the metabolic effects that can be associated with GAHT. Both testosterone and estrogen can influence lipid panels: Testosterone can increase the red blood cell count, and spironolactone may cause hyperkalemia. While the SOC7 previously encouraged assessment of these laboratory values every 3 months, the new guidelines are more flexible in the frequency of testing of asymptomatic individuals as there is no strong evidence from published studies that supports these 3-month intervals.1
Providers are responsible for informing patients about the possible effects of GAHT on fertility. Estrogen often will cause a reduction in spermatogenesis, which may be irreversible. Patients who plan on taking estrogen should be counseled regarding sperm cryopreservation prior to starting GAHT. Even though testosterone inhibits ovulation and induces menstrual suppression, patients often regain their fertility after cessation of testosterone therapy. However, given the significant knowledge deficit about long-term fertility in transmasculine patients, providers should still offer oocyte or embryo cryopreservation.
Health care providers should collaborate with surgeons regarding preoperative and postoperative GAHT. To mitigate the risk of thromboembolism, many surgeons would stop hormones 1-4 weeks before and after gender-affirming surgery. Recent evidence does not support this practice, as studies indicate no increased risk for venous thromboembolism in individuals on GAHT undergoing surgery. These studies are consistent with other well-established guidelines on preoperative management of cisgender women taking estrogen or progestins. As exogenous sex steroids are necessary for bone health in patients who undergo gonadectomy, surgeons and other health care providers should educate patients on the importance of continuing GAHT.
There are many procedures available for gender-affirming surgery. Many of these surgeries involve three regions: the face, chest/breast, and/or genitalia (both internal and external). Prior to making a surgical referral, providers should be familiar with the surgeon’s scope of practice, performance measures, and surgical outcomes.1 For the first time, the SOC8 also addresses the surgical training of the providers who offer these procedures. While gender-affirming surgery can be performed by a variety of different specialists, training and documented supervision (often by an existing expert in gender-affirming surgery) is essential. Maintaining an active practice in these procedures, tracking surgical outcomes, and continuing education within the field of gender-affirming surgery are additional requirements for surgeons performing these complex operations.1
As their name implies, the SOC8 attempts to create a standardized guide to assist practitioners caring for gender-diverse patients. It’s important for providers to be familiar with updates while also recognizing the evolving nature of this rapidly growing field.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
Reference
1. World Professional Association for Transgender Health. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, Version 8. Int J Transgend Health. 2022 Sep 15. doi: 10.1080/26895269.2022.2100644.
In September, the World Professional Association for Transgender Health released its much-anticipated standards of care (SOC8). While this update has unfortunately received intense scrutiny for its guidance about gender-diverse adolescents and youth, the SOC8 is their most evidence-based version to date. Recommendations were developed based on data from independent systematic literature reviews, background reviews, and expert opinions.1 These guidelines also recognize knowledge deficits and are intended to be flexible to meet the individual needs of transgender patients. While the scope of this column will not delve into all 258 pages of these new standards, it will highlight pertinent information on hormonal management.
Ever since the original publication of the standards of care in 1979, gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) has been considered medically necessary. The approach to GAHT depends on the patient’s goals and the age at which the patient is seeking to medically transition. Given the complexity of GAHT for transgender youth and adolescents, this article will focus primarily on adult patients.
There are a few pertinent differences in the management and monitoring of GAHT in adults. For patients assigned female at birth, testosterone is the primary modality by which patients can achieve masculinizing features. GAHT for patients assigned male at birth often consists of estrogen and an androgen-lowering medication. Like its predecessor, SOC8 recommends against prescribing ethinyl estradiol because of its marked association with thromboembolic events.
While the formulations of estrogen (oral, injectable, and patches) and hormone blockers (finasteride, spironolactone, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, and bicalutamide) are discussed in prior standards of care, SOC8 further delineates their utilization. It suggests that transdermal estrogen should be considered in transgender women over the age of 45 who are at high risk for developing a venous thromboembolism or have a previous history of thromboembolism. Furthermore, SOC8 establishes spironolactone as the mainstay for androgen blockage and discourages routine usage of bicalutamide and finasteride because of a lack of safety data and questionable efficacy.1 Even though some patients anecdotally report increased breast growth with progesterone supplementation, there is insufficient evidence to regularly prescribe progesterone for breast development.1
Both WPATH and the Endocrine Society recommend checking serum levels of sex hormones every 3 months during the first year until stable levels are achieved, then once or twice a year thereafter.1 Hormone levels should be maintained at physiologic concentrations of the targeted gender. Some patients on feminizing GAHT often request evaluation of estrone/estradiol ratios as there was an assumption that higher ratios were associated with antagonistic effects on breast development. However, recent published evidence refutes this claim and estrone/estradiol ratios need not be measured.1
In addition to monitoring sex hormone levels, providers should check the metabolic effects that can be associated with GAHT. Both testosterone and estrogen can influence lipid panels: Testosterone can increase the red blood cell count, and spironolactone may cause hyperkalemia. While the SOC7 previously encouraged assessment of these laboratory values every 3 months, the new guidelines are more flexible in the frequency of testing of asymptomatic individuals as there is no strong evidence from published studies that supports these 3-month intervals.1
Providers are responsible for informing patients about the possible effects of GAHT on fertility. Estrogen often will cause a reduction in spermatogenesis, which may be irreversible. Patients who plan on taking estrogen should be counseled regarding sperm cryopreservation prior to starting GAHT. Even though testosterone inhibits ovulation and induces menstrual suppression, patients often regain their fertility after cessation of testosterone therapy. However, given the significant knowledge deficit about long-term fertility in transmasculine patients, providers should still offer oocyte or embryo cryopreservation.
Health care providers should collaborate with surgeons regarding preoperative and postoperative GAHT. To mitigate the risk of thromboembolism, many surgeons would stop hormones 1-4 weeks before and after gender-affirming surgery. Recent evidence does not support this practice, as studies indicate no increased risk for venous thromboembolism in individuals on GAHT undergoing surgery. These studies are consistent with other well-established guidelines on preoperative management of cisgender women taking estrogen or progestins. As exogenous sex steroids are necessary for bone health in patients who undergo gonadectomy, surgeons and other health care providers should educate patients on the importance of continuing GAHT.
There are many procedures available for gender-affirming surgery. Many of these surgeries involve three regions: the face, chest/breast, and/or genitalia (both internal and external). Prior to making a surgical referral, providers should be familiar with the surgeon’s scope of practice, performance measures, and surgical outcomes.1 For the first time, the SOC8 also addresses the surgical training of the providers who offer these procedures. While gender-affirming surgery can be performed by a variety of different specialists, training and documented supervision (often by an existing expert in gender-affirming surgery) is essential. Maintaining an active practice in these procedures, tracking surgical outcomes, and continuing education within the field of gender-affirming surgery are additional requirements for surgeons performing these complex operations.1
As their name implies, the SOC8 attempts to create a standardized guide to assist practitioners caring for gender-diverse patients. It’s important for providers to be familiar with updates while also recognizing the evolving nature of this rapidly growing field.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
Reference
1. World Professional Association for Transgender Health. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, Version 8. Int J Transgend Health. 2022 Sep 15. doi: 10.1080/26895269.2022.2100644.








