User login
Diversity – We’re not one size fits all
The United States has often been described as a “melting pot,” defined as diverse cultures and ethnicities coming together to form the rich fabric of our nation. These days, it seems that our fabric is a bit frayed.
DEIB (diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging) is dawning as a significant conversation. Each and every one of us is unique by age, gender, culture/ethnicity, religion, socioeconomic status, geographical location, race, and sexual identity – to name just a few aspects of our identity. Keeping these differences in mind, it is evident that none of us fits a “one size fits all” mold.
Some of these differences, such as cross-cultural cuisine and holidays, are enjoyed and celebrated as wonderful opportunities to learn from others, embrace our distinctions, and have them beneficially contribute to our lives. Other differences, however, are not understood or embraced and are, in fact, belittled and stigmatized. Sexual identity falls into this category. It behooves us as a country to become more aware and educated about this category in our identities, in order to understand it, quell our unfounded fear, learn to support one another, and improve our collective mental health.
Recent reports have shown that exposing students and teachers to sexual identity diversity education has sparked some backlash from parents and communities alike. Those opposed are citing concerns over introducing children to LGBTQ+ information, either embedded in the school curriculum or made available in school library reading materials. “Children should remain innocent” seems to be the message. Perhaps parents prefer to discuss this topic privately, at home. Either way, teaching about diversity does not damage one’s innocence or deprive parents of private conversations. In fact, it educates children by improving their awareness, tolerance, and acceptance of others’ differences, and can serve as a catalyst to further parental conversation.
There are kids everywhere who are starting to develop and understand their identities. Wouldn’t it be wonderful for them to know that whichever way they identify is okay, that they are not ‘weird’ or ‘different,’ but that in fact we are all different? Wouldn’t it be great for them to be able to explore and discuss their identities and journeys openly, and not have to hide for fear of retribution or bullying?
It is important for these children to know that they are not alone, that they have options, and that they don’t need to contemplate suicide because they believe that their identity makes them not worthy of being in this world.
Starting the conversation early on in life can empower our youth by planting the seed that people are not “one size fits all,” which is the element responsible for our being unique and human. Diversity can be woven into the rich fabric that defines our nation, rather than be a factor that unravels it.
April was National Diversity Awareness Month and we took time to celebrate our country’s cultural melting pot. By embracing our differences, we can show our children and ourselves how to better navigate diversity, which can help us all fit in.
Dr. Jarkon is a psychiatrist and director of the Center for Behavioral Health at the New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine in Old Westbury, N.Y.
The United States has often been described as a “melting pot,” defined as diverse cultures and ethnicities coming together to form the rich fabric of our nation. These days, it seems that our fabric is a bit frayed.
DEIB (diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging) is dawning as a significant conversation. Each and every one of us is unique by age, gender, culture/ethnicity, religion, socioeconomic status, geographical location, race, and sexual identity – to name just a few aspects of our identity. Keeping these differences in mind, it is evident that none of us fits a “one size fits all” mold.
Some of these differences, such as cross-cultural cuisine and holidays, are enjoyed and celebrated as wonderful opportunities to learn from others, embrace our distinctions, and have them beneficially contribute to our lives. Other differences, however, are not understood or embraced and are, in fact, belittled and stigmatized. Sexual identity falls into this category. It behooves us as a country to become more aware and educated about this category in our identities, in order to understand it, quell our unfounded fear, learn to support one another, and improve our collective mental health.
Recent reports have shown that exposing students and teachers to sexual identity diversity education has sparked some backlash from parents and communities alike. Those opposed are citing concerns over introducing children to LGBTQ+ information, either embedded in the school curriculum or made available in school library reading materials. “Children should remain innocent” seems to be the message. Perhaps parents prefer to discuss this topic privately, at home. Either way, teaching about diversity does not damage one’s innocence or deprive parents of private conversations. In fact, it educates children by improving their awareness, tolerance, and acceptance of others’ differences, and can serve as a catalyst to further parental conversation.
There are kids everywhere who are starting to develop and understand their identities. Wouldn’t it be wonderful for them to know that whichever way they identify is okay, that they are not ‘weird’ or ‘different,’ but that in fact we are all different? Wouldn’t it be great for them to be able to explore and discuss their identities and journeys openly, and not have to hide for fear of retribution or bullying?
It is important for these children to know that they are not alone, that they have options, and that they don’t need to contemplate suicide because they believe that their identity makes them not worthy of being in this world.
Starting the conversation early on in life can empower our youth by planting the seed that people are not “one size fits all,” which is the element responsible for our being unique and human. Diversity can be woven into the rich fabric that defines our nation, rather than be a factor that unravels it.
April was National Diversity Awareness Month and we took time to celebrate our country’s cultural melting pot. By embracing our differences, we can show our children and ourselves how to better navigate diversity, which can help us all fit in.
Dr. Jarkon is a psychiatrist and director of the Center for Behavioral Health at the New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine in Old Westbury, N.Y.
The United States has often been described as a “melting pot,” defined as diverse cultures and ethnicities coming together to form the rich fabric of our nation. These days, it seems that our fabric is a bit frayed.
DEIB (diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging) is dawning as a significant conversation. Each and every one of us is unique by age, gender, culture/ethnicity, religion, socioeconomic status, geographical location, race, and sexual identity – to name just a few aspects of our identity. Keeping these differences in mind, it is evident that none of us fits a “one size fits all” mold.
Some of these differences, such as cross-cultural cuisine and holidays, are enjoyed and celebrated as wonderful opportunities to learn from others, embrace our distinctions, and have them beneficially contribute to our lives. Other differences, however, are not understood or embraced and are, in fact, belittled and stigmatized. Sexual identity falls into this category. It behooves us as a country to become more aware and educated about this category in our identities, in order to understand it, quell our unfounded fear, learn to support one another, and improve our collective mental health.
Recent reports have shown that exposing students and teachers to sexual identity diversity education has sparked some backlash from parents and communities alike. Those opposed are citing concerns over introducing children to LGBTQ+ information, either embedded in the school curriculum or made available in school library reading materials. “Children should remain innocent” seems to be the message. Perhaps parents prefer to discuss this topic privately, at home. Either way, teaching about diversity does not damage one’s innocence or deprive parents of private conversations. In fact, it educates children by improving their awareness, tolerance, and acceptance of others’ differences, and can serve as a catalyst to further parental conversation.
There are kids everywhere who are starting to develop and understand their identities. Wouldn’t it be wonderful for them to know that whichever way they identify is okay, that they are not ‘weird’ or ‘different,’ but that in fact we are all different? Wouldn’t it be great for them to be able to explore and discuss their identities and journeys openly, and not have to hide for fear of retribution or bullying?
It is important for these children to know that they are not alone, that they have options, and that they don’t need to contemplate suicide because they believe that their identity makes them not worthy of being in this world.
Starting the conversation early on in life can empower our youth by planting the seed that people are not “one size fits all,” which is the element responsible for our being unique and human. Diversity can be woven into the rich fabric that defines our nation, rather than be a factor that unravels it.
April was National Diversity Awareness Month and we took time to celebrate our country’s cultural melting pot. By embracing our differences, we can show our children and ourselves how to better navigate diversity, which can help us all fit in.
Dr. Jarkon is a psychiatrist and director of the Center for Behavioral Health at the New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine in Old Westbury, N.Y.
Why the approval of MiniMed 780G is a ‘quantum leap’ forward
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There is wonderful news in the field of hybrid closed-loop pump technology because the Medtronic 780G system was just approved. I can’t tell you how happy this makes me because we’ve all been waiting for this seemingly forever and ever. This isn’t just a small upgrade from the 770G. It’s a quantum leap from the 770G to the 780G. The 780G has newer algorithms, a new sensor, and a longer-lasting infusion set.
It’s been used since 2020 in Europe, so we have good data on how well it works. Frankly, I think it works really well. We’ve seen nice improvements in [hemoglobin] A1c, time in range, other glycemic metrics, and patient satisfaction in studies done in Europe.
Now, I’ve never had the system to use in one of my patients. I always say I never know a system until I see it in use in my own patients, but let me tell you what I’ve read.
First, it has something called meal-detection technology with autocorrection boluses every 5 minutes. If this works, it can be a huge win for our patients because the problem my patients have is with mealtime dosing. They often dose late, or they may not dose enough insulin for the carbohydrates. That’s where the issues are.
All these hybrid closed-loop systems, this one included, show that the best improvements in glycemia are overnight. I’m hoping that this one shows some nice improvements in daytime glycemia as well. Stay tuned and I’ll let you know once I’ve been using it.
Next, it has adjustable targets down to 100. This is the lowest target for any hybrid closed-loop system. It has an extended-wear infusion set that lasts for 7 days. This infusion set is already available but works with this new system.
Finally, it has a new sensor. It looks like the old sensors, but it’s the Guardian 4, which requires much fewer finger sticks. Now, I’m not entirely sure about how often one has to do a finger stick. I know one has to do with finger sticking to initiate auto mode, or what they call SmartGuard, but I don’t know whether you ever have to do it again. I know for sure that you have to do it again if you fall out of the automated mode into manual mode. Once you’re in SmartGuard, I believe there are no further finger-stick calibrations required.
If people are already on the 770G system, this is just a software update that is presumably easy to upgrade to the 780G. Now, the physical pieces ... If someone doesn’t already have the Guardian 4 sensor or the extended-wear infusion set, they’ll have to get those. The software update to make the 770G increase to the 780G should just come through the cloud. I don’t know when that’s going to happen.
I do know that preorders for this system, if you want to buy the new physical system, start on May 15. The shipping of the new 780G system should occur in the United States toward the end of this summer.
I’m so excited. I think this is really going to benefit my patients. I can’t wait to start using it and letting patients see how these algorithms work and how they really help patients improve their glucose control.
Anne L. Peters, MD, is a professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She reported conflicts of interest with Abbott Diabetes Care, Becton Dickinson, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Livongo, Medscape, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Omada Health, OptumHealth, Sanofi, Zafgen, Dexcom, MannKind, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There is wonderful news in the field of hybrid closed-loop pump technology because the Medtronic 780G system was just approved. I can’t tell you how happy this makes me because we’ve all been waiting for this seemingly forever and ever. This isn’t just a small upgrade from the 770G. It’s a quantum leap from the 770G to the 780G. The 780G has newer algorithms, a new sensor, and a longer-lasting infusion set.
It’s been used since 2020 in Europe, so we have good data on how well it works. Frankly, I think it works really well. We’ve seen nice improvements in [hemoglobin] A1c, time in range, other glycemic metrics, and patient satisfaction in studies done in Europe.
Now, I’ve never had the system to use in one of my patients. I always say I never know a system until I see it in use in my own patients, but let me tell you what I’ve read.
First, it has something called meal-detection technology with autocorrection boluses every 5 minutes. If this works, it can be a huge win for our patients because the problem my patients have is with mealtime dosing. They often dose late, or they may not dose enough insulin for the carbohydrates. That’s where the issues are.
All these hybrid closed-loop systems, this one included, show that the best improvements in glycemia are overnight. I’m hoping that this one shows some nice improvements in daytime glycemia as well. Stay tuned and I’ll let you know once I’ve been using it.
Next, it has adjustable targets down to 100. This is the lowest target for any hybrid closed-loop system. It has an extended-wear infusion set that lasts for 7 days. This infusion set is already available but works with this new system.
Finally, it has a new sensor. It looks like the old sensors, but it’s the Guardian 4, which requires much fewer finger sticks. Now, I’m not entirely sure about how often one has to do a finger stick. I know one has to do with finger sticking to initiate auto mode, or what they call SmartGuard, but I don’t know whether you ever have to do it again. I know for sure that you have to do it again if you fall out of the automated mode into manual mode. Once you’re in SmartGuard, I believe there are no further finger-stick calibrations required.
If people are already on the 770G system, this is just a software update that is presumably easy to upgrade to the 780G. Now, the physical pieces ... If someone doesn’t already have the Guardian 4 sensor or the extended-wear infusion set, they’ll have to get those. The software update to make the 770G increase to the 780G should just come through the cloud. I don’t know when that’s going to happen.
I do know that preorders for this system, if you want to buy the new physical system, start on May 15. The shipping of the new 780G system should occur in the United States toward the end of this summer.
I’m so excited. I think this is really going to benefit my patients. I can’t wait to start using it and letting patients see how these algorithms work and how they really help patients improve their glucose control.
Anne L. Peters, MD, is a professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She reported conflicts of interest with Abbott Diabetes Care, Becton Dickinson, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Livongo, Medscape, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Omada Health, OptumHealth, Sanofi, Zafgen, Dexcom, MannKind, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There is wonderful news in the field of hybrid closed-loop pump technology because the Medtronic 780G system was just approved. I can’t tell you how happy this makes me because we’ve all been waiting for this seemingly forever and ever. This isn’t just a small upgrade from the 770G. It’s a quantum leap from the 770G to the 780G. The 780G has newer algorithms, a new sensor, and a longer-lasting infusion set.
It’s been used since 2020 in Europe, so we have good data on how well it works. Frankly, I think it works really well. We’ve seen nice improvements in [hemoglobin] A1c, time in range, other glycemic metrics, and patient satisfaction in studies done in Europe.
Now, I’ve never had the system to use in one of my patients. I always say I never know a system until I see it in use in my own patients, but let me tell you what I’ve read.
First, it has something called meal-detection technology with autocorrection boluses every 5 minutes. If this works, it can be a huge win for our patients because the problem my patients have is with mealtime dosing. They often dose late, or they may not dose enough insulin for the carbohydrates. That’s where the issues are.
All these hybrid closed-loop systems, this one included, show that the best improvements in glycemia are overnight. I’m hoping that this one shows some nice improvements in daytime glycemia as well. Stay tuned and I’ll let you know once I’ve been using it.
Next, it has adjustable targets down to 100. This is the lowest target for any hybrid closed-loop system. It has an extended-wear infusion set that lasts for 7 days. This infusion set is already available but works with this new system.
Finally, it has a new sensor. It looks like the old sensors, but it’s the Guardian 4, which requires much fewer finger sticks. Now, I’m not entirely sure about how often one has to do a finger stick. I know one has to do with finger sticking to initiate auto mode, or what they call SmartGuard, but I don’t know whether you ever have to do it again. I know for sure that you have to do it again if you fall out of the automated mode into manual mode. Once you’re in SmartGuard, I believe there are no further finger-stick calibrations required.
If people are already on the 770G system, this is just a software update that is presumably easy to upgrade to the 780G. Now, the physical pieces ... If someone doesn’t already have the Guardian 4 sensor or the extended-wear infusion set, they’ll have to get those. The software update to make the 770G increase to the 780G should just come through the cloud. I don’t know when that’s going to happen.
I do know that preorders for this system, if you want to buy the new physical system, start on May 15. The shipping of the new 780G system should occur in the United States toward the end of this summer.
I’m so excited. I think this is really going to benefit my patients. I can’t wait to start using it and letting patients see how these algorithms work and how they really help patients improve their glucose control.
Anne L. Peters, MD, is a professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She reported conflicts of interest with Abbott Diabetes Care, Becton Dickinson, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Livongo, Medscape, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Omada Health, OptumHealth, Sanofi, Zafgen, Dexcom, MannKind, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Autism and bone health: What you need to know
Many years ago, at the conclusion of a talk I gave on bone health in teens with anorexia nervosa, I was approached by a colleague, Ann Neumeyer, MD, medical director of the Lurie Center for Autism at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who asked about bone health in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
When I explained that there was little information about bone health in this patient population, she suggested that we learn and investigate together. Ann explained that she had observed that some of her patients with ASD had suffered fractures with minimal trauma, raising her concern about their bone health.
This was the beginning of a partnership that led us down the path of many grant submissions, some of which were funded and others that were not, to explore and investigate bone outcomes in children with ASD.
This applies to prepubertal children as well as older children and adolescents. One study showed that 28% and 33% of children with ASD 8-14 years old had very low bone density (z scores of ≤ –2) at the spine and hip, respectively, compared with 0% of typically developing controls.
Studies that have used sophisticated imaging techniques to determine bone strength have shown that it is lower at the forearm and lower leg in children with ASD versus neurotypical children.
These findings are of particular concern during the childhood and teenage years when bone is typically accrued at a rapid rate. A normal rate of bone accrual at this time of life is essential for optimal bone health in later life. While children with ASD gain bone mass at a similar rate as neurotypical controls, they start at a deficit and seem unable to “catch up.”
Further, people with ASD are more prone to certain kinds of fracture than those without the condition. For example, both children and adults with ASD have a high risk for hip fracture, while adult women with ASD have a higher risk for forearm and spine fractures. There is some protection against forearm fractures in children and adult men, probably because of markedly lower levels of physical activity, which would reduce fall risk.
Many of Ann’s patients with ASD had unusual or restricted diets, low levels of physical activity, and were on multiple medications. We have since learned that some factors that contribute to low bone density in ASD include lower levels of weight-bearing physical activity; lower muscle mass; low muscle tone; suboptimal dietary calcium and vitamin D intake; lower vitamin D levels; higher levels of the hormone cortisol, which has deleterious effects on bone; and use of medications that can lower bone density.
In order to mitigate the risk for low bone density and fractures, it is important to optimize physical activity while considering the child’s ability to safely engage in weight-bearing sports.
High-impact sports like gymnastics and jumping, or cross-impact sports like soccer, basketball, field hockey, and lacrosse, are particularly useful in this context, but many patients with ASD are not able to easily engage in typical team sports.
For such children, a prescribed amount of time spent walking, as well as weight and resistance training, could be helpful. The latter would also help increase muscle mass, a key modulator of bone health.
Other strategies include ensuring sufficient intake of calcium and vitamin D through diet and supplements. This can be a particular challenge for children with ASD on specialized diets, such as a gluten-free or dairy-free diet, which are deficient in calcium and vitamin D. Health care providers should check for intake of dairy and dairy products, as well as serum vitamin D levels, and prescribe supplements as needed.
All children should get at least 600 IUs of vitamin D and 1,000-1,300 mg of elemental calcium daily. That said, many with ASD need much higher quantities of vitamin D (1,000-4,000 IUs or more) to maintain levels in the normal range. This is particularly true for dark-skinned children and children with obesity, as well as those who have medical disorders that cause malabsorption.
Higher cortisol levels in the ASD patient population are harder to manage. Efforts to ease anxiety and depression may help reduce cortisol levels. Medications such as protein pump inhibitors and glucocorticosteroids can compromise bone health.
In addition, certain antipsychotics can cause marked elevations in prolactin which, in turn, can lower levels of estrogen and testosterone, which are very important for bone health. In such cases, the clinician should consider switching patients to a different, less detrimental medication or adjust the current medication so that patients receive the lowest possible effective dose.
Obesity is associated with increased fracture risk and with suboptimal bone accrual during childhood, so ensuring a healthy diet is important. This includes avoiding sugary beverages and reducing intake of processed food and juice.
Sometimes, particularly when a child has low bone density and a history of several low-trauma fractures, medications such as bisphosphonates should be considered to increase bone density.
Above all, as physicians who manage ASD, it is essential that we raise awareness about bone health among our colleagues, patients, and their families to help mitigate fracture risk.
Madhusmita Misra, MD, MPH, is chief of the Division of Pediatric Endocrinology at Mass General for Children, Boston.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many years ago, at the conclusion of a talk I gave on bone health in teens with anorexia nervosa, I was approached by a colleague, Ann Neumeyer, MD, medical director of the Lurie Center for Autism at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who asked about bone health in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
When I explained that there was little information about bone health in this patient population, she suggested that we learn and investigate together. Ann explained that she had observed that some of her patients with ASD had suffered fractures with minimal trauma, raising her concern about their bone health.
This was the beginning of a partnership that led us down the path of many grant submissions, some of which were funded and others that were not, to explore and investigate bone outcomes in children with ASD.
This applies to prepubertal children as well as older children and adolescents. One study showed that 28% and 33% of children with ASD 8-14 years old had very low bone density (z scores of ≤ –2) at the spine and hip, respectively, compared with 0% of typically developing controls.
Studies that have used sophisticated imaging techniques to determine bone strength have shown that it is lower at the forearm and lower leg in children with ASD versus neurotypical children.
These findings are of particular concern during the childhood and teenage years when bone is typically accrued at a rapid rate. A normal rate of bone accrual at this time of life is essential for optimal bone health in later life. While children with ASD gain bone mass at a similar rate as neurotypical controls, they start at a deficit and seem unable to “catch up.”
Further, people with ASD are more prone to certain kinds of fracture than those without the condition. For example, both children and adults with ASD have a high risk for hip fracture, while adult women with ASD have a higher risk for forearm and spine fractures. There is some protection against forearm fractures in children and adult men, probably because of markedly lower levels of physical activity, which would reduce fall risk.
Many of Ann’s patients with ASD had unusual or restricted diets, low levels of physical activity, and were on multiple medications. We have since learned that some factors that contribute to low bone density in ASD include lower levels of weight-bearing physical activity; lower muscle mass; low muscle tone; suboptimal dietary calcium and vitamin D intake; lower vitamin D levels; higher levels of the hormone cortisol, which has deleterious effects on bone; and use of medications that can lower bone density.
In order to mitigate the risk for low bone density and fractures, it is important to optimize physical activity while considering the child’s ability to safely engage in weight-bearing sports.
High-impact sports like gymnastics and jumping, or cross-impact sports like soccer, basketball, field hockey, and lacrosse, are particularly useful in this context, but many patients with ASD are not able to easily engage in typical team sports.
For such children, a prescribed amount of time spent walking, as well as weight and resistance training, could be helpful. The latter would also help increase muscle mass, a key modulator of bone health.
Other strategies include ensuring sufficient intake of calcium and vitamin D through diet and supplements. This can be a particular challenge for children with ASD on specialized diets, such as a gluten-free or dairy-free diet, which are deficient in calcium and vitamin D. Health care providers should check for intake of dairy and dairy products, as well as serum vitamin D levels, and prescribe supplements as needed.
All children should get at least 600 IUs of vitamin D and 1,000-1,300 mg of elemental calcium daily. That said, many with ASD need much higher quantities of vitamin D (1,000-4,000 IUs or more) to maintain levels in the normal range. This is particularly true for dark-skinned children and children with obesity, as well as those who have medical disorders that cause malabsorption.
Higher cortisol levels in the ASD patient population are harder to manage. Efforts to ease anxiety and depression may help reduce cortisol levels. Medications such as protein pump inhibitors and glucocorticosteroids can compromise bone health.
In addition, certain antipsychotics can cause marked elevations in prolactin which, in turn, can lower levels of estrogen and testosterone, which are very important for bone health. In such cases, the clinician should consider switching patients to a different, less detrimental medication or adjust the current medication so that patients receive the lowest possible effective dose.
Obesity is associated with increased fracture risk and with suboptimal bone accrual during childhood, so ensuring a healthy diet is important. This includes avoiding sugary beverages and reducing intake of processed food and juice.
Sometimes, particularly when a child has low bone density and a history of several low-trauma fractures, medications such as bisphosphonates should be considered to increase bone density.
Above all, as physicians who manage ASD, it is essential that we raise awareness about bone health among our colleagues, patients, and their families to help mitigate fracture risk.
Madhusmita Misra, MD, MPH, is chief of the Division of Pediatric Endocrinology at Mass General for Children, Boston.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many years ago, at the conclusion of a talk I gave on bone health in teens with anorexia nervosa, I was approached by a colleague, Ann Neumeyer, MD, medical director of the Lurie Center for Autism at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who asked about bone health in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
When I explained that there was little information about bone health in this patient population, she suggested that we learn and investigate together. Ann explained that she had observed that some of her patients with ASD had suffered fractures with minimal trauma, raising her concern about their bone health.
This was the beginning of a partnership that led us down the path of many grant submissions, some of which were funded and others that were not, to explore and investigate bone outcomes in children with ASD.
This applies to prepubertal children as well as older children and adolescents. One study showed that 28% and 33% of children with ASD 8-14 years old had very low bone density (z scores of ≤ –2) at the spine and hip, respectively, compared with 0% of typically developing controls.
Studies that have used sophisticated imaging techniques to determine bone strength have shown that it is lower at the forearm and lower leg in children with ASD versus neurotypical children.
These findings are of particular concern during the childhood and teenage years when bone is typically accrued at a rapid rate. A normal rate of bone accrual at this time of life is essential for optimal bone health in later life. While children with ASD gain bone mass at a similar rate as neurotypical controls, they start at a deficit and seem unable to “catch up.”
Further, people with ASD are more prone to certain kinds of fracture than those without the condition. For example, both children and adults with ASD have a high risk for hip fracture, while adult women with ASD have a higher risk for forearm and spine fractures. There is some protection against forearm fractures in children and adult men, probably because of markedly lower levels of physical activity, which would reduce fall risk.
Many of Ann’s patients with ASD had unusual or restricted diets, low levels of physical activity, and were on multiple medications. We have since learned that some factors that contribute to low bone density in ASD include lower levels of weight-bearing physical activity; lower muscle mass; low muscle tone; suboptimal dietary calcium and vitamin D intake; lower vitamin D levels; higher levels of the hormone cortisol, which has deleterious effects on bone; and use of medications that can lower bone density.
In order to mitigate the risk for low bone density and fractures, it is important to optimize physical activity while considering the child’s ability to safely engage in weight-bearing sports.
High-impact sports like gymnastics and jumping, or cross-impact sports like soccer, basketball, field hockey, and lacrosse, are particularly useful in this context, but many patients with ASD are not able to easily engage in typical team sports.
For such children, a prescribed amount of time spent walking, as well as weight and resistance training, could be helpful. The latter would also help increase muscle mass, a key modulator of bone health.
Other strategies include ensuring sufficient intake of calcium and vitamin D through diet and supplements. This can be a particular challenge for children with ASD on specialized diets, such as a gluten-free or dairy-free diet, which are deficient in calcium and vitamin D. Health care providers should check for intake of dairy and dairy products, as well as serum vitamin D levels, and prescribe supplements as needed.
All children should get at least 600 IUs of vitamin D and 1,000-1,300 mg of elemental calcium daily. That said, many with ASD need much higher quantities of vitamin D (1,000-4,000 IUs or more) to maintain levels in the normal range. This is particularly true for dark-skinned children and children with obesity, as well as those who have medical disorders that cause malabsorption.
Higher cortisol levels in the ASD patient population are harder to manage. Efforts to ease anxiety and depression may help reduce cortisol levels. Medications such as protein pump inhibitors and glucocorticosteroids can compromise bone health.
In addition, certain antipsychotics can cause marked elevations in prolactin which, in turn, can lower levels of estrogen and testosterone, which are very important for bone health. In such cases, the clinician should consider switching patients to a different, less detrimental medication or adjust the current medication so that patients receive the lowest possible effective dose.
Obesity is associated with increased fracture risk and with suboptimal bone accrual during childhood, so ensuring a healthy diet is important. This includes avoiding sugary beverages and reducing intake of processed food and juice.
Sometimes, particularly when a child has low bone density and a history of several low-trauma fractures, medications such as bisphosphonates should be considered to increase bone density.
Above all, as physicians who manage ASD, it is essential that we raise awareness about bone health among our colleagues, patients, and their families to help mitigate fracture risk.
Madhusmita Misra, MD, MPH, is chief of the Division of Pediatric Endocrinology at Mass General for Children, Boston.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation during pregnancy: An alternative to antidepressant treatment?
A growing number of women ask about nonpharmacologic approaches for either the treatment of acute perinatal depression or for relapse prevention during pregnancy.
The last several decades have brought an increasing level of comfort with respect to antidepressant use during pregnancy, which derives from several factors.
First, it’s been well described that there’s an increased risk of relapse and morbidity associated with discontinuation of antidepressants proximate to pregnancy, particularly in women with histories of recurrent disease (JAMA Psychiatry. 2023;80[5]:441-50 and JAMA. 2006;295[5]:499-507).
Second, there’s an obvious increased confidence about using antidepressants during pregnancy given the robust reproductive safety data about antidepressants with respect to both teratogenesis and risk for organ malformation. Other studies also fail to demonstrate a relationship between fetal exposure to antidepressants and risk for subsequent development of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and autism. These latter studies have been reviewed extensively in systematic reviews of meta-analyses addressing this question.
However, there are women who, as they approach the question of antidepressant use during pregnancy, would prefer a nonpharmacologic approach to managing depression in the setting of either a planned pregnancy, or sometimes in the setting of acute onset of depressive symptoms during pregnancy. Other women are more comfortable with the data in hand regarding the reproductive safety of antidepressants and continue antidepressants that have afforded emotional well-being, particularly if the road to well-being or euthymia has been a long one.
Still, we at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) Center for Women’s Mental Health along with multidisciplinary colleagues with whom we engage during our weekly Virtual Rounds community have observed a growing number of women asking about nonpharmacologic approaches for either the treatment of acute perinatal depression or for relapse prevention during pregnancy. They ask about these options for personal reasons, regardless of what we may know (and what we may not know) about existing pharmacologic interventions. In these scenarios, it is important to keep in mind that it is not about what we as clinicians necessarily know about these medicines per se that drives treatment, but rather about the private calculus that women and their partners apply about risk and benefit of pharmacologic treatment during pregnancy.
Nonpharmacologic treatment options
Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT), cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and behavioral activation are therapies all of which have an evidence base with respect to their effectiveness for either the acute treatment of both depression (and perinatal depression specifically) or for mitigating risk for depressive relapse (MBCT). Several investigations are underway evaluating digital apps that utilize MBCT and CBT in these patient populations as well.
New treatments for which we have none or exceedingly sparse data to support use during pregnancy are neurosteroids. We are asked all the time about the use of neurosteroids such as brexanolone or zuranolone during pregnancy. Given the data on effectiveness of these agents for treatment of postpartum depression, the question about use during pregnancy is intuitive. But at this point in time, absent data, their use during pregnancy cannot be recommended.
With respect to newer nonpharmacologic approaches that have been looked at for treatment of major depressive disorder, the Food and Drug Administration has approved transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), a noninvasive form of neuromodulating therapy that use magnetic pulses to stimulate specific regions of the brain that have been implicated in psychiatric illness.
While there are no safety concerns that have been noted about use of TMS, the data regarding its use during pregnancy are still relatively limited, but it has been used to treat certain neurologic conditions during pregnancy. We now have a small randomized controlled study using TMS during pregnancy and multiple small case series suggesting a signal of efficacy in women with perinatal major depressive disorder. Side effects of TMS use during pregnancy have included hypotension, which has sometimes required repositioning of subjects, particularly later in pregnancy. Unlike electroconvulsive therapy, (ECT), often used when clinicians have exhausted other treatment options, TMS has no risk of seizure associated with its use.
TMS is now entering into the clinical arena in a more robust way. In certain settings, insurance companies are reimbursing for TMS treatment more often than was the case previously, making it a more viable option for a larger number of patients. There are also several exciting newer protocols, including theta burst stimulation, a new form of TMS treatment with less of a time commitment, and which may be more cost effective. However, data on this modality of treatment remain limited.
Where TMS fits in treating depression during pregnancy
The real question we are getting asked in clinic, both in person and during virtual rounds with multidisciplinary colleagues from across the world, is where TMS might fit into the algorithm for treating of depression during pregnancy. Where is it appropriate to be thinking about TMS in pregnancy, and where should it perhaps be deferred at this moment (and where is it not appropriate)?
It is probably of limited value (and possibly of potential harm) to switch to TMS in patients who have severe recurrent major depression and who are on maintenance antidepressant, and who believe that a switch to TMS will be effective for relapse prevention; there are simply no data currently suggesting that TMS can be used as a relapse prevention tool, unlike certain other nonpharmacologic interventions.
What about managing relapse of major depressive disorder during pregnancy in a patient who had responded to an antidepressant? We have seen patients with histories of severe recurrent disease who are managed well on antidepressants during pregnancy who then have breakthrough symptoms and inquire about using TMS as an augmentation strategy. Although we don’t have clear data supporting the use of TMS as an adjunct in that setting, in those patients, one could argue that a trial of TMS may be appropriate – as opposed to introducing multiple medicines to recapture euthymia during pregnancy where the benefit is unclear and where more exposure is implied by having to do potentially multiple trials.
Other patients with new onset of depression during pregnancy who, for personal reasons, will not take an antidepressant or pursue other nonpharmacologic interventions will frequently ask about TMS. and the increased availability of TMS in the community in various centers – as opposed to previously where it was more restricted to large academic medical centers.
I think it is a time of excitement in reproductive psychiatry where we have a growing number of tools to treat perinatal depression – from medications to digital tools. These tools – either alone or in combination with medicines that we’ve been using for years – are able to afford women a greater number of choices with respect to the treatment of perinatal depression than was available even 5 years ago. That takes us closer to an ability to use interventions that truly combine patient wishes and “precision perinatal psychiatry,” where we can match effective therapies with the individual clinical presentations and wishes with which patients come to us.
Dr. Cohen is the director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, which provides information resources and conducts clinical care and research in reproductive mental health. He has been a consultant to manufacturers of psychiatric medications. Email Dr. Cohen at [email protected].
A growing number of women ask about nonpharmacologic approaches for either the treatment of acute perinatal depression or for relapse prevention during pregnancy.
The last several decades have brought an increasing level of comfort with respect to antidepressant use during pregnancy, which derives from several factors.
First, it’s been well described that there’s an increased risk of relapse and morbidity associated with discontinuation of antidepressants proximate to pregnancy, particularly in women with histories of recurrent disease (JAMA Psychiatry. 2023;80[5]:441-50 and JAMA. 2006;295[5]:499-507).
Second, there’s an obvious increased confidence about using antidepressants during pregnancy given the robust reproductive safety data about antidepressants with respect to both teratogenesis and risk for organ malformation. Other studies also fail to demonstrate a relationship between fetal exposure to antidepressants and risk for subsequent development of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and autism. These latter studies have been reviewed extensively in systematic reviews of meta-analyses addressing this question.
However, there are women who, as they approach the question of antidepressant use during pregnancy, would prefer a nonpharmacologic approach to managing depression in the setting of either a planned pregnancy, or sometimes in the setting of acute onset of depressive symptoms during pregnancy. Other women are more comfortable with the data in hand regarding the reproductive safety of antidepressants and continue antidepressants that have afforded emotional well-being, particularly if the road to well-being or euthymia has been a long one.
Still, we at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) Center for Women’s Mental Health along with multidisciplinary colleagues with whom we engage during our weekly Virtual Rounds community have observed a growing number of women asking about nonpharmacologic approaches for either the treatment of acute perinatal depression or for relapse prevention during pregnancy. They ask about these options for personal reasons, regardless of what we may know (and what we may not know) about existing pharmacologic interventions. In these scenarios, it is important to keep in mind that it is not about what we as clinicians necessarily know about these medicines per se that drives treatment, but rather about the private calculus that women and their partners apply about risk and benefit of pharmacologic treatment during pregnancy.
Nonpharmacologic treatment options
Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT), cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and behavioral activation are therapies all of which have an evidence base with respect to their effectiveness for either the acute treatment of both depression (and perinatal depression specifically) or for mitigating risk for depressive relapse (MBCT). Several investigations are underway evaluating digital apps that utilize MBCT and CBT in these patient populations as well.
New treatments for which we have none or exceedingly sparse data to support use during pregnancy are neurosteroids. We are asked all the time about the use of neurosteroids such as brexanolone or zuranolone during pregnancy. Given the data on effectiveness of these agents for treatment of postpartum depression, the question about use during pregnancy is intuitive. But at this point in time, absent data, their use during pregnancy cannot be recommended.
With respect to newer nonpharmacologic approaches that have been looked at for treatment of major depressive disorder, the Food and Drug Administration has approved transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), a noninvasive form of neuromodulating therapy that use magnetic pulses to stimulate specific regions of the brain that have been implicated in psychiatric illness.
While there are no safety concerns that have been noted about use of TMS, the data regarding its use during pregnancy are still relatively limited, but it has been used to treat certain neurologic conditions during pregnancy. We now have a small randomized controlled study using TMS during pregnancy and multiple small case series suggesting a signal of efficacy in women with perinatal major depressive disorder. Side effects of TMS use during pregnancy have included hypotension, which has sometimes required repositioning of subjects, particularly later in pregnancy. Unlike electroconvulsive therapy, (ECT), often used when clinicians have exhausted other treatment options, TMS has no risk of seizure associated with its use.
TMS is now entering into the clinical arena in a more robust way. In certain settings, insurance companies are reimbursing for TMS treatment more often than was the case previously, making it a more viable option for a larger number of patients. There are also several exciting newer protocols, including theta burst stimulation, a new form of TMS treatment with less of a time commitment, and which may be more cost effective. However, data on this modality of treatment remain limited.
Where TMS fits in treating depression during pregnancy
The real question we are getting asked in clinic, both in person and during virtual rounds with multidisciplinary colleagues from across the world, is where TMS might fit into the algorithm for treating of depression during pregnancy. Where is it appropriate to be thinking about TMS in pregnancy, and where should it perhaps be deferred at this moment (and where is it not appropriate)?
It is probably of limited value (and possibly of potential harm) to switch to TMS in patients who have severe recurrent major depression and who are on maintenance antidepressant, and who believe that a switch to TMS will be effective for relapse prevention; there are simply no data currently suggesting that TMS can be used as a relapse prevention tool, unlike certain other nonpharmacologic interventions.
What about managing relapse of major depressive disorder during pregnancy in a patient who had responded to an antidepressant? We have seen patients with histories of severe recurrent disease who are managed well on antidepressants during pregnancy who then have breakthrough symptoms and inquire about using TMS as an augmentation strategy. Although we don’t have clear data supporting the use of TMS as an adjunct in that setting, in those patients, one could argue that a trial of TMS may be appropriate – as opposed to introducing multiple medicines to recapture euthymia during pregnancy where the benefit is unclear and where more exposure is implied by having to do potentially multiple trials.
Other patients with new onset of depression during pregnancy who, for personal reasons, will not take an antidepressant or pursue other nonpharmacologic interventions will frequently ask about TMS. and the increased availability of TMS in the community in various centers – as opposed to previously where it was more restricted to large academic medical centers.
I think it is a time of excitement in reproductive psychiatry where we have a growing number of tools to treat perinatal depression – from medications to digital tools. These tools – either alone or in combination with medicines that we’ve been using for years – are able to afford women a greater number of choices with respect to the treatment of perinatal depression than was available even 5 years ago. That takes us closer to an ability to use interventions that truly combine patient wishes and “precision perinatal psychiatry,” where we can match effective therapies with the individual clinical presentations and wishes with which patients come to us.
Dr. Cohen is the director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, which provides information resources and conducts clinical care and research in reproductive mental health. He has been a consultant to manufacturers of psychiatric medications. Email Dr. Cohen at [email protected].
A growing number of women ask about nonpharmacologic approaches for either the treatment of acute perinatal depression or for relapse prevention during pregnancy.
The last several decades have brought an increasing level of comfort with respect to antidepressant use during pregnancy, which derives from several factors.
First, it’s been well described that there’s an increased risk of relapse and morbidity associated with discontinuation of antidepressants proximate to pregnancy, particularly in women with histories of recurrent disease (JAMA Psychiatry. 2023;80[5]:441-50 and JAMA. 2006;295[5]:499-507).
Second, there’s an obvious increased confidence about using antidepressants during pregnancy given the robust reproductive safety data about antidepressants with respect to both teratogenesis and risk for organ malformation. Other studies also fail to demonstrate a relationship between fetal exposure to antidepressants and risk for subsequent development of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and autism. These latter studies have been reviewed extensively in systematic reviews of meta-analyses addressing this question.
However, there are women who, as they approach the question of antidepressant use during pregnancy, would prefer a nonpharmacologic approach to managing depression in the setting of either a planned pregnancy, or sometimes in the setting of acute onset of depressive symptoms during pregnancy. Other women are more comfortable with the data in hand regarding the reproductive safety of antidepressants and continue antidepressants that have afforded emotional well-being, particularly if the road to well-being or euthymia has been a long one.
Still, we at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) Center for Women’s Mental Health along with multidisciplinary colleagues with whom we engage during our weekly Virtual Rounds community have observed a growing number of women asking about nonpharmacologic approaches for either the treatment of acute perinatal depression or for relapse prevention during pregnancy. They ask about these options for personal reasons, regardless of what we may know (and what we may not know) about existing pharmacologic interventions. In these scenarios, it is important to keep in mind that it is not about what we as clinicians necessarily know about these medicines per se that drives treatment, but rather about the private calculus that women and their partners apply about risk and benefit of pharmacologic treatment during pregnancy.
Nonpharmacologic treatment options
Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT), cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and behavioral activation are therapies all of which have an evidence base with respect to their effectiveness for either the acute treatment of both depression (and perinatal depression specifically) or for mitigating risk for depressive relapse (MBCT). Several investigations are underway evaluating digital apps that utilize MBCT and CBT in these patient populations as well.
New treatments for which we have none or exceedingly sparse data to support use during pregnancy are neurosteroids. We are asked all the time about the use of neurosteroids such as brexanolone or zuranolone during pregnancy. Given the data on effectiveness of these agents for treatment of postpartum depression, the question about use during pregnancy is intuitive. But at this point in time, absent data, their use during pregnancy cannot be recommended.
With respect to newer nonpharmacologic approaches that have been looked at for treatment of major depressive disorder, the Food and Drug Administration has approved transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), a noninvasive form of neuromodulating therapy that use magnetic pulses to stimulate specific regions of the brain that have been implicated in psychiatric illness.
While there are no safety concerns that have been noted about use of TMS, the data regarding its use during pregnancy are still relatively limited, but it has been used to treat certain neurologic conditions during pregnancy. We now have a small randomized controlled study using TMS during pregnancy and multiple small case series suggesting a signal of efficacy in women with perinatal major depressive disorder. Side effects of TMS use during pregnancy have included hypotension, which has sometimes required repositioning of subjects, particularly later in pregnancy. Unlike electroconvulsive therapy, (ECT), often used when clinicians have exhausted other treatment options, TMS has no risk of seizure associated with its use.
TMS is now entering into the clinical arena in a more robust way. In certain settings, insurance companies are reimbursing for TMS treatment more often than was the case previously, making it a more viable option for a larger number of patients. There are also several exciting newer protocols, including theta burst stimulation, a new form of TMS treatment with less of a time commitment, and which may be more cost effective. However, data on this modality of treatment remain limited.
Where TMS fits in treating depression during pregnancy
The real question we are getting asked in clinic, both in person and during virtual rounds with multidisciplinary colleagues from across the world, is where TMS might fit into the algorithm for treating of depression during pregnancy. Where is it appropriate to be thinking about TMS in pregnancy, and where should it perhaps be deferred at this moment (and where is it not appropriate)?
It is probably of limited value (and possibly of potential harm) to switch to TMS in patients who have severe recurrent major depression and who are on maintenance antidepressant, and who believe that a switch to TMS will be effective for relapse prevention; there are simply no data currently suggesting that TMS can be used as a relapse prevention tool, unlike certain other nonpharmacologic interventions.
What about managing relapse of major depressive disorder during pregnancy in a patient who had responded to an antidepressant? We have seen patients with histories of severe recurrent disease who are managed well on antidepressants during pregnancy who then have breakthrough symptoms and inquire about using TMS as an augmentation strategy. Although we don’t have clear data supporting the use of TMS as an adjunct in that setting, in those patients, one could argue that a trial of TMS may be appropriate – as opposed to introducing multiple medicines to recapture euthymia during pregnancy where the benefit is unclear and where more exposure is implied by having to do potentially multiple trials.
Other patients with new onset of depression during pregnancy who, for personal reasons, will not take an antidepressant or pursue other nonpharmacologic interventions will frequently ask about TMS. and the increased availability of TMS in the community in various centers – as opposed to previously where it was more restricted to large academic medical centers.
I think it is a time of excitement in reproductive psychiatry where we have a growing number of tools to treat perinatal depression – from medications to digital tools. These tools – either alone or in combination with medicines that we’ve been using for years – are able to afford women a greater number of choices with respect to the treatment of perinatal depression than was available even 5 years ago. That takes us closer to an ability to use interventions that truly combine patient wishes and “precision perinatal psychiatry,” where we can match effective therapies with the individual clinical presentations and wishes with which patients come to us.
Dr. Cohen is the director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, which provides information resources and conducts clinical care and research in reproductive mental health. He has been a consultant to manufacturers of psychiatric medications. Email Dr. Cohen at [email protected].
Surprising brain activity moments before death
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
All the participants in the study I am going to tell you about this week died. And three of them died twice. But their deaths provide us with a fascinating window into the complex electrochemistry of the dying brain. What we might be looking at, indeed, is the physiologic correlate of the near-death experience.
The concept of the near-death experience is culturally ubiquitous. And though the content seems to track along culture lines – Western Christians are more likely to report seeing guardian angels, while Hindus are more likely to report seeing messengers of the god of death – certain factors seem to transcend culture: an out-of-body experience; a feeling of peace; and, of course, the light at the end of the tunnel.
As a materialist, I won’t discuss the possibility that these commonalities reflect some metaphysical structure to the afterlife. More likely, it seems to me, is that the commonalities result from the fact that the experience is mediated by our brains, and our brains, when dying, may be more alike than different.
We are talking about this study, appearing in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, by Jimo Borjigin and her team.
Dr. Borjigin studies the neural correlates of consciousness, perhaps one of the biggest questions in all of science today. To wit,
The study in question follows four unconscious patients –comatose patients, really – as life-sustaining support was withdrawn, up until the moment of death. Three had suffered severe anoxic brain injury in the setting of prolonged cardiac arrest. Though the heart was restarted, the brain damage was severe. The fourth had a large brain hemorrhage. All four patients were thus comatose and, though not brain-dead, unresponsive – with the lowest possible Glasgow Coma Scale score. No response to outside stimuli.
The families had made the decision to withdraw life support – to remove the breathing tube – but agreed to enroll their loved one in the study.
The team applied EEG leads to the head, EKG leads to the chest, and other monitoring equipment to observe the physiologic changes that occurred as the comatose and unresponsive patient died.
As the heart rhythm evolved from this: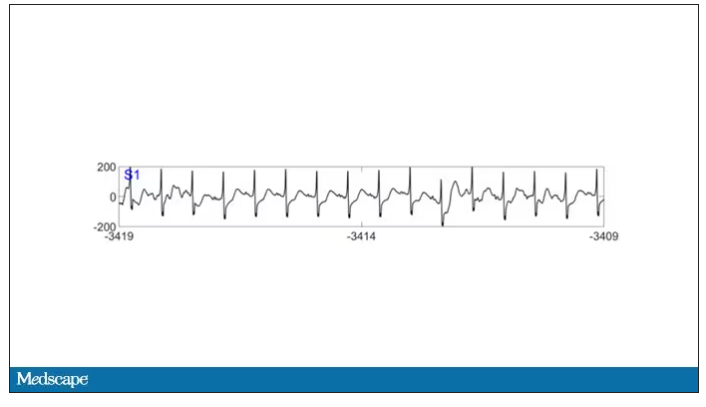
To this: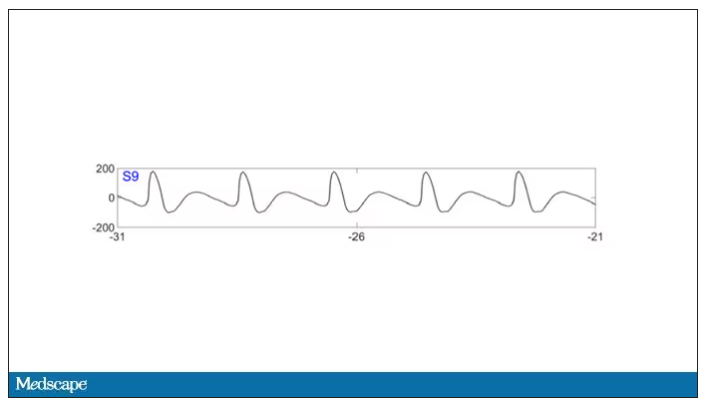
And eventually stopped.
But this is a study about the brain, not the heart.
Prior to the withdrawal of life support, the brain electrical signals looked like this: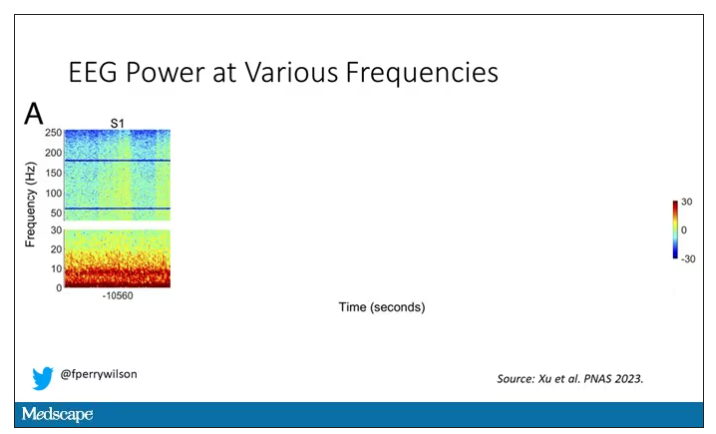
What you see is the EEG power at various frequencies, with red being higher. All the red was down at the low frequencies. Consciousness, at least as we understand it, is a higher-frequency phenomenon.
Right after the breathing tube was removed, the power didn’t change too much, but you can see some increased activity at the higher frequencies.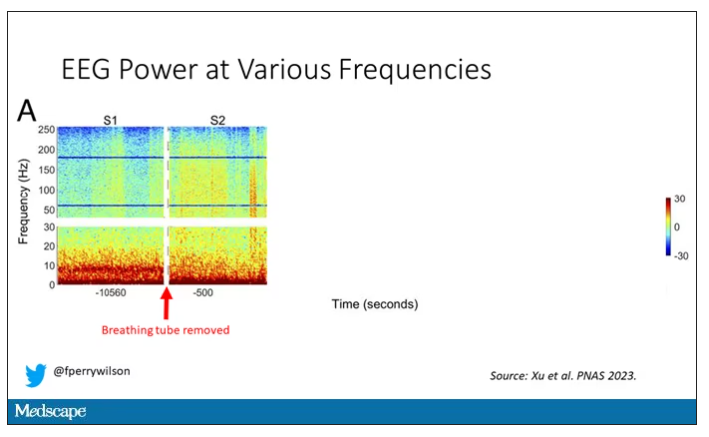
But in two of the four patients, something really surprising happened. Watch what happens as the brain gets closer and closer to death.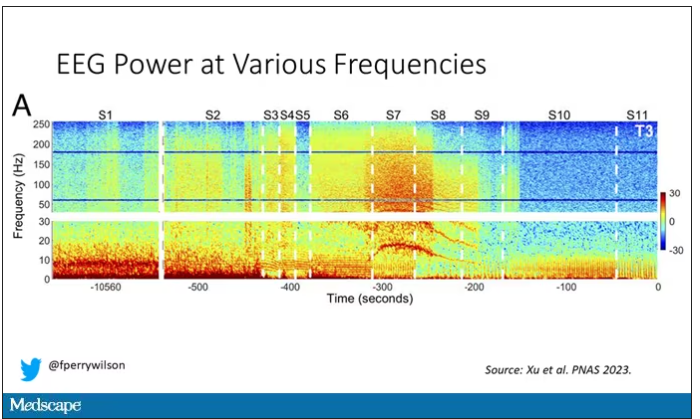
Here, about 300 seconds before death, there was a power surge at the high gamma frequencies.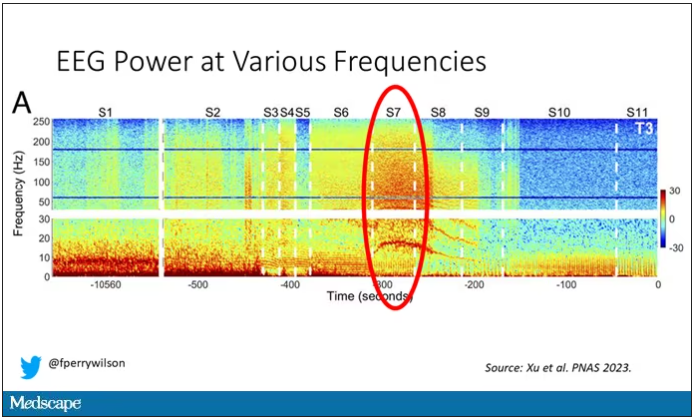
This spike in power occurred in the somatosensory cortex and the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, areas that are associated with conscious experience. It seems that this patient, 5 minutes before death, was experiencing something.
But I know what you’re thinking. This is a brain that is not receiving oxygen. Cells are going to become disordered quickly and start firing randomly – a last gasp, so to speak, before the end. Meaningless noise.
But connectivity mapping tells a different story. The signals seem to have structure.
Those high-frequency power surges increased connectivity in the posterior cortical “hot zone,” an area of the brain many researchers feel is necessary for conscious perception. This figure is not a map of raw brain electrical output like the one I showed before, but of coherence between brain regions in the consciousness hot zone. Those red areas indicate cross-talk – not the disordered scream of dying neurons, but a last set of messages passing back and forth from the parietal and posterior temporal lobes.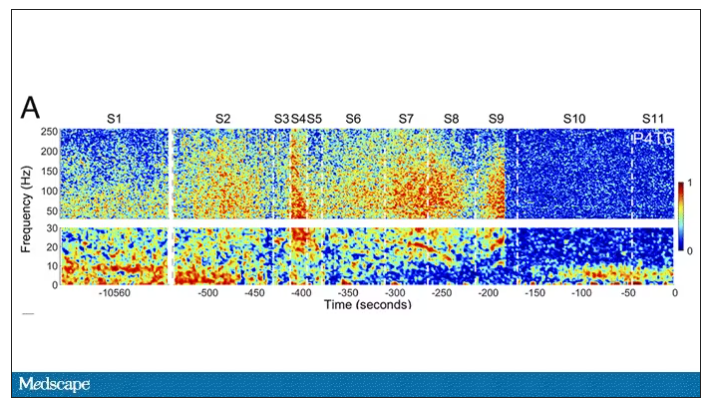
In fact, the electrical patterns of the brains in these patients looked very similar to the patterns seen in dreaming humans, as well as in patients with epilepsy who report sensations of out-of-body experiences.
It’s critical to realize two things here. First, these signals of consciousness were not present before life support was withdrawn. These comatose patients had minimal brain activity; there was no evidence that they were experiencing anything before the process of dying began. These brains are behaving fundamentally differently near death.
But second, we must realize that, although the brains of these individuals, in their last moments, appeared to be acting in a way that conscious brains act, we have no way of knowing if the patients were truly having a conscious experience. As I said, all the patients in the study died. Short of those metaphysics I alluded to earlier, we will have no way to ask them how they experienced their final moments.
Let’s be clear: This study doesn’t answer the question of what happens when we die. It says nothing about life after death or the existence or persistence of the soul. But what it does do is shed light on an incredibly difficult problem in neuroscience: the problem of consciousness. And as studies like this move forward, we may discover that the root of consciousness comes not from the breath of God or the energy of a living universe, but from very specific parts of the very complicated machine that is the brain, acting together to produce something transcendent. And to me, that is no less sublime.
Dr. Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, Yale University, New Haven, Conn. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape. He tweets @fperrywilson and his new book, How Medicine Works and When It Doesn’t, is available now. Dr. Wilson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
All the participants in the study I am going to tell you about this week died. And three of them died twice. But their deaths provide us with a fascinating window into the complex electrochemistry of the dying brain. What we might be looking at, indeed, is the physiologic correlate of the near-death experience.
The concept of the near-death experience is culturally ubiquitous. And though the content seems to track along culture lines – Western Christians are more likely to report seeing guardian angels, while Hindus are more likely to report seeing messengers of the god of death – certain factors seem to transcend culture: an out-of-body experience; a feeling of peace; and, of course, the light at the end of the tunnel.
As a materialist, I won’t discuss the possibility that these commonalities reflect some metaphysical structure to the afterlife. More likely, it seems to me, is that the commonalities result from the fact that the experience is mediated by our brains, and our brains, when dying, may be more alike than different.
We are talking about this study, appearing in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, by Jimo Borjigin and her team.
Dr. Borjigin studies the neural correlates of consciousness, perhaps one of the biggest questions in all of science today. To wit,
The study in question follows four unconscious patients –comatose patients, really – as life-sustaining support was withdrawn, up until the moment of death. Three had suffered severe anoxic brain injury in the setting of prolonged cardiac arrest. Though the heart was restarted, the brain damage was severe. The fourth had a large brain hemorrhage. All four patients were thus comatose and, though not brain-dead, unresponsive – with the lowest possible Glasgow Coma Scale score. No response to outside stimuli.
The families had made the decision to withdraw life support – to remove the breathing tube – but agreed to enroll their loved one in the study.
The team applied EEG leads to the head, EKG leads to the chest, and other monitoring equipment to observe the physiologic changes that occurred as the comatose and unresponsive patient died.
As the heart rhythm evolved from this:
To this:
And eventually stopped.
But this is a study about the brain, not the heart.
Prior to the withdrawal of life support, the brain electrical signals looked like this:
What you see is the EEG power at various frequencies, with red being higher. All the red was down at the low frequencies. Consciousness, at least as we understand it, is a higher-frequency phenomenon.
Right after the breathing tube was removed, the power didn’t change too much, but you can see some increased activity at the higher frequencies.
But in two of the four patients, something really surprising happened. Watch what happens as the brain gets closer and closer to death.
Here, about 300 seconds before death, there was a power surge at the high gamma frequencies.
This spike in power occurred in the somatosensory cortex and the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, areas that are associated with conscious experience. It seems that this patient, 5 minutes before death, was experiencing something.
But I know what you’re thinking. This is a brain that is not receiving oxygen. Cells are going to become disordered quickly and start firing randomly – a last gasp, so to speak, before the end. Meaningless noise.
But connectivity mapping tells a different story. The signals seem to have structure.
Those high-frequency power surges increased connectivity in the posterior cortical “hot zone,” an area of the brain many researchers feel is necessary for conscious perception. This figure is not a map of raw brain electrical output like the one I showed before, but of coherence between brain regions in the consciousness hot zone. Those red areas indicate cross-talk – not the disordered scream of dying neurons, but a last set of messages passing back and forth from the parietal and posterior temporal lobes.
In fact, the electrical patterns of the brains in these patients looked very similar to the patterns seen in dreaming humans, as well as in patients with epilepsy who report sensations of out-of-body experiences.
It’s critical to realize two things here. First, these signals of consciousness were not present before life support was withdrawn. These comatose patients had minimal brain activity; there was no evidence that they were experiencing anything before the process of dying began. These brains are behaving fundamentally differently near death.
But second, we must realize that, although the brains of these individuals, in their last moments, appeared to be acting in a way that conscious brains act, we have no way of knowing if the patients were truly having a conscious experience. As I said, all the patients in the study died. Short of those metaphysics I alluded to earlier, we will have no way to ask them how they experienced their final moments.
Let’s be clear: This study doesn’t answer the question of what happens when we die. It says nothing about life after death or the existence or persistence of the soul. But what it does do is shed light on an incredibly difficult problem in neuroscience: the problem of consciousness. And as studies like this move forward, we may discover that the root of consciousness comes not from the breath of God or the energy of a living universe, but from very specific parts of the very complicated machine that is the brain, acting together to produce something transcendent. And to me, that is no less sublime.
Dr. Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, Yale University, New Haven, Conn. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape. He tweets @fperrywilson and his new book, How Medicine Works and When It Doesn’t, is available now. Dr. Wilson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
All the participants in the study I am going to tell you about this week died. And three of them died twice. But their deaths provide us with a fascinating window into the complex electrochemistry of the dying brain. What we might be looking at, indeed, is the physiologic correlate of the near-death experience.
The concept of the near-death experience is culturally ubiquitous. And though the content seems to track along culture lines – Western Christians are more likely to report seeing guardian angels, while Hindus are more likely to report seeing messengers of the god of death – certain factors seem to transcend culture: an out-of-body experience; a feeling of peace; and, of course, the light at the end of the tunnel.
As a materialist, I won’t discuss the possibility that these commonalities reflect some metaphysical structure to the afterlife. More likely, it seems to me, is that the commonalities result from the fact that the experience is mediated by our brains, and our brains, when dying, may be more alike than different.
We are talking about this study, appearing in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, by Jimo Borjigin and her team.
Dr. Borjigin studies the neural correlates of consciousness, perhaps one of the biggest questions in all of science today. To wit,
The study in question follows four unconscious patients –comatose patients, really – as life-sustaining support was withdrawn, up until the moment of death. Three had suffered severe anoxic brain injury in the setting of prolonged cardiac arrest. Though the heart was restarted, the brain damage was severe. The fourth had a large brain hemorrhage. All four patients were thus comatose and, though not brain-dead, unresponsive – with the lowest possible Glasgow Coma Scale score. No response to outside stimuli.
The families had made the decision to withdraw life support – to remove the breathing tube – but agreed to enroll their loved one in the study.
The team applied EEG leads to the head, EKG leads to the chest, and other monitoring equipment to observe the physiologic changes that occurred as the comatose and unresponsive patient died.
As the heart rhythm evolved from this:
To this:
And eventually stopped.
But this is a study about the brain, not the heart.
Prior to the withdrawal of life support, the brain electrical signals looked like this:
What you see is the EEG power at various frequencies, with red being higher. All the red was down at the low frequencies. Consciousness, at least as we understand it, is a higher-frequency phenomenon.
Right after the breathing tube was removed, the power didn’t change too much, but you can see some increased activity at the higher frequencies.
But in two of the four patients, something really surprising happened. Watch what happens as the brain gets closer and closer to death.
Here, about 300 seconds before death, there was a power surge at the high gamma frequencies.
This spike in power occurred in the somatosensory cortex and the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, areas that are associated with conscious experience. It seems that this patient, 5 minutes before death, was experiencing something.
But I know what you’re thinking. This is a brain that is not receiving oxygen. Cells are going to become disordered quickly and start firing randomly – a last gasp, so to speak, before the end. Meaningless noise.
But connectivity mapping tells a different story. The signals seem to have structure.
Those high-frequency power surges increased connectivity in the posterior cortical “hot zone,” an area of the brain many researchers feel is necessary for conscious perception. This figure is not a map of raw brain electrical output like the one I showed before, but of coherence between brain regions in the consciousness hot zone. Those red areas indicate cross-talk – not the disordered scream of dying neurons, but a last set of messages passing back and forth from the parietal and posterior temporal lobes.
In fact, the electrical patterns of the brains in these patients looked very similar to the patterns seen in dreaming humans, as well as in patients with epilepsy who report sensations of out-of-body experiences.
It’s critical to realize two things here. First, these signals of consciousness were not present before life support was withdrawn. These comatose patients had minimal brain activity; there was no evidence that they were experiencing anything before the process of dying began. These brains are behaving fundamentally differently near death.
But second, we must realize that, although the brains of these individuals, in their last moments, appeared to be acting in a way that conscious brains act, we have no way of knowing if the patients were truly having a conscious experience. As I said, all the patients in the study died. Short of those metaphysics I alluded to earlier, we will have no way to ask them how they experienced their final moments.
Let’s be clear: This study doesn’t answer the question of what happens when we die. It says nothing about life after death or the existence or persistence of the soul. But what it does do is shed light on an incredibly difficult problem in neuroscience: the problem of consciousness. And as studies like this move forward, we may discover that the root of consciousness comes not from the breath of God or the energy of a living universe, but from very specific parts of the very complicated machine that is the brain, acting together to produce something transcendent. And to me, that is no less sublime.
Dr. Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, Yale University, New Haven, Conn. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape. He tweets @fperrywilson and his new book, How Medicine Works and When It Doesn’t, is available now. Dr. Wilson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Getting a white-bagging exemption: A win for the patient, employer, and rheumatologist
Whether it’s filling out a prior authorization form or testifying before Congress, it is an action we perform that ultimately helps our patients achieve that care. We are familiar with many of the obstacles that block the path to the best care and interfere with our patient-doctor relationships. Much work has been done to pass legislation in the states to mitigate some of those obstacles, such as unreasonable step therapy regimens, nonmedical switching, and copay accumulators.
Unfortunately, that state legislation does not cover patients who work for companies that are self-insured. Self-insured employers, which account for about 60% of America’s workers, directly pay for the health benefits offered to employees instead of buying “fully funded” insurance plans. Most of those self-funded plans fall under “ERISA” protections and are regulated by the federal Department of Labor. ERISA stands for Employee Retirement Income Security Act. The law, which was enacted in 1974, also covers employee health plans. These plans must act as a fiduciary, meaning they must look after the well-being of the employees, including their finances and those of the plan itself.
The Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations (CSRO) has learned of a number of issues involving patients who work for self-funded companies, regulated by ERISA. One such issue is that of mandated “white bagging.” White bagging has been discussed in “Rheum for Action” in the past. There is a long list of white-bagging problems, including dosing issues, lack of “chain of custody” with the medications, delays in treatment, mandatory up-front payments by the patient, and wastage of unused medication. However, there is another issue that is of concern not only to the employees (our patients) but to the employer as well.
Employers’ fiduciary responsibility
As mentioned earlier, the employers who self insure are responsible for the financial well-being of their employee and the plan itself. Therefore, if certain practices are mandated within the health plan that harm our patients or the plan financially, the company could be in violation of their fiduciary duty. Rheumatologists have said that buying and billing the drug to the medical side of the health plan in many cases costs much less than white bagging. Conceivably, that could result in breach of an employer’s fiduciary duty to their employee.
Evidence for violating fiduciary duty
CSRO recently received redacted receipts comparing costs between the two models of drug acquisition for a patient in an ERISA plan. White bagging for the patient occurred in 2021, and in 2022 an exemption was granted for the rheumatologist to buy and bill the administered medication. Unfortunately, the exemption to buy and bill in 2023 was denied and continues to be denied (as of this writing). A comparison of the receipts revealed the company was charged over $40,000 for the white-bagged medication in 2021, and the patient’s cost share for that year was $525. Under the traditional buy-and-bill acquisition model in 2022, the company was charged around $12,000 for the medication and the patient’s cost share was $30. There is a clear difference in cost to the employee and plan between the two acquisition models.
Is this major company unknowingly violating its fiduciary duty by mandating white bagging as per their contract with one of the three big pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs)? If so, how does something like this happen with a large national company that has ERISA attorneys looking over the contracts with the PBMs?
Why is white bagging mandated?
Often, white bagging is mandated because the cost of infusions in a hospital outpatient facility can be very high. Nationally, it has been shown that hospitals charge four to five times the cost they paid for the drug, and the 100 most expensive hospitals charge 10-18 times the cost of their drugs. With these up-charges, white bagging could easily be a lower cost for employee and company. But across-the-board mandating of white bagging ignores that physician office–based infusions may offer a much lower cost to employees and the employer.
Another reason large and small self-funded companies may unknowingly sign contracts that are often more profitable to the PBM than to the employer is that the employer pharmacy benefit consultants are paid handsomely by the big PBMs and have been known to “rig” the contract in favor of the PBM, according to Paul Holmes, an ERISA attorney with a focus in pharmacy health plan contracts. Clearly, the PBM profits more with white-bagged medicines billed through the pharmacy (PBM) side of insurance as opposed to buy-and-bill medications that are billed on the medical side of insurance. So mandated white bagging is often included in these contracts, ignoring the lower cost in an infusion suite at a physician’s office.
Suggestions for employers
Employers and employees should be able to obtain the costs of mandated, white-bagged drugs from their PBMs because the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2021 (CAA) mandates that group health plans ensure access to cost data. The employer should also have access to their consultant’s compensation from the PBM as Section 202 in the CAA states that employer benefit consultants must “disclose actual and anticipated cash and non-cash compensation they expect to earn in connection with the sale, renewal, and extension of group health insurance.”
It would be wise for all self-insured companies to use this section to see how much their consultants are being influenced by the company that they are recommending. Additionally, the companies should consider hiring ERISA attorneys that understand not only the legalese of the contract with a PBM but also the pharmacy lingo, such as the difference between maximum allowable cost, average wholesale price, average sales price, and average manufacturer’s price.
Suggestion for the rheumatologist
This leads to a suggestion to rheumatologists trying to get an exemption from mandated white bagging. If a patient has already had white-bagged medication, have them obtain a receipt from the PBM for their charges to the plan for the medication. If the patient has not gone through the white bagging yet, the PBM should be able to tell the plan the cost of the white-bagged medication and the cost to the patient. Compare those costs with what would be charged through buy and bill, and if it is less, present that evidence to the employer and remind them of their fiduciary responsibility to their employees.
Granted, this process may take more effort than filling out a prior authorization, but getting the white-bag exemption will help the patient, the employer, and the rheumatologist in the long run. A win-win-win!
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s Vice President of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate Past President, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. You can reach her at [email protected].
Whether it’s filling out a prior authorization form or testifying before Congress, it is an action we perform that ultimately helps our patients achieve that care. We are familiar with many of the obstacles that block the path to the best care and interfere with our patient-doctor relationships. Much work has been done to pass legislation in the states to mitigate some of those obstacles, such as unreasonable step therapy regimens, nonmedical switching, and copay accumulators.
Unfortunately, that state legislation does not cover patients who work for companies that are self-insured. Self-insured employers, which account for about 60% of America’s workers, directly pay for the health benefits offered to employees instead of buying “fully funded” insurance plans. Most of those self-funded plans fall under “ERISA” protections and are regulated by the federal Department of Labor. ERISA stands for Employee Retirement Income Security Act. The law, which was enacted in 1974, also covers employee health plans. These plans must act as a fiduciary, meaning they must look after the well-being of the employees, including their finances and those of the plan itself.
The Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations (CSRO) has learned of a number of issues involving patients who work for self-funded companies, regulated by ERISA. One such issue is that of mandated “white bagging.” White bagging has been discussed in “Rheum for Action” in the past. There is a long list of white-bagging problems, including dosing issues, lack of “chain of custody” with the medications, delays in treatment, mandatory up-front payments by the patient, and wastage of unused medication. However, there is another issue that is of concern not only to the employees (our patients) but to the employer as well.
Employers’ fiduciary responsibility
As mentioned earlier, the employers who self insure are responsible for the financial well-being of their employee and the plan itself. Therefore, if certain practices are mandated within the health plan that harm our patients or the plan financially, the company could be in violation of their fiduciary duty. Rheumatologists have said that buying and billing the drug to the medical side of the health plan in many cases costs much less than white bagging. Conceivably, that could result in breach of an employer’s fiduciary duty to their employee.
Evidence for violating fiduciary duty
CSRO recently received redacted receipts comparing costs between the two models of drug acquisition for a patient in an ERISA plan. White bagging for the patient occurred in 2021, and in 2022 an exemption was granted for the rheumatologist to buy and bill the administered medication. Unfortunately, the exemption to buy and bill in 2023 was denied and continues to be denied (as of this writing). A comparison of the receipts revealed the company was charged over $40,000 for the white-bagged medication in 2021, and the patient’s cost share for that year was $525. Under the traditional buy-and-bill acquisition model in 2022, the company was charged around $12,000 for the medication and the patient’s cost share was $30. There is a clear difference in cost to the employee and plan between the two acquisition models.
Is this major company unknowingly violating its fiduciary duty by mandating white bagging as per their contract with one of the three big pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs)? If so, how does something like this happen with a large national company that has ERISA attorneys looking over the contracts with the PBMs?
Why is white bagging mandated?
Often, white bagging is mandated because the cost of infusions in a hospital outpatient facility can be very high. Nationally, it has been shown that hospitals charge four to five times the cost they paid for the drug, and the 100 most expensive hospitals charge 10-18 times the cost of their drugs. With these up-charges, white bagging could easily be a lower cost for employee and company. But across-the-board mandating of white bagging ignores that physician office–based infusions may offer a much lower cost to employees and the employer.
Another reason large and small self-funded companies may unknowingly sign contracts that are often more profitable to the PBM than to the employer is that the employer pharmacy benefit consultants are paid handsomely by the big PBMs and have been known to “rig” the contract in favor of the PBM, according to Paul Holmes, an ERISA attorney with a focus in pharmacy health plan contracts. Clearly, the PBM profits more with white-bagged medicines billed through the pharmacy (PBM) side of insurance as opposed to buy-and-bill medications that are billed on the medical side of insurance. So mandated white bagging is often included in these contracts, ignoring the lower cost in an infusion suite at a physician’s office.
Suggestions for employers
Employers and employees should be able to obtain the costs of mandated, white-bagged drugs from their PBMs because the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2021 (CAA) mandates that group health plans ensure access to cost data. The employer should also have access to their consultant’s compensation from the PBM as Section 202 in the CAA states that employer benefit consultants must “disclose actual and anticipated cash and non-cash compensation they expect to earn in connection with the sale, renewal, and extension of group health insurance.”
It would be wise for all self-insured companies to use this section to see how much their consultants are being influenced by the company that they are recommending. Additionally, the companies should consider hiring ERISA attorneys that understand not only the legalese of the contract with a PBM but also the pharmacy lingo, such as the difference between maximum allowable cost, average wholesale price, average sales price, and average manufacturer’s price.
Suggestion for the rheumatologist
This leads to a suggestion to rheumatologists trying to get an exemption from mandated white bagging. If a patient has already had white-bagged medication, have them obtain a receipt from the PBM for their charges to the plan for the medication. If the patient has not gone through the white bagging yet, the PBM should be able to tell the plan the cost of the white-bagged medication and the cost to the patient. Compare those costs with what would be charged through buy and bill, and if it is less, present that evidence to the employer and remind them of their fiduciary responsibility to their employees.
Granted, this process may take more effort than filling out a prior authorization, but getting the white-bag exemption will help the patient, the employer, and the rheumatologist in the long run. A win-win-win!
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s Vice President of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate Past President, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. You can reach her at [email protected].
Whether it’s filling out a prior authorization form or testifying before Congress, it is an action we perform that ultimately helps our patients achieve that care. We are familiar with many of the obstacles that block the path to the best care and interfere with our patient-doctor relationships. Much work has been done to pass legislation in the states to mitigate some of those obstacles, such as unreasonable step therapy regimens, nonmedical switching, and copay accumulators.
Unfortunately, that state legislation does not cover patients who work for companies that are self-insured. Self-insured employers, which account for about 60% of America’s workers, directly pay for the health benefits offered to employees instead of buying “fully funded” insurance plans. Most of those self-funded plans fall under “ERISA” protections and are regulated by the federal Department of Labor. ERISA stands for Employee Retirement Income Security Act. The law, which was enacted in 1974, also covers employee health plans. These plans must act as a fiduciary, meaning they must look after the well-being of the employees, including their finances and those of the plan itself.
The Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations (CSRO) has learned of a number of issues involving patients who work for self-funded companies, regulated by ERISA. One such issue is that of mandated “white bagging.” White bagging has been discussed in “Rheum for Action” in the past. There is a long list of white-bagging problems, including dosing issues, lack of “chain of custody” with the medications, delays in treatment, mandatory up-front payments by the patient, and wastage of unused medication. However, there is another issue that is of concern not only to the employees (our patients) but to the employer as well.
Employers’ fiduciary responsibility
As mentioned earlier, the employers who self insure are responsible for the financial well-being of their employee and the plan itself. Therefore, if certain practices are mandated within the health plan that harm our patients or the plan financially, the company could be in violation of their fiduciary duty. Rheumatologists have said that buying and billing the drug to the medical side of the health plan in many cases costs much less than white bagging. Conceivably, that could result in breach of an employer’s fiduciary duty to their employee.
Evidence for violating fiduciary duty
CSRO recently received redacted receipts comparing costs between the two models of drug acquisition for a patient in an ERISA plan. White bagging for the patient occurred in 2021, and in 2022 an exemption was granted for the rheumatologist to buy and bill the administered medication. Unfortunately, the exemption to buy and bill in 2023 was denied and continues to be denied (as of this writing). A comparison of the receipts revealed the company was charged over $40,000 for the white-bagged medication in 2021, and the patient’s cost share for that year was $525. Under the traditional buy-and-bill acquisition model in 2022, the company was charged around $12,000 for the medication and the patient’s cost share was $30. There is a clear difference in cost to the employee and plan between the two acquisition models.
Is this major company unknowingly violating its fiduciary duty by mandating white bagging as per their contract with one of the three big pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs)? If so, how does something like this happen with a large national company that has ERISA attorneys looking over the contracts with the PBMs?
Why is white bagging mandated?
Often, white bagging is mandated because the cost of infusions in a hospital outpatient facility can be very high. Nationally, it has been shown that hospitals charge four to five times the cost they paid for the drug, and the 100 most expensive hospitals charge 10-18 times the cost of their drugs. With these up-charges, white bagging could easily be a lower cost for employee and company. But across-the-board mandating of white bagging ignores that physician office–based infusions may offer a much lower cost to employees and the employer.
Another reason large and small self-funded companies may unknowingly sign contracts that are often more profitable to the PBM than to the employer is that the employer pharmacy benefit consultants are paid handsomely by the big PBMs and have been known to “rig” the contract in favor of the PBM, according to Paul Holmes, an ERISA attorney with a focus in pharmacy health plan contracts. Clearly, the PBM profits more with white-bagged medicines billed through the pharmacy (PBM) side of insurance as opposed to buy-and-bill medications that are billed on the medical side of insurance. So mandated white bagging is often included in these contracts, ignoring the lower cost in an infusion suite at a physician’s office.
Suggestions for employers
Employers and employees should be able to obtain the costs of mandated, white-bagged drugs from their PBMs because the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2021 (CAA) mandates that group health plans ensure access to cost data. The employer should also have access to their consultant’s compensation from the PBM as Section 202 in the CAA states that employer benefit consultants must “disclose actual and anticipated cash and non-cash compensation they expect to earn in connection with the sale, renewal, and extension of group health insurance.”
It would be wise for all self-insured companies to use this section to see how much their consultants are being influenced by the company that they are recommending. Additionally, the companies should consider hiring ERISA attorneys that understand not only the legalese of the contract with a PBM but also the pharmacy lingo, such as the difference between maximum allowable cost, average wholesale price, average sales price, and average manufacturer’s price.
Suggestion for the rheumatologist
This leads to a suggestion to rheumatologists trying to get an exemption from mandated white bagging. If a patient has already had white-bagged medication, have them obtain a receipt from the PBM for their charges to the plan for the medication. If the patient has not gone through the white bagging yet, the PBM should be able to tell the plan the cost of the white-bagged medication and the cost to the patient. Compare those costs with what would be charged through buy and bill, and if it is less, present that evidence to the employer and remind them of their fiduciary responsibility to their employees.
Granted, this process may take more effort than filling out a prior authorization, but getting the white-bag exemption will help the patient, the employer, and the rheumatologist in the long run. A win-win-win!
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s Vice President of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate Past President, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. You can reach her at [email protected].
Gene Expression Profiling for Melanoma Prognosis: Going Beyond What We See With Our Eyes
Dermatology certainly is the most visual medical specialty. In the current era of powerful electronic imaging and laboratory techniques, the skills of physical diagnosis seem to have become less important in medicine—not so in dermatology, in which the experienced clinician is able to identify many conditions by simply looking at the skin. Of course, dermatologists do heavily rely on dermatopathologists to microscopically visualize biopsies to distinguish diseases. Even as we acknowledge the dominant role of visual recognition, there is increasing progress in making clinical determinations based on molecular events. The era of genomic dermatology is here.
The Genodermatoses
There are more than 500 dermatologic conditions resulting from heritable mutational events.1 The rarity of most of these diseases and variability in phenotypic manifestations presents considerable diagnostic challenges, typically the province of a select group of clinical pediatric dermatologists whose abilities have been developed by experience.2 However, the addition of genomic analysis has now made reliable identification more accessible to a wider group of clinicians.3 The Human Genome Project was arguably the most successful health policy endeavor in human history, promoting the development of massive automated, information theory–driven applications to analyze DNA sequences.4 We all think of DNA analysis as the ultimate means to detect mutations by sequencing whole exomes—and in fact the entire genome of affected individuals searching for mutations—but DNA sequencing often is insufficient to detect mutations in noncoding regions of genes and to identify abnormalities of gene expression (eg, splice variants). Building on the advances in high-throughput nucleic acid sequencing and massive computerized analysis, the field has now taken a quantum leap further to sequence transcribed RNA to detect abnormalities.5
The techniques are straightforward: RNA is isolated and reverse transcribed to complementary DNA. The complementary DNA is amplified and then processed by high-throughput sequencers. The sequences are then identified by computer algorithms. It is possible to fully define the transcriptomes of multiple genes, even reaching the threshold of resolution of gene expression emanating from a single cell.6
Studying Gene Expression for Malignant Melanoma
As much as we rely on visual interpretations, we acknowledge that many conditions look very similar, whether to the naked eye or under the microscope. This is true for rare diseases but also for the rashes we routinely see. A group of investigators recently used RNA transcriptome sequencing to analyze differences between atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, permitting better differentiation of these 2 common conditions.7
One of the greatest challenges confronting dermatologists and their dermatopathologist partners is to distinguish malignant melanoma from benign nevi.8 Despite staining for a number of molecular markers, some lesions defy histopathology, such as distinguishing benign and malignant Spitz nevi; however, recent work on RNA transcriptomes suggests that gene expression may increase confidence in assessing atypical Spitz nevi.9 A 23-gene expression panel has yielded a sensitivity of 91.5% and a specificity of 92.5% in differentiating benign nevi from malignant melanoma.10
From the Research Laboratory to Routine Clinical Use
Undoubtedly, it is a large step from proof-of-concept studies to accepted clinical use. The ultimate achievement for a laboratory technique is to enter approved clinical use. Gene expression panels have now been approved by numerous third-party insurers to help predict future clinical evolution of biopsied melanomas. Although early in situ melanomas are eminently curable by wide excision, lesions that have more concerning characteristics (eg, depth >0.8 mm, ulceration) may progress to metastatic disease. The gratifying success of checkpoint inhibitor therapy has improved the previously dismal outlook for advanced melanomas.11 Dermatologists search for clues to suggest which patients may benefit from adjuvant therapy. Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) has been a standard-of-care technique to help make this determination.12
It has now been demonstrated that gene expression array analysis can provide evidence complementing SLNB results or even independent of SLNB results. In extensive validation studies, a 31-gene expression panel analyzing initial melanoma biopsy specimens showed predictive value for later recurrence and development of metastatic disease.13,14 The gene expression studies have identified patients with negative SLNBs who have gone on to develop metastatic melanomas.15 It has been suggested that gene expression panel diagnosis may reduce the need for invasive SLNBs in patients in whom the surgical procedure may involve risk.16
Looking to the Future
The progress of science is the result of many small steps building on prior work. The terms breakthrough and game changer in medicine have been popularized by the media and rarely are valid. On the contrary, sequential development of methods over many years has preceded the acclaimed successes of medical research; for example, the best-known medical breakthrough—that of Salk’s inactivated polio vaccine—was preceded by the use of an inactivated polio vaccine by Brodie and Park17 in 1935. However, it was the development of tissue culture of poliomyelitis virus by Enders et al18 that provided the methodology to Salk’s group to produce their inactivated polio vaccine.
The ability to go beyond our visual senses will be of great importance in characterizing the variability of skin diseases, especially in skin of color patients; for example, acral melanoma is perhaps the primary melanocytic malignancy in darker-skinned patients and is the target of RNA transcriptomic research.19 Progress is continuing on gene therapy for a growing number of skin conditions.20,21 In vivo correction of abnormal genes is being attempted for a number of inherited cutaneous diseases,22 notably for disorders of skin fragility.23 For now, we welcome the addition of genomic capabilities to the visual practice of dermatology and the capability to go beyond that which we can see with our eyes.
- Feramisco JD, Sadreyev RI, Murray ML, et al. Phenotypic and enotypic analyses of genetic skin disease through the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) database. J Investig Derm. 2009;129:2628-2636.
- Parker JC, Rangu S, Grand KL, et al. Genetic skin disorders: the value of a multidisciplinary clinic. Am J Med Genet A. 2021;185:1159-1167.
- Richert B, Smits G. Clinical and molecular diagnosis of genodermatoses: review and perspectives. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:488-500.
- Green ED, Watson JD, Collins FS. Human genome project: twenty-five years of big biology. Nature. 2015;526:29-31.
- Saeidian AH, Youssefian L, Vahidnezhad H, et al. Research techniques made simple: whole-transcriptome sequencing by RNA-seq for diagnosis of monogenic disorders. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140:1117-1126.e1.
- Deutsch A, McLellan BN, Shinoda K. Single-cell transcriptomics in dermatology. JAAD Int. 2020;1:182-188.
- Liu Y, Wang H, Taylor M, et al. Classification of human chronic inflammatory skin disease based on single-cell immune profiling [published online April 15, 2022]. Sci Immunol. doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.abl9165
- Reimann JDR, Salim S, Velazquez EF, et al. Comparison of melanoma gene expression score with histopathology, fluorescence in situ hybridization, and SNP array for the classification of melanocytic neoplasms. Mod Pathol. 2018;31:1733-1743.
- Hillen LM, Geybels MS, Spassova I, et al. A digital mRNA expression signature to classify challenging spitzoid melanocytic neoplasms. FEBS Open Bio. 2020;10:1326-1341.
- Clarke LE, Flake DD 2nd, Busam K, et al. An independent validation of a gene expression signature to differentiate malignant melanoma from benign melanocytic nevi. Cancer. 2017;123:617-628.
- Stege H, Haist M, Nikfarjam U, et al. The status of adjuvant and neoadjuvant melanoma therapy, new developments and upcoming challenges. Target Oncol. 2021;16:537-552.
- Morrison S, Han D. Re-evaluation of sentinel lymph node biopsy for melanoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2021;22:22.
- Gerami P, Cook RW, Russell MC, et al. Gene expression profiling for molecular staging of cutaneous melanoma in patients with sentinel lymph node biopsy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:780-785.e3.
- Keller J, Schwartz TL, Lizalek JM, et al. Prospective validation of the prognostic 31-gene expression profiling test in primary cutaneous melanoma. Cancer Med. 2019;8:2205-2212.
- Gastman BR, Gerami P, Kurley SJ, et al. Identification of patients at risk for metastasis using a prognostic 31-gene expression profile in subpopulations of melanoma patients with favorable outcomes by standard criteria. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:149-157.
- Vetto JT, Hsueh EC, Gastman BR, et al. Guidance of sentinel lymph node biopsy decisions in patients with T1-T2 melanoma using gene expression profiling. Future Oncol. 2019;15:1207-1217.
- Brodie M, Park W. Active immunization against poliomyelitis. JAMA. 1935;105:1089-1093.
- Enders JF, Weller TH, Robbins FC. Cultivation of the Lansing strain of poliomyelitis virus in cultures of various human embryonic tissues. Science. 1949;109:85-87.
- Li J, Smalley I, Chen Z, et al. Single-cell characterization of the cellular landscape of acral melanoma identifies novel targets for immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28:2131-2146.
- Gorell E, Nguyen N, Lane A, et al. Gene therapy for skin diseases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014;4:A015149.
- Cavazza A, Mavilio F. Gene therapy of skin adhesion disorders (mini review). Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012;13:1868-1876.
- Abdul-Wahab A, Qasim W, McGrath JA. Gene therapies for inherited skin disorders. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2014;33:83-90.
- Bilousova G. Gene therapy for skin fragility diseases: the new generation. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:1634-1637.
Dermatology certainly is the most visual medical specialty. In the current era of powerful electronic imaging and laboratory techniques, the skills of physical diagnosis seem to have become less important in medicine—not so in dermatology, in which the experienced clinician is able to identify many conditions by simply looking at the skin. Of course, dermatologists do heavily rely on dermatopathologists to microscopically visualize biopsies to distinguish diseases. Even as we acknowledge the dominant role of visual recognition, there is increasing progress in making clinical determinations based on molecular events. The era of genomic dermatology is here.
The Genodermatoses
There are more than 500 dermatologic conditions resulting from heritable mutational events.1 The rarity of most of these diseases and variability in phenotypic manifestations presents considerable diagnostic challenges, typically the province of a select group of clinical pediatric dermatologists whose abilities have been developed by experience.2 However, the addition of genomic analysis has now made reliable identification more accessible to a wider group of clinicians.3 The Human Genome Project was arguably the most successful health policy endeavor in human history, promoting the development of massive automated, information theory–driven applications to analyze DNA sequences.4 We all think of DNA analysis as the ultimate means to detect mutations by sequencing whole exomes—and in fact the entire genome of affected individuals searching for mutations—but DNA sequencing often is insufficient to detect mutations in noncoding regions of genes and to identify abnormalities of gene expression (eg, splice variants). Building on the advances in high-throughput nucleic acid sequencing and massive computerized analysis, the field has now taken a quantum leap further to sequence transcribed RNA to detect abnormalities.5
The techniques are straightforward: RNA is isolated and reverse transcribed to complementary DNA. The complementary DNA is amplified and then processed by high-throughput sequencers. The sequences are then identified by computer algorithms. It is possible to fully define the transcriptomes of multiple genes, even reaching the threshold of resolution of gene expression emanating from a single cell.6
Studying Gene Expression for Malignant Melanoma
As much as we rely on visual interpretations, we acknowledge that many conditions look very similar, whether to the naked eye or under the microscope. This is true for rare diseases but also for the rashes we routinely see. A group of investigators recently used RNA transcriptome sequencing to analyze differences between atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, permitting better differentiation of these 2 common conditions.7
One of the greatest challenges confronting dermatologists and their dermatopathologist partners is to distinguish malignant melanoma from benign nevi.8 Despite staining for a number of molecular markers, some lesions defy histopathology, such as distinguishing benign and malignant Spitz nevi; however, recent work on RNA transcriptomes suggests that gene expression may increase confidence in assessing atypical Spitz nevi.9 A 23-gene expression panel has yielded a sensitivity of 91.5% and a specificity of 92.5% in differentiating benign nevi from malignant melanoma.10
From the Research Laboratory to Routine Clinical Use
Undoubtedly, it is a large step from proof-of-concept studies to accepted clinical use. The ultimate achievement for a laboratory technique is to enter approved clinical use. Gene expression panels have now been approved by numerous third-party insurers to help predict future clinical evolution of biopsied melanomas. Although early in situ melanomas are eminently curable by wide excision, lesions that have more concerning characteristics (eg, depth >0.8 mm, ulceration) may progress to metastatic disease. The gratifying success of checkpoint inhibitor therapy has improved the previously dismal outlook for advanced melanomas.11 Dermatologists search for clues to suggest which patients may benefit from adjuvant therapy. Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) has been a standard-of-care technique to help make this determination.12
It has now been demonstrated that gene expression array analysis can provide evidence complementing SLNB results or even independent of SLNB results. In extensive validation studies, a 31-gene expression panel analyzing initial melanoma biopsy specimens showed predictive value for later recurrence and development of metastatic disease.13,14 The gene expression studies have identified patients with negative SLNBs who have gone on to develop metastatic melanomas.15 It has been suggested that gene expression panel diagnosis may reduce the need for invasive SLNBs in patients in whom the surgical procedure may involve risk.16
Looking to the Future
The progress of science is the result of many small steps building on prior work. The terms breakthrough and game changer in medicine have been popularized by the media and rarely are valid. On the contrary, sequential development of methods over many years has preceded the acclaimed successes of medical research; for example, the best-known medical breakthrough—that of Salk’s inactivated polio vaccine—was preceded by the use of an inactivated polio vaccine by Brodie and Park17 in 1935. However, it was the development of tissue culture of poliomyelitis virus by Enders et al18 that provided the methodology to Salk’s group to produce their inactivated polio vaccine.
The ability to go beyond our visual senses will be of great importance in characterizing the variability of skin diseases, especially in skin of color patients; for example, acral melanoma is perhaps the primary melanocytic malignancy in darker-skinned patients and is the target of RNA transcriptomic research.19 Progress is continuing on gene therapy for a growing number of skin conditions.20,21 In vivo correction of abnormal genes is being attempted for a number of inherited cutaneous diseases,22 notably for disorders of skin fragility.23 For now, we welcome the addition of genomic capabilities to the visual practice of dermatology and the capability to go beyond that which we can see with our eyes.
Dermatology certainly is the most visual medical specialty. In the current era of powerful electronic imaging and laboratory techniques, the skills of physical diagnosis seem to have become less important in medicine—not so in dermatology, in which the experienced clinician is able to identify many conditions by simply looking at the skin. Of course, dermatologists do heavily rely on dermatopathologists to microscopically visualize biopsies to distinguish diseases. Even as we acknowledge the dominant role of visual recognition, there is increasing progress in making clinical determinations based on molecular events. The era of genomic dermatology is here.
The Genodermatoses
There are more than 500 dermatologic conditions resulting from heritable mutational events.1 The rarity of most of these diseases and variability in phenotypic manifestations presents considerable diagnostic challenges, typically the province of a select group of clinical pediatric dermatologists whose abilities have been developed by experience.2 However, the addition of genomic analysis has now made reliable identification more accessible to a wider group of clinicians.3 The Human Genome Project was arguably the most successful health policy endeavor in human history, promoting the development of massive automated, information theory–driven applications to analyze DNA sequences.4 We all think of DNA analysis as the ultimate means to detect mutations by sequencing whole exomes—and in fact the entire genome of affected individuals searching for mutations—but DNA sequencing often is insufficient to detect mutations in noncoding regions of genes and to identify abnormalities of gene expression (eg, splice variants). Building on the advances in high-throughput nucleic acid sequencing and massive computerized analysis, the field has now taken a quantum leap further to sequence transcribed RNA to detect abnormalities.5
The techniques are straightforward: RNA is isolated and reverse transcribed to complementary DNA. The complementary DNA is amplified and then processed by high-throughput sequencers. The sequences are then identified by computer algorithms. It is possible to fully define the transcriptomes of multiple genes, even reaching the threshold of resolution of gene expression emanating from a single cell.6
Studying Gene Expression for Malignant Melanoma
As much as we rely on visual interpretations, we acknowledge that many conditions look very similar, whether to the naked eye or under the microscope. This is true for rare diseases but also for the rashes we routinely see. A group of investigators recently used RNA transcriptome sequencing to analyze differences between atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, permitting better differentiation of these 2 common conditions.7
One of the greatest challenges confronting dermatologists and their dermatopathologist partners is to distinguish malignant melanoma from benign nevi.8 Despite staining for a number of molecular markers, some lesions defy histopathology, such as distinguishing benign and malignant Spitz nevi; however, recent work on RNA transcriptomes suggests that gene expression may increase confidence in assessing atypical Spitz nevi.9 A 23-gene expression panel has yielded a sensitivity of 91.5% and a specificity of 92.5% in differentiating benign nevi from malignant melanoma.10
From the Research Laboratory to Routine Clinical Use
Undoubtedly, it is a large step from proof-of-concept studies to accepted clinical use. The ultimate achievement for a laboratory technique is to enter approved clinical use. Gene expression panels have now been approved by numerous third-party insurers to help predict future clinical evolution of biopsied melanomas. Although early in situ melanomas are eminently curable by wide excision, lesions that have more concerning characteristics (eg, depth >0.8 mm, ulceration) may progress to metastatic disease. The gratifying success of checkpoint inhibitor therapy has improved the previously dismal outlook for advanced melanomas.11 Dermatologists search for clues to suggest which patients may benefit from adjuvant therapy. Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) has been a standard-of-care technique to help make this determination.12
It has now been demonstrated that gene expression array analysis can provide evidence complementing SLNB results or even independent of SLNB results. In extensive validation studies, a 31-gene expression panel analyzing initial melanoma biopsy specimens showed predictive value for later recurrence and development of metastatic disease.13,14 The gene expression studies have identified patients with negative SLNBs who have gone on to develop metastatic melanomas.15 It has been suggested that gene expression panel diagnosis may reduce the need for invasive SLNBs in patients in whom the surgical procedure may involve risk.16
Looking to the Future
The progress of science is the result of many small steps building on prior work. The terms breakthrough and game changer in medicine have been popularized by the media and rarely are valid. On the contrary, sequential development of methods over many years has preceded the acclaimed successes of medical research; for example, the best-known medical breakthrough—that of Salk’s inactivated polio vaccine—was preceded by the use of an inactivated polio vaccine by Brodie and Park17 in 1935. However, it was the development of tissue culture of poliomyelitis virus by Enders et al18 that provided the methodology to Salk’s group to produce their inactivated polio vaccine.
The ability to go beyond our visual senses will be of great importance in characterizing the variability of skin diseases, especially in skin of color patients; for example, acral melanoma is perhaps the primary melanocytic malignancy in darker-skinned patients and is the target of RNA transcriptomic research.19 Progress is continuing on gene therapy for a growing number of skin conditions.20,21 In vivo correction of abnormal genes is being attempted for a number of inherited cutaneous diseases,22 notably for disorders of skin fragility.23 For now, we welcome the addition of genomic capabilities to the visual practice of dermatology and the capability to go beyond that which we can see with our eyes.
- Feramisco JD, Sadreyev RI, Murray ML, et al. Phenotypic and enotypic analyses of genetic skin disease through the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) database. J Investig Derm. 2009;129:2628-2636.
- Parker JC, Rangu S, Grand KL, et al. Genetic skin disorders: the value of a multidisciplinary clinic. Am J Med Genet A. 2021;185:1159-1167.
- Richert B, Smits G. Clinical and molecular diagnosis of genodermatoses: review and perspectives. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:488-500.
- Green ED, Watson JD, Collins FS. Human genome project: twenty-five years of big biology. Nature. 2015;526:29-31.
- Saeidian AH, Youssefian L, Vahidnezhad H, et al. Research techniques made simple: whole-transcriptome sequencing by RNA-seq for diagnosis of monogenic disorders. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140:1117-1126.e1.
- Deutsch A, McLellan BN, Shinoda K. Single-cell transcriptomics in dermatology. JAAD Int. 2020;1:182-188.
- Liu Y, Wang H, Taylor M, et al. Classification of human chronic inflammatory skin disease based on single-cell immune profiling [published online April 15, 2022]. Sci Immunol. doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.abl9165
- Reimann JDR, Salim S, Velazquez EF, et al. Comparison of melanoma gene expression score with histopathology, fluorescence in situ hybridization, and SNP array for the classification of melanocytic neoplasms. Mod Pathol. 2018;31:1733-1743.
- Hillen LM, Geybels MS, Spassova I, et al. A digital mRNA expression signature to classify challenging spitzoid melanocytic neoplasms. FEBS Open Bio. 2020;10:1326-1341.
- Clarke LE, Flake DD 2nd, Busam K, et al. An independent validation of a gene expression signature to differentiate malignant melanoma from benign melanocytic nevi. Cancer. 2017;123:617-628.
- Stege H, Haist M, Nikfarjam U, et al. The status of adjuvant and neoadjuvant melanoma therapy, new developments and upcoming challenges. Target Oncol. 2021;16:537-552.
- Morrison S, Han D. Re-evaluation of sentinel lymph node biopsy for melanoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2021;22:22.
- Gerami P, Cook RW, Russell MC, et al. Gene expression profiling for molecular staging of cutaneous melanoma in patients with sentinel lymph node biopsy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:780-785.e3.
- Keller J, Schwartz TL, Lizalek JM, et al. Prospective validation of the prognostic 31-gene expression profiling test in primary cutaneous melanoma. Cancer Med. 2019;8:2205-2212.
- Gastman BR, Gerami P, Kurley SJ, et al. Identification of patients at risk for metastasis using a prognostic 31-gene expression profile in subpopulations of melanoma patients with favorable outcomes by standard criteria. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:149-157.
- Vetto JT, Hsueh EC, Gastman BR, et al. Guidance of sentinel lymph node biopsy decisions in patients with T1-T2 melanoma using gene expression profiling. Future Oncol. 2019;15:1207-1217.
- Brodie M, Park W. Active immunization against poliomyelitis. JAMA. 1935;105:1089-1093.
- Enders JF, Weller TH, Robbins FC. Cultivation of the Lansing strain of poliomyelitis virus in cultures of various human embryonic tissues. Science. 1949;109:85-87.
- Li J, Smalley I, Chen Z, et al. Single-cell characterization of the cellular landscape of acral melanoma identifies novel targets for immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28:2131-2146.
- Gorell E, Nguyen N, Lane A, et al. Gene therapy for skin diseases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014;4:A015149.
- Cavazza A, Mavilio F. Gene therapy of skin adhesion disorders (mini review). Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012;13:1868-1876.
- Abdul-Wahab A, Qasim W, McGrath JA. Gene therapies for inherited skin disorders. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2014;33:83-90.
- Bilousova G. Gene therapy for skin fragility diseases: the new generation. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:1634-1637.
- Feramisco JD, Sadreyev RI, Murray ML, et al. Phenotypic and enotypic analyses of genetic skin disease through the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) database. J Investig Derm. 2009;129:2628-2636.
- Parker JC, Rangu S, Grand KL, et al. Genetic skin disorders: the value of a multidisciplinary clinic. Am J Med Genet A. 2021;185:1159-1167.
- Richert B, Smits G. Clinical and molecular diagnosis of genodermatoses: review and perspectives. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:488-500.
- Green ED, Watson JD, Collins FS. Human genome project: twenty-five years of big biology. Nature. 2015;526:29-31.
- Saeidian AH, Youssefian L, Vahidnezhad H, et al. Research techniques made simple: whole-transcriptome sequencing by RNA-seq for diagnosis of monogenic disorders. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140:1117-1126.e1.
- Deutsch A, McLellan BN, Shinoda K. Single-cell transcriptomics in dermatology. JAAD Int. 2020;1:182-188.
- Liu Y, Wang H, Taylor M, et al. Classification of human chronic inflammatory skin disease based on single-cell immune profiling [published online April 15, 2022]. Sci Immunol. doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.abl9165
- Reimann JDR, Salim S, Velazquez EF, et al. Comparison of melanoma gene expression score with histopathology, fluorescence in situ hybridization, and SNP array for the classification of melanocytic neoplasms. Mod Pathol. 2018;31:1733-1743.
- Hillen LM, Geybels MS, Spassova I, et al. A digital mRNA expression signature to classify challenging spitzoid melanocytic neoplasms. FEBS Open Bio. 2020;10:1326-1341.
- Clarke LE, Flake DD 2nd, Busam K, et al. An independent validation of a gene expression signature to differentiate malignant melanoma from benign melanocytic nevi. Cancer. 2017;123:617-628.
- Stege H, Haist M, Nikfarjam U, et al. The status of adjuvant and neoadjuvant melanoma therapy, new developments and upcoming challenges. Target Oncol. 2021;16:537-552.
- Morrison S, Han D. Re-evaluation of sentinel lymph node biopsy for melanoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2021;22:22.
- Gerami P, Cook RW, Russell MC, et al. Gene expression profiling for molecular staging of cutaneous melanoma in patients with sentinel lymph node biopsy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:780-785.e3.
- Keller J, Schwartz TL, Lizalek JM, et al. Prospective validation of the prognostic 31-gene expression profiling test in primary cutaneous melanoma. Cancer Med. 2019;8:2205-2212.
- Gastman BR, Gerami P, Kurley SJ, et al. Identification of patients at risk for metastasis using a prognostic 31-gene expression profile in subpopulations of melanoma patients with favorable outcomes by standard criteria. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:149-157.
- Vetto JT, Hsueh EC, Gastman BR, et al. Guidance of sentinel lymph node biopsy decisions in patients with T1-T2 melanoma using gene expression profiling. Future Oncol. 2019;15:1207-1217.
- Brodie M, Park W. Active immunization against poliomyelitis. JAMA. 1935;105:1089-1093.
- Enders JF, Weller TH, Robbins FC. Cultivation of the Lansing strain of poliomyelitis virus in cultures of various human embryonic tissues. Science. 1949;109:85-87.
- Li J, Smalley I, Chen Z, et al. Single-cell characterization of the cellular landscape of acral melanoma identifies novel targets for immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28:2131-2146.
- Gorell E, Nguyen N, Lane A, et al. Gene therapy for skin diseases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014;4:A015149.
- Cavazza A, Mavilio F. Gene therapy of skin adhesion disorders (mini review). Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012;13:1868-1876.
- Abdul-Wahab A, Qasim W, McGrath JA. Gene therapies for inherited skin disorders. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2014;33:83-90.
- Bilousova G. Gene therapy for skin fragility diseases: the new generation. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:1634-1637.
Some decisions aren’t right or wrong; they’re just devastating
There is one situation, while not common, that is often among the most difficult for me: the person who must be told at diagnosis that they are already dying. I am still reminded of a patient I saw early in my career.
A woman in her 40s was admitted to the hospital complaining of severe shortness of breath. In retrospect, she had been sick for months. She had not sought help because she was young and thought it would pass – the results of a “bad bug” that she just couldn’t shake.
But in the past few weeks, the persistence of symptoms became associated with weight loss, profound fatigue, loss of appetite, and nausea.
By the time she was hospitalized she was emaciated, though she appeared pregnant – a sign of the fluid that had built up in her abdomen. Imaging showed that her abdomen was filled with disease (carcinomatosis) and her liver and lungs were nearly replaced with metastatic disease.
A biopsy revealed an aggressive cancer that had no identifying histologic marker: carcinoma, not otherwise specified, or cancer of unknown primary.
I still remember seeing her. She had a deer-in-headlights stare that held me as I approached. I introduced myself and sat down so we were eye to eye.
“Tell me what you know,” I said.
“I know I have cancer and they don’t know where it started. I know surgery is not an option and that’s why they’ve asked you to come. Whatever. I’m ready. I want to fight this because I know I can beat it,” she said.
I remember that she looked very sick; her thin face and arms contrasted with her large, distended abdomen. Her breathing was labored, her skin almost gray. For a moment I didn’t know what to say.
As doctors, we like to believe that our decisions are guided by data: the randomized trials and meta-analyses that set standards of care; phase 2 trials that establish evidence (or lack thereof) of activity; case-control studies that suggest the impacts of treatment; and at the very least, case studies that document that “N of 1” experience. We have expert panels and pathways that lay out what treatments we should be using to help ensure access to quality care in every clinic on every corner of every cancer center in the United States.
These data and pathways tell us objectively what we can expect from therapy, who is at most risk for toxicities, and profiles of patients for whom treatment is not likely to be of benefit. In an ideal world, this objectivity would help us help people decide on an approach. But life is not objective, and sometimes individualizing care is as important as data.
In this scenario, I knew only one thing: She was dying. She had an overwhelming tumor burden. But I still asked myself a question that many in, and outside of, oncology ask themselves: Could she be saved?
This question was made even more difficult because she was young. She had her whole life ahead of her. It seemed incongruous that she would be here now, facing the gravity of her situation.
Looking at her, I saw the person, not a data point in a trial or a statistic in a textbook. She was terrified. And she was not ready to die.
I sat down and reviewed what I knew about her cancer and what I did not know. I went through potential treatments we could try and the toxicities associated with each. I made clear that these treatments, based on how sick she was, could kill her.
“Whatever we do,” I said, “you do not have disease that I can cure.”
She cried then, realizing what a horrible situation she was in and that she would no longer go back to her normal life. Indeed, she seemed to grasp that she was probably facing the end of her life and that it could be short.
“My concern is,” I continued, “that treatment could do the exact opposite of what I hope it would do. It could kill you sooner than this cancer will.”
Instead of making a treatment plan, I decided that it would be best to come back another day, so I said my goodbyes and left. Still, I could not stop thinking about her and what I should suggest as her next steps.
I asked colleagues what they would suggest. Some recommended hospice care, others recommended treatment. Clearly, there was no one way to proceed.
One might wonder: Why is it so hard to do the right thing?
Ask any clinician and I think you will hear the same answer: Because we do not have the luxury of certainty.
Am I certain that this person will not benefit from intubation? Am I certain that she has only weeks to live? Am I sure that there are no treatments that will work?
The answer to these questions is no – I am not certain. It is that uncertainty that always makes me pause because it reminds me of my own humanity.
I stopped by the next day to see her surrounded by family. After some pleasantries I took the opportunity to reiterate much of our conversation from the other day. After some questions, I looked at her and asked if she wanted to talk more about her options. I was prepared to suggest treatment, anticipating that she would want it. Instead, she told me she didn’t want to proceed.
“I feel like I’m dying, and if what you have to give me isn’t going to cure me, then I’d prefer not to suffer while it happens. You said it’s up to me. I don’t want it.”
First, do no harm. It’s one of the tenets of medicine – to provide care that will benefit the people who have trusted us with their lives, whether that be longevity, relief of symptoms, or helping them achieve their last wishes. Throughout one’s life, goals might change but that edict remains the same.
But that can be difficult, especially in oncology and especially when one is not prepared for their own end of life. It can be hard for doctors to discuss the end of life; it’s easier to focus on the next treatment, instilling hope that there’s more that can be done. And there are people with end-stage cancer who insist on continuing treatment in the same circumstances, preferring to “die fighting” than to “give up.” Involving supportive and palliative care specialists early has helped in both situations, which is certainly a good thing.
We talked a while more and then arranged for our palliative care team to see her. I wish I could say I was at peace with her decision, but I wasn’t. The truth is, whatever she decided would probably have the same impact: I wouldn’t be able to stop thinking about it.
Dr. Dizon is professor of medicine, department of medicine, at Brown University and director of medical oncology at Rhode Island Hospital, both in Providence, R.I. He disclosed conflicts of interest with Regeneron, AstraZeneca, Clovis, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Kazia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There is one situation, while not common, that is often among the most difficult for me: the person who must be told at diagnosis that they are already dying. I am still reminded of a patient I saw early in my career.
A woman in her 40s was admitted to the hospital complaining of severe shortness of breath. In retrospect, she had been sick for months. She had not sought help because she was young and thought it would pass – the results of a “bad bug” that she just couldn’t shake.
But in the past few weeks, the persistence of symptoms became associated with weight loss, profound fatigue, loss of appetite, and nausea.
By the time she was hospitalized she was emaciated, though she appeared pregnant – a sign of the fluid that had built up in her abdomen. Imaging showed that her abdomen was filled with disease (carcinomatosis) and her liver and lungs were nearly replaced with metastatic disease.
A biopsy revealed an aggressive cancer that had no identifying histologic marker: carcinoma, not otherwise specified, or cancer of unknown primary.
I still remember seeing her. She had a deer-in-headlights stare that held me as I approached. I introduced myself and sat down so we were eye to eye.
“Tell me what you know,” I said.
“I know I have cancer and they don’t know where it started. I know surgery is not an option and that’s why they’ve asked you to come. Whatever. I’m ready. I want to fight this because I know I can beat it,” she said.
I remember that she looked very sick; her thin face and arms contrasted with her large, distended abdomen. Her breathing was labored, her skin almost gray. For a moment I didn’t know what to say.
As doctors, we like to believe that our decisions are guided by data: the randomized trials and meta-analyses that set standards of care; phase 2 trials that establish evidence (or lack thereof) of activity; case-control studies that suggest the impacts of treatment; and at the very least, case studies that document that “N of 1” experience. We have expert panels and pathways that lay out what treatments we should be using to help ensure access to quality care in every clinic on every corner of every cancer center in the United States.
These data and pathways tell us objectively what we can expect from therapy, who is at most risk for toxicities, and profiles of patients for whom treatment is not likely to be of benefit. In an ideal world, this objectivity would help us help people decide on an approach. But life is not objective, and sometimes individualizing care is as important as data.
In this scenario, I knew only one thing: She was dying. She had an overwhelming tumor burden. But I still asked myself a question that many in, and outside of, oncology ask themselves: Could she be saved?
This question was made even more difficult because she was young. She had her whole life ahead of her. It seemed incongruous that she would be here now, facing the gravity of her situation.
Looking at her, I saw the person, not a data point in a trial or a statistic in a textbook. She was terrified. And she was not ready to die.
I sat down and reviewed what I knew about her cancer and what I did not know. I went through potential treatments we could try and the toxicities associated with each. I made clear that these treatments, based on how sick she was, could kill her.
“Whatever we do,” I said, “you do not have disease that I can cure.”
She cried then, realizing what a horrible situation she was in and that she would no longer go back to her normal life. Indeed, she seemed to grasp that she was probably facing the end of her life and that it could be short.
“My concern is,” I continued, “that treatment could do the exact opposite of what I hope it would do. It could kill you sooner than this cancer will.”
Instead of making a treatment plan, I decided that it would be best to come back another day, so I said my goodbyes and left. Still, I could not stop thinking about her and what I should suggest as her next steps.
I asked colleagues what they would suggest. Some recommended hospice care, others recommended treatment. Clearly, there was no one way to proceed.
One might wonder: Why is it so hard to do the right thing?
Ask any clinician and I think you will hear the same answer: Because we do not have the luxury of certainty.
Am I certain that this person will not benefit from intubation? Am I certain that she has only weeks to live? Am I sure that there are no treatments that will work?
The answer to these questions is no – I am not certain. It is that uncertainty that always makes me pause because it reminds me of my own humanity.
I stopped by the next day to see her surrounded by family. After some pleasantries I took the opportunity to reiterate much of our conversation from the other day. After some questions, I looked at her and asked if she wanted to talk more about her options. I was prepared to suggest treatment, anticipating that she would want it. Instead, she told me she didn’t want to proceed.
“I feel like I’m dying, and if what you have to give me isn’t going to cure me, then I’d prefer not to suffer while it happens. You said it’s up to me. I don’t want it.”
First, do no harm. It’s one of the tenets of medicine – to provide care that will benefit the people who have trusted us with their lives, whether that be longevity, relief of symptoms, or helping them achieve their last wishes. Throughout one’s life, goals might change but that edict remains the same.
But that can be difficult, especially in oncology and especially when one is not prepared for their own end of life. It can be hard for doctors to discuss the end of life; it’s easier to focus on the next treatment, instilling hope that there’s more that can be done. And there are people with end-stage cancer who insist on continuing treatment in the same circumstances, preferring to “die fighting” than to “give up.” Involving supportive and palliative care specialists early has helped in both situations, which is certainly a good thing.
We talked a while more and then arranged for our palliative care team to see her. I wish I could say I was at peace with her decision, but I wasn’t. The truth is, whatever she decided would probably have the same impact: I wouldn’t be able to stop thinking about it.
Dr. Dizon is professor of medicine, department of medicine, at Brown University and director of medical oncology at Rhode Island Hospital, both in Providence, R.I. He disclosed conflicts of interest with Regeneron, AstraZeneca, Clovis, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Kazia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There is one situation, while not common, that is often among the most difficult for me: the person who must be told at diagnosis that they are already dying. I am still reminded of a patient I saw early in my career.
A woman in her 40s was admitted to the hospital complaining of severe shortness of breath. In retrospect, she had been sick for months. She had not sought help because she was young and thought it would pass – the results of a “bad bug” that she just couldn’t shake.
But in the past few weeks, the persistence of symptoms became associated with weight loss, profound fatigue, loss of appetite, and nausea.
By the time she was hospitalized she was emaciated, though she appeared pregnant – a sign of the fluid that had built up in her abdomen. Imaging showed that her abdomen was filled with disease (carcinomatosis) and her liver and lungs were nearly replaced with metastatic disease.
A biopsy revealed an aggressive cancer that had no identifying histologic marker: carcinoma, not otherwise specified, or cancer of unknown primary.
I still remember seeing her. She had a deer-in-headlights stare that held me as I approached. I introduced myself and sat down so we were eye to eye.
“Tell me what you know,” I said.
“I know I have cancer and they don’t know where it started. I know surgery is not an option and that’s why they’ve asked you to come. Whatever. I’m ready. I want to fight this because I know I can beat it,” she said.
I remember that she looked very sick; her thin face and arms contrasted with her large, distended abdomen. Her breathing was labored, her skin almost gray. For a moment I didn’t know what to say.
As doctors, we like to believe that our decisions are guided by data: the randomized trials and meta-analyses that set standards of care; phase 2 trials that establish evidence (or lack thereof) of activity; case-control studies that suggest the impacts of treatment; and at the very least, case studies that document that “N of 1” experience. We have expert panels and pathways that lay out what treatments we should be using to help ensure access to quality care in every clinic on every corner of every cancer center in the United States.
These data and pathways tell us objectively what we can expect from therapy, who is at most risk for toxicities, and profiles of patients for whom treatment is not likely to be of benefit. In an ideal world, this objectivity would help us help people decide on an approach. But life is not objective, and sometimes individualizing care is as important as data.
In this scenario, I knew only one thing: She was dying. She had an overwhelming tumor burden. But I still asked myself a question that many in, and outside of, oncology ask themselves: Could she be saved?
This question was made even more difficult because she was young. She had her whole life ahead of her. It seemed incongruous that she would be here now, facing the gravity of her situation.
Looking at her, I saw the person, not a data point in a trial or a statistic in a textbook. She was terrified. And she was not ready to die.
I sat down and reviewed what I knew about her cancer and what I did not know. I went through potential treatments we could try and the toxicities associated with each. I made clear that these treatments, based on how sick she was, could kill her.
“Whatever we do,” I said, “you do not have disease that I can cure.”
She cried then, realizing what a horrible situation she was in and that she would no longer go back to her normal life. Indeed, she seemed to grasp that she was probably facing the end of her life and that it could be short.
“My concern is,” I continued, “that treatment could do the exact opposite of what I hope it would do. It could kill you sooner than this cancer will.”
Instead of making a treatment plan, I decided that it would be best to come back another day, so I said my goodbyes and left. Still, I could not stop thinking about her and what I should suggest as her next steps.
I asked colleagues what they would suggest. Some recommended hospice care, others recommended treatment. Clearly, there was no one way to proceed.
One might wonder: Why is it so hard to do the right thing?
Ask any clinician and I think you will hear the same answer: Because we do not have the luxury of certainty.
Am I certain that this person will not benefit from intubation? Am I certain that she has only weeks to live? Am I sure that there are no treatments that will work?
The answer to these questions is no – I am not certain. It is that uncertainty that always makes me pause because it reminds me of my own humanity.
I stopped by the next day to see her surrounded by family. After some pleasantries I took the opportunity to reiterate much of our conversation from the other day. After some questions, I looked at her and asked if she wanted to talk more about her options. I was prepared to suggest treatment, anticipating that she would want it. Instead, she told me she didn’t want to proceed.
“I feel like I’m dying, and if what you have to give me isn’t going to cure me, then I’d prefer not to suffer while it happens. You said it’s up to me. I don’t want it.”
First, do no harm. It’s one of the tenets of medicine – to provide care that will benefit the people who have trusted us with their lives, whether that be longevity, relief of symptoms, or helping them achieve their last wishes. Throughout one’s life, goals might change but that edict remains the same.
But that can be difficult, especially in oncology and especially when one is not prepared for their own end of life. It can be hard for doctors to discuss the end of life; it’s easier to focus on the next treatment, instilling hope that there’s more that can be done. And there are people with end-stage cancer who insist on continuing treatment in the same circumstances, preferring to “die fighting” than to “give up.” Involving supportive and palliative care specialists early has helped in both situations, which is certainly a good thing.
We talked a while more and then arranged for our palliative care team to see her. I wish I could say I was at peace with her decision, but I wasn’t. The truth is, whatever she decided would probably have the same impact: I wouldn’t be able to stop thinking about it.
Dr. Dizon is professor of medicine, department of medicine, at Brown University and director of medical oncology at Rhode Island Hospital, both in Providence, R.I. He disclosed conflicts of interest with Regeneron, AstraZeneca, Clovis, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Kazia.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
De-pathologizing gender identity: Psychiatry’s role
Treating patients who are transgender or gender diverse (TGGD) requires an understanding of the social and psychological factors that have a unique impact on this population. As clinicians, it is our responsibility to understand the social, cultural, and political issues our patients face, both historically and currently. In this article, we provide information about the nature of gender and gender identity as separate from biological sex and informed by a person’s perception of self as male, female, nonbinary, or other variation.
Psychiatrists must be aware of how individuals who are TGGD have been perceived, classified, and treated by the medical profession, as this history is often a source of mistrust and a barrier to treatment for patients who need psychiatric care. This includes awareness of the “gatekeeping” role that persists in medical institutions today: applying strict eligibility criteria to determine the “fitness” of individuals who are transgender to pursue medical transition, as compared to the informed-consent model that is widely applied to other medical interventions. Our review of minority stress theory, as applicable to this patient population, provides a context and framework for empathic approaches to care for patients who are TGGD. Recognizing barriers to care and ways in which we can create a supportive environment for treatment will allow for tailored approaches that better fit the unique needs of this patient population.
The gender binary
In Western societies, gender has often been viewed as “binary,” oppositional, and directly correlated with physical sex or presumed anatomy.1 The theory of gender essentialism insists that sex and gender are indistinguishable from one another and provide 2 “natural” and distinct categories: women and men. The “gender/sex” binary refers to the belief that individuals born with 2 X chromosomes will inherently develop into and fulfill the social roles of women, and those born with an X and a Y chromosome will develop into and fulfill the social roles of men.1 In this context, “sex” refers to biological characteristics of individuals, including combinations of sex chromosomes, anatomy, and the development of sex characteristics during puberty. The term “gender” refers to the social, cultural, and behavioral aspects of being a man, woman, both, or neither, and “gender identity” refers to one’s internal, individual sense of self and experience of gender (Figure 12). Many Western cultures are now facing destabilization of the gender/sex binary in social, political, and interpersonal contexts.1 This is perhaps most clearly seen in the battle for self-determination and protection by laws affecting individuals who are transgender as well as the determination of other groups to maintain traditional sex and gender roles, often through political action. Historically, individuals who are TGGD have been present in a variety of cultures. For example, most Native American cultures have revered other-gendered individuals, more recently referred to as “two-spirited.” Similarly, the Bugis people of South Sulawesi, Indonesia, recognize 5 genders that exist on a nonbinary spectrum.3
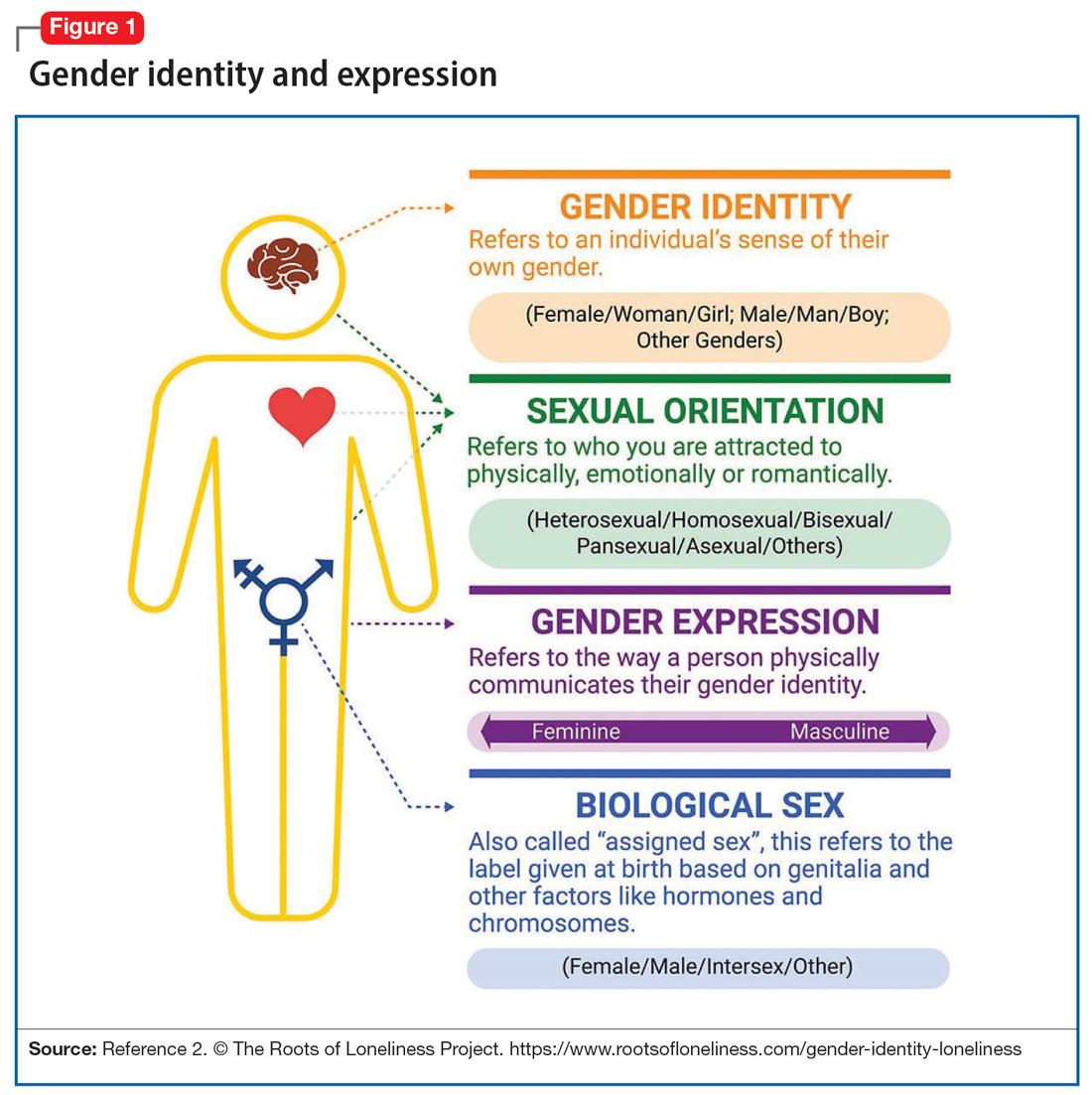
Despite its prevalence in Western society, scientific evidence for the gender/sex binary is lacking. The gender similarities hypothesis states that males and females are similar in most, but not all, psychological variables and is supported by multiple meta-analyses examining psychological gender differences.4 In a 2005 review of 46 meta-analyses of gender-differences, studied through behavior analysis, effect sizes for gender differences were trivial or small in almost 75% of examined variables.5 Analyzing for internal consistency among studies showing large gender/sex differences, Joel et al6 found that, on measures of personality traits, attitudes, interests, and behaviors were rarely homogenous in the brains of males or females. In fact, <1% of study participants showed only masculine or feminine traits, whereas 55% showed a combination, or mosaic, of these traits.6 These findings were supported by further research in behavioral neuroendocrinology that demonstrated a lack of hormonal evidence for 2 distinct sexes. Both estrogen (the “female” hormone) and testosterone (the “male” hormone) are produced by both biological males and females. Further, levels of estradiol do not significantly differ between males and females, and, in fact, in nonpregnant females, estradiol levels are more similar to those of males than to those of pregnant females.1 In the last decade, imaging studies of the human brain have shown that brain structure and connectivity in individuals who are transgender are more similar to those of their experienced gender than of their natal sex.7 In social analyses of intersex individuals (individuals born with ambiguous physical sex characteristics), surgical assignment into the binary gender system did not improve—and often worsened—feelings of isolation and shame.1
The National Institutes of Health defines gender as “socially constructed and enacted roles and behaviors which occur in a historical and cultural context and vary across societies and time.”8 The World Health Organization (WHO) provides a similar definition, and the evidence to support this exists in social-role theory, social-identity theory, and the stereotype-content model. However, despite evidence disputing a gender/sex binary, this method of classifying individuals into a dyad persists in many areas of modern culture, from gender-specific physical spaces (bathrooms, classrooms, store brands), language (pronouns), and laws. This desire for categorization helps fulfill social and psychological needs of groups and individuals by providing group identities and giving structure to the complexity of modern-day life. Identity and group membership provide a sense of belonging, source of self-esteem, and avoidance of ambiguity. Binary gender stereotypes provide expectations that allow anticipation and prediction of our social environments.9 However, the harm of perpetuating the false gender/sex binary is well documented and includes social and economic penalties, extreme violence, and even death. The field of medicine has not been immune from practices that implicitly endorse the gender/sex connection, as seen in the erroneous use of gender in biomedical writings at the highest levels and evidenced in research examining “gender” differences in disease incidence.
Gender diversity as a pathology
The American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) has been a source of pathologizing gender diversity since the 1960s, with the introduction of “transsexualism” in DSM-II10 and “gender identity disorder of childhood” in DSM-III.11 These diagnoses were listed under the headings of “sexual deviations” and “psychosexual disorders” in the respective DSM editions. This illustrates how gender diversity was viewed as a mental illness/defect. As the DSM developed through various revisions, so have these diagnoses. DSM-IV used the diagnosis “gender identity disorder.”12 Psychiatry has evolved away from this line of thinking by focusing on the distress from biological sex characteristics that are “incongruent” with an individual’s gender identity, leading to the development of the gender dysphoria diagnosis.13 While this has been a positive step in psychiatry’s efforts to de-pathologize individuals who are gender-diverse, it raises the question: should such diagnoses be included in the DSM at all?
The gender dysphoria diagnosis continues to be needed by many individuals who are TGGD in order to access gender-affirming health care services. Mental health professionals are placed in a gatekeeping role by the expectation that they provide letters of “support” to indicate an individual is of sound mind and consistent gender identity to have services covered by insurance providers. In this way, the insurance industry and the field of medicine continue to believe that individuals who are TGGD need psychiatric permission and/or counsel regarding their gender identity. This can place psychiatry in a role of controlling access to necessary care while also creating a possible distrust in our ability to provide care to patients who are gender-diverse. This is particularly problematic given the high rates of depression, anxiety, trauma, and substance use within these communities.14 In the WHO’s ICD-11, gender dysphoria was changed to gender incongruence and is contained in the category of “Conditions related to sexual health.”15 This indicates continued evolution of how medicine views individuals who are TGGD, and offers hope that psychiatry and the DSM will follow suit.
Continue to: Minority stress theory
Minority stress theory
Ilan Meyer’s minority stress theory explores how cultural and social factors impact mental health functioning (Figure 216). Minority stress theory, which was originally developed for what at the time was described as the lesbian, gay, and bisexual communities, purports that the higher prevalence of mental health disorders among such individuals is likely due to social stigma, discrimination, and stressors associated with minority status. More recently, minority stress theory has been expanded to provide framework for individuals who are TGGD. Hendricks et al17 explain how distal, proximal, and resilience factors contribute to mental health outcomes among these individuals. Distal factors, such as gender-related discrimination, harassment, violence, and rejection, explain how systemic, cultural, and environmental events lead to overt stress. Proximal factors consist of an individual’s expectation and anticipation of negative and stressful events and the internalization of negative attitudes and prejudice (ie, internalized transphobia). Resilience factors consist of community connectedness and within-group identification and can help mediate the negative effects of distal and proximal factors.
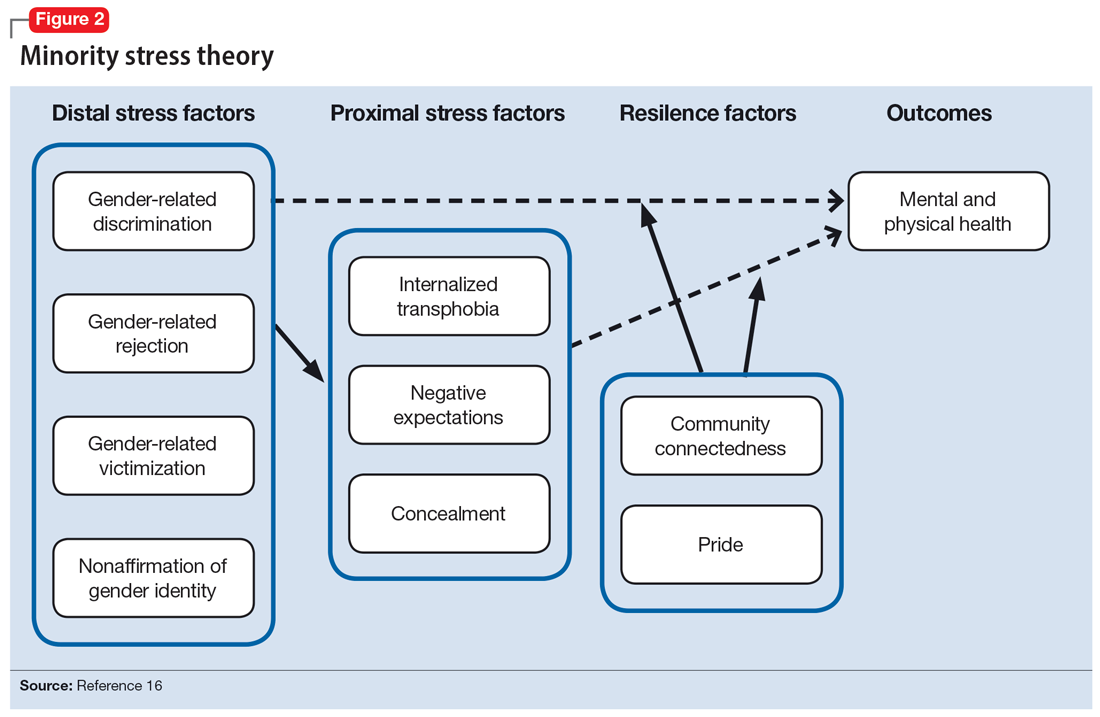
As clinicians, understanding our patients’ experiences and expectations can help us better engage with them and create an environment of safety and healing. Minority stress theory framework suggests that patients may start treatment with distrust or suspicion in light of previous negative experiences. They may also be likely to expect clinicians to be judgmental or to lack understanding of them. The 2015 US Transgender Survey found that 33% of individuals who are TGGD who sought medical treatment in the past year had at least 1 negative experience related to their gender identity (Table 118). Twenty-four percent reported having to educate their clinician about people who are TGGD, while 15% reported the health care professional asked invasive or unnecessary questions about their gender status that were unrelated to their visit. While psychiatry is often distinct from the larger medical field, it is important to understand the negative encounters individuals who are TGGD have likely experienced in medicine, and how those events may skew their feelings about psychiatric treatment. This is especially salient given the higher prevalence of various psychiatric disorders among individuals who are TGGD.18
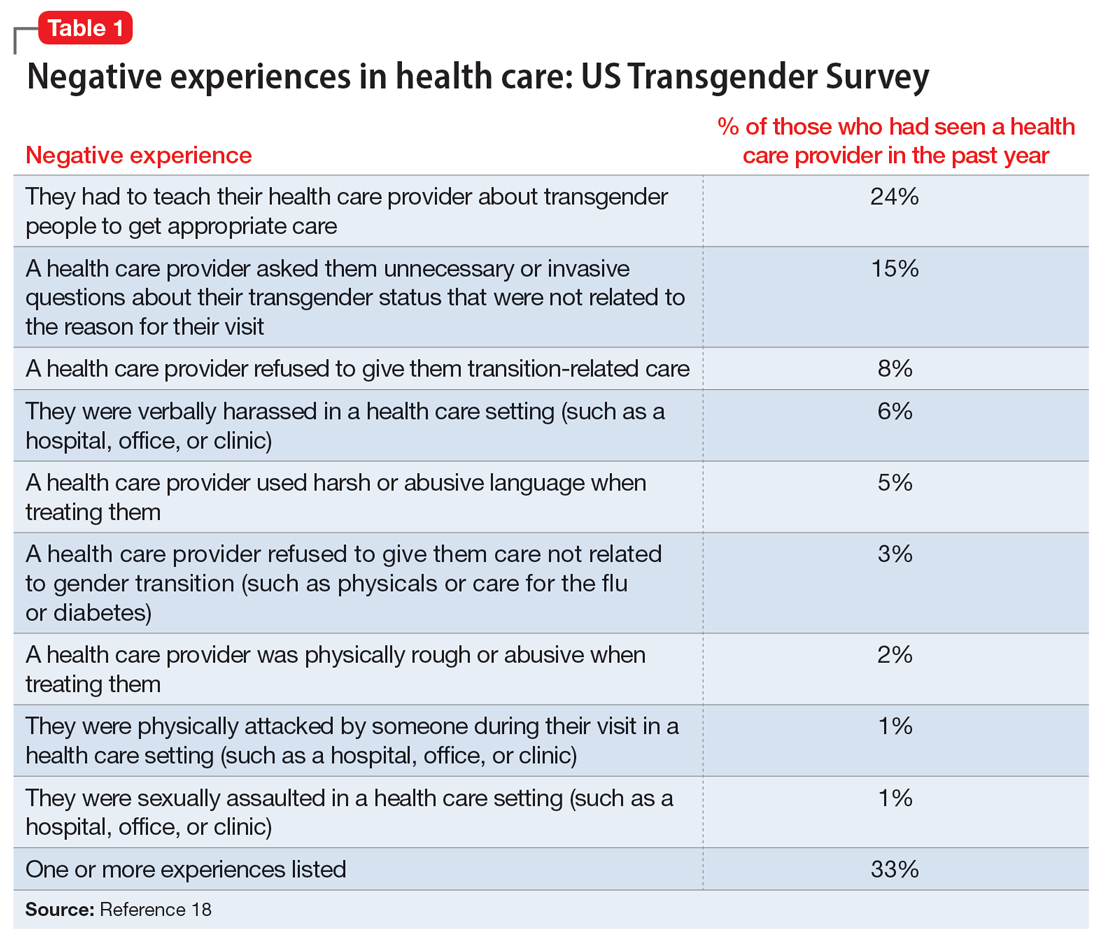
According to the US Transgender Survey, 39% of participants were currently experiencing serious psychological distress, which is nearly 8 times the rate in the US population (5%).18 When extrapolated, this data indicates that we in psychiatry are likely to work with individuals who identify as TGGD, regardless of our expertise. Additionally, research indicates that having access to gender-affirming care—such as hormone replacement therapy, gender-affirming surgery, voice therapy, and other treatments—greatly improves mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and suicidality among individuals who are TGGD.19,20 It is in this way we in psychiatry must do more than just care for our patients by becoming advocates for them to receive the care they need and deserve. While at times we may want to stay out of politics and other public discourse, it is becoming increasingly necessary as health care is entrenched in politics.
Clinical applicability
Because individuals who are TGGD experience higher rates of depression, anxiety, substance use, and other psychiatric disorders,14 it is increasingly likely that many clinicians will be presented with opportunities to treat such individuals. Despite high rates of psychiatric disorders, individuals who are TGGD often avoid treatment due to concerns about being pathologized, stereotyped, and/or encountering professionals who lack the knowledge to treat them as they are.21 Several studies recommend clinicians better equip themselves to appropriately provide services to individuals who are TGGD.21 Some advise seeking education to understand the unique needs of these patients and to help stay current with appropriate terminology and language (Table 222). This also implies not relying on patients to educate clinicians in understanding their specific needs and experiences.
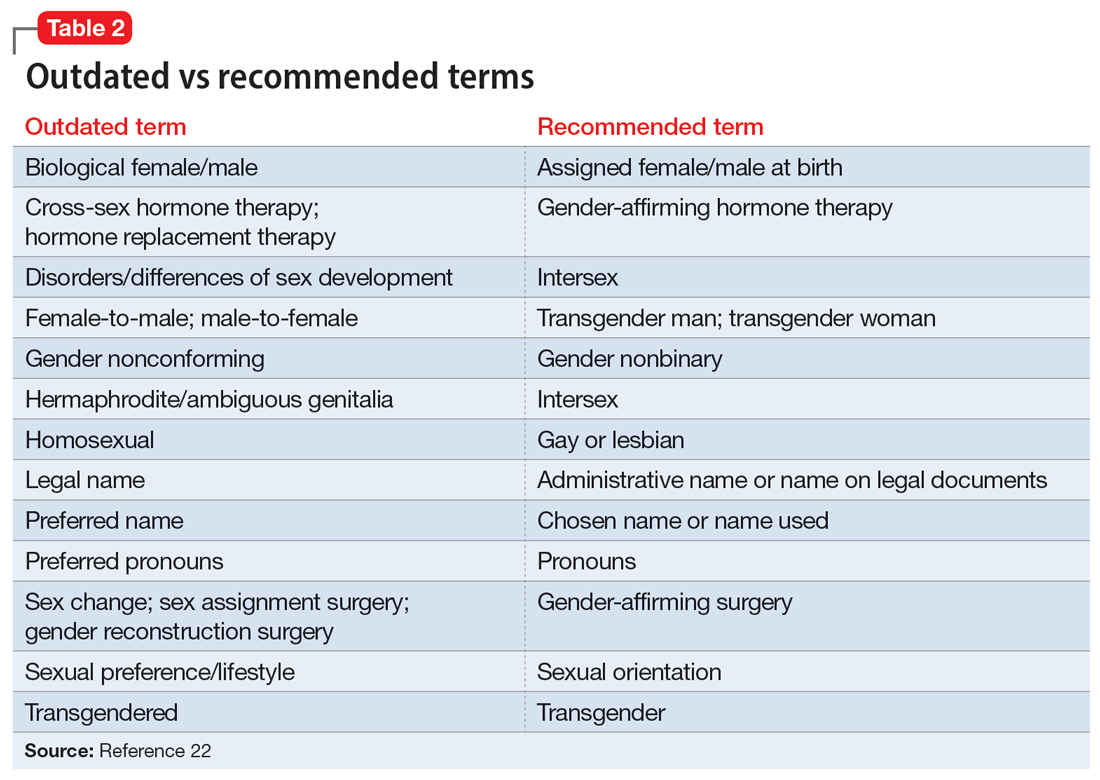
Making assumptions about a patient’s identity is one of the most commonly reported issues by individuals who are TGGD. Therefore, it is critical to avoid making assumptions about patients based on binary stereotypes.23,24 We can circumvent these mistakes by asking every patient for their name and pronouns, and introducing ourselves with our pronouns. This illustrates an openness and understanding of the importance of identity and language, and makes it common practice from the outset. Integrating the use of gender-neutral language into paperwork, intake forms, charting, and conversation will also help avoid the pitfalls of misgendering and making false assumptions. This will also allow for support staff, medical assistants, and others to use correct language with patients. Having a patient’s used name and pronouns visible for everyone who works with the patient is necessary to effectively meet the patient’s needs. Additionally, understanding that the range of experiences and needs for individuals who are TGGD is heterogeneous can help reduce assumptions and ensure we are asking for needed information. It is also important to ask for only relevant information needed to provide treatment.
Continue to: Resources are widely available...
Resources are widely available to aid in the care of individuals who are TGGD. In 2022, the World Professional Association for Transgender Health released new guidelines—Standards of Care 8—for working with individuals who are TGGD.25 While these standards include a section dedicated to mental health, they also provide guidelines on education, assessments, specific demographic groups, hormone therapy, primary care, and sexual health. Additionally, while we may not want the role of gatekeeping for individuals to receive gender-affirming care, we work within a health care and insurance system that continues to require psychiatric assessment for such surgeries. In this role, we must do our part to educate ourselves in how to best provide these assessments and letters of support to help patients receive appropriate and life-saving care.
Finally, in order to provide a more comfortable and affirming space for individuals who are TGGD, develop ways to self-assess and monitor the policies, procedures, and language used within your practice, clinic, or institution. Monitoring the language used in charting to ensure consistency with the individual’s gender identity is important for our own understanding of the patient, and for patients to feel seen. This is especially true given patients’ access to medical records under the Cures Act. Moreover, it is essential to be cognizant of how you present clients to others in consultation or care coordination to ensure the patient is identified correctly and consistently by clinicians and staff.
Bottom Line
Understanding the social, cultural, and medical discrimination faced by patients who are transgender or gender diverse can make us better suited to engage and treat these individuals in an affirming and supportive way.
Related Resources
- World Professional Association of Transgender Health (WPATH) Standards of Care—8th edition. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/26895269.2022.2100644
- The Fenway Institute: National LGBTQIA+ Health Education Center. https://fenwayhealth.org/the-fenway-institute/education/the-national-lgbtia-health-education-center/
1. Morgenroth T, Ryan MK. The effects of gender trouble: an integrative theoretical framework of the perpetuation and disruption of the gender/sex binary. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2021;16(6):1113-1142. doi:10.1177/1745691620902442
2. The Roots of Loneliness Project. Accessed April 8, 2023. https://www.rootsofloneliness.com/gender-identity-loneliness
3. Davies SG. Challenging Gender Norms: Five Genders Among Bugis in Indonesia. Thomson Wadsworth; 2007.
4. Hyde JS. The gender similarities hypothesis. Am Psychol. 2005;60(6):581-592. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.60.6.581
5. Joel D. Beyond the binary: rethinking sex and the brain. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021;122:165-175. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.22.018
6. Joel D, Berman Z, Tavor I, et al. Sex beyond the genitalia: the human brain mosaic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(50):15468-15473. doi:10.1073/pnas.1509654112
7. Palmer BF, Clegg DJ. A universally accepted definition of gender will positively impact societal understanding, acceptance, and appropriateness of health care. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95(10):2235-2243. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.01.031
8. Office of Research on Women’s Health. Sex & Gender. National Institutes of Health. Accessed April 6, 2023. https://orwh.od.nih.gov/sex-gender
9. Morgenroth T, Sendén MG, Lindqvist A, et al. Defending the sex/gender binary: the role of gender identification and need for closure. Soc Psychol Pers Sci. 2021;12(5):731-740.
10. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 2nd ed. American Psychiatric Association; 1968.
11. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association; 1980.
12. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
13. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
14. Wanta JW, Niforatos JD, Durbak E, et al. Mental health diagnoses among transgender patients in the clinical setting: an all-payer electronic health record study. Transgend Health. 2019;4(1):313-315.
15. World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases. 11th ed. World Health Organization; 2019.
16. Meyer IH. Prejudice, social stress, and mental health in lesbian, gay, and bisexual populations: conceptual issues and research evidence. Psychol Bull. 2003;129(5):674-697. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.129.5.674
17. Hendricks ML, Testa RJ. A conceptual framework for clinical work with transgender and gender nonconforming clients: an adaptation of the Minority Stress Model. Profess Psychol: Res Pract. 2012;43(5):460-467. doi:10.1037/a0029597
18. James SE, Herman J, Keisling M, et al. The Report of the 2015 U.S. Transgender Survey. National Center for Transgender Equality; 2016. Accessed April 6, 2023. https://transequality.org/sites/default/files/docs/usts/USTS-Full-Report-Dec17.pdf
19. Almazan AN, Keuroghlian AS. Association between gender-affirming surgeries and mental health outcomes. JAMA Surg. 2021;156(7):611-618. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2021.0952
20. Tordoff DM, Wanta JW, Collin A, et al. Mental health outcomes in transgender and nonbinary youths receiving gender-affirming care. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(2):e220978. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.0978
21. Snow A, Cerel J, Loeffler DN, et al. Barriers to mental health care for transgender and gender-nonconforming adults: a systematic literature review. Health Soc Work. 2019;44(3):149-155. doi:10.1093/hsw/hlz016
22. National LGBTQIA+ Health Education Center. Accessed April 8, 2023. https://www.lgbtqiahealtheducation.org
23. Baldwin A, Dodge B, Schick VR, et al. Transgender and genderqueer individuals’ experiences with health care providers: what’s working, what’s not, and where do we go from here? J Health Care Poor Underserved. 2018;29(4):1300-1318. doi:10.1353/hpu.2018.0097
24. Kcomt L, Gorey KM, Barrett BJ, et al. Healthcare avoidance due to anticipated discrimination among transgender people: a call to create trans-affirmative environments. SSM-Popul Health. 2020;11:100608. doi:10.1016/j.ssmph.2020.100608
25. Coleman E, Radix AE, Bouman WP, et al. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, version 8. Int J Transgender Health. 2022;23(Suppl 1):S1-S259.
Treating patients who are transgender or gender diverse (TGGD) requires an understanding of the social and psychological factors that have a unique impact on this population. As clinicians, it is our responsibility to understand the social, cultural, and political issues our patients face, both historically and currently. In this article, we provide information about the nature of gender and gender identity as separate from biological sex and informed by a person’s perception of self as male, female, nonbinary, or other variation.
Psychiatrists must be aware of how individuals who are TGGD have been perceived, classified, and treated by the medical profession, as this history is often a source of mistrust and a barrier to treatment for patients who need psychiatric care. This includes awareness of the “gatekeeping” role that persists in medical institutions today: applying strict eligibility criteria to determine the “fitness” of individuals who are transgender to pursue medical transition, as compared to the informed-consent model that is widely applied to other medical interventions. Our review of minority stress theory, as applicable to this patient population, provides a context and framework for empathic approaches to care for patients who are TGGD. Recognizing barriers to care and ways in which we can create a supportive environment for treatment will allow for tailored approaches that better fit the unique needs of this patient population.
The gender binary
In Western societies, gender has often been viewed as “binary,” oppositional, and directly correlated with physical sex or presumed anatomy.1 The theory of gender essentialism insists that sex and gender are indistinguishable from one another and provide 2 “natural” and distinct categories: women and men. The “gender/sex” binary refers to the belief that individuals born with 2 X chromosomes will inherently develop into and fulfill the social roles of women, and those born with an X and a Y chromosome will develop into and fulfill the social roles of men.1 In this context, “sex” refers to biological characteristics of individuals, including combinations of sex chromosomes, anatomy, and the development of sex characteristics during puberty. The term “gender” refers to the social, cultural, and behavioral aspects of being a man, woman, both, or neither, and “gender identity” refers to one’s internal, individual sense of self and experience of gender (Figure 12). Many Western cultures are now facing destabilization of the gender/sex binary in social, political, and interpersonal contexts.1 This is perhaps most clearly seen in the battle for self-determination and protection by laws affecting individuals who are transgender as well as the determination of other groups to maintain traditional sex and gender roles, often through political action. Historically, individuals who are TGGD have been present in a variety of cultures. For example, most Native American cultures have revered other-gendered individuals, more recently referred to as “two-spirited.” Similarly, the Bugis people of South Sulawesi, Indonesia, recognize 5 genders that exist on a nonbinary spectrum.3

Despite its prevalence in Western society, scientific evidence for the gender/sex binary is lacking. The gender similarities hypothesis states that males and females are similar in most, but not all, psychological variables and is supported by multiple meta-analyses examining psychological gender differences.4 In a 2005 review of 46 meta-analyses of gender-differences, studied through behavior analysis, effect sizes for gender differences were trivial or small in almost 75% of examined variables.5 Analyzing for internal consistency among studies showing large gender/sex differences, Joel et al6 found that, on measures of personality traits, attitudes, interests, and behaviors were rarely homogenous in the brains of males or females. In fact, <1% of study participants showed only masculine or feminine traits, whereas 55% showed a combination, or mosaic, of these traits.6 These findings were supported by further research in behavioral neuroendocrinology that demonstrated a lack of hormonal evidence for 2 distinct sexes. Both estrogen (the “female” hormone) and testosterone (the “male” hormone) are produced by both biological males and females. Further, levels of estradiol do not significantly differ between males and females, and, in fact, in nonpregnant females, estradiol levels are more similar to those of males than to those of pregnant females.1 In the last decade, imaging studies of the human brain have shown that brain structure and connectivity in individuals who are transgender are more similar to those of their experienced gender than of their natal sex.7 In social analyses of intersex individuals (individuals born with ambiguous physical sex characteristics), surgical assignment into the binary gender system did not improve—and often worsened—feelings of isolation and shame.1
The National Institutes of Health defines gender as “socially constructed and enacted roles and behaviors which occur in a historical and cultural context and vary across societies and time.”8 The World Health Organization (WHO) provides a similar definition, and the evidence to support this exists in social-role theory, social-identity theory, and the stereotype-content model. However, despite evidence disputing a gender/sex binary, this method of classifying individuals into a dyad persists in many areas of modern culture, from gender-specific physical spaces (bathrooms, classrooms, store brands), language (pronouns), and laws. This desire for categorization helps fulfill social and psychological needs of groups and individuals by providing group identities and giving structure to the complexity of modern-day life. Identity and group membership provide a sense of belonging, source of self-esteem, and avoidance of ambiguity. Binary gender stereotypes provide expectations that allow anticipation and prediction of our social environments.9 However, the harm of perpetuating the false gender/sex binary is well documented and includes social and economic penalties, extreme violence, and even death. The field of medicine has not been immune from practices that implicitly endorse the gender/sex connection, as seen in the erroneous use of gender in biomedical writings at the highest levels and evidenced in research examining “gender” differences in disease incidence.
Gender diversity as a pathology
The American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) has been a source of pathologizing gender diversity since the 1960s, with the introduction of “transsexualism” in DSM-II10 and “gender identity disorder of childhood” in DSM-III.11 These diagnoses were listed under the headings of “sexual deviations” and “psychosexual disorders” in the respective DSM editions. This illustrates how gender diversity was viewed as a mental illness/defect. As the DSM developed through various revisions, so have these diagnoses. DSM-IV used the diagnosis “gender identity disorder.”12 Psychiatry has evolved away from this line of thinking by focusing on the distress from biological sex characteristics that are “incongruent” with an individual’s gender identity, leading to the development of the gender dysphoria diagnosis.13 While this has been a positive step in psychiatry’s efforts to de-pathologize individuals who are gender-diverse, it raises the question: should such diagnoses be included in the DSM at all?
The gender dysphoria diagnosis continues to be needed by many individuals who are TGGD in order to access gender-affirming health care services. Mental health professionals are placed in a gatekeeping role by the expectation that they provide letters of “support” to indicate an individual is of sound mind and consistent gender identity to have services covered by insurance providers. In this way, the insurance industry and the field of medicine continue to believe that individuals who are TGGD need psychiatric permission and/or counsel regarding their gender identity. This can place psychiatry in a role of controlling access to necessary care while also creating a possible distrust in our ability to provide care to patients who are gender-diverse. This is particularly problematic given the high rates of depression, anxiety, trauma, and substance use within these communities.14 In the WHO’s ICD-11, gender dysphoria was changed to gender incongruence and is contained in the category of “Conditions related to sexual health.”15 This indicates continued evolution of how medicine views individuals who are TGGD, and offers hope that psychiatry and the DSM will follow suit.
Continue to: Minority stress theory
Minority stress theory
Ilan Meyer’s minority stress theory explores how cultural and social factors impact mental health functioning (Figure 216). Minority stress theory, which was originally developed for what at the time was described as the lesbian, gay, and bisexual communities, purports that the higher prevalence of mental health disorders among such individuals is likely due to social stigma, discrimination, and stressors associated with minority status. More recently, minority stress theory has been expanded to provide framework for individuals who are TGGD. Hendricks et al17 explain how distal, proximal, and resilience factors contribute to mental health outcomes among these individuals. Distal factors, such as gender-related discrimination, harassment, violence, and rejection, explain how systemic, cultural, and environmental events lead to overt stress. Proximal factors consist of an individual’s expectation and anticipation of negative and stressful events and the internalization of negative attitudes and prejudice (ie, internalized transphobia). Resilience factors consist of community connectedness and within-group identification and can help mediate the negative effects of distal and proximal factors.

As clinicians, understanding our patients’ experiences and expectations can help us better engage with them and create an environment of safety and healing. Minority stress theory framework suggests that patients may start treatment with distrust or suspicion in light of previous negative experiences. They may also be likely to expect clinicians to be judgmental or to lack understanding of them. The 2015 US Transgender Survey found that 33% of individuals who are TGGD who sought medical treatment in the past year had at least 1 negative experience related to their gender identity (Table 118). Twenty-four percent reported having to educate their clinician about people who are TGGD, while 15% reported the health care professional asked invasive or unnecessary questions about their gender status that were unrelated to their visit. While psychiatry is often distinct from the larger medical field, it is important to understand the negative encounters individuals who are TGGD have likely experienced in medicine, and how those events may skew their feelings about psychiatric treatment. This is especially salient given the higher prevalence of various psychiatric disorders among individuals who are TGGD.18

According to the US Transgender Survey, 39% of participants were currently experiencing serious psychological distress, which is nearly 8 times the rate in the US population (5%).18 When extrapolated, this data indicates that we in psychiatry are likely to work with individuals who identify as TGGD, regardless of our expertise. Additionally, research indicates that having access to gender-affirming care—such as hormone replacement therapy, gender-affirming surgery, voice therapy, and other treatments—greatly improves mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and suicidality among individuals who are TGGD.19,20 It is in this way we in psychiatry must do more than just care for our patients by becoming advocates for them to receive the care they need and deserve. While at times we may want to stay out of politics and other public discourse, it is becoming increasingly necessary as health care is entrenched in politics.
Clinical applicability
Because individuals who are TGGD experience higher rates of depression, anxiety, substance use, and other psychiatric disorders,14 it is increasingly likely that many clinicians will be presented with opportunities to treat such individuals. Despite high rates of psychiatric disorders, individuals who are TGGD often avoid treatment due to concerns about being pathologized, stereotyped, and/or encountering professionals who lack the knowledge to treat them as they are.21 Several studies recommend clinicians better equip themselves to appropriately provide services to individuals who are TGGD.21 Some advise seeking education to understand the unique needs of these patients and to help stay current with appropriate terminology and language (Table 222). This also implies not relying on patients to educate clinicians in understanding their specific needs and experiences.

Making assumptions about a patient’s identity is one of the most commonly reported issues by individuals who are TGGD. Therefore, it is critical to avoid making assumptions about patients based on binary stereotypes.23,24 We can circumvent these mistakes by asking every patient for their name and pronouns, and introducing ourselves with our pronouns. This illustrates an openness and understanding of the importance of identity and language, and makes it common practice from the outset. Integrating the use of gender-neutral language into paperwork, intake forms, charting, and conversation will also help avoid the pitfalls of misgendering and making false assumptions. This will also allow for support staff, medical assistants, and others to use correct language with patients. Having a patient’s used name and pronouns visible for everyone who works with the patient is necessary to effectively meet the patient’s needs. Additionally, understanding that the range of experiences and needs for individuals who are TGGD is heterogeneous can help reduce assumptions and ensure we are asking for needed information. It is also important to ask for only relevant information needed to provide treatment.
Continue to: Resources are widely available...
Resources are widely available to aid in the care of individuals who are TGGD. In 2022, the World Professional Association for Transgender Health released new guidelines—Standards of Care 8—for working with individuals who are TGGD.25 While these standards include a section dedicated to mental health, they also provide guidelines on education, assessments, specific demographic groups, hormone therapy, primary care, and sexual health. Additionally, while we may not want the role of gatekeeping for individuals to receive gender-affirming care, we work within a health care and insurance system that continues to require psychiatric assessment for such surgeries. In this role, we must do our part to educate ourselves in how to best provide these assessments and letters of support to help patients receive appropriate and life-saving care.
Finally, in order to provide a more comfortable and affirming space for individuals who are TGGD, develop ways to self-assess and monitor the policies, procedures, and language used within your practice, clinic, or institution. Monitoring the language used in charting to ensure consistency with the individual’s gender identity is important for our own understanding of the patient, and for patients to feel seen. This is especially true given patients’ access to medical records under the Cures Act. Moreover, it is essential to be cognizant of how you present clients to others in consultation or care coordination to ensure the patient is identified correctly and consistently by clinicians and staff.
Bottom Line
Understanding the social, cultural, and medical discrimination faced by patients who are transgender or gender diverse can make us better suited to engage and treat these individuals in an affirming and supportive way.
Related Resources
- World Professional Association of Transgender Health (WPATH) Standards of Care—8th edition. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/26895269.2022.2100644
- The Fenway Institute: National LGBTQIA+ Health Education Center. https://fenwayhealth.org/the-fenway-institute/education/the-national-lgbtia-health-education-center/
Treating patients who are transgender or gender diverse (TGGD) requires an understanding of the social and psychological factors that have a unique impact on this population. As clinicians, it is our responsibility to understand the social, cultural, and political issues our patients face, both historically and currently. In this article, we provide information about the nature of gender and gender identity as separate from biological sex and informed by a person’s perception of self as male, female, nonbinary, or other variation.
Psychiatrists must be aware of how individuals who are TGGD have been perceived, classified, and treated by the medical profession, as this history is often a source of mistrust and a barrier to treatment for patients who need psychiatric care. This includes awareness of the “gatekeeping” role that persists in medical institutions today: applying strict eligibility criteria to determine the “fitness” of individuals who are transgender to pursue medical transition, as compared to the informed-consent model that is widely applied to other medical interventions. Our review of minority stress theory, as applicable to this patient population, provides a context and framework for empathic approaches to care for patients who are TGGD. Recognizing barriers to care and ways in which we can create a supportive environment for treatment will allow for tailored approaches that better fit the unique needs of this patient population.
The gender binary
In Western societies, gender has often been viewed as “binary,” oppositional, and directly correlated with physical sex or presumed anatomy.1 The theory of gender essentialism insists that sex and gender are indistinguishable from one another and provide 2 “natural” and distinct categories: women and men. The “gender/sex” binary refers to the belief that individuals born with 2 X chromosomes will inherently develop into and fulfill the social roles of women, and those born with an X and a Y chromosome will develop into and fulfill the social roles of men.1 In this context, “sex” refers to biological characteristics of individuals, including combinations of sex chromosomes, anatomy, and the development of sex characteristics during puberty. The term “gender” refers to the social, cultural, and behavioral aspects of being a man, woman, both, or neither, and “gender identity” refers to one’s internal, individual sense of self and experience of gender (Figure 12). Many Western cultures are now facing destabilization of the gender/sex binary in social, political, and interpersonal contexts.1 This is perhaps most clearly seen in the battle for self-determination and protection by laws affecting individuals who are transgender as well as the determination of other groups to maintain traditional sex and gender roles, often through political action. Historically, individuals who are TGGD have been present in a variety of cultures. For example, most Native American cultures have revered other-gendered individuals, more recently referred to as “two-spirited.” Similarly, the Bugis people of South Sulawesi, Indonesia, recognize 5 genders that exist on a nonbinary spectrum.3

Despite its prevalence in Western society, scientific evidence for the gender/sex binary is lacking. The gender similarities hypothesis states that males and females are similar in most, but not all, psychological variables and is supported by multiple meta-analyses examining psychological gender differences.4 In a 2005 review of 46 meta-analyses of gender-differences, studied through behavior analysis, effect sizes for gender differences were trivial or small in almost 75% of examined variables.5 Analyzing for internal consistency among studies showing large gender/sex differences, Joel et al6 found that, on measures of personality traits, attitudes, interests, and behaviors were rarely homogenous in the brains of males or females. In fact, <1% of study participants showed only masculine or feminine traits, whereas 55% showed a combination, or mosaic, of these traits.6 These findings were supported by further research in behavioral neuroendocrinology that demonstrated a lack of hormonal evidence for 2 distinct sexes. Both estrogen (the “female” hormone) and testosterone (the “male” hormone) are produced by both biological males and females. Further, levels of estradiol do not significantly differ between males and females, and, in fact, in nonpregnant females, estradiol levels are more similar to those of males than to those of pregnant females.1 In the last decade, imaging studies of the human brain have shown that brain structure and connectivity in individuals who are transgender are more similar to those of their experienced gender than of their natal sex.7 In social analyses of intersex individuals (individuals born with ambiguous physical sex characteristics), surgical assignment into the binary gender system did not improve—and often worsened—feelings of isolation and shame.1
The National Institutes of Health defines gender as “socially constructed and enacted roles and behaviors which occur in a historical and cultural context and vary across societies and time.”8 The World Health Organization (WHO) provides a similar definition, and the evidence to support this exists in social-role theory, social-identity theory, and the stereotype-content model. However, despite evidence disputing a gender/sex binary, this method of classifying individuals into a dyad persists in many areas of modern culture, from gender-specific physical spaces (bathrooms, classrooms, store brands), language (pronouns), and laws. This desire for categorization helps fulfill social and psychological needs of groups and individuals by providing group identities and giving structure to the complexity of modern-day life. Identity and group membership provide a sense of belonging, source of self-esteem, and avoidance of ambiguity. Binary gender stereotypes provide expectations that allow anticipation and prediction of our social environments.9 However, the harm of perpetuating the false gender/sex binary is well documented and includes social and economic penalties, extreme violence, and even death. The field of medicine has not been immune from practices that implicitly endorse the gender/sex connection, as seen in the erroneous use of gender in biomedical writings at the highest levels and evidenced in research examining “gender” differences in disease incidence.
Gender diversity as a pathology
The American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) has been a source of pathologizing gender diversity since the 1960s, with the introduction of “transsexualism” in DSM-II10 and “gender identity disorder of childhood” in DSM-III.11 These diagnoses were listed under the headings of “sexual deviations” and “psychosexual disorders” in the respective DSM editions. This illustrates how gender diversity was viewed as a mental illness/defect. As the DSM developed through various revisions, so have these diagnoses. DSM-IV used the diagnosis “gender identity disorder.”12 Psychiatry has evolved away from this line of thinking by focusing on the distress from biological sex characteristics that are “incongruent” with an individual’s gender identity, leading to the development of the gender dysphoria diagnosis.13 While this has been a positive step in psychiatry’s efforts to de-pathologize individuals who are gender-diverse, it raises the question: should such diagnoses be included in the DSM at all?
The gender dysphoria diagnosis continues to be needed by many individuals who are TGGD in order to access gender-affirming health care services. Mental health professionals are placed in a gatekeeping role by the expectation that they provide letters of “support” to indicate an individual is of sound mind and consistent gender identity to have services covered by insurance providers. In this way, the insurance industry and the field of medicine continue to believe that individuals who are TGGD need psychiatric permission and/or counsel regarding their gender identity. This can place psychiatry in a role of controlling access to necessary care while also creating a possible distrust in our ability to provide care to patients who are gender-diverse. This is particularly problematic given the high rates of depression, anxiety, trauma, and substance use within these communities.14 In the WHO’s ICD-11, gender dysphoria was changed to gender incongruence and is contained in the category of “Conditions related to sexual health.”15 This indicates continued evolution of how medicine views individuals who are TGGD, and offers hope that psychiatry and the DSM will follow suit.
Continue to: Minority stress theory
Minority stress theory
Ilan Meyer’s minority stress theory explores how cultural and social factors impact mental health functioning (Figure 216). Minority stress theory, which was originally developed for what at the time was described as the lesbian, gay, and bisexual communities, purports that the higher prevalence of mental health disorders among such individuals is likely due to social stigma, discrimination, and stressors associated with minority status. More recently, minority stress theory has been expanded to provide framework for individuals who are TGGD. Hendricks et al17 explain how distal, proximal, and resilience factors contribute to mental health outcomes among these individuals. Distal factors, such as gender-related discrimination, harassment, violence, and rejection, explain how systemic, cultural, and environmental events lead to overt stress. Proximal factors consist of an individual’s expectation and anticipation of negative and stressful events and the internalization of negative attitudes and prejudice (ie, internalized transphobia). Resilience factors consist of community connectedness and within-group identification and can help mediate the negative effects of distal and proximal factors.

As clinicians, understanding our patients’ experiences and expectations can help us better engage with them and create an environment of safety and healing. Minority stress theory framework suggests that patients may start treatment with distrust or suspicion in light of previous negative experiences. They may also be likely to expect clinicians to be judgmental or to lack understanding of them. The 2015 US Transgender Survey found that 33% of individuals who are TGGD who sought medical treatment in the past year had at least 1 negative experience related to their gender identity (Table 118). Twenty-four percent reported having to educate their clinician about people who are TGGD, while 15% reported the health care professional asked invasive or unnecessary questions about their gender status that were unrelated to their visit. While psychiatry is often distinct from the larger medical field, it is important to understand the negative encounters individuals who are TGGD have likely experienced in medicine, and how those events may skew their feelings about psychiatric treatment. This is especially salient given the higher prevalence of various psychiatric disorders among individuals who are TGGD.18

According to the US Transgender Survey, 39% of participants were currently experiencing serious psychological distress, which is nearly 8 times the rate in the US population (5%).18 When extrapolated, this data indicates that we in psychiatry are likely to work with individuals who identify as TGGD, regardless of our expertise. Additionally, research indicates that having access to gender-affirming care—such as hormone replacement therapy, gender-affirming surgery, voice therapy, and other treatments—greatly improves mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and suicidality among individuals who are TGGD.19,20 It is in this way we in psychiatry must do more than just care for our patients by becoming advocates for them to receive the care they need and deserve. While at times we may want to stay out of politics and other public discourse, it is becoming increasingly necessary as health care is entrenched in politics.
Clinical applicability
Because individuals who are TGGD experience higher rates of depression, anxiety, substance use, and other psychiatric disorders,14 it is increasingly likely that many clinicians will be presented with opportunities to treat such individuals. Despite high rates of psychiatric disorders, individuals who are TGGD often avoid treatment due to concerns about being pathologized, stereotyped, and/or encountering professionals who lack the knowledge to treat them as they are.21 Several studies recommend clinicians better equip themselves to appropriately provide services to individuals who are TGGD.21 Some advise seeking education to understand the unique needs of these patients and to help stay current with appropriate terminology and language (Table 222). This also implies not relying on patients to educate clinicians in understanding their specific needs and experiences.

Making assumptions about a patient’s identity is one of the most commonly reported issues by individuals who are TGGD. Therefore, it is critical to avoid making assumptions about patients based on binary stereotypes.23,24 We can circumvent these mistakes by asking every patient for their name and pronouns, and introducing ourselves with our pronouns. This illustrates an openness and understanding of the importance of identity and language, and makes it common practice from the outset. Integrating the use of gender-neutral language into paperwork, intake forms, charting, and conversation will also help avoid the pitfalls of misgendering and making false assumptions. This will also allow for support staff, medical assistants, and others to use correct language with patients. Having a patient’s used name and pronouns visible for everyone who works with the patient is necessary to effectively meet the patient’s needs. Additionally, understanding that the range of experiences and needs for individuals who are TGGD is heterogeneous can help reduce assumptions and ensure we are asking for needed information. It is also important to ask for only relevant information needed to provide treatment.
Continue to: Resources are widely available...
Resources are widely available to aid in the care of individuals who are TGGD. In 2022, the World Professional Association for Transgender Health released new guidelines—Standards of Care 8—for working with individuals who are TGGD.25 While these standards include a section dedicated to mental health, they also provide guidelines on education, assessments, specific demographic groups, hormone therapy, primary care, and sexual health. Additionally, while we may not want the role of gatekeeping for individuals to receive gender-affirming care, we work within a health care and insurance system that continues to require psychiatric assessment for such surgeries. In this role, we must do our part to educate ourselves in how to best provide these assessments and letters of support to help patients receive appropriate and life-saving care.
Finally, in order to provide a more comfortable and affirming space for individuals who are TGGD, develop ways to self-assess and monitor the policies, procedures, and language used within your practice, clinic, or institution. Monitoring the language used in charting to ensure consistency with the individual’s gender identity is important for our own understanding of the patient, and for patients to feel seen. This is especially true given patients’ access to medical records under the Cures Act. Moreover, it is essential to be cognizant of how you present clients to others in consultation or care coordination to ensure the patient is identified correctly and consistently by clinicians and staff.
Bottom Line
Understanding the social, cultural, and medical discrimination faced by patients who are transgender or gender diverse can make us better suited to engage and treat these individuals in an affirming and supportive way.
Related Resources
- World Professional Association of Transgender Health (WPATH) Standards of Care—8th edition. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/26895269.2022.2100644
- The Fenway Institute: National LGBTQIA+ Health Education Center. https://fenwayhealth.org/the-fenway-institute/education/the-national-lgbtia-health-education-center/
1. Morgenroth T, Ryan MK. The effects of gender trouble: an integrative theoretical framework of the perpetuation and disruption of the gender/sex binary. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2021;16(6):1113-1142. doi:10.1177/1745691620902442
2. The Roots of Loneliness Project. Accessed April 8, 2023. https://www.rootsofloneliness.com/gender-identity-loneliness
3. Davies SG. Challenging Gender Norms: Five Genders Among Bugis in Indonesia. Thomson Wadsworth; 2007.
4. Hyde JS. The gender similarities hypothesis. Am Psychol. 2005;60(6):581-592. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.60.6.581
5. Joel D. Beyond the binary: rethinking sex and the brain. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021;122:165-175. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.22.018
6. Joel D, Berman Z, Tavor I, et al. Sex beyond the genitalia: the human brain mosaic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(50):15468-15473. doi:10.1073/pnas.1509654112
7. Palmer BF, Clegg DJ. A universally accepted definition of gender will positively impact societal understanding, acceptance, and appropriateness of health care. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95(10):2235-2243. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.01.031
8. Office of Research on Women’s Health. Sex & Gender. National Institutes of Health. Accessed April 6, 2023. https://orwh.od.nih.gov/sex-gender
9. Morgenroth T, Sendén MG, Lindqvist A, et al. Defending the sex/gender binary: the role of gender identification and need for closure. Soc Psychol Pers Sci. 2021;12(5):731-740.
10. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 2nd ed. American Psychiatric Association; 1968.
11. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association; 1980.
12. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
13. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
14. Wanta JW, Niforatos JD, Durbak E, et al. Mental health diagnoses among transgender patients in the clinical setting: an all-payer electronic health record study. Transgend Health. 2019;4(1):313-315.
15. World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases. 11th ed. World Health Organization; 2019.
16. Meyer IH. Prejudice, social stress, and mental health in lesbian, gay, and bisexual populations: conceptual issues and research evidence. Psychol Bull. 2003;129(5):674-697. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.129.5.674
17. Hendricks ML, Testa RJ. A conceptual framework for clinical work with transgender and gender nonconforming clients: an adaptation of the Minority Stress Model. Profess Psychol: Res Pract. 2012;43(5):460-467. doi:10.1037/a0029597
18. James SE, Herman J, Keisling M, et al. The Report of the 2015 U.S. Transgender Survey. National Center for Transgender Equality; 2016. Accessed April 6, 2023. https://transequality.org/sites/default/files/docs/usts/USTS-Full-Report-Dec17.pdf
19. Almazan AN, Keuroghlian AS. Association between gender-affirming surgeries and mental health outcomes. JAMA Surg. 2021;156(7):611-618. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2021.0952
20. Tordoff DM, Wanta JW, Collin A, et al. Mental health outcomes in transgender and nonbinary youths receiving gender-affirming care. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(2):e220978. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.0978
21. Snow A, Cerel J, Loeffler DN, et al. Barriers to mental health care for transgender and gender-nonconforming adults: a systematic literature review. Health Soc Work. 2019;44(3):149-155. doi:10.1093/hsw/hlz016
22. National LGBTQIA+ Health Education Center. Accessed April 8, 2023. https://www.lgbtqiahealtheducation.org
23. Baldwin A, Dodge B, Schick VR, et al. Transgender and genderqueer individuals’ experiences with health care providers: what’s working, what’s not, and where do we go from here? J Health Care Poor Underserved. 2018;29(4):1300-1318. doi:10.1353/hpu.2018.0097
24. Kcomt L, Gorey KM, Barrett BJ, et al. Healthcare avoidance due to anticipated discrimination among transgender people: a call to create trans-affirmative environments. SSM-Popul Health. 2020;11:100608. doi:10.1016/j.ssmph.2020.100608
25. Coleman E, Radix AE, Bouman WP, et al. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, version 8. Int J Transgender Health. 2022;23(Suppl 1):S1-S259.
1. Morgenroth T, Ryan MK. The effects of gender trouble: an integrative theoretical framework of the perpetuation and disruption of the gender/sex binary. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2021;16(6):1113-1142. doi:10.1177/1745691620902442
2. The Roots of Loneliness Project. Accessed April 8, 2023. https://www.rootsofloneliness.com/gender-identity-loneliness
3. Davies SG. Challenging Gender Norms: Five Genders Among Bugis in Indonesia. Thomson Wadsworth; 2007.
4. Hyde JS. The gender similarities hypothesis. Am Psychol. 2005;60(6):581-592. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.60.6.581
5. Joel D. Beyond the binary: rethinking sex and the brain. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021;122:165-175. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.22.018
6. Joel D, Berman Z, Tavor I, et al. Sex beyond the genitalia: the human brain mosaic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(50):15468-15473. doi:10.1073/pnas.1509654112
7. Palmer BF, Clegg DJ. A universally accepted definition of gender will positively impact societal understanding, acceptance, and appropriateness of health care. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95(10):2235-2243. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.01.031
8. Office of Research on Women’s Health. Sex & Gender. National Institutes of Health. Accessed April 6, 2023. https://orwh.od.nih.gov/sex-gender
9. Morgenroth T, Sendén MG, Lindqvist A, et al. Defending the sex/gender binary: the role of gender identification and need for closure. Soc Psychol Pers Sci. 2021;12(5):731-740.
10. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 2nd ed. American Psychiatric Association; 1968.
11. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association; 1980.
12. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
13. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
14. Wanta JW, Niforatos JD, Durbak E, et al. Mental health diagnoses among transgender patients in the clinical setting: an all-payer electronic health record study. Transgend Health. 2019;4(1):313-315.
15. World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases. 11th ed. World Health Organization; 2019.
16. Meyer IH. Prejudice, social stress, and mental health in lesbian, gay, and bisexual populations: conceptual issues and research evidence. Psychol Bull. 2003;129(5):674-697. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.129.5.674
17. Hendricks ML, Testa RJ. A conceptual framework for clinical work with transgender and gender nonconforming clients: an adaptation of the Minority Stress Model. Profess Psychol: Res Pract. 2012;43(5):460-467. doi:10.1037/a0029597
18. James SE, Herman J, Keisling M, et al. The Report of the 2015 U.S. Transgender Survey. National Center for Transgender Equality; 2016. Accessed April 6, 2023. https://transequality.org/sites/default/files/docs/usts/USTS-Full-Report-Dec17.pdf
19. Almazan AN, Keuroghlian AS. Association between gender-affirming surgeries and mental health outcomes. JAMA Surg. 2021;156(7):611-618. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2021.0952
20. Tordoff DM, Wanta JW, Collin A, et al. Mental health outcomes in transgender and nonbinary youths receiving gender-affirming care. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(2):e220978. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.0978
21. Snow A, Cerel J, Loeffler DN, et al. Barriers to mental health care for transgender and gender-nonconforming adults: a systematic literature review. Health Soc Work. 2019;44(3):149-155. doi:10.1093/hsw/hlz016
22. National LGBTQIA+ Health Education Center. Accessed April 8, 2023. https://www.lgbtqiahealtheducation.org
23. Baldwin A, Dodge B, Schick VR, et al. Transgender and genderqueer individuals’ experiences with health care providers: what’s working, what’s not, and where do we go from here? J Health Care Poor Underserved. 2018;29(4):1300-1318. doi:10.1353/hpu.2018.0097
24. Kcomt L, Gorey KM, Barrett BJ, et al. Healthcare avoidance due to anticipated discrimination among transgender people: a call to create trans-affirmative environments. SSM-Popul Health. 2020;11:100608. doi:10.1016/j.ssmph.2020.100608
25. Coleman E, Radix AE, Bouman WP, et al. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, version 8. Int J Transgender Health. 2022;23(Suppl 1):S1-S259.
The joys and rewards of an asymmetric life
The benefits of living a balanced life is a very popular concept. But I beg to differ. Balance in one’s life is overrated. Allocating equal time to the various components of one’s life may sound admirable, but it is a recipe for an ordinary life, with no major achievements or a memorable legacy. Scoring a “moonshot” achievement while living a balanced life is highly unlikely.
The benefits of deliberately leading an “asymmetric life” is an epiphany I acquired as a young boy addicted to watching stellar Olympic athletes win gold medals. I dreamed about being the best in the world in a sport, or in something else. As I read about the lives of my Olympic idols, my mind was opened to the fact that each of them led an unbalanced life in the pursuit of their cherished goal to be the best in the world: a gold medalist. I found out that for several years before the Olympic games, these athletes spent a disproportionate amount of their waking time (≥10 hours a day) practicing their sport, strengthening their muscles, building up their stamina, and honing their physical skills and mental toughness. Those sacrifices were necessary—in fact, indispensable—to set themselves apart from us mere mortals. Their social life was quite restricted, and even their educational pursuits had to be reduced or deferred.
I realized at a young age that to be the world’s best athlete, one must lead a purpose-driven life and channel a tremendous amount of time and energy to achieve the cherished goal of an Olympic gold medal. I understood the sacrifices necessary to excel in sports, and concluded the same was also true outside of sports, such as for Nobel Laureates, world-class pianists, prodigious authors, ballet dancers, opera divas, or self-employed entrepreneurs.
As I grew up, I repeatedly heard people praise “the balanced life,” but in my heart, I knew that was a fallacy. I had already decided in high school that I wanted to become a psychiatric physician. I was a premed major in college and very aware that our medical school enrolled only 44 students into the Med 1 class. There were >350 other premed undergraduates. Thus, without hesitation, and with gusto, I deliberately led an unbalanced life, studying countless hours each day to achieve an A grade in all required and elective courses to earn a spot on the Dean’s list. I already had confidence in my academic skills because of my excellent performance in high school, but I was not going to take any chances because I recalled a quote commonly attributed to Thomas Edison: “Genius is 1% inspiration and 99% perspiration.” This is obviously antithetical to living a balanced life.
I matriculated in medical school, and my unbalanced lifestyle continued unabated. Most readers of this journal are fellow physicians who know well the heavy demands of medical school on our lives, in both the preclinical and clinical years. Trying to lead a balanced life during the 4 years of medical school can have disastrous consequences. We all led an “asymmetric existence” with 75% (or more) of our waking hours invested in our careers and 25% (or less) directed to our social lives (and fortunately, our families and friends generally understood). That is what it takes to earn the coveted MD, the equivalent of an Olympic medal for intellectual athletes.
Then came 4 more years of psychiatric residency training, and the long hours of work continued, along with many nights and weekends on call. As a resident, I treasured the modest but precious amount of time I had outside work. I was lucky to have a very supportive and competent wife (a psychologist), who spared me from having to wake up at night to feed our first baby or do various household chores, so I could read the many articles and books on my desk and catch up on my sleep after my frequent night and weekend call shifts.
My unbalanced life continued when I pursued a postresidency fellowship at the National Institutes of Health, where I conducted numerous clinical research trials, brain imaging studies, and postmortem research on a large collection of brains from deceased patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. I worked 12 to 15 hours a day to write up the data I had collected, submit it to scientific journals, and revise it as needed. I knew from the strategic plan I had set for my life that the neuroscience fellowship would launch my academic career, and indeed it did.
Continue to: Reaping the benefits
Reaping the benefits
Fast forward 30 years and you will still find me leading an unbalanced but joyful and fulfilling life. People often ask me how I was able to achieve so much (authoring several hundred scientific publications; publishing 13 books; receiving dozens of grants; editing 3 scientific journals; founding an international schizophrenia society; assuming many leadership positions, including becoming a department chair at 2 universities and being elected to the presidency of several associations; lecturing around the world and making hundreds of scientific presentations at national and international conferences; seeing thousands of patients; teaching, supervising, and mentoring countless medical students, psychiatric residents, and young faculty members; and creating a nonprofit foundation [CURESZ.org] with a former patient who recovered completely after 5 years of home classes and treatment-refractory command hallucinations who then graduated from college with honors in molecular biology after I prescribed clozapine to “cure” her from what was deemed a hopeless and irreversible mental disability1). In all, thanks to my unbalanced life, I have achieved 12 moonshots and each is a major achievement of which I am proud.
My answer to those who ask me how I did all that is simple: I have strategically led an unbalanced life, enjoying every minute of it, and reaping the fruits of my labor. I do not waste an inordinate amount of time watching TV or participating in social media like many others might. And more importantly, despite this unbalanced life, I have been married to my college sweetheart for several decades and have a son and a daughter who are very high achievers and make me proud. I do budget time to regularly take my children and grandchildren on family vacations to exotic locations. I have dinner with my family every night. I am very happy with this so-called unbalanced life. I have received numerous awards and recognitions for my accomplishments, including the Distinguished Scholar Award (the highest academic recognition at The Ohio State University), the coveted Stanley Dean Award for research into schizophrenia from the American College of Psychiatrists, 4 Golden Apple Teaching Awards, and the Daniel Drake Medal, the highest honor that the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine bestows on a faculty member. (Dr. Drake founded the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine 200 years ago, a major moonshot, and among his many accomplishments, he also established the first psychiatric hospital in Ohio, another consequential moonshot. I am sure he led a very productive, unbalanced life, and that is why he is still remembered and revered 200 years later.)
It is said that at the height of his prominence 90 years ago, Sigmund Freud was asked, “What is life all about?” He responded with 2 words: “Liebe und arbeit” (love and work). Importantly, he did not specify which proportions those 2 major functions should occupy in one’s life. It was left up to each individual to make that choice. In the constitution of our country, that freedom of choice is the secret sauce of “the pursuit of happiness.”
1. The CURESZ Foundation. Who we are. Accessed April 11, 2023. https://curesz.org/about/who-we-are/
The benefits of living a balanced life is a very popular concept. But I beg to differ. Balance in one’s life is overrated. Allocating equal time to the various components of one’s life may sound admirable, but it is a recipe for an ordinary life, with no major achievements or a memorable legacy. Scoring a “moonshot” achievement while living a balanced life is highly unlikely.
The benefits of deliberately leading an “asymmetric life” is an epiphany I acquired as a young boy addicted to watching stellar Olympic athletes win gold medals. I dreamed about being the best in the world in a sport, or in something else. As I read about the lives of my Olympic idols, my mind was opened to the fact that each of them led an unbalanced life in the pursuit of their cherished goal to be the best in the world: a gold medalist. I found out that for several years before the Olympic games, these athletes spent a disproportionate amount of their waking time (≥10 hours a day) practicing their sport, strengthening their muscles, building up their stamina, and honing their physical skills and mental toughness. Those sacrifices were necessary—in fact, indispensable—to set themselves apart from us mere mortals. Their social life was quite restricted, and even their educational pursuits had to be reduced or deferred.
I realized at a young age that to be the world’s best athlete, one must lead a purpose-driven life and channel a tremendous amount of time and energy to achieve the cherished goal of an Olympic gold medal. I understood the sacrifices necessary to excel in sports, and concluded the same was also true outside of sports, such as for Nobel Laureates, world-class pianists, prodigious authors, ballet dancers, opera divas, or self-employed entrepreneurs.
As I grew up, I repeatedly heard people praise “the balanced life,” but in my heart, I knew that was a fallacy. I had already decided in high school that I wanted to become a psychiatric physician. I was a premed major in college and very aware that our medical school enrolled only 44 students into the Med 1 class. There were >350 other premed undergraduates. Thus, without hesitation, and with gusto, I deliberately led an unbalanced life, studying countless hours each day to achieve an A grade in all required and elective courses to earn a spot on the Dean’s list. I already had confidence in my academic skills because of my excellent performance in high school, but I was not going to take any chances because I recalled a quote commonly attributed to Thomas Edison: “Genius is 1% inspiration and 99% perspiration.” This is obviously antithetical to living a balanced life.
I matriculated in medical school, and my unbalanced lifestyle continued unabated. Most readers of this journal are fellow physicians who know well the heavy demands of medical school on our lives, in both the preclinical and clinical years. Trying to lead a balanced life during the 4 years of medical school can have disastrous consequences. We all led an “asymmetric existence” with 75% (or more) of our waking hours invested in our careers and 25% (or less) directed to our social lives (and fortunately, our families and friends generally understood). That is what it takes to earn the coveted MD, the equivalent of an Olympic medal for intellectual athletes.
Then came 4 more years of psychiatric residency training, and the long hours of work continued, along with many nights and weekends on call. As a resident, I treasured the modest but precious amount of time I had outside work. I was lucky to have a very supportive and competent wife (a psychologist), who spared me from having to wake up at night to feed our first baby or do various household chores, so I could read the many articles and books on my desk and catch up on my sleep after my frequent night and weekend call shifts.
My unbalanced life continued when I pursued a postresidency fellowship at the National Institutes of Health, where I conducted numerous clinical research trials, brain imaging studies, and postmortem research on a large collection of brains from deceased patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. I worked 12 to 15 hours a day to write up the data I had collected, submit it to scientific journals, and revise it as needed. I knew from the strategic plan I had set for my life that the neuroscience fellowship would launch my academic career, and indeed it did.
Continue to: Reaping the benefits
Reaping the benefits
Fast forward 30 years and you will still find me leading an unbalanced but joyful and fulfilling life. People often ask me how I was able to achieve so much (authoring several hundred scientific publications; publishing 13 books; receiving dozens of grants; editing 3 scientific journals; founding an international schizophrenia society; assuming many leadership positions, including becoming a department chair at 2 universities and being elected to the presidency of several associations; lecturing around the world and making hundreds of scientific presentations at national and international conferences; seeing thousands of patients; teaching, supervising, and mentoring countless medical students, psychiatric residents, and young faculty members; and creating a nonprofit foundation [CURESZ.org] with a former patient who recovered completely after 5 years of home classes and treatment-refractory command hallucinations who then graduated from college with honors in molecular biology after I prescribed clozapine to “cure” her from what was deemed a hopeless and irreversible mental disability1). In all, thanks to my unbalanced life, I have achieved 12 moonshots and each is a major achievement of which I am proud.
My answer to those who ask me how I did all that is simple: I have strategically led an unbalanced life, enjoying every minute of it, and reaping the fruits of my labor. I do not waste an inordinate amount of time watching TV or participating in social media like many others might. And more importantly, despite this unbalanced life, I have been married to my college sweetheart for several decades and have a son and a daughter who are very high achievers and make me proud. I do budget time to regularly take my children and grandchildren on family vacations to exotic locations. I have dinner with my family every night. I am very happy with this so-called unbalanced life. I have received numerous awards and recognitions for my accomplishments, including the Distinguished Scholar Award (the highest academic recognition at The Ohio State University), the coveted Stanley Dean Award for research into schizophrenia from the American College of Psychiatrists, 4 Golden Apple Teaching Awards, and the Daniel Drake Medal, the highest honor that the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine bestows on a faculty member. (Dr. Drake founded the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine 200 years ago, a major moonshot, and among his many accomplishments, he also established the first psychiatric hospital in Ohio, another consequential moonshot. I am sure he led a very productive, unbalanced life, and that is why he is still remembered and revered 200 years later.)
It is said that at the height of his prominence 90 years ago, Sigmund Freud was asked, “What is life all about?” He responded with 2 words: “Liebe und arbeit” (love and work). Importantly, he did not specify which proportions those 2 major functions should occupy in one’s life. It was left up to each individual to make that choice. In the constitution of our country, that freedom of choice is the secret sauce of “the pursuit of happiness.”
The benefits of living a balanced life is a very popular concept. But I beg to differ. Balance in one’s life is overrated. Allocating equal time to the various components of one’s life may sound admirable, but it is a recipe for an ordinary life, with no major achievements or a memorable legacy. Scoring a “moonshot” achievement while living a balanced life is highly unlikely.
The benefits of deliberately leading an “asymmetric life” is an epiphany I acquired as a young boy addicted to watching stellar Olympic athletes win gold medals. I dreamed about being the best in the world in a sport, or in something else. As I read about the lives of my Olympic idols, my mind was opened to the fact that each of them led an unbalanced life in the pursuit of their cherished goal to be the best in the world: a gold medalist. I found out that for several years before the Olympic games, these athletes spent a disproportionate amount of their waking time (≥10 hours a day) practicing their sport, strengthening their muscles, building up their stamina, and honing their physical skills and mental toughness. Those sacrifices were necessary—in fact, indispensable—to set themselves apart from us mere mortals. Their social life was quite restricted, and even their educational pursuits had to be reduced or deferred.
I realized at a young age that to be the world’s best athlete, one must lead a purpose-driven life and channel a tremendous amount of time and energy to achieve the cherished goal of an Olympic gold medal. I understood the sacrifices necessary to excel in sports, and concluded the same was also true outside of sports, such as for Nobel Laureates, world-class pianists, prodigious authors, ballet dancers, opera divas, or self-employed entrepreneurs.
As I grew up, I repeatedly heard people praise “the balanced life,” but in my heart, I knew that was a fallacy. I had already decided in high school that I wanted to become a psychiatric physician. I was a premed major in college and very aware that our medical school enrolled only 44 students into the Med 1 class. There were >350 other premed undergraduates. Thus, without hesitation, and with gusto, I deliberately led an unbalanced life, studying countless hours each day to achieve an A grade in all required and elective courses to earn a spot on the Dean’s list. I already had confidence in my academic skills because of my excellent performance in high school, but I was not going to take any chances because I recalled a quote commonly attributed to Thomas Edison: “Genius is 1% inspiration and 99% perspiration.” This is obviously antithetical to living a balanced life.
I matriculated in medical school, and my unbalanced lifestyle continued unabated. Most readers of this journal are fellow physicians who know well the heavy demands of medical school on our lives, in both the preclinical and clinical years. Trying to lead a balanced life during the 4 years of medical school can have disastrous consequences. We all led an “asymmetric existence” with 75% (or more) of our waking hours invested in our careers and 25% (or less) directed to our social lives (and fortunately, our families and friends generally understood). That is what it takes to earn the coveted MD, the equivalent of an Olympic medal for intellectual athletes.
Then came 4 more years of psychiatric residency training, and the long hours of work continued, along with many nights and weekends on call. As a resident, I treasured the modest but precious amount of time I had outside work. I was lucky to have a very supportive and competent wife (a psychologist), who spared me from having to wake up at night to feed our first baby or do various household chores, so I could read the many articles and books on my desk and catch up on my sleep after my frequent night and weekend call shifts.
My unbalanced life continued when I pursued a postresidency fellowship at the National Institutes of Health, where I conducted numerous clinical research trials, brain imaging studies, and postmortem research on a large collection of brains from deceased patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. I worked 12 to 15 hours a day to write up the data I had collected, submit it to scientific journals, and revise it as needed. I knew from the strategic plan I had set for my life that the neuroscience fellowship would launch my academic career, and indeed it did.
Continue to: Reaping the benefits
Reaping the benefits
Fast forward 30 years and you will still find me leading an unbalanced but joyful and fulfilling life. People often ask me how I was able to achieve so much (authoring several hundred scientific publications; publishing 13 books; receiving dozens of grants; editing 3 scientific journals; founding an international schizophrenia society; assuming many leadership positions, including becoming a department chair at 2 universities and being elected to the presidency of several associations; lecturing around the world and making hundreds of scientific presentations at national and international conferences; seeing thousands of patients; teaching, supervising, and mentoring countless medical students, psychiatric residents, and young faculty members; and creating a nonprofit foundation [CURESZ.org] with a former patient who recovered completely after 5 years of home classes and treatment-refractory command hallucinations who then graduated from college with honors in molecular biology after I prescribed clozapine to “cure” her from what was deemed a hopeless and irreversible mental disability1). In all, thanks to my unbalanced life, I have achieved 12 moonshots and each is a major achievement of which I am proud.
My answer to those who ask me how I did all that is simple: I have strategically led an unbalanced life, enjoying every minute of it, and reaping the fruits of my labor. I do not waste an inordinate amount of time watching TV or participating in social media like many others might. And more importantly, despite this unbalanced life, I have been married to my college sweetheart for several decades and have a son and a daughter who are very high achievers and make me proud. I do budget time to regularly take my children and grandchildren on family vacations to exotic locations. I have dinner with my family every night. I am very happy with this so-called unbalanced life. I have received numerous awards and recognitions for my accomplishments, including the Distinguished Scholar Award (the highest academic recognition at The Ohio State University), the coveted Stanley Dean Award for research into schizophrenia from the American College of Psychiatrists, 4 Golden Apple Teaching Awards, and the Daniel Drake Medal, the highest honor that the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine bestows on a faculty member. (Dr. Drake founded the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine 200 years ago, a major moonshot, and among his many accomplishments, he also established the first psychiatric hospital in Ohio, another consequential moonshot. I am sure he led a very productive, unbalanced life, and that is why he is still remembered and revered 200 years later.)
It is said that at the height of his prominence 90 years ago, Sigmund Freud was asked, “What is life all about?” He responded with 2 words: “Liebe und arbeit” (love and work). Importantly, he did not specify which proportions those 2 major functions should occupy in one’s life. It was left up to each individual to make that choice. In the constitution of our country, that freedom of choice is the secret sauce of “the pursuit of happiness.”
1. The CURESZ Foundation. Who we are. Accessed April 11, 2023. https://curesz.org/about/who-we-are/
1. The CURESZ Foundation. Who we are. Accessed April 11, 2023. https://curesz.org/about/who-we-are/