User login
Liver cancer exacts high financial toll on older adults
In the first year after a diagnosis of HCC, median Medicare payments exceed $65,000 and out-of-pocket costs top $10,000.
Even after adjustment for the presence of cirrhosis and its related costs, patients with HCC still have Medicare payments exceeding $50,000 and out-of-pocket costs topping $7000.
Amit Singal, MD, of UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, and colleagues reported their findings in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Common and costly
HCC, the most common type of primary liver cancer, is a leading cause of death in patients with cirrhosis and is projected to become the third leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States by 2040, the researchers wrote.
The treatment landscape for HCC has changed over the past decade, with expanded surgical options, introduction of radiation-based therapies, and approval of immunotherapies – all of which are costly.
Yet the magnitude of financial burden of HCC therapy has been understudied, the researchers noted.
To investigate, Dr. Singal and colleagues evaluated Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)–Medicare data for 4,525 adults with traditional Medicare coverage who were diagnosed with HCC between 2011 and 2015 and a propensity-matched cohort of 4,525 adults with cirrhosis but no HCC as a comparator group to tease out HCC-specific costs beyond those related to cirrhosis. Patients in Medicare managed care were excluded because their cost information is not available in the database.
In the first year after a diagnosis of HCC, the median total Medicare payments were $66,338 (interquartile range [IQR], $30,931-$158,740) and patient liabilities (a proxy for out-of-pocket costs) were $10,008 (IQR, $5,427-$19,669).
First-year costs were higher for patients with HCC than matched patients without HCC; the former group incurred median incremental Medicare payments of $50,110 (IQR, $14,242-$136,239) and patient liabilities of $7,166 (IQR, $2,401-$16,099), the investigators found.
Patients with early-stage HCC had lower incremental patient liabilities (median, $4,195 vs. $8,238) and Medicare payments (median, $28,207 vs. $59,509) than did their peers with larger tumor burden.
NAFLD notably tied to higher costs
Factors associated with higher HCC-related costs were nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) etiology, higher comorbidities, presence of ascites and hepatic encephalopathy, and larger tumor burden.
The researchers said that the link between NAFLD and higher costs is notable, given that NAFLD is an increasingly common underlying cause of HCC.
The link between larger tumor burden and higher costs underscores “another benefit of HCC surveillance and early detection,” they added.
“By separating the financial liabilities borne by patients and Medicare, we provide a clearer outlook of how cancer-related costs are distributed between patients and public payers,” Dr. Singal and colleagues said.
“Our findings will inform policy interventions and will help formulate better financial supports targeting the most vulnerable HCC patients,” they concluded.
The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Singal has been on advisory boards and served as a consultant for Wako Diagnostics, Glycotest, Exact Sciences, Roche, Genentech, Bayer, Eisai, BMS, Exelixis, AstraZeneca, and TARGET RWE.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the first year after a diagnosis of HCC, median Medicare payments exceed $65,000 and out-of-pocket costs top $10,000.
Even after adjustment for the presence of cirrhosis and its related costs, patients with HCC still have Medicare payments exceeding $50,000 and out-of-pocket costs topping $7000.
Amit Singal, MD, of UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, and colleagues reported their findings in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Common and costly
HCC, the most common type of primary liver cancer, is a leading cause of death in patients with cirrhosis and is projected to become the third leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States by 2040, the researchers wrote.
The treatment landscape for HCC has changed over the past decade, with expanded surgical options, introduction of radiation-based therapies, and approval of immunotherapies – all of which are costly.
Yet the magnitude of financial burden of HCC therapy has been understudied, the researchers noted.
To investigate, Dr. Singal and colleagues evaluated Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)–Medicare data for 4,525 adults with traditional Medicare coverage who were diagnosed with HCC between 2011 and 2015 and a propensity-matched cohort of 4,525 adults with cirrhosis but no HCC as a comparator group to tease out HCC-specific costs beyond those related to cirrhosis. Patients in Medicare managed care were excluded because their cost information is not available in the database.
In the first year after a diagnosis of HCC, the median total Medicare payments were $66,338 (interquartile range [IQR], $30,931-$158,740) and patient liabilities (a proxy for out-of-pocket costs) were $10,008 (IQR, $5,427-$19,669).
First-year costs were higher for patients with HCC than matched patients without HCC; the former group incurred median incremental Medicare payments of $50,110 (IQR, $14,242-$136,239) and patient liabilities of $7,166 (IQR, $2,401-$16,099), the investigators found.
Patients with early-stage HCC had lower incremental patient liabilities (median, $4,195 vs. $8,238) and Medicare payments (median, $28,207 vs. $59,509) than did their peers with larger tumor burden.
NAFLD notably tied to higher costs
Factors associated with higher HCC-related costs were nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) etiology, higher comorbidities, presence of ascites and hepatic encephalopathy, and larger tumor burden.
The researchers said that the link between NAFLD and higher costs is notable, given that NAFLD is an increasingly common underlying cause of HCC.
The link between larger tumor burden and higher costs underscores “another benefit of HCC surveillance and early detection,” they added.
“By separating the financial liabilities borne by patients and Medicare, we provide a clearer outlook of how cancer-related costs are distributed between patients and public payers,” Dr. Singal and colleagues said.
“Our findings will inform policy interventions and will help formulate better financial supports targeting the most vulnerable HCC patients,” they concluded.
The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Singal has been on advisory boards and served as a consultant for Wako Diagnostics, Glycotest, Exact Sciences, Roche, Genentech, Bayer, Eisai, BMS, Exelixis, AstraZeneca, and TARGET RWE.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the first year after a diagnosis of HCC, median Medicare payments exceed $65,000 and out-of-pocket costs top $10,000.
Even after adjustment for the presence of cirrhosis and its related costs, patients with HCC still have Medicare payments exceeding $50,000 and out-of-pocket costs topping $7000.
Amit Singal, MD, of UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, and colleagues reported their findings in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Common and costly
HCC, the most common type of primary liver cancer, is a leading cause of death in patients with cirrhosis and is projected to become the third leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States by 2040, the researchers wrote.
The treatment landscape for HCC has changed over the past decade, with expanded surgical options, introduction of radiation-based therapies, and approval of immunotherapies – all of which are costly.
Yet the magnitude of financial burden of HCC therapy has been understudied, the researchers noted.
To investigate, Dr. Singal and colleagues evaluated Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)–Medicare data for 4,525 adults with traditional Medicare coverage who were diagnosed with HCC between 2011 and 2015 and a propensity-matched cohort of 4,525 adults with cirrhosis but no HCC as a comparator group to tease out HCC-specific costs beyond those related to cirrhosis. Patients in Medicare managed care were excluded because their cost information is not available in the database.
In the first year after a diagnosis of HCC, the median total Medicare payments were $66,338 (interquartile range [IQR], $30,931-$158,740) and patient liabilities (a proxy for out-of-pocket costs) were $10,008 (IQR, $5,427-$19,669).
First-year costs were higher for patients with HCC than matched patients without HCC; the former group incurred median incremental Medicare payments of $50,110 (IQR, $14,242-$136,239) and patient liabilities of $7,166 (IQR, $2,401-$16,099), the investigators found.
Patients with early-stage HCC had lower incremental patient liabilities (median, $4,195 vs. $8,238) and Medicare payments (median, $28,207 vs. $59,509) than did their peers with larger tumor burden.
NAFLD notably tied to higher costs
Factors associated with higher HCC-related costs were nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) etiology, higher comorbidities, presence of ascites and hepatic encephalopathy, and larger tumor burden.
The researchers said that the link between NAFLD and higher costs is notable, given that NAFLD is an increasingly common underlying cause of HCC.
The link between larger tumor burden and higher costs underscores “another benefit of HCC surveillance and early detection,” they added.
“By separating the financial liabilities borne by patients and Medicare, we provide a clearer outlook of how cancer-related costs are distributed between patients and public payers,” Dr. Singal and colleagues said.
“Our findings will inform policy interventions and will help formulate better financial supports targeting the most vulnerable HCC patients,” they concluded.
The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Singal has been on advisory boards and served as a consultant for Wako Diagnostics, Glycotest, Exact Sciences, Roche, Genentech, Bayer, Eisai, BMS, Exelixis, AstraZeneca, and TARGET RWE.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Cancer researcher banned from federal funding for faking data in nearly 400 images in 16 grant applications
according to a U.S. government research watchdog.
Alice C. Chang, PhD, whose publications and grants listed her name as Chun-Ju Chang, received nearly $700,000 in funding from the National Institutes of Health through grant applications that the U.S. Office of Research Integrity said contained fake data. She will be banned from receiving federal grants for a decade – a more severe sanction than ORI has typically imposed in recent years.
In its findings, ORI said Dr. Chang, who was an associate professor of basic medical sciences at Purdue’s College of Veterinary Medicine, West Lafayette, Ind., “knowingly, intentionally, or recklessly falsified and/or fabricated data from the same mouse models or cell lines by reusing the data, with or without manipulation, to represent unrelated experiments from different mouse models or cell lines with different treatments in three hundred eighty-four (384) figure panels in sixteen (16) grant applications.”
Two of the grant applications were funded. Dr. Chang received $688,196 from the National Cancer Institute, a division of NIH, from 2018 to 2019 for “Targeting metformin-directed stem cell fate in triple negative breast cancer.” The other grant ORI says was submitted in 2014 and funded, “Targeting cell polarity machinery to exhaust breast cancer stem cell pool,” does not show up in NIH RePorter. The rest of the grants were not approved.
We found a Chun-Ju Chang who is dean of the College of Life Sciences at China Medical University in Taiwan and has published papers with a group that Chun-Ju Chang at Purdue also published with. She did not immediately respond to our request for comment.
ORI’s finding also stated Dr. Chang faked data in two papers supported by government funding by reusing figures reporting gene expression in mice and cells after drug treatments, relabeling them to say they showed the results of different experiments. According to the agency, she has agreed to request corrections for the papers:
“Leptin–STAT3–G9a Signaling Promotes Obesity-Mediated Breast Cancer Progression,” published in May 2015 in Cancer Research and cited 83 times, according to Clarivate’s Web of Science.
“Retinoic acid directs breast cancer cell state changes through regulation of TET2-PKC-zeta pathway,” published in February 2017 in Oncogene and cited 26 times.
Between the two papers and 15 of the grant applications, ORI said that Dr. Chang reused gene expression data, sometimes with manipulation, in 119 figure panels. She reused other types of data and images in hundreds of figures across multiple grant applications, ORI found.
As well as correcting the two papers, Dr. Chang agreed to a 10-year ban from all federal contracting, including grant funding. She also agreed not to serve in any advisory or consulting role with the U.S. Public Health Service, which includes the NIH, for that time period.
A version of this article first appeared on Retraction Watch.
according to a U.S. government research watchdog.
Alice C. Chang, PhD, whose publications and grants listed her name as Chun-Ju Chang, received nearly $700,000 in funding from the National Institutes of Health through grant applications that the U.S. Office of Research Integrity said contained fake data. She will be banned from receiving federal grants for a decade – a more severe sanction than ORI has typically imposed in recent years.
In its findings, ORI said Dr. Chang, who was an associate professor of basic medical sciences at Purdue’s College of Veterinary Medicine, West Lafayette, Ind., “knowingly, intentionally, or recklessly falsified and/or fabricated data from the same mouse models or cell lines by reusing the data, with or without manipulation, to represent unrelated experiments from different mouse models or cell lines with different treatments in three hundred eighty-four (384) figure panels in sixteen (16) grant applications.”
Two of the grant applications were funded. Dr. Chang received $688,196 from the National Cancer Institute, a division of NIH, from 2018 to 2019 for “Targeting metformin-directed stem cell fate in triple negative breast cancer.” The other grant ORI says was submitted in 2014 and funded, “Targeting cell polarity machinery to exhaust breast cancer stem cell pool,” does not show up in NIH RePorter. The rest of the grants were not approved.
We found a Chun-Ju Chang who is dean of the College of Life Sciences at China Medical University in Taiwan and has published papers with a group that Chun-Ju Chang at Purdue also published with. She did not immediately respond to our request for comment.
ORI’s finding also stated Dr. Chang faked data in two papers supported by government funding by reusing figures reporting gene expression in mice and cells after drug treatments, relabeling them to say they showed the results of different experiments. According to the agency, she has agreed to request corrections for the papers:
“Leptin–STAT3–G9a Signaling Promotes Obesity-Mediated Breast Cancer Progression,” published in May 2015 in Cancer Research and cited 83 times, according to Clarivate’s Web of Science.
“Retinoic acid directs breast cancer cell state changes through regulation of TET2-PKC-zeta pathway,” published in February 2017 in Oncogene and cited 26 times.
Between the two papers and 15 of the grant applications, ORI said that Dr. Chang reused gene expression data, sometimes with manipulation, in 119 figure panels. She reused other types of data and images in hundreds of figures across multiple grant applications, ORI found.
As well as correcting the two papers, Dr. Chang agreed to a 10-year ban from all federal contracting, including grant funding. She also agreed not to serve in any advisory or consulting role with the U.S. Public Health Service, which includes the NIH, for that time period.
A version of this article first appeared on Retraction Watch.
according to a U.S. government research watchdog.
Alice C. Chang, PhD, whose publications and grants listed her name as Chun-Ju Chang, received nearly $700,000 in funding from the National Institutes of Health through grant applications that the U.S. Office of Research Integrity said contained fake data. She will be banned from receiving federal grants for a decade – a more severe sanction than ORI has typically imposed in recent years.
In its findings, ORI said Dr. Chang, who was an associate professor of basic medical sciences at Purdue’s College of Veterinary Medicine, West Lafayette, Ind., “knowingly, intentionally, or recklessly falsified and/or fabricated data from the same mouse models or cell lines by reusing the data, with or without manipulation, to represent unrelated experiments from different mouse models or cell lines with different treatments in three hundred eighty-four (384) figure panels in sixteen (16) grant applications.”
Two of the grant applications were funded. Dr. Chang received $688,196 from the National Cancer Institute, a division of NIH, from 2018 to 2019 for “Targeting metformin-directed stem cell fate in triple negative breast cancer.” The other grant ORI says was submitted in 2014 and funded, “Targeting cell polarity machinery to exhaust breast cancer stem cell pool,” does not show up in NIH RePorter. The rest of the grants were not approved.
We found a Chun-Ju Chang who is dean of the College of Life Sciences at China Medical University in Taiwan and has published papers with a group that Chun-Ju Chang at Purdue also published with. She did not immediately respond to our request for comment.
ORI’s finding also stated Dr. Chang faked data in two papers supported by government funding by reusing figures reporting gene expression in mice and cells after drug treatments, relabeling them to say they showed the results of different experiments. According to the agency, she has agreed to request corrections for the papers:
“Leptin–STAT3–G9a Signaling Promotes Obesity-Mediated Breast Cancer Progression,” published in May 2015 in Cancer Research and cited 83 times, according to Clarivate’s Web of Science.
“Retinoic acid directs breast cancer cell state changes through regulation of TET2-PKC-zeta pathway,” published in February 2017 in Oncogene and cited 26 times.
Between the two papers and 15 of the grant applications, ORI said that Dr. Chang reused gene expression data, sometimes with manipulation, in 119 figure panels. She reused other types of data and images in hundreds of figures across multiple grant applications, ORI found.
As well as correcting the two papers, Dr. Chang agreed to a 10-year ban from all federal contracting, including grant funding. She also agreed not to serve in any advisory or consulting role with the U.S. Public Health Service, which includes the NIH, for that time period.
A version of this article first appeared on Retraction Watch.
Have you heard the one about the cow in the doctor’s office?
Maybe the cow was late for its appointment
It’s been a long day running the front desk at your doctor’s office. People calling in prescriptions, a million appointments, you’ve been running yourself ragged keeping things together. Finally, it’s almost closing time. The last patient of the day has just checked out and you turn back to the waiting room, expecting to see it blessedly empty.
Instead, a 650-pound cow is staring at you.
“I’m sorry, sir or madam, we’re about to close.”
Moo.
“I understand it’s important, but seriously, the doctor’s about to …”
Moo.
“Fine, I’ll see what we can do for you. What’s your insurance?”
Moo Cross Moo Shield.
“Sorry, we don’t take that. You’ll have to go someplace else.”
This is probably not how things went down recently at Orange (Va.) Family Physicians, when they had a cow break into the office. Cows don’t have health insurance.
The intrepid bovine was being transferred to a new home when it jumped off the trailer and wandered an eighth of a mile to Orange Family Physicians, where the cow wranglers found it hanging around outside. Unfortunately, this was a smart cow, and it bolted as it saw the wranglers, crashing through the glass doors into the doctor’s office. Though neither man had ever wrangled a cow from inside a building, they ultimately secured a rope around the cow’s neck and escorted it back outside, tying it to a nearby pole to keep it from further adventures.
One of the wranglers summed up the situation quite nicely on his Facebook page: “You ain’t no cowboy if you don’t rope a calf out of a [doctor’s] office.”
We can see that decision in your eyes
The cliché that eyes are the windows to the soul doesn’t tell the whole story about how telling eyes really are. It’s all about how they move. In a recent study, researchers determined that a type of eye movement known as a saccade reveals your choice before you even decide.
Saccades involve the eyes jumping from one fixation point to another, senior author Alaa Ahmed of the University of Colorado, Boulder, explained in a statement from the university. Saccade vigor was the key in how aligned the type of decisions were made by the 22 study participants.
In the study, subjects walked on a treadmill at varied inclines for a period of time. Then they sat in front of a monitor and a high-speed camera that tracked their eye movements as the monitor presented them with a series of exercise options. The participants had only 4 seconds to choose between them.
After they made their choices, participants went back on the treadmill to perform the exercises they had chosen. The researchers found that participants’ eyes jumped between the options slowly then faster to the option they eventually picked. The more impulsive decision-makers also tended to move their eyes even more rapidly before slowing down after a decision was made, making it pretty conclusive that the eyes were revealing their choices.
The way your eyes shift gives you away without saying a thing. Might be wise, then, to wear sunglasses to your next poker tournament.
Let them eat soap
Okay, we admit it: LOTME spends a lot of time in the bathroom. Today, though, we’re interested in the sinks. Specifically, the P-traps under the sinks. You know, the curvy bit that keeps sewer gas from wafting back into the room?
Well, researchers from the University of Reading (England) recently found some fungi while examining a bunch of sinks on the university’s Whiteknights campus. “It isn’t a big surprise to find fungi in a warm, wet environment. But sinks and P-traps have thus far been overlooked as potential reservoirs of these microorganisms,” they said in a written statement.
Samples collected from 289 P-traps contained “a very similar community of yeasts and molds, showing that sinks in use in public environments share a role as reservoirs of fungal organisms,” they noted.
The fungi living in the traps survived conditions with high temperatures, low pH, and little in the way of nutrients. So what were they eating? Some varieties, they said, “use detergents, found in soap, as a source of carbon-rich food.” We’ll repeat that last part: They used the soap as food.
WARNING: Rant Ahead.
There are a lot of cleaning products for sale that say they will make your home safe by killing 99.9% of germs and bacteria. Not fungi, exactly, but we’re still talking microorganisms. Molds, bacteria, and viruses are all stuff that can infect humans and make them sick.
So you kill 99.9% of them. Great, but that leaves 0.1% that you just made angry. And what do they do next? They learn to eat soap. Then University of Reading investigators find out that all the extra hand washing going on during the COVID-19 pandemic was “clogging up sinks with nasty disease-causing bacteria.”
These are microorganisms we’re talking about people. They’ve been at this for a billion years! Rats can’t beat them, cockroaches won’t stop them – Earth’s ultimate survivors are powerless against the invisible horde.
We’re doomed.
Maybe the cow was late for its appointment
It’s been a long day running the front desk at your doctor’s office. People calling in prescriptions, a million appointments, you’ve been running yourself ragged keeping things together. Finally, it’s almost closing time. The last patient of the day has just checked out and you turn back to the waiting room, expecting to see it blessedly empty.
Instead, a 650-pound cow is staring at you.
“I’m sorry, sir or madam, we’re about to close.”
Moo.
“I understand it’s important, but seriously, the doctor’s about to …”
Moo.
“Fine, I’ll see what we can do for you. What’s your insurance?”
Moo Cross Moo Shield.
“Sorry, we don’t take that. You’ll have to go someplace else.”
This is probably not how things went down recently at Orange (Va.) Family Physicians, when they had a cow break into the office. Cows don’t have health insurance.
The intrepid bovine was being transferred to a new home when it jumped off the trailer and wandered an eighth of a mile to Orange Family Physicians, where the cow wranglers found it hanging around outside. Unfortunately, this was a smart cow, and it bolted as it saw the wranglers, crashing through the glass doors into the doctor’s office. Though neither man had ever wrangled a cow from inside a building, they ultimately secured a rope around the cow’s neck and escorted it back outside, tying it to a nearby pole to keep it from further adventures.
One of the wranglers summed up the situation quite nicely on his Facebook page: “You ain’t no cowboy if you don’t rope a calf out of a [doctor’s] office.”
We can see that decision in your eyes
The cliché that eyes are the windows to the soul doesn’t tell the whole story about how telling eyes really are. It’s all about how they move. In a recent study, researchers determined that a type of eye movement known as a saccade reveals your choice before you even decide.
Saccades involve the eyes jumping from one fixation point to another, senior author Alaa Ahmed of the University of Colorado, Boulder, explained in a statement from the university. Saccade vigor was the key in how aligned the type of decisions were made by the 22 study participants.
In the study, subjects walked on a treadmill at varied inclines for a period of time. Then they sat in front of a monitor and a high-speed camera that tracked their eye movements as the monitor presented them with a series of exercise options. The participants had only 4 seconds to choose between them.
After they made their choices, participants went back on the treadmill to perform the exercises they had chosen. The researchers found that participants’ eyes jumped between the options slowly then faster to the option they eventually picked. The more impulsive decision-makers also tended to move their eyes even more rapidly before slowing down after a decision was made, making it pretty conclusive that the eyes were revealing their choices.
The way your eyes shift gives you away without saying a thing. Might be wise, then, to wear sunglasses to your next poker tournament.
Let them eat soap
Okay, we admit it: LOTME spends a lot of time in the bathroom. Today, though, we’re interested in the sinks. Specifically, the P-traps under the sinks. You know, the curvy bit that keeps sewer gas from wafting back into the room?
Well, researchers from the University of Reading (England) recently found some fungi while examining a bunch of sinks on the university’s Whiteknights campus. “It isn’t a big surprise to find fungi in a warm, wet environment. But sinks and P-traps have thus far been overlooked as potential reservoirs of these microorganisms,” they said in a written statement.
Samples collected from 289 P-traps contained “a very similar community of yeasts and molds, showing that sinks in use in public environments share a role as reservoirs of fungal organisms,” they noted.
The fungi living in the traps survived conditions with high temperatures, low pH, and little in the way of nutrients. So what were they eating? Some varieties, they said, “use detergents, found in soap, as a source of carbon-rich food.” We’ll repeat that last part: They used the soap as food.
WARNING: Rant Ahead.
There are a lot of cleaning products for sale that say they will make your home safe by killing 99.9% of germs and bacteria. Not fungi, exactly, but we’re still talking microorganisms. Molds, bacteria, and viruses are all stuff that can infect humans and make them sick.
So you kill 99.9% of them. Great, but that leaves 0.1% that you just made angry. And what do they do next? They learn to eat soap. Then University of Reading investigators find out that all the extra hand washing going on during the COVID-19 pandemic was “clogging up sinks with nasty disease-causing bacteria.”
These are microorganisms we’re talking about people. They’ve been at this for a billion years! Rats can’t beat them, cockroaches won’t stop them – Earth’s ultimate survivors are powerless against the invisible horde.
We’re doomed.
Maybe the cow was late for its appointment
It’s been a long day running the front desk at your doctor’s office. People calling in prescriptions, a million appointments, you’ve been running yourself ragged keeping things together. Finally, it’s almost closing time. The last patient of the day has just checked out and you turn back to the waiting room, expecting to see it blessedly empty.
Instead, a 650-pound cow is staring at you.
“I’m sorry, sir or madam, we’re about to close.”
Moo.
“I understand it’s important, but seriously, the doctor’s about to …”
Moo.
“Fine, I’ll see what we can do for you. What’s your insurance?”
Moo Cross Moo Shield.
“Sorry, we don’t take that. You’ll have to go someplace else.”
This is probably not how things went down recently at Orange (Va.) Family Physicians, when they had a cow break into the office. Cows don’t have health insurance.
The intrepid bovine was being transferred to a new home when it jumped off the trailer and wandered an eighth of a mile to Orange Family Physicians, where the cow wranglers found it hanging around outside. Unfortunately, this was a smart cow, and it bolted as it saw the wranglers, crashing through the glass doors into the doctor’s office. Though neither man had ever wrangled a cow from inside a building, they ultimately secured a rope around the cow’s neck and escorted it back outside, tying it to a nearby pole to keep it from further adventures.
One of the wranglers summed up the situation quite nicely on his Facebook page: “You ain’t no cowboy if you don’t rope a calf out of a [doctor’s] office.”
We can see that decision in your eyes
The cliché that eyes are the windows to the soul doesn’t tell the whole story about how telling eyes really are. It’s all about how they move. In a recent study, researchers determined that a type of eye movement known as a saccade reveals your choice before you even decide.
Saccades involve the eyes jumping from one fixation point to another, senior author Alaa Ahmed of the University of Colorado, Boulder, explained in a statement from the university. Saccade vigor was the key in how aligned the type of decisions were made by the 22 study participants.
In the study, subjects walked on a treadmill at varied inclines for a period of time. Then they sat in front of a monitor and a high-speed camera that tracked their eye movements as the monitor presented them with a series of exercise options. The participants had only 4 seconds to choose between them.
After they made their choices, participants went back on the treadmill to perform the exercises they had chosen. The researchers found that participants’ eyes jumped between the options slowly then faster to the option they eventually picked. The more impulsive decision-makers also tended to move their eyes even more rapidly before slowing down after a decision was made, making it pretty conclusive that the eyes were revealing their choices.
The way your eyes shift gives you away without saying a thing. Might be wise, then, to wear sunglasses to your next poker tournament.
Let them eat soap
Okay, we admit it: LOTME spends a lot of time in the bathroom. Today, though, we’re interested in the sinks. Specifically, the P-traps under the sinks. You know, the curvy bit that keeps sewer gas from wafting back into the room?
Well, researchers from the University of Reading (England) recently found some fungi while examining a bunch of sinks on the university’s Whiteknights campus. “It isn’t a big surprise to find fungi in a warm, wet environment. But sinks and P-traps have thus far been overlooked as potential reservoirs of these microorganisms,” they said in a written statement.
Samples collected from 289 P-traps contained “a very similar community of yeasts and molds, showing that sinks in use in public environments share a role as reservoirs of fungal organisms,” they noted.
The fungi living in the traps survived conditions with high temperatures, low pH, and little in the way of nutrients. So what were they eating? Some varieties, they said, “use detergents, found in soap, as a source of carbon-rich food.” We’ll repeat that last part: They used the soap as food.
WARNING: Rant Ahead.
There are a lot of cleaning products for sale that say they will make your home safe by killing 99.9% of germs and bacteria. Not fungi, exactly, but we’re still talking microorganisms. Molds, bacteria, and viruses are all stuff that can infect humans and make them sick.
So you kill 99.9% of them. Great, but that leaves 0.1% that you just made angry. And what do they do next? They learn to eat soap. Then University of Reading investigators find out that all the extra hand washing going on during the COVID-19 pandemic was “clogging up sinks with nasty disease-causing bacteria.”
These are microorganisms we’re talking about people. They’ve been at this for a billion years! Rats can’t beat them, cockroaches won’t stop them – Earth’s ultimate survivors are powerless against the invisible horde.
We’re doomed.
Noninvasive laser therapy tied to improved short-term memory
Investigators compared the effect of 1,064 nm of tPBM delivered over a 12-minute session to the right PFC vs. three other treatment arms: delivery of the same intervention to the left PFC, delivery of the intervention at a lower frequency, and a sham intervention.
All participants were shown a series of items prior to the intervention and asked to recall them after the intervention. Those who received tPBM 1,064 nm to the right PFC showed a superior performance of up to 25% in the memory tasks compared with the other groups.
Patients with attention-related conditions, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, “could benefit from this type of treatment, which is safe, simple, and noninvasive, with no side effects,” coinvestigator Dongwei Li, a visiting PhD student at the Centre for Human Brain Health, University of Birmingham, England, said in a news release.
The findings were published online in Science Advances.
Differing wavelengths
The researchers note that “in the past decades,” noninvasive brain stimulation technology using transcranial application of direct or alternating electrical or magnetic fields “has been proven to be useful” in the improvement of working memory (WM).
When applied to the right PFC, tPBM has been shown to improve accuracy and speed of reaction time in WM tasks and improvements in “high-order cognitive functions,” such as sustained attention, emotion, and executive functions.
The investigators wanted to assess the impact of tPBM applied to different parts of the brain and at different wavelengths. They conducted four double-blind, sham-controlled experiments encompassing 90 neurotypical college students (mean age, 22 years). Each student participated in only one of the four experiments.
All completed two different tPBM sessions, separated by a week, in which sham and active tPBM were compared. Two different types of change-detection memory tasks were given: one requiring participants to remember the orientation of a series of items before and after the intervention and one other requiring them to remember the color of the items (experiments 1 and 2).
A series of follow-up experiments focused on comparing different wavelengths (1,064 nm vs. 852 nm) and different stimulation sites (right vs. left PFC; experiments 3 and 4).
EEG recordings were obtained during the intervention and the memory tasks.
Each experiment consisted of one active tPBM session and one sham tPBM session, with sessions consisting of 12 minutes of laser light (or sham) intervention. These sessions were conducted on the first and the seventh day; then, on the eighth day, participants were asked to report (or guess) which session was the active tPBM session.
Stimulating astrocytes
Results showed that, compared with sham tPBM, there was an improvement in WM capacity and scores by the 1,064 nm intervention in the orientation as well as the color task.
Participants who received the targeted treatment were able to remember between four and five test objects, whereas those with the treatment variations were only able to remember between three and four objects.
“These results support the hypothesis that 1,064 nm tPBM on the right PFC enhances WM capacity,” the investigators wrote.
They also found improvements in WM in participants receiving tPBM vs. sham regardless of whether their performance in the WM task was at a low or high level. This finding held true in both the orientation and the color tasks.
“Therefore, participants with good and poor WM capacity improved after 1,064 nm tPBM,” the researchers noted.
In addition, participants were unable to guess or report whether they had received sham or active tPBM.
EEG monitoring showed changes in brain activity that predicted the improvements in memory performance. In particular, 1,064 tPBM applied to the right PFC increased occipitoparietal contralateral delay activity (CDA), with CDA mediating the WM improvement.
This is “consistent with previous research that CDA is indicative of the number of maintained objects in visual working memory,” the investigators wrote.
Pearson correlation analyses showed that the differences in CDA set-size effects between active and sham session “correlated positively” with the behavioral differences between these sessions. For the orientation task, the r was 0.446 (P < .04); and for the color task, the r was .563 (P < .02).
No similar improvements were found with the 852 nm tPBM.
“We need further research to understand exactly why the tPBM is having this positive effect,” coinvestigator Ole Jensen, PhD, professor in translational neuroscience and codirector of the Centre for Human Brain Health, said in the release.
“It’s possible that the light is stimulating the astrocytes – the powerplants – in the nerve cells within the PFC, and this has a positive effect on the cells’ efficiency,” he noted.
Dr. Jensen added that his team “will also be investigating how long the effects might last. Clearly, if these experiments are to lead to a clinical intervention, we will need to see long-lasting benefits.”
Beneficial cognitive, emotional effects
Commenting for this news organization, Francisco Gonzalez-Lima, PhD, professor in the department of psychology, University of Texas at Austin, called the study “well done.”
Dr. Gonzalez-Lima was one of the first researchers to demonstrate that 1,064 nm transcranial infrared laser stimulation “produces beneficial cognitive and emotional effects in humans, including improving visual working memory,” he said.
The current study “reported an additional brain effect linked to the improved visual working memory that consists of an EEG-derived response, which is a new finding,” noted Dr. Gonzales-Lima, who was not involved with the new research.
He added that the same laser method “has been found by the Gonzalez-Lima lab to be effective at improving cognition in older adults and depressed and bipolar patients.”
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, and the National Defence Basic Scientific Research Program of China. The investigators and Dr. Gonzalez-Lima report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators compared the effect of 1,064 nm of tPBM delivered over a 12-minute session to the right PFC vs. three other treatment arms: delivery of the same intervention to the left PFC, delivery of the intervention at a lower frequency, and a sham intervention.
All participants were shown a series of items prior to the intervention and asked to recall them after the intervention. Those who received tPBM 1,064 nm to the right PFC showed a superior performance of up to 25% in the memory tasks compared with the other groups.
Patients with attention-related conditions, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, “could benefit from this type of treatment, which is safe, simple, and noninvasive, with no side effects,” coinvestigator Dongwei Li, a visiting PhD student at the Centre for Human Brain Health, University of Birmingham, England, said in a news release.
The findings were published online in Science Advances.
Differing wavelengths
The researchers note that “in the past decades,” noninvasive brain stimulation technology using transcranial application of direct or alternating electrical or magnetic fields “has been proven to be useful” in the improvement of working memory (WM).
When applied to the right PFC, tPBM has been shown to improve accuracy and speed of reaction time in WM tasks and improvements in “high-order cognitive functions,” such as sustained attention, emotion, and executive functions.
The investigators wanted to assess the impact of tPBM applied to different parts of the brain and at different wavelengths. They conducted four double-blind, sham-controlled experiments encompassing 90 neurotypical college students (mean age, 22 years). Each student participated in only one of the four experiments.
All completed two different tPBM sessions, separated by a week, in which sham and active tPBM were compared. Two different types of change-detection memory tasks were given: one requiring participants to remember the orientation of a series of items before and after the intervention and one other requiring them to remember the color of the items (experiments 1 and 2).
A series of follow-up experiments focused on comparing different wavelengths (1,064 nm vs. 852 nm) and different stimulation sites (right vs. left PFC; experiments 3 and 4).
EEG recordings were obtained during the intervention and the memory tasks.
Each experiment consisted of one active tPBM session and one sham tPBM session, with sessions consisting of 12 minutes of laser light (or sham) intervention. These sessions were conducted on the first and the seventh day; then, on the eighth day, participants were asked to report (or guess) which session was the active tPBM session.
Stimulating astrocytes
Results showed that, compared with sham tPBM, there was an improvement in WM capacity and scores by the 1,064 nm intervention in the orientation as well as the color task.
Participants who received the targeted treatment were able to remember between four and five test objects, whereas those with the treatment variations were only able to remember between three and four objects.
“These results support the hypothesis that 1,064 nm tPBM on the right PFC enhances WM capacity,” the investigators wrote.
They also found improvements in WM in participants receiving tPBM vs. sham regardless of whether their performance in the WM task was at a low or high level. This finding held true in both the orientation and the color tasks.
“Therefore, participants with good and poor WM capacity improved after 1,064 nm tPBM,” the researchers noted.
In addition, participants were unable to guess or report whether they had received sham or active tPBM.
EEG monitoring showed changes in brain activity that predicted the improvements in memory performance. In particular, 1,064 tPBM applied to the right PFC increased occipitoparietal contralateral delay activity (CDA), with CDA mediating the WM improvement.
This is “consistent with previous research that CDA is indicative of the number of maintained objects in visual working memory,” the investigators wrote.
Pearson correlation analyses showed that the differences in CDA set-size effects between active and sham session “correlated positively” with the behavioral differences between these sessions. For the orientation task, the r was 0.446 (P < .04); and for the color task, the r was .563 (P < .02).
No similar improvements were found with the 852 nm tPBM.
“We need further research to understand exactly why the tPBM is having this positive effect,” coinvestigator Ole Jensen, PhD, professor in translational neuroscience and codirector of the Centre for Human Brain Health, said in the release.
“It’s possible that the light is stimulating the astrocytes – the powerplants – in the nerve cells within the PFC, and this has a positive effect on the cells’ efficiency,” he noted.
Dr. Jensen added that his team “will also be investigating how long the effects might last. Clearly, if these experiments are to lead to a clinical intervention, we will need to see long-lasting benefits.”
Beneficial cognitive, emotional effects
Commenting for this news organization, Francisco Gonzalez-Lima, PhD, professor in the department of psychology, University of Texas at Austin, called the study “well done.”
Dr. Gonzalez-Lima was one of the first researchers to demonstrate that 1,064 nm transcranial infrared laser stimulation “produces beneficial cognitive and emotional effects in humans, including improving visual working memory,” he said.
The current study “reported an additional brain effect linked to the improved visual working memory that consists of an EEG-derived response, which is a new finding,” noted Dr. Gonzales-Lima, who was not involved with the new research.
He added that the same laser method “has been found by the Gonzalez-Lima lab to be effective at improving cognition in older adults and depressed and bipolar patients.”
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, and the National Defence Basic Scientific Research Program of China. The investigators and Dr. Gonzalez-Lima report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators compared the effect of 1,064 nm of tPBM delivered over a 12-minute session to the right PFC vs. three other treatment arms: delivery of the same intervention to the left PFC, delivery of the intervention at a lower frequency, and a sham intervention.
All participants were shown a series of items prior to the intervention and asked to recall them after the intervention. Those who received tPBM 1,064 nm to the right PFC showed a superior performance of up to 25% in the memory tasks compared with the other groups.
Patients with attention-related conditions, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, “could benefit from this type of treatment, which is safe, simple, and noninvasive, with no side effects,” coinvestigator Dongwei Li, a visiting PhD student at the Centre for Human Brain Health, University of Birmingham, England, said in a news release.
The findings were published online in Science Advances.
Differing wavelengths
The researchers note that “in the past decades,” noninvasive brain stimulation technology using transcranial application of direct or alternating electrical or magnetic fields “has been proven to be useful” in the improvement of working memory (WM).
When applied to the right PFC, tPBM has been shown to improve accuracy and speed of reaction time in WM tasks and improvements in “high-order cognitive functions,” such as sustained attention, emotion, and executive functions.
The investigators wanted to assess the impact of tPBM applied to different parts of the brain and at different wavelengths. They conducted four double-blind, sham-controlled experiments encompassing 90 neurotypical college students (mean age, 22 years). Each student participated in only one of the four experiments.
All completed two different tPBM sessions, separated by a week, in which sham and active tPBM were compared. Two different types of change-detection memory tasks were given: one requiring participants to remember the orientation of a series of items before and after the intervention and one other requiring them to remember the color of the items (experiments 1 and 2).
A series of follow-up experiments focused on comparing different wavelengths (1,064 nm vs. 852 nm) and different stimulation sites (right vs. left PFC; experiments 3 and 4).
EEG recordings were obtained during the intervention and the memory tasks.
Each experiment consisted of one active tPBM session and one sham tPBM session, with sessions consisting of 12 minutes of laser light (or sham) intervention. These sessions were conducted on the first and the seventh day; then, on the eighth day, participants were asked to report (or guess) which session was the active tPBM session.
Stimulating astrocytes
Results showed that, compared with sham tPBM, there was an improvement in WM capacity and scores by the 1,064 nm intervention in the orientation as well as the color task.
Participants who received the targeted treatment were able to remember between four and five test objects, whereas those with the treatment variations were only able to remember between three and four objects.
“These results support the hypothesis that 1,064 nm tPBM on the right PFC enhances WM capacity,” the investigators wrote.
They also found improvements in WM in participants receiving tPBM vs. sham regardless of whether their performance in the WM task was at a low or high level. This finding held true in both the orientation and the color tasks.
“Therefore, participants with good and poor WM capacity improved after 1,064 nm tPBM,” the researchers noted.
In addition, participants were unable to guess or report whether they had received sham or active tPBM.
EEG monitoring showed changes in brain activity that predicted the improvements in memory performance. In particular, 1,064 tPBM applied to the right PFC increased occipitoparietal contralateral delay activity (CDA), with CDA mediating the WM improvement.
This is “consistent with previous research that CDA is indicative of the number of maintained objects in visual working memory,” the investigators wrote.
Pearson correlation analyses showed that the differences in CDA set-size effects between active and sham session “correlated positively” with the behavioral differences between these sessions. For the orientation task, the r was 0.446 (P < .04); and for the color task, the r was .563 (P < .02).
No similar improvements were found with the 852 nm tPBM.
“We need further research to understand exactly why the tPBM is having this positive effect,” coinvestigator Ole Jensen, PhD, professor in translational neuroscience and codirector of the Centre for Human Brain Health, said in the release.
“It’s possible that the light is stimulating the astrocytes – the powerplants – in the nerve cells within the PFC, and this has a positive effect on the cells’ efficiency,” he noted.
Dr. Jensen added that his team “will also be investigating how long the effects might last. Clearly, if these experiments are to lead to a clinical intervention, we will need to see long-lasting benefits.”
Beneficial cognitive, emotional effects
Commenting for this news organization, Francisco Gonzalez-Lima, PhD, professor in the department of psychology, University of Texas at Austin, called the study “well done.”
Dr. Gonzalez-Lima was one of the first researchers to demonstrate that 1,064 nm transcranial infrared laser stimulation “produces beneficial cognitive and emotional effects in humans, including improving visual working memory,” he said.
The current study “reported an additional brain effect linked to the improved visual working memory that consists of an EEG-derived response, which is a new finding,” noted Dr. Gonzales-Lima, who was not involved with the new research.
He added that the same laser method “has been found by the Gonzalez-Lima lab to be effective at improving cognition in older adults and depressed and bipolar patients.”
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, and the National Defence Basic Scientific Research Program of China. The investigators and Dr. Gonzalez-Lima report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SCIENCE ADVANCES
Terminally ill cancer patients struggle to access psilocybin
In March 2020, when the world was struck by the news of the COVID-19 pandemic, Erinn Baldeschwiler received her own gut punch. She was diagnosed with stage IV metastatic breast cancer and was given about 2 years to live.
Then 48, the mother of two teenagers had just started a new chapter in her life. She’d gotten divorced, moved to a new home, and left a small business she had spent 18 years cultivating. The prospect that her life story might soon be ending, that she wouldn’t see her children grow up, was a twist of fate almost too devastating to bear.
“Are you kidding me that this is happening?” she thought.
But she also wanted to keep learning and growing in her remaining years, to devote them to creating meaningful memories, contemplating her mortality, and trying to find inner peace.
“The last 2 years have kind of been this dance with Lady Death,” she said.
They have also been a dance with Lady Justice.
In March 2021, Ms. Baldeschwiler, along with Michal Bloom, who also has terminal cancer, and their palliative care physician, Sunil Aggarwal, MD, PhD, decided to sue the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) for the right to access psilocybin, the psychoactive ingredient in “magic” mushrooms.
Psilocybin-assisted therapy has been shown to help terminally ill people overcome their fear, anxiety, and despair about death and to experience the kind of peace Ms. Baldeschwiler is seeking.
Psilocybin is illegal in the United States, but the plaintiffs argue they should be able to take the substance through the Right to Try Act. The 2018 federal law says that people with life-threatening conditions who have exhausted all approved treatment options can access drugs that have not yet been approved by the Food and Drug Administration but have passed phase 1 clinical trials.
This case marks the first time patients have fought to use a Schedule I drug under the Right to Try Act.
The push to expand access to psilocybin is picking up steam in the United States. In 2023, facilitated use of psilocybin will become legal in Oregon and Colorado. Recent proposals from the Biden administration and members of Congress could make psilocybin more widely accessible in the next few years.
It is also gaining momentum outside the United States. In Canada, patients are suing the government to help patients obtain psilocybin-assisted therapy for medical purposes.
“I think what we have here is a confluence of events that are driving toward the mandatory opening of a path to access psilocybin for therapeutic use sooner rather than later,” said Kathryn Tucker, lead counsel in the case against the DEA.
Reverberations of Right to Try
The story of Right to Try began with Abigail Burroughs, who was diagnosed with head and neck cancer at age 19.
After conventional therapies failed, Ms. Burroughs’ oncologist recommended cetuximab, a drug targeting EGFR that was experimental at the time. Because the drug was available only through colon cancer trials, she was denied access.
She died in 2001 at age 21.
Ms. Burroughs’ father, Frank Burroughs, formed an organization that in 2003 sued the FDA to provide terminally ill patients access to unapproved drugs. In 2005, they lost, and subsequent attempts to appeal the decision failed.
Still, the case sparked a Right to Try movement.
“Right to Try laws swept the U.S. in a firestorm,” Ms. Tucker said.
Along with the federal law, which passed in 2018, 41 states have enacted Right to Try laws.
The movement intrigued Dr. Aggarwal, codirector of the Advanced Integrative Medical Science (AIMS) Institute in Seattle. Dr. Aggarwal had been treating patients with cannabis, and after taking psilocybin himself and finding it therapeutic, he thought Ms. Baldeschwiler could benefit.
“I always knew that the powerful medicines within Schedule I had a significant role to play in healing,” he said. “That was baked into my decision to become a doctor, to research, and to innovate.”
He applied for the right to cultivate psilocybin mushrooms, but the fungus doesn’t meet Right to Try requirements. He then found a manufacturer willing to supply synthesized psilocybin, but because it’s a Schedule I drug, the manufacturer needed an okay from the DEA.
Dr. Aggarwal joined forces with Ms. Tucker, who has spent 35 years protecting the rights of terminally ill patients. In January 2021, Ms. Tucker contacted the DEA about allowing dying patients, including Ms. Baldeschwiler and Mr. Bloom, to access psilocybin-assisted therapy.
The response, she said, was predictable.
“The DEA’s knee always jerks in the direction of no access,” Ms. Tucker said. “So it said ‘no access.’ “
The reason: In a letter dated February 2021, the DEA said it “has no authority to waive” any requirements of the Controlled Substances Act under Right to Try laws.
Suing the DEA
Dr. Aggarwal and Ms. Tucker did not accept the DEA’s “no access” answer.
They decided to sue.
Dr. Aggarwal and Ms. Tucker took the matter to the Ninth Circuit Court in March 2021. In January 2022, the court dismissed the case after the DEA claimed its initial denial was not final.
The following month, the plaintiffs petitioned the DEA to deliver a concrete answer.
In May, while waiting for a response, demonstrators gathered at the DEA’s headquarters to call for legal access to psilocybin. One of the protesters was Ms. Baldeschwiler, who choked back tears as she told the crowd she was likely missing her last Mother’s Day with her children to attend the event. She was arrested, along with 16 other people.
In late June, the DEA provided its final answer: No access.
In a letter addressed to Ms. Tucker, Thomas W. Prevoznik, the DEA’s deputy assistant administrator, said it “finds no basis” to reconsider its initial denial in February 2021 “because the legal and factual considerations remain unchanged.”
In an appeal, Ms. Tucker wrote: “In denying Petitioners’ requested accommodation in the Final Agency Action, DEA hides behind a smokescreen, neglecting its duty to implement the federal [Right to Try Act] and violating the state [Right to Try law].”
The government’s response is due in January 2023.
Ms. Tucker and her legal team also petitioned the DEA on behalf of Dr. Aggarwal to reschedule psilocybin from Schedule I to Schedule II.
The DEA defines Schedule I substances as “drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse.” But the FDA has designated psilocybin as a breakthrough therapy for depression, which, Ms. Tucker noted, “reflects that there is a currently accepted medical use.”
Nevertheless, in September, the DEA denied Ms. Tucker’s petition to reschedule psilocybin, and her team is now petitioning the Ninth Circuit Court for a review of that decision.
Despite the setbacks, actions from the Biden administration and members of Congress could help improve access.
In July, Senators Cory Booker and Rand Paul introduced the Right to Try Clarification Act to clarify that the federal law includes Schedule I substances. If passed, Ms. Tucker said, it would negate the DEA’s “no access” argument.
And earlier this year, the Biden administration announced plans to establish a federal task force to address the “myriad of complex issues” associated with the anticipated FDA approval of psilocybin to treat depression. The task force will explore “the potential of psychedelic-assisted therapies” to tackle the mental health crisis as well as any “risks to public health” that “may require harm reduction, risk mitigation, and safety monitoring.”
The fight north of the border
In 2016, Canadian resident Thomas Hartle, then 48, awoke from surgery for a bowel obstruction to learn he had stage IV colon cancer.
After another surgery, his doctors believed the tumors were gone. But in 2019, the cancer came back, along with extreme anxiety and distress over his impending death and how his two special-needs children would cope.
Mr. Hartle wanted to try magic mushroom–assisted psychotherapy. The Saskatoon resident sought help from TheraPsil, a Canadian nonprofit organization that advocates for therapeutic psilocybin. They applied for access under Section 56, which allows health officials to exempt patients from certain provisions of drug law.
In 2020, Hartle became the first Canadian to legally obtain psilocybin-assisted therapy.
“It has been nothing short of life changing for me,” Mr. Hartle said at a palliative care conference in Saskatoon this past June. “I am now no longer actively dying. I feel like I am genuinely actively living.”
TheraPsil has obtained Section 56 exemptions for around 60 patients to access psilocybin-assisted therapy as well as 19 health care professionals who are training to become psilocybin-assisted therapists.
But then an election ushered in new health ministers, and in early 2022, the exemptions evaporated. Thousands of patients and health care practitioners on TheraPsil’s waiting list were left in limbo.
Health Canada told CBC News that the rule change came about because “while psilocybin has shown promise in clinical trials for the treatment of some indications, further research is still needed to determine its safety and efficacy.”
As an alternative, TheraPsil began applying for access under Canada’s Special Access Program, which is similar to Right to Try laws in the United States. But Canada’s program doesn’t apply to therapists in training, and the petition process is so slow that many patients die before requests can be approved.
“People like to pretend that the Special Access Program is not political, but it is very political,” said TheraPsil’s CEO, Spencer Hawkswell. “It means a patient and a doctor are asking a politician for access to their medicine, which is absolutely unacceptable.”
Now, TheraPsil is helping patients take the Canadian government to court. In July, Mr. Hartle and seven others with conditions ranging from cancer to chronic pain filed a lawsuit against Canada’s health ministry that challenges the limited legal pathways to the use of psilocybin. The lawsuit argues that patients have a “constitutional right to access psilocybin for medicinal purposes,” and it advocates for access to regulated psilocybin products from licensed dealers, much like Canada’s medical marijuana program already does.
In the filing, TheraPsil said that as of February 2022, it has a wait-list of more than 800 patients who are requesting help in obtaining psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy.
An uncertain future
Despite the groundswell of support, many unknowns remain about the safety of expanding access to psilocybin-assisted therapy.
When Oregon and Colorado launch their psilocybin programs in 2023, the licensed centers will provide testing grounds for the safety and efficacy of broader access to psilocybin for people with depression or terminal cancer as well as those looking to grow spiritually.
Although in clinical trials psilocybin has been found to ease symptoms of depression and end-of-life demoralization for people with life-threatening conditions, it has not been adequately tested in people with a range of mental health problems, traumas, and racial backgrounds.
That uncertainty has given some people pause. In recent months, some researchers and journalists have pushed back against the frenzy over the promise of psychedelics.
In September, David Yaden, PhD, a psychedelics researcher at Johns Hopkins, spoke at the Interdisciplinary Conference on Psychedelic Research in the Netherlands. He encouraged people to pay more attention to potential adverse effects of psychedelics, which could include anything from headaches to lingering dysphoria.
“Oftentimes, we hear only the positive anecdotes,” Dr. Yaden said. “We don’t hear ... neutral or negative ones. So, I think all of those anecdotes need to be part of the picture.”
A recent piece in Wired noted that mentioning the potential harms of psychedelics amid its renaissance has been “taboo,” but the authors cautioned that as clinical trials involving psychedelics grow larger and the drugs become commercialized, “more negative outcomes are likely to transpire.”
But Ms. Baldeschwiler remains steadfast in her pursuit. While it’s important to approach broader access to psychedelics with caution, “end-of-life patients don’t have time to wait,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In March 2020, when the world was struck by the news of the COVID-19 pandemic, Erinn Baldeschwiler received her own gut punch. She was diagnosed with stage IV metastatic breast cancer and was given about 2 years to live.
Then 48, the mother of two teenagers had just started a new chapter in her life. She’d gotten divorced, moved to a new home, and left a small business she had spent 18 years cultivating. The prospect that her life story might soon be ending, that she wouldn’t see her children grow up, was a twist of fate almost too devastating to bear.
“Are you kidding me that this is happening?” she thought.
But she also wanted to keep learning and growing in her remaining years, to devote them to creating meaningful memories, contemplating her mortality, and trying to find inner peace.
“The last 2 years have kind of been this dance with Lady Death,” she said.
They have also been a dance with Lady Justice.
In March 2021, Ms. Baldeschwiler, along with Michal Bloom, who also has terminal cancer, and their palliative care physician, Sunil Aggarwal, MD, PhD, decided to sue the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) for the right to access psilocybin, the psychoactive ingredient in “magic” mushrooms.
Psilocybin-assisted therapy has been shown to help terminally ill people overcome their fear, anxiety, and despair about death and to experience the kind of peace Ms. Baldeschwiler is seeking.
Psilocybin is illegal in the United States, but the plaintiffs argue they should be able to take the substance through the Right to Try Act. The 2018 federal law says that people with life-threatening conditions who have exhausted all approved treatment options can access drugs that have not yet been approved by the Food and Drug Administration but have passed phase 1 clinical trials.
This case marks the first time patients have fought to use a Schedule I drug under the Right to Try Act.
The push to expand access to psilocybin is picking up steam in the United States. In 2023, facilitated use of psilocybin will become legal in Oregon and Colorado. Recent proposals from the Biden administration and members of Congress could make psilocybin more widely accessible in the next few years.
It is also gaining momentum outside the United States. In Canada, patients are suing the government to help patients obtain psilocybin-assisted therapy for medical purposes.
“I think what we have here is a confluence of events that are driving toward the mandatory opening of a path to access psilocybin for therapeutic use sooner rather than later,” said Kathryn Tucker, lead counsel in the case against the DEA.
Reverberations of Right to Try
The story of Right to Try began with Abigail Burroughs, who was diagnosed with head and neck cancer at age 19.
After conventional therapies failed, Ms. Burroughs’ oncologist recommended cetuximab, a drug targeting EGFR that was experimental at the time. Because the drug was available only through colon cancer trials, she was denied access.
She died in 2001 at age 21.
Ms. Burroughs’ father, Frank Burroughs, formed an organization that in 2003 sued the FDA to provide terminally ill patients access to unapproved drugs. In 2005, they lost, and subsequent attempts to appeal the decision failed.
Still, the case sparked a Right to Try movement.
“Right to Try laws swept the U.S. in a firestorm,” Ms. Tucker said.
Along with the federal law, which passed in 2018, 41 states have enacted Right to Try laws.
The movement intrigued Dr. Aggarwal, codirector of the Advanced Integrative Medical Science (AIMS) Institute in Seattle. Dr. Aggarwal had been treating patients with cannabis, and after taking psilocybin himself and finding it therapeutic, he thought Ms. Baldeschwiler could benefit.
“I always knew that the powerful medicines within Schedule I had a significant role to play in healing,” he said. “That was baked into my decision to become a doctor, to research, and to innovate.”
He applied for the right to cultivate psilocybin mushrooms, but the fungus doesn’t meet Right to Try requirements. He then found a manufacturer willing to supply synthesized psilocybin, but because it’s a Schedule I drug, the manufacturer needed an okay from the DEA.
Dr. Aggarwal joined forces with Ms. Tucker, who has spent 35 years protecting the rights of terminally ill patients. In January 2021, Ms. Tucker contacted the DEA about allowing dying patients, including Ms. Baldeschwiler and Mr. Bloom, to access psilocybin-assisted therapy.
The response, she said, was predictable.
“The DEA’s knee always jerks in the direction of no access,” Ms. Tucker said. “So it said ‘no access.’ “
The reason: In a letter dated February 2021, the DEA said it “has no authority to waive” any requirements of the Controlled Substances Act under Right to Try laws.
Suing the DEA
Dr. Aggarwal and Ms. Tucker did not accept the DEA’s “no access” answer.
They decided to sue.
Dr. Aggarwal and Ms. Tucker took the matter to the Ninth Circuit Court in March 2021. In January 2022, the court dismissed the case after the DEA claimed its initial denial was not final.
The following month, the plaintiffs petitioned the DEA to deliver a concrete answer.
In May, while waiting for a response, demonstrators gathered at the DEA’s headquarters to call for legal access to psilocybin. One of the protesters was Ms. Baldeschwiler, who choked back tears as she told the crowd she was likely missing her last Mother’s Day with her children to attend the event. She was arrested, along with 16 other people.
In late June, the DEA provided its final answer: No access.
In a letter addressed to Ms. Tucker, Thomas W. Prevoznik, the DEA’s deputy assistant administrator, said it “finds no basis” to reconsider its initial denial in February 2021 “because the legal and factual considerations remain unchanged.”
In an appeal, Ms. Tucker wrote: “In denying Petitioners’ requested accommodation in the Final Agency Action, DEA hides behind a smokescreen, neglecting its duty to implement the federal [Right to Try Act] and violating the state [Right to Try law].”
The government’s response is due in January 2023.
Ms. Tucker and her legal team also petitioned the DEA on behalf of Dr. Aggarwal to reschedule psilocybin from Schedule I to Schedule II.
The DEA defines Schedule I substances as “drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse.” But the FDA has designated psilocybin as a breakthrough therapy for depression, which, Ms. Tucker noted, “reflects that there is a currently accepted medical use.”
Nevertheless, in September, the DEA denied Ms. Tucker’s petition to reschedule psilocybin, and her team is now petitioning the Ninth Circuit Court for a review of that decision.
Despite the setbacks, actions from the Biden administration and members of Congress could help improve access.
In July, Senators Cory Booker and Rand Paul introduced the Right to Try Clarification Act to clarify that the federal law includes Schedule I substances. If passed, Ms. Tucker said, it would negate the DEA’s “no access” argument.
And earlier this year, the Biden administration announced plans to establish a federal task force to address the “myriad of complex issues” associated with the anticipated FDA approval of psilocybin to treat depression. The task force will explore “the potential of psychedelic-assisted therapies” to tackle the mental health crisis as well as any “risks to public health” that “may require harm reduction, risk mitigation, and safety monitoring.”
The fight north of the border
In 2016, Canadian resident Thomas Hartle, then 48, awoke from surgery for a bowel obstruction to learn he had stage IV colon cancer.
After another surgery, his doctors believed the tumors were gone. But in 2019, the cancer came back, along with extreme anxiety and distress over his impending death and how his two special-needs children would cope.
Mr. Hartle wanted to try magic mushroom–assisted psychotherapy. The Saskatoon resident sought help from TheraPsil, a Canadian nonprofit organization that advocates for therapeutic psilocybin. They applied for access under Section 56, which allows health officials to exempt patients from certain provisions of drug law.
In 2020, Hartle became the first Canadian to legally obtain psilocybin-assisted therapy.
“It has been nothing short of life changing for me,” Mr. Hartle said at a palliative care conference in Saskatoon this past June. “I am now no longer actively dying. I feel like I am genuinely actively living.”
TheraPsil has obtained Section 56 exemptions for around 60 patients to access psilocybin-assisted therapy as well as 19 health care professionals who are training to become psilocybin-assisted therapists.
But then an election ushered in new health ministers, and in early 2022, the exemptions evaporated. Thousands of patients and health care practitioners on TheraPsil’s waiting list were left in limbo.
Health Canada told CBC News that the rule change came about because “while psilocybin has shown promise in clinical trials for the treatment of some indications, further research is still needed to determine its safety and efficacy.”
As an alternative, TheraPsil began applying for access under Canada’s Special Access Program, which is similar to Right to Try laws in the United States. But Canada’s program doesn’t apply to therapists in training, and the petition process is so slow that many patients die before requests can be approved.
“People like to pretend that the Special Access Program is not political, but it is very political,” said TheraPsil’s CEO, Spencer Hawkswell. “It means a patient and a doctor are asking a politician for access to their medicine, which is absolutely unacceptable.”
Now, TheraPsil is helping patients take the Canadian government to court. In July, Mr. Hartle and seven others with conditions ranging from cancer to chronic pain filed a lawsuit against Canada’s health ministry that challenges the limited legal pathways to the use of psilocybin. The lawsuit argues that patients have a “constitutional right to access psilocybin for medicinal purposes,” and it advocates for access to regulated psilocybin products from licensed dealers, much like Canada’s medical marijuana program already does.
In the filing, TheraPsil said that as of February 2022, it has a wait-list of more than 800 patients who are requesting help in obtaining psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy.
An uncertain future
Despite the groundswell of support, many unknowns remain about the safety of expanding access to psilocybin-assisted therapy.
When Oregon and Colorado launch their psilocybin programs in 2023, the licensed centers will provide testing grounds for the safety and efficacy of broader access to psilocybin for people with depression or terminal cancer as well as those looking to grow spiritually.
Although in clinical trials psilocybin has been found to ease symptoms of depression and end-of-life demoralization for people with life-threatening conditions, it has not been adequately tested in people with a range of mental health problems, traumas, and racial backgrounds.
That uncertainty has given some people pause. In recent months, some researchers and journalists have pushed back against the frenzy over the promise of psychedelics.
In September, David Yaden, PhD, a psychedelics researcher at Johns Hopkins, spoke at the Interdisciplinary Conference on Psychedelic Research in the Netherlands. He encouraged people to pay more attention to potential adverse effects of psychedelics, which could include anything from headaches to lingering dysphoria.
“Oftentimes, we hear only the positive anecdotes,” Dr. Yaden said. “We don’t hear ... neutral or negative ones. So, I think all of those anecdotes need to be part of the picture.”
A recent piece in Wired noted that mentioning the potential harms of psychedelics amid its renaissance has been “taboo,” but the authors cautioned that as clinical trials involving psychedelics grow larger and the drugs become commercialized, “more negative outcomes are likely to transpire.”
But Ms. Baldeschwiler remains steadfast in her pursuit. While it’s important to approach broader access to psychedelics with caution, “end-of-life patients don’t have time to wait,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In March 2020, when the world was struck by the news of the COVID-19 pandemic, Erinn Baldeschwiler received her own gut punch. She was diagnosed with stage IV metastatic breast cancer and was given about 2 years to live.
Then 48, the mother of two teenagers had just started a new chapter in her life. She’d gotten divorced, moved to a new home, and left a small business she had spent 18 years cultivating. The prospect that her life story might soon be ending, that she wouldn’t see her children grow up, was a twist of fate almost too devastating to bear.
“Are you kidding me that this is happening?” she thought.
But she also wanted to keep learning and growing in her remaining years, to devote them to creating meaningful memories, contemplating her mortality, and trying to find inner peace.
“The last 2 years have kind of been this dance with Lady Death,” she said.
They have also been a dance with Lady Justice.
In March 2021, Ms. Baldeschwiler, along with Michal Bloom, who also has terminal cancer, and their palliative care physician, Sunil Aggarwal, MD, PhD, decided to sue the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) for the right to access psilocybin, the psychoactive ingredient in “magic” mushrooms.
Psilocybin-assisted therapy has been shown to help terminally ill people overcome their fear, anxiety, and despair about death and to experience the kind of peace Ms. Baldeschwiler is seeking.
Psilocybin is illegal in the United States, but the plaintiffs argue they should be able to take the substance through the Right to Try Act. The 2018 federal law says that people with life-threatening conditions who have exhausted all approved treatment options can access drugs that have not yet been approved by the Food and Drug Administration but have passed phase 1 clinical trials.
This case marks the first time patients have fought to use a Schedule I drug under the Right to Try Act.
The push to expand access to psilocybin is picking up steam in the United States. In 2023, facilitated use of psilocybin will become legal in Oregon and Colorado. Recent proposals from the Biden administration and members of Congress could make psilocybin more widely accessible in the next few years.
It is also gaining momentum outside the United States. In Canada, patients are suing the government to help patients obtain psilocybin-assisted therapy for medical purposes.
“I think what we have here is a confluence of events that are driving toward the mandatory opening of a path to access psilocybin for therapeutic use sooner rather than later,” said Kathryn Tucker, lead counsel in the case against the DEA.
Reverberations of Right to Try
The story of Right to Try began with Abigail Burroughs, who was diagnosed with head and neck cancer at age 19.
After conventional therapies failed, Ms. Burroughs’ oncologist recommended cetuximab, a drug targeting EGFR that was experimental at the time. Because the drug was available only through colon cancer trials, she was denied access.
She died in 2001 at age 21.
Ms. Burroughs’ father, Frank Burroughs, formed an organization that in 2003 sued the FDA to provide terminally ill patients access to unapproved drugs. In 2005, they lost, and subsequent attempts to appeal the decision failed.
Still, the case sparked a Right to Try movement.
“Right to Try laws swept the U.S. in a firestorm,” Ms. Tucker said.
Along with the federal law, which passed in 2018, 41 states have enacted Right to Try laws.
The movement intrigued Dr. Aggarwal, codirector of the Advanced Integrative Medical Science (AIMS) Institute in Seattle. Dr. Aggarwal had been treating patients with cannabis, and after taking psilocybin himself and finding it therapeutic, he thought Ms. Baldeschwiler could benefit.
“I always knew that the powerful medicines within Schedule I had a significant role to play in healing,” he said. “That was baked into my decision to become a doctor, to research, and to innovate.”
He applied for the right to cultivate psilocybin mushrooms, but the fungus doesn’t meet Right to Try requirements. He then found a manufacturer willing to supply synthesized psilocybin, but because it’s a Schedule I drug, the manufacturer needed an okay from the DEA.
Dr. Aggarwal joined forces with Ms. Tucker, who has spent 35 years protecting the rights of terminally ill patients. In January 2021, Ms. Tucker contacted the DEA about allowing dying patients, including Ms. Baldeschwiler and Mr. Bloom, to access psilocybin-assisted therapy.
The response, she said, was predictable.
“The DEA’s knee always jerks in the direction of no access,” Ms. Tucker said. “So it said ‘no access.’ “
The reason: In a letter dated February 2021, the DEA said it “has no authority to waive” any requirements of the Controlled Substances Act under Right to Try laws.
Suing the DEA
Dr. Aggarwal and Ms. Tucker did not accept the DEA’s “no access” answer.
They decided to sue.
Dr. Aggarwal and Ms. Tucker took the matter to the Ninth Circuit Court in March 2021. In January 2022, the court dismissed the case after the DEA claimed its initial denial was not final.
The following month, the plaintiffs petitioned the DEA to deliver a concrete answer.
In May, while waiting for a response, demonstrators gathered at the DEA’s headquarters to call for legal access to psilocybin. One of the protesters was Ms. Baldeschwiler, who choked back tears as she told the crowd she was likely missing her last Mother’s Day with her children to attend the event. She was arrested, along with 16 other people.
In late June, the DEA provided its final answer: No access.
In a letter addressed to Ms. Tucker, Thomas W. Prevoznik, the DEA’s deputy assistant administrator, said it “finds no basis” to reconsider its initial denial in February 2021 “because the legal and factual considerations remain unchanged.”
In an appeal, Ms. Tucker wrote: “In denying Petitioners’ requested accommodation in the Final Agency Action, DEA hides behind a smokescreen, neglecting its duty to implement the federal [Right to Try Act] and violating the state [Right to Try law].”
The government’s response is due in January 2023.
Ms. Tucker and her legal team also petitioned the DEA on behalf of Dr. Aggarwal to reschedule psilocybin from Schedule I to Schedule II.
The DEA defines Schedule I substances as “drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse.” But the FDA has designated psilocybin as a breakthrough therapy for depression, which, Ms. Tucker noted, “reflects that there is a currently accepted medical use.”
Nevertheless, in September, the DEA denied Ms. Tucker’s petition to reschedule psilocybin, and her team is now petitioning the Ninth Circuit Court for a review of that decision.
Despite the setbacks, actions from the Biden administration and members of Congress could help improve access.
In July, Senators Cory Booker and Rand Paul introduced the Right to Try Clarification Act to clarify that the federal law includes Schedule I substances. If passed, Ms. Tucker said, it would negate the DEA’s “no access” argument.
And earlier this year, the Biden administration announced plans to establish a federal task force to address the “myriad of complex issues” associated with the anticipated FDA approval of psilocybin to treat depression. The task force will explore “the potential of psychedelic-assisted therapies” to tackle the mental health crisis as well as any “risks to public health” that “may require harm reduction, risk mitigation, and safety monitoring.”
The fight north of the border
In 2016, Canadian resident Thomas Hartle, then 48, awoke from surgery for a bowel obstruction to learn he had stage IV colon cancer.
After another surgery, his doctors believed the tumors were gone. But in 2019, the cancer came back, along with extreme anxiety and distress over his impending death and how his two special-needs children would cope.
Mr. Hartle wanted to try magic mushroom–assisted psychotherapy. The Saskatoon resident sought help from TheraPsil, a Canadian nonprofit organization that advocates for therapeutic psilocybin. They applied for access under Section 56, which allows health officials to exempt patients from certain provisions of drug law.
In 2020, Hartle became the first Canadian to legally obtain psilocybin-assisted therapy.
“It has been nothing short of life changing for me,” Mr. Hartle said at a palliative care conference in Saskatoon this past June. “I am now no longer actively dying. I feel like I am genuinely actively living.”
TheraPsil has obtained Section 56 exemptions for around 60 patients to access psilocybin-assisted therapy as well as 19 health care professionals who are training to become psilocybin-assisted therapists.
But then an election ushered in new health ministers, and in early 2022, the exemptions evaporated. Thousands of patients and health care practitioners on TheraPsil’s waiting list were left in limbo.
Health Canada told CBC News that the rule change came about because “while psilocybin has shown promise in clinical trials for the treatment of some indications, further research is still needed to determine its safety and efficacy.”
As an alternative, TheraPsil began applying for access under Canada’s Special Access Program, which is similar to Right to Try laws in the United States. But Canada’s program doesn’t apply to therapists in training, and the petition process is so slow that many patients die before requests can be approved.
“People like to pretend that the Special Access Program is not political, but it is very political,” said TheraPsil’s CEO, Spencer Hawkswell. “It means a patient and a doctor are asking a politician for access to their medicine, which is absolutely unacceptable.”
Now, TheraPsil is helping patients take the Canadian government to court. In July, Mr. Hartle and seven others with conditions ranging from cancer to chronic pain filed a lawsuit against Canada’s health ministry that challenges the limited legal pathways to the use of psilocybin. The lawsuit argues that patients have a “constitutional right to access psilocybin for medicinal purposes,” and it advocates for access to regulated psilocybin products from licensed dealers, much like Canada’s medical marijuana program already does.
In the filing, TheraPsil said that as of February 2022, it has a wait-list of more than 800 patients who are requesting help in obtaining psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy.
An uncertain future
Despite the groundswell of support, many unknowns remain about the safety of expanding access to psilocybin-assisted therapy.
When Oregon and Colorado launch their psilocybin programs in 2023, the licensed centers will provide testing grounds for the safety and efficacy of broader access to psilocybin for people with depression or terminal cancer as well as those looking to grow spiritually.
Although in clinical trials psilocybin has been found to ease symptoms of depression and end-of-life demoralization for people with life-threatening conditions, it has not been adequately tested in people with a range of mental health problems, traumas, and racial backgrounds.
That uncertainty has given some people pause. In recent months, some researchers and journalists have pushed back against the frenzy over the promise of psychedelics.
In September, David Yaden, PhD, a psychedelics researcher at Johns Hopkins, spoke at the Interdisciplinary Conference on Psychedelic Research in the Netherlands. He encouraged people to pay more attention to potential adverse effects of psychedelics, which could include anything from headaches to lingering dysphoria.
“Oftentimes, we hear only the positive anecdotes,” Dr. Yaden said. “We don’t hear ... neutral or negative ones. So, I think all of those anecdotes need to be part of the picture.”
A recent piece in Wired noted that mentioning the potential harms of psychedelics amid its renaissance has been “taboo,” but the authors cautioned that as clinical trials involving psychedelics grow larger and the drugs become commercialized, “more negative outcomes are likely to transpire.”
But Ms. Baldeschwiler remains steadfast in her pursuit. While it’s important to approach broader access to psychedelics with caution, “end-of-life patients don’t have time to wait,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should you quit employment to open a practice? These docs share how they did it
“Everyone said private practice is dying,” said Omar Maniya, MD, an emergency physician who left his hospital job for family practice in New Jersey. “But I think it could be one of the best models we have to advance our health care system and prevent burnout – and bring joy back to the practice of medicine.”
But employment doesn’t necessarily mean happiness. In the Medscape “Employed Physicians: Loving the Focus, Hating the Bureaucracy” ” report, more than 1,350 U.S. physicians employed by a health care organization, hospital, large group practice, or other medical group were surveyedabout their work. As the subtitle suggests, many are torn.
In the survey, employed doctors cited three main downsides to the lifestyle: They have less autonomy, more corporate rules than they’d like, and lower earning potential. Nearly one-third say they’re unhappy about their work-life balance, too, which raises the risk for burnout.
Some physicians find that employment has more cons than pros and turn to private practice instead.
A system skewed toward employment
In the mid-1990s, when James Milford, MD, completed his residency, going straight into private practice was the norm. The family physician bucked that trend by joining a large regional medical center in Wisconsin. He spent the next 20+ years working to establish a network of medical clinics.
“It was very satisfying,” Dr. Milford said. “When I started, I had a lot of input, a lot of control.”
Since then, the pendulum has been swinging toward employment. Brieanna Seefeldt, DO, a family physician outside Denver, completed her residency in 2012.
“I told the recruiter I wanted my own practice,” Dr. Seefeldt said, “They said if you’re not independently wealthy, there’s no way.”
Sonal G. Patel, MD, a pediatric neurologist in Bethesda, finished her residency the same year as Dr. Seefeldt. Dr. Patel never even considered private practice.
“I always thought I would have a certain amount of clinic time where I have my regular patients,” she said, “but I’d also be doing hospital rounds and reading EEG studies at the hospital.”
For Dr. Maniya, who completed his residency in 2021, the choice was simple. Growing up, he watched his immigrant parents, both doctors in private practice, struggle to keep up.
“I opted for a big, sophisticated health system,” he said. “I thought we’d be pushing the envelope of what was possible in medicine.”
Becoming disillusioned with employment
All four of these physicians are now in private practice and are much happier.
Within a few years of starting her job, Dr. Seefeldt was one of the top producers in her area but felt tremendous pressure to see more and more patients. The last straw came after an unpaid maternity leave.
“They told me I owed them for my maternity leave, for lack of productivity,” she said. “I was in practice for only 4 years, but already feeling the effects of burnout.”
Dr. Patel only lasted 2 years before realizing employment didn’t suit her.
“There was an excessive amount of hospital calls,” she said. “And there were bureaucratic issues that made it very difficult to practice the way I thought my practice would be.”
It took just 18 months for Dr. Maniya’s light-bulb moment. He was working at a hospital when COVID-19 hit.
“At my big health care system, it took 9 months to come up with a way to get COVID swabs for free,” he said. “At the same time, I was helping out the family business, a private practice. It took me two calls and 48 hours to get free swabs for not just the practice, not just our patients, but the entire city of Hamilton, New Jersey.”
Milford lasted the longest as an employee – nearly 25 years. The end came after a healthcare company with hospitals in 30 states bought out the medical center.
“My control gradually eroded,” he said. “It got to the point where I had no input regarding things like employees or processes we wanted to improve.”
Making the leap to private practice
Private practice can take different forms.
Dr. Seefeldt opted for direct primary care, a model in which her patients pay a set monthly fee for care whenever needed. Her practice doesn’t take any insurance besides Medicaid.
“Direct primary care is about working directly with the patient and cost-conscious, transparent care,” she said. “And I don’t have to deal with insurance.”
For Dr. Patel, working with an accountable care organization made the transition easier. She owns her practice solo but works with a company called Privia for administrative needs. Privia sent a consultant to set up her office in the company’s electronic medical record. Things were up and running within the first week.
Dr. Maniya joined his mother’s practice, easing his way in over 18 months.
And then there’s what Milford did, building a private practice from the ground up.
“We did a lot of Googling, a lot of meeting with accountants, meeting with small business development from the state of Wisconsin,” he said. “We asked people that were in business, ‘What are the things businesses fail on? Not medical practices, but businesses.’” All that research helped him launch successfully.
Making the dollars and cents add up
Moving from employment into private practice takes time, effort, and of course, money. How much of each varies depending on where you live, your specialty, whether you choose to rent or buy office space, staffing needs, and other factors.
Dr. Seefeldt, Dr. Patel, Dr. Milford, and Dr. Maniya illustrate the range.
- Dr. Seefeldt got a home equity loan of $50,000 to cover startup costs – and paid it back within 6 months.
- Purchasing EEG equipment added to Dr. Patel’s budget; she spent $130,000 of her own money to launch her practice in a temporary office and took out a $150,000 loan to finance the buildout of her final space. It took her 3 years to pay it back.
- When Dr. Milford left employment, he borrowed the buildout and startup costs for his practice from his father, a retired surgeon, to the tune of $500,000.
- Dr. Maniya assumed the largest risk. When he took over the family practice, he borrowed $1.5 million to modernize and build a new office. The practice has now quintupled in size. “It’s going great,” he said. “One of our questions is, should we pay back the loan at a faster pace rather than make the minimum payments?”
Several years in, Dr. Patel reports she’s easily making three to four times as much as she would have at a hospital. However, Dr. Maniya’s guaranteed compensation is 10% less than his old job.
“But as a partner in a private practice, if it succeeds, it could be 100%-150% more in a good year,” he said. On the flip side, if the practice runs into financial trouble, so does he. “Does the risk keep me up at night, give me heartburn? You betcha.”
Dr. Milford and Dr. Seefeldt have both chosen to take less compensation than they could, opting to reinvest in and nurture their practices.
“I love it,” said Dr. Milford. “I joke that I have half as much in my pocketbook, twice as much in my heart. But it’s not really half as much, 5 years in. If I weren’t growing the business, I’d be making more than before.”
Private practice is not without challenges
Being the big cheese does have drawbacks. In the current climate, staffing is a persistent issue for doctors in private practice – both maintaining a full staff and managing their employees.
And without the backing of a large corporation, doctors are sometimes called on to do less than pleasant tasks.
“If the toilet gets clogged and the plumber can’t come for a few hours, the patients still need a bathroom,” Dr. Maniya said. “I’ll go in with my $400 shoes and snake the toilet.”
Dr. Milford pointed out that when the buck stops with you, small mistakes can have enormous ramifications. “But with the bad comes the great potential for good. You have the ability to positively affect patients and healthcare, and to make a difference for people. It creates great personal satisfaction.”
Is running your own practice all it’s cracked up to be?
If it’s not yet apparent, all four doctors highly recommend moving from employment to private practice when possible. The autonomy and the improved work-life balance have helped them find the satisfaction they’d been missing while making burnout less likely.
“When you don’t have to spend 30% of your day apologizing to patients for how bad the health care system is, it reignites your passion for why you went into medicine in the first place,” said Dr. Maniya. In his practice, he’s made a conscious decision to pursue a mix of demographics. “Thirty percent of our patients are Medicaid. The vast majority are middle to low income.”
For physicians who are also parents, the ability to set their own schedules is life-changing.
“My son got an award ... and the teacher invited me to the assembly. In a corporate-based world, I’d struggle to be able to go,” said Dr. Seefeldt. As her own boss, she didn’t have to forgo this special event. Instead, she coordinated directly with her scheduled patient to make time for it.
In Medscape’s report, 61% of employed physicians indicated that they don’t have a say on key management decisions. However, doctors who launch private practices embrace the chance to set their own standards.
“We make sure from the minute someone calls they know they’re in good hands, we’re responsive, we address concerns right away. That’s the difference with private practice – the one-on-one connection is huge,” said Dr. Patel.
“This is exactly what I always wanted. It brings me joy knowing we’ve made a difference in these children’s lives, in their parents’ lives,” she concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Everyone said private practice is dying,” said Omar Maniya, MD, an emergency physician who left his hospital job for family practice in New Jersey. “But I think it could be one of the best models we have to advance our health care system and prevent burnout – and bring joy back to the practice of medicine.”
But employment doesn’t necessarily mean happiness. In the Medscape “Employed Physicians: Loving the Focus, Hating the Bureaucracy” ” report, more than 1,350 U.S. physicians employed by a health care organization, hospital, large group practice, or other medical group were surveyedabout their work. As the subtitle suggests, many are torn.
In the survey, employed doctors cited three main downsides to the lifestyle: They have less autonomy, more corporate rules than they’d like, and lower earning potential. Nearly one-third say they’re unhappy about their work-life balance, too, which raises the risk for burnout.
Some physicians find that employment has more cons than pros and turn to private practice instead.
A system skewed toward employment
In the mid-1990s, when James Milford, MD, completed his residency, going straight into private practice was the norm. The family physician bucked that trend by joining a large regional medical center in Wisconsin. He spent the next 20+ years working to establish a network of medical clinics.
“It was very satisfying,” Dr. Milford said. “When I started, I had a lot of input, a lot of control.”
Since then, the pendulum has been swinging toward employment. Brieanna Seefeldt, DO, a family physician outside Denver, completed her residency in 2012.
“I told the recruiter I wanted my own practice,” Dr. Seefeldt said, “They said if you’re not independently wealthy, there’s no way.”
Sonal G. Patel, MD, a pediatric neurologist in Bethesda, finished her residency the same year as Dr. Seefeldt. Dr. Patel never even considered private practice.
“I always thought I would have a certain amount of clinic time where I have my regular patients,” she said, “but I’d also be doing hospital rounds and reading EEG studies at the hospital.”
For Dr. Maniya, who completed his residency in 2021, the choice was simple. Growing up, he watched his immigrant parents, both doctors in private practice, struggle to keep up.
“I opted for a big, sophisticated health system,” he said. “I thought we’d be pushing the envelope of what was possible in medicine.”
Becoming disillusioned with employment
All four of these physicians are now in private practice and are much happier.
Within a few years of starting her job, Dr. Seefeldt was one of the top producers in her area but felt tremendous pressure to see more and more patients. The last straw came after an unpaid maternity leave.
“They told me I owed them for my maternity leave, for lack of productivity,” she said. “I was in practice for only 4 years, but already feeling the effects of burnout.”
Dr. Patel only lasted 2 years before realizing employment didn’t suit her.
“There was an excessive amount of hospital calls,” she said. “And there were bureaucratic issues that made it very difficult to practice the way I thought my practice would be.”
It took just 18 months for Dr. Maniya’s light-bulb moment. He was working at a hospital when COVID-19 hit.
“At my big health care system, it took 9 months to come up with a way to get COVID swabs for free,” he said. “At the same time, I was helping out the family business, a private practice. It took me two calls and 48 hours to get free swabs for not just the practice, not just our patients, but the entire city of Hamilton, New Jersey.”
Milford lasted the longest as an employee – nearly 25 years. The end came after a healthcare company with hospitals in 30 states bought out the medical center.
“My control gradually eroded,” he said. “It got to the point where I had no input regarding things like employees or processes we wanted to improve.”
Making the leap to private practice
Private practice can take different forms.
Dr. Seefeldt opted for direct primary care, a model in which her patients pay a set monthly fee for care whenever needed. Her practice doesn’t take any insurance besides Medicaid.
“Direct primary care is about working directly with the patient and cost-conscious, transparent care,” she said. “And I don’t have to deal with insurance.”
For Dr. Patel, working with an accountable care organization made the transition easier. She owns her practice solo but works with a company called Privia for administrative needs. Privia sent a consultant to set up her office in the company’s electronic medical record. Things were up and running within the first week.
Dr. Maniya joined his mother’s practice, easing his way in over 18 months.
And then there’s what Milford did, building a private practice from the ground up.
“We did a lot of Googling, a lot of meeting with accountants, meeting with small business development from the state of Wisconsin,” he said. “We asked people that were in business, ‘What are the things businesses fail on? Not medical practices, but businesses.’” All that research helped him launch successfully.
Making the dollars and cents add up
Moving from employment into private practice takes time, effort, and of course, money. How much of each varies depending on where you live, your specialty, whether you choose to rent or buy office space, staffing needs, and other factors.
Dr. Seefeldt, Dr. Patel, Dr. Milford, and Dr. Maniya illustrate the range.
- Dr. Seefeldt got a home equity loan of $50,000 to cover startup costs – and paid it back within 6 months.
- Purchasing EEG equipment added to Dr. Patel’s budget; she spent $130,000 of her own money to launch her practice in a temporary office and took out a $150,000 loan to finance the buildout of her final space. It took her 3 years to pay it back.
- When Dr. Milford left employment, he borrowed the buildout and startup costs for his practice from his father, a retired surgeon, to the tune of $500,000.
- Dr. Maniya assumed the largest risk. When he took over the family practice, he borrowed $1.5 million to modernize and build a new office. The practice has now quintupled in size. “It’s going great,” he said. “One of our questions is, should we pay back the loan at a faster pace rather than make the minimum payments?”
Several years in, Dr. Patel reports she’s easily making three to four times as much as she would have at a hospital. However, Dr. Maniya’s guaranteed compensation is 10% less than his old job.
“But as a partner in a private practice, if it succeeds, it could be 100%-150% more in a good year,” he said. On the flip side, if the practice runs into financial trouble, so does he. “Does the risk keep me up at night, give me heartburn? You betcha.”
Dr. Milford and Dr. Seefeldt have both chosen to take less compensation than they could, opting to reinvest in and nurture their practices.
“I love it,” said Dr. Milford. “I joke that I have half as much in my pocketbook, twice as much in my heart. But it’s not really half as much, 5 years in. If I weren’t growing the business, I’d be making more than before.”
Private practice is not without challenges
Being the big cheese does have drawbacks. In the current climate, staffing is a persistent issue for doctors in private practice – both maintaining a full staff and managing their employees.
And without the backing of a large corporation, doctors are sometimes called on to do less than pleasant tasks.
“If the toilet gets clogged and the plumber can’t come for a few hours, the patients still need a bathroom,” Dr. Maniya said. “I’ll go in with my $400 shoes and snake the toilet.”
Dr. Milford pointed out that when the buck stops with you, small mistakes can have enormous ramifications. “But with the bad comes the great potential for good. You have the ability to positively affect patients and healthcare, and to make a difference for people. It creates great personal satisfaction.”
Is running your own practice all it’s cracked up to be?
If it’s not yet apparent, all four doctors highly recommend moving from employment to private practice when possible. The autonomy and the improved work-life balance have helped them find the satisfaction they’d been missing while making burnout less likely.
“When you don’t have to spend 30% of your day apologizing to patients for how bad the health care system is, it reignites your passion for why you went into medicine in the first place,” said Dr. Maniya. In his practice, he’s made a conscious decision to pursue a mix of demographics. “Thirty percent of our patients are Medicaid. The vast majority are middle to low income.”
For physicians who are also parents, the ability to set their own schedules is life-changing.
“My son got an award ... and the teacher invited me to the assembly. In a corporate-based world, I’d struggle to be able to go,” said Dr. Seefeldt. As her own boss, she didn’t have to forgo this special event. Instead, she coordinated directly with her scheduled patient to make time for it.
In Medscape’s report, 61% of employed physicians indicated that they don’t have a say on key management decisions. However, doctors who launch private practices embrace the chance to set their own standards.
“We make sure from the minute someone calls they know they’re in good hands, we’re responsive, we address concerns right away. That’s the difference with private practice – the one-on-one connection is huge,” said Dr. Patel.
“This is exactly what I always wanted. It brings me joy knowing we’ve made a difference in these children’s lives, in their parents’ lives,” she concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Everyone said private practice is dying,” said Omar Maniya, MD, an emergency physician who left his hospital job for family practice in New Jersey. “But I think it could be one of the best models we have to advance our health care system and prevent burnout – and bring joy back to the practice of medicine.”
But employment doesn’t necessarily mean happiness. In the Medscape “Employed Physicians: Loving the Focus, Hating the Bureaucracy” ” report, more than 1,350 U.S. physicians employed by a health care organization, hospital, large group practice, or other medical group were surveyedabout their work. As the subtitle suggests, many are torn.
In the survey, employed doctors cited three main downsides to the lifestyle: They have less autonomy, more corporate rules than they’d like, and lower earning potential. Nearly one-third say they’re unhappy about their work-life balance, too, which raises the risk for burnout.
Some physicians find that employment has more cons than pros and turn to private practice instead.
A system skewed toward employment
In the mid-1990s, when James Milford, MD, completed his residency, going straight into private practice was the norm. The family physician bucked that trend by joining a large regional medical center in Wisconsin. He spent the next 20+ years working to establish a network of medical clinics.
“It was very satisfying,” Dr. Milford said. “When I started, I had a lot of input, a lot of control.”
Since then, the pendulum has been swinging toward employment. Brieanna Seefeldt, DO, a family physician outside Denver, completed her residency in 2012.
“I told the recruiter I wanted my own practice,” Dr. Seefeldt said, “They said if you’re not independently wealthy, there’s no way.”
Sonal G. Patel, MD, a pediatric neurologist in Bethesda, finished her residency the same year as Dr. Seefeldt. Dr. Patel never even considered private practice.
“I always thought I would have a certain amount of clinic time where I have my regular patients,” she said, “but I’d also be doing hospital rounds and reading EEG studies at the hospital.”
For Dr. Maniya, who completed his residency in 2021, the choice was simple. Growing up, he watched his immigrant parents, both doctors in private practice, struggle to keep up.
“I opted for a big, sophisticated health system,” he said. “I thought we’d be pushing the envelope of what was possible in medicine.”
Becoming disillusioned with employment
All four of these physicians are now in private practice and are much happier.
Within a few years of starting her job, Dr. Seefeldt was one of the top producers in her area but felt tremendous pressure to see more and more patients. The last straw came after an unpaid maternity leave.
“They told me I owed them for my maternity leave, for lack of productivity,” she said. “I was in practice for only 4 years, but already feeling the effects of burnout.”
Dr. Patel only lasted 2 years before realizing employment didn’t suit her.
“There was an excessive amount of hospital calls,” she said. “And there were bureaucratic issues that made it very difficult to practice the way I thought my practice would be.”
It took just 18 months for Dr. Maniya’s light-bulb moment. He was working at a hospital when COVID-19 hit.
“At my big health care system, it took 9 months to come up with a way to get COVID swabs for free,” he said. “At the same time, I was helping out the family business, a private practice. It took me two calls and 48 hours to get free swabs for not just the practice, not just our patients, but the entire city of Hamilton, New Jersey.”
Milford lasted the longest as an employee – nearly 25 years. The end came after a healthcare company with hospitals in 30 states bought out the medical center.
“My control gradually eroded,” he said. “It got to the point where I had no input regarding things like employees or processes we wanted to improve.”
Making the leap to private practice
Private practice can take different forms.
Dr. Seefeldt opted for direct primary care, a model in which her patients pay a set monthly fee for care whenever needed. Her practice doesn’t take any insurance besides Medicaid.
“Direct primary care is about working directly with the patient and cost-conscious, transparent care,” she said. “And I don’t have to deal with insurance.”
For Dr. Patel, working with an accountable care organization made the transition easier. She owns her practice solo but works with a company called Privia for administrative needs. Privia sent a consultant to set up her office in the company’s electronic medical record. Things were up and running within the first week.
Dr. Maniya joined his mother’s practice, easing his way in over 18 months.
And then there’s what Milford did, building a private practice from the ground up.
“We did a lot of Googling, a lot of meeting with accountants, meeting with small business development from the state of Wisconsin,” he said. “We asked people that were in business, ‘What are the things businesses fail on? Not medical practices, but businesses.’” All that research helped him launch successfully.
Making the dollars and cents add up
Moving from employment into private practice takes time, effort, and of course, money. How much of each varies depending on where you live, your specialty, whether you choose to rent or buy office space, staffing needs, and other factors.
Dr. Seefeldt, Dr. Patel, Dr. Milford, and Dr. Maniya illustrate the range.
- Dr. Seefeldt got a home equity loan of $50,000 to cover startup costs – and paid it back within 6 months.
- Purchasing EEG equipment added to Dr. Patel’s budget; she spent $130,000 of her own money to launch her practice in a temporary office and took out a $150,000 loan to finance the buildout of her final space. It took her 3 years to pay it back.
- When Dr. Milford left employment, he borrowed the buildout and startup costs for his practice from his father, a retired surgeon, to the tune of $500,000.
- Dr. Maniya assumed the largest risk. When he took over the family practice, he borrowed $1.5 million to modernize and build a new office. The practice has now quintupled in size. “It’s going great,” he said. “One of our questions is, should we pay back the loan at a faster pace rather than make the minimum payments?”
Several years in, Dr. Patel reports she’s easily making three to four times as much as she would have at a hospital. However, Dr. Maniya’s guaranteed compensation is 10% less than his old job.
“But as a partner in a private practice, if it succeeds, it could be 100%-150% more in a good year,” he said. On the flip side, if the practice runs into financial trouble, so does he. “Does the risk keep me up at night, give me heartburn? You betcha.”
Dr. Milford and Dr. Seefeldt have both chosen to take less compensation than they could, opting to reinvest in and nurture their practices.
“I love it,” said Dr. Milford. “I joke that I have half as much in my pocketbook, twice as much in my heart. But it’s not really half as much, 5 years in. If I weren’t growing the business, I’d be making more than before.”
Private practice is not without challenges
Being the big cheese does have drawbacks. In the current climate, staffing is a persistent issue for doctors in private practice – both maintaining a full staff and managing their employees.
And without the backing of a large corporation, doctors are sometimes called on to do less than pleasant tasks.
“If the toilet gets clogged and the plumber can’t come for a few hours, the patients still need a bathroom,” Dr. Maniya said. “I’ll go in with my $400 shoes and snake the toilet.”
Dr. Milford pointed out that when the buck stops with you, small mistakes can have enormous ramifications. “But with the bad comes the great potential for good. You have the ability to positively affect patients and healthcare, and to make a difference for people. It creates great personal satisfaction.”
Is running your own practice all it’s cracked up to be?
If it’s not yet apparent, all four doctors highly recommend moving from employment to private practice when possible. The autonomy and the improved work-life balance have helped them find the satisfaction they’d been missing while making burnout less likely.
“When you don’t have to spend 30% of your day apologizing to patients for how bad the health care system is, it reignites your passion for why you went into medicine in the first place,” said Dr. Maniya. In his practice, he’s made a conscious decision to pursue a mix of demographics. “Thirty percent of our patients are Medicaid. The vast majority are middle to low income.”
For physicians who are also parents, the ability to set their own schedules is life-changing.
“My son got an award ... and the teacher invited me to the assembly. In a corporate-based world, I’d struggle to be able to go,” said Dr. Seefeldt. As her own boss, she didn’t have to forgo this special event. Instead, she coordinated directly with her scheduled patient to make time for it.
In Medscape’s report, 61% of employed physicians indicated that they don’t have a say on key management decisions. However, doctors who launch private practices embrace the chance to set their own standards.
“We make sure from the minute someone calls they know they’re in good hands, we’re responsive, we address concerns right away. That’s the difference with private practice – the one-on-one connection is huge,” said Dr. Patel.
“This is exactly what I always wanted. It brings me joy knowing we’ve made a difference in these children’s lives, in their parents’ lives,” she concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S. sees most flu hospitalizations in a decade
But the number of deaths and outpatient visits for flu or flu-like illnesses was down slightly from the week before, the CDC said in its weekly FluView report.
There were almost 26,000 new hospital admissions involving laboratory-confirmed influenza over those 7 days, up by over 31% from the previous week, based on data from 5,000 hospitals in the HHS Protect system, which tracks and shares COVID-19 data.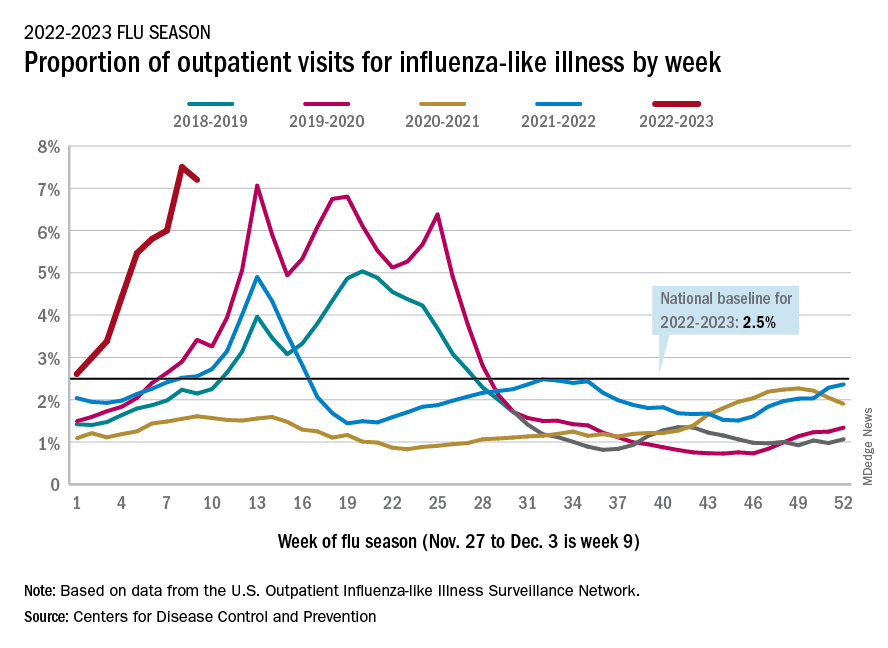
The cumulative hospitalization rate for the 2022-2023 season is 26.0 per 100,000 people, the highest seen at this time of year since 2010-2011, the CDC said, based on data from its Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network, which includes hospitals in select counties in 13 states.
At this point in the 2019-2020 season, just before the COVID-19 pandemic began, the cumulative rate was 3.1 per 100,000 people, the CDC’s data show.
On the positive side, the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness dropped slightly to 7.2%, from 7.5% the week before. But these cases from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network are not laboratory confirmed, so the data could include people with the flu, COVID-19, or respiratory syncytial virus.
The number of confirmed flu deaths for the week of Nov. 27 to Dec. 3 also fell slightly from the last full week of November, 246 vs. 255, but the number of pediatric deaths rose from 2 to 7, and total deaths in children are already up to 21 for 2022-2023. That’s compared to 44 that were reported during all of the 2021-2022 season, the CDC said.
“So far this season, there have been at least 13 million illnesses, 120,000 hospitalizations, and 7,300 deaths from flu,” the agency estimated.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
But the number of deaths and outpatient visits for flu or flu-like illnesses was down slightly from the week before, the CDC said in its weekly FluView report.
There were almost 26,000 new hospital admissions involving laboratory-confirmed influenza over those 7 days, up by over 31% from the previous week, based on data from 5,000 hospitals in the HHS Protect system, which tracks and shares COVID-19 data.
The cumulative hospitalization rate for the 2022-2023 season is 26.0 per 100,000 people, the highest seen at this time of year since 2010-2011, the CDC said, based on data from its Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network, which includes hospitals in select counties in 13 states.
At this point in the 2019-2020 season, just before the COVID-19 pandemic began, the cumulative rate was 3.1 per 100,000 people, the CDC’s data show.
On the positive side, the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness dropped slightly to 7.2%, from 7.5% the week before. But these cases from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network are not laboratory confirmed, so the data could include people with the flu, COVID-19, or respiratory syncytial virus.
The number of confirmed flu deaths for the week of Nov. 27 to Dec. 3 also fell slightly from the last full week of November, 246 vs. 255, but the number of pediatric deaths rose from 2 to 7, and total deaths in children are already up to 21 for 2022-2023. That’s compared to 44 that were reported during all of the 2021-2022 season, the CDC said.
“So far this season, there have been at least 13 million illnesses, 120,000 hospitalizations, and 7,300 deaths from flu,” the agency estimated.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
But the number of deaths and outpatient visits for flu or flu-like illnesses was down slightly from the week before, the CDC said in its weekly FluView report.
There were almost 26,000 new hospital admissions involving laboratory-confirmed influenza over those 7 days, up by over 31% from the previous week, based on data from 5,000 hospitals in the HHS Protect system, which tracks and shares COVID-19 data.
The cumulative hospitalization rate for the 2022-2023 season is 26.0 per 100,000 people, the highest seen at this time of year since 2010-2011, the CDC said, based on data from its Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network, which includes hospitals in select counties in 13 states.
At this point in the 2019-2020 season, just before the COVID-19 pandemic began, the cumulative rate was 3.1 per 100,000 people, the CDC’s data show.
On the positive side, the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness dropped slightly to 7.2%, from 7.5% the week before. But these cases from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network are not laboratory confirmed, so the data could include people with the flu, COVID-19, or respiratory syncytial virus.
The number of confirmed flu deaths for the week of Nov. 27 to Dec. 3 also fell slightly from the last full week of November, 246 vs. 255, but the number of pediatric deaths rose from 2 to 7, and total deaths in children are already up to 21 for 2022-2023. That’s compared to 44 that were reported during all of the 2021-2022 season, the CDC said.
“So far this season, there have been at least 13 million illnesses, 120,000 hospitalizations, and 7,300 deaths from flu,” the agency estimated.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As COVID treatments dwindle, are new ones waiting in the wings?
It was the last monoclonal antibody treatment standing. But less than 10 months after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration gave bebtelovimab its emergency use authorization (EUA) to fight COVID-19, it earlier this month de-authorized it, just as it had for other monoclonal antibody treatments, and for the same reason:
Bebtelovimab couldn’t neutralize the Omicron subvariants BQ.1 and BQ.1.1, the cause of nearly 60% of COVID cases nationally as of November 30.
Next on the chopping block, some predict, will be Evusheld, the combination of tixagevimab and cilgavimab given as a preventive monoclonal antibody to people who are immunocompromised and at high risk of contracting COVID and to those who can’t take the vaccine. In October, the FDA warned that Evusheld was not neutralizing circulating COVID variants.
As the options for treating and preventing COVID decline, will companies rally quickly to develop new ones, or cut their losses in developing treatments that may work for only a few months, given the speed of viral mutations?
But although monoclonal antibody treatments are off the table, at least for now, antiviral drugs – including Paxlovid – are still very much available, and some say underused.
Others suggest it’s time to resurrect interest in convalescent plasma, a treatment used early in the pandemic before drugs or vaccines were here and still authorized for use in those who are immunosuppressed or receiving immunosuppressive treatment.
And on the prevention front, staying up to date with booster vaccines, masking, and taking other precautions should be stressed more, others say, regardless of the number of treatment options, and especially now, as cases rise and people gather for the winter holidays.
‘A major setback’
The bebtelovimab de-authorization was “a major setback,” but an understandable one, said Arturo Casadevall, MD, PhD, professor and chair of molecular microbiology and immunology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore. “Monoclonal antibodies are great drugs. We are in an unfortunate situation in that they are vulnerable to changes in the virus” and can’t offer long-lasting protection.
Supplies of bebtelovimab will be retained, according to the FDA, in case variants susceptible to it return.
“What happened to bebtelovimab is no surprise,” agreed Amesh Adalja, MD, senior scholar at Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security. “This is what is going to happen when you are targeting a virus that mutates a lot.”
Monoclonal antibodies work by binding to the spike protein on the virus surface to prevent it from entering cells.
However, Dr. Adalja doesn’t view the disappearance of monoclonal antibody treatments as a major setback. Monoclonal antibodies were not the primary way COVID was treated, he said.
While he does believe it’s important that more monoclonal antibody treatments be developed, “I think it’s important to remember we still have Paxlovid while everyone is lamenting the loss of bebtelovimab.’’
Antivirals: What’s here, what’s coming
Compared with monoclonal antibodies, “Paxlovid remains a much easier drug to give,” Dr. Adalja told this news organization, because it is taken orally, not intravenously.
And it’s effective. In a recent study, researchers found that adults diagnosed with COVID given Paxlovid within 5 days of diagnosis had a 51% lower hospitalization rate within the next 30 days than those not given it. Another study shows it could also reduce a person’s risk of developing long COVID by 26%.
Paxlovid is underused, Dr. Adalja said, partly because the rebound potential got more press than the effectiveness. When a celebrity got rebound from Paxlovid, he said, that would make the news, overshadowing the research on its effectiveness.
Besides Paxlovid, the antivirals remdesivir (Veklury), given intravenously for 3 days, and molnupiravir (Lagevrio), taken orally, are also still available. Antivirals work by targeting specific parts of the virus to prevent it from multiplying.
In the lab, remdesivir, molnupiravir, and another antiviral, nirmatrelvir, all appear to be effective against both BQ.1.1 (a BA.5 subvariant) and XBB (a BA.2 subvariant), both rapidly rising in the United States, according to a report last week in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The researchers also tested several monoclonal antibodies and found they did not neutralize either of the subvariants BQ.1.1 and XBB.
A new oral antiviral, Xocova (ensitrelvir fumaric acid), from Japanese manufacturer Shionogi, received emergency approval in Japan on November 22. It’s taken once a day for 5 days. The goal is to expand access to it globally, according to the company.
Pardes Biosciences launched a phase 2 trial in September for its oral antiviral drug (PBI-0451), under study as a treatment and preventive for COVID. It expects data by the first quarter of 2023.
Pfizer, which makes Paxlovid, has partnered with Clear Creek Bio to develop another oral antiviral COVID drug.
Other approaches
A receptor protein known as ACE2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2) is the main “doorway” that SARS-CoV-2 uses to enter and infect cells.
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute scientists are developing a “decoy” drug that works by mimicking the ACE2 receptor on the surface of cells; when the virus tries to bind to it, the spike protein is destroyed. Human trials have not yet started.
Other researchers are investigating whether an already-approved drug used to treat a liver disease, Actigall (UDCA/ursodeoxycholic acid), could protect against COVID infection by reducing ACE2.
So far, the researchers have found in early research that people taking UDCA for liver conditions were less likely than those not taking the drug to have severe COVID. They also found that UDCA reduced SARS-CoV-2 infection in human lungs maintained outside the body.
Monoclonal antibody treatments?
After the FDA decision to withdraw the bebtelovimab EUA, which Eli Lilly said it agreed with, the company issued a statement, promising it wasn’t giving up on monoclonal antibody treatments.
“Lilly will continue to search and evaluate monoclonal antibodies to identify potential candidates for clinical development against new variants,” it read in part.
AstraZeneca, which makes Evusheld, is also continuing to work on monoclonal antibody development. According to a spokesperson, “We are also developing a new long-acting antibody combination – AZD5156 – which has been shown in the lab to neutralize emerging new variants and all known variants to date. We are working to accelerate the development of AZD5156 to make it available at the end of 2023.”
The AstraZeneca spokesperson said he could share no more information about what the combination would include.
A convalescent plasma comeback?
Although Paxlovid can help, there are many contraindications to it, such as drug-drug interactions, Dr. Casadevall told this news organization. And now that the monoclonal antibody treatments have been paused, convalescent plasma “is the only antibody-based therapy that is reliably available. Convalescent plasma includes thousands of different antibodies.”
With his colleagues, Dr. Casadevall evaluated plasma samples from 740 patients. Some had received booster vaccines and been infected with Omicron, others had received boosters and not been infected, and still others had not been vaccinated and became infected.
In a report (not yet peer-reviewed), they found the plasma from those who had been infected or boosted within the past 6 months neutralized the new Omicron variants BQ.1.1, XBB.1, and BF.7.
A push for boosters, masks
To get through the coming months, taking precautions like masking and distancing and staying up to date on booster vaccinations, especially for older adults, can make a difference, other experts say.
In a Twitter thread in early December, Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, professor of pediatrics and molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, urged people to take COVID seriously as holiday parties and gatherings occur.
“The single most impactful thing you can do is get your bivalent booster,” he tweeted, as well as give your kids the booster, citing preliminary research that the bivalent mRNA booster broadens immunity against the Omicron subvariants.
For seniors, he said, ‘‘if you get breakthrough COVID, [it’s] really important to get Paxlovid.” Masks will help not only for COVID but also influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and other conditions.
Mitigation measures have largely been abandoned, according to Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute, La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape. In an op-ed in the Los Angeles Times, and on his Twitter feed, he reminds people about masking and urges people to get the bivalent booster.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as of Dec. 8, only 13.5% of people aged 5 and older have gotten an updated booster, despite research that shows an increase in antibodies to BQ.1.1. Recent research has found that the bivalent booster increases antibodies to BQ.1.1 by up to 10-fold, Dr. Topol said.
Dr. Adalja is on advisory boards for Shionogi, GSK, and Pardes. Dr. Casadevall reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It was the last monoclonal antibody treatment standing. But less than 10 months after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration gave bebtelovimab its emergency use authorization (EUA) to fight COVID-19, it earlier this month de-authorized it, just as it had for other monoclonal antibody treatments, and for the same reason:
Bebtelovimab couldn’t neutralize the Omicron subvariants BQ.1 and BQ.1.1, the cause of nearly 60% of COVID cases nationally as of November 30.
Next on the chopping block, some predict, will be Evusheld, the combination of tixagevimab and cilgavimab given as a preventive monoclonal antibody to people who are immunocompromised and at high risk of contracting COVID and to those who can’t take the vaccine. In October, the FDA warned that Evusheld was not neutralizing circulating COVID variants.
As the options for treating and preventing COVID decline, will companies rally quickly to develop new ones, or cut their losses in developing treatments that may work for only a few months, given the speed of viral mutations?
But although monoclonal antibody treatments are off the table, at least for now, antiviral drugs – including Paxlovid – are still very much available, and some say underused.
Others suggest it’s time to resurrect interest in convalescent plasma, a treatment used early in the pandemic before drugs or vaccines were here and still authorized for use in those who are immunosuppressed or receiving immunosuppressive treatment.
And on the prevention front, staying up to date with booster vaccines, masking, and taking other precautions should be stressed more, others say, regardless of the number of treatment options, and especially now, as cases rise and people gather for the winter holidays.
‘A major setback’
The bebtelovimab de-authorization was “a major setback,” but an understandable one, said Arturo Casadevall, MD, PhD, professor and chair of molecular microbiology and immunology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore. “Monoclonal antibodies are great drugs. We are in an unfortunate situation in that they are vulnerable to changes in the virus” and can’t offer long-lasting protection.
Supplies of bebtelovimab will be retained, according to the FDA, in case variants susceptible to it return.
“What happened to bebtelovimab is no surprise,” agreed Amesh Adalja, MD, senior scholar at Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security. “This is what is going to happen when you are targeting a virus that mutates a lot.”
Monoclonal antibodies work by binding to the spike protein on the virus surface to prevent it from entering cells.
However, Dr. Adalja doesn’t view the disappearance of monoclonal antibody treatments as a major setback. Monoclonal antibodies were not the primary way COVID was treated, he said.
While he does believe it’s important that more monoclonal antibody treatments be developed, “I think it’s important to remember we still have Paxlovid while everyone is lamenting the loss of bebtelovimab.’’
Antivirals: What’s here, what’s coming
Compared with monoclonal antibodies, “Paxlovid remains a much easier drug to give,” Dr. Adalja told this news organization, because it is taken orally, not intravenously.
And it’s effective. In a recent study, researchers found that adults diagnosed with COVID given Paxlovid within 5 days of diagnosis had a 51% lower hospitalization rate within the next 30 days than those not given it. Another study shows it could also reduce a person’s risk of developing long COVID by 26%.
Paxlovid is underused, Dr. Adalja said, partly because the rebound potential got more press than the effectiveness. When a celebrity got rebound from Paxlovid, he said, that would make the news, overshadowing the research on its effectiveness.
Besides Paxlovid, the antivirals remdesivir (Veklury), given intravenously for 3 days, and molnupiravir (Lagevrio), taken orally, are also still available. Antivirals work by targeting specific parts of the virus to prevent it from multiplying.
In the lab, remdesivir, molnupiravir, and another antiviral, nirmatrelvir, all appear to be effective against both BQ.1.1 (a BA.5 subvariant) and XBB (a BA.2 subvariant), both rapidly rising in the United States, according to a report last week in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The researchers also tested several monoclonal antibodies and found they did not neutralize either of the subvariants BQ.1.1 and XBB.
A new oral antiviral, Xocova (ensitrelvir fumaric acid), from Japanese manufacturer Shionogi, received emergency approval in Japan on November 22. It’s taken once a day for 5 days. The goal is to expand access to it globally, according to the company.
Pardes Biosciences launched a phase 2 trial in September for its oral antiviral drug (PBI-0451), under study as a treatment and preventive for COVID. It expects data by the first quarter of 2023.
Pfizer, which makes Paxlovid, has partnered with Clear Creek Bio to develop another oral antiviral COVID drug.
Other approaches
A receptor protein known as ACE2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2) is the main “doorway” that SARS-CoV-2 uses to enter and infect cells.
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute scientists are developing a “decoy” drug that works by mimicking the ACE2 receptor on the surface of cells; when the virus tries to bind to it, the spike protein is destroyed. Human trials have not yet started.
Other researchers are investigating whether an already-approved drug used to treat a liver disease, Actigall (UDCA/ursodeoxycholic acid), could protect against COVID infection by reducing ACE2.
So far, the researchers have found in early research that people taking UDCA for liver conditions were less likely than those not taking the drug to have severe COVID. They also found that UDCA reduced SARS-CoV-2 infection in human lungs maintained outside the body.
Monoclonal antibody treatments?
After the FDA decision to withdraw the bebtelovimab EUA, which Eli Lilly said it agreed with, the company issued a statement, promising it wasn’t giving up on monoclonal antibody treatments.
“Lilly will continue to search and evaluate monoclonal antibodies to identify potential candidates for clinical development against new variants,” it read in part.
AstraZeneca, which makes Evusheld, is also continuing to work on monoclonal antibody development. According to a spokesperson, “We are also developing a new long-acting antibody combination – AZD5156 – which has been shown in the lab to neutralize emerging new variants and all known variants to date. We are working to accelerate the development of AZD5156 to make it available at the end of 2023.”
The AstraZeneca spokesperson said he could share no more information about what the combination would include.
A convalescent plasma comeback?
Although Paxlovid can help, there are many contraindications to it, such as drug-drug interactions, Dr. Casadevall told this news organization. And now that the monoclonal antibody treatments have been paused, convalescent plasma “is the only antibody-based therapy that is reliably available. Convalescent plasma includes thousands of different antibodies.”
With his colleagues, Dr. Casadevall evaluated plasma samples from 740 patients. Some had received booster vaccines and been infected with Omicron, others had received boosters and not been infected, and still others had not been vaccinated and became infected.
In a report (not yet peer-reviewed), they found the plasma from those who had been infected or boosted within the past 6 months neutralized the new Omicron variants BQ.1.1, XBB.1, and BF.7.
A push for boosters, masks
To get through the coming months, taking precautions like masking and distancing and staying up to date on booster vaccinations, especially for older adults, can make a difference, other experts say.
In a Twitter thread in early December, Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, professor of pediatrics and molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, urged people to take COVID seriously as holiday parties and gatherings occur.
“The single most impactful thing you can do is get your bivalent booster,” he tweeted, as well as give your kids the booster, citing preliminary research that the bivalent mRNA booster broadens immunity against the Omicron subvariants.
For seniors, he said, ‘‘if you get breakthrough COVID, [it’s] really important to get Paxlovid.” Masks will help not only for COVID but also influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and other conditions.
Mitigation measures have largely been abandoned, according to Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute, La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape. In an op-ed in the Los Angeles Times, and on his Twitter feed, he reminds people about masking and urges people to get the bivalent booster.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as of Dec. 8, only 13.5% of people aged 5 and older have gotten an updated booster, despite research that shows an increase in antibodies to BQ.1.1. Recent research has found that the bivalent booster increases antibodies to BQ.1.1 by up to 10-fold, Dr. Topol said.
Dr. Adalja is on advisory boards for Shionogi, GSK, and Pardes. Dr. Casadevall reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It was the last monoclonal antibody treatment standing. But less than 10 months after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration gave bebtelovimab its emergency use authorization (EUA) to fight COVID-19, it earlier this month de-authorized it, just as it had for other monoclonal antibody treatments, and for the same reason:
Bebtelovimab couldn’t neutralize the Omicron subvariants BQ.1 and BQ.1.1, the cause of nearly 60% of COVID cases nationally as of November 30.
Next on the chopping block, some predict, will be Evusheld, the combination of tixagevimab and cilgavimab given as a preventive monoclonal antibody to people who are immunocompromised and at high risk of contracting COVID and to those who can’t take the vaccine. In October, the FDA warned that Evusheld was not neutralizing circulating COVID variants.
As the options for treating and preventing COVID decline, will companies rally quickly to develop new ones, or cut their losses in developing treatments that may work for only a few months, given the speed of viral mutations?
But although monoclonal antibody treatments are off the table, at least for now, antiviral drugs – including Paxlovid – are still very much available, and some say underused.
Others suggest it’s time to resurrect interest in convalescent plasma, a treatment used early in the pandemic before drugs or vaccines were here and still authorized for use in those who are immunosuppressed or receiving immunosuppressive treatment.
And on the prevention front, staying up to date with booster vaccines, masking, and taking other precautions should be stressed more, others say, regardless of the number of treatment options, and especially now, as cases rise and people gather for the winter holidays.
‘A major setback’
The bebtelovimab de-authorization was “a major setback,” but an understandable one, said Arturo Casadevall, MD, PhD, professor and chair of molecular microbiology and immunology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore. “Monoclonal antibodies are great drugs. We are in an unfortunate situation in that they are vulnerable to changes in the virus” and can’t offer long-lasting protection.
Supplies of bebtelovimab will be retained, according to the FDA, in case variants susceptible to it return.
“What happened to bebtelovimab is no surprise,” agreed Amesh Adalja, MD, senior scholar at Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security. “This is what is going to happen when you are targeting a virus that mutates a lot.”
Monoclonal antibodies work by binding to the spike protein on the virus surface to prevent it from entering cells.
However, Dr. Adalja doesn’t view the disappearance of monoclonal antibody treatments as a major setback. Monoclonal antibodies were not the primary way COVID was treated, he said.
While he does believe it’s important that more monoclonal antibody treatments be developed, “I think it’s important to remember we still have Paxlovid while everyone is lamenting the loss of bebtelovimab.’’
Antivirals: What’s here, what’s coming
Compared with monoclonal antibodies, “Paxlovid remains a much easier drug to give,” Dr. Adalja told this news organization, because it is taken orally, not intravenously.
And it’s effective. In a recent study, researchers found that adults diagnosed with COVID given Paxlovid within 5 days of diagnosis had a 51% lower hospitalization rate within the next 30 days than those not given it. Another study shows it could also reduce a person’s risk of developing long COVID by 26%.
Paxlovid is underused, Dr. Adalja said, partly because the rebound potential got more press than the effectiveness. When a celebrity got rebound from Paxlovid, he said, that would make the news, overshadowing the research on its effectiveness.
Besides Paxlovid, the antivirals remdesivir (Veklury), given intravenously for 3 days, and molnupiravir (Lagevrio), taken orally, are also still available. Antivirals work by targeting specific parts of the virus to prevent it from multiplying.
In the lab, remdesivir, molnupiravir, and another antiviral, nirmatrelvir, all appear to be effective against both BQ.1.1 (a BA.5 subvariant) and XBB (a BA.2 subvariant), both rapidly rising in the United States, according to a report last week in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The researchers also tested several monoclonal antibodies and found they did not neutralize either of the subvariants BQ.1.1 and XBB.
A new oral antiviral, Xocova (ensitrelvir fumaric acid), from Japanese manufacturer Shionogi, received emergency approval in Japan on November 22. It’s taken once a day for 5 days. The goal is to expand access to it globally, according to the company.
Pardes Biosciences launched a phase 2 trial in September for its oral antiviral drug (PBI-0451), under study as a treatment and preventive for COVID. It expects data by the first quarter of 2023.
Pfizer, which makes Paxlovid, has partnered with Clear Creek Bio to develop another oral antiviral COVID drug.
Other approaches
A receptor protein known as ACE2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2) is the main “doorway” that SARS-CoV-2 uses to enter and infect cells.
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute scientists are developing a “decoy” drug that works by mimicking the ACE2 receptor on the surface of cells; when the virus tries to bind to it, the spike protein is destroyed. Human trials have not yet started.
Other researchers are investigating whether an already-approved drug used to treat a liver disease, Actigall (UDCA/ursodeoxycholic acid), could protect against COVID infection by reducing ACE2.
So far, the researchers have found in early research that people taking UDCA for liver conditions were less likely than those not taking the drug to have severe COVID. They also found that UDCA reduced SARS-CoV-2 infection in human lungs maintained outside the body.
Monoclonal antibody treatments?
After the FDA decision to withdraw the bebtelovimab EUA, which Eli Lilly said it agreed with, the company issued a statement, promising it wasn’t giving up on monoclonal antibody treatments.
“Lilly will continue to search and evaluate monoclonal antibodies to identify potential candidates for clinical development against new variants,” it read in part.
AstraZeneca, which makes Evusheld, is also continuing to work on monoclonal antibody development. According to a spokesperson, “We are also developing a new long-acting antibody combination – AZD5156 – which has been shown in the lab to neutralize emerging new variants and all known variants to date. We are working to accelerate the development of AZD5156 to make it available at the end of 2023.”
The AstraZeneca spokesperson said he could share no more information about what the combination would include.
A convalescent plasma comeback?
Although Paxlovid can help, there are many contraindications to it, such as drug-drug interactions, Dr. Casadevall told this news organization. And now that the monoclonal antibody treatments have been paused, convalescent plasma “is the only antibody-based therapy that is reliably available. Convalescent plasma includes thousands of different antibodies.”
With his colleagues, Dr. Casadevall evaluated plasma samples from 740 patients. Some had received booster vaccines and been infected with Omicron, others had received boosters and not been infected, and still others had not been vaccinated and became infected.
In a report (not yet peer-reviewed), they found the plasma from those who had been infected or boosted within the past 6 months neutralized the new Omicron variants BQ.1.1, XBB.1, and BF.7.
A push for boosters, masks
To get through the coming months, taking precautions like masking and distancing and staying up to date on booster vaccinations, especially for older adults, can make a difference, other experts say.
In a Twitter thread in early December, Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, professor of pediatrics and molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, urged people to take COVID seriously as holiday parties and gatherings occur.
“The single most impactful thing you can do is get your bivalent booster,” he tweeted, as well as give your kids the booster, citing preliminary research that the bivalent mRNA booster broadens immunity against the Omicron subvariants.
For seniors, he said, ‘‘if you get breakthrough COVID, [it’s] really important to get Paxlovid.” Masks will help not only for COVID but also influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and other conditions.
Mitigation measures have largely been abandoned, according to Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute, La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape. In an op-ed in the Los Angeles Times, and on his Twitter feed, he reminds people about masking and urges people to get the bivalent booster.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as of Dec. 8, only 13.5% of people aged 5 and older have gotten an updated booster, despite research that shows an increase in antibodies to BQ.1.1. Recent research has found that the bivalent booster increases antibodies to BQ.1.1 by up to 10-fold, Dr. Topol said.
Dr. Adalja is on advisory boards for Shionogi, GSK, and Pardes. Dr. Casadevall reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Low-carb, high-fat, calorie-unrestricted diet improves type 2 diabetes
This was true regardless of an individual’s calorie intake, in the randomized controlled trial published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Patients with T2D who ate a low-carb, high-fat diet (LCHF) lost more weight and saw greater improvements in both glycemic control and insulin resistance than those who ate a high-carb, low-fat diet (HCLF), reported lead author Camilla Dalby Hansen, MD, of University of Southern Denmark, Odense, and colleagues, suggesting that this is an effective, nonpharmaceutical treatment option for T2D.
The trial enrolled 185 patients with T2D, for whom low-calorie diets are often recommended to induce weight loss and improve glycemic control.
The trouble with this common recommendation, the investigators wrote, is that it induces hunger, so few patients stick to it.
“Therefore, calorie-unrestricted diets may be a better alternative to achieve long-term maintenance,” Dr. Hansen and colleagues wrote, noting that this approach “is not widely investigated.”
Study methods and results
In the new study, participants were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to follow the LCHF or HCLF diet for 6 months, with no restriction on calorie intake. Patients were evaluated at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and 9 months (3 months after discontinuation). Parameters included glycemic control, serum lipid levels, and metabolic markers. The final analysis included 165 patients.
While patients in both groups lost weight, those in the LCHF group lost, on average, about 8 pounds more than the HCLF group, a significant difference. While the LCHF diet was associated with greater improvements in glycemic control (HbA1c) than the HCLF diet, it also led to slightly greater increases in LDL levels. In both groups, HDL levels increased, and triglycerides decreased, without significant differences between groups.
The above changes were not sustained 3 months after finishing the diet.
“I believe we have sufficient data to include LCHF as one of the diet options for people with type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Hansen said in a written comment, considering all available data.
Although the diet did lead to significant clinical benefits, she predicted that some patients would still struggle with adherence in the real world.
“The LCHF diet can be difficult for some people to follow,” Dr. Hansen said. “It is a bit more expensive, and it can be difficult to comply to in social gatherings, simply because our society is not suited for this type of diet.”
The magic of unrestricted calories
Jay H. Shubrook, DO, diabetologist and professor at Touro University of California, Vallejo, offered a similar view.
“When you start to fiddle with the diet, it affects not only the person, but all the people they eat with, because eating is a communal experience,” Dr. Shubrook said, in an interview.
Still, he said the present study is “a big deal,” because T2D is a “noncommunicable pandemic,” and “anything we could do that disrupts this process is very important.”
While some may struggle to follow the LCHF diet, Dr. Shubrook predicted better long-term adherence than the low-calorie diet usually recommended.
“What’s magic about this study is because it wasn’t calorie restricted, I think it made it a little bit more flexible for people to continue,” Dr. Shubrook said.
He added that he thinks patients will need a fair amount of coaching and education about food choices in order to lose weight on a diet without calorie restrictions.
Not the first study of its kind
In a written comment, Jeff Volek, PhD, RD, professor at the Ohio State University, Columbus, called the present study “another important piece of work, demonstrating yet again, that a low-carbohydrate eating pattern is superior to a high-carbohydrate approach in people with insulin resistance.”
Yet Dr. Volek, who has conducted numerous studies on low-carbohydrate diets, also said there is “little here that is new or surprising.”
He went on to admonish Dr. Hansen and colleagues for failing to recognize those who have already broken ground in this area.
“Unfortunately, these authors do not give credit to the many researchers who have published extensively on low-carbohydrate diets in the past, and instead make claims about being the first to study a calorie unrestricted low-carb diet in individuals with T2D, which is clearly not the case,” Dr. Volek said. “There is a large body of literature showing similar findings with better control over diet, larger cohorts, longer follow-up, and more comprehensive biomarker assessment.”
He noted that data supporting low-carb diets for T2D have been sufficient since at least 2019, when the American Diabetes Association updated their guidance on the subject.
Citing a paper published in Diabetes Care, he said, “Low-carbohydrate eating patterns, especially very-low-carbohydrate eating patterns, have been shown to reduce A1C and the need for antihyperglycemic medications.”
The study was funded by Novo Nordisk Foundation, Danish Diabetes Academy, Odense University Hospital, and others. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Eli Lilly, Amgen, UCB, and others. Dr. Shubrook disclosed relationships with Abbot, AstraZeneca, Bayer, and others.
This was true regardless of an individual’s calorie intake, in the randomized controlled trial published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Patients with T2D who ate a low-carb, high-fat diet (LCHF) lost more weight and saw greater improvements in both glycemic control and insulin resistance than those who ate a high-carb, low-fat diet (HCLF), reported lead author Camilla Dalby Hansen, MD, of University of Southern Denmark, Odense, and colleagues, suggesting that this is an effective, nonpharmaceutical treatment option for T2D.
The trial enrolled 185 patients with T2D, for whom low-calorie diets are often recommended to induce weight loss and improve glycemic control.
The trouble with this common recommendation, the investigators wrote, is that it induces hunger, so few patients stick to it.
“Therefore, calorie-unrestricted diets may be a better alternative to achieve long-term maintenance,” Dr. Hansen and colleagues wrote, noting that this approach “is not widely investigated.”
Study methods and results
In the new study, participants were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to follow the LCHF or HCLF diet for 6 months, with no restriction on calorie intake. Patients were evaluated at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and 9 months (3 months after discontinuation). Parameters included glycemic control, serum lipid levels, and metabolic markers. The final analysis included 165 patients.
While patients in both groups lost weight, those in the LCHF group lost, on average, about 8 pounds more than the HCLF group, a significant difference. While the LCHF diet was associated with greater improvements in glycemic control (HbA1c) than the HCLF diet, it also led to slightly greater increases in LDL levels. In both groups, HDL levels increased, and triglycerides decreased, without significant differences between groups.
The above changes were not sustained 3 months after finishing the diet.
“I believe we have sufficient data to include LCHF as one of the diet options for people with type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Hansen said in a written comment, considering all available data.
Although the diet did lead to significant clinical benefits, she predicted that some patients would still struggle with adherence in the real world.
“The LCHF diet can be difficult for some people to follow,” Dr. Hansen said. “It is a bit more expensive, and it can be difficult to comply to in social gatherings, simply because our society is not suited for this type of diet.”
The magic of unrestricted calories
Jay H. Shubrook, DO, diabetologist and professor at Touro University of California, Vallejo, offered a similar view.
“When you start to fiddle with the diet, it affects not only the person, but all the people they eat with, because eating is a communal experience,” Dr. Shubrook said, in an interview.
Still, he said the present study is “a big deal,” because T2D is a “noncommunicable pandemic,” and “anything we could do that disrupts this process is very important.”
While some may struggle to follow the LCHF diet, Dr. Shubrook predicted better long-term adherence than the low-calorie diet usually recommended.
“What’s magic about this study is because it wasn’t calorie restricted, I think it made it a little bit more flexible for people to continue,” Dr. Shubrook said.
He added that he thinks patients will need a fair amount of coaching and education about food choices in order to lose weight on a diet without calorie restrictions.
Not the first study of its kind
In a written comment, Jeff Volek, PhD, RD, professor at the Ohio State University, Columbus, called the present study “another important piece of work, demonstrating yet again, that a low-carbohydrate eating pattern is superior to a high-carbohydrate approach in people with insulin resistance.”
Yet Dr. Volek, who has conducted numerous studies on low-carbohydrate diets, also said there is “little here that is new or surprising.”
He went on to admonish Dr. Hansen and colleagues for failing to recognize those who have already broken ground in this area.
“Unfortunately, these authors do not give credit to the many researchers who have published extensively on low-carbohydrate diets in the past, and instead make claims about being the first to study a calorie unrestricted low-carb diet in individuals with T2D, which is clearly not the case,” Dr. Volek said. “There is a large body of literature showing similar findings with better control over diet, larger cohorts, longer follow-up, and more comprehensive biomarker assessment.”
He noted that data supporting low-carb diets for T2D have been sufficient since at least 2019, when the American Diabetes Association updated their guidance on the subject.
Citing a paper published in Diabetes Care, he said, “Low-carbohydrate eating patterns, especially very-low-carbohydrate eating patterns, have been shown to reduce A1C and the need for antihyperglycemic medications.”
The study was funded by Novo Nordisk Foundation, Danish Diabetes Academy, Odense University Hospital, and others. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Eli Lilly, Amgen, UCB, and others. Dr. Shubrook disclosed relationships with Abbot, AstraZeneca, Bayer, and others.
This was true regardless of an individual’s calorie intake, in the randomized controlled trial published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Patients with T2D who ate a low-carb, high-fat diet (LCHF) lost more weight and saw greater improvements in both glycemic control and insulin resistance than those who ate a high-carb, low-fat diet (HCLF), reported lead author Camilla Dalby Hansen, MD, of University of Southern Denmark, Odense, and colleagues, suggesting that this is an effective, nonpharmaceutical treatment option for T2D.
The trial enrolled 185 patients with T2D, for whom low-calorie diets are often recommended to induce weight loss and improve glycemic control.
The trouble with this common recommendation, the investigators wrote, is that it induces hunger, so few patients stick to it.
“Therefore, calorie-unrestricted diets may be a better alternative to achieve long-term maintenance,” Dr. Hansen and colleagues wrote, noting that this approach “is not widely investigated.”
Study methods and results
In the new study, participants were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to follow the LCHF or HCLF diet for 6 months, with no restriction on calorie intake. Patients were evaluated at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and 9 months (3 months after discontinuation). Parameters included glycemic control, serum lipid levels, and metabolic markers. The final analysis included 165 patients.
While patients in both groups lost weight, those in the LCHF group lost, on average, about 8 pounds more than the HCLF group, a significant difference. While the LCHF diet was associated with greater improvements in glycemic control (HbA1c) than the HCLF diet, it also led to slightly greater increases in LDL levels. In both groups, HDL levels increased, and triglycerides decreased, without significant differences between groups.
The above changes were not sustained 3 months after finishing the diet.
“I believe we have sufficient data to include LCHF as one of the diet options for people with type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Hansen said in a written comment, considering all available data.
Although the diet did lead to significant clinical benefits, she predicted that some patients would still struggle with adherence in the real world.
“The LCHF diet can be difficult for some people to follow,” Dr. Hansen said. “It is a bit more expensive, and it can be difficult to comply to in social gatherings, simply because our society is not suited for this type of diet.”
The magic of unrestricted calories
Jay H. Shubrook, DO, diabetologist and professor at Touro University of California, Vallejo, offered a similar view.
“When you start to fiddle with the diet, it affects not only the person, but all the people they eat with, because eating is a communal experience,” Dr. Shubrook said, in an interview.
Still, he said the present study is “a big deal,” because T2D is a “noncommunicable pandemic,” and “anything we could do that disrupts this process is very important.”
While some may struggle to follow the LCHF diet, Dr. Shubrook predicted better long-term adherence than the low-calorie diet usually recommended.
“What’s magic about this study is because it wasn’t calorie restricted, I think it made it a little bit more flexible for people to continue,” Dr. Shubrook said.
He added that he thinks patients will need a fair amount of coaching and education about food choices in order to lose weight on a diet without calorie restrictions.
Not the first study of its kind
In a written comment, Jeff Volek, PhD, RD, professor at the Ohio State University, Columbus, called the present study “another important piece of work, demonstrating yet again, that a low-carbohydrate eating pattern is superior to a high-carbohydrate approach in people with insulin resistance.”
Yet Dr. Volek, who has conducted numerous studies on low-carbohydrate diets, also said there is “little here that is new or surprising.”
He went on to admonish Dr. Hansen and colleagues for failing to recognize those who have already broken ground in this area.
“Unfortunately, these authors do not give credit to the many researchers who have published extensively on low-carbohydrate diets in the past, and instead make claims about being the first to study a calorie unrestricted low-carb diet in individuals with T2D, which is clearly not the case,” Dr. Volek said. “There is a large body of literature showing similar findings with better control over diet, larger cohorts, longer follow-up, and more comprehensive biomarker assessment.”
He noted that data supporting low-carb diets for T2D have been sufficient since at least 2019, when the American Diabetes Association updated their guidance on the subject.
Citing a paper published in Diabetes Care, he said, “Low-carbohydrate eating patterns, especially very-low-carbohydrate eating patterns, have been shown to reduce A1C and the need for antihyperglycemic medications.”
The study was funded by Novo Nordisk Foundation, Danish Diabetes Academy, Odense University Hospital, and others. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Eli Lilly, Amgen, UCB, and others. Dr. Shubrook disclosed relationships with Abbot, AstraZeneca, Bayer, and others.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Direct-acting antivirals tied to better outcomes in chronic Hep C
Eiichi Ogawa, MD, PhD, with the department of general internal medicine, Kyushu University Hospital in Fukuoka, Japan, led the retrospective study of 245,596 adults with CHC. In the new research, which was published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the authors analyzed data from the Optum Clinformatics Data Mart (CDM) database, 2010-2021.
It was important to do the study because of limited and conflicting information – mostly from case reports – on safety of the DAAs when they were approved for CHC in 2014, said coauthor Mindie H. Nguyen, MD, in an interview.
‘DAA treatment is safe’
“The main message is that DAA treatment is safe,” said Dr. Nguyen, of the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center in Palo Alto. In the early days of treatment, physicians were treating the sickest patients with the DAAs, which may have introduced patient selection bias and caused lasting misperceptions about poor safety, she noted.
“I really hope to dispel this myth,” she said, adding that this study also shows improved liver and nonliver outcomes.
Of the total cohort in this study, 40,654 patients had one or more prescriptions for a DAA (without interferon) and 204,942 patients had not been treated.
All-cause mortality reduced by 57%
DAA treatment, vs. no treatment, was linked with a large and significant reduction (57%) in all-cause mortality. That finding was particularly notable, because it was seen regardless of age, sex, race and ethnicity, comorbidities, alcohol use, and presence of hepatocellular carcinoma or cirrhosis.
The authors noted that patients without cirrhosis are a population previously considered to receive less benefit from an HCV cure than patients with cirrhosis.
DAAs were associated with lower risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and decompensation as well as risk of nonliver outcomes, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Lower risk of poor nonliver outcomes
The researchers found that when they compared DAA-treated patients with untreated patients, the incidences per 1,000 person-years of having diabetes were 30.2 vs. 37.2 (P less than .001), and of having kidney disease was 31.1 vs. 34.1 (P less than .001), respectively.
“This retrospective cohort study provides valuable information to physicians,” Noel Deep, MD, chief medical officer at Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo, Wis., said, in an interview.
The study’s size helps confirm DAAs’ safety and benefit, and previously unknown added benefits, in treating CHC, he continued.
Large study confirms, introduces DAA benefits
Dr. Deep, who was not part of the study, noted that DAAs now show much promise in efficacy and tolerability in most people with chronic hepatitis C, including those with concomitant conditions such as CKD.
“Previous studies did not have such large-scale nationwide data. [The findings of the new study] greatly enhance our knowledge of DAA treatment for chronic hepatitis C patients across the spectrum from noncirrhotic to compensated cirrhotic to decompensated cirrhotic,” Dr. Deep said. “The added benefit of improved outcomes for diabetes, CVD, CKD, and nonliver cancers truly surprised me.”
Dr. Deep pointed out some limitations of the study, including that, as the authors acknowledge, only privately insured patients were included so results may not be generalizable to the underinsured/uninsured “who might have other risk factors, poorer health, and fewer resources.”
He added: “The data also may not be reflective of the outcomes in Asians who were, in my opinion, also underrepresented in this study.”
The authors cited the insurance claims database they used as a strength of the study, due to it containing information on 61 million people from across all regions of the United States.
Dr. Ogawa reports grants from Gilead Sciences outside the submitted work. Coauthor Dr. Nguyen reports institutional grants and advisory board fees from Gilead Sciences outside the submitted work. Another coauthor reports speaking/consulting fees from Gilead and Merck Sharp & Dohme outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
The Stanford Center for Population Health Sciences (PHS) supported this study by providing access to the PHS Data Core.
Dr. Deep reports no relevant financial relationships. He serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Eiichi Ogawa, MD, PhD, with the department of general internal medicine, Kyushu University Hospital in Fukuoka, Japan, led the retrospective study of 245,596 adults with CHC. In the new research, which was published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the authors analyzed data from the Optum Clinformatics Data Mart (CDM) database, 2010-2021.
It was important to do the study because of limited and conflicting information – mostly from case reports – on safety of the DAAs when they were approved for CHC in 2014, said coauthor Mindie H. Nguyen, MD, in an interview.
‘DAA treatment is safe’
“The main message is that DAA treatment is safe,” said Dr. Nguyen, of the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center in Palo Alto. In the early days of treatment, physicians were treating the sickest patients with the DAAs, which may have introduced patient selection bias and caused lasting misperceptions about poor safety, she noted.
“I really hope to dispel this myth,” she said, adding that this study also shows improved liver and nonliver outcomes.
Of the total cohort in this study, 40,654 patients had one or more prescriptions for a DAA (without interferon) and 204,942 patients had not been treated.
All-cause mortality reduced by 57%
DAA treatment, vs. no treatment, was linked with a large and significant reduction (57%) in all-cause mortality. That finding was particularly notable, because it was seen regardless of age, sex, race and ethnicity, comorbidities, alcohol use, and presence of hepatocellular carcinoma or cirrhosis.
The authors noted that patients without cirrhosis are a population previously considered to receive less benefit from an HCV cure than patients with cirrhosis.
DAAs were associated with lower risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and decompensation as well as risk of nonliver outcomes, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Lower risk of poor nonliver outcomes
The researchers found that when they compared DAA-treated patients with untreated patients, the incidences per 1,000 person-years of having diabetes were 30.2 vs. 37.2 (P less than .001), and of having kidney disease was 31.1 vs. 34.1 (P less than .001), respectively.
“This retrospective cohort study provides valuable information to physicians,” Noel Deep, MD, chief medical officer at Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo, Wis., said, in an interview.
The study’s size helps confirm DAAs’ safety and benefit, and previously unknown added benefits, in treating CHC, he continued.
Large study confirms, introduces DAA benefits
Dr. Deep, who was not part of the study, noted that DAAs now show much promise in efficacy and tolerability in most people with chronic hepatitis C, including those with concomitant conditions such as CKD.
“Previous studies did not have such large-scale nationwide data. [The findings of the new study] greatly enhance our knowledge of DAA treatment for chronic hepatitis C patients across the spectrum from noncirrhotic to compensated cirrhotic to decompensated cirrhotic,” Dr. Deep said. “The added benefit of improved outcomes for diabetes, CVD, CKD, and nonliver cancers truly surprised me.”
Dr. Deep pointed out some limitations of the study, including that, as the authors acknowledge, only privately insured patients were included so results may not be generalizable to the underinsured/uninsured “who might have other risk factors, poorer health, and fewer resources.”
He added: “The data also may not be reflective of the outcomes in Asians who were, in my opinion, also underrepresented in this study.”
The authors cited the insurance claims database they used as a strength of the study, due to it containing information on 61 million people from across all regions of the United States.
Dr. Ogawa reports grants from Gilead Sciences outside the submitted work. Coauthor Dr. Nguyen reports institutional grants and advisory board fees from Gilead Sciences outside the submitted work. Another coauthor reports speaking/consulting fees from Gilead and Merck Sharp & Dohme outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
The Stanford Center for Population Health Sciences (PHS) supported this study by providing access to the PHS Data Core.
Dr. Deep reports no relevant financial relationships. He serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Eiichi Ogawa, MD, PhD, with the department of general internal medicine, Kyushu University Hospital in Fukuoka, Japan, led the retrospective study of 245,596 adults with CHC. In the new research, which was published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the authors analyzed data from the Optum Clinformatics Data Mart (CDM) database, 2010-2021.
It was important to do the study because of limited and conflicting information – mostly from case reports – on safety of the DAAs when they were approved for CHC in 2014, said coauthor Mindie H. Nguyen, MD, in an interview.
‘DAA treatment is safe’
“The main message is that DAA treatment is safe,” said Dr. Nguyen, of the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center in Palo Alto. In the early days of treatment, physicians were treating the sickest patients with the DAAs, which may have introduced patient selection bias and caused lasting misperceptions about poor safety, she noted.
“I really hope to dispel this myth,” she said, adding that this study also shows improved liver and nonliver outcomes.
Of the total cohort in this study, 40,654 patients had one or more prescriptions for a DAA (without interferon) and 204,942 patients had not been treated.
All-cause mortality reduced by 57%
DAA treatment, vs. no treatment, was linked with a large and significant reduction (57%) in all-cause mortality. That finding was particularly notable, because it was seen regardless of age, sex, race and ethnicity, comorbidities, alcohol use, and presence of hepatocellular carcinoma or cirrhosis.
The authors noted that patients without cirrhosis are a population previously considered to receive less benefit from an HCV cure than patients with cirrhosis.
DAAs were associated with lower risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and decompensation as well as risk of nonliver outcomes, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Lower risk of poor nonliver outcomes
The researchers found that when they compared DAA-treated patients with untreated patients, the incidences per 1,000 person-years of having diabetes were 30.2 vs. 37.2 (P less than .001), and of having kidney disease was 31.1 vs. 34.1 (P less than .001), respectively.
“This retrospective cohort study provides valuable information to physicians,” Noel Deep, MD, chief medical officer at Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo, Wis., said, in an interview.
The study’s size helps confirm DAAs’ safety and benefit, and previously unknown added benefits, in treating CHC, he continued.
Large study confirms, introduces DAA benefits
Dr. Deep, who was not part of the study, noted that DAAs now show much promise in efficacy and tolerability in most people with chronic hepatitis C, including those with concomitant conditions such as CKD.
“Previous studies did not have such large-scale nationwide data. [The findings of the new study] greatly enhance our knowledge of DAA treatment for chronic hepatitis C patients across the spectrum from noncirrhotic to compensated cirrhotic to decompensated cirrhotic,” Dr. Deep said. “The added benefit of improved outcomes for diabetes, CVD, CKD, and nonliver cancers truly surprised me.”
Dr. Deep pointed out some limitations of the study, including that, as the authors acknowledge, only privately insured patients were included so results may not be generalizable to the underinsured/uninsured “who might have other risk factors, poorer health, and fewer resources.”
He added: “The data also may not be reflective of the outcomes in Asians who were, in my opinion, also underrepresented in this study.”
The authors cited the insurance claims database they used as a strength of the study, due to it containing information on 61 million people from across all regions of the United States.
Dr. Ogawa reports grants from Gilead Sciences outside the submitted work. Coauthor Dr. Nguyen reports institutional grants and advisory board fees from Gilead Sciences outside the submitted work. Another coauthor reports speaking/consulting fees from Gilead and Merck Sharp & Dohme outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
The Stanford Center for Population Health Sciences (PHS) supported this study by providing access to the PHS Data Core.
Dr. Deep reports no relevant financial relationships. He serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE



