User login
Sustained Control Reported for Anti–IL-17, Anti–IL-23 Psoriasis Treatments
SAN DIEGO — , but late-breaker data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology show that these types of responses are sustained for as long as patients have remained on therapy.
Of the two, the longer follow up is with the IL-17 inhibitor bimekizumab (Bimzelx). In a 4-year open-label extension study, the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 rate was approximately 85% in treated patients, according to Mark Lebwohl, MD, professor and chairman emeritus of the Department of Dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City
A PASI 90 score signifies that 90% of skin surface area is cleared. The proportion of patients who achieved a PASI 100 score, signifying total clearance, approached 70% at 4 years in the group with the greatest response. PASI 90 and PASI 100 rates at this point were only modestly lower than those reported at the end of the double-blind phase 3 trial when evaluated 3 years earlier.
Follow-up with a novel oral anti-IL-23 inhibitor JNJ-2113 (JNJ-77242113) was only 52 weeks, far shorter. But again, the response for the most effective dose at the end of this period was essentially unchanged from that at 16 weeks. Among those on the highest and most effective test dose of once-daily 100 mg, the PASI 90 at 1 year was 64.3%, a rate that was essentially unchanged from week 16.
No Apparent Loss of Benefit Over Time
“We can really look at those dose-response curves and see that there is, overall, a maintenance of response,” reported Laura K. Ferris, MD, PhD, professor and director of clinical trials, Department of Dermatology, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. In her presentation of the data, she showed similar sustained control for the most effective doses of JNJ-2113 for multiple clinical outcomes, including an investigator’s global assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1, also signifying clear or near clear skin.
Bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits both IL-17A and IL-17F, is already approved for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. The 52-week BE SURE trial, which provided the 478 patients who entered into the BE BRIGHT open label extension study, was published in The New England Journal of Medicine in July 2021.
In the 4-year data reported by Dr. Lebwohl, three groups were compared: Those initially randomized to an every-4-week dosing schedule of bimekizumab over the course of the 52-week BE SURE trial; those randomized to an every-4-week bimekizumab schedule who were then subsequently switched to an every-8-week schedule; and those initiated on the TNF-inhibitor adalimumab (Humira) and were then switched at week 24 to every-4-week bimekizumab.
The PASI 90 responses at 52 weeks in these three groups, respectively, were 91.2%, 89.3%, and 95.2%. At 4 years, this almost clear response was observed in 82.4%, 83.2%, and 87.6%, respectively. At 52 weeks, the PASI 100 responses in these three groups, respectively, were 75.3%, 74.2%, and 72.9%. At 4 years, 61.9%, 58.5%, and 69.5% still had complete skin clearance.
Bimekizumab was well tolerated during the randomized trial, reported Dr. Lebwohl. The rates of nasopharyngitis and oral candidiasis, which were observed in approximately 12% and 8%, respectively, of treated patients during the randomized phase remained at about the same level in the long-term follow up. There were no new safety signals, he said.
JNJ-2113 Is First Potential Oral IL-23 Inhibitor
JNJ-2113 is a first-in-class oral peptide that binds to the IL-23 receptor, blocking the IL-23 signaling pathway. If approved, it would be the first oral therapy targeting IL-23. The 16-week outcomes of the dose-finding FRONTIER 1 phase 2b trial were published in The New England Journal of Medicine earlier this year. The primary endpoint was PASI 75, achieved by 79% of those on the 100 mg twice daily dose at week 16, vs 9% on placebo, and at 52 weeks, was 76%.
“The proportion of patients achieving the FRONTIER 1 primary endpoint was maintained from week 16 to the end of week 52 in the extension study,” Dr. Ferris said, but further pointed out that rates of near or complete clearance achieved at week 16 were also essentially unchanged at week 52. This was true of PASI scores and IGA.
Clearance of psoriatic lesions on the scalp was particularly impressive. By scalp-specific IGA, rates of clear or near clear (0/1) were not just maintained but improved over the course of follow-up, reaching 75.1% at 52 weeks in the highest dose group, she said.
JNJ-2113 was well tolerated in FRONTIER 1 and remained so during long-term follow-up, in the FRONTIER 2 extension study, according to Dr. Ferris. The most common complaints with JNJ-2113, such as nasopharyngitis (18.1% vs 25.7% in placebo), did not appear to differ significantly from placebo and the treatment remained well tolerated over the course of the extended follow-up.
There are limited direct comparisons of different biologics active in the treatment of plaque psoriasis for efficacy and safety, but these data appear to show a depth and durability of benefit for psoriasis that is exceptional, Dr. Lebwohl told this news organization. “The PASI 100 scores achieved by bimekizumab exceed anything we have seen to date,” he said. “And the durability of those exceedingly high scores is remarkable.”
Dr. Lebwohl reports financial relationships with approximately 40 pharmaceutical companies, including UCB Pharma, which developed bimekizumab. Dr. Ferris reports financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen, which is developing JNJ-2113.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — , but late-breaker data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology show that these types of responses are sustained for as long as patients have remained on therapy.
Of the two, the longer follow up is with the IL-17 inhibitor bimekizumab (Bimzelx). In a 4-year open-label extension study, the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 rate was approximately 85% in treated patients, according to Mark Lebwohl, MD, professor and chairman emeritus of the Department of Dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City
A PASI 90 score signifies that 90% of skin surface area is cleared. The proportion of patients who achieved a PASI 100 score, signifying total clearance, approached 70% at 4 years in the group with the greatest response. PASI 90 and PASI 100 rates at this point were only modestly lower than those reported at the end of the double-blind phase 3 trial when evaluated 3 years earlier.
Follow-up with a novel oral anti-IL-23 inhibitor JNJ-2113 (JNJ-77242113) was only 52 weeks, far shorter. But again, the response for the most effective dose at the end of this period was essentially unchanged from that at 16 weeks. Among those on the highest and most effective test dose of once-daily 100 mg, the PASI 90 at 1 year was 64.3%, a rate that was essentially unchanged from week 16.
No Apparent Loss of Benefit Over Time
“We can really look at those dose-response curves and see that there is, overall, a maintenance of response,” reported Laura K. Ferris, MD, PhD, professor and director of clinical trials, Department of Dermatology, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. In her presentation of the data, she showed similar sustained control for the most effective doses of JNJ-2113 for multiple clinical outcomes, including an investigator’s global assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1, also signifying clear or near clear skin.
Bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits both IL-17A and IL-17F, is already approved for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. The 52-week BE SURE trial, which provided the 478 patients who entered into the BE BRIGHT open label extension study, was published in The New England Journal of Medicine in July 2021.
In the 4-year data reported by Dr. Lebwohl, three groups were compared: Those initially randomized to an every-4-week dosing schedule of bimekizumab over the course of the 52-week BE SURE trial; those randomized to an every-4-week bimekizumab schedule who were then subsequently switched to an every-8-week schedule; and those initiated on the TNF-inhibitor adalimumab (Humira) and were then switched at week 24 to every-4-week bimekizumab.
The PASI 90 responses at 52 weeks in these three groups, respectively, were 91.2%, 89.3%, and 95.2%. At 4 years, this almost clear response was observed in 82.4%, 83.2%, and 87.6%, respectively. At 52 weeks, the PASI 100 responses in these three groups, respectively, were 75.3%, 74.2%, and 72.9%. At 4 years, 61.9%, 58.5%, and 69.5% still had complete skin clearance.
Bimekizumab was well tolerated during the randomized trial, reported Dr. Lebwohl. The rates of nasopharyngitis and oral candidiasis, which were observed in approximately 12% and 8%, respectively, of treated patients during the randomized phase remained at about the same level in the long-term follow up. There were no new safety signals, he said.
JNJ-2113 Is First Potential Oral IL-23 Inhibitor
JNJ-2113 is a first-in-class oral peptide that binds to the IL-23 receptor, blocking the IL-23 signaling pathway. If approved, it would be the first oral therapy targeting IL-23. The 16-week outcomes of the dose-finding FRONTIER 1 phase 2b trial were published in The New England Journal of Medicine earlier this year. The primary endpoint was PASI 75, achieved by 79% of those on the 100 mg twice daily dose at week 16, vs 9% on placebo, and at 52 weeks, was 76%.
“The proportion of patients achieving the FRONTIER 1 primary endpoint was maintained from week 16 to the end of week 52 in the extension study,” Dr. Ferris said, but further pointed out that rates of near or complete clearance achieved at week 16 were also essentially unchanged at week 52. This was true of PASI scores and IGA.
Clearance of psoriatic lesions on the scalp was particularly impressive. By scalp-specific IGA, rates of clear or near clear (0/1) were not just maintained but improved over the course of follow-up, reaching 75.1% at 52 weeks in the highest dose group, she said.
JNJ-2113 was well tolerated in FRONTIER 1 and remained so during long-term follow-up, in the FRONTIER 2 extension study, according to Dr. Ferris. The most common complaints with JNJ-2113, such as nasopharyngitis (18.1% vs 25.7% in placebo), did not appear to differ significantly from placebo and the treatment remained well tolerated over the course of the extended follow-up.
There are limited direct comparisons of different biologics active in the treatment of plaque psoriasis for efficacy and safety, but these data appear to show a depth and durability of benefit for psoriasis that is exceptional, Dr. Lebwohl told this news organization. “The PASI 100 scores achieved by bimekizumab exceed anything we have seen to date,” he said. “And the durability of those exceedingly high scores is remarkable.”
Dr. Lebwohl reports financial relationships with approximately 40 pharmaceutical companies, including UCB Pharma, which developed bimekizumab. Dr. Ferris reports financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen, which is developing JNJ-2113.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — , but late-breaker data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology show that these types of responses are sustained for as long as patients have remained on therapy.
Of the two, the longer follow up is with the IL-17 inhibitor bimekizumab (Bimzelx). In a 4-year open-label extension study, the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 rate was approximately 85% in treated patients, according to Mark Lebwohl, MD, professor and chairman emeritus of the Department of Dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City
A PASI 90 score signifies that 90% of skin surface area is cleared. The proportion of patients who achieved a PASI 100 score, signifying total clearance, approached 70% at 4 years in the group with the greatest response. PASI 90 and PASI 100 rates at this point were only modestly lower than those reported at the end of the double-blind phase 3 trial when evaluated 3 years earlier.
Follow-up with a novel oral anti-IL-23 inhibitor JNJ-2113 (JNJ-77242113) was only 52 weeks, far shorter. But again, the response for the most effective dose at the end of this period was essentially unchanged from that at 16 weeks. Among those on the highest and most effective test dose of once-daily 100 mg, the PASI 90 at 1 year was 64.3%, a rate that was essentially unchanged from week 16.
No Apparent Loss of Benefit Over Time
“We can really look at those dose-response curves and see that there is, overall, a maintenance of response,” reported Laura K. Ferris, MD, PhD, professor and director of clinical trials, Department of Dermatology, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. In her presentation of the data, she showed similar sustained control for the most effective doses of JNJ-2113 for multiple clinical outcomes, including an investigator’s global assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1, also signifying clear or near clear skin.
Bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits both IL-17A and IL-17F, is already approved for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. The 52-week BE SURE trial, which provided the 478 patients who entered into the BE BRIGHT open label extension study, was published in The New England Journal of Medicine in July 2021.
In the 4-year data reported by Dr. Lebwohl, three groups were compared: Those initially randomized to an every-4-week dosing schedule of bimekizumab over the course of the 52-week BE SURE trial; those randomized to an every-4-week bimekizumab schedule who were then subsequently switched to an every-8-week schedule; and those initiated on the TNF-inhibitor adalimumab (Humira) and were then switched at week 24 to every-4-week bimekizumab.
The PASI 90 responses at 52 weeks in these three groups, respectively, were 91.2%, 89.3%, and 95.2%. At 4 years, this almost clear response was observed in 82.4%, 83.2%, and 87.6%, respectively. At 52 weeks, the PASI 100 responses in these three groups, respectively, were 75.3%, 74.2%, and 72.9%. At 4 years, 61.9%, 58.5%, and 69.5% still had complete skin clearance.
Bimekizumab was well tolerated during the randomized trial, reported Dr. Lebwohl. The rates of nasopharyngitis and oral candidiasis, which were observed in approximately 12% and 8%, respectively, of treated patients during the randomized phase remained at about the same level in the long-term follow up. There were no new safety signals, he said.
JNJ-2113 Is First Potential Oral IL-23 Inhibitor
JNJ-2113 is a first-in-class oral peptide that binds to the IL-23 receptor, blocking the IL-23 signaling pathway. If approved, it would be the first oral therapy targeting IL-23. The 16-week outcomes of the dose-finding FRONTIER 1 phase 2b trial were published in The New England Journal of Medicine earlier this year. The primary endpoint was PASI 75, achieved by 79% of those on the 100 mg twice daily dose at week 16, vs 9% on placebo, and at 52 weeks, was 76%.
“The proportion of patients achieving the FRONTIER 1 primary endpoint was maintained from week 16 to the end of week 52 in the extension study,” Dr. Ferris said, but further pointed out that rates of near or complete clearance achieved at week 16 were also essentially unchanged at week 52. This was true of PASI scores and IGA.
Clearance of psoriatic lesions on the scalp was particularly impressive. By scalp-specific IGA, rates of clear or near clear (0/1) were not just maintained but improved over the course of follow-up, reaching 75.1% at 52 weeks in the highest dose group, she said.
JNJ-2113 was well tolerated in FRONTIER 1 and remained so during long-term follow-up, in the FRONTIER 2 extension study, according to Dr. Ferris. The most common complaints with JNJ-2113, such as nasopharyngitis (18.1% vs 25.7% in placebo), did not appear to differ significantly from placebo and the treatment remained well tolerated over the course of the extended follow-up.
There are limited direct comparisons of different biologics active in the treatment of plaque psoriasis for efficacy and safety, but these data appear to show a depth and durability of benefit for psoriasis that is exceptional, Dr. Lebwohl told this news organization. “The PASI 100 scores achieved by bimekizumab exceed anything we have seen to date,” he said. “And the durability of those exceedingly high scores is remarkable.”
Dr. Lebwohl reports financial relationships with approximately 40 pharmaceutical companies, including UCB Pharma, which developed bimekizumab. Dr. Ferris reports financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen, which is developing JNJ-2113.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAD 2024
Allergens Present in Most ‘Hypoallergenic’ Baby Cleansers, Study Finds
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Many baby cleansers are marketed as “hypoallergenic,” but these claims are not validated.
- This study assessed the potential allergens and marketing claims in best-selling baby cleansers.
- The researchers collected ingredients and marketing claims of the top 50 best-selling baby body wash products sold on Amazon on April 4, 2023.
- Ingredient lists were checked for potential allergens using the 2020 American Contact Dermatitis Society (ACDS) core allergen series, which lists 90 common allergens for adults and children.
TAKEAWAY:
- In the 50 cleansers tested, 10 allergens were identified. Overall, 94% of the cleansers contained at least one allergen, averaging 2.9 allergens per product; cocamidopropyl betaine (72%), fragrance (64%), and sodium benzoate (54%) were the most common allergens.
- All cleansers had at least five marketing claims, with an average of 10.9 claims per product; the most common claims were “paraben-free” (88%), “phthalate-free” (84%), “tear-free” (74%), and “hypoallergenic” or “allergy-tested” (74%).
- There was no significant difference in the number of allergens in the cleansers marketed as “hypoallergenic” or “allergy tested” compared with cleansers that did not have these claims (P = .843).
- Fewer allergens were found in cleansers endorsed by the National Eczema Association (P = .004) or labeled “synthetic fragrance-free” (P = .003).
- There was a positive correlation between a greater number of allergens and an increased number of marketing claims (r = 0.547, P < .001) and a negative correlation between cost and number of allergens (r = −0.450, P = .001).
IN PRACTICE:
Because marketing claims like “hypoallergenic” may be misleading, “clinicians should counsel parents to carefully examine cleanser ingredients or consider selecting cleansers” endorsed by the National Eczema Association or another international eczema organization, especially for infants and children with a history of atopic dermatitis, the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Sasan D. Noveir, BA, from the University of California, Los Angeles, and coauthors from the division of dermatology at UCLA, was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study only evaluated top-selling products from a single online source at a specific time, which may limit generalizability. Potential allergens not included in the ACDS core series may be present.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not disclose any funding source. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Many baby cleansers are marketed as “hypoallergenic,” but these claims are not validated.
- This study assessed the potential allergens and marketing claims in best-selling baby cleansers.
- The researchers collected ingredients and marketing claims of the top 50 best-selling baby body wash products sold on Amazon on April 4, 2023.
- Ingredient lists were checked for potential allergens using the 2020 American Contact Dermatitis Society (ACDS) core allergen series, which lists 90 common allergens for adults and children.
TAKEAWAY:
- In the 50 cleansers tested, 10 allergens were identified. Overall, 94% of the cleansers contained at least one allergen, averaging 2.9 allergens per product; cocamidopropyl betaine (72%), fragrance (64%), and sodium benzoate (54%) were the most common allergens.
- All cleansers had at least five marketing claims, with an average of 10.9 claims per product; the most common claims were “paraben-free” (88%), “phthalate-free” (84%), “tear-free” (74%), and “hypoallergenic” or “allergy-tested” (74%).
- There was no significant difference in the number of allergens in the cleansers marketed as “hypoallergenic” or “allergy tested” compared with cleansers that did not have these claims (P = .843).
- Fewer allergens were found in cleansers endorsed by the National Eczema Association (P = .004) or labeled “synthetic fragrance-free” (P = .003).
- There was a positive correlation between a greater number of allergens and an increased number of marketing claims (r = 0.547, P < .001) and a negative correlation between cost and number of allergens (r = −0.450, P = .001).
IN PRACTICE:
Because marketing claims like “hypoallergenic” may be misleading, “clinicians should counsel parents to carefully examine cleanser ingredients or consider selecting cleansers” endorsed by the National Eczema Association or another international eczema organization, especially for infants and children with a history of atopic dermatitis, the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Sasan D. Noveir, BA, from the University of California, Los Angeles, and coauthors from the division of dermatology at UCLA, was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study only evaluated top-selling products from a single online source at a specific time, which may limit generalizability. Potential allergens not included in the ACDS core series may be present.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not disclose any funding source. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Many baby cleansers are marketed as “hypoallergenic,” but these claims are not validated.
- This study assessed the potential allergens and marketing claims in best-selling baby cleansers.
- The researchers collected ingredients and marketing claims of the top 50 best-selling baby body wash products sold on Amazon on April 4, 2023.
- Ingredient lists were checked for potential allergens using the 2020 American Contact Dermatitis Society (ACDS) core allergen series, which lists 90 common allergens for adults and children.
TAKEAWAY:
- In the 50 cleansers tested, 10 allergens were identified. Overall, 94% of the cleansers contained at least one allergen, averaging 2.9 allergens per product; cocamidopropyl betaine (72%), fragrance (64%), and sodium benzoate (54%) were the most common allergens.
- All cleansers had at least five marketing claims, with an average of 10.9 claims per product; the most common claims were “paraben-free” (88%), “phthalate-free” (84%), “tear-free” (74%), and “hypoallergenic” or “allergy-tested” (74%).
- There was no significant difference in the number of allergens in the cleansers marketed as “hypoallergenic” or “allergy tested” compared with cleansers that did not have these claims (P = .843).
- Fewer allergens were found in cleansers endorsed by the National Eczema Association (P = .004) or labeled “synthetic fragrance-free” (P = .003).
- There was a positive correlation between a greater number of allergens and an increased number of marketing claims (r = 0.547, P < .001) and a negative correlation between cost and number of allergens (r = −0.450, P = .001).
IN PRACTICE:
Because marketing claims like “hypoallergenic” may be misleading, “clinicians should counsel parents to carefully examine cleanser ingredients or consider selecting cleansers” endorsed by the National Eczema Association or another international eczema organization, especially for infants and children with a history of atopic dermatitis, the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Sasan D. Noveir, BA, from the University of California, Los Angeles, and coauthors from the division of dermatology at UCLA, was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study only evaluated top-selling products from a single online source at a specific time, which may limit generalizability. Potential allergens not included in the ACDS core series may be present.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not disclose any funding source. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Studies Reinforce JAK Inhibitor Efficacy for Most Challenging Alopecia Types
FROM AAD 2024
SAN DIEGO — , according to late-breaking data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
In one study of brepocitinib, the target was cicatricial alopecia (CA), a form of hair loss for which there are no approved therapies. In the other, a subanalysis from phase 3 trials of ritlecitinib for alopecia areata (AA), hair regrowth was shown in the subset of patients who entered the study with alopecia totalis or alopecia universalis (AT/AU).
Reflecting comments from several experts, including one of the late-breaking session moderators, April W. Armstrong, MD, MPH, professor and chief of dermatology, University of California, Los Angeles, said that the CA study, which matched clinical response to changes in CA biomarkers, suggested that the results are a potential breakthrough.
“This is the first placebo-controlled study with an oral JAK inhibitor that not only shows that scarring alopecia can be reversible but also gives insights to the mechanism of action and which patients might respond best,” Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, said in an interview. Dr. Guttman-Yassky, professor of Dermatology and Immunology, and director of the Laboratory of Inflammatory Skin Diseases, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, was the study’s senior investigator.
Scarring Alopecia and Brepocitinib
For the study of scarring alopecia, 49 patients with CA were randomized in a 3:1 ratio to brepocitinib, a first-in-class inhibitor that targets both JAK1 and TYK2, or placebo. Because of the small size of the study, the primary endpoint was the change in CA biomarkers. The secondary outcome was clinical response, but because of a correlation between the two, these were mutually reinforcing.
Of the subtypes, nine patients enrolled in the study had frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA), 16 had lichen planopilaris (LPP) alopecia, and 24 had central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA). All of the forms of CA are more common in women overall and women of color specifically, particularly CCCA. For this analysis, the FFA and LPP subtypes were considered similar for assessing response and were combined.
The data included a comparison of response and safety during the 24-week randomization phase, as well as an additional follow-up conducted after another 24 weeks of open-label treatment. During the second phase, all patients on placebo were switched to active treatment.
Overall, there was a reduction in all four of the key scalp inflammatory biomarkers measured among those in the combined FFA/LLP group. In the placebo group, each of these markers — interferon gamma (IFN-gamma), CCLS, CXCL10, and STAT1 — increased over the same time period. In almost all cases, the differences were statistically significant.
In the CCCA subgroup, the same pattern (an increase among those on placebo but a decrease among those on brepocitinib) was observed for CCLS and CXCL10. For IFN-gamma and STAT1, a rise was observed among those on placebo and those on active treatment, although the rise was greater for placebo.
For clinical response, improvement on brepocitinib was observed on disease activity indexes, particularly among those in the FFA/LLP group, according to Marguerite Meariman, MD, a dermatology resident at Mount Sinai, who presented the results. She called the improvement in clinical activity scores at 48 weeks “dramatic.” Moreover, improvement was apparent within 4 weeks of starting therapy.
For CCCA, a more challenging condition to treat, Dr. Meariman said that no further progression might represent an acceptable response for many patients, but there were also cases of hair regrowth in this subset. Although improvement was not generally on the order seen among those with FFA/LLP, she suggested that there is promise even in these more difficult patients.
Further studies are planned, but Dr. Meariman said that it might be important to focus on early treatment regardless of CA subtype. She noted that patients with less than 5 years disease duration typically did better than those with longer durations.
Ritlecitinib for AT/AU
The analysis of patients with AT/AU was based on a subset analysis from the ALLEGRO phase 2b/3 study of ritlecitinib, which targets JAK3 and TEC kinases. The full results of the ALLEGRO trial were published last year in The Lancet. In the new late-breaker analysis, Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) scores were evaluated on an observed or last-observation-carried-forward basis. Generally, responses in the subgroup of patients with AT/AU, who had a median SALT score of 80.3 (signifying 80.3% hair loss) at baseline, were only modestly lower than those in the overall trial.
At 24 months, about 50% of patients achieved a SALT score of 20, according to Melissa Piliang, MD, chair of Dermatology at the Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio, who presented the data. In this group, as in the non-AT/AU population, responses climbed over time, and these responses have been maintained for as long as patients have remained on therapy.
At the more rigorous threshold of SALT < 10, the proportion of responders was only slightly lower, meaning a substantial proportion of patients with AT/AU “are achieving 90% or more of hair regrowth, so really an excellent response,” Dr. Piliang said.
For the subgroup with AU, specifically, regrowth of eyebrows and eyelashes was also observed in a substantial proportion, according to Dr. Piliang. Attributed to the often-devastating psychological burden of hair loss, patient-reported assessments of these responses global were generally “even better” than those reported by the investigators.
However, Dr. Piliang advised clinicians to treat AA as early as possible. Despite the benefits seen in the AT/AU subgroup, she pointed out that starting treatment before total hair loss is associated with a higher likelihood of complete or nearly complete hair regrowth.
There are no data from the ALLEGRO trial to determine how long hair regrowth persists after discontinuation of ritlecitinib, which has been approved for the treatment of AA, but Dr. Piliang said that patients should be told that lifelong therapy should be expected in the vast majority of individuals, whether or not AA has advanced to AT/AU.
“In my experience with JAK inhibitors, you lose response when you come off these drugs,” she said.
Dr. Meariman reported a financial relationship with AbbVie. Dr. Piliang reported financial relationships with Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Proctor & Gamble. Dr. Armstrong reported financial relationships with more than 30 pharmaceutical companies, including those that manufacture JAK inhibitors. Dr. Guttman-Yassky reported financial relationships with more than 30 companies, including those that manufacture JAK inhibitors.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAD 2024
SAN DIEGO — , according to late-breaking data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
In one study of brepocitinib, the target was cicatricial alopecia (CA), a form of hair loss for which there are no approved therapies. In the other, a subanalysis from phase 3 trials of ritlecitinib for alopecia areata (AA), hair regrowth was shown in the subset of patients who entered the study with alopecia totalis or alopecia universalis (AT/AU).
Reflecting comments from several experts, including one of the late-breaking session moderators, April W. Armstrong, MD, MPH, professor and chief of dermatology, University of California, Los Angeles, said that the CA study, which matched clinical response to changes in CA biomarkers, suggested that the results are a potential breakthrough.
“This is the first placebo-controlled study with an oral JAK inhibitor that not only shows that scarring alopecia can be reversible but also gives insights to the mechanism of action and which patients might respond best,” Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, said in an interview. Dr. Guttman-Yassky, professor of Dermatology and Immunology, and director of the Laboratory of Inflammatory Skin Diseases, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, was the study’s senior investigator.
Scarring Alopecia and Brepocitinib
For the study of scarring alopecia, 49 patients with CA were randomized in a 3:1 ratio to brepocitinib, a first-in-class inhibitor that targets both JAK1 and TYK2, or placebo. Because of the small size of the study, the primary endpoint was the change in CA biomarkers. The secondary outcome was clinical response, but because of a correlation between the two, these were mutually reinforcing.
Of the subtypes, nine patients enrolled in the study had frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA), 16 had lichen planopilaris (LPP) alopecia, and 24 had central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA). All of the forms of CA are more common in women overall and women of color specifically, particularly CCCA. For this analysis, the FFA and LPP subtypes were considered similar for assessing response and were combined.
The data included a comparison of response and safety during the 24-week randomization phase, as well as an additional follow-up conducted after another 24 weeks of open-label treatment. During the second phase, all patients on placebo were switched to active treatment.
Overall, there was a reduction in all four of the key scalp inflammatory biomarkers measured among those in the combined FFA/LLP group. In the placebo group, each of these markers — interferon gamma (IFN-gamma), CCLS, CXCL10, and STAT1 — increased over the same time period. In almost all cases, the differences were statistically significant.
In the CCCA subgroup, the same pattern (an increase among those on placebo but a decrease among those on brepocitinib) was observed for CCLS and CXCL10. For IFN-gamma and STAT1, a rise was observed among those on placebo and those on active treatment, although the rise was greater for placebo.
For clinical response, improvement on brepocitinib was observed on disease activity indexes, particularly among those in the FFA/LLP group, according to Marguerite Meariman, MD, a dermatology resident at Mount Sinai, who presented the results. She called the improvement in clinical activity scores at 48 weeks “dramatic.” Moreover, improvement was apparent within 4 weeks of starting therapy.
For CCCA, a more challenging condition to treat, Dr. Meariman said that no further progression might represent an acceptable response for many patients, but there were also cases of hair regrowth in this subset. Although improvement was not generally on the order seen among those with FFA/LLP, she suggested that there is promise even in these more difficult patients.
Further studies are planned, but Dr. Meariman said that it might be important to focus on early treatment regardless of CA subtype. She noted that patients with less than 5 years disease duration typically did better than those with longer durations.
Ritlecitinib for AT/AU
The analysis of patients with AT/AU was based on a subset analysis from the ALLEGRO phase 2b/3 study of ritlecitinib, which targets JAK3 and TEC kinases. The full results of the ALLEGRO trial were published last year in The Lancet. In the new late-breaker analysis, Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) scores were evaluated on an observed or last-observation-carried-forward basis. Generally, responses in the subgroup of patients with AT/AU, who had a median SALT score of 80.3 (signifying 80.3% hair loss) at baseline, were only modestly lower than those in the overall trial.
At 24 months, about 50% of patients achieved a SALT score of 20, according to Melissa Piliang, MD, chair of Dermatology at the Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio, who presented the data. In this group, as in the non-AT/AU population, responses climbed over time, and these responses have been maintained for as long as patients have remained on therapy.
At the more rigorous threshold of SALT < 10, the proportion of responders was only slightly lower, meaning a substantial proportion of patients with AT/AU “are achieving 90% or more of hair regrowth, so really an excellent response,” Dr. Piliang said.
For the subgroup with AU, specifically, regrowth of eyebrows and eyelashes was also observed in a substantial proportion, according to Dr. Piliang. Attributed to the often-devastating psychological burden of hair loss, patient-reported assessments of these responses global were generally “even better” than those reported by the investigators.
However, Dr. Piliang advised clinicians to treat AA as early as possible. Despite the benefits seen in the AT/AU subgroup, she pointed out that starting treatment before total hair loss is associated with a higher likelihood of complete or nearly complete hair regrowth.
There are no data from the ALLEGRO trial to determine how long hair regrowth persists after discontinuation of ritlecitinib, which has been approved for the treatment of AA, but Dr. Piliang said that patients should be told that lifelong therapy should be expected in the vast majority of individuals, whether or not AA has advanced to AT/AU.
“In my experience with JAK inhibitors, you lose response when you come off these drugs,” she said.
Dr. Meariman reported a financial relationship with AbbVie. Dr. Piliang reported financial relationships with Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Proctor & Gamble. Dr. Armstrong reported financial relationships with more than 30 pharmaceutical companies, including those that manufacture JAK inhibitors. Dr. Guttman-Yassky reported financial relationships with more than 30 companies, including those that manufacture JAK inhibitors.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAD 2024
SAN DIEGO — , according to late-breaking data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
In one study of brepocitinib, the target was cicatricial alopecia (CA), a form of hair loss for which there are no approved therapies. In the other, a subanalysis from phase 3 trials of ritlecitinib for alopecia areata (AA), hair regrowth was shown in the subset of patients who entered the study with alopecia totalis or alopecia universalis (AT/AU).
Reflecting comments from several experts, including one of the late-breaking session moderators, April W. Armstrong, MD, MPH, professor and chief of dermatology, University of California, Los Angeles, said that the CA study, which matched clinical response to changes in CA biomarkers, suggested that the results are a potential breakthrough.
“This is the first placebo-controlled study with an oral JAK inhibitor that not only shows that scarring alopecia can be reversible but also gives insights to the mechanism of action and which patients might respond best,” Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, said in an interview. Dr. Guttman-Yassky, professor of Dermatology and Immunology, and director of the Laboratory of Inflammatory Skin Diseases, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, was the study’s senior investigator.
Scarring Alopecia and Brepocitinib
For the study of scarring alopecia, 49 patients with CA were randomized in a 3:1 ratio to brepocitinib, a first-in-class inhibitor that targets both JAK1 and TYK2, or placebo. Because of the small size of the study, the primary endpoint was the change in CA biomarkers. The secondary outcome was clinical response, but because of a correlation between the two, these were mutually reinforcing.
Of the subtypes, nine patients enrolled in the study had frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA), 16 had lichen planopilaris (LPP) alopecia, and 24 had central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA). All of the forms of CA are more common in women overall and women of color specifically, particularly CCCA. For this analysis, the FFA and LPP subtypes were considered similar for assessing response and were combined.
The data included a comparison of response and safety during the 24-week randomization phase, as well as an additional follow-up conducted after another 24 weeks of open-label treatment. During the second phase, all patients on placebo were switched to active treatment.
Overall, there was a reduction in all four of the key scalp inflammatory biomarkers measured among those in the combined FFA/LLP group. In the placebo group, each of these markers — interferon gamma (IFN-gamma), CCLS, CXCL10, and STAT1 — increased over the same time period. In almost all cases, the differences were statistically significant.
In the CCCA subgroup, the same pattern (an increase among those on placebo but a decrease among those on brepocitinib) was observed for CCLS and CXCL10. For IFN-gamma and STAT1, a rise was observed among those on placebo and those on active treatment, although the rise was greater for placebo.
For clinical response, improvement on brepocitinib was observed on disease activity indexes, particularly among those in the FFA/LLP group, according to Marguerite Meariman, MD, a dermatology resident at Mount Sinai, who presented the results. She called the improvement in clinical activity scores at 48 weeks “dramatic.” Moreover, improvement was apparent within 4 weeks of starting therapy.
For CCCA, a more challenging condition to treat, Dr. Meariman said that no further progression might represent an acceptable response for many patients, but there were also cases of hair regrowth in this subset. Although improvement was not generally on the order seen among those with FFA/LLP, she suggested that there is promise even in these more difficult patients.
Further studies are planned, but Dr. Meariman said that it might be important to focus on early treatment regardless of CA subtype. She noted that patients with less than 5 years disease duration typically did better than those with longer durations.
Ritlecitinib for AT/AU
The analysis of patients with AT/AU was based on a subset analysis from the ALLEGRO phase 2b/3 study of ritlecitinib, which targets JAK3 and TEC kinases. The full results of the ALLEGRO trial were published last year in The Lancet. In the new late-breaker analysis, Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) scores were evaluated on an observed or last-observation-carried-forward basis. Generally, responses in the subgroup of patients with AT/AU, who had a median SALT score of 80.3 (signifying 80.3% hair loss) at baseline, were only modestly lower than those in the overall trial.
At 24 months, about 50% of patients achieved a SALT score of 20, according to Melissa Piliang, MD, chair of Dermatology at the Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio, who presented the data. In this group, as in the non-AT/AU population, responses climbed over time, and these responses have been maintained for as long as patients have remained on therapy.
At the more rigorous threshold of SALT < 10, the proportion of responders was only slightly lower, meaning a substantial proportion of patients with AT/AU “are achieving 90% or more of hair regrowth, so really an excellent response,” Dr. Piliang said.
For the subgroup with AU, specifically, regrowth of eyebrows and eyelashes was also observed in a substantial proportion, according to Dr. Piliang. Attributed to the often-devastating psychological burden of hair loss, patient-reported assessments of these responses global were generally “even better” than those reported by the investigators.
However, Dr. Piliang advised clinicians to treat AA as early as possible. Despite the benefits seen in the AT/AU subgroup, she pointed out that starting treatment before total hair loss is associated with a higher likelihood of complete or nearly complete hair regrowth.
There are no data from the ALLEGRO trial to determine how long hair regrowth persists after discontinuation of ritlecitinib, which has been approved for the treatment of AA, but Dr. Piliang said that patients should be told that lifelong therapy should be expected in the vast majority of individuals, whether or not AA has advanced to AT/AU.
“In my experience with JAK inhibitors, you lose response when you come off these drugs,” she said.
Dr. Meariman reported a financial relationship with AbbVie. Dr. Piliang reported financial relationships with Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Proctor & Gamble. Dr. Armstrong reported financial relationships with more than 30 pharmaceutical companies, including those that manufacture JAK inhibitors. Dr. Guttman-Yassky reported financial relationships with more than 30 companies, including those that manufacture JAK inhibitors.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
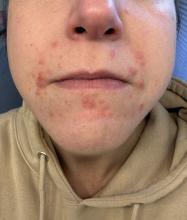
A 35-year-old female presented with a 1-day history of eroded papules and vesicles distributed periorally
.1 While it predominantly affects children, it is important to note that it can also affect adults. Although it is not a life threatening infection, it can cause a painful rash and is highly contagious. The infection is easily spread in multiple ways, including via respiratory droplets, contact with vesicular or nasal secretions, or through fecal-oral transmission. Most cases occur during the summer and fall seasons but individuals can be infected at any time of the year.
HFMD typically starts with a few days of non-specific viral symptoms, such as fever, cough, sore throat, and fatigue. It is then followed by an eruption of intraoral macules and vesicles and a widespread distribution of oval shaped macules that predominantly involve the hands and feet.1 Both children and adults can present atypically. Atypical presentations include vesicles and bullae on extensor surfaces such as the forearms, as well as eruptions on the face or buttocks.2 Other atypical morphologies include eczema herpeticum-like, Gianotti-Crosti-like, and purpuric/petechiae.3 Atypical hand, food, and mouth disease cases are often caused by coxsackievirus A6, however other strains of coxsackievirus can also cause atypical symptoms.2,3
Our 35-year-old female patient presented with eroded papules and vesicles around the mouth. A diagnosis of atypical HFMD was made clinically in the following days when the patient developed the more classic intraoral and acral macules and vesicles.
Similar to our case, HFMD is most often diagnosed clinically. PCR testing from an active vesicle or nasopharyngeal swab can be obtained. Treatment for HFMD is supportive and symptoms generally resolve over 7-10 days. Over-the-counter analgesics, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, as well as oral analgesics that contain lidocaine or diphenhydramine are often helpful3. In this case, our patient improved over the course of seven days without needing therapy.
This case and the photos were submitted by Vanessa Ortega, BS, University of California, San Diego; Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, and Justin Gordon, MD, San Diego Family Dermatology. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023, June 20). Symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease.
2. Drago F et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Aug;77(2):e51-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.03.046.
3. Starkey SY et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2024 Jan-Feb;41(1):23-7. doi: 10.1111/pde.15461.
.1 While it predominantly affects children, it is important to note that it can also affect adults. Although it is not a life threatening infection, it can cause a painful rash and is highly contagious. The infection is easily spread in multiple ways, including via respiratory droplets, contact with vesicular or nasal secretions, or through fecal-oral transmission. Most cases occur during the summer and fall seasons but individuals can be infected at any time of the year.
HFMD typically starts with a few days of non-specific viral symptoms, such as fever, cough, sore throat, and fatigue. It is then followed by an eruption of intraoral macules and vesicles and a widespread distribution of oval shaped macules that predominantly involve the hands and feet.1 Both children and adults can present atypically. Atypical presentations include vesicles and bullae on extensor surfaces such as the forearms, as well as eruptions on the face or buttocks.2 Other atypical morphologies include eczema herpeticum-like, Gianotti-Crosti-like, and purpuric/petechiae.3 Atypical hand, food, and mouth disease cases are often caused by coxsackievirus A6, however other strains of coxsackievirus can also cause atypical symptoms.2,3
Our 35-year-old female patient presented with eroded papules and vesicles around the mouth. A diagnosis of atypical HFMD was made clinically in the following days when the patient developed the more classic intraoral and acral macules and vesicles.
Similar to our case, HFMD is most often diagnosed clinically. PCR testing from an active vesicle or nasopharyngeal swab can be obtained. Treatment for HFMD is supportive and symptoms generally resolve over 7-10 days. Over-the-counter analgesics, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, as well as oral analgesics that contain lidocaine or diphenhydramine are often helpful3. In this case, our patient improved over the course of seven days without needing therapy.
This case and the photos were submitted by Vanessa Ortega, BS, University of California, San Diego; Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, and Justin Gordon, MD, San Diego Family Dermatology. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023, June 20). Symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease.
2. Drago F et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Aug;77(2):e51-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.03.046.
3. Starkey SY et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2024 Jan-Feb;41(1):23-7. doi: 10.1111/pde.15461.
.1 While it predominantly affects children, it is important to note that it can also affect adults. Although it is not a life threatening infection, it can cause a painful rash and is highly contagious. The infection is easily spread in multiple ways, including via respiratory droplets, contact with vesicular or nasal secretions, or through fecal-oral transmission. Most cases occur during the summer and fall seasons but individuals can be infected at any time of the year.
HFMD typically starts with a few days of non-specific viral symptoms, such as fever, cough, sore throat, and fatigue. It is then followed by an eruption of intraoral macules and vesicles and a widespread distribution of oval shaped macules that predominantly involve the hands and feet.1 Both children and adults can present atypically. Atypical presentations include vesicles and bullae on extensor surfaces such as the forearms, as well as eruptions on the face or buttocks.2 Other atypical morphologies include eczema herpeticum-like, Gianotti-Crosti-like, and purpuric/petechiae.3 Atypical hand, food, and mouth disease cases are often caused by coxsackievirus A6, however other strains of coxsackievirus can also cause atypical symptoms.2,3
Our 35-year-old female patient presented with eroded papules and vesicles around the mouth. A diagnosis of atypical HFMD was made clinically in the following days when the patient developed the more classic intraoral and acral macules and vesicles.
Similar to our case, HFMD is most often diagnosed clinically. PCR testing from an active vesicle or nasopharyngeal swab can be obtained. Treatment for HFMD is supportive and symptoms generally resolve over 7-10 days. Over-the-counter analgesics, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, as well as oral analgesics that contain lidocaine or diphenhydramine are often helpful3. In this case, our patient improved over the course of seven days without needing therapy.
This case and the photos were submitted by Vanessa Ortega, BS, University of California, San Diego; Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, and Justin Gordon, MD, San Diego Family Dermatology. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023, June 20). Symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease.
2. Drago F et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Aug;77(2):e51-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.03.046.
3. Starkey SY et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2024 Jan-Feb;41(1):23-7. doi: 10.1111/pde.15461.
Treating Pediatric Vitiligo: Consensus Statement Provides Recommendations
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- While half of all vitiligo cases manifest within the initial two decades of life, no guidelines specifically address the management of vitiligo in children, adolescents, and young adults with vitiligo.
- A protocol was established to formulate consensus recommendations addressing questions related to pediatric vitiligo.
- Overall, 50 articles on topical corticosteroids and/or topical calcineurin inhibitors, five on topical Janus kinase inhibitors, and two each on pseudocatalase and microdermabrasion were included.
- The participants recorded their agreement levels with the formulated statements, using a 5-point Likert scale.
TAKEAWAY:
- TCIs, TCSs, JAK inhibitors, and phototherapy, specifically narrowband ultraviolet (UV)-B light therapy, are mainstay treatments; the combination of UV-B light and topical therapy may enhance initial repigmentation.
- Long-term monitoring for skin cancers is advised, and short outdoor UV exposure is suggested for pediatric patients.
- TCIs, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are recommended as first-line therapy, particularly on the face, applied twice daily for ≥ 3 months; continued use for 6-12 additional months is recommended if repigmentation is observed.
- The choice of TCS class depends on the site and planned usage duration. Short-term use or overlap with TCIs is recommended because of the risk for atrophy with long-term TCS use. Class 5-6 agents are another option.
- For areas with thin skin, TCSs can be considered second-line treatments.
- Topical JAK inhibitors, specifically topical 1.5% ruxolitinib cream, are recommended for patients aged ≥ 12 years, as first- or second-line therapy. Limitation to 10% body surface area is recommended to minimize systemic absorption. Limited evidence exists for children aged < 12 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“Effective therapy requires a focus on long-term therapeutic interventions to maximize the local gain and retention of pigmentation with a trial period of twice-weekly application. Counseling should include discussion of the chronicity of vitiligo and the need for long-term care,” the authors wrote.
LIMITATIONS:
Some of the recommendations were opinion-based because of the scarcity of evidence-based literature.
SOURCE:
The consensus statement was published on March 13 in JAMA Dermatology.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by grants from Vitiligo Research Foundation and Incyte Pharmaceuticals. The majority of authors disclosed financial relationships outside this work; several reported no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- While half of all vitiligo cases manifest within the initial two decades of life, no guidelines specifically address the management of vitiligo in children, adolescents, and young adults with vitiligo.
- A protocol was established to formulate consensus recommendations addressing questions related to pediatric vitiligo.
- Overall, 50 articles on topical corticosteroids and/or topical calcineurin inhibitors, five on topical Janus kinase inhibitors, and two each on pseudocatalase and microdermabrasion were included.
- The participants recorded their agreement levels with the formulated statements, using a 5-point Likert scale.
TAKEAWAY:
- TCIs, TCSs, JAK inhibitors, and phototherapy, specifically narrowband ultraviolet (UV)-B light therapy, are mainstay treatments; the combination of UV-B light and topical therapy may enhance initial repigmentation.
- Long-term monitoring for skin cancers is advised, and short outdoor UV exposure is suggested for pediatric patients.
- TCIs, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are recommended as first-line therapy, particularly on the face, applied twice daily for ≥ 3 months; continued use for 6-12 additional months is recommended if repigmentation is observed.
- The choice of TCS class depends on the site and planned usage duration. Short-term use or overlap with TCIs is recommended because of the risk for atrophy with long-term TCS use. Class 5-6 agents are another option.
- For areas with thin skin, TCSs can be considered second-line treatments.
- Topical JAK inhibitors, specifically topical 1.5% ruxolitinib cream, are recommended for patients aged ≥ 12 years, as first- or second-line therapy. Limitation to 10% body surface area is recommended to minimize systemic absorption. Limited evidence exists for children aged < 12 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“Effective therapy requires a focus on long-term therapeutic interventions to maximize the local gain and retention of pigmentation with a trial period of twice-weekly application. Counseling should include discussion of the chronicity of vitiligo and the need for long-term care,” the authors wrote.
LIMITATIONS:
Some of the recommendations were opinion-based because of the scarcity of evidence-based literature.
SOURCE:
The consensus statement was published on March 13 in JAMA Dermatology.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by grants from Vitiligo Research Foundation and Incyte Pharmaceuticals. The majority of authors disclosed financial relationships outside this work; several reported no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- While half of all vitiligo cases manifest within the initial two decades of life, no guidelines specifically address the management of vitiligo in children, adolescents, and young adults with vitiligo.
- A protocol was established to formulate consensus recommendations addressing questions related to pediatric vitiligo.
- Overall, 50 articles on topical corticosteroids and/or topical calcineurin inhibitors, five on topical Janus kinase inhibitors, and two each on pseudocatalase and microdermabrasion were included.
- The participants recorded their agreement levels with the formulated statements, using a 5-point Likert scale.
TAKEAWAY:
- TCIs, TCSs, JAK inhibitors, and phototherapy, specifically narrowband ultraviolet (UV)-B light therapy, are mainstay treatments; the combination of UV-B light and topical therapy may enhance initial repigmentation.
- Long-term monitoring for skin cancers is advised, and short outdoor UV exposure is suggested for pediatric patients.
- TCIs, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are recommended as first-line therapy, particularly on the face, applied twice daily for ≥ 3 months; continued use for 6-12 additional months is recommended if repigmentation is observed.
- The choice of TCS class depends on the site and planned usage duration. Short-term use or overlap with TCIs is recommended because of the risk for atrophy with long-term TCS use. Class 5-6 agents are another option.
- For areas with thin skin, TCSs can be considered second-line treatments.
- Topical JAK inhibitors, specifically topical 1.5% ruxolitinib cream, are recommended for patients aged ≥ 12 years, as first- or second-line therapy. Limitation to 10% body surface area is recommended to minimize systemic absorption. Limited evidence exists for children aged < 12 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“Effective therapy requires a focus on long-term therapeutic interventions to maximize the local gain and retention of pigmentation with a trial period of twice-weekly application. Counseling should include discussion of the chronicity of vitiligo and the need for long-term care,” the authors wrote.
LIMITATIONS:
Some of the recommendations were opinion-based because of the scarcity of evidence-based literature.
SOURCE:
The consensus statement was published on March 13 in JAMA Dermatology.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by grants from Vitiligo Research Foundation and Incyte Pharmaceuticals. The majority of authors disclosed financial relationships outside this work; several reported no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Sublingual Immunotherapy Safe, Effective for Older Kids
Sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) is as safe and effective for high-risk older children and adolescents as oral immunotherapy (OIT) is for infants and preschoolers, according to new research.
Preliminary data from a study of more than 180 pediatric patients with multiple food allergies showed that while most patients had mild symptoms, none experienced a severe grade 4 reaction during the buildup and maintenance phase of SLIT.
In addition, 70% of those tested at the end of the treatment protocol were able to tolerate 300 mg of their allergen, a success rate nearly as high as that for OIT.
The study was published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.
SLIT has been used successfully in the treatment of environmental allergens such as grass and tree pollen and dust mites. In this study, researchers decided to test SLIT’s effectiveness and safety in the treatment of food allergies in older children.
“We knew that OIT is very effective and safe in infants and toddlers, but there was literature illustrating that for older, school-age kids and adolescents, OIT is not safe enough, as those older age groups tend to have higher risk of severe reaction during treatment,” senior author Edmond Chan, MD, clinical professor of allergy at the University of British Columbia and pediatric allergist at BC Children’s Hospital, both in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, told this news organization. “With that knowledge, we decided to explore SLIT as another first-phase therapy for the older kids.”
The investigators recruited 188 high-risk older children aged 4-18 years for multifood SLIT. Most (61.7%) participants had multiple food allergies. Approximately 68% were male, and the population’s median age was 11.3 years.
Nearly half (48.4%) of participants had atopic dermatitis, 45.2% had asthma, 58.0% had allergic rhinitis, and 2.66% had preexisting eosinophilic esophagitis.
Most (75.0%) of the children were classified as higher risk, and 23 had a history of a grade 3 or 4 reaction before beginning SLIT.
Of the 188 children who were initially enrolled in the study, 173 (92.0%) finished their SLIT buildup phase.
Because the study started when COVID-19 pandemic restrictions were in place, the SLIT protocol mandated that patients be seen virtually. The patients’ caregivers learned how to mix and administer the required doses at home using recipes specially developed by the research team that used products bought at the grocery store.
A wide variety of food allergens were treated, including peanut, other legumes, tree nuts, sesame, other seeds, egg, cow’s milk, fish, wheat, shrimp, and other allergens.
The children built up to 2-mg protein SLIT maintenance over the course of three to five visits under nurse supervision.
After 1-2 years of daily SLIT maintenance, patients were offered a low-dose oral food challenge (OFC; cumulative dose: 300 mg of protein) with the goal of bypassing OIT buildup.
Nearly all patients (93.1%) had symptoms during SLIT buildup, but most were mild grade 1 (52.1%) or 2 (40.4%) reactions. Only one patient had a grade 3 reaction. None of the patients experienced a severe grade 4 reaction.
The most common grade 1 reaction was oral itch, an expected symptom of SLIT, which occurred in 82.7% of the patients.
Four patients (2.10%) received epinephrine during buildup and went to the emergency department. All these patients returned to continue SLIT without further need for epinephrine.
To test the effectiveness of SLIT, the researchers performed 50 low-dose OFCs in 20 patients. Of these food challenges, 35 (70%) were successful, and patients were asked to start daily 300-mg OIT maintenance, thus bypassing OIT buildup.
An additional nine OFCs that were unsuccessful were counseled to self-escalate from 80 mg or higher to 300 mg at home with medical guidance as needed.
“Our preliminary data of 20 patients and 50 low-dose oral food challenges suggest that an initial phase of 1-2 years of 2-mg daily SLIT therapy may be a safe and effective way to bypass the OIT buildup phase without the need for dozens of in-person visits with an allergist,” said Dr. Chan.
“So now we have the best of both worlds. We harness the safety of SLIT for the first 1-2 years, with the effectiveness of OIT for the remainder of the treatment period,” he said.
Adds to Evidence
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Julia Upton, MD, associate professor of pediatrics at the University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, said, “This study adds to the evidence that consistent, low exposure to food drives meaningful desensitization far above the daily dose.” Upton did not participate in the research.
“Prior prospective studies in SLIT demonstrated that small single-digit-milligram doses and time greatly increased the threshold of reaction. This real-world report suggests that a way to utilize that threshold increase is by switching to a commonly used maintenance dose of OIT,” said Dr. Upton.
“Although few patients have been assessed for the 300-mg challenge, this study is notable for the age group of 4-18 years, and that many of the patients had reacted to low doses in the past. It also shows that many families are capable of diluting and mixing their own immunotherapy solutions with store-bought foods under the guidance of an experienced allergy clinic,” she added.
“Overall, evidence is building that by various routes, initial small amounts with minimal updoses, plus the tincture of time, may be preferred to multiple frequent updosing from multiple perspectives, including safety, feasibility, cost, and medical resources. It will also be important to understand the preferences and goals of the patient and family as various regimens become more available,” Dr. Upton concluded.
The study was funded by BC Children’s Hospital Foundation. Dr. Chan reported receiving research support from DVB Technologies; has been a member of advisory boards for Pfizer, Miravo, Medexus, Leo Pharma, Kaleo, DBV, AllerGenis, Sanofi, Genzyme, Bausch Health, Avir Pharma, AstraZeneca, ALK, and Alladapt; and was a colead of the CSACI OIT guidelines. Dr. Upton reported research support/grants from Novartis, Regeneron, Sanofi, ALK Abello, DBV Technologies, CIHR, and SickKids Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Program and fees from Pfizer, ALK Abello, Bausch Health, Astra Zeneca, and Pharming. She serves as an associate editor for Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology and is on the Board of Directors of Canadian Society of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and the Healthcare Advisory Board of Food Allergy Canada.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) is as safe and effective for high-risk older children and adolescents as oral immunotherapy (OIT) is for infants and preschoolers, according to new research.
Preliminary data from a study of more than 180 pediatric patients with multiple food allergies showed that while most patients had mild symptoms, none experienced a severe grade 4 reaction during the buildup and maintenance phase of SLIT.
In addition, 70% of those tested at the end of the treatment protocol were able to tolerate 300 mg of their allergen, a success rate nearly as high as that for OIT.
The study was published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.
SLIT has been used successfully in the treatment of environmental allergens such as grass and tree pollen and dust mites. In this study, researchers decided to test SLIT’s effectiveness and safety in the treatment of food allergies in older children.
“We knew that OIT is very effective and safe in infants and toddlers, but there was literature illustrating that for older, school-age kids and adolescents, OIT is not safe enough, as those older age groups tend to have higher risk of severe reaction during treatment,” senior author Edmond Chan, MD, clinical professor of allergy at the University of British Columbia and pediatric allergist at BC Children’s Hospital, both in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, told this news organization. “With that knowledge, we decided to explore SLIT as another first-phase therapy for the older kids.”
The investigators recruited 188 high-risk older children aged 4-18 years for multifood SLIT. Most (61.7%) participants had multiple food allergies. Approximately 68% were male, and the population’s median age was 11.3 years.
Nearly half (48.4%) of participants had atopic dermatitis, 45.2% had asthma, 58.0% had allergic rhinitis, and 2.66% had preexisting eosinophilic esophagitis.
Most (75.0%) of the children were classified as higher risk, and 23 had a history of a grade 3 or 4 reaction before beginning SLIT.
Of the 188 children who were initially enrolled in the study, 173 (92.0%) finished their SLIT buildup phase.
Because the study started when COVID-19 pandemic restrictions were in place, the SLIT protocol mandated that patients be seen virtually. The patients’ caregivers learned how to mix and administer the required doses at home using recipes specially developed by the research team that used products bought at the grocery store.
A wide variety of food allergens were treated, including peanut, other legumes, tree nuts, sesame, other seeds, egg, cow’s milk, fish, wheat, shrimp, and other allergens.
The children built up to 2-mg protein SLIT maintenance over the course of three to five visits under nurse supervision.
After 1-2 years of daily SLIT maintenance, patients were offered a low-dose oral food challenge (OFC; cumulative dose: 300 mg of protein) with the goal of bypassing OIT buildup.
Nearly all patients (93.1%) had symptoms during SLIT buildup, but most were mild grade 1 (52.1%) or 2 (40.4%) reactions. Only one patient had a grade 3 reaction. None of the patients experienced a severe grade 4 reaction.
The most common grade 1 reaction was oral itch, an expected symptom of SLIT, which occurred in 82.7% of the patients.
Four patients (2.10%) received epinephrine during buildup and went to the emergency department. All these patients returned to continue SLIT without further need for epinephrine.
To test the effectiveness of SLIT, the researchers performed 50 low-dose OFCs in 20 patients. Of these food challenges, 35 (70%) were successful, and patients were asked to start daily 300-mg OIT maintenance, thus bypassing OIT buildup.
An additional nine OFCs that were unsuccessful were counseled to self-escalate from 80 mg or higher to 300 mg at home with medical guidance as needed.
“Our preliminary data of 20 patients and 50 low-dose oral food challenges suggest that an initial phase of 1-2 years of 2-mg daily SLIT therapy may be a safe and effective way to bypass the OIT buildup phase without the need for dozens of in-person visits with an allergist,” said Dr. Chan.
“So now we have the best of both worlds. We harness the safety of SLIT for the first 1-2 years, with the effectiveness of OIT for the remainder of the treatment period,” he said.
Adds to Evidence
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Julia Upton, MD, associate professor of pediatrics at the University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, said, “This study adds to the evidence that consistent, low exposure to food drives meaningful desensitization far above the daily dose.” Upton did not participate in the research.
“Prior prospective studies in SLIT demonstrated that small single-digit-milligram doses and time greatly increased the threshold of reaction. This real-world report suggests that a way to utilize that threshold increase is by switching to a commonly used maintenance dose of OIT,” said Dr. Upton.
“Although few patients have been assessed for the 300-mg challenge, this study is notable for the age group of 4-18 years, and that many of the patients had reacted to low doses in the past. It also shows that many families are capable of diluting and mixing their own immunotherapy solutions with store-bought foods under the guidance of an experienced allergy clinic,” she added.
“Overall, evidence is building that by various routes, initial small amounts with minimal updoses, plus the tincture of time, may be preferred to multiple frequent updosing from multiple perspectives, including safety, feasibility, cost, and medical resources. It will also be important to understand the preferences and goals of the patient and family as various regimens become more available,” Dr. Upton concluded.
The study was funded by BC Children’s Hospital Foundation. Dr. Chan reported receiving research support from DVB Technologies; has been a member of advisory boards for Pfizer, Miravo, Medexus, Leo Pharma, Kaleo, DBV, AllerGenis, Sanofi, Genzyme, Bausch Health, Avir Pharma, AstraZeneca, ALK, and Alladapt; and was a colead of the CSACI OIT guidelines. Dr. Upton reported research support/grants from Novartis, Regeneron, Sanofi, ALK Abello, DBV Technologies, CIHR, and SickKids Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Program and fees from Pfizer, ALK Abello, Bausch Health, Astra Zeneca, and Pharming. She serves as an associate editor for Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology and is on the Board of Directors of Canadian Society of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and the Healthcare Advisory Board of Food Allergy Canada.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) is as safe and effective for high-risk older children and adolescents as oral immunotherapy (OIT) is for infants and preschoolers, according to new research.
Preliminary data from a study of more than 180 pediatric patients with multiple food allergies showed that while most patients had mild symptoms, none experienced a severe grade 4 reaction during the buildup and maintenance phase of SLIT.
In addition, 70% of those tested at the end of the treatment protocol were able to tolerate 300 mg of their allergen, a success rate nearly as high as that for OIT.
The study was published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.
SLIT has been used successfully in the treatment of environmental allergens such as grass and tree pollen and dust mites. In this study, researchers decided to test SLIT’s effectiveness and safety in the treatment of food allergies in older children.
“We knew that OIT is very effective and safe in infants and toddlers, but there was literature illustrating that for older, school-age kids and adolescents, OIT is not safe enough, as those older age groups tend to have higher risk of severe reaction during treatment,” senior author Edmond Chan, MD, clinical professor of allergy at the University of British Columbia and pediatric allergist at BC Children’s Hospital, both in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, told this news organization. “With that knowledge, we decided to explore SLIT as another first-phase therapy for the older kids.”
The investigators recruited 188 high-risk older children aged 4-18 years for multifood SLIT. Most (61.7%) participants had multiple food allergies. Approximately 68% were male, and the population’s median age was 11.3 years.
Nearly half (48.4%) of participants had atopic dermatitis, 45.2% had asthma, 58.0% had allergic rhinitis, and 2.66% had preexisting eosinophilic esophagitis.
Most (75.0%) of the children were classified as higher risk, and 23 had a history of a grade 3 or 4 reaction before beginning SLIT.
Of the 188 children who were initially enrolled in the study, 173 (92.0%) finished their SLIT buildup phase.
Because the study started when COVID-19 pandemic restrictions were in place, the SLIT protocol mandated that patients be seen virtually. The patients’ caregivers learned how to mix and administer the required doses at home using recipes specially developed by the research team that used products bought at the grocery store.
A wide variety of food allergens were treated, including peanut, other legumes, tree nuts, sesame, other seeds, egg, cow’s milk, fish, wheat, shrimp, and other allergens.
The children built up to 2-mg protein SLIT maintenance over the course of three to five visits under nurse supervision.
After 1-2 years of daily SLIT maintenance, patients were offered a low-dose oral food challenge (OFC; cumulative dose: 300 mg of protein) with the goal of bypassing OIT buildup.
Nearly all patients (93.1%) had symptoms during SLIT buildup, but most were mild grade 1 (52.1%) or 2 (40.4%) reactions. Only one patient had a grade 3 reaction. None of the patients experienced a severe grade 4 reaction.
The most common grade 1 reaction was oral itch, an expected symptom of SLIT, which occurred in 82.7% of the patients.
Four patients (2.10%) received epinephrine during buildup and went to the emergency department. All these patients returned to continue SLIT without further need for epinephrine.
To test the effectiveness of SLIT, the researchers performed 50 low-dose OFCs in 20 patients. Of these food challenges, 35 (70%) were successful, and patients were asked to start daily 300-mg OIT maintenance, thus bypassing OIT buildup.
An additional nine OFCs that were unsuccessful were counseled to self-escalate from 80 mg or higher to 300 mg at home with medical guidance as needed.
“Our preliminary data of 20 patients and 50 low-dose oral food challenges suggest that an initial phase of 1-2 years of 2-mg daily SLIT therapy may be a safe and effective way to bypass the OIT buildup phase without the need for dozens of in-person visits with an allergist,” said Dr. Chan.
“So now we have the best of both worlds. We harness the safety of SLIT for the first 1-2 years, with the effectiveness of OIT for the remainder of the treatment period,” he said.
Adds to Evidence
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Julia Upton, MD, associate professor of pediatrics at the University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, said, “This study adds to the evidence that consistent, low exposure to food drives meaningful desensitization far above the daily dose.” Upton did not participate in the research.
“Prior prospective studies in SLIT demonstrated that small single-digit-milligram doses and time greatly increased the threshold of reaction. This real-world report suggests that a way to utilize that threshold increase is by switching to a commonly used maintenance dose of OIT,” said Dr. Upton.
“Although few patients have been assessed for the 300-mg challenge, this study is notable for the age group of 4-18 years, and that many of the patients had reacted to low doses in the past. It also shows that many families are capable of diluting and mixing their own immunotherapy solutions with store-bought foods under the guidance of an experienced allergy clinic,” she added.
“Overall, evidence is building that by various routes, initial small amounts with minimal updoses, plus the tincture of time, may be preferred to multiple frequent updosing from multiple perspectives, including safety, feasibility, cost, and medical resources. It will also be important to understand the preferences and goals of the patient and family as various regimens become more available,” Dr. Upton concluded.
The study was funded by BC Children’s Hospital Foundation. Dr. Chan reported receiving research support from DVB Technologies; has been a member of advisory boards for Pfizer, Miravo, Medexus, Leo Pharma, Kaleo, DBV, AllerGenis, Sanofi, Genzyme, Bausch Health, Avir Pharma, AstraZeneca, ALK, and Alladapt; and was a colead of the CSACI OIT guidelines. Dr. Upton reported research support/grants from Novartis, Regeneron, Sanofi, ALK Abello, DBV Technologies, CIHR, and SickKids Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Program and fees from Pfizer, ALK Abello, Bausch Health, Astra Zeneca, and Pharming. She serves as an associate editor for Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology and is on the Board of Directors of Canadian Society of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and the Healthcare Advisory Board of Food Allergy Canada.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
THE JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY: IN PRACTICE
Inside the 2024 AAD Acne Guidelines: New Therapies Join Old Standbys
SAN DIEGO — Just weeks after the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) published its updated acne management guidelines, a dermatologist who helped write the recommendations provided colleagues with insight into recently approved topical therapies, the importance of multimodal therapy, and a controversial report linking benzoyl peroxide (BP) to the carcinogen benzene.
In regard to topical treatments, the guidelines make a “strong” recommendation for topical retinoids based on “moderate” evidence, Andrea L. Zaenglein, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, Penn State University, Hershey, Pennsylvania, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. The recommendation was based on a pooled analysis of four randomized controlled trials that found patients with acne who used the medications were more likely to have improvement via the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) scale at 12 weeks than were those treated with a vehicle (risk ratio [RR], 1.57; 1.21-2.04).
The updated guidelines were published on January 30 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. The previous guidelines were issued in 2016.
“We have four current retinoids that we use: adapalene, tretinoin, tazarotene, and trifarotene,” Dr. Zaenglein said. “Typically, when we think about retinoids, we think of adapalene as being more tolerable and tazarotene as being more effective. But we also know that they can work to prevent and treat scarring, and they work against comedonal lesions and inflammatory lesions.”
Newer concentrations include tretinoin 0.05% lotion, tazarotene 0.045% lotion, and trifarotene 0.005% cream. She noted that this trifarotene concentration can be helpful for moderate truncal acne and also referred to evidence that whey protein appears to exacerbate that condition. “I always ask teenage kids about that: Are they using those protein powders?”
Recommendations for ‘Multimodal Therapy,’ Especially With Antibiotics
Dr. Zaenglein highlighted a “good practice statement” in the new guidelines that says, “when managing acne with topical medications, we recommend multimodal therapy combining multiple mechanisms of action.”
Topical antibiotics are effective treatments on their own and include erythromycin, clindamycin, and minocycline (Minocin), she said. But the guidelines, which refer to evidence supporting them as “moderate,” do not recommend them as monotherapy because of the risk for antibiotic resistance.
The oral retinoid isotretinoin may be appropriate in conjunction with topical medications, she said, “and we also recommend fixed combination products because they’re associated with increased adherence.”
Dermatologists are familiar with several of these products because “we’ve been using them for years and years,” she said. The guidelines note that “compared to vehicle at 12 weeks, a greater proportion of patients treated with combined BP and topical retinoid achieved IGA success in three RCTs (RR, 2.19; 1.77-2.72).”
Dr. Zaenglein noted that the guidelines recommend that patients taking antibiotics also use benzoyl peroxide, which has “moderate” evidence regarding preventing the development of antibiotic resistance. “Lower strengths tend to be less irritating, and over-the-counter formulations are readily available,” she said, adding that colleagues should make sure to warn patients about the risk of bleaching clothes and towels with BP.
Now, there’s a newly approved treatment, the first fixed-dose triple combination therapy for acne, she said. It combines 1.2% clindamycin, 3.1% benzoyl peroxide, and 0.15% adapalene (Cabtreo) and is Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved for treating acne in patients ages 12 and up.
The new AAD guidelines note that “potential adverse effect profiles of the fixed-dose combinations generally reflect those of the individual agents in summation. Some fixed-dose combination products may be less expensive than prescribing their individual components separately.” The evidence supporting fixed-dose combinations in conjunction with benzoyl peroxide is considered “moderate.”
Dapsone gel, 7.5% (Aczone) is another option for acne. “It’s a topical so you don’t need to do G6PD [glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase] testing,” Dr. Zaenglein said. “It’s well tolerated, and mean total lesions fell by 48.9% vs 43.2% for vehicle,” in a 2018 study, which she said also found that females benefited more than males from this treatment.
Clascoterone 1% cream (Winlevi), approved in 2020, is appropriate for males and females aged 12 and up, Dr. Zaenglein said. She noted that it’s the only topical anti-androgen that can be used in males. However, while it has a “high” level of evidence because of phase 3 clinical trials showing benefits in moderate to severe acne, the AAD guidelines only conditionally recommend this option because the high price of clascoterone “may impact equitable acne treatment access.” The price listed on the website GoodRx (accessed on March 12) lists drugstore prices for a single 60-gram tube as ranging from $590 to $671.
“One of the harder things is trying to figure out where clascoterone fits in our kind of standard combination therapy,” she said. “Much like other hormonal therapies, it works better over the long term.”
Two more topical options per the AAD guidelines are salicylic acid, based on one randomized controlled trial, and azelaic acid (Azelex, Finacea), based on three randomized controlled trials. Both of these recommendations are conditional because of limited evidence: Evidence is considered “low” for salicylic acid and “moderate” for azelaic acid, the guidelines say, and azelaic acid “may be particularly helpful for patients with sensitive skin or darker skin types due to its lightening effect on dyspigmentation.”
As for risk for topical treatments during pregnancy/lactation, the guidelines note that topical therapies other than topical retinoids are “preferred” during pregnancy. Tazarotene is contraindicated during pregnancy, and salicylic acid should be used only in limited areas of exposure. There are no data for dapsone and clascoterone during pregnancy/lactation, and minocycline is “not recommended.”
The guideline authors noted that “available evidence is insufficient to develop a recommendation on the use of topical glycolic acid, sulfur, sodium sulfacetamide, and resorcinol for acne treatment or to make recommendations that compare topical BP, retinoids, antibiotics, and their combinations directly against each other.”
Could BP Post a Risk From Benzene?
Dr. Zaenglein highlighted a recently released report by Valisure, an independent laboratory, which reported finding high levels of the cancer-causing chemical benzene in several acne treatments, including brands such as Clearasil. “They didn’t release all of the ones that they evaluated, but there were a lot ... that we commonly recommend for our patients,” she said.
On March 6, CBS News reported that Valisure “ran tests at various temperatures over 18 days and found some products ‘can form over 800 times the conditionally restricted FDA concentration limit of two parts per million (ppm) for benzene’ in 2 weeks at 50° C (122° F),” but that benzene levels “at room temperature were more modest, ranging from about one to 24 parts per million.”
Dr. Zaenglein said she’s not ready to urge patients to discontinue BP, although in light of the findings, “I will tell them to store it at room temperature or lower.”
For now, it’s important to wait for independent verification of the results, she said. “And then it’s up to the manufacturers to reevaluate the stability of their benzoyl peroxide products with heat.”
Dr. Zaenglein disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Arcutis, Biofrontera, Galderma, and Incyte (grants/research funding), Church & Dwight (consulting fees), and UCB (consulting honoraria).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — Just weeks after the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) published its updated acne management guidelines, a dermatologist who helped write the recommendations provided colleagues with insight into recently approved topical therapies, the importance of multimodal therapy, and a controversial report linking benzoyl peroxide (BP) to the carcinogen benzene.
In regard to topical treatments, the guidelines make a “strong” recommendation for topical retinoids based on “moderate” evidence, Andrea L. Zaenglein, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, Penn State University, Hershey, Pennsylvania, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. The recommendation was based on a pooled analysis of four randomized controlled trials that found patients with acne who used the medications were more likely to have improvement via the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) scale at 12 weeks than were those treated with a vehicle (risk ratio [RR], 1.57; 1.21-2.04).
The updated guidelines were published on January 30 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. The previous guidelines were issued in 2016.
“We have four current retinoids that we use: adapalene, tretinoin, tazarotene, and trifarotene,” Dr. Zaenglein said. “Typically, when we think about retinoids, we think of adapalene as being more tolerable and tazarotene as being more effective. But we also know that they can work to prevent and treat scarring, and they work against comedonal lesions and inflammatory lesions.”
Newer concentrations include tretinoin 0.05% lotion, tazarotene 0.045% lotion, and trifarotene 0.005% cream. She noted that this trifarotene concentration can be helpful for moderate truncal acne and also referred to evidence that whey protein appears to exacerbate that condition. “I always ask teenage kids about that: Are they using those protein powders?”
Recommendations for ‘Multimodal Therapy,’ Especially With Antibiotics
Dr. Zaenglein highlighted a “good practice statement” in the new guidelines that says, “when managing acne with topical medications, we recommend multimodal therapy combining multiple mechanisms of action.”
Topical antibiotics are effective treatments on their own and include erythromycin, clindamycin, and minocycline (Minocin), she said. But the guidelines, which refer to evidence supporting them as “moderate,” do not recommend them as monotherapy because of the risk for antibiotic resistance.
The oral retinoid isotretinoin may be appropriate in conjunction with topical medications, she said, “and we also recommend fixed combination products because they’re associated with increased adherence.”
Dermatologists are familiar with several of these products because “we’ve been using them for years and years,” she said. The guidelines note that “compared to vehicle at 12 weeks, a greater proportion of patients treated with combined BP and topical retinoid achieved IGA success in three RCTs (RR, 2.19; 1.77-2.72).”
Dr. Zaenglein noted that the guidelines recommend that patients taking antibiotics also use benzoyl peroxide, which has “moderate” evidence regarding preventing the development of antibiotic resistance. “Lower strengths tend to be less irritating, and over-the-counter formulations are readily available,” she said, adding that colleagues should make sure to warn patients about the risk of bleaching clothes and towels with BP.
Now, there’s a newly approved treatment, the first fixed-dose triple combination therapy for acne, she said. It combines 1.2% clindamycin, 3.1% benzoyl peroxide, and 0.15% adapalene (Cabtreo) and is Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved for treating acne in patients ages 12 and up.
The new AAD guidelines note that “potential adverse effect profiles of the fixed-dose combinations generally reflect those of the individual agents in summation. Some fixed-dose combination products may be less expensive than prescribing their individual components separately.” The evidence supporting fixed-dose combinations in conjunction with benzoyl peroxide is considered “moderate.”
Dapsone gel, 7.5% (Aczone) is another option for acne. “It’s a topical so you don’t need to do G6PD [glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase] testing,” Dr. Zaenglein said. “It’s well tolerated, and mean total lesions fell by 48.9% vs 43.2% for vehicle,” in a 2018 study, which she said also found that females benefited more than males from this treatment.
Clascoterone 1% cream (Winlevi), approved in 2020, is appropriate for males and females aged 12 and up, Dr. Zaenglein said. She noted that it’s the only topical anti-androgen that can be used in males. However, while it has a “high” level of evidence because of phase 3 clinical trials showing benefits in moderate to severe acne, the AAD guidelines only conditionally recommend this option because the high price of clascoterone “may impact equitable acne treatment access.” The price listed on the website GoodRx (accessed on March 12) lists drugstore prices for a single 60-gram tube as ranging from $590 to $671.
“One of the harder things is trying to figure out where clascoterone fits in our kind of standard combination therapy,” she said. “Much like other hormonal therapies, it works better over the long term.”
Two more topical options per the AAD guidelines are salicylic acid, based on one randomized controlled trial, and azelaic acid (Azelex, Finacea), based on three randomized controlled trials. Both of these recommendations are conditional because of limited evidence: Evidence is considered “low” for salicylic acid and “moderate” for azelaic acid, the guidelines say, and azelaic acid “may be particularly helpful for patients with sensitive skin or darker skin types due to its lightening effect on dyspigmentation.”
As for risk for topical treatments during pregnancy/lactation, the guidelines note that topical therapies other than topical retinoids are “preferred” during pregnancy. Tazarotene is contraindicated during pregnancy, and salicylic acid should be used only in limited areas of exposure. There are no data for dapsone and clascoterone during pregnancy/lactation, and minocycline is “not recommended.”
The guideline authors noted that “available evidence is insufficient to develop a recommendation on the use of topical glycolic acid, sulfur, sodium sulfacetamide, and resorcinol for acne treatment or to make recommendations that compare topical BP, retinoids, antibiotics, and their combinations directly against each other.”
Could BP Post a Risk From Benzene?
Dr. Zaenglein highlighted a recently released report by Valisure, an independent laboratory, which reported finding high levels of the cancer-causing chemical benzene in several acne treatments, including brands such as Clearasil. “They didn’t release all of the ones that they evaluated, but there were a lot ... that we commonly recommend for our patients,” she said.
On March 6, CBS News reported that Valisure “ran tests at various temperatures over 18 days and found some products ‘can form over 800 times the conditionally restricted FDA concentration limit of two parts per million (ppm) for benzene’ in 2 weeks at 50° C (122° F),” but that benzene levels “at room temperature were more modest, ranging from about one to 24 parts per million.”
Dr. Zaenglein said she’s not ready to urge patients to discontinue BP, although in light of the findings, “I will tell them to store it at room temperature or lower.”
For now, it’s important to wait for independent verification of the results, she said. “And then it’s up to the manufacturers to reevaluate the stability of their benzoyl peroxide products with heat.”
Dr. Zaenglein disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Arcutis, Biofrontera, Galderma, and Incyte (grants/research funding), Church & Dwight (consulting fees), and UCB (consulting honoraria).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — Just weeks after the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) published its updated acne management guidelines, a dermatologist who helped write the recommendations provided colleagues with insight into recently approved topical therapies, the importance of multimodal therapy, and a controversial report linking benzoyl peroxide (BP) to the carcinogen benzene.
In regard to topical treatments, the guidelines make a “strong” recommendation for topical retinoids based on “moderate” evidence, Andrea L. Zaenglein, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, Penn State University, Hershey, Pennsylvania, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. The recommendation was based on a pooled analysis of four randomized controlled trials that found patients with acne who used the medications were more likely to have improvement via the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) scale at 12 weeks than were those treated with a vehicle (risk ratio [RR], 1.57; 1.21-2.04).
The updated guidelines were published on January 30 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. The previous guidelines were issued in 2016.
“We have four current retinoids that we use: adapalene, tretinoin, tazarotene, and trifarotene,” Dr. Zaenglein said. “Typically, when we think about retinoids, we think of adapalene as being more tolerable and tazarotene as being more effective. But we also know that they can work to prevent and treat scarring, and they work against comedonal lesions and inflammatory lesions.”
Newer concentrations include tretinoin 0.05% lotion, tazarotene 0.045% lotion, and trifarotene 0.005% cream. She noted that this trifarotene concentration can be helpful for moderate truncal acne and also referred to evidence that whey protein appears to exacerbate that condition. “I always ask teenage kids about that: Are they using those protein powders?”
Recommendations for ‘Multimodal Therapy,’ Especially With Antibiotics
Dr. Zaenglein highlighted a “good practice statement” in the new guidelines that says, “when managing acne with topical medications, we recommend multimodal therapy combining multiple mechanisms of action.”
Topical antibiotics are effective treatments on their own and include erythromycin, clindamycin, and minocycline (Minocin), she said. But the guidelines, which refer to evidence supporting them as “moderate,” do not recommend them as monotherapy because of the risk for antibiotic resistance.
The oral retinoid isotretinoin may be appropriate in conjunction with topical medications, she said, “and we also recommend fixed combination products because they’re associated with increased adherence.”
Dermatologists are familiar with several of these products because “we’ve been using them for years and years,” she said. The guidelines note that “compared to vehicle at 12 weeks, a greater proportion of patients treated with combined BP and topical retinoid achieved IGA success in three RCTs (RR, 2.19; 1.77-2.72).”
Dr. Zaenglein noted that the guidelines recommend that patients taking antibiotics also use benzoyl peroxide, which has “moderate” evidence regarding preventing the development of antibiotic resistance. “Lower strengths tend to be less irritating, and over-the-counter formulations are readily available,” she said, adding that colleagues should make sure to warn patients about the risk of bleaching clothes and towels with BP.
Now, there’s a newly approved treatment, the first fixed-dose triple combination therapy for acne, she said. It combines 1.2% clindamycin, 3.1% benzoyl peroxide, and 0.15% adapalene (Cabtreo) and is Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved for treating acne in patients ages 12 and up.
The new AAD guidelines note that “potential adverse effect profiles of the fixed-dose combinations generally reflect those of the individual agents in summation. Some fixed-dose combination products may be less expensive than prescribing their individual components separately.” The evidence supporting fixed-dose combinations in conjunction with benzoyl peroxide is considered “moderate.”
Dapsone gel, 7.5% (Aczone) is another option for acne. “It’s a topical so you don’t need to do G6PD [glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase] testing,” Dr. Zaenglein said. “It’s well tolerated, and mean total lesions fell by 48.9% vs 43.2% for vehicle,” in a 2018 study, which she said also found that females benefited more than males from this treatment.
Clascoterone 1% cream (Winlevi), approved in 2020, is appropriate for males and females aged 12 and up, Dr. Zaenglein said. She noted that it’s the only topical anti-androgen that can be used in males. However, while it has a “high” level of evidence because of phase 3 clinical trials showing benefits in moderate to severe acne, the AAD guidelines only conditionally recommend this option because the high price of clascoterone “may impact equitable acne treatment access.” The price listed on the website GoodRx (accessed on March 12) lists drugstore prices for a single 60-gram tube as ranging from $590 to $671.
“One of the harder things is trying to figure out where clascoterone fits in our kind of standard combination therapy,” she said. “Much like other hormonal therapies, it works better over the long term.”
Two more topical options per the AAD guidelines are salicylic acid, based on one randomized controlled trial, and azelaic acid (Azelex, Finacea), based on three randomized controlled trials. Both of these recommendations are conditional because of limited evidence: Evidence is considered “low” for salicylic acid and “moderate” for azelaic acid, the guidelines say, and azelaic acid “may be particularly helpful for patients with sensitive skin or darker skin types due to its lightening effect on dyspigmentation.”
As for risk for topical treatments during pregnancy/lactation, the guidelines note that topical therapies other than topical retinoids are “preferred” during pregnancy. Tazarotene is contraindicated during pregnancy, and salicylic acid should be used only in limited areas of exposure. There are no data for dapsone and clascoterone during pregnancy/lactation, and minocycline is “not recommended.”
The guideline authors noted that “available evidence is insufficient to develop a recommendation on the use of topical glycolic acid, sulfur, sodium sulfacetamide, and resorcinol for acne treatment or to make recommendations that compare topical BP, retinoids, antibiotics, and their combinations directly against each other.”
Could BP Post a Risk From Benzene?
Dr. Zaenglein highlighted a recently released report by Valisure, an independent laboratory, which reported finding high levels of the cancer-causing chemical benzene in several acne treatments, including brands such as Clearasil. “They didn’t release all of the ones that they evaluated, but there were a lot ... that we commonly recommend for our patients,” she said.
On March 6, CBS News reported that Valisure “ran tests at various temperatures over 18 days and found some products ‘can form over 800 times the conditionally restricted FDA concentration limit of two parts per million (ppm) for benzene’ in 2 weeks at 50° C (122° F),” but that benzene levels “at room temperature were more modest, ranging from about one to 24 parts per million.”
Dr. Zaenglein said she’s not ready to urge patients to discontinue BP, although in light of the findings, “I will tell them to store it at room temperature or lower.”
For now, it’s important to wait for independent verification of the results, she said. “And then it’s up to the manufacturers to reevaluate the stability of their benzoyl peroxide products with heat.”
Dr. Zaenglein disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Arcutis, Biofrontera, Galderma, and Incyte (grants/research funding), Church & Dwight (consulting fees), and UCB (consulting honoraria).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAD 2024
Latest NCCN Melanoma Guidelines Capture Dynamic of Constantly Evolving Best Practice
SAN DIEGO — that extend a slow divergence from the last set of detailed recommendations released by the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) in 2019.
Based on the constantly evolving science that drives guidelines, the new set of NCCN recommendations reflects the latest iteration of a consensus effort to define best practice, according to Susan M. Swetter, MD, professor of dermatology and director of the Pigmented Lesion and Melanoma Program at Stanford University in California.
Dr. Swetter chaired the committee that developed the most recent NCCN guidelines, released February 12. She also chaired the work group that developed the AAD recommendations, released in 2019. Differences between the two primarily reflect evolving evidence and expert opinion over time.
Next AAD Guidelines More Than 1 Year Away
The AAD guidelines are developed infrequently and in a process that can take years. The next AAD cutaneous melanoma guidelines are not likely to be released until the end of 2025 or in 2026, Dr. Swetter said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology on March 8. In contrast, the NCCN guidelines for cutaneous melanoma are revisited frequently. The last iteration was published only 1 year ago.
Many of the changes in the 2024 NCCN guidelines capture incremental advances rather than a radical departure from previous practice. One example involves shave biopsies. According to a new recommendation, residual pigment or tumor found at the base of a shave procedure, whether for tumor removal or biopsy, should prompt a deeper punch or elliptical biopsy.
The additional biopsy “should be performed immediately and submitted in a separate container to the pathologist,” Dr. Swetter said.
Further, the biopsy should be accompanied with a note to the pathologist that the shave specimen was transected. She added that the Breslow thickness (the measurement of the depth of the melanoma from the top of the granular layer down to the deepest point of the tumor) can accompany each of the two tissue specimens submitted to the pathologist.
This update — like most of the NCCN guidelines — is a category 2A recommendation. Category 1 recommendations signal a high level of evidence, such as a multicenter randomized trial. A 2A recommendation is based on nondefinitive evidence, but it does represent near uniform (≥ 85% agreement) expert consensus.
More Than 50% Consensus Generally Required
The NCCN committee that issues periodic guidelines on cutaneous melanoma is formed by a rotating group of interdisciplinary melanoma specialists. More than 30 academic institutions nationwide are generally represented, and the group includes patient advocates. Typically, no comment or recommendation is provided if the committee cannot generate at least a majority endorsement (≥ 50%) on a given topic.
Overall, the majority of guidelines, including those issued by the NCCN and the AAD, are aligned, except to the degree of the time lag that provides different sets of evidence to consider. The rationale for keeping abreast of the NCCN recommendations is that updates are more frequent, according to Dr. Swetter, who noted that these are available for free once a user has registered on the NCCN website.
Importantly, guidelines not only identify what further steps can be taken to improve diagnostic accuracy or outcomes but what practices can be abandoned to improve the benefit-to-risk ratio. As an example, surgical margins for primary melanomas have been becoming progressively smaller on the basis of evidence that larger margins increase morbidity without improving outcomes.
Although Dr. Swetter acknowledged that “we still haven’t identified the narrowest, most efficacious margins for cutaneous melanoma,” she cited studies now suggesting that margins of 2 cm appear to be sufficient even for advanced T3 and T4 tumors. Prior to the 1970s, margins of 5 cm or greater were common.
There are still many unanswered questions about optimal margins, but the 2023 NCCN guidelines already called for surgical margins of at least 1 cm and no more than 2 cm for large invasive melanomas when clinically measured around the primary tumor. Dr. Swetter said that even smaller margins can be considered “to accommodate function and/or the anatomic location.”
Best Margins for MIS Undefined
So far, there are no randomized trials yet to guide surgical margins or depth for many melanoma subtypes, including melanoma in situ (MIS). These are the types of data, when they become available, that change guidelines.
The list of procedures often performed, but for which there is no specific guidance from NCCN or other organizations, is long. Numerous examples were provided during the AAD symposium on guidelines, during which Dr. Swetter spoke. The bedside diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma with noninvasive testing was one.
Describing the 2-gene molecular assay for the evaluation of a suspected melanoma, Caroline C. Kim, MD, director of the Melanoma and Pigmented Lesion Program at Tufts University in Boston, explained that this tool, which is based on the presence of the LINC00158 gene and the preferentially expressed antigen in melanoma (PRAME), has limited utility as a tool for establishing a diagnosis of melanoma. But, she said, it has reasonably good reliability for ruling out melanoma, thereby providing a basis to avoid or delay further diagnostic steps, such as biopsy.
Skin biopsy, as established in the guidelines, “is still the gold standard,” but there are numerous studies indicating that patients negative for both LINC00158 and PRAME have a low risk for melanoma, she said.
“A double negative result is not 100% effective, but it is high,” said Dr. Kim, who provided several examples whereby she employed the test to follow the patient rather than do invasive testing.
This test is gaining popularity, according to Dr. Kim, who cited several surveys suggesting growing use among clinicians, but she characterized it as an adjunctive approach that should be considered in the context of guidelines. It is an example of an approach that is not yet standard practice but can be helpful if used appropriately, she noted.
Dr. Swetter and Dr. Kim report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — that extend a slow divergence from the last set of detailed recommendations released by the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) in 2019.
Based on the constantly evolving science that drives guidelines, the new set of NCCN recommendations reflects the latest iteration of a consensus effort to define best practice, according to Susan M. Swetter, MD, professor of dermatology and director of the Pigmented Lesion and Melanoma Program at Stanford University in California.
Dr. Swetter chaired the committee that developed the most recent NCCN guidelines, released February 12. She also chaired the work group that developed the AAD recommendations, released in 2019. Differences between the two primarily reflect evolving evidence and expert opinion over time.
Next AAD Guidelines More Than 1 Year Away
The AAD guidelines are developed infrequently and in a process that can take years. The next AAD cutaneous melanoma guidelines are not likely to be released until the end of 2025 or in 2026, Dr. Swetter said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology on March 8. In contrast, the NCCN guidelines for cutaneous melanoma are revisited frequently. The last iteration was published only 1 year ago.
Many of the changes in the 2024 NCCN guidelines capture incremental advances rather than a radical departure from previous practice. One example involves shave biopsies. According to a new recommendation, residual pigment or tumor found at the base of a shave procedure, whether for tumor removal or biopsy, should prompt a deeper punch or elliptical biopsy.
The additional biopsy “should be performed immediately and submitted in a separate container to the pathologist,” Dr. Swetter said.
Further, the biopsy should be accompanied with a note to the pathologist that the shave specimen was transected. She added that the Breslow thickness (the measurement of the depth of the melanoma from the top of the granular layer down to the deepest point of the tumor) can accompany each of the two tissue specimens submitted to the pathologist.
This update — like most of the NCCN guidelines — is a category 2A recommendation. Category 1 recommendations signal a high level of evidence, such as a multicenter randomized trial. A 2A recommendation is based on nondefinitive evidence, but it does represent near uniform (≥ 85% agreement) expert consensus.
More Than 50% Consensus Generally Required
The NCCN committee that issues periodic guidelines on cutaneous melanoma is formed by a rotating group of interdisciplinary melanoma specialists. More than 30 academic institutions nationwide are generally represented, and the group includes patient advocates. Typically, no comment or recommendation is provided if the committee cannot generate at least a majority endorsement (≥ 50%) on a given topic.
Overall, the majority of guidelines, including those issued by the NCCN and the AAD, are aligned, except to the degree of the time lag that provides different sets of evidence to consider. The rationale for keeping abreast of the NCCN recommendations is that updates are more frequent, according to Dr. Swetter, who noted that these are available for free once a user has registered on the NCCN website.
Importantly, guidelines not only identify what further steps can be taken to improve diagnostic accuracy or outcomes but what practices can be abandoned to improve the benefit-to-risk ratio. As an example, surgical margins for primary melanomas have been becoming progressively smaller on the basis of evidence that larger margins increase morbidity without improving outcomes.
Although Dr. Swetter acknowledged that “we still haven’t identified the narrowest, most efficacious margins for cutaneous melanoma,” she cited studies now suggesting that margins of 2 cm appear to be sufficient even for advanced T3 and T4 tumors. Prior to the 1970s, margins of 5 cm or greater were common.
There are still many unanswered questions about optimal margins, but the 2023 NCCN guidelines already called for surgical margins of at least 1 cm and no more than 2 cm for large invasive melanomas when clinically measured around the primary tumor. Dr. Swetter said that even smaller margins can be considered “to accommodate function and/or the anatomic location.”
Best Margins for MIS Undefined
So far, there are no randomized trials yet to guide surgical margins or depth for many melanoma subtypes, including melanoma in situ (MIS). These are the types of data, when they become available, that change guidelines.
The list of procedures often performed, but for which there is no specific guidance from NCCN or other organizations, is long. Numerous examples were provided during the AAD symposium on guidelines, during which Dr. Swetter spoke. The bedside diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma with noninvasive testing was one.
Describing the 2-gene molecular assay for the evaluation of a suspected melanoma, Caroline C. Kim, MD, director of the Melanoma and Pigmented Lesion Program at Tufts University in Boston, explained that this tool, which is based on the presence of the LINC00158 gene and the preferentially expressed antigen in melanoma (PRAME), has limited utility as a tool for establishing a diagnosis of melanoma. But, she said, it has reasonably good reliability for ruling out melanoma, thereby providing a basis to avoid or delay further diagnostic steps, such as biopsy.
Skin biopsy, as established in the guidelines, “is still the gold standard,” but there are numerous studies indicating that patients negative for both LINC00158 and PRAME have a low risk for melanoma, she said.
“A double negative result is not 100% effective, but it is high,” said Dr. Kim, who provided several examples whereby she employed the test to follow the patient rather than do invasive testing.
This test is gaining popularity, according to Dr. Kim, who cited several surveys suggesting growing use among clinicians, but she characterized it as an adjunctive approach that should be considered in the context of guidelines. It is an example of an approach that is not yet standard practice but can be helpful if used appropriately, she noted.
Dr. Swetter and Dr. Kim report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — that extend a slow divergence from the last set of detailed recommendations released by the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) in 2019.
Based on the constantly evolving science that drives guidelines, the new set of NCCN recommendations reflects the latest iteration of a consensus effort to define best practice, according to Susan M. Swetter, MD, professor of dermatology and director of the Pigmented Lesion and Melanoma Program at Stanford University in California.
Dr. Swetter chaired the committee that developed the most recent NCCN guidelines, released February 12. She also chaired the work group that developed the AAD recommendations, released in 2019. Differences between the two primarily reflect evolving evidence and expert opinion over time.
Next AAD Guidelines More Than 1 Year Away
The AAD guidelines are developed infrequently and in a process that can take years. The next AAD cutaneous melanoma guidelines are not likely to be released until the end of 2025 or in 2026, Dr. Swetter said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology on March 8. In contrast, the NCCN guidelines for cutaneous melanoma are revisited frequently. The last iteration was published only 1 year ago.
Many of the changes in the 2024 NCCN guidelines capture incremental advances rather than a radical departure from previous practice. One example involves shave biopsies. According to a new recommendation, residual pigment or tumor found at the base of a shave procedure, whether for tumor removal or biopsy, should prompt a deeper punch or elliptical biopsy.
The additional biopsy “should be performed immediately and submitted in a separate container to the pathologist,” Dr. Swetter said.
Further, the biopsy should be accompanied with a note to the pathologist that the shave specimen was transected. She added that the Breslow thickness (the measurement of the depth of the melanoma from the top of the granular layer down to the deepest point of the tumor) can accompany each of the two tissue specimens submitted to the pathologist.
This update — like most of the NCCN guidelines — is a category 2A recommendation. Category 1 recommendations signal a high level of evidence, such as a multicenter randomized trial. A 2A recommendation is based on nondefinitive evidence, but it does represent near uniform (≥ 85% agreement) expert consensus.
More Than 50% Consensus Generally Required
The NCCN committee that issues periodic guidelines on cutaneous melanoma is formed by a rotating group of interdisciplinary melanoma specialists. More than 30 academic institutions nationwide are generally represented, and the group includes patient advocates. Typically, no comment or recommendation is provided if the committee cannot generate at least a majority endorsement (≥ 50%) on a given topic.
Overall, the majority of guidelines, including those issued by the NCCN and the AAD, are aligned, except to the degree of the time lag that provides different sets of evidence to consider. The rationale for keeping abreast of the NCCN recommendations is that updates are more frequent, according to Dr. Swetter, who noted that these are available for free once a user has registered on the NCCN website.
Importantly, guidelines not only identify what further steps can be taken to improve diagnostic accuracy or outcomes but what practices can be abandoned to improve the benefit-to-risk ratio. As an example, surgical margins for primary melanomas have been becoming progressively smaller on the basis of evidence that larger margins increase morbidity without improving outcomes.
Although Dr. Swetter acknowledged that “we still haven’t identified the narrowest, most efficacious margins for cutaneous melanoma,” she cited studies now suggesting that margins of 2 cm appear to be sufficient even for advanced T3 and T4 tumors. Prior to the 1970s, margins of 5 cm or greater were common.
There are still many unanswered questions about optimal margins, but the 2023 NCCN guidelines already called for surgical margins of at least 1 cm and no more than 2 cm for large invasive melanomas when clinically measured around the primary tumor. Dr. Swetter said that even smaller margins can be considered “to accommodate function and/or the anatomic location.”
Best Margins for MIS Undefined
So far, there are no randomized trials yet to guide surgical margins or depth for many melanoma subtypes, including melanoma in situ (MIS). These are the types of data, when they become available, that change guidelines.
The list of procedures often performed, but for which there is no specific guidance from NCCN or other organizations, is long. Numerous examples were provided during the AAD symposium on guidelines, during which Dr. Swetter spoke. The bedside diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma with noninvasive testing was one.
Describing the 2-gene molecular assay for the evaluation of a suspected melanoma, Caroline C. Kim, MD, director of the Melanoma and Pigmented Lesion Program at Tufts University in Boston, explained that this tool, which is based on the presence of the LINC00158 gene and the preferentially expressed antigen in melanoma (PRAME), has limited utility as a tool for establishing a diagnosis of melanoma. But, she said, it has reasonably good reliability for ruling out melanoma, thereby providing a basis to avoid or delay further diagnostic steps, such as biopsy.
Skin biopsy, as established in the guidelines, “is still the gold standard,” but there are numerous studies indicating that patients negative for both LINC00158 and PRAME have a low risk for melanoma, she said.
“A double negative result is not 100% effective, but it is high,” said Dr. Kim, who provided several examples whereby she employed the test to follow the patient rather than do invasive testing.
This test is gaining popularity, according to Dr. Kim, who cited several surveys suggesting growing use among clinicians, but she characterized it as an adjunctive approach that should be considered in the context of guidelines. It is an example of an approach that is not yet standard practice but can be helpful if used appropriately, she noted.
Dr. Swetter and Dr. Kim report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAD 2024
Sulfites Selected as ACDS Allergen of the Year
by the American Contact Dermatitis Society (ACDS).
Sulfites are currently not found in most screening patch test series, so may be missed as a relevant contact allergen, Donald V. Belsito, MD, emeritus professor in the Department of Dermatology at Columbia University, New York City, said in his presentation on the Allergen of the Year on March 7 at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society in San Diego. Sulfites, he noted, are distinct from sulfates, and the groups do not cross-react with each other.
Sodium disulfite, an inorganic compound, belongs to a group of sulfiting agents, which contain the sulfite ion SO32− and include ammonium sulfite, potassium sulfite, and sodium sulfite, Dr. Belsito said. Sulfites function as antioxidants and preservatives in a range of products including food and beverages, personal care products, and pharmaceuticals.
The type of sulfite allergy diagnosed by patch testing is type IV hypersensitivity or delayed-type hypersensitivity, where patients present with pruritic, red, scaling macules, papulovesicles, and patches, Dr. Belsito told this news organization. “It is not the type I, immediate hypersensitivity that causes hives and, in some cases, anaphylaxis,” he said. Sulfites also can cause these side effects, so correct labeling of food and beverages is important, he noted.
Some common nonoccupational sulfite sources include hair coloring and bleach products, hairspray, tanning lotions, makeup, sunscreens, and deodorants, Dr. Belsito said in his presentation. Medications including topical antifungals, topical corticosteroids, and nasal solutions can be culprits, as can water in swimming pools, he noted.
In occupational settings, sulfites may be present not only in food and drink products but also can be used in production of products, such as those used for sterilization during beer and wine fermentation, Dr. Belsito said. Other potential occupational sources of sulfite exposure include healthcare settings and textile, chemical, rubber, and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
High-sulfite food products (> 100 ppm) to be aware of include dried fruit (raisins and prunes are exceptions), bottled lemon or lime juice (but not frozen products), wine, molasses, grape juice (white, or white, pink, and red sparkling), and pickled cocktail onions, Dr. Belsito said.
“Like other contact allergens, the clinical presentation correlates with exposure,” he added. A study by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) found that 28.8% of patients positive for sulfite allergy on patch testing presented with facial dermatitis, which was not only related to cosmetics and medications used on the face but also from products, such as shampoo, used on the scalp that dripped onto the face. “The scalp is relatively resistant to the expression of contact allergy and may not be involved at all,” he said.
According to the NACDG study, the hands were the second most common site of dermatitis associated with sulfites (20.5%) followed by generalized distribution (13.6%). These sites are to be expected, given the sources of food and beverage, personal care products, and occupational materials, Dr. Belsito said.
“Eczematous dermatitis of the lips is also common in patients with ingested food sources of sulfites,” he said.
Systemic contact dermatitis to sulfites has been documented following oral, rectal, and parental exposure, Dr. Belsito told this news organization. “Systemic dermatitis may present as a scattered/generalized dermatitis, symmetrical drug-related intertriginous and flexural exanthema (also referred to as baboon syndrome), or erythroderma,” he said.
How to Spot Sulfite Allergies
The exclusion of sulfites from most patch test series means that sulfite allergy diagnoses are often missed, despite the wide range of potential exposures, Dr. Belsito said.
“Most cases of allergic contact dermatitis occur at the site of application of the allergen,” he noted. Depending on the location of the dermatitis, a detailed history of exposures that includes cosmetics and topical medications, work-related materials, and foods and beverages might suggest a sulfite allergy, he said.
Given the range of potential clinical presentations and the many and varied exposures to sulfites, Dr. Belsito’s best tip for clinicians is to routinely screen for them and evaluate the many avenues of exposure if a patch test is positive, he said.
For now, he said he does not think additional research is needed on sulfites as allergens; instead, sulfites, such as sodium metabisulfite/sodium disulfite, should be included in all clinicians’ baseline screening series, he said.
The Allergen of the Year was also recently announced in the journal Dermatitis. Authors Samuel F. Ekstein, MS, and Erin M. Warshaw, MD, from the Department of Dermatology, Park Nicollet Health Services, Minneapolis, Minnesota, noted that the ACDS hoped to raise awareness of sulfites as a “significant allergen” and called for their increased inclusion in screening patch test series.
Patients identified with sulfite allergies can find alternative products on the ACDS CAMP (Contact Allergen Management Program) website, Dr. Warshaw said in an interview.
She also highlighted some examples of sulfites as allergens in healthcare settings in particular. She described one patient who presented with dermatitis at the site of three previous hand orthopedic procedures.
“Although surgical cleansers were suspected, the patient reacted to sodium metabisulfite. Review of the operating room contactants confirmed sulfites as preservatives in an injectable anesthetic and antibiotic used for wound irrigation,” she said. Another patient who had been treated for recurrent otitis externa and seborrheic dermatitis was found to be allergic to sulfites in an otic antibiotic suspension as well as in a ketoconazole cream product, she added.
In the paper, Dr. Warshaw and Mr. Ekstein called for the addition of sulfites to the test series. Although the NACDG added sodium metabisulfite to the series in 2017, sulfites are not part of the American Contact Dermatitis Core Series, they wrote. Sodium metabisulfite, they said, was added to the European baseline standard series after review of the 2019-2020 patch test reactivity and clinical relevance data.
The ACDS meeting is held every year the day before the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Dr. Belsito and Dr. Warshaw had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
by the American Contact Dermatitis Society (ACDS).
Sulfites are currently not found in most screening patch test series, so may be missed as a relevant contact allergen, Donald V. Belsito, MD, emeritus professor in the Department of Dermatology at Columbia University, New York City, said in his presentation on the Allergen of the Year on March 7 at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society in San Diego. Sulfites, he noted, are distinct from sulfates, and the groups do not cross-react with each other.
Sodium disulfite, an inorganic compound, belongs to a group of sulfiting agents, which contain the sulfite ion SO32− and include ammonium sulfite, potassium sulfite, and sodium sulfite, Dr. Belsito said. Sulfites function as antioxidants and preservatives in a range of products including food and beverages, personal care products, and pharmaceuticals.
The type of sulfite allergy diagnosed by patch testing is type IV hypersensitivity or delayed-type hypersensitivity, where patients present with pruritic, red, scaling macules, papulovesicles, and patches, Dr. Belsito told this news organization. “It is not the type I, immediate hypersensitivity that causes hives and, in some cases, anaphylaxis,” he said. Sulfites also can cause these side effects, so correct labeling of food and beverages is important, he noted.
Some common nonoccupational sulfite sources include hair coloring and bleach products, hairspray, tanning lotions, makeup, sunscreens, and deodorants, Dr. Belsito said in his presentation. Medications including topical antifungals, topical corticosteroids, and nasal solutions can be culprits, as can water in swimming pools, he noted.
In occupational settings, sulfites may be present not only in food and drink products but also can be used in production of products, such as those used for sterilization during beer and wine fermentation, Dr. Belsito said. Other potential occupational sources of sulfite exposure include healthcare settings and textile, chemical, rubber, and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
High-sulfite food products (> 100 ppm) to be aware of include dried fruit (raisins and prunes are exceptions), bottled lemon or lime juice (but not frozen products), wine, molasses, grape juice (white, or white, pink, and red sparkling), and pickled cocktail onions, Dr. Belsito said.
“Like other contact allergens, the clinical presentation correlates with exposure,” he added. A study by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) found that 28.8% of patients positive for sulfite allergy on patch testing presented with facial dermatitis, which was not only related to cosmetics and medications used on the face but also from products, such as shampoo, used on the scalp that dripped onto the face. “The scalp is relatively resistant to the expression of contact allergy and may not be involved at all,” he said.
According to the NACDG study, the hands were the second most common site of dermatitis associated with sulfites (20.5%) followed by generalized distribution (13.6%). These sites are to be expected, given the sources of food and beverage, personal care products, and occupational materials, Dr. Belsito said.
“Eczematous dermatitis of the lips is also common in patients with ingested food sources of sulfites,” he said.
Systemic contact dermatitis to sulfites has been documented following oral, rectal, and parental exposure, Dr. Belsito told this news organization. “Systemic dermatitis may present as a scattered/generalized dermatitis, symmetrical drug-related intertriginous and flexural exanthema (also referred to as baboon syndrome), or erythroderma,” he said.
How to Spot Sulfite Allergies
The exclusion of sulfites from most patch test series means that sulfite allergy diagnoses are often missed, despite the wide range of potential exposures, Dr. Belsito said.
“Most cases of allergic contact dermatitis occur at the site of application of the allergen,” he noted. Depending on the location of the dermatitis, a detailed history of exposures that includes cosmetics and topical medications, work-related materials, and foods and beverages might suggest a sulfite allergy, he said.
Given the range of potential clinical presentations and the many and varied exposures to sulfites, Dr. Belsito’s best tip for clinicians is to routinely screen for them and evaluate the many avenues of exposure if a patch test is positive, he said.
For now, he said he does not think additional research is needed on sulfites as allergens; instead, sulfites, such as sodium metabisulfite/sodium disulfite, should be included in all clinicians’ baseline screening series, he said.
The Allergen of the Year was also recently announced in the journal Dermatitis. Authors Samuel F. Ekstein, MS, and Erin M. Warshaw, MD, from the Department of Dermatology, Park Nicollet Health Services, Minneapolis, Minnesota, noted that the ACDS hoped to raise awareness of sulfites as a “significant allergen” and called for their increased inclusion in screening patch test series.
Patients identified with sulfite allergies can find alternative products on the ACDS CAMP (Contact Allergen Management Program) website, Dr. Warshaw said in an interview.
She also highlighted some examples of sulfites as allergens in healthcare settings in particular. She described one patient who presented with dermatitis at the site of three previous hand orthopedic procedures.
“Although surgical cleansers were suspected, the patient reacted to sodium metabisulfite. Review of the operating room contactants confirmed sulfites as preservatives in an injectable anesthetic and antibiotic used for wound irrigation,” she said. Another patient who had been treated for recurrent otitis externa and seborrheic dermatitis was found to be allergic to sulfites in an otic antibiotic suspension as well as in a ketoconazole cream product, she added.
In the paper, Dr. Warshaw and Mr. Ekstein called for the addition of sulfites to the test series. Although the NACDG added sodium metabisulfite to the series in 2017, sulfites are not part of the American Contact Dermatitis Core Series, they wrote. Sodium metabisulfite, they said, was added to the European baseline standard series after review of the 2019-2020 patch test reactivity and clinical relevance data.
The ACDS meeting is held every year the day before the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Dr. Belsito and Dr. Warshaw had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
by the American Contact Dermatitis Society (ACDS).
Sulfites are currently not found in most screening patch test series, so may be missed as a relevant contact allergen, Donald V. Belsito, MD, emeritus professor in the Department of Dermatology at Columbia University, New York City, said in his presentation on the Allergen of the Year on March 7 at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society in San Diego. Sulfites, he noted, are distinct from sulfates, and the groups do not cross-react with each other.
Sodium disulfite, an inorganic compound, belongs to a group of sulfiting agents, which contain the sulfite ion SO32− and include ammonium sulfite, potassium sulfite, and sodium sulfite, Dr. Belsito said. Sulfites function as antioxidants and preservatives in a range of products including food and beverages, personal care products, and pharmaceuticals.
The type of sulfite allergy diagnosed by patch testing is type IV hypersensitivity or delayed-type hypersensitivity, where patients present with pruritic, red, scaling macules, papulovesicles, and patches, Dr. Belsito told this news organization. “It is not the type I, immediate hypersensitivity that causes hives and, in some cases, anaphylaxis,” he said. Sulfites also can cause these side effects, so correct labeling of food and beverages is important, he noted.
Some common nonoccupational sulfite sources include hair coloring and bleach products, hairspray, tanning lotions, makeup, sunscreens, and deodorants, Dr. Belsito said in his presentation. Medications including topical antifungals, topical corticosteroids, and nasal solutions can be culprits, as can water in swimming pools, he noted.
In occupational settings, sulfites may be present not only in food and drink products but also can be used in production of products, such as those used for sterilization during beer and wine fermentation, Dr. Belsito said. Other potential occupational sources of sulfite exposure include healthcare settings and textile, chemical, rubber, and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
High-sulfite food products (> 100 ppm) to be aware of include dried fruit (raisins and prunes are exceptions), bottled lemon or lime juice (but not frozen products), wine, molasses, grape juice (white, or white, pink, and red sparkling), and pickled cocktail onions, Dr. Belsito said.
“Like other contact allergens, the clinical presentation correlates with exposure,” he added. A study by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) found that 28.8% of patients positive for sulfite allergy on patch testing presented with facial dermatitis, which was not only related to cosmetics and medications used on the face but also from products, such as shampoo, used on the scalp that dripped onto the face. “The scalp is relatively resistant to the expression of contact allergy and may not be involved at all,” he said.
According to the NACDG study, the hands were the second most common site of dermatitis associated with sulfites (20.5%) followed by generalized distribution (13.6%). These sites are to be expected, given the sources of food and beverage, personal care products, and occupational materials, Dr. Belsito said.
“Eczematous dermatitis of the lips is also common in patients with ingested food sources of sulfites,” he said.
Systemic contact dermatitis to sulfites has been documented following oral, rectal, and parental exposure, Dr. Belsito told this news organization. “Systemic dermatitis may present as a scattered/generalized dermatitis, symmetrical drug-related intertriginous and flexural exanthema (also referred to as baboon syndrome), or erythroderma,” he said.
How to Spot Sulfite Allergies
The exclusion of sulfites from most patch test series means that sulfite allergy diagnoses are often missed, despite the wide range of potential exposures, Dr. Belsito said.
“Most cases of allergic contact dermatitis occur at the site of application of the allergen,” he noted. Depending on the location of the dermatitis, a detailed history of exposures that includes cosmetics and topical medications, work-related materials, and foods and beverages might suggest a sulfite allergy, he said.
Given the range of potential clinical presentations and the many and varied exposures to sulfites, Dr. Belsito’s best tip for clinicians is to routinely screen for them and evaluate the many avenues of exposure if a patch test is positive, he said.
For now, he said he does not think additional research is needed on sulfites as allergens; instead, sulfites, such as sodium metabisulfite/sodium disulfite, should be included in all clinicians’ baseline screening series, he said.
The Allergen of the Year was also recently announced in the journal Dermatitis. Authors Samuel F. Ekstein, MS, and Erin M. Warshaw, MD, from the Department of Dermatology, Park Nicollet Health Services, Minneapolis, Minnesota, noted that the ACDS hoped to raise awareness of sulfites as a “significant allergen” and called for their increased inclusion in screening patch test series.
Patients identified with sulfite allergies can find alternative products on the ACDS CAMP (Contact Allergen Management Program) website, Dr. Warshaw said in an interview.
She also highlighted some examples of sulfites as allergens in healthcare settings in particular. She described one patient who presented with dermatitis at the site of three previous hand orthopedic procedures.
“Although surgical cleansers were suspected, the patient reacted to sodium metabisulfite. Review of the operating room contactants confirmed sulfites as preservatives in an injectable anesthetic and antibiotic used for wound irrigation,” she said. Another patient who had been treated for recurrent otitis externa and seborrheic dermatitis was found to be allergic to sulfites in an otic antibiotic suspension as well as in a ketoconazole cream product, she added.
In the paper, Dr. Warshaw and Mr. Ekstein called for the addition of sulfites to the test series. Although the NACDG added sodium metabisulfite to the series in 2017, sulfites are not part of the American Contact Dermatitis Core Series, they wrote. Sodium metabisulfite, they said, was added to the European baseline standard series after review of the 2019-2020 patch test reactivity and clinical relevance data.
The ACDS meeting is held every year the day before the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Dr. Belsito and Dr. Warshaw had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACDS 2024
TIL for Melanoma: What Are the Costs and Other Challenges to Getting It to Patients?
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved the tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte cell therapy (TIL) for use in certain adults with unresectable or metastatic melanoma. This marks the first time the FDA has allowed a cellular therapy to be marketed for a solid tumor cancer.
Lifileucel is made from a patient’s surgically removed tumor. Tissue from that tumor is then sent to a manufacturing center. Turnaround time to when the drug is ready to be sent back to the cancer center for use is approximately 34 days, according to the drug’s manufacturer, Iovance.
Insurance Adjustments
The cost of the one-time lifileucel treatment is $515,000, according to the manufacturer.
Two investigators in the clinical trials of lifileucel, Allison Betof Warner, MD, of Stanford University, Stanford, California, and Igor Puzanov, MD, of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, New York, shared their expectations regarding factors that would contribute to how much a patient paid for the drug.
Given the drug’s recent approval, the logistical details are still being worked out between cancer centers and insurers regarding how much patients will pay out of pocket for lifileucel, said Dr. Betof Warner, who is assistant professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Medical Oncology at Stanford University.
The associated costs, including the surgery that is needed to procure the TIL cells for expansion into the final drug product, will be different for each patient, she told this publication.
Patients’ costs for lifileucel will vary based on their insurance, explained Dr. Puzanov, chief of melanoma and professor of oncology at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center.
At Roswell Park, “we will work with our regionally-based payers on a case-by-case basis to seek approval for those patients we believe can most benefit from lifileucel,” he said in an interview. Preauthorization will be required, as is standard for many cancer treatments, he added.
Once payer approval is in place, Dr. Puzanov said, he did not anticipate significant delays in access for patients.
Certified centers such as the multidisciplinary team at Roswell Park are ready to treat patients now. Other centers are similarly prepared, especially those involved in the clinical trials of lifileucel, he said.
Logistics and Infrastructure
A position article and guidelines on the management of and best practices for TIL was published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer on February 29. The paper, of which both Dr. Betof Warner and Dr. Puzanov served as authors, noted that one of the barriers to the use of TIL cell therapy in clinical practice is the need for state-of-the art infrastructure at centers that want to offer the treatment. Scheduling, patient referrals, and surgery, as well as the production and infusion of TIL, must be organized and streamlined for successful treatment, the authors wrote.
The two supply chains involved in TIL — the transportation of the tumor tissue from the treatment center to the manufacturer and transport of the TIL infusion product back to the treatment center — must be timely and precise, they emphasized.
Docs Hope TIL Improves in Several Ways
Although the TIL technology is a breakthrough, “we hope to see even better efficacy and lower toxicity as further research looks at ways to improve on the current TIL standard,” Dr. Puzanov said.
More research and dose adjustments may impact patient costs and side effects, he noted. “I am looking to see TILs used in the front line, with or without checkpoint inhibitors.”
Research is needed to explore how to lower the chemotherapy doses and possibly the associated toxicity, he added. Finally, researchers must consider whether high-dose IL-2 therapy — given as part of the TIL cell therapy — could be replaced with other cytokines, or whether the number of doses could be lowered. Another avenue of exploration is engineering genes for cytokines into TILs, he said.
“The key is to think about TIL therapy before you need it — ideally, when the patient is still doing well on their frontline checkpoint inhibition immunotherapy,” Dr. Puzanov said in an interview. That is the time for evaluation, and specialty centers can provide an expert assessment, he said.
“We are constantly working to improve TIL therapy,” Dr. Betof Warner told this publication. More research is needed optimize the regimen to reduce side effects, which would not only make treatment easier for currently eligible patients, but might allow treatment for patients not currently eligible.
“For example, we are looking for ways to reduce the dose of preparative chemotherapy, which prepares the body for the cells to maximize their longevity and efficacy, and to reduce or eliminate the need to give IL-2 after the cell administration,” continued Dr. Betof Warner, who is also Director of Melanoma Medical Oncology, Director of Solid Tumor Cellular Therapy, and Codirector of the Pigmented Lesion and Melanoma Program at Stanford University. “We are also actively studying next-generation TIL therapies to try to increase the efficacy.”
“Lifileucel has about a 30% success rate for melanoma that has progressed after standard therapy; we are working hard to do better than that,” she noted.
In a press release, Iovance summarized the results of the trial that supported the FDA’s accelerated approval of lifileucel. In an open-label single-arm study, including multiple sites worldwide, 73 adults with unresectable or metastatic melanoma who had received at least one previous systemic therapy underwent a lymphodepleting regimen followed by treatments with fludarabine and aldesleukin. Patients then received lifileucel at a median dose of 21.1 x 109 viable cells; the recommended dose ranges from 7.5 x 109 to 72 x 109 cells.
The primary efficacy outcome was objective response rate (ORR). The ORR in the study was 31.5%, and the median time to initial lifileucel response was 1.5 months.
The clinical trials of lifileucel for which Dr. Betof Warner and Dr. Puzanov served as investigators were sponsored by Iovance.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved the tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte cell therapy (TIL) for use in certain adults with unresectable or metastatic melanoma. This marks the first time the FDA has allowed a cellular therapy to be marketed for a solid tumor cancer.
Lifileucel is made from a patient’s surgically removed tumor. Tissue from that tumor is then sent to a manufacturing center. Turnaround time to when the drug is ready to be sent back to the cancer center for use is approximately 34 days, according to the drug’s manufacturer, Iovance.
Insurance Adjustments
The cost of the one-time lifileucel treatment is $515,000, according to the manufacturer.
Two investigators in the clinical trials of lifileucel, Allison Betof Warner, MD, of Stanford University, Stanford, California, and Igor Puzanov, MD, of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, New York, shared their expectations regarding factors that would contribute to how much a patient paid for the drug.
Given the drug’s recent approval, the logistical details are still being worked out between cancer centers and insurers regarding how much patients will pay out of pocket for lifileucel, said Dr. Betof Warner, who is assistant professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Medical Oncology at Stanford University.
The associated costs, including the surgery that is needed to procure the TIL cells for expansion into the final drug product, will be different for each patient, she told this publication.
Patients’ costs for lifileucel will vary based on their insurance, explained Dr. Puzanov, chief of melanoma and professor of oncology at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center.
At Roswell Park, “we will work with our regionally-based payers on a case-by-case basis to seek approval for those patients we believe can most benefit from lifileucel,” he said in an interview. Preauthorization will be required, as is standard for many cancer treatments, he added.
Once payer approval is in place, Dr. Puzanov said, he did not anticipate significant delays in access for patients.
Certified centers such as the multidisciplinary team at Roswell Park are ready to treat patients now. Other centers are similarly prepared, especially those involved in the clinical trials of lifileucel, he said.
Logistics and Infrastructure
A position article and guidelines on the management of and best practices for TIL was published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer on February 29. The paper, of which both Dr. Betof Warner and Dr. Puzanov served as authors, noted that one of the barriers to the use of TIL cell therapy in clinical practice is the need for state-of-the art infrastructure at centers that want to offer the treatment. Scheduling, patient referrals, and surgery, as well as the production and infusion of TIL, must be organized and streamlined for successful treatment, the authors wrote.
The two supply chains involved in TIL — the transportation of the tumor tissue from the treatment center to the manufacturer and transport of the TIL infusion product back to the treatment center — must be timely and precise, they emphasized.
Docs Hope TIL Improves in Several Ways
Although the TIL technology is a breakthrough, “we hope to see even better efficacy and lower toxicity as further research looks at ways to improve on the current TIL standard,” Dr. Puzanov said.
More research and dose adjustments may impact patient costs and side effects, he noted. “I am looking to see TILs used in the front line, with or without checkpoint inhibitors.”
Research is needed to explore how to lower the chemotherapy doses and possibly the associated toxicity, he added. Finally, researchers must consider whether high-dose IL-2 therapy — given as part of the TIL cell therapy — could be replaced with other cytokines, or whether the number of doses could be lowered. Another avenue of exploration is engineering genes for cytokines into TILs, he said.
“The key is to think about TIL therapy before you need it — ideally, when the patient is still doing well on their frontline checkpoint inhibition immunotherapy,” Dr. Puzanov said in an interview. That is the time for evaluation, and specialty centers can provide an expert assessment, he said.
“We are constantly working to improve TIL therapy,” Dr. Betof Warner told this publication. More research is needed optimize the regimen to reduce side effects, which would not only make treatment easier for currently eligible patients, but might allow treatment for patients not currently eligible.
“For example, we are looking for ways to reduce the dose of preparative chemotherapy, which prepares the body for the cells to maximize their longevity and efficacy, and to reduce or eliminate the need to give IL-2 after the cell administration,” continued Dr. Betof Warner, who is also Director of Melanoma Medical Oncology, Director of Solid Tumor Cellular Therapy, and Codirector of the Pigmented Lesion and Melanoma Program at Stanford University. “We are also actively studying next-generation TIL therapies to try to increase the efficacy.”
“Lifileucel has about a 30% success rate for melanoma that has progressed after standard therapy; we are working hard to do better than that,” she noted.
In a press release, Iovance summarized the results of the trial that supported the FDA’s accelerated approval of lifileucel. In an open-label single-arm study, including multiple sites worldwide, 73 adults with unresectable or metastatic melanoma who had received at least one previous systemic therapy underwent a lymphodepleting regimen followed by treatments with fludarabine and aldesleukin. Patients then received lifileucel at a median dose of 21.1 x 109 viable cells; the recommended dose ranges from 7.5 x 109 to 72 x 109 cells.
The primary efficacy outcome was objective response rate (ORR). The ORR in the study was 31.5%, and the median time to initial lifileucel response was 1.5 months.
The clinical trials of lifileucel for which Dr. Betof Warner and Dr. Puzanov served as investigators were sponsored by Iovance.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved the tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte cell therapy (TIL) for use in certain adults with unresectable or metastatic melanoma. This marks the first time the FDA has allowed a cellular therapy to be marketed for a solid tumor cancer.
Lifileucel is made from a patient’s surgically removed tumor. Tissue from that tumor is then sent to a manufacturing center. Turnaround time to when the drug is ready to be sent back to the cancer center for use is approximately 34 days, according to the drug’s manufacturer, Iovance.
Insurance Adjustments
The cost of the one-time lifileucel treatment is $515,000, according to the manufacturer.
Two investigators in the clinical trials of lifileucel, Allison Betof Warner, MD, of Stanford University, Stanford, California, and Igor Puzanov, MD, of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, New York, shared their expectations regarding factors that would contribute to how much a patient paid for the drug.
Given the drug’s recent approval, the logistical details are still being worked out between cancer centers and insurers regarding how much patients will pay out of pocket for lifileucel, said Dr. Betof Warner, who is assistant professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Medical Oncology at Stanford University.
The associated costs, including the surgery that is needed to procure the TIL cells for expansion into the final drug product, will be different for each patient, she told this publication.
Patients’ costs for lifileucel will vary based on their insurance, explained Dr. Puzanov, chief of melanoma and professor of oncology at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center.
At Roswell Park, “we will work with our regionally-based payers on a case-by-case basis to seek approval for those patients we believe can most benefit from lifileucel,” he said in an interview. Preauthorization will be required, as is standard for many cancer treatments, he added.
Once payer approval is in place, Dr. Puzanov said, he did not anticipate significant delays in access for patients.
Certified centers such as the multidisciplinary team at Roswell Park are ready to treat patients now. Other centers are similarly prepared, especially those involved in the clinical trials of lifileucel, he said.
Logistics and Infrastructure
A position article and guidelines on the management of and best practices for TIL was published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer on February 29. The paper, of which both Dr. Betof Warner and Dr. Puzanov served as authors, noted that one of the barriers to the use of TIL cell therapy in clinical practice is the need for state-of-the art infrastructure at centers that want to offer the treatment. Scheduling, patient referrals, and surgery, as well as the production and infusion of TIL, must be organized and streamlined for successful treatment, the authors wrote.
The two supply chains involved in TIL — the transportation of the tumor tissue from the treatment center to the manufacturer and transport of the TIL infusion product back to the treatment center — must be timely and precise, they emphasized.
Docs Hope TIL Improves in Several Ways
Although the TIL technology is a breakthrough, “we hope to see even better efficacy and lower toxicity as further research looks at ways to improve on the current TIL standard,” Dr. Puzanov said.
More research and dose adjustments may impact patient costs and side effects, he noted. “I am looking to see TILs used in the front line, with or without checkpoint inhibitors.”
Research is needed to explore how to lower the chemotherapy doses and possibly the associated toxicity, he added. Finally, researchers must consider whether high-dose IL-2 therapy — given as part of the TIL cell therapy — could be replaced with other cytokines, or whether the number of doses could be lowered. Another avenue of exploration is engineering genes for cytokines into TILs, he said.
“The key is to think about TIL therapy before you need it — ideally, when the patient is still doing well on their frontline checkpoint inhibition immunotherapy,” Dr. Puzanov said in an interview. That is the time for evaluation, and specialty centers can provide an expert assessment, he said.
“We are constantly working to improve TIL therapy,” Dr. Betof Warner told this publication. More research is needed optimize the regimen to reduce side effects, which would not only make treatment easier for currently eligible patients, but might allow treatment for patients not currently eligible.
“For example, we are looking for ways to reduce the dose of preparative chemotherapy, which prepares the body for the cells to maximize their longevity and efficacy, and to reduce or eliminate the need to give IL-2 after the cell administration,” continued Dr. Betof Warner, who is also Director of Melanoma Medical Oncology, Director of Solid Tumor Cellular Therapy, and Codirector of the Pigmented Lesion and Melanoma Program at Stanford University. “We are also actively studying next-generation TIL therapies to try to increase the efficacy.”
“Lifileucel has about a 30% success rate for melanoma that has progressed after standard therapy; we are working hard to do better than that,” she noted.
In a press release, Iovance summarized the results of the trial that supported the FDA’s accelerated approval of lifileucel. In an open-label single-arm study, including multiple sites worldwide, 73 adults with unresectable or metastatic melanoma who had received at least one previous systemic therapy underwent a lymphodepleting regimen followed by treatments with fludarabine and aldesleukin. Patients then received lifileucel at a median dose of 21.1 x 109 viable cells; the recommended dose ranges from 7.5 x 109 to 72 x 109 cells.
The primary efficacy outcome was objective response rate (ORR). The ORR in the study was 31.5%, and the median time to initial lifileucel response was 1.5 months.
The clinical trials of lifileucel for which Dr. Betof Warner and Dr. Puzanov served as investigators were sponsored by Iovance.