User login
Biden’s COVID-19 challenge: 100 million vaccinations in the first 100 days. It won’t be easy.
It’s in the nature of presidential candidates and new presidents to promise big things. Just months after his 1961 inauguration, President John F. Kennedy vowed to send a man to the moon by the end of the decade. That pledge was kept, but many others haven’t been, such as candidate Bill Clinton’s promise to provide universal health care and presidential hopeful George H.W. Bush’s guarantee of no new taxes.
Now, during a once-in-a-century pandemic, incoming President Joe Biden has promised to provide 100 million COVID-19 vaccinations in his first 100 days in office.
“This team will help get … at least 100 million covid vaccine shots into the arms of the American people in the first 100 days,” Biden said during a Dec. 8 news conference introducing key members of his health team.
When first asked about his pledge, the Biden team said the president-elect meant 50 million people would get their two-dose regimen. The incoming administration has since updated this plan, saying it will release vaccine doses as soon as they’re available instead of holding back some of that supply for second doses.
Either way, Biden may run into difficulty meeting that 100 million mark.
“I think it’s an attainable goal. I think it’s going to be extremely challenging,” said Claire Hannan, executive director of the Association of Immunization Managers.
While a pace of 1 million doses a day is “somewhat of an increase over what we’re already doing,” a much higher rate of vaccinations will be necessary to stem the pandemic, said Larry Levitt, executive vice president for health policy at Kaiser Family Foundation. (KHN is an editorially independent program of KFF.) “The Biden administration has plans to rationalize vaccine distribution, but increasing the supply quickly” could be a difficult task.
Under the Trump administration, vaccine deployment has been much slower than Biden’s plan. The rollout began on Dec. 14. Since then, 12 million shots have been given and 31 million doses have been shipped out, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s vaccine tracker.
This sluggishness has been attributed to a lack of communication between the federal government and state and local health departments, not enough funding for large-scale vaccination efforts, and confusing federal guidance on distribution of the vaccines.
The same problems could plague the Biden administration, said experts.
States still aren’t sure how much vaccine they’ll get and whether there will be a sufficient supply, said Dr. Marcus Plescia, chief medical officer for the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, which represents state public health agencies.
“We have been given little information about the amount of vaccine the states will receive in the near future and are of the impression that there may not be 1 million doses available per day in the first 100 days of the Biden administration,” said Dr. Plescia. “Or at least not in the early stages of the 100 days.”
Another challenge has been a lack of funding. Public health departments have had to start vaccination campaigns while also operating testing centers and conducting contact tracing efforts with budgets that have been critically underfunded for years.
“States have to pay for creating the systems, identifying the personnel, training, staffing, tracking people, information campaigns – all the things that go into getting a shot in someone’s arm,” said Jennifer Kates, director of global health & HIV policy at KFF. “They’re having to create an unprecedented mass vaccination program on a shaky foundation.”
The latest covid stimulus bill, signed into law in December, allocates almost $9 billion in funding to the CDC for vaccination efforts. About $4.5 billion is supposed to go to states, territories and tribal organizations, and $3 billion of that is slated to arrive soon.
But it’s not clear that level of funding can sustain mass vaccination campaigns as more groups become eligible for the vaccine.
Biden released a $1.9 trillion plan last week to address covid and the struggling economy. It includes $160 billion to create national vaccination and testing programs, but also earmarks funds for $1,400 stimulus payments to individuals, state and local government aid, extension of unemployment insurance, and financial assistance for schools to reopen safely.
Though it took Congress almost eight months to pass the last covid relief bill after Republican objections to the cost, Biden seems optimistic he’ll get some Republicans on board for his plan. But it’s not yet clear that will work.
There’s also the question of whether outgoing President Donald Trump’s impeachment trial will get in the way of Biden’s legislative priorities.
In addition, states have complained about a lack of guidance and confusing instructions on which groups should be given priority status for vaccination, an issue the Biden administration will need to address.
On Dec. 3, the CDC recommended health care personnel, residents of long-term care facilities, those 75 and older, and front-line essential workers should be immunized first. But on Jan. 12, the CDC shifted course and recommended that everyone over age 65 should be immunized. In a speech Biden gave on Jan. 15 detailing his vaccination plan, he said he would stick to the CDC’s recommendation to prioritize those over 65.
Outgoing Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar also said on Jan. 12 that states that moved their vaccine supply fastest would be prioritized in getting more shipments. It’s not known yet whether the Biden administration’s CDC will stick to this guidance. Critics have said it could make vaccine distribution less equitable.
In general, taking over with a strong vision and clear communication will be key to ramping up vaccine distribution, said Ms. Hannan.
“Everyone needs to understand what the goal is and how it’s going to work,” she said.
A challenge for Biden will be tamping expectations that the vaccine is all that is needed to end the pandemic. Across the country, covid cases are higher than ever, and in many locations officials cannot control the spread.
Public health experts said Biden must amp up efforts to increase testing across the country, as he has suggested he will do by promising to establish a national pandemic testing board.
With so much focus on vaccine distribution, it’s important that this part of the equation not be lost. Right now, “it’s completely all over the map,” said KFF’s Ms. Kates, adding that the federal government will need a “good sense” of who is and is not being tested in different areas in order to “fix” public health capacity.
Jan. 20, 2021, marks the launch of The Biden Promise Tracker, which monitors the 100 most important campaign promises of President Joseph R. Biden. Biden listed the coronavirus and a variety of other health-related issues among his top priorities. You can see the entire list – including improving the economy, responding to calls for racial justice and combating climate change – here. As part of KHN’s partnership with PolitiFact, we will follow the health-related issues and then rate them on whether the promise was achieved: Promise Kept, Promise Broken, Compromise, Stalled, In the Works or Not Yet Rated. We rate the promise not on the president’s intentions or effort, but on verifiable outcomes. PolitiFact previously tracked the promises of President Donald Trump and President Barack Obama.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF, which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
It’s in the nature of presidential candidates and new presidents to promise big things. Just months after his 1961 inauguration, President John F. Kennedy vowed to send a man to the moon by the end of the decade. That pledge was kept, but many others haven’t been, such as candidate Bill Clinton’s promise to provide universal health care and presidential hopeful George H.W. Bush’s guarantee of no new taxes.
Now, during a once-in-a-century pandemic, incoming President Joe Biden has promised to provide 100 million COVID-19 vaccinations in his first 100 days in office.
“This team will help get … at least 100 million covid vaccine shots into the arms of the American people in the first 100 days,” Biden said during a Dec. 8 news conference introducing key members of his health team.
When first asked about his pledge, the Biden team said the president-elect meant 50 million people would get their two-dose regimen. The incoming administration has since updated this plan, saying it will release vaccine doses as soon as they’re available instead of holding back some of that supply for second doses.
Either way, Biden may run into difficulty meeting that 100 million mark.
“I think it’s an attainable goal. I think it’s going to be extremely challenging,” said Claire Hannan, executive director of the Association of Immunization Managers.
While a pace of 1 million doses a day is “somewhat of an increase over what we’re already doing,” a much higher rate of vaccinations will be necessary to stem the pandemic, said Larry Levitt, executive vice president for health policy at Kaiser Family Foundation. (KHN is an editorially independent program of KFF.) “The Biden administration has plans to rationalize vaccine distribution, but increasing the supply quickly” could be a difficult task.
Under the Trump administration, vaccine deployment has been much slower than Biden’s plan. The rollout began on Dec. 14. Since then, 12 million shots have been given and 31 million doses have been shipped out, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s vaccine tracker.
This sluggishness has been attributed to a lack of communication between the federal government and state and local health departments, not enough funding for large-scale vaccination efforts, and confusing federal guidance on distribution of the vaccines.
The same problems could plague the Biden administration, said experts.
States still aren’t sure how much vaccine they’ll get and whether there will be a sufficient supply, said Dr. Marcus Plescia, chief medical officer for the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, which represents state public health agencies.
“We have been given little information about the amount of vaccine the states will receive in the near future and are of the impression that there may not be 1 million doses available per day in the first 100 days of the Biden administration,” said Dr. Plescia. “Or at least not in the early stages of the 100 days.”
Another challenge has been a lack of funding. Public health departments have had to start vaccination campaigns while also operating testing centers and conducting contact tracing efforts with budgets that have been critically underfunded for years.
“States have to pay for creating the systems, identifying the personnel, training, staffing, tracking people, information campaigns – all the things that go into getting a shot in someone’s arm,” said Jennifer Kates, director of global health & HIV policy at KFF. “They’re having to create an unprecedented mass vaccination program on a shaky foundation.”
The latest covid stimulus bill, signed into law in December, allocates almost $9 billion in funding to the CDC for vaccination efforts. About $4.5 billion is supposed to go to states, territories and tribal organizations, and $3 billion of that is slated to arrive soon.
But it’s not clear that level of funding can sustain mass vaccination campaigns as more groups become eligible for the vaccine.
Biden released a $1.9 trillion plan last week to address covid and the struggling economy. It includes $160 billion to create national vaccination and testing programs, but also earmarks funds for $1,400 stimulus payments to individuals, state and local government aid, extension of unemployment insurance, and financial assistance for schools to reopen safely.
Though it took Congress almost eight months to pass the last covid relief bill after Republican objections to the cost, Biden seems optimistic he’ll get some Republicans on board for his plan. But it’s not yet clear that will work.
There’s also the question of whether outgoing President Donald Trump’s impeachment trial will get in the way of Biden’s legislative priorities.
In addition, states have complained about a lack of guidance and confusing instructions on which groups should be given priority status for vaccination, an issue the Biden administration will need to address.
On Dec. 3, the CDC recommended health care personnel, residents of long-term care facilities, those 75 and older, and front-line essential workers should be immunized first. But on Jan. 12, the CDC shifted course and recommended that everyone over age 65 should be immunized. In a speech Biden gave on Jan. 15 detailing his vaccination plan, he said he would stick to the CDC’s recommendation to prioritize those over 65.
Outgoing Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar also said on Jan. 12 that states that moved their vaccine supply fastest would be prioritized in getting more shipments. It’s not known yet whether the Biden administration’s CDC will stick to this guidance. Critics have said it could make vaccine distribution less equitable.
In general, taking over with a strong vision and clear communication will be key to ramping up vaccine distribution, said Ms. Hannan.
“Everyone needs to understand what the goal is and how it’s going to work,” she said.
A challenge for Biden will be tamping expectations that the vaccine is all that is needed to end the pandemic. Across the country, covid cases are higher than ever, and in many locations officials cannot control the spread.
Public health experts said Biden must amp up efforts to increase testing across the country, as he has suggested he will do by promising to establish a national pandemic testing board.
With so much focus on vaccine distribution, it’s important that this part of the equation not be lost. Right now, “it’s completely all over the map,” said KFF’s Ms. Kates, adding that the federal government will need a “good sense” of who is and is not being tested in different areas in order to “fix” public health capacity.
Jan. 20, 2021, marks the launch of The Biden Promise Tracker, which monitors the 100 most important campaign promises of President Joseph R. Biden. Biden listed the coronavirus and a variety of other health-related issues among his top priorities. You can see the entire list – including improving the economy, responding to calls for racial justice and combating climate change – here. As part of KHN’s partnership with PolitiFact, we will follow the health-related issues and then rate them on whether the promise was achieved: Promise Kept, Promise Broken, Compromise, Stalled, In the Works or Not Yet Rated. We rate the promise not on the president’s intentions or effort, but on verifiable outcomes. PolitiFact previously tracked the promises of President Donald Trump and President Barack Obama.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF, which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
It’s in the nature of presidential candidates and new presidents to promise big things. Just months after his 1961 inauguration, President John F. Kennedy vowed to send a man to the moon by the end of the decade. That pledge was kept, but many others haven’t been, such as candidate Bill Clinton’s promise to provide universal health care and presidential hopeful George H.W. Bush’s guarantee of no new taxes.
Now, during a once-in-a-century pandemic, incoming President Joe Biden has promised to provide 100 million COVID-19 vaccinations in his first 100 days in office.
“This team will help get … at least 100 million covid vaccine shots into the arms of the American people in the first 100 days,” Biden said during a Dec. 8 news conference introducing key members of his health team.
When first asked about his pledge, the Biden team said the president-elect meant 50 million people would get their two-dose regimen. The incoming administration has since updated this plan, saying it will release vaccine doses as soon as they’re available instead of holding back some of that supply for second doses.
Either way, Biden may run into difficulty meeting that 100 million mark.
“I think it’s an attainable goal. I think it’s going to be extremely challenging,” said Claire Hannan, executive director of the Association of Immunization Managers.
While a pace of 1 million doses a day is “somewhat of an increase over what we’re already doing,” a much higher rate of vaccinations will be necessary to stem the pandemic, said Larry Levitt, executive vice president for health policy at Kaiser Family Foundation. (KHN is an editorially independent program of KFF.) “The Biden administration has plans to rationalize vaccine distribution, but increasing the supply quickly” could be a difficult task.
Under the Trump administration, vaccine deployment has been much slower than Biden’s plan. The rollout began on Dec. 14. Since then, 12 million shots have been given and 31 million doses have been shipped out, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s vaccine tracker.
This sluggishness has been attributed to a lack of communication between the federal government and state and local health departments, not enough funding for large-scale vaccination efforts, and confusing federal guidance on distribution of the vaccines.
The same problems could plague the Biden administration, said experts.
States still aren’t sure how much vaccine they’ll get and whether there will be a sufficient supply, said Dr. Marcus Plescia, chief medical officer for the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, which represents state public health agencies.
“We have been given little information about the amount of vaccine the states will receive in the near future and are of the impression that there may not be 1 million doses available per day in the first 100 days of the Biden administration,” said Dr. Plescia. “Or at least not in the early stages of the 100 days.”
Another challenge has been a lack of funding. Public health departments have had to start vaccination campaigns while also operating testing centers and conducting contact tracing efforts with budgets that have been critically underfunded for years.
“States have to pay for creating the systems, identifying the personnel, training, staffing, tracking people, information campaigns – all the things that go into getting a shot in someone’s arm,” said Jennifer Kates, director of global health & HIV policy at KFF. “They’re having to create an unprecedented mass vaccination program on a shaky foundation.”
The latest covid stimulus bill, signed into law in December, allocates almost $9 billion in funding to the CDC for vaccination efforts. About $4.5 billion is supposed to go to states, territories and tribal organizations, and $3 billion of that is slated to arrive soon.
But it’s not clear that level of funding can sustain mass vaccination campaigns as more groups become eligible for the vaccine.
Biden released a $1.9 trillion plan last week to address covid and the struggling economy. It includes $160 billion to create national vaccination and testing programs, but also earmarks funds for $1,400 stimulus payments to individuals, state and local government aid, extension of unemployment insurance, and financial assistance for schools to reopen safely.
Though it took Congress almost eight months to pass the last covid relief bill after Republican objections to the cost, Biden seems optimistic he’ll get some Republicans on board for his plan. But it’s not yet clear that will work.
There’s also the question of whether outgoing President Donald Trump’s impeachment trial will get in the way of Biden’s legislative priorities.
In addition, states have complained about a lack of guidance and confusing instructions on which groups should be given priority status for vaccination, an issue the Biden administration will need to address.
On Dec. 3, the CDC recommended health care personnel, residents of long-term care facilities, those 75 and older, and front-line essential workers should be immunized first. But on Jan. 12, the CDC shifted course and recommended that everyone over age 65 should be immunized. In a speech Biden gave on Jan. 15 detailing his vaccination plan, he said he would stick to the CDC’s recommendation to prioritize those over 65.
Outgoing Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar also said on Jan. 12 that states that moved their vaccine supply fastest would be prioritized in getting more shipments. It’s not known yet whether the Biden administration’s CDC will stick to this guidance. Critics have said it could make vaccine distribution less equitable.
In general, taking over with a strong vision and clear communication will be key to ramping up vaccine distribution, said Ms. Hannan.
“Everyone needs to understand what the goal is and how it’s going to work,” she said.
A challenge for Biden will be tamping expectations that the vaccine is all that is needed to end the pandemic. Across the country, covid cases are higher than ever, and in many locations officials cannot control the spread.
Public health experts said Biden must amp up efforts to increase testing across the country, as he has suggested he will do by promising to establish a national pandemic testing board.
With so much focus on vaccine distribution, it’s important that this part of the equation not be lost. Right now, “it’s completely all over the map,” said KFF’s Ms. Kates, adding that the federal government will need a “good sense” of who is and is not being tested in different areas in order to “fix” public health capacity.
Jan. 20, 2021, marks the launch of The Biden Promise Tracker, which monitors the 100 most important campaign promises of President Joseph R. Biden. Biden listed the coronavirus and a variety of other health-related issues among his top priorities. You can see the entire list – including improving the economy, responding to calls for racial justice and combating climate change – here. As part of KHN’s partnership with PolitiFact, we will follow the health-related issues and then rate them on whether the promise was achieved: Promise Kept, Promise Broken, Compromise, Stalled, In the Works or Not Yet Rated. We rate the promise not on the president’s intentions or effort, but on verifiable outcomes. PolitiFact previously tracked the promises of President Donald Trump and President Barack Obama.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF, which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
HHS will drop buprenorphine waiver rule for most physicians
Federal officials on Thursday announced a plan to largely drop the so-called X-waiver requirement for buprenorphine prescriptions for physicians in a bid to remove an administrative procedure widely seen as a barrier to opioid use disorder (OUD) treatment.
The Department of Health & Human Services unveiled new practice guidelines that include an exemption from current certification requirements. The exemption applies to physicians already registered with the Drug Enforcement Administration.
A restriction included in the new HHS policy is a limit of treating no more than 30 patients with buprenorphine for OUD at any one time. There is an exception to this limit for hospital-based physicians, such as those working in emergency departments, HHS said.
, such as buprenorphine, and does not apply to methadone. The new guidelines say the date on which they will take effect will be added after publication in the Federal Register. HHS did not immediately answer a request from this news organization for a more specific timeline.
Welcomed change
The change in prescribing rule was widely welcomed, with the American Medical Association issuing a statement endorsing the revision. The AMA and many prescribers and researchers had seen the X-waiver as a hurdle to address the nation’s opioid epidemic.
There were more than 83,000 deaths attributed to drug overdoses in the United States in the 12 months ending in June 2020. This is the highest number of overdose deaths ever recorded in a 12-month period, HHS said in a press release, which cited data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In a tweet about the new policy, Peter Grinspoon, MD, a Boston internist and author of the memoir “Free Refills: A Doctor Confronts His Addiction,” contrasted the relative ease with which clinicians can give medicines that carry a risk for abuse with the challenge that has existed in trying to provide patients with buprenorphine.
“Absolutely insane that we need a special waiver for buprenorphine to TREAT opioid addiction, but not to prescribe oxycodone, Vicodin, etc., which can get people in trouble in the first place!!” Dr. Grinspoon tweeted.
Patrice Harris, MD, chair of the AMA’s Opioid Task Force and the organization’s immediate past president, said removing the X-waiver requirement can help lessen the stigma associated with this OUD treatment. The AMA had urged HHS to change the regulation.
“With this change, office-based physicians and physician-led teams working with patients to manage their other medical conditions can also treat them for their opioid use disorder without being subjected to a separate and burdensome regulatory regime,” Dr. Harris said in the AMA statement.
Researchers have in recent years sought to highlight what they described as missed opportunities for OUD treatment because of the need for the X-waiver.
Buprenorphine is a cost-effective treatment for opioid use disorder, which reduces the risk of injection-related infections and mortality risk, notes a study published online last month in JAMA Network Open.
However, results showed that fewer than 2% of obstetrician-gynecologists who examined women enrolled in Medicaid were trained to prescribe buprenorphine. The study, which was based on data from 31, 211 ob.gyns. who accepted Medicaid insurance, was created to quantify how many were on the list of Drug Addiction Treatment Act buprenorphine-waived clinicians.
The Drug Addiction Treatment Act has required 8 hours of training for physicians and 24 hours for nurse practitioners and physician assistants for the X-waiver needed to prescribe buprenorphine, the investigators report.
‘X the X-waiver’
Only 10% of recent family residency graduates reported being adequately trained to prescribe buprenorphine and only 7% reported actually prescribing the drug, write Kevin Fiscella, MD, University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center and colleagues in a 2018 Viewpoint article published in JAMA Psychiatry.
In the article, which was subtitled “X the X Waiver,” they called for deregulation of buprenorphine as a way of mainstreaming treatment for OUD.
“The DATA 2000 has failed – too few physicians have obtained X-waivers,” the authors write. “Regulations reinforce the stigma surrounding buprenorphine prescribers and patients who receive it while constraining access and discouraging patient engagement and retention in treatment.”
The change, announced Jan. 14, leaves in place restrictions on prescribing for clinicians other than physicians. On a call with reporters, Adm. Brett P. Giroir, MD, assistant secretary for health, suggested that federal officials should take further steps to remove hurdles to buprenorphine prescriptions.
“Many people will say this has gone too far,” Dr. Giroir said of the drive to end the X-waiver for clinicians. “But I believe more people will say this has not gone far enough.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Federal officials on Thursday announced a plan to largely drop the so-called X-waiver requirement for buprenorphine prescriptions for physicians in a bid to remove an administrative procedure widely seen as a barrier to opioid use disorder (OUD) treatment.
The Department of Health & Human Services unveiled new practice guidelines that include an exemption from current certification requirements. The exemption applies to physicians already registered with the Drug Enforcement Administration.
A restriction included in the new HHS policy is a limit of treating no more than 30 patients with buprenorphine for OUD at any one time. There is an exception to this limit for hospital-based physicians, such as those working in emergency departments, HHS said.
, such as buprenorphine, and does not apply to methadone. The new guidelines say the date on which they will take effect will be added after publication in the Federal Register. HHS did not immediately answer a request from this news organization for a more specific timeline.
Welcomed change
The change in prescribing rule was widely welcomed, with the American Medical Association issuing a statement endorsing the revision. The AMA and many prescribers and researchers had seen the X-waiver as a hurdle to address the nation’s opioid epidemic.
There were more than 83,000 deaths attributed to drug overdoses in the United States in the 12 months ending in June 2020. This is the highest number of overdose deaths ever recorded in a 12-month period, HHS said in a press release, which cited data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In a tweet about the new policy, Peter Grinspoon, MD, a Boston internist and author of the memoir “Free Refills: A Doctor Confronts His Addiction,” contrasted the relative ease with which clinicians can give medicines that carry a risk for abuse with the challenge that has existed in trying to provide patients with buprenorphine.
“Absolutely insane that we need a special waiver for buprenorphine to TREAT opioid addiction, but not to prescribe oxycodone, Vicodin, etc., which can get people in trouble in the first place!!” Dr. Grinspoon tweeted.
Patrice Harris, MD, chair of the AMA’s Opioid Task Force and the organization’s immediate past president, said removing the X-waiver requirement can help lessen the stigma associated with this OUD treatment. The AMA had urged HHS to change the regulation.
“With this change, office-based physicians and physician-led teams working with patients to manage their other medical conditions can also treat them for their opioid use disorder without being subjected to a separate and burdensome regulatory regime,” Dr. Harris said in the AMA statement.
Researchers have in recent years sought to highlight what they described as missed opportunities for OUD treatment because of the need for the X-waiver.
Buprenorphine is a cost-effective treatment for opioid use disorder, which reduces the risk of injection-related infections and mortality risk, notes a study published online last month in JAMA Network Open.
However, results showed that fewer than 2% of obstetrician-gynecologists who examined women enrolled in Medicaid were trained to prescribe buprenorphine. The study, which was based on data from 31, 211 ob.gyns. who accepted Medicaid insurance, was created to quantify how many were on the list of Drug Addiction Treatment Act buprenorphine-waived clinicians.
The Drug Addiction Treatment Act has required 8 hours of training for physicians and 24 hours for nurse practitioners and physician assistants for the X-waiver needed to prescribe buprenorphine, the investigators report.
‘X the X-waiver’
Only 10% of recent family residency graduates reported being adequately trained to prescribe buprenorphine and only 7% reported actually prescribing the drug, write Kevin Fiscella, MD, University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center and colleagues in a 2018 Viewpoint article published in JAMA Psychiatry.
In the article, which was subtitled “X the X Waiver,” they called for deregulation of buprenorphine as a way of mainstreaming treatment for OUD.
“The DATA 2000 has failed – too few physicians have obtained X-waivers,” the authors write. “Regulations reinforce the stigma surrounding buprenorphine prescribers and patients who receive it while constraining access and discouraging patient engagement and retention in treatment.”
The change, announced Jan. 14, leaves in place restrictions on prescribing for clinicians other than physicians. On a call with reporters, Adm. Brett P. Giroir, MD, assistant secretary for health, suggested that federal officials should take further steps to remove hurdles to buprenorphine prescriptions.
“Many people will say this has gone too far,” Dr. Giroir said of the drive to end the X-waiver for clinicians. “But I believe more people will say this has not gone far enough.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Federal officials on Thursday announced a plan to largely drop the so-called X-waiver requirement for buprenorphine prescriptions for physicians in a bid to remove an administrative procedure widely seen as a barrier to opioid use disorder (OUD) treatment.
The Department of Health & Human Services unveiled new practice guidelines that include an exemption from current certification requirements. The exemption applies to physicians already registered with the Drug Enforcement Administration.
A restriction included in the new HHS policy is a limit of treating no more than 30 patients with buprenorphine for OUD at any one time. There is an exception to this limit for hospital-based physicians, such as those working in emergency departments, HHS said.
, such as buprenorphine, and does not apply to methadone. The new guidelines say the date on which they will take effect will be added after publication in the Federal Register. HHS did not immediately answer a request from this news organization for a more specific timeline.
Welcomed change
The change in prescribing rule was widely welcomed, with the American Medical Association issuing a statement endorsing the revision. The AMA and many prescribers and researchers had seen the X-waiver as a hurdle to address the nation’s opioid epidemic.
There were more than 83,000 deaths attributed to drug overdoses in the United States in the 12 months ending in June 2020. This is the highest number of overdose deaths ever recorded in a 12-month period, HHS said in a press release, which cited data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In a tweet about the new policy, Peter Grinspoon, MD, a Boston internist and author of the memoir “Free Refills: A Doctor Confronts His Addiction,” contrasted the relative ease with which clinicians can give medicines that carry a risk for abuse with the challenge that has existed in trying to provide patients with buprenorphine.
“Absolutely insane that we need a special waiver for buprenorphine to TREAT opioid addiction, but not to prescribe oxycodone, Vicodin, etc., which can get people in trouble in the first place!!” Dr. Grinspoon tweeted.
Patrice Harris, MD, chair of the AMA’s Opioid Task Force and the organization’s immediate past president, said removing the X-waiver requirement can help lessen the stigma associated with this OUD treatment. The AMA had urged HHS to change the regulation.
“With this change, office-based physicians and physician-led teams working with patients to manage their other medical conditions can also treat them for their opioid use disorder without being subjected to a separate and burdensome regulatory regime,” Dr. Harris said in the AMA statement.
Researchers have in recent years sought to highlight what they described as missed opportunities for OUD treatment because of the need for the X-waiver.
Buprenorphine is a cost-effective treatment for opioid use disorder, which reduces the risk of injection-related infections and mortality risk, notes a study published online last month in JAMA Network Open.
However, results showed that fewer than 2% of obstetrician-gynecologists who examined women enrolled in Medicaid were trained to prescribe buprenorphine. The study, which was based on data from 31, 211 ob.gyns. who accepted Medicaid insurance, was created to quantify how many were on the list of Drug Addiction Treatment Act buprenorphine-waived clinicians.
The Drug Addiction Treatment Act has required 8 hours of training for physicians and 24 hours for nurse practitioners and physician assistants for the X-waiver needed to prescribe buprenorphine, the investigators report.
‘X the X-waiver’
Only 10% of recent family residency graduates reported being adequately trained to prescribe buprenorphine and only 7% reported actually prescribing the drug, write Kevin Fiscella, MD, University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center and colleagues in a 2018 Viewpoint article published in JAMA Psychiatry.
In the article, which was subtitled “X the X Waiver,” they called for deregulation of buprenorphine as a way of mainstreaming treatment for OUD.
“The DATA 2000 has failed – too few physicians have obtained X-waivers,” the authors write. “Regulations reinforce the stigma surrounding buprenorphine prescribers and patients who receive it while constraining access and discouraging patient engagement and retention in treatment.”
The change, announced Jan. 14, leaves in place restrictions on prescribing for clinicians other than physicians. On a call with reporters, Adm. Brett P. Giroir, MD, assistant secretary for health, suggested that federal officials should take further steps to remove hurdles to buprenorphine prescriptions.
“Many people will say this has gone too far,” Dr. Giroir said of the drive to end the X-waiver for clinicians. “But I believe more people will say this has not gone far enough.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Eliminating hepatitis by 2030: HHS releases new strategic plan
In an effort to counteract alarming trends in rising hepatitis infections, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has developed and released its Viral Hepatitis National Strategic Plan 2021-2025, which aims to eliminate viral hepatitis infection in the United States by 2030.
An estimated 3.3 million people in the United States were chronically infected with hepatitis B (HBV) and hepatitis C (HCV) as of 2016. In addition, the country “is currently facing unprecedented hepatitis A (HAV) outbreaks, while progress in preventing hepatitis B has stalled, and hepatitis C rates nearly tripled from 2011 to 2018,” according to the HHS.
The new plan, “A Roadmap to Elimination for the United States,” builds upon previous initiatives the HHS has made to tackle the diseases and was coordinated by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health through the Office of Infectious Disease and HIV/AIDS Policy.
The plan focuses on HAV, HBV, and HCV, which have the largest impact on the health of the nation, according to the HHS. The plan addresses populations with the highest burden of viral hepatitis based on nationwide data so that resources can be focused there to achieve the greatest impact. Persons who inject drugs are a priority population for all three hepatitis viruses. HAV efforts will also include a focus on the homeless population. HBV efforts will also focus on Asian and Pacific Islander and the Black, non-Hispanic populations, while HCV efforts will include a focus on Black, non-Hispanic people, people born during 1945-1965, people with HIV, and the American Indian/Alaska Native population.
Goal-setting
There are five main goals outlined in the plan, according to the HHS:
- Prevent new hepatitis infections.
- Improve hepatitis-related health outcomes of people with viral hepatitis.
- Reduce hepatitis-related disparities and health inequities.
- Improve hepatitis surveillance and data use.
- Achieve integrated, coordinated efforts that address the viral hepatitis epidemics among all partners and stakeholders.
“The United States will be a place where new viral hepatitis infections are prevented, every person knows their status, and every person with viral hepatitis has high-quality health care and treatment and lives free from stigma and discrimination. This vision includes all people, regardless of age, sex, gender identity, sexual orientation, race, ethnicity, religion, disability, geographic location, or socioeconomic circumstance,” according to the HHS vision statement.
In an effort to counteract alarming trends in rising hepatitis infections, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has developed and released its Viral Hepatitis National Strategic Plan 2021-2025, which aims to eliminate viral hepatitis infection in the United States by 2030.
An estimated 3.3 million people in the United States were chronically infected with hepatitis B (HBV) and hepatitis C (HCV) as of 2016. In addition, the country “is currently facing unprecedented hepatitis A (HAV) outbreaks, while progress in preventing hepatitis B has stalled, and hepatitis C rates nearly tripled from 2011 to 2018,” according to the HHS.
The new plan, “A Roadmap to Elimination for the United States,” builds upon previous initiatives the HHS has made to tackle the diseases and was coordinated by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health through the Office of Infectious Disease and HIV/AIDS Policy.
The plan focuses on HAV, HBV, and HCV, which have the largest impact on the health of the nation, according to the HHS. The plan addresses populations with the highest burden of viral hepatitis based on nationwide data so that resources can be focused there to achieve the greatest impact. Persons who inject drugs are a priority population for all three hepatitis viruses. HAV efforts will also include a focus on the homeless population. HBV efforts will also focus on Asian and Pacific Islander and the Black, non-Hispanic populations, while HCV efforts will include a focus on Black, non-Hispanic people, people born during 1945-1965, people with HIV, and the American Indian/Alaska Native population.
Goal-setting
There are five main goals outlined in the plan, according to the HHS:
- Prevent new hepatitis infections.
- Improve hepatitis-related health outcomes of people with viral hepatitis.
- Reduce hepatitis-related disparities and health inequities.
- Improve hepatitis surveillance and data use.
- Achieve integrated, coordinated efforts that address the viral hepatitis epidemics among all partners and stakeholders.
“The United States will be a place where new viral hepatitis infections are prevented, every person knows their status, and every person with viral hepatitis has high-quality health care and treatment and lives free from stigma and discrimination. This vision includes all people, regardless of age, sex, gender identity, sexual orientation, race, ethnicity, religion, disability, geographic location, or socioeconomic circumstance,” according to the HHS vision statement.
In an effort to counteract alarming trends in rising hepatitis infections, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has developed and released its Viral Hepatitis National Strategic Plan 2021-2025, which aims to eliminate viral hepatitis infection in the United States by 2030.
An estimated 3.3 million people in the United States were chronically infected with hepatitis B (HBV) and hepatitis C (HCV) as of 2016. In addition, the country “is currently facing unprecedented hepatitis A (HAV) outbreaks, while progress in preventing hepatitis B has stalled, and hepatitis C rates nearly tripled from 2011 to 2018,” according to the HHS.
The new plan, “A Roadmap to Elimination for the United States,” builds upon previous initiatives the HHS has made to tackle the diseases and was coordinated by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health through the Office of Infectious Disease and HIV/AIDS Policy.
The plan focuses on HAV, HBV, and HCV, which have the largest impact on the health of the nation, according to the HHS. The plan addresses populations with the highest burden of viral hepatitis based on nationwide data so that resources can be focused there to achieve the greatest impact. Persons who inject drugs are a priority population for all three hepatitis viruses. HAV efforts will also include a focus on the homeless population. HBV efforts will also focus on Asian and Pacific Islander and the Black, non-Hispanic populations, while HCV efforts will include a focus on Black, non-Hispanic people, people born during 1945-1965, people with HIV, and the American Indian/Alaska Native population.
Goal-setting
There are five main goals outlined in the plan, according to the HHS:
- Prevent new hepatitis infections.
- Improve hepatitis-related health outcomes of people with viral hepatitis.
- Reduce hepatitis-related disparities and health inequities.
- Improve hepatitis surveillance and data use.
- Achieve integrated, coordinated efforts that address the viral hepatitis epidemics among all partners and stakeholders.
“The United States will be a place where new viral hepatitis infections are prevented, every person knows their status, and every person with viral hepatitis has high-quality health care and treatment and lives free from stigma and discrimination. This vision includes all people, regardless of age, sex, gender identity, sexual orientation, race, ethnicity, religion, disability, geographic location, or socioeconomic circumstance,” according to the HHS vision statement.
Pressure builds on CDC to prioritize both diabetes types for vaccine
The American Diabetes Association, along with 18 other organizations, has sent a letter to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention urging them to rank people with type 1 diabetes as equally high risk for COVID-19 severity, and therefore vaccination, as those with type 2 diabetes.
On Jan. 12, the CDC recommended states vaccinate all Americans over age 65 and those with underlying health conditions that make them more vulnerable to COVID-19.
Currently, type 2 diabetes is listed among 12 conditions that place adults “at increased risk of severe illness from the virus that causes COVID-19,” with the latter defined as “hospitalization, admission to the intensive care unit, intubation or mechanical ventilation, or death.”
On the other hand, the autoimmune condition type 1 diabetes is among 11 conditions the CDC says “might be at increased risk” for COVID-19, but limited data were available at the time of the last update on Dec. 23, 2020.
“States are utilizing the CDC risk classification when designing their vaccine distribution plans. This raises an obvious concern as it could result in the approximately 1.6 million with type 1 diabetes receiving the vaccination later than others with the same risk,” states the ADA letter, sent to the CDC on Jan. 13.
Representatives from the Endocrine Society, American Association of Clinical Endocrinology, Pediatric Endocrine Society, Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists, and JDRF, among others, cosigned the letter.
Newer data show those with type 1 diabetes at equally high risk
While acknowledging that “early data did not provide as much clarity about the extent to which those with type 1 diabetes are at high risk,” the ADA says newer evidence has emerged, as previously reported by this news organization, that “convincingly demonstrates that COVID-19 severity is more than tripled in individuals with type 1 diabetes.”
The letter also cites another study showing that people with type 1 diabetes “have a 3.3-fold greater risk of severe illness, are 3.9 times more likely to be hospitalized with COVID-19, and have a 3-fold increase in mortality compared to those without type 1 diabetes.”
Those risks, they note, are comparable to the increased risk established for those with type 2 diabetes, as shown in a third study from Scotland, published last month.
Asked for comment, CDC representative Kirsten Nordlund said in an interview, “This list is a living document that will be periodically updated by CDC, and it could rapidly change as the science evolves.”
In addition, Ms. Nordlund said, “Decisions about transitioning to subsequent phases should depend on supply; demand; equitable vaccine distribution; and local, state, or territorial context.”
“Phased vaccine recommendations are meant to be fluid and not restrictive for jurisdictions. It is not necessary to vaccinate all individuals in one phase before initiating the next phase; phases may overlap,” she noted. More information is available here.
Tennessee gives type 1 and type 2 diabetes equal priority for vaccination
Meanwhile, at least one state, Tennessee, has updated its guidance to include both types of diabetes as being priority for COVID-19 vaccination.
Vanderbilt University pediatric endocrinologist Justin M. Gregory, MD, said in an interview: “I was thrilled when our state modified its guidance on December 30th to include both type 1 and type 2 diabetes in the ‘high-risk category.’ Other states have not modified that guidance though.”
It’s unclear how this might play out on the ground, noted Dr. Gregory, who led one of the three studies demonstrating increased COVID-19 risk for people with type 1 diabetes.
“To tell you the truth, I don’t really know how individual organizations dispensing the vaccination [will handle] people who come to their facility saying they have ‘diabetes.’ Individual states set the vaccine-dispensing guidance and individual county health departments and health care systems mirror that guidance,” he said.
Thus, he added, “Although it’s possible an individual nurse may take the ‘I’ll ask you no questions, and you’ll tell me no lies’ approach if someone with type 1 diabetes says they have ‘diabetes’, websites and health department–recorded telephone messages are going to tell people with type 1 diabetes they have to wait further back in line if that is what their state’s guidance directs.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Diabetes Association, along with 18 other organizations, has sent a letter to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention urging them to rank people with type 1 diabetes as equally high risk for COVID-19 severity, and therefore vaccination, as those with type 2 diabetes.
On Jan. 12, the CDC recommended states vaccinate all Americans over age 65 and those with underlying health conditions that make them more vulnerable to COVID-19.
Currently, type 2 diabetes is listed among 12 conditions that place adults “at increased risk of severe illness from the virus that causes COVID-19,” with the latter defined as “hospitalization, admission to the intensive care unit, intubation or mechanical ventilation, or death.”
On the other hand, the autoimmune condition type 1 diabetes is among 11 conditions the CDC says “might be at increased risk” for COVID-19, but limited data were available at the time of the last update on Dec. 23, 2020.
“States are utilizing the CDC risk classification when designing their vaccine distribution plans. This raises an obvious concern as it could result in the approximately 1.6 million with type 1 diabetes receiving the vaccination later than others with the same risk,” states the ADA letter, sent to the CDC on Jan. 13.
Representatives from the Endocrine Society, American Association of Clinical Endocrinology, Pediatric Endocrine Society, Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists, and JDRF, among others, cosigned the letter.
Newer data show those with type 1 diabetes at equally high risk
While acknowledging that “early data did not provide as much clarity about the extent to which those with type 1 diabetes are at high risk,” the ADA says newer evidence has emerged, as previously reported by this news organization, that “convincingly demonstrates that COVID-19 severity is more than tripled in individuals with type 1 diabetes.”
The letter also cites another study showing that people with type 1 diabetes “have a 3.3-fold greater risk of severe illness, are 3.9 times more likely to be hospitalized with COVID-19, and have a 3-fold increase in mortality compared to those without type 1 diabetes.”
Those risks, they note, are comparable to the increased risk established for those with type 2 diabetes, as shown in a third study from Scotland, published last month.
Asked for comment, CDC representative Kirsten Nordlund said in an interview, “This list is a living document that will be periodically updated by CDC, and it could rapidly change as the science evolves.”
In addition, Ms. Nordlund said, “Decisions about transitioning to subsequent phases should depend on supply; demand; equitable vaccine distribution; and local, state, or territorial context.”
“Phased vaccine recommendations are meant to be fluid and not restrictive for jurisdictions. It is not necessary to vaccinate all individuals in one phase before initiating the next phase; phases may overlap,” she noted. More information is available here.
Tennessee gives type 1 and type 2 diabetes equal priority for vaccination
Meanwhile, at least one state, Tennessee, has updated its guidance to include both types of diabetes as being priority for COVID-19 vaccination.
Vanderbilt University pediatric endocrinologist Justin M. Gregory, MD, said in an interview: “I was thrilled when our state modified its guidance on December 30th to include both type 1 and type 2 diabetes in the ‘high-risk category.’ Other states have not modified that guidance though.”
It’s unclear how this might play out on the ground, noted Dr. Gregory, who led one of the three studies demonstrating increased COVID-19 risk for people with type 1 diabetes.
“To tell you the truth, I don’t really know how individual organizations dispensing the vaccination [will handle] people who come to their facility saying they have ‘diabetes.’ Individual states set the vaccine-dispensing guidance and individual county health departments and health care systems mirror that guidance,” he said.
Thus, he added, “Although it’s possible an individual nurse may take the ‘I’ll ask you no questions, and you’ll tell me no lies’ approach if someone with type 1 diabetes says they have ‘diabetes’, websites and health department–recorded telephone messages are going to tell people with type 1 diabetes they have to wait further back in line if that is what their state’s guidance directs.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Diabetes Association, along with 18 other organizations, has sent a letter to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention urging them to rank people with type 1 diabetes as equally high risk for COVID-19 severity, and therefore vaccination, as those with type 2 diabetes.
On Jan. 12, the CDC recommended states vaccinate all Americans over age 65 and those with underlying health conditions that make them more vulnerable to COVID-19.
Currently, type 2 diabetes is listed among 12 conditions that place adults “at increased risk of severe illness from the virus that causes COVID-19,” with the latter defined as “hospitalization, admission to the intensive care unit, intubation or mechanical ventilation, or death.”
On the other hand, the autoimmune condition type 1 diabetes is among 11 conditions the CDC says “might be at increased risk” for COVID-19, but limited data were available at the time of the last update on Dec. 23, 2020.
“States are utilizing the CDC risk classification when designing their vaccine distribution plans. This raises an obvious concern as it could result in the approximately 1.6 million with type 1 diabetes receiving the vaccination later than others with the same risk,” states the ADA letter, sent to the CDC on Jan. 13.
Representatives from the Endocrine Society, American Association of Clinical Endocrinology, Pediatric Endocrine Society, Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists, and JDRF, among others, cosigned the letter.
Newer data show those with type 1 diabetes at equally high risk
While acknowledging that “early data did not provide as much clarity about the extent to which those with type 1 diabetes are at high risk,” the ADA says newer evidence has emerged, as previously reported by this news organization, that “convincingly demonstrates that COVID-19 severity is more than tripled in individuals with type 1 diabetes.”
The letter also cites another study showing that people with type 1 diabetes “have a 3.3-fold greater risk of severe illness, are 3.9 times more likely to be hospitalized with COVID-19, and have a 3-fold increase in mortality compared to those without type 1 diabetes.”
Those risks, they note, are comparable to the increased risk established for those with type 2 diabetes, as shown in a third study from Scotland, published last month.
Asked for comment, CDC representative Kirsten Nordlund said in an interview, “This list is a living document that will be periodically updated by CDC, and it could rapidly change as the science evolves.”
In addition, Ms. Nordlund said, “Decisions about transitioning to subsequent phases should depend on supply; demand; equitable vaccine distribution; and local, state, or territorial context.”
“Phased vaccine recommendations are meant to be fluid and not restrictive for jurisdictions. It is not necessary to vaccinate all individuals in one phase before initiating the next phase; phases may overlap,” she noted. More information is available here.
Tennessee gives type 1 and type 2 diabetes equal priority for vaccination
Meanwhile, at least one state, Tennessee, has updated its guidance to include both types of diabetes as being priority for COVID-19 vaccination.
Vanderbilt University pediatric endocrinologist Justin M. Gregory, MD, said in an interview: “I was thrilled when our state modified its guidance on December 30th to include both type 1 and type 2 diabetes in the ‘high-risk category.’ Other states have not modified that guidance though.”
It’s unclear how this might play out on the ground, noted Dr. Gregory, who led one of the three studies demonstrating increased COVID-19 risk for people with type 1 diabetes.
“To tell you the truth, I don’t really know how individual organizations dispensing the vaccination [will handle] people who come to their facility saying they have ‘diabetes.’ Individual states set the vaccine-dispensing guidance and individual county health departments and health care systems mirror that guidance,” he said.
Thus, he added, “Although it’s possible an individual nurse may take the ‘I’ll ask you no questions, and you’ll tell me no lies’ approach if someone with type 1 diabetes says they have ‘diabetes’, websites and health department–recorded telephone messages are going to tell people with type 1 diabetes they have to wait further back in line if that is what their state’s guidance directs.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Feds authorize $3 billion to boost vaccine rollout
The CDC will send $3 billion to the states to boost a lagging national COVID-19 vaccination program.
The Department of Health and Human Services announced the new funding as only 30% of the more than 22 million doses of vaccine distributed in the U.S. has been injected into Americans’ arms.
Along with the $3 billion, HHS said another $19 billion is headed to states and jurisdictions to boost COVID-19 testing programs. The amount each state will receive will be determined by population.
The news comes days after President-elect Joe Biden said he planned to release all available doses of vaccine after he takes office on Jan. 20. The Trump administration has been holding back millions of doses to ensure supply of vaccine to provide the necessary second dose for those who received the first shot.
“This funding is another timely investment that will strengthen our nation’s efforts to stop the COVID-19 pandemic in America,” CDC Director Robert Redfield, MD, said in a statement. “Particularly now, it is crucial that states and communities have the resources they need to conduct testing, and to distribute and administer safe, high-quality COVID-19 vaccines safely and equitably.”
Federal officials and public health experts, however, expressed concerns this weekend about Biden’s plan.
Outgoing Trump administration officials and others said they worry that doing so will leave providers without enough second doses for people getting the two-shot vaccines.
If Biden releases all available doses and the vaccine-making process has an issue, they said, that could pose a supply risk.
“We have product that is going through QC right now – quality control – for sterility, identity check that we have tens and tens of millions of product. We always will. But batches fail. Sterility fails ... and then you don’t have a product for that second dose,” Alex Azar, secretary of health and human services, told the American Hospital Association on Jan. 8, according to CNN.
“And frankly, talking about that or encouraging that can really undermine a critical public health need, which is that people come back for their second vaccine,” he said.
One of the main roadblocks in the vaccine rollout has been administering the doses that have already been distributed. The U.S. has shipped 22.1 million doses, and 6.6 million first shots have been given, according to the latest CDC data updated Jan. 8. Mr. Azar and other federal health officials have encouraged states to use their current supply and expand vaccine access to more priority groups.
“We would be delighted to learn that jurisdictions have actually administered many more doses than they are presently reporting,” a spokesman for the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services told CNN. “We are encouraging jurisdictions to expand their priority groups as needed to ensure no vaccine is sitting on the shelf after having been delivered to the jurisdiction-directed locations.”
Releasing more vaccines for first doses could create ethical concerns as well, since people getting vaccines expect to get a second dose in the proper amount of time, according to The Week. Biden’s transition team said on Jan. 8 that he won’t delay the second dose but, instead, plans to ramp up production to stay on track.
To do this well, the federal government should create a coordinated vaccine strategy that sets expectations for an around-the-clock operation and help state and local vaccination programs meet their goals, Leana Wen, MD, a professor at George Washington University, wrote in an editorial for The Washington Post.
“The Biden team’s urgency around vaccinations is commendable,” she added in a Twitter post on Jan. 11. “I’d like to see a guarantee that every 1st dose given will be followed with a timely 2nd dose. Otherwise, there are ethical concerns that could add to vaccine hesitancy.”
Biden has pledged that 100 million doses will be administered in his first 100 days in office. He has grown frustrated as concerns grow that his administration could fall short of the promise, according to Politico. His coronavirus response team has noted several challenges, including what they say is a lack of long-term planning by the Trump administration and an initial refusal to share key information.
“We’re uncovering new information each day, and we’re unearthing – of course – more work to be done,” Vivek Murthy, MD, Biden’s nominee for surgeon general, told Politico.
The team has uncovered staffing shortages, technology problems, and issues with health care insurance coverage. The incoming Biden team has developed several initiatives, such as mobile vaccination units and new federal sites to give shots. It could take weeks to get the vaccine rollout on track, the news outlet reported.
“Will this be challenging? Absolutely,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and Biden’s incoming chief medical adviser on the coronavirus, told Politico. “This is an unprecedented effort to vaccinate the entire country over a period of time that’s fighting against people dying at record numbers. To say it’s not a challenge would be unrealistic. Do I think it can be done? Yes.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The CDC will send $3 billion to the states to boost a lagging national COVID-19 vaccination program.
The Department of Health and Human Services announced the new funding as only 30% of the more than 22 million doses of vaccine distributed in the U.S. has been injected into Americans’ arms.
Along with the $3 billion, HHS said another $19 billion is headed to states and jurisdictions to boost COVID-19 testing programs. The amount each state will receive will be determined by population.
The news comes days after President-elect Joe Biden said he planned to release all available doses of vaccine after he takes office on Jan. 20. The Trump administration has been holding back millions of doses to ensure supply of vaccine to provide the necessary second dose for those who received the first shot.
“This funding is another timely investment that will strengthen our nation’s efforts to stop the COVID-19 pandemic in America,” CDC Director Robert Redfield, MD, said in a statement. “Particularly now, it is crucial that states and communities have the resources they need to conduct testing, and to distribute and administer safe, high-quality COVID-19 vaccines safely and equitably.”
Federal officials and public health experts, however, expressed concerns this weekend about Biden’s plan.
Outgoing Trump administration officials and others said they worry that doing so will leave providers without enough second doses for people getting the two-shot vaccines.
If Biden releases all available doses and the vaccine-making process has an issue, they said, that could pose a supply risk.
“We have product that is going through QC right now – quality control – for sterility, identity check that we have tens and tens of millions of product. We always will. But batches fail. Sterility fails ... and then you don’t have a product for that second dose,” Alex Azar, secretary of health and human services, told the American Hospital Association on Jan. 8, according to CNN.
“And frankly, talking about that or encouraging that can really undermine a critical public health need, which is that people come back for their second vaccine,” he said.
One of the main roadblocks in the vaccine rollout has been administering the doses that have already been distributed. The U.S. has shipped 22.1 million doses, and 6.6 million first shots have been given, according to the latest CDC data updated Jan. 8. Mr. Azar and other federal health officials have encouraged states to use their current supply and expand vaccine access to more priority groups.
“We would be delighted to learn that jurisdictions have actually administered many more doses than they are presently reporting,” a spokesman for the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services told CNN. “We are encouraging jurisdictions to expand their priority groups as needed to ensure no vaccine is sitting on the shelf after having been delivered to the jurisdiction-directed locations.”
Releasing more vaccines for first doses could create ethical concerns as well, since people getting vaccines expect to get a second dose in the proper amount of time, according to The Week. Biden’s transition team said on Jan. 8 that he won’t delay the second dose but, instead, plans to ramp up production to stay on track.
To do this well, the federal government should create a coordinated vaccine strategy that sets expectations for an around-the-clock operation and help state and local vaccination programs meet their goals, Leana Wen, MD, a professor at George Washington University, wrote in an editorial for The Washington Post.
“The Biden team’s urgency around vaccinations is commendable,” she added in a Twitter post on Jan. 11. “I’d like to see a guarantee that every 1st dose given will be followed with a timely 2nd dose. Otherwise, there are ethical concerns that could add to vaccine hesitancy.”
Biden has pledged that 100 million doses will be administered in his first 100 days in office. He has grown frustrated as concerns grow that his administration could fall short of the promise, according to Politico. His coronavirus response team has noted several challenges, including what they say is a lack of long-term planning by the Trump administration and an initial refusal to share key information.
“We’re uncovering new information each day, and we’re unearthing – of course – more work to be done,” Vivek Murthy, MD, Biden’s nominee for surgeon general, told Politico.
The team has uncovered staffing shortages, technology problems, and issues with health care insurance coverage. The incoming Biden team has developed several initiatives, such as mobile vaccination units and new federal sites to give shots. It could take weeks to get the vaccine rollout on track, the news outlet reported.
“Will this be challenging? Absolutely,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and Biden’s incoming chief medical adviser on the coronavirus, told Politico. “This is an unprecedented effort to vaccinate the entire country over a period of time that’s fighting against people dying at record numbers. To say it’s not a challenge would be unrealistic. Do I think it can be done? Yes.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The CDC will send $3 billion to the states to boost a lagging national COVID-19 vaccination program.
The Department of Health and Human Services announced the new funding as only 30% of the more than 22 million doses of vaccine distributed in the U.S. has been injected into Americans’ arms.
Along with the $3 billion, HHS said another $19 billion is headed to states and jurisdictions to boost COVID-19 testing programs. The amount each state will receive will be determined by population.
The news comes days after President-elect Joe Biden said he planned to release all available doses of vaccine after he takes office on Jan. 20. The Trump administration has been holding back millions of doses to ensure supply of vaccine to provide the necessary second dose for those who received the first shot.
“This funding is another timely investment that will strengthen our nation’s efforts to stop the COVID-19 pandemic in America,” CDC Director Robert Redfield, MD, said in a statement. “Particularly now, it is crucial that states and communities have the resources they need to conduct testing, and to distribute and administer safe, high-quality COVID-19 vaccines safely and equitably.”
Federal officials and public health experts, however, expressed concerns this weekend about Biden’s plan.
Outgoing Trump administration officials and others said they worry that doing so will leave providers without enough second doses for people getting the two-shot vaccines.
If Biden releases all available doses and the vaccine-making process has an issue, they said, that could pose a supply risk.
“We have product that is going through QC right now – quality control – for sterility, identity check that we have tens and tens of millions of product. We always will. But batches fail. Sterility fails ... and then you don’t have a product for that second dose,” Alex Azar, secretary of health and human services, told the American Hospital Association on Jan. 8, according to CNN.
“And frankly, talking about that or encouraging that can really undermine a critical public health need, which is that people come back for their second vaccine,” he said.
One of the main roadblocks in the vaccine rollout has been administering the doses that have already been distributed. The U.S. has shipped 22.1 million doses, and 6.6 million first shots have been given, according to the latest CDC data updated Jan. 8. Mr. Azar and other federal health officials have encouraged states to use their current supply and expand vaccine access to more priority groups.
“We would be delighted to learn that jurisdictions have actually administered many more doses than they are presently reporting,” a spokesman for the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services told CNN. “We are encouraging jurisdictions to expand their priority groups as needed to ensure no vaccine is sitting on the shelf after having been delivered to the jurisdiction-directed locations.”
Releasing more vaccines for first doses could create ethical concerns as well, since people getting vaccines expect to get a second dose in the proper amount of time, according to The Week. Biden’s transition team said on Jan. 8 that he won’t delay the second dose but, instead, plans to ramp up production to stay on track.
To do this well, the federal government should create a coordinated vaccine strategy that sets expectations for an around-the-clock operation and help state and local vaccination programs meet their goals, Leana Wen, MD, a professor at George Washington University, wrote in an editorial for The Washington Post.
“The Biden team’s urgency around vaccinations is commendable,” she added in a Twitter post on Jan. 11. “I’d like to see a guarantee that every 1st dose given will be followed with a timely 2nd dose. Otherwise, there are ethical concerns that could add to vaccine hesitancy.”
Biden has pledged that 100 million doses will be administered in his first 100 days in office. He has grown frustrated as concerns grow that his administration could fall short of the promise, according to Politico. His coronavirus response team has noted several challenges, including what they say is a lack of long-term planning by the Trump administration and an initial refusal to share key information.
“We’re uncovering new information each day, and we’re unearthing – of course – more work to be done,” Vivek Murthy, MD, Biden’s nominee for surgeon general, told Politico.
The team has uncovered staffing shortages, technology problems, and issues with health care insurance coverage. The incoming Biden team has developed several initiatives, such as mobile vaccination units and new federal sites to give shots. It could take weeks to get the vaccine rollout on track, the news outlet reported.
“Will this be challenging? Absolutely,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and Biden’s incoming chief medical adviser on the coronavirus, told Politico. “This is an unprecedented effort to vaccinate the entire country over a period of time that’s fighting against people dying at record numbers. To say it’s not a challenge would be unrealistic. Do I think it can be done? Yes.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Examining the Interfacility Variation of Social Determinants of Health in the Veterans Health Administration
Social determinants of health (SDoH) are social, economic, environmental, and occupational factors that are known to influence an individual’s health care utilization and clinical outcomes.1,2 Because the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is charged to address both the medical and nonmedical needs of the veteran population, it is increasingly interested in the impact SDoH have on veteran care.3,4 To combat the adverse impact of such factors, the VHA has implemented several large-scale programs across the US that focus on prevalent SDoH, such as homelessness, substance abuse, and alcohol use disorders.5,6 While such risk factors are generally universal in their distribution, variation across regions, between urban and rural spaces, and even within cities has been shown to exist in private settings.7 Understanding such variability potentially could be helpful to US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) policymakers and leaders to better allocate funding and resources to address such issues.
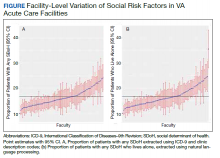
Although previous work has highlighted regional and neighborhood-level variability of SDoH, no study has examined the facility-level variability of commonly encountered social risk factors within the VHA.4,8 The aim of this study was to describe the interfacility variation of 5 common SDoH known to influence health and health outcomes among a national cohort of veterans hospitalized for common medical issues by using administrative data.
Methods
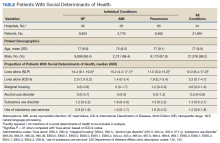
We used a national cohort of veterans aged ≥ 65 years who were hospitalized at a VHA acute care facility with a primary discharge diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction (AMI), heart failure (HF), or pneumonia in 2012. These conditions were chosen because they are publicly reported and frequently used for interfacility comparison.
Using the International Classification of Diseases–9th Revision (ICD-9) and VHA clinical stop codes, we calculated the median documented proportion of patients with any of the following 5 SDoH: lived alone, marginal housing, alcohol use disorder, substance use disorder, and use of substance use services for patients presenting with HF, MI, and pneumonia (Table). These SDoH were chosen because they are intervenable risk factors for which the VHA has several programs (eg, homeless outreach, substance abuse, and tobacco cessation). To examine the variability of these SDoH across VHA facilities, we determined the number of hospitals that had a sufficient number of admissions (≥ 50) to be included in the analyses. We then examined the administratively documented, facility-level variation in the proportion of individuals with any of the 5 SDoH administrative codes and examined the distribution of their use across all qualifying facilities.
Because variability may be due to regional coding differences, we examined the difference in the estimated prevalence of the risk factor lives alone by using a previously developed natural language processing (NLP) program.9 The NLP program is a rule-based system designed to automatically extract information that requires inferencing from clinical notes (eg, discharge summaries and nursing, social work, emergency department physician, primary care, and hospital admission notes). For instance, the program identifies whether there was direct or indirect evidence that the patient did or did not live alone. In addition to extracting data on lives alone, the NLP program has the capacity to extract information on lack of social support and living alone—2 characteristics without VHA interventions, which were not examined here. The NLP program was developed and evaluated using at least 1 year of notes prior to index hospitalization. Because this program was developed and validated on a 2012 data set, we were limited to using a cohort from this year as well.
All analyses were conducted using SAS Version 9.4. The San Francisco VA Medical Center Institutional Review Board approved this study.
Results
In total, 21,991 patients with either HF (9,853), pneumonia (9,362), or AMI (2,776) were identified across 91 VHA facilities. The majority were male (98%) and had a median (SD) age of 77.0 (9.0) years. The median facility-level proportion of veterans who had any of the SDoH risk factors extracted through administrative codes was low across all conditions, ranging from 0.5 to 2.2%. The most prevalent factors among patients admitted for HF, AMI, and pneumonia were lives alone (2.0% [Interquartile range (IQR), 1.0-5.2], 1.4% [IQR, 0-3.4], and 1.9% [IQR, 0.7-5.4]), substance use disorder (1.2% [IQR, 0-2.2], 1.6% [IQR: 0-3.0], and 1.3% [IQR, 0-2.2] and use of substance use services (0.9% [IQR, 0-1.6%], 1.0% [IQR, 0-1.7%], and 1.6% [IQR, 0-2.2%], respectively [Table]).
When utilizing the NLP algorithm, the documented prevalence of lives alone in the free text of the medical record was higher than administrative coding across all conditions (12.3% vs. 2.2%; P < .01). Among each of the 3 assessed conditions, HF (14.4% vs 2.0%, P < .01) had higher levels of lives alone compared with pneumonia (11% vs 1.9%, P < .01), and AMI (10.2% vs 1.4%, P < .01) when using the NLP algorithm. When we examined the documented facility-level variation in the proportion of individuals with any of the 5 SDoH administrative codes or NLP, we found large variability across all facilities—regardless of extraction method (Figure).
Discussion
While SDoH are known to impact health outcomes, the presence of these risk factors in administrative data among individuals hospitalized for common medical issues is low and variable across VHA facilities. Understanding the documented, facility-level variability of these measures may assist the VHA in determining how it invests time and resources—as different facilities may disproportionately serve a higher number of vulnerable individuals. Beyond the VHA, these findings have generalizable lessons for the US health care system, which has come to recognize how these risk factors impact patients’ health.10
Although the proportion of individuals with any of the assessed SDoH identified by administrative data was low, our findings are in line with recent studies that showed other risk factors such as social isolation (0.65%), housing issues (0.19%), and financial strain (0.07%) had similarly low prevalence.8,11 Although the exact prevalence of such factors remains unclear, these findings highlight that SDoH do not appear to be well documented in administrative data. Low coding rates are likely due to the fact that SDoH administrative codes are not tied to financial reimbursement—thus not incentivizing their use by clinicians or hospital systems.
In 2014, an Institute of Medicine report suggested that collection of SDoH in electronic health data as a means to better empower clinicians and health care systems to address social disparities and further support research in SDoH.12 Since then, data collection using SDoH screening tools has become more common across settings, but is not consistently translated to standardized data due to lack of industry consensus and technical barriers.13 To improve this process, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services created “z-codes” for the ICD-10 classification system—a subset of codes that are meant to better capture patients’ underlying social risk.14 It remains to be seen if such administrative codes have improved the documentation of SDoH.
As health care systems have grown to understand the impact of SDoH on health outcomes,other means of collecting these data have evolved.1,10 For example, NLP-based extraction methods and electronic screening tools have been proposed and utilized as alternative for obtaining this information. Our findings suggest that some of these measures (eg, lives alone) often may be documented as part of routine care in the electronic health record, thus highlighting NLP as a tool to obtain such data. However, other studies using NLP technology to extract SDoH have shown this technology is often complicated by quality issues (ie, missing data), complex methods, and poor integration with current information technology infrastructures—thus limiting its use in health care delivery.15-18
While variance among SDoH across a national health care system is natural, it remains an important systems-level characteristic that health care leaders and policymakers should appreciate. As health care systems disperse financial resources and initiate quality improvement initiatives to address SDoH, knowing that not all facilities are equally affected by SDoH should impact allocation of such resources and energies. Although previous work has highlighted regional and neighborhood levels of variation within the VHA and other health care systems, to our knowledge, this is the first study to examine variability at the facility-level within the VHA.2,4,13,19
Limitations
There are several limitations to this study. First, though our findings are in line with previous data in other health care systems, generalizability beyond the VA, which primarily cares for older, male patients, may be limited.8 Though, as the nation’s largest health care system, lessons from the VHA can still be useful for other health care systems as they consider SDoH variation. Second, among the many SDoH previously identified to impact health, our analysis only focused on 5 such variables. Administrative and medical record documentation of other SDoH may be more common and less variable across institutions. Third, while our data suggests facility-level variation in these measures, this may be in part related to variation in coding across facilities. However, the single SDoH variable extracted using NLP also varied at the facility-level, suggesting that coding may not entirely drive the variation observed.
Conclusions
As US health care systems continue to address SDoH, our findings highlight the various challenges in obtaining accurate data on a patient’s social risk. Moreover, these findings highlight the large variability that exists among institutions in a national integrated health care system. Future work should explore the prevalence and variance of other SDoH as a means to help guide resource allocation and prioritize spending to better address SDoH where it is most needed.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NHLBI R01 RO1 HL116522-01A1. Support for VA/CMS data is provided by the US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of Research and Development, Health Services Research and Development, VA Information Resource Center (Project Numbers SDR 02-237 and 98-004).
1. Social determinants of health (SDOH). https://catalyst.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/CAT.17.0312. Published December 1, 2017. Accessed December 8, 2020.
2. Hatef E, Searle KM, Predmore Z, et al. The Impact of Social Determinants of Health on hospitalization in the Veterans Health Administration. Am J Prev Med. 2019;56(6):811-818. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2018.12.012
3. Lushniak BD, Alley DE, Ulin B, Graffunder C. The National Prevention Strategy: leveraging multiple sectors to improve population health. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(2):229-231. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2014.302257
4. Nelson K, Schwartz G, Hernandez S, Simonetti J, Curtis I, Fihn SD. The association between neighborhood environment and mortality: results from a national study of veterans. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32(4):416-422. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3905-x
5. Gundlapalli AV, Redd A, Bolton D, et al. Patient-aligned care team engagement to connect veterans experiencing homelessness with appropriate health care. Med Care. 2017;55 Suppl 9 Suppl 2:S104-S110. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000770
6. Rash CJ, DePhilippis D. Considerations for implementing contingency management in substance abuse treatment clinics: the Veterans Affairs initiative as a model. Perspect Behav Sci. 2019;42(3):479-499. doi:10.1007/s40614-019-00204-3.
7. Ompad DC, Galea S, Caiaffa WT, Vlahov D. Social determinants of the health of urban populations: methodologic considerations. J Urban Health. 2007;84(3 Suppl):i42-i53. doi:10.1007/s11524-007-9168-4
8. Hatef E, Rouhizadeh M, Tia I, et al. Assessing the availability of data on social and behavioral determinants in structured and unstructured electronic health records: a retrospective analysis of a multilevel health care system. JMIR Med Inform. 2019;7(3):e13802. doi:10.2196/13802
9. Conway M, Keyhani S, Christensen L, et al. Moonstone: a novel natural language processing system for inferring social risk from clinical narratives. J Biomed Semantics. 2019;10(1):6. doi:10.1186/s13326-019-0198-0
10. Adler NE, Cutler DM, Fielding JE, et al. Addressing social determinants of health and health disparities: a vital direction for health and health care. Discussion Paper. NAM Perspectives. National Academy of Medicine, Washington, DC. doi:10.31478/201609t
11. Cottrell EK, Dambrun K, Cowburn S, et al. Variation in electronic health record documentation of social determinants of health across a national network of community health centers. Am J Prev Med. 2019;57(6):S65-S73. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2019.07.014
12. Committee on the Recommended Social and Behavioral Domains and Measures for Electronic Health Records, Board on Population Health and Public Health Practice, Institute of Medicine. Capturing Social and Behavioral Domains and Measures in Electronic Health Records: Phase 2. National Academies Press (US); 2015.
13. Gottlieb L, Tobey R, Cantor J, Hessler D, Adler NE. Integrating Social And Medical Data To Improve Population Health: Opportunities And Barriers. Health Aff (Millwood). 2016;35(11):2116-2123. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2016.0723
14. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Service, Office of Minority Health. Z codes utilization among medicare fee-for-service (FFS) beneficiaries in 2017. Published January 2020. Accessed December 8, 2020. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/cms-omh-january2020-zcode-data-highlightpdf.pdf
15. Kharrazi H, Wang C, Scharfstein D. Prospective EHR-based clinical trials: the challenge of missing data. J Gen Intern Med. 2014;29(7):976-978. doi:10.1007/s11606-014-2883-0
16. Weiskopf NG, Weng C. Methods and dimensions of electronic health record data quality assessment: enabling reuse for clinical research. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2013;20(1):144-151. doi:10.1136/amiajnl-2011-000681
17. Anzaldi LJ, Davison A, Boyd CM, Leff B, Kharrazi H. Comparing clinician descriptions of frailty and geriatric syndromes using electronic health records: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2017;17(1):248. doi:10.1186/s12877-017-0645-7
18. Chen T, Dredze M, Weiner JP, Kharrazi H. Identifying vulnerable older adult populations by contextualizing geriatric syndrome information in clinical notes of electronic health records. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2019;26(8-9):787-795. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocz093
19. Raphael E, Gaynes R, Hamad R. Cross-sectional analysis of place-based and racial disparities in hospitalisation rates by disease category in California in 2001 and 2011. BMJ Open. 2019;9(10):e031556. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2019-031556
Social determinants of health (SDoH) are social, economic, environmental, and occupational factors that are known to influence an individual’s health care utilization and clinical outcomes.1,2 Because the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is charged to address both the medical and nonmedical needs of the veteran population, it is increasingly interested in the impact SDoH have on veteran care.3,4 To combat the adverse impact of such factors, the VHA has implemented several large-scale programs across the US that focus on prevalent SDoH, such as homelessness, substance abuse, and alcohol use disorders.5,6 While such risk factors are generally universal in their distribution, variation across regions, between urban and rural spaces, and even within cities has been shown to exist in private settings.7 Understanding such variability potentially could be helpful to US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) policymakers and leaders to better allocate funding and resources to address such issues.
Although previous work has highlighted regional and neighborhood-level variability of SDoH, no study has examined the facility-level variability of commonly encountered social risk factors within the VHA.4,8 The aim of this study was to describe the interfacility variation of 5 common SDoH known to influence health and health outcomes among a national cohort of veterans hospitalized for common medical issues by using administrative data.
Methods
We used a national cohort of veterans aged ≥ 65 years who were hospitalized at a VHA acute care facility with a primary discharge diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction (AMI), heart failure (HF), or pneumonia in 2012. These conditions were chosen because they are publicly reported and frequently used for interfacility comparison.
Using the International Classification of Diseases–9th Revision (ICD-9) and VHA clinical stop codes, we calculated the median documented proportion of patients with any of the following 5 SDoH: lived alone, marginal housing, alcohol use disorder, substance use disorder, and use of substance use services for patients presenting with HF, MI, and pneumonia (Table). These SDoH were chosen because they are intervenable risk factors for which the VHA has several programs (eg, homeless outreach, substance abuse, and tobacco cessation). To examine the variability of these SDoH across VHA facilities, we determined the number of hospitals that had a sufficient number of admissions (≥ 50) to be included in the analyses. We then examined the administratively documented, facility-level variation in the proportion of individuals with any of the 5 SDoH administrative codes and examined the distribution of their use across all qualifying facilities.
Because variability may be due to regional coding differences, we examined the difference in the estimated prevalence of the risk factor lives alone by using a previously developed natural language processing (NLP) program.9 The NLP program is a rule-based system designed to automatically extract information that requires inferencing from clinical notes (eg, discharge summaries and nursing, social work, emergency department physician, primary care, and hospital admission notes). For instance, the program identifies whether there was direct or indirect evidence that the patient did or did not live alone. In addition to extracting data on lives alone, the NLP program has the capacity to extract information on lack of social support and living alone—2 characteristics without VHA interventions, which were not examined here. The NLP program was developed and evaluated using at least 1 year of notes prior to index hospitalization. Because this program was developed and validated on a 2012 data set, we were limited to using a cohort from this year as well.
All analyses were conducted using SAS Version 9.4. The San Francisco VA Medical Center Institutional Review Board approved this study.
Results
In total, 21,991 patients with either HF (9,853), pneumonia (9,362), or AMI (2,776) were identified across 91 VHA facilities. The majority were male (98%) and had a median (SD) age of 77.0 (9.0) years. The median facility-level proportion of veterans who had any of the SDoH risk factors extracted through administrative codes was low across all conditions, ranging from 0.5 to 2.2%. The most prevalent factors among patients admitted for HF, AMI, and pneumonia were lives alone (2.0% [Interquartile range (IQR), 1.0-5.2], 1.4% [IQR, 0-3.4], and 1.9% [IQR, 0.7-5.4]), substance use disorder (1.2% [IQR, 0-2.2], 1.6% [IQR: 0-3.0], and 1.3% [IQR, 0-2.2] and use of substance use services (0.9% [IQR, 0-1.6%], 1.0% [IQR, 0-1.7%], and 1.6% [IQR, 0-2.2%], respectively [Table]).
When utilizing the NLP algorithm, the documented prevalence of lives alone in the free text of the medical record was higher than administrative coding across all conditions (12.3% vs. 2.2%; P < .01). Among each of the 3 assessed conditions, HF (14.4% vs 2.0%, P < .01) had higher levels of lives alone compared with pneumonia (11% vs 1.9%, P < .01), and AMI (10.2% vs 1.4%, P < .01) when using the NLP algorithm. When we examined the documented facility-level variation in the proportion of individuals with any of the 5 SDoH administrative codes or NLP, we found large variability across all facilities—regardless of extraction method (Figure).
Discussion
While SDoH are known to impact health outcomes, the presence of these risk factors in administrative data among individuals hospitalized for common medical issues is low and variable across VHA facilities. Understanding the documented, facility-level variability of these measures may assist the VHA in determining how it invests time and resources—as different facilities may disproportionately serve a higher number of vulnerable individuals. Beyond the VHA, these findings have generalizable lessons for the US health care system, which has come to recognize how these risk factors impact patients’ health.10
Although the proportion of individuals with any of the assessed SDoH identified by administrative data was low, our findings are in line with recent studies that showed other risk factors such as social isolation (0.65%), housing issues (0.19%), and financial strain (0.07%) had similarly low prevalence.8,11 Although the exact prevalence of such factors remains unclear, these findings highlight that SDoH do not appear to be well documented in administrative data. Low coding rates are likely due to the fact that SDoH administrative codes are not tied to financial reimbursement—thus not incentivizing their use by clinicians or hospital systems.
In 2014, an Institute of Medicine report suggested that collection of SDoH in electronic health data as a means to better empower clinicians and health care systems to address social disparities and further support research in SDoH.12 Since then, data collection using SDoH screening tools has become more common across settings, but is not consistently translated to standardized data due to lack of industry consensus and technical barriers.13 To improve this process, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services created “z-codes” for the ICD-10 classification system—a subset of codes that are meant to better capture patients’ underlying social risk.14 It remains to be seen if such administrative codes have improved the documentation of SDoH.
As health care systems have grown to understand the impact of SDoH on health outcomes,other means of collecting these data have evolved.1,10 For example, NLP-based extraction methods and electronic screening tools have been proposed and utilized as alternative for obtaining this information. Our findings suggest that some of these measures (eg, lives alone) often may be documented as part of routine care in the electronic health record, thus highlighting NLP as a tool to obtain such data. However, other studies using NLP technology to extract SDoH have shown this technology is often complicated by quality issues (ie, missing data), complex methods, and poor integration with current information technology infrastructures—thus limiting its use in health care delivery.15-18
While variance among SDoH across a national health care system is natural, it remains an important systems-level characteristic that health care leaders and policymakers should appreciate. As health care systems disperse financial resources and initiate quality improvement initiatives to address SDoH, knowing that not all facilities are equally affected by SDoH should impact allocation of such resources and energies. Although previous work has highlighted regional and neighborhood levels of variation within the VHA and other health care systems, to our knowledge, this is the first study to examine variability at the facility-level within the VHA.2,4,13,19
Limitations
There are several limitations to this study. First, though our findings are in line with previous data in other health care systems, generalizability beyond the VA, which primarily cares for older, male patients, may be limited.8 Though, as the nation’s largest health care system, lessons from the VHA can still be useful for other health care systems as they consider SDoH variation. Second, among the many SDoH previously identified to impact health, our analysis only focused on 5 such variables. Administrative and medical record documentation of other SDoH may be more common and less variable across institutions. Third, while our data suggests facility-level variation in these measures, this may be in part related to variation in coding across facilities. However, the single SDoH variable extracted using NLP also varied at the facility-level, suggesting that coding may not entirely drive the variation observed.
Conclusions
As US health care systems continue to address SDoH, our findings highlight the various challenges in obtaining accurate data on a patient’s social risk. Moreover, these findings highlight the large variability that exists among institutions in a national integrated health care system. Future work should explore the prevalence and variance of other SDoH as a means to help guide resource allocation and prioritize spending to better address SDoH where it is most needed.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NHLBI R01 RO1 HL116522-01A1. Support for VA/CMS data is provided by the US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of Research and Development, Health Services Research and Development, VA Information Resource Center (Project Numbers SDR 02-237 and 98-004).
Social determinants of health (SDoH) are social, economic, environmental, and occupational factors that are known to influence an individual’s health care utilization and clinical outcomes.1,2 Because the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is charged to address both the medical and nonmedical needs of the veteran population, it is increasingly interested in the impact SDoH have on veteran care.3,4 To combat the adverse impact of such factors, the VHA has implemented several large-scale programs across the US that focus on prevalent SDoH, such as homelessness, substance abuse, and alcohol use disorders.5,6 While such risk factors are generally universal in their distribution, variation across regions, between urban and rural spaces, and even within cities has been shown to exist in private settings.7 Understanding such variability potentially could be helpful to US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) policymakers and leaders to better allocate funding and resources to address such issues.
Although previous work has highlighted regional and neighborhood-level variability of SDoH, no study has examined the facility-level variability of commonly encountered social risk factors within the VHA.4,8 The aim of this study was to describe the interfacility variation of 5 common SDoH known to influence health and health outcomes among a national cohort of veterans hospitalized for common medical issues by using administrative data.
Methods
We used a national cohort of veterans aged ≥ 65 years who were hospitalized at a VHA acute care facility with a primary discharge diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction (AMI), heart failure (HF), or pneumonia in 2012. These conditions were chosen because they are publicly reported and frequently used for interfacility comparison.
Using the International Classification of Diseases–9th Revision (ICD-9) and VHA clinical stop codes, we calculated the median documented proportion of patients with any of the following 5 SDoH: lived alone, marginal housing, alcohol use disorder, substance use disorder, and use of substance use services for patients presenting with HF, MI, and pneumonia (Table). These SDoH were chosen because they are intervenable risk factors for which the VHA has several programs (eg, homeless outreach, substance abuse, and tobacco cessation). To examine the variability of these SDoH across VHA facilities, we determined the number of hospitals that had a sufficient number of admissions (≥ 50) to be included in the analyses. We then examined the administratively documented, facility-level variation in the proportion of individuals with any of the 5 SDoH administrative codes and examined the distribution of their use across all qualifying facilities.
Because variability may be due to regional coding differences, we examined the difference in the estimated prevalence of the risk factor lives alone by using a previously developed natural language processing (NLP) program.9 The NLP program is a rule-based system designed to automatically extract information that requires inferencing from clinical notes (eg, discharge summaries and nursing, social work, emergency department physician, primary care, and hospital admission notes). For instance, the program identifies whether there was direct or indirect evidence that the patient did or did not live alone. In addition to extracting data on lives alone, the NLP program has the capacity to extract information on lack of social support and living alone—2 characteristics without VHA interventions, which were not examined here. The NLP program was developed and evaluated using at least 1 year of notes prior to index hospitalization. Because this program was developed and validated on a 2012 data set, we were limited to using a cohort from this year as well.
All analyses were conducted using SAS Version 9.4. The San Francisco VA Medical Center Institutional Review Board approved this study.
Results
In total, 21,991 patients with either HF (9,853), pneumonia (9,362), or AMI (2,776) were identified across 91 VHA facilities. The majority were male (98%) and had a median (SD) age of 77.0 (9.0) years. The median facility-level proportion of veterans who had any of the SDoH risk factors extracted through administrative codes was low across all conditions, ranging from 0.5 to 2.2%. The most prevalent factors among patients admitted for HF, AMI, and pneumonia were lives alone (2.0% [Interquartile range (IQR), 1.0-5.2], 1.4% [IQR, 0-3.4], and 1.9% [IQR, 0.7-5.4]), substance use disorder (1.2% [IQR, 0-2.2], 1.6% [IQR: 0-3.0], and 1.3% [IQR, 0-2.2] and use of substance use services (0.9% [IQR, 0-1.6%], 1.0% [IQR, 0-1.7%], and 1.6% [IQR, 0-2.2%], respectively [Table]).
When utilizing the NLP algorithm, the documented prevalence of lives alone in the free text of the medical record was higher than administrative coding across all conditions (12.3% vs. 2.2%; P < .01). Among each of the 3 assessed conditions, HF (14.4% vs 2.0%, P < .01) had higher levels of lives alone compared with pneumonia (11% vs 1.9%, P < .01), and AMI (10.2% vs 1.4%, P < .01) when using the NLP algorithm. When we examined the documented facility-level variation in the proportion of individuals with any of the 5 SDoH administrative codes or NLP, we found large variability across all facilities—regardless of extraction method (Figure).
Discussion
While SDoH are known to impact health outcomes, the presence of these risk factors in administrative data among individuals hospitalized for common medical issues is low and variable across VHA facilities. Understanding the documented, facility-level variability of these measures may assist the VHA in determining how it invests time and resources—as different facilities may disproportionately serve a higher number of vulnerable individuals. Beyond the VHA, these findings have generalizable lessons for the US health care system, which has come to recognize how these risk factors impact patients’ health.10
Although the proportion of individuals with any of the assessed SDoH identified by administrative data was low, our findings are in line with recent studies that showed other risk factors such as social isolation (0.65%), housing issues (0.19%), and financial strain (0.07%) had similarly low prevalence.8,11 Although the exact prevalence of such factors remains unclear, these findings highlight that SDoH do not appear to be well documented in administrative data. Low coding rates are likely due to the fact that SDoH administrative codes are not tied to financial reimbursement—thus not incentivizing their use by clinicians or hospital systems.
In 2014, an Institute of Medicine report suggested that collection of SDoH in electronic health data as a means to better empower clinicians and health care systems to address social disparities and further support research in SDoH.12 Since then, data collection using SDoH screening tools has become more common across settings, but is not consistently translated to standardized data due to lack of industry consensus and technical barriers.13 To improve this process, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services created “z-codes” for the ICD-10 classification system—a subset of codes that are meant to better capture patients’ underlying social risk.14 It remains to be seen if such administrative codes have improved the documentation of SDoH.
As health care systems have grown to understand the impact of SDoH on health outcomes,other means of collecting these data have evolved.1,10 For example, NLP-based extraction methods and electronic screening tools have been proposed and utilized as alternative for obtaining this information. Our findings suggest that some of these measures (eg, lives alone) often may be documented as part of routine care in the electronic health record, thus highlighting NLP as a tool to obtain such data. However, other studies using NLP technology to extract SDoH have shown this technology is often complicated by quality issues (ie, missing data), complex methods, and poor integration with current information technology infrastructures—thus limiting its use in health care delivery.15-18
While variance among SDoH across a national health care system is natural, it remains an important systems-level characteristic that health care leaders and policymakers should appreciate. As health care systems disperse financial resources and initiate quality improvement initiatives to address SDoH, knowing that not all facilities are equally affected by SDoH should impact allocation of such resources and energies. Although previous work has highlighted regional and neighborhood levels of variation within the VHA and other health care systems, to our knowledge, this is the first study to examine variability at the facility-level within the VHA.2,4,13,19
Limitations
There are several limitations to this study. First, though our findings are in line with previous data in other health care systems, generalizability beyond the VA, which primarily cares for older, male patients, may be limited.8 Though, as the nation’s largest health care system, lessons from the VHA can still be useful for other health care systems as they consider SDoH variation. Second, among the many SDoH previously identified to impact health, our analysis only focused on 5 such variables. Administrative and medical record documentation of other SDoH may be more common and less variable across institutions. Third, while our data suggests facility-level variation in these measures, this may be in part related to variation in coding across facilities. However, the single SDoH variable extracted using NLP also varied at the facility-level, suggesting that coding may not entirely drive the variation observed.
Conclusions
As US health care systems continue to address SDoH, our findings highlight the various challenges in obtaining accurate data on a patient’s social risk. Moreover, these findings highlight the large variability that exists among institutions in a national integrated health care system. Future work should explore the prevalence and variance of other SDoH as a means to help guide resource allocation and prioritize spending to better address SDoH where it is most needed.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NHLBI R01 RO1 HL116522-01A1. Support for VA/CMS data is provided by the US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of Research and Development, Health Services Research and Development, VA Information Resource Center (Project Numbers SDR 02-237 and 98-004).
1. Social determinants of health (SDOH). https://catalyst.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/CAT.17.0312. Published December 1, 2017. Accessed December 8, 2020.
2. Hatef E, Searle KM, Predmore Z, et al. The Impact of Social Determinants of Health on hospitalization in the Veterans Health Administration. Am J Prev Med. 2019;56(6):811-818. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2018.12.012
3. Lushniak BD, Alley DE, Ulin B, Graffunder C. The National Prevention Strategy: leveraging multiple sectors to improve population health. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(2):229-231. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2014.302257
4. Nelson K, Schwartz G, Hernandez S, Simonetti J, Curtis I, Fihn SD. The association between neighborhood environment and mortality: results from a national study of veterans. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32(4):416-422. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3905-x
5. Gundlapalli AV, Redd A, Bolton D, et al. Patient-aligned care team engagement to connect veterans experiencing homelessness with appropriate health care. Med Care. 2017;55 Suppl 9 Suppl 2:S104-S110. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000770
6. Rash CJ, DePhilippis D. Considerations for implementing contingency management in substance abuse treatment clinics: the Veterans Affairs initiative as a model. Perspect Behav Sci. 2019;42(3):479-499. doi:10.1007/s40614-019-00204-3.
7. Ompad DC, Galea S, Caiaffa WT, Vlahov D. Social determinants of the health of urban populations: methodologic considerations. J Urban Health. 2007;84(3 Suppl):i42-i53. doi:10.1007/s11524-007-9168-4
8. Hatef E, Rouhizadeh M, Tia I, et al. Assessing the availability of data on social and behavioral determinants in structured and unstructured electronic health records: a retrospective analysis of a multilevel health care system. JMIR Med Inform. 2019;7(3):e13802. doi:10.2196/13802
9. Conway M, Keyhani S, Christensen L, et al. Moonstone: a novel natural language processing system for inferring social risk from clinical narratives. J Biomed Semantics. 2019;10(1):6. doi:10.1186/s13326-019-0198-0
10. Adler NE, Cutler DM, Fielding JE, et al. Addressing social determinants of health and health disparities: a vital direction for health and health care. Discussion Paper. NAM Perspectives. National Academy of Medicine, Washington, DC. doi:10.31478/201609t
11. Cottrell EK, Dambrun K, Cowburn S, et al. Variation in electronic health record documentation of social determinants of health across a national network of community health centers. Am J Prev Med. 2019;57(6):S65-S73. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2019.07.014
12. Committee on the Recommended Social and Behavioral Domains and Measures for Electronic Health Records, Board on Population Health and Public Health Practice, Institute of Medicine. Capturing Social and Behavioral Domains and Measures in Electronic Health Records: Phase 2. National Academies Press (US); 2015.
13. Gottlieb L, Tobey R, Cantor J, Hessler D, Adler NE. Integrating Social And Medical Data To Improve Population Health: Opportunities And Barriers. Health Aff (Millwood). 2016;35(11):2116-2123. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2016.0723
14. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Service, Office of Minority Health. Z codes utilization among medicare fee-for-service (FFS) beneficiaries in 2017. Published January 2020. Accessed December 8, 2020. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/cms-omh-january2020-zcode-data-highlightpdf.pdf
15. Kharrazi H, Wang C, Scharfstein D. Prospective EHR-based clinical trials: the challenge of missing data. J Gen Intern Med. 2014;29(7):976-978. doi:10.1007/s11606-014-2883-0
16. Weiskopf NG, Weng C. Methods and dimensions of electronic health record data quality assessment: enabling reuse for clinical research. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2013;20(1):144-151. doi:10.1136/amiajnl-2011-000681
17. Anzaldi LJ, Davison A, Boyd CM, Leff B, Kharrazi H. Comparing clinician descriptions of frailty and geriatric syndromes using electronic health records: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2017;17(1):248. doi:10.1186/s12877-017-0645-7
18. Chen T, Dredze M, Weiner JP, Kharrazi H. Identifying vulnerable older adult populations by contextualizing geriatric syndrome information in clinical notes of electronic health records. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2019;26(8-9):787-795. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocz093
19. Raphael E, Gaynes R, Hamad R. Cross-sectional analysis of place-based and racial disparities in hospitalisation rates by disease category in California in 2001 and 2011. BMJ Open. 2019;9(10):e031556. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2019-031556
1. Social determinants of health (SDOH). https://catalyst.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/CAT.17.0312. Published December 1, 2017. Accessed December 8, 2020.
2. Hatef E, Searle KM, Predmore Z, et al. The Impact of Social Determinants of Health on hospitalization in the Veterans Health Administration. Am J Prev Med. 2019;56(6):811-818. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2018.12.012
3. Lushniak BD, Alley DE, Ulin B, Graffunder C. The National Prevention Strategy: leveraging multiple sectors to improve population health. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(2):229-231. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2014.302257
4. Nelson K, Schwartz G, Hernandez S, Simonetti J, Curtis I, Fihn SD. The association between neighborhood environment and mortality: results from a national study of veterans. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32(4):416-422. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3905-x
5. Gundlapalli AV, Redd A, Bolton D, et al. Patient-aligned care team engagement to connect veterans experiencing homelessness with appropriate health care. Med Care. 2017;55 Suppl 9 Suppl 2:S104-S110. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000770
6. Rash CJ, DePhilippis D. Considerations for implementing contingency management in substance abuse treatment clinics: the Veterans Affairs initiative as a model. Perspect Behav Sci. 2019;42(3):479-499. doi:10.1007/s40614-019-00204-3.
7. Ompad DC, Galea S, Caiaffa WT, Vlahov D. Social determinants of the health of urban populations: methodologic considerations. J Urban Health. 2007;84(3 Suppl):i42-i53. doi:10.1007/s11524-007-9168-4
8. Hatef E, Rouhizadeh M, Tia I, et al. Assessing the availability of data on social and behavioral determinants in structured and unstructured electronic health records: a retrospective analysis of a multilevel health care system. JMIR Med Inform. 2019;7(3):e13802. doi:10.2196/13802
9. Conway M, Keyhani S, Christensen L, et al. Moonstone: a novel natural language processing system for inferring social risk from clinical narratives. J Biomed Semantics. 2019;10(1):6. doi:10.1186/s13326-019-0198-0
10. Adler NE, Cutler DM, Fielding JE, et al. Addressing social determinants of health and health disparities: a vital direction for health and health care. Discussion Paper. NAM Perspectives. National Academy of Medicine, Washington, DC. doi:10.31478/201609t
11. Cottrell EK, Dambrun K, Cowburn S, et al. Variation in electronic health record documentation of social determinants of health across a national network of community health centers. Am J Prev Med. 2019;57(6):S65-S73. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2019.07.014
12. Committee on the Recommended Social and Behavioral Domains and Measures for Electronic Health Records, Board on Population Health and Public Health Practice, Institute of Medicine. Capturing Social and Behavioral Domains and Measures in Electronic Health Records: Phase 2. National Academies Press (US); 2015.
13. Gottlieb L, Tobey R, Cantor J, Hessler D, Adler NE. Integrating Social And Medical Data To Improve Population Health: Opportunities And Barriers. Health Aff (Millwood). 2016;35(11):2116-2123. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2016.0723
14. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Service, Office of Minority Health. Z codes utilization among medicare fee-for-service (FFS) beneficiaries in 2017. Published January 2020. Accessed December 8, 2020. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/cms-omh-january2020-zcode-data-highlightpdf.pdf
15. Kharrazi H, Wang C, Scharfstein D. Prospective EHR-based clinical trials: the challenge of missing data. J Gen Intern Med. 2014;29(7):976-978. doi:10.1007/s11606-014-2883-0
16. Weiskopf NG, Weng C. Methods and dimensions of electronic health record data quality assessment: enabling reuse for clinical research. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2013;20(1):144-151. doi:10.1136/amiajnl-2011-000681
17. Anzaldi LJ, Davison A, Boyd CM, Leff B, Kharrazi H. Comparing clinician descriptions of frailty and geriatric syndromes using electronic health records: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2017;17(1):248. doi:10.1186/s12877-017-0645-7
18. Chen T, Dredze M, Weiner JP, Kharrazi H. Identifying vulnerable older adult populations by contextualizing geriatric syndrome information in clinical notes of electronic health records. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2019;26(8-9):787-795. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocz093
19. Raphael E, Gaynes R, Hamad R. Cross-sectional analysis of place-based and racial disparities in hospitalisation rates by disease category in California in 2001 and 2011. BMJ Open. 2019;9(10):e031556. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2019-031556
“To Conserve Fighting Strength”: The Role of Military Culture in the Delivery of Care
Since 2001, nearly 2,000 US military service members have sustained traumatically acquired limb loss while serving in conflict zones primarily in Afghanistan and Iraq.1 Although most of these patients receive acute and long-term care in a military health facility, polytrauma programs within the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) treat other military patients with traumatic injuries while others receive specialized care in civilian medical programs. The Military Advanced Training Center (MATC) at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center (WRNMMC) provides a comprehensive rehabilitation program for patients with acquired traumatic limb loss.2
In this paper, we argue that receiving long-term care in military settings provides unique value for military patients because of the background therapeutic work such settings can provide. Currently, there are policy discussions that center on consolidating military health care under the oversight of the Defense Health Agency. This approach would develop a more centralized administration while also pursuing other measures to improve efficiency. When evaluating the current system, one key question remains: Would military service members and dependents seeking specific care or long-term rehabilitation programs be more effectively treated in nonmilitary settings?
Based on qualitative research, we argue that keeping a diverse range of military health programs has a positive and therapeutic impact. We also argue that the emergent literature about the importance of military culture to patients and the need for military cultural competence training for nonmilitary clinicians coupled with the results of a qualitative study of former patients at WRNMMC demonstrate that the social context at military treatment facilities offers a positive therapeutic impact.3
Program Description
This article is grounded in research conducted in the US Armed Forces Amputee Patient Care Program at WRNMMC. The study received WRNMMC Institutional Review Board approval in February 2012 and again for the continuation study in January 2015. The lead investigator for the research project was a medical anthropologist who worked with a research unit in the WRNMMC Department of Rehabilitation.
The main period of data collection occurred in 2 waves, the first between 2012 and 2014 and the second between 2015 and 2019. Patients arrived at WRNMMC within several days from the site of their injuries (nearly all were from Iraq and Afghanistan) via military medical facilities in Germany. After a period of recovery from the acute phase of their injuries, patients transitioned to outpatient housing and began their longer phase of care in the outpatient MATC.
On MATC admission, patients were assigned an occupational therapist, physical therapist, and prosthetist. In addition, rehabilitation physicians and orthopedic surgeons oversaw patient care. Social work and other programs provided additional services as needed.2 Patients were treated primarily for their orthopedic and extremity trauma and for neuropsychiatric injuries, such as mild traumatic brain injury. Other behavioral health services were available to support patients who reported symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, anxiety, depression, or other neuropsychological issues.
Patients had multiple daily appointments that shifted throughout the duration of their care. Initially a patient might have 2 physical therapy and 2 occupational therapy appointments daily, with each session lasting about an hour. Appointments with the orthotics and prosthetics service, which could be considerably longer were added as needed. These appointments required multiple castings, fittings, adjustments, and other activities. This also was the case with wound care, behavioral health, and other services and departments.
Cultural Competency
A recently published special issue of Academic Psychiatry described the important role that basic knowledge of military culture plays in effective care delivery to active-duty service members, guard and reserve, and veteran patients and families.4 Reger and colleagues also emphasized the importance of awareness of military culture to civilian clinicians particularly those providing care to service members.5
This concern with gaps in knowledge about recognizing the realities of military culture has given rise to an emergent literature on military cultural competence training for clinical providers.6 Cultural competence in health care settings is understood to be the practice of providing care within a social framework that acknowledges the social and cultural background of patients.7 In the military context, as in others, these discussions often are limited to behavioral health settings.8 This emergent literature provides researchers with important insights into understanding the scope and scale of military culture and the importance of delivering culturally competent care.
Beyond the concept of cultural competence, recognizing the importance of culture can be used to understand positive therapeutic impacts. In discussions of culture, service-members, veterans, and family members are shown to have adopted a set of ideas, values, roles, and behaviors. Mastering an awareness of those attributes is part of the process of delivering culturally competent care. At WRNMMC and other military treatment facilities, those attributes are “baked in” to the delivery of service—even when that service is provided by civilians. How that process operates is important to understanding the impact of the organization of clinical care.
Methods
Data were extracted from research conducted between 2012 and 2014 that investigated how former patients evaluated their posttreatment lives considering the care received in the MATC at WRNMMC. We used a lightly structured set of interview questions and categories in each interview that focused on 3 themes in the individual’s pathway to injury: education, joining their branch of service, injury experience. The focus was on developing an understanding of how events antecedent to the injury experience could influence the rehabilitation experience and postcare life. The second focus was on the experience of rehabilitation and to learn how the individual navigated community living after leaving care.
Results
Thirty-five participants with lower extremity amputations were recruited who had been discharged from the Amputee Patient Care Program ≥ 12 months prior to the study (Table 1). Participants were interviewed either over the telephone, or when possible, in person. Interviews were based on a lightly structured schedule designed to elicit accounts of community integration, which attended to reports of belongingness supported by accounts of social engagement in work, school, family, and social events. Interviews were analyzed using a modified content analysis approach. The study did not rely on a structured interview, but as is the case with many qualitative and ethnographic interviews, each session shared themes in common, such as questions about injury experience, rehabilitation experience, life after care (work, school, relationships), and so forth. Interviews were conducted by the lead author who was a medical anthropologist with training in health services research.
Participants generally described their post-care lives as “successful” that had been built on “good outcomes.” We left these concepts loosely defined to grant participants latitude in developing their own definitions for these ideas. That said, there is reason to view participants' lives as meeting specific criteria of success (Table 2). For example:
- 16 participants attended higher education postrehabilitation;
- 18 participants were working, or had worked, at the time of the interview;
- There was overlap between these groups and the total that had worked or attended school was 33 of 35; and
- 2 participants who had neither worked nor attended school were still recovering from injury complications at the time of the interview.
Family and relationships were other areas of success (Table 3). Twenty-three participants were currently in long-term relationships, including a mix of marriage and cohabitation households, while 3 were recently divorced and 2 were divorced for a longer term. Of the 5 participants who had been divorced, 3 were interested in pursuing new relationships. All 5 of these participants had children and were actively involved in their lives. Seven participants were not in relationships. Two participants did not have or seek relationships because of complications associated with their ongoing recovery.
Whether considering the claims of participants, or how the literature conceptualizes successful community living, the evidence of success is supported by the accounts of work, school, and relationships. The attribution of these successes, in part, to the MATC rehabilitation program is important to understand because of the implications that this has on program value. Three features of the program continually emerged in interviews: recovering alongside peers, routine access to the entire treatment team, and ongoing relationships with key health care providers (HCPs).
Working Alongside Peers
Peers are an important element in how former patients remember their time in the rehabilitation program at WRNMMC. One benefit of recovering alongside peers is that it changes patients’ experiences of time. Being with other military patients creates a transitional time that participants said they valued as they shifted from the immediacy of their deployment experiences to the longer term demands of recovery and community reintegration.9 Additionally, sharing the clinical space with patients who had come before allowed participants to visualize a living timeline of their proposed recovery.
For most former patients, remembering the social intensity of their rehabilitation program is an important element in their narratives of recovery. The participants in our study do not necessarily maintain ties with their former peers, but nearly all of them point to support from other patients as being key in their own recovery from both the physical and psychological consequences of their injury.
Routine Access to the Treatment Team
The weekly amputee clinics that put surgeons, physicians, occupational and physical therapists, social workers, and prosthetists in a room with each patient worked to alleviate stress and anxiety in participants’ minds around the complexities of their injuries and care. One of the benefits of a group meeting is that it reduces the risk of miscommunication among HCPs and between HCPs and patients.7,10
These weekly sessions with HCPs and patients led to a second advantage; they promoted patient autonomy and participation in clinical decisions. Patients were able to negotiate clinical goals with their HCPs and then act on them almost immediately. In addition, patients with complex physical injuries, often with neurological or psychiatric comorbidities, were able to describe the full range of their challenges, and HCPs had an opportunity to check in with patients about the problems they faced and level of severity.
The ability to marshal clinical HCPs to attend weekly meetings of this nature with patients may be key for distinguishing military health care from VHA and civilian counterparts. More research on how clinical team/ patient meetings occur in other settings is needed. But one of the hallmark features of these clinic meetings at WRNMMC was their open-endedness. Patients typically were not bound by 15 minute or other temporally delimited meeting intervals. This research indicates that in military health care, the patient is the leader.
Continuity of Care
Continuity of care is a well-understood benefit to working with the same HCP. There were additional unanticipated benefits to assigning patients to HCPs with whom they had worked. The long-term period of care (5-24 months) gave patients the opportunity to develop multifaceted relationships with their HCPs and empowered them to advocate and negotiate for their outcome goals. In addition, the majority of frontline HCPs in physical and occupational therapy were civil ians (all prosthetic providers were civilians). These ongoing relationships had the impact of socializing clinicians into the expectations of military culture (around physical training, endurance and resilience, and disregard of pain).
Physical and occupational therapists occupied multiple roles for their patients, including being teachers, coaches, and sounding boards. Participants frequently described the way that their physical or occupational therapist could, on one hand, push them to achieve more in terms of physical functioning. But on the other hand, participants also talked about the emotional and psychological support they could receive based both on the long duration of their work with their care providers.
Conclusions
The ability to recover alongside peers, have access to the whole treatment team and develop long-term relationships with key care HCPs served as drivers for positive recovery. The impact of these 3 drivers of the social organization of the Amputee Patient Care Program represent an opportunity to highlight the role that the social context of military health care to use in achieving positive therapeutic outcomes. Former patients of the WRNMMC program could rely on a familiar and dependable social context for their care. This social context draws heavily on elements of military culture that structure the preinjury worlds of work and life that patients occupied. Based on these results we argue that the presence of rehabilitation and other clinical units in military medical settings offers an important value to patients and HCPs.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Center for Rehabilitation Science Research, Department of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, MD (awards HU0001-11-1-0004 and HU0001-15-2-0003).
1. Grimm PD, Mauntel TC, Potter BK. Combat and noncombat musculoskeletal injuries in the US military. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2019;27(3):84-91. doi:10.1097/JSA.0000000000000246
2. Gajewski D, Granville R. The United States Armed Forces Amputee Patient Care Program. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2006;14(10 Spec No.):S183-S187. doi:10.5435/00124635-200600001-00040
3. Messinger S, Bozorghadad S, Pasquina P. Social relationships in rehabilitation and their impact on positive outcomes among amputees with lower limb loss at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center. J Rehabil Med. 2018;50(1):86-93. doi:10.2340/16501977-2274
4. Meyer EG. The importance of understanding military culture. Acad Psychiatry. 2015;39(4):416-418. doi:10.1007/s40596-015-0285-1
5. Reger MA, Etherage JR, Reger GM, Gahm GA. Civilian psychologists in an army culture: the ethical challenge of cultural competence. Mil Psychol. 2008;20(1):21-35. doi:10.1080/08995600701753144
6. Convoy S, Westphal RJ. The importance of developing military cultural competence. J Emerg Nurs. 2013;39(6):591-594. doi:10.1016/j.jen.2013.08.010
7. Campinha-Bacote J. The process of cultural competence in the delivery of healthcare services: a model of care. J Transcult Nurs. 2002;13(3):181-201. doi:10.1177/10459602013003003
8. Meyer EG, Hall-Clark BN, Hamaoka D, Peterson AL. Assessment of military cultural competence: a pilot study. Acad Psychiatry. 2015;39(4):382-388. doi:10.1007/s40596-015-0328-7
9. Messinger SD. Rehabilitating time: multiple temporalities among military clinicians and patients. Med Anthropol. 2010;29(2):150-169. doi:10.1080/01459741003715383
10. Williams MV, Davis T, Parker RM, Weiss BD. The role of health literacy in patient-physician communication. Fam Med. 2002;34(5):383-389.
Since 2001, nearly 2,000 US military service members have sustained traumatically acquired limb loss while serving in conflict zones primarily in Afghanistan and Iraq.1 Although most of these patients receive acute and long-term care in a military health facility, polytrauma programs within the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) treat other military patients with traumatic injuries while others receive specialized care in civilian medical programs. The Military Advanced Training Center (MATC) at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center (WRNMMC) provides a comprehensive rehabilitation program for patients with acquired traumatic limb loss.2
In this paper, we argue that receiving long-term care in military settings provides unique value for military patients because of the background therapeutic work such settings can provide. Currently, there are policy discussions that center on consolidating military health care under the oversight of the Defense Health Agency. This approach would develop a more centralized administration while also pursuing other measures to improve efficiency. When evaluating the current system, one key question remains: Would military service members and dependents seeking specific care or long-term rehabilitation programs be more effectively treated in nonmilitary settings?
Based on qualitative research, we argue that keeping a diverse range of military health programs has a positive and therapeutic impact. We also argue that the emergent literature about the importance of military culture to patients and the need for military cultural competence training for nonmilitary clinicians coupled with the results of a qualitative study of former patients at WRNMMC demonstrate that the social context at military treatment facilities offers a positive therapeutic impact.3
Program Description
This article is grounded in research conducted in the US Armed Forces Amputee Patient Care Program at WRNMMC. The study received WRNMMC Institutional Review Board approval in February 2012 and again for the continuation study in January 2015. The lead investigator for the research project was a medical anthropologist who worked with a research unit in the WRNMMC Department of Rehabilitation.
The main period of data collection occurred in 2 waves, the first between 2012 and 2014 and the second between 2015 and 2019. Patients arrived at WRNMMC within several days from the site of their injuries (nearly all were from Iraq and Afghanistan) via military medical facilities in Germany. After a period of recovery from the acute phase of their injuries, patients transitioned to outpatient housing and began their longer phase of care in the outpatient MATC.
On MATC admission, patients were assigned an occupational therapist, physical therapist, and prosthetist. In addition, rehabilitation physicians and orthopedic surgeons oversaw patient care. Social work and other programs provided additional services as needed.2 Patients were treated primarily for their orthopedic and extremity trauma and for neuropsychiatric injuries, such as mild traumatic brain injury. Other behavioral health services were available to support patients who reported symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, anxiety, depression, or other neuropsychological issues.
Patients had multiple daily appointments that shifted throughout the duration of their care. Initially a patient might have 2 physical therapy and 2 occupational therapy appointments daily, with each session lasting about an hour. Appointments with the orthotics and prosthetics service, which could be considerably longer were added as needed. These appointments required multiple castings, fittings, adjustments, and other activities. This also was the case with wound care, behavioral health, and other services and departments.
Cultural Competency
A recently published special issue of Academic Psychiatry described the important role that basic knowledge of military culture plays in effective care delivery to active-duty service members, guard and reserve, and veteran patients and families.4 Reger and colleagues also emphasized the importance of awareness of military culture to civilian clinicians particularly those providing care to service members.5
This concern with gaps in knowledge about recognizing the realities of military culture has given rise to an emergent literature on military cultural competence training for clinical providers.6 Cultural competence in health care settings is understood to be the practice of providing care within a social framework that acknowledges the social and cultural background of patients.7 In the military context, as in others, these discussions often are limited to behavioral health settings.8 This emergent literature provides researchers with important insights into understanding the scope and scale of military culture and the importance of delivering culturally competent care.
Beyond the concept of cultural competence, recognizing the importance of culture can be used to understand positive therapeutic impacts. In discussions of culture, service-members, veterans, and family members are shown to have adopted a set of ideas, values, roles, and behaviors. Mastering an awareness of those attributes is part of the process of delivering culturally competent care. At WRNMMC and other military treatment facilities, those attributes are “baked in” to the delivery of service—even when that service is provided by civilians. How that process operates is important to understanding the impact of the organization of clinical care.
Methods
Data were extracted from research conducted between 2012 and 2014 that investigated how former patients evaluated their posttreatment lives considering the care received in the MATC at WRNMMC. We used a lightly structured set of interview questions and categories in each interview that focused on 3 themes in the individual’s pathway to injury: education, joining their branch of service, injury experience. The focus was on developing an understanding of how events antecedent to the injury experience could influence the rehabilitation experience and postcare life. The second focus was on the experience of rehabilitation and to learn how the individual navigated community living after leaving care.
Results
Thirty-five participants with lower extremity amputations were recruited who had been discharged from the Amputee Patient Care Program ≥ 12 months prior to the study (Table 1). Participants were interviewed either over the telephone, or when possible, in person. Interviews were based on a lightly structured schedule designed to elicit accounts of community integration, which attended to reports of belongingness supported by accounts of social engagement in work, school, family, and social events. Interviews were analyzed using a modified content analysis approach. The study did not rely on a structured interview, but as is the case with many qualitative and ethnographic interviews, each session shared themes in common, such as questions about injury experience, rehabilitation experience, life after care (work, school, relationships), and so forth. Interviews were conducted by the lead author who was a medical anthropologist with training in health services research.
Participants generally described their post-care lives as “successful” that had been built on “good outcomes.” We left these concepts loosely defined to grant participants latitude in developing their own definitions for these ideas. That said, there is reason to view participants' lives as meeting specific criteria of success (Table 2). For example:
- 16 participants attended higher education postrehabilitation;
- 18 participants were working, or had worked, at the time of the interview;
- There was overlap between these groups and the total that had worked or attended school was 33 of 35; and
- 2 participants who had neither worked nor attended school were still recovering from injury complications at the time of the interview.
Family and relationships were other areas of success (Table 3). Twenty-three participants were currently in long-term relationships, including a mix of marriage and cohabitation households, while 3 were recently divorced and 2 were divorced for a longer term. Of the 5 participants who had been divorced, 3 were interested in pursuing new relationships. All 5 of these participants had children and were actively involved in their lives. Seven participants were not in relationships. Two participants did not have or seek relationships because of complications associated with their ongoing recovery.
Whether considering the claims of participants, or how the literature conceptualizes successful community living, the evidence of success is supported by the accounts of work, school, and relationships. The attribution of these successes, in part, to the MATC rehabilitation program is important to understand because of the implications that this has on program value. Three features of the program continually emerged in interviews: recovering alongside peers, routine access to the entire treatment team, and ongoing relationships with key health care providers (HCPs).
Working Alongside Peers
Peers are an important element in how former patients remember their time in the rehabilitation program at WRNMMC. One benefit of recovering alongside peers is that it changes patients’ experiences of time. Being with other military patients creates a transitional time that participants said they valued as they shifted from the immediacy of their deployment experiences to the longer term demands of recovery and community reintegration.9 Additionally, sharing the clinical space with patients who had come before allowed participants to visualize a living timeline of their proposed recovery.
For most former patients, remembering the social intensity of their rehabilitation program is an important element in their narratives of recovery. The participants in our study do not necessarily maintain ties with their former peers, but nearly all of them point to support from other patients as being key in their own recovery from both the physical and psychological consequences of their injury.
Routine Access to the Treatment Team
The weekly amputee clinics that put surgeons, physicians, occupational and physical therapists, social workers, and prosthetists in a room with each patient worked to alleviate stress and anxiety in participants’ minds around the complexities of their injuries and care. One of the benefits of a group meeting is that it reduces the risk of miscommunication among HCPs and between HCPs and patients.7,10
These weekly sessions with HCPs and patients led to a second advantage; they promoted patient autonomy and participation in clinical decisions. Patients were able to negotiate clinical goals with their HCPs and then act on them almost immediately. In addition, patients with complex physical injuries, often with neurological or psychiatric comorbidities, were able to describe the full range of their challenges, and HCPs had an opportunity to check in with patients about the problems they faced and level of severity.
The ability to marshal clinical HCPs to attend weekly meetings of this nature with patients may be key for distinguishing military health care from VHA and civilian counterparts. More research on how clinical team/ patient meetings occur in other settings is needed. But one of the hallmark features of these clinic meetings at WRNMMC was their open-endedness. Patients typically were not bound by 15 minute or other temporally delimited meeting intervals. This research indicates that in military health care, the patient is the leader.
Continuity of Care
Continuity of care is a well-understood benefit to working with the same HCP. There were additional unanticipated benefits to assigning patients to HCPs with whom they had worked. The long-term period of care (5-24 months) gave patients the opportunity to develop multifaceted relationships with their HCPs and empowered them to advocate and negotiate for their outcome goals. In addition, the majority of frontline HCPs in physical and occupational therapy were civil ians (all prosthetic providers were civilians). These ongoing relationships had the impact of socializing clinicians into the expectations of military culture (around physical training, endurance and resilience, and disregard of pain).
Physical and occupational therapists occupied multiple roles for their patients, including being teachers, coaches, and sounding boards. Participants frequently described the way that their physical or occupational therapist could, on one hand, push them to achieve more in terms of physical functioning. But on the other hand, participants also talked about the emotional and psychological support they could receive based both on the long duration of their work with their care providers.
Conclusions
The ability to recover alongside peers, have access to the whole treatment team and develop long-term relationships with key care HCPs served as drivers for positive recovery. The impact of these 3 drivers of the social organization of the Amputee Patient Care Program represent an opportunity to highlight the role that the social context of military health care to use in achieving positive therapeutic outcomes. Former patients of the WRNMMC program could rely on a familiar and dependable social context for their care. This social context draws heavily on elements of military culture that structure the preinjury worlds of work and life that patients occupied. Based on these results we argue that the presence of rehabilitation and other clinical units in military medical settings offers an important value to patients and HCPs.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Center for Rehabilitation Science Research, Department of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, MD (awards HU0001-11-1-0004 and HU0001-15-2-0003).
Since 2001, nearly 2,000 US military service members have sustained traumatically acquired limb loss while serving in conflict zones primarily in Afghanistan and Iraq.1 Although most of these patients receive acute and long-term care in a military health facility, polytrauma programs within the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) treat other military patients with traumatic injuries while others receive specialized care in civilian medical programs. The Military Advanced Training Center (MATC) at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center (WRNMMC) provides a comprehensive rehabilitation program for patients with acquired traumatic limb loss.2
In this paper, we argue that receiving long-term care in military settings provides unique value for military patients because of the background therapeutic work such settings can provide. Currently, there are policy discussions that center on consolidating military health care under the oversight of the Defense Health Agency. This approach would develop a more centralized administration while also pursuing other measures to improve efficiency. When evaluating the current system, one key question remains: Would military service members and dependents seeking specific care or long-term rehabilitation programs be more effectively treated in nonmilitary settings?
Based on qualitative research, we argue that keeping a diverse range of military health programs has a positive and therapeutic impact. We also argue that the emergent literature about the importance of military culture to patients and the need for military cultural competence training for nonmilitary clinicians coupled with the results of a qualitative study of former patients at WRNMMC demonstrate that the social context at military treatment facilities offers a positive therapeutic impact.3
Program Description
This article is grounded in research conducted in the US Armed Forces Amputee Patient Care Program at WRNMMC. The study received WRNMMC Institutional Review Board approval in February 2012 and again for the continuation study in January 2015. The lead investigator for the research project was a medical anthropologist who worked with a research unit in the WRNMMC Department of Rehabilitation.
The main period of data collection occurred in 2 waves, the first between 2012 and 2014 and the second between 2015 and 2019. Patients arrived at WRNMMC within several days from the site of their injuries (nearly all were from Iraq and Afghanistan) via military medical facilities in Germany. After a period of recovery from the acute phase of their injuries, patients transitioned to outpatient housing and began their longer phase of care in the outpatient MATC.
On MATC admission, patients were assigned an occupational therapist, physical therapist, and prosthetist. In addition, rehabilitation physicians and orthopedic surgeons oversaw patient care. Social work and other programs provided additional services as needed.2 Patients were treated primarily for their orthopedic and extremity trauma and for neuropsychiatric injuries, such as mild traumatic brain injury. Other behavioral health services were available to support patients who reported symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, anxiety, depression, or other neuropsychological issues.
Patients had multiple daily appointments that shifted throughout the duration of their care. Initially a patient might have 2 physical therapy and 2 occupational therapy appointments daily, with each session lasting about an hour. Appointments with the orthotics and prosthetics service, which could be considerably longer were added as needed. These appointments required multiple castings, fittings, adjustments, and other activities. This also was the case with wound care, behavioral health, and other services and departments.
Cultural Competency
A recently published special issue of Academic Psychiatry described the important role that basic knowledge of military culture plays in effective care delivery to active-duty service members, guard and reserve, and veteran patients and families.4 Reger and colleagues also emphasized the importance of awareness of military culture to civilian clinicians particularly those providing care to service members.5
This concern with gaps in knowledge about recognizing the realities of military culture has given rise to an emergent literature on military cultural competence training for clinical providers.6 Cultural competence in health care settings is understood to be the practice of providing care within a social framework that acknowledges the social and cultural background of patients.7 In the military context, as in others, these discussions often are limited to behavioral health settings.8 This emergent literature provides researchers with important insights into understanding the scope and scale of military culture and the importance of delivering culturally competent care.
Beyond the concept of cultural competence, recognizing the importance of culture can be used to understand positive therapeutic impacts. In discussions of culture, service-members, veterans, and family members are shown to have adopted a set of ideas, values, roles, and behaviors. Mastering an awareness of those attributes is part of the process of delivering culturally competent care. At WRNMMC and other military treatment facilities, those attributes are “baked in” to the delivery of service—even when that service is provided by civilians. How that process operates is important to understanding the impact of the organization of clinical care.
Methods
Data were extracted from research conducted between 2012 and 2014 that investigated how former patients evaluated their posttreatment lives considering the care received in the MATC at WRNMMC. We used a lightly structured set of interview questions and categories in each interview that focused on 3 themes in the individual’s pathway to injury: education, joining their branch of service, injury experience. The focus was on developing an understanding of how events antecedent to the injury experience could influence the rehabilitation experience and postcare life. The second focus was on the experience of rehabilitation and to learn how the individual navigated community living after leaving care.
Results
Thirty-five participants with lower extremity amputations were recruited who had been discharged from the Amputee Patient Care Program ≥ 12 months prior to the study (Table 1). Participants were interviewed either over the telephone, or when possible, in person. Interviews were based on a lightly structured schedule designed to elicit accounts of community integration, which attended to reports of belongingness supported by accounts of social engagement in work, school, family, and social events. Interviews were analyzed using a modified content analysis approach. The study did not rely on a structured interview, but as is the case with many qualitative and ethnographic interviews, each session shared themes in common, such as questions about injury experience, rehabilitation experience, life after care (work, school, relationships), and so forth. Interviews were conducted by the lead author who was a medical anthropologist with training in health services research.
Participants generally described their post-care lives as “successful” that had been built on “good outcomes.” We left these concepts loosely defined to grant participants latitude in developing their own definitions for these ideas. That said, there is reason to view participants' lives as meeting specific criteria of success (Table 2). For example:
- 16 participants attended higher education postrehabilitation;
- 18 participants were working, or had worked, at the time of the interview;
- There was overlap between these groups and the total that had worked or attended school was 33 of 35; and
- 2 participants who had neither worked nor attended school were still recovering from injury complications at the time of the interview.
Family and relationships were other areas of success (Table 3). Twenty-three participants were currently in long-term relationships, including a mix of marriage and cohabitation households, while 3 were recently divorced and 2 were divorced for a longer term. Of the 5 participants who had been divorced, 3 were interested in pursuing new relationships. All 5 of these participants had children and were actively involved in their lives. Seven participants were not in relationships. Two participants did not have or seek relationships because of complications associated with their ongoing recovery.
Whether considering the claims of participants, or how the literature conceptualizes successful community living, the evidence of success is supported by the accounts of work, school, and relationships. The attribution of these successes, in part, to the MATC rehabilitation program is important to understand because of the implications that this has on program value. Three features of the program continually emerged in interviews: recovering alongside peers, routine access to the entire treatment team, and ongoing relationships with key health care providers (HCPs).
Working Alongside Peers
Peers are an important element in how former patients remember their time in the rehabilitation program at WRNMMC. One benefit of recovering alongside peers is that it changes patients’ experiences of time. Being with other military patients creates a transitional time that participants said they valued as they shifted from the immediacy of their deployment experiences to the longer term demands of recovery and community reintegration.9 Additionally, sharing the clinical space with patients who had come before allowed participants to visualize a living timeline of their proposed recovery.
For most former patients, remembering the social intensity of their rehabilitation program is an important element in their narratives of recovery. The participants in our study do not necessarily maintain ties with their former peers, but nearly all of them point to support from other patients as being key in their own recovery from both the physical and psychological consequences of their injury.
Routine Access to the Treatment Team
The weekly amputee clinics that put surgeons, physicians, occupational and physical therapists, social workers, and prosthetists in a room with each patient worked to alleviate stress and anxiety in participants’ minds around the complexities of their injuries and care. One of the benefits of a group meeting is that it reduces the risk of miscommunication among HCPs and between HCPs and patients.7,10
These weekly sessions with HCPs and patients led to a second advantage; they promoted patient autonomy and participation in clinical decisions. Patients were able to negotiate clinical goals with their HCPs and then act on them almost immediately. In addition, patients with complex physical injuries, often with neurological or psychiatric comorbidities, were able to describe the full range of their challenges, and HCPs had an opportunity to check in with patients about the problems they faced and level of severity.
The ability to marshal clinical HCPs to attend weekly meetings of this nature with patients may be key for distinguishing military health care from VHA and civilian counterparts. More research on how clinical team/ patient meetings occur in other settings is needed. But one of the hallmark features of these clinic meetings at WRNMMC was their open-endedness. Patients typically were not bound by 15 minute or other temporally delimited meeting intervals. This research indicates that in military health care, the patient is the leader.
Continuity of Care
Continuity of care is a well-understood benefit to working with the same HCP. There were additional unanticipated benefits to assigning patients to HCPs with whom they had worked. The long-term period of care (5-24 months) gave patients the opportunity to develop multifaceted relationships with their HCPs and empowered them to advocate and negotiate for their outcome goals. In addition, the majority of frontline HCPs in physical and occupational therapy were civil ians (all prosthetic providers were civilians). These ongoing relationships had the impact of socializing clinicians into the expectations of military culture (around physical training, endurance and resilience, and disregard of pain).
Physical and occupational therapists occupied multiple roles for their patients, including being teachers, coaches, and sounding boards. Participants frequently described the way that their physical or occupational therapist could, on one hand, push them to achieve more in terms of physical functioning. But on the other hand, participants also talked about the emotional and psychological support they could receive based both on the long duration of their work with their care providers.
Conclusions
The ability to recover alongside peers, have access to the whole treatment team and develop long-term relationships with key care HCPs served as drivers for positive recovery. The impact of these 3 drivers of the social organization of the Amputee Patient Care Program represent an opportunity to highlight the role that the social context of military health care to use in achieving positive therapeutic outcomes. Former patients of the WRNMMC program could rely on a familiar and dependable social context for their care. This social context draws heavily on elements of military culture that structure the preinjury worlds of work and life that patients occupied. Based on these results we argue that the presence of rehabilitation and other clinical units in military medical settings offers an important value to patients and HCPs.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Center for Rehabilitation Science Research, Department of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, MD (awards HU0001-11-1-0004 and HU0001-15-2-0003).
1. Grimm PD, Mauntel TC, Potter BK. Combat and noncombat musculoskeletal injuries in the US military. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2019;27(3):84-91. doi:10.1097/JSA.0000000000000246
2. Gajewski D, Granville R. The United States Armed Forces Amputee Patient Care Program. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2006;14(10 Spec No.):S183-S187. doi:10.5435/00124635-200600001-00040
3. Messinger S, Bozorghadad S, Pasquina P. Social relationships in rehabilitation and their impact on positive outcomes among amputees with lower limb loss at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center. J Rehabil Med. 2018;50(1):86-93. doi:10.2340/16501977-2274
4. Meyer EG. The importance of understanding military culture. Acad Psychiatry. 2015;39(4):416-418. doi:10.1007/s40596-015-0285-1
5. Reger MA, Etherage JR, Reger GM, Gahm GA. Civilian psychologists in an army culture: the ethical challenge of cultural competence. Mil Psychol. 2008;20(1):21-35. doi:10.1080/08995600701753144
6. Convoy S, Westphal RJ. The importance of developing military cultural competence. J Emerg Nurs. 2013;39(6):591-594. doi:10.1016/j.jen.2013.08.010
7. Campinha-Bacote J. The process of cultural competence in the delivery of healthcare services: a model of care. J Transcult Nurs. 2002;13(3):181-201. doi:10.1177/10459602013003003
8. Meyer EG, Hall-Clark BN, Hamaoka D, Peterson AL. Assessment of military cultural competence: a pilot study. Acad Psychiatry. 2015;39(4):382-388. doi:10.1007/s40596-015-0328-7
9. Messinger SD. Rehabilitating time: multiple temporalities among military clinicians and patients. Med Anthropol. 2010;29(2):150-169. doi:10.1080/01459741003715383
10. Williams MV, Davis T, Parker RM, Weiss BD. The role of health literacy in patient-physician communication. Fam Med. 2002;34(5):383-389.
1. Grimm PD, Mauntel TC, Potter BK. Combat and noncombat musculoskeletal injuries in the US military. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2019;27(3):84-91. doi:10.1097/JSA.0000000000000246
2. Gajewski D, Granville R. The United States Armed Forces Amputee Patient Care Program. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2006;14(10 Spec No.):S183-S187. doi:10.5435/00124635-200600001-00040
3. Messinger S, Bozorghadad S, Pasquina P. Social relationships in rehabilitation and their impact on positive outcomes among amputees with lower limb loss at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center. J Rehabil Med. 2018;50(1):86-93. doi:10.2340/16501977-2274
4. Meyer EG. The importance of understanding military culture. Acad Psychiatry. 2015;39(4):416-418. doi:10.1007/s40596-015-0285-1
5. Reger MA, Etherage JR, Reger GM, Gahm GA. Civilian psychologists in an army culture: the ethical challenge of cultural competence. Mil Psychol. 2008;20(1):21-35. doi:10.1080/08995600701753144
6. Convoy S, Westphal RJ. The importance of developing military cultural competence. J Emerg Nurs. 2013;39(6):591-594. doi:10.1016/j.jen.2013.08.010
7. Campinha-Bacote J. The process of cultural competence in the delivery of healthcare services: a model of care. J Transcult Nurs. 2002;13(3):181-201. doi:10.1177/10459602013003003
8. Meyer EG, Hall-Clark BN, Hamaoka D, Peterson AL. Assessment of military cultural competence: a pilot study. Acad Psychiatry. 2015;39(4):382-388. doi:10.1007/s40596-015-0328-7
9. Messinger SD. Rehabilitating time: multiple temporalities among military clinicians and patients. Med Anthropol. 2010;29(2):150-169. doi:10.1080/01459741003715383
10. Williams MV, Davis T, Parker RM, Weiss BD. The role of health literacy in patient-physician communication. Fam Med. 2002;34(5):383-389.
Perception of Executive Order on Medicare Pay for Advanced Practice Providers: A Study of Comments From Medical Professionals
The ability of advanced practice providers (APPs) to practice independently has been a recent topic of discussion among both the medical community and legislatures. Advanced practice provider is an umbrella term that includes physician assistants (PAs) and advanced practice registered nurses, including nurse practitioners (NPs), clinical nurse specialists, certified nurse-midwives, and certified registered nurse anesthetists. Since Congress passed the Balanced Budget Act of 1997, APPs can bill and be paid independently if they are not practicing incident to a physician or in a facility.1 Currently, NPs can practice independently in 27 states and Washington, DC. Physician assistants are required to practice under the supervision of a physician; however, the extent of supervision varies by state.2 Advocates for broadening the scope of practice for APPs argue that NPs and PAs will help to fill the physician deficit, particularly in primary care and rural regions. It has been projected that by 2025, the United States will require an additional 46,000 primary care providers to meet growing medical needs.3
On October 3, 2019, President Donald Trump issued the Executive Order on Protecting and Improving Medicare for Our Nation’s Seniors, in which he proposed an alternative to “Medicare for all.”4 This order instructed the Secretary of Health and Human Services to prepare a regulation that would “eliminate burdensome regulatory billing requirements, conditions of participation, supervision requirements, benefit definitions and all other licensure requirements . . . that are more stringent than applicable Federal or State laws require and that limit professionals from practicing at the top of their field.” Furthermore, President Trump proposed that “services provided by clinicians, including physicians, physician assistants, and nurse practitioners, are appropriately reimbursed in accordance with the work performed rather than the clinician’s occupation.”4
In response to the executive order, members of the medical community utilized Reddit, an online public forum, and Medscape, a medical news website, to vocalize opinions on the executive order.5,6 Our goal was to analyze the characteristics of those who participated in the discussion and their points of view on the plan to broaden the scope of practice and change the Medicare reimbursement plans for APPs.
Methods
All comments on the October 3, 2019, Medscape article, “Trump Executive Order Seeks Proposals on Medicare Pay for NPs, PAs,”5 and the corresponding Reddit discussion on this article6 were reviewed and characterized by the type of commenter—doctor of medicine (MD)/doctor of osteopathic medicine (DO), NP/RN/certified registered nurse anesthetist, PA, medical student, PA student, NP student, pharmacist, dietician, emergency medical technician, scribe, or unknown—as identified in their username, title, or in the text of the comment. Gender of the commenter was recorded when provided. Commenters were further grouped by their support or lack of support for the executive order based on their comments. Patients’ comments underwent further qualitative analysis to identify general themes.
All analyses were conducted with RStudio statistical software. Analyses were reported as proportions. Variables were compared by χ2 and Fisher exact tests. Odds ratios with 95% CIs were calculated. P<.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
A total of 352 comments (130 on Medscape and 222 on Reddit) posted by 155 unique users (57 on Medscape and 98 on Reddit) were included in the analysis (Table 1). Of the 51 Medscape commenters who identified a gender, 60.7% were male and 39.2% were female. Reddit commenters did not identify a gender. Commenters included MD and DO physicians (43.2%), NPs/RNs/certified registered nurse anesthetists (13.5%), medical students (11.0%), PAs (9.7%), pharmacists (3.2%), NP students (1.9%), PA students (1.3%), emergency medical technicians (1.3%), dieticians (0.6%), and scribes (0.6%). Physicians (54.5% vs 36.73%; P=.032) and NPs (22.8% vs 8.2%; P=.009) made up a larger percentage of all comments on Medscape compared to Reddit, where medical students were more prevalent (16.3% vs 1.8%; P=.005). Nursing students and PA students more commonly posted on Reddit (4.08% of Reddit commenters vs 1.75% of Medscape commenters), though this difference did not achieve statistical significance.
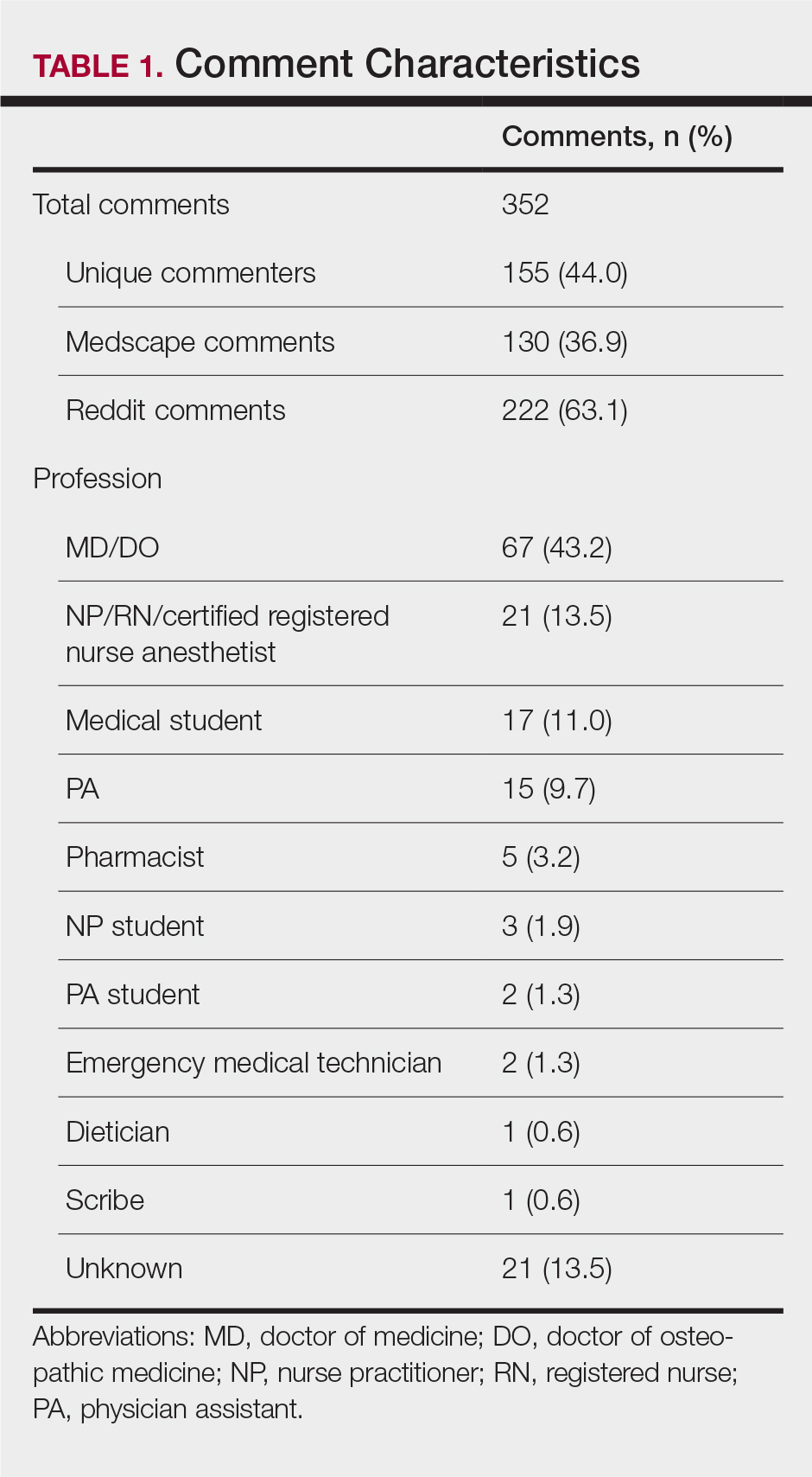
A majority of commenters did not support the executive order, with only 20.6% approving of the plan, 54.8% disapproving, and 24.5% remaining neutral (Figure). Advanced practice providers—NPs, PAs, NP/PA students, and APPs not otherwise specified—were more likely to support the executive order, with 52.3% voicing their support compared to only 4.8% of physicians and medical students expressing support (P<.0001). Similarly, physicians and medical students were more likely to disapprove of the order, with 75.0% voicing concerns compared to only 27.3% of APPs dissenting (P<.0001). A similar percentage of both physicians/medical students and APPs remained neutral (20.2% vs 18.2%). Commenters on Medscape were more likely to voice support for the executive order than those on Reddit (36.8% vs 11.2%; P=.0002), likely due to the higher percentage of NP and PA comments on the former.
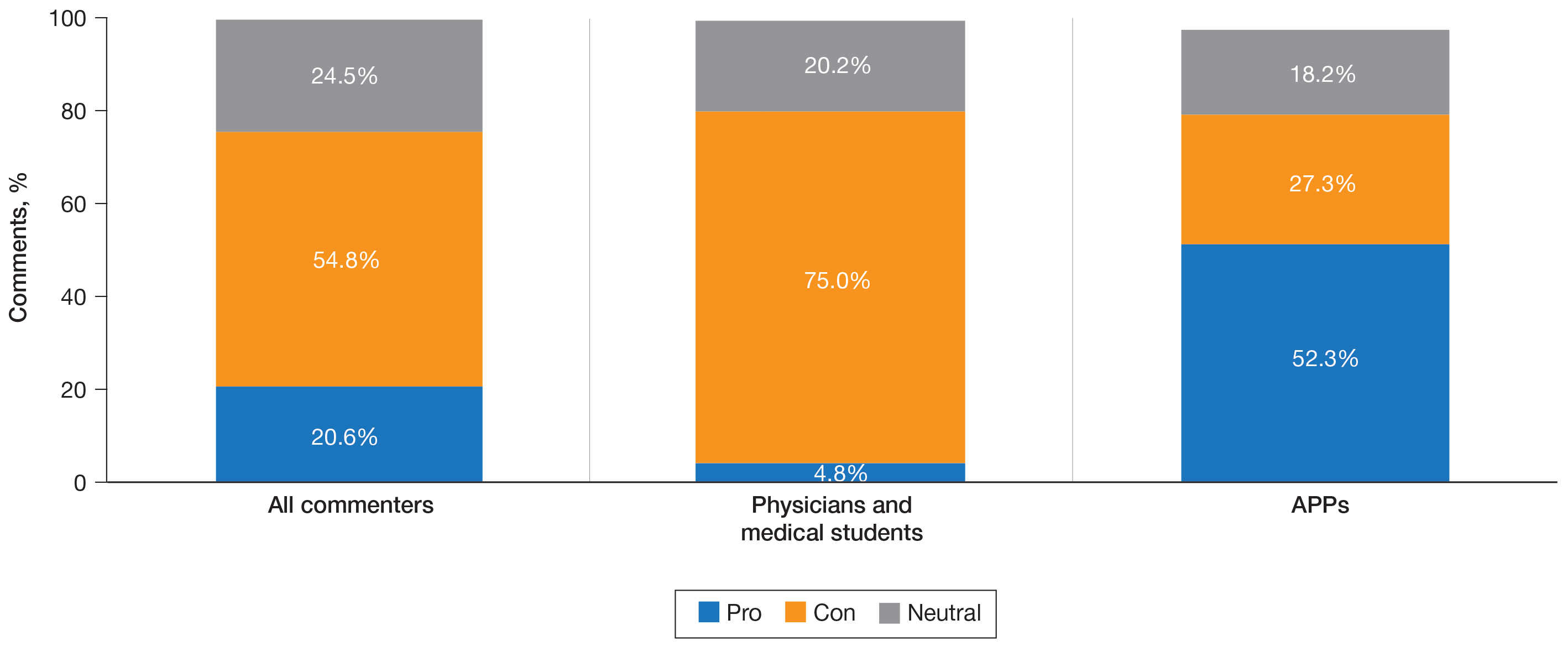
Overall, the most commonly discussed topic was provider reimbursement (22.6% of all comments)(Table 2). Physicians and medical students were more likely to discuss physician expertise compared to APPs (32.1% vs 4.5%; P<.001). They also were more likely to raise concerns that the executive order would discourage future generations of physicians from pursuing medicine (15.5% vs 0%; P=.01). Advanced practice providers were more likely than physicians/medical students to comment on the breadth of NP and/or PA training (38.6% vs 19.0%; P=.02). The eTable shows representative comments for each theme encountered.
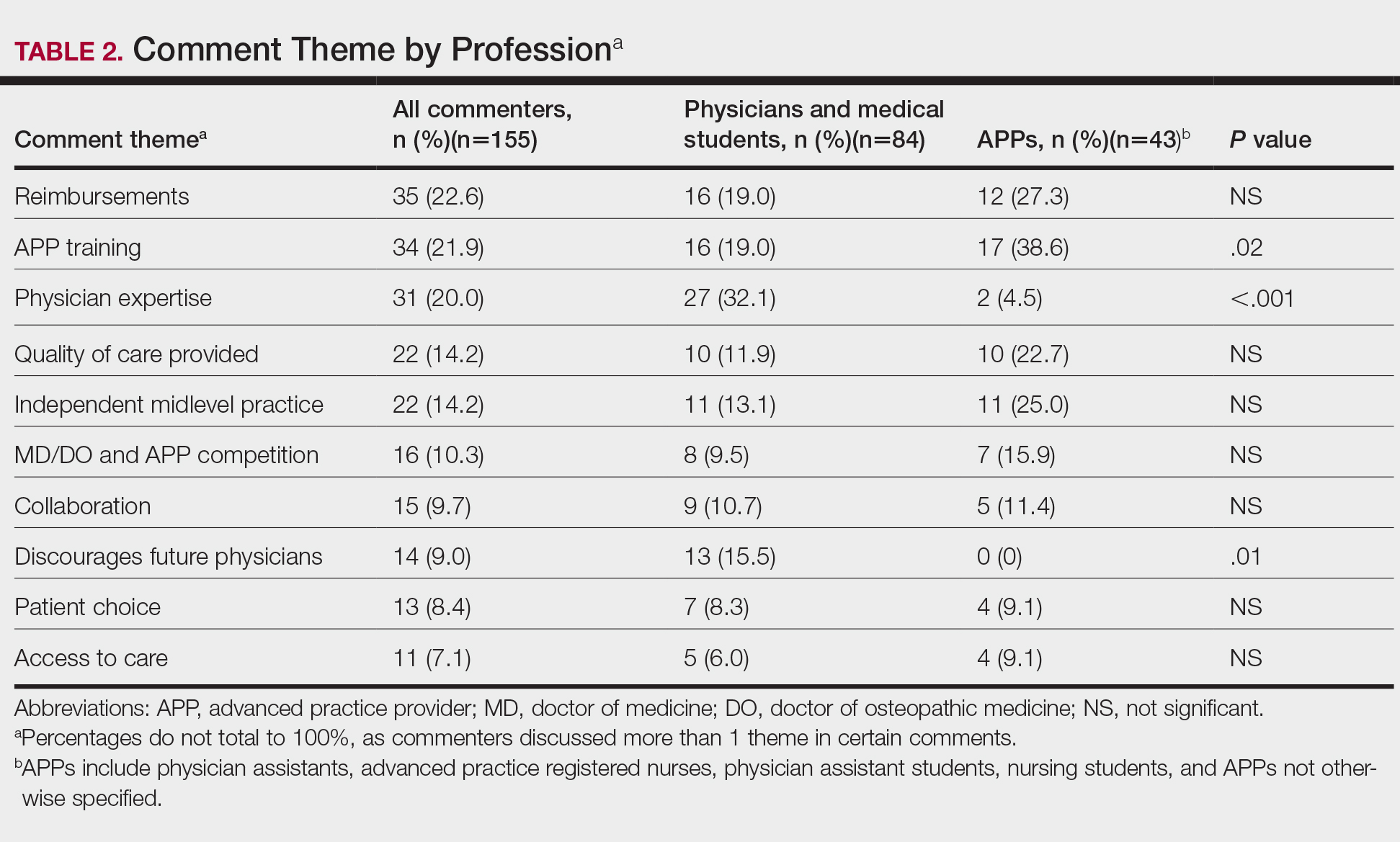
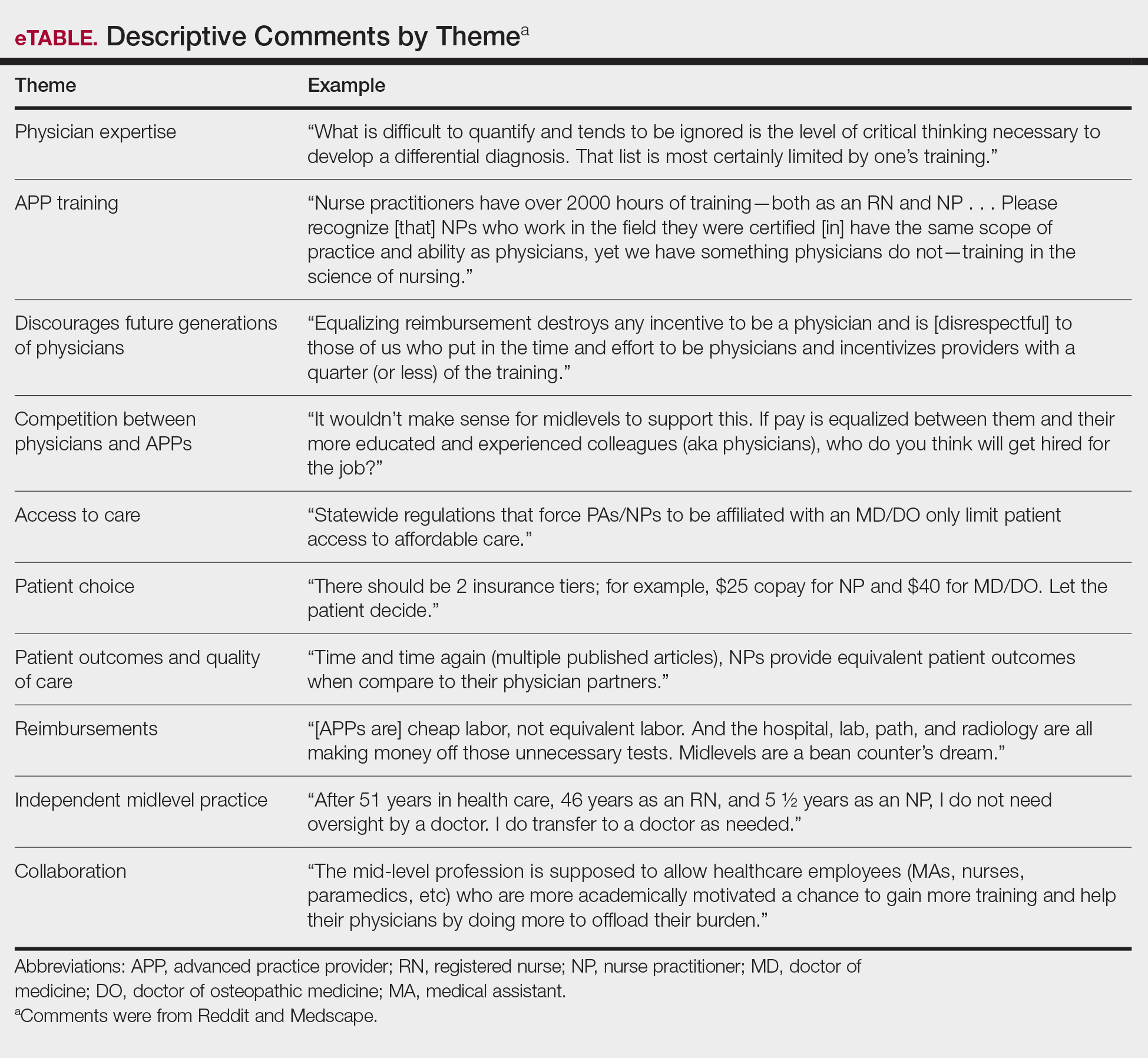
A subgroup analysis of the comments written by physicians supporting the executive order (n=4) and APPs disapproving of the order (n=12) was performed to identify the dissenting opinions. Physicians who supported the order discussed the need for improved pay for equal work (n=3), the competency of NP and PA training (n=2), the ability of a practice to generate more profit from APPs (n=1), and possible benefits of APPs providing primary care while MDs perform more specialized care (n=1). Of the APPs who did not support the order, there were 4 PAs, 2 registered nurses, 2 NPs, 2 NP students, and 2 PA students. The most common themes discussed were the differences in APP education and training (n=6), lack of desire for further responsibilities (n=4), and the adequacy of the current scope of practice (n=3).
Comment
President Trump’s executive order follows a trend of decreasing required oversight of APPs; however, this study indicates that these policies would face pushback from many physicians. These results are consistent with a prior study that analyzed 309 comments on an article in The New York Times made by physicians, APPs, patients, and laypeople, in which 24.7% had mistrust of APPs and 14.9% had concerns over APP supervision compared to 9% who supported APP independent practice.7 It is clear that there is a serious divide in opinion that threatens to harm the existing collaborations between physicians and APPs.
Primary Care Coverage With APPs
In the comments analyzed in our study, supporters of the executive order argued that an increase in APPs practicing independently would provide much-needed primary care coverage to patients in underserved regions. However, APPs are instead well represented across most specialties, with a majority in dermatology. Of the 4 million procedures billed independently by APPs in 2012, 54.8% were in the field of dermatology.8 The employment of APPs by dermatologists has grown from 28% of practices in 2005 to 46% in 2014, making this issue of particular importance to our field.9,10
Education and Training of APPs
In our analysis, many physicians cited concerns about the education and training of APPs. Dermatologists receive approximately 10,000 hours of training over the course of residency. Per the American Academy of Physician Assistants, PAs spend more than 2000 hours over a 26-month period on various clinical rotations, “with an emphasis on primary care.”11 There are multiple routes to become an advanced practice RN with varying classroom and clinical requirements, with one pathway requiring a bachelor of science in nursing, followed by a master’s degree requiring 500 to 700 hours of supervised clinical work. Although the Dermatology Nurses’ Association and Society of Dermatology Physician Assistants (http://www.dermpa.org) provide online modules, annual conventions with training workshops, and short fellowship programs, neither have formal guidelines on minimum requirements to diagnose and treat dermatologic conditions.2 Despite the lack of formalized dermatologic training, APPs billed for 13.4% of all dermatology procedures submitted to Medicare in 2015.12
Quality of Patient Care
In our study, physicians also voiced concern over reduced quality of patient care. In a review of 33,647 skin cancer screening examinations, PAs biopsied an average of 39.4 skin lesions, while dermatologists biopsied an average of 25.4 skin lesions to diagnose 1 case of melanoma.13 In addition, nonphysician providers accounted for 37.9% of defendants in 174 legal cases related to injury from cutaneous laser surgery.14 Before further laws are enacted regarding the independent practice and billing by NPs and PAs in the field of dermatology, further research is needed to address patient outcomes and safety.
Limitations
This study was subject to several limitations. Because of a lack of other sources offering discussions on the topic, our sample size was limited. Self-identification of users presents a challenge, as an individual can pose as a physician or APP without validation of credentials. Although great care was taken to minimize bias, grouping comments into broad categories may misinterpret a poster’s intentions. Furthermore, the data collected represent only a small proportion of the medical community—readers of Medscape and Reddit who have the motivation to create a user profile and post a comment rather than put their efforts into lobbying or contacting legislators. Those posting may have stronger political opinions or more poignant experiences than the general public. Although selection bias impacts the generalizability of our findings, this analysis allows for deeper insight into the beliefs of a vocal subset of the medical community who may not have the opportunity to present their opinions elsewhere.
Conclusion
Our analysis of the response to President Trump’s executive order reveals that a rollout of these regulations would be met with strong opposition. On October 29, 2019, more than 100 professional organizations, including the American Medical Association and the American Academy of Dermatology, wrote a letter to the Secretary of Health and Human Services that eloquently echoed the sentiments of the physician commenters in this study: “Scope of practice of health care professionals should be based on standardized, adequate training and demonstrated competence in patient care, not politics. While all health care professionals share an important role in providing care to patients, their skillset is not interchangeable with that of a fully trained physician.”15 The executive order would lead to a major shift in the current medical landscape, and as such, it is prudent that these concerns are addressed.
- Balanced Budget Act of 1997, 42 USC §1395x (1997). Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/PLAW-105publ33/html/PLAW-105publ33.htm
- State practice environment. American Association of Nurse Practitioners. Updated October 20, 2020. Accessed December 8, 2020. https://www.aanp.org/advocacy/state/state-practice-environment
- Petterson SM, Liaw WR, Phillips RL Jr, et al. Projecting US primary care physician workforce needs: 2010-2015. Ann Fam Med. 2012;10:503-509.
- United States, Executive Office of the President [Donald Trump]. Executive Order 13890: Protecting and Improving Medicare for Our Nation’s Seniors. October 3, 2019. Fed Regist. 2019;84:53573-53576.
- Young KD. Trump executive order seeks proposals on Medicare pay for NPs, PAs. Medscape. Published October 3, 2019. Accessed December 8, 2020. https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/919415
- Trump seeks proposals on Medicare pay for NPs, PAs. Reddit. Accessed December 8, 2020. https://www.reddit.com/r/medicine/comments/ddy03w/trump_seeks_proposals_on_medicare_pay_for_nps_pas/
- Martin E, Huang WW, Strowd LC, et al. Public perception of ethical issues in dermatology: evidenced by New York Times commenters. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:1571-1577.
- Coldiron B, Ratnarathorn M. Scope of physician procedures independently billed by mid-level providers in the office setting. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:1153-1159.
- Resneck JS Jr. Dermatology practice consolidation fueled by private equity investment: potential consequences for the specialty and patients. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:13-14.
- Ehrlich A, Kostecki J, Olkaba H. Trends in dermatology practices and the implications for the workforce. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:746-752.
- Become a PA. American Academy of Physician Assistants. Accessed December 8, 2020. https://www.aapa.org/career-central/become-a-pa/.
- Zhang M, Zippin J, Kaffenberger B. Trends and scope of dermatology procedures billed by advanced practice professionals from 2012 through 2015. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1040-1044.
- Anderson AM, Matsumoto M, Saul MI, et al. Accuracy of skin cancer diagnosis of physician assistants compared with dermatologists in a large health care system. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:569-573.
- Jalian HR, Jalian CA, Avram MM. Common causes of injury and legal action in laser surgery. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:188-193.
- American Medical Association. Open letter to the Honorable Alex M. Azar II. Published October 29, 2019. Accessed December 11, 2020. https://searchlf.ama-assn.org/undefined/documentDownload?uri=%2Funstructured%2Fbinary%2Fletter%2FLETTERS%2F2019-10-29-Final-Sign-on-re-10-3-Executive-Order.pdf
The ability of advanced practice providers (APPs) to practice independently has been a recent topic of discussion among both the medical community and legislatures. Advanced practice provider is an umbrella term that includes physician assistants (PAs) and advanced practice registered nurses, including nurse practitioners (NPs), clinical nurse specialists, certified nurse-midwives, and certified registered nurse anesthetists. Since Congress passed the Balanced Budget Act of 1997, APPs can bill and be paid independently if they are not practicing incident to a physician or in a facility.1 Currently, NPs can practice independently in 27 states and Washington, DC. Physician assistants are required to practice under the supervision of a physician; however, the extent of supervision varies by state.2 Advocates for broadening the scope of practice for APPs argue that NPs and PAs will help to fill the physician deficit, particularly in primary care and rural regions. It has been projected that by 2025, the United States will require an additional 46,000 primary care providers to meet growing medical needs.3
On October 3, 2019, President Donald Trump issued the Executive Order on Protecting and Improving Medicare for Our Nation’s Seniors, in which he proposed an alternative to “Medicare for all.”4 This order instructed the Secretary of Health and Human Services to prepare a regulation that would “eliminate burdensome regulatory billing requirements, conditions of participation, supervision requirements, benefit definitions and all other licensure requirements . . . that are more stringent than applicable Federal or State laws require and that limit professionals from practicing at the top of their field.” Furthermore, President Trump proposed that “services provided by clinicians, including physicians, physician assistants, and nurse practitioners, are appropriately reimbursed in accordance with the work performed rather than the clinician’s occupation.”4
In response to the executive order, members of the medical community utilized Reddit, an online public forum, and Medscape, a medical news website, to vocalize opinions on the executive order.5,6 Our goal was to analyze the characteristics of those who participated in the discussion and their points of view on the plan to broaden the scope of practice and change the Medicare reimbursement plans for APPs.
Methods
All comments on the October 3, 2019, Medscape article, “Trump Executive Order Seeks Proposals on Medicare Pay for NPs, PAs,”5 and the corresponding Reddit discussion on this article6 were reviewed and characterized by the type of commenter—doctor of medicine (MD)/doctor of osteopathic medicine (DO), NP/RN/certified registered nurse anesthetist, PA, medical student, PA student, NP student, pharmacist, dietician, emergency medical technician, scribe, or unknown—as identified in their username, title, or in the text of the comment. Gender of the commenter was recorded when provided. Commenters were further grouped by their support or lack of support for the executive order based on their comments. Patients’ comments underwent further qualitative analysis to identify general themes.
All analyses were conducted with RStudio statistical software. Analyses were reported as proportions. Variables were compared by χ2 and Fisher exact tests. Odds ratios with 95% CIs were calculated. P<.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
A total of 352 comments (130 on Medscape and 222 on Reddit) posted by 155 unique users (57 on Medscape and 98 on Reddit) were included in the analysis (Table 1). Of the 51 Medscape commenters who identified a gender, 60.7% were male and 39.2% were female. Reddit commenters did not identify a gender. Commenters included MD and DO physicians (43.2%), NPs/RNs/certified registered nurse anesthetists (13.5%), medical students (11.0%), PAs (9.7%), pharmacists (3.2%), NP students (1.9%), PA students (1.3%), emergency medical technicians (1.3%), dieticians (0.6%), and scribes (0.6%). Physicians (54.5% vs 36.73%; P=.032) and NPs (22.8% vs 8.2%; P=.009) made up a larger percentage of all comments on Medscape compared to Reddit, where medical students were more prevalent (16.3% vs 1.8%; P=.005). Nursing students and PA students more commonly posted on Reddit (4.08% of Reddit commenters vs 1.75% of Medscape commenters), though this difference did not achieve statistical significance.

A majority of commenters did not support the executive order, with only 20.6% approving of the plan, 54.8% disapproving, and 24.5% remaining neutral (Figure). Advanced practice providers—NPs, PAs, NP/PA students, and APPs not otherwise specified—were more likely to support the executive order, with 52.3% voicing their support compared to only 4.8% of physicians and medical students expressing support (P<.0001). Similarly, physicians and medical students were more likely to disapprove of the order, with 75.0% voicing concerns compared to only 27.3% of APPs dissenting (P<.0001). A similar percentage of both physicians/medical students and APPs remained neutral (20.2% vs 18.2%). Commenters on Medscape were more likely to voice support for the executive order than those on Reddit (36.8% vs 11.2%; P=.0002), likely due to the higher percentage of NP and PA comments on the former.

Overall, the most commonly discussed topic was provider reimbursement (22.6% of all comments)(Table 2). Physicians and medical students were more likely to discuss physician expertise compared to APPs (32.1% vs 4.5%; P<.001). They also were more likely to raise concerns that the executive order would discourage future generations of physicians from pursuing medicine (15.5% vs 0%; P=.01). Advanced practice providers were more likely than physicians/medical students to comment on the breadth of NP and/or PA training (38.6% vs 19.0%; P=.02). The eTable shows representative comments for each theme encountered.


A subgroup analysis of the comments written by physicians supporting the executive order (n=4) and APPs disapproving of the order (n=12) was performed to identify the dissenting opinions. Physicians who supported the order discussed the need for improved pay for equal work (n=3), the competency of NP and PA training (n=2), the ability of a practice to generate more profit from APPs (n=1), and possible benefits of APPs providing primary care while MDs perform more specialized care (n=1). Of the APPs who did not support the order, there were 4 PAs, 2 registered nurses, 2 NPs, 2 NP students, and 2 PA students. The most common themes discussed were the differences in APP education and training (n=6), lack of desire for further responsibilities (n=4), and the adequacy of the current scope of practice (n=3).
Comment
President Trump’s executive order follows a trend of decreasing required oversight of APPs; however, this study indicates that these policies would face pushback from many physicians. These results are consistent with a prior study that analyzed 309 comments on an article in The New York Times made by physicians, APPs, patients, and laypeople, in which 24.7% had mistrust of APPs and 14.9% had concerns over APP supervision compared to 9% who supported APP independent practice.7 It is clear that there is a serious divide in opinion that threatens to harm the existing collaborations between physicians and APPs.
Primary Care Coverage With APPs
In the comments analyzed in our study, supporters of the executive order argued that an increase in APPs practicing independently would provide much-needed primary care coverage to patients in underserved regions. However, APPs are instead well represented across most specialties, with a majority in dermatology. Of the 4 million procedures billed independently by APPs in 2012, 54.8% were in the field of dermatology.8 The employment of APPs by dermatologists has grown from 28% of practices in 2005 to 46% in 2014, making this issue of particular importance to our field.9,10
Education and Training of APPs
In our analysis, many physicians cited concerns about the education and training of APPs. Dermatologists receive approximately 10,000 hours of training over the course of residency. Per the American Academy of Physician Assistants, PAs spend more than 2000 hours over a 26-month period on various clinical rotations, “with an emphasis on primary care.”11 There are multiple routes to become an advanced practice RN with varying classroom and clinical requirements, with one pathway requiring a bachelor of science in nursing, followed by a master’s degree requiring 500 to 700 hours of supervised clinical work. Although the Dermatology Nurses’ Association and Society of Dermatology Physician Assistants (http://www.dermpa.org) provide online modules, annual conventions with training workshops, and short fellowship programs, neither have formal guidelines on minimum requirements to diagnose and treat dermatologic conditions.2 Despite the lack of formalized dermatologic training, APPs billed for 13.4% of all dermatology procedures submitted to Medicare in 2015.12
Quality of Patient Care
In our study, physicians also voiced concern over reduced quality of patient care. In a review of 33,647 skin cancer screening examinations, PAs biopsied an average of 39.4 skin lesions, while dermatologists biopsied an average of 25.4 skin lesions to diagnose 1 case of melanoma.13 In addition, nonphysician providers accounted for 37.9% of defendants in 174 legal cases related to injury from cutaneous laser surgery.14 Before further laws are enacted regarding the independent practice and billing by NPs and PAs in the field of dermatology, further research is needed to address patient outcomes and safety.
Limitations
This study was subject to several limitations. Because of a lack of other sources offering discussions on the topic, our sample size was limited. Self-identification of users presents a challenge, as an individual can pose as a physician or APP without validation of credentials. Although great care was taken to minimize bias, grouping comments into broad categories may misinterpret a poster’s intentions. Furthermore, the data collected represent only a small proportion of the medical community—readers of Medscape and Reddit who have the motivation to create a user profile and post a comment rather than put their efforts into lobbying or contacting legislators. Those posting may have stronger political opinions or more poignant experiences than the general public. Although selection bias impacts the generalizability of our findings, this analysis allows for deeper insight into the beliefs of a vocal subset of the medical community who may not have the opportunity to present their opinions elsewhere.
Conclusion
Our analysis of the response to President Trump’s executive order reveals that a rollout of these regulations would be met with strong opposition. On October 29, 2019, more than 100 professional organizations, including the American Medical Association and the American Academy of Dermatology, wrote a letter to the Secretary of Health and Human Services that eloquently echoed the sentiments of the physician commenters in this study: “Scope of practice of health care professionals should be based on standardized, adequate training and demonstrated competence in patient care, not politics. While all health care professionals share an important role in providing care to patients, their skillset is not interchangeable with that of a fully trained physician.”15 The executive order would lead to a major shift in the current medical landscape, and as such, it is prudent that these concerns are addressed.
The ability of advanced practice providers (APPs) to practice independently has been a recent topic of discussion among both the medical community and legislatures. Advanced practice provider is an umbrella term that includes physician assistants (PAs) and advanced practice registered nurses, including nurse practitioners (NPs), clinical nurse specialists, certified nurse-midwives, and certified registered nurse anesthetists. Since Congress passed the Balanced Budget Act of 1997, APPs can bill and be paid independently if they are not practicing incident to a physician or in a facility.1 Currently, NPs can practice independently in 27 states and Washington, DC. Physician assistants are required to practice under the supervision of a physician; however, the extent of supervision varies by state.2 Advocates for broadening the scope of practice for APPs argue that NPs and PAs will help to fill the physician deficit, particularly in primary care and rural regions. It has been projected that by 2025, the United States will require an additional 46,000 primary care providers to meet growing medical needs.3
On October 3, 2019, President Donald Trump issued the Executive Order on Protecting and Improving Medicare for Our Nation’s Seniors, in which he proposed an alternative to “Medicare for all.”4 This order instructed the Secretary of Health and Human Services to prepare a regulation that would “eliminate burdensome regulatory billing requirements, conditions of participation, supervision requirements, benefit definitions and all other licensure requirements . . . that are more stringent than applicable Federal or State laws require and that limit professionals from practicing at the top of their field.” Furthermore, President Trump proposed that “services provided by clinicians, including physicians, physician assistants, and nurse practitioners, are appropriately reimbursed in accordance with the work performed rather than the clinician’s occupation.”4
In response to the executive order, members of the medical community utilized Reddit, an online public forum, and Medscape, a medical news website, to vocalize opinions on the executive order.5,6 Our goal was to analyze the characteristics of those who participated in the discussion and their points of view on the plan to broaden the scope of practice and change the Medicare reimbursement plans for APPs.
Methods
All comments on the October 3, 2019, Medscape article, “Trump Executive Order Seeks Proposals on Medicare Pay for NPs, PAs,”5 and the corresponding Reddit discussion on this article6 were reviewed and characterized by the type of commenter—doctor of medicine (MD)/doctor of osteopathic medicine (DO), NP/RN/certified registered nurse anesthetist, PA, medical student, PA student, NP student, pharmacist, dietician, emergency medical technician, scribe, or unknown—as identified in their username, title, or in the text of the comment. Gender of the commenter was recorded when provided. Commenters were further grouped by their support or lack of support for the executive order based on their comments. Patients’ comments underwent further qualitative analysis to identify general themes.
All analyses were conducted with RStudio statistical software. Analyses were reported as proportions. Variables were compared by χ2 and Fisher exact tests. Odds ratios with 95% CIs were calculated. P<.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
A total of 352 comments (130 on Medscape and 222 on Reddit) posted by 155 unique users (57 on Medscape and 98 on Reddit) were included in the analysis (Table 1). Of the 51 Medscape commenters who identified a gender, 60.7% were male and 39.2% were female. Reddit commenters did not identify a gender. Commenters included MD and DO physicians (43.2%), NPs/RNs/certified registered nurse anesthetists (13.5%), medical students (11.0%), PAs (9.7%), pharmacists (3.2%), NP students (1.9%), PA students (1.3%), emergency medical technicians (1.3%), dieticians (0.6%), and scribes (0.6%). Physicians (54.5% vs 36.73%; P=.032) and NPs (22.8% vs 8.2%; P=.009) made up a larger percentage of all comments on Medscape compared to Reddit, where medical students were more prevalent (16.3% vs 1.8%; P=.005). Nursing students and PA students more commonly posted on Reddit (4.08% of Reddit commenters vs 1.75% of Medscape commenters), though this difference did not achieve statistical significance.

A majority of commenters did not support the executive order, with only 20.6% approving of the plan, 54.8% disapproving, and 24.5% remaining neutral (Figure). Advanced practice providers—NPs, PAs, NP/PA students, and APPs not otherwise specified—were more likely to support the executive order, with 52.3% voicing their support compared to only 4.8% of physicians and medical students expressing support (P<.0001). Similarly, physicians and medical students were more likely to disapprove of the order, with 75.0% voicing concerns compared to only 27.3% of APPs dissenting (P<.0001). A similar percentage of both physicians/medical students and APPs remained neutral (20.2% vs 18.2%). Commenters on Medscape were more likely to voice support for the executive order than those on Reddit (36.8% vs 11.2%; P=.0002), likely due to the higher percentage of NP and PA comments on the former.

Overall, the most commonly discussed topic was provider reimbursement (22.6% of all comments)(Table 2). Physicians and medical students were more likely to discuss physician expertise compared to APPs (32.1% vs 4.5%; P<.001). They also were more likely to raise concerns that the executive order would discourage future generations of physicians from pursuing medicine (15.5% vs 0%; P=.01). Advanced practice providers were more likely than physicians/medical students to comment on the breadth of NP and/or PA training (38.6% vs 19.0%; P=.02). The eTable shows representative comments for each theme encountered.


A subgroup analysis of the comments written by physicians supporting the executive order (n=4) and APPs disapproving of the order (n=12) was performed to identify the dissenting opinions. Physicians who supported the order discussed the need for improved pay for equal work (n=3), the competency of NP and PA training (n=2), the ability of a practice to generate more profit from APPs (n=1), and possible benefits of APPs providing primary care while MDs perform more specialized care (n=1). Of the APPs who did not support the order, there were 4 PAs, 2 registered nurses, 2 NPs, 2 NP students, and 2 PA students. The most common themes discussed were the differences in APP education and training (n=6), lack of desire for further responsibilities (n=4), and the adequacy of the current scope of practice (n=3).
Comment
President Trump’s executive order follows a trend of decreasing required oversight of APPs; however, this study indicates that these policies would face pushback from many physicians. These results are consistent with a prior study that analyzed 309 comments on an article in The New York Times made by physicians, APPs, patients, and laypeople, in which 24.7% had mistrust of APPs and 14.9% had concerns over APP supervision compared to 9% who supported APP independent practice.7 It is clear that there is a serious divide in opinion that threatens to harm the existing collaborations between physicians and APPs.
Primary Care Coverage With APPs
In the comments analyzed in our study, supporters of the executive order argued that an increase in APPs practicing independently would provide much-needed primary care coverage to patients in underserved regions. However, APPs are instead well represented across most specialties, with a majority in dermatology. Of the 4 million procedures billed independently by APPs in 2012, 54.8% were in the field of dermatology.8 The employment of APPs by dermatologists has grown from 28% of practices in 2005 to 46% in 2014, making this issue of particular importance to our field.9,10
Education and Training of APPs
In our analysis, many physicians cited concerns about the education and training of APPs. Dermatologists receive approximately 10,000 hours of training over the course of residency. Per the American Academy of Physician Assistants, PAs spend more than 2000 hours over a 26-month period on various clinical rotations, “with an emphasis on primary care.”11 There are multiple routes to become an advanced practice RN with varying classroom and clinical requirements, with one pathway requiring a bachelor of science in nursing, followed by a master’s degree requiring 500 to 700 hours of supervised clinical work. Although the Dermatology Nurses’ Association and Society of Dermatology Physician Assistants (http://www.dermpa.org) provide online modules, annual conventions with training workshops, and short fellowship programs, neither have formal guidelines on minimum requirements to diagnose and treat dermatologic conditions.2 Despite the lack of formalized dermatologic training, APPs billed for 13.4% of all dermatology procedures submitted to Medicare in 2015.12
Quality of Patient Care
In our study, physicians also voiced concern over reduced quality of patient care. In a review of 33,647 skin cancer screening examinations, PAs biopsied an average of 39.4 skin lesions, while dermatologists biopsied an average of 25.4 skin lesions to diagnose 1 case of melanoma.13 In addition, nonphysician providers accounted for 37.9% of defendants in 174 legal cases related to injury from cutaneous laser surgery.14 Before further laws are enacted regarding the independent practice and billing by NPs and PAs in the field of dermatology, further research is needed to address patient outcomes and safety.
Limitations
This study was subject to several limitations. Because of a lack of other sources offering discussions on the topic, our sample size was limited. Self-identification of users presents a challenge, as an individual can pose as a physician or APP without validation of credentials. Although great care was taken to minimize bias, grouping comments into broad categories may misinterpret a poster’s intentions. Furthermore, the data collected represent only a small proportion of the medical community—readers of Medscape and Reddit who have the motivation to create a user profile and post a comment rather than put their efforts into lobbying or contacting legislators. Those posting may have stronger political opinions or more poignant experiences than the general public. Although selection bias impacts the generalizability of our findings, this analysis allows for deeper insight into the beliefs of a vocal subset of the medical community who may not have the opportunity to present their opinions elsewhere.
Conclusion
Our analysis of the response to President Trump’s executive order reveals that a rollout of these regulations would be met with strong opposition. On October 29, 2019, more than 100 professional organizations, including the American Medical Association and the American Academy of Dermatology, wrote a letter to the Secretary of Health and Human Services that eloquently echoed the sentiments of the physician commenters in this study: “Scope of practice of health care professionals should be based on standardized, adequate training and demonstrated competence in patient care, not politics. While all health care professionals share an important role in providing care to patients, their skillset is not interchangeable with that of a fully trained physician.”15 The executive order would lead to a major shift in the current medical landscape, and as such, it is prudent that these concerns are addressed.
- Balanced Budget Act of 1997, 42 USC §1395x (1997). Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/PLAW-105publ33/html/PLAW-105publ33.htm
- State practice environment. American Association of Nurse Practitioners. Updated October 20, 2020. Accessed December 8, 2020. https://www.aanp.org/advocacy/state/state-practice-environment
- Petterson SM, Liaw WR, Phillips RL Jr, et al. Projecting US primary care physician workforce needs: 2010-2015. Ann Fam Med. 2012;10:503-509.
- United States, Executive Office of the President [Donald Trump]. Executive Order 13890: Protecting and Improving Medicare for Our Nation’s Seniors. October 3, 2019. Fed Regist. 2019;84:53573-53576.
- Young KD. Trump executive order seeks proposals on Medicare pay for NPs, PAs. Medscape. Published October 3, 2019. Accessed December 8, 2020. https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/919415
- Trump seeks proposals on Medicare pay for NPs, PAs. Reddit. Accessed December 8, 2020. https://www.reddit.com/r/medicine/comments/ddy03w/trump_seeks_proposals_on_medicare_pay_for_nps_pas/
- Martin E, Huang WW, Strowd LC, et al. Public perception of ethical issues in dermatology: evidenced by New York Times commenters. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:1571-1577.
- Coldiron B, Ratnarathorn M. Scope of physician procedures independently billed by mid-level providers in the office setting. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:1153-1159.
- Resneck JS Jr. Dermatology practice consolidation fueled by private equity investment: potential consequences for the specialty and patients. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:13-14.
- Ehrlich A, Kostecki J, Olkaba H. Trends in dermatology practices and the implications for the workforce. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:746-752.
- Become a PA. American Academy of Physician Assistants. Accessed December 8, 2020. https://www.aapa.org/career-central/become-a-pa/.
- Zhang M, Zippin J, Kaffenberger B. Trends and scope of dermatology procedures billed by advanced practice professionals from 2012 through 2015. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1040-1044.
- Anderson AM, Matsumoto M, Saul MI, et al. Accuracy of skin cancer diagnosis of physician assistants compared with dermatologists in a large health care system. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:569-573.
- Jalian HR, Jalian CA, Avram MM. Common causes of injury and legal action in laser surgery. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:188-193.
- American Medical Association. Open letter to the Honorable Alex M. Azar II. Published October 29, 2019. Accessed December 11, 2020. https://searchlf.ama-assn.org/undefined/documentDownload?uri=%2Funstructured%2Fbinary%2Fletter%2FLETTERS%2F2019-10-29-Final-Sign-on-re-10-3-Executive-Order.pdf
- Balanced Budget Act of 1997, 42 USC §1395x (1997). Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/PLAW-105publ33/html/PLAW-105publ33.htm
- State practice environment. American Association of Nurse Practitioners. Updated October 20, 2020. Accessed December 8, 2020. https://www.aanp.org/advocacy/state/state-practice-environment
- Petterson SM, Liaw WR, Phillips RL Jr, et al. Projecting US primary care physician workforce needs: 2010-2015. Ann Fam Med. 2012;10:503-509.
- United States, Executive Office of the President [Donald Trump]. Executive Order 13890: Protecting and Improving Medicare for Our Nation’s Seniors. October 3, 2019. Fed Regist. 2019;84:53573-53576.
- Young KD. Trump executive order seeks proposals on Medicare pay for NPs, PAs. Medscape. Published October 3, 2019. Accessed December 8, 2020. https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/919415
- Trump seeks proposals on Medicare pay for NPs, PAs. Reddit. Accessed December 8, 2020. https://www.reddit.com/r/medicine/comments/ddy03w/trump_seeks_proposals_on_medicare_pay_for_nps_pas/
- Martin E, Huang WW, Strowd LC, et al. Public perception of ethical issues in dermatology: evidenced by New York Times commenters. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:1571-1577.
- Coldiron B, Ratnarathorn M. Scope of physician procedures independently billed by mid-level providers in the office setting. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:1153-1159.
- Resneck JS Jr. Dermatology practice consolidation fueled by private equity investment: potential consequences for the specialty and patients. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:13-14.
- Ehrlich A, Kostecki J, Olkaba H. Trends in dermatology practices and the implications for the workforce. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:746-752.
- Become a PA. American Academy of Physician Assistants. Accessed December 8, 2020. https://www.aapa.org/career-central/become-a-pa/.
- Zhang M, Zippin J, Kaffenberger B. Trends and scope of dermatology procedures billed by advanced practice professionals from 2012 through 2015. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1040-1044.
- Anderson AM, Matsumoto M, Saul MI, et al. Accuracy of skin cancer diagnosis of physician assistants compared with dermatologists in a large health care system. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:569-573.
- Jalian HR, Jalian CA, Avram MM. Common causes of injury and legal action in laser surgery. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:188-193.
- American Medical Association. Open letter to the Honorable Alex M. Azar II. Published October 29, 2019. Accessed December 11, 2020. https://searchlf.ama-assn.org/undefined/documentDownload?uri=%2Funstructured%2Fbinary%2Fletter%2FLETTERS%2F2019-10-29-Final-Sign-on-re-10-3-Executive-Order.pdf
Practice Points
- On October 3, 2019, President Donald Trump issued the Executive Order on Protecting and Improving Medicare for Our Nation’s Seniors, in which he proposed eliminating supervision requirements for advanced practice providers (APPs) and equalizing Medicare reimbursements among APPs and physicians.
- In a review of comments posted on online forums for medical professionals, a majority of medical professionals disapproved of the executive order.
- Advanced practice providers were more likely to support the plan, citing the breadth of their experience, whereas physicians were more likely to disapprove based on their extensive training within their specialty.
Rural Residency Curricula: Potential Target for Improved Access to Care?
To the Editor:
There is an irrefutable trend toward urban dermatology practice in the United States, leading to growing problems with rural access to care. The provision of rural clinical experiences and telehealth in dermatology residency training might increase the likelihood of trainees establishing a rural practice.
In 2017, the American Academy of Dermatology released an updated statement supporting direct patient access to board-certified dermatologists in an effort to reduce morbidity and mortality associated with skin disease.1 Twenty percent of the US population lives in a rural and medically underserved location, yet these areas remain largely underserved, in part because of an irrefutable trend toward urban dermatology practice.2-4 Successful approaches to improving rural access to dermatology care are poorly defined in the literature.
Several variables have been shown to influence a young physician’s decision to establish a clinical practice in geographically isolated areas, including rural upbringing, longitudinal rural clinical experiences during medical training, and family influences.5 Location of residency training is an additional variable that impacts practice location, though migration following dermatology residency is a complex phenomenon. However, training location does not guarantee retention of dermatology graduates in any particular geographic area.6 Practice incentives and stipends might encourage rural dermatology practice, yet these programs are underfunded. Last, telemedicine in dermatology (including teledermatology and teledermoscopy), though not always an ideal substitute for a live visit, can improve access to care in geographically isolated or underserved areas in general.7-9
Focused recruitment of medical students interested in rural dermatology practice to accredited dermatology residency programs aligned with this goal represents another approach to improve geographic diversity in the field of dermatology. Online access to this information would be useful for both applicants and their mentors.
We assessed viewable online curricula related to rural dermatology and telemedicine experiences at all Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME)–accredited residency programs. Telemedicine experiences at Veterans Health Administration (VHA) health systems also were assessed.
Methods
This study was exempt from review by the institutional review board at the University of Minnesota (Minneapolis, Minnesota)(IRB #STUDY00004915) because no human subjects were involved. Online curricula of all ACGME-accredited dermatology residency programs in the United States and Puerto Rico were reviewed from November to December 2018. The following information was recorded: specialized “rural-track” training; optional elective time in rural settings; teledermatology training; and teledermoscopy training.
Additionally, population density at each program’s primary location was determined using US Census Bureau data and with consideration to communities contained within particular Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSAs)(eTable). Data were obtained from the VHA system to assess teledermatology services at VHA locations affiliated with residency programs.
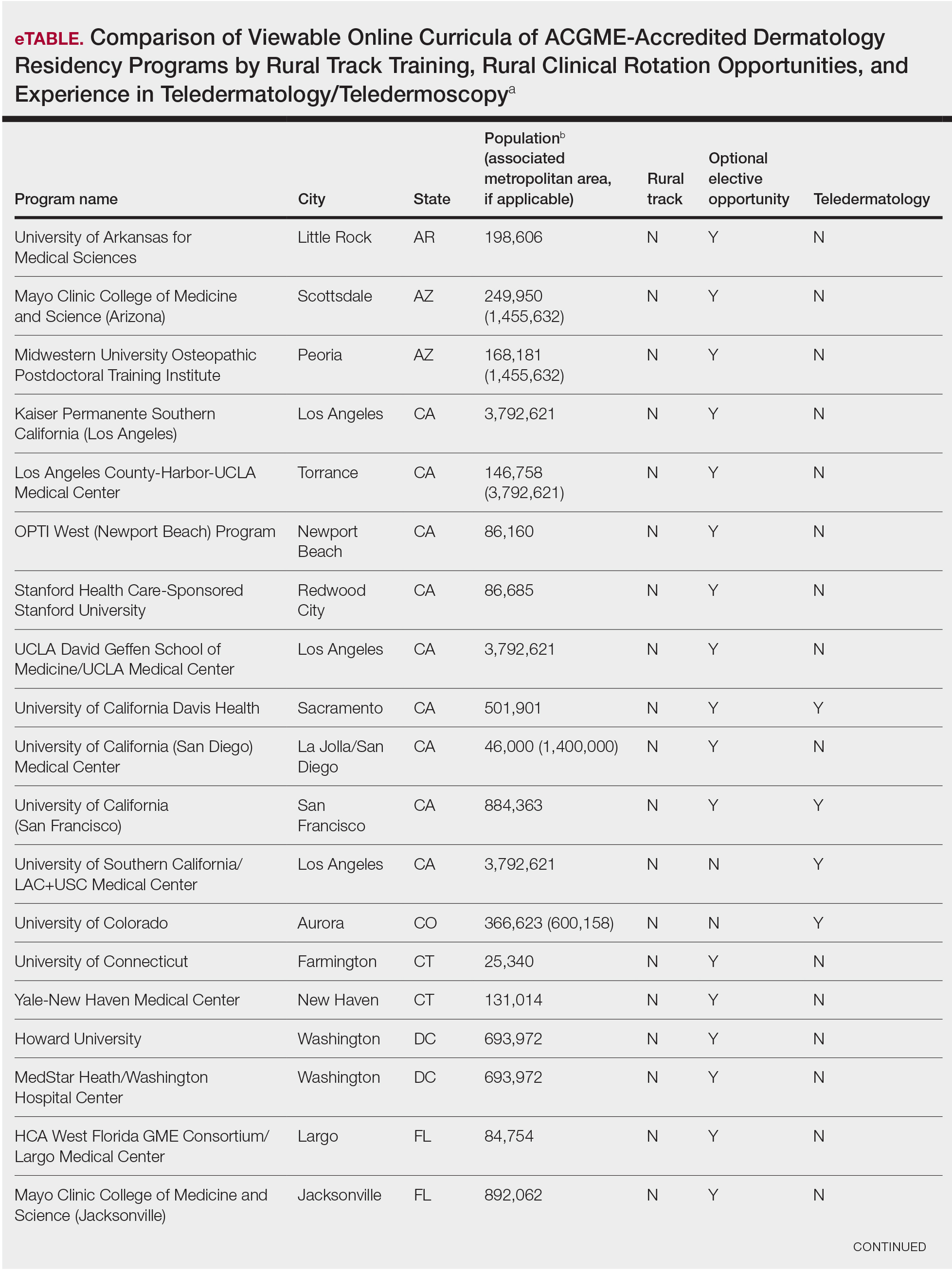
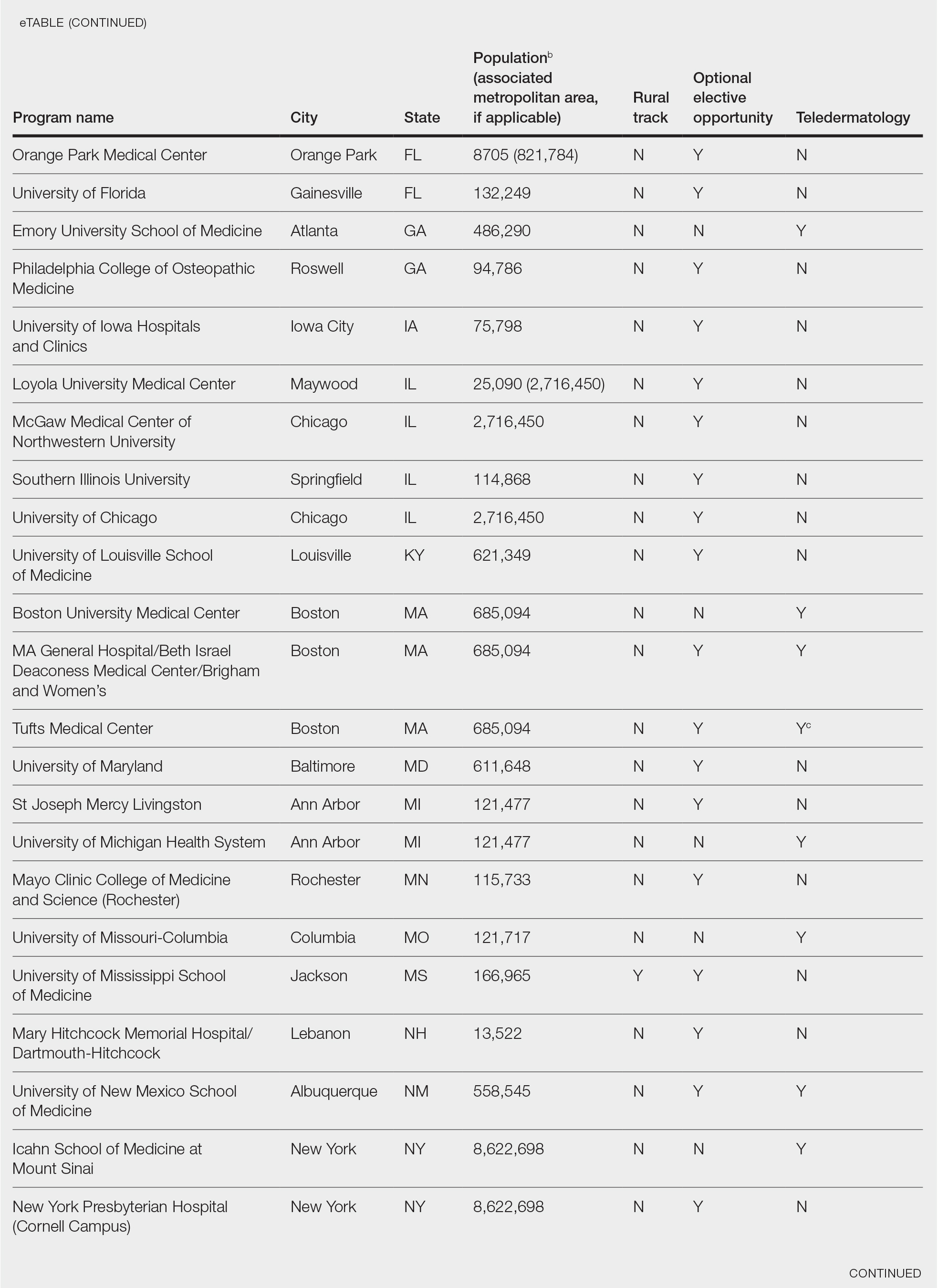
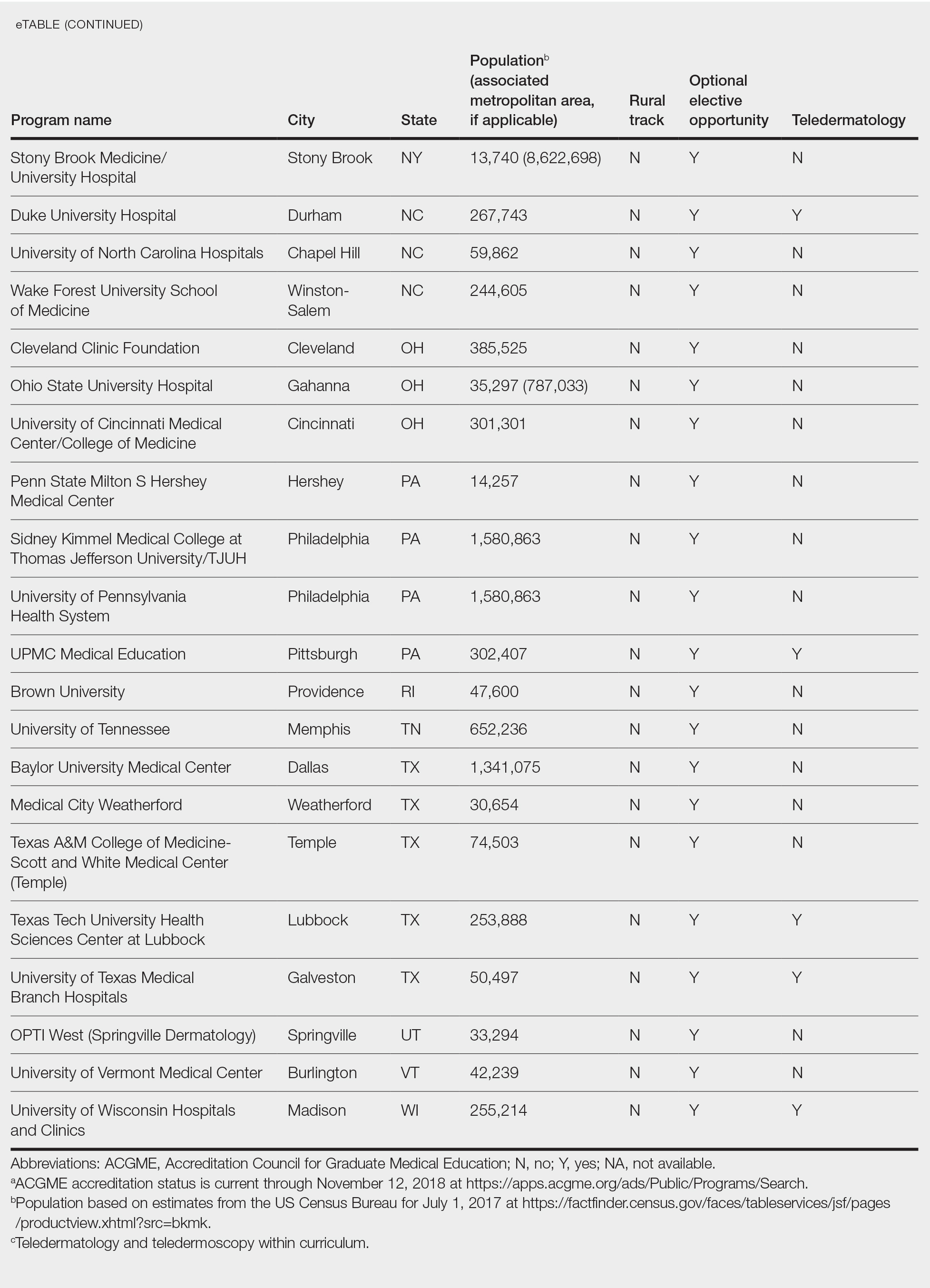
Results
Of 154 dermatology residency programs identified in the United States and Puerto Rico, 142 were accredited at the time of data collection. Fifteen (10%) were based in communities of 50,000 individuals or fewer that were not near a large metropolitan area. One program (<1%) offered a specific rural track. Fifty-six programs (39%) cited optional rotations or clinical electives, or both, that could be utilized for a rural experience. Eighteen (12%) offered teledermatology experiences and 1 (<1%) offered teledermoscopy during training. Fifty-three programs (37%) offered a rotation at a VHA hospital that had an active teledermatology service.
Comment
Program websites are a free and easily accessible means of acquiring relevant information. The paucity of readily available data on rural dermatology and teledermatology opportunities is unfortunate and a detriment to dermatology residency applicants interested in rural practice, which may result in a missed opportunity to foster a true passion for rural medicine. A brief comment on a website can be impactful, leading to a postgraduate year 4 dermatology elective rotation at a prospective fellowship training site or a rural dermatology experience.
The paucity of dermatologists working directly in rural areas has led to development of teledermatology initiatives to reach deeply into underserved regions. One of the largest providers of teledermatology is the VHA, which standardized its teledermatology efforts in 2012 and provides remarkable educational opportunities for dermatology residents. However, many residency program and VHA websites provide no information about the participation of dermatology residents in the provision of teledermatology services.
A limitation of this study is that it is based on online published curricula. Dermatology residency programs with excellent rural curricula that are not published online might exist.
Residency program directors with an interest in geographic diversity are encouraged to provide rural and teledermatology opportunities and to update these offerings on their websites, which is a simple modifiable strategy that can impact the rural dermatology care gap by recruiting students interested in filling this role. These efforts should be studied to determine whether this strategy impacts resident selection as well as whether focused rural and telemedicine exposure during training increases the likelihood of establishing a rural dermatology practice in the future.
- American Academy of Dermatology. Position statement on access to specialty care and direct access to dermatologic care. Revised May 20, 2017. Accessed December 13, 2020. https://server.aad.org/forms/Policies/Uploads/PS/PS-Access%20to%20Specialty%20Care%20and%20Direct%20Access%20to%20Dermatologic%20Care.pdf
- Dill MJ, Salsberg ES. The Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projections Through 2025. Center for Workforce Studies, Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC); November 2008. Accessed December 13, 2020. http://innovationlabs.com/pa_future/1/background_docs/AAMC%20Complexities%20of%20physician%20demand,%202008.pdf
- Glazer AM, Rigel DS. Analysis of trends in geographic distribution of US dermatology workforce density. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:472-473.
- Yoo JY, Rigel DS. Trends in dermatology: geographic density of US dermatologists. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:779.
- Feng H, Berk-Krauss J, Feng PW, et al. Comparison of dermatologist density between urban and rural counties in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1265-1271.
- Landow SM, Oh DH, Weinstock MA. Teledermatology within the Veterans Health Administration, 2002-2014. Telemed J E Health. 2015;21:769-773.
- Armstrong AW, Kwong MW, Ledo L, et al. Practice models and challenges in teledermatology: a study of collective experiences from teledermatologists. PloS One. 2011;6:e28687.
- Lewis H, Becevic M, Myers D, et al. Dermatology ECHO—an innovative solution to address limited access to dermatology expertise. Rural Remote Health. 2018;18:4415.
- Edison KE, Dyer JA, Whited JD, et al. Practice gaps. the barriers and the promise of teledermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2012:148:650-651.
To the Editor:
There is an irrefutable trend toward urban dermatology practice in the United States, leading to growing problems with rural access to care. The provision of rural clinical experiences and telehealth in dermatology residency training might increase the likelihood of trainees establishing a rural practice.
In 2017, the American Academy of Dermatology released an updated statement supporting direct patient access to board-certified dermatologists in an effort to reduce morbidity and mortality associated with skin disease.1 Twenty percent of the US population lives in a rural and medically underserved location, yet these areas remain largely underserved, in part because of an irrefutable trend toward urban dermatology practice.2-4 Successful approaches to improving rural access to dermatology care are poorly defined in the literature.
Several variables have been shown to influence a young physician’s decision to establish a clinical practice in geographically isolated areas, including rural upbringing, longitudinal rural clinical experiences during medical training, and family influences.5 Location of residency training is an additional variable that impacts practice location, though migration following dermatology residency is a complex phenomenon. However, training location does not guarantee retention of dermatology graduates in any particular geographic area.6 Practice incentives and stipends might encourage rural dermatology practice, yet these programs are underfunded. Last, telemedicine in dermatology (including teledermatology and teledermoscopy), though not always an ideal substitute for a live visit, can improve access to care in geographically isolated or underserved areas in general.7-9
Focused recruitment of medical students interested in rural dermatology practice to accredited dermatology residency programs aligned with this goal represents another approach to improve geographic diversity in the field of dermatology. Online access to this information would be useful for both applicants and their mentors.
We assessed viewable online curricula related to rural dermatology and telemedicine experiences at all Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME)–accredited residency programs. Telemedicine experiences at Veterans Health Administration (VHA) health systems also were assessed.
Methods
This study was exempt from review by the institutional review board at the University of Minnesota (Minneapolis, Minnesota)(IRB #STUDY00004915) because no human subjects were involved. Online curricula of all ACGME-accredited dermatology residency programs in the United States and Puerto Rico were reviewed from November to December 2018. The following information was recorded: specialized “rural-track” training; optional elective time in rural settings; teledermatology training; and teledermoscopy training.
Additionally, population density at each program’s primary location was determined using US Census Bureau data and with consideration to communities contained within particular Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSAs)(eTable). Data were obtained from the VHA system to assess teledermatology services at VHA locations affiliated with residency programs.



Results
Of 154 dermatology residency programs identified in the United States and Puerto Rico, 142 were accredited at the time of data collection. Fifteen (10%) were based in communities of 50,000 individuals or fewer that were not near a large metropolitan area. One program (<1%) offered a specific rural track. Fifty-six programs (39%) cited optional rotations or clinical electives, or both, that could be utilized for a rural experience. Eighteen (12%) offered teledermatology experiences and 1 (<1%) offered teledermoscopy during training. Fifty-three programs (37%) offered a rotation at a VHA hospital that had an active teledermatology service.
Comment
Program websites are a free and easily accessible means of acquiring relevant information. The paucity of readily available data on rural dermatology and teledermatology opportunities is unfortunate and a detriment to dermatology residency applicants interested in rural practice, which may result in a missed opportunity to foster a true passion for rural medicine. A brief comment on a website can be impactful, leading to a postgraduate year 4 dermatology elective rotation at a prospective fellowship training site or a rural dermatology experience.
The paucity of dermatologists working directly in rural areas has led to development of teledermatology initiatives to reach deeply into underserved regions. One of the largest providers of teledermatology is the VHA, which standardized its teledermatology efforts in 2012 and provides remarkable educational opportunities for dermatology residents. However, many residency program and VHA websites provide no information about the participation of dermatology residents in the provision of teledermatology services.
A limitation of this study is that it is based on online published curricula. Dermatology residency programs with excellent rural curricula that are not published online might exist.
Residency program directors with an interest in geographic diversity are encouraged to provide rural and teledermatology opportunities and to update these offerings on their websites, which is a simple modifiable strategy that can impact the rural dermatology care gap by recruiting students interested in filling this role. These efforts should be studied to determine whether this strategy impacts resident selection as well as whether focused rural and telemedicine exposure during training increases the likelihood of establishing a rural dermatology practice in the future.
To the Editor:
There is an irrefutable trend toward urban dermatology practice in the United States, leading to growing problems with rural access to care. The provision of rural clinical experiences and telehealth in dermatology residency training might increase the likelihood of trainees establishing a rural practice.
In 2017, the American Academy of Dermatology released an updated statement supporting direct patient access to board-certified dermatologists in an effort to reduce morbidity and mortality associated with skin disease.1 Twenty percent of the US population lives in a rural and medically underserved location, yet these areas remain largely underserved, in part because of an irrefutable trend toward urban dermatology practice.2-4 Successful approaches to improving rural access to dermatology care are poorly defined in the literature.
Several variables have been shown to influence a young physician’s decision to establish a clinical practice in geographically isolated areas, including rural upbringing, longitudinal rural clinical experiences during medical training, and family influences.5 Location of residency training is an additional variable that impacts practice location, though migration following dermatology residency is a complex phenomenon. However, training location does not guarantee retention of dermatology graduates in any particular geographic area.6 Practice incentives and stipends might encourage rural dermatology practice, yet these programs are underfunded. Last, telemedicine in dermatology (including teledermatology and teledermoscopy), though not always an ideal substitute for a live visit, can improve access to care in geographically isolated or underserved areas in general.7-9
Focused recruitment of medical students interested in rural dermatology practice to accredited dermatology residency programs aligned with this goal represents another approach to improve geographic diversity in the field of dermatology. Online access to this information would be useful for both applicants and their mentors.
We assessed viewable online curricula related to rural dermatology and telemedicine experiences at all Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME)–accredited residency programs. Telemedicine experiences at Veterans Health Administration (VHA) health systems also were assessed.
Methods
This study was exempt from review by the institutional review board at the University of Minnesota (Minneapolis, Minnesota)(IRB #STUDY00004915) because no human subjects were involved. Online curricula of all ACGME-accredited dermatology residency programs in the United States and Puerto Rico were reviewed from November to December 2018. The following information was recorded: specialized “rural-track” training; optional elective time in rural settings; teledermatology training; and teledermoscopy training.
Additionally, population density at each program’s primary location was determined using US Census Bureau data and with consideration to communities contained within particular Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSAs)(eTable). Data were obtained from the VHA system to assess teledermatology services at VHA locations affiliated with residency programs.



Results
Of 154 dermatology residency programs identified in the United States and Puerto Rico, 142 were accredited at the time of data collection. Fifteen (10%) were based in communities of 50,000 individuals or fewer that were not near a large metropolitan area. One program (<1%) offered a specific rural track. Fifty-six programs (39%) cited optional rotations or clinical electives, or both, that could be utilized for a rural experience. Eighteen (12%) offered teledermatology experiences and 1 (<1%) offered teledermoscopy during training. Fifty-three programs (37%) offered a rotation at a VHA hospital that had an active teledermatology service.
Comment
Program websites are a free and easily accessible means of acquiring relevant information. The paucity of readily available data on rural dermatology and teledermatology opportunities is unfortunate and a detriment to dermatology residency applicants interested in rural practice, which may result in a missed opportunity to foster a true passion for rural medicine. A brief comment on a website can be impactful, leading to a postgraduate year 4 dermatology elective rotation at a prospective fellowship training site or a rural dermatology experience.
The paucity of dermatologists working directly in rural areas has led to development of teledermatology initiatives to reach deeply into underserved regions. One of the largest providers of teledermatology is the VHA, which standardized its teledermatology efforts in 2012 and provides remarkable educational opportunities for dermatology residents. However, many residency program and VHA websites provide no information about the participation of dermatology residents in the provision of teledermatology services.
A limitation of this study is that it is based on online published curricula. Dermatology residency programs with excellent rural curricula that are not published online might exist.
Residency program directors with an interest in geographic diversity are encouraged to provide rural and teledermatology opportunities and to update these offerings on their websites, which is a simple modifiable strategy that can impact the rural dermatology care gap by recruiting students interested in filling this role. These efforts should be studied to determine whether this strategy impacts resident selection as well as whether focused rural and telemedicine exposure during training increases the likelihood of establishing a rural dermatology practice in the future.
- American Academy of Dermatology. Position statement on access to specialty care and direct access to dermatologic care. Revised May 20, 2017. Accessed December 13, 2020. https://server.aad.org/forms/Policies/Uploads/PS/PS-Access%20to%20Specialty%20Care%20and%20Direct%20Access%20to%20Dermatologic%20Care.pdf
- Dill MJ, Salsberg ES. The Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projections Through 2025. Center for Workforce Studies, Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC); November 2008. Accessed December 13, 2020. http://innovationlabs.com/pa_future/1/background_docs/AAMC%20Complexities%20of%20physician%20demand,%202008.pdf
- Glazer AM, Rigel DS. Analysis of trends in geographic distribution of US dermatology workforce density. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:472-473.
- Yoo JY, Rigel DS. Trends in dermatology: geographic density of US dermatologists. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:779.
- Feng H, Berk-Krauss J, Feng PW, et al. Comparison of dermatologist density between urban and rural counties in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1265-1271.
- Landow SM, Oh DH, Weinstock MA. Teledermatology within the Veterans Health Administration, 2002-2014. Telemed J E Health. 2015;21:769-773.
- Armstrong AW, Kwong MW, Ledo L, et al. Practice models and challenges in teledermatology: a study of collective experiences from teledermatologists. PloS One. 2011;6:e28687.
- Lewis H, Becevic M, Myers D, et al. Dermatology ECHO—an innovative solution to address limited access to dermatology expertise. Rural Remote Health. 2018;18:4415.
- Edison KE, Dyer JA, Whited JD, et al. Practice gaps. the barriers and the promise of teledermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2012:148:650-651.
- American Academy of Dermatology. Position statement on access to specialty care and direct access to dermatologic care. Revised May 20, 2017. Accessed December 13, 2020. https://server.aad.org/forms/Policies/Uploads/PS/PS-Access%20to%20Specialty%20Care%20and%20Direct%20Access%20to%20Dermatologic%20Care.pdf
- Dill MJ, Salsberg ES. The Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projections Through 2025. Center for Workforce Studies, Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC); November 2008. Accessed December 13, 2020. http://innovationlabs.com/pa_future/1/background_docs/AAMC%20Complexities%20of%20physician%20demand,%202008.pdf
- Glazer AM, Rigel DS. Analysis of trends in geographic distribution of US dermatology workforce density. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:472-473.
- Yoo JY, Rigel DS. Trends in dermatology: geographic density of US dermatologists. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:779.
- Feng H, Berk-Krauss J, Feng PW, et al. Comparison of dermatologist density between urban and rural counties in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1265-1271.
- Landow SM, Oh DH, Weinstock MA. Teledermatology within the Veterans Health Administration, 2002-2014. Telemed J E Health. 2015;21:769-773.
- Armstrong AW, Kwong MW, Ledo L, et al. Practice models and challenges in teledermatology: a study of collective experiences from teledermatologists. PloS One. 2011;6:e28687.
- Lewis H, Becevic M, Myers D, et al. Dermatology ECHO—an innovative solution to address limited access to dermatology expertise. Rural Remote Health. 2018;18:4415.
- Edison KE, Dyer JA, Whited JD, et al. Practice gaps. the barriers and the promise of teledermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2012:148:650-651.
Practice Points
- Access to dermatologic care in rural areas is a growing problem.
- Dermatology residency programs can influence medical students and resident dermatologists to provide care in rural and geographically isolated areas.
- Presenting detailed curricula that impact access to care on residency program websites could attract applicants with these career goals.
New dietary guidelines omit recommended cuts to sugar, alcohol intake
Although the new guidelines were informed by an advisory committee’s scientific report, officials omitted certain recommendations that would have reduced allowances for added sugars and alcohol intake.
The 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans “carried forward the committee’s emphasis on limiting these dietary components, but did not include changes to quantitative recommendations, as there was not a preponderance of evidence in the material the committee reviewed to support specific changes, as required by law,” the agencies said in a news release.
The guidelines encourage Americans to “Make Every Bite Count” through four overarching suggestions:
- Follow a healthy dietary pattern at every life stage.
- Customize nutrient-dense food and beverage choices to reflect preferences, cultural traditions, and budgets.
- Focus on meeting dietary needs from five food groups – vegetables, fruits, grains, dairy and fortified soy alternatives, and proteins – and stay within calorie limits.
- Limit foods and beverages that are higher in added sugars, saturated fat, and sodium, and limit alcoholic beverages.
The guidance “can help all Americans lead healthier lives by making every bite count,” Secretary of Agriculture Sonny Perdue said.
Proposed cutoffs rejected
The guidelines omit a recommendation from the advisory committee’s scientific report to reduce intake of added sugars from less than 10% of calories to less than 6% of calories.
It also omits a recommendation that men and women who drink alcohol limit themselves to one drink per day. It maintains guidance from the 2015-2020 edition that allows two drinks per day for men.
The agencies published a document explaining why they omitted the advisory committee›s conclusions.
The American Heart Association in July had praised the suggestion to reduce added sugars. The proposed change would have helped “steer the public toward a more heart-healthy path in their daily diets,” Mitchell S.V. Elkind, MD, president of the AHA, said at the time. The association would “strongly oppose any efforts to weaken these recommendations,” he added.
In its response to the new guidelines, Dr. Elkind praised the emphasis on a healthy diet “at every life stage” but called out a missed opportunity.
“We are disappointed that USDA and HHS did not accept all of the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee’s science-based recommendations in the final guidelines for 2020, including the recommendation to lower added sugars consumption to less than 6% of calories,” he said in a prepared statement.
Guidance for infants and toddlers
The guidelines advise that for about the first 6 months of life, infants should exclusively receive breast milk. Infants should continue to receive breast milk through at least the first year of life, and longer if desired. Infants should be fed iron-fortified infant formula during the first year of life when breast milk is unavailable, and infants should receive supplemental vitamin D soon after birth, the guidelines advise.
At about 6 months, infants should be introduced to a variety of nutrient-dense complementary foods, including potentially allergenic foods. Infants should eat foods that are rich in iron and zinc, particularly if they are fed breast milk.
The guidelines also include dietary and caloric advice for pregnant and lactating women with daily or weekly amounts of food from different groups and subgroups.
Dr. Elkind highlighted the significance of these additions.
“We are pleased that for the first time, the guidelines provide recommendations for pregnant and breastfeeding women as well as infants and toddlers, underscoring the importance of maternal health and proper nutrition across the lifespan,” he said.
For all ages
From 12 months through older adulthood, people should follow a healthy dietary pattern to meet nutrient needs, help achieve a healthy body weight, and reduce the risk of chronic disease.
According to the guidelines, core elements of a healthy diet include:
- Vegetables of all types (dark green; red and orange; beans, peas, and lentils; starchy; and other types).
- Fruits (especially whole fruit).
- Grains, at least half of which are whole grain.
- Dairy, including fat-free or low-fat milk, yogurt, and cheese, and lactose-free versions; and fortified soy beverages and yogurt as alternatives.
- Protein foods, including lean meats, poultry, and eggs; seafood; beans, peas, and lentils; and nuts, seeds, and soy products.
- Oils, including vegetable oils and oils in food, such as seafood and nuts.
The guidelines spell out limits to added sugars, sodium, saturated fat, and alcohol. The recommendation to limit added sugars to less than 10% of calories per day starts at age 2 years. Before age 2, foods and beverages with added sugars should be avoided.
Saturated fat should be limited to less than 10% of calories per day starting at age 2. And sodium intake should be limited to 2,300 mg/day for those age 14 and older, but just 1,200 mg/day for toddlers, 1,500 mg/day for children aged 4-8, and 1,800 mg/day for children 9-13.
“Adults of legal drinking age can choose not to drink or to drink in moderation by limiting intake to 2 drinks or less in a day for men and 1 drink or less in a day for women, when alcohol is consumed,” the agencies said. “Drinking less is better for health than drinking more. There are some adults who should not drink alcohol, such as women who are pregnant.”
An appendix includes estimated calorie needs based on a person’s age, sex, height, weight, and level of physical activity. A need to lose, maintain, or gain weight are among the factors that influence how many calories should be consumed, the guidelines note.
The guidelines are designed for use by health care professionals and policymakers. The USDA has launched a new MyPlate website to help consumers incorporate the dietary guidance.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although the new guidelines were informed by an advisory committee’s scientific report, officials omitted certain recommendations that would have reduced allowances for added sugars and alcohol intake.
The 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans “carried forward the committee’s emphasis on limiting these dietary components, but did not include changes to quantitative recommendations, as there was not a preponderance of evidence in the material the committee reviewed to support specific changes, as required by law,” the agencies said in a news release.
The guidelines encourage Americans to “Make Every Bite Count” through four overarching suggestions:
- Follow a healthy dietary pattern at every life stage.
- Customize nutrient-dense food and beverage choices to reflect preferences, cultural traditions, and budgets.
- Focus on meeting dietary needs from five food groups – vegetables, fruits, grains, dairy and fortified soy alternatives, and proteins – and stay within calorie limits.
- Limit foods and beverages that are higher in added sugars, saturated fat, and sodium, and limit alcoholic beverages.
The guidance “can help all Americans lead healthier lives by making every bite count,” Secretary of Agriculture Sonny Perdue said.
Proposed cutoffs rejected
The guidelines omit a recommendation from the advisory committee’s scientific report to reduce intake of added sugars from less than 10% of calories to less than 6% of calories.
It also omits a recommendation that men and women who drink alcohol limit themselves to one drink per day. It maintains guidance from the 2015-2020 edition that allows two drinks per day for men.
The agencies published a document explaining why they omitted the advisory committee›s conclusions.
The American Heart Association in July had praised the suggestion to reduce added sugars. The proposed change would have helped “steer the public toward a more heart-healthy path in their daily diets,” Mitchell S.V. Elkind, MD, president of the AHA, said at the time. The association would “strongly oppose any efforts to weaken these recommendations,” he added.
In its response to the new guidelines, Dr. Elkind praised the emphasis on a healthy diet “at every life stage” but called out a missed opportunity.
“We are disappointed that USDA and HHS did not accept all of the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee’s science-based recommendations in the final guidelines for 2020, including the recommendation to lower added sugars consumption to less than 6% of calories,” he said in a prepared statement.
Guidance for infants and toddlers
The guidelines advise that for about the first 6 months of life, infants should exclusively receive breast milk. Infants should continue to receive breast milk through at least the first year of life, and longer if desired. Infants should be fed iron-fortified infant formula during the first year of life when breast milk is unavailable, and infants should receive supplemental vitamin D soon after birth, the guidelines advise.
At about 6 months, infants should be introduced to a variety of nutrient-dense complementary foods, including potentially allergenic foods. Infants should eat foods that are rich in iron and zinc, particularly if they are fed breast milk.
The guidelines also include dietary and caloric advice for pregnant and lactating women with daily or weekly amounts of food from different groups and subgroups.
Dr. Elkind highlighted the significance of these additions.
“We are pleased that for the first time, the guidelines provide recommendations for pregnant and breastfeeding women as well as infants and toddlers, underscoring the importance of maternal health and proper nutrition across the lifespan,” he said.
For all ages
From 12 months through older adulthood, people should follow a healthy dietary pattern to meet nutrient needs, help achieve a healthy body weight, and reduce the risk of chronic disease.
According to the guidelines, core elements of a healthy diet include:
- Vegetables of all types (dark green; red and orange; beans, peas, and lentils; starchy; and other types).
- Fruits (especially whole fruit).
- Grains, at least half of which are whole grain.
- Dairy, including fat-free or low-fat milk, yogurt, and cheese, and lactose-free versions; and fortified soy beverages and yogurt as alternatives.
- Protein foods, including lean meats, poultry, and eggs; seafood; beans, peas, and lentils; and nuts, seeds, and soy products.
- Oils, including vegetable oils and oils in food, such as seafood and nuts.
The guidelines spell out limits to added sugars, sodium, saturated fat, and alcohol. The recommendation to limit added sugars to less than 10% of calories per day starts at age 2 years. Before age 2, foods and beverages with added sugars should be avoided.
Saturated fat should be limited to less than 10% of calories per day starting at age 2. And sodium intake should be limited to 2,300 mg/day for those age 14 and older, but just 1,200 mg/day for toddlers, 1,500 mg/day for children aged 4-8, and 1,800 mg/day for children 9-13.
“Adults of legal drinking age can choose not to drink or to drink in moderation by limiting intake to 2 drinks or less in a day for men and 1 drink or less in a day for women, when alcohol is consumed,” the agencies said. “Drinking less is better for health than drinking more. There are some adults who should not drink alcohol, such as women who are pregnant.”
An appendix includes estimated calorie needs based on a person’s age, sex, height, weight, and level of physical activity. A need to lose, maintain, or gain weight are among the factors that influence how many calories should be consumed, the guidelines note.
The guidelines are designed for use by health care professionals and policymakers. The USDA has launched a new MyPlate website to help consumers incorporate the dietary guidance.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although the new guidelines were informed by an advisory committee’s scientific report, officials omitted certain recommendations that would have reduced allowances for added sugars and alcohol intake.
The 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans “carried forward the committee’s emphasis on limiting these dietary components, but did not include changes to quantitative recommendations, as there was not a preponderance of evidence in the material the committee reviewed to support specific changes, as required by law,” the agencies said in a news release.
The guidelines encourage Americans to “Make Every Bite Count” through four overarching suggestions:
- Follow a healthy dietary pattern at every life stage.
- Customize nutrient-dense food and beverage choices to reflect preferences, cultural traditions, and budgets.
- Focus on meeting dietary needs from five food groups – vegetables, fruits, grains, dairy and fortified soy alternatives, and proteins – and stay within calorie limits.
- Limit foods and beverages that are higher in added sugars, saturated fat, and sodium, and limit alcoholic beverages.
The guidance “can help all Americans lead healthier lives by making every bite count,” Secretary of Agriculture Sonny Perdue said.
Proposed cutoffs rejected
The guidelines omit a recommendation from the advisory committee’s scientific report to reduce intake of added sugars from less than 10% of calories to less than 6% of calories.
It also omits a recommendation that men and women who drink alcohol limit themselves to one drink per day. It maintains guidance from the 2015-2020 edition that allows two drinks per day for men.
The agencies published a document explaining why they omitted the advisory committee›s conclusions.
The American Heart Association in July had praised the suggestion to reduce added sugars. The proposed change would have helped “steer the public toward a more heart-healthy path in their daily diets,” Mitchell S.V. Elkind, MD, president of the AHA, said at the time. The association would “strongly oppose any efforts to weaken these recommendations,” he added.
In its response to the new guidelines, Dr. Elkind praised the emphasis on a healthy diet “at every life stage” but called out a missed opportunity.
“We are disappointed that USDA and HHS did not accept all of the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee’s science-based recommendations in the final guidelines for 2020, including the recommendation to lower added sugars consumption to less than 6% of calories,” he said in a prepared statement.
Guidance for infants and toddlers
The guidelines advise that for about the first 6 months of life, infants should exclusively receive breast milk. Infants should continue to receive breast milk through at least the first year of life, and longer if desired. Infants should be fed iron-fortified infant formula during the first year of life when breast milk is unavailable, and infants should receive supplemental vitamin D soon after birth, the guidelines advise.
At about 6 months, infants should be introduced to a variety of nutrient-dense complementary foods, including potentially allergenic foods. Infants should eat foods that are rich in iron and zinc, particularly if they are fed breast milk.
The guidelines also include dietary and caloric advice for pregnant and lactating women with daily or weekly amounts of food from different groups and subgroups.
Dr. Elkind highlighted the significance of these additions.
“We are pleased that for the first time, the guidelines provide recommendations for pregnant and breastfeeding women as well as infants and toddlers, underscoring the importance of maternal health and proper nutrition across the lifespan,” he said.
For all ages
From 12 months through older adulthood, people should follow a healthy dietary pattern to meet nutrient needs, help achieve a healthy body weight, and reduce the risk of chronic disease.
According to the guidelines, core elements of a healthy diet include:
- Vegetables of all types (dark green; red and orange; beans, peas, and lentils; starchy; and other types).
- Fruits (especially whole fruit).
- Grains, at least half of which are whole grain.
- Dairy, including fat-free or low-fat milk, yogurt, and cheese, and lactose-free versions; and fortified soy beverages and yogurt as alternatives.
- Protein foods, including lean meats, poultry, and eggs; seafood; beans, peas, and lentils; and nuts, seeds, and soy products.
- Oils, including vegetable oils and oils in food, such as seafood and nuts.
The guidelines spell out limits to added sugars, sodium, saturated fat, and alcohol. The recommendation to limit added sugars to less than 10% of calories per day starts at age 2 years. Before age 2, foods and beverages with added sugars should be avoided.
Saturated fat should be limited to less than 10% of calories per day starting at age 2. And sodium intake should be limited to 2,300 mg/day for those age 14 and older, but just 1,200 mg/day for toddlers, 1,500 mg/day for children aged 4-8, and 1,800 mg/day for children 9-13.
“Adults of legal drinking age can choose not to drink or to drink in moderation by limiting intake to 2 drinks or less in a day for men and 1 drink or less in a day for women, when alcohol is consumed,” the agencies said. “Drinking less is better for health than drinking more. There are some adults who should not drink alcohol, such as women who are pregnant.”
An appendix includes estimated calorie needs based on a person’s age, sex, height, weight, and level of physical activity. A need to lose, maintain, or gain weight are among the factors that influence how many calories should be consumed, the guidelines note.
The guidelines are designed for use by health care professionals and policymakers. The USDA has launched a new MyPlate website to help consumers incorporate the dietary guidance.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.