User login
Early GI symptoms in COVID-19 may indicate fecal transmission
Fecal-oral transmission may be part of the COVID-19 clinical picture, according to two reports published in Gastroenterology. The researchers find that RNA and proteins from SARS-CoV-2, the viral cause of COVID-19, are shed in feces early in infection and persist after respiratory symptoms abate.
But the discovery is preliminary. “There is evidence of the virus in stool, but not evidence of infectious virus,” David A. Johnson, MD, professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at the Eastern Virginia School of Medicine in Norfolk, told Medscape Medical News.
The findings are not entirely unexpected. Both of the coronaviruses behind SARS and MERS are shed in stool, Jinyang Gu, MD, from Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in Shanghai, China, and colleagues, note in one of the newly published articles.
In addition, as COVID-19 spread beyond China, clinicians began noticing initial mild gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms in some patients, including diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, preceding the hallmark fever, dry cough, and dyspnea. The first patient diagnosed in the United States with COVID-19 reported having 2 days of nausea and vomiting, with viral RNA detected in fecal and respiratory specimens, according to an earlier report.
Gu and colleagues warn that initial investigations would likely have not considered cases that manifested initially only as mild gastrointestinal symptoms.
Although early reports indicated that only about 10% of people with COVID-19 have GI symptoms, it isn’t known whether some infected individuals have only GI symptoms, Johnson said.
The GI manifestations are consistent with the distribution of ACE2 receptors, which serve as entry points for SARS-CoV-2, as well as SARS-CoV-1, which causes SARS. The receptors are most abundant in the cell membranes of lung AT2 cells, as well as in enterocytes in the ileum and colon.
“Altogether, many efforts should be made to be alert on the initial digestive symptoms of COVID-19 for early detection, early diagnosis, early isolation and early intervention,” Gu and colleagues conclude.
But Johnson cautions, “gastroenterologists are not the ones managing diagnosis of COVID-19. It is diagnosed as a respiratory illness, but we are seeing concomitant gastrointestinal shedding in stool and saliva, and GI symptoms.”
Samples From 73 Patients Studied
In the second article published, Fei Xiao, MD, of Sun Yat-sen University in Guangdong Province, China, and colleagues report detecting viral RNA in samples from the mouths, noses, throats, urine, and feces of 73 patients hospitalized during the first 2 weeks of February.
Of the 73 hospitalized patients, 39 (53.24%; 25 males and 14 females) had viral RNA in their feces, present from 1 to 12 days. Seventeen (23.29%) of the patients continued to have viral RNA in their stool after respiratory symptoms had improved.
One patient underwent endoscopy. There was no evidence of damage to the GI epithelium, but the clinicians detected slightly elevated levels of lymphocytes and plasma cells.
The researcher used laser scanning confocal microscopy to analyze samples taken during the endoscopy. They found evidence of both ACE2 receptors and viral nucleocapsid proteins in the gastric, duodenal, and rectal glandular epithelial cells.
Finding evidence of SARS-CoV-2 throughout the GI system, if not direct infectivity, suggests a fecal-oral route of transmission, the researchers conclude. “Our immunofluorescent data showed that ACE2 protein, a cell receptor for SARS-CoV-2, is abundantly expressed in the glandular cells of gastric, duodenal and rectal epithelia, supporting the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the host cells.”
Detection of viral RNA at different time points in infection, they write, suggests that the virions are continually secreted and therefore likely infectious, which is under investigation. “Prevention of fecal-oral transmission should be taken into consideration to control the spread of the virus,” they write.
Current recommendations do not require that patients’ fecal samples be tested before being considered noninfectious. However, given their findings and evidence from other studies, Xiao and colleagues recommend that real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) testing of fecal samples be added to current protocols.
Johnson offers practical suggestions based on the “potty hygiene” suggestions he gives to patients dealing with fecal shedding in Clostridioides difficile infection.
“To combat the microaerosolization of C. diff spores, I have patients do a complete bacteriocidal washing out of the toilet bowl, as well as clean surface areas and especially toothbrushes.” Keeping the bowl closed when not in use is important too in preventing “fecal-oral transmission of remnants” of toilet contents, he adds.
The new papers add to other reports suggesting that virus-bearing droplets may reach people in various ways, Johnson said. “Maybe the virus isn’t only spread by a cough or a sneeze.”
The researchers and commentator have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fecal-oral transmission may be part of the COVID-19 clinical picture, according to two reports published in Gastroenterology. The researchers find that RNA and proteins from SARS-CoV-2, the viral cause of COVID-19, are shed in feces early in infection and persist after respiratory symptoms abate.
But the discovery is preliminary. “There is evidence of the virus in stool, but not evidence of infectious virus,” David A. Johnson, MD, professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at the Eastern Virginia School of Medicine in Norfolk, told Medscape Medical News.
The findings are not entirely unexpected. Both of the coronaviruses behind SARS and MERS are shed in stool, Jinyang Gu, MD, from Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in Shanghai, China, and colleagues, note in one of the newly published articles.
In addition, as COVID-19 spread beyond China, clinicians began noticing initial mild gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms in some patients, including diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, preceding the hallmark fever, dry cough, and dyspnea. The first patient diagnosed in the United States with COVID-19 reported having 2 days of nausea and vomiting, with viral RNA detected in fecal and respiratory specimens, according to an earlier report.
Gu and colleagues warn that initial investigations would likely have not considered cases that manifested initially only as mild gastrointestinal symptoms.
Although early reports indicated that only about 10% of people with COVID-19 have GI symptoms, it isn’t known whether some infected individuals have only GI symptoms, Johnson said.
The GI manifestations are consistent with the distribution of ACE2 receptors, which serve as entry points for SARS-CoV-2, as well as SARS-CoV-1, which causes SARS. The receptors are most abundant in the cell membranes of lung AT2 cells, as well as in enterocytes in the ileum and colon.
“Altogether, many efforts should be made to be alert on the initial digestive symptoms of COVID-19 for early detection, early diagnosis, early isolation and early intervention,” Gu and colleagues conclude.
But Johnson cautions, “gastroenterologists are not the ones managing diagnosis of COVID-19. It is diagnosed as a respiratory illness, but we are seeing concomitant gastrointestinal shedding in stool and saliva, and GI symptoms.”
Samples From 73 Patients Studied
In the second article published, Fei Xiao, MD, of Sun Yat-sen University in Guangdong Province, China, and colleagues report detecting viral RNA in samples from the mouths, noses, throats, urine, and feces of 73 patients hospitalized during the first 2 weeks of February.
Of the 73 hospitalized patients, 39 (53.24%; 25 males and 14 females) had viral RNA in their feces, present from 1 to 12 days. Seventeen (23.29%) of the patients continued to have viral RNA in their stool after respiratory symptoms had improved.
One patient underwent endoscopy. There was no evidence of damage to the GI epithelium, but the clinicians detected slightly elevated levels of lymphocytes and plasma cells.
The researcher used laser scanning confocal microscopy to analyze samples taken during the endoscopy. They found evidence of both ACE2 receptors and viral nucleocapsid proteins in the gastric, duodenal, and rectal glandular epithelial cells.
Finding evidence of SARS-CoV-2 throughout the GI system, if not direct infectivity, suggests a fecal-oral route of transmission, the researchers conclude. “Our immunofluorescent data showed that ACE2 protein, a cell receptor for SARS-CoV-2, is abundantly expressed in the glandular cells of gastric, duodenal and rectal epithelia, supporting the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the host cells.”
Detection of viral RNA at different time points in infection, they write, suggests that the virions are continually secreted and therefore likely infectious, which is under investigation. “Prevention of fecal-oral transmission should be taken into consideration to control the spread of the virus,” they write.
Current recommendations do not require that patients’ fecal samples be tested before being considered noninfectious. However, given their findings and evidence from other studies, Xiao and colleagues recommend that real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) testing of fecal samples be added to current protocols.
Johnson offers practical suggestions based on the “potty hygiene” suggestions he gives to patients dealing with fecal shedding in Clostridioides difficile infection.
“To combat the microaerosolization of C. diff spores, I have patients do a complete bacteriocidal washing out of the toilet bowl, as well as clean surface areas and especially toothbrushes.” Keeping the bowl closed when not in use is important too in preventing “fecal-oral transmission of remnants” of toilet contents, he adds.
The new papers add to other reports suggesting that virus-bearing droplets may reach people in various ways, Johnson said. “Maybe the virus isn’t only spread by a cough or a sneeze.”
The researchers and commentator have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fecal-oral transmission may be part of the COVID-19 clinical picture, according to two reports published in Gastroenterology. The researchers find that RNA and proteins from SARS-CoV-2, the viral cause of COVID-19, are shed in feces early in infection and persist after respiratory symptoms abate.
But the discovery is preliminary. “There is evidence of the virus in stool, but not evidence of infectious virus,” David A. Johnson, MD, professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at the Eastern Virginia School of Medicine in Norfolk, told Medscape Medical News.
The findings are not entirely unexpected. Both of the coronaviruses behind SARS and MERS are shed in stool, Jinyang Gu, MD, from Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in Shanghai, China, and colleagues, note in one of the newly published articles.
In addition, as COVID-19 spread beyond China, clinicians began noticing initial mild gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms in some patients, including diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, preceding the hallmark fever, dry cough, and dyspnea. The first patient diagnosed in the United States with COVID-19 reported having 2 days of nausea and vomiting, with viral RNA detected in fecal and respiratory specimens, according to an earlier report.
Gu and colleagues warn that initial investigations would likely have not considered cases that manifested initially only as mild gastrointestinal symptoms.
Although early reports indicated that only about 10% of people with COVID-19 have GI symptoms, it isn’t known whether some infected individuals have only GI symptoms, Johnson said.
The GI manifestations are consistent with the distribution of ACE2 receptors, which serve as entry points for SARS-CoV-2, as well as SARS-CoV-1, which causes SARS. The receptors are most abundant in the cell membranes of lung AT2 cells, as well as in enterocytes in the ileum and colon.
“Altogether, many efforts should be made to be alert on the initial digestive symptoms of COVID-19 for early detection, early diagnosis, early isolation and early intervention,” Gu and colleagues conclude.
But Johnson cautions, “gastroenterologists are not the ones managing diagnosis of COVID-19. It is diagnosed as a respiratory illness, but we are seeing concomitant gastrointestinal shedding in stool and saliva, and GI symptoms.”
Samples From 73 Patients Studied
In the second article published, Fei Xiao, MD, of Sun Yat-sen University in Guangdong Province, China, and colleagues report detecting viral RNA in samples from the mouths, noses, throats, urine, and feces of 73 patients hospitalized during the first 2 weeks of February.
Of the 73 hospitalized patients, 39 (53.24%; 25 males and 14 females) had viral RNA in their feces, present from 1 to 12 days. Seventeen (23.29%) of the patients continued to have viral RNA in their stool after respiratory symptoms had improved.
One patient underwent endoscopy. There was no evidence of damage to the GI epithelium, but the clinicians detected slightly elevated levels of lymphocytes and plasma cells.
The researcher used laser scanning confocal microscopy to analyze samples taken during the endoscopy. They found evidence of both ACE2 receptors and viral nucleocapsid proteins in the gastric, duodenal, and rectal glandular epithelial cells.
Finding evidence of SARS-CoV-2 throughout the GI system, if not direct infectivity, suggests a fecal-oral route of transmission, the researchers conclude. “Our immunofluorescent data showed that ACE2 protein, a cell receptor for SARS-CoV-2, is abundantly expressed in the glandular cells of gastric, duodenal and rectal epithelia, supporting the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the host cells.”
Detection of viral RNA at different time points in infection, they write, suggests that the virions are continually secreted and therefore likely infectious, which is under investigation. “Prevention of fecal-oral transmission should be taken into consideration to control the spread of the virus,” they write.
Current recommendations do not require that patients’ fecal samples be tested before being considered noninfectious. However, given their findings and evidence from other studies, Xiao and colleagues recommend that real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) testing of fecal samples be added to current protocols.
Johnson offers practical suggestions based on the “potty hygiene” suggestions he gives to patients dealing with fecal shedding in Clostridioides difficile infection.
“To combat the microaerosolization of C. diff spores, I have patients do a complete bacteriocidal washing out of the toilet bowl, as well as clean surface areas and especially toothbrushes.” Keeping the bowl closed when not in use is important too in preventing “fecal-oral transmission of remnants” of toilet contents, he adds.
The new papers add to other reports suggesting that virus-bearing droplets may reach people in various ways, Johnson said. “Maybe the virus isn’t only spread by a cough or a sneeze.”
The researchers and commentator have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Risk factors for death from COVID-19 identified in Wuhan patients
Patients who did not survive hospitalization for COVID-19 in Wuhan were more likely to be older, have comorbidities, and elevated D-dimer, according to the first study to examine risk factors associated with death among adults hospitalized with COVID-19. “Older age, showing signs of sepsis on admission, underlying diseases like high blood pressure and diabetes, and the prolonged use of noninvasive ventilation were important factors in the deaths of these patients,” coauthor Zhibo Liu said in a news release. Abnormal blood clotting was part of the clinical picture too.
Fei Zhou, MD, from the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and colleagues conducted a retrospective, observational, multicenter cohort study of 191 patients, 137 of whom were discharged and 54 of whom died in the hospital.
The study, published online today in The Lancet, included all adult inpatients with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 from Jinyintan Hospital and Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital who had been discharged or died by January 31 of this year. Severely ill patients in the province were transferred to these hospitals until February 1.
The researchers compared demographic, clinical, treatment, and laboratory data from electronic medical records between survivors and those who succumbed to the disease. The analysis also tested serial samples for viral RNA. Overall, 91 (48%) of the 191 patients had comorbidity. Most common was hypertension (30%), followed by diabetes (19%) and coronary heart disease (8%).
The odds of dying in the hospital increased with age (odds ratio 1.10; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.17; per year increase in age), higher Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score (5.65, 2.61-12.23; P < .0001), and D-dimer level exceeding 1 mcg/L on admission. The SOFA was previously called the “sepsis-related organ failure assessment score” and assesses rate of organ failure in intensive care units. Elevated D-dimer indicates increased risk of abnormal blood clotting, such as deep vein thrombosis.
Nonsurvivors compared with survivors had higher frequencies of respiratory failure (98% vs 36%), sepsis (100%, vs 42%), and secondary infections (50% vs 1%).
The average age of survivors was 52 years compared to 69 for those who died. Liu cited weakening of the immune system and increased inflammation, which damages organs and also promotes viral replication, as explanations for the age effect.
From the time of initial symptoms, median time to discharge from the hospital was 22 days. Average time to death was 18.5 days.
Fever persisted for a median of 12 days among all patients, and cough persisted for a median 19 days; 45% of the survivors were still coughing on discharge. In survivors, shortness of breath improved after 13 days, but persisted until death in the others.
Viral shedding persisted for a median duration of 20 days in survivors, ranging from 8 to 37. The virus (SARS-CoV-2) was detectable in nonsurvivors until death. Antiviral treatment did not curtail viral shedding.
But the viral shedding data come with a caveat. “The extended viral shedding noted in our study has important implications for guiding decisions around isolation precautions and antiviral treatment in patients with confirmed COVID-19 infection. However, we need to be clear that viral shedding time should not be confused with other self-isolation guidance for people who may have been exposed to COVID-19 but do not have symptoms, as this guidance is based on the incubation time of the virus,” explained colead author Bin Cao.
“Older age, elevated D-dimer levels, and high SOFA score could help clinicians to identify at an early stage those patients with COVID-19 who have poor prognosis. Prolonged viral shedding provides the rationale for a strategy of isolation of infected patients and optimal antiviral interventions in the future,” the researchers conclude.
A limitation in interpreting the findings of the study is that hospitalized patients do not represent the entire infected population. The researchers caution that “the number of deaths does not reflect the true mortality of COVID-19.” They also note that they did not have enough genetic material to accurately assess duration of viral shedding.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients who did not survive hospitalization for COVID-19 in Wuhan were more likely to be older, have comorbidities, and elevated D-dimer, according to the first study to examine risk factors associated with death among adults hospitalized with COVID-19. “Older age, showing signs of sepsis on admission, underlying diseases like high blood pressure and diabetes, and the prolonged use of noninvasive ventilation were important factors in the deaths of these patients,” coauthor Zhibo Liu said in a news release. Abnormal blood clotting was part of the clinical picture too.
Fei Zhou, MD, from the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and colleagues conducted a retrospective, observational, multicenter cohort study of 191 patients, 137 of whom were discharged and 54 of whom died in the hospital.
The study, published online today in The Lancet, included all adult inpatients with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 from Jinyintan Hospital and Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital who had been discharged or died by January 31 of this year. Severely ill patients in the province were transferred to these hospitals until February 1.
The researchers compared demographic, clinical, treatment, and laboratory data from electronic medical records between survivors and those who succumbed to the disease. The analysis also tested serial samples for viral RNA. Overall, 91 (48%) of the 191 patients had comorbidity. Most common was hypertension (30%), followed by diabetes (19%) and coronary heart disease (8%).
The odds of dying in the hospital increased with age (odds ratio 1.10; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.17; per year increase in age), higher Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score (5.65, 2.61-12.23; P < .0001), and D-dimer level exceeding 1 mcg/L on admission. The SOFA was previously called the “sepsis-related organ failure assessment score” and assesses rate of organ failure in intensive care units. Elevated D-dimer indicates increased risk of abnormal blood clotting, such as deep vein thrombosis.
Nonsurvivors compared with survivors had higher frequencies of respiratory failure (98% vs 36%), sepsis (100%, vs 42%), and secondary infections (50% vs 1%).
The average age of survivors was 52 years compared to 69 for those who died. Liu cited weakening of the immune system and increased inflammation, which damages organs and also promotes viral replication, as explanations for the age effect.
From the time of initial symptoms, median time to discharge from the hospital was 22 days. Average time to death was 18.5 days.
Fever persisted for a median of 12 days among all patients, and cough persisted for a median 19 days; 45% of the survivors were still coughing on discharge. In survivors, shortness of breath improved after 13 days, but persisted until death in the others.
Viral shedding persisted for a median duration of 20 days in survivors, ranging from 8 to 37. The virus (SARS-CoV-2) was detectable in nonsurvivors until death. Antiviral treatment did not curtail viral shedding.
But the viral shedding data come with a caveat. “The extended viral shedding noted in our study has important implications for guiding decisions around isolation precautions and antiviral treatment in patients with confirmed COVID-19 infection. However, we need to be clear that viral shedding time should not be confused with other self-isolation guidance for people who may have been exposed to COVID-19 but do not have symptoms, as this guidance is based on the incubation time of the virus,” explained colead author Bin Cao.
“Older age, elevated D-dimer levels, and high SOFA score could help clinicians to identify at an early stage those patients with COVID-19 who have poor prognosis. Prolonged viral shedding provides the rationale for a strategy of isolation of infected patients and optimal antiviral interventions in the future,” the researchers conclude.
A limitation in interpreting the findings of the study is that hospitalized patients do not represent the entire infected population. The researchers caution that “the number of deaths does not reflect the true mortality of COVID-19.” They also note that they did not have enough genetic material to accurately assess duration of viral shedding.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients who did not survive hospitalization for COVID-19 in Wuhan were more likely to be older, have comorbidities, and elevated D-dimer, according to the first study to examine risk factors associated with death among adults hospitalized with COVID-19. “Older age, showing signs of sepsis on admission, underlying diseases like high blood pressure and diabetes, and the prolonged use of noninvasive ventilation were important factors in the deaths of these patients,” coauthor Zhibo Liu said in a news release. Abnormal blood clotting was part of the clinical picture too.
Fei Zhou, MD, from the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and colleagues conducted a retrospective, observational, multicenter cohort study of 191 patients, 137 of whom were discharged and 54 of whom died in the hospital.
The study, published online today in The Lancet, included all adult inpatients with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 from Jinyintan Hospital and Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital who had been discharged or died by January 31 of this year. Severely ill patients in the province were transferred to these hospitals until February 1.
The researchers compared demographic, clinical, treatment, and laboratory data from electronic medical records between survivors and those who succumbed to the disease. The analysis also tested serial samples for viral RNA. Overall, 91 (48%) of the 191 patients had comorbidity. Most common was hypertension (30%), followed by diabetes (19%) and coronary heart disease (8%).
The odds of dying in the hospital increased with age (odds ratio 1.10; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.17; per year increase in age), higher Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score (5.65, 2.61-12.23; P < .0001), and D-dimer level exceeding 1 mcg/L on admission. The SOFA was previously called the “sepsis-related organ failure assessment score” and assesses rate of organ failure in intensive care units. Elevated D-dimer indicates increased risk of abnormal blood clotting, such as deep vein thrombosis.
Nonsurvivors compared with survivors had higher frequencies of respiratory failure (98% vs 36%), sepsis (100%, vs 42%), and secondary infections (50% vs 1%).
The average age of survivors was 52 years compared to 69 for those who died. Liu cited weakening of the immune system and increased inflammation, which damages organs and also promotes viral replication, as explanations for the age effect.
From the time of initial symptoms, median time to discharge from the hospital was 22 days. Average time to death was 18.5 days.
Fever persisted for a median of 12 days among all patients, and cough persisted for a median 19 days; 45% of the survivors were still coughing on discharge. In survivors, shortness of breath improved after 13 days, but persisted until death in the others.
Viral shedding persisted for a median duration of 20 days in survivors, ranging from 8 to 37. The virus (SARS-CoV-2) was detectable in nonsurvivors until death. Antiviral treatment did not curtail viral shedding.
But the viral shedding data come with a caveat. “The extended viral shedding noted in our study has important implications for guiding decisions around isolation precautions and antiviral treatment in patients with confirmed COVID-19 infection. However, we need to be clear that viral shedding time should not be confused with other self-isolation guidance for people who may have been exposed to COVID-19 but do not have symptoms, as this guidance is based on the incubation time of the virus,” explained colead author Bin Cao.
“Older age, elevated D-dimer levels, and high SOFA score could help clinicians to identify at an early stage those patients with COVID-19 who have poor prognosis. Prolonged viral shedding provides the rationale for a strategy of isolation of infected patients and optimal antiviral interventions in the future,” the researchers conclude.
A limitation in interpreting the findings of the study is that hospitalized patients do not represent the entire infected population. The researchers caution that “the number of deaths does not reflect the true mortality of COVID-19.” They also note that they did not have enough genetic material to accurately assess duration of viral shedding.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WHO declares COVID-19 outbreak a pandemic
The World Health Organization has formally declared the COVID-19 outbreak a pandemic.

“WHO has been assessing this outbreak around the clock and we are deeply concerned both by the alarming levels of spread and severity, and by the alarming levels of inaction,” WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said during a March 11 press briefing. “We therefore made the assessment that COVID-19 can be characterized as a pandemic.”
He noted that this is the first time a coronavirus has been seen as a pandemic.
The Director-General cautioned that just looking at the number of countries affected, 114 countries, “does not tell the full story. ... We cannot say this loudly enough, or clearly enough, or often enough: All countries can still change the course of this pandemic.”
He reiterated the need for a whole-of-government and a whole-of-society approach to dealing with this, including taking precautions such as isolating, testing, and treating every case and tracing every contact, as well as readying hospitals and health care professionals.
“Let’s look out for each other, because we need each other,” he said.
The World Health Organization has formally declared the COVID-19 outbreak a pandemic.

“WHO has been assessing this outbreak around the clock and we are deeply concerned both by the alarming levels of spread and severity, and by the alarming levels of inaction,” WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said during a March 11 press briefing. “We therefore made the assessment that COVID-19 can be characterized as a pandemic.”
He noted that this is the first time a coronavirus has been seen as a pandemic.
The Director-General cautioned that just looking at the number of countries affected, 114 countries, “does not tell the full story. ... We cannot say this loudly enough, or clearly enough, or often enough: All countries can still change the course of this pandemic.”
He reiterated the need for a whole-of-government and a whole-of-society approach to dealing with this, including taking precautions such as isolating, testing, and treating every case and tracing every contact, as well as readying hospitals and health care professionals.
“Let’s look out for each other, because we need each other,” he said.
The World Health Organization has formally declared the COVID-19 outbreak a pandemic.

“WHO has been assessing this outbreak around the clock and we are deeply concerned both by the alarming levels of spread and severity, and by the alarming levels of inaction,” WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said during a March 11 press briefing. “We therefore made the assessment that COVID-19 can be characterized as a pandemic.”
He noted that this is the first time a coronavirus has been seen as a pandemic.
The Director-General cautioned that just looking at the number of countries affected, 114 countries, “does not tell the full story. ... We cannot say this loudly enough, or clearly enough, or often enough: All countries can still change the course of this pandemic.”
He reiterated the need for a whole-of-government and a whole-of-society approach to dealing with this, including taking precautions such as isolating, testing, and treating every case and tracing every contact, as well as readying hospitals and health care professionals.
“Let’s look out for each other, because we need each other,” he said.
Managing children’s fear, anxiety in the age of COVID-19
With coronavirus disease (COVID-19) reaching epidemic proportions, many US children are growing increasingly anxious about what this means for their own health and safety and that of their friends and family.
The constantly changing numbers of people affected by the virus and the evolving situation mean daily life for many children is affected in some way, with school trips, sports tournaments, and family vacations being postponed or canceled.
All children may have a heightened level of worry, and some who are normally anxious might be obsessing more about handwashing or getting sick.
Experts say there are ways to manage this fear to help children feel safe and appropriately informed.
Clinicians and other adults should provide children with honest and accurate information geared to their age and developmental level, said David Fassler, MD, clinical professor of psychiatry, University of Vermont Larner College of Medicine, Burlington, and member of the Consumer Issues Committee of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.
That said, it’s also acceptable to let children know that some questions can’t be answered, said Fassler.
Be truthful, calm
“This is partly because the information keeps changing as we learn more about how the virus spreads, how to best protect communities, and how to treat people who get sick,” he added.
Clinicians and parents should remind children “that there are a lot of adults who are working very hard to keep them safe,” said Eli R. Lebowitz, PhD, associate professor in the Child Study Center, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, who directs a program for anxiety.
It’s important for adults to pay attention not only to what they say to children but also how they say it, said Lebowitz. He highlighted the importance of talking about the virus “in a calm and matter-of-fact way” rather than in an anxious way.
“If you look scared or tense or your voice is conveying that you’re really scared, the child is going to absorb that and feel anxious as well,” he noted.
This advice also applies when adults are discussing the issue among themselves. They should be aware that “children are listening” and are picking up any anxiety or panic adults are expressing.
Children are soaking up information about this virus from the Internet, the media, friends, teachers, and elsewhere. Lebowitz suggests asking children what they have already heard, which provides an opportunity to correct rumors and inaccurate information.
“A child might have a very inflated sense of what the actual risk is. For example, they may think that anyone who gets the virus dies,” he said.
Myth busting
Adults should let children know that not everything they hear from friends or on the Internet “is necessarily correct,” he added.
Some children who have experienced serious illness or losses may be particularly vulnerable to experiencing intense reactions to graphic news reports or images of illness or death and may need extra support, said Fassler.
Adults could use the “framework of knowledge” that children already have, said Lebowitz. He noted that all children are aware of sickness.
“They know people get sick, and they themselves have probably been sick, so you can tell them that this is a sickness like a bad flu,” he said.
Children should be encouraged to approach adults they trust, such as their pediatrician, a parent, or a teacher, with their questions, said Lebowitz. “Those are the people who are able to give them the most accurate information.”
Fassler noted that accurate, up-to-date information is available via fact sheets developed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization.
Although it’s helpful and appropriate to be reassuring, Fassler advises not to make unrealistic promises.
“It’s fine to tell kids that you’ll deal with whatever happens, even if it means altering travel plans or work schedules, but you can’t promise that no one in your state or community will get sick,” he said.
Maintain healthy habits
Physicians and other adults can tell children “in an age-appropriate way” how the virus is transmitted and what the symptoms are, but it’s important to emphasize that most people who are sick don’t have COVID-19, said Lebowitz.
“I would emphasize that the people who are the sickest are the elderly who are already sick, rather than healthy younger people,” he said.
Lebowitz recommends continuing to follow guidelines on staying healthy, including coughing into a sleeve instead of your hand and regular handwashing.
It’s also important at this time for children to maintain healthy habits – getting enough physical activity and sleep, eating well, and being outside – because this regime will go a long way toward reducing anxiety, said Lebowitz. Deep breathing and muscle-relaxing exercises can also help, he said.
Lebowitz also suggests maintaining a supportive attitude and showing “some acceptance and validation of what children are feeling, as well as some confidence that they can cope and tolerate feeling uncomfortable sometimes, that they can handle some anxiety.”
While accepting that the child could be anxious, it’s important not to encourage excessive avoidance or unhealthy coping strategies. Fassler and Lebowitz agree that children who are overly anxious or preoccupied with concerns about the coronavirus should be evaluated by a trained, qualified mental health professional.
Signs that a child may need additional help include ongoing sleep difficulties, intrusive thoughts or worries, obsessive-compulsive behaviors, or reluctance or refusal to go to school, said Fassler.
The good news is that most children are resilient, said Fassler. “They’ll adjust, adapt, and go on with their lives.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With coronavirus disease (COVID-19) reaching epidemic proportions, many US children are growing increasingly anxious about what this means for their own health and safety and that of their friends and family.
The constantly changing numbers of people affected by the virus and the evolving situation mean daily life for many children is affected in some way, with school trips, sports tournaments, and family vacations being postponed or canceled.
All children may have a heightened level of worry, and some who are normally anxious might be obsessing more about handwashing or getting sick.
Experts say there are ways to manage this fear to help children feel safe and appropriately informed.
Clinicians and other adults should provide children with honest and accurate information geared to their age and developmental level, said David Fassler, MD, clinical professor of psychiatry, University of Vermont Larner College of Medicine, Burlington, and member of the Consumer Issues Committee of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.
That said, it’s also acceptable to let children know that some questions can’t be answered, said Fassler.
Be truthful, calm
“This is partly because the information keeps changing as we learn more about how the virus spreads, how to best protect communities, and how to treat people who get sick,” he added.
Clinicians and parents should remind children “that there are a lot of adults who are working very hard to keep them safe,” said Eli R. Lebowitz, PhD, associate professor in the Child Study Center, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, who directs a program for anxiety.
It’s important for adults to pay attention not only to what they say to children but also how they say it, said Lebowitz. He highlighted the importance of talking about the virus “in a calm and matter-of-fact way” rather than in an anxious way.
“If you look scared or tense or your voice is conveying that you’re really scared, the child is going to absorb that and feel anxious as well,” he noted.
This advice also applies when adults are discussing the issue among themselves. They should be aware that “children are listening” and are picking up any anxiety or panic adults are expressing.
Children are soaking up information about this virus from the Internet, the media, friends, teachers, and elsewhere. Lebowitz suggests asking children what they have already heard, which provides an opportunity to correct rumors and inaccurate information.
“A child might have a very inflated sense of what the actual risk is. For example, they may think that anyone who gets the virus dies,” he said.
Myth busting
Adults should let children know that not everything they hear from friends or on the Internet “is necessarily correct,” he added.
Some children who have experienced serious illness or losses may be particularly vulnerable to experiencing intense reactions to graphic news reports or images of illness or death and may need extra support, said Fassler.
Adults could use the “framework of knowledge” that children already have, said Lebowitz. He noted that all children are aware of sickness.
“They know people get sick, and they themselves have probably been sick, so you can tell them that this is a sickness like a bad flu,” he said.
Children should be encouraged to approach adults they trust, such as their pediatrician, a parent, or a teacher, with their questions, said Lebowitz. “Those are the people who are able to give them the most accurate information.”
Fassler noted that accurate, up-to-date information is available via fact sheets developed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization.
Although it’s helpful and appropriate to be reassuring, Fassler advises not to make unrealistic promises.
“It’s fine to tell kids that you’ll deal with whatever happens, even if it means altering travel plans or work schedules, but you can’t promise that no one in your state or community will get sick,” he said.
Maintain healthy habits
Physicians and other adults can tell children “in an age-appropriate way” how the virus is transmitted and what the symptoms are, but it’s important to emphasize that most people who are sick don’t have COVID-19, said Lebowitz.
“I would emphasize that the people who are the sickest are the elderly who are already sick, rather than healthy younger people,” he said.
Lebowitz recommends continuing to follow guidelines on staying healthy, including coughing into a sleeve instead of your hand and regular handwashing.
It’s also important at this time for children to maintain healthy habits – getting enough physical activity and sleep, eating well, and being outside – because this regime will go a long way toward reducing anxiety, said Lebowitz. Deep breathing and muscle-relaxing exercises can also help, he said.
Lebowitz also suggests maintaining a supportive attitude and showing “some acceptance and validation of what children are feeling, as well as some confidence that they can cope and tolerate feeling uncomfortable sometimes, that they can handle some anxiety.”
While accepting that the child could be anxious, it’s important not to encourage excessive avoidance or unhealthy coping strategies. Fassler and Lebowitz agree that children who are overly anxious or preoccupied with concerns about the coronavirus should be evaluated by a trained, qualified mental health professional.
Signs that a child may need additional help include ongoing sleep difficulties, intrusive thoughts or worries, obsessive-compulsive behaviors, or reluctance or refusal to go to school, said Fassler.
The good news is that most children are resilient, said Fassler. “They’ll adjust, adapt, and go on with their lives.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With coronavirus disease (COVID-19) reaching epidemic proportions, many US children are growing increasingly anxious about what this means for their own health and safety and that of their friends and family.
The constantly changing numbers of people affected by the virus and the evolving situation mean daily life for many children is affected in some way, with school trips, sports tournaments, and family vacations being postponed or canceled.
All children may have a heightened level of worry, and some who are normally anxious might be obsessing more about handwashing or getting sick.
Experts say there are ways to manage this fear to help children feel safe and appropriately informed.
Clinicians and other adults should provide children with honest and accurate information geared to their age and developmental level, said David Fassler, MD, clinical professor of psychiatry, University of Vermont Larner College of Medicine, Burlington, and member of the Consumer Issues Committee of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.
That said, it’s also acceptable to let children know that some questions can’t be answered, said Fassler.
Be truthful, calm
“This is partly because the information keeps changing as we learn more about how the virus spreads, how to best protect communities, and how to treat people who get sick,” he added.
Clinicians and parents should remind children “that there are a lot of adults who are working very hard to keep them safe,” said Eli R. Lebowitz, PhD, associate professor in the Child Study Center, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, who directs a program for anxiety.
It’s important for adults to pay attention not only to what they say to children but also how they say it, said Lebowitz. He highlighted the importance of talking about the virus “in a calm and matter-of-fact way” rather than in an anxious way.
“If you look scared or tense or your voice is conveying that you’re really scared, the child is going to absorb that and feel anxious as well,” he noted.
This advice also applies when adults are discussing the issue among themselves. They should be aware that “children are listening” and are picking up any anxiety or panic adults are expressing.
Children are soaking up information about this virus from the Internet, the media, friends, teachers, and elsewhere. Lebowitz suggests asking children what they have already heard, which provides an opportunity to correct rumors and inaccurate information.
“A child might have a very inflated sense of what the actual risk is. For example, they may think that anyone who gets the virus dies,” he said.
Myth busting
Adults should let children know that not everything they hear from friends or on the Internet “is necessarily correct,” he added.
Some children who have experienced serious illness or losses may be particularly vulnerable to experiencing intense reactions to graphic news reports or images of illness or death and may need extra support, said Fassler.
Adults could use the “framework of knowledge” that children already have, said Lebowitz. He noted that all children are aware of sickness.
“They know people get sick, and they themselves have probably been sick, so you can tell them that this is a sickness like a bad flu,” he said.
Children should be encouraged to approach adults they trust, such as their pediatrician, a parent, or a teacher, with their questions, said Lebowitz. “Those are the people who are able to give them the most accurate information.”
Fassler noted that accurate, up-to-date information is available via fact sheets developed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization.
Although it’s helpful and appropriate to be reassuring, Fassler advises not to make unrealistic promises.
“It’s fine to tell kids that you’ll deal with whatever happens, even if it means altering travel plans or work schedules, but you can’t promise that no one in your state or community will get sick,” he said.
Maintain healthy habits
Physicians and other adults can tell children “in an age-appropriate way” how the virus is transmitted and what the symptoms are, but it’s important to emphasize that most people who are sick don’t have COVID-19, said Lebowitz.
“I would emphasize that the people who are the sickest are the elderly who are already sick, rather than healthy younger people,” he said.
Lebowitz recommends continuing to follow guidelines on staying healthy, including coughing into a sleeve instead of your hand and regular handwashing.
It’s also important at this time for children to maintain healthy habits – getting enough physical activity and sleep, eating well, and being outside – because this regime will go a long way toward reducing anxiety, said Lebowitz. Deep breathing and muscle-relaxing exercises can also help, he said.
Lebowitz also suggests maintaining a supportive attitude and showing “some acceptance and validation of what children are feeling, as well as some confidence that they can cope and tolerate feeling uncomfortable sometimes, that they can handle some anxiety.”
While accepting that the child could be anxious, it’s important not to encourage excessive avoidance or unhealthy coping strategies. Fassler and Lebowitz agree that children who are overly anxious or preoccupied with concerns about the coronavirus should be evaluated by a trained, qualified mental health professional.
Signs that a child may need additional help include ongoing sleep difficulties, intrusive thoughts or worries, obsessive-compulsive behaviors, or reluctance or refusal to go to school, said Fassler.
The good news is that most children are resilient, said Fassler. “They’ll adjust, adapt, and go on with their lives.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rapid Development of Perifolliculitis Following Mesotherapy
To the Editor:
Mesotherapy, also known as intradermotherapy, is a cosmetic procedure in which multiple intradermal or subcutaneous injections of homeopathic substances, vitamins, chemicals, and plant extracts are administered.1 First conceived in Europe, mesotherapy is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration but is gaining popularity in the United States as an alternative cosmetic procedure for various purposes, including lipolysis, body contouring, stretch marks, acne scars, actinic damage, and skin rejuvenation.1,2 We report a case of a healthy woman who developed perifolliculitis, transaminitis, and neutropenia 2 weeks after mesotherapy administration to the face, neck, and chest. We also review other potential side effects of this procedure.
A 36-year-old woman with no notable medical history presented to the emergency department with a worsening pruritic and painful rash on the face, chest, and neck of 2 weeks’ duration. The rash had developed 3 days after the patient received mesotherapy with an unknown substance for cosmetic rejuvenation; the rash was localized only to the injection sites. She did not note any fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, arthralgia, or upper respiratory tract symptoms. She further denied starting any new medications, herbal products, or topical therapies apart from the procedure she had received 2 weeks prior.
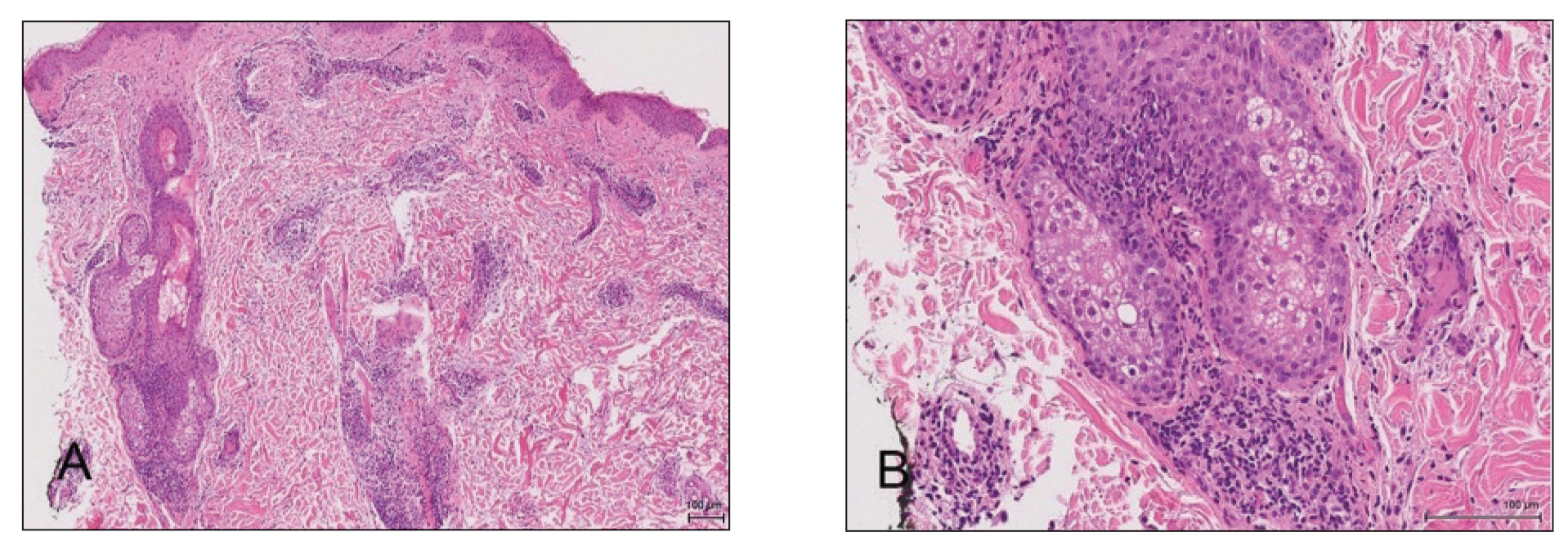
The patient was found to be in no acute distress and vital signs were stable. Laboratory testing was remarkable for elevations in alanine aminotransferase (62 U/L [reference range, 10–40 U/L]) and aspartate aminotransferase (72 U/L [reference range 10–30 U/L]). Moreover, she had an absolute neutrophil count of 0.5×103 cells/µL (reference range 1.8–8.0×103 cells/µL). An electrolyte panel, creatinine level, and urinalysis were normal. Physical examination revealed numerous 4- to 5-mm erythematous papules in a gridlike distribution across the face, neck, and chest (Figure 1). No pustules or nodules were present. There was no discharge, crust, excoriations, or secondary lesions. Additionally, there was no lymphadenopathy and no mucous membrane or ocular involvement.

A 4-mm punch biopsy from a representative papule on the right lateral aspect of the neck demonstrated a perifollicular and perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with some focal granulomatous changes. No polarizable foreign body material was found (Figure 2). Bacterial, fungal, mycobacterial, and skin cultures were obtained, and results were all negative after several weeks.
A diagnosis of perifolliculitis from the mesotherapy procedure was on the top of the differential vs a fast-growing mycobacterial or granulomatous reaction. The patient was started on a prednisone taper at 40 mg once daily tapered down completely over 3 weeks in addition to triamcinolone cream 0.1% applied 2 to 4 times daily as needed. Although she did not return to our outpatient clinic for follow-up, she informed us that her rash had improved 1 month after starting the prednisone taper. She was later lost to follow-up. It is unclear if the transaminitis and neutropenia were related to the materials injected during the mesotherapy procedure or from long-standing health issues.
Mesotherapy promises aesthetic benefits through a minimally invasive procedure and therefore is rapidly gaining popularity in aesthetic spas and treatment centers. Due to the lack of regulation in treatment protocols and substances used, there have been numerous reported cases of adverse side effects following mesotherapy, such as pain, allergic reactions, urticaria, panniculitis, ulceration, hair loss, necrosis, paraffinoma, cutaneous tuberculosis, and rapidly growing nontuberculous mycobacterial infections.1-5 More serious side effects also have been reported, such as permanent scarring, deformities, delirium, and massive subcutaneous emphysema (Table).2,4-18
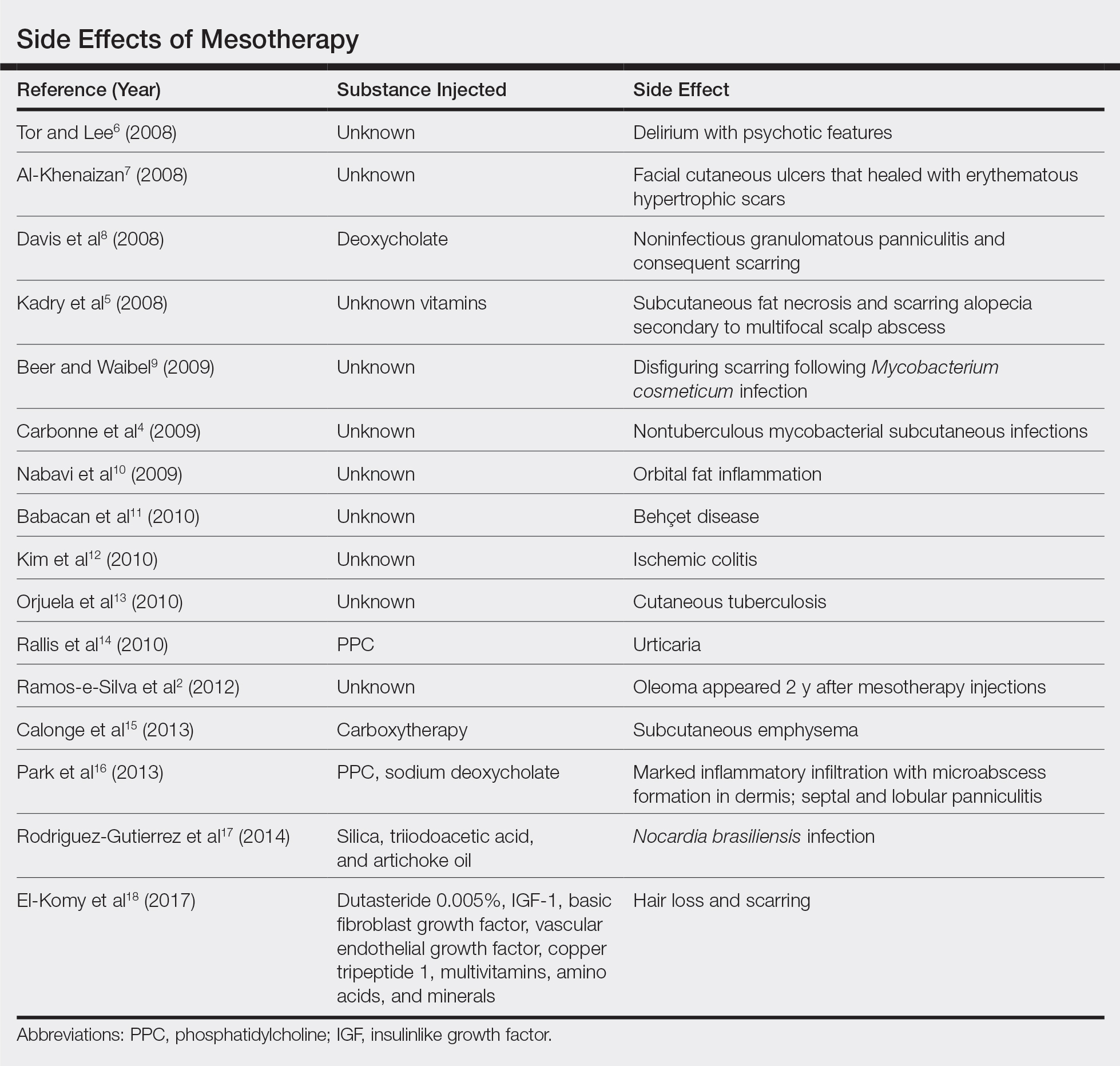
Given the potential complications of mesotherapy documented in the literature, we believe clinical investigations and trials must be performed to appropriately assess the safety and efficacy of this potentially hazardous procedure. Because there currently is insufficient research showing why certain patients are developing these adverse side effects, aesthetic spas and treatment centers should inform patients of all potential side effects associated with mesotherapy for the patient to make an informed decision about the procedure. Mesotherapy should be a point of focus for both the US Food and Drug Administration and researchers to determine its efficacy, safety, and standardization of the procedure.
- Bishara AS, Ibrahim AE, Dibo SA. Cosmetic mesotherapy: between scientific evidence, science fiction, and lucrative business. Aesth Plast Surg. 2008;32:842-849.
- Ramos-e-Silva M, Pereira AL, Ramos-e-Silva S, et al. Oleoma: a rare complication of mesotherapy for cellulite. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:162-167.
- Rotunda AM, Kolodney MS. Mesotherapy and phosphatidylcholine injections: historical clarification and review. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:465-480.
- Carbonne A, Brossier F, Arnaud I, et al. Outbreak of nontuberculous mycobacterial subcutaneous infections related to multiple mesotherapy injections. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:1961-1964.
- Kadry R, Hamadah I, Al-Issa A, et al. Multifocal scalp abscess with subcutaneous fat necrosis and scarring alopecia as a complication of scalp mesotherapy. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7:72-73.
- Tor PC, Lee TS. Delirium with psychotic features possibly associated with mesotherapy. Psychosomatics. 2008;49:273-274.
- Al-Khenaizan S. Facial cutaneous ulcers following mesotherapy. Dermatol Surg. 2008;34:832-834.
- Davis MD, Wright TI, Shehan JM. A complication of mesotherapy: noninfectious granulomatous panniculitis. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:808-809.
- Beer K, Waibel J. Disfiguring scarring following mesotherapy-associated Mycobacterium cosmeticum infection. J Drugs Dermatol. 2009;8:391-393.
- Nabavi CB, Minckler DS, Tao JP. Histologic features of mesotherapy-induced orbital fat inflammation. Opthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;25:69-70.
- Babacan T, Onat AM, Pehlivan Y, et al. A case of Behçet’s disease diagnosed by the panniculitis after mesotherapy. Rheumatol Int. 2010;30:1657-1659.
- Kim JB, Moon W, Park SJ, et al. Ischemic colitis after mesotherapy combined with anti-obesity medications. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:1537-1540.
- Orjuela D, Puerto G, Mejia G, et al. Cutaneous tuberculosis after mesotherapy: report of six cases. Biomedica. 2010;30:321-326.
- Rallis E, Kintzoglou S, Moussatou V, et al. Mesotherapy-induced urticaria. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1355-1356.
- Calonge WM, Lesbros-Pantoflickova D, Hodina M, et al. Massive subcutaneous emphysema after carbon dioxide mesotherapy. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2013;37:194-197.
- Park EJ, Kim HS, Kim M, et al. Histological changes after treatment for localized fat deposits with phosphatidylcholine and sodium deoxycholate. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2013;3:240-243.
- Rodriguez-Gutierrez G, Toussaint S, Hernandez-Castro R, et al. Norcardia brasiliensis infection: an emergent suppurative granuloma after mesotherapy. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:888-890.
- El-Komy M, Hassan A, Tawdy A, et al. Hair loss at injection sites of mesotherapy for alopecia [published online February 3, 2017]. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2017;16:E28-E30.
To the Editor:
Mesotherapy, also known as intradermotherapy, is a cosmetic procedure in which multiple intradermal or subcutaneous injections of homeopathic substances, vitamins, chemicals, and plant extracts are administered.1 First conceived in Europe, mesotherapy is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration but is gaining popularity in the United States as an alternative cosmetic procedure for various purposes, including lipolysis, body contouring, stretch marks, acne scars, actinic damage, and skin rejuvenation.1,2 We report a case of a healthy woman who developed perifolliculitis, transaminitis, and neutropenia 2 weeks after mesotherapy administration to the face, neck, and chest. We also review other potential side effects of this procedure.
A 36-year-old woman with no notable medical history presented to the emergency department with a worsening pruritic and painful rash on the face, chest, and neck of 2 weeks’ duration. The rash had developed 3 days after the patient received mesotherapy with an unknown substance for cosmetic rejuvenation; the rash was localized only to the injection sites. She did not note any fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, arthralgia, or upper respiratory tract symptoms. She further denied starting any new medications, herbal products, or topical therapies apart from the procedure she had received 2 weeks prior.
The patient was found to be in no acute distress and vital signs were stable. Laboratory testing was remarkable for elevations in alanine aminotransferase (62 U/L [reference range, 10–40 U/L]) and aspartate aminotransferase (72 U/L [reference range 10–30 U/L]). Moreover, she had an absolute neutrophil count of 0.5×103 cells/µL (reference range 1.8–8.0×103 cells/µL). An electrolyte panel, creatinine level, and urinalysis were normal. Physical examination revealed numerous 4- to 5-mm erythematous papules in a gridlike distribution across the face, neck, and chest (Figure 1). No pustules or nodules were present. There was no discharge, crust, excoriations, or secondary lesions. Additionally, there was no lymphadenopathy and no mucous membrane or ocular involvement.

A 4-mm punch biopsy from a representative papule on the right lateral aspect of the neck demonstrated a perifollicular and perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with some focal granulomatous changes. No polarizable foreign body material was found (Figure 2). Bacterial, fungal, mycobacterial, and skin cultures were obtained, and results were all negative after several weeks.

A diagnosis of perifolliculitis from the mesotherapy procedure was on the top of the differential vs a fast-growing mycobacterial or granulomatous reaction. The patient was started on a prednisone taper at 40 mg once daily tapered down completely over 3 weeks in addition to triamcinolone cream 0.1% applied 2 to 4 times daily as needed. Although she did not return to our outpatient clinic for follow-up, she informed us that her rash had improved 1 month after starting the prednisone taper. She was later lost to follow-up. It is unclear if the transaminitis and neutropenia were related to the materials injected during the mesotherapy procedure or from long-standing health issues.
Mesotherapy promises aesthetic benefits through a minimally invasive procedure and therefore is rapidly gaining popularity in aesthetic spas and treatment centers. Due to the lack of regulation in treatment protocols and substances used, there have been numerous reported cases of adverse side effects following mesotherapy, such as pain, allergic reactions, urticaria, panniculitis, ulceration, hair loss, necrosis, paraffinoma, cutaneous tuberculosis, and rapidly growing nontuberculous mycobacterial infections.1-5 More serious side effects also have been reported, such as permanent scarring, deformities, delirium, and massive subcutaneous emphysema (Table).2,4-18

Given the potential complications of mesotherapy documented in the literature, we believe clinical investigations and trials must be performed to appropriately assess the safety and efficacy of this potentially hazardous procedure. Because there currently is insufficient research showing why certain patients are developing these adverse side effects, aesthetic spas and treatment centers should inform patients of all potential side effects associated with mesotherapy for the patient to make an informed decision about the procedure. Mesotherapy should be a point of focus for both the US Food and Drug Administration and researchers to determine its efficacy, safety, and standardization of the procedure.
To the Editor:
Mesotherapy, also known as intradermotherapy, is a cosmetic procedure in which multiple intradermal or subcutaneous injections of homeopathic substances, vitamins, chemicals, and plant extracts are administered.1 First conceived in Europe, mesotherapy is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration but is gaining popularity in the United States as an alternative cosmetic procedure for various purposes, including lipolysis, body contouring, stretch marks, acne scars, actinic damage, and skin rejuvenation.1,2 We report a case of a healthy woman who developed perifolliculitis, transaminitis, and neutropenia 2 weeks after mesotherapy administration to the face, neck, and chest. We also review other potential side effects of this procedure.
A 36-year-old woman with no notable medical history presented to the emergency department with a worsening pruritic and painful rash on the face, chest, and neck of 2 weeks’ duration. The rash had developed 3 days after the patient received mesotherapy with an unknown substance for cosmetic rejuvenation; the rash was localized only to the injection sites. She did not note any fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, arthralgia, or upper respiratory tract symptoms. She further denied starting any new medications, herbal products, or topical therapies apart from the procedure she had received 2 weeks prior.
The patient was found to be in no acute distress and vital signs were stable. Laboratory testing was remarkable for elevations in alanine aminotransferase (62 U/L [reference range, 10–40 U/L]) and aspartate aminotransferase (72 U/L [reference range 10–30 U/L]). Moreover, she had an absolute neutrophil count of 0.5×103 cells/µL (reference range 1.8–8.0×103 cells/µL). An electrolyte panel, creatinine level, and urinalysis were normal. Physical examination revealed numerous 4- to 5-mm erythematous papules in a gridlike distribution across the face, neck, and chest (Figure 1). No pustules or nodules were present. There was no discharge, crust, excoriations, or secondary lesions. Additionally, there was no lymphadenopathy and no mucous membrane or ocular involvement.

A 4-mm punch biopsy from a representative papule on the right lateral aspect of the neck demonstrated a perifollicular and perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with some focal granulomatous changes. No polarizable foreign body material was found (Figure 2). Bacterial, fungal, mycobacterial, and skin cultures were obtained, and results were all negative after several weeks.

A diagnosis of perifolliculitis from the mesotherapy procedure was on the top of the differential vs a fast-growing mycobacterial or granulomatous reaction. The patient was started on a prednisone taper at 40 mg once daily tapered down completely over 3 weeks in addition to triamcinolone cream 0.1% applied 2 to 4 times daily as needed. Although she did not return to our outpatient clinic for follow-up, she informed us that her rash had improved 1 month after starting the prednisone taper. She was later lost to follow-up. It is unclear if the transaminitis and neutropenia were related to the materials injected during the mesotherapy procedure or from long-standing health issues.
Mesotherapy promises aesthetic benefits through a minimally invasive procedure and therefore is rapidly gaining popularity in aesthetic spas and treatment centers. Due to the lack of regulation in treatment protocols and substances used, there have been numerous reported cases of adverse side effects following mesotherapy, such as pain, allergic reactions, urticaria, panniculitis, ulceration, hair loss, necrosis, paraffinoma, cutaneous tuberculosis, and rapidly growing nontuberculous mycobacterial infections.1-5 More serious side effects also have been reported, such as permanent scarring, deformities, delirium, and massive subcutaneous emphysema (Table).2,4-18

Given the potential complications of mesotherapy documented in the literature, we believe clinical investigations and trials must be performed to appropriately assess the safety and efficacy of this potentially hazardous procedure. Because there currently is insufficient research showing why certain patients are developing these adverse side effects, aesthetic spas and treatment centers should inform patients of all potential side effects associated with mesotherapy for the patient to make an informed decision about the procedure. Mesotherapy should be a point of focus for both the US Food and Drug Administration and researchers to determine its efficacy, safety, and standardization of the procedure.
- Bishara AS, Ibrahim AE, Dibo SA. Cosmetic mesotherapy: between scientific evidence, science fiction, and lucrative business. Aesth Plast Surg. 2008;32:842-849.
- Ramos-e-Silva M, Pereira AL, Ramos-e-Silva S, et al. Oleoma: a rare complication of mesotherapy for cellulite. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:162-167.
- Rotunda AM, Kolodney MS. Mesotherapy and phosphatidylcholine injections: historical clarification and review. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:465-480.
- Carbonne A, Brossier F, Arnaud I, et al. Outbreak of nontuberculous mycobacterial subcutaneous infections related to multiple mesotherapy injections. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:1961-1964.
- Kadry R, Hamadah I, Al-Issa A, et al. Multifocal scalp abscess with subcutaneous fat necrosis and scarring alopecia as a complication of scalp mesotherapy. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7:72-73.
- Tor PC, Lee TS. Delirium with psychotic features possibly associated with mesotherapy. Psychosomatics. 2008;49:273-274.
- Al-Khenaizan S. Facial cutaneous ulcers following mesotherapy. Dermatol Surg. 2008;34:832-834.
- Davis MD, Wright TI, Shehan JM. A complication of mesotherapy: noninfectious granulomatous panniculitis. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:808-809.
- Beer K, Waibel J. Disfiguring scarring following mesotherapy-associated Mycobacterium cosmeticum infection. J Drugs Dermatol. 2009;8:391-393.
- Nabavi CB, Minckler DS, Tao JP. Histologic features of mesotherapy-induced orbital fat inflammation. Opthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;25:69-70.
- Babacan T, Onat AM, Pehlivan Y, et al. A case of Behçet’s disease diagnosed by the panniculitis after mesotherapy. Rheumatol Int. 2010;30:1657-1659.
- Kim JB, Moon W, Park SJ, et al. Ischemic colitis after mesotherapy combined with anti-obesity medications. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:1537-1540.
- Orjuela D, Puerto G, Mejia G, et al. Cutaneous tuberculosis after mesotherapy: report of six cases. Biomedica. 2010;30:321-326.
- Rallis E, Kintzoglou S, Moussatou V, et al. Mesotherapy-induced urticaria. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1355-1356.
- Calonge WM, Lesbros-Pantoflickova D, Hodina M, et al. Massive subcutaneous emphysema after carbon dioxide mesotherapy. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2013;37:194-197.
- Park EJ, Kim HS, Kim M, et al. Histological changes after treatment for localized fat deposits with phosphatidylcholine and sodium deoxycholate. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2013;3:240-243.
- Rodriguez-Gutierrez G, Toussaint S, Hernandez-Castro R, et al. Norcardia brasiliensis infection: an emergent suppurative granuloma after mesotherapy. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:888-890.
- El-Komy M, Hassan A, Tawdy A, et al. Hair loss at injection sites of mesotherapy for alopecia [published online February 3, 2017]. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2017;16:E28-E30.
- Bishara AS, Ibrahim AE, Dibo SA. Cosmetic mesotherapy: between scientific evidence, science fiction, and lucrative business. Aesth Plast Surg. 2008;32:842-849.
- Ramos-e-Silva M, Pereira AL, Ramos-e-Silva S, et al. Oleoma: a rare complication of mesotherapy for cellulite. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:162-167.
- Rotunda AM, Kolodney MS. Mesotherapy and phosphatidylcholine injections: historical clarification and review. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:465-480.
- Carbonne A, Brossier F, Arnaud I, et al. Outbreak of nontuberculous mycobacterial subcutaneous infections related to multiple mesotherapy injections. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:1961-1964.
- Kadry R, Hamadah I, Al-Issa A, et al. Multifocal scalp abscess with subcutaneous fat necrosis and scarring alopecia as a complication of scalp mesotherapy. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7:72-73.
- Tor PC, Lee TS. Delirium with psychotic features possibly associated with mesotherapy. Psychosomatics. 2008;49:273-274.
- Al-Khenaizan S. Facial cutaneous ulcers following mesotherapy. Dermatol Surg. 2008;34:832-834.
- Davis MD, Wright TI, Shehan JM. A complication of mesotherapy: noninfectious granulomatous panniculitis. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:808-809.
- Beer K, Waibel J. Disfiguring scarring following mesotherapy-associated Mycobacterium cosmeticum infection. J Drugs Dermatol. 2009;8:391-393.
- Nabavi CB, Minckler DS, Tao JP. Histologic features of mesotherapy-induced orbital fat inflammation. Opthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;25:69-70.
- Babacan T, Onat AM, Pehlivan Y, et al. A case of Behçet’s disease diagnosed by the panniculitis after mesotherapy. Rheumatol Int. 2010;30:1657-1659.
- Kim JB, Moon W, Park SJ, et al. Ischemic colitis after mesotherapy combined with anti-obesity medications. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:1537-1540.
- Orjuela D, Puerto G, Mejia G, et al. Cutaneous tuberculosis after mesotherapy: report of six cases. Biomedica. 2010;30:321-326.
- Rallis E, Kintzoglou S, Moussatou V, et al. Mesotherapy-induced urticaria. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1355-1356.
- Calonge WM, Lesbros-Pantoflickova D, Hodina M, et al. Massive subcutaneous emphysema after carbon dioxide mesotherapy. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2013;37:194-197.
- Park EJ, Kim HS, Kim M, et al. Histological changes after treatment for localized fat deposits with phosphatidylcholine and sodium deoxycholate. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2013;3:240-243.
- Rodriguez-Gutierrez G, Toussaint S, Hernandez-Castro R, et al. Norcardia brasiliensis infection: an emergent suppurative granuloma after mesotherapy. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:888-890.
- El-Komy M, Hassan A, Tawdy A, et al. Hair loss at injection sites of mesotherapy for alopecia [published online February 3, 2017]. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2017;16:E28-E30.
Practice Points
- Mesotherapy—the delivery of vitamins, chemicals, and plant extracts directly into the dermis via injections—is a common procedure performed in both medical and nonmedical settings for cosmetic rejuvenation.
- Complications can occur from mesotherapy treatment.
- Patients should be advised to seek medical care with US Food and Drug Administration–approved cosmetic techniques and substances only
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection in a Hepatitis B Virus–Positive Psoriasis Patient Treated With Ustekinumab
To the Editor:
The incidence of psoriasis in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)–infected patients is similar to the general population, but it usually becomes more severe as immunosuppression increases. Additionally, it tends to be more resistant to conventional therapies, and the incidence and severity of psoriatic arthropathy is increased. Psoriasis often worsens at the time of HIV primary infection.1 We describe a case of a patient with hepatitis B virus (HBV) whose severe plaque psoriasis was controlled on ustekinumab; he was later diagnosed with HIV infection.
A 42-year-old man with HBV treated with entecavir (HBV DNA viral load, <20 copies/mL [inactive carrier, <2000 copies/mL]) presented to our dermatology unit with severe plaque psoriasis (psoriasis area and severity index 23) that caused notable psychologic difficulties such as anxiety and depression. Treatment was attempted with cyclosporine; acitretin; psoralen plus UVA; infliximab; adalimumab; and eventually ustekinumab (45 mg every 3 months), which controlled the condition well (psoriasis area and severity index 0) in an almost completely sustained manner.
Serologic tests requested at one of his analytical control appointments 2 years after initiating treatment with ustekinumab revealed he was HIV positive. The patient reported unprotected sexual intercourse 4 months prior. He was referred to the infectious disease unit and was classified in subtype A1 of HIV infection (CD4 count, 583 cells/µL [reference range, 500-1200 cells/µL]; viral load, 159,268 copies/mL [rapid progression to AIDS, >100,000 copies/mL]). Treatment was initiated with raltegravir, ritonavir, darunavir, and abacavir; tolerance was suitable. Because of the patient’s history of severe psoriasis, treatment with ustekinumab was maintained. Normally, treatment with this drug would be contraindicated in patients with HIV, as it can lead to viral reactivation. Four years after his HIV diagnosis, neither the patient’s cutaneous nor HIV-associated condition had worsened.
For patients with HIV and mild or moderate psoriasis, topical therapies (eg, corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues, tazarotene) are recommended, similar to patients who are HIV negative. Human immunodeficiency virus–positive patients with severe psoriasis who do not respond to topical treatment should receive phototherapy (UVB or psoralen plus UVA) or acitretin along with their antiretroviral drugs.2 In refractory cases, immunosuppressants, including cyclosporine, methotrexate, or tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors, might be used, though experience with them is limited.3,4 Maintaining antiretroviral therapy and prophylaxis against opportunist disease is important in patients who receive such immunosuppressants, as is close monitoring of the viral load.
Ustekinumab is an IL-12/IL-23 monoclonal antibody indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, active psoriatic arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease. It is contraindicated in patients with clinically important active infections, such as HBV and hepatitis C virus infections.5 However, it was shown to be safe in a group of 18 patients with HBV who had received antiviral prophylaxis6; a degree of reactivation was observed in similar patients who received no such prophylaxis and in others with hepatitis C virus infection.7 The simultaneous use of methotrexate with ustekinumab in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis does not appear to affect the safety of the latter drug.8 Paparizos et al9 described a patient with HIV controlled with antiretroviral drugs who was treated with ustekinumab for psoriasis; no adverse effects were observed.
We report the case of a patient with HBV and psoriasis who was treated with ustekinumab and later became infected with HIV. His ustekinumab treatment was maintained without subsequent cutaneous or systemic complications.
- Menon K, Van Voorhees V, Bebo B, et al. Psoriasis in patients with HIV infection: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:291-299.
- Chiricozzi A, Saraceno R, Cannizzaro MV. Complete resolution of erythrodermic psoriasis in an HIV and HCV patient unresponsive to antipsoriatic treatments after highly active antiretroviral therapy. Dermatology. 2012;225:333-337.
- Barco D, Puig L, Alomar A. Treatment of moderate-severe psoriasis with etanercept in patients with chronic human immunodeficiency virus infection. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2010;101(suppl 1):77-81.
- Lindsey SF, Weiss J, Lee ES, et al. Treatment of severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis with adalimumab in an HIV positive patient. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:869-871.
- Rustin MH. Long-term safety of biologics in the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: review of the current data. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167(suppl 3):3-11.
- Navarro R, Vilarrasa E, Herranz P, et al. Safety and effectiveness of ustekinumab and antitumour necrosis factor therapy in patients with psoriasis and chronic viral hepatitis B or C: a retrospective, multicentre study in a clinical setting. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:609-616.
- Chiu HY, Chen CH, Wu MS, et al. The safety profile of ustekinumab in the treatment of patients with psoriasis and concurrent hepatitis B or C. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:1295-1303.
- Weitz JE, Ritchlin CT. Ustekinumab: targeting the IL-17 pathway to improve outcomes in psoriatic arthritis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2014;14:515-526.
- Paparizos V, Rallis E, Kirsten L, et al. Ustekinumab for the treatment of HIV psoriasis. J Dermatol Treat. 2012;23:398-399.
To the Editor:
The incidence of psoriasis in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)–infected patients is similar to the general population, but it usually becomes more severe as immunosuppression increases. Additionally, it tends to be more resistant to conventional therapies, and the incidence and severity of psoriatic arthropathy is increased. Psoriasis often worsens at the time of HIV primary infection.1 We describe a case of a patient with hepatitis B virus (HBV) whose severe plaque psoriasis was controlled on ustekinumab; he was later diagnosed with HIV infection.
A 42-year-old man with HBV treated with entecavir (HBV DNA viral load, <20 copies/mL [inactive carrier, <2000 copies/mL]) presented to our dermatology unit with severe plaque psoriasis (psoriasis area and severity index 23) that caused notable psychologic difficulties such as anxiety and depression. Treatment was attempted with cyclosporine; acitretin; psoralen plus UVA; infliximab; adalimumab; and eventually ustekinumab (45 mg every 3 months), which controlled the condition well (psoriasis area and severity index 0) in an almost completely sustained manner.
Serologic tests requested at one of his analytical control appointments 2 years after initiating treatment with ustekinumab revealed he was HIV positive. The patient reported unprotected sexual intercourse 4 months prior. He was referred to the infectious disease unit and was classified in subtype A1 of HIV infection (CD4 count, 583 cells/µL [reference range, 500-1200 cells/µL]; viral load, 159,268 copies/mL [rapid progression to AIDS, >100,000 copies/mL]). Treatment was initiated with raltegravir, ritonavir, darunavir, and abacavir; tolerance was suitable. Because of the patient’s history of severe psoriasis, treatment with ustekinumab was maintained. Normally, treatment with this drug would be contraindicated in patients with HIV, as it can lead to viral reactivation. Four years after his HIV diagnosis, neither the patient’s cutaneous nor HIV-associated condition had worsened.
For patients with HIV and mild or moderate psoriasis, topical therapies (eg, corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues, tazarotene) are recommended, similar to patients who are HIV negative. Human immunodeficiency virus–positive patients with severe psoriasis who do not respond to topical treatment should receive phototherapy (UVB or psoralen plus UVA) or acitretin along with their antiretroviral drugs.2 In refractory cases, immunosuppressants, including cyclosporine, methotrexate, or tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors, might be used, though experience with them is limited.3,4 Maintaining antiretroviral therapy and prophylaxis against opportunist disease is important in patients who receive such immunosuppressants, as is close monitoring of the viral load.
Ustekinumab is an IL-12/IL-23 monoclonal antibody indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, active psoriatic arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease. It is contraindicated in patients with clinically important active infections, such as HBV and hepatitis C virus infections.5 However, it was shown to be safe in a group of 18 patients with HBV who had received antiviral prophylaxis6; a degree of reactivation was observed in similar patients who received no such prophylaxis and in others with hepatitis C virus infection.7 The simultaneous use of methotrexate with ustekinumab in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis does not appear to affect the safety of the latter drug.8 Paparizos et al9 described a patient with HIV controlled with antiretroviral drugs who was treated with ustekinumab for psoriasis; no adverse effects were observed.
We report the case of a patient with HBV and psoriasis who was treated with ustekinumab and later became infected with HIV. His ustekinumab treatment was maintained without subsequent cutaneous or systemic complications.
To the Editor:
The incidence of psoriasis in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)–infected patients is similar to the general population, but it usually becomes more severe as immunosuppression increases. Additionally, it tends to be more resistant to conventional therapies, and the incidence and severity of psoriatic arthropathy is increased. Psoriasis often worsens at the time of HIV primary infection.1 We describe a case of a patient with hepatitis B virus (HBV) whose severe plaque psoriasis was controlled on ustekinumab; he was later diagnosed with HIV infection.
A 42-year-old man with HBV treated with entecavir (HBV DNA viral load, <20 copies/mL [inactive carrier, <2000 copies/mL]) presented to our dermatology unit with severe plaque psoriasis (psoriasis area and severity index 23) that caused notable psychologic difficulties such as anxiety and depression. Treatment was attempted with cyclosporine; acitretin; psoralen plus UVA; infliximab; adalimumab; and eventually ustekinumab (45 mg every 3 months), which controlled the condition well (psoriasis area and severity index 0) in an almost completely sustained manner.
Serologic tests requested at one of his analytical control appointments 2 years after initiating treatment with ustekinumab revealed he was HIV positive. The patient reported unprotected sexual intercourse 4 months prior. He was referred to the infectious disease unit and was classified in subtype A1 of HIV infection (CD4 count, 583 cells/µL [reference range, 500-1200 cells/µL]; viral load, 159,268 copies/mL [rapid progression to AIDS, >100,000 copies/mL]). Treatment was initiated with raltegravir, ritonavir, darunavir, and abacavir; tolerance was suitable. Because of the patient’s history of severe psoriasis, treatment with ustekinumab was maintained. Normally, treatment with this drug would be contraindicated in patients with HIV, as it can lead to viral reactivation. Four years after his HIV diagnosis, neither the patient’s cutaneous nor HIV-associated condition had worsened.
For patients with HIV and mild or moderate psoriasis, topical therapies (eg, corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues, tazarotene) are recommended, similar to patients who are HIV negative. Human immunodeficiency virus–positive patients with severe psoriasis who do not respond to topical treatment should receive phototherapy (UVB or psoralen plus UVA) or acitretin along with their antiretroviral drugs.2 In refractory cases, immunosuppressants, including cyclosporine, methotrexate, or tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors, might be used, though experience with them is limited.3,4 Maintaining antiretroviral therapy and prophylaxis against opportunist disease is important in patients who receive such immunosuppressants, as is close monitoring of the viral load.
Ustekinumab is an IL-12/IL-23 monoclonal antibody indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, active psoriatic arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease. It is contraindicated in patients with clinically important active infections, such as HBV and hepatitis C virus infections.5 However, it was shown to be safe in a group of 18 patients with HBV who had received antiviral prophylaxis6; a degree of reactivation was observed in similar patients who received no such prophylaxis and in others with hepatitis C virus infection.7 The simultaneous use of methotrexate with ustekinumab in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis does not appear to affect the safety of the latter drug.8 Paparizos et al9 described a patient with HIV controlled with antiretroviral drugs who was treated with ustekinumab for psoriasis; no adverse effects were observed.
We report the case of a patient with HBV and psoriasis who was treated with ustekinumab and later became infected with HIV. His ustekinumab treatment was maintained without subsequent cutaneous or systemic complications.
- Menon K, Van Voorhees V, Bebo B, et al. Psoriasis in patients with HIV infection: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:291-299.
- Chiricozzi A, Saraceno R, Cannizzaro MV. Complete resolution of erythrodermic psoriasis in an HIV and HCV patient unresponsive to antipsoriatic treatments after highly active antiretroviral therapy. Dermatology. 2012;225:333-337.
- Barco D, Puig L, Alomar A. Treatment of moderate-severe psoriasis with etanercept in patients with chronic human immunodeficiency virus infection. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2010;101(suppl 1):77-81.
- Lindsey SF, Weiss J, Lee ES, et al. Treatment of severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis with adalimumab in an HIV positive patient. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:869-871.
- Rustin MH. Long-term safety of biologics in the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: review of the current data. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167(suppl 3):3-11.
- Navarro R, Vilarrasa E, Herranz P, et al. Safety and effectiveness of ustekinumab and antitumour necrosis factor therapy in patients with psoriasis and chronic viral hepatitis B or C: a retrospective, multicentre study in a clinical setting. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:609-616.
- Chiu HY, Chen CH, Wu MS, et al. The safety profile of ustekinumab in the treatment of patients with psoriasis and concurrent hepatitis B or C. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:1295-1303.
- Weitz JE, Ritchlin CT. Ustekinumab: targeting the IL-17 pathway to improve outcomes in psoriatic arthritis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2014;14:515-526.
- Paparizos V, Rallis E, Kirsten L, et al. Ustekinumab for the treatment of HIV psoriasis. J Dermatol Treat. 2012;23:398-399.
- Menon K, Van Voorhees V, Bebo B, et al. Psoriasis in patients with HIV infection: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:291-299.
- Chiricozzi A, Saraceno R, Cannizzaro MV. Complete resolution of erythrodermic psoriasis in an HIV and HCV patient unresponsive to antipsoriatic treatments after highly active antiretroviral therapy. Dermatology. 2012;225:333-337.
- Barco D, Puig L, Alomar A. Treatment of moderate-severe psoriasis with etanercept in patients with chronic human immunodeficiency virus infection. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2010;101(suppl 1):77-81.
- Lindsey SF, Weiss J, Lee ES, et al. Treatment of severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis with adalimumab in an HIV positive patient. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:869-871.
- Rustin MH. Long-term safety of biologics in the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: review of the current data. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167(suppl 3):3-11.
- Navarro R, Vilarrasa E, Herranz P, et al. Safety and effectiveness of ustekinumab and antitumour necrosis factor therapy in patients with psoriasis and chronic viral hepatitis B or C: a retrospective, multicentre study in a clinical setting. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:609-616.
- Chiu HY, Chen CH, Wu MS, et al. The safety profile of ustekinumab in the treatment of patients with psoriasis and concurrent hepatitis B or C. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:1295-1303.
- Weitz JE, Ritchlin CT. Ustekinumab: targeting the IL-17 pathway to improve outcomes in psoriatic arthritis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2014;14:515-526.
- Paparizos V, Rallis E, Kirsten L, et al. Ustekinumab for the treatment of HIV psoriasis. J Dermatol Treat. 2012;23:398-399.
Practice Points
- Psoriasis in patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) tends to be more resistant to conventional therapies.
- Experience is limited in the use of immunosuppressants and biologics to treat psoriasis in HIV patients.
- Maintaining antiretroviral therapy and prophylaxis against opportunist disease is important in HIV patients who receive biologics, as is close monitoring of the viral load.
COVID-19 update: Transmission 5% or less among close contacts
The transmission rate of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was 1%-5% among 38,000 Chinese people in close contact with infected patients, according to the chief epidemiologist of the Chinese Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing, Zunyou Wu, MD, PhD, who gave an update on the epidemic at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
The rate of spread to family members – the driver of the infection in China – was 10% early in the outbreak, but fell to 3% with quicker recognition and isolation. The overall numbers are lower than might have been expected, and an important insight for clinicians trying to contain the outbreak in the United States.
, but their ability to spread the infection dropped after that, Dr. Wu and others said at a special COVID-19 session at the meeting, which was scheduled to be in Boston, but was held online instead because of concerns about spreading the virus. The session has been posted.
Transmission from presymptomatic people is rare. Shedding persists to some degree for 7-12 days in mild/moderate cases, but 2 weeks or more in severe cases.
Dr. Wu said the numbers in China are moving in the right direction, which means that containment efforts there have worked.
The virus emerged in Wuhan, the capital of Hubei province in central China, in connection with a wildlife food market in December 2019. Bats are thought to be the reservoir, with perhaps an intermediate step between civet cats and raccoon dogs. Officials shut down the market.
Essentially, the entire population of China, more than a billion people, was told to stay home for 10 days to interrupt the transmission cycle after the virus spread throughout the country in a few weeks, and almost 60 million people in Hubei were put behind a cordon sanitaire, where they have been for 50 days and will remain “for a while,” Dr. Wu said.
It’s led to a steep drop in new cases and deaths in China since mid-February; both are now more common outside China than inside, and international numbers are lower than they were at the peak in China.
Meanwhile, there’s been no evidence of perinatal transmission; the virus has not been detected in amniotic fluid, cord blood, neonatal throat swabs, or breast milk. Maternal morbidity appears to be similar to uninfected women. “The data around pregnancy are reassuring,” said John Brooks, MD, chief medical officers for HIV/AIDS prevention at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, who has been involved with CDC’s containment efforts.
There’s no data yet for immunocompromised people, but for people with HIV, he said, “we think the risk of severe illness would be greater” with lower CD4 counts and unsuppressed viral loads. “People living with HIV should take precautions against this new virus,” including having at least a 30-day supply of HIV medications; keeping up flu and pneumonia vaccinations; and having a care plan if quarantined. Setting up telemedicine might be a good idea.
The usual incubation period for COVID-19 is 4-6 days but can be longer. Recovery time is about 2 weeks in mild cases and 3-6 weeks in more severe cases. People who die do so within 2 months of symptom onset.
The most common symptoms among hospitalized patients in China are fever, dry cough, fatigue, and headache. Truly asymptomatic cases are not common; most go on to develop symptoms. There have been reports of diarrhea before other symptoms by a day or two, but it’s probably a red herring. The virus has been isolated from stool, but there is no evidence of fecal-oral transmission, Dr. Wu said.
Eighty percent of COVID-19 cases are mild or moderate and most patients recover spontaneously, especially middle aged and younger people. There is no meaningful difference in distribution between the sexes.
There are limited pediatric data perhaps due to underreporting, “but we know [children] experience milder illness than adults,” the CDC’s Dr. Brooks said.
He pegged the latest case fatality estimate at 0.5% to 3.5%, which is considerably higher than seasonal flu, but might well drop as more mild cases are detected and added to the denominator, he said.
For now, death rates top 5% in adults over 60 years old and climb further with increasing age, approaching 16% in people 80 years or older. Patients with hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and chronic respiratory illness are at increased risk. The ultimate cause of death is acute respiratory distress syndrome, said Ralph Baric, PhD, a coronavirus expert and epidemiology professor at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, who also presented at the meeting.
Several drug and vaccine candidates are under study for the infection. An intriguing possibility is that angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors might help. Hypertension is a known risk factor for severe infection; the virus makes use of ACE receptor pathways to infect airway epithelial cells; and there have been reports of ACE inhibitors having effect against the virus that caused severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), another coronavirus outbreak in 2003.
“I think it’s a very good idea to go back and re-explore use of these drugs,” Dr. Baric said.
The presenters didn’t have any relevant disclosures.
The transmission rate of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was 1%-5% among 38,000 Chinese people in close contact with infected patients, according to the chief epidemiologist of the Chinese Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing, Zunyou Wu, MD, PhD, who gave an update on the epidemic at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
The rate of spread to family members – the driver of the infection in China – was 10% early in the outbreak, but fell to 3% with quicker recognition and isolation. The overall numbers are lower than might have been expected, and an important insight for clinicians trying to contain the outbreak in the United States.
, but their ability to spread the infection dropped after that, Dr. Wu and others said at a special COVID-19 session at the meeting, which was scheduled to be in Boston, but was held online instead because of concerns about spreading the virus. The session has been posted.
Transmission from presymptomatic people is rare. Shedding persists to some degree for 7-12 days in mild/moderate cases, but 2 weeks or more in severe cases.
Dr. Wu said the numbers in China are moving in the right direction, which means that containment efforts there have worked.
The virus emerged in Wuhan, the capital of Hubei province in central China, in connection with a wildlife food market in December 2019. Bats are thought to be the reservoir, with perhaps an intermediate step between civet cats and raccoon dogs. Officials shut down the market.
Essentially, the entire population of China, more than a billion people, was told to stay home for 10 days to interrupt the transmission cycle after the virus spread throughout the country in a few weeks, and almost 60 million people in Hubei were put behind a cordon sanitaire, where they have been for 50 days and will remain “for a while,” Dr. Wu said.
It’s led to a steep drop in new cases and deaths in China since mid-February; both are now more common outside China than inside, and international numbers are lower than they were at the peak in China.
Meanwhile, there’s been no evidence of perinatal transmission; the virus has not been detected in amniotic fluid, cord blood, neonatal throat swabs, or breast milk. Maternal morbidity appears to be similar to uninfected women. “The data around pregnancy are reassuring,” said John Brooks, MD, chief medical officers for HIV/AIDS prevention at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, who has been involved with CDC’s containment efforts.
There’s no data yet for immunocompromised people, but for people with HIV, he said, “we think the risk of severe illness would be greater” with lower CD4 counts and unsuppressed viral loads. “People living with HIV should take precautions against this new virus,” including having at least a 30-day supply of HIV medications; keeping up flu and pneumonia vaccinations; and having a care plan if quarantined. Setting up telemedicine might be a good idea.
The usual incubation period for COVID-19 is 4-6 days but can be longer. Recovery time is about 2 weeks in mild cases and 3-6 weeks in more severe cases. People who die do so within 2 months of symptom onset.
The most common symptoms among hospitalized patients in China are fever, dry cough, fatigue, and headache. Truly asymptomatic cases are not common; most go on to develop symptoms. There have been reports of diarrhea before other symptoms by a day or two, but it’s probably a red herring. The virus has been isolated from stool, but there is no evidence of fecal-oral transmission, Dr. Wu said.
Eighty percent of COVID-19 cases are mild or moderate and most patients recover spontaneously, especially middle aged and younger people. There is no meaningful difference in distribution between the sexes.
There are limited pediatric data perhaps due to underreporting, “but we know [children] experience milder illness than adults,” the CDC’s Dr. Brooks said.
He pegged the latest case fatality estimate at 0.5% to 3.5%, which is considerably higher than seasonal flu, but might well drop as more mild cases are detected and added to the denominator, he said.
For now, death rates top 5% in adults over 60 years old and climb further with increasing age, approaching 16% in people 80 years or older. Patients with hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and chronic respiratory illness are at increased risk. The ultimate cause of death is acute respiratory distress syndrome, said Ralph Baric, PhD, a coronavirus expert and epidemiology professor at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, who also presented at the meeting.
Several drug and vaccine candidates are under study for the infection. An intriguing possibility is that angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors might help. Hypertension is a known risk factor for severe infection; the virus makes use of ACE receptor pathways to infect airway epithelial cells; and there have been reports of ACE inhibitors having effect against the virus that caused severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), another coronavirus outbreak in 2003.
“I think it’s a very good idea to go back and re-explore use of these drugs,” Dr. Baric said.
The presenters didn’t have any relevant disclosures.
The transmission rate of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was 1%-5% among 38,000 Chinese people in close contact with infected patients, according to the chief epidemiologist of the Chinese Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing, Zunyou Wu, MD, PhD, who gave an update on the epidemic at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
The rate of spread to family members – the driver of the infection in China – was 10% early in the outbreak, but fell to 3% with quicker recognition and isolation. The overall numbers are lower than might have been expected, and an important insight for clinicians trying to contain the outbreak in the United States.
, but their ability to spread the infection dropped after that, Dr. Wu and others said at a special COVID-19 session at the meeting, which was scheduled to be in Boston, but was held online instead because of concerns about spreading the virus. The session has been posted.
Transmission from presymptomatic people is rare. Shedding persists to some degree for 7-12 days in mild/moderate cases, but 2 weeks or more in severe cases.
Dr. Wu said the numbers in China are moving in the right direction, which means that containment efforts there have worked.
The virus emerged in Wuhan, the capital of Hubei province in central China, in connection with a wildlife food market in December 2019. Bats are thought to be the reservoir, with perhaps an intermediate step between civet cats and raccoon dogs. Officials shut down the market.
Essentially, the entire population of China, more than a billion people, was told to stay home for 10 days to interrupt the transmission cycle after the virus spread throughout the country in a few weeks, and almost 60 million people in Hubei were put behind a cordon sanitaire, where they have been for 50 days and will remain “for a while,” Dr. Wu said.
It’s led to a steep drop in new cases and deaths in China since mid-February; both are now more common outside China than inside, and international numbers are lower than they were at the peak in China.
Meanwhile, there’s been no evidence of perinatal transmission; the virus has not been detected in amniotic fluid, cord blood, neonatal throat swabs, or breast milk. Maternal morbidity appears to be similar to uninfected women. “The data around pregnancy are reassuring,” said John Brooks, MD, chief medical officers for HIV/AIDS prevention at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, who has been involved with CDC’s containment efforts.
There’s no data yet for immunocompromised people, but for people with HIV, he said, “we think the risk of severe illness would be greater” with lower CD4 counts and unsuppressed viral loads. “People living with HIV should take precautions against this new virus,” including having at least a 30-day supply of HIV medications; keeping up flu and pneumonia vaccinations; and having a care plan if quarantined. Setting up telemedicine might be a good idea.
The usual incubation period for COVID-19 is 4-6 days but can be longer. Recovery time is about 2 weeks in mild cases and 3-6 weeks in more severe cases. People who die do so within 2 months of symptom onset.
The most common symptoms among hospitalized patients in China are fever, dry cough, fatigue, and headache. Truly asymptomatic cases are not common; most go on to develop symptoms. There have been reports of diarrhea before other symptoms by a day or two, but it’s probably a red herring. The virus has been isolated from stool, but there is no evidence of fecal-oral transmission, Dr. Wu said.
Eighty percent of COVID-19 cases are mild or moderate and most patients recover spontaneously, especially middle aged and younger people. There is no meaningful difference in distribution between the sexes.
There are limited pediatric data perhaps due to underreporting, “but we know [children] experience milder illness than adults,” the CDC’s Dr. Brooks said.
He pegged the latest case fatality estimate at 0.5% to 3.5%, which is considerably higher than seasonal flu, but might well drop as more mild cases are detected and added to the denominator, he said.
For now, death rates top 5% in adults over 60 years old and climb further with increasing age, approaching 16% in people 80 years or older. Patients with hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and chronic respiratory illness are at increased risk. The ultimate cause of death is acute respiratory distress syndrome, said Ralph Baric, PhD, a coronavirus expert and epidemiology professor at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, who also presented at the meeting.
Several drug and vaccine candidates are under study for the infection. An intriguing possibility is that angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors might help. Hypertension is a known risk factor for severe infection; the virus makes use of ACE receptor pathways to infect airway epithelial cells; and there have been reports of ACE inhibitors having effect against the virus that caused severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), another coronavirus outbreak in 2003.
“I think it’s a very good idea to go back and re-explore use of these drugs,” Dr. Baric said.
The presenters didn’t have any relevant disclosures.
FROM CROI 2020
FDA cancels or postpones meetings amid COVID-19 concerns
Officials at the Food and Drug Administration’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research are taking the precautionary step of canceling or postponing advisory committee meetings and limiting staff travel in an effort to help curb the spread of the COVID-19.
“The outbreak of respiratory illness caused by a novel coronavirus, COVID-19, that started in China is spreading to other countries, including the United States,” CDER Director Janet Woodcock, MD, said in a memo to CDER staff. “As a precaution, FDA is canceling foreign official agency travel and limiting domestic travel to mission critical only, effective immediately and through April.”
Additionally, the memo notes that “CDER-organized external meetings, conferences, and workshops will be postponed or canceled from March 10 through April.”
“To mitigate the impact on our work, I encourage you to hold meetings with external stakeholders through teleconference, when possible,” she wrote.
Thus far, only a few CDER events on the FDA’s meeting webpage are listed as being canceled or postponed. Some of the affected meetings include a March 10 public meeting on patient-focused drug development for stimulant-use disorder, a March 11 meeting of the Nonprescription Drug Advisory Committee, and a March 30 public meeting on patient-focused drug development for vitiligo, all of which are postponed until further notice. The Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research also has postponed until further notice its U.S.–Japan Cellular and Gene Therapy Conference, originally scheduled for March 12.
Dr. Woodcock also noted in the memo that in relation to inspections, “we plan to use technology and established agreements with our foreign counterparts to minimize disruptions to the drug supply chain and to applications under review, so that Americans can continue to get their medications.”
Officials at the Food and Drug Administration’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research are taking the precautionary step of canceling or postponing advisory committee meetings and limiting staff travel in an effort to help curb the spread of the COVID-19.
“The outbreak of respiratory illness caused by a novel coronavirus, COVID-19, that started in China is spreading to other countries, including the United States,” CDER Director Janet Woodcock, MD, said in a memo to CDER staff. “As a precaution, FDA is canceling foreign official agency travel and limiting domestic travel to mission critical only, effective immediately and through April.”
Additionally, the memo notes that “CDER-organized external meetings, conferences, and workshops will be postponed or canceled from March 10 through April.”
“To mitigate the impact on our work, I encourage you to hold meetings with external stakeholders through teleconference, when possible,” she wrote.
Thus far, only a few CDER events on the FDA’s meeting webpage are listed as being canceled or postponed. Some of the affected meetings include a March 10 public meeting on patient-focused drug development for stimulant-use disorder, a March 11 meeting of the Nonprescription Drug Advisory Committee, and a March 30 public meeting on patient-focused drug development for vitiligo, all of which are postponed until further notice. The Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research also has postponed until further notice its U.S.–Japan Cellular and Gene Therapy Conference, originally scheduled for March 12.
Dr. Woodcock also noted in the memo that in relation to inspections, “we plan to use technology and established agreements with our foreign counterparts to minimize disruptions to the drug supply chain and to applications under review, so that Americans can continue to get their medications.”
Officials at the Food and Drug Administration’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research are taking the precautionary step of canceling or postponing advisory committee meetings and limiting staff travel in an effort to help curb the spread of the COVID-19.
“The outbreak of respiratory illness caused by a novel coronavirus, COVID-19, that started in China is spreading to other countries, including the United States,” CDER Director Janet Woodcock, MD, said in a memo to CDER staff. “As a precaution, FDA is canceling foreign official agency travel and limiting domestic travel to mission critical only, effective immediately and through April.”
Additionally, the memo notes that “CDER-organized external meetings, conferences, and workshops will be postponed or canceled from March 10 through April.”
“To mitigate the impact on our work, I encourage you to hold meetings with external stakeholders through teleconference, when possible,” she wrote.
Thus far, only a few CDER events on the FDA’s meeting webpage are listed as being canceled or postponed. Some of the affected meetings include a March 10 public meeting on patient-focused drug development for stimulant-use disorder, a March 11 meeting of the Nonprescription Drug Advisory Committee, and a March 30 public meeting on patient-focused drug development for vitiligo, all of which are postponed until further notice. The Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research also has postponed until further notice its U.S.–Japan Cellular and Gene Therapy Conference, originally scheduled for March 12.
Dr. Woodcock also noted in the memo that in relation to inspections, “we plan to use technology and established agreements with our foreign counterparts to minimize disruptions to the drug supply chain and to applications under review, so that Americans can continue to get their medications.”
Internal Medicine 2020 canceled
The American College of Physicians has recently joined the list of medical-specialty organizations to have canceled an upcoming meeting because of the ongoing COVID-19 (coronavirus disease) outbreak.
according to a statement from the organization.
“ACP’s decision is based on recent reports from the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) of rapidly escalating concerns about the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), and in recognition of the vital role of internal medicine physicians in diagnosing, managing, and caring for their patients and communities on the front lines,” according to the announcement.
The ACP is offering a refund to those who have already registered to attend the meeting.
The organization has included responses on its website to a number of frequently asked questions related to the cancellation. One response notes that ACP is offering paid registrants an opportunity to apply their meeting registration credit toward a 30-hour CME package, “which will be made available as soon as possible.” This package, named ACP CME 30, “will comprise curated, online lectures originally scheduled for live presentation at Internal Medicine Meeting 2020.”
The American College of Physicians has recently joined the list of medical-specialty organizations to have canceled an upcoming meeting because of the ongoing COVID-19 (coronavirus disease) outbreak.
according to a statement from the organization.
“ACP’s decision is based on recent reports from the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) of rapidly escalating concerns about the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), and in recognition of the vital role of internal medicine physicians in diagnosing, managing, and caring for their patients and communities on the front lines,” according to the announcement.
The ACP is offering a refund to those who have already registered to attend the meeting.
The organization has included responses on its website to a number of frequently asked questions related to the cancellation. One response notes that ACP is offering paid registrants an opportunity to apply their meeting registration credit toward a 30-hour CME package, “which will be made available as soon as possible.” This package, named ACP CME 30, “will comprise curated, online lectures originally scheduled for live presentation at Internal Medicine Meeting 2020.”
The American College of Physicians has recently joined the list of medical-specialty organizations to have canceled an upcoming meeting because of the ongoing COVID-19 (coronavirus disease) outbreak.
according to a statement from the organization.
“ACP’s decision is based on recent reports from the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) of rapidly escalating concerns about the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), and in recognition of the vital role of internal medicine physicians in diagnosing, managing, and caring for their patients and communities on the front lines,” according to the announcement.
The ACP is offering a refund to those who have already registered to attend the meeting.
The organization has included responses on its website to a number of frequently asked questions related to the cancellation. One response notes that ACP is offering paid registrants an opportunity to apply their meeting registration credit toward a 30-hour CME package, “which will be made available as soon as possible.” This package, named ACP CME 30, “will comprise curated, online lectures originally scheduled for live presentation at Internal Medicine Meeting 2020.”
More postpartum weight gain with dolutegravir-based ART
Women with HIV on dolutegravir-based antiretroviral therapy (ART) protocols had higher weights through 18 months of the postpartum period than women on efavirenz-based therapy, according to a recent study. However, women taking dolutegravir had similar postpartum weights to women who did not have HIV infection.
The results were shared by Jennifer Jao, MD, MPH, of Northwestern University, Chicago, in a video presentation of the research during the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting because of concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
Dr. Jao, an internal medicine physician and pediatrician, and colleagues looked at the association between dolutegravir and postpartum weight for women with HIV, compared with women with HIV who were taking efavirenz-based ART and women who did not have HIV infection.
Though there was no significant difference among the three groups for body mass index at 4 weeks post partum (all were between 24 and 26 kg/m2), postpartum weight for the dolutegravir group was significantly higher.
Using a mixed models statistical approach that adjusted for potentially confounding variables, Dr. Jao and associates found that women on a dolutegravir-based regiment weighed an average of 5 kg more postpartum than women on an efavirenz-based regiment. (P less than .01).
Further adjustment that included CD4 count, viral load, and ART status at conception didn’t change the results from the original approach that included such variables as age, breastfeeding duration , gestational diabetes status, and second and third trimester weight gain (P = .04).
The study was a secondary analysis of the Tshilo Dikotla study conducted in Botswana. Dr. Jao said that the study addressed the known association of dolutegravir-based ART with higher weight gain than other ART regimens. Seeing how postpartum weight varies by regimen is important because “postpartum weight retention impacts cardiometabolic risk,” added Dr. Jao.
Of a total of 406 women, 170 were on dolutegravir-based therapy, 114 were on efavirenz-based therapy, and 122 weren’t HIV infected. Overall, the women on efavirenz-based therapy were older, with a median age of 33 years, compared with 28.5 and 25 years for the dolutegravir group and those without HIV, respectively. This and all other between-group differences were statistically significant at P less than .01.
Women without HIV had lower gravidity, with a median one pregnancy, compared with three in the other two groups. Other significant differences included a higher rate of weight gain in the second and third trimesters for the non–HIV-infected group, who gained at a rate of 0.3 kg/week, compared with 0.1 and 0.2 kg/week for the efavirenz and dolutegravir groups, respectively. Breastfeeding duration was longer in the non–HIV-infected group as well.
Finally, 86% of women on efavirenz-based therapy were on ART at the time of conception, compared with just 35.3% of women on dolutegravir-based treatment.
“Further studies to assess mechanisms of postpartum weight retention are needed,” said Dr. Jao.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Jao reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jao J et al. CROI 2020, Poster 00772.
Women with HIV on dolutegravir-based antiretroviral therapy (ART) protocols had higher weights through 18 months of the postpartum period than women on efavirenz-based therapy, according to a recent study. However, women taking dolutegravir had similar postpartum weights to women who did not have HIV infection.
The results were shared by Jennifer Jao, MD, MPH, of Northwestern University, Chicago, in a video presentation of the research during the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting because of concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
Dr. Jao, an internal medicine physician and pediatrician, and colleagues looked at the association between dolutegravir and postpartum weight for women with HIV, compared with women with HIV who were taking efavirenz-based ART and women who did not have HIV infection.
Though there was no significant difference among the three groups for body mass index at 4 weeks post partum (all were between 24 and 26 kg/m2), postpartum weight for the dolutegravir group was significantly higher.
Using a mixed models statistical approach that adjusted for potentially confounding variables, Dr. Jao and associates found that women on a dolutegravir-based regiment weighed an average of 5 kg more postpartum than women on an efavirenz-based regiment. (P less than .01).
Further adjustment that included CD4 count, viral load, and ART status at conception didn’t change the results from the original approach that included such variables as age, breastfeeding duration , gestational diabetes status, and second and third trimester weight gain (P = .04).
The study was a secondary analysis of the Tshilo Dikotla study conducted in Botswana. Dr. Jao said that the study addressed the known association of dolutegravir-based ART with higher weight gain than other ART regimens. Seeing how postpartum weight varies by regimen is important because “postpartum weight retention impacts cardiometabolic risk,” added Dr. Jao.
Of a total of 406 women, 170 were on dolutegravir-based therapy, 114 were on efavirenz-based therapy, and 122 weren’t HIV infected. Overall, the women on efavirenz-based therapy were older, with a median age of 33 years, compared with 28.5 and 25 years for the dolutegravir group and those without HIV, respectively. This and all other between-group differences were statistically significant at P less than .01.
Women without HIV had lower gravidity, with a median one pregnancy, compared with three in the other two groups. Other significant differences included a higher rate of weight gain in the second and third trimesters for the non–HIV-infected group, who gained at a rate of 0.3 kg/week, compared with 0.1 and 0.2 kg/week for the efavirenz and dolutegravir groups, respectively. Breastfeeding duration was longer in the non–HIV-infected group as well.
Finally, 86% of women on efavirenz-based therapy were on ART at the time of conception, compared with just 35.3% of women on dolutegravir-based treatment.
“Further studies to assess mechanisms of postpartum weight retention are needed,” said Dr. Jao.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Jao reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jao J et al. CROI 2020, Poster 00772.
Women with HIV on dolutegravir-based antiretroviral therapy (ART) protocols had higher weights through 18 months of the postpartum period than women on efavirenz-based therapy, according to a recent study. However, women taking dolutegravir had similar postpartum weights to women who did not have HIV infection.
The results were shared by Jennifer Jao, MD, MPH, of Northwestern University, Chicago, in a video presentation of the research during the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting because of concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
Dr. Jao, an internal medicine physician and pediatrician, and colleagues looked at the association between dolutegravir and postpartum weight for women with HIV, compared with women with HIV who were taking efavirenz-based ART and women who did not have HIV infection.
Though there was no significant difference among the three groups for body mass index at 4 weeks post partum (all were between 24 and 26 kg/m2), postpartum weight for the dolutegravir group was significantly higher.
Using a mixed models statistical approach that adjusted for potentially confounding variables, Dr. Jao and associates found that women on a dolutegravir-based regiment weighed an average of 5 kg more postpartum than women on an efavirenz-based regiment. (P less than .01).
Further adjustment that included CD4 count, viral load, and ART status at conception didn’t change the results from the original approach that included such variables as age, breastfeeding duration , gestational diabetes status, and second and third trimester weight gain (P = .04).
The study was a secondary analysis of the Tshilo Dikotla study conducted in Botswana. Dr. Jao said that the study addressed the known association of dolutegravir-based ART with higher weight gain than other ART regimens. Seeing how postpartum weight varies by regimen is important because “postpartum weight retention impacts cardiometabolic risk,” added Dr. Jao.
Of a total of 406 women, 170 were on dolutegravir-based therapy, 114 were on efavirenz-based therapy, and 122 weren’t HIV infected. Overall, the women on efavirenz-based therapy were older, with a median age of 33 years, compared with 28.5 and 25 years for the dolutegravir group and those without HIV, respectively. This and all other between-group differences were statistically significant at P less than .01.
Women without HIV had lower gravidity, with a median one pregnancy, compared with three in the other two groups. Other significant differences included a higher rate of weight gain in the second and third trimesters for the non–HIV-infected group, who gained at a rate of 0.3 kg/week, compared with 0.1 and 0.2 kg/week for the efavirenz and dolutegravir groups, respectively. Breastfeeding duration was longer in the non–HIV-infected group as well.
Finally, 86% of women on efavirenz-based therapy were on ART at the time of conception, compared with just 35.3% of women on dolutegravir-based treatment.
“Further studies to assess mechanisms of postpartum weight retention are needed,” said Dr. Jao.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Jao reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jao J et al. CROI 2020, Poster 00772.
FROM CROI 2020
