User login
Do You Have Patients With JAKne — JAK Inhibitor–Associated Acne? Here’s What to Know
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A 62-year-old Black female presented with an epidermal inclusion cyst on her left upper back
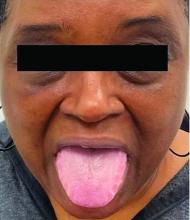
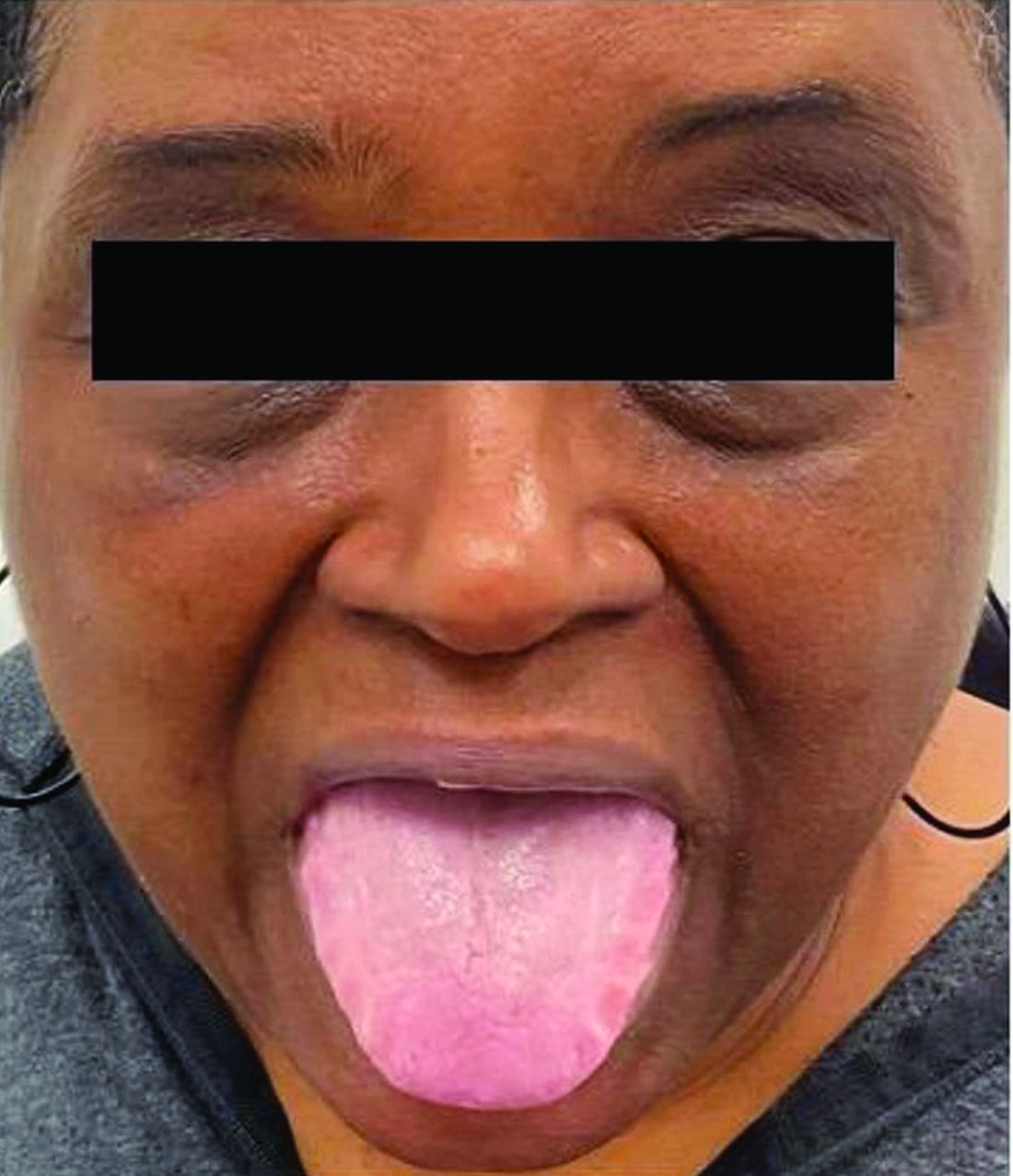
This heterogeneous disorder can present with a wide range of clinical manifestations, including dermatological symptoms that may be the first or predominant feature. Systemic amyloidosis is characterized by macroglossia, periorbital purpura, and waxy skin plaques. Lateral scalloping of the tongue may be seen due to impingement of the teeth. Cutaneous amyloidosis occurs when amyloid is deposited in the skin, without internal organ involvement. Variants of cutaneous amyloidosis include macular, lichen, nodular and biphasic.
This condition requires a thorough diagnostic workup, including serum and urine protein electrophoresis and biopsy of the affected tissue. Biopsy of a cutaneous amyloidosis lesion will show fractured, amorphous, eosinophilic material in the dermis. Pigment and epidermal changes are often found with cutaneous amyloidosis, including hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and epidermal atrophy. Stains that may be used include Congo red showing apple-green birefringence, thioflavin T, and crystal violet.
If untreated, the prognosis is generally poor, related to the extent of organ involvement. Cardiac involvement, a common feature of systemic amyloidosis, can lead to restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Management strategies include steroids, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation. Medications include dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and melphalan.
This patient went undiagnosed for several years until she began experiencing cardiac issues, including syncope, angina, and restrictive cardiomyopathy with heart failure. A cardiac biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis. This patient is currently awaiting a heart transplant. Early diagnosis of amyloidosis is vital, as it can help prevent severe complications such as heart involvement, significantly impacting the patient’s prognosis and quality of life. When amyloidosis is suspected based on dermatological findings, it is essential to distinguish it from other conditions, such as chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleromyxedema, and lipoid proteinosis. Early identification of characteristic skin lesions and systemic features can lead to timely interventions, more favorable outcomes, and reduction in the risk of advanced organ damage.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Cael Aoki and Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Bartos, of Imperial Dermatology, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Clin Liver Dis. 2004 Nov;8(4):915-30, x. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.06.009.
2. Bolognia JL et al. (2017). Dermatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
3. Mehrotra K et al. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Aug;11(8):WC01-WC05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/24273.10334.
4. Banypersad SM et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012 Apr;1(2):e000364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.111.000364.
5. Bustamante JG, Zaidi SRH. Amyloidosis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
This heterogeneous disorder can present with a wide range of clinical manifestations, including dermatological symptoms that may be the first or predominant feature. Systemic amyloidosis is characterized by macroglossia, periorbital purpura, and waxy skin plaques. Lateral scalloping of the tongue may be seen due to impingement of the teeth. Cutaneous amyloidosis occurs when amyloid is deposited in the skin, without internal organ involvement. Variants of cutaneous amyloidosis include macular, lichen, nodular and biphasic.
This condition requires a thorough diagnostic workup, including serum and urine protein electrophoresis and biopsy of the affected tissue. Biopsy of a cutaneous amyloidosis lesion will show fractured, amorphous, eosinophilic material in the dermis. Pigment and epidermal changes are often found with cutaneous amyloidosis, including hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and epidermal atrophy. Stains that may be used include Congo red showing apple-green birefringence, thioflavin T, and crystal violet.
If untreated, the prognosis is generally poor, related to the extent of organ involvement. Cardiac involvement, a common feature of systemic amyloidosis, can lead to restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Management strategies include steroids, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation. Medications include dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and melphalan.
This patient went undiagnosed for several years until she began experiencing cardiac issues, including syncope, angina, and restrictive cardiomyopathy with heart failure. A cardiac biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis. This patient is currently awaiting a heart transplant. Early diagnosis of amyloidosis is vital, as it can help prevent severe complications such as heart involvement, significantly impacting the patient’s prognosis and quality of life. When amyloidosis is suspected based on dermatological findings, it is essential to distinguish it from other conditions, such as chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleromyxedema, and lipoid proteinosis. Early identification of characteristic skin lesions and systemic features can lead to timely interventions, more favorable outcomes, and reduction in the risk of advanced organ damage.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Cael Aoki and Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Bartos, of Imperial Dermatology, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Clin Liver Dis. 2004 Nov;8(4):915-30, x. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.06.009.
2. Bolognia JL et al. (2017). Dermatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
3. Mehrotra K et al. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Aug;11(8):WC01-WC05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/24273.10334.
4. Banypersad SM et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012 Apr;1(2):e000364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.111.000364.
5. Bustamante JG, Zaidi SRH. Amyloidosis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
This heterogeneous disorder can present with a wide range of clinical manifestations, including dermatological symptoms that may be the first or predominant feature. Systemic amyloidosis is characterized by macroglossia, periorbital purpura, and waxy skin plaques. Lateral scalloping of the tongue may be seen due to impingement of the teeth. Cutaneous amyloidosis occurs when amyloid is deposited in the skin, without internal organ involvement. Variants of cutaneous amyloidosis include macular, lichen, nodular and biphasic.
This condition requires a thorough diagnostic workup, including serum and urine protein electrophoresis and biopsy of the affected tissue. Biopsy of a cutaneous amyloidosis lesion will show fractured, amorphous, eosinophilic material in the dermis. Pigment and epidermal changes are often found with cutaneous amyloidosis, including hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and epidermal atrophy. Stains that may be used include Congo red showing apple-green birefringence, thioflavin T, and crystal violet.
If untreated, the prognosis is generally poor, related to the extent of organ involvement. Cardiac involvement, a common feature of systemic amyloidosis, can lead to restrictive cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Management strategies include steroids, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation. Medications include dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and melphalan.
This patient went undiagnosed for several years until she began experiencing cardiac issues, including syncope, angina, and restrictive cardiomyopathy with heart failure. A cardiac biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis. This patient is currently awaiting a heart transplant. Early diagnosis of amyloidosis is vital, as it can help prevent severe complications such as heart involvement, significantly impacting the patient’s prognosis and quality of life. When amyloidosis is suspected based on dermatological findings, it is essential to distinguish it from other conditions, such as chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, scleromyxedema, and lipoid proteinosis. Early identification of characteristic skin lesions and systemic features can lead to timely interventions, more favorable outcomes, and reduction in the risk of advanced organ damage.
The case and photo were submitted by Ms. Cael Aoki and Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Davie, Florida, and Dr. Bartos, of Imperial Dermatology, Hollywood, Florida. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Clin Liver Dis. 2004 Nov;8(4):915-30, x. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.06.009.
2. Bolognia JL et al. (2017). Dermatology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
3. Mehrotra K et al. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Aug;11(8):WC01-WC05. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/24273.10334.
4. Banypersad SM et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012 Apr;1(2):e000364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.111.000364.
5. Bustamante JG, Zaidi SRH. Amyloidosis. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
Study Identifies Oral Antibiotics Linked to Severe Cutaneous Reactions
according to a large, population-based, nested case-control study of older adults, spanning two decades.
The findings, published online in JAMA, “underscore the importance of judicious prescribing, with preferential use of antibiotics associated with a lower risk when clinically appropriate,” noted senior author David Juurlink, MD, PhD, professor of medicine; pediatrics; and health policy, management and evaluation at the University of Toronto, and head of the Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology Division at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, also in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and coauthors.
“We hope our study raises awareness about the importance of drug allergy and gains support for future studies to improve drug allergy care,” lead author Erika Lee, MD, clinical immunology and allergy lecturer at the University of Toronto’s Drug Allergy Clinic, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, said in an interview. “It is important to recognize symptoms and signs of a severe drug rash and promptly stop culprit drugs to prevent worsening reaction.”
Serious cADRs are “a group of rare but potentially life-threatening drug hypersensitivity reactions involving the skin and, frequently, internal organs,” the authors wrote. “Typically delayed in onset, these reactions include drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) — the most severe cADR, which has a reported mortality of 20%-40%,” they noted.
Speculation Without Data
Although it has been speculated that some oral antibiotics are more likely than others to be associated with serious cADRs, there have been no population-based studies examining this, they added.
The study included adults aged 66 years or older and used administrative health databases in Ontario, spanning from April 1, 2002, to March 31, 2022. Data on antibiotic use were taken from the Ontario Drug Benefit database. The Canadian Institute for Health Information (CIHI) National Ambulatory Care Reporting System was used to obtain data on emergency department (ED) visits for cADRs, while the CIHI Discharge Abstract Database was used to identify hospitalizations for cADRs. Finally, demographic information and outpatient healthcare utilization data were obtained from the Registered Persons Database and the Ontario Health Insurance Plan database, respectively.
A cohort of 21,758 older adults (median age, 75 years; 64.1% women) who had an ED visit or hospitalization for serious cADRs within 60 days of receiving antibiotic therapy was matched by age and sex with 87,025 antibiotic-treated controls who did not have a cutaneous reaction.
The median duration of antibiotic prescription was 7 days among cases and controls, and among the cases, the median latency period between antibiotic prescriptions and hospital visits for cADRs was 14 days. Most of the case patients went to the ED only (86.9%), and the rest were hospitalized.
The most commonly prescribed antibiotic class was penicillins (28.9%), followed by cephalosporins (18.2%), fluoroquinolones (16.5%), macrolides (14.8%), nitrofurantoin (8.6%), and sulfonamides (6.2%). Less commonly used antibiotics (“other” antibiotics) accounted for 6.9%.
Macrolide antibiotics were used as the reference because they are rarely associated with serious cADRs, noted the authors, and the multivariable analysis, adjusted for risk factors associated with serious cADRs, including malignancy, chronic liver disease, chronic kidney disease, and HIV.
After multivariable adjustment, relative to macrolides, sulfonamides were most strongly associated with serious cADRs (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.9) but so were all other antibiotic classes, including cephalosporins (aOR, 2.6), “other” antibiotics (aOR, 2.3), nitrofurantoin (aOR, 2.2), penicillins (aOR, 1.4), and fluoroquinolones (aOR,1.3).
In the secondary analysis, the crude rate of ED visits or hospitalizations for cADRs was highest for cephalosporins (4.92 per 1000 prescriptions), followed by sulfonamides (3.22 per 1000 prescriptions). Among hospitalized patients, the median length of stay was 6 days, with 9.6% requiring transfer to a critical care unit and 5.3% dying in the hospital.
Hospitalizations, ED Visits Not Studied Previously
“Notably, the rate of antibiotic-associated serious cADRs leading to an ED visit or hospitalization has not been previously studied,” noted the authors. “We found that at least two hospital encounters for serious cADRs ensued for every 1000 antibiotic prescriptions. This rate is considerably higher than suggested by studies that examine only SJS/TEN and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms.”
Dr. Lee also emphasized the previously unreported findings about nitrofurantoin. “It is surprising to find that nitrofurantoin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic for urinary tract infection, is also associated with an increased risk of severe drug rash,” she said in an interview.
“This finding highlights a potential novel risk at a population-based level and should be further explored in other populations to verify this association,” the authors wrote.
Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security in Baltimore, Maryland, and a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America, who was not involved in the study, agreed that the nitrofurantoin finding was surprising, but he was not surprised that sulfonamides were high on the list.
“The study reinforces that antibiotics are not benign medications to be dispensed injudiciously,” he said in an interview. “Antibiotics have risks, including serious skin reactions, as well as the fostering of antibiotic resistance. Clinicians should always first ask themselves if their patient actually merits an antibiotic and then assess what is the safest antibiotic for the purpose, bearing in mind that certain antibiotics are more likely to result in adverse reactions than others.”
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The study was conducted at ICES, which is funded in part by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care. One coauthor reported receiving compensation from the British Journal of Dermatology as reviewer and section editor, the American Academy of Dermatology as guidelines writer, Canadian Dermatology Today as manuscript writer, and the National Eczema Association and the Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health as consultant; as well as receiving research grants to the coauthor’s institution from the National Eczema Association, Eczema Society of Canada, Canadian Dermatology Foundation, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, US National Institutes of Health, and PSI Foundation. Another coauthor reported receiving grants from AbbVie, Bausch Health, Celgene, Lilly, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, L’Oréal, Novartis, Organon, Pfizer, Sandoz, Amgen, and Boehringer Ingelheim; receiving payment or honoraria for speaking from Sanofi China; participating on advisory boards for LEO Pharma, Novartis, Sanofi, and Union Therapeutics; and receiving equipment donation from L’Oréal. Dr. Adalja reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a large, population-based, nested case-control study of older adults, spanning two decades.
The findings, published online in JAMA, “underscore the importance of judicious prescribing, with preferential use of antibiotics associated with a lower risk when clinically appropriate,” noted senior author David Juurlink, MD, PhD, professor of medicine; pediatrics; and health policy, management and evaluation at the University of Toronto, and head of the Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology Division at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, also in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and coauthors.
“We hope our study raises awareness about the importance of drug allergy and gains support for future studies to improve drug allergy care,” lead author Erika Lee, MD, clinical immunology and allergy lecturer at the University of Toronto’s Drug Allergy Clinic, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, said in an interview. “It is important to recognize symptoms and signs of a severe drug rash and promptly stop culprit drugs to prevent worsening reaction.”
Serious cADRs are “a group of rare but potentially life-threatening drug hypersensitivity reactions involving the skin and, frequently, internal organs,” the authors wrote. “Typically delayed in onset, these reactions include drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) — the most severe cADR, which has a reported mortality of 20%-40%,” they noted.
Speculation Without Data
Although it has been speculated that some oral antibiotics are more likely than others to be associated with serious cADRs, there have been no population-based studies examining this, they added.
The study included adults aged 66 years or older and used administrative health databases in Ontario, spanning from April 1, 2002, to March 31, 2022. Data on antibiotic use were taken from the Ontario Drug Benefit database. The Canadian Institute for Health Information (CIHI) National Ambulatory Care Reporting System was used to obtain data on emergency department (ED) visits for cADRs, while the CIHI Discharge Abstract Database was used to identify hospitalizations for cADRs. Finally, demographic information and outpatient healthcare utilization data were obtained from the Registered Persons Database and the Ontario Health Insurance Plan database, respectively.
A cohort of 21,758 older adults (median age, 75 years; 64.1% women) who had an ED visit or hospitalization for serious cADRs within 60 days of receiving antibiotic therapy was matched by age and sex with 87,025 antibiotic-treated controls who did not have a cutaneous reaction.
The median duration of antibiotic prescription was 7 days among cases and controls, and among the cases, the median latency period between antibiotic prescriptions and hospital visits for cADRs was 14 days. Most of the case patients went to the ED only (86.9%), and the rest were hospitalized.
The most commonly prescribed antibiotic class was penicillins (28.9%), followed by cephalosporins (18.2%), fluoroquinolones (16.5%), macrolides (14.8%), nitrofurantoin (8.6%), and sulfonamides (6.2%). Less commonly used antibiotics (“other” antibiotics) accounted for 6.9%.
Macrolide antibiotics were used as the reference because they are rarely associated with serious cADRs, noted the authors, and the multivariable analysis, adjusted for risk factors associated with serious cADRs, including malignancy, chronic liver disease, chronic kidney disease, and HIV.
After multivariable adjustment, relative to macrolides, sulfonamides were most strongly associated with serious cADRs (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.9) but so were all other antibiotic classes, including cephalosporins (aOR, 2.6), “other” antibiotics (aOR, 2.3), nitrofurantoin (aOR, 2.2), penicillins (aOR, 1.4), and fluoroquinolones (aOR,1.3).
In the secondary analysis, the crude rate of ED visits or hospitalizations for cADRs was highest for cephalosporins (4.92 per 1000 prescriptions), followed by sulfonamides (3.22 per 1000 prescriptions). Among hospitalized patients, the median length of stay was 6 days, with 9.6% requiring transfer to a critical care unit and 5.3% dying in the hospital.
Hospitalizations, ED Visits Not Studied Previously
“Notably, the rate of antibiotic-associated serious cADRs leading to an ED visit or hospitalization has not been previously studied,” noted the authors. “We found that at least two hospital encounters for serious cADRs ensued for every 1000 antibiotic prescriptions. This rate is considerably higher than suggested by studies that examine only SJS/TEN and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms.”
Dr. Lee also emphasized the previously unreported findings about nitrofurantoin. “It is surprising to find that nitrofurantoin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic for urinary tract infection, is also associated with an increased risk of severe drug rash,” she said in an interview.
“This finding highlights a potential novel risk at a population-based level and should be further explored in other populations to verify this association,” the authors wrote.
Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security in Baltimore, Maryland, and a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America, who was not involved in the study, agreed that the nitrofurantoin finding was surprising, but he was not surprised that sulfonamides were high on the list.
“The study reinforces that antibiotics are not benign medications to be dispensed injudiciously,” he said in an interview. “Antibiotics have risks, including serious skin reactions, as well as the fostering of antibiotic resistance. Clinicians should always first ask themselves if their patient actually merits an antibiotic and then assess what is the safest antibiotic for the purpose, bearing in mind that certain antibiotics are more likely to result in adverse reactions than others.”
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The study was conducted at ICES, which is funded in part by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care. One coauthor reported receiving compensation from the British Journal of Dermatology as reviewer and section editor, the American Academy of Dermatology as guidelines writer, Canadian Dermatology Today as manuscript writer, and the National Eczema Association and the Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health as consultant; as well as receiving research grants to the coauthor’s institution from the National Eczema Association, Eczema Society of Canada, Canadian Dermatology Foundation, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, US National Institutes of Health, and PSI Foundation. Another coauthor reported receiving grants from AbbVie, Bausch Health, Celgene, Lilly, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, L’Oréal, Novartis, Organon, Pfizer, Sandoz, Amgen, and Boehringer Ingelheim; receiving payment or honoraria for speaking from Sanofi China; participating on advisory boards for LEO Pharma, Novartis, Sanofi, and Union Therapeutics; and receiving equipment donation from L’Oréal. Dr. Adalja reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a large, population-based, nested case-control study of older adults, spanning two decades.
The findings, published online in JAMA, “underscore the importance of judicious prescribing, with preferential use of antibiotics associated with a lower risk when clinically appropriate,” noted senior author David Juurlink, MD, PhD, professor of medicine; pediatrics; and health policy, management and evaluation at the University of Toronto, and head of the Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology Division at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, also in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and coauthors.
“We hope our study raises awareness about the importance of drug allergy and gains support for future studies to improve drug allergy care,” lead author Erika Lee, MD, clinical immunology and allergy lecturer at the University of Toronto’s Drug Allergy Clinic, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, said in an interview. “It is important to recognize symptoms and signs of a severe drug rash and promptly stop culprit drugs to prevent worsening reaction.”
Serious cADRs are “a group of rare but potentially life-threatening drug hypersensitivity reactions involving the skin and, frequently, internal organs,” the authors wrote. “Typically delayed in onset, these reactions include drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) — the most severe cADR, which has a reported mortality of 20%-40%,” they noted.
Speculation Without Data
Although it has been speculated that some oral antibiotics are more likely than others to be associated with serious cADRs, there have been no population-based studies examining this, they added.
The study included adults aged 66 years or older and used administrative health databases in Ontario, spanning from April 1, 2002, to March 31, 2022. Data on antibiotic use were taken from the Ontario Drug Benefit database. The Canadian Institute for Health Information (CIHI) National Ambulatory Care Reporting System was used to obtain data on emergency department (ED) visits for cADRs, while the CIHI Discharge Abstract Database was used to identify hospitalizations for cADRs. Finally, demographic information and outpatient healthcare utilization data were obtained from the Registered Persons Database and the Ontario Health Insurance Plan database, respectively.
A cohort of 21,758 older adults (median age, 75 years; 64.1% women) who had an ED visit or hospitalization for serious cADRs within 60 days of receiving antibiotic therapy was matched by age and sex with 87,025 antibiotic-treated controls who did not have a cutaneous reaction.
The median duration of antibiotic prescription was 7 days among cases and controls, and among the cases, the median latency period between antibiotic prescriptions and hospital visits for cADRs was 14 days. Most of the case patients went to the ED only (86.9%), and the rest were hospitalized.
The most commonly prescribed antibiotic class was penicillins (28.9%), followed by cephalosporins (18.2%), fluoroquinolones (16.5%), macrolides (14.8%), nitrofurantoin (8.6%), and sulfonamides (6.2%). Less commonly used antibiotics (“other” antibiotics) accounted for 6.9%.
Macrolide antibiotics were used as the reference because they are rarely associated with serious cADRs, noted the authors, and the multivariable analysis, adjusted for risk factors associated with serious cADRs, including malignancy, chronic liver disease, chronic kidney disease, and HIV.
After multivariable adjustment, relative to macrolides, sulfonamides were most strongly associated with serious cADRs (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.9) but so were all other antibiotic classes, including cephalosporins (aOR, 2.6), “other” antibiotics (aOR, 2.3), nitrofurantoin (aOR, 2.2), penicillins (aOR, 1.4), and fluoroquinolones (aOR,1.3).
In the secondary analysis, the crude rate of ED visits or hospitalizations for cADRs was highest for cephalosporins (4.92 per 1000 prescriptions), followed by sulfonamides (3.22 per 1000 prescriptions). Among hospitalized patients, the median length of stay was 6 days, with 9.6% requiring transfer to a critical care unit and 5.3% dying in the hospital.
Hospitalizations, ED Visits Not Studied Previously
“Notably, the rate of antibiotic-associated serious cADRs leading to an ED visit or hospitalization has not been previously studied,” noted the authors. “We found that at least two hospital encounters for serious cADRs ensued for every 1000 antibiotic prescriptions. This rate is considerably higher than suggested by studies that examine only SJS/TEN and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms.”
Dr. Lee also emphasized the previously unreported findings about nitrofurantoin. “It is surprising to find that nitrofurantoin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic for urinary tract infection, is also associated with an increased risk of severe drug rash,” she said in an interview.
“This finding highlights a potential novel risk at a population-based level and should be further explored in other populations to verify this association,” the authors wrote.
Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security in Baltimore, Maryland, and a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America, who was not involved in the study, agreed that the nitrofurantoin finding was surprising, but he was not surprised that sulfonamides were high on the list.
“The study reinforces that antibiotics are not benign medications to be dispensed injudiciously,” he said in an interview. “Antibiotics have risks, including serious skin reactions, as well as the fostering of antibiotic resistance. Clinicians should always first ask themselves if their patient actually merits an antibiotic and then assess what is the safest antibiotic for the purpose, bearing in mind that certain antibiotics are more likely to result in adverse reactions than others.”
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The study was conducted at ICES, which is funded in part by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care. One coauthor reported receiving compensation from the British Journal of Dermatology as reviewer and section editor, the American Academy of Dermatology as guidelines writer, Canadian Dermatology Today as manuscript writer, and the National Eczema Association and the Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health as consultant; as well as receiving research grants to the coauthor’s institution from the National Eczema Association, Eczema Society of Canada, Canadian Dermatology Foundation, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, US National Institutes of Health, and PSI Foundation. Another coauthor reported receiving grants from AbbVie, Bausch Health, Celgene, Lilly, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, L’Oréal, Novartis, Organon, Pfizer, Sandoz, Amgen, and Boehringer Ingelheim; receiving payment or honoraria for speaking from Sanofi China; participating on advisory boards for LEO Pharma, Novartis, Sanofi, and Union Therapeutics; and receiving equipment donation from L’Oréal. Dr. Adalja reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA
Light Therapy, Phototherapy, Photobiomodulation: New Ways to Heal With Light
A surprising therapy is showing promise for chronic pain, vision loss, and muscle recovery, among other conditions.
It’s not a pill, an injection, or surgery.
It’s light.
Yes, light. The thing that appears when you open the curtains, flip a switch, or strike a match.
Light illuminates our world and helps us see. Early human trials suggest it may help us heal in new ways as well.
“Phototherapy is still in its infancy,” said Mohab Ibrahim, MD, PhD, a professor of anesthesiology at the University of Arizona, Tucson, who studies the effects of light on chronic pain. “There are so many questions, a lot of things we do not understand yet. But that’s where it gets interesting. What we can conclude is that different colors of light can influence different biological functions.”
This growing field goes by several names. Light therapy. Phototherapy. Photobiomodulation.
It leverages known effects of light on human health — such as skin exposure to ultraviolet light producing vitamin D or blue light’s power to regulate human body clocks — to take light as medicine in surprising new directions.
New Science, Old Idea
The science is young, but the concept of using light to restore health is thousands of years old.
Hippocrates prescribed sunbathing to patients at his medical center on the Greek island of Kos in 400 BC. Florence Nightingale promoted sunshine, along with fresh air, as prerequisites for recovery in hospitals during the Civil War. A Danish doctor, Niels Finsen, won the Nobel Prize in 1903 for developing ultraviolet lamps to treat a tuberculosis-related skin condition. And worried parents of the 1930s sat their babies in front of mercury arc lamps, bought at the drugstore, to discourage rickets.
Today, light therapy is widely used in medicine for newborn jaundice, psoriasis, and seasonal affective disorder and in light-activated treatments for cancers of the esophagus and lungs, as well as for actinic keratosis, a skin condition that can lead to cancer.
But researchers are finding that light may be capable of far more, particularly in conditions with few treatment options or where available drugs have unwanted side effects.
How Red Light Could Restore Vision
When 100 midlife and older adults, aged 53-91, with the dry form of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) were treated with an experimental red-light therapy or a sham therapy, the light treatment group showed signs of improved vision, as measured on a standard eye chart.
Volunteers received the therapy three times a week for 3-5 weeks, every 4 months for 2 years. By the study’s end, 67% of those treated with light could read an additional five letters on the chart, and 20% could read 10 or more. About 7% developed geographic atrophy — the most advanced, vision-threatening stage of dry AMD — compared with 24% in the sham group.
The study, called LIGHTSITE III, was conducted at 10 ophthalmology centers across the United States. The device they used — the Valeda Light Delivery System from medical device company LumiThera — is available in Europe and now being reviewed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Exposure to red light at the wavelengths used in the study likely revitalizes failing mitochondria — the power plants inside cells — so they produce more energy, the researchers say.
“This is the first therapy for dry AMD that’s actually shown a benefit in improving vision,” said study coauthor Richard Rosen, MD, chair of ophthalmology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and chief of Retinal Services at the New York Eye and Ear Infirmary in New York City. “Supplements called AREDS can reduce progression, and in wet AMD we can improve vision loss with injections. But in dry AMD, none of the treatments studied in the past have improved it.”
AMD develops when the eyes can’t break down natural by-products, which glom together as clumps of protein called drusen. Drusen can lodge under the retina, eventually damaging tissue.
“Retinal epithelial cells, a single layer of cells that cares for the photoreceptors in the eyes, are there for life,” Dr. Rosen said. “They have a tremendous capacity to repair themselves, but things [such as aging and smoking] get in the way.”
“I’m proposing,” Dr. Rosen said, “that by boosting energy levels in cells [with red light], we’re improving normal repair mechanisms.”
Lab studies support this idea.
In a 2017 mouse study from the University College London Institute of Ophthalmology in England, retinal function improved by 25% in old mice exposed to red light. And a 2019 study from the Ophthalmological Research Foundation, Oviedo, Spain, found that exposure to blue light harmed the mitochondria in retina cells, while red light somewhat counteracted the losses.
If cleared by the FDA — which the company anticipated could happen in 2024 — LumiThera’s light delivery device will likely be most useful in the beginning stages of dry AMD, Dr. Rosen said. “I think treatment of early dry AMD will be huge.”
Eventually, light therapy may also be valuable in treating or managing glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy.
For now, Dr. Rosen recommended that clinicians and consumers with AMD skip over-the-counter (OTC) red-light therapy devices currently on the market.
“We don’t know what kind of light the devices produce,” he said. “The wavelengths can vary. The eyes are delicate. Experimenting on your own may be hazardous to your vision.”
Green Light for Pain Relief
On his way to the pharmacy to pick up pain relievers for a headache, Dr. Ibrahim passed Gene C. Reid Park in Tucson. Recalling how his brother eased headaches by sitting in his backyard, Dr. Ibrahim pulled over.
“Reid Park is probably one of the greenest areas of Tucson,” said Dr. Ibrahim, who also serves as medical director of the Comprehensive Center for Pain & Addiction at Banner-University Medical Center Phoenix in Arizona. “I spent a half hour or 40 minutes there, and my headache felt better.”
Being outdoors in a green space may be soothing for lots of reasons, like the quiet or the fresh air. But there’s also sunlight reflected off and shining through greenery. The experience inspired Dr. Ibrahim to take a closer look at the effects of green light on chronic pain.
In his 2021 study of 29 people with migraines, participants reported that, after daily exposure to green light for 10 weeks, the number of days per month when they had headaches fell from 7.9 to 2.4 for those who had episodic migraines and from 22.3 to 9.4 for those with chronic migraines. In another 2021 study, 21 people with fibromyalgia who had green light therapy for 10 weeks said their average, self-reported pain intensity fell from 8.4 to 4.9 on a 10-point scale used at the University of Arizona’s pain clinic.
Volunteers in both studies got their light therapy at home, switching on green LED lights while they listened to music, read a book, relaxed, or exercised for 1 or 2 hours daily. The lights were within their field of vision, but they did not look directly at them.
Dr. Ibrahim now has funding from the Department of Defense and Department of Veterans Affairs to find out why green light alters pain perception.
“What we know is that the visual system is connected to certain areas of the brain that also modulate pain,” he said. “We are trying to understand the connection.”
Padma Gulur, MD, a professor of anesthesiology and population health and director of Pain Management Strategy and Opioid Surveillance at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, saw similar results in a 2023 study of 45 people with fibromyalgia. But instead of using a light source, volunteers wore glasses with clear, green, or blue lenses for 4 hours a day.
After 2 weeks, 33% in the green lens group reduced their use of opioids by 10% or more, compared with 11% in the blue lens group and 8% who wore clear lenses. Previous studies have found green light affects levels of the feel-good brain chemical serotonin and stimulates the body’s own opioid system, the authors noted.
“Green light helps your body control and reduce pain,” Dr. Gulur said. It “seems to help with pain relief by affecting the body’s natural pain management system. This effect appears to play a crucial role in antinociception — reducing the sensation of pain; antiallodynia — preventing normal, nonpainful stimuli from causing pain; and antihyperalgesia — reducing heightened sensitivity to pain.”
Light therapy could help pain patients reduce their dose of opioids or even forgo the drugs altogether, Dr. Gulur said. “It is our hope this will become a useful adjuvant therapy to manage pain.”
In the University of Arizona studies, some patients on green-light therapy stopped their medications completely. Even if they didn’t, other benefits appeared. “They had improved quality of life, decreased depression and anxiety, and improved sleep,” Dr. Ibrahim said.
But not just any green light or green-tinted glasses will work, both researchers said. “We have found there are specific frequencies of green light that give this benefit,” Dr. Gulur said. “OTC products may not be helpful for that reason.”
While Dr. Ibrahim said it could be possible for healthcare practitioners and consumers to consult his studies and put together an inexpensive green-light device at home while carefully following the protocol participants used in the studies , it would first be a good idea for patients to talk with their family doctor or a pain specialist.
“A headache is not always just a headache,” Dr. Ibrahim said. “It could be some other abnormality that needs diagnosis and treatment. If you have long-lasting pain or pain that’s getting worse, it’s always better to discuss it with your physician.”
Helping Muscles Recover With Red Light
Intense exercise — whether it’s a sprint at the end of a morning run, an extra set of biceps curls, or a weekend of all-day DIY home improvement projects — can temporarily damage muscle, causing soreness, inflammation, and even swelling. Phototherapy with red and near-infrared light is widely used by sports trainers, physical therapists, and athletes to aid in recovery. It may even work better than a trendy plunge in an ice bath, according to a 2019 Texas State University review.
But how does it work? Jamie Ghigiarelli, PhD, professor of Allied Health & Kinesiology at Hofstra University in Hempstead, New York, looked closely at signs of inflammation and muscle damage in 12 athletes to find out.
Study participants overtaxed their muscles with rounds of chin-ups, high-speed sprints, and repeated bench presses. Afterward, they relaxed in a full-body red-light therapy bed or in a similar bed without lights.
The results, published in 2020, showed that blood levels of creatine kinase — an enzyme that’s elevated by muscle damage — were 18% lower 1-3 days after exercising for the light-bed group than for the control group.
“Photobiomodulation seems to help with muscle recovery,” Dr. Ghigiarelli said.
Red light at wavelengths from 650 to 820 nm can enter muscle cells, where it is absorbed by mitochondria and boosts their energy production, he said. At the time of his research, some exercise science researchers and athletes thought using light therapy before an event might also increase athletic performance, but according to Dr. Ghigiarelli, that use has not panned out.
Handheld red light and near-infrared light devices for muscle recovery are widely available, but it’s important to do your homework before buying one.
“You want to choose a device with the right energy production — the right wavelength of light, the right power — to be safe and effective,” he said.
For details, he recommends consulting a 2019 paper in The Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy called “Clinical and scientific recommendations for the use of photobiomodulation therapy in exercise performance enhancement and post-exercise recovery: Current evidence and future directions.”
The paper, from the Laboratory of Phototherapy and Innovative Technologies in Health at the Universidade Nove de Julho in Sao Paulo, Brazil, recommends that for small muscle groups like the biceps or triceps, use red-light lasers or LED devices with a wavelength of 640 nm for red light or 950 nm for infrared light, at a power of 50-200 mW per diode for single-probe device types, at a dose of 20-60 J, given 5-10 minutes after exercise.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A surprising therapy is showing promise for chronic pain, vision loss, and muscle recovery, among other conditions.
It’s not a pill, an injection, or surgery.
It’s light.
Yes, light. The thing that appears when you open the curtains, flip a switch, or strike a match.
Light illuminates our world and helps us see. Early human trials suggest it may help us heal in new ways as well.
“Phototherapy is still in its infancy,” said Mohab Ibrahim, MD, PhD, a professor of anesthesiology at the University of Arizona, Tucson, who studies the effects of light on chronic pain. “There are so many questions, a lot of things we do not understand yet. But that’s where it gets interesting. What we can conclude is that different colors of light can influence different biological functions.”
This growing field goes by several names. Light therapy. Phototherapy. Photobiomodulation.
It leverages known effects of light on human health — such as skin exposure to ultraviolet light producing vitamin D or blue light’s power to regulate human body clocks — to take light as medicine in surprising new directions.
New Science, Old Idea
The science is young, but the concept of using light to restore health is thousands of years old.
Hippocrates prescribed sunbathing to patients at his medical center on the Greek island of Kos in 400 BC. Florence Nightingale promoted sunshine, along with fresh air, as prerequisites for recovery in hospitals during the Civil War. A Danish doctor, Niels Finsen, won the Nobel Prize in 1903 for developing ultraviolet lamps to treat a tuberculosis-related skin condition. And worried parents of the 1930s sat their babies in front of mercury arc lamps, bought at the drugstore, to discourage rickets.
Today, light therapy is widely used in medicine for newborn jaundice, psoriasis, and seasonal affective disorder and in light-activated treatments for cancers of the esophagus and lungs, as well as for actinic keratosis, a skin condition that can lead to cancer.
But researchers are finding that light may be capable of far more, particularly in conditions with few treatment options or where available drugs have unwanted side effects.
How Red Light Could Restore Vision
When 100 midlife and older adults, aged 53-91, with the dry form of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) were treated with an experimental red-light therapy or a sham therapy, the light treatment group showed signs of improved vision, as measured on a standard eye chart.
Volunteers received the therapy three times a week for 3-5 weeks, every 4 months for 2 years. By the study’s end, 67% of those treated with light could read an additional five letters on the chart, and 20% could read 10 or more. About 7% developed geographic atrophy — the most advanced, vision-threatening stage of dry AMD — compared with 24% in the sham group.
The study, called LIGHTSITE III, was conducted at 10 ophthalmology centers across the United States. The device they used — the Valeda Light Delivery System from medical device company LumiThera — is available in Europe and now being reviewed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Exposure to red light at the wavelengths used in the study likely revitalizes failing mitochondria — the power plants inside cells — so they produce more energy, the researchers say.
“This is the first therapy for dry AMD that’s actually shown a benefit in improving vision,” said study coauthor Richard Rosen, MD, chair of ophthalmology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and chief of Retinal Services at the New York Eye and Ear Infirmary in New York City. “Supplements called AREDS can reduce progression, and in wet AMD we can improve vision loss with injections. But in dry AMD, none of the treatments studied in the past have improved it.”
AMD develops when the eyes can’t break down natural by-products, which glom together as clumps of protein called drusen. Drusen can lodge under the retina, eventually damaging tissue.
“Retinal epithelial cells, a single layer of cells that cares for the photoreceptors in the eyes, are there for life,” Dr. Rosen said. “They have a tremendous capacity to repair themselves, but things [such as aging and smoking] get in the way.”
“I’m proposing,” Dr. Rosen said, “that by boosting energy levels in cells [with red light], we’re improving normal repair mechanisms.”
Lab studies support this idea.
In a 2017 mouse study from the University College London Institute of Ophthalmology in England, retinal function improved by 25% in old mice exposed to red light. And a 2019 study from the Ophthalmological Research Foundation, Oviedo, Spain, found that exposure to blue light harmed the mitochondria in retina cells, while red light somewhat counteracted the losses.
If cleared by the FDA — which the company anticipated could happen in 2024 — LumiThera’s light delivery device will likely be most useful in the beginning stages of dry AMD, Dr. Rosen said. “I think treatment of early dry AMD will be huge.”
Eventually, light therapy may also be valuable in treating or managing glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy.
For now, Dr. Rosen recommended that clinicians and consumers with AMD skip over-the-counter (OTC) red-light therapy devices currently on the market.
“We don’t know what kind of light the devices produce,” he said. “The wavelengths can vary. The eyes are delicate. Experimenting on your own may be hazardous to your vision.”
Green Light for Pain Relief
On his way to the pharmacy to pick up pain relievers for a headache, Dr. Ibrahim passed Gene C. Reid Park in Tucson. Recalling how his brother eased headaches by sitting in his backyard, Dr. Ibrahim pulled over.
“Reid Park is probably one of the greenest areas of Tucson,” said Dr. Ibrahim, who also serves as medical director of the Comprehensive Center for Pain & Addiction at Banner-University Medical Center Phoenix in Arizona. “I spent a half hour or 40 minutes there, and my headache felt better.”
Being outdoors in a green space may be soothing for lots of reasons, like the quiet or the fresh air. But there’s also sunlight reflected off and shining through greenery. The experience inspired Dr. Ibrahim to take a closer look at the effects of green light on chronic pain.
In his 2021 study of 29 people with migraines, participants reported that, after daily exposure to green light for 10 weeks, the number of days per month when they had headaches fell from 7.9 to 2.4 for those who had episodic migraines and from 22.3 to 9.4 for those with chronic migraines. In another 2021 study, 21 people with fibromyalgia who had green light therapy for 10 weeks said their average, self-reported pain intensity fell from 8.4 to 4.9 on a 10-point scale used at the University of Arizona’s pain clinic.
Volunteers in both studies got their light therapy at home, switching on green LED lights while they listened to music, read a book, relaxed, or exercised for 1 or 2 hours daily. The lights were within their field of vision, but they did not look directly at them.
Dr. Ibrahim now has funding from the Department of Defense and Department of Veterans Affairs to find out why green light alters pain perception.
“What we know is that the visual system is connected to certain areas of the brain that also modulate pain,” he said. “We are trying to understand the connection.”
Padma Gulur, MD, a professor of anesthesiology and population health and director of Pain Management Strategy and Opioid Surveillance at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, saw similar results in a 2023 study of 45 people with fibromyalgia. But instead of using a light source, volunteers wore glasses with clear, green, or blue lenses for 4 hours a day.
After 2 weeks, 33% in the green lens group reduced their use of opioids by 10% or more, compared with 11% in the blue lens group and 8% who wore clear lenses. Previous studies have found green light affects levels of the feel-good brain chemical serotonin and stimulates the body’s own opioid system, the authors noted.
“Green light helps your body control and reduce pain,” Dr. Gulur said. It “seems to help with pain relief by affecting the body’s natural pain management system. This effect appears to play a crucial role in antinociception — reducing the sensation of pain; antiallodynia — preventing normal, nonpainful stimuli from causing pain; and antihyperalgesia — reducing heightened sensitivity to pain.”
Light therapy could help pain patients reduce their dose of opioids or even forgo the drugs altogether, Dr. Gulur said. “It is our hope this will become a useful adjuvant therapy to manage pain.”
In the University of Arizona studies, some patients on green-light therapy stopped their medications completely. Even if they didn’t, other benefits appeared. “They had improved quality of life, decreased depression and anxiety, and improved sleep,” Dr. Ibrahim said.
But not just any green light or green-tinted glasses will work, both researchers said. “We have found there are specific frequencies of green light that give this benefit,” Dr. Gulur said. “OTC products may not be helpful for that reason.”
While Dr. Ibrahim said it could be possible for healthcare practitioners and consumers to consult his studies and put together an inexpensive green-light device at home while carefully following the protocol participants used in the studies , it would first be a good idea for patients to talk with their family doctor or a pain specialist.
“A headache is not always just a headache,” Dr. Ibrahim said. “It could be some other abnormality that needs diagnosis and treatment. If you have long-lasting pain or pain that’s getting worse, it’s always better to discuss it with your physician.”
Helping Muscles Recover With Red Light
Intense exercise — whether it’s a sprint at the end of a morning run, an extra set of biceps curls, or a weekend of all-day DIY home improvement projects — can temporarily damage muscle, causing soreness, inflammation, and even swelling. Phototherapy with red and near-infrared light is widely used by sports trainers, physical therapists, and athletes to aid in recovery. It may even work better than a trendy plunge in an ice bath, according to a 2019 Texas State University review.
But how does it work? Jamie Ghigiarelli, PhD, professor of Allied Health & Kinesiology at Hofstra University in Hempstead, New York, looked closely at signs of inflammation and muscle damage in 12 athletes to find out.
Study participants overtaxed their muscles with rounds of chin-ups, high-speed sprints, and repeated bench presses. Afterward, they relaxed in a full-body red-light therapy bed or in a similar bed without lights.
The results, published in 2020, showed that blood levels of creatine kinase — an enzyme that’s elevated by muscle damage — were 18% lower 1-3 days after exercising for the light-bed group than for the control group.
“Photobiomodulation seems to help with muscle recovery,” Dr. Ghigiarelli said.
Red light at wavelengths from 650 to 820 nm can enter muscle cells, where it is absorbed by mitochondria and boosts their energy production, he said. At the time of his research, some exercise science researchers and athletes thought using light therapy before an event might also increase athletic performance, but according to Dr. Ghigiarelli, that use has not panned out.
Handheld red light and near-infrared light devices for muscle recovery are widely available, but it’s important to do your homework before buying one.
“You want to choose a device with the right energy production — the right wavelength of light, the right power — to be safe and effective,” he said.
For details, he recommends consulting a 2019 paper in The Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy called “Clinical and scientific recommendations for the use of photobiomodulation therapy in exercise performance enhancement and post-exercise recovery: Current evidence and future directions.”
The paper, from the Laboratory of Phototherapy and Innovative Technologies in Health at the Universidade Nove de Julho in Sao Paulo, Brazil, recommends that for small muscle groups like the biceps or triceps, use red-light lasers or LED devices with a wavelength of 640 nm for red light or 950 nm for infrared light, at a power of 50-200 mW per diode for single-probe device types, at a dose of 20-60 J, given 5-10 minutes after exercise.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A surprising therapy is showing promise for chronic pain, vision loss, and muscle recovery, among other conditions.
It’s not a pill, an injection, or surgery.
It’s light.
Yes, light. The thing that appears when you open the curtains, flip a switch, or strike a match.
Light illuminates our world and helps us see. Early human trials suggest it may help us heal in new ways as well.
“Phototherapy is still in its infancy,” said Mohab Ibrahim, MD, PhD, a professor of anesthesiology at the University of Arizona, Tucson, who studies the effects of light on chronic pain. “There are so many questions, a lot of things we do not understand yet. But that’s where it gets interesting. What we can conclude is that different colors of light can influence different biological functions.”
This growing field goes by several names. Light therapy. Phototherapy. Photobiomodulation.
It leverages known effects of light on human health — such as skin exposure to ultraviolet light producing vitamin D or blue light’s power to regulate human body clocks — to take light as medicine in surprising new directions.
New Science, Old Idea
The science is young, but the concept of using light to restore health is thousands of years old.
Hippocrates prescribed sunbathing to patients at his medical center on the Greek island of Kos in 400 BC. Florence Nightingale promoted sunshine, along with fresh air, as prerequisites for recovery in hospitals during the Civil War. A Danish doctor, Niels Finsen, won the Nobel Prize in 1903 for developing ultraviolet lamps to treat a tuberculosis-related skin condition. And worried parents of the 1930s sat their babies in front of mercury arc lamps, bought at the drugstore, to discourage rickets.
Today, light therapy is widely used in medicine for newborn jaundice, psoriasis, and seasonal affective disorder and in light-activated treatments for cancers of the esophagus and lungs, as well as for actinic keratosis, a skin condition that can lead to cancer.
But researchers are finding that light may be capable of far more, particularly in conditions with few treatment options or where available drugs have unwanted side effects.
How Red Light Could Restore Vision
When 100 midlife and older adults, aged 53-91, with the dry form of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) were treated with an experimental red-light therapy or a sham therapy, the light treatment group showed signs of improved vision, as measured on a standard eye chart.
Volunteers received the therapy three times a week for 3-5 weeks, every 4 months for 2 years. By the study’s end, 67% of those treated with light could read an additional five letters on the chart, and 20% could read 10 or more. About 7% developed geographic atrophy — the most advanced, vision-threatening stage of dry AMD — compared with 24% in the sham group.
The study, called LIGHTSITE III, was conducted at 10 ophthalmology centers across the United States. The device they used — the Valeda Light Delivery System from medical device company LumiThera — is available in Europe and now being reviewed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Exposure to red light at the wavelengths used in the study likely revitalizes failing mitochondria — the power plants inside cells — so they produce more energy, the researchers say.
“This is the first therapy for dry AMD that’s actually shown a benefit in improving vision,” said study coauthor Richard Rosen, MD, chair of ophthalmology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and chief of Retinal Services at the New York Eye and Ear Infirmary in New York City. “Supplements called AREDS can reduce progression, and in wet AMD we can improve vision loss with injections. But in dry AMD, none of the treatments studied in the past have improved it.”
AMD develops when the eyes can’t break down natural by-products, which glom together as clumps of protein called drusen. Drusen can lodge under the retina, eventually damaging tissue.
“Retinal epithelial cells, a single layer of cells that cares for the photoreceptors in the eyes, are there for life,” Dr. Rosen said. “They have a tremendous capacity to repair themselves, but things [such as aging and smoking] get in the way.”
“I’m proposing,” Dr. Rosen said, “that by boosting energy levels in cells [with red light], we’re improving normal repair mechanisms.”
Lab studies support this idea.
In a 2017 mouse study from the University College London Institute of Ophthalmology in England, retinal function improved by 25% in old mice exposed to red light. And a 2019 study from the Ophthalmological Research Foundation, Oviedo, Spain, found that exposure to blue light harmed the mitochondria in retina cells, while red light somewhat counteracted the losses.
If cleared by the FDA — which the company anticipated could happen in 2024 — LumiThera’s light delivery device will likely be most useful in the beginning stages of dry AMD, Dr. Rosen said. “I think treatment of early dry AMD will be huge.”
Eventually, light therapy may also be valuable in treating or managing glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy.
For now, Dr. Rosen recommended that clinicians and consumers with AMD skip over-the-counter (OTC) red-light therapy devices currently on the market.
“We don’t know what kind of light the devices produce,” he said. “The wavelengths can vary. The eyes are delicate. Experimenting on your own may be hazardous to your vision.”
Green Light for Pain Relief
On his way to the pharmacy to pick up pain relievers for a headache, Dr. Ibrahim passed Gene C. Reid Park in Tucson. Recalling how his brother eased headaches by sitting in his backyard, Dr. Ibrahim pulled over.
“Reid Park is probably one of the greenest areas of Tucson,” said Dr. Ibrahim, who also serves as medical director of the Comprehensive Center for Pain & Addiction at Banner-University Medical Center Phoenix in Arizona. “I spent a half hour or 40 minutes there, and my headache felt better.”
Being outdoors in a green space may be soothing for lots of reasons, like the quiet or the fresh air. But there’s also sunlight reflected off and shining through greenery. The experience inspired Dr. Ibrahim to take a closer look at the effects of green light on chronic pain.
In his 2021 study of 29 people with migraines, participants reported that, after daily exposure to green light for 10 weeks, the number of days per month when they had headaches fell from 7.9 to 2.4 for those who had episodic migraines and from 22.3 to 9.4 for those with chronic migraines. In another 2021 study, 21 people with fibromyalgia who had green light therapy for 10 weeks said their average, self-reported pain intensity fell from 8.4 to 4.9 on a 10-point scale used at the University of Arizona’s pain clinic.
Volunteers in both studies got their light therapy at home, switching on green LED lights while they listened to music, read a book, relaxed, or exercised for 1 or 2 hours daily. The lights were within their field of vision, but they did not look directly at them.
Dr. Ibrahim now has funding from the Department of Defense and Department of Veterans Affairs to find out why green light alters pain perception.
“What we know is that the visual system is connected to certain areas of the brain that also modulate pain,” he said. “We are trying to understand the connection.”
Padma Gulur, MD, a professor of anesthesiology and population health and director of Pain Management Strategy and Opioid Surveillance at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, saw similar results in a 2023 study of 45 people with fibromyalgia. But instead of using a light source, volunteers wore glasses with clear, green, or blue lenses for 4 hours a day.
After 2 weeks, 33% in the green lens group reduced their use of opioids by 10% or more, compared with 11% in the blue lens group and 8% who wore clear lenses. Previous studies have found green light affects levels of the feel-good brain chemical serotonin and stimulates the body’s own opioid system, the authors noted.
“Green light helps your body control and reduce pain,” Dr. Gulur said. It “seems to help with pain relief by affecting the body’s natural pain management system. This effect appears to play a crucial role in antinociception — reducing the sensation of pain; antiallodynia — preventing normal, nonpainful stimuli from causing pain; and antihyperalgesia — reducing heightened sensitivity to pain.”
Light therapy could help pain patients reduce their dose of opioids or even forgo the drugs altogether, Dr. Gulur said. “It is our hope this will become a useful adjuvant therapy to manage pain.”
In the University of Arizona studies, some patients on green-light therapy stopped their medications completely. Even if they didn’t, other benefits appeared. “They had improved quality of life, decreased depression and anxiety, and improved sleep,” Dr. Ibrahim said.
But not just any green light or green-tinted glasses will work, both researchers said. “We have found there are specific frequencies of green light that give this benefit,” Dr. Gulur said. “OTC products may not be helpful for that reason.”
While Dr. Ibrahim said it could be possible for healthcare practitioners and consumers to consult his studies and put together an inexpensive green-light device at home while carefully following the protocol participants used in the studies , it would first be a good idea for patients to talk with their family doctor or a pain specialist.
“A headache is not always just a headache,” Dr. Ibrahim said. “It could be some other abnormality that needs diagnosis and treatment. If you have long-lasting pain or pain that’s getting worse, it’s always better to discuss it with your physician.”
Helping Muscles Recover With Red Light
Intense exercise — whether it’s a sprint at the end of a morning run, an extra set of biceps curls, or a weekend of all-day DIY home improvement projects — can temporarily damage muscle, causing soreness, inflammation, and even swelling. Phototherapy with red and near-infrared light is widely used by sports trainers, physical therapists, and athletes to aid in recovery. It may even work better than a trendy plunge in an ice bath, according to a 2019 Texas State University review.
But how does it work? Jamie Ghigiarelli, PhD, professor of Allied Health & Kinesiology at Hofstra University in Hempstead, New York, looked closely at signs of inflammation and muscle damage in 12 athletes to find out.
Study participants overtaxed their muscles with rounds of chin-ups, high-speed sprints, and repeated bench presses. Afterward, they relaxed in a full-body red-light therapy bed or in a similar bed without lights.
The results, published in 2020, showed that blood levels of creatine kinase — an enzyme that’s elevated by muscle damage — were 18% lower 1-3 days after exercising for the light-bed group than for the control group.
“Photobiomodulation seems to help with muscle recovery,” Dr. Ghigiarelli said.
Red light at wavelengths from 650 to 820 nm can enter muscle cells, where it is absorbed by mitochondria and boosts their energy production, he said. At the time of his research, some exercise science researchers and athletes thought using light therapy before an event might also increase athletic performance, but according to Dr. Ghigiarelli, that use has not panned out.
Handheld red light and near-infrared light devices for muscle recovery are widely available, but it’s important to do your homework before buying one.
“You want to choose a device with the right energy production — the right wavelength of light, the right power — to be safe and effective,” he said.
For details, he recommends consulting a 2019 paper in The Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy called “Clinical and scientific recommendations for the use of photobiomodulation therapy in exercise performance enhancement and post-exercise recovery: Current evidence and future directions.”
The paper, from the Laboratory of Phototherapy and Innovative Technologies in Health at the Universidade Nove de Julho in Sao Paulo, Brazil, recommends that for small muscle groups like the biceps or triceps, use red-light lasers or LED devices with a wavelength of 640 nm for red light or 950 nm for infrared light, at a power of 50-200 mW per diode for single-probe device types, at a dose of 20-60 J, given 5-10 minutes after exercise.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Management, Evaluation of Chronic Itch in Older Adults
WASHINGTON — , Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, said at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in older patients hosted by the GW School of Medicine & Health Sciences.
“We found a few years ago that eosinophils seem to differentiate this group, and now we’re finding that IgE and CBC [complete blood count] differential can help you get a little better sense of who has an immune-driven itch vs something more neuropathic,” said Dr. Kwatra, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, who founded and directed the Johns Hopkins Itch Center before coming to the University of Maryland in 2023. Not all patients with immune-driven itch will have these biomarkers, “but it’s a helpful tool,” he said.
CPUO is the term that is increasingly being used, he said, to describe intense, chronic pruritus without primary skin lesions or rashes and without any known systemic cause. It becomes more common as people get older and is sometimes debilitating. The initial evaluation should be kept “simple and straightforward,” he advised, with heightened concern for underlying malignancy in those who present with an itch of less than 12 months’ duration.
Biologics, JAK Inhibitors: Case Reports, Ongoing Research
Research conducted by Dr. Kwatra and Jaya Manjunath, a fourth-year medical student at The George Washington University, Washington, documented higher levels of Th2-associated cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with CPUO who had elevated IgE or eosinophil levels, or both than in patients with itch who had low IgE and eosinophil levels. The patients with higher levels also had a greater response to off-label treatment with immunomodulatory therapy.
“Multiple Th2-related inflammatory markers, like IL [interleukin]-5 and eotaxin-3, were reduced after dupilumab” in patients who responded to the therapy, said Ms. Manjunath, who co-presented the meeting session on chronic itch with Dr. Kwatra. Other changes in the plasma cytokine profile included a reduction in the serum level of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine, which is a biomarker for atopic dermatitis. The research is under review for publication.
Meanwhile, a phase 3 trial (LIBERTY-CPUO-CHIC) of dupilumab for CPUO is currently underway, Dr. Kwatra noted. Investigators are randomizing patients with severe pruritus (Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale [WI-NRS] ≥ 7) to dupilumab or placebo for 12 or 24 weeks.
In one of several cases shared by Dr. Kwatra and Ms. Manjunath, a 71-year-old Black woman with a 6-month history of generalized itch (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease was found to have elevated eosinophil levels and a negative malignancy workup. Previous therapies included antihistamines and topical steroids. She was started on a 600-mg loading dose of subcutaneous dupilumab followed by 300 mg every 14 days. At the 2-month follow-up, her WI-NRS score was 0.
Because “dupilumab is off label right now for this form of itch, oftentimes our first line is methotrexate,” Dr. Kwatra said. Patients “can have a good response with this therapeutic.”
He also described the case of a 72-year-old Black woman with total body itch for 2 years (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of seasonal allergies, thyroid disease, and hypertension. Previous therapies included prednisone, antihistamines, topical steroids, and gabapentin. The patient was found to have high IgE (447 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.9%), was started on methotrexate, and had an itch score of 0 at the 8-month follow-up.
JAK inhibitors may also have a role in the management of CPUO. A phase 2 nonrandomized controlled trial of abrocitinib for adults with prurigo nodularis (PN) or CPUO, recently published in JAMA Dermatology, showed itch scores decreased by 53.7% in the CPUO group (and 78.3% in the PN group) after 12 weeks of treatment with oral abrocitinib 200 mg daily. Patients had significant improvements in quality of life and no serious adverse events, said Dr. Kwatra, the lead author of the paper.
One of these patients was a 73-year-old White man who had experienced total body itch for 1.5 years (predominantly affecting his upper extremities; WI-NRS = 10) and a history of ascending aortic aneurysm, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. Previous failed therapies included dupilumab (> 6 months), topical steroids, tacrolimus, and antihistamines. Labs showed elevated IgE (456 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (11.7%). After 12 weeks of treatment with abrocitinib, the WI-NRS decreased to 2.
PD-1 Inhibitors As a Trigger
Chronic pruritus caused by the anticancer PD-1 inhibitors is becoming more common as the utilization of these immune checkpoint inhibitors increases, Dr. Kwatra noted. “You don’t see much in the skin, but [these patients have] very high IgE and eosinophils,” he said. “We’ve been seeing more reports recently of utilizing agents that target type 2 inflammation off label for PD-1 inhibitor–related skin manifestations.”
One such patient with PD-1 inhibitor–induced pruritus was a 65-year-old White man with metastatic melanoma who reported a 6-month history of itching that began 3 weeks after the start of treatment with the PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab. His WI-NRS score was 10 despite treatment with topical steroids and antihistamines. He had a history of psoriasis. Labs showed elevated IgE (1350 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.5%). At a 4-month follow-up after treatment with off-label dupilumab (a 600-mg subcutaneous loading dose followed by 300 mg every 14 days), his WI-NRS score was 0.
In a paper recently published in JAAD International, Dr. Kwatra, Ms. Manjunath, and coinvestigators reported on a series of 15 patients who developed chronic pruritus following an immune stimulus exposure, including immunotherapy and vaccination (2024 Apr 7:16:97-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jdin.2024.03.022). Most immunotherapy-treated patients experienced pruritus during treatment or after 21-60 days of receiving treatment, and the patients with vaccine-stimulated pruritus (after Tdap and messenger RNA COVID-19 vaccination) developed pruritus within a week of vaccination.
In addition to the elevated levels of IgE and eosinophils, plasma cytokine analysis showed elevated levels of IL-5, thymic stromal lymphopoietin, and other Th2-related cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with immune-stimulated pruritus compared with healthy controls, Ms. Manjunath said at the meeting.
When a Malignancy Workup Becomes Important
The initial part of any diagnostic workup for CPUO should include CBC with differential, liver function tests, renal function tests, and thyroid function testing, said Kwatra, referring to a diagnostic algorithm he developed, which was published as part of a CME review in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022.
Then, as indicated by risk factors in the history and physical, one could order other tests such as HIV serology, hepatitis B/C serologies, bullous pemphigoid testing, chest x-rays, evaluation for gammopathies, stool examination for ova and parasites, or heavy metal testing. “Do you do everything at once? We like to keep it straightforward,” Dr. Kwatra said. “Depending on the patient’s risk factors, you could order more or less.”
A malignancy workup should be strongly considered in patients whose itch duration is less than 12 months — and especially if the duration is less than 3 months — with an emphasis on cancers more frequently associated with itch: Hematologic and hepatobiliary cancers. This is “when concern should be heightened ... when there should be a lower threshold for workup,” he said.
The 12-month recommendation stems from a Danish cohort study published in 2014 that demonstrated a twofold increased incidence of cancer among patients with pruritus in the first 3 months after the diagnosis of pruritus. The 1-year absolute cancer risk was 1.63%.
Other risk factors for underlying malignancy or malignancy development in patients with CPUO include age older than 60 years, male sex, liver disease, and current or prior smoking, according to another study, noted Dr. Kwatra.
Dr. Kwatra disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, and other companies and an investigator for Galderma, Incyte, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Manjunath served as the codirector of the ElderDerm conference.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — , Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, said at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in older patients hosted by the GW School of Medicine & Health Sciences.
“We found a few years ago that eosinophils seem to differentiate this group, and now we’re finding that IgE and CBC [complete blood count] differential can help you get a little better sense of who has an immune-driven itch vs something more neuropathic,” said Dr. Kwatra, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, who founded and directed the Johns Hopkins Itch Center before coming to the University of Maryland in 2023. Not all patients with immune-driven itch will have these biomarkers, “but it’s a helpful tool,” he said.
CPUO is the term that is increasingly being used, he said, to describe intense, chronic pruritus without primary skin lesions or rashes and without any known systemic cause. It becomes more common as people get older and is sometimes debilitating. The initial evaluation should be kept “simple and straightforward,” he advised, with heightened concern for underlying malignancy in those who present with an itch of less than 12 months’ duration.
Biologics, JAK Inhibitors: Case Reports, Ongoing Research
Research conducted by Dr. Kwatra and Jaya Manjunath, a fourth-year medical student at The George Washington University, Washington, documented higher levels of Th2-associated cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with CPUO who had elevated IgE or eosinophil levels, or both than in patients with itch who had low IgE and eosinophil levels. The patients with higher levels also had a greater response to off-label treatment with immunomodulatory therapy.
“Multiple Th2-related inflammatory markers, like IL [interleukin]-5 and eotaxin-3, were reduced after dupilumab” in patients who responded to the therapy, said Ms. Manjunath, who co-presented the meeting session on chronic itch with Dr. Kwatra. Other changes in the plasma cytokine profile included a reduction in the serum level of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine, which is a biomarker for atopic dermatitis. The research is under review for publication.
Meanwhile, a phase 3 trial (LIBERTY-CPUO-CHIC) of dupilumab for CPUO is currently underway, Dr. Kwatra noted. Investigators are randomizing patients with severe pruritus (Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale [WI-NRS] ≥ 7) to dupilumab or placebo for 12 or 24 weeks.
In one of several cases shared by Dr. Kwatra and Ms. Manjunath, a 71-year-old Black woman with a 6-month history of generalized itch (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease was found to have elevated eosinophil levels and a negative malignancy workup. Previous therapies included antihistamines and topical steroids. She was started on a 600-mg loading dose of subcutaneous dupilumab followed by 300 mg every 14 days. At the 2-month follow-up, her WI-NRS score was 0.
Because “dupilumab is off label right now for this form of itch, oftentimes our first line is methotrexate,” Dr. Kwatra said. Patients “can have a good response with this therapeutic.”
He also described the case of a 72-year-old Black woman with total body itch for 2 years (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of seasonal allergies, thyroid disease, and hypertension. Previous therapies included prednisone, antihistamines, topical steroids, and gabapentin. The patient was found to have high IgE (447 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.9%), was started on methotrexate, and had an itch score of 0 at the 8-month follow-up.
JAK inhibitors may also have a role in the management of CPUO. A phase 2 nonrandomized controlled trial of abrocitinib for adults with prurigo nodularis (PN) or CPUO, recently published in JAMA Dermatology, showed itch scores decreased by 53.7% in the CPUO group (and 78.3% in the PN group) after 12 weeks of treatment with oral abrocitinib 200 mg daily. Patients had significant improvements in quality of life and no serious adverse events, said Dr. Kwatra, the lead author of the paper.
One of these patients was a 73-year-old White man who had experienced total body itch for 1.5 years (predominantly affecting his upper extremities; WI-NRS = 10) and a history of ascending aortic aneurysm, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. Previous failed therapies included dupilumab (> 6 months), topical steroids, tacrolimus, and antihistamines. Labs showed elevated IgE (456 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (11.7%). After 12 weeks of treatment with abrocitinib, the WI-NRS decreased to 2.
PD-1 Inhibitors As a Trigger
Chronic pruritus caused by the anticancer PD-1 inhibitors is becoming more common as the utilization of these immune checkpoint inhibitors increases, Dr. Kwatra noted. “You don’t see much in the skin, but [these patients have] very high IgE and eosinophils,” he said. “We’ve been seeing more reports recently of utilizing agents that target type 2 inflammation off label for PD-1 inhibitor–related skin manifestations.”
One such patient with PD-1 inhibitor–induced pruritus was a 65-year-old White man with metastatic melanoma who reported a 6-month history of itching that began 3 weeks after the start of treatment with the PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab. His WI-NRS score was 10 despite treatment with topical steroids and antihistamines. He had a history of psoriasis. Labs showed elevated IgE (1350 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.5%). At a 4-month follow-up after treatment with off-label dupilumab (a 600-mg subcutaneous loading dose followed by 300 mg every 14 days), his WI-NRS score was 0.
In a paper recently published in JAAD International, Dr. Kwatra, Ms. Manjunath, and coinvestigators reported on a series of 15 patients who developed chronic pruritus following an immune stimulus exposure, including immunotherapy and vaccination (2024 Apr 7:16:97-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jdin.2024.03.022). Most immunotherapy-treated patients experienced pruritus during treatment or after 21-60 days of receiving treatment, and the patients with vaccine-stimulated pruritus (after Tdap and messenger RNA COVID-19 vaccination) developed pruritus within a week of vaccination.
In addition to the elevated levels of IgE and eosinophils, plasma cytokine analysis showed elevated levels of IL-5, thymic stromal lymphopoietin, and other Th2-related cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with immune-stimulated pruritus compared with healthy controls, Ms. Manjunath said at the meeting.
When a Malignancy Workup Becomes Important
The initial part of any diagnostic workup for CPUO should include CBC with differential, liver function tests, renal function tests, and thyroid function testing, said Kwatra, referring to a diagnostic algorithm he developed, which was published as part of a CME review in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022.
Then, as indicated by risk factors in the history and physical, one could order other tests such as HIV serology, hepatitis B/C serologies, bullous pemphigoid testing, chest x-rays, evaluation for gammopathies, stool examination for ova and parasites, or heavy metal testing. “Do you do everything at once? We like to keep it straightforward,” Dr. Kwatra said. “Depending on the patient’s risk factors, you could order more or less.”
A malignancy workup should be strongly considered in patients whose itch duration is less than 12 months — and especially if the duration is less than 3 months — with an emphasis on cancers more frequently associated with itch: Hematologic and hepatobiliary cancers. This is “when concern should be heightened ... when there should be a lower threshold for workup,” he said.
The 12-month recommendation stems from a Danish cohort study published in 2014 that demonstrated a twofold increased incidence of cancer among patients with pruritus in the first 3 months after the diagnosis of pruritus. The 1-year absolute cancer risk was 1.63%.
Other risk factors for underlying malignancy or malignancy development in patients with CPUO include age older than 60 years, male sex, liver disease, and current or prior smoking, according to another study, noted Dr. Kwatra.
Dr. Kwatra disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, and other companies and an investigator for Galderma, Incyte, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Manjunath served as the codirector of the ElderDerm conference.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — , Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, said at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in older patients hosted by the GW School of Medicine & Health Sciences.
“We found a few years ago that eosinophils seem to differentiate this group, and now we’re finding that IgE and CBC [complete blood count] differential can help you get a little better sense of who has an immune-driven itch vs something more neuropathic,” said Dr. Kwatra, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, who founded and directed the Johns Hopkins Itch Center before coming to the University of Maryland in 2023. Not all patients with immune-driven itch will have these biomarkers, “but it’s a helpful tool,” he said.
CPUO is the term that is increasingly being used, he said, to describe intense, chronic pruritus without primary skin lesions or rashes and without any known systemic cause. It becomes more common as people get older and is sometimes debilitating. The initial evaluation should be kept “simple and straightforward,” he advised, with heightened concern for underlying malignancy in those who present with an itch of less than 12 months’ duration.
Biologics, JAK Inhibitors: Case Reports, Ongoing Research
Research conducted by Dr. Kwatra and Jaya Manjunath, a fourth-year medical student at The George Washington University, Washington, documented higher levels of Th2-associated cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with CPUO who had elevated IgE or eosinophil levels, or both than in patients with itch who had low IgE and eosinophil levels. The patients with higher levels also had a greater response to off-label treatment with immunomodulatory therapy.
“Multiple Th2-related inflammatory markers, like IL [interleukin]-5 and eotaxin-3, were reduced after dupilumab” in patients who responded to the therapy, said Ms. Manjunath, who co-presented the meeting session on chronic itch with Dr. Kwatra. Other changes in the plasma cytokine profile included a reduction in the serum level of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine, which is a biomarker for atopic dermatitis. The research is under review for publication.
Meanwhile, a phase 3 trial (LIBERTY-CPUO-CHIC) of dupilumab for CPUO is currently underway, Dr. Kwatra noted. Investigators are randomizing patients with severe pruritus (Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale [WI-NRS] ≥ 7) to dupilumab or placebo for 12 or 24 weeks.
In one of several cases shared by Dr. Kwatra and Ms. Manjunath, a 71-year-old Black woman with a 6-month history of generalized itch (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease was found to have elevated eosinophil levels and a negative malignancy workup. Previous therapies included antihistamines and topical steroids. She was started on a 600-mg loading dose of subcutaneous dupilumab followed by 300 mg every 14 days. At the 2-month follow-up, her WI-NRS score was 0.
Because “dupilumab is off label right now for this form of itch, oftentimes our first line is methotrexate,” Dr. Kwatra said. Patients “can have a good response with this therapeutic.”
He also described the case of a 72-year-old Black woman with total body itch for 2 years (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of seasonal allergies, thyroid disease, and hypertension. Previous therapies included prednisone, antihistamines, topical steroids, and gabapentin. The patient was found to have high IgE (447 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.9%), was started on methotrexate, and had an itch score of 0 at the 8-month follow-up.
JAK inhibitors may also have a role in the management of CPUO. A phase 2 nonrandomized controlled trial of abrocitinib for adults with prurigo nodularis (PN) or CPUO, recently published in JAMA Dermatology, showed itch scores decreased by 53.7% in the CPUO group (and 78.3% in the PN group) after 12 weeks of treatment with oral abrocitinib 200 mg daily. Patients had significant improvements in quality of life and no serious adverse events, said Dr. Kwatra, the lead author of the paper.
One of these patients was a 73-year-old White man who had experienced total body itch for 1.5 years (predominantly affecting his upper extremities; WI-NRS = 10) and a history of ascending aortic aneurysm, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. Previous failed therapies included dupilumab (> 6 months), topical steroids, tacrolimus, and antihistamines. Labs showed elevated IgE (456 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (11.7%). After 12 weeks of treatment with abrocitinib, the WI-NRS decreased to 2.
PD-1 Inhibitors As a Trigger
Chronic pruritus caused by the anticancer PD-1 inhibitors is becoming more common as the utilization of these immune checkpoint inhibitors increases, Dr. Kwatra noted. “You don’t see much in the skin, but [these patients have] very high IgE and eosinophils,” he said. “We’ve been seeing more reports recently of utilizing agents that target type 2 inflammation off label for PD-1 inhibitor–related skin manifestations.”
One such patient with PD-1 inhibitor–induced pruritus was a 65-year-old White man with metastatic melanoma who reported a 6-month history of itching that began 3 weeks after the start of treatment with the PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab. His WI-NRS score was 10 despite treatment with topical steroids and antihistamines. He had a history of psoriasis. Labs showed elevated IgE (1350 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.5%). At a 4-month follow-up after treatment with off-label dupilumab (a 600-mg subcutaneous loading dose followed by 300 mg every 14 days), his WI-NRS score was 0.
In a paper recently published in JAAD International, Dr. Kwatra, Ms. Manjunath, and coinvestigators reported on a series of 15 patients who developed chronic pruritus following an immune stimulus exposure, including immunotherapy and vaccination (2024 Apr 7:16:97-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jdin.2024.03.022). Most immunotherapy-treated patients experienced pruritus during treatment or after 21-60 days of receiving treatment, and the patients with vaccine-stimulated pruritus (after Tdap and messenger RNA COVID-19 vaccination) developed pruritus within a week of vaccination.
In addition to the elevated levels of IgE and eosinophils, plasma cytokine analysis showed elevated levels of IL-5, thymic stromal lymphopoietin, and other Th2-related cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with immune-stimulated pruritus compared with healthy controls, Ms. Manjunath said at the meeting.
When a Malignancy Workup Becomes Important
The initial part of any diagnostic workup for CPUO should include CBC with differential, liver function tests, renal function tests, and thyroid function testing, said Kwatra, referring to a diagnostic algorithm he developed, which was published as part of a CME review in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022.
Then, as indicated by risk factors in the history and physical, one could order other tests such as HIV serology, hepatitis B/C serologies, bullous pemphigoid testing, chest x-rays, evaluation for gammopathies, stool examination for ova and parasites, or heavy metal testing. “Do you do everything at once? We like to keep it straightforward,” Dr. Kwatra said. “Depending on the patient’s risk factors, you could order more or less.”
A malignancy workup should be strongly considered in patients whose itch duration is less than 12 months — and especially if the duration is less than 3 months — with an emphasis on cancers more frequently associated with itch: Hematologic and hepatobiliary cancers. This is “when concern should be heightened ... when there should be a lower threshold for workup,” he said.
The 12-month recommendation stems from a Danish cohort study published in 2014 that demonstrated a twofold increased incidence of cancer among patients with pruritus in the first 3 months after the diagnosis of pruritus. The 1-year absolute cancer risk was 1.63%.
Other risk factors for underlying malignancy or malignancy development in patients with CPUO include age older than 60 years, male sex, liver disease, and current or prior smoking, according to another study, noted Dr. Kwatra.
Dr. Kwatra disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, and other companies and an investigator for Galderma, Incyte, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Manjunath served as the codirector of the ElderDerm conference.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ELDERDERM 2024
Case Series: Upadacitinib Effective for Granulomatous Cheilitis
TOPLINE:
in a small retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Granulomatous cheilitis is a rare, nonnecrotizing granulomatous inflammatory disorder characterized by intermittent or persistent swelling of the lips.
- In a retrospective case series of five patients (median age, 30 years; four women) with granulomatous cheilitis resistant to systemic treatments at a Belgian hospital between June 2023 and March 2024, all five were treated with a high dose of upadacitinib (30 mg daily).
- The primary endpoint was objective clinical improvement in lip swelling and infiltration over a median follow-up of 7.2 months.
- Three patients had concomitant dormant Crohn’s disease (CD); a secondary outcome was disease activity in these patients.
TAKEAWAY:
- Upadacitinib treatment resulted in a complete response in four patients (80%) within a median of 3.8 months and a partial response in one patient.
- CD remained dormant in the three patients with CD.
- The safety profile of upadacitinib was favorable, and no serious adverse events were reported. Two patients experienced headaches, acne, mild changes in lipids, and/or transaminitis.
IN PRACTICE:
“Upadacitinib was effective in treating patients with recalcitrant and long-lasting granulomatous cheilitis, even in cases of concomitant CD, which could substantially improve the quality of life of affected patients,” the authors wrote. More studies are needed to confirm these results in larger groups of patients over longer periods of time, “and with other JAK inhibitors.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Axel De Greef, MD, Department of Dermatology, Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc, Université catholique de Louvain (UCLouvain), Brussels, Belgium. It was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and short follow-up may limit the generalizability of the findings to a larger population of patients with granulomatous cheilitis.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not report any funding sources. Some authors reported receiving nonfinancial support and personal fees from various pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
in a small retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Granulomatous cheilitis is a rare, nonnecrotizing granulomatous inflammatory disorder characterized by intermittent or persistent swelling of the lips.
- In a retrospective case series of five patients (median age, 30 years; four women) with granulomatous cheilitis resistant to systemic treatments at a Belgian hospital between June 2023 and March 2024, all five were treated with a high dose of upadacitinib (30 mg daily).
- The primary endpoint was objective clinical improvement in lip swelling and infiltration over a median follow-up of 7.2 months.
- Three patients had concomitant dormant Crohn’s disease (CD); a secondary outcome was disease activity in these patients.
TAKEAWAY:
- Upadacitinib treatment resulted in a complete response in four patients (80%) within a median of 3.8 months and a partial response in one patient.
- CD remained dormant in the three patients with CD.
- The safety profile of upadacitinib was favorable, and no serious adverse events were reported. Two patients experienced headaches, acne, mild changes in lipids, and/or transaminitis.
IN PRACTICE:
“Upadacitinib was effective in treating patients with recalcitrant and long-lasting granulomatous cheilitis, even in cases of concomitant CD, which could substantially improve the quality of life of affected patients,” the authors wrote. More studies are needed to confirm these results in larger groups of patients over longer periods of time, “and with other JAK inhibitors.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Axel De Greef, MD, Department of Dermatology, Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc, Université catholique de Louvain (UCLouvain), Brussels, Belgium. It was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and short follow-up may limit the generalizability of the findings to a larger population of patients with granulomatous cheilitis.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not report any funding sources. Some authors reported receiving nonfinancial support and personal fees from various pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
in a small retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Granulomatous cheilitis is a rare, nonnecrotizing granulomatous inflammatory disorder characterized by intermittent or persistent swelling of the lips.
- In a retrospective case series of five patients (median age, 30 years; four women) with granulomatous cheilitis resistant to systemic treatments at a Belgian hospital between June 2023 and March 2024, all five were treated with a high dose of upadacitinib (30 mg daily).
- The primary endpoint was objective clinical improvement in lip swelling and infiltration over a median follow-up of 7.2 months.
- Three patients had concomitant dormant Crohn’s disease (CD); a secondary outcome was disease activity in these patients.
TAKEAWAY:
- Upadacitinib treatment resulted in a complete response in four patients (80%) within a median of 3.8 months and a partial response in one patient.
- CD remained dormant in the three patients with CD.
- The safety profile of upadacitinib was favorable, and no serious adverse events were reported. Two patients experienced headaches, acne, mild changes in lipids, and/or transaminitis.
IN PRACTICE:
“Upadacitinib was effective in treating patients with recalcitrant and long-lasting granulomatous cheilitis, even in cases of concomitant CD, which could substantially improve the quality of life of affected patients,” the authors wrote. More studies are needed to confirm these results in larger groups of patients over longer periods of time, “and with other JAK inhibitors.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Axel De Greef, MD, Department of Dermatology, Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc, Université catholique de Louvain (UCLouvain), Brussels, Belgium. It was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and short follow-up may limit the generalizability of the findings to a larger population of patients with granulomatous cheilitis.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not report any funding sources. Some authors reported receiving nonfinancial support and personal fees from various pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A young adult with a 1-year history of erythema, papules, and pustules on her cheeks and skin
. It typically presents with a sudden onset of papules, pustules, cysts, painful inflammatory nodules, and erythema on the centrofacial areas. The etiology is unknown but has been speculated to be hormone-related as it is more common in women and can be triggered by acute changes such as stress or medications.
Because of overlapping symptoms with other conditions, an accurate clinical assessment is crucial. Typically, there are no comedones and about half of the patients have a history of acne. Some cases have shown a possible link between pyoderma faciale with inflammatory bowel disease, thyroid disease and liver disease, highlighting the importance of considering these associations in treatment decisions.
Treatment options for pyoderma faciale include isotretinoin, corticosteroids, dapsone, and antibiotics such as doxycycline. Isotretinoin is usually the first-line treatment, with dapsone reserved for cases where other methods have failed. Despite concerns about isotretinoin exacerbating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), there has been at least one reported case where a patient with ulcerative colitis who had pyoderma faciale that was successfully treated with isotretinoin with no adverse effects.
Isotretinoin has been shown to be effective in treating pyoderma faciale by significantly reducing inflammation and scarring. This is imperative because the scarring from pyoderma faciale can be disfiguring and psychologically harmful for patients. Therefore, an early diagnosis and effective treatment method are essential in preventing these scars and improving patients’ confidence and overall dermatological care.
This patient’s initial bacterial culture was negative. She was treated with a course of low dose isotretinoin. Prednisone was initiated two weeks before starting isotretinoin and then was tapered off during the first month of isotretinoin treatment. The patient was also started on spironolactone. The course of isotretinoin was 9 months. She has remained clear and still takes oral contraceptive pills and low dose spironolactone.
This case and the photos were submitted by Ms. Towe, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Donna Bilu Martin, MD, of Premier Dermatology, MD, Aventura, Florida. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Angileri L et al. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021 Feb;32(1):110-3. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2019.1628175.
Coutinho JC et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2016 Sep-Oct;91(5 suppl 1):151-3. doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20164943.
Rosen T and Unkefer RP. Cutis. 1999 Aug;64(2):107-9.
. It typically presents with a sudden onset of papules, pustules, cysts, painful inflammatory nodules, and erythema on the centrofacial areas. The etiology is unknown but has been speculated to be hormone-related as it is more common in women and can be triggered by acute changes such as stress or medications.
Because of overlapping symptoms with other conditions, an accurate clinical assessment is crucial. Typically, there are no comedones and about half of the patients have a history of acne. Some cases have shown a possible link between pyoderma faciale with inflammatory bowel disease, thyroid disease and liver disease, highlighting the importance of considering these associations in treatment decisions.
Treatment options for pyoderma faciale include isotretinoin, corticosteroids, dapsone, and antibiotics such as doxycycline. Isotretinoin is usually the first-line treatment, with dapsone reserved for cases where other methods have failed. Despite concerns about isotretinoin exacerbating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), there has been at least one reported case where a patient with ulcerative colitis who had pyoderma faciale that was successfully treated with isotretinoin with no adverse effects.
Isotretinoin has been shown to be effective in treating pyoderma faciale by significantly reducing inflammation and scarring. This is imperative because the scarring from pyoderma faciale can be disfiguring and psychologically harmful for patients. Therefore, an early diagnosis and effective treatment method are essential in preventing these scars and improving patients’ confidence and overall dermatological care.
This patient’s initial bacterial culture was negative. She was treated with a course of low dose isotretinoin. Prednisone was initiated two weeks before starting isotretinoin and then was tapered off during the first month of isotretinoin treatment. The patient was also started on spironolactone. The course of isotretinoin was 9 months. She has remained clear and still takes oral contraceptive pills and low dose spironolactone.
This case and the photos were submitted by Ms. Towe, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Donna Bilu Martin, MD, of Premier Dermatology, MD, Aventura, Florida. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Angileri L et al. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021 Feb;32(1):110-3. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2019.1628175.
Coutinho JC et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2016 Sep-Oct;91(5 suppl 1):151-3. doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20164943.
Rosen T and Unkefer RP. Cutis. 1999 Aug;64(2):107-9.
. It typically presents with a sudden onset of papules, pustules, cysts, painful inflammatory nodules, and erythema on the centrofacial areas. The etiology is unknown but has been speculated to be hormone-related as it is more common in women and can be triggered by acute changes such as stress or medications.
Because of overlapping symptoms with other conditions, an accurate clinical assessment is crucial. Typically, there are no comedones and about half of the patients have a history of acne. Some cases have shown a possible link between pyoderma faciale with inflammatory bowel disease, thyroid disease and liver disease, highlighting the importance of considering these associations in treatment decisions.
Treatment options for pyoderma faciale include isotretinoin, corticosteroids, dapsone, and antibiotics such as doxycycline. Isotretinoin is usually the first-line treatment, with dapsone reserved for cases where other methods have failed. Despite concerns about isotretinoin exacerbating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), there has been at least one reported case where a patient with ulcerative colitis who had pyoderma faciale that was successfully treated with isotretinoin with no adverse effects.
Isotretinoin has been shown to be effective in treating pyoderma faciale by significantly reducing inflammation and scarring. This is imperative because the scarring from pyoderma faciale can be disfiguring and psychologically harmful for patients. Therefore, an early diagnosis and effective treatment method are essential in preventing these scars and improving patients’ confidence and overall dermatological care.
This patient’s initial bacterial culture was negative. She was treated with a course of low dose isotretinoin. Prednisone was initiated two weeks before starting isotretinoin and then was tapered off during the first month of isotretinoin treatment. The patient was also started on spironolactone. The course of isotretinoin was 9 months. She has remained clear and still takes oral contraceptive pills and low dose spironolactone.
This case and the photos were submitted by Ms. Towe, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Donna Bilu Martin, MD, of Premier Dermatology, MD, Aventura, Florida. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Angileri L et al. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021 Feb;32(1):110-3. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2019.1628175.
Coutinho JC et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2016 Sep-Oct;91(5 suppl 1):151-3. doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20164943.
Rosen T and Unkefer RP. Cutis. 1999 Aug;64(2):107-9.
Several Skin Conditions More Likely in Children With Obesity
TORONTO — results of new research show.
The retrospective cohort study found markedly higher rates of skin infections, atopic dermatitis (AD), and acanthosis nigricans among children with overweight, compared with children with average weight.
“Many conditions associated with obesity are strong predictors of cardiovascular mortality as these children age, so doctors can play a key role in advocating for weight loss strategies in this population,” lead study author Samantha Epstein, third-year medical student at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio, said in an interview. The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Previous research has linked obesity, a chronic inflammatory condition, to psoriasis, AD, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), acne vulgaris, infections, and rosacea in adults. However, there’s scant research exploring the connection between obesity and cutaneous conditions in children.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, childhood obesity is defined as a body mass index, which is weight in kg divided by the square of height in m2, at or above the 95th percentile for age and sex in children aged 2 years or older.
For the study, Ms. Epstein and coauthor Sonal D. Shah, MD, associate professor, Department of Dermatology, Case Western Reserve University, and a board-certified pediatric dermatologist accessed a large national research database and used diagnostic codes to identify over 1 million children (mean age, 8.5 years). Most (about 44%) were White; about one-quarter were Black. The groups were propensity matched, so there were about equal numbers of youngsters with and without obesity and of boys and girls.
They collected data on AD, HS, rosacea, psoriasis, and acanthosis nigricans (a thickened purplish discoloration typically found in body folds around the armpits, groin, and neck). They also gathered information on comorbidities.
Acanthosis nigricans, which is linked to metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and insulin resistance , was more prevalent among children with obesity (20,885 cases in the with-obesity group and 336 in the without-obesity group, for a relative risk [RR] of 62.16 and an odds ratio [OR] of 64.38).
Skin and subcutaneous tissue infections were also more common among those with obesity (14,795 cases) vs 4720 cases among those without obesity (RR, 3.14; OR, 3.2). As for AD, there were 11,892 cases in the with-obesity group and 2983 in the without-obesity group (RR, 3.99; OR, 4.06). There were 1166 cases of psoriasis among those with obesity and 408 among those without obesity (RR, 2.86; OR, 2.88).
HS (587 cases in the with-obesity group and 70 in the without-obesity group; RR, 8.39; OR, 8.39) and rosacea (351 in the with-obesity group and 138 in the without-obesity group; RR, 2.54; OR, 2.55) were the least common skin conditions.
Higher Comorbidity Rates
Compared with their average-weight counterparts, the children with obesity had higher rates of comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes. Ms. Epstein noted that children with diabetes and obesity had increased risks for every skin condition except for infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue when compared with children without obesity.
Such infections were the most common skin conditions among children without obesity. “This was expected just due to the fact that children are outside, they’re playing in the grass and the dirt, and they get infected,” said Ms. Epstein. Still, these infections were three times more common in youngsters with obesity.
Although acanthosis nigricans is “highly correlated” with type 2 diabetes, “not as many children as we would expect in this population have developed type 2 diabetes,” said Ms. Epstein. This might make some sense, though, because these children are still quite young. “When dermatologists recognize this skin condition, they can advocate for weight loss management to try to prevent it.”
Other conditions seen more often in the overweight children with overweight included: hypertension, hyperlipidemia, obstructive sleep apnea, polycystic ovarian syndrome, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, major depressive disorder, depressive episodes, and anxiety (all P < .001).
Commenting on the results, Sonia Havele, MD, a pediatrician and dermatology resident at Children’s Mercy Hospital, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview that the study reflects trends that she and her colleagues see in clinic: There are more common skin conditions in their patients with obesity.
She agreed that it offers an opening for education. “The results of this study highlight the opportunity we have as pediatric dermatologists to provide additional counseling on obesity and offer referrals to our colleagues in endocrinology, gastroenterology, and nutrition if needed.”
No conflicts of interest were reported.
TORONTO — results of new research show.
The retrospective cohort study found markedly higher rates of skin infections, atopic dermatitis (AD), and acanthosis nigricans among children with overweight, compared with children with average weight.
“Many conditions associated with obesity are strong predictors of cardiovascular mortality as these children age, so doctors can play a key role in advocating for weight loss strategies in this population,” lead study author Samantha Epstein, third-year medical student at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio, said in an interview. The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Previous research has linked obesity, a chronic inflammatory condition, to psoriasis, AD, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), acne vulgaris, infections, and rosacea in adults. However, there’s scant research exploring the connection between obesity and cutaneous conditions in children.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, childhood obesity is defined as a body mass index, which is weight in kg divided by the square of height in m2, at or above the 95th percentile for age and sex in children aged 2 years or older.
For the study, Ms. Epstein and coauthor Sonal D. Shah, MD, associate professor, Department of Dermatology, Case Western Reserve University, and a board-certified pediatric dermatologist accessed a large national research database and used diagnostic codes to identify over 1 million children (mean age, 8.5 years). Most (about 44%) were White; about one-quarter were Black. The groups were propensity matched, so there were about equal numbers of youngsters with and without obesity and of boys and girls.
They collected data on AD, HS, rosacea, psoriasis, and acanthosis nigricans (a thickened purplish discoloration typically found in body folds around the armpits, groin, and neck). They also gathered information on comorbidities.
Acanthosis nigricans, which is linked to metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and insulin resistance , was more prevalent among children with obesity (20,885 cases in the with-obesity group and 336 in the without-obesity group, for a relative risk [RR] of 62.16 and an odds ratio [OR] of 64.38).
Skin and subcutaneous tissue infections were also more common among those with obesity (14,795 cases) vs 4720 cases among those without obesity (RR, 3.14; OR, 3.2). As for AD, there were 11,892 cases in the with-obesity group and 2983 in the without-obesity group (RR, 3.99; OR, 4.06). There were 1166 cases of psoriasis among those with obesity and 408 among those without obesity (RR, 2.86; OR, 2.88).
HS (587 cases in the with-obesity group and 70 in the without-obesity group; RR, 8.39; OR, 8.39) and rosacea (351 in the with-obesity group and 138 in the without-obesity group; RR, 2.54; OR, 2.55) were the least common skin conditions.
Higher Comorbidity Rates
Compared with their average-weight counterparts, the children with obesity had higher rates of comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes. Ms. Epstein noted that children with diabetes and obesity had increased risks for every skin condition except for infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue when compared with children without obesity.
Such infections were the most common skin conditions among children without obesity. “This was expected just due to the fact that children are outside, they’re playing in the grass and the dirt, and they get infected,” said Ms. Epstein. Still, these infections were three times more common in youngsters with obesity.
Although acanthosis nigricans is “highly correlated” with type 2 diabetes, “not as many children as we would expect in this population have developed type 2 diabetes,” said Ms. Epstein. This might make some sense, though, because these children are still quite young. “When dermatologists recognize this skin condition, they can advocate for weight loss management to try to prevent it.”
Other conditions seen more often in the overweight children with overweight included: hypertension, hyperlipidemia, obstructive sleep apnea, polycystic ovarian syndrome, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, major depressive disorder, depressive episodes, and anxiety (all P < .001).
Commenting on the results, Sonia Havele, MD, a pediatrician and dermatology resident at Children’s Mercy Hospital, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview that the study reflects trends that she and her colleagues see in clinic: There are more common skin conditions in their patients with obesity.
She agreed that it offers an opening for education. “The results of this study highlight the opportunity we have as pediatric dermatologists to provide additional counseling on obesity and offer referrals to our colleagues in endocrinology, gastroenterology, and nutrition if needed.”
No conflicts of interest were reported.
TORONTO — results of new research show.
The retrospective cohort study found markedly higher rates of skin infections, atopic dermatitis (AD), and acanthosis nigricans among children with overweight, compared with children with average weight.
“Many conditions associated with obesity are strong predictors of cardiovascular mortality as these children age, so doctors can play a key role in advocating for weight loss strategies in this population,” lead study author Samantha Epstein, third-year medical student at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio, said in an interview. The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Previous research has linked obesity, a chronic inflammatory condition, to psoriasis, AD, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), acne vulgaris, infections, and rosacea in adults. However, there’s scant research exploring the connection between obesity and cutaneous conditions in children.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, childhood obesity is defined as a body mass index, which is weight in kg divided by the square of height in m2, at or above the 95th percentile for age and sex in children aged 2 years or older.
For the study, Ms. Epstein and coauthor Sonal D. Shah, MD, associate professor, Department of Dermatology, Case Western Reserve University, and a board-certified pediatric dermatologist accessed a large national research database and used diagnostic codes to identify over 1 million children (mean age, 8.5 years). Most (about 44%) were White; about one-quarter were Black. The groups were propensity matched, so there were about equal numbers of youngsters with and without obesity and of boys and girls.
They collected data on AD, HS, rosacea, psoriasis, and acanthosis nigricans (a thickened purplish discoloration typically found in body folds around the armpits, groin, and neck). They also gathered information on comorbidities.
Acanthosis nigricans, which is linked to metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and insulin resistance , was more prevalent among children with obesity (20,885 cases in the with-obesity group and 336 in the without-obesity group, for a relative risk [RR] of 62.16 and an odds ratio [OR] of 64.38).
Skin and subcutaneous tissue infections were also more common among those with obesity (14,795 cases) vs 4720 cases among those without obesity (RR, 3.14; OR, 3.2). As for AD, there were 11,892 cases in the with-obesity group and 2983 in the without-obesity group (RR, 3.99; OR, 4.06). There were 1166 cases of psoriasis among those with obesity and 408 among those without obesity (RR, 2.86; OR, 2.88).
HS (587 cases in the with-obesity group and 70 in the without-obesity group; RR, 8.39; OR, 8.39) and rosacea (351 in the with-obesity group and 138 in the without-obesity group; RR, 2.54; OR, 2.55) were the least common skin conditions.
Higher Comorbidity Rates
Compared with their average-weight counterparts, the children with obesity had higher rates of comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes. Ms. Epstein noted that children with diabetes and obesity had increased risks for every skin condition except for infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue when compared with children without obesity.
Such infections were the most common skin conditions among children without obesity. “This was expected just due to the fact that children are outside, they’re playing in the grass and the dirt, and they get infected,” said Ms. Epstein. Still, these infections were three times more common in youngsters with obesity.
Although acanthosis nigricans is “highly correlated” with type 2 diabetes, “not as many children as we would expect in this population have developed type 2 diabetes,” said Ms. Epstein. This might make some sense, though, because these children are still quite young. “When dermatologists recognize this skin condition, they can advocate for weight loss management to try to prevent it.”
Other conditions seen more often in the overweight children with overweight included: hypertension, hyperlipidemia, obstructive sleep apnea, polycystic ovarian syndrome, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, major depressive disorder, depressive episodes, and anxiety (all P < .001).
Commenting on the results, Sonia Havele, MD, a pediatrician and dermatology resident at Children’s Mercy Hospital, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview that the study reflects trends that she and her colleagues see in clinic: There are more common skin conditions in their patients with obesity.
She agreed that it offers an opening for education. “The results of this study highlight the opportunity we have as pediatric dermatologists to provide additional counseling on obesity and offer referrals to our colleagues in endocrinology, gastroenterology, and nutrition if needed.”
No conflicts of interest were reported.
FROM SPD 2024
Dermatoporosis in Older Adults: A Condition That Requires Holistic, Creative Management
WASHINGTON — and conveys the skin’s vulnerability to serious medical complications, said Adam Friedman, MD, at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient.
Key features of dermatoporosis include atrophic skin, solar purpura, white pseudoscars, easily acquired skin lacerations and tears, bruises, and delayed healing. “We’re going to see more of this, and it will more and more be a chief complaint of patients,” said Dr. Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University (GWU) in Washington, and co-chair of the meeting. GWU hosted the conference, describing it as a first-of-its-kind meeting dedicated to improving dermatologic care for older adults.
Dermatoporosis was described in the literature in 2007 by dermatologists at the University of Geneva in Switzerland. “It is not only a cosmetic problem,” Dr. Friedman said. “This is a medical problem ... which can absolutely lead to comorbidities [such as deep dissecting hematomas] that are a huge strain on the healthcare system.”
Dermatologists can meet the moment with holistic, creative combination treatment and counseling approaches aimed at improving the mechanical strength of skin and preventing potential complications in older patients, Dr. Friedman said at the meeting.
He described the case of a 76-year-old woman who presented with dermatoporosis on her arms involving pronounced skin atrophy, solar purpura, and a small covered laceration. “This was a patient who was both devastated by the appearance” and impacted by the pain and burden of dressing frequent wounds, said Dr. Friedman, who is also the director of the Residency Program, of Translational Research, and of Supportive Oncodermatology, all within the Department of Dermatology at GWU.
With 11 months of topical treatment that included daily application of calcipotriene 0.05% ointment and nightly application of tazarotene 0.045% lotion and oral supplementation with 1000-mg vitamin C twice daily and 1000-mg citrus bioflavonoid complex daily, as well as no changes to the medications she took for various comorbidities, the solar purpura improved significantly and “we made a huge difference in the integrity of her skin,” he said.
Dr. Friedman also described this case in a recently published article in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology titled “What’s Old Is New: An Emerging Focus on Dermatoporosis”.
Likely Pathophysiology
Advancing age and chronic ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure are the chief drivers of dermatoporosis. In addition to UVA and UVB light, other secondary drivers include genetic susceptibility, topical and systematic corticosteroid use, and anticoagulant treatment.
Its pathogenesis is not well described in the literature but is easy to envision, Dr. Friedman said. For one, both advancing age and exposure to UV light lead to a reduction in hygroscopic glycosaminoglycans, including hyaluronate (HA), and the impact of this diminishment is believed to go “beyond [the loss of] buoyancy,” he noted. Researchers have “been showing these are not just water-loving molecules, they also have some biologic properties” relating to keratinocyte production and epidermal turnover that appear to be intricately linked to the pathogenesis of dermatoporosis.
HAs have been shown to interact with the cell surface receptor CD44 to stimulate keratinocyte proliferation, and low levels of CD44 have been reported in skin with dermatoporosis compared with a younger control population. (A newly characterized organelle, the hyaluronosome, serves as an HA factory and contains CD44 and heparin-binding epidermal growth factor, Dr. Friedman noted. Inadequate functioning may be involved in skin atrophy.)
Advancing age also brings an increase in matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)–1, –2, and –3, which are “the demolition workers of the skin,” and downregulation of a tissue inhibitor of MMPs, he said.
Adding insult to injury, dermis-penetrating UVA also activates MMPs, “obliterating collagen and elastin.” UVB generates DNA photoproducts, including oxidative stress and damaging skin cell DNA. “That UV light induces breakdown [of the skin] through different mechanisms and inhibits buildup is a simple concept I think our patients can understand,” Dr. Friedman said.
Multifaceted Treatment
For an older adult, “there is never a wrong time to start sun-protective measures” to prevent or try to halt the progression of dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman said, noting that “UV radiation is an immunosuppressant, so there are many good reasons to start” if the adult is not already taking measures on a regular basis.
Potential treatments for the syndrome of dermatoporosis are backed by few clinical studies, but dermatologists are skilled at translating the use of products from one disease state to another based on understandings of pathophysiology and mechanistic pathways, Dr. Friedman commented in an interview after the meeting.
For instance, “from decades of research, we know what retinoids will do to the skin,” he said in the interview. “We know they will turn on collagen-1 and -3 genes in the skin, and that they will increase the production of glycosaminoglycans ... By understanding the biology, we can translate this to dermatoporosis.” These changes were demonstrated, for instance, in a small study of topical retinol in older adults.
Studies of topical alpha hydroxy acid (AHA), moreover, have demonstrated epidermal thickening and firmness, and “some studies show they can limit steroid-induced atrophy,” Dr. Friedman said at the meeting. “And things like lactic acid and urea are super accessible.”
Topical dehydroepiandrosterone is backed by even less data than retinoids or AHAs are, “but it’s still something to consider” as part of a multimechanistic approach to dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman shared, noting that a small study demonstrated beneficial effects on epidermal atrophy in aging skin.
The use of vitamin D analogues such as calcipotriene, which is approved for the treatment of psoriasis, may also be promising. “One concept is that [vitamin D analogues] increase calcium concentrations in the epidermis, and calcium is so central to keratinocyte differentiation” and epidermal function that calcipotriene in combination with topical steroid therapy has been shown to limit skin atrophy, he noted.
Nutritionally, low protein intake is a known problem in the older population and is associated with increased skin fragility and poorer healing. From a prevention and treatment standpoint, therefore, patients can be counseled to be attentive to their diets, Dr. Friedman said. Experts have recommended a higher protein intake for older adults than for younger adults; in 2013, an international group recommended a protein intake of 1-1.5 g/kg/d for healthy older adults and more for those with acute or chronic illness.
“Patients love talking about diet and skin disease ... and they love over-the-counter nutraceuticals as well because they want something natural,” Dr. Friedman said. “I like using bioflavonoids in combination with vitamin C, which can be effective especially for solar purpura.”
A 6-week randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial involving 67 patients with purpura associated with aging found a 50% reduction in purpura lesions among those took a particular citrus bioflavonoid blend twice daily. “I thought this was a pretty well-done study,” he said, noting that patient self-assessment and investigator global assessment were utilized.
Skin Injury and Wound Prevention
In addition to recommending gentle skin cleansers and daily moisturizing, dermatologists should talk to their older patients with dermatoporosis about their home environments. “What is it like? Is there furniture with sharp edges?” Dr. Friedman advised. If so, could they use sleeves or protectors on their arms or legs “to protect against injury?”
In a later meeting session about lower-extremity wounds on geriatric patients, Michael Stempel, DPM, assistant professor of medicine and surgery and chief of podiatry at GWU, said that he was happy to hear the term dermatoporosis being used because like diabetes, it’s a risk factor for developing lower-extremity wounds and poor wound healing.
He shared the case of an older woman with dermatoporosis who “tripped and skinned her knee against a step and then self-treated it for over a month by pouring hydrogen peroxide over it and letting air get to it.” The wound developed into “full-thickness tissue loss,” said Dr. Stempel, also medical director of the Wound Healing and Limb Preservation Center at GWU Hospital.
Misperceptions are common among older patients about how a simple wound should be managed; for instance, the adage “just let it get air” is not uncommon. This makes anticipatory guidance about basic wound care — such as the importance of a moist and occlusive environment and the safe use of hydrogen peroxide — especially important for patients with dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman commented after the meeting.
Dermatoporosis is quantifiable, Dr. Friedman said during the meeting, with a scoring system having been developed by the researchers in Switzerland who originally coined the term. Its use in practice is unnecessary, but its existence is “nice to share with patients who feel bothered because oftentimes, patients feel it’s been dismissed by other providers,” he said. “Telling your patients there’s an actual name for their problem, and that there are ways to quantify and measure changes over time, is validating.”
Its recognition as a medical condition, Dr. Friedman added, also enables the dermatologist to bring it up and counsel appropriately — without a patient feeling shame — when it is identified in the context of a skin excision, treatment of a primary inflammatory skin disease, or management of another dermatologic problem.
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a consultant/advisory board member for L’Oréal, La Roche-Posay, Galderma, and other companies; a speaker for Regeneron/Sanofi, Incyte, BMD, and Janssen; and has grants from Pfizer, Lilly, Incyte, and other companies. Dr. Stempel reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — and conveys the skin’s vulnerability to serious medical complications, said Adam Friedman, MD, at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient.
Key features of dermatoporosis include atrophic skin, solar purpura, white pseudoscars, easily acquired skin lacerations and tears, bruises, and delayed healing. “We’re going to see more of this, and it will more and more be a chief complaint of patients,” said Dr. Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University (GWU) in Washington, and co-chair of the meeting. GWU hosted the conference, describing it as a first-of-its-kind meeting dedicated to improving dermatologic care for older adults.
Dermatoporosis was described in the literature in 2007 by dermatologists at the University of Geneva in Switzerland. “It is not only a cosmetic problem,” Dr. Friedman said. “This is a medical problem ... which can absolutely lead to comorbidities [such as deep dissecting hematomas] that are a huge strain on the healthcare system.”
Dermatologists can meet the moment with holistic, creative combination treatment and counseling approaches aimed at improving the mechanical strength of skin and preventing potential complications in older patients, Dr. Friedman said at the meeting.
He described the case of a 76-year-old woman who presented with dermatoporosis on her arms involving pronounced skin atrophy, solar purpura, and a small covered laceration. “This was a patient who was both devastated by the appearance” and impacted by the pain and burden of dressing frequent wounds, said Dr. Friedman, who is also the director of the Residency Program, of Translational Research, and of Supportive Oncodermatology, all within the Department of Dermatology at GWU.
With 11 months of topical treatment that included daily application of calcipotriene 0.05% ointment and nightly application of tazarotene 0.045% lotion and oral supplementation with 1000-mg vitamin C twice daily and 1000-mg citrus bioflavonoid complex daily, as well as no changes to the medications she took for various comorbidities, the solar purpura improved significantly and “we made a huge difference in the integrity of her skin,” he said.
Dr. Friedman also described this case in a recently published article in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology titled “What’s Old Is New: An Emerging Focus on Dermatoporosis”.
Likely Pathophysiology
Advancing age and chronic ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure are the chief drivers of dermatoporosis. In addition to UVA and UVB light, other secondary drivers include genetic susceptibility, topical and systematic corticosteroid use, and anticoagulant treatment.
Its pathogenesis is not well described in the literature but is easy to envision, Dr. Friedman said. For one, both advancing age and exposure to UV light lead to a reduction in hygroscopic glycosaminoglycans, including hyaluronate (HA), and the impact of this diminishment is believed to go “beyond [the loss of] buoyancy,” he noted. Researchers have “been showing these are not just water-loving molecules, they also have some biologic properties” relating to keratinocyte production and epidermal turnover that appear to be intricately linked to the pathogenesis of dermatoporosis.
HAs have been shown to interact with the cell surface receptor CD44 to stimulate keratinocyte proliferation, and low levels of CD44 have been reported in skin with dermatoporosis compared with a younger control population. (A newly characterized organelle, the hyaluronosome, serves as an HA factory and contains CD44 and heparin-binding epidermal growth factor, Dr. Friedman noted. Inadequate functioning may be involved in skin atrophy.)
Advancing age also brings an increase in matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)–1, –2, and –3, which are “the demolition workers of the skin,” and downregulation of a tissue inhibitor of MMPs, he said.
Adding insult to injury, dermis-penetrating UVA also activates MMPs, “obliterating collagen and elastin.” UVB generates DNA photoproducts, including oxidative stress and damaging skin cell DNA. “That UV light induces breakdown [of the skin] through different mechanisms and inhibits buildup is a simple concept I think our patients can understand,” Dr. Friedman said.
Multifaceted Treatment
For an older adult, “there is never a wrong time to start sun-protective measures” to prevent or try to halt the progression of dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman said, noting that “UV radiation is an immunosuppressant, so there are many good reasons to start” if the adult is not already taking measures on a regular basis.
Potential treatments for the syndrome of dermatoporosis are backed by few clinical studies, but dermatologists are skilled at translating the use of products from one disease state to another based on understandings of pathophysiology and mechanistic pathways, Dr. Friedman commented in an interview after the meeting.
For instance, “from decades of research, we know what retinoids will do to the skin,” he said in the interview. “We know they will turn on collagen-1 and -3 genes in the skin, and that they will increase the production of glycosaminoglycans ... By understanding the biology, we can translate this to dermatoporosis.” These changes were demonstrated, for instance, in a small study of topical retinol in older adults.
Studies of topical alpha hydroxy acid (AHA), moreover, have demonstrated epidermal thickening and firmness, and “some studies show they can limit steroid-induced atrophy,” Dr. Friedman said at the meeting. “And things like lactic acid and urea are super accessible.”
Topical dehydroepiandrosterone is backed by even less data than retinoids or AHAs are, “but it’s still something to consider” as part of a multimechanistic approach to dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman shared, noting that a small study demonstrated beneficial effects on epidermal atrophy in aging skin.
The use of vitamin D analogues such as calcipotriene, which is approved for the treatment of psoriasis, may also be promising. “One concept is that [vitamin D analogues] increase calcium concentrations in the epidermis, and calcium is so central to keratinocyte differentiation” and epidermal function that calcipotriene in combination with topical steroid therapy has been shown to limit skin atrophy, he noted.
Nutritionally, low protein intake is a known problem in the older population and is associated with increased skin fragility and poorer healing. From a prevention and treatment standpoint, therefore, patients can be counseled to be attentive to their diets, Dr. Friedman said. Experts have recommended a higher protein intake for older adults than for younger adults; in 2013, an international group recommended a protein intake of 1-1.5 g/kg/d for healthy older adults and more for those with acute or chronic illness.
“Patients love talking about diet and skin disease ... and they love over-the-counter nutraceuticals as well because they want something natural,” Dr. Friedman said. “I like using bioflavonoids in combination with vitamin C, which can be effective especially for solar purpura.”
A 6-week randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial involving 67 patients with purpura associated with aging found a 50% reduction in purpura lesions among those took a particular citrus bioflavonoid blend twice daily. “I thought this was a pretty well-done study,” he said, noting that patient self-assessment and investigator global assessment were utilized.
Skin Injury and Wound Prevention
In addition to recommending gentle skin cleansers and daily moisturizing, dermatologists should talk to their older patients with dermatoporosis about their home environments. “What is it like? Is there furniture with sharp edges?” Dr. Friedman advised. If so, could they use sleeves or protectors on their arms or legs “to protect against injury?”
In a later meeting session about lower-extremity wounds on geriatric patients, Michael Stempel, DPM, assistant professor of medicine and surgery and chief of podiatry at GWU, said that he was happy to hear the term dermatoporosis being used because like diabetes, it’s a risk factor for developing lower-extremity wounds and poor wound healing.
He shared the case of an older woman with dermatoporosis who “tripped and skinned her knee against a step and then self-treated it for over a month by pouring hydrogen peroxide over it and letting air get to it.” The wound developed into “full-thickness tissue loss,” said Dr. Stempel, also medical director of the Wound Healing and Limb Preservation Center at GWU Hospital.
Misperceptions are common among older patients about how a simple wound should be managed; for instance, the adage “just let it get air” is not uncommon. This makes anticipatory guidance about basic wound care — such as the importance of a moist and occlusive environment and the safe use of hydrogen peroxide — especially important for patients with dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman commented after the meeting.
Dermatoporosis is quantifiable, Dr. Friedman said during the meeting, with a scoring system having been developed by the researchers in Switzerland who originally coined the term. Its use in practice is unnecessary, but its existence is “nice to share with patients who feel bothered because oftentimes, patients feel it’s been dismissed by other providers,” he said. “Telling your patients there’s an actual name for their problem, and that there are ways to quantify and measure changes over time, is validating.”
Its recognition as a medical condition, Dr. Friedman added, also enables the dermatologist to bring it up and counsel appropriately — without a patient feeling shame — when it is identified in the context of a skin excision, treatment of a primary inflammatory skin disease, or management of another dermatologic problem.
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a consultant/advisory board member for L’Oréal, La Roche-Posay, Galderma, and other companies; a speaker for Regeneron/Sanofi, Incyte, BMD, and Janssen; and has grants from Pfizer, Lilly, Incyte, and other companies. Dr. Stempel reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — and conveys the skin’s vulnerability to serious medical complications, said Adam Friedman, MD, at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient.
Key features of dermatoporosis include atrophic skin, solar purpura, white pseudoscars, easily acquired skin lacerations and tears, bruises, and delayed healing. “We’re going to see more of this, and it will more and more be a chief complaint of patients,” said Dr. Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University (GWU) in Washington, and co-chair of the meeting. GWU hosted the conference, describing it as a first-of-its-kind meeting dedicated to improving dermatologic care for older adults.
Dermatoporosis was described in the literature in 2007 by dermatologists at the University of Geneva in Switzerland. “It is not only a cosmetic problem,” Dr. Friedman said. “This is a medical problem ... which can absolutely lead to comorbidities [such as deep dissecting hematomas] that are a huge strain on the healthcare system.”
Dermatologists can meet the moment with holistic, creative combination treatment and counseling approaches aimed at improving the mechanical strength of skin and preventing potential complications in older patients, Dr. Friedman said at the meeting.
He described the case of a 76-year-old woman who presented with dermatoporosis on her arms involving pronounced skin atrophy, solar purpura, and a small covered laceration. “This was a patient who was both devastated by the appearance” and impacted by the pain and burden of dressing frequent wounds, said Dr. Friedman, who is also the director of the Residency Program, of Translational Research, and of Supportive Oncodermatology, all within the Department of Dermatology at GWU.
With 11 months of topical treatment that included daily application of calcipotriene 0.05% ointment and nightly application of tazarotene 0.045% lotion and oral supplementation with 1000-mg vitamin C twice daily and 1000-mg citrus bioflavonoid complex daily, as well as no changes to the medications she took for various comorbidities, the solar purpura improved significantly and “we made a huge difference in the integrity of her skin,” he said.
Dr. Friedman also described this case in a recently published article in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology titled “What’s Old Is New: An Emerging Focus on Dermatoporosis”.
Likely Pathophysiology
Advancing age and chronic ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure are the chief drivers of dermatoporosis. In addition to UVA and UVB light, other secondary drivers include genetic susceptibility, topical and systematic corticosteroid use, and anticoagulant treatment.
Its pathogenesis is not well described in the literature but is easy to envision, Dr. Friedman said. For one, both advancing age and exposure to UV light lead to a reduction in hygroscopic glycosaminoglycans, including hyaluronate (HA), and the impact of this diminishment is believed to go “beyond [the loss of] buoyancy,” he noted. Researchers have “been showing these are not just water-loving molecules, they also have some biologic properties” relating to keratinocyte production and epidermal turnover that appear to be intricately linked to the pathogenesis of dermatoporosis.
HAs have been shown to interact with the cell surface receptor CD44 to stimulate keratinocyte proliferation, and low levels of CD44 have been reported in skin with dermatoporosis compared with a younger control population. (A newly characterized organelle, the hyaluronosome, serves as an HA factory and contains CD44 and heparin-binding epidermal growth factor, Dr. Friedman noted. Inadequate functioning may be involved in skin atrophy.)
Advancing age also brings an increase in matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)–1, –2, and –3, which are “the demolition workers of the skin,” and downregulation of a tissue inhibitor of MMPs, he said.
Adding insult to injury, dermis-penetrating UVA also activates MMPs, “obliterating collagen and elastin.” UVB generates DNA photoproducts, including oxidative stress and damaging skin cell DNA. “That UV light induces breakdown [of the skin] through different mechanisms and inhibits buildup is a simple concept I think our patients can understand,” Dr. Friedman said.
Multifaceted Treatment
For an older adult, “there is never a wrong time to start sun-protective measures” to prevent or try to halt the progression of dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman said, noting that “UV radiation is an immunosuppressant, so there are many good reasons to start” if the adult is not already taking measures on a regular basis.
Potential treatments for the syndrome of dermatoporosis are backed by few clinical studies, but dermatologists are skilled at translating the use of products from one disease state to another based on understandings of pathophysiology and mechanistic pathways, Dr. Friedman commented in an interview after the meeting.
For instance, “from decades of research, we know what retinoids will do to the skin,” he said in the interview. “We know they will turn on collagen-1 and -3 genes in the skin, and that they will increase the production of glycosaminoglycans ... By understanding the biology, we can translate this to dermatoporosis.” These changes were demonstrated, for instance, in a small study of topical retinol in older adults.
Studies of topical alpha hydroxy acid (AHA), moreover, have demonstrated epidermal thickening and firmness, and “some studies show they can limit steroid-induced atrophy,” Dr. Friedman said at the meeting. “And things like lactic acid and urea are super accessible.”
Topical dehydroepiandrosterone is backed by even less data than retinoids or AHAs are, “but it’s still something to consider” as part of a multimechanistic approach to dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman shared, noting that a small study demonstrated beneficial effects on epidermal atrophy in aging skin.
The use of vitamin D analogues such as calcipotriene, which is approved for the treatment of psoriasis, may also be promising. “One concept is that [vitamin D analogues] increase calcium concentrations in the epidermis, and calcium is so central to keratinocyte differentiation” and epidermal function that calcipotriene in combination with topical steroid therapy has been shown to limit skin atrophy, he noted.
Nutritionally, low protein intake is a known problem in the older population and is associated with increased skin fragility and poorer healing. From a prevention and treatment standpoint, therefore, patients can be counseled to be attentive to their diets, Dr. Friedman said. Experts have recommended a higher protein intake for older adults than for younger adults; in 2013, an international group recommended a protein intake of 1-1.5 g/kg/d for healthy older adults and more for those with acute or chronic illness.
“Patients love talking about diet and skin disease ... and they love over-the-counter nutraceuticals as well because they want something natural,” Dr. Friedman said. “I like using bioflavonoids in combination with vitamin C, which can be effective especially for solar purpura.”
A 6-week randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial involving 67 patients with purpura associated with aging found a 50% reduction in purpura lesions among those took a particular citrus bioflavonoid blend twice daily. “I thought this was a pretty well-done study,” he said, noting that patient self-assessment and investigator global assessment were utilized.
Skin Injury and Wound Prevention
In addition to recommending gentle skin cleansers and daily moisturizing, dermatologists should talk to their older patients with dermatoporosis about their home environments. “What is it like? Is there furniture with sharp edges?” Dr. Friedman advised. If so, could they use sleeves or protectors on their arms or legs “to protect against injury?”
In a later meeting session about lower-extremity wounds on geriatric patients, Michael Stempel, DPM, assistant professor of medicine and surgery and chief of podiatry at GWU, said that he was happy to hear the term dermatoporosis being used because like diabetes, it’s a risk factor for developing lower-extremity wounds and poor wound healing.
He shared the case of an older woman with dermatoporosis who “tripped and skinned her knee against a step and then self-treated it for over a month by pouring hydrogen peroxide over it and letting air get to it.” The wound developed into “full-thickness tissue loss,” said Dr. Stempel, also medical director of the Wound Healing and Limb Preservation Center at GWU Hospital.
Misperceptions are common among older patients about how a simple wound should be managed; for instance, the adage “just let it get air” is not uncommon. This makes anticipatory guidance about basic wound care — such as the importance of a moist and occlusive environment and the safe use of hydrogen peroxide — especially important for patients with dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman commented after the meeting.
Dermatoporosis is quantifiable, Dr. Friedman said during the meeting, with a scoring system having been developed by the researchers in Switzerland who originally coined the term. Its use in practice is unnecessary, but its existence is “nice to share with patients who feel bothered because oftentimes, patients feel it’s been dismissed by other providers,” he said. “Telling your patients there’s an actual name for their problem, and that there are ways to quantify and measure changes over time, is validating.”
Its recognition as a medical condition, Dr. Friedman added, also enables the dermatologist to bring it up and counsel appropriately — without a patient feeling shame — when it is identified in the context of a skin excision, treatment of a primary inflammatory skin disease, or management of another dermatologic problem.
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a consultant/advisory board member for L’Oréal, La Roche-Posay, Galderma, and other companies; a speaker for Regeneron/Sanofi, Incyte, BMD, and Janssen; and has grants from Pfizer, Lilly, Incyte, and other companies. Dr. Stempel reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ELDERDERM 2024
Study Finds Potential benefits of Spironolactone for Women with HS
TOPLINE:
according to the results of a single-center retrospective study.
METHODOLOGY:
- This retrospective study included 157 women (median age, 36.5 years) with HS who received spironolactone for at least 3 months between 2000 and 2021 at Michigan Medicine outpatient dermatology clinics. The majority of patients were White (59%) or Black (37%) individuals.
- The median prescribed dose was 100 mg/d, the most common dose was 50-100 mg/d, and the median time spironolactone was initiated was 8.8 years after HS was diagnosed.
- Improvement status was classified on the basis of objective clinician assessments, including documented reductions in the lesion count, pain, and symptoms.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 31 patients (20%) showed improvements with spironolactone treatment.
- A shorter duration between the diagnosis of HS and the initiation of spironolactone was associated with improvement (P = .047).
- Axillary involvement (P = .003), the use of intralesional steroids (P = .015), previous treatments (P = .023), and previous treatment failures (P = .030) were linked to a lack of improvement with spironolactone.
- Patients with Hurley stage III were 85% less likely to experience improvement with spironolactone (P = .036).
IN PRACTICE:
Spironolactone, which has antiandrogenic properties, “may be beneficial for patients with mild HS, notably those at Hurley stage I if implemented early as a primary or ancillary treatment,” the authors concluded, adding that prospective, multicenter studies are needed to “elucidate further the safety and efficacy of spironolactone for treating HS.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Suma V. Gangidi, BS, Carle Illinois College of Medicine, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, and was published online in the International Journal of Women’s Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Retrospective design can introduce inherent biases, including the potential for missing or misclassified data. Additionally, the study was conducted at a single center, which may limit the generalizability, and findings were also limited by lack of standardized objective measures for assessing treatment improvement, presence of confounding variables from concomitant treatments, small sample size, and potential multicollinearity.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not receive any funding. One author declared ties with various pharmaceutical companies. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
according to the results of a single-center retrospective study.
METHODOLOGY:
- This retrospective study included 157 women (median age, 36.5 years) with HS who received spironolactone for at least 3 months between 2000 and 2021 at Michigan Medicine outpatient dermatology clinics. The majority of patients were White (59%) or Black (37%) individuals.
- The median prescribed dose was 100 mg/d, the most common dose was 50-100 mg/d, and the median time spironolactone was initiated was 8.8 years after HS was diagnosed.
- Improvement status was classified on the basis of objective clinician assessments, including documented reductions in the lesion count, pain, and symptoms.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 31 patients (20%) showed improvements with spironolactone treatment.
- A shorter duration between the diagnosis of HS and the initiation of spironolactone was associated with improvement (P = .047).
- Axillary involvement (P = .003), the use of intralesional steroids (P = .015), previous treatments (P = .023), and previous treatment failures (P = .030) were linked to a lack of improvement with spironolactone.
- Patients with Hurley stage III were 85% less likely to experience improvement with spironolactone (P = .036).
IN PRACTICE:
Spironolactone, which has antiandrogenic properties, “may be beneficial for patients with mild HS, notably those at Hurley stage I if implemented early as a primary or ancillary treatment,” the authors concluded, adding that prospective, multicenter studies are needed to “elucidate further the safety and efficacy of spironolactone for treating HS.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Suma V. Gangidi, BS, Carle Illinois College of Medicine, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, and was published online in the International Journal of Women’s Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Retrospective design can introduce inherent biases, including the potential for missing or misclassified data. Additionally, the study was conducted at a single center, which may limit the generalizability, and findings were also limited by lack of standardized objective measures for assessing treatment improvement, presence of confounding variables from concomitant treatments, small sample size, and potential multicollinearity.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not receive any funding. One author declared ties with various pharmaceutical companies. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
according to the results of a single-center retrospective study.
METHODOLOGY:
- This retrospective study included 157 women (median age, 36.5 years) with HS who received spironolactone for at least 3 months between 2000 and 2021 at Michigan Medicine outpatient dermatology clinics. The majority of patients were White (59%) or Black (37%) individuals.
- The median prescribed dose was 100 mg/d, the most common dose was 50-100 mg/d, and the median time spironolactone was initiated was 8.8 years after HS was diagnosed.
- Improvement status was classified on the basis of objective clinician assessments, including documented reductions in the lesion count, pain, and symptoms.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 31 patients (20%) showed improvements with spironolactone treatment.
- A shorter duration between the diagnosis of HS and the initiation of spironolactone was associated with improvement (P = .047).
- Axillary involvement (P = .003), the use of intralesional steroids (P = .015), previous treatments (P = .023), and previous treatment failures (P = .030) were linked to a lack of improvement with spironolactone.
- Patients with Hurley stage III were 85% less likely to experience improvement with spironolactone (P = .036).
IN PRACTICE:
Spironolactone, which has antiandrogenic properties, “may be beneficial for patients with mild HS, notably those at Hurley stage I if implemented early as a primary or ancillary treatment,” the authors concluded, adding that prospective, multicenter studies are needed to “elucidate further the safety and efficacy of spironolactone for treating HS.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Suma V. Gangidi, BS, Carle Illinois College of Medicine, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, and was published online in the International Journal of Women’s Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Retrospective design can introduce inherent biases, including the potential for missing or misclassified data. Additionally, the study was conducted at a single center, which may limit the generalizability, and findings were also limited by lack of standardized objective measures for assessing treatment improvement, presence of confounding variables from concomitant treatments, small sample size, and potential multicollinearity.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not receive any funding. One author declared ties with various pharmaceutical companies. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.