User login
Adjuvant nivolumab plus ipilimumab shows strong results in resected stage IV melanoma
Results of the
IMMUNED was a multicenter German double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial conducted by the Dermatologic Cooperative Oncology Group. It included 167 patients with resected stage IV melanoma and no evidence of disease who were randomized to adjuvant nivolumab (Opdivo) plus placebo, nivolumab plus ipilimumab (Yervoy), or double placebo, with relapse-free survival as the primary outcome, Merrick I. Ross, MD, explained at a forum on cutaneous malignancies jointly presented by Postgraduate Institute for Medicine and Global Academy for Medical Education.
“The patients who received adjuvant ipilimumab and nivolumab had amazing 24-month outcomes: a relapse-free survival of 70% versus 42% with nivolumab and 14% with placebo,” observed Dr. Ross, professor of surgical oncology and chief of the melanoma section at the University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
“It’s not a long-term survival outcome, but we’ll see what happens long term. This could be a very interesting approach to move forward with,” he commented.
By way of background, the cancer surgeon noted that nivolumab has achieved standard-of-care status as adjuvant immunotherapy in patients with resected stage IIIB-C and stage IV melanoma, largely on the strength of the CheckMate-238 trial, which randomized 906 such patients at 130 academic centers in 25 countries to 1 year of adjuvant therapy with either intravenous nivolumab or ipilimumab. In the study, nivolumab emerged as the clear winner, with a 4-year recurrence-free survival of 51.7%, compared with 41.2% for ipilimumab, for a 29% relative risk reduction. Ipilimumab was associated with greater toxicity.
The between-group difference in relapse-free survival in the overall study population also held true in the subgroup comprised of 169 CheckMate 238 participants with resected stage IV melanoma and no evidence of disease at enrollment, Dr. Ross noted.
In the IMMUNED trial, the superior outcome achieved with adjuvant nivolumab plus ipilimumab came at the cost of significantly greater toxicity than with nivolumab alone. Treatment-related adverse events led to medication discontinuation in 62% of the dual-adjuvant therapy group, compared with 13% of those on adjuvant nivolumab.
IMMUNED was funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Dr. Ross reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same company.
Results of the
IMMUNED was a multicenter German double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial conducted by the Dermatologic Cooperative Oncology Group. It included 167 patients with resected stage IV melanoma and no evidence of disease who were randomized to adjuvant nivolumab (Opdivo) plus placebo, nivolumab plus ipilimumab (Yervoy), or double placebo, with relapse-free survival as the primary outcome, Merrick I. Ross, MD, explained at a forum on cutaneous malignancies jointly presented by Postgraduate Institute for Medicine and Global Academy for Medical Education.
“The patients who received adjuvant ipilimumab and nivolumab had amazing 24-month outcomes: a relapse-free survival of 70% versus 42% with nivolumab and 14% with placebo,” observed Dr. Ross, professor of surgical oncology and chief of the melanoma section at the University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
“It’s not a long-term survival outcome, but we’ll see what happens long term. This could be a very interesting approach to move forward with,” he commented.
By way of background, the cancer surgeon noted that nivolumab has achieved standard-of-care status as adjuvant immunotherapy in patients with resected stage IIIB-C and stage IV melanoma, largely on the strength of the CheckMate-238 trial, which randomized 906 such patients at 130 academic centers in 25 countries to 1 year of adjuvant therapy with either intravenous nivolumab or ipilimumab. In the study, nivolumab emerged as the clear winner, with a 4-year recurrence-free survival of 51.7%, compared with 41.2% for ipilimumab, for a 29% relative risk reduction. Ipilimumab was associated with greater toxicity.
The between-group difference in relapse-free survival in the overall study population also held true in the subgroup comprised of 169 CheckMate 238 participants with resected stage IV melanoma and no evidence of disease at enrollment, Dr. Ross noted.
In the IMMUNED trial, the superior outcome achieved with adjuvant nivolumab plus ipilimumab came at the cost of significantly greater toxicity than with nivolumab alone. Treatment-related adverse events led to medication discontinuation in 62% of the dual-adjuvant therapy group, compared with 13% of those on adjuvant nivolumab.
IMMUNED was funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Dr. Ross reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same company.
Results of the
IMMUNED was a multicenter German double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial conducted by the Dermatologic Cooperative Oncology Group. It included 167 patients with resected stage IV melanoma and no evidence of disease who were randomized to adjuvant nivolumab (Opdivo) plus placebo, nivolumab plus ipilimumab (Yervoy), or double placebo, with relapse-free survival as the primary outcome, Merrick I. Ross, MD, explained at a forum on cutaneous malignancies jointly presented by Postgraduate Institute for Medicine and Global Academy for Medical Education.
“The patients who received adjuvant ipilimumab and nivolumab had amazing 24-month outcomes: a relapse-free survival of 70% versus 42% with nivolumab and 14% with placebo,” observed Dr. Ross, professor of surgical oncology and chief of the melanoma section at the University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
“It’s not a long-term survival outcome, but we’ll see what happens long term. This could be a very interesting approach to move forward with,” he commented.
By way of background, the cancer surgeon noted that nivolumab has achieved standard-of-care status as adjuvant immunotherapy in patients with resected stage IIIB-C and stage IV melanoma, largely on the strength of the CheckMate-238 trial, which randomized 906 such patients at 130 academic centers in 25 countries to 1 year of adjuvant therapy with either intravenous nivolumab or ipilimumab. In the study, nivolumab emerged as the clear winner, with a 4-year recurrence-free survival of 51.7%, compared with 41.2% for ipilimumab, for a 29% relative risk reduction. Ipilimumab was associated with greater toxicity.
The between-group difference in relapse-free survival in the overall study population also held true in the subgroup comprised of 169 CheckMate 238 participants with resected stage IV melanoma and no evidence of disease at enrollment, Dr. Ross noted.
In the IMMUNED trial, the superior outcome achieved with adjuvant nivolumab plus ipilimumab came at the cost of significantly greater toxicity than with nivolumab alone. Treatment-related adverse events led to medication discontinuation in 62% of the dual-adjuvant therapy group, compared with 13% of those on adjuvant nivolumab.
IMMUNED was funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Dr. Ross reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same company.
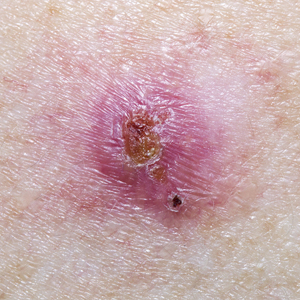
Telltale dermoscopic features of melanomas lacking pigment reviewed
by familiarity with a handful of dermoscopic features specific to melanomas lacking significant pigment, Steven Q. Wang, MD, said at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar, held virtually this year.
These features emerged from a major study conducted on five continents by members of the International Dermoscopy Society. The investigators developed a simple, eight-variable model, which demonstrated a sensitivity of 70% and specificity of 56% for diagnosis of melanoma. And while that’s a markedly worse performance than when dermoscopy is used for detection of pigmented melanomas, where sensitivities in excess of 90% and specificities greater than 70% are typical, it’s nonetheless a significant improvement over naked-eye evaluation of these challenging pigment-deprived melanomas, noted Dr. Wang, director of dermatologic surgery and dermatology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Basking Ridge (N.J.)
Using the predictive model developed in the international study to evaluate lesions lacking pigment, a diagnosis of melanoma is made provided two conditions are met: The lesion can have no more than three milia-like cysts, and it has to possess one or more of seven positive dermoscopic findings. The strongest predictor of melanoma in the study was the presence of a blue-white veil, which in univariate analysis was associated with a 13-fold increased likelihood of melanoma.
The other positive predictors were irregularly shaped depigmentation, more than one shade of pink, predominant central vessels, irregularly sized or distributed brown dots or globules, multiple blue-gray dots, and dotted and linear irregular vessels.
Dr. Wang emphasized that, when dermoscopy and clinical skin examination of a featureless hypomelanotic or amelanotic lesion yield ambiguous findings, frequent vigilant follow-up is a viable strategy to detect early melanoma – provided the lesion is superficial.
“The reality is not all melanomas are the same. The superficial spreading melanomas and lentigo melanomas grow very, very slowly: less than 0.1 mm per month. Those are the types of lesions you can monitor. But there is one type of lesion you should never, ever monitor: nodular lesions. They are the type of lesions that can do your patient harm because nodular melanomas can grow really fast. So my key takeaway message is, if you see a nodule and you don’t know what it is, take it off,” the dermatologist said.
Dermoscopy in the hands of experienced users has repeatedly been shown to improve diagnostic accuracy by more than 25%. But there is an additional very important reason to embrace dermoscopy in daily clinical practice, according to Dr. Wang: “When you put the scope on an individual, you slow down the exam and patients feels like you’re paying more attention to them.”
That’s worthwhile because the No. 1 complaint voiced by patients who make their way to Sloan Kettering for a second opinion is that their prior skin examination by an outside physician wasn’t thorough. They’re often angry about it. And while it’s true that incorporating dermoscopy does make for a lengthier skin examination, the additional time involved is actually minimal. Dr. Wang cited a randomized, prospective, multicenter study which documented that the median time required to conduct a thorough complete skin examination without dermoscopy was 70 seconds versus 142 seconds with dermoscopy.
Dr. Wang reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
by familiarity with a handful of dermoscopic features specific to melanomas lacking significant pigment, Steven Q. Wang, MD, said at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar, held virtually this year.
These features emerged from a major study conducted on five continents by members of the International Dermoscopy Society. The investigators developed a simple, eight-variable model, which demonstrated a sensitivity of 70% and specificity of 56% for diagnosis of melanoma. And while that’s a markedly worse performance than when dermoscopy is used for detection of pigmented melanomas, where sensitivities in excess of 90% and specificities greater than 70% are typical, it’s nonetheless a significant improvement over naked-eye evaluation of these challenging pigment-deprived melanomas, noted Dr. Wang, director of dermatologic surgery and dermatology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Basking Ridge (N.J.)
Using the predictive model developed in the international study to evaluate lesions lacking pigment, a diagnosis of melanoma is made provided two conditions are met: The lesion can have no more than three milia-like cysts, and it has to possess one or more of seven positive dermoscopic findings. The strongest predictor of melanoma in the study was the presence of a blue-white veil, which in univariate analysis was associated with a 13-fold increased likelihood of melanoma.
The other positive predictors were irregularly shaped depigmentation, more than one shade of pink, predominant central vessels, irregularly sized or distributed brown dots or globules, multiple blue-gray dots, and dotted and linear irregular vessels.
Dr. Wang emphasized that, when dermoscopy and clinical skin examination of a featureless hypomelanotic or amelanotic lesion yield ambiguous findings, frequent vigilant follow-up is a viable strategy to detect early melanoma – provided the lesion is superficial.
“The reality is not all melanomas are the same. The superficial spreading melanomas and lentigo melanomas grow very, very slowly: less than 0.1 mm per month. Those are the types of lesions you can monitor. But there is one type of lesion you should never, ever monitor: nodular lesions. They are the type of lesions that can do your patient harm because nodular melanomas can grow really fast. So my key takeaway message is, if you see a nodule and you don’t know what it is, take it off,” the dermatologist said.
Dermoscopy in the hands of experienced users has repeatedly been shown to improve diagnostic accuracy by more than 25%. But there is an additional very important reason to embrace dermoscopy in daily clinical practice, according to Dr. Wang: “When you put the scope on an individual, you slow down the exam and patients feels like you’re paying more attention to them.”
That’s worthwhile because the No. 1 complaint voiced by patients who make their way to Sloan Kettering for a second opinion is that their prior skin examination by an outside physician wasn’t thorough. They’re often angry about it. And while it’s true that incorporating dermoscopy does make for a lengthier skin examination, the additional time involved is actually minimal. Dr. Wang cited a randomized, prospective, multicenter study which documented that the median time required to conduct a thorough complete skin examination without dermoscopy was 70 seconds versus 142 seconds with dermoscopy.
Dr. Wang reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
by familiarity with a handful of dermoscopic features specific to melanomas lacking significant pigment, Steven Q. Wang, MD, said at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar, held virtually this year.
These features emerged from a major study conducted on five continents by members of the International Dermoscopy Society. The investigators developed a simple, eight-variable model, which demonstrated a sensitivity of 70% and specificity of 56% for diagnosis of melanoma. And while that’s a markedly worse performance than when dermoscopy is used for detection of pigmented melanomas, where sensitivities in excess of 90% and specificities greater than 70% are typical, it’s nonetheless a significant improvement over naked-eye evaluation of these challenging pigment-deprived melanomas, noted Dr. Wang, director of dermatologic surgery and dermatology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Basking Ridge (N.J.)
Using the predictive model developed in the international study to evaluate lesions lacking pigment, a diagnosis of melanoma is made provided two conditions are met: The lesion can have no more than three milia-like cysts, and it has to possess one or more of seven positive dermoscopic findings. The strongest predictor of melanoma in the study was the presence of a blue-white veil, which in univariate analysis was associated with a 13-fold increased likelihood of melanoma.
The other positive predictors were irregularly shaped depigmentation, more than one shade of pink, predominant central vessels, irregularly sized or distributed brown dots or globules, multiple blue-gray dots, and dotted and linear irregular vessels.
Dr. Wang emphasized that, when dermoscopy and clinical skin examination of a featureless hypomelanotic or amelanotic lesion yield ambiguous findings, frequent vigilant follow-up is a viable strategy to detect early melanoma – provided the lesion is superficial.
“The reality is not all melanomas are the same. The superficial spreading melanomas and lentigo melanomas grow very, very slowly: less than 0.1 mm per month. Those are the types of lesions you can monitor. But there is one type of lesion you should never, ever monitor: nodular lesions. They are the type of lesions that can do your patient harm because nodular melanomas can grow really fast. So my key takeaway message is, if you see a nodule and you don’t know what it is, take it off,” the dermatologist said.
Dermoscopy in the hands of experienced users has repeatedly been shown to improve diagnostic accuracy by more than 25%. But there is an additional very important reason to embrace dermoscopy in daily clinical practice, according to Dr. Wang: “When you put the scope on an individual, you slow down the exam and patients feels like you’re paying more attention to them.”
That’s worthwhile because the No. 1 complaint voiced by patients who make their way to Sloan Kettering for a second opinion is that their prior skin examination by an outside physician wasn’t thorough. They’re often angry about it. And while it’s true that incorporating dermoscopy does make for a lengthier skin examination, the additional time involved is actually minimal. Dr. Wang cited a randomized, prospective, multicenter study which documented that the median time required to conduct a thorough complete skin examination without dermoscopy was 70 seconds versus 142 seconds with dermoscopy.
Dr. Wang reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
FROM MEDSCAPELIVE LAS VEGAS DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Skin Cancer Management During the COVID-19 Pandemic
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome novel coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has presented a unique challenge to providing essential care to patients. Increased demand for health care workers and medical supplies, in addition to the risk for COVID-19 infection and asymptomatic transmission of SARS-CoV-2 among health care workers and patients, prompted the delay of nonessential services during the surge of cases this summer.1 Key considerations for continuing operation included current and projected COVID-19 cases in the region, ability to implement telehealth, staffing availability, personal protective equipment availability, and office capacity.2 Providing care that is deemed essential often was determined by the urgency of the treatment or service.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services outlined a strategy to stratify patients, based on level of acuity, during the COVID-19 surge3:
- Low-acuity treatments or services: includes routine primary, specialty, or preventive care visits. They should be postponed; telehealth follow-ups should be considered.
- Intermediate-acuity treatments or services: includes pediatric and neonatal care, follow-up visits for existing conditions, and evaluation of new symptoms (including those consistent with COVID-19). These services should initially be evaluated using telehealth, then triaged to the appropriate site and level of care.
- High-acuity treatments or services: address symptoms consistent with COVID-19 or other severe disease, of which the lack of in-person evaluation would result in harm to the patient.
Employees in hospitals and health care clinics were classified as essential, but dermatologists were not given explicit direction regarding clinic operation. Many practices have restricted services, especially those in an area of higher COVID-19 prevalence. However, the challenge of determining day-to-day operation may have been left to the provider in most cases.4 As many states in the United States continue to relax restrictions, total cases and the rate of positivity of COVID-19 have been sharply rising again, after months of decline,5 which suggests increased transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and potential resurgence of the high case burden on our health care system. Furthermore, a lack of a widely distributed vaccine or herd immunity suggests we will need to take many of the same precautions as in the first surge.6
In general, patients with cancer have been found to be at greater risk for adverse outcomes and mortality after COVID-19.7 Therefore, resource rationing is particularly concerning for patients with skin cancer, including melanoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, mycosis fungoides, and keratinocyte carcinoma. Triaging patients based on level of acuity, type of skin cancer, disease burden, host immunosuppression, and risk for progression must be carefully considered in this population.2 Treatment and follow-up present additional challenges.
Guidelines provided by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) and the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) elaborated on key considerations for the treatment of melanoma, keratinocyte carcinoma, and Merkel cell carcinoma during the COVID-19 pandemic.8-10 Guidelines from the NCCN concentrated on clear divisions between disease stages to determine provider response. Guidelines for melanoma patients proposed by the ESMO assign tiers by value-based priority in various treatment settings, which offered flexibility to providers as the COVID-19 landscape continued to change. Recommendations from the NCCN and ESMO are summarized in Tables 1 to 5.



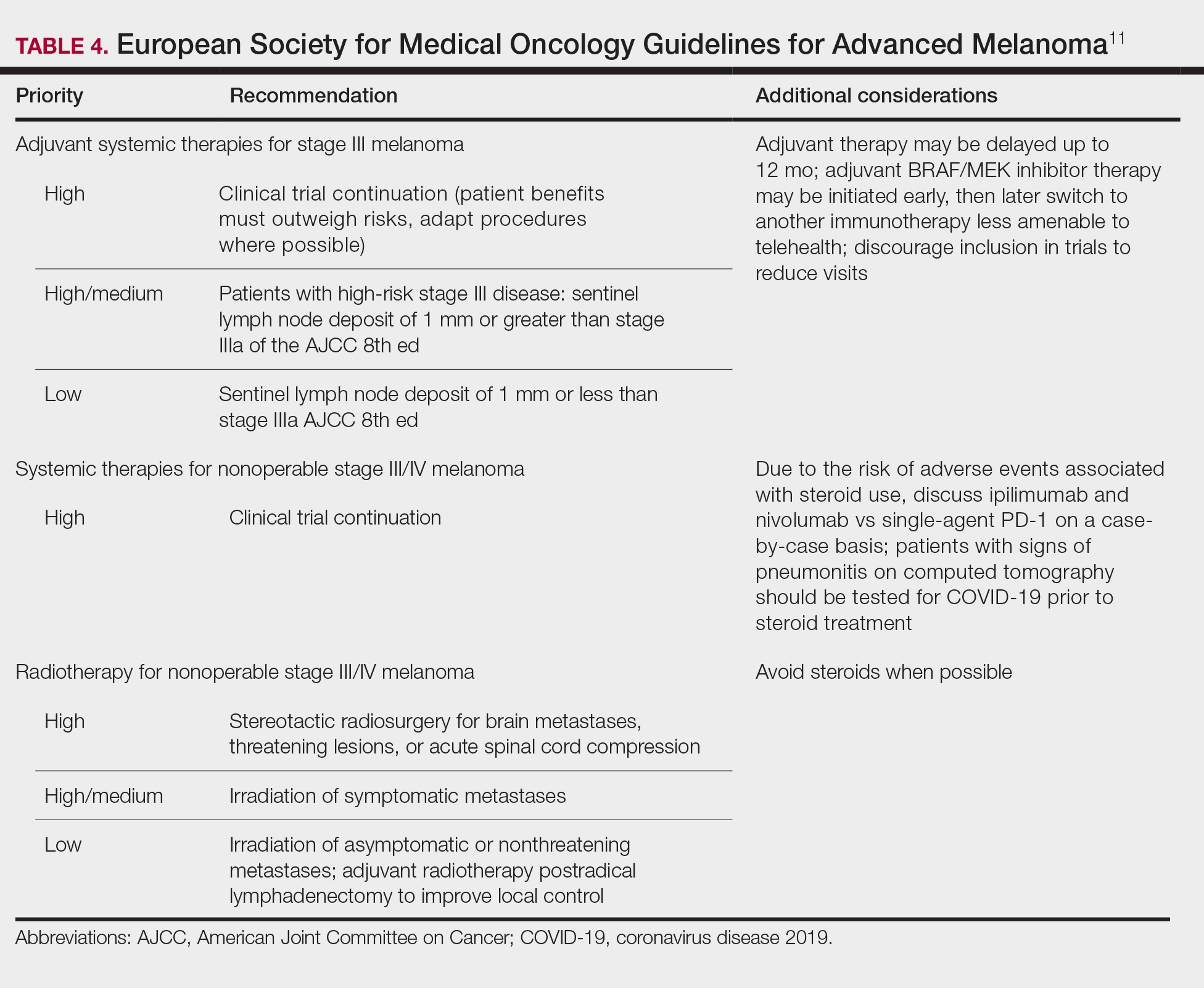
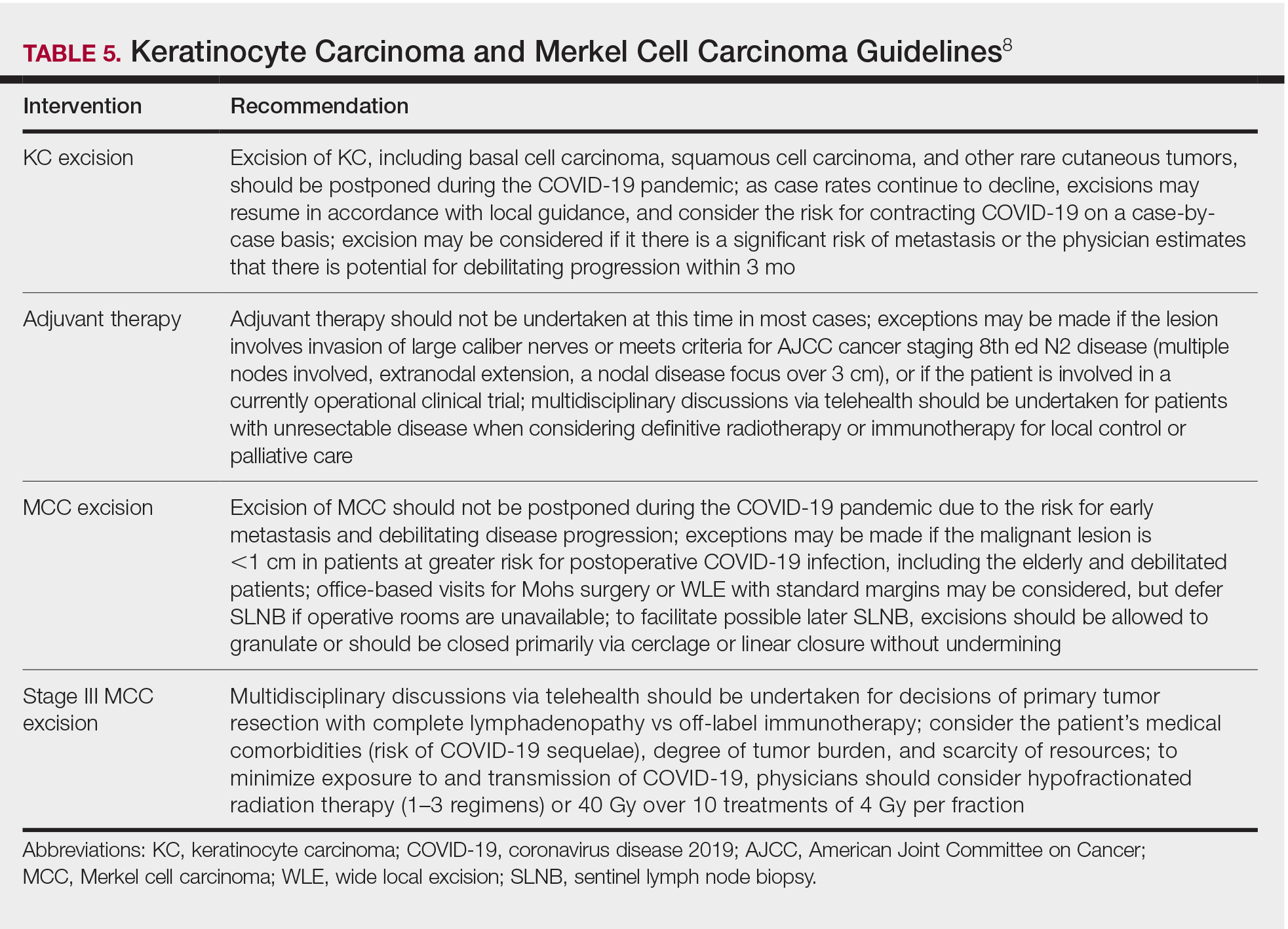
Although these guidelines initially may have been proposed to delay treatment of lower-acuity tumors, such delay might not be feasible given the unknown duration of this pandemic and future disease waves. One review of several studies, which addressed the outcomes on melanoma survival following the surgical delay recommended by the NCCN, revealed contradictory evidence.12 Further, sufficiently powered studies will be needed to better understand the impact of delaying treatment during the summer COVID-19 surge on patients with skin cancer. Therefore, physicians must triage patients accordingly to manage and treat while also preventing disease spread.
Tips for Performing Dermatologic Surgery
Careful consideration should be made to protect both the patient and staff during office-based excisional surgery during the COVID-19 pandemic. To minimize the risk of transmission of SARS-CoV-2, patients and staff should (1) be screened for symptoms of COVID-19 at least 48 hours prior to entering the office via telephone screening questions, and (2) follow proper hygiene and contact procedures once entering the office. Consider obtaining a nasal polymerase chain reaction swab or saliva test 48 hours prior to the procedure if the patient is undergoing a head and neck procedure or there is risk for transmission.
Guidelines from the ESMO recommended that all patients undergoing surgery or therapy should be swabbed for SARS-CoV-2 before each treatment.11 Patients should wear a mask, remain 6-feet apart in the waiting room, and avoid touching objects until they enter the procedure room. Objects that the patient must touch, such as pens, should be cleaned immediately after such contact with either alcohol or soap and water for 20 seconds.
Office capacity should be reduced by allowing no more than 1 person to accompany the patient and ensuring the presence of only the minimum staff needed for the procedure. Staff who are deemed necessary should wear a mask continuously and gloves during patient contact.
Once in the procedure room, providers might be at elevated risk of contracting COVID-19 or transmitting SARS-CoV-2. A properly fitted N95 respirator and a face shield are recommended, especially for facial cases. N95 respirators can be reused by following the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendations for reuse and decontamination techniques,13 which may include protecting the N95 respirator with a surgical mask and storing it in a paper bag when not in use. Consider testing asymptomatic patients in facial cases when they cannot wear a mask.
Steps should be taken to reduce in-person visits. Dissolving sutures can help avoid return visits. Follow-up visits and postprocedural questions should be managed by telehealth. However, patients with a high-risk underlying conditions (eg, posttransplantation, immunosuppressed) should continue to obtain regular skin checks because they are at higher risk for more aggressive malignancies, such as Merkel cell carcinoma.
Conclusion
The future trajectory of the COVID-19 pandemic is uncertain. Dermatologists should continue providing care for patients with skin cancer while mitigating the risk for COVID-19 infection and transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Guidelines provided by the NCCN and ESMO should help providers triage patients. Decisions should be made case by case, keeping in mind the availability of resources and practicing in compliance with local guidance.
- Moletta L, Pierobon ES, Capovilla G, et al. International guidelines and recommendations for surgery during COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review. Int J Surg. 2020;79:180-188.
- Ueda M, Martins R, Hendrie PC, et al. Managing cancer care during the COVID-19 pandemic: agility and collaboration toward common goal. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2020:1-4.
- Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Non-emergent, elective medical services, and treatment recommendations. Published April 7, 2020. Accessed October 15, 2020. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/cms-non-emergent-elective-medical-recommendations.pdf
- Muddasani S, Housholder A, Fleischer AB. An assessment of United States dermatology practices during the COVID-19 outbreak. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;31:436-438.
- Coronavirus Resource Center, Johns Hopkins University & Medicine. Rate of positive tests in the US and states over time. Updated December 11, 2020. Accessed December 11, 2020. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/testing/individual-states
- Middleton J, Lopes H, Michelson K, et al. Planning for a second wave pandemic of COVID-19 and planning for winter: a statement from the Association of Schools of Public Health in the European Region. Int J Public Health. 2020;65:1525-1527.
- Liang W, Guan W, Chen R, et al. Cancer patients in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a nationwide analysis in China. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:335-337.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Advisory statement for non-melanoma skin cancer care during the COVID-19 pandemic (version 4). Published May 22, 2020. Accessed December 11, 2020. https://www.nccn.org/covid-19/pdf/NCCN-NMSC.pdf
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Short-term recommendations for cutaneous melanoma management during COVID-19 pandemic (version 3). Published May 6, 2020. Accessed December 11, 2020. www.nccn.org/covid-19/pdf/Melanoma.pdf - Conforti C, Giuffrida R, Di Meo N, et al. Management of advanced melanoma in the COVID-19 era. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e13444.
- ESMO [European Society for Medical Oncology]. Cancer patient management during the COVID-19 pandemic. Accessed Decemeber 11, 2020. https://www.esmo.org/guidelines/cancer-patient-management-during-the-covid-19-pandemic?hit=ehp
- Guhan S, Boland G, Tanabe K, et al. Surgical delay and mortality for primary cutaneous melanoma [published online July 22, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.07.078
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Implementing filtering facepiece respirator (FFR) reuse, including reuse after decontamination, when there are known shortages of N95 respirators. Updated October 19, 2020. Accessed December 11, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/ppe-strategy/decontamination-reuse-respirators.html
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome novel coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has presented a unique challenge to providing essential care to patients. Increased demand for health care workers and medical supplies, in addition to the risk for COVID-19 infection and asymptomatic transmission of SARS-CoV-2 among health care workers and patients, prompted the delay of nonessential services during the surge of cases this summer.1 Key considerations for continuing operation included current and projected COVID-19 cases in the region, ability to implement telehealth, staffing availability, personal protective equipment availability, and office capacity.2 Providing care that is deemed essential often was determined by the urgency of the treatment or service.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services outlined a strategy to stratify patients, based on level of acuity, during the COVID-19 surge3:
- Low-acuity treatments or services: includes routine primary, specialty, or preventive care visits. They should be postponed; telehealth follow-ups should be considered.
- Intermediate-acuity treatments or services: includes pediatric and neonatal care, follow-up visits for existing conditions, and evaluation of new symptoms (including those consistent with COVID-19). These services should initially be evaluated using telehealth, then triaged to the appropriate site and level of care.
- High-acuity treatments or services: address symptoms consistent with COVID-19 or other severe disease, of which the lack of in-person evaluation would result in harm to the patient.
Employees in hospitals and health care clinics were classified as essential, but dermatologists were not given explicit direction regarding clinic operation. Many practices have restricted services, especially those in an area of higher COVID-19 prevalence. However, the challenge of determining day-to-day operation may have been left to the provider in most cases.4 As many states in the United States continue to relax restrictions, total cases and the rate of positivity of COVID-19 have been sharply rising again, after months of decline,5 which suggests increased transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and potential resurgence of the high case burden on our health care system. Furthermore, a lack of a widely distributed vaccine or herd immunity suggests we will need to take many of the same precautions as in the first surge.6
In general, patients with cancer have been found to be at greater risk for adverse outcomes and mortality after COVID-19.7 Therefore, resource rationing is particularly concerning for patients with skin cancer, including melanoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, mycosis fungoides, and keratinocyte carcinoma. Triaging patients based on level of acuity, type of skin cancer, disease burden, host immunosuppression, and risk for progression must be carefully considered in this population.2 Treatment and follow-up present additional challenges.
Guidelines provided by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) and the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) elaborated on key considerations for the treatment of melanoma, keratinocyte carcinoma, and Merkel cell carcinoma during the COVID-19 pandemic.8-10 Guidelines from the NCCN concentrated on clear divisions between disease stages to determine provider response. Guidelines for melanoma patients proposed by the ESMO assign tiers by value-based priority in various treatment settings, which offered flexibility to providers as the COVID-19 landscape continued to change. Recommendations from the NCCN and ESMO are summarized in Tables 1 to 5.





Although these guidelines initially may have been proposed to delay treatment of lower-acuity tumors, such delay might not be feasible given the unknown duration of this pandemic and future disease waves. One review of several studies, which addressed the outcomes on melanoma survival following the surgical delay recommended by the NCCN, revealed contradictory evidence.12 Further, sufficiently powered studies will be needed to better understand the impact of delaying treatment during the summer COVID-19 surge on patients with skin cancer. Therefore, physicians must triage patients accordingly to manage and treat while also preventing disease spread.
Tips for Performing Dermatologic Surgery
Careful consideration should be made to protect both the patient and staff during office-based excisional surgery during the COVID-19 pandemic. To minimize the risk of transmission of SARS-CoV-2, patients and staff should (1) be screened for symptoms of COVID-19 at least 48 hours prior to entering the office via telephone screening questions, and (2) follow proper hygiene and contact procedures once entering the office. Consider obtaining a nasal polymerase chain reaction swab or saliva test 48 hours prior to the procedure if the patient is undergoing a head and neck procedure or there is risk for transmission.
Guidelines from the ESMO recommended that all patients undergoing surgery or therapy should be swabbed for SARS-CoV-2 before each treatment.11 Patients should wear a mask, remain 6-feet apart in the waiting room, and avoid touching objects until they enter the procedure room. Objects that the patient must touch, such as pens, should be cleaned immediately after such contact with either alcohol or soap and water for 20 seconds.
Office capacity should be reduced by allowing no more than 1 person to accompany the patient and ensuring the presence of only the minimum staff needed for the procedure. Staff who are deemed necessary should wear a mask continuously and gloves during patient contact.
Once in the procedure room, providers might be at elevated risk of contracting COVID-19 or transmitting SARS-CoV-2. A properly fitted N95 respirator and a face shield are recommended, especially for facial cases. N95 respirators can be reused by following the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendations for reuse and decontamination techniques,13 which may include protecting the N95 respirator with a surgical mask and storing it in a paper bag when not in use. Consider testing asymptomatic patients in facial cases when they cannot wear a mask.
Steps should be taken to reduce in-person visits. Dissolving sutures can help avoid return visits. Follow-up visits and postprocedural questions should be managed by telehealth. However, patients with a high-risk underlying conditions (eg, posttransplantation, immunosuppressed) should continue to obtain regular skin checks because they are at higher risk for more aggressive malignancies, such as Merkel cell carcinoma.
Conclusion
The future trajectory of the COVID-19 pandemic is uncertain. Dermatologists should continue providing care for patients with skin cancer while mitigating the risk for COVID-19 infection and transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Guidelines provided by the NCCN and ESMO should help providers triage patients. Decisions should be made case by case, keeping in mind the availability of resources and practicing in compliance with local guidance.
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome novel coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has presented a unique challenge to providing essential care to patients. Increased demand for health care workers and medical supplies, in addition to the risk for COVID-19 infection and asymptomatic transmission of SARS-CoV-2 among health care workers and patients, prompted the delay of nonessential services during the surge of cases this summer.1 Key considerations for continuing operation included current and projected COVID-19 cases in the region, ability to implement telehealth, staffing availability, personal protective equipment availability, and office capacity.2 Providing care that is deemed essential often was determined by the urgency of the treatment or service.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services outlined a strategy to stratify patients, based on level of acuity, during the COVID-19 surge3:
- Low-acuity treatments or services: includes routine primary, specialty, or preventive care visits. They should be postponed; telehealth follow-ups should be considered.
- Intermediate-acuity treatments or services: includes pediatric and neonatal care, follow-up visits for existing conditions, and evaluation of new symptoms (including those consistent with COVID-19). These services should initially be evaluated using telehealth, then triaged to the appropriate site and level of care.
- High-acuity treatments or services: address symptoms consistent with COVID-19 or other severe disease, of which the lack of in-person evaluation would result in harm to the patient.
Employees in hospitals and health care clinics were classified as essential, but dermatologists were not given explicit direction regarding clinic operation. Many practices have restricted services, especially those in an area of higher COVID-19 prevalence. However, the challenge of determining day-to-day operation may have been left to the provider in most cases.4 As many states in the United States continue to relax restrictions, total cases and the rate of positivity of COVID-19 have been sharply rising again, after months of decline,5 which suggests increased transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and potential resurgence of the high case burden on our health care system. Furthermore, a lack of a widely distributed vaccine or herd immunity suggests we will need to take many of the same precautions as in the first surge.6
In general, patients with cancer have been found to be at greater risk for adverse outcomes and mortality after COVID-19.7 Therefore, resource rationing is particularly concerning for patients with skin cancer, including melanoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, mycosis fungoides, and keratinocyte carcinoma. Triaging patients based on level of acuity, type of skin cancer, disease burden, host immunosuppression, and risk for progression must be carefully considered in this population.2 Treatment and follow-up present additional challenges.
Guidelines provided by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) and the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) elaborated on key considerations for the treatment of melanoma, keratinocyte carcinoma, and Merkel cell carcinoma during the COVID-19 pandemic.8-10 Guidelines from the NCCN concentrated on clear divisions between disease stages to determine provider response. Guidelines for melanoma patients proposed by the ESMO assign tiers by value-based priority in various treatment settings, which offered flexibility to providers as the COVID-19 landscape continued to change. Recommendations from the NCCN and ESMO are summarized in Tables 1 to 5.





Although these guidelines initially may have been proposed to delay treatment of lower-acuity tumors, such delay might not be feasible given the unknown duration of this pandemic and future disease waves. One review of several studies, which addressed the outcomes on melanoma survival following the surgical delay recommended by the NCCN, revealed contradictory evidence.12 Further, sufficiently powered studies will be needed to better understand the impact of delaying treatment during the summer COVID-19 surge on patients with skin cancer. Therefore, physicians must triage patients accordingly to manage and treat while also preventing disease spread.
Tips for Performing Dermatologic Surgery
Careful consideration should be made to protect both the patient and staff during office-based excisional surgery during the COVID-19 pandemic. To minimize the risk of transmission of SARS-CoV-2, patients and staff should (1) be screened for symptoms of COVID-19 at least 48 hours prior to entering the office via telephone screening questions, and (2) follow proper hygiene and contact procedures once entering the office. Consider obtaining a nasal polymerase chain reaction swab or saliva test 48 hours prior to the procedure if the patient is undergoing a head and neck procedure or there is risk for transmission.
Guidelines from the ESMO recommended that all patients undergoing surgery or therapy should be swabbed for SARS-CoV-2 before each treatment.11 Patients should wear a mask, remain 6-feet apart in the waiting room, and avoid touching objects until they enter the procedure room. Objects that the patient must touch, such as pens, should be cleaned immediately after such contact with either alcohol or soap and water for 20 seconds.
Office capacity should be reduced by allowing no more than 1 person to accompany the patient and ensuring the presence of only the minimum staff needed for the procedure. Staff who are deemed necessary should wear a mask continuously and gloves during patient contact.
Once in the procedure room, providers might be at elevated risk of contracting COVID-19 or transmitting SARS-CoV-2. A properly fitted N95 respirator and a face shield are recommended, especially for facial cases. N95 respirators can be reused by following the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendations for reuse and decontamination techniques,13 which may include protecting the N95 respirator with a surgical mask and storing it in a paper bag when not in use. Consider testing asymptomatic patients in facial cases when they cannot wear a mask.
Steps should be taken to reduce in-person visits. Dissolving sutures can help avoid return visits. Follow-up visits and postprocedural questions should be managed by telehealth. However, patients with a high-risk underlying conditions (eg, posttransplantation, immunosuppressed) should continue to obtain regular skin checks because they are at higher risk for more aggressive malignancies, such as Merkel cell carcinoma.
Conclusion
The future trajectory of the COVID-19 pandemic is uncertain. Dermatologists should continue providing care for patients with skin cancer while mitigating the risk for COVID-19 infection and transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Guidelines provided by the NCCN and ESMO should help providers triage patients. Decisions should be made case by case, keeping in mind the availability of resources and practicing in compliance with local guidance.
- Moletta L, Pierobon ES, Capovilla G, et al. International guidelines and recommendations for surgery during COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review. Int J Surg. 2020;79:180-188.
- Ueda M, Martins R, Hendrie PC, et al. Managing cancer care during the COVID-19 pandemic: agility and collaboration toward common goal. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2020:1-4.
- Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Non-emergent, elective medical services, and treatment recommendations. Published April 7, 2020. Accessed October 15, 2020. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/cms-non-emergent-elective-medical-recommendations.pdf
- Muddasani S, Housholder A, Fleischer AB. An assessment of United States dermatology practices during the COVID-19 outbreak. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;31:436-438.
- Coronavirus Resource Center, Johns Hopkins University & Medicine. Rate of positive tests in the US and states over time. Updated December 11, 2020. Accessed December 11, 2020. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/testing/individual-states
- Middleton J, Lopes H, Michelson K, et al. Planning for a second wave pandemic of COVID-19 and planning for winter: a statement from the Association of Schools of Public Health in the European Region. Int J Public Health. 2020;65:1525-1527.
- Liang W, Guan W, Chen R, et al. Cancer patients in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a nationwide analysis in China. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:335-337.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Advisory statement for non-melanoma skin cancer care during the COVID-19 pandemic (version 4). Published May 22, 2020. Accessed December 11, 2020. https://www.nccn.org/covid-19/pdf/NCCN-NMSC.pdf
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Short-term recommendations for cutaneous melanoma management during COVID-19 pandemic (version 3). Published May 6, 2020. Accessed December 11, 2020. www.nccn.org/covid-19/pdf/Melanoma.pdf - Conforti C, Giuffrida R, Di Meo N, et al. Management of advanced melanoma in the COVID-19 era. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e13444.
- ESMO [European Society for Medical Oncology]. Cancer patient management during the COVID-19 pandemic. Accessed Decemeber 11, 2020. https://www.esmo.org/guidelines/cancer-patient-management-during-the-covid-19-pandemic?hit=ehp
- Guhan S, Boland G, Tanabe K, et al. Surgical delay and mortality for primary cutaneous melanoma [published online July 22, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.07.078
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Implementing filtering facepiece respirator (FFR) reuse, including reuse after decontamination, when there are known shortages of N95 respirators. Updated October 19, 2020. Accessed December 11, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/ppe-strategy/decontamination-reuse-respirators.html
- Moletta L, Pierobon ES, Capovilla G, et al. International guidelines and recommendations for surgery during COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review. Int J Surg. 2020;79:180-188.
- Ueda M, Martins R, Hendrie PC, et al. Managing cancer care during the COVID-19 pandemic: agility and collaboration toward common goal. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2020:1-4.
- Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Non-emergent, elective medical services, and treatment recommendations. Published April 7, 2020. Accessed October 15, 2020. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/cms-non-emergent-elective-medical-recommendations.pdf
- Muddasani S, Housholder A, Fleischer AB. An assessment of United States dermatology practices during the COVID-19 outbreak. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;31:436-438.
- Coronavirus Resource Center, Johns Hopkins University & Medicine. Rate of positive tests in the US and states over time. Updated December 11, 2020. Accessed December 11, 2020. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/testing/individual-states
- Middleton J, Lopes H, Michelson K, et al. Planning for a second wave pandemic of COVID-19 and planning for winter: a statement from the Association of Schools of Public Health in the European Region. Int J Public Health. 2020;65:1525-1527.
- Liang W, Guan W, Chen R, et al. Cancer patients in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a nationwide analysis in China. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:335-337.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Advisory statement for non-melanoma skin cancer care during the COVID-19 pandemic (version 4). Published May 22, 2020. Accessed December 11, 2020. https://www.nccn.org/covid-19/pdf/NCCN-NMSC.pdf
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Short-term recommendations for cutaneous melanoma management during COVID-19 pandemic (version 3). Published May 6, 2020. Accessed December 11, 2020. www.nccn.org/covid-19/pdf/Melanoma.pdf - Conforti C, Giuffrida R, Di Meo N, et al. Management of advanced melanoma in the COVID-19 era. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e13444.
- ESMO [European Society for Medical Oncology]. Cancer patient management during the COVID-19 pandemic. Accessed Decemeber 11, 2020. https://www.esmo.org/guidelines/cancer-patient-management-during-the-covid-19-pandemic?hit=ehp
- Guhan S, Boland G, Tanabe K, et al. Surgical delay and mortality for primary cutaneous melanoma [published online July 22, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.07.078
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Implementing filtering facepiece respirator (FFR) reuse, including reuse after decontamination, when there are known shortages of N95 respirators. Updated October 19, 2020. Accessed December 11, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/ppe-strategy/decontamination-reuse-respirators.html
Practice Points
- Consider the rate of cases and transmission in your area during a pandemic surge when triaging surgical and nonsurgical cases.
- If performing head and neck surgical procedures or cosmetic procedures in which the patient cannot wear a mask, consider testing them 24 to 48 hours before the procedure.
- Follow Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines concerning screening asymptomatic patients. Also, follow CDC guidelines on testing patients who have had prior infections.
- Ensure proper personal protective equipment for yourself and staff, including the use of properly fitting N95 respirators and face shields.
Skin Cancer Screening and Prevention During the COVID-19 Pandemic
On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) a pandemic, leading to an abrupt widespread shift to teledermatology, with postponement of nonessential in-office medical and surgical services, according to American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) recommendations.1 Perspectives have been offered regarding skin cancer management during the pandemic2; however, the current literature is lacking guidance on skin cancer screening and prevention during the COVID-19 era.
Preliminary data show a 34.3% reduction in skin cancer referrals from February to April 2020 compared to the same period in 2019. The authors also presented a subsequent reduction in the number of skin cancer diagnoses in March 2020 compared to March 2019.3 Although the COVID-19 public health emergency should be prioritized by all health care workers, the duty to maintain disease prevention remains.
We aim to provide recommendations for this urgent topic. Our goal is finding balance in preventing an increase in the incidence of and mortality from skin cancer that results from delayed detection, while conserving personalprotective equipment and minimizing exposure, by patients and clinical personnel, to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. A primary benefit of skin cancer screening lies in the ability to detect melanoma, which is associated with higher mortality than the more common nonmelanoma skin cancers, basal and cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas. We place preeminence on screening directed toward detecting melanoma. The main screening method that dermatologists employ is the total-body skin examination (TBSE). Another widely encouraged and utilized component in skin cancer prevention is patient education, emphasizing avoidance of risk factors, undertaking protective factors, and providing clear instructions for performing the patient-led skin self-examination (SSE).
Teledermatology Essentials for Skin Cancer Screening
Arguably, dermatology possesses the most potential for successfully utilizing telemedicine. Teledermatology has become widely implemented across the United States, secondary to the implications of the current pandemic. A report by Perkins and colleagues4 provided a positive outlook in the preliminary transition to teledermatology beginning in March 2020, though reported time of use was relatively short (3 weeks). A May 2020 article in Dermatology News provided tips for implementing telemedicine for practices.5
We agree with the comprehensive screening algorithm for teledermatology presented by Perkins and colleagues4 (Figure 1A in their report) and recommend the following for the screening and prevention of skin cancer:
• Patients with any characteristics of increased risk, including a personal or family history of melanoma, large congenital nevi, many melanotic nevi, dysplastic nevi, and Fitzpatrick skin types I and II,6 should be prioritized for an in-person visit for TBSE.
• Immunosuppressed patients, particularly organ transplant recipients and those with a history of skin cancer, should be prioritized for an in-person visit for TBSE.
• Established patients evaluated and determined to be at average risk for skin cancer should be offered a teledermatology visit. Suspicious findings during these visits should be prioritized for an in-person visit, with subsequent biopsy and follow-up.
• New patients should be offered a teledermatology visit.
These recommendations must be reviewed alongside each patient’s risk for travel and being present in person as well as other factors that might place the patient at increased risk for COVID-19.
Total-body skin examination, a widely used tool in the dermatologist’s tool kit, presents minimal risk to patients while providing important data for each dermatology patient’s profile, ultimately directing patient care. The role of TBSE in skin cancer screening and prevention has been in discussion even prior to the current pandemic. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has not declared a role for TBSE in recent years; however, USPSTF recommendations are formulated using data from all forms of screening, not only dermatologist-led interventions. Accordingly, USPSTF recommendations target primary care. The AAD has released statements addressing the role of TBSE and skin cancer prevention in the past, when necessary, to provide clarity.7
There is no clear definition of SSE or guidelines on how to educate a patient to perform regular SSE; however, the AAD provides patients with resources on how to perform an SSE.8 Just as dermatologists would provide education, advice, and guidance by directing patients to the AAD website for the SSE during an in-person visit, we encourage dermatologists to continue this practice during all teledermatology visits.
The role of teledermatology in skin cancer screening and prevention is limited; dermatologists will not be able to adequately perform TBSE as it would be done at in-person visits. Furthermore, the true implications of teledermatology compared to in-person visits during the COVID-19 pandemic have yet to be realized and analyzed. It is nonetheless important to appreciate that teledermatology holds great promise of benefit in skin cancer prevention, especially in the form of patient education by dermatologists. Practices in the realm of screening and prevention by health care professionals should be continually addressed during the pandemic; it is important to consider the implications associated with delays in diagnosis and treatment.
Teledermatology Limitations and Recommendations for High-Quality Visits
A benefit of video consultation (VC) vs telephone visits is visual interaction—the crux of dermatology. A 2019 study investigated VC experiences among providers and patients in the primary care setting. Benefits of VC were reported to include convenience for working patients and patients with mobility or mental health problems, visual cues, building rapport, and improving communication.9
Despite these benefits, VC is not without limitations. Many technical factors create variability in the quality of teledermatology VCs for a melanocytic lesion, including patient environment and lighting, color distortion, video resolution, and Internet connection. We make the following recommendations:
• Environment: Locate or create a dedicated space for teledermatology visits that is well lit, private, and has minimal background noise. Place the device on a level surface, center yourself in the frame, and keep the camera at eye level.
• Lighting: Use neutral lighting, placing the light source in front of you but behind the camera of the device. Avoid placing light sources, such as a window, behind you.
• Video resolution: Regardless of the type of camera (eg, integrated webcam, external camera), close out all other running software programs to optimize bandwidth during the visit.
• Internet connection: Use a wired connection (via an Ethernet cable) instead of a Wi-Fi connection to greatly decrease the chance of losing the connection during the visit. It also is faster than Wi-Fi.
• Addressing specific lesions: Patients should keep the device in place, repositioning themselves to show the lesions rather than moving the device by hand.
• Video capacity: Test your device’s video capacity beforehand, which can be as simple as video-calling a family member or friend from your designated space. Feedback regarding video and audio quality will help fine-tune your setup.
• Instructions to the patient: Provide clear instructions to the patient when photographs of specific lesions are needed for further review. Specify what view(s) you need and whether size or bilateral comparison is needed. A web post by VisualDx10 provides advice to patients on taking high-quality photographs.
Final Thoughts
Teledermatology indubitably presents a learning curve for dermatologists and patients. As with other technological advances in society, we are optimistic that, first, the confidence level in teledermatology use will increase, and, second, evidence-based data will pave the way to enhance this experience. We realize the inherent limitation of accessibility to certain technologies, which is regrettably far from equitable. Patients need a personal device equipped with audio and video; access to a high-quality Internet connection; some degree of technological literacy; and a quiet private location.
We hope to learn from all experiences during the current pandemic. Future innovation in teledermatology and in telemedicine generally should aim to address technological inequities to allow for the delivery of quality care to as many patients as possible.
- American Academy of Dermatology. Everyday health and preparedness steps in clinic Updated April 4, 2020. Accessed December 17, 2020. https://assets.ctfassets.net/1ny4yoiyrqia/4LNCNjucOonbQx7aC970x/b56b540957ddad94dcc61949b8e3acc9/COVID-19_Preparedness_30Apr2020.pdf
- Geskin LJ, Trager MH, Aasi SZ, et al. Perspectives on the recommendations for skin cancer management during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:295-296.
- Earnshaw CH, Hunter HJA, McMullen E, et al. Reduction in skin cancer diagnosis, and overall cancer referrals, during the COVID-19 pandemic. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:792-794.
- Perkins S, Cohen JM, Nelson CA, et al. Teledermatology in the era of COVID-19: experience of an academic department of dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:E43-E44.
- Marina F. COVID-19: telehealth at the forefront of the pandemic. Dermatology News. May 12, 2020. Accessed December 17, 2020. www.mdedge.com/dermatology/article/222089/coronavirus-updates/covid-19-telehealth-forefront-pandemic?channel=52
- Watts CG, Dieng M, Morton RL, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for identification, screening and follow-up of individuals at high risk of primary cutaneous melanoma: a systematic review. Br J Dermatol. 2015;172:33-47.
- Rosamilia LL. “Doctor, do I need a skin check?” Cutis. 2019;103:290-291.
- Detect skin cancer: how to perform a skin self-exam. American Academy of Dermatology. Accessed December 17, 2020. www.aad.org/public/diseases/skin-cancer/find/check-skin
- Donaghy E, Atherton H, Hammersley V, et al. Acceptability, benefits, and challenges of video consulting: a qualitative study in primary care. Br J Gen Pract. 2019;69:E586-E594.
- How to take the best photos for teledermatology. VisualDx. Accessed December 17, 2020. https://info.visualdx.com/l/11412/2020-03-31/6h4hdz
On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) a pandemic, leading to an abrupt widespread shift to teledermatology, with postponement of nonessential in-office medical and surgical services, according to American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) recommendations.1 Perspectives have been offered regarding skin cancer management during the pandemic2; however, the current literature is lacking guidance on skin cancer screening and prevention during the COVID-19 era.
Preliminary data show a 34.3% reduction in skin cancer referrals from February to April 2020 compared to the same period in 2019. The authors also presented a subsequent reduction in the number of skin cancer diagnoses in March 2020 compared to March 2019.3 Although the COVID-19 public health emergency should be prioritized by all health care workers, the duty to maintain disease prevention remains.
We aim to provide recommendations for this urgent topic. Our goal is finding balance in preventing an increase in the incidence of and mortality from skin cancer that results from delayed detection, while conserving personalprotective equipment and minimizing exposure, by patients and clinical personnel, to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. A primary benefit of skin cancer screening lies in the ability to detect melanoma, which is associated with higher mortality than the more common nonmelanoma skin cancers, basal and cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas. We place preeminence on screening directed toward detecting melanoma. The main screening method that dermatologists employ is the total-body skin examination (TBSE). Another widely encouraged and utilized component in skin cancer prevention is patient education, emphasizing avoidance of risk factors, undertaking protective factors, and providing clear instructions for performing the patient-led skin self-examination (SSE).
Teledermatology Essentials for Skin Cancer Screening
Arguably, dermatology possesses the most potential for successfully utilizing telemedicine. Teledermatology has become widely implemented across the United States, secondary to the implications of the current pandemic. A report by Perkins and colleagues4 provided a positive outlook in the preliminary transition to teledermatology beginning in March 2020, though reported time of use was relatively short (3 weeks). A May 2020 article in Dermatology News provided tips for implementing telemedicine for practices.5
We agree with the comprehensive screening algorithm for teledermatology presented by Perkins and colleagues4 (Figure 1A in their report) and recommend the following for the screening and prevention of skin cancer:
• Patients with any characteristics of increased risk, including a personal or family history of melanoma, large congenital nevi, many melanotic nevi, dysplastic nevi, and Fitzpatrick skin types I and II,6 should be prioritized for an in-person visit for TBSE.
• Immunosuppressed patients, particularly organ transplant recipients and those with a history of skin cancer, should be prioritized for an in-person visit for TBSE.
• Established patients evaluated and determined to be at average risk for skin cancer should be offered a teledermatology visit. Suspicious findings during these visits should be prioritized for an in-person visit, with subsequent biopsy and follow-up.
• New patients should be offered a teledermatology visit.
These recommendations must be reviewed alongside each patient’s risk for travel and being present in person as well as other factors that might place the patient at increased risk for COVID-19.
Total-body skin examination, a widely used tool in the dermatologist’s tool kit, presents minimal risk to patients while providing important data for each dermatology patient’s profile, ultimately directing patient care. The role of TBSE in skin cancer screening and prevention has been in discussion even prior to the current pandemic. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has not declared a role for TBSE in recent years; however, USPSTF recommendations are formulated using data from all forms of screening, not only dermatologist-led interventions. Accordingly, USPSTF recommendations target primary care. The AAD has released statements addressing the role of TBSE and skin cancer prevention in the past, when necessary, to provide clarity.7
There is no clear definition of SSE or guidelines on how to educate a patient to perform regular SSE; however, the AAD provides patients with resources on how to perform an SSE.8 Just as dermatologists would provide education, advice, and guidance by directing patients to the AAD website for the SSE during an in-person visit, we encourage dermatologists to continue this practice during all teledermatology visits.
The role of teledermatology in skin cancer screening and prevention is limited; dermatologists will not be able to adequately perform TBSE as it would be done at in-person visits. Furthermore, the true implications of teledermatology compared to in-person visits during the COVID-19 pandemic have yet to be realized and analyzed. It is nonetheless important to appreciate that teledermatology holds great promise of benefit in skin cancer prevention, especially in the form of patient education by dermatologists. Practices in the realm of screening and prevention by health care professionals should be continually addressed during the pandemic; it is important to consider the implications associated with delays in diagnosis and treatment.
Teledermatology Limitations and Recommendations for High-Quality Visits
A benefit of video consultation (VC) vs telephone visits is visual interaction—the crux of dermatology. A 2019 study investigated VC experiences among providers and patients in the primary care setting. Benefits of VC were reported to include convenience for working patients and patients with mobility or mental health problems, visual cues, building rapport, and improving communication.9
Despite these benefits, VC is not without limitations. Many technical factors create variability in the quality of teledermatology VCs for a melanocytic lesion, including patient environment and lighting, color distortion, video resolution, and Internet connection. We make the following recommendations:
• Environment: Locate or create a dedicated space for teledermatology visits that is well lit, private, and has minimal background noise. Place the device on a level surface, center yourself in the frame, and keep the camera at eye level.
• Lighting: Use neutral lighting, placing the light source in front of you but behind the camera of the device. Avoid placing light sources, such as a window, behind you.
• Video resolution: Regardless of the type of camera (eg, integrated webcam, external camera), close out all other running software programs to optimize bandwidth during the visit.
• Internet connection: Use a wired connection (via an Ethernet cable) instead of a Wi-Fi connection to greatly decrease the chance of losing the connection during the visit. It also is faster than Wi-Fi.
• Addressing specific lesions: Patients should keep the device in place, repositioning themselves to show the lesions rather than moving the device by hand.
• Video capacity: Test your device’s video capacity beforehand, which can be as simple as video-calling a family member or friend from your designated space. Feedback regarding video and audio quality will help fine-tune your setup.
• Instructions to the patient: Provide clear instructions to the patient when photographs of specific lesions are needed for further review. Specify what view(s) you need and whether size or bilateral comparison is needed. A web post by VisualDx10 provides advice to patients on taking high-quality photographs.
Final Thoughts
Teledermatology indubitably presents a learning curve for dermatologists and patients. As with other technological advances in society, we are optimistic that, first, the confidence level in teledermatology use will increase, and, second, evidence-based data will pave the way to enhance this experience. We realize the inherent limitation of accessibility to certain technologies, which is regrettably far from equitable. Patients need a personal device equipped with audio and video; access to a high-quality Internet connection; some degree of technological literacy; and a quiet private location.
We hope to learn from all experiences during the current pandemic. Future innovation in teledermatology and in telemedicine generally should aim to address technological inequities to allow for the delivery of quality care to as many patients as possible.
On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) a pandemic, leading to an abrupt widespread shift to teledermatology, with postponement of nonessential in-office medical and surgical services, according to American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) recommendations.1 Perspectives have been offered regarding skin cancer management during the pandemic2; however, the current literature is lacking guidance on skin cancer screening and prevention during the COVID-19 era.
Preliminary data show a 34.3% reduction in skin cancer referrals from February to April 2020 compared to the same period in 2019. The authors also presented a subsequent reduction in the number of skin cancer diagnoses in March 2020 compared to March 2019.3 Although the COVID-19 public health emergency should be prioritized by all health care workers, the duty to maintain disease prevention remains.
We aim to provide recommendations for this urgent topic. Our goal is finding balance in preventing an increase in the incidence of and mortality from skin cancer that results from delayed detection, while conserving personalprotective equipment and minimizing exposure, by patients and clinical personnel, to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. A primary benefit of skin cancer screening lies in the ability to detect melanoma, which is associated with higher mortality than the more common nonmelanoma skin cancers, basal and cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas. We place preeminence on screening directed toward detecting melanoma. The main screening method that dermatologists employ is the total-body skin examination (TBSE). Another widely encouraged and utilized component in skin cancer prevention is patient education, emphasizing avoidance of risk factors, undertaking protective factors, and providing clear instructions for performing the patient-led skin self-examination (SSE).
Teledermatology Essentials for Skin Cancer Screening
Arguably, dermatology possesses the most potential for successfully utilizing telemedicine. Teledermatology has become widely implemented across the United States, secondary to the implications of the current pandemic. A report by Perkins and colleagues4 provided a positive outlook in the preliminary transition to teledermatology beginning in March 2020, though reported time of use was relatively short (3 weeks). A May 2020 article in Dermatology News provided tips for implementing telemedicine for practices.5
We agree with the comprehensive screening algorithm for teledermatology presented by Perkins and colleagues4 (Figure 1A in their report) and recommend the following for the screening and prevention of skin cancer:
• Patients with any characteristics of increased risk, including a personal or family history of melanoma, large congenital nevi, many melanotic nevi, dysplastic nevi, and Fitzpatrick skin types I and II,6 should be prioritized for an in-person visit for TBSE.
• Immunosuppressed patients, particularly organ transplant recipients and those with a history of skin cancer, should be prioritized for an in-person visit for TBSE.
• Established patients evaluated and determined to be at average risk for skin cancer should be offered a teledermatology visit. Suspicious findings during these visits should be prioritized for an in-person visit, with subsequent biopsy and follow-up.
• New patients should be offered a teledermatology visit.
These recommendations must be reviewed alongside each patient’s risk for travel and being present in person as well as other factors that might place the patient at increased risk for COVID-19.
Total-body skin examination, a widely used tool in the dermatologist’s tool kit, presents minimal risk to patients while providing important data for each dermatology patient’s profile, ultimately directing patient care. The role of TBSE in skin cancer screening and prevention has been in discussion even prior to the current pandemic. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has not declared a role for TBSE in recent years; however, USPSTF recommendations are formulated using data from all forms of screening, not only dermatologist-led interventions. Accordingly, USPSTF recommendations target primary care. The AAD has released statements addressing the role of TBSE and skin cancer prevention in the past, when necessary, to provide clarity.7
There is no clear definition of SSE or guidelines on how to educate a patient to perform regular SSE; however, the AAD provides patients with resources on how to perform an SSE.8 Just as dermatologists would provide education, advice, and guidance by directing patients to the AAD website for the SSE during an in-person visit, we encourage dermatologists to continue this practice during all teledermatology visits.
The role of teledermatology in skin cancer screening and prevention is limited; dermatologists will not be able to adequately perform TBSE as it would be done at in-person visits. Furthermore, the true implications of teledermatology compared to in-person visits during the COVID-19 pandemic have yet to be realized and analyzed. It is nonetheless important to appreciate that teledermatology holds great promise of benefit in skin cancer prevention, especially in the form of patient education by dermatologists. Practices in the realm of screening and prevention by health care professionals should be continually addressed during the pandemic; it is important to consider the implications associated with delays in diagnosis and treatment.
Teledermatology Limitations and Recommendations for High-Quality Visits
A benefit of video consultation (VC) vs telephone visits is visual interaction—the crux of dermatology. A 2019 study investigated VC experiences among providers and patients in the primary care setting. Benefits of VC were reported to include convenience for working patients and patients with mobility or mental health problems, visual cues, building rapport, and improving communication.9
Despite these benefits, VC is not without limitations. Many technical factors create variability in the quality of teledermatology VCs for a melanocytic lesion, including patient environment and lighting, color distortion, video resolution, and Internet connection. We make the following recommendations:
• Environment: Locate or create a dedicated space for teledermatology visits that is well lit, private, and has minimal background noise. Place the device on a level surface, center yourself in the frame, and keep the camera at eye level.
• Lighting: Use neutral lighting, placing the light source in front of you but behind the camera of the device. Avoid placing light sources, such as a window, behind you.
• Video resolution: Regardless of the type of camera (eg, integrated webcam, external camera), close out all other running software programs to optimize bandwidth during the visit.
• Internet connection: Use a wired connection (via an Ethernet cable) instead of a Wi-Fi connection to greatly decrease the chance of losing the connection during the visit. It also is faster than Wi-Fi.
• Addressing specific lesions: Patients should keep the device in place, repositioning themselves to show the lesions rather than moving the device by hand.
• Video capacity: Test your device’s video capacity beforehand, which can be as simple as video-calling a family member or friend from your designated space. Feedback regarding video and audio quality will help fine-tune your setup.
• Instructions to the patient: Provide clear instructions to the patient when photographs of specific lesions are needed for further review. Specify what view(s) you need and whether size or bilateral comparison is needed. A web post by VisualDx10 provides advice to patients on taking high-quality photographs.
Final Thoughts
Teledermatology indubitably presents a learning curve for dermatologists and patients. As with other technological advances in society, we are optimistic that, first, the confidence level in teledermatology use will increase, and, second, evidence-based data will pave the way to enhance this experience. We realize the inherent limitation of accessibility to certain technologies, which is regrettably far from equitable. Patients need a personal device equipped with audio and video; access to a high-quality Internet connection; some degree of technological literacy; and a quiet private location.
We hope to learn from all experiences during the current pandemic. Future innovation in teledermatology and in telemedicine generally should aim to address technological inequities to allow for the delivery of quality care to as many patients as possible.
- American Academy of Dermatology. Everyday health and preparedness steps in clinic Updated April 4, 2020. Accessed December 17, 2020. https://assets.ctfassets.net/1ny4yoiyrqia/4LNCNjucOonbQx7aC970x/b56b540957ddad94dcc61949b8e3acc9/COVID-19_Preparedness_30Apr2020.pdf
- Geskin LJ, Trager MH, Aasi SZ, et al. Perspectives on the recommendations for skin cancer management during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:295-296.
- Earnshaw CH, Hunter HJA, McMullen E, et al. Reduction in skin cancer diagnosis, and overall cancer referrals, during the COVID-19 pandemic. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:792-794.
- Perkins S, Cohen JM, Nelson CA, et al. Teledermatology in the era of COVID-19: experience of an academic department of dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:E43-E44.
- Marina F. COVID-19: telehealth at the forefront of the pandemic. Dermatology News. May 12, 2020. Accessed December 17, 2020. www.mdedge.com/dermatology/article/222089/coronavirus-updates/covid-19-telehealth-forefront-pandemic?channel=52
- Watts CG, Dieng M, Morton RL, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for identification, screening and follow-up of individuals at high risk of primary cutaneous melanoma: a systematic review. Br J Dermatol. 2015;172:33-47.
- Rosamilia LL. “Doctor, do I need a skin check?” Cutis. 2019;103:290-291.
- Detect skin cancer: how to perform a skin self-exam. American Academy of Dermatology. Accessed December 17, 2020. www.aad.org/public/diseases/skin-cancer/find/check-skin
- Donaghy E, Atherton H, Hammersley V, et al. Acceptability, benefits, and challenges of video consulting: a qualitative study in primary care. Br J Gen Pract. 2019;69:E586-E594.
- How to take the best photos for teledermatology. VisualDx. Accessed December 17, 2020. https://info.visualdx.com/l/11412/2020-03-31/6h4hdz
- American Academy of Dermatology. Everyday health and preparedness steps in clinic Updated April 4, 2020. Accessed December 17, 2020. https://assets.ctfassets.net/1ny4yoiyrqia/4LNCNjucOonbQx7aC970x/b56b540957ddad94dcc61949b8e3acc9/COVID-19_Preparedness_30Apr2020.pdf
- Geskin LJ, Trager MH, Aasi SZ, et al. Perspectives on the recommendations for skin cancer management during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:295-296.
- Earnshaw CH, Hunter HJA, McMullen E, et al. Reduction in skin cancer diagnosis, and overall cancer referrals, during the COVID-19 pandemic. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:792-794.
- Perkins S, Cohen JM, Nelson CA, et al. Teledermatology in the era of COVID-19: experience of an academic department of dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:E43-E44.
- Marina F. COVID-19: telehealth at the forefront of the pandemic. Dermatology News. May 12, 2020. Accessed December 17, 2020. www.mdedge.com/dermatology/article/222089/coronavirus-updates/covid-19-telehealth-forefront-pandemic?channel=52
- Watts CG, Dieng M, Morton RL, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for identification, screening and follow-up of individuals at high risk of primary cutaneous melanoma: a systematic review. Br J Dermatol. 2015;172:33-47.
- Rosamilia LL. “Doctor, do I need a skin check?” Cutis. 2019;103:290-291.
- Detect skin cancer: how to perform a skin self-exam. American Academy of Dermatology. Accessed December 17, 2020. www.aad.org/public/diseases/skin-cancer/find/check-skin
- Donaghy E, Atherton H, Hammersley V, et al. Acceptability, benefits, and challenges of video consulting: a qualitative study in primary care. Br J Gen Pract. 2019;69:E586-E594.
- How to take the best photos for teledermatology. VisualDx. Accessed December 17, 2020. https://info.visualdx.com/l/11412/2020-03-31/6h4hdz
Practice Points
- It is important for dermatologists to maintain skin cancer screening and prevention efforts during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic.
- Patient populations at increased risk for skin cancer should be prioritized for in-person evaluations, but teledermatology should be considered for initial examination in new patients and patients at average risk for skin cancer.
- Teledermatology presents a learning curve for dermatologists and patients, but the confidence level will increase, and evidence-based data will pave the way to enhance this experience.
Skin Cancer in the US Military
There are numerous intrinsic risks that military servicemembers face, such as the dangers of combat, handling firearms, operating ships and heavy machinery, undersea diving, and aircraft operations. Multiple studies also have identified an increased risk for melanomas and keratinocyte cancers in those who have served on active duty.
Epidemiology
Differences in demographics are important to consider given the differences among races in the risks of skin cancers. Important racial demographic differences exist between the US Military and the general US population. Racial demographic differences also exist among the various military branches themselves. The US population is 61.0% White, 20.7% racial minorities (defined as Black or African American, Asian, American Indian or Alaska native, Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander, multiracial, or unknown), and 18.3% Hispanic or Latino (Hispanic or Latino was not listed as a component of racial minorities).1 According to 2018 data, the US Military population is 52.9% White, 31.0% racial minorities, and 16.1% Hispanic or Latino.2 The percentage of White military members was highest in the US Marine Corps (58.4%) and lowest in the US Navy (46.5%). The percentage of racial minorities was highest in the US Navy (38.0%) and lowest in the US Marine Corps (20.0%).2 The percentage of Hispanic and Latino military members was highest in the US Marine Corps (21.6%) and lowest in the US Air Force (14.5%).2
Melanoma in Military Members
It is estimated that the annual incidence rate of melanoma in the United States is 27 per 100,000 individuals for non-Hispanic Whites, 5 per 100,000 for Hispanics, and 1 per 100,000 for Black individuals and Asians/Pacific Islanders.3 Three studies have reviewed melanoma incidence in relation to service in the US Military.
A 2011 retrospective tumor registries study of US veterans aged 45 years or older demonstrated increased incidences of melanoma compared with the general population.4 With age, the melanoma incidence per 100,000 person-years increased in White veterans compared to their civilian counterparts (aged 45 to 49 years, 33.62 vs 27.49; aged 50 to 54 years, 49.76 vs 32.18; aged 55 to 59 years, 178.48 vs 39.17).4 An increased melanoma incidence of 62% also was seen in active-duty servicemembers aged 18 to 56 years compared to their age-matched civilian peers in a 2014 retrospective cohort study.5
Melanoma rates also vary depending on military service branch. Across 3 separate studies, service in the US Air Force was associated with the highest risk for melanoma development. A surveillance report of cancer incidence in active-duty US Armed Forces personnel between 2000 and 2011 conducted by the Defense Medical Surveillance System showed an incidence rate (per 100,000 person-years) for melanoma of 10.5 in all services, and a rate of 15.5 in the US Air Force vs 8.6 in the US Army, further highlighting the disparity between the services.6 The 2014 study also demonstrated a melanoma incidence rate of 17.80 in active-duty
Keratinocyte Cancers in Military Members
Although less well studied than melanoma, keratinocyte-derived skin cancers represent a major source of disease burden both during and after active-duty service. In a retrospective chart review of dermatology patients seen at the 86th Combat Support Hospital at Ibn Sina Hospital in Baghdad, Iraq, during a 6-month period in 2008, 8% of 2696 total visits were identified to be due to skin cancer, with the overwhelming majority being for keratinocyte cancers.7 A 1993 retrospective chart review of World War II veterans referred for Mohs micrographic surgery showed a considerably higher incidence in those who served in the Pacific Theater compared to those who served in the European Theater. Despite having approximately equal characteristics—age, skin type, and cumulative time spent outdoors—between the 2 groups, military servicemembers deployed to the Pacific represented 66% of the patients with basal cell carcinoma and 68% of the patients with squamous cell carcinoma.8
Contributing Factors
There are many factors related to military service that are likely to contribute to the increased risk for skin cancer. Based on a review of the literature, we have found an increased exposure to UV radiation, low utilization of sun-protective strategies, and low overall education regarding the risks for UV exposure to be the primary contributors to increased risks for skin cancer.
UV exposure is the primary mitigatable risk factor for developing melanoma and keratinocyte cancers.9,10 In a 2015 study of 212 military servicemembers returning from deployments in Iraq and Afghanistan, 77% reported spending more than 4 hours per day working directly in the bright sun, with 64% spending more than 75% of the average day in the bright sun.11 A 1984 study of World War II veterans diagnosed with melanoma also showed that 34% of those with melanoma had prior deployments to the tropics compared to 6% in age-matched controls.12
Even in those not deployed to overseas locations, military work still frequently involves prolonged sun exposure. In a 2015 cross-sectional study of US Air Force maintenance squadrons at Travis Air Force Base in Fairfield, California (N=356), 67% of those surveyed reported having careers that frequently involved direct sun exposure.13 This occupational sun exposure may be worsened by increased UV exposure during recreational activities, as active-duty military servicemembers may reasonably be expected to engage in more outdoor exercise and leisure activities than their civilian counterparts.
Other occupation-specific risk factors also may affect skin cancer rates in certain populations. In a study of aircraft personnel that included male military and civilian pilots, a meta-standardized incidence ratio for melanoma of 3.42 was identified compared to controls not involved in aircraft work.14 Theories to explain this increased incidence of melanoma include increased exposure to ionizing radiation at high altitudes, exposure to aviation-related chemicals, and alterations in circadian rhythm.14,15
This increased sun exposure is compounded by the overall low rates of sun protection among military members. Of those returning from Iraq and Afghanistan in the 2015 study, less than 30% of servicemembers reported routine access to sunscreen, and only 13% stated that they routinely applied sunscreen when exposed to the sun. Of this same group, only 23% endorsed that the military made them very aware of their risk for skin cancer.11 The low rates of sunscreen usage by those deployed to an active combat zone may partially be explained by the assumption that those individuals placed more emphasis on the acute dangers of combat rather than the perceived future dangers of skin cancer. A decreased availability of sunscreen for deployed military servicemembers, particularly those located at small austere bases where supplies are likely to be limited, likely makes the use of sunscreen even more difficult.
However, even within the continental United States, active-duty military servicemembers still exhibit low rates of sunscreen usage. In the 2015 study of US Air Force personnel in maintenance squadrons in California, less than 11% of those surveyed reported using sunscreen most of the time despite high rates of outdoor work.13
Another factor likely contributing to increased sun exposure and decreased sun-protection practices is the so-called invincibility complex, which is a common set of egocentric beliefs that leads to a perception that an individual is not likely to suffer the consequences of engaging in risky behaviors. Despite knowledge of the dangers associated with risky activity, individuals with an invincibility complex are more likely to view potential consequences as relevant only to others, not to themselves.16 A study of adolescent smokers in the Netherlands examined why subjects continue to smoke, despite knowledge of the potentially deadly consequences of smoking. Three common rationalizing beliefs were found: trivialization of the immediate consequences, that their smoking is only temporary and they have time in the future to stop, and that they have control over how much they smoke and can prevent fatal consequences with moderation.17 Such an invincibility complex is thought to directly run counter to the efforts of public health and educational campaigns. This belief set is thought to at least partially explain why adolescents in Australia are the most knowledgeable age cohort regarding the dangers of UV exposure but the least likely to engage in skin-protective measures.18 This inflated sense of invincibility may be leading active-duty military servicemembers to engage in unhealthy sun-exposure practices regardless of knowledge of the associated risks.
Members of the military may be uniquely susceptible to this invincibility complex. Growing evidence suggests that exposure to life-threatening circumstances may lead to long-lasting alterations in threat assessment.19,20 A 2008 study of Iraq veterans returning from deployment found that direct exposure to violent combat and human trauma was associated with an increased perceived degree of invincibility and a higher propensity to engage in risky behaviors after returning from deployment.19 Additionally, it has been speculated that individuals with a higher degree of perceived invincibility may be more likely to pursue military service, as a higher degree of self-confidence in the face of the often dangerous circumstances of military operations may be advantageous.20
In addition to scarce use of sun-protective strategies, military servicemembers also tend to lack awareness of the potential short-term and long-term harm from UV radiation. In a 2016 study of veterans undergoing treatment for skin cancer, patients reported inadequate education about skin cancer risks and strategies to decrease their chances of developing it.21 Sunscreen is less frequently used in males, specifically those aged 18 to 30 years; this demographic makes up 55.7% of the active-duty population.2,22 Low income also has been associated with decreased sunscreen use; junior enlisted military servicemembers (ranks E1-E4) make up 43.8% of the military’s ranks and make less than the average annual American household income.2,23,24
Prevention and Risk-Mitigation Strategies
Although many of the risk factors in the US Military promoting skin cancer are intrinsic to the occupation, certain steps could help minimize servicemembers’ risks. To be effective, any attempt to decrease the risk for skin cancer in the US Military must take into consideration the environment in which the military operates. To complete their mission, military personnel often are required to operate for extended periods outdoors in areas of high UV exposure, such as the deserts of Iraq or the mountains of Afghanistan. Outdoor work at times of peak sunlight often is required for successful mission completion, thus it would be ineffective to simply give blanket advice to avoid sun exposure.
Another important factor is the impact that official policy plays in shaping the daily actions of individual military servicemembers. In a hierarchical organization such as the US Military, unit commanders have substantial authority over the behaviors of their subordinates. Thus, strategies to mitigate skin cancer risks should be aimed at the individual servicemembers and unit commanders and at a policy level. Ultimately, a 3-pronged approach built on education, access to sun-protective gear, and increased availability to sunscreen is recommended.
Education
The foundation for any skin cancer prevention strategies should be built on the education of individual military servicemembers. The majority of active-duty members and veterans did not believe the military did enough to actively educate them on the risks for developing skin cancer.21 An effective educational program should focus on prevention and detection. Prevention programs should explain the role of UV exposure in the development of skin cancer, the intrinsic risks of UV exposure associated with outdoor activities, and strategies that can be implemented to reduce UV exposure and lifetime risk of skin cancer development. In a study of German outdoor workers, displays of support and concern by management regarding UV protection were associated with increases in sun-protective behaviors among the employees.25
Because patient self-examinations have been shown to be associated with earlier melanoma diagnosis and a more superficial depth at diagnosis, detection programs also should focus on the identification of suspicious skin lesions, such as by teaching the ABCDEs of melanoma.26 Among the general population, educational campaigns have been shown to be effective at reducing melanoma mortality.27,28
Access to Sun-Protective Gear
The second aspect of reducing skin cancer risk should be aiming to protect military servicemembers from UV exposure. Any prevention strategy must fit within the military’s broader tactical and strategic framework.
The use of photoprotective strategies rather than the outright avoidance of sun exposure should be implemented to minimize the deleterious effects of outdoor work. The most recent study of the UV-protective properties of US Military uniforms found all tested uniforms to have either very good or excellent UV protection, with UV protection factors (UPFs) ranging from 35 to 50+.29 However, this study was performed in 2002, and the majority of the uniforms tested are no longer in service. More up-to-date UPF information for existing military uniforms is not currently available. Most military commands wear baseball hat–style covers when operating outdoors, which generally provide good photoprotection with UPF ratings of 35 to 50 over the protected areas.29 Unfortunately, these types of headgear offer less photoprotection than do wide-brimmed hats, which have demonstrated improved photoprotection, particularly of the neck, cheeks, ears, and chin.30 A wide-brimmed hat, known as the boonie hat, was originally proposed for military use in 1966 to provide protection of servicemembers’ faces and necks from the intense sun of Vietnam. Currently, the use of the boonie hat typically is prohibited for units not engaged in combat or combat-support roles and requires authorization by the unit-level commander.31 Because of its perception as “unmilitary appearing” by many unit commanders and its restriction of use to combat-related units, the boonie hat is not consistently used. Increasing the use of this type of wide-brimmed hat would be an important asset in decreasing chronic UV exposure in military servicemembers, particularly on those parts of the body where skin cancer occurrence is the greatest.32 Policies should be aimed at increasing the use of the boonie hat, both through expanding its availability to troops in non–combat-related fields and by encouraging unit commanders to authorize its use in their units.
Sunscreen Availability
Improving the use of sunscreen is another impactful strategy that could be undertaken to decrease the risk for skin cancer in military servicemembers. The use of sunscreen is low in both those deployed overseas and those stationed within the United States. Improving access to sunscreen, particularly in the deployed setting, also could reduce barriers to use. Providing sunscreen directly to servicemembers, either when issuing gear or integrated within Meals Ready to Eat, could remove both the financial and logistical barriers to sunscreen utilization. Centralized troop-gathering locations, such as dining facilities, could be utilized both for the mass distribution of sunscreen and to display educational material. Unit commanders also could mandate times for servicemembers to stop work and apply sunscreen at regularly scheduled intervals.
The composition and delivery vehicle of sunscreen may have an impact on its efficacy and ease of use in the field. The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) recommends using sunscreen that is broad spectrum, sun protection factor (SPF) 30 or greater, and water resistant.33 However, the AAD does not make a recommendation of whether to use a physical sunscreen (such as titanium dioxide) or a chemical sunscreen. If applied in equal amounts, a chemical sunscreen and a physical sunscreen with an equal SPF should offer the same UV protection. However, a study in the British Journal of Dermatology showed that subjects applied only two-thirds the quantity of physical sunscreen compared to those applying chemical sunscreen, achieving approximately only one-half the SPF as provided by the chemical sunscreen.34 Because sunscreen is only effective when it is used, consideration should be given to the preferences of the military population when selecting sunscreens. A review of consumer preferences of sunscreen qualities showed that sunscreens that were nongreasy and did not leave a residue were given the most favorable rankings.35 In recent years, sunscreen sprays have become increasingly popular. When adequately applied, sprays have been shown to be equally effective as sunscreen lotions.36 However, although recommendations have been issued by both the AAD and the US Food and Drug Administration on the application of sunscreen lotion to adequately cover exposed skin, no such recommendations have been given for sunscreen sprays.33 Some safety concerns also remain regarding the flammability of aerosol sunscreens, which could be exacerbated in a combat situation.37
However, there are some obvious downsides to sunscreen use. During certain operational tasks, particularly in combat settings, it may not be feasible or even safe to stop working to apply sunscreen at the 2-hour intervals required for effective UV protection.38 Water exposure or large amounts of perspiration also would cause sunscreen to lose effectiveness earlier than expected. Logistically, it may be challenging to regularly supply sunscreen to small austere bases in remote locations.
Final Thoughts
The men and women of our armed forces already undertake great risk in the defense of our country. It should be ensured that their risk for developing skin cancer is made as low as possible, while still allowing them to successfully accomplish their mission. Multiple studies have shown servicemembers to be at an increased risk for skin cancer, particularly melanoma. We believe the primary factor behind this increased risk is occupational UV exposure, which is compounded by the suboptimal use of sun-protective strategies. By educating our servicemembers about their risk for skin cancer and promoting increased UV protection, we can effectively reduce the burden of skin cancer on our active-duty servicemembers and veterans.
- QuickFacts. United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/PST045219
- 2018 Demographics Profile. Military OneSource. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.militaryonesource.mil/reports-and-surveys/infographics/active-duty-member-and-family-demographics
- Cancer Facts & Figures 2019. American Cancer Society. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/cancer-facts-figures-2019.html
- Zhou J, Enewold L, Zahm SH, et al. Melanoma incidence rates among whites in the U.S. Military. Cancer Epidemiol. 2011;20:318-323.
- Lea CS, Efird JT, Toland AE, et al. Melanoma incidence rates in active duty military personnel compared with a population-based registry in the United States, 2000-2007. Military Med. 2014;179:247-253.
- Armed Forces Health Surveillance Center. Incident diagnoses of cancers and cancer-related deaths, active component, US Armed Forces, 2000-2011. MSMR. 2012;19:18-22.
- Henning JS, Firoz BF. Combat dermatology: the prevalence of skin disease in a deployed dermatology clinic in Iraq. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:210-214.
- Ramani ML, Bennett RG. High prevalence of skin-cancer in World-War-II servicemen stationed in the Pacific Theater. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28:733-737.
- Schmitt J, Seidler A, Diepgen TL, et al. Occupational ultraviolet light exposure increases the risk for the development of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:291-307.
- Armstrong BK, Kricker A. The epidemiology of UV induced skin cancer. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2001;63:8-18.
- Powers JG, Patel NA, Powers EM, et al. Skin cancer risk factors and preventative behaviors among United States military veterans deployed to Iraq and Afghanistan. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:2871-2873.
- Brown J, Kopf AW, Rica DS, et al. Malignant melanoma in World War II veterans. Int J Dermatol. 1984;23:661-663.
- Parker G, Williams B, Driggers P. Sun exposure knowledge and practices survey of maintenance squadrons at Travis AFB. Military Med. 2015;180:26-31.
- Buja A, Lange JH, Perissinotto E, et al. Cancer incidence among male military and civil pilots and flight attendants: an analysis on published data. Toxicol Ind Health. 2005;21:273-282.
- Wilkison BD, Wong EB. Skin cancer in military pilots: a special population with special risk factors. Cutis. 2017;100:218-220.
- Wickman ME, Anderson NLR, Smith Greenberg C. The adolescent perception of invincibility and its influence on teen acceptance of health promotion strategies. J Pediatr Nurs. 2008;23:460-468.
- Schreuders M, Krooneman NT, van den Putte B, et al. Boy smokers’ rationalisations for engaging in potentially fatal behaviour: in-depth interviews in the Netherlands. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15:767.
- Eastabrook S, Chang P, Taylor MF. Melanoma risk: adolescent females’ perspectives on skin protection pre/post-viewing a ultraviolet photoaged photograph of their own facial sun damage. Glob Health Promot. 2018;25:23-32.
- Killgore WD, Cotting DI, Thomas JL, et al. Post-combat invincibility: violent combat experiences are associated with increased risk-taking propensity following deployment. J Psychiatr Res. 2008;42:1112-1121.
- Killgore WD, Kelley A, Balkin TJ. So you think you’re bulletproof: development and validation of the Invincibility Belief Index (IBI). Military Med. 2010;175:499-508.
- McGrath JM, Fisher V, Krejci-Manwaring J. Skin cancer warnings and the need for new preventive campaigns: a pilot study. Am J Prevent Med. 2016;50:E62-E63.
- Thieden E, Philipsen PA, Sandby-Moller J, et al. Sunscreen use related to UV exposure, age, sex, and occupation based on personal dosimeter readings and sun-exposure behavior diaries. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:967-973.
- Holman DM, Berkowitz Z, Guy GP Jr, et al. Patterns of sunscreen use on the face and other exposed skin among US adults. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:83-92.e1.
- Military Pay Tables & Information. Defense Finance and Accounting Service website. Accessed December 21, 2020. https://www.dfas.mil/militarymembers/payentitlements/Pay-Tables.html
- Schilling L, Schneider S, Gorig T, et al. “Lost in the sun”—the key role of perceived workplace support for sun-protective behavior in outdoor workers. Am J Ind Med. 2018;61:929-938.
- Uliasz A, Lebwohl M. Patient education and regular surveillance results in earlier diagnosis of second primary melanoma. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:575-577.
- MacKie RM, Hole D. Audit of public education campaign to encourage earlier detection of malignant melanoma. BMJ. 1992;304:1012-1015.
- Berwick M, Begg CB, Fine JA, et al. Screening for cutaneous melanoma by skin self-examination. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996;88:17-23.
- Winterhalter C, DiLuna K, Bide M. Characterization of the ultraviolet protection of combat uniform fabrics. US Army Soldier and Biological Chemical Command Soldier Systems Center technical report Natick/TR-02/006. Published January 21, 2002. Accessed December 21, 2021. https://apps.dtic.mil/dtic/tr/fulltext/u2/a398572.pdf
- Gies P, Javorniczky J, Roy C, et al. Measurements of the UVR protection provided by hats used at school. Photochem Photobiol. 2006;82:750-754.
- Stanton S. Headgear. In: Stanton S. US Army Uniforms of the Vietnam War. Stackpole Books; 1992:26-61.
- Richmond-Sinclair NM, Pandeya N, Ware RS, et al. Incidence of basal cell carcinoma multiplicity and detailed anatomic distribution: longitudinal study of an Australian population. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:323-328.
- How to select a sunscreen. American Academy of Dermatology. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.aad.org/sun-protection/how-to-select-sunscreen
- Diffey BL, Grice J. The influence of sunscreen type on photoprotection. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:103-105.
- Xu S, Kwa M, Agarwal A, et al. Sunscreen product performance and other determinants of consumer preferences. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:920-927.
- Ou-Yang H, Stanfield J, Cole C, et al. High-SPF sunscreens (SPF ≥ 70) may provide ultraviolet protection above minimal recommended levels by adequately compensating for lower sunscreen user application amounts. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:1220-1227.
- O’Connor A. Is sunscreen flammable? The New York Times. June 6, 2012. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://well.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/06/06/is-sunscreen-flammable/
- Prevent skin cancer. American Academy of Dermatology. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.aad.org/public/spot-skin-cancer/learn-about-skin-cancer/prevent
There are numerous intrinsic risks that military servicemembers face, such as the dangers of combat, handling firearms, operating ships and heavy machinery, undersea diving, and aircraft operations. Multiple studies also have identified an increased risk for melanomas and keratinocyte cancers in those who have served on active duty.
Epidemiology
Differences in demographics are important to consider given the differences among races in the risks of skin cancers. Important racial demographic differences exist between the US Military and the general US population. Racial demographic differences also exist among the various military branches themselves. The US population is 61.0% White, 20.7% racial minorities (defined as Black or African American, Asian, American Indian or Alaska native, Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander, multiracial, or unknown), and 18.3% Hispanic or Latino (Hispanic or Latino was not listed as a component of racial minorities).1 According to 2018 data, the US Military population is 52.9% White, 31.0% racial minorities, and 16.1% Hispanic or Latino.2 The percentage of White military members was highest in the US Marine Corps (58.4%) and lowest in the US Navy (46.5%). The percentage of racial minorities was highest in the US Navy (38.0%) and lowest in the US Marine Corps (20.0%).2 The percentage of Hispanic and Latino military members was highest in the US Marine Corps (21.6%) and lowest in the US Air Force (14.5%).2
Melanoma in Military Members
It is estimated that the annual incidence rate of melanoma in the United States is 27 per 100,000 individuals for non-Hispanic Whites, 5 per 100,000 for Hispanics, and 1 per 100,000 for Black individuals and Asians/Pacific Islanders.3 Three studies have reviewed melanoma incidence in relation to service in the US Military.
A 2011 retrospective tumor registries study of US veterans aged 45 years or older demonstrated increased incidences of melanoma compared with the general population.4 With age, the melanoma incidence per 100,000 person-years increased in White veterans compared to their civilian counterparts (aged 45 to 49 years, 33.62 vs 27.49; aged 50 to 54 years, 49.76 vs 32.18; aged 55 to 59 years, 178.48 vs 39.17).4 An increased melanoma incidence of 62% also was seen in active-duty servicemembers aged 18 to 56 years compared to their age-matched civilian peers in a 2014 retrospective cohort study.5
Melanoma rates also vary depending on military service branch. Across 3 separate studies, service in the US Air Force was associated with the highest risk for melanoma development. A surveillance report of cancer incidence in active-duty US Armed Forces personnel between 2000 and 2011 conducted by the Defense Medical Surveillance System showed an incidence rate (per 100,000 person-years) for melanoma of 10.5 in all services, and a rate of 15.5 in the US Air Force vs 8.6 in the US Army, further highlighting the disparity between the services.6 The 2014 study also demonstrated a melanoma incidence rate of 17.80 in active-duty
Keratinocyte Cancers in Military Members
Although less well studied than melanoma, keratinocyte-derived skin cancers represent a major source of disease burden both during and after active-duty service. In a retrospective chart review of dermatology patients seen at the 86th Combat Support Hospital at Ibn Sina Hospital in Baghdad, Iraq, during a 6-month period in 2008, 8% of 2696 total visits were identified to be due to skin cancer, with the overwhelming majority being for keratinocyte cancers.7 A 1993 retrospective chart review of World War II veterans referred for Mohs micrographic surgery showed a considerably higher incidence in those who served in the Pacific Theater compared to those who served in the European Theater. Despite having approximately equal characteristics—age, skin type, and cumulative time spent outdoors—between the 2 groups, military servicemembers deployed to the Pacific represented 66% of the patients with basal cell carcinoma and 68% of the patients with squamous cell carcinoma.8
Contributing Factors
There are many factors related to military service that are likely to contribute to the increased risk for skin cancer. Based on a review of the literature, we have found an increased exposure to UV radiation, low utilization of sun-protective strategies, and low overall education regarding the risks for UV exposure to be the primary contributors to increased risks for skin cancer.
UV exposure is the primary mitigatable risk factor for developing melanoma and keratinocyte cancers.9,10 In a 2015 study of 212 military servicemembers returning from deployments in Iraq and Afghanistan, 77% reported spending more than 4 hours per day working directly in the bright sun, with 64% spending more than 75% of the average day in the bright sun.11 A 1984 study of World War II veterans diagnosed with melanoma also showed that 34% of those with melanoma had prior deployments to the tropics compared to 6% in age-matched controls.12
Even in those not deployed to overseas locations, military work still frequently involves prolonged sun exposure. In a 2015 cross-sectional study of US Air Force maintenance squadrons at Travis Air Force Base in Fairfield, California (N=356), 67% of those surveyed reported having careers that frequently involved direct sun exposure.13 This occupational sun exposure may be worsened by increased UV exposure during recreational activities, as active-duty military servicemembers may reasonably be expected to engage in more outdoor exercise and leisure activities than their civilian counterparts.
Other occupation-specific risk factors also may affect skin cancer rates in certain populations. In a study of aircraft personnel that included male military and civilian pilots, a meta-standardized incidence ratio for melanoma of 3.42 was identified compared to controls not involved in aircraft work.14 Theories to explain this increased incidence of melanoma include increased exposure to ionizing radiation at high altitudes, exposure to aviation-related chemicals, and alterations in circadian rhythm.14,15
This increased sun exposure is compounded by the overall low rates of sun protection among military members. Of those returning from Iraq and Afghanistan in the 2015 study, less than 30% of servicemembers reported routine access to sunscreen, and only 13% stated that they routinely applied sunscreen when exposed to the sun. Of this same group, only 23% endorsed that the military made them very aware of their risk for skin cancer.11 The low rates of sunscreen usage by those deployed to an active combat zone may partially be explained by the assumption that those individuals placed more emphasis on the acute dangers of combat rather than the perceived future dangers of skin cancer. A decreased availability of sunscreen for deployed military servicemembers, particularly those located at small austere bases where supplies are likely to be limited, likely makes the use of sunscreen even more difficult.
However, even within the continental United States, active-duty military servicemembers still exhibit low rates of sunscreen usage. In the 2015 study of US Air Force personnel in maintenance squadrons in California, less than 11% of those surveyed reported using sunscreen most of the time despite high rates of outdoor work.13
Another factor likely contributing to increased sun exposure and decreased sun-protection practices is the so-called invincibility complex, which is a common set of egocentric beliefs that leads to a perception that an individual is not likely to suffer the consequences of engaging in risky behaviors. Despite knowledge of the dangers associated with risky activity, individuals with an invincibility complex are more likely to view potential consequences as relevant only to others, not to themselves.16 A study of adolescent smokers in the Netherlands examined why subjects continue to smoke, despite knowledge of the potentially deadly consequences of smoking. Three common rationalizing beliefs were found: trivialization of the immediate consequences, that their smoking is only temporary and they have time in the future to stop, and that they have control over how much they smoke and can prevent fatal consequences with moderation.17 Such an invincibility complex is thought to directly run counter to the efforts of public health and educational campaigns. This belief set is thought to at least partially explain why adolescents in Australia are the most knowledgeable age cohort regarding the dangers of UV exposure but the least likely to engage in skin-protective measures.18 This inflated sense of invincibility may be leading active-duty military servicemembers to engage in unhealthy sun-exposure practices regardless of knowledge of the associated risks.
Members of the military may be uniquely susceptible to this invincibility complex. Growing evidence suggests that exposure to life-threatening circumstances may lead to long-lasting alterations in threat assessment.19,20 A 2008 study of Iraq veterans returning from deployment found that direct exposure to violent combat and human trauma was associated with an increased perceived degree of invincibility and a higher propensity to engage in risky behaviors after returning from deployment.19 Additionally, it has been speculated that individuals with a higher degree of perceived invincibility may be more likely to pursue military service, as a higher degree of self-confidence in the face of the often dangerous circumstances of military operations may be advantageous.20
In addition to scarce use of sun-protective strategies, military servicemembers also tend to lack awareness of the potential short-term and long-term harm from UV radiation. In a 2016 study of veterans undergoing treatment for skin cancer, patients reported inadequate education about skin cancer risks and strategies to decrease their chances of developing it.21 Sunscreen is less frequently used in males, specifically those aged 18 to 30 years; this demographic makes up 55.7% of the active-duty population.2,22 Low income also has been associated with decreased sunscreen use; junior enlisted military servicemembers (ranks E1-E4) make up 43.8% of the military’s ranks and make less than the average annual American household income.2,23,24
Prevention and Risk-Mitigation Strategies
Although many of the risk factors in the US Military promoting skin cancer are intrinsic to the occupation, certain steps could help minimize servicemembers’ risks. To be effective, any attempt to decrease the risk for skin cancer in the US Military must take into consideration the environment in which the military operates. To complete their mission, military personnel often are required to operate for extended periods outdoors in areas of high UV exposure, such as the deserts of Iraq or the mountains of Afghanistan. Outdoor work at times of peak sunlight often is required for successful mission completion, thus it would be ineffective to simply give blanket advice to avoid sun exposure.
Another important factor is the impact that official policy plays in shaping the daily actions of individual military servicemembers. In a hierarchical organization such as the US Military, unit commanders have substantial authority over the behaviors of their subordinates. Thus, strategies to mitigate skin cancer risks should be aimed at the individual servicemembers and unit commanders and at a policy level. Ultimately, a 3-pronged approach built on education, access to sun-protective gear, and increased availability to sunscreen is recommended.
Education
The foundation for any skin cancer prevention strategies should be built on the education of individual military servicemembers. The majority of active-duty members and veterans did not believe the military did enough to actively educate them on the risks for developing skin cancer.21 An effective educational program should focus on prevention and detection. Prevention programs should explain the role of UV exposure in the development of skin cancer, the intrinsic risks of UV exposure associated with outdoor activities, and strategies that can be implemented to reduce UV exposure and lifetime risk of skin cancer development. In a study of German outdoor workers, displays of support and concern by management regarding UV protection were associated with increases in sun-protective behaviors among the employees.25
Because patient self-examinations have been shown to be associated with earlier melanoma diagnosis and a more superficial depth at diagnosis, detection programs also should focus on the identification of suspicious skin lesions, such as by teaching the ABCDEs of melanoma.26 Among the general population, educational campaigns have been shown to be effective at reducing melanoma mortality.27,28
Access to Sun-Protective Gear
The second aspect of reducing skin cancer risk should be aiming to protect military servicemembers from UV exposure. Any prevention strategy must fit within the military’s broader tactical and strategic framework.
The use of photoprotective strategies rather than the outright avoidance of sun exposure should be implemented to minimize the deleterious effects of outdoor work. The most recent study of the UV-protective properties of US Military uniforms found all tested uniforms to have either very good or excellent UV protection, with UV protection factors (UPFs) ranging from 35 to 50+.29 However, this study was performed in 2002, and the majority of the uniforms tested are no longer in service. More up-to-date UPF information for existing military uniforms is not currently available. Most military commands wear baseball hat–style covers when operating outdoors, which generally provide good photoprotection with UPF ratings of 35 to 50 over the protected areas.29 Unfortunately, these types of headgear offer less photoprotection than do wide-brimmed hats, which have demonstrated improved photoprotection, particularly of the neck, cheeks, ears, and chin.30 A wide-brimmed hat, known as the boonie hat, was originally proposed for military use in 1966 to provide protection of servicemembers’ faces and necks from the intense sun of Vietnam. Currently, the use of the boonie hat typically is prohibited for units not engaged in combat or combat-support roles and requires authorization by the unit-level commander.31 Because of its perception as “unmilitary appearing” by many unit commanders and its restriction of use to combat-related units, the boonie hat is not consistently used. Increasing the use of this type of wide-brimmed hat would be an important asset in decreasing chronic UV exposure in military servicemembers, particularly on those parts of the body where skin cancer occurrence is the greatest.32 Policies should be aimed at increasing the use of the boonie hat, both through expanding its availability to troops in non–combat-related fields and by encouraging unit commanders to authorize its use in their units.
Sunscreen Availability
Improving the use of sunscreen is another impactful strategy that could be undertaken to decrease the risk for skin cancer in military servicemembers. The use of sunscreen is low in both those deployed overseas and those stationed within the United States. Improving access to sunscreen, particularly in the deployed setting, also could reduce barriers to use. Providing sunscreen directly to servicemembers, either when issuing gear or integrated within Meals Ready to Eat, could remove both the financial and logistical barriers to sunscreen utilization. Centralized troop-gathering locations, such as dining facilities, could be utilized both for the mass distribution of sunscreen and to display educational material. Unit commanders also could mandate times for servicemembers to stop work and apply sunscreen at regularly scheduled intervals.
The composition and delivery vehicle of sunscreen may have an impact on its efficacy and ease of use in the field. The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) recommends using sunscreen that is broad spectrum, sun protection factor (SPF) 30 or greater, and water resistant.33 However, the AAD does not make a recommendation of whether to use a physical sunscreen (such as titanium dioxide) or a chemical sunscreen. If applied in equal amounts, a chemical sunscreen and a physical sunscreen with an equal SPF should offer the same UV protection. However, a study in the British Journal of Dermatology showed that subjects applied only two-thirds the quantity of physical sunscreen compared to those applying chemical sunscreen, achieving approximately only one-half the SPF as provided by the chemical sunscreen.34 Because sunscreen is only effective when it is used, consideration should be given to the preferences of the military population when selecting sunscreens. A review of consumer preferences of sunscreen qualities showed that sunscreens that were nongreasy and did not leave a residue were given the most favorable rankings.35 In recent years, sunscreen sprays have become increasingly popular. When adequately applied, sprays have been shown to be equally effective as sunscreen lotions.36 However, although recommendations have been issued by both the AAD and the US Food and Drug Administration on the application of sunscreen lotion to adequately cover exposed skin, no such recommendations have been given for sunscreen sprays.33 Some safety concerns also remain regarding the flammability of aerosol sunscreens, which could be exacerbated in a combat situation.37
However, there are some obvious downsides to sunscreen use. During certain operational tasks, particularly in combat settings, it may not be feasible or even safe to stop working to apply sunscreen at the 2-hour intervals required for effective UV protection.38 Water exposure or large amounts of perspiration also would cause sunscreen to lose effectiveness earlier than expected. Logistically, it may be challenging to regularly supply sunscreen to small austere bases in remote locations.
Final Thoughts
The men and women of our armed forces already undertake great risk in the defense of our country. It should be ensured that their risk for developing skin cancer is made as low as possible, while still allowing them to successfully accomplish their mission. Multiple studies have shown servicemembers to be at an increased risk for skin cancer, particularly melanoma. We believe the primary factor behind this increased risk is occupational UV exposure, which is compounded by the suboptimal use of sun-protective strategies. By educating our servicemembers about their risk for skin cancer and promoting increased UV protection, we can effectively reduce the burden of skin cancer on our active-duty servicemembers and veterans.
There are numerous intrinsic risks that military servicemembers face, such as the dangers of combat, handling firearms, operating ships and heavy machinery, undersea diving, and aircraft operations. Multiple studies also have identified an increased risk for melanomas and keratinocyte cancers in those who have served on active duty.
Epidemiology
Differences in demographics are important to consider given the differences among races in the risks of skin cancers. Important racial demographic differences exist between the US Military and the general US population. Racial demographic differences also exist among the various military branches themselves. The US population is 61.0% White, 20.7% racial minorities (defined as Black or African American, Asian, American Indian or Alaska native, Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander, multiracial, or unknown), and 18.3% Hispanic or Latino (Hispanic or Latino was not listed as a component of racial minorities).1 According to 2018 data, the US Military population is 52.9% White, 31.0% racial minorities, and 16.1% Hispanic or Latino.2 The percentage of White military members was highest in the US Marine Corps (58.4%) and lowest in the US Navy (46.5%). The percentage of racial minorities was highest in the US Navy (38.0%) and lowest in the US Marine Corps (20.0%).2 The percentage of Hispanic and Latino military members was highest in the US Marine Corps (21.6%) and lowest in the US Air Force (14.5%).2
Melanoma in Military Members
It is estimated that the annual incidence rate of melanoma in the United States is 27 per 100,000 individuals for non-Hispanic Whites, 5 per 100,000 for Hispanics, and 1 per 100,000 for Black individuals and Asians/Pacific Islanders.3 Three studies have reviewed melanoma incidence in relation to service in the US Military.
A 2011 retrospective tumor registries study of US veterans aged 45 years or older demonstrated increased incidences of melanoma compared with the general population.4 With age, the melanoma incidence per 100,000 person-years increased in White veterans compared to their civilian counterparts (aged 45 to 49 years, 33.62 vs 27.49; aged 50 to 54 years, 49.76 vs 32.18; aged 55 to 59 years, 178.48 vs 39.17).4 An increased melanoma incidence of 62% also was seen in active-duty servicemembers aged 18 to 56 years compared to their age-matched civilian peers in a 2014 retrospective cohort study.5
Melanoma rates also vary depending on military service branch. Across 3 separate studies, service in the US Air Force was associated with the highest risk for melanoma development. A surveillance report of cancer incidence in active-duty US Armed Forces personnel between 2000 and 2011 conducted by the Defense Medical Surveillance System showed an incidence rate (per 100,000 person-years) for melanoma of 10.5 in all services, and a rate of 15.5 in the US Air Force vs 8.6 in the US Army, further highlighting the disparity between the services.6 The 2014 study also demonstrated a melanoma incidence rate of 17.80 in active-duty
Keratinocyte Cancers in Military Members
Although less well studied than melanoma, keratinocyte-derived skin cancers represent a major source of disease burden both during and after active-duty service. In a retrospective chart review of dermatology patients seen at the 86th Combat Support Hospital at Ibn Sina Hospital in Baghdad, Iraq, during a 6-month period in 2008, 8% of 2696 total visits were identified to be due to skin cancer, with the overwhelming majority being for keratinocyte cancers.7 A 1993 retrospective chart review of World War II veterans referred for Mohs micrographic surgery showed a considerably higher incidence in those who served in the Pacific Theater compared to those who served in the European Theater. Despite having approximately equal characteristics—age, skin type, and cumulative time spent outdoors—between the 2 groups, military servicemembers deployed to the Pacific represented 66% of the patients with basal cell carcinoma and 68% of the patients with squamous cell carcinoma.8
Contributing Factors
There are many factors related to military service that are likely to contribute to the increased risk for skin cancer. Based on a review of the literature, we have found an increased exposure to UV radiation, low utilization of sun-protective strategies, and low overall education regarding the risks for UV exposure to be the primary contributors to increased risks for skin cancer.
UV exposure is the primary mitigatable risk factor for developing melanoma and keratinocyte cancers.9,10 In a 2015 study of 212 military servicemembers returning from deployments in Iraq and Afghanistan, 77% reported spending more than 4 hours per day working directly in the bright sun, with 64% spending more than 75% of the average day in the bright sun.11 A 1984 study of World War II veterans diagnosed with melanoma also showed that 34% of those with melanoma had prior deployments to the tropics compared to 6% in age-matched controls.12
Even in those not deployed to overseas locations, military work still frequently involves prolonged sun exposure. In a 2015 cross-sectional study of US Air Force maintenance squadrons at Travis Air Force Base in Fairfield, California (N=356), 67% of those surveyed reported having careers that frequently involved direct sun exposure.13 This occupational sun exposure may be worsened by increased UV exposure during recreational activities, as active-duty military servicemembers may reasonably be expected to engage in more outdoor exercise and leisure activities than their civilian counterparts.
Other occupation-specific risk factors also may affect skin cancer rates in certain populations. In a study of aircraft personnel that included male military and civilian pilots, a meta-standardized incidence ratio for melanoma of 3.42 was identified compared to controls not involved in aircraft work.14 Theories to explain this increased incidence of melanoma include increased exposure to ionizing radiation at high altitudes, exposure to aviation-related chemicals, and alterations in circadian rhythm.14,15
This increased sun exposure is compounded by the overall low rates of sun protection among military members. Of those returning from Iraq and Afghanistan in the 2015 study, less than 30% of servicemembers reported routine access to sunscreen, and only 13% stated that they routinely applied sunscreen when exposed to the sun. Of this same group, only 23% endorsed that the military made them very aware of their risk for skin cancer.11 The low rates of sunscreen usage by those deployed to an active combat zone may partially be explained by the assumption that those individuals placed more emphasis on the acute dangers of combat rather than the perceived future dangers of skin cancer. A decreased availability of sunscreen for deployed military servicemembers, particularly those located at small austere bases where supplies are likely to be limited, likely makes the use of sunscreen even more difficult.
However, even within the continental United States, active-duty military servicemembers still exhibit low rates of sunscreen usage. In the 2015 study of US Air Force personnel in maintenance squadrons in California, less than 11% of those surveyed reported using sunscreen most of the time despite high rates of outdoor work.13
Another factor likely contributing to increased sun exposure and decreased sun-protection practices is the so-called invincibility complex, which is a common set of egocentric beliefs that leads to a perception that an individual is not likely to suffer the consequences of engaging in risky behaviors. Despite knowledge of the dangers associated with risky activity, individuals with an invincibility complex are more likely to view potential consequences as relevant only to others, not to themselves.16 A study of adolescent smokers in the Netherlands examined why subjects continue to smoke, despite knowledge of the potentially deadly consequences of smoking. Three common rationalizing beliefs were found: trivialization of the immediate consequences, that their smoking is only temporary and they have time in the future to stop, and that they have control over how much they smoke and can prevent fatal consequences with moderation.17 Such an invincibility complex is thought to directly run counter to the efforts of public health and educational campaigns. This belief set is thought to at least partially explain why adolescents in Australia are the most knowledgeable age cohort regarding the dangers of UV exposure but the least likely to engage in skin-protective measures.18 This inflated sense of invincibility may be leading active-duty military servicemembers to engage in unhealthy sun-exposure practices regardless of knowledge of the associated risks.
Members of the military may be uniquely susceptible to this invincibility complex. Growing evidence suggests that exposure to life-threatening circumstances may lead to long-lasting alterations in threat assessment.19,20 A 2008 study of Iraq veterans returning from deployment found that direct exposure to violent combat and human trauma was associated with an increased perceived degree of invincibility and a higher propensity to engage in risky behaviors after returning from deployment.19 Additionally, it has been speculated that individuals with a higher degree of perceived invincibility may be more likely to pursue military service, as a higher degree of self-confidence in the face of the often dangerous circumstances of military operations may be advantageous.20
In addition to scarce use of sun-protective strategies, military servicemembers also tend to lack awareness of the potential short-term and long-term harm from UV radiation. In a 2016 study of veterans undergoing treatment for skin cancer, patients reported inadequate education about skin cancer risks and strategies to decrease their chances of developing it.21 Sunscreen is less frequently used in males, specifically those aged 18 to 30 years; this demographic makes up 55.7% of the active-duty population.2,22 Low income also has been associated with decreased sunscreen use; junior enlisted military servicemembers (ranks E1-E4) make up 43.8% of the military’s ranks and make less than the average annual American household income.2,23,24
Prevention and Risk-Mitigation Strategies
Although many of the risk factors in the US Military promoting skin cancer are intrinsic to the occupation, certain steps could help minimize servicemembers’ risks. To be effective, any attempt to decrease the risk for skin cancer in the US Military must take into consideration the environment in which the military operates. To complete their mission, military personnel often are required to operate for extended periods outdoors in areas of high UV exposure, such as the deserts of Iraq or the mountains of Afghanistan. Outdoor work at times of peak sunlight often is required for successful mission completion, thus it would be ineffective to simply give blanket advice to avoid sun exposure.
Another important factor is the impact that official policy plays in shaping the daily actions of individual military servicemembers. In a hierarchical organization such as the US Military, unit commanders have substantial authority over the behaviors of their subordinates. Thus, strategies to mitigate skin cancer risks should be aimed at the individual servicemembers and unit commanders and at a policy level. Ultimately, a 3-pronged approach built on education, access to sun-protective gear, and increased availability to sunscreen is recommended.
Education
The foundation for any skin cancer prevention strategies should be built on the education of individual military servicemembers. The majority of active-duty members and veterans did not believe the military did enough to actively educate them on the risks for developing skin cancer.21 An effective educational program should focus on prevention and detection. Prevention programs should explain the role of UV exposure in the development of skin cancer, the intrinsic risks of UV exposure associated with outdoor activities, and strategies that can be implemented to reduce UV exposure and lifetime risk of skin cancer development. In a study of German outdoor workers, displays of support and concern by management regarding UV protection were associated with increases in sun-protective behaviors among the employees.25
Because patient self-examinations have been shown to be associated with earlier melanoma diagnosis and a more superficial depth at diagnosis, detection programs also should focus on the identification of suspicious skin lesions, such as by teaching the ABCDEs of melanoma.26 Among the general population, educational campaigns have been shown to be effective at reducing melanoma mortality.27,28
Access to Sun-Protective Gear
The second aspect of reducing skin cancer risk should be aiming to protect military servicemembers from UV exposure. Any prevention strategy must fit within the military’s broader tactical and strategic framework.
The use of photoprotective strategies rather than the outright avoidance of sun exposure should be implemented to minimize the deleterious effects of outdoor work. The most recent study of the UV-protective properties of US Military uniforms found all tested uniforms to have either very good or excellent UV protection, with UV protection factors (UPFs) ranging from 35 to 50+.29 However, this study was performed in 2002, and the majority of the uniforms tested are no longer in service. More up-to-date UPF information for existing military uniforms is not currently available. Most military commands wear baseball hat–style covers when operating outdoors, which generally provide good photoprotection with UPF ratings of 35 to 50 over the protected areas.29 Unfortunately, these types of headgear offer less photoprotection than do wide-brimmed hats, which have demonstrated improved photoprotection, particularly of the neck, cheeks, ears, and chin.30 A wide-brimmed hat, known as the boonie hat, was originally proposed for military use in 1966 to provide protection of servicemembers’ faces and necks from the intense sun of Vietnam. Currently, the use of the boonie hat typically is prohibited for units not engaged in combat or combat-support roles and requires authorization by the unit-level commander.31 Because of its perception as “unmilitary appearing” by many unit commanders and its restriction of use to combat-related units, the boonie hat is not consistently used. Increasing the use of this type of wide-brimmed hat would be an important asset in decreasing chronic UV exposure in military servicemembers, particularly on those parts of the body where skin cancer occurrence is the greatest.32 Policies should be aimed at increasing the use of the boonie hat, both through expanding its availability to troops in non–combat-related fields and by encouraging unit commanders to authorize its use in their units.
Sunscreen Availability
Improving the use of sunscreen is another impactful strategy that could be undertaken to decrease the risk for skin cancer in military servicemembers. The use of sunscreen is low in both those deployed overseas and those stationed within the United States. Improving access to sunscreen, particularly in the deployed setting, also could reduce barriers to use. Providing sunscreen directly to servicemembers, either when issuing gear or integrated within Meals Ready to Eat, could remove both the financial and logistical barriers to sunscreen utilization. Centralized troop-gathering locations, such as dining facilities, could be utilized both for the mass distribution of sunscreen and to display educational material. Unit commanders also could mandate times for servicemembers to stop work and apply sunscreen at regularly scheduled intervals.
The composition and delivery vehicle of sunscreen may have an impact on its efficacy and ease of use in the field. The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) recommends using sunscreen that is broad spectrum, sun protection factor (SPF) 30 or greater, and water resistant.33 However, the AAD does not make a recommendation of whether to use a physical sunscreen (such as titanium dioxide) or a chemical sunscreen. If applied in equal amounts, a chemical sunscreen and a physical sunscreen with an equal SPF should offer the same UV protection. However, a study in the British Journal of Dermatology showed that subjects applied only two-thirds the quantity of physical sunscreen compared to those applying chemical sunscreen, achieving approximately only one-half the SPF as provided by the chemical sunscreen.34 Because sunscreen is only effective when it is used, consideration should be given to the preferences of the military population when selecting sunscreens. A review of consumer preferences of sunscreen qualities showed that sunscreens that were nongreasy and did not leave a residue were given the most favorable rankings.35 In recent years, sunscreen sprays have become increasingly popular. When adequately applied, sprays have been shown to be equally effective as sunscreen lotions.36 However, although recommendations have been issued by both the AAD and the US Food and Drug Administration on the application of sunscreen lotion to adequately cover exposed skin, no such recommendations have been given for sunscreen sprays.33 Some safety concerns also remain regarding the flammability of aerosol sunscreens, which could be exacerbated in a combat situation.37
However, there are some obvious downsides to sunscreen use. During certain operational tasks, particularly in combat settings, it may not be feasible or even safe to stop working to apply sunscreen at the 2-hour intervals required for effective UV protection.38 Water exposure or large amounts of perspiration also would cause sunscreen to lose effectiveness earlier than expected. Logistically, it may be challenging to regularly supply sunscreen to small austere bases in remote locations.
Final Thoughts
The men and women of our armed forces already undertake great risk in the defense of our country. It should be ensured that their risk for developing skin cancer is made as low as possible, while still allowing them to successfully accomplish their mission. Multiple studies have shown servicemembers to be at an increased risk for skin cancer, particularly melanoma. We believe the primary factor behind this increased risk is occupational UV exposure, which is compounded by the suboptimal use of sun-protective strategies. By educating our servicemembers about their risk for skin cancer and promoting increased UV protection, we can effectively reduce the burden of skin cancer on our active-duty servicemembers and veterans.
- QuickFacts. United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/PST045219
- 2018 Demographics Profile. Military OneSource. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.militaryonesource.mil/reports-and-surveys/infographics/active-duty-member-and-family-demographics
- Cancer Facts & Figures 2019. American Cancer Society. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/cancer-facts-figures-2019.html
- Zhou J, Enewold L, Zahm SH, et al. Melanoma incidence rates among whites in the U.S. Military. Cancer Epidemiol. 2011;20:318-323.
- Lea CS, Efird JT, Toland AE, et al. Melanoma incidence rates in active duty military personnel compared with a population-based registry in the United States, 2000-2007. Military Med. 2014;179:247-253.
- Armed Forces Health Surveillance Center. Incident diagnoses of cancers and cancer-related deaths, active component, US Armed Forces, 2000-2011. MSMR. 2012;19:18-22.
- Henning JS, Firoz BF. Combat dermatology: the prevalence of skin disease in a deployed dermatology clinic in Iraq. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:210-214.
- Ramani ML, Bennett RG. High prevalence of skin-cancer in World-War-II servicemen stationed in the Pacific Theater. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28:733-737.
- Schmitt J, Seidler A, Diepgen TL, et al. Occupational ultraviolet light exposure increases the risk for the development of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:291-307.
- Armstrong BK, Kricker A. The epidemiology of UV induced skin cancer. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2001;63:8-18.
- Powers JG, Patel NA, Powers EM, et al. Skin cancer risk factors and preventative behaviors among United States military veterans deployed to Iraq and Afghanistan. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:2871-2873.
- Brown J, Kopf AW, Rica DS, et al. Malignant melanoma in World War II veterans. Int J Dermatol. 1984;23:661-663.
- Parker G, Williams B, Driggers P. Sun exposure knowledge and practices survey of maintenance squadrons at Travis AFB. Military Med. 2015;180:26-31.
- Buja A, Lange JH, Perissinotto E, et al. Cancer incidence among male military and civil pilots and flight attendants: an analysis on published data. Toxicol Ind Health. 2005;21:273-282.
- Wilkison BD, Wong EB. Skin cancer in military pilots: a special population with special risk factors. Cutis. 2017;100:218-220.
- Wickman ME, Anderson NLR, Smith Greenberg C. The adolescent perception of invincibility and its influence on teen acceptance of health promotion strategies. J Pediatr Nurs. 2008;23:460-468.
- Schreuders M, Krooneman NT, van den Putte B, et al. Boy smokers’ rationalisations for engaging in potentially fatal behaviour: in-depth interviews in the Netherlands. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15:767.
- Eastabrook S, Chang P, Taylor MF. Melanoma risk: adolescent females’ perspectives on skin protection pre/post-viewing a ultraviolet photoaged photograph of their own facial sun damage. Glob Health Promot. 2018;25:23-32.
- Killgore WD, Cotting DI, Thomas JL, et al. Post-combat invincibility: violent combat experiences are associated with increased risk-taking propensity following deployment. J Psychiatr Res. 2008;42:1112-1121.
- Killgore WD, Kelley A, Balkin TJ. So you think you’re bulletproof: development and validation of the Invincibility Belief Index (IBI). Military Med. 2010;175:499-508.
- McGrath JM, Fisher V, Krejci-Manwaring J. Skin cancer warnings and the need for new preventive campaigns: a pilot study. Am J Prevent Med. 2016;50:E62-E63.
- Thieden E, Philipsen PA, Sandby-Moller J, et al. Sunscreen use related to UV exposure, age, sex, and occupation based on personal dosimeter readings and sun-exposure behavior diaries. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:967-973.
- Holman DM, Berkowitz Z, Guy GP Jr, et al. Patterns of sunscreen use on the face and other exposed skin among US adults. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:83-92.e1.
- Military Pay Tables & Information. Defense Finance and Accounting Service website. Accessed December 21, 2020. https://www.dfas.mil/militarymembers/payentitlements/Pay-Tables.html
- Schilling L, Schneider S, Gorig T, et al. “Lost in the sun”—the key role of perceived workplace support for sun-protective behavior in outdoor workers. Am J Ind Med. 2018;61:929-938.
- Uliasz A, Lebwohl M. Patient education and regular surveillance results in earlier diagnosis of second primary melanoma. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:575-577.
- MacKie RM, Hole D. Audit of public education campaign to encourage earlier detection of malignant melanoma. BMJ. 1992;304:1012-1015.
- Berwick M, Begg CB, Fine JA, et al. Screening for cutaneous melanoma by skin self-examination. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996;88:17-23.
- Winterhalter C, DiLuna K, Bide M. Characterization of the ultraviolet protection of combat uniform fabrics. US Army Soldier and Biological Chemical Command Soldier Systems Center technical report Natick/TR-02/006. Published January 21, 2002. Accessed December 21, 2021. https://apps.dtic.mil/dtic/tr/fulltext/u2/a398572.pdf
- Gies P, Javorniczky J, Roy C, et al. Measurements of the UVR protection provided by hats used at school. Photochem Photobiol. 2006;82:750-754.
- Stanton S. Headgear. In: Stanton S. US Army Uniforms of the Vietnam War. Stackpole Books; 1992:26-61.
- Richmond-Sinclair NM, Pandeya N, Ware RS, et al. Incidence of basal cell carcinoma multiplicity and detailed anatomic distribution: longitudinal study of an Australian population. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:323-328.
- How to select a sunscreen. American Academy of Dermatology. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.aad.org/sun-protection/how-to-select-sunscreen
- Diffey BL, Grice J. The influence of sunscreen type on photoprotection. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:103-105.
- Xu S, Kwa M, Agarwal A, et al. Sunscreen product performance and other determinants of consumer preferences. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:920-927.
- Ou-Yang H, Stanfield J, Cole C, et al. High-SPF sunscreens (SPF ≥ 70) may provide ultraviolet protection above minimal recommended levels by adequately compensating for lower sunscreen user application amounts. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:1220-1227.
- O’Connor A. Is sunscreen flammable? The New York Times. June 6, 2012. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://well.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/06/06/is-sunscreen-flammable/
- Prevent skin cancer. American Academy of Dermatology. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.aad.org/public/spot-skin-cancer/learn-about-skin-cancer/prevent
- QuickFacts. United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/PST045219
- 2018 Demographics Profile. Military OneSource. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.militaryonesource.mil/reports-and-surveys/infographics/active-duty-member-and-family-demographics
- Cancer Facts & Figures 2019. American Cancer Society. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/cancer-facts-figures-2019.html
- Zhou J, Enewold L, Zahm SH, et al. Melanoma incidence rates among whites in the U.S. Military. Cancer Epidemiol. 2011;20:318-323.
- Lea CS, Efird JT, Toland AE, et al. Melanoma incidence rates in active duty military personnel compared with a population-based registry in the United States, 2000-2007. Military Med. 2014;179:247-253.
- Armed Forces Health Surveillance Center. Incident diagnoses of cancers and cancer-related deaths, active component, US Armed Forces, 2000-2011. MSMR. 2012;19:18-22.
- Henning JS, Firoz BF. Combat dermatology: the prevalence of skin disease in a deployed dermatology clinic in Iraq. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:210-214.
- Ramani ML, Bennett RG. High prevalence of skin-cancer in World-War-II servicemen stationed in the Pacific Theater. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28:733-737.
- Schmitt J, Seidler A, Diepgen TL, et al. Occupational ultraviolet light exposure increases the risk for the development of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:291-307.
- Armstrong BK, Kricker A. The epidemiology of UV induced skin cancer. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2001;63:8-18.
- Powers JG, Patel NA, Powers EM, et al. Skin cancer risk factors and preventative behaviors among United States military veterans deployed to Iraq and Afghanistan. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:2871-2873.
- Brown J, Kopf AW, Rica DS, et al. Malignant melanoma in World War II veterans. Int J Dermatol. 1984;23:661-663.
- Parker G, Williams B, Driggers P. Sun exposure knowledge and practices survey of maintenance squadrons at Travis AFB. Military Med. 2015;180:26-31.
- Buja A, Lange JH, Perissinotto E, et al. Cancer incidence among male military and civil pilots and flight attendants: an analysis on published data. Toxicol Ind Health. 2005;21:273-282.
- Wilkison BD, Wong EB. Skin cancer in military pilots: a special population with special risk factors. Cutis. 2017;100:218-220.
- Wickman ME, Anderson NLR, Smith Greenberg C. The adolescent perception of invincibility and its influence on teen acceptance of health promotion strategies. J Pediatr Nurs. 2008;23:460-468.
- Schreuders M, Krooneman NT, van den Putte B, et al. Boy smokers’ rationalisations for engaging in potentially fatal behaviour: in-depth interviews in the Netherlands. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15:767.
- Eastabrook S, Chang P, Taylor MF. Melanoma risk: adolescent females’ perspectives on skin protection pre/post-viewing a ultraviolet photoaged photograph of their own facial sun damage. Glob Health Promot. 2018;25:23-32.
- Killgore WD, Cotting DI, Thomas JL, et al. Post-combat invincibility: violent combat experiences are associated with increased risk-taking propensity following deployment. J Psychiatr Res. 2008;42:1112-1121.
- Killgore WD, Kelley A, Balkin TJ. So you think you’re bulletproof: development and validation of the Invincibility Belief Index (IBI). Military Med. 2010;175:499-508.
- McGrath JM, Fisher V, Krejci-Manwaring J. Skin cancer warnings and the need for new preventive campaigns: a pilot study. Am J Prevent Med. 2016;50:E62-E63.
- Thieden E, Philipsen PA, Sandby-Moller J, et al. Sunscreen use related to UV exposure, age, sex, and occupation based on personal dosimeter readings and sun-exposure behavior diaries. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:967-973.
- Holman DM, Berkowitz Z, Guy GP Jr, et al. Patterns of sunscreen use on the face and other exposed skin among US adults. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:83-92.e1.
- Military Pay Tables & Information. Defense Finance and Accounting Service website. Accessed December 21, 2020. https://www.dfas.mil/militarymembers/payentitlements/Pay-Tables.html
- Schilling L, Schneider S, Gorig T, et al. “Lost in the sun”—the key role of perceived workplace support for sun-protective behavior in outdoor workers. Am J Ind Med. 2018;61:929-938.
- Uliasz A, Lebwohl M. Patient education and regular surveillance results in earlier diagnosis of second primary melanoma. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:575-577.
- MacKie RM, Hole D. Audit of public education campaign to encourage earlier detection of malignant melanoma. BMJ. 1992;304:1012-1015.
- Berwick M, Begg CB, Fine JA, et al. Screening for cutaneous melanoma by skin self-examination. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996;88:17-23.
- Winterhalter C, DiLuna K, Bide M. Characterization of the ultraviolet protection of combat uniform fabrics. US Army Soldier and Biological Chemical Command Soldier Systems Center technical report Natick/TR-02/006. Published January 21, 2002. Accessed December 21, 2021. https://apps.dtic.mil/dtic/tr/fulltext/u2/a398572.pdf
- Gies P, Javorniczky J, Roy C, et al. Measurements of the UVR protection provided by hats used at school. Photochem Photobiol. 2006;82:750-754.
- Stanton S. Headgear. In: Stanton S. US Army Uniforms of the Vietnam War. Stackpole Books; 1992:26-61.
- Richmond-Sinclair NM, Pandeya N, Ware RS, et al. Incidence of basal cell carcinoma multiplicity and detailed anatomic distribution: longitudinal study of an Australian population. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:323-328.
- How to select a sunscreen. American Academy of Dermatology. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.aad.org/sun-protection/how-to-select-sunscreen
- Diffey BL, Grice J. The influence of sunscreen type on photoprotection. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:103-105.
- Xu S, Kwa M, Agarwal A, et al. Sunscreen product performance and other determinants of consumer preferences. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:920-927.
- Ou-Yang H, Stanfield J, Cole C, et al. High-SPF sunscreens (SPF ≥ 70) may provide ultraviolet protection above minimal recommended levels by adequately compensating for lower sunscreen user application amounts. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:1220-1227.
- O’Connor A. Is sunscreen flammable? The New York Times. June 6, 2012. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://well.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/06/06/is-sunscreen-flammable/
- Prevent skin cancer. American Academy of Dermatology. Accessed December 15, 2020. https://www.aad.org/public/spot-skin-cancer/learn-about-skin-cancer/prevent
Practice Points
- An increased risk for melanoma and keratinocyte carcinomas has been identified in those who have served in the US Military.
- UV radiation exposure, low utilization of sun-protective strategies, and low overall education regarding the risks of UV exposure appear to be the primary contributors to increased risks of skin cancer in this population.
- Improving education for military servicemembers on the risks of UV exposure, increasing utilization of sun-protective clothing, and improving access and utilization of sunscreen are viable options to decrease the risk for cutaneous malignancies in US Military servicemembers.
COVID-19 vaccines and cancer patients: 4 things to know
Earlier this week, Medscape spoke with Nora Disis, MD, about vaccinating cancer patients. Disis is a medical oncologist and director of both the Institute of Translational Health Sciences and the Cancer Vaccine Institute, the University of Washington, Seattle, Washington. As editor-in-chief of JAMA Oncology, she has watched COVID-19 developments in the oncology community over the past year.
Here are a few themes that Disis said oncologists should be aware of as vaccines eventually begin reaching cancer patients.
We should expect cancer patients to respond to vaccines. Historically, some believed that cancer patients would be unable to mount an immune response to vaccines. Data on other viral vaccines have shown otherwise. For example, there has been a long history of studies of flu vaccination in cancer patients, and in general, those vaccines confer protection. Likewise for pneumococcal vaccine, which, generally speaking, cancer patients should receive.
Special cases may include hematologic malignancies in which the immune system has been destroyed and profound immunosuppression occurs. Data on immunization during this immunosuppressed period are scarce, but what data are available suggest that once cancer patients are through this immunosuppressed period, they can be vaccinated successfully.
The type of vaccine will probably be important for cancer patients. Currently, there are 61 coronavirus vaccines in human clinical trials, and 17 have reached the final stages of testing. At least 85 preclinical vaccines are under active investigation in animals.
Both the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna COVID vaccines are mRNA type. There are many other types, including protein-based vaccines, viral vector vaccines based on adenoviruses, and inactivated or attenuated coronavirus vaccines.
The latter vaccines, particularly attenuated live virus vaccines, may not be a good choice for cancer patients. Especially in those with rapidly progressing disease or on chemotherapy, attenuated live viruses may cause a low-grade infection.
Incidentally, the technology used in the genetic, or mRNA, vaccines developed by both Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna was initially developed for fighting cancer, and studies have shown that patients can generate immune responses to cancer-associated proteins with this type of vaccine.
These genetic vaccines could turn out to be the most effective for cancer patients, especially those with solid tumors.
Our understanding is very limited right now. Neither the Pfizer-BioNTech nor the Moderna early data discuss cancer patients. Two of the most important questions for cancer patients are dosing and booster scheduling. Potential defects in lymphocyte function among cancer patients may require unique initial dosing and booster schedules. In terms of timing, it is unclear how active therapy might affect a patient’s immune response to vaccination and whether vaccines should be timed with therapy cycles.
Vaccine access may depend on whether cancer patients are viewed as a vulnerable population. Those at higher risk for severe COVID-19 clearly have a greater need for vaccination. While there are data suggesting that cancer patients are at higher risk, they are a bit murky, in part because cancer patients are a heterogeneous group. For example, there are data suggesting that lung and blood cancer patients fare worse. There is also a suggestion that, like in the general population, COVID risk in cancer patients remains driven by comorbidities.
It is likely, then, that personalized risk factors such as type of cancer therapy, site of disease, and comorbidities will shape individual choices about vaccination among cancer patients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Earlier this week, Medscape spoke with Nora Disis, MD, about vaccinating cancer patients. Disis is a medical oncologist and director of both the Institute of Translational Health Sciences and the Cancer Vaccine Institute, the University of Washington, Seattle, Washington. As editor-in-chief of JAMA Oncology, she has watched COVID-19 developments in the oncology community over the past year.
Here are a few themes that Disis said oncologists should be aware of as vaccines eventually begin reaching cancer patients.
We should expect cancer patients to respond to vaccines. Historically, some believed that cancer patients would be unable to mount an immune response to vaccines. Data on other viral vaccines have shown otherwise. For example, there has been a long history of studies of flu vaccination in cancer patients, and in general, those vaccines confer protection. Likewise for pneumococcal vaccine, which, generally speaking, cancer patients should receive.
Special cases may include hematologic malignancies in which the immune system has been destroyed and profound immunosuppression occurs. Data on immunization during this immunosuppressed period are scarce, but what data are available suggest that once cancer patients are through this immunosuppressed period, they can be vaccinated successfully.
The type of vaccine will probably be important for cancer patients. Currently, there are 61 coronavirus vaccines in human clinical trials, and 17 have reached the final stages of testing. At least 85 preclinical vaccines are under active investigation in animals.
Both the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna COVID vaccines are mRNA type. There are many other types, including protein-based vaccines, viral vector vaccines based on adenoviruses, and inactivated or attenuated coronavirus vaccines.
The latter vaccines, particularly attenuated live virus vaccines, may not be a good choice for cancer patients. Especially in those with rapidly progressing disease or on chemotherapy, attenuated live viruses may cause a low-grade infection.
Incidentally, the technology used in the genetic, or mRNA, vaccines developed by both Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna was initially developed for fighting cancer, and studies have shown that patients can generate immune responses to cancer-associated proteins with this type of vaccine.
These genetic vaccines could turn out to be the most effective for cancer patients, especially those with solid tumors.
Our understanding is very limited right now. Neither the Pfizer-BioNTech nor the Moderna early data discuss cancer patients. Two of the most important questions for cancer patients are dosing and booster scheduling. Potential defects in lymphocyte function among cancer patients may require unique initial dosing and booster schedules. In terms of timing, it is unclear how active therapy might affect a patient’s immune response to vaccination and whether vaccines should be timed with therapy cycles.
Vaccine access may depend on whether cancer patients are viewed as a vulnerable population. Those at higher risk for severe COVID-19 clearly have a greater need for vaccination. While there are data suggesting that cancer patients are at higher risk, they are a bit murky, in part because cancer patients are a heterogeneous group. For example, there are data suggesting that lung and blood cancer patients fare worse. There is also a suggestion that, like in the general population, COVID risk in cancer patients remains driven by comorbidities.
It is likely, then, that personalized risk factors such as type of cancer therapy, site of disease, and comorbidities will shape individual choices about vaccination among cancer patients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Earlier this week, Medscape spoke with Nora Disis, MD, about vaccinating cancer patients. Disis is a medical oncologist and director of both the Institute of Translational Health Sciences and the Cancer Vaccine Institute, the University of Washington, Seattle, Washington. As editor-in-chief of JAMA Oncology, she has watched COVID-19 developments in the oncology community over the past year.
Here are a few themes that Disis said oncologists should be aware of as vaccines eventually begin reaching cancer patients.
We should expect cancer patients to respond to vaccines. Historically, some believed that cancer patients would be unable to mount an immune response to vaccines. Data on other viral vaccines have shown otherwise. For example, there has been a long history of studies of flu vaccination in cancer patients, and in general, those vaccines confer protection. Likewise for pneumococcal vaccine, which, generally speaking, cancer patients should receive.
Special cases may include hematologic malignancies in which the immune system has been destroyed and profound immunosuppression occurs. Data on immunization during this immunosuppressed period are scarce, but what data are available suggest that once cancer patients are through this immunosuppressed period, they can be vaccinated successfully.
The type of vaccine will probably be important for cancer patients. Currently, there are 61 coronavirus vaccines in human clinical trials, and 17 have reached the final stages of testing. At least 85 preclinical vaccines are under active investigation in animals.
Both the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna COVID vaccines are mRNA type. There are many other types, including protein-based vaccines, viral vector vaccines based on adenoviruses, and inactivated or attenuated coronavirus vaccines.
The latter vaccines, particularly attenuated live virus vaccines, may not be a good choice for cancer patients. Especially in those with rapidly progressing disease or on chemotherapy, attenuated live viruses may cause a low-grade infection.
Incidentally, the technology used in the genetic, or mRNA, vaccines developed by both Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna was initially developed for fighting cancer, and studies have shown that patients can generate immune responses to cancer-associated proteins with this type of vaccine.
These genetic vaccines could turn out to be the most effective for cancer patients, especially those with solid tumors.
Our understanding is very limited right now. Neither the Pfizer-BioNTech nor the Moderna early data discuss cancer patients. Two of the most important questions for cancer patients are dosing and booster scheduling. Potential defects in lymphocyte function among cancer patients may require unique initial dosing and booster schedules. In terms of timing, it is unclear how active therapy might affect a patient’s immune response to vaccination and whether vaccines should be timed with therapy cycles.
Vaccine access may depend on whether cancer patients are viewed as a vulnerable population. Those at higher risk for severe COVID-19 clearly have a greater need for vaccination. While there are data suggesting that cancer patients are at higher risk, they are a bit murky, in part because cancer patients are a heterogeneous group. For example, there are data suggesting that lung and blood cancer patients fare worse. There is also a suggestion that, like in the general population, COVID risk in cancer patients remains driven by comorbidities.
It is likely, then, that personalized risk factors such as type of cancer therapy, site of disease, and comorbidities will shape individual choices about vaccination among cancer patients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How should we evaluate the benefit of immunotherapy combinations?
Every medical oncologist who has described a combination chemotherapy regimen to a patient with advanced cancer has likely been asked whether the benefits of tumor shrinkage, disease-free survival (DFS), and overall survival are worth the risks of adverse events (AEs).
Single-agent immunotherapy and, more recently, combinations of immunotherapy drugs have been approved for a variety of metastatic tumors. In general, combination immunotherapy regimens have more AEs and a higher frequency of premature treatment discontinuation for toxicity.
Michael Postow, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, reflected on new ways to evaluate the benefits and risks of immunotherapy combinations during a plenary session on novel combinations at the American Association for Cancer Research’s Virtual Special Conference on Tumor Immunology and Immunotherapy.
Potential targets
As with chemotherapy drugs, immunotherapy combinations make the most sense when drugs targeting independent processes are employed.
As described in a paper published in Nature in 2011, the process for recruiting the immune system to combat cancer is as follows:
- Dendritic cells must sample antigens derived from the tumor.
- The dendritic cells must receive an activation signal so they promote immunity rather than tolerance.
- The tumor antigen–loaded dendritic cells need to generate protective T-cell responses, instead of T-regulatory responses, in lymphoid tissues.
- Cancer antigen–specific T cells must enter tumor tissues.
- Tumor-derived mechanisms for promoting immunosuppression need to be circumvented.
Since each step in the cascade is a potential therapeutic target, there are large numbers of potential drug combinations.
Measuring impact
Conventional measurements of tumor response may not be adequately sensitive to the impact from immunotherapy drugs. A case in point is sipuleucel-T, which is approved to treat advanced prostate cancer.
In the pivotal phase 3 trial, only 1 of 341 patients receiving sipuleucel-T achieved a partial response by RECIST criteria. Only 2.6% of patients had a 50% reduction in prostate-specific antigen levels. Nonetheless, a 4.1-month improvement in median overall survival was achieved. These results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The discrepancy between tumor shrinkage and survival benefit for immunotherapy is not unexpected. As many as 10% of patients treated with ipilimumab (ipi) for stage IV malignant melanoma have progressive disease by tumor size but experience prolongation of survival, according to guidelines published in Clinical Cancer Research.
Accurate assessment of the ultimate efficacy of immunotherapy over time would benefit patients and clinicians since immune checkpoint inhibitors are often administered for several years, are financially costly, and treatment-associated AEs emerge unpredictably at any time.
Curtailing the duration of ineffective treatment could be valuable from many perspectives.
Immunotherapy combinations in metastatic melanoma
In the CheckMate 067 study, there was an improvement in response, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival for nivolumab (nivo) plus ipi or nivo alone, in comparison with ipi alone, in patients with advanced melanoma. Initial results from this trial were published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2017.
At a minimum follow-up of 60 months, the 5-year overall survival was 52% for the nivo/ipi regimen, 44% for nivo alone, and 26% for ipi alone. These results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2019.
The trial was not statistically powered to conclude whether the overall survival for the combination was superior to that of single-agent nivo alone, but both nivo regimens were superior to ipi alone.
Unfortunately, the combination also produced the highest treatment-related AE rates – 59% with nivo/ipi, 23% with nivo, and 28% with ipi in 2019. In the 2017 report, the combination regimen had more than twice as many premature treatment discontinuations as the other two study arms.
Is there a better way to quantify the risk-benefit ratio and explain it to patients?
Alternative strategies for assessing benefit: Treatment-free survival
Researchers have proposed treatment-free survival (TFS) as a potential new metric to characterize not only antitumor activity but also toxicity experienced after the cessation of therapy and before initiation of subsequent systemic therapy or death.
TFS is defined as the area between Kaplan-Meier curves from immunotherapy cessation until the reinitiation of systemic therapy or death. All patients who began immunotherapy are included – not just those achieving response or concluding a predefined number of cycles of treatment.
The curves can be partitioned into states with and without toxicity to establish a unique endpoint: time to cessation of both immunotherapy and toxicity.
Researchers conducted a pooled analysis of 3-year follow-up data from the 1,077 patients who participated in CheckMate 069, testing nivo/ipi versus nivo alone, and CheckMate 067, comparing nivo/ipi, nivo alone, and ipi alone. The results were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The TFS without grade 3 or higher AEs was 28% for nivo/ipi, 11% for nivo alone, and 23% for ipi alone. The restricted mean time without either treatment or grade 3 or greater AEs was 10.1 months, 4.1 months, and 8.5 months, respectively.
TFS incentivizes the use of regimens that have:
- A short duration of treatment
- Prolonged time to subsequent therapy or death
- Only mild AEs of brief duration.
A higher TFS corresponds with the goals that patients and their providers would have for a treatment regimen.
Adaptive models provide clues about benefit from extended therapy
In contrast to cytotoxic chemotherapy and molecularly targeted agents, benefit from immune-targeted therapy can deepen and persist after treatment discontinuation.
In advanced melanoma, researchers observed that overall survival was similar for patients who discontinued nivo/ipi because of AEs during the induction phase of treatment and those who did not. These results were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
This observation has led to an individualized, adaptive approach to de-escalating combination immunotherapy, described in Clinical Cancer Research. The approach is dubbed “SMART,” which stands for sequential multiple assignment randomized trial designs.
With the SMART approach, each stage of a trial corresponds to an important treatment decision point. The goal is to define the population of patients who can safely discontinue treatment based on response, rather than doing so after the development of AEs.
In the Adapt-IT prospective study, 60 patients with advanced melanoma with poor prognostic features were given two doses of nivo/ipi followed by a CT scan at week 6. They were triaged to stopping ipi and proceeding with maintenance therapy with nivo alone or continuing the combination for an additional two cycles of treatment. Results from this trial were presented at ASCO 2020 (abstract 10003).
The investigators found that 68% of patients had no tumor burden increase at week 6 and could discontinue ipi. For those patients, their response rate of 57% approached the expected results from a full course of ipi.
At median follow-up of 22.3 months, median response duration, PFS, and overall survival had not been reached for the responders who received an abbreviated course of the combination regimen.
There were two observations that suggested the first two cycles of treatment drove not only toxicity but also tumor control:
- The rate of grade 3-4 toxicity from only two cycles was high (57%).
- Of the 19 patients (32% of the original 60 patients) who had progressive disease after two cycles of nivo/ipi, there were no responders with continued therapy.
Dr. Postow commented that, in correlative studies conducted as part of Adapt-IT, the Ki-67 of CD8-positive T cells increased after the initial dose of nivo/ipi. However, proliferation did not continue with subsequent cycles (that is, Ki-67 did not continue to rise).
When they examined markers of T-cell stimulation such as inducible costimulator of CD8-positive T cells, the researchers observed the same effect. The “immune boost” occurred with cycle one but not after subsequent doses of the nivo/ipi combination.
Although unproven in clinical trials at this time, these data suggest that response and risks of toxicity may not support giving patients more than one cycle of combination treatment.
More nuanced ways of assessing tumor growth
Dr. Postow noted that judgment about treatment effects over time are often made by displaying spider plots of changes from baseline tumor size from “time zero” – the time at which combination therapy is commenced.
He speculated that it might be worthwhile to give a dose or two of immune-targeted monotherapy (such as a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor alone) before time zero, measure tumor growth prior to and after the single agent, and reserve using combination immunotherapy only for those patients who do not experience a dampening of the growth curve.
Patients whose tumor growth kinetics are improved with single-agent treatment could be spared the additional toxicity (and uncertain additive benefit) from the second agent.
Treatment optimization: More than ‘messaging’
Oncology practice has passed through a long era of “more is better,” an era that gave rise to intensive cytotoxic chemotherapy for hematologic and solid tumors in the metastatic and adjuvant settings. In some cases, that approach proved to be curative, but not in all.
More recently, because of better staging, improved outcomes with newer technology and treatments, and concern about immediate- and late-onset health risks, there has been an effort to deintensify therapy when it can be done safely.
Once a treatment regimen and treatment duration become established, however, patients and their physicians are reluctant to deintensity therapy.
Dr. Postow’s presentation demonstrated that, with regard to immunotherapy combinations – as in other realms of medical practice – science can lead the way to treatment optimization for individual patients.
We have the potential to reassure patients that treatment de-escalation is a rational and personalized component of treatment optimization through the combination of:
- Identifying new endpoints to quantify treatment benefits and risks.
- SMART trial designs.
- Innovative ways to assess tumor response during each phase of a treatment course.
Precision assessment of immunotherapy effect in individual patients can be a key part of precision medicine.
Dr. Postow disclosed relationships with Aduro, Array BioPharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Incyte, Infinity, Merck, NewLink Genetics, Novartis, and RGenix.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
Every medical oncologist who has described a combination chemotherapy regimen to a patient with advanced cancer has likely been asked whether the benefits of tumor shrinkage, disease-free survival (DFS), and overall survival are worth the risks of adverse events (AEs).
Single-agent immunotherapy and, more recently, combinations of immunotherapy drugs have been approved for a variety of metastatic tumors. In general, combination immunotherapy regimens have more AEs and a higher frequency of premature treatment discontinuation for toxicity.
Michael Postow, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, reflected on new ways to evaluate the benefits and risks of immunotherapy combinations during a plenary session on novel combinations at the American Association for Cancer Research’s Virtual Special Conference on Tumor Immunology and Immunotherapy.
Potential targets
As with chemotherapy drugs, immunotherapy combinations make the most sense when drugs targeting independent processes are employed.
As described in a paper published in Nature in 2011, the process for recruiting the immune system to combat cancer is as follows:
- Dendritic cells must sample antigens derived from the tumor.
- The dendritic cells must receive an activation signal so they promote immunity rather than tolerance.
- The tumor antigen–loaded dendritic cells need to generate protective T-cell responses, instead of T-regulatory responses, in lymphoid tissues.
- Cancer antigen–specific T cells must enter tumor tissues.
- Tumor-derived mechanisms for promoting immunosuppression need to be circumvented.
Since each step in the cascade is a potential therapeutic target, there are large numbers of potential drug combinations.
Measuring impact
Conventional measurements of tumor response may not be adequately sensitive to the impact from immunotherapy drugs. A case in point is sipuleucel-T, which is approved to treat advanced prostate cancer.
In the pivotal phase 3 trial, only 1 of 341 patients receiving sipuleucel-T achieved a partial response by RECIST criteria. Only 2.6% of patients had a 50% reduction in prostate-specific antigen levels. Nonetheless, a 4.1-month improvement in median overall survival was achieved. These results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The discrepancy between tumor shrinkage and survival benefit for immunotherapy is not unexpected. As many as 10% of patients treated with ipilimumab (ipi) for stage IV malignant melanoma have progressive disease by tumor size but experience prolongation of survival, according to guidelines published in Clinical Cancer Research.
Accurate assessment of the ultimate efficacy of immunotherapy over time would benefit patients and clinicians since immune checkpoint inhibitors are often administered for several years, are financially costly, and treatment-associated AEs emerge unpredictably at any time.
Curtailing the duration of ineffective treatment could be valuable from many perspectives.
Immunotherapy combinations in metastatic melanoma
In the CheckMate 067 study, there was an improvement in response, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival for nivolumab (nivo) plus ipi or nivo alone, in comparison with ipi alone, in patients with advanced melanoma. Initial results from this trial were published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2017.
At a minimum follow-up of 60 months, the 5-year overall survival was 52% for the nivo/ipi regimen, 44% for nivo alone, and 26% for ipi alone. These results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2019.
The trial was not statistically powered to conclude whether the overall survival for the combination was superior to that of single-agent nivo alone, but both nivo regimens were superior to ipi alone.
Unfortunately, the combination also produced the highest treatment-related AE rates – 59% with nivo/ipi, 23% with nivo, and 28% with ipi in 2019. In the 2017 report, the combination regimen had more than twice as many premature treatment discontinuations as the other two study arms.
Is there a better way to quantify the risk-benefit ratio and explain it to patients?
Alternative strategies for assessing benefit: Treatment-free survival
Researchers have proposed treatment-free survival (TFS) as a potential new metric to characterize not only antitumor activity but also toxicity experienced after the cessation of therapy and before initiation of subsequent systemic therapy or death.
TFS is defined as the area between Kaplan-Meier curves from immunotherapy cessation until the reinitiation of systemic therapy or death. All patients who began immunotherapy are included – not just those achieving response or concluding a predefined number of cycles of treatment.
The curves can be partitioned into states with and without toxicity to establish a unique endpoint: time to cessation of both immunotherapy and toxicity.
Researchers conducted a pooled analysis of 3-year follow-up data from the 1,077 patients who participated in CheckMate 069, testing nivo/ipi versus nivo alone, and CheckMate 067, comparing nivo/ipi, nivo alone, and ipi alone. The results were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The TFS without grade 3 or higher AEs was 28% for nivo/ipi, 11% for nivo alone, and 23% for ipi alone. The restricted mean time without either treatment or grade 3 or greater AEs was 10.1 months, 4.1 months, and 8.5 months, respectively.
TFS incentivizes the use of regimens that have:
- A short duration of treatment
- Prolonged time to subsequent therapy or death
- Only mild AEs of brief duration.
A higher TFS corresponds with the goals that patients and their providers would have for a treatment regimen.
Adaptive models provide clues about benefit from extended therapy
In contrast to cytotoxic chemotherapy and molecularly targeted agents, benefit from immune-targeted therapy can deepen and persist after treatment discontinuation.
In advanced melanoma, researchers observed that overall survival was similar for patients who discontinued nivo/ipi because of AEs during the induction phase of treatment and those who did not. These results were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
This observation has led to an individualized, adaptive approach to de-escalating combination immunotherapy, described in Clinical Cancer Research. The approach is dubbed “SMART,” which stands for sequential multiple assignment randomized trial designs.
With the SMART approach, each stage of a trial corresponds to an important treatment decision point. The goal is to define the population of patients who can safely discontinue treatment based on response, rather than doing so after the development of AEs.
In the Adapt-IT prospective study, 60 patients with advanced melanoma with poor prognostic features were given two doses of nivo/ipi followed by a CT scan at week 6. They were triaged to stopping ipi and proceeding with maintenance therapy with nivo alone or continuing the combination for an additional two cycles of treatment. Results from this trial were presented at ASCO 2020 (abstract 10003).
The investigators found that 68% of patients had no tumor burden increase at week 6 and could discontinue ipi. For those patients, their response rate of 57% approached the expected results from a full course of ipi.
At median follow-up of 22.3 months, median response duration, PFS, and overall survival had not been reached for the responders who received an abbreviated course of the combination regimen.
There were two observations that suggested the first two cycles of treatment drove not only toxicity but also tumor control:
- The rate of grade 3-4 toxicity from only two cycles was high (57%).
- Of the 19 patients (32% of the original 60 patients) who had progressive disease after two cycles of nivo/ipi, there were no responders with continued therapy.
Dr. Postow commented that, in correlative studies conducted as part of Adapt-IT, the Ki-67 of CD8-positive T cells increased after the initial dose of nivo/ipi. However, proliferation did not continue with subsequent cycles (that is, Ki-67 did not continue to rise).
When they examined markers of T-cell stimulation such as inducible costimulator of CD8-positive T cells, the researchers observed the same effect. The “immune boost” occurred with cycle one but not after subsequent doses of the nivo/ipi combination.
Although unproven in clinical trials at this time, these data suggest that response and risks of toxicity may not support giving patients more than one cycle of combination treatment.
More nuanced ways of assessing tumor growth
Dr. Postow noted that judgment about treatment effects over time are often made by displaying spider plots of changes from baseline tumor size from “time zero” – the time at which combination therapy is commenced.
He speculated that it might be worthwhile to give a dose or two of immune-targeted monotherapy (such as a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor alone) before time zero, measure tumor growth prior to and after the single agent, and reserve using combination immunotherapy only for those patients who do not experience a dampening of the growth curve.
Patients whose tumor growth kinetics are improved with single-agent treatment could be spared the additional toxicity (and uncertain additive benefit) from the second agent.
Treatment optimization: More than ‘messaging’
Oncology practice has passed through a long era of “more is better,” an era that gave rise to intensive cytotoxic chemotherapy for hematologic and solid tumors in the metastatic and adjuvant settings. In some cases, that approach proved to be curative, but not in all.
More recently, because of better staging, improved outcomes with newer technology and treatments, and concern about immediate- and late-onset health risks, there has been an effort to deintensify therapy when it can be done safely.
Once a treatment regimen and treatment duration become established, however, patients and their physicians are reluctant to deintensity therapy.
Dr. Postow’s presentation demonstrated that, with regard to immunotherapy combinations – as in other realms of medical practice – science can lead the way to treatment optimization for individual patients.
We have the potential to reassure patients that treatment de-escalation is a rational and personalized component of treatment optimization through the combination of:
- Identifying new endpoints to quantify treatment benefits and risks.
- SMART trial designs.
- Innovative ways to assess tumor response during each phase of a treatment course.
Precision assessment of immunotherapy effect in individual patients can be a key part of precision medicine.
Dr. Postow disclosed relationships with Aduro, Array BioPharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Incyte, Infinity, Merck, NewLink Genetics, Novartis, and RGenix.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
Every medical oncologist who has described a combination chemotherapy regimen to a patient with advanced cancer has likely been asked whether the benefits of tumor shrinkage, disease-free survival (DFS), and overall survival are worth the risks of adverse events (AEs).
Single-agent immunotherapy and, more recently, combinations of immunotherapy drugs have been approved for a variety of metastatic tumors. In general, combination immunotherapy regimens have more AEs and a higher frequency of premature treatment discontinuation for toxicity.
Michael Postow, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, reflected on new ways to evaluate the benefits and risks of immunotherapy combinations during a plenary session on novel combinations at the American Association for Cancer Research’s Virtual Special Conference on Tumor Immunology and Immunotherapy.
Potential targets
As with chemotherapy drugs, immunotherapy combinations make the most sense when drugs targeting independent processes are employed.
As described in a paper published in Nature in 2011, the process for recruiting the immune system to combat cancer is as follows:
- Dendritic cells must sample antigens derived from the tumor.
- The dendritic cells must receive an activation signal so they promote immunity rather than tolerance.
- The tumor antigen–loaded dendritic cells need to generate protective T-cell responses, instead of T-regulatory responses, in lymphoid tissues.
- Cancer antigen–specific T cells must enter tumor tissues.
- Tumor-derived mechanisms for promoting immunosuppression need to be circumvented.
Since each step in the cascade is a potential therapeutic target, there are large numbers of potential drug combinations.
Measuring impact
Conventional measurements of tumor response may not be adequately sensitive to the impact from immunotherapy drugs. A case in point is sipuleucel-T, which is approved to treat advanced prostate cancer.
In the pivotal phase 3 trial, only 1 of 341 patients receiving sipuleucel-T achieved a partial response by RECIST criteria. Only 2.6% of patients had a 50% reduction in prostate-specific antigen levels. Nonetheless, a 4.1-month improvement in median overall survival was achieved. These results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The discrepancy between tumor shrinkage and survival benefit for immunotherapy is not unexpected. As many as 10% of patients treated with ipilimumab (ipi) for stage IV malignant melanoma have progressive disease by tumor size but experience prolongation of survival, according to guidelines published in Clinical Cancer Research.
Accurate assessment of the ultimate efficacy of immunotherapy over time would benefit patients and clinicians since immune checkpoint inhibitors are often administered for several years, are financially costly, and treatment-associated AEs emerge unpredictably at any time.
Curtailing the duration of ineffective treatment could be valuable from many perspectives.
Immunotherapy combinations in metastatic melanoma
In the CheckMate 067 study, there was an improvement in response, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival for nivolumab (nivo) plus ipi or nivo alone, in comparison with ipi alone, in patients with advanced melanoma. Initial results from this trial were published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2017.
At a minimum follow-up of 60 months, the 5-year overall survival was 52% for the nivo/ipi regimen, 44% for nivo alone, and 26% for ipi alone. These results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2019.
The trial was not statistically powered to conclude whether the overall survival for the combination was superior to that of single-agent nivo alone, but both nivo regimens were superior to ipi alone.
Unfortunately, the combination also produced the highest treatment-related AE rates – 59% with nivo/ipi, 23% with nivo, and 28% with ipi in 2019. In the 2017 report, the combination regimen had more than twice as many premature treatment discontinuations as the other two study arms.
Is there a better way to quantify the risk-benefit ratio and explain it to patients?
Alternative strategies for assessing benefit: Treatment-free survival
Researchers have proposed treatment-free survival (TFS) as a potential new metric to characterize not only antitumor activity but also toxicity experienced after the cessation of therapy and before initiation of subsequent systemic therapy or death.
TFS is defined as the area between Kaplan-Meier curves from immunotherapy cessation until the reinitiation of systemic therapy or death. All patients who began immunotherapy are included – not just those achieving response or concluding a predefined number of cycles of treatment.
The curves can be partitioned into states with and without toxicity to establish a unique endpoint: time to cessation of both immunotherapy and toxicity.
Researchers conducted a pooled analysis of 3-year follow-up data from the 1,077 patients who participated in CheckMate 069, testing nivo/ipi versus nivo alone, and CheckMate 067, comparing nivo/ipi, nivo alone, and ipi alone. The results were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The TFS without grade 3 or higher AEs was 28% for nivo/ipi, 11% for nivo alone, and 23% for ipi alone. The restricted mean time without either treatment or grade 3 or greater AEs was 10.1 months, 4.1 months, and 8.5 months, respectively.
TFS incentivizes the use of regimens that have:
- A short duration of treatment
- Prolonged time to subsequent therapy or death
- Only mild AEs of brief duration.
A higher TFS corresponds with the goals that patients and their providers would have for a treatment regimen.
Adaptive models provide clues about benefit from extended therapy
In contrast to cytotoxic chemotherapy and molecularly targeted agents, benefit from immune-targeted therapy can deepen and persist after treatment discontinuation.
In advanced melanoma, researchers observed that overall survival was similar for patients who discontinued nivo/ipi because of AEs during the induction phase of treatment and those who did not. These results were published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
This observation has led to an individualized, adaptive approach to de-escalating combination immunotherapy, described in Clinical Cancer Research. The approach is dubbed “SMART,” which stands for sequential multiple assignment randomized trial designs.
With the SMART approach, each stage of a trial corresponds to an important treatment decision point. The goal is to define the population of patients who can safely discontinue treatment based on response, rather than doing so after the development of AEs.
In the Adapt-IT prospective study, 60 patients with advanced melanoma with poor prognostic features were given two doses of nivo/ipi followed by a CT scan at week 6. They were triaged to stopping ipi and proceeding with maintenance therapy with nivo alone or continuing the combination for an additional two cycles of treatment. Results from this trial were presented at ASCO 2020 (abstract 10003).
The investigators found that 68% of patients had no tumor burden increase at week 6 and could discontinue ipi. For those patients, their response rate of 57% approached the expected results from a full course of ipi.
At median follow-up of 22.3 months, median response duration, PFS, and overall survival had not been reached for the responders who received an abbreviated course of the combination regimen.
There were two observations that suggested the first two cycles of treatment drove not only toxicity but also tumor control:
- The rate of grade 3-4 toxicity from only two cycles was high (57%).
- Of the 19 patients (32% of the original 60 patients) who had progressive disease after two cycles of nivo/ipi, there were no responders with continued therapy.
Dr. Postow commented that, in correlative studies conducted as part of Adapt-IT, the Ki-67 of CD8-positive T cells increased after the initial dose of nivo/ipi. However, proliferation did not continue with subsequent cycles (that is, Ki-67 did not continue to rise).
When they examined markers of T-cell stimulation such as inducible costimulator of CD8-positive T cells, the researchers observed the same effect. The “immune boost” occurred with cycle one but not after subsequent doses of the nivo/ipi combination.
Although unproven in clinical trials at this time, these data suggest that response and risks of toxicity may not support giving patients more than one cycle of combination treatment.
More nuanced ways of assessing tumor growth
Dr. Postow noted that judgment about treatment effects over time are often made by displaying spider plots of changes from baseline tumor size from “time zero” – the time at which combination therapy is commenced.
He speculated that it might be worthwhile to give a dose or two of immune-targeted monotherapy (such as a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor alone) before time zero, measure tumor growth prior to and after the single agent, and reserve using combination immunotherapy only for those patients who do not experience a dampening of the growth curve.
Patients whose tumor growth kinetics are improved with single-agent treatment could be spared the additional toxicity (and uncertain additive benefit) from the second agent.
Treatment optimization: More than ‘messaging’
Oncology practice has passed through a long era of “more is better,” an era that gave rise to intensive cytotoxic chemotherapy for hematologic and solid tumors in the metastatic and adjuvant settings. In some cases, that approach proved to be curative, but not in all.
More recently, because of better staging, improved outcomes with newer technology and treatments, and concern about immediate- and late-onset health risks, there has been an effort to deintensify therapy when it can be done safely.
Once a treatment regimen and treatment duration become established, however, patients and their physicians are reluctant to deintensity therapy.
Dr. Postow’s presentation demonstrated that, with regard to immunotherapy combinations – as in other realms of medical practice – science can lead the way to treatment optimization for individual patients.
We have the potential to reassure patients that treatment de-escalation is a rational and personalized component of treatment optimization through the combination of:
- Identifying new endpoints to quantify treatment benefits and risks.
- SMART trial designs.
- Innovative ways to assess tumor response during each phase of a treatment course.
Precision assessment of immunotherapy effect in individual patients can be a key part of precision medicine.
Dr. Postow disclosed relationships with Aduro, Array BioPharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Incyte, Infinity, Merck, NewLink Genetics, Novartis, and RGenix.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
FROM AACR: TUMOR IMMUNOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
Phase 1 study: Beta-blocker may improve melanoma treatment response
Response rates were high without dose-limiting toxicities in a small phase 1 study that evaluated the addition of propranolol to pembrolizumab in treatment-naive patients with metastatic melanoma.
“To our knowledge, this effort is the,” wrote the two co-first authors, Shipra Gandhi, MD, and Manu Pandey, MBBS, from the Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, N.Y., and coauthors.
The need for combinations built on anti-PD1 checkpoint inhibitor therapy strategies in metastatic melanoma that safely improve outcomes is underscored by the high (59%) grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse event (TRAE) rates when an anti-CTLA4 agent (ipilimumab) was added to an anti-PD-1 agent (nivolumab), they noted. In contrast, a TRAE rate of only 17% has been reported with pembrolizumab monotherapy.
The phase 1b study was stimulated by preclinical, retrospective observations of improved overall survival (OS) in cancer patients treated with beta-blockers. These were preceded by murine melanoma studies showing decreased tumor growth and metastasis with the nonselective beta-blocker propranolol. “Propranolol exerts an antitumor effect,” the authors stated, “by favorably modulating the tumor microenvironment (TME) by decreasing myeloid-derived suppressor cells and increasing CD8+ T-cell and natural killer cells in the TME.” Other research in a melanoma model in chronically-stressed mice has demonstrated synergy between an anti-PD1 antibody and propranolol.
“We know that stress can have a significant negative effect on health, but the extent to which stress may impact the outcome of cancer therapy is not well understood at all,” Dr. Ghandi said in a statement provided by Roswell Park. “We set out to better understand this relationship and to explore its implications for cancer treatment.”
The investigators recruited nine White adults (median age 65 years) with treatment-naive, histologically confirmed unresectable stage III or IV melanoma and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0 or 1 to the open-label, single arm, nonrandomized, single-center, dose-finding study. Patients received standard of care intravenous pembrolizumab 200 mg every 3 weeks and, in three groups, propranolol doses of 10 mg, 20 mg, or 30 mg twice a day until 2 years on study or disease progression or the development of dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs). Assessing the safety and efficacy (overall response rate [ORR] within 6 months of starting therapy) of pembrolizumab with the increasing doses of propranolol and selecting the recommended phase 2 dose were the study’s primary objectives.
Objective responses (complete or partial responses) were reported in seven of the nine patients, with partial tumor responses in two patients in the propranolol 10-mg group, two partial responses in the 20-mg group, and three partial responses in the 30-mg group.
While all patients experienced TRAEs, only one was above grade 2. The most commonly reported TRAEs were fatigue, rash and vitiligo, reported in four of the nine patients. Two patients in the 20-mg twice-a-day group discontinued therapy because of TRAEs (hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and labyrinthitis). No DLTs were observed at any of the three dose levels, and no deaths occurred on study treatment.
The authors said that propranolol 30 mg twice a day was chosen as the recommended phase 2 dose, because in combination with pembrolizumab, there were no DLTs, and preliminary antitumor efficacy was observed in all three patients. Also, in all three patients, the investigators observed a trend toward higher CD8+T-cell percentage, higher ratios of CD8+T-cell/ Treg and CD8+T-cell/ polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells. They underscored, however, that the small size and significant heterogeneity in biomarkers made a statistically sound and meaningful interpretation of biomarkers for deciding the phase 2 dose difficult.
“In repurposing propranolol,” Dr. Pandey said in the Roswell statement, “we’ve gained important insights on how to manage stress in people with cancer – who can face dangerously elevated levels of mental and physical stress related to their diagnosis and treatment.”
In an interview, one of the two senior authors, Elizabeth Repasky, PhD, professor of oncology and immunology at Roswell Park, said, “it’s exciting that an extremely inexpensive drug like propranolol that could be used in every country around the world could have an impact on cancer by blocking stress, especially chronic stress.” Her murine research showing that adding propranolol to immunotherapy or radiotherapy or chemotherapy improved tumor growth control provided rationale for the current study.
“The breakthrough in this study is that it reveals the immune system as the best target to look at, and shows that what stress reduction is doing is improving a patient’s immune response to his or her own tumor,” Dr. Repasky said. “The mind/body connection is so important, but we have not had a handle on how to study it,” she added.
Further research funded by Herd of Hope grants at Roswell will look at tumor effects of propranolol and nonpharmacological reducers of chronic stress such as exercise, meditation, yoga, and Tai Chi, with first studies in breast cancer.
The study was funded by Roswell Park, private, and NIH grants. The authors had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Gandhi S et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 30. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2381
Response rates were high without dose-limiting toxicities in a small phase 1 study that evaluated the addition of propranolol to pembrolizumab in treatment-naive patients with metastatic melanoma.
“To our knowledge, this effort is the,” wrote the two co-first authors, Shipra Gandhi, MD, and Manu Pandey, MBBS, from the Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, N.Y., and coauthors.
The need for combinations built on anti-PD1 checkpoint inhibitor therapy strategies in metastatic melanoma that safely improve outcomes is underscored by the high (59%) grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse event (TRAE) rates when an anti-CTLA4 agent (ipilimumab) was added to an anti-PD-1 agent (nivolumab), they noted. In contrast, a TRAE rate of only 17% has been reported with pembrolizumab monotherapy.
The phase 1b study was stimulated by preclinical, retrospective observations of improved overall survival (OS) in cancer patients treated with beta-blockers. These were preceded by murine melanoma studies showing decreased tumor growth and metastasis with the nonselective beta-blocker propranolol. “Propranolol exerts an antitumor effect,” the authors stated, “by favorably modulating the tumor microenvironment (TME) by decreasing myeloid-derived suppressor cells and increasing CD8+ T-cell and natural killer cells in the TME.” Other research in a melanoma model in chronically-stressed mice has demonstrated synergy between an anti-PD1 antibody and propranolol.
“We know that stress can have a significant negative effect on health, but the extent to which stress may impact the outcome of cancer therapy is not well understood at all,” Dr. Ghandi said in a statement provided by Roswell Park. “We set out to better understand this relationship and to explore its implications for cancer treatment.”
The investigators recruited nine White adults (median age 65 years) with treatment-naive, histologically confirmed unresectable stage III or IV melanoma and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0 or 1 to the open-label, single arm, nonrandomized, single-center, dose-finding study. Patients received standard of care intravenous pembrolizumab 200 mg every 3 weeks and, in three groups, propranolol doses of 10 mg, 20 mg, or 30 mg twice a day until 2 years on study or disease progression or the development of dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs). Assessing the safety and efficacy (overall response rate [ORR] within 6 months of starting therapy) of pembrolizumab with the increasing doses of propranolol and selecting the recommended phase 2 dose were the study’s primary objectives.
Objective responses (complete or partial responses) were reported in seven of the nine patients, with partial tumor responses in two patients in the propranolol 10-mg group, two partial responses in the 20-mg group, and three partial responses in the 30-mg group.
While all patients experienced TRAEs, only one was above grade 2. The most commonly reported TRAEs were fatigue, rash and vitiligo, reported in four of the nine patients. Two patients in the 20-mg twice-a-day group discontinued therapy because of TRAEs (hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and labyrinthitis). No DLTs were observed at any of the three dose levels, and no deaths occurred on study treatment.
The authors said that propranolol 30 mg twice a day was chosen as the recommended phase 2 dose, because in combination with pembrolizumab, there were no DLTs, and preliminary antitumor efficacy was observed in all three patients. Also, in all three patients, the investigators observed a trend toward higher CD8+T-cell percentage, higher ratios of CD8+T-cell/ Treg and CD8+T-cell/ polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells. They underscored, however, that the small size and significant heterogeneity in biomarkers made a statistically sound and meaningful interpretation of biomarkers for deciding the phase 2 dose difficult.
“In repurposing propranolol,” Dr. Pandey said in the Roswell statement, “we’ve gained important insights on how to manage stress in people with cancer – who can face dangerously elevated levels of mental and physical stress related to their diagnosis and treatment.”
In an interview, one of the two senior authors, Elizabeth Repasky, PhD, professor of oncology and immunology at Roswell Park, said, “it’s exciting that an extremely inexpensive drug like propranolol that could be used in every country around the world could have an impact on cancer by blocking stress, especially chronic stress.” Her murine research showing that adding propranolol to immunotherapy or radiotherapy or chemotherapy improved tumor growth control provided rationale for the current study.
“The breakthrough in this study is that it reveals the immune system as the best target to look at, and shows that what stress reduction is doing is improving a patient’s immune response to his or her own tumor,” Dr. Repasky said. “The mind/body connection is so important, but we have not had a handle on how to study it,” she added.
Further research funded by Herd of Hope grants at Roswell will look at tumor effects of propranolol and nonpharmacological reducers of chronic stress such as exercise, meditation, yoga, and Tai Chi, with first studies in breast cancer.
The study was funded by Roswell Park, private, and NIH grants. The authors had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Gandhi S et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 30. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2381
Response rates were high without dose-limiting toxicities in a small phase 1 study that evaluated the addition of propranolol to pembrolizumab in treatment-naive patients with metastatic melanoma.
“To our knowledge, this effort is the,” wrote the two co-first authors, Shipra Gandhi, MD, and Manu Pandey, MBBS, from the Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, N.Y., and coauthors.
The need for combinations built on anti-PD1 checkpoint inhibitor therapy strategies in metastatic melanoma that safely improve outcomes is underscored by the high (59%) grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse event (TRAE) rates when an anti-CTLA4 agent (ipilimumab) was added to an anti-PD-1 agent (nivolumab), they noted. In contrast, a TRAE rate of only 17% has been reported with pembrolizumab monotherapy.
The phase 1b study was stimulated by preclinical, retrospective observations of improved overall survival (OS) in cancer patients treated with beta-blockers. These were preceded by murine melanoma studies showing decreased tumor growth and metastasis with the nonselective beta-blocker propranolol. “Propranolol exerts an antitumor effect,” the authors stated, “by favorably modulating the tumor microenvironment (TME) by decreasing myeloid-derived suppressor cells and increasing CD8+ T-cell and natural killer cells in the TME.” Other research in a melanoma model in chronically-stressed mice has demonstrated synergy between an anti-PD1 antibody and propranolol.
“We know that stress can have a significant negative effect on health, but the extent to which stress may impact the outcome of cancer therapy is not well understood at all,” Dr. Ghandi said in a statement provided by Roswell Park. “We set out to better understand this relationship and to explore its implications for cancer treatment.”
The investigators recruited nine White adults (median age 65 years) with treatment-naive, histologically confirmed unresectable stage III or IV melanoma and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0 or 1 to the open-label, single arm, nonrandomized, single-center, dose-finding study. Patients received standard of care intravenous pembrolizumab 200 mg every 3 weeks and, in three groups, propranolol doses of 10 mg, 20 mg, or 30 mg twice a day until 2 years on study or disease progression or the development of dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs). Assessing the safety and efficacy (overall response rate [ORR] within 6 months of starting therapy) of pembrolizumab with the increasing doses of propranolol and selecting the recommended phase 2 dose were the study’s primary objectives.
Objective responses (complete or partial responses) were reported in seven of the nine patients, with partial tumor responses in two patients in the propranolol 10-mg group, two partial responses in the 20-mg group, and three partial responses in the 30-mg group.
While all patients experienced TRAEs, only one was above grade 2. The most commonly reported TRAEs were fatigue, rash and vitiligo, reported in four of the nine patients. Two patients in the 20-mg twice-a-day group discontinued therapy because of TRAEs (hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and labyrinthitis). No DLTs were observed at any of the three dose levels, and no deaths occurred on study treatment.
The authors said that propranolol 30 mg twice a day was chosen as the recommended phase 2 dose, because in combination with pembrolizumab, there were no DLTs, and preliminary antitumor efficacy was observed in all three patients. Also, in all three patients, the investigators observed a trend toward higher CD8+T-cell percentage, higher ratios of CD8+T-cell/ Treg and CD8+T-cell/ polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells. They underscored, however, that the small size and significant heterogeneity in biomarkers made a statistically sound and meaningful interpretation of biomarkers for deciding the phase 2 dose difficult.
“In repurposing propranolol,” Dr. Pandey said in the Roswell statement, “we’ve gained important insights on how to manage stress in people with cancer – who can face dangerously elevated levels of mental and physical stress related to their diagnosis and treatment.”
In an interview, one of the two senior authors, Elizabeth Repasky, PhD, professor of oncology and immunology at Roswell Park, said, “it’s exciting that an extremely inexpensive drug like propranolol that could be used in every country around the world could have an impact on cancer by blocking stress, especially chronic stress.” Her murine research showing that adding propranolol to immunotherapy or radiotherapy or chemotherapy improved tumor growth control provided rationale for the current study.
“The breakthrough in this study is that it reveals the immune system as the best target to look at, and shows that what stress reduction is doing is improving a patient’s immune response to his or her own tumor,” Dr. Repasky said. “The mind/body connection is so important, but we have not had a handle on how to study it,” she added.
Further research funded by Herd of Hope grants at Roswell will look at tumor effects of propranolol and nonpharmacological reducers of chronic stress such as exercise, meditation, yoga, and Tai Chi, with first studies in breast cancer.
The study was funded by Roswell Park, private, and NIH grants. The authors had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Gandhi S et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 30. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2381
FROM CLINICAL CANCER RESEARCH
Mobile Apps for Professional Dermatology Education: An Objective Review
With today’s technology, it is easier than ever to access web-based tools that enrich traditional dermatology education. The literature supports the use of these innovative platforms to enhance learning at the student and trainee levels. A controlled study of pediatric residents showed that online modules effectively supplemented clinical experience with atopic dermatitis.1 In a randomized diagnostic study of medical students, practice with an image-based web application (app) that teaches rapid recognition of melanoma proved more effective than learning a rule-based algorithm.2 Given the visual nature of dermatology, pattern recognition is an essential skill that is fostered through experience and is only made more accessible with technology.
With the added benefit of convenience and accessibility, mobile apps can supplement experiential learning. Mirroring the overall growth of mobile apps, the number of available dermatology apps has increased.3 Dermatology mobile apps serve purposes ranging from quick reference tools to comprehensive modules, journals, and question banks. At an academic hospital in Taiwan, both nondermatology and dermatology trainees’ examination performance improved after 3 weeks of using a smartphone-based wallpaper learning module displaying morphologic characteristics of fungi.4 With the expansion of virtual microscopy, mobile apps also have been created as a learning tool for dermatopathology, giving trainees the flexibility and autonomy to view slides on their own time.5 Nevertheless, the literature on dermatology mobile apps designed for the education of medical students and trainees is limited, demonstrating a need for further investigation.
Prior studies have reviewed dermatology apps for patients and practicing dermatologists.6-8 Herein, we focus on mobile apps targeting students and residents learning dermatology. General dermatology reference apps and educational aid apps have grown by 33% and 32%, respectively, from 2014 to 2017.3 As with any resource meant to educate future and current medical providers, there must be an objective review process in place to ensure accurate, unbiased, evidence-based teaching.
Well-organized, comprehensive information and a user-friendly interface are additional factors of importance when selecting an educational mobile app. When discussing supplemental resources, accessibility and affordability also are priorities given the high cost of a medical education at baseline. Overall, there is a need for a standardized method to evaluate the key factors of an educational mobile app that make it appropriate for this demographic. We conducted a search of mobile apps relating to dermatology education for students and residents.
Methods
We searched for publicly available mobile apps relating to dermatology education in the App Store (Apple Inc) from September to November 2019 using the search terms dermatology education, dermoscopy education, melanoma education, skin cancer education, psoriasis education, rosacea education, acne education, eczema education, dermal fillers education, and Mohs surgery education. We excluded apps that were not in English, were created for a conference, cost more than $5 to download, or did not include a specific dermatology education section. In this way, we hoped to evaluate apps that were relevant, accessible, and affordable.
We modeled our study after a review of patient education apps performed by Masud et al6 and utilized their quantified grading rubric (scale of 1 to 4). We found their established criteria—educational objectives, content, accuracy, design, and conflict of interest—to be equally applicable for evaluating apps designed for professional education.6 Each app earned a minimum of 1 point and a maximum of 4 points per criterion. One point was given if the app did not fulfill the criterion, 2 points for minimally fulfilling the criterion, 3 points for mostly fulfilling the criterion, and 4 points if the criterion was completely fulfilled. Two medical students (E.H. and N.C.)—one at the preclinical stage and the other at the clinical stage of medical education—reviewed the apps using the given rubric, then discussed and resolved any discrepancies in points assigned. A dermatology resident (M.A.) independently reviewed the apps using the given rubric.
The mean of the student score and the resident score was calculated for each category. The sum of the averages for each category was considered the final score for an app, determining its overall quality. Apps with a total score of 5 to 10 were considered poor and inadequate for education. A total score of 10.5 to 15 indicated that an app was somewhat adequate (ie, useful for education in some aspects but falling short in others). Apps that were considered adequate for education, across all or most criteria, received a total score ranging from 15.5 to 20.
Results
Our search generated 130 apps. After applying exclusion criteria, 42 apps were eligible for review. At the time of publication, 36 of these apps were still available. The possible range of scores based on the rubric was 5 to 20. The actual range of scores was 7 to 20. Of the 36 apps, 2 (5.6%) were poor, 16 (44.4%) were somewhat adequate, and 18 (50%) were adequate. Formats included primary resources, such as clinical decision support tools, journals, references, and a podcast (Table 1). Additionally, interactive learning tools included games, learning modules, and apps for self-evaluation (Table 2). Thirty apps covered general dermatology; others focused on skin cancer (n=5) and cosmetic dermatology (n=1). Regarding cost, 29 apps were free to download, whereas 7 charged a fee (mean price, $2.56).

Comment
In addition to the convenience of having an educational tool in their white-coat pocket, learners of dermatology have been shown to benefit from supplementing their curriculum with mobile apps, which sets the stage for formal integration of mobile apps into dermatology teaching in the future.8 Prior to widespread adoption, mobile apps must be evaluated for content and utility, starting with an objective rubric.
Without official scientific standards in place, it was unsurprising that only half of the dermatology education applications were classified as adequate in this study. Among the types of apps offered—clinical decision support tools, journals, references, podcast, games, learning modules, and self-evaluation—certain categories scored higher than others. App formats with the highest average score (16.5 out of 20) were journals and podcast.
One barrier to utilization of these apps was that a subscription to the journals and podcast was required to obtain access to all available content. Students and trainees can seek out library resources at their academic institutions to take advantage of journal subscriptions available to them at no additional cost. Dermatology residents can take advantage of their complimentary membership in the American Academy of Dermatology for a free subscription to AAD Dialogues in Dermatology (otherwise $179 annually for nonresident members and $320 annually for nonmembers).
On the other hand, learning module was the lowest-rated format (average score, 11.3 out of 20), with only Medical Student: Dermatology qualifying as adequate (total score, 16). This finding is worrisome given that students and residents might look to learning modules for quick targeted lessons on specific topics.
The lowest-scoring app, a clinical decision support tool called Naturelize, received a total score of 7. Although it listed the indications and contraindications for dermal filler types to be used in different locations on the face, there was a clear conflict of interest, oversimplified design, and little evidence-based education, mirroring the current state of cosmetic dermatology training in residency, in which trainees think they are inadequately prepared for aesthetic procedures and comparative effectiveness research is lacking.9-11
At the opposite end of the spectrum, MyDermPath+ was a reference app with a total score of 20. The app cited credible authors with a medical degree (MD) and had an easy-to-use, well-designed interface, including a reference guide, differential builder, and quiz for a range of topics within dermatology. As a free download without in-app purchases or advertisements, there was no evidence of conflict of interest. The position of a dermatopathology app as the top dermatology education mobile app might reflect an increased emphasis on dermatopathology education in residency as well as a transition to digitization of slides.5
The second-highest scoring apps (total score of 19 points) were Dermatology Database and VisualDx. Both were references covering a wide range of dermatology topics. Dermatology Database was a comprehensive search tool for diseases, drugs, procedures, and terms that was simple and entirely free to use but did not cite references. VisualDx, as its name suggests, offered quality clinical images, complete guides with references, and a unique differential builder. An annual subscription is $399.99, but the process to gain free access through a participating academic institution was simple.
Games were a unique mobile app format; however, 2 of 3 games scored in the somewhat adequate range. The game DiagnosUs, which tested users’ ability to differentiate skin cancer and psoriasis from dermatitis on clinical images, would benefit from more comprehensive content as well as professional verification of true diagnoses, which earned the app 2 points in both the content and accuracy categories. The Unusual Suspects tested the ABCDE algorithm in a short learning module, followed by a simple game that involved identification of melanoma in a timed setting. Although the design was novel and interactive, the game was limited to the same 5 melanoma tumors overlaid on pictures of normal skin. The narrow scope earned 1 point for content, the redundancy in the game earned 3 points for design, and the lack of real clinical images earned 2 points for educational objectives. Although game-format mobile apps have the capability to challenge the user’s knowledge with a built-in feedback or reward system, improvements should be made to ensure that apps are equally educational as they are engaging.
AAD Dialogues in Dermatology was the only app in the form of a podcast and provided expert interviews along with disclosures, transcripts, commentary, and references. More than half the content in the app could not be accessed without a subscription, earning 2.5 points in the conflict of interest category. Additionally, several flaws resulted in a design score of 2.5, including inconsistent availability of transcripts, poor quality of sound on some episodes, difficulty distinguishing new episodes from those already played, and a glitch that removed the episode duration. Still, the app was a valuable and comprehensive resource, with clear objectives and cited references. With improvements in content, affordability, and user experience, apps in unique formats such as games and podcasts might appeal to kinesthetic and auditory learners.
An important factor to consider when discussing mobile apps for students and residents is cost. With rising prices of board examinations and preparation materials, supplementary study tools should not come with an exorbitant price tag. Therefore, we limited our evaluation to apps that were free or cost less than $5 to download. Even so, subscriptions and other in-app purchases were an obstacle in one-third of apps, ranging from $4.99 to unlock additional content in Rash Decisions to $69.99 to access most topics in Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas. The highest-rated app in our study, MyDermPath+, historically cost $19.99 to download but became free with a grant from the Sulzberger Foundation.12 An initial investment to develop quality apps for the purpose of dermatology education might pay off in the end.
To evaluate the apps from the perspective of the target demographic of this study, 2 medical students—one in the preclinical stage and the other in the clinical stage of medical education—and a dermatology resident graded the apps. Certain limitations exist in this type of study, including differing learning styles, which might influence the types of apps that evaluators found most impactful to their education. Interestingly, some apps earned a higher resident score than student score. In particular, RightSite (a reference that helps with anatomically correct labeling) and Mohs Surgery Appropriate Use Criteria (a clinical decision support tool to determine whether to perform Mohs surgery) each had a 3-point discrepancy (data not shown). A resident might benefit from these practical apps in day-to-day practice, but a student would be less likely to find them useful as a learning tool.
Still, by defining adequate teaching value using specific categories of educational objectives, content, accuracy, design, and conflict of interest, we attempted to minimize the effect of personal preference on the grading process. Although we acknowledge a degree of subjectivity, we found that utilizing a previously published rubric with defined criteria was crucial in remaining unbiased.
Conclusion
Further studies should evaluate additional apps available on Apple’s iPad (tablet), as well as those on other operating systems, including Google’s Android. To ensure the existence of mobile apps as adequate education tools, they should be peer reviewed prior to publication or before widespread use by future and current providers at the minimum. To maximize free access to highly valuable resources available in the palm of their hand, students and trainees should contact the library at their academic institution.
- Craddock MF, Blondin HM, Youssef MJ, et al. Online education improves pediatric residents' understanding of atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:64-69.
- Lacy FA, Coman GC, Holliday AC, et al. Assessment of smartphone application for teaching intuitive visual diagnosis of melanoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:730-731.
- Flaten HK, St Claire C, Schlager E, et al. Growth of mobile applications in dermatology--2017 update. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24:13.
- Liu R-F, Wang F-Y, Yen H, et al. A new mobile learning module using smartphone wallpapers in identification of medical fungi for medical students and residents. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:458-462.
- Shahriari N, Grant-Kels J, Murphy MJ. Dermatopathology education in the era of modern technology. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:763-771.
- Masud A, Shafi S, Rao BK. Mobile medical apps for patient education: a graded review of available dermatology apps. Cutis. 2018;101:141-144.
- Mercer JM. An array of mobile apps for dermatologists. J Cutan Med Surg. 2014;18:295-297.
- Tongdee E, Markowitz O. Mobile app rankings in dermatology. Cutis. 2018;102:252-256.
- Kirby JS, Adgerson CN, Anderson BE. A survey of dermatology resident education in cosmetic procedures. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:e23-e28.
- Waldman A, Sobanko JF, Alam M. Practice and educational gaps in cosmetic dermatologic surgery. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:341-346.
- Nielson CB, Harb JN, Motaparthi K. Education in cosmetic procedural dermatology: resident experiences and perceptions. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2019;12:E70-E72.
- Hanna MG, Parwani AV, Pantanowitz L, et al. Smartphone applications: a contemporary resource for dermatopathology. J Pathol Inform. 2015;6:44.
With today’s technology, it is easier than ever to access web-based tools that enrich traditional dermatology education. The literature supports the use of these innovative platforms to enhance learning at the student and trainee levels. A controlled study of pediatric residents showed that online modules effectively supplemented clinical experience with atopic dermatitis.1 In a randomized diagnostic study of medical students, practice with an image-based web application (app) that teaches rapid recognition of melanoma proved more effective than learning a rule-based algorithm.2 Given the visual nature of dermatology, pattern recognition is an essential skill that is fostered through experience and is only made more accessible with technology.
With the added benefit of convenience and accessibility, mobile apps can supplement experiential learning. Mirroring the overall growth of mobile apps, the number of available dermatology apps has increased.3 Dermatology mobile apps serve purposes ranging from quick reference tools to comprehensive modules, journals, and question banks. At an academic hospital in Taiwan, both nondermatology and dermatology trainees’ examination performance improved after 3 weeks of using a smartphone-based wallpaper learning module displaying morphologic characteristics of fungi.4 With the expansion of virtual microscopy, mobile apps also have been created as a learning tool for dermatopathology, giving trainees the flexibility and autonomy to view slides on their own time.5 Nevertheless, the literature on dermatology mobile apps designed for the education of medical students and trainees is limited, demonstrating a need for further investigation.
Prior studies have reviewed dermatology apps for patients and practicing dermatologists.6-8 Herein, we focus on mobile apps targeting students and residents learning dermatology. General dermatology reference apps and educational aid apps have grown by 33% and 32%, respectively, from 2014 to 2017.3 As with any resource meant to educate future and current medical providers, there must be an objective review process in place to ensure accurate, unbiased, evidence-based teaching.
Well-organized, comprehensive information and a user-friendly interface are additional factors of importance when selecting an educational mobile app. When discussing supplemental resources, accessibility and affordability also are priorities given the high cost of a medical education at baseline. Overall, there is a need for a standardized method to evaluate the key factors of an educational mobile app that make it appropriate for this demographic. We conducted a search of mobile apps relating to dermatology education for students and residents.
Methods
We searched for publicly available mobile apps relating to dermatology education in the App Store (Apple Inc) from September to November 2019 using the search terms dermatology education, dermoscopy education, melanoma education, skin cancer education, psoriasis education, rosacea education, acne education, eczema education, dermal fillers education, and Mohs surgery education. We excluded apps that were not in English, were created for a conference, cost more than $5 to download, or did not include a specific dermatology education section. In this way, we hoped to evaluate apps that were relevant, accessible, and affordable.
We modeled our study after a review of patient education apps performed by Masud et al6 and utilized their quantified grading rubric (scale of 1 to 4). We found their established criteria—educational objectives, content, accuracy, design, and conflict of interest—to be equally applicable for evaluating apps designed for professional education.6 Each app earned a minimum of 1 point and a maximum of 4 points per criterion. One point was given if the app did not fulfill the criterion, 2 points for minimally fulfilling the criterion, 3 points for mostly fulfilling the criterion, and 4 points if the criterion was completely fulfilled. Two medical students (E.H. and N.C.)—one at the preclinical stage and the other at the clinical stage of medical education—reviewed the apps using the given rubric, then discussed and resolved any discrepancies in points assigned. A dermatology resident (M.A.) independently reviewed the apps using the given rubric.
The mean of the student score and the resident score was calculated for each category. The sum of the averages for each category was considered the final score for an app, determining its overall quality. Apps with a total score of 5 to 10 were considered poor and inadequate for education. A total score of 10.5 to 15 indicated that an app was somewhat adequate (ie, useful for education in some aspects but falling short in others). Apps that were considered adequate for education, across all or most criteria, received a total score ranging from 15.5 to 20.
Results
Our search generated 130 apps. After applying exclusion criteria, 42 apps were eligible for review. At the time of publication, 36 of these apps were still available. The possible range of scores based on the rubric was 5 to 20. The actual range of scores was 7 to 20. Of the 36 apps, 2 (5.6%) were poor, 16 (44.4%) were somewhat adequate, and 18 (50%) were adequate. Formats included primary resources, such as clinical decision support tools, journals, references, and a podcast (Table 1). Additionally, interactive learning tools included games, learning modules, and apps for self-evaluation (Table 2). Thirty apps covered general dermatology; others focused on skin cancer (n=5) and cosmetic dermatology (n=1). Regarding cost, 29 apps were free to download, whereas 7 charged a fee (mean price, $2.56).


Comment
In addition to the convenience of having an educational tool in their white-coat pocket, learners of dermatology have been shown to benefit from supplementing their curriculum with mobile apps, which sets the stage for formal integration of mobile apps into dermatology teaching in the future.8 Prior to widespread adoption, mobile apps must be evaluated for content and utility, starting with an objective rubric.
Without official scientific standards in place, it was unsurprising that only half of the dermatology education applications were classified as adequate in this study. Among the types of apps offered—clinical decision support tools, journals, references, podcast, games, learning modules, and self-evaluation—certain categories scored higher than others. App formats with the highest average score (16.5 out of 20) were journals and podcast.
One barrier to utilization of these apps was that a subscription to the journals and podcast was required to obtain access to all available content. Students and trainees can seek out library resources at their academic institutions to take advantage of journal subscriptions available to them at no additional cost. Dermatology residents can take advantage of their complimentary membership in the American Academy of Dermatology for a free subscription to AAD Dialogues in Dermatology (otherwise $179 annually for nonresident members and $320 annually for nonmembers).
On the other hand, learning module was the lowest-rated format (average score, 11.3 out of 20), with only Medical Student: Dermatology qualifying as adequate (total score, 16). This finding is worrisome given that students and residents might look to learning modules for quick targeted lessons on specific topics.
The lowest-scoring app, a clinical decision support tool called Naturelize, received a total score of 7. Although it listed the indications and contraindications for dermal filler types to be used in different locations on the face, there was a clear conflict of interest, oversimplified design, and little evidence-based education, mirroring the current state of cosmetic dermatology training in residency, in which trainees think they are inadequately prepared for aesthetic procedures and comparative effectiveness research is lacking.9-11
At the opposite end of the spectrum, MyDermPath+ was a reference app with a total score of 20. The app cited credible authors with a medical degree (MD) and had an easy-to-use, well-designed interface, including a reference guide, differential builder, and quiz for a range of topics within dermatology. As a free download without in-app purchases or advertisements, there was no evidence of conflict of interest. The position of a dermatopathology app as the top dermatology education mobile app might reflect an increased emphasis on dermatopathology education in residency as well as a transition to digitization of slides.5
The second-highest scoring apps (total score of 19 points) were Dermatology Database and VisualDx. Both were references covering a wide range of dermatology topics. Dermatology Database was a comprehensive search tool for diseases, drugs, procedures, and terms that was simple and entirely free to use but did not cite references. VisualDx, as its name suggests, offered quality clinical images, complete guides with references, and a unique differential builder. An annual subscription is $399.99, but the process to gain free access through a participating academic institution was simple.
Games were a unique mobile app format; however, 2 of 3 games scored in the somewhat adequate range. The game DiagnosUs, which tested users’ ability to differentiate skin cancer and psoriasis from dermatitis on clinical images, would benefit from more comprehensive content as well as professional verification of true diagnoses, which earned the app 2 points in both the content and accuracy categories. The Unusual Suspects tested the ABCDE algorithm in a short learning module, followed by a simple game that involved identification of melanoma in a timed setting. Although the design was novel and interactive, the game was limited to the same 5 melanoma tumors overlaid on pictures of normal skin. The narrow scope earned 1 point for content, the redundancy in the game earned 3 points for design, and the lack of real clinical images earned 2 points for educational objectives. Although game-format mobile apps have the capability to challenge the user’s knowledge with a built-in feedback or reward system, improvements should be made to ensure that apps are equally educational as they are engaging.
AAD Dialogues in Dermatology was the only app in the form of a podcast and provided expert interviews along with disclosures, transcripts, commentary, and references. More than half the content in the app could not be accessed without a subscription, earning 2.5 points in the conflict of interest category. Additionally, several flaws resulted in a design score of 2.5, including inconsistent availability of transcripts, poor quality of sound on some episodes, difficulty distinguishing new episodes from those already played, and a glitch that removed the episode duration. Still, the app was a valuable and comprehensive resource, with clear objectives and cited references. With improvements in content, affordability, and user experience, apps in unique formats such as games and podcasts might appeal to kinesthetic and auditory learners.
An important factor to consider when discussing mobile apps for students and residents is cost. With rising prices of board examinations and preparation materials, supplementary study tools should not come with an exorbitant price tag. Therefore, we limited our evaluation to apps that were free or cost less than $5 to download. Even so, subscriptions and other in-app purchases were an obstacle in one-third of apps, ranging from $4.99 to unlock additional content in Rash Decisions to $69.99 to access most topics in Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas. The highest-rated app in our study, MyDermPath+, historically cost $19.99 to download but became free with a grant from the Sulzberger Foundation.12 An initial investment to develop quality apps for the purpose of dermatology education might pay off in the end.
To evaluate the apps from the perspective of the target demographic of this study, 2 medical students—one in the preclinical stage and the other in the clinical stage of medical education—and a dermatology resident graded the apps. Certain limitations exist in this type of study, including differing learning styles, which might influence the types of apps that evaluators found most impactful to their education. Interestingly, some apps earned a higher resident score than student score. In particular, RightSite (a reference that helps with anatomically correct labeling) and Mohs Surgery Appropriate Use Criteria (a clinical decision support tool to determine whether to perform Mohs surgery) each had a 3-point discrepancy (data not shown). A resident might benefit from these practical apps in day-to-day practice, but a student would be less likely to find them useful as a learning tool.
Still, by defining adequate teaching value using specific categories of educational objectives, content, accuracy, design, and conflict of interest, we attempted to minimize the effect of personal preference on the grading process. Although we acknowledge a degree of subjectivity, we found that utilizing a previously published rubric with defined criteria was crucial in remaining unbiased.
Conclusion
Further studies should evaluate additional apps available on Apple’s iPad (tablet), as well as those on other operating systems, including Google’s Android. To ensure the existence of mobile apps as adequate education tools, they should be peer reviewed prior to publication or before widespread use by future and current providers at the minimum. To maximize free access to highly valuable resources available in the palm of their hand, students and trainees should contact the library at their academic institution.
With today’s technology, it is easier than ever to access web-based tools that enrich traditional dermatology education. The literature supports the use of these innovative platforms to enhance learning at the student and trainee levels. A controlled study of pediatric residents showed that online modules effectively supplemented clinical experience with atopic dermatitis.1 In a randomized diagnostic study of medical students, practice with an image-based web application (app) that teaches rapid recognition of melanoma proved more effective than learning a rule-based algorithm.2 Given the visual nature of dermatology, pattern recognition is an essential skill that is fostered through experience and is only made more accessible with technology.
With the added benefit of convenience and accessibility, mobile apps can supplement experiential learning. Mirroring the overall growth of mobile apps, the number of available dermatology apps has increased.3 Dermatology mobile apps serve purposes ranging from quick reference tools to comprehensive modules, journals, and question banks. At an academic hospital in Taiwan, both nondermatology and dermatology trainees’ examination performance improved after 3 weeks of using a smartphone-based wallpaper learning module displaying morphologic characteristics of fungi.4 With the expansion of virtual microscopy, mobile apps also have been created as a learning tool for dermatopathology, giving trainees the flexibility and autonomy to view slides on their own time.5 Nevertheless, the literature on dermatology mobile apps designed for the education of medical students and trainees is limited, demonstrating a need for further investigation.
Prior studies have reviewed dermatology apps for patients and practicing dermatologists.6-8 Herein, we focus on mobile apps targeting students and residents learning dermatology. General dermatology reference apps and educational aid apps have grown by 33% and 32%, respectively, from 2014 to 2017.3 As with any resource meant to educate future and current medical providers, there must be an objective review process in place to ensure accurate, unbiased, evidence-based teaching.
Well-organized, comprehensive information and a user-friendly interface are additional factors of importance when selecting an educational mobile app. When discussing supplemental resources, accessibility and affordability also are priorities given the high cost of a medical education at baseline. Overall, there is a need for a standardized method to evaluate the key factors of an educational mobile app that make it appropriate for this demographic. We conducted a search of mobile apps relating to dermatology education for students and residents.
Methods
We searched for publicly available mobile apps relating to dermatology education in the App Store (Apple Inc) from September to November 2019 using the search terms dermatology education, dermoscopy education, melanoma education, skin cancer education, psoriasis education, rosacea education, acne education, eczema education, dermal fillers education, and Mohs surgery education. We excluded apps that were not in English, were created for a conference, cost more than $5 to download, or did not include a specific dermatology education section. In this way, we hoped to evaluate apps that were relevant, accessible, and affordable.
We modeled our study after a review of patient education apps performed by Masud et al6 and utilized their quantified grading rubric (scale of 1 to 4). We found their established criteria—educational objectives, content, accuracy, design, and conflict of interest—to be equally applicable for evaluating apps designed for professional education.6 Each app earned a minimum of 1 point and a maximum of 4 points per criterion. One point was given if the app did not fulfill the criterion, 2 points for minimally fulfilling the criterion, 3 points for mostly fulfilling the criterion, and 4 points if the criterion was completely fulfilled. Two medical students (E.H. and N.C.)—one at the preclinical stage and the other at the clinical stage of medical education—reviewed the apps using the given rubric, then discussed and resolved any discrepancies in points assigned. A dermatology resident (M.A.) independently reviewed the apps using the given rubric.
The mean of the student score and the resident score was calculated for each category. The sum of the averages for each category was considered the final score for an app, determining its overall quality. Apps with a total score of 5 to 10 were considered poor and inadequate for education. A total score of 10.5 to 15 indicated that an app was somewhat adequate (ie, useful for education in some aspects but falling short in others). Apps that were considered adequate for education, across all or most criteria, received a total score ranging from 15.5 to 20.
Results
Our search generated 130 apps. After applying exclusion criteria, 42 apps were eligible for review. At the time of publication, 36 of these apps were still available. The possible range of scores based on the rubric was 5 to 20. The actual range of scores was 7 to 20. Of the 36 apps, 2 (5.6%) were poor, 16 (44.4%) were somewhat adequate, and 18 (50%) were adequate. Formats included primary resources, such as clinical decision support tools, journals, references, and a podcast (Table 1). Additionally, interactive learning tools included games, learning modules, and apps for self-evaluation (Table 2). Thirty apps covered general dermatology; others focused on skin cancer (n=5) and cosmetic dermatology (n=1). Regarding cost, 29 apps were free to download, whereas 7 charged a fee (mean price, $2.56).


Comment
In addition to the convenience of having an educational tool in their white-coat pocket, learners of dermatology have been shown to benefit from supplementing their curriculum with mobile apps, which sets the stage for formal integration of mobile apps into dermatology teaching in the future.8 Prior to widespread adoption, mobile apps must be evaluated for content and utility, starting with an objective rubric.
Without official scientific standards in place, it was unsurprising that only half of the dermatology education applications were classified as adequate in this study. Among the types of apps offered—clinical decision support tools, journals, references, podcast, games, learning modules, and self-evaluation—certain categories scored higher than others. App formats with the highest average score (16.5 out of 20) were journals and podcast.
One barrier to utilization of these apps was that a subscription to the journals and podcast was required to obtain access to all available content. Students and trainees can seek out library resources at their academic institutions to take advantage of journal subscriptions available to them at no additional cost. Dermatology residents can take advantage of their complimentary membership in the American Academy of Dermatology for a free subscription to AAD Dialogues in Dermatology (otherwise $179 annually for nonresident members and $320 annually for nonmembers).
On the other hand, learning module was the lowest-rated format (average score, 11.3 out of 20), with only Medical Student: Dermatology qualifying as adequate (total score, 16). This finding is worrisome given that students and residents might look to learning modules for quick targeted lessons on specific topics.
The lowest-scoring app, a clinical decision support tool called Naturelize, received a total score of 7. Although it listed the indications and contraindications for dermal filler types to be used in different locations on the face, there was a clear conflict of interest, oversimplified design, and little evidence-based education, mirroring the current state of cosmetic dermatology training in residency, in which trainees think they are inadequately prepared for aesthetic procedures and comparative effectiveness research is lacking.9-11
At the opposite end of the spectrum, MyDermPath+ was a reference app with a total score of 20. The app cited credible authors with a medical degree (MD) and had an easy-to-use, well-designed interface, including a reference guide, differential builder, and quiz for a range of topics within dermatology. As a free download without in-app purchases or advertisements, there was no evidence of conflict of interest. The position of a dermatopathology app as the top dermatology education mobile app might reflect an increased emphasis on dermatopathology education in residency as well as a transition to digitization of slides.5
The second-highest scoring apps (total score of 19 points) were Dermatology Database and VisualDx. Both were references covering a wide range of dermatology topics. Dermatology Database was a comprehensive search tool for diseases, drugs, procedures, and terms that was simple and entirely free to use but did not cite references. VisualDx, as its name suggests, offered quality clinical images, complete guides with references, and a unique differential builder. An annual subscription is $399.99, but the process to gain free access through a participating academic institution was simple.
Games were a unique mobile app format; however, 2 of 3 games scored in the somewhat adequate range. The game DiagnosUs, which tested users’ ability to differentiate skin cancer and psoriasis from dermatitis on clinical images, would benefit from more comprehensive content as well as professional verification of true diagnoses, which earned the app 2 points in both the content and accuracy categories. The Unusual Suspects tested the ABCDE algorithm in a short learning module, followed by a simple game that involved identification of melanoma in a timed setting. Although the design was novel and interactive, the game was limited to the same 5 melanoma tumors overlaid on pictures of normal skin. The narrow scope earned 1 point for content, the redundancy in the game earned 3 points for design, and the lack of real clinical images earned 2 points for educational objectives. Although game-format mobile apps have the capability to challenge the user’s knowledge with a built-in feedback or reward system, improvements should be made to ensure that apps are equally educational as they are engaging.
AAD Dialogues in Dermatology was the only app in the form of a podcast and provided expert interviews along with disclosures, transcripts, commentary, and references. More than half the content in the app could not be accessed without a subscription, earning 2.5 points in the conflict of interest category. Additionally, several flaws resulted in a design score of 2.5, including inconsistent availability of transcripts, poor quality of sound on some episodes, difficulty distinguishing new episodes from those already played, and a glitch that removed the episode duration. Still, the app was a valuable and comprehensive resource, with clear objectives and cited references. With improvements in content, affordability, and user experience, apps in unique formats such as games and podcasts might appeal to kinesthetic and auditory learners.
An important factor to consider when discussing mobile apps for students and residents is cost. With rising prices of board examinations and preparation materials, supplementary study tools should not come with an exorbitant price tag. Therefore, we limited our evaluation to apps that were free or cost less than $5 to download. Even so, subscriptions and other in-app purchases were an obstacle in one-third of apps, ranging from $4.99 to unlock additional content in Rash Decisions to $69.99 to access most topics in Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas. The highest-rated app in our study, MyDermPath+, historically cost $19.99 to download but became free with a grant from the Sulzberger Foundation.12 An initial investment to develop quality apps for the purpose of dermatology education might pay off in the end.
To evaluate the apps from the perspective of the target demographic of this study, 2 medical students—one in the preclinical stage and the other in the clinical stage of medical education—and a dermatology resident graded the apps. Certain limitations exist in this type of study, including differing learning styles, which might influence the types of apps that evaluators found most impactful to their education. Interestingly, some apps earned a higher resident score than student score. In particular, RightSite (a reference that helps with anatomically correct labeling) and Mohs Surgery Appropriate Use Criteria (a clinical decision support tool to determine whether to perform Mohs surgery) each had a 3-point discrepancy (data not shown). A resident might benefit from these practical apps in day-to-day practice, but a student would be less likely to find them useful as a learning tool.
Still, by defining adequate teaching value using specific categories of educational objectives, content, accuracy, design, and conflict of interest, we attempted to minimize the effect of personal preference on the grading process. Although we acknowledge a degree of subjectivity, we found that utilizing a previously published rubric with defined criteria was crucial in remaining unbiased.
Conclusion
Further studies should evaluate additional apps available on Apple’s iPad (tablet), as well as those on other operating systems, including Google’s Android. To ensure the existence of mobile apps as adequate education tools, they should be peer reviewed prior to publication or before widespread use by future and current providers at the minimum. To maximize free access to highly valuable resources available in the palm of their hand, students and trainees should contact the library at their academic institution.
- Craddock MF, Blondin HM, Youssef MJ, et al. Online education improves pediatric residents' understanding of atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:64-69.
- Lacy FA, Coman GC, Holliday AC, et al. Assessment of smartphone application for teaching intuitive visual diagnosis of melanoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:730-731.
- Flaten HK, St Claire C, Schlager E, et al. Growth of mobile applications in dermatology--2017 update. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24:13.
- Liu R-F, Wang F-Y, Yen H, et al. A new mobile learning module using smartphone wallpapers in identification of medical fungi for medical students and residents. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:458-462.
- Shahriari N, Grant-Kels J, Murphy MJ. Dermatopathology education in the era of modern technology. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:763-771.
- Masud A, Shafi S, Rao BK. Mobile medical apps for patient education: a graded review of available dermatology apps. Cutis. 2018;101:141-144.
- Mercer JM. An array of mobile apps for dermatologists. J Cutan Med Surg. 2014;18:295-297.
- Tongdee E, Markowitz O. Mobile app rankings in dermatology. Cutis. 2018;102:252-256.
- Kirby JS, Adgerson CN, Anderson BE. A survey of dermatology resident education in cosmetic procedures. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:e23-e28.
- Waldman A, Sobanko JF, Alam M. Practice and educational gaps in cosmetic dermatologic surgery. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:341-346.
- Nielson CB, Harb JN, Motaparthi K. Education in cosmetic procedural dermatology: resident experiences and perceptions. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2019;12:E70-E72.
- Hanna MG, Parwani AV, Pantanowitz L, et al. Smartphone applications: a contemporary resource for dermatopathology. J Pathol Inform. 2015;6:44.
- Craddock MF, Blondin HM, Youssef MJ, et al. Online education improves pediatric residents' understanding of atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:64-69.
- Lacy FA, Coman GC, Holliday AC, et al. Assessment of smartphone application for teaching intuitive visual diagnosis of melanoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:730-731.
- Flaten HK, St Claire C, Schlager E, et al. Growth of mobile applications in dermatology--2017 update. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24:13.
- Liu R-F, Wang F-Y, Yen H, et al. A new mobile learning module using smartphone wallpapers in identification of medical fungi for medical students and residents. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:458-462.
- Shahriari N, Grant-Kels J, Murphy MJ. Dermatopathology education in the era of modern technology. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:763-771.
- Masud A, Shafi S, Rao BK. Mobile medical apps for patient education: a graded review of available dermatology apps. Cutis. 2018;101:141-144.
- Mercer JM. An array of mobile apps for dermatologists. J Cutan Med Surg. 2014;18:295-297.
- Tongdee E, Markowitz O. Mobile app rankings in dermatology. Cutis. 2018;102:252-256.
- Kirby JS, Adgerson CN, Anderson BE. A survey of dermatology resident education in cosmetic procedures. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:e23-e28.
- Waldman A, Sobanko JF, Alam M. Practice and educational gaps in cosmetic dermatologic surgery. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:341-346.
- Nielson CB, Harb JN, Motaparthi K. Education in cosmetic procedural dermatology: resident experiences and perceptions. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2019;12:E70-E72.
- Hanna MG, Parwani AV, Pantanowitz L, et al. Smartphone applications: a contemporary resource for dermatopathology. J Pathol Inform. 2015;6:44.
Practice Points
- Mobile applications (apps) are a convenient way to learn dermatology, but there is no objective method to assess their quality.
- To determine which apps are most useful for education, we performed a graded review of dermatology apps targeted to students and residents.
- By applying a rubric to 36 affordable apps, we identified 18 (50%) with adequate teaching value.
Reliability of Biopsy Margin Status for Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common type of skin cancer frequently encountered in both dermatology and primary care settings.1 When biopsies of these neoplasms are performed to confirm the diagnosis, pathology reports may indicate positive or negative margin status. No guidelines exist for reporting biopsy margin status for BCC, resulting in varied reporting practices among dermatopathologists. Furthermore, the terminology used to describe margin status can be ambiguous and differs among pathologists; language such as “approaches the margin” or “margins appear free” may be used, with nonuniform interpretation between pathologists and providers, leading to variability in patient management.2
When interpreting a negative margin status on a pathology report, one must question if the BCC extends beyond the margin in unexamined sections of the specimen, which could be the result of an irregular tumor growth pattern or tissue processing. It has been estimated that less than 2% of the peripheral surgical margin is ultimately examined when serial cross-sections are prepared histologically (the bread loaf technique). However, this estimation would depend on several variables, including the number and thickness of sections and the amount of tissue discarded during processing.3 Importantly, reports of a false-negative margin could lead both the clinician and patient to believe that the neoplasm has been completely removed, which could have serious consequences.
Our study sought to determine the reliability of negative biopsy margin status for BCC. We examined BCC biopsy specimens initially determined to have uninvolved margins on routine tissue processing and determined the proportion with truly negative margins after complete tissue block sectioning of the initial biopsy specimen. We felt this technique was a more accurate measurement of true margin status than examination of a re-excision specimen. We also identified any factors that were predictive of positive true margins.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective study evaluating tissue samples collected at Geisinger Health System (Danville, Pennsylvania) from January to December 2016. Specimens were queried via the electronic database system at our institution (CoPath). We included BCC biopsy specimens with negative histologic margins on initial assessment that subsequently had block exhaust levels routinely ordered. These levels are cut every 100 to 150 µm, generating approximately 8 glass slides. We excluded all tumors that did not fit these criteria as well as those in patients younger than 18 years. Data collection was performed utilizing specimen pathology reports in addition to the note from the corresponding clinician office visit from the institution’s electronic medical record (Epic). Appropriate statistical calculations were performed. This study was approved by an institutional review board at our institution, which is required for all research involving human participants. This served to ensure the proper review and storage of patients’ protected health information.
Results
The search yielded a total of 122 specimens from 104 patients after appropriate exclusions. We examined a total of 122 BCC biopsy specimens with negative initial margins: 121 (99.2%) shave biopsies and 1 (0.8%) punch biopsy. Of 122 specimens with negative initial margins, 53 (43.4%) were found to have a truly positive margin based on the presence of either tumor or stroma at the lateral or deep tissue edge after complete tissue block sectioning. Sixty-nine (56.6%) specimens had clear margins and were categorized as truly negative after complete tissue block sectioning. Specimens with positive and negative final margin status did not differ significantly with respect to patient age; gender; biopsy technique; number of gross specimen sections; or tumor characteristics, including location, size, and subtype (Table)(P>.05).
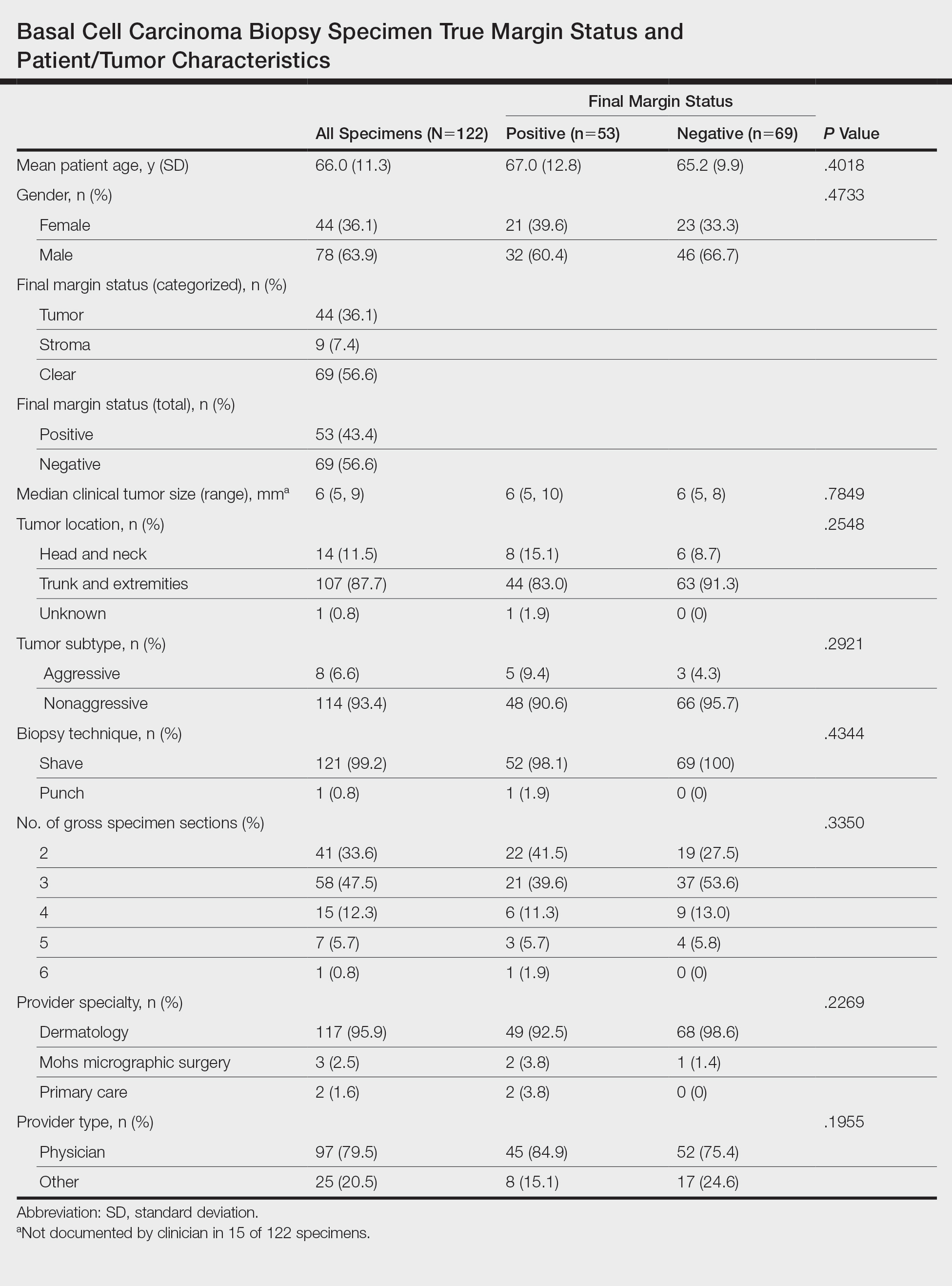
We also examined the type of treatment performed, which varied and included curettage, electrodesiccation and curettage, excision, and Mohs micrographic surgery. Clinicians, who were not made aware of the exhaust level protocol, chose not to pursue further treatment in 6 (4.9%) of the cases because of negative biopsy margins. Four (66.7%) of the 6 providers were physicians, and 2 (33.3%) were advanced practitioners. All of the providers practiced within the Department of Dermatology.
Comment
Our findings support prior smaller studies investigating this topic. A prospective study by Schnebelen et al4 examined 27 BCC biopsy specimens and found that 8 (30%) were erroneously classified as negative on routine examination. This study similarly determined true margin status by assessing the margins at complete tissue block exhaustion.4 Willardson et al5 also demonstrated the poor predictive value of margin status based on the presence of residual BCC in subsequent excisions. They found that 34 (24%) of 143 cases with negative biopsy margins contained residual tumor in the corresponding excision.5
Our study revealed that almost half of BCC biopsy specimens that had negative histologic margins with routine sectioning had truly positive margins on complete block exhaustion. This finding was independent of multiple factors, including tumor subtype, indicating that even nonaggressive tumors are prone to false-negative margin reports. We also found that reports of negative margins persuaded some clinicians to forgo definitive treatment. This study serves to remind clinicians of the limitations of margin assessment and provides impetus for dermatopathologists to consider modifying how margin status is reported.
Limitations of this study include a small number of cases and limited generalizability. Institutions that routinely examine more levels of each biopsy specimen may be less likely to erroneously categorize a positive margin as negative. Furthermore, despite exhausting the tissue block, we still may have underestimated the number of cases with truly positive margins, as this method inherently does not allow for complete margin examination.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Geisinger Department of Dermatopathology and the Geisinger Biostatistics & Research Data Core (Danville, Pennsylvania) for their assistance with our project.
- Lukowiak TM, Aizman L, Perz A, et al. Association of age, sex, race, and geographic region with variation of the ratio of basal cell to squamous cell carcinomas in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:1149-1276.
- Abide JM, Nahai F, Bennett RG. The meaning of surgical margins. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984;73:492-497.
- Kimyai-Asadi A, Goldberg LH, Jih MH. Accuracy of serial transverse cross-sections in detecting residual basal cell carcinoma at the surgical margins of an elliptical excision specimen. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:469-473.
- Schnebelen AM, Gardner JM, Shalin SC. Margin status in shave biopsies of nonmelanoma skin cancers: is it worth reporting? Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:678-681.
- Willardson HB, Lombardo J, Raines M, et al. Predictive value of basal cell carcinoma biopsies with negative margins: a retrospective cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:42-46.
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common type of skin cancer frequently encountered in both dermatology and primary care settings.1 When biopsies of these neoplasms are performed to confirm the diagnosis, pathology reports may indicate positive or negative margin status. No guidelines exist for reporting biopsy margin status for BCC, resulting in varied reporting practices among dermatopathologists. Furthermore, the terminology used to describe margin status can be ambiguous and differs among pathologists; language such as “approaches the margin” or “margins appear free” may be used, with nonuniform interpretation between pathologists and providers, leading to variability in patient management.2
When interpreting a negative margin status on a pathology report, one must question if the BCC extends beyond the margin in unexamined sections of the specimen, which could be the result of an irregular tumor growth pattern or tissue processing. It has been estimated that less than 2% of the peripheral surgical margin is ultimately examined when serial cross-sections are prepared histologically (the bread loaf technique). However, this estimation would depend on several variables, including the number and thickness of sections and the amount of tissue discarded during processing.3 Importantly, reports of a false-negative margin could lead both the clinician and patient to believe that the neoplasm has been completely removed, which could have serious consequences.
Our study sought to determine the reliability of negative biopsy margin status for BCC. We examined BCC biopsy specimens initially determined to have uninvolved margins on routine tissue processing and determined the proportion with truly negative margins after complete tissue block sectioning of the initial biopsy specimen. We felt this technique was a more accurate measurement of true margin status than examination of a re-excision specimen. We also identified any factors that were predictive of positive true margins.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective study evaluating tissue samples collected at Geisinger Health System (Danville, Pennsylvania) from January to December 2016. Specimens were queried via the electronic database system at our institution (CoPath). We included BCC biopsy specimens with negative histologic margins on initial assessment that subsequently had block exhaust levels routinely ordered. These levels are cut every 100 to 150 µm, generating approximately 8 glass slides. We excluded all tumors that did not fit these criteria as well as those in patients younger than 18 years. Data collection was performed utilizing specimen pathology reports in addition to the note from the corresponding clinician office visit from the institution’s electronic medical record (Epic). Appropriate statistical calculations were performed. This study was approved by an institutional review board at our institution, which is required for all research involving human participants. This served to ensure the proper review and storage of patients’ protected health information.
Results
The search yielded a total of 122 specimens from 104 patients after appropriate exclusions. We examined a total of 122 BCC biopsy specimens with negative initial margins: 121 (99.2%) shave biopsies and 1 (0.8%) punch biopsy. Of 122 specimens with negative initial margins, 53 (43.4%) were found to have a truly positive margin based on the presence of either tumor or stroma at the lateral or deep tissue edge after complete tissue block sectioning. Sixty-nine (56.6%) specimens had clear margins and were categorized as truly negative after complete tissue block sectioning. Specimens with positive and negative final margin status did not differ significantly with respect to patient age; gender; biopsy technique; number of gross specimen sections; or tumor characteristics, including location, size, and subtype (Table)(P>.05).

We also examined the type of treatment performed, which varied and included curettage, electrodesiccation and curettage, excision, and Mohs micrographic surgery. Clinicians, who were not made aware of the exhaust level protocol, chose not to pursue further treatment in 6 (4.9%) of the cases because of negative biopsy margins. Four (66.7%) of the 6 providers were physicians, and 2 (33.3%) were advanced practitioners. All of the providers practiced within the Department of Dermatology.
Comment
Our findings support prior smaller studies investigating this topic. A prospective study by Schnebelen et al4 examined 27 BCC biopsy specimens and found that 8 (30%) were erroneously classified as negative on routine examination. This study similarly determined true margin status by assessing the margins at complete tissue block exhaustion.4 Willardson et al5 also demonstrated the poor predictive value of margin status based on the presence of residual BCC in subsequent excisions. They found that 34 (24%) of 143 cases with negative biopsy margins contained residual tumor in the corresponding excision.5
Our study revealed that almost half of BCC biopsy specimens that had negative histologic margins with routine sectioning had truly positive margins on complete block exhaustion. This finding was independent of multiple factors, including tumor subtype, indicating that even nonaggressive tumors are prone to false-negative margin reports. We also found that reports of negative margins persuaded some clinicians to forgo definitive treatment. This study serves to remind clinicians of the limitations of margin assessment and provides impetus for dermatopathologists to consider modifying how margin status is reported.
Limitations of this study include a small number of cases and limited generalizability. Institutions that routinely examine more levels of each biopsy specimen may be less likely to erroneously categorize a positive margin as negative. Furthermore, despite exhausting the tissue block, we still may have underestimated the number of cases with truly positive margins, as this method inherently does not allow for complete margin examination.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Geisinger Department of Dermatopathology and the Geisinger Biostatistics & Research Data Core (Danville, Pennsylvania) for their assistance with our project.
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common type of skin cancer frequently encountered in both dermatology and primary care settings.1 When biopsies of these neoplasms are performed to confirm the diagnosis, pathology reports may indicate positive or negative margin status. No guidelines exist for reporting biopsy margin status for BCC, resulting in varied reporting practices among dermatopathologists. Furthermore, the terminology used to describe margin status can be ambiguous and differs among pathologists; language such as “approaches the margin” or “margins appear free” may be used, with nonuniform interpretation between pathologists and providers, leading to variability in patient management.2
When interpreting a negative margin status on a pathology report, one must question if the BCC extends beyond the margin in unexamined sections of the specimen, which could be the result of an irregular tumor growth pattern or tissue processing. It has been estimated that less than 2% of the peripheral surgical margin is ultimately examined when serial cross-sections are prepared histologically (the bread loaf technique). However, this estimation would depend on several variables, including the number and thickness of sections and the amount of tissue discarded during processing.3 Importantly, reports of a false-negative margin could lead both the clinician and patient to believe that the neoplasm has been completely removed, which could have serious consequences.
Our study sought to determine the reliability of negative biopsy margin status for BCC. We examined BCC biopsy specimens initially determined to have uninvolved margins on routine tissue processing and determined the proportion with truly negative margins after complete tissue block sectioning of the initial biopsy specimen. We felt this technique was a more accurate measurement of true margin status than examination of a re-excision specimen. We also identified any factors that were predictive of positive true margins.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective study evaluating tissue samples collected at Geisinger Health System (Danville, Pennsylvania) from January to December 2016. Specimens were queried via the electronic database system at our institution (CoPath). We included BCC biopsy specimens with negative histologic margins on initial assessment that subsequently had block exhaust levels routinely ordered. These levels are cut every 100 to 150 µm, generating approximately 8 glass slides. We excluded all tumors that did not fit these criteria as well as those in patients younger than 18 years. Data collection was performed utilizing specimen pathology reports in addition to the note from the corresponding clinician office visit from the institution’s electronic medical record (Epic). Appropriate statistical calculations were performed. This study was approved by an institutional review board at our institution, which is required for all research involving human participants. This served to ensure the proper review and storage of patients’ protected health information.
Results
The search yielded a total of 122 specimens from 104 patients after appropriate exclusions. We examined a total of 122 BCC biopsy specimens with negative initial margins: 121 (99.2%) shave biopsies and 1 (0.8%) punch biopsy. Of 122 specimens with negative initial margins, 53 (43.4%) were found to have a truly positive margin based on the presence of either tumor or stroma at the lateral or deep tissue edge after complete tissue block sectioning. Sixty-nine (56.6%) specimens had clear margins and were categorized as truly negative after complete tissue block sectioning. Specimens with positive and negative final margin status did not differ significantly with respect to patient age; gender; biopsy technique; number of gross specimen sections; or tumor characteristics, including location, size, and subtype (Table)(P>.05).

We also examined the type of treatment performed, which varied and included curettage, electrodesiccation and curettage, excision, and Mohs micrographic surgery. Clinicians, who were not made aware of the exhaust level protocol, chose not to pursue further treatment in 6 (4.9%) of the cases because of negative biopsy margins. Four (66.7%) of the 6 providers were physicians, and 2 (33.3%) were advanced practitioners. All of the providers practiced within the Department of Dermatology.
Comment
Our findings support prior smaller studies investigating this topic. A prospective study by Schnebelen et al4 examined 27 BCC biopsy specimens and found that 8 (30%) were erroneously classified as negative on routine examination. This study similarly determined true margin status by assessing the margins at complete tissue block exhaustion.4 Willardson et al5 also demonstrated the poor predictive value of margin status based on the presence of residual BCC in subsequent excisions. They found that 34 (24%) of 143 cases with negative biopsy margins contained residual tumor in the corresponding excision.5
Our study revealed that almost half of BCC biopsy specimens that had negative histologic margins with routine sectioning had truly positive margins on complete block exhaustion. This finding was independent of multiple factors, including tumor subtype, indicating that even nonaggressive tumors are prone to false-negative margin reports. We also found that reports of negative margins persuaded some clinicians to forgo definitive treatment. This study serves to remind clinicians of the limitations of margin assessment and provides impetus for dermatopathologists to consider modifying how margin status is reported.
Limitations of this study include a small number of cases and limited generalizability. Institutions that routinely examine more levels of each biopsy specimen may be less likely to erroneously categorize a positive margin as negative. Furthermore, despite exhausting the tissue block, we still may have underestimated the number of cases with truly positive margins, as this method inherently does not allow for complete margin examination.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Geisinger Department of Dermatopathology and the Geisinger Biostatistics & Research Data Core (Danville, Pennsylvania) for their assistance with our project.
- Lukowiak TM, Aizman L, Perz A, et al. Association of age, sex, race, and geographic region with variation of the ratio of basal cell to squamous cell carcinomas in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:1149-1276.
- Abide JM, Nahai F, Bennett RG. The meaning of surgical margins. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984;73:492-497.
- Kimyai-Asadi A, Goldberg LH, Jih MH. Accuracy of serial transverse cross-sections in detecting residual basal cell carcinoma at the surgical margins of an elliptical excision specimen. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:469-473.
- Schnebelen AM, Gardner JM, Shalin SC. Margin status in shave biopsies of nonmelanoma skin cancers: is it worth reporting? Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:678-681.
- Willardson HB, Lombardo J, Raines M, et al. Predictive value of basal cell carcinoma biopsies with negative margins: a retrospective cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:42-46.
- Lukowiak TM, Aizman L, Perz A, et al. Association of age, sex, race, and geographic region with variation of the ratio of basal cell to squamous cell carcinomas in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:1149-1276.
- Abide JM, Nahai F, Bennett RG. The meaning of surgical margins. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984;73:492-497.
- Kimyai-Asadi A, Goldberg LH, Jih MH. Accuracy of serial transverse cross-sections in detecting residual basal cell carcinoma at the surgical margins of an elliptical excision specimen. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:469-473.
- Schnebelen AM, Gardner JM, Shalin SC. Margin status in shave biopsies of nonmelanoma skin cancers: is it worth reporting? Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:678-681.
- Willardson HB, Lombardo J, Raines M, et al. Predictive value of basal cell carcinoma biopsies with negative margins: a retrospective cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:42-46.
Practice Points
- Clinicians must recognize the limitations of margin assessment of biopsy specimens and not rely on margin status to dictate treatment.
- Dermatopathologists should consider modifying how margin status is reported, either by omitting it or clarifying its limitations on the pathology report.