User login
Sea Buckthorn
A member of the Elaeagnaceae family, Hippophae rhamnoides, better known as sea buckthorn, is a high-altitude wild shrub endemic to Europe and Asia with edible fruits and a lengthy record of use in traditional Chinese medicine.1-6 Used as a health supplement and consumed in the diet throughout the world,5 sea buckthorn berries, seeds, and leaves have been used in traditional medicine to treat burns/injuries, edema, hypertension, inflammation, skin grafts, ulcers, and wounds.4,7
This hardy plant is associated with a wide range of biologic activities, including anti-atherogenic, anti-atopic dermatitis, antibacterial, anticancer, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-psoriasis, anti-sebum, anti-stress, anti-tumor, cytoprotective, hepatoprotective, immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, radioprotective, and tissue regenerative functions.4,5,8-11
Key Constituents
Functional constituents identified in sea buckthorn include alkaloids, carotenoids, flavonoids, lignans, organic acids, phenolic acids, proanthocyanidins, polyunsaturated acids (including omega-3, -6, -7, and -9), steroids, tannins, terpenoids, and volatile oils, as well as nutritional compounds such as minerals, proteins, and vitamins.4,5,11 Sea buckthorn pericarp oil contains copious amounts of saturated palmitic acid (29%-36%) and omega-7 unsaturated palmitoleic acid (36%-48%), which fosters cutaneous and mucosal epithelialization, as well as linoleic (10%-12%) and oleic (4%-6%) acids.12,6 Significant amounts of carotenoids as well as alpha‐linolenic fatty acid (38%), linoleic (36%), oleic (13%), and palmitic (7%) acids are present in sea buckthorn seed oil.6
Polysaccharides
In an expansive review on the pharmacological activities of sea buckthorn polysaccharides, Teng and colleagues reported in April 2024 that 20 diverse polysaccharides have been culled from sea buckthorn and exhibited various healthy activities, including antioxidant, anti-fatigue, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, anti-tumor, hepatoprotective, hypoglycemic, and immunoregulation, and regulation of intestinal flora activities.1
Proanthocyanidins and Anti-Aging
In 2023, Liu and colleagues investigated the anti–skin aging impact of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins in D-galactose-induced aging in mice given the known free radical scavenging activity of these compounds. They found the proanthocyanidins mitigated D-galactose-induced aging and can augment the total antioxidant capacity of the body. Sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can further attenuate the effects of skin aging by regulating the TGF-beta1/Smads pathway and MMPs/TIMP system, thus amplifying collagen I and tropoelastin content.13
A year earlier, many of the same investigators assessed the possible protective activity of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins against cutaneous aging engendered by oxidative stress from hydrogen peroxide. The compounds amplified superoxide dismutase and glutathione antioxidant functions. The extracts also fostered collagen I production in aging human skin fibroblasts via the TGF-beta1/Smads pathway and hindered collagen I degradation by regulating the MMPs/TIMPs system, which maintained extracellular matrix integrity. Senescent cell migration was also promoted with 100 mcg/mL of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins. The researchers concluded that this sets the stage for investigating how sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can be incorporated in cosmetic formulations.14 In a separate study, Liu and colleagues demonstrated that sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can attenuate oxidative damage and protect mitochondrial function.9
Acne and Barrier Functions
The extracts of H rhamnoides and Cassia fistula in a combined formulation were found to be effective in lowering skin sebum content in humans with grade I and grade II acne vulgaris in a 2014 single-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, split-face study with two groups of 25 patients each (aged 18-37 years).15 Khan and colleagues have also reported that a sea buckthorn oil-in-water emulsion improved barrier function in human skin as tested by a tewameter and corneometer (noninvasive probes) in 13 healthy males with a mean age of 27 ± 4.8 years.16
Anti-Aging, Antioxidant, Antibacterial, Skin-Whitening Activity
Zaman and colleagues reported in 2011 that results from an in vivo study of the effects of a sea buckthorn fruit extract topical cream on stratum corneum water content and transepidermal water loss indicated that the formulation enhanced cell surface integrin expression thus facilitating collagen contraction.17
In 2012, Khan and colleagues reported amelioration in skin elasticity, thus achieving an anti-aging result, from the use of a water-in-oil–based hydroalcoholic cream loaded with fruit extract of H rhamnoides, as measured with a Cutometer.18 The previous year, some of the same researchers reported that the antioxidants and flavonoids found in a topical sea buckthorn formulation could decrease cutaneous melanin and erythema levels.
More recently, Gęgotek and colleagues found that sea buckthorn seed oil prevented redox balance and lipid metabolism disturbances in skin fibroblasts and keratinocytes caused by UVA or UVB. They suggested that such findings point to the potential of this natural agent to confer anti-inflammatory properties and photoprotection to the skin.19
In 2020, Ivanišová and colleagues investigated the antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of H rhamnoides 100% oil, 100% juice, dry berries, and tea (dry berries, leaves, and twigs). They found that all of the studied sea buckthorn products displayed high antioxidant activity (identified through DPPH radical scavenging and molybdenum reducing antioxidant power tests). Sea buckthorn juice contained the highest total content of polyphenols, flavonoids, and carotenoids. All of the tested products also exhibited substantial antibacterial activity against the tested microbes.20
Burns and Wound Healing
In a preclinical study of the effects of sea buckthorn leaf extracts on wound healing in albino rats using an excision-punch wound model in 2005, Gupta and colleagues found that twice daily topical application of the aqueous leaf extract fostered wound healing. This was indicated by higher hydroxyproline and protein levels, a diminished wound area, and lower lipid peroxide levels. The investigators suggested that sea buckthorn may facilitate wound healing at least in part because of elevated antioxidant activity in the granulation tissue.3
A year later, Wang and colleagues reported on observations of using H rhamnoides oil, a traditional Chinese herbal medicine derived from sea buckthorn fruit, as a burn treatment. In the study, 151 burn patients received an H rhamnoides oil dressing (changed every other day until wound healing) that was covered with a disinfecting dressing. The dressing reduced swelling and effusion, and alleviated pain, with patients receiving the sea buckthorn dressing experiencing greater apparent exudation reduction, pain reduction, and more rapid epithelial cell growth and wound healing than controls (treated only with Vaseline gauze). The difference between the two groups was statistically significant.21
Conclusion
Sea buckthorn has been used for hundreds if not thousands of years in traditional medical applications, including for dermatologic purposes. Emerging data appear to support the use of this dynamic plant for consideration in dermatologic applications. As is often the case, much more work is necessary in the form of randomized controlled trials to determine the effectiveness of sea buckthorn formulations as well as the most appropriate avenues of research or uses for dermatologic application of this traditionally used botanical agent.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as a e-commerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Teng H et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Apr 24;324:117809. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117809.
2. Wang Z et al. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Apr;263(Pt 1):130206. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130206.
3. Gupta A et al. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2005 Jun;4(2):88-92. doi: 10.1177/1534734605277401.
4. Pundir S et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Feb 10;266:113434. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113434.
5. Ma QG et al. J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Mar 29;71(12):4769-4788. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06916.
6. Poljšak N et al. Phytother Res. 2020 Feb;34(2):254-269. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6524. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6524.
7. Upadhyay NK et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:659705. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nep189.
8. Suryakumar G, Gupta A. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Nov 18;138(2):268-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.09.024.
9. Liu K et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 8;13:914146. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.914146.
10. Akhtar N et al. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2010 Jan;2(1):13-7. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.62698.
11. Ren R et al. RSC Adv. 2020 Dec 17;10(73):44654-44671. doi: 10.1039/d0ra06488b.
12. Ito H et al. Burns. 2014 May;40(3):511-9. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2013.08.011.
13. Liu X et al. Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Dec 7;12(2):1082-1094. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3823.
14. Liu X at al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 25;11(10):1900. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101900.
15. Khan BA, Akhtar N. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2014 Aug;31(4):229-234. doi: 10.5114/pdia.2014.40934.
16. Khan BA, Akhtar N. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2014 Nov;27(6):1919-22.
17. Khan AB et al. African J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;5(8):1092-5.
18. Khan BA, Akhtar N, Braga VA. Trop J Pharm Res. 2012;11(6):955-62.
19. Gęgotek A et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Aug 23;7(9):110. doi: 10.3390/antiox7090110.
20. Ivanišová E et al. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment. 2020 Apr-Jun;19(2):195-205. doi: 10.17306/J.AFS.0809.
21. Wang ZY, Luo XL, He CP. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2006 Jan;26(1):124-5.
A member of the Elaeagnaceae family, Hippophae rhamnoides, better known as sea buckthorn, is a high-altitude wild shrub endemic to Europe and Asia with edible fruits and a lengthy record of use in traditional Chinese medicine.1-6 Used as a health supplement and consumed in the diet throughout the world,5 sea buckthorn berries, seeds, and leaves have been used in traditional medicine to treat burns/injuries, edema, hypertension, inflammation, skin grafts, ulcers, and wounds.4,7
This hardy plant is associated with a wide range of biologic activities, including anti-atherogenic, anti-atopic dermatitis, antibacterial, anticancer, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-psoriasis, anti-sebum, anti-stress, anti-tumor, cytoprotective, hepatoprotective, immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, radioprotective, and tissue regenerative functions.4,5,8-11
Key Constituents
Functional constituents identified in sea buckthorn include alkaloids, carotenoids, flavonoids, lignans, organic acids, phenolic acids, proanthocyanidins, polyunsaturated acids (including omega-3, -6, -7, and -9), steroids, tannins, terpenoids, and volatile oils, as well as nutritional compounds such as minerals, proteins, and vitamins.4,5,11 Sea buckthorn pericarp oil contains copious amounts of saturated palmitic acid (29%-36%) and omega-7 unsaturated palmitoleic acid (36%-48%), which fosters cutaneous and mucosal epithelialization, as well as linoleic (10%-12%) and oleic (4%-6%) acids.12,6 Significant amounts of carotenoids as well as alpha‐linolenic fatty acid (38%), linoleic (36%), oleic (13%), and palmitic (7%) acids are present in sea buckthorn seed oil.6
Polysaccharides
In an expansive review on the pharmacological activities of sea buckthorn polysaccharides, Teng and colleagues reported in April 2024 that 20 diverse polysaccharides have been culled from sea buckthorn and exhibited various healthy activities, including antioxidant, anti-fatigue, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, anti-tumor, hepatoprotective, hypoglycemic, and immunoregulation, and regulation of intestinal flora activities.1
Proanthocyanidins and Anti-Aging
In 2023, Liu and colleagues investigated the anti–skin aging impact of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins in D-galactose-induced aging in mice given the known free radical scavenging activity of these compounds. They found the proanthocyanidins mitigated D-galactose-induced aging and can augment the total antioxidant capacity of the body. Sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can further attenuate the effects of skin aging by regulating the TGF-beta1/Smads pathway and MMPs/TIMP system, thus amplifying collagen I and tropoelastin content.13
A year earlier, many of the same investigators assessed the possible protective activity of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins against cutaneous aging engendered by oxidative stress from hydrogen peroxide. The compounds amplified superoxide dismutase and glutathione antioxidant functions. The extracts also fostered collagen I production in aging human skin fibroblasts via the TGF-beta1/Smads pathway and hindered collagen I degradation by regulating the MMPs/TIMPs system, which maintained extracellular matrix integrity. Senescent cell migration was also promoted with 100 mcg/mL of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins. The researchers concluded that this sets the stage for investigating how sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can be incorporated in cosmetic formulations.14 In a separate study, Liu and colleagues demonstrated that sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can attenuate oxidative damage and protect mitochondrial function.9
Acne and Barrier Functions
The extracts of H rhamnoides and Cassia fistula in a combined formulation were found to be effective in lowering skin sebum content in humans with grade I and grade II acne vulgaris in a 2014 single-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, split-face study with two groups of 25 patients each (aged 18-37 years).15 Khan and colleagues have also reported that a sea buckthorn oil-in-water emulsion improved barrier function in human skin as tested by a tewameter and corneometer (noninvasive probes) in 13 healthy males with a mean age of 27 ± 4.8 years.16
Anti-Aging, Antioxidant, Antibacterial, Skin-Whitening Activity
Zaman and colleagues reported in 2011 that results from an in vivo study of the effects of a sea buckthorn fruit extract topical cream on stratum corneum water content and transepidermal water loss indicated that the formulation enhanced cell surface integrin expression thus facilitating collagen contraction.17
In 2012, Khan and colleagues reported amelioration in skin elasticity, thus achieving an anti-aging result, from the use of a water-in-oil–based hydroalcoholic cream loaded with fruit extract of H rhamnoides, as measured with a Cutometer.18 The previous year, some of the same researchers reported that the antioxidants and flavonoids found in a topical sea buckthorn formulation could decrease cutaneous melanin and erythema levels.
More recently, Gęgotek and colleagues found that sea buckthorn seed oil prevented redox balance and lipid metabolism disturbances in skin fibroblasts and keratinocytes caused by UVA or UVB. They suggested that such findings point to the potential of this natural agent to confer anti-inflammatory properties and photoprotection to the skin.19
In 2020, Ivanišová and colleagues investigated the antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of H rhamnoides 100% oil, 100% juice, dry berries, and tea (dry berries, leaves, and twigs). They found that all of the studied sea buckthorn products displayed high antioxidant activity (identified through DPPH radical scavenging and molybdenum reducing antioxidant power tests). Sea buckthorn juice contained the highest total content of polyphenols, flavonoids, and carotenoids. All of the tested products also exhibited substantial antibacterial activity against the tested microbes.20
Burns and Wound Healing
In a preclinical study of the effects of sea buckthorn leaf extracts on wound healing in albino rats using an excision-punch wound model in 2005, Gupta and colleagues found that twice daily topical application of the aqueous leaf extract fostered wound healing. This was indicated by higher hydroxyproline and protein levels, a diminished wound area, and lower lipid peroxide levels. The investigators suggested that sea buckthorn may facilitate wound healing at least in part because of elevated antioxidant activity in the granulation tissue.3
A year later, Wang and colleagues reported on observations of using H rhamnoides oil, a traditional Chinese herbal medicine derived from sea buckthorn fruit, as a burn treatment. In the study, 151 burn patients received an H rhamnoides oil dressing (changed every other day until wound healing) that was covered with a disinfecting dressing. The dressing reduced swelling and effusion, and alleviated pain, with patients receiving the sea buckthorn dressing experiencing greater apparent exudation reduction, pain reduction, and more rapid epithelial cell growth and wound healing than controls (treated only with Vaseline gauze). The difference between the two groups was statistically significant.21
Conclusion
Sea buckthorn has been used for hundreds if not thousands of years in traditional medical applications, including for dermatologic purposes. Emerging data appear to support the use of this dynamic plant for consideration in dermatologic applications. As is often the case, much more work is necessary in the form of randomized controlled trials to determine the effectiveness of sea buckthorn formulations as well as the most appropriate avenues of research or uses for dermatologic application of this traditionally used botanical agent.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as a e-commerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Teng H et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Apr 24;324:117809. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117809.
2. Wang Z et al. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Apr;263(Pt 1):130206. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130206.
3. Gupta A et al. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2005 Jun;4(2):88-92. doi: 10.1177/1534734605277401.
4. Pundir S et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Feb 10;266:113434. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113434.
5. Ma QG et al. J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Mar 29;71(12):4769-4788. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06916.
6. Poljšak N et al. Phytother Res. 2020 Feb;34(2):254-269. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6524. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6524.
7. Upadhyay NK et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:659705. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nep189.
8. Suryakumar G, Gupta A. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Nov 18;138(2):268-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.09.024.
9. Liu K et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 8;13:914146. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.914146.
10. Akhtar N et al. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2010 Jan;2(1):13-7. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.62698.
11. Ren R et al. RSC Adv. 2020 Dec 17;10(73):44654-44671. doi: 10.1039/d0ra06488b.
12. Ito H et al. Burns. 2014 May;40(3):511-9. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2013.08.011.
13. Liu X et al. Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Dec 7;12(2):1082-1094. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3823.
14. Liu X at al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 25;11(10):1900. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101900.
15. Khan BA, Akhtar N. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2014 Aug;31(4):229-234. doi: 10.5114/pdia.2014.40934.
16. Khan BA, Akhtar N. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2014 Nov;27(6):1919-22.
17. Khan AB et al. African J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;5(8):1092-5.
18. Khan BA, Akhtar N, Braga VA. Trop J Pharm Res. 2012;11(6):955-62.
19. Gęgotek A et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Aug 23;7(9):110. doi: 10.3390/antiox7090110.
20. Ivanišová E et al. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment. 2020 Apr-Jun;19(2):195-205. doi: 10.17306/J.AFS.0809.
21. Wang ZY, Luo XL, He CP. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2006 Jan;26(1):124-5.
A member of the Elaeagnaceae family, Hippophae rhamnoides, better known as sea buckthorn, is a high-altitude wild shrub endemic to Europe and Asia with edible fruits and a lengthy record of use in traditional Chinese medicine.1-6 Used as a health supplement and consumed in the diet throughout the world,5 sea buckthorn berries, seeds, and leaves have been used in traditional medicine to treat burns/injuries, edema, hypertension, inflammation, skin grafts, ulcers, and wounds.4,7
This hardy plant is associated with a wide range of biologic activities, including anti-atherogenic, anti-atopic dermatitis, antibacterial, anticancer, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-psoriasis, anti-sebum, anti-stress, anti-tumor, cytoprotective, hepatoprotective, immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, radioprotective, and tissue regenerative functions.4,5,8-11
Key Constituents
Functional constituents identified in sea buckthorn include alkaloids, carotenoids, flavonoids, lignans, organic acids, phenolic acids, proanthocyanidins, polyunsaturated acids (including omega-3, -6, -7, and -9), steroids, tannins, terpenoids, and volatile oils, as well as nutritional compounds such as minerals, proteins, and vitamins.4,5,11 Sea buckthorn pericarp oil contains copious amounts of saturated palmitic acid (29%-36%) and omega-7 unsaturated palmitoleic acid (36%-48%), which fosters cutaneous and mucosal epithelialization, as well as linoleic (10%-12%) and oleic (4%-6%) acids.12,6 Significant amounts of carotenoids as well as alpha‐linolenic fatty acid (38%), linoleic (36%), oleic (13%), and palmitic (7%) acids are present in sea buckthorn seed oil.6
Polysaccharides
In an expansive review on the pharmacological activities of sea buckthorn polysaccharides, Teng and colleagues reported in April 2024 that 20 diverse polysaccharides have been culled from sea buckthorn and exhibited various healthy activities, including antioxidant, anti-fatigue, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, anti-tumor, hepatoprotective, hypoglycemic, and immunoregulation, and regulation of intestinal flora activities.1
Proanthocyanidins and Anti-Aging
In 2023, Liu and colleagues investigated the anti–skin aging impact of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins in D-galactose-induced aging in mice given the known free radical scavenging activity of these compounds. They found the proanthocyanidins mitigated D-galactose-induced aging and can augment the total antioxidant capacity of the body. Sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can further attenuate the effects of skin aging by regulating the TGF-beta1/Smads pathway and MMPs/TIMP system, thus amplifying collagen I and tropoelastin content.13
A year earlier, many of the same investigators assessed the possible protective activity of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins against cutaneous aging engendered by oxidative stress from hydrogen peroxide. The compounds amplified superoxide dismutase and glutathione antioxidant functions. The extracts also fostered collagen I production in aging human skin fibroblasts via the TGF-beta1/Smads pathway and hindered collagen I degradation by regulating the MMPs/TIMPs system, which maintained extracellular matrix integrity. Senescent cell migration was also promoted with 100 mcg/mL of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins. The researchers concluded that this sets the stage for investigating how sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can be incorporated in cosmetic formulations.14 In a separate study, Liu and colleagues demonstrated that sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can attenuate oxidative damage and protect mitochondrial function.9
Acne and Barrier Functions
The extracts of H rhamnoides and Cassia fistula in a combined formulation were found to be effective in lowering skin sebum content in humans with grade I and grade II acne vulgaris in a 2014 single-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, split-face study with two groups of 25 patients each (aged 18-37 years).15 Khan and colleagues have also reported that a sea buckthorn oil-in-water emulsion improved barrier function in human skin as tested by a tewameter and corneometer (noninvasive probes) in 13 healthy males with a mean age of 27 ± 4.8 years.16
Anti-Aging, Antioxidant, Antibacterial, Skin-Whitening Activity
Zaman and colleagues reported in 2011 that results from an in vivo study of the effects of a sea buckthorn fruit extract topical cream on stratum corneum water content and transepidermal water loss indicated that the formulation enhanced cell surface integrin expression thus facilitating collagen contraction.17
In 2012, Khan and colleagues reported amelioration in skin elasticity, thus achieving an anti-aging result, from the use of a water-in-oil–based hydroalcoholic cream loaded with fruit extract of H rhamnoides, as measured with a Cutometer.18 The previous year, some of the same researchers reported that the antioxidants and flavonoids found in a topical sea buckthorn formulation could decrease cutaneous melanin and erythema levels.
More recently, Gęgotek and colleagues found that sea buckthorn seed oil prevented redox balance and lipid metabolism disturbances in skin fibroblasts and keratinocytes caused by UVA or UVB. They suggested that such findings point to the potential of this natural agent to confer anti-inflammatory properties and photoprotection to the skin.19
In 2020, Ivanišová and colleagues investigated the antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of H rhamnoides 100% oil, 100% juice, dry berries, and tea (dry berries, leaves, and twigs). They found that all of the studied sea buckthorn products displayed high antioxidant activity (identified through DPPH radical scavenging and molybdenum reducing antioxidant power tests). Sea buckthorn juice contained the highest total content of polyphenols, flavonoids, and carotenoids. All of the tested products also exhibited substantial antibacterial activity against the tested microbes.20
Burns and Wound Healing
In a preclinical study of the effects of sea buckthorn leaf extracts on wound healing in albino rats using an excision-punch wound model in 2005, Gupta and colleagues found that twice daily topical application of the aqueous leaf extract fostered wound healing. This was indicated by higher hydroxyproline and protein levels, a diminished wound area, and lower lipid peroxide levels. The investigators suggested that sea buckthorn may facilitate wound healing at least in part because of elevated antioxidant activity in the granulation tissue.3
A year later, Wang and colleagues reported on observations of using H rhamnoides oil, a traditional Chinese herbal medicine derived from sea buckthorn fruit, as a burn treatment. In the study, 151 burn patients received an H rhamnoides oil dressing (changed every other day until wound healing) that was covered with a disinfecting dressing. The dressing reduced swelling and effusion, and alleviated pain, with patients receiving the sea buckthorn dressing experiencing greater apparent exudation reduction, pain reduction, and more rapid epithelial cell growth and wound healing than controls (treated only with Vaseline gauze). The difference between the two groups was statistically significant.21
Conclusion
Sea buckthorn has been used for hundreds if not thousands of years in traditional medical applications, including for dermatologic purposes. Emerging data appear to support the use of this dynamic plant for consideration in dermatologic applications. As is often the case, much more work is necessary in the form of randomized controlled trials to determine the effectiveness of sea buckthorn formulations as well as the most appropriate avenues of research or uses for dermatologic application of this traditionally used botanical agent.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as a e-commerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Teng H et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Apr 24;324:117809. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117809.
2. Wang Z et al. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Apr;263(Pt 1):130206. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130206.
3. Gupta A et al. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2005 Jun;4(2):88-92. doi: 10.1177/1534734605277401.
4. Pundir S et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Feb 10;266:113434. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113434.
5. Ma QG et al. J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Mar 29;71(12):4769-4788. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06916.
6. Poljšak N et al. Phytother Res. 2020 Feb;34(2):254-269. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6524. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6524.
7. Upadhyay NK et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:659705. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nep189.
8. Suryakumar G, Gupta A. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Nov 18;138(2):268-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.09.024.
9. Liu K et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 8;13:914146. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.914146.
10. Akhtar N et al. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2010 Jan;2(1):13-7. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.62698.
11. Ren R et al. RSC Adv. 2020 Dec 17;10(73):44654-44671. doi: 10.1039/d0ra06488b.
12. Ito H et al. Burns. 2014 May;40(3):511-9. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2013.08.011.
13. Liu X et al. Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Dec 7;12(2):1082-1094. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3823.
14. Liu X at al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 25;11(10):1900. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101900.
15. Khan BA, Akhtar N. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2014 Aug;31(4):229-234. doi: 10.5114/pdia.2014.40934.
16. Khan BA, Akhtar N. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2014 Nov;27(6):1919-22.
17. Khan AB et al. African J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;5(8):1092-5.
18. Khan BA, Akhtar N, Braga VA. Trop J Pharm Res. 2012;11(6):955-62.
19. Gęgotek A et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Aug 23;7(9):110. doi: 10.3390/antiox7090110.
20. Ivanišová E et al. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment. 2020 Apr-Jun;19(2):195-205. doi: 10.17306/J.AFS.0809.
21. Wang ZY, Luo XL, He CP. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2006 Jan;26(1):124-5.
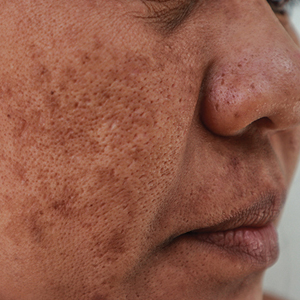
New Cosmeceutical as Effective as Cysteamine for Facial Melasma
A presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2024 Congress.
“Melasyl is a new potent melanogenesis inhibitor that exhibits a unique mode of action while preserving melanocyte integrity,” Mukta Sachdev, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology at Manipal Hospital in Bangalore, India, said at a late-breaking news session.
Both the serum and the cysteamine cream lightened participants’ skin to a similar extent, according to the modified Melasma Area and Severity Index (mMASI), with respective reductions of 4.19 and 3.81 points over a period of 4 months from baseline values of 11.15 and 10.93.
The mMASI score ranges from 0 to 24, with the lowest score representing the least and the highest score the most severe hyperpigmentation of the skin.
But the serum performed better than the cream by another measure. Judged by investigators blinded to which preparation study participants had been using, there was a significantly higher reduction in the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score from baseline among those treated with the serum than among those treated with the cream (−51.85% vs −39.06%; P = .0163).
Moreover, after 4 months of treatment, there were significantly more participants with clear or almost clear skin with the serum than with the cream (17.46% vs 7.81%; P = .0163), Sachdev reported.
Other skin parameters relative to melasma, such as the brightness of skin tone and evenness of the improvement, improved more in the participants using the serum vs cream, she said.
With “no side effects, no local skin reactions,” Sachdev said, “quality of life improved significantly and similarly, and almost all subjects in both groups were very satisfied with their treatment options.”
Active Ingredients
Margarida Gonçalo, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Coimbra, in Portugal, who co-chaired the late-breaking news session, commented: “It’s really nice to have new products to treat such a devastating disease.”
Session co-chair, Lidia Rudnicka, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology, Medical University of Warsaw, in Poland, and president of the Polish Dermatological Society, wanted to know more about the active ingredients of the serum and the study’s design.
Sachdev replied that the serum also contains other ingredients that provide “antioxidant protection” and moisturization. These include retinyl palmitate, which works on the dermal-epidermal junction, and hyaluronic acid, as well as “soothing agents,” such as the medicinal herb Centella asiatica, she said.
Study Design
Conducted at a single center in India, the study involved 127 adults aged 20-50 years with melasma. For inclusion, the participants had to have facial epidermal or mixed melasma (phototypes III-V) for more than 1 year; those with dermal melasma were excluded.
Participants were randomly allocated to receive either the serum, which was applied topically to the areas of interest twice a day in the morning and then at bedtime (n = 63), or cysteamine cream (n = 64), which was applied once a day in addition to a neutral moisturizer. Treatment was for 4 months, with an on-site visit every month.
All participants were supplied with the same sunscreen/ultraviolet protector applied twice a day (once in the morning and again at midday) and a neutral hydrating cleanser that was used in the morning and evening.
Practical Implications
Over 4 months, both products showed significant improvement in melasma without reaching a plateau, Sachdev reported, with the serum demonstrating superior efficacy and tolerability, as judged by the investigators.
The study suggests that the serum is a promising non-hydroquinone treatment for melasma, she said. Hydroquinone-containing topical preparations are used to depigment the skin, but their long-term use can be limited for safety reasons.
“When products like this demonstrate improvement, it is something for the dermatologist to think about because we now have newer ingredients, which are safer and well tolerated,” she continued, noting that there appeared to be no risk for exogenous ochronosis, which can occur with long-term application of hydroquinone.
“So, I think the armamentarium of non-hydroquinone products for the treatment of melasma is rapidly expanding, and there are studies now with clinically proven efficacy,” Sachdev concluded.
The study was supported by L’Oréal France La Roche-Posay, which launched Melasyl in March 2024. Sachdev reported receipt of research support and honoraria from the company. Gonçalo and Rudnicka were not involved in the study and had no relevant conflicts of interest to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2024 Congress.
“Melasyl is a new potent melanogenesis inhibitor that exhibits a unique mode of action while preserving melanocyte integrity,” Mukta Sachdev, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology at Manipal Hospital in Bangalore, India, said at a late-breaking news session.
Both the serum and the cysteamine cream lightened participants’ skin to a similar extent, according to the modified Melasma Area and Severity Index (mMASI), with respective reductions of 4.19 and 3.81 points over a period of 4 months from baseline values of 11.15 and 10.93.
The mMASI score ranges from 0 to 24, with the lowest score representing the least and the highest score the most severe hyperpigmentation of the skin.
But the serum performed better than the cream by another measure. Judged by investigators blinded to which preparation study participants had been using, there was a significantly higher reduction in the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score from baseline among those treated with the serum than among those treated with the cream (−51.85% vs −39.06%; P = .0163).
Moreover, after 4 months of treatment, there were significantly more participants with clear or almost clear skin with the serum than with the cream (17.46% vs 7.81%; P = .0163), Sachdev reported.
Other skin parameters relative to melasma, such as the brightness of skin tone and evenness of the improvement, improved more in the participants using the serum vs cream, she said.
With “no side effects, no local skin reactions,” Sachdev said, “quality of life improved significantly and similarly, and almost all subjects in both groups were very satisfied with their treatment options.”
Active Ingredients
Margarida Gonçalo, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Coimbra, in Portugal, who co-chaired the late-breaking news session, commented: “It’s really nice to have new products to treat such a devastating disease.”
Session co-chair, Lidia Rudnicka, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology, Medical University of Warsaw, in Poland, and president of the Polish Dermatological Society, wanted to know more about the active ingredients of the serum and the study’s design.
Sachdev replied that the serum also contains other ingredients that provide “antioxidant protection” and moisturization. These include retinyl palmitate, which works on the dermal-epidermal junction, and hyaluronic acid, as well as “soothing agents,” such as the medicinal herb Centella asiatica, she said.
Study Design
Conducted at a single center in India, the study involved 127 adults aged 20-50 years with melasma. For inclusion, the participants had to have facial epidermal or mixed melasma (phototypes III-V) for more than 1 year; those with dermal melasma were excluded.
Participants were randomly allocated to receive either the serum, which was applied topically to the areas of interest twice a day in the morning and then at bedtime (n = 63), or cysteamine cream (n = 64), which was applied once a day in addition to a neutral moisturizer. Treatment was for 4 months, with an on-site visit every month.
All participants were supplied with the same sunscreen/ultraviolet protector applied twice a day (once in the morning and again at midday) and a neutral hydrating cleanser that was used in the morning and evening.
Practical Implications
Over 4 months, both products showed significant improvement in melasma without reaching a plateau, Sachdev reported, with the serum demonstrating superior efficacy and tolerability, as judged by the investigators.
The study suggests that the serum is a promising non-hydroquinone treatment for melasma, she said. Hydroquinone-containing topical preparations are used to depigment the skin, but their long-term use can be limited for safety reasons.
“When products like this demonstrate improvement, it is something for the dermatologist to think about because we now have newer ingredients, which are safer and well tolerated,” she continued, noting that there appeared to be no risk for exogenous ochronosis, which can occur with long-term application of hydroquinone.
“So, I think the armamentarium of non-hydroquinone products for the treatment of melasma is rapidly expanding, and there are studies now with clinically proven efficacy,” Sachdev concluded.
The study was supported by L’Oréal France La Roche-Posay, which launched Melasyl in March 2024. Sachdev reported receipt of research support and honoraria from the company. Gonçalo and Rudnicka were not involved in the study and had no relevant conflicts of interest to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2024 Congress.
“Melasyl is a new potent melanogenesis inhibitor that exhibits a unique mode of action while preserving melanocyte integrity,” Mukta Sachdev, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology at Manipal Hospital in Bangalore, India, said at a late-breaking news session.
Both the serum and the cysteamine cream lightened participants’ skin to a similar extent, according to the modified Melasma Area and Severity Index (mMASI), with respective reductions of 4.19 and 3.81 points over a period of 4 months from baseline values of 11.15 and 10.93.
The mMASI score ranges from 0 to 24, with the lowest score representing the least and the highest score the most severe hyperpigmentation of the skin.
But the serum performed better than the cream by another measure. Judged by investigators blinded to which preparation study participants had been using, there was a significantly higher reduction in the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score from baseline among those treated with the serum than among those treated with the cream (−51.85% vs −39.06%; P = .0163).
Moreover, after 4 months of treatment, there were significantly more participants with clear or almost clear skin with the serum than with the cream (17.46% vs 7.81%; P = .0163), Sachdev reported.
Other skin parameters relative to melasma, such as the brightness of skin tone and evenness of the improvement, improved more in the participants using the serum vs cream, she said.
With “no side effects, no local skin reactions,” Sachdev said, “quality of life improved significantly and similarly, and almost all subjects in both groups were very satisfied with their treatment options.”
Active Ingredients
Margarida Gonçalo, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Coimbra, in Portugal, who co-chaired the late-breaking news session, commented: “It’s really nice to have new products to treat such a devastating disease.”
Session co-chair, Lidia Rudnicka, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology, Medical University of Warsaw, in Poland, and president of the Polish Dermatological Society, wanted to know more about the active ingredients of the serum and the study’s design.
Sachdev replied that the serum also contains other ingredients that provide “antioxidant protection” and moisturization. These include retinyl palmitate, which works on the dermal-epidermal junction, and hyaluronic acid, as well as “soothing agents,” such as the medicinal herb Centella asiatica, she said.
Study Design
Conducted at a single center in India, the study involved 127 adults aged 20-50 years with melasma. For inclusion, the participants had to have facial epidermal or mixed melasma (phototypes III-V) for more than 1 year; those with dermal melasma were excluded.
Participants were randomly allocated to receive either the serum, which was applied topically to the areas of interest twice a day in the morning and then at bedtime (n = 63), or cysteamine cream (n = 64), which was applied once a day in addition to a neutral moisturizer. Treatment was for 4 months, with an on-site visit every month.
All participants were supplied with the same sunscreen/ultraviolet protector applied twice a day (once in the morning and again at midday) and a neutral hydrating cleanser that was used in the morning and evening.
Practical Implications
Over 4 months, both products showed significant improvement in melasma without reaching a plateau, Sachdev reported, with the serum demonstrating superior efficacy and tolerability, as judged by the investigators.
The study suggests that the serum is a promising non-hydroquinone treatment for melasma, she said. Hydroquinone-containing topical preparations are used to depigment the skin, but their long-term use can be limited for safety reasons.
“When products like this demonstrate improvement, it is something for the dermatologist to think about because we now have newer ingredients, which are safer and well tolerated,” she continued, noting that there appeared to be no risk for exogenous ochronosis, which can occur with long-term application of hydroquinone.
“So, I think the armamentarium of non-hydroquinone products for the treatment of melasma is rapidly expanding, and there are studies now with clinically proven efficacy,” Sachdev concluded.
The study was supported by L’Oréal France La Roche-Posay, which launched Melasyl in March 2024. Sachdev reported receipt of research support and honoraria from the company. Gonçalo and Rudnicka were not involved in the study and had no relevant conflicts of interest to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EADV 2024
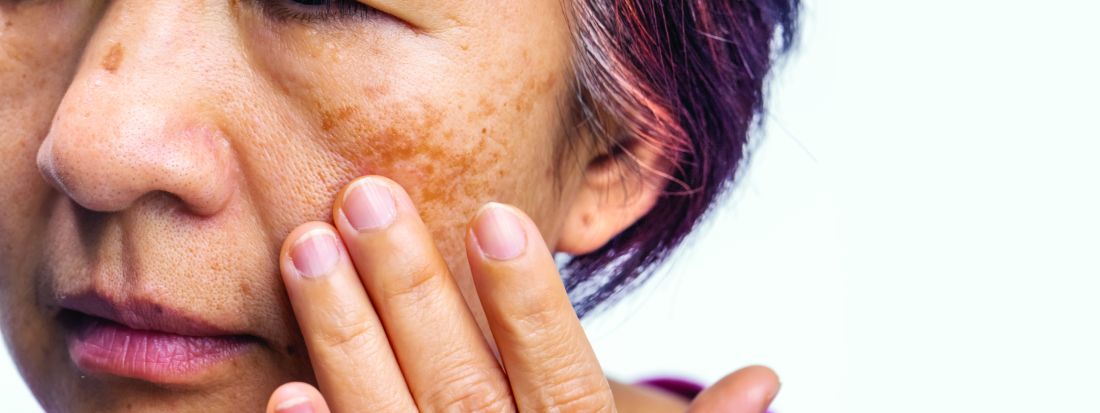
Melasma Risk Factors: A Matched Cohort Study Using Data From the All of Us Research Program
To the Editor:
Melasma (also known as chloasma) is characterized by symmetric hyperpigmented patches affecting sun-exposed areas. Women commonly develop this condition during pregnancy, suggesting a connection between melasma and increased female sex hormone levels.1 Other hypothesized risk factors include sun exposure, genetic susceptibility, estrogen and/or progesterone therapy, and thyroid abnormalities but have not been corroborated.2 Treatment options are limited because the pathogenesis is poorly understood; thus, we aimed to analyze melasma risk factors using a national database with a nested case-control approach.
We conducted a matched case-control study using the Registered Tier dataset (version 7) from the National Institute of Health’s All of Us Research Program (https://allofus.nih.gov/), which is available to authorized users through the program’s Researcher Workbench and includes more than 413,000 total participants enrolled from May 1, 2018, through July 1, 2022. Cases included patients 18 years and older with a diagnosis of melasma (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification code L81.1 [Chloasma]; concept ID 4264234 [Chloasma]; and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine [SNOMED] code 36209000 [Chloasma]), and controls without a diagnosis of melasma were matched in a 1:10 ratio based on age, sex, and self-reported race. Concept IDs and SNOMED codes were used to identify individuals in each cohort with a diagnosis of alcohol dependence (concept IDs 433753, 435243, 4218106; SNOMED codes 15167005, 66590003, 7200002), depression (concept ID 440383; SNOMED code 35489007), hypothyroidism (concept ID 140673; SNOMED code 40930008), hyperthyroidism (concept ID 4142479; SNOMED code 34486009), anxiety (concept IDs 441542, 442077, 434613; SNOMED codes 48694002, 197480006, 21897009), tobacco dependence (concept IDs 37109023, 437264, 4099811; SNOMED codes 16077091000119107, 89765005, 191887008), or obesity (concept IDs 433736 and 434005; SNOMED codes 414916001 and 238136002), or with a history of radiation therapy (concept IDs 4085340, 4311117, 4061844, 4029715; SNOMED codes 24803000, 85983004, 200861004, 108290001) or hormonal medications containing estrogen and/or progesterone, including oral medications and implants (concept IDs 21602445, 40254009, 21602514, 21603814, 19049228, 21602529, 1549080, 1551673, 1549254, 21602472, 21602446, 21602450, 21602515, 21602566, 21602473, 21602567, 21602488, 21602585, 1596779, 1586808, 21602524). In our case cohort, diagnoses and exposures to treatments were only considered for analysis if they occurred prior to melasma diagnosis.
Multivariate logistic regression was performed to calculate odds ratios and P values between melasma and each comorbidity or exposure to the treatments specified. Statistical significance was set at P<.05.
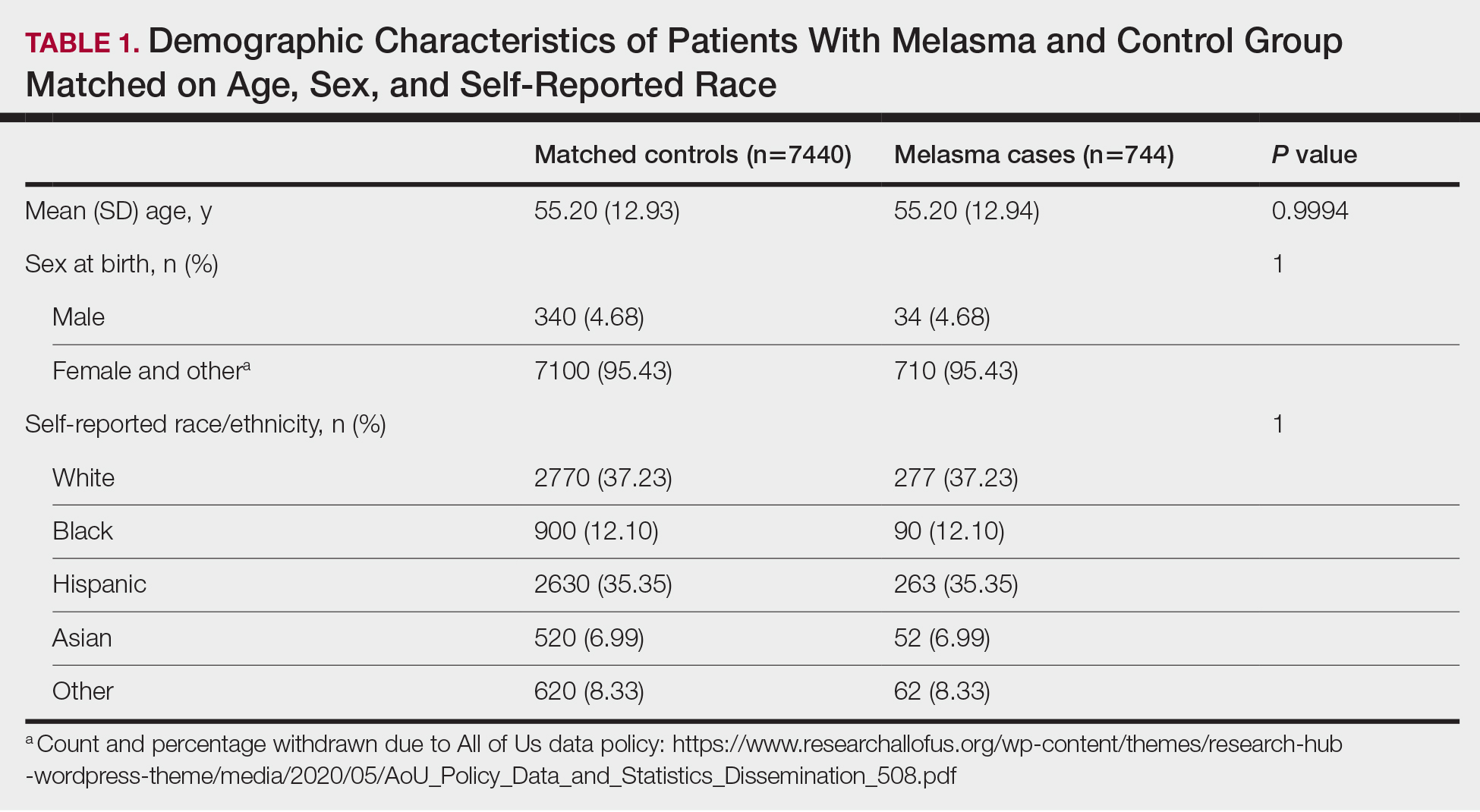
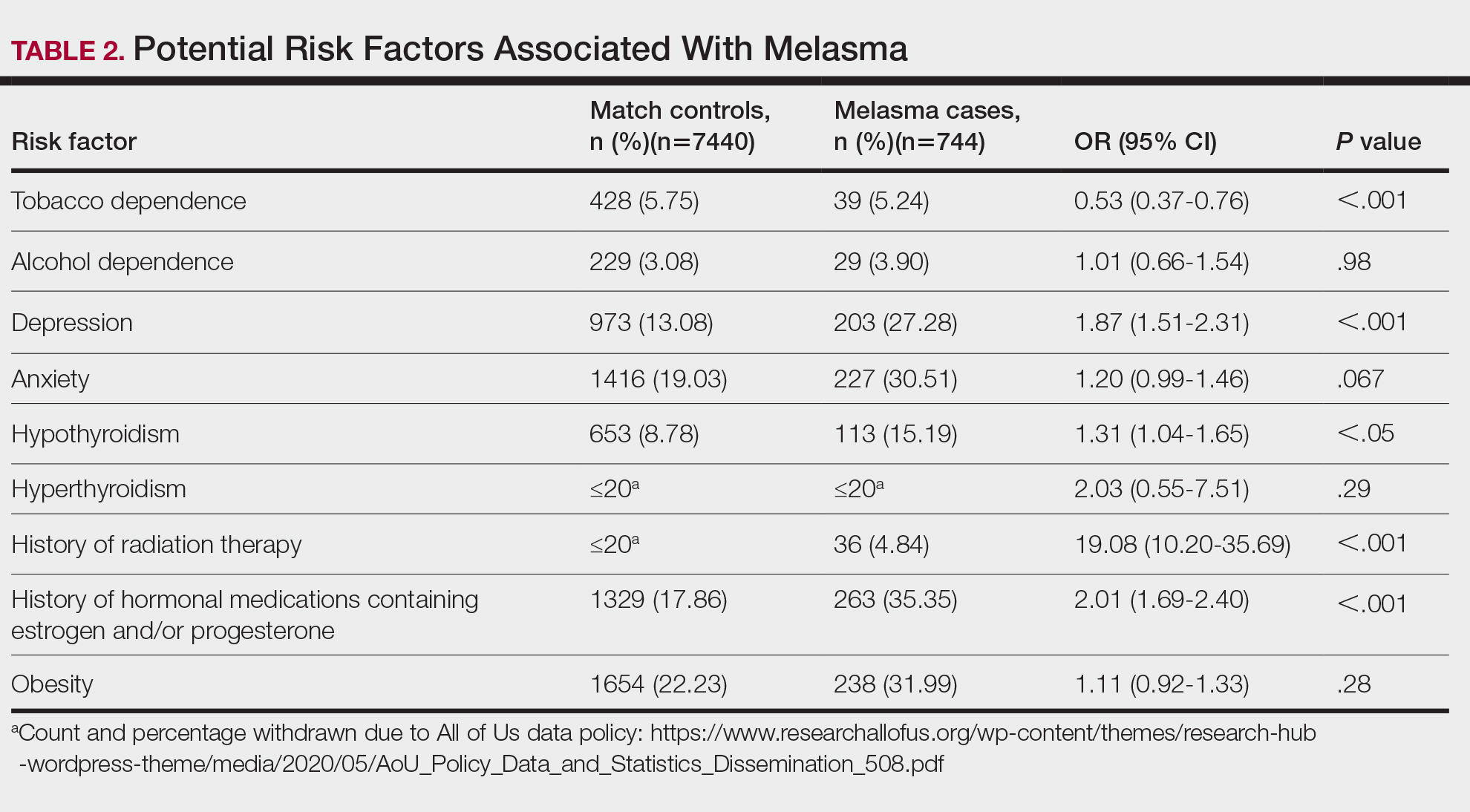
We identified 744 melasma cases (mean age, 55.20 years; 95.43% female; 12.10% Black) and 7440 controls with similar demographics (ie, age, sex, race/ethnicity) between groups (all P>.05 [Table 1]). Patients with a melasma diagnosis were more likely to have a pre-existing diagnosis of depression (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.51-2.31 [P<.001]) or hypothyroidism (OR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.04-1.65 [P<.05]), or a history of radiation therapy (OR, 19.08; 95% CI, 10.20-35.69 [P<.001]) and/or estrogen and/or progesterone therapy (OR, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.69-2.40 [P<.001]) prior to melasma diagnosis. A diagnosis of anxiety prior to melasma diagnosis trended toward an association with melasma (P=.067). Pre-existing alcohol dependence, obesity, and hyperthyroidism were not associated with melasma (P=.98, P=.28, and P=.29, respectively). A diagnosis of tobacco dependence was associated with a decreased melasma risk (OR, 0.53, 95% CI, 0.37-0.76)[P<.001])(Table 2).
Our study results suggest that pre-existing depression was a risk factor for subsequent melasma diagnosis. Depression may exacerbate stress, leading to increased activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis as well as increased levels of cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone, which subsequently act on melanocytes to increase melanogenesis.3 A retrospective study of 254 participants, including 127 with melasma, showed that increased melasma severity was associated with higher rates of depression (P=.002)2; however, the risk for melasma following a depression diagnosis has not been reported.
Our results also showed that hypothyroidism was associated with an increased risk for melasma. On a cellular level, hypothyroidism can cause systemic inflammation, potentailly leading to increased stress and melanogenesis via activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.4 These findings are similar to a systematic review and meta-analysis reporting increased thyroid-stimulating hormone, anti–thyroid peroxidase, and antithyroglobulin antibody levels associated with increased melasma risk (mean difference between cases and controls, 0.33 [95% CI, 0.18-0.47]; pooled association, P=.020; mean difference between cases and controls, 0.28 [95% CI, 0.01-0.55], respectively).5
Patients in our cohort who had a history of radiation therapy were 19 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to findings of a survey-based study of 421 breast cancer survivors in which 336 (79.81%) reported hyperpigmentation in irradiated areas.6 Patients in our cohort who had a history of estrogen and/or progesterone therapy were 2 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to a case-control study of 207 patients with melasma and 207 controls that showed combined oral contraceptives increased risk for melasma (OR, 1.23 [95% CI, 1.08-1.41; P<.01).3
Tobacco use is not a well-known protective factor against melasma. Prior studies have indicated that tobacco smoking activates melanocytes via the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway, leading to hyperpigmentation.7 Although exposure to cigarette smoke decreases angiogenesis and would more likely lead to hyperpigmentation, nicotine exposure has been shown to increase angiogenesis, which could lead to increased blood flow and partially explain the protection against melasma demonstrated in our cohort.8 Future studies are needed to explore this relationship.
Limitations of our study include lack of information about melasma severity and information about prior melasma treatment in our cohort as well as possible misdiagnosis reported in the dataset.
Our results demonstrated that pre-existing depression and hypothyroidism as well as a history of radiation or estrogen and/or progesterone therapies are potential risk factors for melasma. Therefore, we recommend that patients with melasma be screened for depression and thyroid dysfunction, and patients undergoing radiation therapy or starting estrogen and/or progesterone therapy should be counseled on their increased risk for melasma. Future studies are needed to determine whether treatment of comorbidities such as hypothyroidism and depression improve melasma severity. The decreased risk for melasma associated with tobacco use also requires further investigation.
Acknowledgments—The All of Us Research Program is supported by the National Institutes of Health, Office of the Director: Regional Medical Centers: 1 OT2 OD026549; 1 OT2 OD026554; 1 OT2 OD026557; 1 OT2 OD026556; 1 OT2 OD026550; 1 OT2 OD 026552; 1 OT2 OD026553; 1 OT2 OD026548; 1 OT2 OD026551; 1 OT2 OD026555; IAA #: AOD 16037; Federally Qualified Health Centers: HHSN 263201600085U; Data and Research Center: 5 U2C OD023196; Biobank: 1 U24 OD023121; The Participant Center: U24 OD023176; Participant Technology Systems Center: 1 U24 OD023163; Communications and Engagement: 3 OT2 OD023205; 3 OT2 OD023206; and Community Partners: 1 OT2 OD025277; 3 OT2 OD025315; 1 OT2 OD025337; 1 OT2 OD025276.
In addition, the All of Us Research Program would not be possible without the partnership of its participants, who we gratefully acknowledge for their contributions and without whom this research would not have been possible. We also thank the All of Us Research Program for making the participant data examined in this study available to us.
- Filoni A, Mariano M, Cameli N. Melasma: how hormones can modulate skin pigmentation. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019;18:458-463. doi:10.1111/jocd.12877
- Platsidaki E, Efstathiou V, Markantoni V, et al. Self-esteem, depression, anxiety and quality of life in patients with melasma living in a sunny mediterranean area: results from a prospective cross-sectional study. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023;13:1127-1136. doi:10.1007/s13555-023-00915-1
- Handel AC, Lima PB, Tonolli VM, et al. Risk factors for facial melasma in women: a case-control study. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:588-594. doi:10.1111/bjd.13059
- Erge E, Kiziltunc C, Balci SB, et al. A novel inflammatory marker for the diagnosis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: platelet-count-to-lymphocyte-count ratio (published January 22, 2023). Diseases. 2023;11:15. doi:10.3390/diseases11010015
- Kheradmand M, Afshari M, Damiani G, et al. Melasma and thyroid disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:1231-1238. doi:10.1111/ijd.14497
- Chu CN, Hu KC, Wu RS, et al. Radiation-irritated skin and hyperpigmentation may impact the quality of life of breast cancer patients after whole breast radiotherapy (published March 31, 2021). BMC Cancer. 2021;21:330. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-08047-5
- Nakamura M, Ueda Y, Hayashi M, et al. Tobacco smoke-induced skin pigmentation is mediated by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22:556-558. doi:10.1111/exd.12170
- Ejaz S, Lim CW. Toxicological overview of cigarette smoking on angiogenesis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2005;20:335-344. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2005.03.011
To the Editor:
Melasma (also known as chloasma) is characterized by symmetric hyperpigmented patches affecting sun-exposed areas. Women commonly develop this condition during pregnancy, suggesting a connection between melasma and increased female sex hormone levels.1 Other hypothesized risk factors include sun exposure, genetic susceptibility, estrogen and/or progesterone therapy, and thyroid abnormalities but have not been corroborated.2 Treatment options are limited because the pathogenesis is poorly understood; thus, we aimed to analyze melasma risk factors using a national database with a nested case-control approach.
We conducted a matched case-control study using the Registered Tier dataset (version 7) from the National Institute of Health’s All of Us Research Program (https://allofus.nih.gov/), which is available to authorized users through the program’s Researcher Workbench and includes more than 413,000 total participants enrolled from May 1, 2018, through July 1, 2022. Cases included patients 18 years and older with a diagnosis of melasma (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification code L81.1 [Chloasma]; concept ID 4264234 [Chloasma]; and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine [SNOMED] code 36209000 [Chloasma]), and controls without a diagnosis of melasma were matched in a 1:10 ratio based on age, sex, and self-reported race. Concept IDs and SNOMED codes were used to identify individuals in each cohort with a diagnosis of alcohol dependence (concept IDs 433753, 435243, 4218106; SNOMED codes 15167005, 66590003, 7200002), depression (concept ID 440383; SNOMED code 35489007), hypothyroidism (concept ID 140673; SNOMED code 40930008), hyperthyroidism (concept ID 4142479; SNOMED code 34486009), anxiety (concept IDs 441542, 442077, 434613; SNOMED codes 48694002, 197480006, 21897009), tobacco dependence (concept IDs 37109023, 437264, 4099811; SNOMED codes 16077091000119107, 89765005, 191887008), or obesity (concept IDs 433736 and 434005; SNOMED codes 414916001 and 238136002), or with a history of radiation therapy (concept IDs 4085340, 4311117, 4061844, 4029715; SNOMED codes 24803000, 85983004, 200861004, 108290001) or hormonal medications containing estrogen and/or progesterone, including oral medications and implants (concept IDs 21602445, 40254009, 21602514, 21603814, 19049228, 21602529, 1549080, 1551673, 1549254, 21602472, 21602446, 21602450, 21602515, 21602566, 21602473, 21602567, 21602488, 21602585, 1596779, 1586808, 21602524). In our case cohort, diagnoses and exposures to treatments were only considered for analysis if they occurred prior to melasma diagnosis.
Multivariate logistic regression was performed to calculate odds ratios and P values between melasma and each comorbidity or exposure to the treatments specified. Statistical significance was set at P<.05.
We identified 744 melasma cases (mean age, 55.20 years; 95.43% female; 12.10% Black) and 7440 controls with similar demographics (ie, age, sex, race/ethnicity) between groups (all P>.05 [Table 1]). Patients with a melasma diagnosis were more likely to have a pre-existing diagnosis of depression (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.51-2.31 [P<.001]) or hypothyroidism (OR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.04-1.65 [P<.05]), or a history of radiation therapy (OR, 19.08; 95% CI, 10.20-35.69 [P<.001]) and/or estrogen and/or progesterone therapy (OR, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.69-2.40 [P<.001]) prior to melasma diagnosis. A diagnosis of anxiety prior to melasma diagnosis trended toward an association with melasma (P=.067). Pre-existing alcohol dependence, obesity, and hyperthyroidism were not associated with melasma (P=.98, P=.28, and P=.29, respectively). A diagnosis of tobacco dependence was associated with a decreased melasma risk (OR, 0.53, 95% CI, 0.37-0.76)[P<.001])(Table 2).
Our study results suggest that pre-existing depression was a risk factor for subsequent melasma diagnosis. Depression may exacerbate stress, leading to increased activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis as well as increased levels of cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone, which subsequently act on melanocytes to increase melanogenesis.3 A retrospective study of 254 participants, including 127 with melasma, showed that increased melasma severity was associated with higher rates of depression (P=.002)2; however, the risk for melasma following a depression diagnosis has not been reported.
Our results also showed that hypothyroidism was associated with an increased risk for melasma. On a cellular level, hypothyroidism can cause systemic inflammation, potentailly leading to increased stress and melanogenesis via activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.4 These findings are similar to a systematic review and meta-analysis reporting increased thyroid-stimulating hormone, anti–thyroid peroxidase, and antithyroglobulin antibody levels associated with increased melasma risk (mean difference between cases and controls, 0.33 [95% CI, 0.18-0.47]; pooled association, P=.020; mean difference between cases and controls, 0.28 [95% CI, 0.01-0.55], respectively).5
Patients in our cohort who had a history of radiation therapy were 19 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to findings of a survey-based study of 421 breast cancer survivors in which 336 (79.81%) reported hyperpigmentation in irradiated areas.6 Patients in our cohort who had a history of estrogen and/or progesterone therapy were 2 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to a case-control study of 207 patients with melasma and 207 controls that showed combined oral contraceptives increased risk for melasma (OR, 1.23 [95% CI, 1.08-1.41; P<.01).3
Tobacco use is not a well-known protective factor against melasma. Prior studies have indicated that tobacco smoking activates melanocytes via the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway, leading to hyperpigmentation.7 Although exposure to cigarette smoke decreases angiogenesis and would more likely lead to hyperpigmentation, nicotine exposure has been shown to increase angiogenesis, which could lead to increased blood flow and partially explain the protection against melasma demonstrated in our cohort.8 Future studies are needed to explore this relationship.


Limitations of our study include lack of information about melasma severity and information about prior melasma treatment in our cohort as well as possible misdiagnosis reported in the dataset.
Our results demonstrated that pre-existing depression and hypothyroidism as well as a history of radiation or estrogen and/or progesterone therapies are potential risk factors for melasma. Therefore, we recommend that patients with melasma be screened for depression and thyroid dysfunction, and patients undergoing radiation therapy or starting estrogen and/or progesterone therapy should be counseled on their increased risk for melasma. Future studies are needed to determine whether treatment of comorbidities such as hypothyroidism and depression improve melasma severity. The decreased risk for melasma associated with tobacco use also requires further investigation.
Acknowledgments—The All of Us Research Program is supported by the National Institutes of Health, Office of the Director: Regional Medical Centers: 1 OT2 OD026549; 1 OT2 OD026554; 1 OT2 OD026557; 1 OT2 OD026556; 1 OT2 OD026550; 1 OT2 OD 026552; 1 OT2 OD026553; 1 OT2 OD026548; 1 OT2 OD026551; 1 OT2 OD026555; IAA #: AOD 16037; Federally Qualified Health Centers: HHSN 263201600085U; Data and Research Center: 5 U2C OD023196; Biobank: 1 U24 OD023121; The Participant Center: U24 OD023176; Participant Technology Systems Center: 1 U24 OD023163; Communications and Engagement: 3 OT2 OD023205; 3 OT2 OD023206; and Community Partners: 1 OT2 OD025277; 3 OT2 OD025315; 1 OT2 OD025337; 1 OT2 OD025276.
In addition, the All of Us Research Program would not be possible without the partnership of its participants, who we gratefully acknowledge for their contributions and without whom this research would not have been possible. We also thank the All of Us Research Program for making the participant data examined in this study available to us.
To the Editor:
Melasma (also known as chloasma) is characterized by symmetric hyperpigmented patches affecting sun-exposed areas. Women commonly develop this condition during pregnancy, suggesting a connection between melasma and increased female sex hormone levels.1 Other hypothesized risk factors include sun exposure, genetic susceptibility, estrogen and/or progesterone therapy, and thyroid abnormalities but have not been corroborated.2 Treatment options are limited because the pathogenesis is poorly understood; thus, we aimed to analyze melasma risk factors using a national database with a nested case-control approach.
We conducted a matched case-control study using the Registered Tier dataset (version 7) from the National Institute of Health’s All of Us Research Program (https://allofus.nih.gov/), which is available to authorized users through the program’s Researcher Workbench and includes more than 413,000 total participants enrolled from May 1, 2018, through July 1, 2022. Cases included patients 18 years and older with a diagnosis of melasma (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification code L81.1 [Chloasma]; concept ID 4264234 [Chloasma]; and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine [SNOMED] code 36209000 [Chloasma]), and controls without a diagnosis of melasma were matched in a 1:10 ratio based on age, sex, and self-reported race. Concept IDs and SNOMED codes were used to identify individuals in each cohort with a diagnosis of alcohol dependence (concept IDs 433753, 435243, 4218106; SNOMED codes 15167005, 66590003, 7200002), depression (concept ID 440383; SNOMED code 35489007), hypothyroidism (concept ID 140673; SNOMED code 40930008), hyperthyroidism (concept ID 4142479; SNOMED code 34486009), anxiety (concept IDs 441542, 442077, 434613; SNOMED codes 48694002, 197480006, 21897009), tobacco dependence (concept IDs 37109023, 437264, 4099811; SNOMED codes 16077091000119107, 89765005, 191887008), or obesity (concept IDs 433736 and 434005; SNOMED codes 414916001 and 238136002), or with a history of radiation therapy (concept IDs 4085340, 4311117, 4061844, 4029715; SNOMED codes 24803000, 85983004, 200861004, 108290001) or hormonal medications containing estrogen and/or progesterone, including oral medications and implants (concept IDs 21602445, 40254009, 21602514, 21603814, 19049228, 21602529, 1549080, 1551673, 1549254, 21602472, 21602446, 21602450, 21602515, 21602566, 21602473, 21602567, 21602488, 21602585, 1596779, 1586808, 21602524). In our case cohort, diagnoses and exposures to treatments were only considered for analysis if they occurred prior to melasma diagnosis.
Multivariate logistic regression was performed to calculate odds ratios and P values between melasma and each comorbidity or exposure to the treatments specified. Statistical significance was set at P<.05.
We identified 744 melasma cases (mean age, 55.20 years; 95.43% female; 12.10% Black) and 7440 controls with similar demographics (ie, age, sex, race/ethnicity) between groups (all P>.05 [Table 1]). Patients with a melasma diagnosis were more likely to have a pre-existing diagnosis of depression (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.51-2.31 [P<.001]) or hypothyroidism (OR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.04-1.65 [P<.05]), or a history of radiation therapy (OR, 19.08; 95% CI, 10.20-35.69 [P<.001]) and/or estrogen and/or progesterone therapy (OR, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.69-2.40 [P<.001]) prior to melasma diagnosis. A diagnosis of anxiety prior to melasma diagnosis trended toward an association with melasma (P=.067). Pre-existing alcohol dependence, obesity, and hyperthyroidism were not associated with melasma (P=.98, P=.28, and P=.29, respectively). A diagnosis of tobacco dependence was associated with a decreased melasma risk (OR, 0.53, 95% CI, 0.37-0.76)[P<.001])(Table 2).
Our study results suggest that pre-existing depression was a risk factor for subsequent melasma diagnosis. Depression may exacerbate stress, leading to increased activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis as well as increased levels of cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone, which subsequently act on melanocytes to increase melanogenesis.3 A retrospective study of 254 participants, including 127 with melasma, showed that increased melasma severity was associated with higher rates of depression (P=.002)2; however, the risk for melasma following a depression diagnosis has not been reported.
Our results also showed that hypothyroidism was associated with an increased risk for melasma. On a cellular level, hypothyroidism can cause systemic inflammation, potentailly leading to increased stress and melanogenesis via activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.4 These findings are similar to a systematic review and meta-analysis reporting increased thyroid-stimulating hormone, anti–thyroid peroxidase, and antithyroglobulin antibody levels associated with increased melasma risk (mean difference between cases and controls, 0.33 [95% CI, 0.18-0.47]; pooled association, P=.020; mean difference between cases and controls, 0.28 [95% CI, 0.01-0.55], respectively).5
Patients in our cohort who had a history of radiation therapy were 19 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to findings of a survey-based study of 421 breast cancer survivors in which 336 (79.81%) reported hyperpigmentation in irradiated areas.6 Patients in our cohort who had a history of estrogen and/or progesterone therapy were 2 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to a case-control study of 207 patients with melasma and 207 controls that showed combined oral contraceptives increased risk for melasma (OR, 1.23 [95% CI, 1.08-1.41; P<.01).3
Tobacco use is not a well-known protective factor against melasma. Prior studies have indicated that tobacco smoking activates melanocytes via the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway, leading to hyperpigmentation.7 Although exposure to cigarette smoke decreases angiogenesis and would more likely lead to hyperpigmentation, nicotine exposure has been shown to increase angiogenesis, which could lead to increased blood flow and partially explain the protection against melasma demonstrated in our cohort.8 Future studies are needed to explore this relationship.


Limitations of our study include lack of information about melasma severity and information about prior melasma treatment in our cohort as well as possible misdiagnosis reported in the dataset.
Our results demonstrated that pre-existing depression and hypothyroidism as well as a history of radiation or estrogen and/or progesterone therapies are potential risk factors for melasma. Therefore, we recommend that patients with melasma be screened for depression and thyroid dysfunction, and patients undergoing radiation therapy or starting estrogen and/or progesterone therapy should be counseled on their increased risk for melasma. Future studies are needed to determine whether treatment of comorbidities such as hypothyroidism and depression improve melasma severity. The decreased risk for melasma associated with tobacco use also requires further investigation.
Acknowledgments—The All of Us Research Program is supported by the National Institutes of Health, Office of the Director: Regional Medical Centers: 1 OT2 OD026549; 1 OT2 OD026554; 1 OT2 OD026557; 1 OT2 OD026556; 1 OT2 OD026550; 1 OT2 OD 026552; 1 OT2 OD026553; 1 OT2 OD026548; 1 OT2 OD026551; 1 OT2 OD026555; IAA #: AOD 16037; Federally Qualified Health Centers: HHSN 263201600085U; Data and Research Center: 5 U2C OD023196; Biobank: 1 U24 OD023121; The Participant Center: U24 OD023176; Participant Technology Systems Center: 1 U24 OD023163; Communications and Engagement: 3 OT2 OD023205; 3 OT2 OD023206; and Community Partners: 1 OT2 OD025277; 3 OT2 OD025315; 1 OT2 OD025337; 1 OT2 OD025276.
In addition, the All of Us Research Program would not be possible without the partnership of its participants, who we gratefully acknowledge for their contributions and without whom this research would not have been possible. We also thank the All of Us Research Program for making the participant data examined in this study available to us.
- Filoni A, Mariano M, Cameli N. Melasma: how hormones can modulate skin pigmentation. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019;18:458-463. doi:10.1111/jocd.12877
- Platsidaki E, Efstathiou V, Markantoni V, et al. Self-esteem, depression, anxiety and quality of life in patients with melasma living in a sunny mediterranean area: results from a prospective cross-sectional study. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023;13:1127-1136. doi:10.1007/s13555-023-00915-1
- Handel AC, Lima PB, Tonolli VM, et al. Risk factors for facial melasma in women: a case-control study. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:588-594. doi:10.1111/bjd.13059
- Erge E, Kiziltunc C, Balci SB, et al. A novel inflammatory marker for the diagnosis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: platelet-count-to-lymphocyte-count ratio (published January 22, 2023). Diseases. 2023;11:15. doi:10.3390/diseases11010015
- Kheradmand M, Afshari M, Damiani G, et al. Melasma and thyroid disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:1231-1238. doi:10.1111/ijd.14497
- Chu CN, Hu KC, Wu RS, et al. Radiation-irritated skin and hyperpigmentation may impact the quality of life of breast cancer patients after whole breast radiotherapy (published March 31, 2021). BMC Cancer. 2021;21:330. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-08047-5
- Nakamura M, Ueda Y, Hayashi M, et al. Tobacco smoke-induced skin pigmentation is mediated by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22:556-558. doi:10.1111/exd.12170
- Ejaz S, Lim CW. Toxicological overview of cigarette smoking on angiogenesis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2005;20:335-344. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2005.03.011
- Filoni A, Mariano M, Cameli N. Melasma: how hormones can modulate skin pigmentation. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019;18:458-463. doi:10.1111/jocd.12877
- Platsidaki E, Efstathiou V, Markantoni V, et al. Self-esteem, depression, anxiety and quality of life in patients with melasma living in a sunny mediterranean area: results from a prospective cross-sectional study. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023;13:1127-1136. doi:10.1007/s13555-023-00915-1
- Handel AC, Lima PB, Tonolli VM, et al. Risk factors for facial melasma in women: a case-control study. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:588-594. doi:10.1111/bjd.13059
- Erge E, Kiziltunc C, Balci SB, et al. A novel inflammatory marker for the diagnosis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: platelet-count-to-lymphocyte-count ratio (published January 22, 2023). Diseases. 2023;11:15. doi:10.3390/diseases11010015
- Kheradmand M, Afshari M, Damiani G, et al. Melasma and thyroid disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:1231-1238. doi:10.1111/ijd.14497
- Chu CN, Hu KC, Wu RS, et al. Radiation-irritated skin and hyperpigmentation may impact the quality of life of breast cancer patients after whole breast radiotherapy (published March 31, 2021). BMC Cancer. 2021;21:330. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-08047-5
- Nakamura M, Ueda Y, Hayashi M, et al. Tobacco smoke-induced skin pigmentation is mediated by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22:556-558. doi:10.1111/exd.12170
- Ejaz S, Lim CW. Toxicological overview of cigarette smoking on angiogenesis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2005;20:335-344. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2005.03.011
Practice Points
- Treatment options for melasma are limited due to its poorly understood pathogenesis.
- Depression and hypothyroidism and/or history of exposure to radiation and hormonal therapies may increase melasma risk.
- We recommend that patients with melasma be screened for depression and thyroid dysfunction. Patients undergoing radiation therapy or starting estrogen and/ or progesterone therapy should be counseled on the increased risk for melasma.
US Dermatologic Drug Approvals Rose Between 2012 and 2022
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Only five new drugs for diseases treated mostly by dermatologists were approved by the FDA between 1999 and 2009.
- In a cross-sectional analysis to characterize the frequency and degree of innovation of dermatologic drugs approved more recently, researchers identified new and supplemental dermatologic drugs approved between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2022, from FDA lists, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services CenterWatch, and peer-reviewed articles.
- They used five proxy measures to estimate each drug’s degree of innovation: FDA designation (first in class, advance in class, or addition to class), independent clinical usefulness ratings, and benefit ratings by health technology assessment organizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- The study authors identified 52 new drug applications and 26 supplemental new indications approved by the FDA for dermatologic indications between 2012 and 2022.
- Of the 52 new drugs, the researchers categorized 11 (21%) as first in class and 13 (25%) as first in indication.
- An analysis of benefit ratings available for 38 of the drugs showed that 15 (39%) were rated as being clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
- Of the 10 supplemental new indications with ratings by any organization, 3 (30%) were rated as clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
IN PRACTICE:
While innovative drug development in dermatology may have increased, “these findings also highlight opportunities to develop more truly innovative dermatologic agents, particularly for diseases with unmet therapeutic need,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Samir Kamat, MD, of the Medical Education Department at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, and corresponding author Ravi Gupta, MD, MSHP, of the Internal Medicine Division at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research. The study was published online as a research letter on December 20, 2023, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
They include the use of individual indications to assess clinical usefulness and benefit ratings. Many drugs, particularly supplemental indications, lacked such ratings. Reformulations of already marketed drugs or indications were not included.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Kamat and Dr. Gupta had no relevant disclosures. Three coauthors reported having received financial support outside of the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Only five new drugs for diseases treated mostly by dermatologists were approved by the FDA between 1999 and 2009.
- In a cross-sectional analysis to characterize the frequency and degree of innovation of dermatologic drugs approved more recently, researchers identified new and supplemental dermatologic drugs approved between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2022, from FDA lists, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services CenterWatch, and peer-reviewed articles.
- They used five proxy measures to estimate each drug’s degree of innovation: FDA designation (first in class, advance in class, or addition to class), independent clinical usefulness ratings, and benefit ratings by health technology assessment organizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- The study authors identified 52 new drug applications and 26 supplemental new indications approved by the FDA for dermatologic indications between 2012 and 2022.
- Of the 52 new drugs, the researchers categorized 11 (21%) as first in class and 13 (25%) as first in indication.
- An analysis of benefit ratings available for 38 of the drugs showed that 15 (39%) were rated as being clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
- Of the 10 supplemental new indications with ratings by any organization, 3 (30%) were rated as clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
IN PRACTICE:
While innovative drug development in dermatology may have increased, “these findings also highlight opportunities to develop more truly innovative dermatologic agents, particularly for diseases with unmet therapeutic need,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Samir Kamat, MD, of the Medical Education Department at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, and corresponding author Ravi Gupta, MD, MSHP, of the Internal Medicine Division at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research. The study was published online as a research letter on December 20, 2023, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
They include the use of individual indications to assess clinical usefulness and benefit ratings. Many drugs, particularly supplemental indications, lacked such ratings. Reformulations of already marketed drugs or indications were not included.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Kamat and Dr. Gupta had no relevant disclosures. Three coauthors reported having received financial support outside of the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Only five new drugs for diseases treated mostly by dermatologists were approved by the FDA between 1999 and 2009.
- In a cross-sectional analysis to characterize the frequency and degree of innovation of dermatologic drugs approved more recently, researchers identified new and supplemental dermatologic drugs approved between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2022, from FDA lists, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services CenterWatch, and peer-reviewed articles.
- They used five proxy measures to estimate each drug’s degree of innovation: FDA designation (first in class, advance in class, or addition to class), independent clinical usefulness ratings, and benefit ratings by health technology assessment organizations.
TAKEAWAY:
- The study authors identified 52 new drug applications and 26 supplemental new indications approved by the FDA for dermatologic indications between 2012 and 2022.
- Of the 52 new drugs, the researchers categorized 11 (21%) as first in class and 13 (25%) as first in indication.
- An analysis of benefit ratings available for 38 of the drugs showed that 15 (39%) were rated as being clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
- Of the 10 supplemental new indications with ratings by any organization, 3 (30%) were rated as clinically useful or having high added therapeutic benefit.
IN PRACTICE:
While innovative drug development in dermatology may have increased, “these findings also highlight opportunities to develop more truly innovative dermatologic agents, particularly for diseases with unmet therapeutic need,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Samir Kamat, MD, of the Medical Education Department at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, and corresponding author Ravi Gupta, MD, MSHP, of the Internal Medicine Division at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research. The study was published online as a research letter on December 20, 2023, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
They include the use of individual indications to assess clinical usefulness and benefit ratings. Many drugs, particularly supplemental indications, lacked such ratings. Reformulations of already marketed drugs or indications were not included.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Kamat and Dr. Gupta had no relevant disclosures. Three coauthors reported having received financial support outside of the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Tips, contraindications for superficial chemical peels reviewed
CHICAGO – Heather Woolery-Lloyd, MD, says she’s generally “risk averse,” but when it comes to superficial chemical peels, she’s in her comfort zone.
Superficial peeling is “one of the most common cosmetic procedures that I do,” Dr. Woolery-Lloyd, director of the skin of color division in the dermatology department at the University of Miami, said at the Pigmentary Disorders Exchange Symposium.
In her practice, .
Contraindications are an active bacterial infection, open wounds, and active herpes simplex virus. “If someone looks like they even have a remnant of a cold sore, I tell them to come back,” she said.
Setting expectations for patients is critical, Dr. Woolery-Lloyd said, as a series of superficial peels is needed before the desired results are evident.
The peel she uses most is salicylic acid, a beta-hydroxy acid, at a strength of 20%-30%. “It’s very effective on our acne patients,” she said at the meeting, provided by MedscapeLIVE! “If you’re just starting with peels, I think this is a very safe one. You don’t have to time it, and you don’t have to neutralize it,” and at lower concentrations, is “very safe.”
Dr. Woolery-Lloyd provided these other tips during her presentation:
- Even superficial peels can be uncomfortable, she noted, so she keeps a fan nearby to use when needed to help with discomfort.
- Find the peel you’re comfortable with, master that peel, and don’t jump from peel to peel. Get familiar with the side effects and how to predict results.
- Stop retinoids up to 7 days before a peel. Consider placing the patient on hydroquinone before the chemical peel to decrease the risk of hyperpigmentation.
- Before the procedure, prep the skin with acetone or alcohol. Applying petrolatum helps protect around the eyes, alar crease, and other sensitive areas, “or anywhere you’re concerned about the depth of the peel.”
- Application with rough gauze helps avoid the waste that comes with makeup sponges soaking up the product. It also helps add exfoliation.
- Have everything ready before starting the procedure, including (depending on the peel), a neutralizer or soapless cleanser. Although peels are generally safe, you want to be able to remove one quickly, if needed, without having to leave the room.
- Start with the lowest concentration (salicylic acid or glycolic acid) then titrate up. Ask patients about any reactions they experienced with the previous peel before making the decision on the next concentration.
- For a peel to treat hyperpigmentation, she recommends one peel about every 4 weeks for a series of 5-6 peels.
- After a peel, the patient should use a mineral sunscreen; chemical sunscreens will sting.
Know your comfort zone
Conference chair Pearl Grimes, MD, director of The Vitiligo & Pigmentation Institute of Southern California in Los Angeles, said superficial peels are best for dermatologists new to peeling until they gain comfort with experience.
Superficial and medium-depth peels work well for mild to moderate photoaging, she said at the meeting.
“We know that in darker skin we have more intrinsic aging rather than photoaging. We have more textural changes, hyperpigmentation,” Dr. Grimes said.
For Fitzpatrick skin types I-III, she said, “you can do superficial, medium, and deep peels.” For darker skin types, “I typically stay in the superficial, medium range.”
She said that she uses retinoids to exfoliate before a superficial peel but added, “you’ve got to stop them early because retinoids can make a superficial peel a medium-depth peel.”
Taking photos is important before any procedure, she said, as is spending time with patients clarifying their outcome expectations.
“I love peeling,” Dr. Grimes said. “And it’s cost effective. If you don’t want to spend a ton of money, it’s amazing what you can achieve with chemical peeling.”
When asked by a member of the audience whether they avoid superficial peels in women who are pregnant or breastfeeding, both Dr. Woolery-Lloyd and Dr. Grimes said they do avoid them in those patients.
Dr. Grimes said she tells her patients, especially in the first trimester, “I am the most conservative woman on the planet. I do nothing during the first trimester.”
Dr. Woolery-Lloyd has been a speaker for Ortho Dermatologics, Loreal and EPI, and has done research for Pfizer, Galderma, Allergan, Arcutis, Vyne, Merz, and Eirion. She has been on advisory boards for Loreal, Allergan, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfize,r and Merz. Dr. Grimes reports grant/research Support from Clinuvel Pharmaceuticals, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, LASEROPTEK, L’Oréal USA, Pfizer, Procter & Gamble, skinbetter science, and Versicolor Technologies, and is on the speakers bureau/receives honoraria for non-CME for Incyte and Procter & Gamble; and is a consultant or is on the advisory board for L’Oréal USA and Procter & Gamble. She has stock options in Versicolor Technologies.
CHICAGO – Heather Woolery-Lloyd, MD, says she’s generally “risk averse,” but when it comes to superficial chemical peels, she’s in her comfort zone.
Superficial peeling is “one of the most common cosmetic procedures that I do,” Dr. Woolery-Lloyd, director of the skin of color division in the dermatology department at the University of Miami, said at the Pigmentary Disorders Exchange Symposium.
In her practice, .
Contraindications are an active bacterial infection, open wounds, and active herpes simplex virus. “If someone looks like they even have a remnant of a cold sore, I tell them to come back,” she said.
Setting expectations for patients is critical, Dr. Woolery-Lloyd said, as a series of superficial peels is needed before the desired results are evident.
The peel she uses most is salicylic acid, a beta-hydroxy acid, at a strength of 20%-30%. “It’s very effective on our acne patients,” she said at the meeting, provided by MedscapeLIVE! “If you’re just starting with peels, I think this is a very safe one. You don’t have to time it, and you don’t have to neutralize it,” and at lower concentrations, is “very safe.”
Dr. Woolery-Lloyd provided these other tips during her presentation:
- Even superficial peels can be uncomfortable, she noted, so she keeps a fan nearby to use when needed to help with discomfort.
- Find the peel you’re comfortable with, master that peel, and don’t jump from peel to peel. Get familiar with the side effects and how to predict results.
- Stop retinoids up to 7 days before a peel. Consider placing the patient on hydroquinone before the chemical peel to decrease the risk of hyperpigmentation.
- Before the procedure, prep the skin with acetone or alcohol. Applying petrolatum helps protect around the eyes, alar crease, and other sensitive areas, “or anywhere you’re concerned about the depth of the peel.”
- Application with rough gauze helps avoid the waste that comes with makeup sponges soaking up the product. It also helps add exfoliation.
- Have everything ready before starting the procedure, including (depending on the peel), a neutralizer or soapless cleanser. Although peels are generally safe, you want to be able to remove one quickly, if needed, without having to leave the room.
- Start with the lowest concentration (salicylic acid or glycolic acid) then titrate up. Ask patients about any reactions they experienced with the previous peel before making the decision on the next concentration.
- For a peel to treat hyperpigmentation, she recommends one peel about every 4 weeks for a series of 5-6 peels.
- After a peel, the patient should use a mineral sunscreen; chemical sunscreens will sting.
Know your comfort zone
Conference chair Pearl Grimes, MD, director of The Vitiligo & Pigmentation Institute of Southern California in Los Angeles, said superficial peels are best for dermatologists new to peeling until they gain comfort with experience.
Superficial and medium-depth peels work well for mild to moderate photoaging, she said at the meeting.
“We know that in darker skin we have more intrinsic aging rather than photoaging. We have more textural changes, hyperpigmentation,” Dr. Grimes said.
For Fitzpatrick skin types I-III, she said, “you can do superficial, medium, and deep peels.” For darker skin types, “I typically stay in the superficial, medium range.”
She said that she uses retinoids to exfoliate before a superficial peel but added, “you’ve got to stop them early because retinoids can make a superficial peel a medium-depth peel.”
Taking photos is important before any procedure, she said, as is spending time with patients clarifying their outcome expectations.
“I love peeling,” Dr. Grimes said. “And it’s cost effective. If you don’t want to spend a ton of money, it’s amazing what you can achieve with chemical peeling.”
When asked by a member of the audience whether they avoid superficial peels in women who are pregnant or breastfeeding, both Dr. Woolery-Lloyd and Dr. Grimes said they do avoid them in those patients.
Dr. Grimes said she tells her patients, especially in the first trimester, “I am the most conservative woman on the planet. I do nothing during the first trimester.”
Dr. Woolery-Lloyd has been a speaker for Ortho Dermatologics, Loreal and EPI, and has done research for Pfizer, Galderma, Allergan, Arcutis, Vyne, Merz, and Eirion. She has been on advisory boards for Loreal, Allergan, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfize,r and Merz. Dr. Grimes reports grant/research Support from Clinuvel Pharmaceuticals, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, LASEROPTEK, L’Oréal USA, Pfizer, Procter & Gamble, skinbetter science, and Versicolor Technologies, and is on the speakers bureau/receives honoraria for non-CME for Incyte and Procter & Gamble; and is a consultant or is on the advisory board for L’Oréal USA and Procter & Gamble. She has stock options in Versicolor Technologies.
CHICAGO – Heather Woolery-Lloyd, MD, says she’s generally “risk averse,” but when it comes to superficial chemical peels, she’s in her comfort zone.
Superficial peeling is “one of the most common cosmetic procedures that I do,” Dr. Woolery-Lloyd, director of the skin of color division in the dermatology department at the University of Miami, said at the Pigmentary Disorders Exchange Symposium.
In her practice, .
Contraindications are an active bacterial infection, open wounds, and active herpes simplex virus. “If someone looks like they even have a remnant of a cold sore, I tell them to come back,” she said.
Setting expectations for patients is critical, Dr. Woolery-Lloyd said, as a series of superficial peels is needed before the desired results are evident.
The peel she uses most is salicylic acid, a beta-hydroxy acid, at a strength of 20%-30%. “It’s very effective on our acne patients,” she said at the meeting, provided by MedscapeLIVE! “If you’re just starting with peels, I think this is a very safe one. You don’t have to time it, and you don’t have to neutralize it,” and at lower concentrations, is “very safe.”
Dr. Woolery-Lloyd provided these other tips during her presentation:
- Even superficial peels can be uncomfortable, she noted, so she keeps a fan nearby to use when needed to help with discomfort.
- Find the peel you’re comfortable with, master that peel, and don’t jump from peel to peel. Get familiar with the side effects and how to predict results.
- Stop retinoids up to 7 days before a peel. Consider placing the patient on hydroquinone before the chemical peel to decrease the risk of hyperpigmentation.
- Before the procedure, prep the skin with acetone or alcohol. Applying petrolatum helps protect around the eyes, alar crease, and other sensitive areas, “or anywhere you’re concerned about the depth of the peel.”
- Application with rough gauze helps avoid the waste that comes with makeup sponges soaking up the product. It also helps add exfoliation.
- Have everything ready before starting the procedure, including (depending on the peel), a neutralizer or soapless cleanser. Although peels are generally safe, you want to be able to remove one quickly, if needed, without having to leave the room.
- Start with the lowest concentration (salicylic acid or glycolic acid) then titrate up. Ask patients about any reactions they experienced with the previous peel before making the decision on the next concentration.
- For a peel to treat hyperpigmentation, she recommends one peel about every 4 weeks for a series of 5-6 peels.
- After a peel, the patient should use a mineral sunscreen; chemical sunscreens will sting.
Know your comfort zone
Conference chair Pearl Grimes, MD, director of The Vitiligo & Pigmentation Institute of Southern California in Los Angeles, said superficial peels are best for dermatologists new to peeling until they gain comfort with experience.
Superficial and medium-depth peels work well for mild to moderate photoaging, she said at the meeting.
“We know that in darker skin we have more intrinsic aging rather than photoaging. We have more textural changes, hyperpigmentation,” Dr. Grimes said.
For Fitzpatrick skin types I-III, she said, “you can do superficial, medium, and deep peels.” For darker skin types, “I typically stay in the superficial, medium range.”
She said that she uses retinoids to exfoliate before a superficial peel but added, “you’ve got to stop them early because retinoids can make a superficial peel a medium-depth peel.”
Taking photos is important before any procedure, she said, as is spending time with patients clarifying their outcome expectations.
“I love peeling,” Dr. Grimes said. “And it’s cost effective. If you don’t want to spend a ton of money, it’s amazing what you can achieve with chemical peeling.”
When asked by a member of the audience whether they avoid superficial peels in women who are pregnant or breastfeeding, both Dr. Woolery-Lloyd and Dr. Grimes said they do avoid them in those patients.
Dr. Grimes said she tells her patients, especially in the first trimester, “I am the most conservative woman on the planet. I do nothing during the first trimester.”
Dr. Woolery-Lloyd has been a speaker for Ortho Dermatologics, Loreal and EPI, and has done research for Pfizer, Galderma, Allergan, Arcutis, Vyne, Merz, and Eirion. She has been on advisory boards for Loreal, Allergan, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfize,r and Merz. Dr. Grimes reports grant/research Support from Clinuvel Pharmaceuticals, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, LASEROPTEK, L’Oréal USA, Pfizer, Procter & Gamble, skinbetter science, and Versicolor Technologies, and is on the speakers bureau/receives honoraria for non-CME for Incyte and Procter & Gamble; and is a consultant or is on the advisory board for L’Oréal USA and Procter & Gamble. She has stock options in Versicolor Technologies.
AT THE MEDSCAPE LIVE! PIGMENTARY DISORDERS SYMPOSIUM
SPF is only the start when recommending sunscreens
CHICAGO – at the inaugural Pigmentary Disorders Exchange Symposium.
Among the first factors physicians should consider before recommending sunscreen are a patient’s Fitzpatrick skin type, risks for burning or tanning, underlying skin disorders, and medications the patient is taking, Dr. Taylor, professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said at the meeting, provided by MedscapeLIVE! If patients are on hypertensives, for example, medications can make them more photosensitive.
Consider skin type
Dr. Taylor said she was dismayed by the results of a recent study, which found that 43% of dermatologists who responded to a survey reported that they never, rarely, or only sometimes took a patient’s skin type into account when making sunscreen recommendations. The article is referenced in a 2022 expert panel consensus paper she coauthored on photoprotection “for skin of all color.” But she pointed out that considering skin type alone is inadequate.
Questions for patients in joint decision-making should include lifestyle and work choices such as whether they work inside or outside, and how much sun exposure they get in a typical day. Heat and humidity levels should also be considered as should a patient’s susceptibility to dyspigmentation. “That could be overall darkening of the skin, mottled hyperpigmentation, actinic dyspigmentation, and, of course, propensity for skin cancer,” she said.
Use differs by race
Dr. Taylor, who is also vice chair for diversity, equity and inclusion in the department of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, pointed out that sunscreen use differs considerably by race.
In study of 8,952 adults in the United States who reported that they were sun sensitive found that a subset of adults with skin of color were significantly less likely to use sunscreen when compared with non-Hispanic White adults: Non-Hispanic Black (adjusted odds ratio, 0.43); non-Hispanic Asian (aOR. 0.54); and Hispanic (aOR, 0.70) adults.
In the study, non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic adults were significantly less likely to use sunscreens with an SPF greater than 15. In addition, non-Hispanic Black, non-Hispanic Asian, and Hispanic adults were significantly more likely than non-Hispanic Whites to wear long sleeves when outside. Such differences are important to keep in mind when advising patients about sunscreens, she said.
Protection for lighter-colored skin
Dr. Taylor said that, for patients with lighter skin tones, “we really want to protect against ultraviolet B as well as ultraviolet A, particularly ultraviolet A2. Ultraviolet radiation is going to cause DNA damage.” Patients with Fitzpatrick skin types I, II, or III are most susceptible to the effects of UVB with sunburn inflammation, which will cause erythema and tanning, and immunosuppression.
“For those who are I, II, and III, we do want to recommend a broad-spectrum, photostable sunscreen with a critical wavelength of 370 nanometers, which is going to protect from both UVB and UVA2,” she said.
Sunscreen recommendations are meant to be paired with advice to avoid midday sun from 10 a.m. to 2 p.m., wearing protective clothing and accessories, and seeking shade, she noted.
Dr. Taylor said, for those patients with lighter skin who are more susceptible to photodamage and premature aging, physicians should recommend sunscreens that contain DNA repair enzymes such as photolyases and sunscreens that contain antioxidants that can prevent or reverse DNA damage. “The exogenous form of these lyases have been manufactured and added to sunscreens,” Dr. Taylor said. “They’re readily available in the United States. That is something to consider for patients with significant photodamage.”
Retinoids can also help alleviate or reverse photodamage, she added.
Protection for darker-colored skin
“Many people of color do not believe they need sunscreen,” Dr. Taylor said. But studies show that, although there may be more intrinsic protection, sunscreen is still needed.
Over 30 years ago, Halder and colleagues reported that melanin in skin of color can filter two to five times more UV radiation, and in a paper on the photoprotective role of melanin, Kaidbey and colleagues found that skin types V and VI had an intrinsic SPF of 13 when compared with those who have lighter complexions, which had an SPF of 3.
Sunburns seem to occur less frequently in people with skin of color, but that may be because erythema is less apparent in people with darker skin tones or because of differences in personal definitions of sunburn, Dr. Taylor said.
“Skin of color can and does sustain sunburns and sunscreen will help prevent that,” she said, adding that a recommendation of an SPF 30 is likely sufficient for these patients. Dr. Taylor noted that sunscreens for patients with darker skin often cost substantially more than those for lighter skin, and that should be considered in recommendations.
Tinted sunscreens
Dr. Taylor said that, while broad-spectrum photostable sunscreens protect against UVB and UVA 2, they don’t protect from visible light and UVA1. Two methods to add that protection are using inorganic tinted sunscreens that contain iron oxide or pigmentary titanium dioxide. Dr. Taylor was a coauthor of a practical guide to tinted sunscreens published in 2022.
“For iron oxide, we want a concentration of 3% or greater,” she said, adding that the percentage often is not known because if it is contained in a sunscreen, it is listed as an inactive ingredient.
Another method to address visible light and UVA1 is the use of antioxidant-containing sunscreens with vitamin E, vitamin C, or licochalcone A, Dr. Taylor said.
During the question-and-answer period following her presentation, Amit Pandya, MD, adjunct professor of dermatology at University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, asked why “every makeup, every sunscreen, just says iron oxide,” since it is known that visible light will cause pigmentation, especially in those with darker skin tones.
He urged pushing for a law that would require listing the percentage of iron oxide on products to assure it is sufficient, according to what the literature recommends.
Conference Chair Pearl Grimes, MD, director of the Vitiligo and Pigmentation Institute of Southern California, Los Angeles, said that she recommends tinted sunscreens almost exclusively for her patients, but those with darker skin colors struggle to match color.
Dr. Taylor referred to an analysis published in 2022 of 58 over-the counter sunscreens, which found that only 38% of tinted sunscreens was available in more than one shade, “which is a problem for many of our patients.” She said that providing samples with different hues and tactile sensations may help patients find the right product.
Dr. Taylor disclosed being on the advisory boards for AbbVie, Avita Medical, Beiersdorf, Biorez, Eli Lily, EPI Health, Evolus, Galderma, Hugel America, Johnson and Johnson, L’Oreal USA, MedScape, Pfizer, Scientis US, UCB, Vichy Laboratories. She is a consultant for Arcutis Biothermapeutics, Beiersdorf, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cara Therapeutics, Dior, and Sanofi. She has done contracted research for Allergan Aesthetics, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Croma-Pharma, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer, and has an ownership interest in Armis Scientific, GloGetter, and Piction Health.
Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
CHICAGO – at the inaugural Pigmentary Disorders Exchange Symposium.
Among the first factors physicians should consider before recommending sunscreen are a patient’s Fitzpatrick skin type, risks for burning or tanning, underlying skin disorders, and medications the patient is taking, Dr. Taylor, professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said at the meeting, provided by MedscapeLIVE! If patients are on hypertensives, for example, medications can make them more photosensitive.
Consider skin type
Dr. Taylor said she was dismayed by the results of a recent study, which found that 43% of dermatologists who responded to a survey reported that they never, rarely, or only sometimes took a patient’s skin type into account when making sunscreen recommendations. The article is referenced in a 2022 expert panel consensus paper she coauthored on photoprotection “for skin of all color.” But she pointed out that considering skin type alone is inadequate.
Questions for patients in joint decision-making should include lifestyle and work choices such as whether they work inside or outside, and how much sun exposure they get in a typical day. Heat and humidity levels should also be considered as should a patient’s susceptibility to dyspigmentation. “That could be overall darkening of the skin, mottled hyperpigmentation, actinic dyspigmentation, and, of course, propensity for skin cancer,” she said.
Use differs by race
Dr. Taylor, who is also vice chair for diversity, equity and inclusion in the department of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, pointed out that sunscreen use differs considerably by race.
In study of 8,952 adults in the United States who reported that they were sun sensitive found that a subset of adults with skin of color were significantly less likely to use sunscreen when compared with non-Hispanic White adults: Non-Hispanic Black (adjusted odds ratio, 0.43); non-Hispanic Asian (aOR. 0.54); and Hispanic (aOR, 0.70) adults.
In the study, non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic adults were significantly less likely to use sunscreens with an SPF greater than 15. In addition, non-Hispanic Black, non-Hispanic Asian, and Hispanic adults were significantly more likely than non-Hispanic Whites to wear long sleeves when outside. Such differences are important to keep in mind when advising patients about sunscreens, she said.
Protection for lighter-colored skin
Dr. Taylor said that, for patients with lighter skin tones, “we really want to protect against ultraviolet B as well as ultraviolet A, particularly ultraviolet A2. Ultraviolet radiation is going to cause DNA damage.” Patients with Fitzpatrick skin types I, II, or III are most susceptible to the effects of UVB with sunburn inflammation, which will cause erythema and tanning, and immunosuppression.
“For those who are I, II, and III, we do want to recommend a broad-spectrum, photostable sunscreen with a critical wavelength of 370 nanometers, which is going to protect from both UVB and UVA2,” she said.
Sunscreen recommendations are meant to be paired with advice to avoid midday sun from 10 a.m. to 2 p.m., wearing protective clothing and accessories, and seeking shade, she noted.
Dr. Taylor said, for those patients with lighter skin who are more susceptible to photodamage and premature aging, physicians should recommend sunscreens that contain DNA repair enzymes such as photolyases and sunscreens that contain antioxidants that can prevent or reverse DNA damage. “The exogenous form of these lyases have been manufactured and added to sunscreens,” Dr. Taylor said. “They’re readily available in the United States. That is something to consider for patients with significant photodamage.”
Retinoids can also help alleviate or reverse photodamage, she added.
Protection for darker-colored skin
“Many people of color do not believe they need sunscreen,” Dr. Taylor said. But studies show that, although there may be more intrinsic protection, sunscreen is still needed.
Over 30 years ago, Halder and colleagues reported that melanin in skin of color can filter two to five times more UV radiation, and in a paper on the photoprotective role of melanin, Kaidbey and colleagues found that skin types V and VI had an intrinsic SPF of 13 when compared with those who have lighter complexions, which had an SPF of 3.
Sunburns seem to occur less frequently in people with skin of color, but that may be because erythema is less apparent in people with darker skin tones or because of differences in personal definitions of sunburn, Dr. Taylor said.
“Skin of color can and does sustain sunburns and sunscreen will help prevent that,” she said, adding that a recommendation of an SPF 30 is likely sufficient for these patients. Dr. Taylor noted that sunscreens for patients with darker skin often cost substantially more than those for lighter skin, and that should be considered in recommendations.
Tinted sunscreens
Dr. Taylor said that, while broad-spectrum photostable sunscreens protect against UVB and UVA 2, they don’t protect from visible light and UVA1. Two methods to add that protection are using inorganic tinted sunscreens that contain iron oxide or pigmentary titanium dioxide. Dr. Taylor was a coauthor of a practical guide to tinted sunscreens published in 2022.
“For iron oxide, we want a concentration of 3% or greater,” she said, adding that the percentage often is not known because if it is contained in a sunscreen, it is listed as an inactive ingredient.
Another method to address visible light and UVA1 is the use of antioxidant-containing sunscreens with vitamin E, vitamin C, or licochalcone A, Dr. Taylor said.
During the question-and-answer period following her presentation, Amit Pandya, MD, adjunct professor of dermatology at University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, asked why “every makeup, every sunscreen, just says iron oxide,” since it is known that visible light will cause pigmentation, especially in those with darker skin tones.
He urged pushing for a law that would require listing the percentage of iron oxide on products to assure it is sufficient, according to what the literature recommends.
Conference Chair Pearl Grimes, MD, director of the Vitiligo and Pigmentation Institute of Southern California, Los Angeles, said that she recommends tinted sunscreens almost exclusively for her patients, but those with darker skin colors struggle to match color.
Dr. Taylor referred to an analysis published in 2022 of 58 over-the counter sunscreens, which found that only 38% of tinted sunscreens was available in more than one shade, “which is a problem for many of our patients.” She said that providing samples with different hues and tactile sensations may help patients find the right product.
Dr. Taylor disclosed being on the advisory boards for AbbVie, Avita Medical, Beiersdorf, Biorez, Eli Lily, EPI Health, Evolus, Galderma, Hugel America, Johnson and Johnson, L’Oreal USA, MedScape, Pfizer, Scientis US, UCB, Vichy Laboratories. She is a consultant for Arcutis Biothermapeutics, Beiersdorf, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cara Therapeutics, Dior, and Sanofi. She has done contracted research for Allergan Aesthetics, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Croma-Pharma, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer, and has an ownership interest in Armis Scientific, GloGetter, and Piction Health.
Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
CHICAGO – at the inaugural Pigmentary Disorders Exchange Symposium.
Among the first factors physicians should consider before recommending sunscreen are a patient’s Fitzpatrick skin type, risks for burning or tanning, underlying skin disorders, and medications the patient is taking, Dr. Taylor, professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said at the meeting, provided by MedscapeLIVE! If patients are on hypertensives, for example, medications can make them more photosensitive.
Consider skin type
Dr. Taylor said she was dismayed by the results of a recent study, which found that 43% of dermatologists who responded to a survey reported that they never, rarely, or only sometimes took a patient’s skin type into account when making sunscreen recommendations. The article is referenced in a 2022 expert panel consensus paper she coauthored on photoprotection “for skin of all color.” But she pointed out that considering skin type alone is inadequate.
Questions for patients in joint decision-making should include lifestyle and work choices such as whether they work inside or outside, and how much sun exposure they get in a typical day. Heat and humidity levels should also be considered as should a patient’s susceptibility to dyspigmentation. “That could be overall darkening of the skin, mottled hyperpigmentation, actinic dyspigmentation, and, of course, propensity for skin cancer,” she said.
Use differs by race
Dr. Taylor, who is also vice chair for diversity, equity and inclusion in the department of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, pointed out that sunscreen use differs considerably by race.
In study of 8,952 adults in the United States who reported that they were sun sensitive found that a subset of adults with skin of color were significantly less likely to use sunscreen when compared with non-Hispanic White adults: Non-Hispanic Black (adjusted odds ratio, 0.43); non-Hispanic Asian (aOR. 0.54); and Hispanic (aOR, 0.70) adults.
In the study, non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic adults were significantly less likely to use sunscreens with an SPF greater than 15. In addition, non-Hispanic Black, non-Hispanic Asian, and Hispanic adults were significantly more likely than non-Hispanic Whites to wear long sleeves when outside. Such differences are important to keep in mind when advising patients about sunscreens, she said.
Protection for lighter-colored skin
Dr. Taylor said that, for patients with lighter skin tones, “we really want to protect against ultraviolet B as well as ultraviolet A, particularly ultraviolet A2. Ultraviolet radiation is going to cause DNA damage.” Patients with Fitzpatrick skin types I, II, or III are most susceptible to the effects of UVB with sunburn inflammation, which will cause erythema and tanning, and immunosuppression.
“For those who are I, II, and III, we do want to recommend a broad-spectrum, photostable sunscreen with a critical wavelength of 370 nanometers, which is going to protect from both UVB and UVA2,” she said.
Sunscreen recommendations are meant to be paired with advice to avoid midday sun from 10 a.m. to 2 p.m., wearing protective clothing and accessories, and seeking shade, she noted.
Dr. Taylor said, for those patients with lighter skin who are more susceptible to photodamage and premature aging, physicians should recommend sunscreens that contain DNA repair enzymes such as photolyases and sunscreens that contain antioxidants that can prevent or reverse DNA damage. “The exogenous form of these lyases have been manufactured and added to sunscreens,” Dr. Taylor said. “They’re readily available in the United States. That is something to consider for patients with significant photodamage.”
Retinoids can also help alleviate or reverse photodamage, she added.
Protection for darker-colored skin
“Many people of color do not believe they need sunscreen,” Dr. Taylor said. But studies show that, although there may be more intrinsic protection, sunscreen is still needed.
Over 30 years ago, Halder and colleagues reported that melanin in skin of color can filter two to five times more UV radiation, and in a paper on the photoprotective role of melanin, Kaidbey and colleagues found that skin types V and VI had an intrinsic SPF of 13 when compared with those who have lighter complexions, which had an SPF of 3.
Sunburns seem to occur less frequently in people with skin of color, but that may be because erythema is less apparent in people with darker skin tones or because of differences in personal definitions of sunburn, Dr. Taylor said.
“Skin of color can and does sustain sunburns and sunscreen will help prevent that,” she said, adding that a recommendation of an SPF 30 is likely sufficient for these patients. Dr. Taylor noted that sunscreens for patients with darker skin often cost substantially more than those for lighter skin, and that should be considered in recommendations.
Tinted sunscreens
Dr. Taylor said that, while broad-spectrum photostable sunscreens protect against UVB and UVA 2, they don’t protect from visible light and UVA1. Two methods to add that protection are using inorganic tinted sunscreens that contain iron oxide or pigmentary titanium dioxide. Dr. Taylor was a coauthor of a practical guide to tinted sunscreens published in 2022.
“For iron oxide, we want a concentration of 3% or greater,” she said, adding that the percentage often is not known because if it is contained in a sunscreen, it is listed as an inactive ingredient.
Another method to address visible light and UVA1 is the use of antioxidant-containing sunscreens with vitamin E, vitamin C, or licochalcone A, Dr. Taylor said.
During the question-and-answer period following her presentation, Amit Pandya, MD, adjunct professor of dermatology at University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, asked why “every makeup, every sunscreen, just says iron oxide,” since it is known that visible light will cause pigmentation, especially in those with darker skin tones.
He urged pushing for a law that would require listing the percentage of iron oxide on products to assure it is sufficient, according to what the literature recommends.
Conference Chair Pearl Grimes, MD, director of the Vitiligo and Pigmentation Institute of Southern California, Los Angeles, said that she recommends tinted sunscreens almost exclusively for her patients, but those with darker skin colors struggle to match color.
Dr. Taylor referred to an analysis published in 2022 of 58 over-the counter sunscreens, which found that only 38% of tinted sunscreens was available in more than one shade, “which is a problem for many of our patients.” She said that providing samples with different hues and tactile sensations may help patients find the right product.
Dr. Taylor disclosed being on the advisory boards for AbbVie, Avita Medical, Beiersdorf, Biorez, Eli Lily, EPI Health, Evolus, Galderma, Hugel America, Johnson and Johnson, L’Oreal USA, MedScape, Pfizer, Scientis US, UCB, Vichy Laboratories. She is a consultant for Arcutis Biothermapeutics, Beiersdorf, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cara Therapeutics, Dior, and Sanofi. She has done contracted research for Allergan Aesthetics, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Croma-Pharma, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer, and has an ownership interest in Armis Scientific, GloGetter, and Piction Health.
Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT THE MEDSCAPELIVE! PIGMENTARY DISORDERS SYMPOSIUM
Picosecond laser applications continue to expand
PHOENIX – Ever since PicoSure became the first picosecond laser cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of unwanted tattoos and pigmented lesions in 2012, new uses for this technology continue to expand.
Now, These include PicoWay, PicoSure, Enlighten, PicoPlus, PiQo4, and Quanta Pico, among others.
“PicoWay technology has integrated nicely into my practice in Houston, the most ethnically diverse city in the country, with its ability to safely treat a number of various benign, congenital, and acquired epidermal and dermal pigmented lesions with ultrashort pulse duration and low thermal impact, which greatly reduces the risk of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation even in darker skin types,” Paul M. Friedman, MD, director of the Dermatology and Laser Surgery Center, Houston, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery.
He emphasized the importance of therapeutic clinical endpoints, noting that with q-switched lasers, “you’re looking for immediate whitening, whereas with picosecond lasers, your endpoint is slight whitening or slight darkening depending on wavelength, indication, and skin type. The ability to fractionate picosecond pulses has also allowed us to utilize this technology for photoaging as well as acne scarring.”
The PicoWay system includes a 730-nm picosecond titanium sapphire handpiece, which is FDA cleared for treatment of benign pigmented lesions and blue and green tattoo removal. Dr. Friedman said that he has seen good clinical results using the handpiece for café-au-lait macules, particularly in skin of color.
In an abstract presented at the ASLMS meeting, he and his colleagues presented a retrospective review of 12 patients with café-au-lait macules with Fitzpatrick skin types III-VI who were treated with the PicoWay 730 nm handpiece between April 2021 and January 2023. Patients received a mean of 3.1 treatments at intervals that ranged from 5 to 40 weeks. Clinical photographs were graded by three board-certified dermatologists using a 5-point visual analogue scale.
Overall, patients were rated to have a mean improvement of 26%-50%. Two patients achieved 100% clearance after four to five treatment sessions. “Café-au-lait macules with smooth borders responded less well to laser treatment, confirming prior studies at our center,” he said. “We often educate parents that café-au-lait macules may recur over time, especially with repeated sun exposure.”
Treating melasma
Dr. Friedman’s go-to devices for melasma include the low-density, low-energy 1,927-nm fractional diode laser; the 1,064 nm picosecond Nd:YAG, the low-fluence 1,064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG with a nanosecond pulse duration, and the 595-nm pulsed dye laser for lesions exhibiting underlying vascularity. He said that combining therapies that target pigment and vasculature may be ideal to prevent relapses. “Melasma is a multifactorial condition so by improving patient education and expectation alongside advances in laser treatment of melasma, we have ultimately improved our ability to treat this condition,” he said.
“We’re approaching it from all angles, with ultraviolet photography and spectrocolorimetry, behavioral modifications, topical skin-lightening agents, broad spectrum sunscreens with protection against visible light, and oral tranexamic acid in advanced cases. Then, we intervene with these energy-based modalities, and the bottom line is, less energy and density is more, with lengthened treatment intervals. In 2023, we’re better than we’ve ever been in terms of our ability to safely and effectively improve melasma.”
Novel lasers
Dr. Friedman also described the UltraClear, a novel ablative fractional 2,910-nm erbium-doped glass fiber laser that delivers a customized blend of ablation and coagulation based on the patient’s condition, skin type, and tolerability for down time. He provided an overview of the versatility of what he described as highly customizable technology for conditions such as photoaging and dyschromia in patients of various skin types, making it a very versatile platform in his practice.
The AVAVA MIRIA system is a “next generation” laser “where you’re able to use a focal point. Basically, you’re treating the skin from the inside out in a 3D manner and you’re able to focus intradermally up to 1 mm with high energy 1,064 nm or 1,550 nm,” he said. “It’s a unique conical geometry that spares the epidermis, combined with sapphire tip cooling and images the skin at the same time with the potential for personalized treatments of dyschromia and photoaging in all skin types. It’s truly remarkable where the technology is heading.”
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, Acclaro, Merz Aesthetics, Solta Medical, and Cytrellis. He has conducted contracted research for Sofwave and is a member of the speakers bureau for Solta Medical and Candela.
PHOENIX – Ever since PicoSure became the first picosecond laser cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of unwanted tattoos and pigmented lesions in 2012, new uses for this technology continue to expand.
Now, These include PicoWay, PicoSure, Enlighten, PicoPlus, PiQo4, and Quanta Pico, among others.
“PicoWay technology has integrated nicely into my practice in Houston, the most ethnically diverse city in the country, with its ability to safely treat a number of various benign, congenital, and acquired epidermal and dermal pigmented lesions with ultrashort pulse duration and low thermal impact, which greatly reduces the risk of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation even in darker skin types,” Paul M. Friedman, MD, director of the Dermatology and Laser Surgery Center, Houston, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery.
He emphasized the importance of therapeutic clinical endpoints, noting that with q-switched lasers, “you’re looking for immediate whitening, whereas with picosecond lasers, your endpoint is slight whitening or slight darkening depending on wavelength, indication, and skin type. The ability to fractionate picosecond pulses has also allowed us to utilize this technology for photoaging as well as acne scarring.”
The PicoWay system includes a 730-nm picosecond titanium sapphire handpiece, which is FDA cleared for treatment of benign pigmented lesions and blue and green tattoo removal. Dr. Friedman said that he has seen good clinical results using the handpiece for café-au-lait macules, particularly in skin of color.
In an abstract presented at the ASLMS meeting, he and his colleagues presented a retrospective review of 12 patients with café-au-lait macules with Fitzpatrick skin types III-VI who were treated with the PicoWay 730 nm handpiece between April 2021 and January 2023. Patients received a mean of 3.1 treatments at intervals that ranged from 5 to 40 weeks. Clinical photographs were graded by three board-certified dermatologists using a 5-point visual analogue scale.
Overall, patients were rated to have a mean improvement of 26%-50%. Two patients achieved 100% clearance after four to five treatment sessions. “Café-au-lait macules with smooth borders responded less well to laser treatment, confirming prior studies at our center,” he said. “We often educate parents that café-au-lait macules may recur over time, especially with repeated sun exposure.”
Treating melasma
Dr. Friedman’s go-to devices for melasma include the low-density, low-energy 1,927-nm fractional diode laser; the 1,064 nm picosecond Nd:YAG, the low-fluence 1,064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG with a nanosecond pulse duration, and the 595-nm pulsed dye laser for lesions exhibiting underlying vascularity. He said that combining therapies that target pigment and vasculature may be ideal to prevent relapses. “Melasma is a multifactorial condition so by improving patient education and expectation alongside advances in laser treatment of melasma, we have ultimately improved our ability to treat this condition,” he said.
“We’re approaching it from all angles, with ultraviolet photography and spectrocolorimetry, behavioral modifications, topical skin-lightening agents, broad spectrum sunscreens with protection against visible light, and oral tranexamic acid in advanced cases. Then, we intervene with these energy-based modalities, and the bottom line is, less energy and density is more, with lengthened treatment intervals. In 2023, we’re better than we’ve ever been in terms of our ability to safely and effectively improve melasma.”
Novel lasers
Dr. Friedman also described the UltraClear, a novel ablative fractional 2,910-nm erbium-doped glass fiber laser that delivers a customized blend of ablation and coagulation based on the patient’s condition, skin type, and tolerability for down time. He provided an overview of the versatility of what he described as highly customizable technology for conditions such as photoaging and dyschromia in patients of various skin types, making it a very versatile platform in his practice.
The AVAVA MIRIA system is a “next generation” laser “where you’re able to use a focal point. Basically, you’re treating the skin from the inside out in a 3D manner and you’re able to focus intradermally up to 1 mm with high energy 1,064 nm or 1,550 nm,” he said. “It’s a unique conical geometry that spares the epidermis, combined with sapphire tip cooling and images the skin at the same time with the potential for personalized treatments of dyschromia and photoaging in all skin types. It’s truly remarkable where the technology is heading.”
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, Acclaro, Merz Aesthetics, Solta Medical, and Cytrellis. He has conducted contracted research for Sofwave and is a member of the speakers bureau for Solta Medical and Candela.
PHOENIX – Ever since PicoSure became the first picosecond laser cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of unwanted tattoos and pigmented lesions in 2012, new uses for this technology continue to expand.
Now, These include PicoWay, PicoSure, Enlighten, PicoPlus, PiQo4, and Quanta Pico, among others.
“PicoWay technology has integrated nicely into my practice in Houston, the most ethnically diverse city in the country, with its ability to safely treat a number of various benign, congenital, and acquired epidermal and dermal pigmented lesions with ultrashort pulse duration and low thermal impact, which greatly reduces the risk of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation even in darker skin types,” Paul M. Friedman, MD, director of the Dermatology and Laser Surgery Center, Houston, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery.
He emphasized the importance of therapeutic clinical endpoints, noting that with q-switched lasers, “you’re looking for immediate whitening, whereas with picosecond lasers, your endpoint is slight whitening or slight darkening depending on wavelength, indication, and skin type. The ability to fractionate picosecond pulses has also allowed us to utilize this technology for photoaging as well as acne scarring.”
The PicoWay system includes a 730-nm picosecond titanium sapphire handpiece, which is FDA cleared for treatment of benign pigmented lesions and blue and green tattoo removal. Dr. Friedman said that he has seen good clinical results using the handpiece for café-au-lait macules, particularly in skin of color.
In an abstract presented at the ASLMS meeting, he and his colleagues presented a retrospective review of 12 patients with café-au-lait macules with Fitzpatrick skin types III-VI who were treated with the PicoWay 730 nm handpiece between April 2021 and January 2023. Patients received a mean of 3.1 treatments at intervals that ranged from 5 to 40 weeks. Clinical photographs were graded by three board-certified dermatologists using a 5-point visual analogue scale.
Overall, patients were rated to have a mean improvement of 26%-50%. Two patients achieved 100% clearance after four to five treatment sessions. “Café-au-lait macules with smooth borders responded less well to laser treatment, confirming prior studies at our center,” he said. “We often educate parents that café-au-lait macules may recur over time, especially with repeated sun exposure.”
Treating melasma
Dr. Friedman’s go-to devices for melasma include the low-density, low-energy 1,927-nm fractional diode laser; the 1,064 nm picosecond Nd:YAG, the low-fluence 1,064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG with a nanosecond pulse duration, and the 595-nm pulsed dye laser for lesions exhibiting underlying vascularity. He said that combining therapies that target pigment and vasculature may be ideal to prevent relapses. “Melasma is a multifactorial condition so by improving patient education and expectation alongside advances in laser treatment of melasma, we have ultimately improved our ability to treat this condition,” he said.
“We’re approaching it from all angles, with ultraviolet photography and spectrocolorimetry, behavioral modifications, topical skin-lightening agents, broad spectrum sunscreens with protection against visible light, and oral tranexamic acid in advanced cases. Then, we intervene with these energy-based modalities, and the bottom line is, less energy and density is more, with lengthened treatment intervals. In 2023, we’re better than we’ve ever been in terms of our ability to safely and effectively improve melasma.”
Novel lasers
Dr. Friedman also described the UltraClear, a novel ablative fractional 2,910-nm erbium-doped glass fiber laser that delivers a customized blend of ablation and coagulation based on the patient’s condition, skin type, and tolerability for down time. He provided an overview of the versatility of what he described as highly customizable technology for conditions such as photoaging and dyschromia in patients of various skin types, making it a very versatile platform in his practice.
The AVAVA MIRIA system is a “next generation” laser “where you’re able to use a focal point. Basically, you’re treating the skin from the inside out in a 3D manner and you’re able to focus intradermally up to 1 mm with high energy 1,064 nm or 1,550 nm,” he said. “It’s a unique conical geometry that spares the epidermis, combined with sapphire tip cooling and images the skin at the same time with the potential for personalized treatments of dyschromia and photoaging in all skin types. It’s truly remarkable where the technology is heading.”
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, Acclaro, Merz Aesthetics, Solta Medical, and Cytrellis. He has conducted contracted research for Sofwave and is a member of the speakers bureau for Solta Medical and Candela.
FROM ASLMS 2023
Study eyes sunscreens marketed to individuals with skin of color
, and more than 40% contain a UV blocker that may create a white cast.
Those are among the findings from a study by Michelle Xiong, a medical student at Brown University, Providence, R.I., and Erin M. Warshaw, MD, of the department of dermatology at Park Nicollet/Health Partners Health Services, Minneapolis, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“There is increasing awareness of the negative effects of ultraviolet (UV) light in individuals with skin of color (SOC), especially in regards to pigmentation disorders induced and/or exacerbated by UV exposure,” the authors wrote. “As a result, there has been a surge in sunscreens marketed to this population. We aimed to characterize cost, marketing claims, and potential allergenic ingredients in sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC.”
Between December 2021 and October 2022, the researchers used the following search terms on Google: “sunscreen” plus “skin of 36 color,” “dark skin,” “brown skin,” “LatinX skin,” and/or “Black skin.” They extracted price, marketing claims, and ingredients from manufacturers’ websites and used 90 allergens contained in the American Contact Dermatitis Society 2020 Core series to identify potential allergens. Next, they combined cross-reactors/synonyms into allergen categories based on ACDS Contact Allergen Management Plan (CAMP) cross-reactor classification. If multiple ingredients in a sunscreen were represented by a single allergen category, it was counted only once. A similar approach was utilized for marketing categories.
A total of 12 sunscreens were included in the analysis: Absolute Joi, Black Girl Sunscreen, Black Girl Sunscreen Make It Matte, Bolden SPF Brightening Moisturizer, Eleven on the Defense Unrivaled Sun Serum, Kinlo Golden Rays Sunscreen, Live Tinted Hueguard 3-in-1 Mineral Sunscreen, Mele Dew The Most Sheer Moisturizer SPF30 Broad Spectrum Sunscreen, Mele No Shade Sunscreen Oil, Specific Beauty Active Radiance Day Moi, Unsun Mineral Sunscreen, and Urban Skin Rx Complexion Protection. Their average cost was $19.30 per ounce (range, $6.33-$50.00) and common marketing claims for these products were “no white cast” (91.7%), being free of an ingredient (83.3%), and “moisturizing” (75%).
Of the 12 sunscreens, 7 (58.3%) contained a chemical sunscreen agent, 5 (41.7%) contained a physical UV blocker, and all contained at least one allergen. The average number of allergens per product was 4.7, most commonly fragrance/botanicals (83.3%), tocopherol (83.3%), sodium benzoates/derivatives (58.3%), and sorbitan sesquiolate/derivatives (58.3%).
“Average cost of sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC was $19.30/oz, much higher than the median price of $3.32/oz reported in a separate study of 65 popular sunscreens,” the study authors wrote. “As many of the sunscreens in our study were sold by smaller businesses, higher prices may be due to higher production costs or a perceived smaller market.”
The authors expressed surprise that five sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC contained a physical UV blocker which may create a white cast. They contacted the manufacturers of these five sunscreens and confirmed that three used micronized formulations. “While ingested/inhaled nanoparticles of titanium dioxide may cause tissue effects, most studies of topical products show excellent safety,” they wrote.
They also noted that the average of 4.7 allergens per product observed in the analysis was similar to the average of 4.9 seen in a separate study of 52 popular sunscreens. “However, that study only included 34 allergens while this study evaluated 90 allergens,” the authors wrote. “Consumers and providers should be aware sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC may cause allergic contact dermatitis,” they commented.
“It is interesting to see how costly these products are now compared to store bought and general commercially available sunscreens several years ago,” said Lawrence J. Green, clinical professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study. “However, to me that is not surprising as products marketed and targeted to specific populations are often priced at a premium. It wasn’t clear to me how many of these specialized online SOC sunscreens are tinted. I wish the authors had compared the cost of tinted sunscreens in general to nontinted sunscreens because tinted ones are more useful for SOC, because when rubbed in, they can readily match SOC and can also offer protection in the visible light spectrum.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures; the study had no funding source. Dr. Green disclosed that he is a speaker, consultant, or investigator for many pharmaceutical companies.
, and more than 40% contain a UV blocker that may create a white cast.
Those are among the findings from a study by Michelle Xiong, a medical student at Brown University, Providence, R.I., and Erin M. Warshaw, MD, of the department of dermatology at Park Nicollet/Health Partners Health Services, Minneapolis, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“There is increasing awareness of the negative effects of ultraviolet (UV) light in individuals with skin of color (SOC), especially in regards to pigmentation disorders induced and/or exacerbated by UV exposure,” the authors wrote. “As a result, there has been a surge in sunscreens marketed to this population. We aimed to characterize cost, marketing claims, and potential allergenic ingredients in sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC.”
Between December 2021 and October 2022, the researchers used the following search terms on Google: “sunscreen” plus “skin of 36 color,” “dark skin,” “brown skin,” “LatinX skin,” and/or “Black skin.” They extracted price, marketing claims, and ingredients from manufacturers’ websites and used 90 allergens contained in the American Contact Dermatitis Society 2020 Core series to identify potential allergens. Next, they combined cross-reactors/synonyms into allergen categories based on ACDS Contact Allergen Management Plan (CAMP) cross-reactor classification. If multiple ingredients in a sunscreen were represented by a single allergen category, it was counted only once. A similar approach was utilized for marketing categories.
A total of 12 sunscreens were included in the analysis: Absolute Joi, Black Girl Sunscreen, Black Girl Sunscreen Make It Matte, Bolden SPF Brightening Moisturizer, Eleven on the Defense Unrivaled Sun Serum, Kinlo Golden Rays Sunscreen, Live Tinted Hueguard 3-in-1 Mineral Sunscreen, Mele Dew The Most Sheer Moisturizer SPF30 Broad Spectrum Sunscreen, Mele No Shade Sunscreen Oil, Specific Beauty Active Radiance Day Moi, Unsun Mineral Sunscreen, and Urban Skin Rx Complexion Protection. Their average cost was $19.30 per ounce (range, $6.33-$50.00) and common marketing claims for these products were “no white cast” (91.7%), being free of an ingredient (83.3%), and “moisturizing” (75%).
Of the 12 sunscreens, 7 (58.3%) contained a chemical sunscreen agent, 5 (41.7%) contained a physical UV blocker, and all contained at least one allergen. The average number of allergens per product was 4.7, most commonly fragrance/botanicals (83.3%), tocopherol (83.3%), sodium benzoates/derivatives (58.3%), and sorbitan sesquiolate/derivatives (58.3%).
“Average cost of sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC was $19.30/oz, much higher than the median price of $3.32/oz reported in a separate study of 65 popular sunscreens,” the study authors wrote. “As many of the sunscreens in our study were sold by smaller businesses, higher prices may be due to higher production costs or a perceived smaller market.”
The authors expressed surprise that five sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC contained a physical UV blocker which may create a white cast. They contacted the manufacturers of these five sunscreens and confirmed that three used micronized formulations. “While ingested/inhaled nanoparticles of titanium dioxide may cause tissue effects, most studies of topical products show excellent safety,” they wrote.
They also noted that the average of 4.7 allergens per product observed in the analysis was similar to the average of 4.9 seen in a separate study of 52 popular sunscreens. “However, that study only included 34 allergens while this study evaluated 90 allergens,” the authors wrote. “Consumers and providers should be aware sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC may cause allergic contact dermatitis,” they commented.
“It is interesting to see how costly these products are now compared to store bought and general commercially available sunscreens several years ago,” said Lawrence J. Green, clinical professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study. “However, to me that is not surprising as products marketed and targeted to specific populations are often priced at a premium. It wasn’t clear to me how many of these specialized online SOC sunscreens are tinted. I wish the authors had compared the cost of tinted sunscreens in general to nontinted sunscreens because tinted ones are more useful for SOC, because when rubbed in, they can readily match SOC and can also offer protection in the visible light spectrum.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures; the study had no funding source. Dr. Green disclosed that he is a speaker, consultant, or investigator for many pharmaceutical companies.
, and more than 40% contain a UV blocker that may create a white cast.
Those are among the findings from a study by Michelle Xiong, a medical student at Brown University, Providence, R.I., and Erin M. Warshaw, MD, of the department of dermatology at Park Nicollet/Health Partners Health Services, Minneapolis, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“There is increasing awareness of the negative effects of ultraviolet (UV) light in individuals with skin of color (SOC), especially in regards to pigmentation disorders induced and/or exacerbated by UV exposure,” the authors wrote. “As a result, there has been a surge in sunscreens marketed to this population. We aimed to characterize cost, marketing claims, and potential allergenic ingredients in sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC.”
Between December 2021 and October 2022, the researchers used the following search terms on Google: “sunscreen” plus “skin of 36 color,” “dark skin,” “brown skin,” “LatinX skin,” and/or “Black skin.” They extracted price, marketing claims, and ingredients from manufacturers’ websites and used 90 allergens contained in the American Contact Dermatitis Society 2020 Core series to identify potential allergens. Next, they combined cross-reactors/synonyms into allergen categories based on ACDS Contact Allergen Management Plan (CAMP) cross-reactor classification. If multiple ingredients in a sunscreen were represented by a single allergen category, it was counted only once. A similar approach was utilized for marketing categories.
A total of 12 sunscreens were included in the analysis: Absolute Joi, Black Girl Sunscreen, Black Girl Sunscreen Make It Matte, Bolden SPF Brightening Moisturizer, Eleven on the Defense Unrivaled Sun Serum, Kinlo Golden Rays Sunscreen, Live Tinted Hueguard 3-in-1 Mineral Sunscreen, Mele Dew The Most Sheer Moisturizer SPF30 Broad Spectrum Sunscreen, Mele No Shade Sunscreen Oil, Specific Beauty Active Radiance Day Moi, Unsun Mineral Sunscreen, and Urban Skin Rx Complexion Protection. Their average cost was $19.30 per ounce (range, $6.33-$50.00) and common marketing claims for these products were “no white cast” (91.7%), being free of an ingredient (83.3%), and “moisturizing” (75%).
Of the 12 sunscreens, 7 (58.3%) contained a chemical sunscreen agent, 5 (41.7%) contained a physical UV blocker, and all contained at least one allergen. The average number of allergens per product was 4.7, most commonly fragrance/botanicals (83.3%), tocopherol (83.3%), sodium benzoates/derivatives (58.3%), and sorbitan sesquiolate/derivatives (58.3%).
“Average cost of sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC was $19.30/oz, much higher than the median price of $3.32/oz reported in a separate study of 65 popular sunscreens,” the study authors wrote. “As many of the sunscreens in our study were sold by smaller businesses, higher prices may be due to higher production costs or a perceived smaller market.”
The authors expressed surprise that five sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC contained a physical UV blocker which may create a white cast. They contacted the manufacturers of these five sunscreens and confirmed that three used micronized formulations. “While ingested/inhaled nanoparticles of titanium dioxide may cause tissue effects, most studies of topical products show excellent safety,” they wrote.
They also noted that the average of 4.7 allergens per product observed in the analysis was similar to the average of 4.9 seen in a separate study of 52 popular sunscreens. “However, that study only included 34 allergens while this study evaluated 90 allergens,” the authors wrote. “Consumers and providers should be aware sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC may cause allergic contact dermatitis,” they commented.
“It is interesting to see how costly these products are now compared to store bought and general commercially available sunscreens several years ago,” said Lawrence J. Green, clinical professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study. “However, to me that is not surprising as products marketed and targeted to specific populations are often priced at a premium. It wasn’t clear to me how many of these specialized online SOC sunscreens are tinted. I wish the authors had compared the cost of tinted sunscreens in general to nontinted sunscreens because tinted ones are more useful for SOC, because when rubbed in, they can readily match SOC and can also offer protection in the visible light spectrum.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures; the study had no funding source. Dr. Green disclosed that he is a speaker, consultant, or investigator for many pharmaceutical companies.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Saururus chinensis
Also known as Asian or Chinese lizard’s tail (or Sam-baekcho in Korea), Saururus chinensis is an East Asian plant used in traditional medicine for various indications including edema, gonorrhea, jaundice, hypertension, leproma, pneumonia, and rheumatoid arthritis.1,2 Specifically, Korean traditional medicine practitioners as well as Native Americans and early colonists in what is now the United States used the botanical to treat cancer, edema, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions.2-4 Modern research has produced evidence supporting the use of this plant in the dermatologic realm. This column focuses on the relevant bench science and possible applications.
Various beneficial effects
In 2008, Yoo et al. found that the ethanol extract of the dried aerial parts of S. chinensis exhibit anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and antinociceptive properties, which they suggested may partially account for the established therapeutic effects of the plant.2 Also, Lee et al. reported in 2012 on the antiproliferative effects against human cancer cell lines of neolignans found in S. chinensis.5
Antioxidant properties have been associated with S. chinensis. In 2014, Kim et al. reported that S. chinensis extract attenuated the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated neuroinflammatory response in BV-2 microglia cells, a result that the authors partly ascribed to the antioxidant constituents (particularly quercetin) of the plant.3
Atopic dermatitis
In 2008, Choi et al. determined that the leaves of S. chinensis impeded the formation of atopic dermatitis–like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice caused by repeated application of picryl chloride, potentially by stimulating the Th1 cell response, thus modulating Th1/Th2 imbalance. They concluded that S. chinensis has potential as an adjunct treatment option for atopic dermatitis.6
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Bae et al. studied the anti-inflammatory properties of sauchinone, a lignan derived from S. chinensis reputed to exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective activity,7 using LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. They found that the lignan lowered tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha synthesis by inhibiting the c-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 phosphorylation pathway, accounting for the anti-inflammatory effects of the S. chinensis constituent.8
More recently, Zhang et al. determined that the ethanol extract of S. chinensis leaves impaired proinflammatory gene expression by blocking the TAK1/AP-1 pathway in LPS-treated RAW264.7 macrophages. They suggested that such suppression is a significant step in the anti-inflammatory function exhibited by the plant.1
Photoprotection
Park et al. investigated in 2013 the beneficial effects of sauchinone. Specifically, they studied potential photoprotective effects of the lignan against UVB in HaCaT human epidermal keratinocytes. They found that sauchinone (5-40 mcm) conferred significant protection as evaluated by cell viability and a toxicity assay. At 20-40 mcm, sauchinone blocked the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)–1 proteins and decrease of type 1 collagen engendered by UVB exposure. The investigators further discovered that sauchinone diminished the synthesis of reactive oxygen species. Overall, they determined that sauchinone imparted protection by suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 MAPK signaling through the activation of oxidative defense enzymes.7
Potential use as a depigmenting agent
In 2009, Seo et al. isolated the lignans manassantin A and B from S. chinensis and determined that these compounds dose-dependently impeded melanin synthesis in alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)–activated melanoma B16 cells. They also noted that manassantin A suppressed forskolin- or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX)–induced melanin production and diminished cellular levels of IBMX-inducible tyrosinase protein. The lignan had no effect on the catalytic activity of cell-free tyrosinase, an important enzyme in melanin pigment production. The researchers concluded that their results suggest the potential for S. chinensis to be used to treat hyperpigmentation disorders.9
Two years later Lee et al. found that manassantin A, derived from S. chinensis, steadily suppressed the cAMP elevator IBMX- or dibutyryl cAMP-induced melanin synthesis in B16 cells or in melan-a melanocytes by down-regulating the expression of tyrosinase or the TRP1 gene. The lignan also inhibited microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) induction via the IBMX-activated cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) pathway, thus preventing the Ser-133 phosphorylation of CREB. The researchers concluded that this molecular disruption of melanin production suggests the potential for the use of manassantin A as a skin depigmenting agent.10
That same year, another S. chinensis lignan gained interest. Yun et al. investigated the effects of the S. chinensis lignan component saucerneol D on melanin synthesis in cAMP-elevated melanocytes. They found that the lignan efficiently impeded melanin product in B16 melanoma cells stimulated with alpha-MSH or other cAMP elevators. Saucerneol D was also credited with down-regulating alpha-MSH–induced gene expression of tyrosinase at the transcription level in B16 cells, suppressing alpha-MSH–induced phosphorylation of CREB in the cells, and inhibiting MITF induction. The investigators concluded that their results point to the potential of the S. chinensis lignan saucerneol D for the treatment of hyperpigmentation disorders.11
In 2012, Chang et al. observed that an extract of S. chinensis and one of its constituent lignans, manassantin B, prevented melanosome transport in normal human melanocytes and Melan-a melanocytes, by interrupting the interaction between melanophilin and myosin Va. The investigators concluded that as a substance that can hinder melanosome transport, manassantin B displays potential for use as depigmenting product.12
The following year, Lee et al. studied the effects of S. chinensis extracts on the melanogenesis signaling pathway activated by alpha-MSH, finding dose-dependent inhibition without provoking cytotoxicity in B16F10 cells. Further, the team found evidence that the depigmenting activity exhibited by S. chinensis extracts may occur as a result of MITF and tyrosinase expression stemming from elevated activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). They concluded that their results support further examination of S. chinensis for its potential to contribute to skin whitening.5
Conclusion
Multiple lignan constituents in this plant-derived ingredient appear to yield anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, photoprotective, and antitumor properties. Its inhibitory effects on melanin production and its antiaging abilities make it worthy of further study and consideration of inclusion in antiaging skin care products.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in the office and as an e-commerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Zhang J et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:114400.
2. Yoo HJ et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Nov 20;120(2):282-6.
3. Kim BW et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 16;14:502.
4. Lee DH et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(5):772-9.
5. Lee YJ et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(8):1361-6.
6. Choi MS et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Jan;31(1):51-6.
7. Park G et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(7):1134-9.
8. Bae HB et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Sep;10(9):1022-8.
9. Seo CS et al. Phytother Res. 2009 Nov;23(11):1531-6.
10. Lee HD et al. Exp Dermatol. 2011 Sep;20(9):761-3.
11. Yun JY et al. Arch Pharm Res. 2011 Aug;34(8):1339-45.
12. Chang H et al. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012 Nov;25(6):765-72.
Also known as Asian or Chinese lizard’s tail (or Sam-baekcho in Korea), Saururus chinensis is an East Asian plant used in traditional medicine for various indications including edema, gonorrhea, jaundice, hypertension, leproma, pneumonia, and rheumatoid arthritis.1,2 Specifically, Korean traditional medicine practitioners as well as Native Americans and early colonists in what is now the United States used the botanical to treat cancer, edema, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions.2-4 Modern research has produced evidence supporting the use of this plant in the dermatologic realm. This column focuses on the relevant bench science and possible applications.
Various beneficial effects
In 2008, Yoo et al. found that the ethanol extract of the dried aerial parts of S. chinensis exhibit anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and antinociceptive properties, which they suggested may partially account for the established therapeutic effects of the plant.2 Also, Lee et al. reported in 2012 on the antiproliferative effects against human cancer cell lines of neolignans found in S. chinensis.5
Antioxidant properties have been associated with S. chinensis. In 2014, Kim et al. reported that S. chinensis extract attenuated the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated neuroinflammatory response in BV-2 microglia cells, a result that the authors partly ascribed to the antioxidant constituents (particularly quercetin) of the plant.3
Atopic dermatitis
In 2008, Choi et al. determined that the leaves of S. chinensis impeded the formation of atopic dermatitis–like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice caused by repeated application of picryl chloride, potentially by stimulating the Th1 cell response, thus modulating Th1/Th2 imbalance. They concluded that S. chinensis has potential as an adjunct treatment option for atopic dermatitis.6
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Bae et al. studied the anti-inflammatory properties of sauchinone, a lignan derived from S. chinensis reputed to exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective activity,7 using LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. They found that the lignan lowered tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha synthesis by inhibiting the c-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 phosphorylation pathway, accounting for the anti-inflammatory effects of the S. chinensis constituent.8
More recently, Zhang et al. determined that the ethanol extract of S. chinensis leaves impaired proinflammatory gene expression by blocking the TAK1/AP-1 pathway in LPS-treated RAW264.7 macrophages. They suggested that such suppression is a significant step in the anti-inflammatory function exhibited by the plant.1
Photoprotection
Park et al. investigated in 2013 the beneficial effects of sauchinone. Specifically, they studied potential photoprotective effects of the lignan against UVB in HaCaT human epidermal keratinocytes. They found that sauchinone (5-40 mcm) conferred significant protection as evaluated by cell viability and a toxicity assay. At 20-40 mcm, sauchinone blocked the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)–1 proteins and decrease of type 1 collagen engendered by UVB exposure. The investigators further discovered that sauchinone diminished the synthesis of reactive oxygen species. Overall, they determined that sauchinone imparted protection by suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 MAPK signaling through the activation of oxidative defense enzymes.7
Potential use as a depigmenting agent
In 2009, Seo et al. isolated the lignans manassantin A and B from S. chinensis and determined that these compounds dose-dependently impeded melanin synthesis in alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)–activated melanoma B16 cells. They also noted that manassantin A suppressed forskolin- or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX)–induced melanin production and diminished cellular levels of IBMX-inducible tyrosinase protein. The lignan had no effect on the catalytic activity of cell-free tyrosinase, an important enzyme in melanin pigment production. The researchers concluded that their results suggest the potential for S. chinensis to be used to treat hyperpigmentation disorders.9
Two years later Lee et al. found that manassantin A, derived from S. chinensis, steadily suppressed the cAMP elevator IBMX- or dibutyryl cAMP-induced melanin synthesis in B16 cells or in melan-a melanocytes by down-regulating the expression of tyrosinase or the TRP1 gene. The lignan also inhibited microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) induction via the IBMX-activated cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) pathway, thus preventing the Ser-133 phosphorylation of CREB. The researchers concluded that this molecular disruption of melanin production suggests the potential for the use of manassantin A as a skin depigmenting agent.10
That same year, another S. chinensis lignan gained interest. Yun et al. investigated the effects of the S. chinensis lignan component saucerneol D on melanin synthesis in cAMP-elevated melanocytes. They found that the lignan efficiently impeded melanin product in B16 melanoma cells stimulated with alpha-MSH or other cAMP elevators. Saucerneol D was also credited with down-regulating alpha-MSH–induced gene expression of tyrosinase at the transcription level in B16 cells, suppressing alpha-MSH–induced phosphorylation of CREB in the cells, and inhibiting MITF induction. The investigators concluded that their results point to the potential of the S. chinensis lignan saucerneol D for the treatment of hyperpigmentation disorders.11
In 2012, Chang et al. observed that an extract of S. chinensis and one of its constituent lignans, manassantin B, prevented melanosome transport in normal human melanocytes and Melan-a melanocytes, by interrupting the interaction between melanophilin and myosin Va. The investigators concluded that as a substance that can hinder melanosome transport, manassantin B displays potential for use as depigmenting product.12
The following year, Lee et al. studied the effects of S. chinensis extracts on the melanogenesis signaling pathway activated by alpha-MSH, finding dose-dependent inhibition without provoking cytotoxicity in B16F10 cells. Further, the team found evidence that the depigmenting activity exhibited by S. chinensis extracts may occur as a result of MITF and tyrosinase expression stemming from elevated activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). They concluded that their results support further examination of S. chinensis for its potential to contribute to skin whitening.5
Conclusion
Multiple lignan constituents in this plant-derived ingredient appear to yield anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, photoprotective, and antitumor properties. Its inhibitory effects on melanin production and its antiaging abilities make it worthy of further study and consideration of inclusion in antiaging skin care products.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in the office and as an e-commerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Zhang J et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:114400.
2. Yoo HJ et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Nov 20;120(2):282-6.
3. Kim BW et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 16;14:502.
4. Lee DH et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(5):772-9.
5. Lee YJ et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(8):1361-6.
6. Choi MS et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Jan;31(1):51-6.
7. Park G et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(7):1134-9.
8. Bae HB et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Sep;10(9):1022-8.
9. Seo CS et al. Phytother Res. 2009 Nov;23(11):1531-6.
10. Lee HD et al. Exp Dermatol. 2011 Sep;20(9):761-3.
11. Yun JY et al. Arch Pharm Res. 2011 Aug;34(8):1339-45.
12. Chang H et al. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012 Nov;25(6):765-72.
Also known as Asian or Chinese lizard’s tail (or Sam-baekcho in Korea), Saururus chinensis is an East Asian plant used in traditional medicine for various indications including edema, gonorrhea, jaundice, hypertension, leproma, pneumonia, and rheumatoid arthritis.1,2 Specifically, Korean traditional medicine practitioners as well as Native Americans and early colonists in what is now the United States used the botanical to treat cancer, edema, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions.2-4 Modern research has produced evidence supporting the use of this plant in the dermatologic realm. This column focuses on the relevant bench science and possible applications.
Various beneficial effects
In 2008, Yoo et al. found that the ethanol extract of the dried aerial parts of S. chinensis exhibit anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and antinociceptive properties, which they suggested may partially account for the established therapeutic effects of the plant.2 Also, Lee et al. reported in 2012 on the antiproliferative effects against human cancer cell lines of neolignans found in S. chinensis.5
Antioxidant properties have been associated with S. chinensis. In 2014, Kim et al. reported that S. chinensis extract attenuated the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated neuroinflammatory response in BV-2 microglia cells, a result that the authors partly ascribed to the antioxidant constituents (particularly quercetin) of the plant.3
Atopic dermatitis
In 2008, Choi et al. determined that the leaves of S. chinensis impeded the formation of atopic dermatitis–like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice caused by repeated application of picryl chloride, potentially by stimulating the Th1 cell response, thus modulating Th1/Th2 imbalance. They concluded that S. chinensis has potential as an adjunct treatment option for atopic dermatitis.6
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Bae et al. studied the anti-inflammatory properties of sauchinone, a lignan derived from S. chinensis reputed to exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective activity,7 using LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. They found that the lignan lowered tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha synthesis by inhibiting the c-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 phosphorylation pathway, accounting for the anti-inflammatory effects of the S. chinensis constituent.8
More recently, Zhang et al. determined that the ethanol extract of S. chinensis leaves impaired proinflammatory gene expression by blocking the TAK1/AP-1 pathway in LPS-treated RAW264.7 macrophages. They suggested that such suppression is a significant step in the anti-inflammatory function exhibited by the plant.1
Photoprotection
Park et al. investigated in 2013 the beneficial effects of sauchinone. Specifically, they studied potential photoprotective effects of the lignan against UVB in HaCaT human epidermal keratinocytes. They found that sauchinone (5-40 mcm) conferred significant protection as evaluated by cell viability and a toxicity assay. At 20-40 mcm, sauchinone blocked the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)–1 proteins and decrease of type 1 collagen engendered by UVB exposure. The investigators further discovered that sauchinone diminished the synthesis of reactive oxygen species. Overall, they determined that sauchinone imparted protection by suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 MAPK signaling through the activation of oxidative defense enzymes.7
Potential use as a depigmenting agent
In 2009, Seo et al. isolated the lignans manassantin A and B from S. chinensis and determined that these compounds dose-dependently impeded melanin synthesis in alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)–activated melanoma B16 cells. They also noted that manassantin A suppressed forskolin- or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX)–induced melanin production and diminished cellular levels of IBMX-inducible tyrosinase protein. The lignan had no effect on the catalytic activity of cell-free tyrosinase, an important enzyme in melanin pigment production. The researchers concluded that their results suggest the potential for S. chinensis to be used to treat hyperpigmentation disorders.9
Two years later Lee et al. found that manassantin A, derived from S. chinensis, steadily suppressed the cAMP elevator IBMX- or dibutyryl cAMP-induced melanin synthesis in B16 cells or in melan-a melanocytes by down-regulating the expression of tyrosinase or the TRP1 gene. The lignan also inhibited microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) induction via the IBMX-activated cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) pathway, thus preventing the Ser-133 phosphorylation of CREB. The researchers concluded that this molecular disruption of melanin production suggests the potential for the use of manassantin A as a skin depigmenting agent.10
That same year, another S. chinensis lignan gained interest. Yun et al. investigated the effects of the S. chinensis lignan component saucerneol D on melanin synthesis in cAMP-elevated melanocytes. They found that the lignan efficiently impeded melanin product in B16 melanoma cells stimulated with alpha-MSH or other cAMP elevators. Saucerneol D was also credited with down-regulating alpha-MSH–induced gene expression of tyrosinase at the transcription level in B16 cells, suppressing alpha-MSH–induced phosphorylation of CREB in the cells, and inhibiting MITF induction. The investigators concluded that their results point to the potential of the S. chinensis lignan saucerneol D for the treatment of hyperpigmentation disorders.11
In 2012, Chang et al. observed that an extract of S. chinensis and one of its constituent lignans, manassantin B, prevented melanosome transport in normal human melanocytes and Melan-a melanocytes, by interrupting the interaction between melanophilin and myosin Va. The investigators concluded that as a substance that can hinder melanosome transport, manassantin B displays potential for use as depigmenting product.12
The following year, Lee et al. studied the effects of S. chinensis extracts on the melanogenesis signaling pathway activated by alpha-MSH, finding dose-dependent inhibition without provoking cytotoxicity in B16F10 cells. Further, the team found evidence that the depigmenting activity exhibited by S. chinensis extracts may occur as a result of MITF and tyrosinase expression stemming from elevated activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). They concluded that their results support further examination of S. chinensis for its potential to contribute to skin whitening.5
Conclusion
Multiple lignan constituents in this plant-derived ingredient appear to yield anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, photoprotective, and antitumor properties. Its inhibitory effects on melanin production and its antiaging abilities make it worthy of further study and consideration of inclusion in antiaging skin care products.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in the office and as an e-commerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Zhang J et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:114400.
2. Yoo HJ et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Nov 20;120(2):282-6.
3. Kim BW et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 16;14:502.
4. Lee DH et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(5):772-9.
5. Lee YJ et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(8):1361-6.
6. Choi MS et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Jan;31(1):51-6.
7. Park G et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(7):1134-9.
8. Bae HB et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Sep;10(9):1022-8.
9. Seo CS et al. Phytother Res. 2009 Nov;23(11):1531-6.
10. Lee HD et al. Exp Dermatol. 2011 Sep;20(9):761-3.
11. Yun JY et al. Arch Pharm Res. 2011 Aug;34(8):1339-45.
12. Chang H et al. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012 Nov;25(6):765-72.
Novel platform harnesses 3D laser technology for skin treatments
in all skin types, according to speakers at a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy.
The products feature “focal point technology,” which pairs 3D laser targeting with an integrated high-resolution imaging system (IntelliView), to help the user guide treatments at selectable depths. They have been cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for use in skin resurfacing procedures, and to treat benign pigmented lesions of the skin, including hyperpigmentation, and were created by Dieter Manstein, MD, PhD, Rox Anderson, MD, and Henry Chan, MD, of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Irina Erenburg, PhD, CEO of AVAVA, the company that markets the products.
dermally focused treatment with Focal Point Technology. The coagulation zone, in dark purple, shows a deep conical lesion that extends 1.3 mm deep with significant epidermal sparing.
At the meeting, Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser & Cosmetic Center, described focal point technology as an adjustable intradermally focused laser platform guided by real-time visual mapping to ensure the precise dose and depth of energy as the user performs treatments. “This is the key for rejuvenation,” he said. “You can go to different depths of the skin. You can be superficial for dyschromia and maybe a little bit different for wrinkles. If you want to treat scars, you go a little bit deeper. Coagulation occurs at these different depths.”
The collimated beam from conventional lasers affects all tissue in its path. The laser beam from the AVAVA product, however, creates a cone-shaped profile of injury in the dermis that minimizes the area of epidermal damage, making it safe in skin of color, according to Dr. Avram. “The beam comes to a focal point in the dermis at the depth that you want it to,” he explained during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s where the energy is going to focus and it bypasses the dermal/epidermal junction, which traditional fractional lasers cannot. What’s interesting about this platform is that you have a wavelength for skin rejuvenation, then you have wavelengths for pigment, which allows you to treat conditions like melasma at different depths.”
The AVAVA high-speed IntelliView imaging system features 10-micron resolution, “so you get exquisite imaging that can help guide your treatments,” he said. It also features image acquisition and storage with artificial intelligence algorithm interrogation and the ability to personalize treatments to the patient’s specific skin type. Commercial availability is expected in the first half of 2023, Dr. Avram said.
In a separate presentation, New York-based cosmetic dermatologist Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who has been involved in clinical trials of AVAVA’s focal point technology, said that patients “feel less pain and have less down time than we saw previously with other nonablative, fractional technologies.”
Downtime involves “just some mild redness,” he said, adding that he is encouraged by early results seen to date, and that “there appears to be some unique capabilities that will be borne out as the clinical studies progress.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, and Revelle. He is an investigator for Endo and holds ownership and/or shareholder interest in Cytrellis and La Jolla NanoMedical. Dr. Geronemus disclosed having financial relationships with numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
in all skin types, according to speakers at a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy.
The products feature “focal point technology,” which pairs 3D laser targeting with an integrated high-resolution imaging system (IntelliView), to help the user guide treatments at selectable depths. They have been cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for use in skin resurfacing procedures, and to treat benign pigmented lesions of the skin, including hyperpigmentation, and were created by Dieter Manstein, MD, PhD, Rox Anderson, MD, and Henry Chan, MD, of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Irina Erenburg, PhD, CEO of AVAVA, the company that markets the products.
dermally focused treatment with Focal Point Technology. The coagulation zone, in dark purple, shows a deep conical lesion that extends 1.3 mm deep with significant epidermal sparing.
At the meeting, Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser & Cosmetic Center, described focal point technology as an adjustable intradermally focused laser platform guided by real-time visual mapping to ensure the precise dose and depth of energy as the user performs treatments. “This is the key for rejuvenation,” he said. “You can go to different depths of the skin. You can be superficial for dyschromia and maybe a little bit different for wrinkles. If you want to treat scars, you go a little bit deeper. Coagulation occurs at these different depths.”
The collimated beam from conventional lasers affects all tissue in its path. The laser beam from the AVAVA product, however, creates a cone-shaped profile of injury in the dermis that minimizes the area of epidermal damage, making it safe in skin of color, according to Dr. Avram. “The beam comes to a focal point in the dermis at the depth that you want it to,” he explained during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s where the energy is going to focus and it bypasses the dermal/epidermal junction, which traditional fractional lasers cannot. What’s interesting about this platform is that you have a wavelength for skin rejuvenation, then you have wavelengths for pigment, which allows you to treat conditions like melasma at different depths.”
The AVAVA high-speed IntelliView imaging system features 10-micron resolution, “so you get exquisite imaging that can help guide your treatments,” he said. It also features image acquisition and storage with artificial intelligence algorithm interrogation and the ability to personalize treatments to the patient’s specific skin type. Commercial availability is expected in the first half of 2023, Dr. Avram said.
In a separate presentation, New York-based cosmetic dermatologist Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who has been involved in clinical trials of AVAVA’s focal point technology, said that patients “feel less pain and have less down time than we saw previously with other nonablative, fractional technologies.”
Downtime involves “just some mild redness,” he said, adding that he is encouraged by early results seen to date, and that “there appears to be some unique capabilities that will be borne out as the clinical studies progress.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, and Revelle. He is an investigator for Endo and holds ownership and/or shareholder interest in Cytrellis and La Jolla NanoMedical. Dr. Geronemus disclosed having financial relationships with numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
in all skin types, according to speakers at a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy.
The products feature “focal point technology,” which pairs 3D laser targeting with an integrated high-resolution imaging system (IntelliView), to help the user guide treatments at selectable depths. They have been cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for use in skin resurfacing procedures, and to treat benign pigmented lesions of the skin, including hyperpigmentation, and were created by Dieter Manstein, MD, PhD, Rox Anderson, MD, and Henry Chan, MD, of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Irina Erenburg, PhD, CEO of AVAVA, the company that markets the products.
dermally focused treatment with Focal Point Technology. The coagulation zone, in dark purple, shows a deep conical lesion that extends 1.3 mm deep with significant epidermal sparing.
At the meeting, Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser & Cosmetic Center, described focal point technology as an adjustable intradermally focused laser platform guided by real-time visual mapping to ensure the precise dose and depth of energy as the user performs treatments. “This is the key for rejuvenation,” he said. “You can go to different depths of the skin. You can be superficial for dyschromia and maybe a little bit different for wrinkles. If you want to treat scars, you go a little bit deeper. Coagulation occurs at these different depths.”
The collimated beam from conventional lasers affects all tissue in its path. The laser beam from the AVAVA product, however, creates a cone-shaped profile of injury in the dermis that minimizes the area of epidermal damage, making it safe in skin of color, according to Dr. Avram. “The beam comes to a focal point in the dermis at the depth that you want it to,” he explained during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s where the energy is going to focus and it bypasses the dermal/epidermal junction, which traditional fractional lasers cannot. What’s interesting about this platform is that you have a wavelength for skin rejuvenation, then you have wavelengths for pigment, which allows you to treat conditions like melasma at different depths.”
The AVAVA high-speed IntelliView imaging system features 10-micron resolution, “so you get exquisite imaging that can help guide your treatments,” he said. It also features image acquisition and storage with artificial intelligence algorithm interrogation and the ability to personalize treatments to the patient’s specific skin type. Commercial availability is expected in the first half of 2023, Dr. Avram said.
In a separate presentation, New York-based cosmetic dermatologist Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who has been involved in clinical trials of AVAVA’s focal point technology, said that patients “feel less pain and have less down time than we saw previously with other nonablative, fractional technologies.”
Downtime involves “just some mild redness,” he said, adding that he is encouraged by early results seen to date, and that “there appears to be some unique capabilities that will be borne out as the clinical studies progress.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, and Revelle. He is an investigator for Endo and holds ownership and/or shareholder interest in Cytrellis and La Jolla NanoMedical. Dr. Geronemus disclosed having financial relationships with numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE