User login
New DEA CME mandate affects 2 million prescribers
The Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023 mandates that all Drug Enforcement Administration–registered physicians and health care providers complete a one-time, 8-hour CME training on managing and treating opioid and other substance abuse disorders. This requirement goes into effect on June 27, 2023. New DEA registrants must also comply. Veterinarians are exempt.
A DEA registration is required to prescribe any controlled substance. The DEA categorizes these as Schedule I-V, with V being the least likely to be abused (Table 1). For example, opioids like fentanyl, oxycodone, and morphine are Schedule II. Medications without abuse potential are not scheduled.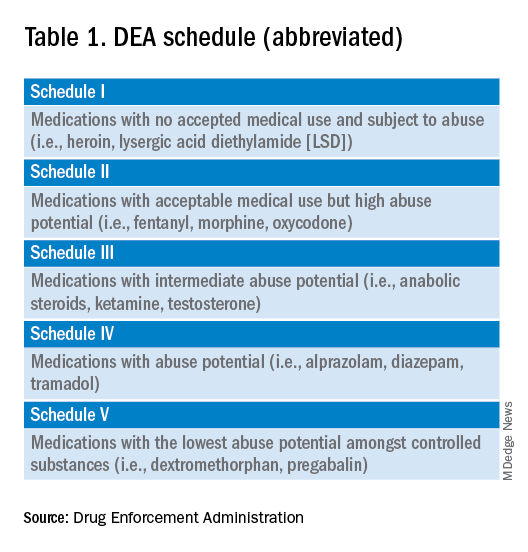
Will 16 million hours of opioid education save lives?
One should not underestimate the sweeping scope of this new federal requirement. DEA registrants include physicians and other health care providers such as nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and dentists. That is 8 hours per provider x 2 million providers: 16 million hours of CME!
Many states already require 1 or more hours of opioid training and pain management as part of their relicensure requirements (Table 2). To avoid redundancy, the DEA-mandated 8-hour training satisfies the various states’ requirements. 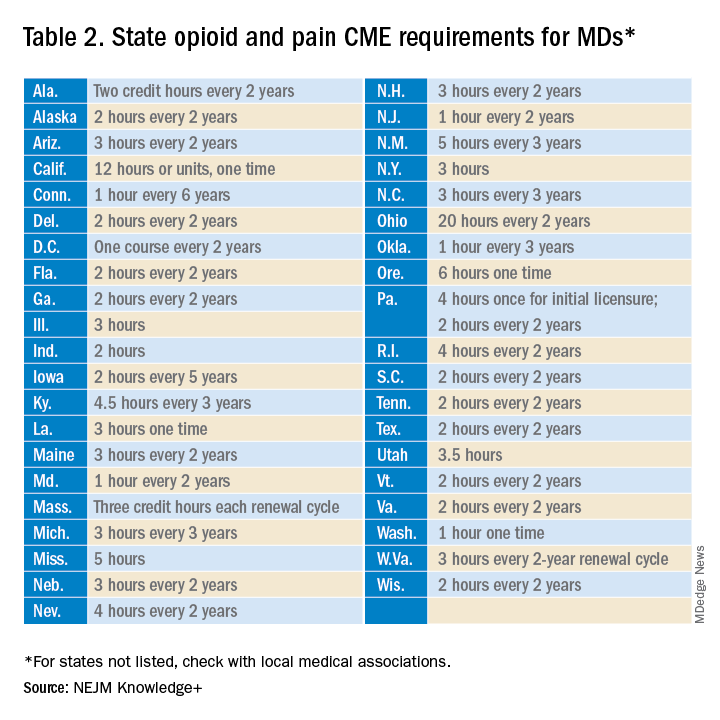
An uncompensated mandate
Physicians are no strangers to lifelong learning and most eagerly pursue educational opportunities. Though some physicians may have CME time and stipends allocated by their employers, many others, such as the approximately 50,000 locum tenens doctors, do not. However, as enthusiastic as these physicians may be about this new CME course, they will likely lose a day of seeing patients (and income) to comply with this new obligation.
Not just pain doctors
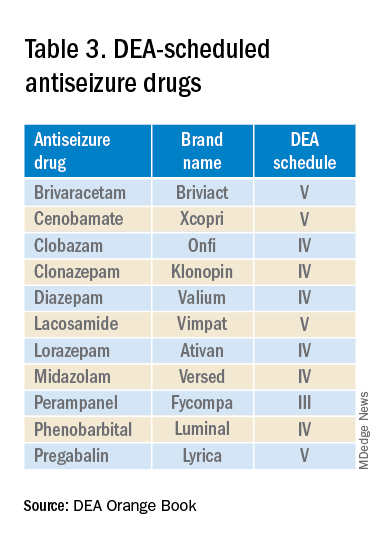
The mandate’s broad brush includes many health care providers who hold DEA certificates but do not prescribe opioids. For example, as a general neurologist and epileptologist, I do not treat patients with chronic pain and cannot remember the last time I wrote an opioid prescription. However, I frequently prescribe lacosamide, a Schedule V drug. A surprisingly large number of antiseizure drugs are Schedule III, IV, or V drugs (Table 3).
Real-world abuse?
How often scheduled antiseizure drugs are diverted or abused in an epilepsy population is unknown but appears to be infrequent. For example, perampanel abuse has not been reported despite its classification as a Schedule III drug. Anecdotally, in more than 40 years of clinical practice, I have never known a patient with epilepsy to abuse their antiseizure medications.
Take the course
Many organizations are happy to charge for the new 8-hour course. For example, the Tennessee Medical Association offers the training for $299 online or $400 in person. Materials from Elite Learning satisfy the 8-hour requirement for $80. However, NEJM Knowledge+ provides a complimentary 10-hour DEA-compliant course.
I recently completed the NEJM course. The information was thorough and took the whole 10 hours to finish. As excellent as it was, the content was only tangentially relevant to my clinical practice.
Conclusions
To obtain or renew a DEA certificate, neurologists, epilepsy specialists, and many other health care providers must comply with the new 8-hour CME opioid training mandate. Because the course requires 1 day to complete, health care providers would be prudent to obtain their CME well before their DEA certificate expires.
Though efforts to control the morbidity and mortality of the opioid epidemic are laudatory, perhaps the training should be more targeted to physicians who actually prescribe opioids rather than every DEA registrant. In the meantime, whether 16 million CME hours will save lives remains to be seen.
Dr. Wilner is professor of neurology at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis. He reported a conflict of interest with Accordant Health Services.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023 mandates that all Drug Enforcement Administration–registered physicians and health care providers complete a one-time, 8-hour CME training on managing and treating opioid and other substance abuse disorders. This requirement goes into effect on June 27, 2023. New DEA registrants must also comply. Veterinarians are exempt.
A DEA registration is required to prescribe any controlled substance. The DEA categorizes these as Schedule I-V, with V being the least likely to be abused (Table 1). For example, opioids like fentanyl, oxycodone, and morphine are Schedule II. Medications without abuse potential are not scheduled.
Will 16 million hours of opioid education save lives?
One should not underestimate the sweeping scope of this new federal requirement. DEA registrants include physicians and other health care providers such as nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and dentists. That is 8 hours per provider x 2 million providers: 16 million hours of CME!
Many states already require 1 or more hours of opioid training and pain management as part of their relicensure requirements (Table 2). To avoid redundancy, the DEA-mandated 8-hour training satisfies the various states’ requirements. 
An uncompensated mandate
Physicians are no strangers to lifelong learning and most eagerly pursue educational opportunities. Though some physicians may have CME time and stipends allocated by their employers, many others, such as the approximately 50,000 locum tenens doctors, do not. However, as enthusiastic as these physicians may be about this new CME course, they will likely lose a day of seeing patients (and income) to comply with this new obligation.
Not just pain doctors
The mandate’s broad brush includes many health care providers who hold DEA certificates but do not prescribe opioids. For example, as a general neurologist and epileptologist, I do not treat patients with chronic pain and cannot remember the last time I wrote an opioid prescription. However, I frequently prescribe lacosamide, a Schedule V drug. A surprisingly large number of antiseizure drugs are Schedule III, IV, or V drugs (Table 3).

Real-world abuse?
How often scheduled antiseizure drugs are diverted or abused in an epilepsy population is unknown but appears to be infrequent. For example, perampanel abuse has not been reported despite its classification as a Schedule III drug. Anecdotally, in more than 40 years of clinical practice, I have never known a patient with epilepsy to abuse their antiseizure medications.
Take the course
Many organizations are happy to charge for the new 8-hour course. For example, the Tennessee Medical Association offers the training for $299 online or $400 in person. Materials from Elite Learning satisfy the 8-hour requirement for $80. However, NEJM Knowledge+ provides a complimentary 10-hour DEA-compliant course.
I recently completed the NEJM course. The information was thorough and took the whole 10 hours to finish. As excellent as it was, the content was only tangentially relevant to my clinical practice.
Conclusions
To obtain or renew a DEA certificate, neurologists, epilepsy specialists, and many other health care providers must comply with the new 8-hour CME opioid training mandate. Because the course requires 1 day to complete, health care providers would be prudent to obtain their CME well before their DEA certificate expires.
Though efforts to control the morbidity and mortality of the opioid epidemic are laudatory, perhaps the training should be more targeted to physicians who actually prescribe opioids rather than every DEA registrant. In the meantime, whether 16 million CME hours will save lives remains to be seen.
Dr. Wilner is professor of neurology at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis. He reported a conflict of interest with Accordant Health Services.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023 mandates that all Drug Enforcement Administration–registered physicians and health care providers complete a one-time, 8-hour CME training on managing and treating opioid and other substance abuse disorders. This requirement goes into effect on June 27, 2023. New DEA registrants must also comply. Veterinarians are exempt.
A DEA registration is required to prescribe any controlled substance. The DEA categorizes these as Schedule I-V, with V being the least likely to be abused (Table 1). For example, opioids like fentanyl, oxycodone, and morphine are Schedule II. Medications without abuse potential are not scheduled.
Will 16 million hours of opioid education save lives?
One should not underestimate the sweeping scope of this new federal requirement. DEA registrants include physicians and other health care providers such as nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and dentists. That is 8 hours per provider x 2 million providers: 16 million hours of CME!
Many states already require 1 or more hours of opioid training and pain management as part of their relicensure requirements (Table 2). To avoid redundancy, the DEA-mandated 8-hour training satisfies the various states’ requirements. 
An uncompensated mandate
Physicians are no strangers to lifelong learning and most eagerly pursue educational opportunities. Though some physicians may have CME time and stipends allocated by their employers, many others, such as the approximately 50,000 locum tenens doctors, do not. However, as enthusiastic as these physicians may be about this new CME course, they will likely lose a day of seeing patients (and income) to comply with this new obligation.
Not just pain doctors
The mandate’s broad brush includes many health care providers who hold DEA certificates but do not prescribe opioids. For example, as a general neurologist and epileptologist, I do not treat patients with chronic pain and cannot remember the last time I wrote an opioid prescription. However, I frequently prescribe lacosamide, a Schedule V drug. A surprisingly large number of antiseizure drugs are Schedule III, IV, or V drugs (Table 3).

Real-world abuse?
How often scheduled antiseizure drugs are diverted or abused in an epilepsy population is unknown but appears to be infrequent. For example, perampanel abuse has not been reported despite its classification as a Schedule III drug. Anecdotally, in more than 40 years of clinical practice, I have never known a patient with epilepsy to abuse their antiseizure medications.
Take the course
Many organizations are happy to charge for the new 8-hour course. For example, the Tennessee Medical Association offers the training for $299 online or $400 in person. Materials from Elite Learning satisfy the 8-hour requirement for $80. However, NEJM Knowledge+ provides a complimentary 10-hour DEA-compliant course.
I recently completed the NEJM course. The information was thorough and took the whole 10 hours to finish. As excellent as it was, the content was only tangentially relevant to my clinical practice.
Conclusions
To obtain or renew a DEA certificate, neurologists, epilepsy specialists, and many other health care providers must comply with the new 8-hour CME opioid training mandate. Because the course requires 1 day to complete, health care providers would be prudent to obtain their CME well before their DEA certificate expires.
Though efforts to control the morbidity and mortality of the opioid epidemic are laudatory, perhaps the training should be more targeted to physicians who actually prescribe opioids rather than every DEA registrant. In the meantime, whether 16 million CME hours will save lives remains to be seen.
Dr. Wilner is professor of neurology at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis. He reported a conflict of interest with Accordant Health Services.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Migraine device expands treatment possibilities
AUSTIN, TEX – Migraine treatment and prevention is challenging in any population, but some present even more difficulties. Pregnant women and pediatric patients are two such groups where physicians and patients may be hesitant to use drugs.
Neuromodulation devices are proven alternatives to medical interventions, and the remote electrical neuromodulation device Nerivio (Theranica) was cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for acute treatment of migraine patients aged 12 and over in 2021. In March 2023, the agency expanded the clearance to include prevention of migration in adolescents aged 12 and over as well as adults.
Two studies presented at the annual meeting of the American Headache Society showed The latter study yielded similar findings to adults and was used by FDA in its decision to expand the device’s indication in adolescents in 2023, according to Teshamae Monteith, MD, who presented the study at a poster session.
The device, worn on the arm, allows the user to modulate the intensity of the stimulation so that it activates nociceptive pain receptors, but not in a painful way. “Each [patient] raises the intensity until it feels strong, yet comfortable, and when that happens, they activate the nociceptive receptors and the arm sends a signal all the way back up to the brainstem, where the pain control area is. Activating it causes the release of neurotransmitters that inhibit pain. That inhibition is a global pain inhibition mechanism, which causes inhibition of the migraine pain, and also the symptoms associated with migraine like photophobia and vomiting,” said Alit Stark-Inbar, PhD, who presented the study of treatment of pregnant women during a poster session.
Declining treatment days over time in adolescents
Dr. Monteith’s team studied high-frequency remote electrical neuromodulation device use in adolescents who had migraine on 10 days or more per month. They also required at least three treatment days in months 2 and 3 to control for the possibility that patients might stop using the device because they couldn’t afford it or for some reason other than efficacy or because their migraines went away.
The study included 83 adolescents aged 12-17 (mean, 15.9 years, 89% female). In the first month of use, the mean number of migraine treatment days was 12.6, which dropped to 9.0 in month 2 (P < .001), and 7.4 in month 3 (P < .001 from month 2). At 2 hours after treatment, 61.9% had pain relief, 24.5% had freedom from pain, 67.4% had functional disability relief, and 41.3% had functional disability freedom.
“It parallels the findings of the randomized, sham-controlled study in adults. The safety profile was excellent with just one person complaining of minor discomfort of the arm that resolved after treatment. The combination of the exceedingly safe profile and the likelihood of efficacy based on using monthly migraine treatment days as a proxy, the FDA decided to clear this for an adolescent indication,” said Dr. Monteith, associate professor of clinical neurology and chief of the headache division at the University of Miami.
The device design is convenient, according to Dr. Monteith. “The arm is just an easy place to stimulate. It’s a wearable device, and it’s 45 minutes [of treatment] and it’s app controlled. You know adolescents like their technology. They can track their symptoms here, and there’s some biobehavioral power to this because they can do biobehavioral exercises in addition to receiving the simulation,” she said.
The fact that the device is discrete is also an advantage for adolescents in school. “You have to go to the nurse to get your medication versus a device, you can just put it on, it’s easy, no one sees it, and no one’s making fun of you,” said Dr. Monteith.
Advantages for adolescents
The device offers a useful alternative to medication, according to Alan M. Rapoport, MD, who was asked for comment on the adolescent study. “I’d rather not give medication and certainly not preventive medication to an adolescent,” he said. He noted that over-the-counter acute care migraine medications such as aspirin or acetaminophen and combination medications with caffeine, as well as prescription medications such as triptans, “all have possible side effects, and when used to an increased extent can even cause medication overuse headache, increasing the severity and frequency of headache and migraine days per month,” Dr. Rapoport said. Using an effective device with almost no side effects is preferable to any of these acute care medications, especially if there are several headaches a month,” he said. Some newer medications that block calcitonin gene-related peptide might be quite effective when they are approved for adolescents, and should have few adverse events, he added.
In the past, Dr. Rapoport has favored biofeedback training for acute and especially preventive treatment of migraine in adolescents. “[Remote electrical neuromodulation] seems to do just as well, children enjoy it, and it’s easier for a patient to do at home,” said Dr. Rapoport.
Biofeedback training is usually taught to patients by a PhD psychologist. Once the patients have been on the biofeedback equipment and learn the techniques, they can practice on their own at home without equipment. “This new device treatment using Nerivio for acute care and prevention of migraine in adults and children 12 and older, where they can easily apply the device in almost any situation, whether they are at home or possibly even in school or out and about, looks very promising,” said Dr. Rapoport. It is quite effective and has almost no adverse events, which is what you really want, especially for adolescents,” he said.
Also asked to comment on the study of remote electrical neuromodulation use in adolescents, Abraham Avi Ashkenazi, MD, director of the Headache Clinic at Shaare Zedek Medical Center in Jerusalem, who attended the session, was enthusiastic, and said he has begun using it in his own practice. “It shows that remote electrical neuromodulation can not only be effective for the acute migraine attack, but also has a potential preventive effect on future migraine attacks. [This] actually makes sense, because we know that the more migraine attacks a person has, the more likely they are to progress to a more chronic form of the disease,” he said in an interview.
Asked what distinguishes REN from other neuromodulation therapies such as vagus nerve stimulation or transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), Dr. Ashkenazi said: “It’s just a different way of modulating the brain system via a different mechanism. In both ways, though, the advantage is that there are literally no adverse effects, as opposed to drug treatment.”
An alternative during pregnancy
Adolescents aren’t the only population where there is reluctance to use medication. Physicians have been prescribing the device for pregnant women, who are reluctant to take medication due to concerns effects on the fetus. However, pregnant women were not included in the pivotal studies. “They expect it to be safe. This study was done in order to validate that assumption. We reached out to women who either used the device during pregnancy or women from the same database who started it using afterwards, but did not use it during the pregnancy,” said Dr. Stark-Inbar, vice president of medical information at Theranica.
The study included 140 women, 59 in the remote electrical neuromodulation device group and 81 controls. The primary endpoint was gestational age, which was 38 weeks and 5 days in the remote electrical neuromodulation device group and 39 weeks among controls (P = .150). There were no significant between-group differences with respect to newborn birth weight, miscarriage rate, preterm birth rate, birth defect rate, developmental milestone rate, or emergency department visit rate.
Dr. Monteith and Dr. Ashkenazi have no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Rapoport advises AbbVie, Biohaven, Cala Health, Dr. Reddy’s, Pfizer, Satsuma, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, and Theranica. He is on the speakers bureau of AbbVie, Dr. Reddy’s, Impel, Pfizer and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries. Dr. Rapoport is the editor-in-chief of Neurology Reviews and on the editorial board of CNS Drugs.
AUSTIN, TEX – Migraine treatment and prevention is challenging in any population, but some present even more difficulties. Pregnant women and pediatric patients are two such groups where physicians and patients may be hesitant to use drugs.
Neuromodulation devices are proven alternatives to medical interventions, and the remote electrical neuromodulation device Nerivio (Theranica) was cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for acute treatment of migraine patients aged 12 and over in 2021. In March 2023, the agency expanded the clearance to include prevention of migration in adolescents aged 12 and over as well as adults.
Two studies presented at the annual meeting of the American Headache Society showed The latter study yielded similar findings to adults and was used by FDA in its decision to expand the device’s indication in adolescents in 2023, according to Teshamae Monteith, MD, who presented the study at a poster session.
The device, worn on the arm, allows the user to modulate the intensity of the stimulation so that it activates nociceptive pain receptors, but not in a painful way. “Each [patient] raises the intensity until it feels strong, yet comfortable, and when that happens, they activate the nociceptive receptors and the arm sends a signal all the way back up to the brainstem, where the pain control area is. Activating it causes the release of neurotransmitters that inhibit pain. That inhibition is a global pain inhibition mechanism, which causes inhibition of the migraine pain, and also the symptoms associated with migraine like photophobia and vomiting,” said Alit Stark-Inbar, PhD, who presented the study of treatment of pregnant women during a poster session.
Declining treatment days over time in adolescents
Dr. Monteith’s team studied high-frequency remote electrical neuromodulation device use in adolescents who had migraine on 10 days or more per month. They also required at least three treatment days in months 2 and 3 to control for the possibility that patients might stop using the device because they couldn’t afford it or for some reason other than efficacy or because their migraines went away.
The study included 83 adolescents aged 12-17 (mean, 15.9 years, 89% female). In the first month of use, the mean number of migraine treatment days was 12.6, which dropped to 9.0 in month 2 (P < .001), and 7.4 in month 3 (P < .001 from month 2). At 2 hours after treatment, 61.9% had pain relief, 24.5% had freedom from pain, 67.4% had functional disability relief, and 41.3% had functional disability freedom.
“It parallels the findings of the randomized, sham-controlled study in adults. The safety profile was excellent with just one person complaining of minor discomfort of the arm that resolved after treatment. The combination of the exceedingly safe profile and the likelihood of efficacy based on using monthly migraine treatment days as a proxy, the FDA decided to clear this for an adolescent indication,” said Dr. Monteith, associate professor of clinical neurology and chief of the headache division at the University of Miami.
The device design is convenient, according to Dr. Monteith. “The arm is just an easy place to stimulate. It’s a wearable device, and it’s 45 minutes [of treatment] and it’s app controlled. You know adolescents like their technology. They can track their symptoms here, and there’s some biobehavioral power to this because they can do biobehavioral exercises in addition to receiving the simulation,” she said.
The fact that the device is discrete is also an advantage for adolescents in school. “You have to go to the nurse to get your medication versus a device, you can just put it on, it’s easy, no one sees it, and no one’s making fun of you,” said Dr. Monteith.
Advantages for adolescents
The device offers a useful alternative to medication, according to Alan M. Rapoport, MD, who was asked for comment on the adolescent study. “I’d rather not give medication and certainly not preventive medication to an adolescent,” he said. He noted that over-the-counter acute care migraine medications such as aspirin or acetaminophen and combination medications with caffeine, as well as prescription medications such as triptans, “all have possible side effects, and when used to an increased extent can even cause medication overuse headache, increasing the severity and frequency of headache and migraine days per month,” Dr. Rapoport said. Using an effective device with almost no side effects is preferable to any of these acute care medications, especially if there are several headaches a month,” he said. Some newer medications that block calcitonin gene-related peptide might be quite effective when they are approved for adolescents, and should have few adverse events, he added.
In the past, Dr. Rapoport has favored biofeedback training for acute and especially preventive treatment of migraine in adolescents. “[Remote electrical neuromodulation] seems to do just as well, children enjoy it, and it’s easier for a patient to do at home,” said Dr. Rapoport.
Biofeedback training is usually taught to patients by a PhD psychologist. Once the patients have been on the biofeedback equipment and learn the techniques, they can practice on their own at home without equipment. “This new device treatment using Nerivio for acute care and prevention of migraine in adults and children 12 and older, where they can easily apply the device in almost any situation, whether they are at home or possibly even in school or out and about, looks very promising,” said Dr. Rapoport. It is quite effective and has almost no adverse events, which is what you really want, especially for adolescents,” he said.
Also asked to comment on the study of remote electrical neuromodulation use in adolescents, Abraham Avi Ashkenazi, MD, director of the Headache Clinic at Shaare Zedek Medical Center in Jerusalem, who attended the session, was enthusiastic, and said he has begun using it in his own practice. “It shows that remote electrical neuromodulation can not only be effective for the acute migraine attack, but also has a potential preventive effect on future migraine attacks. [This] actually makes sense, because we know that the more migraine attacks a person has, the more likely they are to progress to a more chronic form of the disease,” he said in an interview.
Asked what distinguishes REN from other neuromodulation therapies such as vagus nerve stimulation or transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), Dr. Ashkenazi said: “It’s just a different way of modulating the brain system via a different mechanism. In both ways, though, the advantage is that there are literally no adverse effects, as opposed to drug treatment.”
An alternative during pregnancy
Adolescents aren’t the only population where there is reluctance to use medication. Physicians have been prescribing the device for pregnant women, who are reluctant to take medication due to concerns effects on the fetus. However, pregnant women were not included in the pivotal studies. “They expect it to be safe. This study was done in order to validate that assumption. We reached out to women who either used the device during pregnancy or women from the same database who started it using afterwards, but did not use it during the pregnancy,” said Dr. Stark-Inbar, vice president of medical information at Theranica.
The study included 140 women, 59 in the remote electrical neuromodulation device group and 81 controls. The primary endpoint was gestational age, which was 38 weeks and 5 days in the remote electrical neuromodulation device group and 39 weeks among controls (P = .150). There were no significant between-group differences with respect to newborn birth weight, miscarriage rate, preterm birth rate, birth defect rate, developmental milestone rate, or emergency department visit rate.
Dr. Monteith and Dr. Ashkenazi have no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Rapoport advises AbbVie, Biohaven, Cala Health, Dr. Reddy’s, Pfizer, Satsuma, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, and Theranica. He is on the speakers bureau of AbbVie, Dr. Reddy’s, Impel, Pfizer and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries. Dr. Rapoport is the editor-in-chief of Neurology Reviews and on the editorial board of CNS Drugs.
AUSTIN, TEX – Migraine treatment and prevention is challenging in any population, but some present even more difficulties. Pregnant women and pediatric patients are two such groups where physicians and patients may be hesitant to use drugs.
Neuromodulation devices are proven alternatives to medical interventions, and the remote electrical neuromodulation device Nerivio (Theranica) was cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for acute treatment of migraine patients aged 12 and over in 2021. In March 2023, the agency expanded the clearance to include prevention of migration in adolescents aged 12 and over as well as adults.
Two studies presented at the annual meeting of the American Headache Society showed The latter study yielded similar findings to adults and was used by FDA in its decision to expand the device’s indication in adolescents in 2023, according to Teshamae Monteith, MD, who presented the study at a poster session.
The device, worn on the arm, allows the user to modulate the intensity of the stimulation so that it activates nociceptive pain receptors, but not in a painful way. “Each [patient] raises the intensity until it feels strong, yet comfortable, and when that happens, they activate the nociceptive receptors and the arm sends a signal all the way back up to the brainstem, where the pain control area is. Activating it causes the release of neurotransmitters that inhibit pain. That inhibition is a global pain inhibition mechanism, which causes inhibition of the migraine pain, and also the symptoms associated with migraine like photophobia and vomiting,” said Alit Stark-Inbar, PhD, who presented the study of treatment of pregnant women during a poster session.
Declining treatment days over time in adolescents
Dr. Monteith’s team studied high-frequency remote electrical neuromodulation device use in adolescents who had migraine on 10 days or more per month. They also required at least three treatment days in months 2 and 3 to control for the possibility that patients might stop using the device because they couldn’t afford it or for some reason other than efficacy or because their migraines went away.
The study included 83 adolescents aged 12-17 (mean, 15.9 years, 89% female). In the first month of use, the mean number of migraine treatment days was 12.6, which dropped to 9.0 in month 2 (P < .001), and 7.4 in month 3 (P < .001 from month 2). At 2 hours after treatment, 61.9% had pain relief, 24.5% had freedom from pain, 67.4% had functional disability relief, and 41.3% had functional disability freedom.
“It parallels the findings of the randomized, sham-controlled study in adults. The safety profile was excellent with just one person complaining of minor discomfort of the arm that resolved after treatment. The combination of the exceedingly safe profile and the likelihood of efficacy based on using monthly migraine treatment days as a proxy, the FDA decided to clear this for an adolescent indication,” said Dr. Monteith, associate professor of clinical neurology and chief of the headache division at the University of Miami.
The device design is convenient, according to Dr. Monteith. “The arm is just an easy place to stimulate. It’s a wearable device, and it’s 45 minutes [of treatment] and it’s app controlled. You know adolescents like their technology. They can track their symptoms here, and there’s some biobehavioral power to this because they can do biobehavioral exercises in addition to receiving the simulation,” she said.
The fact that the device is discrete is also an advantage for adolescents in school. “You have to go to the nurse to get your medication versus a device, you can just put it on, it’s easy, no one sees it, and no one’s making fun of you,” said Dr. Monteith.
Advantages for adolescents
The device offers a useful alternative to medication, according to Alan M. Rapoport, MD, who was asked for comment on the adolescent study. “I’d rather not give medication and certainly not preventive medication to an adolescent,” he said. He noted that over-the-counter acute care migraine medications such as aspirin or acetaminophen and combination medications with caffeine, as well as prescription medications such as triptans, “all have possible side effects, and when used to an increased extent can even cause medication overuse headache, increasing the severity and frequency of headache and migraine days per month,” Dr. Rapoport said. Using an effective device with almost no side effects is preferable to any of these acute care medications, especially if there are several headaches a month,” he said. Some newer medications that block calcitonin gene-related peptide might be quite effective when they are approved for adolescents, and should have few adverse events, he added.
In the past, Dr. Rapoport has favored biofeedback training for acute and especially preventive treatment of migraine in adolescents. “[Remote electrical neuromodulation] seems to do just as well, children enjoy it, and it’s easier for a patient to do at home,” said Dr. Rapoport.
Biofeedback training is usually taught to patients by a PhD psychologist. Once the patients have been on the biofeedback equipment and learn the techniques, they can practice on their own at home without equipment. “This new device treatment using Nerivio for acute care and prevention of migraine in adults and children 12 and older, where they can easily apply the device in almost any situation, whether they are at home or possibly even in school or out and about, looks very promising,” said Dr. Rapoport. It is quite effective and has almost no adverse events, which is what you really want, especially for adolescents,” he said.
Also asked to comment on the study of remote electrical neuromodulation use in adolescents, Abraham Avi Ashkenazi, MD, director of the Headache Clinic at Shaare Zedek Medical Center in Jerusalem, who attended the session, was enthusiastic, and said he has begun using it in his own practice. “It shows that remote electrical neuromodulation can not only be effective for the acute migraine attack, but also has a potential preventive effect on future migraine attacks. [This] actually makes sense, because we know that the more migraine attacks a person has, the more likely they are to progress to a more chronic form of the disease,” he said in an interview.
Asked what distinguishes REN from other neuromodulation therapies such as vagus nerve stimulation or transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), Dr. Ashkenazi said: “It’s just a different way of modulating the brain system via a different mechanism. In both ways, though, the advantage is that there are literally no adverse effects, as opposed to drug treatment.”
An alternative during pregnancy
Adolescents aren’t the only population where there is reluctance to use medication. Physicians have been prescribing the device for pregnant women, who are reluctant to take medication due to concerns effects on the fetus. However, pregnant women were not included in the pivotal studies. “They expect it to be safe. This study was done in order to validate that assumption. We reached out to women who either used the device during pregnancy or women from the same database who started it using afterwards, but did not use it during the pregnancy,” said Dr. Stark-Inbar, vice president of medical information at Theranica.
The study included 140 women, 59 in the remote electrical neuromodulation device group and 81 controls. The primary endpoint was gestational age, which was 38 weeks and 5 days in the remote electrical neuromodulation device group and 39 weeks among controls (P = .150). There were no significant between-group differences with respect to newborn birth weight, miscarriage rate, preterm birth rate, birth defect rate, developmental milestone rate, or emergency department visit rate.
Dr. Monteith and Dr. Ashkenazi have no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Rapoport advises AbbVie, Biohaven, Cala Health, Dr. Reddy’s, Pfizer, Satsuma, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, and Theranica. He is on the speakers bureau of AbbVie, Dr. Reddy’s, Impel, Pfizer and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries. Dr. Rapoport is the editor-in-chief of Neurology Reviews and on the editorial board of CNS Drugs.
AT AHS 2023
Consider mental health and social factors in management of sickle cell disease
Complications from sickle cell disease (SCD) can affect education and life opportunities, and these complications have been associated with social determinants of health such as socioeconomic status, depression, health literacy, and level of education, according to Kelly M. Harris, PhD, of Washington University in St. Louis, and colleagues.
Pain is a hallmark of SCD, and “the current climate around pain management and opioid use has specific implications for individuals with [SCD], especially youth,” Dr. Harris said in an interview.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers analyzed 2,264 participants (average age, 27.9 years; 56.2% were female) in the Sickle Cell Disease Implementation Consortium a study that includes patient assessment, treatment, and creation of a longitudinal registry.
The participants completed the Adult Sickle Cell Quality of Life Measurement Information System to provide data on the frequency and severity of pain episodes related to SCD over the past 12 months. Multivariable regression analysis was used to examine the associations of education, employment, and mental health with pain frequency and severity.
Overall, 79.8% of participants reported severe pain, and 47.8% reported more than four episodes of pain in the past year.
Notably, 20% of the participants were diagnosed with depression, and increased pain frequency was significantly associated with depression, although no significant association appeared between pain severity and depression, the researchers said.
A total of 47% of the participants reported using pain medication and 49% reported using hydroxyurea. In addition, 628 participants (28.0%) underwent regular blood transfusions.
Neither education level nor income was associated with increased pain frequency or severity. Age younger than 18 years was significantly associated with both pain frequency and severity, as was daily used of pain medication. Unemployment and female sex also were associated with increased pain frequency.
The findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design that prevents conclusions of causality, and by the reliance on patient reports of depression, which likely led to underreporting, the researchers noted.
However, the results are consistent with previous studies suggesting that pain and negative feelings were associated with reduced quality of life in SCD patients, especially younger patients, and support the need to screen SCD patients for depression, especially those who report more severe and/or more frequent pain, they said.
Take a comprehensive approach to a complex condition
“When treating pain, we cannot just rely on medication,” Dr. Harris said. “It is important that providers consider the full experiences of patients and pursue holistic and comprehensive treatment approaches to reducing pain. Screening for depression should be a regular practice, particularly for patients experiencing frequent and/or severe pain.
“Racial discrimination, stigma, and bias impact pain diagnosis and treatment for individuals with SCD,” said Dr. Harris. “Increasing awareness of the associations between depression and pain frequency and severity ... may help address these barriers.”
Data highlight treatment gaps
Alexander A. Boucher, MD, a member of the division of pediatric hematology and oncology at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, noted the researchers included patients as young as midadolescence, with a majority being under 35 years old. “The 18- to 30-year-old range is an especially high-risk age window for increased acute health care utilization, even compared with other chronic adolescent/young adult conditions. “The demographics in the study group also reasonably approximate those for young adults with SCD in urban centers. By taking a multicenter approach across a several-state region, I believe the findings offer better generalizability, since health care access and mental health access can vary state-by-state,” and the current results show a more standard experience.
“It was a bit surprising that female [sex] maintained such an association with pain across the different components of the study,” and that the pain peak was in the 25- to 34-year-old age range, said Dr. Boucher. However, anecdotally, the late teens and early 20s “can be laden with mental health concerns due to the life transitions that accompany most people at that time. The note that hydroxyurea use was associated with more pain and depression symptoms was interesting, and serves as a reminder that what is happening to the red blood cells and in the blood vessels, such as red blood cell breakdown, sickling, and vaso-occlusion are only a part of what causes pain, and hydroxyurea is not likely to play a role in mitigating mental health aspects of pain.”
The findings that overall pain frequency and related pain medication use were associated with higher depression rates “may in part reflect a blind spot for physicians and medical teams, who often resort back to physical pain-based heuristics.” Physicians may misunderstand chronic pain and its management and look for quick fixes for pain out of uncertainty or urgency, said Dr. Boucher. “This serves to diminish the perspectives of patients as people first (not embodiments of a disease) and can lead to missed opportunities to tackle mental health challenges.”
Barriers and limitations
There are barriers to mental health screening in hematology care,” Dr. Boucher said. First, most hematologists are not experts in mental health and while they may have some from their medical training in these disorders, it can be difficult to maintain the level of health literacy needed to stay up to date on treatments. Second, depression screening may not be part of regular patient intake and the Patient Health Questionnaire–2 or PHQ-9 offer only short-term (2-week) snapshots of depression.
“Perhaps most critically, even if we do successfully screen, the access to mental health specialists is severely limited, just as it is across the medical landscape, so intervention opportunities may be suboptimal,” said Dr. Boucher. The problem is magnified if, as the current study suggests, the rates of depression in SCD are approximately three times greater than the population overall.
In the current study, “the fact that only half of those who self-reported depression symptoms actually had depression documented as a diagnosis in their medical records suggests that we are missing a lot of patients affected by mental health disturbances.”
This study is limited in measurement of the contribution of social determinants of health, he said, as they were primarily focused on employment status and income. The study does not describe other factors like support systems, housing, and transportation.
“I would like to see studies that not only identify associated drivers of pain, but also offer evidence for successful interventions,” Dr. Boucher said, and these studies should include patient-centered interventions versus disease-centered interventions.
Undertreatment persists
Other concerns with sickle cell anemia include the underuse of hydroxyurea to reduce complications associated with the disease such as pain, stroke, and even early death. Another recent study in JAMA Network Open suggested that use of hydroxyurea remained low in children and youth despite the issuing of guidelines, and that underserved populations were especially affected. In that study, the researchers found that the patients’ annual days’ supply of hydroxyurea in New York state did not change significantly after the guideline update.
SCD also has been associated with increased risk of other poor outcomes, such as stillbirth and increased risk of poor COVID-19–related outcomes and COVID-19–related deaths.
The study by Dr. Harris and colleagues was supported by the National Institutes of Health through the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities. Dr. Harris had no financial conflicts to disclose. The hydroxyurea study was supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the NHLBI. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Boucher disclosed conducting research with SCL Behring, but had no relevant financial conflicts.
Complications from sickle cell disease (SCD) can affect education and life opportunities, and these complications have been associated with social determinants of health such as socioeconomic status, depression, health literacy, and level of education, according to Kelly M. Harris, PhD, of Washington University in St. Louis, and colleagues.
Pain is a hallmark of SCD, and “the current climate around pain management and opioid use has specific implications for individuals with [SCD], especially youth,” Dr. Harris said in an interview.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers analyzed 2,264 participants (average age, 27.9 years; 56.2% were female) in the Sickle Cell Disease Implementation Consortium a study that includes patient assessment, treatment, and creation of a longitudinal registry.
The participants completed the Adult Sickle Cell Quality of Life Measurement Information System to provide data on the frequency and severity of pain episodes related to SCD over the past 12 months. Multivariable regression analysis was used to examine the associations of education, employment, and mental health with pain frequency and severity.
Overall, 79.8% of participants reported severe pain, and 47.8% reported more than four episodes of pain in the past year.
Notably, 20% of the participants were diagnosed with depression, and increased pain frequency was significantly associated with depression, although no significant association appeared between pain severity and depression, the researchers said.
A total of 47% of the participants reported using pain medication and 49% reported using hydroxyurea. In addition, 628 participants (28.0%) underwent regular blood transfusions.
Neither education level nor income was associated with increased pain frequency or severity. Age younger than 18 years was significantly associated with both pain frequency and severity, as was daily used of pain medication. Unemployment and female sex also were associated with increased pain frequency.
The findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design that prevents conclusions of causality, and by the reliance on patient reports of depression, which likely led to underreporting, the researchers noted.
However, the results are consistent with previous studies suggesting that pain and negative feelings were associated with reduced quality of life in SCD patients, especially younger patients, and support the need to screen SCD patients for depression, especially those who report more severe and/or more frequent pain, they said.
Take a comprehensive approach to a complex condition
“When treating pain, we cannot just rely on medication,” Dr. Harris said. “It is important that providers consider the full experiences of patients and pursue holistic and comprehensive treatment approaches to reducing pain. Screening for depression should be a regular practice, particularly for patients experiencing frequent and/or severe pain.
“Racial discrimination, stigma, and bias impact pain diagnosis and treatment for individuals with SCD,” said Dr. Harris. “Increasing awareness of the associations between depression and pain frequency and severity ... may help address these barriers.”
Data highlight treatment gaps
Alexander A. Boucher, MD, a member of the division of pediatric hematology and oncology at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, noted the researchers included patients as young as midadolescence, with a majority being under 35 years old. “The 18- to 30-year-old range is an especially high-risk age window for increased acute health care utilization, even compared with other chronic adolescent/young adult conditions. “The demographics in the study group also reasonably approximate those for young adults with SCD in urban centers. By taking a multicenter approach across a several-state region, I believe the findings offer better generalizability, since health care access and mental health access can vary state-by-state,” and the current results show a more standard experience.
“It was a bit surprising that female [sex] maintained such an association with pain across the different components of the study,” and that the pain peak was in the 25- to 34-year-old age range, said Dr. Boucher. However, anecdotally, the late teens and early 20s “can be laden with mental health concerns due to the life transitions that accompany most people at that time. The note that hydroxyurea use was associated with more pain and depression symptoms was interesting, and serves as a reminder that what is happening to the red blood cells and in the blood vessels, such as red blood cell breakdown, sickling, and vaso-occlusion are only a part of what causes pain, and hydroxyurea is not likely to play a role in mitigating mental health aspects of pain.”
The findings that overall pain frequency and related pain medication use were associated with higher depression rates “may in part reflect a blind spot for physicians and medical teams, who often resort back to physical pain-based heuristics.” Physicians may misunderstand chronic pain and its management and look for quick fixes for pain out of uncertainty or urgency, said Dr. Boucher. “This serves to diminish the perspectives of patients as people first (not embodiments of a disease) and can lead to missed opportunities to tackle mental health challenges.”
Barriers and limitations
There are barriers to mental health screening in hematology care,” Dr. Boucher said. First, most hematologists are not experts in mental health and while they may have some from their medical training in these disorders, it can be difficult to maintain the level of health literacy needed to stay up to date on treatments. Second, depression screening may not be part of regular patient intake and the Patient Health Questionnaire–2 or PHQ-9 offer only short-term (2-week) snapshots of depression.
“Perhaps most critically, even if we do successfully screen, the access to mental health specialists is severely limited, just as it is across the medical landscape, so intervention opportunities may be suboptimal,” said Dr. Boucher. The problem is magnified if, as the current study suggests, the rates of depression in SCD are approximately three times greater than the population overall.
In the current study, “the fact that only half of those who self-reported depression symptoms actually had depression documented as a diagnosis in their medical records suggests that we are missing a lot of patients affected by mental health disturbances.”
This study is limited in measurement of the contribution of social determinants of health, he said, as they were primarily focused on employment status and income. The study does not describe other factors like support systems, housing, and transportation.
“I would like to see studies that not only identify associated drivers of pain, but also offer evidence for successful interventions,” Dr. Boucher said, and these studies should include patient-centered interventions versus disease-centered interventions.
Undertreatment persists
Other concerns with sickle cell anemia include the underuse of hydroxyurea to reduce complications associated with the disease such as pain, stroke, and even early death. Another recent study in JAMA Network Open suggested that use of hydroxyurea remained low in children and youth despite the issuing of guidelines, and that underserved populations were especially affected. In that study, the researchers found that the patients’ annual days’ supply of hydroxyurea in New York state did not change significantly after the guideline update.
SCD also has been associated with increased risk of other poor outcomes, such as stillbirth and increased risk of poor COVID-19–related outcomes and COVID-19–related deaths.
The study by Dr. Harris and colleagues was supported by the National Institutes of Health through the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities. Dr. Harris had no financial conflicts to disclose. The hydroxyurea study was supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the NHLBI. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Boucher disclosed conducting research with SCL Behring, but had no relevant financial conflicts.
Complications from sickle cell disease (SCD) can affect education and life opportunities, and these complications have been associated with social determinants of health such as socioeconomic status, depression, health literacy, and level of education, according to Kelly M. Harris, PhD, of Washington University in St. Louis, and colleagues.
Pain is a hallmark of SCD, and “the current climate around pain management and opioid use has specific implications for individuals with [SCD], especially youth,” Dr. Harris said in an interview.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers analyzed 2,264 participants (average age, 27.9 years; 56.2% were female) in the Sickle Cell Disease Implementation Consortium a study that includes patient assessment, treatment, and creation of a longitudinal registry.
The participants completed the Adult Sickle Cell Quality of Life Measurement Information System to provide data on the frequency and severity of pain episodes related to SCD over the past 12 months. Multivariable regression analysis was used to examine the associations of education, employment, and mental health with pain frequency and severity.
Overall, 79.8% of participants reported severe pain, and 47.8% reported more than four episodes of pain in the past year.
Notably, 20% of the participants were diagnosed with depression, and increased pain frequency was significantly associated with depression, although no significant association appeared between pain severity and depression, the researchers said.
A total of 47% of the participants reported using pain medication and 49% reported using hydroxyurea. In addition, 628 participants (28.0%) underwent regular blood transfusions.
Neither education level nor income was associated with increased pain frequency or severity. Age younger than 18 years was significantly associated with both pain frequency and severity, as was daily used of pain medication. Unemployment and female sex also were associated with increased pain frequency.
The findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design that prevents conclusions of causality, and by the reliance on patient reports of depression, which likely led to underreporting, the researchers noted.
However, the results are consistent with previous studies suggesting that pain and negative feelings were associated with reduced quality of life in SCD patients, especially younger patients, and support the need to screen SCD patients for depression, especially those who report more severe and/or more frequent pain, they said.
Take a comprehensive approach to a complex condition
“When treating pain, we cannot just rely on medication,” Dr. Harris said. “It is important that providers consider the full experiences of patients and pursue holistic and comprehensive treatment approaches to reducing pain. Screening for depression should be a regular practice, particularly for patients experiencing frequent and/or severe pain.
“Racial discrimination, stigma, and bias impact pain diagnosis and treatment for individuals with SCD,” said Dr. Harris. “Increasing awareness of the associations between depression and pain frequency and severity ... may help address these barriers.”
Data highlight treatment gaps
Alexander A. Boucher, MD, a member of the division of pediatric hematology and oncology at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, noted the researchers included patients as young as midadolescence, with a majority being under 35 years old. “The 18- to 30-year-old range is an especially high-risk age window for increased acute health care utilization, even compared with other chronic adolescent/young adult conditions. “The demographics in the study group also reasonably approximate those for young adults with SCD in urban centers. By taking a multicenter approach across a several-state region, I believe the findings offer better generalizability, since health care access and mental health access can vary state-by-state,” and the current results show a more standard experience.
“It was a bit surprising that female [sex] maintained such an association with pain across the different components of the study,” and that the pain peak was in the 25- to 34-year-old age range, said Dr. Boucher. However, anecdotally, the late teens and early 20s “can be laden with mental health concerns due to the life transitions that accompany most people at that time. The note that hydroxyurea use was associated with more pain and depression symptoms was interesting, and serves as a reminder that what is happening to the red blood cells and in the blood vessels, such as red blood cell breakdown, sickling, and vaso-occlusion are only a part of what causes pain, and hydroxyurea is not likely to play a role in mitigating mental health aspects of pain.”
The findings that overall pain frequency and related pain medication use were associated with higher depression rates “may in part reflect a blind spot for physicians and medical teams, who often resort back to physical pain-based heuristics.” Physicians may misunderstand chronic pain and its management and look for quick fixes for pain out of uncertainty or urgency, said Dr. Boucher. “This serves to diminish the perspectives of patients as people first (not embodiments of a disease) and can lead to missed opportunities to tackle mental health challenges.”
Barriers and limitations
There are barriers to mental health screening in hematology care,” Dr. Boucher said. First, most hematologists are not experts in mental health and while they may have some from their medical training in these disorders, it can be difficult to maintain the level of health literacy needed to stay up to date on treatments. Second, depression screening may not be part of regular patient intake and the Patient Health Questionnaire–2 or PHQ-9 offer only short-term (2-week) snapshots of depression.
“Perhaps most critically, even if we do successfully screen, the access to mental health specialists is severely limited, just as it is across the medical landscape, so intervention opportunities may be suboptimal,” said Dr. Boucher. The problem is magnified if, as the current study suggests, the rates of depression in SCD are approximately three times greater than the population overall.
In the current study, “the fact that only half of those who self-reported depression symptoms actually had depression documented as a diagnosis in their medical records suggests that we are missing a lot of patients affected by mental health disturbances.”
This study is limited in measurement of the contribution of social determinants of health, he said, as they were primarily focused on employment status and income. The study does not describe other factors like support systems, housing, and transportation.
“I would like to see studies that not only identify associated drivers of pain, but also offer evidence for successful interventions,” Dr. Boucher said, and these studies should include patient-centered interventions versus disease-centered interventions.
Undertreatment persists
Other concerns with sickle cell anemia include the underuse of hydroxyurea to reduce complications associated with the disease such as pain, stroke, and even early death. Another recent study in JAMA Network Open suggested that use of hydroxyurea remained low in children and youth despite the issuing of guidelines, and that underserved populations were especially affected. In that study, the researchers found that the patients’ annual days’ supply of hydroxyurea in New York state did not change significantly after the guideline update.
SCD also has been associated with increased risk of other poor outcomes, such as stillbirth and increased risk of poor COVID-19–related outcomes and COVID-19–related deaths.
The study by Dr. Harris and colleagues was supported by the National Institutes of Health through the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities. Dr. Harris had no financial conflicts to disclose. The hydroxyurea study was supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the NHLBI. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Boucher disclosed conducting research with SCL Behring, but had no relevant financial conflicts.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Are you a physician ... or a vending machine?
When we address this problem with patients, some become immediately defensive, making it difficult to modify treatment regimens. It’s almost as if people believe that they have a “right” to their medications and nobody should dare take them away. Even when I think the interaction goes relatively smoothly, the outcome usually shows otherwise.
I will decrease gabapentin from 3,200 mg per day and they will come back with cyclobenzaprine from the urgent care center down the block.
I try to stop an abused amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, and not only do the drugs show up in the urine toxicology test a month later (from the brother’s girlfriend’s sister) but the screening will be positive for cocaine (from the sister’s boyfriend’s brother) and probably alprazolam, too.
People want what they want, and I believe what they want is the overwhelming need not to feel, and especially to not feel our natural and uncomfortable states of pain, sadness, anxiety, fatigue, and discomfort (sometimes all at once). They will use anything orally or intravenously or nasally to make those feelings go away.
I am an addiction specialist so I write this commentary out of care and concern and recognition of how much, pain both physical and psychic, people suffer.
Perhaps we as physicians are conditioned to believe that we must prescribe “something” to the patient who is uncomfortable and sitting in front of us. In general we are sympathetic to the needs of those who come to us in distress, and we try our best to help reduce their symptoms.
I know that we cannot simply “fire” people, because these patients are ours to take care of; they are our responsibility, though this is our overused response to “difficult” patients.
And I know that we have insufficient replacements for these medications. We stopped prescribing oxycodone and now people are on gabapentin in the highest doses, diversion is up, and so is its abuse.
Many of us regularly teach about breathing and mindfulness. I discuss trauma and talk therapy. I order physical therapy and walking regimens and podcasts. But our relationship is transactional, and in prescribing a medication, I have shown them that I am hearing them. I hate this feeling of being trapped.
I spend much of my day negotiating and drive home at night feeling like nothing more than a vending machine.
Dr. Hambright is with the department of addiction medicine at Samaritan Daytop Village, Ellenville, N.Y., and Samadhi Recovery Community Outreach Center, Kingston, N.Y. She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When we address this problem with patients, some become immediately defensive, making it difficult to modify treatment regimens. It’s almost as if people believe that they have a “right” to their medications and nobody should dare take them away. Even when I think the interaction goes relatively smoothly, the outcome usually shows otherwise.
I will decrease gabapentin from 3,200 mg per day and they will come back with cyclobenzaprine from the urgent care center down the block.
I try to stop an abused amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, and not only do the drugs show up in the urine toxicology test a month later (from the brother’s girlfriend’s sister) but the screening will be positive for cocaine (from the sister’s boyfriend’s brother) and probably alprazolam, too.
People want what they want, and I believe what they want is the overwhelming need not to feel, and especially to not feel our natural and uncomfortable states of pain, sadness, anxiety, fatigue, and discomfort (sometimes all at once). They will use anything orally or intravenously or nasally to make those feelings go away.
I am an addiction specialist so I write this commentary out of care and concern and recognition of how much, pain both physical and psychic, people suffer.
Perhaps we as physicians are conditioned to believe that we must prescribe “something” to the patient who is uncomfortable and sitting in front of us. In general we are sympathetic to the needs of those who come to us in distress, and we try our best to help reduce their symptoms.
I know that we cannot simply “fire” people, because these patients are ours to take care of; they are our responsibility, though this is our overused response to “difficult” patients.
And I know that we have insufficient replacements for these medications. We stopped prescribing oxycodone and now people are on gabapentin in the highest doses, diversion is up, and so is its abuse.
Many of us regularly teach about breathing and mindfulness. I discuss trauma and talk therapy. I order physical therapy and walking regimens and podcasts. But our relationship is transactional, and in prescribing a medication, I have shown them that I am hearing them. I hate this feeling of being trapped.
I spend much of my day negotiating and drive home at night feeling like nothing more than a vending machine.
Dr. Hambright is with the department of addiction medicine at Samaritan Daytop Village, Ellenville, N.Y., and Samadhi Recovery Community Outreach Center, Kingston, N.Y. She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When we address this problem with patients, some become immediately defensive, making it difficult to modify treatment regimens. It’s almost as if people believe that they have a “right” to their medications and nobody should dare take them away. Even when I think the interaction goes relatively smoothly, the outcome usually shows otherwise.
I will decrease gabapentin from 3,200 mg per day and they will come back with cyclobenzaprine from the urgent care center down the block.
I try to stop an abused amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, and not only do the drugs show up in the urine toxicology test a month later (from the brother’s girlfriend’s sister) but the screening will be positive for cocaine (from the sister’s boyfriend’s brother) and probably alprazolam, too.
People want what they want, and I believe what they want is the overwhelming need not to feel, and especially to not feel our natural and uncomfortable states of pain, sadness, anxiety, fatigue, and discomfort (sometimes all at once). They will use anything orally or intravenously or nasally to make those feelings go away.
I am an addiction specialist so I write this commentary out of care and concern and recognition of how much, pain both physical and psychic, people suffer.
Perhaps we as physicians are conditioned to believe that we must prescribe “something” to the patient who is uncomfortable and sitting in front of us. In general we are sympathetic to the needs of those who come to us in distress, and we try our best to help reduce their symptoms.
I know that we cannot simply “fire” people, because these patients are ours to take care of; they are our responsibility, though this is our overused response to “difficult” patients.
And I know that we have insufficient replacements for these medications. We stopped prescribing oxycodone and now people are on gabapentin in the highest doses, diversion is up, and so is its abuse.
Many of us regularly teach about breathing and mindfulness. I discuss trauma and talk therapy. I order physical therapy and walking regimens and podcasts. But our relationship is transactional, and in prescribing a medication, I have shown them that I am hearing them. I hate this feeling of being trapped.
I spend much of my day negotiating and drive home at night feeling like nothing more than a vending machine.
Dr. Hambright is with the department of addiction medicine at Samaritan Daytop Village, Ellenville, N.Y., and Samadhi Recovery Community Outreach Center, Kingston, N.Y. She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Regular exercise may boost pain tolerance
new research suggests.
In a large observational study of more than 10,000 adults, researchers found those who consistently engage in moderate to vigorous physical activity over the 7- to 8-year study period reported the highest pain tolerance. However, the results also showed that even light exercise was associated with greater pain tolerance.
“There were indications that both total amount of physical activity over time, as well as the direction of change in activity level over time matters to how high your pain tolerance is,” lead investigator Anders Pedersen Årnes, PT, MPH, research fellow and adviser at the University Hospital of North Norway, affiliated with the University of Tromsø, said in an interview. “As an observational study, this points toward the possibility that increased physical activity might increase pain tolerance.”
The findings were published online in PLOS One.
Anything is better than nothing
The researchers drew from the prospective, population-based Tromsø health study, a health survey that draws on surveys conducted periodically since 1974 among residents in northern Norway.
The study included 10,732 participants who completed surveys in 2007-2008 and again in 2015-2016.
Data on physical activity, experimental pain tolerance, sex, sociodemographic covariates, and chronic pain was collected through questionnaires, biological samples and clinical examination.
Pain tolerance was measured using the cold-pressor test (CPT), in which participants submerge their hand in icy water for as long as possible.
CPT tolerance was 7%, 14%, and 16% higher respectively for light, moderate, and vigorous consistent exercise across the two surveys versus the sedentary group.
“Engaging in habitual physical activity in leisure time is associated with higher pain tolerance,” Mr. Årnes said. “Any kind of activity over time is better than being sedentary.”
The researchers also found that people who were sedentary at baseline who reported greater physical activity at follow-up also had higher pain tolerance than those who remained sedentary, although this finding was not statistically significant.
This highest pain tolerance was noted in people who engaged in moderate to vigorous exercise over time, with a 20.4-second longer performance in the CPT than those who were consistently sedentary (P < .001; 95% confidence interval, 13.7-27.1).
There was no significant difference in pain tolerance between men and women and all participants experienced a decline in tolerance over time.
“Results indicate that a positive change in physical activity level over time was associated with higher pain tolerance,” Mr. Årnes said. “Your total activity level might decide how much, as more seems to be better.”
More work needed
The long follow-up and large number of patients are two strengths of the study, Steven Cohen, MD, chief of pain medicine and professor of anesthesiology, neurology, physical medicine & rehabilitation and psychiatry at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in an interview.
“This study explored the relationship between general physical activity levels and one form of acute pain, but data from other studies show a benefit for other forms of pain,” said Dr. Cohen, who was not part of the research. “Taken together, this suggests that exercise is beneficial for individuals living with pain.”
The findings demonstrate an association between exercise and pain tolerance and other research has shown evidence of a cause-and-effect relationship, Dr. Cohen said. However, “more work is needed to determine what mediates these effects.”
Questions also remain about how exercise might impact tolerance or risk for chronic pain, he added.
Investigators are now working on a follow-up study of how the effect of exercise on pain tolerance might influence chronic pain risk, Mr. Årnes said.
The study received no specific funding. Mr. Årnes and Dr. Cohen reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
In a large observational study of more than 10,000 adults, researchers found those who consistently engage in moderate to vigorous physical activity over the 7- to 8-year study period reported the highest pain tolerance. However, the results also showed that even light exercise was associated with greater pain tolerance.
“There were indications that both total amount of physical activity over time, as well as the direction of change in activity level over time matters to how high your pain tolerance is,” lead investigator Anders Pedersen Årnes, PT, MPH, research fellow and adviser at the University Hospital of North Norway, affiliated with the University of Tromsø, said in an interview. “As an observational study, this points toward the possibility that increased physical activity might increase pain tolerance.”
The findings were published online in PLOS One.
Anything is better than nothing
The researchers drew from the prospective, population-based Tromsø health study, a health survey that draws on surveys conducted periodically since 1974 among residents in northern Norway.
The study included 10,732 participants who completed surveys in 2007-2008 and again in 2015-2016.
Data on physical activity, experimental pain tolerance, sex, sociodemographic covariates, and chronic pain was collected through questionnaires, biological samples and clinical examination.
Pain tolerance was measured using the cold-pressor test (CPT), in which participants submerge their hand in icy water for as long as possible.
CPT tolerance was 7%, 14%, and 16% higher respectively for light, moderate, and vigorous consistent exercise across the two surveys versus the sedentary group.
“Engaging in habitual physical activity in leisure time is associated with higher pain tolerance,” Mr. Årnes said. “Any kind of activity over time is better than being sedentary.”
The researchers also found that people who were sedentary at baseline who reported greater physical activity at follow-up also had higher pain tolerance than those who remained sedentary, although this finding was not statistically significant.
This highest pain tolerance was noted in people who engaged in moderate to vigorous exercise over time, with a 20.4-second longer performance in the CPT than those who were consistently sedentary (P < .001; 95% confidence interval, 13.7-27.1).
There was no significant difference in pain tolerance between men and women and all participants experienced a decline in tolerance over time.
“Results indicate that a positive change in physical activity level over time was associated with higher pain tolerance,” Mr. Årnes said. “Your total activity level might decide how much, as more seems to be better.”
More work needed
The long follow-up and large number of patients are two strengths of the study, Steven Cohen, MD, chief of pain medicine and professor of anesthesiology, neurology, physical medicine & rehabilitation and psychiatry at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in an interview.
“This study explored the relationship between general physical activity levels and one form of acute pain, but data from other studies show a benefit for other forms of pain,” said Dr. Cohen, who was not part of the research. “Taken together, this suggests that exercise is beneficial for individuals living with pain.”
The findings demonstrate an association between exercise and pain tolerance and other research has shown evidence of a cause-and-effect relationship, Dr. Cohen said. However, “more work is needed to determine what mediates these effects.”
Questions also remain about how exercise might impact tolerance or risk for chronic pain, he added.
Investigators are now working on a follow-up study of how the effect of exercise on pain tolerance might influence chronic pain risk, Mr. Årnes said.
The study received no specific funding. Mr. Årnes and Dr. Cohen reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
In a large observational study of more than 10,000 adults, researchers found those who consistently engage in moderate to vigorous physical activity over the 7- to 8-year study period reported the highest pain tolerance. However, the results also showed that even light exercise was associated with greater pain tolerance.
“There were indications that both total amount of physical activity over time, as well as the direction of change in activity level over time matters to how high your pain tolerance is,” lead investigator Anders Pedersen Årnes, PT, MPH, research fellow and adviser at the University Hospital of North Norway, affiliated with the University of Tromsø, said in an interview. “As an observational study, this points toward the possibility that increased physical activity might increase pain tolerance.”
The findings were published online in PLOS One.
Anything is better than nothing
The researchers drew from the prospective, population-based Tromsø health study, a health survey that draws on surveys conducted periodically since 1974 among residents in northern Norway.
The study included 10,732 participants who completed surveys in 2007-2008 and again in 2015-2016.
Data on physical activity, experimental pain tolerance, sex, sociodemographic covariates, and chronic pain was collected through questionnaires, biological samples and clinical examination.
Pain tolerance was measured using the cold-pressor test (CPT), in which participants submerge their hand in icy water for as long as possible.
CPT tolerance was 7%, 14%, and 16% higher respectively for light, moderate, and vigorous consistent exercise across the two surveys versus the sedentary group.
“Engaging in habitual physical activity in leisure time is associated with higher pain tolerance,” Mr. Årnes said. “Any kind of activity over time is better than being sedentary.”
The researchers also found that people who were sedentary at baseline who reported greater physical activity at follow-up also had higher pain tolerance than those who remained sedentary, although this finding was not statistically significant.
This highest pain tolerance was noted in people who engaged in moderate to vigorous exercise over time, with a 20.4-second longer performance in the CPT than those who were consistently sedentary (P < .001; 95% confidence interval, 13.7-27.1).
There was no significant difference in pain tolerance between men and women and all participants experienced a decline in tolerance over time.
“Results indicate that a positive change in physical activity level over time was associated with higher pain tolerance,” Mr. Årnes said. “Your total activity level might decide how much, as more seems to be better.”
More work needed
The long follow-up and large number of patients are two strengths of the study, Steven Cohen, MD, chief of pain medicine and professor of anesthesiology, neurology, physical medicine & rehabilitation and psychiatry at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in an interview.
“This study explored the relationship between general physical activity levels and one form of acute pain, but data from other studies show a benefit for other forms of pain,” said Dr. Cohen, who was not part of the research. “Taken together, this suggests that exercise is beneficial for individuals living with pain.”
The findings demonstrate an association between exercise and pain tolerance and other research has shown evidence of a cause-and-effect relationship, Dr. Cohen said. However, “more work is needed to determine what mediates these effects.”
Questions also remain about how exercise might impact tolerance or risk for chronic pain, he added.
Investigators are now working on a follow-up study of how the effect of exercise on pain tolerance might influence chronic pain risk, Mr. Årnes said.
The study received no specific funding. Mr. Årnes and Dr. Cohen reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PLOS ONE
Positive top-line results for cannabinoid-based med for nerve pain
, new top-line results released by Zelira Therapeutics suggest.
“The implications of these results for patients are incredibly promising,” principal investigator Bryan Doner, DO, medical director of HealthyWays Integrated Wellness Solutions, Gibsonia, Pa., said in a news release.
“Through this rigorously designed study, we have demonstrated that ZLT-L-007 is a safe, effective, and well-tolerated alternative for patients who would typically seek a Lyrica-level of pain relief,” he added.
The observational, nonblinded trial tested the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of ZLT-L-007 against pregabalin in 60 adults with diabetic nerve pain.
The study had three groups with 20 patients each (pregabalin alone, pregabalin plus ZLT-L-007, and ZLT-L-007 alone).
Top-line results show the study met its primary endpoint for change in daily pain severity as measured by the percent change from baseline at 30, 60, and 90 days on the Numerical Rating Scale.
For the pregabalin-only group, there was a reduction in symptom severity at all follow-up points, ranging from 20% to 35% (median percent change from baseline), the company said.
For the ZLT-L-007 only group, there was about a 33% reduction in symptom severity at 30 days, and 71% and 78% reduction, respectively, at 60 and 90 days, suggesting a larger improvement in symptom severity than with pregabalin alone, the company said.
For the pregabalin plus ZLT-L-007 group, there was a moderate 20% reduction in symptom severity at 30 days, but a larger reduction at 60 and 90 days (50% and 72%, respectively), which indicates substantially greater improvement in symptom severity than with pregabalin alone, the company said.
The study also met secondary endpoints, including significant decreases in daily pain severity as measured by the Visual Analog Scale and measurable changes in the short-form McGill Pain Questionnaire and Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory.
Dr. Doner noted that the top-line data showed “no serious adverse events, and participants’ blood pressure and other safety vitals remained unaffected throughout. This confirms that ZLT-L-007 is a well-tolerated product that delivers statistically significant pain relief, surpassing the levels achieved by Lyrica.”
The company plans to report additional insights from the full study, as they become available, during fiscal year 2023-2024.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new top-line results released by Zelira Therapeutics suggest.
“The implications of these results for patients are incredibly promising,” principal investigator Bryan Doner, DO, medical director of HealthyWays Integrated Wellness Solutions, Gibsonia, Pa., said in a news release.
“Through this rigorously designed study, we have demonstrated that ZLT-L-007 is a safe, effective, and well-tolerated alternative for patients who would typically seek a Lyrica-level of pain relief,” he added.
The observational, nonblinded trial tested the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of ZLT-L-007 against pregabalin in 60 adults with diabetic nerve pain.
The study had three groups with 20 patients each (pregabalin alone, pregabalin plus ZLT-L-007, and ZLT-L-007 alone).
Top-line results show the study met its primary endpoint for change in daily pain severity as measured by the percent change from baseline at 30, 60, and 90 days on the Numerical Rating Scale.
For the pregabalin-only group, there was a reduction in symptom severity at all follow-up points, ranging from 20% to 35% (median percent change from baseline), the company said.
For the ZLT-L-007 only group, there was about a 33% reduction in symptom severity at 30 days, and 71% and 78% reduction, respectively, at 60 and 90 days, suggesting a larger improvement in symptom severity than with pregabalin alone, the company said.
For the pregabalin plus ZLT-L-007 group, there was a moderate 20% reduction in symptom severity at 30 days, but a larger reduction at 60 and 90 days (50% and 72%, respectively), which indicates substantially greater improvement in symptom severity than with pregabalin alone, the company said.
The study also met secondary endpoints, including significant decreases in daily pain severity as measured by the Visual Analog Scale and measurable changes in the short-form McGill Pain Questionnaire and Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory.
Dr. Doner noted that the top-line data showed “no serious adverse events, and participants’ blood pressure and other safety vitals remained unaffected throughout. This confirms that ZLT-L-007 is a well-tolerated product that delivers statistically significant pain relief, surpassing the levels achieved by Lyrica.”
The company plans to report additional insights from the full study, as they become available, during fiscal year 2023-2024.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new top-line results released by Zelira Therapeutics suggest.
“The implications of these results for patients are incredibly promising,” principal investigator Bryan Doner, DO, medical director of HealthyWays Integrated Wellness Solutions, Gibsonia, Pa., said in a news release.
“Through this rigorously designed study, we have demonstrated that ZLT-L-007 is a safe, effective, and well-tolerated alternative for patients who would typically seek a Lyrica-level of pain relief,” he added.
The observational, nonblinded trial tested the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of ZLT-L-007 against pregabalin in 60 adults with diabetic nerve pain.
The study had three groups with 20 patients each (pregabalin alone, pregabalin plus ZLT-L-007, and ZLT-L-007 alone).
Top-line results show the study met its primary endpoint for change in daily pain severity as measured by the percent change from baseline at 30, 60, and 90 days on the Numerical Rating Scale.
For the pregabalin-only group, there was a reduction in symptom severity at all follow-up points, ranging from 20% to 35% (median percent change from baseline), the company said.
For the ZLT-L-007 only group, there was about a 33% reduction in symptom severity at 30 days, and 71% and 78% reduction, respectively, at 60 and 90 days, suggesting a larger improvement in symptom severity than with pregabalin alone, the company said.
For the pregabalin plus ZLT-L-007 group, there was a moderate 20% reduction in symptom severity at 30 days, but a larger reduction at 60 and 90 days (50% and 72%, respectively), which indicates substantially greater improvement in symptom severity than with pregabalin alone, the company said.
The study also met secondary endpoints, including significant decreases in daily pain severity as measured by the Visual Analog Scale and measurable changes in the short-form McGill Pain Questionnaire and Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory.
Dr. Doner noted that the top-line data showed “no serious adverse events, and participants’ blood pressure and other safety vitals remained unaffected throughout. This confirms that ZLT-L-007 is a well-tolerated product that delivers statistically significant pain relief, surpassing the levels achieved by Lyrica.”
The company plans to report additional insights from the full study, as they become available, during fiscal year 2023-2024.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Exercise and empathy can help back pain patients in primary care
Treatment of chronic back pain remains a challenge for primary care physicians, and a new Cochrane Review confirms previous studies suggesting that analgesics and antidepressants fall short in terms of relief.
Data from another Cochrane Review support the value of exercise for chronic low back pain, although it is often underused, and the Food and Drug Administration’s recent approval of a spinal cord stimulation device for chronic back pain opens the door for another alternative.
Regardless of treatment type, however, patients report that empathy and clear communication from their doctors go a long way in their satisfaction with pain management, according to another recent study.
Exercise helps when patients adhere
The objective of the Cochrane Review on “Exercise therapy for chronic low back pain” was to determine whether exercise improves pain and functioning for people with chronic low back pain, compared with no treatment, usual care, or other common treatments, corresponding author Jill Hayden, PhD, of Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S., said in an interview.
When back pain is chronic, it is expensive in terms of health care costs and lost work hours, said Dr. Hayden. “Exercise is promoted in many guidelines and is often recommended for, and used by, people with chronic low back pain.” However, “systematic reviews have found only small treatment effects, with considerable variation across individual trials.”
The 2021 review is one of the largest in the Cochrane Library, and included 249 trials and 24,486 study participants. However, Dr. Hayden said she had been disappointed by the methodological limitations of many of the trials. “The field is saturated with small exercise trials, many of which suffer from poor planning, conduct, and reporting due to limited resources.”
In the current review, “we found that exercise is likely to be effective for chronic low back pain. Overall, 3 months after the start of treatment, people receiving exercise treatment rated their pain an average of 15 points better on a scale of 0-100, and functional limitations were 7 points better, compared to people who had no treatment or usual care,” said Dr. Hayden.
Barriers to the use of exercise to treat pain may include fear of movement on the part of patients, she noted.
“Although our related network meta-analysis found some differences between specific types of exercise, we found all exercise types are more effective than minimal treatment,” she said. “People with chronic low back pain should be encouraged to do exercises that they enjoy and will do consistently to promote adherence.”
Limitations of medications
Both the safety and effectiveness of analgesics and antidepressants for pain in general and back pain in particular have come under scrutiny in recent research. A study published online in the British Medical Journal of patients with acute low back pain found that, although some medications were associated with large reductions in pain intensity, compared with placebo, the quality of the studies was “low or very low confidence,” according to a Medscape report on the findings.
This conclusion was supported in a large-scale analysis of the safety and effectiveness of antidepressants in chronic pain conditions, including back pain.
A new Cochrane Review led by a team of researchers in the United Kingdom found inadequate evidence to support the effectiveness of most antidepressants used for chronic pain, including amitriptyline, fluoxetine, citalopram, paroxetine, sertraline, and duloxetine.
“While chronic pain remains one of the top causes of daily disability worldwide, clinicians’ choices at offering interventions are getting fewer, especially if they tend toward a medical model and want a pharmacological solution,” corresponding author Tamar Pincus, PhD, of the University of Southampton (England), said in an interview. “We now know that opioids harm patients, and the evidence for common analgesics such as paracetamol and ibuprofen, for some conditions such as back pain, suggest they are not effective and might cause harm. This leaves clinicians with few options, and the most common prescription, supported by guidelines, is antidepressants.”
The study found moderate evidence that duloxetine can reduce pain in the short term and improve physical activity and some evidence that milnacipran might also be effective, Dr. Pincus said. “For all other antidepressants, including the commonly prescribed amitriptyline, the evidence was poor. Of importance, the average length of trials was 10 weeks, so long-term effects for all antidepressants remain unknown, and side effects and adverse events were reported poorly, so we also don’t know if any antidepressants are harmful.”
The takeaway message for the management of back pain in particular? “If a clinician and a patient decide together that it would be a good idea to try an antidepressant to reduce pain, they should consider starting with duloxetine, the drug with supporting evidence,” she said.
Physician attitude matters
Antidepressants may not have much impact on chronic pain, but a physician’s empathy and support do, according to data from a registry study of more than 1,300 individuals.
Despite efforts and guidelines from multiple medical organizations to promote optimal pain management, “much remains unknown regarding how the patient-physician interaction affects the process of delivering medical care for chronic low back pain and, ultimately, patient satisfaction,” John C. Licciardone, DO, of the University of North Texas Health Science Center, Fort Worth, and colleagues wrote in Annals of Family Medicine.
Previous studies have examined the relationship between clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction, but data on patient satisfaction with medical care for chronic low back pain specifically are limited, they said.
The researchers reviewed data from a national pain registry of adults aged 21-79 years that included self-reported measures of physician communication and empathy, prescribing data for opioids, and outcomes data for pain intensity, physical function, and health-related quality of life.
In a multivariate analysis, physician empathy and physician communication showed the strongest associations with patient satisfaction (P < .001).
The researchers found a negligible correlation between opioid prescription and perceived physician empathy and communication, “although current physician prescribing of opioids was also associated with patient satisfaction,” they wrote.
“Our findings pertaining to physician empathy are intriguing because they do not necessarily involve a therapeutic alliance with the patient based on collaborative communication or the expectation of a therapeutic effect via pharmacotherapy,” the researchers wrote .
The findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design that prevented conclusions about cause and effect, the researchers noted. “It is possible that prior improvements in pain intensity, physical function, or [health-related quality of life] might have prompted participants to report more favorable ratings for physician empathy, physician communication, or patient satisfaction at registry enrollment.” However, the study supports the view that patients with low back pain in particular value physicians who validate their concerns and symptoms, and who make an effort to communicate treatment plans clearly.
Back pain patients continue to challenge primary care
“Back pain is a major issue in U.S. health care, in part because too many people have tough physical jobs or longstanding injuries that become chronic,” William Golden, MD, professor of medicine and public health at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, said in an interview.
“There are no magic bullets for a lot of back pain patients, so empathy and support are key drivers,” he noted. “Helping patients maximize functionality as opposed to seeking mythical cures is the stronger line of visit discussions, but that takes a bit of time and skill in interviewing.
“It is fairly well established that duloxetine is useful in pain management, especially when present with mood disorders, either primary or secondary to the back-related disability,” said Dr. Golden. “Greater dissemination of its utility is probably useful, as is the side effect profile of the drug as well,” given the “nasty discontinuation syndrome when the treatment is reduced or stopped.”
Looking ahead, “more research is needed about microsurgery, namely for whom and for what anatomic presentations,” said Dr. Golden. Other topics for further research include a better understanding about medical marijuana and pain management and its interactions and side effects with other opioids and muscle relaxants. “Polypharmacy is still an issue in this class of patient,” and many of these patients are frustrated and angry “so the psychosocial skills of the PCP can be greatly tested as well,” he said.
Empathy promotes patient adherence to treatment
The new opioid prescription guidelines have increased interest among clinicians in how to improve patient satisfaction with the care for back pain provided, Noel Deep, MD, said in an interview. “These studies address this concern and bring forth an important aspect of the physician-patient relationship, namely the human touch and empathy.”
“I have been a strong proponent of the trust and relationship between a physician and patient; displaying empathy and increased and transparent communication between the physician and the patient has always resulted in better relationships and better outcomes for patients, especially those dealing with chronic health concerns,” said Dr. Deep, who is a general internist in a multispecialty group practice with Aspirus Antigo (Wisc.) Clinic and the chief medical officer and a staff physician at Aspirus Langlade Hospital, also in Antigo.
Potential barriers to effective pain management include beliefs and attitudes on the part of patients, Dr. Deep noted. “Physicians lacking adequate time to communicate effectively with the patient and describe nonopioid and nonsurgical interventions would be another potential barrier.” Other issues include the time and effort, as well as cost, associated with interventions such as physical therapy and other nondrug and nonsurgical interventions. Issues with family and social support and health literacy are also potential barriers to pain management.
Clinical takeaways
Low back pain is one of the most common reasons for a visit in primary care and can be “chronic and debilitating,” Grace Lin, MD, an internal medicine physician and primary care provider at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview.
“One issue with the Cochrane Review on exercise is that the studies on exercise were heterogeneous, so it’s difficult to know whether there is a particular kind of exercise that would be most effective and should be recommended to patients,” she said.
Furthermore, she said, “there is a physical therapist shortage in the U.S. I practice in a major city with a large health care system, and it can still take months to get an appointment with a physical therapist.” Also, insurance coverage may limit which therapists a patient can see and how many visits they can have.
“On the clinician side, I think physicians need to be better informed about the evidence base for back pain treatment, namely that exercise is effective and that, long term, analgesics are not,” Dr. Lin said. “This might decrease overprescription of ineffective analgesics and encourage more education about and referrals to physical therapy.”
“Physicians should continue to educate patients that physical therapy is the first-line treatment for back pain and that pain medications are secondary,” she said. “I think that analgesics can be effective for the short term to get people to a point where they feel well enough to do physical therapy. Duloxetine also appears to be moderately effective for chronic low back pain, in part because it may also help address coexisting depression and anxiety,” but these options should be reserved for adjuncts to physical therapy for back pain.
The findings from the study on empathy and communication suggest that the main challenges to these behaviors are systemic, said Dr. Lin.
“Our health care system is not conducive to treating chronic back pain,” she said. Primary care visits that last for 15 or 20 minutes are not long enough to diagnose and counsel patients on such a complex problem as chronic low back pain. Since back pain is usually not the only issue the primary care physician is dealing with during that visit, this can lead to patients feeling like their doctor isn’t listening to them and doesn’t care about their pain.
“We need to better understand the mechanisms by which people develop chronic, debilitating back pain,” Dr. Lin said. “I think if we understood this better, more effective and targeted treatments, both pharmacological and nonpharmacological, could be developed.”
The Annals of Family Medicine study received no outside funding, and the researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The Cochrane Reviews was supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research’s Health Technology Assessment program, and the authors had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Golden and Dr. Deep had no financial conflicts to disclose and serve on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Lin disclosed receiving research funding from the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review and the National Institutes of Health.
Treatment of chronic back pain remains a challenge for primary care physicians, and a new Cochrane Review confirms previous studies suggesting that analgesics and antidepressants fall short in terms of relief.
Data from another Cochrane Review support the value of exercise for chronic low back pain, although it is often underused, and the Food and Drug Administration’s recent approval of a spinal cord stimulation device for chronic back pain opens the door for another alternative.
Regardless of treatment type, however, patients report that empathy and clear communication from their doctors go a long way in their satisfaction with pain management, according to another recent study.
Exercise helps when patients adhere
The objective of the Cochrane Review on “Exercise therapy for chronic low back pain” was to determine whether exercise improves pain and functioning for people with chronic low back pain, compared with no treatment, usual care, or other common treatments, corresponding author Jill Hayden, PhD, of Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S., said in an interview.
When back pain is chronic, it is expensive in terms of health care costs and lost work hours, said Dr. Hayden. “Exercise is promoted in many guidelines and is often recommended for, and used by, people with chronic low back pain.” However, “systematic reviews have found only small treatment effects, with considerable variation across individual trials.”
The 2021 review is one of the largest in the Cochrane Library, and included 249 trials and 24,486 study participants. However, Dr. Hayden said she had been disappointed by the methodological limitations of many of the trials. “The field is saturated with small exercise trials, many of which suffer from poor planning, conduct, and reporting due to limited resources.”
In the current review, “we found that exercise is likely to be effective for chronic low back pain. Overall, 3 months after the start of treatment, people receiving exercise treatment rated their pain an average of 15 points better on a scale of 0-100, and functional limitations were 7 points better, compared to people who had no treatment or usual care,” said Dr. Hayden.
Barriers to the use of exercise to treat pain may include fear of movement on the part of patients, she noted.
“Although our related network meta-analysis found some differences between specific types of exercise, we found all exercise types are more effective than minimal treatment,” she said. “People with chronic low back pain should be encouraged to do exercises that they enjoy and will do consistently to promote adherence.”
Limitations of medications
Both the safety and effectiveness of analgesics and antidepressants for pain in general and back pain in particular have come under scrutiny in recent research. A study published online in the British Medical Journal of patients with acute low back pain found that, although some medications were associated with large reductions in pain intensity, compared with placebo, the quality of the studies was “low or very low confidence,” according to a Medscape report on the findings.
This conclusion was supported in a large-scale analysis of the safety and effectiveness of antidepressants in chronic pain conditions, including back pain.
A new Cochrane Review led by a team of researchers in the United Kingdom found inadequate evidence to support the effectiveness of most antidepressants used for chronic pain, including amitriptyline, fluoxetine, citalopram, paroxetine, sertraline, and duloxetine.
“While chronic pain remains one of the top causes of daily disability worldwide, clinicians’ choices at offering interventions are getting fewer, especially if they tend toward a medical model and want a pharmacological solution,” corresponding author Tamar Pincus, PhD, of the University of Southampton (England), said in an interview. “We now know that opioids harm patients, and the evidence for common analgesics such as paracetamol and ibuprofen, for some conditions such as back pain, suggest they are not effective and might cause harm. This leaves clinicians with few options, and the most common prescription, supported by guidelines, is antidepressants.”
The study found moderate evidence that duloxetine can reduce pain in the short term and improve physical activity and some evidence that milnacipran might also be effective, Dr. Pincus said. “For all other antidepressants, including the commonly prescribed amitriptyline, the evidence was poor. Of importance, the average length of trials was 10 weeks, so long-term effects for all antidepressants remain unknown, and side effects and adverse events were reported poorly, so we also don’t know if any antidepressants are harmful.”
The takeaway message for the management of back pain in particular? “If a clinician and a patient decide together that it would be a good idea to try an antidepressant to reduce pain, they should consider starting with duloxetine, the drug with supporting evidence,” she said.
Physician attitude matters
Antidepressants may not have much impact on chronic pain, but a physician’s empathy and support do, according to data from a registry study of more than 1,300 individuals.
Despite efforts and guidelines from multiple medical organizations to promote optimal pain management, “much remains unknown regarding how the patient-physician interaction affects the process of delivering medical care for chronic low back pain and, ultimately, patient satisfaction,” John C. Licciardone, DO, of the University of North Texas Health Science Center, Fort Worth, and colleagues wrote in Annals of Family Medicine.
Previous studies have examined the relationship between clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction, but data on patient satisfaction with medical care for chronic low back pain specifically are limited, they said.
The researchers reviewed data from a national pain registry of adults aged 21-79 years that included self-reported measures of physician communication and empathy, prescribing data for opioids, and outcomes data for pain intensity, physical function, and health-related quality of life.
In a multivariate analysis, physician empathy and physician communication showed the strongest associations with patient satisfaction (P < .001).
The researchers found a negligible correlation between opioid prescription and perceived physician empathy and communication, “although current physician prescribing of opioids was also associated with patient satisfaction,” they wrote.
“Our findings pertaining to physician empathy are intriguing because they do not necessarily involve a therapeutic alliance with the patient based on collaborative communication or the expectation of a therapeutic effect via pharmacotherapy,” the researchers wrote .
The findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design that prevented conclusions about cause and effect, the researchers noted. “It is possible that prior improvements in pain intensity, physical function, or [health-related quality of life] might have prompted participants to report more favorable ratings for physician empathy, physician communication, or patient satisfaction at registry enrollment.” However, the study supports the view that patients with low back pain in particular value physicians who validate their concerns and symptoms, and who make an effort to communicate treatment plans clearly.
Back pain patients continue to challenge primary care
“Back pain is a major issue in U.S. health care, in part because too many people have tough physical jobs or longstanding injuries that become chronic,” William Golden, MD, professor of medicine and public health at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, said in an interview.
“There are no magic bullets for a lot of back pain patients, so empathy and support are key drivers,” he noted. “Helping patients maximize functionality as opposed to seeking mythical cures is the stronger line of visit discussions, but that takes a bit of time and skill in interviewing.
“It is fairly well established that duloxetine is useful in pain management, especially when present with mood disorders, either primary or secondary to the back-related disability,” said Dr. Golden. “Greater dissemination of its utility is probably useful, as is the side effect profile of the drug as well,” given the “nasty discontinuation syndrome when the treatment is reduced or stopped.”
Looking ahead, “more research is needed about microsurgery, namely for whom and for what anatomic presentations,” said Dr. Golden. Other topics for further research include a better understanding about medical marijuana and pain management and its interactions and side effects with other opioids and muscle relaxants. “Polypharmacy is still an issue in this class of patient,” and many of these patients are frustrated and angry “so the psychosocial skills of the PCP can be greatly tested as well,” he said.
Empathy promotes patient adherence to treatment
The new opioid prescription guidelines have increased interest among clinicians in how to improve patient satisfaction with the care for back pain provided, Noel Deep, MD, said in an interview. “These studies address this concern and bring forth an important aspect of the physician-patient relationship, namely the human touch and empathy.”
“I have been a strong proponent of the trust and relationship between a physician and patient; displaying empathy and increased and transparent communication between the physician and the patient has always resulted in better relationships and better outcomes for patients, especially those dealing with chronic health concerns,” said Dr. Deep, who is a general internist in a multispecialty group practice with Aspirus Antigo (Wisc.) Clinic and the chief medical officer and a staff physician at Aspirus Langlade Hospital, also in Antigo.
Potential barriers to effective pain management include beliefs and attitudes on the part of patients, Dr. Deep noted. “Physicians lacking adequate time to communicate effectively with the patient and describe nonopioid and nonsurgical interventions would be another potential barrier.” Other issues include the time and effort, as well as cost, associated with interventions such as physical therapy and other nondrug and nonsurgical interventions. Issues with family and social support and health literacy are also potential barriers to pain management.
Clinical takeaways
Low back pain is one of the most common reasons for a visit in primary care and can be “chronic and debilitating,” Grace Lin, MD, an internal medicine physician and primary care provider at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview.
“One issue with the Cochrane Review on exercise is that the studies on exercise were heterogeneous, so it’s difficult to know whether there is a particular kind of exercise that would be most effective and should be recommended to patients,” she said.
Furthermore, she said, “there is a physical therapist shortage in the U.S. I practice in a major city with a large health care system, and it can still take months to get an appointment with a physical therapist.” Also, insurance coverage may limit which therapists a patient can see and how many visits they can have.
“On the clinician side, I think physicians need to be better informed about the evidence base for back pain treatment, namely that exercise is effective and that, long term, analgesics are not,” Dr. Lin said. “This might decrease overprescription of ineffective analgesics and encourage more education about and referrals to physical therapy.”
“Physicians should continue to educate patients that physical therapy is the first-line treatment for back pain and that pain medications are secondary,” she said. “I think that analgesics can be effective for the short term to get people to a point where they feel well enough to do physical therapy. Duloxetine also appears to be moderately effective for chronic low back pain, in part because it may also help address coexisting depression and anxiety,” but these options should be reserved for adjuncts to physical therapy for back pain.
The findings from the study on empathy and communication suggest that the main challenges to these behaviors are systemic, said Dr. Lin.
“Our health care system is not conducive to treating chronic back pain,” she said. Primary care visits that last for 15 or 20 minutes are not long enough to diagnose and counsel patients on such a complex problem as chronic low back pain. Since back pain is usually not the only issue the primary care physician is dealing with during that visit, this can lead to patients feeling like their doctor isn’t listening to them and doesn’t care about their pain.
“We need to better understand the mechanisms by which people develop chronic, debilitating back pain,” Dr. Lin said. “I think if we understood this better, more effective and targeted treatments, both pharmacological and nonpharmacological, could be developed.”
The Annals of Family Medicine study received no outside funding, and the researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The Cochrane Reviews was supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research’s Health Technology Assessment program, and the authors had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Golden and Dr. Deep had no financial conflicts to disclose and serve on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Lin disclosed receiving research funding from the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review and the National Institutes of Health.
Treatment of chronic back pain remains a challenge for primary care physicians, and a new Cochrane Review confirms previous studies suggesting that analgesics and antidepressants fall short in terms of relief.
Data from another Cochrane Review support the value of exercise for chronic low back pain, although it is often underused, and the Food and Drug Administration’s recent approval of a spinal cord stimulation device for chronic back pain opens the door for another alternative.
Regardless of treatment type, however, patients report that empathy and clear communication from their doctors go a long way in their satisfaction with pain management, according to another recent study.
Exercise helps when patients adhere
The objective of the Cochrane Review on “Exercise therapy for chronic low back pain” was to determine whether exercise improves pain and functioning for people with chronic low back pain, compared with no treatment, usual care, or other common treatments, corresponding author Jill Hayden, PhD, of Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S., said in an interview.
When back pain is chronic, it is expensive in terms of health care costs and lost work hours, said Dr. Hayden. “Exercise is promoted in many guidelines and is often recommended for, and used by, people with chronic low back pain.” However, “systematic reviews have found only small treatment effects, with considerable variation across individual trials.”
The 2021 review is one of the largest in the Cochrane Library, and included 249 trials and 24,486 study participants. However, Dr. Hayden said she had been disappointed by the methodological limitations of many of the trials. “The field is saturated with small exercise trials, many of which suffer from poor planning, conduct, and reporting due to limited resources.”
In the current review, “we found that exercise is likely to be effective for chronic low back pain. Overall, 3 months after the start of treatment, people receiving exercise treatment rated their pain an average of 15 points better on a scale of 0-100, and functional limitations were 7 points better, compared to people who had no treatment or usual care,” said Dr. Hayden.
Barriers to the use of exercise to treat pain may include fear of movement on the part of patients, she noted.
“Although our related network meta-analysis found some differences between specific types of exercise, we found all exercise types are more effective than minimal treatment,” she said. “People with chronic low back pain should be encouraged to do exercises that they enjoy and will do consistently to promote adherence.”
Limitations of medications
Both the safety and effectiveness of analgesics and antidepressants for pain in general and back pain in particular have come under scrutiny in recent research. A study published online in the British Medical Journal of patients with acute low back pain found that, although some medications were associated with large reductions in pain intensity, compared with placebo, the quality of the studies was “low or very low confidence,” according to a Medscape report on the findings.
This conclusion was supported in a large-scale analysis of the safety and effectiveness of antidepressants in chronic pain conditions, including back pain.
A new Cochrane Review led by a team of researchers in the United Kingdom found inadequate evidence to support the effectiveness of most antidepressants used for chronic pain, including amitriptyline, fluoxetine, citalopram, paroxetine, sertraline, and duloxetine.
“While chronic pain remains one of the top causes of daily disability worldwide, clinicians’ choices at offering interventions are getting fewer, especially if they tend toward a medical model and want a pharmacological solution,” corresponding author Tamar Pincus, PhD, of the University of Southampton (England), said in an interview. “We now know that opioids harm patients, and the evidence for common analgesics such as paracetamol and ibuprofen, for some conditions such as back pain, suggest they are not effective and might cause harm. This leaves clinicians with few options, and the most common prescription, supported by guidelines, is antidepressants.”
The study found moderate evidence that duloxetine can reduce pain in the short term and improve physical activity and some evidence that milnacipran might also be effective, Dr. Pincus said. “For all other antidepressants, including the commonly prescribed amitriptyline, the evidence was poor. Of importance, the average length of trials was 10 weeks, so long-term effects for all antidepressants remain unknown, and side effects and adverse events were reported poorly, so we also don’t know if any antidepressants are harmful.”
The takeaway message for the management of back pain in particular? “If a clinician and a patient decide together that it would be a good idea to try an antidepressant to reduce pain, they should consider starting with duloxetine, the drug with supporting evidence,” she said.
Physician attitude matters
Antidepressants may not have much impact on chronic pain, but a physician’s empathy and support do, according to data from a registry study of more than 1,300 individuals.
Despite efforts and guidelines from multiple medical organizations to promote optimal pain management, “much remains unknown regarding how the patient-physician interaction affects the process of delivering medical care for chronic low back pain and, ultimately, patient satisfaction,” John C. Licciardone, DO, of the University of North Texas Health Science Center, Fort Worth, and colleagues wrote in Annals of Family Medicine.
Previous studies have examined the relationship between clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction, but data on patient satisfaction with medical care for chronic low back pain specifically are limited, they said.
The researchers reviewed data from a national pain registry of adults aged 21-79 years that included self-reported measures of physician communication and empathy, prescribing data for opioids, and outcomes data for pain intensity, physical function, and health-related quality of life.
In a multivariate analysis, physician empathy and physician communication showed the strongest associations with patient satisfaction (P < .001).
The researchers found a negligible correlation between opioid prescription and perceived physician empathy and communication, “although current physician prescribing of opioids was also associated with patient satisfaction,” they wrote.
“Our findings pertaining to physician empathy are intriguing because they do not necessarily involve a therapeutic alliance with the patient based on collaborative communication or the expectation of a therapeutic effect via pharmacotherapy,” the researchers wrote .
The findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design that prevented conclusions about cause and effect, the researchers noted. “It is possible that prior improvements in pain intensity, physical function, or [health-related quality of life] might have prompted participants to report more favorable ratings for physician empathy, physician communication, or patient satisfaction at registry enrollment.” However, the study supports the view that patients with low back pain in particular value physicians who validate their concerns and symptoms, and who make an effort to communicate treatment plans clearly.
Back pain patients continue to challenge primary care
“Back pain is a major issue in U.S. health care, in part because too many people have tough physical jobs or longstanding injuries that become chronic,” William Golden, MD, professor of medicine and public health at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, said in an interview.
“There are no magic bullets for a lot of back pain patients, so empathy and support are key drivers,” he noted. “Helping patients maximize functionality as opposed to seeking mythical cures is the stronger line of visit discussions, but that takes a bit of time and skill in interviewing.
“It is fairly well established that duloxetine is useful in pain management, especially when present with mood disorders, either primary or secondary to the back-related disability,” said Dr. Golden. “Greater dissemination of its utility is probably useful, as is the side effect profile of the drug as well,” given the “nasty discontinuation syndrome when the treatment is reduced or stopped.”
Looking ahead, “more research is needed about microsurgery, namely for whom and for what anatomic presentations,” said Dr. Golden. Other topics for further research include a better understanding about medical marijuana and pain management and its interactions and side effects with other opioids and muscle relaxants. “Polypharmacy is still an issue in this class of patient,” and many of these patients are frustrated and angry “so the psychosocial skills of the PCP can be greatly tested as well,” he said.
Empathy promotes patient adherence to treatment
The new opioid prescription guidelines have increased interest among clinicians in how to improve patient satisfaction with the care for back pain provided, Noel Deep, MD, said in an interview. “These studies address this concern and bring forth an important aspect of the physician-patient relationship, namely the human touch and empathy.”
“I have been a strong proponent of the trust and relationship between a physician and patient; displaying empathy and increased and transparent communication between the physician and the patient has always resulted in better relationships and better outcomes for patients, especially those dealing with chronic health concerns,” said Dr. Deep, who is a general internist in a multispecialty group practice with Aspirus Antigo (Wisc.) Clinic and the chief medical officer and a staff physician at Aspirus Langlade Hospital, also in Antigo.
Potential barriers to effective pain management include beliefs and attitudes on the part of patients, Dr. Deep noted. “Physicians lacking adequate time to communicate effectively with the patient and describe nonopioid and nonsurgical interventions would be another potential barrier.” Other issues include the time and effort, as well as cost, associated with interventions such as physical therapy and other nondrug and nonsurgical interventions. Issues with family and social support and health literacy are also potential barriers to pain management.
Clinical takeaways
Low back pain is one of the most common reasons for a visit in primary care and can be “chronic and debilitating,” Grace Lin, MD, an internal medicine physician and primary care provider at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview.
“One issue with the Cochrane Review on exercise is that the studies on exercise were heterogeneous, so it’s difficult to know whether there is a particular kind of exercise that would be most effective and should be recommended to patients,” she said.
Furthermore, she said, “there is a physical therapist shortage in the U.S. I practice in a major city with a large health care system, and it can still take months to get an appointment with a physical therapist.” Also, insurance coverage may limit which therapists a patient can see and how many visits they can have.
“On the clinician side, I think physicians need to be better informed about the evidence base for back pain treatment, namely that exercise is effective and that, long term, analgesics are not,” Dr. Lin said. “This might decrease overprescription of ineffective analgesics and encourage more education about and referrals to physical therapy.”
“Physicians should continue to educate patients that physical therapy is the first-line treatment for back pain and that pain medications are secondary,” she said. “I think that analgesics can be effective for the short term to get people to a point where they feel well enough to do physical therapy. Duloxetine also appears to be moderately effective for chronic low back pain, in part because it may also help address coexisting depression and anxiety,” but these options should be reserved for adjuncts to physical therapy for back pain.
The findings from the study on empathy and communication suggest that the main challenges to these behaviors are systemic, said Dr. Lin.
“Our health care system is not conducive to treating chronic back pain,” she said. Primary care visits that last for 15 or 20 minutes are not long enough to diagnose and counsel patients on such a complex problem as chronic low back pain. Since back pain is usually not the only issue the primary care physician is dealing with during that visit, this can lead to patients feeling like their doctor isn’t listening to them and doesn’t care about their pain.
“We need to better understand the mechanisms by which people develop chronic, debilitating back pain,” Dr. Lin said. “I think if we understood this better, more effective and targeted treatments, both pharmacological and nonpharmacological, could be developed.”
The Annals of Family Medicine study received no outside funding, and the researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The Cochrane Reviews was supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research’s Health Technology Assessment program, and the authors had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Golden and Dr. Deep had no financial conflicts to disclose and serve on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Lin disclosed receiving research funding from the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review and the National Institutes of Health.
Researchers locate signals in brain related to chronic pain
a new study in Nature Neuroscience concluded.
The researchers used the devices on four patients who had felt endless nerve pain for more than a year. The devices recorded several times a day, which could pave “the way for implanted devices to one day predict pain signals or even short-circuit them,” The New York Times reported.
The study says the pain “was associated with electrical fluctuations in the orbitofrontal cortex, an area involved in emotion regulation, self-evaluation, and decision-making,” The Times reported. “The research suggests that such patterns of brain activity could serve as biomarkers to guide diagnosis and treatment for millions of people with shooting or burning chronic pain linked to a damaged nervous system.”
Ajay Wasan, MD, and a pain specialist at the University of Pittsburgh who was not involved in the study praised it to the Times.
“The study really advances a whole generation of research that has shown that the functioning of the brain is really important to processing and perceiving pain,” he said.
Chronic pain is defined as persistent or recurring and lasting more than three months. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says about 20% of Americans experience it. It has been linked with depression, Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias, suicide, and substance use.
Yet, the study’s authors noted, “pain severity is often measured through subjective report, while objective biomarkers that may guide diagnosis and treatment are lacking.”
Medtronic provided devices for the study. The study authors reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
a new study in Nature Neuroscience concluded.
The researchers used the devices on four patients who had felt endless nerve pain for more than a year. The devices recorded several times a day, which could pave “the way for implanted devices to one day predict pain signals or even short-circuit them,” The New York Times reported.
The study says the pain “was associated with electrical fluctuations in the orbitofrontal cortex, an area involved in emotion regulation, self-evaluation, and decision-making,” The Times reported. “The research suggests that such patterns of brain activity could serve as biomarkers to guide diagnosis and treatment for millions of people with shooting or burning chronic pain linked to a damaged nervous system.”
Ajay Wasan, MD, and a pain specialist at the University of Pittsburgh who was not involved in the study praised it to the Times.
“The study really advances a whole generation of research that has shown that the functioning of the brain is really important to processing and perceiving pain,” he said.
Chronic pain is defined as persistent or recurring and lasting more than three months. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says about 20% of Americans experience it. It has been linked with depression, Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias, suicide, and substance use.
Yet, the study’s authors noted, “pain severity is often measured through subjective report, while objective biomarkers that may guide diagnosis and treatment are lacking.”
Medtronic provided devices for the study. The study authors reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
a new study in Nature Neuroscience concluded.
The researchers used the devices on four patients who had felt endless nerve pain for more than a year. The devices recorded several times a day, which could pave “the way for implanted devices to one day predict pain signals or even short-circuit them,” The New York Times reported.
The study says the pain “was associated with electrical fluctuations in the orbitofrontal cortex, an area involved in emotion regulation, self-evaluation, and decision-making,” The Times reported. “The research suggests that such patterns of brain activity could serve as biomarkers to guide diagnosis and treatment for millions of people with shooting or burning chronic pain linked to a damaged nervous system.”
Ajay Wasan, MD, and a pain specialist at the University of Pittsburgh who was not involved in the study praised it to the Times.
“The study really advances a whole generation of research that has shown that the functioning of the brain is really important to processing and perceiving pain,” he said.
Chronic pain is defined as persistent or recurring and lasting more than three months. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says about 20% of Americans experience it. It has been linked with depression, Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias, suicide, and substance use.
Yet, the study’s authors noted, “pain severity is often measured through subjective report, while objective biomarkers that may guide diagnosis and treatment are lacking.”
Medtronic provided devices for the study. The study authors reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
FDA OKs spinal cord stimulation devices for chronic back pain
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indication for Abbott Laboratories’ spinal cord stimulation (SCS) devices to include treatment of chronic back pain in patients who have not had, or are not eligible for, back surgery, the company has announced.
The new indication spans all of Abbott’s SCS devices in the United States, which include the recharge-free Proclaim SCS family and the rechargeable Eterna SCS platform.
The devices feature the company’s proprietary, low-energy BurstDR stimulation waveform, a form of stimulation therapy that uses bursts of mild electrical energy without causing an abnormal tingling sensation to help disrupt pain signals before they can reach the brain, the company explained.
The expanded indication was supported by results from the DISTINCT study, which enrolled 270 adults suffering from severe, disabling chronic back pain for an average of more than 12 years and who were not eligible for surgery.
The study showed that significantly more patients who were treated with SCS achieved significant improvements in back pain, function, quality of life, and psychological status than peers treated with conservative medical management.
“To date, we have struggled with how to treat people who weren’t considered a good surgical candidate because we didn’t have clear, data-driven treatment options for non-surgical back pain,” Timothy Deer, MD, president and CEO of the Spine and Nerve Centers of the Virginias in Charleston, W.Va., said in a news release.
“This new indication for Abbott’s SCS devices, together with BurstDR stimulation, allows physicians the ability to identify and treat a new group of people, providing them with relief from chronic back pain,” Dr. Deer said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indication for Abbott Laboratories’ spinal cord stimulation (SCS) devices to include treatment of chronic back pain in patients who have not had, or are not eligible for, back surgery, the company has announced.
The new indication spans all of Abbott’s SCS devices in the United States, which include the recharge-free Proclaim SCS family and the rechargeable Eterna SCS platform.
The devices feature the company’s proprietary, low-energy BurstDR stimulation waveform, a form of stimulation therapy that uses bursts of mild electrical energy without causing an abnormal tingling sensation to help disrupt pain signals before they can reach the brain, the company explained.
The expanded indication was supported by results from the DISTINCT study, which enrolled 270 adults suffering from severe, disabling chronic back pain for an average of more than 12 years and who were not eligible for surgery.
The study showed that significantly more patients who were treated with SCS achieved significant improvements in back pain, function, quality of life, and psychological status than peers treated with conservative medical management.
“To date, we have struggled with how to treat people who weren’t considered a good surgical candidate because we didn’t have clear, data-driven treatment options for non-surgical back pain,” Timothy Deer, MD, president and CEO of the Spine and Nerve Centers of the Virginias in Charleston, W.Va., said in a news release.
“This new indication for Abbott’s SCS devices, together with BurstDR stimulation, allows physicians the ability to identify and treat a new group of people, providing them with relief from chronic back pain,” Dr. Deer said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indication for Abbott Laboratories’ spinal cord stimulation (SCS) devices to include treatment of chronic back pain in patients who have not had, or are not eligible for, back surgery, the company has announced.
The new indication spans all of Abbott’s SCS devices in the United States, which include the recharge-free Proclaim SCS family and the rechargeable Eterna SCS platform.
The devices feature the company’s proprietary, low-energy BurstDR stimulation waveform, a form of stimulation therapy that uses bursts of mild electrical energy without causing an abnormal tingling sensation to help disrupt pain signals before they can reach the brain, the company explained.
The expanded indication was supported by results from the DISTINCT study, which enrolled 270 adults suffering from severe, disabling chronic back pain for an average of more than 12 years and who were not eligible for surgery.
The study showed that significantly more patients who were treated with SCS achieved significant improvements in back pain, function, quality of life, and psychological status than peers treated with conservative medical management.
“To date, we have struggled with how to treat people who weren’t considered a good surgical candidate because we didn’t have clear, data-driven treatment options for non-surgical back pain,” Timothy Deer, MD, president and CEO of the Spine and Nerve Centers of the Virginias in Charleston, W.Va., said in a news release.
“This new indication for Abbott’s SCS devices, together with BurstDR stimulation, allows physicians the ability to identify and treat a new group of people, providing them with relief from chronic back pain,” Dr. Deer said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medication-assisted recovery for opioid use disorder: A guide
Medication-assisted recovery (MAR)—the preferred terminology for the service formerly known as medication-assisted treatment—entails a comprehensive set of interventions for managing opioid use disorder (OUD), including medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD). Despite the benefits of MAR—reducing opioid use, opioid-related mortality, and health care costs1-3—only 11% of patients with a diagnosis of OUD received MOUD in 2020.3
Primary care physicians, including family physicians, are well positioned to provide MAR across the patient’s lifespan. However, many family medicine clinicians do not possess the logistical knowledge or resources to implement this service.4 In this article, we describe options for, and barriers to, MAR and societal issues that have an impact on the care of these patients.
Pathophysiology of OUD
Opioids relieve pain by stimulating μ-opioid receptors and activating the brain’s reward system. These pleasurable effects motivate repeated use.5 Frequent opioid exposure causes neuroadaptation, tolerance, and dependence. For patients with OUD who are misusing illicit or prescription opioids, periods of abstinence following neuroadaptation lead to withdrawal symptoms that vary in intensity, depending on the drug, dose, and duration of use. Upregulated noradrenergic tone and dopamine deficiency manifest as numerous signs and symptoms of withdrawal, including5:
- Physiologic: secretory (diaphoresis, rhinorrhea, lacrimation, vomiting, diarrhea) and stimulatory (mydriasis, piloerection, hypertension, tachycardia, insomnia)
- Psychological: pain, cravings, dysphoria, anxiety.
A single episode of opioid withdrawal is not directly life-threatening, but untreated episodes can progressively amplify negative feedback and reinforce continued opioid use.6 Left untreated, withdrawal can be terminal.
Medication-assisted recovery: Effective intervention
MAR services that integrate medical, behavioral, and psychosocial programs can reduce mortality from OUD 2-fold.7,8 A meta-analysis found that, when MAR services are rendered in primary care, treatment retention improves by 25% (number needed to treat [NNT] = 6) and ongoing illicit opioid use is reduced by 50% (NNT = 6), relative to care at a specialty clinic9—highlighting a role for family medicine clinicians in treating OUD.
All 3 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved MOUD (methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone) reduce cravings; 2 (methadone and buprenorphine) mitigate withdrawal symptoms by activating the μ-opioid receptor; and naltrexone diminishes the reinforcing effects of use (TABLE10-12). It is crucial to recognize the pharmacologic distinctions among MOUD because untreated withdrawal syndromes increase dropout from treatment programs and subsequent relapse.13
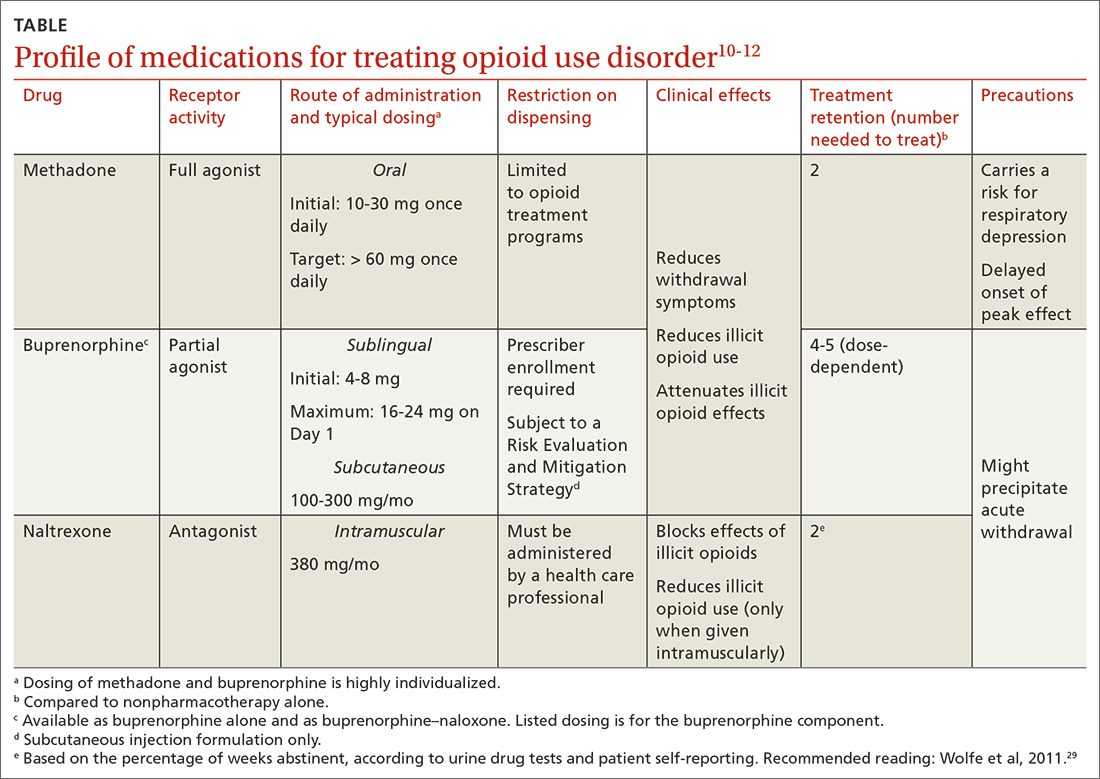
The Hx of medication-assisted recovery
To understand the landscape of MAR, it is important to understand the history of opioid treatment in the United States. In 1966, Congress passed the Narcotic Addiction Rehabilitation Act (NARA), which secured federal assistance by which state and local governments could develop drug treatment programs.14 NARA permitted legal offenders with OUD to be civilly committed to treatment programs, rather than prosecuted. However, limited resources and a burgeoning population led, instead, to low-cost outpatient programs saddled by strict requirements that lacked a basis for improving clinical outcomes.
Continue to: At the time NARA...
At the time NARA was passed by Congress, OUD was viewed—inaccurately—as a criminal problem, not a medical one. Subsequent legislation was crafted through that lens, which has placed a heavy burden on patients until today.14 Although medical understanding of OUD has advanced tremendously over the past 50 years, treatment remains siloed from mainstream medicine, even in primary care.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to MAR, and relapse is common. Patient-specific factors and the availability of resources should be considered when designing the most individualized, advantageous plan for MAR.
Methadone
Background. Methadone has the most extensive history for treating OUD and consistently has demonstrated efficacy.13 A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing methadone to nonpharmacotherapy alone found that methadone improved treatment retention by an absolute 57% (NNT = 2).10
Methadone was approved by the FDA for detoxification and maintenance treatment in the early 1970s, although the Narcotic Addict Treatment Act (NATA) of 1974 restricted dispensing of maintenance treatment to highly regulated clinics known as opioid treatment programs (OTPs).14 NATA required the treating physician to register with the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) and to comply with conservative dosing regimens and observed dosing.
Over time, regulations evolved to give the physician greater flexibility in developing a care plan, allowing “take-home” doses, and improving patients’ access to care. Although access to methadone for the treatment of OUD remains limited to federally certified OTPs, regulations facilitate incorporation of a whole-person approach to care, including counseling, individual and group therapy, and toxicology testing.7
Continue to: Clinical considerations
Clinical considerations. Methadone requires slow titration. For patients starting methadone as an outpatient, federal law15 limits the initial dose to 30 mg and requires physician documentation when the first-day total dosage exceeds 40 mg. This dosing constraint makes it challenging to provide care because a daily dosage ≥ 60 mg has been found to produce, first, higher program retention (relative risk = 1.36; 95% CI, 1.13-1.63) and, second, greater reduction in illicit opioid use (relative risk = 1.59; 95% CI, 1.16-2.18) than is seen in patients who receive a lower daily dosage.16
Due to a prolonged elimination half-life, methadone reaches steady-state in 3 to 5 days. Patients and their families should be educated that withdrawal symptoms might not feel fully managed in the first few days of therapy and that time is required to experience safely the regimen’s full effects.
Aggressive dose-titration during methadone induction can result in drug accumulation and respiratory depression. The risk for methadone-related mortality is highest in the first 2 weeks of therapy, mostly related to overdose potential if the drug is combined with other opioids.17
Buprenorphine
Background. The prescribing rate for buprenorphine, particularly in primary care, is accelerating.18 A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials found that11:
- compared to placebo, buprenorphine, at any dosage, improves treatment retention by an absolute 21% to 28% (NNT = 4-5)
- patients receiving high-dose buprenorphine (≥ 16 mg/d) had fewer evident cases of illicit opioid use.
Unlike methadone, buprenorphine exerts partial agonism at the μ-opioid receptor, resulting in a so-called ceiling effect that significantly reduces the adverse effect profile, including respiratory depression and euphoria, relative to a full-agonist opioid, such as methadone.19
Continue to: Whereas accessing methadone...
Whereas accessing methadone is limited to OTPs, buprenorphine is available for office-based treatment. By hosting OUD treatment and primary care in the same place, primary care physicians can provide comprehensive medical care including and beyond OUD, thereby improving retention and managing comorbidity.20
Integrated models involving support staff—eg, nurses, behavioral health providers, and pharmacists—have produced the greatest success with office-based treatment models.21 Office-based treatment normalizes OUD as a chronic disease managed by the primary care physician, enabling concurrent harm-reduction strategies; medication reconciliation; and convenient, regular prescribing intervals (eg, every 30 days).22 Nevertheless, access to buprenorphine is limited. Because buprenorphine is a controlled substance, the Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act of 2008 prevents initial prescribing of buprenorphine without in-person evaluation. Telehealth consultations increased access to buprenorphine through temporary exceptions during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, revised rules and regulations for telehealth visits for these controlled substances are forthcoming from the DEA as temporary exceptions for telehealth consultations come to an end. Additionally, prescribing buprenorphine for OUD requires that the treating physician undergo specific training and obtain qualifications, which have evolved over time through federal legislation.
The Drug Addiction Treatment Act of 2000 (DATA 2000) authorized what is known as an X-waiver, which allows physicians to prescribe controlled substances for office-based treatment of OUD, provided that:
- they are registered to do so with the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration and the DEA
- they have had subspecialty training in addiction or completed an 8-hour training course
- they are able to refer patients to appropriate counseling and ancillary services.
DATA 2000 restricted patient panel sizes to 30 patients in the first year, expanding thereafter upon appropriate certification.
The Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016 (CARA) and the Substance Use Disorder Prevention that Promotes Opioid Recovery and Treatment for Patients and Communities Act of 2018 (the SUPPORT Act) collectively extended prescribing authority for MOUD to other qualifying practitioners (eg, advanced practice clinicians). Despite these attempts to expand access to services, the overdose death rate has continued to increase.
Continue to: To further expand access to MAR...
To further expand access to MAR, the US Department of Health and Human Services updated its practice guidelines in April 2021, allowing clinicians to bypass X-waiver training requirements by applying for a notification-of-intent (NOI) buprenorphine waiver.a However, clinicians are still limited to prescribing buprenorphine for 30 patients at a time. Clinicians who undergo complete X-waiver training may prescribe for 100 patients in the first year and, if eligible, 275 patients thereafter.
In addition, as a component of the Consolidation Appropriations Act of 2023, Congress passed the Mainstreaming Addiction Treatment Act of 2021, or MAT 2021, and Medication Access and Training Expansion Act of 2021, or MATE 2021. MAT eliminated the X-waiver, NOI, and restrictions on the number of patients for whom a provider could prescribe buprenorphine, under federal authority; however, restrictions within one’s state might limit the ability to prescribe buprenorphine. MATE 2021 is an educational requirement for licensing by the DEA (at application and renewal) that will require prescribers to complete 8 hours of training in substance use disorders starting in June 2023.
Use of the monthly injectable extended-release buprenorphine productb is limited by an FDA Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program, which requires specialized training and certification by the prescriber, distributor, and administering clinician. REMS reduces buprenorphine accessibility due to time, cost, and regulatory barriers; although such restrictions have been instituted with the patient’s safety in mind, any limitation to buprenorphine prescribing, apart from controlled substance licensure, serves only to limit access to a primary component of MAR.
Clinical considerations. Due to the competitive nature of buprenorphine and its high affinity for the μ-opioid receptor, the drug can displace other opioid agonists and precipitate acute withdrawal. The withdrawal experience can thereby condition fear and disfavor toward buprenorphine among patients.
It is vital, therefore, that (1) patients’ expectations for treatment be managed appropriately and (2) the treating physician be prepared to provide additional buprenorphine for adequate maintenance doses and utilize adjunct comfort agents (clonidine, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, ondansetron) to manage acute withdrawal symptoms. Newer buprenorphine dosing strategies, such as micro-induction and macro-induction, have emerged to curtail these risks.23,24 This is an evolving area of MAR; newer low-threshold initiation strategies25 (see “Low-threshold MOUD prescribing models,” in the text that follows) and evidence that supports micro-induction26 might eliminate the practice of requiring active withdrawal for treatment.
Continue to: Regardless of the strategy...
Regardless of the strategy for dosing buprenorphine, it’s critical that patients be educated on how to initiate treatment outside a clinical setting, such as at home, where they occupy a familiar haven during a potentially uncomfortable time and can be as effective at initiation as they would be in a clinical setting, with no difference in precipitation of adverse effects.
At-home induction might be more appropriate for patients who are not yet in significant enough withdrawal while in the physician's office.27 Guidance should be provided on dosing instructions, self-assessment of withdrawal symptoms, and, if applicable, patience with the slow-dissolving sublingual tablet or film formulation.
Naltrexone
Background. Naltrexone is available as an oral tablet and an extended-release, once-monthly intramuscular injection; the latter has demonstrated superiority in MAR.28 Oral naltrexone has limited supporting evidence, is inferior to other MOUD options, and should not be used to treat OUD.7 Altogether, approval of naltrexone for OUD is controversial, due to potentially unethical trials and approval processes,29 although a multicenter randomized controlled trial demonstrated the drug’s noninferiority with respect to treatment retention relative to buprenorphine.30 Used over time, naltrexone does not relieve withdrawal symptoms but can reduce cravings.
Clinical considerations. There are numerous clinical barriers that limit the use of naltrexone.
First, patients should be abstinent from opioids for 7 to 14 days prior to starting therapy; usually, this means undergoing medically supervised withdrawal in a controlled environment. This is an obvious limitation for patients who are constrained financially—those who lack, or have inadequate, health insurance or are unable to be away from their job for an extended time.
Continue to: Second, because naltrexone...
Second, because naltrexone does not address withdrawal symptoms, supportive therapies should be incorporated into the treatment plan, including:
- clonidine for hyperadrenergic symptoms (anxiety, diaphoresis, hypertension)
- nonopioid analgesics for pain
- antiemetics, such as ondansetron and metoclopramide, for nausea or vomiting
- loperamide for diarrhea
- diphenhydramine for insomnia.
Third, patients taking naltrexone have a diminished response to opioids. This complicates pain management in the event of an emergent surgical procedure.
Last, when naltrexone wears off, patients are effectively opioid-naïve, which increases the risk for overdose in those who stop therapy abruptly.29 The increased risk for overdose should be communicated to all patients with OUD who are being treated with naltrexone.
This nonopioid option is appealing to policymakers and is often prioritized in the criminal justice system; however, the decreased efficacy of naltrexone (compared to methadone and buprenorphine), potential for overdose, and challenges in initiating treatment are concerning and limit the drug’s use in many real-world settings.
Because naltrexone is not a controlled substance, regulations regarding maintaining inventory and distribution are more flexible.
Continue to: Overall, the cost-effectiveness...
Overall, the cost-effectiveness of intramuscular naltrexone is unclear. State-administered insurance programs vary in their requirements for coverage of naltrexone treatment.31
Comprehensive medication reconciliation is vital
Overall fragmentation of care within OTPs places patients at risk for adverse events, such as drug interactions.32 Under Title 42 of the US Code,33 patients must provide written consent for an OTP provider to disclose their history of a substance use disorder. Allowing the patient to decide which medical providers can access their treatment records for an OUD benefits patient confidentiality but poses numerous issues worth exploring.
All prescribed controlled substances are recorded in the prescription drug monitoring program, or PDMP, a state-level electronic database accessible to health care professionals to inform prescribing decisions and identify drug interactions. The PDMP has substantially reduced opioid overprescribing and improved identification of patients at risk for overdose or misuse of opioids.
Unlike all other controlled substances, however, prescriptions ordered by an OTP are not recorded in the PDMP (although there are recent exceptions to this scenario). Without such information, a physician might not have important information about the patient when making medical decisions—placing the patient at risk for harmful outcomes, such as drug–drug and drug–disease interactions.
For example: Methadone is associated with a prolonged QT interval,34 increasing the risk for a fatal arrhythmia. Concurrent QT-prolonging medications, such as azithromycin and citalopram, further increase this risk.35 Because methadone dispensing is isolated from the patient’s medical record, the clinician who prescribes MOUD has an incomplete patient history and could make a potentially fatal treatment decision.
Continue to: Diversion is unlikely
Diversion is unlikely
Health care providers often express concern about diversion in MOUD. However, misuse and diversion rates of methadone and buprenorphine have declined steadily since 2011, and, in fact, are actually lower than the diversion rate of prescription antibiotics.36
Regardless, diversion of buprenorphine should not be a concern for physicians prescribing MOUD. Although a prescriber might worry about manipulation of the formulation of buprenorphine for intravenous administration, addition of naloxone to buprenorphine in tablet form diminishes the potential for overdose. Additionally, the ceiling effect of buprenorphine limits the likelihood of significant respiratory depression and euphoria.
Should buprenorphine reach a patient for whom it was not prescribed, it is highly unlikely that an overdose would result. Rather, the medication would protect against the effects of illicit opioids and relieve withdrawal symptoms. Most people with OUD who have misused buprenorphine have done so to relieve withdrawal symptoms,37 not to experience intoxication.
Health care deserts
So-called health care deserts in parts of the United States are an ongoing problem that disproportionately affects lower-income and segregated Black and Hispanic communities38—communities that shoulder the highest burden of OUD and OUD-related mortality39 and whose populace is in greatest need of MAR. Even when health care is accessible in such a desert, some clinicians and pharmacies refuse to prescribe or dispense MOUD because of the accompanying stigma of OUD.
A MAR desert, like a pharmacy desert, is a geographic region—one without access to a MAR or an OTP provider, thereby preventing patients from reaching appropriate care; for some patients, having to travel to the nearest provider can render treatment inaccessible.40
Continue to: Efforts are in place to identify...
Efforts are in place to identify areas at greatest need of OUD-related medical services, such as heat maps that identify areas of increased utilization of emergency medical services for opioid overdose. State-run programs have been implemented to increase access, such as the Illinois Helpline (https://helplineil.org) that provides support and resources for patients, friends, family, and providers.
Novel solutions
Key strategies to increase access to care and slow the opioid epidemic include low-threshold prescribing of MOUD and mobile OTPs.41
Low-threshold MOUD prescribing models. Adoption of one of these models in a medical practice that provides MAR might increase absolute enrollment. A low-threshold prescribing model involves42:
- same-day treatment
- leniency with respect to abstinence periods and a concomitant substance use disorder
- enhanced accessibility to MOUD through nontraditional medical settings.
Low-threshold prescribing is flexible in regard to patients’ needs and bypasses many of the barriers discussed in this article. Impressive multicenter success has been achieved by the CA Bridge program in California (https://cabridge.org), including an increase in recognition of OUD, treatment initiations, and outpatient engagement.25
The cost-effectiveness of low-threshold MOUD prescribing programs remains to be determined.
Mobile OTPs. In July 2021, the DEA authorized a mobile component to existing OTP registrants that is permitted to dispense methadone and buprenorphine. Mobile units are physically separate from the OTP but have similar functions, depending on available space. Services that cannot be provided on the mobile unit of an OTP must be available at its brick-and-mortar location.7 Logistically, OTP registrants no longer need a separate registration to implement a mobile unit, thus expanding care to patients in underserved or remote areas who often encounter barriers to access.43
Conclusion
Understanding the distinct clinical and accessibility benefits and limitations among available MOUD is essential for prescribing clinicians. Accessing treatment is limited by federal regulation, stigma, and the existence of health care deserts that limit access to necessary care for patients with OUD. Newer harm-reduction models, such as low-threshold prescribing and mobile OTPs, represent progress, but many patients remain untreated.
a At buprenorphine.samhsa.gov/forms/select-practitioner-type.php
b Sold under the brand name Sublocade.
CORRESPONDENCE
Jennie B. Jarrett, PharmD, MMedEd, Department of Pharmacy Practice, University of Illinois Chicago College of Pharmacy, 833 South Wood Street (MC 886), Chicago, IL 60612; [email protected]
1. Baser O, Chalk M, Fiellin DA, et al. Cost and utilization outcomes of opioid-dependence treatments. Am J Manag Care. 2011;17(suppl 8):S235-S248.
2. Gibson A, Degenhardt L, Mattick RP, et al. Exposure to opioid maintenance treatment reduces long-term mortality. Addiction. 2008;103:462-468. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2007.02090.x
3. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States: Results From the 2020 National Survey on Drug Use and Health. HHS Publication PEP21-07-01-003, NSDUH Series H-56. 2021. Accessed March 19, 2023. www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt35325/NSDUHFFRPDFWHTMLFiles2020/2020NSDUHFFR1PDFW102121.pdf
4. Haffajee RL, Andraka-Christou B, Attermann J, et al. A mixed-method comparison of physician-reported beliefs about and barriers to treatment with medications for opioid use disorder. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2020;15:69. doi: 10.1186/s13011-020-00312-3
5. Kosten TR, George TP. The neurobiology of opioid dependence: implications for treatment. Sci Pract Perspect. 2002;1:13-20. doi: 10.1151/spp021113
6. Koob GF. Neurobiology of opioid addiction: opponent process, hyperkatifeia, and negative reinforcement. Biol Psychiatry. 2020;87:44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.05.023
7. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Medications for Opioid Use Disorder. For Health care and Addiction Professionals, Policymakers, Patients, and Families. Treatment Improvement Protocol TIP 63. Publication No. PEP21-02-01-002. 2021. Accessed March 19, 2023. https://store.samhsa.gov/sites/default/files/pep21-02-01-002.pdf
8. Sordo L, Barrio G, Bravo MJ, et al. Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2017;357:j1550. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1550
9. Korownyk C, Perry D, Ton J, et al. Opioid use disorder in primary care: PEER umbrella systematic review of systematic reviews. Can Fam Physician. 2019;65:e194-e206.
10. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, et al. Methadone maintenance therapy versus no opioid replacement therapy for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;(3):CD002209. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002209.pub2
11. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, et al. Buprenorphine maintenance versus placebo or methadone maintenance for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(2):CD002207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002207.pub4
12. Krupitsky E, Nunes EV, Ling W, et al. Injectable extended-release naltrexone for opioid dependence: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2011;377:1506-1513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60358-9
13. Soyka M, Zingg C, Koller G, et al. Retention rate and substance use in methadone and buprenorphine maintenance therapy and predictors of outcome: results from a randomized study. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008;11:641-653. doi: 10.1017/S146114570700836X
14. Institute of Medicine Committee on Federal Regulation of Methadone Treatment; Rettig R, Yarmolinsky A, eds. Federal Regulation of Methadone Treatment. National Academies Press; 1995.
15. 42 eCFR §8. Medication assisted treatment for opioid use disorders. Revised March 15, 2023. Accessed March 23, 2023. www.ecfr.gov/current/title-42/chapter-I/subchapter-A/part-8?toc=1
16. Faggiano F, Vigna-Taglianti F, Versino E, et al. Methadone maintenance at different dosages for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(3):CD002208. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002208
17. Baxter LE Sr, Campbell A, Deshields M, et al. Safe methadone induction and stabilization: report of an expert panel. J Addict Med. 2013;7:377-386. doi: 10.1097/01.ADM.0000435321.39251.d7
18. Olfson M, Zhang VS, Schoenbaum M, et al. Trends in buprenorphine treatment in the United States, 2009-2018. JAMA. 2020;323:276-277. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.18913
19. Walsh SL, Preston KL, Stitzer ML, et al. Clinical pharmacology of buprenorphine: ceiling effects at high doses. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1994;55:569-580. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1994.71
20. Walley AY, Palmisano J, Sorensen-Alawad A, et al. Engagement and substance dependence in a primary care-based addiction treatment program for people infected with HIV and people at high-risk for HIV infection. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2015;59:59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2015.07.007
21. Lagisetty P, Klasa K, Bush C, et al. Primary care models for treating opioid use disorders: what actually works? A systematic review. PloS One. 2017;12:e0186315. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186315
22. Du CX, Shi J, Tetrault JM, et al. Primary care and medication management characteristics among patients receiving office-based opioid treatment with buprenorphine. Fam Pract. 2022;39:234-240. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmab166
23. Herring AA, Vosooghi AA, Luftig J, et al. High-dose buprenorphine induction in the emergency department for treatment of opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2117128. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.17128
24. Hämmig R, Kemter A, Strasser J, et al. Use of microdoses for induction of buprenorphine treatment with overlapping full opioid agonist use: the Bernese method. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2016;7:99-105. doi: 10.2147/SAR.S109919
25. Snyder H, Kalmin MM, Moulin A, et al. Rapid adoption of low-threshold buprenorphine treatment at California emergency departments participating in the CA Bridge Program. Ann Emerg Med. 2021;78:759-772. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2021.05.024
26. Wong JSH, Nikoo M, Westenberg JN, et al. Comparing rapid micro-induction and standard induction of buprenorphine/naloxone for treatment of opioid use disorder: protocol for an open-label, parallel-group, superiority, randomized controlled trial. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2021;16:11. doi: 10.1186/s13722-021-00220-2
27. Lee JD, Vocci F, Fiellin DA. Unobserved “home” induction onto buprenorphine. J Addict Med. 2014;8:299-308. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000059
28. Krupitsky E, Zvartau E, Blokhina E, et al. Randomized trial of long-acting sustained-release naltrexone implant vs oral naltrexone or placebo for preventing relapse to opioid dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69:973-981. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2012.1a
29. Wolfe D, Carrieri MP, Dasgupta N, et al. Concerns about injectable naltrexone for opioid dependence. Lancet. 2011;377:1468-1470. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62056-9
30. Tanum L, Solli KK, Latif ZEH, et al. Effectiveness of injectable extended-release naltrexone vs daily buprenorphine–naloxone for opioid dependence: a randomized clinical noninferiority trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74:1197-1205. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.3206
31. Murphy SM, Polsky D, Lee JD, et al. Cost-effectiveness of extended release naltrexone to prevent relapse among criminal justice-involved individuals with a history of opioid use disorder. Addiction. 2017;112:1440-1450. doi: 10.1111/add.13807
32. Ferrari A, Coccia CPR, Bertolini A, et al. Methadone—metabolism, pharmacokinetics and interactions. Pharmacol Res. 2004;50:551-559. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2004.05.002
33. 42 eCFR Part 2. Confidentiality of substance use disorder patient records. January 18, 2017. Accessed March 23, 2023. www.ecfr.gov/current/title-42/chapter-I/subchapter-A/part-2
34. Kao DP, Haigney MCP, Mehler PS, et al. Arrhythmia associated with buprenorphine and methadone reported to the Food and Drug Administration. Addiction. 2015;110:1468-1475. doi: 10.1111/add.13013
35. Tisdale JE, Chung MK, Campbell KB, et al; . Drug-induced arrhythmias: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;142:e214-e233. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000905
36. Leshner AI, Mancher M, eds. Barriers to broader use of medications to treat opioid use disorder. In: Medications for Opioid Use Disorder Save Lives. National Academies Press; 2019:109-136.
37. Chilcoat HD, Amick HR, Sherwood MR, et al. Buprenorphine in the United States: Motives for abuse, misuse, and diversion. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2019;104:148-157. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat. 2019.07.005
38. Qato DM, Daviglus ML, Wilder J, et al. “Pharmacy deserts” are prevalent in Chicago’s predominantly minority communities, raising medication access concerns. Health Aff (Millwood). 2014;33:1958-1965. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2013.1397
39. Mason M, Soliman R, Kim HS, et al. Disparities by sex and race and ethnicity in death rates due to opioid overdose among adults 55 years or older, 1999 to 2019. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5:e2142982. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.42982
40. Rosenblum A, Cleland CM, Fong C, et al. Distance traveled and cross-state commuting to opioid treatment programs in the United States. J Environ Public Health. 2011;2011:948789. doi: 10.1155/2011/948789
41. Chan B, Hoffman KA, Bougatsos C, et al. Mobile methadone medication units: a brief history, scoping review and research opportunity. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2021;129:108483. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2021.108483
42. Jakubowski A, Fox A. Defining low-threshold buprenorphine treatment. J Addict Med. 2020;14:95-98. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000555
43. Messmer SE, Elmes AT, Jimenez AD, et al. Outcomes of a mobile medical unit for low-threshold buprenorphine access targeting opioid overdose hot spots in Chicago. J Subst Use Addict Treat. 2023;209054. doi: 10.1016/j.josat.2023.209054
Medication-assisted recovery (MAR)—the preferred terminology for the service formerly known as medication-assisted treatment—entails a comprehensive set of interventions for managing opioid use disorder (OUD), including medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD). Despite the benefits of MAR—reducing opioid use, opioid-related mortality, and health care costs1-3—only 11% of patients with a diagnosis of OUD received MOUD in 2020.3
Primary care physicians, including family physicians, are well positioned to provide MAR across the patient’s lifespan. However, many family medicine clinicians do not possess the logistical knowledge or resources to implement this service.4 In this article, we describe options for, and barriers to, MAR and societal issues that have an impact on the care of these patients.
Pathophysiology of OUD
Opioids relieve pain by stimulating μ-opioid receptors and activating the brain’s reward system. These pleasurable effects motivate repeated use.5 Frequent opioid exposure causes neuroadaptation, tolerance, and dependence. For patients with OUD who are misusing illicit or prescription opioids, periods of abstinence following neuroadaptation lead to withdrawal symptoms that vary in intensity, depending on the drug, dose, and duration of use. Upregulated noradrenergic tone and dopamine deficiency manifest as numerous signs and symptoms of withdrawal, including5:
- Physiologic: secretory (diaphoresis, rhinorrhea, lacrimation, vomiting, diarrhea) and stimulatory (mydriasis, piloerection, hypertension, tachycardia, insomnia)
- Psychological: pain, cravings, dysphoria, anxiety.
A single episode of opioid withdrawal is not directly life-threatening, but untreated episodes can progressively amplify negative feedback and reinforce continued opioid use.6 Left untreated, withdrawal can be terminal.

Medication-assisted recovery: Effective intervention
MAR services that integrate medical, behavioral, and psychosocial programs can reduce mortality from OUD 2-fold.7,8 A meta-analysis found that, when MAR services are rendered in primary care, treatment retention improves by 25% (number needed to treat [NNT] = 6) and ongoing illicit opioid use is reduced by 50% (NNT = 6), relative to care at a specialty clinic9—highlighting a role for family medicine clinicians in treating OUD.
All 3 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved MOUD (methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone) reduce cravings; 2 (methadone and buprenorphine) mitigate withdrawal symptoms by activating the μ-opioid receptor; and naltrexone diminishes the reinforcing effects of use (TABLE10-12). It is crucial to recognize the pharmacologic distinctions among MOUD because untreated withdrawal syndromes increase dropout from treatment programs and subsequent relapse.13

The Hx of medication-assisted recovery
To understand the landscape of MAR, it is important to understand the history of opioid treatment in the United States. In 1966, Congress passed the Narcotic Addiction Rehabilitation Act (NARA), which secured federal assistance by which state and local governments could develop drug treatment programs.14 NARA permitted legal offenders with OUD to be civilly committed to treatment programs, rather than prosecuted. However, limited resources and a burgeoning population led, instead, to low-cost outpatient programs saddled by strict requirements that lacked a basis for improving clinical outcomes.
Continue to: At the time NARA...
At the time NARA was passed by Congress, OUD was viewed—inaccurately—as a criminal problem, not a medical one. Subsequent legislation was crafted through that lens, which has placed a heavy burden on patients until today.14 Although medical understanding of OUD has advanced tremendously over the past 50 years, treatment remains siloed from mainstream medicine, even in primary care.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to MAR, and relapse is common. Patient-specific factors and the availability of resources should be considered when designing the most individualized, advantageous plan for MAR.
Methadone
Background. Methadone has the most extensive history for treating OUD and consistently has demonstrated efficacy.13 A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing methadone to nonpharmacotherapy alone found that methadone improved treatment retention by an absolute 57% (NNT = 2).10
Methadone was approved by the FDA for detoxification and maintenance treatment in the early 1970s, although the Narcotic Addict Treatment Act (NATA) of 1974 restricted dispensing of maintenance treatment to highly regulated clinics known as opioid treatment programs (OTPs).14 NATA required the treating physician to register with the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) and to comply with conservative dosing regimens and observed dosing.
Over time, regulations evolved to give the physician greater flexibility in developing a care plan, allowing “take-home” doses, and improving patients’ access to care. Although access to methadone for the treatment of OUD remains limited to federally certified OTPs, regulations facilitate incorporation of a whole-person approach to care, including counseling, individual and group therapy, and toxicology testing.7
Continue to: Clinical considerations
Clinical considerations. Methadone requires slow titration. For patients starting methadone as an outpatient, federal law15 limits the initial dose to 30 mg and requires physician documentation when the first-day total dosage exceeds 40 mg. This dosing constraint makes it challenging to provide care because a daily dosage ≥ 60 mg has been found to produce, first, higher program retention (relative risk = 1.36; 95% CI, 1.13-1.63) and, second, greater reduction in illicit opioid use (relative risk = 1.59; 95% CI, 1.16-2.18) than is seen in patients who receive a lower daily dosage.16
Due to a prolonged elimination half-life, methadone reaches steady-state in 3 to 5 days. Patients and their families should be educated that withdrawal symptoms might not feel fully managed in the first few days of therapy and that time is required to experience safely the regimen’s full effects.
Aggressive dose-titration during methadone induction can result in drug accumulation and respiratory depression. The risk for methadone-related mortality is highest in the first 2 weeks of therapy, mostly related to overdose potential if the drug is combined with other opioids.17
Buprenorphine
Background. The prescribing rate for buprenorphine, particularly in primary care, is accelerating.18 A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials found that11:
- compared to placebo, buprenorphine, at any dosage, improves treatment retention by an absolute 21% to 28% (NNT = 4-5)
- patients receiving high-dose buprenorphine (≥ 16 mg/d) had fewer evident cases of illicit opioid use.
Unlike methadone, buprenorphine exerts partial agonism at the μ-opioid receptor, resulting in a so-called ceiling effect that significantly reduces the adverse effect profile, including respiratory depression and euphoria, relative to a full-agonist opioid, such as methadone.19
Continue to: Whereas accessing methadone...
Whereas accessing methadone is limited to OTPs, buprenorphine is available for office-based treatment. By hosting OUD treatment and primary care in the same place, primary care physicians can provide comprehensive medical care including and beyond OUD, thereby improving retention and managing comorbidity.20
Integrated models involving support staff—eg, nurses, behavioral health providers, and pharmacists—have produced the greatest success with office-based treatment models.21 Office-based treatment normalizes OUD as a chronic disease managed by the primary care physician, enabling concurrent harm-reduction strategies; medication reconciliation; and convenient, regular prescribing intervals (eg, every 30 days).22 Nevertheless, access to buprenorphine is limited. Because buprenorphine is a controlled substance, the Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act of 2008 prevents initial prescribing of buprenorphine without in-person evaluation. Telehealth consultations increased access to buprenorphine through temporary exceptions during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, revised rules and regulations for telehealth visits for these controlled substances are forthcoming from the DEA as temporary exceptions for telehealth consultations come to an end. Additionally, prescribing buprenorphine for OUD requires that the treating physician undergo specific training and obtain qualifications, which have evolved over time through federal legislation.
The Drug Addiction Treatment Act of 2000 (DATA 2000) authorized what is known as an X-waiver, which allows physicians to prescribe controlled substances for office-based treatment of OUD, provided that:
- they are registered to do so with the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration and the DEA
- they have had subspecialty training in addiction or completed an 8-hour training course
- they are able to refer patients to appropriate counseling and ancillary services.
DATA 2000 restricted patient panel sizes to 30 patients in the first year, expanding thereafter upon appropriate certification.
The Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016 (CARA) and the Substance Use Disorder Prevention that Promotes Opioid Recovery and Treatment for Patients and Communities Act of 2018 (the SUPPORT Act) collectively extended prescribing authority for MOUD to other qualifying practitioners (eg, advanced practice clinicians). Despite these attempts to expand access to services, the overdose death rate has continued to increase.
Continue to: To further expand access to MAR...
To further expand access to MAR, the US Department of Health and Human Services updated its practice guidelines in April 2021, allowing clinicians to bypass X-waiver training requirements by applying for a notification-of-intent (NOI) buprenorphine waiver.a However, clinicians are still limited to prescribing buprenorphine for 30 patients at a time. Clinicians who undergo complete X-waiver training may prescribe for 100 patients in the first year and, if eligible, 275 patients thereafter.
In addition, as a component of the Consolidation Appropriations Act of 2023, Congress passed the Mainstreaming Addiction Treatment Act of 2021, or MAT 2021, and Medication Access and Training Expansion Act of 2021, or MATE 2021. MAT eliminated the X-waiver, NOI, and restrictions on the number of patients for whom a provider could prescribe buprenorphine, under federal authority; however, restrictions within one’s state might limit the ability to prescribe buprenorphine. MATE 2021 is an educational requirement for licensing by the DEA (at application and renewal) that will require prescribers to complete 8 hours of training in substance use disorders starting in June 2023.
Use of the monthly injectable extended-release buprenorphine productb is limited by an FDA Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program, which requires specialized training and certification by the prescriber, distributor, and administering clinician. REMS reduces buprenorphine accessibility due to time, cost, and regulatory barriers; although such restrictions have been instituted with the patient’s safety in mind, any limitation to buprenorphine prescribing, apart from controlled substance licensure, serves only to limit access to a primary component of MAR.
Clinical considerations. Due to the competitive nature of buprenorphine and its high affinity for the μ-opioid receptor, the drug can displace other opioid agonists and precipitate acute withdrawal. The withdrawal experience can thereby condition fear and disfavor toward buprenorphine among patients.
It is vital, therefore, that (1) patients’ expectations for treatment be managed appropriately and (2) the treating physician be prepared to provide additional buprenorphine for adequate maintenance doses and utilize adjunct comfort agents (clonidine, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, ondansetron) to manage acute withdrawal symptoms. Newer buprenorphine dosing strategies, such as micro-induction and macro-induction, have emerged to curtail these risks.23,24 This is an evolving area of MAR; newer low-threshold initiation strategies25 (see “Low-threshold MOUD prescribing models,” in the text that follows) and evidence that supports micro-induction26 might eliminate the practice of requiring active withdrawal for treatment.
Continue to: Regardless of the strategy...
Regardless of the strategy for dosing buprenorphine, it’s critical that patients be educated on how to initiate treatment outside a clinical setting, such as at home, where they occupy a familiar haven during a potentially uncomfortable time and can be as effective at initiation as they would be in a clinical setting, with no difference in precipitation of adverse effects.
At-home induction might be more appropriate for patients who are not yet in significant enough withdrawal while in the physician's office.27 Guidance should be provided on dosing instructions, self-assessment of withdrawal symptoms, and, if applicable, patience with the slow-dissolving sublingual tablet or film formulation.
Naltrexone
Background. Naltrexone is available as an oral tablet and an extended-release, once-monthly intramuscular injection; the latter has demonstrated superiority in MAR.28 Oral naltrexone has limited supporting evidence, is inferior to other MOUD options, and should not be used to treat OUD.7 Altogether, approval of naltrexone for OUD is controversial, due to potentially unethical trials and approval processes,29 although a multicenter randomized controlled trial demonstrated the drug’s noninferiority with respect to treatment retention relative to buprenorphine.30 Used over time, naltrexone does not relieve withdrawal symptoms but can reduce cravings.
Clinical considerations. There are numerous clinical barriers that limit the use of naltrexone.
First, patients should be abstinent from opioids for 7 to 14 days prior to starting therapy; usually, this means undergoing medically supervised withdrawal in a controlled environment. This is an obvious limitation for patients who are constrained financially—those who lack, or have inadequate, health insurance or are unable to be away from their job for an extended time.
Continue to: Second, because naltrexone...
Second, because naltrexone does not address withdrawal symptoms, supportive therapies should be incorporated into the treatment plan, including:
- clonidine for hyperadrenergic symptoms (anxiety, diaphoresis, hypertension)
- nonopioid analgesics for pain
- antiemetics, such as ondansetron and metoclopramide, for nausea or vomiting
- loperamide for diarrhea
- diphenhydramine for insomnia.
Third, patients taking naltrexone have a diminished response to opioids. This complicates pain management in the event of an emergent surgical procedure.
Last, when naltrexone wears off, patients are effectively opioid-naïve, which increases the risk for overdose in those who stop therapy abruptly.29 The increased risk for overdose should be communicated to all patients with OUD who are being treated with naltrexone.
This nonopioid option is appealing to policymakers and is often prioritized in the criminal justice system; however, the decreased efficacy of naltrexone (compared to methadone and buprenorphine), potential for overdose, and challenges in initiating treatment are concerning and limit the drug’s use in many real-world settings.
Because naltrexone is not a controlled substance, regulations regarding maintaining inventory and distribution are more flexible.
Continue to: Overall, the cost-effectiveness...
Overall, the cost-effectiveness of intramuscular naltrexone is unclear. State-administered insurance programs vary in their requirements for coverage of naltrexone treatment.31
Comprehensive medication reconciliation is vital
Overall fragmentation of care within OTPs places patients at risk for adverse events, such as drug interactions.32 Under Title 42 of the US Code,33 patients must provide written consent for an OTP provider to disclose their history of a substance use disorder. Allowing the patient to decide which medical providers can access their treatment records for an OUD benefits patient confidentiality but poses numerous issues worth exploring.
All prescribed controlled substances are recorded in the prescription drug monitoring program, or PDMP, a state-level electronic database accessible to health care professionals to inform prescribing decisions and identify drug interactions. The PDMP has substantially reduced opioid overprescribing and improved identification of patients at risk for overdose or misuse of opioids.
Unlike all other controlled substances, however, prescriptions ordered by an OTP are not recorded in the PDMP (although there are recent exceptions to this scenario). Without such information, a physician might not have important information about the patient when making medical decisions—placing the patient at risk for harmful outcomes, such as drug–drug and drug–disease interactions.
For example: Methadone is associated with a prolonged QT interval,34 increasing the risk for a fatal arrhythmia. Concurrent QT-prolonging medications, such as azithromycin and citalopram, further increase this risk.35 Because methadone dispensing is isolated from the patient’s medical record, the clinician who prescribes MOUD has an incomplete patient history and could make a potentially fatal treatment decision.
Continue to: Diversion is unlikely
Diversion is unlikely
Health care providers often express concern about diversion in MOUD. However, misuse and diversion rates of methadone and buprenorphine have declined steadily since 2011, and, in fact, are actually lower than the diversion rate of prescription antibiotics.36
Regardless, diversion of buprenorphine should not be a concern for physicians prescribing MOUD. Although a prescriber might worry about manipulation of the formulation of buprenorphine for intravenous administration, addition of naloxone to buprenorphine in tablet form diminishes the potential for overdose. Additionally, the ceiling effect of buprenorphine limits the likelihood of significant respiratory depression and euphoria.
Should buprenorphine reach a patient for whom it was not prescribed, it is highly unlikely that an overdose would result. Rather, the medication would protect against the effects of illicit opioids and relieve withdrawal symptoms. Most people with OUD who have misused buprenorphine have done so to relieve withdrawal symptoms,37 not to experience intoxication.
Health care deserts
So-called health care deserts in parts of the United States are an ongoing problem that disproportionately affects lower-income and segregated Black and Hispanic communities38—communities that shoulder the highest burden of OUD and OUD-related mortality39 and whose populace is in greatest need of MAR. Even when health care is accessible in such a desert, some clinicians and pharmacies refuse to prescribe or dispense MOUD because of the accompanying stigma of OUD.
A MAR desert, like a pharmacy desert, is a geographic region—one without access to a MAR or an OTP provider, thereby preventing patients from reaching appropriate care; for some patients, having to travel to the nearest provider can render treatment inaccessible.40
Continue to: Efforts are in place to identify...
Efforts are in place to identify areas at greatest need of OUD-related medical services, such as heat maps that identify areas of increased utilization of emergency medical services for opioid overdose. State-run programs have been implemented to increase access, such as the Illinois Helpline (https://helplineil.org) that provides support and resources for patients, friends, family, and providers.
Novel solutions
Key strategies to increase access to care and slow the opioid epidemic include low-threshold prescribing of MOUD and mobile OTPs.41
Low-threshold MOUD prescribing models. Adoption of one of these models in a medical practice that provides MAR might increase absolute enrollment. A low-threshold prescribing model involves42:
- same-day treatment
- leniency with respect to abstinence periods and a concomitant substance use disorder
- enhanced accessibility to MOUD through nontraditional medical settings.
Low-threshold prescribing is flexible in regard to patients’ needs and bypasses many of the barriers discussed in this article. Impressive multicenter success has been achieved by the CA Bridge program in California (https://cabridge.org), including an increase in recognition of OUD, treatment initiations, and outpatient engagement.25
The cost-effectiveness of low-threshold MOUD prescribing programs remains to be determined.
Mobile OTPs. In July 2021, the DEA authorized a mobile component to existing OTP registrants that is permitted to dispense methadone and buprenorphine. Mobile units are physically separate from the OTP but have similar functions, depending on available space. Services that cannot be provided on the mobile unit of an OTP must be available at its brick-and-mortar location.7 Logistically, OTP registrants no longer need a separate registration to implement a mobile unit, thus expanding care to patients in underserved or remote areas who often encounter barriers to access.43
Conclusion
Understanding the distinct clinical and accessibility benefits and limitations among available MOUD is essential for prescribing clinicians. Accessing treatment is limited by federal regulation, stigma, and the existence of health care deserts that limit access to necessary care for patients with OUD. Newer harm-reduction models, such as low-threshold prescribing and mobile OTPs, represent progress, but many patients remain untreated.
a At buprenorphine.samhsa.gov/forms/select-practitioner-type.php
b Sold under the brand name Sublocade.
CORRESPONDENCE
Jennie B. Jarrett, PharmD, MMedEd, Department of Pharmacy Practice, University of Illinois Chicago College of Pharmacy, 833 South Wood Street (MC 886), Chicago, IL 60612; [email protected]
Medication-assisted recovery (MAR)—the preferred terminology for the service formerly known as medication-assisted treatment—entails a comprehensive set of interventions for managing opioid use disorder (OUD), including medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD). Despite the benefits of MAR—reducing opioid use, opioid-related mortality, and health care costs1-3—only 11% of patients with a diagnosis of OUD received MOUD in 2020.3
Primary care physicians, including family physicians, are well positioned to provide MAR across the patient’s lifespan. However, many family medicine clinicians do not possess the logistical knowledge or resources to implement this service.4 In this article, we describe options for, and barriers to, MAR and societal issues that have an impact on the care of these patients.
Pathophysiology of OUD
Opioids relieve pain by stimulating μ-opioid receptors and activating the brain’s reward system. These pleasurable effects motivate repeated use.5 Frequent opioid exposure causes neuroadaptation, tolerance, and dependence. For patients with OUD who are misusing illicit or prescription opioids, periods of abstinence following neuroadaptation lead to withdrawal symptoms that vary in intensity, depending on the drug, dose, and duration of use. Upregulated noradrenergic tone and dopamine deficiency manifest as numerous signs and symptoms of withdrawal, including5:
- Physiologic: secretory (diaphoresis, rhinorrhea, lacrimation, vomiting, diarrhea) and stimulatory (mydriasis, piloerection, hypertension, tachycardia, insomnia)
- Psychological: pain, cravings, dysphoria, anxiety.
A single episode of opioid withdrawal is not directly life-threatening, but untreated episodes can progressively amplify negative feedback and reinforce continued opioid use.6 Left untreated, withdrawal can be terminal.

Medication-assisted recovery: Effective intervention
MAR services that integrate medical, behavioral, and psychosocial programs can reduce mortality from OUD 2-fold.7,8 A meta-analysis found that, when MAR services are rendered in primary care, treatment retention improves by 25% (number needed to treat [NNT] = 6) and ongoing illicit opioid use is reduced by 50% (NNT = 6), relative to care at a specialty clinic9—highlighting a role for family medicine clinicians in treating OUD.
All 3 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved MOUD (methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone) reduce cravings; 2 (methadone and buprenorphine) mitigate withdrawal symptoms by activating the μ-opioid receptor; and naltrexone diminishes the reinforcing effects of use (TABLE10-12). It is crucial to recognize the pharmacologic distinctions among MOUD because untreated withdrawal syndromes increase dropout from treatment programs and subsequent relapse.13

The Hx of medication-assisted recovery
To understand the landscape of MAR, it is important to understand the history of opioid treatment in the United States. In 1966, Congress passed the Narcotic Addiction Rehabilitation Act (NARA), which secured federal assistance by which state and local governments could develop drug treatment programs.14 NARA permitted legal offenders with OUD to be civilly committed to treatment programs, rather than prosecuted. However, limited resources and a burgeoning population led, instead, to low-cost outpatient programs saddled by strict requirements that lacked a basis for improving clinical outcomes.
Continue to: At the time NARA...
At the time NARA was passed by Congress, OUD was viewed—inaccurately—as a criminal problem, not a medical one. Subsequent legislation was crafted through that lens, which has placed a heavy burden on patients until today.14 Although medical understanding of OUD has advanced tremendously over the past 50 years, treatment remains siloed from mainstream medicine, even in primary care.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to MAR, and relapse is common. Patient-specific factors and the availability of resources should be considered when designing the most individualized, advantageous plan for MAR.
Methadone
Background. Methadone has the most extensive history for treating OUD and consistently has demonstrated efficacy.13 A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing methadone to nonpharmacotherapy alone found that methadone improved treatment retention by an absolute 57% (NNT = 2).10
Methadone was approved by the FDA for detoxification and maintenance treatment in the early 1970s, although the Narcotic Addict Treatment Act (NATA) of 1974 restricted dispensing of maintenance treatment to highly regulated clinics known as opioid treatment programs (OTPs).14 NATA required the treating physician to register with the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) and to comply with conservative dosing regimens and observed dosing.
Over time, regulations evolved to give the physician greater flexibility in developing a care plan, allowing “take-home” doses, and improving patients’ access to care. Although access to methadone for the treatment of OUD remains limited to federally certified OTPs, regulations facilitate incorporation of a whole-person approach to care, including counseling, individual and group therapy, and toxicology testing.7
Continue to: Clinical considerations
Clinical considerations. Methadone requires slow titration. For patients starting methadone as an outpatient, federal law15 limits the initial dose to 30 mg and requires physician documentation when the first-day total dosage exceeds 40 mg. This dosing constraint makes it challenging to provide care because a daily dosage ≥ 60 mg has been found to produce, first, higher program retention (relative risk = 1.36; 95% CI, 1.13-1.63) and, second, greater reduction in illicit opioid use (relative risk = 1.59; 95% CI, 1.16-2.18) than is seen in patients who receive a lower daily dosage.16
Due to a prolonged elimination half-life, methadone reaches steady-state in 3 to 5 days. Patients and their families should be educated that withdrawal symptoms might not feel fully managed in the first few days of therapy and that time is required to experience safely the regimen’s full effects.
Aggressive dose-titration during methadone induction can result in drug accumulation and respiratory depression. The risk for methadone-related mortality is highest in the first 2 weeks of therapy, mostly related to overdose potential if the drug is combined with other opioids.17
Buprenorphine
Background. The prescribing rate for buprenorphine, particularly in primary care, is accelerating.18 A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials found that11:
- compared to placebo, buprenorphine, at any dosage, improves treatment retention by an absolute 21% to 28% (NNT = 4-5)
- patients receiving high-dose buprenorphine (≥ 16 mg/d) had fewer evident cases of illicit opioid use.
Unlike methadone, buprenorphine exerts partial agonism at the μ-opioid receptor, resulting in a so-called ceiling effect that significantly reduces the adverse effect profile, including respiratory depression and euphoria, relative to a full-agonist opioid, such as methadone.19
Continue to: Whereas accessing methadone...
Whereas accessing methadone is limited to OTPs, buprenorphine is available for office-based treatment. By hosting OUD treatment and primary care in the same place, primary care physicians can provide comprehensive medical care including and beyond OUD, thereby improving retention and managing comorbidity.20
Integrated models involving support staff—eg, nurses, behavioral health providers, and pharmacists—have produced the greatest success with office-based treatment models.21 Office-based treatment normalizes OUD as a chronic disease managed by the primary care physician, enabling concurrent harm-reduction strategies; medication reconciliation; and convenient, regular prescribing intervals (eg, every 30 days).22 Nevertheless, access to buprenorphine is limited. Because buprenorphine is a controlled substance, the Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act of 2008 prevents initial prescribing of buprenorphine without in-person evaluation. Telehealth consultations increased access to buprenorphine through temporary exceptions during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, revised rules and regulations for telehealth visits for these controlled substances are forthcoming from the DEA as temporary exceptions for telehealth consultations come to an end. Additionally, prescribing buprenorphine for OUD requires that the treating physician undergo specific training and obtain qualifications, which have evolved over time through federal legislation.
The Drug Addiction Treatment Act of 2000 (DATA 2000) authorized what is known as an X-waiver, which allows physicians to prescribe controlled substances for office-based treatment of OUD, provided that:
- they are registered to do so with the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration and the DEA
- they have had subspecialty training in addiction or completed an 8-hour training course
- they are able to refer patients to appropriate counseling and ancillary services.
DATA 2000 restricted patient panel sizes to 30 patients in the first year, expanding thereafter upon appropriate certification.
The Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016 (CARA) and the Substance Use Disorder Prevention that Promotes Opioid Recovery and Treatment for Patients and Communities Act of 2018 (the SUPPORT Act) collectively extended prescribing authority for MOUD to other qualifying practitioners (eg, advanced practice clinicians). Despite these attempts to expand access to services, the overdose death rate has continued to increase.
Continue to: To further expand access to MAR...
To further expand access to MAR, the US Department of Health and Human Services updated its practice guidelines in April 2021, allowing clinicians to bypass X-waiver training requirements by applying for a notification-of-intent (NOI) buprenorphine waiver.a However, clinicians are still limited to prescribing buprenorphine for 30 patients at a time. Clinicians who undergo complete X-waiver training may prescribe for 100 patients in the first year and, if eligible, 275 patients thereafter.
In addition, as a component of the Consolidation Appropriations Act of 2023, Congress passed the Mainstreaming Addiction Treatment Act of 2021, or MAT 2021, and Medication Access and Training Expansion Act of 2021, or MATE 2021. MAT eliminated the X-waiver, NOI, and restrictions on the number of patients for whom a provider could prescribe buprenorphine, under federal authority; however, restrictions within one’s state might limit the ability to prescribe buprenorphine. MATE 2021 is an educational requirement for licensing by the DEA (at application and renewal) that will require prescribers to complete 8 hours of training in substance use disorders starting in June 2023.
Use of the monthly injectable extended-release buprenorphine productb is limited by an FDA Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program, which requires specialized training and certification by the prescriber, distributor, and administering clinician. REMS reduces buprenorphine accessibility due to time, cost, and regulatory barriers; although such restrictions have been instituted with the patient’s safety in mind, any limitation to buprenorphine prescribing, apart from controlled substance licensure, serves only to limit access to a primary component of MAR.
Clinical considerations. Due to the competitive nature of buprenorphine and its high affinity for the μ-opioid receptor, the drug can displace other opioid agonists and precipitate acute withdrawal. The withdrawal experience can thereby condition fear and disfavor toward buprenorphine among patients.
It is vital, therefore, that (1) patients’ expectations for treatment be managed appropriately and (2) the treating physician be prepared to provide additional buprenorphine for adequate maintenance doses and utilize adjunct comfort agents (clonidine, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, ondansetron) to manage acute withdrawal symptoms. Newer buprenorphine dosing strategies, such as micro-induction and macro-induction, have emerged to curtail these risks.23,24 This is an evolving area of MAR; newer low-threshold initiation strategies25 (see “Low-threshold MOUD prescribing models,” in the text that follows) and evidence that supports micro-induction26 might eliminate the practice of requiring active withdrawal for treatment.
Continue to: Regardless of the strategy...
Regardless of the strategy for dosing buprenorphine, it’s critical that patients be educated on how to initiate treatment outside a clinical setting, such as at home, where they occupy a familiar haven during a potentially uncomfortable time and can be as effective at initiation as they would be in a clinical setting, with no difference in precipitation of adverse effects.
At-home induction might be more appropriate for patients who are not yet in significant enough withdrawal while in the physician's office.27 Guidance should be provided on dosing instructions, self-assessment of withdrawal symptoms, and, if applicable, patience with the slow-dissolving sublingual tablet or film formulation.
Naltrexone
Background. Naltrexone is available as an oral tablet and an extended-release, once-monthly intramuscular injection; the latter has demonstrated superiority in MAR.28 Oral naltrexone has limited supporting evidence, is inferior to other MOUD options, and should not be used to treat OUD.7 Altogether, approval of naltrexone for OUD is controversial, due to potentially unethical trials and approval processes,29 although a multicenter randomized controlled trial demonstrated the drug’s noninferiority with respect to treatment retention relative to buprenorphine.30 Used over time, naltrexone does not relieve withdrawal symptoms but can reduce cravings.
Clinical considerations. There are numerous clinical barriers that limit the use of naltrexone.
First, patients should be abstinent from opioids for 7 to 14 days prior to starting therapy; usually, this means undergoing medically supervised withdrawal in a controlled environment. This is an obvious limitation for patients who are constrained financially—those who lack, or have inadequate, health insurance or are unable to be away from their job for an extended time.
Continue to: Second, because naltrexone...
Second, because naltrexone does not address withdrawal symptoms, supportive therapies should be incorporated into the treatment plan, including:
- clonidine for hyperadrenergic symptoms (anxiety, diaphoresis, hypertension)
- nonopioid analgesics for pain
- antiemetics, such as ondansetron and metoclopramide, for nausea or vomiting
- loperamide for diarrhea
- diphenhydramine for insomnia.
Third, patients taking naltrexone have a diminished response to opioids. This complicates pain management in the event of an emergent surgical procedure.
Last, when naltrexone wears off, patients are effectively opioid-naïve, which increases the risk for overdose in those who stop therapy abruptly.29 The increased risk for overdose should be communicated to all patients with OUD who are being treated with naltrexone.
This nonopioid option is appealing to policymakers and is often prioritized in the criminal justice system; however, the decreased efficacy of naltrexone (compared to methadone and buprenorphine), potential for overdose, and challenges in initiating treatment are concerning and limit the drug’s use in many real-world settings.
Because naltrexone is not a controlled substance, regulations regarding maintaining inventory and distribution are more flexible.
Continue to: Overall, the cost-effectiveness...
Overall, the cost-effectiveness of intramuscular naltrexone is unclear. State-administered insurance programs vary in their requirements for coverage of naltrexone treatment.31
Comprehensive medication reconciliation is vital
Overall fragmentation of care within OTPs places patients at risk for adverse events, such as drug interactions.32 Under Title 42 of the US Code,33 patients must provide written consent for an OTP provider to disclose their history of a substance use disorder. Allowing the patient to decide which medical providers can access their treatment records for an OUD benefits patient confidentiality but poses numerous issues worth exploring.
All prescribed controlled substances are recorded in the prescription drug monitoring program, or PDMP, a state-level electronic database accessible to health care professionals to inform prescribing decisions and identify drug interactions. The PDMP has substantially reduced opioid overprescribing and improved identification of patients at risk for overdose or misuse of opioids.
Unlike all other controlled substances, however, prescriptions ordered by an OTP are not recorded in the PDMP (although there are recent exceptions to this scenario). Without such information, a physician might not have important information about the patient when making medical decisions—placing the patient at risk for harmful outcomes, such as drug–drug and drug–disease interactions.
For example: Methadone is associated with a prolonged QT interval,34 increasing the risk for a fatal arrhythmia. Concurrent QT-prolonging medications, such as azithromycin and citalopram, further increase this risk.35 Because methadone dispensing is isolated from the patient’s medical record, the clinician who prescribes MOUD has an incomplete patient history and could make a potentially fatal treatment decision.
Continue to: Diversion is unlikely
Diversion is unlikely
Health care providers often express concern about diversion in MOUD. However, misuse and diversion rates of methadone and buprenorphine have declined steadily since 2011, and, in fact, are actually lower than the diversion rate of prescription antibiotics.36
Regardless, diversion of buprenorphine should not be a concern for physicians prescribing MOUD. Although a prescriber might worry about manipulation of the formulation of buprenorphine for intravenous administration, addition of naloxone to buprenorphine in tablet form diminishes the potential for overdose. Additionally, the ceiling effect of buprenorphine limits the likelihood of significant respiratory depression and euphoria.
Should buprenorphine reach a patient for whom it was not prescribed, it is highly unlikely that an overdose would result. Rather, the medication would protect against the effects of illicit opioids and relieve withdrawal symptoms. Most people with OUD who have misused buprenorphine have done so to relieve withdrawal symptoms,37 not to experience intoxication.
Health care deserts
So-called health care deserts in parts of the United States are an ongoing problem that disproportionately affects lower-income and segregated Black and Hispanic communities38—communities that shoulder the highest burden of OUD and OUD-related mortality39 and whose populace is in greatest need of MAR. Even when health care is accessible in such a desert, some clinicians and pharmacies refuse to prescribe or dispense MOUD because of the accompanying stigma of OUD.
A MAR desert, like a pharmacy desert, is a geographic region—one without access to a MAR or an OTP provider, thereby preventing patients from reaching appropriate care; for some patients, having to travel to the nearest provider can render treatment inaccessible.40
Continue to: Efforts are in place to identify...
Efforts are in place to identify areas at greatest need of OUD-related medical services, such as heat maps that identify areas of increased utilization of emergency medical services for opioid overdose. State-run programs have been implemented to increase access, such as the Illinois Helpline (https://helplineil.org) that provides support and resources for patients, friends, family, and providers.
Novel solutions
Key strategies to increase access to care and slow the opioid epidemic include low-threshold prescribing of MOUD and mobile OTPs.41
Low-threshold MOUD prescribing models. Adoption of one of these models in a medical practice that provides MAR might increase absolute enrollment. A low-threshold prescribing model involves42:
- same-day treatment
- leniency with respect to abstinence periods and a concomitant substance use disorder
- enhanced accessibility to MOUD through nontraditional medical settings.
Low-threshold prescribing is flexible in regard to patients’ needs and bypasses many of the barriers discussed in this article. Impressive multicenter success has been achieved by the CA Bridge program in California (https://cabridge.org), including an increase in recognition of OUD, treatment initiations, and outpatient engagement.25
The cost-effectiveness of low-threshold MOUD prescribing programs remains to be determined.
Mobile OTPs. In July 2021, the DEA authorized a mobile component to existing OTP registrants that is permitted to dispense methadone and buprenorphine. Mobile units are physically separate from the OTP but have similar functions, depending on available space. Services that cannot be provided on the mobile unit of an OTP must be available at its brick-and-mortar location.7 Logistically, OTP registrants no longer need a separate registration to implement a mobile unit, thus expanding care to patients in underserved or remote areas who often encounter barriers to access.43
Conclusion
Understanding the distinct clinical and accessibility benefits and limitations among available MOUD is essential for prescribing clinicians. Accessing treatment is limited by federal regulation, stigma, and the existence of health care deserts that limit access to necessary care for patients with OUD. Newer harm-reduction models, such as low-threshold prescribing and mobile OTPs, represent progress, but many patients remain untreated.
a At buprenorphine.samhsa.gov/forms/select-practitioner-type.php
b Sold under the brand name Sublocade.
CORRESPONDENCE
Jennie B. Jarrett, PharmD, MMedEd, Department of Pharmacy Practice, University of Illinois Chicago College of Pharmacy, 833 South Wood Street (MC 886), Chicago, IL 60612; [email protected]
1. Baser O, Chalk M, Fiellin DA, et al. Cost and utilization outcomes of opioid-dependence treatments. Am J Manag Care. 2011;17(suppl 8):S235-S248.
2. Gibson A, Degenhardt L, Mattick RP, et al. Exposure to opioid maintenance treatment reduces long-term mortality. Addiction. 2008;103:462-468. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2007.02090.x
3. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States: Results From the 2020 National Survey on Drug Use and Health. HHS Publication PEP21-07-01-003, NSDUH Series H-56. 2021. Accessed March 19, 2023. www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt35325/NSDUHFFRPDFWHTMLFiles2020/2020NSDUHFFR1PDFW102121.pdf
4. Haffajee RL, Andraka-Christou B, Attermann J, et al. A mixed-method comparison of physician-reported beliefs about and barriers to treatment with medications for opioid use disorder. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2020;15:69. doi: 10.1186/s13011-020-00312-3
5. Kosten TR, George TP. The neurobiology of opioid dependence: implications for treatment. Sci Pract Perspect. 2002;1:13-20. doi: 10.1151/spp021113
6. Koob GF. Neurobiology of opioid addiction: opponent process, hyperkatifeia, and negative reinforcement. Biol Psychiatry. 2020;87:44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.05.023
7. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Medications for Opioid Use Disorder. For Health care and Addiction Professionals, Policymakers, Patients, and Families. Treatment Improvement Protocol TIP 63. Publication No. PEP21-02-01-002. 2021. Accessed March 19, 2023. https://store.samhsa.gov/sites/default/files/pep21-02-01-002.pdf
8. Sordo L, Barrio G, Bravo MJ, et al. Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2017;357:j1550. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1550
9. Korownyk C, Perry D, Ton J, et al. Opioid use disorder in primary care: PEER umbrella systematic review of systematic reviews. Can Fam Physician. 2019;65:e194-e206.
10. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, et al. Methadone maintenance therapy versus no opioid replacement therapy for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;(3):CD002209. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002209.pub2
11. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, et al. Buprenorphine maintenance versus placebo or methadone maintenance for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(2):CD002207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002207.pub4
12. Krupitsky E, Nunes EV, Ling W, et al. Injectable extended-release naltrexone for opioid dependence: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2011;377:1506-1513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60358-9
13. Soyka M, Zingg C, Koller G, et al. Retention rate and substance use in methadone and buprenorphine maintenance therapy and predictors of outcome: results from a randomized study. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008;11:641-653. doi: 10.1017/S146114570700836X
14. Institute of Medicine Committee on Federal Regulation of Methadone Treatment; Rettig R, Yarmolinsky A, eds. Federal Regulation of Methadone Treatment. National Academies Press; 1995.
15. 42 eCFR §8. Medication assisted treatment for opioid use disorders. Revised March 15, 2023. Accessed March 23, 2023. www.ecfr.gov/current/title-42/chapter-I/subchapter-A/part-8?toc=1
16. Faggiano F, Vigna-Taglianti F, Versino E, et al. Methadone maintenance at different dosages for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(3):CD002208. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002208
17. Baxter LE Sr, Campbell A, Deshields M, et al. Safe methadone induction and stabilization: report of an expert panel. J Addict Med. 2013;7:377-386. doi: 10.1097/01.ADM.0000435321.39251.d7
18. Olfson M, Zhang VS, Schoenbaum M, et al. Trends in buprenorphine treatment in the United States, 2009-2018. JAMA. 2020;323:276-277. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.18913
19. Walsh SL, Preston KL, Stitzer ML, et al. Clinical pharmacology of buprenorphine: ceiling effects at high doses. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1994;55:569-580. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1994.71
20. Walley AY, Palmisano J, Sorensen-Alawad A, et al. Engagement and substance dependence in a primary care-based addiction treatment program for people infected with HIV and people at high-risk for HIV infection. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2015;59:59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2015.07.007
21. Lagisetty P, Klasa K, Bush C, et al. Primary care models for treating opioid use disorders: what actually works? A systematic review. PloS One. 2017;12:e0186315. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186315
22. Du CX, Shi J, Tetrault JM, et al. Primary care and medication management characteristics among patients receiving office-based opioid treatment with buprenorphine. Fam Pract. 2022;39:234-240. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmab166
23. Herring AA, Vosooghi AA, Luftig J, et al. High-dose buprenorphine induction in the emergency department for treatment of opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2117128. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.17128
24. Hämmig R, Kemter A, Strasser J, et al. Use of microdoses for induction of buprenorphine treatment with overlapping full opioid agonist use: the Bernese method. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2016;7:99-105. doi: 10.2147/SAR.S109919
25. Snyder H, Kalmin MM, Moulin A, et al. Rapid adoption of low-threshold buprenorphine treatment at California emergency departments participating in the CA Bridge Program. Ann Emerg Med. 2021;78:759-772. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2021.05.024
26. Wong JSH, Nikoo M, Westenberg JN, et al. Comparing rapid micro-induction and standard induction of buprenorphine/naloxone for treatment of opioid use disorder: protocol for an open-label, parallel-group, superiority, randomized controlled trial. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2021;16:11. doi: 10.1186/s13722-021-00220-2
27. Lee JD, Vocci F, Fiellin DA. Unobserved “home” induction onto buprenorphine. J Addict Med. 2014;8:299-308. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000059
28. Krupitsky E, Zvartau E, Blokhina E, et al. Randomized trial of long-acting sustained-release naltrexone implant vs oral naltrexone or placebo for preventing relapse to opioid dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69:973-981. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2012.1a
29. Wolfe D, Carrieri MP, Dasgupta N, et al. Concerns about injectable naltrexone for opioid dependence. Lancet. 2011;377:1468-1470. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62056-9
30. Tanum L, Solli KK, Latif ZEH, et al. Effectiveness of injectable extended-release naltrexone vs daily buprenorphine–naloxone for opioid dependence: a randomized clinical noninferiority trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74:1197-1205. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.3206
31. Murphy SM, Polsky D, Lee JD, et al. Cost-effectiveness of extended release naltrexone to prevent relapse among criminal justice-involved individuals with a history of opioid use disorder. Addiction. 2017;112:1440-1450. doi: 10.1111/add.13807
32. Ferrari A, Coccia CPR, Bertolini A, et al. Methadone—metabolism, pharmacokinetics and interactions. Pharmacol Res. 2004;50:551-559. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2004.05.002
33. 42 eCFR Part 2. Confidentiality of substance use disorder patient records. January 18, 2017. Accessed March 23, 2023. www.ecfr.gov/current/title-42/chapter-I/subchapter-A/part-2
34. Kao DP, Haigney MCP, Mehler PS, et al. Arrhythmia associated with buprenorphine and methadone reported to the Food and Drug Administration. Addiction. 2015;110:1468-1475. doi: 10.1111/add.13013
35. Tisdale JE, Chung MK, Campbell KB, et al; . Drug-induced arrhythmias: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;142:e214-e233. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000905
36. Leshner AI, Mancher M, eds. Barriers to broader use of medications to treat opioid use disorder. In: Medications for Opioid Use Disorder Save Lives. National Academies Press; 2019:109-136.
37. Chilcoat HD, Amick HR, Sherwood MR, et al. Buprenorphine in the United States: Motives for abuse, misuse, and diversion. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2019;104:148-157. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat. 2019.07.005
38. Qato DM, Daviglus ML, Wilder J, et al. “Pharmacy deserts” are prevalent in Chicago’s predominantly minority communities, raising medication access concerns. Health Aff (Millwood). 2014;33:1958-1965. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2013.1397
39. Mason M, Soliman R, Kim HS, et al. Disparities by sex and race and ethnicity in death rates due to opioid overdose among adults 55 years or older, 1999 to 2019. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5:e2142982. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.42982
40. Rosenblum A, Cleland CM, Fong C, et al. Distance traveled and cross-state commuting to opioid treatment programs in the United States. J Environ Public Health. 2011;2011:948789. doi: 10.1155/2011/948789
41. Chan B, Hoffman KA, Bougatsos C, et al. Mobile methadone medication units: a brief history, scoping review and research opportunity. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2021;129:108483. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2021.108483
42. Jakubowski A, Fox A. Defining low-threshold buprenorphine treatment. J Addict Med. 2020;14:95-98. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000555
43. Messmer SE, Elmes AT, Jimenez AD, et al. Outcomes of a mobile medical unit for low-threshold buprenorphine access targeting opioid overdose hot spots in Chicago. J Subst Use Addict Treat. 2023;209054. doi: 10.1016/j.josat.2023.209054
1. Baser O, Chalk M, Fiellin DA, et al. Cost and utilization outcomes of opioid-dependence treatments. Am J Manag Care. 2011;17(suppl 8):S235-S248.
2. Gibson A, Degenhardt L, Mattick RP, et al. Exposure to opioid maintenance treatment reduces long-term mortality. Addiction. 2008;103:462-468. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2007.02090.x
3. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States: Results From the 2020 National Survey on Drug Use and Health. HHS Publication PEP21-07-01-003, NSDUH Series H-56. 2021. Accessed March 19, 2023. www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt35325/NSDUHFFRPDFWHTMLFiles2020/2020NSDUHFFR1PDFW102121.pdf
4. Haffajee RL, Andraka-Christou B, Attermann J, et al. A mixed-method comparison of physician-reported beliefs about and barriers to treatment with medications for opioid use disorder. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2020;15:69. doi: 10.1186/s13011-020-00312-3
5. Kosten TR, George TP. The neurobiology of opioid dependence: implications for treatment. Sci Pract Perspect. 2002;1:13-20. doi: 10.1151/spp021113
6. Koob GF. Neurobiology of opioid addiction: opponent process, hyperkatifeia, and negative reinforcement. Biol Psychiatry. 2020;87:44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.05.023
7. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Medications for Opioid Use Disorder. For Health care and Addiction Professionals, Policymakers, Patients, and Families. Treatment Improvement Protocol TIP 63. Publication No. PEP21-02-01-002. 2021. Accessed March 19, 2023. https://store.samhsa.gov/sites/default/files/pep21-02-01-002.pdf
8. Sordo L, Barrio G, Bravo MJ, et al. Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2017;357:j1550. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1550
9. Korownyk C, Perry D, Ton J, et al. Opioid use disorder in primary care: PEER umbrella systematic review of systematic reviews. Can Fam Physician. 2019;65:e194-e206.
10. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, et al. Methadone maintenance therapy versus no opioid replacement therapy for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;(3):CD002209. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002209.pub2
11. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, et al. Buprenorphine maintenance versus placebo or methadone maintenance for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(2):CD002207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002207.pub4
12. Krupitsky E, Nunes EV, Ling W, et al. Injectable extended-release naltrexone for opioid dependence: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2011;377:1506-1513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60358-9
13. Soyka M, Zingg C, Koller G, et al. Retention rate and substance use in methadone and buprenorphine maintenance therapy and predictors of outcome: results from a randomized study. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008;11:641-653. doi: 10.1017/S146114570700836X
14. Institute of Medicine Committee on Federal Regulation of Methadone Treatment; Rettig R, Yarmolinsky A, eds. Federal Regulation of Methadone Treatment. National Academies Press; 1995.
15. 42 eCFR §8. Medication assisted treatment for opioid use disorders. Revised March 15, 2023. Accessed March 23, 2023. www.ecfr.gov/current/title-42/chapter-I/subchapter-A/part-8?toc=1
16. Faggiano F, Vigna-Taglianti F, Versino E, et al. Methadone maintenance at different dosages for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(3):CD002208. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002208
17. Baxter LE Sr, Campbell A, Deshields M, et al. Safe methadone induction and stabilization: report of an expert panel. J Addict Med. 2013;7:377-386. doi: 10.1097/01.ADM.0000435321.39251.d7
18. Olfson M, Zhang VS, Schoenbaum M, et al. Trends in buprenorphine treatment in the United States, 2009-2018. JAMA. 2020;323:276-277. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.18913
19. Walsh SL, Preston KL, Stitzer ML, et al. Clinical pharmacology of buprenorphine: ceiling effects at high doses. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1994;55:569-580. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1994.71
20. Walley AY, Palmisano J, Sorensen-Alawad A, et al. Engagement and substance dependence in a primary care-based addiction treatment program for people infected with HIV and people at high-risk for HIV infection. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2015;59:59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2015.07.007
21. Lagisetty P, Klasa K, Bush C, et al. Primary care models for treating opioid use disorders: what actually works? A systematic review. PloS One. 2017;12:e0186315. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186315
22. Du CX, Shi J, Tetrault JM, et al. Primary care and medication management characteristics among patients receiving office-based opioid treatment with buprenorphine. Fam Pract. 2022;39:234-240. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmab166
23. Herring AA, Vosooghi AA, Luftig J, et al. High-dose buprenorphine induction in the emergency department for treatment of opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2117128. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.17128
24. Hämmig R, Kemter A, Strasser J, et al. Use of microdoses for induction of buprenorphine treatment with overlapping full opioid agonist use: the Bernese method. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2016;7:99-105. doi: 10.2147/SAR.S109919
25. Snyder H, Kalmin MM, Moulin A, et al. Rapid adoption of low-threshold buprenorphine treatment at California emergency departments participating in the CA Bridge Program. Ann Emerg Med. 2021;78:759-772. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2021.05.024
26. Wong JSH, Nikoo M, Westenberg JN, et al. Comparing rapid micro-induction and standard induction of buprenorphine/naloxone for treatment of opioid use disorder: protocol for an open-label, parallel-group, superiority, randomized controlled trial. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2021;16:11. doi: 10.1186/s13722-021-00220-2
27. Lee JD, Vocci F, Fiellin DA. Unobserved “home” induction onto buprenorphine. J Addict Med. 2014;8:299-308. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000059
28. Krupitsky E, Zvartau E, Blokhina E, et al. Randomized trial of long-acting sustained-release naltrexone implant vs oral naltrexone or placebo for preventing relapse to opioid dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69:973-981. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2012.1a
29. Wolfe D, Carrieri MP, Dasgupta N, et al. Concerns about injectable naltrexone for opioid dependence. Lancet. 2011;377:1468-1470. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62056-9
30. Tanum L, Solli KK, Latif ZEH, et al. Effectiveness of injectable extended-release naltrexone vs daily buprenorphine–naloxone for opioid dependence: a randomized clinical noninferiority trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74:1197-1205. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.3206
31. Murphy SM, Polsky D, Lee JD, et al. Cost-effectiveness of extended release naltrexone to prevent relapse among criminal justice-involved individuals with a history of opioid use disorder. Addiction. 2017;112:1440-1450. doi: 10.1111/add.13807
32. Ferrari A, Coccia CPR, Bertolini A, et al. Methadone—metabolism, pharmacokinetics and interactions. Pharmacol Res. 2004;50:551-559. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2004.05.002
33. 42 eCFR Part 2. Confidentiality of substance use disorder patient records. January 18, 2017. Accessed March 23, 2023. www.ecfr.gov/current/title-42/chapter-I/subchapter-A/part-2
34. Kao DP, Haigney MCP, Mehler PS, et al. Arrhythmia associated with buprenorphine and methadone reported to the Food and Drug Administration. Addiction. 2015;110:1468-1475. doi: 10.1111/add.13013
35. Tisdale JE, Chung MK, Campbell KB, et al; . Drug-induced arrhythmias: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;142:e214-e233. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000905
36. Leshner AI, Mancher M, eds. Barriers to broader use of medications to treat opioid use disorder. In: Medications for Opioid Use Disorder Save Lives. National Academies Press; 2019:109-136.
37. Chilcoat HD, Amick HR, Sherwood MR, et al. Buprenorphine in the United States: Motives for abuse, misuse, and diversion. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2019;104:148-157. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat. 2019.07.005
38. Qato DM, Daviglus ML, Wilder J, et al. “Pharmacy deserts” are prevalent in Chicago’s predominantly minority communities, raising medication access concerns. Health Aff (Millwood). 2014;33:1958-1965. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2013.1397
39. Mason M, Soliman R, Kim HS, et al. Disparities by sex and race and ethnicity in death rates due to opioid overdose among adults 55 years or older, 1999 to 2019. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5:e2142982. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.42982
40. Rosenblum A, Cleland CM, Fong C, et al. Distance traveled and cross-state commuting to opioid treatment programs in the United States. J Environ Public Health. 2011;2011:948789. doi: 10.1155/2011/948789
41. Chan B, Hoffman KA, Bougatsos C, et al. Mobile methadone medication units: a brief history, scoping review and research opportunity. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2021;129:108483. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2021.108483
42. Jakubowski A, Fox A. Defining low-threshold buprenorphine treatment. J Addict Med. 2020;14:95-98. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000555
43. Messmer SE, Elmes AT, Jimenez AD, et al. Outcomes of a mobile medical unit for low-threshold buprenorphine access targeting opioid overdose hot spots in Chicago. J Subst Use Addict Treat. 2023;209054. doi: 10.1016/j.josat.2023.209054
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
› Consider resource availability (eg, treatment programs and regulatory barriers), in addition to patient- and medicationspecific factors, when designing the most individualized, advantageous medication-assisted recovery plan, to reduce the risk for mortality. B
› Schedule early (< 2 weeks) and frequent follow-up with patients who are starting medications for opioid use disorder (particularly methadone), to manage risk when mortality is highest and to support recovery. C
› Set and manage patient expectations for control of withdrawal symptoms when initiating medications for opioid use disorder (particularly buprenorphine). B
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series