User login
Risk factors found for respiratory AEs in children following OSA surgery
Underlying cardiac disease, airway anomalies, and younger age each independently boosted the risk of severe perioperative respiratory adverse events (PRAE) in children undergoing adenotonsillectomy to treat obstructive sleep apnea, in a review of 374 patients treated at a single Canadian tertiary-referral center.
In contrast, the analysis failed to show independent, significant effects from any assessed polysomnography or oximetry parameters on the rate of postoperative respiratory complications. The utility of preoperative polysomnography or oximetry for risk stratification is questionable for pediatric patients scheduled to adenotonsillectomy to treat obstructive sleep apnea, wrote Sherri L. Katz, MD, of the University of Ottawa, and associates in a recent report published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, although they also added that making these assessments may be “unavoidable” because of their need for diagnosing obstructive sleep apnea and determining the need for surgery.
Despite this caveat, “overall our study results highlight the need to better define the complex interaction between comorbidities, age, nocturnal respiratory events, and gas exchange abnormalities in predicting risk for PRAE” after adenotonsillectomy, the researchers wrote. These findings “are consistent with existing clinical care guidelines,” and “cardiac and craniofacial conditions have been associated with risk of postoperative complications in other studies.”
The analysis used data collected from all children aged 0-18 years who underwent polysomnography assessment followed by adenotonsillectomy at one Canadian tertiary-referral center, Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario in Ottawa, during 2010-2016. Their median age was just over 6 years, and 39 patients (10%) were younger than 3 years at the time of their surgery. More than three-quarters of the patients, 286, had at least one identified comorbidity, and nearly half had at least two comorbidities. Polysomnography identified sleep-disordered breathing in 344 of the children (92%), and diagnosed obstructive sleep apnea in 256 (68%), including 148 (43% of the full cohort) with a severe apnea-hypopnea index.
Sixty-six of the children (18%) had at least one severe PRAE that required intervention. Specifically these were either oxygen desaturations requiring intervention or need for airway or ventilatory support with interventions such as jaw thrust, oral or nasal airway placement, bag and mask ventilation, or endotracheal intubation.
A multivariate regression analysis of the measured comorbidity, polysomnography, and oximetry parameters, as well as age, identified three factors that independently linked with a statistically significant increase in the rate of severe PRAE: airway anomaly, underlying cardiac disease, and young age. Patients with an airway anomaly had a 219% increased rate of PRAE, compared with those with no anomaly; patients with underlying cardiac disease had a 109% increased rate, compared with those without cardiac disease; and patients aged younger than 3 years had a 310% higher rate of PRAE, compared with the children aged 6 years or older, while children aged 3-5 years had a 121% higher rate of PRAE, compared with older children.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Katz has received honoraria for speaking from Biogen that had no relevance to the study.
SOURCE: Katz SL et al. J Clin Sleep Med. 2020 Jan 15;16(1):41-8.
This well-conducted, retrospective, chart-review study adds important information to the published literature about risk stratification for children in a tertiary-referral population undergoing adenotonsillectomy. Their findings indicate that younger children remain at higher risk as well as those children with complex comorbid medical disease. They also show that children with severe sleep apnea or significant oxyhemoglobin desaturation are likewise at higher risk of postoperative respiratory compromise – emphasizing the need for preoperative polysomnography – particularly in a tertiary setting where many patients have medical comorbidities.
Despite the strengths of this study in assessing perioperative risk for respiratory compromise in a referral population with highly prevalent medical comorbidities, this study does not provide significant insight into the management of otherwise healthy children in a community setting who are undergoing adenotonsillectomy. This is important because a large number of adenotonsillectomies are performed outside of a tertiary-referral center and many of these children may not have undergone preoperative polysomnography to stratify risk. The utility of preoperative polysomnography in the evaluation of all children undergoing adenotonsillectomy remains controversial, with diverging recommendations from two major U.S. medical groups.
This study does not address the utility of polysomnography in community-based populations of otherwise healthy children. It is imperative to accurately ascertain risk so perioperative planning can ensure the safety of children at higher risk following adenotonsillectomy; however, there remains a paucity of studies assessing the cost-effectiveness as well as the positive and negative predictive value of polysomnographic findings. This study highlights the need for community-based studies of otherwise healthy children undergoing adenotonsillectomy to ensure that children at risk receive appropriate monitoring in an inpatient setting whereas those at lesser risk are not unnecessarily hospitalized postoperatively.
Heidi V. Connolly, MD, and Laura E. Tomaselli, MD, are pediatric sleep medicine physicians, and Margo K. McKenna Benoit, MD, is an otolaryngologist at the University of Rochester (N.Y.). They made these comments in a commentary that accompanied the published report ( J Clin Sleep Med. 2020 Jan 15;16[1]:3-4 ). They had no disclosures.
This well-conducted, retrospective, chart-review study adds important information to the published literature about risk stratification for children in a tertiary-referral population undergoing adenotonsillectomy. Their findings indicate that younger children remain at higher risk as well as those children with complex comorbid medical disease. They also show that children with severe sleep apnea or significant oxyhemoglobin desaturation are likewise at higher risk of postoperative respiratory compromise – emphasizing the need for preoperative polysomnography – particularly in a tertiary setting where many patients have medical comorbidities.
Despite the strengths of this study in assessing perioperative risk for respiratory compromise in a referral population with highly prevalent medical comorbidities, this study does not provide significant insight into the management of otherwise healthy children in a community setting who are undergoing adenotonsillectomy. This is important because a large number of adenotonsillectomies are performed outside of a tertiary-referral center and many of these children may not have undergone preoperative polysomnography to stratify risk. The utility of preoperative polysomnography in the evaluation of all children undergoing adenotonsillectomy remains controversial, with diverging recommendations from two major U.S. medical groups.
This study does not address the utility of polysomnography in community-based populations of otherwise healthy children. It is imperative to accurately ascertain risk so perioperative planning can ensure the safety of children at higher risk following adenotonsillectomy; however, there remains a paucity of studies assessing the cost-effectiveness as well as the positive and negative predictive value of polysomnographic findings. This study highlights the need for community-based studies of otherwise healthy children undergoing adenotonsillectomy to ensure that children at risk receive appropriate monitoring in an inpatient setting whereas those at lesser risk are not unnecessarily hospitalized postoperatively.
Heidi V. Connolly, MD, and Laura E. Tomaselli, MD, are pediatric sleep medicine physicians, and Margo K. McKenna Benoit, MD, is an otolaryngologist at the University of Rochester (N.Y.). They made these comments in a commentary that accompanied the published report ( J Clin Sleep Med. 2020 Jan 15;16[1]:3-4 ). They had no disclosures.
This well-conducted, retrospective, chart-review study adds important information to the published literature about risk stratification for children in a tertiary-referral population undergoing adenotonsillectomy. Their findings indicate that younger children remain at higher risk as well as those children with complex comorbid medical disease. They also show that children with severe sleep apnea or significant oxyhemoglobin desaturation are likewise at higher risk of postoperative respiratory compromise – emphasizing the need for preoperative polysomnography – particularly in a tertiary setting where many patients have medical comorbidities.
Despite the strengths of this study in assessing perioperative risk for respiratory compromise in a referral population with highly prevalent medical comorbidities, this study does not provide significant insight into the management of otherwise healthy children in a community setting who are undergoing adenotonsillectomy. This is important because a large number of adenotonsillectomies are performed outside of a tertiary-referral center and many of these children may not have undergone preoperative polysomnography to stratify risk. The utility of preoperative polysomnography in the evaluation of all children undergoing adenotonsillectomy remains controversial, with diverging recommendations from two major U.S. medical groups.
This study does not address the utility of polysomnography in community-based populations of otherwise healthy children. It is imperative to accurately ascertain risk so perioperative planning can ensure the safety of children at higher risk following adenotonsillectomy; however, there remains a paucity of studies assessing the cost-effectiveness as well as the positive and negative predictive value of polysomnographic findings. This study highlights the need for community-based studies of otherwise healthy children undergoing adenotonsillectomy to ensure that children at risk receive appropriate monitoring in an inpatient setting whereas those at lesser risk are not unnecessarily hospitalized postoperatively.
Heidi V. Connolly, MD, and Laura E. Tomaselli, MD, are pediatric sleep medicine physicians, and Margo K. McKenna Benoit, MD, is an otolaryngologist at the University of Rochester (N.Y.). They made these comments in a commentary that accompanied the published report ( J Clin Sleep Med. 2020 Jan 15;16[1]:3-4 ). They had no disclosures.
Underlying cardiac disease, airway anomalies, and younger age each independently boosted the risk of severe perioperative respiratory adverse events (PRAE) in children undergoing adenotonsillectomy to treat obstructive sleep apnea, in a review of 374 patients treated at a single Canadian tertiary-referral center.
In contrast, the analysis failed to show independent, significant effects from any assessed polysomnography or oximetry parameters on the rate of postoperative respiratory complications. The utility of preoperative polysomnography or oximetry for risk stratification is questionable for pediatric patients scheduled to adenotonsillectomy to treat obstructive sleep apnea, wrote Sherri L. Katz, MD, of the University of Ottawa, and associates in a recent report published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, although they also added that making these assessments may be “unavoidable” because of their need for diagnosing obstructive sleep apnea and determining the need for surgery.
Despite this caveat, “overall our study results highlight the need to better define the complex interaction between comorbidities, age, nocturnal respiratory events, and gas exchange abnormalities in predicting risk for PRAE” after adenotonsillectomy, the researchers wrote. These findings “are consistent with existing clinical care guidelines,” and “cardiac and craniofacial conditions have been associated with risk of postoperative complications in other studies.”
The analysis used data collected from all children aged 0-18 years who underwent polysomnography assessment followed by adenotonsillectomy at one Canadian tertiary-referral center, Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario in Ottawa, during 2010-2016. Their median age was just over 6 years, and 39 patients (10%) were younger than 3 years at the time of their surgery. More than three-quarters of the patients, 286, had at least one identified comorbidity, and nearly half had at least two comorbidities. Polysomnography identified sleep-disordered breathing in 344 of the children (92%), and diagnosed obstructive sleep apnea in 256 (68%), including 148 (43% of the full cohort) with a severe apnea-hypopnea index.
Sixty-six of the children (18%) had at least one severe PRAE that required intervention. Specifically these were either oxygen desaturations requiring intervention or need for airway or ventilatory support with interventions such as jaw thrust, oral or nasal airway placement, bag and mask ventilation, or endotracheal intubation.
A multivariate regression analysis of the measured comorbidity, polysomnography, and oximetry parameters, as well as age, identified three factors that independently linked with a statistically significant increase in the rate of severe PRAE: airway anomaly, underlying cardiac disease, and young age. Patients with an airway anomaly had a 219% increased rate of PRAE, compared with those with no anomaly; patients with underlying cardiac disease had a 109% increased rate, compared with those without cardiac disease; and patients aged younger than 3 years had a 310% higher rate of PRAE, compared with the children aged 6 years or older, while children aged 3-5 years had a 121% higher rate of PRAE, compared with older children.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Katz has received honoraria for speaking from Biogen that had no relevance to the study.
SOURCE: Katz SL et al. J Clin Sleep Med. 2020 Jan 15;16(1):41-8.
Underlying cardiac disease, airway anomalies, and younger age each independently boosted the risk of severe perioperative respiratory adverse events (PRAE) in children undergoing adenotonsillectomy to treat obstructive sleep apnea, in a review of 374 patients treated at a single Canadian tertiary-referral center.
In contrast, the analysis failed to show independent, significant effects from any assessed polysomnography or oximetry parameters on the rate of postoperative respiratory complications. The utility of preoperative polysomnography or oximetry for risk stratification is questionable for pediatric patients scheduled to adenotonsillectomy to treat obstructive sleep apnea, wrote Sherri L. Katz, MD, of the University of Ottawa, and associates in a recent report published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, although they also added that making these assessments may be “unavoidable” because of their need for diagnosing obstructive sleep apnea and determining the need for surgery.
Despite this caveat, “overall our study results highlight the need to better define the complex interaction between comorbidities, age, nocturnal respiratory events, and gas exchange abnormalities in predicting risk for PRAE” after adenotonsillectomy, the researchers wrote. These findings “are consistent with existing clinical care guidelines,” and “cardiac and craniofacial conditions have been associated with risk of postoperative complications in other studies.”
The analysis used data collected from all children aged 0-18 years who underwent polysomnography assessment followed by adenotonsillectomy at one Canadian tertiary-referral center, Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario in Ottawa, during 2010-2016. Their median age was just over 6 years, and 39 patients (10%) were younger than 3 years at the time of their surgery. More than three-quarters of the patients, 286, had at least one identified comorbidity, and nearly half had at least two comorbidities. Polysomnography identified sleep-disordered breathing in 344 of the children (92%), and diagnosed obstructive sleep apnea in 256 (68%), including 148 (43% of the full cohort) with a severe apnea-hypopnea index.
Sixty-six of the children (18%) had at least one severe PRAE that required intervention. Specifically these were either oxygen desaturations requiring intervention or need for airway or ventilatory support with interventions such as jaw thrust, oral or nasal airway placement, bag and mask ventilation, or endotracheal intubation.
A multivariate regression analysis of the measured comorbidity, polysomnography, and oximetry parameters, as well as age, identified three factors that independently linked with a statistically significant increase in the rate of severe PRAE: airway anomaly, underlying cardiac disease, and young age. Patients with an airway anomaly had a 219% increased rate of PRAE, compared with those with no anomaly; patients with underlying cardiac disease had a 109% increased rate, compared with those without cardiac disease; and patients aged younger than 3 years had a 310% higher rate of PRAE, compared with the children aged 6 years or older, while children aged 3-5 years had a 121% higher rate of PRAE, compared with older children.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Katz has received honoraria for speaking from Biogen that had no relevance to the study.
SOURCE: Katz SL et al. J Clin Sleep Med. 2020 Jan 15;16(1):41-8.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL SLEEP MEDICINE
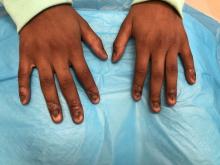
Nail dystrophy and nail plate thinning
At a follow-up visit, a biopsy of the skin on the fingertips was performed, which showed lichenoid lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate with associated hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, and acanthosis.
No fungal elements were seen. The findings were consistent with lichen planus.
The patient was started on hydroxychloroquine. It was recommended she start a 6-week course of oral prednisone, but the mother was opposed to systemic treatment because of potential side effects.
She continued topical betamethasone without much change. Topical tacrolimus later was recommended to use on off days of betamethasone, which led to no improvement. Narrow-band UVB also was started with minimal improvement. Unfortunately,
Nail lichen planus (NLP) in children is not a common condition.1 In a recent series from Chiheb et al., NLP was reported in 90 patients, of which 40% were children; a quarter of the patients reported having extracutaneous involvement as well.2 In another childhood LP series,14 % of the children presented with nail disease.3 It can be a severe disease that, if not treated aggressively, may lead to destruction of the nail bed. This condition seems to be more prevalent in boys than girls and more prevalent in African American children.3 Unfortunately, in this patient’s case, the mother was hesitant to use systemic therapy and aggressive treatment was delayed.
Possible but not clear associations with autoimmune conditions such as vitiligo, autoimmune thyroiditis, myasthenia gravis, alopecia areata, thymoma, autoimmune polyendocrinopathy, atopic dermatitis, and lichen nitidus have been described in children with LP.
The clinical characteristics of NLP include nail plate thinning with longitudinal ridging and fissuring, with or without pterygium; trachyonychia; and erythema of the lunula when the nail matrix is involved. When the nail bed is affected, the patient can present with onycholysis with or without subungual hyperkeratosis and violaceous hue of the nail bed.4 NLP can have three different clinical presentations described by Tosti et al., which include typical NLP, 20‐nail dystrophy (trachyonychia), and idiopathic nail atrophy. Idiopathic nail atrophy is described solely in children as an acute and rapid progression that leads to destruction of the nail within months, which appears to be the clinical presentation in our patient.
The differential diagnosis of nail dystrophy in children includes infectious processes such as onychomycosis, especially when children present with onycholysis and subungual hyperkeratosis. Because of this, it is recommended to perform a nail culture or submit a sample of nail clippings for microscopic evaluation to confirm the diagnosis of onychomycosis prior to starting systemic therapy in children. Fingernail involvement without toenail involvement is an unusual presentation of onychomycosis.
Twenty-nail dystrophy – also known as trachyonychia – can be caused by several inflammatory skin conditions such as lichen planus, psoriasis, eczema, pemphigus vulgaris, and alopecia areata. Clinically, there is uniformly monomorphic thinning of the nail plate with longitudinal ridging without splitting or pterygium.1 This is a benign condition and should not cause scarring. About 10% of the cases of 20-nail dystrophy are caused by lichen planus.
Nail psoriasis is characterized by nail pitting, oil spots on the nail plate, leukonychia, subungual hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis, as well as nail crumbling, which were not seen in our patient. Although her initial presentation was of 20-nail dystrophy, which also can be a presentation of nail psoriasis, its rapid evolution with associated nail atrophy and pterygium make it unlikely to be psoriasis in this particular patient.
Patients with pachyonychia congenita – which is a genetic disorder or keratinization caused by mutations on several genes encoding keratin such as K6a, K16, K17, K6b, and possibly K6c – present with nail thickening (pachyonychia) and discoloration of the nails, as well as pincer nails. These patients also present with oral leukokeratosis and focal palmoplantar keratoderma.
The main treatment of lichen planus is potent topical corticosteroids.
For nail disease, topical treatment may not be effective and systemic treatment may be necessary. Systemic corticosteroids have been used in several pediatric series varying from a short course given at a dose of 1- 2 mg/kg per day for 2 weeks to a longer 3-month course followed by tapering.3 There are several protocols of intramuscular triamcinolone at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg in children in once a month injections for about 3 months that have been reported successful with minimal side effects.1 Other medications reported useful in patients with NLP include dapsone and acitretin. Other treatment options include narrow-band UVB and PUVA.3
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Arch Dermatol. 2001 Aug;137(8):1027-32.
2. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2015 Jan;142(1):21-5.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Jan-Feb;31(1):59-67.
4. Dermatological diseases, in “Nails: Diagnosis, Therapy, and Surgery,” 3rd ed. (Oxford: Elsevier Saunders, 2005, p. 105).
At a follow-up visit, a biopsy of the skin on the fingertips was performed, which showed lichenoid lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate with associated hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, and acanthosis.
No fungal elements were seen. The findings were consistent with lichen planus.
The patient was started on hydroxychloroquine. It was recommended she start a 6-week course of oral prednisone, but the mother was opposed to systemic treatment because of potential side effects.
She continued topical betamethasone without much change. Topical tacrolimus later was recommended to use on off days of betamethasone, which led to no improvement. Narrow-band UVB also was started with minimal improvement. Unfortunately,
Nail lichen planus (NLP) in children is not a common condition.1 In a recent series from Chiheb et al., NLP was reported in 90 patients, of which 40% were children; a quarter of the patients reported having extracutaneous involvement as well.2 In another childhood LP series,14 % of the children presented with nail disease.3 It can be a severe disease that, if not treated aggressively, may lead to destruction of the nail bed. This condition seems to be more prevalent in boys than girls and more prevalent in African American children.3 Unfortunately, in this patient’s case, the mother was hesitant to use systemic therapy and aggressive treatment was delayed.
Possible but not clear associations with autoimmune conditions such as vitiligo, autoimmune thyroiditis, myasthenia gravis, alopecia areata, thymoma, autoimmune polyendocrinopathy, atopic dermatitis, and lichen nitidus have been described in children with LP.
The clinical characteristics of NLP include nail plate thinning with longitudinal ridging and fissuring, with or without pterygium; trachyonychia; and erythema of the lunula when the nail matrix is involved. When the nail bed is affected, the patient can present with onycholysis with or without subungual hyperkeratosis and violaceous hue of the nail bed.4 NLP can have three different clinical presentations described by Tosti et al., which include typical NLP, 20‐nail dystrophy (trachyonychia), and idiopathic nail atrophy. Idiopathic nail atrophy is described solely in children as an acute and rapid progression that leads to destruction of the nail within months, which appears to be the clinical presentation in our patient.
The differential diagnosis of nail dystrophy in children includes infectious processes such as onychomycosis, especially when children present with onycholysis and subungual hyperkeratosis. Because of this, it is recommended to perform a nail culture or submit a sample of nail clippings for microscopic evaluation to confirm the diagnosis of onychomycosis prior to starting systemic therapy in children. Fingernail involvement without toenail involvement is an unusual presentation of onychomycosis.
Twenty-nail dystrophy – also known as trachyonychia – can be caused by several inflammatory skin conditions such as lichen planus, psoriasis, eczema, pemphigus vulgaris, and alopecia areata. Clinically, there is uniformly monomorphic thinning of the nail plate with longitudinal ridging without splitting or pterygium.1 This is a benign condition and should not cause scarring. About 10% of the cases of 20-nail dystrophy are caused by lichen planus.
Nail psoriasis is characterized by nail pitting, oil spots on the nail plate, leukonychia, subungual hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis, as well as nail crumbling, which were not seen in our patient. Although her initial presentation was of 20-nail dystrophy, which also can be a presentation of nail psoriasis, its rapid evolution with associated nail atrophy and pterygium make it unlikely to be psoriasis in this particular patient.
Patients with pachyonychia congenita – which is a genetic disorder or keratinization caused by mutations on several genes encoding keratin such as K6a, K16, K17, K6b, and possibly K6c – present with nail thickening (pachyonychia) and discoloration of the nails, as well as pincer nails. These patients also present with oral leukokeratosis and focal palmoplantar keratoderma.
The main treatment of lichen planus is potent topical corticosteroids.
For nail disease, topical treatment may not be effective and systemic treatment may be necessary. Systemic corticosteroids have been used in several pediatric series varying from a short course given at a dose of 1- 2 mg/kg per day for 2 weeks to a longer 3-month course followed by tapering.3 There are several protocols of intramuscular triamcinolone at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg in children in once a month injections for about 3 months that have been reported successful with minimal side effects.1 Other medications reported useful in patients with NLP include dapsone and acitretin. Other treatment options include narrow-band UVB and PUVA.3
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Arch Dermatol. 2001 Aug;137(8):1027-32.
2. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2015 Jan;142(1):21-5.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Jan-Feb;31(1):59-67.
4. Dermatological diseases, in “Nails: Diagnosis, Therapy, and Surgery,” 3rd ed. (Oxford: Elsevier Saunders, 2005, p. 105).
At a follow-up visit, a biopsy of the skin on the fingertips was performed, which showed lichenoid lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate with associated hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, and acanthosis.
No fungal elements were seen. The findings were consistent with lichen planus.
The patient was started on hydroxychloroquine. It was recommended she start a 6-week course of oral prednisone, but the mother was opposed to systemic treatment because of potential side effects.
She continued topical betamethasone without much change. Topical tacrolimus later was recommended to use on off days of betamethasone, which led to no improvement. Narrow-band UVB also was started with minimal improvement. Unfortunately,
Nail lichen planus (NLP) in children is not a common condition.1 In a recent series from Chiheb et al., NLP was reported in 90 patients, of which 40% were children; a quarter of the patients reported having extracutaneous involvement as well.2 In another childhood LP series,14 % of the children presented with nail disease.3 It can be a severe disease that, if not treated aggressively, may lead to destruction of the nail bed. This condition seems to be more prevalent in boys than girls and more prevalent in African American children.3 Unfortunately, in this patient’s case, the mother was hesitant to use systemic therapy and aggressive treatment was delayed.
Possible but not clear associations with autoimmune conditions such as vitiligo, autoimmune thyroiditis, myasthenia gravis, alopecia areata, thymoma, autoimmune polyendocrinopathy, atopic dermatitis, and lichen nitidus have been described in children with LP.
The clinical characteristics of NLP include nail plate thinning with longitudinal ridging and fissuring, with or without pterygium; trachyonychia; and erythema of the lunula when the nail matrix is involved. When the nail bed is affected, the patient can present with onycholysis with or without subungual hyperkeratosis and violaceous hue of the nail bed.4 NLP can have three different clinical presentations described by Tosti et al., which include typical NLP, 20‐nail dystrophy (trachyonychia), and idiopathic nail atrophy. Idiopathic nail atrophy is described solely in children as an acute and rapid progression that leads to destruction of the nail within months, which appears to be the clinical presentation in our patient.
The differential diagnosis of nail dystrophy in children includes infectious processes such as onychomycosis, especially when children present with onycholysis and subungual hyperkeratosis. Because of this, it is recommended to perform a nail culture or submit a sample of nail clippings for microscopic evaluation to confirm the diagnosis of onychomycosis prior to starting systemic therapy in children. Fingernail involvement without toenail involvement is an unusual presentation of onychomycosis.
Twenty-nail dystrophy – also known as trachyonychia – can be caused by several inflammatory skin conditions such as lichen planus, psoriasis, eczema, pemphigus vulgaris, and alopecia areata. Clinically, there is uniformly monomorphic thinning of the nail plate with longitudinal ridging without splitting or pterygium.1 This is a benign condition and should not cause scarring. About 10% of the cases of 20-nail dystrophy are caused by lichen planus.
Nail psoriasis is characterized by nail pitting, oil spots on the nail plate, leukonychia, subungual hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis, as well as nail crumbling, which were not seen in our patient. Although her initial presentation was of 20-nail dystrophy, which also can be a presentation of nail psoriasis, its rapid evolution with associated nail atrophy and pterygium make it unlikely to be psoriasis in this particular patient.
Patients with pachyonychia congenita – which is a genetic disorder or keratinization caused by mutations on several genes encoding keratin such as K6a, K16, K17, K6b, and possibly K6c – present with nail thickening (pachyonychia) and discoloration of the nails, as well as pincer nails. These patients also present with oral leukokeratosis and focal palmoplantar keratoderma.
The main treatment of lichen planus is potent topical corticosteroids.
For nail disease, topical treatment may not be effective and systemic treatment may be necessary. Systemic corticosteroids have been used in several pediatric series varying from a short course given at a dose of 1- 2 mg/kg per day for 2 weeks to a longer 3-month course followed by tapering.3 There are several protocols of intramuscular triamcinolone at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg in children in once a month injections for about 3 months that have been reported successful with minimal side effects.1 Other medications reported useful in patients with NLP include dapsone and acitretin. Other treatment options include narrow-band UVB and PUVA.3
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Arch Dermatol. 2001 Aug;137(8):1027-32.
2. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2015 Jan;142(1):21-5.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Jan-Feb;31(1):59-67.
4. Dermatological diseases, in “Nails: Diagnosis, Therapy, and Surgery,” 3rd ed. (Oxford: Elsevier Saunders, 2005, p. 105).
An 8-year-old female child comes to our pediatric dermatology clinic for evaluation of onychomycosis on her fingernails. The mother stated the child started developing funny-looking nails 1 year prior to the visit. It started with only two fingernails affected and now has spread to all her fingernails. Her toenails are not involved.
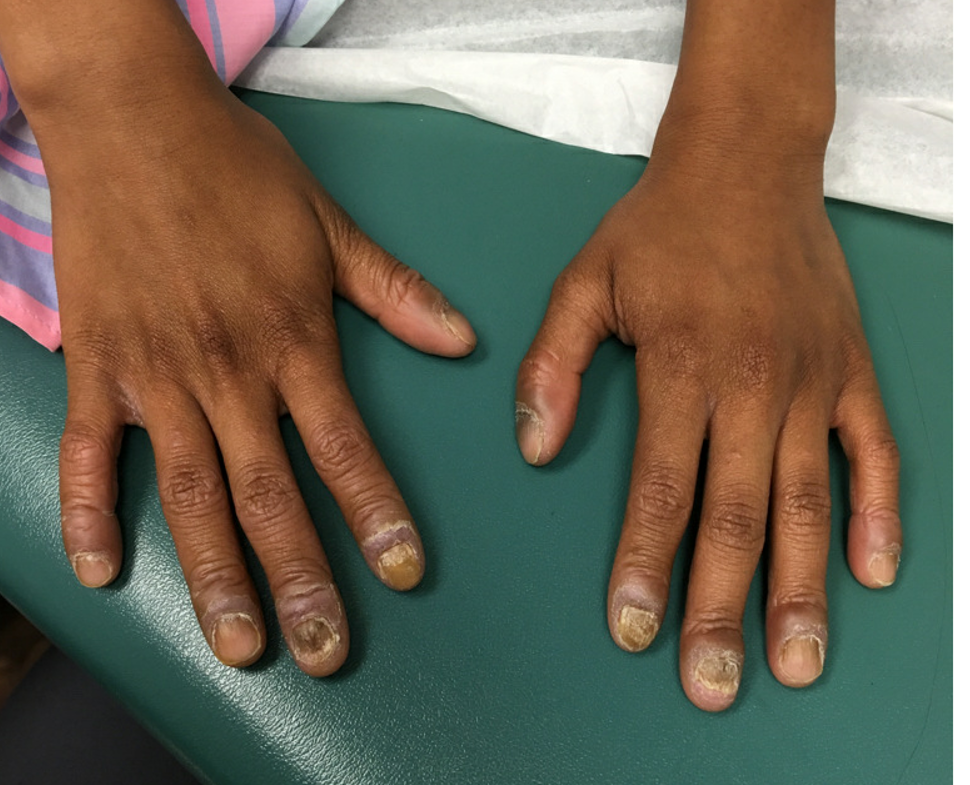
She denied any pain or itching. She initially was treated with topical antifungal medications as well as tea tree oil, apple cider vinegar, and a 6-week course of oral griseofulvin without any improvement. Her nails progressively have gotten much worse. She has no history of atopic dermatitis or any other skin conditions. She denied any joint pain, sun sensitivity, hair loss, or any other symptoms. The mother denied any family history of nail fungus, ringworm, psoriasis, or eczema.
She likes to play basketball and enjoys arts and crafts. She has a cat and a dog; neither of them have any skin problems.
On physical examination, there is nail dystrophy with nail plate thinning and longitudinal fissuring of all fingernails but not of the toenails. She also has hyperpigmented violaceous plaques on the surrounding periungual skin. There are no other skin lesions, and there are no oral or genital lesions. There is no scalp involvement or hair loss. At follow-up several months later, she had complete destruction of the nail plate with scar formation.
A fungal culture was performed, as well as microscopic analysis of the nail with periodic acid fast and giemsa stains, which showed no fungal organisms.
She initially was treated with topical betamethasone twice a day for 6 weeks and then 2 weeks on and 2 weeks off without much change.
Play it as it lies: Handling lying by kids
“Not my son!” your patient’s parent rants. “If he lies to me, he will regret it for a long time.” While your first reaction may be to agree that a child lying to a parent crosses a kind of moral line in the sand, lying is a far more nuanced part of parenting worth a deeper understanding.
In order to lie, a child has to develop cognitive and social understanding. Typically developing children look to see what is interesting to others, called “joint attention,” at around 12-18 months. Failure to do this is one of the early signs of autism reflecting atypical social understanding. At around 3.5 years, children may attempt to deceive if they have broken a rule. The study demonstrating this may sound a lot like home: Children are left alone with a tempting toy but told not to touch it. Although they do touch it while the adult is out of sight, they say rather sweetly (and eventually convincingly) that they did not, even though the toy was clearly moved! While boys generally have more behavior problems, girls and children with better verbal skills achieve deceit at an earlier age, some as young as 2 years. At this stage, children become aware that the adult can’t know exactly what they know. If the parent shows high emotion to what they consider a lie, this can be a topic for testing! Children with ADHD often lack the inhibition needed for early mastery of deception, and children with autism later or not at all. They don’t see the social point to lying nor can they fake a facial expression. They have a case of intractable honesty!
The inability to refrain from telling the truth can result in social rejection, for example when a child rats on a peer for a trivial misdeed in class. Even though he is speaking the truth and “following the (teacher’s) rules,” he did not see that the cost of breaking the (peer) social rules was more important. By age 6 years, children typically figure out that what another person thinks may not be true – their belief may be incorrect or a “false belief.” This understanding is called Theory of Mind, missing or delayed in autism. Only 40% of high-functioning children with autism passed false belief testing at ages 6- to 13-years-old, compared with 95% of typical age-matched peers (Physiol Behav. 2010 Jun 1;100[3]:268-76). The percentage of children on the spectrum understanding false beliefs more closely matched that of preschoolers (39%). At a later age and given extra time to think, some children with autism can do better at this kind of perspective taking, but many continue having difficulty understanding thoughts of others, especially social expectations or motivations (such as flirting, status seeking, and making an excuse) even as adults. This can impair social relationships even when desire to fit in and IQ are otherwise high.
On the other hand, ADHD is a common condition in which “lying” comes from saying the first thing that comes to mind even if the child knows otherwise. A wise parent of one of my patients with ADHD told me about her “30 second rule” where she would give her child that extra time and walk away briefly to “be sure that is what you wanted to say,” with praise rather than give a consequence for changing the story to the truth. This is an important concept we pediatricians need to know: Punishing lying in children tends to result in more, not less, lying and more sneakiness. Instead, parents need to be advised to recall the origins of the word discipline as being “to teach.”
When children lie there are four basic scenarios: They may not know the rules, they may know but have something they want more, they may be impulsive, or they may have developed an attitude of seeking to con the adults whom they feel are mean as a way to have some power in the relationship and get back at them. Clearly, we do not want to push children to this fourth resort by harsh reactions to lying. We have seen particular difficulty with harsh reactions to lying in parents from strong, rule-oriented careers such as police officers, military, and ministers. Asking “How would your parent have handled this?” often will reveal reasons for their tough but backfiring stance.
Lying can work to get what one wants and nearly all children try it. As with other new milestones, children practice this “skill,” much to parents’ dismay. Parents generally can tell if children are lying; they see it on their faces, hear the story from siblings, or see evidence of what happened. Lying provides an important opportunity for the adult to stop, take some breaths, touch the child, and empathize: “It is hard to admit a mistake. I know you did not mean to do it. But you are young, and I know that you are good and honest inside, and will get stronger and braver at telling the truth as you get older. Will you promise to try harder?” In some cases a consequence may be appropriate, for example if something was broken. Usually, simply empathizing and focusing on the expectation for improvement will increase the child’s desire to please the parents rather than get back at them. Actual rewards for honesty improve truth telling by 1.5 times if the reward is big enough.
But it is important to recognize that we all make split second tactical decisions about our actions based on how safe we feel in the situation and our knowledge of social rules and costs. Children over time need to learn that it is safe to tell the truth among family members and that they will not be harshly dealt with. It is a subtle task, but important to learn that deception is a tool that can be important used judiciously when required socially (I have a curfew) or in dangerous situations (I did not see the thug), but can undermine relationships and should not be used with your allies (family and friends).
But parenting involves lying also, which can be a model for the child. Sarcasm is a peculiar form of problematic adult lying. The adults say the opposite or an exaggeration of what they really mean, usually with a smirk or other nonverbal cue to their intent. This is confusing, if not infuriating, to immature children or those who do not understand this twisted communication. It is best to avoid sarcasm with children, or at least be sure to explain it so the children gain understanding over time.
Parents need to “lie” to their children to some extent to reassure and allow for development of confidence. What adult hasn’t said “It’s going to be all right” about a looming storm, car crash, or illness, when actually there is uncertainty. Children count on adults to keep them safe emotionally and physically from things they can’t yet handle. To move forward developmentally, children need adults to be brave leaders, even when the adults don’t feel confident. Some parents think their children must know the “truth” in every instance. Those children are often painfully anxious and overwhelmed.
There is plenty of time for more facts later when the child has the thinking and emotional power to handle the truth.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS (www.CHADIS.com). She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
“Not my son!” your patient’s parent rants. “If he lies to me, he will regret it for a long time.” While your first reaction may be to agree that a child lying to a parent crosses a kind of moral line in the sand, lying is a far more nuanced part of parenting worth a deeper understanding.
In order to lie, a child has to develop cognitive and social understanding. Typically developing children look to see what is interesting to others, called “joint attention,” at around 12-18 months. Failure to do this is one of the early signs of autism reflecting atypical social understanding. At around 3.5 years, children may attempt to deceive if they have broken a rule. The study demonstrating this may sound a lot like home: Children are left alone with a tempting toy but told not to touch it. Although they do touch it while the adult is out of sight, they say rather sweetly (and eventually convincingly) that they did not, even though the toy was clearly moved! While boys generally have more behavior problems, girls and children with better verbal skills achieve deceit at an earlier age, some as young as 2 years. At this stage, children become aware that the adult can’t know exactly what they know. If the parent shows high emotion to what they consider a lie, this can be a topic for testing! Children with ADHD often lack the inhibition needed for early mastery of deception, and children with autism later or not at all. They don’t see the social point to lying nor can they fake a facial expression. They have a case of intractable honesty!
The inability to refrain from telling the truth can result in social rejection, for example when a child rats on a peer for a trivial misdeed in class. Even though he is speaking the truth and “following the (teacher’s) rules,” he did not see that the cost of breaking the (peer) social rules was more important. By age 6 years, children typically figure out that what another person thinks may not be true – their belief may be incorrect or a “false belief.” This understanding is called Theory of Mind, missing or delayed in autism. Only 40% of high-functioning children with autism passed false belief testing at ages 6- to 13-years-old, compared with 95% of typical age-matched peers (Physiol Behav. 2010 Jun 1;100[3]:268-76). The percentage of children on the spectrum understanding false beliefs more closely matched that of preschoolers (39%). At a later age and given extra time to think, some children with autism can do better at this kind of perspective taking, but many continue having difficulty understanding thoughts of others, especially social expectations or motivations (such as flirting, status seeking, and making an excuse) even as adults. This can impair social relationships even when desire to fit in and IQ are otherwise high.
On the other hand, ADHD is a common condition in which “lying” comes from saying the first thing that comes to mind even if the child knows otherwise. A wise parent of one of my patients with ADHD told me about her “30 second rule” where she would give her child that extra time and walk away briefly to “be sure that is what you wanted to say,” with praise rather than give a consequence for changing the story to the truth. This is an important concept we pediatricians need to know: Punishing lying in children tends to result in more, not less, lying and more sneakiness. Instead, parents need to be advised to recall the origins of the word discipline as being “to teach.”
When children lie there are four basic scenarios: They may not know the rules, they may know but have something they want more, they may be impulsive, or they may have developed an attitude of seeking to con the adults whom they feel are mean as a way to have some power in the relationship and get back at them. Clearly, we do not want to push children to this fourth resort by harsh reactions to lying. We have seen particular difficulty with harsh reactions to lying in parents from strong, rule-oriented careers such as police officers, military, and ministers. Asking “How would your parent have handled this?” often will reveal reasons for their tough but backfiring stance.
Lying can work to get what one wants and nearly all children try it. As with other new milestones, children practice this “skill,” much to parents’ dismay. Parents generally can tell if children are lying; they see it on their faces, hear the story from siblings, or see evidence of what happened. Lying provides an important opportunity for the adult to stop, take some breaths, touch the child, and empathize: “It is hard to admit a mistake. I know you did not mean to do it. But you are young, and I know that you are good and honest inside, and will get stronger and braver at telling the truth as you get older. Will you promise to try harder?” In some cases a consequence may be appropriate, for example if something was broken. Usually, simply empathizing and focusing on the expectation for improvement will increase the child’s desire to please the parents rather than get back at them. Actual rewards for honesty improve truth telling by 1.5 times if the reward is big enough.
But it is important to recognize that we all make split second tactical decisions about our actions based on how safe we feel in the situation and our knowledge of social rules and costs. Children over time need to learn that it is safe to tell the truth among family members and that they will not be harshly dealt with. It is a subtle task, but important to learn that deception is a tool that can be important used judiciously when required socially (I have a curfew) or in dangerous situations (I did not see the thug), but can undermine relationships and should not be used with your allies (family and friends).
But parenting involves lying also, which can be a model for the child. Sarcasm is a peculiar form of problematic adult lying. The adults say the opposite or an exaggeration of what they really mean, usually with a smirk or other nonverbal cue to their intent. This is confusing, if not infuriating, to immature children or those who do not understand this twisted communication. It is best to avoid sarcasm with children, or at least be sure to explain it so the children gain understanding over time.
Parents need to “lie” to their children to some extent to reassure and allow for development of confidence. What adult hasn’t said “It’s going to be all right” about a looming storm, car crash, or illness, when actually there is uncertainty. Children count on adults to keep them safe emotionally and physically from things they can’t yet handle. To move forward developmentally, children need adults to be brave leaders, even when the adults don’t feel confident. Some parents think their children must know the “truth” in every instance. Those children are often painfully anxious and overwhelmed.
There is plenty of time for more facts later when the child has the thinking and emotional power to handle the truth.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS (www.CHADIS.com). She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
“Not my son!” your patient’s parent rants. “If he lies to me, he will regret it for a long time.” While your first reaction may be to agree that a child lying to a parent crosses a kind of moral line in the sand, lying is a far more nuanced part of parenting worth a deeper understanding.
In order to lie, a child has to develop cognitive and social understanding. Typically developing children look to see what is interesting to others, called “joint attention,” at around 12-18 months. Failure to do this is one of the early signs of autism reflecting atypical social understanding. At around 3.5 years, children may attempt to deceive if they have broken a rule. The study demonstrating this may sound a lot like home: Children are left alone with a tempting toy but told not to touch it. Although they do touch it while the adult is out of sight, they say rather sweetly (and eventually convincingly) that they did not, even though the toy was clearly moved! While boys generally have more behavior problems, girls and children with better verbal skills achieve deceit at an earlier age, some as young as 2 years. At this stage, children become aware that the adult can’t know exactly what they know. If the parent shows high emotion to what they consider a lie, this can be a topic for testing! Children with ADHD often lack the inhibition needed for early mastery of deception, and children with autism later or not at all. They don’t see the social point to lying nor can they fake a facial expression. They have a case of intractable honesty!
The inability to refrain from telling the truth can result in social rejection, for example when a child rats on a peer for a trivial misdeed in class. Even though he is speaking the truth and “following the (teacher’s) rules,” he did not see that the cost of breaking the (peer) social rules was more important. By age 6 years, children typically figure out that what another person thinks may not be true – their belief may be incorrect or a “false belief.” This understanding is called Theory of Mind, missing or delayed in autism. Only 40% of high-functioning children with autism passed false belief testing at ages 6- to 13-years-old, compared with 95% of typical age-matched peers (Physiol Behav. 2010 Jun 1;100[3]:268-76). The percentage of children on the spectrum understanding false beliefs more closely matched that of preschoolers (39%). At a later age and given extra time to think, some children with autism can do better at this kind of perspective taking, but many continue having difficulty understanding thoughts of others, especially social expectations or motivations (such as flirting, status seeking, and making an excuse) even as adults. This can impair social relationships even when desire to fit in and IQ are otherwise high.
On the other hand, ADHD is a common condition in which “lying” comes from saying the first thing that comes to mind even if the child knows otherwise. A wise parent of one of my patients with ADHD told me about her “30 second rule” where she would give her child that extra time and walk away briefly to “be sure that is what you wanted to say,” with praise rather than give a consequence for changing the story to the truth. This is an important concept we pediatricians need to know: Punishing lying in children tends to result in more, not less, lying and more sneakiness. Instead, parents need to be advised to recall the origins of the word discipline as being “to teach.”
When children lie there are four basic scenarios: They may not know the rules, they may know but have something they want more, they may be impulsive, or they may have developed an attitude of seeking to con the adults whom they feel are mean as a way to have some power in the relationship and get back at them. Clearly, we do not want to push children to this fourth resort by harsh reactions to lying. We have seen particular difficulty with harsh reactions to lying in parents from strong, rule-oriented careers such as police officers, military, and ministers. Asking “How would your parent have handled this?” often will reveal reasons for their tough but backfiring stance.
Lying can work to get what one wants and nearly all children try it. As with other new milestones, children practice this “skill,” much to parents’ dismay. Parents generally can tell if children are lying; they see it on their faces, hear the story from siblings, or see evidence of what happened. Lying provides an important opportunity for the adult to stop, take some breaths, touch the child, and empathize: “It is hard to admit a mistake. I know you did not mean to do it. But you are young, and I know that you are good and honest inside, and will get stronger and braver at telling the truth as you get older. Will you promise to try harder?” In some cases a consequence may be appropriate, for example if something was broken. Usually, simply empathizing and focusing on the expectation for improvement will increase the child’s desire to please the parents rather than get back at them. Actual rewards for honesty improve truth telling by 1.5 times if the reward is big enough.
But it is important to recognize that we all make split second tactical decisions about our actions based on how safe we feel in the situation and our knowledge of social rules and costs. Children over time need to learn that it is safe to tell the truth among family members and that they will not be harshly dealt with. It is a subtle task, but important to learn that deception is a tool that can be important used judiciously when required socially (I have a curfew) or in dangerous situations (I did not see the thug), but can undermine relationships and should not be used with your allies (family and friends).
But parenting involves lying also, which can be a model for the child. Sarcasm is a peculiar form of problematic adult lying. The adults say the opposite or an exaggeration of what they really mean, usually with a smirk or other nonverbal cue to their intent. This is confusing, if not infuriating, to immature children or those who do not understand this twisted communication. It is best to avoid sarcasm with children, or at least be sure to explain it so the children gain understanding over time.
Parents need to “lie” to their children to some extent to reassure and allow for development of confidence. What adult hasn’t said “It’s going to be all right” about a looming storm, car crash, or illness, when actually there is uncertainty. Children count on adults to keep them safe emotionally and physically from things they can’t yet handle. To move forward developmentally, children need adults to be brave leaders, even when the adults don’t feel confident. Some parents think their children must know the “truth” in every instance. Those children are often painfully anxious and overwhelmed.
There is plenty of time for more facts later when the child has the thinking and emotional power to handle the truth.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS (www.CHADIS.com). She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
Critical care admissions up for pediatric opioid poisonings
ORLANDO – The proportion of children and adolescents admitted to critical care for serious poisonings has increased in recent years, according to authors of a study of more than 750,000 reported opioid exposures.
Critical care units were involved in 10% of pediatric opioid poisoning cases registered in 2015-2018, up from 7% in 2005-2009, reported Megan E. Land, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, and coinvestigators.
Attempted suicide has represented an increasingly large proportion of pediatric opioid poisonings from 2005 to 2018, according to the researchers, based on retrospective analysis of cases reported to U.S. poison centers.
Mortality related to these pediatric poisonings increased over time, and among children and adolescents admitted to a pediatric ICU, CPR and naloxone use also increased over time, Dr. Land and associates noted.
These said Dr. Land, who presented the findings at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
“I think that this really requires a two-pronged approach,” she explained. “One is that we need to increase mental health resources for kids to address adolescent suicidality, and secondly, we need to decrease access to opioids in the hands of pediatric patients by decreasing prescribing and then also getting those that are unused out of the homes.”
Jeffrey Zimmerman, MD, past president of SCCM, said these findings on pediatric opioid poisonings represent the “iceberg tip” of a much larger societal issue that has impacts well beyond critical care.
“I think acutely, we’re well equipped to deal with the situation in terms of interventions,” Dr. Zimmerman said in an interview. “The bigger issue is dealing with what happens afterward, when the patient leaves the ICU in the hospital.”
When the issue is chronic opioid use among adolescents or children, critical care specialists can help by initiating opioid tapering in the hospital setting, rather than allowing the complete weaning process to play out at home, he said.
All clinicians can help prevent future injury by asking questions of the child and family to ensure that any opiates and other prescription medications at home are locked up, he added.
“These aren’t very glamorous things, but they’re common sense, and there’s more need for this common sense now than there ever has been,” Dr. Zimmerman concluded.
The study by Dr. Land and colleagues included data on primary opioid ingestions registered at 55 poison control centers in the United States. They assessed trends over three time periods: 2005-2009, 2010-2014, and 2015-2018.
They found that children under 19 years of age accounted for 28% of the 753,592 opioid poisonings reported over that time period.
The overall number of reported opioid poisonings among children declined somewhat since about 2010. However, the proportion admitted to a critical care unit increased from 7% in the 2005-2009 period to 10% in the 2015-2018 period, said Dr. Land, who added that the probability of a moderate or major effect increased by 0.55% and 0.11% per year, respectively, over the 14 years studied.
Mortality – 0.21% overall – increased from 0.18% in the earliest era to 0.28% in the most recent era, according to the investigators.
Suicidal intent increased from 14% in the earliest era to 21% in the most recent era, and was linked to near tenfold odds of undergoing a pediatric ICU procedure, Dr. Land and colleagues reported.
Among those children admitted to a pediatric ICU, use of CPR increased from 1% to 3% in the earliest and latest time periods, respectively; likewise, naloxone administration increased from 42% to 51% over those two time periods. By contrast, there was no change in use of mechanical ventilation (12%) or vasopressors (3%) over time, they added.
The opioids most commonly linked to pediatric ICU procedures were fentanyl (odds ratio, 12), heroin (OR, 11), and methadone (OR, 15).
Some funding for the study came from the Georgia Poison Center. Dr. Land had no disclosures relevant to the research.
SOURCE: Land M et al. Crit Care Med. 2020 doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000618708.38414.ea.
ORLANDO – The proportion of children and adolescents admitted to critical care for serious poisonings has increased in recent years, according to authors of a study of more than 750,000 reported opioid exposures.
Critical care units were involved in 10% of pediatric opioid poisoning cases registered in 2015-2018, up from 7% in 2005-2009, reported Megan E. Land, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, and coinvestigators.
Attempted suicide has represented an increasingly large proportion of pediatric opioid poisonings from 2005 to 2018, according to the researchers, based on retrospective analysis of cases reported to U.S. poison centers.
Mortality related to these pediatric poisonings increased over time, and among children and adolescents admitted to a pediatric ICU, CPR and naloxone use also increased over time, Dr. Land and associates noted.
These said Dr. Land, who presented the findings at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
“I think that this really requires a two-pronged approach,” she explained. “One is that we need to increase mental health resources for kids to address adolescent suicidality, and secondly, we need to decrease access to opioids in the hands of pediatric patients by decreasing prescribing and then also getting those that are unused out of the homes.”
Jeffrey Zimmerman, MD, past president of SCCM, said these findings on pediatric opioid poisonings represent the “iceberg tip” of a much larger societal issue that has impacts well beyond critical care.
“I think acutely, we’re well equipped to deal with the situation in terms of interventions,” Dr. Zimmerman said in an interview. “The bigger issue is dealing with what happens afterward, when the patient leaves the ICU in the hospital.”
When the issue is chronic opioid use among adolescents or children, critical care specialists can help by initiating opioid tapering in the hospital setting, rather than allowing the complete weaning process to play out at home, he said.
All clinicians can help prevent future injury by asking questions of the child and family to ensure that any opiates and other prescription medications at home are locked up, he added.
“These aren’t very glamorous things, but they’re common sense, and there’s more need for this common sense now than there ever has been,” Dr. Zimmerman concluded.
The study by Dr. Land and colleagues included data on primary opioid ingestions registered at 55 poison control centers in the United States. They assessed trends over three time periods: 2005-2009, 2010-2014, and 2015-2018.
They found that children under 19 years of age accounted for 28% of the 753,592 opioid poisonings reported over that time period.
The overall number of reported opioid poisonings among children declined somewhat since about 2010. However, the proportion admitted to a critical care unit increased from 7% in the 2005-2009 period to 10% in the 2015-2018 period, said Dr. Land, who added that the probability of a moderate or major effect increased by 0.55% and 0.11% per year, respectively, over the 14 years studied.
Mortality – 0.21% overall – increased from 0.18% in the earliest era to 0.28% in the most recent era, according to the investigators.
Suicidal intent increased from 14% in the earliest era to 21% in the most recent era, and was linked to near tenfold odds of undergoing a pediatric ICU procedure, Dr. Land and colleagues reported.
Among those children admitted to a pediatric ICU, use of CPR increased from 1% to 3% in the earliest and latest time periods, respectively; likewise, naloxone administration increased from 42% to 51% over those two time periods. By contrast, there was no change in use of mechanical ventilation (12%) or vasopressors (3%) over time, they added.
The opioids most commonly linked to pediatric ICU procedures were fentanyl (odds ratio, 12), heroin (OR, 11), and methadone (OR, 15).
Some funding for the study came from the Georgia Poison Center. Dr. Land had no disclosures relevant to the research.
SOURCE: Land M et al. Crit Care Med. 2020 doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000618708.38414.ea.
ORLANDO – The proportion of children and adolescents admitted to critical care for serious poisonings has increased in recent years, according to authors of a study of more than 750,000 reported opioid exposures.
Critical care units were involved in 10% of pediatric opioid poisoning cases registered in 2015-2018, up from 7% in 2005-2009, reported Megan E. Land, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, and coinvestigators.
Attempted suicide has represented an increasingly large proportion of pediatric opioid poisonings from 2005 to 2018, according to the researchers, based on retrospective analysis of cases reported to U.S. poison centers.
Mortality related to these pediatric poisonings increased over time, and among children and adolescents admitted to a pediatric ICU, CPR and naloxone use also increased over time, Dr. Land and associates noted.
These said Dr. Land, who presented the findings at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
“I think that this really requires a two-pronged approach,” she explained. “One is that we need to increase mental health resources for kids to address adolescent suicidality, and secondly, we need to decrease access to opioids in the hands of pediatric patients by decreasing prescribing and then also getting those that are unused out of the homes.”
Jeffrey Zimmerman, MD, past president of SCCM, said these findings on pediatric opioid poisonings represent the “iceberg tip” of a much larger societal issue that has impacts well beyond critical care.
“I think acutely, we’re well equipped to deal with the situation in terms of interventions,” Dr. Zimmerman said in an interview. “The bigger issue is dealing with what happens afterward, when the patient leaves the ICU in the hospital.”
When the issue is chronic opioid use among adolescents or children, critical care specialists can help by initiating opioid tapering in the hospital setting, rather than allowing the complete weaning process to play out at home, he said.
All clinicians can help prevent future injury by asking questions of the child and family to ensure that any opiates and other prescription medications at home are locked up, he added.
“These aren’t very glamorous things, but they’re common sense, and there’s more need for this common sense now than there ever has been,” Dr. Zimmerman concluded.
The study by Dr. Land and colleagues included data on primary opioid ingestions registered at 55 poison control centers in the United States. They assessed trends over three time periods: 2005-2009, 2010-2014, and 2015-2018.
They found that children under 19 years of age accounted for 28% of the 753,592 opioid poisonings reported over that time period.
The overall number of reported opioid poisonings among children declined somewhat since about 2010. However, the proportion admitted to a critical care unit increased from 7% in the 2005-2009 period to 10% in the 2015-2018 period, said Dr. Land, who added that the probability of a moderate or major effect increased by 0.55% and 0.11% per year, respectively, over the 14 years studied.
Mortality – 0.21% overall – increased from 0.18% in the earliest era to 0.28% in the most recent era, according to the investigators.
Suicidal intent increased from 14% in the earliest era to 21% in the most recent era, and was linked to near tenfold odds of undergoing a pediatric ICU procedure, Dr. Land and colleagues reported.
Among those children admitted to a pediatric ICU, use of CPR increased from 1% to 3% in the earliest and latest time periods, respectively; likewise, naloxone administration increased from 42% to 51% over those two time periods. By contrast, there was no change in use of mechanical ventilation (12%) or vasopressors (3%) over time, they added.
The opioids most commonly linked to pediatric ICU procedures were fentanyl (odds ratio, 12), heroin (OR, 11), and methadone (OR, 15).
Some funding for the study came from the Georgia Poison Center. Dr. Land had no disclosures relevant to the research.
SOURCE: Land M et al. Crit Care Med. 2020 doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000618708.38414.ea.
REPORTING FROM CCC49
Infection with 2019 novel coronavirus extends to infants
between Dec. 8, 2019, and Feb. 6, 2020, based on data from the Chinese central government and local health departments.
“As of February 6, 2020, China reported 31,211 confirmed cases of COVID-19 and 637 fatalities,” wrote Min Wei, MD, of Wuhan University, China, and colleagues. However, “few infections in children have been reported.”
In a research letter published in JAMA, the investigators reviewed data from nine infants aged 28 days to 1 year who were hospitalized with a diagnosis of COVID-19 between Dec. 8, 2019, and Feb. 6, 2020. The ages of the infants ranged from 1 month to 11 months, and seven were female. The patients included two children from Beijing, two from Hainan, and one each from the areas of Guangdong, Anhui, Shanghai, Zhejiang, and Guizhou.
All infected infants had at least one infected family member, and the infants’ infections occurred after the family members’ infections; seven infants lived in Wuhan or had family members who had visited Wuhan.
One of the infants had no symptoms but tested positive for the 2019 novel coronavirus, and two others had a diagnosis but missing information on any symptoms. Fever occurred in four patients, and mild upper respiratory tract symptoms occurred in two patients.
None of the infants died, and none reported severe complications or the need for intensive care or mechanical ventilation, the investigators said. The fact that most of the infants were female might suggest that they are more susceptible to the virus than males, although overall COVID-19 viral infections have been more common in adult men, especially those with chronic comorbidities, Dr. Wei and associates noted.
The study findings were limited by the small sample size and lack of symptom data for some patients, the researchers said. However, the results confirm that the COVID-19 virus is transmissible to infants younger than 1 year, and adult caregivers should exercise protective measures including wearing masks, washing hands before contact with infants, and routinely sterilizing toys and tableware, they emphasized.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Wei M et al. JAMA. 2020 Feb 14. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2131.
between Dec. 8, 2019, and Feb. 6, 2020, based on data from the Chinese central government and local health departments.
“As of February 6, 2020, China reported 31,211 confirmed cases of COVID-19 and 637 fatalities,” wrote Min Wei, MD, of Wuhan University, China, and colleagues. However, “few infections in children have been reported.”
In a research letter published in JAMA, the investigators reviewed data from nine infants aged 28 days to 1 year who were hospitalized with a diagnosis of COVID-19 between Dec. 8, 2019, and Feb. 6, 2020. The ages of the infants ranged from 1 month to 11 months, and seven were female. The patients included two children from Beijing, two from Hainan, and one each from the areas of Guangdong, Anhui, Shanghai, Zhejiang, and Guizhou.
All infected infants had at least one infected family member, and the infants’ infections occurred after the family members’ infections; seven infants lived in Wuhan or had family members who had visited Wuhan.
One of the infants had no symptoms but tested positive for the 2019 novel coronavirus, and two others had a diagnosis but missing information on any symptoms. Fever occurred in four patients, and mild upper respiratory tract symptoms occurred in two patients.
None of the infants died, and none reported severe complications or the need for intensive care or mechanical ventilation, the investigators said. The fact that most of the infants were female might suggest that they are more susceptible to the virus than males, although overall COVID-19 viral infections have been more common in adult men, especially those with chronic comorbidities, Dr. Wei and associates noted.
The study findings were limited by the small sample size and lack of symptom data for some patients, the researchers said. However, the results confirm that the COVID-19 virus is transmissible to infants younger than 1 year, and adult caregivers should exercise protective measures including wearing masks, washing hands before contact with infants, and routinely sterilizing toys and tableware, they emphasized.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Wei M et al. JAMA. 2020 Feb 14. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2131.
between Dec. 8, 2019, and Feb. 6, 2020, based on data from the Chinese central government and local health departments.
“As of February 6, 2020, China reported 31,211 confirmed cases of COVID-19 and 637 fatalities,” wrote Min Wei, MD, of Wuhan University, China, and colleagues. However, “few infections in children have been reported.”
In a research letter published in JAMA, the investigators reviewed data from nine infants aged 28 days to 1 year who were hospitalized with a diagnosis of COVID-19 between Dec. 8, 2019, and Feb. 6, 2020. The ages of the infants ranged from 1 month to 11 months, and seven were female. The patients included two children from Beijing, two from Hainan, and one each from the areas of Guangdong, Anhui, Shanghai, Zhejiang, and Guizhou.
All infected infants had at least one infected family member, and the infants’ infections occurred after the family members’ infections; seven infants lived in Wuhan or had family members who had visited Wuhan.
One of the infants had no symptoms but tested positive for the 2019 novel coronavirus, and two others had a diagnosis but missing information on any symptoms. Fever occurred in four patients, and mild upper respiratory tract symptoms occurred in two patients.
None of the infants died, and none reported severe complications or the need for intensive care or mechanical ventilation, the investigators said. The fact that most of the infants were female might suggest that they are more susceptible to the virus than males, although overall COVID-19 viral infections have been more common in adult men, especially those with chronic comorbidities, Dr. Wei and associates noted.
The study findings were limited by the small sample size and lack of symptom data for some patients, the researchers said. However, the results confirm that the COVID-19 virus is transmissible to infants younger than 1 year, and adult caregivers should exercise protective measures including wearing masks, washing hands before contact with infants, and routinely sterilizing toys and tableware, they emphasized.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Wei M et al. JAMA. 2020 Feb 14. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2131.
FROM JAMA
Psychopharmacology for aggression? Our field’s ‘nonconsensus’ and the risks
A 13-year-old boy with ADHD, combined type, presents to his family physician with his parents. His parents called for an appointment outside of his routine follow-up care to discuss what they should do to address their son’s new “aggressive behaviors.” He will throw objects when angry, yell, and slam doors at home when he is told to turn off video games. He used to play soccer but doesn’t anymore. He has maintained very good grades and friends. There is not a concern for substance abuse at this time.He speaks in curt sentences during the appointment, and he has his arms crossed or is looking out of the window the entire time.
His parents share in front on him that he has always been a “difficult child” (their words), but they now are struggling to adjust to his aggressive tendencies as he ages. He is growing bigger and angrier. He will not attend therapy and will not see a consultation psychiatrist in the office. A variety of stimulant trials including Ritalin and amphetamine preparations to manage impulsivity in ADHD were ineffective to curb his aggression, and he doesn’t want to take any medication.
They ask, what do we do? They are not worried for their safety but living like this is eroding their quality of life as a family, and the dynamic seems destined to get worse before it gets better.
They wonder, is there a next medication step to manage his aggression?
A family physician presented the above situation to me in my role as a child and adolescent psychiatrist in the medical home. It led us to a fruitful discussion of aggression and what can be done to help families who are all too often in situations like the above, then in your office looking for immediate solutions. The questions are, what can be done with an aggressive child, even and especially without the child’s buy-in to work on that as a problem?
Psychoeducation can go a long way in helping families rethink aggression as a symptom of something deeper, either in the environment or a diagnosis, although we all can empathize with the desire to reconcile the above behavior immediately.
Characterize the aggression
First, it can be helpful to identify a child’s aggression type. There are two types of aggression, reactive and proactive. We most often see reactive aggression in our clinics, which is aggression as a defensive and impulsive response to something in the environment (often limit-setting, as above). Proactive aggression is premeditated and may appear as aggression for aggression’s sake without the emotional drive behind it.
Secondly, it also can be helpful to know that externalizing and internalizing symptoms can represent different sides of the same coin, with the proverbial “coin” as “emotion” and the associated behaviors (throwing objects, in the above example) as the “signs” that there is a complex difficulty in managing painful emotions. Some children (and adults too!) tend to “externalize” strong emotions as aggression or irritability with others, while others “internalize” them by retreating with internal suffering such as “anxiety and depression.” These styles also can be similar among children and their parents.
With those two points in mind, it’s important to consider the diagnosis, which would guide treatment. It’s generally agreed upon that “reactive aggression” is more likely to be related to underlying untreated ADHD, or a depressive or anxiety disorder. This is much more amenable to treatment than aggression related to oppositional defiant disorder or conduct disorder, which are more defined by proactive forms of aggression.
You can pick up on family dynamics that may inadvertently reinforce the same behaviors they so wish to change. In the above example, the parents have clearly identified their son as “the problem.” You can imagine the difficulty of going to school and being a “problem,” and then coming home and feeling the same way. This negative perception can erode a child’s self-esteem over time, which may appear as disengagement or simply not caring in an appointment. It may become harder and harder to engage the child in psychotherapy or even in taking a medication as their only means of resistance to that painful notion about oneself as the “problem.”
It can be useful to begin appointments with “what is going well?” (in the example above, he “has friends and is maintaining grades”) and “what do you like most about your child?” As we all know, positive reinforcement is more powerful than its counterpart. Also problems in a family often are complex, and may involve many family members needing to change to meet their goals, not just the child.
Why you should try behavioral interventions first
Behavioral interventions are the first step always. Parents can do behavioral interventions and change their parenting and family environment through their own behavioral changes – commonly called parent management training. They can assess antecedents of aggression and their own responses, which may contribute or perpetuate a cycle of the aggression – such as giving attention or giving in to fewer limitations to avoid a fight. This small but important point can help protect against a feeling of helplessness that a child will not engage in therapy or skills-building.
In answering the clinician’s question about what to do next, I often feel like the question embedded in this is “what medication is next?” There is a felt pressure to do something “right now” conveyed to a clinician. This drives the impulse to prescribe something immediately – and likely more risky and with less of an evidence base – even before trying the known psychotherapy interventions that have the most evidence to change aggressive tendencies.
In looking deeper into this consultation case, I also found more “food for thought” for one’s thinking about aggression and psychopharmacology in cases like the above: Aggression isn’t an uncomplicated symptom that one can address immediately, and therefore we cannot rely on symptom-specific management to eradicate it. This is similar to prescribing Tylenol to manage a general ache or pain; if the pain persists, we want to know the “whys” of the pain persisting.
Thankfully, there are ways that a parent can better understand behaviors with this philosophy in mind. Applied Behavioral Analysis1 offers some helpful ideas, not only for children with autism spectrum disorder, but that can be applied to one’s understanding of other’s behavior in general. ABA pays attention to antecedents, perpetuating factors, and consequences as well as their interplay in understanding behaviors. You can encourage a family – rather than wanting to “get rid of a problem behavior” – to try to understand it and come up, with help from a psychotherapist or other professional, with a deeper evaluation of the behavior and a specific, collaborative plan.
Most experts see that ADHD, anxiety disorders, depressive disorders, and unrecognized learning disabilities, in sum, are more common underpinnings than not with aggressive children. This also can be confounded by an environment with parents who have those diagnoses untreated as well. Aggression should raise a red flag in our clinics to consider the above even if a family or child simply says aggression is the one issue, and it’s only the child with the issue.
While there have been attempts to find a “spot treatment” for aggression in a medication, medications not only fail to address the underlying issues many times, but have little evidence that support them and may do more harm long term than good.2
Kids need outlets for “normal aggressive drives.” And puberty, as in the case above, is a time of intense emotions of all varieties. In the example above, you may notice that the child is no longer playing soccer, which was likely serving some protective function in many ways for him and as a positive outlet for aggression. In the same way, you may see that kids who are more sedentary or idle (playing unrestricted video games now instead of sports, ) would benefit from revisiting outlets or finding new ones as a family.
Consider medications if the underlying diagnosis merits it
We generally seek to find and treat the underlying diagnosis, if it exists, in the following ways.
If a child has ADHD, as in the case above, you can trial a stimulant or an alpha-adrenergic agent to target impulsivity if that is suspected as the driver of aggression. This may include guanfacine (long-acting Intuniv at night, but I would choose lower dosing such as 0.5 mg to 1 mg at bedtime) to manage ADHD. However, the evidence base that management of ADHD improves aggressive behaviors at all or on their own, is scant. In addition, these medications can represent more harm than good as well, although they are perceived as more innocuous than their antipsychotic counterparts. For example, some patients can begin to have bed-wetting accidents in the evening or become sleepy in classes, which can further erode their sense of self-confidence even if this is clearly attributable to a medication side effect and resolves once the agent is reduced or removed.
In the same way to reorient to diagnosis with children with aggression, you can consider an SSRI for an anxiety disorder or irritable depression. But know that it’s a rare thing for children to say specifically that they are struggling with their emotions, whether they are angry, sad, or nervous and that a deeper dive into this may be warranted. Data by Connor DF et al.3 may indicate anxiety disorders should be highest on one’s differential diagnosis in aggression, followed by consideration for ADHD, which may be a different assumption than one would expect.
Mood stabilizers –lamotrigine (Lamictal), divalproex sodium (Depakote), and lithium – and antipsychotics – aripiprazole (Abilify) and risperidone (Risperdal) – are risky medications and the use of them contradicts the first point, agreed upon by most experts, that diagnosis should drive treatment. One is hardly ever treating a young child for psychosis or bipolar disorder in these circumstances of episodic, reactive aggression. Antipsychotics also carry the notorious risks of metabolic syndrome, among other risks to overall health, which becomes an additive risk over time and potentially into adulthood. I once heard in my child adolescent psychiatry training the haunting phase, “yes, they can ‘work’ quickly but they can work ‘almost too well,’ ” meaning they can sedate or tranquilize an aggressive child when the real goal should be to understand, diagnose, and intervene in ways that see the “big picture” of aggression.
Benzodiazepines generally are avoided in children due to disinhibition and often not even considered, in these circumstances, as they are in adults to manage agitation or aggression, due to this fact.
In many instances in working with families, our role in primary care can be one of illuminating children’s behaviors not just as symptoms to treat, but to understand deeply. This is as true for aggression as it is for anxiety.
Finally, I am reminded of the common question I receive from adult patients in primary care who ask me if anyone has yet made a medication to lose weight that’s safe and effective. Then the counseling commences on our fantasies, from our patients and ourselves, about what medications can do for us and our risks therein.
Dr. Pawlowski is an adult, adolescent, and child psychiatrist at the University of Vermont Medical Center and assistant professor of psychiatry at the Larner College of Medicine at UVM in Burlington. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. ABA in the Treatment of Aggressive Behavior Disorder and Lack of Impulse Control.
2. Managing Aggression in Children: A Practical Approach, The Carlat Child Psychiatry Report, May 2010, The Explosive Child.
3. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2006 May;37[1]:1-14.
A 13-year-old boy with ADHD, combined type, presents to his family physician with his parents. His parents called for an appointment outside of his routine follow-up care to discuss what they should do to address their son’s new “aggressive behaviors.” He will throw objects when angry, yell, and slam doors at home when he is told to turn off video games. He used to play soccer but doesn’t anymore. He has maintained very good grades and friends. There is not a concern for substance abuse at this time.He speaks in curt sentences during the appointment, and he has his arms crossed or is looking out of the window the entire time.
His parents share in front on him that he has always been a “difficult child” (their words), but they now are struggling to adjust to his aggressive tendencies as he ages. He is growing bigger and angrier. He will not attend therapy and will not see a consultation psychiatrist in the office. A variety of stimulant trials including Ritalin and amphetamine preparations to manage impulsivity in ADHD were ineffective to curb his aggression, and he doesn’t want to take any medication.
They ask, what do we do? They are not worried for their safety but living like this is eroding their quality of life as a family, and the dynamic seems destined to get worse before it gets better.
They wonder, is there a next medication step to manage his aggression?
A family physician presented the above situation to me in my role as a child and adolescent psychiatrist in the medical home. It led us to a fruitful discussion of aggression and what can be done to help families who are all too often in situations like the above, then in your office looking for immediate solutions. The questions are, what can be done with an aggressive child, even and especially without the child’s buy-in to work on that as a problem?
Psychoeducation can go a long way in helping families rethink aggression as a symptom of something deeper, either in the environment or a diagnosis, although we all can empathize with the desire to reconcile the above behavior immediately.
Characterize the aggression
First, it can be helpful to identify a child’s aggression type. There are two types of aggression, reactive and proactive. We most often see reactive aggression in our clinics, which is aggression as a defensive and impulsive response to something in the environment (often limit-setting, as above). Proactive aggression is premeditated and may appear as aggression for aggression’s sake without the emotional drive behind it.
Secondly, it also can be helpful to know that externalizing and internalizing symptoms can represent different sides of the same coin, with the proverbial “coin” as “emotion” and the associated behaviors (throwing objects, in the above example) as the “signs” that there is a complex difficulty in managing painful emotions. Some children (and adults too!) tend to “externalize” strong emotions as aggression or irritability with others, while others “internalize” them by retreating with internal suffering such as “anxiety and depression.” These styles also can be similar among children and their parents.
With those two points in mind, it’s important to consider the diagnosis, which would guide treatment. It’s generally agreed upon that “reactive aggression” is more likely to be related to underlying untreated ADHD, or a depressive or anxiety disorder. This is much more amenable to treatment than aggression related to oppositional defiant disorder or conduct disorder, which are more defined by proactive forms of aggression.
You can pick up on family dynamics that may inadvertently reinforce the same behaviors they so wish to change. In the above example, the parents have clearly identified their son as “the problem.” You can imagine the difficulty of going to school and being a “problem,” and then coming home and feeling the same way. This negative perception can erode a child’s self-esteem over time, which may appear as disengagement or simply not caring in an appointment. It may become harder and harder to engage the child in psychotherapy or even in taking a medication as their only means of resistance to that painful notion about oneself as the “problem.”
It can be useful to begin appointments with “what is going well?” (in the example above, he “has friends and is maintaining grades”) and “what do you like most about your child?” As we all know, positive reinforcement is more powerful than its counterpart. Also problems in a family often are complex, and may involve many family members needing to change to meet their goals, not just the child.
Why you should try behavioral interventions first
Behavioral interventions are the first step always. Parents can do behavioral interventions and change their parenting and family environment through their own behavioral changes – commonly called parent management training. They can assess antecedents of aggression and their own responses, which may contribute or perpetuate a cycle of the aggression – such as giving attention or giving in to fewer limitations to avoid a fight. This small but important point can help protect against a feeling of helplessness that a child will not engage in therapy or skills-building.
In answering the clinician’s question about what to do next, I often feel like the question embedded in this is “what medication is next?” There is a felt pressure to do something “right now” conveyed to a clinician. This drives the impulse to prescribe something immediately – and likely more risky and with less of an evidence base – even before trying the known psychotherapy interventions that have the most evidence to change aggressive tendencies.
In looking deeper into this consultation case, I also found more “food for thought” for one’s thinking about aggression and psychopharmacology in cases like the above: Aggression isn’t an uncomplicated symptom that one can address immediately, and therefore we cannot rely on symptom-specific management to eradicate it. This is similar to prescribing Tylenol to manage a general ache or pain; if the pain persists, we want to know the “whys” of the pain persisting.
Thankfully, there are ways that a parent can better understand behaviors with this philosophy in mind. Applied Behavioral Analysis1 offers some helpful ideas, not only for children with autism spectrum disorder, but that can be applied to one’s understanding of other’s behavior in general. ABA pays attention to antecedents, perpetuating factors, and consequences as well as their interplay in understanding behaviors. You can encourage a family – rather than wanting to “get rid of a problem behavior” – to try to understand it and come up, with help from a psychotherapist or other professional, with a deeper evaluation of the behavior and a specific, collaborative plan.
Most experts see that ADHD, anxiety disorders, depressive disorders, and unrecognized learning disabilities, in sum, are more common underpinnings than not with aggressive children. This also can be confounded by an environment with parents who have those diagnoses untreated as well. Aggression should raise a red flag in our clinics to consider the above even if a family or child simply says aggression is the one issue, and it’s only the child with the issue.
While there have been attempts to find a “spot treatment” for aggression in a medication, medications not only fail to address the underlying issues many times, but have little evidence that support them and may do more harm long term than good.2
Kids need outlets for “normal aggressive drives.” And puberty, as in the case above, is a time of intense emotions of all varieties. In the example above, you may notice that the child is no longer playing soccer, which was likely serving some protective function in many ways for him and as a positive outlet for aggression. In the same way, you may see that kids who are more sedentary or idle (playing unrestricted video games now instead of sports, ) would benefit from revisiting outlets or finding new ones as a family.
Consider medications if the underlying diagnosis merits it
We generally seek to find and treat the underlying diagnosis, if it exists, in the following ways.
If a child has ADHD, as in the case above, you can trial a stimulant or an alpha-adrenergic agent to target impulsivity if that is suspected as the driver of aggression. This may include guanfacine (long-acting Intuniv at night, but I would choose lower dosing such as 0.5 mg to 1 mg at bedtime) to manage ADHD. However, the evidence base that management of ADHD improves aggressive behaviors at all or on their own, is scant. In addition, these medications can represent more harm than good as well, although they are perceived as more innocuous than their antipsychotic counterparts. For example, some patients can begin to have bed-wetting accidents in the evening or become sleepy in classes, which can further erode their sense of self-confidence even if this is clearly attributable to a medication side effect and resolves once the agent is reduced or removed.
In the same way to reorient to diagnosis with children with aggression, you can consider an SSRI for an anxiety disorder or irritable depression. But know that it’s a rare thing for children to say specifically that they are struggling with their emotions, whether they are angry, sad, or nervous and that a deeper dive into this may be warranted. Data by Connor DF et al.3 may indicate anxiety disorders should be highest on one’s differential diagnosis in aggression, followed by consideration for ADHD, which may be a different assumption than one would expect.
Mood stabilizers –lamotrigine (Lamictal), divalproex sodium (Depakote), and lithium – and antipsychotics – aripiprazole (Abilify) and risperidone (Risperdal) – are risky medications and the use of them contradicts the first point, agreed upon by most experts, that diagnosis should drive treatment. One is hardly ever treating a young child for psychosis or bipolar disorder in these circumstances of episodic, reactive aggression. Antipsychotics also carry the notorious risks of metabolic syndrome, among other risks to overall health, which becomes an additive risk over time and potentially into adulthood. I once heard in my child adolescent psychiatry training the haunting phase, “yes, they can ‘work’ quickly but they can work ‘almost too well,’ ” meaning they can sedate or tranquilize an aggressive child when the real goal should be to understand, diagnose, and intervene in ways that see the “big picture” of aggression.
Benzodiazepines generally are avoided in children due to disinhibition and often not even considered, in these circumstances, as they are in adults to manage agitation or aggression, due to this fact.
In many instances in working with families, our role in primary care can be one of illuminating children’s behaviors not just as symptoms to treat, but to understand deeply. This is as true for aggression as it is for anxiety.
Finally, I am reminded of the common question I receive from adult patients in primary care who ask me if anyone has yet made a medication to lose weight that’s safe and effective. Then the counseling commences on our fantasies, from our patients and ourselves, about what medications can do for us and our risks therein.
Dr. Pawlowski is an adult, adolescent, and child psychiatrist at the University of Vermont Medical Center and assistant professor of psychiatry at the Larner College of Medicine at UVM in Burlington. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. ABA in the Treatment of Aggressive Behavior Disorder and Lack of Impulse Control.
2. Managing Aggression in Children: A Practical Approach, The Carlat Child Psychiatry Report, May 2010, The Explosive Child.
3. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2006 May;37[1]:1-14.
A 13-year-old boy with ADHD, combined type, presents to his family physician with his parents. His parents called for an appointment outside of his routine follow-up care to discuss what they should do to address their son’s new “aggressive behaviors.” He will throw objects when angry, yell, and slam doors at home when he is told to turn off video games. He used to play soccer but doesn’t anymore. He has maintained very good grades and friends. There is not a concern for substance abuse at this time.He speaks in curt sentences during the appointment, and he has his arms crossed or is looking out of the window the entire time.
His parents share in front on him that he has always been a “difficult child” (their words), but they now are struggling to adjust to his aggressive tendencies as he ages. He is growing bigger and angrier. He will not attend therapy and will not see a consultation psychiatrist in the office. A variety of stimulant trials including Ritalin and amphetamine preparations to manage impulsivity in ADHD were ineffective to curb his aggression, and he doesn’t want to take any medication.
They ask, what do we do? They are not worried for their safety but living like this is eroding their quality of life as a family, and the dynamic seems destined to get worse before it gets better.
They wonder, is there a next medication step to manage his aggression?
A family physician presented the above situation to me in my role as a child and adolescent psychiatrist in the medical home. It led us to a fruitful discussion of aggression and what can be done to help families who are all too often in situations like the above, then in your office looking for immediate solutions. The questions are, what can be done with an aggressive child, even and especially without the child’s buy-in to work on that as a problem?
Psychoeducation can go a long way in helping families rethink aggression as a symptom of something deeper, either in the environment or a diagnosis, although we all can empathize with the desire to reconcile the above behavior immediately.
Characterize the aggression
First, it can be helpful to identify a child’s aggression type. There are two types of aggression, reactive and proactive. We most often see reactive aggression in our clinics, which is aggression as a defensive and impulsive response to something in the environment (often limit-setting, as above). Proactive aggression is premeditated and may appear as aggression for aggression’s sake without the emotional drive behind it.
Secondly, it also can be helpful to know that externalizing and internalizing symptoms can represent different sides of the same coin, with the proverbial “coin” as “emotion” and the associated behaviors (throwing objects, in the above example) as the “signs” that there is a complex difficulty in managing painful emotions. Some children (and adults too!) tend to “externalize” strong emotions as aggression or irritability with others, while others “internalize” them by retreating with internal suffering such as “anxiety and depression.” These styles also can be similar among children and their parents.
With those two points in mind, it’s important to consider the diagnosis, which would guide treatment. It’s generally agreed upon that “reactive aggression” is more likely to be related to underlying untreated ADHD, or a depressive or anxiety disorder. This is much more amenable to treatment than aggression related to oppositional defiant disorder or conduct disorder, which are more defined by proactive forms of aggression.
You can pick up on family dynamics that may inadvertently reinforce the same behaviors they so wish to change. In the above example, the parents have clearly identified their son as “the problem.” You can imagine the difficulty of going to school and being a “problem,” and then coming home and feeling the same way. This negative perception can erode a child’s self-esteem over time, which may appear as disengagement or simply not caring in an appointment. It may become harder and harder to engage the child in psychotherapy or even in taking a medication as their only means of resistance to that painful notion about oneself as the “problem.”
It can be useful to begin appointments with “what is going well?” (in the example above, he “has friends and is maintaining grades”) and “what do you like most about your child?” As we all know, positive reinforcement is more powerful than its counterpart. Also problems in a family often are complex, and may involve many family members needing to change to meet their goals, not just the child.
Why you should try behavioral interventions first
Behavioral interventions are the first step always. Parents can do behavioral interventions and change their parenting and family environment through their own behavioral changes – commonly called parent management training. They can assess antecedents of aggression and their own responses, which may contribute or perpetuate a cycle of the aggression – such as giving attention or giving in to fewer limitations to avoid a fight. This small but important point can help protect against a feeling of helplessness that a child will not engage in therapy or skills-building.
In answering the clinician’s question about what to do next, I often feel like the question embedded in this is “what medication is next?” There is a felt pressure to do something “right now” conveyed to a clinician. This drives the impulse to prescribe something immediately – and likely more risky and with less of an evidence base – even before trying the known psychotherapy interventions that have the most evidence to change aggressive tendencies.
In looking deeper into this consultation case, I also found more “food for thought” for one’s thinking about aggression and psychopharmacology in cases like the above: Aggression isn’t an uncomplicated symptom that one can address immediately, and therefore we cannot rely on symptom-specific management to eradicate it. This is similar to prescribing Tylenol to manage a general ache or pain; if the pain persists, we want to know the “whys” of the pain persisting.
Thankfully, there are ways that a parent can better understand behaviors with this philosophy in mind. Applied Behavioral Analysis1 offers some helpful ideas, not only for children with autism spectrum disorder, but that can be applied to one’s understanding of other’s behavior in general. ABA pays attention to antecedents, perpetuating factors, and consequences as well as their interplay in understanding behaviors. You can encourage a family – rather than wanting to “get rid of a problem behavior” – to try to understand it and come up, with help from a psychotherapist or other professional, with a deeper evaluation of the behavior and a specific, collaborative plan.
Most experts see that ADHD, anxiety disorders, depressive disorders, and unrecognized learning disabilities, in sum, are more common underpinnings than not with aggressive children. This also can be confounded by an environment with parents who have those diagnoses untreated as well. Aggression should raise a red flag in our clinics to consider the above even if a family or child simply says aggression is the one issue, and it’s only the child with the issue.
While there have been attempts to find a “spot treatment” for aggression in a medication, medications not only fail to address the underlying issues many times, but have little evidence that support them and may do more harm long term than good.2
Kids need outlets for “normal aggressive drives.” And puberty, as in the case above, is a time of intense emotions of all varieties. In the example above, you may notice that the child is no longer playing soccer, which was likely serving some protective function in many ways for him and as a positive outlet for aggression. In the same way, you may see that kids who are more sedentary or idle (playing unrestricted video games now instead of sports, ) would benefit from revisiting outlets or finding new ones as a family.
Consider medications if the underlying diagnosis merits it
We generally seek to find and treat the underlying diagnosis, if it exists, in the following ways.
If a child has ADHD, as in the case above, you can trial a stimulant or an alpha-adrenergic agent to target impulsivity if that is suspected as the driver of aggression. This may include guanfacine (long-acting Intuniv at night, but I would choose lower dosing such as 0.5 mg to 1 mg at bedtime) to manage ADHD. However, the evidence base that management of ADHD improves aggressive behaviors at all or on their own, is scant. In addition, these medications can represent more harm than good as well, although they are perceived as more innocuous than their antipsychotic counterparts. For example, some patients can begin to have bed-wetting accidents in the evening or become sleepy in classes, which can further erode their sense of self-confidence even if this is clearly attributable to a medication side effect and resolves once the agent is reduced or removed.
In the same way to reorient to diagnosis with children with aggression, you can consider an SSRI for an anxiety disorder or irritable depression. But know that it’s a rare thing for children to say specifically that they are struggling with their emotions, whether they are angry, sad, or nervous and that a deeper dive into this may be warranted. Data by Connor DF et al.3 may indicate anxiety disorders should be highest on one’s differential diagnosis in aggression, followed by consideration for ADHD, which may be a different assumption than one would expect.
Mood stabilizers –lamotrigine (Lamictal), divalproex sodium (Depakote), and lithium – and antipsychotics – aripiprazole (Abilify) and risperidone (Risperdal) – are risky medications and the use of them contradicts the first point, agreed upon by most experts, that diagnosis should drive treatment. One is hardly ever treating a young child for psychosis or bipolar disorder in these circumstances of episodic, reactive aggression. Antipsychotics also carry the notorious risks of metabolic syndrome, among other risks to overall health, which becomes an additive risk over time and potentially into adulthood. I once heard in my child adolescent psychiatry training the haunting phase, “yes, they can ‘work’ quickly but they can work ‘almost too well,’ ” meaning they can sedate or tranquilize an aggressive child when the real goal should be to understand, diagnose, and intervene in ways that see the “big picture” of aggression.
Benzodiazepines generally are avoided in children due to disinhibition and often not even considered, in these circumstances, as they are in adults to manage agitation or aggression, due to this fact.
In many instances in working with families, our role in primary care can be one of illuminating children’s behaviors not just as symptoms to treat, but to understand deeply. This is as true for aggression as it is for anxiety.
Finally, I am reminded of the common question I receive from adult patients in primary care who ask me if anyone has yet made a medication to lose weight that’s safe and effective. Then the counseling commences on our fantasies, from our patients and ourselves, about what medications can do for us and our risks therein.
Dr. Pawlowski is an adult, adolescent, and child psychiatrist at the University of Vermont Medical Center and assistant professor of psychiatry at the Larner College of Medicine at UVM in Burlington. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. ABA in the Treatment of Aggressive Behavior Disorder and Lack of Impulse Control.
2. Managing Aggression in Children: A Practical Approach, The Carlat Child Psychiatry Report, May 2010, The Explosive Child.
3. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2006 May;37[1]:1-14.
Flu increases activity but not its severity

The CDC’s latest report shows that 6.8% of outpatients visiting health care providers had influenza-like illness during the week ending Feb. 8. That’s up from the previous week’s 6.6%, but that rise of 0.2 percentage points is smaller than the 0.6-point rises that occurred each of the 2 weeks before, and that could mean that activity is slowing.
That slowing, however, is not noticeable from this week’s map, which puts 41 states (there were 35 last week) and Puerto Rico in the red at the highest level of activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale and another three states in the “high” range with levels of 8 or 9, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
That leaves Nevada and Oregon at level 7; Alaska, Florida, and the District of Columbia at level 5; Idaho at level 3, and Delaware with insufficient data (it was at level 5 last week), the CDC said.
The 2019-2020 season’s high activity, fortunately, has not translated into high severity, as overall hospitalization and mortality rates continue to remain at fairly typical levels. Hospitalization rates are elevated among children and young adults, however, and pediatric deaths are now up to 92, the CDC said, which is high for this point in the season.

The CDC’s latest report shows that 6.8% of outpatients visiting health care providers had influenza-like illness during the week ending Feb. 8. That’s up from the previous week’s 6.6%, but that rise of 0.2 percentage points is smaller than the 0.6-point rises that occurred each of the 2 weeks before, and that could mean that activity is slowing.
That slowing, however, is not noticeable from this week’s map, which puts 41 states (there were 35 last week) and Puerto Rico in the red at the highest level of activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale and another three states in the “high” range with levels of 8 or 9, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
That leaves Nevada and Oregon at level 7; Alaska, Florida, and the District of Columbia at level 5; Idaho at level 3, and Delaware with insufficient data (it was at level 5 last week), the CDC said.
The 2019-2020 season’s high activity, fortunately, has not translated into high severity, as overall hospitalization and mortality rates continue to remain at fairly typical levels. Hospitalization rates are elevated among children and young adults, however, and pediatric deaths are now up to 92, the CDC said, which is high for this point in the season.

The CDC’s latest report shows that 6.8% of outpatients visiting health care providers had influenza-like illness during the week ending Feb. 8. That’s up from the previous week’s 6.6%, but that rise of 0.2 percentage points is smaller than the 0.6-point rises that occurred each of the 2 weeks before, and that could mean that activity is slowing.
That slowing, however, is not noticeable from this week’s map, which puts 41 states (there were 35 last week) and Puerto Rico in the red at the highest level of activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale and another three states in the “high” range with levels of 8 or 9, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
That leaves Nevada and Oregon at level 7; Alaska, Florida, and the District of Columbia at level 5; Idaho at level 3, and Delaware with insufficient data (it was at level 5 last week), the CDC said.
The 2019-2020 season’s high activity, fortunately, has not translated into high severity, as overall hospitalization and mortality rates continue to remain at fairly typical levels. Hospitalization rates are elevated among children and young adults, however, and pediatric deaths are now up to 92, the CDC said, which is high for this point in the season.
Newborn transfer may not reflect true rate of complications
Neonatal transfer was the factor most often associated with unexpected, severe complications at birth, particularly at hospitals that had the highest rates of complications, according to a cross-sectional study published online in JAMA Network Open (2020;3[2]:e1919498).
Mark A. Clapp, MD, MPH, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, and colleagues wrote. “Thus, if this metric is to be used in its current form, it would appear that accreditors, regulatory bodies, and payers should consider adjusting for or stratifying by a hospital’s level of neonatal care to avoid disincentivizing against appropriate transfers.”
The Joint Commission recently included unexpected complications in term newborns as a marker of quality of obstetric care, but it does not currently recommend any risk adjustment for the metric. The authors aimed to learn which factors regarding patients and hospitals were associated with such complications. Severe, unexpected newborn complications include death, seizure, use of assisted ventilation for at least 6 hours, transfer to another facility, or a 5-minute Apgar score of 3 or less.
“This measure has been proposed to serve as a balancing measure to maternal metrics, such as the rate of nulliparous, term, singleton, vertex-presenting cesarean deliveries,” the authors explained.
This study was supported by a Health Policy Award from the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
This story first appeared on Medscape.
Neonatal transfer was the factor most often associated with unexpected, severe complications at birth, particularly at hospitals that had the highest rates of complications, according to a cross-sectional study published online in JAMA Network Open (2020;3[2]:e1919498).
Mark A. Clapp, MD, MPH, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, and colleagues wrote. “Thus, if this metric is to be used in its current form, it would appear that accreditors, regulatory bodies, and payers should consider adjusting for or stratifying by a hospital’s level of neonatal care to avoid disincentivizing against appropriate transfers.”
The Joint Commission recently included unexpected complications in term newborns as a marker of quality of obstetric care, but it does not currently recommend any risk adjustment for the metric. The authors aimed to learn which factors regarding patients and hospitals were associated with such complications. Severe, unexpected newborn complications include death, seizure, use of assisted ventilation for at least 6 hours, transfer to another facility, or a 5-minute Apgar score of 3 or less.
“This measure has been proposed to serve as a balancing measure to maternal metrics, such as the rate of nulliparous, term, singleton, vertex-presenting cesarean deliveries,” the authors explained.
This study was supported by a Health Policy Award from the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
This story first appeared on Medscape.
Neonatal transfer was the factor most often associated with unexpected, severe complications at birth, particularly at hospitals that had the highest rates of complications, according to a cross-sectional study published online in JAMA Network Open (2020;3[2]:e1919498).
Mark A. Clapp, MD, MPH, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, and colleagues wrote. “Thus, if this metric is to be used in its current form, it would appear that accreditors, regulatory bodies, and payers should consider adjusting for or stratifying by a hospital’s level of neonatal care to avoid disincentivizing against appropriate transfers.”
The Joint Commission recently included unexpected complications in term newborns as a marker of quality of obstetric care, but it does not currently recommend any risk adjustment for the metric. The authors aimed to learn which factors regarding patients and hospitals were associated with such complications. Severe, unexpected newborn complications include death, seizure, use of assisted ventilation for at least 6 hours, transfer to another facility, or a 5-minute Apgar score of 3 or less.
“This measure has been proposed to serve as a balancing measure to maternal metrics, such as the rate of nulliparous, term, singleton, vertex-presenting cesarean deliveries,” the authors explained.
This study was supported by a Health Policy Award from the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
This story first appeared on Medscape.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Broadly Distributed Vascular Macules in a Pediatric Patient
The Diagnosis: Capillary Malformation-Arteriovenous Malformation Syndrome
Capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation (CM-AVM) was suspected, and a sample of the patient's blood was sent for a diagnostic genetic workup. DNA sequencing evaluated the following 5 genes that have been implicated in telangiectasia or AVM disorders: ACVRL1 (activin A receptorlike type 1), ENG (endoglin), GDF2 (growth differentiation factor 2), RASA1 (RAS p21 protein activator 1), and SMAD4 (SMAD family member 4). The patient was found to be heterozygous for a known pathogenic splice-site mutation in the RASA1 gene, consistent with a diagnosis of CM-AVM.
Capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation presents with multiple small cutaneous CMs and associated arteriovenous fistulas as well as high-flow AVMs located in the soft tissues, bones, or central nervous system (CNS). Occasionally, the cutaneous CMs are surrounded by a blanched halo.1 Because of the potential for CNS involvement in CM-AVM, our patient was further evaluated with spine and brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The brain MRI revealed 2 right occipital pole and fusiform gyral AVMs (Figure). No vascular abnormalities were found in the spine. The patient was referred to interventional neuroradiology to assess the feasibility of ablation to reduce the risk for complications, including intracranial hemorrhage.
Compared to other well-established congenital vascular disorders, CM-AVM has only recently been described in the literature. It was first reported by Eerola and colleagues2 in 2003. They studied several families with CMs and identified heterozygous inactivating RASA1 mutations in 6 families manifesting atypical CMs that were multiple small, round to oval, and pinkish red.2
It has been estimated that RASA1 mutations contribute to 68% of CM-AVM cases. Another gene--EPHB4 (EPH receptor B4)--has been implicated in patients with RASA1-negative disease. Two separate subtypes for patients with CM-AVM have been described: (1) CM-AVM type 1 for patients with RASA1 mutations, and (2) CM-AVM type 2 for those with EPHB4 mutations.3
Both CM-AVM types are characterized by small multifocal CMs and an increased risk for CNS fast-flow vascular malformations.4 It has been suggested that there are morphologic differences between the cutaneous manifestations of the 2 types. For example, one group stated Bier spots are more frequently observed in CM-AVM type 2. This same group suggested telangiectases seen primarily on the lips but also in the perioral region and on the upper thorax were seen in CM-AVM type 2 but not in CM-AVM type 1.4 In our patient, it is plausible that the pinpoint red macules on the lips and oral mucosa could be confused for telangiectases (quiz image [bottom]). At this time, we do not feel that there is sufficient evidence to clinically distinguish between CM-AVM types 1 and 2.
Central nervous system involvement seems to be more common in patients with CM-AVM type 1 (10%) than those with CM-AVM type 2 (3%).1,4 Of the 2 CM-AVM type 2 patients found to have intracranial AVMs in one study, both were found to have vein of Galen aneurysmal malformations (VGAMs).4 The study examining CNS involvement in CM-AVM type 1 did not comment on the percentage of VGAMs seen in all patients.1 However, in the retrospective component of the study, the authors reported that in 161 patients with CM-AVM type 1, 24 AVMs were observed, 6 of which were intracranial. Half of these intracranial AVMs were at the vein of Galen, demonstrating that VGAMs are seen in both types of CM-AVM.1 Further study is necessary to better characterize potential phenotypic differences between the 2 forms of CM-AVM.
Overall, the annual risk for hemorrhage associated with brain AVMs is approximately 2% per year.5 Because the morbidity and mortality of undiagnosed CNS malformations is high, it is recommended that patients with both types of CM-AVM undergo spine and brain MRI evaluation. If CNS malformations are identified, patients should be referred to interventional neuroradiology to assess the feasibility of ablation.
It is unclear if patients who initially screen negative for AVMs will go on to develop these fast-flow lesions later. We have noted that new CMs develop over time in our patients. Therefore, it does not seem far-fetched to hypothesize that AVMs of CNS are similarly dynamic. Ultimately, we recommend ongoing screening for brain and spinal AVMs at regular intervals, determined by discussions of risks and benefits between the treating team and patient/family.
It is important to distinguish CM-AVM from hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), as the distinction affects patient management. Unlike the AVMs found in HHT, AVMs in CM-AVM seldom are found in the lungs or liver.1 Thus, asymptomatic patients with HHT, but not CM-AVM, often are screened for pulmonary AVMs.
The diagnosis of HHT is based on the following 4 findings: spontaneous and recurrent epistaxis; multiple mucocutaneous telangiectasia at characteristic sites, including the lips, oral cavity, fingers, and nose; visceral involvement, such as gastrointestinal, pulmonary, cerebral, or hepatic AVMs; and a first-degree relative with the disorder. Three of the criteria are required for diagnosis.
Notably, the lesions seen in HHT and CM-AVM are morphologically different. Our patient did have 1-mm red macules on the lower lip that had clinical features overlapping with telangiectases, but other cutaneous findings including the presence of red macules and small patches, some with blanched halos, were clearly characteristic of CMs, not telangiectases.6 Furthermore, our patient did not have a personal history of epistaxis or a family history of any affected first-degree relatives. Finally, individuals with HHT tend to develop symptoms later in life compared to patients with CM-AVM, starting with epistaxis at 12 years of age.6
Patients with Henoch-Schönlein purpura also present in childhood but typically demonstrate palpable purpura and acute abdominal pain. Patients with Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome present with CM and venous malformation but also typically display limb overgrowth. Most patients with Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome are born with a port-wine stain.
Diffuse neonatal hemangiomatosis is characterized by multiple progressive, rapidly growing cutaneous hemangiomas associated with widespread visceral hemangiomas in the liver, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, brain, and meninges. Our patient's macules were much more slowly progressive.
- Revencu N, Boon LM, Mendola A, et al. RASA1 mutations and associated phenotypes in 68 families with capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation. Hum Mutat. 2013;34:1632-1641.
- Eerola I, Boon LM, Mulliken JB, et al. Capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation, a new clinical and genetic disorder caused by RASA1 mutations. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;73:1240-1249.
- Yu J, Streicher JL, Medne L, et al. EPHB4 mutation implicated in capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation syndrome: a case report. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:227-230.
- Amyere M, Revencu N, Helaers R, et al. Germline loss-of-function mutations in EPHB4 cause a second form of capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation (CM-AVM2) deregulating RAS-MAPK signaling. Circulation. 2017;136:1037-1048.
- Mohr JP, Parides MK, Stapf C, et al. Medical management with or without interventional therapy for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations (ARUBA): a multicentre, non-blinded, randomised trial. Lancet. 2014;383:614-621.
- Edwards LR, Blechman AB, Zlotoff BJ. RASA1 mutation in a family with capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation syndrome: a discussion of the differential diagnosis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;35:e9-e12.
The Diagnosis: Capillary Malformation-Arteriovenous Malformation Syndrome
Capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation (CM-AVM) was suspected, and a sample of the patient's blood was sent for a diagnostic genetic workup. DNA sequencing evaluated the following 5 genes that have been implicated in telangiectasia or AVM disorders: ACVRL1 (activin A receptorlike type 1), ENG (endoglin), GDF2 (growth differentiation factor 2), RASA1 (RAS p21 protein activator 1), and SMAD4 (SMAD family member 4). The patient was found to be heterozygous for a known pathogenic splice-site mutation in the RASA1 gene, consistent with a diagnosis of CM-AVM.
Capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation presents with multiple small cutaneous CMs and associated arteriovenous fistulas as well as high-flow AVMs located in the soft tissues, bones, or central nervous system (CNS). Occasionally, the cutaneous CMs are surrounded by a blanched halo.1 Because of the potential for CNS involvement in CM-AVM, our patient was further evaluated with spine and brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The brain MRI revealed 2 right occipital pole and fusiform gyral AVMs (Figure). No vascular abnormalities were found in the spine. The patient was referred to interventional neuroradiology to assess the feasibility of ablation to reduce the risk for complications, including intracranial hemorrhage.

Compared to other well-established congenital vascular disorders, CM-AVM has only recently been described in the literature. It was first reported by Eerola and colleagues2 in 2003. They studied several families with CMs and identified heterozygous inactivating RASA1 mutations in 6 families manifesting atypical CMs that were multiple small, round to oval, and pinkish red.2
It has been estimated that RASA1 mutations contribute to 68% of CM-AVM cases. Another gene--EPHB4 (EPH receptor B4)--has been implicated in patients with RASA1-negative disease. Two separate subtypes for patients with CM-AVM have been described: (1) CM-AVM type 1 for patients with RASA1 mutations, and (2) CM-AVM type 2 for those with EPHB4 mutations.3
Both CM-AVM types are characterized by small multifocal CMs and an increased risk for CNS fast-flow vascular malformations.4 It has been suggested that there are morphologic differences between the cutaneous manifestations of the 2 types. For example, one group stated Bier spots are more frequently observed in CM-AVM type 2. This same group suggested telangiectases seen primarily on the lips but also in the perioral region and on the upper thorax were seen in CM-AVM type 2 but not in CM-AVM type 1.4 In our patient, it is plausible that the pinpoint red macules on the lips and oral mucosa could be confused for telangiectases (quiz image [bottom]). At this time, we do not feel that there is sufficient evidence to clinically distinguish between CM-AVM types 1 and 2.
Central nervous system involvement seems to be more common in patients with CM-AVM type 1 (10%) than those with CM-AVM type 2 (3%).1,4 Of the 2 CM-AVM type 2 patients found to have intracranial AVMs in one study, both were found to have vein of Galen aneurysmal malformations (VGAMs).4 The study examining CNS involvement in CM-AVM type 1 did not comment on the percentage of VGAMs seen in all patients.1 However, in the retrospective component of the study, the authors reported that in 161 patients with CM-AVM type 1, 24 AVMs were observed, 6 of which were intracranial. Half of these intracranial AVMs were at the vein of Galen, demonstrating that VGAMs are seen in both types of CM-AVM.1 Further study is necessary to better characterize potential phenotypic differences between the 2 forms of CM-AVM.
Overall, the annual risk for hemorrhage associated with brain AVMs is approximately 2% per year.5 Because the morbidity and mortality of undiagnosed CNS malformations is high, it is recommended that patients with both types of CM-AVM undergo spine and brain MRI evaluation. If CNS malformations are identified, patients should be referred to interventional neuroradiology to assess the feasibility of ablation.
It is unclear if patients who initially screen negative for AVMs will go on to develop these fast-flow lesions later. We have noted that new CMs develop over time in our patients. Therefore, it does not seem far-fetched to hypothesize that AVMs of CNS are similarly dynamic. Ultimately, we recommend ongoing screening for brain and spinal AVMs at regular intervals, determined by discussions of risks and benefits between the treating team and patient/family.
It is important to distinguish CM-AVM from hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), as the distinction affects patient management. Unlike the AVMs found in HHT, AVMs in CM-AVM seldom are found in the lungs or liver.1 Thus, asymptomatic patients with HHT, but not CM-AVM, often are screened for pulmonary AVMs.
The diagnosis of HHT is based on the following 4 findings: spontaneous and recurrent epistaxis; multiple mucocutaneous telangiectasia at characteristic sites, including the lips, oral cavity, fingers, and nose; visceral involvement, such as gastrointestinal, pulmonary, cerebral, or hepatic AVMs; and a first-degree relative with the disorder. Three of the criteria are required for diagnosis.
Notably, the lesions seen in HHT and CM-AVM are morphologically different. Our patient did have 1-mm red macules on the lower lip that had clinical features overlapping with telangiectases, but other cutaneous findings including the presence of red macules and small patches, some with blanched halos, were clearly characteristic of CMs, not telangiectases.6 Furthermore, our patient did not have a personal history of epistaxis or a family history of any affected first-degree relatives. Finally, individuals with HHT tend to develop symptoms later in life compared to patients with CM-AVM, starting with epistaxis at 12 years of age.6
Patients with Henoch-Schönlein purpura also present in childhood but typically demonstrate palpable purpura and acute abdominal pain. Patients with Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome present with CM and venous malformation but also typically display limb overgrowth. Most patients with Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome are born with a port-wine stain.
Diffuse neonatal hemangiomatosis is characterized by multiple progressive, rapidly growing cutaneous hemangiomas associated with widespread visceral hemangiomas in the liver, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, brain, and meninges. Our patient's macules were much more slowly progressive.
The Diagnosis: Capillary Malformation-Arteriovenous Malformation Syndrome
Capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation (CM-AVM) was suspected, and a sample of the patient's blood was sent for a diagnostic genetic workup. DNA sequencing evaluated the following 5 genes that have been implicated in telangiectasia or AVM disorders: ACVRL1 (activin A receptorlike type 1), ENG (endoglin), GDF2 (growth differentiation factor 2), RASA1 (RAS p21 protein activator 1), and SMAD4 (SMAD family member 4). The patient was found to be heterozygous for a known pathogenic splice-site mutation in the RASA1 gene, consistent with a diagnosis of CM-AVM.
Capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation presents with multiple small cutaneous CMs and associated arteriovenous fistulas as well as high-flow AVMs located in the soft tissues, bones, or central nervous system (CNS). Occasionally, the cutaneous CMs are surrounded by a blanched halo.1 Because of the potential for CNS involvement in CM-AVM, our patient was further evaluated with spine and brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The brain MRI revealed 2 right occipital pole and fusiform gyral AVMs (Figure). No vascular abnormalities were found in the spine. The patient was referred to interventional neuroradiology to assess the feasibility of ablation to reduce the risk for complications, including intracranial hemorrhage.

Compared to other well-established congenital vascular disorders, CM-AVM has only recently been described in the literature. It was first reported by Eerola and colleagues2 in 2003. They studied several families with CMs and identified heterozygous inactivating RASA1 mutations in 6 families manifesting atypical CMs that were multiple small, round to oval, and pinkish red.2
It has been estimated that RASA1 mutations contribute to 68% of CM-AVM cases. Another gene--EPHB4 (EPH receptor B4)--has been implicated in patients with RASA1-negative disease. Two separate subtypes for patients with CM-AVM have been described: (1) CM-AVM type 1 for patients with RASA1 mutations, and (2) CM-AVM type 2 for those with EPHB4 mutations.3
Both CM-AVM types are characterized by small multifocal CMs and an increased risk for CNS fast-flow vascular malformations.4 It has been suggested that there are morphologic differences between the cutaneous manifestations of the 2 types. For example, one group stated Bier spots are more frequently observed in CM-AVM type 2. This same group suggested telangiectases seen primarily on the lips but also in the perioral region and on the upper thorax were seen in CM-AVM type 2 but not in CM-AVM type 1.4 In our patient, it is plausible that the pinpoint red macules on the lips and oral mucosa could be confused for telangiectases (quiz image [bottom]). At this time, we do not feel that there is sufficient evidence to clinically distinguish between CM-AVM types 1 and 2.
Central nervous system involvement seems to be more common in patients with CM-AVM type 1 (10%) than those with CM-AVM type 2 (3%).1,4 Of the 2 CM-AVM type 2 patients found to have intracranial AVMs in one study, both were found to have vein of Galen aneurysmal malformations (VGAMs).4 The study examining CNS involvement in CM-AVM type 1 did not comment on the percentage of VGAMs seen in all patients.1 However, in the retrospective component of the study, the authors reported that in 161 patients with CM-AVM type 1, 24 AVMs were observed, 6 of which were intracranial. Half of these intracranial AVMs were at the vein of Galen, demonstrating that VGAMs are seen in both types of CM-AVM.1 Further study is necessary to better characterize potential phenotypic differences between the 2 forms of CM-AVM.
Overall, the annual risk for hemorrhage associated with brain AVMs is approximately 2% per year.5 Because the morbidity and mortality of undiagnosed CNS malformations is high, it is recommended that patients with both types of CM-AVM undergo spine and brain MRI evaluation. If CNS malformations are identified, patients should be referred to interventional neuroradiology to assess the feasibility of ablation.
It is unclear if patients who initially screen negative for AVMs will go on to develop these fast-flow lesions later. We have noted that new CMs develop over time in our patients. Therefore, it does not seem far-fetched to hypothesize that AVMs of CNS are similarly dynamic. Ultimately, we recommend ongoing screening for brain and spinal AVMs at regular intervals, determined by discussions of risks and benefits between the treating team and patient/family.
It is important to distinguish CM-AVM from hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), as the distinction affects patient management. Unlike the AVMs found in HHT, AVMs in CM-AVM seldom are found in the lungs or liver.1 Thus, asymptomatic patients with HHT, but not CM-AVM, often are screened for pulmonary AVMs.
The diagnosis of HHT is based on the following 4 findings: spontaneous and recurrent epistaxis; multiple mucocutaneous telangiectasia at characteristic sites, including the lips, oral cavity, fingers, and nose; visceral involvement, such as gastrointestinal, pulmonary, cerebral, or hepatic AVMs; and a first-degree relative with the disorder. Three of the criteria are required for diagnosis.
Notably, the lesions seen in HHT and CM-AVM are morphologically different. Our patient did have 1-mm red macules on the lower lip that had clinical features overlapping with telangiectases, but other cutaneous findings including the presence of red macules and small patches, some with blanched halos, were clearly characteristic of CMs, not telangiectases.6 Furthermore, our patient did not have a personal history of epistaxis or a family history of any affected first-degree relatives. Finally, individuals with HHT tend to develop symptoms later in life compared to patients with CM-AVM, starting with epistaxis at 12 years of age.6
Patients with Henoch-Schönlein purpura also present in childhood but typically demonstrate palpable purpura and acute abdominal pain. Patients with Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome present with CM and venous malformation but also typically display limb overgrowth. Most patients with Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome are born with a port-wine stain.
Diffuse neonatal hemangiomatosis is characterized by multiple progressive, rapidly growing cutaneous hemangiomas associated with widespread visceral hemangiomas in the liver, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, brain, and meninges. Our patient's macules were much more slowly progressive.
- Revencu N, Boon LM, Mendola A, et al. RASA1 mutations and associated phenotypes in 68 families with capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation. Hum Mutat. 2013;34:1632-1641.
- Eerola I, Boon LM, Mulliken JB, et al. Capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation, a new clinical and genetic disorder caused by RASA1 mutations. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;73:1240-1249.
- Yu J, Streicher JL, Medne L, et al. EPHB4 mutation implicated in capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation syndrome: a case report. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:227-230.
- Amyere M, Revencu N, Helaers R, et al. Germline loss-of-function mutations in EPHB4 cause a second form of capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation (CM-AVM2) deregulating RAS-MAPK signaling. Circulation. 2017;136:1037-1048.
- Mohr JP, Parides MK, Stapf C, et al. Medical management with or without interventional therapy for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations (ARUBA): a multicentre, non-blinded, randomised trial. Lancet. 2014;383:614-621.
- Edwards LR, Blechman AB, Zlotoff BJ. RASA1 mutation in a family with capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation syndrome: a discussion of the differential diagnosis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;35:e9-e12.
- Revencu N, Boon LM, Mendola A, et al. RASA1 mutations and associated phenotypes in 68 families with capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation. Hum Mutat. 2013;34:1632-1641.
- Eerola I, Boon LM, Mulliken JB, et al. Capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation, a new clinical and genetic disorder caused by RASA1 mutations. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;73:1240-1249.
- Yu J, Streicher JL, Medne L, et al. EPHB4 mutation implicated in capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation syndrome: a case report. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:227-230.
- Amyere M, Revencu N, Helaers R, et al. Germline loss-of-function mutations in EPHB4 cause a second form of capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation (CM-AVM2) deregulating RAS-MAPK signaling. Circulation. 2017;136:1037-1048.
- Mohr JP, Parides MK, Stapf C, et al. Medical management with or without interventional therapy for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations (ARUBA): a multicentre, non-blinded, randomised trial. Lancet. 2014;383:614-621.
- Edwards LR, Blechman AB, Zlotoff BJ. RASA1 mutation in a family with capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation syndrome: a discussion of the differential diagnosis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;35:e9-e12.
A 2-year-old girl presented with an erythematous macule on the left nasal sidewall that had been present since birth as well as other similar-appearing macules that had slowly evolved over the last 2 years. The patient was born via normal spontaneous vaginal delivery to healthy parents. She had 2 healthy siblings. Her parents reported that she was otherwise growing and developing normally. The patient had no history of epistaxis, and there was no family history of vascular anomalies. Physical examination revealed 2- to 6-mm vascular macules that blanched with pressure and filled quickly thereafter on the left nasal sidewall, upper (top) and lower extremities, and trunk. Some macules were surrounded by blanched halos. Several 1-mm red macules also were noted on the exterior and interior of the mucosal lower lip (bottom).
AAN publishes guideline on the treatment of sleep problems in children with autism
The guideline was published online ahead of print Feb. 12 in Neurology.
“While up to 40% of children and teens in the general population will have sleep problems at some point during their childhood, such problems usually lessen with age,” lead author Ashura Williams Buckley, MD, director of the Sleep and Neurodevelopment Service at the National Institute of Mental Health in Bethesda, Md., said in a press release. “For children and teens with autism, sleep problems are more common and more likely to persist, resulting in poor health and poor quality of life. Some sleep problems may be directly related to autism, but others are not. Regardless, autism symptoms may make sleep problems worse.”
Few evidence-based treatments are available
Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues developed the current guideline to evaluate which pharmacologic, behavioral, and complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) interventions improve bedtime resistance, sleep onset latency, sleep continuity, total sleep time, and daytime behavior in children and adolescents with ASD. The panel evaluated 900 abstracts of articles that had been included in systematic reviews, as well as 1,087 additional abstracts. One hundred thirty-nine articles were potentially relevant, 12 met criteria for data extraction, and eight were rated class III or higher and were included in the panel’s review.
The authors observed what they called a dearth of evidence-based treatments for sleep dysregulation in ASD. Evidence indicates that melatonin, with or without cognitive–behavioral therapy (CBT), improves several sleep outcomes, compared with placebo. “Evidence for other interventions is largely lacking,” wrote Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues. They observed a lack of long-term safety data for melatonin in children, which they considered concerning, because melatonin affects the hypothalamic–gonadal axis and can potentially influence pubertal development.
Screening for comorbid conditions and concomitant medications
The guideline recommends that clinicians assess children with ASD and sleep disturbances for coexisting conditions and concomitant medications that could be contributing to these sleep disturbances. They should ensure that children receive appropriate treatment for coexisting conditions and adjust or discontinue potentially problematic medications appropriately, according to the guideline.
Furthermore, clinicians should counsel parents or guardians about behavioral strategies as a first-line treatment for improving sleep function. These strategies could be administered alone or with pharmacologic or neutraceutical approaches as needed, according to the authors. Suggested behavioral approaches include unmodified extinction (i.e., imposing a bedtime and ignoring a child’s protests), graduated extinction (i.e., ignoring protests for a specified period before responding), positive routines (i.e., establishing pre-bedtime calming rituals), and bedtime fading (i.e., putting a child to bed close to the time he or she begins to fall asleep).
If a child’s contributing coexisting conditions and medications have been addressed and behavioral strategies have not been helpful, clinicians should offer melatonin, according to the guideline. Because over-the-counter formulations contain variable concentrations of melatonin, clinicians should write a prescription for it or recommend high-purity pharmaceutical grade melatonin. The initial dose should be 1-3 mg/day at 60-30 minutes before bedtime. The dose can be titrated to 10 mg/day. Clinicians also should counsel children and their parents about potential adverse events of melatonin and the lack of long-term safety data, according to the guideline.
In addition, clinicians should advise children and parents that no evidence supports the routine use of weighted blankets or specialized mattress technology for improving sleep. Parents who ask about weighted blankets should be told that the reviewed trial reported no serious adverse events with this intervention, and that blankets could be a reasonable nonpharmacologic approach for some patients, according to the guideline.
Optimal outcome measures are undefined
Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues also suggested areas for future research. Investigators have not yet defined optimal outcome measures (e.g., questionnaires, polysomnography, and actigraphy) that balance tolerability and accuracy, they wrote. Clinically important differences for most measures also have yet to be determined. Researchers should investigate whether long-term adverse events are associated with chronic melatonin use and study patients with ASD and comorbid mood disorders, wrote the authors. “Research tying the underlying neurobiology in early-life sleep disruption to behavior might help clinicians and researchers understand which treatments might work for which people with ASD,” they concluded.
The AAN supported the development of the guideline. Dr. Williams Buckley had no conflicts of interest. Six authors had conflicts of interest that the AAN deemed not significant enough to prevent their participation in the development of the guideline.
SOURCE: Williams Buckley A et al. Neurology. 2020;94:393-405. doi: 10.1212/WNL0000000000009033.
The guideline was published online ahead of print Feb. 12 in Neurology.
“While up to 40% of children and teens in the general population will have sleep problems at some point during their childhood, such problems usually lessen with age,” lead author Ashura Williams Buckley, MD, director of the Sleep and Neurodevelopment Service at the National Institute of Mental Health in Bethesda, Md., said in a press release. “For children and teens with autism, sleep problems are more common and more likely to persist, resulting in poor health and poor quality of life. Some sleep problems may be directly related to autism, but others are not. Regardless, autism symptoms may make sleep problems worse.”
Few evidence-based treatments are available
Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues developed the current guideline to evaluate which pharmacologic, behavioral, and complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) interventions improve bedtime resistance, sleep onset latency, sleep continuity, total sleep time, and daytime behavior in children and adolescents with ASD. The panel evaluated 900 abstracts of articles that had been included in systematic reviews, as well as 1,087 additional abstracts. One hundred thirty-nine articles were potentially relevant, 12 met criteria for data extraction, and eight were rated class III or higher and were included in the panel’s review.
The authors observed what they called a dearth of evidence-based treatments for sleep dysregulation in ASD. Evidence indicates that melatonin, with or without cognitive–behavioral therapy (CBT), improves several sleep outcomes, compared with placebo. “Evidence for other interventions is largely lacking,” wrote Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues. They observed a lack of long-term safety data for melatonin in children, which they considered concerning, because melatonin affects the hypothalamic–gonadal axis and can potentially influence pubertal development.
Screening for comorbid conditions and concomitant medications
The guideline recommends that clinicians assess children with ASD and sleep disturbances for coexisting conditions and concomitant medications that could be contributing to these sleep disturbances. They should ensure that children receive appropriate treatment for coexisting conditions and adjust or discontinue potentially problematic medications appropriately, according to the guideline.
Furthermore, clinicians should counsel parents or guardians about behavioral strategies as a first-line treatment for improving sleep function. These strategies could be administered alone or with pharmacologic or neutraceutical approaches as needed, according to the authors. Suggested behavioral approaches include unmodified extinction (i.e., imposing a bedtime and ignoring a child’s protests), graduated extinction (i.e., ignoring protests for a specified period before responding), positive routines (i.e., establishing pre-bedtime calming rituals), and bedtime fading (i.e., putting a child to bed close to the time he or she begins to fall asleep).
If a child’s contributing coexisting conditions and medications have been addressed and behavioral strategies have not been helpful, clinicians should offer melatonin, according to the guideline. Because over-the-counter formulations contain variable concentrations of melatonin, clinicians should write a prescription for it or recommend high-purity pharmaceutical grade melatonin. The initial dose should be 1-3 mg/day at 60-30 minutes before bedtime. The dose can be titrated to 10 mg/day. Clinicians also should counsel children and their parents about potential adverse events of melatonin and the lack of long-term safety data, according to the guideline.
In addition, clinicians should advise children and parents that no evidence supports the routine use of weighted blankets or specialized mattress technology for improving sleep. Parents who ask about weighted blankets should be told that the reviewed trial reported no serious adverse events with this intervention, and that blankets could be a reasonable nonpharmacologic approach for some patients, according to the guideline.
Optimal outcome measures are undefined
Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues also suggested areas for future research. Investigators have not yet defined optimal outcome measures (e.g., questionnaires, polysomnography, and actigraphy) that balance tolerability and accuracy, they wrote. Clinically important differences for most measures also have yet to be determined. Researchers should investigate whether long-term adverse events are associated with chronic melatonin use and study patients with ASD and comorbid mood disorders, wrote the authors. “Research tying the underlying neurobiology in early-life sleep disruption to behavior might help clinicians and researchers understand which treatments might work for which people with ASD,” they concluded.
The AAN supported the development of the guideline. Dr. Williams Buckley had no conflicts of interest. Six authors had conflicts of interest that the AAN deemed not significant enough to prevent their participation in the development of the guideline.
SOURCE: Williams Buckley A et al. Neurology. 2020;94:393-405. doi: 10.1212/WNL0000000000009033.
The guideline was published online ahead of print Feb. 12 in Neurology.
“While up to 40% of children and teens in the general population will have sleep problems at some point during their childhood, such problems usually lessen with age,” lead author Ashura Williams Buckley, MD, director of the Sleep and Neurodevelopment Service at the National Institute of Mental Health in Bethesda, Md., said in a press release. “For children and teens with autism, sleep problems are more common and more likely to persist, resulting in poor health and poor quality of life. Some sleep problems may be directly related to autism, but others are not. Regardless, autism symptoms may make sleep problems worse.”
Few evidence-based treatments are available
Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues developed the current guideline to evaluate which pharmacologic, behavioral, and complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) interventions improve bedtime resistance, sleep onset latency, sleep continuity, total sleep time, and daytime behavior in children and adolescents with ASD. The panel evaluated 900 abstracts of articles that had been included in systematic reviews, as well as 1,087 additional abstracts. One hundred thirty-nine articles were potentially relevant, 12 met criteria for data extraction, and eight were rated class III or higher and were included in the panel’s review.
The authors observed what they called a dearth of evidence-based treatments for sleep dysregulation in ASD. Evidence indicates that melatonin, with or without cognitive–behavioral therapy (CBT), improves several sleep outcomes, compared with placebo. “Evidence for other interventions is largely lacking,” wrote Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues. They observed a lack of long-term safety data for melatonin in children, which they considered concerning, because melatonin affects the hypothalamic–gonadal axis and can potentially influence pubertal development.
Screening for comorbid conditions and concomitant medications
The guideline recommends that clinicians assess children with ASD and sleep disturbances for coexisting conditions and concomitant medications that could be contributing to these sleep disturbances. They should ensure that children receive appropriate treatment for coexisting conditions and adjust or discontinue potentially problematic medications appropriately, according to the guideline.
Furthermore, clinicians should counsel parents or guardians about behavioral strategies as a first-line treatment for improving sleep function. These strategies could be administered alone or with pharmacologic or neutraceutical approaches as needed, according to the authors. Suggested behavioral approaches include unmodified extinction (i.e., imposing a bedtime and ignoring a child’s protests), graduated extinction (i.e., ignoring protests for a specified period before responding), positive routines (i.e., establishing pre-bedtime calming rituals), and bedtime fading (i.e., putting a child to bed close to the time he or she begins to fall asleep).
If a child’s contributing coexisting conditions and medications have been addressed and behavioral strategies have not been helpful, clinicians should offer melatonin, according to the guideline. Because over-the-counter formulations contain variable concentrations of melatonin, clinicians should write a prescription for it or recommend high-purity pharmaceutical grade melatonin. The initial dose should be 1-3 mg/day at 60-30 minutes before bedtime. The dose can be titrated to 10 mg/day. Clinicians also should counsel children and their parents about potential adverse events of melatonin and the lack of long-term safety data, according to the guideline.
In addition, clinicians should advise children and parents that no evidence supports the routine use of weighted blankets or specialized mattress technology for improving sleep. Parents who ask about weighted blankets should be told that the reviewed trial reported no serious adverse events with this intervention, and that blankets could be a reasonable nonpharmacologic approach for some patients, according to the guideline.
Optimal outcome measures are undefined
Dr. Williams Buckley and colleagues also suggested areas for future research. Investigators have not yet defined optimal outcome measures (e.g., questionnaires, polysomnography, and actigraphy) that balance tolerability and accuracy, they wrote. Clinically important differences for most measures also have yet to be determined. Researchers should investigate whether long-term adverse events are associated with chronic melatonin use and study patients with ASD and comorbid mood disorders, wrote the authors. “Research tying the underlying neurobiology in early-life sleep disruption to behavior might help clinicians and researchers understand which treatments might work for which people with ASD,” they concluded.
The AAN supported the development of the guideline. Dr. Williams Buckley had no conflicts of interest. Six authors had conflicts of interest that the AAN deemed not significant enough to prevent their participation in the development of the guideline.
SOURCE: Williams Buckley A et al. Neurology. 2020;94:393-405. doi: 10.1212/WNL0000000000009033.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Key clinical point: The AAN has published a guideline on the treatment of sleep problems in children with autism.
Major finding: The guideline recommends behavioral strategies as a first-line treatment.
Study details: A review of 1,987 peer-reviewed studies.
Disclosures: The AAN funded the development of the guideline. The first author had no conflicts of interest, and the other authors had no significant conflicts.
Source: Williams Buckley A et al. Neurology. 2020;94:393-405. doi: 10.1212/WNL0000000000009033.