User login
Hyperpigmented Flexural Plaques, Hypohidrosis, and Hypotrichosis
The Diagnosis: Lelis Syndrome
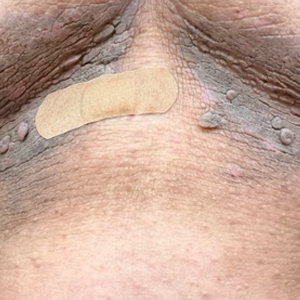
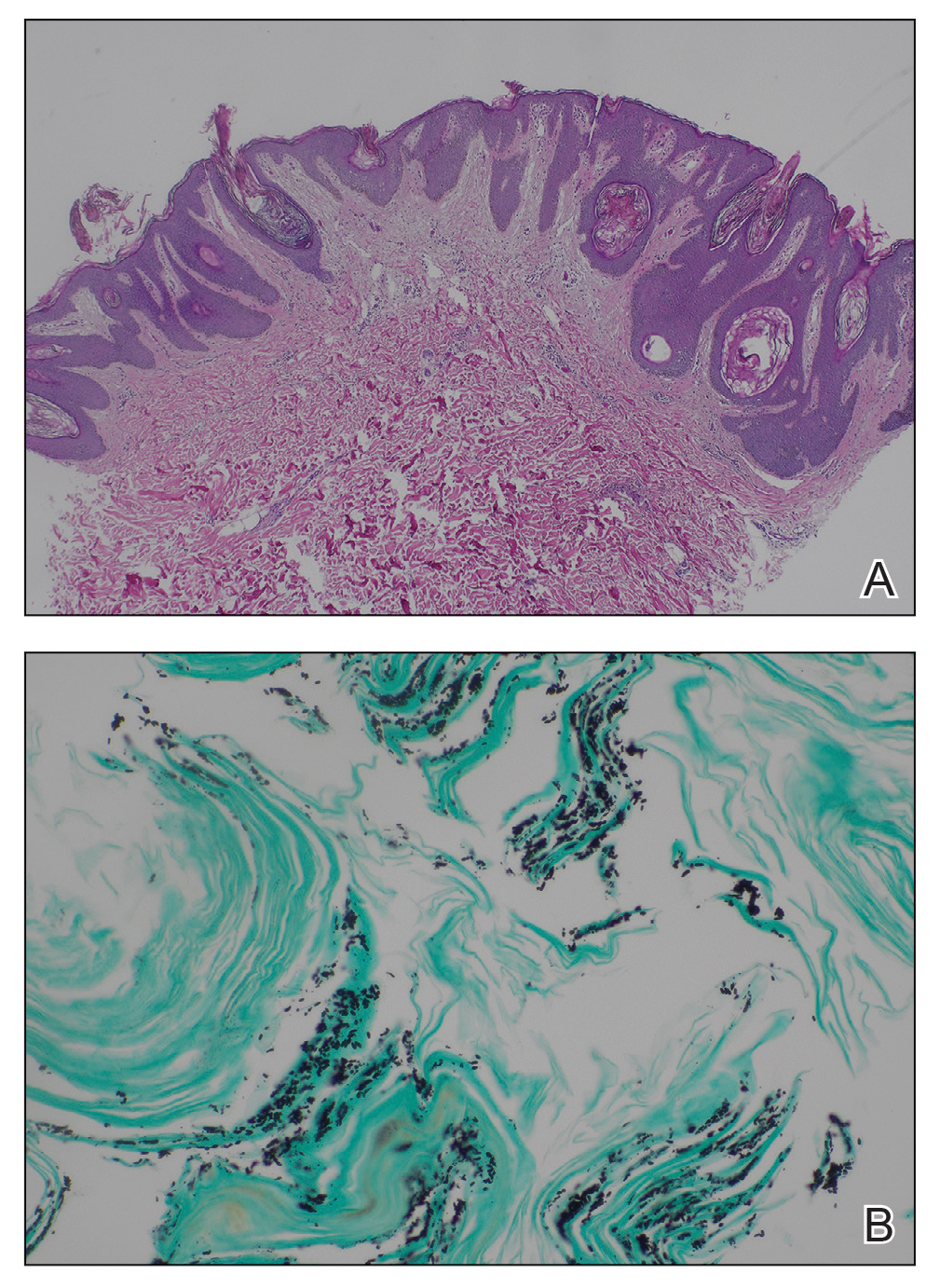
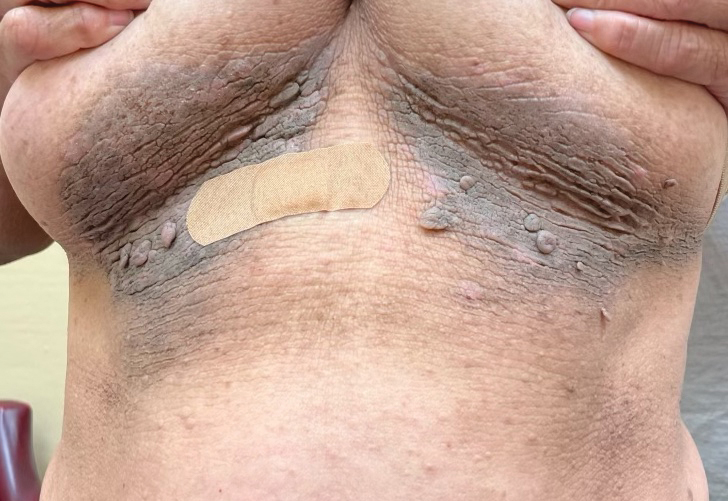
Histopathology revealed spongiotic dermatitis with marked acanthosis and hyperkeratosis (Figure, A) with fungal colonization of the stratum corneum (Figure, B). Our patient was diagnosed with Lelis syndrome (also referred to as ectodermal dysplasia with acanthosis nigricans syndrome), a rare condition with hypotrichosis and hypohidrosis resulting from ectodermal dysplasia.1,2 The pruritic rash was diagnosed as chronic dermatitis due to fungal colonization in the setting of acanthosis nigricans. The fungal infection was treated with a 4-week course of oral fluconazole 200 mg/wk, ketoconazole cream 2% twice daily, and discontinuation of topical steroids, resulting in the thinning of the plaques on the neck and antecubital fossae as well as resolution of the pruritus. Following antifungal treatment, our patient was started on tazarotene cream 0.1% for acanthosis nigricans.
Ectodermal dysplasias are inherited disorders with abnormalities of the skin, hair, sweat glands, nails, teeth, and sometimes internal organs.3 Patients with Lelis syndrome may have other manifestations of ectodermal dysplasia in addition to hypohidrosis and hypotrichosis, including deafness and abnormal dentition,1,3 as seen in our patient. Intellectual disability has been described in many types of ectodermal dysplasia, including Lelis syndrome, but the association may be obscured by neurologic damage after repeat episodes of hyperthermia in infancy due to anhidrosis or hypohidrosis.4
When evaluating the differential diagnoses, the presence of hypotrichosis and hypohidrosis indicating ectodermal dysplasia is key. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis presents with hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and focal acanthosis on histopathology. It can present on the neck and antecubital fossae; however, it is not associated with hypohidrosis and hypotrichosis.5 Although activating fibroblast growth factor receptor, FGFR, mutations have been implicated in the development of acanthosis nigricans in a variety of syndromes, these diagnoses are associated with abnormalities in skeletal development such as craniosynostosis and short stature; hypotrichosis and hypohidrosis are not seen.6,7 HAIR-AN (hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance, and acanthosis nigricans) syndrome typically presents in the prepubertal period with obesity and insulin resistance; acanthosis nigricans and alopecia can occur due to insulin resistance and hyperandrogenism, but concurrent clitoromegaly and hirsutism are common.6 Sudden onset of extensive acanthosis nigricans also is among the paraneoplastic dermatoses; it has been associated with multiple malignancies, but in these cases, hypotrichosis and hypohidrosis are not observed. Adenocarcinomas are the most common neoplasms associated with paraneoplastic acanthosis nigricans, which occurs through growth factor secretion by tumor cells stimulating hyperkeratosis and papillomatosis.6
Lelis syndrome is rare, and our case is unique because the patient had severe manifestations of acanthosis nigricans and hypotrichosis. Because the inheritance pattern and specific genetics of the condition have not been fully elucidated, the diagnosis primarily is clinical.1,8 Diagnosis may be complicated by the variety of other signs that can accompany acanthosis nigricans, hypohidrosis, and hypotrichosis.1,2 The condition also may alter or obscure presentation of other dermatologic conditions, as in our case.
Although there is no cure for Lelis syndrome, one case report described treatment with acitretin that resulted in marked improvement of the patient’s hyperkeratosis and acanthosis nigricans.9 Due to lack of health insurance coverage of acitretin, our patient was started on tazarotene cream 0.1% for acanthosis nigricans. General treatment of ectodermal dysplasia primarily consists of multidisciplinary symptom management, including careful monitoring of temperature and heat intolerance as well as provision of dental prosthetics.4,10 For ectodermal dysplasias caused by identified genetic mutations, prenatal interventions targeting gene pathways offer potentially curative treatment.10 However, for Lelis syndrome, along with many other disorders of ectodermal dysplasia, mitigation of signs and symptoms remains the primary treatment objective. Despite its rarity, increased awareness of Lelis syndrome is important to increase knowledge of ectodermal dysplasia syndromes and allow for the investigation of potential treatment options.
- Steiner CE, Cintra ML, Marques-de-Faria AP. Ectodermal dysplasia with acanthosis nigricans (Lelis syndrome). Am J Med Genet. 2002;113:381-384. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.10787
- Lelis J. Autosomal recessive ectodermal dysplasia. Cutis. 1992; 49:435-437.
- Itin PH, Fistarol SK. Ectodermal dysplasias. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2004;131C:45-51. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.30033
- Blüschke G, Nüsken KD, Schneider H. Prevalence and prevention of severe complications of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in infancy. Early Hum Dev. 2010;86:397-399. doi:10.1016/j .earlhumdev.2010.04.008
- Le C, Bedocs PM. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459130/
- Das A, Datta D, Kassir M, et al. Acanthosis nigricans: a review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19:1857-1865. doi:10.1111/jocd.13544
- Torley D, Bellus GA, Munro CS. Genes, growth factors and acanthosis nigricans. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:1096-1101. doi:10 .1046/j.1365-2133.2002.05150.x
- van Steensel MAM, van der Hout AH. Lelis syndrome may be a manifestation of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Am J Med Genet A. 2009;149A:1612-1613. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.32945
- Yoshimura AM, Neves Ferreira Velho PE, Ferreira Magalhães R, et al. Lelis’ syndrome: treatment with acitretin. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47: 1330-1331. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2008.03874.x
- Schneider H. Ectodermal dysplasias: new perspectives on the treatment of so far immedicable genetic disorders. Front Genet. 2022;13:1000744. doi:10.3389/fgene.2022.1000744
The Diagnosis: Lelis Syndrome
Histopathology revealed spongiotic dermatitis with marked acanthosis and hyperkeratosis (Figure, A) with fungal colonization of the stratum corneum (Figure, B). Our patient was diagnosed with Lelis syndrome (also referred to as ectodermal dysplasia with acanthosis nigricans syndrome), a rare condition with hypotrichosis and hypohidrosis resulting from ectodermal dysplasia.1,2 The pruritic rash was diagnosed as chronic dermatitis due to fungal colonization in the setting of acanthosis nigricans. The fungal infection was treated with a 4-week course of oral fluconazole 200 mg/wk, ketoconazole cream 2% twice daily, and discontinuation of topical steroids, resulting in the thinning of the plaques on the neck and antecubital fossae as well as resolution of the pruritus. Following antifungal treatment, our patient was started on tazarotene cream 0.1% for acanthosis nigricans.

Ectodermal dysplasias are inherited disorders with abnormalities of the skin, hair, sweat glands, nails, teeth, and sometimes internal organs.3 Patients with Lelis syndrome may have other manifestations of ectodermal dysplasia in addition to hypohidrosis and hypotrichosis, including deafness and abnormal dentition,1,3 as seen in our patient. Intellectual disability has been described in many types of ectodermal dysplasia, including Lelis syndrome, but the association may be obscured by neurologic damage after repeat episodes of hyperthermia in infancy due to anhidrosis or hypohidrosis.4
When evaluating the differential diagnoses, the presence of hypotrichosis and hypohidrosis indicating ectodermal dysplasia is key. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis presents with hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and focal acanthosis on histopathology. It can present on the neck and antecubital fossae; however, it is not associated with hypohidrosis and hypotrichosis.5 Although activating fibroblast growth factor receptor, FGFR, mutations have been implicated in the development of acanthosis nigricans in a variety of syndromes, these diagnoses are associated with abnormalities in skeletal development such as craniosynostosis and short stature; hypotrichosis and hypohidrosis are not seen.6,7 HAIR-AN (hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance, and acanthosis nigricans) syndrome typically presents in the prepubertal period with obesity and insulin resistance; acanthosis nigricans and alopecia can occur due to insulin resistance and hyperandrogenism, but concurrent clitoromegaly and hirsutism are common.6 Sudden onset of extensive acanthosis nigricans also is among the paraneoplastic dermatoses; it has been associated with multiple malignancies, but in these cases, hypotrichosis and hypohidrosis are not observed. Adenocarcinomas are the most common neoplasms associated with paraneoplastic acanthosis nigricans, which occurs through growth factor secretion by tumor cells stimulating hyperkeratosis and papillomatosis.6
Lelis syndrome is rare, and our case is unique because the patient had severe manifestations of acanthosis nigricans and hypotrichosis. Because the inheritance pattern and specific genetics of the condition have not been fully elucidated, the diagnosis primarily is clinical.1,8 Diagnosis may be complicated by the variety of other signs that can accompany acanthosis nigricans, hypohidrosis, and hypotrichosis.1,2 The condition also may alter or obscure presentation of other dermatologic conditions, as in our case.
Although there is no cure for Lelis syndrome, one case report described treatment with acitretin that resulted in marked improvement of the patient’s hyperkeratosis and acanthosis nigricans.9 Due to lack of health insurance coverage of acitretin, our patient was started on tazarotene cream 0.1% for acanthosis nigricans. General treatment of ectodermal dysplasia primarily consists of multidisciplinary symptom management, including careful monitoring of temperature and heat intolerance as well as provision of dental prosthetics.4,10 For ectodermal dysplasias caused by identified genetic mutations, prenatal interventions targeting gene pathways offer potentially curative treatment.10 However, for Lelis syndrome, along with many other disorders of ectodermal dysplasia, mitigation of signs and symptoms remains the primary treatment objective. Despite its rarity, increased awareness of Lelis syndrome is important to increase knowledge of ectodermal dysplasia syndromes and allow for the investigation of potential treatment options.
The Diagnosis: Lelis Syndrome
Histopathology revealed spongiotic dermatitis with marked acanthosis and hyperkeratosis (Figure, A) with fungal colonization of the stratum corneum (Figure, B). Our patient was diagnosed with Lelis syndrome (also referred to as ectodermal dysplasia with acanthosis nigricans syndrome), a rare condition with hypotrichosis and hypohidrosis resulting from ectodermal dysplasia.1,2 The pruritic rash was diagnosed as chronic dermatitis due to fungal colonization in the setting of acanthosis nigricans. The fungal infection was treated with a 4-week course of oral fluconazole 200 mg/wk, ketoconazole cream 2% twice daily, and discontinuation of topical steroids, resulting in the thinning of the plaques on the neck and antecubital fossae as well as resolution of the pruritus. Following antifungal treatment, our patient was started on tazarotene cream 0.1% for acanthosis nigricans.

Ectodermal dysplasias are inherited disorders with abnormalities of the skin, hair, sweat glands, nails, teeth, and sometimes internal organs.3 Patients with Lelis syndrome may have other manifestations of ectodermal dysplasia in addition to hypohidrosis and hypotrichosis, including deafness and abnormal dentition,1,3 as seen in our patient. Intellectual disability has been described in many types of ectodermal dysplasia, including Lelis syndrome, but the association may be obscured by neurologic damage after repeat episodes of hyperthermia in infancy due to anhidrosis or hypohidrosis.4
When evaluating the differential diagnoses, the presence of hypotrichosis and hypohidrosis indicating ectodermal dysplasia is key. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis presents with hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and focal acanthosis on histopathology. It can present on the neck and antecubital fossae; however, it is not associated with hypohidrosis and hypotrichosis.5 Although activating fibroblast growth factor receptor, FGFR, mutations have been implicated in the development of acanthosis nigricans in a variety of syndromes, these diagnoses are associated with abnormalities in skeletal development such as craniosynostosis and short stature; hypotrichosis and hypohidrosis are not seen.6,7 HAIR-AN (hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance, and acanthosis nigricans) syndrome typically presents in the prepubertal period with obesity and insulin resistance; acanthosis nigricans and alopecia can occur due to insulin resistance and hyperandrogenism, but concurrent clitoromegaly and hirsutism are common.6 Sudden onset of extensive acanthosis nigricans also is among the paraneoplastic dermatoses; it has been associated with multiple malignancies, but in these cases, hypotrichosis and hypohidrosis are not observed. Adenocarcinomas are the most common neoplasms associated with paraneoplastic acanthosis nigricans, which occurs through growth factor secretion by tumor cells stimulating hyperkeratosis and papillomatosis.6
Lelis syndrome is rare, and our case is unique because the patient had severe manifestations of acanthosis nigricans and hypotrichosis. Because the inheritance pattern and specific genetics of the condition have not been fully elucidated, the diagnosis primarily is clinical.1,8 Diagnosis may be complicated by the variety of other signs that can accompany acanthosis nigricans, hypohidrosis, and hypotrichosis.1,2 The condition also may alter or obscure presentation of other dermatologic conditions, as in our case.
Although there is no cure for Lelis syndrome, one case report described treatment with acitretin that resulted in marked improvement of the patient’s hyperkeratosis and acanthosis nigricans.9 Due to lack of health insurance coverage of acitretin, our patient was started on tazarotene cream 0.1% for acanthosis nigricans. General treatment of ectodermal dysplasia primarily consists of multidisciplinary symptom management, including careful monitoring of temperature and heat intolerance as well as provision of dental prosthetics.4,10 For ectodermal dysplasias caused by identified genetic mutations, prenatal interventions targeting gene pathways offer potentially curative treatment.10 However, for Lelis syndrome, along with many other disorders of ectodermal dysplasia, mitigation of signs and symptoms remains the primary treatment objective. Despite its rarity, increased awareness of Lelis syndrome is important to increase knowledge of ectodermal dysplasia syndromes and allow for the investigation of potential treatment options.
- Steiner CE, Cintra ML, Marques-de-Faria AP. Ectodermal dysplasia with acanthosis nigricans (Lelis syndrome). Am J Med Genet. 2002;113:381-384. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.10787
- Lelis J. Autosomal recessive ectodermal dysplasia. Cutis. 1992; 49:435-437.
- Itin PH, Fistarol SK. Ectodermal dysplasias. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2004;131C:45-51. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.30033
- Blüschke G, Nüsken KD, Schneider H. Prevalence and prevention of severe complications of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in infancy. Early Hum Dev. 2010;86:397-399. doi:10.1016/j .earlhumdev.2010.04.008
- Le C, Bedocs PM. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459130/
- Das A, Datta D, Kassir M, et al. Acanthosis nigricans: a review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19:1857-1865. doi:10.1111/jocd.13544
- Torley D, Bellus GA, Munro CS. Genes, growth factors and acanthosis nigricans. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:1096-1101. doi:10 .1046/j.1365-2133.2002.05150.x
- van Steensel MAM, van der Hout AH. Lelis syndrome may be a manifestation of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Am J Med Genet A. 2009;149A:1612-1613. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.32945
- Yoshimura AM, Neves Ferreira Velho PE, Ferreira Magalhães R, et al. Lelis’ syndrome: treatment with acitretin. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47: 1330-1331. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2008.03874.x
- Schneider H. Ectodermal dysplasias: new perspectives on the treatment of so far immedicable genetic disorders. Front Genet. 2022;13:1000744. doi:10.3389/fgene.2022.1000744
- Steiner CE, Cintra ML, Marques-de-Faria AP. Ectodermal dysplasia with acanthosis nigricans (Lelis syndrome). Am J Med Genet. 2002;113:381-384. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.10787
- Lelis J. Autosomal recessive ectodermal dysplasia. Cutis. 1992; 49:435-437.
- Itin PH, Fistarol SK. Ectodermal dysplasias. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2004;131C:45-51. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.30033
- Blüschke G, Nüsken KD, Schneider H. Prevalence and prevention of severe complications of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in infancy. Early Hum Dev. 2010;86:397-399. doi:10.1016/j .earlhumdev.2010.04.008
- Le C, Bedocs PM. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459130/
- Das A, Datta D, Kassir M, et al. Acanthosis nigricans: a review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19:1857-1865. doi:10.1111/jocd.13544
- Torley D, Bellus GA, Munro CS. Genes, growth factors and acanthosis nigricans. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:1096-1101. doi:10 .1046/j.1365-2133.2002.05150.x
- van Steensel MAM, van der Hout AH. Lelis syndrome may be a manifestation of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Am J Med Genet A. 2009;149A:1612-1613. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.32945
- Yoshimura AM, Neves Ferreira Velho PE, Ferreira Magalhães R, et al. Lelis’ syndrome: treatment with acitretin. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47: 1330-1331. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2008.03874.x
- Schneider H. Ectodermal dysplasias: new perspectives on the treatment of so far immedicable genetic disorders. Front Genet. 2022;13:1000744. doi:10.3389/fgene.2022.1000744
A 61-year-old woman with a history of hypohidrosis and deafness presented with a pruritic rash on the neck and antecubital fossae of several years’ duration. Prior treatment with topical corticosteroids failed to resolve the rash. Physical examination revealed thick, velvety, hyperpigmented plaques on the inframammary folds, axillae, groin, posterior neck, and antecubital fossae with lichenification of the latter 2 areas. Many pedunculated papules were seen on the face, chest, shoulders, and trunk, as well as diffuse hair thinning, particularly of the frontal and vertex scalp. Eyebrows, eyelashes, and axillary hair were absent. Two 5-mm punch biopsies of the antecubital fossa and inframammary fold were obtained for histopathologic analysis.
Commentary: Vaginal Estrogen Therapy, ILC, And Oral Estrogen Receptor Degraders In Breast Cancer, December 2023
Prior studies show inconsistent outcomes in patients with invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) and data in premenopausal women is limited. The retrospective cohort study by Yoon and colleagues analyzed the data from three databases and included 225,938 premenopausal women with stage I-III ILC or invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) in their study to evaluate survival trends in young women with ILC. In the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database, patients with ILC vs IDC showed superior breast cancer severity score (BCSS) outcomes during the first 10 years after diagnosis (HR 0.73; P < .001); similar results were seen in the Asan Medical Center Research (AMCR) database (HR 0.50; 95% CI 0.29-0.86; P = .01). After 10 years, the trend reversed, and BCSS outcomes worsened by 80% in patients with ILC in the SEER database (HR 1.80; P < .001). This was also seen in both the Korean Breast Cancer Registry (HR 2.79; 95% CI 1.32-5.88; P = .007) and AMCR database (HR 2.23; 95% CI 1.04-4.79; P = .04). These findings remained consistent after adjusting for tumor characteristics including age, stage, tumor grade, hormone receptor status, and after controlling for treatment with chemotherapy and radiation. In addition, in the SEER database, the histologic type exerted a statistically significant time-dependent association with BCSS, with ILC showing decreasing BCSS over time (time interaction HR 1.93; 95% CI 1.78-2.10; P < .001). Furthermore, on annual hazard function analysis, the ILC annual peak event of BCSS occurred 5 years after diagnosis, whereas the IDC recurrence events peaked at 5 years before diagnosis, suggesting a higher late recurrence rate for ILC. These findings may have implications on the duration of endocrine therapy used in these patients given concern for worse long-term outcomes in premenopausal patients with ILC.
Oral selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERD) have recently emerged as a new therapeutic mechanism for patients with hormone receptor–positive breast cancer who have developed resistance to other endocrine therapies. Two of these agents, elacestrant and camizestrant, have demonstrated statistically significant progression-free survival benefit in these populations, particularly in tumors with ESR1 mutations. The efficacy of these agents in tumors with ESR1 wild-type subgroup remains uncertain. A meta-analysis by Wong and colleagues of individual patient data from four randomized clinical trials (ACELERA, AMEERA-3, EMERALD, and SERENA-2) included 1290 patients with hormone receptor–positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative metastatic breast cancer who received oral SERD or endocrine therapies (ET) of the physician's choice. In the overall cohort, oral SERD showed improved progression-free survival (PFS) outcomes compared with ET of the physician's choice (HR 0.783; 95% CI 0.681-0.900; P < .001). This was also noted in the subgroup of patients with ESR1 mutations (HR 0.557; 95% CI 0.440-0.705; P < .001); although no significant PFS benefit was observed with oral SERD in the ESR1 wild-type subgroup (HR 0.944; 95% CI 0.783-1.138; P = .543). These results suggest that the PFS benefit observed with oral SERD is mainly seen in patients with ESR1-mutated tumors, and, therefore, these drugs should be prescribed accordingly.
Additional Reference
- Cold S, Cold F, Jensen M-B, et al. Systemic or vaginal hormone therapy after early breast cancer: A Danish observational cohort study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022;114:1347–1354. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djac112
Prior studies show inconsistent outcomes in patients with invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) and data in premenopausal women is limited. The retrospective cohort study by Yoon and colleagues analyzed the data from three databases and included 225,938 premenopausal women with stage I-III ILC or invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) in their study to evaluate survival trends in young women with ILC. In the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database, patients with ILC vs IDC showed superior breast cancer severity score (BCSS) outcomes during the first 10 years after diagnosis (HR 0.73; P < .001); similar results were seen in the Asan Medical Center Research (AMCR) database (HR 0.50; 95% CI 0.29-0.86; P = .01). After 10 years, the trend reversed, and BCSS outcomes worsened by 80% in patients with ILC in the SEER database (HR 1.80; P < .001). This was also seen in both the Korean Breast Cancer Registry (HR 2.79; 95% CI 1.32-5.88; P = .007) and AMCR database (HR 2.23; 95% CI 1.04-4.79; P = .04). These findings remained consistent after adjusting for tumor characteristics including age, stage, tumor grade, hormone receptor status, and after controlling for treatment with chemotherapy and radiation. In addition, in the SEER database, the histologic type exerted a statistically significant time-dependent association with BCSS, with ILC showing decreasing BCSS over time (time interaction HR 1.93; 95% CI 1.78-2.10; P < .001). Furthermore, on annual hazard function analysis, the ILC annual peak event of BCSS occurred 5 years after diagnosis, whereas the IDC recurrence events peaked at 5 years before diagnosis, suggesting a higher late recurrence rate for ILC. These findings may have implications on the duration of endocrine therapy used in these patients given concern for worse long-term outcomes in premenopausal patients with ILC.
Oral selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERD) have recently emerged as a new therapeutic mechanism for patients with hormone receptor–positive breast cancer who have developed resistance to other endocrine therapies. Two of these agents, elacestrant and camizestrant, have demonstrated statistically significant progression-free survival benefit in these populations, particularly in tumors with ESR1 mutations. The efficacy of these agents in tumors with ESR1 wild-type subgroup remains uncertain. A meta-analysis by Wong and colleagues of individual patient data from four randomized clinical trials (ACELERA, AMEERA-3, EMERALD, and SERENA-2) included 1290 patients with hormone receptor–positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative metastatic breast cancer who received oral SERD or endocrine therapies (ET) of the physician's choice. In the overall cohort, oral SERD showed improved progression-free survival (PFS) outcomes compared with ET of the physician's choice (HR 0.783; 95% CI 0.681-0.900; P < .001). This was also noted in the subgroup of patients with ESR1 mutations (HR 0.557; 95% CI 0.440-0.705; P < .001); although no significant PFS benefit was observed with oral SERD in the ESR1 wild-type subgroup (HR 0.944; 95% CI 0.783-1.138; P = .543). These results suggest that the PFS benefit observed with oral SERD is mainly seen in patients with ESR1-mutated tumors, and, therefore, these drugs should be prescribed accordingly.
Additional Reference
- Cold S, Cold F, Jensen M-B, et al. Systemic or vaginal hormone therapy after early breast cancer: A Danish observational cohort study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022;114:1347–1354. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djac112
Prior studies show inconsistent outcomes in patients with invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) and data in premenopausal women is limited. The retrospective cohort study by Yoon and colleagues analyzed the data from three databases and included 225,938 premenopausal women with stage I-III ILC or invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) in their study to evaluate survival trends in young women with ILC. In the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database, patients with ILC vs IDC showed superior breast cancer severity score (BCSS) outcomes during the first 10 years after diagnosis (HR 0.73; P < .001); similar results were seen in the Asan Medical Center Research (AMCR) database (HR 0.50; 95% CI 0.29-0.86; P = .01). After 10 years, the trend reversed, and BCSS outcomes worsened by 80% in patients with ILC in the SEER database (HR 1.80; P < .001). This was also seen in both the Korean Breast Cancer Registry (HR 2.79; 95% CI 1.32-5.88; P = .007) and AMCR database (HR 2.23; 95% CI 1.04-4.79; P = .04). These findings remained consistent after adjusting for tumor characteristics including age, stage, tumor grade, hormone receptor status, and after controlling for treatment with chemotherapy and radiation. In addition, in the SEER database, the histologic type exerted a statistically significant time-dependent association with BCSS, with ILC showing decreasing BCSS over time (time interaction HR 1.93; 95% CI 1.78-2.10; P < .001). Furthermore, on annual hazard function analysis, the ILC annual peak event of BCSS occurred 5 years after diagnosis, whereas the IDC recurrence events peaked at 5 years before diagnosis, suggesting a higher late recurrence rate for ILC. These findings may have implications on the duration of endocrine therapy used in these patients given concern for worse long-term outcomes in premenopausal patients with ILC.
Oral selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERD) have recently emerged as a new therapeutic mechanism for patients with hormone receptor–positive breast cancer who have developed resistance to other endocrine therapies. Two of these agents, elacestrant and camizestrant, have demonstrated statistically significant progression-free survival benefit in these populations, particularly in tumors with ESR1 mutations. The efficacy of these agents in tumors with ESR1 wild-type subgroup remains uncertain. A meta-analysis by Wong and colleagues of individual patient data from four randomized clinical trials (ACELERA, AMEERA-3, EMERALD, and SERENA-2) included 1290 patients with hormone receptor–positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative metastatic breast cancer who received oral SERD or endocrine therapies (ET) of the physician's choice. In the overall cohort, oral SERD showed improved progression-free survival (PFS) outcomes compared with ET of the physician's choice (HR 0.783; 95% CI 0.681-0.900; P < .001). This was also noted in the subgroup of patients with ESR1 mutations (HR 0.557; 95% CI 0.440-0.705; P < .001); although no significant PFS benefit was observed with oral SERD in the ESR1 wild-type subgroup (HR 0.944; 95% CI 0.783-1.138; P = .543). These results suggest that the PFS benefit observed with oral SERD is mainly seen in patients with ESR1-mutated tumors, and, therefore, these drugs should be prescribed accordingly.
Additional Reference
- Cold S, Cold F, Jensen M-B, et al. Systemic or vaginal hormone therapy after early breast cancer: A Danish observational cohort study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022;114:1347–1354. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djac112
Predictors of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections in RA after booster dose vaccination
Key clinical point: Findings from this real-world study identified the protective and risk factors associated with SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections (BI) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who had no COVID-19 infection and received the booster dose of anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
Major finding: Older patients who were age > 50 years (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 0.38; P = .004) and patients receiving conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (aHR 0.52; P = .021) had a significantly lower risk for BI, whereas patients receiving anti-interleukin 6 receptor (aHR 2.01; P = 0.039) and anti-CD20 (aHR 2.88; P = .011) treatments had ~2 and ~3 times higher risks for BI, respectively.
Study details: This prospective study included participants who had never been diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 and had received three doses of the anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, of whom 194 had RA and 1002 were control individuals.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Italian Ministry of Health and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Picchianti-Diamanti A et al. Older age, a high titre of neutralising antibodies and therapy with conventional DMARDs are associated with protection from breakthrough infection in rheumatoid arthritis patients after the booster dose of anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Vaccines. 2023;11(11):1684 (Nov 2). doi: 10.3390/vaccines11111684
Key clinical point: Findings from this real-world study identified the protective and risk factors associated with SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections (BI) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who had no COVID-19 infection and received the booster dose of anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
Major finding: Older patients who were age > 50 years (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 0.38; P = .004) and patients receiving conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (aHR 0.52; P = .021) had a significantly lower risk for BI, whereas patients receiving anti-interleukin 6 receptor (aHR 2.01; P = 0.039) and anti-CD20 (aHR 2.88; P = .011) treatments had ~2 and ~3 times higher risks for BI, respectively.
Study details: This prospective study included participants who had never been diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 and had received three doses of the anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, of whom 194 had RA and 1002 were control individuals.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Italian Ministry of Health and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Picchianti-Diamanti A et al. Older age, a high titre of neutralising antibodies and therapy with conventional DMARDs are associated with protection from breakthrough infection in rheumatoid arthritis patients after the booster dose of anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Vaccines. 2023;11(11):1684 (Nov 2). doi: 10.3390/vaccines11111684
Key clinical point: Findings from this real-world study identified the protective and risk factors associated with SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections (BI) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who had no COVID-19 infection and received the booster dose of anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
Major finding: Older patients who were age > 50 years (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 0.38; P = .004) and patients receiving conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (aHR 0.52; P = .021) had a significantly lower risk for BI, whereas patients receiving anti-interleukin 6 receptor (aHR 2.01; P = 0.039) and anti-CD20 (aHR 2.88; P = .011) treatments had ~2 and ~3 times higher risks for BI, respectively.
Study details: This prospective study included participants who had never been diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 and had received three doses of the anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, of whom 194 had RA and 1002 were control individuals.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Italian Ministry of Health and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Picchianti-Diamanti A et al. Older age, a high titre of neutralising antibodies and therapy with conventional DMARDs are associated with protection from breakthrough infection in rheumatoid arthritis patients after the booster dose of anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Vaccines. 2023;11(11):1684 (Nov 2). doi: 10.3390/vaccines11111684
Insights on methotrexate safety with combination therapies in early RA
Key clinical point: Patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) had a higher frequency of adverse events (AE) with methotrexate + tociluzumab vs methotrexate + active conventional treatment (ACT), which restricted their ability to tolerate the target dose of 25 mg methotrexate per week.
Major finding: The risk for methotrexate-associated AE was significantly higher (hazard ratio 1.48; 95% CI 1.20-1.84) and the proportion of patients able to tolerate 25 mg methotrexate per week at 24 weeks was significantly lower (odds ratio 0.25; P < .001) in the methotrexate + tocilizumab vs methotrexate + ACT group. However, the risks for methotrexate-associated AE were comparable for methotrexate +ACT and the combinations of methotrexate with other biologics like certolizumab-pegol or abatacept.
Study details: This post hoc analysis of the phase 4 NORD-STAR trial included 812 treatment-naive patients with early RA who were randomly assigned to receive methotrexate in combination with ACT, certolizumab-pegol, abatacept, or tocilizumab.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any specific funding. Some authors declared receiving grants, contracts, payments, honoraria, or consulting fees from or having other ties with various sources.
Source: Lend K et al. Methotrexate safety and efficacy in combination therapies in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: A post-hoc analysis of a randomized controlled trial (NORD-STAR). Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023 (Oct 17). doi: 10.1002/art.42730
Key clinical point: Patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) had a higher frequency of adverse events (AE) with methotrexate + tociluzumab vs methotrexate + active conventional treatment (ACT), which restricted their ability to tolerate the target dose of 25 mg methotrexate per week.
Major finding: The risk for methotrexate-associated AE was significantly higher (hazard ratio 1.48; 95% CI 1.20-1.84) and the proportion of patients able to tolerate 25 mg methotrexate per week at 24 weeks was significantly lower (odds ratio 0.25; P < .001) in the methotrexate + tocilizumab vs methotrexate + ACT group. However, the risks for methotrexate-associated AE were comparable for methotrexate +ACT and the combinations of methotrexate with other biologics like certolizumab-pegol or abatacept.
Study details: This post hoc analysis of the phase 4 NORD-STAR trial included 812 treatment-naive patients with early RA who were randomly assigned to receive methotrexate in combination with ACT, certolizumab-pegol, abatacept, or tocilizumab.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any specific funding. Some authors declared receiving grants, contracts, payments, honoraria, or consulting fees from or having other ties with various sources.
Source: Lend K et al. Methotrexate safety and efficacy in combination therapies in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: A post-hoc analysis of a randomized controlled trial (NORD-STAR). Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023 (Oct 17). doi: 10.1002/art.42730
Key clinical point: Patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) had a higher frequency of adverse events (AE) with methotrexate + tociluzumab vs methotrexate + active conventional treatment (ACT), which restricted their ability to tolerate the target dose of 25 mg methotrexate per week.
Major finding: The risk for methotrexate-associated AE was significantly higher (hazard ratio 1.48; 95% CI 1.20-1.84) and the proportion of patients able to tolerate 25 mg methotrexate per week at 24 weeks was significantly lower (odds ratio 0.25; P < .001) in the methotrexate + tocilizumab vs methotrexate + ACT group. However, the risks for methotrexate-associated AE were comparable for methotrexate +ACT and the combinations of methotrexate with other biologics like certolizumab-pegol or abatacept.
Study details: This post hoc analysis of the phase 4 NORD-STAR trial included 812 treatment-naive patients with early RA who were randomly assigned to receive methotrexate in combination with ACT, certolizumab-pegol, abatacept, or tocilizumab.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any specific funding. Some authors declared receiving grants, contracts, payments, honoraria, or consulting fees from or having other ties with various sources.
Source: Lend K et al. Methotrexate safety and efficacy in combination therapies in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: A post-hoc analysis of a randomized controlled trial (NORD-STAR). Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023 (Oct 17). doi: 10.1002/art.42730
Sustained remission tied to better outcomes than sustained LDA in early RA
Key clinical point: Patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who achieved disease remission and sustained it for 10 years had significantly lower structural progression and functional impairment than those who continued to have low disease activity (LDA).
Major finding: Patients with sustained remission vs sustained LDA had significantly lower mean 10-year structural progression (van der Heijde-modified Total Sharp Score 4.06 vs 14.59; P < .001) and 10-year functional impairment (Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index 0.14 vs 0.53; P < .001) scores.
Study details: This study analyzed the data of 252 patients with early RA from the ESPOIR cohort, of whom 48 patients were in sustained remission and 135 patients had sustained LDA.
Disclosures: The ESPOIR cohort was supported by grants from Merck Sharp & Dohme and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ruyssen-Witrand A et al. Ten-year radiographic and functional outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis patients in remission compared to patients in low disease activity. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25:207 (Oct 20). doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03176-7
Key clinical point: Patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who achieved disease remission and sustained it for 10 years had significantly lower structural progression and functional impairment than those who continued to have low disease activity (LDA).
Major finding: Patients with sustained remission vs sustained LDA had significantly lower mean 10-year structural progression (van der Heijde-modified Total Sharp Score 4.06 vs 14.59; P < .001) and 10-year functional impairment (Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index 0.14 vs 0.53; P < .001) scores.
Study details: This study analyzed the data of 252 patients with early RA from the ESPOIR cohort, of whom 48 patients were in sustained remission and 135 patients had sustained LDA.
Disclosures: The ESPOIR cohort was supported by grants from Merck Sharp & Dohme and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ruyssen-Witrand A et al. Ten-year radiographic and functional outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis patients in remission compared to patients in low disease activity. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25:207 (Oct 20). doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03176-7
Key clinical point: Patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who achieved disease remission and sustained it for 10 years had significantly lower structural progression and functional impairment than those who continued to have low disease activity (LDA).
Major finding: Patients with sustained remission vs sustained LDA had significantly lower mean 10-year structural progression (van der Heijde-modified Total Sharp Score 4.06 vs 14.59; P < .001) and 10-year functional impairment (Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index 0.14 vs 0.53; P < .001) scores.
Study details: This study analyzed the data of 252 patients with early RA from the ESPOIR cohort, of whom 48 patients were in sustained remission and 135 patients had sustained LDA.
Disclosures: The ESPOIR cohort was supported by grants from Merck Sharp & Dohme and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ruyssen-Witrand A et al. Ten-year radiographic and functional outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis patients in remission compared to patients in low disease activity. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25:207 (Oct 20). doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03176-7
Four-fold higher risk for interstitial lung abnormalities in RA patients with a history of smoking
Key clinical point: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) increased the prevalence of interstitial lung abnormalities (ILA) in participants with a history of smoking, which in turn led to a significant increase in the mortality rate.
Major finding: ILA were ~4 times more prevalent in individuals with a history of smoking who did vs did not have RA (adjusted odds ratio 4.15; 95% CI 2.17-7.97). Among patients with RA and a record of smoking, mortality risk was ~3 times higher in those with ILA or indeterminate ILA findings vs those without ILA (adjusted hazard ratio 2.86; 95% CI 1.33-6.16).
Study details: This cross-sectional prospective study included participants with a current or past history of smoking from the COPDGene cohort, of whom 83 participants had RA and were compared with 8725 individuals without RA.
Disclosures: COPDGene was supported by the US National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and others. Several authors declared receiving consulting fees, grant support, research support, or having other ties with various sources.
Source: McDermott GC et al. Prevalence and mortality associations of interstitial lung abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis within a multicentre prospective cohort of smokers. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023;62(SI3):SI286-SI295 (Oct 23). doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead277
Key clinical point: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) increased the prevalence of interstitial lung abnormalities (ILA) in participants with a history of smoking, which in turn led to a significant increase in the mortality rate.
Major finding: ILA were ~4 times more prevalent in individuals with a history of smoking who did vs did not have RA (adjusted odds ratio 4.15; 95% CI 2.17-7.97). Among patients with RA and a record of smoking, mortality risk was ~3 times higher in those with ILA or indeterminate ILA findings vs those without ILA (adjusted hazard ratio 2.86; 95% CI 1.33-6.16).
Study details: This cross-sectional prospective study included participants with a current or past history of smoking from the COPDGene cohort, of whom 83 participants had RA and were compared with 8725 individuals without RA.
Disclosures: COPDGene was supported by the US National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and others. Several authors declared receiving consulting fees, grant support, research support, or having other ties with various sources.
Source: McDermott GC et al. Prevalence and mortality associations of interstitial lung abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis within a multicentre prospective cohort of smokers. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023;62(SI3):SI286-SI295 (Oct 23). doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead277
Key clinical point: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) increased the prevalence of interstitial lung abnormalities (ILA) in participants with a history of smoking, which in turn led to a significant increase in the mortality rate.
Major finding: ILA were ~4 times more prevalent in individuals with a history of smoking who did vs did not have RA (adjusted odds ratio 4.15; 95% CI 2.17-7.97). Among patients with RA and a record of smoking, mortality risk was ~3 times higher in those with ILA or indeterminate ILA findings vs those without ILA (adjusted hazard ratio 2.86; 95% CI 1.33-6.16).
Study details: This cross-sectional prospective study included participants with a current or past history of smoking from the COPDGene cohort, of whom 83 participants had RA and were compared with 8725 individuals without RA.
Disclosures: COPDGene was supported by the US National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and others. Several authors declared receiving consulting fees, grant support, research support, or having other ties with various sources.
Source: McDermott GC et al. Prevalence and mortality associations of interstitial lung abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis within a multicentre prospective cohort of smokers. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023;62(SI3):SI286-SI295 (Oct 23). doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead277
Meta-analysis assesses hepatitis B reactivation risk in anti-IL-6-treated RA
Key clinical point: The risk for hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation was substantially high in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and chronic HBV infection who were treated with anti-interleukin-6 (anti-IL-6), with the risk being ~5 times higher in the absence of antiviral prophylaxis.
Major finding: The HBV reactivation rate was 6.7% in patients with chronic HBV infection, with the value further increasing to 31% in patients without antiviral prophylaxis. In patients with resolved HBV infection, the HBV reactivation rate remained ~0% irrespective of antiviral prophylaxis administration.
Study details: This meta-analysis of 19 studies included 372 anti-IL-6-treated patients with RA who had chronic (n = 41) or resolved (n = 279) HBV infection, of whom 19 patients received antiviral prophylaxis.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. Two authors declared receiving honoraria, speaker fees, or research grants from or participating in advisory boards of various sources.
Source: Katelani S et al. HBV reactivation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-interleukin-6: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023;62(SI3):SI252-SI259 (Oct 23). doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead243
Key clinical point: The risk for hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation was substantially high in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and chronic HBV infection who were treated with anti-interleukin-6 (anti-IL-6), with the risk being ~5 times higher in the absence of antiviral prophylaxis.
Major finding: The HBV reactivation rate was 6.7% in patients with chronic HBV infection, with the value further increasing to 31% in patients without antiviral prophylaxis. In patients with resolved HBV infection, the HBV reactivation rate remained ~0% irrespective of antiviral prophylaxis administration.
Study details: This meta-analysis of 19 studies included 372 anti-IL-6-treated patients with RA who had chronic (n = 41) or resolved (n = 279) HBV infection, of whom 19 patients received antiviral prophylaxis.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. Two authors declared receiving honoraria, speaker fees, or research grants from or participating in advisory boards of various sources.
Source: Katelani S et al. HBV reactivation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-interleukin-6: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023;62(SI3):SI252-SI259 (Oct 23). doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead243
Key clinical point: The risk for hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation was substantially high in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and chronic HBV infection who were treated with anti-interleukin-6 (anti-IL-6), with the risk being ~5 times higher in the absence of antiviral prophylaxis.
Major finding: The HBV reactivation rate was 6.7% in patients with chronic HBV infection, with the value further increasing to 31% in patients without antiviral prophylaxis. In patients with resolved HBV infection, the HBV reactivation rate remained ~0% irrespective of antiviral prophylaxis administration.
Study details: This meta-analysis of 19 studies included 372 anti-IL-6-treated patients with RA who had chronic (n = 41) or resolved (n = 279) HBV infection, of whom 19 patients received antiviral prophylaxis.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. Two authors declared receiving honoraria, speaker fees, or research grants from or participating in advisory boards of various sources.
Source: Katelani S et al. HBV reactivation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-interleukin-6: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023;62(SI3):SI252-SI259 (Oct 23). doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead243
Two-fold higher risk for serious infections with tofacitinib vs bDMARD in older RA patients
Key clinical point: Compared with biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARD), tofacitinib increased the risk for serious infections (SI) in older patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA; age ≥ 69 years).
Major finding: The risk for non-fatal SI in the tofacitinib vs bDMARD treatment group was ~2 times higher in patients age 69 years (hazard ratio [HR] ~2.00; 95% CI ~1.02 to ~4.00) and ~2.8 times higher in those age ≥ 76 years (HR ~2.8; 95% CI 1.3 to ~6.4).
Study details: This observational cohort study included 1687 patients with RA enrolled in 2238 different treatment courses (TC), of which 345 and 1893 TC involved tofacitinib and bDMARD, respectively.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Pfizer. Several authors declared receiving speaker fees, consulting fees, research grants, or conference expenditures from or having other ties with various sources, including Pfizer.
Source: Riek M et al. Serious infection risk of tofacitinib compared to biologics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated in routine clinical care. Sci Rep. 2023;13:17776 (Oct 18). doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44841-w
Key clinical point: Compared with biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARD), tofacitinib increased the risk for serious infections (SI) in older patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA; age ≥ 69 years).
Major finding: The risk for non-fatal SI in the tofacitinib vs bDMARD treatment group was ~2 times higher in patients age 69 years (hazard ratio [HR] ~2.00; 95% CI ~1.02 to ~4.00) and ~2.8 times higher in those age ≥ 76 years (HR ~2.8; 95% CI 1.3 to ~6.4).
Study details: This observational cohort study included 1687 patients with RA enrolled in 2238 different treatment courses (TC), of which 345 and 1893 TC involved tofacitinib and bDMARD, respectively.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Pfizer. Several authors declared receiving speaker fees, consulting fees, research grants, or conference expenditures from or having other ties with various sources, including Pfizer.
Source: Riek M et al. Serious infection risk of tofacitinib compared to biologics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated in routine clinical care. Sci Rep. 2023;13:17776 (Oct 18). doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44841-w
Key clinical point: Compared with biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARD), tofacitinib increased the risk for serious infections (SI) in older patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA; age ≥ 69 years).
Major finding: The risk for non-fatal SI in the tofacitinib vs bDMARD treatment group was ~2 times higher in patients age 69 years (hazard ratio [HR] ~2.00; 95% CI ~1.02 to ~4.00) and ~2.8 times higher in those age ≥ 76 years (HR ~2.8; 95% CI 1.3 to ~6.4).
Study details: This observational cohort study included 1687 patients with RA enrolled in 2238 different treatment courses (TC), of which 345 and 1893 TC involved tofacitinib and bDMARD, respectively.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Pfizer. Several authors declared receiving speaker fees, consulting fees, research grants, or conference expenditures from or having other ties with various sources, including Pfizer.
Source: Riek M et al. Serious infection risk of tofacitinib compared to biologics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated in routine clinical care. Sci Rep. 2023;13:17776 (Oct 18). doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44841-w
Real-world study demonstrates cons of tapering DMARD in well-controlled RA
Key clinical point: Tapering biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARD) or both b/tsDMARD and conventional synthetic (cs) DMARD increased the risk for disease flares in patients with well-controlled rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Major finding: Compared with patients whose medication was not tapered, the risk for flares was 31 times higher in the b/tsDMARD taper group (hazard ratio [HR] 31.43; P < .0001) and 18 times higher in the b/tsDMARD and csDMARD taper group (HR 18.45; P = .0039).
Study details: This 2-year prospective cohort study included 131 patients with RA who were on stable b/tsDMARD with or without csDMARD and achieved remission or low disease activity, of whom 39.7% underwent a DMARD taper.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Autoimmune Association - Young Investigator Grant Award. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Tageldin M et al. A real-world 2-year prospective study of medication tapering in patients with well-controlled rheumatoid arthritis within the rheumatoid arthritis medication tapering (RHEUMTAP) cohort. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023;62(Suppl 4):iv8-iv13 (Oct 19). doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead430
Key clinical point: Tapering biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARD) or both b/tsDMARD and conventional synthetic (cs) DMARD increased the risk for disease flares in patients with well-controlled rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Major finding: Compared with patients whose medication was not tapered, the risk for flares was 31 times higher in the b/tsDMARD taper group (hazard ratio [HR] 31.43; P < .0001) and 18 times higher in the b/tsDMARD and csDMARD taper group (HR 18.45; P = .0039).
Study details: This 2-year prospective cohort study included 131 patients with RA who were on stable b/tsDMARD with or without csDMARD and achieved remission or low disease activity, of whom 39.7% underwent a DMARD taper.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Autoimmune Association - Young Investigator Grant Award. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Tageldin M et al. A real-world 2-year prospective study of medication tapering in patients with well-controlled rheumatoid arthritis within the rheumatoid arthritis medication tapering (RHEUMTAP) cohort. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023;62(Suppl 4):iv8-iv13 (Oct 19). doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead430
Key clinical point: Tapering biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARD) or both b/tsDMARD and conventional synthetic (cs) DMARD increased the risk for disease flares in patients with well-controlled rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Major finding: Compared with patients whose medication was not tapered, the risk for flares was 31 times higher in the b/tsDMARD taper group (hazard ratio [HR] 31.43; P < .0001) and 18 times higher in the b/tsDMARD and csDMARD taper group (HR 18.45; P = .0039).
Study details: This 2-year prospective cohort study included 131 patients with RA who were on stable b/tsDMARD with or without csDMARD and achieved remission or low disease activity, of whom 39.7% underwent a DMARD taper.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Autoimmune Association - Young Investigator Grant Award. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Tageldin M et al. A real-world 2-year prospective study of medication tapering in patients with well-controlled rheumatoid arthritis within the rheumatoid arthritis medication tapering (RHEUMTAP) cohort. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023;62(Suppl 4):iv8-iv13 (Oct 19). doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead430
Herpes zoster subunit vaccine can be recommended in JAKi-treated RA
Key clinical point: In a vulnerable population of individuals with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) receiving Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi), the herpes zoster subunit (HZ/su) vaccine elicited a serological immune response in most patients and had an acceptable safety profile.
Major finding: The geometric mean concentration of vaccine-specific antibody levels increased from 2317 ng/mL prevaccination to 26,916 ng/mL postvaccination (P < .0001) in patients with RA, with 80.5% of patients showing a ≥4-fold increase in antibody levels. After vaccination, only 6.5% of patients reported an increase in RA disease activity, and adverse events were mostly mild or moderate.
Study details: Findings are from a phase 4 trial including 82 patients with RA treated using JAKi and 51 control individuals without rheumatic diseases, all of whom received two doses of the HZ/su vaccine.
Disclosures: Two authors declared receiving support or research funds for the present study from various sources. T Bergström declared receiving payments or honoraria from GlaxoSmithKline. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Källmark H et al. Serologic immunogenicity and safety of herpes zoster subunit vaccine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving Janus kinase inhibitors. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023 (Oct 18). Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead552.
Key clinical point: In a vulnerable population of individuals with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) receiving Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi), the herpes zoster subunit (HZ/su) vaccine elicited a serological immune response in most patients and had an acceptable safety profile.
Major finding: The geometric mean concentration of vaccine-specific antibody levels increased from 2317 ng/mL prevaccination to 26,916 ng/mL postvaccination (P < .0001) in patients with RA, with 80.5% of patients showing a ≥4-fold increase in antibody levels. After vaccination, only 6.5% of patients reported an increase in RA disease activity, and adverse events were mostly mild or moderate.
Study details: Findings are from a phase 4 trial including 82 patients with RA treated using JAKi and 51 control individuals without rheumatic diseases, all of whom received two doses of the HZ/su vaccine.
Disclosures: Two authors declared receiving support or research funds for the present study from various sources. T Bergström declared receiving payments or honoraria from GlaxoSmithKline. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Källmark H et al. Serologic immunogenicity and safety of herpes zoster subunit vaccine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving Janus kinase inhibitors. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023 (Oct 18). Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead552.
Key clinical point: In a vulnerable population of individuals with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) receiving Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi), the herpes zoster subunit (HZ/su) vaccine elicited a serological immune response in most patients and had an acceptable safety profile.
Major finding: The geometric mean concentration of vaccine-specific antibody levels increased from 2317 ng/mL prevaccination to 26,916 ng/mL postvaccination (P < .0001) in patients with RA, with 80.5% of patients showing a ≥4-fold increase in antibody levels. After vaccination, only 6.5% of patients reported an increase in RA disease activity, and adverse events were mostly mild or moderate.
Study details: Findings are from a phase 4 trial including 82 patients with RA treated using JAKi and 51 control individuals without rheumatic diseases, all of whom received two doses of the HZ/su vaccine.
Disclosures: Two authors declared receiving support or research funds for the present study from various sources. T Bergström declared receiving payments or honoraria from GlaxoSmithKline. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Källmark H et al. Serologic immunogenicity and safety of herpes zoster subunit vaccine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving Janus kinase inhibitors. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023 (Oct 18). Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead552.