User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Irregular and long periods linked to NAFLD
Long or irregular menstrual cycles in relatively young women are linked an increased risk of both prevalent and incident nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), according to a cross-sectional study that included data on more than 70,000 women.
“Our results indicate that menstrual irregularity, which is easier to diagnose and usually presented earlier than PCOS [polycystic ovary syndrome] highlights the possibility of identifying premenopausal women at risk of developing NAFLD,” reported a team of authors primarily from Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, South Korea.
The study evaluated women aged younger than 40 years who were participating in the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study, which involves a comprehensive biennial health examination at health centers in South Korea. Of the 135,090 women enrolled over a 6-year period who had at least one follow-up examination, 72,092 were available for analysis after excluding for a sizable list of confounding factors such as liver disease and infections; exposure to steatogenic medications, such as corticosteroids; hysterectomy; and pregnancy.
NAFLD prevalence climbs with longer menses
Of these women, 36.378 (27.7%) had menstrual cycles of 26-30 days and were identified as the index group. The prevalence of NAFLD in this group was 5.8%. For those with a menstrual cycle of 31-39 days, the prevalence rate climbed to 7.2%. For those with a menstrual cycle of at least 40 days or too irregular to estimate, the prevalence was 9.7%. The prevalence was 7.1% for those with a menstrual cycle less than 21 days.
The results of this study were published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
In those without NAFLD at baseline who were then followed for a mean of 4.4 years, there were 4,524 incident cases of NAFLD. Incidence density was calculated per 103 patient-years. In the index group, the rate was 18.4. It climbed to 20.2 for those with a menstrual cycle of 31-39 days and then to 22.9 for those with a menstrual cycle of at least 40 days. For those with a cycle of fewer than 21 days, the rate was 26.8.
After adjusting for age, body mass index, insulin resistance, and other confounders, the hazard ratio for incident NAFLD for those with long or irregular menstrual cycles compared with the incident group corresponded with a 22% increased risk (HR, 1.22; 95% confidence interval, 1.14-1.31). When calculated in a time-dependent analysis, the risk of NAFLD was increased by almost 50% (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.38-1.60).
Risk persists with PCOS exclusion
PCOS has previously been associated with increased risk of NAFLD, but the association between long or irregular menstrual cycles and NAFLD persisted after women with PCOS were excluded.
The mechanism that links menstrual irregularity with NAFLD is unclear, but the investigators said that estrogen exposure is implicated. In addition to a previously reported associated between low estradiol levels and antiestrogens such as tamoxifen with increased risk of NAFLD, they cited studies associating estrogen replacement therapy with a reduced risk of NAFLD. The role of estrogen in suppressing inflammation, oxidative stress, and insulin resistance are all activities that might link more regular menses with a reduced risk of NAFLD, the authors contended.
Women older than 40 years were excluded from this analysis to reduce the possibility of perimenopausal changes as a confounding factor.
Of study limitations acknowledged by the investigators, the presence of NAFLD was diagnosed on ultrasonography rather than histology. Information on sex hormone or prolactin levels was not captured in relation to NAFLD incidence, and the lack of exposure to estrogen replacement therapy and oral contraceptives was based on self-reports from the participants.
Still, the large study size and the consistency of results after adjustment for multiple risk factors argue that long and irregular menstrual cycles do identify women at risk for NAFLD. One implication is that irregular menses can be a marker for NAFLD risk.
“Our findings do not prove a causal relationship, but they show that long or irregular menstrual cycles were significantly associated with an increased risk of developing NAFLD,” said Seungho Ryu, MD, PhD, a professor at the Sungkyunkwan University. Senior author of this study, Dr. Ryu emphasized in an interview that the association “was not explained by obesity or any other risk factor for NAFLD.”
Lifestyle changes may lower risk
The message is that “young women with long or irregular menstrual cycles may benefit from lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of NAFLD,” Dr. Ryu stated.
The Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation, which was started in 1994, has not evaluated NAFLD, but it did show a relationship between longer menstrual cycles and more cardiometabolic risk factors, according to Nanette Santoro MD, professor and chair, department of obstetrics & gynecology, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
This suggests that others are “thinking along the same lines,” but in discussing this study with this news organization, she characterized some of the design elements as well as some of the findings in this study as “peculiar.”
In addition to a “very, very narrow definition of regular cycles,” she questioned the consistent hazard ratio for NAFLD for those with long cycles relative to other types of irregular menses. Presuming that the group with longer cycles would have included at least some patients with undiagnosed PCOS, she was would have expected that the risk would have been highest in this group. While conceding that differences in body composition of Korean women is a potential explanation for this apparent discrepancy, “I would like to see confirmed in other samples of women with more detailed metabolic assessments to understand who is at risk,” she said.
Not least problematic for the strength of the conclusions, the hazard ratio for NAFLD among women with long or irregular menstrual cycles was “pretty low.” She described this as a level at which the risk “is very susceptible to confounding and unlikely to influence clinical practice.”
Anuja Dokras, MD, PHD, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology and director of the PCOS Center at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, also questioned whether undiagnosed PCOS might have skewed the data.
“There is increasing data on the association between PCOS and NAFLD. Irregular menses is a key criterion for PCOS, and PCOS is the commonest reason for anovulation,” she said. Dr. Dokras therefore considered it possible that patients with unrecognized PCOS were included in the study, weakening the claim that risk of NAFLD and long menstrual cycles remains significant after controlling for PCOS.
Dr. Ryu and coinvestigators, Dr. Santoro, and Dr. Dokras reported no potential conflicts of interest.
Long or irregular menstrual cycles in relatively young women are linked an increased risk of both prevalent and incident nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), according to a cross-sectional study that included data on more than 70,000 women.
“Our results indicate that menstrual irregularity, which is easier to diagnose and usually presented earlier than PCOS [polycystic ovary syndrome] highlights the possibility of identifying premenopausal women at risk of developing NAFLD,” reported a team of authors primarily from Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, South Korea.
The study evaluated women aged younger than 40 years who were participating in the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study, which involves a comprehensive biennial health examination at health centers in South Korea. Of the 135,090 women enrolled over a 6-year period who had at least one follow-up examination, 72,092 were available for analysis after excluding for a sizable list of confounding factors such as liver disease and infections; exposure to steatogenic medications, such as corticosteroids; hysterectomy; and pregnancy.
NAFLD prevalence climbs with longer menses
Of these women, 36.378 (27.7%) had menstrual cycles of 26-30 days and were identified as the index group. The prevalence of NAFLD in this group was 5.8%. For those with a menstrual cycle of 31-39 days, the prevalence rate climbed to 7.2%. For those with a menstrual cycle of at least 40 days or too irregular to estimate, the prevalence was 9.7%. The prevalence was 7.1% for those with a menstrual cycle less than 21 days.
The results of this study were published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
In those without NAFLD at baseline who were then followed for a mean of 4.4 years, there were 4,524 incident cases of NAFLD. Incidence density was calculated per 103 patient-years. In the index group, the rate was 18.4. It climbed to 20.2 for those with a menstrual cycle of 31-39 days and then to 22.9 for those with a menstrual cycle of at least 40 days. For those with a cycle of fewer than 21 days, the rate was 26.8.
After adjusting for age, body mass index, insulin resistance, and other confounders, the hazard ratio for incident NAFLD for those with long or irregular menstrual cycles compared with the incident group corresponded with a 22% increased risk (HR, 1.22; 95% confidence interval, 1.14-1.31). When calculated in a time-dependent analysis, the risk of NAFLD was increased by almost 50% (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.38-1.60).
Risk persists with PCOS exclusion
PCOS has previously been associated with increased risk of NAFLD, but the association between long or irregular menstrual cycles and NAFLD persisted after women with PCOS were excluded.
The mechanism that links menstrual irregularity with NAFLD is unclear, but the investigators said that estrogen exposure is implicated. In addition to a previously reported associated between low estradiol levels and antiestrogens such as tamoxifen with increased risk of NAFLD, they cited studies associating estrogen replacement therapy with a reduced risk of NAFLD. The role of estrogen in suppressing inflammation, oxidative stress, and insulin resistance are all activities that might link more regular menses with a reduced risk of NAFLD, the authors contended.
Women older than 40 years were excluded from this analysis to reduce the possibility of perimenopausal changes as a confounding factor.
Of study limitations acknowledged by the investigators, the presence of NAFLD was diagnosed on ultrasonography rather than histology. Information on sex hormone or prolactin levels was not captured in relation to NAFLD incidence, and the lack of exposure to estrogen replacement therapy and oral contraceptives was based on self-reports from the participants.
Still, the large study size and the consistency of results after adjustment for multiple risk factors argue that long and irregular menstrual cycles do identify women at risk for NAFLD. One implication is that irregular menses can be a marker for NAFLD risk.
“Our findings do not prove a causal relationship, but they show that long or irregular menstrual cycles were significantly associated with an increased risk of developing NAFLD,” said Seungho Ryu, MD, PhD, a professor at the Sungkyunkwan University. Senior author of this study, Dr. Ryu emphasized in an interview that the association “was not explained by obesity or any other risk factor for NAFLD.”
Lifestyle changes may lower risk
The message is that “young women with long or irregular menstrual cycles may benefit from lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of NAFLD,” Dr. Ryu stated.
The Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation, which was started in 1994, has not evaluated NAFLD, but it did show a relationship between longer menstrual cycles and more cardiometabolic risk factors, according to Nanette Santoro MD, professor and chair, department of obstetrics & gynecology, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
This suggests that others are “thinking along the same lines,” but in discussing this study with this news organization, she characterized some of the design elements as well as some of the findings in this study as “peculiar.”
In addition to a “very, very narrow definition of regular cycles,” she questioned the consistent hazard ratio for NAFLD for those with long cycles relative to other types of irregular menses. Presuming that the group with longer cycles would have included at least some patients with undiagnosed PCOS, she was would have expected that the risk would have been highest in this group. While conceding that differences in body composition of Korean women is a potential explanation for this apparent discrepancy, “I would like to see confirmed in other samples of women with more detailed metabolic assessments to understand who is at risk,” she said.
Not least problematic for the strength of the conclusions, the hazard ratio for NAFLD among women with long or irregular menstrual cycles was “pretty low.” She described this as a level at which the risk “is very susceptible to confounding and unlikely to influence clinical practice.”
Anuja Dokras, MD, PHD, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology and director of the PCOS Center at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, also questioned whether undiagnosed PCOS might have skewed the data.
“There is increasing data on the association between PCOS and NAFLD. Irregular menses is a key criterion for PCOS, and PCOS is the commonest reason for anovulation,” she said. Dr. Dokras therefore considered it possible that patients with unrecognized PCOS were included in the study, weakening the claim that risk of NAFLD and long menstrual cycles remains significant after controlling for PCOS.
Dr. Ryu and coinvestigators, Dr. Santoro, and Dr. Dokras reported no potential conflicts of interest.
Long or irregular menstrual cycles in relatively young women are linked an increased risk of both prevalent and incident nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), according to a cross-sectional study that included data on more than 70,000 women.
“Our results indicate that menstrual irregularity, which is easier to diagnose and usually presented earlier than PCOS [polycystic ovary syndrome] highlights the possibility of identifying premenopausal women at risk of developing NAFLD,” reported a team of authors primarily from Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, South Korea.
The study evaluated women aged younger than 40 years who were participating in the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study, which involves a comprehensive biennial health examination at health centers in South Korea. Of the 135,090 women enrolled over a 6-year period who had at least one follow-up examination, 72,092 were available for analysis after excluding for a sizable list of confounding factors such as liver disease and infections; exposure to steatogenic medications, such as corticosteroids; hysterectomy; and pregnancy.
NAFLD prevalence climbs with longer menses
Of these women, 36.378 (27.7%) had menstrual cycles of 26-30 days and were identified as the index group. The prevalence of NAFLD in this group was 5.8%. For those with a menstrual cycle of 31-39 days, the prevalence rate climbed to 7.2%. For those with a menstrual cycle of at least 40 days or too irregular to estimate, the prevalence was 9.7%. The prevalence was 7.1% for those with a menstrual cycle less than 21 days.
The results of this study were published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
In those without NAFLD at baseline who were then followed for a mean of 4.4 years, there were 4,524 incident cases of NAFLD. Incidence density was calculated per 103 patient-years. In the index group, the rate was 18.4. It climbed to 20.2 for those with a menstrual cycle of 31-39 days and then to 22.9 for those with a menstrual cycle of at least 40 days. For those with a cycle of fewer than 21 days, the rate was 26.8.
After adjusting for age, body mass index, insulin resistance, and other confounders, the hazard ratio for incident NAFLD for those with long or irregular menstrual cycles compared with the incident group corresponded with a 22% increased risk (HR, 1.22; 95% confidence interval, 1.14-1.31). When calculated in a time-dependent analysis, the risk of NAFLD was increased by almost 50% (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.38-1.60).
Risk persists with PCOS exclusion
PCOS has previously been associated with increased risk of NAFLD, but the association between long or irregular menstrual cycles and NAFLD persisted after women with PCOS were excluded.
The mechanism that links menstrual irregularity with NAFLD is unclear, but the investigators said that estrogen exposure is implicated. In addition to a previously reported associated between low estradiol levels and antiestrogens such as tamoxifen with increased risk of NAFLD, they cited studies associating estrogen replacement therapy with a reduced risk of NAFLD. The role of estrogen in suppressing inflammation, oxidative stress, and insulin resistance are all activities that might link more regular menses with a reduced risk of NAFLD, the authors contended.
Women older than 40 years were excluded from this analysis to reduce the possibility of perimenopausal changes as a confounding factor.
Of study limitations acknowledged by the investigators, the presence of NAFLD was diagnosed on ultrasonography rather than histology. Information on sex hormone or prolactin levels was not captured in relation to NAFLD incidence, and the lack of exposure to estrogen replacement therapy and oral contraceptives was based on self-reports from the participants.
Still, the large study size and the consistency of results after adjustment for multiple risk factors argue that long and irregular menstrual cycles do identify women at risk for NAFLD. One implication is that irregular menses can be a marker for NAFLD risk.
“Our findings do not prove a causal relationship, but they show that long or irregular menstrual cycles were significantly associated with an increased risk of developing NAFLD,” said Seungho Ryu, MD, PhD, a professor at the Sungkyunkwan University. Senior author of this study, Dr. Ryu emphasized in an interview that the association “was not explained by obesity or any other risk factor for NAFLD.”
Lifestyle changes may lower risk
The message is that “young women with long or irregular menstrual cycles may benefit from lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of NAFLD,” Dr. Ryu stated.
The Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation, which was started in 1994, has not evaluated NAFLD, but it did show a relationship between longer menstrual cycles and more cardiometabolic risk factors, according to Nanette Santoro MD, professor and chair, department of obstetrics & gynecology, University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
This suggests that others are “thinking along the same lines,” but in discussing this study with this news organization, she characterized some of the design elements as well as some of the findings in this study as “peculiar.”
In addition to a “very, very narrow definition of regular cycles,” she questioned the consistent hazard ratio for NAFLD for those with long cycles relative to other types of irregular menses. Presuming that the group with longer cycles would have included at least some patients with undiagnosed PCOS, she was would have expected that the risk would have been highest in this group. While conceding that differences in body composition of Korean women is a potential explanation for this apparent discrepancy, “I would like to see confirmed in other samples of women with more detailed metabolic assessments to understand who is at risk,” she said.
Not least problematic for the strength of the conclusions, the hazard ratio for NAFLD among women with long or irregular menstrual cycles was “pretty low.” She described this as a level at which the risk “is very susceptible to confounding and unlikely to influence clinical practice.”
Anuja Dokras, MD, PHD, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology and director of the PCOS Center at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, also questioned whether undiagnosed PCOS might have skewed the data.
“There is increasing data on the association between PCOS and NAFLD. Irregular menses is a key criterion for PCOS, and PCOS is the commonest reason for anovulation,” she said. Dr. Dokras therefore considered it possible that patients with unrecognized PCOS were included in the study, weakening the claim that risk of NAFLD and long menstrual cycles remains significant after controlling for PCOS.
Dr. Ryu and coinvestigators, Dr. Santoro, and Dr. Dokras reported no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGY & METABOLISM
Cardiac arrest survival lower in COVID-19 inpatients
Survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest was roughly one-third lower in patients with COVID-19 infections compared to uninfected patients, based on data from nearly 25,000 individuals.
Survival rates of less than 3% were reported in the United States and China for patients who suffered in-hospital cardiac arrest (IHCA) while infected with COVID-19 early in the pandemic, but the data came from small, single-center studies in overwhelmed hospitals, wrote Saket Girotra, MD, of the University of Iowa, Iowa City, and fellow American Heart Association Get With the Guidelines–Resuscitation Investigators. Whether these early reports reflect the broader experience of patients with COVID-19 in hospitals in the United States remains unknown.
In a study published as a research letter in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed data from the American Heart Association Get With the Guidelines–Resuscitation registry. The registry collects detailed information on patients aged 18 years and older who experience cardiac arrest at participating hospitals in the United States. The study population included 24,915 patients aged 18 years and older from 286 hospitals who experienced IHCA during March–December 2020. The mean age of the patients was 64.7 years; 61.1% were White, 24.8% were Black, 3.8% were of other race or ethnicity, and 10.3% were of unknown race or ethnicity.
The primary outcomes were survival to discharge and return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) for at least 20 minutes.
A total of 5,916 patients (23.7%) had suspected or confirmed COVID-19 infections, and infected patients were more likely to be younger, male, and Black. Patients with COVID-19 infections also were significantly more likely than noninfected patients to have nonshockable rhythm, pneumonia, respiratory insufficiency, or sepsis, and to be on mechanical ventilation or vasopressors when the IHCA occurred, the researchers noted.
Survival rates to hospital discharge were 11.9% for COVID-19 patients, compared with 23.5% for noninfected patients (adjusted relative risk, 0.65; P < .001). ROSC was 53.7% and 63.6%, for infected and noninfected patients, respectively (aRR, 0.86; P < .001).
COVID-19 patients also were more likely than noninfected patients to receive delayed defibrillation, the researchers said. “Although delays in resuscitation, especially defibrillation, may have contributed to lower survival, the negative association of COVID-19 with survival in this study was consistent across subgroups, including patients who received timely treatment with defibrillation and epinephrine.”
The extremely low survival rate in early pandemic studies likely reflected the overwhelming burden on health systems at the time, the researchers said in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including potential confounding from unmeasured variables, the use of a quality improvement registry that may not reflect nonparticipating hospitals, and potential false-positive COVID-19 cases. However, the result support findings from recent studies of multiple centers and extend clinical knowledge by comparing infected and noninfected patients from a larger group of hospitals than previously studied, the researchers said.
“We believe that these data will be relevant to health care providers and hospital administrators as the COVID-19 pandemic continues,” they concluded.
Think beyond COVID-19 for cardiac care
“Early during the pandemic, questions were raised whether COVID-19 patients should be treated with CPR,” Dr. Girotra said in an interview. “This was because initial studies had found a dismal survival of 0%-3% in COVID patients treated with CPR. The potential of transmitting the virus to health care professionals during CPR further heightened these concerns. We wanted to know whether the poor survival reported in these initial studies were broadly representative.”
Dr. Girotra said that some of the study findings were surprising. “We found that of all patients with IHCA in 2020 in our study, one in four were suspected or confirmed to have COVID-19 infection. We were surprised by the magnitude of COVID’s impact on the cardiac arrest incidence.”
The implications for clinical decision-making are to think outside of COVID-19 infection, said Dr. Girotra. In the current study, “Although overall survival of cardiac arrest in COVID-positive patients was 30% lower, compared to non-COVID patients, it was not as poor as previously reported. COVID-19 infection alone should not be considered the sole factor for making decisions regarding CPR.
“Over the past 2 decades, we have experienced large gains in survival for in-hospital cardiac arrest. However, the COVID-19 pandemic has eroded these gains,” said Dr. Girotra. “Future studies are needed to monitor the impact of any new variants on cardiac arrest care,” as well as studies “to see whether we return to the prepandemic levels of IHCA survival once the pandemic recedes.”
Dr. Girotra has no relevant financial disclosures.
Survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest was roughly one-third lower in patients with COVID-19 infections compared to uninfected patients, based on data from nearly 25,000 individuals.
Survival rates of less than 3% were reported in the United States and China for patients who suffered in-hospital cardiac arrest (IHCA) while infected with COVID-19 early in the pandemic, but the data came from small, single-center studies in overwhelmed hospitals, wrote Saket Girotra, MD, of the University of Iowa, Iowa City, and fellow American Heart Association Get With the Guidelines–Resuscitation Investigators. Whether these early reports reflect the broader experience of patients with COVID-19 in hospitals in the United States remains unknown.
In a study published as a research letter in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed data from the American Heart Association Get With the Guidelines–Resuscitation registry. The registry collects detailed information on patients aged 18 years and older who experience cardiac arrest at participating hospitals in the United States. The study population included 24,915 patients aged 18 years and older from 286 hospitals who experienced IHCA during March–December 2020. The mean age of the patients was 64.7 years; 61.1% were White, 24.8% were Black, 3.8% were of other race or ethnicity, and 10.3% were of unknown race or ethnicity.
The primary outcomes were survival to discharge and return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) for at least 20 minutes.
A total of 5,916 patients (23.7%) had suspected or confirmed COVID-19 infections, and infected patients were more likely to be younger, male, and Black. Patients with COVID-19 infections also were significantly more likely than noninfected patients to have nonshockable rhythm, pneumonia, respiratory insufficiency, or sepsis, and to be on mechanical ventilation or vasopressors when the IHCA occurred, the researchers noted.
Survival rates to hospital discharge were 11.9% for COVID-19 patients, compared with 23.5% for noninfected patients (adjusted relative risk, 0.65; P < .001). ROSC was 53.7% and 63.6%, for infected and noninfected patients, respectively (aRR, 0.86; P < .001).
COVID-19 patients also were more likely than noninfected patients to receive delayed defibrillation, the researchers said. “Although delays in resuscitation, especially defibrillation, may have contributed to lower survival, the negative association of COVID-19 with survival in this study was consistent across subgroups, including patients who received timely treatment with defibrillation and epinephrine.”
The extremely low survival rate in early pandemic studies likely reflected the overwhelming burden on health systems at the time, the researchers said in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including potential confounding from unmeasured variables, the use of a quality improvement registry that may not reflect nonparticipating hospitals, and potential false-positive COVID-19 cases. However, the result support findings from recent studies of multiple centers and extend clinical knowledge by comparing infected and noninfected patients from a larger group of hospitals than previously studied, the researchers said.
“We believe that these data will be relevant to health care providers and hospital administrators as the COVID-19 pandemic continues,” they concluded.
Think beyond COVID-19 for cardiac care
“Early during the pandemic, questions were raised whether COVID-19 patients should be treated with CPR,” Dr. Girotra said in an interview. “This was because initial studies had found a dismal survival of 0%-3% in COVID patients treated with CPR. The potential of transmitting the virus to health care professionals during CPR further heightened these concerns. We wanted to know whether the poor survival reported in these initial studies were broadly representative.”
Dr. Girotra said that some of the study findings were surprising. “We found that of all patients with IHCA in 2020 in our study, one in four were suspected or confirmed to have COVID-19 infection. We were surprised by the magnitude of COVID’s impact on the cardiac arrest incidence.”
The implications for clinical decision-making are to think outside of COVID-19 infection, said Dr. Girotra. In the current study, “Although overall survival of cardiac arrest in COVID-positive patients was 30% lower, compared to non-COVID patients, it was not as poor as previously reported. COVID-19 infection alone should not be considered the sole factor for making decisions regarding CPR.
“Over the past 2 decades, we have experienced large gains in survival for in-hospital cardiac arrest. However, the COVID-19 pandemic has eroded these gains,” said Dr. Girotra. “Future studies are needed to monitor the impact of any new variants on cardiac arrest care,” as well as studies “to see whether we return to the prepandemic levels of IHCA survival once the pandemic recedes.”
Dr. Girotra has no relevant financial disclosures.
Survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest was roughly one-third lower in patients with COVID-19 infections compared to uninfected patients, based on data from nearly 25,000 individuals.
Survival rates of less than 3% were reported in the United States and China for patients who suffered in-hospital cardiac arrest (IHCA) while infected with COVID-19 early in the pandemic, but the data came from small, single-center studies in overwhelmed hospitals, wrote Saket Girotra, MD, of the University of Iowa, Iowa City, and fellow American Heart Association Get With the Guidelines–Resuscitation Investigators. Whether these early reports reflect the broader experience of patients with COVID-19 in hospitals in the United States remains unknown.
In a study published as a research letter in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed data from the American Heart Association Get With the Guidelines–Resuscitation registry. The registry collects detailed information on patients aged 18 years and older who experience cardiac arrest at participating hospitals in the United States. The study population included 24,915 patients aged 18 years and older from 286 hospitals who experienced IHCA during March–December 2020. The mean age of the patients was 64.7 years; 61.1% were White, 24.8% were Black, 3.8% were of other race or ethnicity, and 10.3% were of unknown race or ethnicity.
The primary outcomes were survival to discharge and return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) for at least 20 minutes.
A total of 5,916 patients (23.7%) had suspected or confirmed COVID-19 infections, and infected patients were more likely to be younger, male, and Black. Patients with COVID-19 infections also were significantly more likely than noninfected patients to have nonshockable rhythm, pneumonia, respiratory insufficiency, or sepsis, and to be on mechanical ventilation or vasopressors when the IHCA occurred, the researchers noted.
Survival rates to hospital discharge were 11.9% for COVID-19 patients, compared with 23.5% for noninfected patients (adjusted relative risk, 0.65; P < .001). ROSC was 53.7% and 63.6%, for infected and noninfected patients, respectively (aRR, 0.86; P < .001).
COVID-19 patients also were more likely than noninfected patients to receive delayed defibrillation, the researchers said. “Although delays in resuscitation, especially defibrillation, may have contributed to lower survival, the negative association of COVID-19 with survival in this study was consistent across subgroups, including patients who received timely treatment with defibrillation and epinephrine.”
The extremely low survival rate in early pandemic studies likely reflected the overwhelming burden on health systems at the time, the researchers said in their discussion.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including potential confounding from unmeasured variables, the use of a quality improvement registry that may not reflect nonparticipating hospitals, and potential false-positive COVID-19 cases. However, the result support findings from recent studies of multiple centers and extend clinical knowledge by comparing infected and noninfected patients from a larger group of hospitals than previously studied, the researchers said.
“We believe that these data will be relevant to health care providers and hospital administrators as the COVID-19 pandemic continues,” they concluded.
Think beyond COVID-19 for cardiac care
“Early during the pandemic, questions were raised whether COVID-19 patients should be treated with CPR,” Dr. Girotra said in an interview. “This was because initial studies had found a dismal survival of 0%-3% in COVID patients treated with CPR. The potential of transmitting the virus to health care professionals during CPR further heightened these concerns. We wanted to know whether the poor survival reported in these initial studies were broadly representative.”
Dr. Girotra said that some of the study findings were surprising. “We found that of all patients with IHCA in 2020 in our study, one in four were suspected or confirmed to have COVID-19 infection. We were surprised by the magnitude of COVID’s impact on the cardiac arrest incidence.”
The implications for clinical decision-making are to think outside of COVID-19 infection, said Dr. Girotra. In the current study, “Although overall survival of cardiac arrest in COVID-positive patients was 30% lower, compared to non-COVID patients, it was not as poor as previously reported. COVID-19 infection alone should not be considered the sole factor for making decisions regarding CPR.
“Over the past 2 decades, we have experienced large gains in survival for in-hospital cardiac arrest. However, the COVID-19 pandemic has eroded these gains,” said Dr. Girotra. “Future studies are needed to monitor the impact of any new variants on cardiac arrest care,” as well as studies “to see whether we return to the prepandemic levels of IHCA survival once the pandemic recedes.”
Dr. Girotra has no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Analysis questions tocilizumab in ventilated COVID patients
A new statistical analysis of an existing meta-analysis reaffirms a finding that hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who are on simple oxygen or noninvasive ventilation can benefit from treatment with the arthritis drug tocilizumab (Actemra) in conjunction with corticosteroids. But the report also casts doubt on the effectiveness of tocilizumab in patients who are on ventilators.
“Clinicians should prescribe steroids and tocilizumab for hospitalized patients needing simple oxygen or noninvasive ventilation,” epidemiologist and study coauthor James (Jay) Brophy, MD, PhD, of McGill University, Montreal, said in an interview. “Further research is required to answer the question of whether tocilizumab is beneficial in patients requiring invasive ventilation, and consideration of participation in further tocilizumab studies seems reasonable.”
The new analysis was published Feb. 28, 2022, in JAMA Network Open.
The initial meta-analysis, published in 2021 in JAMA, was conducted by the WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies Working Group. It analyzed the results of 27 randomized trials that explored the use of interleukin-6 antagonists, including tocilizumab, and found that “28-day all-cause mortality was lower among patients who received IL-6 antagonists, compared with those who received usual care or placebo (summary odds ratio, 0.86). The summary ORs for the association of IL-6 antagonist treatment with 28-day all-cause mortality were 0.78 with concomitant administration of corticosteroids versus 1.09 without administration of corticosteroids.”
For the new report, researchers conducted a Bayesian statistical analysis of 15 studies within the meta-analysis that specifically examined the use of the rheumatoid arthritis drug tocilizumab. “Bayesian analysis allows one to make direct probability statements regarding the exact magnitude and the certainty of any benefit,” Dr. Brophy said. “This provides clinicians with the information they require to make well-informed decisions.”
The analysis estimated that the probability of a “clinically meaningful association” (absolute mortality risk difference, >1%) because of use of tocilizumab was higher than 95% in patients receiving simple oxygen and higher than 90% in those receiving noninvasive ventilation. But the probability was only about 67% higher in those receiving invasive mechanical ventilation.
Also, the researchers estimated that about 72% of future tocilizumab studies in patients on invasive mechanical ventilation would show a benefit.
The new analysis findings don’t add much to existing knowledge, said nephrologist David E. Leaf, MD, MMSc, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, who’s studied tocilizumab in COVID-19.
“The signal seems to be consistent that there is a greater benefit of tocilizumab in less ill patients than those who are more ill – e.g., those who are receiving invasive mechanical ventilation,” Dr. Leaf said in an interview. “This is interesting because in clinical practice the opposite approach is often undertaken, with tocilizumab use only being used in the sickest patients, even though the patients most likely to benefit seem to be those who are less ill.”
Clinically, he said, “hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should receive tocilizumab unless they have a clear contraindication and assuming it can be administered relatively early in their disease course. Earlier administration, before the onset of irreversible organ injury, is likely to have greater benefit.”
Dr. Leaf also noted it’s unknown whether the drug is helpful in several groups – patients presenting later in the course of COVID-19 illness, patients with additional infections, and immunocompromised patients.
It’s also not clear if tocilizumab benefits patients with lower levels of C-reactive protein, Shruti Gupta, MD, MPH, a nephrologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, said in an interview. The RECOVERY trial, for example, limited subjects to those with C-reactive protein of at least 75 mg/L.
Dr. Leaf and Dr. Gupta coauthored a 2021 cohort study analyzing mortality rates in patients with COVID-19 who were treated with tocilizumab versus those who were not.
No study funding was reported. Dr. Brophy, Dr. Leaf, and Dr. Gupta disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One study author reported participating in one of the randomized clinical trials included in the analysis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new statistical analysis of an existing meta-analysis reaffirms a finding that hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who are on simple oxygen or noninvasive ventilation can benefit from treatment with the arthritis drug tocilizumab (Actemra) in conjunction with corticosteroids. But the report also casts doubt on the effectiveness of tocilizumab in patients who are on ventilators.
“Clinicians should prescribe steroids and tocilizumab for hospitalized patients needing simple oxygen or noninvasive ventilation,” epidemiologist and study coauthor James (Jay) Brophy, MD, PhD, of McGill University, Montreal, said in an interview. “Further research is required to answer the question of whether tocilizumab is beneficial in patients requiring invasive ventilation, and consideration of participation in further tocilizumab studies seems reasonable.”
The new analysis was published Feb. 28, 2022, in JAMA Network Open.
The initial meta-analysis, published in 2021 in JAMA, was conducted by the WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies Working Group. It analyzed the results of 27 randomized trials that explored the use of interleukin-6 antagonists, including tocilizumab, and found that “28-day all-cause mortality was lower among patients who received IL-6 antagonists, compared with those who received usual care or placebo (summary odds ratio, 0.86). The summary ORs for the association of IL-6 antagonist treatment with 28-day all-cause mortality were 0.78 with concomitant administration of corticosteroids versus 1.09 without administration of corticosteroids.”
For the new report, researchers conducted a Bayesian statistical analysis of 15 studies within the meta-analysis that specifically examined the use of the rheumatoid arthritis drug tocilizumab. “Bayesian analysis allows one to make direct probability statements regarding the exact magnitude and the certainty of any benefit,” Dr. Brophy said. “This provides clinicians with the information they require to make well-informed decisions.”
The analysis estimated that the probability of a “clinically meaningful association” (absolute mortality risk difference, >1%) because of use of tocilizumab was higher than 95% in patients receiving simple oxygen and higher than 90% in those receiving noninvasive ventilation. But the probability was only about 67% higher in those receiving invasive mechanical ventilation.
Also, the researchers estimated that about 72% of future tocilizumab studies in patients on invasive mechanical ventilation would show a benefit.
The new analysis findings don’t add much to existing knowledge, said nephrologist David E. Leaf, MD, MMSc, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, who’s studied tocilizumab in COVID-19.
“The signal seems to be consistent that there is a greater benefit of tocilizumab in less ill patients than those who are more ill – e.g., those who are receiving invasive mechanical ventilation,” Dr. Leaf said in an interview. “This is interesting because in clinical practice the opposite approach is often undertaken, with tocilizumab use only being used in the sickest patients, even though the patients most likely to benefit seem to be those who are less ill.”
Clinically, he said, “hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should receive tocilizumab unless they have a clear contraindication and assuming it can be administered relatively early in their disease course. Earlier administration, before the onset of irreversible organ injury, is likely to have greater benefit.”
Dr. Leaf also noted it’s unknown whether the drug is helpful in several groups – patients presenting later in the course of COVID-19 illness, patients with additional infections, and immunocompromised patients.
It’s also not clear if tocilizumab benefits patients with lower levels of C-reactive protein, Shruti Gupta, MD, MPH, a nephrologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, said in an interview. The RECOVERY trial, for example, limited subjects to those with C-reactive protein of at least 75 mg/L.
Dr. Leaf and Dr. Gupta coauthored a 2021 cohort study analyzing mortality rates in patients with COVID-19 who were treated with tocilizumab versus those who were not.
No study funding was reported. Dr. Brophy, Dr. Leaf, and Dr. Gupta disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One study author reported participating in one of the randomized clinical trials included in the analysis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new statistical analysis of an existing meta-analysis reaffirms a finding that hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who are on simple oxygen or noninvasive ventilation can benefit from treatment with the arthritis drug tocilizumab (Actemra) in conjunction with corticosteroids. But the report also casts doubt on the effectiveness of tocilizumab in patients who are on ventilators.
“Clinicians should prescribe steroids and tocilizumab for hospitalized patients needing simple oxygen or noninvasive ventilation,” epidemiologist and study coauthor James (Jay) Brophy, MD, PhD, of McGill University, Montreal, said in an interview. “Further research is required to answer the question of whether tocilizumab is beneficial in patients requiring invasive ventilation, and consideration of participation in further tocilizumab studies seems reasonable.”
The new analysis was published Feb. 28, 2022, in JAMA Network Open.
The initial meta-analysis, published in 2021 in JAMA, was conducted by the WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies Working Group. It analyzed the results of 27 randomized trials that explored the use of interleukin-6 antagonists, including tocilizumab, and found that “28-day all-cause mortality was lower among patients who received IL-6 antagonists, compared with those who received usual care or placebo (summary odds ratio, 0.86). The summary ORs for the association of IL-6 antagonist treatment with 28-day all-cause mortality were 0.78 with concomitant administration of corticosteroids versus 1.09 without administration of corticosteroids.”
For the new report, researchers conducted a Bayesian statistical analysis of 15 studies within the meta-analysis that specifically examined the use of the rheumatoid arthritis drug tocilizumab. “Bayesian analysis allows one to make direct probability statements regarding the exact magnitude and the certainty of any benefit,” Dr. Brophy said. “This provides clinicians with the information they require to make well-informed decisions.”
The analysis estimated that the probability of a “clinically meaningful association” (absolute mortality risk difference, >1%) because of use of tocilizumab was higher than 95% in patients receiving simple oxygen and higher than 90% in those receiving noninvasive ventilation. But the probability was only about 67% higher in those receiving invasive mechanical ventilation.
Also, the researchers estimated that about 72% of future tocilizumab studies in patients on invasive mechanical ventilation would show a benefit.
The new analysis findings don’t add much to existing knowledge, said nephrologist David E. Leaf, MD, MMSc, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, who’s studied tocilizumab in COVID-19.
“The signal seems to be consistent that there is a greater benefit of tocilizumab in less ill patients than those who are more ill – e.g., those who are receiving invasive mechanical ventilation,” Dr. Leaf said in an interview. “This is interesting because in clinical practice the opposite approach is often undertaken, with tocilizumab use only being used in the sickest patients, even though the patients most likely to benefit seem to be those who are less ill.”
Clinically, he said, “hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should receive tocilizumab unless they have a clear contraindication and assuming it can be administered relatively early in their disease course. Earlier administration, before the onset of irreversible organ injury, is likely to have greater benefit.”
Dr. Leaf also noted it’s unknown whether the drug is helpful in several groups – patients presenting later in the course of COVID-19 illness, patients with additional infections, and immunocompromised patients.
It’s also not clear if tocilizumab benefits patients with lower levels of C-reactive protein, Shruti Gupta, MD, MPH, a nephrologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, said in an interview. The RECOVERY trial, for example, limited subjects to those with C-reactive protein of at least 75 mg/L.
Dr. Leaf and Dr. Gupta coauthored a 2021 cohort study analyzing mortality rates in patients with COVID-19 who were treated with tocilizumab versus those who were not.
No study funding was reported. Dr. Brophy, Dr. Leaf, and Dr. Gupta disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One study author reported participating in one of the randomized clinical trials included in the analysis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Self-care tips for clinicians as COVID-19 lingers
LAS VEGAS – according to Jon A. Levenson, MD.
“There are those who will need mental health treatment, so creating an easy way to reach out for help and facilitate linkage with care is critically important,” Dr. Levenson, associate professor of psychiatry at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, said during an annual psychopharmacology update held by the Nevada Psychiatric Association. “The vast majority of our workforce will thrive with proper support. But what can each of us do to take care of ourselves?”
Step one is to recognize common stress reactions as well as signs of distress. He offered the oxygen mask metaphor, the idea that before we can take care of and support anyone else, we must first take care of ourselves. “When people are stressed, they don’t always think about the oxygen mask metaphor,” Dr. Levenson said. Step two is to practice and model self-care by adopting principles often discussed in acceptance and commitment therapy: to focus on what you can control, not on what you can’t control.
“We can’t control the amount of toilet paper at the grocery store, how long the pandemic will last, or how others have reacted,” Dr. Levenson said. “We also can’t control other people’s motives, predict what will happen, or the actions of others, including whether they will follow social distancing guidelines or not.”
How about what we can control? One is a positive attitude, “which can sustain people during times of intense stress,” he said. “Other things that we can do include turn off the news and find fun and enriching activities to do at home, whether it be playing a game with family or reaching out to friends through an iPad or a smartphone. You can also follow [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] recommendations, control your own social distancing, and limit social media activity, which can be stressful. We can also control our kindness and grace.” He added that resilience does not mean “snapping back” to how you were before the pandemic, but rather “learning to integrate the adverse experiences into who you are and growing with them, which is sometimes known as posttraumatic growth.”
Dr. Levenson encouraged health care workers to use their coping resources, connect to others, and cultivate their values and purpose in life as they navigate these challenging times. “You also want to promote realistic optimism; find a way to stay positive,” he said. “We emphasize to our staff that while you won’t forget this time, focus on what you can control – your positive relationships – and remind yourself of your values and sources of gratitude. Figure out, and reflect on, what you care about, and then care about it. Remind yourself in a deliberate, purposeful way what anchors you to your job, which in the health care setting tends to be a desire to care for others, to assist those in need, and to work in teams. We also encourage staff to refrain from judgment. Guilt is a normal and near-universal response to this stressor, but there are many ways to contribute without a judgmental or guilty tone.”
Other tips for self-support are to remind yourself that it is not selfish to take breaks. “The needs of your patients are not more important than your own needs,” Dr. Levenson said. “Working nonstop can put you at higher risk for stress, exhaustion, and illness. You may need to give yourself more time to step back and recover from workplace challenges or extended coverage for peers; this is important. We remind our staff that your work may feel more emotionally draining than usual because everything is more intense overall during the COVID-19 pandemic. This reminder helps staff normalize what they already may be experiencing, and in turn, to further support each other.”
Soothing activities to relieve stress include meditation, prayer, deep and slow breathing, relaxation exercises, yoga, mindfulness, stretching, staying hydrated, eating healthfully, exercise, and getting sufficient sleep. Other stress management tips include avoiding excessive alcohol intake, reaching out to others, asking for assistance, and delegating when possible. “We want to promote psychological flexibility: the ability to stay in contact with the present moment,” he said. “We encourage our peers to be aware of unpleasant thoughts and feelings, and to try to redirect negative thought patterns to a proactive problem-solving approach; this includes choosing one’s behaviors based on the situation and personal values.”
Dr. Levenson reported having no disclosures related to his presentation.
LAS VEGAS – according to Jon A. Levenson, MD.
“There are those who will need mental health treatment, so creating an easy way to reach out for help and facilitate linkage with care is critically important,” Dr. Levenson, associate professor of psychiatry at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, said during an annual psychopharmacology update held by the Nevada Psychiatric Association. “The vast majority of our workforce will thrive with proper support. But what can each of us do to take care of ourselves?”
Step one is to recognize common stress reactions as well as signs of distress. He offered the oxygen mask metaphor, the idea that before we can take care of and support anyone else, we must first take care of ourselves. “When people are stressed, they don’t always think about the oxygen mask metaphor,” Dr. Levenson said. Step two is to practice and model self-care by adopting principles often discussed in acceptance and commitment therapy: to focus on what you can control, not on what you can’t control.
“We can’t control the amount of toilet paper at the grocery store, how long the pandemic will last, or how others have reacted,” Dr. Levenson said. “We also can’t control other people’s motives, predict what will happen, or the actions of others, including whether they will follow social distancing guidelines or not.”
How about what we can control? One is a positive attitude, “which can sustain people during times of intense stress,” he said. “Other things that we can do include turn off the news and find fun and enriching activities to do at home, whether it be playing a game with family or reaching out to friends through an iPad or a smartphone. You can also follow [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] recommendations, control your own social distancing, and limit social media activity, which can be stressful. We can also control our kindness and grace.” He added that resilience does not mean “snapping back” to how you were before the pandemic, but rather “learning to integrate the adverse experiences into who you are and growing with them, which is sometimes known as posttraumatic growth.”
Dr. Levenson encouraged health care workers to use their coping resources, connect to others, and cultivate their values and purpose in life as they navigate these challenging times. “You also want to promote realistic optimism; find a way to stay positive,” he said. “We emphasize to our staff that while you won’t forget this time, focus on what you can control – your positive relationships – and remind yourself of your values and sources of gratitude. Figure out, and reflect on, what you care about, and then care about it. Remind yourself in a deliberate, purposeful way what anchors you to your job, which in the health care setting tends to be a desire to care for others, to assist those in need, and to work in teams. We also encourage staff to refrain from judgment. Guilt is a normal and near-universal response to this stressor, but there are many ways to contribute without a judgmental or guilty tone.”
Other tips for self-support are to remind yourself that it is not selfish to take breaks. “The needs of your patients are not more important than your own needs,” Dr. Levenson said. “Working nonstop can put you at higher risk for stress, exhaustion, and illness. You may need to give yourself more time to step back and recover from workplace challenges or extended coverage for peers; this is important. We remind our staff that your work may feel more emotionally draining than usual because everything is more intense overall during the COVID-19 pandemic. This reminder helps staff normalize what they already may be experiencing, and in turn, to further support each other.”
Soothing activities to relieve stress include meditation, prayer, deep and slow breathing, relaxation exercises, yoga, mindfulness, stretching, staying hydrated, eating healthfully, exercise, and getting sufficient sleep. Other stress management tips include avoiding excessive alcohol intake, reaching out to others, asking for assistance, and delegating when possible. “We want to promote psychological flexibility: the ability to stay in contact with the present moment,” he said. “We encourage our peers to be aware of unpleasant thoughts and feelings, and to try to redirect negative thought patterns to a proactive problem-solving approach; this includes choosing one’s behaviors based on the situation and personal values.”
Dr. Levenson reported having no disclosures related to his presentation.
LAS VEGAS – according to Jon A. Levenson, MD.
“There are those who will need mental health treatment, so creating an easy way to reach out for help and facilitate linkage with care is critically important,” Dr. Levenson, associate professor of psychiatry at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, said during an annual psychopharmacology update held by the Nevada Psychiatric Association. “The vast majority of our workforce will thrive with proper support. But what can each of us do to take care of ourselves?”
Step one is to recognize common stress reactions as well as signs of distress. He offered the oxygen mask metaphor, the idea that before we can take care of and support anyone else, we must first take care of ourselves. “When people are stressed, they don’t always think about the oxygen mask metaphor,” Dr. Levenson said. Step two is to practice and model self-care by adopting principles often discussed in acceptance and commitment therapy: to focus on what you can control, not on what you can’t control.
“We can’t control the amount of toilet paper at the grocery store, how long the pandemic will last, or how others have reacted,” Dr. Levenson said. “We also can’t control other people’s motives, predict what will happen, or the actions of others, including whether they will follow social distancing guidelines or not.”
How about what we can control? One is a positive attitude, “which can sustain people during times of intense stress,” he said. “Other things that we can do include turn off the news and find fun and enriching activities to do at home, whether it be playing a game with family or reaching out to friends through an iPad or a smartphone. You can also follow [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] recommendations, control your own social distancing, and limit social media activity, which can be stressful. We can also control our kindness and grace.” He added that resilience does not mean “snapping back” to how you were before the pandemic, but rather “learning to integrate the adverse experiences into who you are and growing with them, which is sometimes known as posttraumatic growth.”
Dr. Levenson encouraged health care workers to use their coping resources, connect to others, and cultivate their values and purpose in life as they navigate these challenging times. “You also want to promote realistic optimism; find a way to stay positive,” he said. “We emphasize to our staff that while you won’t forget this time, focus on what you can control – your positive relationships – and remind yourself of your values and sources of gratitude. Figure out, and reflect on, what you care about, and then care about it. Remind yourself in a deliberate, purposeful way what anchors you to your job, which in the health care setting tends to be a desire to care for others, to assist those in need, and to work in teams. We also encourage staff to refrain from judgment. Guilt is a normal and near-universal response to this stressor, but there are many ways to contribute without a judgmental or guilty tone.”
Other tips for self-support are to remind yourself that it is not selfish to take breaks. “The needs of your patients are not more important than your own needs,” Dr. Levenson said. “Working nonstop can put you at higher risk for stress, exhaustion, and illness. You may need to give yourself more time to step back and recover from workplace challenges or extended coverage for peers; this is important. We remind our staff that your work may feel more emotionally draining than usual because everything is more intense overall during the COVID-19 pandemic. This reminder helps staff normalize what they already may be experiencing, and in turn, to further support each other.”
Soothing activities to relieve stress include meditation, prayer, deep and slow breathing, relaxation exercises, yoga, mindfulness, stretching, staying hydrated, eating healthfully, exercise, and getting sufficient sleep. Other stress management tips include avoiding excessive alcohol intake, reaching out to others, asking for assistance, and delegating when possible. “We want to promote psychological flexibility: the ability to stay in contact with the present moment,” he said. “We encourage our peers to be aware of unpleasant thoughts and feelings, and to try to redirect negative thought patterns to a proactive problem-solving approach; this includes choosing one’s behaviors based on the situation and personal values.”
Dr. Levenson reported having no disclosures related to his presentation.
AT NPA 2022
B-cell therapy for MS may impact COVID-19 vaccination
, according to a new retrospective analysis. The link is particularly strong among B-cell depleting drugs.
“A lot of patients ask us if having MS by itself affects the vaccine response. We did not find that, but it’s about the disease-modifying therapy that a patient is being treated with,” Tirisham Gyang, MD, said in an interview. Dr. Gyang presented the study at a poster session during the annual meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
“These patients (on DMTs) had decreased neutralizing antibody levels to the vaccine after they received it. We also saw a similar marker in drugs that modulate the sphingosine S-1 receptor. These patients also had a lower titer. It wasn’t statistically significant, but we think it’s positive. It was underpowered because there was a small number of patients in that subgroup,” said Dr. Gyang, assistant professor of neurology at The Ohio State University.
The results can inform vaccine strategies among people with MS, but the issue remains complex. “I don’t know that we could do a blanket statement and say, if you wait this amount of time, everybody will be okay. It’s a very individualized approach, and patients need to discuss timing of vaccines with their providers, because we know that waiting is better. It’s preferable to wait until towards the end of the dosing cycle. The other factor is making sure that the MS is well treated,” said Dr. Gyang.
The researchers prospectively followed 83 MS patients at the The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. Among the cohort, 71% were female. Fifty-one subjects had serum samples analyzed following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination, and they were compared with 38 health care worker controls.
After vaccination, people with MS had about 2.4-fold lower levels of half-maximal neutralization titer (NT50) values compared with health care worker controls. This appeared to be driven primarily by DMTs. There was a more than ninefold reduction in the neutralizing antibody (nAb) response among 13 patients on B-cell depleting agents, compared with no therapy or other therapies (P < .001). Among of individuals on these agents, 61.5% had no detectable nAb.
The researchers also found an association between postvaccine NT50 values and when the vaccine was received compared with the last infusion of B-cell depleting agents. Every additional day since the previous infusion was associated with a 3.7% increase in NT50 value (P = .0032).
The average length of exposure to B-cell depleting agents was 24 months and the median was 25 months. There was no association between length of time on a B-cell depleting agent and NT50 values after vaccination (Spearman correlation 0.35, P = .24).
Subanalyses by sex and vaccine type revealed no differences in nAb levels.
The study did not look at T-cell responses after vaccination or the effect of T-cell depleting agents, and T cells likely still provide some protection, according to Dr. Gyang. “Even though the vaccine response may not be as robust as it would have been if they were not on the drug, there is still some degree of protection,” she said.
Some answers, more questions
The study is important, even though it was presented at the time that the COVID-19 Omicron variant surge was waning. “COVID still remains a major concern. Even though it seems to be on the wane at the moment, that doesn’t mean it will be on the wane next week,” said Mark Gudesblatt, MD, medical director at South Shore Neurologic Associates (Patchogue, N.Y.), who was asked to comment on the study.
He noted that about 21% of patients in the study who received a vaccination had no detectable antibodies. “That’s a problem. You need to pick a medication that works, but not if the medication puts you at risk for other problems, especially in the world of now, where we know there are viral pandemics that occur. And that calls into question: What if you’re immunocompromised and you get a flu vaccine or a tetanus vaccine? How much do we know about the vaccination response to most of these? No one really considers [vaccine response] when choosing a medication,” said Dr. Gudesblatt.
The results broadly confirm what has been seen in other studies, though its focus on the humoral response is a limitation, according to Patricia Coyle, MD, professor of neurology and director of Stony Brook (N.Y.) MS Comprehensive Care Center. “For example, there have been independent studies with the (anti-CD-20 therapies) that indicate that they have a normal cell-mediated vaccine response to the COVID vaccine, even though the antibody response may be impaired in a significant number of individuals, though as you continue to vaccinate the antibody response seems to get better,” Dr. Coyle said in an interview.
Dr. Gyang has served as consultant for Genentech, Horizon Therapeutics, Greenwich Biosciences and EMD Serono. Dr. Gudesblatt has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Coyle has consulted or received speaker fees from Accordant, Alexion, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, Horizon Therapeutics, Janssen, Mylan, Novartis, Sanofi Genzyme, TG Therapeutics, and Viela Bio. Dr. Coyle has received research funding from Actelion, Alkermes, Celgene, CorEvitas LLC, Genentech/Roche, MedDay, Novartis, and Sanofi Genzyme.
, according to a new retrospective analysis. The link is particularly strong among B-cell depleting drugs.
“A lot of patients ask us if having MS by itself affects the vaccine response. We did not find that, but it’s about the disease-modifying therapy that a patient is being treated with,” Tirisham Gyang, MD, said in an interview. Dr. Gyang presented the study at a poster session during the annual meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
“These patients (on DMTs) had decreased neutralizing antibody levels to the vaccine after they received it. We also saw a similar marker in drugs that modulate the sphingosine S-1 receptor. These patients also had a lower titer. It wasn’t statistically significant, but we think it’s positive. It was underpowered because there was a small number of patients in that subgroup,” said Dr. Gyang, assistant professor of neurology at The Ohio State University.
The results can inform vaccine strategies among people with MS, but the issue remains complex. “I don’t know that we could do a blanket statement and say, if you wait this amount of time, everybody will be okay. It’s a very individualized approach, and patients need to discuss timing of vaccines with their providers, because we know that waiting is better. It’s preferable to wait until towards the end of the dosing cycle. The other factor is making sure that the MS is well treated,” said Dr. Gyang.
The researchers prospectively followed 83 MS patients at the The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. Among the cohort, 71% were female. Fifty-one subjects had serum samples analyzed following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination, and they were compared with 38 health care worker controls.
After vaccination, people with MS had about 2.4-fold lower levels of half-maximal neutralization titer (NT50) values compared with health care worker controls. This appeared to be driven primarily by DMTs. There was a more than ninefold reduction in the neutralizing antibody (nAb) response among 13 patients on B-cell depleting agents, compared with no therapy or other therapies (P < .001). Among of individuals on these agents, 61.5% had no detectable nAb.
The researchers also found an association between postvaccine NT50 values and when the vaccine was received compared with the last infusion of B-cell depleting agents. Every additional day since the previous infusion was associated with a 3.7% increase in NT50 value (P = .0032).
The average length of exposure to B-cell depleting agents was 24 months and the median was 25 months. There was no association between length of time on a B-cell depleting agent and NT50 values after vaccination (Spearman correlation 0.35, P = .24).
Subanalyses by sex and vaccine type revealed no differences in nAb levels.
The study did not look at T-cell responses after vaccination or the effect of T-cell depleting agents, and T cells likely still provide some protection, according to Dr. Gyang. “Even though the vaccine response may not be as robust as it would have been if they were not on the drug, there is still some degree of protection,” she said.
Some answers, more questions
The study is important, even though it was presented at the time that the COVID-19 Omicron variant surge was waning. “COVID still remains a major concern. Even though it seems to be on the wane at the moment, that doesn’t mean it will be on the wane next week,” said Mark Gudesblatt, MD, medical director at South Shore Neurologic Associates (Patchogue, N.Y.), who was asked to comment on the study.
He noted that about 21% of patients in the study who received a vaccination had no detectable antibodies. “That’s a problem. You need to pick a medication that works, but not if the medication puts you at risk for other problems, especially in the world of now, where we know there are viral pandemics that occur. And that calls into question: What if you’re immunocompromised and you get a flu vaccine or a tetanus vaccine? How much do we know about the vaccination response to most of these? No one really considers [vaccine response] when choosing a medication,” said Dr. Gudesblatt.
The results broadly confirm what has been seen in other studies, though its focus on the humoral response is a limitation, according to Patricia Coyle, MD, professor of neurology and director of Stony Brook (N.Y.) MS Comprehensive Care Center. “For example, there have been independent studies with the (anti-CD-20 therapies) that indicate that they have a normal cell-mediated vaccine response to the COVID vaccine, even though the antibody response may be impaired in a significant number of individuals, though as you continue to vaccinate the antibody response seems to get better,” Dr. Coyle said in an interview.
Dr. Gyang has served as consultant for Genentech, Horizon Therapeutics, Greenwich Biosciences and EMD Serono. Dr. Gudesblatt has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Coyle has consulted or received speaker fees from Accordant, Alexion, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, Horizon Therapeutics, Janssen, Mylan, Novartis, Sanofi Genzyme, TG Therapeutics, and Viela Bio. Dr. Coyle has received research funding from Actelion, Alkermes, Celgene, CorEvitas LLC, Genentech/Roche, MedDay, Novartis, and Sanofi Genzyme.
, according to a new retrospective analysis. The link is particularly strong among B-cell depleting drugs.
“A lot of patients ask us if having MS by itself affects the vaccine response. We did not find that, but it’s about the disease-modifying therapy that a patient is being treated with,” Tirisham Gyang, MD, said in an interview. Dr. Gyang presented the study at a poster session during the annual meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
“These patients (on DMTs) had decreased neutralizing antibody levels to the vaccine after they received it. We also saw a similar marker in drugs that modulate the sphingosine S-1 receptor. These patients also had a lower titer. It wasn’t statistically significant, but we think it’s positive. It was underpowered because there was a small number of patients in that subgroup,” said Dr. Gyang, assistant professor of neurology at The Ohio State University.
The results can inform vaccine strategies among people with MS, but the issue remains complex. “I don’t know that we could do a blanket statement and say, if you wait this amount of time, everybody will be okay. It’s a very individualized approach, and patients need to discuss timing of vaccines with their providers, because we know that waiting is better. It’s preferable to wait until towards the end of the dosing cycle. The other factor is making sure that the MS is well treated,” said Dr. Gyang.
The researchers prospectively followed 83 MS patients at the The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. Among the cohort, 71% were female. Fifty-one subjects had serum samples analyzed following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination, and they were compared with 38 health care worker controls.
After vaccination, people with MS had about 2.4-fold lower levels of half-maximal neutralization titer (NT50) values compared with health care worker controls. This appeared to be driven primarily by DMTs. There was a more than ninefold reduction in the neutralizing antibody (nAb) response among 13 patients on B-cell depleting agents, compared with no therapy or other therapies (P < .001). Among of individuals on these agents, 61.5% had no detectable nAb.
The researchers also found an association between postvaccine NT50 values and when the vaccine was received compared with the last infusion of B-cell depleting agents. Every additional day since the previous infusion was associated with a 3.7% increase in NT50 value (P = .0032).
The average length of exposure to B-cell depleting agents was 24 months and the median was 25 months. There was no association between length of time on a B-cell depleting agent and NT50 values after vaccination (Spearman correlation 0.35, P = .24).
Subanalyses by sex and vaccine type revealed no differences in nAb levels.
The study did not look at T-cell responses after vaccination or the effect of T-cell depleting agents, and T cells likely still provide some protection, according to Dr. Gyang. “Even though the vaccine response may not be as robust as it would have been if they were not on the drug, there is still some degree of protection,” she said.
Some answers, more questions
The study is important, even though it was presented at the time that the COVID-19 Omicron variant surge was waning. “COVID still remains a major concern. Even though it seems to be on the wane at the moment, that doesn’t mean it will be on the wane next week,” said Mark Gudesblatt, MD, medical director at South Shore Neurologic Associates (Patchogue, N.Y.), who was asked to comment on the study.
He noted that about 21% of patients in the study who received a vaccination had no detectable antibodies. “That’s a problem. You need to pick a medication that works, but not if the medication puts you at risk for other problems, especially in the world of now, where we know there are viral pandemics that occur. And that calls into question: What if you’re immunocompromised and you get a flu vaccine or a tetanus vaccine? How much do we know about the vaccination response to most of these? No one really considers [vaccine response] when choosing a medication,” said Dr. Gudesblatt.
The results broadly confirm what has been seen in other studies, though its focus on the humoral response is a limitation, according to Patricia Coyle, MD, professor of neurology and director of Stony Brook (N.Y.) MS Comprehensive Care Center. “For example, there have been independent studies with the (anti-CD-20 therapies) that indicate that they have a normal cell-mediated vaccine response to the COVID vaccine, even though the antibody response may be impaired in a significant number of individuals, though as you continue to vaccinate the antibody response seems to get better,” Dr. Coyle said in an interview.
Dr. Gyang has served as consultant for Genentech, Horizon Therapeutics, Greenwich Biosciences and EMD Serono. Dr. Gudesblatt has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Coyle has consulted or received speaker fees from Accordant, Alexion, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, Horizon Therapeutics, Janssen, Mylan, Novartis, Sanofi Genzyme, TG Therapeutics, and Viela Bio. Dr. Coyle has received research funding from Actelion, Alkermes, Celgene, CorEvitas LLC, Genentech/Roche, MedDay, Novartis, and Sanofi Genzyme.
FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2022
Unusual tongue markings
Well-demarcated, map-like tongue markings are consistent with migratory glossitis, also called geographic tongue, and can be recognized by its distinct clinical appearance. If performed, a biopsy would show psoriasiform mucositis.
Migratory glossitis is an uncommon condition found mostly in adults and occasionally in children. The prevalence may be as high as 2.5% globally and it may occur in conjunction with psoriasis, sharing some histologic features.1 (On close inspection, this patient was noted to have plaques on his elbows that were consistent with psoriasis.) While an immunogenic cause is suspected, the exact etiology is unknown.
Patients may develop these clinical findings quickly and just as quickly they may resolve. Discomfort and taste disturbances rarely occur. Hot, spicy, or acidic foods may be a contributing trigger. Tobacco-use appears to be protective. The presence of ulceration should prompt evaluation for a different diagnosis, such as erosive lichen planus, leukoplakia, candidiasis, or Behçet syndrome.
With minimal symptoms, treatment is rarely needed. Patients with any discomfort can be treated with topical lidocaine 2% swish and spit mouthwash, topical tacrolimus, or topical steroids.
The patient in this case was reassured that the diagnosis was not concerning and he was observed without active treatment. His psoriasis was treated with topical clobetasol ointment 0.05%. He has continued to have intermittent flares that he has yet to associate with any specific dietary causes.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Shareef S, Ettefagh L. Geographic tongue. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 3, 2021. Accessed February 25, 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554466/

Well-demarcated, map-like tongue markings are consistent with migratory glossitis, also called geographic tongue, and can be recognized by its distinct clinical appearance. If performed, a biopsy would show psoriasiform mucositis.
Migratory glossitis is an uncommon condition found mostly in adults and occasionally in children. The prevalence may be as high as 2.5% globally and it may occur in conjunction with psoriasis, sharing some histologic features.1 (On close inspection, this patient was noted to have plaques on his elbows that were consistent with psoriasis.) While an immunogenic cause is suspected, the exact etiology is unknown.
Patients may develop these clinical findings quickly and just as quickly they may resolve. Discomfort and taste disturbances rarely occur. Hot, spicy, or acidic foods may be a contributing trigger. Tobacco-use appears to be protective. The presence of ulceration should prompt evaluation for a different diagnosis, such as erosive lichen planus, leukoplakia, candidiasis, or Behçet syndrome.
With minimal symptoms, treatment is rarely needed. Patients with any discomfort can be treated with topical lidocaine 2% swish and spit mouthwash, topical tacrolimus, or topical steroids.
The patient in this case was reassured that the diagnosis was not concerning and he was observed without active treatment. His psoriasis was treated with topical clobetasol ointment 0.05%. He has continued to have intermittent flares that he has yet to associate with any specific dietary causes.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).

Well-demarcated, map-like tongue markings are consistent with migratory glossitis, also called geographic tongue, and can be recognized by its distinct clinical appearance. If performed, a biopsy would show psoriasiform mucositis.
Migratory glossitis is an uncommon condition found mostly in adults and occasionally in children. The prevalence may be as high as 2.5% globally and it may occur in conjunction with psoriasis, sharing some histologic features.1 (On close inspection, this patient was noted to have plaques on his elbows that were consistent with psoriasis.) While an immunogenic cause is suspected, the exact etiology is unknown.
Patients may develop these clinical findings quickly and just as quickly they may resolve. Discomfort and taste disturbances rarely occur. Hot, spicy, or acidic foods may be a contributing trigger. Tobacco-use appears to be protective. The presence of ulceration should prompt evaluation for a different diagnosis, such as erosive lichen planus, leukoplakia, candidiasis, or Behçet syndrome.
With minimal symptoms, treatment is rarely needed. Patients with any discomfort can be treated with topical lidocaine 2% swish and spit mouthwash, topical tacrolimus, or topical steroids.
The patient in this case was reassured that the diagnosis was not concerning and he was observed without active treatment. His psoriasis was treated with topical clobetasol ointment 0.05%. He has continued to have intermittent flares that he has yet to associate with any specific dietary causes.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Shareef S, Ettefagh L. Geographic tongue. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 3, 2021. Accessed February 25, 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554466/
1. Shareef S, Ettefagh L. Geographic tongue. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 3, 2021. Accessed February 25, 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554466/
First possible case of deer-to-human COVID transmission identified
according a new preprint study that hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed.
Typically, humans spread the virus to deer, and then deer spread it to other deer. But new evidence suggests that the virus could spill over from deer into humans. The researchers identified a COVID-19 case in someone from Ontario who had recently been in contact with deer.
“This particular case, while raising a red flag, doesn’t seem to be hugely alarming,” Finlay Maguire, PhD, one of the study authors and an epidemiologist at Dalhousie University, told CBC News.
“While we haven’t seen [transmission from deer to humans] happen directly, we sampled from the human case around the same time we sampled from the deer, and we sampled from around the same location,” he said. “There is also a plausible link by which it could have happened, in that the individual involved is known to have had considerable contact with deer.”
Dr. Maguire and colleagues have been monitoring the spread of the coronavirus among animals. They analyzed nasal swabs and lymph node samples taken from hundreds of deer that were killed by hunters in fall 2021 in southwestern and eastern Ontario. Among 298 sampled deer, 17 tested positive -- all from southwestern Ontario.
During the analysis, they found a “highly divergent” coronavirus lineage, which means a cluster of samples with many mutations. Around the same time, they found a genetically similar version in a person from the same region.
The study points to the need for better surveillance of the coronavirus, Dr. Maguire told CBC News, including in humans, animals, plants, and the broader environment. Researchers aren’t quite sure how deer contract the virus from humans, but it could happen through contaminated water, direct contact, food, farming, or other animals such as mink.
The coronavirus lineage identified in the study is different from what’s circulating among humans now, and it’s not related to the Delta or Omicron variants. The closest genetic relative came from samples taken from humans and mink in Michigan in 2020, which means the divergent lineage mutated and evolved over time.
“It’s reassuring that we found no evidence of further transmission, during a time when we were doing a lot of sampling and a lot of sequencing,” Samira Mubareka, MD, one of the study authors and a virologist at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, told CBC News.
“If we continue to do this surveillance, we’ll get a much better sense of what the actual risk is,” she said.
So far, the coronavirus has been found in wild white-tailed deer in the northeastern United States and central Canadian provinces.
Other known cases of transmission from animals to humans have been identified in farmed mink and potentially hamsters, the news outlet reported. But for the most part, humans transmit the virus to animals and are most likely to catch the virus from other people.
At the same time, the Public Health Agency of Canada has issued guidance for hunters, trappers, and those who handle wild deer. People should wear gloves, goggles, and a mask when they could be exposed to respiratory tissues and fluids, especially indoors.
Coronaviruses are killed by normal cooking temperatures, the agency said, and there has been no evidence that cooked venison can spread the virus.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according a new preprint study that hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed.
Typically, humans spread the virus to deer, and then deer spread it to other deer. But new evidence suggests that the virus could spill over from deer into humans. The researchers identified a COVID-19 case in someone from Ontario who had recently been in contact with deer.
“This particular case, while raising a red flag, doesn’t seem to be hugely alarming,” Finlay Maguire, PhD, one of the study authors and an epidemiologist at Dalhousie University, told CBC News.
“While we haven’t seen [transmission from deer to humans] happen directly, we sampled from the human case around the same time we sampled from the deer, and we sampled from around the same location,” he said. “There is also a plausible link by which it could have happened, in that the individual involved is known to have had considerable contact with deer.”
Dr. Maguire and colleagues have been monitoring the spread of the coronavirus among animals. They analyzed nasal swabs and lymph node samples taken from hundreds of deer that were killed by hunters in fall 2021 in southwestern and eastern Ontario. Among 298 sampled deer, 17 tested positive -- all from southwestern Ontario.
During the analysis, they found a “highly divergent” coronavirus lineage, which means a cluster of samples with many mutations. Around the same time, they found a genetically similar version in a person from the same region.
The study points to the need for better surveillance of the coronavirus, Dr. Maguire told CBC News, including in humans, animals, plants, and the broader environment. Researchers aren’t quite sure how deer contract the virus from humans, but it could happen through contaminated water, direct contact, food, farming, or other animals such as mink.
The coronavirus lineage identified in the study is different from what’s circulating among humans now, and it’s not related to the Delta or Omicron variants. The closest genetic relative came from samples taken from humans and mink in Michigan in 2020, which means the divergent lineage mutated and evolved over time.
“It’s reassuring that we found no evidence of further transmission, during a time when we were doing a lot of sampling and a lot of sequencing,” Samira Mubareka, MD, one of the study authors and a virologist at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, told CBC News.
“If we continue to do this surveillance, we’ll get a much better sense of what the actual risk is,” she said.
So far, the coronavirus has been found in wild white-tailed deer in the northeastern United States and central Canadian provinces.
Other known cases of transmission from animals to humans have been identified in farmed mink and potentially hamsters, the news outlet reported. But for the most part, humans transmit the virus to animals and are most likely to catch the virus from other people.
At the same time, the Public Health Agency of Canada has issued guidance for hunters, trappers, and those who handle wild deer. People should wear gloves, goggles, and a mask when they could be exposed to respiratory tissues and fluids, especially indoors.
Coronaviruses are killed by normal cooking temperatures, the agency said, and there has been no evidence that cooked venison can spread the virus.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according a new preprint study that hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed.
Typically, humans spread the virus to deer, and then deer spread it to other deer. But new evidence suggests that the virus could spill over from deer into humans. The researchers identified a COVID-19 case in someone from Ontario who had recently been in contact with deer.
“This particular case, while raising a red flag, doesn’t seem to be hugely alarming,” Finlay Maguire, PhD, one of the study authors and an epidemiologist at Dalhousie University, told CBC News.
“While we haven’t seen [transmission from deer to humans] happen directly, we sampled from the human case around the same time we sampled from the deer, and we sampled from around the same location,” he said. “There is also a plausible link by which it could have happened, in that the individual involved is known to have had considerable contact with deer.”
Dr. Maguire and colleagues have been monitoring the spread of the coronavirus among animals. They analyzed nasal swabs and lymph node samples taken from hundreds of deer that were killed by hunters in fall 2021 in southwestern and eastern Ontario. Among 298 sampled deer, 17 tested positive -- all from southwestern Ontario.
During the analysis, they found a “highly divergent” coronavirus lineage, which means a cluster of samples with many mutations. Around the same time, they found a genetically similar version in a person from the same region.
The study points to the need for better surveillance of the coronavirus, Dr. Maguire told CBC News, including in humans, animals, plants, and the broader environment. Researchers aren’t quite sure how deer contract the virus from humans, but it could happen through contaminated water, direct contact, food, farming, or other animals such as mink.
The coronavirus lineage identified in the study is different from what’s circulating among humans now, and it’s not related to the Delta or Omicron variants. The closest genetic relative came from samples taken from humans and mink in Michigan in 2020, which means the divergent lineage mutated and evolved over time.
“It’s reassuring that we found no evidence of further transmission, during a time when we were doing a lot of sampling and a lot of sequencing,” Samira Mubareka, MD, one of the study authors and a virologist at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, told CBC News.
“If we continue to do this surveillance, we’ll get a much better sense of what the actual risk is,” she said.
So far, the coronavirus has been found in wild white-tailed deer in the northeastern United States and central Canadian provinces.
Other known cases of transmission from animals to humans have been identified in farmed mink and potentially hamsters, the news outlet reported. But for the most part, humans transmit the virus to animals and are most likely to catch the virus from other people.
At the same time, the Public Health Agency of Canada has issued guidance for hunters, trappers, and those who handle wild deer. People should wear gloves, goggles, and a mask when they could be exposed to respiratory tissues and fluids, especially indoors.
Coronaviruses are killed by normal cooking temperatures, the agency said, and there has been no evidence that cooked venison can spread the virus.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
GI involvement may signal risk for MIS-C after COVID
While evaluating an adolescent who had endured a several-day history of vomiting and diarrhea, I mentioned the likelihood of a viral causation, including SARS-CoV-2 infection. His well-informed mother responded, “He has no respiratory symptoms. Does COVID cause GI disease?”
Indeed, not only is the gastrointestinal tract a potential portal of entry of the virus but it may well be the site of mediation of both local and remote injury and thus a harbinger of more severe clinical phenotypes.
As we learn more about the clinical spectrum of COVID, it is becoming increasingly clear that certain features of GI tract involvement may allow us to establish a timeline of the clinical course and perhaps predict the outcome.
The GI tract’s involvement isn’t surprising
The ways in which the GI tract serves as a target organ of SARS-CoV-2 have been postulated in the literature. In part, this is related to the presence of abundant receptors for SARS-CoV-2 cell binding and internalization. The virus uses angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors to enter various cells. These receptors are highly expressed on not only lung cells but also enterocytes. Binding of SARS-CoV-2 to ACE2 receptors allows GI involvement, leading to microscopic mucosal inflammation, increased permeability, and altered intestinal absorption.
The clinical GI manifestations of this include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, which may be the earliest, or sole, symptoms of COVID-19, often noted before the onset of fever or respiratory symptoms. In fact, John Ong, MBBS, and colleagues, in a discussion about patients with primary GI SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptoms, use the term “GI-COVID.”
Clinical course of GI manifestations
After SARS-CoV-2 exposure, adults most commonly present with respiratory symptoms, with GI symptoms reported in 10%-15% of cases. However, the overall incidence of GI involvement during SARS-CoV-2 infection varies according to age, with children more likely than adults to manifest intestinal symptoms.
There are also differences in incidence reported when comparing hospitalized with nonhospitalized individuals. In early reports from the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, 11%-43% of hospitalized adult patients manifested GI symptoms. Of note, the presence of GI symptoms was associated with more severe disease and thus predictive of outcomes in those admitted to hospitals.
In a multicenter study that assessed pediatric inpatients with COVID-19, GI manifestations were present in 57% of patients and were the first manifestation in 14%. Adjusted by confounding factors, those with GI symptoms had a higher risk for pediatric intensive care unit admission. Patients admitted to the PICU also had higher serum C-reactive protein and aspartate aminotransferase values.
Emerging data on MIS-C
In previously healthy children and adolescents, the severe, life-threatening complication of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) may present 2-6 weeks after acute infection with SARS-CoV-2. MIS-C appears to be an immune activation syndrome and is presumed to be the delayed immunologic sequelae of mild/asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. This response manifests as hyperinflammation in conjunction with a peak in antibody production a few weeks later.
One report of 186 children with MIS-C in the United States noted that the involved organ system included the GI tract in 92%, followed by cardiovascular in 80%, hematologic in 76%, mucocutaneous in 74%, and respiratory in 70%. Affected children were hospitalized for a median of 7 days, with 80% requiring intensive care, 20% receiving mechanical ventilation, and 48% receiving vasoactive support; 2% died. In a similar study of patients hospitalized in New York, 88% had GI symptoms (abdominal pain, vomiting, and/or diarrhea). A retrospective chart review of patients with MIS-C found that the majority had GI symptoms with any portion of the GI tract potentially involved, but ileal and colonic inflammation predominated.
Elizabeth Whittaker, MD, and colleagues described the clinical characteristics of children in eight hospitals in England who met criteria for MIS-C that were temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2. At presentation, all of the patients manifested fever and nonspecific GI symptoms, including vomiting (45%), abdominal pain (53%), and diarrhea (52%). During hospitalization, 50% developed shock with evidence of myocardial dysfunction.
Ermias D. Belay, MD, and colleagues described the clinical characteristics of a large cohort of patients with MIS-C that were reported to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Of 1,733 patients identified, GI symptoms were reported in 53%-67%. Over half developed hypotension or shock and were admitted for intensive care. Younger children more frequently presented with abdominal pain in contrast with adolescents, who more frequently manifest respiratory symptoms.
In a multicenter retrospective study of Italian children with COVID-19 that was conducted from the onset of the pandemic to early 2021, GI symptoms were noted in 38%. These manifestations were mild and self-limiting, comparable to other viral intestinal infections. However, a subset of children (9.5%) had severe GI manifestations of MIS-C, defined as a medical and/or radiologic diagnosis of acute abdomen, appendicitis, intussusception, pancreatitis, abdominal fluid collection, or diffuse adenomesenteritis requiring surgical consultation. Overall, 42% of this group underwent surgery. The authors noted that the clinical presentation of abdominal pain, lymphopenia, and increased C-reactive protein and ferritin levels were associated with a 9- to 30-fold increased probability of these severe sequelae. In addition, the severity of the GI manifestations was correlated with age (5-10 years: overall response, 8.33; >10 years: OR, 6.37). Again, the presence of GI symptoms was a harbinger of hospitalization and PICU admission.
Given that GI symptoms are a common presentation of MIS-C, its diagnosis may be delayed as clinicians first consider other GI/viral infections, inflammatory bowel disease, or Kawasaki disease. Prompt identification of GI involvement and awareness of the potential outcomes may guide the management and improve the outcome.
These studies provide a clear picture of the differential presenting features of COVID-19 and MIS-C. Although there may be other environmental/genetic factors that govern the incidence, impact, and manifestations, COVID’s status as an ongoing pandemic gives these observations worldwide relevance. This is evident in a recent report documenting pronounced GI symptoms in African children with COVID-19.
It should be noted, however, that the published data cited here reflect the impact of the initial variants of SARS-CoV-2. The GI binding, effects, and aftermath of infection with the Delta and Omicron variants is not yet known.
Cause and effect, or simply coincidental?
Some insight into MIS-C pathogenesis was provided by Lael M. Yonker, MD, and colleagues in their analysis of biospecimens from 100 children: 19 with MIS-C, 26 with acute COVID-19, and 55 controls. They demonstrated that in children with MIS-C the prolonged presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the GI tract led to the release of zonulin, a biomarker of intestinal permeability, with subsequent trafficking of SARS-CoV-2 antigens into the bloodstream, leading to hyperinflammation. They were then able to decrease plasma SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen levels and inflammatory markers, with resulting clinical improvement after administration of larazotide, a zonulin antagonist.
These observations regarding the potential mechanism and triggers of MIS-C may offer biomarkers for early detection and/or strategies for prevention and treatment of MIS-C.
Bottom line
The GI tract is the target of an immune-mediated inflammatory response that is triggered by SARS-CoV-2, with MIS-C being the major manifestation of the resultant high degree of inflammation. These observations will allow an increased awareness of nonrespiratory symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infection by clinicians working in emergency departments and primary care settings.
Clues that may enhance the ability of pediatric clinicians to recognize the potential for severe GI involvement include the occurrence of abdominal pain, leukopenia, and elevated inflammatory markers. Their presence should raise suspicion of MIS-C and lead to early evaluation.
Of note, COVID-19 mRNA vaccination is associated with a lower incidence of MIS-C in adolescents. This underscores the importance of COVID vaccination for all eligible children. Yet, we clearly have our work cut out for us. Of 107 children with MIS-C who were hospitalized in France, 31% were adolescents eligible for vaccination; however, none had been fully vaccinated. At the end of 2021, CDC data noted that less than 1% of vaccine-eligible children (12-17 years) were fully vaccinated.
The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine is now authorized for receipt by children aged 5-11 years, the age group that is at highest risk for MIS-C. However, despite the approval of vaccines for these younger children, there is limited access in some parts of the United States at a time of rising incidence.
We look forward to broad availability of pediatric vaccination strategies. In addition, with the intense focus on safe and effective therapeutics for SARS-CoV-2 infection, we hope to soon have strategies to prevent and/or treat the life-threatening manifestations and long-term consequences of MIS-C. For example, the recently reported central role of the gut microbiota in immunity against SARS-CoV-2 infection offer the possibility that “microbiota modulation” may both reduce GI injury and enhance vaccine efficacy.
Dr. Balistreri has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
William F. Balistreri, MD, is the Dorothy M.M. Kersten Professor of Pediatrics; director emeritus, Pediatric Liver Care Center; medical director emeritus, liver transplantation; and professor, University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, department of pediatrics, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. He has served as director of the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Cincinnati Children’s for 25 years and frequently covers gastroenterology, liver, and nutrition-related topics for this news organization. Dr Balistreri is currently editor-in-chief of the Journal of Pediatrics, having previously served as editor-in-chief of several journals and textbooks. He also became the first pediatrician to act as president of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. In his spare time, he coaches youth lacrosse.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While evaluating an adolescent who had endured a several-day history of vomiting and diarrhea, I mentioned the likelihood of a viral causation, including SARS-CoV-2 infection. His well-informed mother responded, “He has no respiratory symptoms. Does COVID cause GI disease?”
Indeed, not only is the gastrointestinal tract a potential portal of entry of the virus but it may well be the site of mediation of both local and remote injury and thus a harbinger of more severe clinical phenotypes.
As we learn more about the clinical spectrum of COVID, it is becoming increasingly clear that certain features of GI tract involvement may allow us to establish a timeline of the clinical course and perhaps predict the outcome.
The GI tract’s involvement isn’t surprising
The ways in which the GI tract serves as a target organ of SARS-CoV-2 have been postulated in the literature. In part, this is related to the presence of abundant receptors for SARS-CoV-2 cell binding and internalization. The virus uses angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors to enter various cells. These receptors are highly expressed on not only lung cells but also enterocytes. Binding of SARS-CoV-2 to ACE2 receptors allows GI involvement, leading to microscopic mucosal inflammation, increased permeability, and altered intestinal absorption.
The clinical GI manifestations of this include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, which may be the earliest, or sole, symptoms of COVID-19, often noted before the onset of fever or respiratory symptoms. In fact, John Ong, MBBS, and colleagues, in a discussion about patients with primary GI SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptoms, use the term “GI-COVID.”
Clinical course of GI manifestations
After SARS-CoV-2 exposure, adults most commonly present with respiratory symptoms, with GI symptoms reported in 10%-15% of cases. However, the overall incidence of GI involvement during SARS-CoV-2 infection varies according to age, with children more likely than adults to manifest intestinal symptoms.
There are also differences in incidence reported when comparing hospitalized with nonhospitalized individuals. In early reports from the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, 11%-43% of hospitalized adult patients manifested GI symptoms. Of note, the presence of GI symptoms was associated with more severe disease and thus predictive of outcomes in those admitted to hospitals.
In a multicenter study that assessed pediatric inpatients with COVID-19, GI manifestations were present in 57% of patients and were the first manifestation in 14%. Adjusted by confounding factors, those with GI symptoms had a higher risk for pediatric intensive care unit admission. Patients admitted to the PICU also had higher serum C-reactive protein and aspartate aminotransferase values.
Emerging data on MIS-C
In previously healthy children and adolescents, the severe, life-threatening complication of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) may present 2-6 weeks after acute infection with SARS-CoV-2. MIS-C appears to be an immune activation syndrome and is presumed to be the delayed immunologic sequelae of mild/asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. This response manifests as hyperinflammation in conjunction with a peak in antibody production a few weeks later.
One report of 186 children with MIS-C in the United States noted that the involved organ system included the GI tract in 92%, followed by cardiovascular in 80%, hematologic in 76%, mucocutaneous in 74%, and respiratory in 70%. Affected children were hospitalized for a median of 7 days, with 80% requiring intensive care, 20% receiving mechanical ventilation, and 48% receiving vasoactive support; 2% died. In a similar study of patients hospitalized in New York, 88% had GI symptoms (abdominal pain, vomiting, and/or diarrhea). A retrospective chart review of patients with MIS-C found that the majority had GI symptoms with any portion of the GI tract potentially involved, but ileal and colonic inflammation predominated.
Elizabeth Whittaker, MD, and colleagues described the clinical characteristics of children in eight hospitals in England who met criteria for MIS-C that were temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2. At presentation, all of the patients manifested fever and nonspecific GI symptoms, including vomiting (45%), abdominal pain (53%), and diarrhea (52%). During hospitalization, 50% developed shock with evidence of myocardial dysfunction.
Ermias D. Belay, MD, and colleagues described the clinical characteristics of a large cohort of patients with MIS-C that were reported to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Of 1,733 patients identified, GI symptoms were reported in 53%-67%. Over half developed hypotension or shock and were admitted for intensive care. Younger children more frequently presented with abdominal pain in contrast with adolescents, who more frequently manifest respiratory symptoms.
In a multicenter retrospective study of Italian children with COVID-19 that was conducted from the onset of the pandemic to early 2021, GI symptoms were noted in 38%. These manifestations were mild and self-limiting, comparable to other viral intestinal infections. However, a subset of children (9.5%) had severe GI manifestations of MIS-C, defined as a medical and/or radiologic diagnosis of acute abdomen, appendicitis, intussusception, pancreatitis, abdominal fluid collection, or diffuse adenomesenteritis requiring surgical consultation. Overall, 42% of this group underwent surgery. The authors noted that the clinical presentation of abdominal pain, lymphopenia, and increased C-reactive protein and ferritin levels were associated with a 9- to 30-fold increased probability of these severe sequelae. In addition, the severity of the GI manifestations was correlated with age (5-10 years: overall response, 8.33; >10 years: OR, 6.37). Again, the presence of GI symptoms was a harbinger of hospitalization and PICU admission.
Given that GI symptoms are a common presentation of MIS-C, its diagnosis may be delayed as clinicians first consider other GI/viral infections, inflammatory bowel disease, or Kawasaki disease. Prompt identification of GI involvement and awareness of the potential outcomes may guide the management and improve the outcome.
These studies provide a clear picture of the differential presenting features of COVID-19 and MIS-C. Although there may be other environmental/genetic factors that govern the incidence, impact, and manifestations, COVID’s status as an ongoing pandemic gives these observations worldwide relevance. This is evident in a recent report documenting pronounced GI symptoms in African children with COVID-19.
It should be noted, however, that the published data cited here reflect the impact of the initial variants of SARS-CoV-2. The GI binding, effects, and aftermath of infection with the Delta and Omicron variants is not yet known.
Cause and effect, or simply coincidental?
Some insight into MIS-C pathogenesis was provided by Lael M. Yonker, MD, and colleagues in their analysis of biospecimens from 100 children: 19 with MIS-C, 26 with acute COVID-19, and 55 controls. They demonstrated that in children with MIS-C the prolonged presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the GI tract led to the release of zonulin, a biomarker of intestinal permeability, with subsequent trafficking of SARS-CoV-2 antigens into the bloodstream, leading to hyperinflammation. They were then able to decrease plasma SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen levels and inflammatory markers, with resulting clinical improvement after administration of larazotide, a zonulin antagonist.
These observations regarding the potential mechanism and triggers of MIS-C may offer biomarkers for early detection and/or strategies for prevention and treatment of MIS-C.
Bottom line
The GI tract is the target of an immune-mediated inflammatory response that is triggered by SARS-CoV-2, with MIS-C being the major manifestation of the resultant high degree of inflammation. These observations will allow an increased awareness of nonrespiratory symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infection by clinicians working in emergency departments and primary care settings.
Clues that may enhance the ability of pediatric clinicians to recognize the potential for severe GI involvement include the occurrence of abdominal pain, leukopenia, and elevated inflammatory markers. Their presence should raise suspicion of MIS-C and lead to early evaluation.
Of note, COVID-19 mRNA vaccination is associated with a lower incidence of MIS-C in adolescents. This underscores the importance of COVID vaccination for all eligible children. Yet, we clearly have our work cut out for us. Of 107 children with MIS-C who were hospitalized in France, 31% were adolescents eligible for vaccination; however, none had been fully vaccinated. At the end of 2021, CDC data noted that less than 1% of vaccine-eligible children (12-17 years) were fully vaccinated.
The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine is now authorized for receipt by children aged 5-11 years, the age group that is at highest risk for MIS-C. However, despite the approval of vaccines for these younger children, there is limited access in some parts of the United States at a time of rising incidence.
We look forward to broad availability of pediatric vaccination strategies. In addition, with the intense focus on safe and effective therapeutics for SARS-CoV-2 infection, we hope to soon have strategies to prevent and/or treat the life-threatening manifestations and long-term consequences of MIS-C. For example, the recently reported central role of the gut microbiota in immunity against SARS-CoV-2 infection offer the possibility that “microbiota modulation” may both reduce GI injury and enhance vaccine efficacy.
Dr. Balistreri has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
William F. Balistreri, MD, is the Dorothy M.M. Kersten Professor of Pediatrics; director emeritus, Pediatric Liver Care Center; medical director emeritus, liver transplantation; and professor, University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, department of pediatrics, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. He has served as director of the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Cincinnati Children’s for 25 years and frequently covers gastroenterology, liver, and nutrition-related topics for this news organization. Dr Balistreri is currently editor-in-chief of the Journal of Pediatrics, having previously served as editor-in-chief of several journals and textbooks. He also became the first pediatrician to act as president of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. In his spare time, he coaches youth lacrosse.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
While evaluating an adolescent who had endured a several-day history of vomiting and diarrhea, I mentioned the likelihood of a viral causation, including SARS-CoV-2 infection. His well-informed mother responded, “He has no respiratory symptoms. Does COVID cause GI disease?”
Indeed, not only is the gastrointestinal tract a potential portal of entry of the virus but it may well be the site of mediation of both local and remote injury and thus a harbinger of more severe clinical phenotypes.
As we learn more about the clinical spectrum of COVID, it is becoming increasingly clear that certain features of GI tract involvement may allow us to establish a timeline of the clinical course and perhaps predict the outcome.
The GI tract’s involvement isn’t surprising
The ways in which the GI tract serves as a target organ of SARS-CoV-2 have been postulated in the literature. In part, this is related to the presence of abundant receptors for SARS-CoV-2 cell binding and internalization. The virus uses angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors to enter various cells. These receptors are highly expressed on not only lung cells but also enterocytes. Binding of SARS-CoV-2 to ACE2 receptors allows GI involvement, leading to microscopic mucosal inflammation, increased permeability, and altered intestinal absorption.
The clinical GI manifestations of this include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, which may be the earliest, or sole, symptoms of COVID-19, often noted before the onset of fever or respiratory symptoms. In fact, John Ong, MBBS, and colleagues, in a discussion about patients with primary GI SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptoms, use the term “GI-COVID.”
Clinical course of GI manifestations
After SARS-CoV-2 exposure, adults most commonly present with respiratory symptoms, with GI symptoms reported in 10%-15% of cases. However, the overall incidence of GI involvement during SARS-CoV-2 infection varies according to age, with children more likely than adults to manifest intestinal symptoms.
There are also differences in incidence reported when comparing hospitalized with nonhospitalized individuals. In early reports from the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, 11%-43% of hospitalized adult patients manifested GI symptoms. Of note, the presence of GI symptoms was associated with more severe disease and thus predictive of outcomes in those admitted to hospitals.
In a multicenter study that assessed pediatric inpatients with COVID-19, GI manifestations were present in 57% of patients and were the first manifestation in 14%. Adjusted by confounding factors, those with GI symptoms had a higher risk for pediatric intensive care unit admission. Patients admitted to the PICU also had higher serum C-reactive protein and aspartate aminotransferase values.
Emerging data on MIS-C
In previously healthy children and adolescents, the severe, life-threatening complication of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) may present 2-6 weeks after acute infection with SARS-CoV-2. MIS-C appears to be an immune activation syndrome and is presumed to be the delayed immunologic sequelae of mild/asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. This response manifests as hyperinflammation in conjunction with a peak in antibody production a few weeks later.
One report of 186 children with MIS-C in the United States noted that the involved organ system included the GI tract in 92%, followed by cardiovascular in 80%, hematologic in 76%, mucocutaneous in 74%, and respiratory in 70%. Affected children were hospitalized for a median of 7 days, with 80% requiring intensive care, 20% receiving mechanical ventilation, and 48% receiving vasoactive support; 2% died. In a similar study of patients hospitalized in New York, 88% had GI symptoms (abdominal pain, vomiting, and/or diarrhea). A retrospective chart review of patients with MIS-C found that the majority had GI symptoms with any portion of the GI tract potentially involved, but ileal and colonic inflammation predominated.
Elizabeth Whittaker, MD, and colleagues described the clinical characteristics of children in eight hospitals in England who met criteria for MIS-C that were temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2. At presentation, all of the patients manifested fever and nonspecific GI symptoms, including vomiting (45%), abdominal pain (53%), and diarrhea (52%). During hospitalization, 50% developed shock with evidence of myocardial dysfunction.
Ermias D. Belay, MD, and colleagues described the clinical characteristics of a large cohort of patients with MIS-C that were reported to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Of 1,733 patients identified, GI symptoms were reported in 53%-67%. Over half developed hypotension or shock and were admitted for intensive care. Younger children more frequently presented with abdominal pain in contrast with adolescents, who more frequently manifest respiratory symptoms.
In a multicenter retrospective study of Italian children with COVID-19 that was conducted from the onset of the pandemic to early 2021, GI symptoms were noted in 38%. These manifestations were mild and self-limiting, comparable to other viral intestinal infections. However, a subset of children (9.5%) had severe GI manifestations of MIS-C, defined as a medical and/or radiologic diagnosis of acute abdomen, appendicitis, intussusception, pancreatitis, abdominal fluid collection, or diffuse adenomesenteritis requiring surgical consultation. Overall, 42% of this group underwent surgery. The authors noted that the clinical presentation of abdominal pain, lymphopenia, and increased C-reactive protein and ferritin levels were associated with a 9- to 30-fold increased probability of these severe sequelae. In addition, the severity of the GI manifestations was correlated with age (5-10 years: overall response, 8.33; >10 years: OR, 6.37). Again, the presence of GI symptoms was a harbinger of hospitalization and PICU admission.
Given that GI symptoms are a common presentation of MIS-C, its diagnosis may be delayed as clinicians first consider other GI/viral infections, inflammatory bowel disease, or Kawasaki disease. Prompt identification of GI involvement and awareness of the potential outcomes may guide the management and improve the outcome.
These studies provide a clear picture of the differential presenting features of COVID-19 and MIS-C. Although there may be other environmental/genetic factors that govern the incidence, impact, and manifestations, COVID’s status as an ongoing pandemic gives these observations worldwide relevance. This is evident in a recent report documenting pronounced GI symptoms in African children with COVID-19.
It should be noted, however, that the published data cited here reflect the impact of the initial variants of SARS-CoV-2. The GI binding, effects, and aftermath of infection with the Delta and Omicron variants is not yet known.
Cause and effect, or simply coincidental?
Some insight into MIS-C pathogenesis was provided by Lael M. Yonker, MD, and colleagues in their analysis of biospecimens from 100 children: 19 with MIS-C, 26 with acute COVID-19, and 55 controls. They demonstrated that in children with MIS-C the prolonged presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the GI tract led to the release of zonulin, a biomarker of intestinal permeability, with subsequent trafficking of SARS-CoV-2 antigens into the bloodstream, leading to hyperinflammation. They were then able to decrease plasma SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen levels and inflammatory markers, with resulting clinical improvement after administration of larazotide, a zonulin antagonist.
These observations regarding the potential mechanism and triggers of MIS-C may offer biomarkers for early detection and/or strategies for prevention and treatment of MIS-C.
Bottom line
The GI tract is the target of an immune-mediated inflammatory response that is triggered by SARS-CoV-2, with MIS-C being the major manifestation of the resultant high degree of inflammation. These observations will allow an increased awareness of nonrespiratory symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infection by clinicians working in emergency departments and primary care settings.
Clues that may enhance the ability of pediatric clinicians to recognize the potential for severe GI involvement include the occurrence of abdominal pain, leukopenia, and elevated inflammatory markers. Their presence should raise suspicion of MIS-C and lead to early evaluation.
Of note, COVID-19 mRNA vaccination is associated with a lower incidence of MIS-C in adolescents. This underscores the importance of COVID vaccination for all eligible children. Yet, we clearly have our work cut out for us. Of 107 children with MIS-C who were hospitalized in France, 31% were adolescents eligible for vaccination; however, none had been fully vaccinated. At the end of 2021, CDC data noted that less than 1% of vaccine-eligible children (12-17 years) were fully vaccinated.
The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine is now authorized for receipt by children aged 5-11 years, the age group that is at highest risk for MIS-C. However, despite the approval of vaccines for these younger children, there is limited access in some parts of the United States at a time of rising incidence.
We look forward to broad availability of pediatric vaccination strategies. In addition, with the intense focus on safe and effective therapeutics for SARS-CoV-2 infection, we hope to soon have strategies to prevent and/or treat the life-threatening manifestations and long-term consequences of MIS-C. For example, the recently reported central role of the gut microbiota in immunity against SARS-CoV-2 infection offer the possibility that “microbiota modulation” may both reduce GI injury and enhance vaccine efficacy.
Dr. Balistreri has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
William F. Balistreri, MD, is the Dorothy M.M. Kersten Professor of Pediatrics; director emeritus, Pediatric Liver Care Center; medical director emeritus, liver transplantation; and professor, University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, department of pediatrics, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. He has served as director of the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Cincinnati Children’s for 25 years and frequently covers gastroenterology, liver, and nutrition-related topics for this news organization. Dr Balistreri is currently editor-in-chief of the Journal of Pediatrics, having previously served as editor-in-chief of several journals and textbooks. He also became the first pediatrician to act as president of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. In his spare time, he coaches youth lacrosse.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: New cases down to pre-Omicron level
New cases of COVID-19 in U.S. children dropped for the fifth consecutive week, but the rate of decline slowed considerably, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The national count of new cases has now fallen for five straight weeks since peaking Jan. 14-20, and this week’s figure is the lowest since the pre-Omicron days of mid-November, based on data collected by the AAP and CHA from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.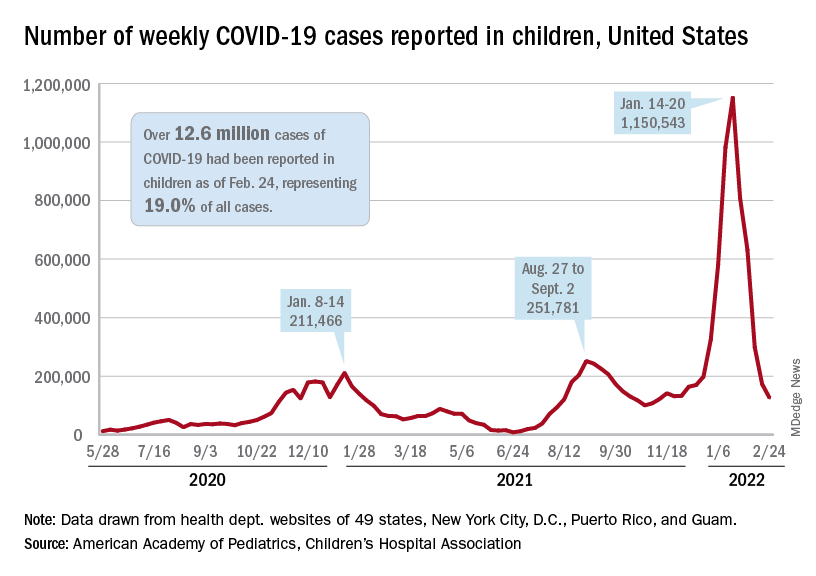
Over 12.6 million pediatric cases have been reported by those jurisdictions since the start of the pandemic, representing 19.0% of all cases in the United States, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
The highest cumulative rate among the states, 27.5%, can be found in Vermont, followed by New Hampshire (26.7%) and Alaska (26.6%). Alabama’s 12.1% is lower than any other jurisdiction, but the state stopped reporting during the summer of 2021, just as the Delta surge was beginning. The next two lowest states, Florida (12.8%) and Utah (13.9%), both define children as those aged 0-14 years, so the state with the lowest rate and no qualifiers is Idaho at 14.3%, the AAP/CHA data show.
The downward trend in new cases is reflected in other national measures. The daily rate of new hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 years was 0.32 per 100,000 population on Feb. 26, which is a drop of 75% since admissions peaked at 1.25 per 100,000 on Jan. 15, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The most recent 7-day average (Feb. 20-26) for child admissions with confirmed COVID-19 was 237 per day, compared with 914 per day during the peak week of Jan. 10-16. Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID, measured as a percentage of all ED visits by age group, are down even more. The 7-day average was 1.2% on Feb. 25 for children aged 0-11 years, compared with a peak of 13.9% in mid-January, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. The current rates for older children are even lower.
The decline of the Omicron surge over the last few weeks is allowing states to end mask mandates in schools around the country. The governors of California, Oregon, and Washington just announced that their states will be lifting their mask requirements on March 11, and New York State will end its mandate on March 2, while New York City is scheduled to go mask-free as of March 7, according to District Administration.
Those types of government moves, however, do not seem to be entirely supported by the public. In a survey conducted Feb. 9-21 by the Kaiser Family Foundation, 43% of the 1,502 respondents said that all students and staff should be required to wear masks in schools, while 40% said that there should be no mask requirements at all.
New cases of COVID-19 in U.S. children dropped for the fifth consecutive week, but the rate of decline slowed considerably, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The national count of new cases has now fallen for five straight weeks since peaking Jan. 14-20, and this week’s figure is the lowest since the pre-Omicron days of mid-November, based on data collected by the AAP and CHA from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Over 12.6 million pediatric cases have been reported by those jurisdictions since the start of the pandemic, representing 19.0% of all cases in the United States, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
The highest cumulative rate among the states, 27.5%, can be found in Vermont, followed by New Hampshire (26.7%) and Alaska (26.6%). Alabama’s 12.1% is lower than any other jurisdiction, but the state stopped reporting during the summer of 2021, just as the Delta surge was beginning. The next two lowest states, Florida (12.8%) and Utah (13.9%), both define children as those aged 0-14 years, so the state with the lowest rate and no qualifiers is Idaho at 14.3%, the AAP/CHA data show.
The downward trend in new cases is reflected in other national measures. The daily rate of new hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 years was 0.32 per 100,000 population on Feb. 26, which is a drop of 75% since admissions peaked at 1.25 per 100,000 on Jan. 15, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The most recent 7-day average (Feb. 20-26) for child admissions with confirmed COVID-19 was 237 per day, compared with 914 per day during the peak week of Jan. 10-16. Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID, measured as a percentage of all ED visits by age group, are down even more. The 7-day average was 1.2% on Feb. 25 for children aged 0-11 years, compared with a peak of 13.9% in mid-January, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. The current rates for older children are even lower.
The decline of the Omicron surge over the last few weeks is allowing states to end mask mandates in schools around the country. The governors of California, Oregon, and Washington just announced that their states will be lifting their mask requirements on March 11, and New York State will end its mandate on March 2, while New York City is scheduled to go mask-free as of March 7, according to District Administration.
Those types of government moves, however, do not seem to be entirely supported by the public. In a survey conducted Feb. 9-21 by the Kaiser Family Foundation, 43% of the 1,502 respondents said that all students and staff should be required to wear masks in schools, while 40% said that there should be no mask requirements at all.
New cases of COVID-19 in U.S. children dropped for the fifth consecutive week, but the rate of decline slowed considerably, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The national count of new cases has now fallen for five straight weeks since peaking Jan. 14-20, and this week’s figure is the lowest since the pre-Omicron days of mid-November, based on data collected by the AAP and CHA from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Over 12.6 million pediatric cases have been reported by those jurisdictions since the start of the pandemic, representing 19.0% of all cases in the United States, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
The highest cumulative rate among the states, 27.5%, can be found in Vermont, followed by New Hampshire (26.7%) and Alaska (26.6%). Alabama’s 12.1% is lower than any other jurisdiction, but the state stopped reporting during the summer of 2021, just as the Delta surge was beginning. The next two lowest states, Florida (12.8%) and Utah (13.9%), both define children as those aged 0-14 years, so the state with the lowest rate and no qualifiers is Idaho at 14.3%, the AAP/CHA data show.
The downward trend in new cases is reflected in other national measures. The daily rate of new hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 years was 0.32 per 100,000 population on Feb. 26, which is a drop of 75% since admissions peaked at 1.25 per 100,000 on Jan. 15, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The most recent 7-day average (Feb. 20-26) for child admissions with confirmed COVID-19 was 237 per day, compared with 914 per day during the peak week of Jan. 10-16. Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID, measured as a percentage of all ED visits by age group, are down even more. The 7-day average was 1.2% on Feb. 25 for children aged 0-11 years, compared with a peak of 13.9% in mid-January, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. The current rates for older children are even lower.
The decline of the Omicron surge over the last few weeks is allowing states to end mask mandates in schools around the country. The governors of California, Oregon, and Washington just announced that their states will be lifting their mask requirements on March 11, and New York State will end its mandate on March 2, while New York City is scheduled to go mask-free as of March 7, according to District Administration.
Those types of government moves, however, do not seem to be entirely supported by the public. In a survey conducted Feb. 9-21 by the Kaiser Family Foundation, 43% of the 1,502 respondents said that all students and staff should be required to wear masks in schools, while 40% said that there should be no mask requirements at all.
Immediate postpartum IUD insertion increases expulsion risk
Expulsion of intrauterine devices was significantly more likely when the devices were inserted within the first 3 days after delivery compared with later insertions, based on data from more than 300,000 women.
Intrauterine devices are effective contraception, and current guidelines support immediate postpartum IUD insertion as a safe, effective, and convenient option, Mary Anne Armstrong, MA, of Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Oakland, and colleagues wrote. Although IUD expulsion rates are low overall, data from previous studies suggest that timing of insertion may affect expulsion rates, and that breastfeeding may play a role.
In the Association of Perforation and Expulsion of Intrauterine Devices (APEX-IUD) cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed data from the electronic health records at four sites; the study population included women aged 50 years and younger who underwent IUD insertion between 2001 and 2018.
The women were grouped by postpartum status and timing of IUD placement: 0-3 days, 4 days to 6 weeks, 6-14 weeks, 14-52 weeks, and nonpostpartum (defined as more than 52 weeks or no evidence of delivery).
The researchers also compared expulsion rates in postpartum women who were and were not breastfeeding at the time of IUD insertion based on clinical records, diagnostic codes, or questionnaires at well-baby visits.
The total study population included 326,658 women with a mean age of 32.0 years; 42% were non-Hispanic White, 17.2% were Hispanic other, 13.0% were Hispanic White, 11.9% were Asian or Pacific Islander, 8.7% were non-Hispanic Black, and 0.2% were Hispanic Black. Approximately 80% of the IUDs were levonorgestrel releasing.
A total of 8,943 expulsions were reported, for an overall expulsion rate of 13.94 per 1,000 person-years.
The adjusted hazard ratios for IUD expulsion were 5.34, 1.22, 1.06, and 1.43 for women with insertion times, respectively, of 0-3 days, 4 days to 6 or fewer weeks, 6-14 weeks, and 14-52 weeks. Women with nonpostpartum IUD insertion served as the referent.
The 5-year cumulative incidence of IUD expulsion was highest with placement between 0 and 3 days post partum and lowest with placement at 6-14 weeks postpartum (10.73% and 3.18%, respectively).
“Within the group with IUD insertions 0-3 days postpartum, the highest expulsion rates were discovered within 12 weeks of insertion, with the highest incidence rate occurring at week 6 (844 per 1,000 person-years), a time women are commonly seen post delivery,” the researchers noted.
In a subcohort of 94,817 women with known breastfeeding status, the 5-year cumulative incidence of expulsion was 3.49% for breastfeeding women and 4.57% for nonbreastfeeding women, with an adjusted HR of 0.71 for breastfeeding versus not breastfeeding.
“While women who accept immediate postpartum IUD placement report high satisfaction rates, information on women’s preferences and satisfaction associated with different timing of postpartum placement would also be helpful to understand the benefit-risk profile,” the researchers wrote in their discussion of the findings. “The fact that most expulsions in the immediate postpartum group occurred early presents an opportunity to mitigate risk of unrecognized expulsion and unintended pregnancy via counseling on signs of expulsion and follow-up examination.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential misclassification of exposures and the primary outcome of expulsion, especially since some postpartum women may be lactating whether or not they are breastfeeding, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the combination of complete and partial expulsions, and the dating of IUD expulsion based on when it came to medical attention, which was not necessarily when it occurred. More data are needed on the potential association between lactational amenorrhea and lower expulsion risk among postpartum women who are breastfeeding.
However, the results were strengthened by the large and diverse study population, the use of linked mother-infant records to identify exposures, and the use electronic health records to identify outcomes, and the data can inform patient counseling for postpartum IUDs, the researchers concluded.
Study reflects findings from Europe
“The FDA mandated this study in response to a European study, EURAS-IUD1, a European prospective observational study that enrolled 61,448 participants between 2006 and 2012,” Ms. Armstrong said in an interview. In the European study “women breastfeeding at the time of device insertion or with the device inserted at 36 weeks’ postpartum or less had higher risk of uterine perforation. The FDA wanted to know if the risks were similar in the United States population”
The APEX-IUD study was designed to reflect current United States clinical practice. “The aims of APEX-IUD are to evaluate risk of IUD-related uterine perforation and device expulsion among women who are breastfeeding or within 12 months postpartum at insertion. The perforation outcome is addressed in a separate paper,” Ms. Armstrong noted.
“We were not surprised by the findings; they aligned with previous findings and confirm the overall safety of intrauterine devices,” said Ms. Armstrong. “Data from this study provides IUD expulsion risk estimates that can be used to inform clinical practice and preinsertion counseling. IUD insertions 0-3 days postpartum might decrease the risk of unintended pregnancy and provide more convenience and efficiency for new mothers. This has proven to be especially important during the pandemic. The higher risk of expulsion at 0-3 days post partum must be balanced with the low IUD-related uterine perforation risk to provide a comprehensive picture that aids in clinical decision-making.
“Potential barriers to postpartum IUD placement include lack of provision of education on the range of contraceptive options available during prenatal care and failure or inability of hospital inpatient units to stock the intrauterine devices for use when needed,” said Ms. Armstrong.
Looking ahead, “future research could evaluate risk factors for partial versus complete expulsions, the association of preinsertion counseling with recognition of potential expulsions and corresponding IUD failure rates, and whether ultrasound verification of IUD position in the uterus after insertion is associated with expulsion risk,” she said.
Identifying risk factors informs patient counseling
“The current study examines breastfeeding at time of IUD insertion as a risk factor for expulsion,” Iris Krishna, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview. “There is biologic plausibility that breastfeeding may be a risk factor of IUD expulsion. Breastfeeding stimulates secretion of oxytocin, a hormone which plays a key role in the contraction of the uterus during labor and uterine involution postpartum. It also plays a key role in the contraction of milk ducts to allow for milk letdown. Because of its dual role some mothers may occasionally report uterine cramping with breastfeeding. Prior studies have suggested that breastfeeding may be associated with an increased risk of uterine perforation with postpartum IUD placement, but how breastfeeding may contribute to risk of IUD expulsion has not been studied extensively.”
The current data are consistent with previous studies suggesting the highest risk of IUD expulsion is with placement in the immediate postpartum period (0-3 days). “In a subcohort analysis by breastfeeding status, the risk of IUD expulsion was lower for women who were breastfeeding versus not breastfeeding;” however, “these findings may be due to amenorrhea that can also be seen with breastfeeding,” Dr. Krishna said. “Menstrual bleeding is an independent risk factor for IUD expulsion and not having menstrual bleeding while breastfeeding may lower risk of expulsion.
“Patients should be counseled on the benefits of immediate postpartum IUD placement, the risk of IUD expulsion, and alternative contraception options to be able to make an informed decision about the right contraception for them,” Dr. Krishna emphasized. “Clinicians can reassure patients that the uterine cramping they may feel while breastfeeding does not appear to increase the risk of IUD expulsion and that the amenorrhea that may result from breastfeeding also may lower the risk of IUD expulsion.”
The study was supported by Bayer through support to RTI Health Solutions, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Kaiser Permanente Southern California, Kaiser Permanente Washington, and the Regenstrief Institute. Ms. Armstrong and several coauthors disclosed support from Bayer during the study. Dr. Krishna had no relevant disclosures.
Expulsion of intrauterine devices was significantly more likely when the devices were inserted within the first 3 days after delivery compared with later insertions, based on data from more than 300,000 women.
Intrauterine devices are effective contraception, and current guidelines support immediate postpartum IUD insertion as a safe, effective, and convenient option, Mary Anne Armstrong, MA, of Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Oakland, and colleagues wrote. Although IUD expulsion rates are low overall, data from previous studies suggest that timing of insertion may affect expulsion rates, and that breastfeeding may play a role.
In the Association of Perforation and Expulsion of Intrauterine Devices (APEX-IUD) cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed data from the electronic health records at four sites; the study population included women aged 50 years and younger who underwent IUD insertion between 2001 and 2018.
The women were grouped by postpartum status and timing of IUD placement: 0-3 days, 4 days to 6 weeks, 6-14 weeks, 14-52 weeks, and nonpostpartum (defined as more than 52 weeks or no evidence of delivery).
The researchers also compared expulsion rates in postpartum women who were and were not breastfeeding at the time of IUD insertion based on clinical records, diagnostic codes, or questionnaires at well-baby visits.
The total study population included 326,658 women with a mean age of 32.0 years; 42% were non-Hispanic White, 17.2% were Hispanic other, 13.0% were Hispanic White, 11.9% were Asian or Pacific Islander, 8.7% were non-Hispanic Black, and 0.2% were Hispanic Black. Approximately 80% of the IUDs were levonorgestrel releasing.
A total of 8,943 expulsions were reported, for an overall expulsion rate of 13.94 per 1,000 person-years.
The adjusted hazard ratios for IUD expulsion were 5.34, 1.22, 1.06, and 1.43 for women with insertion times, respectively, of 0-3 days, 4 days to 6 or fewer weeks, 6-14 weeks, and 14-52 weeks. Women with nonpostpartum IUD insertion served as the referent.
The 5-year cumulative incidence of IUD expulsion was highest with placement between 0 and 3 days post partum and lowest with placement at 6-14 weeks postpartum (10.73% and 3.18%, respectively).
“Within the group with IUD insertions 0-3 days postpartum, the highest expulsion rates were discovered within 12 weeks of insertion, with the highest incidence rate occurring at week 6 (844 per 1,000 person-years), a time women are commonly seen post delivery,” the researchers noted.
In a subcohort of 94,817 women with known breastfeeding status, the 5-year cumulative incidence of expulsion was 3.49% for breastfeeding women and 4.57% for nonbreastfeeding women, with an adjusted HR of 0.71 for breastfeeding versus not breastfeeding.
“While women who accept immediate postpartum IUD placement report high satisfaction rates, information on women’s preferences and satisfaction associated with different timing of postpartum placement would also be helpful to understand the benefit-risk profile,” the researchers wrote in their discussion of the findings. “The fact that most expulsions in the immediate postpartum group occurred early presents an opportunity to mitigate risk of unrecognized expulsion and unintended pregnancy via counseling on signs of expulsion and follow-up examination.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential misclassification of exposures and the primary outcome of expulsion, especially since some postpartum women may be lactating whether or not they are breastfeeding, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the combination of complete and partial expulsions, and the dating of IUD expulsion based on when it came to medical attention, which was not necessarily when it occurred. More data are needed on the potential association between lactational amenorrhea and lower expulsion risk among postpartum women who are breastfeeding.
However, the results were strengthened by the large and diverse study population, the use of linked mother-infant records to identify exposures, and the use electronic health records to identify outcomes, and the data can inform patient counseling for postpartum IUDs, the researchers concluded.
Study reflects findings from Europe
“The FDA mandated this study in response to a European study, EURAS-IUD1, a European prospective observational study that enrolled 61,448 participants between 2006 and 2012,” Ms. Armstrong said in an interview. In the European study “women breastfeeding at the time of device insertion or with the device inserted at 36 weeks’ postpartum or less had higher risk of uterine perforation. The FDA wanted to know if the risks were similar in the United States population”
The APEX-IUD study was designed to reflect current United States clinical practice. “The aims of APEX-IUD are to evaluate risk of IUD-related uterine perforation and device expulsion among women who are breastfeeding or within 12 months postpartum at insertion. The perforation outcome is addressed in a separate paper,” Ms. Armstrong noted.
“We were not surprised by the findings; they aligned with previous findings and confirm the overall safety of intrauterine devices,” said Ms. Armstrong. “Data from this study provides IUD expulsion risk estimates that can be used to inform clinical practice and preinsertion counseling. IUD insertions 0-3 days postpartum might decrease the risk of unintended pregnancy and provide more convenience and efficiency for new mothers. This has proven to be especially important during the pandemic. The higher risk of expulsion at 0-3 days post partum must be balanced with the low IUD-related uterine perforation risk to provide a comprehensive picture that aids in clinical decision-making.
“Potential barriers to postpartum IUD placement include lack of provision of education on the range of contraceptive options available during prenatal care and failure or inability of hospital inpatient units to stock the intrauterine devices for use when needed,” said Ms. Armstrong.
Looking ahead, “future research could evaluate risk factors for partial versus complete expulsions, the association of preinsertion counseling with recognition of potential expulsions and corresponding IUD failure rates, and whether ultrasound verification of IUD position in the uterus after insertion is associated with expulsion risk,” she said.
Identifying risk factors informs patient counseling
“The current study examines breastfeeding at time of IUD insertion as a risk factor for expulsion,” Iris Krishna, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview. “There is biologic plausibility that breastfeeding may be a risk factor of IUD expulsion. Breastfeeding stimulates secretion of oxytocin, a hormone which plays a key role in the contraction of the uterus during labor and uterine involution postpartum. It also plays a key role in the contraction of milk ducts to allow for milk letdown. Because of its dual role some mothers may occasionally report uterine cramping with breastfeeding. Prior studies have suggested that breastfeeding may be associated with an increased risk of uterine perforation with postpartum IUD placement, but how breastfeeding may contribute to risk of IUD expulsion has not been studied extensively.”
The current data are consistent with previous studies suggesting the highest risk of IUD expulsion is with placement in the immediate postpartum period (0-3 days). “In a subcohort analysis by breastfeeding status, the risk of IUD expulsion was lower for women who were breastfeeding versus not breastfeeding;” however, “these findings may be due to amenorrhea that can also be seen with breastfeeding,” Dr. Krishna said. “Menstrual bleeding is an independent risk factor for IUD expulsion and not having menstrual bleeding while breastfeeding may lower risk of expulsion.
“Patients should be counseled on the benefits of immediate postpartum IUD placement, the risk of IUD expulsion, and alternative contraception options to be able to make an informed decision about the right contraception for them,” Dr. Krishna emphasized. “Clinicians can reassure patients that the uterine cramping they may feel while breastfeeding does not appear to increase the risk of IUD expulsion and that the amenorrhea that may result from breastfeeding also may lower the risk of IUD expulsion.”
The study was supported by Bayer through support to RTI Health Solutions, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Kaiser Permanente Southern California, Kaiser Permanente Washington, and the Regenstrief Institute. Ms. Armstrong and several coauthors disclosed support from Bayer during the study. Dr. Krishna had no relevant disclosures.
Expulsion of intrauterine devices was significantly more likely when the devices were inserted within the first 3 days after delivery compared with later insertions, based on data from more than 300,000 women.
Intrauterine devices are effective contraception, and current guidelines support immediate postpartum IUD insertion as a safe, effective, and convenient option, Mary Anne Armstrong, MA, of Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Oakland, and colleagues wrote. Although IUD expulsion rates are low overall, data from previous studies suggest that timing of insertion may affect expulsion rates, and that breastfeeding may play a role.
In the Association of Perforation and Expulsion of Intrauterine Devices (APEX-IUD) cohort study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers reviewed data from the electronic health records at four sites; the study population included women aged 50 years and younger who underwent IUD insertion between 2001 and 2018.
The women were grouped by postpartum status and timing of IUD placement: 0-3 days, 4 days to 6 weeks, 6-14 weeks, 14-52 weeks, and nonpostpartum (defined as more than 52 weeks or no evidence of delivery).
The researchers also compared expulsion rates in postpartum women who were and were not breastfeeding at the time of IUD insertion based on clinical records, diagnostic codes, or questionnaires at well-baby visits.
The total study population included 326,658 women with a mean age of 32.0 years; 42% were non-Hispanic White, 17.2% were Hispanic other, 13.0% were Hispanic White, 11.9% were Asian or Pacific Islander, 8.7% were non-Hispanic Black, and 0.2% were Hispanic Black. Approximately 80% of the IUDs were levonorgestrel releasing.
A total of 8,943 expulsions were reported, for an overall expulsion rate of 13.94 per 1,000 person-years.
The adjusted hazard ratios for IUD expulsion were 5.34, 1.22, 1.06, and 1.43 for women with insertion times, respectively, of 0-3 days, 4 days to 6 or fewer weeks, 6-14 weeks, and 14-52 weeks. Women with nonpostpartum IUD insertion served as the referent.
The 5-year cumulative incidence of IUD expulsion was highest with placement between 0 and 3 days post partum and lowest with placement at 6-14 weeks postpartum (10.73% and 3.18%, respectively).
“Within the group with IUD insertions 0-3 days postpartum, the highest expulsion rates were discovered within 12 weeks of insertion, with the highest incidence rate occurring at week 6 (844 per 1,000 person-years), a time women are commonly seen post delivery,” the researchers noted.
In a subcohort of 94,817 women with known breastfeeding status, the 5-year cumulative incidence of expulsion was 3.49% for breastfeeding women and 4.57% for nonbreastfeeding women, with an adjusted HR of 0.71 for breastfeeding versus not breastfeeding.
“While women who accept immediate postpartum IUD placement report high satisfaction rates, information on women’s preferences and satisfaction associated with different timing of postpartum placement would also be helpful to understand the benefit-risk profile,” the researchers wrote in their discussion of the findings. “The fact that most expulsions in the immediate postpartum group occurred early presents an opportunity to mitigate risk of unrecognized expulsion and unintended pregnancy via counseling on signs of expulsion and follow-up examination.”
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential misclassification of exposures and the primary outcome of expulsion, especially since some postpartum women may be lactating whether or not they are breastfeeding, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the combination of complete and partial expulsions, and the dating of IUD expulsion based on when it came to medical attention, which was not necessarily when it occurred. More data are needed on the potential association between lactational amenorrhea and lower expulsion risk among postpartum women who are breastfeeding.
However, the results were strengthened by the large and diverse study population, the use of linked mother-infant records to identify exposures, and the use electronic health records to identify outcomes, and the data can inform patient counseling for postpartum IUDs, the researchers concluded.
Study reflects findings from Europe
“The FDA mandated this study in response to a European study, EURAS-IUD1, a European prospective observational study that enrolled 61,448 participants between 2006 and 2012,” Ms. Armstrong said in an interview. In the European study “women breastfeeding at the time of device insertion or with the device inserted at 36 weeks’ postpartum or less had higher risk of uterine perforation. The FDA wanted to know if the risks were similar in the United States population”
The APEX-IUD study was designed to reflect current United States clinical practice. “The aims of APEX-IUD are to evaluate risk of IUD-related uterine perforation and device expulsion among women who are breastfeeding or within 12 months postpartum at insertion. The perforation outcome is addressed in a separate paper,” Ms. Armstrong noted.
“We were not surprised by the findings; they aligned with previous findings and confirm the overall safety of intrauterine devices,” said Ms. Armstrong. “Data from this study provides IUD expulsion risk estimates that can be used to inform clinical practice and preinsertion counseling. IUD insertions 0-3 days postpartum might decrease the risk of unintended pregnancy and provide more convenience and efficiency for new mothers. This has proven to be especially important during the pandemic. The higher risk of expulsion at 0-3 days post partum must be balanced with the low IUD-related uterine perforation risk to provide a comprehensive picture that aids in clinical decision-making.
“Potential barriers to postpartum IUD placement include lack of provision of education on the range of contraceptive options available during prenatal care and failure or inability of hospital inpatient units to stock the intrauterine devices for use when needed,” said Ms. Armstrong.
Looking ahead, “future research could evaluate risk factors for partial versus complete expulsions, the association of preinsertion counseling with recognition of potential expulsions and corresponding IUD failure rates, and whether ultrasound verification of IUD position in the uterus after insertion is associated with expulsion risk,” she said.
Identifying risk factors informs patient counseling
“The current study examines breastfeeding at time of IUD insertion as a risk factor for expulsion,” Iris Krishna, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview. “There is biologic plausibility that breastfeeding may be a risk factor of IUD expulsion. Breastfeeding stimulates secretion of oxytocin, a hormone which plays a key role in the contraction of the uterus during labor and uterine involution postpartum. It also plays a key role in the contraction of milk ducts to allow for milk letdown. Because of its dual role some mothers may occasionally report uterine cramping with breastfeeding. Prior studies have suggested that breastfeeding may be associated with an increased risk of uterine perforation with postpartum IUD placement, but how breastfeeding may contribute to risk of IUD expulsion has not been studied extensively.”
The current data are consistent with previous studies suggesting the highest risk of IUD expulsion is with placement in the immediate postpartum period (0-3 days). “In a subcohort analysis by breastfeeding status, the risk of IUD expulsion was lower for women who were breastfeeding versus not breastfeeding;” however, “these findings may be due to amenorrhea that can also be seen with breastfeeding,” Dr. Krishna said. “Menstrual bleeding is an independent risk factor for IUD expulsion and not having menstrual bleeding while breastfeeding may lower risk of expulsion.
“Patients should be counseled on the benefits of immediate postpartum IUD placement, the risk of IUD expulsion, and alternative contraception options to be able to make an informed decision about the right contraception for them,” Dr. Krishna emphasized. “Clinicians can reassure patients that the uterine cramping they may feel while breastfeeding does not appear to increase the risk of IUD expulsion and that the amenorrhea that may result from breastfeeding also may lower the risk of IUD expulsion.”
The study was supported by Bayer through support to RTI Health Solutions, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, Kaiser Permanente Southern California, Kaiser Permanente Washington, and the Regenstrief Institute. Ms. Armstrong and several coauthors disclosed support from Bayer during the study. Dr. Krishna had no relevant disclosures.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN