User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Coffee and the brain: ‘Concerning’ new data
according to the results of a large study.
“With coffee intake, moderation is the key, and especially high levels of consumption may have adverse long-term effects on the brain,” said study investigator Elina Hypponen, PhD, professor of nutritional and genetic epidemiology and director of the Australian Center for Precision Health at the University of South Australia.
“These new data are concerning, and there is a need to conduct further carefully controlled studies to clarify the effects of coffee on the brain.”
The study was published online June 24 in Nutritional Neuroscience.
Potent stimulant
Coffee is a potent nervous system stimulant and is among the most popular nonalcoholic beverages. Some previous research suggests it benefits the brain, but the investigators noted that other research shows a negative or U-shaped relationship.
To investigate, the researchers examined data from the U.K. Biobank, a long-term prospective epidemiologic study of more than 500,000 participants aged 37-73 years who were recruited in 22 assessment centers in the United Kingdom between March 2006 and October 2010.
During the baseline assessment, information was gathered using touchscreen questionnaires, verbal interviews, and physical examinations that involved collection of blood, urine, and saliva samples. An imaging substudy was incorporated in 2014, the goal of which was to conduct brain, heart, and body MRI imaging for 100,000 participants.
The investigators conducted analyses on disease outcomes for 398,646 participants for whom information on habitual coffee consumption was available. Brain volume analyses were conducted in 17,702 participants for whom valid brain imaging data were available.
Participants reported coffee intake in cups per day. Researchers grouped coffee consumption into seven categories: nondrinkers, decaffeinated coffee drinkers, and caffeinated coffee drinkers who consumed less than 1 cup/d, 1-2 cups/d, 3-4 cups/d, 5-6 cups/d, and more than 6 cups/d.
The reference category was those who consumed 1-2 cups/d, rather than those who abstained from coffee, because persons who abstain are more likely to be at suboptimal health.
“Comparing the health of coffee drinkers to the health of those choosing to abstain from coffee will typically lead to an impression of a health benefit, even if there would not be one,” said Dr. Hypponen.
The researchers obtained total and regional brain volumes from the MRI imaging substudy starting 4-6 years after baseline assessment. They accessed information on incident dementia and stroke using primary care data, hospital admission electronic health records, national death registers, and self-reported medical conditions.
Covariates included socioeconomic, health, and other factors, such as smoking, alcohol and tea consumption, physical activity, stressful life events, and body mass index.
The investigators found that there was a linear inverse association between coffee consumption and total brain volume (fully adjusted beta per cup, –1.42; 95% confidence interval, –1.89 to –0.94), with consistent patterns for gray matter, white matter, and hippocampal volumes.
There was no evidence to support an association with white matter hyperintensity (WMH) volume (beta –0.01; 95% CI, –0.07 to 0.05).
Higher consumption, higher risk
The analysis also revealed a nonlinear association between coffee consumption and the odds of dementia (P nonlinearity = .0001), with slightly higher odds seen with non–coffee drinkers and decaffeinated-coffee drinkers and more notable increases for participants in the highest categories of coffee consumption compared with light coffee drinkers.
After adjustment for all covariates, the odds ratio of dementia among persons in the category of coffee intake was 1.53 (95% CI, 1.28-1.83). After full adjustments, the association with heavy coffee consumption and stroke was not significant, although “we can’t exclude a weak effect,” said Dr. Hypponen.
“For the highest coffee consumption group, the data support an association which may be anywhere from 0% to 37% higher odds of stroke after full adjustment,” she added.
People at risk for hypertension may develop “unpleasant sensations” and stop drinking coffee before a serious adverse event occurs, said Dr. Hypponen. In a previous study, she and her colleagues showed that those who have genetically higher blood pressure tend to drink less coffee than their counterparts without the condition.
“This type of effect might be expected to naturally limit the adverse effects of coffee on the risk of stroke,” said Dr. Hypponen.
The odds remained elevated for participants drinking more than 6 cups/d after the researchers accounted for sleep quality. There were no differences in risk between men and women or by age.
An examination of the consumption of tea, which often contains caffeine, did not show an association with brain volume or the odds of dementia or stroke.
“We don’t know whether the difference between associations seen for coffee and tea intake reflects the difference in related caffeine intake or some other explanation, such as dehydration or effects operating through blood cholesterol,” said Dr. Hypponen.
Although reverse causation is possible, there’s no reason to believe that it is relevant to the study results. Genetic evidence suggests a causal role of higher coffee intake on risk for Alzheimer’s disease. In addition, results of a clinical trial support the association between higher caffeine intake and smaller gray matter volume, said Dr. Hypponen.
The mechanisms linking coffee consumption to brain volumes and dementia are not well established. However, Dr. Hypponen noted that caffeine has been used to induce apoptosis in cancer studies using glial cells.
“Furthermore, adenosine receptors, which mediate many of the effects of caffeine in the brain, have been suggested to influence the release of growth factors, which in turn can have an influence on astrocyte proliferation and angiogenesis in the brain,” she said.
Some types of coffee contain cafestol, which increases blood cholesterol and can have adverse effects though related mechanisms, said Dr. Hypponen.
The mechanism may also involve dehydration, which may have a harmful effect on the brain. The study suggested a correlation between dehydration and high coffee intake. “Of course, if this is the case, it is good news, as then we can do something about it simply by drinking some water every time we have a cup of coffee,” she said.
Misleading conclusions
Coffee contains antioxidants, and although previous studies have suggested it might be beneficial, this hypothesis is “too simplistic,” said Dr. Hypponen. “While coffee is not going to be all ‘bad’ either, there are a lot of controversies and suggestions about beneficial effects of coffee which may not be true, or at least do not reflect the full story.”
If the drinking of coffee is at least partly determined by an individual’s health status, then that would often lead to misleading conclusions in observational studies, said Dr. Hypponen.
“When one uses as a comparison people who already have poor health and who do not drink coffee because of that, coffee intake will by default appear beneficial simply because there are more people with disease among those choosing abstinence,” she said.
Before now, there was “very little evidence about the association between coffee intake and brain morphology,” and the studies that were conducted were relatively small, said Dr. Hypponen.
One of these smaller studies included a group of women aged 13-30 years. It found that coffee consumption was not associated with total brain volumes, but the findings suggested a U-shaped association with hippocampal volume; higher values were seen both for nondrinkers and the groups with higher consumption.
A small study of elderly patients with diabetes showed no evidence of an association with white matter volume, but there was a possible age-dependent association with gray matter volume.
The largest of the earlier studies had results that were very similar to those of the current study, suggesting that increasing coffee intake is associated with smaller hippocampal volumes, said Dr. Hypponen.
One of the study’s limitations included the fact that full dietary information was available only for a subsample and that factors such as dehydration were measured at baseline rather than at the time of brain MRI.
Another possible study limitation was the use of self-reported data and the fact that lifestyle changes may have occurred between baseline and MRI or covariate measurement.
In addition, the study is subject to a healthy-volunteer bias, and its implications are restricted to White British persons. The association needs to be studied in other ethnic populations, the authors noted.
A reason to cut back?
Commenting on the findings, Walter Willett, MD, DrPH, professor of epidemiology and nutrition, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, said the study is large and quite well done.
“It does raise questions about an increase in risk of dementia with six or more cups of coffee per day,” said Dr. Willett. “At the same time, it provides reassurance about lack of adverse effects of coffee for those consuming three or four cups per day, and little increase in risk, if any, with five cups per day.”
It’s not entirely clear whether the increase in risk with six or more cups of coffee per day represents a “true effect” of coffee, inasmuch as the study did not seem to adjust fully for dietary factors, high consumption of alcohol, or past smoking, said Dr. Willett.
The findings don’t suggest that coffee lovers should give up their Java. “But six or more cups per day is a lot, and those who drink that much might consider cutting back a bit while research continues,” said Dr. Willett.
The study was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to the results of a large study.
“With coffee intake, moderation is the key, and especially high levels of consumption may have adverse long-term effects on the brain,” said study investigator Elina Hypponen, PhD, professor of nutritional and genetic epidemiology and director of the Australian Center for Precision Health at the University of South Australia.
“These new data are concerning, and there is a need to conduct further carefully controlled studies to clarify the effects of coffee on the brain.”
The study was published online June 24 in Nutritional Neuroscience.
Potent stimulant
Coffee is a potent nervous system stimulant and is among the most popular nonalcoholic beverages. Some previous research suggests it benefits the brain, but the investigators noted that other research shows a negative or U-shaped relationship.
To investigate, the researchers examined data from the U.K. Biobank, a long-term prospective epidemiologic study of more than 500,000 participants aged 37-73 years who were recruited in 22 assessment centers in the United Kingdom between March 2006 and October 2010.
During the baseline assessment, information was gathered using touchscreen questionnaires, verbal interviews, and physical examinations that involved collection of blood, urine, and saliva samples. An imaging substudy was incorporated in 2014, the goal of which was to conduct brain, heart, and body MRI imaging for 100,000 participants.
The investigators conducted analyses on disease outcomes for 398,646 participants for whom information on habitual coffee consumption was available. Brain volume analyses were conducted in 17,702 participants for whom valid brain imaging data were available.
Participants reported coffee intake in cups per day. Researchers grouped coffee consumption into seven categories: nondrinkers, decaffeinated coffee drinkers, and caffeinated coffee drinkers who consumed less than 1 cup/d, 1-2 cups/d, 3-4 cups/d, 5-6 cups/d, and more than 6 cups/d.
The reference category was those who consumed 1-2 cups/d, rather than those who abstained from coffee, because persons who abstain are more likely to be at suboptimal health.
“Comparing the health of coffee drinkers to the health of those choosing to abstain from coffee will typically lead to an impression of a health benefit, even if there would not be one,” said Dr. Hypponen.
The researchers obtained total and regional brain volumes from the MRI imaging substudy starting 4-6 years after baseline assessment. They accessed information on incident dementia and stroke using primary care data, hospital admission electronic health records, national death registers, and self-reported medical conditions.
Covariates included socioeconomic, health, and other factors, such as smoking, alcohol and tea consumption, physical activity, stressful life events, and body mass index.
The investigators found that there was a linear inverse association between coffee consumption and total brain volume (fully adjusted beta per cup, –1.42; 95% confidence interval, –1.89 to –0.94), with consistent patterns for gray matter, white matter, and hippocampal volumes.
There was no evidence to support an association with white matter hyperintensity (WMH) volume (beta –0.01; 95% CI, –0.07 to 0.05).
Higher consumption, higher risk
The analysis also revealed a nonlinear association between coffee consumption and the odds of dementia (P nonlinearity = .0001), with slightly higher odds seen with non–coffee drinkers and decaffeinated-coffee drinkers and more notable increases for participants in the highest categories of coffee consumption compared with light coffee drinkers.
After adjustment for all covariates, the odds ratio of dementia among persons in the category of coffee intake was 1.53 (95% CI, 1.28-1.83). After full adjustments, the association with heavy coffee consumption and stroke was not significant, although “we can’t exclude a weak effect,” said Dr. Hypponen.
“For the highest coffee consumption group, the data support an association which may be anywhere from 0% to 37% higher odds of stroke after full adjustment,” she added.
People at risk for hypertension may develop “unpleasant sensations” and stop drinking coffee before a serious adverse event occurs, said Dr. Hypponen. In a previous study, she and her colleagues showed that those who have genetically higher blood pressure tend to drink less coffee than their counterparts without the condition.
“This type of effect might be expected to naturally limit the adverse effects of coffee on the risk of stroke,” said Dr. Hypponen.
The odds remained elevated for participants drinking more than 6 cups/d after the researchers accounted for sleep quality. There were no differences in risk between men and women or by age.
An examination of the consumption of tea, which often contains caffeine, did not show an association with brain volume or the odds of dementia or stroke.
“We don’t know whether the difference between associations seen for coffee and tea intake reflects the difference in related caffeine intake or some other explanation, such as dehydration or effects operating through blood cholesterol,” said Dr. Hypponen.
Although reverse causation is possible, there’s no reason to believe that it is relevant to the study results. Genetic evidence suggests a causal role of higher coffee intake on risk for Alzheimer’s disease. In addition, results of a clinical trial support the association between higher caffeine intake and smaller gray matter volume, said Dr. Hypponen.
The mechanisms linking coffee consumption to brain volumes and dementia are not well established. However, Dr. Hypponen noted that caffeine has been used to induce apoptosis in cancer studies using glial cells.
“Furthermore, adenosine receptors, which mediate many of the effects of caffeine in the brain, have been suggested to influence the release of growth factors, which in turn can have an influence on astrocyte proliferation and angiogenesis in the brain,” she said.
Some types of coffee contain cafestol, which increases blood cholesterol and can have adverse effects though related mechanisms, said Dr. Hypponen.
The mechanism may also involve dehydration, which may have a harmful effect on the brain. The study suggested a correlation between dehydration and high coffee intake. “Of course, if this is the case, it is good news, as then we can do something about it simply by drinking some water every time we have a cup of coffee,” she said.
Misleading conclusions
Coffee contains antioxidants, and although previous studies have suggested it might be beneficial, this hypothesis is “too simplistic,” said Dr. Hypponen. “While coffee is not going to be all ‘bad’ either, there are a lot of controversies and suggestions about beneficial effects of coffee which may not be true, or at least do not reflect the full story.”
If the drinking of coffee is at least partly determined by an individual’s health status, then that would often lead to misleading conclusions in observational studies, said Dr. Hypponen.
“When one uses as a comparison people who already have poor health and who do not drink coffee because of that, coffee intake will by default appear beneficial simply because there are more people with disease among those choosing abstinence,” she said.
Before now, there was “very little evidence about the association between coffee intake and brain morphology,” and the studies that were conducted were relatively small, said Dr. Hypponen.
One of these smaller studies included a group of women aged 13-30 years. It found that coffee consumption was not associated with total brain volumes, but the findings suggested a U-shaped association with hippocampal volume; higher values were seen both for nondrinkers and the groups with higher consumption.
A small study of elderly patients with diabetes showed no evidence of an association with white matter volume, but there was a possible age-dependent association with gray matter volume.
The largest of the earlier studies had results that were very similar to those of the current study, suggesting that increasing coffee intake is associated with smaller hippocampal volumes, said Dr. Hypponen.
One of the study’s limitations included the fact that full dietary information was available only for a subsample and that factors such as dehydration were measured at baseline rather than at the time of brain MRI.
Another possible study limitation was the use of self-reported data and the fact that lifestyle changes may have occurred between baseline and MRI or covariate measurement.
In addition, the study is subject to a healthy-volunteer bias, and its implications are restricted to White British persons. The association needs to be studied in other ethnic populations, the authors noted.
A reason to cut back?
Commenting on the findings, Walter Willett, MD, DrPH, professor of epidemiology and nutrition, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, said the study is large and quite well done.
“It does raise questions about an increase in risk of dementia with six or more cups of coffee per day,” said Dr. Willett. “At the same time, it provides reassurance about lack of adverse effects of coffee for those consuming three or four cups per day, and little increase in risk, if any, with five cups per day.”
It’s not entirely clear whether the increase in risk with six or more cups of coffee per day represents a “true effect” of coffee, inasmuch as the study did not seem to adjust fully for dietary factors, high consumption of alcohol, or past smoking, said Dr. Willett.
The findings don’t suggest that coffee lovers should give up their Java. “But six or more cups per day is a lot, and those who drink that much might consider cutting back a bit while research continues,” said Dr. Willett.
The study was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to the results of a large study.
“With coffee intake, moderation is the key, and especially high levels of consumption may have adverse long-term effects on the brain,” said study investigator Elina Hypponen, PhD, professor of nutritional and genetic epidemiology and director of the Australian Center for Precision Health at the University of South Australia.
“These new data are concerning, and there is a need to conduct further carefully controlled studies to clarify the effects of coffee on the brain.”
The study was published online June 24 in Nutritional Neuroscience.
Potent stimulant
Coffee is a potent nervous system stimulant and is among the most popular nonalcoholic beverages. Some previous research suggests it benefits the brain, but the investigators noted that other research shows a negative or U-shaped relationship.
To investigate, the researchers examined data from the U.K. Biobank, a long-term prospective epidemiologic study of more than 500,000 participants aged 37-73 years who were recruited in 22 assessment centers in the United Kingdom between March 2006 and October 2010.
During the baseline assessment, information was gathered using touchscreen questionnaires, verbal interviews, and physical examinations that involved collection of blood, urine, and saliva samples. An imaging substudy was incorporated in 2014, the goal of which was to conduct brain, heart, and body MRI imaging for 100,000 participants.
The investigators conducted analyses on disease outcomes for 398,646 participants for whom information on habitual coffee consumption was available. Brain volume analyses were conducted in 17,702 participants for whom valid brain imaging data were available.
Participants reported coffee intake in cups per day. Researchers grouped coffee consumption into seven categories: nondrinkers, decaffeinated coffee drinkers, and caffeinated coffee drinkers who consumed less than 1 cup/d, 1-2 cups/d, 3-4 cups/d, 5-6 cups/d, and more than 6 cups/d.
The reference category was those who consumed 1-2 cups/d, rather than those who abstained from coffee, because persons who abstain are more likely to be at suboptimal health.
“Comparing the health of coffee drinkers to the health of those choosing to abstain from coffee will typically lead to an impression of a health benefit, even if there would not be one,” said Dr. Hypponen.
The researchers obtained total and regional brain volumes from the MRI imaging substudy starting 4-6 years after baseline assessment. They accessed information on incident dementia and stroke using primary care data, hospital admission electronic health records, national death registers, and self-reported medical conditions.
Covariates included socioeconomic, health, and other factors, such as smoking, alcohol and tea consumption, physical activity, stressful life events, and body mass index.
The investigators found that there was a linear inverse association between coffee consumption and total brain volume (fully adjusted beta per cup, –1.42; 95% confidence interval, –1.89 to –0.94), with consistent patterns for gray matter, white matter, and hippocampal volumes.
There was no evidence to support an association with white matter hyperintensity (WMH) volume (beta –0.01; 95% CI, –0.07 to 0.05).
Higher consumption, higher risk
The analysis also revealed a nonlinear association between coffee consumption and the odds of dementia (P nonlinearity = .0001), with slightly higher odds seen with non–coffee drinkers and decaffeinated-coffee drinkers and more notable increases for participants in the highest categories of coffee consumption compared with light coffee drinkers.
After adjustment for all covariates, the odds ratio of dementia among persons in the category of coffee intake was 1.53 (95% CI, 1.28-1.83). After full adjustments, the association with heavy coffee consumption and stroke was not significant, although “we can’t exclude a weak effect,” said Dr. Hypponen.
“For the highest coffee consumption group, the data support an association which may be anywhere from 0% to 37% higher odds of stroke after full adjustment,” she added.
People at risk for hypertension may develop “unpleasant sensations” and stop drinking coffee before a serious adverse event occurs, said Dr. Hypponen. In a previous study, she and her colleagues showed that those who have genetically higher blood pressure tend to drink less coffee than their counterparts without the condition.
“This type of effect might be expected to naturally limit the adverse effects of coffee on the risk of stroke,” said Dr. Hypponen.
The odds remained elevated for participants drinking more than 6 cups/d after the researchers accounted for sleep quality. There were no differences in risk between men and women or by age.
An examination of the consumption of tea, which often contains caffeine, did not show an association with brain volume or the odds of dementia or stroke.
“We don’t know whether the difference between associations seen for coffee and tea intake reflects the difference in related caffeine intake or some other explanation, such as dehydration or effects operating through blood cholesterol,” said Dr. Hypponen.
Although reverse causation is possible, there’s no reason to believe that it is relevant to the study results. Genetic evidence suggests a causal role of higher coffee intake on risk for Alzheimer’s disease. In addition, results of a clinical trial support the association between higher caffeine intake and smaller gray matter volume, said Dr. Hypponen.
The mechanisms linking coffee consumption to brain volumes and dementia are not well established. However, Dr. Hypponen noted that caffeine has been used to induce apoptosis in cancer studies using glial cells.
“Furthermore, adenosine receptors, which mediate many of the effects of caffeine in the brain, have been suggested to influence the release of growth factors, which in turn can have an influence on astrocyte proliferation and angiogenesis in the brain,” she said.
Some types of coffee contain cafestol, which increases blood cholesterol and can have adverse effects though related mechanisms, said Dr. Hypponen.
The mechanism may also involve dehydration, which may have a harmful effect on the brain. The study suggested a correlation between dehydration and high coffee intake. “Of course, if this is the case, it is good news, as then we can do something about it simply by drinking some water every time we have a cup of coffee,” she said.
Misleading conclusions
Coffee contains antioxidants, and although previous studies have suggested it might be beneficial, this hypothesis is “too simplistic,” said Dr. Hypponen. “While coffee is not going to be all ‘bad’ either, there are a lot of controversies and suggestions about beneficial effects of coffee which may not be true, or at least do not reflect the full story.”
If the drinking of coffee is at least partly determined by an individual’s health status, then that would often lead to misleading conclusions in observational studies, said Dr. Hypponen.
“When one uses as a comparison people who already have poor health and who do not drink coffee because of that, coffee intake will by default appear beneficial simply because there are more people with disease among those choosing abstinence,” she said.
Before now, there was “very little evidence about the association between coffee intake and brain morphology,” and the studies that were conducted were relatively small, said Dr. Hypponen.
One of these smaller studies included a group of women aged 13-30 years. It found that coffee consumption was not associated with total brain volumes, but the findings suggested a U-shaped association with hippocampal volume; higher values were seen both for nondrinkers and the groups with higher consumption.
A small study of elderly patients with diabetes showed no evidence of an association with white matter volume, but there was a possible age-dependent association with gray matter volume.
The largest of the earlier studies had results that were very similar to those of the current study, suggesting that increasing coffee intake is associated with smaller hippocampal volumes, said Dr. Hypponen.
One of the study’s limitations included the fact that full dietary information was available only for a subsample and that factors such as dehydration were measured at baseline rather than at the time of brain MRI.
Another possible study limitation was the use of self-reported data and the fact that lifestyle changes may have occurred between baseline and MRI or covariate measurement.
In addition, the study is subject to a healthy-volunteer bias, and its implications are restricted to White British persons. The association needs to be studied in other ethnic populations, the authors noted.
A reason to cut back?
Commenting on the findings, Walter Willett, MD, DrPH, professor of epidemiology and nutrition, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, said the study is large and quite well done.
“It does raise questions about an increase in risk of dementia with six or more cups of coffee per day,” said Dr. Willett. “At the same time, it provides reassurance about lack of adverse effects of coffee for those consuming three or four cups per day, and little increase in risk, if any, with five cups per day.”
It’s not entirely clear whether the increase in risk with six or more cups of coffee per day represents a “true effect” of coffee, inasmuch as the study did not seem to adjust fully for dietary factors, high consumption of alcohol, or past smoking, said Dr. Willett.
The findings don’t suggest that coffee lovers should give up their Java. “But six or more cups per day is a lot, and those who drink that much might consider cutting back a bit while research continues,” said Dr. Willett.
The study was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NUTRITIONAL NEUROSCIENCE
Study estimates carbon footprint reduction of virtual isotretinoin visits
: A reduction of 5,137 kg of greenhouse gas emissions in carbon dioxide equivalents.
In what they say is “one of the first studies to evaluate the environmental impact of any aspect of dermatology,” the authors of the retrospective cross-sectional study identified patients who had virtual visits for isotretinoin management between March 25 and May 29, 2020, – the period during which all such visits were conducted virtually in keeping with hospital recommendations to minimize the spread of COVID-19.
The investigators, from the department of dermatology and the department of civil and environmental engineering at West Virginia University, Morgantown, then counted the number of virtual visits that occurred during this period and through Dec. 1, 2020, (175 virtual visits), calculated the distance patients would have traveled round-trip had these visits been in-person, and converted miles saved into the environmental impact using U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and Federal Highway Administration data and relevant EPA standards.
Most patients had elected to continue virtual visits after May 29, the point at which patients were given the option to return to the WVUH clinic. (Patients who initiated treatment during the 2-month identification period were not included.)
The investigators determined that virtual management of isotretinoin saved a median of 37.8 miles per visit during the study period of March 25 to Dec. 1, and estimated that the virtual visits reduced total travel by 14,450 miles. For the analysis, patients were assumed to use light-duty vehicles.
In addition to calculating the reduction in emissions during the study period (5,137 kg of CO2equivalents) they used patient census data from 2019 to 2020 and data from the study period to project the mileage – and the associated emissions – that would be saved annually if all in-person visits for isotretinoin management occurred virtually.
Their calculation for a projected emissions reduction with 1 year of all-virtual isotretinoin management was 49,400 kg of greenhouse gas emissions in CO2equivalents. This is the emission load released when 24,690 kg of coal are burned or 6.3 million smartphones are charged, the researchers wrote.
“Considering that more than 1,000,000 prescriptions of isotretinoin are authorized annually in the United States, the environmental impact could be magnified if virtual delivery of isotretinoin care is adopted on a national scale,” they commented.“Given the serious consequences of global climate change, analysis of the environmental impact of all fields of medicine, including dermatology, is warranted,” they added.
The reduced greenhouse gas emissions are “definitely [being taken] into consideration for future decisions about virtual visits” in the department of dermatology, said Zachary Zinn, MD, residency director and associate professor in the department of dermatology at West Virginia University, Morgantown, who is the senior author of the study. “The main benefit of virtual care in my opinion,” he said in an interview, “is the potential to reduce our carbon footprint.”
Justin Lee, MD, an intern at WVU and the study’s first author, said that the research team was motivated to think about how they “could reduce the negative environmental impact of practicing dermatology” after they read a paper about the environmental impact of endoscopy, written by a gastroenterologist.
In the study, no pregnancies occurred and monthly tests were performed, but “formal assessment of pregnancy risk with virtual isotretinoin management would be warranted,” Dr. Lee and coauthors wrote, noting too that, while no differences were seen with respect to isotretinoin side effects, these were not formally analyzed.
Dr. Zinn said that he and colleagues at WVUH are currently conducting clinical trials to assess the quality and efficacy of virtual care for patients with acne, atopic dermatitis, and psoriasis. Delivering care virtually “will be easier to do if there are data supporting [its] quality and efficacy,” he said. Rosacea is another condition that may be amendable to virtual care, he noted.
Meanwhile, he said, isotretinoin management is “well suited” for virtual visits. When initiating isotretinoin treatment, Dr. Zinn now “proactively inquires” if patients would like to pursue their follow-up visits virtually. “I’ll note that it will save the time and decrease the burden of travel, including the financial cost as well as the environmental cost of travel,” he said, estimating that about half of their management visits are currently virtual.
Asked about the study, Misha Rosenbach, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said the reduced carbon footprint calculated by the researchers and its downstream health benefits “should be taken into consideration by [dermatology] departments, insurers and policymakers” when making decisions about teledermatology.
While environmental impact is “not something I think most institutions are considering for virtual versus in-person care, they should be. And some are,” said Dr. Rosenbach, a founder and cochair of the American Academy of Dermatology Expert Resource Group for Climate Change and Environmental Issues.
Limitations of the study include the generalizability of the results. The impact of virtual isotretinoin management “may be less in predominantly urban areas” than it is in predominately rural West Virginia, the study authors note. And in the case of West Virginia, travel to a local laboratory and pharmacy offsets some of the environmental benefits for the virtual care, they noted. Such travel wasn’t accounted for in the study, but it was found to be a fraction of travel to the WVU hospital clinic. (Patients traveled a median of 5.8 miles to a lab 2.4 times from March 25 to Dec. 1, 2020.)
Dr. Lee will start his dermatology residency at WVU next year. The study was funded by a grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation. The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest, according to Dr. Lee.
: A reduction of 5,137 kg of greenhouse gas emissions in carbon dioxide equivalents.
In what they say is “one of the first studies to evaluate the environmental impact of any aspect of dermatology,” the authors of the retrospective cross-sectional study identified patients who had virtual visits for isotretinoin management between March 25 and May 29, 2020, – the period during which all such visits were conducted virtually in keeping with hospital recommendations to minimize the spread of COVID-19.
The investigators, from the department of dermatology and the department of civil and environmental engineering at West Virginia University, Morgantown, then counted the number of virtual visits that occurred during this period and through Dec. 1, 2020, (175 virtual visits), calculated the distance patients would have traveled round-trip had these visits been in-person, and converted miles saved into the environmental impact using U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and Federal Highway Administration data and relevant EPA standards.
Most patients had elected to continue virtual visits after May 29, the point at which patients were given the option to return to the WVUH clinic. (Patients who initiated treatment during the 2-month identification period were not included.)
The investigators determined that virtual management of isotretinoin saved a median of 37.8 miles per visit during the study period of March 25 to Dec. 1, and estimated that the virtual visits reduced total travel by 14,450 miles. For the analysis, patients were assumed to use light-duty vehicles.
In addition to calculating the reduction in emissions during the study period (5,137 kg of CO2equivalents) they used patient census data from 2019 to 2020 and data from the study period to project the mileage – and the associated emissions – that would be saved annually if all in-person visits for isotretinoin management occurred virtually.
Their calculation for a projected emissions reduction with 1 year of all-virtual isotretinoin management was 49,400 kg of greenhouse gas emissions in CO2equivalents. This is the emission load released when 24,690 kg of coal are burned or 6.3 million smartphones are charged, the researchers wrote.
“Considering that more than 1,000,000 prescriptions of isotretinoin are authorized annually in the United States, the environmental impact could be magnified if virtual delivery of isotretinoin care is adopted on a national scale,” they commented.“Given the serious consequences of global climate change, analysis of the environmental impact of all fields of medicine, including dermatology, is warranted,” they added.
The reduced greenhouse gas emissions are “definitely [being taken] into consideration for future decisions about virtual visits” in the department of dermatology, said Zachary Zinn, MD, residency director and associate professor in the department of dermatology at West Virginia University, Morgantown, who is the senior author of the study. “The main benefit of virtual care in my opinion,” he said in an interview, “is the potential to reduce our carbon footprint.”
Justin Lee, MD, an intern at WVU and the study’s first author, said that the research team was motivated to think about how they “could reduce the negative environmental impact of practicing dermatology” after they read a paper about the environmental impact of endoscopy, written by a gastroenterologist.
In the study, no pregnancies occurred and monthly tests were performed, but “formal assessment of pregnancy risk with virtual isotretinoin management would be warranted,” Dr. Lee and coauthors wrote, noting too that, while no differences were seen with respect to isotretinoin side effects, these were not formally analyzed.
Dr. Zinn said that he and colleagues at WVUH are currently conducting clinical trials to assess the quality and efficacy of virtual care for patients with acne, atopic dermatitis, and psoriasis. Delivering care virtually “will be easier to do if there are data supporting [its] quality and efficacy,” he said. Rosacea is another condition that may be amendable to virtual care, he noted.
Meanwhile, he said, isotretinoin management is “well suited” for virtual visits. When initiating isotretinoin treatment, Dr. Zinn now “proactively inquires” if patients would like to pursue their follow-up visits virtually. “I’ll note that it will save the time and decrease the burden of travel, including the financial cost as well as the environmental cost of travel,” he said, estimating that about half of their management visits are currently virtual.
Asked about the study, Misha Rosenbach, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said the reduced carbon footprint calculated by the researchers and its downstream health benefits “should be taken into consideration by [dermatology] departments, insurers and policymakers” when making decisions about teledermatology.
While environmental impact is “not something I think most institutions are considering for virtual versus in-person care, they should be. And some are,” said Dr. Rosenbach, a founder and cochair of the American Academy of Dermatology Expert Resource Group for Climate Change and Environmental Issues.
Limitations of the study include the generalizability of the results. The impact of virtual isotretinoin management “may be less in predominantly urban areas” than it is in predominately rural West Virginia, the study authors note. And in the case of West Virginia, travel to a local laboratory and pharmacy offsets some of the environmental benefits for the virtual care, they noted. Such travel wasn’t accounted for in the study, but it was found to be a fraction of travel to the WVU hospital clinic. (Patients traveled a median of 5.8 miles to a lab 2.4 times from March 25 to Dec. 1, 2020.)
Dr. Lee will start his dermatology residency at WVU next year. The study was funded by a grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation. The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest, according to Dr. Lee.
: A reduction of 5,137 kg of greenhouse gas emissions in carbon dioxide equivalents.
In what they say is “one of the first studies to evaluate the environmental impact of any aspect of dermatology,” the authors of the retrospective cross-sectional study identified patients who had virtual visits for isotretinoin management between March 25 and May 29, 2020, – the period during which all such visits were conducted virtually in keeping with hospital recommendations to minimize the spread of COVID-19.
The investigators, from the department of dermatology and the department of civil and environmental engineering at West Virginia University, Morgantown, then counted the number of virtual visits that occurred during this period and through Dec. 1, 2020, (175 virtual visits), calculated the distance patients would have traveled round-trip had these visits been in-person, and converted miles saved into the environmental impact using U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and Federal Highway Administration data and relevant EPA standards.
Most patients had elected to continue virtual visits after May 29, the point at which patients were given the option to return to the WVUH clinic. (Patients who initiated treatment during the 2-month identification period were not included.)
The investigators determined that virtual management of isotretinoin saved a median of 37.8 miles per visit during the study period of March 25 to Dec. 1, and estimated that the virtual visits reduced total travel by 14,450 miles. For the analysis, patients were assumed to use light-duty vehicles.
In addition to calculating the reduction in emissions during the study period (5,137 kg of CO2equivalents) they used patient census data from 2019 to 2020 and data from the study period to project the mileage – and the associated emissions – that would be saved annually if all in-person visits for isotretinoin management occurred virtually.
Their calculation for a projected emissions reduction with 1 year of all-virtual isotretinoin management was 49,400 kg of greenhouse gas emissions in CO2equivalents. This is the emission load released when 24,690 kg of coal are burned or 6.3 million smartphones are charged, the researchers wrote.
“Considering that more than 1,000,000 prescriptions of isotretinoin are authorized annually in the United States, the environmental impact could be magnified if virtual delivery of isotretinoin care is adopted on a national scale,” they commented.“Given the serious consequences of global climate change, analysis of the environmental impact of all fields of medicine, including dermatology, is warranted,” they added.
The reduced greenhouse gas emissions are “definitely [being taken] into consideration for future decisions about virtual visits” in the department of dermatology, said Zachary Zinn, MD, residency director and associate professor in the department of dermatology at West Virginia University, Morgantown, who is the senior author of the study. “The main benefit of virtual care in my opinion,” he said in an interview, “is the potential to reduce our carbon footprint.”
Justin Lee, MD, an intern at WVU and the study’s first author, said that the research team was motivated to think about how they “could reduce the negative environmental impact of practicing dermatology” after they read a paper about the environmental impact of endoscopy, written by a gastroenterologist.
In the study, no pregnancies occurred and monthly tests were performed, but “formal assessment of pregnancy risk with virtual isotretinoin management would be warranted,” Dr. Lee and coauthors wrote, noting too that, while no differences were seen with respect to isotretinoin side effects, these were not formally analyzed.
Dr. Zinn said that he and colleagues at WVUH are currently conducting clinical trials to assess the quality and efficacy of virtual care for patients with acne, atopic dermatitis, and psoriasis. Delivering care virtually “will be easier to do if there are data supporting [its] quality and efficacy,” he said. Rosacea is another condition that may be amendable to virtual care, he noted.
Meanwhile, he said, isotretinoin management is “well suited” for virtual visits. When initiating isotretinoin treatment, Dr. Zinn now “proactively inquires” if patients would like to pursue their follow-up visits virtually. “I’ll note that it will save the time and decrease the burden of travel, including the financial cost as well as the environmental cost of travel,” he said, estimating that about half of their management visits are currently virtual.
Asked about the study, Misha Rosenbach, MD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said the reduced carbon footprint calculated by the researchers and its downstream health benefits “should be taken into consideration by [dermatology] departments, insurers and policymakers” when making decisions about teledermatology.
While environmental impact is “not something I think most institutions are considering for virtual versus in-person care, they should be. And some are,” said Dr. Rosenbach, a founder and cochair of the American Academy of Dermatology Expert Resource Group for Climate Change and Environmental Issues.
Limitations of the study include the generalizability of the results. The impact of virtual isotretinoin management “may be less in predominantly urban areas” than it is in predominately rural West Virginia, the study authors note. And in the case of West Virginia, travel to a local laboratory and pharmacy offsets some of the environmental benefits for the virtual care, they noted. Such travel wasn’t accounted for in the study, but it was found to be a fraction of travel to the WVU hospital clinic. (Patients traveled a median of 5.8 miles to a lab 2.4 times from March 25 to Dec. 1, 2020.)
Dr. Lee will start his dermatology residency at WVU next year. The study was funded by a grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation. The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest, according to Dr. Lee.
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
ARBs equal ACE inhibitors for hypertension, and better tolerated
In the largest comparison of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) and ACE inhibitors to date, a study of nearly 2.3 million patients starting the drugs as monotherapy shows no significant differences between the two in the long-term prevention of hypertension-related cardiovascular events.
However, side effects were notably lower with ARBs.
“This is a very large, well-executed observational study that confirms that ARBs appear to have fewer side effects than ACE inhibitors, and no unexpected ARB side effects were detected,” senior author George Hripcsak, MD, professor and chair of biomedical informatics at Columbia University, New York, told this news organization.
“Despite being equally guideline-recommended first-line therapies for hypertension, these results support preferentially starting ARBs rather than ACE inhibitors when initiating treatment for hypertension for physicians and patients considering renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibition,” the authors added in the study, published online July 26, 2021, in the journal Hypertension.
They noted that both drug classes have been on the market a long time, with proven efficacy in hypertension and “a wide availability of inexpensive generic forms.”
They also stressed that their findings only apply to patients with hypertension for whom a RAS inhibitor would be the best choice of therapy.
Commenting on the research, George Bakris, MD, of the American Heart Association’s Comprehensive Hypertension Center at the University of Chicago, said the findings were consistent with his experience in prescribing as well as researching the two drug classes.
“I have been in practice for over 30 years and studied both classes, including head-to-head prospective trials to assess blood pressure, and found in many cases better blood pressure lowering by some ARBs and always better tolerability,” he told this news organization. “I think this study confirms and extends my thoughts between the two classes of blood pressure–lowering agents.”
Head-to-head comparisons of ACE inhibitors and ARBs limited to date
ACE inhibitors and ARBs each have extensive evidence supporting their roles as first-line medications in the treatment of hypertension, and each have the strongest recommendations in international guidelines.
However, ACE inhibitors are prescribed more commonly than ARBs as the first-line drug for lowering blood pressure, and head-to-head comparisons of the two are limited, with conflicting results.
For the study, Dr. Hripcsak and colleagues evaluated data on almost 3 million patients starting monotherapy with an ACE inhibitor or ARB for the first time between 1996 and 2018 in the United States, Germany, and South Korea, who had no history of heart disease or stroke.
They identified a total of 2,297,881 patients initiating ACE inhibitors and 673,938 starting ARBs. Among new users of ACE inhibitors, most received lisinopril (80%), followed by ramipril and enalapril, while most patients prescribed ARBs received losartan (45%), followed by valsartan and olmesartan.
With follow-up times ranging from about 4 months to more than 18 months, the data show no statistically significant differences between ACE inhibitors versus ARBs in the primary outcomes of acute myocardial infarction (hazard ratio, 1.11), heart failure (HR, 1.03), stroke (HR, 1.07), or composite cardiovascular events (HR, 1.06).
For secondary and safety outcomes, including an analysis of 51 possible side effects, ACE inhibitors, compared with ARBs, were associated with a significantly higher risk of angioedema (HR, 3.31; P < .01), cough (HR, 1.32; P < .01), acute pancreatitis (HR, 1.32; P = .02), gastrointestinal bleeding (HR, 1.18; P = .04), and abnormal weight loss (HR, 1.18; P = .04).
While the link between ACE inhibitors and pancreatitis has been previously reported, the association with GI bleeding may be a novel finding, with no prior studies comparing those effects in the two drug classes, the authors noted.
Despite most patients taking just a couple of drugs in either class, Dr. Hripcsak said, “we don’t expect that other drugs from those classes will have fewer differences. It is possible, of course, but that is not our expectation.”
Results only applicable to those starting therapy with RAS inhibitors
First author RuiJun Chen, MD, added that, importantly, the results may not apply to patients switching therapies or adding on therapy, “such as for the patient whose hypertension is not effectively controlled with one drug and requires the addition of a second medication,” he said in an interview.
“Also, the suggestion of preferentially prescribing ARBs only applies to those patients and providers intending to control blood pressure through RAS inhibition,” said Dr. Chen, an assistant professor in translational data science and informatics at Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, Pa., who was a National Library of Medicine postdoctoral fellow at Columbia University at the time of the study.
Hence, he stressed the results do not extend to other classes of recommended first-line blood pressure medications.
“Essentially, since this is an ACE inhibitor versus ARB study, we would not claim that ARBs are preferred over all other types of hypertension medications which were not studied here,” the researchers emphasize.
In addition to ARBs and ACE inhibitors, other medications recommended by the AHA/American College of Cardiology in the 2017 “Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults” for the primary treatment of hypertension include thiazide diuretics and calcium channel blockers.
The study received support from the National Library of Medicine and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health; the National Science Foundation; and the Ministries of Health & Welfare and of Trade, Industry & Energy of the Republic of Korea. Dr. Hripcsak reported receiving grants from the National Library of Medicine during the study and grants from Janssen Research outside the submitted work. Dr. Bakris reported being a consultant for Merck, KBP Biosciences, and Ionis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the largest comparison of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) and ACE inhibitors to date, a study of nearly 2.3 million patients starting the drugs as monotherapy shows no significant differences between the two in the long-term prevention of hypertension-related cardiovascular events.
However, side effects were notably lower with ARBs.
“This is a very large, well-executed observational study that confirms that ARBs appear to have fewer side effects than ACE inhibitors, and no unexpected ARB side effects were detected,” senior author George Hripcsak, MD, professor and chair of biomedical informatics at Columbia University, New York, told this news organization.
“Despite being equally guideline-recommended first-line therapies for hypertension, these results support preferentially starting ARBs rather than ACE inhibitors when initiating treatment for hypertension for physicians and patients considering renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibition,” the authors added in the study, published online July 26, 2021, in the journal Hypertension.
They noted that both drug classes have been on the market a long time, with proven efficacy in hypertension and “a wide availability of inexpensive generic forms.”
They also stressed that their findings only apply to patients with hypertension for whom a RAS inhibitor would be the best choice of therapy.
Commenting on the research, George Bakris, MD, of the American Heart Association’s Comprehensive Hypertension Center at the University of Chicago, said the findings were consistent with his experience in prescribing as well as researching the two drug classes.
“I have been in practice for over 30 years and studied both classes, including head-to-head prospective trials to assess blood pressure, and found in many cases better blood pressure lowering by some ARBs and always better tolerability,” he told this news organization. “I think this study confirms and extends my thoughts between the two classes of blood pressure–lowering agents.”
Head-to-head comparisons of ACE inhibitors and ARBs limited to date
ACE inhibitors and ARBs each have extensive evidence supporting their roles as first-line medications in the treatment of hypertension, and each have the strongest recommendations in international guidelines.
However, ACE inhibitors are prescribed more commonly than ARBs as the first-line drug for lowering blood pressure, and head-to-head comparisons of the two are limited, with conflicting results.
For the study, Dr. Hripcsak and colleagues evaluated data on almost 3 million patients starting monotherapy with an ACE inhibitor or ARB for the first time between 1996 and 2018 in the United States, Germany, and South Korea, who had no history of heart disease or stroke.
They identified a total of 2,297,881 patients initiating ACE inhibitors and 673,938 starting ARBs. Among new users of ACE inhibitors, most received lisinopril (80%), followed by ramipril and enalapril, while most patients prescribed ARBs received losartan (45%), followed by valsartan and olmesartan.
With follow-up times ranging from about 4 months to more than 18 months, the data show no statistically significant differences between ACE inhibitors versus ARBs in the primary outcomes of acute myocardial infarction (hazard ratio, 1.11), heart failure (HR, 1.03), stroke (HR, 1.07), or composite cardiovascular events (HR, 1.06).
For secondary and safety outcomes, including an analysis of 51 possible side effects, ACE inhibitors, compared with ARBs, were associated with a significantly higher risk of angioedema (HR, 3.31; P < .01), cough (HR, 1.32; P < .01), acute pancreatitis (HR, 1.32; P = .02), gastrointestinal bleeding (HR, 1.18; P = .04), and abnormal weight loss (HR, 1.18; P = .04).
While the link between ACE inhibitors and pancreatitis has been previously reported, the association with GI bleeding may be a novel finding, with no prior studies comparing those effects in the two drug classes, the authors noted.
Despite most patients taking just a couple of drugs in either class, Dr. Hripcsak said, “we don’t expect that other drugs from those classes will have fewer differences. It is possible, of course, but that is not our expectation.”
Results only applicable to those starting therapy with RAS inhibitors
First author RuiJun Chen, MD, added that, importantly, the results may not apply to patients switching therapies or adding on therapy, “such as for the patient whose hypertension is not effectively controlled with one drug and requires the addition of a second medication,” he said in an interview.
“Also, the suggestion of preferentially prescribing ARBs only applies to those patients and providers intending to control blood pressure through RAS inhibition,” said Dr. Chen, an assistant professor in translational data science and informatics at Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, Pa., who was a National Library of Medicine postdoctoral fellow at Columbia University at the time of the study.
Hence, he stressed the results do not extend to other classes of recommended first-line blood pressure medications.
“Essentially, since this is an ACE inhibitor versus ARB study, we would not claim that ARBs are preferred over all other types of hypertension medications which were not studied here,” the researchers emphasize.
In addition to ARBs and ACE inhibitors, other medications recommended by the AHA/American College of Cardiology in the 2017 “Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults” for the primary treatment of hypertension include thiazide diuretics and calcium channel blockers.
The study received support from the National Library of Medicine and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health; the National Science Foundation; and the Ministries of Health & Welfare and of Trade, Industry & Energy of the Republic of Korea. Dr. Hripcsak reported receiving grants from the National Library of Medicine during the study and grants from Janssen Research outside the submitted work. Dr. Bakris reported being a consultant for Merck, KBP Biosciences, and Ionis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the largest comparison of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) and ACE inhibitors to date, a study of nearly 2.3 million patients starting the drugs as monotherapy shows no significant differences between the two in the long-term prevention of hypertension-related cardiovascular events.
However, side effects were notably lower with ARBs.
“This is a very large, well-executed observational study that confirms that ARBs appear to have fewer side effects than ACE inhibitors, and no unexpected ARB side effects were detected,” senior author George Hripcsak, MD, professor and chair of biomedical informatics at Columbia University, New York, told this news organization.
“Despite being equally guideline-recommended first-line therapies for hypertension, these results support preferentially starting ARBs rather than ACE inhibitors when initiating treatment for hypertension for physicians and patients considering renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibition,” the authors added in the study, published online July 26, 2021, in the journal Hypertension.
They noted that both drug classes have been on the market a long time, with proven efficacy in hypertension and “a wide availability of inexpensive generic forms.”
They also stressed that their findings only apply to patients with hypertension for whom a RAS inhibitor would be the best choice of therapy.
Commenting on the research, George Bakris, MD, of the American Heart Association’s Comprehensive Hypertension Center at the University of Chicago, said the findings were consistent with his experience in prescribing as well as researching the two drug classes.
“I have been in practice for over 30 years and studied both classes, including head-to-head prospective trials to assess blood pressure, and found in many cases better blood pressure lowering by some ARBs and always better tolerability,” he told this news organization. “I think this study confirms and extends my thoughts between the two classes of blood pressure–lowering agents.”
Head-to-head comparisons of ACE inhibitors and ARBs limited to date
ACE inhibitors and ARBs each have extensive evidence supporting their roles as first-line medications in the treatment of hypertension, and each have the strongest recommendations in international guidelines.
However, ACE inhibitors are prescribed more commonly than ARBs as the first-line drug for lowering blood pressure, and head-to-head comparisons of the two are limited, with conflicting results.
For the study, Dr. Hripcsak and colleagues evaluated data on almost 3 million patients starting monotherapy with an ACE inhibitor or ARB for the first time between 1996 and 2018 in the United States, Germany, and South Korea, who had no history of heart disease or stroke.
They identified a total of 2,297,881 patients initiating ACE inhibitors and 673,938 starting ARBs. Among new users of ACE inhibitors, most received lisinopril (80%), followed by ramipril and enalapril, while most patients prescribed ARBs received losartan (45%), followed by valsartan and olmesartan.
With follow-up times ranging from about 4 months to more than 18 months, the data show no statistically significant differences between ACE inhibitors versus ARBs in the primary outcomes of acute myocardial infarction (hazard ratio, 1.11), heart failure (HR, 1.03), stroke (HR, 1.07), or composite cardiovascular events (HR, 1.06).
For secondary and safety outcomes, including an analysis of 51 possible side effects, ACE inhibitors, compared with ARBs, were associated with a significantly higher risk of angioedema (HR, 3.31; P < .01), cough (HR, 1.32; P < .01), acute pancreatitis (HR, 1.32; P = .02), gastrointestinal bleeding (HR, 1.18; P = .04), and abnormal weight loss (HR, 1.18; P = .04).
While the link between ACE inhibitors and pancreatitis has been previously reported, the association with GI bleeding may be a novel finding, with no prior studies comparing those effects in the two drug classes, the authors noted.
Despite most patients taking just a couple of drugs in either class, Dr. Hripcsak said, “we don’t expect that other drugs from those classes will have fewer differences. It is possible, of course, but that is not our expectation.”
Results only applicable to those starting therapy with RAS inhibitors
First author RuiJun Chen, MD, added that, importantly, the results may not apply to patients switching therapies or adding on therapy, “such as for the patient whose hypertension is not effectively controlled with one drug and requires the addition of a second medication,” he said in an interview.
“Also, the suggestion of preferentially prescribing ARBs only applies to those patients and providers intending to control blood pressure through RAS inhibition,” said Dr. Chen, an assistant professor in translational data science and informatics at Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, Pa., who was a National Library of Medicine postdoctoral fellow at Columbia University at the time of the study.
Hence, he stressed the results do not extend to other classes of recommended first-line blood pressure medications.
“Essentially, since this is an ACE inhibitor versus ARB study, we would not claim that ARBs are preferred over all other types of hypertension medications which were not studied here,” the researchers emphasize.
In addition to ARBs and ACE inhibitors, other medications recommended by the AHA/American College of Cardiology in the 2017 “Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults” for the primary treatment of hypertension include thiazide diuretics and calcium channel blockers.
The study received support from the National Library of Medicine and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health; the National Science Foundation; and the Ministries of Health & Welfare and of Trade, Industry & Energy of the Republic of Korea. Dr. Hripcsak reported receiving grants from the National Library of Medicine during the study and grants from Janssen Research outside the submitted work. Dr. Bakris reported being a consultant for Merck, KBP Biosciences, and Ionis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More on GRADE: Cognitive deficits linked to CV risk factors in T2D
In type 2 diabetes (T2D), a greater degree of hyperlipidemia and hypertension, although not hyperglycemia, was associated with measurable cognitive impairment even among patients with only a 4-year mean disease duration, according to a substudy of the GRADE trial.
The association of these cardiovascular (CV) risk factors with impairments in cognition has been reported before, but the findings are notable because the mean duration of T2D was short in a relatively healthy study population, reported a multicenter team of investigators.
The relative impairments in cognitive function “may not be clinically significant given the very small size of the differences,” conceded the authors of this study, led by José A. Luchsinger, MD, but they are consistent with previous reports of the same association in older patients with a longer duration of diabetes. In other words, the data suggest the risk of cognitive loss from CV risk factors in T2D patients begins early.
“A potential explanation for the small differences, compared with those previously reported, is that the GRADE cohort is relatively young with a healthier cardiovascular profile and shorter diabetes duration compared with other studies,” reported the investigators, whose results were published online July 20, 2021, in Diabetes Care.
99% complete cognitive assessments
In the GRADE (Glycemia Reduction Approaches in Diabetes: Comparative Effectiveness) trial, 5,018 (99.4%) of the 5,047 enrolled patients completed a battery of cognitive assessments at baseline. Patients were excluded from this study if they had any major CV event in the previous year, if they had T2D for more than 10 years, if they had significant renal impairment, and if they had any history of stage 3 or greater heart failure. Their mean age was 56.7 years.
By cross-sectional analysis, cognitive evaluations, including the Digit Symbol Substitution Test (DSST) and the Spanish English Verbal Learning Test, were evaluated in relation to baseline LDL cholesterol levels, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, hemoglobin A1c, and statin use.
Unlike previous studies in T2D patients, no relationship was observed between cognitive function and A1c level at baseline. However, LDL cholesterol greater than 100 mg/dL was associated with cognitive impairment as measured with the DSST after adjustment for age, sex, education, and general health. The mean difference relative to LDL cholesterol below 70 mg/dL was only 1.8 points, but this was highly significant (P < .001).
Similarly, significant but modest cognitive impairment on DSST score after adjustment for variables were seen for those with a systolic BP between 120 mg and <140 mg relative to either <120 mm Hg or at least 140 mm Hg (P = .014). The same was seen for diastolic BPs of 80 to <90 when compared with either <80 mm Hg or to 90 mm Hg or higher (P = .01).
For those taking statins versus no statins at baseline, there was a 1.4-point mean advantage in DSST score after adjusting for variables (P < .001).
Modest cognitive impairments recorded
Again, the absolute mean differences in the DSST cognitive scores, despite their statistical significance, were modest, according to the authors. In general, the mean difference was rarely greater than 2.0 points and often 1.0 point or less. The authors acknowledged that these changes are of an uncertain clinical significance, but they considered the findings consistent with the association of CV risk factors with cognitive deficits in older T2DM patients or T2DM patients with longer duration of disease.
One difference between this GRADE substudy and previous studies was the lack of an association between cognitive impairment and hyperglycemia. In the ACCORD trial for example, increased levels of blood glycemia were associated with lower performance on numerous tests of cognitive function.
In the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT), poorer glycemic control was related to poorer performance on tests of executive function.
Both of those studies also linked hypertension and hyperlipidemia with cognitive deficits, but given that patients in ACCORD had T2DM of substantially longer duration and those in DCCT were older, “it seems reasonable to speculate that, in patients with diabetes duration of less than 10 years, the association between hyperglycemia and cognitive performance may not yet be evident,” the GRADE authors reported.
GRADE trial compares drugs in four classes
The GRADE trial was conducted to compare four classes of T2D therapies for long-term glycemic control as expressed by A1c control over time. The results of the trial, presented recently at the 2021 annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association, found that insulin glargine and the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist liraglutide performed best on the primary endpoint of maintaining A1c below 7.0%. Both performed significantly better than the sulfonylurea glimepiride and the dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitor sitagliptin.
This substudy of baseline cognitive function in the relatively large GRADE trial provided a unique opportunity to evaluate the impact of CV risk factors in patients with T2D of relatively short duration.
While the data support the adverse impact of inadequately controlled modifiable risk factors on cognitive function in T2D patients, David R. Matthews, DPhil, BM, BCh, emeritus professor of diabetes medicine at the University of Oxford (England), noted that the association was weak and advised a cautious interpretation.
“The effect size is very small indeed. The data are found as a subset of multiple testing,” he said in an interview. He suggested the associations might be the result of “data farming,” and he emphasized that the relationships between these risk factors and cognitive deficits are associations that do not imply causation.
Nevertheless, and despite their unclear clinical implications, Dr. Matthews said that these data might still have a message.
“It is another reminder that for many reasons we all need to be alert to the need for lowering hyperlipidemia and hypertension to normal levels – the benefits may not just be limited to cardiovascular outcome,” Dr. Matthews stated.
The lead author of the study, Dr. Luchsinger, also cautioned against overinterpreting the data.
While the data show that “lipid and blood pressure control within recommended guidelines are associated with marginally better cognitive function in patients with type 2 diabetes of less than 5 years duration on average,” he added that “the study is limited by its cross-sectional nature.”
He indicated that further analysis will be helpful in assessing the implications.
“Longitudinal analyses of the same group of individuals will be conducted next year,” noted Dr. Luchsinger, associate professor of medicine and epidemiology, Columbia University Medical Center, New York.
Dr. Luchsinger reported financial relationships with vTv therapeutics. Dr. Matthews reported no potential conflicts of interest.
In type 2 diabetes (T2D), a greater degree of hyperlipidemia and hypertension, although not hyperglycemia, was associated with measurable cognitive impairment even among patients with only a 4-year mean disease duration, according to a substudy of the GRADE trial.
The association of these cardiovascular (CV) risk factors with impairments in cognition has been reported before, but the findings are notable because the mean duration of T2D was short in a relatively healthy study population, reported a multicenter team of investigators.
The relative impairments in cognitive function “may not be clinically significant given the very small size of the differences,” conceded the authors of this study, led by José A. Luchsinger, MD, but they are consistent with previous reports of the same association in older patients with a longer duration of diabetes. In other words, the data suggest the risk of cognitive loss from CV risk factors in T2D patients begins early.
“A potential explanation for the small differences, compared with those previously reported, is that the GRADE cohort is relatively young with a healthier cardiovascular profile and shorter diabetes duration compared with other studies,” reported the investigators, whose results were published online July 20, 2021, in Diabetes Care.
99% complete cognitive assessments
In the GRADE (Glycemia Reduction Approaches in Diabetes: Comparative Effectiveness) trial, 5,018 (99.4%) of the 5,047 enrolled patients completed a battery of cognitive assessments at baseline. Patients were excluded from this study if they had any major CV event in the previous year, if they had T2D for more than 10 years, if they had significant renal impairment, and if they had any history of stage 3 or greater heart failure. Their mean age was 56.7 years.
By cross-sectional analysis, cognitive evaluations, including the Digit Symbol Substitution Test (DSST) and the Spanish English Verbal Learning Test, were evaluated in relation to baseline LDL cholesterol levels, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, hemoglobin A1c, and statin use.
Unlike previous studies in T2D patients, no relationship was observed between cognitive function and A1c level at baseline. However, LDL cholesterol greater than 100 mg/dL was associated with cognitive impairment as measured with the DSST after adjustment for age, sex, education, and general health. The mean difference relative to LDL cholesterol below 70 mg/dL was only 1.8 points, but this was highly significant (P < .001).
Similarly, significant but modest cognitive impairment on DSST score after adjustment for variables were seen for those with a systolic BP between 120 mg and <140 mg relative to either <120 mm Hg or at least 140 mm Hg (P = .014). The same was seen for diastolic BPs of 80 to <90 when compared with either <80 mm Hg or to 90 mm Hg or higher (P = .01).
For those taking statins versus no statins at baseline, there was a 1.4-point mean advantage in DSST score after adjusting for variables (P < .001).
Modest cognitive impairments recorded
Again, the absolute mean differences in the DSST cognitive scores, despite their statistical significance, were modest, according to the authors. In general, the mean difference was rarely greater than 2.0 points and often 1.0 point or less. The authors acknowledged that these changes are of an uncertain clinical significance, but they considered the findings consistent with the association of CV risk factors with cognitive deficits in older T2DM patients or T2DM patients with longer duration of disease.
One difference between this GRADE substudy and previous studies was the lack of an association between cognitive impairment and hyperglycemia. In the ACCORD trial for example, increased levels of blood glycemia were associated with lower performance on numerous tests of cognitive function.
In the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT), poorer glycemic control was related to poorer performance on tests of executive function.
Both of those studies also linked hypertension and hyperlipidemia with cognitive deficits, but given that patients in ACCORD had T2DM of substantially longer duration and those in DCCT were older, “it seems reasonable to speculate that, in patients with diabetes duration of less than 10 years, the association between hyperglycemia and cognitive performance may not yet be evident,” the GRADE authors reported.
GRADE trial compares drugs in four classes
The GRADE trial was conducted to compare four classes of T2D therapies for long-term glycemic control as expressed by A1c control over time. The results of the trial, presented recently at the 2021 annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association, found that insulin glargine and the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist liraglutide performed best on the primary endpoint of maintaining A1c below 7.0%. Both performed significantly better than the sulfonylurea glimepiride and the dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitor sitagliptin.
This substudy of baseline cognitive function in the relatively large GRADE trial provided a unique opportunity to evaluate the impact of CV risk factors in patients with T2D of relatively short duration.
While the data support the adverse impact of inadequately controlled modifiable risk factors on cognitive function in T2D patients, David R. Matthews, DPhil, BM, BCh, emeritus professor of diabetes medicine at the University of Oxford (England), noted that the association was weak and advised a cautious interpretation.
“The effect size is very small indeed. The data are found as a subset of multiple testing,” he said in an interview. He suggested the associations might be the result of “data farming,” and he emphasized that the relationships between these risk factors and cognitive deficits are associations that do not imply causation.
Nevertheless, and despite their unclear clinical implications, Dr. Matthews said that these data might still have a message.
“It is another reminder that for many reasons we all need to be alert to the need for lowering hyperlipidemia and hypertension to normal levels – the benefits may not just be limited to cardiovascular outcome,” Dr. Matthews stated.
The lead author of the study, Dr. Luchsinger, also cautioned against overinterpreting the data.
While the data show that “lipid and blood pressure control within recommended guidelines are associated with marginally better cognitive function in patients with type 2 diabetes of less than 5 years duration on average,” he added that “the study is limited by its cross-sectional nature.”
He indicated that further analysis will be helpful in assessing the implications.
“Longitudinal analyses of the same group of individuals will be conducted next year,” noted Dr. Luchsinger, associate professor of medicine and epidemiology, Columbia University Medical Center, New York.
Dr. Luchsinger reported financial relationships with vTv therapeutics. Dr. Matthews reported no potential conflicts of interest.
In type 2 diabetes (T2D), a greater degree of hyperlipidemia and hypertension, although not hyperglycemia, was associated with measurable cognitive impairment even among patients with only a 4-year mean disease duration, according to a substudy of the GRADE trial.
The association of these cardiovascular (CV) risk factors with impairments in cognition has been reported before, but the findings are notable because the mean duration of T2D was short in a relatively healthy study population, reported a multicenter team of investigators.
The relative impairments in cognitive function “may not be clinically significant given the very small size of the differences,” conceded the authors of this study, led by José A. Luchsinger, MD, but they are consistent with previous reports of the same association in older patients with a longer duration of diabetes. In other words, the data suggest the risk of cognitive loss from CV risk factors in T2D patients begins early.
“A potential explanation for the small differences, compared with those previously reported, is that the GRADE cohort is relatively young with a healthier cardiovascular profile and shorter diabetes duration compared with other studies,” reported the investigators, whose results were published online July 20, 2021, in Diabetes Care.
99% complete cognitive assessments
In the GRADE (Glycemia Reduction Approaches in Diabetes: Comparative Effectiveness) trial, 5,018 (99.4%) of the 5,047 enrolled patients completed a battery of cognitive assessments at baseline. Patients were excluded from this study if they had any major CV event in the previous year, if they had T2D for more than 10 years, if they had significant renal impairment, and if they had any history of stage 3 or greater heart failure. Their mean age was 56.7 years.
By cross-sectional analysis, cognitive evaluations, including the Digit Symbol Substitution Test (DSST) and the Spanish English Verbal Learning Test, were evaluated in relation to baseline LDL cholesterol levels, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, hemoglobin A1c, and statin use.
Unlike previous studies in T2D patients, no relationship was observed between cognitive function and A1c level at baseline. However, LDL cholesterol greater than 100 mg/dL was associated with cognitive impairment as measured with the DSST after adjustment for age, sex, education, and general health. The mean difference relative to LDL cholesterol below 70 mg/dL was only 1.8 points, but this was highly significant (P < .001).
Similarly, significant but modest cognitive impairment on DSST score after adjustment for variables were seen for those with a systolic BP between 120 mg and <140 mg relative to either <120 mm Hg or at least 140 mm Hg (P = .014). The same was seen for diastolic BPs of 80 to <90 when compared with either <80 mm Hg or to 90 mm Hg or higher (P = .01).
For those taking statins versus no statins at baseline, there was a 1.4-point mean advantage in DSST score after adjusting for variables (P < .001).
Modest cognitive impairments recorded
Again, the absolute mean differences in the DSST cognitive scores, despite their statistical significance, were modest, according to the authors. In general, the mean difference was rarely greater than 2.0 points and often 1.0 point or less. The authors acknowledged that these changes are of an uncertain clinical significance, but they considered the findings consistent with the association of CV risk factors with cognitive deficits in older T2DM patients or T2DM patients with longer duration of disease.
One difference between this GRADE substudy and previous studies was the lack of an association between cognitive impairment and hyperglycemia. In the ACCORD trial for example, increased levels of blood glycemia were associated with lower performance on numerous tests of cognitive function.
In the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT), poorer glycemic control was related to poorer performance on tests of executive function.
Both of those studies also linked hypertension and hyperlipidemia with cognitive deficits, but given that patients in ACCORD had T2DM of substantially longer duration and those in DCCT were older, “it seems reasonable to speculate that, in patients with diabetes duration of less than 10 years, the association between hyperglycemia and cognitive performance may not yet be evident,” the GRADE authors reported.
GRADE trial compares drugs in four classes
The GRADE trial was conducted to compare four classes of T2D therapies for long-term glycemic control as expressed by A1c control over time. The results of the trial, presented recently at the 2021 annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association, found that insulin glargine and the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist liraglutide performed best on the primary endpoint of maintaining A1c below 7.0%. Both performed significantly better than the sulfonylurea glimepiride and the dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitor sitagliptin.
This substudy of baseline cognitive function in the relatively large GRADE trial provided a unique opportunity to evaluate the impact of CV risk factors in patients with T2D of relatively short duration.
While the data support the adverse impact of inadequately controlled modifiable risk factors on cognitive function in T2D patients, David R. Matthews, DPhil, BM, BCh, emeritus professor of diabetes medicine at the University of Oxford (England), noted that the association was weak and advised a cautious interpretation.
“The effect size is very small indeed. The data are found as a subset of multiple testing,” he said in an interview. He suggested the associations might be the result of “data farming,” and he emphasized that the relationships between these risk factors and cognitive deficits are associations that do not imply causation.
Nevertheless, and despite their unclear clinical implications, Dr. Matthews said that these data might still have a message.
“It is another reminder that for many reasons we all need to be alert to the need for lowering hyperlipidemia and hypertension to normal levels – the benefits may not just be limited to cardiovascular outcome,” Dr. Matthews stated.
The lead author of the study, Dr. Luchsinger, also cautioned against overinterpreting the data.
While the data show that “lipid and blood pressure control within recommended guidelines are associated with marginally better cognitive function in patients with type 2 diabetes of less than 5 years duration on average,” he added that “the study is limited by its cross-sectional nature.”
He indicated that further analysis will be helpful in assessing the implications.
“Longitudinal analyses of the same group of individuals will be conducted next year,” noted Dr. Luchsinger, associate professor of medicine and epidemiology, Columbia University Medical Center, New York.
Dr. Luchsinger reported financial relationships with vTv therapeutics. Dr. Matthews reported no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM DIABETES CARE
When it comes to young women, regular check-ins support ongoing PrEP use
The secret, said Gonasagrie Nair, MBChB, faculty of medicine and health sciences at Stellenbosch University, Zimbabwe, is offering intensive wraparound services to support teenagers – a lesson that may be useful as adolescent and family medicine professionals in the United States begin to roll out HIV prevention in their clinics.
This is important in the United States because cisgender Black women make up 60% of all new HIV cases in the United States while accounting for just 14% of the overall U.S. population. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has found that only about 1% of Black Americans who could benefit from PrEP have access to it.
“Younger women and adolescent girls in particular face a number of cultural and social challenges that impact their ability to make decisions related to their own health,” said Dr. Nair, who presented the data at the International AIDS Society (IAS) Conference 2021. “The adherence support provided by this study empowered them to make choices and stick to these choices,” she said.
In total, 247 women and girls aged 16 to 21 who were without HIV were enrolled in the Reversing the Epidemic in Africa with Choices in HIV Prevention (REACH) trial in two sites in South Africa and one each in Uganda and Zimbabwe beginning in February 2019. One-third of the participants were minors; the average age was 18.2 years.
The women were good candidates for PrEP. More than 1 in 3 of the women started the study with a sexually transmitted infection (STI), the most prevalent of which was chlamydia. This is often a good marker for condomless sex. Of the participants, 89% had a primary sex partner; a quarter of those thought their partner was having sex with other people. Only 7% of participants reported being very worried about acquiring HIV. More than 1 in 3 (39%) weren’t worried about HIV at all. This conforms to previous data suggesting that those who could most benefit from PrEP often don’t perceive their own vulnerability.
In the study, the women were randomly assigned two groups. In one group, the participants used the dapivirine ring for 6 months; in the other, participants used oral PrEP for 6 months. The participants then swapped prevention methods and used the alternative method for 6 more months. After a year of trying both methods, the women will be asked to choose one of the two prevention method or to stop PrEP altogether. At the IAS conference, the researchers reported interim data from the first year of the study, before the girls had the opportunity to choose for themselves.
During that first year, girls received intensive adherence support, including daily or weekly text check-ins, phone check-ins, peer buddy support, additional onsite counseling visits, access to adherence support groups, participation in online support groups via apps such as WhatsApp, and in-person social events designed to empower young women and to teach them skills. Support included discussion of adherence, contraceptives, and STIs. In addition, when girls came in for study visits, staff provided feedback on how adherent the girls had been, as determined on the basis of residual levels of dapivirine in the rings or, with regard to oral pills, drug levels as determined with blood spots.
Girls were considered to have had high adherence if they were found to have oral PrEP concentrations equivalent to four or more doses per week or if residual levels of dapivirine in their rings were 0.1071 mg/d. Moderate adherence was the equivalent of one to three doses of oral PrEP a week or dapivirine levels between 0.0321 mg/d and 0.1071 mg/d.
In total, 95.6% of ring users showed some adherence to the ring. Of those, adherence was high for 50.2%; 49.8% used the ring perfectly. For oral PrEP, 98.5% showed some level of PrEP use; for 58.6%, lab results suggested adherence high enough to provide protection from HIV, and 22% took their pills at least six times a week. Between the two arms, 54.3% of all participants used the medication sufficiently to be protected from HIV.
One person acquired HIV during the study. Dr. Nair did not say which study arm that participant was in or how adherent that person has been to their prevention method.
That level of adherence is on par with studies in the United States, which have found 56% adherence to PrEP among adolescent and young men who have sex with men. But the level of adherence is far higher than has been found in other studies that tested oral PrEP among women who did not have a partner with HIV. In particular, the VOICE and FEM-PrEP trials were both stopped early for lack of adherence. In those placebo-controlled oral-PrEP trials, fewer than 25% of participants used the oral prevention pills. Although adherence to the vaginal ring was estimated to be 61% for women older than 25 in the ASPIRE trial, it was effectively zero among women aged 18 to 21 years. Adherence has been the “bugaboo of efficacy for PrEP in young women,” said Judith Auerbach, PhD, independent science and policy consultant and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco. But health care professionals have a long way to go to support young people in general in using PrEP.
“Yes, this shows improvement compared to previous studies,” Dr. Auerbach told this news organization. “But is it sufficient to have an epidemiological impact at the population level?”
Medical Advocacy and Outreach (MAO) is an HIV clinic and services program in Montgomery, Alabama, that offers a clinic specifically for some of their 144 clients to receive oral PrEP. In addition to in-person testing, MAO offers home HIV testing and lab work and televisits to support the college students they serve in taking PrEP whether they’re at school or at home on break. Currently, MAO provides a series of support groups and other social support programs for their clients living with HIV, but there are none for those receiving PrEP. The organization is in the process of hiring a social worker for the PrEP side of the clinic.
Until that person is on board, “I’m their support system in an unofficial capacity,” Shericka Williams, MPH, told this news organization. She runs education programs at MAO and handles all the phone calls from PrEP clients. “My title changes a lot, but the one I like to go with most often is the PrEP navigator,” she said.
She said she was intrigued by the dapivirine ring and oral PrEP data but said that currently, the women they serve are still learning that PrEP is for them, too. The women report that all the ads and all the information they receive is aimed at gay or bisexual men or transgender women. It takes a while for them to recognize that they could benefit, so a lot of the work that Ms. Williams does is focused on explaining the benefit of PrEP.
In MAO, the number of women receiving PrEP fluctuates more than for men. Mostly, women start PrEP because of they are in a relationship with someone who receives HIV care from MAO’s other wing – women who potentially would experience less vulnerability to HIV if their partners had undetectable viral loads. The other reason women take it is because they suspect that their partner is cheating or because they are in abusive relationships in which they want their partner to use a condom but the partner won’t. As in the PrEP trials, they often see women discontinue PrEP when they leave those relationships. In part, her job is to educate women regarding all the ways PrEP could serve them.
“Most of the time, they’re just no longer in that relationship, and they’re just taking some time for themselves,” she said in an interview. “We definitely try to bring up other reasons to stay on PrEP, but we don’t want to seem like we’re bullying someone to stay on it.”
Dr. Nair, Dr. Auerbach, and Ms. Williams report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The secret, said Gonasagrie Nair, MBChB, faculty of medicine and health sciences at Stellenbosch University, Zimbabwe, is offering intensive wraparound services to support teenagers – a lesson that may be useful as adolescent and family medicine professionals in the United States begin to roll out HIV prevention in their clinics.
This is important in the United States because cisgender Black women make up 60% of all new HIV cases in the United States while accounting for just 14% of the overall U.S. population. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has found that only about 1% of Black Americans who could benefit from PrEP have access to it.
“Younger women and adolescent girls in particular face a number of cultural and social challenges that impact their ability to make decisions related to their own health,” said Dr. Nair, who presented the data at the International AIDS Society (IAS) Conference 2021. “The adherence support provided by this study empowered them to make choices and stick to these choices,” she said.
In total, 247 women and girls aged 16 to 21 who were without HIV were enrolled in the Reversing the Epidemic in Africa with Choices in HIV Prevention (REACH) trial in two sites in South Africa and one each in Uganda and Zimbabwe beginning in February 2019. One-third of the participants were minors; the average age was 18.2 years.
The women were good candidates for PrEP. More than 1 in 3 of the women started the study with a sexually transmitted infection (STI), the most prevalent of which was chlamydia. This is often a good marker for condomless sex. Of the participants, 89% had a primary sex partner; a quarter of those thought their partner was having sex with other people. Only 7% of participants reported being very worried about acquiring HIV. More than 1 in 3 (39%) weren’t worried about HIV at all. This conforms to previous data suggesting that those who could most benefit from PrEP often don’t perceive their own vulnerability.
In the study, the women were randomly assigned two groups. In one group, the participants used the dapivirine ring for 6 months; in the other, participants used oral PrEP for 6 months. The participants then swapped prevention methods and used the alternative method for 6 more months. After a year of trying both methods, the women will be asked to choose one of the two prevention method or to stop PrEP altogether. At the IAS conference, the researchers reported interim data from the first year of the study, before the girls had the opportunity to choose for themselves.
During that first year, girls received intensive adherence support, including daily or weekly text check-ins, phone check-ins, peer buddy support, additional onsite counseling visits, access to adherence support groups, participation in online support groups via apps such as WhatsApp, and in-person social events designed to empower young women and to teach them skills. Support included discussion of adherence, contraceptives, and STIs. In addition, when girls came in for study visits, staff provided feedback on how adherent the girls had been, as determined on the basis of residual levels of dapivirine in the rings or, with regard to oral pills, drug levels as determined with blood spots.
Girls were considered to have had high adherence if they were found to have oral PrEP concentrations equivalent to four or more doses per week or if residual levels of dapivirine in their rings were 0.1071 mg/d. Moderate adherence was the equivalent of one to three doses of oral PrEP a week or dapivirine levels between 0.0321 mg/d and 0.1071 mg/d.
In total, 95.6% of ring users showed some adherence to the ring. Of those, adherence was high for 50.2%; 49.8% used the ring perfectly. For oral PrEP, 98.5% showed some level of PrEP use; for 58.6%, lab results suggested adherence high enough to provide protection from HIV, and 22% took their pills at least six times a week. Between the two arms, 54.3% of all participants used the medication sufficiently to be protected from HIV.
One person acquired HIV during the study. Dr. Nair did not say which study arm that participant was in or how adherent that person has been to their prevention method.
That level of adherence is on par with studies in the United States, which have found 56% adherence to PrEP among adolescent and young men who have sex with men. But the level of adherence is far higher than has been found in other studies that tested oral PrEP among women who did not have a partner with HIV. In particular, the VOICE and FEM-PrEP trials were both stopped early for lack of adherence. In those placebo-controlled oral-PrEP trials, fewer than 25% of participants used the oral prevention pills. Although adherence to the vaginal ring was estimated to be 61% for women older than 25 in the ASPIRE trial, it was effectively zero among women aged 18 to 21 years. Adherence has been the “bugaboo of efficacy for PrEP in young women,” said Judith Auerbach, PhD, independent science and policy consultant and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco. But health care professionals have a long way to go to support young people in general in using PrEP.
“Yes, this shows improvement compared to previous studies,” Dr. Auerbach told this news organization. “But is it sufficient to have an epidemiological impact at the population level?”
Medical Advocacy and Outreach (MAO) is an HIV clinic and services program in Montgomery, Alabama, that offers a clinic specifically for some of their 144 clients to receive oral PrEP. In addition to in-person testing, MAO offers home HIV testing and lab work and televisits to support the college students they serve in taking PrEP whether they’re at school or at home on break. Currently, MAO provides a series of support groups and other social support programs for their clients living with HIV, but there are none for those receiving PrEP. The organization is in the process of hiring a social worker for the PrEP side of the clinic.
Until that person is on board, “I’m their support system in an unofficial capacity,” Shericka Williams, MPH, told this news organization. She runs education programs at MAO and handles all the phone calls from PrEP clients. “My title changes a lot, but the one I like to go with most often is the PrEP navigator,” she said.
She said she was intrigued by the dapivirine ring and oral PrEP data but said that currently, the women they serve are still learning that PrEP is for them, too. The women report that all the ads and all the information they receive is aimed at gay or bisexual men or transgender women. It takes a while for them to recognize that they could benefit, so a lot of the work that Ms. Williams does is focused on explaining the benefit of PrEP.
In MAO, the number of women receiving PrEP fluctuates more than for men. Mostly, women start PrEP because of they are in a relationship with someone who receives HIV care from MAO’s other wing – women who potentially would experience less vulnerability to HIV if their partners had undetectable viral loads. The other reason women take it is because they suspect that their partner is cheating or because they are in abusive relationships in which they want their partner to use a condom but the partner won’t. As in the PrEP trials, they often see women discontinue PrEP when they leave those relationships. In part, her job is to educate women regarding all the ways PrEP could serve them.
“Most of the time, they’re just no longer in that relationship, and they’re just taking some time for themselves,” she said in an interview. “We definitely try to bring up other reasons to stay on PrEP, but we don’t want to seem like we’re bullying someone to stay on it.”
Dr. Nair, Dr. Auerbach, and Ms. Williams report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The secret, said Gonasagrie Nair, MBChB, faculty of medicine and health sciences at Stellenbosch University, Zimbabwe, is offering intensive wraparound services to support teenagers – a lesson that may be useful as adolescent and family medicine professionals in the United States begin to roll out HIV prevention in their clinics.
This is important in the United States because cisgender Black women make up 60% of all new HIV cases in the United States while accounting for just 14% of the overall U.S. population. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has found that only about 1% of Black Americans who could benefit from PrEP have access to it.
“Younger women and adolescent girls in particular face a number of cultural and social challenges that impact their ability to make decisions related to their own health,” said Dr. Nair, who presented the data at the International AIDS Society (IAS) Conference 2021. “The adherence support provided by this study empowered them to make choices and stick to these choices,” she said.
In total, 247 women and girls aged 16 to 21 who were without HIV were enrolled in the Reversing the Epidemic in Africa with Choices in HIV Prevention (REACH) trial in two sites in South Africa and one each in Uganda and Zimbabwe beginning in February 2019. One-third of the participants were minors; the average age was 18.2 years.
The women were good candidates for PrEP. More than 1 in 3 of the women started the study with a sexually transmitted infection (STI), the most prevalent of which was chlamydia. This is often a good marker for condomless sex. Of the participants, 89% had a primary sex partner; a quarter of those thought their partner was having sex with other people. Only 7% of participants reported being very worried about acquiring HIV. More than 1 in 3 (39%) weren’t worried about HIV at all. This conforms to previous data suggesting that those who could most benefit from PrEP often don’t perceive their own vulnerability.
In the study, the women were randomly assigned two groups. In one group, the participants used the dapivirine ring for 6 months; in the other, participants used oral PrEP for 6 months. The participants then swapped prevention methods and used the alternative method for 6 more months. After a year of trying both methods, the women will be asked to choose one of the two prevention method or to stop PrEP altogether. At the IAS conference, the researchers reported interim data from the first year of the study, before the girls had the opportunity to choose for themselves.
During that first year, girls received intensive adherence support, including daily or weekly text check-ins, phone check-ins, peer buddy support, additional onsite counseling visits, access to adherence support groups, participation in online support groups via apps such as WhatsApp, and in-person social events designed to empower young women and to teach them skills. Support included discussion of adherence, contraceptives, and STIs. In addition, when girls came in for study visits, staff provided feedback on how adherent the girls had been, as determined on the basis of residual levels of dapivirine in the rings or, with regard to oral pills, drug levels as determined with blood spots.
Girls were considered to have had high adherence if they were found to have oral PrEP concentrations equivalent to four or more doses per week or if residual levels of dapivirine in their rings were 0.1071 mg/d. Moderate adherence was the equivalent of one to three doses of oral PrEP a week or dapivirine levels between 0.0321 mg/d and 0.1071 mg/d.
In total, 95.6% of ring users showed some adherence to the ring. Of those, adherence was high for 50.2%; 49.8% used the ring perfectly. For oral PrEP, 98.5% showed some level of PrEP use; for 58.6%, lab results suggested adherence high enough to provide protection from HIV, and 22% took their pills at least six times a week. Between the two arms, 54.3% of all participants used the medication sufficiently to be protected from HIV.
One person acquired HIV during the study. Dr. Nair did not say which study arm that participant was in or how adherent that person has been to their prevention method.
That level of adherence is on par with studies in the United States, which have found 56% adherence to PrEP among adolescent and young men who have sex with men. But the level of adherence is far higher than has been found in other studies that tested oral PrEP among women who did not have a partner with HIV. In particular, the VOICE and FEM-PrEP trials were both stopped early for lack of adherence. In those placebo-controlled oral-PrEP trials, fewer than 25% of participants used the oral prevention pills. Although adherence to the vaginal ring was estimated to be 61% for women older than 25 in the ASPIRE trial, it was effectively zero among women aged 18 to 21 years. Adherence has been the “bugaboo of efficacy for PrEP in young women,” said Judith Auerbach, PhD, independent science and policy consultant and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco. But health care professionals have a long way to go to support young people in general in using PrEP.
“Yes, this shows improvement compared to previous studies,” Dr. Auerbach told this news organization. “But is it sufficient to have an epidemiological impact at the population level?”
Medical Advocacy and Outreach (MAO) is an HIV clinic and services program in Montgomery, Alabama, that offers a clinic specifically for some of their 144 clients to receive oral PrEP. In addition to in-person testing, MAO offers home HIV testing and lab work and televisits to support the college students they serve in taking PrEP whether they’re at school or at home on break. Currently, MAO provides a series of support groups and other social support programs for their clients living with HIV, but there are none for those receiving PrEP. The organization is in the process of hiring a social worker for the PrEP side of the clinic.
Until that person is on board, “I’m their support system in an unofficial capacity,” Shericka Williams, MPH, told this news organization. She runs education programs at MAO and handles all the phone calls from PrEP clients. “My title changes a lot, but the one I like to go with most often is the PrEP navigator,” she said.
She said she was intrigued by the dapivirine ring and oral PrEP data but said that currently, the women they serve are still learning that PrEP is for them, too. The women report that all the ads and all the information they receive is aimed at gay or bisexual men or transgender women. It takes a while for them to recognize that they could benefit, so a lot of the work that Ms. Williams does is focused on explaining the benefit of PrEP.
In MAO, the number of women receiving PrEP fluctuates more than for men. Mostly, women start PrEP because of they are in a relationship with someone who receives HIV care from MAO’s other wing – women who potentially would experience less vulnerability to HIV if their partners had undetectable viral loads. The other reason women take it is because they suspect that their partner is cheating or because they are in abusive relationships in which they want their partner to use a condom but the partner won’t. As in the PrEP trials, they often see women discontinue PrEP when they leave those relationships. In part, her job is to educate women regarding all the ways PrEP could serve them.
“Most of the time, they’re just no longer in that relationship, and they’re just taking some time for themselves,” she said in an interview. “We definitely try to bring up other reasons to stay on PrEP, but we don’t want to seem like we’re bullying someone to stay on it.”
Dr. Nair, Dr. Auerbach, and Ms. Williams report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vaccine breakthrough cases rising with Delta: Here’s what that means
At a recent town hall meeting in Cincinnati, President Joe Biden was asked about COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths rising in response to the Delta variant.
Touting the importance of vaccination, “We have a pandemic for those who haven’t gotten a vaccination. It’s that basic, that simple,” President Biden said at the event, which was broadcast live on CNN.
“If you’re vaccinated, you’re not going to be hospitalized, not going to the ICU unit, and not going to die,” he said, adding “you’re not going to get COVID if you have these vaccinations.”
Unfortunately, it’s not so simple. Fully vaccinated people continue to be well protected against severe disease and death, even with Delta, Because of that, many experts continue to advise caution, even if fully vaccinated.
“I was disappointed,” Leana Wen, MD, MSc, an emergency physician and visiting professor of health policy and management at George Washington University’s Milken School of Public Health in Washington, told CNN in response to the president’s statement.
“I actually thought he was answering questions as if it were a month ago. He’s not really meeting the realities of what’s happening on the ground,” she said. “I think he may have led people astray.”
Vaccines still work
Recent cases support Dr. Wen’s claim. Fully vaccinated Olympic athletes, wedding guests, healthcare workers, and even White House staff have recently tested positive. So what gives?
The vast majority of these illnesses are mild, and public health officials say they are to be expected.
“The vaccines were designed to keep us out of the hospital and to keep us from dying. That was the whole purpose of the vaccine and they’re even more successful than we anticipated,” says William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University in Nashville.
As good as they are, these shots aren’t perfect. Their protection differs from person to person depending on age and underlying health. People with immune function that’s weakened because of age or a health condition can still become seriously ill, and, in very rare cases, die after vaccination.
When people are infected with Delta, they carry approximately 1,000 times more virus compared with previous versions of the virus, according to a recent study. All that virus can overwhelm even the strong protection from the vaccines.
“Three months ago, breakthroughs didn’t occur nearly at this rate because there was just so much less virus exposure in the community,” said Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis.
Breakthroughs by the numbers
In Los Angeles County, where 69% of residents over age 12 have been fully vaccinated, COVID-19 cases are rising, and so, too, are cases that break through the protection of the vaccine.
In June, fully vaccinated people accounted for 20%, or 1 in 5, COVID cases in the county, which is the most populous in the United States. The increase mirrors Delta’s rise. The proportion of breakthrough cases is up from 11% in May, 5% in April, and 2% in March, according to the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health.
In the United Kingdom, which is collecting the best information on infections caused by variants, the estimated effectiveness of the vaccines to prevent an illness that causes symptoms dropped by about 10 points against Delta compared with Alpha (or B.1.1.7).
After two doses, vaccines prevent symptomatic infection about 79% of the time against Delta, according to data compiled by Public Health England. They are still highly effective at preventing hospitalization, 96% after two doses.
Out of 229,218 COVID infections in the United Kingdom between February and July 19, 28,773 — or 12.5% — were in fully vaccinated people. Of those breakthrough infections, 1,101, or 3.8%, required a visit to an emergency room, according to Public Health England. Just 474, or 2.9%, of fully vaccinated people required hospital admission, and 229, or less than 1%, died.
Unanswered questions
One of the biggest questions about breakthrough cases is how often people who have it may pass the virus to others.
“We know the vaccine reduces the likelihood of carrying the virus and the amount of virus you would carry,” Dr. Wen told CNN. But we don’t yet know whether a vaccinated person with a breakthrough infection may still be contagious to others.
For that reason, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says that fully vaccinated people still need to be tested if they have symptoms and shouldn’t be out in public for at least 10 days after a positive test.
How should fully vaccinated people behave? That depends a lot on their underlying health and whether or not they have vulnerable people around them.
If you’re older or immunocompromised, Dr. Schaffner recommends what he calls the “belt-and-suspenders approach,” in other words, do everything you can to stay safe.
“Get vaccinated for sure, but since we can’t be absolutely certain that the vaccines are going to be optimally protective and you are particularly susceptible to serious disease, you would be well advised to adopt at least one and perhaps more of the other mitigation measures,” he said.
These include wearing a mask, social distancing, making sure your spaces are well ventilated, and not spending prolonged periods of time indoors in crowded places.
Taking young children to visit vaccinated, elderly grandparents demands extra caution, again, with Delta circulating, particularly as they go back to school and start mixing with other kids.
Dr. Schaffner recommends explaining the ground rules before the visit: Hugs around the waist. No kissing. Wearing a mask while indoors with them.
Other important unanswered questions are whether breakthrough infections can lead to prolonged symptoms, or “long covid.” Most experts think that’s less likely in vaccinated people.
And Dr. Osterholm said it will be important to see whether there’s anything unusual about the breakthrough cases happening in the community.
“I think some of us have been challenged by the number of clusters that we’ve seen,” he said. “I think that really needs to be examined more.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
At a recent town hall meeting in Cincinnati, President Joe Biden was asked about COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths rising in response to the Delta variant.
Touting the importance of vaccination, “We have a pandemic for those who haven’t gotten a vaccination. It’s that basic, that simple,” President Biden said at the event, which was broadcast live on CNN.
“If you’re vaccinated, you’re not going to be hospitalized, not going to the ICU unit, and not going to die,” he said, adding “you’re not going to get COVID if you have these vaccinations.”
Unfortunately, it’s not so simple. Fully vaccinated people continue to be well protected against severe disease and death, even with Delta, Because of that, many experts continue to advise caution, even if fully vaccinated.
“I was disappointed,” Leana Wen, MD, MSc, an emergency physician and visiting professor of health policy and management at George Washington University’s Milken School of Public Health in Washington, told CNN in response to the president’s statement.
“I actually thought he was answering questions as if it were a month ago. He’s not really meeting the realities of what’s happening on the ground,” she said. “I think he may have led people astray.”
Vaccines still work
Recent cases support Dr. Wen’s claim. Fully vaccinated Olympic athletes, wedding guests, healthcare workers, and even White House staff have recently tested positive. So what gives?
The vast majority of these illnesses are mild, and public health officials say they are to be expected.
“The vaccines were designed to keep us out of the hospital and to keep us from dying. That was the whole purpose of the vaccine and they’re even more successful than we anticipated,” says William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University in Nashville.
As good as they are, these shots aren’t perfect. Their protection differs from person to person depending on age and underlying health. People with immune function that’s weakened because of age or a health condition can still become seriously ill, and, in very rare cases, die after vaccination.
When people are infected with Delta, they carry approximately 1,000 times more virus compared with previous versions of the virus, according to a recent study. All that virus can overwhelm even the strong protection from the vaccines.
“Three months ago, breakthroughs didn’t occur nearly at this rate because there was just so much less virus exposure in the community,” said Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis.
Breakthroughs by the numbers
In Los Angeles County, where 69% of residents over age 12 have been fully vaccinated, COVID-19 cases are rising, and so, too, are cases that break through the protection of the vaccine.
In June, fully vaccinated people accounted for 20%, or 1 in 5, COVID cases in the county, which is the most populous in the United States. The increase mirrors Delta’s rise. The proportion of breakthrough cases is up from 11% in May, 5% in April, and 2% in March, according to the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health.
In the United Kingdom, which is collecting the best information on infections caused by variants, the estimated effectiveness of the vaccines to prevent an illness that causes symptoms dropped by about 10 points against Delta compared with Alpha (or B.1.1.7).
After two doses, vaccines prevent symptomatic infection about 79% of the time against Delta, according to data compiled by Public Health England. They are still highly effective at preventing hospitalization, 96% after two doses.
Out of 229,218 COVID infections in the United Kingdom between February and July 19, 28,773 — or 12.5% — were in fully vaccinated people. Of those breakthrough infections, 1,101, or 3.8%, required a visit to an emergency room, according to Public Health England. Just 474, or 2.9%, of fully vaccinated people required hospital admission, and 229, or less than 1%, died.
Unanswered questions
One of the biggest questions about breakthrough cases is how often people who have it may pass the virus to others.
“We know the vaccine reduces the likelihood of carrying the virus and the amount of virus you would carry,” Dr. Wen told CNN. But we don’t yet know whether a vaccinated person with a breakthrough infection may still be contagious to others.
For that reason, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says that fully vaccinated people still need to be tested if they have symptoms and shouldn’t be out in public for at least 10 days after a positive test.
How should fully vaccinated people behave? That depends a lot on their underlying health and whether or not they have vulnerable people around them.
If you’re older or immunocompromised, Dr. Schaffner recommends what he calls the “belt-and-suspenders approach,” in other words, do everything you can to stay safe.
“Get vaccinated for sure, but since we can’t be absolutely certain that the vaccines are going to be optimally protective and you are particularly susceptible to serious disease, you would be well advised to adopt at least one and perhaps more of the other mitigation measures,” he said.
These include wearing a mask, social distancing, making sure your spaces are well ventilated, and not spending prolonged periods of time indoors in crowded places.
Taking young children to visit vaccinated, elderly grandparents demands extra caution, again, with Delta circulating, particularly as they go back to school and start mixing with other kids.
Dr. Schaffner recommends explaining the ground rules before the visit: Hugs around the waist. No kissing. Wearing a mask while indoors with them.
Other important unanswered questions are whether breakthrough infections can lead to prolonged symptoms, or “long covid.” Most experts think that’s less likely in vaccinated people.
And Dr. Osterholm said it will be important to see whether there’s anything unusual about the breakthrough cases happening in the community.
“I think some of us have been challenged by the number of clusters that we’ve seen,” he said. “I think that really needs to be examined more.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
At a recent town hall meeting in Cincinnati, President Joe Biden was asked about COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths rising in response to the Delta variant.
Touting the importance of vaccination, “We have a pandemic for those who haven’t gotten a vaccination. It’s that basic, that simple,” President Biden said at the event, which was broadcast live on CNN.
“If you’re vaccinated, you’re not going to be hospitalized, not going to the ICU unit, and not going to die,” he said, adding “you’re not going to get COVID if you have these vaccinations.”
Unfortunately, it’s not so simple. Fully vaccinated people continue to be well protected against severe disease and death, even with Delta, Because of that, many experts continue to advise caution, even if fully vaccinated.
“I was disappointed,” Leana Wen, MD, MSc, an emergency physician and visiting professor of health policy and management at George Washington University’s Milken School of Public Health in Washington, told CNN in response to the president’s statement.
“I actually thought he was answering questions as if it were a month ago. He’s not really meeting the realities of what’s happening on the ground,” she said. “I think he may have led people astray.”
Vaccines still work
Recent cases support Dr. Wen’s claim. Fully vaccinated Olympic athletes, wedding guests, healthcare workers, and even White House staff have recently tested positive. So what gives?
The vast majority of these illnesses are mild, and public health officials say they are to be expected.
“The vaccines were designed to keep us out of the hospital and to keep us from dying. That was the whole purpose of the vaccine and they’re even more successful than we anticipated,” says William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease expert at Vanderbilt University in Nashville.
As good as they are, these shots aren’t perfect. Their protection differs from person to person depending on age and underlying health. People with immune function that’s weakened because of age or a health condition can still become seriously ill, and, in very rare cases, die after vaccination.
When people are infected with Delta, they carry approximately 1,000 times more virus compared with previous versions of the virus, according to a recent study. All that virus can overwhelm even the strong protection from the vaccines.
“Three months ago, breakthroughs didn’t occur nearly at this rate because there was just so much less virus exposure in the community,” said Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota in Minneapolis.
Breakthroughs by the numbers
In Los Angeles County, where 69% of residents over age 12 have been fully vaccinated, COVID-19 cases are rising, and so, too, are cases that break through the protection of the vaccine.
In June, fully vaccinated people accounted for 20%, or 1 in 5, COVID cases in the county, which is the most populous in the United States. The increase mirrors Delta’s rise. The proportion of breakthrough cases is up from 11% in May, 5% in April, and 2% in March, according to the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health.
In the United Kingdom, which is collecting the best information on infections caused by variants, the estimated effectiveness of the vaccines to prevent an illness that causes symptoms dropped by about 10 points against Delta compared with Alpha (or B.1.1.7).
After two doses, vaccines prevent symptomatic infection about 79% of the time against Delta, according to data compiled by Public Health England. They are still highly effective at preventing hospitalization, 96% after two doses.
Out of 229,218 COVID infections in the United Kingdom between February and July 19, 28,773 — or 12.5% — were in fully vaccinated people. Of those breakthrough infections, 1,101, or 3.8%, required a visit to an emergency room, according to Public Health England. Just 474, or 2.9%, of fully vaccinated people required hospital admission, and 229, or less than 1%, died.
Unanswered questions
One of the biggest questions about breakthrough cases is how often people who have it may pass the virus to others.
“We know the vaccine reduces the likelihood of carrying the virus and the amount of virus you would carry,” Dr. Wen told CNN. But we don’t yet know whether a vaccinated person with a breakthrough infection may still be contagious to others.
For that reason, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says that fully vaccinated people still need to be tested if they have symptoms and shouldn’t be out in public for at least 10 days after a positive test.
How should fully vaccinated people behave? That depends a lot on their underlying health and whether or not they have vulnerable people around them.
If you’re older or immunocompromised, Dr. Schaffner recommends what he calls the “belt-and-suspenders approach,” in other words, do everything you can to stay safe.
“Get vaccinated for sure, but since we can’t be absolutely certain that the vaccines are going to be optimally protective and you are particularly susceptible to serious disease, you would be well advised to adopt at least one and perhaps more of the other mitigation measures,” he said.
These include wearing a mask, social distancing, making sure your spaces are well ventilated, and not spending prolonged periods of time indoors in crowded places.
Taking young children to visit vaccinated, elderly grandparents demands extra caution, again, with Delta circulating, particularly as they go back to school and start mixing with other kids.
Dr. Schaffner recommends explaining the ground rules before the visit: Hugs around the waist. No kissing. Wearing a mask while indoors with them.
Other important unanswered questions are whether breakthrough infections can lead to prolonged symptoms, or “long covid.” Most experts think that’s less likely in vaccinated people.
And Dr. Osterholm said it will be important to see whether there’s anything unusual about the breakthrough cases happening in the community.
“I think some of us have been challenged by the number of clusters that we’ve seen,” he said. “I think that really needs to be examined more.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Diabetes duration linked to increasing heart failure risk
In a multivariable analysis the rate of incident heart failure increased steadily and significantly as diabetes duration increased. Among the 168 study subjects (2% of the total study group) who had diabetes for at least 15 years, the subsequent incidence of heart failure was nearly threefold higher than among the 4,802 subjects (49%) who never had diabetes or prediabetes, reported Justin B. Echouffo-Tcheugui, MD, PhD, and coauthors in an article published in JACC Heart Failure.
People with prediabetes (32% of the study population) had a significant but modest increased rate of incident heart failure that was 16% higher than in control subjects who never developed diabetes. People with diabetes for durations of 0-4.9 years, 5.0-9.9 years, or 10-14.9 years, had steadily increasing relative incident heart failure rates of 29%, 97%, and 210%, respectively, compared with controls, reported Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui, an endocrinologist at Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore.
Similar rates of HFrEF and HFpEF
Among all 1,841 people in the dataset with diabetes for any length of time each additional 5 years of the disorder linked with a significant, relative 17% increase in the rate of incident heart failure. Incidence of heart failure rose even more sharply with added duration among those with a hemoglobin A1c of 7% or greater, compared with those with better glycemic control. And the rate of incident heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) roughly matched the rate of incident heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
The study dataset included 9,734 adults enrolled into the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study, and during a median follow-up of 22.5 years they had nearly 2,000 episodes of either hospitalization or death secondary to incident heart failure. This included 617 (31%) events involving HFpEF, 495 events (25%) involving HFrEF, and 876 unclassified heart failure events.
The cohort averaged 63 years of age; 58% were women, 23% were Black, and 77% were White (the study design excluded people with other racial and ethnic backgrounds). The study design also excluded people with a history of heart failure or coronary artery disease, as well as those diagnosed with diabetes prior to age 18 resulting in a study group that presumably mostly had type 2 diabetes when diabetes was present. The report provided no data on the specific numbers of patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
“It’s not surprising that a longer duration of diabetes is associated with heart failure, but the etiology remains problematic,” commented Robert H. Eckel, MD, an endocrinologist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. “The impact of diabetes on incident heart failure is not well know, particularly duration of diabetes,” although disorders often found in patients with diabetes, such as hypertension and diabetic cardiomyopathy, likely have roles in causing heart failure, he said.
Diabetes duration may signal need for an SGLT2 inhibitor
“With emerging novel treatments like the SGLT2 [sodium-glucose cotransporter 2] inhibitors for preventing heart failure hospitalizations and deaths in patients with type 2 diabetes, this is a timely analysis,” Dr. Eckel said in an interview.
“There is no question that with increased duration of type 2 diabetes” the need for an agent from the SGLT2-inhibitor class increases. Although, because of the proven protection these drugs give against heart failure events and progression of chronic kidney disease, treatment with this drug class should start early in patients with type 2 diabetes, he added.
Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui and his coauthors agreed, citing two important clinical take-aways from their findings:
First, interventions that delay the onset of diabetes may potentially reduce incident heart failure; second, patients with diabetes might benefit from cardioprotective treatments such as SGLT2 inhibitors, the report said.
“Our observations suggest the potential prognostic relevance of diabetes duration in assessing heart failure,” the authors wrote. Integrating diabetes duration into heart failure risk estimation in people with diabetes “could help refine the selection of high-risk individuals who may derive the greatest absolute benefit from aggressive cardioprotective therapies such as SGLT2 inhibitors.”
The analysis also identified several other demographic and clinical factors that influenced the relative effect of diabetes duration. Longer duration was linked with higher rates of incident heart failure in women compared with men, in Blacks compared with Whites, in people younger than 65 compared with older people, in people with an A1c of 7% or higher, and in those with a body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or greater.
The ARIC study and the analyses run by Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui and his coauthors received no commercial funding. Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui and Dr. Eckel had no relevant disclosures.
In a multivariable analysis the rate of incident heart failure increased steadily and significantly as diabetes duration increased. Among the 168 study subjects (2% of the total study group) who had diabetes for at least 15 years, the subsequent incidence of heart failure was nearly threefold higher than among the 4,802 subjects (49%) who never had diabetes or prediabetes, reported Justin B. Echouffo-Tcheugui, MD, PhD, and coauthors in an article published in JACC Heart Failure.
People with prediabetes (32% of the study population) had a significant but modest increased rate of incident heart failure that was 16% higher than in control subjects who never developed diabetes. People with diabetes for durations of 0-4.9 years, 5.0-9.9 years, or 10-14.9 years, had steadily increasing relative incident heart failure rates of 29%, 97%, and 210%, respectively, compared with controls, reported Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui, an endocrinologist at Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore.
Similar rates of HFrEF and HFpEF
Among all 1,841 people in the dataset with diabetes for any length of time each additional 5 years of the disorder linked with a significant, relative 17% increase in the rate of incident heart failure. Incidence of heart failure rose even more sharply with added duration among those with a hemoglobin A1c of 7% or greater, compared with those with better glycemic control. And the rate of incident heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) roughly matched the rate of incident heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
The study dataset included 9,734 adults enrolled into the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study, and during a median follow-up of 22.5 years they had nearly 2,000 episodes of either hospitalization or death secondary to incident heart failure. This included 617 (31%) events involving HFpEF, 495 events (25%) involving HFrEF, and 876 unclassified heart failure events.
The cohort averaged 63 years of age; 58% were women, 23% were Black, and 77% were White (the study design excluded people with other racial and ethnic backgrounds). The study design also excluded people with a history of heart failure or coronary artery disease, as well as those diagnosed with diabetes prior to age 18 resulting in a study group that presumably mostly had type 2 diabetes when diabetes was present. The report provided no data on the specific numbers of patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
“It’s not surprising that a longer duration of diabetes is associated with heart failure, but the etiology remains problematic,” commented Robert H. Eckel, MD, an endocrinologist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. “The impact of diabetes on incident heart failure is not well know, particularly duration of diabetes,” although disorders often found in patients with diabetes, such as hypertension and diabetic cardiomyopathy, likely have roles in causing heart failure, he said.
Diabetes duration may signal need for an SGLT2 inhibitor
“With emerging novel treatments like the SGLT2 [sodium-glucose cotransporter 2] inhibitors for preventing heart failure hospitalizations and deaths in patients with type 2 diabetes, this is a timely analysis,” Dr. Eckel said in an interview.
“There is no question that with increased duration of type 2 diabetes” the need for an agent from the SGLT2-inhibitor class increases. Although, because of the proven protection these drugs give against heart failure events and progression of chronic kidney disease, treatment with this drug class should start early in patients with type 2 diabetes, he added.
Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui and his coauthors agreed, citing two important clinical take-aways from their findings:
First, interventions that delay the onset of diabetes may potentially reduce incident heart failure; second, patients with diabetes might benefit from cardioprotective treatments such as SGLT2 inhibitors, the report said.
“Our observations suggest the potential prognostic relevance of diabetes duration in assessing heart failure,” the authors wrote. Integrating diabetes duration into heart failure risk estimation in people with diabetes “could help refine the selection of high-risk individuals who may derive the greatest absolute benefit from aggressive cardioprotective therapies such as SGLT2 inhibitors.”
The analysis also identified several other demographic and clinical factors that influenced the relative effect of diabetes duration. Longer duration was linked with higher rates of incident heart failure in women compared with men, in Blacks compared with Whites, in people younger than 65 compared with older people, in people with an A1c of 7% or higher, and in those with a body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or greater.
The ARIC study and the analyses run by Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui and his coauthors received no commercial funding. Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui and Dr. Eckel had no relevant disclosures.
In a multivariable analysis the rate of incident heart failure increased steadily and significantly as diabetes duration increased. Among the 168 study subjects (2% of the total study group) who had diabetes for at least 15 years, the subsequent incidence of heart failure was nearly threefold higher than among the 4,802 subjects (49%) who never had diabetes or prediabetes, reported Justin B. Echouffo-Tcheugui, MD, PhD, and coauthors in an article published in JACC Heart Failure.
People with prediabetes (32% of the study population) had a significant but modest increased rate of incident heart failure that was 16% higher than in control subjects who never developed diabetes. People with diabetes for durations of 0-4.9 years, 5.0-9.9 years, or 10-14.9 years, had steadily increasing relative incident heart failure rates of 29%, 97%, and 210%, respectively, compared with controls, reported Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui, an endocrinologist at Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore.
Similar rates of HFrEF and HFpEF
Among all 1,841 people in the dataset with diabetes for any length of time each additional 5 years of the disorder linked with a significant, relative 17% increase in the rate of incident heart failure. Incidence of heart failure rose even more sharply with added duration among those with a hemoglobin A1c of 7% or greater, compared with those with better glycemic control. And the rate of incident heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) roughly matched the rate of incident heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
The study dataset included 9,734 adults enrolled into the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study, and during a median follow-up of 22.5 years they had nearly 2,000 episodes of either hospitalization or death secondary to incident heart failure. This included 617 (31%) events involving HFpEF, 495 events (25%) involving HFrEF, and 876 unclassified heart failure events.
The cohort averaged 63 years of age; 58% were women, 23% were Black, and 77% were White (the study design excluded people with other racial and ethnic backgrounds). The study design also excluded people with a history of heart failure or coronary artery disease, as well as those diagnosed with diabetes prior to age 18 resulting in a study group that presumably mostly had type 2 diabetes when diabetes was present. The report provided no data on the specific numbers of patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
“It’s not surprising that a longer duration of diabetes is associated with heart failure, but the etiology remains problematic,” commented Robert H. Eckel, MD, an endocrinologist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. “The impact of diabetes on incident heart failure is not well know, particularly duration of diabetes,” although disorders often found in patients with diabetes, such as hypertension and diabetic cardiomyopathy, likely have roles in causing heart failure, he said.
Diabetes duration may signal need for an SGLT2 inhibitor
“With emerging novel treatments like the SGLT2 [sodium-glucose cotransporter 2] inhibitors for preventing heart failure hospitalizations and deaths in patients with type 2 diabetes, this is a timely analysis,” Dr. Eckel said in an interview.
“There is no question that with increased duration of type 2 diabetes” the need for an agent from the SGLT2-inhibitor class increases. Although, because of the proven protection these drugs give against heart failure events and progression of chronic kidney disease, treatment with this drug class should start early in patients with type 2 diabetes, he added.
Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui and his coauthors agreed, citing two important clinical take-aways from their findings:
First, interventions that delay the onset of diabetes may potentially reduce incident heart failure; second, patients with diabetes might benefit from cardioprotective treatments such as SGLT2 inhibitors, the report said.
“Our observations suggest the potential prognostic relevance of diabetes duration in assessing heart failure,” the authors wrote. Integrating diabetes duration into heart failure risk estimation in people with diabetes “could help refine the selection of high-risk individuals who may derive the greatest absolute benefit from aggressive cardioprotective therapies such as SGLT2 inhibitors.”
The analysis also identified several other demographic and clinical factors that influenced the relative effect of diabetes duration. Longer duration was linked with higher rates of incident heart failure in women compared with men, in Blacks compared with Whites, in people younger than 65 compared with older people, in people with an A1c of 7% or higher, and in those with a body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or greater.
The ARIC study and the analyses run by Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui and his coauthors received no commercial funding. Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui and Dr. Eckel had no relevant disclosures.
FROM JACC HEART FAILURE
Hand ulceration
A 45-year-old man presented to a south Texas emergency department with a red, tender, edematous left hand. Earlier that day, he had been working in an oil field when his hand suddenly began to hurt.
On physical exam, puncture wounds were visible at the metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb and the interphalangeal joint, dorsal aspect; the area was surrounded by necrotic black tissue (FIGURE). Additionally, erythema with extensive edema extended distally to the proximal interphalangeal joints of each digit. Upon palpation, the area was warm, firm, and tender, with the edema tracking proximally to his mid-forearm.
The patient had a temperature of 99.5 °F; his other vital signs were normal. His past medical history included hypertension.
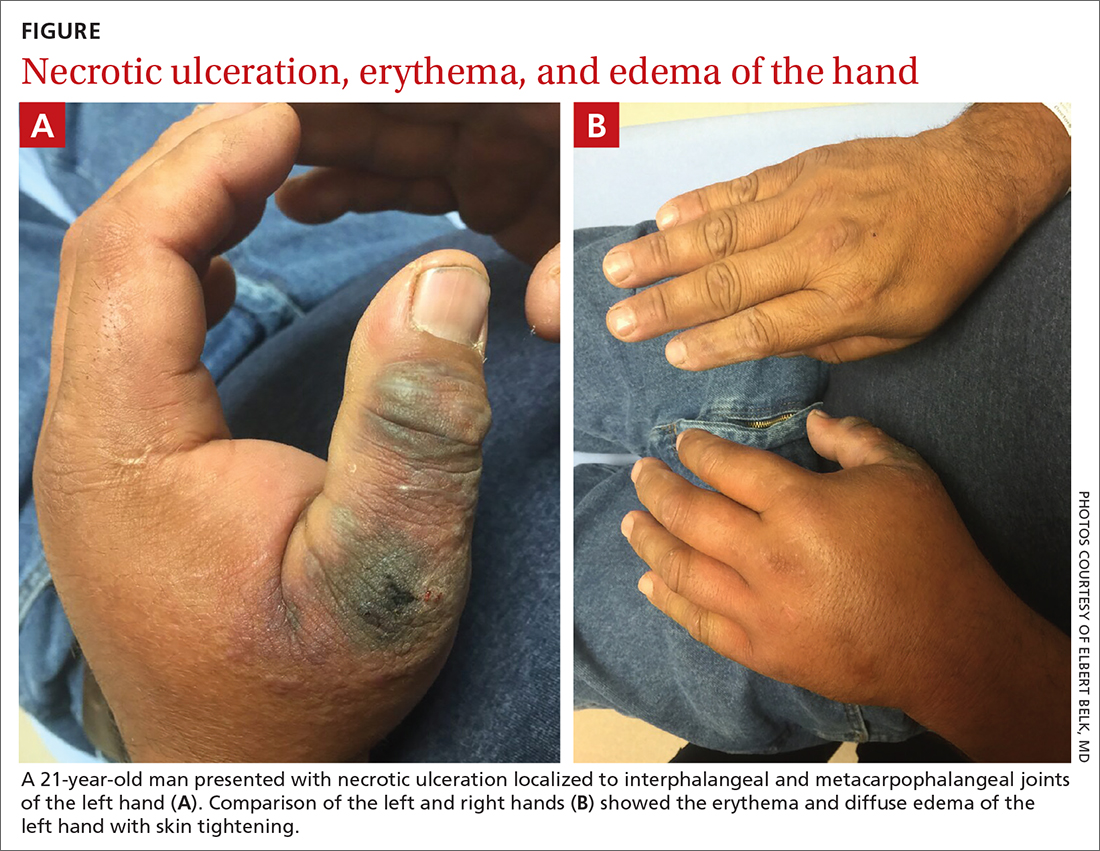
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Dx: Cellulitis, compartment syndrome by scorpion sting
Based on the necrotic puncture wounds, unilateral distribution of the swelling, and the patient’s acknowledgement that he’d seen a scorpion in his work environment prior to symptom onset, he was given a diagnosis of cellulitis with secondary compartment syndrome following a scorpion sting.
A geographic problem
In the United States, there are approximately 17,000 reported cases of scorpion stings every year, with fewer than 11 related deaths reported between 1999 and 2014.1 These cases tend to follow a geographic distribution along the American Southwest, with the highest incidence occurring in Arizona, followed by Texas; the majority of cases occur during the summer months.1
The most clinically relevant scorpion in the United States is the Centruroides sculpturatus, also known as the Arizona bark scorpion.2Centruroides spp can be recognized by a slender, yellow to light brown or tan body measuring 1.3 cm to 7.6 cm in length. There is a tubercule at the base of the stringer, a defining characteristic of the species.3
Urgent care is necessary for more severe symptoms
The most common complaint following a scorpion sting tends to be pain (88.7%), followed by numbness, edema, and erythema.1 Other signs and symptoms include muscle spasms, hypertension, and salivation. Symptoms can persist for 10 to 48 hours. Cardiovascular collapse and disseminated intravascular coagulation are 2 potentially fatal complications of a scorpion sting.
The diagnosis is made clinically based on history and physical exam findings; a complete blood count, coagulation panel, and creatine kinase and amylase/lipase bloodwork may be ordered to assess for end-organ complications. Local serious complications, such as compartment syndrome, should be urgently referred for surgical management.
Continue to: Signs of compartment syndrome...
Signs of compartment syndrome include tense, swollen compartments and pain with passive stretching of muscles within the compartment. Rapid progression of symptoms, as seen in this case, is also a red flag.
Differential diagnosis includes necrotizing fasciitis
The differential diagnosis includes uncomplicated cellulitis, as well as necrotizing fasciitis and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) cellulitis.
Necrotizing fasciitis. The lack of subcutaneous crackles and pain that is out of proportion to touch, as well as relatively normal vital signs, ruled out a diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis in this case.
Community-acquired MRSA is seen with purulent cellulitis. However, this patient had no purulent discharge.
Antivenom is only needed for severe cases
Treatment is primarily supportive; all patients should have the wound thoroughly cleaned, and pain can be controlled using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or opioid therapy.2 Tetanus prophylaxis should be given. The Centruroides antivenom, Anascorp, should be considered for patients with severe symptoms, including loss of muscle control, roving or abnormal eye movements, slurred speech, respiratory distress, excessive salivation, frothing at the mouth, and vomiting.4 In most cases, local poison control centers should be consulted for advice on management and to answer questions about antivenom availability.
Our patient was admitted to the hospital and an urgent surgery consult was obtained. The surgeon performed a fasciotomy to treat the compartment syndrome, and the patient survived without loss of his hand or arm.
1. Kang AM, Brooks DE. Nationwide scorpion exposures reported to US poison control centers from 2005 to 2015. J Med Toxicol. 2017;13:158-165. doi: 10.1007/s13181-016-0594-0
2. Barish RA, Arnold T. Scorpion Stings. Merck Manual. Updated April 2020. Accessed June 26, 2021. https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/injuries-poisoning/bites-and-stings/scorpion-stings
3. González-Santillán E, Possani LD. North American scorpion species of public health importance with reappraisal of historical epidemiology. Acta Trop. 2018;187:264-274. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.08.002
4. Anascorp. Package insert. Accredo Health Group, Inc; 2011.
A 45-year-old man presented to a south Texas emergency department with a red, tender, edematous left hand. Earlier that day, he had been working in an oil field when his hand suddenly began to hurt.
On physical exam, puncture wounds were visible at the metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb and the interphalangeal joint, dorsal aspect; the area was surrounded by necrotic black tissue (FIGURE). Additionally, erythema with extensive edema extended distally to the proximal interphalangeal joints of each digit. Upon palpation, the area was warm, firm, and tender, with the edema tracking proximally to his mid-forearm.
The patient had a temperature of 99.5 °F; his other vital signs were normal. His past medical history included hypertension.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Dx: Cellulitis, compartment syndrome by scorpion sting
Based on the necrotic puncture wounds, unilateral distribution of the swelling, and the patient’s acknowledgement that he’d seen a scorpion in his work environment prior to symptom onset, he was given a diagnosis of cellulitis with secondary compartment syndrome following a scorpion sting.
A geographic problem
In the United States, there are approximately 17,000 reported cases of scorpion stings every year, with fewer than 11 related deaths reported between 1999 and 2014.1 These cases tend to follow a geographic distribution along the American Southwest, with the highest incidence occurring in Arizona, followed by Texas; the majority of cases occur during the summer months.1
The most clinically relevant scorpion in the United States is the Centruroides sculpturatus, also known as the Arizona bark scorpion.2Centruroides spp can be recognized by a slender, yellow to light brown or tan body measuring 1.3 cm to 7.6 cm in length. There is a tubercule at the base of the stringer, a defining characteristic of the species.3
Urgent care is necessary for more severe symptoms
The most common complaint following a scorpion sting tends to be pain (88.7%), followed by numbness, edema, and erythema.1 Other signs and symptoms include muscle spasms, hypertension, and salivation. Symptoms can persist for 10 to 48 hours. Cardiovascular collapse and disseminated intravascular coagulation are 2 potentially fatal complications of a scorpion sting.
The diagnosis is made clinically based on history and physical exam findings; a complete blood count, coagulation panel, and creatine kinase and amylase/lipase bloodwork may be ordered to assess for end-organ complications. Local serious complications, such as compartment syndrome, should be urgently referred for surgical management.
Continue to: Signs of compartment syndrome...
Signs of compartment syndrome include tense, swollen compartments and pain with passive stretching of muscles within the compartment. Rapid progression of symptoms, as seen in this case, is also a red flag.
Differential diagnosis includes necrotizing fasciitis
The differential diagnosis includes uncomplicated cellulitis, as well as necrotizing fasciitis and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) cellulitis.
Necrotizing fasciitis. The lack of subcutaneous crackles and pain that is out of proportion to touch, as well as relatively normal vital signs, ruled out a diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis in this case.
Community-acquired MRSA is seen with purulent cellulitis. However, this patient had no purulent discharge.
Antivenom is only needed for severe cases
Treatment is primarily supportive; all patients should have the wound thoroughly cleaned, and pain can be controlled using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or opioid therapy.2 Tetanus prophylaxis should be given. The Centruroides antivenom, Anascorp, should be considered for patients with severe symptoms, including loss of muscle control, roving or abnormal eye movements, slurred speech, respiratory distress, excessive salivation, frothing at the mouth, and vomiting.4 In most cases, local poison control centers should be consulted for advice on management and to answer questions about antivenom availability.
Our patient was admitted to the hospital and an urgent surgery consult was obtained. The surgeon performed a fasciotomy to treat the compartment syndrome, and the patient survived without loss of his hand or arm.
A 45-year-old man presented to a south Texas emergency department with a red, tender, edematous left hand. Earlier that day, he had been working in an oil field when his hand suddenly began to hurt.
On physical exam, puncture wounds were visible at the metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb and the interphalangeal joint, dorsal aspect; the area was surrounded by necrotic black tissue (FIGURE). Additionally, erythema with extensive edema extended distally to the proximal interphalangeal joints of each digit. Upon palpation, the area was warm, firm, and tender, with the edema tracking proximally to his mid-forearm.
The patient had a temperature of 99.5 °F; his other vital signs were normal. His past medical history included hypertension.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Dx: Cellulitis, compartment syndrome by scorpion sting
Based on the necrotic puncture wounds, unilateral distribution of the swelling, and the patient’s acknowledgement that he’d seen a scorpion in his work environment prior to symptom onset, he was given a diagnosis of cellulitis with secondary compartment syndrome following a scorpion sting.
A geographic problem
In the United States, there are approximately 17,000 reported cases of scorpion stings every year, with fewer than 11 related deaths reported between 1999 and 2014.1 These cases tend to follow a geographic distribution along the American Southwest, with the highest incidence occurring in Arizona, followed by Texas; the majority of cases occur during the summer months.1
The most clinically relevant scorpion in the United States is the Centruroides sculpturatus, also known as the Arizona bark scorpion.2Centruroides spp can be recognized by a slender, yellow to light brown or tan body measuring 1.3 cm to 7.6 cm in length. There is a tubercule at the base of the stringer, a defining characteristic of the species.3
Urgent care is necessary for more severe symptoms
The most common complaint following a scorpion sting tends to be pain (88.7%), followed by numbness, edema, and erythema.1 Other signs and symptoms include muscle spasms, hypertension, and salivation. Symptoms can persist for 10 to 48 hours. Cardiovascular collapse and disseminated intravascular coagulation are 2 potentially fatal complications of a scorpion sting.
The diagnosis is made clinically based on history and physical exam findings; a complete blood count, coagulation panel, and creatine kinase and amylase/lipase bloodwork may be ordered to assess for end-organ complications. Local serious complications, such as compartment syndrome, should be urgently referred for surgical management.
Continue to: Signs of compartment syndrome...
Signs of compartment syndrome include tense, swollen compartments and pain with passive stretching of muscles within the compartment. Rapid progression of symptoms, as seen in this case, is also a red flag.
Differential diagnosis includes necrotizing fasciitis
The differential diagnosis includes uncomplicated cellulitis, as well as necrotizing fasciitis and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) cellulitis.
Necrotizing fasciitis. The lack of subcutaneous crackles and pain that is out of proportion to touch, as well as relatively normal vital signs, ruled out a diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis in this case.
Community-acquired MRSA is seen with purulent cellulitis. However, this patient had no purulent discharge.
Antivenom is only needed for severe cases
Treatment is primarily supportive; all patients should have the wound thoroughly cleaned, and pain can be controlled using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or opioid therapy.2 Tetanus prophylaxis should be given. The Centruroides antivenom, Anascorp, should be considered for patients with severe symptoms, including loss of muscle control, roving or abnormal eye movements, slurred speech, respiratory distress, excessive salivation, frothing at the mouth, and vomiting.4 In most cases, local poison control centers should be consulted for advice on management and to answer questions about antivenom availability.
Our patient was admitted to the hospital and an urgent surgery consult was obtained. The surgeon performed a fasciotomy to treat the compartment syndrome, and the patient survived without loss of his hand or arm.
1. Kang AM, Brooks DE. Nationwide scorpion exposures reported to US poison control centers from 2005 to 2015. J Med Toxicol. 2017;13:158-165. doi: 10.1007/s13181-016-0594-0
2. Barish RA, Arnold T. Scorpion Stings. Merck Manual. Updated April 2020. Accessed June 26, 2021. https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/injuries-poisoning/bites-and-stings/scorpion-stings
3. González-Santillán E, Possani LD. North American scorpion species of public health importance with reappraisal of historical epidemiology. Acta Trop. 2018;187:264-274. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.08.002
4. Anascorp. Package insert. Accredo Health Group, Inc; 2011.
1. Kang AM, Brooks DE. Nationwide scorpion exposures reported to US poison control centers from 2005 to 2015. J Med Toxicol. 2017;13:158-165. doi: 10.1007/s13181-016-0594-0
2. Barish RA, Arnold T. Scorpion Stings. Merck Manual. Updated April 2020. Accessed June 26, 2021. https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/injuries-poisoning/bites-and-stings/scorpion-stings
3. González-Santillán E, Possani LD. North American scorpion species of public health importance with reappraisal of historical epidemiology. Acta Trop. 2018;187:264-274. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.08.002
4. Anascorp. Package insert. Accredo Health Group, Inc; 2011.
Call to Action: Multidisciplinary panel urges coordinated care for ‘NASH epidemic’
A multidisciplinary panel of U.S. experts released a “Call to Action” for improved screening, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) on July 26, an effort organized by the American Gastroenterological Association in collaboration with seven other U.S. medical organizations including several endocrinology groups.
The published statement, “Preparing for the NASH Epidemic: A Call to Action,” proposes several urgent steps for the U.S. clinical community to provide better-focused and better-coordinated care for patients at risk for developing or having NAFLD or NASH, particularly among “emerging” at-risk cohorts such as patients with diabetes and obesity. It appears in the journals Gastroenterology, Diabetes Care, Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, and Obesity.
The statement’s central pitch is that improvements in care won’t be possible unless the several medical specialties that deal with affected or at-risk patients stop working “in separate silos,” and instead create “a collective action plan,” and also organize multidisciplinary teams that “integrate primary care, hepatology, obesity medicine, endocrinology, and diabetology via well-defined care pathways.”
“The overarching goal” is a “unified, international public health response to NAFLD and NASH,” said the statement, which stemmed from a conference held in July 2020 that included representatives from not only the lead gastroenterology group but also the American Diabetes Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, The Endocrine Society, The American Academy of Family Physicians, The Obesity Society, and the American College of Osteopathic Family Physicians.
The statement cites sobering prevalence numbers, with estimates that NAFLD exists in more than half the patients with type 2 diabetes, while NASH affects about a third, rates that translate into many millions of affected Americans, given recent estimates that the U.S. prevalence of type 2 diabetes exceeds 30 million people. And the numbers continue to rise along with increases in the prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
“It’s an enormously common disease, and there are not enough gastroenterologists, to say nothing of hepatologists, to care for every patient with NAFLD,” said Anna Mae Diehl, MD, a gastroenterologist and professor at Duke University in Durham, N.C., who was not involved with the conference nor in writing the statement.
Clinical care pathways coming soon
Another key part of this initiative is development of clinical care pathways that will have “careful explication of each step in screening, diagnosis, and treatment,” and will be designed to inform the practice of primary care physicians (PCPs) as well as clinicians from the various specialties that deal with these patients.
The clinical care pathways are on track to come out later in 2021, said Fasiha Kanwal, MD, a professor and chief of gastroenterology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, and lead author on the Call to Action document.
“The Pathways will include practical recommendations about whom to screen and when to refer, and the criteria primary care physicians can use for diagnosis and risk stratification,” Dr. Kanwal said in an interview. “Patients can benefit from a standardized approach.”
The new document also includes results from a recent survey about NAFLD and NASH management completed by 751 U.S. physicians, including 401 (53%) primary care physicians, 175 gastroenterologists, (23%) and 175 endocrinologists (23%; percentages total 99% because of rounding).
The results showed “significant gaps in knowledge about whom to screen and how to diagnose and treat patients at high risk for NASH,” concluded the statement’s authors. Barely more than a third of the respondents knew that almost all patients with severe obesity likely have NAFLD, and fewer than half the endocrinologists and the primary care physicians appreciated that NAFLD is very common among patients with type 2 diabetes.
‘Understanding of NAFLD is not there’
“I applaud this effort that calls attention to an emerging public health problem. This paper and survey are great ideas. The findings are not surprising, but they’re important,” said Dr. Diehl said in an interview. “Much more needs to be done” including changes in social behavior and government policies.
“The public’s understanding of NAFLD is not there,” and many physicians also have an incomplete understanding of NAFLD and more serious stages of metabolic liver disease. “Physicians know that patients with obesity are at risk for heart disease, diabetes, and stroke, but they may not always be aware that these patients can also have cirrhosis,” noted Dr. Diehl, who published in 2019 a call to action for NAFLD of her own with some associates.
“My referrals are fueled by primary care physicians who recognize patients with significant liver disease. It would be great to outline recommended practice; I have no doubt that providers will embrace this,” as well as the broader concept of multidisciplinary teams, another focus of the statement. Dr. Diehl cited the “Cancer Center model,” where an oncologist takes primary responsibility for caring for a cancer patient while coordinating care with other specialists, an approach facilitated by EMRs that allow seamless data and chart sharing and something that many health systems have either already adopted or are moving toward.
She said the NASH Call to Action may help catalyze broader application of this model to many more patients with NAFLD or NASH, and noted that some U.S. centers already use this approach – including Dr. Diehl’s program at Duke – which brings together her gastroenterology colleagues with cardiologists, radiologists, endocrinologists, and bariatric surgeons. But she noted that for most patients with metabolic liver disease, the hub clinician needs to be a PCP, especially for patients with earlier-stage disease, because the number of affected patients is so huge.
“Key steps toward establishing such teams include establishing protocols for risk stratification and referral, definition of roles and responsibilities, and buy-in from institutions and payers. Clearly a lot of work needs to occur to get to these multidisciplinary teams,” said Dr. Kanwal.
Ralph A. DeFronzo, MD, professor and deputy director of the Texas Diabetes Institute at UT Health San Antonio, who was not involved with the conference or statement, had a different take on what the future of NASH and NAFLD care may look like.
“Endocrinologists, hepatologists, and obesity experts will work within their individual specialties to diagnose and manage NASH,” he said in an interview. But he acknowledged that “an integrated effort by specialists would be important” to help “primary care physicians who are less familiar with the disease.”
Controversy over pioglitazone?
Dr. DeFronzo endorsed development of clinical care pathways as “important,” but also as a potential source of “controversy, especially with respect to treatment.”
The Call to Action statement cites lifestyle-based therapies, such as an appropriate diet; regular, moderate exercise; and elimination when possible of obesogenic medications as cornerstone interventions for patients with NAFLD or early-stage NASH, interventions that can be prescribed by PCPs. For patients with NASH and stage 2 or worse fibrosis, the statement endorses liver-directed pharmacotherapy. While noting that no agents currently carry a Food and Drug Administration–approved indication for treating NASH, the statement cites evidence that 800 IU/day of vitamin E improves steatosis in patients with NASH but not type 2 diabetes.
For patients with type 2 diabetes, the statement notes that results from five randomized trials indicated that pioglitazone could reverse steatohepatitis, findings that led to its recommendation in guidelines from a modest circle of medical groups, including the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. However, the 2021 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes from the American Diabetes Association gives these agents limited endorsement, saying: “Pioglitazone, vitamin E treatment, and liraglutide treatment of biopsy-proven nonalcoholic steatohepatitis have each been shown to improve liver histology, but effects on longer-term clinical outcomes are not known.”
“The strongest evidence by far is for pioglitazone for treating NAFLD and NASH,” said Dr. DeFronzo, a vocal proponent of the drug for this indication. But he added that “hepatologists don’t feel comfortable with drugs from the thiazolidinedione class,” which includes pioglitazone.
“We don’t yet know how to optimally configure the health system for NAFLD and NASH to make it more efficient and helpful to patients, but models exist, and the approach is evolving,” said Dr. Diehl.
Dr. Diehl and Dr. Kanwal had no relevant disclosures. Dr. DeFronzo has been a speaker on behalf of AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk, has been an adviser to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Intarcia, and Janssen, and has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Janssen and Merck.
A multidisciplinary panel of U.S. experts released a “Call to Action” for improved screening, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) on July 26, an effort organized by the American Gastroenterological Association in collaboration with seven other U.S. medical organizations including several endocrinology groups.
The published statement, “Preparing for the NASH Epidemic: A Call to Action,” proposes several urgent steps for the U.S. clinical community to provide better-focused and better-coordinated care for patients at risk for developing or having NAFLD or NASH, particularly among “emerging” at-risk cohorts such as patients with diabetes and obesity. It appears in the journals Gastroenterology, Diabetes Care, Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, and Obesity.
The statement’s central pitch is that improvements in care won’t be possible unless the several medical specialties that deal with affected or at-risk patients stop working “in separate silos,” and instead create “a collective action plan,” and also organize multidisciplinary teams that “integrate primary care, hepatology, obesity medicine, endocrinology, and diabetology via well-defined care pathways.”
“The overarching goal” is a “unified, international public health response to NAFLD and NASH,” said the statement, which stemmed from a conference held in July 2020 that included representatives from not only the lead gastroenterology group but also the American Diabetes Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, The Endocrine Society, The American Academy of Family Physicians, The Obesity Society, and the American College of Osteopathic Family Physicians.
The statement cites sobering prevalence numbers, with estimates that NAFLD exists in more than half the patients with type 2 diabetes, while NASH affects about a third, rates that translate into many millions of affected Americans, given recent estimates that the U.S. prevalence of type 2 diabetes exceeds 30 million people. And the numbers continue to rise along with increases in the prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
“It’s an enormously common disease, and there are not enough gastroenterologists, to say nothing of hepatologists, to care for every patient with NAFLD,” said Anna Mae Diehl, MD, a gastroenterologist and professor at Duke University in Durham, N.C., who was not involved with the conference nor in writing the statement.
Clinical care pathways coming soon
Another key part of this initiative is development of clinical care pathways that will have “careful explication of each step in screening, diagnosis, and treatment,” and will be designed to inform the practice of primary care physicians (PCPs) as well as clinicians from the various specialties that deal with these patients.
The clinical care pathways are on track to come out later in 2021, said Fasiha Kanwal, MD, a professor and chief of gastroenterology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, and lead author on the Call to Action document.
“The Pathways will include practical recommendations about whom to screen and when to refer, and the criteria primary care physicians can use for diagnosis and risk stratification,” Dr. Kanwal said in an interview. “Patients can benefit from a standardized approach.”
The new document also includes results from a recent survey about NAFLD and NASH management completed by 751 U.S. physicians, including 401 (53%) primary care physicians, 175 gastroenterologists, (23%) and 175 endocrinologists (23%; percentages total 99% because of rounding).
The results showed “significant gaps in knowledge about whom to screen and how to diagnose and treat patients at high risk for NASH,” concluded the statement’s authors. Barely more than a third of the respondents knew that almost all patients with severe obesity likely have NAFLD, and fewer than half the endocrinologists and the primary care physicians appreciated that NAFLD is very common among patients with type 2 diabetes.
‘Understanding of NAFLD is not there’
“I applaud this effort that calls attention to an emerging public health problem. This paper and survey are great ideas. The findings are not surprising, but they’re important,” said Dr. Diehl said in an interview. “Much more needs to be done” including changes in social behavior and government policies.
“The public’s understanding of NAFLD is not there,” and many physicians also have an incomplete understanding of NAFLD and more serious stages of metabolic liver disease. “Physicians know that patients with obesity are at risk for heart disease, diabetes, and stroke, but they may not always be aware that these patients can also have cirrhosis,” noted Dr. Diehl, who published in 2019 a call to action for NAFLD of her own with some associates.
“My referrals are fueled by primary care physicians who recognize patients with significant liver disease. It would be great to outline recommended practice; I have no doubt that providers will embrace this,” as well as the broader concept of multidisciplinary teams, another focus of the statement. Dr. Diehl cited the “Cancer Center model,” where an oncologist takes primary responsibility for caring for a cancer patient while coordinating care with other specialists, an approach facilitated by EMRs that allow seamless data and chart sharing and something that many health systems have either already adopted or are moving toward.
She said the NASH Call to Action may help catalyze broader application of this model to many more patients with NAFLD or NASH, and noted that some U.S. centers already use this approach – including Dr. Diehl’s program at Duke – which brings together her gastroenterology colleagues with cardiologists, radiologists, endocrinologists, and bariatric surgeons. But she noted that for most patients with metabolic liver disease, the hub clinician needs to be a PCP, especially for patients with earlier-stage disease, because the number of affected patients is so huge.
“Key steps toward establishing such teams include establishing protocols for risk stratification and referral, definition of roles and responsibilities, and buy-in from institutions and payers. Clearly a lot of work needs to occur to get to these multidisciplinary teams,” said Dr. Kanwal.
Ralph A. DeFronzo, MD, professor and deputy director of the Texas Diabetes Institute at UT Health San Antonio, who was not involved with the conference or statement, had a different take on what the future of NASH and NAFLD care may look like.
“Endocrinologists, hepatologists, and obesity experts will work within their individual specialties to diagnose and manage NASH,” he said in an interview. But he acknowledged that “an integrated effort by specialists would be important” to help “primary care physicians who are less familiar with the disease.”
Controversy over pioglitazone?
Dr. DeFronzo endorsed development of clinical care pathways as “important,” but also as a potential source of “controversy, especially with respect to treatment.”
The Call to Action statement cites lifestyle-based therapies, such as an appropriate diet; regular, moderate exercise; and elimination when possible of obesogenic medications as cornerstone interventions for patients with NAFLD or early-stage NASH, interventions that can be prescribed by PCPs. For patients with NASH and stage 2 or worse fibrosis, the statement endorses liver-directed pharmacotherapy. While noting that no agents currently carry a Food and Drug Administration–approved indication for treating NASH, the statement cites evidence that 800 IU/day of vitamin E improves steatosis in patients with NASH but not type 2 diabetes.
For patients with type 2 diabetes, the statement notes that results from five randomized trials indicated that pioglitazone could reverse steatohepatitis, findings that led to its recommendation in guidelines from a modest circle of medical groups, including the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. However, the 2021 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes from the American Diabetes Association gives these agents limited endorsement, saying: “Pioglitazone, vitamin E treatment, and liraglutide treatment of biopsy-proven nonalcoholic steatohepatitis have each been shown to improve liver histology, but effects on longer-term clinical outcomes are not known.”
“The strongest evidence by far is for pioglitazone for treating NAFLD and NASH,” said Dr. DeFronzo, a vocal proponent of the drug for this indication. But he added that “hepatologists don’t feel comfortable with drugs from the thiazolidinedione class,” which includes pioglitazone.
“We don’t yet know how to optimally configure the health system for NAFLD and NASH to make it more efficient and helpful to patients, but models exist, and the approach is evolving,” said Dr. Diehl.
Dr. Diehl and Dr. Kanwal had no relevant disclosures. Dr. DeFronzo has been a speaker on behalf of AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk, has been an adviser to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Intarcia, and Janssen, and has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Janssen and Merck.
A multidisciplinary panel of U.S. experts released a “Call to Action” for improved screening, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) on July 26, an effort organized by the American Gastroenterological Association in collaboration with seven other U.S. medical organizations including several endocrinology groups.
The published statement, “Preparing for the NASH Epidemic: A Call to Action,” proposes several urgent steps for the U.S. clinical community to provide better-focused and better-coordinated care for patients at risk for developing or having NAFLD or NASH, particularly among “emerging” at-risk cohorts such as patients with diabetes and obesity. It appears in the journals Gastroenterology, Diabetes Care, Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, and Obesity.
The statement’s central pitch is that improvements in care won’t be possible unless the several medical specialties that deal with affected or at-risk patients stop working “in separate silos,” and instead create “a collective action plan,” and also organize multidisciplinary teams that “integrate primary care, hepatology, obesity medicine, endocrinology, and diabetology via well-defined care pathways.”
“The overarching goal” is a “unified, international public health response to NAFLD and NASH,” said the statement, which stemmed from a conference held in July 2020 that included representatives from not only the lead gastroenterology group but also the American Diabetes Association, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, The Endocrine Society, The American Academy of Family Physicians, The Obesity Society, and the American College of Osteopathic Family Physicians.
The statement cites sobering prevalence numbers, with estimates that NAFLD exists in more than half the patients with type 2 diabetes, while NASH affects about a third, rates that translate into many millions of affected Americans, given recent estimates that the U.S. prevalence of type 2 diabetes exceeds 30 million people. And the numbers continue to rise along with increases in the prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
“It’s an enormously common disease, and there are not enough gastroenterologists, to say nothing of hepatologists, to care for every patient with NAFLD,” said Anna Mae Diehl, MD, a gastroenterologist and professor at Duke University in Durham, N.C., who was not involved with the conference nor in writing the statement.
Clinical care pathways coming soon
Another key part of this initiative is development of clinical care pathways that will have “careful explication of each step in screening, diagnosis, and treatment,” and will be designed to inform the practice of primary care physicians (PCPs) as well as clinicians from the various specialties that deal with these patients.
The clinical care pathways are on track to come out later in 2021, said Fasiha Kanwal, MD, a professor and chief of gastroenterology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, and lead author on the Call to Action document.
“The Pathways will include practical recommendations about whom to screen and when to refer, and the criteria primary care physicians can use for diagnosis and risk stratification,” Dr. Kanwal said in an interview. “Patients can benefit from a standardized approach.”
The new document also includes results from a recent survey about NAFLD and NASH management completed by 751 U.S. physicians, including 401 (53%) primary care physicians, 175 gastroenterologists, (23%) and 175 endocrinologists (23%; percentages total 99% because of rounding).
The results showed “significant gaps in knowledge about whom to screen and how to diagnose and treat patients at high risk for NASH,” concluded the statement’s authors. Barely more than a third of the respondents knew that almost all patients with severe obesity likely have NAFLD, and fewer than half the endocrinologists and the primary care physicians appreciated that NAFLD is very common among patients with type 2 diabetes.
‘Understanding of NAFLD is not there’
“I applaud this effort that calls attention to an emerging public health problem. This paper and survey are great ideas. The findings are not surprising, but they’re important,” said Dr. Diehl said in an interview. “Much more needs to be done” including changes in social behavior and government policies.
“The public’s understanding of NAFLD is not there,” and many physicians also have an incomplete understanding of NAFLD and more serious stages of metabolic liver disease. “Physicians know that patients with obesity are at risk for heart disease, diabetes, and stroke, but they may not always be aware that these patients can also have cirrhosis,” noted Dr. Diehl, who published in 2019 a call to action for NAFLD of her own with some associates.
“My referrals are fueled by primary care physicians who recognize patients with significant liver disease. It would be great to outline recommended practice; I have no doubt that providers will embrace this,” as well as the broader concept of multidisciplinary teams, another focus of the statement. Dr. Diehl cited the “Cancer Center model,” where an oncologist takes primary responsibility for caring for a cancer patient while coordinating care with other specialists, an approach facilitated by EMRs that allow seamless data and chart sharing and something that many health systems have either already adopted or are moving toward.
She said the NASH Call to Action may help catalyze broader application of this model to many more patients with NAFLD or NASH, and noted that some U.S. centers already use this approach – including Dr. Diehl’s program at Duke – which brings together her gastroenterology colleagues with cardiologists, radiologists, endocrinologists, and bariatric surgeons. But she noted that for most patients with metabolic liver disease, the hub clinician needs to be a PCP, especially for patients with earlier-stage disease, because the number of affected patients is so huge.
“Key steps toward establishing such teams include establishing protocols for risk stratification and referral, definition of roles and responsibilities, and buy-in from institutions and payers. Clearly a lot of work needs to occur to get to these multidisciplinary teams,” said Dr. Kanwal.
Ralph A. DeFronzo, MD, professor and deputy director of the Texas Diabetes Institute at UT Health San Antonio, who was not involved with the conference or statement, had a different take on what the future of NASH and NAFLD care may look like.
“Endocrinologists, hepatologists, and obesity experts will work within their individual specialties to diagnose and manage NASH,” he said in an interview. But he acknowledged that “an integrated effort by specialists would be important” to help “primary care physicians who are less familiar with the disease.”
Controversy over pioglitazone?
Dr. DeFronzo endorsed development of clinical care pathways as “important,” but also as a potential source of “controversy, especially with respect to treatment.”
The Call to Action statement cites lifestyle-based therapies, such as an appropriate diet; regular, moderate exercise; and elimination when possible of obesogenic medications as cornerstone interventions for patients with NAFLD or early-stage NASH, interventions that can be prescribed by PCPs. For patients with NASH and stage 2 or worse fibrosis, the statement endorses liver-directed pharmacotherapy. While noting that no agents currently carry a Food and Drug Administration–approved indication for treating NASH, the statement cites evidence that 800 IU/day of vitamin E improves steatosis in patients with NASH but not type 2 diabetes.
For patients with type 2 diabetes, the statement notes that results from five randomized trials indicated that pioglitazone could reverse steatohepatitis, findings that led to its recommendation in guidelines from a modest circle of medical groups, including the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. However, the 2021 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes from the American Diabetes Association gives these agents limited endorsement, saying: “Pioglitazone, vitamin E treatment, and liraglutide treatment of biopsy-proven nonalcoholic steatohepatitis have each been shown to improve liver histology, but effects on longer-term clinical outcomes are not known.”
“The strongest evidence by far is for pioglitazone for treating NAFLD and NASH,” said Dr. DeFronzo, a vocal proponent of the drug for this indication. But he added that “hepatologists don’t feel comfortable with drugs from the thiazolidinedione class,” which includes pioglitazone.
“We don’t yet know how to optimally configure the health system for NAFLD and NASH to make it more efficient and helpful to patients, but models exist, and the approach is evolving,” said Dr. Diehl.
Dr. Diehl and Dr. Kanwal had no relevant disclosures. Dr. DeFronzo has been a speaker on behalf of AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk, has been an adviser to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Intarcia, and Janssen, and has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Janssen and Merck.
No link between childhood vaccinations and allergies or asthma
A meta-analysis by Australian researchers found no link between childhood vaccinations and an increase in allergies and asthma. In fact, children who received the BCG vaccine actually had a lesser incidence of eczema than other children, but there was no difference shown in any of the allergies or asthma.
The researchers, in a report published in the journal Allergy, write, “We found no evidence that childhood vaccination with commonly administered vaccines was associated with increased risk of later allergic disease.”
“Allergies have increased worldwide in the last 50 years, and in developed countries, earlier,” said study author Caroline J. Lodge, PhD, principal research fellow at the University of Melbourne, in an interview. “In developing countries, it is still a crisis.” No one knows why, she said. That was the reason for the recent study.
Allergic diseases such as allergic rhinitis (hay fever) and food allergies have a serious influence on quality of life, and the incidence is growing. According to the Global Asthma Network, there are 334 million people living with asthma. Between 2%-10% of adults have atopic eczema, and more than a 250,000 people have food allergies. This coincides temporally with an increase in mass vaccination of children.
Unlike the controversy surrounding vaccinations and autism, which has long been debunked as baseless, a hygiene hypothesis postulates that when children acquire immunity from many diseases, they become vulnerable to allergic reactions. Thanks to vaccinations, children in the developed world now are routinely immune to dozens of diseases.
That immunity leads to suppression of a major antibody response, increasing sensitivity to allergens and allergic disease. Suspicion of a link with childhood vaccinations has been used by opponents of vaccines in lobbying campaigns jeopardizing the sustainability of vaccine programs. In recent days, for example, the state of Tennessee has halted a program to encourage vaccination for COVID-19 as well as all other vaccinations, the result of pressure on the state by anti-vaccination lobbying.
But the Melbourne researchers reported that the meta-analysis of 42 published research studies doesn’t support the vaccine–allergy hypothesis. Using PubMed and EMBASE records between January 1946 and January 2018, researchers selected studies to be included in the analysis, looking for allergic outcomes in children given BCG or vaccines for measles or pertussis. Thirty-five publications reported cohort studies, and seven were based on randomized controlled trials.
The Australian study is not the only one showing the same lack of linkage between vaccination and allergy. The International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) found no association between mass vaccination and atopic disease. A 1998 Swedish study of 669 children found no differences in the incidence of allergic diseases between those who received pertussis vaccine and those who did not.
“The bottom line is that vaccines prevent infectious diseases,” said Matthew B. Laurens, associate professor of pediatrics at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, in an interview. Dr. Laurens was not part of the Australian study.
“Large-scale epidemiological studies do not support the theory that vaccines are associated with an increased risk of allergy or asthma,” he stressed. “Parents should not be deterred from vaccinating their children because of fears that this would increase risks of allergy and/or asthma.”
Dr. Lodge and Dr. Laurens have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A meta-analysis by Australian researchers found no link between childhood vaccinations and an increase in allergies and asthma. In fact, children who received the BCG vaccine actually had a lesser incidence of eczema than other children, but there was no difference shown in any of the allergies or asthma.
The researchers, in a report published in the journal Allergy, write, “We found no evidence that childhood vaccination with commonly administered vaccines was associated with increased risk of later allergic disease.”
“Allergies have increased worldwide in the last 50 years, and in developed countries, earlier,” said study author Caroline J. Lodge, PhD, principal research fellow at the University of Melbourne, in an interview. “In developing countries, it is still a crisis.” No one knows why, she said. That was the reason for the recent study.
Allergic diseases such as allergic rhinitis (hay fever) and food allergies have a serious influence on quality of life, and the incidence is growing. According to the Global Asthma Network, there are 334 million people living with asthma. Between 2%-10% of adults have atopic eczema, and more than a 250,000 people have food allergies. This coincides temporally with an increase in mass vaccination of children.
Unlike the controversy surrounding vaccinations and autism, which has long been debunked as baseless, a hygiene hypothesis postulates that when children acquire immunity from many diseases, they become vulnerable to allergic reactions. Thanks to vaccinations, children in the developed world now are routinely immune to dozens of diseases.
That immunity leads to suppression of a major antibody response, increasing sensitivity to allergens and allergic disease. Suspicion of a link with childhood vaccinations has been used by opponents of vaccines in lobbying campaigns jeopardizing the sustainability of vaccine programs. In recent days, for example, the state of Tennessee has halted a program to encourage vaccination for COVID-19 as well as all other vaccinations, the result of pressure on the state by anti-vaccination lobbying.
But the Melbourne researchers reported that the meta-analysis of 42 published research studies doesn’t support the vaccine–allergy hypothesis. Using PubMed and EMBASE records between January 1946 and January 2018, researchers selected studies to be included in the analysis, looking for allergic outcomes in children given BCG or vaccines for measles or pertussis. Thirty-five publications reported cohort studies, and seven were based on randomized controlled trials.
The Australian study is not the only one showing the same lack of linkage between vaccination and allergy. The International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) found no association between mass vaccination and atopic disease. A 1998 Swedish study of 669 children found no differences in the incidence of allergic diseases between those who received pertussis vaccine and those who did not.
“The bottom line is that vaccines prevent infectious diseases,” said Matthew B. Laurens, associate professor of pediatrics at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, in an interview. Dr. Laurens was not part of the Australian study.
“Large-scale epidemiological studies do not support the theory that vaccines are associated with an increased risk of allergy or asthma,” he stressed. “Parents should not be deterred from vaccinating their children because of fears that this would increase risks of allergy and/or asthma.”
Dr. Lodge and Dr. Laurens have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A meta-analysis by Australian researchers found no link between childhood vaccinations and an increase in allergies and asthma. In fact, children who received the BCG vaccine actually had a lesser incidence of eczema than other children, but there was no difference shown in any of the allergies or asthma.
The researchers, in a report published in the journal Allergy, write, “We found no evidence that childhood vaccination with commonly administered vaccines was associated with increased risk of later allergic disease.”
“Allergies have increased worldwide in the last 50 years, and in developed countries, earlier,” said study author Caroline J. Lodge, PhD, principal research fellow at the University of Melbourne, in an interview. “In developing countries, it is still a crisis.” No one knows why, she said. That was the reason for the recent study.
Allergic diseases such as allergic rhinitis (hay fever) and food allergies have a serious influence on quality of life, and the incidence is growing. According to the Global Asthma Network, there are 334 million people living with asthma. Between 2%-10% of adults have atopic eczema, and more than a 250,000 people have food allergies. This coincides temporally with an increase in mass vaccination of children.
Unlike the controversy surrounding vaccinations and autism, which has long been debunked as baseless, a hygiene hypothesis postulates that when children acquire immunity from many diseases, they become vulnerable to allergic reactions. Thanks to vaccinations, children in the developed world now are routinely immune to dozens of diseases.
That immunity leads to suppression of a major antibody response, increasing sensitivity to allergens and allergic disease. Suspicion of a link with childhood vaccinations has been used by opponents of vaccines in lobbying campaigns jeopardizing the sustainability of vaccine programs. In recent days, for example, the state of Tennessee has halted a program to encourage vaccination for COVID-19 as well as all other vaccinations, the result of pressure on the state by anti-vaccination lobbying.
But the Melbourne researchers reported that the meta-analysis of 42 published research studies doesn’t support the vaccine–allergy hypothesis. Using PubMed and EMBASE records between January 1946 and January 2018, researchers selected studies to be included in the analysis, looking for allergic outcomes in children given BCG or vaccines for measles or pertussis. Thirty-five publications reported cohort studies, and seven were based on randomized controlled trials.
The Australian study is not the only one showing the same lack of linkage between vaccination and allergy. The International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) found no association between mass vaccination and atopic disease. A 1998 Swedish study of 669 children found no differences in the incidence of allergic diseases between those who received pertussis vaccine and those who did not.
“The bottom line is that vaccines prevent infectious diseases,” said Matthew B. Laurens, associate professor of pediatrics at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, in an interview. Dr. Laurens was not part of the Australian study.
“Large-scale epidemiological studies do not support the theory that vaccines are associated with an increased risk of allergy or asthma,” he stressed. “Parents should not be deterred from vaccinating their children because of fears that this would increase risks of allergy and/or asthma.”
Dr. Lodge and Dr. Laurens have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.