User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
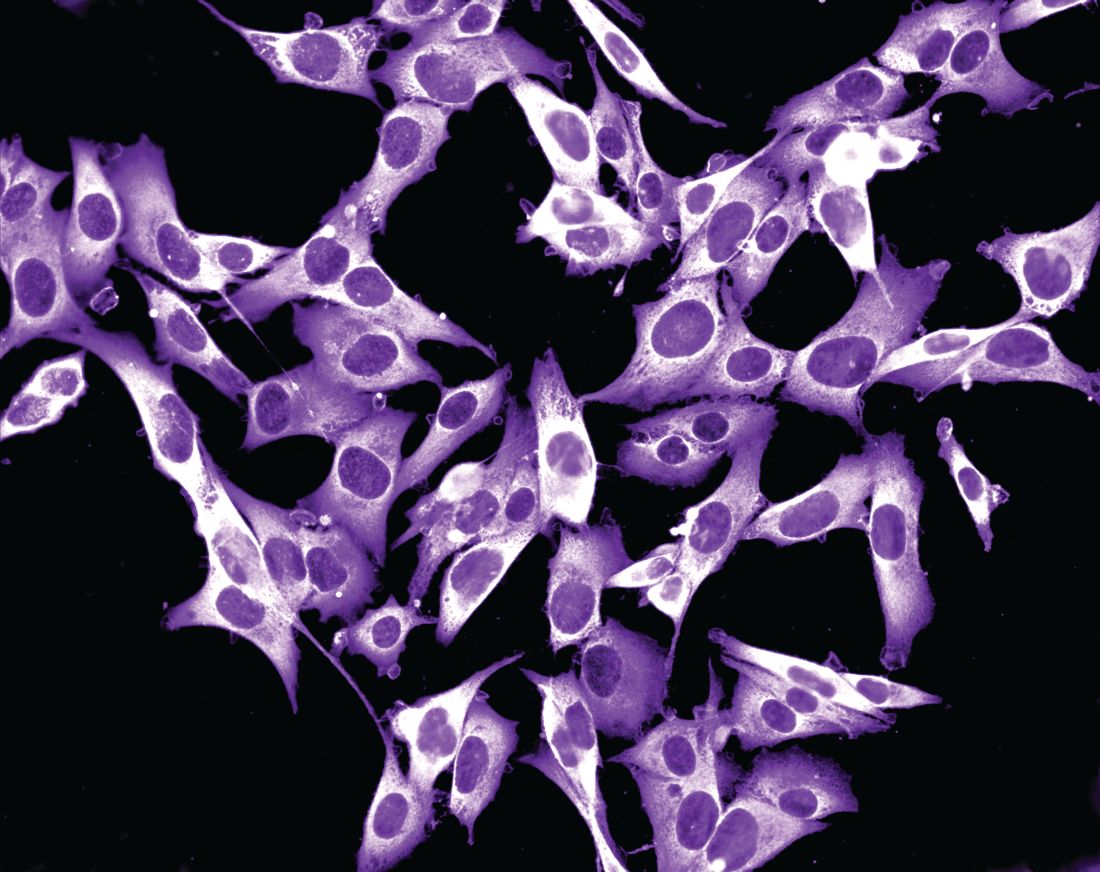
Study spotlights clinicopathologic features, survival outcomes of pediatric melanoma
.
“Cutaneous melanomas are rare in children and much less common in adolescents than in later life,” researchers led by Mary-Ann El Sharouni, PhD, wrote in the study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. “Management of these young patients currently follows guidelines developed for adults. Better understanding of melanoma occurring in the first 2 decades of life is, therefore, warranted.”
Drawing from two datasets – one from the Netherlands and the other from Melanoma Institute Australia (MIA) at the University of Sydney – Dr. El Sharouni of the MIA and of the department of dermatology at University Medical Center Utrecht in the Netherlands, and colleagues, evaluated all patients younger than 20 years of age who were diagnosed with invasive melanoma between January 2000 and December 2014. The pooled cohort included 397 Dutch and 117 Australian individuals. Of these, 62 were children and 452 were adolescents. To determine melanoma subtypes, the researchers reevaluated pathology reports and used multivariate Cox models to calculate recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS).
The median Breslow thickness was 2.7 mm in children and 1.0 mm in adolescents. Most patients (83%) had conventional melanoma, which consisted of superficial spreading, nodular, desmoplastic, and acral lentiginous forms, while 78 had spitzoid melanoma and 8 had melanoma associated with a congenital nevus. The 10-year RFS was 91.5% in children and 86.4% in adolescents (P =.32), while the 10-year OS was 100% in children and 92.7% in adolescents (P = .09).
On multivariable analysis, which was possible only for the adolescent cohort because of the small number of children, ulceration status and anatomic site were associated with RFS and OS, whereas age, sex, mitotic index, sentinel node status, and melanoma subtype were not. Breslow thickness > 4 mm was associated with worse RFS. As for affected anatomic site, those with melanomas located on the upper and lower limbs had a better overall RFS and OS compared with those who had head or neck melanomas.
The authors acknowledged certain limitation of the analysis, including its retrospective design and the small number of children. “Our data suggest that adolescent melanomas are often similar to adult-type melanomas, whilst those which occur in young children frequently occur via different molecular mechanisms,” they concluded. “In the future it is likely that further understanding of these molecular mechanisms and ability to classify melanomas based on their molecular characteristics will assist in further refining prognostic estimates and possible guiding treatment for young patients with melanoma.”
Rebecca M. Thiede, MD, assistant program director of the division of dermatology at the University of Arizona, Tucson, who was asked to comment on the study, said that the analysis “greatly contributes to dermatology, as we are still learning the differences between melanoma in children and adolescents versus adults.
This study found that adolescents with melanoma had worse survival if mitosis were present and/or located on head/neck, which could aid in aggressiveness of treatment.”
A key strength of analysis, she continued, is the large sample size of 514 patients, “given that melanoma in this population is very rare. A limitation which [the researchers] brought up is the discrepancy of diagnosis via histopathology of melanoma in children versus adults. The study relied on the pathology report given the retrospective nature of this [analysis, and it] was based on Australian and Dutch populations, which may limit its scope in other countries.”
Dr. El Sharouni was supported by a research fellowship grant from the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV), while two of her coauthors, Richard A. Scolyer, MD, and John F. Thompson, MD, were recipients of an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council Program Grant. The study was also supported by a research program grant from Cancer Institute New South Wales. Dr. Thiede reported having no financial disclosures.
.
“Cutaneous melanomas are rare in children and much less common in adolescents than in later life,” researchers led by Mary-Ann El Sharouni, PhD, wrote in the study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. “Management of these young patients currently follows guidelines developed for adults. Better understanding of melanoma occurring in the first 2 decades of life is, therefore, warranted.”
Drawing from two datasets – one from the Netherlands and the other from Melanoma Institute Australia (MIA) at the University of Sydney – Dr. El Sharouni of the MIA and of the department of dermatology at University Medical Center Utrecht in the Netherlands, and colleagues, evaluated all patients younger than 20 years of age who were diagnosed with invasive melanoma between January 2000 and December 2014. The pooled cohort included 397 Dutch and 117 Australian individuals. Of these, 62 were children and 452 were adolescents. To determine melanoma subtypes, the researchers reevaluated pathology reports and used multivariate Cox models to calculate recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS).
The median Breslow thickness was 2.7 mm in children and 1.0 mm in adolescents. Most patients (83%) had conventional melanoma, which consisted of superficial spreading, nodular, desmoplastic, and acral lentiginous forms, while 78 had spitzoid melanoma and 8 had melanoma associated with a congenital nevus. The 10-year RFS was 91.5% in children and 86.4% in adolescents (P =.32), while the 10-year OS was 100% in children and 92.7% in adolescents (P = .09).
On multivariable analysis, which was possible only for the adolescent cohort because of the small number of children, ulceration status and anatomic site were associated with RFS and OS, whereas age, sex, mitotic index, sentinel node status, and melanoma subtype were not. Breslow thickness > 4 mm was associated with worse RFS. As for affected anatomic site, those with melanomas located on the upper and lower limbs had a better overall RFS and OS compared with those who had head or neck melanomas.
The authors acknowledged certain limitation of the analysis, including its retrospective design and the small number of children. “Our data suggest that adolescent melanomas are often similar to adult-type melanomas, whilst those which occur in young children frequently occur via different molecular mechanisms,” they concluded. “In the future it is likely that further understanding of these molecular mechanisms and ability to classify melanomas based on their molecular characteristics will assist in further refining prognostic estimates and possible guiding treatment for young patients with melanoma.”
Rebecca M. Thiede, MD, assistant program director of the division of dermatology at the University of Arizona, Tucson, who was asked to comment on the study, said that the analysis “greatly contributes to dermatology, as we are still learning the differences between melanoma in children and adolescents versus adults.
This study found that adolescents with melanoma had worse survival if mitosis were present and/or located on head/neck, which could aid in aggressiveness of treatment.”
A key strength of analysis, she continued, is the large sample size of 514 patients, “given that melanoma in this population is very rare. A limitation which [the researchers] brought up is the discrepancy of diagnosis via histopathology of melanoma in children versus adults. The study relied on the pathology report given the retrospective nature of this [analysis, and it] was based on Australian and Dutch populations, which may limit its scope in other countries.”
Dr. El Sharouni was supported by a research fellowship grant from the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV), while two of her coauthors, Richard A. Scolyer, MD, and John F. Thompson, MD, were recipients of an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council Program Grant. The study was also supported by a research program grant from Cancer Institute New South Wales. Dr. Thiede reported having no financial disclosures.
.
“Cutaneous melanomas are rare in children and much less common in adolescents than in later life,” researchers led by Mary-Ann El Sharouni, PhD, wrote in the study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. “Management of these young patients currently follows guidelines developed for adults. Better understanding of melanoma occurring in the first 2 decades of life is, therefore, warranted.”
Drawing from two datasets – one from the Netherlands and the other from Melanoma Institute Australia (MIA) at the University of Sydney – Dr. El Sharouni of the MIA and of the department of dermatology at University Medical Center Utrecht in the Netherlands, and colleagues, evaluated all patients younger than 20 years of age who were diagnosed with invasive melanoma between January 2000 and December 2014. The pooled cohort included 397 Dutch and 117 Australian individuals. Of these, 62 were children and 452 were adolescents. To determine melanoma subtypes, the researchers reevaluated pathology reports and used multivariate Cox models to calculate recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS).
The median Breslow thickness was 2.7 mm in children and 1.0 mm in adolescents. Most patients (83%) had conventional melanoma, which consisted of superficial spreading, nodular, desmoplastic, and acral lentiginous forms, while 78 had spitzoid melanoma and 8 had melanoma associated with a congenital nevus. The 10-year RFS was 91.5% in children and 86.4% in adolescents (P =.32), while the 10-year OS was 100% in children and 92.7% in adolescents (P = .09).
On multivariable analysis, which was possible only for the adolescent cohort because of the small number of children, ulceration status and anatomic site were associated with RFS and OS, whereas age, sex, mitotic index, sentinel node status, and melanoma subtype were not. Breslow thickness > 4 mm was associated with worse RFS. As for affected anatomic site, those with melanomas located on the upper and lower limbs had a better overall RFS and OS compared with those who had head or neck melanomas.
The authors acknowledged certain limitation of the analysis, including its retrospective design and the small number of children. “Our data suggest that adolescent melanomas are often similar to adult-type melanomas, whilst those which occur in young children frequently occur via different molecular mechanisms,” they concluded. “In the future it is likely that further understanding of these molecular mechanisms and ability to classify melanomas based on their molecular characteristics will assist in further refining prognostic estimates and possible guiding treatment for young patients with melanoma.”
Rebecca M. Thiede, MD, assistant program director of the division of dermatology at the University of Arizona, Tucson, who was asked to comment on the study, said that the analysis “greatly contributes to dermatology, as we are still learning the differences between melanoma in children and adolescents versus adults.
This study found that adolescents with melanoma had worse survival if mitosis were present and/or located on head/neck, which could aid in aggressiveness of treatment.”
A key strength of analysis, she continued, is the large sample size of 514 patients, “given that melanoma in this population is very rare. A limitation which [the researchers] brought up is the discrepancy of diagnosis via histopathology of melanoma in children versus adults. The study relied on the pathology report given the retrospective nature of this [analysis, and it] was based on Australian and Dutch populations, which may limit its scope in other countries.”
Dr. El Sharouni was supported by a research fellowship grant from the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV), while two of her coauthors, Richard A. Scolyer, MD, and John F. Thompson, MD, were recipients of an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council Program Grant. The study was also supported by a research program grant from Cancer Institute New South Wales. Dr. Thiede reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Infantile hemangioma: Analysis underscores importance of early propranolol treatment
, results from a post-hoc analysis of phase 2 and 3 clinical trial data showed.
“It is widely accepted that oral propranolol should be started early to improve the success rate, but proposed thresholds have lacked supportive data,” researchers led by Christine Léauté-Labrèze, MD, of the department of dermatology at Pellegrin Children’s Hospital, Bordeaux, France, wrote in the study, which was published online in Pediatric Dermatology. In the pivotal phase 2/3 trial of propranolol of 460 infants, published in 2015, the mean initiation of treatment was 104 days, they added, but “in real-life studies, most infants are referred later than this.”
In addition, a European expert consensus panel set the ideal age for a patient to be seen by a specialist at between 3 and 5 weeks of age, while an American Academy of Pediatrics Clinical Practice Guideline set the ideal age at 1 month.
To determine factors associated with a higher success rate with oral propranolol treatment, such as age at treatment initiation, the researchers analyzed data from the pivotal phase 2-3 clinical trial of oral propranolol in IH. They used Generalized Additive Model (GAM) charts with Generalized Linear Models (GLM), then a rule discovery algorithm, to identify subgroups presenting a high probability of occurrence of the predefined outcome: success at 6 months of treatment (defined as complete or nearly complete resolution of the target hemangioma). Study coauthors were Ilona J. Frieden, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, and director of the UCSF Birthmarks & Vascular Anomalies Center; and Alain Delarue, MD, of medical affairs at Pierre Fabre Dermatologie, Lavaur, France, which markets the pediatric formulation of propranolol approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2014 for treating IH.
They found that patients who started oral propranolol 3 mg/kg/day before the age of 10 weeks had a success rate of 86%, while those who started treatment after 10 weeks of age had a success rate of 60%. “Our clinical experience suggested that starting early propranolol gave better results on infantile hemangiomas; however, we were surprised” by the significance of the difference, the three study authors stated in an e-mail reply to this news organization.
“It therefore seemed essential to communicate the importance of early treatment to maximize the possibilities of recovery for children. Our findings support early treatment of at-risk infantile hemangiomas, without waiting for complications such as ulceration and/or functional consequences,” they added.
In their e-mail reply, the authors stated that treatment of high-risk IH should be initiated whenever possible before 10 weeks of age. Ideally, infants should be examined by a practitioner between 2 and 5 weeks of age and referred to a specialized center if they have features of an at-risk IH. Tools such as the Infantile Hemangioma Referral Score (IHReS) and consensus guidelines such as the AAP Clinical Practice Guideline “can help guide clinicians seeing newborns and young infants to recognize which IH may need early intervention,” they stated.
For rural-based providers whose patients and their families may not live close to an expert center, the study authors especially recommend using the IHReS scoring tool, which is readily available online and “will be very helpful in assessing whether patients need referral.” For those who do, they added, “triage using photographs is an excellent way to reach out to a referral center for advice and possible urgent referral.” In addition, a recent study emphasized that telemedicine using either live interactive portals or store-and-forward can be helpful in evaluation and management of patients with IH.
Dr. Léauté-Labrèze and colleagues acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, including the fact that it was performed post-hoc on an existing study and the challenge of translating its findings into clinical practice.
The three study authors were also authors of the 2015 NEJM study; Dr. Léauté-Labrèze was the lead author.
Dr. Léauté-Labrèze disclosed that she has served as a speaker and consultant for Pierre Fabre. Dr. Delarue is an employee of the company. Dr. Frieden reported having no disclosures relevant to the analysis.
, results from a post-hoc analysis of phase 2 and 3 clinical trial data showed.
“It is widely accepted that oral propranolol should be started early to improve the success rate, but proposed thresholds have lacked supportive data,” researchers led by Christine Léauté-Labrèze, MD, of the department of dermatology at Pellegrin Children’s Hospital, Bordeaux, France, wrote in the study, which was published online in Pediatric Dermatology. In the pivotal phase 2/3 trial of propranolol of 460 infants, published in 2015, the mean initiation of treatment was 104 days, they added, but “in real-life studies, most infants are referred later than this.”
In addition, a European expert consensus panel set the ideal age for a patient to be seen by a specialist at between 3 and 5 weeks of age, while an American Academy of Pediatrics Clinical Practice Guideline set the ideal age at 1 month.
To determine factors associated with a higher success rate with oral propranolol treatment, such as age at treatment initiation, the researchers analyzed data from the pivotal phase 2-3 clinical trial of oral propranolol in IH. They used Generalized Additive Model (GAM) charts with Generalized Linear Models (GLM), then a rule discovery algorithm, to identify subgroups presenting a high probability of occurrence of the predefined outcome: success at 6 months of treatment (defined as complete or nearly complete resolution of the target hemangioma). Study coauthors were Ilona J. Frieden, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, and director of the UCSF Birthmarks & Vascular Anomalies Center; and Alain Delarue, MD, of medical affairs at Pierre Fabre Dermatologie, Lavaur, France, which markets the pediatric formulation of propranolol approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2014 for treating IH.
They found that patients who started oral propranolol 3 mg/kg/day before the age of 10 weeks had a success rate of 86%, while those who started treatment after 10 weeks of age had a success rate of 60%. “Our clinical experience suggested that starting early propranolol gave better results on infantile hemangiomas; however, we were surprised” by the significance of the difference, the three study authors stated in an e-mail reply to this news organization.
“It therefore seemed essential to communicate the importance of early treatment to maximize the possibilities of recovery for children. Our findings support early treatment of at-risk infantile hemangiomas, without waiting for complications such as ulceration and/or functional consequences,” they added.
In their e-mail reply, the authors stated that treatment of high-risk IH should be initiated whenever possible before 10 weeks of age. Ideally, infants should be examined by a practitioner between 2 and 5 weeks of age and referred to a specialized center if they have features of an at-risk IH. Tools such as the Infantile Hemangioma Referral Score (IHReS) and consensus guidelines such as the AAP Clinical Practice Guideline “can help guide clinicians seeing newborns and young infants to recognize which IH may need early intervention,” they stated.
For rural-based providers whose patients and their families may not live close to an expert center, the study authors especially recommend using the IHReS scoring tool, which is readily available online and “will be very helpful in assessing whether patients need referral.” For those who do, they added, “triage using photographs is an excellent way to reach out to a referral center for advice and possible urgent referral.” In addition, a recent study emphasized that telemedicine using either live interactive portals or store-and-forward can be helpful in evaluation and management of patients with IH.
Dr. Léauté-Labrèze and colleagues acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, including the fact that it was performed post-hoc on an existing study and the challenge of translating its findings into clinical practice.
The three study authors were also authors of the 2015 NEJM study; Dr. Léauté-Labrèze was the lead author.
Dr. Léauté-Labrèze disclosed that she has served as a speaker and consultant for Pierre Fabre. Dr. Delarue is an employee of the company. Dr. Frieden reported having no disclosures relevant to the analysis.
, results from a post-hoc analysis of phase 2 and 3 clinical trial data showed.
“It is widely accepted that oral propranolol should be started early to improve the success rate, but proposed thresholds have lacked supportive data,” researchers led by Christine Léauté-Labrèze, MD, of the department of dermatology at Pellegrin Children’s Hospital, Bordeaux, France, wrote in the study, which was published online in Pediatric Dermatology. In the pivotal phase 2/3 trial of propranolol of 460 infants, published in 2015, the mean initiation of treatment was 104 days, they added, but “in real-life studies, most infants are referred later than this.”
In addition, a European expert consensus panel set the ideal age for a patient to be seen by a specialist at between 3 and 5 weeks of age, while an American Academy of Pediatrics Clinical Practice Guideline set the ideal age at 1 month.
To determine factors associated with a higher success rate with oral propranolol treatment, such as age at treatment initiation, the researchers analyzed data from the pivotal phase 2-3 clinical trial of oral propranolol in IH. They used Generalized Additive Model (GAM) charts with Generalized Linear Models (GLM), then a rule discovery algorithm, to identify subgroups presenting a high probability of occurrence of the predefined outcome: success at 6 months of treatment (defined as complete or nearly complete resolution of the target hemangioma). Study coauthors were Ilona J. Frieden, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, and director of the UCSF Birthmarks & Vascular Anomalies Center; and Alain Delarue, MD, of medical affairs at Pierre Fabre Dermatologie, Lavaur, France, which markets the pediatric formulation of propranolol approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2014 for treating IH.
They found that patients who started oral propranolol 3 mg/kg/day before the age of 10 weeks had a success rate of 86%, while those who started treatment after 10 weeks of age had a success rate of 60%. “Our clinical experience suggested that starting early propranolol gave better results on infantile hemangiomas; however, we were surprised” by the significance of the difference, the three study authors stated in an e-mail reply to this news organization.
“It therefore seemed essential to communicate the importance of early treatment to maximize the possibilities of recovery for children. Our findings support early treatment of at-risk infantile hemangiomas, without waiting for complications such as ulceration and/or functional consequences,” they added.
In their e-mail reply, the authors stated that treatment of high-risk IH should be initiated whenever possible before 10 weeks of age. Ideally, infants should be examined by a practitioner between 2 and 5 weeks of age and referred to a specialized center if they have features of an at-risk IH. Tools such as the Infantile Hemangioma Referral Score (IHReS) and consensus guidelines such as the AAP Clinical Practice Guideline “can help guide clinicians seeing newborns and young infants to recognize which IH may need early intervention,” they stated.
For rural-based providers whose patients and their families may not live close to an expert center, the study authors especially recommend using the IHReS scoring tool, which is readily available online and “will be very helpful in assessing whether patients need referral.” For those who do, they added, “triage using photographs is an excellent way to reach out to a referral center for advice and possible urgent referral.” In addition, a recent study emphasized that telemedicine using either live interactive portals or store-and-forward can be helpful in evaluation and management of patients with IH.
Dr. Léauté-Labrèze and colleagues acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, including the fact that it was performed post-hoc on an existing study and the challenge of translating its findings into clinical practice.
The three study authors were also authors of the 2015 NEJM study; Dr. Léauté-Labrèze was the lead author.
Dr. Léauté-Labrèze disclosed that she has served as a speaker and consultant for Pierre Fabre. Dr. Delarue is an employee of the company. Dr. Frieden reported having no disclosures relevant to the analysis.
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
Screen all patients for cannabis use before surgery: Guideline
All patients who undergo procedures that require regional or general anesthesia should be asked if, how often, and in what forms they use the drug, according to recommendations from the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine.
One reason: Patients who regularly use cannabis may experience worse pain and nausea after surgery and may require more opioid analgesia, the group said.
The society’s recommendations – published in Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine – are the first guidelines in the United States to cover cannabis use as it relates to surgery, the group said.
Possible interactions
Use of cannabis has increased in recent years, and researchers have been concerned that the drug may interact with anesthesia and complicate pain management. Few studies have evaluated interactions between cannabis and anesthetic agents, however, according to the authors of the new guidelines.
“With the rising prevalence of both medical and recreational cannabis use in the general population, anesthesiologists, surgeons, and perioperative physicians must have an understanding of the effects of cannabis on physiology in order to provide safe perioperative care,” the guideline said.
“Before surgery, anesthesiologists should ask patients if they use cannabis – whether medicinally or recreationally – and be prepared to possibly change the anesthesia plan or delay the procedure in certain situations,” Samer Narouze, MD, PhD, ASRA president and senior author of the guidelines, said in a news release about the recommendations.
Although some patients may use cannabis to relieve pain, research shows that “regular users may have more pain and nausea after surgery, not less, and may need more medications, including opioids, to manage the discomfort,” said Dr. Narouze, chairman of the Center for Pain Medicine at Western Reserve Hospital in Cuyahoga Falls, Ohio.
Risks for vomiting, heart attack
The new recommendations were created by a committee of 13 experts, including anesthesiologists, chronic pain physicians, and a patient advocate. Shalini Shah, MD, vice chair of anesthesiology at the University of California, Irvine, was lead author of the document.
Four of 21 recommendations were classified as grade A, meaning that following them would be expected to provide substantial benefits. Those recommendations are to screen all patients before surgery; postpone elective surgery for patients who have altered mental status or impaired decision-making capacity at the time of surgery; counsel frequent, heavy users about the potential for cannabis use to impair postoperative pain control; and counsel pregnant patients about the risks of cannabis use to unborn children.
The authors cited studies to support their recommendations, including one showing that long-term cannabis use was associated with a 20% increase in the incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting, a leading complaint of surgery patients. Other research has shown that cannabis use is linked to more pain and use of opioids after surgery.
Other recommendations include delaying elective surgery for at least 2 hours after a patient has smoked cannabis, owing to an increased risk for heart attack, and considering adjustment of ventilation settings during surgery for regular smokers of cannabis. Research has shown that smoking cannabis may be a rare trigger for myocardial infarction and is associated with airway inflammation and self-reported respiratory symptoms.
Nevertheless, doctors should not conduct universal toxicology screening, given a lack of evidence supporting this practice, the guideline stated.
The authors did not have enough information to make recommendations about reducing cannabis use before surgery or adjusting opioid prescriptions after surgery for patients who use cannabis, they said.
Kenneth Finn, MD, president of the American Board of Pain Medicine, welcomed the publication of the new guidelines. Dr. Finn, who practices at Springs Rehabilitation in Colorado Springs, has edited a textbook about cannabis in medicine and founded the International Academy on the Science and Impact of Cannabis.
“The vast majority of medical providers really have no idea about cannabis and what its impacts are on the human body,” Dr. Finn said.
For one, it can interact with numerous other drugs, including warfarin.
Guideline coauthor Eugene R. Viscusi, MD, professor of anesthesiology at the Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, emphasized that, while cannabis may be perceived as “natural,” it should not be considered differently from manufactured drugs.
Cannabis and cannabinoids represent “a class of very potent and pharmacologically active compounds,” Dr. Viscusi said in an interview. While researchers continue to assess possible medically beneficial effects of cannabis compounds, clinicians also need to be aware of the risks.
“The literature continues to emerge, and while we are always hopeful for good news, as physicians, we need to be very well versed on potential risks, especially in a high-risk situation like surgery,” he said.
Dr. Shah has consulted for companies that develop medical devices and drugs. Dr. Finn is the editor of the textbook, “Cannabis in Medicine: An Evidence-Based Approach” (Springer: New York, 2020), for which he receives royalties.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
All patients who undergo procedures that require regional or general anesthesia should be asked if, how often, and in what forms they use the drug, according to recommendations from the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine.
One reason: Patients who regularly use cannabis may experience worse pain and nausea after surgery and may require more opioid analgesia, the group said.
The society’s recommendations – published in Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine – are the first guidelines in the United States to cover cannabis use as it relates to surgery, the group said.
Possible interactions
Use of cannabis has increased in recent years, and researchers have been concerned that the drug may interact with anesthesia and complicate pain management. Few studies have evaluated interactions between cannabis and anesthetic agents, however, according to the authors of the new guidelines.
“With the rising prevalence of both medical and recreational cannabis use in the general population, anesthesiologists, surgeons, and perioperative physicians must have an understanding of the effects of cannabis on physiology in order to provide safe perioperative care,” the guideline said.
“Before surgery, anesthesiologists should ask patients if they use cannabis – whether medicinally or recreationally – and be prepared to possibly change the anesthesia plan or delay the procedure in certain situations,” Samer Narouze, MD, PhD, ASRA president and senior author of the guidelines, said in a news release about the recommendations.
Although some patients may use cannabis to relieve pain, research shows that “regular users may have more pain and nausea after surgery, not less, and may need more medications, including opioids, to manage the discomfort,” said Dr. Narouze, chairman of the Center for Pain Medicine at Western Reserve Hospital in Cuyahoga Falls, Ohio.
Risks for vomiting, heart attack
The new recommendations were created by a committee of 13 experts, including anesthesiologists, chronic pain physicians, and a patient advocate. Shalini Shah, MD, vice chair of anesthesiology at the University of California, Irvine, was lead author of the document.
Four of 21 recommendations were classified as grade A, meaning that following them would be expected to provide substantial benefits. Those recommendations are to screen all patients before surgery; postpone elective surgery for patients who have altered mental status or impaired decision-making capacity at the time of surgery; counsel frequent, heavy users about the potential for cannabis use to impair postoperative pain control; and counsel pregnant patients about the risks of cannabis use to unborn children.
The authors cited studies to support their recommendations, including one showing that long-term cannabis use was associated with a 20% increase in the incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting, a leading complaint of surgery patients. Other research has shown that cannabis use is linked to more pain and use of opioids after surgery.
Other recommendations include delaying elective surgery for at least 2 hours after a patient has smoked cannabis, owing to an increased risk for heart attack, and considering adjustment of ventilation settings during surgery for regular smokers of cannabis. Research has shown that smoking cannabis may be a rare trigger for myocardial infarction and is associated with airway inflammation and self-reported respiratory symptoms.
Nevertheless, doctors should not conduct universal toxicology screening, given a lack of evidence supporting this practice, the guideline stated.
The authors did not have enough information to make recommendations about reducing cannabis use before surgery or adjusting opioid prescriptions after surgery for patients who use cannabis, they said.
Kenneth Finn, MD, president of the American Board of Pain Medicine, welcomed the publication of the new guidelines. Dr. Finn, who practices at Springs Rehabilitation in Colorado Springs, has edited a textbook about cannabis in medicine and founded the International Academy on the Science and Impact of Cannabis.
“The vast majority of medical providers really have no idea about cannabis and what its impacts are on the human body,” Dr. Finn said.
For one, it can interact with numerous other drugs, including warfarin.
Guideline coauthor Eugene R. Viscusi, MD, professor of anesthesiology at the Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, emphasized that, while cannabis may be perceived as “natural,” it should not be considered differently from manufactured drugs.
Cannabis and cannabinoids represent “a class of very potent and pharmacologically active compounds,” Dr. Viscusi said in an interview. While researchers continue to assess possible medically beneficial effects of cannabis compounds, clinicians also need to be aware of the risks.
“The literature continues to emerge, and while we are always hopeful for good news, as physicians, we need to be very well versed on potential risks, especially in a high-risk situation like surgery,” he said.
Dr. Shah has consulted for companies that develop medical devices and drugs. Dr. Finn is the editor of the textbook, “Cannabis in Medicine: An Evidence-Based Approach” (Springer: New York, 2020), for which he receives royalties.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
All patients who undergo procedures that require regional or general anesthesia should be asked if, how often, and in what forms they use the drug, according to recommendations from the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine.
One reason: Patients who regularly use cannabis may experience worse pain and nausea after surgery and may require more opioid analgesia, the group said.
The society’s recommendations – published in Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine – are the first guidelines in the United States to cover cannabis use as it relates to surgery, the group said.
Possible interactions
Use of cannabis has increased in recent years, and researchers have been concerned that the drug may interact with anesthesia and complicate pain management. Few studies have evaluated interactions between cannabis and anesthetic agents, however, according to the authors of the new guidelines.
“With the rising prevalence of both medical and recreational cannabis use in the general population, anesthesiologists, surgeons, and perioperative physicians must have an understanding of the effects of cannabis on physiology in order to provide safe perioperative care,” the guideline said.
“Before surgery, anesthesiologists should ask patients if they use cannabis – whether medicinally or recreationally – and be prepared to possibly change the anesthesia plan or delay the procedure in certain situations,” Samer Narouze, MD, PhD, ASRA president and senior author of the guidelines, said in a news release about the recommendations.
Although some patients may use cannabis to relieve pain, research shows that “regular users may have more pain and nausea after surgery, not less, and may need more medications, including opioids, to manage the discomfort,” said Dr. Narouze, chairman of the Center for Pain Medicine at Western Reserve Hospital in Cuyahoga Falls, Ohio.
Risks for vomiting, heart attack
The new recommendations were created by a committee of 13 experts, including anesthesiologists, chronic pain physicians, and a patient advocate. Shalini Shah, MD, vice chair of anesthesiology at the University of California, Irvine, was lead author of the document.
Four of 21 recommendations were classified as grade A, meaning that following them would be expected to provide substantial benefits. Those recommendations are to screen all patients before surgery; postpone elective surgery for patients who have altered mental status or impaired decision-making capacity at the time of surgery; counsel frequent, heavy users about the potential for cannabis use to impair postoperative pain control; and counsel pregnant patients about the risks of cannabis use to unborn children.
The authors cited studies to support their recommendations, including one showing that long-term cannabis use was associated with a 20% increase in the incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting, a leading complaint of surgery patients. Other research has shown that cannabis use is linked to more pain and use of opioids after surgery.
Other recommendations include delaying elective surgery for at least 2 hours after a patient has smoked cannabis, owing to an increased risk for heart attack, and considering adjustment of ventilation settings during surgery for regular smokers of cannabis. Research has shown that smoking cannabis may be a rare trigger for myocardial infarction and is associated with airway inflammation and self-reported respiratory symptoms.
Nevertheless, doctors should not conduct universal toxicology screening, given a lack of evidence supporting this practice, the guideline stated.
The authors did not have enough information to make recommendations about reducing cannabis use before surgery or adjusting opioid prescriptions after surgery for patients who use cannabis, they said.
Kenneth Finn, MD, president of the American Board of Pain Medicine, welcomed the publication of the new guidelines. Dr. Finn, who practices at Springs Rehabilitation in Colorado Springs, has edited a textbook about cannabis in medicine and founded the International Academy on the Science and Impact of Cannabis.
“The vast majority of medical providers really have no idea about cannabis and what its impacts are on the human body,” Dr. Finn said.
For one, it can interact with numerous other drugs, including warfarin.
Guideline coauthor Eugene R. Viscusi, MD, professor of anesthesiology at the Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, emphasized that, while cannabis may be perceived as “natural,” it should not be considered differently from manufactured drugs.
Cannabis and cannabinoids represent “a class of very potent and pharmacologically active compounds,” Dr. Viscusi said in an interview. While researchers continue to assess possible medically beneficial effects of cannabis compounds, clinicians also need to be aware of the risks.
“The literature continues to emerge, and while we are always hopeful for good news, as physicians, we need to be very well versed on potential risks, especially in a high-risk situation like surgery,” he said.
Dr. Shah has consulted for companies that develop medical devices and drugs. Dr. Finn is the editor of the textbook, “Cannabis in Medicine: An Evidence-Based Approach” (Springer: New York, 2020), for which he receives royalties.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM REGIONAL ANETHESIA AND MEDICINE
Do collagen supplements benefit the skin?
SAN DIEGO – When patients ask if collagen supplements can benefit their skin, what should you tell them?
According to Ava Shamban, MD, a dermatologist who practices in Santa Monica, Calif., And in her opinion, more research is needed to establish knowledge of the effects and physiologic mechanism of collagen supplementation.
“Collagen is the most abundant protein in the skin; it is found only in animal flesh like meat and fish that contain connective tissue,” she said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium. “We produce less collagen as we age. External factors can slow down our collagen production, including smoking, sun exposure, lack of sleep/exercise, and alcohol consumption.”
Though human studies are lacking, some trials have found that collagen supplements may improve skin hydration and elasticity. “Maybe there’s some benefit, but the digestive process breaks collagen down into amino acids, so I don’t buy it,” she said.
At the meeting, Dr. Shamban discussed other topics related to the effect of supplements and nutrition on the skin:
Can Nutrafol reverse permanent hair loss? “It definitely doesn’t do that,” she said. “Can it help regrow hair? Perhaps.” Nutrafol is an over-the-counter supplement that aims to relieve moderate hair thinning or strengthen hair to prevent breakage, and is physician-formulated with medical-grade ingredients that target root causes of thinning such as stress, lifestyle, hormones, and nutrition.
As for biotin, “we now know that high levels of biotin can actually cause hair loss,” she said. “If you have advanced hair loss, supplements may not work for you. There is no hair regrowth supplement that can bring back a dead hair follicle. Can it help a miniaturized hair follicle? Maybe. Platelet-rich plasma injections have been shown to stimulate hair growth, but only if the follicle is miniaturized, not if it’s totally gone.”
How does the human microbiome affect skin? In a review of sequencing surveys of healthy adults, “the composition of microbial communities was found to be primarily dependent on the physiology of the skin site, with changes in the relative abundance of bacterial taxa associated with moist, dry, and sebaceous environments,” the authors reported . “The microbiome is the genetic material of all the microbes that live inside the body, including bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and viruses,” Dr. Shamban said. “The more diverse the microbiota is, the healthier it’s considered. That diversity is enriched through a diet full of various vegetables and fruits.”
Nearly all adults are colonized with Cutibacterium acnes (formerly Propionibacterium acnes), but only a minority have acne, which highlights the importance of studying diseases in the broader context of host genetics, immune or barrier defects, the microbiome, and the environment, she added. For example, the decreased diversity of the skin microbiome in people with atopic dermatitis has been linked to a reduction in environmental biodiversity in the areas surrounding their homes.
Do adaptogens have a role in skin care? Adaptogens such as ashwagandha, elderberry, ginseng, licorice root, neem, moringa, and reishi mushrooms have been used in Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine for centuries and are purported to promote adaptability, resilience, and survival of living organisms in stress. They appear to affect the neuroendocrine immune system and at low doses may function as mild stress mimetics.
“The idea is that combining adaptogens into skin care can reinforce and support the skin’s resistance against stressors that can accelerate visible signs of aging,” said Dr. Shamban. “They share some similarities with antioxidants in that their main purpose is to protect the body from external stressors such as UV rays, oxidation, and pollution.” More studies should be conducted to verify effectiveness, she said, “but Eastern practices that have incorporated it for centuries shouldn’t be fully dismissed. Most doctors believe adaptogens are safe, but how they interact with the mechanics of the body’s stress response system remains a mystery.”
Embrace the consumption of micronutrients. Inspired by work from dermatologist Zoe Diana Draelos, MD, Dr. Shamban advises patients to eat a “rainbow of different colored foods” every day, especially those rich in vitamins A, C, and E. Green foods are generally rich in vitamin E, brown foods are rich in trace minerals, and blue/purple foods are rich in antioxidants. “It’s always best to get nutrients from a rich, healthy diet, but sometimes our skin requires extra help,” she said.
A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study by French researchers, which showed that skin is prone to seasonal changes during the winter, particularly in exposed areas, also looked at whether a daily micronutrient supplement with ingredients that included green tea extract, blackcurrant seed oil, and magnesium, had an impact on the negative effects of winter weather on the skin. “The data indicate that oral micronutrient supplementation can be a safe treatment, with no serious side effects, and may prevent or even eliminate the negative effects of winter on the skin,” she said.
Dr. Shamban disclosed that she conducts clinical trials for many pharmaceutical and device companies.
SAN DIEGO – When patients ask if collagen supplements can benefit their skin, what should you tell them?
According to Ava Shamban, MD, a dermatologist who practices in Santa Monica, Calif., And in her opinion, more research is needed to establish knowledge of the effects and physiologic mechanism of collagen supplementation.
“Collagen is the most abundant protein in the skin; it is found only in animal flesh like meat and fish that contain connective tissue,” she said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium. “We produce less collagen as we age. External factors can slow down our collagen production, including smoking, sun exposure, lack of sleep/exercise, and alcohol consumption.”
Though human studies are lacking, some trials have found that collagen supplements may improve skin hydration and elasticity. “Maybe there’s some benefit, but the digestive process breaks collagen down into amino acids, so I don’t buy it,” she said.
At the meeting, Dr. Shamban discussed other topics related to the effect of supplements and nutrition on the skin:
Can Nutrafol reverse permanent hair loss? “It definitely doesn’t do that,” she said. “Can it help regrow hair? Perhaps.” Nutrafol is an over-the-counter supplement that aims to relieve moderate hair thinning or strengthen hair to prevent breakage, and is physician-formulated with medical-grade ingredients that target root causes of thinning such as stress, lifestyle, hormones, and nutrition.
As for biotin, “we now know that high levels of biotin can actually cause hair loss,” she said. “If you have advanced hair loss, supplements may not work for you. There is no hair regrowth supplement that can bring back a dead hair follicle. Can it help a miniaturized hair follicle? Maybe. Platelet-rich plasma injections have been shown to stimulate hair growth, but only if the follicle is miniaturized, not if it’s totally gone.”
How does the human microbiome affect skin? In a review of sequencing surveys of healthy adults, “the composition of microbial communities was found to be primarily dependent on the physiology of the skin site, with changes in the relative abundance of bacterial taxa associated with moist, dry, and sebaceous environments,” the authors reported . “The microbiome is the genetic material of all the microbes that live inside the body, including bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and viruses,” Dr. Shamban said. “The more diverse the microbiota is, the healthier it’s considered. That diversity is enriched through a diet full of various vegetables and fruits.”
Nearly all adults are colonized with Cutibacterium acnes (formerly Propionibacterium acnes), but only a minority have acne, which highlights the importance of studying diseases in the broader context of host genetics, immune or barrier defects, the microbiome, and the environment, she added. For example, the decreased diversity of the skin microbiome in people with atopic dermatitis has been linked to a reduction in environmental biodiversity in the areas surrounding their homes.
Do adaptogens have a role in skin care? Adaptogens such as ashwagandha, elderberry, ginseng, licorice root, neem, moringa, and reishi mushrooms have been used in Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine for centuries and are purported to promote adaptability, resilience, and survival of living organisms in stress. They appear to affect the neuroendocrine immune system and at low doses may function as mild stress mimetics.
“The idea is that combining adaptogens into skin care can reinforce and support the skin’s resistance against stressors that can accelerate visible signs of aging,” said Dr. Shamban. “They share some similarities with antioxidants in that their main purpose is to protect the body from external stressors such as UV rays, oxidation, and pollution.” More studies should be conducted to verify effectiveness, she said, “but Eastern practices that have incorporated it for centuries shouldn’t be fully dismissed. Most doctors believe adaptogens are safe, but how they interact with the mechanics of the body’s stress response system remains a mystery.”
Embrace the consumption of micronutrients. Inspired by work from dermatologist Zoe Diana Draelos, MD, Dr. Shamban advises patients to eat a “rainbow of different colored foods” every day, especially those rich in vitamins A, C, and E. Green foods are generally rich in vitamin E, brown foods are rich in trace minerals, and blue/purple foods are rich in antioxidants. “It’s always best to get nutrients from a rich, healthy diet, but sometimes our skin requires extra help,” she said.
A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study by French researchers, which showed that skin is prone to seasonal changes during the winter, particularly in exposed areas, also looked at whether a daily micronutrient supplement with ingredients that included green tea extract, blackcurrant seed oil, and magnesium, had an impact on the negative effects of winter weather on the skin. “The data indicate that oral micronutrient supplementation can be a safe treatment, with no serious side effects, and may prevent or even eliminate the negative effects of winter on the skin,” she said.
Dr. Shamban disclosed that she conducts clinical trials for many pharmaceutical and device companies.
SAN DIEGO – When patients ask if collagen supplements can benefit their skin, what should you tell them?
According to Ava Shamban, MD, a dermatologist who practices in Santa Monica, Calif., And in her opinion, more research is needed to establish knowledge of the effects and physiologic mechanism of collagen supplementation.
“Collagen is the most abundant protein in the skin; it is found only in animal flesh like meat and fish that contain connective tissue,” she said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium. “We produce less collagen as we age. External factors can slow down our collagen production, including smoking, sun exposure, lack of sleep/exercise, and alcohol consumption.”
Though human studies are lacking, some trials have found that collagen supplements may improve skin hydration and elasticity. “Maybe there’s some benefit, but the digestive process breaks collagen down into amino acids, so I don’t buy it,” she said.
At the meeting, Dr. Shamban discussed other topics related to the effect of supplements and nutrition on the skin:
Can Nutrafol reverse permanent hair loss? “It definitely doesn’t do that,” she said. “Can it help regrow hair? Perhaps.” Nutrafol is an over-the-counter supplement that aims to relieve moderate hair thinning or strengthen hair to prevent breakage, and is physician-formulated with medical-grade ingredients that target root causes of thinning such as stress, lifestyle, hormones, and nutrition.
As for biotin, “we now know that high levels of biotin can actually cause hair loss,” she said. “If you have advanced hair loss, supplements may not work for you. There is no hair regrowth supplement that can bring back a dead hair follicle. Can it help a miniaturized hair follicle? Maybe. Platelet-rich plasma injections have been shown to stimulate hair growth, but only if the follicle is miniaturized, not if it’s totally gone.”
How does the human microbiome affect skin? In a review of sequencing surveys of healthy adults, “the composition of microbial communities was found to be primarily dependent on the physiology of the skin site, with changes in the relative abundance of bacterial taxa associated with moist, dry, and sebaceous environments,” the authors reported . “The microbiome is the genetic material of all the microbes that live inside the body, including bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and viruses,” Dr. Shamban said. “The more diverse the microbiota is, the healthier it’s considered. That diversity is enriched through a diet full of various vegetables and fruits.”
Nearly all adults are colonized with Cutibacterium acnes (formerly Propionibacterium acnes), but only a minority have acne, which highlights the importance of studying diseases in the broader context of host genetics, immune or barrier defects, the microbiome, and the environment, she added. For example, the decreased diversity of the skin microbiome in people with atopic dermatitis has been linked to a reduction in environmental biodiversity in the areas surrounding their homes.
Do adaptogens have a role in skin care? Adaptogens such as ashwagandha, elderberry, ginseng, licorice root, neem, moringa, and reishi mushrooms have been used in Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine for centuries and are purported to promote adaptability, resilience, and survival of living organisms in stress. They appear to affect the neuroendocrine immune system and at low doses may function as mild stress mimetics.
“The idea is that combining adaptogens into skin care can reinforce and support the skin’s resistance against stressors that can accelerate visible signs of aging,” said Dr. Shamban. “They share some similarities with antioxidants in that their main purpose is to protect the body from external stressors such as UV rays, oxidation, and pollution.” More studies should be conducted to verify effectiveness, she said, “but Eastern practices that have incorporated it for centuries shouldn’t be fully dismissed. Most doctors believe adaptogens are safe, but how they interact with the mechanics of the body’s stress response system remains a mystery.”
Embrace the consumption of micronutrients. Inspired by work from dermatologist Zoe Diana Draelos, MD, Dr. Shamban advises patients to eat a “rainbow of different colored foods” every day, especially those rich in vitamins A, C, and E. Green foods are generally rich in vitamin E, brown foods are rich in trace minerals, and blue/purple foods are rich in antioxidants. “It’s always best to get nutrients from a rich, healthy diet, but sometimes our skin requires extra help,” she said.
A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study by French researchers, which showed that skin is prone to seasonal changes during the winter, particularly in exposed areas, also looked at whether a daily micronutrient supplement with ingredients that included green tea extract, blackcurrant seed oil, and magnesium, had an impact on the negative effects of winter weather on the skin. “The data indicate that oral micronutrient supplementation can be a safe treatment, with no serious side effects, and may prevent or even eliminate the negative effects of winter on the skin,” she said.
Dr. Shamban disclosed that she conducts clinical trials for many pharmaceutical and device companies.
AT MOAS 2022
Berdazimer gel under review at FDA for treating molluscum contagiosum
, the manufacturer announced.
If the submission is accepted by the FDA, the topical product could be approved in the first quarter of 2024, according to a press release from Novan, the manufacturer. If approved, it would be the first-in-class topical treatment for MC, the common, contagious viral skin infection that affects approximately six million individuals in the United States each year, most of them children aged 1-14 years, the statement noted. No FDA-approved therapies currently exist for the condition, which causes unsightly lesions on the face, trunk, limbs, and axillae that may persist untreated for a period of years.
The active ingredient in berdazimer gel 10.3% is berdazimer sodium, a nitric oxide–releasing agent. A 3.4% formulation is in development for the topical treatment of acne, according to the company.
The submission for FDA approval is based on data from the B-SIMPLE4 study, a phase 3 randomized trial of nearly 900 individuals with MC aged 6 months and older (mean age, 6.6 years), with 3-70 raised lesions. Participants were randomized to treatment with berdazimer gel 10.3% or a vehicle gel applied in a thin layer to all lesions once daily for 12 weeks. The results were published in JAMA Dermatology.
The primary outcome was complete clearance of all lesions. At 12 weeks, 32.4% of patients in the berdazimer group achieved this outcome vs. 19.7% of those in the vehicle group (P < .001). Overall adverse event rates were low in both groups; 4.1% of patients on berdazimer and 0.7% of those on the vehicle experienced adverse events that led to discontinuation of treatment. The most common adverse events across both groups were application-site pain and erythema, and most of these were mild or moderate.
, the manufacturer announced.
If the submission is accepted by the FDA, the topical product could be approved in the first quarter of 2024, according to a press release from Novan, the manufacturer. If approved, it would be the first-in-class topical treatment for MC, the common, contagious viral skin infection that affects approximately six million individuals in the United States each year, most of them children aged 1-14 years, the statement noted. No FDA-approved therapies currently exist for the condition, which causes unsightly lesions on the face, trunk, limbs, and axillae that may persist untreated for a period of years.
The active ingredient in berdazimer gel 10.3% is berdazimer sodium, a nitric oxide–releasing agent. A 3.4% formulation is in development for the topical treatment of acne, according to the company.
The submission for FDA approval is based on data from the B-SIMPLE4 study, a phase 3 randomized trial of nearly 900 individuals with MC aged 6 months and older (mean age, 6.6 years), with 3-70 raised lesions. Participants were randomized to treatment with berdazimer gel 10.3% or a vehicle gel applied in a thin layer to all lesions once daily for 12 weeks. The results were published in JAMA Dermatology.
The primary outcome was complete clearance of all lesions. At 12 weeks, 32.4% of patients in the berdazimer group achieved this outcome vs. 19.7% of those in the vehicle group (P < .001). Overall adverse event rates were low in both groups; 4.1% of patients on berdazimer and 0.7% of those on the vehicle experienced adverse events that led to discontinuation of treatment. The most common adverse events across both groups were application-site pain and erythema, and most of these were mild or moderate.
, the manufacturer announced.
If the submission is accepted by the FDA, the topical product could be approved in the first quarter of 2024, according to a press release from Novan, the manufacturer. If approved, it would be the first-in-class topical treatment for MC, the common, contagious viral skin infection that affects approximately six million individuals in the United States each year, most of them children aged 1-14 years, the statement noted. No FDA-approved therapies currently exist for the condition, which causes unsightly lesions on the face, trunk, limbs, and axillae that may persist untreated for a period of years.
The active ingredient in berdazimer gel 10.3% is berdazimer sodium, a nitric oxide–releasing agent. A 3.4% formulation is in development for the topical treatment of acne, according to the company.
The submission for FDA approval is based on data from the B-SIMPLE4 study, a phase 3 randomized trial of nearly 900 individuals with MC aged 6 months and older (mean age, 6.6 years), with 3-70 raised lesions. Participants were randomized to treatment with berdazimer gel 10.3% or a vehicle gel applied in a thin layer to all lesions once daily for 12 weeks. The results were published in JAMA Dermatology.
The primary outcome was complete clearance of all lesions. At 12 weeks, 32.4% of patients in the berdazimer group achieved this outcome vs. 19.7% of those in the vehicle group (P < .001). Overall adverse event rates were low in both groups; 4.1% of patients on berdazimer and 0.7% of those on the vehicle experienced adverse events that led to discontinuation of treatment. The most common adverse events across both groups were application-site pain and erythema, and most of these were mild or moderate.
Five thoughts on the Damar Hamlin collapse
The obvious first statement is that it’s neither wise nor appropriate to speculate on the specifics of Damar Hamlin’s cardiac event during a football game on Jan. 2 (including the possibility of commotio cordis) or his ongoing care. The public nature of his collapse induces intense curiosity but people with illness deserve privacy. Privacy in health care is in short supply. I disagree strongly with those who say his doctors ought to be giving public updates. That’s up to the family.
But there are important general concepts to consider about this incident. These include ...
Cardiac arrest can happen to anyone
People with structural heart disease or other chronic illnesses have a higher risk of arrhythmia, but the notion that athletes are immune from cardiac arrest is wrong. This sentence almost seems too obvious to write, but to this day, I hear clinicians express surprise that an athletic person has heart disease.
Survival turns on rapid and effective intervention
In the old days of electrophysiology, we used to test implantable cardioverter-defibrillators during an implant procedure by inducing ventricular fibrillation (VF) and watching the device convert it. Thankfully, trials have shown that this is no longer necessary for most implants.
When you induce VF In the EP lab, you learn quickly that a) it causes loss of consciousness in a matter of seconds, b) rapid defibrillation restores consciousness, often without the patients knowing or remembering they passed out, and c) the failure of the shock to terminate VF results in deterioration in a matter of 1-2 minutes. Even 1 minute in VF feels so long.
Need is an appropriate word in VF treatment
Clinicians often use the verb need. As in, this patient needs this pill or this procedure. It’s rarely appropriate.
But in the case of treating VF, patients truly need rapid defibrillation. Survival of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is low because there just aren’t enough automated external defibrillators (AEDs) or people trained to use them. A study of patients who had out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in Denmark found that 30-day survival almost doubled (28.8% vs. 16.4%), when the nearest AED was accessible.
Bystanders must act
The public messages are simple: If a person loses consciousness in front of you, and is not breathing normally, assume it is a cardiac arrest, call 911 to get professional help, and start hands-only chest compressions. Don’t spend time checking for a pulse or trying to wake the person. If this is not a cardiac arrest, they will soon tell you to stop compressing their chest. Seconds matter.
Chest compressions are important but what is really needed is defibrillation. A crucial step in CPR is to send someone to get an AED and get the pads attached. If this is a shockable rhythm, deliver the shock. Hamlin’s collapse emphasizes the importance of the AED; without it, his survival to the hospital would have been unlikely.
Widespread preparticipation screening of young athletes remains a bad idea
Whenever cardiac arrest occurs in an athlete, in such a public way, people think about prevention. Surely it is better to prevent such an event than react to it, goes the thinking. The argument against this idea has four prongs:
The incidence of cardiac disease in a young athlete is extremely low, which sets up a situation where most “positive” tests are false positive. A false positive screening ECG or echocardiogram can create harm in multiple ways. One is the risk from downstream procedures, but worse is the inappropriate disqualification from sport. Healthwise, few harms could be greater than creating long-term fear of exercise in someone.
There is also the problem of false-negative screening tests. An ECG may be normal in the setting of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. And a normal echocardiogram does not exclude arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy or other genetic causes of cardiac arrest. In a 2018 study from a major sports cardiology center in London, 6 of the 8 sudden cardiac deaths in their series were in athletes who had no detectable abnormalities on screening.
Even when disease is found, it’s not clear that prohibiting participation in sports prevents sudden death. Many previous class III recommendations against participation in sport now carry class II – may be considered – designations.
Finally, screening for any disease loses value as treatments improve. Public education regarding rapid intervention with CPR and AED use is the best treatment option. A great example is the case of Christian Erikson, a Danish soccer player who suffered cardiac arrest during a match at the European Championships in 2021 and was rapidly defibrillated on the field. Therapy was so effective that he was conscious and able to wave to fans on his way out of the stadium. He has now returned to elite competition.
Proponents of screening might oppose my take by saying that National Football League players are intensely screened. But this is different from widespread screening of high school and college athletes. It might sound harsh to say, but professional teams have dualities of interests in the health of their athletes given the million-dollar contracts.
What’s more, professional teams can afford to hire expert cardiologists to perform the testing. This would likely reduce the rate of false-positive findings, compared with screening in the community setting. I often have young people referred to me because of asymptomatic bradycardia found during athletic screening – an obviously normal finding.
Conclusions
As long as there are sports, there will be athletes who suffer cardiac arrest.
We can both hope for Hamlin’s full recovery and learn lessons to help reduce the rate of death from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. This mostly involves education on how to help fellow humans and a public health commitment to access to AEDs.
John Mandrola, MD, practices cardiac electrophysiology in Louisville, Ky. and is a writer and podcaster for Medscape. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The obvious first statement is that it’s neither wise nor appropriate to speculate on the specifics of Damar Hamlin’s cardiac event during a football game on Jan. 2 (including the possibility of commotio cordis) or his ongoing care. The public nature of his collapse induces intense curiosity but people with illness deserve privacy. Privacy in health care is in short supply. I disagree strongly with those who say his doctors ought to be giving public updates. That’s up to the family.
But there are important general concepts to consider about this incident. These include ...
Cardiac arrest can happen to anyone
People with structural heart disease or other chronic illnesses have a higher risk of arrhythmia, but the notion that athletes are immune from cardiac arrest is wrong. This sentence almost seems too obvious to write, but to this day, I hear clinicians express surprise that an athletic person has heart disease.
Survival turns on rapid and effective intervention
In the old days of electrophysiology, we used to test implantable cardioverter-defibrillators during an implant procedure by inducing ventricular fibrillation (VF) and watching the device convert it. Thankfully, trials have shown that this is no longer necessary for most implants.
When you induce VF In the EP lab, you learn quickly that a) it causes loss of consciousness in a matter of seconds, b) rapid defibrillation restores consciousness, often without the patients knowing or remembering they passed out, and c) the failure of the shock to terminate VF results in deterioration in a matter of 1-2 minutes. Even 1 minute in VF feels so long.
Need is an appropriate word in VF treatment
Clinicians often use the verb need. As in, this patient needs this pill or this procedure. It’s rarely appropriate.
But in the case of treating VF, patients truly need rapid defibrillation. Survival of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is low because there just aren’t enough automated external defibrillators (AEDs) or people trained to use them. A study of patients who had out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in Denmark found that 30-day survival almost doubled (28.8% vs. 16.4%), when the nearest AED was accessible.
Bystanders must act
The public messages are simple: If a person loses consciousness in front of you, and is not breathing normally, assume it is a cardiac arrest, call 911 to get professional help, and start hands-only chest compressions. Don’t spend time checking for a pulse or trying to wake the person. If this is not a cardiac arrest, they will soon tell you to stop compressing their chest. Seconds matter.
Chest compressions are important but what is really needed is defibrillation. A crucial step in CPR is to send someone to get an AED and get the pads attached. If this is a shockable rhythm, deliver the shock. Hamlin’s collapse emphasizes the importance of the AED; without it, his survival to the hospital would have been unlikely.
Widespread preparticipation screening of young athletes remains a bad idea
Whenever cardiac arrest occurs in an athlete, in such a public way, people think about prevention. Surely it is better to prevent such an event than react to it, goes the thinking. The argument against this idea has four prongs:
The incidence of cardiac disease in a young athlete is extremely low, which sets up a situation where most “positive” tests are false positive. A false positive screening ECG or echocardiogram can create harm in multiple ways. One is the risk from downstream procedures, but worse is the inappropriate disqualification from sport. Healthwise, few harms could be greater than creating long-term fear of exercise in someone.
There is also the problem of false-negative screening tests. An ECG may be normal in the setting of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. And a normal echocardiogram does not exclude arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy or other genetic causes of cardiac arrest. In a 2018 study from a major sports cardiology center in London, 6 of the 8 sudden cardiac deaths in their series were in athletes who had no detectable abnormalities on screening.
Even when disease is found, it’s not clear that prohibiting participation in sports prevents sudden death. Many previous class III recommendations against participation in sport now carry class II – may be considered – designations.
Finally, screening for any disease loses value as treatments improve. Public education regarding rapid intervention with CPR and AED use is the best treatment option. A great example is the case of Christian Erikson, a Danish soccer player who suffered cardiac arrest during a match at the European Championships in 2021 and was rapidly defibrillated on the field. Therapy was so effective that he was conscious and able to wave to fans on his way out of the stadium. He has now returned to elite competition.
Proponents of screening might oppose my take by saying that National Football League players are intensely screened. But this is different from widespread screening of high school and college athletes. It might sound harsh to say, but professional teams have dualities of interests in the health of their athletes given the million-dollar contracts.
What’s more, professional teams can afford to hire expert cardiologists to perform the testing. This would likely reduce the rate of false-positive findings, compared with screening in the community setting. I often have young people referred to me because of asymptomatic bradycardia found during athletic screening – an obviously normal finding.
Conclusions
As long as there are sports, there will be athletes who suffer cardiac arrest.
We can both hope for Hamlin’s full recovery and learn lessons to help reduce the rate of death from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. This mostly involves education on how to help fellow humans and a public health commitment to access to AEDs.
John Mandrola, MD, practices cardiac electrophysiology in Louisville, Ky. and is a writer and podcaster for Medscape. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The obvious first statement is that it’s neither wise nor appropriate to speculate on the specifics of Damar Hamlin’s cardiac event during a football game on Jan. 2 (including the possibility of commotio cordis) or his ongoing care. The public nature of his collapse induces intense curiosity but people with illness deserve privacy. Privacy in health care is in short supply. I disagree strongly with those who say his doctors ought to be giving public updates. That’s up to the family.
But there are important general concepts to consider about this incident. These include ...
Cardiac arrest can happen to anyone
People with structural heart disease or other chronic illnesses have a higher risk of arrhythmia, but the notion that athletes are immune from cardiac arrest is wrong. This sentence almost seems too obvious to write, but to this day, I hear clinicians express surprise that an athletic person has heart disease.
Survival turns on rapid and effective intervention
In the old days of electrophysiology, we used to test implantable cardioverter-defibrillators during an implant procedure by inducing ventricular fibrillation (VF) and watching the device convert it. Thankfully, trials have shown that this is no longer necessary for most implants.
When you induce VF In the EP lab, you learn quickly that a) it causes loss of consciousness in a matter of seconds, b) rapid defibrillation restores consciousness, often without the patients knowing or remembering they passed out, and c) the failure of the shock to terminate VF results in deterioration in a matter of 1-2 minutes. Even 1 minute in VF feels so long.
Need is an appropriate word in VF treatment
Clinicians often use the verb need. As in, this patient needs this pill or this procedure. It’s rarely appropriate.
But in the case of treating VF, patients truly need rapid defibrillation. Survival of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is low because there just aren’t enough automated external defibrillators (AEDs) or people trained to use them. A study of patients who had out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in Denmark found that 30-day survival almost doubled (28.8% vs. 16.4%), when the nearest AED was accessible.
Bystanders must act
The public messages are simple: If a person loses consciousness in front of you, and is not breathing normally, assume it is a cardiac arrest, call 911 to get professional help, and start hands-only chest compressions. Don’t spend time checking for a pulse or trying to wake the person. If this is not a cardiac arrest, they will soon tell you to stop compressing their chest. Seconds matter.
Chest compressions are important but what is really needed is defibrillation. A crucial step in CPR is to send someone to get an AED and get the pads attached. If this is a shockable rhythm, deliver the shock. Hamlin’s collapse emphasizes the importance of the AED; without it, his survival to the hospital would have been unlikely.
Widespread preparticipation screening of young athletes remains a bad idea
Whenever cardiac arrest occurs in an athlete, in such a public way, people think about prevention. Surely it is better to prevent such an event than react to it, goes the thinking. The argument against this idea has four prongs:
The incidence of cardiac disease in a young athlete is extremely low, which sets up a situation where most “positive” tests are false positive. A false positive screening ECG or echocardiogram can create harm in multiple ways. One is the risk from downstream procedures, but worse is the inappropriate disqualification from sport. Healthwise, few harms could be greater than creating long-term fear of exercise in someone.
There is also the problem of false-negative screening tests. An ECG may be normal in the setting of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. And a normal echocardiogram does not exclude arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy or other genetic causes of cardiac arrest. In a 2018 study from a major sports cardiology center in London, 6 of the 8 sudden cardiac deaths in their series were in athletes who had no detectable abnormalities on screening.
Even when disease is found, it’s not clear that prohibiting participation in sports prevents sudden death. Many previous class III recommendations against participation in sport now carry class II – may be considered – designations.
Finally, screening for any disease loses value as treatments improve. Public education regarding rapid intervention with CPR and AED use is the best treatment option. A great example is the case of Christian Erikson, a Danish soccer player who suffered cardiac arrest during a match at the European Championships in 2021 and was rapidly defibrillated on the field. Therapy was so effective that he was conscious and able to wave to fans on his way out of the stadium. He has now returned to elite competition.
Proponents of screening might oppose my take by saying that National Football League players are intensely screened. But this is different from widespread screening of high school and college athletes. It might sound harsh to say, but professional teams have dualities of interests in the health of their athletes given the million-dollar contracts.
What’s more, professional teams can afford to hire expert cardiologists to perform the testing. This would likely reduce the rate of false-positive findings, compared with screening in the community setting. I often have young people referred to me because of asymptomatic bradycardia found during athletic screening – an obviously normal finding.
Conclusions
As long as there are sports, there will be athletes who suffer cardiac arrest.
We can both hope for Hamlin’s full recovery and learn lessons to help reduce the rate of death from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. This mostly involves education on how to help fellow humans and a public health commitment to access to AEDs.
John Mandrola, MD, practices cardiac electrophysiology in Louisville, Ky. and is a writer and podcaster for Medscape. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Small study finds high dose vitamin D relieved toxic erythema of chemotherapy
seen on an inpatient dermatology consultative service.
Currently, chemotherapy cessation, delay, or dose modification are the “only reliable methods of resolving TEC,” and supportive agents such as topical corticosteroids, topical keratolytics, and pain control are associated with variable and “relatively slow improvement involving 2 to 4 weeks of recovery after chemotherapy interruption,” Cuong V. Nguyen, MD, of the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues, wrote in a research letter.
Onset of TEC in the six patients occurred a mean of 8.5 days after chemotherapy. Vitamin D – 50,000 IU for one patient and 100,000 IU for the others – was administered a mean of 4.3 days from rash onset and again in 7 days. Triamcinolone, 0.1%, or clobetasol, 0.05%, ointments were also prescribed.
All patients experienced symptomatic improvement in pain, pruritus, or swelling within a day of the first vitamin D treatment, and improvement in redness within 1 to 4 days, the authors said. The second treatment was administered for residual symptoms.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology and director of the supportive oncodermatology clinic at George Washington University, Washington, said that supporting patients through the “expected, disabling and often treatment-limiting side effects of oncologic therapies” is an area that is “in its infancy” and is characterized by limited evidence-based approaches.
“Creativity is therefore a must,” he said, commenting on the research letter. “Practice starts with anecdote, and this is certainly an exciting finding ... I look forward to trialing this with our patients at GW.”
Five of the six patients had a hematologic condition that required induction chemotherapy before hematopoietic stem cell transplant, and one was receiving regorafenib for treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Diagnosis of TEC was established by clinical presentation, and five of the six patients underwent a biopsy. Biopsy findings were consistent with a TEC diagnosis in three patients, and showed nonspecific perivascular dermatitis in two, the investigators reported.
Further research is needed to determine optimal dosing, “delineate safety concerns and potential role in cancer treatment, and establish whether a durable response in patients with continuous chemotherapy, such as in an outpatient setting, is possible,” they said.
Dr. Nguyen and his coauthors reported no conflict of interest disclosures.
seen on an inpatient dermatology consultative service.
Currently, chemotherapy cessation, delay, or dose modification are the “only reliable methods of resolving TEC,” and supportive agents such as topical corticosteroids, topical keratolytics, and pain control are associated with variable and “relatively slow improvement involving 2 to 4 weeks of recovery after chemotherapy interruption,” Cuong V. Nguyen, MD, of the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues, wrote in a research letter.
Onset of TEC in the six patients occurred a mean of 8.5 days after chemotherapy. Vitamin D – 50,000 IU for one patient and 100,000 IU for the others – was administered a mean of 4.3 days from rash onset and again in 7 days. Triamcinolone, 0.1%, or clobetasol, 0.05%, ointments were also prescribed.
All patients experienced symptomatic improvement in pain, pruritus, or swelling within a day of the first vitamin D treatment, and improvement in redness within 1 to 4 days, the authors said. The second treatment was administered for residual symptoms.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology and director of the supportive oncodermatology clinic at George Washington University, Washington, said that supporting patients through the “expected, disabling and often treatment-limiting side effects of oncologic therapies” is an area that is “in its infancy” and is characterized by limited evidence-based approaches.
“Creativity is therefore a must,” he said, commenting on the research letter. “Practice starts with anecdote, and this is certainly an exciting finding ... I look forward to trialing this with our patients at GW.”
Five of the six patients had a hematologic condition that required induction chemotherapy before hematopoietic stem cell transplant, and one was receiving regorafenib for treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Diagnosis of TEC was established by clinical presentation, and five of the six patients underwent a biopsy. Biopsy findings were consistent with a TEC diagnosis in three patients, and showed nonspecific perivascular dermatitis in two, the investigators reported.
Further research is needed to determine optimal dosing, “delineate safety concerns and potential role in cancer treatment, and establish whether a durable response in patients with continuous chemotherapy, such as in an outpatient setting, is possible,” they said.
Dr. Nguyen and his coauthors reported no conflict of interest disclosures.
seen on an inpatient dermatology consultative service.
Currently, chemotherapy cessation, delay, or dose modification are the “only reliable methods of resolving TEC,” and supportive agents such as topical corticosteroids, topical keratolytics, and pain control are associated with variable and “relatively slow improvement involving 2 to 4 weeks of recovery after chemotherapy interruption,” Cuong V. Nguyen, MD, of the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues, wrote in a research letter.
Onset of TEC in the six patients occurred a mean of 8.5 days after chemotherapy. Vitamin D – 50,000 IU for one patient and 100,000 IU for the others – was administered a mean of 4.3 days from rash onset and again in 7 days. Triamcinolone, 0.1%, or clobetasol, 0.05%, ointments were also prescribed.
All patients experienced symptomatic improvement in pain, pruritus, or swelling within a day of the first vitamin D treatment, and improvement in redness within 1 to 4 days, the authors said. The second treatment was administered for residual symptoms.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology and director of the supportive oncodermatology clinic at George Washington University, Washington, said that supporting patients through the “expected, disabling and often treatment-limiting side effects of oncologic therapies” is an area that is “in its infancy” and is characterized by limited evidence-based approaches.
“Creativity is therefore a must,” he said, commenting on the research letter. “Practice starts with anecdote, and this is certainly an exciting finding ... I look forward to trialing this with our patients at GW.”
Five of the six patients had a hematologic condition that required induction chemotherapy before hematopoietic stem cell transplant, and one was receiving regorafenib for treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Diagnosis of TEC was established by clinical presentation, and five of the six patients underwent a biopsy. Biopsy findings were consistent with a TEC diagnosis in three patients, and showed nonspecific perivascular dermatitis in two, the investigators reported.
Further research is needed to determine optimal dosing, “delineate safety concerns and potential role in cancer treatment, and establish whether a durable response in patients with continuous chemotherapy, such as in an outpatient setting, is possible,” they said.
Dr. Nguyen and his coauthors reported no conflict of interest disclosures.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
ED doctors call private equity staffing practices illegal and seek to ban them
Thirty-three states plus the District of Columbia have rules on their books against the so-called corporate practice of medicine. But over the years, critics say, companies have successfully sidestepped bans on owning medical practices by buying or establishing local staffing groups that are nominally owned by doctors and restricting the physicians’ authority so they have no direct control.
These laws and regulations, which started appearing nearly a century ago, were meant to fight the commercialization of medicine, maintain the independence and authority of physicians, and prioritize the doctor-patient relationship over the interests of investors and shareholders.
Those campaigning for stiffer enforcement of the laws say that physician-staffing firms owned by private equity investors are the most egregious offenders. Private equity-backed staffing companies manage a quarter of the nation’s emergency departments, according to a Raleigh, N.C.–based doctor who runs a job site for ED physicians. The two largest are Nashville, Tenn.–based Envision Healthcare, owned by investment giant KKR & Co., and Knoxville, Tenn.–based TeamHealth, owned by Blackstone.
Court filings in multiple states, including California, Missouri, Texas, and Tennessee, have called out Envision and TeamHealth for allegedly using doctor groups as straw men to sidestep corporate practice laws. But those filings have typically been in financial cases involving wrongful termination, breach of contract, and overbilling.
Now, physicians and consumer advocates around the country are anticipating a California lawsuit against Envision, scheduled to start in January 2024 in federal court. The plaintiff in the case, Milwaukee-based American Academy of Emergency Medicine Physician Group, alleges that Envision uses shell business structures to retain de facto ownership of ED staffing groups, and it is asking the court to declare them illegal.
“We’re not asking them to pay money, and we will not accept being paid to drop the case,” said David Millstein, lead attorney for the plaintiff. “We are simply asking the court to ban this practice model.”
‘Possibility to reverberate throughout the country’
The physician group believes a victory would lead to a prohibition of the practice across California – and not just in ERs, but for other staff provided by Envision and TeamHealth, including in anesthesiology and hospital medicine. The California Medical Association supports the lawsuit, saying it “will shape the boundaries of California’s prohibition on the corporate practice of medicine.”
The plaintiff – along with many doctors, nurses, and consumer advocates, as well as some lawmakers – hopes that success in the case will spur regulators and prosecutors in other states to take corporate medicine prohibitions more seriously. “Any decision anywhere in the country that says the corporate ownership of a medical practice is illegal has the possibility to reverberate throughout the country, absolutely – and I hope that it would,” said Julie Mayfield, a state senator in North Carolina.
But the push to reinvigorate laws restricting the corporate practice of medicine has plenty of skeptics, who view it as an effort to return to a golden era in medicine that is long gone or may never have existed to begin with. The genie is out of the bottle, they say, noting that the profit motive has penetrated every corner of health care and that nearly 70% of physicians in the United States are now employed by corporations and hospitals.
The corporate practice of medicine doctrine has “a very interesting and not a very flattering history,” said Barak Richman, a law professor at Duke University. “The medical profession was trying to assert its professional dominance that accrued a lot of benefits to itself in ways that were not terribly beneficial to patients or to the market.”
The California case involves Placentia-Linda Hospital in Orange County, where the plaintiff physician group lost its ED management contract to Envision. The complaint alleges that Envision uses the same business model at numerous hospitals around the state.
“Envision exercises profound and pervasive direct and indirect control and/or influence over the medical practice, making decisions which bear directly and indirectly on the practice of medicine, rendering physicians as mere employees, and diminishing physician independence and freedom from commercial interests,” according to the complaint.
Envision said the company is compliant with state laws and that its operating structure is common in the health care industry. “Legal challenges to that structure have proved meritless,” Envision wrote in an email. It added that “care decisions have and always will be between clinicians and patients.”
TeamHealth, an indirect target in the case, said its “world-class operating team” provides management services that “allow clinicians to focus on the practice of medicine and patient care through a structure commonly utilized by hospitals, health systems, and other providers across the country.”
State rules vary widely
State laws and regulations governing the corporate practice of medicine vary widely on multiple factors, including whether there are exceptions for nonprofit organizations, how much of doctors’ revenue outside management firms can keep, who can own the equipment, and how violations are punished. New York, Texas, and California are considered to have among the toughest restrictions, while Florida and 16 other states have none.
Kirk Ogrosky, a partner at the law firm Goodwin Procter, said this kind of management structure predates the arrival of private equity in the industry. “I would be surprised if a company that is interested in investing in this space screwed up the formation documents; it would shock me,” Mr. Ogrosky said.
Private equity–backed firms have been attracted to EDs in recent years because they are profitable and because they have been able to charge inflated amounts for out-of-network care – at least until a federal law cracked down on surprise billing. Envision and TeamHealth prioritize profits, critics say, by maximizing revenue, cutting costs, and consolidating smaller practices into ever-larger groups – to the point of regional dominance.
Envision and TeamHealth are privately owned, which makes it difficult to find reliable data on their finances and the extent of their market penetration.
Leon Adelman, MD, cofounder and CEO of Ivy Clinicians, a Raleigh, N.C.–based startup job site for emergency physicians, has spent 18 months piecing together data and found that private equity–backed staffing firms run 25% of the nation’s EDs. TeamHealth and Envision have the two largest shares, with 8.6% and 8.3%, respectively, Dr. Adelman said.
Other estimates put private equity’s penetration of ERs at closer to 40%.
Doctors push for investigations
So far, efforts by emergency physicians and others to challenge private equity staffing firms over their alleged violations have yielded frustrating results.
An advocacy group called Take Medicine Back, formed last year by a handful of ED physicians, sent a letter in July to North Carolina Attorney General Josh Stein, asking him to investigate violations of the ban on the corporate practice of medicine. And because Mr. Stein holds a senior position at the National Association of Attorneys General, the letter also asked him to take the lead in persuading his fellow AGs to “launch a multi-state investigation into the widespread lack of enforcement” of corporate practice of medicine laws.
The group’s leader, Mitchell Li, MD, said he was initially disappointed by the response he received from Mr. Stein’s office, which promised to review his request, saying it raised complex legal issues about the corporate practice of medicine in the state. But Dr. Li is now more hopeful, since he has secured a January appointment with officials in Mr. Stein’s office.
Robert McNamara, MD, a cofounder of Dr. Li’s group and chair of emergency medicine at Temple University’s Lewis Katz School of Medicine, drafted complaints to the Texas Medical Board, along with Houston physician David Hoyer, MD, asking the board to intervene against two doctors accused of fronting for professional entities controlled by Envision and TeamHealth. In both cases, the board declined to intervene.
Dr. McNamara, who serves as the chief medical officer of the physicians’ group in the California Envision case, also filed a complaint with Pennsylvania Attorney General Josh Shapiro, alleging that a group called Emergency Care Services of Pennsylvania PC, which was trying to contract with ED physicians of the Crozer Keystone Health System, was wholly owned by TeamHealth and serving as a shell to avoid scrutiny.
A senior official in Mr. Shapiro’s office responded, saying the complaint had been referred to two state agencies, but Dr. McNamara said he has heard nothing back in more than 3 years.
Differing views on private equity’s role
Proponents of private equity ownership say it has brought a lot of good to health care. Jamal Hagler, vice president of research at the American Investment Council, said private equity brings expertise to hospital systems, “whether it’s to hire new staff, grow and open up to new markets, integrate new technologies, or develop new technologies.”
But many physicians who have worked for private equity companies say their mission is not compatible with the best practice of medicine. They cite an emphasis on speed and high patient volume over safety; a preference for lesser-trained, cheaper medical providers; and treatment protocols unsuitable for certain patients.
Sean Jones, MD, an emergency physician in Asheville, N.C., said his first full-time job was at a Florida hospital, where EmCare, a subsidiary of Envision, ran the ED. Dr. Jones said EmCare, in collaboration with the hospital’s owner, pushed doctors to meet performance goals related to wait times and treatments, which were not always good for patients.
For example, if a patient came in with abnormally high heart and respiratory rates – signs of sepsis – doctors were expected to give them large amounts of fluids and antibiotics within an hour, Dr. Jones said. But those symptoms could also be caused by a panic attack or heart failure.
“You don’t want to give a patient with heart failure 2 or 3 liters of fluid, and I would get emails saying, ‘You didn’t do this,’ ” he said. “Well, no, I didn’t, because the reason they couldn’t breathe was they had too much fluid in their lungs.”
Envision said the company’s 25,000 clinicians, “like all clinicians, exercise their independent judgment to provide quality, compassionate, clinically appropriate care.”
Dr. Jones felt otherwise. “We don’t need some MBAs telling us what to do,” he said.
This story was produced by KHN, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation. Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Thirty-three states plus the District of Columbia have rules on their books against the so-called corporate practice of medicine. But over the years, critics say, companies have successfully sidestepped bans on owning medical practices by buying or establishing local staffing groups that are nominally owned by doctors and restricting the physicians’ authority so they have no direct control.
These laws and regulations, which started appearing nearly a century ago, were meant to fight the commercialization of medicine, maintain the independence and authority of physicians, and prioritize the doctor-patient relationship over the interests of investors and shareholders.
Those campaigning for stiffer enforcement of the laws say that physician-staffing firms owned by private equity investors are the most egregious offenders. Private equity-backed staffing companies manage a quarter of the nation’s emergency departments, according to a Raleigh, N.C.–based doctor who runs a job site for ED physicians. The two largest are Nashville, Tenn.–based Envision Healthcare, owned by investment giant KKR & Co., and Knoxville, Tenn.–based TeamHealth, owned by Blackstone.
Court filings in multiple states, including California, Missouri, Texas, and Tennessee, have called out Envision and TeamHealth for allegedly using doctor groups as straw men to sidestep corporate practice laws. But those filings have typically been in financial cases involving wrongful termination, breach of contract, and overbilling.
Now, physicians and consumer advocates around the country are anticipating a California lawsuit against Envision, scheduled to start in January 2024 in federal court. The plaintiff in the case, Milwaukee-based American Academy of Emergency Medicine Physician Group, alleges that Envision uses shell business structures to retain de facto ownership of ED staffing groups, and it is asking the court to declare them illegal.
“We’re not asking them to pay money, and we will not accept being paid to drop the case,” said David Millstein, lead attorney for the plaintiff. “We are simply asking the court to ban this practice model.”
‘Possibility to reverberate throughout the country’
The physician group believes a victory would lead to a prohibition of the practice across California – and not just in ERs, but for other staff provided by Envision and TeamHealth, including in anesthesiology and hospital medicine. The California Medical Association supports the lawsuit, saying it “will shape the boundaries of California’s prohibition on the corporate practice of medicine.”
The plaintiff – along with many doctors, nurses, and consumer advocates, as well as some lawmakers – hopes that success in the case will spur regulators and prosecutors in other states to take corporate medicine prohibitions more seriously. “Any decision anywhere in the country that says the corporate ownership of a medical practice is illegal has the possibility to reverberate throughout the country, absolutely – and I hope that it would,” said Julie Mayfield, a state senator in North Carolina.
But the push to reinvigorate laws restricting the corporate practice of medicine has plenty of skeptics, who view it as an effort to return to a golden era in medicine that is long gone or may never have existed to begin with. The genie is out of the bottle, they say, noting that the profit motive has penetrated every corner of health care and that nearly 70% of physicians in the United States are now employed by corporations and hospitals.
The corporate practice of medicine doctrine has “a very interesting and not a very flattering history,” said Barak Richman, a law professor at Duke University. “The medical profession was trying to assert its professional dominance that accrued a lot of benefits to itself in ways that were not terribly beneficial to patients or to the market.”
The California case involves Placentia-Linda Hospital in Orange County, where the plaintiff physician group lost its ED management contract to Envision. The complaint alleges that Envision uses the same business model at numerous hospitals around the state.
“Envision exercises profound and pervasive direct and indirect control and/or influence over the medical practice, making decisions which bear directly and indirectly on the practice of medicine, rendering physicians as mere employees, and diminishing physician independence and freedom from commercial interests,” according to the complaint.
Envision said the company is compliant with state laws and that its operating structure is common in the health care industry. “Legal challenges to that structure have proved meritless,” Envision wrote in an email. It added that “care decisions have and always will be between clinicians and patients.”
TeamHealth, an indirect target in the case, said its “world-class operating team” provides management services that “allow clinicians to focus on the practice of medicine and patient care through a structure commonly utilized by hospitals, health systems, and other providers across the country.”
State rules vary widely
State laws and regulations governing the corporate practice of medicine vary widely on multiple factors, including whether there are exceptions for nonprofit organizations, how much of doctors’ revenue outside management firms can keep, who can own the equipment, and how violations are punished. New York, Texas, and California are considered to have among the toughest restrictions, while Florida and 16 other states have none.
Kirk Ogrosky, a partner at the law firm Goodwin Procter, said this kind of management structure predates the arrival of private equity in the industry. “I would be surprised if a company that is interested in investing in this space screwed up the formation documents; it would shock me,” Mr. Ogrosky said.
Private equity–backed firms have been attracted to EDs in recent years because they are profitable and because they have been able to charge inflated amounts for out-of-network care – at least until a federal law cracked down on surprise billing. Envision and TeamHealth prioritize profits, critics say, by maximizing revenue, cutting costs, and consolidating smaller practices into ever-larger groups – to the point of regional dominance.
Envision and TeamHealth are privately owned, which makes it difficult to find reliable data on their finances and the extent of their market penetration.
Leon Adelman, MD, cofounder and CEO of Ivy Clinicians, a Raleigh, N.C.–based startup job site for emergency physicians, has spent 18 months piecing together data and found that private equity–backed staffing firms run 25% of the nation’s EDs. TeamHealth and Envision have the two largest shares, with 8.6% and 8.3%, respectively, Dr. Adelman said.
Other estimates put private equity’s penetration of ERs at closer to 40%.
Doctors push for investigations
So far, efforts by emergency physicians and others to challenge private equity staffing firms over their alleged violations have yielded frustrating results.
An advocacy group called Take Medicine Back, formed last year by a handful of ED physicians, sent a letter in July to North Carolina Attorney General Josh Stein, asking him to investigate violations of the ban on the corporate practice of medicine. And because Mr. Stein holds a senior position at the National Association of Attorneys General, the letter also asked him to take the lead in persuading his fellow AGs to “launch a multi-state investigation into the widespread lack of enforcement” of corporate practice of medicine laws.
The group’s leader, Mitchell Li, MD, said he was initially disappointed by the response he received from Mr. Stein’s office, which promised to review his request, saying it raised complex legal issues about the corporate practice of medicine in the state. But Dr. Li is now more hopeful, since he has secured a January appointment with officials in Mr. Stein’s office.
Robert McNamara, MD, a cofounder of Dr. Li’s group and chair of emergency medicine at Temple University’s Lewis Katz School of Medicine, drafted complaints to the Texas Medical Board, along with Houston physician David Hoyer, MD, asking the board to intervene against two doctors accused of fronting for professional entities controlled by Envision and TeamHealth. In both cases, the board declined to intervene.
Dr. McNamara, who serves as the chief medical officer of the physicians’ group in the California Envision case, also filed a complaint with Pennsylvania Attorney General Josh Shapiro, alleging that a group called Emergency Care Services of Pennsylvania PC, which was trying to contract with ED physicians of the Crozer Keystone Health System, was wholly owned by TeamHealth and serving as a shell to avoid scrutiny.
A senior official in Mr. Shapiro’s office responded, saying the complaint had been referred to two state agencies, but Dr. McNamara said he has heard nothing back in more than 3 years.
Differing views on private equity’s role
Proponents of private equity ownership say it has brought a lot of good to health care. Jamal Hagler, vice president of research at the American Investment Council, said private equity brings expertise to hospital systems, “whether it’s to hire new staff, grow and open up to new markets, integrate new technologies, or develop new technologies.”
But many physicians who have worked for private equity companies say their mission is not compatible with the best practice of medicine. They cite an emphasis on speed and high patient volume over safety; a preference for lesser-trained, cheaper medical providers; and treatment protocols unsuitable for certain patients.
Sean Jones, MD, an emergency physician in Asheville, N.C., said his first full-time job was at a Florida hospital, where EmCare, a subsidiary of Envision, ran the ED. Dr. Jones said EmCare, in collaboration with the hospital’s owner, pushed doctors to meet performance goals related to wait times and treatments, which were not always good for patients.
For example, if a patient came in with abnormally high heart and respiratory rates – signs of sepsis – doctors were expected to give them large amounts of fluids and antibiotics within an hour, Dr. Jones said. But those symptoms could also be caused by a panic attack or heart failure.
“You don’t want to give a patient with heart failure 2 or 3 liters of fluid, and I would get emails saying, ‘You didn’t do this,’ ” he said. “Well, no, I didn’t, because the reason they couldn’t breathe was they had too much fluid in their lungs.”
Envision said the company’s 25,000 clinicians, “like all clinicians, exercise their independent judgment to provide quality, compassionate, clinically appropriate care.”
Dr. Jones felt otherwise. “We don’t need some MBAs telling us what to do,” he said.
This story was produced by KHN, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation. Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Thirty-three states plus the District of Columbia have rules on their books against the so-called corporate practice of medicine. But over the years, critics say, companies have successfully sidestepped bans on owning medical practices by buying or establishing local staffing groups that are nominally owned by doctors and restricting the physicians’ authority so they have no direct control.
These laws and regulations, which started appearing nearly a century ago, were meant to fight the commercialization of medicine, maintain the independence and authority of physicians, and prioritize the doctor-patient relationship over the interests of investors and shareholders.
Those campaigning for stiffer enforcement of the laws say that physician-staffing firms owned by private equity investors are the most egregious offenders. Private equity-backed staffing companies manage a quarter of the nation’s emergency departments, according to a Raleigh, N.C.–based doctor who runs a job site for ED physicians. The two largest are Nashville, Tenn.–based Envision Healthcare, owned by investment giant KKR & Co., and Knoxville, Tenn.–based TeamHealth, owned by Blackstone.
Court filings in multiple states, including California, Missouri, Texas, and Tennessee, have called out Envision and TeamHealth for allegedly using doctor groups as straw men to sidestep corporate practice laws. But those filings have typically been in financial cases involving wrongful termination, breach of contract, and overbilling.
Now, physicians and consumer advocates around the country are anticipating a California lawsuit against Envision, scheduled to start in January 2024 in federal court. The plaintiff in the case, Milwaukee-based American Academy of Emergency Medicine Physician Group, alleges that Envision uses shell business structures to retain de facto ownership of ED staffing groups, and it is asking the court to declare them illegal.
“We’re not asking them to pay money, and we will not accept being paid to drop the case,” said David Millstein, lead attorney for the plaintiff. “We are simply asking the court to ban this practice model.”
‘Possibility to reverberate throughout the country’
The physician group believes a victory would lead to a prohibition of the practice across California – and not just in ERs, but for other staff provided by Envision and TeamHealth, including in anesthesiology and hospital medicine. The California Medical Association supports the lawsuit, saying it “will shape the boundaries of California’s prohibition on the corporate practice of medicine.”
The plaintiff – along with many doctors, nurses, and consumer advocates, as well as some lawmakers – hopes that success in the case will spur regulators and prosecutors in other states to take corporate medicine prohibitions more seriously. “Any decision anywhere in the country that says the corporate ownership of a medical practice is illegal has the possibility to reverberate throughout the country, absolutely – and I hope that it would,” said Julie Mayfield, a state senator in North Carolina.
But the push to reinvigorate laws restricting the corporate practice of medicine has plenty of skeptics, who view it as an effort to return to a golden era in medicine that is long gone or may never have existed to begin with. The genie is out of the bottle, they say, noting that the profit motive has penetrated every corner of health care and that nearly 70% of physicians in the United States are now employed by corporations and hospitals.
The corporate practice of medicine doctrine has “a very interesting and not a very flattering history,” said Barak Richman, a law professor at Duke University. “The medical profession was trying to assert its professional dominance that accrued a lot of benefits to itself in ways that were not terribly beneficial to patients or to the market.”
The California case involves Placentia-Linda Hospital in Orange County, where the plaintiff physician group lost its ED management contract to Envision. The complaint alleges that Envision uses the same business model at numerous hospitals around the state.
“Envision exercises profound and pervasive direct and indirect control and/or influence over the medical practice, making decisions which bear directly and indirectly on the practice of medicine, rendering physicians as mere employees, and diminishing physician independence and freedom from commercial interests,” according to the complaint.
Envision said the company is compliant with state laws and that its operating structure is common in the health care industry. “Legal challenges to that structure have proved meritless,” Envision wrote in an email. It added that “care decisions have and always will be between clinicians and patients.”
TeamHealth, an indirect target in the case, said its “world-class operating team” provides management services that “allow clinicians to focus on the practice of medicine and patient care through a structure commonly utilized by hospitals, health systems, and other providers across the country.”
State rules vary widely
State laws and regulations governing the corporate practice of medicine vary widely on multiple factors, including whether there are exceptions for nonprofit organizations, how much of doctors’ revenue outside management firms can keep, who can own the equipment, and how violations are punished. New York, Texas, and California are considered to have among the toughest restrictions, while Florida and 16 other states have none.
Kirk Ogrosky, a partner at the law firm Goodwin Procter, said this kind of management structure predates the arrival of private equity in the industry. “I would be surprised if a company that is interested in investing in this space screwed up the formation documents; it would shock me,” Mr. Ogrosky said.
Private equity–backed firms have been attracted to EDs in recent years because they are profitable and because they have been able to charge inflated amounts for out-of-network care – at least until a federal law cracked down on surprise billing. Envision and TeamHealth prioritize profits, critics say, by maximizing revenue, cutting costs, and consolidating smaller practices into ever-larger groups – to the point of regional dominance.
Envision and TeamHealth are privately owned, which makes it difficult to find reliable data on their finances and the extent of their market penetration.
Leon Adelman, MD, cofounder and CEO of Ivy Clinicians, a Raleigh, N.C.–based startup job site for emergency physicians, has spent 18 months piecing together data and found that private equity–backed staffing firms run 25% of the nation’s EDs. TeamHealth and Envision have the two largest shares, with 8.6% and 8.3%, respectively, Dr. Adelman said.
Other estimates put private equity’s penetration of ERs at closer to 40%.
Doctors push for investigations
So far, efforts by emergency physicians and others to challenge private equity staffing firms over their alleged violations have yielded frustrating results.
An advocacy group called Take Medicine Back, formed last year by a handful of ED physicians, sent a letter in July to North Carolina Attorney General Josh Stein, asking him to investigate violations of the ban on the corporate practice of medicine. And because Mr. Stein holds a senior position at the National Association of Attorneys General, the letter also asked him to take the lead in persuading his fellow AGs to “launch a multi-state investigation into the widespread lack of enforcement” of corporate practice of medicine laws.
The group’s leader, Mitchell Li, MD, said he was initially disappointed by the response he received from Mr. Stein’s office, which promised to review his request, saying it raised complex legal issues about the corporate practice of medicine in the state. But Dr. Li is now more hopeful, since he has secured a January appointment with officials in Mr. Stein’s office.
Robert McNamara, MD, a cofounder of Dr. Li’s group and chair of emergency medicine at Temple University’s Lewis Katz School of Medicine, drafted complaints to the Texas Medical Board, along with Houston physician David Hoyer, MD, asking the board to intervene against two doctors accused of fronting for professional entities controlled by Envision and TeamHealth. In both cases, the board declined to intervene.
Dr. McNamara, who serves as the chief medical officer of the physicians’ group in the California Envision case, also filed a complaint with Pennsylvania Attorney General Josh Shapiro, alleging that a group called Emergency Care Services of Pennsylvania PC, which was trying to contract with ED physicians of the Crozer Keystone Health System, was wholly owned by TeamHealth and serving as a shell to avoid scrutiny.
A senior official in Mr. Shapiro’s office responded, saying the complaint had been referred to two state agencies, but Dr. McNamara said he has heard nothing back in more than 3 years.
Differing views on private equity’s role
Proponents of private equity ownership say it has brought a lot of good to health care. Jamal Hagler, vice president of research at the American Investment Council, said private equity brings expertise to hospital systems, “whether it’s to hire new staff, grow and open up to new markets, integrate new technologies, or develop new technologies.”
But many physicians who have worked for private equity companies say their mission is not compatible with the best practice of medicine. They cite an emphasis on speed and high patient volume over safety; a preference for lesser-trained, cheaper medical providers; and treatment protocols unsuitable for certain patients.
Sean Jones, MD, an emergency physician in Asheville, N.C., said his first full-time job was at a Florida hospital, where EmCare, a subsidiary of Envision, ran the ED. Dr. Jones said EmCare, in collaboration with the hospital’s owner, pushed doctors to meet performance goals related to wait times and treatments, which were not always good for patients.
For example, if a patient came in with abnormally high heart and respiratory rates – signs of sepsis – doctors were expected to give them large amounts of fluids and antibiotics within an hour, Dr. Jones said. But those symptoms could also be caused by a panic attack or heart failure.
“You don’t want to give a patient with heart failure 2 or 3 liters of fluid, and I would get emails saying, ‘You didn’t do this,’ ” he said. “Well, no, I didn’t, because the reason they couldn’t breathe was they had too much fluid in their lungs.”
Envision said the company’s 25,000 clinicians, “like all clinicians, exercise their independent judgment to provide quality, compassionate, clinically appropriate care.”
Dr. Jones felt otherwise. “We don’t need some MBAs telling us what to do,” he said.
This story was produced by KHN, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation. Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Medical practice gave 8,000 patients cancer for Christmas
We wish you a merry Christmas and a happy heart failure
Does anyone really like it when places of business send out cards or messages for the holidays? A card from a truly small family business is one thing, but when you start getting emails from multibillion dollar corporations, it feels a bit dishonest. And that’s not even mentioning the potential blowback when things go wrong.
Now, you may wonder how a company could possibly mess up something so simple. “We wish you a merry Christmas and a happy New Year.” Not that difficult. Unless you’re Askern Medical Practice in Doncaster, England. Instead of expressing a simple expression of joy for the holiday season, Askern informed all 8,000 of its patients that they had aggressive lung cancer with metastases and they needed to fill out a DS1500 form, which entitles terminal patients to certain benefits.
It only took an hour for Askern to recognize its mistake and send a second text apologizing and adding in the appropriate season’s greetings, but obviously the damage was done. Presumably patients who were last at the doctor to have their cold treated were able to shrug off the text, or simply didn’t see it before the correction came through, but obviously many patients had concerns directly related to cancer and panicked. They called in but were by and large unable to reach anyone at the practice. Some patients close by even went to center itself to clear things up.
One patient, Mr. Carl Chegwin, raised an excellent point about the debacle: “What if that message was meant for someone, and then they are told it’s a Christmas message, then again told, ‘Oh no, that was actually meant for you?’ ” The old double backtrack into yes, you actually do have cancer has got to be a candidate for worst Christmas gift of all. Yes, even worse than socks.
Genes know it: You are when you eat
There’s been a lot of recent research on intermittent fasting and what it can and can’t do for one’s health. Much of it has focused on participants’ metabolic rates, but a study just published in Cell Metabolism shows how time-restricted feeding (TRF) has an impact on gene expression, the process through which genes are activated and respond to their environment by creating proteins.
The research conducted by Satchidananda Panda, PhD, of the Salk Institute and his team involved two groups of mice, one with free access to food and the other with a daily 9-hour feeding window. Analysis of tissue samples collected from 22 organ groups revealed that nearly 80% of mouse genes responded to TRF. Interestingly, 40% of the genes in the hypothalamus, adrenal gland, and pancreas, which handle hormone regulation, were affected, suggesting that TRF could potentially aid in diabetes and stress disorder management, the investigators said in a written statement.
The researchers also found that TRF aligned the circadian rhythms of multiple organs of the body, which brings sleep into the picture. “Time-restricted eating synchronized the circadian rhythms to have two major waves: one during fasting, and another just after eating. We suspect this allows the body to coordinate different processes,” said Dr. Panda, whose previous research looked at TRF in firefighters, who typically work on shift schedules.
Time-restricted eating, it appears, affects gene expression throughout the body and allows interconnected organ systems to work smoothly. It’s not just about eating. Go figure.
This group practice reduced stress for everyone
It’s been awhile since we checked in on the good folks at Maharishi International University in Fairfield, Iowa – fictional home of the Fighting Transcendentalists [MAHARISHI RULES!] – but we just have to mention their long-term effort to reduce the national stress.
Way back in the year 2000, a group from MIU began practicing transcendental meditation. The size of the group increased over the next few years and eventually reached 1,725 in 2006. That number is important because it represents the square root of 1% of the U.S. population. When that “transition threshold was achieved,” the university explained in a written statement, “all stress indicators immediately started decreasing.”
By stress indicators they mean the U.S. stress index, the mean of eight variables – murder, rape, assault, robbery, infant mortality, drug deaths, vehicle fatalities, and child deaths by injuries – that the study investigators used to track the effectiveness of the meditation program, they said in the World Journal of Social Science.
After 2011, “when the size of the group size began to decline the rate of decrease in stress slowed and then it reversed and began to increase,” MIU reported.
Coauthor Dr. Kenneth Cavanaugh of MIU explained the process: “This study used state-of-the-art methods of time series regression analysis for eliminating potential alternative explanations due to intrinsic preexisting trends and fluctuations in the data. We carefully studied potential alternative explanations in terms of changes in economic conditions, political leadership, population demographics, and policing strategies. None of these factors could account for the results.”
Since we here at LOTME are serious professional journalists, the use of quotes means we are not making this up. Here’s one more thing in quotes: “A grant for 75 million dollars from the Howard and Alice Settle Foundation provided stipends for participants to be in the group and provided funding to bring several hundred visiting [meditation] experts from India to further augment the MIU group.”
Who needs to make up stuff? Not us.
We wish you a merry Christmas and a happy heart failure
Does anyone really like it when places of business send out cards or messages for the holidays? A card from a truly small family business is one thing, but when you start getting emails from multibillion dollar corporations, it feels a bit dishonest. And that’s not even mentioning the potential blowback when things go wrong.
Now, you may wonder how a company could possibly mess up something so simple. “We wish you a merry Christmas and a happy New Year.” Not that difficult. Unless you’re Askern Medical Practice in Doncaster, England. Instead of expressing a simple expression of joy for the holiday season, Askern informed all 8,000 of its patients that they had aggressive lung cancer with metastases and they needed to fill out a DS1500 form, which entitles terminal patients to certain benefits.
It only took an hour for Askern to recognize its mistake and send a second text apologizing and adding in the appropriate season’s greetings, but obviously the damage was done. Presumably patients who were last at the doctor to have their cold treated were able to shrug off the text, or simply didn’t see it before the correction came through, but obviously many patients had concerns directly related to cancer and panicked. They called in but were by and large unable to reach anyone at the practice. Some patients close by even went to center itself to clear things up.
One patient, Mr. Carl Chegwin, raised an excellent point about the debacle: “What if that message was meant for someone, and then they are told it’s a Christmas message, then again told, ‘Oh no, that was actually meant for you?’ ” The old double backtrack into yes, you actually do have cancer has got to be a candidate for worst Christmas gift of all. Yes, even worse than socks.
Genes know it: You are when you eat
There’s been a lot of recent research on intermittent fasting and what it can and can’t do for one’s health. Much of it has focused on participants’ metabolic rates, but a study just published in Cell Metabolism shows how time-restricted feeding (TRF) has an impact on gene expression, the process through which genes are activated and respond to their environment by creating proteins.
The research conducted by Satchidananda Panda, PhD, of the Salk Institute and his team involved two groups of mice, one with free access to food and the other with a daily 9-hour feeding window. Analysis of tissue samples collected from 22 organ groups revealed that nearly 80% of mouse genes responded to TRF. Interestingly, 40% of the genes in the hypothalamus, adrenal gland, and pancreas, which handle hormone regulation, were affected, suggesting that TRF could potentially aid in diabetes and stress disorder management, the investigators said in a written statement.
The researchers also found that TRF aligned the circadian rhythms of multiple organs of the body, which brings sleep into the picture. “Time-restricted eating synchronized the circadian rhythms to have two major waves: one during fasting, and another just after eating. We suspect this allows the body to coordinate different processes,” said Dr. Panda, whose previous research looked at TRF in firefighters, who typically work on shift schedules.
Time-restricted eating, it appears, affects gene expression throughout the body and allows interconnected organ systems to work smoothly. It’s not just about eating. Go figure.
This group practice reduced stress for everyone
It’s been awhile since we checked in on the good folks at Maharishi International University in Fairfield, Iowa – fictional home of the Fighting Transcendentalists [MAHARISHI RULES!] – but we just have to mention their long-term effort to reduce the national stress.
Way back in the year 2000, a group from MIU began practicing transcendental meditation. The size of the group increased over the next few years and eventually reached 1,725 in 2006. That number is important because it represents the square root of 1% of the U.S. population. When that “transition threshold was achieved,” the university explained in a written statement, “all stress indicators immediately started decreasing.”
By stress indicators they mean the U.S. stress index, the mean of eight variables – murder, rape, assault, robbery, infant mortality, drug deaths, vehicle fatalities, and child deaths by injuries – that the study investigators used to track the effectiveness of the meditation program, they said in the World Journal of Social Science.
After 2011, “when the size of the group size began to decline the rate of decrease in stress slowed and then it reversed and began to increase,” MIU reported.
Coauthor Dr. Kenneth Cavanaugh of MIU explained the process: “This study used state-of-the-art methods of time series regression analysis for eliminating potential alternative explanations due to intrinsic preexisting trends and fluctuations in the data. We carefully studied potential alternative explanations in terms of changes in economic conditions, political leadership, population demographics, and policing strategies. None of these factors could account for the results.”
Since we here at LOTME are serious professional journalists, the use of quotes means we are not making this up. Here’s one more thing in quotes: “A grant for 75 million dollars from the Howard and Alice Settle Foundation provided stipends for participants to be in the group and provided funding to bring several hundred visiting [meditation] experts from India to further augment the MIU group.”
Who needs to make up stuff? Not us.
We wish you a merry Christmas and a happy heart failure
Does anyone really like it when places of business send out cards or messages for the holidays? A card from a truly small family business is one thing, but when you start getting emails from multibillion dollar corporations, it feels a bit dishonest. And that’s not even mentioning the potential blowback when things go wrong.
Now, you may wonder how a company could possibly mess up something so simple. “We wish you a merry Christmas and a happy New Year.” Not that difficult. Unless you’re Askern Medical Practice in Doncaster, England. Instead of expressing a simple expression of joy for the holiday season, Askern informed all 8,000 of its patients that they had aggressive lung cancer with metastases and they needed to fill out a DS1500 form, which entitles terminal patients to certain benefits.
It only took an hour for Askern to recognize its mistake and send a second text apologizing and adding in the appropriate season’s greetings, but obviously the damage was done. Presumably patients who were last at the doctor to have their cold treated were able to shrug off the text, or simply didn’t see it before the correction came through, but obviously many patients had concerns directly related to cancer and panicked. They called in but were by and large unable to reach anyone at the practice. Some patients close by even went to center itself to clear things up.
One patient, Mr. Carl Chegwin, raised an excellent point about the debacle: “What if that message was meant for someone, and then they are told it’s a Christmas message, then again told, ‘Oh no, that was actually meant for you?’ ” The old double backtrack into yes, you actually do have cancer has got to be a candidate for worst Christmas gift of all. Yes, even worse than socks.
Genes know it: You are when you eat
There’s been a lot of recent research on intermittent fasting and what it can and can’t do for one’s health. Much of it has focused on participants’ metabolic rates, but a study just published in Cell Metabolism shows how time-restricted feeding (TRF) has an impact on gene expression, the process through which genes are activated and respond to their environment by creating proteins.
The research conducted by Satchidananda Panda, PhD, of the Salk Institute and his team involved two groups of mice, one with free access to food and the other with a daily 9-hour feeding window. Analysis of tissue samples collected from 22 organ groups revealed that nearly 80% of mouse genes responded to TRF. Interestingly, 40% of the genes in the hypothalamus, adrenal gland, and pancreas, which handle hormone regulation, were affected, suggesting that TRF could potentially aid in diabetes and stress disorder management, the investigators said in a written statement.
The researchers also found that TRF aligned the circadian rhythms of multiple organs of the body, which brings sleep into the picture. “Time-restricted eating synchronized the circadian rhythms to have two major waves: one during fasting, and another just after eating. We suspect this allows the body to coordinate different processes,” said Dr. Panda, whose previous research looked at TRF in firefighters, who typically work on shift schedules.
Time-restricted eating, it appears, affects gene expression throughout the body and allows interconnected organ systems to work smoothly. It’s not just about eating. Go figure.
This group practice reduced stress for everyone
It’s been awhile since we checked in on the good folks at Maharishi International University in Fairfield, Iowa – fictional home of the Fighting Transcendentalists [MAHARISHI RULES!] – but we just have to mention their long-term effort to reduce the national stress.
Way back in the year 2000, a group from MIU began practicing transcendental meditation. The size of the group increased over the next few years and eventually reached 1,725 in 2006. That number is important because it represents the square root of 1% of the U.S. population. When that “transition threshold was achieved,” the university explained in a written statement, “all stress indicators immediately started decreasing.”
By stress indicators they mean the U.S. stress index, the mean of eight variables – murder, rape, assault, robbery, infant mortality, drug deaths, vehicle fatalities, and child deaths by injuries – that the study investigators used to track the effectiveness of the meditation program, they said in the World Journal of Social Science.
After 2011, “when the size of the group size began to decline the rate of decrease in stress slowed and then it reversed and began to increase,” MIU reported.
Coauthor Dr. Kenneth Cavanaugh of MIU explained the process: “This study used state-of-the-art methods of time series regression analysis for eliminating potential alternative explanations due to intrinsic preexisting trends and fluctuations in the data. We carefully studied potential alternative explanations in terms of changes in economic conditions, political leadership, population demographics, and policing strategies. None of these factors could account for the results.”
Since we here at LOTME are serious professional journalists, the use of quotes means we are not making this up. Here’s one more thing in quotes: “A grant for 75 million dollars from the Howard and Alice Settle Foundation provided stipends for participants to be in the group and provided funding to bring several hundred visiting [meditation] experts from India to further augment the MIU group.”
Who needs to make up stuff? Not us.
Oral Propranolol Used as Adjunct Therapy in Cutaneous Angiosarcoma
To the Editor:
Angiosarcoma is a malignancy of the vascular endothelium that most commonly presents on the skin.1 Patients diagnosed with cutaneous angiosarcoma, which is a rare and aggressive malignancy, have a 5-year survival rate of approximately 30%.2,3 Angiosarcoma can be seen in the setting of chronic lymphedema; radiation therapy; and sporadically in elderly patients, where it is commonly seen on the head and neck. Presentation on the head and neck has been associated with worse outcomes, with a projected overall 10-year survival rate of 13.8%; the survival rate is lower if the tumor is surgically unresectable or larger in size. Metastasis can occur via both lymphatic and hematogenous routes, with pulmonary and hepatic metastases most frequently observed.1 Prognostications of poor outcomes for patients with head and neck cutaneous angiosarcoma via a 5-year survival rate were identified in a meta-analysis and included the following: patient age older than 70 years, larger tumors, tumor location of scalp vs face, nonsurgical treatments, and lack of clear margins on histology.2
Treatment of angiosarcoma historically has encompassed both surgical resection and adjuvant radiation therapy with suboptimal success. Evidence supporting various treatment regimens remains sparse due to the low incidence of the neoplasm. Although surgical resection is the only documented curative treatment, cutaneous angiosarcomas frequently are found to have positive surgical margins and require adjuvant radiation. Use of high-dose radiation (>50 Gy) with application over a wide treatment area such as total scalp irradiation is recommended.4 Although radiation has been found to diminish local recurrence rates, it has not substantially affected rates of distant disease recurrence.1 Cytotoxic chemotherapy has clinical utility in minimizing progression, but standard regimens afford a progression-free survival of only months.3 Adjuvant treatment with paclitaxel has been shown to have improved efficacy in scalp angiosarcoma vs other visceral sites, showing a nonprogression rate of 42% at 4 months after treatment.5 More recently, targeted chemotherapeutics, including the vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor bevacizumab and tyrosine kinase inhibitor sorafenib, have shown some survival benefit, but it is unclear if these agents are superior to traditional cytotoxic agents.4,6-10 A phase 2 study of paclitaxel administered weekly with or without bevacizumab showed similar progression-free survival and overall survival, albeit at the expense of added toxicity experienced by participants in the combined group.10
The addition of the nonselective β-adrenergic blocker propranolol to the treatment armamentarium, which was pursued due to its utility in the treatment of benign infantile hemangioma and demonstrated ability to limit the expression of adrenergic receptors in angiosarcoma, has gained clinical attention for possible augmentation of cutaneous angiosarcoma therapy.11-14 Propranolol has been shown to reduce metastasis in other neoplasms—both vascular and nonvascular—and may play a role as an adjuvant treatment to current therapies in angiosarcoma.15-20 We report a patient with cutaneous angiosarcoma (T2 classification) with disease-free survival of nearly 6 years without evidence of recurrence in the setting of continuous propranolol use supplementary to chemotherapy and radiation.
A 78-year-old man with a history of multiple basal cell carcinomas, hypertension, and remote smoking history presented to the dermatology clinic with an enlarging red-brown plaque on the scalp of 2 months’ duration. The lesion had grown rapidly to involve the forehead, right temple, preauricular region, and parietal scalp. At presentation, the tumor measured more than 20 cm in diameter at its greatest point (Figure 1). Physical examination revealed a 6-mm purple nodule within the lesion on the patient’s right parietal scalp. No clinical lymphadenopathy was appreciated at the time of diagnosis. Punch biopsies of the right parietal scalp nodule and right temple patch showed findings consistent with angiosarcoma with diffuse cytoplasmic staining of CD31 in atypical endothelial cells and no staining for human herpesvirus 8 (Figure 2). Concurrent computed tomography of the head showed thickening of the right epidermis, dermis, and deeper scalp tissues, but there was no evidence of skull involvement. Computed tomography of the thorax, abdomen, and pelvis showed no evidence of metastatic disease. After a diagnostic workup, the patient was diagnosed with T2bN0M0 angiosarcoma.
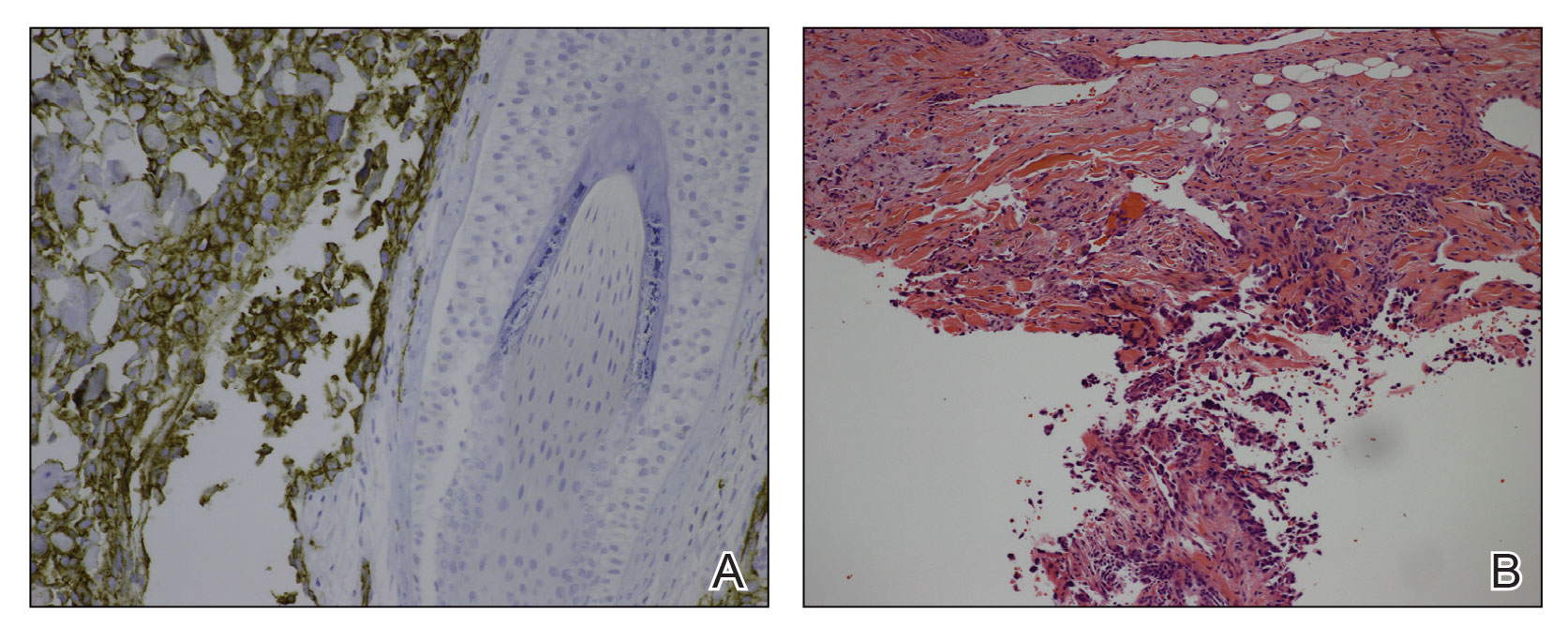
The lesion was determined to be nonresectable due to the extent of the patient’s cutaneous disease. The patient was started on a regimen of paclitaxel, scalp radiation, and oral propranolol. Propranolol 40 mg twice daily was initiated at the time of diagnosis with a plan to continue indefinitely. Starting 1 month after staging, the patient completed 10 weekly cycles of paclitaxel, and he was treated with 60 Gy of scalp radiation in 30 fractions, starting with the second cycle of paclitaxel. He tolerated both well with no reported adverse events. Repeat computed tomography performed 1 month after completion of chemotherapy and radiation showed no evidence of a mass or fluid collection in subcutaneous scalp tissues and no evidence of metastatic disease. This correlated with an observed clinical regression at 1 month and complete clinical response at 5 months with residual hemosiderin and radiation changes. The area of prior disease involvement subsequently evolved from violet to dusky gray in appearance to an eventual complete resolution 26 months after diagnosis, accompanied by atrophic radiation-induced sequelae (Figure 3).
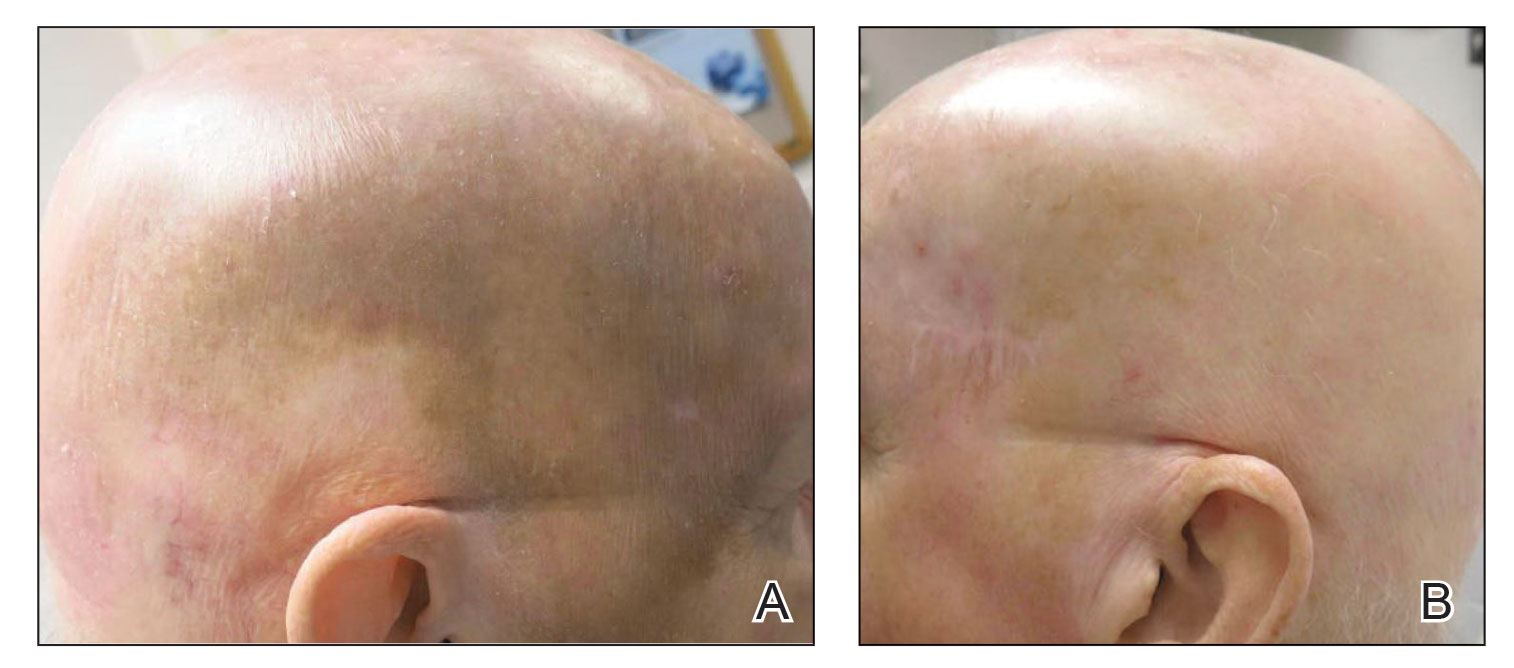
The patient’s postchemotherapy course was complicated by hospitalization for a suspected malignant pleural effusion. Analysis revealed growing ground-glass opacities and nodules in the right lower lung lobe. A thoracentesis with cytology studies was negative for malignancy. Continued monitoring over 19 months demonstrated eventual resolution of those findings. He experienced notable complication from local radiation therapy to the scalp with chronic cutaneous ulceration refractory to wound care and surgical intervention. The patient did not exhibit additional signs or symptoms concerning for recurrence or metastasis and was followed by dermatology and oncology until he died nearly 5 years after initial diagnosis due to complications from acute hypoxic respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19. The last imaging obtained showed no convincing evidence of metastasis, though spinal imaging within a month of his death showed lesions favored to represent benign angiomatous growths. His survival after diagnosis ultimately reached 57 months without confirmed disease recurrence and cause of death unrelated to malignancy history, which is a markedly long documented survival for this extent of disease.
Cutaneous angiosarcoma is an aggressive yet rare malignancy without effective treatments for prolonging survival or eradicating disease. Cutaneous angiosarcoma of the head and neck has a reported 10-year survival rate of 13.8%.1 Although angiosarcoma in any location holds a bleak prognosis, cutaneous angiosarcoma of the scalp with a T2 classification has a 2-year survival rate of 0%. Moreover, even if remission is achieved, disease is highly recurrent, typically within months with the current standard of care.3,21,22
Emerging evidence for the possible role of β-adrenergic receptor blockade in the treatment of malignant vascular neoplasms is promising. Microarrays from a host of vascular growths have demonstrated expression of β-adrenergic receptors in 77% of sampled angiosarcoma specimens in addition to strong expression in infantile hemangiomas, hemangiomas, hemangioendotheliomas, and vascular malformations.19 Research findings have further verified the validity of this approach with the demonstration of b1-, b2-, and b3- adrenergic receptor expression by angiosarcoma cell lines. Propranolol subsequently was shown to effectively target proliferation of these cells and induce apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner and moreover be synergistic in effect with other chemotherapies.15 Several genes have exhibited differential expression between control tumor cells and propranolol-treated cells. Specifically, target genes including AXL (a receptor tyrosine kinase associated with cell adhesion, proliferation, and apoptosis and found to upregulated in melanoma and leukemia) and ERBB receptor feedback inhibitor 1 (receptor tyrosine kinase, with ERBB family members commonly overexpressed or mutated in the setting malignancy) have been posited as possible explanatory factors in the observed angiosarcoma response to propranolol.23
Several cases describing propranolol use as an adjunctive therapy for angiosarcoma suggest a beneficial role in clinical medicine. One case report described propranolol monotherapy for lesion to our patient, with a resultant reduction in Ki-67 as a measure of proliferative index within 1 week of initiating propranolol therapy.13 Propranolol also has been shown to halt or slow progression of metastatic disease in visceral and metastatic angiosarcomas.12-14 In combination with oral etoposide and cyclophosphamide, maintenance propranolol therapy in 7 cases of advanced cutaneous angiosarcoma resulted in 1 complete response and 3 very good partial responses, with a median progression-free survival of 11 months.11 Larger-scale studies have not been published, but the growing number of case reports and case series warrants further investigation of the utility of propranolol as an adjunct to current therapies in advanced angiosarcoma.
- Abraham JA, Hornicek FJ, Kaufman AM, et al. Treatment and outcome of 82 patients with angiosarcoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:1953-1967.
- Shin JY, Roh SG, Lee NH, et al. Predisposing factors for poor prognosis of angiosarcoma of the scalp and face: systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck. 2017;39:380-386.
- Fury MG, Antonescu CR, Zee KJV, et al. A 14-year retrospective review of angiosarcoma: clinical characteristics, prognostic factors, and treatment outcomes with surgery and chemotherapy. Cancer. 2005;11:241-247.
- Dossett LA, Harrington M, Cruse CW, et al. Cutaneous angiosarcoma. Curr Probl Cancer. 2015;39:258-263.
- Penel N, Bui BN, Bay JO, et al. Phase II trial of weekly paclitaxel for unresectable angiosarcoma: the ANGIOTAX study. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:5269-5274.
- Agulnik M, Yarber JL, Okuno SH, et al. An open-label, multicenter, phase II study of bevacizumab for the treatment of angiosarcoma and epithelioid hemangioendotheliomas. Ann Oncol. 2013;24:257-263.
- Maki RG, D’Adamo DR, Keohan ML, et al. Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with metastatic or recurrent sarcomas. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3133-3140.
- Ishida Y, Otsuka A, Kabashima K. Cutaneous angiosarcoma: update on biology and latest treatment. Curr Opin Oncol. 2018;30:107-112.
- Ray-Coquard I, Italiano A, Bompas E, et al. Sorafenib for patients with advanced angiosarcoma: a phase II trial from the French Sarcoma Group (GSF/GETO). Oncologist. 2012;17:260-266.
- Ray-Coquard IL, Domont J, Tresch-Bruneel E, et al. Paclitaxel given once per week with or without bevacizumab in patients with advanced angiosarcoma: a randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:2797-2802.
- Pasquier E, Andre N, Street J, et al. Effective management of advanced angiosarcoma by the synergistic combination of propranolol and vinblastine-based metronomic chemotherapy: a bench to bedside study. EBioMedicine. 2016;6:87-95.
- Banavali S, Pasquier E, Andre N. Targeted therapy with propranolol and metronomic chemotherapy combination: sustained complete response of a relapsing metastatic angiosarcoma. Ecancermedicalscience. 2015;9:499.
- Chow W, Amaya CN, Rains S, et al. Growth attenuation of cutaneous angiosarcoma with propranolol-mediated beta-blockade. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1226-1229.
- Daguze J, Saint-Jean M, Peuvrel L, et al. Visceral metastatic angiosarcoma treated effectively with oral cyclophosphamide combined with propranolol. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:497-499.
- Stiles JM, Amaya C, Rains S, et al. Targeting of beta adrenergic receptors results in therapeutic efficacy against models of hemangioendothelioma and angiosarcoma. PLoS One. 2013;8:e60021.
- Chang PY, Chung CH, Chang WC, et al. The effect of propranolol on the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: a nationwide population-based study. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0216828.
- De Giorgi V, Grazzini M, Benemei S, et al. Propranolol for off-label treatment of patients with melanoma: results from a cohort study. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:e172908.
- Rico M, Baglioni M, Bondarenko M, et al. Metformin and propranolol combination prevents cancer progression and metastasis in different breast cancer models. Oncotarget. 2017;8:2874-2889.
- Chisholm KM, Chang KW, Truong MT, et al. β-Adrenergic receptor expression in vascular tumors. Mod Pathol. 2012;25:1446-1451.
- Leaute-Labreze C, Dumas de la Roque E, Hubiche T, et al. Propranolol for severe hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2649-2651.
- Maddox JC, Evans HL. Angiosarcoma of skin and soft tissue: a study of forty-four cases. Cancer. 1981;48:1907-1921.
- Morgan MB, Swann M, Somach S, et al. Cutaneous angiosarcoma: a case series with prognostic correlation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:867-874.
- Zhou S, Liu P, Jiang W, et al. Identification of potential target genes associated with the effect of propranolol on angiosarcoma via microarray analysis. Oncol Lett. 2017;13:4267-4275.
To the Editor:
Angiosarcoma is a malignancy of the vascular endothelium that most commonly presents on the skin.1 Patients diagnosed with cutaneous angiosarcoma, which is a rare and aggressive malignancy, have a 5-year survival rate of approximately 30%.2,3 Angiosarcoma can be seen in the setting of chronic lymphedema; radiation therapy; and sporadically in elderly patients, where it is commonly seen on the head and neck. Presentation on the head and neck has been associated with worse outcomes, with a projected overall 10-year survival rate of 13.8%; the survival rate is lower if the tumor is surgically unresectable or larger in size. Metastasis can occur via both lymphatic and hematogenous routes, with pulmonary and hepatic metastases most frequently observed.1 Prognostications of poor outcomes for patients with head and neck cutaneous angiosarcoma via a 5-year survival rate were identified in a meta-analysis and included the following: patient age older than 70 years, larger tumors, tumor location of scalp vs face, nonsurgical treatments, and lack of clear margins on histology.2
Treatment of angiosarcoma historically has encompassed both surgical resection and adjuvant radiation therapy with suboptimal success. Evidence supporting various treatment regimens remains sparse due to the low incidence of the neoplasm. Although surgical resection is the only documented curative treatment, cutaneous angiosarcomas frequently are found to have positive surgical margins and require adjuvant radiation. Use of high-dose radiation (>50 Gy) with application over a wide treatment area such as total scalp irradiation is recommended.4 Although radiation has been found to diminish local recurrence rates, it has not substantially affected rates of distant disease recurrence.1 Cytotoxic chemotherapy has clinical utility in minimizing progression, but standard regimens afford a progression-free survival of only months.3 Adjuvant treatment with paclitaxel has been shown to have improved efficacy in scalp angiosarcoma vs other visceral sites, showing a nonprogression rate of 42% at 4 months after treatment.5 More recently, targeted chemotherapeutics, including the vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor bevacizumab and tyrosine kinase inhibitor sorafenib, have shown some survival benefit, but it is unclear if these agents are superior to traditional cytotoxic agents.4,6-10 A phase 2 study of paclitaxel administered weekly with or without bevacizumab showed similar progression-free survival and overall survival, albeit at the expense of added toxicity experienced by participants in the combined group.10
The addition of the nonselective β-adrenergic blocker propranolol to the treatment armamentarium, which was pursued due to its utility in the treatment of benign infantile hemangioma and demonstrated ability to limit the expression of adrenergic receptors in angiosarcoma, has gained clinical attention for possible augmentation of cutaneous angiosarcoma therapy.11-14 Propranolol has been shown to reduce metastasis in other neoplasms—both vascular and nonvascular—and may play a role as an adjuvant treatment to current therapies in angiosarcoma.15-20 We report a patient with cutaneous angiosarcoma (T2 classification) with disease-free survival of nearly 6 years without evidence of recurrence in the setting of continuous propranolol use supplementary to chemotherapy and radiation.

A 78-year-old man with a history of multiple basal cell carcinomas, hypertension, and remote smoking history presented to the dermatology clinic with an enlarging red-brown plaque on the scalp of 2 months’ duration. The lesion had grown rapidly to involve the forehead, right temple, preauricular region, and parietal scalp. At presentation, the tumor measured more than 20 cm in diameter at its greatest point (Figure 1). Physical examination revealed a 6-mm purple nodule within the lesion on the patient’s right parietal scalp. No clinical lymphadenopathy was appreciated at the time of diagnosis. Punch biopsies of the right parietal scalp nodule and right temple patch showed findings consistent with angiosarcoma with diffuse cytoplasmic staining of CD31 in atypical endothelial cells and no staining for human herpesvirus 8 (Figure 2). Concurrent computed tomography of the head showed thickening of the right epidermis, dermis, and deeper scalp tissues, but there was no evidence of skull involvement. Computed tomography of the thorax, abdomen, and pelvis showed no evidence of metastatic disease. After a diagnostic workup, the patient was diagnosed with T2bN0M0 angiosarcoma.

The lesion was determined to be nonresectable due to the extent of the patient’s cutaneous disease. The patient was started on a regimen of paclitaxel, scalp radiation, and oral propranolol. Propranolol 40 mg twice daily was initiated at the time of diagnosis with a plan to continue indefinitely. Starting 1 month after staging, the patient completed 10 weekly cycles of paclitaxel, and he was treated with 60 Gy of scalp radiation in 30 fractions, starting with the second cycle of paclitaxel. He tolerated both well with no reported adverse events. Repeat computed tomography performed 1 month after completion of chemotherapy and radiation showed no evidence of a mass or fluid collection in subcutaneous scalp tissues and no evidence of metastatic disease. This correlated with an observed clinical regression at 1 month and complete clinical response at 5 months with residual hemosiderin and radiation changes. The area of prior disease involvement subsequently evolved from violet to dusky gray in appearance to an eventual complete resolution 26 months after diagnosis, accompanied by atrophic radiation-induced sequelae (Figure 3).

The patient’s postchemotherapy course was complicated by hospitalization for a suspected malignant pleural effusion. Analysis revealed growing ground-glass opacities and nodules in the right lower lung lobe. A thoracentesis with cytology studies was negative for malignancy. Continued monitoring over 19 months demonstrated eventual resolution of those findings. He experienced notable complication from local radiation therapy to the scalp with chronic cutaneous ulceration refractory to wound care and surgical intervention. The patient did not exhibit additional signs or symptoms concerning for recurrence or metastasis and was followed by dermatology and oncology until he died nearly 5 years after initial diagnosis due to complications from acute hypoxic respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19. The last imaging obtained showed no convincing evidence of metastasis, though spinal imaging within a month of his death showed lesions favored to represent benign angiomatous growths. His survival after diagnosis ultimately reached 57 months without confirmed disease recurrence and cause of death unrelated to malignancy history, which is a markedly long documented survival for this extent of disease.
Cutaneous angiosarcoma is an aggressive yet rare malignancy without effective treatments for prolonging survival or eradicating disease. Cutaneous angiosarcoma of the head and neck has a reported 10-year survival rate of 13.8%.1 Although angiosarcoma in any location holds a bleak prognosis, cutaneous angiosarcoma of the scalp with a T2 classification has a 2-year survival rate of 0%. Moreover, even if remission is achieved, disease is highly recurrent, typically within months with the current standard of care.3,21,22
Emerging evidence for the possible role of β-adrenergic receptor blockade in the treatment of malignant vascular neoplasms is promising. Microarrays from a host of vascular growths have demonstrated expression of β-adrenergic receptors in 77% of sampled angiosarcoma specimens in addition to strong expression in infantile hemangiomas, hemangiomas, hemangioendotheliomas, and vascular malformations.19 Research findings have further verified the validity of this approach with the demonstration of b1-, b2-, and b3- adrenergic receptor expression by angiosarcoma cell lines. Propranolol subsequently was shown to effectively target proliferation of these cells and induce apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner and moreover be synergistic in effect with other chemotherapies.15 Several genes have exhibited differential expression between control tumor cells and propranolol-treated cells. Specifically, target genes including AXL (a receptor tyrosine kinase associated with cell adhesion, proliferation, and apoptosis and found to upregulated in melanoma and leukemia) and ERBB receptor feedback inhibitor 1 (receptor tyrosine kinase, with ERBB family members commonly overexpressed or mutated in the setting malignancy) have been posited as possible explanatory factors in the observed angiosarcoma response to propranolol.23
Several cases describing propranolol use as an adjunctive therapy for angiosarcoma suggest a beneficial role in clinical medicine. One case report described propranolol monotherapy for lesion to our patient, with a resultant reduction in Ki-67 as a measure of proliferative index within 1 week of initiating propranolol therapy.13 Propranolol also has been shown to halt or slow progression of metastatic disease in visceral and metastatic angiosarcomas.12-14 In combination with oral etoposide and cyclophosphamide, maintenance propranolol therapy in 7 cases of advanced cutaneous angiosarcoma resulted in 1 complete response and 3 very good partial responses, with a median progression-free survival of 11 months.11 Larger-scale studies have not been published, but the growing number of case reports and case series warrants further investigation of the utility of propranolol as an adjunct to current therapies in advanced angiosarcoma.
To the Editor:
Angiosarcoma is a malignancy of the vascular endothelium that most commonly presents on the skin.1 Patients diagnosed with cutaneous angiosarcoma, which is a rare and aggressive malignancy, have a 5-year survival rate of approximately 30%.2,3 Angiosarcoma can be seen in the setting of chronic lymphedema; radiation therapy; and sporadically in elderly patients, where it is commonly seen on the head and neck. Presentation on the head and neck has been associated with worse outcomes, with a projected overall 10-year survival rate of 13.8%; the survival rate is lower if the tumor is surgically unresectable or larger in size. Metastasis can occur via both lymphatic and hematogenous routes, with pulmonary and hepatic metastases most frequently observed.1 Prognostications of poor outcomes for patients with head and neck cutaneous angiosarcoma via a 5-year survival rate were identified in a meta-analysis and included the following: patient age older than 70 years, larger tumors, tumor location of scalp vs face, nonsurgical treatments, and lack of clear margins on histology.2
Treatment of angiosarcoma historically has encompassed both surgical resection and adjuvant radiation therapy with suboptimal success. Evidence supporting various treatment regimens remains sparse due to the low incidence of the neoplasm. Although surgical resection is the only documented curative treatment, cutaneous angiosarcomas frequently are found to have positive surgical margins and require adjuvant radiation. Use of high-dose radiation (>50 Gy) with application over a wide treatment area such as total scalp irradiation is recommended.4 Although radiation has been found to diminish local recurrence rates, it has not substantially affected rates of distant disease recurrence.1 Cytotoxic chemotherapy has clinical utility in minimizing progression, but standard regimens afford a progression-free survival of only months.3 Adjuvant treatment with paclitaxel has been shown to have improved efficacy in scalp angiosarcoma vs other visceral sites, showing a nonprogression rate of 42% at 4 months after treatment.5 More recently, targeted chemotherapeutics, including the vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor bevacizumab and tyrosine kinase inhibitor sorafenib, have shown some survival benefit, but it is unclear if these agents are superior to traditional cytotoxic agents.4,6-10 A phase 2 study of paclitaxel administered weekly with or without bevacizumab showed similar progression-free survival and overall survival, albeit at the expense of added toxicity experienced by participants in the combined group.10
The addition of the nonselective β-adrenergic blocker propranolol to the treatment armamentarium, which was pursued due to its utility in the treatment of benign infantile hemangioma and demonstrated ability to limit the expression of adrenergic receptors in angiosarcoma, has gained clinical attention for possible augmentation of cutaneous angiosarcoma therapy.11-14 Propranolol has been shown to reduce metastasis in other neoplasms—both vascular and nonvascular—and may play a role as an adjuvant treatment to current therapies in angiosarcoma.15-20 We report a patient with cutaneous angiosarcoma (T2 classification) with disease-free survival of nearly 6 years without evidence of recurrence in the setting of continuous propranolol use supplementary to chemotherapy and radiation.

A 78-year-old man with a history of multiple basal cell carcinomas, hypertension, and remote smoking history presented to the dermatology clinic with an enlarging red-brown plaque on the scalp of 2 months’ duration. The lesion had grown rapidly to involve the forehead, right temple, preauricular region, and parietal scalp. At presentation, the tumor measured more than 20 cm in diameter at its greatest point (Figure 1). Physical examination revealed a 6-mm purple nodule within the lesion on the patient’s right parietal scalp. No clinical lymphadenopathy was appreciated at the time of diagnosis. Punch biopsies of the right parietal scalp nodule and right temple patch showed findings consistent with angiosarcoma with diffuse cytoplasmic staining of CD31 in atypical endothelial cells and no staining for human herpesvirus 8 (Figure 2). Concurrent computed tomography of the head showed thickening of the right epidermis, dermis, and deeper scalp tissues, but there was no evidence of skull involvement. Computed tomography of the thorax, abdomen, and pelvis showed no evidence of metastatic disease. After a diagnostic workup, the patient was diagnosed with T2bN0M0 angiosarcoma.

The lesion was determined to be nonresectable due to the extent of the patient’s cutaneous disease. The patient was started on a regimen of paclitaxel, scalp radiation, and oral propranolol. Propranolol 40 mg twice daily was initiated at the time of diagnosis with a plan to continue indefinitely. Starting 1 month after staging, the patient completed 10 weekly cycles of paclitaxel, and he was treated with 60 Gy of scalp radiation in 30 fractions, starting with the second cycle of paclitaxel. He tolerated both well with no reported adverse events. Repeat computed tomography performed 1 month after completion of chemotherapy and radiation showed no evidence of a mass or fluid collection in subcutaneous scalp tissues and no evidence of metastatic disease. This correlated with an observed clinical regression at 1 month and complete clinical response at 5 months with residual hemosiderin and radiation changes. The area of prior disease involvement subsequently evolved from violet to dusky gray in appearance to an eventual complete resolution 26 months after diagnosis, accompanied by atrophic radiation-induced sequelae (Figure 3).

The patient’s postchemotherapy course was complicated by hospitalization for a suspected malignant pleural effusion. Analysis revealed growing ground-glass opacities and nodules in the right lower lung lobe. A thoracentesis with cytology studies was negative for malignancy. Continued monitoring over 19 months demonstrated eventual resolution of those findings. He experienced notable complication from local radiation therapy to the scalp with chronic cutaneous ulceration refractory to wound care and surgical intervention. The patient did not exhibit additional signs or symptoms concerning for recurrence or metastasis and was followed by dermatology and oncology until he died nearly 5 years after initial diagnosis due to complications from acute hypoxic respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19. The last imaging obtained showed no convincing evidence of metastasis, though spinal imaging within a month of his death showed lesions favored to represent benign angiomatous growths. His survival after diagnosis ultimately reached 57 months without confirmed disease recurrence and cause of death unrelated to malignancy history, which is a markedly long documented survival for this extent of disease.
Cutaneous angiosarcoma is an aggressive yet rare malignancy without effective treatments for prolonging survival or eradicating disease. Cutaneous angiosarcoma of the head and neck has a reported 10-year survival rate of 13.8%.1 Although angiosarcoma in any location holds a bleak prognosis, cutaneous angiosarcoma of the scalp with a T2 classification has a 2-year survival rate of 0%. Moreover, even if remission is achieved, disease is highly recurrent, typically within months with the current standard of care.3,21,22
Emerging evidence for the possible role of β-adrenergic receptor blockade in the treatment of malignant vascular neoplasms is promising. Microarrays from a host of vascular growths have demonstrated expression of β-adrenergic receptors in 77% of sampled angiosarcoma specimens in addition to strong expression in infantile hemangiomas, hemangiomas, hemangioendotheliomas, and vascular malformations.19 Research findings have further verified the validity of this approach with the demonstration of b1-, b2-, and b3- adrenergic receptor expression by angiosarcoma cell lines. Propranolol subsequently was shown to effectively target proliferation of these cells and induce apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner and moreover be synergistic in effect with other chemotherapies.15 Several genes have exhibited differential expression between control tumor cells and propranolol-treated cells. Specifically, target genes including AXL (a receptor tyrosine kinase associated with cell adhesion, proliferation, and apoptosis and found to upregulated in melanoma and leukemia) and ERBB receptor feedback inhibitor 1 (receptor tyrosine kinase, with ERBB family members commonly overexpressed or mutated in the setting malignancy) have been posited as possible explanatory factors in the observed angiosarcoma response to propranolol.23
Several cases describing propranolol use as an adjunctive therapy for angiosarcoma suggest a beneficial role in clinical medicine. One case report described propranolol monotherapy for lesion to our patient, with a resultant reduction in Ki-67 as a measure of proliferative index within 1 week of initiating propranolol therapy.13 Propranolol also has been shown to halt or slow progression of metastatic disease in visceral and metastatic angiosarcomas.12-14 In combination with oral etoposide and cyclophosphamide, maintenance propranolol therapy in 7 cases of advanced cutaneous angiosarcoma resulted in 1 complete response and 3 very good partial responses, with a median progression-free survival of 11 months.11 Larger-scale studies have not been published, but the growing number of case reports and case series warrants further investigation of the utility of propranolol as an adjunct to current therapies in advanced angiosarcoma.
- Abraham JA, Hornicek FJ, Kaufman AM, et al. Treatment and outcome of 82 patients with angiosarcoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:1953-1967.
- Shin JY, Roh SG, Lee NH, et al. Predisposing factors for poor prognosis of angiosarcoma of the scalp and face: systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck. 2017;39:380-386.
- Fury MG, Antonescu CR, Zee KJV, et al. A 14-year retrospective review of angiosarcoma: clinical characteristics, prognostic factors, and treatment outcomes with surgery and chemotherapy. Cancer. 2005;11:241-247.
- Dossett LA, Harrington M, Cruse CW, et al. Cutaneous angiosarcoma. Curr Probl Cancer. 2015;39:258-263.
- Penel N, Bui BN, Bay JO, et al. Phase II trial of weekly paclitaxel for unresectable angiosarcoma: the ANGIOTAX study. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:5269-5274.
- Agulnik M, Yarber JL, Okuno SH, et al. An open-label, multicenter, phase II study of bevacizumab for the treatment of angiosarcoma and epithelioid hemangioendotheliomas. Ann Oncol. 2013;24:257-263.
- Maki RG, D’Adamo DR, Keohan ML, et al. Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with metastatic or recurrent sarcomas. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3133-3140.
- Ishida Y, Otsuka A, Kabashima K. Cutaneous angiosarcoma: update on biology and latest treatment. Curr Opin Oncol. 2018;30:107-112.
- Ray-Coquard I, Italiano A, Bompas E, et al. Sorafenib for patients with advanced angiosarcoma: a phase II trial from the French Sarcoma Group (GSF/GETO). Oncologist. 2012;17:260-266.
- Ray-Coquard IL, Domont J, Tresch-Bruneel E, et al. Paclitaxel given once per week with or without bevacizumab in patients with advanced angiosarcoma: a randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:2797-2802.
- Pasquier E, Andre N, Street J, et al. Effective management of advanced angiosarcoma by the synergistic combination of propranolol and vinblastine-based metronomic chemotherapy: a bench to bedside study. EBioMedicine. 2016;6:87-95.
- Banavali S, Pasquier E, Andre N. Targeted therapy with propranolol and metronomic chemotherapy combination: sustained complete response of a relapsing metastatic angiosarcoma. Ecancermedicalscience. 2015;9:499.
- Chow W, Amaya CN, Rains S, et al. Growth attenuation of cutaneous angiosarcoma with propranolol-mediated beta-blockade. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1226-1229.
- Daguze J, Saint-Jean M, Peuvrel L, et al. Visceral metastatic angiosarcoma treated effectively with oral cyclophosphamide combined with propranolol. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:497-499.
- Stiles JM, Amaya C, Rains S, et al. Targeting of beta adrenergic receptors results in therapeutic efficacy against models of hemangioendothelioma and angiosarcoma. PLoS One. 2013;8:e60021.
- Chang PY, Chung CH, Chang WC, et al. The effect of propranolol on the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: a nationwide population-based study. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0216828.
- De Giorgi V, Grazzini M, Benemei S, et al. Propranolol for off-label treatment of patients with melanoma: results from a cohort study. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:e172908.
- Rico M, Baglioni M, Bondarenko M, et al. Metformin and propranolol combination prevents cancer progression and metastasis in different breast cancer models. Oncotarget. 2017;8:2874-2889.
- Chisholm KM, Chang KW, Truong MT, et al. β-Adrenergic receptor expression in vascular tumors. Mod Pathol. 2012;25:1446-1451.
- Leaute-Labreze C, Dumas de la Roque E, Hubiche T, et al. Propranolol for severe hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2649-2651.
- Maddox JC, Evans HL. Angiosarcoma of skin and soft tissue: a study of forty-four cases. Cancer. 1981;48:1907-1921.
- Morgan MB, Swann M, Somach S, et al. Cutaneous angiosarcoma: a case series with prognostic correlation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:867-874.
- Zhou S, Liu P, Jiang W, et al. Identification of potential target genes associated with the effect of propranolol on angiosarcoma via microarray analysis. Oncol Lett. 2017;13:4267-4275.
- Abraham JA, Hornicek FJ, Kaufman AM, et al. Treatment and outcome of 82 patients with angiosarcoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:1953-1967.
- Shin JY, Roh SG, Lee NH, et al. Predisposing factors for poor prognosis of angiosarcoma of the scalp and face: systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck. 2017;39:380-386.
- Fury MG, Antonescu CR, Zee KJV, et al. A 14-year retrospective review of angiosarcoma: clinical characteristics, prognostic factors, and treatment outcomes with surgery and chemotherapy. Cancer. 2005;11:241-247.
- Dossett LA, Harrington M, Cruse CW, et al. Cutaneous angiosarcoma. Curr Probl Cancer. 2015;39:258-263.
- Penel N, Bui BN, Bay JO, et al. Phase II trial of weekly paclitaxel for unresectable angiosarcoma: the ANGIOTAX study. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:5269-5274.
- Agulnik M, Yarber JL, Okuno SH, et al. An open-label, multicenter, phase II study of bevacizumab for the treatment of angiosarcoma and epithelioid hemangioendotheliomas. Ann Oncol. 2013;24:257-263.
- Maki RG, D’Adamo DR, Keohan ML, et al. Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with metastatic or recurrent sarcomas. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3133-3140.
- Ishida Y, Otsuka A, Kabashima K. Cutaneous angiosarcoma: update on biology and latest treatment. Curr Opin Oncol. 2018;30:107-112.
- Ray-Coquard I, Italiano A, Bompas E, et al. Sorafenib for patients with advanced angiosarcoma: a phase II trial from the French Sarcoma Group (GSF/GETO). Oncologist. 2012;17:260-266.
- Ray-Coquard IL, Domont J, Tresch-Bruneel E, et al. Paclitaxel given once per week with or without bevacizumab in patients with advanced angiosarcoma: a randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:2797-2802.
- Pasquier E, Andre N, Street J, et al. Effective management of advanced angiosarcoma by the synergistic combination of propranolol and vinblastine-based metronomic chemotherapy: a bench to bedside study. EBioMedicine. 2016;6:87-95.
- Banavali S, Pasquier E, Andre N. Targeted therapy with propranolol and metronomic chemotherapy combination: sustained complete response of a relapsing metastatic angiosarcoma. Ecancermedicalscience. 2015;9:499.
- Chow W, Amaya CN, Rains S, et al. Growth attenuation of cutaneous angiosarcoma with propranolol-mediated beta-blockade. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1226-1229.
- Daguze J, Saint-Jean M, Peuvrel L, et al. Visceral metastatic angiosarcoma treated effectively with oral cyclophosphamide combined with propranolol. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:497-499.
- Stiles JM, Amaya C, Rains S, et al. Targeting of beta adrenergic receptors results in therapeutic efficacy against models of hemangioendothelioma and angiosarcoma. PLoS One. 2013;8:e60021.
- Chang PY, Chung CH, Chang WC, et al. The effect of propranolol on the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: a nationwide population-based study. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0216828.
- De Giorgi V, Grazzini M, Benemei S, et al. Propranolol for off-label treatment of patients with melanoma: results from a cohort study. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:e172908.
- Rico M, Baglioni M, Bondarenko M, et al. Metformin and propranolol combination prevents cancer progression and metastasis in different breast cancer models. Oncotarget. 2017;8:2874-2889.
- Chisholm KM, Chang KW, Truong MT, et al. β-Adrenergic receptor expression in vascular tumors. Mod Pathol. 2012;25:1446-1451.
- Leaute-Labreze C, Dumas de la Roque E, Hubiche T, et al. Propranolol for severe hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2649-2651.
- Maddox JC, Evans HL. Angiosarcoma of skin and soft tissue: a study of forty-four cases. Cancer. 1981;48:1907-1921.
- Morgan MB, Swann M, Somach S, et al. Cutaneous angiosarcoma: a case series with prognostic correlation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:867-874.
- Zhou S, Liu P, Jiang W, et al. Identification of potential target genes associated with the effect of propranolol on angiosarcoma via microarray analysis. Oncol Lett. 2017;13:4267-4275.
PRACTICE POINTS
- In one classic presentation, cutaneous angiosarcoma characteristically appears as a bruiselike patch on the head and neck of an elderly gentleman.
- Although cutaneous angiosarcoma typically portends a poor prognosis at the time of diagnosis, adjunctive oral propranolol may be a promising and relatively benign therapy, posited to afford benefit in a manner similar to its efficacy in the treatment of infantile hemangiomas.