User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Previously unknown viral families hide in the darnedest places
You and me and baby makes 10,003
If you were a virus hunter, looking for your next big virus discovery, where would you go? The wholesale seafood market in Wuhan? A gathering of unmasked anti-vaxxers in the heartland of America? The frozen snot fields of northwest Siberia?
How about babies? Well, it’s too late now, because that’s what Dennis Sandris Nielsen, PhD, of the University of Copenhagen, and his associates did, and they hit the mother lode. Actually, it was more like the infant load, if we’re being honest here.
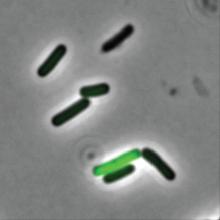
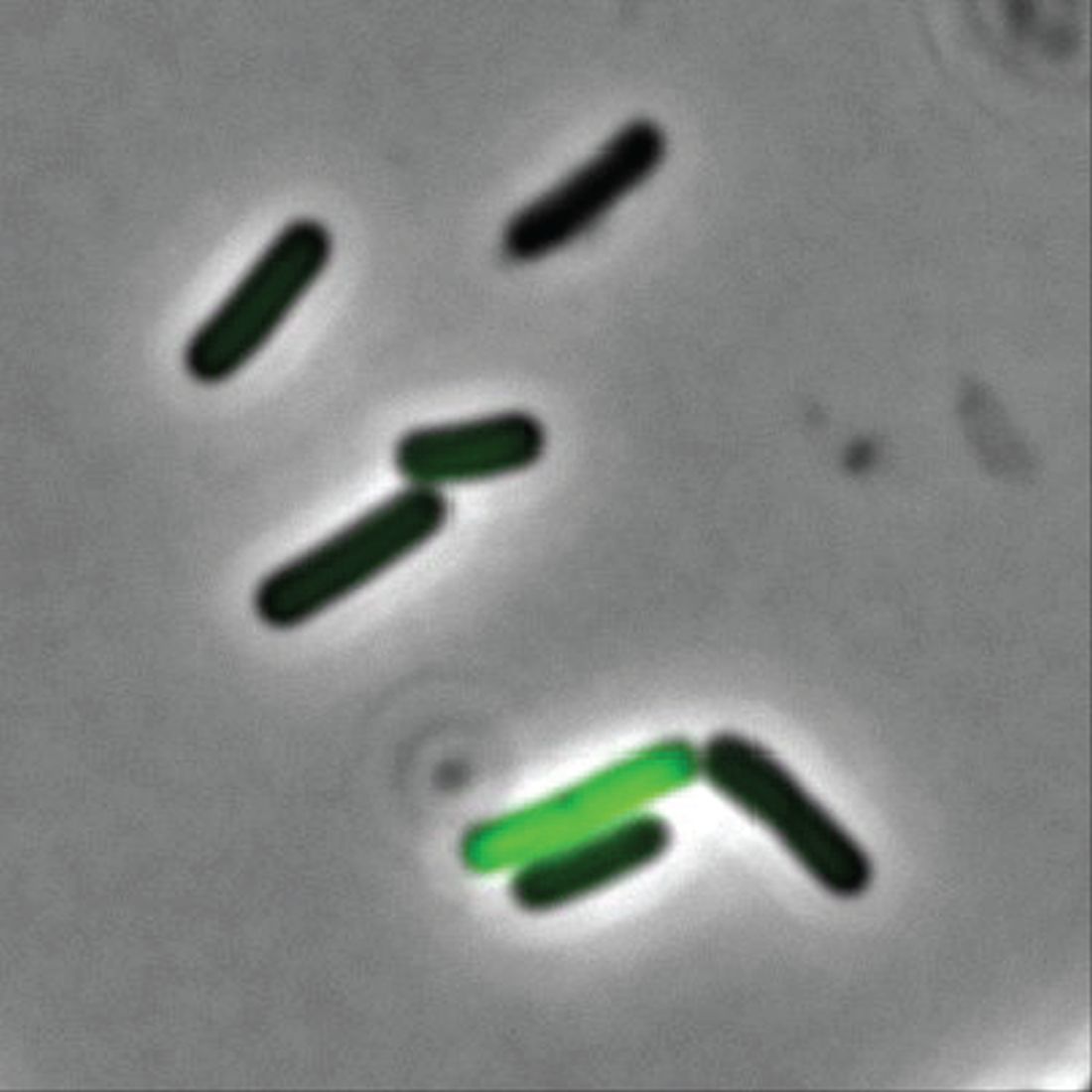
“We found an exceptional number of unknown viruses in the faeces of these babies,” Dr. Nielsen said in a written statement from the university. (The study was published in Nature Microbiology, so we get the English spelling of feces.)
The investigators mapped the gut “viromes” of 647 healthy Danish 1-year-old children over the course of 5 years and found 10,000 species of viruses distributed across 248 different viral families, of which only 16 were already known. Incredible stuff, but then things took a turn for the cute. “The researchers named the remaining 232 unknown viral families after the children whose diapers made the study possible. As a result, new viral families include names like Sylvesterviridae, Rigmorviridae and Tristanviridae,” the university said.
About 90% of the viruses found in the feces are bacterial viruses, aka bacteriophages, which have bacteria as their hosts and don’t attack the children’s cells, so they don’t cause disease. The other 10%, however, are eukaryotic: They use human cells as hosts, so they can be either friend or foe. “It is thought-provoking that all children run around with 10-20 of these virus types that infect human cells. So, there is a constant viral infection taking place, which apparently doesn’t make them sick,” Dr. Nielsen said.
Doesn’t make them sick? Riiiight. The thought that this gives rise to now? People love babies. Everyone wants to pick up the baby. Now we know why. Because the viruses want us to! Well, those cute little faces aren’t fooling us anymore. No more babies for us. Everyone should stay away from babies and their evil little eukaryotic viruses. STOP THE BABIES!
[Editor’s note: After a short timeout, we explained to the staff that the human species actually needs babies for its survival. They calmed down, picked up their crayons, and quietly went back to work.]
Fooled them. Stop the babies!
At least someone out there appreciates hospital food
Life in Alaska is not for the meek. It’s dark half the year. Summer is 3 weeks in July. And somehow, there’s a moose in line ahead of you at the doctor’s office. To make matters worse, it’s arguing about insurance. “What do you mean, you’ve heard the Moo Cross Moo Shield joke before?”
One might expect that Providence Alaska Health Park, located near downtown Anchorage, the largest city in Alaska by a massive margin, might be safe from ungulate invasion. Nope. In recent days, a young moose has taken to hanging around Providence campus, and it just could not find anything to eat. Remember, it may be early April, but this is Alaska. It’s still winter there. The ground’s still covered in snow.
Eventually, the gears in our young moose friend’s mind turned and it settled on a course of action: “Hey, those are some nice-looking plants behind that door over there. …” And that’s how Providence Alaska Health ended up with a moose munching on decorative potted plants in the hospital lobby.
Funnily enough, the moose didn’t even make a big scene. It just walked through the automatic doors and started chowing down. Security only found out because a tenant called them. Naturally though, once security made the announcement that a massive wild animal had been spotted in the building, the lobby was evacuated. … What do you mean, half the hospital came around to see it? Apparently, even though Alaskans have to fight moose herds on their daily commute, a lot of people wanted to see our moose friend do its thing.
“That’s crazy,” a woman in scrubs said in a video as she snapped a photo with her phone.
“This is the best. Like, what’s the code for this?” asked another bystander.
Despite security’s best efforts to shoo the moose out with barricades and offers of tasty branches, our furry friend left of its own volition, presumably irritated that his breakfast had become a spectator sport. But it didn’t go far. It hung around the front drive for a while, then went around the back of the building for a nap. What has four hooves and still doesn’t give a crap? Bob Moose-o! How you doing?
That click sounded stressed
How can people tell that you’re stressed? Maybe you get irritable and a little snappy. Some people have an inability to concentrate or focus. Eating that muffin when you weren’t really hungry could be a sign you’re not relaxed.
Did you know that your computer can be an indicator of your stress levels?
We tend to be working when we’re using computers, right? That can be a stressor in itself. Well, some researchers at ETH Zürich decided to have a look at the situation. Surprisingly, at least to us, one in three Swiss employees experience workplace stress, which makes us wonder what the percentage is in this country.
The Swiss researchers developed a model that tells how stressed someone is just by the way they use their computer mouse or type. The results of their study showed that those who were stressed clicked and tapped differently than participants who were more relaxed.
Stressed people click “more often and less precisely and cover longer distances on the screen,” while the relaxed take “shorter, more direct routes to reach their destination and take more time doing so,” study author Mara Nägelin explained in a written statement from ETH (Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule, or Swiss Federal Institute of Technology) Zürich.
Ever find when you’re frustrated and in a rush you end up making more mistakes? Same deal. Coauthor Jasmine Kerr noted that “increased levels of stress negatively impact our brain’s ability to process information.” Which totally is going to affect how we move.
Hopefully, these results can give insight to companies on how stressed their employees are and the effect it has on their work performance, eventually leading to, guess what, more research on how to alleviate workplace stress in general, which can benefit us all.
So if you find yourself in the office working on your computer like it’s a game of Perfection and time is running out, take a beat. Maybe try a stress-relieving breathing technique. Nonstressed people, according to the study, take fewer and longer pauses on their computers. Perfection on the job may mean relaxing first.
You and me and baby makes 10,003
If you were a virus hunter, looking for your next big virus discovery, where would you go? The wholesale seafood market in Wuhan? A gathering of unmasked anti-vaxxers in the heartland of America? The frozen snot fields of northwest Siberia?
How about babies? Well, it’s too late now, because that’s what Dennis Sandris Nielsen, PhD, of the University of Copenhagen, and his associates did, and they hit the mother lode. Actually, it was more like the infant load, if we’re being honest here.
“We found an exceptional number of unknown viruses in the faeces of these babies,” Dr. Nielsen said in a written statement from the university. (The study was published in Nature Microbiology, so we get the English spelling of feces.)
The investigators mapped the gut “viromes” of 647 healthy Danish 1-year-old children over the course of 5 years and found 10,000 species of viruses distributed across 248 different viral families, of which only 16 were already known. Incredible stuff, but then things took a turn for the cute. “The researchers named the remaining 232 unknown viral families after the children whose diapers made the study possible. As a result, new viral families include names like Sylvesterviridae, Rigmorviridae and Tristanviridae,” the university said.
About 90% of the viruses found in the feces are bacterial viruses, aka bacteriophages, which have bacteria as their hosts and don’t attack the children’s cells, so they don’t cause disease. The other 10%, however, are eukaryotic: They use human cells as hosts, so they can be either friend or foe. “It is thought-provoking that all children run around with 10-20 of these virus types that infect human cells. So, there is a constant viral infection taking place, which apparently doesn’t make them sick,” Dr. Nielsen said.
Doesn’t make them sick? Riiiight. The thought that this gives rise to now? People love babies. Everyone wants to pick up the baby. Now we know why. Because the viruses want us to! Well, those cute little faces aren’t fooling us anymore. No more babies for us. Everyone should stay away from babies and their evil little eukaryotic viruses. STOP THE BABIES!
[Editor’s note: After a short timeout, we explained to the staff that the human species actually needs babies for its survival. They calmed down, picked up their crayons, and quietly went back to work.]
Fooled them. Stop the babies!
At least someone out there appreciates hospital food
Life in Alaska is not for the meek. It’s dark half the year. Summer is 3 weeks in July. And somehow, there’s a moose in line ahead of you at the doctor’s office. To make matters worse, it’s arguing about insurance. “What do you mean, you’ve heard the Moo Cross Moo Shield joke before?”
One might expect that Providence Alaska Health Park, located near downtown Anchorage, the largest city in Alaska by a massive margin, might be safe from ungulate invasion. Nope. In recent days, a young moose has taken to hanging around Providence campus, and it just could not find anything to eat. Remember, it may be early April, but this is Alaska. It’s still winter there. The ground’s still covered in snow.
Eventually, the gears in our young moose friend’s mind turned and it settled on a course of action: “Hey, those are some nice-looking plants behind that door over there. …” And that’s how Providence Alaska Health ended up with a moose munching on decorative potted plants in the hospital lobby.
Funnily enough, the moose didn’t even make a big scene. It just walked through the automatic doors and started chowing down. Security only found out because a tenant called them. Naturally though, once security made the announcement that a massive wild animal had been spotted in the building, the lobby was evacuated. … What do you mean, half the hospital came around to see it? Apparently, even though Alaskans have to fight moose herds on their daily commute, a lot of people wanted to see our moose friend do its thing.
“That’s crazy,” a woman in scrubs said in a video as she snapped a photo with her phone.
“This is the best. Like, what’s the code for this?” asked another bystander.
Despite security’s best efforts to shoo the moose out with barricades and offers of tasty branches, our furry friend left of its own volition, presumably irritated that his breakfast had become a spectator sport. But it didn’t go far. It hung around the front drive for a while, then went around the back of the building for a nap. What has four hooves and still doesn’t give a crap? Bob Moose-o! How you doing?
That click sounded stressed
How can people tell that you’re stressed? Maybe you get irritable and a little snappy. Some people have an inability to concentrate or focus. Eating that muffin when you weren’t really hungry could be a sign you’re not relaxed.
Did you know that your computer can be an indicator of your stress levels?
We tend to be working when we’re using computers, right? That can be a stressor in itself. Well, some researchers at ETH Zürich decided to have a look at the situation. Surprisingly, at least to us, one in three Swiss employees experience workplace stress, which makes us wonder what the percentage is in this country.
The Swiss researchers developed a model that tells how stressed someone is just by the way they use their computer mouse or type. The results of their study showed that those who were stressed clicked and tapped differently than participants who were more relaxed.
Stressed people click “more often and less precisely and cover longer distances on the screen,” while the relaxed take “shorter, more direct routes to reach their destination and take more time doing so,” study author Mara Nägelin explained in a written statement from ETH (Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule, or Swiss Federal Institute of Technology) Zürich.
Ever find when you’re frustrated and in a rush you end up making more mistakes? Same deal. Coauthor Jasmine Kerr noted that “increased levels of stress negatively impact our brain’s ability to process information.” Which totally is going to affect how we move.
Hopefully, these results can give insight to companies on how stressed their employees are and the effect it has on their work performance, eventually leading to, guess what, more research on how to alleviate workplace stress in general, which can benefit us all.
So if you find yourself in the office working on your computer like it’s a game of Perfection and time is running out, take a beat. Maybe try a stress-relieving breathing technique. Nonstressed people, according to the study, take fewer and longer pauses on their computers. Perfection on the job may mean relaxing first.
You and me and baby makes 10,003
If you were a virus hunter, looking for your next big virus discovery, where would you go? The wholesale seafood market in Wuhan? A gathering of unmasked anti-vaxxers in the heartland of America? The frozen snot fields of northwest Siberia?
How about babies? Well, it’s too late now, because that’s what Dennis Sandris Nielsen, PhD, of the University of Copenhagen, and his associates did, and they hit the mother lode. Actually, it was more like the infant load, if we’re being honest here.
“We found an exceptional number of unknown viruses in the faeces of these babies,” Dr. Nielsen said in a written statement from the university. (The study was published in Nature Microbiology, so we get the English spelling of feces.)
The investigators mapped the gut “viromes” of 647 healthy Danish 1-year-old children over the course of 5 years and found 10,000 species of viruses distributed across 248 different viral families, of which only 16 were already known. Incredible stuff, but then things took a turn for the cute. “The researchers named the remaining 232 unknown viral families after the children whose diapers made the study possible. As a result, new viral families include names like Sylvesterviridae, Rigmorviridae and Tristanviridae,” the university said.
About 90% of the viruses found in the feces are bacterial viruses, aka bacteriophages, which have bacteria as their hosts and don’t attack the children’s cells, so they don’t cause disease. The other 10%, however, are eukaryotic: They use human cells as hosts, so they can be either friend or foe. “It is thought-provoking that all children run around with 10-20 of these virus types that infect human cells. So, there is a constant viral infection taking place, which apparently doesn’t make them sick,” Dr. Nielsen said.
Doesn’t make them sick? Riiiight. The thought that this gives rise to now? People love babies. Everyone wants to pick up the baby. Now we know why. Because the viruses want us to! Well, those cute little faces aren’t fooling us anymore. No more babies for us. Everyone should stay away from babies and their evil little eukaryotic viruses. STOP THE BABIES!
[Editor’s note: After a short timeout, we explained to the staff that the human species actually needs babies for its survival. They calmed down, picked up their crayons, and quietly went back to work.]
Fooled them. Stop the babies!
At least someone out there appreciates hospital food
Life in Alaska is not for the meek. It’s dark half the year. Summer is 3 weeks in July. And somehow, there’s a moose in line ahead of you at the doctor’s office. To make matters worse, it’s arguing about insurance. “What do you mean, you’ve heard the Moo Cross Moo Shield joke before?”
One might expect that Providence Alaska Health Park, located near downtown Anchorage, the largest city in Alaska by a massive margin, might be safe from ungulate invasion. Nope. In recent days, a young moose has taken to hanging around Providence campus, and it just could not find anything to eat. Remember, it may be early April, but this is Alaska. It’s still winter there. The ground’s still covered in snow.
Eventually, the gears in our young moose friend’s mind turned and it settled on a course of action: “Hey, those are some nice-looking plants behind that door over there. …” And that’s how Providence Alaska Health ended up with a moose munching on decorative potted plants in the hospital lobby.
Funnily enough, the moose didn’t even make a big scene. It just walked through the automatic doors and started chowing down. Security only found out because a tenant called them. Naturally though, once security made the announcement that a massive wild animal had been spotted in the building, the lobby was evacuated. … What do you mean, half the hospital came around to see it? Apparently, even though Alaskans have to fight moose herds on their daily commute, a lot of people wanted to see our moose friend do its thing.
“That’s crazy,” a woman in scrubs said in a video as she snapped a photo with her phone.
“This is the best. Like, what’s the code for this?” asked another bystander.
Despite security’s best efforts to shoo the moose out with barricades and offers of tasty branches, our furry friend left of its own volition, presumably irritated that his breakfast had become a spectator sport. But it didn’t go far. It hung around the front drive for a while, then went around the back of the building for a nap. What has four hooves and still doesn’t give a crap? Bob Moose-o! How you doing?
That click sounded stressed
How can people tell that you’re stressed? Maybe you get irritable and a little snappy. Some people have an inability to concentrate or focus. Eating that muffin when you weren’t really hungry could be a sign you’re not relaxed.
Did you know that your computer can be an indicator of your stress levels?
We tend to be working when we’re using computers, right? That can be a stressor in itself. Well, some researchers at ETH Zürich decided to have a look at the situation. Surprisingly, at least to us, one in three Swiss employees experience workplace stress, which makes us wonder what the percentage is in this country.
The Swiss researchers developed a model that tells how stressed someone is just by the way they use their computer mouse or type. The results of their study showed that those who were stressed clicked and tapped differently than participants who were more relaxed.
Stressed people click “more often and less precisely and cover longer distances on the screen,” while the relaxed take “shorter, more direct routes to reach their destination and take more time doing so,” study author Mara Nägelin explained in a written statement from ETH (Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule, or Swiss Federal Institute of Technology) Zürich.
Ever find when you’re frustrated and in a rush you end up making more mistakes? Same deal. Coauthor Jasmine Kerr noted that “increased levels of stress negatively impact our brain’s ability to process information.” Which totally is going to affect how we move.
Hopefully, these results can give insight to companies on how stressed their employees are and the effect it has on their work performance, eventually leading to, guess what, more research on how to alleviate workplace stress in general, which can benefit us all.
So if you find yourself in the office working on your computer like it’s a game of Perfection and time is running out, take a beat. Maybe try a stress-relieving breathing technique. Nonstressed people, according to the study, take fewer and longer pauses on their computers. Perfection on the job may mean relaxing first.
Lack of food for thought: Starve a bacterium, feed an infection
A whole new, tiny level of hangry
Ever been so hungry that everything just got on your nerves? Maybe you feel a little snappy right now? Like you’ll just lash out unless you get something to eat? Been there. And so have bacteria.
New research shows that some bacteria go into a full-on Hulk smash if they’re not getting the nutrients they need by releasing toxins into the body. Sounds like a bacterial temper tantrum.
Even though two cells may be genetically identical, they don’t always behave the same in a bacterial community. Some do their job and stay in line, but some evil twins rage out and make people sick by releasing toxins into the environment, Adam Rosenthal, PhD, of the University of North Carolina and his colleagues discovered.
To figure out why some cells were all business as usual while others were not, the investigators looked at Clostridium perfringens, a bacterium found in the intestines of humans and other vertebrates. When the C. perfringens cells were fed a little acetate to munch on, the hangry cells calmed down faster than a kid with a bag of fruit snacks, reducing toxin levels. Some cells even disappeared, falling in line with their model-citizen counterparts.
So what does this really mean? More research, duh. Now that we know nutrients play a role in toxicity, it may open the door to finding a way to fight against antibiotic resistance in humans and reduce antibiotic use in the food industry.
So think to yourself. Are you bothered for no reason? Getting a little testy with your friends and coworkers? Maybe you just haven’t eaten in a while. You’re literally not alone. Even a single-cell organism can behave based on its hunger levels.
Now go have a snack. Your bacteria are getting restless.
The very hangry iguana?
Imagine yourself on a warm, sunny tropical beach. You are enjoying a piece of cake as you take in the slow beat of the waves lapping against the shore. Life is as good as it could be.
Then you feel a presence nearby. Hostility. Hunger. A set of feral, covetous eyes in the nearby jungle. A reptilian beast stalks you, and its all-encompassing sweet tooth desires your cake.
Wait, hold on, what?
As an unfortunate 3-year-old on vacation in Costa Rica found out, there’s at least one iguana in the world out there with a taste for sugar (better than a taste for blood, we suppose).
While out on the beach, the lizard darted out of nowhere, bit the girl on the back of the hand, and stole her cake. Still not the worst party guest ever. The child was taken to a local clinic, where the wound was cleaned and a 5-day antibiotic treatment (lizards carry salmonella) was provided. Things seemed fine, and the girl returned home without incident.
But of course, that’s not the end of the story. Five months later, the girl’s parents noticed a red bump at the wound site. Over the next 3 months, the surrounding skin grew red and painful. A trip to the hospital in California revealed that she had a ganglion cyst and a discharge of pus. Turns out our cake-obsessed lizard friend did give the little girl a gift: the first known human case of Mycobacterium marinum infection following an iguana bite on record.
M. marinum, which causes a disease similar to tuberculosis, typically infects fish but can infect humans if skin wounds are exposed to contaminated water. It’s also resistant to most antibiotics, which is why the first round didn’t clear up the infection. A second round of more-potent antibiotics seems to be working well.
So, to sum up, this poor child got bitten by a lizard, had her cake stolen, and contracted a rare illness in exchange. For a 3-year-old, that’s gotta be in the top-10 worst days ever. Unless, of course, we’re actually living in the Marvel universe (sorry, multiverse at this point). Then we’re totally going to see the emergence of the new superhero Iguana Girl in 15 years or so. Keep your eyes open.
No allergies? Let them give up cake
Allergy season is already here – starting earlier every year, it seems – and many people are not happy about it. So unhappy, actually, that there’s a list of things they would be willing to give up for a year to get rid of their of allergies, according to a survey conducted by OnePoll on behalf of Flonase.
Nearly 40% of 2,000 respondents with allergies would go a year without eating cake or chocolate or playing video games in exchange for allergy-free status, the survey results show. Almost as many would forgo coffee (38%) or pizza (37%) for a year, while 36% would stay off social media and 31% would take a pay cut or give up their smartphones, the Independent reported.
More than half of the allergic Americans – 54%, to be exact – who were polled this past winter – Feb. 24 to March 1, to be exact – consider allergy symptoms to be the most frustrating part of the spring. Annoying things that were less frustrating to the group included mosquitoes (41%), filing tax returns (38%), and daylight savings time (37%).
The Trump arraignment circus, of course, occurred too late to make the list, as did the big “We’re going back to the office! No wait, we’re closing the office forever!” email extravaganza and emotional roller coaster. That second one, however, did not get nearly as much media coverage.
A whole new, tiny level of hangry
Ever been so hungry that everything just got on your nerves? Maybe you feel a little snappy right now? Like you’ll just lash out unless you get something to eat? Been there. And so have bacteria.
New research shows that some bacteria go into a full-on Hulk smash if they’re not getting the nutrients they need by releasing toxins into the body. Sounds like a bacterial temper tantrum.
Even though two cells may be genetically identical, they don’t always behave the same in a bacterial community. Some do their job and stay in line, but some evil twins rage out and make people sick by releasing toxins into the environment, Adam Rosenthal, PhD, of the University of North Carolina and his colleagues discovered.
To figure out why some cells were all business as usual while others were not, the investigators looked at Clostridium perfringens, a bacterium found in the intestines of humans and other vertebrates. When the C. perfringens cells were fed a little acetate to munch on, the hangry cells calmed down faster than a kid with a bag of fruit snacks, reducing toxin levels. Some cells even disappeared, falling in line with their model-citizen counterparts.
So what does this really mean? More research, duh. Now that we know nutrients play a role in toxicity, it may open the door to finding a way to fight against antibiotic resistance in humans and reduce antibiotic use in the food industry.
So think to yourself. Are you bothered for no reason? Getting a little testy with your friends and coworkers? Maybe you just haven’t eaten in a while. You’re literally not alone. Even a single-cell organism can behave based on its hunger levels.
Now go have a snack. Your bacteria are getting restless.
The very hangry iguana?
Imagine yourself on a warm, sunny tropical beach. You are enjoying a piece of cake as you take in the slow beat of the waves lapping against the shore. Life is as good as it could be.
Then you feel a presence nearby. Hostility. Hunger. A set of feral, covetous eyes in the nearby jungle. A reptilian beast stalks you, and its all-encompassing sweet tooth desires your cake.
Wait, hold on, what?
As an unfortunate 3-year-old on vacation in Costa Rica found out, there’s at least one iguana in the world out there with a taste for sugar (better than a taste for blood, we suppose).
While out on the beach, the lizard darted out of nowhere, bit the girl on the back of the hand, and stole her cake. Still not the worst party guest ever. The child was taken to a local clinic, where the wound was cleaned and a 5-day antibiotic treatment (lizards carry salmonella) was provided. Things seemed fine, and the girl returned home without incident.
But of course, that’s not the end of the story. Five months later, the girl’s parents noticed a red bump at the wound site. Over the next 3 months, the surrounding skin grew red and painful. A trip to the hospital in California revealed that she had a ganglion cyst and a discharge of pus. Turns out our cake-obsessed lizard friend did give the little girl a gift: the first known human case of Mycobacterium marinum infection following an iguana bite on record.
M. marinum, which causes a disease similar to tuberculosis, typically infects fish but can infect humans if skin wounds are exposed to contaminated water. It’s also resistant to most antibiotics, which is why the first round didn’t clear up the infection. A second round of more-potent antibiotics seems to be working well.
So, to sum up, this poor child got bitten by a lizard, had her cake stolen, and contracted a rare illness in exchange. For a 3-year-old, that’s gotta be in the top-10 worst days ever. Unless, of course, we’re actually living in the Marvel universe (sorry, multiverse at this point). Then we’re totally going to see the emergence of the new superhero Iguana Girl in 15 years or so. Keep your eyes open.
No allergies? Let them give up cake
Allergy season is already here – starting earlier every year, it seems – and many people are not happy about it. So unhappy, actually, that there’s a list of things they would be willing to give up for a year to get rid of their of allergies, according to a survey conducted by OnePoll on behalf of Flonase.
Nearly 40% of 2,000 respondents with allergies would go a year without eating cake or chocolate or playing video games in exchange for allergy-free status, the survey results show. Almost as many would forgo coffee (38%) or pizza (37%) for a year, while 36% would stay off social media and 31% would take a pay cut or give up their smartphones, the Independent reported.
More than half of the allergic Americans – 54%, to be exact – who were polled this past winter – Feb. 24 to March 1, to be exact – consider allergy symptoms to be the most frustrating part of the spring. Annoying things that were less frustrating to the group included mosquitoes (41%), filing tax returns (38%), and daylight savings time (37%).
The Trump arraignment circus, of course, occurred too late to make the list, as did the big “We’re going back to the office! No wait, we’re closing the office forever!” email extravaganza and emotional roller coaster. That second one, however, did not get nearly as much media coverage.
A whole new, tiny level of hangry
Ever been so hungry that everything just got on your nerves? Maybe you feel a little snappy right now? Like you’ll just lash out unless you get something to eat? Been there. And so have bacteria.
New research shows that some bacteria go into a full-on Hulk smash if they’re not getting the nutrients they need by releasing toxins into the body. Sounds like a bacterial temper tantrum.
Even though two cells may be genetically identical, they don’t always behave the same in a bacterial community. Some do their job and stay in line, but some evil twins rage out and make people sick by releasing toxins into the environment, Adam Rosenthal, PhD, of the University of North Carolina and his colleagues discovered.
To figure out why some cells were all business as usual while others were not, the investigators looked at Clostridium perfringens, a bacterium found in the intestines of humans and other vertebrates. When the C. perfringens cells were fed a little acetate to munch on, the hangry cells calmed down faster than a kid with a bag of fruit snacks, reducing toxin levels. Some cells even disappeared, falling in line with their model-citizen counterparts.
So what does this really mean? More research, duh. Now that we know nutrients play a role in toxicity, it may open the door to finding a way to fight against antibiotic resistance in humans and reduce antibiotic use in the food industry.
So think to yourself. Are you bothered for no reason? Getting a little testy with your friends and coworkers? Maybe you just haven’t eaten in a while. You’re literally not alone. Even a single-cell organism can behave based on its hunger levels.
Now go have a snack. Your bacteria are getting restless.
The very hangry iguana?
Imagine yourself on a warm, sunny tropical beach. You are enjoying a piece of cake as you take in the slow beat of the waves lapping against the shore. Life is as good as it could be.
Then you feel a presence nearby. Hostility. Hunger. A set of feral, covetous eyes in the nearby jungle. A reptilian beast stalks you, and its all-encompassing sweet tooth desires your cake.
Wait, hold on, what?
As an unfortunate 3-year-old on vacation in Costa Rica found out, there’s at least one iguana in the world out there with a taste for sugar (better than a taste for blood, we suppose).
While out on the beach, the lizard darted out of nowhere, bit the girl on the back of the hand, and stole her cake. Still not the worst party guest ever. The child was taken to a local clinic, where the wound was cleaned and a 5-day antibiotic treatment (lizards carry salmonella) was provided. Things seemed fine, and the girl returned home without incident.
But of course, that’s not the end of the story. Five months later, the girl’s parents noticed a red bump at the wound site. Over the next 3 months, the surrounding skin grew red and painful. A trip to the hospital in California revealed that she had a ganglion cyst and a discharge of pus. Turns out our cake-obsessed lizard friend did give the little girl a gift: the first known human case of Mycobacterium marinum infection following an iguana bite on record.
M. marinum, which causes a disease similar to tuberculosis, typically infects fish but can infect humans if skin wounds are exposed to contaminated water. It’s also resistant to most antibiotics, which is why the first round didn’t clear up the infection. A second round of more-potent antibiotics seems to be working well.
So, to sum up, this poor child got bitten by a lizard, had her cake stolen, and contracted a rare illness in exchange. For a 3-year-old, that’s gotta be in the top-10 worst days ever. Unless, of course, we’re actually living in the Marvel universe (sorry, multiverse at this point). Then we’re totally going to see the emergence of the new superhero Iguana Girl in 15 years or so. Keep your eyes open.
No allergies? Let them give up cake
Allergy season is already here – starting earlier every year, it seems – and many people are not happy about it. So unhappy, actually, that there’s a list of things they would be willing to give up for a year to get rid of their of allergies, according to a survey conducted by OnePoll on behalf of Flonase.
Nearly 40% of 2,000 respondents with allergies would go a year without eating cake or chocolate or playing video games in exchange for allergy-free status, the survey results show. Almost as many would forgo coffee (38%) or pizza (37%) for a year, while 36% would stay off social media and 31% would take a pay cut or give up their smartphones, the Independent reported.
More than half of the allergic Americans – 54%, to be exact – who were polled this past winter – Feb. 24 to March 1, to be exact – consider allergy symptoms to be the most frustrating part of the spring. Annoying things that were less frustrating to the group included mosquitoes (41%), filing tax returns (38%), and daylight savings time (37%).
The Trump arraignment circus, of course, occurred too late to make the list, as did the big “We’re going back to the office! No wait, we’re closing the office forever!” email extravaganza and emotional roller coaster. That second one, however, did not get nearly as much media coverage.
Deadly bacteria in recalled eye drops can spread person-to-person
according to a new report.
Scientists are concerned that the once-rare treatment-resistant bacteria found in the eyedrops can spread person-to-person, posing a risk of becoming a recurrent problem in the United States, The New York Times reported.
In January, EzriCare and Delsam Pharma artificial tears and ointment products were recalled after being linked to the bacterium P. aeruginosa. The bacteria have caused at least 68 infections, including three deaths and at least eight cases of blindness. The eyedrops were imported to the United States from India, and many of the cases occurred after the bacteria spread person-to-person at a long-term care facility in Connecticut, according to the Times, which cited FDA and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention lead investigator Maroya Walters, PhD.
Dr. Walters said the cases that caused death or blindness were traced to the EzriCare artificial tears product.
“It’s very hard to get rid of,” University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill infectious disease specialist David van Duin, MD, PhD, told the Times, noting that the bacteria cling to sink drains, water faucets, and other moist places.
The FDA said it had halted the import of the recalled products and has since visited the plant in India where they were made, which is owned by Global Pharma Healthcare. In a citation to the company dated March 2, the FDA listed nearly a dozen problems, such as dirty equipment and the absence of safety procedures and tests.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
according to a new report.
Scientists are concerned that the once-rare treatment-resistant bacteria found in the eyedrops can spread person-to-person, posing a risk of becoming a recurrent problem in the United States, The New York Times reported.
In January, EzriCare and Delsam Pharma artificial tears and ointment products were recalled after being linked to the bacterium P. aeruginosa. The bacteria have caused at least 68 infections, including three deaths and at least eight cases of blindness. The eyedrops were imported to the United States from India, and many of the cases occurred after the bacteria spread person-to-person at a long-term care facility in Connecticut, according to the Times, which cited FDA and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention lead investigator Maroya Walters, PhD.
Dr. Walters said the cases that caused death or blindness were traced to the EzriCare artificial tears product.
“It’s very hard to get rid of,” University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill infectious disease specialist David van Duin, MD, PhD, told the Times, noting that the bacteria cling to sink drains, water faucets, and other moist places.
The FDA said it had halted the import of the recalled products and has since visited the plant in India where they were made, which is owned by Global Pharma Healthcare. In a citation to the company dated March 2, the FDA listed nearly a dozen problems, such as dirty equipment and the absence of safety procedures and tests.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
according to a new report.
Scientists are concerned that the once-rare treatment-resistant bacteria found in the eyedrops can spread person-to-person, posing a risk of becoming a recurrent problem in the United States, The New York Times reported.
In January, EzriCare and Delsam Pharma artificial tears and ointment products were recalled after being linked to the bacterium P. aeruginosa. The bacteria have caused at least 68 infections, including three deaths and at least eight cases of blindness. The eyedrops were imported to the United States from India, and many of the cases occurred after the bacteria spread person-to-person at a long-term care facility in Connecticut, according to the Times, which cited FDA and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention lead investigator Maroya Walters, PhD.
Dr. Walters said the cases that caused death or blindness were traced to the EzriCare artificial tears product.
“It’s very hard to get rid of,” University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill infectious disease specialist David van Duin, MD, PhD, told the Times, noting that the bacteria cling to sink drains, water faucets, and other moist places.
The FDA said it had halted the import of the recalled products and has since visited the plant in India where they were made, which is owned by Global Pharma Healthcare. In a citation to the company dated March 2, the FDA listed nearly a dozen problems, such as dirty equipment and the absence of safety procedures and tests.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
‘Excess’ deaths surging, but why?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
“Excess deaths.” You’ve heard the phrase countless times by now. It is one of the myriad of previously esoteric epidemiology terms that the pandemic brought squarely into the zeitgeist.
As a sort of standard candle of the performance of a state or a region or a country in terms of health care, it has a lot of utility – if for nothing more than Monday-morning quarterbacking. But this week, I want to dig in on the concept a bit because, according to a new study, the excess death gap between the United States and Western Europe has never been higher.
You might imagine that the best way to figure this out is for some group of intelligent people to review each death and decide, somehow, whether it was expected or not. But aside from being impractical, this would end up being somewhat subjective. That older person who died from pneumonia – was that an expected death? Could it have been avoided?
Rather, the calculation of excess mortality relies on large numbers and statistical inference to compare an expected number of deaths with those that are observed.
The difference is excess mortality, even if you can never be sure whether any particular death was expected or not.
As always, however, the devil is in the details. What data do you use to define the expected number of deaths?
There are options here. Probably the most straightforward analysis uses past data from the country of interest. You look at annual deaths over some historical period of time and compare those numbers with the rates today. Two issues need to be accounted for here: population growth – a larger population will have more deaths, so you need to adjust the historical population with current levels, and demographic shifts – an older or more male population will have more deaths, so you need to adjust for that as well.
But provided you take care of those factors, you can estimate fairly well how many deaths you can expect to see in any given period of time.
Still, you should see right away that excess mortality is a relative concept. If you think that, just perhaps, the United States has some systematic failure to deliver care that has been stable and persistent over time, you wouldn’t capture that failing in an excess mortality calculation that uses U.S. historical data as the baseline.
The best way to get around that is to use data from other countries, and that’s just what this article – a rare single-author piece by Patrick Heuveline – does, calculating excess deaths in the United States by standardizing our mortality rates to the five largest Western European countries: the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy, and Spain.
Controlling for the differences in the demographics of that European population, here is the expected number of deaths in the United States over the past 5 years.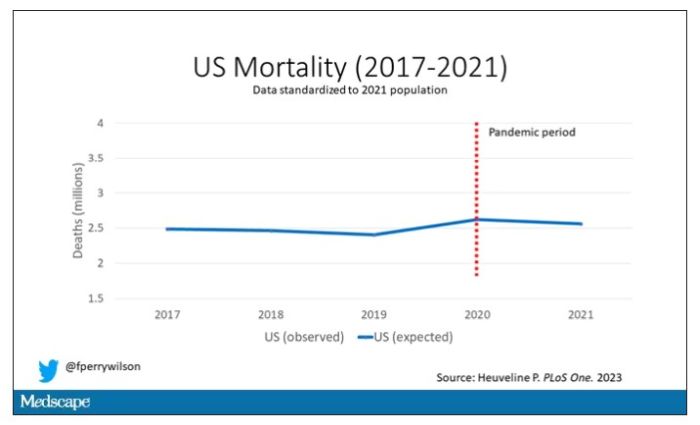
Note that there is a small uptick in expected deaths in 2020, reflecting the pandemic, which returns to baseline levels by 2021. This is because that’s what happened in Europe; by 2021, the excess mortality due to COVID-19 was quite low.
Here are the actual deaths in the US during that time.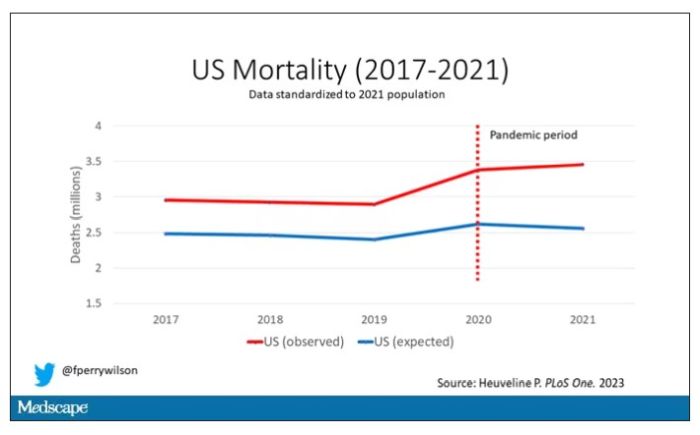
Highlighted here in green, then, is the excess mortality over time in the United States.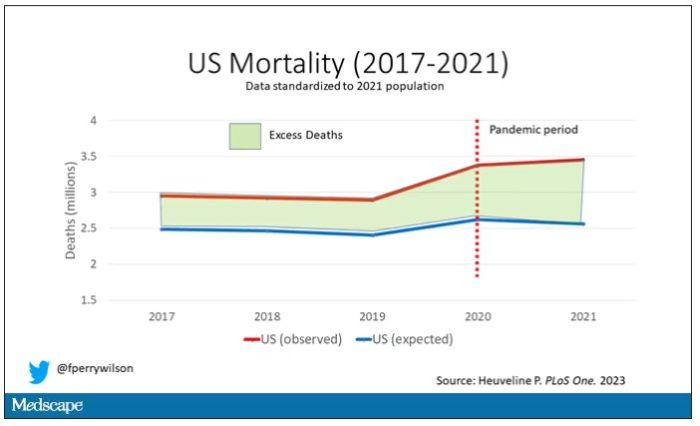
There are some fascinating and concerning findings here.
First of all, you can see that even before the pandemic, the United States has an excess mortality problem. This is not entirely a surprise; we’ve known that so-called “deaths of despair,” those due to alcohol abuse, drug overdoses, and suicide, are at an all-time high and tend to affect a “prime of life” population that would not otherwise be expected to die. In fact, fully 50% of the excess deaths in the United States occur in those between ages 15 and 64.
Excess deaths are also a concerning percentage of total deaths. In 2017, 17% of total deaths in the United States could be considered “excess.” In 2021, that number had doubled to 35%. Nearly 900,000 individuals in the United States died in 2021 who perhaps didn’t need to.
The obvious culprit to blame here is COVID, but COVID-associated excess deaths only explain about 50% of the excess we see in 2021. The rest reflect something even more concerning: a worsening of the failures of the past, perhaps exacerbated by the pandemic but not due to the virus itself.
Of course, we started this discussion acknowledging that the calculation of excess mortality is exquisitely dependent on how you model the expected number of deaths, and I’m sure some will take issue with the use of European numbers when applied to Americans. After all, Europe has, by and large, a robust public health service, socialized medicine, and healthcare that does not run the risk of bankrupting its citizens. How can we compare our outcomes to a place like that?
How indeed.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale University’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven,Conn. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
“Excess deaths.” You’ve heard the phrase countless times by now. It is one of the myriad of previously esoteric epidemiology terms that the pandemic brought squarely into the zeitgeist.
As a sort of standard candle of the performance of a state or a region or a country in terms of health care, it has a lot of utility – if for nothing more than Monday-morning quarterbacking. But this week, I want to dig in on the concept a bit because, according to a new study, the excess death gap between the United States and Western Europe has never been higher.
You might imagine that the best way to figure this out is for some group of intelligent people to review each death and decide, somehow, whether it was expected or not. But aside from being impractical, this would end up being somewhat subjective. That older person who died from pneumonia – was that an expected death? Could it have been avoided?
Rather, the calculation of excess mortality relies on large numbers and statistical inference to compare an expected number of deaths with those that are observed.
The difference is excess mortality, even if you can never be sure whether any particular death was expected or not.
As always, however, the devil is in the details. What data do you use to define the expected number of deaths?
There are options here. Probably the most straightforward analysis uses past data from the country of interest. You look at annual deaths over some historical period of time and compare those numbers with the rates today. Two issues need to be accounted for here: population growth – a larger population will have more deaths, so you need to adjust the historical population with current levels, and demographic shifts – an older or more male population will have more deaths, so you need to adjust for that as well.
But provided you take care of those factors, you can estimate fairly well how many deaths you can expect to see in any given period of time.
Still, you should see right away that excess mortality is a relative concept. If you think that, just perhaps, the United States has some systematic failure to deliver care that has been stable and persistent over time, you wouldn’t capture that failing in an excess mortality calculation that uses U.S. historical data as the baseline.
The best way to get around that is to use data from other countries, and that’s just what this article – a rare single-author piece by Patrick Heuveline – does, calculating excess deaths in the United States by standardizing our mortality rates to the five largest Western European countries: the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy, and Spain.
Controlling for the differences in the demographics of that European population, here is the expected number of deaths in the United States over the past 5 years.
Note that there is a small uptick in expected deaths in 2020, reflecting the pandemic, which returns to baseline levels by 2021. This is because that’s what happened in Europe; by 2021, the excess mortality due to COVID-19 was quite low.
Here are the actual deaths in the US during that time.
Highlighted here in green, then, is the excess mortality over time in the United States.
There are some fascinating and concerning findings here.
First of all, you can see that even before the pandemic, the United States has an excess mortality problem. This is not entirely a surprise; we’ve known that so-called “deaths of despair,” those due to alcohol abuse, drug overdoses, and suicide, are at an all-time high and tend to affect a “prime of life” population that would not otherwise be expected to die. In fact, fully 50% of the excess deaths in the United States occur in those between ages 15 and 64.
Excess deaths are also a concerning percentage of total deaths. In 2017, 17% of total deaths in the United States could be considered “excess.” In 2021, that number had doubled to 35%. Nearly 900,000 individuals in the United States died in 2021 who perhaps didn’t need to.
The obvious culprit to blame here is COVID, but COVID-associated excess deaths only explain about 50% of the excess we see in 2021. The rest reflect something even more concerning: a worsening of the failures of the past, perhaps exacerbated by the pandemic but not due to the virus itself.
Of course, we started this discussion acknowledging that the calculation of excess mortality is exquisitely dependent on how you model the expected number of deaths, and I’m sure some will take issue with the use of European numbers when applied to Americans. After all, Europe has, by and large, a robust public health service, socialized medicine, and healthcare that does not run the risk of bankrupting its citizens. How can we compare our outcomes to a place like that?
How indeed.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale University’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven,Conn. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
“Excess deaths.” You’ve heard the phrase countless times by now. It is one of the myriad of previously esoteric epidemiology terms that the pandemic brought squarely into the zeitgeist.
As a sort of standard candle of the performance of a state or a region or a country in terms of health care, it has a lot of utility – if for nothing more than Monday-morning quarterbacking. But this week, I want to dig in on the concept a bit because, according to a new study, the excess death gap between the United States and Western Europe has never been higher.
You might imagine that the best way to figure this out is for some group of intelligent people to review each death and decide, somehow, whether it was expected or not. But aside from being impractical, this would end up being somewhat subjective. That older person who died from pneumonia – was that an expected death? Could it have been avoided?
Rather, the calculation of excess mortality relies on large numbers and statistical inference to compare an expected number of deaths with those that are observed.
The difference is excess mortality, even if you can never be sure whether any particular death was expected or not.
As always, however, the devil is in the details. What data do you use to define the expected number of deaths?
There are options here. Probably the most straightforward analysis uses past data from the country of interest. You look at annual deaths over some historical period of time and compare those numbers with the rates today. Two issues need to be accounted for here: population growth – a larger population will have more deaths, so you need to adjust the historical population with current levels, and demographic shifts – an older or more male population will have more deaths, so you need to adjust for that as well.
But provided you take care of those factors, you can estimate fairly well how many deaths you can expect to see in any given period of time.
Still, you should see right away that excess mortality is a relative concept. If you think that, just perhaps, the United States has some systematic failure to deliver care that has been stable and persistent over time, you wouldn’t capture that failing in an excess mortality calculation that uses U.S. historical data as the baseline.
The best way to get around that is to use data from other countries, and that’s just what this article – a rare single-author piece by Patrick Heuveline – does, calculating excess deaths in the United States by standardizing our mortality rates to the five largest Western European countries: the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy, and Spain.
Controlling for the differences in the demographics of that European population, here is the expected number of deaths in the United States over the past 5 years.
Note that there is a small uptick in expected deaths in 2020, reflecting the pandemic, which returns to baseline levels by 2021. This is because that’s what happened in Europe; by 2021, the excess mortality due to COVID-19 was quite low.
Here are the actual deaths in the US during that time.
Highlighted here in green, then, is the excess mortality over time in the United States.
There are some fascinating and concerning findings here.
First of all, you can see that even before the pandemic, the United States has an excess mortality problem. This is not entirely a surprise; we’ve known that so-called “deaths of despair,” those due to alcohol abuse, drug overdoses, and suicide, are at an all-time high and tend to affect a “prime of life” population that would not otherwise be expected to die. In fact, fully 50% of the excess deaths in the United States occur in those between ages 15 and 64.
Excess deaths are also a concerning percentage of total deaths. In 2017, 17% of total deaths in the United States could be considered “excess.” In 2021, that number had doubled to 35%. Nearly 900,000 individuals in the United States died in 2021 who perhaps didn’t need to.
The obvious culprit to blame here is COVID, but COVID-associated excess deaths only explain about 50% of the excess we see in 2021. The rest reflect something even more concerning: a worsening of the failures of the past, perhaps exacerbated by the pandemic but not due to the virus itself.
Of course, we started this discussion acknowledging that the calculation of excess mortality is exquisitely dependent on how you model the expected number of deaths, and I’m sure some will take issue with the use of European numbers when applied to Americans. After all, Europe has, by and large, a robust public health service, socialized medicine, and healthcare that does not run the risk of bankrupting its citizens. How can we compare our outcomes to a place like that?
How indeed.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale University’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven,Conn. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Telehealth services tied to a major reduction in opioid overdose deaths
, a new study of Medicare beneficiaries shows.
Telehealth services for opioid use disorder (OUD) were used far more often during the pandemic than before COVID-19, and those who used them were 33% less likely to die of a drug overdose.
Investigators also found a significant increase in MOUD use during the pandemic. Fatal drug overdoses were 59% less likely among individuals who received MOUD from an opioid treatment program and 38% less likely among those treated with buprenorphine in an office-based setting.
The results come as policymakers are preparing for the end of the public health emergency that prompted the expansion of OUD-related telehealth and MOUD prescribing and are deciding whether to make those expansions permanent.
“The expansion of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic appears to have had positive effects on patients receiving MOUD, improved retention among patients who received MOUD, and lowered risks for both nonfatal and fatal overdose,” lead investigator Christopher M. Jones, PharmD, DrPH, director of the National Center for Injury Prevention and Control at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia, told this news organization. “Our results suggest that telehealth is a valuable tool in the toolbox for expanding access to and improving retention on MOUD.”
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Increase in treatment
The study included 105,162 Medicare beneficiaries who began OUD treatment between March and August in 2019 (prepandemic cohort; 67.6%
aged 45-74 years), and 70,479 who began treatment between March and August of 2020 (pandemic cohort; 66.3% aged 45-74 years).
Participants had not received OUD treatment in the 6 months leading up to study enrollment and were followed for 6 months after treatment began.
Significantly more study participants received OUD-related telehealth services during the pandemic than prior to 2019 (19.6% vs. 0.6%; P < .001). Receipt of MOUD was also significantly higher in the pandemic cohort (12.6% vs. 10.8%; P < .001).
The rate of drug overdose deaths was higher in the pandemic cohort (5.1 deaths vs. 3.7 deaths per 1,000 beneficiaries; P < .001). But the percentage of deaths from drug overdoses did not differ between groups (4.8% in the prepandemic cohort vs. 5.1% in the pandemic cohort; P = .49).
In the pandemic cohort, fatal drug overdoses were 33% less likely among those who received OUD-related telehealth services (adjusted odds ratio, 0.67; 95% confidence interval, 0.48-0.92); 59% less likely among those who received MOUD from opioid treatment programs (aOR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.25-0.68), and 38% less likely among those who received buprenorphine in office-based settings (aOR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.43-0.91).
Risk of fatal overdose was significantly lower among women and those aged 65 years and older. There were no significant differences in risk based on urban or rural residency or on ethnicity.
“Against the backdrop of a highly potent illicit drug supply driven by illicit fentanyl and fentanyl analogues and historically large increases in overdose deaths during the COVID-19 pandemic, MOUD was still highly effective at reducing risk for fatal overdose,” Dr. Jones said.
While the use of buprenorphine in office-based settings was associated with a decreased risk of overdose death, use of extended-release naltrexone was not.
“Prior research has demonstrated the effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone in the treatment of opioid use disorder,” Dr. Jones said. “However, research has also shown that patients have challenges getting started, or inducted, on extended-release naltrexone.”
An earlier study by Dr. Jones and colleagues showed that rates of retention were lower with extended-release naltrexone, compared with buprenorphine in office-based settings or MOUD from opioid treatment programs.
The new study included only a small number of individuals who were receiving extended-release naltrexone, which may have influenced the findings. In addition, challenges with induction and retention may be driving the results, Dr. Jones noted.
“Efforts to improve induction and retention with extended-release naltrexone are important areas for future research and clinical practice,” he added.
An important engagement tool
A number of questions about telehealth care for OUD remain, including whether increased access to care accounts for the reduction in drug overdose risk that the investigators found or whether other factors are at play.
“There is still more we need to understand about telehealth, such as the quality of care provided and the particular aspects of care provided by telehealth and how this influences health outcomes,” Dr. Jones said.
The results also suggest treatments for OUD are still not finding their way to patients who might benefit, he added.
“Despite the positive findings and the prior research showing that MOUD is highly effective, we found that only one in five patients received telehealth services and only one in eight received any MOUD. This really underscores the need to expand these services across clinical settings,” he added.
These and earlier findings demonstrate the potential benefits of continuing pandemic-era expansion of OUD-related telehealth services and MOUD access, Dr. Jones said.
In preparation for the end of the public health emergency on May 1, the Drug Enforcement Agency recently released a proposal that would allow providers to prescribe a 30-day supply of buprenorphine, but for patients to receive additional prescriptions, a face-to-face meeting would be required. The proposal has drawn criticism from addiction medicine specialists.
The current study didn’t explore if or how the proposal might affect patients with OUD or whether it could blunt the positive effects of the findings.
“Prior research shows that keeping individuals engaged in treatment, including on medications, is a critical part of reducing the negative health and social impacts of opioid use disorder. Our results suggest that telehealth can be an important tool in helping patients engage in and stay connected in care,” said Dr. Jones.
The study was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Johnson reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study of Medicare beneficiaries shows.
Telehealth services for opioid use disorder (OUD) were used far more often during the pandemic than before COVID-19, and those who used them were 33% less likely to die of a drug overdose.
Investigators also found a significant increase in MOUD use during the pandemic. Fatal drug overdoses were 59% less likely among individuals who received MOUD from an opioid treatment program and 38% less likely among those treated with buprenorphine in an office-based setting.
The results come as policymakers are preparing for the end of the public health emergency that prompted the expansion of OUD-related telehealth and MOUD prescribing and are deciding whether to make those expansions permanent.
“The expansion of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic appears to have had positive effects on patients receiving MOUD, improved retention among patients who received MOUD, and lowered risks for both nonfatal and fatal overdose,” lead investigator Christopher M. Jones, PharmD, DrPH, director of the National Center for Injury Prevention and Control at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia, told this news organization. “Our results suggest that telehealth is a valuable tool in the toolbox for expanding access to and improving retention on MOUD.”
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Increase in treatment
The study included 105,162 Medicare beneficiaries who began OUD treatment between March and August in 2019 (prepandemic cohort; 67.6%
aged 45-74 years), and 70,479 who began treatment between March and August of 2020 (pandemic cohort; 66.3% aged 45-74 years).
Participants had not received OUD treatment in the 6 months leading up to study enrollment and were followed for 6 months after treatment began.
Significantly more study participants received OUD-related telehealth services during the pandemic than prior to 2019 (19.6% vs. 0.6%; P < .001). Receipt of MOUD was also significantly higher in the pandemic cohort (12.6% vs. 10.8%; P < .001).
The rate of drug overdose deaths was higher in the pandemic cohort (5.1 deaths vs. 3.7 deaths per 1,000 beneficiaries; P < .001). But the percentage of deaths from drug overdoses did not differ between groups (4.8% in the prepandemic cohort vs. 5.1% in the pandemic cohort; P = .49).
In the pandemic cohort, fatal drug overdoses were 33% less likely among those who received OUD-related telehealth services (adjusted odds ratio, 0.67; 95% confidence interval, 0.48-0.92); 59% less likely among those who received MOUD from opioid treatment programs (aOR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.25-0.68), and 38% less likely among those who received buprenorphine in office-based settings (aOR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.43-0.91).
Risk of fatal overdose was significantly lower among women and those aged 65 years and older. There were no significant differences in risk based on urban or rural residency or on ethnicity.
“Against the backdrop of a highly potent illicit drug supply driven by illicit fentanyl and fentanyl analogues and historically large increases in overdose deaths during the COVID-19 pandemic, MOUD was still highly effective at reducing risk for fatal overdose,” Dr. Jones said.
While the use of buprenorphine in office-based settings was associated with a decreased risk of overdose death, use of extended-release naltrexone was not.
“Prior research has demonstrated the effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone in the treatment of opioid use disorder,” Dr. Jones said. “However, research has also shown that patients have challenges getting started, or inducted, on extended-release naltrexone.”
An earlier study by Dr. Jones and colleagues showed that rates of retention were lower with extended-release naltrexone, compared with buprenorphine in office-based settings or MOUD from opioid treatment programs.
The new study included only a small number of individuals who were receiving extended-release naltrexone, which may have influenced the findings. In addition, challenges with induction and retention may be driving the results, Dr. Jones noted.
“Efforts to improve induction and retention with extended-release naltrexone are important areas for future research and clinical practice,” he added.
An important engagement tool
A number of questions about telehealth care for OUD remain, including whether increased access to care accounts for the reduction in drug overdose risk that the investigators found or whether other factors are at play.
“There is still more we need to understand about telehealth, such as the quality of care provided and the particular aspects of care provided by telehealth and how this influences health outcomes,” Dr. Jones said.
The results also suggest treatments for OUD are still not finding their way to patients who might benefit, he added.
“Despite the positive findings and the prior research showing that MOUD is highly effective, we found that only one in five patients received telehealth services and only one in eight received any MOUD. This really underscores the need to expand these services across clinical settings,” he added.
These and earlier findings demonstrate the potential benefits of continuing pandemic-era expansion of OUD-related telehealth services and MOUD access, Dr. Jones said.
In preparation for the end of the public health emergency on May 1, the Drug Enforcement Agency recently released a proposal that would allow providers to prescribe a 30-day supply of buprenorphine, but for patients to receive additional prescriptions, a face-to-face meeting would be required. The proposal has drawn criticism from addiction medicine specialists.
The current study didn’t explore if or how the proposal might affect patients with OUD or whether it could blunt the positive effects of the findings.
“Prior research shows that keeping individuals engaged in treatment, including on medications, is a critical part of reducing the negative health and social impacts of opioid use disorder. Our results suggest that telehealth can be an important tool in helping patients engage in and stay connected in care,” said Dr. Jones.
The study was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Johnson reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study of Medicare beneficiaries shows.
Telehealth services for opioid use disorder (OUD) were used far more often during the pandemic than before COVID-19, and those who used them were 33% less likely to die of a drug overdose.
Investigators also found a significant increase in MOUD use during the pandemic. Fatal drug overdoses were 59% less likely among individuals who received MOUD from an opioid treatment program and 38% less likely among those treated with buprenorphine in an office-based setting.
The results come as policymakers are preparing for the end of the public health emergency that prompted the expansion of OUD-related telehealth and MOUD prescribing and are deciding whether to make those expansions permanent.
“The expansion of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic appears to have had positive effects on patients receiving MOUD, improved retention among patients who received MOUD, and lowered risks for both nonfatal and fatal overdose,” lead investigator Christopher M. Jones, PharmD, DrPH, director of the National Center for Injury Prevention and Control at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia, told this news organization. “Our results suggest that telehealth is a valuable tool in the toolbox for expanding access to and improving retention on MOUD.”
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Increase in treatment
The study included 105,162 Medicare beneficiaries who began OUD treatment between March and August in 2019 (prepandemic cohort; 67.6%
aged 45-74 years), and 70,479 who began treatment between March and August of 2020 (pandemic cohort; 66.3% aged 45-74 years).
Participants had not received OUD treatment in the 6 months leading up to study enrollment and were followed for 6 months after treatment began.
Significantly more study participants received OUD-related telehealth services during the pandemic than prior to 2019 (19.6% vs. 0.6%; P < .001). Receipt of MOUD was also significantly higher in the pandemic cohort (12.6% vs. 10.8%; P < .001).
The rate of drug overdose deaths was higher in the pandemic cohort (5.1 deaths vs. 3.7 deaths per 1,000 beneficiaries; P < .001). But the percentage of deaths from drug overdoses did not differ between groups (4.8% in the prepandemic cohort vs. 5.1% in the pandemic cohort; P = .49).
In the pandemic cohort, fatal drug overdoses were 33% less likely among those who received OUD-related telehealth services (adjusted odds ratio, 0.67; 95% confidence interval, 0.48-0.92); 59% less likely among those who received MOUD from opioid treatment programs (aOR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.25-0.68), and 38% less likely among those who received buprenorphine in office-based settings (aOR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.43-0.91).
Risk of fatal overdose was significantly lower among women and those aged 65 years and older. There were no significant differences in risk based on urban or rural residency or on ethnicity.
“Against the backdrop of a highly potent illicit drug supply driven by illicit fentanyl and fentanyl analogues and historically large increases in overdose deaths during the COVID-19 pandemic, MOUD was still highly effective at reducing risk for fatal overdose,” Dr. Jones said.
While the use of buprenorphine in office-based settings was associated with a decreased risk of overdose death, use of extended-release naltrexone was not.
“Prior research has demonstrated the effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone in the treatment of opioid use disorder,” Dr. Jones said. “However, research has also shown that patients have challenges getting started, or inducted, on extended-release naltrexone.”
An earlier study by Dr. Jones and colleagues showed that rates of retention were lower with extended-release naltrexone, compared with buprenorphine in office-based settings or MOUD from opioid treatment programs.
The new study included only a small number of individuals who were receiving extended-release naltrexone, which may have influenced the findings. In addition, challenges with induction and retention may be driving the results, Dr. Jones noted.
“Efforts to improve induction and retention with extended-release naltrexone are important areas for future research and clinical practice,” he added.
An important engagement tool
A number of questions about telehealth care for OUD remain, including whether increased access to care accounts for the reduction in drug overdose risk that the investigators found or whether other factors are at play.
“There is still more we need to understand about telehealth, such as the quality of care provided and the particular aspects of care provided by telehealth and how this influences health outcomes,” Dr. Jones said.
The results also suggest treatments for OUD are still not finding their way to patients who might benefit, he added.
“Despite the positive findings and the prior research showing that MOUD is highly effective, we found that only one in five patients received telehealth services and only one in eight received any MOUD. This really underscores the need to expand these services across clinical settings,” he added.
These and earlier findings demonstrate the potential benefits of continuing pandemic-era expansion of OUD-related telehealth services and MOUD access, Dr. Jones said.
In preparation for the end of the public health emergency on May 1, the Drug Enforcement Agency recently released a proposal that would allow providers to prescribe a 30-day supply of buprenorphine, but for patients to receive additional prescriptions, a face-to-face meeting would be required. The proposal has drawn criticism from addiction medicine specialists.
The current study didn’t explore if or how the proposal might affect patients with OUD or whether it could blunt the positive effects of the findings.
“Prior research shows that keeping individuals engaged in treatment, including on medications, is a critical part of reducing the negative health and social impacts of opioid use disorder. Our results suggest that telehealth can be an important tool in helping patients engage in and stay connected in care,” said Dr. Jones.
The study was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Johnson reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA PSYCHIATRY
Tranq-contaminated fentanyl now in 48 states, DEA warns
The DEA warning comes on the heels of a Food and Drug Administration announcement that it would begin more closely monitoring imports of the raw materials and bulk shipments of xylazine, also known as “tranq” and “zombie drug.”
Xylazine was first approved by the FDA in 1972 as a sedative and analgesic for use only in animals, but is increasingly being detected in illicit street drugs, and is often mixed with fentanyl, cocaine, and methamphetamine.
The FDA warned in November that naloxone (Narcan) would not reverse xylazine-related overdoses because the tranquilizer is not an opioid. It does suppress respiration and repeated exposures may lead to dependence and withdrawal, said the agency. Users are also experiencing severe necrosis at injection sites.
“Xylazine is making the deadliest drug threat our country has ever faced, fentanyl, even deadlier,” said DEA Administrator Anne Milgram in a statement. “The DEA Laboratory System is reporting that in 2022 approximately 23% of fentanyl powder and 7% of fentanyl pills seized by the DEA contained xylazine.”
Xylazine use has spread quickly, from its start in the Philadelphia area to the Northeast, the South, and most recently the West.
Citing data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the DEA said that 66% of the 107,735 overdose deaths for the year ending August 2022 involved synthetic opioids such as fentanyl. The DEA said that the Sinaloa Cartel and Jalisco Cartel in Mexico, using chemicals sourced from China, are primarily responsible for trafficking fentanyl in the United States.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The DEA warning comes on the heels of a Food and Drug Administration announcement that it would begin more closely monitoring imports of the raw materials and bulk shipments of xylazine, also known as “tranq” and “zombie drug.”
Xylazine was first approved by the FDA in 1972 as a sedative and analgesic for use only in animals, but is increasingly being detected in illicit street drugs, and is often mixed with fentanyl, cocaine, and methamphetamine.
The FDA warned in November that naloxone (Narcan) would not reverse xylazine-related overdoses because the tranquilizer is not an opioid. It does suppress respiration and repeated exposures may lead to dependence and withdrawal, said the agency. Users are also experiencing severe necrosis at injection sites.
“Xylazine is making the deadliest drug threat our country has ever faced, fentanyl, even deadlier,” said DEA Administrator Anne Milgram in a statement. “The DEA Laboratory System is reporting that in 2022 approximately 23% of fentanyl powder and 7% of fentanyl pills seized by the DEA contained xylazine.”
Xylazine use has spread quickly, from its start in the Philadelphia area to the Northeast, the South, and most recently the West.
Citing data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the DEA said that 66% of the 107,735 overdose deaths for the year ending August 2022 involved synthetic opioids such as fentanyl. The DEA said that the Sinaloa Cartel and Jalisco Cartel in Mexico, using chemicals sourced from China, are primarily responsible for trafficking fentanyl in the United States.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The DEA warning comes on the heels of a Food and Drug Administration announcement that it would begin more closely monitoring imports of the raw materials and bulk shipments of xylazine, also known as “tranq” and “zombie drug.”
Xylazine was first approved by the FDA in 1972 as a sedative and analgesic for use only in animals, but is increasingly being detected in illicit street drugs, and is often mixed with fentanyl, cocaine, and methamphetamine.
The FDA warned in November that naloxone (Narcan) would not reverse xylazine-related overdoses because the tranquilizer is not an opioid. It does suppress respiration and repeated exposures may lead to dependence and withdrawal, said the agency. Users are also experiencing severe necrosis at injection sites.
“Xylazine is making the deadliest drug threat our country has ever faced, fentanyl, even deadlier,” said DEA Administrator Anne Milgram in a statement. “The DEA Laboratory System is reporting that in 2022 approximately 23% of fentanyl powder and 7% of fentanyl pills seized by the DEA contained xylazine.”
Xylazine use has spread quickly, from its start in the Philadelphia area to the Northeast, the South, and most recently the West.
Citing data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the DEA said that 66% of the 107,735 overdose deaths for the year ending August 2022 involved synthetic opioids such as fentanyl. The DEA said that the Sinaloa Cartel and Jalisco Cartel in Mexico, using chemicals sourced from China, are primarily responsible for trafficking fentanyl in the United States.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Sweaty treatment for social anxiety could pass the sniff test
Getting sweet on sweat
Are you the sort of person who struggles in social situations? Have the past 3 years been a secret respite from the terror and exhaustion of meeting new people? We understand your plight. People kind of suck. And you don’t have to look far to be reminded of it.
Unfortunately, on occasion we all have to interact with other human beings. If you suffer from social anxiety, this is not a fun thing to do. But new research indicates that there may be a way to alleviate the stress for those with social anxiety: armpits.
Specifically, sweat from the armpits of other people. Yes, this means a group of scientists gathered up some volunteers and collected their armpit sweat while the volunteers watched a variety of movies (horror, comedy, romance, etc.). Our condolences to the poor unpaid interns tasked with gathering the sweat.
Once they had their precious new medicine, the researchers took a group of women and administered a round of mindfulness therapy. Some of the participants then received the various sweats, while the rest were forced to smell only clean air. (The horror!) Lo and behold, the sweat groups had their anxiety scores reduced by about 40% after their therapy, compared with just 17% in the control group.
The researchers also found that the source of the sweat didn’t matter. Their study subjects responded the same to sweat excreted during a scary movie as they did to sweat from a comedy, a result that surprised the researchers. They suggested chemosignals in the sweat may affect the treatment response and advised further research. Which means more sweat collection! They plan on testing emotionally neutral movies next time, and if we can make a humble suggestion, they also should try the sweatiest movies.
Before the Food and Drug Administration can approve armpit sweat as a treatment for social anxiety, we have some advice for those shut-in introverts out there. Next time you have to interact with rabid extroverts, instead of shaking their hands, walk up to them and take a deep whiff of their armpits. Establish dominance. Someone will feel awkward, and science has proved it won’t be you.
The puff that vaccinates
Ever been shot with a Nerf gun or hit with a foam pool tube? More annoying than painful, right? If we asked if you’d rather get pelted with one of those than receive a traditional vaccine injection, you would choose the former. Maybe someday you actually will.
During the boredom of the early pandemic lockdown, Jeremiah Gassensmith, PhD, of the department of chemistry and biochemistry at the University of Texas, Dallas, ordered a compressed gas–powered jet injection system to fool around with at home. Hey, who didn’t? Anyway, when it was time to go back to the lab he handed it over to one of his grad students, Yalini Wijesundara, and asked her to see what could be done with it.
In her tinkering she found that the jet injector could deliver metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) that can hold a bunch of different materials, like proteins and nucleic acids, through the skin.
Thus the “MOF-Jet” was born!
Jet injectors are nothing new, but they hurt. The MOF-Jet, however, is practically painless and cheaper than the gene guns that veterinarians use to inject biological cargo attached to the surface of a metal microparticle.
Changing the carrier gas also changes the time needed to break down the MOF and thus alters delivery of the drug inside. “If you shoot it with carbon dioxide, it will release its cargo faster within cells; if you use regular air, it will take 4 or 5 days,” Ms. Wijesundara explained in a written statement. That means the same drug could be released over different timescales without changing its formulation.
While testing on onion cells and mice, Ms. Wijesundara noted that it was as easy as “pointing and shooting” to distribute the puff of gas into the cells. A saving grace to those with needle anxiety. Not that we would know anything about needle anxiety.
More testing needs to be done before bringing this technology to human use, obviously, but we’re looking forward to saying goodbye to that dreaded prick and hello to a puff.
Your hippocampus is showing
Brain anatomy is one of the many, many things that’s not really our thing, but we do know a cool picture when we see one. Case in point: The image just below, which happens to be a full-scale, single-cell resolution model of the CA1 region of the hippocampus that “replicates the structure and architecture of the area, along with the position and relative connectivity of the neurons,” according to a statement from the Human Brain Project.
“We have performed a data mining operation on high resolution images of the human hippocampus, obtained from the BigBrain database. The position of individual neurons has been derived from a detailed analysis of these images,” said senior author Michele Migliore, PhD, of the Italian National Research Council’s Institute of Biophysics in Palermo.
Yes, he did say BigBrain database. BigBrain is – we checked and it’s definitely not this – a 3D model of a brain that was sectioned into 7,404 slices just 20 micrometers thick and then scanned by MRI. Digital reconstruction of those slices was done by supercomputer and the results are now available for analysis.
Dr. Migliore and his associates developed an image-processing algorithm to obtain neuronal positioning distribution and an algorithm to generate neuronal connectivity by approximating the shapes of dendrites and axons. (Our brains are starting to hurt just trying to write this.) “Some fit into narrow cones, others have a broad complex extension that can be approximated by dedicated geometrical volumes, and the connectivity to nearby neurons changes accordingly,” explained lead author Daniela Gandolfi of the University of Modena (Italy) and Reggio Emilia.
The investigators have made their dataset and the extraction methodology available on the EBRAINS platform and through the Human Brain Project and are moving on to other brain regions. And then, once everyone can find their way in and around the old gray matter, it should bring an end to conversations like this, which no doubt occur between male and female neuroscientists every day:
“Arnold, I think we’re lost.”
“Don’t worry, Bev, I know where I’m going.”
“Stop and ask this lady for directions.”
“I said I can find it.”
“Just ask her.”
“Fine. Excuse me, ma’am, can you tell us how to get to the corpora quadrigemina from here?
Getting sweet on sweat
Are you the sort of person who struggles in social situations? Have the past 3 years been a secret respite from the terror and exhaustion of meeting new people? We understand your plight. People kind of suck. And you don’t have to look far to be reminded of it.
Unfortunately, on occasion we all have to interact with other human beings. If you suffer from social anxiety, this is not a fun thing to do. But new research indicates that there may be a way to alleviate the stress for those with social anxiety: armpits.
Specifically, sweat from the armpits of other people. Yes, this means a group of scientists gathered up some volunteers and collected their armpit sweat while the volunteers watched a variety of movies (horror, comedy, romance, etc.). Our condolences to the poor unpaid interns tasked with gathering the sweat.
Once they had their precious new medicine, the researchers took a group of women and administered a round of mindfulness therapy. Some of the participants then received the various sweats, while the rest were forced to smell only clean air. (The horror!) Lo and behold, the sweat groups had their anxiety scores reduced by about 40% after their therapy, compared with just 17% in the control group.
The researchers also found that the source of the sweat didn’t matter. Their study subjects responded the same to sweat excreted during a scary movie as they did to sweat from a comedy, a result that surprised the researchers. They suggested chemosignals in the sweat may affect the treatment response and advised further research. Which means more sweat collection! They plan on testing emotionally neutral movies next time, and if we can make a humble suggestion, they also should try the sweatiest movies.
Before the Food and Drug Administration can approve armpit sweat as a treatment for social anxiety, we have some advice for those shut-in introverts out there. Next time you have to interact with rabid extroverts, instead of shaking their hands, walk up to them and take a deep whiff of their armpits. Establish dominance. Someone will feel awkward, and science has proved it won’t be you.
The puff that vaccinates
Ever been shot with a Nerf gun or hit with a foam pool tube? More annoying than painful, right? If we asked if you’d rather get pelted with one of those than receive a traditional vaccine injection, you would choose the former. Maybe someday you actually will.
During the boredom of the early pandemic lockdown, Jeremiah Gassensmith, PhD, of the department of chemistry and biochemistry at the University of Texas, Dallas, ordered a compressed gas–powered jet injection system to fool around with at home. Hey, who didn’t? Anyway, when it was time to go back to the lab he handed it over to one of his grad students, Yalini Wijesundara, and asked her to see what could be done with it.
In her tinkering she found that the jet injector could deliver metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) that can hold a bunch of different materials, like proteins and nucleic acids, through the skin.
Thus the “MOF-Jet” was born!
Jet injectors are nothing new, but they hurt. The MOF-Jet, however, is practically painless and cheaper than the gene guns that veterinarians use to inject biological cargo attached to the surface of a metal microparticle.
Changing the carrier gas also changes the time needed to break down the MOF and thus alters delivery of the drug inside. “If you shoot it with carbon dioxide, it will release its cargo faster within cells; if you use regular air, it will take 4 or 5 days,” Ms. Wijesundara explained in a written statement. That means the same drug could be released over different timescales without changing its formulation.
While testing on onion cells and mice, Ms. Wijesundara noted that it was as easy as “pointing and shooting” to distribute the puff of gas into the cells. A saving grace to those with needle anxiety. Not that we would know anything about needle anxiety.
More testing needs to be done before bringing this technology to human use, obviously, but we’re looking forward to saying goodbye to that dreaded prick and hello to a puff.
Your hippocampus is showing
Brain anatomy is one of the many, many things that’s not really our thing, but we do know a cool picture when we see one. Case in point: The image just below, which happens to be a full-scale, single-cell resolution model of the CA1 region of the hippocampus that “replicates the structure and architecture of the area, along with the position and relative connectivity of the neurons,” according to a statement from the Human Brain Project.
“We have performed a data mining operation on high resolution images of the human hippocampus, obtained from the BigBrain database. The position of individual neurons has been derived from a detailed analysis of these images,” said senior author Michele Migliore, PhD, of the Italian National Research Council’s Institute of Biophysics in Palermo.
Yes, he did say BigBrain database. BigBrain is – we checked and it’s definitely not this – a 3D model of a brain that was sectioned into 7,404 slices just 20 micrometers thick and then scanned by MRI. Digital reconstruction of those slices was done by supercomputer and the results are now available for analysis.
Dr. Migliore and his associates developed an image-processing algorithm to obtain neuronal positioning distribution and an algorithm to generate neuronal connectivity by approximating the shapes of dendrites and axons. (Our brains are starting to hurt just trying to write this.) “Some fit into narrow cones, others have a broad complex extension that can be approximated by dedicated geometrical volumes, and the connectivity to nearby neurons changes accordingly,” explained lead author Daniela Gandolfi of the University of Modena (Italy) and Reggio Emilia.
The investigators have made their dataset and the extraction methodology available on the EBRAINS platform and through the Human Brain Project and are moving on to other brain regions. And then, once everyone can find their way in and around the old gray matter, it should bring an end to conversations like this, which no doubt occur between male and female neuroscientists every day:
“Arnold, I think we’re lost.”
“Don’t worry, Bev, I know where I’m going.”
“Stop and ask this lady for directions.”
“I said I can find it.”
“Just ask her.”
“Fine. Excuse me, ma’am, can you tell us how to get to the corpora quadrigemina from here?
Getting sweet on sweat
Are you the sort of person who struggles in social situations? Have the past 3 years been a secret respite from the terror and exhaustion of meeting new people? We understand your plight. People kind of suck. And you don’t have to look far to be reminded of it.
Unfortunately, on occasion we all have to interact with other human beings. If you suffer from social anxiety, this is not a fun thing to do. But new research indicates that there may be a way to alleviate the stress for those with social anxiety: armpits.
Specifically, sweat from the armpits of other people. Yes, this means a group of scientists gathered up some volunteers and collected their armpit sweat while the volunteers watched a variety of movies (horror, comedy, romance, etc.). Our condolences to the poor unpaid interns tasked with gathering the sweat.
Once they had their precious new medicine, the researchers took a group of women and administered a round of mindfulness therapy. Some of the participants then received the various sweats, while the rest were forced to smell only clean air. (The horror!) Lo and behold, the sweat groups had their anxiety scores reduced by about 40% after their therapy, compared with just 17% in the control group.
The researchers also found that the source of the sweat didn’t matter. Their study subjects responded the same to sweat excreted during a scary movie as they did to sweat from a comedy, a result that surprised the researchers. They suggested chemosignals in the sweat may affect the treatment response and advised further research. Which means more sweat collection! They plan on testing emotionally neutral movies next time, and if we can make a humble suggestion, they also should try the sweatiest movies.
Before the Food and Drug Administration can approve armpit sweat as a treatment for social anxiety, we have some advice for those shut-in introverts out there. Next time you have to interact with rabid extroverts, instead of shaking their hands, walk up to them and take a deep whiff of their armpits. Establish dominance. Someone will feel awkward, and science has proved it won’t be you.
The puff that vaccinates
Ever been shot with a Nerf gun or hit with a foam pool tube? More annoying than painful, right? If we asked if you’d rather get pelted with one of those than receive a traditional vaccine injection, you would choose the former. Maybe someday you actually will.
During the boredom of the early pandemic lockdown, Jeremiah Gassensmith, PhD, of the department of chemistry and biochemistry at the University of Texas, Dallas, ordered a compressed gas–powered jet injection system to fool around with at home. Hey, who didn’t? Anyway, when it was time to go back to the lab he handed it over to one of his grad students, Yalini Wijesundara, and asked her to see what could be done with it.
In her tinkering she found that the jet injector could deliver metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) that can hold a bunch of different materials, like proteins and nucleic acids, through the skin.
Thus the “MOF-Jet” was born!
Jet injectors are nothing new, but they hurt. The MOF-Jet, however, is practically painless and cheaper than the gene guns that veterinarians use to inject biological cargo attached to the surface of a metal microparticle.
Changing the carrier gas also changes the time needed to break down the MOF and thus alters delivery of the drug inside. “If you shoot it with carbon dioxide, it will release its cargo faster within cells; if you use regular air, it will take 4 or 5 days,” Ms. Wijesundara explained in a written statement. That means the same drug could be released over different timescales without changing its formulation.
While testing on onion cells and mice, Ms. Wijesundara noted that it was as easy as “pointing and shooting” to distribute the puff of gas into the cells. A saving grace to those with needle anxiety. Not that we would know anything about needle anxiety.
More testing needs to be done before bringing this technology to human use, obviously, but we’re looking forward to saying goodbye to that dreaded prick and hello to a puff.
Your hippocampus is showing
Brain anatomy is one of the many, many things that’s not really our thing, but we do know a cool picture when we see one. Case in point: The image just below, which happens to be a full-scale, single-cell resolution model of the CA1 region of the hippocampus that “replicates the structure and architecture of the area, along with the position and relative connectivity of the neurons,” according to a statement from the Human Brain Project.
“We have performed a data mining operation on high resolution images of the human hippocampus, obtained from the BigBrain database. The position of individual neurons has been derived from a detailed analysis of these images,” said senior author Michele Migliore, PhD, of the Italian National Research Council’s Institute of Biophysics in Palermo.
Yes, he did say BigBrain database. BigBrain is – we checked and it’s definitely not this – a 3D model of a brain that was sectioned into 7,404 slices just 20 micrometers thick and then scanned by MRI. Digital reconstruction of those slices was done by supercomputer and the results are now available for analysis.
Dr. Migliore and his associates developed an image-processing algorithm to obtain neuronal positioning distribution and an algorithm to generate neuronal connectivity by approximating the shapes of dendrites and axons. (Our brains are starting to hurt just trying to write this.) “Some fit into narrow cones, others have a broad complex extension that can be approximated by dedicated geometrical volumes, and the connectivity to nearby neurons changes accordingly,” explained lead author Daniela Gandolfi of the University of Modena (Italy) and Reggio Emilia.
The investigators have made their dataset and the extraction methodology available on the EBRAINS platform and through the Human Brain Project and are moving on to other brain regions. And then, once everyone can find their way in and around the old gray matter, it should bring an end to conversations like this, which no doubt occur between male and female neuroscientists every day:
“Arnold, I think we’re lost.”
“Don’t worry, Bev, I know where I’m going.”
“Stop and ask this lady for directions.”
“I said I can find it.”
“Just ask her.”
“Fine. Excuse me, ma’am, can you tell us how to get to the corpora quadrigemina from here?
Commotio cordis underrecognized, undertreated outside of sports
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) due to commotio cordis occurs more frequently in non–sport-related settings than is commonly thought, resulting in lower rates of resuscitation and increased mortality, especially among young women, a new review suggests.
The condition is rare, caused by an often fatal arrhythmia secondary to a blunt, nonpenetrating impact over the precordium, without direct structural damage to the heart itself. Common causes in nonsport settings include assault, motor vehicle accidents (MVAs), and daily activities such as occupational accidents.
“We found a stark difference in mortality outcomes between non–sport-related commotio cordis compared to sport-related events,” at 88% vs. 66%, Han S. Lim, MBBS, PhD, of the University of Melbourne, and Austin Health, Heidelberg, Australia, told this news organization. “Rates of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) (27% vs. 97%) and defibrillation (17% vs. 81%) were considerably lower in the non–sport-related events.”
“Although still being male-predominant, of concern, we saw a higher proportion of females in non–sport-related commotio cordis due to assault, MVAs, and other activities,” he noted. Such events may occur “in secluded domestic settings, may not be witnessed, or may occur as intentional harm, whereby the witness could also be the perpetrator, reducing the likelihood of prompt diagnosis, CPR, and defibrillation administration.”
The study was published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
Young women affected
Dr. Lim and colleagues searched the literature through 2021 for all cases of commotio cordis. Three hundred and thirty-four cases from among 53 citations were included in the analysis; of those, 121 (36%) occurred in non–sport-related settings, including assault (76%), MVAs (7%), and daily activities (16%). “Daily activities” comprised activities that were expected in a person’s day-to-day routine such as falls, play fighting (in children), and occupational accidents.
Non–sport-related cases primarily involved nonprojectile etiologies (95%), including bodily contact (79%), such as impacts from fists, feet, and knees; impacts with handlebars or steering wheels; and solid stick-like weapons and flat surfaces.
Sport-related cases involved a significantly higher proportion of projectiles (94% vs. 5%) and occurred across a range of sports, mostly at the competitive level (66%).
Both sport-related and non–sport-related commotio cordis affected a similar younger demographic (mean age, 19; mostly males). No statistically significant differences between the two groups were seen with regard to previous cardiac history or family history of cardiac disease, or in arrhythmias on electrocardiogram, biomarkers, or imaging findings.
However, in non–sport-related events, the proportion of females affected was significantly higher (13% vs. 2%), as was mortality (88% vs. 66%). Rates were lower for CPR (27% vs. 97%) and defibrillation use (17% vs. 81%), and resuscitation was more commonly delayed beyond 3 minutes (80% vs. 5%).
The finding that more than a third of reported cases were non–sport-related “is higher than previously reported, and included data from 15 different countries,” the authors noted.
Study limitations included the use of data only from published studies, inclusion of a case series limited to fatal cases, small sample sizes, and lack of consistent reporting of demographic data, mechanisms, investigation results, management, and outcomes.
Increased awareness ‘essential’
Dr. Lim and colleagues concluded that increased awareness of non–sport-related commotio cordis is “essential” for early recognition, resuscitation, and mortality reduction.
Jim Cheung, MD, chair of the American College of Cardiology’s electrophysiology section, “completely agrees.” Greater awareness among the general population could reduce barriers to CPR and automated external defibrillator (AED) use, he said, which in turn, can lead to improved survival.
Furthermore, Dr. Cheung added, “This study underscores the importance of ensuring that non–cardiology-trained physicians such as emergency medicine physicians and trauma surgeons who might encounter patients with non–sports-related commotio cordis recognize the entity during the course of treatment.”
Because the review relied only on published cases, “it may not represent the true breadth of cases that are occurring in the real world,” he noted. “I suspect that cases that occur outside of sports-related activities, such as MVAs and assault, are more likely to be underreported and that the true proportion of non–sports-related commotio cordis may be significantly higher than 36%.” Increased reporting of cases as part of an international commotio cordis registry would help provide additional insights, he suggested.
“There is a common misperception that SCA only occurs among older patients and patients with known coronary artery disease or heart failure,” he said. “For us to move the needle on improving SCA survival, we will need to tackle the problem from multiple angles including increasing public awareness, training the public on CPR and AED use, and improving access to AEDs by addressing structural barriers.”
Dr. Cheung pointed to ongoing efforts by nonprofit, patient-driven organizations such as the SADS Foundation and Omar Carter Foundation, and professional societies such as the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, and Heart Rhythm Society, to direct public awareness campaigns and legislative proposals to address this problem.
Similar efforts are underway among cardiac societies and SCA awareness groups in Australia, Dr. Lim said.
No funding or relevant financial relationships were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) due to commotio cordis occurs more frequently in non–sport-related settings than is commonly thought, resulting in lower rates of resuscitation and increased mortality, especially among young women, a new review suggests.
The condition is rare, caused by an often fatal arrhythmia secondary to a blunt, nonpenetrating impact over the precordium, without direct structural damage to the heart itself. Common causes in nonsport settings include assault, motor vehicle accidents (MVAs), and daily activities such as occupational accidents.
“We found a stark difference in mortality outcomes between non–sport-related commotio cordis compared to sport-related events,” at 88% vs. 66%, Han S. Lim, MBBS, PhD, of the University of Melbourne, and Austin Health, Heidelberg, Australia, told this news organization. “Rates of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) (27% vs. 97%) and defibrillation (17% vs. 81%) were considerably lower in the non–sport-related events.”
“Although still being male-predominant, of concern, we saw a higher proportion of females in non–sport-related commotio cordis due to assault, MVAs, and other activities,” he noted. Such events may occur “in secluded domestic settings, may not be witnessed, or may occur as intentional harm, whereby the witness could also be the perpetrator, reducing the likelihood of prompt diagnosis, CPR, and defibrillation administration.”
The study was published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
Young women affected
Dr. Lim and colleagues searched the literature through 2021 for all cases of commotio cordis. Three hundred and thirty-four cases from among 53 citations were included in the analysis; of those, 121 (36%) occurred in non–sport-related settings, including assault (76%), MVAs (7%), and daily activities (16%). “Daily activities” comprised activities that were expected in a person’s day-to-day routine such as falls, play fighting (in children), and occupational accidents.
Non–sport-related cases primarily involved nonprojectile etiologies (95%), including bodily contact (79%), such as impacts from fists, feet, and knees; impacts with handlebars or steering wheels; and solid stick-like weapons and flat surfaces.
Sport-related cases involved a significantly higher proportion of projectiles (94% vs. 5%) and occurred across a range of sports, mostly at the competitive level (66%).
Both sport-related and non–sport-related commotio cordis affected a similar younger demographic (mean age, 19; mostly males). No statistically significant differences between the two groups were seen with regard to previous cardiac history or family history of cardiac disease, or in arrhythmias on electrocardiogram, biomarkers, or imaging findings.
However, in non–sport-related events, the proportion of females affected was significantly higher (13% vs. 2%), as was mortality (88% vs. 66%). Rates were lower for CPR (27% vs. 97%) and defibrillation use (17% vs. 81%), and resuscitation was more commonly delayed beyond 3 minutes (80% vs. 5%).
The finding that more than a third of reported cases were non–sport-related “is higher than previously reported, and included data from 15 different countries,” the authors noted.
Study limitations included the use of data only from published studies, inclusion of a case series limited to fatal cases, small sample sizes, and lack of consistent reporting of demographic data, mechanisms, investigation results, management, and outcomes.
Increased awareness ‘essential’
Dr. Lim and colleagues concluded that increased awareness of non–sport-related commotio cordis is “essential” for early recognition, resuscitation, and mortality reduction.
Jim Cheung, MD, chair of the American College of Cardiology’s electrophysiology section, “completely agrees.” Greater awareness among the general population could reduce barriers to CPR and automated external defibrillator (AED) use, he said, which in turn, can lead to improved survival.
Furthermore, Dr. Cheung added, “This study underscores the importance of ensuring that non–cardiology-trained physicians such as emergency medicine physicians and trauma surgeons who might encounter patients with non–sports-related commotio cordis recognize the entity during the course of treatment.”
Because the review relied only on published cases, “it may not represent the true breadth of cases that are occurring in the real world,” he noted. “I suspect that cases that occur outside of sports-related activities, such as MVAs and assault, are more likely to be underreported and that the true proportion of non–sports-related commotio cordis may be significantly higher than 36%.” Increased reporting of cases as part of an international commotio cordis registry would help provide additional insights, he suggested.
“There is a common misperception that SCA only occurs among older patients and patients with known coronary artery disease or heart failure,” he said. “For us to move the needle on improving SCA survival, we will need to tackle the problem from multiple angles including increasing public awareness, training the public on CPR and AED use, and improving access to AEDs by addressing structural barriers.”
Dr. Cheung pointed to ongoing efforts by nonprofit, patient-driven organizations such as the SADS Foundation and Omar Carter Foundation, and professional societies such as the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, and Heart Rhythm Society, to direct public awareness campaigns and legislative proposals to address this problem.
Similar efforts are underway among cardiac societies and SCA awareness groups in Australia, Dr. Lim said.
No funding or relevant financial relationships were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) due to commotio cordis occurs more frequently in non–sport-related settings than is commonly thought, resulting in lower rates of resuscitation and increased mortality, especially among young women, a new review suggests.
The condition is rare, caused by an often fatal arrhythmia secondary to a blunt, nonpenetrating impact over the precordium, without direct structural damage to the heart itself. Common causes in nonsport settings include assault, motor vehicle accidents (MVAs), and daily activities such as occupational accidents.
“We found a stark difference in mortality outcomes between non–sport-related commotio cordis compared to sport-related events,” at 88% vs. 66%, Han S. Lim, MBBS, PhD, of the University of Melbourne, and Austin Health, Heidelberg, Australia, told this news organization. “Rates of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) (27% vs. 97%) and defibrillation (17% vs. 81%) were considerably lower in the non–sport-related events.”
“Although still being male-predominant, of concern, we saw a higher proportion of females in non–sport-related commotio cordis due to assault, MVAs, and other activities,” he noted. Such events may occur “in secluded domestic settings, may not be witnessed, or may occur as intentional harm, whereby the witness could also be the perpetrator, reducing the likelihood of prompt diagnosis, CPR, and defibrillation administration.”
The study was published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
Young women affected
Dr. Lim and colleagues searched the literature through 2021 for all cases of commotio cordis. Three hundred and thirty-four cases from among 53 citations were included in the analysis; of those, 121 (36%) occurred in non–sport-related settings, including assault (76%), MVAs (7%), and daily activities (16%). “Daily activities” comprised activities that were expected in a person’s day-to-day routine such as falls, play fighting (in children), and occupational accidents.
Non–sport-related cases primarily involved nonprojectile etiologies (95%), including bodily contact (79%), such as impacts from fists, feet, and knees; impacts with handlebars or steering wheels; and solid stick-like weapons and flat surfaces.
Sport-related cases involved a significantly higher proportion of projectiles (94% vs. 5%) and occurred across a range of sports, mostly at the competitive level (66%).
Both sport-related and non–sport-related commotio cordis affected a similar younger demographic (mean age, 19; mostly males). No statistically significant differences between the two groups were seen with regard to previous cardiac history or family history of cardiac disease, or in arrhythmias on electrocardiogram, biomarkers, or imaging findings.
However, in non–sport-related events, the proportion of females affected was significantly higher (13% vs. 2%), as was mortality (88% vs. 66%). Rates were lower for CPR (27% vs. 97%) and defibrillation use (17% vs. 81%), and resuscitation was more commonly delayed beyond 3 minutes (80% vs. 5%).
The finding that more than a third of reported cases were non–sport-related “is higher than previously reported, and included data from 15 different countries,” the authors noted.
Study limitations included the use of data only from published studies, inclusion of a case series limited to fatal cases, small sample sizes, and lack of consistent reporting of demographic data, mechanisms, investigation results, management, and outcomes.
Increased awareness ‘essential’
Dr. Lim and colleagues concluded that increased awareness of non–sport-related commotio cordis is “essential” for early recognition, resuscitation, and mortality reduction.
Jim Cheung, MD, chair of the American College of Cardiology’s electrophysiology section, “completely agrees.” Greater awareness among the general population could reduce barriers to CPR and automated external defibrillator (AED) use, he said, which in turn, can lead to improved survival.
Furthermore, Dr. Cheung added, “This study underscores the importance of ensuring that non–cardiology-trained physicians such as emergency medicine physicians and trauma surgeons who might encounter patients with non–sports-related commotio cordis recognize the entity during the course of treatment.”
Because the review relied only on published cases, “it may not represent the true breadth of cases that are occurring in the real world,” he noted. “I suspect that cases that occur outside of sports-related activities, such as MVAs and assault, are more likely to be underreported and that the true proportion of non–sports-related commotio cordis may be significantly higher than 36%.” Increased reporting of cases as part of an international commotio cordis registry would help provide additional insights, he suggested.
“There is a common misperception that SCA only occurs among older patients and patients with known coronary artery disease or heart failure,” he said. “For us to move the needle on improving SCA survival, we will need to tackle the problem from multiple angles including increasing public awareness, training the public on CPR and AED use, and improving access to AEDs by addressing structural barriers.”
Dr. Cheung pointed to ongoing efforts by nonprofit, patient-driven organizations such as the SADS Foundation and Omar Carter Foundation, and professional societies such as the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, and Heart Rhythm Society, to direct public awareness campaigns and legislative proposals to address this problem.
Similar efforts are underway among cardiac societies and SCA awareness groups in Australia, Dr. Lim said.
No funding or relevant financial relationships were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JACC: CLINICAL ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
Luxe vacations, private jets: Medical device maker, surgeon to pay $46 million penalty in kickback scheme
according to experts familiar with the federal Anti-Kickback Statute.
Historically, enforcement actions have primarily focused on the person or organization offering the perks – and not necessarily the physicians accepting it, Steven W. Ortquist, founder and principal of Arete Compliance Solutions, LLC, in Phoenix, told this news organization.
But that’s changing.
“In recent years, we are seeing a trend toward holding physicians and others on the receiving end of the inducement accountable as well,” said Mr. Ortquist, who is a past board member and president of the Health Care Compliance Association. He noted that authorities usually pursue the inducing company first before moving on to individual clinicians or practices.
The Department of Justice followed a similar pattern in a recently announced kickback settlement that ensnared an intraocular lens distributor, an ophthalmology equipment supplier, two CEOs, and a surgeon. Precision Lens must pay more than $43 million for offering high-end vacations and other expensive perks to surgeons who used its cataract products.
The verdict marks the end of a 6-week civil jury trial, where evidence emerged that Paul Ehlen, owner of Precision Lens and its parent company, Cameron-Ehlen Group, maintained a secret “slush fund” for paying kickbacks to ophthalmic surgeons. The inducement scheme netted the Minnesota-based company millions in sales and led to the submission of 64,575 false Medicare claims from 2006 to 2015, a violation of the Anti-Kickback Statute and the False Claims Act.
According to court documents, physicians received luxury travel and entertainment packages, including skiing, fishing, and golfing excursions at exclusive destinations, often traveling via private jet to attend Broadway musicals and major sporting events. Mr. Ehlen and company representatives also sold frequent flyer miles to physicians at a steep discount, allowing them to take personal and business trips below fair market value.
Federal authorities initially announced an investigation into the business practices of Precision Lens in 2017 after receiving a whistleblower complaint from Kipp Fesenmaier, a former executive at Sightpath Medical, an ophthalmology supplier and “corporate partner” of Precision Lens. Mr. Fesenmaier alleged that both companies were involved in an inducement scheme.
Sightpath Medical and its CEO, James Tiffany, agreed to a $12 million settlement to resolve the kickback allegations.
The Department of Justice subsequently investigated Jitendra Swarup, MD, an ophthalmologist and cataract surgeon who allegedly received “unlawful remuneration from Sightpath, Precision, and Ehlen” and filed false insurance claims. In addition to accepting expensive hunting and fishing trips from the medical device companies, Dr. Swarup was paid more than $100,000 per year for consulting services he did not fully render.
Dr. Swarup agreed to a nearly $3 million settlement and participation in a 3-year corporate integrity agreement with the Office of Inspector General. In exchange for compliance with such contracts, the OIG permits physicians to continue participating in Medicare, Medicaid, and other federal health care programs.
In a statement from attorneys, Precision Lens and Mr. Ehlen pledged to appeal the verdict and “defend ... our wholly appropriate actions” while remaining focused on their commitment to health care clinicians and manufacturers.
‘Endless’ opportunities for inducement
Unfortunately, opportunities for inducement are “endless,” experts say. Extravagant trips, dinners, and gifts can trigger a violation, but so can nearly anything of value.
Just last year, Biotronik reached a $12.95 million settlement amid allegations that company representatives wined and dined physicians to induce their use of its pacemakers and defibrillators. To date, no physicians have been charged.
But after a record-breaking number of whistleblower judgments last fiscal year totaling more than $2 billion, physicians should take note, Radha Bhatnagar, Esq, director of compliance at The CM Group, told the news organization.
“When manufacturers offer physicians kickbacks with the added element of fraudulent Medicare or Medicaid reimbursements, that is typically when manufacturers and individuals face civil and criminal liability,” said Ms. Bhatnagar, something the Department of Justice alluded to when announcing a settlement involving 15 Texas physicians last year.
In another case, Kingsley R. Chin, an orthopedic surgeon and designer of a spinal implant, was indicted in 2021 for paying millions of dollars in sham consulting fees to physicians who used his products. At least six surgeons who accepted money from Dr. Chin were later named in a civil case and ordered to pay $3.3 million in penalties.
Jason Montone, DO, an orthopedic surgeon who accepted the illicit payments, agreed to a plea deal with a reduced prison sentence, 1 year of supervised release, and a fine of $379,000.
Although Dr. Chin’s sentencing hasn’t been announced, violating kickback laws can result in a sentence of up to 10 years.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
according to experts familiar with the federal Anti-Kickback Statute.
Historically, enforcement actions have primarily focused on the person or organization offering the perks – and not necessarily the physicians accepting it, Steven W. Ortquist, founder and principal of Arete Compliance Solutions, LLC, in Phoenix, told this news organization.
But that’s changing.
“In recent years, we are seeing a trend toward holding physicians and others on the receiving end of the inducement accountable as well,” said Mr. Ortquist, who is a past board member and president of the Health Care Compliance Association. He noted that authorities usually pursue the inducing company first before moving on to individual clinicians or practices.
The Department of Justice followed a similar pattern in a recently announced kickback settlement that ensnared an intraocular lens distributor, an ophthalmology equipment supplier, two CEOs, and a surgeon. Precision Lens must pay more than $43 million for offering high-end vacations and other expensive perks to surgeons who used its cataract products.
The verdict marks the end of a 6-week civil jury trial, where evidence emerged that Paul Ehlen, owner of Precision Lens and its parent company, Cameron-Ehlen Group, maintained a secret “slush fund” for paying kickbacks to ophthalmic surgeons. The inducement scheme netted the Minnesota-based company millions in sales and led to the submission of 64,575 false Medicare claims from 2006 to 2015, a violation of the Anti-Kickback Statute and the False Claims Act.
According to court documents, physicians received luxury travel and entertainment packages, including skiing, fishing, and golfing excursions at exclusive destinations, often traveling via private jet to attend Broadway musicals and major sporting events. Mr. Ehlen and company representatives also sold frequent flyer miles to physicians at a steep discount, allowing them to take personal and business trips below fair market value.
Federal authorities initially announced an investigation into the business practices of Precision Lens in 2017 after receiving a whistleblower complaint from Kipp Fesenmaier, a former executive at Sightpath Medical, an ophthalmology supplier and “corporate partner” of Precision Lens. Mr. Fesenmaier alleged that both companies were involved in an inducement scheme.
Sightpath Medical and its CEO, James Tiffany, agreed to a $12 million settlement to resolve the kickback allegations.
The Department of Justice subsequently investigated Jitendra Swarup, MD, an ophthalmologist and cataract surgeon who allegedly received “unlawful remuneration from Sightpath, Precision, and Ehlen” and filed false insurance claims. In addition to accepting expensive hunting and fishing trips from the medical device companies, Dr. Swarup was paid more than $100,000 per year for consulting services he did not fully render.
Dr. Swarup agreed to a nearly $3 million settlement and participation in a 3-year corporate integrity agreement with the Office of Inspector General. In exchange for compliance with such contracts, the OIG permits physicians to continue participating in Medicare, Medicaid, and other federal health care programs.
In a statement from attorneys, Precision Lens and Mr. Ehlen pledged to appeal the verdict and “defend ... our wholly appropriate actions” while remaining focused on their commitment to health care clinicians and manufacturers.
‘Endless’ opportunities for inducement
Unfortunately, opportunities for inducement are “endless,” experts say. Extravagant trips, dinners, and gifts can trigger a violation, but so can nearly anything of value.
Just last year, Biotronik reached a $12.95 million settlement amid allegations that company representatives wined and dined physicians to induce their use of its pacemakers and defibrillators. To date, no physicians have been charged.
But after a record-breaking number of whistleblower judgments last fiscal year totaling more than $2 billion, physicians should take note, Radha Bhatnagar, Esq, director of compliance at The CM Group, told the news organization.
“When manufacturers offer physicians kickbacks with the added element of fraudulent Medicare or Medicaid reimbursements, that is typically when manufacturers and individuals face civil and criminal liability,” said Ms. Bhatnagar, something the Department of Justice alluded to when announcing a settlement involving 15 Texas physicians last year.
In another case, Kingsley R. Chin, an orthopedic surgeon and designer of a spinal implant, was indicted in 2021 for paying millions of dollars in sham consulting fees to physicians who used his products. At least six surgeons who accepted money from Dr. Chin were later named in a civil case and ordered to pay $3.3 million in penalties.
Jason Montone, DO, an orthopedic surgeon who accepted the illicit payments, agreed to a plea deal with a reduced prison sentence, 1 year of supervised release, and a fine of $379,000.
Although Dr. Chin’s sentencing hasn’t been announced, violating kickback laws can result in a sentence of up to 10 years.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
according to experts familiar with the federal Anti-Kickback Statute.
Historically, enforcement actions have primarily focused on the person or organization offering the perks – and not necessarily the physicians accepting it, Steven W. Ortquist, founder and principal of Arete Compliance Solutions, LLC, in Phoenix, told this news organization.
But that’s changing.
“In recent years, we are seeing a trend toward holding physicians and others on the receiving end of the inducement accountable as well,” said Mr. Ortquist, who is a past board member and president of the Health Care Compliance Association. He noted that authorities usually pursue the inducing company first before moving on to individual clinicians or practices.
The Department of Justice followed a similar pattern in a recently announced kickback settlement that ensnared an intraocular lens distributor, an ophthalmology equipment supplier, two CEOs, and a surgeon. Precision Lens must pay more than $43 million for offering high-end vacations and other expensive perks to surgeons who used its cataract products.
The verdict marks the end of a 6-week civil jury trial, where evidence emerged that Paul Ehlen, owner of Precision Lens and its parent company, Cameron-Ehlen Group, maintained a secret “slush fund” for paying kickbacks to ophthalmic surgeons. The inducement scheme netted the Minnesota-based company millions in sales and led to the submission of 64,575 false Medicare claims from 2006 to 2015, a violation of the Anti-Kickback Statute and the False Claims Act.
According to court documents, physicians received luxury travel and entertainment packages, including skiing, fishing, and golfing excursions at exclusive destinations, often traveling via private jet to attend Broadway musicals and major sporting events. Mr. Ehlen and company representatives also sold frequent flyer miles to physicians at a steep discount, allowing them to take personal and business trips below fair market value.
Federal authorities initially announced an investigation into the business practices of Precision Lens in 2017 after receiving a whistleblower complaint from Kipp Fesenmaier, a former executive at Sightpath Medical, an ophthalmology supplier and “corporate partner” of Precision Lens. Mr. Fesenmaier alleged that both companies were involved in an inducement scheme.
Sightpath Medical and its CEO, James Tiffany, agreed to a $12 million settlement to resolve the kickback allegations.
The Department of Justice subsequently investigated Jitendra Swarup, MD, an ophthalmologist and cataract surgeon who allegedly received “unlawful remuneration from Sightpath, Precision, and Ehlen” and filed false insurance claims. In addition to accepting expensive hunting and fishing trips from the medical device companies, Dr. Swarup was paid more than $100,000 per year for consulting services he did not fully render.
Dr. Swarup agreed to a nearly $3 million settlement and participation in a 3-year corporate integrity agreement with the Office of Inspector General. In exchange for compliance with such contracts, the OIG permits physicians to continue participating in Medicare, Medicaid, and other federal health care programs.
In a statement from attorneys, Precision Lens and Mr. Ehlen pledged to appeal the verdict and “defend ... our wholly appropriate actions” while remaining focused on their commitment to health care clinicians and manufacturers.
‘Endless’ opportunities for inducement
Unfortunately, opportunities for inducement are “endless,” experts say. Extravagant trips, dinners, and gifts can trigger a violation, but so can nearly anything of value.
Just last year, Biotronik reached a $12.95 million settlement amid allegations that company representatives wined and dined physicians to induce their use of its pacemakers and defibrillators. To date, no physicians have been charged.
But after a record-breaking number of whistleblower judgments last fiscal year totaling more than $2 billion, physicians should take note, Radha Bhatnagar, Esq, director of compliance at The CM Group, told the news organization.
“When manufacturers offer physicians kickbacks with the added element of fraudulent Medicare or Medicaid reimbursements, that is typically when manufacturers and individuals face civil and criminal liability,” said Ms. Bhatnagar, something the Department of Justice alluded to when announcing a settlement involving 15 Texas physicians last year.
In another case, Kingsley R. Chin, an orthopedic surgeon and designer of a spinal implant, was indicted in 2021 for paying millions of dollars in sham consulting fees to physicians who used his products. At least six surgeons who accepted money from Dr. Chin were later named in a civil case and ordered to pay $3.3 million in penalties.
Jason Montone, DO, an orthopedic surgeon who accepted the illicit payments, agreed to a plea deal with a reduced prison sentence, 1 year of supervised release, and a fine of $379,000.
Although Dr. Chin’s sentencing hasn’t been announced, violating kickback laws can result in a sentence of up to 10 years.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
ED doc and group owe $13.5M after patient’s serious brain injury
according to a report in the Idaho Capital Sun.
The suit, which took nearly 5 years after filing to wend its way through the courts, stems from an incident that took place in the early morning of March 29, 2016. An Ada County resident peered into the family bathroom and discovered that her husband, Carl B. Stiefel, lay on the floor confused and vomiting and complaining of a severe headache. Recently, the man had experienced several of these same symptoms, plus sinus congestion, dizziness, and tinnitus.
As Mr. Stiefel’s confusion worsened, his wife called for an ambulance, which arrived at the local hospital emergency department (ED) at 4:12 AM. Within approximately 11 minutes, the patient was examined by a doctor and later underwent a cranial CT scan, which a second doctor said showed “no intracranial process.”
Mr. Stiefel’s condition improved somewhat, although his dizziness persisted, leaving him still unable to walk. At this point, his primary ED doctor admitted him to the hospital for “benign positional vertigo.” The doctor also joined colleagues in suggesting that the patient might well be a candidate for an MRI, just in case his condition failed to improve over the next few hours.
But the transfer from the ED to the main hospital reportedly took at least 3 hours, during which time Mr. Stiefel’s condition deteriorated. Once admitted, he was observed by a healthcare provider — the news report doesn’t indicate precisely who — to be “delirious without meaningful interaction.” At least 4 hours would pass before the patient was seen by still another doctor, as the plaintiffs later claimed.
The patient remained disoriented and restless as the day unfolded. The MRI contemplated earlier was finally ordered, but the scan wasn’t available for several hours, according to nursing notes cited by the plaintiffs in their lawsuit.
Finally, the scan was administered at about 5:50 PM, almost 12 hours since Mr. Stiefel had first arrived at the ED. It showed that he had a torn artery in his neck and was experiencing a stroke. This was, clearly, a very different diagnosis from the one that his admitting doctor had entered into his notes.
A surgeon operated to repair the arterial tear, but the patient’s condition continued to worsen. Over the next 3 weeks, Mr. Stiefel went from the hospital to a local rehab facility, and back to the hospital with bacterial meningitis. Ultimately, he was diagnosed with “an irreparable brain injury,” which ultimately left him disabled and unable to work.
At this point, he and his wife sued a broad range of defendants — a radiology group, individual healthcare providers employed by the hospital, the primary ED physician, and that doctor’s emergency medicine group. In the nearly 5 intervening years, each of the named defendants settled, except the ED doctor and the emergency medicine group.
The two remaining defendants vigorously contested the claims against them, denying “any and all allegations of responsibility and liability” and contending that the patient’s injuries resulted from unforeseen complications rather than the care that had been administered.
The Ada County jury disagreed, however. It found that the primary ED doctor — and by extension the group to which the doctor belonged — did in fact negligently and recklessly fail to meet the proper standard of care, leading directly to the patient’s life-altering injuries.
For this failure, the jury awarded the plaintiffs $13.5 million, well over the state’s current inflation-adjusted cap of $400,000. (To date, Idaho’s largest med-mal award is nearly $30 million, handed down more than 20 years ago.)
At press time, there was no word of an appeal.
Man sues dentist, ends up changing state medical malpractice law
In a surprise move, the Connecticut Supreme Court in mid-February reversed its own precedent regarding a 2005 law requiring certain pre-litigation steps be taken before state residents are permitted to file a medical malpractice claim, as a story in the Claims Journal reports.
In its 2011 review of that earlier law — passed to ensure that complainants had a reasonable basis for their claims — the high court went the legislature one better. It held that state courts had no “personal jurisdiction” in adjudicating malpractice claims in the absence of required supporting documents — specifically, a proper certificate and opinion letter from “a similar healthcare provider.”
For the past 12 years, this meant that any suit lacking the proper documents could not only be halted but dismissed with prejudice, meaning that such a case couldn’t be refiled.
That interpretation of the law was eventually challenged, however, by a Connecticut man who sued his dentist. Filed in 2018, the suit alleged that, during a root canal, the dentist had failed to properly diagnose and treat his patient’s dental abscess, which ultimately required surgery.
Complying with what he regarded as state law, the man attached a letter of opinion to his complaint, which testified to the merits of his claim. But, in a twist with significant consequences, the letter was written by an endodontist, not a general dentist. In response, the dentist’s attorneys submitted a motion to dismiss to the trial court, arguing that the plaintiff had breached the “similar provider” provision and that therefore the opinion letter was defective and the entire suit should be dismissed.
The trial court agreed — and the Connecticut Appellate Court went on to affirm the lower-court ruling. The case might have ended there, but the plaintiff appealed to the Connecticut Supreme Court, which agreed to review the appellate court finding.
In a 6-0 decision, the high court looked back on its 2011 interpretation of the med-mal statute, which in the intervening years had given rise to “a body of case law.” The problem with that body of law, the justices argued, was that it had “imposed substantially greater burdens on plaintiffs than the legislature intended” — and it did so “by allowing potentially curable, technical, pre-litigation defects to defeat otherwise meritorious malpractice actions, sometimes after several years of litigation.”
In short, said the justices, there was nothing in the original statute that required a court to dismiss a suit once it found a letter of opinion to be deficient. This was a “curable” defect, one that shouldn’t be allowed to derail an otherwise meritorious claim.
As for the case that prompted the high court’s latest review — that is, the Connecticut man’s suit against his dentist — the justices found that the appellate court had also erred when it tossed out the endodontist’s opinion letter. Technically, the dentist might not have been an endodontist, said the justices, but he had in fact practiced in the field during the course of a long career, so close enough.
The justices kicked the case back to the trial court, with instructions that it deny the defendant’s motion to dismiss.
Stakeholders divided over new awards cap
Last month, Iowa Gov. Kim Reynolds signed a bill into law that limits the amount of noneconomic damages a successful med-mal plaintiff can collect, explains a story posted on Radio Iowa, among other news sites.
Under the new law, the limit for suits involving hospitals is capped at $2 million — while those involving all other healthcare providers are capped at $1 million. Beginning in 2028, those caps will be adjusted annually for inflation by 2.1%.
“When mistakes happen, Iowans deserve compensation, but arbitrary multimillion-dollar awards do more than that,” said Gov. Reynolds. “They act as a tax on all Iowans by raising the cost of care. They drive medical clinics out of business and medical students out of state.”
The CEO of Knoxville Hospital and Clinics — a well-known regional provider — agreed, saying that the new law helped to make Iowa “a more attractive place to practice medicine.”
But most Democrats in the GOP-controlled legislature — and 16 Republicans — voted against the legislation. For her part, House Minority Leader Jennifer Konfrst said there was absolutely no evidence that states with caps fared any better with medical workforce shortages than states without caps.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a report in the Idaho Capital Sun.
The suit, which took nearly 5 years after filing to wend its way through the courts, stems from an incident that took place in the early morning of March 29, 2016. An Ada County resident peered into the family bathroom and discovered that her husband, Carl B. Stiefel, lay on the floor confused and vomiting and complaining of a severe headache. Recently, the man had experienced several of these same symptoms, plus sinus congestion, dizziness, and tinnitus.
As Mr. Stiefel’s confusion worsened, his wife called for an ambulance, which arrived at the local hospital emergency department (ED) at 4:12 AM. Within approximately 11 minutes, the patient was examined by a doctor and later underwent a cranial CT scan, which a second doctor said showed “no intracranial process.”
Mr. Stiefel’s condition improved somewhat, although his dizziness persisted, leaving him still unable to walk. At this point, his primary ED doctor admitted him to the hospital for “benign positional vertigo.” The doctor also joined colleagues in suggesting that the patient might well be a candidate for an MRI, just in case his condition failed to improve over the next few hours.
But the transfer from the ED to the main hospital reportedly took at least 3 hours, during which time Mr. Stiefel’s condition deteriorated. Once admitted, he was observed by a healthcare provider — the news report doesn’t indicate precisely who — to be “delirious without meaningful interaction.” At least 4 hours would pass before the patient was seen by still another doctor, as the plaintiffs later claimed.
The patient remained disoriented and restless as the day unfolded. The MRI contemplated earlier was finally ordered, but the scan wasn’t available for several hours, according to nursing notes cited by the plaintiffs in their lawsuit.
Finally, the scan was administered at about 5:50 PM, almost 12 hours since Mr. Stiefel had first arrived at the ED. It showed that he had a torn artery in his neck and was experiencing a stroke. This was, clearly, a very different diagnosis from the one that his admitting doctor had entered into his notes.
A surgeon operated to repair the arterial tear, but the patient’s condition continued to worsen. Over the next 3 weeks, Mr. Stiefel went from the hospital to a local rehab facility, and back to the hospital with bacterial meningitis. Ultimately, he was diagnosed with “an irreparable brain injury,” which ultimately left him disabled and unable to work.
At this point, he and his wife sued a broad range of defendants — a radiology group, individual healthcare providers employed by the hospital, the primary ED physician, and that doctor’s emergency medicine group. In the nearly 5 intervening years, each of the named defendants settled, except the ED doctor and the emergency medicine group.
The two remaining defendants vigorously contested the claims against them, denying “any and all allegations of responsibility and liability” and contending that the patient’s injuries resulted from unforeseen complications rather than the care that had been administered.
The Ada County jury disagreed, however. It found that the primary ED doctor — and by extension the group to which the doctor belonged — did in fact negligently and recklessly fail to meet the proper standard of care, leading directly to the patient’s life-altering injuries.
For this failure, the jury awarded the plaintiffs $13.5 million, well over the state’s current inflation-adjusted cap of $400,000. (To date, Idaho’s largest med-mal award is nearly $30 million, handed down more than 20 years ago.)
At press time, there was no word of an appeal.
Man sues dentist, ends up changing state medical malpractice law
In a surprise move, the Connecticut Supreme Court in mid-February reversed its own precedent regarding a 2005 law requiring certain pre-litigation steps be taken before state residents are permitted to file a medical malpractice claim, as a story in the Claims Journal reports.
In its 2011 review of that earlier law — passed to ensure that complainants had a reasonable basis for their claims — the high court went the legislature one better. It held that state courts had no “personal jurisdiction” in adjudicating malpractice claims in the absence of required supporting documents — specifically, a proper certificate and opinion letter from “a similar healthcare provider.”
For the past 12 years, this meant that any suit lacking the proper documents could not only be halted but dismissed with prejudice, meaning that such a case couldn’t be refiled.
That interpretation of the law was eventually challenged, however, by a Connecticut man who sued his dentist. Filed in 2018, the suit alleged that, during a root canal, the dentist had failed to properly diagnose and treat his patient’s dental abscess, which ultimately required surgery.
Complying with what he regarded as state law, the man attached a letter of opinion to his complaint, which testified to the merits of his claim. But, in a twist with significant consequences, the letter was written by an endodontist, not a general dentist. In response, the dentist’s attorneys submitted a motion to dismiss to the trial court, arguing that the plaintiff had breached the “similar provider” provision and that therefore the opinion letter was defective and the entire suit should be dismissed.
The trial court agreed — and the Connecticut Appellate Court went on to affirm the lower-court ruling. The case might have ended there, but the plaintiff appealed to the Connecticut Supreme Court, which agreed to review the appellate court finding.
In a 6-0 decision, the high court looked back on its 2011 interpretation of the med-mal statute, which in the intervening years had given rise to “a body of case law.” The problem with that body of law, the justices argued, was that it had “imposed substantially greater burdens on plaintiffs than the legislature intended” — and it did so “by allowing potentially curable, technical, pre-litigation defects to defeat otherwise meritorious malpractice actions, sometimes after several years of litigation.”
In short, said the justices, there was nothing in the original statute that required a court to dismiss a suit once it found a letter of opinion to be deficient. This was a “curable” defect, one that shouldn’t be allowed to derail an otherwise meritorious claim.
As for the case that prompted the high court’s latest review — that is, the Connecticut man’s suit against his dentist — the justices found that the appellate court had also erred when it tossed out the endodontist’s opinion letter. Technically, the dentist might not have been an endodontist, said the justices, but he had in fact practiced in the field during the course of a long career, so close enough.
The justices kicked the case back to the trial court, with instructions that it deny the defendant’s motion to dismiss.
Stakeholders divided over new awards cap
Last month, Iowa Gov. Kim Reynolds signed a bill into law that limits the amount of noneconomic damages a successful med-mal plaintiff can collect, explains a story posted on Radio Iowa, among other news sites.
Under the new law, the limit for suits involving hospitals is capped at $2 million — while those involving all other healthcare providers are capped at $1 million. Beginning in 2028, those caps will be adjusted annually for inflation by 2.1%.
“When mistakes happen, Iowans deserve compensation, but arbitrary multimillion-dollar awards do more than that,” said Gov. Reynolds. “They act as a tax on all Iowans by raising the cost of care. They drive medical clinics out of business and medical students out of state.”
The CEO of Knoxville Hospital and Clinics — a well-known regional provider — agreed, saying that the new law helped to make Iowa “a more attractive place to practice medicine.”
But most Democrats in the GOP-controlled legislature — and 16 Republicans — voted against the legislation. For her part, House Minority Leader Jennifer Konfrst said there was absolutely no evidence that states with caps fared any better with medical workforce shortages than states without caps.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a report in the Idaho Capital Sun.
The suit, which took nearly 5 years after filing to wend its way through the courts, stems from an incident that took place in the early morning of March 29, 2016. An Ada County resident peered into the family bathroom and discovered that her husband, Carl B. Stiefel, lay on the floor confused and vomiting and complaining of a severe headache. Recently, the man had experienced several of these same symptoms, plus sinus congestion, dizziness, and tinnitus.
As Mr. Stiefel’s confusion worsened, his wife called for an ambulance, which arrived at the local hospital emergency department (ED) at 4:12 AM. Within approximately 11 minutes, the patient was examined by a doctor and later underwent a cranial CT scan, which a second doctor said showed “no intracranial process.”
Mr. Stiefel’s condition improved somewhat, although his dizziness persisted, leaving him still unable to walk. At this point, his primary ED doctor admitted him to the hospital for “benign positional vertigo.” The doctor also joined colleagues in suggesting that the patient might well be a candidate for an MRI, just in case his condition failed to improve over the next few hours.
But the transfer from the ED to the main hospital reportedly took at least 3 hours, during which time Mr. Stiefel’s condition deteriorated. Once admitted, he was observed by a healthcare provider — the news report doesn’t indicate precisely who — to be “delirious without meaningful interaction.” At least 4 hours would pass before the patient was seen by still another doctor, as the plaintiffs later claimed.
The patient remained disoriented and restless as the day unfolded. The MRI contemplated earlier was finally ordered, but the scan wasn’t available for several hours, according to nursing notes cited by the plaintiffs in their lawsuit.
Finally, the scan was administered at about 5:50 PM, almost 12 hours since Mr. Stiefel had first arrived at the ED. It showed that he had a torn artery in his neck and was experiencing a stroke. This was, clearly, a very different diagnosis from the one that his admitting doctor had entered into his notes.
A surgeon operated to repair the arterial tear, but the patient’s condition continued to worsen. Over the next 3 weeks, Mr. Stiefel went from the hospital to a local rehab facility, and back to the hospital with bacterial meningitis. Ultimately, he was diagnosed with “an irreparable brain injury,” which ultimately left him disabled and unable to work.
At this point, he and his wife sued a broad range of defendants — a radiology group, individual healthcare providers employed by the hospital, the primary ED physician, and that doctor’s emergency medicine group. In the nearly 5 intervening years, each of the named defendants settled, except the ED doctor and the emergency medicine group.
The two remaining defendants vigorously contested the claims against them, denying “any and all allegations of responsibility and liability” and contending that the patient’s injuries resulted from unforeseen complications rather than the care that had been administered.
The Ada County jury disagreed, however. It found that the primary ED doctor — and by extension the group to which the doctor belonged — did in fact negligently and recklessly fail to meet the proper standard of care, leading directly to the patient’s life-altering injuries.
For this failure, the jury awarded the plaintiffs $13.5 million, well over the state’s current inflation-adjusted cap of $400,000. (To date, Idaho’s largest med-mal award is nearly $30 million, handed down more than 20 years ago.)
At press time, there was no word of an appeal.
Man sues dentist, ends up changing state medical malpractice law
In a surprise move, the Connecticut Supreme Court in mid-February reversed its own precedent regarding a 2005 law requiring certain pre-litigation steps be taken before state residents are permitted to file a medical malpractice claim, as a story in the Claims Journal reports.
In its 2011 review of that earlier law — passed to ensure that complainants had a reasonable basis for their claims — the high court went the legislature one better. It held that state courts had no “personal jurisdiction” in adjudicating malpractice claims in the absence of required supporting documents — specifically, a proper certificate and opinion letter from “a similar healthcare provider.”
For the past 12 years, this meant that any suit lacking the proper documents could not only be halted but dismissed with prejudice, meaning that such a case couldn’t be refiled.
That interpretation of the law was eventually challenged, however, by a Connecticut man who sued his dentist. Filed in 2018, the suit alleged that, during a root canal, the dentist had failed to properly diagnose and treat his patient’s dental abscess, which ultimately required surgery.
Complying with what he regarded as state law, the man attached a letter of opinion to his complaint, which testified to the merits of his claim. But, in a twist with significant consequences, the letter was written by an endodontist, not a general dentist. In response, the dentist’s attorneys submitted a motion to dismiss to the trial court, arguing that the plaintiff had breached the “similar provider” provision and that therefore the opinion letter was defective and the entire suit should be dismissed.
The trial court agreed — and the Connecticut Appellate Court went on to affirm the lower-court ruling. The case might have ended there, but the plaintiff appealed to the Connecticut Supreme Court, which agreed to review the appellate court finding.
In a 6-0 decision, the high court looked back on its 2011 interpretation of the med-mal statute, which in the intervening years had given rise to “a body of case law.” The problem with that body of law, the justices argued, was that it had “imposed substantially greater burdens on plaintiffs than the legislature intended” — and it did so “by allowing potentially curable, technical, pre-litigation defects to defeat otherwise meritorious malpractice actions, sometimes after several years of litigation.”
In short, said the justices, there was nothing in the original statute that required a court to dismiss a suit once it found a letter of opinion to be deficient. This was a “curable” defect, one that shouldn’t be allowed to derail an otherwise meritorious claim.
As for the case that prompted the high court’s latest review — that is, the Connecticut man’s suit against his dentist — the justices found that the appellate court had also erred when it tossed out the endodontist’s opinion letter. Technically, the dentist might not have been an endodontist, said the justices, but he had in fact practiced in the field during the course of a long career, so close enough.
The justices kicked the case back to the trial court, with instructions that it deny the defendant’s motion to dismiss.
Stakeholders divided over new awards cap
Last month, Iowa Gov. Kim Reynolds signed a bill into law that limits the amount of noneconomic damages a successful med-mal plaintiff can collect, explains a story posted on Radio Iowa, among other news sites.
Under the new law, the limit for suits involving hospitals is capped at $2 million — while those involving all other healthcare providers are capped at $1 million. Beginning in 2028, those caps will be adjusted annually for inflation by 2.1%.
“When mistakes happen, Iowans deserve compensation, but arbitrary multimillion-dollar awards do more than that,” said Gov. Reynolds. “They act as a tax on all Iowans by raising the cost of care. They drive medical clinics out of business and medical students out of state.”
The CEO of Knoxville Hospital and Clinics — a well-known regional provider — agreed, saying that the new law helped to make Iowa “a more attractive place to practice medicine.”
But most Democrats in the GOP-controlled legislature — and 16 Republicans — voted against the legislation. For her part, House Minority Leader Jennifer Konfrst said there was absolutely no evidence that states with caps fared any better with medical workforce shortages than states without caps.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.