User login
-
From Baghdad to Boston: The Making of a Blood Cancer Specialist
Today, she practices hematology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and is a leading advocate for palliative care in oncology.
In an interview, Dr. El-Jawahri spoke about her journey from Baghdad to Boston and the future of palliative medicine in hematology.
Question: Where did you grow up?
Dr. El-Jawahri: My family is from Baghdad, Iraq, and I was born there. We moved to the States when I was 14. I came to Michigan not speaking a word of English. My parents — my father is a mechanical engineer, and my mom is a computer engineer — chose to live in a very white neighborhood in Farmington Hills, in the suburbs of Detroit. The neighborhood did not have any immigrants or Arab Americans. There are a lot of Arab Americans in Michigan, but they chose for me not to hang out with them early on so that I could learn the language. It was a really good choice.
Question: What happened to your college friend?
Dr. El-Jawahri: She had a brain tumor and ended up receiving intensive care at the end of life. We had a lot of conversations about her wishes and desires, but none of those were honored. Her ending was not something that she wanted, nor did it honor her memory.
Question: What do you think went wrong?
Dr. El-Jawahri: She was getting treatment for her family’s sake. The idea of losing her was too hard for them. I remember vividly the conversations where she would say, “I just hope I don’t end up in the hospital at the end of life.” We had that conversation explicitly. But because we were young, her family was very involved in her care. A lot of the decision-making was very complicated.
Question: How did this experience change your career path?
Dr. El-Jawahri: I went into medicine specifically to become an oncologist and cure cancer. The naive 20-year-old in me said, “Nobody should die this miserable death. I’m going to go in, and I’m going to cure it.”
Question: How did palliative medicine become your major focus?
Dr. El-Jawahri: During my first year at Harvard Medical School, I took a course that’s called “Living With Life-Threatening Illness.” It allows medical students to spend their entire first year getting to know a patient living with a serious illness. We’d spend weekly coffee or lunch breaks with them, where we’d hear about their experiences. After every weekly meeting with a patient, we also had a group meeting with several students and group facilitators to talk about — and process — the interactions we had with patients. I was assigned a woman who was living with metastatic breast cancer. I was also introduced to the field of palliative care and how it helps patients manage complex symptoms and process and cope with a difficult diagnosis. It also cultivates the understanding to make informed decisions about their care. That’s when I knew what I wanted to do for the rest of my life — figure out ways to integrate these palliative and supportive care concepts and improve the lived experience of patients and families within the oncology setting.
Question: What happened next?
Dr. El-Jawahri: When I was a first-year intern, I went to residency at Massachusetts General Hospital. I was on an oncology service and admitted a young college student who was diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia. She was an athlete, and every time she went up the stairs to her dorm, she was getting very short of breath. She went to a walk-in clinic because when you’re 20 and you’re healthy, you don’t think you need anything. They did some blood work, and 2 hours later, they called her and said, “You probably have leukemia. You need to go to the emergency department immediately.” There she saw an emergency doctor who said, “You will be admitted to the hospital. You have leukemia. I’m calling an oncologist, and you’ll probably have to start chemotherapy within the next day or two.”
Question: What was that experience like for the patient?
Dr. El-Jawahri: I’ve never seen someone so scared. The first question she asked me was about her family, who were from North Carolina. She said, “It feels like everybody thinks that I’m dying. Do you think my family will have time to get here?” They were in a car driving over. This is not a unique story in this population. Unfortunately, these patients experience the most traumatic way of being diagnosed and probably the most traumatic experience in oncology. They’re being abducted into a hospital environment, losing all control and starting immediate therapy. Then, for the first 4-6 weeks, they experience immense toxicity, side effects like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and mucositis, where they have painful mouth and throat sores that require intravenous pain medications. This causes real posttraumatic stress. After seeing that woman, I made the decision to work in leukemia and transplants to try to make things a little bit better for these patients.
Question: How did the patient fare?
Dr. El-Jawahri: She actually did great and was cured of her disease. Many of our patients with leukemia, especially younger ones, do well in terms of survival. But they struggle with the trauma of their diagnosis and the distress of the acute treatment period. Even in the curative setting, helping patients to cope with a traumatic diagnosis can have a big impact on their quality of life, how they feel, and their long-term outcomes in terms of psychological stress, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress. But so often, our patients with leukemia are not offered palliative care and supportive care because they’re going to be cured.
Question: What is an important lesson from your research into palliative care in hematology?
Dr. El-Jawahri: We can make things better for patients and families by integrating palliative care clinicians into the care of patients. Patients receiving palliative care are more likely to document their end-of-life preferences and discuss them with their clinicians, and they’re less likely to be hospitalized at the end of life. When you ask patients with cancer where do they want to die, many of patients say, “I want to die at home. I don’t want to be in a hospital.” A lot of the work I’m doing now is focused on creating digital apps with components of palliative care and supportive care interventions. Patients can administer these interventions to themselves and learn how to effectively cope and deal with their illness. Some patients may do well with a digital app, but others may actually need the in-person touch. Some may need a hybrid approach. One of the other future directions for us is thinking about how we optimize supportive care interventions. Which ones do we give to which patient?
Question: Considering all that you’ve learned since college, how do you think your sick friend should have been treated?
Dr. El-Jawahri: She was neither introduced to the term palliative care nor to palliative care specialists. Now the standard of care — especially in patients with advanced cancer — is to integrate palliative care clinicians early in the course of illness. We would have loved for her to have a palliative care clinician who didn’t replace the oncologist but rather helped the patient, family, and oncologist communicate more effectively with one another. We hear all the time from patients who say different things to their oncologist than to their palliative care clinician. It’s not like my friend wasn’t able to communicate with her oncologist. But maybe part of it was that she wanted to not disappoint her oncologist [by ending treatment].
Question: Could you tell me about the research you presented at ASCO 2024 regarding 115 adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome who were receiving non-intensive chemotherapy?
Dr. El-Jawahri: These patients receive therapy that requires frequent clinic visits and often substantially impairs their quality of life. We know this population often does not engage in any timely discussion with their clinicians about their end-of-life care preferences. This multisite randomized clinical trial assigned patients to receive usual oncology care [with palliative care consultations only upon request] vs to see palliative care clinicians monthly in the outpatient setting and twice weekly every time they were hospitalized. The intervention focused on how to help patients manage their symptoms and end-of-life communication in particular. The primary outcome of the study was time from the documentation of end-of-life care preferences to death.
Question: What did you learn?
Dr. El-Jawahri: This is one of the first studies to highlight the impact of palliative care integration on end-of-life care preferences and discussions and documentation in this population. Patients receiving the palliative care intervention were much more likely to discuss their end-of-life care preferences (96.5% vs 68.4%; P < .001). More importantly, those receiving the intervention had a much longer time from documentation of end-of-life care preferences to death. On average, patients in the palliative care intervention group vs the usual care group had a mean of 41 vs 1.5 days from documentation of their preferences to death (P < .001). In the intervention group, these conversations were happening early enough for patients to plan, talk to their families, and discuss their wishes. In the usual care group, they were happening acutely while these patients were dying. We also learned that patients receiving palliative care intervention were less likely to be hospitalized at the end of life (70.6% vs 91.9%; P = .031) and had better quality of life (138.6 vs 125.5; P = .010).
Question: What’s next for your research in this area?
Dr. El-Jawahri: We are doing a large-scale randomized, comparative effectiveness trial of specialty palliative care vs primary palliative care in 11,150 patients with acute myeloid leukemia across 20 institutions in the United States. We expect results in 2028.
Question: What are you hoping to understand?
Dr. El-Jawahri: We will never have enough specialty palliative care clinicians to take care of all patients with serious illness. As a result, we have to learn how palliative care works: How does it improve outcomes? How do we potentially take what palliative care clinicians do and try to integrate it into regular oncology practice? A lot of the work that I’m excited about now regards what we call primary palliative care. How do we train oncology clinicians to incorporate palliative care skills in their practices so we’re able to better meet the needs of our patients and their families? What we’d love to understand from future research is which patient populations need specialty palliative care and which patients can do just fine with an oncology clinician who has a lot of good palliative care skills integrated into their practice.
Dr. El-Jawahri disclosed consulting for Incyte and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Today, she practices hematology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and is a leading advocate for palliative care in oncology.
In an interview, Dr. El-Jawahri spoke about her journey from Baghdad to Boston and the future of palliative medicine in hematology.
Question: Where did you grow up?
Dr. El-Jawahri: My family is from Baghdad, Iraq, and I was born there. We moved to the States when I was 14. I came to Michigan not speaking a word of English. My parents — my father is a mechanical engineer, and my mom is a computer engineer — chose to live in a very white neighborhood in Farmington Hills, in the suburbs of Detroit. The neighborhood did not have any immigrants or Arab Americans. There are a lot of Arab Americans in Michigan, but they chose for me not to hang out with them early on so that I could learn the language. It was a really good choice.
Question: What happened to your college friend?
Dr. El-Jawahri: She had a brain tumor and ended up receiving intensive care at the end of life. We had a lot of conversations about her wishes and desires, but none of those were honored. Her ending was not something that she wanted, nor did it honor her memory.
Question: What do you think went wrong?
Dr. El-Jawahri: She was getting treatment for her family’s sake. The idea of losing her was too hard for them. I remember vividly the conversations where she would say, “I just hope I don’t end up in the hospital at the end of life.” We had that conversation explicitly. But because we were young, her family was very involved in her care. A lot of the decision-making was very complicated.
Question: How did this experience change your career path?
Dr. El-Jawahri: I went into medicine specifically to become an oncologist and cure cancer. The naive 20-year-old in me said, “Nobody should die this miserable death. I’m going to go in, and I’m going to cure it.”
Question: How did palliative medicine become your major focus?
Dr. El-Jawahri: During my first year at Harvard Medical School, I took a course that’s called “Living With Life-Threatening Illness.” It allows medical students to spend their entire first year getting to know a patient living with a serious illness. We’d spend weekly coffee or lunch breaks with them, where we’d hear about their experiences. After every weekly meeting with a patient, we also had a group meeting with several students and group facilitators to talk about — and process — the interactions we had with patients. I was assigned a woman who was living with metastatic breast cancer. I was also introduced to the field of palliative care and how it helps patients manage complex symptoms and process and cope with a difficult diagnosis. It also cultivates the understanding to make informed decisions about their care. That’s when I knew what I wanted to do for the rest of my life — figure out ways to integrate these palliative and supportive care concepts and improve the lived experience of patients and families within the oncology setting.
Question: What happened next?
Dr. El-Jawahri: When I was a first-year intern, I went to residency at Massachusetts General Hospital. I was on an oncology service and admitted a young college student who was diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia. She was an athlete, and every time she went up the stairs to her dorm, she was getting very short of breath. She went to a walk-in clinic because when you’re 20 and you’re healthy, you don’t think you need anything. They did some blood work, and 2 hours later, they called her and said, “You probably have leukemia. You need to go to the emergency department immediately.” There she saw an emergency doctor who said, “You will be admitted to the hospital. You have leukemia. I’m calling an oncologist, and you’ll probably have to start chemotherapy within the next day or two.”
Question: What was that experience like for the patient?
Dr. El-Jawahri: I’ve never seen someone so scared. The first question she asked me was about her family, who were from North Carolina. She said, “It feels like everybody thinks that I’m dying. Do you think my family will have time to get here?” They were in a car driving over. This is not a unique story in this population. Unfortunately, these patients experience the most traumatic way of being diagnosed and probably the most traumatic experience in oncology. They’re being abducted into a hospital environment, losing all control and starting immediate therapy. Then, for the first 4-6 weeks, they experience immense toxicity, side effects like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and mucositis, where they have painful mouth and throat sores that require intravenous pain medications. This causes real posttraumatic stress. After seeing that woman, I made the decision to work in leukemia and transplants to try to make things a little bit better for these patients.
Question: How did the patient fare?
Dr. El-Jawahri: She actually did great and was cured of her disease. Many of our patients with leukemia, especially younger ones, do well in terms of survival. But they struggle with the trauma of their diagnosis and the distress of the acute treatment period. Even in the curative setting, helping patients to cope with a traumatic diagnosis can have a big impact on their quality of life, how they feel, and their long-term outcomes in terms of psychological stress, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress. But so often, our patients with leukemia are not offered palliative care and supportive care because they’re going to be cured.
Question: What is an important lesson from your research into palliative care in hematology?
Dr. El-Jawahri: We can make things better for patients and families by integrating palliative care clinicians into the care of patients. Patients receiving palliative care are more likely to document their end-of-life preferences and discuss them with their clinicians, and they’re less likely to be hospitalized at the end of life. When you ask patients with cancer where do they want to die, many of patients say, “I want to die at home. I don’t want to be in a hospital.” A lot of the work I’m doing now is focused on creating digital apps with components of palliative care and supportive care interventions. Patients can administer these interventions to themselves and learn how to effectively cope and deal with their illness. Some patients may do well with a digital app, but others may actually need the in-person touch. Some may need a hybrid approach. One of the other future directions for us is thinking about how we optimize supportive care interventions. Which ones do we give to which patient?
Question: Considering all that you’ve learned since college, how do you think your sick friend should have been treated?
Dr. El-Jawahri: She was neither introduced to the term palliative care nor to palliative care specialists. Now the standard of care — especially in patients with advanced cancer — is to integrate palliative care clinicians early in the course of illness. We would have loved for her to have a palliative care clinician who didn’t replace the oncologist but rather helped the patient, family, and oncologist communicate more effectively with one another. We hear all the time from patients who say different things to their oncologist than to their palliative care clinician. It’s not like my friend wasn’t able to communicate with her oncologist. But maybe part of it was that she wanted to not disappoint her oncologist [by ending treatment].
Question: Could you tell me about the research you presented at ASCO 2024 regarding 115 adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome who were receiving non-intensive chemotherapy?
Dr. El-Jawahri: These patients receive therapy that requires frequent clinic visits and often substantially impairs their quality of life. We know this population often does not engage in any timely discussion with their clinicians about their end-of-life care preferences. This multisite randomized clinical trial assigned patients to receive usual oncology care [with palliative care consultations only upon request] vs to see palliative care clinicians monthly in the outpatient setting and twice weekly every time they were hospitalized. The intervention focused on how to help patients manage their symptoms and end-of-life communication in particular. The primary outcome of the study was time from the documentation of end-of-life care preferences to death.
Question: What did you learn?
Dr. El-Jawahri: This is one of the first studies to highlight the impact of palliative care integration on end-of-life care preferences and discussions and documentation in this population. Patients receiving the palliative care intervention were much more likely to discuss their end-of-life care preferences (96.5% vs 68.4%; P < .001). More importantly, those receiving the intervention had a much longer time from documentation of end-of-life care preferences to death. On average, patients in the palliative care intervention group vs the usual care group had a mean of 41 vs 1.5 days from documentation of their preferences to death (P < .001). In the intervention group, these conversations were happening early enough for patients to plan, talk to their families, and discuss their wishes. In the usual care group, they were happening acutely while these patients were dying. We also learned that patients receiving palliative care intervention were less likely to be hospitalized at the end of life (70.6% vs 91.9%; P = .031) and had better quality of life (138.6 vs 125.5; P = .010).
Question: What’s next for your research in this area?
Dr. El-Jawahri: We are doing a large-scale randomized, comparative effectiveness trial of specialty palliative care vs primary palliative care in 11,150 patients with acute myeloid leukemia across 20 institutions in the United States. We expect results in 2028.
Question: What are you hoping to understand?
Dr. El-Jawahri: We will never have enough specialty palliative care clinicians to take care of all patients with serious illness. As a result, we have to learn how palliative care works: How does it improve outcomes? How do we potentially take what palliative care clinicians do and try to integrate it into regular oncology practice? A lot of the work that I’m excited about now regards what we call primary palliative care. How do we train oncology clinicians to incorporate palliative care skills in their practices so we’re able to better meet the needs of our patients and their families? What we’d love to understand from future research is which patient populations need specialty palliative care and which patients can do just fine with an oncology clinician who has a lot of good palliative care skills integrated into their practice.
Dr. El-Jawahri disclosed consulting for Incyte and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Today, she practices hematology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and is a leading advocate for palliative care in oncology.
In an interview, Dr. El-Jawahri spoke about her journey from Baghdad to Boston and the future of palliative medicine in hematology.
Question: Where did you grow up?
Dr. El-Jawahri: My family is from Baghdad, Iraq, and I was born there. We moved to the States when I was 14. I came to Michigan not speaking a word of English. My parents — my father is a mechanical engineer, and my mom is a computer engineer — chose to live in a very white neighborhood in Farmington Hills, in the suburbs of Detroit. The neighborhood did not have any immigrants or Arab Americans. There are a lot of Arab Americans in Michigan, but they chose for me not to hang out with them early on so that I could learn the language. It was a really good choice.
Question: What happened to your college friend?
Dr. El-Jawahri: She had a brain tumor and ended up receiving intensive care at the end of life. We had a lot of conversations about her wishes and desires, but none of those were honored. Her ending was not something that she wanted, nor did it honor her memory.
Question: What do you think went wrong?
Dr. El-Jawahri: She was getting treatment for her family’s sake. The idea of losing her was too hard for them. I remember vividly the conversations where she would say, “I just hope I don’t end up in the hospital at the end of life.” We had that conversation explicitly. But because we were young, her family was very involved in her care. A lot of the decision-making was very complicated.
Question: How did this experience change your career path?
Dr. El-Jawahri: I went into medicine specifically to become an oncologist and cure cancer. The naive 20-year-old in me said, “Nobody should die this miserable death. I’m going to go in, and I’m going to cure it.”
Question: How did palliative medicine become your major focus?
Dr. El-Jawahri: During my first year at Harvard Medical School, I took a course that’s called “Living With Life-Threatening Illness.” It allows medical students to spend their entire first year getting to know a patient living with a serious illness. We’d spend weekly coffee or lunch breaks with them, where we’d hear about their experiences. After every weekly meeting with a patient, we also had a group meeting with several students and group facilitators to talk about — and process — the interactions we had with patients. I was assigned a woman who was living with metastatic breast cancer. I was also introduced to the field of palliative care and how it helps patients manage complex symptoms and process and cope with a difficult diagnosis. It also cultivates the understanding to make informed decisions about their care. That’s when I knew what I wanted to do for the rest of my life — figure out ways to integrate these palliative and supportive care concepts and improve the lived experience of patients and families within the oncology setting.
Question: What happened next?
Dr. El-Jawahri: When I was a first-year intern, I went to residency at Massachusetts General Hospital. I was on an oncology service and admitted a young college student who was diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia. She was an athlete, and every time she went up the stairs to her dorm, she was getting very short of breath. She went to a walk-in clinic because when you’re 20 and you’re healthy, you don’t think you need anything. They did some blood work, and 2 hours later, they called her and said, “You probably have leukemia. You need to go to the emergency department immediately.” There she saw an emergency doctor who said, “You will be admitted to the hospital. You have leukemia. I’m calling an oncologist, and you’ll probably have to start chemotherapy within the next day or two.”
Question: What was that experience like for the patient?
Dr. El-Jawahri: I’ve never seen someone so scared. The first question she asked me was about her family, who were from North Carolina. She said, “It feels like everybody thinks that I’m dying. Do you think my family will have time to get here?” They were in a car driving over. This is not a unique story in this population. Unfortunately, these patients experience the most traumatic way of being diagnosed and probably the most traumatic experience in oncology. They’re being abducted into a hospital environment, losing all control and starting immediate therapy. Then, for the first 4-6 weeks, they experience immense toxicity, side effects like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and mucositis, where they have painful mouth and throat sores that require intravenous pain medications. This causes real posttraumatic stress. After seeing that woman, I made the decision to work in leukemia and transplants to try to make things a little bit better for these patients.
Question: How did the patient fare?
Dr. El-Jawahri: She actually did great and was cured of her disease. Many of our patients with leukemia, especially younger ones, do well in terms of survival. But they struggle with the trauma of their diagnosis and the distress of the acute treatment period. Even in the curative setting, helping patients to cope with a traumatic diagnosis can have a big impact on their quality of life, how they feel, and their long-term outcomes in terms of psychological stress, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress. But so often, our patients with leukemia are not offered palliative care and supportive care because they’re going to be cured.
Question: What is an important lesson from your research into palliative care in hematology?
Dr. El-Jawahri: We can make things better for patients and families by integrating palliative care clinicians into the care of patients. Patients receiving palliative care are more likely to document their end-of-life preferences and discuss them with their clinicians, and they’re less likely to be hospitalized at the end of life. When you ask patients with cancer where do they want to die, many of patients say, “I want to die at home. I don’t want to be in a hospital.” A lot of the work I’m doing now is focused on creating digital apps with components of palliative care and supportive care interventions. Patients can administer these interventions to themselves and learn how to effectively cope and deal with their illness. Some patients may do well with a digital app, but others may actually need the in-person touch. Some may need a hybrid approach. One of the other future directions for us is thinking about how we optimize supportive care interventions. Which ones do we give to which patient?
Question: Considering all that you’ve learned since college, how do you think your sick friend should have been treated?
Dr. El-Jawahri: She was neither introduced to the term palliative care nor to palliative care specialists. Now the standard of care — especially in patients with advanced cancer — is to integrate palliative care clinicians early in the course of illness. We would have loved for her to have a palliative care clinician who didn’t replace the oncologist but rather helped the patient, family, and oncologist communicate more effectively with one another. We hear all the time from patients who say different things to their oncologist than to their palliative care clinician. It’s not like my friend wasn’t able to communicate with her oncologist. But maybe part of it was that she wanted to not disappoint her oncologist [by ending treatment].
Question: Could you tell me about the research you presented at ASCO 2024 regarding 115 adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome who were receiving non-intensive chemotherapy?
Dr. El-Jawahri: These patients receive therapy that requires frequent clinic visits and often substantially impairs their quality of life. We know this population often does not engage in any timely discussion with their clinicians about their end-of-life care preferences. This multisite randomized clinical trial assigned patients to receive usual oncology care [with palliative care consultations only upon request] vs to see palliative care clinicians monthly in the outpatient setting and twice weekly every time they were hospitalized. The intervention focused on how to help patients manage their symptoms and end-of-life communication in particular. The primary outcome of the study was time from the documentation of end-of-life care preferences to death.
Question: What did you learn?
Dr. El-Jawahri: This is one of the first studies to highlight the impact of palliative care integration on end-of-life care preferences and discussions and documentation in this population. Patients receiving the palliative care intervention were much more likely to discuss their end-of-life care preferences (96.5% vs 68.4%; P < .001). More importantly, those receiving the intervention had a much longer time from documentation of end-of-life care preferences to death. On average, patients in the palliative care intervention group vs the usual care group had a mean of 41 vs 1.5 days from documentation of their preferences to death (P < .001). In the intervention group, these conversations were happening early enough for patients to plan, talk to their families, and discuss their wishes. In the usual care group, they were happening acutely while these patients were dying. We also learned that patients receiving palliative care intervention were less likely to be hospitalized at the end of life (70.6% vs 91.9%; P = .031) and had better quality of life (138.6 vs 125.5; P = .010).
Question: What’s next for your research in this area?
Dr. El-Jawahri: We are doing a large-scale randomized, comparative effectiveness trial of specialty palliative care vs primary palliative care in 11,150 patients with acute myeloid leukemia across 20 institutions in the United States. We expect results in 2028.
Question: What are you hoping to understand?
Dr. El-Jawahri: We will never have enough specialty palliative care clinicians to take care of all patients with serious illness. As a result, we have to learn how palliative care works: How does it improve outcomes? How do we potentially take what palliative care clinicians do and try to integrate it into regular oncology practice? A lot of the work that I’m excited about now regards what we call primary palliative care. How do we train oncology clinicians to incorporate palliative care skills in their practices so we’re able to better meet the needs of our patients and their families? What we’d love to understand from future research is which patient populations need specialty palliative care and which patients can do just fine with an oncology clinician who has a lot of good palliative care skills integrated into their practice.
Dr. El-Jawahri disclosed consulting for Incyte and Novartis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer Treatment 101: A Primer for Non-Oncologists
The remaining 700,000 or so often proceed to chemotherapy either immediately or upon cancer recurrence, spread, or newly recognized metastases. “Cures” after that point are rare.
I’m speaking in generalities, understanding that each cancer and each patient is unique.
Chemotherapy
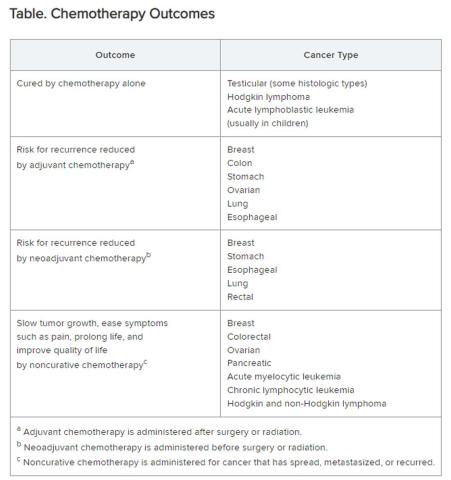
Chemotherapy alone can cure a small number of cancer types. When added to radiation or surgery, chemotherapy can help to cure a wider range of cancer types. As an add-on, chemotherapy can extend the length and quality of life for many patients with cancer. Since chemotherapy is by definition “toxic,” it can also shorten the duration or harm the quality of life and provide false hope. The Table summarizes what chemotherapy can and cannot achieve in selected cancer types.
Careful, compassionate communication between patient and physician is key. Goals and expectations must be clearly understood.
Organized chemotherapeutic efforts are further categorized as first line, second line, and third line.
First-line treatment. The initial round of recommended chemotherapy for a specific cancer. It is typically considered the most effective treatment for that type and stage of cancer on the basis of current research and clinical trials.
Second-line treatment. This is the treatment used if the first-line chemotherapy doesn’t work as desired. Reasons to switch to second-line chemo include:
- Lack of response (the tumor failed to shrink).
- Progression (the cancer may have grown or spread further).
- Adverse side effects were too severe to continue.
The drugs used in second-line chemo will typically be different from those used in first line, sometimes because cancer cells can develop resistance to chemotherapy drugs over time. Moreover, the goal of second-line chemo may differ from that of first-line therapy. Rather than chiefly aiming for a cure, second-line treatment might focus on slowing cancer growth, managing symptoms, or improving quality of life. Unfortunately, not every type of cancer has a readily available second-line option.
Third-line treatment. Third-line options come into play when both the initial course of chemo (first line) and the subsequent treatment (second line) have failed to achieve remission or control the cancer’s spread. Owing to the progressive nature of advanced cancers, patients might not be eligible or healthy enough for third-line therapy. Depending on cancer type, the patient’s general health, and response to previous treatments, third-line options could include:
- New or different chemotherapy drugs compared with prior lines.
- Surgery to debulk the tumor.
- Radiation for symptom control.
- Targeted therapy: drugs designed to target specific vulnerabilities in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: agents that help the body’s immune system fight cancer cells.
- Clinical trials testing new or investigational treatments, which may be applicable at any time, depending on the questions being addressed.
The goals of third-line therapy may shift from aiming for a cure to managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and potentially slowing cancer growth. The decision to pursue third-line therapy involves careful consideration by the doctor and patient, weighing the potential benefits and risks of treatment considering the individual’s overall health and specific situation.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about the potential outcomes of third-line therapy. Although remission may be unlikely, third-line therapy can still play a role in managing the disease.
Navigating advanced cancer treatment is very complex. The patient and physician must together consider detailed explanations and clarifications to set expectations and make informed decisions about care.
Interventions to Consider Earlier
In traditional clinical oncology practice, other interventions are possible, but these may not be offered until treatment has reached the third line:
- Molecular testing.
- Palliation.
- Clinical trials.
- Innovative testing to guide targeted therapy by ascertaining which agents are most likely (or not likely at all) to be effective.
I would argue that the patient’s interests are better served by considering and offering these other interventions much earlier, even before starting first-line chemotherapy.
Molecular testing. The best time for molecular testing of a new malignant tumor is typically at the time of diagnosis. Here’s why:
- Molecular testing helps identify specific genetic mutations in the cancer cells. This information can be crucial for selecting targeted therapies that are most effective against those specific mutations. Early detection allows for the most treatment options. For example, for non–small cell lung cancer, early is best because treatment and outcomes may well be changed by test results.
- Knowing the tumor’s molecular makeup can help determine whether a patient qualifies for clinical trials of new drugs designed for specific mutations.
- Some molecular markers can offer information about the tumor’s aggressiveness and potential for metastasis so that prognosis can be informed.
Molecular testing can be a valuable tool throughout a cancer patient’s journey. With genetically diverse tumors, the initial biopsy might not capture the full picture. Molecular testing of circulating tumor DNA can be used to monitor a patient’s response to treatment and detect potential mutations that might arise during treatment resistance. Retesting after metastasis can provide additional information that can aid in treatment decisions.
Palliative care. The ideal time to discuss palliative care with a patient with cancer is early in the diagnosis and treatment process. Palliative care is not the same as hospice care; it isn’t just about end-of-life. Palliative care focuses on improving a patient’s quality of life throughout cancer treatment. Palliative care specialists can address a wide range of symptoms a patient might experience from cancer or its treatment, including pain, fatigue, nausea, and anxiety.
Early discussions allow for a more comprehensive care plan. Open communication about all treatment options, including palliative care, empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care goals and preferences.
Specific situations where discussing palliative care might be appropriate are:
- Soon after a cancer diagnosis.
- If the patient experiences significant side effects from cancer treatment.
- When considering different treatment options, palliative care can complement those treatments.
- In advanced stages of cancer, to focus on comfort and quality of life.
Clinical trials. Participation in a clinical trial to explore new or investigational treatments should always be considered.
In theory, clinical trials should be an option at any time in the patient’s course. But the organized clinical trial experience may not be available or appropriate. Then, the individual becomes a de facto “clinical trial with an n of 1.” Read this brief open-access blog post at Cancer Commons to learn more about that circumstance.
Innovative testing. The best choice of chemotherapeutic or targeted therapies is often unclear. The clinician is likely to follow published guidelines, often from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
These are evidence based and driven by consensus of experts. But guideline-recommended therapy is not always effective, and weeks or months can pass before this ineffectiveness becomes apparent. Thus, many researchers and companies are seeking methods of testing each patient’s specific cancer to determine in advance, or very quickly, whether a particular drug is likely to be effective.
Read more about these leading innovations:
SAGE Oncotest: Entering the Next Generation of Tailored Cancer Treatment
Alibrex: A New Blood Test to Reveal Whether a Cancer Treatment is Working
PARIS Test Uses Lab-Grown Mini-Tumors to Find a Patient’s Best Treatment
Using Live Cells from Patients to Find the Right Cancer Drug
Other innovative therapies under investigation could even be agnostic to cancer type:
Treating Pancreatic Cancer: Could Metabolism — Not Genomics — Be the Key?
High-Energy Blue Light Powers a Promising New Treatment to Destroy Cancer Cells
All-Clear Follow-Up: Hydrogen Peroxide Appears to Treat Oral and Skin Lesions
Cancer is a tough nut to crack. Many people and organizations are trying very hard. So much is being learned. Some approaches will be effective. We can all hope.
Dr. Lundberg, editor in chief, Cancer Commons, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The remaining 700,000 or so often proceed to chemotherapy either immediately or upon cancer recurrence, spread, or newly recognized metastases. “Cures” after that point are rare.
I’m speaking in generalities, understanding that each cancer and each patient is unique.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy alone can cure a small number of cancer types. When added to radiation or surgery, chemotherapy can help to cure a wider range of cancer types. As an add-on, chemotherapy can extend the length and quality of life for many patients with cancer. Since chemotherapy is by definition “toxic,” it can also shorten the duration or harm the quality of life and provide false hope. The Table summarizes what chemotherapy can and cannot achieve in selected cancer types.
Careful, compassionate communication between patient and physician is key. Goals and expectations must be clearly understood.
Organized chemotherapeutic efforts are further categorized as first line, second line, and third line.
First-line treatment. The initial round of recommended chemotherapy for a specific cancer. It is typically considered the most effective treatment for that type and stage of cancer on the basis of current research and clinical trials.
Second-line treatment. This is the treatment used if the first-line chemotherapy doesn’t work as desired. Reasons to switch to second-line chemo include:
- Lack of response (the tumor failed to shrink).
- Progression (the cancer may have grown or spread further).
- Adverse side effects were too severe to continue.
The drugs used in second-line chemo will typically be different from those used in first line, sometimes because cancer cells can develop resistance to chemotherapy drugs over time. Moreover, the goal of second-line chemo may differ from that of first-line therapy. Rather than chiefly aiming for a cure, second-line treatment might focus on slowing cancer growth, managing symptoms, or improving quality of life. Unfortunately, not every type of cancer has a readily available second-line option.
Third-line treatment. Third-line options come into play when both the initial course of chemo (first line) and the subsequent treatment (second line) have failed to achieve remission or control the cancer’s spread. Owing to the progressive nature of advanced cancers, patients might not be eligible or healthy enough for third-line therapy. Depending on cancer type, the patient’s general health, and response to previous treatments, third-line options could include:
- New or different chemotherapy drugs compared with prior lines.
- Surgery to debulk the tumor.
- Radiation for symptom control.
- Targeted therapy: drugs designed to target specific vulnerabilities in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: agents that help the body’s immune system fight cancer cells.
- Clinical trials testing new or investigational treatments, which may be applicable at any time, depending on the questions being addressed.
The goals of third-line therapy may shift from aiming for a cure to managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and potentially slowing cancer growth. The decision to pursue third-line therapy involves careful consideration by the doctor and patient, weighing the potential benefits and risks of treatment considering the individual’s overall health and specific situation.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about the potential outcomes of third-line therapy. Although remission may be unlikely, third-line therapy can still play a role in managing the disease.
Navigating advanced cancer treatment is very complex. The patient and physician must together consider detailed explanations and clarifications to set expectations and make informed decisions about care.
Interventions to Consider Earlier
In traditional clinical oncology practice, other interventions are possible, but these may not be offered until treatment has reached the third line:
- Molecular testing.
- Palliation.
- Clinical trials.
- Innovative testing to guide targeted therapy by ascertaining which agents are most likely (or not likely at all) to be effective.
I would argue that the patient’s interests are better served by considering and offering these other interventions much earlier, even before starting first-line chemotherapy.
Molecular testing. The best time for molecular testing of a new malignant tumor is typically at the time of diagnosis. Here’s why:
- Molecular testing helps identify specific genetic mutations in the cancer cells. This information can be crucial for selecting targeted therapies that are most effective against those specific mutations. Early detection allows for the most treatment options. For example, for non–small cell lung cancer, early is best because treatment and outcomes may well be changed by test results.
- Knowing the tumor’s molecular makeup can help determine whether a patient qualifies for clinical trials of new drugs designed for specific mutations.
- Some molecular markers can offer information about the tumor’s aggressiveness and potential for metastasis so that prognosis can be informed.
Molecular testing can be a valuable tool throughout a cancer patient’s journey. With genetically diverse tumors, the initial biopsy might not capture the full picture. Molecular testing of circulating tumor DNA can be used to monitor a patient’s response to treatment and detect potential mutations that might arise during treatment resistance. Retesting after metastasis can provide additional information that can aid in treatment decisions.
Palliative care. The ideal time to discuss palliative care with a patient with cancer is early in the diagnosis and treatment process. Palliative care is not the same as hospice care; it isn’t just about end-of-life. Palliative care focuses on improving a patient’s quality of life throughout cancer treatment. Palliative care specialists can address a wide range of symptoms a patient might experience from cancer or its treatment, including pain, fatigue, nausea, and anxiety.
Early discussions allow for a more comprehensive care plan. Open communication about all treatment options, including palliative care, empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care goals and preferences.
Specific situations where discussing palliative care might be appropriate are:
- Soon after a cancer diagnosis.
- If the patient experiences significant side effects from cancer treatment.
- When considering different treatment options, palliative care can complement those treatments.
- In advanced stages of cancer, to focus on comfort and quality of life.
Clinical trials. Participation in a clinical trial to explore new or investigational treatments should always be considered.
In theory, clinical trials should be an option at any time in the patient’s course. But the organized clinical trial experience may not be available or appropriate. Then, the individual becomes a de facto “clinical trial with an n of 1.” Read this brief open-access blog post at Cancer Commons to learn more about that circumstance.
Innovative testing. The best choice of chemotherapeutic or targeted therapies is often unclear. The clinician is likely to follow published guidelines, often from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
These are evidence based and driven by consensus of experts. But guideline-recommended therapy is not always effective, and weeks or months can pass before this ineffectiveness becomes apparent. Thus, many researchers and companies are seeking methods of testing each patient’s specific cancer to determine in advance, or very quickly, whether a particular drug is likely to be effective.
Read more about these leading innovations:
SAGE Oncotest: Entering the Next Generation of Tailored Cancer Treatment
Alibrex: A New Blood Test to Reveal Whether a Cancer Treatment is Working
PARIS Test Uses Lab-Grown Mini-Tumors to Find a Patient’s Best Treatment
Using Live Cells from Patients to Find the Right Cancer Drug
Other innovative therapies under investigation could even be agnostic to cancer type:
Treating Pancreatic Cancer: Could Metabolism — Not Genomics — Be the Key?
High-Energy Blue Light Powers a Promising New Treatment to Destroy Cancer Cells
All-Clear Follow-Up: Hydrogen Peroxide Appears to Treat Oral and Skin Lesions
Cancer is a tough nut to crack. Many people and organizations are trying very hard. So much is being learned. Some approaches will be effective. We can all hope.
Dr. Lundberg, editor in chief, Cancer Commons, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The remaining 700,000 or so often proceed to chemotherapy either immediately or upon cancer recurrence, spread, or newly recognized metastases. “Cures” after that point are rare.
I’m speaking in generalities, understanding that each cancer and each patient is unique.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy alone can cure a small number of cancer types. When added to radiation or surgery, chemotherapy can help to cure a wider range of cancer types. As an add-on, chemotherapy can extend the length and quality of life for many patients with cancer. Since chemotherapy is by definition “toxic,” it can also shorten the duration or harm the quality of life and provide false hope. The Table summarizes what chemotherapy can and cannot achieve in selected cancer types.
Careful, compassionate communication between patient and physician is key. Goals and expectations must be clearly understood.
Organized chemotherapeutic efforts are further categorized as first line, second line, and third line.
First-line treatment. The initial round of recommended chemotherapy for a specific cancer. It is typically considered the most effective treatment for that type and stage of cancer on the basis of current research and clinical trials.
Second-line treatment. This is the treatment used if the first-line chemotherapy doesn’t work as desired. Reasons to switch to second-line chemo include:
- Lack of response (the tumor failed to shrink).
- Progression (the cancer may have grown or spread further).
- Adverse side effects were too severe to continue.
The drugs used in second-line chemo will typically be different from those used in first line, sometimes because cancer cells can develop resistance to chemotherapy drugs over time. Moreover, the goal of second-line chemo may differ from that of first-line therapy. Rather than chiefly aiming for a cure, second-line treatment might focus on slowing cancer growth, managing symptoms, or improving quality of life. Unfortunately, not every type of cancer has a readily available second-line option.
Third-line treatment. Third-line options come into play when both the initial course of chemo (first line) and the subsequent treatment (second line) have failed to achieve remission or control the cancer’s spread. Owing to the progressive nature of advanced cancers, patients might not be eligible or healthy enough for third-line therapy. Depending on cancer type, the patient’s general health, and response to previous treatments, third-line options could include:
- New or different chemotherapy drugs compared with prior lines.
- Surgery to debulk the tumor.
- Radiation for symptom control.
- Targeted therapy: drugs designed to target specific vulnerabilities in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: agents that help the body’s immune system fight cancer cells.
- Clinical trials testing new or investigational treatments, which may be applicable at any time, depending on the questions being addressed.
The goals of third-line therapy may shift from aiming for a cure to managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and potentially slowing cancer growth. The decision to pursue third-line therapy involves careful consideration by the doctor and patient, weighing the potential benefits and risks of treatment considering the individual’s overall health and specific situation.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about the potential outcomes of third-line therapy. Although remission may be unlikely, third-line therapy can still play a role in managing the disease.
Navigating advanced cancer treatment is very complex. The patient and physician must together consider detailed explanations and clarifications to set expectations and make informed decisions about care.
Interventions to Consider Earlier
In traditional clinical oncology practice, other interventions are possible, but these may not be offered until treatment has reached the third line:
- Molecular testing.
- Palliation.
- Clinical trials.
- Innovative testing to guide targeted therapy by ascertaining which agents are most likely (or not likely at all) to be effective.
I would argue that the patient’s interests are better served by considering and offering these other interventions much earlier, even before starting first-line chemotherapy.
Molecular testing. The best time for molecular testing of a new malignant tumor is typically at the time of diagnosis. Here’s why:
- Molecular testing helps identify specific genetic mutations in the cancer cells. This information can be crucial for selecting targeted therapies that are most effective against those specific mutations. Early detection allows for the most treatment options. For example, for non–small cell lung cancer, early is best because treatment and outcomes may well be changed by test results.
- Knowing the tumor’s molecular makeup can help determine whether a patient qualifies for clinical trials of new drugs designed for specific mutations.
- Some molecular markers can offer information about the tumor’s aggressiveness and potential for metastasis so that prognosis can be informed.
Molecular testing can be a valuable tool throughout a cancer patient’s journey. With genetically diverse tumors, the initial biopsy might not capture the full picture. Molecular testing of circulating tumor DNA can be used to monitor a patient’s response to treatment and detect potential mutations that might arise during treatment resistance. Retesting after metastasis can provide additional information that can aid in treatment decisions.
Palliative care. The ideal time to discuss palliative care with a patient with cancer is early in the diagnosis and treatment process. Palliative care is not the same as hospice care; it isn’t just about end-of-life. Palliative care focuses on improving a patient’s quality of life throughout cancer treatment. Palliative care specialists can address a wide range of symptoms a patient might experience from cancer or its treatment, including pain, fatigue, nausea, and anxiety.
Early discussions allow for a more comprehensive care plan. Open communication about all treatment options, including palliative care, empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care goals and preferences.
Specific situations where discussing palliative care might be appropriate are:
- Soon after a cancer diagnosis.
- If the patient experiences significant side effects from cancer treatment.
- When considering different treatment options, palliative care can complement those treatments.
- In advanced stages of cancer, to focus on comfort and quality of life.
Clinical trials. Participation in a clinical trial to explore new or investigational treatments should always be considered.
In theory, clinical trials should be an option at any time in the patient’s course. But the organized clinical trial experience may not be available or appropriate. Then, the individual becomes a de facto “clinical trial with an n of 1.” Read this brief open-access blog post at Cancer Commons to learn more about that circumstance.
Innovative testing. The best choice of chemotherapeutic or targeted therapies is often unclear. The clinician is likely to follow published guidelines, often from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
These are evidence based and driven by consensus of experts. But guideline-recommended therapy is not always effective, and weeks or months can pass before this ineffectiveness becomes apparent. Thus, many researchers and companies are seeking methods of testing each patient’s specific cancer to determine in advance, or very quickly, whether a particular drug is likely to be effective.
Read more about these leading innovations:
SAGE Oncotest: Entering the Next Generation of Tailored Cancer Treatment
Alibrex: A New Blood Test to Reveal Whether a Cancer Treatment is Working
PARIS Test Uses Lab-Grown Mini-Tumors to Find a Patient’s Best Treatment
Using Live Cells from Patients to Find the Right Cancer Drug
Other innovative therapies under investigation could even be agnostic to cancer type:
Treating Pancreatic Cancer: Could Metabolism — Not Genomics — Be the Key?
High-Energy Blue Light Powers a Promising New Treatment to Destroy Cancer Cells
All-Clear Follow-Up: Hydrogen Peroxide Appears to Treat Oral and Skin Lesions
Cancer is a tough nut to crack. Many people and organizations are trying very hard. So much is being learned. Some approaches will be effective. We can all hope.
Dr. Lundberg, editor in chief, Cancer Commons, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians Lament Over Reliance on Relative Value Units: Survey
Most physicians oppose the way standardized relative value units (RVUs) are used to determine performance and compensation, according to Medscape’s 2024 Physicians and RVUs Report. About 6 in 10 survey respondents were unhappy with how RVUs affected them financially, while 7 in 10 said RVUs were poor measures of productivity.
The report analyzed 2024 survey data from 1005 practicing physicians who earn RVUs.
“I’m already mad that the medical field is controlled by health insurers and what they pay and authorize,” said an anesthesiologist in New York. “Then [that approach] is transferred to medical offices and hospitals, where physicians are paid by RVUs.”
Most physicians surveyed produced between 4000 and 8000 RVUs per year. Roughly one in six were high RVU generators, generating more than 10,000 annually.
In most cases, the metric influences earning potential — 42% of doctors surveyed said RVUs affect their salaries to some degree. One quarter said their salary was based entirely on RVUs. More than three fourths of physicians who received performance bonuses said they must meet RVU targets to do so.
“The current RVU system encourages unnecessary procedures, hurting patients,” said an orthopedic surgeon in Maine.
Nearly three fourths of practitioners surveyed said they occasionally to frequently felt pressure to take on more patients as a result of this system.
“I know numerous primary care doctors and specialists who have been forced to increase patient volume to meet RVU goals, and none is happy about it,” said Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist with Stanford Hospital in Palo Alto, California. “Plus, patients are definitely not happy about being rushed.”
More than half of respondents said they occasionally or frequently felt compelled by their employer to use higher-level coding, which interferes with a physician’s ethical responsibility to the patient, said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a bioethicist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City.
“Rather than rewarding excellence or good outcomes, you’re kind of rewarding procedures and volume,” said Dr. Caplan. “It’s more than pressure; it’s expected.”
Nearly 6 in 10 physicians said that the method for calculating reimbursements was unfair. Almost half said that they weren’t happy with how their workplace uses RVUs.
A few respondents said that their RVU model, which is often based on what Dr. Patel called an “overly complicated algorithm,” did not account for the time spent on tasks or the fact that some patients miss appointments. RVUs also rely on factors outside the control of a physician, such as location and patient volume, said one doctor.
The model can also lower the level of care patients receive, Dr. Patel said.
“I know primary care doctors who work in RVU-based systems and simply cannot take the necessary time — even if it’s 30-45 minutes — to thoroughly assess a patient, when the model forces them to take on 15-minute encounters.”
Finally, over half of clinicians said alternatives to the RVU system would be more effective, and 77% suggested including qualitative data. One respondent recommended incorporating time spent doing paperwork and communicating with patients, complexity of conditions, and medication management.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most physicians oppose the way standardized relative value units (RVUs) are used to determine performance and compensation, according to Medscape’s 2024 Physicians and RVUs Report. About 6 in 10 survey respondents were unhappy with how RVUs affected them financially, while 7 in 10 said RVUs were poor measures of productivity.
The report analyzed 2024 survey data from 1005 practicing physicians who earn RVUs.
“I’m already mad that the medical field is controlled by health insurers and what they pay and authorize,” said an anesthesiologist in New York. “Then [that approach] is transferred to medical offices and hospitals, where physicians are paid by RVUs.”
Most physicians surveyed produced between 4000 and 8000 RVUs per year. Roughly one in six were high RVU generators, generating more than 10,000 annually.
In most cases, the metric influences earning potential — 42% of doctors surveyed said RVUs affect their salaries to some degree. One quarter said their salary was based entirely on RVUs. More than three fourths of physicians who received performance bonuses said they must meet RVU targets to do so.
“The current RVU system encourages unnecessary procedures, hurting patients,” said an orthopedic surgeon in Maine.
Nearly three fourths of practitioners surveyed said they occasionally to frequently felt pressure to take on more patients as a result of this system.
“I know numerous primary care doctors and specialists who have been forced to increase patient volume to meet RVU goals, and none is happy about it,” said Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist with Stanford Hospital in Palo Alto, California. “Plus, patients are definitely not happy about being rushed.”
More than half of respondents said they occasionally or frequently felt compelled by their employer to use higher-level coding, which interferes with a physician’s ethical responsibility to the patient, said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a bioethicist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City.
“Rather than rewarding excellence or good outcomes, you’re kind of rewarding procedures and volume,” said Dr. Caplan. “It’s more than pressure; it’s expected.”
Nearly 6 in 10 physicians said that the method for calculating reimbursements was unfair. Almost half said that they weren’t happy with how their workplace uses RVUs.
A few respondents said that their RVU model, which is often based on what Dr. Patel called an “overly complicated algorithm,” did not account for the time spent on tasks or the fact that some patients miss appointments. RVUs also rely on factors outside the control of a physician, such as location and patient volume, said one doctor.
The model can also lower the level of care patients receive, Dr. Patel said.
“I know primary care doctors who work in RVU-based systems and simply cannot take the necessary time — even if it’s 30-45 minutes — to thoroughly assess a patient, when the model forces them to take on 15-minute encounters.”
Finally, over half of clinicians said alternatives to the RVU system would be more effective, and 77% suggested including qualitative data. One respondent recommended incorporating time spent doing paperwork and communicating with patients, complexity of conditions, and medication management.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most physicians oppose the way standardized relative value units (RVUs) are used to determine performance and compensation, according to Medscape’s 2024 Physicians and RVUs Report. About 6 in 10 survey respondents were unhappy with how RVUs affected them financially, while 7 in 10 said RVUs were poor measures of productivity.
The report analyzed 2024 survey data from 1005 practicing physicians who earn RVUs.
“I’m already mad that the medical field is controlled by health insurers and what they pay and authorize,” said an anesthesiologist in New York. “Then [that approach] is transferred to medical offices and hospitals, where physicians are paid by RVUs.”
Most physicians surveyed produced between 4000 and 8000 RVUs per year. Roughly one in six were high RVU generators, generating more than 10,000 annually.
In most cases, the metric influences earning potential — 42% of doctors surveyed said RVUs affect their salaries to some degree. One quarter said their salary was based entirely on RVUs. More than three fourths of physicians who received performance bonuses said they must meet RVU targets to do so.
“The current RVU system encourages unnecessary procedures, hurting patients,” said an orthopedic surgeon in Maine.
Nearly three fourths of practitioners surveyed said they occasionally to frequently felt pressure to take on more patients as a result of this system.
“I know numerous primary care doctors and specialists who have been forced to increase patient volume to meet RVU goals, and none is happy about it,” said Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist with Stanford Hospital in Palo Alto, California. “Plus, patients are definitely not happy about being rushed.”
More than half of respondents said they occasionally or frequently felt compelled by their employer to use higher-level coding, which interferes with a physician’s ethical responsibility to the patient, said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a bioethicist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City.
“Rather than rewarding excellence or good outcomes, you’re kind of rewarding procedures and volume,” said Dr. Caplan. “It’s more than pressure; it’s expected.”
Nearly 6 in 10 physicians said that the method for calculating reimbursements was unfair. Almost half said that they weren’t happy with how their workplace uses RVUs.
A few respondents said that their RVU model, which is often based on what Dr. Patel called an “overly complicated algorithm,” did not account for the time spent on tasks or the fact that some patients miss appointments. RVUs also rely on factors outside the control of a physician, such as location and patient volume, said one doctor.
The model can also lower the level of care patients receive, Dr. Patel said.
“I know primary care doctors who work in RVU-based systems and simply cannot take the necessary time — even if it’s 30-45 minutes — to thoroughly assess a patient, when the model forces them to take on 15-minute encounters.”
Finally, over half of clinicians said alternatives to the RVU system would be more effective, and 77% suggested including qualitative data. One respondent recommended incorporating time spent doing paperwork and communicating with patients, complexity of conditions, and medication management.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Multiple Myeloma: New Treatments Aid Patient Subgroups
“The introduction of treatments such as elranatamab (Elrexfio) is allowing patients with multiple myeloma, which is still incurable for now, to have different options and achieve long periods of remission, thus improving their survival,” she added. “This therapeutic innovation is highly effective and well tolerated in patients with relapse or refractory multiple myeloma.” The overall response rate is “up to 61%, early, deep, and long-lasting.”
In an interview with El Médico Interactivo, Dr. Mateos explained the new approaches to multiple myeloma. She highlighted the effectiveness of new treatments and reviewed the latest data on this disease, which were presented at the recent European Hematology Association Congress.
What is the incidence rate of multiple myeloma in the Spanish population?
Multiple myeloma has an incidence of approximately 4-5 new cases per 100,000 inhabitants per year. This means that around 3000 new cases are diagnosed each year in Spain. As with most tumors, multiple myeloma is generally slightly more common in males than females. It is the third most frequent hematologic cancer in men (1757 new cases) and women (1325 new cases), behind lymphoma and leukemias.
At what age is it most often diagnosed?
It affects older people, with recent reports indicating around 68-69 years as the median age. Although more young people are being diagnosed with multiple myeloma, analyses of how this hematologic cancer affects the general population show that it generally impacts patients over age 65 years.
What is the typical survival prognosis?
Thanks to research and therapeutic innovation, the prognosis has changed significantly over the past 20-25 years. Today, if a patient with multiple myeloma receives a diagnosis and does not exhibit poor prognostic characteristics (and this description fits approximately 70%-80% of patients with multiple myeloma), it is realistic to expect a survival exceeding 10 years. A few years ago, this outcome was unimaginable, but a significant amount of therapeutic innovation has made it possible. That’s why I emphasize that it is realistic to provide these data with such a positive outlook.
Is multiple myeloma a refractory type of cancer?
It was a refractory type of cancer. Twenty years ago, there were no treatment options, and therefore survival was around 2-3 years, because treatment mainly consisted of using alkylating agents and corticosteroids. This is what made it refractory.
With the emergence of new therapeutic innovations, patients have been responding better and their responses are lasting longer. Although there is still a group of patients, about 10%-15%, with a poor prognosis and refractory disease, those with standard risk are responding better to different therapies.
Although most patients will eventually exhaust the treatments, which until now were primarily triple-drug regimens (such as proteasome inhibitors, immunomodulators, and antiCD38 antibodies), the introduction of new therapies is extending the duration of responses.
Is the risk for relapse high?
It is very high, in the sense that almost all patients with multiple myeloma eventually relapse. However, we hope that there soon will be some patients who do not relapse.
What are the typical pathologic manifestations of this cancer? Does it affect everyone equally, or in specific ways in each person?
In multiple myeloma, we often say there are multiple myelomas. Clinically, the disease presents in most patients, around 80%, with two clinical manifestations: anemia and bone lesions. Less frequently, patients may also have kidney failure, hypercalcemia, and a higher tendency toward infection. Behind this rather common symptomatology, from a molecular and genetic perspective, each myeloma is practically unique, adding complexity to its treatment. Therefore, ultimately, myelomas end up being refractory.
Elranatamab is a new therapeutic tool. For which patients is it recommended?
It is a bispecific monoclonal antibody that corresponds to the new monotherapy strategies we have for treating patients with multiple myeloma. On the one hand, it targets damaged plasma cells, which are the patient’s tumor cells, and on the other, it binds the patient’s T cells and redirects them to the tumor niche. When this happens, the T cell activates and destroys the tumor cell.
This medication has been approved for patients with relapsed myeloma who have received traditional drugs for their treatment. We know well that patients who have already received proteasome inhibitors, immunomodulators, and anti-CD38 antibodies typically need something new after treatment. Before, there were no other options, and we would reuse what had been previously used. Now we have elranatamab, a bispecific monoclonal antibody targeting a new receptor that has shown significant responses as monotherapy.
More than 60% of patients respond, and more than 30% achieve complete remission. The key is the response duration and progression-free survival of almost a year and a half. This is the longest progression-free survival we have seen to date in previous lines. Therefore, it fills the needs we had for these relapsed or refractory myeloma patients.
What advantages does this new treatment offer?
It represents a therapeutic innovation because, as mentioned, it achieves a response in more than 60% of patients, and around 35% achieve complete remission. The median response duration has not been reached yet. Progression-free survival is 17.2 months, almost a year and a half, and overall survival is almost two years.
Furthermore, it is administered as subcutaneous monotherapy weekly for the first six cycles and then every 15 days. It has a good safety profile, although some adverse events are known, so we have strategies to combat or mitigate them, making the treatment generally well tolerated.
What side effects are being observed?
They are manageable. When the drug is first administered, patients may experience what we call a cytokine release syndrome, which is a result of the treatment’s mechanism. However, we can predict very well when it occurs, usually 2 days after the first doses, and we have strategies to mitigate it.
The second most common adverse event we need to be cautious about is infection. Nowadays, before starting treatment, patients update their vaccination schedule, receive antiviral prophylaxis, and receive prophylaxis against certain germs, resulting in reduced infections. However, infections are probably the adverse events we need to be most careful about when treating the patient.
We must ensure that prophylaxis is performed, and if fever occurs and an infection is suspected, cultures and all kinds of studies must be done to identify and treat it properly.
How does elranatamab change the treatment of an incurable disease? Does it bring us closer to a cure or to making multiple myeloma a manageable chronic disease?
With the already approved elranatamab, the most important aspect is that it adds another treatment option for patients with myeloma. With the progression-free survival data I indicated, life expectancy is increased, with a good quality of life and acceptable safety.
Obviously, elranatamab is still under study and development, even in early lines, including in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma. When we are choosing first-line therapy, we select the best patients by combining traditional drugs with these new immunotherapies, such as elranatamab, it is likely that we are much closer to offering a cure to specific subgroups.
Although it won’t happen in all cases, I believe it will be applicable to a significant subgroup of patients, making chronicity of the disease a reality we are already approaching. Each day, we encounter more patients receiving different lines of treatment and ultimately meeting their life expectancy with myeloma. Even though some may die, it is often due to causes not related to myeloma. This is the most important contribution of these innovations, such as elranatamab.
Dr. Mateos reported receiving honoraria from Janssen, Celgene, Takeda, Amgen, GSK, AbbVie, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Stemline, Oncopeptides, and Kite for delivering lectures and for participating in advisory boards.
This story was translated from El Médico Interactivo, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
“The introduction of treatments such as elranatamab (Elrexfio) is allowing patients with multiple myeloma, which is still incurable for now, to have different options and achieve long periods of remission, thus improving their survival,” she added. “This therapeutic innovation is highly effective and well tolerated in patients with relapse or refractory multiple myeloma.” The overall response rate is “up to 61%, early, deep, and long-lasting.”
In an interview with El Médico Interactivo, Dr. Mateos explained the new approaches to multiple myeloma. She highlighted the effectiveness of new treatments and reviewed the latest data on this disease, which were presented at the recent European Hematology Association Congress.
What is the incidence rate of multiple myeloma in the Spanish population?
Multiple myeloma has an incidence of approximately 4-5 new cases per 100,000 inhabitants per year. This means that around 3000 new cases are diagnosed each year in Spain. As with most tumors, multiple myeloma is generally slightly more common in males than females. It is the third most frequent hematologic cancer in men (1757 new cases) and women (1325 new cases), behind lymphoma and leukemias.
At what age is it most often diagnosed?
It affects older people, with recent reports indicating around 68-69 years as the median age. Although more young people are being diagnosed with multiple myeloma, analyses of how this hematologic cancer affects the general population show that it generally impacts patients over age 65 years.
What is the typical survival prognosis?
Thanks to research and therapeutic innovation, the prognosis has changed significantly over the past 20-25 years. Today, if a patient with multiple myeloma receives a diagnosis and does not exhibit poor prognostic characteristics (and this description fits approximately 70%-80% of patients with multiple myeloma), it is realistic to expect a survival exceeding 10 years. A few years ago, this outcome was unimaginable, but a significant amount of therapeutic innovation has made it possible. That’s why I emphasize that it is realistic to provide these data with such a positive outlook.
Is multiple myeloma a refractory type of cancer?
It was a refractory type of cancer. Twenty years ago, there were no treatment options, and therefore survival was around 2-3 years, because treatment mainly consisted of using alkylating agents and corticosteroids. This is what made it refractory.
With the emergence of new therapeutic innovations, patients have been responding better and their responses are lasting longer. Although there is still a group of patients, about 10%-15%, with a poor prognosis and refractory disease, those with standard risk are responding better to different therapies.
Although most patients will eventually exhaust the treatments, which until now were primarily triple-drug regimens (such as proteasome inhibitors, immunomodulators, and antiCD38 antibodies), the introduction of new therapies is extending the duration of responses.
Is the risk for relapse high?
It is very high, in the sense that almost all patients with multiple myeloma eventually relapse. However, we hope that there soon will be some patients who do not relapse.
What are the typical pathologic manifestations of this cancer? Does it affect everyone equally, or in specific ways in each person?
In multiple myeloma, we often say there are multiple myelomas. Clinically, the disease presents in most patients, around 80%, with two clinical manifestations: anemia and bone lesions. Less frequently, patients may also have kidney failure, hypercalcemia, and a higher tendency toward infection. Behind this rather common symptomatology, from a molecular and genetic perspective, each myeloma is practically unique, adding complexity to its treatment. Therefore, ultimately, myelomas end up being refractory.
Elranatamab is a new therapeutic tool. For which patients is it recommended?
It is a bispecific monoclonal antibody that corresponds to the new monotherapy strategies we have for treating patients with multiple myeloma. On the one hand, it targets damaged plasma cells, which are the patient’s tumor cells, and on the other, it binds the patient’s T cells and redirects them to the tumor niche. When this happens, the T cell activates and destroys the tumor cell.
This medication has been approved for patients with relapsed myeloma who have received traditional drugs for their treatment. We know well that patients who have already received proteasome inhibitors, immunomodulators, and anti-CD38 antibodies typically need something new after treatment. Before, there were no other options, and we would reuse what had been previously used. Now we have elranatamab, a bispecific monoclonal antibody targeting a new receptor that has shown significant responses as monotherapy.
More than 60% of patients respond, and more than 30% achieve complete remission. The key is the response duration and progression-free survival of almost a year and a half. This is the longest progression-free survival we have seen to date in previous lines. Therefore, it fills the needs we had for these relapsed or refractory myeloma patients.
What advantages does this new treatment offer?
It represents a therapeutic innovation because, as mentioned, it achieves a response in more than 60% of patients, and around 35% achieve complete remission. The median response duration has not been reached yet. Progression-free survival is 17.2 months, almost a year and a half, and overall survival is almost two years.
Furthermore, it is administered as subcutaneous monotherapy weekly for the first six cycles and then every 15 days. It has a good safety profile, although some adverse events are known, so we have strategies to combat or mitigate them, making the treatment generally well tolerated.
What side effects are being observed?
They are manageable. When the drug is first administered, patients may experience what we call a cytokine release syndrome, which is a result of the treatment’s mechanism. However, we can predict very well when it occurs, usually 2 days after the first doses, and we have strategies to mitigate it.
The second most common adverse event we need to be cautious about is infection. Nowadays, before starting treatment, patients update their vaccination schedule, receive antiviral prophylaxis, and receive prophylaxis against certain germs, resulting in reduced infections. However, infections are probably the adverse events we need to be most careful about when treating the patient.
We must ensure that prophylaxis is performed, and if fever occurs and an infection is suspected, cultures and all kinds of studies must be done to identify and treat it properly.
How does elranatamab change the treatment of an incurable disease? Does it bring us closer to a cure or to making multiple myeloma a manageable chronic disease?
With the already approved elranatamab, the most important aspect is that it adds another treatment option for patients with myeloma. With the progression-free survival data I indicated, life expectancy is increased, with a good quality of life and acceptable safety.
Obviously, elranatamab is still under study and development, even in early lines, including in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma. When we are choosing first-line therapy, we select the best patients by combining traditional drugs with these new immunotherapies, such as elranatamab, it is likely that we are much closer to offering a cure to specific subgroups.
Although it won’t happen in all cases, I believe it will be applicable to a significant subgroup of patients, making chronicity of the disease a reality we are already approaching. Each day, we encounter more patients receiving different lines of treatment and ultimately meeting their life expectancy with myeloma. Even though some may die, it is often due to causes not related to myeloma. This is the most important contribution of these innovations, such as elranatamab.
Dr. Mateos reported receiving honoraria from Janssen, Celgene, Takeda, Amgen, GSK, AbbVie, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Stemline, Oncopeptides, and Kite for delivering lectures and for participating in advisory boards.
This story was translated from El Médico Interactivo, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
“The introduction of treatments such as elranatamab (Elrexfio) is allowing patients with multiple myeloma, which is still incurable for now, to have different options and achieve long periods of remission, thus improving their survival,” she added. “This therapeutic innovation is highly effective and well tolerated in patients with relapse or refractory multiple myeloma.” The overall response rate is “up to 61%, early, deep, and long-lasting.”
In an interview with El Médico Interactivo, Dr. Mateos explained the new approaches to multiple myeloma. She highlighted the effectiveness of new treatments and reviewed the latest data on this disease, which were presented at the recent European Hematology Association Congress.
What is the incidence rate of multiple myeloma in the Spanish population?
Multiple myeloma has an incidence of approximately 4-5 new cases per 100,000 inhabitants per year. This means that around 3000 new cases are diagnosed each year in Spain. As with most tumors, multiple myeloma is generally slightly more common in males than females. It is the third most frequent hematologic cancer in men (1757 new cases) and women (1325 new cases), behind lymphoma and leukemias.
At what age is it most often diagnosed?
It affects older people, with recent reports indicating around 68-69 years as the median age. Although more young people are being diagnosed with multiple myeloma, analyses of how this hematologic cancer affects the general population show that it generally impacts patients over age 65 years.
What is the typical survival prognosis?
Thanks to research and therapeutic innovation, the prognosis has changed significantly over the past 20-25 years. Today, if a patient with multiple myeloma receives a diagnosis and does not exhibit poor prognostic characteristics (and this description fits approximately 70%-80% of patients with multiple myeloma), it is realistic to expect a survival exceeding 10 years. A few years ago, this outcome was unimaginable, but a significant amount of therapeutic innovation has made it possible. That’s why I emphasize that it is realistic to provide these data with such a positive outlook.
Is multiple myeloma a refractory type of cancer?
It was a refractory type of cancer. Twenty years ago, there were no treatment options, and therefore survival was around 2-3 years, because treatment mainly consisted of using alkylating agents and corticosteroids. This is what made it refractory.
With the emergence of new therapeutic innovations, patients have been responding better and their responses are lasting longer. Although there is still a group of patients, about 10%-15%, with a poor prognosis and refractory disease, those with standard risk are responding better to different therapies.
Although most patients will eventually exhaust the treatments, which until now were primarily triple-drug regimens (such as proteasome inhibitors, immunomodulators, and antiCD38 antibodies), the introduction of new therapies is extending the duration of responses.
Is the risk for relapse high?
It is very high, in the sense that almost all patients with multiple myeloma eventually relapse. However, we hope that there soon will be some patients who do not relapse.
What are the typical pathologic manifestations of this cancer? Does it affect everyone equally, or in specific ways in each person?
In multiple myeloma, we often say there are multiple myelomas. Clinically, the disease presents in most patients, around 80%, with two clinical manifestations: anemia and bone lesions. Less frequently, patients may also have kidney failure, hypercalcemia, and a higher tendency toward infection. Behind this rather common symptomatology, from a molecular and genetic perspective, each myeloma is practically unique, adding complexity to its treatment. Therefore, ultimately, myelomas end up being refractory.
Elranatamab is a new therapeutic tool. For which patients is it recommended?
It is a bispecific monoclonal antibody that corresponds to the new monotherapy strategies we have for treating patients with multiple myeloma. On the one hand, it targets damaged plasma cells, which are the patient’s tumor cells, and on the other, it binds the patient’s T cells and redirects them to the tumor niche. When this happens, the T cell activates and destroys the tumor cell.
This medication has been approved for patients with relapsed myeloma who have received traditional drugs for their treatment. We know well that patients who have already received proteasome inhibitors, immunomodulators, and anti-CD38 antibodies typically need something new after treatment. Before, there were no other options, and we would reuse what had been previously used. Now we have elranatamab, a bispecific monoclonal antibody targeting a new receptor that has shown significant responses as monotherapy.
More than 60% of patients respond, and more than 30% achieve complete remission. The key is the response duration and progression-free survival of almost a year and a half. This is the longest progression-free survival we have seen to date in previous lines. Therefore, it fills the needs we had for these relapsed or refractory myeloma patients.
What advantages does this new treatment offer?
It represents a therapeutic innovation because, as mentioned, it achieves a response in more than 60% of patients, and around 35% achieve complete remission. The median response duration has not been reached yet. Progression-free survival is 17.2 months, almost a year and a half, and overall survival is almost two years.
Furthermore, it is administered as subcutaneous monotherapy weekly for the first six cycles and then every 15 days. It has a good safety profile, although some adverse events are known, so we have strategies to combat or mitigate them, making the treatment generally well tolerated.
What side effects are being observed?
They are manageable. When the drug is first administered, patients may experience what we call a cytokine release syndrome, which is a result of the treatment’s mechanism. However, we can predict very well when it occurs, usually 2 days after the first doses, and we have strategies to mitigate it.
The second most common adverse event we need to be cautious about is infection. Nowadays, before starting treatment, patients update their vaccination schedule, receive antiviral prophylaxis, and receive prophylaxis against certain germs, resulting in reduced infections. However, infections are probably the adverse events we need to be most careful about when treating the patient.
We must ensure that prophylaxis is performed, and if fever occurs and an infection is suspected, cultures and all kinds of studies must be done to identify and treat it properly.
How does elranatamab change the treatment of an incurable disease? Does it bring us closer to a cure or to making multiple myeloma a manageable chronic disease?
With the already approved elranatamab, the most important aspect is that it adds another treatment option for patients with myeloma. With the progression-free survival data I indicated, life expectancy is increased, with a good quality of life and acceptable safety.
Obviously, elranatamab is still under study and development, even in early lines, including in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma. When we are choosing first-line therapy, we select the best patients by combining traditional drugs with these new immunotherapies, such as elranatamab, it is likely that we are much closer to offering a cure to specific subgroups.
Although it won’t happen in all cases, I believe it will be applicable to a significant subgroup of patients, making chronicity of the disease a reality we are already approaching. Each day, we encounter more patients receiving different lines of treatment and ultimately meeting their life expectancy with myeloma. Even though some may die, it is often due to causes not related to myeloma. This is the most important contribution of these innovations, such as elranatamab.
Dr. Mateos reported receiving honoraria from Janssen, Celgene, Takeda, Amgen, GSK, AbbVie, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Stemline, Oncopeptides, and Kite for delivering lectures and for participating in advisory boards.
This story was translated from El Médico Interactivo, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When Childhood Cancer Survivors Face Sexual Challenges
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Issues Complete Response Letter for Myeloma Drug
On August 20, Regeneron announced that it had received a complete response letter from the FDA regarding its Biologics License Application for linvoseltamab, citing issues at a third-party manufacturer.
More specifically, Regeneron said in a company press release that the FDA issued the complete response letter based on findings from “a preapproval inspection at a third-party fill/finish manufacturer for another company’s product candidate.”
The third-party manufacturer told Regeneron it believes that the issues have been resolved, Regeneron said, and that facility is now awaiting a follow-up FDA inspection in the “coming months.”
Regeneron noted that this “anticipated outcome” from the FDA preapproval inspection had been disclosed previously during a company earnings call on August 1.
On that call, Regeneron had discussed the FDA’s concerns about the third-party manufacturer and anticipated that “any potential FDA approval for linvoseltamab is likely to be delayed beyond the August 22 PDUFA date.”
Regeneron had initially filed a Biologics License Application for its bispecific antibody in 2023, based on findings from the phase 1/2 single arm LINKER-MM1 trial.
In the latest published trial findings, investigators reported that, at a median follow-up of about 14 months, 71% of the 117 patients receiving 200 mg of linvoseltamab achieved an overall response, with 50% achieving a complete response. The probability of survival at 12 months was 75.3%.
This would have been the first approval for linvoseltamab, which would have joined two agents already on the US market for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: teclistamab (Tecvayli, Janssen) and elranatamab (Elrexfio, Pfizer).
Pricing information for linvoseltamab is not yet available, but its competitors teclistamab and elranatamab are reported to cost around $40,000 per month.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On August 20, Regeneron announced that it had received a complete response letter from the FDA regarding its Biologics License Application for linvoseltamab, citing issues at a third-party manufacturer.
More specifically, Regeneron said in a company press release that the FDA issued the complete response letter based on findings from “a preapproval inspection at a third-party fill/finish manufacturer for another company’s product candidate.”
The third-party manufacturer told Regeneron it believes that the issues have been resolved, Regeneron said, and that facility is now awaiting a follow-up FDA inspection in the “coming months.”
Regeneron noted that this “anticipated outcome” from the FDA preapproval inspection had been disclosed previously during a company earnings call on August 1.
On that call, Regeneron had discussed the FDA’s concerns about the third-party manufacturer and anticipated that “any potential FDA approval for linvoseltamab is likely to be delayed beyond the August 22 PDUFA date.”
Regeneron had initially filed a Biologics License Application for its bispecific antibody in 2023, based on findings from the phase 1/2 single arm LINKER-MM1 trial.
In the latest published trial findings, investigators reported that, at a median follow-up of about 14 months, 71% of the 117 patients receiving 200 mg of linvoseltamab achieved an overall response, with 50% achieving a complete response. The probability of survival at 12 months was 75.3%.
This would have been the first approval for linvoseltamab, which would have joined two agents already on the US market for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: teclistamab (Tecvayli, Janssen) and elranatamab (Elrexfio, Pfizer).
Pricing information for linvoseltamab is not yet available, but its competitors teclistamab and elranatamab are reported to cost around $40,000 per month.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
On August 20, Regeneron announced that it had received a complete response letter from the FDA regarding its Biologics License Application for linvoseltamab, citing issues at a third-party manufacturer.
More specifically, Regeneron said in a company press release that the FDA issued the complete response letter based on findings from “a preapproval inspection at a third-party fill/finish manufacturer for another company’s product candidate.”
The third-party manufacturer told Regeneron it believes that the issues have been resolved, Regeneron said, and that facility is now awaiting a follow-up FDA inspection in the “coming months.”
Regeneron noted that this “anticipated outcome” from the FDA preapproval inspection had been disclosed previously during a company earnings call on August 1.
On that call, Regeneron had discussed the FDA’s concerns about the third-party manufacturer and anticipated that “any potential FDA approval for linvoseltamab is likely to be delayed beyond the August 22 PDUFA date.”
Regeneron had initially filed a Biologics License Application for its bispecific antibody in 2023, based on findings from the phase 1/2 single arm LINKER-MM1 trial.
In the latest published trial findings, investigators reported that, at a median follow-up of about 14 months, 71% of the 117 patients receiving 200 mg of linvoseltamab achieved an overall response, with 50% achieving a complete response. The probability of survival at 12 months was 75.3%.
This would have been the first approval for linvoseltamab, which would have joined two agents already on the US market for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: teclistamab (Tecvayli, Janssen) and elranatamab (Elrexfio, Pfizer).
Pricing information for linvoseltamab is not yet available, but its competitors teclistamab and elranatamab are reported to cost around $40,000 per month.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Diagnosing, Treating Rashes In Patients on Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
WASHINGTON, DC — and with judicious usage and dosing of prednisone when deemed necessary, Blair Allais, MD, said during a session on supportive oncodermatology at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient hosted by the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
“It’s important when you see these patients to be as specific as possible” based on morphology and histopathology, and to treat the rashes in a similar way as in the non-ICI setting,” said Dr. Allais, a dermato-oncologist at the Inova Schar Cancer Institute, Fairfax, Virginia.
cirAEs are the most frequently reported and most visible adverse effects of checkpoint inhibition — a treatment that has emerged as a standard therapy for many malignancies since the first ICI was approved in 2011 for metastatic melanoma.
And contrary to what the phenomenon of immunosenescence might suggest, older patients are no less prone to cirAEs than younger patients. “You’d think you’d have fewer rashes and side effects as you age, but that’s not true,” said Dr. Allais, who completed a fellowship in cutaneous oncology after her dermatology residency.
A 2021 multicenter international cohort study of over 900 patients aged ≥ 80 years treated with single-agent ICIs for cancer did not find any significant differences in the development of immune-related adverse events among those younger than 85, those aged 85-89 years, and those 90 and older. Neither did the ELDERS study in the United Kingdom; this prospective observational study found similar rates of high-grade and low-grade immune toxicity in its two cohorts of patients ≥ 70 and < 70 years of age.
At the meeting, Dr. Allais, who coauthored a 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs, reviewed recent developments and provided the following advice:
New diagnostic criteria: “Really exciting” news for more precise diagnosis and optimal therapy of cirAEs, Dr. Allais said, is a position paper published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer that offers consensus-based diagnostic criteria for the 10 most common types of dermatologic immune-related adverse events and an overall diagnostic framework. “Luckily, through the work of a Delphi consensus group, we can now have [more diagnostic specificity],” which is important for both clinical care and research, she said.
Most cirAEs have typically been reported nonspecifically as “rash,” but diagnosing a rash subtype is “critical in tailoring appropriate therapy that it is both effective and the least detrimental to the oncology treatment plan for patients with cancer,” the group’s coauthors wrote.
The 10 core diagnoses include psoriasis, eczematous dermatitis, vitiligo, Grover disease, eruptive atypical squamous proliferation, and bullous pemphigoid. Outside of the core diagnoses are other nonspecific presentations that require evaluation to arrive at a diagnosis, if possible, or to reveal data that can allow for targeted therapy and severity grading, the group explains in its paper.
“To prednisone or not to prednisone”: The development of cirAEs is associated with reduced mortality and improved cancer outcomes, making the use of immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids a therapeutic dilemma. “Patients who get these rashes usually do better with respect to their cancer, so the concern has been, if we affect how they respond to their immunotherapy, we may minimize that improvement in mortality,” said Dr. Allais, also assistant professor at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and clinical assistant professor of dermatology at George Washington University.
A widely discussed study published in 2015 reported on 254 patients with melanoma who developed an immune-related adverse event during treatment with ipilimumab — approximately one third of whom required systemic corticosteroids — and concluded that systemic corticosteroids did not affect overall survival or time to (cancer) treatment failure. This study from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, “was the first large study looking at this question,” she said, and the subsequent message for several years in conferences and the literature was that steroids do not affect the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors.
“But the study was not without limitations,” Dr. Allais said, “because the patients who got prednisone were mainly those with higher-grade toxicities,” while those not treated with corticosteroids had either no toxicities or low-grade toxicities. “If higher-grade toxicities were associated with better (antitumor) response, the steroids may have just [blunted] that benefit.”
The current totality of data available in the literature suggests that corticosteroids may indeed have an impact on the efficacy of ICI therapy. “Subsequent studies have come out in the community that have shown that we should probably think twice about giving prednisone to some patients, particularly within the first 50 days of ICI treatment, and that we should be mindful of the dose,” Dr. Allais said.
The takeaways from these studies — all published in the past few years — are to use prednisone early and liberally for life-threatening toxicity, to use it at the lowest dose and for the shortest course when there is not an appropriate alternative, to avoid it for diagnoses that are not treated with prednisone outside the ICI setting, and to “have a plan” for a steroid-sparing agent to use after prednisone, she said.
Dr. Allais recommends heightened consideration during the first 50 days of ICI treatment based on a multicenter retrospective study that found a significant association between use of high-dose glucocorticoids (≥ 60 mg prednisone equivalent once a day) within 8 weeks of anti–programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) monotherapy initiation and poorer progression-free and overall survival. The study covered a cohort of 947 patients with advanced melanoma treated with anti–PD-1 monotherapy between 2009 and 2019, 54% of whom developed immune-related adverse events.
This study and other recent studies addressing the association between steroids and survival outcomes in patients with immune-related adverse events during ICI therapy are described in Dr. Allais’ 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs.
Approach to morbilliform eruptions: This rash is “super common” in patients on ICIs, occurring generally within 2-3 weeks of starting treatment. “It tends to be self-limited and can recur with future infusions,” Dr. Allais said.
Systemic steroids should be reserved for severe or refractory eruptions. “Usually, I treat the patients with topical steroids, and I manage their expectations (that the rash may recur with subsequent infusions), but I closely follow them up” within 2-3 weeks, she said. It’s important to rule out a severe cutaneous adverse drug eruption, of course, and to start high-dose systemic steroids immediately if necessary. “Antibiotics are a big culprit” and often can be discontinued.
Soak and smear: “I’m obsessed” with this technique of a 20-minute soak in plain water followed by application of steroid ointment, said Dr. Allais, referring to a small study published in 2005 that reported a complete response after 2 weeks in 60% of patients with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other inflammatory skin conditions (none had cancer), who had failed prior systemic therapy. All patients had at least a 75% response.
The method offers a way to “avoid the systemic immunosuppression we’d get with prednisone,” she said. One just needs to make sure the older patient can get in and out of their tub safely.
ICI-induced bullous pemphigoid (BP): BP occurs more frequently in the ICI setting, compared with the general population, with a median time to development of 8.5 months after ICI initiation. It is associated in this setting with improved tumor response, but “many oncologists stop anticancer treatment because of this diagnosis,” she said.
In the supportive oncodermatology space, however, ICI-induced BP exemplifies the value of tailored treatment regimens, she said. A small multi-institutional retrospective cohort study published in 2023 identified 35 cases of ICI-BP among 5636 ICI-treated patients and found that 8 out of 11 patients who received biologic therapy (rituximab, omalizumab, or dupilumab) had a complete response to ICI-BP without flares following subsequent ICI cycles. And while statistical significance was not reached, the study showed that no cancer-related outcomes were worsened.
“If you see someone with ICI-induced BP and they have a lot of involvement, you could start them on steroids and get that steroid-sparing agent initiated for approval. ... And if IgE is elevated, you might reach for omalizumab,” said Dr. Allais, noting that her favored treatment overall is dupilumab.
Risk factors for the development of ICI-induced BP include age > 70, skin cancer, and having an initial response to ICI on first imaging, the latter of which “I find fascinating ... because imaging occurs within the first 12 weeks of treatment, but we don’t see BP popping up until 8.5 months into treatment,” she noted. “So maybe there’s a baseline risk factor that could predispose them.”
Caution with antibiotics: “I try to avoid antibiotics in the ICI setting,” Dr. Allais said, in deference to the “ever-important microbiome.” Studies have demonstrated that the microbiomes of responders to ICI treatment are different from those of nonresponders, she said.
And a “fascinating” study of patients with melanoma undergoing ICI therapy showed not only a higher abundance of Ruminococcaceae bacteria in responders vs nonresponders but a significant impact of dietary fiber. High dietary fiber was associated with significantly improved overall survival in the patients on ICI, with the most pronounced benefit in patients with good fiber intake and no probiotic use. “Even wilder, their T cells changed,” she said. “They had a high expression of genes related to T-cell activation ... so more tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.”
A retrospective study of 568 patients with stages III and IV melanoma treated with ICI showed that those exposed to antibiotics prior to ICI had significantly worse overall survival than those not exposed to antibiotics. “Think before you give them,” Dr. Allais said. “And try to tell your older patients to eat beans and greens.”
Dr. Allais reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON, DC — and with judicious usage and dosing of prednisone when deemed necessary, Blair Allais, MD, said during a session on supportive oncodermatology at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient hosted by the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
“It’s important when you see these patients to be as specific as possible” based on morphology and histopathology, and to treat the rashes in a similar way as in the non-ICI setting,” said Dr. Allais, a dermato-oncologist at the Inova Schar Cancer Institute, Fairfax, Virginia.
cirAEs are the most frequently reported and most visible adverse effects of checkpoint inhibition — a treatment that has emerged as a standard therapy for many malignancies since the first ICI was approved in 2011 for metastatic melanoma.
And contrary to what the phenomenon of immunosenescence might suggest, older patients are no less prone to cirAEs than younger patients. “You’d think you’d have fewer rashes and side effects as you age, but that’s not true,” said Dr. Allais, who completed a fellowship in cutaneous oncology after her dermatology residency.
A 2021 multicenter international cohort study of over 900 patients aged ≥ 80 years treated with single-agent ICIs for cancer did not find any significant differences in the development of immune-related adverse events among those younger than 85, those aged 85-89 years, and those 90 and older. Neither did the ELDERS study in the United Kingdom; this prospective observational study found similar rates of high-grade and low-grade immune toxicity in its two cohorts of patients ≥ 70 and < 70 years of age.
At the meeting, Dr. Allais, who coauthored a 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs, reviewed recent developments and provided the following advice:
New diagnostic criteria: “Really exciting” news for more precise diagnosis and optimal therapy of cirAEs, Dr. Allais said, is a position paper published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer that offers consensus-based diagnostic criteria for the 10 most common types of dermatologic immune-related adverse events and an overall diagnostic framework. “Luckily, through the work of a Delphi consensus group, we can now have [more diagnostic specificity],” which is important for both clinical care and research, she said.
Most cirAEs have typically been reported nonspecifically as “rash,” but diagnosing a rash subtype is “critical in tailoring appropriate therapy that it is both effective and the least detrimental to the oncology treatment plan for patients with cancer,” the group’s coauthors wrote.
The 10 core diagnoses include psoriasis, eczematous dermatitis, vitiligo, Grover disease, eruptive atypical squamous proliferation, and bullous pemphigoid. Outside of the core diagnoses are other nonspecific presentations that require evaluation to arrive at a diagnosis, if possible, or to reveal data that can allow for targeted therapy and severity grading, the group explains in its paper.
“To prednisone or not to prednisone”: The development of cirAEs is associated with reduced mortality and improved cancer outcomes, making the use of immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids a therapeutic dilemma. “Patients who get these rashes usually do better with respect to their cancer, so the concern has been, if we affect how they respond to their immunotherapy, we may minimize that improvement in mortality,” said Dr. Allais, also assistant professor at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and clinical assistant professor of dermatology at George Washington University.
A widely discussed study published in 2015 reported on 254 patients with melanoma who developed an immune-related adverse event during treatment with ipilimumab — approximately one third of whom required systemic corticosteroids — and concluded that systemic corticosteroids did not affect overall survival or time to (cancer) treatment failure. This study from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, “was the first large study looking at this question,” she said, and the subsequent message for several years in conferences and the literature was that steroids do not affect the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors.
“But the study was not without limitations,” Dr. Allais said, “because the patients who got prednisone were mainly those with higher-grade toxicities,” while those not treated with corticosteroids had either no toxicities or low-grade toxicities. “If higher-grade toxicities were associated with better (antitumor) response, the steroids may have just [blunted] that benefit.”
The current totality of data available in the literature suggests that corticosteroids may indeed have an impact on the efficacy of ICI therapy. “Subsequent studies have come out in the community that have shown that we should probably think twice about giving prednisone to some patients, particularly within the first 50 days of ICI treatment, and that we should be mindful of the dose,” Dr. Allais said.
The takeaways from these studies — all published in the past few years — are to use prednisone early and liberally for life-threatening toxicity, to use it at the lowest dose and for the shortest course when there is not an appropriate alternative, to avoid it for diagnoses that are not treated with prednisone outside the ICI setting, and to “have a plan” for a steroid-sparing agent to use after prednisone, she said.
Dr. Allais recommends heightened consideration during the first 50 days of ICI treatment based on a multicenter retrospective study that found a significant association between use of high-dose glucocorticoids (≥ 60 mg prednisone equivalent once a day) within 8 weeks of anti–programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) monotherapy initiation and poorer progression-free and overall survival. The study covered a cohort of 947 patients with advanced melanoma treated with anti–PD-1 monotherapy between 2009 and 2019, 54% of whom developed immune-related adverse events.
This study and other recent studies addressing the association between steroids and survival outcomes in patients with immune-related adverse events during ICI therapy are described in Dr. Allais’ 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs.
Approach to morbilliform eruptions: This rash is “super common” in patients on ICIs, occurring generally within 2-3 weeks of starting treatment. “It tends to be self-limited and can recur with future infusions,” Dr. Allais said.
Systemic steroids should be reserved for severe or refractory eruptions. “Usually, I treat the patients with topical steroids, and I manage their expectations (that the rash may recur with subsequent infusions), but I closely follow them up” within 2-3 weeks, she said. It’s important to rule out a severe cutaneous adverse drug eruption, of course, and to start high-dose systemic steroids immediately if necessary. “Antibiotics are a big culprit” and often can be discontinued.
Soak and smear: “I’m obsessed” with this technique of a 20-minute soak in plain water followed by application of steroid ointment, said Dr. Allais, referring to a small study published in 2005 that reported a complete response after 2 weeks in 60% of patients with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other inflammatory skin conditions (none had cancer), who had failed prior systemic therapy. All patients had at least a 75% response.
The method offers a way to “avoid the systemic immunosuppression we’d get with prednisone,” she said. One just needs to make sure the older patient can get in and out of their tub safely.
ICI-induced bullous pemphigoid (BP): BP occurs more frequently in the ICI setting, compared with the general population, with a median time to development of 8.5 months after ICI initiation. It is associated in this setting with improved tumor response, but “many oncologists stop anticancer treatment because of this diagnosis,” she said.
In the supportive oncodermatology space, however, ICI-induced BP exemplifies the value of tailored treatment regimens, she said. A small multi-institutional retrospective cohort study published in 2023 identified 35 cases of ICI-BP among 5636 ICI-treated patients and found that 8 out of 11 patients who received biologic therapy (rituximab, omalizumab, or dupilumab) had a complete response to ICI-BP without flares following subsequent ICI cycles. And while statistical significance was not reached, the study showed that no cancer-related outcomes were worsened.
“If you see someone with ICI-induced BP and they have a lot of involvement, you could start them on steroids and get that steroid-sparing agent initiated for approval. ... And if IgE is elevated, you might reach for omalizumab,” said Dr. Allais, noting that her favored treatment overall is dupilumab.
Risk factors for the development of ICI-induced BP include age > 70, skin cancer, and having an initial response to ICI on first imaging, the latter of which “I find fascinating ... because imaging occurs within the first 12 weeks of treatment, but we don’t see BP popping up until 8.5 months into treatment,” she noted. “So maybe there’s a baseline risk factor that could predispose them.”
Caution with antibiotics: “I try to avoid antibiotics in the ICI setting,” Dr. Allais said, in deference to the “ever-important microbiome.” Studies have demonstrated that the microbiomes of responders to ICI treatment are different from those of nonresponders, she said.
And a “fascinating” study of patients with melanoma undergoing ICI therapy showed not only a higher abundance of Ruminococcaceae bacteria in responders vs nonresponders but a significant impact of dietary fiber. High dietary fiber was associated with significantly improved overall survival in the patients on ICI, with the most pronounced benefit in patients with good fiber intake and no probiotic use. “Even wilder, their T cells changed,” she said. “They had a high expression of genes related to T-cell activation ... so more tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.”
A retrospective study of 568 patients with stages III and IV melanoma treated with ICI showed that those exposed to antibiotics prior to ICI had significantly worse overall survival than those not exposed to antibiotics. “Think before you give them,” Dr. Allais said. “And try to tell your older patients to eat beans and greens.”
Dr. Allais reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON, DC — and with judicious usage and dosing of prednisone when deemed necessary, Blair Allais, MD, said during a session on supportive oncodermatology at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient hosted by the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
“It’s important when you see these patients to be as specific as possible” based on morphology and histopathology, and to treat the rashes in a similar way as in the non-ICI setting,” said Dr. Allais, a dermato-oncologist at the Inova Schar Cancer Institute, Fairfax, Virginia.
cirAEs are the most frequently reported and most visible adverse effects of checkpoint inhibition — a treatment that has emerged as a standard therapy for many malignancies since the first ICI was approved in 2011 for metastatic melanoma.
And contrary to what the phenomenon of immunosenescence might suggest, older patients are no less prone to cirAEs than younger patients. “You’d think you’d have fewer rashes and side effects as you age, but that’s not true,” said Dr. Allais, who completed a fellowship in cutaneous oncology after her dermatology residency.
A 2021 multicenter international cohort study of over 900 patients aged ≥ 80 years treated with single-agent ICIs for cancer did not find any significant differences in the development of immune-related adverse events among those younger than 85, those aged 85-89 years, and those 90 and older. Neither did the ELDERS study in the United Kingdom; this prospective observational study found similar rates of high-grade and low-grade immune toxicity in its two cohorts of patients ≥ 70 and < 70 years of age.
At the meeting, Dr. Allais, who coauthored a 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs, reviewed recent developments and provided the following advice:
New diagnostic criteria: “Really exciting” news for more precise diagnosis and optimal therapy of cirAEs, Dr. Allais said, is a position paper published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer that offers consensus-based diagnostic criteria for the 10 most common types of dermatologic immune-related adverse events and an overall diagnostic framework. “Luckily, through the work of a Delphi consensus group, we can now have [more diagnostic specificity],” which is important for both clinical care and research, she said.
Most cirAEs have typically been reported nonspecifically as “rash,” but diagnosing a rash subtype is “critical in tailoring appropriate therapy that it is both effective and the least detrimental to the oncology treatment plan for patients with cancer,” the group’s coauthors wrote.
The 10 core diagnoses include psoriasis, eczematous dermatitis, vitiligo, Grover disease, eruptive atypical squamous proliferation, and bullous pemphigoid. Outside of the core diagnoses are other nonspecific presentations that require evaluation to arrive at a diagnosis, if possible, or to reveal data that can allow for targeted therapy and severity grading, the group explains in its paper.
“To prednisone or not to prednisone”: The development of cirAEs is associated with reduced mortality and improved cancer outcomes, making the use of immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids a therapeutic dilemma. “Patients who get these rashes usually do better with respect to their cancer, so the concern has been, if we affect how they respond to their immunotherapy, we may minimize that improvement in mortality,” said Dr. Allais, also assistant professor at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, and clinical assistant professor of dermatology at George Washington University.
A widely discussed study published in 2015 reported on 254 patients with melanoma who developed an immune-related adverse event during treatment with ipilimumab — approximately one third of whom required systemic corticosteroids — and concluded that systemic corticosteroids did not affect overall survival or time to (cancer) treatment failure. This study from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, “was the first large study looking at this question,” she said, and the subsequent message for several years in conferences and the literature was that steroids do not affect the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors.
“But the study was not without limitations,” Dr. Allais said, “because the patients who got prednisone were mainly those with higher-grade toxicities,” while those not treated with corticosteroids had either no toxicities or low-grade toxicities. “If higher-grade toxicities were associated with better (antitumor) response, the steroids may have just [blunted] that benefit.”
The current totality of data available in the literature suggests that corticosteroids may indeed have an impact on the efficacy of ICI therapy. “Subsequent studies have come out in the community that have shown that we should probably think twice about giving prednisone to some patients, particularly within the first 50 days of ICI treatment, and that we should be mindful of the dose,” Dr. Allais said.
The takeaways from these studies — all published in the past few years — are to use prednisone early and liberally for life-threatening toxicity, to use it at the lowest dose and for the shortest course when there is not an appropriate alternative, to avoid it for diagnoses that are not treated with prednisone outside the ICI setting, and to “have a plan” for a steroid-sparing agent to use after prednisone, she said.
Dr. Allais recommends heightened consideration during the first 50 days of ICI treatment based on a multicenter retrospective study that found a significant association between use of high-dose glucocorticoids (≥ 60 mg prednisone equivalent once a day) within 8 weeks of anti–programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) monotherapy initiation and poorer progression-free and overall survival. The study covered a cohort of 947 patients with advanced melanoma treated with anti–PD-1 monotherapy between 2009 and 2019, 54% of whom developed immune-related adverse events.
This study and other recent studies addressing the association between steroids and survival outcomes in patients with immune-related adverse events during ICI therapy are described in Dr. Allais’ 2023 review of cirAEs from ICIs.
Approach to morbilliform eruptions: This rash is “super common” in patients on ICIs, occurring generally within 2-3 weeks of starting treatment. “It tends to be self-limited and can recur with future infusions,” Dr. Allais said.
Systemic steroids should be reserved for severe or refractory eruptions. “Usually, I treat the patients with topical steroids, and I manage their expectations (that the rash may recur with subsequent infusions), but I closely follow them up” within 2-3 weeks, she said. It’s important to rule out a severe cutaneous adverse drug eruption, of course, and to start high-dose systemic steroids immediately if necessary. “Antibiotics are a big culprit” and often can be discontinued.
Soak and smear: “I’m obsessed” with this technique of a 20-minute soak in plain water followed by application of steroid ointment, said Dr. Allais, referring to a small study published in 2005 that reported a complete response after 2 weeks in 60% of patients with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and other inflammatory skin conditions (none had cancer), who had failed prior systemic therapy. All patients had at least a 75% response.
The method offers a way to “avoid the systemic immunosuppression we’d get with prednisone,” she said. One just needs to make sure the older patient can get in and out of their tub safely.
ICI-induced bullous pemphigoid (BP): BP occurs more frequently in the ICI setting, compared with the general population, with a median time to development of 8.5 months after ICI initiation. It is associated in this setting with improved tumor response, but “many oncologists stop anticancer treatment because of this diagnosis,” she said.
In the supportive oncodermatology space, however, ICI-induced BP exemplifies the value of tailored treatment regimens, she said. A small multi-institutional retrospective cohort study published in 2023 identified 35 cases of ICI-BP among 5636 ICI-treated patients and found that 8 out of 11 patients who received biologic therapy (rituximab, omalizumab, or dupilumab) had a complete response to ICI-BP without flares following subsequent ICI cycles. And while statistical significance was not reached, the study showed that no cancer-related outcomes were worsened.
“If you see someone with ICI-induced BP and they have a lot of involvement, you could start them on steroids and get that steroid-sparing agent initiated for approval. ... And if IgE is elevated, you might reach for omalizumab,” said Dr. Allais, noting that her favored treatment overall is dupilumab.
Risk factors for the development of ICI-induced BP include age > 70, skin cancer, and having an initial response to ICI on first imaging, the latter of which “I find fascinating ... because imaging occurs within the first 12 weeks of treatment, but we don’t see BP popping up until 8.5 months into treatment,” she noted. “So maybe there’s a baseline risk factor that could predispose them.”
Caution with antibiotics: “I try to avoid antibiotics in the ICI setting,” Dr. Allais said, in deference to the “ever-important microbiome.” Studies have demonstrated that the microbiomes of responders to ICI treatment are different from those of nonresponders, she said.
And a “fascinating” study of patients with melanoma undergoing ICI therapy showed not only a higher abundance of Ruminococcaceae bacteria in responders vs nonresponders but a significant impact of dietary fiber. High dietary fiber was associated with significantly improved overall survival in the patients on ICI, with the most pronounced benefit in patients with good fiber intake and no probiotic use. “Even wilder, their T cells changed,” she said. “They had a high expression of genes related to T-cell activation ... so more tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.”
A retrospective study of 568 patients with stages III and IV melanoma treated with ICI showed that those exposed to antibiotics prior to ICI had significantly worse overall survival than those not exposed to antibiotics. “Think before you give them,” Dr. Allais said. “And try to tell your older patients to eat beans and greens.”
Dr. Allais reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ELDERDERM 2024
Doctors Are Seeking Professional Coaches More Often. Here’s Why
When Andrea Austin, MD, an emergency medicine specialist, left the military in 2020, she knew the adjustment to civilian life and practice might be difficult. To help smooth the transition, she reached out to a physician mentor who also had a professional coaching certificate. After a conversation, Dr. Austin signed up for 6 months of career coaching.
It was time well spent, according to Dr. Austin, who today is a coach herself. “It was really the first time I had the ability to choose what I wanted to do, and that required a mindset shift,” she explains. “A big part of coaching is helping physicians discover their agency so that they can make the best career choices.”
Physicians have long lacked the coaching resources typically made available to corporate executives. But that’s changing. In today’s high-pressure environment, where doctors are burning out at a rapid pace, coaching can sometimes be an avenue to staying in the field, especially if that coach is a fellow physician who understands what you’re facing.
With a physician shortage that the Association of American Medical Colleges expects to hit 86,000 in the next decade or so, coaching could be a stone worth turning over. A 2024 report in JAMA Network Open found that coaching provided by physician peers led to a significant reduction in interpersonal disengagement and burnout.
“What I think is exciting about coaching is that it allows you to better understand yourself and know your strengths and weaknesses,” said Dr. Austin. “It might seem simple, but many ‘soft skills’ aren’t considered mainstream in medicine. Coaching allows us to understand them and ourselves better.”
Why Are Doctors Using Coaches?
Although it’s hard to put a number on how many physicians are turning to coaches, the number of coaches available for doctors is growing rapidly. The American Medical Women’s Association maintains a database of physician coaches. According to deputy director Jodi Godfrey, MS, RDN, the number of members who have added coaching to their skill set has tripled in the past 4 years. “Many cite burnout as the reason they sought coaching support, and then they decided to go on to get certified in coaching.”
The pandemic is one reason physician coaching has grown, said Elizabeth Esparaz, MD, an ophthalmologist and physician coach. “Since the pandemic, the word ‘burnout’ is thrown around a good deal.” And the causes are clear. “Doctors are facing longer hours, they must make split-second decisions, they’re multitasking, and they have less support staff.”
Among her coaching clients, Dr. Austin has noticed other common struggles: fears of litigation, time scarcity with patients, declining reimbursement that hasn’t kept up with inflation, and loss of autonomy because of the corporatization of healthcare.
Coaching, Dr. Esparaz believes, can be an antidote to many of these issues. “Coaches help doctors see their strengths and find better ways of applying them,” she said. “We help them move forward, and also see their blind spots.”
Clarity, Goals, and Making the Right Choices
Physician coaching comes in a variety of flavors — some one on one, and others in the form of group sessions. All, however, serve the purpose of helping physicians gain career clarity. “Sometimes clients realize their job may not be working for them, but that there are things they can do to change that without having to leave the field,” said Jattu Senesie, MD, a former ob.gyn. who is now a physician coach.
Dr. Esparaz works with doctors to establish SMART goals: specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time based. She gave the example of learning how to set boundaries. “If a physician is asked to create a presentation for work, I encourage them to ask for compensation or administrative time before committing to unpaid tasks.”
Another big issue: charting. It’s increasingly burdensome, and many doctors find it encroaching on their home lives. “If we can identify a problem like that, we can come up with a strategy for mitigating it,” Dr. Esparaz said. This might include setting a goal of getting 80% of charting completed immediately after the patient encounter on the busiest clinic day of the week. The client tests the experiment and then revisits it with the coach to discuss what worked and what didn’t, refining the process until it has freed up the physician’s home life.
The younger generation of doctors often struggles with career choices, too, because it’s the first time they are without structure, said Dr. Senesie. There’s med school and residency, which puts a framework around every move a doctor makes. But once they become attending physicians, the choices are endless. “Coaching can help them find a new structure and systems that will allow them to thrive.”
Although mentoring has been a well-embraced concept for decades, it “hits a wall,” at some point in terms of what it can offer, Dr. Austin said. That’s where coaching can take over. “There’s a point where a mentor cannot help someone self-actualize. As a coach, you don’t need to know everything about a doctor’s life, but you can help them learn to ask themselves the right questions to solve problems.”
Should You Stay or Should You Go?
Dr. Austin’s approach begins with the premise that healthcare today is challenging and dysfunctional — but doctors still have agency. She has worked with clients on the verge of leaving the field and helped them find their way back.
“They have a light bulb moment and open up to the idea that they have much to give still,” she said. “We take an inventory to help them better communicate their needs and make changes, and I help them connect to their values. Sometimes that exercise allows them to reframe their current work environment.”
Not every doctor who goes through coaching remains in the field. But “that’s the exception, not the rule,” Dr. Austin said. And that’s okay. “If that’s the outcome, coaching probably helped them get to that point faster, and with an informed decision.”
Dr. Senesie has been coaching for about a decade, and in that time, she’s seen a shift that goes beyond figuring out career goals. “Doctors are more aware of the need for well-being today. The pandemic made it impossible to ignore what doesn’t work for us. When I work with clients, we look for ways to make the job more tenable.”
According to Dr. Senesie, younger doctors are looking for that balance at the outset. “They want to be physicians, but they also want a life,” she said. “It’s a challenge for them because in addition to that mindset, they’re also coming out with more debt than older generations. They want out from underneath that.”
When It’s Time to Find a Physician Coach
Wondering whether coaching is right for you? Consider these symptoms:
- You need help setting boundaries at work.
- You feel like you’re sacrificing your own well-being for your job.
- You’re using maladaptive strategies to cope with the stress at work.
- You’ve reached a point where you are considering leaving the field.
If you’re interested in finding a physician coach, there are several places to begin your search, word of mouth being one of them. “Conferences and social media can also expose you to coaches,” suggested Dr. Esparaz. There are different methods and approaches to coaching. So, as you research, “make sure the coach you choose has techniques and a framework that fit what you’re after.”
Dr. Austin warned that it is an unregulated industry, so buyer beware. To ensure you’re getting an accredited physician coach, look for people who have obtained an International Coach Federation (ICF) accreditation. These coaches will hold an associate certified coach credential, which requires at least 60 hours of coaching-specific training approved by the ICF, in addition to other assessments and education.
Ensure that the coach you choose is within your budget. “There are some people charging astronomical rates out there,” Dr. Austin said. “If you’re burned out or struggling, it can be easy to reach for your credit card.”
Dr. Austin also cautioned doctors seeking a coach to avoid promises that sound too good to be true. Some coaching can have a gaslighting quality to it, she warned, “suggesting it can allow you to endure any environment.” But positive self-talk alone won’t cure an abusive or discriminatory situation. “If a client describes a toxic work environment,” the coach has an “ethical imperative” to help that person protect themselves.
A Side Gig or a New Career Path
After Dr. Austin’s experience with her coach, she made the choice to continue as an emergency physician part-time while starting her own coaching business. “It’s important for me personally to keep in touch with what’s happening on the ground, but I have no judgment for anyone who chooses to leave clinical practice to become a coach.”
When Dr. Senesie looks back on her own struggles as a clinician, she recognizes the state of burnout she was in 10 years ago. “I knew there was an issue, but I didn’t have the mindset to find a way to make it work,” she said. “I left the field when I was at my depths of burnout, which is generally not the best way to go about it.”
Guidance might have allowed her to take into account other avenues and helped her remain in the field, said Dr. Senesie. She has since learned that “there are many ways to practice medicine, and the way we’ve gone about it traditionally has worked for some, but not necessarily for everyone.”
There may be more possibilities than you think. By helping you assess your path and make meaningful changes, a physician coach might be the key to remaining in the field you love.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Andrea Austin, MD, an emergency medicine specialist, left the military in 2020, she knew the adjustment to civilian life and practice might be difficult. To help smooth the transition, she reached out to a physician mentor who also had a professional coaching certificate. After a conversation, Dr. Austin signed up for 6 months of career coaching.
It was time well spent, according to Dr. Austin, who today is a coach herself. “It was really the first time I had the ability to choose what I wanted to do, and that required a mindset shift,” she explains. “A big part of coaching is helping physicians discover their agency so that they can make the best career choices.”
Physicians have long lacked the coaching resources typically made available to corporate executives. But that’s changing. In today’s high-pressure environment, where doctors are burning out at a rapid pace, coaching can sometimes be an avenue to staying in the field, especially if that coach is a fellow physician who understands what you’re facing.
With a physician shortage that the Association of American Medical Colleges expects to hit 86,000 in the next decade or so, coaching could be a stone worth turning over. A 2024 report in JAMA Network Open found that coaching provided by physician peers led to a significant reduction in interpersonal disengagement and burnout.
“What I think is exciting about coaching is that it allows you to better understand yourself and know your strengths and weaknesses,” said Dr. Austin. “It might seem simple, but many ‘soft skills’ aren’t considered mainstream in medicine. Coaching allows us to understand them and ourselves better.”
Why Are Doctors Using Coaches?
Although it’s hard to put a number on how many physicians are turning to coaches, the number of coaches available for doctors is growing rapidly. The American Medical Women’s Association maintains a database of physician coaches. According to deputy director Jodi Godfrey, MS, RDN, the number of members who have added coaching to their skill set has tripled in the past 4 years. “Many cite burnout as the reason they sought coaching support, and then they decided to go on to get certified in coaching.”
The pandemic is one reason physician coaching has grown, said Elizabeth Esparaz, MD, an ophthalmologist and physician coach. “Since the pandemic, the word ‘burnout’ is thrown around a good deal.” And the causes are clear. “Doctors are facing longer hours, they must make split-second decisions, they’re multitasking, and they have less support staff.”
Among her coaching clients, Dr. Austin has noticed other common struggles: fears of litigation, time scarcity with patients, declining reimbursement that hasn’t kept up with inflation, and loss of autonomy because of the corporatization of healthcare.
Coaching, Dr. Esparaz believes, can be an antidote to many of these issues. “Coaches help doctors see their strengths and find better ways of applying them,” she said. “We help them move forward, and also see their blind spots.”
Clarity, Goals, and Making the Right Choices
Physician coaching comes in a variety of flavors — some one on one, and others in the form of group sessions. All, however, serve the purpose of helping physicians gain career clarity. “Sometimes clients realize their job may not be working for them, but that there are things they can do to change that without having to leave the field,” said Jattu Senesie, MD, a former ob.gyn. who is now a physician coach.
Dr. Esparaz works with doctors to establish SMART goals: specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time based. She gave the example of learning how to set boundaries. “If a physician is asked to create a presentation for work, I encourage them to ask for compensation or administrative time before committing to unpaid tasks.”
Another big issue: charting. It’s increasingly burdensome, and many doctors find it encroaching on their home lives. “If we can identify a problem like that, we can come up with a strategy for mitigating it,” Dr. Esparaz said. This might include setting a goal of getting 80% of charting completed immediately after the patient encounter on the busiest clinic day of the week. The client tests the experiment and then revisits it with the coach to discuss what worked and what didn’t, refining the process until it has freed up the physician’s home life.
The younger generation of doctors often struggles with career choices, too, because it’s the first time they are without structure, said Dr. Senesie. There’s med school and residency, which puts a framework around every move a doctor makes. But once they become attending physicians, the choices are endless. “Coaching can help them find a new structure and systems that will allow them to thrive.”
Although mentoring has been a well-embraced concept for decades, it “hits a wall,” at some point in terms of what it can offer, Dr. Austin said. That’s where coaching can take over. “There’s a point where a mentor cannot help someone self-actualize. As a coach, you don’t need to know everything about a doctor’s life, but you can help them learn to ask themselves the right questions to solve problems.”
Should You Stay or Should You Go?
Dr. Austin’s approach begins with the premise that healthcare today is challenging and dysfunctional — but doctors still have agency. She has worked with clients on the verge of leaving the field and helped them find their way back.
“They have a light bulb moment and open up to the idea that they have much to give still,” she said. “We take an inventory to help them better communicate their needs and make changes, and I help them connect to their values. Sometimes that exercise allows them to reframe their current work environment.”
Not every doctor who goes through coaching remains in the field. But “that’s the exception, not the rule,” Dr. Austin said. And that’s okay. “If that’s the outcome, coaching probably helped them get to that point faster, and with an informed decision.”
Dr. Senesie has been coaching for about a decade, and in that time, she’s seen a shift that goes beyond figuring out career goals. “Doctors are more aware of the need for well-being today. The pandemic made it impossible to ignore what doesn’t work for us. When I work with clients, we look for ways to make the job more tenable.”
According to Dr. Senesie, younger doctors are looking for that balance at the outset. “They want to be physicians, but they also want a life,” she said. “It’s a challenge for them because in addition to that mindset, they’re also coming out with more debt than older generations. They want out from underneath that.”
When It’s Time to Find a Physician Coach
Wondering whether coaching is right for you? Consider these symptoms:
- You need help setting boundaries at work.
- You feel like you’re sacrificing your own well-being for your job.
- You’re using maladaptive strategies to cope with the stress at work.
- You’ve reached a point where you are considering leaving the field.
If you’re interested in finding a physician coach, there are several places to begin your search, word of mouth being one of them. “Conferences and social media can also expose you to coaches,” suggested Dr. Esparaz. There are different methods and approaches to coaching. So, as you research, “make sure the coach you choose has techniques and a framework that fit what you’re after.”
Dr. Austin warned that it is an unregulated industry, so buyer beware. To ensure you’re getting an accredited physician coach, look for people who have obtained an International Coach Federation (ICF) accreditation. These coaches will hold an associate certified coach credential, which requires at least 60 hours of coaching-specific training approved by the ICF, in addition to other assessments and education.
Ensure that the coach you choose is within your budget. “There are some people charging astronomical rates out there,” Dr. Austin said. “If you’re burned out or struggling, it can be easy to reach for your credit card.”
Dr. Austin also cautioned doctors seeking a coach to avoid promises that sound too good to be true. Some coaching can have a gaslighting quality to it, she warned, “suggesting it can allow you to endure any environment.” But positive self-talk alone won’t cure an abusive or discriminatory situation. “If a client describes a toxic work environment,” the coach has an “ethical imperative” to help that person protect themselves.
A Side Gig or a New Career Path
After Dr. Austin’s experience with her coach, she made the choice to continue as an emergency physician part-time while starting her own coaching business. “It’s important for me personally to keep in touch with what’s happening on the ground, but I have no judgment for anyone who chooses to leave clinical practice to become a coach.”
When Dr. Senesie looks back on her own struggles as a clinician, she recognizes the state of burnout she was in 10 years ago. “I knew there was an issue, but I didn’t have the mindset to find a way to make it work,” she said. “I left the field when I was at my depths of burnout, which is generally not the best way to go about it.”
Guidance might have allowed her to take into account other avenues and helped her remain in the field, said Dr. Senesie. She has since learned that “there are many ways to practice medicine, and the way we’ve gone about it traditionally has worked for some, but not necessarily for everyone.”
There may be more possibilities than you think. By helping you assess your path and make meaningful changes, a physician coach might be the key to remaining in the field you love.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Andrea Austin, MD, an emergency medicine specialist, left the military in 2020, she knew the adjustment to civilian life and practice might be difficult. To help smooth the transition, she reached out to a physician mentor who also had a professional coaching certificate. After a conversation, Dr. Austin signed up for 6 months of career coaching.
It was time well spent, according to Dr. Austin, who today is a coach herself. “It was really the first time I had the ability to choose what I wanted to do, and that required a mindset shift,” she explains. “A big part of coaching is helping physicians discover their agency so that they can make the best career choices.”
Physicians have long lacked the coaching resources typically made available to corporate executives. But that’s changing. In today’s high-pressure environment, where doctors are burning out at a rapid pace, coaching can sometimes be an avenue to staying in the field, especially if that coach is a fellow physician who understands what you’re facing.
With a physician shortage that the Association of American Medical Colleges expects to hit 86,000 in the next decade or so, coaching could be a stone worth turning over. A 2024 report in JAMA Network Open found that coaching provided by physician peers led to a significant reduction in interpersonal disengagement and burnout.
“What I think is exciting about coaching is that it allows you to better understand yourself and know your strengths and weaknesses,” said Dr. Austin. “It might seem simple, but many ‘soft skills’ aren’t considered mainstream in medicine. Coaching allows us to understand them and ourselves better.”
Why Are Doctors Using Coaches?
Although it’s hard to put a number on how many physicians are turning to coaches, the number of coaches available for doctors is growing rapidly. The American Medical Women’s Association maintains a database of physician coaches. According to deputy director Jodi Godfrey, MS, RDN, the number of members who have added coaching to their skill set has tripled in the past 4 years. “Many cite burnout as the reason they sought coaching support, and then they decided to go on to get certified in coaching.”
The pandemic is one reason physician coaching has grown, said Elizabeth Esparaz, MD, an ophthalmologist and physician coach. “Since the pandemic, the word ‘burnout’ is thrown around a good deal.” And the causes are clear. “Doctors are facing longer hours, they must make split-second decisions, they’re multitasking, and they have less support staff.”
Among her coaching clients, Dr. Austin has noticed other common struggles: fears of litigation, time scarcity with patients, declining reimbursement that hasn’t kept up with inflation, and loss of autonomy because of the corporatization of healthcare.
Coaching, Dr. Esparaz believes, can be an antidote to many of these issues. “Coaches help doctors see their strengths and find better ways of applying them,” she said. “We help them move forward, and also see their blind spots.”
Clarity, Goals, and Making the Right Choices
Physician coaching comes in a variety of flavors — some one on one, and others in the form of group sessions. All, however, serve the purpose of helping physicians gain career clarity. “Sometimes clients realize their job may not be working for them, but that there are things they can do to change that without having to leave the field,” said Jattu Senesie, MD, a former ob.gyn. who is now a physician coach.
Dr. Esparaz works with doctors to establish SMART goals: specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time based. She gave the example of learning how to set boundaries. “If a physician is asked to create a presentation for work, I encourage them to ask for compensation or administrative time before committing to unpaid tasks.”
Another big issue: charting. It’s increasingly burdensome, and many doctors find it encroaching on their home lives. “If we can identify a problem like that, we can come up with a strategy for mitigating it,” Dr. Esparaz said. This might include setting a goal of getting 80% of charting completed immediately after the patient encounter on the busiest clinic day of the week. The client tests the experiment and then revisits it with the coach to discuss what worked and what didn’t, refining the process until it has freed up the physician’s home life.
The younger generation of doctors often struggles with career choices, too, because it’s the first time they are without structure, said Dr. Senesie. There’s med school and residency, which puts a framework around every move a doctor makes. But once they become attending physicians, the choices are endless. “Coaching can help them find a new structure and systems that will allow them to thrive.”
Although mentoring has been a well-embraced concept for decades, it “hits a wall,” at some point in terms of what it can offer, Dr. Austin said. That’s where coaching can take over. “There’s a point where a mentor cannot help someone self-actualize. As a coach, you don’t need to know everything about a doctor’s life, but you can help them learn to ask themselves the right questions to solve problems.”
Should You Stay or Should You Go?
Dr. Austin’s approach begins with the premise that healthcare today is challenging and dysfunctional — but doctors still have agency. She has worked with clients on the verge of leaving the field and helped them find their way back.
“They have a light bulb moment and open up to the idea that they have much to give still,” she said. “We take an inventory to help them better communicate their needs and make changes, and I help them connect to their values. Sometimes that exercise allows them to reframe their current work environment.”
Not every doctor who goes through coaching remains in the field. But “that’s the exception, not the rule,” Dr. Austin said. And that’s okay. “If that’s the outcome, coaching probably helped them get to that point faster, and with an informed decision.”
Dr. Senesie has been coaching for about a decade, and in that time, she’s seen a shift that goes beyond figuring out career goals. “Doctors are more aware of the need for well-being today. The pandemic made it impossible to ignore what doesn’t work for us. When I work with clients, we look for ways to make the job more tenable.”
According to Dr. Senesie, younger doctors are looking for that balance at the outset. “They want to be physicians, but they also want a life,” she said. “It’s a challenge for them because in addition to that mindset, they’re also coming out with more debt than older generations. They want out from underneath that.”
When It’s Time to Find a Physician Coach
Wondering whether coaching is right for you? Consider these symptoms:
- You need help setting boundaries at work.
- You feel like you’re sacrificing your own well-being for your job.
- You’re using maladaptive strategies to cope with the stress at work.
- You’ve reached a point where you are considering leaving the field.
If you’re interested in finding a physician coach, there are several places to begin your search, word of mouth being one of them. “Conferences and social media can also expose you to coaches,” suggested Dr. Esparaz. There are different methods and approaches to coaching. So, as you research, “make sure the coach you choose has techniques and a framework that fit what you’re after.”
Dr. Austin warned that it is an unregulated industry, so buyer beware. To ensure you’re getting an accredited physician coach, look for people who have obtained an International Coach Federation (ICF) accreditation. These coaches will hold an associate certified coach credential, which requires at least 60 hours of coaching-specific training approved by the ICF, in addition to other assessments and education.
Ensure that the coach you choose is within your budget. “There are some people charging astronomical rates out there,” Dr. Austin said. “If you’re burned out or struggling, it can be easy to reach for your credit card.”
Dr. Austin also cautioned doctors seeking a coach to avoid promises that sound too good to be true. Some coaching can have a gaslighting quality to it, she warned, “suggesting it can allow you to endure any environment.” But positive self-talk alone won’t cure an abusive or discriminatory situation. “If a client describes a toxic work environment,” the coach has an “ethical imperative” to help that person protect themselves.
A Side Gig or a New Career Path
After Dr. Austin’s experience with her coach, she made the choice to continue as an emergency physician part-time while starting her own coaching business. “It’s important for me personally to keep in touch with what’s happening on the ground, but I have no judgment for anyone who chooses to leave clinical practice to become a coach.”
When Dr. Senesie looks back on her own struggles as a clinician, she recognizes the state of burnout she was in 10 years ago. “I knew there was an issue, but I didn’t have the mindset to find a way to make it work,” she said. “I left the field when I was at my depths of burnout, which is generally not the best way to go about it.”
Guidance might have allowed her to take into account other avenues and helped her remain in the field, said Dr. Senesie. She has since learned that “there are many ways to practice medicine, and the way we’ve gone about it traditionally has worked for some, but not necessarily for everyone.”
There may be more possibilities than you think. By helping you assess your path and make meaningful changes, a physician coach might be the key to remaining in the field you love.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FTC Interim Report on Pharmacy Middlemen Is First Step of Many Needed in Addressing Drug Costs, Access
Rising consolidation among pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) allows the companies to profit at the expense of patients and independent pharmacists. That’s the conclusion of a recent Federal Trade Commission (FTC) report on interim findings from the agency’s ongoing investigation of PBMs.
Lawmakers are increasingly scrutinizing the industry amid growing concern among physicians and consumers about how PBMs exploit their market dominance. The top six PBMs managed 94% of US drug claims in 2023, with the majority handled by the industry’s three giants: CVS Caremark, Cigna’s Express Scripts, and United Healthcare’s OptumRx.
PBMs manage prescription drug benefits for health insurers, Medicare Part D drug plans, and large employers. They act as middlemen between health insurers and pharmacies, developing formularies of covered drugs and promising savings from the discounts and rebates they negotiate with drugmakers.
The FTC’s interim report found that the giant PBMs often exercise significant control over what drugs are available and at what price and which pharmacies patients can use to access their prescribed medications. Consumers suffer as a result, the report concluded.
Madelaine A. Feldman, MD, vice president for advocacy and government affairs for the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations, shared her perspective on the FTC report in an email Q&A with this news organization. She is affiliated with The Rheumatology Group, based in Metairie, Louisiana.
Dr. Feldman has long tracked the PBM industry and appeared as a witness before influential government panels, including the House Energy and Commerce Committee. She has highlighted for lawmakers the challenges physicians face in helping patients get needed medicines.
For example, she shared cases of PBMs steering patients toward the more expensive of three widely used rheumatoid arthritis medicines that have a similar mechanism of action, the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, Dr. Feldman said.
One of the drugs cost roughly half of the other two — about $30,000 per year vs $65,000-$70,000. Yet only the two expensive drugs were included in the PBM formulary. As a result, the cheapest drug holds only a sliver of market share; the remainder is dominated by the two expensive products, she told the House Oversight and Accountability Committee in 2021.
This Q&A has been edited for length and clarity.
What would you want federal and state policymakers to do in response to the FTC’s report?
I think Congress needs to clearly delineate the differences between anticompetitive pharmacy issues, drug pricing issues, and their effect on formulary construction issues.
Lawmakers should demand more transparency and consider legislation that would remove perverse incentives that prompt PBMs to choose higher priced drugs for their formularies.
That may require other regulatory or legislative actions to ensure lower prices (not higher kickbacks) are incentivized. Ultimately, in order to gain true competition within the health insurance business, these oligopolies of multiple businesses need to be broken up. Anything less seems to be nibbling around the edges and allows the Big Three to continue their “whack-a mole” in circumventing piecemeal regulatory and legislative policies.
You’ve followed PBM practices closely for many years. Was there anything in this interim FTC report that surprised you?
Though not surprised, I am glad that it was released because it had been a year in investigation and there were many requests for some type of substantive report.
Two things that are missing that I feel are paramount are investigating how the three big PBMs are causing physical harm to patients as a result of the profit component in formulary construction and the profound financial impact of hidden PBM profit centers in self-insured employer health plans.
What we have seen over the years is the result of the perverse incentives for the PBMs to prefer the most profitable medications on their formularies.
They use utilization management tools such as step therapy, nonmedical switching, and exclusions to maintain their formularies’ profitability. These tools have been shown to delay and deny the proper care of patients, resulting in not just monetary but physical harm as well.
I would think the physical harm done to patients in manipulating the formularies should be addressed in this report as well and, in fact, may be the most important aspect of consumer protection of this issue.
In terms of the FTC’s mission to not “unduly burden” legitimate business, I would like to see the sector of self-insured employers addressed.
The report details how PBMs steer prescriptions to their affiliated pharmacies. The FTC says that can push smaller pharmacies out of the market, ultimately leading to higher costs and lower quality services for people. What’s your perspective?
Having more community pharmacies is better than having less. We are seeing more “pharmacy deserts” in rural areas as a result of many community pharmacies having to close.
The FTC voted 4-1 to allow staff to issue the interim report, with Commissioner Melissa Holyoak voting no. And some FTC commissioners seem divided on the usefulness of the report. Why?
Commissioner Holyoak states the “the Report leaves us without a better understanding of the competition concerns surrounding PBMs or how consumers are impacted by PBM practices.”
I do agree with her that the harm to patients’ medical status was not even addressed as far as I could tell in this report. There are multiple news articles and reports on the harms inflicted upon patients by the UM tools that drive the construction of ever changing formularies, all based on contracting with manufacturers that result in the highest profit for the PBM.
Holyoak also states, “Among other critical conclusions, the Report does not address the seemingly contradictory conclusions in the 2005 Report that PBMs, including vertically owned PBMs, generated cost savings for consumers.”
That may be true, but in 2005, the rise of PBMs was just beginning and the huge vertical and horizontal integration had yet to begin. Also, 2005 was still in the beginning of the biologic drug deluge, which did create competition to get on the formulary. Since then, PBMs have done nothing to control the rise in prices but instead, apparently have used the competition to get higher price concessions from manufacturers based on a percentage of the list price to line their pockets.
Commissioner Ferguson agreed with releasing the report but he had many issues with this report including the lack of PBM response.
I do agree with him that the FTC should have used some type of “force” to get the information they needed from the PBMs. The Big Three are known for obfuscation and delaying providing information to legislative and regulatory agencies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Rising consolidation among pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) allows the companies to profit at the expense of patients and independent pharmacists. That’s the conclusion of a recent Federal Trade Commission (FTC) report on interim findings from the agency’s ongoing investigation of PBMs.
Lawmakers are increasingly scrutinizing the industry amid growing concern among physicians and consumers about how PBMs exploit their market dominance. The top six PBMs managed 94% of US drug claims in 2023, with the majority handled by the industry’s three giants: CVS Caremark, Cigna’s Express Scripts, and United Healthcare’s OptumRx.
PBMs manage prescription drug benefits for health insurers, Medicare Part D drug plans, and large employers. They act as middlemen between health insurers and pharmacies, developing formularies of covered drugs and promising savings from the discounts and rebates they negotiate with drugmakers.
The FTC’s interim report found that the giant PBMs often exercise significant control over what drugs are available and at what price and which pharmacies patients can use to access their prescribed medications. Consumers suffer as a result, the report concluded.
Madelaine A. Feldman, MD, vice president for advocacy and government affairs for the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations, shared her perspective on the FTC report in an email Q&A with this news organization. She is affiliated with The Rheumatology Group, based in Metairie, Louisiana.
Dr. Feldman has long tracked the PBM industry and appeared as a witness before influential government panels, including the House Energy and Commerce Committee. She has highlighted for lawmakers the challenges physicians face in helping patients get needed medicines.
For example, she shared cases of PBMs steering patients toward the more expensive of three widely used rheumatoid arthritis medicines that have a similar mechanism of action, the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, Dr. Feldman said.
One of the drugs cost roughly half of the other two — about $30,000 per year vs $65,000-$70,000. Yet only the two expensive drugs were included in the PBM formulary. As a result, the cheapest drug holds only a sliver of market share; the remainder is dominated by the two expensive products, she told the House Oversight and Accountability Committee in 2021.
This Q&A has been edited for length and clarity.
What would you want federal and state policymakers to do in response to the FTC’s report?
I think Congress needs to clearly delineate the differences between anticompetitive pharmacy issues, drug pricing issues, and their effect on formulary construction issues.
Lawmakers should demand more transparency and consider legislation that would remove perverse incentives that prompt PBMs to choose higher priced drugs for their formularies.
That may require other regulatory or legislative actions to ensure lower prices (not higher kickbacks) are incentivized. Ultimately, in order to gain true competition within the health insurance business, these oligopolies of multiple businesses need to be broken up. Anything less seems to be nibbling around the edges and allows the Big Three to continue their “whack-a mole” in circumventing piecemeal regulatory and legislative policies.
You’ve followed PBM practices closely for many years. Was there anything in this interim FTC report that surprised you?
Though not surprised, I am glad that it was released because it had been a year in investigation and there were many requests for some type of substantive report.
Two things that are missing that I feel are paramount are investigating how the three big PBMs are causing physical harm to patients as a result of the profit component in formulary construction and the profound financial impact of hidden PBM profit centers in self-insured employer health plans.
What we have seen over the years is the result of the perverse incentives for the PBMs to prefer the most profitable medications on their formularies.
They use utilization management tools such as step therapy, nonmedical switching, and exclusions to maintain their formularies’ profitability. These tools have been shown to delay and deny the proper care of patients, resulting in not just monetary but physical harm as well.
I would think the physical harm done to patients in manipulating the formularies should be addressed in this report as well and, in fact, may be the most important aspect of consumer protection of this issue.
In terms of the FTC’s mission to not “unduly burden” legitimate business, I would like to see the sector of self-insured employers addressed.
The report details how PBMs steer prescriptions to their affiliated pharmacies. The FTC says that can push smaller pharmacies out of the market, ultimately leading to higher costs and lower quality services for people. What’s your perspective?
Having more community pharmacies is better than having less. We are seeing more “pharmacy deserts” in rural areas as a result of many community pharmacies having to close.
The FTC voted 4-1 to allow staff to issue the interim report, with Commissioner Melissa Holyoak voting no. And some FTC commissioners seem divided on the usefulness of the report. Why?
Commissioner Holyoak states the “the Report leaves us without a better understanding of the competition concerns surrounding PBMs or how consumers are impacted by PBM practices.”
I do agree with her that the harm to patients’ medical status was not even addressed as far as I could tell in this report. There are multiple news articles and reports on the harms inflicted upon patients by the UM tools that drive the construction of ever changing formularies, all based on contracting with manufacturers that result in the highest profit for the PBM.
Holyoak also states, “Among other critical conclusions, the Report does not address the seemingly contradictory conclusions in the 2005 Report that PBMs, including vertically owned PBMs, generated cost savings for consumers.”
That may be true, but in 2005, the rise of PBMs was just beginning and the huge vertical and horizontal integration had yet to begin. Also, 2005 was still in the beginning of the biologic drug deluge, which did create competition to get on the formulary. Since then, PBMs have done nothing to control the rise in prices but instead, apparently have used the competition to get higher price concessions from manufacturers based on a percentage of the list price to line their pockets.
Commissioner Ferguson agreed with releasing the report but he had many issues with this report including the lack of PBM response.
I do agree with him that the FTC should have used some type of “force” to get the information they needed from the PBMs. The Big Three are known for obfuscation and delaying providing information to legislative and regulatory agencies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Rising consolidation among pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) allows the companies to profit at the expense of patients and independent pharmacists. That’s the conclusion of a recent Federal Trade Commission (FTC) report on interim findings from the agency’s ongoing investigation of PBMs.
Lawmakers are increasingly scrutinizing the industry amid growing concern among physicians and consumers about how PBMs exploit their market dominance. The top six PBMs managed 94% of US drug claims in 2023, with the majority handled by the industry’s three giants: CVS Caremark, Cigna’s Express Scripts, and United Healthcare’s OptumRx.
PBMs manage prescription drug benefits for health insurers, Medicare Part D drug plans, and large employers. They act as middlemen between health insurers and pharmacies, developing formularies of covered drugs and promising savings from the discounts and rebates they negotiate with drugmakers.
The FTC’s interim report found that the giant PBMs often exercise significant control over what drugs are available and at what price and which pharmacies patients can use to access their prescribed medications. Consumers suffer as a result, the report concluded.
Madelaine A. Feldman, MD, vice president for advocacy and government affairs for the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations, shared her perspective on the FTC report in an email Q&A with this news organization. She is affiliated with The Rheumatology Group, based in Metairie, Louisiana.
Dr. Feldman has long tracked the PBM industry and appeared as a witness before influential government panels, including the House Energy and Commerce Committee. She has highlighted for lawmakers the challenges physicians face in helping patients get needed medicines.
For example, she shared cases of PBMs steering patients toward the more expensive of three widely used rheumatoid arthritis medicines that have a similar mechanism of action, the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, Dr. Feldman said.
One of the drugs cost roughly half of the other two — about $30,000 per year vs $65,000-$70,000. Yet only the two expensive drugs were included in the PBM formulary. As a result, the cheapest drug holds only a sliver of market share; the remainder is dominated by the two expensive products, she told the House Oversight and Accountability Committee in 2021.
This Q&A has been edited for length and clarity.
What would you want federal and state policymakers to do in response to the FTC’s report?
I think Congress needs to clearly delineate the differences between anticompetitive pharmacy issues, drug pricing issues, and their effect on formulary construction issues.
Lawmakers should demand more transparency and consider legislation that would remove perverse incentives that prompt PBMs to choose higher priced drugs for their formularies.
That may require other regulatory or legislative actions to ensure lower prices (not higher kickbacks) are incentivized. Ultimately, in order to gain true competition within the health insurance business, these oligopolies of multiple businesses need to be broken up. Anything less seems to be nibbling around the edges and allows the Big Three to continue their “whack-a mole” in circumventing piecemeal regulatory and legislative policies.
You’ve followed PBM practices closely for many years. Was there anything in this interim FTC report that surprised you?
Though not surprised, I am glad that it was released because it had been a year in investigation and there were many requests for some type of substantive report.
Two things that are missing that I feel are paramount are investigating how the three big PBMs are causing physical harm to patients as a result of the profit component in formulary construction and the profound financial impact of hidden PBM profit centers in self-insured employer health plans.
What we have seen over the years is the result of the perverse incentives for the PBMs to prefer the most profitable medications on their formularies.
They use utilization management tools such as step therapy, nonmedical switching, and exclusions to maintain their formularies’ profitability. These tools have been shown to delay and deny the proper care of patients, resulting in not just monetary but physical harm as well.
I would think the physical harm done to patients in manipulating the formularies should be addressed in this report as well and, in fact, may be the most important aspect of consumer protection of this issue.
In terms of the FTC’s mission to not “unduly burden” legitimate business, I would like to see the sector of self-insured employers addressed.
The report details how PBMs steer prescriptions to their affiliated pharmacies. The FTC says that can push smaller pharmacies out of the market, ultimately leading to higher costs and lower quality services for people. What’s your perspective?
Having more community pharmacies is better than having less. We are seeing more “pharmacy deserts” in rural areas as a result of many community pharmacies having to close.
The FTC voted 4-1 to allow staff to issue the interim report, with Commissioner Melissa Holyoak voting no. And some FTC commissioners seem divided on the usefulness of the report. Why?
Commissioner Holyoak states the “the Report leaves us without a better understanding of the competition concerns surrounding PBMs or how consumers are impacted by PBM practices.”
I do agree with her that the harm to patients’ medical status was not even addressed as far as I could tell in this report. There are multiple news articles and reports on the harms inflicted upon patients by the UM tools that drive the construction of ever changing formularies, all based on contracting with manufacturers that result in the highest profit for the PBM.
Holyoak also states, “Among other critical conclusions, the Report does not address the seemingly contradictory conclusions in the 2005 Report that PBMs, including vertically owned PBMs, generated cost savings for consumers.”
That may be true, but in 2005, the rise of PBMs was just beginning and the huge vertical and horizontal integration had yet to begin. Also, 2005 was still in the beginning of the biologic drug deluge, which did create competition to get on the formulary. Since then, PBMs have done nothing to control the rise in prices but instead, apparently have used the competition to get higher price concessions from manufacturers based on a percentage of the list price to line their pockets.
Commissioner Ferguson agreed with releasing the report but he had many issues with this report including the lack of PBM response.
I do agree with him that the FTC should have used some type of “force” to get the information they needed from the PBMs. The Big Three are known for obfuscation and delaying providing information to legislative and regulatory agencies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Approves Axatilimab for Chronic GVHD
Chronic GVHD is a potentially life-threatening complication of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation that develops in about 50% of transplant recipients.
The first-in-class treatment for chronic GVHD is a monoclonal antibody that targets the colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1) receptor. Approval for axatilimab followed priority review of Incyte’s Biologic License Application and was based on findings from the open-label phase 2 AGAVE-201 trial.
Study participants had chronic GVHD after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and had failed to respond to at least two prior lines of systemic therapy (median, four lines of therapy). Prior therapies included ruxolitinib, belumosudil, and ibrutinib in 74%, 23%, and 31% of patients, respectively. Overall, 239 patients were enrolled at 121 study sites and were randomly assigned 1:1:1 to three doses.
The FDA recommended dose of axatilimab is 0.3 mg/kg (to a maximum of 35 mg) as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes every 2 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Other doses tested in the AGAVE-201 trial were 1 mg/kg every 2 weeks and 3 mg/kg every 4 weeks.
The trial measured overall response rate over the first six cycles (24 weeks). In the 79 patients who received the recommended 0.3-mg/kg dose, the overall response rate was 75%, and the median time to first response was 1.5 months (range, 0.9-5.1). The median duration of response — measured from first response to progression, death, or switch to a new systemic therapy for chronic GVHD — was 1.9 months.
In those who responded to the therapy, there were no deaths or new therapies required in 60% of patients.
The most common adverse reactions, occurring in 15% or more patients, included increased aspartate aminotransferase, infection (pathogen unspecified), increased alanine aminotransferase, decreased phosphate, decreased hemoglobin, musculoskeletal pain, increased lipase, fatigue, increased amylase, increased calcium, increased creatine phosphokinase, nausea, headache, diarrhea, cough, pyrexia, and dyspnea.
In the AGAVE-201 trial results, researchers noted that drug discontinuation from treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 6% of patients in the 0.3-mg/kg cohort, in 22% in the 1-mg/kg cohort, and in 18% in the 3-mg/kg cohort. Fatal treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 1.3% of patients in the 0.3-mg/kg cohort.
“Advanced chronic GVHD is characterized by the development of fibrotic tissue across multiple organ systems, including most commonly the skin and mucosa, and can be extremely difficult to treat, leading to high rates of morbidity and mortality,” lead study author Daniel Wolff, MD, PhD, head of the GVHD Center at the University Hospital Regensburg, Germany, said in a company press release. “I am excited that Niktimvo is designed to specifically target key drivers of inflammation and fibrosis in chronic GVHD, and I am highly encouraged by the robust responses observed across all organs and patient subgroups within the heavily pretreated population enrolled in the AGAVE-201 trial. I look forward to having a new and differentiated treatment option for my patients who need additional therapies to address this very difficult to manage, debilitating, disease.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic GVHD is a potentially life-threatening complication of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation that develops in about 50% of transplant recipients.
The first-in-class treatment for chronic GVHD is a monoclonal antibody that targets the colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1) receptor. Approval for axatilimab followed priority review of Incyte’s Biologic License Application and was based on findings from the open-label phase 2 AGAVE-201 trial.
Study participants had chronic GVHD after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and had failed to respond to at least two prior lines of systemic therapy (median, four lines of therapy). Prior therapies included ruxolitinib, belumosudil, and ibrutinib in 74%, 23%, and 31% of patients, respectively. Overall, 239 patients were enrolled at 121 study sites and were randomly assigned 1:1:1 to three doses.
The FDA recommended dose of axatilimab is 0.3 mg/kg (to a maximum of 35 mg) as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes every 2 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Other doses tested in the AGAVE-201 trial were 1 mg/kg every 2 weeks and 3 mg/kg every 4 weeks.
The trial measured overall response rate over the first six cycles (24 weeks). In the 79 patients who received the recommended 0.3-mg/kg dose, the overall response rate was 75%, and the median time to first response was 1.5 months (range, 0.9-5.1). The median duration of response — measured from first response to progression, death, or switch to a new systemic therapy for chronic GVHD — was 1.9 months.
In those who responded to the therapy, there were no deaths or new therapies required in 60% of patients.
The most common adverse reactions, occurring in 15% or more patients, included increased aspartate aminotransferase, infection (pathogen unspecified), increased alanine aminotransferase, decreased phosphate, decreased hemoglobin, musculoskeletal pain, increased lipase, fatigue, increased amylase, increased calcium, increased creatine phosphokinase, nausea, headache, diarrhea, cough, pyrexia, and dyspnea.
In the AGAVE-201 trial results, researchers noted that drug discontinuation from treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 6% of patients in the 0.3-mg/kg cohort, in 22% in the 1-mg/kg cohort, and in 18% in the 3-mg/kg cohort. Fatal treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 1.3% of patients in the 0.3-mg/kg cohort.
“Advanced chronic GVHD is characterized by the development of fibrotic tissue across multiple organ systems, including most commonly the skin and mucosa, and can be extremely difficult to treat, leading to high rates of morbidity and mortality,” lead study author Daniel Wolff, MD, PhD, head of the GVHD Center at the University Hospital Regensburg, Germany, said in a company press release. “I am excited that Niktimvo is designed to specifically target key drivers of inflammation and fibrosis in chronic GVHD, and I am highly encouraged by the robust responses observed across all organs and patient subgroups within the heavily pretreated population enrolled in the AGAVE-201 trial. I look forward to having a new and differentiated treatment option for my patients who need additional therapies to address this very difficult to manage, debilitating, disease.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic GVHD is a potentially life-threatening complication of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation that develops in about 50% of transplant recipients.
The first-in-class treatment for chronic GVHD is a monoclonal antibody that targets the colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1) receptor. Approval for axatilimab followed priority review of Incyte’s Biologic License Application and was based on findings from the open-label phase 2 AGAVE-201 trial.
Study participants had chronic GVHD after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and had failed to respond to at least two prior lines of systemic therapy (median, four lines of therapy). Prior therapies included ruxolitinib, belumosudil, and ibrutinib in 74%, 23%, and 31% of patients, respectively. Overall, 239 patients were enrolled at 121 study sites and were randomly assigned 1:1:1 to three doses.
The FDA recommended dose of axatilimab is 0.3 mg/kg (to a maximum of 35 mg) as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes every 2 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Other doses tested in the AGAVE-201 trial were 1 mg/kg every 2 weeks and 3 mg/kg every 4 weeks.
The trial measured overall response rate over the first six cycles (24 weeks). In the 79 patients who received the recommended 0.3-mg/kg dose, the overall response rate was 75%, and the median time to first response was 1.5 months (range, 0.9-5.1). The median duration of response — measured from first response to progression, death, or switch to a new systemic therapy for chronic GVHD — was 1.9 months.
In those who responded to the therapy, there were no deaths or new therapies required in 60% of patients.
The most common adverse reactions, occurring in 15% or more patients, included increased aspartate aminotransferase, infection (pathogen unspecified), increased alanine aminotransferase, decreased phosphate, decreased hemoglobin, musculoskeletal pain, increased lipase, fatigue, increased amylase, increased calcium, increased creatine phosphokinase, nausea, headache, diarrhea, cough, pyrexia, and dyspnea.
In the AGAVE-201 trial results, researchers noted that drug discontinuation from treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 6% of patients in the 0.3-mg/kg cohort, in 22% in the 1-mg/kg cohort, and in 18% in the 3-mg/kg cohort. Fatal treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 1.3% of patients in the 0.3-mg/kg cohort.
“Advanced chronic GVHD is characterized by the development of fibrotic tissue across multiple organ systems, including most commonly the skin and mucosa, and can be extremely difficult to treat, leading to high rates of morbidity and mortality,” lead study author Daniel Wolff, MD, PhD, head of the GVHD Center at the University Hospital Regensburg, Germany, said in a company press release. “I am excited that Niktimvo is designed to specifically target key drivers of inflammation and fibrosis in chronic GVHD, and I am highly encouraged by the robust responses observed across all organs and patient subgroups within the heavily pretreated population enrolled in the AGAVE-201 trial. I look forward to having a new and differentiated treatment option for my patients who need additional therapies to address this very difficult to manage, debilitating, disease.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.