User login
The case for molecular classification of vascular anomalies presented
according to Beth Drolet, MD.
“We now know that 75%-80% of vascular malformations have gene mutations that make the cells either live longer, grow faster, or make them bigger in size,” Dr. Drolet, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said during the Society for Pediatric Dermatology pre-AAD meeting. “The basic binary premise of the current ISSVA [International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies] classification dividing vascular anomalies into tumors and malformations is wrong; the biology is not that straightforward. It may be helpful to differentiate between an infantile hemangioma and a capillary malformation during infancy as the hemangioma will grow in the next month, but we now know that patients with capillary malformations also have significant overgrowth of their tissue. We’ve all seen that; it just takes years, not months for us to notice it.”
The change in thinking about the root causes of vascular anomalies, she noted, stems from scientific advances in the understanding of embryonic mosaicism, DNA variation that happens after the zygote is formed, but before birth. “We know that each cell in a zygote will undergo 40 cell divisions before a baby is born,” she said. “Those cell divisions are not as neat as we thought they were. That cell and DNA duplication is actually quite messy, so there are mutations that happen purely because of embryonic cell division.”
Everyone is born with 120 somatic mutations per cell, she continued, “so we have multiple genomes in one human. Not all of those mutations are going to cause disease. Not all of those are going to be functional. About 10% of those mutations will actually be in a coding region of the gene and have the potential to change the function of the protein. If it changes the function of the protein so that the cell can’t survive, that cell dies off, but it gives the cell an advantage. It grows a little bit faster, let’s say. That cell survives, divides, producing a line of cells that can cause disease.”
In 2011, Dr. Drolet and colleagues from the Hemangioma Investigator Group and the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA) launched a multisite collaborative group to investigate the role of mosaic genetics in patients with vascular anomalies and discrepancy of growth. To date, 365 patients are enrolled, and the researchers have sequenced 97 of 165 affected tissue samples collected. “What’s nice about the registry is that we enrolled a wide spectrum of diseases: very mild diseases that might be treated by dermatologists to complex, syndromic diseases that might end up in an interdisciplinary vascular anomalies clinic,” she said.
For gene sequencing, the researchers drew from solid tumor biology and used next-generation sequencing with semi-target hybrid capture, “so we’re only looking at a subset of genes,” she said. “Right now, the chip we’re using has 180 cancer-related genes. It sequences the entire exome of the gene with a high depth of coverage, usually over 1,000 X. We use a specific pipeline that can detect very low allele frequency mutation: down to 1%, and robust criteria to determine variant pathogenicity.”
In 75% of tissue samples so far, the researchers have found a gene mutation in one of 13 genes: AKT1, AKT3, BRAF, GNA11, GNAQ, KRAS, MAP2K1, NRAS, PIK3CA, PIK3R1, PTPN11, RASA1, and TEK. According to Dr. Drolet, the common thread in these 13 genes is that they are implicated in cancer and have direct control over the cell cycle. “They’re intracellular proteins that control the cell cycle,” she explained. “These are proteins that are in the cell but interact with transmembrane proteins that receive extracellular messengers of cell growth”.
Understanding and recognizing genetic conditions is complicated, she said, because it involves determining which gene is altered, where in the DNA the gene is altered, how the gene variation will influence the function of the protein, and what tissue expresses that gene. “Then you get your phenotype,” Dr. Drolet said. “If you add mosaicism onto that, you have several additional variables. You need to know: When in embryogenesis did the mutation occur? What region of the body is affected? What cell lineage is affected? That predicts what phenotype you’re going to have.”
While molecular classification efforts continue to be refined, Dr. Drolet incorporates genotyping at every opportunity, like when she counsels parents of a baby born with a vascular stain on its face. “What can we tell them about what else might be wrong? What can we tell them about how this will change over time? What can we tell them about how we can treat it? I think genotyping absolutely helps to clarify that for me,” she said. “I can’t use that alone, but it gives me another piece of evidence to help do a better job in predicting when I need to screen, what I need to screen for, and what might happen in the future. If you combine your genotype with your clinical exam, I really do believe we can start to offer some prognostication for our families, to say, ‘this is the degree of overgrowth we may see over time; these are the complications I predict that you might have.’ ”
Even the vascular stain can give you a clue. “If it’s light and lacey, you probably don’t have a lot of cell cycle activation,” Dr. Drolet said. “If it’s dark and there’s blebs and you’ve got some bleeding at a young age, you’ve got a highly activated mutation, and there’s everything in between.”
Dr. Drolet disclosed that she is a consultant for Venthera and Novartis and is a board member for the Isthmus Project. She also holds intellectual property rights in and is a patent holder for Peds Derm Development Group. Dr. Drolet has also received funding from the Spirit Foundation, Kayleigh’s Crew Endowment, the SPD, PeDRA, and the National Institutes of Health.
according to Beth Drolet, MD.
“We now know that 75%-80% of vascular malformations have gene mutations that make the cells either live longer, grow faster, or make them bigger in size,” Dr. Drolet, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said during the Society for Pediatric Dermatology pre-AAD meeting. “The basic binary premise of the current ISSVA [International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies] classification dividing vascular anomalies into tumors and malformations is wrong; the biology is not that straightforward. It may be helpful to differentiate between an infantile hemangioma and a capillary malformation during infancy as the hemangioma will grow in the next month, but we now know that patients with capillary malformations also have significant overgrowth of their tissue. We’ve all seen that; it just takes years, not months for us to notice it.”
The change in thinking about the root causes of vascular anomalies, she noted, stems from scientific advances in the understanding of embryonic mosaicism, DNA variation that happens after the zygote is formed, but before birth. “We know that each cell in a zygote will undergo 40 cell divisions before a baby is born,” she said. “Those cell divisions are not as neat as we thought they were. That cell and DNA duplication is actually quite messy, so there are mutations that happen purely because of embryonic cell division.”
Everyone is born with 120 somatic mutations per cell, she continued, “so we have multiple genomes in one human. Not all of those mutations are going to cause disease. Not all of those are going to be functional. About 10% of those mutations will actually be in a coding region of the gene and have the potential to change the function of the protein. If it changes the function of the protein so that the cell can’t survive, that cell dies off, but it gives the cell an advantage. It grows a little bit faster, let’s say. That cell survives, divides, producing a line of cells that can cause disease.”
In 2011, Dr. Drolet and colleagues from the Hemangioma Investigator Group and the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA) launched a multisite collaborative group to investigate the role of mosaic genetics in patients with vascular anomalies and discrepancy of growth. To date, 365 patients are enrolled, and the researchers have sequenced 97 of 165 affected tissue samples collected. “What’s nice about the registry is that we enrolled a wide spectrum of diseases: very mild diseases that might be treated by dermatologists to complex, syndromic diseases that might end up in an interdisciplinary vascular anomalies clinic,” she said.
For gene sequencing, the researchers drew from solid tumor biology and used next-generation sequencing with semi-target hybrid capture, “so we’re only looking at a subset of genes,” she said. “Right now, the chip we’re using has 180 cancer-related genes. It sequences the entire exome of the gene with a high depth of coverage, usually over 1,000 X. We use a specific pipeline that can detect very low allele frequency mutation: down to 1%, and robust criteria to determine variant pathogenicity.”
In 75% of tissue samples so far, the researchers have found a gene mutation in one of 13 genes: AKT1, AKT3, BRAF, GNA11, GNAQ, KRAS, MAP2K1, NRAS, PIK3CA, PIK3R1, PTPN11, RASA1, and TEK. According to Dr. Drolet, the common thread in these 13 genes is that they are implicated in cancer and have direct control over the cell cycle. “They’re intracellular proteins that control the cell cycle,” she explained. “These are proteins that are in the cell but interact with transmembrane proteins that receive extracellular messengers of cell growth”.
Understanding and recognizing genetic conditions is complicated, she said, because it involves determining which gene is altered, where in the DNA the gene is altered, how the gene variation will influence the function of the protein, and what tissue expresses that gene. “Then you get your phenotype,” Dr. Drolet said. “If you add mosaicism onto that, you have several additional variables. You need to know: When in embryogenesis did the mutation occur? What region of the body is affected? What cell lineage is affected? That predicts what phenotype you’re going to have.”
While molecular classification efforts continue to be refined, Dr. Drolet incorporates genotyping at every opportunity, like when she counsels parents of a baby born with a vascular stain on its face. “What can we tell them about what else might be wrong? What can we tell them about how this will change over time? What can we tell them about how we can treat it? I think genotyping absolutely helps to clarify that for me,” she said. “I can’t use that alone, but it gives me another piece of evidence to help do a better job in predicting when I need to screen, what I need to screen for, and what might happen in the future. If you combine your genotype with your clinical exam, I really do believe we can start to offer some prognostication for our families, to say, ‘this is the degree of overgrowth we may see over time; these are the complications I predict that you might have.’ ”
Even the vascular stain can give you a clue. “If it’s light and lacey, you probably don’t have a lot of cell cycle activation,” Dr. Drolet said. “If it’s dark and there’s blebs and you’ve got some bleeding at a young age, you’ve got a highly activated mutation, and there’s everything in between.”
Dr. Drolet disclosed that she is a consultant for Venthera and Novartis and is a board member for the Isthmus Project. She also holds intellectual property rights in and is a patent holder for Peds Derm Development Group. Dr. Drolet has also received funding from the Spirit Foundation, Kayleigh’s Crew Endowment, the SPD, PeDRA, and the National Institutes of Health.
according to Beth Drolet, MD.
“We now know that 75%-80% of vascular malformations have gene mutations that make the cells either live longer, grow faster, or make them bigger in size,” Dr. Drolet, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said during the Society for Pediatric Dermatology pre-AAD meeting. “The basic binary premise of the current ISSVA [International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies] classification dividing vascular anomalies into tumors and malformations is wrong; the biology is not that straightforward. It may be helpful to differentiate between an infantile hemangioma and a capillary malformation during infancy as the hemangioma will grow in the next month, but we now know that patients with capillary malformations also have significant overgrowth of their tissue. We’ve all seen that; it just takes years, not months for us to notice it.”
The change in thinking about the root causes of vascular anomalies, she noted, stems from scientific advances in the understanding of embryonic mosaicism, DNA variation that happens after the zygote is formed, but before birth. “We know that each cell in a zygote will undergo 40 cell divisions before a baby is born,” she said. “Those cell divisions are not as neat as we thought they were. That cell and DNA duplication is actually quite messy, so there are mutations that happen purely because of embryonic cell division.”
Everyone is born with 120 somatic mutations per cell, she continued, “so we have multiple genomes in one human. Not all of those mutations are going to cause disease. Not all of those are going to be functional. About 10% of those mutations will actually be in a coding region of the gene and have the potential to change the function of the protein. If it changes the function of the protein so that the cell can’t survive, that cell dies off, but it gives the cell an advantage. It grows a little bit faster, let’s say. That cell survives, divides, producing a line of cells that can cause disease.”
In 2011, Dr. Drolet and colleagues from the Hemangioma Investigator Group and the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA) launched a multisite collaborative group to investigate the role of mosaic genetics in patients with vascular anomalies and discrepancy of growth. To date, 365 patients are enrolled, and the researchers have sequenced 97 of 165 affected tissue samples collected. “What’s nice about the registry is that we enrolled a wide spectrum of diseases: very mild diseases that might be treated by dermatologists to complex, syndromic diseases that might end up in an interdisciplinary vascular anomalies clinic,” she said.
For gene sequencing, the researchers drew from solid tumor biology and used next-generation sequencing with semi-target hybrid capture, “so we’re only looking at a subset of genes,” she said. “Right now, the chip we’re using has 180 cancer-related genes. It sequences the entire exome of the gene with a high depth of coverage, usually over 1,000 X. We use a specific pipeline that can detect very low allele frequency mutation: down to 1%, and robust criteria to determine variant pathogenicity.”
In 75% of tissue samples so far, the researchers have found a gene mutation in one of 13 genes: AKT1, AKT3, BRAF, GNA11, GNAQ, KRAS, MAP2K1, NRAS, PIK3CA, PIK3R1, PTPN11, RASA1, and TEK. According to Dr. Drolet, the common thread in these 13 genes is that they are implicated in cancer and have direct control over the cell cycle. “They’re intracellular proteins that control the cell cycle,” she explained. “These are proteins that are in the cell but interact with transmembrane proteins that receive extracellular messengers of cell growth”.
Understanding and recognizing genetic conditions is complicated, she said, because it involves determining which gene is altered, where in the DNA the gene is altered, how the gene variation will influence the function of the protein, and what tissue expresses that gene. “Then you get your phenotype,” Dr. Drolet said. “If you add mosaicism onto that, you have several additional variables. You need to know: When in embryogenesis did the mutation occur? What region of the body is affected? What cell lineage is affected? That predicts what phenotype you’re going to have.”
While molecular classification efforts continue to be refined, Dr. Drolet incorporates genotyping at every opportunity, like when she counsels parents of a baby born with a vascular stain on its face. “What can we tell them about what else might be wrong? What can we tell them about how this will change over time? What can we tell them about how we can treat it? I think genotyping absolutely helps to clarify that for me,” she said. “I can’t use that alone, but it gives me another piece of evidence to help do a better job in predicting when I need to screen, what I need to screen for, and what might happen in the future. If you combine your genotype with your clinical exam, I really do believe we can start to offer some prognostication for our families, to say, ‘this is the degree of overgrowth we may see over time; these are the complications I predict that you might have.’ ”
Even the vascular stain can give you a clue. “If it’s light and lacey, you probably don’t have a lot of cell cycle activation,” Dr. Drolet said. “If it’s dark and there’s blebs and you’ve got some bleeding at a young age, you’ve got a highly activated mutation, and there’s everything in between.”
Dr. Drolet disclosed that she is a consultant for Venthera and Novartis and is a board member for the Isthmus Project. She also holds intellectual property rights in and is a patent holder for Peds Derm Development Group. Dr. Drolet has also received funding from the Spirit Foundation, Kayleigh’s Crew Endowment, the SPD, PeDRA, and the National Institutes of Health.
FROM THE SPD PRE-AAD MEETING
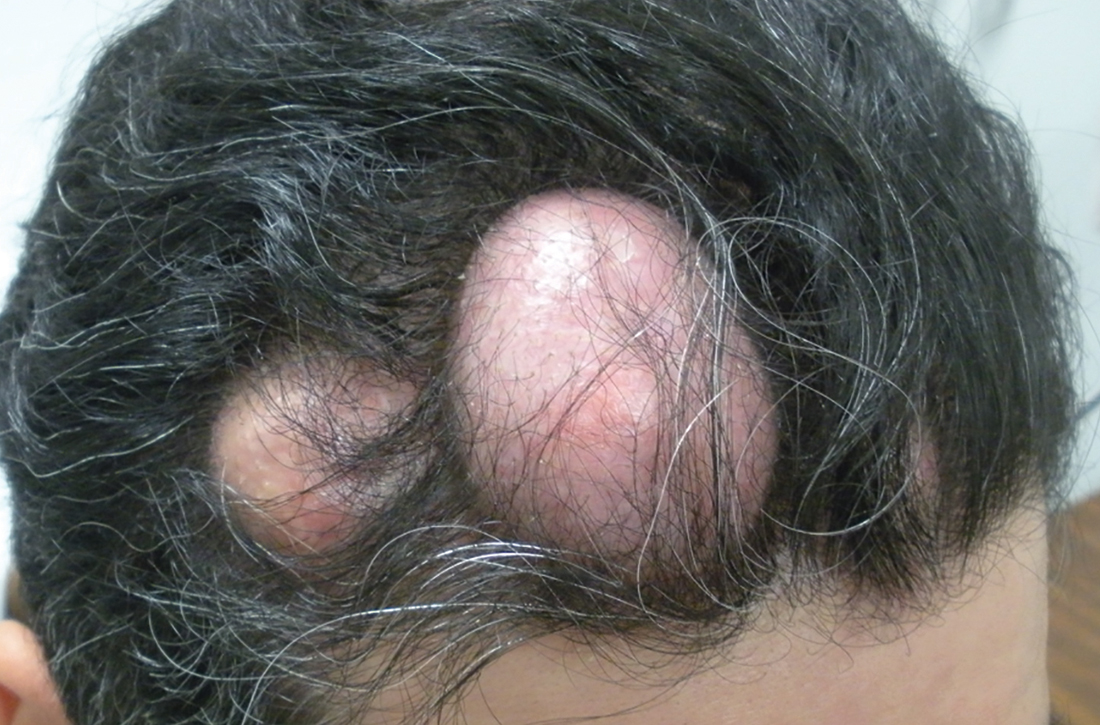
Numerous large nodules on scalp
A 31-year-old Hispanic man presented for evaluation of numerous disfiguring growths on his scalp. They first appeared when he was 19 years old. A review of his family history revealed that his father had 2 “cysts” on his body.
The patient had 10 nodules on his scalp and upper back (Figures 1A and 1B). The ones on his scalp lacked puncta and appeared in a “turban tumor” configuration. The lesions were pink, smooth, and semisoft, and ranged in size from 1 to 6 cm.
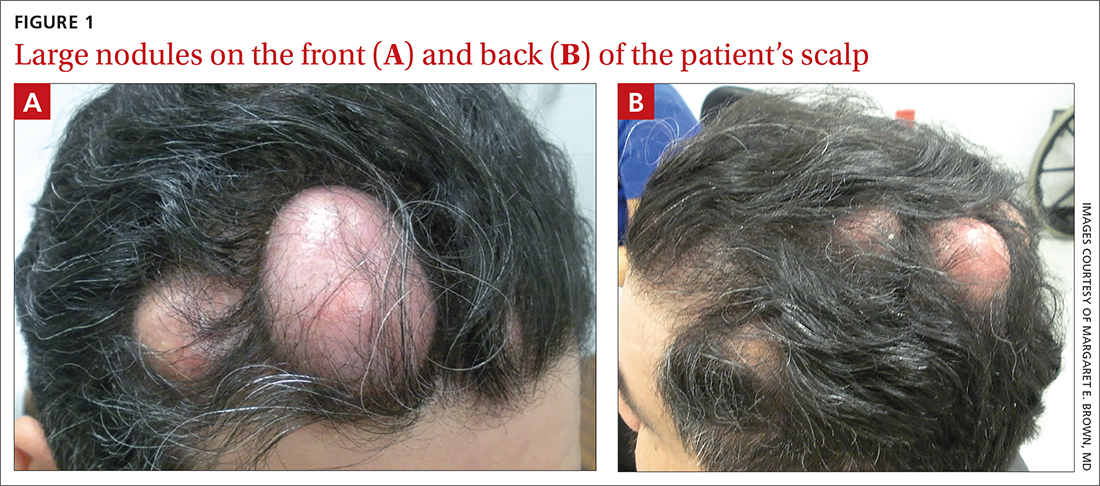
Six years earlier, the patient had been seen for evaluation of 20 protuberant nodules. At the time, he had been referred to plastic surgery, where 15 lesions were excised. No other treatment was reported by the patient during the 6-year gap between exams.
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Pilar cysts
Pilar cysts (PC), also known as trichilemma cysts, wen, or isthmus-catagen cysts, are benign cysts that manifest as smooth, firm, well-circumscribed, pink nodules. PCs originate from the follicular isthmus of the hair’s external root sheath1 and are found in 5% to 10% of the US population.2 Possible sites of appearance include the face, neck, trunk, and extremities, although 90% of PCs develop on the scalp.1 They tend to have an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance with linkages to the short arm of chromosome 3.3 PCs can occasionally become inflamed following infection or trauma.
Characteristic histology of PCs demonstrates semisolid, keratin-filled, subepidermal cysts lined by stratified epithelium without a granular layer (trichilemmal keratinization). Lesions excised from this patient’s scalp showed 2 subtypes of PCs: nonproliferating (FIGURE 2A) and proliferating (FIGURE 2B). Subtypes appear similar on exam but can be differentiated on histology.
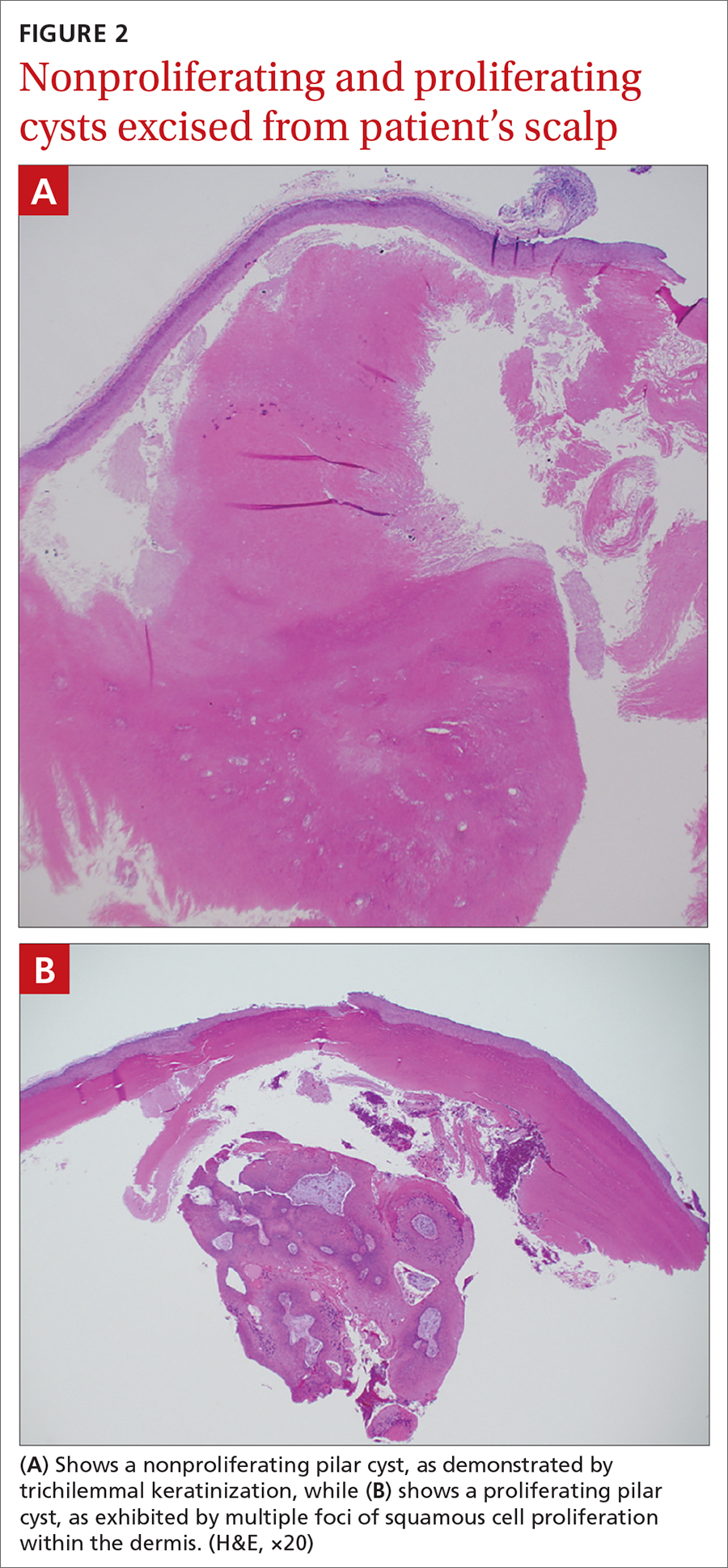
With gradual growth, proliferating PCs can reach up to 25 cm in diameter.1 Rapid growth, size > 5 cm, infiltration, or a non-scalp location may indicate malignancy.4
Differential diagnosis includes lipomas
The differential diagnosis for a lesion such as this includes epidermal inclusion cysts, dermoid cysts, and lipomas. Epidermal inclusion cysts have a punctum, whereas PCs do not. Dermoid cysts are single congenital lesions that manifest much earlier than PCs. Lipomas are easily movable rubbery bulges that appear more frequently in lipid-dense areas of the body.
For this patient, the striking turban tumor–like presentation, with numerous large cysts on the scalp, initially inspired a differential diagnosis including several genetic tumor syndromes. However, unlike the association between Gardner syndrome and numerous epidermoid cysts or Brooke-Spiegler syndrome and spiradenomas, no syndromes have been linked to numerous trichilemmal cysts.
Continue to: Excision is effective
Excision is effective
Excision is the treatment of choice for both proliferating and nonproliferating PCs.5 The local recurrence rate of proliferating PCs is 3.7% with a rare likelihood of transformation to trichilemmal carcinoma.6
Our patient continues to be followed in clinic for monitoring and periodic excision of bothersome cysts.
1. Ramaswamy AS, Manjunatha HK, Sunilkumar B, et al. Morphological spectrum of pilar cysts. N Am J Med Sci. 2013;5:124-128. http://doi.org/10.4103/1947-2714.107532
2. Ibrahim AE, Barikian A, Janom H, et al. Numerous recurrent trichilemmal cysts of the scalp: differential diagnosis and surgical management. J Craniofac Surg. 2012;23:e164-168. http://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e31824cdbd2
3. Adya KA, Inamadar AC, Palit A. Multiple firm mobile swellings over the scalp. Int J Trichology. 2012;4:98-99. http://doi.org/10.4103/0974-7753.96906
4. Folpe AL, Reisenauer AK, Mentzel T, et al. Proliferating trichilemmal tumors: clinicopathologic evaluation is a guide to biologic behavior. J Cutan Pathol. 2003;30:492-498. http://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0560.2003.00041.x
5. Leppard BJ, Sanderson KV. The natural history of trichilemmal cysts. Br J Dermatol. 1976;94:379-390. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.1976.tb06115.x
6. Kim UG, Kook DB, Kim TH, et al. Trichilemmal carcinoma from proliferating trichilemmal cyst on the posterior neck. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2017;18:50-53. http://doi.org/10.7181/acfs.2017.18.1.50
A 31-year-old Hispanic man presented for evaluation of numerous disfiguring growths on his scalp. They first appeared when he was 19 years old. A review of his family history revealed that his father had 2 “cysts” on his body.
The patient had 10 nodules on his scalp and upper back (Figures 1A and 1B). The ones on his scalp lacked puncta and appeared in a “turban tumor” configuration. The lesions were pink, smooth, and semisoft, and ranged in size from 1 to 6 cm.

Six years earlier, the patient had been seen for evaluation of 20 protuberant nodules. At the time, he had been referred to plastic surgery, where 15 lesions were excised. No other treatment was reported by the patient during the 6-year gap between exams.
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Pilar cysts
Pilar cysts (PC), also known as trichilemma cysts, wen, or isthmus-catagen cysts, are benign cysts that manifest as smooth, firm, well-circumscribed, pink nodules. PCs originate from the follicular isthmus of the hair’s external root sheath1 and are found in 5% to 10% of the US population.2 Possible sites of appearance include the face, neck, trunk, and extremities, although 90% of PCs develop on the scalp.1 They tend to have an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance with linkages to the short arm of chromosome 3.3 PCs can occasionally become inflamed following infection or trauma.
Characteristic histology of PCs demonstrates semisolid, keratin-filled, subepidermal cysts lined by stratified epithelium without a granular layer (trichilemmal keratinization). Lesions excised from this patient’s scalp showed 2 subtypes of PCs: nonproliferating (FIGURE 2A) and proliferating (FIGURE 2B). Subtypes appear similar on exam but can be differentiated on histology.

With gradual growth, proliferating PCs can reach up to 25 cm in diameter.1 Rapid growth, size > 5 cm, infiltration, or a non-scalp location may indicate malignancy.4
Differential diagnosis includes lipomas
The differential diagnosis for a lesion such as this includes epidermal inclusion cysts, dermoid cysts, and lipomas. Epidermal inclusion cysts have a punctum, whereas PCs do not. Dermoid cysts are single congenital lesions that manifest much earlier than PCs. Lipomas are easily movable rubbery bulges that appear more frequently in lipid-dense areas of the body.
For this patient, the striking turban tumor–like presentation, with numerous large cysts on the scalp, initially inspired a differential diagnosis including several genetic tumor syndromes. However, unlike the association between Gardner syndrome and numerous epidermoid cysts or Brooke-Spiegler syndrome and spiradenomas, no syndromes have been linked to numerous trichilemmal cysts.
Continue to: Excision is effective
Excision is effective
Excision is the treatment of choice for both proliferating and nonproliferating PCs.5 The local recurrence rate of proliferating PCs is 3.7% with a rare likelihood of transformation to trichilemmal carcinoma.6
Our patient continues to be followed in clinic for monitoring and periodic excision of bothersome cysts.
A 31-year-old Hispanic man presented for evaluation of numerous disfiguring growths on his scalp. They first appeared when he was 19 years old. A review of his family history revealed that his father had 2 “cysts” on his body.
The patient had 10 nodules on his scalp and upper back (Figures 1A and 1B). The ones on his scalp lacked puncta and appeared in a “turban tumor” configuration. The lesions were pink, smooth, and semisoft, and ranged in size from 1 to 6 cm.

Six years earlier, the patient had been seen for evaluation of 20 protuberant nodules. At the time, he had been referred to plastic surgery, where 15 lesions were excised. No other treatment was reported by the patient during the 6-year gap between exams.
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Pilar cysts
Pilar cysts (PC), also known as trichilemma cysts, wen, or isthmus-catagen cysts, are benign cysts that manifest as smooth, firm, well-circumscribed, pink nodules. PCs originate from the follicular isthmus of the hair’s external root sheath1 and are found in 5% to 10% of the US population.2 Possible sites of appearance include the face, neck, trunk, and extremities, although 90% of PCs develop on the scalp.1 They tend to have an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance with linkages to the short arm of chromosome 3.3 PCs can occasionally become inflamed following infection or trauma.
Characteristic histology of PCs demonstrates semisolid, keratin-filled, subepidermal cysts lined by stratified epithelium without a granular layer (trichilemmal keratinization). Lesions excised from this patient’s scalp showed 2 subtypes of PCs: nonproliferating (FIGURE 2A) and proliferating (FIGURE 2B). Subtypes appear similar on exam but can be differentiated on histology.

With gradual growth, proliferating PCs can reach up to 25 cm in diameter.1 Rapid growth, size > 5 cm, infiltration, or a non-scalp location may indicate malignancy.4
Differential diagnosis includes lipomas
The differential diagnosis for a lesion such as this includes epidermal inclusion cysts, dermoid cysts, and lipomas. Epidermal inclusion cysts have a punctum, whereas PCs do not. Dermoid cysts are single congenital lesions that manifest much earlier than PCs. Lipomas are easily movable rubbery bulges that appear more frequently in lipid-dense areas of the body.
For this patient, the striking turban tumor–like presentation, with numerous large cysts on the scalp, initially inspired a differential diagnosis including several genetic tumor syndromes. However, unlike the association between Gardner syndrome and numerous epidermoid cysts or Brooke-Spiegler syndrome and spiradenomas, no syndromes have been linked to numerous trichilemmal cysts.
Continue to: Excision is effective
Excision is effective
Excision is the treatment of choice for both proliferating and nonproliferating PCs.5 The local recurrence rate of proliferating PCs is 3.7% with a rare likelihood of transformation to trichilemmal carcinoma.6
Our patient continues to be followed in clinic for monitoring and periodic excision of bothersome cysts.
1. Ramaswamy AS, Manjunatha HK, Sunilkumar B, et al. Morphological spectrum of pilar cysts. N Am J Med Sci. 2013;5:124-128. http://doi.org/10.4103/1947-2714.107532
2. Ibrahim AE, Barikian A, Janom H, et al. Numerous recurrent trichilemmal cysts of the scalp: differential diagnosis and surgical management. J Craniofac Surg. 2012;23:e164-168. http://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e31824cdbd2
3. Adya KA, Inamadar AC, Palit A. Multiple firm mobile swellings over the scalp. Int J Trichology. 2012;4:98-99. http://doi.org/10.4103/0974-7753.96906
4. Folpe AL, Reisenauer AK, Mentzel T, et al. Proliferating trichilemmal tumors: clinicopathologic evaluation is a guide to biologic behavior. J Cutan Pathol. 2003;30:492-498. http://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0560.2003.00041.x
5. Leppard BJ, Sanderson KV. The natural history of trichilemmal cysts. Br J Dermatol. 1976;94:379-390. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.1976.tb06115.x
6. Kim UG, Kook DB, Kim TH, et al. Trichilemmal carcinoma from proliferating trichilemmal cyst on the posterior neck. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2017;18:50-53. http://doi.org/10.7181/acfs.2017.18.1.50
1. Ramaswamy AS, Manjunatha HK, Sunilkumar B, et al. Morphological spectrum of pilar cysts. N Am J Med Sci. 2013;5:124-128. http://doi.org/10.4103/1947-2714.107532
2. Ibrahim AE, Barikian A, Janom H, et al. Numerous recurrent trichilemmal cysts of the scalp: differential diagnosis and surgical management. J Craniofac Surg. 2012;23:e164-168. http://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e31824cdbd2
3. Adya KA, Inamadar AC, Palit A. Multiple firm mobile swellings over the scalp. Int J Trichology. 2012;4:98-99. http://doi.org/10.4103/0974-7753.96906
4. Folpe AL, Reisenauer AK, Mentzel T, et al. Proliferating trichilemmal tumors: clinicopathologic evaluation is a guide to biologic behavior. J Cutan Pathol. 2003;30:492-498. http://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0560.2003.00041.x
5. Leppard BJ, Sanderson KV. The natural history of trichilemmal cysts. Br J Dermatol. 1976;94:379-390. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.1976.tb06115.x
6. Kim UG, Kook DB, Kim TH, et al. Trichilemmal carcinoma from proliferating trichilemmal cyst on the posterior neck. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2017;18:50-53. http://doi.org/10.7181/acfs.2017.18.1.50
Stable, supportive shoes reduce walking pain in severe knee OA
Wearing stable, supportive footwear reduces knee pain to a significantly greater extent than what’s felt with flat, flexible shoes in patients with severe knee osteoarthritis, according to results of a randomized, controlled trial presented at the OARSI 2021 World Congress.
Clinical guidelines for knee OA emphasize the importance of patients self-managing their condition with exercise, weight control, and appropriate footwear. However, there is limited evidence on which footwear is best, and some guidelines advocate stable supportive shoes based solely on expert opinion, Kade Paterson, PhD, of the University of Melbourne told the conference, sponsored by Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
“Recent research suggests that another type of shoe style – termed flat, flexible shoes – may be more beneficial,” Dr. Paterson said, citing a randomized, controlled trial that found greater improvement in pain and function with flat flexible shoes, compared with neutral tennis shoes. “Flat, flexible shoes are generally lighter, and have thinner, more flexible soles.”
In this study, which was published earlier this year in Annals of Internal Medicine, 164 individuals with knee OA who had experienced knee pain on most days of the past month were randomized to wear either stable, supportive shoes or flat, flexible shoes for at least 6 hours a day for 6 months. Six of each shoe type – three male styles and three female styles – were offered, having been chosen based on a survey in which participants were asked about a selection of commercially available shoes they were most likely to wear.
Researchers found participants who wore the stable, supportive shoes had significantly greater reductions in knee pain on walking during the previous week, representing a mean difference of 1.1 units on an 11-point numerical rating scale. More patients in the stable, supportive shoe arm of the study achieved minimal clinically important difference in pain than did those in the flat, flexible shoe group.
Stable, supportive shoes were also associated with greater improvements in knee-related quality of life scores and greater improvements in overall pain. However, there was no significant difference between the two groups in function. Patients wearing flat, flexible shoes reported significantly more adverse events – mainly onset of or increases in knee pain.
Dr. Paterson said the results were surprising, given previous research suggesting a benefit from lighter flat, flexible shoes. “Some previous research showed that those shoes reduced knee joint forces that were associated with pain and reduced it more than stable, supportive shoes, and based on the biomechanical research, we thought would be flat, flexible shoes,” he said in an interview.
Another observation to come from the study was the poor quality of most patients’ everyday shoes. Dr. Paterson said that most of the participants’ usual shoes were very old, and many were also wearing inappropriate footwear for knee OA, including shoes with heels or slippers.
“We would strongly recommend that clinicians ask patients to even bring in their most commonly worn shoes and then recommend new shoes, and based on our data, certainly stable supportive shoes,” he said.
Commenting on the findings, Jos Runhaar, PhD, of Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, said this study provided high-quality evidence for this specific intervention in this specific group of patients, namely those with more severe, end-stage OA who had long-lasting changes in their foot posture and gait.
“Based on this, I would say that restoring the original posture of the foot – because that’s how the stable, supportive shoes are probably designed – is more beneficial than actually supporting the natural gait that people are already adapted to at that stage,” Dr. Runhaar said in an interview.
Dr. Paterson noted that the findings of the study were not generalizable to people with mild knee OA, and also that the study did not compare either shoe type with participants’ usual shoes.
The study and three authors were supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. No conflicts of interest were declared.
Wearing stable, supportive footwear reduces knee pain to a significantly greater extent than what’s felt with flat, flexible shoes in patients with severe knee osteoarthritis, according to results of a randomized, controlled trial presented at the OARSI 2021 World Congress.
Clinical guidelines for knee OA emphasize the importance of patients self-managing their condition with exercise, weight control, and appropriate footwear. However, there is limited evidence on which footwear is best, and some guidelines advocate stable supportive shoes based solely on expert opinion, Kade Paterson, PhD, of the University of Melbourne told the conference, sponsored by Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
“Recent research suggests that another type of shoe style – termed flat, flexible shoes – may be more beneficial,” Dr. Paterson said, citing a randomized, controlled trial that found greater improvement in pain and function with flat flexible shoes, compared with neutral tennis shoes. “Flat, flexible shoes are generally lighter, and have thinner, more flexible soles.”
In this study, which was published earlier this year in Annals of Internal Medicine, 164 individuals with knee OA who had experienced knee pain on most days of the past month were randomized to wear either stable, supportive shoes or flat, flexible shoes for at least 6 hours a day for 6 months. Six of each shoe type – three male styles and three female styles – were offered, having been chosen based on a survey in which participants were asked about a selection of commercially available shoes they were most likely to wear.
Researchers found participants who wore the stable, supportive shoes had significantly greater reductions in knee pain on walking during the previous week, representing a mean difference of 1.1 units on an 11-point numerical rating scale. More patients in the stable, supportive shoe arm of the study achieved minimal clinically important difference in pain than did those in the flat, flexible shoe group.
Stable, supportive shoes were also associated with greater improvements in knee-related quality of life scores and greater improvements in overall pain. However, there was no significant difference between the two groups in function. Patients wearing flat, flexible shoes reported significantly more adverse events – mainly onset of or increases in knee pain.
Dr. Paterson said the results were surprising, given previous research suggesting a benefit from lighter flat, flexible shoes. “Some previous research showed that those shoes reduced knee joint forces that were associated with pain and reduced it more than stable, supportive shoes, and based on the biomechanical research, we thought would be flat, flexible shoes,” he said in an interview.
Another observation to come from the study was the poor quality of most patients’ everyday shoes. Dr. Paterson said that most of the participants’ usual shoes were very old, and many were also wearing inappropriate footwear for knee OA, including shoes with heels or slippers.
“We would strongly recommend that clinicians ask patients to even bring in their most commonly worn shoes and then recommend new shoes, and based on our data, certainly stable supportive shoes,” he said.
Commenting on the findings, Jos Runhaar, PhD, of Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, said this study provided high-quality evidence for this specific intervention in this specific group of patients, namely those with more severe, end-stage OA who had long-lasting changes in their foot posture and gait.
“Based on this, I would say that restoring the original posture of the foot – because that’s how the stable, supportive shoes are probably designed – is more beneficial than actually supporting the natural gait that people are already adapted to at that stage,” Dr. Runhaar said in an interview.
Dr. Paterson noted that the findings of the study were not generalizable to people with mild knee OA, and also that the study did not compare either shoe type with participants’ usual shoes.
The study and three authors were supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. No conflicts of interest were declared.
Wearing stable, supportive footwear reduces knee pain to a significantly greater extent than what’s felt with flat, flexible shoes in patients with severe knee osteoarthritis, according to results of a randomized, controlled trial presented at the OARSI 2021 World Congress.
Clinical guidelines for knee OA emphasize the importance of patients self-managing their condition with exercise, weight control, and appropriate footwear. However, there is limited evidence on which footwear is best, and some guidelines advocate stable supportive shoes based solely on expert opinion, Kade Paterson, PhD, of the University of Melbourne told the conference, sponsored by Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
“Recent research suggests that another type of shoe style – termed flat, flexible shoes – may be more beneficial,” Dr. Paterson said, citing a randomized, controlled trial that found greater improvement in pain and function with flat flexible shoes, compared with neutral tennis shoes. “Flat, flexible shoes are generally lighter, and have thinner, more flexible soles.”
In this study, which was published earlier this year in Annals of Internal Medicine, 164 individuals with knee OA who had experienced knee pain on most days of the past month were randomized to wear either stable, supportive shoes or flat, flexible shoes for at least 6 hours a day for 6 months. Six of each shoe type – three male styles and three female styles – were offered, having been chosen based on a survey in which participants were asked about a selection of commercially available shoes they were most likely to wear.
Researchers found participants who wore the stable, supportive shoes had significantly greater reductions in knee pain on walking during the previous week, representing a mean difference of 1.1 units on an 11-point numerical rating scale. More patients in the stable, supportive shoe arm of the study achieved minimal clinically important difference in pain than did those in the flat, flexible shoe group.
Stable, supportive shoes were also associated with greater improvements in knee-related quality of life scores and greater improvements in overall pain. However, there was no significant difference between the two groups in function. Patients wearing flat, flexible shoes reported significantly more adverse events – mainly onset of or increases in knee pain.
Dr. Paterson said the results were surprising, given previous research suggesting a benefit from lighter flat, flexible shoes. “Some previous research showed that those shoes reduced knee joint forces that were associated with pain and reduced it more than stable, supportive shoes, and based on the biomechanical research, we thought would be flat, flexible shoes,” he said in an interview.
Another observation to come from the study was the poor quality of most patients’ everyday shoes. Dr. Paterson said that most of the participants’ usual shoes were very old, and many were also wearing inappropriate footwear for knee OA, including shoes with heels or slippers.
“We would strongly recommend that clinicians ask patients to even bring in their most commonly worn shoes and then recommend new shoes, and based on our data, certainly stable supportive shoes,” he said.
Commenting on the findings, Jos Runhaar, PhD, of Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, said this study provided high-quality evidence for this specific intervention in this specific group of patients, namely those with more severe, end-stage OA who had long-lasting changes in their foot posture and gait.
“Based on this, I would say that restoring the original posture of the foot – because that’s how the stable, supportive shoes are probably designed – is more beneficial than actually supporting the natural gait that people are already adapted to at that stage,” Dr. Runhaar said in an interview.
Dr. Paterson noted that the findings of the study were not generalizable to people with mild knee OA, and also that the study did not compare either shoe type with participants’ usual shoes.
The study and three authors were supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. No conflicts of interest were declared.
FROM OARSI 2021
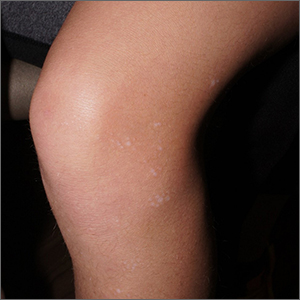
White macules on knee
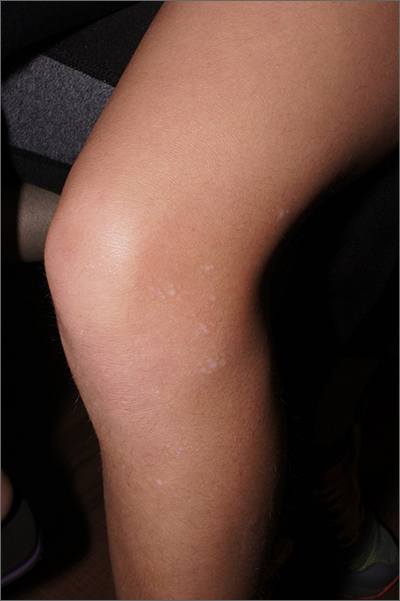
The ivory white appearance and slight atrophy of the lesions raised the possibility of extragenital lichen sclerosus (LS). A 4-mm punch biopsy confirmed the diagnosis.
LS occurs in all races and is an uncommon, chronic inflammatory disease that most often affects the vulva and perianal mucosa in postmenopausal women.1 That said, it can also affect men and children, and manifest in places such as the trunk and neck. Extragenital lesions may appear ivory white, as in this case, or may resemble ecchymoses and raise alarm for possible abuse.
When LS is present on the extremities, a complete skin surface exam, including external genitalia, is warranted. LS is thought to be an autoimmune disease and is associated with vitiligo, autoimmune thyroid disease, and morphea.
In cases of suspected LS, it’s important to biopsy the full thickness of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. It is helpful to include an area of normal skin in the sample, as the findings are subtle and best contrasted with the architecture of unaffected skin. For this patient, a 4-mm punch biopsy was sufficient, but an incisional biopsy would be more appropriate for a larger patch or plaque.
Treatment options are based on a small case series and a few small randomized controlled trials. Medications include topical steroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, systemic retinoids, and topical estrogens.
In this case, the patient was advised to apply topical clobetasol 0.05% cream bid to the affected area for 2 weeks, then twice weekly for 4 weeks. She had partial clearance with this approach, but small macules later appeared on her dorsal foot; the treatment was repeated.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)
1. Tong LX, Sun GS, Teng JMC. Pediatric lichen sclerosus: a review of the epidemiology and treatment options. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:593-599. doi: 10.1111/pde.12615

The ivory white appearance and slight atrophy of the lesions raised the possibility of extragenital lichen sclerosus (LS). A 4-mm punch biopsy confirmed the diagnosis.
LS occurs in all races and is an uncommon, chronic inflammatory disease that most often affects the vulva and perianal mucosa in postmenopausal women.1 That said, it can also affect men and children, and manifest in places such as the trunk and neck. Extragenital lesions may appear ivory white, as in this case, or may resemble ecchymoses and raise alarm for possible abuse.
When LS is present on the extremities, a complete skin surface exam, including external genitalia, is warranted. LS is thought to be an autoimmune disease and is associated with vitiligo, autoimmune thyroid disease, and morphea.
In cases of suspected LS, it’s important to biopsy the full thickness of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. It is helpful to include an area of normal skin in the sample, as the findings are subtle and best contrasted with the architecture of unaffected skin. For this patient, a 4-mm punch biopsy was sufficient, but an incisional biopsy would be more appropriate for a larger patch or plaque.
Treatment options are based on a small case series and a few small randomized controlled trials. Medications include topical steroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, systemic retinoids, and topical estrogens.
In this case, the patient was advised to apply topical clobetasol 0.05% cream bid to the affected area for 2 weeks, then twice weekly for 4 weeks. She had partial clearance with this approach, but small macules later appeared on her dorsal foot; the treatment was repeated.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)

The ivory white appearance and slight atrophy of the lesions raised the possibility of extragenital lichen sclerosus (LS). A 4-mm punch biopsy confirmed the diagnosis.
LS occurs in all races and is an uncommon, chronic inflammatory disease that most often affects the vulva and perianal mucosa in postmenopausal women.1 That said, it can also affect men and children, and manifest in places such as the trunk and neck. Extragenital lesions may appear ivory white, as in this case, or may resemble ecchymoses and raise alarm for possible abuse.
When LS is present on the extremities, a complete skin surface exam, including external genitalia, is warranted. LS is thought to be an autoimmune disease and is associated with vitiligo, autoimmune thyroid disease, and morphea.
In cases of suspected LS, it’s important to biopsy the full thickness of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. It is helpful to include an area of normal skin in the sample, as the findings are subtle and best contrasted with the architecture of unaffected skin. For this patient, a 4-mm punch biopsy was sufficient, but an incisional biopsy would be more appropriate for a larger patch or plaque.
Treatment options are based on a small case series and a few small randomized controlled trials. Medications include topical steroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, systemic retinoids, and topical estrogens.
In this case, the patient was advised to apply topical clobetasol 0.05% cream bid to the affected area for 2 weeks, then twice weekly for 4 weeks. She had partial clearance with this approach, but small macules later appeared on her dorsal foot; the treatment was repeated.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)
1. Tong LX, Sun GS, Teng JMC. Pediatric lichen sclerosus: a review of the epidemiology and treatment options. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:593-599. doi: 10.1111/pde.12615
1. Tong LX, Sun GS, Teng JMC. Pediatric lichen sclerosus: a review of the epidemiology and treatment options. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:593-599. doi: 10.1111/pde.12615
Any bone break increases risk for subsequent fracture in older women
No matter where an initial fracture occurs in a postmenopausal woman, there is a subsequent increased risk of another fracture, with the risk surprisingly highest in the youngest postmenopausal group and among certain minorities, new data indicate.
“To our knowledge, no previous prospective study has reported detailed patterns of subsequent fracture locations after initial fracture according to age strata among women in the U.S.,” the authors noted in their article, published online May 5, 2021, in EClinicalMedicine.
The results show that a first fracture of the lower arm or wrist; upper arm; or shoulder, upper leg, knee, lower leg, or ankle – as well as those of the hip or pelvis – were associated with an approximately three- to sixfold increased risk for subsequent fractures. The findings have important implications for clinicians, said lead author Carolyn J. Crandall, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles.
“By not paying attention to which types of fractures increase the risk of future fractures, we are missing the opportunity to identify people at increased risk of future fracture and counsel them regarding risk reduction,” she said in a press statement.
Commenting on the research, Michael R. McClung, MD, stressed this message to clinicians needs to be underscored.
“This paper is one of a series of papers highlighting the fact that having a previous fracture is a risk factor for subsequent fractures,” he said in an interview.
“This has been known for a very long time, but it is a point still not appreciated by patients and primary care doctors, so having another study pointing this out is important,” emphasized Dr. McClung, of the Oregon Osteoporosis Center in Portland.
30% of women’s health initiative participants had a fracture
For the study, Dr. Crandall and colleagues evaluated data on 157,282 women between the ages of 50 and 79 who were enrolled in the Women’s Health Initiative between 1993 and 2018.
The women were a mean age of 63.1 years and 47,126 (30%) experienced an incident fracture during the study period.
With a mean follow-up of 15.4 years, each type of fracture was associated with an increased risk of a subsequent fracture after adjusting for age, race/ethnicity, body mass index, hormone therapy use, and other factors.
A wide range of initial risk fractures – including an initial lower arm or wrist fracture (adjusted hazard ratio, 4.80), upper arm or shoulder fracture (aHR, 5.06), upper leg fracture (aHR, 5.11), knee fracture (aHR, 5.03), lower leg/ankle fracture (aHR, 4.10), and spinal fracture (aHR, 6.69) – increased the risk of sustaining a subsequent hip fracture.
For initial fractures of the lower arm or wrist, there was an increased risk of a subsequent fracture of the upper arm/shoulder, upper leg, knee, lower leg/ankle, hip/pelvis, and spine (aHRs ranged from 2.63 to 5.68).
“The finding that knee fracture has the same prognostic value for subsequent fracture as hip or wrist fracture is a novel key finding, as knee fracture is generally not considered ‘osteoporotic’,” the authors noted.
The risk of fracture after sustaining an initial hip or pelvis fracture was exceptionally high – with as much as a 27-fold higher risk of a subsequent upper leg (nonhip) fracture (aHR, 27.18).
“Thirty-four percent of women who experienced initial hip or pelvis fracture experienced a subsequent nonhip fracture,” the authors noted.
However, the risks associated with an initial hip fracture are already well established, and the study’s more notable findings are the risks of other bone breaks, Dr. Crandall told this news organization.
“The (increased risk with hip fracture) is a rather substantial result,” she said. “However, the more major point of this study is that no matter where the initial fracture happened, the risk of the future fracture was elevated.”
Don’t disregard risks in younger women, racial/ethnic groups
The findings regarding age are also important. The highest risk was observed in the youngest postmenopausal age group of 50-59 years (aHR, 6.45), which decreased slightly in the 60- to 69-year age group (aHR, 6.04) and further decreased in the 70- to 79-year age group (aHR, 4.99).
“This was a surprise, and it highlights that clinicians should not disregard initial fractures among young postmenopausal women,” Dr. Crandall told this news organization.
Even greater increased risks for a subsequent fracture following an initial lower extremity fracture were observed in non-Hispanic Black women, Hispanic or Latina women, and women of Asian Pacific Islander ethnicity, ranging from ninefold to 14-fold, versus a sevenfold risk among non-Hispanic White women.
“This has public health implications because it means that we may have been missing the opportunity to prevent fractures among younger postmenopausal women and underrepresented racial/ethnic groups,” Dr. Crandall noted.
Is risk greatest 1-2 years after the initial fracture?
The findings suggest that current treatment guidelines may need to be revisited in light of inconsistencies regarding when, and for which fracture types, to initiate treatment.
“It will be important to determine whether existing risk calculators can be adapted (or new calculators developed) to help refine decision-making to determine which of the women with fractures other than hip or vertebral fractures should be treated,” the authors wrote.
Dr. McClung said a randomized, controlled trial of osteoporosis treatment in people who present with all types of fractures would help determine whether having a knee or a wrist fracture does indeed warrant such therapy.
He further commented that future studies should evaluate the shorter- versus longer-term risks.
“The most recent research suggests that the risk of having a second fracture is much higher in the first year or 2 after the first or incident fracture,” he observed. “So, the next stage in research with this dataset would be to ask not what happens over a 10-year time frame but what happens over the first year or 2 after the fracture.”
The study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Crandall reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. McClung reported being a consultant and on the speakers bureau for Amgen and being a speaker for Alexion.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No matter where an initial fracture occurs in a postmenopausal woman, there is a subsequent increased risk of another fracture, with the risk surprisingly highest in the youngest postmenopausal group and among certain minorities, new data indicate.
“To our knowledge, no previous prospective study has reported detailed patterns of subsequent fracture locations after initial fracture according to age strata among women in the U.S.,” the authors noted in their article, published online May 5, 2021, in EClinicalMedicine.
The results show that a first fracture of the lower arm or wrist; upper arm; or shoulder, upper leg, knee, lower leg, or ankle – as well as those of the hip or pelvis – were associated with an approximately three- to sixfold increased risk for subsequent fractures. The findings have important implications for clinicians, said lead author Carolyn J. Crandall, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles.
“By not paying attention to which types of fractures increase the risk of future fractures, we are missing the opportunity to identify people at increased risk of future fracture and counsel them regarding risk reduction,” she said in a press statement.
Commenting on the research, Michael R. McClung, MD, stressed this message to clinicians needs to be underscored.
“This paper is one of a series of papers highlighting the fact that having a previous fracture is a risk factor for subsequent fractures,” he said in an interview.
“This has been known for a very long time, but it is a point still not appreciated by patients and primary care doctors, so having another study pointing this out is important,” emphasized Dr. McClung, of the Oregon Osteoporosis Center in Portland.
30% of women’s health initiative participants had a fracture
For the study, Dr. Crandall and colleagues evaluated data on 157,282 women between the ages of 50 and 79 who were enrolled in the Women’s Health Initiative between 1993 and 2018.
The women were a mean age of 63.1 years and 47,126 (30%) experienced an incident fracture during the study period.
With a mean follow-up of 15.4 years, each type of fracture was associated with an increased risk of a subsequent fracture after adjusting for age, race/ethnicity, body mass index, hormone therapy use, and other factors.
A wide range of initial risk fractures – including an initial lower arm or wrist fracture (adjusted hazard ratio, 4.80), upper arm or shoulder fracture (aHR, 5.06), upper leg fracture (aHR, 5.11), knee fracture (aHR, 5.03), lower leg/ankle fracture (aHR, 4.10), and spinal fracture (aHR, 6.69) – increased the risk of sustaining a subsequent hip fracture.
For initial fractures of the lower arm or wrist, there was an increased risk of a subsequent fracture of the upper arm/shoulder, upper leg, knee, lower leg/ankle, hip/pelvis, and spine (aHRs ranged from 2.63 to 5.68).
“The finding that knee fracture has the same prognostic value for subsequent fracture as hip or wrist fracture is a novel key finding, as knee fracture is generally not considered ‘osteoporotic’,” the authors noted.
The risk of fracture after sustaining an initial hip or pelvis fracture was exceptionally high – with as much as a 27-fold higher risk of a subsequent upper leg (nonhip) fracture (aHR, 27.18).
“Thirty-four percent of women who experienced initial hip or pelvis fracture experienced a subsequent nonhip fracture,” the authors noted.
However, the risks associated with an initial hip fracture are already well established, and the study’s more notable findings are the risks of other bone breaks, Dr. Crandall told this news organization.
“The (increased risk with hip fracture) is a rather substantial result,” she said. “However, the more major point of this study is that no matter where the initial fracture happened, the risk of the future fracture was elevated.”
Don’t disregard risks in younger women, racial/ethnic groups
The findings regarding age are also important. The highest risk was observed in the youngest postmenopausal age group of 50-59 years (aHR, 6.45), which decreased slightly in the 60- to 69-year age group (aHR, 6.04) and further decreased in the 70- to 79-year age group (aHR, 4.99).
“This was a surprise, and it highlights that clinicians should not disregard initial fractures among young postmenopausal women,” Dr. Crandall told this news organization.
Even greater increased risks for a subsequent fracture following an initial lower extremity fracture were observed in non-Hispanic Black women, Hispanic or Latina women, and women of Asian Pacific Islander ethnicity, ranging from ninefold to 14-fold, versus a sevenfold risk among non-Hispanic White women.
“This has public health implications because it means that we may have been missing the opportunity to prevent fractures among younger postmenopausal women and underrepresented racial/ethnic groups,” Dr. Crandall noted.
Is risk greatest 1-2 years after the initial fracture?
The findings suggest that current treatment guidelines may need to be revisited in light of inconsistencies regarding when, and for which fracture types, to initiate treatment.
“It will be important to determine whether existing risk calculators can be adapted (or new calculators developed) to help refine decision-making to determine which of the women with fractures other than hip or vertebral fractures should be treated,” the authors wrote.
Dr. McClung said a randomized, controlled trial of osteoporosis treatment in people who present with all types of fractures would help determine whether having a knee or a wrist fracture does indeed warrant such therapy.
He further commented that future studies should evaluate the shorter- versus longer-term risks.
“The most recent research suggests that the risk of having a second fracture is much higher in the first year or 2 after the first or incident fracture,” he observed. “So, the next stage in research with this dataset would be to ask not what happens over a 10-year time frame but what happens over the first year or 2 after the fracture.”
The study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Crandall reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. McClung reported being a consultant and on the speakers bureau for Amgen and being a speaker for Alexion.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No matter where an initial fracture occurs in a postmenopausal woman, there is a subsequent increased risk of another fracture, with the risk surprisingly highest in the youngest postmenopausal group and among certain minorities, new data indicate.
“To our knowledge, no previous prospective study has reported detailed patterns of subsequent fracture locations after initial fracture according to age strata among women in the U.S.,” the authors noted in their article, published online May 5, 2021, in EClinicalMedicine.
The results show that a first fracture of the lower arm or wrist; upper arm; or shoulder, upper leg, knee, lower leg, or ankle – as well as those of the hip or pelvis – were associated with an approximately three- to sixfold increased risk for subsequent fractures. The findings have important implications for clinicians, said lead author Carolyn J. Crandall, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles.
“By not paying attention to which types of fractures increase the risk of future fractures, we are missing the opportunity to identify people at increased risk of future fracture and counsel them regarding risk reduction,” she said in a press statement.
Commenting on the research, Michael R. McClung, MD, stressed this message to clinicians needs to be underscored.
“This paper is one of a series of papers highlighting the fact that having a previous fracture is a risk factor for subsequent fractures,” he said in an interview.
“This has been known for a very long time, but it is a point still not appreciated by patients and primary care doctors, so having another study pointing this out is important,” emphasized Dr. McClung, of the Oregon Osteoporosis Center in Portland.
30% of women’s health initiative participants had a fracture
For the study, Dr. Crandall and colleagues evaluated data on 157,282 women between the ages of 50 and 79 who were enrolled in the Women’s Health Initiative between 1993 and 2018.
The women were a mean age of 63.1 years and 47,126 (30%) experienced an incident fracture during the study period.
With a mean follow-up of 15.4 years, each type of fracture was associated with an increased risk of a subsequent fracture after adjusting for age, race/ethnicity, body mass index, hormone therapy use, and other factors.
A wide range of initial risk fractures – including an initial lower arm or wrist fracture (adjusted hazard ratio, 4.80), upper arm or shoulder fracture (aHR, 5.06), upper leg fracture (aHR, 5.11), knee fracture (aHR, 5.03), lower leg/ankle fracture (aHR, 4.10), and spinal fracture (aHR, 6.69) – increased the risk of sustaining a subsequent hip fracture.
For initial fractures of the lower arm or wrist, there was an increased risk of a subsequent fracture of the upper arm/shoulder, upper leg, knee, lower leg/ankle, hip/pelvis, and spine (aHRs ranged from 2.63 to 5.68).
“The finding that knee fracture has the same prognostic value for subsequent fracture as hip or wrist fracture is a novel key finding, as knee fracture is generally not considered ‘osteoporotic’,” the authors noted.
The risk of fracture after sustaining an initial hip or pelvis fracture was exceptionally high – with as much as a 27-fold higher risk of a subsequent upper leg (nonhip) fracture (aHR, 27.18).
“Thirty-four percent of women who experienced initial hip or pelvis fracture experienced a subsequent nonhip fracture,” the authors noted.
However, the risks associated with an initial hip fracture are already well established, and the study’s more notable findings are the risks of other bone breaks, Dr. Crandall told this news organization.
“The (increased risk with hip fracture) is a rather substantial result,” she said. “However, the more major point of this study is that no matter where the initial fracture happened, the risk of the future fracture was elevated.”
Don’t disregard risks in younger women, racial/ethnic groups
The findings regarding age are also important. The highest risk was observed in the youngest postmenopausal age group of 50-59 years (aHR, 6.45), which decreased slightly in the 60- to 69-year age group (aHR, 6.04) and further decreased in the 70- to 79-year age group (aHR, 4.99).
“This was a surprise, and it highlights that clinicians should not disregard initial fractures among young postmenopausal women,” Dr. Crandall told this news organization.
Even greater increased risks for a subsequent fracture following an initial lower extremity fracture were observed in non-Hispanic Black women, Hispanic or Latina women, and women of Asian Pacific Islander ethnicity, ranging from ninefold to 14-fold, versus a sevenfold risk among non-Hispanic White women.
“This has public health implications because it means that we may have been missing the opportunity to prevent fractures among younger postmenopausal women and underrepresented racial/ethnic groups,” Dr. Crandall noted.
Is risk greatest 1-2 years after the initial fracture?
The findings suggest that current treatment guidelines may need to be revisited in light of inconsistencies regarding when, and for which fracture types, to initiate treatment.
“It will be important to determine whether existing risk calculators can be adapted (or new calculators developed) to help refine decision-making to determine which of the women with fractures other than hip or vertebral fractures should be treated,” the authors wrote.
Dr. McClung said a randomized, controlled trial of osteoporosis treatment in people who present with all types of fractures would help determine whether having a knee or a wrist fracture does indeed warrant such therapy.
He further commented that future studies should evaluate the shorter- versus longer-term risks.
“The most recent research suggests that the risk of having a second fracture is much higher in the first year or 2 after the first or incident fracture,” he observed. “So, the next stage in research with this dataset would be to ask not what happens over a 10-year time frame but what happens over the first year or 2 after the fracture.”
The study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Crandall reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. McClung reported being a consultant and on the speakers bureau for Amgen and being a speaker for Alexion.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Smart prescribing strategies improve antibiotic stewardship
“Antibiotic stewardship is never easy, and sometimes it is very difficult to differentiate what is going on with a patient in the clinical setting,” said Valerie M. Vaughn, MD, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, at SHM Converge, the annual conference of the Society of Hospital Medicine.
“We know from studies that 20% of hospitalized patients who receive an antibiotic have an adverse drug event from that antibiotic within 30 days,” said Dr. Vaughn.
Dr. Vaughn identified several practical ways in which hospitalists can reduce antibiotic overuse, including in the management of patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
Identify asymptomatic bacteriuria
One key area in which hospitalists can improve antibiotic stewardship is in recognizing asymptomatic bacteriuria and the harms associated with treatment, Dr. Vaughn said. For example, a common scenario for hospitalists might involve and 80-year-old woman with dementia, who can provide little in the way of history, and whose chest x-ray can’t rule out an underlying infection. This patient might have a positive urine culture, but no other signs of a urinary tract infection. “We know that asymptomatic bacteriuria is very common in hospitalized patients,” especially elderly women living in nursing home settings, she noted.
In cases of asymptomatic bacteriuria, data show that antibiotic treatment does not improve outcomes, and in fact may increase the risk of subsequent UTI, said Dr. Vaughn. Elderly patients also are at increased risk for developing antibiotic-related adverse events, especially Clostridioides difficile. Asymptomatic bacteriuria is any bacteria in the urine in the absence of signs or symptoms of a UTI, even if lab tests show pyuria, nitrates, and resistant bacteria. These lab results are often associated with inappropriate antibiotic use. “The laboratory tests can’t distinguish between asymptomatic bacteriuria and a UTI, only the symptoms can,” she emphasized.
Contain treatment of community-acquired pneumonia
Another practical point for reducing antibiotics in the hospital setting is to limit treatment of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) to 5 days when possible. Duration matters because for many diseases, shorter durations of antibiotic treatments are just as effective as longer durations based on the latest evidence. “This is a change in dogma,” from previous thinking that patients must complete a full course, and that anything less might promote antibiotic resistance, she said.
“In fact, longer antibiotic durations kill off more healthy, normal flora, select for resistant pathogens, increase the risk of C. difficile, and increase the risk of side effects,” she said.
Ultimately, the right treatment duration for pneumonia depends on several factors including patient factors, disease, clinical stability, and rate of improvement. However, a good rule of thumb is that approximately 89% of CAP patients need only 5 days of antibiotics as long as they are afebrile for 48 hours and have 1 or fewer vital sign abnormalities by day 5 of treatment. “We do need to prescribe longer durations for patients with complications,” she emphasized.
Revisit need for antibiotics at discharge
Hospitalists also can practice antibiotic stewardship by considering four points at patient discharge, said Dr. Vaughn.
First, consider whether antibiotics can be stopped. For example, antibiotics are not needed on discharge if infection is no longer the most likely diagnosis, or if the course of antibiotics has been completed, as is often the case for patients hospitalized with CAP, she noted.
Second, if the antibiotics can’t be stopped at the time of discharge, consider whether the preferred agent is being used. Third, be sure the patient is receiving the minimum duration of antibiotics, and fourth, be sure that the dose, indication, and total planned duration with start and stop dates is written in the discharge summary, said Dr. Vaughn. “This helps with communication to our outpatient providers as well as with education to the patients themselves.”
Bacterial coinfections rare in COVID-19
Dr. Vaughn concluded the session with data from a study she conducted with colleagues on the use of empiric antibacterial therapy and community-onset bacterial coinfection in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. The study included 1,667 patients at 32 hospitals in Michigan. The number of patients treated with antibiotics varied widely among hospitals, from 30% to as much as 90%, Dr. Vaughn said.
“What we found was that more than half of hospitalized patients with COVID (57%) received empiric antibiotic therapy in the first few days of hospitalization,” she said.
However, “despite all the antibiotic use, community-onset bacterial coinfections were rare,” and occurred in only 3.5% of the patients, meaning that the number needed to treat with antibiotics to prevent a single case was about 20.
Predictors of community-onset co-infections in the patients included older age, more severe disease, patients coming from nursing homes, and those with lower BMI or kidney disease, said Dr. Vaughn. She and her team also found that procalcitonin’s positive predictive value was 9.3%, but the negative predictive value was 98.3%, so these patients were extremely likely to have no coinfection.
Dr. Vaughn said that in her practice she might order procalcitonin when considering stopping antibiotics in a patient with COVID-19 and make a decision based on the negative predictive value, but she emphasized that she does not use it in the converse situation to rely on a positive value when deciding whether to start antibiotics in these patients.
Dr. Vaughn had no financial conflicts to disclose.
“Antibiotic stewardship is never easy, and sometimes it is very difficult to differentiate what is going on with a patient in the clinical setting,” said Valerie M. Vaughn, MD, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, at SHM Converge, the annual conference of the Society of Hospital Medicine.
“We know from studies that 20% of hospitalized patients who receive an antibiotic have an adverse drug event from that antibiotic within 30 days,” said Dr. Vaughn.
Dr. Vaughn identified several practical ways in which hospitalists can reduce antibiotic overuse, including in the management of patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
Identify asymptomatic bacteriuria
One key area in which hospitalists can improve antibiotic stewardship is in recognizing asymptomatic bacteriuria and the harms associated with treatment, Dr. Vaughn said. For example, a common scenario for hospitalists might involve and 80-year-old woman with dementia, who can provide little in the way of history, and whose chest x-ray can’t rule out an underlying infection. This patient might have a positive urine culture, but no other signs of a urinary tract infection. “We know that asymptomatic bacteriuria is very common in hospitalized patients,” especially elderly women living in nursing home settings, she noted.
In cases of asymptomatic bacteriuria, data show that antibiotic treatment does not improve outcomes, and in fact may increase the risk of subsequent UTI, said Dr. Vaughn. Elderly patients also are at increased risk for developing antibiotic-related adverse events, especially Clostridioides difficile. Asymptomatic bacteriuria is any bacteria in the urine in the absence of signs or symptoms of a UTI, even if lab tests show pyuria, nitrates, and resistant bacteria. These lab results are often associated with inappropriate antibiotic use. “The laboratory tests can’t distinguish between asymptomatic bacteriuria and a UTI, only the symptoms can,” she emphasized.
Contain treatment of community-acquired pneumonia
Another practical point for reducing antibiotics in the hospital setting is to limit treatment of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) to 5 days when possible. Duration matters because for many diseases, shorter durations of antibiotic treatments are just as effective as longer durations based on the latest evidence. “This is a change in dogma,” from previous thinking that patients must complete a full course, and that anything less might promote antibiotic resistance, she said.
“In fact, longer antibiotic durations kill off more healthy, normal flora, select for resistant pathogens, increase the risk of C. difficile, and increase the risk of side effects,” she said.
Ultimately, the right treatment duration for pneumonia depends on several factors including patient factors, disease, clinical stability, and rate of improvement. However, a good rule of thumb is that approximately 89% of CAP patients need only 5 days of antibiotics as long as they are afebrile for 48 hours and have 1 or fewer vital sign abnormalities by day 5 of treatment. “We do need to prescribe longer durations for patients with complications,” she emphasized.
Revisit need for antibiotics at discharge
Hospitalists also can practice antibiotic stewardship by considering four points at patient discharge, said Dr. Vaughn.
First, consider whether antibiotics can be stopped. For example, antibiotics are not needed on discharge if infection is no longer the most likely diagnosis, or if the course of antibiotics has been completed, as is often the case for patients hospitalized with CAP, she noted.
Second, if the antibiotics can’t be stopped at the time of discharge, consider whether the preferred agent is being used. Third, be sure the patient is receiving the minimum duration of antibiotics, and fourth, be sure that the dose, indication, and total planned duration with start and stop dates is written in the discharge summary, said Dr. Vaughn. “This helps with communication to our outpatient providers as well as with education to the patients themselves.”
Bacterial coinfections rare in COVID-19
Dr. Vaughn concluded the session with data from a study she conducted with colleagues on the use of empiric antibacterial therapy and community-onset bacterial coinfection in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. The study included 1,667 patients at 32 hospitals in Michigan. The number of patients treated with antibiotics varied widely among hospitals, from 30% to as much as 90%, Dr. Vaughn said.
“What we found was that more than half of hospitalized patients with COVID (57%) received empiric antibiotic therapy in the first few days of hospitalization,” she said.
However, “despite all the antibiotic use, community-onset bacterial coinfections were rare,” and occurred in only 3.5% of the patients, meaning that the number needed to treat with antibiotics to prevent a single case was about 20.
Predictors of community-onset co-infections in the patients included older age, more severe disease, patients coming from nursing homes, and those with lower BMI or kidney disease, said Dr. Vaughn. She and her team also found that procalcitonin’s positive predictive value was 9.3%, but the negative predictive value was 98.3%, so these patients were extremely likely to have no coinfection.
Dr. Vaughn said that in her practice she might order procalcitonin when considering stopping antibiotics in a patient with COVID-19 and make a decision based on the negative predictive value, but she emphasized that she does not use it in the converse situation to rely on a positive value when deciding whether to start antibiotics in these patients.
Dr. Vaughn had no financial conflicts to disclose.
“Antibiotic stewardship is never easy, and sometimes it is very difficult to differentiate what is going on with a patient in the clinical setting,” said Valerie M. Vaughn, MD, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, at SHM Converge, the annual conference of the Society of Hospital Medicine.
“We know from studies that 20% of hospitalized patients who receive an antibiotic have an adverse drug event from that antibiotic within 30 days,” said Dr. Vaughn.
Dr. Vaughn identified several practical ways in which hospitalists can reduce antibiotic overuse, including in the management of patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
Identify asymptomatic bacteriuria
One key area in which hospitalists can improve antibiotic stewardship is in recognizing asymptomatic bacteriuria and the harms associated with treatment, Dr. Vaughn said. For example, a common scenario for hospitalists might involve and 80-year-old woman with dementia, who can provide little in the way of history, and whose chest x-ray can’t rule out an underlying infection. This patient might have a positive urine culture, but no other signs of a urinary tract infection. “We know that asymptomatic bacteriuria is very common in hospitalized patients,” especially elderly women living in nursing home settings, she noted.
In cases of asymptomatic bacteriuria, data show that antibiotic treatment does not improve outcomes, and in fact may increase the risk of subsequent UTI, said Dr. Vaughn. Elderly patients also are at increased risk for developing antibiotic-related adverse events, especially Clostridioides difficile. Asymptomatic bacteriuria is any bacteria in the urine in the absence of signs or symptoms of a UTI, even if lab tests show pyuria, nitrates, and resistant bacteria. These lab results are often associated with inappropriate antibiotic use. “The laboratory tests can’t distinguish between asymptomatic bacteriuria and a UTI, only the symptoms can,” she emphasized.
Contain treatment of community-acquired pneumonia
Another practical point for reducing antibiotics in the hospital setting is to limit treatment of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) to 5 days when possible. Duration matters because for many diseases, shorter durations of antibiotic treatments are just as effective as longer durations based on the latest evidence. “This is a change in dogma,” from previous thinking that patients must complete a full course, and that anything less might promote antibiotic resistance, she said.
“In fact, longer antibiotic durations kill off more healthy, normal flora, select for resistant pathogens, increase the risk of C. difficile, and increase the risk of side effects,” she said.
Ultimately, the right treatment duration for pneumonia depends on several factors including patient factors, disease, clinical stability, and rate of improvement. However, a good rule of thumb is that approximately 89% of CAP patients need only 5 days of antibiotics as long as they are afebrile for 48 hours and have 1 or fewer vital sign abnormalities by day 5 of treatment. “We do need to prescribe longer durations for patients with complications,” she emphasized.
Revisit need for antibiotics at discharge
Hospitalists also can practice antibiotic stewardship by considering four points at patient discharge, said Dr. Vaughn.
First, consider whether antibiotics can be stopped. For example, antibiotics are not needed on discharge if infection is no longer the most likely diagnosis, or if the course of antibiotics has been completed, as is often the case for patients hospitalized with CAP, she noted.
Second, if the antibiotics can’t be stopped at the time of discharge, consider whether the preferred agent is being used. Third, be sure the patient is receiving the minimum duration of antibiotics, and fourth, be sure that the dose, indication, and total planned duration with start and stop dates is written in the discharge summary, said Dr. Vaughn. “This helps with communication to our outpatient providers as well as with education to the patients themselves.”
Bacterial coinfections rare in COVID-19
Dr. Vaughn concluded the session with data from a study she conducted with colleagues on the use of empiric antibacterial therapy and community-onset bacterial coinfection in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. The study included 1,667 patients at 32 hospitals in Michigan. The number of patients treated with antibiotics varied widely among hospitals, from 30% to as much as 90%, Dr. Vaughn said.
“What we found was that more than half of hospitalized patients with COVID (57%) received empiric antibiotic therapy in the first few days of hospitalization,” she said.
However, “despite all the antibiotic use, community-onset bacterial coinfections were rare,” and occurred in only 3.5% of the patients, meaning that the number needed to treat with antibiotics to prevent a single case was about 20.
Predictors of community-onset co-infections in the patients included older age, more severe disease, patients coming from nursing homes, and those with lower BMI or kidney disease, said Dr. Vaughn. She and her team also found that procalcitonin’s positive predictive value was 9.3%, but the negative predictive value was 98.3%, so these patients were extremely likely to have no coinfection.
Dr. Vaughn said that in her practice she might order procalcitonin when considering stopping antibiotics in a patient with COVID-19 and make a decision based on the negative predictive value, but she emphasized that she does not use it in the converse situation to rely on a positive value when deciding whether to start antibiotics in these patients.
Dr. Vaughn had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM SHM CONVERGE 2021
Mentor-mentee relationships in hospital medicine
Your mentor has been looking for someone to help lead a new project in your division, and tells you she’s been having a hard time finding someone – but that you would be great. The project isn’t something you are very interested in doing and you’re already swamped with other projects, but the mentor seems to need the help. What do you do?
Mentor-mentee relationships can be deeply beneficial, but the dynamics – in this situation and many others – can be complex. At SHM Converge, the annual conference of the Society of Hospital Medicine, panelists offered guidance on how best to navigate this terrain.
Vineet Arora, MD, MAPP, MHM, associate chief medical officer for clinical learning environment at the University of Chicago, suggested that, in the situation involving the mentor’s request to an uncertain mentee, the mentee should not give an immediate answer, but consider the pros and cons.
“It’s tough when it’s somebody who’s directly overseeing you,” she said. “If you’re really truly the best person, they’re going to want you in the job, and maybe they’ll make it work for you.” She said it would be important to find out why the mentor is having trouble finding someone, and suggested the mentee could find someone with whom to discuss it.
Calling mentoring a “team sport,” Dr. Arora described several types: the traditional mentor who helps many aspects of a mentee’s career, a “coach” who helps on a specific project or topic, a “sponsor” that can help elevate a mentee to a bigger opportunity, and a “connector” who can help a mentee begin new career relationships.
“Don’t invest in just one person,” she said. “Try to get that personal board of directors.”
She mentioned six things all mentors should do: Choose mentees carefully, establish a mentorship team, run a tight ship, head off rifts or resolve them, prepare for transitions when they take a new position and might have a new relationship with a mentee, and don’t commit “mentorship malpractice.”
Mentoring is a two-way street, with both people benefiting and learning, but mentoring can have its troubles, either through active, dysfunctional behavior that’s easy to spot, or passive behavior, such as the “bottleneck” problem when a mentor is too preoccupied with his or her own priorities to mentor well, the “country clubber” who mentors only for popularity and social capital but doesn’t do the work required, and the “world traveler” who is sought after but has little time for day-to-day mentoring.
Valerie Vaughan, MD, MSc, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Utah, described four “golden rules” of being a mentee. First, find a CAPE mentor (for capable, availability, projects of interest, and easy to get along with). Then, be respectful of a mentor’s time, communicate effectively, and be engaged and energizing.
“Mentors typically don’t get paid to mentor and so a lot of them are doing it because they find joy for doing it,” Dr. Vaughan said. “So as much as you can as a mentee, try to be the person who brings energy to the mentor-mentee relationship. It’s up to you to drive projects forward.”
Valerie Press, MD, MPH, SFHM, associate professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, offered tips for men who are mentoring women. She said that, while cross-gender mentorship is common and important, gender-based stereotypes and “unconscious assumptions” are alive and well. Women, she noted, have less access to mentorship and sponsorship, are paid less for the same work, and have high rates of attrition.
Male mentors have to meet the challenge of thinking outside of their own lived experience, combating stereotypes, and addressing these gender-based career disparities, she said.
She suggested that male mentors, for one thing, “rewrite gender scripts,” with comments such as, “This is a difficult situation, but I have confidence in you! What do you think your next move should be?” They should also “learn from each other on how to change the power dynamic,” and start and participate in conversations involving emotions, since they can be clues to what a mentee is experiencing.
When it comes to pushing for better policies, “be an upstander, not a bystander,” Dr. Press said.
“Use your organizational power and your social capital,” she said. “Use your voice to help make more equitable policies. Don’t just leave it to the women’s committee to come up with solutions to lack of lactation rooms, or paternity and maternity leave, or better daycare. These are family issues and everybody issues.”
Maylyn S. Martinez, MD, clinical associate professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, suggested that mentors for physicians from minority groups should resist the tendency to view their interests narrowly.
“Don’t assume that their interests are going to center on their gender or minority status – invite them to be on projects that have nothing to do with that,” she said. They should also not be encouraged to do projects that won’t help with career advancement any more than others would be encouraged to take on such projects.
“Be the solution,” she said. “Not the problem.”
Your mentor has been looking for someone to help lead a new project in your division, and tells you she’s been having a hard time finding someone – but that you would be great. The project isn’t something you are very interested in doing and you’re already swamped with other projects, but the mentor seems to need the help. What do you do?
Mentor-mentee relationships can be deeply beneficial, but the dynamics – in this situation and many others – can be complex. At SHM Converge, the annual conference of the Society of Hospital Medicine, panelists offered guidance on how best to navigate this terrain.
Vineet Arora, MD, MAPP, MHM, associate chief medical officer for clinical learning environment at the University of Chicago, suggested that, in the situation involving the mentor’s request to an uncertain mentee, the mentee should not give an immediate answer, but consider the pros and cons.
“It’s tough when it’s somebody who’s directly overseeing you,” she said. “If you’re really truly the best person, they’re going to want you in the job, and maybe they’ll make it work for you.” She said it would be important to find out why the mentor is having trouble finding someone, and suggested the mentee could find someone with whom to discuss it.
Calling mentoring a “team sport,” Dr. Arora described several types: the traditional mentor who helps many aspects of a mentee’s career, a “coach” who helps on a specific project or topic, a “sponsor” that can help elevate a mentee to a bigger opportunity, and a “connector” who can help a mentee begin new career relationships.
“Don’t invest in just one person,” she said. “Try to get that personal board of directors.”
She mentioned six things all mentors should do: Choose mentees carefully, establish a mentorship team, run a tight ship, head off rifts or resolve them, prepare for transitions when they take a new position and might have a new relationship with a mentee, and don’t commit “mentorship malpractice.”
Mentoring is a two-way street, with both people benefiting and learning, but mentoring can have its troubles, either through active, dysfunctional behavior that’s easy to spot, or passive behavior, such as the “bottleneck” problem when a mentor is too preoccupied with his or her own priorities to mentor well, the “country clubber” who mentors only for popularity and social capital but doesn’t do the work required, and the “world traveler” who is sought after but has little time for day-to-day mentoring.
Valerie Vaughan, MD, MSc, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Utah, described four “golden rules” of being a mentee. First, find a CAPE mentor (for capable, availability, projects of interest, and easy to get along with). Then, be respectful of a mentor’s time, communicate effectively, and be engaged and energizing.
“Mentors typically don’t get paid to mentor and so a lot of them are doing it because they find joy for doing it,” Dr. Vaughan said. “So as much as you can as a mentee, try to be the person who brings energy to the mentor-mentee relationship. It’s up to you to drive projects forward.”
Valerie Press, MD, MPH, SFHM, associate professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, offered tips for men who are mentoring women. She said that, while cross-gender mentorship is common and important, gender-based stereotypes and “unconscious assumptions” are alive and well. Women, she noted, have less access to mentorship and sponsorship, are paid less for the same work, and have high rates of attrition.
Male mentors have to meet the challenge of thinking outside of their own lived experience, combating stereotypes, and addressing these gender-based career disparities, she said.
She suggested that male mentors, for one thing, “rewrite gender scripts,” with comments such as, “This is a difficult situation, but I have confidence in you! What do you think your next move should be?” They should also “learn from each other on how to change the power dynamic,” and start and participate in conversations involving emotions, since they can be clues to what a mentee is experiencing.
When it comes to pushing for better policies, “be an upstander, not a bystander,” Dr. Press said.
“Use your organizational power and your social capital,” she said. “Use your voice to help make more equitable policies. Don’t just leave it to the women’s committee to come up with solutions to lack of lactation rooms, or paternity and maternity leave, or better daycare. These are family issues and everybody issues.”
Maylyn S. Martinez, MD, clinical associate professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, suggested that mentors for physicians from minority groups should resist the tendency to view their interests narrowly.
“Don’t assume that their interests are going to center on their gender or minority status – invite them to be on projects that have nothing to do with that,” she said. They should also not be encouraged to do projects that won’t help with career advancement any more than others would be encouraged to take on such projects.
“Be the solution,” she said. “Not the problem.”
Your mentor has been looking for someone to help lead a new project in your division, and tells you she’s been having a hard time finding someone – but that you would be great. The project isn’t something you are very interested in doing and you’re already swamped with other projects, but the mentor seems to need the help. What do you do?
Mentor-mentee relationships can be deeply beneficial, but the dynamics – in this situation and many others – can be complex. At SHM Converge, the annual conference of the Society of Hospital Medicine, panelists offered guidance on how best to navigate this terrain.
Vineet Arora, MD, MAPP, MHM, associate chief medical officer for clinical learning environment at the University of Chicago, suggested that, in the situation involving the mentor’s request to an uncertain mentee, the mentee should not give an immediate answer, but consider the pros and cons.
“It’s tough when it’s somebody who’s directly overseeing you,” she said. “If you’re really truly the best person, they’re going to want you in the job, and maybe they’ll make it work for you.” She said it would be important to find out why the mentor is having trouble finding someone, and suggested the mentee could find someone with whom to discuss it.
Calling mentoring a “team sport,” Dr. Arora described several types: the traditional mentor who helps many aspects of a mentee’s career, a “coach” who helps on a specific project or topic, a “sponsor” that can help elevate a mentee to a bigger opportunity, and a “connector” who can help a mentee begin new career relationships.
“Don’t invest in just one person,” she said. “Try to get that personal board of directors.”
She mentioned six things all mentors should do: Choose mentees carefully, establish a mentorship team, run a tight ship, head off rifts or resolve them, prepare for transitions when they take a new position and might have a new relationship with a mentee, and don’t commit “mentorship malpractice.”
Mentoring is a two-way street, with both people benefiting and learning, but mentoring can have its troubles, either through active, dysfunctional behavior that’s easy to spot, or passive behavior, such as the “bottleneck” problem when a mentor is too preoccupied with his or her own priorities to mentor well, the “country clubber” who mentors only for popularity and social capital but doesn’t do the work required, and the “world traveler” who is sought after but has little time for day-to-day mentoring.
Valerie Vaughan, MD, MSc, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Utah, described four “golden rules” of being a mentee. First, find a CAPE mentor (for capable, availability, projects of interest, and easy to get along with). Then, be respectful of a mentor’s time, communicate effectively, and be engaged and energizing.
“Mentors typically don’t get paid to mentor and so a lot of them are doing it because they find joy for doing it,” Dr. Vaughan said. “So as much as you can as a mentee, try to be the person who brings energy to the mentor-mentee relationship. It’s up to you to drive projects forward.”
Valerie Press, MD, MPH, SFHM, associate professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, offered tips for men who are mentoring women. She said that, while cross-gender mentorship is common and important, gender-based stereotypes and “unconscious assumptions” are alive and well. Women, she noted, have less access to mentorship and sponsorship, are paid less for the same work, and have high rates of attrition.
Male mentors have to meet the challenge of thinking outside of their own lived experience, combating stereotypes, and addressing these gender-based career disparities, she said.
She suggested that male mentors, for one thing, “rewrite gender scripts,” with comments such as, “This is a difficult situation, but I have confidence in you! What do you think your next move should be?” They should also “learn from each other on how to change the power dynamic,” and start and participate in conversations involving emotions, since they can be clues to what a mentee is experiencing.
When it comes to pushing for better policies, “be an upstander, not a bystander,” Dr. Press said.
“Use your organizational power and your social capital,” she said. “Use your voice to help make more equitable policies. Don’t just leave it to the women’s committee to come up with solutions to lack of lactation rooms, or paternity and maternity leave, or better daycare. These are family issues and everybody issues.”
Maylyn S. Martinez, MD, clinical associate professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, suggested that mentors for physicians from minority groups should resist the tendency to view their interests narrowly.
“Don’t assume that their interests are going to center on their gender or minority status – invite them to be on projects that have nothing to do with that,” she said. They should also not be encouraged to do projects that won’t help with career advancement any more than others would be encouraged to take on such projects.
“Be the solution,” she said. “Not the problem.”
FROM SHM CONVERGE 2021
18-year-old woman • chest pain • shortness of breath • electrocardiogram abnormality • Dx?
THE CASE
An 18-year-old woman with no significant past medical history presented to the emergency department complaining of midsternal chest pain and mild shortness of breath, which had been intermittent for the past several months. She denied any history of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism risk factors, such as oral contraceptive use.
Laboratory values were within normal limits. An electrocardiogram (EKG), however, showed T-wave inversions in leads V1 and V2, and physical examination revealed decreased breath sounds in the right lung base. A chest radiograph and subsequent chest computed tomography (CT) were ordered.
The initial radiograph (FIGURE 1) showed a large right anterior mediastinal mass; the CT revealed fat, fluid, soft tissue, and ossification within the mass (FIGURE 2). The CT also showed evidence of local mass effect on the right atrium, as well as compressive atelectasis in the adjacent right lung, contributing to the patient’s EKG abnormality and physical exam findings.
THE DIAGNOSIS
Based on the patient’s clinical history and imaging findings, which were consistent with a benign well-differentiated teratoma, she was given a diagnosis of anterior mediastinal teratoma.
DISCUSSION
Teratomas are tumors composed of pluripotent stem cells that carry elements from all 3 of the embryologic layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm).1 There are 3 classifications of teratomas: mature (well-differentiated), immature (poorly differentiated), and malignant.
Tumors of germ cell origin are rare within the anterior mediastinum, accounting for 1% to 3% of total reported cases.2 Among anterior mediastinal masses, germ cell tumors such as teratomas, seminomas, and nonseminomatous tumors comprise approximately 15% of adult and 24% of pediatric anterior mediastinal tumors.3
It is reported that up to 60% of patients with mediastinal teratomas present with no signs or symptoms upon diagnosis.4 When the mass is large, patients can develop chest pain or shortness of breath relating to tumor mass effect. In rare instances, there can be hemoptysis or trichoptysis, pathognomonic for teratomas with bronchial communication.5 Physical exam findings are also nonspecific and may include decreased breath sounds secondary to compressive atelectasis with large tumor burden.
Continue to: Radiographic imaging...
Radiographic imaging is essential to elucidate the diagnosis. Chest radiograph can show an intrathoracic mass, and CT can provide further characterization, such as density and precise location.
Location of mass guides differential
Localizing an intrathoracic mass in the anterior, middle, or posterior mediastinum allows for narrowing of the differential diagnosis (TABLE6). The main diagnostic consideration for a middle mediastinal or hilar mass is primary carcinoma. Posterior mediastinal masses, on the other hand, are generally of benign etiology and may include neurogenic tumors, foregut duplication cysts, or, in rare cases, extramedullary hematopoiesis.
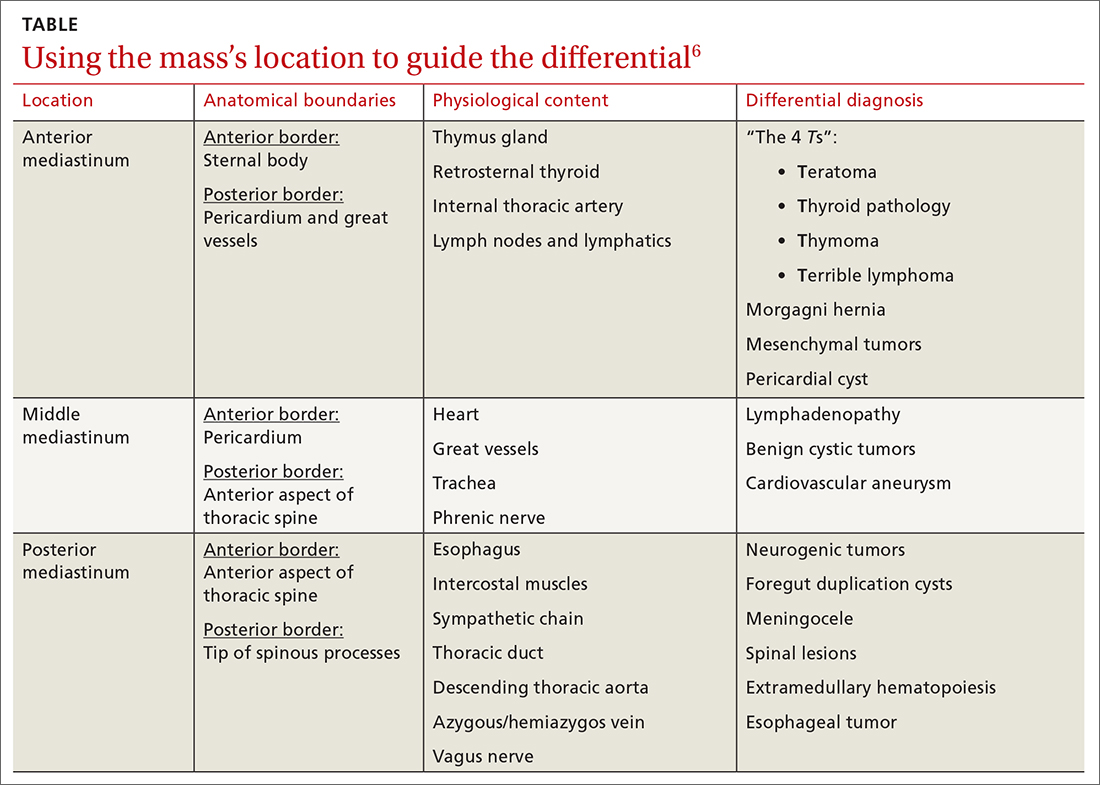
The differential diagnosis of anterior mediastinal masses can be separated into 4 main categories of disease, colloquially known as the “4 Ts”:
Teratoma. Mixed tissue densities seen on CT relate to the multiple tissue types originating from the embryologic germ cell layers.Frequently, there will be fat, fluid, and calcifications.
Thyroid pathology. A goiter or thyroid cancer can manifest with endocrine dysfunction, such as thyroid-stimulating hormone and T3/T4 abnormalities. A thyroid mass tends to sit more superiorly than do other anterior mediastinal masses and may be confirmed using a nuclear scan looking for increased radioactive iodine uptake.
Continue to: Thymoma
Thymoma. The diagnostic features include parathymic syndromes such as myasthenia gravis (30%-50% of thymoma cases7,8) and pure red cell aplasia (5% of thymoma cases9).
“Terrible” lymphoma. The most effective way to differentiate an anterior mediastinal mass due to lymphadenopathy (secondary to lymphoma) is to perform a tissue sample biopsy.
Also consider, as part of the differential for anterior mediastinal masses, such things as mesenchymal tumors, Morgagni hernia (anterior diaphragmatic defect), and pericardial cysts (fluid attenuating and usually located at the right cardiophrenic angle).
Surgical resection is effective
The treatment for anterior mediastinal teratoma is surgical resection.10 A complete surgical resection is typically curative and provides adequate therapy for symptom resolution.
The standard surgical approach involves gaining access to the anterior mediastinum via a median sternotomy. When there is extensive tumor involvement of the hemithorax, clamshell thoracotomy is preferred, requiring incisions in both the left and right hemithoraxes.11
Continue to: Our patient
Our patient underwent resection of the tumor; the subsequent pathology report for the specimen (FIGURE 3) confirmed the diagnosis. There was no abnormal enhancement or vascular invasion to suggest aggressive or malignant potential.
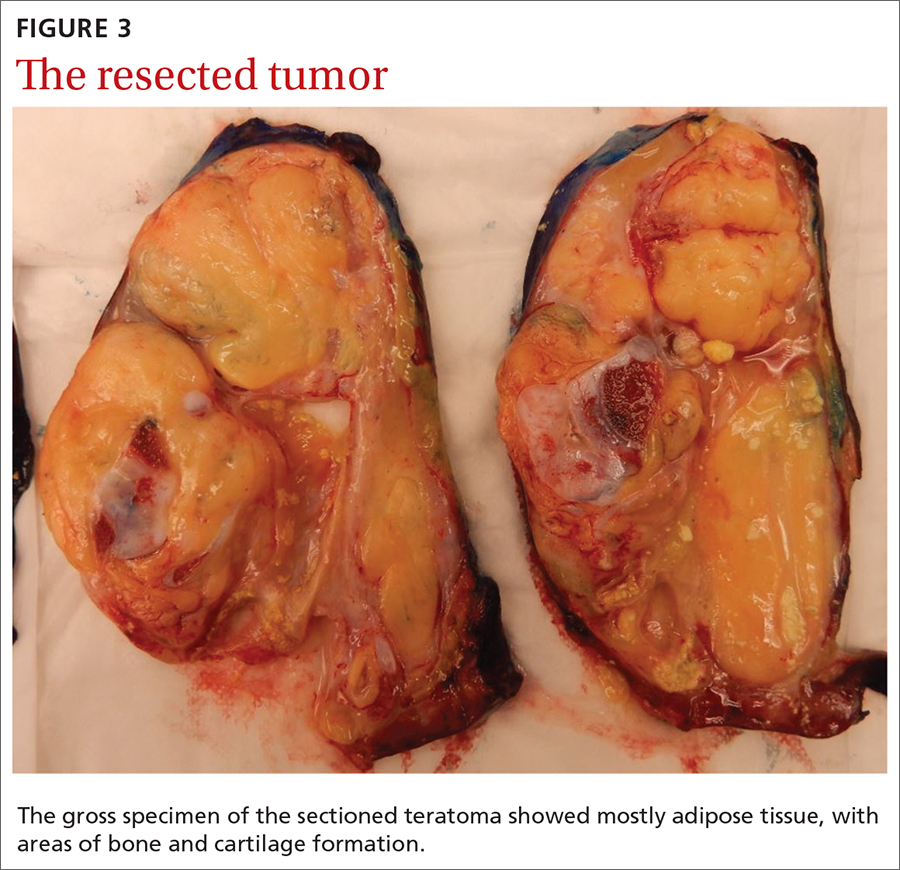
THE TAKEAWAY
Patients frequently present with nonspecific and vague chest complaints. This case points to the importance of obtaining a thorough clinical history and conducting a complete physical examination to guide additional work-up and radiographic imaging.
CORRESPONDENCE
Cassie Tran, MD, 320 E North Avenue, Pittsburgh, PA 15212; [email protected]
1. Chen C, Zheng H, Jiang S. An unusual case of giant mediastinal teratoma with malignant transformation. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;86:302-304.
2. Nichols CR. Mediastinal germ cell tumors: clinical features and biologic correlates. Chest. 1991;99:472. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.2.472
3. Mulen B, Richardson JD. Primary anterior mediastinal tumors in children and adults. Ann Thorac Surg. 1986;42:338. doi: 10.1016/S0003-4975(10)62751-8
4. Carter B, Okumura M, Detterbeck F, et al. Approaching the patient with an anterior mediastinal mass: a guide for radiologists. J Thorac Oncol. 2014;9 (9 suppl 2):S100-S118.
5. Dar RA, Mushtaque M, Wani SH, et al. Giant intrapulmonary teratoma: a rare case. Case Rep Pulmonol. 2011;2011:298653.
6. Whitten C, Khan S, Munneke G, et al. A diagnostic approach to mediastinal abnormalities. RadioGraphics. 2007;27:657-672.
7. Osserman KE, Genkins G. Studies in myasthenia gravis: review of a 20-year experience in over 1200 patients. Mt Sinai J Med. 1971;38:497-537.
8. Marx A, Muller-Hermelink HK, Strobel P. The role of thymomas in the development of myasthenia gravis. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2003;998:223-236.
9. Rosai J, Levine GD. Tumors of the thymus. In: Firminger HI, ed. Atlas of Tumor Pathology. Washington, DC: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology; 1976: 34-212.
10. Yendamuri S. Resection of a giant mediastinal teratoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;102:e401-e402.
11. Yokoyama Y, Chen F, Date H. Surgical resection of a giant mediastinal teratoma occupying the entire left hemithorax. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;62:255-257.
THE CASE
An 18-year-old woman with no significant past medical history presented to the emergency department complaining of midsternal chest pain and mild shortness of breath, which had been intermittent for the past several months. She denied any history of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism risk factors, such as oral contraceptive use.
Laboratory values were within normal limits. An electrocardiogram (EKG), however, showed T-wave inversions in leads V1 and V2, and physical examination revealed decreased breath sounds in the right lung base. A chest radiograph and subsequent chest computed tomography (CT) were ordered.

The initial radiograph (FIGURE 1) showed a large right anterior mediastinal mass; the CT revealed fat, fluid, soft tissue, and ossification within the mass (FIGURE 2). The CT also showed evidence of local mass effect on the right atrium, as well as compressive atelectasis in the adjacent right lung, contributing to the patient’s EKG abnormality and physical exam findings.

THE DIAGNOSIS
Based on the patient’s clinical history and imaging findings, which were consistent with a benign well-differentiated teratoma, she was given a diagnosis of anterior mediastinal teratoma.
DISCUSSION
Teratomas are tumors composed of pluripotent stem cells that carry elements from all 3 of the embryologic layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm).1 There are 3 classifications of teratomas: mature (well-differentiated), immature (poorly differentiated), and malignant.
Tumors of germ cell origin are rare within the anterior mediastinum, accounting for 1% to 3% of total reported cases.2 Among anterior mediastinal masses, germ cell tumors such as teratomas, seminomas, and nonseminomatous tumors comprise approximately 15% of adult and 24% of pediatric anterior mediastinal tumors.3
It is reported that up to 60% of patients with mediastinal teratomas present with no signs or symptoms upon diagnosis.4 When the mass is large, patients can develop chest pain or shortness of breath relating to tumor mass effect. In rare instances, there can be hemoptysis or trichoptysis, pathognomonic for teratomas with bronchial communication.5 Physical exam findings are also nonspecific and may include decreased breath sounds secondary to compressive atelectasis with large tumor burden.
Continue to: Radiographic imaging...
Radiographic imaging is essential to elucidate the diagnosis. Chest radiograph can show an intrathoracic mass, and CT can provide further characterization, such as density and precise location.
Location of mass guides differential
Localizing an intrathoracic mass in the anterior, middle, or posterior mediastinum allows for narrowing of the differential diagnosis (TABLE6). The main diagnostic consideration for a middle mediastinal or hilar mass is primary carcinoma. Posterior mediastinal masses, on the other hand, are generally of benign etiology and may include neurogenic tumors, foregut duplication cysts, or, in rare cases, extramedullary hematopoiesis.

The differential diagnosis of anterior mediastinal masses can be separated into 4 main categories of disease, colloquially known as the “4 Ts”:
Teratoma. Mixed tissue densities seen on CT relate to the multiple tissue types originating from the embryologic germ cell layers.Frequently, there will be fat, fluid, and calcifications.
Thyroid pathology. A goiter or thyroid cancer can manifest with endocrine dysfunction, such as thyroid-stimulating hormone and T3/T4 abnormalities. A thyroid mass tends to sit more superiorly than do other anterior mediastinal masses and may be confirmed using a nuclear scan looking for increased radioactive iodine uptake.
Continue to: Thymoma
Thymoma. The diagnostic features include parathymic syndromes such as myasthenia gravis (30%-50% of thymoma cases7,8) and pure red cell aplasia (5% of thymoma cases9).
“Terrible” lymphoma. The most effective way to differentiate an anterior mediastinal mass due to lymphadenopathy (secondary to lymphoma) is to perform a tissue sample biopsy.
Also consider, as part of the differential for anterior mediastinal masses, such things as mesenchymal tumors, Morgagni hernia (anterior diaphragmatic defect), and pericardial cysts (fluid attenuating and usually located at the right cardiophrenic angle).
Surgical resection is effective
The treatment for anterior mediastinal teratoma is surgical resection.10 A complete surgical resection is typically curative and provides adequate therapy for symptom resolution.
The standard surgical approach involves gaining access to the anterior mediastinum via a median sternotomy. When there is extensive tumor involvement of the hemithorax, clamshell thoracotomy is preferred, requiring incisions in both the left and right hemithoraxes.11
Continue to: Our patient
Our patient underwent resection of the tumor; the subsequent pathology report for the specimen (FIGURE 3) confirmed the diagnosis. There was no abnormal enhancement or vascular invasion to suggest aggressive or malignant potential.

THE TAKEAWAY
Patients frequently present with nonspecific and vague chest complaints. This case points to the importance of obtaining a thorough clinical history and conducting a complete physical examination to guide additional work-up and radiographic imaging.
CORRESPONDENCE
Cassie Tran, MD, 320 E North Avenue, Pittsburgh, PA 15212; [email protected]
THE CASE
An 18-year-old woman with no significant past medical history presented to the emergency department complaining of midsternal chest pain and mild shortness of breath, which had been intermittent for the past several months. She denied any history of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism risk factors, such as oral contraceptive use.
Laboratory values were within normal limits. An electrocardiogram (EKG), however, showed T-wave inversions in leads V1 and V2, and physical examination revealed decreased breath sounds in the right lung base. A chest radiograph and subsequent chest computed tomography (CT) were ordered.

The initial radiograph (FIGURE 1) showed a large right anterior mediastinal mass; the CT revealed fat, fluid, soft tissue, and ossification within the mass (FIGURE 2). The CT also showed evidence of local mass effect on the right atrium, as well as compressive atelectasis in the adjacent right lung, contributing to the patient’s EKG abnormality and physical exam findings.

THE DIAGNOSIS
Based on the patient’s clinical history and imaging findings, which were consistent with a benign well-differentiated teratoma, she was given a diagnosis of anterior mediastinal teratoma.
DISCUSSION
Teratomas are tumors composed of pluripotent stem cells that carry elements from all 3 of the embryologic layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm).1 There are 3 classifications of teratomas: mature (well-differentiated), immature (poorly differentiated), and malignant.
Tumors of germ cell origin are rare within the anterior mediastinum, accounting for 1% to 3% of total reported cases.2 Among anterior mediastinal masses, germ cell tumors such as teratomas, seminomas, and nonseminomatous tumors comprise approximately 15% of adult and 24% of pediatric anterior mediastinal tumors.3
It is reported that up to 60% of patients with mediastinal teratomas present with no signs or symptoms upon diagnosis.4 When the mass is large, patients can develop chest pain or shortness of breath relating to tumor mass effect. In rare instances, there can be hemoptysis or trichoptysis, pathognomonic for teratomas with bronchial communication.5 Physical exam findings are also nonspecific and may include decreased breath sounds secondary to compressive atelectasis with large tumor burden.
Continue to: Radiographic imaging...
Radiographic imaging is essential to elucidate the diagnosis. Chest radiograph can show an intrathoracic mass, and CT can provide further characterization, such as density and precise location.
Location of mass guides differential
Localizing an intrathoracic mass in the anterior, middle, or posterior mediastinum allows for narrowing of the differential diagnosis (TABLE6). The main diagnostic consideration for a middle mediastinal or hilar mass is primary carcinoma. Posterior mediastinal masses, on the other hand, are generally of benign etiology and may include neurogenic tumors, foregut duplication cysts, or, in rare cases, extramedullary hematopoiesis.

The differential diagnosis of anterior mediastinal masses can be separated into 4 main categories of disease, colloquially known as the “4 Ts”:
Teratoma. Mixed tissue densities seen on CT relate to the multiple tissue types originating from the embryologic germ cell layers.Frequently, there will be fat, fluid, and calcifications.
Thyroid pathology. A goiter or thyroid cancer can manifest with endocrine dysfunction, such as thyroid-stimulating hormone and T3/T4 abnormalities. A thyroid mass tends to sit more superiorly than do other anterior mediastinal masses and may be confirmed using a nuclear scan looking for increased radioactive iodine uptake.
Continue to: Thymoma
Thymoma. The diagnostic features include parathymic syndromes such as myasthenia gravis (30%-50% of thymoma cases7,8) and pure red cell aplasia (5% of thymoma cases9).
“Terrible” lymphoma. The most effective way to differentiate an anterior mediastinal mass due to lymphadenopathy (secondary to lymphoma) is to perform a tissue sample biopsy.
Also consider, as part of the differential for anterior mediastinal masses, such things as mesenchymal tumors, Morgagni hernia (anterior diaphragmatic defect), and pericardial cysts (fluid attenuating and usually located at the right cardiophrenic angle).
Surgical resection is effective
The treatment for anterior mediastinal teratoma is surgical resection.10 A complete surgical resection is typically curative and provides adequate therapy for symptom resolution.
The standard surgical approach involves gaining access to the anterior mediastinum via a median sternotomy. When there is extensive tumor involvement of the hemithorax, clamshell thoracotomy is preferred, requiring incisions in both the left and right hemithoraxes.11
Continue to: Our patient
Our patient underwent resection of the tumor; the subsequent pathology report for the specimen (FIGURE 3) confirmed the diagnosis. There was no abnormal enhancement or vascular invasion to suggest aggressive or malignant potential.

THE TAKEAWAY
Patients frequently present with nonspecific and vague chest complaints. This case points to the importance of obtaining a thorough clinical history and conducting a complete physical examination to guide additional work-up and radiographic imaging.
CORRESPONDENCE
Cassie Tran, MD, 320 E North Avenue, Pittsburgh, PA 15212; [email protected]
1. Chen C, Zheng H, Jiang S. An unusual case of giant mediastinal teratoma with malignant transformation. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;86:302-304.
2. Nichols CR. Mediastinal germ cell tumors: clinical features and biologic correlates. Chest. 1991;99:472. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.2.472
3. Mulen B, Richardson JD. Primary anterior mediastinal tumors in children and adults. Ann Thorac Surg. 1986;42:338. doi: 10.1016/S0003-4975(10)62751-8
4. Carter B, Okumura M, Detterbeck F, et al. Approaching the patient with an anterior mediastinal mass: a guide for radiologists. J Thorac Oncol. 2014;9 (9 suppl 2):S100-S118.
5. Dar RA, Mushtaque M, Wani SH, et al. Giant intrapulmonary teratoma: a rare case. Case Rep Pulmonol. 2011;2011:298653.
6. Whitten C, Khan S, Munneke G, et al. A diagnostic approach to mediastinal abnormalities. RadioGraphics. 2007;27:657-672.
7. Osserman KE, Genkins G. Studies in myasthenia gravis: review of a 20-year experience in over 1200 patients. Mt Sinai J Med. 1971;38:497-537.
8. Marx A, Muller-Hermelink HK, Strobel P. The role of thymomas in the development of myasthenia gravis. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2003;998:223-236.
9. Rosai J, Levine GD. Tumors of the thymus. In: Firminger HI, ed. Atlas of Tumor Pathology. Washington, DC: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology; 1976: 34-212.
10. Yendamuri S. Resection of a giant mediastinal teratoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;102:e401-e402.
11. Yokoyama Y, Chen F, Date H. Surgical resection of a giant mediastinal teratoma occupying the entire left hemithorax. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;62:255-257.
1. Chen C, Zheng H, Jiang S. An unusual case of giant mediastinal teratoma with malignant transformation. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;86:302-304.
2. Nichols CR. Mediastinal germ cell tumors: clinical features and biologic correlates. Chest. 1991;99:472. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.2.472
3. Mulen B, Richardson JD. Primary anterior mediastinal tumors in children and adults. Ann Thorac Surg. 1986;42:338. doi: 10.1016/S0003-4975(10)62751-8
4. Carter B, Okumura M, Detterbeck F, et al. Approaching the patient with an anterior mediastinal mass: a guide for radiologists. J Thorac Oncol. 2014;9 (9 suppl 2):S100-S118.
5. Dar RA, Mushtaque M, Wani SH, et al. Giant intrapulmonary teratoma: a rare case. Case Rep Pulmonol. 2011;2011:298653.
6. Whitten C, Khan S, Munneke G, et al. A diagnostic approach to mediastinal abnormalities. RadioGraphics. 2007;27:657-672.
7. Osserman KE, Genkins G. Studies in myasthenia gravis: review of a 20-year experience in over 1200 patients. Mt Sinai J Med. 1971;38:497-537.
8. Marx A, Muller-Hermelink HK, Strobel P. The role of thymomas in the development of myasthenia gravis. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2003;998:223-236.
9. Rosai J, Levine GD. Tumors of the thymus. In: Firminger HI, ed. Atlas of Tumor Pathology. Washington, DC: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology; 1976: 34-212.
10. Yendamuri S. Resection of a giant mediastinal teratoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;102:e401-e402.
11. Yokoyama Y, Chen F, Date H. Surgical resection of a giant mediastinal teratoma occupying the entire left hemithorax. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;62:255-257.
CDC recommends use of Pfizer’s COVID vaccine in 12- to 15-year-olds
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s director Rochelle Walensky, MD, signed off on an advisory panel’s recommendation May 12 endorsing the use of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in adolescents aged 12-15 years.
Earlier in the day the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted 14-0 in favor of the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine in younger teens.
Dr. Walensky said in an official statement.
The Food and Drug Administration on May 10 issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine for the prevention of COVID-19 in individuals 12-15 years old. The FDA first cleared the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine through an EUA in December 2020 for those ages 16 and older. Pfizer this month also initiated steps with the FDA toward a full approval of its vaccine.
Dr. Walenksy urged parents to seriously consider vaccinating their children.
“Understandably, some parents want more information before their children receive a vaccine,” she said. “I encourage parents with questions to talk to your child’s healthcare provider or your family doctor to learn more about the vaccine.”
Vaccine “safe and effective”
Separately, the American Academy of Pediatrics issued a statement May 12 in support of vaccinating all children ages 12 and older who are eligible for the federally authorized COVID-19 vaccine.
“As a pediatrician and a parent, I have looked forward to getting my own children and patients vaccinated, and I am thrilled that those ages 12 and older can now be protected,” said AAP President Lee Savio Beers, MD, in a statement. “The data continue to show that this vaccine is safe and effective. I urge all parents to call their pediatrician to learn more about how to get their children and teens vaccinated.”
The expanded clearance for the Pfizer vaccine is seen as a critical step for allowing teens to resume activities on which they missed out during the pandemic.
“We’ve seen the harm done to children’s mental and emotional health as they’ve missed out on so many experiences during the pandemic,” Dr. Beers said. “Vaccinating children will protect them and allow them to fully engage in all of the activities – school, sports, socializing with friends and family – that are so important to their health and development.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s director Rochelle Walensky, MD, signed off on an advisory panel’s recommendation May 12 endorsing the use of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in adolescents aged 12-15 years.
Earlier in the day the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted 14-0 in favor of the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine in younger teens.
Dr. Walensky said in an official statement.
The Food and Drug Administration on May 10 issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine for the prevention of COVID-19 in individuals 12-15 years old. The FDA first cleared the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine through an EUA in December 2020 for those ages 16 and older. Pfizer this month also initiated steps with the FDA toward a full approval of its vaccine.
Dr. Walenksy urged parents to seriously consider vaccinating their children.
“Understandably, some parents want more information before their children receive a vaccine,” she said. “I encourage parents with questions to talk to your child’s healthcare provider or your family doctor to learn more about the vaccine.”
Vaccine “safe and effective”
Separately, the American Academy of Pediatrics issued a statement May 12 in support of vaccinating all children ages 12 and older who are eligible for the federally authorized COVID-19 vaccine.
“As a pediatrician and a parent, I have looked forward to getting my own children and patients vaccinated, and I am thrilled that those ages 12 and older can now be protected,” said AAP President Lee Savio Beers, MD, in a statement. “The data continue to show that this vaccine is safe and effective. I urge all parents to call their pediatrician to learn more about how to get their children and teens vaccinated.”
The expanded clearance for the Pfizer vaccine is seen as a critical step for allowing teens to resume activities on which they missed out during the pandemic.
“We’ve seen the harm done to children’s mental and emotional health as they’ve missed out on so many experiences during the pandemic,” Dr. Beers said. “Vaccinating children will protect them and allow them to fully engage in all of the activities – school, sports, socializing with friends and family – that are so important to their health and development.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s director Rochelle Walensky, MD, signed off on an advisory panel’s recommendation May 12 endorsing the use of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in adolescents aged 12-15 years.
Earlier in the day the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted 14-0 in favor of the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine in younger teens.
Dr. Walensky said in an official statement.
The Food and Drug Administration on May 10 issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine for the prevention of COVID-19 in individuals 12-15 years old. The FDA first cleared the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine through an EUA in December 2020 for those ages 16 and older. Pfizer this month also initiated steps with the FDA toward a full approval of its vaccine.
Dr. Walenksy urged parents to seriously consider vaccinating their children.
“Understandably, some parents want more information before their children receive a vaccine,” she said. “I encourage parents with questions to talk to your child’s healthcare provider or your family doctor to learn more about the vaccine.”
Vaccine “safe and effective”
Separately, the American Academy of Pediatrics issued a statement May 12 in support of vaccinating all children ages 12 and older who are eligible for the federally authorized COVID-19 vaccine.
“As a pediatrician and a parent, I have looked forward to getting my own children and patients vaccinated, and I am thrilled that those ages 12 and older can now be protected,” said AAP President Lee Savio Beers, MD, in a statement. “The data continue to show that this vaccine is safe and effective. I urge all parents to call their pediatrician to learn more about how to get their children and teens vaccinated.”
The expanded clearance for the Pfizer vaccine is seen as a critical step for allowing teens to resume activities on which they missed out during the pandemic.
“We’ve seen the harm done to children’s mental and emotional health as they’ve missed out on so many experiences during the pandemic,” Dr. Beers said. “Vaccinating children will protect them and allow them to fully engage in all of the activities – school, sports, socializing with friends and family – that are so important to their health and development.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Does surgery for colorectal liver metastases release tumor cells?
For patients with colorectal liver metastasis (CLM), surgical resection is the only hope for cure, but conventional hepatectomy involves mechanical manipulation that could release tumor cells into the bloodstream and result in further spread.
To minimize this risk, an alternative method was introduced in 1992 – an anterior approach for open right hepatectomies, which involves less manipulation. However, a trial that compared the two surgical approaches showed no difference between the two in reducing intraoperative tumor cell dissemination.
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) were detected in 6 of 22 patients (27%) in the anterior hepatectomy group and in 5 of 21 (24%) patients in the conventional hepatectomy group, the study authors reported.
Operating time was longer with the anterior approach (221 vs. 171 minutes), but intraoperative and postoperative outcomes were similar for the two approaches. Median overall and disease-free survival were also similar (55 vs. 73 months and 48 vs. 40 months, respectively), as were recurrence patterns, reported Nuh N. Rahbari, MD, and colleagues. Dr. Rahbari is affiliated with the University of Heidelberg (Germany).
The findings were published online Nov. 4, 2020, in JAMA Surgery.
This “timely” trial “addresses the concerns of many liver surgeons about detaching and shedding cancer cells into the hepatic veins during the initial mobilization of the right lobe,” comment the authors of an accompanying editorial, Iswanto Sucandy, MD, from the Digestive Health Institute, AdventHealth, Tampa, and Allan Tsung, MD, from Ohio State University, Columbus.
“The medial rotation to get the right lobe out of its anatomical confinement is often mechanically rigorous (and potentially traumatic to the tumor and remaining parenchyma), but it is very helpful in facilitating later steps of the operation,” they wrote. “It seems intuitive and easy to extrapolate that this maneuver can increase the release of CTCs into the systemic circulation, thus leading to an inferior oncological outcome.”
However, this assumption appears to be unfounded in light of results from this latest study, they pointed out.
“The most likely reason for these findings is that surgical techniques for CLM resection play a minor role, compared with those of tumor biology and patient responses in affecting the metastatic cascade,” they suggested.
Tumor cell spread remains a concern
About 70% of patients experience hepatic or extrahepatic recurrence after conventional hepatectomy, noted the study authors, so the concern over tumor cell spread during surgical manipulation remains.
Although their study was limited by small sample size, the absence of bone marrow samples for eight patients, and early discontinuation of the study per protocol, the authors said the findings “do not support further efforts to reduce tumor cell dissemination and subsequent disease recurrence by minimizing intraoperative manipulation.”
The findings should “rather prompt strategies to prevent spontaneous tumor cell dissemination and to target minimal residual disease after potentially curative resection.”
The editorialists added that the results of this study provide further insights and points for discussion regarding the benefits of minimally invasive approaches to liver surgery, which have been shown in several studies to decrease dissemination of CTCs by reducing surgical manipulation of tumors.
The study was supported by the department of surgery at the University of Heidelberg. The study authors and the editorialists disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For patients with colorectal liver metastasis (CLM), surgical resection is the only hope for cure, but conventional hepatectomy involves mechanical manipulation that could release tumor cells into the bloodstream and result in further spread.
To minimize this risk, an alternative method was introduced in 1992 – an anterior approach for open right hepatectomies, which involves less manipulation. However, a trial that compared the two surgical approaches showed no difference between the two in reducing intraoperative tumor cell dissemination.
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) were detected in 6 of 22 patients (27%) in the anterior hepatectomy group and in 5 of 21 (24%) patients in the conventional hepatectomy group, the study authors reported.
Operating time was longer with the anterior approach (221 vs. 171 minutes), but intraoperative and postoperative outcomes were similar for the two approaches. Median overall and disease-free survival were also similar (55 vs. 73 months and 48 vs. 40 months, respectively), as were recurrence patterns, reported Nuh N. Rahbari, MD, and colleagues. Dr. Rahbari is affiliated with the University of Heidelberg (Germany).
The findings were published online Nov. 4, 2020, in JAMA Surgery.
This “timely” trial “addresses the concerns of many liver surgeons about detaching and shedding cancer cells into the hepatic veins during the initial mobilization of the right lobe,” comment the authors of an accompanying editorial, Iswanto Sucandy, MD, from the Digestive Health Institute, AdventHealth, Tampa, and Allan Tsung, MD, from Ohio State University, Columbus.
“The medial rotation to get the right lobe out of its anatomical confinement is often mechanically rigorous (and potentially traumatic to the tumor and remaining parenchyma), but it is very helpful in facilitating later steps of the operation,” they wrote. “It seems intuitive and easy to extrapolate that this maneuver can increase the release of CTCs into the systemic circulation, thus leading to an inferior oncological outcome.”
However, this assumption appears to be unfounded in light of results from this latest study, they pointed out.
“The most likely reason for these findings is that surgical techniques for CLM resection play a minor role, compared with those of tumor biology and patient responses in affecting the metastatic cascade,” they suggested.
Tumor cell spread remains a concern
About 70% of patients experience hepatic or extrahepatic recurrence after conventional hepatectomy, noted the study authors, so the concern over tumor cell spread during surgical manipulation remains.
Although their study was limited by small sample size, the absence of bone marrow samples for eight patients, and early discontinuation of the study per protocol, the authors said the findings “do not support further efforts to reduce tumor cell dissemination and subsequent disease recurrence by minimizing intraoperative manipulation.”
The findings should “rather prompt strategies to prevent spontaneous tumor cell dissemination and to target minimal residual disease after potentially curative resection.”
The editorialists added that the results of this study provide further insights and points for discussion regarding the benefits of minimally invasive approaches to liver surgery, which have been shown in several studies to decrease dissemination of CTCs by reducing surgical manipulation of tumors.
The study was supported by the department of surgery at the University of Heidelberg. The study authors and the editorialists disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For patients with colorectal liver metastasis (CLM), surgical resection is the only hope for cure, but conventional hepatectomy involves mechanical manipulation that could release tumor cells into the bloodstream and result in further spread.
To minimize this risk, an alternative method was introduced in 1992 – an anterior approach for open right hepatectomies, which involves less manipulation. However, a trial that compared the two surgical approaches showed no difference between the two in reducing intraoperative tumor cell dissemination.
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) were detected in 6 of 22 patients (27%) in the anterior hepatectomy group and in 5 of 21 (24%) patients in the conventional hepatectomy group, the study authors reported.
Operating time was longer with the anterior approach (221 vs. 171 minutes), but intraoperative and postoperative outcomes were similar for the two approaches. Median overall and disease-free survival were also similar (55 vs. 73 months and 48 vs. 40 months, respectively), as were recurrence patterns, reported Nuh N. Rahbari, MD, and colleagues. Dr. Rahbari is affiliated with the University of Heidelberg (Germany).
The findings were published online Nov. 4, 2020, in JAMA Surgery.
This “timely” trial “addresses the concerns of many liver surgeons about detaching and shedding cancer cells into the hepatic veins during the initial mobilization of the right lobe,” comment the authors of an accompanying editorial, Iswanto Sucandy, MD, from the Digestive Health Institute, AdventHealth, Tampa, and Allan Tsung, MD, from Ohio State University, Columbus.
“The medial rotation to get the right lobe out of its anatomical confinement is often mechanically rigorous (and potentially traumatic to the tumor and remaining parenchyma), but it is very helpful in facilitating later steps of the operation,” they wrote. “It seems intuitive and easy to extrapolate that this maneuver can increase the release of CTCs into the systemic circulation, thus leading to an inferior oncological outcome.”
However, this assumption appears to be unfounded in light of results from this latest study, they pointed out.
“The most likely reason for these findings is that surgical techniques for CLM resection play a minor role, compared with those of tumor biology and patient responses in affecting the metastatic cascade,” they suggested.
Tumor cell spread remains a concern
About 70% of patients experience hepatic or extrahepatic recurrence after conventional hepatectomy, noted the study authors, so the concern over tumor cell spread during surgical manipulation remains.
Although their study was limited by small sample size, the absence of bone marrow samples for eight patients, and early discontinuation of the study per protocol, the authors said the findings “do not support further efforts to reduce tumor cell dissemination and subsequent disease recurrence by minimizing intraoperative manipulation.”
The findings should “rather prompt strategies to prevent spontaneous tumor cell dissemination and to target minimal residual disease after potentially curative resection.”
The editorialists added that the results of this study provide further insights and points for discussion regarding the benefits of minimally invasive approaches to liver surgery, which have been shown in several studies to decrease dissemination of CTCs by reducing surgical manipulation of tumors.
The study was supported by the department of surgery at the University of Heidelberg. The study authors and the editorialists disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.