User login
Dark Brown Hyperkeratotic Nodule on the Back
The Diagnosis: Seborrheic Keratosis-like Melanoma
Seborrheic keratosis (SK) is a benign neoplasm commonly encountered on the skin and frequently diagnosed by clinical examination alone. Seborrheic keratosis-like melanomas are melanomas that clinically or dermatoscopically resemble SKs and thus can be challenging to accurately diagnose. Melanomas can have a hyperkeratotic or verrucous appearance1-3 and can even exhibit dermatoscopic and microscopic features that are found in SKs such as comedolike openings and milialike cysts as well as acanthosis and pseudohorn cysts, respectively.2
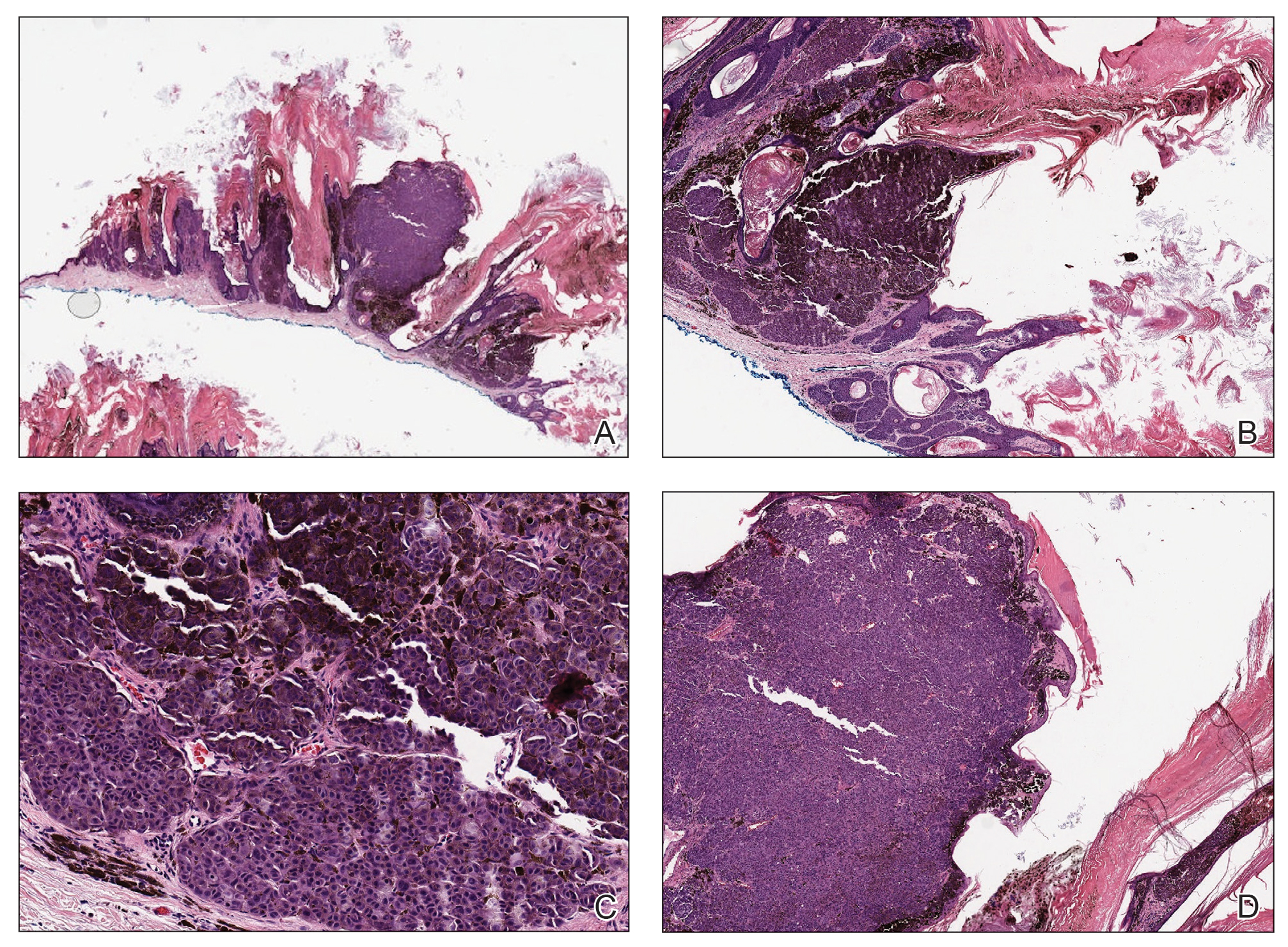
In our patient, histopathology revealed SK-like architecture with hyperorthokeratosis, papillomatosis, pseudohorn cyst formation, and basaloid acanthosis (Figure). However, within the lesion was an asymmetric proliferation of nested atypical melanocytes with melanin pigment production. The atypical melanocytes filled and expanded papillomatous projections without notable pagetoid growth and extended into the dermis. There was a background congenital nevus component. These findings were diagnostic of invasive malignant melanoma, extending to a Breslow depth of 5.5 mm. A follow-up sentinel lymph node biopsy was negative for metastatic melanoma. The clinical and histologic findings did not show melanoma in the surrounding skin to suggest colonization of an SK by an adjacent melanoma. The clinical history of a long-standing lesion in conjunction with a congenital nevus component on histology favored a diagnosis of melanoma arising in association with a congenital nevus with an SK-like architecture rather than arising in a preexisting SK or de novo melanoma.
Because our patient did not have multiple widespread SKs and reported rapid growth in the lesion in the last 6 months, there was concern for a malignant neoplasm. However, in patients with numerous SKs or areas of chronically sun-damaged skin, it can be difficult to identify suspicious lesions. It is important for clinicians to remain aware of SK-like melanomas and have a lower threshold for biopsy of any changing or symptomatic lesion that clinically resembles an SK. In our case, the history of change and the markedly different clinical appearance of the lesion in comparison to our patient's SKs prompted the biopsy. Criteria have been proposed to help differentiate these entities under dermoscopy, with melanoma showing the presence of the blue-black sign, pigment network, pseudopods or streaks, and/or the blue-white veil.4
Cutaneous metastases classically present as dermal nodules, plaques, or ulcers.5,6 A rare pigmented case of metastatic breast adenocarcinoma clinically mimicking melanoma has been reported.7 There is limited literature on the dermoscopic features of cutaneous metastases, but it appears that polymorphic vascular patterns are most common.5,8 The possibility of a metastatic melanoma involving an SK is a theoretical consideration, but there was no prior history of melanoma in our patient, and the histologic findings were consistent with primary melanoma. There was no histologic evidence of pigmented metastatic breast carcinoma or metastatic lung carcinoma.
Pigmented malignant hidroacanthoma simplex and pigmented porocarcinomas are rare malignant sweat gland tumors.9-11 Their benign counterparts are the more commonly encountered hidroacanthoma simplex (intraepidermal poroma) and poroma. Pigmented malignant hidroacanthoma simplex has been reported to clinically mimic an irritated SK.10 The histopathology of our case did not have features of malignant hidroacanthoma simplex or porocarcinoma. Pigmented squamous cell carcinoma is an uncommon variant of squamous cell carcinoma, and histopathology would reveal proliferation of atypical keratinocytes.12
- Saggini A, Cota C, Lora V, et al. Uncommon histopathological variants of malignant melanoma. part 2. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:321-342.
- Klebanov N, Gunasekera N, Lin WM, et al. The clinical spectrum of cutaneous melanoma morphology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:178-188.
- Tran PT, Truong AK, Munday W, et al. Verrucous melanoma masquerading as a seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030/qt1m07k7fm.
- Carrera C, Segura S, Aguilera P. Dermoscopic clues for diagnosing melanomas that resemble seborrheic keratosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:544-551.
- Strickley JD, Jenson AB, Jung JY. Cutaneous metastasis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2019;33:173-197.
- Chernoff KA, Marghoob AA, Lacouture ME. Dermoscopic findings in cutaneous metastases. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:429-433.
- Marti N, Molina I, Monteagudo C, et al. Cutaneous metastasis of breast carcinoma mimicking malignant melanoma in scalp. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:12.
- Kelati A, Gallouj S. Dermoscopy of skin metastases from breast cancer: two case reports. J Med Case Rep. 2018;12:273.
- Ishida M, Hotta M, Kushima R, et al. A case of porocarcinoma arising in pigmented hidroacanthoma simplex with multiple lymph node, liver and bone metastases. J Cutan Pathol. 2011;38:227-231.
- Lee JY, Lin MH. Pigmented malignant hidroacanthoma simplex mimicking irritated seborrheic keratosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:705-708.
- Ueo T, Kashima K, Daa T, et al. Porocarcinoma arising in pigmented hidroacanthoma simplex. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:500-503.
- Motta de Morais P, Schettini A, Rocha J, et al. Pigmented squamous cell carcinoma: case report and importance of differential diagnosis. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:96-98.
The Diagnosis: Seborrheic Keratosis-like Melanoma
Seborrheic keratosis (SK) is a benign neoplasm commonly encountered on the skin and frequently diagnosed by clinical examination alone. Seborrheic keratosis-like melanomas are melanomas that clinically or dermatoscopically resemble SKs and thus can be challenging to accurately diagnose. Melanomas can have a hyperkeratotic or verrucous appearance1-3 and can even exhibit dermatoscopic and microscopic features that are found in SKs such as comedolike openings and milialike cysts as well as acanthosis and pseudohorn cysts, respectively.2
In our patient, histopathology revealed SK-like architecture with hyperorthokeratosis, papillomatosis, pseudohorn cyst formation, and basaloid acanthosis (Figure). However, within the lesion was an asymmetric proliferation of nested atypical melanocytes with melanin pigment production. The atypical melanocytes filled and expanded papillomatous projections without notable pagetoid growth and extended into the dermis. There was a background congenital nevus component. These findings were diagnostic of invasive malignant melanoma, extending to a Breslow depth of 5.5 mm. A follow-up sentinel lymph node biopsy was negative for metastatic melanoma. The clinical and histologic findings did not show melanoma in the surrounding skin to suggest colonization of an SK by an adjacent melanoma. The clinical history of a long-standing lesion in conjunction with a congenital nevus component on histology favored a diagnosis of melanoma arising in association with a congenital nevus with an SK-like architecture rather than arising in a preexisting SK or de novo melanoma.

Because our patient did not have multiple widespread SKs and reported rapid growth in the lesion in the last 6 months, there was concern for a malignant neoplasm. However, in patients with numerous SKs or areas of chronically sun-damaged skin, it can be difficult to identify suspicious lesions. It is important for clinicians to remain aware of SK-like melanomas and have a lower threshold for biopsy of any changing or symptomatic lesion that clinically resembles an SK. In our case, the history of change and the markedly different clinical appearance of the lesion in comparison to our patient's SKs prompted the biopsy. Criteria have been proposed to help differentiate these entities under dermoscopy, with melanoma showing the presence of the blue-black sign, pigment network, pseudopods or streaks, and/or the blue-white veil.4
Cutaneous metastases classically present as dermal nodules, plaques, or ulcers.5,6 A rare pigmented case of metastatic breast adenocarcinoma clinically mimicking melanoma has been reported.7 There is limited literature on the dermoscopic features of cutaneous metastases, but it appears that polymorphic vascular patterns are most common.5,8 The possibility of a metastatic melanoma involving an SK is a theoretical consideration, but there was no prior history of melanoma in our patient, and the histologic findings were consistent with primary melanoma. There was no histologic evidence of pigmented metastatic breast carcinoma or metastatic lung carcinoma.
Pigmented malignant hidroacanthoma simplex and pigmented porocarcinomas are rare malignant sweat gland tumors.9-11 Their benign counterparts are the more commonly encountered hidroacanthoma simplex (intraepidermal poroma) and poroma. Pigmented malignant hidroacanthoma simplex has been reported to clinically mimic an irritated SK.10 The histopathology of our case did not have features of malignant hidroacanthoma simplex or porocarcinoma. Pigmented squamous cell carcinoma is an uncommon variant of squamous cell carcinoma, and histopathology would reveal proliferation of atypical keratinocytes.12
The Diagnosis: Seborrheic Keratosis-like Melanoma
Seborrheic keratosis (SK) is a benign neoplasm commonly encountered on the skin and frequently diagnosed by clinical examination alone. Seborrheic keratosis-like melanomas are melanomas that clinically or dermatoscopically resemble SKs and thus can be challenging to accurately diagnose. Melanomas can have a hyperkeratotic or verrucous appearance1-3 and can even exhibit dermatoscopic and microscopic features that are found in SKs such as comedolike openings and milialike cysts as well as acanthosis and pseudohorn cysts, respectively.2
In our patient, histopathology revealed SK-like architecture with hyperorthokeratosis, papillomatosis, pseudohorn cyst formation, and basaloid acanthosis (Figure). However, within the lesion was an asymmetric proliferation of nested atypical melanocytes with melanin pigment production. The atypical melanocytes filled and expanded papillomatous projections without notable pagetoid growth and extended into the dermis. There was a background congenital nevus component. These findings were diagnostic of invasive malignant melanoma, extending to a Breslow depth of 5.5 mm. A follow-up sentinel lymph node biopsy was negative for metastatic melanoma. The clinical and histologic findings did not show melanoma in the surrounding skin to suggest colonization of an SK by an adjacent melanoma. The clinical history of a long-standing lesion in conjunction with a congenital nevus component on histology favored a diagnosis of melanoma arising in association with a congenital nevus with an SK-like architecture rather than arising in a preexisting SK or de novo melanoma.

Because our patient did not have multiple widespread SKs and reported rapid growth in the lesion in the last 6 months, there was concern for a malignant neoplasm. However, in patients with numerous SKs or areas of chronically sun-damaged skin, it can be difficult to identify suspicious lesions. It is important for clinicians to remain aware of SK-like melanomas and have a lower threshold for biopsy of any changing or symptomatic lesion that clinically resembles an SK. In our case, the history of change and the markedly different clinical appearance of the lesion in comparison to our patient's SKs prompted the biopsy. Criteria have been proposed to help differentiate these entities under dermoscopy, with melanoma showing the presence of the blue-black sign, pigment network, pseudopods or streaks, and/or the blue-white veil.4
Cutaneous metastases classically present as dermal nodules, plaques, or ulcers.5,6 A rare pigmented case of metastatic breast adenocarcinoma clinically mimicking melanoma has been reported.7 There is limited literature on the dermoscopic features of cutaneous metastases, but it appears that polymorphic vascular patterns are most common.5,8 The possibility of a metastatic melanoma involving an SK is a theoretical consideration, but there was no prior history of melanoma in our patient, and the histologic findings were consistent with primary melanoma. There was no histologic evidence of pigmented metastatic breast carcinoma or metastatic lung carcinoma.
Pigmented malignant hidroacanthoma simplex and pigmented porocarcinomas are rare malignant sweat gland tumors.9-11 Their benign counterparts are the more commonly encountered hidroacanthoma simplex (intraepidermal poroma) and poroma. Pigmented malignant hidroacanthoma simplex has been reported to clinically mimic an irritated SK.10 The histopathology of our case did not have features of malignant hidroacanthoma simplex or porocarcinoma. Pigmented squamous cell carcinoma is an uncommon variant of squamous cell carcinoma, and histopathology would reveal proliferation of atypical keratinocytes.12
- Saggini A, Cota C, Lora V, et al. Uncommon histopathological variants of malignant melanoma. part 2. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:321-342.
- Klebanov N, Gunasekera N, Lin WM, et al. The clinical spectrum of cutaneous melanoma morphology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:178-188.
- Tran PT, Truong AK, Munday W, et al. Verrucous melanoma masquerading as a seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030/qt1m07k7fm.
- Carrera C, Segura S, Aguilera P. Dermoscopic clues for diagnosing melanomas that resemble seborrheic keratosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:544-551.
- Strickley JD, Jenson AB, Jung JY. Cutaneous metastasis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2019;33:173-197.
- Chernoff KA, Marghoob AA, Lacouture ME. Dermoscopic findings in cutaneous metastases. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:429-433.
- Marti N, Molina I, Monteagudo C, et al. Cutaneous metastasis of breast carcinoma mimicking malignant melanoma in scalp. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:12.
- Kelati A, Gallouj S. Dermoscopy of skin metastases from breast cancer: two case reports. J Med Case Rep. 2018;12:273.
- Ishida M, Hotta M, Kushima R, et al. A case of porocarcinoma arising in pigmented hidroacanthoma simplex with multiple lymph node, liver and bone metastases. J Cutan Pathol. 2011;38:227-231.
- Lee JY, Lin MH. Pigmented malignant hidroacanthoma simplex mimicking irritated seborrheic keratosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:705-708.
- Ueo T, Kashima K, Daa T, et al. Porocarcinoma arising in pigmented hidroacanthoma simplex. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:500-503.
- Motta de Morais P, Schettini A, Rocha J, et al. Pigmented squamous cell carcinoma: case report and importance of differential diagnosis. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:96-98.
- Saggini A, Cota C, Lora V, et al. Uncommon histopathological variants of malignant melanoma. part 2. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:321-342.
- Klebanov N, Gunasekera N, Lin WM, et al. The clinical spectrum of cutaneous melanoma morphology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:178-188.
- Tran PT, Truong AK, Munday W, et al. Verrucous melanoma masquerading as a seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030/qt1m07k7fm.
- Carrera C, Segura S, Aguilera P. Dermoscopic clues for diagnosing melanomas that resemble seborrheic keratosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:544-551.
- Strickley JD, Jenson AB, Jung JY. Cutaneous metastasis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2019;33:173-197.
- Chernoff KA, Marghoob AA, Lacouture ME. Dermoscopic findings in cutaneous metastases. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:429-433.
- Marti N, Molina I, Monteagudo C, et al. Cutaneous metastasis of breast carcinoma mimicking malignant melanoma in scalp. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:12.
- Kelati A, Gallouj S. Dermoscopy of skin metastases from breast cancer: two case reports. J Med Case Rep. 2018;12:273.
- Ishida M, Hotta M, Kushima R, et al. A case of porocarcinoma arising in pigmented hidroacanthoma simplex with multiple lymph node, liver and bone metastases. J Cutan Pathol. 2011;38:227-231.
- Lee JY, Lin MH. Pigmented malignant hidroacanthoma simplex mimicking irritated seborrheic keratosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:705-708.
- Ueo T, Kashima K, Daa T, et al. Porocarcinoma arising in pigmented hidroacanthoma simplex. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:500-503.
- Motta de Morais P, Schettini A, Rocha J, et al. Pigmented squamous cell carcinoma: case report and importance of differential diagnosis. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:96-98.
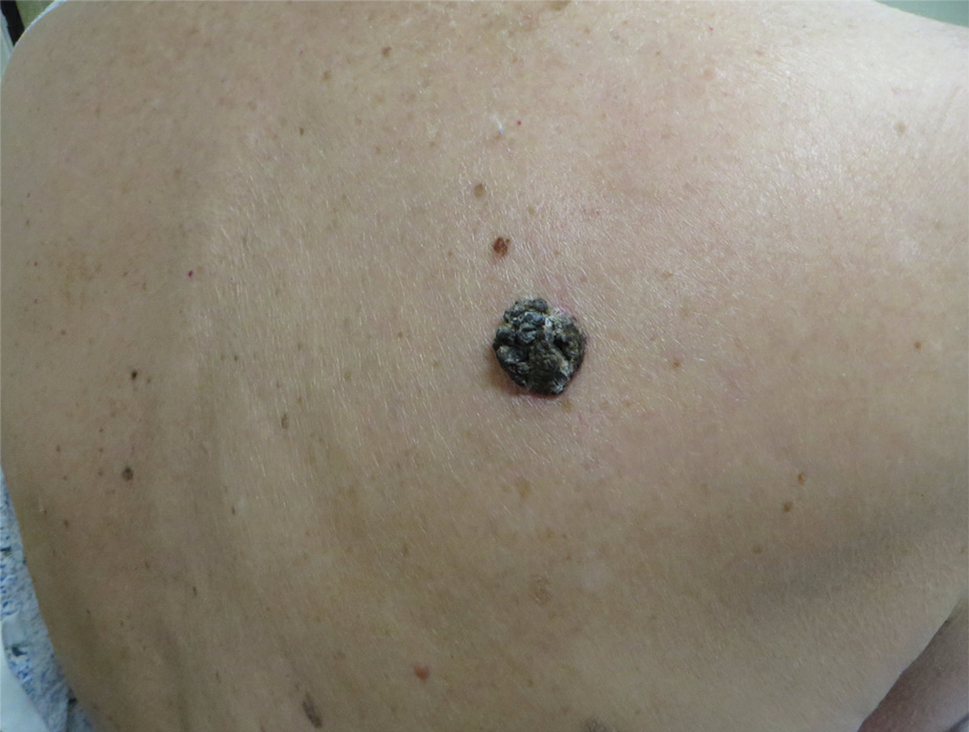
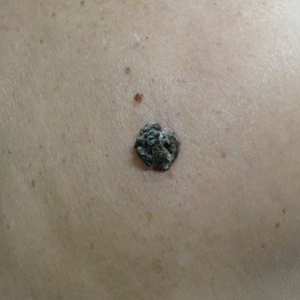
A 71-year-old woman presented with a persistent asymptomatic lesion on the right upper back that had recently increased in size and changed in color, shape, and texture. The lesion had been present for many years. Physical examination revealed a 1.5-cm, dark brown, hyperkeratotic nodule with no identifiable pigment network on dermatoscopy. The patient had no personal history of melanoma but did have a history of stage I non–small cell lung cancer. A review of systems was noncontributory. A shave biopsy of the lesion was performed.
New guidelines advise expanded use of high-flow nasal oxygen for patients with ARDS
Hospitalized patients with acute respiratory failure can benefit from high-flow nasal oxygen in certain settings, according to a new clinical guideline from the American College of Physicians.
High-flow nasal oxygen (HFNO) has demonstrated advantages including improved oxygenation and ventilation, wrote Arianne K. Baldomero, MD, of Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Health Care System and the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and colleagues. “However, the comparative benefits and harms of HFNO in clinical outcomes, including mortality, intubation, hospital length of stay, patient comfort, clearance of airway secretions, and reduced work of breathing are not well known.”
In the guideline, published in Annals of Internal Medicine, the authors recommend the use of high-flow nasal oxygen in hospitalized patients for initial or postextubation management of acute respiratory failure. The target population includes those patients treated in hospital wards, EDs, intermediate/step-down units, and ICUs.
Use of HFNO therapy as a form of noninvasive respiratory support for hospitalized patients has increased in recent years. The treatment involves delivering warm, humidified oxygen via nasal cannula at a flow level higher than the patient’s inspiratory flow.
Potential benefits of HFNO include greater patient comfort, improved compliance, and psychological benefits, according to the authors. HFNO also can be used as respiratory support in critically ill patients for a number of indications including respiratory failure or support post extubation; however, treatment of patients with COVID-19 and related conditions were not considered in the guideline.
The guideline was based on evidence comparing HFNO with conventional oxygen therapy (COT) and noninvasive ventilation (NIV). The authors reviewed 29 randomized, controlled trials that showed clinically meaningful outcomes in HFNO patients, as well as similar rates of, or reductions in, mortality, intubations, and hospital-acquired pneumonia, and increased reports of patient comfort. Data also supported the safety of HFNO with few, if any, contraindications other than problems with fitting the nasal cannula.
Across several trials comparing HFNO and NIV for initial management of acute respiratory failure, HFNO reduced all-cause mortality, intubation, and hospital-acquired pneumonia, although the authors categorized the results as “low-certainty evidence.” HFNO was not more effective than NIV for postextubation management. Based trials comparing HFNO and COT for postextubation management, the authors concluded that HFNO may reduce rates of reintubation and improve patient comfort, also with low-certainty evidence.
The research was limited by a lack of studies comparing HFNO with NIV or COT for acute respiratory failure in patients who were post lung transplantation, or for those with pulmonary embolism, pulmonary arterial hypertension, or asthma, the authors said. Other limitations included the variation in study design, study populations, and treatment protocols across the included studies. Additional research is needed to better identify the patients most likely to benefit from HFNO, according to type of acute respiratory failure.
Despite these limitations, the results support the guideline recommendation for HFNO in cases of acute respiratory failure and postextubation management. However, “broad applicability, including required clinician and health system experience and resource use, remains unknown,” the authors concluded.
Research catches up with practice
The guidelines are important at this time because “the medical literature over the past 3-4 years is catching up to what hospitalists, pulmonologists, and critical care specialists have been doing clinically over the past 6-8 years with perceived better results, Jacqueline W. Fincher, MD, MACP, President of the American College of Physicians, said in an interview.
“HFNO has been used to a varying degree over the last 6-8 years by physicians with much-perceived improved benefit in patients who are hypoxemic on usual noninvasive therapy or conventional oxygen therapy with the impending need for intubation or post extubation,” Dr. Fincher said. “During the COVID pandemic particularly with the attack on the respiratory system with COVID pneumonia and frequently associated ARDS [acute respiratory distress syndrome], the use of HFNO has been enormously helpful in trying to keep patients well oxygenated without having to intubate or reintubate them.
“We now have the medical literature that supports what has been seen clinically to make the recommendations and guidelines based on the scientific evidence,” Dr. Fincher added. “If we can avoid intubation associated with the patient being sedated, unable to eat, talk, or meaningfully participate in their care or get the patient off the ventilator sooner for the same reasons, then we have significantly improved the quality of their care, decreased their risk of infection, decreased their days in the ICU and the hospital, we will have succeeded in providing the best care possible. The availability of HFNO, with much greater comfort to the patient than being intubated, is a great tool in the toolbox of respiratory care.”
Dr. Fincher said she was not surprised by any of the recommendations. “We knew the use of HFNO helped but we were surprised by the evidence of the degree to which it is enormously helpful to patients.
“The good news is that HFNO is readily available at most hospitals, but it really requires an intensive care unit and a team of physicians, nurses, and respiratory therapists to be familiar with its use and work closely together to monitor the patient for significant changes in their respiratory status to titrate therapy,” she noted.
Looking ahead, some areas in need of more research that might impact updates to the guidelines include “What are some areas in need of more research that might impact future updates to these guidelines? Specifics on whether initiating HFNO earlier in the course of the patient’s hypoxemic illness is better or worse, as well as the use of HFNO outside of the ICU setting,” Dr. Fincher said. “The needed monitoring of the patient to know whether their respiratory status was deteriorating and how fast would be critical along with the specific indications for titration of the HFNO.”
The evidence review was commissioned and funded by the ACP. The data come from work supported by and conducted at the Minneapolis VA Health Care System. Lead author Dr. Baldomero was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
Hospitalized patients with acute respiratory failure can benefit from high-flow nasal oxygen in certain settings, according to a new clinical guideline from the American College of Physicians.
High-flow nasal oxygen (HFNO) has demonstrated advantages including improved oxygenation and ventilation, wrote Arianne K. Baldomero, MD, of Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Health Care System and the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and colleagues. “However, the comparative benefits and harms of HFNO in clinical outcomes, including mortality, intubation, hospital length of stay, patient comfort, clearance of airway secretions, and reduced work of breathing are not well known.”
In the guideline, published in Annals of Internal Medicine, the authors recommend the use of high-flow nasal oxygen in hospitalized patients for initial or postextubation management of acute respiratory failure. The target population includes those patients treated in hospital wards, EDs, intermediate/step-down units, and ICUs.
Use of HFNO therapy as a form of noninvasive respiratory support for hospitalized patients has increased in recent years. The treatment involves delivering warm, humidified oxygen via nasal cannula at a flow level higher than the patient’s inspiratory flow.
Potential benefits of HFNO include greater patient comfort, improved compliance, and psychological benefits, according to the authors. HFNO also can be used as respiratory support in critically ill patients for a number of indications including respiratory failure or support post extubation; however, treatment of patients with COVID-19 and related conditions were not considered in the guideline.
The guideline was based on evidence comparing HFNO with conventional oxygen therapy (COT) and noninvasive ventilation (NIV). The authors reviewed 29 randomized, controlled trials that showed clinically meaningful outcomes in HFNO patients, as well as similar rates of, or reductions in, mortality, intubations, and hospital-acquired pneumonia, and increased reports of patient comfort. Data also supported the safety of HFNO with few, if any, contraindications other than problems with fitting the nasal cannula.
Across several trials comparing HFNO and NIV for initial management of acute respiratory failure, HFNO reduced all-cause mortality, intubation, and hospital-acquired pneumonia, although the authors categorized the results as “low-certainty evidence.” HFNO was not more effective than NIV for postextubation management. Based trials comparing HFNO and COT for postextubation management, the authors concluded that HFNO may reduce rates of reintubation and improve patient comfort, also with low-certainty evidence.
The research was limited by a lack of studies comparing HFNO with NIV or COT for acute respiratory failure in patients who were post lung transplantation, or for those with pulmonary embolism, pulmonary arterial hypertension, or asthma, the authors said. Other limitations included the variation in study design, study populations, and treatment protocols across the included studies. Additional research is needed to better identify the patients most likely to benefit from HFNO, according to type of acute respiratory failure.
Despite these limitations, the results support the guideline recommendation for HFNO in cases of acute respiratory failure and postextubation management. However, “broad applicability, including required clinician and health system experience and resource use, remains unknown,” the authors concluded.
Research catches up with practice
The guidelines are important at this time because “the medical literature over the past 3-4 years is catching up to what hospitalists, pulmonologists, and critical care specialists have been doing clinically over the past 6-8 years with perceived better results, Jacqueline W. Fincher, MD, MACP, President of the American College of Physicians, said in an interview.
“HFNO has been used to a varying degree over the last 6-8 years by physicians with much-perceived improved benefit in patients who are hypoxemic on usual noninvasive therapy or conventional oxygen therapy with the impending need for intubation or post extubation,” Dr. Fincher said. “During the COVID pandemic particularly with the attack on the respiratory system with COVID pneumonia and frequently associated ARDS [acute respiratory distress syndrome], the use of HFNO has been enormously helpful in trying to keep patients well oxygenated without having to intubate or reintubate them.
“We now have the medical literature that supports what has been seen clinically to make the recommendations and guidelines based on the scientific evidence,” Dr. Fincher added. “If we can avoid intubation associated with the patient being sedated, unable to eat, talk, or meaningfully participate in their care or get the patient off the ventilator sooner for the same reasons, then we have significantly improved the quality of their care, decreased their risk of infection, decreased their days in the ICU and the hospital, we will have succeeded in providing the best care possible. The availability of HFNO, with much greater comfort to the patient than being intubated, is a great tool in the toolbox of respiratory care.”
Dr. Fincher said she was not surprised by any of the recommendations. “We knew the use of HFNO helped but we were surprised by the evidence of the degree to which it is enormously helpful to patients.
“The good news is that HFNO is readily available at most hospitals, but it really requires an intensive care unit and a team of physicians, nurses, and respiratory therapists to be familiar with its use and work closely together to monitor the patient for significant changes in their respiratory status to titrate therapy,” she noted.
Looking ahead, some areas in need of more research that might impact updates to the guidelines include “What are some areas in need of more research that might impact future updates to these guidelines? Specifics on whether initiating HFNO earlier in the course of the patient’s hypoxemic illness is better or worse, as well as the use of HFNO outside of the ICU setting,” Dr. Fincher said. “The needed monitoring of the patient to know whether their respiratory status was deteriorating and how fast would be critical along with the specific indications for titration of the HFNO.”
The evidence review was commissioned and funded by the ACP. The data come from work supported by and conducted at the Minneapolis VA Health Care System. Lead author Dr. Baldomero was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
Hospitalized patients with acute respiratory failure can benefit from high-flow nasal oxygen in certain settings, according to a new clinical guideline from the American College of Physicians.
High-flow nasal oxygen (HFNO) has demonstrated advantages including improved oxygenation and ventilation, wrote Arianne K. Baldomero, MD, of Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Health Care System and the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and colleagues. “However, the comparative benefits and harms of HFNO in clinical outcomes, including mortality, intubation, hospital length of stay, patient comfort, clearance of airway secretions, and reduced work of breathing are not well known.”
In the guideline, published in Annals of Internal Medicine, the authors recommend the use of high-flow nasal oxygen in hospitalized patients for initial or postextubation management of acute respiratory failure. The target population includes those patients treated in hospital wards, EDs, intermediate/step-down units, and ICUs.
Use of HFNO therapy as a form of noninvasive respiratory support for hospitalized patients has increased in recent years. The treatment involves delivering warm, humidified oxygen via nasal cannula at a flow level higher than the patient’s inspiratory flow.
Potential benefits of HFNO include greater patient comfort, improved compliance, and psychological benefits, according to the authors. HFNO also can be used as respiratory support in critically ill patients for a number of indications including respiratory failure or support post extubation; however, treatment of patients with COVID-19 and related conditions were not considered in the guideline.
The guideline was based on evidence comparing HFNO with conventional oxygen therapy (COT) and noninvasive ventilation (NIV). The authors reviewed 29 randomized, controlled trials that showed clinically meaningful outcomes in HFNO patients, as well as similar rates of, or reductions in, mortality, intubations, and hospital-acquired pneumonia, and increased reports of patient comfort. Data also supported the safety of HFNO with few, if any, contraindications other than problems with fitting the nasal cannula.
Across several trials comparing HFNO and NIV for initial management of acute respiratory failure, HFNO reduced all-cause mortality, intubation, and hospital-acquired pneumonia, although the authors categorized the results as “low-certainty evidence.” HFNO was not more effective than NIV for postextubation management. Based trials comparing HFNO and COT for postextubation management, the authors concluded that HFNO may reduce rates of reintubation and improve patient comfort, also with low-certainty evidence.
The research was limited by a lack of studies comparing HFNO with NIV or COT for acute respiratory failure in patients who were post lung transplantation, or for those with pulmonary embolism, pulmonary arterial hypertension, or asthma, the authors said. Other limitations included the variation in study design, study populations, and treatment protocols across the included studies. Additional research is needed to better identify the patients most likely to benefit from HFNO, according to type of acute respiratory failure.
Despite these limitations, the results support the guideline recommendation for HFNO in cases of acute respiratory failure and postextubation management. However, “broad applicability, including required clinician and health system experience and resource use, remains unknown,” the authors concluded.
Research catches up with practice
The guidelines are important at this time because “the medical literature over the past 3-4 years is catching up to what hospitalists, pulmonologists, and critical care specialists have been doing clinically over the past 6-8 years with perceived better results, Jacqueline W. Fincher, MD, MACP, President of the American College of Physicians, said in an interview.
“HFNO has been used to a varying degree over the last 6-8 years by physicians with much-perceived improved benefit in patients who are hypoxemic on usual noninvasive therapy or conventional oxygen therapy with the impending need for intubation or post extubation,” Dr. Fincher said. “During the COVID pandemic particularly with the attack on the respiratory system with COVID pneumonia and frequently associated ARDS [acute respiratory distress syndrome], the use of HFNO has been enormously helpful in trying to keep patients well oxygenated without having to intubate or reintubate them.
“We now have the medical literature that supports what has been seen clinically to make the recommendations and guidelines based on the scientific evidence,” Dr. Fincher added. “If we can avoid intubation associated with the patient being sedated, unable to eat, talk, or meaningfully participate in their care or get the patient off the ventilator sooner for the same reasons, then we have significantly improved the quality of their care, decreased their risk of infection, decreased their days in the ICU and the hospital, we will have succeeded in providing the best care possible. The availability of HFNO, with much greater comfort to the patient than being intubated, is a great tool in the toolbox of respiratory care.”
Dr. Fincher said she was not surprised by any of the recommendations. “We knew the use of HFNO helped but we were surprised by the evidence of the degree to which it is enormously helpful to patients.
“The good news is that HFNO is readily available at most hospitals, but it really requires an intensive care unit and a team of physicians, nurses, and respiratory therapists to be familiar with its use and work closely together to monitor the patient for significant changes in their respiratory status to titrate therapy,” she noted.
Looking ahead, some areas in need of more research that might impact updates to the guidelines include “What are some areas in need of more research that might impact future updates to these guidelines? Specifics on whether initiating HFNO earlier in the course of the patient’s hypoxemic illness is better or worse, as well as the use of HFNO outside of the ICU setting,” Dr. Fincher said. “The needed monitoring of the patient to know whether their respiratory status was deteriorating and how fast would be critical along with the specific indications for titration of the HFNO.”
The evidence review was commissioned and funded by the ACP. The data come from work supported by and conducted at the Minneapolis VA Health Care System. Lead author Dr. Baldomero was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
FROM THE ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
How does fragmented care affect IBD outcomes?
Poor continuity of care may lead to worse outcomes among patients with active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to data from more than 20,000 veterans.
Even in the Veterans Health Administration health care system, which “may provide the ideal environment for care coordination,” patients with active IBD had “substantial variation” in dispersion of care, leading to more frequent surgical interventions, corticosteroid use, and hospitalizations, reported lead author Shirley Cohen-Mekelburg, MD, MS, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues.
“Health care in the United States is marked by substantial fragmentation, with patients pursuing and receiving care from multiple clinicians, often at different institutions,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Network Open. “Fragmented care has been associated with poor chronic disease outcomes, higher health care use, duplication in testing, and increased costs of care.”
In the VHA, these issues prompted creation of the Patient Aligned Care Team (PACT), a medical home model in which primary care physicians coordinate clinical teams of specialists and other health care practitioners. But coordination can be challenging with chronic medical conditions like IBD, according to Dr. Cohen-Mekelburg and colleagues.
“High-quality care for IBD includes not only disease-specific management of symptoms but also disease-specific preventive care, such as immunizations and cancer screening, to prevent associated adverse outcomes,” the investigators wrote. “Identifying which physician is responsible for managing each aspect of care requires some degree of coordination and makes patients with IBD vulnerable to care fragmentation.”
Worse outcomes tied to poor first-year continuity
To evaluate care fragmentation within the VHA, the investigators identified 20,079 veterans with IBD who had at least one outpatient encounter with the system between the beginning of 2002 and the end of 2014. Continuity of care (COC) was calculated with the Bice-Boxerman COC index, which measures how much a patient’s care is connected with a distinct physician. The investigators used the first year COC as the primary independent variable.
In the first year of care, the median COC index was 0.24 (interquartile range, 0.13-0.46). The investigators noted that this figure was lower than reported by previous studies involving patients with several other chronic conditions, including IBD.
After controlling for covariates and adjusting for facility-related clustering, the investigators found a lower COC index in the first year was associated with a higher rate of worse outcomes in the subsequent 2 years, including surgical interventions (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.72; 95% confidence interval, 1.43-2.07), hospitalizations (aHR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.06-1.47), and outpatient flares requiring corticosteroids (aHR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.01-1.22). Conversely, improving COC index score by 0.1 reduced risk of outpatient flare (aHR, 0.69; 95%CI, 0.58-0.82), hospitalization (aHR, 0.57; 95%CI, 0.41-0.79), and surgical intervention (aHR, 0.25; 95% CI, 0.16-0.38).
Further analyses showed that the relationship between lower COC and worse outcomes carried across measures such as baseline use of an immunomodulator or biological agent, as well as subgroups such as patients with nonsevere IBD and nonsurgical patients.
Among those treated by a VHA gastroenterologist, a lower level of COC was associated with a higher rate of surgical interventions, but not hospitalizations or outpatient flares. Physician-specific COC index scores were highest for primary care providers (0.54), followed by gastroenterologists (0.25) and surgeons (0.17). However, lower physician-specific COC scores did not translate to worse IBD outcomes.
“The level of COC among patients with IBD in the present VHA cohort was ... lower than the values described in previous studies of veterans in the VHA system, including a study of VHA-Medicare dual enrollees who were especially prone to fragmented care because of their ability to seek care both inside and outside of the VHA system,” the investigators wrote, referring to a 2018 study. “The difference in COC among patients with IBD vs. patients without IBD is likely multifactorial and may be associated with confusion about physician accountability and lack of focus on coordination in IBD multidisciplinary care. Patients with IBD require care by primary care providers, gastroenterologists, and surgeons, but the delineation of responsibility by physician is often unclear.”
‘Better care, not just more care,’ is needed
“These outcomes cannot be improved with a more robust treatment armamentarium alone,” according to Jason K. Hou, MD, MS, AGAF, FACG, interim chief of gastroenterology and hepatology at Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center and associate professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who cowrote a simultaneously published editorial, which was also authored by David I. Fudman, MD.
“Examples exist of improving care coordination and outcomes through patient-aligned care teams in primary care and medical specialty homes for IBD,” Dr. Hou said in an interview. “However, significant barriers to widespread implementation remain.”
Dr. Hou offered several possible approaches to overcome these barriers.
“We need improved methods to identify and follow high-risk patients most likely to have complications and health care utilization,” he said. “We need an investment by payers and health care systems on care coordination so the identified high-risk patients can receive timely testing, referral, and treatment. These changes require reevaluation of how the health care system incentivizes health care to provide better care, not just more care.”
The investigators reported grants from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and the National Institutes of Health and financial relationships with AbbVie, UCB, and Takeda. Dr. Hou reported no conflicts of interest.
Help your patients better understand their IBD treatment options by sharing AGA's patient education, "Living with IBD," in the AGA GI Patient Center at www.gastro.org/IBD.
Poor continuity of care may lead to worse outcomes among patients with active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to data from more than 20,000 veterans.
Even in the Veterans Health Administration health care system, which “may provide the ideal environment for care coordination,” patients with active IBD had “substantial variation” in dispersion of care, leading to more frequent surgical interventions, corticosteroid use, and hospitalizations, reported lead author Shirley Cohen-Mekelburg, MD, MS, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues.
“Health care in the United States is marked by substantial fragmentation, with patients pursuing and receiving care from multiple clinicians, often at different institutions,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Network Open. “Fragmented care has been associated with poor chronic disease outcomes, higher health care use, duplication in testing, and increased costs of care.”
In the VHA, these issues prompted creation of the Patient Aligned Care Team (PACT), a medical home model in which primary care physicians coordinate clinical teams of specialists and other health care practitioners. But coordination can be challenging with chronic medical conditions like IBD, according to Dr. Cohen-Mekelburg and colleagues.
“High-quality care for IBD includes not only disease-specific management of symptoms but also disease-specific preventive care, such as immunizations and cancer screening, to prevent associated adverse outcomes,” the investigators wrote. “Identifying which physician is responsible for managing each aspect of care requires some degree of coordination and makes patients with IBD vulnerable to care fragmentation.”
Worse outcomes tied to poor first-year continuity
To evaluate care fragmentation within the VHA, the investigators identified 20,079 veterans with IBD who had at least one outpatient encounter with the system between the beginning of 2002 and the end of 2014. Continuity of care (COC) was calculated with the Bice-Boxerman COC index, which measures how much a patient’s care is connected with a distinct physician. The investigators used the first year COC as the primary independent variable.
In the first year of care, the median COC index was 0.24 (interquartile range, 0.13-0.46). The investigators noted that this figure was lower than reported by previous studies involving patients with several other chronic conditions, including IBD.
After controlling for covariates and adjusting for facility-related clustering, the investigators found a lower COC index in the first year was associated with a higher rate of worse outcomes in the subsequent 2 years, including surgical interventions (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.72; 95% confidence interval, 1.43-2.07), hospitalizations (aHR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.06-1.47), and outpatient flares requiring corticosteroids (aHR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.01-1.22). Conversely, improving COC index score by 0.1 reduced risk of outpatient flare (aHR, 0.69; 95%CI, 0.58-0.82), hospitalization (aHR, 0.57; 95%CI, 0.41-0.79), and surgical intervention (aHR, 0.25; 95% CI, 0.16-0.38).
Further analyses showed that the relationship between lower COC and worse outcomes carried across measures such as baseline use of an immunomodulator or biological agent, as well as subgroups such as patients with nonsevere IBD and nonsurgical patients.
Among those treated by a VHA gastroenterologist, a lower level of COC was associated with a higher rate of surgical interventions, but not hospitalizations or outpatient flares. Physician-specific COC index scores were highest for primary care providers (0.54), followed by gastroenterologists (0.25) and surgeons (0.17). However, lower physician-specific COC scores did not translate to worse IBD outcomes.
“The level of COC among patients with IBD in the present VHA cohort was ... lower than the values described in previous studies of veterans in the VHA system, including a study of VHA-Medicare dual enrollees who were especially prone to fragmented care because of their ability to seek care both inside and outside of the VHA system,” the investigators wrote, referring to a 2018 study. “The difference in COC among patients with IBD vs. patients without IBD is likely multifactorial and may be associated with confusion about physician accountability and lack of focus on coordination in IBD multidisciplinary care. Patients with IBD require care by primary care providers, gastroenterologists, and surgeons, but the delineation of responsibility by physician is often unclear.”
‘Better care, not just more care,’ is needed
“These outcomes cannot be improved with a more robust treatment armamentarium alone,” according to Jason K. Hou, MD, MS, AGAF, FACG, interim chief of gastroenterology and hepatology at Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center and associate professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who cowrote a simultaneously published editorial, which was also authored by David I. Fudman, MD.
“Examples exist of improving care coordination and outcomes through patient-aligned care teams in primary care and medical specialty homes for IBD,” Dr. Hou said in an interview. “However, significant barriers to widespread implementation remain.”
Dr. Hou offered several possible approaches to overcome these barriers.
“We need improved methods to identify and follow high-risk patients most likely to have complications and health care utilization,” he said. “We need an investment by payers and health care systems on care coordination so the identified high-risk patients can receive timely testing, referral, and treatment. These changes require reevaluation of how the health care system incentivizes health care to provide better care, not just more care.”
The investigators reported grants from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and the National Institutes of Health and financial relationships with AbbVie, UCB, and Takeda. Dr. Hou reported no conflicts of interest.
Help your patients better understand their IBD treatment options by sharing AGA's patient education, "Living with IBD," in the AGA GI Patient Center at www.gastro.org/IBD.
Poor continuity of care may lead to worse outcomes among patients with active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to data from more than 20,000 veterans.
Even in the Veterans Health Administration health care system, which “may provide the ideal environment for care coordination,” patients with active IBD had “substantial variation” in dispersion of care, leading to more frequent surgical interventions, corticosteroid use, and hospitalizations, reported lead author Shirley Cohen-Mekelburg, MD, MS, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues.
“Health care in the United States is marked by substantial fragmentation, with patients pursuing and receiving care from multiple clinicians, often at different institutions,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Network Open. “Fragmented care has been associated with poor chronic disease outcomes, higher health care use, duplication in testing, and increased costs of care.”
In the VHA, these issues prompted creation of the Patient Aligned Care Team (PACT), a medical home model in which primary care physicians coordinate clinical teams of specialists and other health care practitioners. But coordination can be challenging with chronic medical conditions like IBD, according to Dr. Cohen-Mekelburg and colleagues.
“High-quality care for IBD includes not only disease-specific management of symptoms but also disease-specific preventive care, such as immunizations and cancer screening, to prevent associated adverse outcomes,” the investigators wrote. “Identifying which physician is responsible for managing each aspect of care requires some degree of coordination and makes patients with IBD vulnerable to care fragmentation.”
Worse outcomes tied to poor first-year continuity
To evaluate care fragmentation within the VHA, the investigators identified 20,079 veterans with IBD who had at least one outpatient encounter with the system between the beginning of 2002 and the end of 2014. Continuity of care (COC) was calculated with the Bice-Boxerman COC index, which measures how much a patient’s care is connected with a distinct physician. The investigators used the first year COC as the primary independent variable.
In the first year of care, the median COC index was 0.24 (interquartile range, 0.13-0.46). The investigators noted that this figure was lower than reported by previous studies involving patients with several other chronic conditions, including IBD.
After controlling for covariates and adjusting for facility-related clustering, the investigators found a lower COC index in the first year was associated with a higher rate of worse outcomes in the subsequent 2 years, including surgical interventions (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.72; 95% confidence interval, 1.43-2.07), hospitalizations (aHR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.06-1.47), and outpatient flares requiring corticosteroids (aHR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.01-1.22). Conversely, improving COC index score by 0.1 reduced risk of outpatient flare (aHR, 0.69; 95%CI, 0.58-0.82), hospitalization (aHR, 0.57; 95%CI, 0.41-0.79), and surgical intervention (aHR, 0.25; 95% CI, 0.16-0.38).
Further analyses showed that the relationship between lower COC and worse outcomes carried across measures such as baseline use of an immunomodulator or biological agent, as well as subgroups such as patients with nonsevere IBD and nonsurgical patients.
Among those treated by a VHA gastroenterologist, a lower level of COC was associated with a higher rate of surgical interventions, but not hospitalizations or outpatient flares. Physician-specific COC index scores were highest for primary care providers (0.54), followed by gastroenterologists (0.25) and surgeons (0.17). However, lower physician-specific COC scores did not translate to worse IBD outcomes.
“The level of COC among patients with IBD in the present VHA cohort was ... lower than the values described in previous studies of veterans in the VHA system, including a study of VHA-Medicare dual enrollees who were especially prone to fragmented care because of their ability to seek care both inside and outside of the VHA system,” the investigators wrote, referring to a 2018 study. “The difference in COC among patients with IBD vs. patients without IBD is likely multifactorial and may be associated with confusion about physician accountability and lack of focus on coordination in IBD multidisciplinary care. Patients with IBD require care by primary care providers, gastroenterologists, and surgeons, but the delineation of responsibility by physician is often unclear.”
‘Better care, not just more care,’ is needed
“These outcomes cannot be improved with a more robust treatment armamentarium alone,” according to Jason K. Hou, MD, MS, AGAF, FACG, interim chief of gastroenterology and hepatology at Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center and associate professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who cowrote a simultaneously published editorial, which was also authored by David I. Fudman, MD.
“Examples exist of improving care coordination and outcomes through patient-aligned care teams in primary care and medical specialty homes for IBD,” Dr. Hou said in an interview. “However, significant barriers to widespread implementation remain.”
Dr. Hou offered several possible approaches to overcome these barriers.
“We need improved methods to identify and follow high-risk patients most likely to have complications and health care utilization,” he said. “We need an investment by payers and health care systems on care coordination so the identified high-risk patients can receive timely testing, referral, and treatment. These changes require reevaluation of how the health care system incentivizes health care to provide better care, not just more care.”
The investigators reported grants from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and the National Institutes of Health and financial relationships with AbbVie, UCB, and Takeda. Dr. Hou reported no conflicts of interest.
Help your patients better understand their IBD treatment options by sharing AGA's patient education, "Living with IBD," in the AGA GI Patient Center at www.gastro.org/IBD.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Patient benefits justify price of new lupus nephritis drugs
The prices of two new drugs that have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of lupus nephritis are in “reasonable alignment” with the drugs’ estimated benefits for patients with the disease, the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review has determined.
“Both belimumab [Benlysta] and voclosporin [Lupkynis] are important new treatment options,” Steven Pearson, MD, president of ICER, observed in a summary of the report’s findings.
“Despite remaining uncertainty about both treatments’ longer-term outcomes, their estimated net prices appear to be aligned with their anticipated clinical benefits. ... For patients and clinicians to have responsibly priced options specifically indicated for lupus nephritis is a win for patients and the entire health system,” Dr. Pearson added.
The estimated annual price of belimumab is approximately $43,000 per patient; the estimated annual price for voclosporin is approximately $92,000 per patient.
The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio for belimumab is approximately $90,0000 per quality-adjusted life-year; the corresponding value for voclosporin is higher, at approximately $149,000 per QALY, the ICER authors noted.
The report was published by ICER in April 2021.
Large unmet need for treatment of lupus nephritis
In their report, the ICER reviewed belimumab, a parenteral B-lymphocyte inhibitor, as well as voclosporin, an oral calcineurin inhibitor, as initial treatment of patients with lupus nephritis. Lupus nephritis is a serious complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Belimumab was first approved for the treatment of lupus in adults in the United States in March 2011. In April 2019, it was approved for use for the same indication for children aged 5 years and older. The FDA expanded the indication in December 2020 to include adults with active lupus nephritis who are receiving standard therapy.
Voclosporin was approved for the treatment of lupus nephritis in January 2021.
In the pivotal trials for the two agents, each drug was added to standard induction therapy for lupus nephritis, which consisted of high-dose corticosteroids combined with either mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) or cyclophosphamide.
Compared with standard therapy alone, belimumab increased the complete renal response and the primary efficacy renal response at 2 years. With voclosporin, complete response was nearly doubled, and there was marked increased in partial response at 1 year, compared with standard therapy alone.
Neither drug appeared to increase the adverse-event rate or the rate of discontinuations, compared with standard therapy, although the FDA did add a black box warning regarding the possible risk for serious infections and malignancies with voclosporin use.
“There is a very large unmet need for the treatment of lupus nephritis,” Chris Phillips, MD, of Paducah (Ky.) Rheumatology said in an interview.
“A very large percentage of patients who do not achieve complete remission on traditional treatments have side effects or contraindications to these treatments, so we’ve needed new ones for sure,” he stressed.
The ICER authors made it clear that there is considerable uncertainty as to how short-term assessment of each of the two drugs’ performance might translate into meaningful long-term outcomes for patients, especially given that SLE is a lifelong illness.
On the other hand, “there are a lot of attributes for both of these new drugs that suggest there is potential for kidney benefit over time,” Brad Rovin, MD, professor of medicine and pathology at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, said in an interview.
For example, data from the BLISS-LN study, reported by Dr. Rovin during a meeting last year, suggest that belimumab reduces the flare rate and appears to stabilize kidney function over time, compared with standard therapy alone.
“BLISS-LN was 2 years long, so it gave us an opportunity to look at kidney function over a longer period of time than most of our prior trials in lupus nephritis,” he explained.
“The stabilization of kidney function is important, because it suggests that belimumab has a kidney protective effect, while a decrease in lupus nephritis flares is also important, because each time the disease flares, you can accumulate chronic tissue damage, which can eventually cause end-stage renal disease [ESRD],” he said.
Dr. Rovin also pointed out that the BLISS-LN trial results indicate that patients who achieve a urine protein level less than 700 mg/d after the first year of treatment do very well on long-term follow-up – another hint that belimumab may have long-term benefits for kidney function.
Voclosporin is a calcineurin inhibitor, which are protective of podocytes. “When you start to lose too many podocytes, the kidney can again progress onto ESRD, so this is again an extra benefit of the calcineurin inhibitors in the context of kidney disease that affects the glomeruli,” he noted.
“So both of these drugs have these interesting attributes that go beyond, or at least are maybe tied to, their immunosuppressive actions, but they do offer some kidney protective effects,” he reaffirmed.
Black patients underrepresented in trials
The ICER authors voiced concern over the fact that individuals most at risk for SLE – mostly Black patients, but also patients of other racial groups – were underrepresented in clinical trials that evaluated both agents.
“We cannot stress enough that the results are highly uncertain due to the small numbers of Black patients in the available clinical trials and the lack of data on differences among subgroups in long-term outcomes,” they stated.
This is not an academic issue, Dr. Phillips pointed out. Responses to both MMF and cyclophosphamide differ among persons of different races, “so it’s not unreasonable to consider that there could be racial differences in treatment responses to both drugs, and these definitely need to be investigated.”
This is not an academic issue, Dr. Phillips said, because there are racial disparities in how patients respond to both MMF and cyclophosphamide – “so it’s not unreasonable to consider that there could be racial differences in treatment responses to both drugs, and these definitely need to be investigated.”
The ICER authors appear to agree. They urged the manufacturers of the two new agents to expand their research to include adequate representation of lupus nephritis patients from Black and other non-White communities.
However, it is somewhat reassuring that the pivotal voclosporin trial enrolled about 30% of Hispanic patients and that about 17% of participants in the BLISS-LN trial were also Hispanic, Dr. Rovin pointed out.
This is important because Hispanic patients can have very aggressive disease, as can Black patients, he noted. There is some evidence to suggest both drugs are effective in aggressive disease.
The ICER also pointed out that the length of time that both drugs can be used prior to tapering of treatment, after which patients receive standard maintenance therapy alone, has yet to be established.
This is important, Dr. Rovin and Dr. Phillips agreed, because calcineurin inhibitors are known to be nephrotoxic, and both drugs are immunosuppressive. At least with respect to voclosporin, there is some cause of concern regarding prolonged use of the drug for patients with kidney disease.
“We don’t want patients to be on an immunosuppressive drug forever if they don’t need to be,” Dr. Rovin emphasized.
“But we are seeing really long-term remission in the setting of other inflammatory diseases, like vasculitis with rituximab. So there is hope that we can achieve the same thing in lupus. If we use drugs that target T cells in the immune system, like voclosporin, or B cells, like belimumab, maybe we can ‘reset’ the immune system and get rid of potentially autoreactive cells that could allow long-lasting disease remission, which is an unanswered question but an intriguing possibility,” he concluded.
Dr. Rovin has served as a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Phillips disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The prices of two new drugs that have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of lupus nephritis are in “reasonable alignment” with the drugs’ estimated benefits for patients with the disease, the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review has determined.
“Both belimumab [Benlysta] and voclosporin [Lupkynis] are important new treatment options,” Steven Pearson, MD, president of ICER, observed in a summary of the report’s findings.
“Despite remaining uncertainty about both treatments’ longer-term outcomes, their estimated net prices appear to be aligned with their anticipated clinical benefits. ... For patients and clinicians to have responsibly priced options specifically indicated for lupus nephritis is a win for patients and the entire health system,” Dr. Pearson added.
The estimated annual price of belimumab is approximately $43,000 per patient; the estimated annual price for voclosporin is approximately $92,000 per patient.
The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio for belimumab is approximately $90,0000 per quality-adjusted life-year; the corresponding value for voclosporin is higher, at approximately $149,000 per QALY, the ICER authors noted.
The report was published by ICER in April 2021.
Large unmet need for treatment of lupus nephritis
In their report, the ICER reviewed belimumab, a parenteral B-lymphocyte inhibitor, as well as voclosporin, an oral calcineurin inhibitor, as initial treatment of patients with lupus nephritis. Lupus nephritis is a serious complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Belimumab was first approved for the treatment of lupus in adults in the United States in March 2011. In April 2019, it was approved for use for the same indication for children aged 5 years and older. The FDA expanded the indication in December 2020 to include adults with active lupus nephritis who are receiving standard therapy.
Voclosporin was approved for the treatment of lupus nephritis in January 2021.
In the pivotal trials for the two agents, each drug was added to standard induction therapy for lupus nephritis, which consisted of high-dose corticosteroids combined with either mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) or cyclophosphamide.
Compared with standard therapy alone, belimumab increased the complete renal response and the primary efficacy renal response at 2 years. With voclosporin, complete response was nearly doubled, and there was marked increased in partial response at 1 year, compared with standard therapy alone.
Neither drug appeared to increase the adverse-event rate or the rate of discontinuations, compared with standard therapy, although the FDA did add a black box warning regarding the possible risk for serious infections and malignancies with voclosporin use.
“There is a very large unmet need for the treatment of lupus nephritis,” Chris Phillips, MD, of Paducah (Ky.) Rheumatology said in an interview.
“A very large percentage of patients who do not achieve complete remission on traditional treatments have side effects or contraindications to these treatments, so we’ve needed new ones for sure,” he stressed.
The ICER authors made it clear that there is considerable uncertainty as to how short-term assessment of each of the two drugs’ performance might translate into meaningful long-term outcomes for patients, especially given that SLE is a lifelong illness.
On the other hand, “there are a lot of attributes for both of these new drugs that suggest there is potential for kidney benefit over time,” Brad Rovin, MD, professor of medicine and pathology at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, said in an interview.
For example, data from the BLISS-LN study, reported by Dr. Rovin during a meeting last year, suggest that belimumab reduces the flare rate and appears to stabilize kidney function over time, compared with standard therapy alone.
“BLISS-LN was 2 years long, so it gave us an opportunity to look at kidney function over a longer period of time than most of our prior trials in lupus nephritis,” he explained.
“The stabilization of kidney function is important, because it suggests that belimumab has a kidney protective effect, while a decrease in lupus nephritis flares is also important, because each time the disease flares, you can accumulate chronic tissue damage, which can eventually cause end-stage renal disease [ESRD],” he said.
Dr. Rovin also pointed out that the BLISS-LN trial results indicate that patients who achieve a urine protein level less than 700 mg/d after the first year of treatment do very well on long-term follow-up – another hint that belimumab may have long-term benefits for kidney function.
Voclosporin is a calcineurin inhibitor, which are protective of podocytes. “When you start to lose too many podocytes, the kidney can again progress onto ESRD, so this is again an extra benefit of the calcineurin inhibitors in the context of kidney disease that affects the glomeruli,” he noted.
“So both of these drugs have these interesting attributes that go beyond, or at least are maybe tied to, their immunosuppressive actions, but they do offer some kidney protective effects,” he reaffirmed.
Black patients underrepresented in trials
The ICER authors voiced concern over the fact that individuals most at risk for SLE – mostly Black patients, but also patients of other racial groups – were underrepresented in clinical trials that evaluated both agents.
“We cannot stress enough that the results are highly uncertain due to the small numbers of Black patients in the available clinical trials and the lack of data on differences among subgroups in long-term outcomes,” they stated.
This is not an academic issue, Dr. Phillips pointed out. Responses to both MMF and cyclophosphamide differ among persons of different races, “so it’s not unreasonable to consider that there could be racial differences in treatment responses to both drugs, and these definitely need to be investigated.”
This is not an academic issue, Dr. Phillips said, because there are racial disparities in how patients respond to both MMF and cyclophosphamide – “so it’s not unreasonable to consider that there could be racial differences in treatment responses to both drugs, and these definitely need to be investigated.”
The ICER authors appear to agree. They urged the manufacturers of the two new agents to expand their research to include adequate representation of lupus nephritis patients from Black and other non-White communities.
However, it is somewhat reassuring that the pivotal voclosporin trial enrolled about 30% of Hispanic patients and that about 17% of participants in the BLISS-LN trial were also Hispanic, Dr. Rovin pointed out.
This is important because Hispanic patients can have very aggressive disease, as can Black patients, he noted. There is some evidence to suggest both drugs are effective in aggressive disease.
The ICER also pointed out that the length of time that both drugs can be used prior to tapering of treatment, after which patients receive standard maintenance therapy alone, has yet to be established.
This is important, Dr. Rovin and Dr. Phillips agreed, because calcineurin inhibitors are known to be nephrotoxic, and both drugs are immunosuppressive. At least with respect to voclosporin, there is some cause of concern regarding prolonged use of the drug for patients with kidney disease.
“We don’t want patients to be on an immunosuppressive drug forever if they don’t need to be,” Dr. Rovin emphasized.
“But we are seeing really long-term remission in the setting of other inflammatory diseases, like vasculitis with rituximab. So there is hope that we can achieve the same thing in lupus. If we use drugs that target T cells in the immune system, like voclosporin, or B cells, like belimumab, maybe we can ‘reset’ the immune system and get rid of potentially autoreactive cells that could allow long-lasting disease remission, which is an unanswered question but an intriguing possibility,” he concluded.
Dr. Rovin has served as a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Phillips disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The prices of two new drugs that have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of lupus nephritis are in “reasonable alignment” with the drugs’ estimated benefits for patients with the disease, the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review has determined.
“Both belimumab [Benlysta] and voclosporin [Lupkynis] are important new treatment options,” Steven Pearson, MD, president of ICER, observed in a summary of the report’s findings.
“Despite remaining uncertainty about both treatments’ longer-term outcomes, their estimated net prices appear to be aligned with their anticipated clinical benefits. ... For patients and clinicians to have responsibly priced options specifically indicated for lupus nephritis is a win for patients and the entire health system,” Dr. Pearson added.
The estimated annual price of belimumab is approximately $43,000 per patient; the estimated annual price for voclosporin is approximately $92,000 per patient.
The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio for belimumab is approximately $90,0000 per quality-adjusted life-year; the corresponding value for voclosporin is higher, at approximately $149,000 per QALY, the ICER authors noted.
The report was published by ICER in April 2021.
Large unmet need for treatment of lupus nephritis
In their report, the ICER reviewed belimumab, a parenteral B-lymphocyte inhibitor, as well as voclosporin, an oral calcineurin inhibitor, as initial treatment of patients with lupus nephritis. Lupus nephritis is a serious complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Belimumab was first approved for the treatment of lupus in adults in the United States in March 2011. In April 2019, it was approved for use for the same indication for children aged 5 years and older. The FDA expanded the indication in December 2020 to include adults with active lupus nephritis who are receiving standard therapy.
Voclosporin was approved for the treatment of lupus nephritis in January 2021.
In the pivotal trials for the two agents, each drug was added to standard induction therapy for lupus nephritis, which consisted of high-dose corticosteroids combined with either mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) or cyclophosphamide.
Compared with standard therapy alone, belimumab increased the complete renal response and the primary efficacy renal response at 2 years. With voclosporin, complete response was nearly doubled, and there was marked increased in partial response at 1 year, compared with standard therapy alone.
Neither drug appeared to increase the adverse-event rate or the rate of discontinuations, compared with standard therapy, although the FDA did add a black box warning regarding the possible risk for serious infections and malignancies with voclosporin use.
“There is a very large unmet need for the treatment of lupus nephritis,” Chris Phillips, MD, of Paducah (Ky.) Rheumatology said in an interview.
“A very large percentage of patients who do not achieve complete remission on traditional treatments have side effects or contraindications to these treatments, so we’ve needed new ones for sure,” he stressed.
The ICER authors made it clear that there is considerable uncertainty as to how short-term assessment of each of the two drugs’ performance might translate into meaningful long-term outcomes for patients, especially given that SLE is a lifelong illness.
On the other hand, “there are a lot of attributes for both of these new drugs that suggest there is potential for kidney benefit over time,” Brad Rovin, MD, professor of medicine and pathology at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, said in an interview.
For example, data from the BLISS-LN study, reported by Dr. Rovin during a meeting last year, suggest that belimumab reduces the flare rate and appears to stabilize kidney function over time, compared with standard therapy alone.
“BLISS-LN was 2 years long, so it gave us an opportunity to look at kidney function over a longer period of time than most of our prior trials in lupus nephritis,” he explained.
“The stabilization of kidney function is important, because it suggests that belimumab has a kidney protective effect, while a decrease in lupus nephritis flares is also important, because each time the disease flares, you can accumulate chronic tissue damage, which can eventually cause end-stage renal disease [ESRD],” he said.
Dr. Rovin also pointed out that the BLISS-LN trial results indicate that patients who achieve a urine protein level less than 700 mg/d after the first year of treatment do very well on long-term follow-up – another hint that belimumab may have long-term benefits for kidney function.
Voclosporin is a calcineurin inhibitor, which are protective of podocytes. “When you start to lose too many podocytes, the kidney can again progress onto ESRD, so this is again an extra benefit of the calcineurin inhibitors in the context of kidney disease that affects the glomeruli,” he noted.
“So both of these drugs have these interesting attributes that go beyond, or at least are maybe tied to, their immunosuppressive actions, but they do offer some kidney protective effects,” he reaffirmed.
Black patients underrepresented in trials
The ICER authors voiced concern over the fact that individuals most at risk for SLE – mostly Black patients, but also patients of other racial groups – were underrepresented in clinical trials that evaluated both agents.
“We cannot stress enough that the results are highly uncertain due to the small numbers of Black patients in the available clinical trials and the lack of data on differences among subgroups in long-term outcomes,” they stated.
This is not an academic issue, Dr. Phillips pointed out. Responses to both MMF and cyclophosphamide differ among persons of different races, “so it’s not unreasonable to consider that there could be racial differences in treatment responses to both drugs, and these definitely need to be investigated.”
This is not an academic issue, Dr. Phillips said, because there are racial disparities in how patients respond to both MMF and cyclophosphamide – “so it’s not unreasonable to consider that there could be racial differences in treatment responses to both drugs, and these definitely need to be investigated.”
The ICER authors appear to agree. They urged the manufacturers of the two new agents to expand their research to include adequate representation of lupus nephritis patients from Black and other non-White communities.
However, it is somewhat reassuring that the pivotal voclosporin trial enrolled about 30% of Hispanic patients and that about 17% of participants in the BLISS-LN trial were also Hispanic, Dr. Rovin pointed out.
This is important because Hispanic patients can have very aggressive disease, as can Black patients, he noted. There is some evidence to suggest both drugs are effective in aggressive disease.
The ICER also pointed out that the length of time that both drugs can be used prior to tapering of treatment, after which patients receive standard maintenance therapy alone, has yet to be established.
This is important, Dr. Rovin and Dr. Phillips agreed, because calcineurin inhibitors are known to be nephrotoxic, and both drugs are immunosuppressive. At least with respect to voclosporin, there is some cause of concern regarding prolonged use of the drug for patients with kidney disease.
“We don’t want patients to be on an immunosuppressive drug forever if they don’t need to be,” Dr. Rovin emphasized.
“But we are seeing really long-term remission in the setting of other inflammatory diseases, like vasculitis with rituximab. So there is hope that we can achieve the same thing in lupus. If we use drugs that target T cells in the immune system, like voclosporin, or B cells, like belimumab, maybe we can ‘reset’ the immune system and get rid of potentially autoreactive cells that could allow long-lasting disease remission, which is an unanswered question but an intriguing possibility,” he concluded.
Dr. Rovin has served as a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Phillips disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: Contraception April 2021
Patients receive the full range of contraception options when providers are educated on the proper use and spectrum of contraceptive options. When an educational intervention was introduced in three countries (Democratic Republic of Congo, Somalia, and Pakistan), aimed at training providers on counseling and provision of immediate postpartum LARC, a significant number of women opted for LARC. This was in comparison to countries that did not implement this educational intervention (Rwanda, Syria, Yemen). The rate of LARC adoption was 10.01% versus 0.77%, respectively in countries providing the educational intervention versus those that did not.
The copper IUD has long been utilized for emergency contraception, providing nearly 100% efficacy in pregnancy prevention, as well as long-acting, reversible contraception. Recently, the levonorgestrel (LNG) IUD was considered for similar use as emergency contraception. Turok et al studied the pregnancy rate of the LNG IUD compared the copper IUD and found that the LNG IUD was noninferior to the copper IUD when used for emergency contraception, with pregnancy rates of 1 in 317 (LNG) compared to 0 in 321 (copper). LNG IUDs are often more readily available in OBGYN offices and could improve access to higher efficacy emergency contraception compared to traditional emergency contraceptive pills.
When placing IUDs, providers have a range of devices to measure the length of the uterus for correct IUD placement, including endometrial biopsy pipelles, uterine sounds, both plastic and metal, as well as the device inserters. In a biomechanical ex vivo analysis, Duncan et al examined the maximum force generated for IUD placement with the levonorgestrel placement instrument, the copper IUD placement instrument, and a metal sound. Using their model, the investigators found that the metal sound caused uterine perforation, but the plastic IUD placement device did not. Although the study authors utilized the device inserters themselves, we recommend the use of plastic uterine sounds or biopsy pipelles over the device inserters in accordance with IUD packaging instructions. IUD packaging should not be opened until both the ability to access the uterine cavity and appropriate uterine size are determined to avoid needing to discard the IUD.
Patients receive the full range of contraception options when providers are educated on the proper use and spectrum of contraceptive options. When an educational intervention was introduced in three countries (Democratic Republic of Congo, Somalia, and Pakistan), aimed at training providers on counseling and provision of immediate postpartum LARC, a significant number of women opted for LARC. This was in comparison to countries that did not implement this educational intervention (Rwanda, Syria, Yemen). The rate of LARC adoption was 10.01% versus 0.77%, respectively in countries providing the educational intervention versus those that did not.
The copper IUD has long been utilized for emergency contraception, providing nearly 100% efficacy in pregnancy prevention, as well as long-acting, reversible contraception. Recently, the levonorgestrel (LNG) IUD was considered for similar use as emergency contraception. Turok et al studied the pregnancy rate of the LNG IUD compared the copper IUD and found that the LNG IUD was noninferior to the copper IUD when used for emergency contraception, with pregnancy rates of 1 in 317 (LNG) compared to 0 in 321 (copper). LNG IUDs are often more readily available in OBGYN offices and could improve access to higher efficacy emergency contraception compared to traditional emergency contraceptive pills.
When placing IUDs, providers have a range of devices to measure the length of the uterus for correct IUD placement, including endometrial biopsy pipelles, uterine sounds, both plastic and metal, as well as the device inserters. In a biomechanical ex vivo analysis, Duncan et al examined the maximum force generated for IUD placement with the levonorgestrel placement instrument, the copper IUD placement instrument, and a metal sound. Using their model, the investigators found that the metal sound caused uterine perforation, but the plastic IUD placement device did not. Although the study authors utilized the device inserters themselves, we recommend the use of plastic uterine sounds or biopsy pipelles over the device inserters in accordance with IUD packaging instructions. IUD packaging should not be opened until both the ability to access the uterine cavity and appropriate uterine size are determined to avoid needing to discard the IUD.
Patients receive the full range of contraception options when providers are educated on the proper use and spectrum of contraceptive options. When an educational intervention was introduced in three countries (Democratic Republic of Congo, Somalia, and Pakistan), aimed at training providers on counseling and provision of immediate postpartum LARC, a significant number of women opted for LARC. This was in comparison to countries that did not implement this educational intervention (Rwanda, Syria, Yemen). The rate of LARC adoption was 10.01% versus 0.77%, respectively in countries providing the educational intervention versus those that did not.
The copper IUD has long been utilized for emergency contraception, providing nearly 100% efficacy in pregnancy prevention, as well as long-acting, reversible contraception. Recently, the levonorgestrel (LNG) IUD was considered for similar use as emergency contraception. Turok et al studied the pregnancy rate of the LNG IUD compared the copper IUD and found that the LNG IUD was noninferior to the copper IUD when used for emergency contraception, with pregnancy rates of 1 in 317 (LNG) compared to 0 in 321 (copper). LNG IUDs are often more readily available in OBGYN offices and could improve access to higher efficacy emergency contraception compared to traditional emergency contraceptive pills.
When placing IUDs, providers have a range of devices to measure the length of the uterus for correct IUD placement, including endometrial biopsy pipelles, uterine sounds, both plastic and metal, as well as the device inserters. In a biomechanical ex vivo analysis, Duncan et al examined the maximum force generated for IUD placement with the levonorgestrel placement instrument, the copper IUD placement instrument, and a metal sound. Using their model, the investigators found that the metal sound caused uterine perforation, but the plastic IUD placement device did not. Although the study authors utilized the device inserters themselves, we recommend the use of plastic uterine sounds or biopsy pipelles over the device inserters in accordance with IUD packaging instructions. IUD packaging should not be opened until both the ability to access the uterine cavity and appropriate uterine size are determined to avoid needing to discard the IUD.
Commentary: Functional assessment developed for older adults with sickle cell disease
As individuals with sickle cell disease (SCD) are living longer than ever before there is a greater need to focus on maintaining and improving function and independence in this growing population. In the general population, impairments in functional measures such as usual gait speed, grip strength, Timed Up and Go, and cognition are associated with adverse health outcomes such as falls, fractures, loss of independence, and death.
Adults with SCD experience multiple complications such as avascular necrosis of the joints, retinopathy, and strokes that lead to functional limitations similar to those experienced by geriatric populations. However, functional assessments are not routinely performed during clinic visits with older adults with SCD.
In order to address this gap in care, my colleagues and I developed the first functional assessment for older adults with SCD, called the Sickle Cell Disease Functional Assessment (SCD-FA). This assessment will allow providers to evaluate the capabilities and vulnerabilities of older adults with SCD.
We assessed the feasibility of administering the SCD-FA in a prospective cohort pilot study. We enrolled 40 adults with SCD (20 older adults aged at least 50 years and 20 younger adults aged 18-49 years as a comparison group). All participants were assessed at steady-state.
For the SCD-FA, we selected geriatric assessment measures across seven domains: functional status, comorbid medical conditions, psychological state, social support, nutritional status, cognition, and medications. Several of these measures were previously validated in an oncology geriatric assessment and enriched with additional physical and cognitive measures to evaluate conditions at the intersection of SCD and geriatrics.
In September 2020, we published a protocol describing the methods and rationale for selecting measures for the SCD-FA in Pilot and Feasibility Studies.1 The preliminary data was presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology in December 2020 and was included in the annual Hematology and Aging Poster Walk.
The results of this pilot study showed that the SCD-FA is feasible (91% of participants who consented completed the SCD-FA), acceptable (95% reported the length as appropriate and had no difficulty understanding the measures), and safe with no adverse events.2 On physical performance testing, both younger and older participants had results consistent with accelerated aging with a functional age at least 20-30 years older than their chronological age.2
The majority of the participants (63%) had a usual gait speed slower than the speed required to safely cross the street at an intersection, and 25% had a gait speed slower than 1 m/s, which has been associated with increased mortality in the general population.3,4
Benefits to management
The SCD-FA can improve management of adults with SCD by:
- Characterizing their capabilities and physiological age, identifying individuals at high risk for functional decline and death early identifying targets for interventions that have been successful in geriatrics,5 assessing risk of toxicity from curative therapies, and evaluating functional response to SCD-specific therapies.
The SCD-FA provides a framework for developing exercise interventions to target functional impairments. This work supports our goal of improving the quality of life and longevity for people with SCD.
Dr. Oyedeji is a senior hematology Fellow at the department of medicine, division of hematology, Duke University, Durham, N.C. She reported that she has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2020;6:131.
2. Blood. 2020;136(Supplement 1):26-7.
3. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2005;42(4):535-46.
4. JAMA. 2011;305(1):50-8.
5. South Med J. 1994;87(5):S83-7.
As individuals with sickle cell disease (SCD) are living longer than ever before there is a greater need to focus on maintaining and improving function and independence in this growing population. In the general population, impairments in functional measures such as usual gait speed, grip strength, Timed Up and Go, and cognition are associated with adverse health outcomes such as falls, fractures, loss of independence, and death.
Adults with SCD experience multiple complications such as avascular necrosis of the joints, retinopathy, and strokes that lead to functional limitations similar to those experienced by geriatric populations. However, functional assessments are not routinely performed during clinic visits with older adults with SCD.
In order to address this gap in care, my colleagues and I developed the first functional assessment for older adults with SCD, called the Sickle Cell Disease Functional Assessment (SCD-FA). This assessment will allow providers to evaluate the capabilities and vulnerabilities of older adults with SCD.
We assessed the feasibility of administering the SCD-FA in a prospective cohort pilot study. We enrolled 40 adults with SCD (20 older adults aged at least 50 years and 20 younger adults aged 18-49 years as a comparison group). All participants were assessed at steady-state.
For the SCD-FA, we selected geriatric assessment measures across seven domains: functional status, comorbid medical conditions, psychological state, social support, nutritional status, cognition, and medications. Several of these measures were previously validated in an oncology geriatric assessment and enriched with additional physical and cognitive measures to evaluate conditions at the intersection of SCD and geriatrics.
In September 2020, we published a protocol describing the methods and rationale for selecting measures for the SCD-FA in Pilot and Feasibility Studies.1 The preliminary data was presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology in December 2020 and was included in the annual Hematology and Aging Poster Walk.
The results of this pilot study showed that the SCD-FA is feasible (91% of participants who consented completed the SCD-FA), acceptable (95% reported the length as appropriate and had no difficulty understanding the measures), and safe with no adverse events.2 On physical performance testing, both younger and older participants had results consistent with accelerated aging with a functional age at least 20-30 years older than their chronological age.2
The majority of the participants (63%) had a usual gait speed slower than the speed required to safely cross the street at an intersection, and 25% had a gait speed slower than 1 m/s, which has been associated with increased mortality in the general population.3,4
Benefits to management
The SCD-FA can improve management of adults with SCD by:
- Characterizing their capabilities and physiological age, identifying individuals at high risk for functional decline and death early identifying targets for interventions that have been successful in geriatrics,5 assessing risk of toxicity from curative therapies, and evaluating functional response to SCD-specific therapies.
The SCD-FA provides a framework for developing exercise interventions to target functional impairments. This work supports our goal of improving the quality of life and longevity for people with SCD.
Dr. Oyedeji is a senior hematology Fellow at the department of medicine, division of hematology, Duke University, Durham, N.C. She reported that she has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2020;6:131.
2. Blood. 2020;136(Supplement 1):26-7.
3. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2005;42(4):535-46.
4. JAMA. 2011;305(1):50-8.
5. South Med J. 1994;87(5):S83-7.
As individuals with sickle cell disease (SCD) are living longer than ever before there is a greater need to focus on maintaining and improving function and independence in this growing population. In the general population, impairments in functional measures such as usual gait speed, grip strength, Timed Up and Go, and cognition are associated with adverse health outcomes such as falls, fractures, loss of independence, and death.
Adults with SCD experience multiple complications such as avascular necrosis of the joints, retinopathy, and strokes that lead to functional limitations similar to those experienced by geriatric populations. However, functional assessments are not routinely performed during clinic visits with older adults with SCD.
In order to address this gap in care, my colleagues and I developed the first functional assessment for older adults with SCD, called the Sickle Cell Disease Functional Assessment (SCD-FA). This assessment will allow providers to evaluate the capabilities and vulnerabilities of older adults with SCD.
We assessed the feasibility of administering the SCD-FA in a prospective cohort pilot study. We enrolled 40 adults with SCD (20 older adults aged at least 50 years and 20 younger adults aged 18-49 years as a comparison group). All participants were assessed at steady-state.
For the SCD-FA, we selected geriatric assessment measures across seven domains: functional status, comorbid medical conditions, psychological state, social support, nutritional status, cognition, and medications. Several of these measures were previously validated in an oncology geriatric assessment and enriched with additional physical and cognitive measures to evaluate conditions at the intersection of SCD and geriatrics.
In September 2020, we published a protocol describing the methods and rationale for selecting measures for the SCD-FA in Pilot and Feasibility Studies.1 The preliminary data was presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology in December 2020 and was included in the annual Hematology and Aging Poster Walk.
The results of this pilot study showed that the SCD-FA is feasible (91% of participants who consented completed the SCD-FA), acceptable (95% reported the length as appropriate and had no difficulty understanding the measures), and safe with no adverse events.2 On physical performance testing, both younger and older participants had results consistent with accelerated aging with a functional age at least 20-30 years older than their chronological age.2
The majority of the participants (63%) had a usual gait speed slower than the speed required to safely cross the street at an intersection, and 25% had a gait speed slower than 1 m/s, which has been associated with increased mortality in the general population.3,4
Benefits to management
The SCD-FA can improve management of adults with SCD by:
- Characterizing their capabilities and physiological age, identifying individuals at high risk for functional decline and death early identifying targets for interventions that have been successful in geriatrics,5 assessing risk of toxicity from curative therapies, and evaluating functional response to SCD-specific therapies.
The SCD-FA provides a framework for developing exercise interventions to target functional impairments. This work supports our goal of improving the quality of life and longevity for people with SCD.
Dr. Oyedeji is a senior hematology Fellow at the department of medicine, division of hematology, Duke University, Durham, N.C. She reported that she has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2020;6:131.
2. Blood. 2020;136(Supplement 1):26-7.
3. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2005;42(4):535-46.
4. JAMA. 2011;305(1):50-8.
5. South Med J. 1994;87(5):S83-7.
Is it time for universal genetic testing in colorectal cancer?
A prospective study of universal genetic testing suggested that one in six colorectal cancer patients have an inherited genetic predisposition to the cancer. More than half of the patients with genetic mutations identified in this study would have been missed if the patients had undergone genetic testing based on current practice. In 11% of patients, the genetic findings led to a change in treatment, including the type of surgery or targeted cancer therapy.
These results were presented at the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics annual meeting and published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
“This study shows the limitations of relying on current clinical practice guidelines for genetic evaluation, which prioritize age of cancer diagnosis and family cancer history,” said investigator Niloy Jewel Samadder, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Phoenix.
“We were surprised that more than 50% of the patients with a genetic mutation would not have been identified had we relied on national practice guidelines or only used a small colon cancer-specific gene panel, as is commonly employed in clinical practice. The fact that more than 10% of patients actually had changes in the type of surgery or chemo/immunotherapy they received gives the strongest indicator of how genetics can revolutionize and individualize cancer care,” Dr. Samadder said.
He added that identifying a germline predisposition has multiple values, including understanding the reason patients and their family members develop specific cancers, preventing the development of new cancers in patients and family members by providing targeted prevention and screening for those at genetic risk, and improving survival in patients with a genetic driver of cancer via targeted therapy.
Study details
The researchers used a next-generation sequencing platform with more than 80 genes in colorectal cancer patients (not selected for age or family history) receiving care at Mayo Clinic Cancer Centers between April 1, 2018, and March 31, 2020.
The study included 361 patients with a median age of 57 years. Pathogenic germline variants were identified in 56 patients (15.5%), including 44 patients with moderate and high penetrance cancer susceptibility genes.
Younger age (under 50 years old) was associated with having a germline mutation, but “more importantly, gender, family cancer history, and stage of cancer were not,” Dr. Samadder said.
“The current clinical guidelines rely heavily on these characteristics to determine who should and should not be referred for genetic testing,” he continued. “Our study suggests that even older patients with colorectal cancer have a high rate of having pathogenic germline mutations [12%], so restricting genetic testing to only those under age 50 will miss a substantial portion of patients who might benefit from this test.”
Genetic testing for all
“Our findings support the broad use of genetic testing in all colorectal cancer patients, regardless of age, gender, ethnicity, family cancer history, or stage of cancer,” Dr. Samadder said.
“This study adds to a growing body of literature that provides evidence that cancer susceptibility due to variants in single genes is more common than previously appreciated,” said Marc S. Williams, MD, president of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. “Current testing guidelines seem to be relatively insensitive and miss opportunities for testing of patients.”
Dr. Williams noted that 11% of patients in this study had a change in disease management related to a genetic testing result, which is “a relatively modest impact.”
“Another potential advantage of [universal] testing was the opportunity to test at-risk relatives,” Dr. Williams added. “However, only 16% of eligible individuals pursued testing. This is consistent with other studies and represents an opportunity for testing new ways to improve uptake of cascade screening.”
Dr. Williams said rigorous prospective studies enrolling large numbers of patients from diverse backgrounds are needed to inform the development and updating of genetic testing guidelines.
He disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Samadder disclosed relationships with Janssen Research and Development, Recursion Pharmaceuticals, and Cancer Prevention Pharmaceuticals. The research was funded by the Mayo Clinic, Desert Mountain Members’ CARE Foundation, David and Twila Woods Foundation, and the Gerstner Foundation.
A prospective study of universal genetic testing suggested that one in six colorectal cancer patients have an inherited genetic predisposition to the cancer. More than half of the patients with genetic mutations identified in this study would have been missed if the patients had undergone genetic testing based on current practice. In 11% of patients, the genetic findings led to a change in treatment, including the type of surgery or targeted cancer therapy.
These results were presented at the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics annual meeting and published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
“This study shows the limitations of relying on current clinical practice guidelines for genetic evaluation, which prioritize age of cancer diagnosis and family cancer history,” said investigator Niloy Jewel Samadder, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Phoenix.
“We were surprised that more than 50% of the patients with a genetic mutation would not have been identified had we relied on national practice guidelines or only used a small colon cancer-specific gene panel, as is commonly employed in clinical practice. The fact that more than 10% of patients actually had changes in the type of surgery or chemo/immunotherapy they received gives the strongest indicator of how genetics can revolutionize and individualize cancer care,” Dr. Samadder said.
He added that identifying a germline predisposition has multiple values, including understanding the reason patients and their family members develop specific cancers, preventing the development of new cancers in patients and family members by providing targeted prevention and screening for those at genetic risk, and improving survival in patients with a genetic driver of cancer via targeted therapy.
Study details
The researchers used a next-generation sequencing platform with more than 80 genes in colorectal cancer patients (not selected for age or family history) receiving care at Mayo Clinic Cancer Centers between April 1, 2018, and March 31, 2020.
The study included 361 patients with a median age of 57 years. Pathogenic germline variants were identified in 56 patients (15.5%), including 44 patients with moderate and high penetrance cancer susceptibility genes.
Younger age (under 50 years old) was associated with having a germline mutation, but “more importantly, gender, family cancer history, and stage of cancer were not,” Dr. Samadder said.
“The current clinical guidelines rely heavily on these characteristics to determine who should and should not be referred for genetic testing,” he continued. “Our study suggests that even older patients with colorectal cancer have a high rate of having pathogenic germline mutations [12%], so restricting genetic testing to only those under age 50 will miss a substantial portion of patients who might benefit from this test.”
Genetic testing for all
“Our findings support the broad use of genetic testing in all colorectal cancer patients, regardless of age, gender, ethnicity, family cancer history, or stage of cancer,” Dr. Samadder said.
“This study adds to a growing body of literature that provides evidence that cancer susceptibility due to variants in single genes is more common than previously appreciated,” said Marc S. Williams, MD, president of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. “Current testing guidelines seem to be relatively insensitive and miss opportunities for testing of patients.”
Dr. Williams noted that 11% of patients in this study had a change in disease management related to a genetic testing result, which is “a relatively modest impact.”
“Another potential advantage of [universal] testing was the opportunity to test at-risk relatives,” Dr. Williams added. “However, only 16% of eligible individuals pursued testing. This is consistent with other studies and represents an opportunity for testing new ways to improve uptake of cascade screening.”
Dr. Williams said rigorous prospective studies enrolling large numbers of patients from diverse backgrounds are needed to inform the development and updating of genetic testing guidelines.
He disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Samadder disclosed relationships with Janssen Research and Development, Recursion Pharmaceuticals, and Cancer Prevention Pharmaceuticals. The research was funded by the Mayo Clinic, Desert Mountain Members’ CARE Foundation, David and Twila Woods Foundation, and the Gerstner Foundation.
A prospective study of universal genetic testing suggested that one in six colorectal cancer patients have an inherited genetic predisposition to the cancer. More than half of the patients with genetic mutations identified in this study would have been missed if the patients had undergone genetic testing based on current practice. In 11% of patients, the genetic findings led to a change in treatment, including the type of surgery or targeted cancer therapy.
These results were presented at the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics annual meeting and published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
“This study shows the limitations of relying on current clinical practice guidelines for genetic evaluation, which prioritize age of cancer diagnosis and family cancer history,” said investigator Niloy Jewel Samadder, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Phoenix.
“We were surprised that more than 50% of the patients with a genetic mutation would not have been identified had we relied on national practice guidelines or only used a small colon cancer-specific gene panel, as is commonly employed in clinical practice. The fact that more than 10% of patients actually had changes in the type of surgery or chemo/immunotherapy they received gives the strongest indicator of how genetics can revolutionize and individualize cancer care,” Dr. Samadder said.
He added that identifying a germline predisposition has multiple values, including understanding the reason patients and their family members develop specific cancers, preventing the development of new cancers in patients and family members by providing targeted prevention and screening for those at genetic risk, and improving survival in patients with a genetic driver of cancer via targeted therapy.
Study details
The researchers used a next-generation sequencing platform with more than 80 genes in colorectal cancer patients (not selected for age or family history) receiving care at Mayo Clinic Cancer Centers between April 1, 2018, and March 31, 2020.
The study included 361 patients with a median age of 57 years. Pathogenic germline variants were identified in 56 patients (15.5%), including 44 patients with moderate and high penetrance cancer susceptibility genes.
Younger age (under 50 years old) was associated with having a germline mutation, but “more importantly, gender, family cancer history, and stage of cancer were not,” Dr. Samadder said.
“The current clinical guidelines rely heavily on these characteristics to determine who should and should not be referred for genetic testing,” he continued. “Our study suggests that even older patients with colorectal cancer have a high rate of having pathogenic germline mutations [12%], so restricting genetic testing to only those under age 50 will miss a substantial portion of patients who might benefit from this test.”
Genetic testing for all
“Our findings support the broad use of genetic testing in all colorectal cancer patients, regardless of age, gender, ethnicity, family cancer history, or stage of cancer,” Dr. Samadder said.
“This study adds to a growing body of literature that provides evidence that cancer susceptibility due to variants in single genes is more common than previously appreciated,” said Marc S. Williams, MD, president of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. “Current testing guidelines seem to be relatively insensitive and miss opportunities for testing of patients.”
Dr. Williams noted that 11% of patients in this study had a change in disease management related to a genetic testing result, which is “a relatively modest impact.”
“Another potential advantage of [universal] testing was the opportunity to test at-risk relatives,” Dr. Williams added. “However, only 16% of eligible individuals pursued testing. This is consistent with other studies and represents an opportunity for testing new ways to improve uptake of cascade screening.”
Dr. Williams said rigorous prospective studies enrolling large numbers of patients from diverse backgrounds are needed to inform the development and updating of genetic testing guidelines.
He disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Samadder disclosed relationships with Janssen Research and Development, Recursion Pharmaceuticals, and Cancer Prevention Pharmaceuticals. The research was funded by the Mayo Clinic, Desert Mountain Members’ CARE Foundation, David and Twila Woods Foundation, and the Gerstner Foundation.
FROM ACMG 2021
Efficacy and safety of daily low-dose colchicine after recent MI
Background: Clinical evidence supports the role of inflammation in atherosclerosis and its complications. Colchicine (Colcrys) in an orally administered potent anti-inflammatory that is currently used to treat gout and pericarditis.
Study design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, investigator-initiated trial.
Setting: Funded by Canadian Institute of Health and Research, 167 centers in 12 different countries. Centers were predominately located in Canada, South America, and Europe.
Synopsis: In this study, 4,745 patients with a MI within the last 30 days and treated according to national guidelines were enrolled. There were multiple exclusion criteria including severe heart, renal, and/or hepatic failure. The mean age of patients was 60.6 years. Patients were followed for a median of 22.6 months. The primary endpoint was a composite of death from cardiovascular causes, resuscitated cardiac arrest, MI, stroke, or urgent hospitalization for angina leading to coronary revascularization.
The primary endpoint occurred in 5.5% of patients in the colchicine group and 7.1% of those in the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.77). This was largely because of a decreased incidence of stroke in the colchicine group compared to placebo (0.2% vs 0.8%) and decreased urgent hospitalizations for unstable angina leading to revascularization (1.1% vs 2.1%).
Nausea was more common in the colchicine group as well as pneumonia which was reported as a serious adverse event (0.9% compared to 0.4% in placebo).
Limitations included short follow-up and significant exclusion criteria.
Bottom line: In patients following a recent myocardial infraction, the use of low-dose colchicine at 0.5 mg daily led to a significantly lower percentage of ischemic cardiovascular events compared to placebo.
Citation: Tardif JC et al. Efficacy and safety of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 26;381:2497-505.
Dr. Qazi is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, Ill.
Background: Clinical evidence supports the role of inflammation in atherosclerosis and its complications. Colchicine (Colcrys) in an orally administered potent anti-inflammatory that is currently used to treat gout and pericarditis.
Study design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, investigator-initiated trial.
Setting: Funded by Canadian Institute of Health and Research, 167 centers in 12 different countries. Centers were predominately located in Canada, South America, and Europe.
Synopsis: In this study, 4,745 patients with a MI within the last 30 days and treated according to national guidelines were enrolled. There were multiple exclusion criteria including severe heart, renal, and/or hepatic failure. The mean age of patients was 60.6 years. Patients were followed for a median of 22.6 months. The primary endpoint was a composite of death from cardiovascular causes, resuscitated cardiac arrest, MI, stroke, or urgent hospitalization for angina leading to coronary revascularization.
The primary endpoint occurred in 5.5% of patients in the colchicine group and 7.1% of those in the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.77). This was largely because of a decreased incidence of stroke in the colchicine group compared to placebo (0.2% vs 0.8%) and decreased urgent hospitalizations for unstable angina leading to revascularization (1.1% vs 2.1%).
Nausea was more common in the colchicine group as well as pneumonia which was reported as a serious adverse event (0.9% compared to 0.4% in placebo).
Limitations included short follow-up and significant exclusion criteria.
Bottom line: In patients following a recent myocardial infraction, the use of low-dose colchicine at 0.5 mg daily led to a significantly lower percentage of ischemic cardiovascular events compared to placebo.
Citation: Tardif JC et al. Efficacy and safety of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 26;381:2497-505.
Dr. Qazi is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, Ill.
Background: Clinical evidence supports the role of inflammation in atherosclerosis and its complications. Colchicine (Colcrys) in an orally administered potent anti-inflammatory that is currently used to treat gout and pericarditis.
Study design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, investigator-initiated trial.
Setting: Funded by Canadian Institute of Health and Research, 167 centers in 12 different countries. Centers were predominately located in Canada, South America, and Europe.
Synopsis: In this study, 4,745 patients with a MI within the last 30 days and treated according to national guidelines were enrolled. There were multiple exclusion criteria including severe heart, renal, and/or hepatic failure. The mean age of patients was 60.6 years. Patients were followed for a median of 22.6 months. The primary endpoint was a composite of death from cardiovascular causes, resuscitated cardiac arrest, MI, stroke, or urgent hospitalization for angina leading to coronary revascularization.
The primary endpoint occurred in 5.5% of patients in the colchicine group and 7.1% of those in the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.77). This was largely because of a decreased incidence of stroke in the colchicine group compared to placebo (0.2% vs 0.8%) and decreased urgent hospitalizations for unstable angina leading to revascularization (1.1% vs 2.1%).
Nausea was more common in the colchicine group as well as pneumonia which was reported as a serious adverse event (0.9% compared to 0.4% in placebo).
Limitations included short follow-up and significant exclusion criteria.
Bottom line: In patients following a recent myocardial infraction, the use of low-dose colchicine at 0.5 mg daily led to a significantly lower percentage of ischemic cardiovascular events compared to placebo.
Citation: Tardif JC et al. Efficacy and safety of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 26;381:2497-505.
Dr. Qazi is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, Ill.
Le Petit Prince: Lessons From a Beloved Fable for Our Current Time
”Good evening,“ said the little prince politely.
”Good evening,“ said the snake.
”What planet have I fallen on?“ asked the little prince.
”On the planet Earth, in Africa,“ replied the snake.
”Oh… Then there are no people on Earth?”
”This is the desert. There are no people in the desert. The Earth is big,“ said the snake.
The little prince sat down on a stone and looked up at the sky.
”I wonder,“ he said, “if the stars are lit up so that each of us can find his own star again. Look at my planet. It is right above us… But how far away is it?” 1
Le Petit Prince is one of the twentieth century’s most widely read fables.1 Written in 1943 by the French aviator and novelist Antoine de Saint-Exupéry, it tells the story of a young prince who inhabits a small planet in outer space with his muse, a fragile and dainty rose. The prince loves his rose and goes to great lengths to protect her, but her constant needs prove too much for him to bear. One day he decides to leave her and sets out on a journey across the universe. Along the way he stops at several different planets and interacts with their sole inhabitants, each of whom performs a bizarre and arguably pointless activity. The prince leaves each planet confused and despondent—for no place or person has proven more inspiring than his own planet or rose—until he arrives on Earth, where he meets a snake, a fox, and the novel’s unnamed narrator. Their company is a welcome relief for the travel-weary prince, who learns important lessons about love, friendship, and “matters of consequence.” Toward the novel’s end, the snake promises to deliver the little prince home if he allows himself to be bitten. The prince obliges in order to be with his rose, and he soon disappears. The story concludes with the narrator looking up at the stars, wondering if the prince is somewhere among them.
One interpretation of Le Petit Prince is that life is more beautiful when the things that give it meaning are recognized and cherished, but there is a heavy irony behind this theme. The story was published during one of the lowest points in the Second World War, when France was still in the grips of its German oppressors. Saint-Exupéry himself had fled to the United States years earlier and composed Le Petit Prince during a time of personal upheaval. In short, nothing about the context of the book’s birth seemed to inspire its rosy message.
Now, almost 80 years after the first publication of Le Petit Prince, we find ourselves in a similarly jarring and unpredictable time. As calamitous global events unfold around us, it is difficult not to feel overwhelmed. For healthcare workers, the crush of patient care has made us feel vulnerable—first to a virus that might infect us and our loved ones, and second, to the overwhelming sense of despair when caring for patients who ultimately die despite our best efforts. Pandemics are a time of physical and social disruption, and while it has been 100 years since we experienced one like this, they are a repeated part of the history of life on our planet. What would the little prince see if he landed in our clinics, hospitals, nursing homes, testing centers, or vaccination facilities today? Would he observe patients saying good-bye to family members on tablets and cell phones because their loved ones are not allowed to visit in person? Would he see healthcare workers struggling to resuscitate dying patients in a crowded emergency department or intensive care unit? Would he see long lines of cars filled with people waiting for tests or vaccines? Would he see government officials and public health workers agonizing over decisions about steps that could reduce spread but impose economic hardship on many?
There has been much debate about whether Le Petit Prince is a children’s story or a message for adults disguised as a children’s fable. Perhaps the answer is that it is both, for many children’s stories were actually written for adults. Despite the fragility and delicacy of the book, there is clearly a haunting and deep irony inherent in what it is, in effect, a most savage critique of the world at war.
Two themes that emerge in the novel resonate widely now: isolation and death. Each character the little prince meets is alone, mirroring the long periods of social distancing we have experienced over the past year. And while death is never explicitly mentioned in the book, it seems to be lurking throughout, especially when the prince disappears from Earth after being bitten by the snake. Currently, we have almost become numb to the reported daily death counts—each one alone would have evoked outrage in more usual times. One might imagine that Saint-Exupéry wrote this fable in part to help people cope with the deaths of their loved ones.
And when you are comforted (time soothes all sorrows) you will be happy to have known me. You will always be my friend. You will want to laugh with me. And from time to time you will open your window, so, just for the pleasure of it ... And your friends will be astonished to see you laughing whilst gazing at the sky! And so you will say to them, “Yes, stars always make me laugh!”
Over the past year, both authors of this essay have seen people turn to Le Petit Prince to cope with death. One of us observed a daughter reading the book to her mother at her intensive care bedside on the day she died. The other received a copy as thanks from the wife of a young man who died after 18 months of punishing chemotherapy for sarcoma. Inside the cover was a picture of her husband and the inscription, “Please share this book with someone you love—it’s meant to be read out loud—and remember James.” And so I did, with my grandson Sebastian, who listened to the story with the imagination, wonder, and curiosity of a 6-year-old—he had many questions.
Perhaps the fable that has comforted our patients and their families during their time of despair can do the same for us. Like the prince, who returns to his rose after a difficult journey, we might find solace in the people and things that give our lives their deepest meaning. Thereafter, we might return, rejuvenated, to the clinics, emergency departments, and inpatient wards where our daily work must continue. While the scale of the problems around us makes it feel like any step we take towards preserving our hope will be moot, Le Petit Prince teaches us there is value in making the effort. And there is even a chance that we will find, to our surprise, and against our more cynical judgment, a small rose pushing itself up towards the light.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Rita Charon (Columbia University), Pam Hartzband (Harvard University), Raphael Rush (University of Toronto), and Emily Silverman (University of California San Francisco) for their comments on earlier versions of this essay. None were compensated. We thank Sebastian, James’ wife, and our other patient’s daughter for giving permission to include them in the story.
1. de Saint-Exupéry A. The Little Prince. Harcourt Brace; 1961.
”Good evening,“ said the little prince politely.
”Good evening,“ said the snake.
”What planet have I fallen on?“ asked the little prince.
”On the planet Earth, in Africa,“ replied the snake.
”Oh… Then there are no people on Earth?”
”This is the desert. There are no people in the desert. The Earth is big,“ said the snake.
The little prince sat down on a stone and looked up at the sky.
”I wonder,“ he said, “if the stars are lit up so that each of us can find his own star again. Look at my planet. It is right above us… But how far away is it?” 1
Le Petit Prince is one of the twentieth century’s most widely read fables.1 Written in 1943 by the French aviator and novelist Antoine de Saint-Exupéry, it tells the story of a young prince who inhabits a small planet in outer space with his muse, a fragile and dainty rose. The prince loves his rose and goes to great lengths to protect her, but her constant needs prove too much for him to bear. One day he decides to leave her and sets out on a journey across the universe. Along the way he stops at several different planets and interacts with their sole inhabitants, each of whom performs a bizarre and arguably pointless activity. The prince leaves each planet confused and despondent—for no place or person has proven more inspiring than his own planet or rose—until he arrives on Earth, where he meets a snake, a fox, and the novel’s unnamed narrator. Their company is a welcome relief for the travel-weary prince, who learns important lessons about love, friendship, and “matters of consequence.” Toward the novel’s end, the snake promises to deliver the little prince home if he allows himself to be bitten. The prince obliges in order to be with his rose, and he soon disappears. The story concludes with the narrator looking up at the stars, wondering if the prince is somewhere among them.
One interpretation of Le Petit Prince is that life is more beautiful when the things that give it meaning are recognized and cherished, but there is a heavy irony behind this theme. The story was published during one of the lowest points in the Second World War, when France was still in the grips of its German oppressors. Saint-Exupéry himself had fled to the United States years earlier and composed Le Petit Prince during a time of personal upheaval. In short, nothing about the context of the book’s birth seemed to inspire its rosy message.
Now, almost 80 years after the first publication of Le Petit Prince, we find ourselves in a similarly jarring and unpredictable time. As calamitous global events unfold around us, it is difficult not to feel overwhelmed. For healthcare workers, the crush of patient care has made us feel vulnerable—first to a virus that might infect us and our loved ones, and second, to the overwhelming sense of despair when caring for patients who ultimately die despite our best efforts. Pandemics are a time of physical and social disruption, and while it has been 100 years since we experienced one like this, they are a repeated part of the history of life on our planet. What would the little prince see if he landed in our clinics, hospitals, nursing homes, testing centers, or vaccination facilities today? Would he observe patients saying good-bye to family members on tablets and cell phones because their loved ones are not allowed to visit in person? Would he see healthcare workers struggling to resuscitate dying patients in a crowded emergency department or intensive care unit? Would he see long lines of cars filled with people waiting for tests or vaccines? Would he see government officials and public health workers agonizing over decisions about steps that could reduce spread but impose economic hardship on many?
There has been much debate about whether Le Petit Prince is a children’s story or a message for adults disguised as a children’s fable. Perhaps the answer is that it is both, for many children’s stories were actually written for adults. Despite the fragility and delicacy of the book, there is clearly a haunting and deep irony inherent in what it is, in effect, a most savage critique of the world at war.
Two themes that emerge in the novel resonate widely now: isolation and death. Each character the little prince meets is alone, mirroring the long periods of social distancing we have experienced over the past year. And while death is never explicitly mentioned in the book, it seems to be lurking throughout, especially when the prince disappears from Earth after being bitten by the snake. Currently, we have almost become numb to the reported daily death counts—each one alone would have evoked outrage in more usual times. One might imagine that Saint-Exupéry wrote this fable in part to help people cope with the deaths of their loved ones.
And when you are comforted (time soothes all sorrows) you will be happy to have known me. You will always be my friend. You will want to laugh with me. And from time to time you will open your window, so, just for the pleasure of it ... And your friends will be astonished to see you laughing whilst gazing at the sky! And so you will say to them, “Yes, stars always make me laugh!”
Over the past year, both authors of this essay have seen people turn to Le Petit Prince to cope with death. One of us observed a daughter reading the book to her mother at her intensive care bedside on the day she died. The other received a copy as thanks from the wife of a young man who died after 18 months of punishing chemotherapy for sarcoma. Inside the cover was a picture of her husband and the inscription, “Please share this book with someone you love—it’s meant to be read out loud—and remember James.” And so I did, with my grandson Sebastian, who listened to the story with the imagination, wonder, and curiosity of a 6-year-old—he had many questions.
Perhaps the fable that has comforted our patients and their families during their time of despair can do the same for us. Like the prince, who returns to his rose after a difficult journey, we might find solace in the people and things that give our lives their deepest meaning. Thereafter, we might return, rejuvenated, to the clinics, emergency departments, and inpatient wards where our daily work must continue. While the scale of the problems around us makes it feel like any step we take towards preserving our hope will be moot, Le Petit Prince teaches us there is value in making the effort. And there is even a chance that we will find, to our surprise, and against our more cynical judgment, a small rose pushing itself up towards the light.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Rita Charon (Columbia University), Pam Hartzband (Harvard University), Raphael Rush (University of Toronto), and Emily Silverman (University of California San Francisco) for their comments on earlier versions of this essay. None were compensated. We thank Sebastian, James’ wife, and our other patient’s daughter for giving permission to include them in the story.
”Good evening,“ said the little prince politely.
”Good evening,“ said the snake.
”What planet have I fallen on?“ asked the little prince.
”On the planet Earth, in Africa,“ replied the snake.
”Oh… Then there are no people on Earth?”
”This is the desert. There are no people in the desert. The Earth is big,“ said the snake.
The little prince sat down on a stone and looked up at the sky.
”I wonder,“ he said, “if the stars are lit up so that each of us can find his own star again. Look at my planet. It is right above us… But how far away is it?” 1
Le Petit Prince is one of the twentieth century’s most widely read fables.1 Written in 1943 by the French aviator and novelist Antoine de Saint-Exupéry, it tells the story of a young prince who inhabits a small planet in outer space with his muse, a fragile and dainty rose. The prince loves his rose and goes to great lengths to protect her, but her constant needs prove too much for him to bear. One day he decides to leave her and sets out on a journey across the universe. Along the way he stops at several different planets and interacts with their sole inhabitants, each of whom performs a bizarre and arguably pointless activity. The prince leaves each planet confused and despondent—for no place or person has proven more inspiring than his own planet or rose—until he arrives on Earth, where he meets a snake, a fox, and the novel’s unnamed narrator. Their company is a welcome relief for the travel-weary prince, who learns important lessons about love, friendship, and “matters of consequence.” Toward the novel’s end, the snake promises to deliver the little prince home if he allows himself to be bitten. The prince obliges in order to be with his rose, and he soon disappears. The story concludes with the narrator looking up at the stars, wondering if the prince is somewhere among them.
One interpretation of Le Petit Prince is that life is more beautiful when the things that give it meaning are recognized and cherished, but there is a heavy irony behind this theme. The story was published during one of the lowest points in the Second World War, when France was still in the grips of its German oppressors. Saint-Exupéry himself had fled to the United States years earlier and composed Le Petit Prince during a time of personal upheaval. In short, nothing about the context of the book’s birth seemed to inspire its rosy message.
Now, almost 80 years after the first publication of Le Petit Prince, we find ourselves in a similarly jarring and unpredictable time. As calamitous global events unfold around us, it is difficult not to feel overwhelmed. For healthcare workers, the crush of patient care has made us feel vulnerable—first to a virus that might infect us and our loved ones, and second, to the overwhelming sense of despair when caring for patients who ultimately die despite our best efforts. Pandemics are a time of physical and social disruption, and while it has been 100 years since we experienced one like this, they are a repeated part of the history of life on our planet. What would the little prince see if he landed in our clinics, hospitals, nursing homes, testing centers, or vaccination facilities today? Would he observe patients saying good-bye to family members on tablets and cell phones because their loved ones are not allowed to visit in person? Would he see healthcare workers struggling to resuscitate dying patients in a crowded emergency department or intensive care unit? Would he see long lines of cars filled with people waiting for tests or vaccines? Would he see government officials and public health workers agonizing over decisions about steps that could reduce spread but impose economic hardship on many?
There has been much debate about whether Le Petit Prince is a children’s story or a message for adults disguised as a children’s fable. Perhaps the answer is that it is both, for many children’s stories were actually written for adults. Despite the fragility and delicacy of the book, there is clearly a haunting and deep irony inherent in what it is, in effect, a most savage critique of the world at war.
Two themes that emerge in the novel resonate widely now: isolation and death. Each character the little prince meets is alone, mirroring the long periods of social distancing we have experienced over the past year. And while death is never explicitly mentioned in the book, it seems to be lurking throughout, especially when the prince disappears from Earth after being bitten by the snake. Currently, we have almost become numb to the reported daily death counts—each one alone would have evoked outrage in more usual times. One might imagine that Saint-Exupéry wrote this fable in part to help people cope with the deaths of their loved ones.
And when you are comforted (time soothes all sorrows) you will be happy to have known me. You will always be my friend. You will want to laugh with me. And from time to time you will open your window, so, just for the pleasure of it ... And your friends will be astonished to see you laughing whilst gazing at the sky! And so you will say to them, “Yes, stars always make me laugh!”
Over the past year, both authors of this essay have seen people turn to Le Petit Prince to cope with death. One of us observed a daughter reading the book to her mother at her intensive care bedside on the day she died. The other received a copy as thanks from the wife of a young man who died after 18 months of punishing chemotherapy for sarcoma. Inside the cover was a picture of her husband and the inscription, “Please share this book with someone you love—it’s meant to be read out loud—and remember James.” And so I did, with my grandson Sebastian, who listened to the story with the imagination, wonder, and curiosity of a 6-year-old—he had many questions.
Perhaps the fable that has comforted our patients and their families during their time of despair can do the same for us. Like the prince, who returns to his rose after a difficult journey, we might find solace in the people and things that give our lives their deepest meaning. Thereafter, we might return, rejuvenated, to the clinics, emergency departments, and inpatient wards where our daily work must continue. While the scale of the problems around us makes it feel like any step we take towards preserving our hope will be moot, Le Petit Prince teaches us there is value in making the effort. And there is even a chance that we will find, to our surprise, and against our more cynical judgment, a small rose pushing itself up towards the light.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Rita Charon (Columbia University), Pam Hartzband (Harvard University), Raphael Rush (University of Toronto), and Emily Silverman (University of California San Francisco) for their comments on earlier versions of this essay. None were compensated. We thank Sebastian, James’ wife, and our other patient’s daughter for giving permission to include them in the story.
1. de Saint-Exupéry A. The Little Prince. Harcourt Brace; 1961.
1. de Saint-Exupéry A. The Little Prince. Harcourt Brace; 1961.
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine
USPSTF makes 2 major changes to its lung cancer screening recs
REFERENCES
- American Academy of Family Physicians. Lung cancer: lung cancer screening in adults. AAFP Clinical Preventive Service Recommendations. Accessed April 26, 2021. www.aafp.org/family-physician/patient-care/clinical-recommendations/all-clinical-recommendations/lung-cancer.html
- USPSTF. Screening for lung cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325:962-970. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1117
- Jonas DE, Reuland DS, Reddy, SM, et al. Screening for lung cancer with low-dose computed tomography: updated evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2021;325:971-987. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0377
- Henderson LM, Rivera MP, Basch E. Broadened eligibility for lung cancer screening: challenges and uncertainty for implementation and equity. JAMA. 2021;325:939-941. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26422
- Meza R, Jeon J, Toumazis I, et al. Evaluation of the benefits and harms of lung cancer screening with low-dose computed tomography: modeling study for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2021;325:988-997. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1077
REFERENCES
- American Academy of Family Physicians. Lung cancer: lung cancer screening in adults. AAFP Clinical Preventive Service Recommendations. Accessed April 26, 2021. www.aafp.org/family-physician/patient-care/clinical-recommendations/all-clinical-recommendations/lung-cancer.html
- USPSTF. Screening for lung cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325:962-970. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1117
- Jonas DE, Reuland DS, Reddy, SM, et al. Screening for lung cancer with low-dose computed tomography: updated evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2021;325:971-987. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0377
- Henderson LM, Rivera MP, Basch E. Broadened eligibility for lung cancer screening: challenges and uncertainty for implementation and equity. JAMA. 2021;325:939-941. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26422
- Meza R, Jeon J, Toumazis I, et al. Evaluation of the benefits and harms of lung cancer screening with low-dose computed tomography: modeling study for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2021;325:988-997. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1077
REFERENCES
- American Academy of Family Physicians. Lung cancer: lung cancer screening in adults. AAFP Clinical Preventive Service Recommendations. Accessed April 26, 2021. www.aafp.org/family-physician/patient-care/clinical-recommendations/all-clinical-recommendations/lung-cancer.html
- USPSTF. Screening for lung cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325:962-970. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1117
- Jonas DE, Reuland DS, Reddy, SM, et al. Screening for lung cancer with low-dose computed tomography: updated evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2021;325:971-987. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0377
- Henderson LM, Rivera MP, Basch E. Broadened eligibility for lung cancer screening: challenges and uncertainty for implementation and equity. JAMA. 2021;325:939-941. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26422
- Meza R, Jeon J, Toumazis I, et al. Evaluation of the benefits and harms of lung cancer screening with low-dose computed tomography: modeling study for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2021;325:988-997. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1077