User login
Papules on the Breast, Flank, and Arm Following Breast Cancer Treatment
The Diagnosis: Acquired Cutaneous Lymphangiectasia
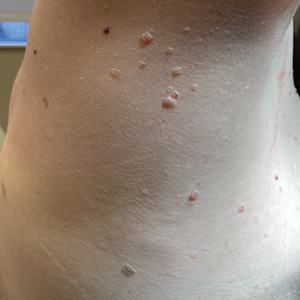
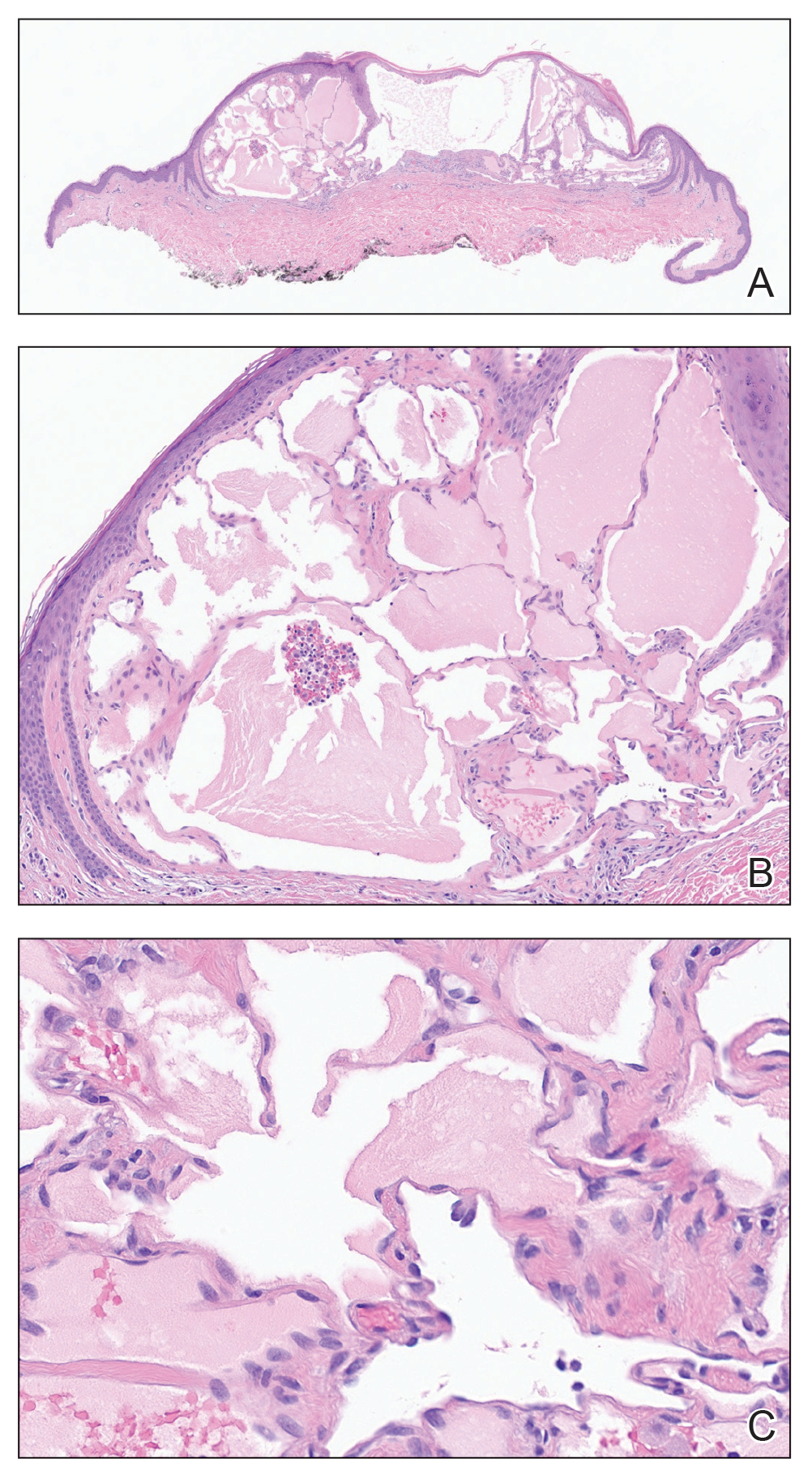
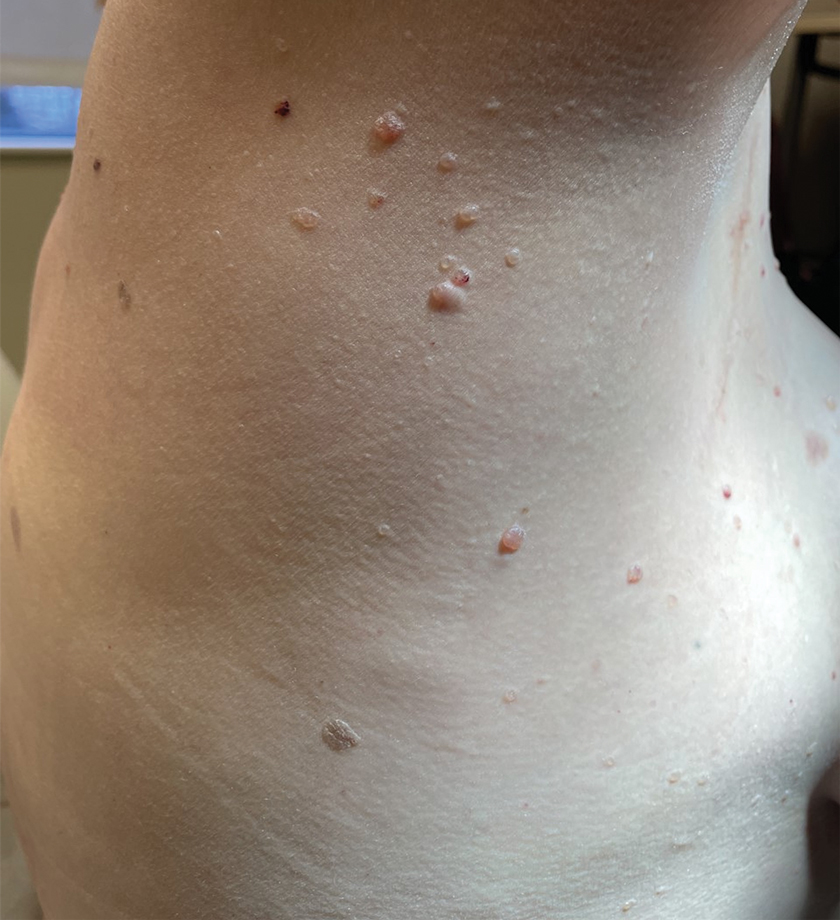
Histopathology showed a cluster of widely ectatic, thin-walled lymphatic spaces immediately subjacent to the epidermis and flanked by an epidermal collarette (Figure, A). The vessels did not extend any further than the papillary dermis and were not accompanied by any notable inflammation (Figure, B). A single layer of bland endothelial cells lined each lymphatic space (Figure, C). A diagnosis of acquired cutaneous lymphangiectasia secondary to surgical and radiation treatment of breast cancer was made. Clinical monitoring was recommended, but no treatment was required unless symptoms arose. At 2-year follow-up, she continued to do well.
Acquired cutaneous lymphangiectasia is characterized by benign dilations of surface lymphatic vessels, likely resulting from disruption of the lymphatic system.1 This finding most commonly occurs on the external genitalia following combined surgical and radiation treatment of malignancy, though in a minority of cases it is seen with surgical or radiation treatment alone.2 Acquired cutaneous lymphangiectasia secondary to radical mastectomy for breast cancer was first reported in 1956 in a patient with persistent ipsilateral lymphadenopathy.3 The presentation in a patient with Cowden syndrome is rare. Cowden syndrome (also called PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome) is a rare autosomal-dominant disorder caused by mutations in the tumor suppressor phosphatase and tensin homolog gene, PTEN. It is characterized by multiple hamartomas and substantially increased risk for breast, endometrial, and thyroid malignancy.4 In addition to breast cancer, our patient had a history of papillary thyroid carcinoma, cerebellar dysplastic gangliocytoma, and multiple cutaneous fibromas and angiolipomas.
A diagnosis of syringomas—benign tumors that arise from the intraepidermal aspect of eccrine sweat ducts— could be considered in the differential diagnosis. Cases of eruptive syringoma on the breast have been reported, but the biopsy would show a circumscribed proliferation of tadpole-shaped tubules comprised of secretory cells in a sclerotic stroma.5 Hidrocystomas are benign sweat gland cysts that present on the face, especially around the eyes, but rarely have been reported on the trunk, particularly the axillae.6 Although they clinically manifest as translucent papules, histopathology shows fluid-filled cysts lined by a layer of secretory columnar epithelium.7 Metastatic breast carcinoma was considered, given the patient’s history of breast cancer. Cutaneous metastases often are found on the chest wall but also can occur at distant sites. Histopathology can reveal various patterns, including islands of tumor cells with glandular formation or single files of cells infiltrating through dermal collagen.
Angiosarcoma also must be considered in the setting of any vasoformative proliferation arising on previously irradiated skin. Angiosarcomas can sometimes be well differentiated with paradoxically bland cytomorphology but characteristically have anastomosing vessels and infiltrative architecture, which were not identified in our patient. Other diagnostic features of angiosarcoma include endothelial nuclear atypia, multilayering, and mitoses. Radiation-associated angiosarcomas amplify MYC, a transcription factor that affects multiple aspects of the cell cycle and is an oncogene implicated in several different types of malignancy.8 MYC immunohistochemistry testing should be performed whenever a vasoformative proliferation on irradiated skin is partially sampled or shows any features concerning for angiosarcoma. Lastly, the term postradiation atypical vascular lesion has been introduced to describe discrete papular proliferations that show close histopathologic overlap with lymphangioma/lymphatic malformations. In contrast, atypical vascular lesions show wedge-shaped intradermal growth that can cause diagnostic confusion with well-differentiated angiosarcoma. Unlike angiosarcomas, they do not express MYC. Postradiation atypical vascular lesions sometimes have an associated inflammatory infiltrate.9 Considerable histomorphologic overlap among lymphangiomas, atypical vascular lesions, and well-differentiated angiosarcomas exists; thus, lesions should be removed in their perceived totality whenever possible to help permit diagnostic distinction. In our patient, the abrupt discontinuation of vessels at the interface of the papillary and reticular dermis was reassuring of benignancy.
Our patient’s diagnosis of acquired cutaneous lymphangiectasia was a benign adverse effect of prior breast cancer treatments. This case demonstrates a rare dermatologic sequela that may arise in patients who receive surgical or radiation treatment of breast cancer. Given the heightened risk for angiosarcoma after radiation therapy as well as the increased risk for malignancy in patients with Cowden syndrome, biopsy can be an important diagnostic step in the management of these patients.
- Valdés F, Peteiro C, Toribio J. Acquired lymphangiectases and breast cancer. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2007;98:347-350.
- Chiyomaru K, Nishigori C. Acquired lymphangiectasia associated with treatment for preceding malignant neoplasm: a retrospective series of 73 Japanese patients. AMA Arch Derm. 2009;145:841-842.
- Plotnick H, Richfield D. Tuberous lymphangiectatic varices secondary to radical mastectomy. AMA Arch Derm. 1956;74:466-468.
- Pilarski R, Burt R, Kohlman W, et al. Cowden syndrome and the PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome: systematic review and revised diagnostic criteria. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105:1607-1616.
- Müller CSL, Tilgen W, Pföhler C. Clinicopathological diversity of syringomas: a study on current clinical and histopathologic concepts. Dermatoendocrinol. 2009;1:282-288.
- Anzai S, Goto M, Fujiwara S, et al. Apocrine hidrocystoma: a case report and analysis of 167 Japanese cases. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:702-703.
- Sarabi K, Khachemoune A. Hidrocystomas—a brief review. MedGenMed. 2006;8:57.
- Ahmadi SE, Rahimi S, Zarandi B, et al. MYC: a multipurpose oncogene with prognostic and therapeutic implications in blood malignancies. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:121. doi:10.1186/s13045-021-01111-4
- Ronen S, Ivan D, Torres-Cabala CA, et al. Post-radiation vascular lesions of the breast. J Cutan Pathol. 2019;46:52-58.
The Diagnosis: Acquired Cutaneous Lymphangiectasia
Histopathology showed a cluster of widely ectatic, thin-walled lymphatic spaces immediately subjacent to the epidermis and flanked by an epidermal collarette (Figure, A). The vessels did not extend any further than the papillary dermis and were not accompanied by any notable inflammation (Figure, B). A single layer of bland endothelial cells lined each lymphatic space (Figure, C). A diagnosis of acquired cutaneous lymphangiectasia secondary to surgical and radiation treatment of breast cancer was made. Clinical monitoring was recommended, but no treatment was required unless symptoms arose. At 2-year follow-up, she continued to do well.

Acquired cutaneous lymphangiectasia is characterized by benign dilations of surface lymphatic vessels, likely resulting from disruption of the lymphatic system.1 This finding most commonly occurs on the external genitalia following combined surgical and radiation treatment of malignancy, though in a minority of cases it is seen with surgical or radiation treatment alone.2 Acquired cutaneous lymphangiectasia secondary to radical mastectomy for breast cancer was first reported in 1956 in a patient with persistent ipsilateral lymphadenopathy.3 The presentation in a patient with Cowden syndrome is rare. Cowden syndrome (also called PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome) is a rare autosomal-dominant disorder caused by mutations in the tumor suppressor phosphatase and tensin homolog gene, PTEN. It is characterized by multiple hamartomas and substantially increased risk for breast, endometrial, and thyroid malignancy.4 In addition to breast cancer, our patient had a history of papillary thyroid carcinoma, cerebellar dysplastic gangliocytoma, and multiple cutaneous fibromas and angiolipomas.
A diagnosis of syringomas—benign tumors that arise from the intraepidermal aspect of eccrine sweat ducts— could be considered in the differential diagnosis. Cases of eruptive syringoma on the breast have been reported, but the biopsy would show a circumscribed proliferation of tadpole-shaped tubules comprised of secretory cells in a sclerotic stroma.5 Hidrocystomas are benign sweat gland cysts that present on the face, especially around the eyes, but rarely have been reported on the trunk, particularly the axillae.6 Although they clinically manifest as translucent papules, histopathology shows fluid-filled cysts lined by a layer of secretory columnar epithelium.7 Metastatic breast carcinoma was considered, given the patient’s history of breast cancer. Cutaneous metastases often are found on the chest wall but also can occur at distant sites. Histopathology can reveal various patterns, including islands of tumor cells with glandular formation or single files of cells infiltrating through dermal collagen.
Angiosarcoma also must be considered in the setting of any vasoformative proliferation arising on previously irradiated skin. Angiosarcomas can sometimes be well differentiated with paradoxically bland cytomorphology but characteristically have anastomosing vessels and infiltrative architecture, which were not identified in our patient. Other diagnostic features of angiosarcoma include endothelial nuclear atypia, multilayering, and mitoses. Radiation-associated angiosarcomas amplify MYC, a transcription factor that affects multiple aspects of the cell cycle and is an oncogene implicated in several different types of malignancy.8 MYC immunohistochemistry testing should be performed whenever a vasoformative proliferation on irradiated skin is partially sampled or shows any features concerning for angiosarcoma. Lastly, the term postradiation atypical vascular lesion has been introduced to describe discrete papular proliferations that show close histopathologic overlap with lymphangioma/lymphatic malformations. In contrast, atypical vascular lesions show wedge-shaped intradermal growth that can cause diagnostic confusion with well-differentiated angiosarcoma. Unlike angiosarcomas, they do not express MYC. Postradiation atypical vascular lesions sometimes have an associated inflammatory infiltrate.9 Considerable histomorphologic overlap among lymphangiomas, atypical vascular lesions, and well-differentiated angiosarcomas exists; thus, lesions should be removed in their perceived totality whenever possible to help permit diagnostic distinction. In our patient, the abrupt discontinuation of vessels at the interface of the papillary and reticular dermis was reassuring of benignancy.
Our patient’s diagnosis of acquired cutaneous lymphangiectasia was a benign adverse effect of prior breast cancer treatments. This case demonstrates a rare dermatologic sequela that may arise in patients who receive surgical or radiation treatment of breast cancer. Given the heightened risk for angiosarcoma after radiation therapy as well as the increased risk for malignancy in patients with Cowden syndrome, biopsy can be an important diagnostic step in the management of these patients.
The Diagnosis: Acquired Cutaneous Lymphangiectasia
Histopathology showed a cluster of widely ectatic, thin-walled lymphatic spaces immediately subjacent to the epidermis and flanked by an epidermal collarette (Figure, A). The vessels did not extend any further than the papillary dermis and were not accompanied by any notable inflammation (Figure, B). A single layer of bland endothelial cells lined each lymphatic space (Figure, C). A diagnosis of acquired cutaneous lymphangiectasia secondary to surgical and radiation treatment of breast cancer was made. Clinical monitoring was recommended, but no treatment was required unless symptoms arose. At 2-year follow-up, she continued to do well.

Acquired cutaneous lymphangiectasia is characterized by benign dilations of surface lymphatic vessels, likely resulting from disruption of the lymphatic system.1 This finding most commonly occurs on the external genitalia following combined surgical and radiation treatment of malignancy, though in a minority of cases it is seen with surgical or radiation treatment alone.2 Acquired cutaneous lymphangiectasia secondary to radical mastectomy for breast cancer was first reported in 1956 in a patient with persistent ipsilateral lymphadenopathy.3 The presentation in a patient with Cowden syndrome is rare. Cowden syndrome (also called PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome) is a rare autosomal-dominant disorder caused by mutations in the tumor suppressor phosphatase and tensin homolog gene, PTEN. It is characterized by multiple hamartomas and substantially increased risk for breast, endometrial, and thyroid malignancy.4 In addition to breast cancer, our patient had a history of papillary thyroid carcinoma, cerebellar dysplastic gangliocytoma, and multiple cutaneous fibromas and angiolipomas.
A diagnosis of syringomas—benign tumors that arise from the intraepidermal aspect of eccrine sweat ducts— could be considered in the differential diagnosis. Cases of eruptive syringoma on the breast have been reported, but the biopsy would show a circumscribed proliferation of tadpole-shaped tubules comprised of secretory cells in a sclerotic stroma.5 Hidrocystomas are benign sweat gland cysts that present on the face, especially around the eyes, but rarely have been reported on the trunk, particularly the axillae.6 Although they clinically manifest as translucent papules, histopathology shows fluid-filled cysts lined by a layer of secretory columnar epithelium.7 Metastatic breast carcinoma was considered, given the patient’s history of breast cancer. Cutaneous metastases often are found on the chest wall but also can occur at distant sites. Histopathology can reveal various patterns, including islands of tumor cells with glandular formation or single files of cells infiltrating through dermal collagen.
Angiosarcoma also must be considered in the setting of any vasoformative proliferation arising on previously irradiated skin. Angiosarcomas can sometimes be well differentiated with paradoxically bland cytomorphology but characteristically have anastomosing vessels and infiltrative architecture, which were not identified in our patient. Other diagnostic features of angiosarcoma include endothelial nuclear atypia, multilayering, and mitoses. Radiation-associated angiosarcomas amplify MYC, a transcription factor that affects multiple aspects of the cell cycle and is an oncogene implicated in several different types of malignancy.8 MYC immunohistochemistry testing should be performed whenever a vasoformative proliferation on irradiated skin is partially sampled or shows any features concerning for angiosarcoma. Lastly, the term postradiation atypical vascular lesion has been introduced to describe discrete papular proliferations that show close histopathologic overlap with lymphangioma/lymphatic malformations. In contrast, atypical vascular lesions show wedge-shaped intradermal growth that can cause diagnostic confusion with well-differentiated angiosarcoma. Unlike angiosarcomas, they do not express MYC. Postradiation atypical vascular lesions sometimes have an associated inflammatory infiltrate.9 Considerable histomorphologic overlap among lymphangiomas, atypical vascular lesions, and well-differentiated angiosarcomas exists; thus, lesions should be removed in their perceived totality whenever possible to help permit diagnostic distinction. In our patient, the abrupt discontinuation of vessels at the interface of the papillary and reticular dermis was reassuring of benignancy.
Our patient’s diagnosis of acquired cutaneous lymphangiectasia was a benign adverse effect of prior breast cancer treatments. This case demonstrates a rare dermatologic sequela that may arise in patients who receive surgical or radiation treatment of breast cancer. Given the heightened risk for angiosarcoma after radiation therapy as well as the increased risk for malignancy in patients with Cowden syndrome, biopsy can be an important diagnostic step in the management of these patients.
- Valdés F, Peteiro C, Toribio J. Acquired lymphangiectases and breast cancer. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2007;98:347-350.
- Chiyomaru K, Nishigori C. Acquired lymphangiectasia associated with treatment for preceding malignant neoplasm: a retrospective series of 73 Japanese patients. AMA Arch Derm. 2009;145:841-842.
- Plotnick H, Richfield D. Tuberous lymphangiectatic varices secondary to radical mastectomy. AMA Arch Derm. 1956;74:466-468.
- Pilarski R, Burt R, Kohlman W, et al. Cowden syndrome and the PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome: systematic review and revised diagnostic criteria. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105:1607-1616.
- Müller CSL, Tilgen W, Pföhler C. Clinicopathological diversity of syringomas: a study on current clinical and histopathologic concepts. Dermatoendocrinol. 2009;1:282-288.
- Anzai S, Goto M, Fujiwara S, et al. Apocrine hidrocystoma: a case report and analysis of 167 Japanese cases. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:702-703.
- Sarabi K, Khachemoune A. Hidrocystomas—a brief review. MedGenMed. 2006;8:57.
- Ahmadi SE, Rahimi S, Zarandi B, et al. MYC: a multipurpose oncogene with prognostic and therapeutic implications in blood malignancies. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:121. doi:10.1186/s13045-021-01111-4
- Ronen S, Ivan D, Torres-Cabala CA, et al. Post-radiation vascular lesions of the breast. J Cutan Pathol. 2019;46:52-58.
- Valdés F, Peteiro C, Toribio J. Acquired lymphangiectases and breast cancer. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2007;98:347-350.
- Chiyomaru K, Nishigori C. Acquired lymphangiectasia associated with treatment for preceding malignant neoplasm: a retrospective series of 73 Japanese patients. AMA Arch Derm. 2009;145:841-842.
- Plotnick H, Richfield D. Tuberous lymphangiectatic varices secondary to radical mastectomy. AMA Arch Derm. 1956;74:466-468.
- Pilarski R, Burt R, Kohlman W, et al. Cowden syndrome and the PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome: systematic review and revised diagnostic criteria. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105:1607-1616.
- Müller CSL, Tilgen W, Pföhler C. Clinicopathological diversity of syringomas: a study on current clinical and histopathologic concepts. Dermatoendocrinol. 2009;1:282-288.
- Anzai S, Goto M, Fujiwara S, et al. Apocrine hidrocystoma: a case report and analysis of 167 Japanese cases. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:702-703.
- Sarabi K, Khachemoune A. Hidrocystomas—a brief review. MedGenMed. 2006;8:57.
- Ahmadi SE, Rahimi S, Zarandi B, et al. MYC: a multipurpose oncogene with prognostic and therapeutic implications in blood malignancies. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:121. doi:10.1186/s13045-021-01111-4
- Ronen S, Ivan D, Torres-Cabala CA, et al. Post-radiation vascular lesions of the breast. J Cutan Pathol. 2019;46:52-58.
A 47-year-old woman with Cowden syndrome presented to the dermatology clinic with asymptomatic papules on and near the right breast that had increased in number over the last year. She had a medical history of breast cancer treated with mastectomy, chemotherapy, and radiation; papillary thyroid carcinoma treated with thyroidectomy and subsequent thyroid hormone replacement; dysplastic cerebellar gangliocytoma treated with surgical excision; and multiple cutaneous fibromas and angiolipomas. Physical examination revealed multiple clustered, 1- to 5-mm, translucent to red papules on the right breast, flank, and upper arm. A shave biopsy of a papule from the right lateral breast was performed.
RUBY: ‘A Huge Win’ for Patients With Advanced or Recurrent Endometrial Cancer
The benefit of the combination of the programmed death protein 1 (PD-1) inhibitor dostarlimab (Jemperli) and chemotherapy was even more pronounced among patients with DNA mismatch repair deficient/microsatellite instability high (dMMR/MSI-H) tumors.
These results, from the second interim analysis of the phase 3 ENGOT-EN6-NSGO/GOG-3031/RUBY trial, were cheered by audience members when they were reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO)’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer, held in San Diego, California.
“Overall survival benefit to the addition of PD-1 inhibitor to chemotherapy upfront for patients with advanced and recurrent MSI-high endometrial cancer: SOLD!” said invited discussant Gini Fleming, medical director of gynecologic oncology at the University of Chicago.
“I think this is a huge win for our patients. It’s something that none of us have seen before over many years of working with endometrial cancer and should be incorporated into everybody’s practice as of yesterday,” she said.
Continued Improvement
Results from the first interim analysis of the trial showed that dostarlimab and chemotherapy significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) in the dMMR/MSI-H population, and there was an early trend toward improved overall survival, compared with chemotherapy plus placebo.
As Matthew A. Powell, MD from Washington University School of Medicine in Saint Louis, Missouri reported at SGO 2024, that early trend has become an undeniable survival advantage.
At a median follow-up of 37.2 months, the median overall survival was 44.6 months for patients randomized to the combination, compared with 28.2 months for those assigned to chemotherapy plus placebo.
The respective 3-year overall survival (OS) rates were 54.9% and 42.9%, translating into a hazard ratio (HR) for death with dostarlimab/chemotherapy of 0.69 (P = .002).
Among the subset of patients with dMMR/MSI-H tumors the survival benefit conferred by the combination was even greater, with median OS not reached in the dostarlimab group vs 31.4 months in the chemotherapy-alone arm, with respective 3-year OS rates of 78% and 46%. This difference translated into a HR for death with the combination of 0.32 (P = .0002) for patients with deficient mismatch-repair cancers.
“Dostarlimab plus carboplatin-paclitaxel chemotherapy demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful overall survival improvements in the overall population, a substantial unprecedented overall survival benefit in patients with defective mismatch-repair tumors, and a clinically meaningful; 7-month improvement in the OS difference in patients with proficient mismatch-repair tumors,” Dr. Powell said.
RUBY Details
The trial was conducted in 494 patients with primary advanced stage III or IV or first recurrent endometrial cancer who received first-line treatment with standard chemotherapy with carboplatin (area under the concentration–time curve, 5 mg/mL per minute) and paclitaxel (175 mg/m2 of body surface area), every 3 weeks (six cycles). They were also randomized to receive either dostarlimab (1000 mg) or dostarlimab placebo every 6 weeks for up to 3 years.
Within the cohort, 118 patients (23.9%) had dMMR/MSI-H tumors.
At the time of the first interim analysis the estimated progression-free survival at 24 months in the dMMR–MSI-H subgroup was 61.4% in the dostarlimab group vs 15.7 in the placebo group (HR for progression or death, 0.28; P < .001). For the entire cohort, progression-free survival at 24 months was 36.1% vs 18.1% (HR, 0.64; P < .001).
A prespecified exploratory analysis of progression-free survival in proficient MMR, microsatellite stable (MSS) patients was also done, and a clinically relevant benefit was observed.
Overall survival at that time also favored dostarlimab, although it was only mature for 33% of the population. But at 24 months, OS rates were 71.3% vs 56.0% among placebo recipients; this difference approached but did not reach statistical significance.
The overall response rate in the dMMR–MSI-H population vs the placebo group was 77.6% vs 69%, respectively, and 68.1% and 63.4% in the pMMR/MSS population.
The most common adverse events observed were nausea, alopecia, and fatigue. Grade 3 and higher adverse events at the most recent follow-up were more frequent in the dostarlimab group than in the placebo group (72.2% vs 60.2%).
“Importantly, safety was maintained” at the second interim analysis, Dr. Powell said.
“No new safety signals were noted, no new deaths related to therapy were noted with the subsequent 1-year additional analysis time,” he said.
What’s Next?
Dr. Fleming reviewed potential strategies for further improving care of patients with advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer during her discussion.
“What are the next directions for patients with MSI-high disease? Well, obviously could we use immune checkpoint inhibitors without chemotherapy and not compromise results? There are two ongoing trials or trials that we’re awaiting results of that have compared single-agent immune checkpoint inhibitor to just chemotherapy in mismatch repair-deficient advanced disease, and hopefully we can extrapolate from these trials to determine if this might be a more patient-friendly and equally effective strategy, but we don’t yet know,” she said.
Dr. Fleming also noted that ongoing or planned clinical trials will address questions about potential options for patients with MSI-H tumors whose disease progresses on frontline chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Other trials are assessing whether combining radiotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors will be effective in treating patients with earlier-stage tumors, or whether the addition of a PARP inhibitor might offer additional benefit for these patients.
“Immune checkpoint inhibitor should be given first line to patients with advanced/recurrent microsatellite [instability] endometrial cancer, and they should be considered as front line in patients with microsatellite stable disease. At this point, unfortunately, we have no reasonable predictive factors to know which of those patients with microsatellite stable disease will truly benefit. Multiple other agents are being tested in this setting, and will hopefully prove useful in subgroups,” she said.
The study is funded by GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Powell reports grants/research support from GSK and honoraria/consultation fees from AstraZeneca, Clovis Oncology, Eisai, GSK, Immunogen, and Merck. Dr. Fleming reports serving as an institutional principal investigator for trials sponsored by multiple companies, not including GSK.
The benefit of the combination of the programmed death protein 1 (PD-1) inhibitor dostarlimab (Jemperli) and chemotherapy was even more pronounced among patients with DNA mismatch repair deficient/microsatellite instability high (dMMR/MSI-H) tumors.
These results, from the second interim analysis of the phase 3 ENGOT-EN6-NSGO/GOG-3031/RUBY trial, were cheered by audience members when they were reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO)’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer, held in San Diego, California.
“Overall survival benefit to the addition of PD-1 inhibitor to chemotherapy upfront for patients with advanced and recurrent MSI-high endometrial cancer: SOLD!” said invited discussant Gini Fleming, medical director of gynecologic oncology at the University of Chicago.
“I think this is a huge win for our patients. It’s something that none of us have seen before over many years of working with endometrial cancer and should be incorporated into everybody’s practice as of yesterday,” she said.
Continued Improvement
Results from the first interim analysis of the trial showed that dostarlimab and chemotherapy significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) in the dMMR/MSI-H population, and there was an early trend toward improved overall survival, compared with chemotherapy plus placebo.
As Matthew A. Powell, MD from Washington University School of Medicine in Saint Louis, Missouri reported at SGO 2024, that early trend has become an undeniable survival advantage.
At a median follow-up of 37.2 months, the median overall survival was 44.6 months for patients randomized to the combination, compared with 28.2 months for those assigned to chemotherapy plus placebo.
The respective 3-year overall survival (OS) rates were 54.9% and 42.9%, translating into a hazard ratio (HR) for death with dostarlimab/chemotherapy of 0.69 (P = .002).
Among the subset of patients with dMMR/MSI-H tumors the survival benefit conferred by the combination was even greater, with median OS not reached in the dostarlimab group vs 31.4 months in the chemotherapy-alone arm, with respective 3-year OS rates of 78% and 46%. This difference translated into a HR for death with the combination of 0.32 (P = .0002) for patients with deficient mismatch-repair cancers.
“Dostarlimab plus carboplatin-paclitaxel chemotherapy demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful overall survival improvements in the overall population, a substantial unprecedented overall survival benefit in patients with defective mismatch-repair tumors, and a clinically meaningful; 7-month improvement in the OS difference in patients with proficient mismatch-repair tumors,” Dr. Powell said.
RUBY Details
The trial was conducted in 494 patients with primary advanced stage III or IV or first recurrent endometrial cancer who received first-line treatment with standard chemotherapy with carboplatin (area under the concentration–time curve, 5 mg/mL per minute) and paclitaxel (175 mg/m2 of body surface area), every 3 weeks (six cycles). They were also randomized to receive either dostarlimab (1000 mg) or dostarlimab placebo every 6 weeks for up to 3 years.
Within the cohort, 118 patients (23.9%) had dMMR/MSI-H tumors.
At the time of the first interim analysis the estimated progression-free survival at 24 months in the dMMR–MSI-H subgroup was 61.4% in the dostarlimab group vs 15.7 in the placebo group (HR for progression or death, 0.28; P < .001). For the entire cohort, progression-free survival at 24 months was 36.1% vs 18.1% (HR, 0.64; P < .001).
A prespecified exploratory analysis of progression-free survival in proficient MMR, microsatellite stable (MSS) patients was also done, and a clinically relevant benefit was observed.
Overall survival at that time also favored dostarlimab, although it was only mature for 33% of the population. But at 24 months, OS rates were 71.3% vs 56.0% among placebo recipients; this difference approached but did not reach statistical significance.
The overall response rate in the dMMR–MSI-H population vs the placebo group was 77.6% vs 69%, respectively, and 68.1% and 63.4% in the pMMR/MSS population.
The most common adverse events observed were nausea, alopecia, and fatigue. Grade 3 and higher adverse events at the most recent follow-up were more frequent in the dostarlimab group than in the placebo group (72.2% vs 60.2%).
“Importantly, safety was maintained” at the second interim analysis, Dr. Powell said.
“No new safety signals were noted, no new deaths related to therapy were noted with the subsequent 1-year additional analysis time,” he said.
What’s Next?
Dr. Fleming reviewed potential strategies for further improving care of patients with advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer during her discussion.
“What are the next directions for patients with MSI-high disease? Well, obviously could we use immune checkpoint inhibitors without chemotherapy and not compromise results? There are two ongoing trials or trials that we’re awaiting results of that have compared single-agent immune checkpoint inhibitor to just chemotherapy in mismatch repair-deficient advanced disease, and hopefully we can extrapolate from these trials to determine if this might be a more patient-friendly and equally effective strategy, but we don’t yet know,” she said.
Dr. Fleming also noted that ongoing or planned clinical trials will address questions about potential options for patients with MSI-H tumors whose disease progresses on frontline chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Other trials are assessing whether combining radiotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors will be effective in treating patients with earlier-stage tumors, or whether the addition of a PARP inhibitor might offer additional benefit for these patients.
“Immune checkpoint inhibitor should be given first line to patients with advanced/recurrent microsatellite [instability] endometrial cancer, and they should be considered as front line in patients with microsatellite stable disease. At this point, unfortunately, we have no reasonable predictive factors to know which of those patients with microsatellite stable disease will truly benefit. Multiple other agents are being tested in this setting, and will hopefully prove useful in subgroups,” she said.
The study is funded by GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Powell reports grants/research support from GSK and honoraria/consultation fees from AstraZeneca, Clovis Oncology, Eisai, GSK, Immunogen, and Merck. Dr. Fleming reports serving as an institutional principal investigator for trials sponsored by multiple companies, not including GSK.
The benefit of the combination of the programmed death protein 1 (PD-1) inhibitor dostarlimab (Jemperli) and chemotherapy was even more pronounced among patients with DNA mismatch repair deficient/microsatellite instability high (dMMR/MSI-H) tumors.
These results, from the second interim analysis of the phase 3 ENGOT-EN6-NSGO/GOG-3031/RUBY trial, were cheered by audience members when they were reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO)’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer, held in San Diego, California.
“Overall survival benefit to the addition of PD-1 inhibitor to chemotherapy upfront for patients with advanced and recurrent MSI-high endometrial cancer: SOLD!” said invited discussant Gini Fleming, medical director of gynecologic oncology at the University of Chicago.
“I think this is a huge win for our patients. It’s something that none of us have seen before over many years of working with endometrial cancer and should be incorporated into everybody’s practice as of yesterday,” she said.
Continued Improvement
Results from the first interim analysis of the trial showed that dostarlimab and chemotherapy significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) in the dMMR/MSI-H population, and there was an early trend toward improved overall survival, compared with chemotherapy plus placebo.
As Matthew A. Powell, MD from Washington University School of Medicine in Saint Louis, Missouri reported at SGO 2024, that early trend has become an undeniable survival advantage.
At a median follow-up of 37.2 months, the median overall survival was 44.6 months for patients randomized to the combination, compared with 28.2 months for those assigned to chemotherapy plus placebo.
The respective 3-year overall survival (OS) rates were 54.9% and 42.9%, translating into a hazard ratio (HR) for death with dostarlimab/chemotherapy of 0.69 (P = .002).
Among the subset of patients with dMMR/MSI-H tumors the survival benefit conferred by the combination was even greater, with median OS not reached in the dostarlimab group vs 31.4 months in the chemotherapy-alone arm, with respective 3-year OS rates of 78% and 46%. This difference translated into a HR for death with the combination of 0.32 (P = .0002) for patients with deficient mismatch-repair cancers.
“Dostarlimab plus carboplatin-paclitaxel chemotherapy demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful overall survival improvements in the overall population, a substantial unprecedented overall survival benefit in patients with defective mismatch-repair tumors, and a clinically meaningful; 7-month improvement in the OS difference in patients with proficient mismatch-repair tumors,” Dr. Powell said.
RUBY Details
The trial was conducted in 494 patients with primary advanced stage III or IV or first recurrent endometrial cancer who received first-line treatment with standard chemotherapy with carboplatin (area under the concentration–time curve, 5 mg/mL per minute) and paclitaxel (175 mg/m2 of body surface area), every 3 weeks (six cycles). They were also randomized to receive either dostarlimab (1000 mg) or dostarlimab placebo every 6 weeks for up to 3 years.
Within the cohort, 118 patients (23.9%) had dMMR/MSI-H tumors.
At the time of the first interim analysis the estimated progression-free survival at 24 months in the dMMR–MSI-H subgroup was 61.4% in the dostarlimab group vs 15.7 in the placebo group (HR for progression or death, 0.28; P < .001). For the entire cohort, progression-free survival at 24 months was 36.1% vs 18.1% (HR, 0.64; P < .001).
A prespecified exploratory analysis of progression-free survival in proficient MMR, microsatellite stable (MSS) patients was also done, and a clinically relevant benefit was observed.
Overall survival at that time also favored dostarlimab, although it was only mature for 33% of the population. But at 24 months, OS rates were 71.3% vs 56.0% among placebo recipients; this difference approached but did not reach statistical significance.
The overall response rate in the dMMR–MSI-H population vs the placebo group was 77.6% vs 69%, respectively, and 68.1% and 63.4% in the pMMR/MSS population.
The most common adverse events observed were nausea, alopecia, and fatigue. Grade 3 and higher adverse events at the most recent follow-up were more frequent in the dostarlimab group than in the placebo group (72.2% vs 60.2%).
“Importantly, safety was maintained” at the second interim analysis, Dr. Powell said.
“No new safety signals were noted, no new deaths related to therapy were noted with the subsequent 1-year additional analysis time,” he said.
What’s Next?
Dr. Fleming reviewed potential strategies for further improving care of patients with advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer during her discussion.
“What are the next directions for patients with MSI-high disease? Well, obviously could we use immune checkpoint inhibitors without chemotherapy and not compromise results? There are two ongoing trials or trials that we’re awaiting results of that have compared single-agent immune checkpoint inhibitor to just chemotherapy in mismatch repair-deficient advanced disease, and hopefully we can extrapolate from these trials to determine if this might be a more patient-friendly and equally effective strategy, but we don’t yet know,” she said.
Dr. Fleming also noted that ongoing or planned clinical trials will address questions about potential options for patients with MSI-H tumors whose disease progresses on frontline chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Other trials are assessing whether combining radiotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors will be effective in treating patients with earlier-stage tumors, or whether the addition of a PARP inhibitor might offer additional benefit for these patients.
“Immune checkpoint inhibitor should be given first line to patients with advanced/recurrent microsatellite [instability] endometrial cancer, and they should be considered as front line in patients with microsatellite stable disease. At this point, unfortunately, we have no reasonable predictive factors to know which of those patients with microsatellite stable disease will truly benefit. Multiple other agents are being tested in this setting, and will hopefully prove useful in subgroups,” she said.
The study is funded by GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Powell reports grants/research support from GSK and honoraria/consultation fees from AstraZeneca, Clovis Oncology, Eisai, GSK, Immunogen, and Merck. Dr. Fleming reports serving as an institutional principal investigator for trials sponsored by multiple companies, not including GSK.
FROM SGO 2024
Sustained Control Reported for Anti–IL-17, Anti–IL-23 Psoriasis Treatments
SAN DIEGO — , but late-breaker data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology show that these types of responses are sustained for as long as patients have remained on therapy.
Of the two, the longer follow up is with the IL-17 inhibitor bimekizumab (Bimzelx). In a 4-year open-label extension study, the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 rate was approximately 85% in treated patients, according to Mark Lebwohl, MD, professor and chairman emeritus of the Department of Dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City
A PASI 90 score signifies that 90% of skin surface area is cleared. The proportion of patients who achieved a PASI 100 score, signifying total clearance, approached 70% at 4 years in the group with the greatest response. PASI 90 and PASI 100 rates at this point were only modestly lower than those reported at the end of the double-blind phase 3 trial when evaluated 3 years earlier.
Follow-up with a novel oral anti-IL-23 inhibitor JNJ-2113 (JNJ-77242113) was only 52 weeks, far shorter. But again, the response for the most effective dose at the end of this period was essentially unchanged from that at 16 weeks. Among those on the highest and most effective test dose of once-daily 100 mg, the PASI 90 at 1 year was 64.3%, a rate that was essentially unchanged from week 16.
No Apparent Loss of Benefit Over Time
“We can really look at those dose-response curves and see that there is, overall, a maintenance of response,” reported Laura K. Ferris, MD, PhD, professor and director of clinical trials, Department of Dermatology, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. In her presentation of the data, she showed similar sustained control for the most effective doses of JNJ-2113 for multiple clinical outcomes, including an investigator’s global assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1, also signifying clear or near clear skin.
Bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits both IL-17A and IL-17F, is already approved for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. The 52-week BE SURE trial, which provided the 478 patients who entered into the BE BRIGHT open label extension study, was published in The New England Journal of Medicine in July 2021.
In the 4-year data reported by Dr. Lebwohl, three groups were compared: Those initially randomized to an every-4-week dosing schedule of bimekizumab over the course of the 52-week BE SURE trial; those randomized to an every-4-week bimekizumab schedule who were then subsequently switched to an every-8-week schedule; and those initiated on the TNF-inhibitor adalimumab (Humira) and were then switched at week 24 to every-4-week bimekizumab.
The PASI 90 responses at 52 weeks in these three groups, respectively, were 91.2%, 89.3%, and 95.2%. At 4 years, this almost clear response was observed in 82.4%, 83.2%, and 87.6%, respectively. At 52 weeks, the PASI 100 responses in these three groups, respectively, were 75.3%, 74.2%, and 72.9%. At 4 years, 61.9%, 58.5%, and 69.5% still had complete skin clearance.
Bimekizumab was well tolerated during the randomized trial, reported Dr. Lebwohl. The rates of nasopharyngitis and oral candidiasis, which were observed in approximately 12% and 8%, respectively, of treated patients during the randomized phase remained at about the same level in the long-term follow up. There were no new safety signals, he said.
JNJ-2113 Is First Potential Oral IL-23 Inhibitor
JNJ-2113 is a first-in-class oral peptide that binds to the IL-23 receptor, blocking the IL-23 signaling pathway. If approved, it would be the first oral therapy targeting IL-23. The 16-week outcomes of the dose-finding FRONTIER 1 phase 2b trial were published in The New England Journal of Medicine earlier this year. The primary endpoint was PASI 75, achieved by 79% of those on the 100 mg twice daily dose at week 16, vs 9% on placebo, and at 52 weeks, was 76%.
“The proportion of patients achieving the FRONTIER 1 primary endpoint was maintained from week 16 to the end of week 52 in the extension study,” Dr. Ferris said, but further pointed out that rates of near or complete clearance achieved at week 16 were also essentially unchanged at week 52. This was true of PASI scores and IGA.
Clearance of psoriatic lesions on the scalp was particularly impressive. By scalp-specific IGA, rates of clear or near clear (0/1) were not just maintained but improved over the course of follow-up, reaching 75.1% at 52 weeks in the highest dose group, she said.
JNJ-2113 was well tolerated in FRONTIER 1 and remained so during long-term follow-up, in the FRONTIER 2 extension study, according to Dr. Ferris. The most common complaints with JNJ-2113, such as nasopharyngitis (18.1% vs 25.7% in placebo), did not appear to differ significantly from placebo and the treatment remained well tolerated over the course of the extended follow-up.
There are limited direct comparisons of different biologics active in the treatment of plaque psoriasis for efficacy and safety, but these data appear to show a depth and durability of benefit for psoriasis that is exceptional, Dr. Lebwohl told this news organization. “The PASI 100 scores achieved by bimekizumab exceed anything we have seen to date,” he said. “And the durability of those exceedingly high scores is remarkable.”
Dr. Lebwohl reports financial relationships with approximately 40 pharmaceutical companies, including UCB Pharma, which developed bimekizumab. Dr. Ferris reports financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen, which is developing JNJ-2113.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — , but late-breaker data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology show that these types of responses are sustained for as long as patients have remained on therapy.
Of the two, the longer follow up is with the IL-17 inhibitor bimekizumab (Bimzelx). In a 4-year open-label extension study, the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 rate was approximately 85% in treated patients, according to Mark Lebwohl, MD, professor and chairman emeritus of the Department of Dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City
A PASI 90 score signifies that 90% of skin surface area is cleared. The proportion of patients who achieved a PASI 100 score, signifying total clearance, approached 70% at 4 years in the group with the greatest response. PASI 90 and PASI 100 rates at this point were only modestly lower than those reported at the end of the double-blind phase 3 trial when evaluated 3 years earlier.
Follow-up with a novel oral anti-IL-23 inhibitor JNJ-2113 (JNJ-77242113) was only 52 weeks, far shorter. But again, the response for the most effective dose at the end of this period was essentially unchanged from that at 16 weeks. Among those on the highest and most effective test dose of once-daily 100 mg, the PASI 90 at 1 year was 64.3%, a rate that was essentially unchanged from week 16.
No Apparent Loss of Benefit Over Time
“We can really look at those dose-response curves and see that there is, overall, a maintenance of response,” reported Laura K. Ferris, MD, PhD, professor and director of clinical trials, Department of Dermatology, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. In her presentation of the data, she showed similar sustained control for the most effective doses of JNJ-2113 for multiple clinical outcomes, including an investigator’s global assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1, also signifying clear or near clear skin.
Bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits both IL-17A and IL-17F, is already approved for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. The 52-week BE SURE trial, which provided the 478 patients who entered into the BE BRIGHT open label extension study, was published in The New England Journal of Medicine in July 2021.
In the 4-year data reported by Dr. Lebwohl, three groups were compared: Those initially randomized to an every-4-week dosing schedule of bimekizumab over the course of the 52-week BE SURE trial; those randomized to an every-4-week bimekizumab schedule who were then subsequently switched to an every-8-week schedule; and those initiated on the TNF-inhibitor adalimumab (Humira) and were then switched at week 24 to every-4-week bimekizumab.
The PASI 90 responses at 52 weeks in these three groups, respectively, were 91.2%, 89.3%, and 95.2%. At 4 years, this almost clear response was observed in 82.4%, 83.2%, and 87.6%, respectively. At 52 weeks, the PASI 100 responses in these three groups, respectively, were 75.3%, 74.2%, and 72.9%. At 4 years, 61.9%, 58.5%, and 69.5% still had complete skin clearance.
Bimekizumab was well tolerated during the randomized trial, reported Dr. Lebwohl. The rates of nasopharyngitis and oral candidiasis, which were observed in approximately 12% and 8%, respectively, of treated patients during the randomized phase remained at about the same level in the long-term follow up. There were no new safety signals, he said.
JNJ-2113 Is First Potential Oral IL-23 Inhibitor
JNJ-2113 is a first-in-class oral peptide that binds to the IL-23 receptor, blocking the IL-23 signaling pathway. If approved, it would be the first oral therapy targeting IL-23. The 16-week outcomes of the dose-finding FRONTIER 1 phase 2b trial were published in The New England Journal of Medicine earlier this year. The primary endpoint was PASI 75, achieved by 79% of those on the 100 mg twice daily dose at week 16, vs 9% on placebo, and at 52 weeks, was 76%.
“The proportion of patients achieving the FRONTIER 1 primary endpoint was maintained from week 16 to the end of week 52 in the extension study,” Dr. Ferris said, but further pointed out that rates of near or complete clearance achieved at week 16 were also essentially unchanged at week 52. This was true of PASI scores and IGA.
Clearance of psoriatic lesions on the scalp was particularly impressive. By scalp-specific IGA, rates of clear or near clear (0/1) were not just maintained but improved over the course of follow-up, reaching 75.1% at 52 weeks in the highest dose group, she said.
JNJ-2113 was well tolerated in FRONTIER 1 and remained so during long-term follow-up, in the FRONTIER 2 extension study, according to Dr. Ferris. The most common complaints with JNJ-2113, such as nasopharyngitis (18.1% vs 25.7% in placebo), did not appear to differ significantly from placebo and the treatment remained well tolerated over the course of the extended follow-up.
There are limited direct comparisons of different biologics active in the treatment of plaque psoriasis for efficacy and safety, but these data appear to show a depth and durability of benefit for psoriasis that is exceptional, Dr. Lebwohl told this news organization. “The PASI 100 scores achieved by bimekizumab exceed anything we have seen to date,” he said. “And the durability of those exceedingly high scores is remarkable.”
Dr. Lebwohl reports financial relationships with approximately 40 pharmaceutical companies, including UCB Pharma, which developed bimekizumab. Dr. Ferris reports financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen, which is developing JNJ-2113.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — , but late-breaker data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology show that these types of responses are sustained for as long as patients have remained on therapy.
Of the two, the longer follow up is with the IL-17 inhibitor bimekizumab (Bimzelx). In a 4-year open-label extension study, the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 rate was approximately 85% in treated patients, according to Mark Lebwohl, MD, professor and chairman emeritus of the Department of Dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City
A PASI 90 score signifies that 90% of skin surface area is cleared. The proportion of patients who achieved a PASI 100 score, signifying total clearance, approached 70% at 4 years in the group with the greatest response. PASI 90 and PASI 100 rates at this point were only modestly lower than those reported at the end of the double-blind phase 3 trial when evaluated 3 years earlier.
Follow-up with a novel oral anti-IL-23 inhibitor JNJ-2113 (JNJ-77242113) was only 52 weeks, far shorter. But again, the response for the most effective dose at the end of this period was essentially unchanged from that at 16 weeks. Among those on the highest and most effective test dose of once-daily 100 mg, the PASI 90 at 1 year was 64.3%, a rate that was essentially unchanged from week 16.
No Apparent Loss of Benefit Over Time
“We can really look at those dose-response curves and see that there is, overall, a maintenance of response,” reported Laura K. Ferris, MD, PhD, professor and director of clinical trials, Department of Dermatology, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. In her presentation of the data, she showed similar sustained control for the most effective doses of JNJ-2113 for multiple clinical outcomes, including an investigator’s global assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1, also signifying clear or near clear skin.
Bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits both IL-17A and IL-17F, is already approved for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. The 52-week BE SURE trial, which provided the 478 patients who entered into the BE BRIGHT open label extension study, was published in The New England Journal of Medicine in July 2021.
In the 4-year data reported by Dr. Lebwohl, three groups were compared: Those initially randomized to an every-4-week dosing schedule of bimekizumab over the course of the 52-week BE SURE trial; those randomized to an every-4-week bimekizumab schedule who were then subsequently switched to an every-8-week schedule; and those initiated on the TNF-inhibitor adalimumab (Humira) and were then switched at week 24 to every-4-week bimekizumab.
The PASI 90 responses at 52 weeks in these three groups, respectively, were 91.2%, 89.3%, and 95.2%. At 4 years, this almost clear response was observed in 82.4%, 83.2%, and 87.6%, respectively. At 52 weeks, the PASI 100 responses in these three groups, respectively, were 75.3%, 74.2%, and 72.9%. At 4 years, 61.9%, 58.5%, and 69.5% still had complete skin clearance.
Bimekizumab was well tolerated during the randomized trial, reported Dr. Lebwohl. The rates of nasopharyngitis and oral candidiasis, which were observed in approximately 12% and 8%, respectively, of treated patients during the randomized phase remained at about the same level in the long-term follow up. There were no new safety signals, he said.
JNJ-2113 Is First Potential Oral IL-23 Inhibitor
JNJ-2113 is a first-in-class oral peptide that binds to the IL-23 receptor, blocking the IL-23 signaling pathway. If approved, it would be the first oral therapy targeting IL-23. The 16-week outcomes of the dose-finding FRONTIER 1 phase 2b trial were published in The New England Journal of Medicine earlier this year. The primary endpoint was PASI 75, achieved by 79% of those on the 100 mg twice daily dose at week 16, vs 9% on placebo, and at 52 weeks, was 76%.
“The proportion of patients achieving the FRONTIER 1 primary endpoint was maintained from week 16 to the end of week 52 in the extension study,” Dr. Ferris said, but further pointed out that rates of near or complete clearance achieved at week 16 were also essentially unchanged at week 52. This was true of PASI scores and IGA.
Clearance of psoriatic lesions on the scalp was particularly impressive. By scalp-specific IGA, rates of clear or near clear (0/1) were not just maintained but improved over the course of follow-up, reaching 75.1% at 52 weeks in the highest dose group, she said.
JNJ-2113 was well tolerated in FRONTIER 1 and remained so during long-term follow-up, in the FRONTIER 2 extension study, according to Dr. Ferris. The most common complaints with JNJ-2113, such as nasopharyngitis (18.1% vs 25.7% in placebo), did not appear to differ significantly from placebo and the treatment remained well tolerated over the course of the extended follow-up.
There are limited direct comparisons of different biologics active in the treatment of plaque psoriasis for efficacy and safety, but these data appear to show a depth and durability of benefit for psoriasis that is exceptional, Dr. Lebwohl told this news organization. “The PASI 100 scores achieved by bimekizumab exceed anything we have seen to date,” he said. “And the durability of those exceedingly high scores is remarkable.”
Dr. Lebwohl reports financial relationships with approximately 40 pharmaceutical companies, including UCB Pharma, which developed bimekizumab. Dr. Ferris reports financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen, which is developing JNJ-2113.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAD 2024
Summertime and Mosquitoes Are Breeding
There are over 3700 types of mosquitoes worldwide and over 200 types in the continental United States, of which only 12 are associated with transmitting diseases to humans. The majority are just a nuisance. Since they cannot readily be distinguished, strategies to prevent any bites are recommended.
West Nile Virus
In the US, West Nile virus (WNV) is the leading cause of neuroinvasive arboviral disease. Just hearing the name took me back to New York in 1999 when sightings of dead birds around the city and boroughs were reported daily. The virus was isolated that same year. The enzootic circle occurs between mosquitoes and birds, which are the primary vertebrate host via the bite of Culex mosquitoes. After a bite from an infected mosquito, humans are usually a dead-end host since the level and duration of viremia needed to infect another mosquito is insufficient.
Human-to-human transmission is documented through blood transfusion and solid organ transplantation. Vertical transmission is rarely described. Initially isolated in New York, WNV quickly spread across North America and has been isolated in every continent except Antarctica. Most cases occur in the summer and autumn.
Most infected individuals are asymptomatic. Those who do develop symptoms have fever, headache, myalgia, arthralgia, nausea, vomiting, and a transient rash. Less than 1% develop meningitis/encephalitis symptoms similar to other causes of aseptic meningitis. Those with encephalitis in addition to fever and headache may have altered mental status and focal neurologic deficits including flaccid paralysis or movement disorders.
Detection of anti-WNV IgM antibodies (AB) in serum or CSF is the most common way to make the diagnosis. IgM AB usually is present within 3-8 days after onset of symptoms and persists up to 90 days. Data from ArboNET, the national arboviral surveillance system managed by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and state health departments, reveal that from 1999 to 2022 there were 56,575 cases of WNV including 28,684 cases of neuroinvasive disease. In 2023 there were 2,406 and 1,599 cases, respectively. Those historic totals for WNV are 10 times greater than the totals for all the other etiologies of neuroinvasive arboviral diseases in the US combined (Jamestown Canyon, LaCrosse, St. Louis, and Eastern Equine encephalitis n = 1813).
Remember to include WNV in your differential of a febrile patient with neurologic symptoms, mosquito bites, blood transfusions, and organ transplantation. Treatment is supportive care.
The US began screening all blood donations for WNV in 2003. Organ donor screening is not universal.
Dengue
Dengue, another arbovirus, is transmitted by bites of infected Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes, which prefer to feed during the daytime. There are four dengue virus serotypes: DENV-1 DENV-2, DENV-3 and DENV-4. In endemic areas, all four serotypes are usually co-circulating and people can be infected by each one.
Long-term immunity is type specific. Heterologous protection lasts only a few months. Dengue is endemic throughout the tropics and subtropics of Asia, Africa, and the Americas. Approximately 53% of the world’s population live in an area where dengue transmission can occur. In the US, most cases are reported from Puerto Rico. Dengue is endemic in the following US territories: Puerto Rico, US Virgin Islands, American Samoa, and free associated states. Most cases reported on the mainland are travel related. However, locally acquired dengue has been reported. From 2010 to 2023 Hawaii reported 250 cases, Florida 438, and Texas 40 locally acquired cases. During that same period, Puerto Rico reported more than 32,000 cases. It is the leading cause of febrile illness for travelers returning from the Caribbean, Latin America, and South Asia. Peru is currently experiencing an outbreak with more than 25,000 cases reported since January 2024. Most cases of dengue occur in adolescents and young adults. Severe disease occurs most often in infants, those with underlying chronic disease, pregnant women, and persons infected with dengue for the second time.
Symptoms range from a mild febrile illness to severe disease associated with hemorrhage and shock. Onset is usually 7-10 days after infection and symptoms include high fever, severe headache, retro-orbital pain, arthralgia and myalgias, nausea, and vomiting; some may develop a generalized rash.
The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies dengue as 1) dengue with or without warning signs for progression of disease and 2) severe dengue. Warning signs for disease progression include abdominal pain or tenderness, persistent vomiting, fluid accumulation (e.g., ascites, pericardial or pleural effusion), mucosal bleeding, restlessness, postural hypotension, liver enlargement greater than 2 cm. Severe dengue is defined as any sign of severe plasma leakage leading to shock, severe bleeding or organ failure, or fluid accumulation with respiratory distress. Management is supportive care.
Prevention: In the US, Dengvaxia, a live attenuated tetravalent vaccine, is approved for use in children aged 9–16 years with laboratory-confirmed previous dengue virus infection and living in areas where dengue is endemic. It is administered at 0, 6, and 12 months. It is not available for purchase on the mainland. Continued control of the vector and personal protection is necessary to prevent recurrent infections.
CHIKV
Chikungunya (CHIKV), which means “that which bends up” in the Mkonde language of Tanzania, refers to the appearance of the person with severe usually symmetric arthralgias characteristic for this infection that otherwise is often clinically confused with dengue and Zika. It too is transmitted by A. aegypti and A. albopictus and is prevalent in tropical Africa, Asia, Central and South America, and the Caribbean. Like dengue it is predominantly an urban disease. The WHO reported the first case in the Western Hemisphere in Saint Martin in December 2013. By August 2014, 31 additional territories and Caribbean or South American countries reported 576,535 suspected cases. Florida first reported locally acquired CHIKV in June 2014. By December an additional 11 cases had been identified. Texas reported one case in 2015. Diagnosis is with IgM ab or PCR. Treatment is supportive with most recovering from acute illness within 2 weeks. Data in adults indicate 40-52% may develop chronic or recurrent joint pain.
Prevention: IXCHIQ, a live attenuated vaccine, was licensed in November 2023 and recommended by the CDC in February 2024 for use in persons at least 18 years of age with travel to destinations where there is a CHIKV outbreak. It may be considered for persons traveling to a country or territory without an outbreak but with evidence of CHIKV transmission among humans within the last 5 years and those staying in endemic areas for a cumulative period of at least 6 months over a 2-year period. Specific recommendations for lab workers and persons older than 65 years were also made. This is good news for your older patients who may be participating in mission trips, volunteering, studying abroad, or just vacationing in an endemic area. Adolescent vaccine trials are ongoing and pediatric trials will soon be initiated. In addition, vector control and use of personal protective measures cannot be emphasized enough.
There are several other mosquito borne diseases, however our discussion here is limited to three. Why these three? WNV as a reminder that it is the most common neuroinvasive agent in the US. Dengue and CHIKV because they are not endemic in the US so they might not routinely be considered in febrile patients; both diseases have been reported and acquired on the mainland and your patients may travel to an endemic area and return home with an unwanted souvenir. You will be ready for them.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
Suggested Reading
Chikungunya. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/recommendations.html.
Fagrem AC et al. West Nile and Other Nationally Notifiable Arboviral Diseases–United States, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 Aug 25;72(34):901-906.
Fever in Returned Travelers, Travel Medicine (Fourth Edition). 2019. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-54696-6.00056-2.
Paz-Baily et al. Dengue Vaccine: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, United States, 2021 MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021 Dec 17;70(6):1-16).
Staples JE and Fischer M. Chikungunya virus in the Americas — what a vectorborne pathogen can do. N Engl J Med. 2014 Sep 4;371(10):887-9.
Mosquitoes and Diseases A-Z, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/mosquitoes/about/diseases.html.
There are over 3700 types of mosquitoes worldwide and over 200 types in the continental United States, of which only 12 are associated with transmitting diseases to humans. The majority are just a nuisance. Since they cannot readily be distinguished, strategies to prevent any bites are recommended.
West Nile Virus
In the US, West Nile virus (WNV) is the leading cause of neuroinvasive arboviral disease. Just hearing the name took me back to New York in 1999 when sightings of dead birds around the city and boroughs were reported daily. The virus was isolated that same year. The enzootic circle occurs between mosquitoes and birds, which are the primary vertebrate host via the bite of Culex mosquitoes. After a bite from an infected mosquito, humans are usually a dead-end host since the level and duration of viremia needed to infect another mosquito is insufficient.
Human-to-human transmission is documented through blood transfusion and solid organ transplantation. Vertical transmission is rarely described. Initially isolated in New York, WNV quickly spread across North America and has been isolated in every continent except Antarctica. Most cases occur in the summer and autumn.
Most infected individuals are asymptomatic. Those who do develop symptoms have fever, headache, myalgia, arthralgia, nausea, vomiting, and a transient rash. Less than 1% develop meningitis/encephalitis symptoms similar to other causes of aseptic meningitis. Those with encephalitis in addition to fever and headache may have altered mental status and focal neurologic deficits including flaccid paralysis or movement disorders.
Detection of anti-WNV IgM antibodies (AB) in serum or CSF is the most common way to make the diagnosis. IgM AB usually is present within 3-8 days after onset of symptoms and persists up to 90 days. Data from ArboNET, the national arboviral surveillance system managed by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and state health departments, reveal that from 1999 to 2022 there were 56,575 cases of WNV including 28,684 cases of neuroinvasive disease. In 2023 there were 2,406 and 1,599 cases, respectively. Those historic totals for WNV are 10 times greater than the totals for all the other etiologies of neuroinvasive arboviral diseases in the US combined (Jamestown Canyon, LaCrosse, St. Louis, and Eastern Equine encephalitis n = 1813).
Remember to include WNV in your differential of a febrile patient with neurologic symptoms, mosquito bites, blood transfusions, and organ transplantation. Treatment is supportive care.
The US began screening all blood donations for WNV in 2003. Organ donor screening is not universal.
Dengue
Dengue, another arbovirus, is transmitted by bites of infected Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes, which prefer to feed during the daytime. There are four dengue virus serotypes: DENV-1 DENV-2, DENV-3 and DENV-4. In endemic areas, all four serotypes are usually co-circulating and people can be infected by each one.
Long-term immunity is type specific. Heterologous protection lasts only a few months. Dengue is endemic throughout the tropics and subtropics of Asia, Africa, and the Americas. Approximately 53% of the world’s population live in an area where dengue transmission can occur. In the US, most cases are reported from Puerto Rico. Dengue is endemic in the following US territories: Puerto Rico, US Virgin Islands, American Samoa, and free associated states. Most cases reported on the mainland are travel related. However, locally acquired dengue has been reported. From 2010 to 2023 Hawaii reported 250 cases, Florida 438, and Texas 40 locally acquired cases. During that same period, Puerto Rico reported more than 32,000 cases. It is the leading cause of febrile illness for travelers returning from the Caribbean, Latin America, and South Asia. Peru is currently experiencing an outbreak with more than 25,000 cases reported since January 2024. Most cases of dengue occur in adolescents and young adults. Severe disease occurs most often in infants, those with underlying chronic disease, pregnant women, and persons infected with dengue for the second time.
Symptoms range from a mild febrile illness to severe disease associated with hemorrhage and shock. Onset is usually 7-10 days after infection and symptoms include high fever, severe headache, retro-orbital pain, arthralgia and myalgias, nausea, and vomiting; some may develop a generalized rash.
The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies dengue as 1) dengue with or without warning signs for progression of disease and 2) severe dengue. Warning signs for disease progression include abdominal pain or tenderness, persistent vomiting, fluid accumulation (e.g., ascites, pericardial or pleural effusion), mucosal bleeding, restlessness, postural hypotension, liver enlargement greater than 2 cm. Severe dengue is defined as any sign of severe plasma leakage leading to shock, severe bleeding or organ failure, or fluid accumulation with respiratory distress. Management is supportive care.
Prevention: In the US, Dengvaxia, a live attenuated tetravalent vaccine, is approved for use in children aged 9–16 years with laboratory-confirmed previous dengue virus infection and living in areas where dengue is endemic. It is administered at 0, 6, and 12 months. It is not available for purchase on the mainland. Continued control of the vector and personal protection is necessary to prevent recurrent infections.
CHIKV
Chikungunya (CHIKV), which means “that which bends up” in the Mkonde language of Tanzania, refers to the appearance of the person with severe usually symmetric arthralgias characteristic for this infection that otherwise is often clinically confused with dengue and Zika. It too is transmitted by A. aegypti and A. albopictus and is prevalent in tropical Africa, Asia, Central and South America, and the Caribbean. Like dengue it is predominantly an urban disease. The WHO reported the first case in the Western Hemisphere in Saint Martin in December 2013. By August 2014, 31 additional territories and Caribbean or South American countries reported 576,535 suspected cases. Florida first reported locally acquired CHIKV in June 2014. By December an additional 11 cases had been identified. Texas reported one case in 2015. Diagnosis is with IgM ab or PCR. Treatment is supportive with most recovering from acute illness within 2 weeks. Data in adults indicate 40-52% may develop chronic or recurrent joint pain.
Prevention: IXCHIQ, a live attenuated vaccine, was licensed in November 2023 and recommended by the CDC in February 2024 for use in persons at least 18 years of age with travel to destinations where there is a CHIKV outbreak. It may be considered for persons traveling to a country or territory without an outbreak but with evidence of CHIKV transmission among humans within the last 5 years and those staying in endemic areas for a cumulative period of at least 6 months over a 2-year period. Specific recommendations for lab workers and persons older than 65 years were also made. This is good news for your older patients who may be participating in mission trips, volunteering, studying abroad, or just vacationing in an endemic area. Adolescent vaccine trials are ongoing and pediatric trials will soon be initiated. In addition, vector control and use of personal protective measures cannot be emphasized enough.
There are several other mosquito borne diseases, however our discussion here is limited to three. Why these three? WNV as a reminder that it is the most common neuroinvasive agent in the US. Dengue and CHIKV because they are not endemic in the US so they might not routinely be considered in febrile patients; both diseases have been reported and acquired on the mainland and your patients may travel to an endemic area and return home with an unwanted souvenir. You will be ready for them.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
Suggested Reading
Chikungunya. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/recommendations.html.
Fagrem AC et al. West Nile and Other Nationally Notifiable Arboviral Diseases–United States, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 Aug 25;72(34):901-906.
Fever in Returned Travelers, Travel Medicine (Fourth Edition). 2019. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-54696-6.00056-2.
Paz-Baily et al. Dengue Vaccine: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, United States, 2021 MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021 Dec 17;70(6):1-16).
Staples JE and Fischer M. Chikungunya virus in the Americas — what a vectorborne pathogen can do. N Engl J Med. 2014 Sep 4;371(10):887-9.
Mosquitoes and Diseases A-Z, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/mosquitoes/about/diseases.html.
There are over 3700 types of mosquitoes worldwide and over 200 types in the continental United States, of which only 12 are associated with transmitting diseases to humans. The majority are just a nuisance. Since they cannot readily be distinguished, strategies to prevent any bites are recommended.
West Nile Virus
In the US, West Nile virus (WNV) is the leading cause of neuroinvasive arboviral disease. Just hearing the name took me back to New York in 1999 when sightings of dead birds around the city and boroughs were reported daily. The virus was isolated that same year. The enzootic circle occurs between mosquitoes and birds, which are the primary vertebrate host via the bite of Culex mosquitoes. After a bite from an infected mosquito, humans are usually a dead-end host since the level and duration of viremia needed to infect another mosquito is insufficient.
Human-to-human transmission is documented through blood transfusion and solid organ transplantation. Vertical transmission is rarely described. Initially isolated in New York, WNV quickly spread across North America and has been isolated in every continent except Antarctica. Most cases occur in the summer and autumn.
Most infected individuals are asymptomatic. Those who do develop symptoms have fever, headache, myalgia, arthralgia, nausea, vomiting, and a transient rash. Less than 1% develop meningitis/encephalitis symptoms similar to other causes of aseptic meningitis. Those with encephalitis in addition to fever and headache may have altered mental status and focal neurologic deficits including flaccid paralysis or movement disorders.
Detection of anti-WNV IgM antibodies (AB) in serum or CSF is the most common way to make the diagnosis. IgM AB usually is present within 3-8 days after onset of symptoms and persists up to 90 days. Data from ArboNET, the national arboviral surveillance system managed by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and state health departments, reveal that from 1999 to 2022 there were 56,575 cases of WNV including 28,684 cases of neuroinvasive disease. In 2023 there were 2,406 and 1,599 cases, respectively. Those historic totals for WNV are 10 times greater than the totals for all the other etiologies of neuroinvasive arboviral diseases in the US combined (Jamestown Canyon, LaCrosse, St. Louis, and Eastern Equine encephalitis n = 1813).
Remember to include WNV in your differential of a febrile patient with neurologic symptoms, mosquito bites, blood transfusions, and organ transplantation. Treatment is supportive care.
The US began screening all blood donations for WNV in 2003. Organ donor screening is not universal.
Dengue
Dengue, another arbovirus, is transmitted by bites of infected Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes, which prefer to feed during the daytime. There are four dengue virus serotypes: DENV-1 DENV-2, DENV-3 and DENV-4. In endemic areas, all four serotypes are usually co-circulating and people can be infected by each one.
Long-term immunity is type specific. Heterologous protection lasts only a few months. Dengue is endemic throughout the tropics and subtropics of Asia, Africa, and the Americas. Approximately 53% of the world’s population live in an area where dengue transmission can occur. In the US, most cases are reported from Puerto Rico. Dengue is endemic in the following US territories: Puerto Rico, US Virgin Islands, American Samoa, and free associated states. Most cases reported on the mainland are travel related. However, locally acquired dengue has been reported. From 2010 to 2023 Hawaii reported 250 cases, Florida 438, and Texas 40 locally acquired cases. During that same period, Puerto Rico reported more than 32,000 cases. It is the leading cause of febrile illness for travelers returning from the Caribbean, Latin America, and South Asia. Peru is currently experiencing an outbreak with more than 25,000 cases reported since January 2024. Most cases of dengue occur in adolescents and young adults. Severe disease occurs most often in infants, those with underlying chronic disease, pregnant women, and persons infected with dengue for the second time.
Symptoms range from a mild febrile illness to severe disease associated with hemorrhage and shock. Onset is usually 7-10 days after infection and symptoms include high fever, severe headache, retro-orbital pain, arthralgia and myalgias, nausea, and vomiting; some may develop a generalized rash.
The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies dengue as 1) dengue with or without warning signs for progression of disease and 2) severe dengue. Warning signs for disease progression include abdominal pain or tenderness, persistent vomiting, fluid accumulation (e.g., ascites, pericardial or pleural effusion), mucosal bleeding, restlessness, postural hypotension, liver enlargement greater than 2 cm. Severe dengue is defined as any sign of severe plasma leakage leading to shock, severe bleeding or organ failure, or fluid accumulation with respiratory distress. Management is supportive care.
Prevention: In the US, Dengvaxia, a live attenuated tetravalent vaccine, is approved for use in children aged 9–16 years with laboratory-confirmed previous dengue virus infection and living in areas where dengue is endemic. It is administered at 0, 6, and 12 months. It is not available for purchase on the mainland. Continued control of the vector and personal protection is necessary to prevent recurrent infections.
CHIKV
Chikungunya (CHIKV), which means “that which bends up” in the Mkonde language of Tanzania, refers to the appearance of the person with severe usually symmetric arthralgias characteristic for this infection that otherwise is often clinically confused with dengue and Zika. It too is transmitted by A. aegypti and A. albopictus and is prevalent in tropical Africa, Asia, Central and South America, and the Caribbean. Like dengue it is predominantly an urban disease. The WHO reported the first case in the Western Hemisphere in Saint Martin in December 2013. By August 2014, 31 additional territories and Caribbean or South American countries reported 576,535 suspected cases. Florida first reported locally acquired CHIKV in June 2014. By December an additional 11 cases had been identified. Texas reported one case in 2015. Diagnosis is with IgM ab or PCR. Treatment is supportive with most recovering from acute illness within 2 weeks. Data in adults indicate 40-52% may develop chronic or recurrent joint pain.
Prevention: IXCHIQ, a live attenuated vaccine, was licensed in November 2023 and recommended by the CDC in February 2024 for use in persons at least 18 years of age with travel to destinations where there is a CHIKV outbreak. It may be considered for persons traveling to a country or territory without an outbreak but with evidence of CHIKV transmission among humans within the last 5 years and those staying in endemic areas for a cumulative period of at least 6 months over a 2-year period. Specific recommendations for lab workers and persons older than 65 years were also made. This is good news for your older patients who may be participating in mission trips, volunteering, studying abroad, or just vacationing in an endemic area. Adolescent vaccine trials are ongoing and pediatric trials will soon be initiated. In addition, vector control and use of personal protective measures cannot be emphasized enough.
There are several other mosquito borne diseases, however our discussion here is limited to three. Why these three? WNV as a reminder that it is the most common neuroinvasive agent in the US. Dengue and CHIKV because they are not endemic in the US so they might not routinely be considered in febrile patients; both diseases have been reported and acquired on the mainland and your patients may travel to an endemic area and return home with an unwanted souvenir. You will be ready for them.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
Suggested Reading
Chikungunya. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/recommendations.html.
Fagrem AC et al. West Nile and Other Nationally Notifiable Arboviral Diseases–United States, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 Aug 25;72(34):901-906.
Fever in Returned Travelers, Travel Medicine (Fourth Edition). 2019. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-54696-6.00056-2.
Paz-Baily et al. Dengue Vaccine: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, United States, 2021 MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021 Dec 17;70(6):1-16).
Staples JE and Fischer M. Chikungunya virus in the Americas — what a vectorborne pathogen can do. N Engl J Med. 2014 Sep 4;371(10):887-9.
Mosquitoes and Diseases A-Z, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/mosquitoes/about/diseases.html.
Phase 2 Results: Zerlasiran siRNA Drug Lowers Lp(a) by 90%
Silence Therapeutics shared positive topline 36-week data from its ongoing phase 2 study of zerlasiran, a long-acting agent directed at lowering Lp(a) levels.
In a statement, the company said the study shows a highly significant reduction from baseline in Lp(a) levels with zerlasiran compared with placebo at 36 weeks, the primary endpoint.
Zerlasiran (formerly known as SLN360), is a short interfering RNA (siRNA) agent, or “ gene silencing” therapy. It binds to and temporarily blocks the action of the LPA gene which encodes for apolipoprotein(a), a dominant and a rate-limiting component in the hepatic synthesis of the Lp(a) particle.
A previous phase 1 study showed that single subcutaneous doses of the drug, ranging from 30 mg to 600 mg, produced a dose-dependent reduction in Lp(a) plasma levels at 45-60 days.
The current double-blind placebo-controlled phase 2 trial — known as ALPACAR-360 — enrolled 178 patients at high risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular events who had elevated levels of Lp(a), ie, ≥ 125 nmol/L (median baseline Lp(a) was approximately 215 nmol/L). They were randomized to zerlasiran or placebo.
Zerlasiran was administered at 300 mg subcutaneously every 16 or 24 weeks or at 450 mg every 24 weeks.
The 60-week study is ongoing, and secondary endpoints, including change in Lp(a) from baseline to 48 weeks (end of treatment period) and 60 weeks (end of study) and potential effects on other lipids/lipoproteins, will be evaluated.
Silence says it plans to report topline 48-week data from the ALPACAR-360 study in the second quarter of this year.
Elevated levels of Lp(a) represent a genetic risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is believed to affect approximately 20% of the population. Although there are currently no approved Lp(a)-lowering therapies, several drug candidates are in late-stage clinical testing.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Silence Therapeutics shared positive topline 36-week data from its ongoing phase 2 study of zerlasiran, a long-acting agent directed at lowering Lp(a) levels.
In a statement, the company said the study shows a highly significant reduction from baseline in Lp(a) levels with zerlasiran compared with placebo at 36 weeks, the primary endpoint.
Zerlasiran (formerly known as SLN360), is a short interfering RNA (siRNA) agent, or “ gene silencing” therapy. It binds to and temporarily blocks the action of the LPA gene which encodes for apolipoprotein(a), a dominant and a rate-limiting component in the hepatic synthesis of the Lp(a) particle.
A previous phase 1 study showed that single subcutaneous doses of the drug, ranging from 30 mg to 600 mg, produced a dose-dependent reduction in Lp(a) plasma levels at 45-60 days.
The current double-blind placebo-controlled phase 2 trial — known as ALPACAR-360 — enrolled 178 patients at high risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular events who had elevated levels of Lp(a), ie, ≥ 125 nmol/L (median baseline Lp(a) was approximately 215 nmol/L). They were randomized to zerlasiran or placebo.
Zerlasiran was administered at 300 mg subcutaneously every 16 or 24 weeks or at 450 mg every 24 weeks.
The 60-week study is ongoing, and secondary endpoints, including change in Lp(a) from baseline to 48 weeks (end of treatment period) and 60 weeks (end of study) and potential effects on other lipids/lipoproteins, will be evaluated.
Silence says it plans to report topline 48-week data from the ALPACAR-360 study in the second quarter of this year.
Elevated levels of Lp(a) represent a genetic risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is believed to affect approximately 20% of the population. Although there are currently no approved Lp(a)-lowering therapies, several drug candidates are in late-stage clinical testing.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Silence Therapeutics shared positive topline 36-week data from its ongoing phase 2 study of zerlasiran, a long-acting agent directed at lowering Lp(a) levels.
In a statement, the company said the study shows a highly significant reduction from baseline in Lp(a) levels with zerlasiran compared with placebo at 36 weeks, the primary endpoint.
Zerlasiran (formerly known as SLN360), is a short interfering RNA (siRNA) agent, or “ gene silencing” therapy. It binds to and temporarily blocks the action of the LPA gene which encodes for apolipoprotein(a), a dominant and a rate-limiting component in the hepatic synthesis of the Lp(a) particle.
A previous phase 1 study showed that single subcutaneous doses of the drug, ranging from 30 mg to 600 mg, produced a dose-dependent reduction in Lp(a) plasma levels at 45-60 days.
The current double-blind placebo-controlled phase 2 trial — known as ALPACAR-360 — enrolled 178 patients at high risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular events who had elevated levels of Lp(a), ie, ≥ 125 nmol/L (median baseline Lp(a) was approximately 215 nmol/L). They were randomized to zerlasiran or placebo.
Zerlasiran was administered at 300 mg subcutaneously every 16 or 24 weeks or at 450 mg every 24 weeks.
The 60-week study is ongoing, and secondary endpoints, including change in Lp(a) from baseline to 48 weeks (end of treatment period) and 60 weeks (end of study) and potential effects on other lipids/lipoproteins, will be evaluated.
Silence says it plans to report topline 48-week data from the ALPACAR-360 study in the second quarter of this year.
Elevated levels of Lp(a) represent a genetic risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is believed to affect approximately 20% of the population. Although there are currently no approved Lp(a)-lowering therapies, several drug candidates are in late-stage clinical testing.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cell-Free DNA Blood Test Has High Accuracy for Detecting Colorectal Cancer
, according to a new study.
The cfDNA blood test had 83% sensitivity for CRC, 90% specificity for advanced neoplasia, and 13% sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions. Other noninvasive screening methods have sensitivity from 67% to 94% for CRC and 22% to 43% for advanced precancerous lesions.
“The results of the study are a promising step toward developing more convenient tools to detect colorectal cancer early while it is more easily treated,” said senior author William M. Grady, MD, AGAF, medical director of the Gastrointestinal Cancer Prevention Program at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle.
“The test, which has an accuracy rate for colon cancer detection similar to stool tests used for early detection of cancer, could offer an alternative for patients who may otherwise decline current screening options,” he said.
The study was published online on March 14 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Analyzing the Blood Test’s Accuracy
Dr. Grady and colleagues conducted a multisite clinical trial called ECLIPSE, which compared the sensitivity and specificity of a cfDNA blood test (Shield, Guardant Health) against that obtained with colonoscopy, the gold standard for CRC screening. Guardant led and funded the study.
Guardant’s Shield test is designed to detect CRC through genomic alterations, aberrant methylation status, and fragmentomic patterns, which show up as an “abnormal signal detected” result. Similar blood tests are being developed as “liquid biopsy” tests for other emerging cancer screenings as well.
The study included 7861 people with average CRC risk who underwent routine screening with colonoscopy at 265 sites in the United States, including primary care and endoscopy centers in academic and community-based institutions. Eligible people were aged 45-84 years (average age, 60 years), and 53.7% were women. The race and ethnicity characteristics of the participants closely mirrored the demographic distribution in the 2020 US Census.
Overall, 54 of 65 (83.1%) participants with colonoscopy-detected CRC had a positive cfDNA blood test. However, 11 participants (16.9%) with CRC had a negative test.
The cfDNA blood test identified 42 of 48 stage I, II, or III CRCs, indicating a sensitivity of 87.5%, including 65% for stage I cancers, 100% for stage II cancers, and 100% for stage III cancers. The test also identified all 10 of the stage IV CRC cases. There were no substantial differences in sensitivity for CRC based on primary tumor location, tumor histologic grade, or demographic characteristics.
Among participants without advanced colorectal neoplasia on colonoscopy, 89.6% had a negative cfDNA blood test, and 10.4% had a positive test.
Among those with a negative colonoscopy — with no CRC, advanced precancerous lesions, or nonadvanced precancerous lesions — specificity was 89.9%.
Among 1116 participants with advanced precancerous lesions identified as the most advanced lesion on colonoscopy, the cfDNA blood test was positive for 147, indicating a sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions of 13.2%.
Although the blood test has sensitivity similar to stool-based tests for CRC, the accuracy is lower than it is with colonoscopy, which remains the current gold standard for CRC screening, Dr. Grady said.
“Colorectal cancer is common and very preventable with screening, but only about 50% to 60% of people who are eligible for screening actually take those tests,” he said. “Getting people to be screened for cancer works best when we offer them screening options and then let them choose what works best for them.”
Future Research
Colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among US adults and is now the third most diagnosed cancer for people younger than 50 years, Dr. Grady said. Although overall CRC death rates have declined in recent years, the rates among those younger than 55 years have increased since the mid-2000s.
“When colorectal cancer is found earlier and the cancer has not yet spread throughout the body, patient outcomes are much better, as reflected in 5-year survival being much better. It makes sense that an effective blood-based test could have a potential role, in particular for those not getting screened yet,” said Joshua Melson, MD, AGAF, clinical professor of medicine and director of the High-Risk Clinic for Gastrointestinal Cancers at the University of Arizona Cancer Center in Tucson.
Dr. Melson, who wasn’t involved with this study, noted that blood-based testing shows promise for cancer detection but needs additional support for real-world implementation. For instance, the Shield blood test has difficulty detecting precancerous lesions, and it remains unclear what the optimal intervals for repeat testing would be after a negative test, he said. In addition, screening programs will need to ensure they have capacity to effectively deal with a positive test result.
“For a screening program to actually work, when a noninvasive test (whether blood-based or stool-based) is read as positive, those patients need to have a follow-up colonoscopy,” he said.
Proper communication with patients will be important as well, said Gloria Coronado, PhD, associate director of Population Sciences at the University of Arizona Cancer Center, Tucson. Dr. Coronado, who wasn’t involved with this study, has developed CRC screening messages for specific patient populations and studied patient reactions to CRC blood tests.
In a study by Dr. Coronado and colleagues, among more than 2000 patients who passively declined fecal testing and had an upcoming clinic visit, CRC screening proportions were 17.5 percentage points higher in the group offered the blood test vs those offered usual care. In qualitative interviews, one patient said of the blood-based testing option, “I was screaming hallelujah!”
“Patients believed that a blood test would be more accurate than a stool-based test. However, for the detection of advanced adenomas, the reverse is true,” she said. “It will be important to balance the high acceptance and enthusiasm for the blood test with the lower performance of the blood test compared to other tests already on the market.”
In a statement accompanying the study’s publication, the American Gastroenterological Association welcomed these results as an exciting development, but cautioned that a blood-based test was not interchangeable with colonoscopy.
“The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) has determined it will cover a blood test for colorectal cancer screening every three years if the test achieves 74% sensitivity for CRC, 90% specificity, and FDA approval,” the statement reads. “However, a blood test that meets only the CMS criteria will be inferior to current recommended tests and should not be recommended to replace current tests. Such a test could be recommended for patients who decline all other recommended tests, since any screening is better than no screening at all.”
Dr. Grady is a paid member of Guardant’s scientific advisory board and advised on the design and procedure of the clinical trial and data analysis. Dr. Melson previously served as consultant for Guardant. Dr. Coronado reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
, according to a new study.
The cfDNA blood test had 83% sensitivity for CRC, 90% specificity for advanced neoplasia, and 13% sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions. Other noninvasive screening methods have sensitivity from 67% to 94% for CRC and 22% to 43% for advanced precancerous lesions.
“The results of the study are a promising step toward developing more convenient tools to detect colorectal cancer early while it is more easily treated,” said senior author William M. Grady, MD, AGAF, medical director of the Gastrointestinal Cancer Prevention Program at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle.
“The test, which has an accuracy rate for colon cancer detection similar to stool tests used for early detection of cancer, could offer an alternative for patients who may otherwise decline current screening options,” he said.
The study was published online on March 14 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Analyzing the Blood Test’s Accuracy
Dr. Grady and colleagues conducted a multisite clinical trial called ECLIPSE, which compared the sensitivity and specificity of a cfDNA blood test (Shield, Guardant Health) against that obtained with colonoscopy, the gold standard for CRC screening. Guardant led and funded the study.
Guardant’s Shield test is designed to detect CRC through genomic alterations, aberrant methylation status, and fragmentomic patterns, which show up as an “abnormal signal detected” result. Similar blood tests are being developed as “liquid biopsy” tests for other emerging cancer screenings as well.
The study included 7861 people with average CRC risk who underwent routine screening with colonoscopy at 265 sites in the United States, including primary care and endoscopy centers in academic and community-based institutions. Eligible people were aged 45-84 years (average age, 60 years), and 53.7% were women. The race and ethnicity characteristics of the participants closely mirrored the demographic distribution in the 2020 US Census.
Overall, 54 of 65 (83.1%) participants with colonoscopy-detected CRC had a positive cfDNA blood test. However, 11 participants (16.9%) with CRC had a negative test.
The cfDNA blood test identified 42 of 48 stage I, II, or III CRCs, indicating a sensitivity of 87.5%, including 65% for stage I cancers, 100% for stage II cancers, and 100% for stage III cancers. The test also identified all 10 of the stage IV CRC cases. There were no substantial differences in sensitivity for CRC based on primary tumor location, tumor histologic grade, or demographic characteristics.
Among participants without advanced colorectal neoplasia on colonoscopy, 89.6% had a negative cfDNA blood test, and 10.4% had a positive test.
Among those with a negative colonoscopy — with no CRC, advanced precancerous lesions, or nonadvanced precancerous lesions — specificity was 89.9%.
Among 1116 participants with advanced precancerous lesions identified as the most advanced lesion on colonoscopy, the cfDNA blood test was positive for 147, indicating a sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions of 13.2%.
Although the blood test has sensitivity similar to stool-based tests for CRC, the accuracy is lower than it is with colonoscopy, which remains the current gold standard for CRC screening, Dr. Grady said.
“Colorectal cancer is common and very preventable with screening, but only about 50% to 60% of people who are eligible for screening actually take those tests,” he said. “Getting people to be screened for cancer works best when we offer them screening options and then let them choose what works best for them.”
Future Research
Colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among US adults and is now the third most diagnosed cancer for people younger than 50 years, Dr. Grady said. Although overall CRC death rates have declined in recent years, the rates among those younger than 55 years have increased since the mid-2000s.
“When colorectal cancer is found earlier and the cancer has not yet spread throughout the body, patient outcomes are much better, as reflected in 5-year survival being much better. It makes sense that an effective blood-based test could have a potential role, in particular for those not getting screened yet,” said Joshua Melson, MD, AGAF, clinical professor of medicine and director of the High-Risk Clinic for Gastrointestinal Cancers at the University of Arizona Cancer Center in Tucson.
Dr. Melson, who wasn’t involved with this study, noted that blood-based testing shows promise for cancer detection but needs additional support for real-world implementation. For instance, the Shield blood test has difficulty detecting precancerous lesions, and it remains unclear what the optimal intervals for repeat testing would be after a negative test, he said. In addition, screening programs will need to ensure they have capacity to effectively deal with a positive test result.
“For a screening program to actually work, when a noninvasive test (whether blood-based or stool-based) is read as positive, those patients need to have a follow-up colonoscopy,” he said.
Proper communication with patients will be important as well, said Gloria Coronado, PhD, associate director of Population Sciences at the University of Arizona Cancer Center, Tucson. Dr. Coronado, who wasn’t involved with this study, has developed CRC screening messages for specific patient populations and studied patient reactions to CRC blood tests.
In a study by Dr. Coronado and colleagues, among more than 2000 patients who passively declined fecal testing and had an upcoming clinic visit, CRC screening proportions were 17.5 percentage points higher in the group offered the blood test vs those offered usual care. In qualitative interviews, one patient said of the blood-based testing option, “I was screaming hallelujah!”
“Patients believed that a blood test would be more accurate than a stool-based test. However, for the detection of advanced adenomas, the reverse is true,” she said. “It will be important to balance the high acceptance and enthusiasm for the blood test with the lower performance of the blood test compared to other tests already on the market.”
In a statement accompanying the study’s publication, the American Gastroenterological Association welcomed these results as an exciting development, but cautioned that a blood-based test was not interchangeable with colonoscopy.
“The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) has determined it will cover a blood test for colorectal cancer screening every three years if the test achieves 74% sensitivity for CRC, 90% specificity, and FDA approval,” the statement reads. “However, a blood test that meets only the CMS criteria will be inferior to current recommended tests and should not be recommended to replace current tests. Such a test could be recommended for patients who decline all other recommended tests, since any screening is better than no screening at all.”
Dr. Grady is a paid member of Guardant’s scientific advisory board and advised on the design and procedure of the clinical trial and data analysis. Dr. Melson previously served as consultant for Guardant. Dr. Coronado reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
, according to a new study.
The cfDNA blood test had 83% sensitivity for CRC, 90% specificity for advanced neoplasia, and 13% sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions. Other noninvasive screening methods have sensitivity from 67% to 94% for CRC and 22% to 43% for advanced precancerous lesions.
“The results of the study are a promising step toward developing more convenient tools to detect colorectal cancer early while it is more easily treated,” said senior author William M. Grady, MD, AGAF, medical director of the Gastrointestinal Cancer Prevention Program at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle.
“The test, which has an accuracy rate for colon cancer detection similar to stool tests used for early detection of cancer, could offer an alternative for patients who may otherwise decline current screening options,” he said.
The study was published online on March 14 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Analyzing the Blood Test’s Accuracy
Dr. Grady and colleagues conducted a multisite clinical trial called ECLIPSE, which compared the sensitivity and specificity of a cfDNA blood test (Shield, Guardant Health) against that obtained with colonoscopy, the gold standard for CRC screening. Guardant led and funded the study.
Guardant’s Shield test is designed to detect CRC through genomic alterations, aberrant methylation status, and fragmentomic patterns, which show up as an “abnormal signal detected” result. Similar blood tests are being developed as “liquid biopsy” tests for other emerging cancer screenings as well.
The study included 7861 people with average CRC risk who underwent routine screening with colonoscopy at 265 sites in the United States, including primary care and endoscopy centers in academic and community-based institutions. Eligible people were aged 45-84 years (average age, 60 years), and 53.7% were women. The race and ethnicity characteristics of the participants closely mirrored the demographic distribution in the 2020 US Census.
Overall, 54 of 65 (83.1%) participants with colonoscopy-detected CRC had a positive cfDNA blood test. However, 11 participants (16.9%) with CRC had a negative test.
The cfDNA blood test identified 42 of 48 stage I, II, or III CRCs, indicating a sensitivity of 87.5%, including 65% for stage I cancers, 100% for stage II cancers, and 100% for stage III cancers. The test also identified all 10 of the stage IV CRC cases. There were no substantial differences in sensitivity for CRC based on primary tumor location, tumor histologic grade, or demographic characteristics.
Among participants without advanced colorectal neoplasia on colonoscopy, 89.6% had a negative cfDNA blood test, and 10.4% had a positive test.
Among those with a negative colonoscopy — with no CRC, advanced precancerous lesions, or nonadvanced precancerous lesions — specificity was 89.9%.
Among 1116 participants with advanced precancerous lesions identified as the most advanced lesion on colonoscopy, the cfDNA blood test was positive for 147, indicating a sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions of 13.2%.
Although the blood test has sensitivity similar to stool-based tests for CRC, the accuracy is lower than it is with colonoscopy, which remains the current gold standard for CRC screening, Dr. Grady said.
“Colorectal cancer is common and very preventable with screening, but only about 50% to 60% of people who are eligible for screening actually take those tests,” he said. “Getting people to be screened for cancer works best when we offer them screening options and then let them choose what works best for them.”
Future Research
Colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among US adults and is now the third most diagnosed cancer for people younger than 50 years, Dr. Grady said. Although overall CRC death rates have declined in recent years, the rates among those younger than 55 years have increased since the mid-2000s.
“When colorectal cancer is found earlier and the cancer has not yet spread throughout the body, patient outcomes are much better, as reflected in 5-year survival being much better. It makes sense that an effective blood-based test could have a potential role, in particular for those not getting screened yet,” said Joshua Melson, MD, AGAF, clinical professor of medicine and director of the High-Risk Clinic for Gastrointestinal Cancers at the University of Arizona Cancer Center in Tucson.
Dr. Melson, who wasn’t involved with this study, noted that blood-based testing shows promise for cancer detection but needs additional support for real-world implementation. For instance, the Shield blood test has difficulty detecting precancerous lesions, and it remains unclear what the optimal intervals for repeat testing would be after a negative test, he said. In addition, screening programs will need to ensure they have capacity to effectively deal with a positive test result.
“For a screening program to actually work, when a noninvasive test (whether blood-based or stool-based) is read as positive, those patients need to have a follow-up colonoscopy,” he said.
Proper communication with patients will be important as well, said Gloria Coronado, PhD, associate director of Population Sciences at the University of Arizona Cancer Center, Tucson. Dr. Coronado, who wasn’t involved with this study, has developed CRC screening messages for specific patient populations and studied patient reactions to CRC blood tests.
In a study by Dr. Coronado and colleagues, among more than 2000 patients who passively declined fecal testing and had an upcoming clinic visit, CRC screening proportions were 17.5 percentage points higher in the group offered the blood test vs those offered usual care. In qualitative interviews, one patient said of the blood-based testing option, “I was screaming hallelujah!”
“Patients believed that a blood test would be more accurate than a stool-based test. However, for the detection of advanced adenomas, the reverse is true,” she said. “It will be important to balance the high acceptance and enthusiasm for the blood test with the lower performance of the blood test compared to other tests already on the market.”
In a statement accompanying the study’s publication, the American Gastroenterological Association welcomed these results as an exciting development, but cautioned that a blood-based test was not interchangeable with colonoscopy.
“The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) has determined it will cover a blood test for colorectal cancer screening every three years if the test achieves 74% sensitivity for CRC, 90% specificity, and FDA approval,” the statement reads. “However, a blood test that meets only the CMS criteria will be inferior to current recommended tests and should not be recommended to replace current tests. Such a test could be recommended for patients who decline all other recommended tests, since any screening is better than no screening at all.”
Dr. Grady is a paid member of Guardant’s scientific advisory board and advised on the design and procedure of the clinical trial and data analysis. Dr. Melson previously served as consultant for Guardant. Dr. Coronado reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
FROM NEJM
Combining Targeted Drugs and Radiation in Breast Cancer: What’s Safe?
One reason is studies of new drugs typically exclude concurrent radiotherapy, said Kathy Miller, MD, a contributor to this news organization and professor of oncology and medicine at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana.
If trials evaluating new targeted therapies included concurrent radiotherapy, it would be challenging to identify whether toxicities came from the drug itself, the radiation, or the combination, Dr. Miller explained.
Given the limited evidence, “we tend to be cautious and conservative” and not combine therapies that “we don’t know are safe or appropriate for patients,” said Chirag Shah, MD, director of breast radiology at the Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio.
Below is a guide to what we do and don’t know about combining radiotherapy and systemic treatments in breast cancer.
1. Immunotherapy plus radiotherapy likely safe but evidence is limited
Safety data on combining immune checkpoint inhibitors and radiotherapy in breast cancer are limited because concurrent radiotherapy has typically been excluded in pivotal trials.
The 2020 KEYNOTE-522 trial did provide a rare look at concurrent radiotherapy and immunotherapy in early triple-negative breast cancer. The analysis found “no safety concerns” with concurrent radiotherapy and pembrolizumab, lead investigator Peter Schmid, MD, of Queen Mary University of London, England, told this news organization.
Research on other solid tumor types also suggests that radiotherapy “can be considered safe” alongside immunotherapy, the authors of a recent ESTRO consensus said.
Despite evidence indicating radiotherapy alongside immunotherapy can be safe in patients with breast cancer, “certain aspects, such as patient selection, total dose, and dose per fraction, remain open for debate to achieve the best therapeutic outcomes,” the ESTRO experts cautioned.
2. CDK4/6 inhibitors may be offered with radiotherapy in some settings, not others
CDK4/6 inhibitors are now standard of care for first- or second-line treatment in patients with advanced or metastatic hormone receptor–positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)–negative breast cancer.
“Unfortunately, we found no information regarding concurrent radiotherapy in the adjuvant setting” in pivotal trials for palbociclib, abemaciclib, and ribociclib, the ESTRO authors said. In the pivotal trials for palbociclib and abemaciclib, patients had to discontinue immunotherapy before initiating radiotherapy, and in the trial for ribociclib, palliative radiotherapy was allowed for relieving bone pain only.
However, in 2023, a team of experts from 12 countries attempted to piece together the available evidence, publishing a meta-analysis of 11 retrospective studies on the safety of CDK4/6 inhibitors given concurrently with radiotherapy in patients with metastatic disease.
Although most of these studies had small patient populations, the analysis revealed that CDK4/6 inhibitors given concurrently with radiotherapy in patients with metastatic breast cancer led to a similar side-effect profile to that observed in trials of the inhibitors given sequentially with adjuvant radiotherapy.
“These findings suggest that the simultaneous administration of CDK4/6 inhibitors and radiotherapy is generally well tolerated,” the ESTRO authors concluded but added that CDK4/6 inhibitors and concomitant radiotherapy should be investigated more in the adjuvant locoregional, whole brain, and intracranial stereotactic radiotherapy settings.
The expert panel did note, however, that CDK4/6 inhibitors and concomitant radiotherapy “could be offered” during palliative and ablative extracranial radiotherapy.
3. Only offer poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors plus radiotherapy in clinical trial setting
PARP inhibitors olaparib (Lynparza) and talazoprib (Talzenna) are standard of care in patients with metastatic breast cancer who have BRCA1/2 gene mutations. Olaparib is also indicated for high-risk early breast cancer following neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy.
But data on combining PARP inhibitors with radiotherapy in breast cancer also remain limited.
One ongoing phase 2 trial, comparing olaparib plus radiotherapy to radiotherapy alone in 300 people with inflammatory breast cancer, is aiming to tease out the safety of the combination and whether it improves local control in patients with aggressive disease.
“The desire is to explore the exciting possibility that low doses of PARP inhibition may radiosensitize tumor cells more than normal tissues,” Reshma Jagsi, MD, chair of the Department of Radiation Oncology at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia, who is leading the study.
Because of potential good or bad interactions between new systemic therapies and radiotherapy, “intentional trial design” is important, Dr. Jagsi said, so we “know the best way to combine treatments in practice to optimize outcomes.”
But given the evidence to date, the ESTRO experts advised waiting until “further research provides more comprehensive safety and efficacy data” in the primary, adjuvant, and metastatic settings. The experts also advised not offering PARP inhibitors and concomitant radiotherapy to treat advanced breast cancer outside of clinical trials.
4. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors (PI3K) inhibitors, mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors, and newer targeted agents should not be offered concurrently with radiotherapy
Clinical trial data on the safety of combining PI3K and mTOR inhibitors with radiation are thin, especially in advanced breast cancer. Typically, radiotherapy within 4 weeks before randomization, or 2 weeks for palliative radiation, was excluded in pivotal trials.
For this reason, the ESTRO team recommended that concurrent radiation with either PI3K inhibitors or mTOR inhibitors “should not be offered.”
ESTRO also cautioned against providing radiation concurrently with newer anti-HER2 tyrosine-kinase drugs, such as neratinib or tucatinib, or newer antibody-drug conjugates such as trastuzumab deruxtecan, until more data emerge on the safety of these combinations.
5. Combining older HER2-targeted drugs and radiotherapy generally safe
The ESTRO authors agreed that older anti-HER2 drugs trastuzumab (Herceptin), pertuzumab (Perjeta), and lapatinib (Tykerb) can be safely used concurrently with locoregional radiotherapy as well.
One of the biggest concerns in the field is how to combine radiation with systemic therapies in the setting of brain metastases, and the data on these older anti-HER2 drugs are relatively clear that it’s safe, Dr. Miller said.
For instance, in a 2019 study of 84 patients with 487 brain metastases, stereotactic radiosurgery given alongside lapatinib led to significantly higher rates of complete responses than stereotactic radiosurgery alone (35% vs 11%) with no increased risk for radiation necrosis.
The ESTRO team agreed, noting that the latest evidence supports the use of trastuzumab, pertuzumab, or lapatinib alongside radiotherapy for whole brain and ablative intracranial stereotactic radiotherapy.
As for older antibody-drug conjugates, trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) plus radiotherapy “might be considered” during adjuvant locoregional radiotherapy for breast cancer but should not be offered for whole brain and ablative intracranial stereotactic radiotherapy, the ESTRO team said.
Dr. Jagsi declared the following conflicts in a recent 2024 publication: Stock options for advisory board role in Equity Quotient; grants or contracts from Genentech; and expert witness for Kleinbard, LLC, and Hawks Quindel Law. In the Keynote-522 trial publication Dr. Schmid declared relationships with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Eisai, Hoffmann-La Roche, Genetech, Merck, Novartis, and Pfizer. Dr. Shah reported consulting for Impedimed, Videra Surgical, and PreludeDX.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
One reason is studies of new drugs typically exclude concurrent radiotherapy, said Kathy Miller, MD, a contributor to this news organization and professor of oncology and medicine at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana.
If trials evaluating new targeted therapies included concurrent radiotherapy, it would be challenging to identify whether toxicities came from the drug itself, the radiation, or the combination, Dr. Miller explained.
Given the limited evidence, “we tend to be cautious and conservative” and not combine therapies that “we don’t know are safe or appropriate for patients,” said Chirag Shah, MD, director of breast radiology at the Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio.
Below is a guide to what we do and don’t know about combining radiotherapy and systemic treatments in breast cancer.
1. Immunotherapy plus radiotherapy likely safe but evidence is limited
Safety data on combining immune checkpoint inhibitors and radiotherapy in breast cancer are limited because concurrent radiotherapy has typically been excluded in pivotal trials.
The 2020 KEYNOTE-522 trial did provide a rare look at concurrent radiotherapy and immunotherapy in early triple-negative breast cancer. The analysis found “no safety concerns” with concurrent radiotherapy and pembrolizumab, lead investigator Peter Schmid, MD, of Queen Mary University of London, England, told this news organization.
Research on other solid tumor types also suggests that radiotherapy “can be considered safe” alongside immunotherapy, the authors of a recent ESTRO consensus said.
Despite evidence indicating radiotherapy alongside immunotherapy can be safe in patients with breast cancer, “certain aspects, such as patient selection, total dose, and dose per fraction, remain open for debate to achieve the best therapeutic outcomes,” the ESTRO experts cautioned.
2. CDK4/6 inhibitors may be offered with radiotherapy in some settings, not others
CDK4/6 inhibitors are now standard of care for first- or second-line treatment in patients with advanced or metastatic hormone receptor–positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)–negative breast cancer.
“Unfortunately, we found no information regarding concurrent radiotherapy in the adjuvant setting” in pivotal trials for palbociclib, abemaciclib, and ribociclib, the ESTRO authors said. In the pivotal trials for palbociclib and abemaciclib, patients had to discontinue immunotherapy before initiating radiotherapy, and in the trial for ribociclib, palliative radiotherapy was allowed for relieving bone pain only.
However, in 2023, a team of experts from 12 countries attempted to piece together the available evidence, publishing a meta-analysis of 11 retrospective studies on the safety of CDK4/6 inhibitors given concurrently with radiotherapy in patients with metastatic disease.
Although most of these studies had small patient populations, the analysis revealed that CDK4/6 inhibitors given concurrently with radiotherapy in patients with metastatic breast cancer led to a similar side-effect profile to that observed in trials of the inhibitors given sequentially with adjuvant radiotherapy.
“These findings suggest that the simultaneous administration of CDK4/6 inhibitors and radiotherapy is generally well tolerated,” the ESTRO authors concluded but added that CDK4/6 inhibitors and concomitant radiotherapy should be investigated more in the adjuvant locoregional, whole brain, and intracranial stereotactic radiotherapy settings.
The expert panel did note, however, that CDK4/6 inhibitors and concomitant radiotherapy “could be offered” during palliative and ablative extracranial radiotherapy.
3. Only offer poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors plus radiotherapy in clinical trial setting
PARP inhibitors olaparib (Lynparza) and talazoprib (Talzenna) are standard of care in patients with metastatic breast cancer who have BRCA1/2 gene mutations. Olaparib is also indicated for high-risk early breast cancer following neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy.
But data on combining PARP inhibitors with radiotherapy in breast cancer also remain limited.
One ongoing phase 2 trial, comparing olaparib plus radiotherapy to radiotherapy alone in 300 people with inflammatory breast cancer, is aiming to tease out the safety of the combination and whether it improves local control in patients with aggressive disease.
“The desire is to explore the exciting possibility that low doses of PARP inhibition may radiosensitize tumor cells more than normal tissues,” Reshma Jagsi, MD, chair of the Department of Radiation Oncology at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia, who is leading the study.
Because of potential good or bad interactions between new systemic therapies and radiotherapy, “intentional trial design” is important, Dr. Jagsi said, so we “know the best way to combine treatments in practice to optimize outcomes.”
But given the evidence to date, the ESTRO experts advised waiting until “further research provides more comprehensive safety and efficacy data” in the primary, adjuvant, and metastatic settings. The experts also advised not offering PARP inhibitors and concomitant radiotherapy to treat advanced breast cancer outside of clinical trials.
4. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors (PI3K) inhibitors, mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors, and newer targeted agents should not be offered concurrently with radiotherapy
Clinical trial data on the safety of combining PI3K and mTOR inhibitors with radiation are thin, especially in advanced breast cancer. Typically, radiotherapy within 4 weeks before randomization, or 2 weeks for palliative radiation, was excluded in pivotal trials.
For this reason, the ESTRO team recommended that concurrent radiation with either PI3K inhibitors or mTOR inhibitors “should not be offered.”
ESTRO also cautioned against providing radiation concurrently with newer anti-HER2 tyrosine-kinase drugs, such as neratinib or tucatinib, or newer antibody-drug conjugates such as trastuzumab deruxtecan, until more data emerge on the safety of these combinations.
5. Combining older HER2-targeted drugs and radiotherapy generally safe
The ESTRO authors agreed that older anti-HER2 drugs trastuzumab (Herceptin), pertuzumab (Perjeta), and lapatinib (Tykerb) can be safely used concurrently with locoregional radiotherapy as well.
One of the biggest concerns in the field is how to combine radiation with systemic therapies in the setting of brain metastases, and the data on these older anti-HER2 drugs are relatively clear that it’s safe, Dr. Miller said.
For instance, in a 2019 study of 84 patients with 487 brain metastases, stereotactic radiosurgery given alongside lapatinib led to significantly higher rates of complete responses than stereotactic radiosurgery alone (35% vs 11%) with no increased risk for radiation necrosis.
The ESTRO team agreed, noting that the latest evidence supports the use of trastuzumab, pertuzumab, or lapatinib alongside radiotherapy for whole brain and ablative intracranial stereotactic radiotherapy.
As for older antibody-drug conjugates, trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) plus radiotherapy “might be considered” during adjuvant locoregional radiotherapy for breast cancer but should not be offered for whole brain and ablative intracranial stereotactic radiotherapy, the ESTRO team said.
Dr. Jagsi declared the following conflicts in a recent 2024 publication: Stock options for advisory board role in Equity Quotient; grants or contracts from Genentech; and expert witness for Kleinbard, LLC, and Hawks Quindel Law. In the Keynote-522 trial publication Dr. Schmid declared relationships with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Eisai, Hoffmann-La Roche, Genetech, Merck, Novartis, and Pfizer. Dr. Shah reported consulting for Impedimed, Videra Surgical, and PreludeDX.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
One reason is studies of new drugs typically exclude concurrent radiotherapy, said Kathy Miller, MD, a contributor to this news organization and professor of oncology and medicine at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, Indiana.
If trials evaluating new targeted therapies included concurrent radiotherapy, it would be challenging to identify whether toxicities came from the drug itself, the radiation, or the combination, Dr. Miller explained.
Given the limited evidence, “we tend to be cautious and conservative” and not combine therapies that “we don’t know are safe or appropriate for patients,” said Chirag Shah, MD, director of breast radiology at the Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio.
Below is a guide to what we do and don’t know about combining radiotherapy and systemic treatments in breast cancer.
1. Immunotherapy plus radiotherapy likely safe but evidence is limited
Safety data on combining immune checkpoint inhibitors and radiotherapy in breast cancer are limited because concurrent radiotherapy has typically been excluded in pivotal trials.
The 2020 KEYNOTE-522 trial did provide a rare look at concurrent radiotherapy and immunotherapy in early triple-negative breast cancer. The analysis found “no safety concerns” with concurrent radiotherapy and pembrolizumab, lead investigator Peter Schmid, MD, of Queen Mary University of London, England, told this news organization.
Research on other solid tumor types also suggests that radiotherapy “can be considered safe” alongside immunotherapy, the authors of a recent ESTRO consensus said.
Despite evidence indicating radiotherapy alongside immunotherapy can be safe in patients with breast cancer, “certain aspects, such as patient selection, total dose, and dose per fraction, remain open for debate to achieve the best therapeutic outcomes,” the ESTRO experts cautioned.
2. CDK4/6 inhibitors may be offered with radiotherapy in some settings, not others
CDK4/6 inhibitors are now standard of care for first- or second-line treatment in patients with advanced or metastatic hormone receptor–positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)–negative breast cancer.
“Unfortunately, we found no information regarding concurrent radiotherapy in the adjuvant setting” in pivotal trials for palbociclib, abemaciclib, and ribociclib, the ESTRO authors said. In the pivotal trials for palbociclib and abemaciclib, patients had to discontinue immunotherapy before initiating radiotherapy, and in the trial for ribociclib, palliative radiotherapy was allowed for relieving bone pain only.
However, in 2023, a team of experts from 12 countries attempted to piece together the available evidence, publishing a meta-analysis of 11 retrospective studies on the safety of CDK4/6 inhibitors given concurrently with radiotherapy in patients with metastatic disease.
Although most of these studies had small patient populations, the analysis revealed that CDK4/6 inhibitors given concurrently with radiotherapy in patients with metastatic breast cancer led to a similar side-effect profile to that observed in trials of the inhibitors given sequentially with adjuvant radiotherapy.
“These findings suggest that the simultaneous administration of CDK4/6 inhibitors and radiotherapy is generally well tolerated,” the ESTRO authors concluded but added that CDK4/6 inhibitors and concomitant radiotherapy should be investigated more in the adjuvant locoregional, whole brain, and intracranial stereotactic radiotherapy settings.
The expert panel did note, however, that CDK4/6 inhibitors and concomitant radiotherapy “could be offered” during palliative and ablative extracranial radiotherapy.
3. Only offer poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors plus radiotherapy in clinical trial setting
PARP inhibitors olaparib (Lynparza) and talazoprib (Talzenna) are standard of care in patients with metastatic breast cancer who have BRCA1/2 gene mutations. Olaparib is also indicated for high-risk early breast cancer following neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy.
But data on combining PARP inhibitors with radiotherapy in breast cancer also remain limited.
One ongoing phase 2 trial, comparing olaparib plus radiotherapy to radiotherapy alone in 300 people with inflammatory breast cancer, is aiming to tease out the safety of the combination and whether it improves local control in patients with aggressive disease.
“The desire is to explore the exciting possibility that low doses of PARP inhibition may radiosensitize tumor cells more than normal tissues,” Reshma Jagsi, MD, chair of the Department of Radiation Oncology at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia, who is leading the study.
Because of potential good or bad interactions between new systemic therapies and radiotherapy, “intentional trial design” is important, Dr. Jagsi said, so we “know the best way to combine treatments in practice to optimize outcomes.”
But given the evidence to date, the ESTRO experts advised waiting until “further research provides more comprehensive safety and efficacy data” in the primary, adjuvant, and metastatic settings. The experts also advised not offering PARP inhibitors and concomitant radiotherapy to treat advanced breast cancer outside of clinical trials.
4. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors (PI3K) inhibitors, mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors, and newer targeted agents should not be offered concurrently with radiotherapy
Clinical trial data on the safety of combining PI3K and mTOR inhibitors with radiation are thin, especially in advanced breast cancer. Typically, radiotherapy within 4 weeks before randomization, or 2 weeks for palliative radiation, was excluded in pivotal trials.
For this reason, the ESTRO team recommended that concurrent radiation with either PI3K inhibitors or mTOR inhibitors “should not be offered.”
ESTRO also cautioned against providing radiation concurrently with newer anti-HER2 tyrosine-kinase drugs, such as neratinib or tucatinib, or newer antibody-drug conjugates such as trastuzumab deruxtecan, until more data emerge on the safety of these combinations.
5. Combining older HER2-targeted drugs and radiotherapy generally safe
The ESTRO authors agreed that older anti-HER2 drugs trastuzumab (Herceptin), pertuzumab (Perjeta), and lapatinib (Tykerb) can be safely used concurrently with locoregional radiotherapy as well.
One of the biggest concerns in the field is how to combine radiation with systemic therapies in the setting of brain metastases, and the data on these older anti-HER2 drugs are relatively clear that it’s safe, Dr. Miller said.
For instance, in a 2019 study of 84 patients with 487 brain metastases, stereotactic radiosurgery given alongside lapatinib led to significantly higher rates of complete responses than stereotactic radiosurgery alone (35% vs 11%) with no increased risk for radiation necrosis.
The ESTRO team agreed, noting that the latest evidence supports the use of trastuzumab, pertuzumab, or lapatinib alongside radiotherapy for whole brain and ablative intracranial stereotactic radiotherapy.
As for older antibody-drug conjugates, trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) plus radiotherapy “might be considered” during adjuvant locoregional radiotherapy for breast cancer but should not be offered for whole brain and ablative intracranial stereotactic radiotherapy, the ESTRO team said.
Dr. Jagsi declared the following conflicts in a recent 2024 publication: Stock options for advisory board role in Equity Quotient; grants or contracts from Genentech; and expert witness for Kleinbard, LLC, and Hawks Quindel Law. In the Keynote-522 trial publication Dr. Schmid declared relationships with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Eisai, Hoffmann-La Roche, Genetech, Merck, Novartis, and Pfizer. Dr. Shah reported consulting for Impedimed, Videra Surgical, and PreludeDX.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pediatrics Takes a Hit, Whereas Emergency Medicine Recovers on Match Day
As US medical school graduates learned Friday, March 15, where they would spend their residencies, new Match Day 2024 data showed a loss of interest in pediatrics, whereas emergency medicine regained popularity after concern over last year’s unfilled positions.
Hospitals and medical groups offered 41,503 residency positions in 2024, a 3% increase from last year, according to the data released by the National Resident Matching Program.
But though the number of pediatric residency slots increased slightly from last year, 8% of available positions remained unfilled in 2024 compared with about 3% last year.
Physician leaders and policymakers alike pay keen attention to Match Day results because they can signal future shortages in certain specialties, including primary care. Unfilled slots also can raise concerns over too many residency programs in a specialty.
Medical students’ interest in pediatrics continues to decline in part because it pays less than other specialties, Bryan Carmody, MD, MPH, a pediatric nephrologist known for his medical school commentaries, told this news organization. The number of pediatric applicants from US medical schools peaked in 2015 and has fallen since, he said.
“There’s been a lot of soul searching ... this week, with people speculating about lots of (reasons),” Dr. Carmody said. “I don’t think it’s even debt. You can look at the number of unfilled positions, and it correlates with the expected earning potential of those specialties.”
Family medicine, for example, filled about 88% of its positions this year.
Ob.gyn. residencies retained their popularity despite concerns over abortion and reproductive health rights in many states. The specialty filled 99.6% of its positions, a very slight improvement over last year’s 99% rate.
Though ob.gyn. applicants might prefer programs in states where there are more liberal policies around reproductive health, many won’t be in a position where they can choose that because of the limited number of ob.gyn. slots, Dr. Carmody said.
Unfilled residency slots likely will be filled through the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP). Applicants who did not match in the first round participate in SOAP for one of the 2562 positions in 787 programs that went unfilled after the matching algorithm was processed. A total of 2575 positions were placed in SOAP, including positions in programs that did not participate in the algorithm phase of the process. There were 83 fewer positions in SOAP in 2024, a decrease of 3.1% compared with last year’s Match. More detailed data on SOAP results will be released later this year.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
As US medical school graduates learned Friday, March 15, where they would spend their residencies, new Match Day 2024 data showed a loss of interest in pediatrics, whereas emergency medicine regained popularity after concern over last year’s unfilled positions.
Hospitals and medical groups offered 41,503 residency positions in 2024, a 3% increase from last year, according to the data released by the National Resident Matching Program.
But though the number of pediatric residency slots increased slightly from last year, 8% of available positions remained unfilled in 2024 compared with about 3% last year.
Physician leaders and policymakers alike pay keen attention to Match Day results because they can signal future shortages in certain specialties, including primary care. Unfilled slots also can raise concerns over too many residency programs in a specialty.
Medical students’ interest in pediatrics continues to decline in part because it pays less than other specialties, Bryan Carmody, MD, MPH, a pediatric nephrologist known for his medical school commentaries, told this news organization. The number of pediatric applicants from US medical schools peaked in 2015 and has fallen since, he said.
“There’s been a lot of soul searching ... this week, with people speculating about lots of (reasons),” Dr. Carmody said. “I don’t think it’s even debt. You can look at the number of unfilled positions, and it correlates with the expected earning potential of those specialties.”
Family medicine, for example, filled about 88% of its positions this year.
Ob.gyn. residencies retained their popularity despite concerns over abortion and reproductive health rights in many states. The specialty filled 99.6% of its positions, a very slight improvement over last year’s 99% rate.
Though ob.gyn. applicants might prefer programs in states where there are more liberal policies around reproductive health, many won’t be in a position where they can choose that because of the limited number of ob.gyn. slots, Dr. Carmody said.
Unfilled residency slots likely will be filled through the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP). Applicants who did not match in the first round participate in SOAP for one of the 2562 positions in 787 programs that went unfilled after the matching algorithm was processed. A total of 2575 positions were placed in SOAP, including positions in programs that did not participate in the algorithm phase of the process. There were 83 fewer positions in SOAP in 2024, a decrease of 3.1% compared with last year’s Match. More detailed data on SOAP results will be released later this year.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
As US medical school graduates learned Friday, March 15, where they would spend their residencies, new Match Day 2024 data showed a loss of interest in pediatrics, whereas emergency medicine regained popularity after concern over last year’s unfilled positions.
Hospitals and medical groups offered 41,503 residency positions in 2024, a 3% increase from last year, according to the data released by the National Resident Matching Program.
But though the number of pediatric residency slots increased slightly from last year, 8% of available positions remained unfilled in 2024 compared with about 3% last year.
Physician leaders and policymakers alike pay keen attention to Match Day results because they can signal future shortages in certain specialties, including primary care. Unfilled slots also can raise concerns over too many residency programs in a specialty.
Medical students’ interest in pediatrics continues to decline in part because it pays less than other specialties, Bryan Carmody, MD, MPH, a pediatric nephrologist known for his medical school commentaries, told this news organization. The number of pediatric applicants from US medical schools peaked in 2015 and has fallen since, he said.
“There’s been a lot of soul searching ... this week, with people speculating about lots of (reasons),” Dr. Carmody said. “I don’t think it’s even debt. You can look at the number of unfilled positions, and it correlates with the expected earning potential of those specialties.”
Family medicine, for example, filled about 88% of its positions this year.
Ob.gyn. residencies retained their popularity despite concerns over abortion and reproductive health rights in many states. The specialty filled 99.6% of its positions, a very slight improvement over last year’s 99% rate.
Though ob.gyn. applicants might prefer programs in states where there are more liberal policies around reproductive health, many won’t be in a position where they can choose that because of the limited number of ob.gyn. slots, Dr. Carmody said.
Unfilled residency slots likely will be filled through the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP). Applicants who did not match in the first round participate in SOAP for one of the 2562 positions in 787 programs that went unfilled after the matching algorithm was processed. A total of 2575 positions were placed in SOAP, including positions in programs that did not participate in the algorithm phase of the process. There were 83 fewer positions in SOAP in 2024, a decrease of 3.1% compared with last year’s Match. More detailed data on SOAP results will be released later this year.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In Unexpected Finding, Clemastine Fumarate Linked to Worsening Symptoms in MS
WEST PALM BEACH, FLORIDA — An over-the-counter antihistamine that had shown potential for treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS) in animal studies was linked to significant worsening of symptoms in humans, new trial data suggested.
,” investigators said.
The inexpensive antihistamine had been touted as a potential MS treatment following promising early findings, and some patients are reportedly taking it on an off-label basis. It was one of four approved drugs in an ongoing trial led by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) to investigate the drugs’ efficacy in the treatment of MS.
“Most patients on the other drugs progressed much slower compared to their baseline,” said senior investigator Bibi Bielekova, MD, with NIAID. “When we compare the results in clemastine arm with all other patients treated with the remaining drugs, the probability that our patients progressed by chance is lower than 0.01%.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
TRAP-MS Trial
The OTC antihistamine clemastine has been available for decades under the brand names Tavist and Dayhist. In addition to findings from mouse studies, results from a small clinical trial reported in 2017 suggested that clemastine may promote myelin repair. Other animal studies and another small study with healthy volunteers also suggested the drug may reduce immune activity.
Clemastine fumarate is one of four drugs in the ongoing TRAP-MS phase 1/2 trial, which is sponsored by NIAID. The study is designed to determine what effects, if any, the drugs have on MS biomarkers either alone or in combination.
Other drugs in the study include the diabetes drug pioglitazone (Actos), the muscle relaxant dantrolene (Ryanodex, Revonto, and Dantrium), and the idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis drug pirfenidone (Pirespa).
An estimated 250 adults with MS were expected to be enrolled in the trial, which began in 2017 and is scheduled to reach its primary completion in 2025.
Per the study protocol, nine patients in the clemastine arm were assigned to receive 8 mg/d (divided into three doses of 2, 2, and 4 mg). Cerebrospinal fluid samples were collected at baseline and 6 months after clemastine treatment began.
Worsening Symptoms
The three patients whose worsening symptoms triggered stopping criteria when they demonstrated increased disability five times faster than their 18-month baseline, researchers reported.
These participants had increased levels of C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate and gained weight, which study authors said were “suggestive of systemic pro-inflammatory state.”
“We found that clemastine treatment causes significant changes in purinergic metabolism,” lead author Joanna Kocot, PhD, a NIAID fellow, said during the ACTRIMS presentation. “We also confirmed that this toxic effect of clemastine was because of pyroptosis,” a form of cell death.
None of the remaining 55 patients treated with other TRAP-MS therapies triggered safety criteria, which study authors said offered “evidence for clemastine toxicity.”
Demographic information was not provided, but the patients on clemastine with worsening symptoms were older, more disabled, and more obese than the other six patients in the clemastine arm, Dr. Bielekova said during the conference presentation.
‘Undesirable’ or ‘Premature’?
Commenting on the findings, Paul J. Tesar, PhD, professor of innovative therapeutics at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine in Cleveland, said the findings are unexpected.
“Compared to previous trials, the TRAP-MS trial included different patient populations and treated them with clemastine for a longer time period, so it is hard to make direct comparisons,” said Dr. Tesar, who studies MS and did not take part in the new study. “From the limited data disclosed thus far, it does seem likely that clemastine is causing toxicity, possibly through increased inflammation, and accelerating disease progression.”
In the big picture, he said, “while clemastine trials have been important steps toward a first-in-class remyelinating drug, the promiscuous nature of clemastine — it binds to many protein targets — and its known side effects make it undesirable as a mainstay treatment for people with multiple sclerosis.”
Hundreds or perhaps thousands of patients with MS may already take the drug because of the early positive findings, said Ari Green, MD, medical director of the University of California at San Francisco Multiple Sclerosis Center and lead author of the initial 2017 clinical trial on clemastine and myelin repair.
Dr. Green, who was not involved in the new study, said he is skeptical of the findings.
“We can’t conclude much about an effect based on three patients, and the risk that this is a chance effect is extraordinarily high,” he said. “It’s premature to make any attribution of what they saw to clemastine itself.”
Dr. Bielekova disagreed, and said she stands by the findings.
The pyroptosis score, derived from CSF biomarkers, was elevated in MS and higher in progressive MS than in relapsing-remitting MS, she said, adding that pyroptosis correlates with how fast people with MS accumulate disability.
“From all drugs we tested, only clemastine increased this CSF pyroptosis score,” Dr. Bielekova said.
Regardless, Dr. Green urged caution when considering whether to use the drug.
“Nobody should take clemastine without the supervision of a doctor,” he said. “It’s actually best done in the context of clinical trials.”
NIAID funded the study, and the authors had no disclosures. Dr. Tesar is cofounder of Convelo Therapeutics, a biotechnology company developing remyelinating therapeutics for MS. Dr. Green said he is conducting studies related to clemastine, but they do not have industry funding.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WEST PALM BEACH, FLORIDA — An over-the-counter antihistamine that had shown potential for treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS) in animal studies was linked to significant worsening of symptoms in humans, new trial data suggested.
,” investigators said.
The inexpensive antihistamine had been touted as a potential MS treatment following promising early findings, and some patients are reportedly taking it on an off-label basis. It was one of four approved drugs in an ongoing trial led by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) to investigate the drugs’ efficacy in the treatment of MS.
“Most patients on the other drugs progressed much slower compared to their baseline,” said senior investigator Bibi Bielekova, MD, with NIAID. “When we compare the results in clemastine arm with all other patients treated with the remaining drugs, the probability that our patients progressed by chance is lower than 0.01%.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
TRAP-MS Trial
The OTC antihistamine clemastine has been available for decades under the brand names Tavist and Dayhist. In addition to findings from mouse studies, results from a small clinical trial reported in 2017 suggested that clemastine may promote myelin repair. Other animal studies and another small study with healthy volunteers also suggested the drug may reduce immune activity.
Clemastine fumarate is one of four drugs in the ongoing TRAP-MS phase 1/2 trial, which is sponsored by NIAID. The study is designed to determine what effects, if any, the drugs have on MS biomarkers either alone or in combination.
Other drugs in the study include the diabetes drug pioglitazone (Actos), the muscle relaxant dantrolene (Ryanodex, Revonto, and Dantrium), and the idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis drug pirfenidone (Pirespa).
An estimated 250 adults with MS were expected to be enrolled in the trial, which began in 2017 and is scheduled to reach its primary completion in 2025.
Per the study protocol, nine patients in the clemastine arm were assigned to receive 8 mg/d (divided into three doses of 2, 2, and 4 mg). Cerebrospinal fluid samples were collected at baseline and 6 months after clemastine treatment began.
Worsening Symptoms
The three patients whose worsening symptoms triggered stopping criteria when they demonstrated increased disability five times faster than their 18-month baseline, researchers reported.
These participants had increased levels of C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate and gained weight, which study authors said were “suggestive of systemic pro-inflammatory state.”
“We found that clemastine treatment causes significant changes in purinergic metabolism,” lead author Joanna Kocot, PhD, a NIAID fellow, said during the ACTRIMS presentation. “We also confirmed that this toxic effect of clemastine was because of pyroptosis,” a form of cell death.
None of the remaining 55 patients treated with other TRAP-MS therapies triggered safety criteria, which study authors said offered “evidence for clemastine toxicity.”
Demographic information was not provided, but the patients on clemastine with worsening symptoms were older, more disabled, and more obese than the other six patients in the clemastine arm, Dr. Bielekova said during the conference presentation.
‘Undesirable’ or ‘Premature’?
Commenting on the findings, Paul J. Tesar, PhD, professor of innovative therapeutics at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine in Cleveland, said the findings are unexpected.
“Compared to previous trials, the TRAP-MS trial included different patient populations and treated them with clemastine for a longer time period, so it is hard to make direct comparisons,” said Dr. Tesar, who studies MS and did not take part in the new study. “From the limited data disclosed thus far, it does seem likely that clemastine is causing toxicity, possibly through increased inflammation, and accelerating disease progression.”
In the big picture, he said, “while clemastine trials have been important steps toward a first-in-class remyelinating drug, the promiscuous nature of clemastine — it binds to many protein targets — and its known side effects make it undesirable as a mainstay treatment for people with multiple sclerosis.”
Hundreds or perhaps thousands of patients with MS may already take the drug because of the early positive findings, said Ari Green, MD, medical director of the University of California at San Francisco Multiple Sclerosis Center and lead author of the initial 2017 clinical trial on clemastine and myelin repair.
Dr. Green, who was not involved in the new study, said he is skeptical of the findings.
“We can’t conclude much about an effect based on three patients, and the risk that this is a chance effect is extraordinarily high,” he said. “It’s premature to make any attribution of what they saw to clemastine itself.”
Dr. Bielekova disagreed, and said she stands by the findings.
The pyroptosis score, derived from CSF biomarkers, was elevated in MS and higher in progressive MS than in relapsing-remitting MS, she said, adding that pyroptosis correlates with how fast people with MS accumulate disability.
“From all drugs we tested, only clemastine increased this CSF pyroptosis score,” Dr. Bielekova said.
Regardless, Dr. Green urged caution when considering whether to use the drug.
“Nobody should take clemastine without the supervision of a doctor,” he said. “It’s actually best done in the context of clinical trials.”
NIAID funded the study, and the authors had no disclosures. Dr. Tesar is cofounder of Convelo Therapeutics, a biotechnology company developing remyelinating therapeutics for MS. Dr. Green said he is conducting studies related to clemastine, but they do not have industry funding.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WEST PALM BEACH, FLORIDA — An over-the-counter antihistamine that had shown potential for treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS) in animal studies was linked to significant worsening of symptoms in humans, new trial data suggested.
,” investigators said.
The inexpensive antihistamine had been touted as a potential MS treatment following promising early findings, and some patients are reportedly taking it on an off-label basis. It was one of four approved drugs in an ongoing trial led by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) to investigate the drugs’ efficacy in the treatment of MS.
“Most patients on the other drugs progressed much slower compared to their baseline,” said senior investigator Bibi Bielekova, MD, with NIAID. “When we compare the results in clemastine arm with all other patients treated with the remaining drugs, the probability that our patients progressed by chance is lower than 0.01%.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
TRAP-MS Trial
The OTC antihistamine clemastine has been available for decades under the brand names Tavist and Dayhist. In addition to findings from mouse studies, results from a small clinical trial reported in 2017 suggested that clemastine may promote myelin repair. Other animal studies and another small study with healthy volunteers also suggested the drug may reduce immune activity.
Clemastine fumarate is one of four drugs in the ongoing TRAP-MS phase 1/2 trial, which is sponsored by NIAID. The study is designed to determine what effects, if any, the drugs have on MS biomarkers either alone or in combination.
Other drugs in the study include the diabetes drug pioglitazone (Actos), the muscle relaxant dantrolene (Ryanodex, Revonto, and Dantrium), and the idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis drug pirfenidone (Pirespa).
An estimated 250 adults with MS were expected to be enrolled in the trial, which began in 2017 and is scheduled to reach its primary completion in 2025.
Per the study protocol, nine patients in the clemastine arm were assigned to receive 8 mg/d (divided into three doses of 2, 2, and 4 mg). Cerebrospinal fluid samples were collected at baseline and 6 months after clemastine treatment began.
Worsening Symptoms
The three patients whose worsening symptoms triggered stopping criteria when they demonstrated increased disability five times faster than their 18-month baseline, researchers reported.
These participants had increased levels of C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate and gained weight, which study authors said were “suggestive of systemic pro-inflammatory state.”
“We found that clemastine treatment causes significant changes in purinergic metabolism,” lead author Joanna Kocot, PhD, a NIAID fellow, said during the ACTRIMS presentation. “We also confirmed that this toxic effect of clemastine was because of pyroptosis,” a form of cell death.
None of the remaining 55 patients treated with other TRAP-MS therapies triggered safety criteria, which study authors said offered “evidence for clemastine toxicity.”
Demographic information was not provided, but the patients on clemastine with worsening symptoms were older, more disabled, and more obese than the other six patients in the clemastine arm, Dr. Bielekova said during the conference presentation.
‘Undesirable’ or ‘Premature’?
Commenting on the findings, Paul J. Tesar, PhD, professor of innovative therapeutics at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine in Cleveland, said the findings are unexpected.
“Compared to previous trials, the TRAP-MS trial included different patient populations and treated them with clemastine for a longer time period, so it is hard to make direct comparisons,” said Dr. Tesar, who studies MS and did not take part in the new study. “From the limited data disclosed thus far, it does seem likely that clemastine is causing toxicity, possibly through increased inflammation, and accelerating disease progression.”
In the big picture, he said, “while clemastine trials have been important steps toward a first-in-class remyelinating drug, the promiscuous nature of clemastine — it binds to many protein targets — and its known side effects make it undesirable as a mainstay treatment for people with multiple sclerosis.”
Hundreds or perhaps thousands of patients with MS may already take the drug because of the early positive findings, said Ari Green, MD, medical director of the University of California at San Francisco Multiple Sclerosis Center and lead author of the initial 2017 clinical trial on clemastine and myelin repair.
Dr. Green, who was not involved in the new study, said he is skeptical of the findings.
“We can’t conclude much about an effect based on three patients, and the risk that this is a chance effect is extraordinarily high,” he said. “It’s premature to make any attribution of what they saw to clemastine itself.”
Dr. Bielekova disagreed, and said she stands by the findings.
The pyroptosis score, derived from CSF biomarkers, was elevated in MS and higher in progressive MS than in relapsing-remitting MS, she said, adding that pyroptosis correlates with how fast people with MS accumulate disability.
“From all drugs we tested, only clemastine increased this CSF pyroptosis score,” Dr. Bielekova said.
Regardless, Dr. Green urged caution when considering whether to use the drug.
“Nobody should take clemastine without the supervision of a doctor,” he said. “It’s actually best done in the context of clinical trials.”
NIAID funded the study, and the authors had no disclosures. Dr. Tesar is cofounder of Convelo Therapeutics, a biotechnology company developing remyelinating therapeutics for MS. Dr. Green said he is conducting studies related to clemastine, but they do not have industry funding.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2024
FDA Approves New Esophageal Cancer Drug
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved tislelizumab-jsgr (Tevimbra, BeiGene Ltd.) as second-line monotherapy for certain adult patients with unresectable or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
Specifically, the novel checkpoint inhibitor is approved for patients with ESCC after prior systemic chemotherapy that did not include a programmed death–ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor.
Approval was based on findings from the open-label, phase 3 RATIONALE 302 trial showing a statistically significant and clinically meaningful overall survival benefit with tislelizumab vs investigator’s choice of chemotherapy.
Study participants included 512 adults enrolled at 123 research sites in 11 countries in Europe, Asia, and North America. Patients were randomly assigned to receive intravenous tislelizumab, a humanized immunoglobulin G4 anti-programmed cell death protein 1 monoclonal antibody, at a dose of 200 mg every 3 weeks or investigator’s choice of standard chemotherapy with paclitaxel, docetaxel, or irinotecan until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or study withdrawal.
Median overall survival in the intention-to-treat population, the primary study endpoint, was 8.6 months vs 6.3 months in the chemotherapy arms (hazard ratio [HR], 0.70). The survival benefit was observed across predefined subgroups, including baseline PD-L1 status and region. The new agent was also associated with improved overall response rate (20.4% vs 9.8%) and more durable response (median duration of response of 7.1 vs 4.0 months; HR, 0.42) compared with chemotherapy.
The most common adverse reactions for tislelizumab, each occurring in at least 20% of treated patients, included increased glucose and decreased hemoglobin, lymphocytes, sodium, and albumin as well as increased alkaline phosphatase, anemia, fatigue, increased aspartate aminotransferase, musculoskeletal pain, decreased weight, increased alanine aminotransferase, and cough.
Fewer patients in the tislelizumab arm experienced grade 3 or greater treatment-emergent adverse events compared with the chemotherapy arm (46% vs 68%, respectively), and fewer patients discontinued tislelizumab vs chemotherapy due to such an event (7% vs 14%).
“Patients diagnosed with advanced or metastasized ESCC, the most common histologic subtype of esophageal cancer, often progress following initial therapy and are in need of new options,” Syma Iqbal, MD, of the Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, stated in the BeiGene release. “The RATIONALE 302 trial showed that patients with previously treated ESCC who received Tevimbra saw a clinically meaningful survival benefit, highlighting its potential as an important treatment option for these patients.”
The approval, which was deferred in 2022 due to COVID-19-related restrictions, marks the first for the agent in the United States. Tislelizumab should be available in the United States in the second half of 2024, BeiGene noted.
The FDA is also reviewing a Biologics License Application for the agent as a first-line treatment for patients with unresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic ESCC and for those with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma, BeiGene announced in a press release.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved tislelizumab-jsgr (Tevimbra, BeiGene Ltd.) as second-line monotherapy for certain adult patients with unresectable or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
Specifically, the novel checkpoint inhibitor is approved for patients with ESCC after prior systemic chemotherapy that did not include a programmed death–ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor.
Approval was based on findings from the open-label, phase 3 RATIONALE 302 trial showing a statistically significant and clinically meaningful overall survival benefit with tislelizumab vs investigator’s choice of chemotherapy.
Study participants included 512 adults enrolled at 123 research sites in 11 countries in Europe, Asia, and North America. Patients were randomly assigned to receive intravenous tislelizumab, a humanized immunoglobulin G4 anti-programmed cell death protein 1 monoclonal antibody, at a dose of 200 mg every 3 weeks or investigator’s choice of standard chemotherapy with paclitaxel, docetaxel, or irinotecan until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or study withdrawal.
Median overall survival in the intention-to-treat population, the primary study endpoint, was 8.6 months vs 6.3 months in the chemotherapy arms (hazard ratio [HR], 0.70). The survival benefit was observed across predefined subgroups, including baseline PD-L1 status and region. The new agent was also associated with improved overall response rate (20.4% vs 9.8%) and more durable response (median duration of response of 7.1 vs 4.0 months; HR, 0.42) compared with chemotherapy.
The most common adverse reactions for tislelizumab, each occurring in at least 20% of treated patients, included increased glucose and decreased hemoglobin, lymphocytes, sodium, and albumin as well as increased alkaline phosphatase, anemia, fatigue, increased aspartate aminotransferase, musculoskeletal pain, decreased weight, increased alanine aminotransferase, and cough.
Fewer patients in the tislelizumab arm experienced grade 3 or greater treatment-emergent adverse events compared with the chemotherapy arm (46% vs 68%, respectively), and fewer patients discontinued tislelizumab vs chemotherapy due to such an event (7% vs 14%).
“Patients diagnosed with advanced or metastasized ESCC, the most common histologic subtype of esophageal cancer, often progress following initial therapy and are in need of new options,” Syma Iqbal, MD, of the Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, stated in the BeiGene release. “The RATIONALE 302 trial showed that patients with previously treated ESCC who received Tevimbra saw a clinically meaningful survival benefit, highlighting its potential as an important treatment option for these patients.”
The approval, which was deferred in 2022 due to COVID-19-related restrictions, marks the first for the agent in the United States. Tislelizumab should be available in the United States in the second half of 2024, BeiGene noted.
The FDA is also reviewing a Biologics License Application for the agent as a first-line treatment for patients with unresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic ESCC and for those with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma, BeiGene announced in a press release.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved tislelizumab-jsgr (Tevimbra, BeiGene Ltd.) as second-line monotherapy for certain adult patients with unresectable or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
Specifically, the novel checkpoint inhibitor is approved for patients with ESCC after prior systemic chemotherapy that did not include a programmed death–ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor.
Approval was based on findings from the open-label, phase 3 RATIONALE 302 trial showing a statistically significant and clinically meaningful overall survival benefit with tislelizumab vs investigator’s choice of chemotherapy.
Study participants included 512 adults enrolled at 123 research sites in 11 countries in Europe, Asia, and North America. Patients were randomly assigned to receive intravenous tislelizumab, a humanized immunoglobulin G4 anti-programmed cell death protein 1 monoclonal antibody, at a dose of 200 mg every 3 weeks or investigator’s choice of standard chemotherapy with paclitaxel, docetaxel, or irinotecan until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or study withdrawal.
Median overall survival in the intention-to-treat population, the primary study endpoint, was 8.6 months vs 6.3 months in the chemotherapy arms (hazard ratio [HR], 0.70). The survival benefit was observed across predefined subgroups, including baseline PD-L1 status and region. The new agent was also associated with improved overall response rate (20.4% vs 9.8%) and more durable response (median duration of response of 7.1 vs 4.0 months; HR, 0.42) compared with chemotherapy.
The most common adverse reactions for tislelizumab, each occurring in at least 20% of treated patients, included increased glucose and decreased hemoglobin, lymphocytes, sodium, and albumin as well as increased alkaline phosphatase, anemia, fatigue, increased aspartate aminotransferase, musculoskeletal pain, decreased weight, increased alanine aminotransferase, and cough.
Fewer patients in the tislelizumab arm experienced grade 3 or greater treatment-emergent adverse events compared with the chemotherapy arm (46% vs 68%, respectively), and fewer patients discontinued tislelizumab vs chemotherapy due to such an event (7% vs 14%).
“Patients diagnosed with advanced or metastasized ESCC, the most common histologic subtype of esophageal cancer, often progress following initial therapy and are in need of new options,” Syma Iqbal, MD, of the Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, stated in the BeiGene release. “The RATIONALE 302 trial showed that patients with previously treated ESCC who received Tevimbra saw a clinically meaningful survival benefit, highlighting its potential as an important treatment option for these patients.”
The approval, which was deferred in 2022 due to COVID-19-related restrictions, marks the first for the agent in the United States. Tislelizumab should be available in the United States in the second half of 2024, BeiGene noted.
The FDA is also reviewing a Biologics License Application for the agent as a first-line treatment for patients with unresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic ESCC and for those with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma, BeiGene announced in a press release.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.