User login
Common meds link to sudden cardiac arrest in type 2 diabetes
HAMBURG, Germany – , shows the first such analysis of real-world, primary care data.
People with type 2 diabetes who do not have a history of CVD have almost three times the risk of SCA if they take antipsychotic medications and nearly double the risk if they take certain antibiotics that prolong the QT interval, notably, macrolides and fluoroquinolones.
“These data show that commonly prescribed drugs - antipsychotic medications, used by about 3% of people with type 2 diabetes, and antibiotics, taken by 5% to 10%, convey an increased risk of sudden cardiac arrest in those without a history of cardiovascular disease,” said Peter Harms, MSc, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Another drug associated with an increase in SCA among patients with diabetes was domperidone, an antinausea medication.
“Perhaps these drugs could be avoided in some cases, and GPs should be more aware of the possible consequences of their use,” he added. “If the patient has type 2 diabetes, then maybe it’s better to avoid some of these medications and try and cope without them, or at least find an alternative antibiotic.”
Mr. Harms, an epidemiologist from Amsterdam University Medical Centers, highlighted that their study was unique because the investigators drew upon primary care data. “These data are extensive, and we find a lot of associations which are very real.”
SCA is associated with 50% of all cardiac deaths and accounts for 20% of all mortality in high-income countries. Of those people who experience SCA, 80% of cases prove fatal.
“As the name suggests, it is difficult to predict because it is sudden, especially in people without a cardiovascular disease history,” Mr. Harms pointed out in an interview with this news organization. He highlighted that “around half of those who experience SCA, often between the ages of 40 and 60 years, have never seen a cardiologist, but many do have type 2 diabetes.
“We need to better understand how to recognize people at risk of SCA, know who to watch and how to prevent these events,” he emphasized.
Vladimira Fejfarova, MD, comoderated the session and commented on the study. “From the clinical point of view, it’s necessary to evaluate risk factors that can contribute to sudden cardiac arrest.”
Overall, the researchers found that, among people with type 2 diabetes who do not have a history of CVD, hypoglycemia, severe hypertension, dyslipidemia, and use of QTc-prolonging medications are associated with SCA risk. Among people with type 2 diabetes and CVD, albuminuria and heart failure are associated with SCA risk.
Dr. Fejfarova added: “With type 2 diabetes and also type 1, we need to look more at adverse events, especially when treating infections with macrolides, but also mycotic infections, because antimycotic drugs are known to influence QT intervals that could contribute to sudden cardiac arrest.
“We need to be more cautious with prescribing certain antibiotics that have these side effects in our patients with diabetes,” asserted Dr. Fejfarova, from the Diabetes Centre, Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Prague.
Type 2 diabetes doubles the risk of SCA
The researcher decided to investigate the population of people with type 2 diabetes because their risk of SCD is around twice that of those without type 2 diabetes. Because these patients have relatively frequent checkups with general practitioners, Mr. Harms turned to primary care databases that contained comprehensive and relatively routine information on risk indicators.
Longitudinal associations between clinical characteristics of 3,919 patients with type 2 diabetes – both those with and those without a history of CVD – and SCA (a total of 689 patients) were determined.
Cases were found in the AmsteRdam REsuscitation STtudies (ARREST) registry of out-of-hospital resuscitation attempts by emergency medical services in the Dutch region of Noord-Holland from 2010 to 2019. Case patients were matched with up to five control patients. The control group comprised people with type 2 diabetes who had not experienced an SCA. Control patients were sourced from the same primary care practices who were of similar age and sex. Clinical measurements, including blood pressure and blood glucose readings, medication use, and medical history for the 5 years leading up to an SCA, were obtained from general practice records. A multivariable analysis was performed, and results were stratified for people with and for those without a history of CVD.
Of particular interest were drugs that interfere with cardiac function, including some prokinetic, antibiotic, and antipsychotic medications. All of the drugs are known to be associated with a change in QTc prolongation. Examples include domperidone (QTc-prolonging prokinetic), macrolides and fluoroquinolones (QTc-prolonging antibiotics), and haloperidol (a QTc-prolonging antipsychotic).
Antibiotic and antipsychotic use might contribute to SCA in T2D
Case patients and control patients were similar in age, hemoglobin A1c level, and other characteristics with the exception that more patients with SCA had a history of CVD (40.0% vs. 29.4%).
“Looking at the associations in the overall population, insulin use was strongly associated with SCA risk [hazard ratio, 2.38] and perhaps this was an indicator of severity of type 2 diabetes,” remarked Mr. Harms. “Also, unsurprisingly, a history of arrhythmia [HR, 1.68] and, more surprisingly, prokinetic drug use [HR, 1.66; 95% confidence interval, 1.20-2.31], specifically those known for QTc-prolongation, were associated with SCA.”
Among people who had experienced an SCA and who did not have a history of CVD (337 case patients/2,023 control patients), QTc-prolonging antipsychotic medication use was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.87, and antibiotic medication use was associated with SCA at an HR of 1.66. A low fasting glucose level (< 4.5 mmol/mol) was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.5; severely high systolic blood pressure (> 180 mm Hg) was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.21; low HDL cholesterol level, with an HR of 1.35; and high LDL cholesterol level (> 2.6 mmol/L), with an HR of 1.64.
Among people with a history of CVD (352 case patients/1,207 control patients), associations between albuminuria and SCA were moderate (HR, 1.54) and severe (HR, 1.55); heart failure was associated with SCA at an HR of 1.85 (95% CI, 1.50-2.29).
Comoderator Dr. Fejfarova added that, in addition to the findings from Dr. Harms’ study, other research presented in the same session highlighted the importance of checking patients for the presence of arrhythmias that could lead to the development of atrioventricular blocks, sinus node diseases, and SCA.
Mr. Harms and Dr. Fejfarova have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HAMBURG, Germany – , shows the first such analysis of real-world, primary care data.
People with type 2 diabetes who do not have a history of CVD have almost three times the risk of SCA if they take antipsychotic medications and nearly double the risk if they take certain antibiotics that prolong the QT interval, notably, macrolides and fluoroquinolones.
“These data show that commonly prescribed drugs - antipsychotic medications, used by about 3% of people with type 2 diabetes, and antibiotics, taken by 5% to 10%, convey an increased risk of sudden cardiac arrest in those without a history of cardiovascular disease,” said Peter Harms, MSc, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Another drug associated with an increase in SCA among patients with diabetes was domperidone, an antinausea medication.
“Perhaps these drugs could be avoided in some cases, and GPs should be more aware of the possible consequences of their use,” he added. “If the patient has type 2 diabetes, then maybe it’s better to avoid some of these medications and try and cope without them, or at least find an alternative antibiotic.”
Mr. Harms, an epidemiologist from Amsterdam University Medical Centers, highlighted that their study was unique because the investigators drew upon primary care data. “These data are extensive, and we find a lot of associations which are very real.”
SCA is associated with 50% of all cardiac deaths and accounts for 20% of all mortality in high-income countries. Of those people who experience SCA, 80% of cases prove fatal.
“As the name suggests, it is difficult to predict because it is sudden, especially in people without a cardiovascular disease history,” Mr. Harms pointed out in an interview with this news organization. He highlighted that “around half of those who experience SCA, often between the ages of 40 and 60 years, have never seen a cardiologist, but many do have type 2 diabetes.
“We need to better understand how to recognize people at risk of SCA, know who to watch and how to prevent these events,” he emphasized.
Vladimira Fejfarova, MD, comoderated the session and commented on the study. “From the clinical point of view, it’s necessary to evaluate risk factors that can contribute to sudden cardiac arrest.”
Overall, the researchers found that, among people with type 2 diabetes who do not have a history of CVD, hypoglycemia, severe hypertension, dyslipidemia, and use of QTc-prolonging medications are associated with SCA risk. Among people with type 2 diabetes and CVD, albuminuria and heart failure are associated with SCA risk.
Dr. Fejfarova added: “With type 2 diabetes and also type 1, we need to look more at adverse events, especially when treating infections with macrolides, but also mycotic infections, because antimycotic drugs are known to influence QT intervals that could contribute to sudden cardiac arrest.
“We need to be more cautious with prescribing certain antibiotics that have these side effects in our patients with diabetes,” asserted Dr. Fejfarova, from the Diabetes Centre, Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Prague.
Type 2 diabetes doubles the risk of SCA
The researcher decided to investigate the population of people with type 2 diabetes because their risk of SCD is around twice that of those without type 2 diabetes. Because these patients have relatively frequent checkups with general practitioners, Mr. Harms turned to primary care databases that contained comprehensive and relatively routine information on risk indicators.
Longitudinal associations between clinical characteristics of 3,919 patients with type 2 diabetes – both those with and those without a history of CVD – and SCA (a total of 689 patients) were determined.
Cases were found in the AmsteRdam REsuscitation STtudies (ARREST) registry of out-of-hospital resuscitation attempts by emergency medical services in the Dutch region of Noord-Holland from 2010 to 2019. Case patients were matched with up to five control patients. The control group comprised people with type 2 diabetes who had not experienced an SCA. Control patients were sourced from the same primary care practices who were of similar age and sex. Clinical measurements, including blood pressure and blood glucose readings, medication use, and medical history for the 5 years leading up to an SCA, were obtained from general practice records. A multivariable analysis was performed, and results were stratified for people with and for those without a history of CVD.
Of particular interest were drugs that interfere with cardiac function, including some prokinetic, antibiotic, and antipsychotic medications. All of the drugs are known to be associated with a change in QTc prolongation. Examples include domperidone (QTc-prolonging prokinetic), macrolides and fluoroquinolones (QTc-prolonging antibiotics), and haloperidol (a QTc-prolonging antipsychotic).
Antibiotic and antipsychotic use might contribute to SCA in T2D
Case patients and control patients were similar in age, hemoglobin A1c level, and other characteristics with the exception that more patients with SCA had a history of CVD (40.0% vs. 29.4%).
“Looking at the associations in the overall population, insulin use was strongly associated with SCA risk [hazard ratio, 2.38] and perhaps this was an indicator of severity of type 2 diabetes,” remarked Mr. Harms. “Also, unsurprisingly, a history of arrhythmia [HR, 1.68] and, more surprisingly, prokinetic drug use [HR, 1.66; 95% confidence interval, 1.20-2.31], specifically those known for QTc-prolongation, were associated with SCA.”
Among people who had experienced an SCA and who did not have a history of CVD (337 case patients/2,023 control patients), QTc-prolonging antipsychotic medication use was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.87, and antibiotic medication use was associated with SCA at an HR of 1.66. A low fasting glucose level (< 4.5 mmol/mol) was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.5; severely high systolic blood pressure (> 180 mm Hg) was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.21; low HDL cholesterol level, with an HR of 1.35; and high LDL cholesterol level (> 2.6 mmol/L), with an HR of 1.64.
Among people with a history of CVD (352 case patients/1,207 control patients), associations between albuminuria and SCA were moderate (HR, 1.54) and severe (HR, 1.55); heart failure was associated with SCA at an HR of 1.85 (95% CI, 1.50-2.29).
Comoderator Dr. Fejfarova added that, in addition to the findings from Dr. Harms’ study, other research presented in the same session highlighted the importance of checking patients for the presence of arrhythmias that could lead to the development of atrioventricular blocks, sinus node diseases, and SCA.
Mr. Harms and Dr. Fejfarova have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HAMBURG, Germany – , shows the first such analysis of real-world, primary care data.
People with type 2 diabetes who do not have a history of CVD have almost three times the risk of SCA if they take antipsychotic medications and nearly double the risk if they take certain antibiotics that prolong the QT interval, notably, macrolides and fluoroquinolones.
“These data show that commonly prescribed drugs - antipsychotic medications, used by about 3% of people with type 2 diabetes, and antibiotics, taken by 5% to 10%, convey an increased risk of sudden cardiac arrest in those without a history of cardiovascular disease,” said Peter Harms, MSc, who presented the study at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Another drug associated with an increase in SCA among patients with diabetes was domperidone, an antinausea medication.
“Perhaps these drugs could be avoided in some cases, and GPs should be more aware of the possible consequences of their use,” he added. “If the patient has type 2 diabetes, then maybe it’s better to avoid some of these medications and try and cope without them, or at least find an alternative antibiotic.”
Mr. Harms, an epidemiologist from Amsterdam University Medical Centers, highlighted that their study was unique because the investigators drew upon primary care data. “These data are extensive, and we find a lot of associations which are very real.”
SCA is associated with 50% of all cardiac deaths and accounts for 20% of all mortality in high-income countries. Of those people who experience SCA, 80% of cases prove fatal.
“As the name suggests, it is difficult to predict because it is sudden, especially in people without a cardiovascular disease history,” Mr. Harms pointed out in an interview with this news organization. He highlighted that “around half of those who experience SCA, often between the ages of 40 and 60 years, have never seen a cardiologist, but many do have type 2 diabetes.
“We need to better understand how to recognize people at risk of SCA, know who to watch and how to prevent these events,” he emphasized.
Vladimira Fejfarova, MD, comoderated the session and commented on the study. “From the clinical point of view, it’s necessary to evaluate risk factors that can contribute to sudden cardiac arrest.”
Overall, the researchers found that, among people with type 2 diabetes who do not have a history of CVD, hypoglycemia, severe hypertension, dyslipidemia, and use of QTc-prolonging medications are associated with SCA risk. Among people with type 2 diabetes and CVD, albuminuria and heart failure are associated with SCA risk.
Dr. Fejfarova added: “With type 2 diabetes and also type 1, we need to look more at adverse events, especially when treating infections with macrolides, but also mycotic infections, because antimycotic drugs are known to influence QT intervals that could contribute to sudden cardiac arrest.
“We need to be more cautious with prescribing certain antibiotics that have these side effects in our patients with diabetes,” asserted Dr. Fejfarova, from the Diabetes Centre, Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Prague.
Type 2 diabetes doubles the risk of SCA
The researcher decided to investigate the population of people with type 2 diabetes because their risk of SCD is around twice that of those without type 2 diabetes. Because these patients have relatively frequent checkups with general practitioners, Mr. Harms turned to primary care databases that contained comprehensive and relatively routine information on risk indicators.
Longitudinal associations between clinical characteristics of 3,919 patients with type 2 diabetes – both those with and those without a history of CVD – and SCA (a total of 689 patients) were determined.
Cases were found in the AmsteRdam REsuscitation STtudies (ARREST) registry of out-of-hospital resuscitation attempts by emergency medical services in the Dutch region of Noord-Holland from 2010 to 2019. Case patients were matched with up to five control patients. The control group comprised people with type 2 diabetes who had not experienced an SCA. Control patients were sourced from the same primary care practices who were of similar age and sex. Clinical measurements, including blood pressure and blood glucose readings, medication use, and medical history for the 5 years leading up to an SCA, were obtained from general practice records. A multivariable analysis was performed, and results were stratified for people with and for those without a history of CVD.
Of particular interest were drugs that interfere with cardiac function, including some prokinetic, antibiotic, and antipsychotic medications. All of the drugs are known to be associated with a change in QTc prolongation. Examples include domperidone (QTc-prolonging prokinetic), macrolides and fluoroquinolones (QTc-prolonging antibiotics), and haloperidol (a QTc-prolonging antipsychotic).
Antibiotic and antipsychotic use might contribute to SCA in T2D
Case patients and control patients were similar in age, hemoglobin A1c level, and other characteristics with the exception that more patients with SCA had a history of CVD (40.0% vs. 29.4%).
“Looking at the associations in the overall population, insulin use was strongly associated with SCA risk [hazard ratio, 2.38] and perhaps this was an indicator of severity of type 2 diabetes,” remarked Mr. Harms. “Also, unsurprisingly, a history of arrhythmia [HR, 1.68] and, more surprisingly, prokinetic drug use [HR, 1.66; 95% confidence interval, 1.20-2.31], specifically those known for QTc-prolongation, were associated with SCA.”
Among people who had experienced an SCA and who did not have a history of CVD (337 case patients/2,023 control patients), QTc-prolonging antipsychotic medication use was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.87, and antibiotic medication use was associated with SCA at an HR of 1.66. A low fasting glucose level (< 4.5 mmol/mol) was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.5; severely high systolic blood pressure (> 180 mm Hg) was associated with SCA at an HR of 2.21; low HDL cholesterol level, with an HR of 1.35; and high LDL cholesterol level (> 2.6 mmol/L), with an HR of 1.64.
Among people with a history of CVD (352 case patients/1,207 control patients), associations between albuminuria and SCA were moderate (HR, 1.54) and severe (HR, 1.55); heart failure was associated with SCA at an HR of 1.85 (95% CI, 1.50-2.29).
Comoderator Dr. Fejfarova added that, in addition to the findings from Dr. Harms’ study, other research presented in the same session highlighted the importance of checking patients for the presence of arrhythmias that could lead to the development of atrioventricular blocks, sinus node diseases, and SCA.
Mr. Harms and Dr. Fejfarova have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT EASD 2023
Employment vs. private practice: Who’s happier?
Alexandra Kharazi, MD, a California-based cardiothoracic surgeon, previously worked as an employed physician and is now in private practice. Though she appreciates that there are some trade-offs to working with her small group of three surgeons, Dr. Kharazi has no qualms about her choice.
“For me, it’s an issue of autonomy,” she said. “While I have to work a lot of hours, I don’t have to adhere to a strict schedule. I also don’t have to follow specific policies and rules.”
In contrast, Cassandra Boduch, MD, an employed psychiatrist with PsychPlus in Houston, is very satisfied with working as an employee. “I looked into private practice, but no one really prepares you for the complications that come with it,” she said. “There’s a lot more that goes into it than people realize.”
By hanging up her own shingle, Dr. Kharazi may be living a rapidly shrinking dream. According to the American Medical Association, between 2012 and 2022, the share of physicians working in private practice fell from 60% to 47%. The share of physicians working in hospitals as direct employees or contractors increased from about 6% to about 10% during the same time period.
, according to the AMA.
Though the traditional dream of owning your own practice may be slipping away, are employed physicians less happy than are their self-employed peers? By many measures, the answer is no.
In Medscape’s Employed Physicians Report 2023, doctors weighed in on the pros and cons of their jobs.
When asked what they like most about their jobs, employed physician respondents reported “not having to run a business” as their number-one benefit, followed closely by a stable income. The fact that employers pay for malpractice insurance ranked third, followed by work-life balance.
“We get no business classes in medical school or residency,” said one employed physician. “Having a good salary feels good,” said another. Yet another respondent chimed in: “Running a practice as a small business has become undoable over the past 10-12 years.”
And 50% of employed physicians said that they were “very satisfied/satisfied” with their degree of autonomy.
Still, employed physicians also had plenty to say about the downsides of their jobs.
Many pointed to “feeling like a cog in the machine,” and one doctor pointed to the hassle of dealing with bureaucracy. Others complained about the fact that nonphysicians ran the business and lacked an understanding of what physicians really need from their jobs. When asked whether administrative rules made sense, 63% of physician respondents said that yes, the rules make sense for the business; but, only 52% said that the rules make sense for the doctors themselves.
Other complaints included the requirement to reach high productivity targets and too low an income potential. In the 9 years since Medscape’s 2104 Employed Physicians Report, the share of employed doctors paid on a straight salary has declined from 46% to 31%. Those compensated on a base salary plus productivity targets and other performance metrics rose from 13% in 2014 to 32% now.
“Many doctors go into private practice because of the freedom it brings and the potential financial incentives,” added Dr. Boduch. “I know that many doctors have a dream of working for themselves, and in many cases, that works out great for them.”
Dr. Boduch noted that in her job as chief medical officer at PsychPlus, she still has flexibility plus the perks of working with a bigger practice. In this scenario, Dr. Boduch said, the company can negotiate with insurance companies, allowing her the financial rewards of private practice.
What’s right for you?
“I think it might be somewhat generational,” said Cody Futch, senior recruiting executive at AMN Healthcare. “It used to be that fewer hospitals offered employment, so private practice was the way to go. Now, there are fewer privates because hospitals and corporations are buying them up.”
This reality has potentially shaped the way younger generations approach their workplace. Also, Gen Z tends to have less intention to stay with a current employer for the long term than did their parents. “Older physicians were trained to expect they’d run their own business and build it over the years,” said Mr. Futch. “The younger generations look at it as a job, something they may want to switch in a few years. It’s a combination of candidates wanting more options, and also the fact that there are more options to be employed.”
Along those lines, younger generations in general tend to place work-life balance as a higher priority than do older generations, and employed physicians place this equation high on the list as well. In the Employed Physicians Report 2023, 54% said that they are satisfied or better with their work-life balance, up from 51% in the 2022 report.
With that in mind, Dr. Kharazi noted that flexibility is one of the chief reasons why she likes private practice. “If my kid has an event I want to attend, I don’t have to adhere to a strict schedule,” she said.
Satisfaction as an employee vs. employed doctor sometimes changes based on the type of medicine you practice too. With specialties that tend to be primarily outpatient, such as dermatology and allergy, private practice may be the best option regardless. “Hospitals don’t seek out those specialists as much and the specialists can operate successfully without a hospital,” said Mr. Futch.
Hospitals try to incentivize doctors with perks like hefty sign-on bonuses, student loan forgiveness, plenty of vacation time, and more. They also put money into marketing their doctors, a time-consuming and expensive aspect that is tough to shoulder in private practice, especially in the early years. Mr. Futch adds that many doctors view employment as a more stable option. “As the government changes reimbursement policies, the income from private practice fluctuates,” he said. “So many doctors worry that if they buy into a private practice, it is a risky endeavor.”
Hospitals aren’t always a sure bet in that regard, either: They go through tough financial times, lay off staff, or make salary cuts. Historically, however, employment tends to be the safer route, which can make it an attractive option.
Ultimately, the pros and cons of each scenario are individual. It’s up to physicians to do their own math and balance sheet before making a decision.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Alexandra Kharazi, MD, a California-based cardiothoracic surgeon, previously worked as an employed physician and is now in private practice. Though she appreciates that there are some trade-offs to working with her small group of three surgeons, Dr. Kharazi has no qualms about her choice.
“For me, it’s an issue of autonomy,” she said. “While I have to work a lot of hours, I don’t have to adhere to a strict schedule. I also don’t have to follow specific policies and rules.”
In contrast, Cassandra Boduch, MD, an employed psychiatrist with PsychPlus in Houston, is very satisfied with working as an employee. “I looked into private practice, but no one really prepares you for the complications that come with it,” she said. “There’s a lot more that goes into it than people realize.”
By hanging up her own shingle, Dr. Kharazi may be living a rapidly shrinking dream. According to the American Medical Association, between 2012 and 2022, the share of physicians working in private practice fell from 60% to 47%. The share of physicians working in hospitals as direct employees or contractors increased from about 6% to about 10% during the same time period.
, according to the AMA.
Though the traditional dream of owning your own practice may be slipping away, are employed physicians less happy than are their self-employed peers? By many measures, the answer is no.
In Medscape’s Employed Physicians Report 2023, doctors weighed in on the pros and cons of their jobs.
When asked what they like most about their jobs, employed physician respondents reported “not having to run a business” as their number-one benefit, followed closely by a stable income. The fact that employers pay for malpractice insurance ranked third, followed by work-life balance.
“We get no business classes in medical school or residency,” said one employed physician. “Having a good salary feels good,” said another. Yet another respondent chimed in: “Running a practice as a small business has become undoable over the past 10-12 years.”
And 50% of employed physicians said that they were “very satisfied/satisfied” with their degree of autonomy.
Still, employed physicians also had plenty to say about the downsides of their jobs.
Many pointed to “feeling like a cog in the machine,” and one doctor pointed to the hassle of dealing with bureaucracy. Others complained about the fact that nonphysicians ran the business and lacked an understanding of what physicians really need from their jobs. When asked whether administrative rules made sense, 63% of physician respondents said that yes, the rules make sense for the business; but, only 52% said that the rules make sense for the doctors themselves.
Other complaints included the requirement to reach high productivity targets and too low an income potential. In the 9 years since Medscape’s 2104 Employed Physicians Report, the share of employed doctors paid on a straight salary has declined from 46% to 31%. Those compensated on a base salary plus productivity targets and other performance metrics rose from 13% in 2014 to 32% now.
“Many doctors go into private practice because of the freedom it brings and the potential financial incentives,” added Dr. Boduch. “I know that many doctors have a dream of working for themselves, and in many cases, that works out great for them.”
Dr. Boduch noted that in her job as chief medical officer at PsychPlus, she still has flexibility plus the perks of working with a bigger practice. In this scenario, Dr. Boduch said, the company can negotiate with insurance companies, allowing her the financial rewards of private practice.
What’s right for you?
“I think it might be somewhat generational,” said Cody Futch, senior recruiting executive at AMN Healthcare. “It used to be that fewer hospitals offered employment, so private practice was the way to go. Now, there are fewer privates because hospitals and corporations are buying them up.”
This reality has potentially shaped the way younger generations approach their workplace. Also, Gen Z tends to have less intention to stay with a current employer for the long term than did their parents. “Older physicians were trained to expect they’d run their own business and build it over the years,” said Mr. Futch. “The younger generations look at it as a job, something they may want to switch in a few years. It’s a combination of candidates wanting more options, and also the fact that there are more options to be employed.”
Along those lines, younger generations in general tend to place work-life balance as a higher priority than do older generations, and employed physicians place this equation high on the list as well. In the Employed Physicians Report 2023, 54% said that they are satisfied or better with their work-life balance, up from 51% in the 2022 report.
With that in mind, Dr. Kharazi noted that flexibility is one of the chief reasons why she likes private practice. “If my kid has an event I want to attend, I don’t have to adhere to a strict schedule,” she said.
Satisfaction as an employee vs. employed doctor sometimes changes based on the type of medicine you practice too. With specialties that tend to be primarily outpatient, such as dermatology and allergy, private practice may be the best option regardless. “Hospitals don’t seek out those specialists as much and the specialists can operate successfully without a hospital,” said Mr. Futch.
Hospitals try to incentivize doctors with perks like hefty sign-on bonuses, student loan forgiveness, plenty of vacation time, and more. They also put money into marketing their doctors, a time-consuming and expensive aspect that is tough to shoulder in private practice, especially in the early years. Mr. Futch adds that many doctors view employment as a more stable option. “As the government changes reimbursement policies, the income from private practice fluctuates,” he said. “So many doctors worry that if they buy into a private practice, it is a risky endeavor.”
Hospitals aren’t always a sure bet in that regard, either: They go through tough financial times, lay off staff, or make salary cuts. Historically, however, employment tends to be the safer route, which can make it an attractive option.
Ultimately, the pros and cons of each scenario are individual. It’s up to physicians to do their own math and balance sheet before making a decision.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Alexandra Kharazi, MD, a California-based cardiothoracic surgeon, previously worked as an employed physician and is now in private practice. Though she appreciates that there are some trade-offs to working with her small group of three surgeons, Dr. Kharazi has no qualms about her choice.
“For me, it’s an issue of autonomy,” she said. “While I have to work a lot of hours, I don’t have to adhere to a strict schedule. I also don’t have to follow specific policies and rules.”
In contrast, Cassandra Boduch, MD, an employed psychiatrist with PsychPlus in Houston, is very satisfied with working as an employee. “I looked into private practice, but no one really prepares you for the complications that come with it,” she said. “There’s a lot more that goes into it than people realize.”
By hanging up her own shingle, Dr. Kharazi may be living a rapidly shrinking dream. According to the American Medical Association, between 2012 and 2022, the share of physicians working in private practice fell from 60% to 47%. The share of physicians working in hospitals as direct employees or contractors increased from about 6% to about 10% during the same time period.
, according to the AMA.
Though the traditional dream of owning your own practice may be slipping away, are employed physicians less happy than are their self-employed peers? By many measures, the answer is no.
In Medscape’s Employed Physicians Report 2023, doctors weighed in on the pros and cons of their jobs.
When asked what they like most about their jobs, employed physician respondents reported “not having to run a business” as their number-one benefit, followed closely by a stable income. The fact that employers pay for malpractice insurance ranked third, followed by work-life balance.
“We get no business classes in medical school or residency,” said one employed physician. “Having a good salary feels good,” said another. Yet another respondent chimed in: “Running a practice as a small business has become undoable over the past 10-12 years.”
And 50% of employed physicians said that they were “very satisfied/satisfied” with their degree of autonomy.
Still, employed physicians also had plenty to say about the downsides of their jobs.
Many pointed to “feeling like a cog in the machine,” and one doctor pointed to the hassle of dealing with bureaucracy. Others complained about the fact that nonphysicians ran the business and lacked an understanding of what physicians really need from their jobs. When asked whether administrative rules made sense, 63% of physician respondents said that yes, the rules make sense for the business; but, only 52% said that the rules make sense for the doctors themselves.
Other complaints included the requirement to reach high productivity targets and too low an income potential. In the 9 years since Medscape’s 2104 Employed Physicians Report, the share of employed doctors paid on a straight salary has declined from 46% to 31%. Those compensated on a base salary plus productivity targets and other performance metrics rose from 13% in 2014 to 32% now.
“Many doctors go into private practice because of the freedom it brings and the potential financial incentives,” added Dr. Boduch. “I know that many doctors have a dream of working for themselves, and in many cases, that works out great for them.”
Dr. Boduch noted that in her job as chief medical officer at PsychPlus, she still has flexibility plus the perks of working with a bigger practice. In this scenario, Dr. Boduch said, the company can negotiate with insurance companies, allowing her the financial rewards of private practice.
What’s right for you?
“I think it might be somewhat generational,” said Cody Futch, senior recruiting executive at AMN Healthcare. “It used to be that fewer hospitals offered employment, so private practice was the way to go. Now, there are fewer privates because hospitals and corporations are buying them up.”
This reality has potentially shaped the way younger generations approach their workplace. Also, Gen Z tends to have less intention to stay with a current employer for the long term than did their parents. “Older physicians were trained to expect they’d run their own business and build it over the years,” said Mr. Futch. “The younger generations look at it as a job, something they may want to switch in a few years. It’s a combination of candidates wanting more options, and also the fact that there are more options to be employed.”
Along those lines, younger generations in general tend to place work-life balance as a higher priority than do older generations, and employed physicians place this equation high on the list as well. In the Employed Physicians Report 2023, 54% said that they are satisfied or better with their work-life balance, up from 51% in the 2022 report.
With that in mind, Dr. Kharazi noted that flexibility is one of the chief reasons why she likes private practice. “If my kid has an event I want to attend, I don’t have to adhere to a strict schedule,” she said.
Satisfaction as an employee vs. employed doctor sometimes changes based on the type of medicine you practice too. With specialties that tend to be primarily outpatient, such as dermatology and allergy, private practice may be the best option regardless. “Hospitals don’t seek out those specialists as much and the specialists can operate successfully without a hospital,” said Mr. Futch.
Hospitals try to incentivize doctors with perks like hefty sign-on bonuses, student loan forgiveness, plenty of vacation time, and more. They also put money into marketing their doctors, a time-consuming and expensive aspect that is tough to shoulder in private practice, especially in the early years. Mr. Futch adds that many doctors view employment as a more stable option. “As the government changes reimbursement policies, the income from private practice fluctuates,” he said. “So many doctors worry that if they buy into a private practice, it is a risky endeavor.”
Hospitals aren’t always a sure bet in that regard, either: They go through tough financial times, lay off staff, or make salary cuts. Historically, however, employment tends to be the safer route, which can make it an attractive option.
Ultimately, the pros and cons of each scenario are individual. It’s up to physicians to do their own math and balance sheet before making a decision.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Exercise as good as Viagra for ED: Study
, according to a new analysis of the best research to date on aerobic exercise and erectile function.
The study, published in The Journal of Sexual Medicine, found that aerobic activities – such as walking or cycling – improved erectile function in all men with erectile dysfunction, regardless of body weight, overall health, or medication use. Men with the most severe erectile dysfunction saw the greatest benefit.
“This study provides physicians and patients the proof needed to definitively recommend aerobic activity as part of ED management,” said study author Larry E. Miller, PhD, president, Miller Scientific Consulting, Johnson City, Tenn.
Doctors have long known that erectile function is linked to cardiovascular health, but there is limited high-quality evidence on the impact of exercise on the disorder.
The researchers scoured the scientific literature and found 11 randomized, controlled trials – a preferred study design where participants are randomly assigned to receive an intervention or not. Of the 1,100 men involved in the studies, 600 were assigned to “experimental” groups that typically exercised for 30 to 60 minutes, three to five times a week, while 500 were assigned to “control” groups with no exercise plan.
The worse the ED was, the more exercise helped, the researchers found. On a standardized scale of 6 to 30, men with severe ED who exercised reported a 5-point improvement in erectile function. Those with mild and moderate ED saw improvements of 2 and 3 points, respectively.
By comparison, phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors – like sildenafil (Viagra) or tadalafil (Cialis) – can lead to improvements of 4 to 8 points, the study authors note. And testosterone replacement therapy can lead to an improvement of 2 points.
“We were particularly impressed by the finding that men with more severe erectile dysfunction saw greater improvements with exercise, and these improvements were similar to those seen in men taking” drugs like Viagra, Dr. Miller said.
ED and heart health
Erectile dysfunction can often be traced to the same causes as cardiovascular disease, including inflammation, a narrowing of the arteries (endothelial dysfunction), or a hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis).
“It’s important to recognize that erectile dysfunction can often serve as an indicator or barometer of underlying cardiovascular health,” said Amy Pearlman, MD, a urologist specializing in male sexual health at Prime Institute in Miami.
Dr. Pearlman was not involved in the study but thinks the results make sense. “It stands to reason that any intervention aimed at enhancing cardiovascular health may also have a positive impact on erectile health.”
But what was surprising was that aerobic exercise reduced symptoms on par with medications like Viagra, said urologist Rahul Mehan, MD, founder of East Valley Urology Center, in Mesa, Ariz. (Dr. Mehan was also not involved in the study.)
While erectile dysfunction medications are generally affordable and accessible, some patients don’t want to take them or can’t tolerate the side effects. These can include “headache, heartburn, nausea, flushing, and pain in muscles, back, arms, or legs,” said Dr. Mehan. He adds, “Everyone can exercise.”
Some doctors, including Dr. Mehan, already recommend exercise to their patients with ED.
Now they can tell patients that it’s “a proven approach backed by high-quality data from randomized studies,” Dr. Miller said. “Exercise is low risk and affordable, making it an ideal first-line treatment option for erectile difficulties, especially for patients unwilling or unable to use medications.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a new analysis of the best research to date on aerobic exercise and erectile function.
The study, published in The Journal of Sexual Medicine, found that aerobic activities – such as walking or cycling – improved erectile function in all men with erectile dysfunction, regardless of body weight, overall health, or medication use. Men with the most severe erectile dysfunction saw the greatest benefit.
“This study provides physicians and patients the proof needed to definitively recommend aerobic activity as part of ED management,” said study author Larry E. Miller, PhD, president, Miller Scientific Consulting, Johnson City, Tenn.
Doctors have long known that erectile function is linked to cardiovascular health, but there is limited high-quality evidence on the impact of exercise on the disorder.
The researchers scoured the scientific literature and found 11 randomized, controlled trials – a preferred study design where participants are randomly assigned to receive an intervention or not. Of the 1,100 men involved in the studies, 600 were assigned to “experimental” groups that typically exercised for 30 to 60 minutes, three to five times a week, while 500 were assigned to “control” groups with no exercise plan.
The worse the ED was, the more exercise helped, the researchers found. On a standardized scale of 6 to 30, men with severe ED who exercised reported a 5-point improvement in erectile function. Those with mild and moderate ED saw improvements of 2 and 3 points, respectively.
By comparison, phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors – like sildenafil (Viagra) or tadalafil (Cialis) – can lead to improvements of 4 to 8 points, the study authors note. And testosterone replacement therapy can lead to an improvement of 2 points.
“We were particularly impressed by the finding that men with more severe erectile dysfunction saw greater improvements with exercise, and these improvements were similar to those seen in men taking” drugs like Viagra, Dr. Miller said.
ED and heart health
Erectile dysfunction can often be traced to the same causes as cardiovascular disease, including inflammation, a narrowing of the arteries (endothelial dysfunction), or a hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis).
“It’s important to recognize that erectile dysfunction can often serve as an indicator or barometer of underlying cardiovascular health,” said Amy Pearlman, MD, a urologist specializing in male sexual health at Prime Institute in Miami.
Dr. Pearlman was not involved in the study but thinks the results make sense. “It stands to reason that any intervention aimed at enhancing cardiovascular health may also have a positive impact on erectile health.”
But what was surprising was that aerobic exercise reduced symptoms on par with medications like Viagra, said urologist Rahul Mehan, MD, founder of East Valley Urology Center, in Mesa, Ariz. (Dr. Mehan was also not involved in the study.)
While erectile dysfunction medications are generally affordable and accessible, some patients don’t want to take them or can’t tolerate the side effects. These can include “headache, heartburn, nausea, flushing, and pain in muscles, back, arms, or legs,” said Dr. Mehan. He adds, “Everyone can exercise.”
Some doctors, including Dr. Mehan, already recommend exercise to their patients with ED.
Now they can tell patients that it’s “a proven approach backed by high-quality data from randomized studies,” Dr. Miller said. “Exercise is low risk and affordable, making it an ideal first-line treatment option for erectile difficulties, especially for patients unwilling or unable to use medications.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a new analysis of the best research to date on aerobic exercise and erectile function.
The study, published in The Journal of Sexual Medicine, found that aerobic activities – such as walking or cycling – improved erectile function in all men with erectile dysfunction, regardless of body weight, overall health, or medication use. Men with the most severe erectile dysfunction saw the greatest benefit.
“This study provides physicians and patients the proof needed to definitively recommend aerobic activity as part of ED management,” said study author Larry E. Miller, PhD, president, Miller Scientific Consulting, Johnson City, Tenn.
Doctors have long known that erectile function is linked to cardiovascular health, but there is limited high-quality evidence on the impact of exercise on the disorder.
The researchers scoured the scientific literature and found 11 randomized, controlled trials – a preferred study design where participants are randomly assigned to receive an intervention or not. Of the 1,100 men involved in the studies, 600 were assigned to “experimental” groups that typically exercised for 30 to 60 minutes, three to five times a week, while 500 were assigned to “control” groups with no exercise plan.
The worse the ED was, the more exercise helped, the researchers found. On a standardized scale of 6 to 30, men with severe ED who exercised reported a 5-point improvement in erectile function. Those with mild and moderate ED saw improvements of 2 and 3 points, respectively.
By comparison, phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors – like sildenafil (Viagra) or tadalafil (Cialis) – can lead to improvements of 4 to 8 points, the study authors note. And testosterone replacement therapy can lead to an improvement of 2 points.
“We were particularly impressed by the finding that men with more severe erectile dysfunction saw greater improvements with exercise, and these improvements were similar to those seen in men taking” drugs like Viagra, Dr. Miller said.
ED and heart health
Erectile dysfunction can often be traced to the same causes as cardiovascular disease, including inflammation, a narrowing of the arteries (endothelial dysfunction), or a hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis).
“It’s important to recognize that erectile dysfunction can often serve as an indicator or barometer of underlying cardiovascular health,” said Amy Pearlman, MD, a urologist specializing in male sexual health at Prime Institute in Miami.
Dr. Pearlman was not involved in the study but thinks the results make sense. “It stands to reason that any intervention aimed at enhancing cardiovascular health may also have a positive impact on erectile health.”
But what was surprising was that aerobic exercise reduced symptoms on par with medications like Viagra, said urologist Rahul Mehan, MD, founder of East Valley Urology Center, in Mesa, Ariz. (Dr. Mehan was also not involved in the study.)
While erectile dysfunction medications are generally affordable and accessible, some patients don’t want to take them or can’t tolerate the side effects. These can include “headache, heartburn, nausea, flushing, and pain in muscles, back, arms, or legs,” said Dr. Mehan. He adds, “Everyone can exercise.”
Some doctors, including Dr. Mehan, already recommend exercise to their patients with ED.
Now they can tell patients that it’s “a proven approach backed by high-quality data from randomized studies,” Dr. Miller said. “Exercise is low risk and affordable, making it an ideal first-line treatment option for erectile difficulties, especially for patients unwilling or unable to use medications.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New calculator tool estimates fracture risk on dialysis
VANCOUVER – A new calculator that predicts short-term fracture risk at both 1 year and 3 years in patients on dialysis performed well in a study presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
The tool will soon be available on QxMD Calculate, which provides free decision-support tools for physicians, said presenter Andrea Cowan, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Western Ontario, London.
Dialysis patients have an approximately fivefold increased risk for fracture, Dr. Cowan noted, compared with the general population. However, treatments to prevent fracture risk are relatively limited and can have significant side effects. Therefore, “you really want to make sure that the person you’re targeting for treatment is actually going to be at a reasonable risk of fracture,” she said.
The Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) is useful, but it estimates 10-year fracture risk, which is too long of a time frame to be useful for dialysis patients who experience a 50% 5-year mortality, according to Dr. Cowan. It does not take kidney failure or severe hyperparathyroidism into account, and it also requires information like bone mineral density, which poses an additional burden for a dialysis patient already undergoing multiple tests.
The new calculator could also be useful for research because it doesn’t rely on clinical data that might not be generally available, such as parental fracture, smoking status, or body mass index. “There’s a move towards things like pragmatic trials, which use more routinely collected data, have broader inclusion criteria, and are often more cost efficient to run. This calculator should be relatively easy to implement in trials using routinely collected data to perhaps define a subgroup of patients who may be at high risk of fracture without having to apply really cumbersome tools,” Dr. Cowan said.
The researchers included 11,599 patients between ages 40 and 89 years who were treated at a single center in Ontario between 2010 and 2017. The mean age was 66.18 years, 38.6% were women, 64.1% had diabetes, 11.9% had liver disease, and median time on dialysis was 0.81 years. The patients’ median parathyroid hormone level was 30 pmol/L.
At 3 years, the cumulative incidence of any fracture was 7.36% (95% confidence interval, 6.89-7.85), including 2.62% for hip fracture (95% CI, 2.34-2.93), 1.36% for spine fracture (95% CI, 1.16-1.59), 1.93% for wrist or forearm (95% CI, 1.69-2.20), and 2.15% for the pelvis (95% CI, 1.89-2.43). The incidence for all fractures at 1 year was 2.93 (95% CI, 2.62-3.26).
Variables associated with fracture risk included female sex (hazard ratio, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.27-1.67), a previous fracture more than 1 year in the past (HR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.37-2.00), a fracture in the past year (HR, 3.63; 95% CI, 2.86-4.60), and proton pump inhibitor use (HR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.04-1.45). After inclusion of vitamin D use, steroid use, time on dialysis, calcium levels, phosphate levels, presence of diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and chronic liver disease, the full model had an area under the curve of 77.7 at 1 year (95% CI, 73.3-84.4) and 69.9 at 3 years (95% CI, 68.0-72.2). For hip fracture, the model had an AUC of 80.1 at 1 year (95% CI, 77.0-83.5) and 71.9 at 3 years (95% CI, 70.1-74.2).
During the Q&A session, Dr. Cowan was asked how the tool could be implemented clinically. She said that it could have value in discussing fracture prediction and prevention with patients, but it could also increase fracture risk awareness among nephrologists. “I need to convince a lot of my colleagues because they’re focused on other things, so having this [calculator] I think is both good from a patient as well as a practitioner perspective. And the treatments that we have in people with end-stage renal disease are limited, so you want to know that you’re really targeting the high-risk person before you potentially put them on denosumab and increase the risk of severe hypercalcemia and things like that,” Dr. Cowan said.
The study points out the challenges of predicting fracture risk for specific populations, according to session comoderator Evelyn Hsieh, MD. She noted that the study needs follow-up. “I don’t think they had gotten to a validation [in a separate cohort] yet,” said Dr. Hsieh, an associate professor of medicine (rheumatology) and epidemiology (chronic diseases) at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Dr. Cowan and Dr. Hsieh have no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VANCOUVER – A new calculator that predicts short-term fracture risk at both 1 year and 3 years in patients on dialysis performed well in a study presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
The tool will soon be available on QxMD Calculate, which provides free decision-support tools for physicians, said presenter Andrea Cowan, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Western Ontario, London.
Dialysis patients have an approximately fivefold increased risk for fracture, Dr. Cowan noted, compared with the general population. However, treatments to prevent fracture risk are relatively limited and can have significant side effects. Therefore, “you really want to make sure that the person you’re targeting for treatment is actually going to be at a reasonable risk of fracture,” she said.
The Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) is useful, but it estimates 10-year fracture risk, which is too long of a time frame to be useful for dialysis patients who experience a 50% 5-year mortality, according to Dr. Cowan. It does not take kidney failure or severe hyperparathyroidism into account, and it also requires information like bone mineral density, which poses an additional burden for a dialysis patient already undergoing multiple tests.
The new calculator could also be useful for research because it doesn’t rely on clinical data that might not be generally available, such as parental fracture, smoking status, or body mass index. “There’s a move towards things like pragmatic trials, which use more routinely collected data, have broader inclusion criteria, and are often more cost efficient to run. This calculator should be relatively easy to implement in trials using routinely collected data to perhaps define a subgroup of patients who may be at high risk of fracture without having to apply really cumbersome tools,” Dr. Cowan said.
The researchers included 11,599 patients between ages 40 and 89 years who were treated at a single center in Ontario between 2010 and 2017. The mean age was 66.18 years, 38.6% were women, 64.1% had diabetes, 11.9% had liver disease, and median time on dialysis was 0.81 years. The patients’ median parathyroid hormone level was 30 pmol/L.
At 3 years, the cumulative incidence of any fracture was 7.36% (95% confidence interval, 6.89-7.85), including 2.62% for hip fracture (95% CI, 2.34-2.93), 1.36% for spine fracture (95% CI, 1.16-1.59), 1.93% for wrist or forearm (95% CI, 1.69-2.20), and 2.15% for the pelvis (95% CI, 1.89-2.43). The incidence for all fractures at 1 year was 2.93 (95% CI, 2.62-3.26).
Variables associated with fracture risk included female sex (hazard ratio, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.27-1.67), a previous fracture more than 1 year in the past (HR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.37-2.00), a fracture in the past year (HR, 3.63; 95% CI, 2.86-4.60), and proton pump inhibitor use (HR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.04-1.45). After inclusion of vitamin D use, steroid use, time on dialysis, calcium levels, phosphate levels, presence of diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and chronic liver disease, the full model had an area under the curve of 77.7 at 1 year (95% CI, 73.3-84.4) and 69.9 at 3 years (95% CI, 68.0-72.2). For hip fracture, the model had an AUC of 80.1 at 1 year (95% CI, 77.0-83.5) and 71.9 at 3 years (95% CI, 70.1-74.2).
During the Q&A session, Dr. Cowan was asked how the tool could be implemented clinically. She said that it could have value in discussing fracture prediction and prevention with patients, but it could also increase fracture risk awareness among nephrologists. “I need to convince a lot of my colleagues because they’re focused on other things, so having this [calculator] I think is both good from a patient as well as a practitioner perspective. And the treatments that we have in people with end-stage renal disease are limited, so you want to know that you’re really targeting the high-risk person before you potentially put them on denosumab and increase the risk of severe hypercalcemia and things like that,” Dr. Cowan said.
The study points out the challenges of predicting fracture risk for specific populations, according to session comoderator Evelyn Hsieh, MD. She noted that the study needs follow-up. “I don’t think they had gotten to a validation [in a separate cohort] yet,” said Dr. Hsieh, an associate professor of medicine (rheumatology) and epidemiology (chronic diseases) at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Dr. Cowan and Dr. Hsieh have no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VANCOUVER – A new calculator that predicts short-term fracture risk at both 1 year and 3 years in patients on dialysis performed well in a study presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
The tool will soon be available on QxMD Calculate, which provides free decision-support tools for physicians, said presenter Andrea Cowan, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Western Ontario, London.
Dialysis patients have an approximately fivefold increased risk for fracture, Dr. Cowan noted, compared with the general population. However, treatments to prevent fracture risk are relatively limited and can have significant side effects. Therefore, “you really want to make sure that the person you’re targeting for treatment is actually going to be at a reasonable risk of fracture,” she said.
The Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) is useful, but it estimates 10-year fracture risk, which is too long of a time frame to be useful for dialysis patients who experience a 50% 5-year mortality, according to Dr. Cowan. It does not take kidney failure or severe hyperparathyroidism into account, and it also requires information like bone mineral density, which poses an additional burden for a dialysis patient already undergoing multiple tests.
The new calculator could also be useful for research because it doesn’t rely on clinical data that might not be generally available, such as parental fracture, smoking status, or body mass index. “There’s a move towards things like pragmatic trials, which use more routinely collected data, have broader inclusion criteria, and are often more cost efficient to run. This calculator should be relatively easy to implement in trials using routinely collected data to perhaps define a subgroup of patients who may be at high risk of fracture without having to apply really cumbersome tools,” Dr. Cowan said.
The researchers included 11,599 patients between ages 40 and 89 years who were treated at a single center in Ontario between 2010 and 2017. The mean age was 66.18 years, 38.6% were women, 64.1% had diabetes, 11.9% had liver disease, and median time on dialysis was 0.81 years. The patients’ median parathyroid hormone level was 30 pmol/L.
At 3 years, the cumulative incidence of any fracture was 7.36% (95% confidence interval, 6.89-7.85), including 2.62% for hip fracture (95% CI, 2.34-2.93), 1.36% for spine fracture (95% CI, 1.16-1.59), 1.93% for wrist or forearm (95% CI, 1.69-2.20), and 2.15% for the pelvis (95% CI, 1.89-2.43). The incidence for all fractures at 1 year was 2.93 (95% CI, 2.62-3.26).
Variables associated with fracture risk included female sex (hazard ratio, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.27-1.67), a previous fracture more than 1 year in the past (HR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.37-2.00), a fracture in the past year (HR, 3.63; 95% CI, 2.86-4.60), and proton pump inhibitor use (HR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.04-1.45). After inclusion of vitamin D use, steroid use, time on dialysis, calcium levels, phosphate levels, presence of diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and chronic liver disease, the full model had an area under the curve of 77.7 at 1 year (95% CI, 73.3-84.4) and 69.9 at 3 years (95% CI, 68.0-72.2). For hip fracture, the model had an AUC of 80.1 at 1 year (95% CI, 77.0-83.5) and 71.9 at 3 years (95% CI, 70.1-74.2).
During the Q&A session, Dr. Cowan was asked how the tool could be implemented clinically. She said that it could have value in discussing fracture prediction and prevention with patients, but it could also increase fracture risk awareness among nephrologists. “I need to convince a lot of my colleagues because they’re focused on other things, so having this [calculator] I think is both good from a patient as well as a practitioner perspective. And the treatments that we have in people with end-stage renal disease are limited, so you want to know that you’re really targeting the high-risk person before you potentially put them on denosumab and increase the risk of severe hypercalcemia and things like that,” Dr. Cowan said.
The study points out the challenges of predicting fracture risk for specific populations, according to session comoderator Evelyn Hsieh, MD. She noted that the study needs follow-up. “I don’t think they had gotten to a validation [in a separate cohort] yet,” said Dr. Hsieh, an associate professor of medicine (rheumatology) and epidemiology (chronic diseases) at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Dr. Cowan and Dr. Hsieh have no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ASBMR 2023
Frustrating facial lesions
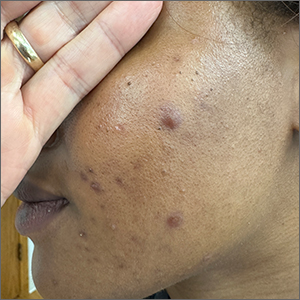
These tender nodules are classic for cystic acne and are common in women older than 20 years. Instead of outgrowing acne in their teenage years, some people (such as this patient) develop frequent tender cystic acne lesions that often heal with hyperpigmented scars.
Acne is the most prevalent chronic skin condition in the United States, affecting up to 50 million people.1 Approximately 12% of adult women are affected.2 The main contributing factors include increased sebum production, follicular hyperkeratinization, microbial follicular colonization with Propionibacterium acnes, and an inflammatory reaction.3
Treatment is available in both topical and oral forms. Topical antibiotics are used predominantly for treating mild-to-moderate inflammatory acne. They are not recommended as monotherapy due to the risk for bacterial resistance; this can be prevented by adding benzoyl peroxide, which exfoliates and acts as an antibacterial agent. Clindamycin 1% solution or gel is the preferred topical antibiotic for treatment of acne.4
Topical retinoids can be used as monotherapy or in combination with antibiotics. They also can be used for maintenance after treatment goals are reached and systemic antibiotics are discontinued. Retinoids generally are applied in the evening because the sun weakens their effect. Patients on retinoids also are more sensitive to the sun and should be counseled to use sunscreen daily. Counseling on pregnancy risks and appropriate use of contraception also should be offered to patients using retinoids. It is advisable to consider the use of combination oral contraceptives, particularly in women who have adult-onset acne or experience flare-ups around the time of their menstrual cycle.3
Azelaic acid has anticomedonal, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties and may be effective in treating mild-to-moderate inflammatory acne and hyperpigmentation. Salicylic acid also has comedolytic properties, although there have been limited studies examining its effectiveness. Both azelaic and salicylic acid are considered safe for use in pregnancy.
Oral antibiotics are recommended in the treatment of moderate-to-severe acne. Both doxycycline and minocycline are more effective than tetracycline for treating acne, with no clear superiority between the two.4 Macrolides also can be effective in treating acne, although their use should be limited to those who cannot tolerate tetracyclines. Systemic antibiotic use should be limited to 3 to 4 months due to decreasing efficacy over time and to minimize the development of bacterial resistance. If treatment goals are attained, the antibiotics can be replaced with retinoids.
Oral isotretinoin is reserved for treatment of severe nodular acne or moderate acne that is treatment resistant. Patients should be counseled on contraceptive methods, as isotretinoin is highly teratogenic and therefore prescribed through the iPLEDGE program.3,4
Given this patient’s persistent symptoms despite use of topical antibiotics and topical tretinoin, she decided to try oral antibiotics (doxycycline 100 mg twice daily) for 3 months and to start long-term oral contraceptives. If her symptoms continue, she will enroll in the iPLEDGE program and start treatment with oral isotretinoin.
Photo courtesy of Ayo Sorunke, MD. Text courtesy of Ayo Sorunke, MD, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University, Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. White GM. Recent findings in the epidemiologic evidence, classification, and subtypes of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39:S34-S37. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(98)70442-6
2. Goulden V, Stables GI, Cunliffe WJ. Prevalence of facial acne in adults. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:577-580.
3. Titus S, Hodge J. Diagnosis and treatment of acne. Am Fam Physician. 2012;86:734-740.
4. Zaenglein AL, Pathy AL, Schlosser BJ, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:945-973.e33. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2015.12.037

These tender nodules are classic for cystic acne and are common in women older than 20 years. Instead of outgrowing acne in their teenage years, some people (such as this patient) develop frequent tender cystic acne lesions that often heal with hyperpigmented scars.
Acne is the most prevalent chronic skin condition in the United States, affecting up to 50 million people.1 Approximately 12% of adult women are affected.2 The main contributing factors include increased sebum production, follicular hyperkeratinization, microbial follicular colonization with Propionibacterium acnes, and an inflammatory reaction.3
Treatment is available in both topical and oral forms. Topical antibiotics are used predominantly for treating mild-to-moderate inflammatory acne. They are not recommended as monotherapy due to the risk for bacterial resistance; this can be prevented by adding benzoyl peroxide, which exfoliates and acts as an antibacterial agent. Clindamycin 1% solution or gel is the preferred topical antibiotic for treatment of acne.4
Topical retinoids can be used as monotherapy or in combination with antibiotics. They also can be used for maintenance after treatment goals are reached and systemic antibiotics are discontinued. Retinoids generally are applied in the evening because the sun weakens their effect. Patients on retinoids also are more sensitive to the sun and should be counseled to use sunscreen daily. Counseling on pregnancy risks and appropriate use of contraception also should be offered to patients using retinoids. It is advisable to consider the use of combination oral contraceptives, particularly in women who have adult-onset acne or experience flare-ups around the time of their menstrual cycle.3
Azelaic acid has anticomedonal, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties and may be effective in treating mild-to-moderate inflammatory acne and hyperpigmentation. Salicylic acid also has comedolytic properties, although there have been limited studies examining its effectiveness. Both azelaic and salicylic acid are considered safe for use in pregnancy.
Oral antibiotics are recommended in the treatment of moderate-to-severe acne. Both doxycycline and minocycline are more effective than tetracycline for treating acne, with no clear superiority between the two.4 Macrolides also can be effective in treating acne, although their use should be limited to those who cannot tolerate tetracyclines. Systemic antibiotic use should be limited to 3 to 4 months due to decreasing efficacy over time and to minimize the development of bacterial resistance. If treatment goals are attained, the antibiotics can be replaced with retinoids.
Oral isotretinoin is reserved for treatment of severe nodular acne or moderate acne that is treatment resistant. Patients should be counseled on contraceptive methods, as isotretinoin is highly teratogenic and therefore prescribed through the iPLEDGE program.3,4
Given this patient’s persistent symptoms despite use of topical antibiotics and topical tretinoin, she decided to try oral antibiotics (doxycycline 100 mg twice daily) for 3 months and to start long-term oral contraceptives. If her symptoms continue, she will enroll in the iPLEDGE program and start treatment with oral isotretinoin.
Photo courtesy of Ayo Sorunke, MD. Text courtesy of Ayo Sorunke, MD, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University, Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.

These tender nodules are classic for cystic acne and are common in women older than 20 years. Instead of outgrowing acne in their teenage years, some people (such as this patient) develop frequent tender cystic acne lesions that often heal with hyperpigmented scars.
Acne is the most prevalent chronic skin condition in the United States, affecting up to 50 million people.1 Approximately 12% of adult women are affected.2 The main contributing factors include increased sebum production, follicular hyperkeratinization, microbial follicular colonization with Propionibacterium acnes, and an inflammatory reaction.3
Treatment is available in both topical and oral forms. Topical antibiotics are used predominantly for treating mild-to-moderate inflammatory acne. They are not recommended as monotherapy due to the risk for bacterial resistance; this can be prevented by adding benzoyl peroxide, which exfoliates and acts as an antibacterial agent. Clindamycin 1% solution or gel is the preferred topical antibiotic for treatment of acne.4
Topical retinoids can be used as monotherapy or in combination with antibiotics. They also can be used for maintenance after treatment goals are reached and systemic antibiotics are discontinued. Retinoids generally are applied in the evening because the sun weakens their effect. Patients on retinoids also are more sensitive to the sun and should be counseled to use sunscreen daily. Counseling on pregnancy risks and appropriate use of contraception also should be offered to patients using retinoids. It is advisable to consider the use of combination oral contraceptives, particularly in women who have adult-onset acne or experience flare-ups around the time of their menstrual cycle.3
Azelaic acid has anticomedonal, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties and may be effective in treating mild-to-moderate inflammatory acne and hyperpigmentation. Salicylic acid also has comedolytic properties, although there have been limited studies examining its effectiveness. Both azelaic and salicylic acid are considered safe for use in pregnancy.
Oral antibiotics are recommended in the treatment of moderate-to-severe acne. Both doxycycline and minocycline are more effective than tetracycline for treating acne, with no clear superiority between the two.4 Macrolides also can be effective in treating acne, although their use should be limited to those who cannot tolerate tetracyclines. Systemic antibiotic use should be limited to 3 to 4 months due to decreasing efficacy over time and to minimize the development of bacterial resistance. If treatment goals are attained, the antibiotics can be replaced with retinoids.
Oral isotretinoin is reserved for treatment of severe nodular acne or moderate acne that is treatment resistant. Patients should be counseled on contraceptive methods, as isotretinoin is highly teratogenic and therefore prescribed through the iPLEDGE program.3,4
Given this patient’s persistent symptoms despite use of topical antibiotics and topical tretinoin, she decided to try oral antibiotics (doxycycline 100 mg twice daily) for 3 months and to start long-term oral contraceptives. If her symptoms continue, she will enroll in the iPLEDGE program and start treatment with oral isotretinoin.
Photo courtesy of Ayo Sorunke, MD. Text courtesy of Ayo Sorunke, MD, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University, Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. White GM. Recent findings in the epidemiologic evidence, classification, and subtypes of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39:S34-S37. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(98)70442-6
2. Goulden V, Stables GI, Cunliffe WJ. Prevalence of facial acne in adults. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:577-580.
3. Titus S, Hodge J. Diagnosis and treatment of acne. Am Fam Physician. 2012;86:734-740.
4. Zaenglein AL, Pathy AL, Schlosser BJ, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:945-973.e33. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2015.12.037
1. White GM. Recent findings in the epidemiologic evidence, classification, and subtypes of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39:S34-S37. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(98)70442-6
2. Goulden V, Stables GI, Cunliffe WJ. Prevalence of facial acne in adults. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:577-580.
3. Titus S, Hodge J. Diagnosis and treatment of acne. Am Fam Physician. 2012;86:734-740.
4. Zaenglein AL, Pathy AL, Schlosser BJ, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:945-973.e33. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2015.12.037
Asthma with EoE linked to earlier hospitalization
, according to a new analysis of data from HCA Healthcare.
Not much work has been done on the overlap between the two conditions, both of which are believed to be driven by the action of both eosinophils and helper T cells, according to Linda Pham, DO, who presented the research at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST).
“I have a colleague who is interested in GI and he’s really interested in EOE. We thought it would be nice to look at those populations of patients to see if there’s a correlation between them aside from just the atopic disease,” said Dr. Pham, who is an internal medicine resident at Riverside (Calif.) Community Hospital.
The findings underscore the need for assessing individual patient risk. “Having another concomitant disease like EoE, or maybe like atopic dermatitis, might cause you to have more severe [asthma] exacerbations causing you to go into the hospital more. I think if patients have more of these diseases, doctors can be more cognizant that they need to really be on top of treatment and make sure that [their patients] are aware of themselves so that if their symptoms exacerbate, they can go to the hospital and seek care,” said Dr. Pham.
The study was a retrospective analysis of 3,678,812 patients with asthma and 5,823 patients with both EoE and asthma. The data was drawn from 185 HCA hospitals, with records between 2016 and 2021.
The incidence of both asthma and asthma with EoE remained stable between 2016 and 2021. Dr. Pham pointed out that there are good methods to diagnose both conditions, which suggests that existing treatments are effective enough to be limiting the need for emergency treatment, according to Dr. Pham.
Among patients hospitalized with asthma alone, 72.55% were female, while 27.45% were male (P < .001). The numbers were much more evenly split among those with asthma and EoE, at 51.78% and 48.22%, respectively. The differing gender statistics aren’t easy to explain. “It’s not quite clear whether it’s because they just have more severe symptoms, or if it is other factors causing women to seek care more than their male counterparts. It could be personal biases, or it could be the asthma itself that is more severe in women,” said Dr. Pham.
When they broke down the analysis by sex, the researchers found that male EoE patients without asthma were a mean value of 5.517 years older than male EoE patients with asthma, and the mean difference was 5.480 years in female patients (P < .001 for both).
Although the direct cause of earlier hospitalization among patients with concomitant EoE and asthma is unclear, Dr. Pham speculated that the combination of atopic diseases may be leading to a stronger inflammatory response.
It remains to be seen if a similar relationship occurs with other atopic diseases, and future research could examine other factors. “I think it’d be good to look at not just age and gender, but BMI and occupation, things like that,” said Dr. Pham.
The study was of particular interest to Michelle Robertson, MD, who was in the audience. She is the director for clinical services at the Airborne Hazards and Burn Pits Center of Excellence at the New Jersey War-Related Illness and Injury Study Center. “We see a significant number of [veterans] who have been diagnosed with both asthma and eosinophilic esophagitis, and our thinking is that that is likely related to some of the military exposures: In particular, [what the] deployed veterans encountered in the Gulf War, [such as] the smoke from burn pits, sand and dust storms, and smoke from oil well fires. Our thinking is that the particulate matter, the PM 2.5, the very, very tiny particles, may be either sensitizing the lung area and/or esophagus and predisposing them to having those symptoms when they return home,” said Dr. Robertson, in an interview.
Particles in this size range may be able to bypass the protected areas of the nose and the lungs to reach the alveoli, where they could potentially interfere with the transfer of air between the lungs and the rest of the body, which could in turn lead to a variety of inflammatory conditions, according to Dr. Robertson.
She noted that particle exposure varies with a soldier’s wartime occupation, with higher exposures among mechanics and burn pit managers, for example. However, the highest levels of exposure do not predict later illness, which is a natural prompt for future research. “The second part of this whole pathophysiology is susceptibility. Is there something about those people that do get sick that makes them more susceptible than folks that don’t, even though they both have the same jobs?”
Dr. Pham and Dr. Robertson have no relevant financial disclosures.
, according to a new analysis of data from HCA Healthcare.
Not much work has been done on the overlap between the two conditions, both of which are believed to be driven by the action of both eosinophils and helper T cells, according to Linda Pham, DO, who presented the research at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST).
“I have a colleague who is interested in GI and he’s really interested in EOE. We thought it would be nice to look at those populations of patients to see if there’s a correlation between them aside from just the atopic disease,” said Dr. Pham, who is an internal medicine resident at Riverside (Calif.) Community Hospital.
The findings underscore the need for assessing individual patient risk. “Having another concomitant disease like EoE, or maybe like atopic dermatitis, might cause you to have more severe [asthma] exacerbations causing you to go into the hospital more. I think if patients have more of these diseases, doctors can be more cognizant that they need to really be on top of treatment and make sure that [their patients] are aware of themselves so that if their symptoms exacerbate, they can go to the hospital and seek care,” said Dr. Pham.
The study was a retrospective analysis of 3,678,812 patients with asthma and 5,823 patients with both EoE and asthma. The data was drawn from 185 HCA hospitals, with records between 2016 and 2021.
The incidence of both asthma and asthma with EoE remained stable between 2016 and 2021. Dr. Pham pointed out that there are good methods to diagnose both conditions, which suggests that existing treatments are effective enough to be limiting the need for emergency treatment, according to Dr. Pham.
Among patients hospitalized with asthma alone, 72.55% were female, while 27.45% were male (P < .001). The numbers were much more evenly split among those with asthma and EoE, at 51.78% and 48.22%, respectively. The differing gender statistics aren’t easy to explain. “It’s not quite clear whether it’s because they just have more severe symptoms, or if it is other factors causing women to seek care more than their male counterparts. It could be personal biases, or it could be the asthma itself that is more severe in women,” said Dr. Pham.
When they broke down the analysis by sex, the researchers found that male EoE patients without asthma were a mean value of 5.517 years older than male EoE patients with asthma, and the mean difference was 5.480 years in female patients (P < .001 for both).
Although the direct cause of earlier hospitalization among patients with concomitant EoE and asthma is unclear, Dr. Pham speculated that the combination of atopic diseases may be leading to a stronger inflammatory response.
It remains to be seen if a similar relationship occurs with other atopic diseases, and future research could examine other factors. “I think it’d be good to look at not just age and gender, but BMI and occupation, things like that,” said Dr. Pham.
The study was of particular interest to Michelle Robertson, MD, who was in the audience. She is the director for clinical services at the Airborne Hazards and Burn Pits Center of Excellence at the New Jersey War-Related Illness and Injury Study Center. “We see a significant number of [veterans] who have been diagnosed with both asthma and eosinophilic esophagitis, and our thinking is that that is likely related to some of the military exposures: In particular, [what the] deployed veterans encountered in the Gulf War, [such as] the smoke from burn pits, sand and dust storms, and smoke from oil well fires. Our thinking is that the particulate matter, the PM 2.5, the very, very tiny particles, may be either sensitizing the lung area and/or esophagus and predisposing them to having those symptoms when they return home,” said Dr. Robertson, in an interview.
Particles in this size range may be able to bypass the protected areas of the nose and the lungs to reach the alveoli, where they could potentially interfere with the transfer of air between the lungs and the rest of the body, which could in turn lead to a variety of inflammatory conditions, according to Dr. Robertson.
She noted that particle exposure varies with a soldier’s wartime occupation, with higher exposures among mechanics and burn pit managers, for example. However, the highest levels of exposure do not predict later illness, which is a natural prompt for future research. “The second part of this whole pathophysiology is susceptibility. Is there something about those people that do get sick that makes them more susceptible than folks that don’t, even though they both have the same jobs?”
Dr. Pham and Dr. Robertson have no relevant financial disclosures.
, according to a new analysis of data from HCA Healthcare.
Not much work has been done on the overlap between the two conditions, both of which are believed to be driven by the action of both eosinophils and helper T cells, according to Linda Pham, DO, who presented the research at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST).
“I have a colleague who is interested in GI and he’s really interested in EOE. We thought it would be nice to look at those populations of patients to see if there’s a correlation between them aside from just the atopic disease,” said Dr. Pham, who is an internal medicine resident at Riverside (Calif.) Community Hospital.
The findings underscore the need for assessing individual patient risk. “Having another concomitant disease like EoE, or maybe like atopic dermatitis, might cause you to have more severe [asthma] exacerbations causing you to go into the hospital more. I think if patients have more of these diseases, doctors can be more cognizant that they need to really be on top of treatment and make sure that [their patients] are aware of themselves so that if their symptoms exacerbate, they can go to the hospital and seek care,” said Dr. Pham.
The study was a retrospective analysis of 3,678,812 patients with asthma and 5,823 patients with both EoE and asthma. The data was drawn from 185 HCA hospitals, with records between 2016 and 2021.
The incidence of both asthma and asthma with EoE remained stable between 2016 and 2021. Dr. Pham pointed out that there are good methods to diagnose both conditions, which suggests that existing treatments are effective enough to be limiting the need for emergency treatment, according to Dr. Pham.
Among patients hospitalized with asthma alone, 72.55% were female, while 27.45% were male (P < .001). The numbers were much more evenly split among those with asthma and EoE, at 51.78% and 48.22%, respectively. The differing gender statistics aren’t easy to explain. “It’s not quite clear whether it’s because they just have more severe symptoms, or if it is other factors causing women to seek care more than their male counterparts. It could be personal biases, or it could be the asthma itself that is more severe in women,” said Dr. Pham.
When they broke down the analysis by sex, the researchers found that male EoE patients without asthma were a mean value of 5.517 years older than male EoE patients with asthma, and the mean difference was 5.480 years in female patients (P < .001 for both).
Although the direct cause of earlier hospitalization among patients with concomitant EoE and asthma is unclear, Dr. Pham speculated that the combination of atopic diseases may be leading to a stronger inflammatory response.
It remains to be seen if a similar relationship occurs with other atopic diseases, and future research could examine other factors. “I think it’d be good to look at not just age and gender, but BMI and occupation, things like that,” said Dr. Pham.
The study was of particular interest to Michelle Robertson, MD, who was in the audience. She is the director for clinical services at the Airborne Hazards and Burn Pits Center of Excellence at the New Jersey War-Related Illness and Injury Study Center. “We see a significant number of [veterans] who have been diagnosed with both asthma and eosinophilic esophagitis, and our thinking is that that is likely related to some of the military exposures: In particular, [what the] deployed veterans encountered in the Gulf War, [such as] the smoke from burn pits, sand and dust storms, and smoke from oil well fires. Our thinking is that the particulate matter, the PM 2.5, the very, very tiny particles, may be either sensitizing the lung area and/or esophagus and predisposing them to having those symptoms when they return home,” said Dr. Robertson, in an interview.
Particles in this size range may be able to bypass the protected areas of the nose and the lungs to reach the alveoli, where they could potentially interfere with the transfer of air between the lungs and the rest of the body, which could in turn lead to a variety of inflammatory conditions, according to Dr. Robertson.
She noted that particle exposure varies with a soldier’s wartime occupation, with higher exposures among mechanics and burn pit managers, for example. However, the highest levels of exposure do not predict later illness, which is a natural prompt for future research. “The second part of this whole pathophysiology is susceptibility. Is there something about those people that do get sick that makes them more susceptible than folks that don’t, even though they both have the same jobs?”
Dr. Pham and Dr. Robertson have no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM CHEST 2023
MS, DMTs, and pregnancy: Beware of over-caution regarding treatment
MILAN – The news about multiple sclerosis (MS) and child-bearing in women is largely good, a researcher told colleagues at the 9th Joint ECTRIMS-ACTRIMS Meeting. However, there are still uncertainties about the timing of medical treatment for MS before, during, and after pregnancy.
Epidemiologist Emmanuelle Leray, PhD, of French School of Public Health in Rennes, urged neurologists to not be too eager to take women off medication – or too slow to put them back on it. “MS should not be undertreated due to a desire for pregnancy, as there are several options that are possible and compatible with pregnancy,” she said. As for after pregnancy, when women face a well-known high risk of MS rebound, “we can reasonably assume that women with active MS need to be advised to restart rapid, highly effective DMT [disease-modifying therapy] soon after delivery,” she said.
Women are more likely than men to develop MS, and they often do so during child-bearing years. Pregnancy among women with MS has become more common over the years: A 2018 Neurology study examined U.S. data from 2006 to 2014 and reported that the annual adjusted proportion of women with MS and pregnancy increased from 7.91% to 9.47%.
While it appears that women with MS get pregnant less often than the age-matched general population, that “doesn’t mean that fertility is impaired. It probably rather reflects the impact of an early diagnosis of MS on associated consequences regarding psychological and physical impact,” Dr. Leray said. “Regarding pregnancy outcomes, there is no evidence of an increased risk of prematurity or adverse neonatal outcomes. That’s why we can assume that multiple sclerosis will not impact the course of pregnancy and does not make a pregnancy at-risk.”
But some treatments may be harmful to the fetus, she said. Teriflunomide must be stopped before pregnancy. Natalizumab and fingolimod-siponimod raise the risk of rebound, and alternate drugs should be considered before pregnancy. However, anti–CD 20 drugs and cladribine “may be a relevant option because their use before pregnancy may provide effective disease control without exposing the fetus or the baby.”
Should women be on MS drugs at all during pregnancy, a period when MS typically wanes? “The recommendation is to discontinue disease-modifying therapy before conception,” Dr. Leray said. “However, we know now that some DMTs can be used safely during pregnancy, especially injectables.” Specifically, beta interferon and glatiramer acetate can be used safely during pregnancy, she said.
The biggest hurdle comes after pregnancy, when women face a high risk of MS rebound. The relapse rate has fallen in recent years from about 30% to 11%-14%, Dr. Leray said, possibly because of the rise of more effective treatment. But the risk, she said, is still significant.
What can clinicians do to avert relapse? According to Dr. Leray, research has failed to support several possible alternatives to DMTs – high-dose corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, and hormonal treatment. “There was no evidence of efficacy of any of these strategies, both in randomized clinical trials and in real-world studies.”
For now, it seems best to restart DMTs as soon as possible after delivery, Dr. Leray said. She urged colleagues to keep in mind that it takes about 3 months for DMTs to reach full efficacy – and research suggests the highest risk of relapse is during the first 3 months after delivery. “That has to be taken into account in the therapeutic strategy,” she said.
Dr. Leray reports consulting/lecture/travel grants from Biogen, Genzyme, MedDay, Merck, Novartis, and Roche.
MILAN – The news about multiple sclerosis (MS) and child-bearing in women is largely good, a researcher told colleagues at the 9th Joint ECTRIMS-ACTRIMS Meeting. However, there are still uncertainties about the timing of medical treatment for MS before, during, and after pregnancy.
Epidemiologist Emmanuelle Leray, PhD, of French School of Public Health in Rennes, urged neurologists to not be too eager to take women off medication – or too slow to put them back on it. “MS should not be undertreated due to a desire for pregnancy, as there are several options that are possible and compatible with pregnancy,” she said. As for after pregnancy, when women face a well-known high risk of MS rebound, “we can reasonably assume that women with active MS need to be advised to restart rapid, highly effective DMT [disease-modifying therapy] soon after delivery,” she said.
Women are more likely than men to develop MS, and they often do so during child-bearing years. Pregnancy among women with MS has become more common over the years: A 2018 Neurology study examined U.S. data from 2006 to 2014 and reported that the annual adjusted proportion of women with MS and pregnancy increased from 7.91% to 9.47%.
While it appears that women with MS get pregnant less often than the age-matched general population, that “doesn’t mean that fertility is impaired. It probably rather reflects the impact of an early diagnosis of MS on associated consequences regarding psychological and physical impact,” Dr. Leray said. “Regarding pregnancy outcomes, there is no evidence of an increased risk of prematurity or adverse neonatal outcomes. That’s why we can assume that multiple sclerosis will not impact the course of pregnancy and does not make a pregnancy at-risk.”
But some treatments may be harmful to the fetus, she said. Teriflunomide must be stopped before pregnancy. Natalizumab and fingolimod-siponimod raise the risk of rebound, and alternate drugs should be considered before pregnancy. However, anti–CD 20 drugs and cladribine “may be a relevant option because their use before pregnancy may provide effective disease control without exposing the fetus or the baby.”
Should women be on MS drugs at all during pregnancy, a period when MS typically wanes? “The recommendation is to discontinue disease-modifying therapy before conception,” Dr. Leray said. “However, we know now that some DMTs can be used safely during pregnancy, especially injectables.” Specifically, beta interferon and glatiramer acetate can be used safely during pregnancy, she said.
The biggest hurdle comes after pregnancy, when women face a high risk of MS rebound. The relapse rate has fallen in recent years from about 30% to 11%-14%, Dr. Leray said, possibly because of the rise of more effective treatment. But the risk, she said, is still significant.
What can clinicians do to avert relapse? According to Dr. Leray, research has failed to support several possible alternatives to DMTs – high-dose corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, and hormonal treatment. “There was no evidence of efficacy of any of these strategies, both in randomized clinical trials and in real-world studies.”
For now, it seems best to restart DMTs as soon as possible after delivery, Dr. Leray said. She urged colleagues to keep in mind that it takes about 3 months for DMTs to reach full efficacy – and research suggests the highest risk of relapse is during the first 3 months after delivery. “That has to be taken into account in the therapeutic strategy,” she said.
Dr. Leray reports consulting/lecture/travel grants from Biogen, Genzyme, MedDay, Merck, Novartis, and Roche.
MILAN – The news about multiple sclerosis (MS) and child-bearing in women is largely good, a researcher told colleagues at the 9th Joint ECTRIMS-ACTRIMS Meeting. However, there are still uncertainties about the timing of medical treatment for MS before, during, and after pregnancy.
Epidemiologist Emmanuelle Leray, PhD, of French School of Public Health in Rennes, urged neurologists to not be too eager to take women off medication – or too slow to put them back on it. “MS should not be undertreated due to a desire for pregnancy, as there are several options that are possible and compatible with pregnancy,” she said. As for after pregnancy, when women face a well-known high risk of MS rebound, “we can reasonably assume that women with active MS need to be advised to restart rapid, highly effective DMT [disease-modifying therapy] soon after delivery,” she said.
Women are more likely than men to develop MS, and they often do so during child-bearing years. Pregnancy among women with MS has become more common over the years: A 2018 Neurology study examined U.S. data from 2006 to 2014 and reported that the annual adjusted proportion of women with MS and pregnancy increased from 7.91% to 9.47%.
While it appears that women with MS get pregnant less often than the age-matched general population, that “doesn’t mean that fertility is impaired. It probably rather reflects the impact of an early diagnosis of MS on associated consequences regarding psychological and physical impact,” Dr. Leray said. “Regarding pregnancy outcomes, there is no evidence of an increased risk of prematurity or adverse neonatal outcomes. That’s why we can assume that multiple sclerosis will not impact the course of pregnancy and does not make a pregnancy at-risk.”
But some treatments may be harmful to the fetus, she said. Teriflunomide must be stopped before pregnancy. Natalizumab and fingolimod-siponimod raise the risk of rebound, and alternate drugs should be considered before pregnancy. However, anti–CD 20 drugs and cladribine “may be a relevant option because their use before pregnancy may provide effective disease control without exposing the fetus or the baby.”
Should women be on MS drugs at all during pregnancy, a period when MS typically wanes? “The recommendation is to discontinue disease-modifying therapy before conception,” Dr. Leray said. “However, we know now that some DMTs can be used safely during pregnancy, especially injectables.” Specifically, beta interferon and glatiramer acetate can be used safely during pregnancy, she said.
The biggest hurdle comes after pregnancy, when women face a high risk of MS rebound. The relapse rate has fallen in recent years from about 30% to 11%-14%, Dr. Leray said, possibly because of the rise of more effective treatment. But the risk, she said, is still significant.
What can clinicians do to avert relapse? According to Dr. Leray, research has failed to support several possible alternatives to DMTs – high-dose corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, and hormonal treatment. “There was no evidence of efficacy of any of these strategies, both in randomized clinical trials and in real-world studies.”
For now, it seems best to restart DMTs as soon as possible after delivery, Dr. Leray said. She urged colleagues to keep in mind that it takes about 3 months for DMTs to reach full efficacy – and research suggests the highest risk of relapse is during the first 3 months after delivery. “That has to be taken into account in the therapeutic strategy,” she said.
Dr. Leray reports consulting/lecture/travel grants from Biogen, Genzyme, MedDay, Merck, Novartis, and Roche.
AT ECTRIMS 2023
LSD use triples among young adults with depression
TOPLINE:
The increase was especially high among young adults and those earning less than $75,000 a year.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators analyzed responses of 478,500 adult respondents to the NSDUH, a cross-sectional, in-person survey administered by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration between 2008 and 2019.
- Respondents were questioned about past-month and past-year LSD use and past-year depression.
- Investigators conducted statistical analysis between December 2022 and June 2023.
TAKEAWAY:
- Past-year use of LSD increased significantly more among adults with major depression, increasing from 0.5% in 2008 to 1.8% in 2019 (prevalence difference, 1.3% [95% confidence interval, 1.0%-1.6%]) compared with adults without major depression.
- This difference was particularly pronounced among young adults with depression age 34 years or younger (PD for age 18-25 years, 3.3% [95% CI, 2.5%-4.2%]; PD for age 26-34 years, 2.7% [95% CI, 1.6%-3.8%]).
- The increase was also higher among those earning less than $75,000 per year (PD for < $20,000, 1.9% [95% CI, 1.3%-2.6%]; PD for $20,000-$49,999, 1.5% [95% CI, 1.0%-2.1%]; PD for $50,000-$74,999, 1.3% [95% CI, 0.7%-2.0%]).
- Use of other hallucinogen classes either decreased or increased only among select age groups or time frames; the use of LSD consistently increased among every observed age group from 2002 to 2019.
IN PRACTICE:
“Future research should aim to understand the motivations for LSD use as well as the directionality between nonmedical LSD use and depression. As the evaluation of LSD as a potential psychiatric treatment continues, public health efforts to promote safe and evidence-based use of psychedelics are critical,” the investigators write.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Deborah S. Hasin, PhD, of Columbia University’s department of psychiatry, New York, and published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations include the use of self-reporting measures in the NSDUH and the lack of information about motives for or doses of LSD use.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The increase was especially high among young adults and those earning less than $75,000 a year.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators analyzed responses of 478,500 adult respondents to the NSDUH, a cross-sectional, in-person survey administered by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration between 2008 and 2019.
- Respondents were questioned about past-month and past-year LSD use and past-year depression.
- Investigators conducted statistical analysis between December 2022 and June 2023.
TAKEAWAY:
- Past-year use of LSD increased significantly more among adults with major depression, increasing from 0.5% in 2008 to 1.8% in 2019 (prevalence difference, 1.3% [95% confidence interval, 1.0%-1.6%]) compared with adults without major depression.
- This difference was particularly pronounced among young adults with depression age 34 years or younger (PD for age 18-25 years, 3.3% [95% CI, 2.5%-4.2%]; PD for age 26-34 years, 2.7% [95% CI, 1.6%-3.8%]).
- The increase was also higher among those earning less than $75,000 per year (PD for < $20,000, 1.9% [95% CI, 1.3%-2.6%]; PD for $20,000-$49,999, 1.5% [95% CI, 1.0%-2.1%]; PD for $50,000-$74,999, 1.3% [95% CI, 0.7%-2.0%]).
- Use of other hallucinogen classes either decreased or increased only among select age groups or time frames; the use of LSD consistently increased among every observed age group from 2002 to 2019.
IN PRACTICE:
“Future research should aim to understand the motivations for LSD use as well as the directionality between nonmedical LSD use and depression. As the evaluation of LSD as a potential psychiatric treatment continues, public health efforts to promote safe and evidence-based use of psychedelics are critical,” the investigators write.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Deborah S. Hasin, PhD, of Columbia University’s department of psychiatry, New York, and published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations include the use of self-reporting measures in the NSDUH and the lack of information about motives for or doses of LSD use.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The increase was especially high among young adults and those earning less than $75,000 a year.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators analyzed responses of 478,500 adult respondents to the NSDUH, a cross-sectional, in-person survey administered by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration between 2008 and 2019.
- Respondents were questioned about past-month and past-year LSD use and past-year depression.
- Investigators conducted statistical analysis between December 2022 and June 2023.
TAKEAWAY:
- Past-year use of LSD increased significantly more among adults with major depression, increasing from 0.5% in 2008 to 1.8% in 2019 (prevalence difference, 1.3% [95% confidence interval, 1.0%-1.6%]) compared with adults without major depression.
- This difference was particularly pronounced among young adults with depression age 34 years or younger (PD for age 18-25 years, 3.3% [95% CI, 2.5%-4.2%]; PD for age 26-34 years, 2.7% [95% CI, 1.6%-3.8%]).
- The increase was also higher among those earning less than $75,000 per year (PD for < $20,000, 1.9% [95% CI, 1.3%-2.6%]; PD for $20,000-$49,999, 1.5% [95% CI, 1.0%-2.1%]; PD for $50,000-$74,999, 1.3% [95% CI, 0.7%-2.0%]).
- Use of other hallucinogen classes either decreased or increased only among select age groups or time frames; the use of LSD consistently increased among every observed age group from 2002 to 2019.
IN PRACTICE:
“Future research should aim to understand the motivations for LSD use as well as the directionality between nonmedical LSD use and depression. As the evaluation of LSD as a potential psychiatric treatment continues, public health efforts to promote safe and evidence-based use of psychedelics are critical,” the investigators write.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Deborah S. Hasin, PhD, of Columbia University’s department of psychiatry, New York, and published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations include the use of self-reporting measures in the NSDUH and the lack of information about motives for or doses of LSD use.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA PSYCHIATRY
CMS ‘million hearts’ CVD risk reduction model works
TOPLINE:
The Million Hearts Model, a U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) initiative that encouraged and paid health care organizations to assess and reduce cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, reduced first-time myocardial infarction (MI) and strokes among Medicare beneficiaries without significant changes in Medicare spending, a randomized trial finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed the Million Hearts CVD Risk Reduction Model in a pragmatic, cluster-randomized trial among 342 health care organizations – half in the intervention group and half in the standard care control group.
- Among 218,684 medium- or high-risk Medicare beneficiaries (median age, 72 years), 130,578 were in the intervention group in which Medicare paid for guideline-concordant care including routine CVD risk assessment, and 88,286 were in the standard care group.
- Outcomes included first time CVD events (for instance, MI, stroke, transient ischemic attack), combined first-time CVD events and CVD deaths, and Medicare spending.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median follow-up of 4.3 years, the intervention group had a 3.3% lower rate of CVD events than the control group (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.97; 90% confidence interval, 0.93-1.00; P = .09) and a 4.2% lower rate of combined first-time CVD events and CVD deaths (HR, 0.96; 90% CI, 0.93-0.99; P = .02).
- These relative effects represent an absolute re.duction of 0.3 percentage points in the probability of a CVD event over 5 years (7.8% intervention vs 8.1%) and 0.4 percentage points in the probability of a CVD event or CVD death over 5 years (9.3% intervention vs. 9.7% control).
- The intervention group also had a 4.3% lower death rate (HR, 0.96; 90% CI, 0.93-0.98; P = .01; absolute reduction of 0.5 percentage points over 5 years).
- Analyses by cause of death showed the largest relative declines (10.6%) among deaths due to coronary heart disease and CVD.
- There was no significant between-group difference in Medicare spending on CVD events or in overall Medicare Parts A and B spending.
IN PRACTICE:
“The model was unique in paying for overall CVD risk reduction, measured by a novel, longitudinal risk calculator, rather than tying performance-based payments to control of individual risk factors,” the authors write.
“The encouraging findings from the Million Hearts Model suggest that modernized payment models may be an affirmative strategy to [incentivize guideline-concordant CVD preventive care and improve outcomes], though further work is needed to ensure that these models are patient-centric, optimally deployed, and equity-enhancing,” add the editorial writers.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Laura Blue, PhD, Mathematica, Washington, was published online in JAMA, with an accompanying editorial.
LIMITATIONS:
The main limitation is nonparticipation of many of the organizations (516 were randomly assigned to one of the study groups, 342 participated) and incomplete entry of beneficiary data into the registry, which could have led to systematic differences between the two groups. Bias due to the selective participation of organizations and beneficiaries cannot be ruled out.
DISCLOSURES:
Funding for the study was provided by CMS, Department of Health & Human Services. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The Million Hearts Model, a U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) initiative that encouraged and paid health care organizations to assess and reduce cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, reduced first-time myocardial infarction (MI) and strokes among Medicare beneficiaries without significant changes in Medicare spending, a randomized trial finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed the Million Hearts CVD Risk Reduction Model in a pragmatic, cluster-randomized trial among 342 health care organizations – half in the intervention group and half in the standard care control group.
- Among 218,684 medium- or high-risk Medicare beneficiaries (median age, 72 years), 130,578 were in the intervention group in which Medicare paid for guideline-concordant care including routine CVD risk assessment, and 88,286 were in the standard care group.
- Outcomes included first time CVD events (for instance, MI, stroke, transient ischemic attack), combined first-time CVD events and CVD deaths, and Medicare spending.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median follow-up of 4.3 years, the intervention group had a 3.3% lower rate of CVD events than the control group (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.97; 90% confidence interval, 0.93-1.00; P = .09) and a 4.2% lower rate of combined first-time CVD events and CVD deaths (HR, 0.96; 90% CI, 0.93-0.99; P = .02).
- These relative effects represent an absolute re.duction of 0.3 percentage points in the probability of a CVD event over 5 years (7.8% intervention vs 8.1%) and 0.4 percentage points in the probability of a CVD event or CVD death over 5 years (9.3% intervention vs. 9.7% control).
- The intervention group also had a 4.3% lower death rate (HR, 0.96; 90% CI, 0.93-0.98; P = .01; absolute reduction of 0.5 percentage points over 5 years).
- Analyses by cause of death showed the largest relative declines (10.6%) among deaths due to coronary heart disease and CVD.
- There was no significant between-group difference in Medicare spending on CVD events or in overall Medicare Parts A and B spending.
IN PRACTICE:
“The model was unique in paying for overall CVD risk reduction, measured by a novel, longitudinal risk calculator, rather than tying performance-based payments to control of individual risk factors,” the authors write.
“The encouraging findings from the Million Hearts Model suggest that modernized payment models may be an affirmative strategy to [incentivize guideline-concordant CVD preventive care and improve outcomes], though further work is needed to ensure that these models are patient-centric, optimally deployed, and equity-enhancing,” add the editorial writers.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Laura Blue, PhD, Mathematica, Washington, was published online in JAMA, with an accompanying editorial.
LIMITATIONS:
The main limitation is nonparticipation of many of the organizations (516 were randomly assigned to one of the study groups, 342 participated) and incomplete entry of beneficiary data into the registry, which could have led to systematic differences between the two groups. Bias due to the selective participation of organizations and beneficiaries cannot be ruled out.
DISCLOSURES:
Funding for the study was provided by CMS, Department of Health & Human Services. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The Million Hearts Model, a U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) initiative that encouraged and paid health care organizations to assess and reduce cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, reduced first-time myocardial infarction (MI) and strokes among Medicare beneficiaries without significant changes in Medicare spending, a randomized trial finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers assessed the Million Hearts CVD Risk Reduction Model in a pragmatic, cluster-randomized trial among 342 health care organizations – half in the intervention group and half in the standard care control group.
- Among 218,684 medium- or high-risk Medicare beneficiaries (median age, 72 years), 130,578 were in the intervention group in which Medicare paid for guideline-concordant care including routine CVD risk assessment, and 88,286 were in the standard care group.
- Outcomes included first time CVD events (for instance, MI, stroke, transient ischemic attack), combined first-time CVD events and CVD deaths, and Medicare spending.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median follow-up of 4.3 years, the intervention group had a 3.3% lower rate of CVD events than the control group (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.97; 90% confidence interval, 0.93-1.00; P = .09) and a 4.2% lower rate of combined first-time CVD events and CVD deaths (HR, 0.96; 90% CI, 0.93-0.99; P = .02).
- These relative effects represent an absolute re.duction of 0.3 percentage points in the probability of a CVD event over 5 years (7.8% intervention vs 8.1%) and 0.4 percentage points in the probability of a CVD event or CVD death over 5 years (9.3% intervention vs. 9.7% control).
- The intervention group also had a 4.3% lower death rate (HR, 0.96; 90% CI, 0.93-0.98; P = .01; absolute reduction of 0.5 percentage points over 5 years).
- Analyses by cause of death showed the largest relative declines (10.6%) among deaths due to coronary heart disease and CVD.
- There was no significant between-group difference in Medicare spending on CVD events or in overall Medicare Parts A and B spending.
IN PRACTICE:
“The model was unique in paying for overall CVD risk reduction, measured by a novel, longitudinal risk calculator, rather than tying performance-based payments to control of individual risk factors,” the authors write.
“The encouraging findings from the Million Hearts Model suggest that modernized payment models may be an affirmative strategy to [incentivize guideline-concordant CVD preventive care and improve outcomes], though further work is needed to ensure that these models are patient-centric, optimally deployed, and equity-enhancing,” add the editorial writers.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Laura Blue, PhD, Mathematica, Washington, was published online in JAMA, with an accompanying editorial.
LIMITATIONS:
The main limitation is nonparticipation of many of the organizations (516 were randomly assigned to one of the study groups, 342 participated) and incomplete entry of beneficiary data into the registry, which could have led to systematic differences between the two groups. Bias due to the selective participation of organizations and beneficiaries cannot be ruled out.
DISCLOSURES:
Funding for the study was provided by CMS, Department of Health & Human Services. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chemo-immunotherapy good, adding a PARP inhibitor better in endometrial cancer?
MADRID – Research presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting 2023 underline the benefit of adding immunotherapy to chemotherapy in advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer, and question whether adding the PARP inhibitor olaparib to the chemo-immunotherapy combination could provide further benefit.
In the AtTEnd trial, presented on Oct. 21, more than 550 patients with advanced newly diagnosed or recurrent disease were randomized to the antiprogrammed death–ligand 1 (PD-L1) antibody atezolizumab (Tecentriq) or placebo plus chemotherapy followed by maintenance atezolizumab or placebo.
– 28.1% vs. 17% at 2 years. The PFS benefit was much more pronounced among patients with mismatch repair-deficient (dMMR) disease – 50.4% vs. 16% at 2 years. Mismatch repair-deficient disease patients receiving atezolizumab also demonstrated an early overall survival benefit, according to findings from the interim analysis.
In the DUO-E trial, presented during the same Oct. 21 session, nearly 720 patients with newly diagnosed advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer were randomized to one of three groups: Chemotherapy alone with maintenance placebo, chemotherapy plus durvalumab (Imfinzi) with maintenance durvalumab, or chemotherapy plus durvalumab with maintenance durvalumab and the PARP inhibitor olaparib.
The results, published simultaneously in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, showed that adding durvalumab to chemotherapy followed by maintenance durvalumab with or without olaparib led to a significant improvement in PFS, compared with chemotherapy alone. As in the AtTEnd trial, this PFS was also more pronounced in dMMR patients.
Overall, Andrés Cervantes, MD, PhD, from the University of Valencia, Spain, and president of ESMO, explained that this research marks “very positive data for women with gynecological cancers,” with immunotherapy now incorporated into the standard of care.
However, an expert questioned whether the DUO-E trial clearly demonstrated the benefit of adding olaparib to immuno- and chemotherapy and whether certain subsets of patients may be more likely to benefit from the PARP inhibitor.
Inside AtTEnd
A growing body of research has shown that single agent immunotherapy is effective in treating endometrial cancer, particularly in tumors with dMMR, and that immunotherapy and chemotherapy may have a synergistic effect.
David S. P. Tan, MD, PhD, National University Cancer Institute, Singapore, who was not involved in the studies, commented that “the molecular classification of endometrial cancer is now leading us to areas that we didn’t think before [were] possible.”
The rationale for combining immunotherapy with chemotherapy, Dr. Tan explained, is that “the cytotoxicity you get from chemotherapy is partly dependent on immune activity within the tumor, and so it makes sense” to combine them.
This approach was borne out by recent positive PFS results from the NRG-GY018 trial of pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in advanced endometrial cancer as well as from the RUBY trial of dostarlimab in primary advanced or recurrent disease.
To further investigate this chemo-immunotherapy strategy, the AtTEnd team enrolled patients with newly diagnosed or recurrent stage III-IV disease who had received no prior systemic chemotherapy for recurrence within the previous 6 months.
Overall, 551 patients from 89 sites across 10 countries were randomized to standard first-line chemotherapy – carboplatin plus paclitaxel – with either atezolizumab or placebo, followed by maintenance atezolizumab or placebo, which continued until confirmed disease progression.
The median age in the intention-to-treat population was 64-67 years. Nearly 23% of patients had dMMR tumors, and 67.2% had recurrent disease.
The baseline characteristics were well balanced and distributed between arms in the dMMR and all-comers population, said Nicoletta Colombo, MD, University of Milan–Bicocca, European Institute of Oncology Istituto di Ricovero e Cura a Carattere Scientifico, Italy, who presented the findings at ESMO.
Over a median follow up of 26.2 months, Dr. Colombo and colleagues observed a statistically significant improvement in PFS in the dMMR arm in favor of atezolizumab (hazard ratio, 0.36; P = .0005). At 2 years, 50.4% of patients receiving the immunotherapy were progression-free, compared with 16.0% in the placebo arm.
In all-comers, the PFS improvement with atezolizumab was less pronounced but remained significant (HR, 0.74; P = .0219).
A secondary analysis revealed, among dMMR patients, atezolizumab was associated with an overall survival advantage over placebo (HR, 0.41), with 75% of patients still alive at 2 years vs. 54.2% in the placebo arm. Dr. Colombo also noted a “clear trend” for improved overall survival with atezolizumab as well (HR, 0.82; P = .0483), but no PFS or overall survival benefit was seen with atezolizumab in MMR proficient (pMMR) patients.
Dr. Colombo said the safety profile of atezolizumab plus chemotherapy was “manageable,” with no differences in the rates of “major side effects,” although there was an increase in the rate of treatment-related grade ≥ 3 adverse events in the atezolizumab group (25.8% vs. 14.1%).
Dr. Tan noted that the AtTEnd trial revealed comparable results to earlier trials in this space but underlined that the survival curves in the interim analysis revealed a “red zone” of dMMR patients who do not respond to the combination and in whom immunotherapy is “not sufficient.”
Alongside this, Dr. Tan flagged a “blue zone” of dMMR patients who plateaued in both PFS and overall survival after 2 years. The question for these patients at this point is whether they need to continue immunotherapy beyond 24 months, he said.
But overall, Dr. Tan noted, the AtTEnd data “continue to validate practice-changing therapy for dMMR endometrial cancer patients” with immunotherapy plus chemotherapy, with the lack of benefit in pMMR disease underscoring an “unmet medical need.”
Inside DUO-E
The burning question, however, was whether adding a PARP inhibitor to immunotherapy and chemotherapy would boost the survival outcomes further.
The DUO-E trial involved patients with newly diagnosed stage III/IV or recurrent endometrial cancer who had not received systematic therapy for advanced disease and were naive to both PARP inhibitors and immune-mediated therapy.
Overall, 718 patients were randomized to one of three arms: Chemotherapy alone followed by maintenance placebo, chemotherapy plus durvalumab with maintenance durvalumab, or chemotherapy plus durvalumab with maintenance durvalumab plus olaparib.
Maintenance was continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, or the patients met another discontinuation criteria.
About half of patients were newly diagnosed, half had recurrent disease, and approximately one-fifth had dMMR disease, said Shannon Westin, MD, from the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, who presented the findings.
Compared with placebo plus chemotherapy, patients in both the durvalumab alone and durvalumab plus olaparib arms experienced a significant improvement in PFS (HR, 0.71; P = .003; and HR, 0.55; P < .0001, respectively).
This effect was amplified in dMMR patients with durvalumab (HR, 0.42) as well as with durvalumab plus olaparib (HR, 0.41).
In pMMR patients, PFS benefit was stronger in the durvalumab-olaparib arm vs. durvalumab (HR, 0.57 vs. 0.77).
Although the overall survival analysis remains exploratory, Dr. Westin noted a trend toward better overall survival in the two treatment arms vs. placebo (HR, 0.77 with durvalumab, and HR, 0.59 with durvalumab plus olaparib).
However, adding olaparib to the equation increased the rate of grade ≥ 3 adverse events – 67.2% vs. 54.9% with durvalumab and 56.4% with chemotherapy alone in the overall analysis. The addition of olaparib also led to treatment discontinuation in 24.4% of patients vs. 20.9% in the durvalumab arm and 18.6% in the chemotherapy alone arm.
Domenica Lorusso, MD, PhD, who was not involved in the study, commented that the marginal PFS benefit of adding olaparib in DUO-E is “not surprising” because the bar set by immunotherapy is “so high in this population that it’s very difficult” to go any higher.
But the results in pMMR patients reveal “a clear additional benefit” to olaparib, said Dr. Lorusso, from Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milan.
“The main limitation of the trial,” she continued, “is that it was not powered to make a formal comparison between the two experimental arms.”
So, what then is the added benefit of olaparib? “Unfortunately, that remains an unanswered question,” Dr. Lorusso said.
AtTEnd was sponsored by the Mario Negri Institute for Pharmacological Research.
DUO-E was funded by AstraZeneca.
Dr. Colombo declares relationships with AstraZeneca, Clovis Oncology, Esai, GSK, Immunogen, Mersana, MSD/Merck, Nuvation Bio, OncXerna, Pieris, Roche, and Novocure.
Dr. Tan declares relationships with AstraZeneca, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Bayer, Roche, MSD, Genmab, Esai, PMV, BioNTech, Ellipses Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck Serono, Takeda, and Clovis.
Dr. Westin declares relationships with AstraZeneca, Avenge Bio, Bayer, Bio-Path, Clovis, Genentech/Roche, GSK, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Mereo, Novartis, Nuvectis, and Zentalis; and consulting and advisory roles for AstraZeneca, Caris, Clovis, Eisai, EQRx, Genentech/Roche, Gilead, GSK, Immunocore, ImmunoGen, Lilly, Merck, Mersana, Mereo, NGM Bio, Nuvectis, Seagen, Verastem, Vincerx, Zentalis, and ZielBio.
Dr. Lorusso declares relationships with PharmaMar, Merck Serono, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Clovis, Tesaro/GSK, Genmab, Immunogen, and Roche.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MADRID – Research presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting 2023 underline the benefit of adding immunotherapy to chemotherapy in advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer, and question whether adding the PARP inhibitor olaparib to the chemo-immunotherapy combination could provide further benefit.
In the AtTEnd trial, presented on Oct. 21, more than 550 patients with advanced newly diagnosed or recurrent disease were randomized to the antiprogrammed death–ligand 1 (PD-L1) antibody atezolizumab (Tecentriq) or placebo plus chemotherapy followed by maintenance atezolizumab or placebo.
– 28.1% vs. 17% at 2 years. The PFS benefit was much more pronounced among patients with mismatch repair-deficient (dMMR) disease – 50.4% vs. 16% at 2 years. Mismatch repair-deficient disease patients receiving atezolizumab also demonstrated an early overall survival benefit, according to findings from the interim analysis.
In the DUO-E trial, presented during the same Oct. 21 session, nearly 720 patients with newly diagnosed advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer were randomized to one of three groups: Chemotherapy alone with maintenance placebo, chemotherapy plus durvalumab (Imfinzi) with maintenance durvalumab, or chemotherapy plus durvalumab with maintenance durvalumab and the PARP inhibitor olaparib.
The results, published simultaneously in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, showed that adding durvalumab to chemotherapy followed by maintenance durvalumab with or without olaparib led to a significant improvement in PFS, compared with chemotherapy alone. As in the AtTEnd trial, this PFS was also more pronounced in dMMR patients.
Overall, Andrés Cervantes, MD, PhD, from the University of Valencia, Spain, and president of ESMO, explained that this research marks “very positive data for women with gynecological cancers,” with immunotherapy now incorporated into the standard of care.
However, an expert questioned whether the DUO-E trial clearly demonstrated the benefit of adding olaparib to immuno- and chemotherapy and whether certain subsets of patients may be more likely to benefit from the PARP inhibitor.
Inside AtTEnd
A growing body of research has shown that single agent immunotherapy is effective in treating endometrial cancer, particularly in tumors with dMMR, and that immunotherapy and chemotherapy may have a synergistic effect.
David S. P. Tan, MD, PhD, National University Cancer Institute, Singapore, who was not involved in the studies, commented that “the molecular classification of endometrial cancer is now leading us to areas that we didn’t think before [were] possible.”
The rationale for combining immunotherapy with chemotherapy, Dr. Tan explained, is that “the cytotoxicity you get from chemotherapy is partly dependent on immune activity within the tumor, and so it makes sense” to combine them.
This approach was borne out by recent positive PFS results from the NRG-GY018 trial of pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in advanced endometrial cancer as well as from the RUBY trial of dostarlimab in primary advanced or recurrent disease.
To further investigate this chemo-immunotherapy strategy, the AtTEnd team enrolled patients with newly diagnosed or recurrent stage III-IV disease who had received no prior systemic chemotherapy for recurrence within the previous 6 months.
Overall, 551 patients from 89 sites across 10 countries were randomized to standard first-line chemotherapy – carboplatin plus paclitaxel – with either atezolizumab or placebo, followed by maintenance atezolizumab or placebo, which continued until confirmed disease progression.
The median age in the intention-to-treat population was 64-67 years. Nearly 23% of patients had dMMR tumors, and 67.2% had recurrent disease.
The baseline characteristics were well balanced and distributed between arms in the dMMR and all-comers population, said Nicoletta Colombo, MD, University of Milan–Bicocca, European Institute of Oncology Istituto di Ricovero e Cura a Carattere Scientifico, Italy, who presented the findings at ESMO.
Over a median follow up of 26.2 months, Dr. Colombo and colleagues observed a statistically significant improvement in PFS in the dMMR arm in favor of atezolizumab (hazard ratio, 0.36; P = .0005). At 2 years, 50.4% of patients receiving the immunotherapy were progression-free, compared with 16.0% in the placebo arm.
In all-comers, the PFS improvement with atezolizumab was less pronounced but remained significant (HR, 0.74; P = .0219).
A secondary analysis revealed, among dMMR patients, atezolizumab was associated with an overall survival advantage over placebo (HR, 0.41), with 75% of patients still alive at 2 years vs. 54.2% in the placebo arm. Dr. Colombo also noted a “clear trend” for improved overall survival with atezolizumab as well (HR, 0.82; P = .0483), but no PFS or overall survival benefit was seen with atezolizumab in MMR proficient (pMMR) patients.
Dr. Colombo said the safety profile of atezolizumab plus chemotherapy was “manageable,” with no differences in the rates of “major side effects,” although there was an increase in the rate of treatment-related grade ≥ 3 adverse events in the atezolizumab group (25.8% vs. 14.1%).
Dr. Tan noted that the AtTEnd trial revealed comparable results to earlier trials in this space but underlined that the survival curves in the interim analysis revealed a “red zone” of dMMR patients who do not respond to the combination and in whom immunotherapy is “not sufficient.”
Alongside this, Dr. Tan flagged a “blue zone” of dMMR patients who plateaued in both PFS and overall survival after 2 years. The question for these patients at this point is whether they need to continue immunotherapy beyond 24 months, he said.
But overall, Dr. Tan noted, the AtTEnd data “continue to validate practice-changing therapy for dMMR endometrial cancer patients” with immunotherapy plus chemotherapy, with the lack of benefit in pMMR disease underscoring an “unmet medical need.”
Inside DUO-E
The burning question, however, was whether adding a PARP inhibitor to immunotherapy and chemotherapy would boost the survival outcomes further.
The DUO-E trial involved patients with newly diagnosed stage III/IV or recurrent endometrial cancer who had not received systematic therapy for advanced disease and were naive to both PARP inhibitors and immune-mediated therapy.
Overall, 718 patients were randomized to one of three arms: Chemotherapy alone followed by maintenance placebo, chemotherapy plus durvalumab with maintenance durvalumab, or chemotherapy plus durvalumab with maintenance durvalumab plus olaparib.
Maintenance was continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, or the patients met another discontinuation criteria.
About half of patients were newly diagnosed, half had recurrent disease, and approximately one-fifth had dMMR disease, said Shannon Westin, MD, from the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, who presented the findings.
Compared with placebo plus chemotherapy, patients in both the durvalumab alone and durvalumab plus olaparib arms experienced a significant improvement in PFS (HR, 0.71; P = .003; and HR, 0.55; P < .0001, respectively).
This effect was amplified in dMMR patients with durvalumab (HR, 0.42) as well as with durvalumab plus olaparib (HR, 0.41).
In pMMR patients, PFS benefit was stronger in the durvalumab-olaparib arm vs. durvalumab (HR, 0.57 vs. 0.77).
Although the overall survival analysis remains exploratory, Dr. Westin noted a trend toward better overall survival in the two treatment arms vs. placebo (HR, 0.77 with durvalumab, and HR, 0.59 with durvalumab plus olaparib).
However, adding olaparib to the equation increased the rate of grade ≥ 3 adverse events – 67.2% vs. 54.9% with durvalumab and 56.4% with chemotherapy alone in the overall analysis. The addition of olaparib also led to treatment discontinuation in 24.4% of patients vs. 20.9% in the durvalumab arm and 18.6% in the chemotherapy alone arm.
Domenica Lorusso, MD, PhD, who was not involved in the study, commented that the marginal PFS benefit of adding olaparib in DUO-E is “not surprising” because the bar set by immunotherapy is “so high in this population that it’s very difficult” to go any higher.
But the results in pMMR patients reveal “a clear additional benefit” to olaparib, said Dr. Lorusso, from Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milan.
“The main limitation of the trial,” she continued, “is that it was not powered to make a formal comparison between the two experimental arms.”
So, what then is the added benefit of olaparib? “Unfortunately, that remains an unanswered question,” Dr. Lorusso said.
AtTEnd was sponsored by the Mario Negri Institute for Pharmacological Research.
DUO-E was funded by AstraZeneca.
Dr. Colombo declares relationships with AstraZeneca, Clovis Oncology, Esai, GSK, Immunogen, Mersana, MSD/Merck, Nuvation Bio, OncXerna, Pieris, Roche, and Novocure.
Dr. Tan declares relationships with AstraZeneca, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Bayer, Roche, MSD, Genmab, Esai, PMV, BioNTech, Ellipses Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck Serono, Takeda, and Clovis.
Dr. Westin declares relationships with AstraZeneca, Avenge Bio, Bayer, Bio-Path, Clovis, Genentech/Roche, GSK, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Mereo, Novartis, Nuvectis, and Zentalis; and consulting and advisory roles for AstraZeneca, Caris, Clovis, Eisai, EQRx, Genentech/Roche, Gilead, GSK, Immunocore, ImmunoGen, Lilly, Merck, Mersana, Mereo, NGM Bio, Nuvectis, Seagen, Verastem, Vincerx, Zentalis, and ZielBio.
Dr. Lorusso declares relationships with PharmaMar, Merck Serono, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Clovis, Tesaro/GSK, Genmab, Immunogen, and Roche.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MADRID – Research presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting 2023 underline the benefit of adding immunotherapy to chemotherapy in advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer, and question whether adding the PARP inhibitor olaparib to the chemo-immunotherapy combination could provide further benefit.
In the AtTEnd trial, presented on Oct. 21, more than 550 patients with advanced newly diagnosed or recurrent disease were randomized to the antiprogrammed death–ligand 1 (PD-L1) antibody atezolizumab (Tecentriq) or placebo plus chemotherapy followed by maintenance atezolizumab or placebo.
– 28.1% vs. 17% at 2 years. The PFS benefit was much more pronounced among patients with mismatch repair-deficient (dMMR) disease – 50.4% vs. 16% at 2 years. Mismatch repair-deficient disease patients receiving atezolizumab also demonstrated an early overall survival benefit, according to findings from the interim analysis.
In the DUO-E trial, presented during the same Oct. 21 session, nearly 720 patients with newly diagnosed advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer were randomized to one of three groups: Chemotherapy alone with maintenance placebo, chemotherapy plus durvalumab (Imfinzi) with maintenance durvalumab, or chemotherapy plus durvalumab with maintenance durvalumab and the PARP inhibitor olaparib.
The results, published simultaneously in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, showed that adding durvalumab to chemotherapy followed by maintenance durvalumab with or without olaparib led to a significant improvement in PFS, compared with chemotherapy alone. As in the AtTEnd trial, this PFS was also more pronounced in dMMR patients.
Overall, Andrés Cervantes, MD, PhD, from the University of Valencia, Spain, and president of ESMO, explained that this research marks “very positive data for women with gynecological cancers,” with immunotherapy now incorporated into the standard of care.
However, an expert questioned whether the DUO-E trial clearly demonstrated the benefit of adding olaparib to immuno- and chemotherapy and whether certain subsets of patients may be more likely to benefit from the PARP inhibitor.
Inside AtTEnd
A growing body of research has shown that single agent immunotherapy is effective in treating endometrial cancer, particularly in tumors with dMMR, and that immunotherapy and chemotherapy may have a synergistic effect.
David S. P. Tan, MD, PhD, National University Cancer Institute, Singapore, who was not involved in the studies, commented that “the molecular classification of endometrial cancer is now leading us to areas that we didn’t think before [were] possible.”
The rationale for combining immunotherapy with chemotherapy, Dr. Tan explained, is that “the cytotoxicity you get from chemotherapy is partly dependent on immune activity within the tumor, and so it makes sense” to combine them.
This approach was borne out by recent positive PFS results from the NRG-GY018 trial of pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in advanced endometrial cancer as well as from the RUBY trial of dostarlimab in primary advanced or recurrent disease.
To further investigate this chemo-immunotherapy strategy, the AtTEnd team enrolled patients with newly diagnosed or recurrent stage III-IV disease who had received no prior systemic chemotherapy for recurrence within the previous 6 months.
Overall, 551 patients from 89 sites across 10 countries were randomized to standard first-line chemotherapy – carboplatin plus paclitaxel – with either atezolizumab or placebo, followed by maintenance atezolizumab or placebo, which continued until confirmed disease progression.
The median age in the intention-to-treat population was 64-67 years. Nearly 23% of patients had dMMR tumors, and 67.2% had recurrent disease.
The baseline characteristics were well balanced and distributed between arms in the dMMR and all-comers population, said Nicoletta Colombo, MD, University of Milan–Bicocca, European Institute of Oncology Istituto di Ricovero e Cura a Carattere Scientifico, Italy, who presented the findings at ESMO.
Over a median follow up of 26.2 months, Dr. Colombo and colleagues observed a statistically significant improvement in PFS in the dMMR arm in favor of atezolizumab (hazard ratio, 0.36; P = .0005). At 2 years, 50.4% of patients receiving the immunotherapy were progression-free, compared with 16.0% in the placebo arm.
In all-comers, the PFS improvement with atezolizumab was less pronounced but remained significant (HR, 0.74; P = .0219).
A secondary analysis revealed, among dMMR patients, atezolizumab was associated with an overall survival advantage over placebo (HR, 0.41), with 75% of patients still alive at 2 years vs. 54.2% in the placebo arm. Dr. Colombo also noted a “clear trend” for improved overall survival with atezolizumab as well (HR, 0.82; P = .0483), but no PFS or overall survival benefit was seen with atezolizumab in MMR proficient (pMMR) patients.
Dr. Colombo said the safety profile of atezolizumab plus chemotherapy was “manageable,” with no differences in the rates of “major side effects,” although there was an increase in the rate of treatment-related grade ≥ 3 adverse events in the atezolizumab group (25.8% vs. 14.1%).
Dr. Tan noted that the AtTEnd trial revealed comparable results to earlier trials in this space but underlined that the survival curves in the interim analysis revealed a “red zone” of dMMR patients who do not respond to the combination and in whom immunotherapy is “not sufficient.”
Alongside this, Dr. Tan flagged a “blue zone” of dMMR patients who plateaued in both PFS and overall survival after 2 years. The question for these patients at this point is whether they need to continue immunotherapy beyond 24 months, he said.
But overall, Dr. Tan noted, the AtTEnd data “continue to validate practice-changing therapy for dMMR endometrial cancer patients” with immunotherapy plus chemotherapy, with the lack of benefit in pMMR disease underscoring an “unmet medical need.”
Inside DUO-E
The burning question, however, was whether adding a PARP inhibitor to immunotherapy and chemotherapy would boost the survival outcomes further.
The DUO-E trial involved patients with newly diagnosed stage III/IV or recurrent endometrial cancer who had not received systematic therapy for advanced disease and were naive to both PARP inhibitors and immune-mediated therapy.
Overall, 718 patients were randomized to one of three arms: Chemotherapy alone followed by maintenance placebo, chemotherapy plus durvalumab with maintenance durvalumab, or chemotherapy plus durvalumab with maintenance durvalumab plus olaparib.
Maintenance was continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, or the patients met another discontinuation criteria.
About half of patients were newly diagnosed, half had recurrent disease, and approximately one-fifth had dMMR disease, said Shannon Westin, MD, from the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, who presented the findings.
Compared with placebo plus chemotherapy, patients in both the durvalumab alone and durvalumab plus olaparib arms experienced a significant improvement in PFS (HR, 0.71; P = .003; and HR, 0.55; P < .0001, respectively).
This effect was amplified in dMMR patients with durvalumab (HR, 0.42) as well as with durvalumab plus olaparib (HR, 0.41).
In pMMR patients, PFS benefit was stronger in the durvalumab-olaparib arm vs. durvalumab (HR, 0.57 vs. 0.77).
Although the overall survival analysis remains exploratory, Dr. Westin noted a trend toward better overall survival in the two treatment arms vs. placebo (HR, 0.77 with durvalumab, and HR, 0.59 with durvalumab plus olaparib).
However, adding olaparib to the equation increased the rate of grade ≥ 3 adverse events – 67.2% vs. 54.9% with durvalumab and 56.4% with chemotherapy alone in the overall analysis. The addition of olaparib also led to treatment discontinuation in 24.4% of patients vs. 20.9% in the durvalumab arm and 18.6% in the chemotherapy alone arm.
Domenica Lorusso, MD, PhD, who was not involved in the study, commented that the marginal PFS benefit of adding olaparib in DUO-E is “not surprising” because the bar set by immunotherapy is “so high in this population that it’s very difficult” to go any higher.
But the results in pMMR patients reveal “a clear additional benefit” to olaparib, said Dr. Lorusso, from Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milan.
“The main limitation of the trial,” she continued, “is that it was not powered to make a formal comparison between the two experimental arms.”
So, what then is the added benefit of olaparib? “Unfortunately, that remains an unanswered question,” Dr. Lorusso said.
AtTEnd was sponsored by the Mario Negri Institute for Pharmacological Research.
DUO-E was funded by AstraZeneca.
Dr. Colombo declares relationships with AstraZeneca, Clovis Oncology, Esai, GSK, Immunogen, Mersana, MSD/Merck, Nuvation Bio, OncXerna, Pieris, Roche, and Novocure.
Dr. Tan declares relationships with AstraZeneca, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Bayer, Roche, MSD, Genmab, Esai, PMV, BioNTech, Ellipses Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck Serono, Takeda, and Clovis.
Dr. Westin declares relationships with AstraZeneca, Avenge Bio, Bayer, Bio-Path, Clovis, Genentech/Roche, GSK, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Mereo, Novartis, Nuvectis, and Zentalis; and consulting and advisory roles for AstraZeneca, Caris, Clovis, Eisai, EQRx, Genentech/Roche, Gilead, GSK, Immunocore, ImmunoGen, Lilly, Merck, Mersana, Mereo, NGM Bio, Nuvectis, Seagen, Verastem, Vincerx, Zentalis, and ZielBio.
Dr. Lorusso declares relationships with PharmaMar, Merck Serono, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Clovis, Tesaro/GSK, Genmab, Immunogen, and Roche.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESMO 2023