User login
Sociogenomics may explain race disparities in breast cancer mortality
Racial differences in cancer outcomes are widespread. Studies indicate that Black people face higher rates of mortality for most cancers than their White counterparts. To bridge this racial gap, researchers need to investigate the biological effects of structural racism and discrimination on cancer outcomes, experts say.
“As a physician, I always like to think that I can influence care in that if I just find the right drugs, help patients understand what their options are, it will help them,” said Ruth Carlos, MD, a radiologist with the University of Michigan Hospital, Ann Arbor. But these things alone are often not enough, because a large proportion of the variation in cancer outcomes is attributable to neighborhood social conditions and the physical environment. “It is incredibly important for us to start to understand just how the neighborhood exerts this effect.”
In a commentary published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, Dr. Carlos and colleagues highlighted the limitations of previous studies aimed at identifying the causes of racial differences in cancer outcomes. They call upon researchers to turn instead to the long-underexamined biological effects of structural racism and discrimination that contribute to these differences.
In the past, studies on the role of race in health outcomes largely looked at race as a proxy for genetic predisposition. But such an interpretation is flawed, because no genes are specific for a racial or ethnic group, Dr. Carlos and coauthors wrote. Researchers have shown that the vast majority of genetic variation occurs within, rather than between groups.
In an analysis published in Science, researchers reported that within-group differences account for more than 90% of genetic variation.
“Using race in these analyses was not necessarily wrong, but the inferences may have been flawed or incomplete,” Dr. Carlos said. On one hand, looking at genetic predisposition has led to important insights, such as the link between mutations in the BRCA gene and increased risk for breast and ovarian cancer.
However, genetic variation alone is not enough to explain the disparities in cancer outcomes between racial and ethnic groups. The fact that breast cancer can be more aggressive in Black women raises several questions, Dr. Carlos said. Is the cancer worse because Black women have a specific genetic predisposition? Is it worse because Black women exist in a society that marginalizes them and exposes them to increased stress, which in turn produces bad outcomes? Or, could it be both?
Despite progress in the screening, diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer, Black women are 40% more likely to die from the disease than White women. At the time of diagnosis, Black women are more likely to have high-grade, more aggressive breast cancer molecular subtypes, and to have had their cancer spread to the lymph nodes. They also tend to be diagnosed at more advanced stages of breast cancer while at the same time, experience higher rates of false-positive screening results.
Although researchers have hypothesized that genetic differences related to African or European ancestry might contribute, studies have not turned up any differences in cancer susceptibility genes by race. Other factors, such as racial differences in the stage of presentation, molecular subtypes, and disparities in treatment, have also emerged as potential culprits.
In her commentary, Dr. Carlos and colleagues wrote that disparities in breast cancer outcomes previously attributed to race need to be examined from multiple angles. This means looking at both the complex interactions between social conditions and policies, which encompass racism both at the individual and structural level, and stressors such as the experience of discrimination in addition to potential biological and genetic contributions.
Many studies now provide evidence for the harmful effects of racism on health. For breast cancer, specifically, studies also suggest that factors such as racial segregation can influence the stage at which Black women get diagnosed and their likelihood of dying from the disease.
However, an important question that remains is what biological changes occur in women exposed to the kind of persistent low-level stress that is associated with structural racism and discrimination, Dr. Carlos said. “We don’t know what stress pathways actually manifest in the body and how they eventually produce the disease.” Studies to address this issue are important, “especially if you would like to develop interventions to prevent or mitigate disease.”
To address this issue, Dr. Carlos and colleagues called upon the research community to conduct both studies that delineate the underlying biology as well as those that test potential interventions – particularly those associated with breast cancer screening outcomes – to try to shed light on why Black women receive more false positives and diagnoses of more aggressive cancer.
Interventions that can target these specific biological pathways could potentially reduce the negative effects of structural racism and discrimination as well as the effects of other social factors that contribute to breast cancer outcomes, “to ultimately help enhance clinical outcomes and close persistent disparities gaps,” the authors wrote.
Racial differences in cancer outcomes are widespread. Studies indicate that Black people face higher rates of mortality for most cancers than their White counterparts. To bridge this racial gap, researchers need to investigate the biological effects of structural racism and discrimination on cancer outcomes, experts say.
“As a physician, I always like to think that I can influence care in that if I just find the right drugs, help patients understand what their options are, it will help them,” said Ruth Carlos, MD, a radiologist with the University of Michigan Hospital, Ann Arbor. But these things alone are often not enough, because a large proportion of the variation in cancer outcomes is attributable to neighborhood social conditions and the physical environment. “It is incredibly important for us to start to understand just how the neighborhood exerts this effect.”
In a commentary published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, Dr. Carlos and colleagues highlighted the limitations of previous studies aimed at identifying the causes of racial differences in cancer outcomes. They call upon researchers to turn instead to the long-underexamined biological effects of structural racism and discrimination that contribute to these differences.
In the past, studies on the role of race in health outcomes largely looked at race as a proxy for genetic predisposition. But such an interpretation is flawed, because no genes are specific for a racial or ethnic group, Dr. Carlos and coauthors wrote. Researchers have shown that the vast majority of genetic variation occurs within, rather than between groups.
In an analysis published in Science, researchers reported that within-group differences account for more than 90% of genetic variation.
“Using race in these analyses was not necessarily wrong, but the inferences may have been flawed or incomplete,” Dr. Carlos said. On one hand, looking at genetic predisposition has led to important insights, such as the link between mutations in the BRCA gene and increased risk for breast and ovarian cancer.
However, genetic variation alone is not enough to explain the disparities in cancer outcomes between racial and ethnic groups. The fact that breast cancer can be more aggressive in Black women raises several questions, Dr. Carlos said. Is the cancer worse because Black women have a specific genetic predisposition? Is it worse because Black women exist in a society that marginalizes them and exposes them to increased stress, which in turn produces bad outcomes? Or, could it be both?
Despite progress in the screening, diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer, Black women are 40% more likely to die from the disease than White women. At the time of diagnosis, Black women are more likely to have high-grade, more aggressive breast cancer molecular subtypes, and to have had their cancer spread to the lymph nodes. They also tend to be diagnosed at more advanced stages of breast cancer while at the same time, experience higher rates of false-positive screening results.
Although researchers have hypothesized that genetic differences related to African or European ancestry might contribute, studies have not turned up any differences in cancer susceptibility genes by race. Other factors, such as racial differences in the stage of presentation, molecular subtypes, and disparities in treatment, have also emerged as potential culprits.
In her commentary, Dr. Carlos and colleagues wrote that disparities in breast cancer outcomes previously attributed to race need to be examined from multiple angles. This means looking at both the complex interactions between social conditions and policies, which encompass racism both at the individual and structural level, and stressors such as the experience of discrimination in addition to potential biological and genetic contributions.
Many studies now provide evidence for the harmful effects of racism on health. For breast cancer, specifically, studies also suggest that factors such as racial segregation can influence the stage at which Black women get diagnosed and their likelihood of dying from the disease.
However, an important question that remains is what biological changes occur in women exposed to the kind of persistent low-level stress that is associated with structural racism and discrimination, Dr. Carlos said. “We don’t know what stress pathways actually manifest in the body and how they eventually produce the disease.” Studies to address this issue are important, “especially if you would like to develop interventions to prevent or mitigate disease.”
To address this issue, Dr. Carlos and colleagues called upon the research community to conduct both studies that delineate the underlying biology as well as those that test potential interventions – particularly those associated with breast cancer screening outcomes – to try to shed light on why Black women receive more false positives and diagnoses of more aggressive cancer.
Interventions that can target these specific biological pathways could potentially reduce the negative effects of structural racism and discrimination as well as the effects of other social factors that contribute to breast cancer outcomes, “to ultimately help enhance clinical outcomes and close persistent disparities gaps,” the authors wrote.
Racial differences in cancer outcomes are widespread. Studies indicate that Black people face higher rates of mortality for most cancers than their White counterparts. To bridge this racial gap, researchers need to investigate the biological effects of structural racism and discrimination on cancer outcomes, experts say.
“As a physician, I always like to think that I can influence care in that if I just find the right drugs, help patients understand what their options are, it will help them,” said Ruth Carlos, MD, a radiologist with the University of Michigan Hospital, Ann Arbor. But these things alone are often not enough, because a large proportion of the variation in cancer outcomes is attributable to neighborhood social conditions and the physical environment. “It is incredibly important for us to start to understand just how the neighborhood exerts this effect.”
In a commentary published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, Dr. Carlos and colleagues highlighted the limitations of previous studies aimed at identifying the causes of racial differences in cancer outcomes. They call upon researchers to turn instead to the long-underexamined biological effects of structural racism and discrimination that contribute to these differences.
In the past, studies on the role of race in health outcomes largely looked at race as a proxy for genetic predisposition. But such an interpretation is flawed, because no genes are specific for a racial or ethnic group, Dr. Carlos and coauthors wrote. Researchers have shown that the vast majority of genetic variation occurs within, rather than between groups.
In an analysis published in Science, researchers reported that within-group differences account for more than 90% of genetic variation.
“Using race in these analyses was not necessarily wrong, but the inferences may have been flawed or incomplete,” Dr. Carlos said. On one hand, looking at genetic predisposition has led to important insights, such as the link between mutations in the BRCA gene and increased risk for breast and ovarian cancer.
However, genetic variation alone is not enough to explain the disparities in cancer outcomes between racial and ethnic groups. The fact that breast cancer can be more aggressive in Black women raises several questions, Dr. Carlos said. Is the cancer worse because Black women have a specific genetic predisposition? Is it worse because Black women exist in a society that marginalizes them and exposes them to increased stress, which in turn produces bad outcomes? Or, could it be both?
Despite progress in the screening, diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer, Black women are 40% more likely to die from the disease than White women. At the time of diagnosis, Black women are more likely to have high-grade, more aggressive breast cancer molecular subtypes, and to have had their cancer spread to the lymph nodes. They also tend to be diagnosed at more advanced stages of breast cancer while at the same time, experience higher rates of false-positive screening results.
Although researchers have hypothesized that genetic differences related to African or European ancestry might contribute, studies have not turned up any differences in cancer susceptibility genes by race. Other factors, such as racial differences in the stage of presentation, molecular subtypes, and disparities in treatment, have also emerged as potential culprits.
In her commentary, Dr. Carlos and colleagues wrote that disparities in breast cancer outcomes previously attributed to race need to be examined from multiple angles. This means looking at both the complex interactions between social conditions and policies, which encompass racism both at the individual and structural level, and stressors such as the experience of discrimination in addition to potential biological and genetic contributions.
Many studies now provide evidence for the harmful effects of racism on health. For breast cancer, specifically, studies also suggest that factors such as racial segregation can influence the stage at which Black women get diagnosed and their likelihood of dying from the disease.
However, an important question that remains is what biological changes occur in women exposed to the kind of persistent low-level stress that is associated with structural racism and discrimination, Dr. Carlos said. “We don’t know what stress pathways actually manifest in the body and how they eventually produce the disease.” Studies to address this issue are important, “especially if you would like to develop interventions to prevent or mitigate disease.”
To address this issue, Dr. Carlos and colleagues called upon the research community to conduct both studies that delineate the underlying biology as well as those that test potential interventions – particularly those associated with breast cancer screening outcomes – to try to shed light on why Black women receive more false positives and diagnoses of more aggressive cancer.
Interventions that can target these specific biological pathways could potentially reduce the negative effects of structural racism and discrimination as well as the effects of other social factors that contribute to breast cancer outcomes, “to ultimately help enhance clinical outcomes and close persistent disparities gaps,” the authors wrote.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Will the headache field embrace rofecoxib?
In June, the Concord, Mass.–based company Tremeau Pharmaceuticals announced that the Food and Drug Administration was letting it proceed with a phase 3 clinical trial to test rofecoxib, the once-bestselling painkiller known as Vioxx, in patients with migraine.
The anti-inflammatory drug, a cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor, received its first FDA approval in 1999 and became widely prescribed for arthritis and acute pain. In 2004 it was withdrawn by its manufacturer, Merck, after being shown to raise the risk of cardiovascular events.
In clinical trials and in real-world epidemiological studies, rofecoxib was associated with elevated heart attack, stroke, and related deaths; one 2005 study estimated that it had been responsible for some 38,000 excess deaths in the United States before being withdrawn. In 2007 Merck, beset with allegations that it had suppressed and mischaracterized rofecoxib’s safety data, paid out nearly $5 billion to settle thousands of lawsuits filed by patients and their families.
, an indication for which it received an orphan drug designation in 2017 and the agency’s green light for trials in 2020.
Brad Sippy, Tremeau’s chief executive officer, said that his company chose the two indications in part because both patient populations have low cardiovascular risk. Migraine patients are generally younger than the arthritis populations formerly treated with rofecoxib and are unlikely to take the drug for more than a day or 2 at time, avoiding the risks associated with extended exposure.
A crowded market
The past several years have seen the emergence of a cornucopia of new migraine treatments, including monoclonal antibodies such as erenumab (Aimovig, Amgen), which help prevent attacks by blocking the vasodilator calcitonin gene-related peptide, or CGRP. In addition to the standard arsenal of triptans and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for acute pain relief, migraine patients can now choose among serotonin-blocking agents such as lasmiditan (Reyvow, Eli Lilly), known as “ditans,” and small-molecule CGRP antagonists such as ubrogepant (Ubrelvy, Abbie), known as “gepants.” Some NSAIDs, including one COX inhibitor, have been formulated into rapidly absorbed powders or liquids for migraine.
Mr. Sippy said he sees a role for rofecoxib even in this crowded space. “Migraine as you know is a multimodal situation – few people say that only one drug works for them,” he said. “We think this is an option that would basically be like a high dose of ibuprofen,” but with less frequent dosing and lower gastrointestinal and platelet effects compared with ibuprofen and other NSAIDs.
An improved formulation
Rofecoxib “crosses the blood brain barrier very readily – better than other COX inhibitors on the market,” Mr. Sippy added. “It was well absorbed in its original formulation, and our product is even better absorbed than the original – we estimate it’s probably an hour quicker to [peak concentration].” In addition, he said, “our formulation is more efficient at delivering the drug so we don’t need as much active ingredient – our 17.5 milligrams gets you the same systemic exposure as 25 milligrams of the old product.”
A different mechanism of action
Neurologist Alan M. Rapoport, MD, editor-in-chief of Neurology Reviews and professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said that he was “cautiously optimistic” that “if used correctly and not too frequently, [rofecoxib] will find its niche in migraine treatment.”
“Patients liked Vioxx,” said Dr. Rapoport, past president of the International Headache Society. Even people currently on prevention “need to have an acute care drug handy.” While some patients on monoclonal antibodies have had success with gepants for acute care, “these both target the same pathway. It’s always nice to have options with a different mechanism of action.”
One of the arguments Tremeau has cited for reintroducing rofecoxib has been an urgent need for alternatives to opioid painkillers. Indeed some analysts have linked the demise of Vioxx with a subsequent increase in opioid prescribing.
Dr. Rapoport noted that he never prescribes opioids or butalbital, a barbiturate, for migraine, and that most headache specialists avoid them in clinical practice. But in the emergency setting, he said, patients receive them all too frequently.
Mr. Sippy said that opioid prescribing, while not unknown in migraine, was a bigger problem in hemophilic arthropathy, the first indication his company has pursued for rofecoxib. People with hemophilia “have a kind of arthritis that would respond well to an anti-inflammatory drug but they can’t take NSAIDs due to bleeding risk. This is why so many end up on opioids. Rofecoxib, as a COX-2 inhibitor, doesn’t have any effect on platelet aggregation, which would make it another option.”
No unique risks at prescribed doses
The migraine indication originally started out narrower: Patients with both migraine and bleeding disorders. “But in talking with the FDA, they encouraged us to develop it for migraine,” Mr. Sippy said. The company is considering pursuing a third indication: menstrual pain co-occurring with migraine. Tremeau has not ruled out seeking an indication in patients with arthritis who cannot take other painkillers, whether opioids or NSAIDs.
Five years ago, when Tremeau first announced its plans to bring rofecoxib back – indeed the company was set up for that purpose and has only this and another COX-2 inhibitor in development – some experts warned that there is little to prevent the drug from being used off-label, whether in higher doses or for other diseases.
“That’s something else we’re seeking to solve in addition to going for younger populations,” said Mr. Sippy, who worked at Merck during the Vioxx crisis and later headed neurology at Sunovion before starting his own company.
“We’re going for the former middle dose as our high dose and now we know that you don’t want to take more than the prescribed amount. If it doesn’t work you get off it; you don’t want to dose-creep on it. That’s been a key insight: At the appropriate dose, this product has no unique risk relative to the drug class and potentially some unique benefits,” he said.
Risk versus benefit
Joseph Ross, MD, a health policy researcher at Yale University in New Haven, Conn., who in a 2018 editorial expressed concerns about rofecoxib’s revival, said in an email that he felt its use in migraine could be justified, with caveats.
During Vioxx’s original approval and time on the market, “there was a cardiovascular risk associated with use that was not being transparently and clearly reported to patients and clinicians,” Dr. Ross said.
“In terms of testing the product for use in patients with migraine – a population of generally younger patients at lower risk of cardiovascular disease – my only concern is that the risk is clearly communicated and that there is adequate postmarket safety surveillance,” he said. “If patients are making fully informed decisions, the potential benefit of the drug with respect to pain control may be worth the risks.”
Dr. Rapoport serves as an adviser for AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Cala Health, Collegium Pharmaceutical, Satsuma, Teva, Theranica and Xoc; he is on the speakers bureau of AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Impel, Lundbeck, and Teva. Dr. Ross disclosed research support from Johnson and Johnson, the Medical Device Innovation Consortium, and the Laura and John Arnold Foundation, along with government grants; he is also an expert witness in a lawsuit against Biogen.
In June, the Concord, Mass.–based company Tremeau Pharmaceuticals announced that the Food and Drug Administration was letting it proceed with a phase 3 clinical trial to test rofecoxib, the once-bestselling painkiller known as Vioxx, in patients with migraine.
The anti-inflammatory drug, a cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor, received its first FDA approval in 1999 and became widely prescribed for arthritis and acute pain. In 2004 it was withdrawn by its manufacturer, Merck, after being shown to raise the risk of cardiovascular events.
In clinical trials and in real-world epidemiological studies, rofecoxib was associated with elevated heart attack, stroke, and related deaths; one 2005 study estimated that it had been responsible for some 38,000 excess deaths in the United States before being withdrawn. In 2007 Merck, beset with allegations that it had suppressed and mischaracterized rofecoxib’s safety data, paid out nearly $5 billion to settle thousands of lawsuits filed by patients and their families.
, an indication for which it received an orphan drug designation in 2017 and the agency’s green light for trials in 2020.
Brad Sippy, Tremeau’s chief executive officer, said that his company chose the two indications in part because both patient populations have low cardiovascular risk. Migraine patients are generally younger than the arthritis populations formerly treated with rofecoxib and are unlikely to take the drug for more than a day or 2 at time, avoiding the risks associated with extended exposure.
A crowded market
The past several years have seen the emergence of a cornucopia of new migraine treatments, including monoclonal antibodies such as erenumab (Aimovig, Amgen), which help prevent attacks by blocking the vasodilator calcitonin gene-related peptide, or CGRP. In addition to the standard arsenal of triptans and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for acute pain relief, migraine patients can now choose among serotonin-blocking agents such as lasmiditan (Reyvow, Eli Lilly), known as “ditans,” and small-molecule CGRP antagonists such as ubrogepant (Ubrelvy, Abbie), known as “gepants.” Some NSAIDs, including one COX inhibitor, have been formulated into rapidly absorbed powders or liquids for migraine.
Mr. Sippy said he sees a role for rofecoxib even in this crowded space. “Migraine as you know is a multimodal situation – few people say that only one drug works for them,” he said. “We think this is an option that would basically be like a high dose of ibuprofen,” but with less frequent dosing and lower gastrointestinal and platelet effects compared with ibuprofen and other NSAIDs.
An improved formulation
Rofecoxib “crosses the blood brain barrier very readily – better than other COX inhibitors on the market,” Mr. Sippy added. “It was well absorbed in its original formulation, and our product is even better absorbed than the original – we estimate it’s probably an hour quicker to [peak concentration].” In addition, he said, “our formulation is more efficient at delivering the drug so we don’t need as much active ingredient – our 17.5 milligrams gets you the same systemic exposure as 25 milligrams of the old product.”
A different mechanism of action
Neurologist Alan M. Rapoport, MD, editor-in-chief of Neurology Reviews and professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said that he was “cautiously optimistic” that “if used correctly and not too frequently, [rofecoxib] will find its niche in migraine treatment.”
“Patients liked Vioxx,” said Dr. Rapoport, past president of the International Headache Society. Even people currently on prevention “need to have an acute care drug handy.” While some patients on monoclonal antibodies have had success with gepants for acute care, “these both target the same pathway. It’s always nice to have options with a different mechanism of action.”
One of the arguments Tremeau has cited for reintroducing rofecoxib has been an urgent need for alternatives to opioid painkillers. Indeed some analysts have linked the demise of Vioxx with a subsequent increase in opioid prescribing.
Dr. Rapoport noted that he never prescribes opioids or butalbital, a barbiturate, for migraine, and that most headache specialists avoid them in clinical practice. But in the emergency setting, he said, patients receive them all too frequently.
Mr. Sippy said that opioid prescribing, while not unknown in migraine, was a bigger problem in hemophilic arthropathy, the first indication his company has pursued for rofecoxib. People with hemophilia “have a kind of arthritis that would respond well to an anti-inflammatory drug but they can’t take NSAIDs due to bleeding risk. This is why so many end up on opioids. Rofecoxib, as a COX-2 inhibitor, doesn’t have any effect on platelet aggregation, which would make it another option.”
No unique risks at prescribed doses
The migraine indication originally started out narrower: Patients with both migraine and bleeding disorders. “But in talking with the FDA, they encouraged us to develop it for migraine,” Mr. Sippy said. The company is considering pursuing a third indication: menstrual pain co-occurring with migraine. Tremeau has not ruled out seeking an indication in patients with arthritis who cannot take other painkillers, whether opioids or NSAIDs.
Five years ago, when Tremeau first announced its plans to bring rofecoxib back – indeed the company was set up for that purpose and has only this and another COX-2 inhibitor in development – some experts warned that there is little to prevent the drug from being used off-label, whether in higher doses or for other diseases.
“That’s something else we’re seeking to solve in addition to going for younger populations,” said Mr. Sippy, who worked at Merck during the Vioxx crisis and later headed neurology at Sunovion before starting his own company.
“We’re going for the former middle dose as our high dose and now we know that you don’t want to take more than the prescribed amount. If it doesn’t work you get off it; you don’t want to dose-creep on it. That’s been a key insight: At the appropriate dose, this product has no unique risk relative to the drug class and potentially some unique benefits,” he said.
Risk versus benefit
Joseph Ross, MD, a health policy researcher at Yale University in New Haven, Conn., who in a 2018 editorial expressed concerns about rofecoxib’s revival, said in an email that he felt its use in migraine could be justified, with caveats.
During Vioxx’s original approval and time on the market, “there was a cardiovascular risk associated with use that was not being transparently and clearly reported to patients and clinicians,” Dr. Ross said.
“In terms of testing the product for use in patients with migraine – a population of generally younger patients at lower risk of cardiovascular disease – my only concern is that the risk is clearly communicated and that there is adequate postmarket safety surveillance,” he said. “If patients are making fully informed decisions, the potential benefit of the drug with respect to pain control may be worth the risks.”
Dr. Rapoport serves as an adviser for AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Cala Health, Collegium Pharmaceutical, Satsuma, Teva, Theranica and Xoc; he is on the speakers bureau of AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Impel, Lundbeck, and Teva. Dr. Ross disclosed research support from Johnson and Johnson, the Medical Device Innovation Consortium, and the Laura and John Arnold Foundation, along with government grants; he is also an expert witness in a lawsuit against Biogen.
In June, the Concord, Mass.–based company Tremeau Pharmaceuticals announced that the Food and Drug Administration was letting it proceed with a phase 3 clinical trial to test rofecoxib, the once-bestselling painkiller known as Vioxx, in patients with migraine.
The anti-inflammatory drug, a cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor, received its first FDA approval in 1999 and became widely prescribed for arthritis and acute pain. In 2004 it was withdrawn by its manufacturer, Merck, after being shown to raise the risk of cardiovascular events.
In clinical trials and in real-world epidemiological studies, rofecoxib was associated with elevated heart attack, stroke, and related deaths; one 2005 study estimated that it had been responsible for some 38,000 excess deaths in the United States before being withdrawn. In 2007 Merck, beset with allegations that it had suppressed and mischaracterized rofecoxib’s safety data, paid out nearly $5 billion to settle thousands of lawsuits filed by patients and their families.
, an indication for which it received an orphan drug designation in 2017 and the agency’s green light for trials in 2020.
Brad Sippy, Tremeau’s chief executive officer, said that his company chose the two indications in part because both patient populations have low cardiovascular risk. Migraine patients are generally younger than the arthritis populations formerly treated with rofecoxib and are unlikely to take the drug for more than a day or 2 at time, avoiding the risks associated with extended exposure.
A crowded market
The past several years have seen the emergence of a cornucopia of new migraine treatments, including monoclonal antibodies such as erenumab (Aimovig, Amgen), which help prevent attacks by blocking the vasodilator calcitonin gene-related peptide, or CGRP. In addition to the standard arsenal of triptans and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for acute pain relief, migraine patients can now choose among serotonin-blocking agents such as lasmiditan (Reyvow, Eli Lilly), known as “ditans,” and small-molecule CGRP antagonists such as ubrogepant (Ubrelvy, Abbie), known as “gepants.” Some NSAIDs, including one COX inhibitor, have been formulated into rapidly absorbed powders or liquids for migraine.
Mr. Sippy said he sees a role for rofecoxib even in this crowded space. “Migraine as you know is a multimodal situation – few people say that only one drug works for them,” he said. “We think this is an option that would basically be like a high dose of ibuprofen,” but with less frequent dosing and lower gastrointestinal and platelet effects compared with ibuprofen and other NSAIDs.
An improved formulation
Rofecoxib “crosses the blood brain barrier very readily – better than other COX inhibitors on the market,” Mr. Sippy added. “It was well absorbed in its original formulation, and our product is even better absorbed than the original – we estimate it’s probably an hour quicker to [peak concentration].” In addition, he said, “our formulation is more efficient at delivering the drug so we don’t need as much active ingredient – our 17.5 milligrams gets you the same systemic exposure as 25 milligrams of the old product.”
A different mechanism of action
Neurologist Alan M. Rapoport, MD, editor-in-chief of Neurology Reviews and professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said that he was “cautiously optimistic” that “if used correctly and not too frequently, [rofecoxib] will find its niche in migraine treatment.”
“Patients liked Vioxx,” said Dr. Rapoport, past president of the International Headache Society. Even people currently on prevention “need to have an acute care drug handy.” While some patients on monoclonal antibodies have had success with gepants for acute care, “these both target the same pathway. It’s always nice to have options with a different mechanism of action.”
One of the arguments Tremeau has cited for reintroducing rofecoxib has been an urgent need for alternatives to opioid painkillers. Indeed some analysts have linked the demise of Vioxx with a subsequent increase in opioid prescribing.
Dr. Rapoport noted that he never prescribes opioids or butalbital, a barbiturate, for migraine, and that most headache specialists avoid them in clinical practice. But in the emergency setting, he said, patients receive them all too frequently.
Mr. Sippy said that opioid prescribing, while not unknown in migraine, was a bigger problem in hemophilic arthropathy, the first indication his company has pursued for rofecoxib. People with hemophilia “have a kind of arthritis that would respond well to an anti-inflammatory drug but they can’t take NSAIDs due to bleeding risk. This is why so many end up on opioids. Rofecoxib, as a COX-2 inhibitor, doesn’t have any effect on platelet aggregation, which would make it another option.”
No unique risks at prescribed doses
The migraine indication originally started out narrower: Patients with both migraine and bleeding disorders. “But in talking with the FDA, they encouraged us to develop it for migraine,” Mr. Sippy said. The company is considering pursuing a third indication: menstrual pain co-occurring with migraine. Tremeau has not ruled out seeking an indication in patients with arthritis who cannot take other painkillers, whether opioids or NSAIDs.
Five years ago, when Tremeau first announced its plans to bring rofecoxib back – indeed the company was set up for that purpose and has only this and another COX-2 inhibitor in development – some experts warned that there is little to prevent the drug from being used off-label, whether in higher doses or for other diseases.
“That’s something else we’re seeking to solve in addition to going for younger populations,” said Mr. Sippy, who worked at Merck during the Vioxx crisis and later headed neurology at Sunovion before starting his own company.
“We’re going for the former middle dose as our high dose and now we know that you don’t want to take more than the prescribed amount. If it doesn’t work you get off it; you don’t want to dose-creep on it. That’s been a key insight: At the appropriate dose, this product has no unique risk relative to the drug class and potentially some unique benefits,” he said.
Risk versus benefit
Joseph Ross, MD, a health policy researcher at Yale University in New Haven, Conn., who in a 2018 editorial expressed concerns about rofecoxib’s revival, said in an email that he felt its use in migraine could be justified, with caveats.
During Vioxx’s original approval and time on the market, “there was a cardiovascular risk associated with use that was not being transparently and clearly reported to patients and clinicians,” Dr. Ross said.
“In terms of testing the product for use in patients with migraine – a population of generally younger patients at lower risk of cardiovascular disease – my only concern is that the risk is clearly communicated and that there is adequate postmarket safety surveillance,” he said. “If patients are making fully informed decisions, the potential benefit of the drug with respect to pain control may be worth the risks.”
Dr. Rapoport serves as an adviser for AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Cala Health, Collegium Pharmaceutical, Satsuma, Teva, Theranica and Xoc; he is on the speakers bureau of AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Impel, Lundbeck, and Teva. Dr. Ross disclosed research support from Johnson and Johnson, the Medical Device Innovation Consortium, and the Laura and John Arnold Foundation, along with government grants; he is also an expert witness in a lawsuit against Biogen.
Mobile devices ‘addictive by design’: Obesity is one of many health effects
Wireless devices, like smart phones and tablets, appear to induce compulsive or even addictive use in many individuals, leading to adverse health consequences that are likely to be curtailed only through often difficult behavior modification, according to a pediatric endocrinologist’s take on the problem.
While the summary was based in part on the analysis of 234 published papers drawn from the medical literature, the lead author, Nidhi Gupta, MD, said the data reinforce her own clinical experience.
“As a pediatric endocrinologist, the trend in smartphone-associated health disorders, such as obesity, sleep, and behavior issues, worries me,” Dr. Gupta, director of KAP Pediatric Endocrinology, Nashville, Tenn., said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Based on her search of the medical literature, the available data raise concern. In one study she cited, for example, each hour per day of screen time was found to translate into a body mass index increase of 0.5 to 0.7 kg/m2 (P < .001).
With this type of progressive rise in BMI comes prediabetes, dyslipidemia, and other metabolic disorders associated with major health risks, including cardiovascular disease. And there are others. Dr. Gupta cited data suggesting screen time before bed disturbs sleep, which has its own set of health risks.
“When I say health, it includes physical health, mental health, and emotional health,” said Dr. Gupta.
In the U.S. and other countries with a growing obesity epidemic, lack of physical activity and unhealthy eating are widely considered the major culprits. Excessive screen time contributes to both.
“When we are engaged with our devices, we are often snacking subconsciously and not very mindful that we are making unhealthy choices,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem is that there is a vicious circle. Compulsive use of devices follows the same loop as other types of addictive behaviors, according to Dr. Gupta. She traced overuse of wireless devices to the dopaminergic system, which is a powerful neuroendocrine-mediated process of craving, response, and reward.
Like fat, sugar, and salt, which provoke a neuroendocrine reward signal, the chimes and buzzes of a cell phone provide their own cues for reward in the form of a dopamine surge. As a result, these become the “triggers of an irresistible and irrational urge to check our device that makes the dopamine go high in our brain,” Dr. Gupta explained.
Although the vicious cycle can be thwarted by turning off the device, Dr. Gupta characterized this as “impractical” when smartphones are so vital to daily communication. Rather, Dr. Gupta advocated a program of moderation, reserving the phone for useful tasks without succumbing to the siren song of apps that waste time.
The most conspicuous culprit is social media, which Dr. Gupta considers to be among the most Pavlovian triggers of cell phone addiction. However, she acknowledged that participation in social media has its justifications.
“I, myself, use social media for my own branding and marketing,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem that users have is distinguishing between screen time that does and does not have value, according to Dr. Gupta. She indicated that many of those overusing their smart devices are being driven by the dopaminergic reward system, which is generally divorced from the real goals of life, such as personal satisfaction and activity that is rewarding monetarily or in other ways.
“I am not asking for these devices to be thrown out the window. I am advocating for moderation, balance, and real-life engagement,” Dr. Gupta said at the meeting, held in Atlanta and virtually.
She outlined a long list of practical suggestions, including turning off the alarms, chimes, and messages that engage the user into the vicious dopaminergic-reward system loop. She suggested mindfulness so that the user can distinguish between valuable device use and activity that is simply procrastination.
“The devices are designed to be addictive. They are designed to manipulate our brain,” she said. “Eliminate the reward. Let’s try to make our devices boring, unappealing, or enticing so that they only work as tools.”
The medical literature is filled with data that support the potential harms of excessive screen use, leading many others to make some of the same points. In 2017, Thomas N. Robinson, MD, professor of child health at Stanford (Calif.) University, reviewed data showing an association between screen media exposure and obesity in children and adolescents.
“This is an area crying out for more research,” Dr. Robinson said in an interview. The problem of screen time, sedentary behavior, and weight gain has been an issue since the television was invented, which was the point he made in his 2017 paper, but he agreed that the problem is only getting worse.
“Digital technology has become ubiquitous, touching nearly every aspect of people’s lives,” he said. Yet, as evidence grows that overuse of this technology can be harmful, it is creating a problem without a clear solution.
“There are few data about the efficacy of specific strategies to reduce harmful impacts of digital screen use,” he said.
While some of the solutions that Dr. Gupta described make sense, they are more easily described than executed. The dopaminergic reward system is strong and largely experienced subconsciously. Recruiting patients to recognize that dopaminergic rewards are not rewards in any true sense is already a challenge. Enlisting patients to take the difficult steps to avoid the behavioral cues might be even more difficult.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Robinson report no potential conflicts of interest.
Wireless devices, like smart phones and tablets, appear to induce compulsive or even addictive use in many individuals, leading to adverse health consequences that are likely to be curtailed only through often difficult behavior modification, according to a pediatric endocrinologist’s take on the problem.
While the summary was based in part on the analysis of 234 published papers drawn from the medical literature, the lead author, Nidhi Gupta, MD, said the data reinforce her own clinical experience.
“As a pediatric endocrinologist, the trend in smartphone-associated health disorders, such as obesity, sleep, and behavior issues, worries me,” Dr. Gupta, director of KAP Pediatric Endocrinology, Nashville, Tenn., said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Based on her search of the medical literature, the available data raise concern. In one study she cited, for example, each hour per day of screen time was found to translate into a body mass index increase of 0.5 to 0.7 kg/m2 (P < .001).
With this type of progressive rise in BMI comes prediabetes, dyslipidemia, and other metabolic disorders associated with major health risks, including cardiovascular disease. And there are others. Dr. Gupta cited data suggesting screen time before bed disturbs sleep, which has its own set of health risks.
“When I say health, it includes physical health, mental health, and emotional health,” said Dr. Gupta.
In the U.S. and other countries with a growing obesity epidemic, lack of physical activity and unhealthy eating are widely considered the major culprits. Excessive screen time contributes to both.
“When we are engaged with our devices, we are often snacking subconsciously and not very mindful that we are making unhealthy choices,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem is that there is a vicious circle. Compulsive use of devices follows the same loop as other types of addictive behaviors, according to Dr. Gupta. She traced overuse of wireless devices to the dopaminergic system, which is a powerful neuroendocrine-mediated process of craving, response, and reward.
Like fat, sugar, and salt, which provoke a neuroendocrine reward signal, the chimes and buzzes of a cell phone provide their own cues for reward in the form of a dopamine surge. As a result, these become the “triggers of an irresistible and irrational urge to check our device that makes the dopamine go high in our brain,” Dr. Gupta explained.
Although the vicious cycle can be thwarted by turning off the device, Dr. Gupta characterized this as “impractical” when smartphones are so vital to daily communication. Rather, Dr. Gupta advocated a program of moderation, reserving the phone for useful tasks without succumbing to the siren song of apps that waste time.
The most conspicuous culprit is social media, which Dr. Gupta considers to be among the most Pavlovian triggers of cell phone addiction. However, she acknowledged that participation in social media has its justifications.
“I, myself, use social media for my own branding and marketing,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem that users have is distinguishing between screen time that does and does not have value, according to Dr. Gupta. She indicated that many of those overusing their smart devices are being driven by the dopaminergic reward system, which is generally divorced from the real goals of life, such as personal satisfaction and activity that is rewarding monetarily or in other ways.
“I am not asking for these devices to be thrown out the window. I am advocating for moderation, balance, and real-life engagement,” Dr. Gupta said at the meeting, held in Atlanta and virtually.
She outlined a long list of practical suggestions, including turning off the alarms, chimes, and messages that engage the user into the vicious dopaminergic-reward system loop. She suggested mindfulness so that the user can distinguish between valuable device use and activity that is simply procrastination.
“The devices are designed to be addictive. They are designed to manipulate our brain,” she said. “Eliminate the reward. Let’s try to make our devices boring, unappealing, or enticing so that they only work as tools.”
The medical literature is filled with data that support the potential harms of excessive screen use, leading many others to make some of the same points. In 2017, Thomas N. Robinson, MD, professor of child health at Stanford (Calif.) University, reviewed data showing an association between screen media exposure and obesity in children and adolescents.
“This is an area crying out for more research,” Dr. Robinson said in an interview. The problem of screen time, sedentary behavior, and weight gain has been an issue since the television was invented, which was the point he made in his 2017 paper, but he agreed that the problem is only getting worse.
“Digital technology has become ubiquitous, touching nearly every aspect of people’s lives,” he said. Yet, as evidence grows that overuse of this technology can be harmful, it is creating a problem without a clear solution.
“There are few data about the efficacy of specific strategies to reduce harmful impacts of digital screen use,” he said.
While some of the solutions that Dr. Gupta described make sense, they are more easily described than executed. The dopaminergic reward system is strong and largely experienced subconsciously. Recruiting patients to recognize that dopaminergic rewards are not rewards in any true sense is already a challenge. Enlisting patients to take the difficult steps to avoid the behavioral cues might be even more difficult.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Robinson report no potential conflicts of interest.
Wireless devices, like smart phones and tablets, appear to induce compulsive or even addictive use in many individuals, leading to adverse health consequences that are likely to be curtailed only through often difficult behavior modification, according to a pediatric endocrinologist’s take on the problem.
While the summary was based in part on the analysis of 234 published papers drawn from the medical literature, the lead author, Nidhi Gupta, MD, said the data reinforce her own clinical experience.
“As a pediatric endocrinologist, the trend in smartphone-associated health disorders, such as obesity, sleep, and behavior issues, worries me,” Dr. Gupta, director of KAP Pediatric Endocrinology, Nashville, Tenn., said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Based on her search of the medical literature, the available data raise concern. In one study she cited, for example, each hour per day of screen time was found to translate into a body mass index increase of 0.5 to 0.7 kg/m2 (P < .001).
With this type of progressive rise in BMI comes prediabetes, dyslipidemia, and other metabolic disorders associated with major health risks, including cardiovascular disease. And there are others. Dr. Gupta cited data suggesting screen time before bed disturbs sleep, which has its own set of health risks.
“When I say health, it includes physical health, mental health, and emotional health,” said Dr. Gupta.
In the U.S. and other countries with a growing obesity epidemic, lack of physical activity and unhealthy eating are widely considered the major culprits. Excessive screen time contributes to both.
“When we are engaged with our devices, we are often snacking subconsciously and not very mindful that we are making unhealthy choices,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem is that there is a vicious circle. Compulsive use of devices follows the same loop as other types of addictive behaviors, according to Dr. Gupta. She traced overuse of wireless devices to the dopaminergic system, which is a powerful neuroendocrine-mediated process of craving, response, and reward.
Like fat, sugar, and salt, which provoke a neuroendocrine reward signal, the chimes and buzzes of a cell phone provide their own cues for reward in the form of a dopamine surge. As a result, these become the “triggers of an irresistible and irrational urge to check our device that makes the dopamine go high in our brain,” Dr. Gupta explained.
Although the vicious cycle can be thwarted by turning off the device, Dr. Gupta characterized this as “impractical” when smartphones are so vital to daily communication. Rather, Dr. Gupta advocated a program of moderation, reserving the phone for useful tasks without succumbing to the siren song of apps that waste time.
The most conspicuous culprit is social media, which Dr. Gupta considers to be among the most Pavlovian triggers of cell phone addiction. However, she acknowledged that participation in social media has its justifications.
“I, myself, use social media for my own branding and marketing,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem that users have is distinguishing between screen time that does and does not have value, according to Dr. Gupta. She indicated that many of those overusing their smart devices are being driven by the dopaminergic reward system, which is generally divorced from the real goals of life, such as personal satisfaction and activity that is rewarding monetarily or in other ways.
“I am not asking for these devices to be thrown out the window. I am advocating for moderation, balance, and real-life engagement,” Dr. Gupta said at the meeting, held in Atlanta and virtually.
She outlined a long list of practical suggestions, including turning off the alarms, chimes, and messages that engage the user into the vicious dopaminergic-reward system loop. She suggested mindfulness so that the user can distinguish between valuable device use and activity that is simply procrastination.
“The devices are designed to be addictive. They are designed to manipulate our brain,” she said. “Eliminate the reward. Let’s try to make our devices boring, unappealing, or enticing so that they only work as tools.”
The medical literature is filled with data that support the potential harms of excessive screen use, leading many others to make some of the same points. In 2017, Thomas N. Robinson, MD, professor of child health at Stanford (Calif.) University, reviewed data showing an association between screen media exposure and obesity in children and adolescents.
“This is an area crying out for more research,” Dr. Robinson said in an interview. The problem of screen time, sedentary behavior, and weight gain has been an issue since the television was invented, which was the point he made in his 2017 paper, but he agreed that the problem is only getting worse.
“Digital technology has become ubiquitous, touching nearly every aspect of people’s lives,” he said. Yet, as evidence grows that overuse of this technology can be harmful, it is creating a problem without a clear solution.
“There are few data about the efficacy of specific strategies to reduce harmful impacts of digital screen use,” he said.
While some of the solutions that Dr. Gupta described make sense, they are more easily described than executed. The dopaminergic reward system is strong and largely experienced subconsciously. Recruiting patients to recognize that dopaminergic rewards are not rewards in any true sense is already a challenge. Enlisting patients to take the difficult steps to avoid the behavioral cues might be even more difficult.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Robinson report no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM ENDO 2022
Food insecurity drives poor glycemic control
People with diabetes who had a poor-quality diet and food insecurity were significantly more likely to have poor glycemic and cholesterol control than were those with a healthier diet and food security, based on data from a national study of more than 2,000 individuals.
The American Diabetes Association recommends a high-quality diet for people with diabetes (PWD) to achieve treatment goals; however, roughly 18% of PWD in the United States are food insecure and/or have a poor-quality diet, Sarah S. Casagrande, PhD, of DLH Corporation, Silver Spring, Md., and colleagues wrote in a poster presented at the annual scientific sessions of the ADA in New Orleans.
To examine the impact of food insecurity and diet quality on diabetes and lipid management, the researchers reviewed data from 2,075 adults with self-reported diabetes who completed the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys between 2013 and 2018.
Diet quality was divided into quartiles based on the 2015 Healthy Eating Index. Food insecurity was assessed using a standard 10-item questionnaire including questions about running out of food and not being able to afford more, reducing meal sizes, eating less or not at all, and going hungry because of lack of money for food.
The logistic regression analysis controlled for factors including sociodemographics, health care use, smoking, diabetes medications, blood pressure medication use, cholesterol medication use, and body mass index.
Overall, 17.6% of the participants were food insecure and had a low-quality diet, 14.2% were food insecure with a high-quality diet, 33.1% were food secure with a low-quality diet, and 35.2% were food secure with a high-quality diet.
PWD in the food insecure/low-quality diet group were significantly more likely to be younger, non-Hispanic black or Hispanic, and uninsured compared to those in the food secure/high-quality diet group (P < .001 for all).
When the researchers examined glycemic control, they found that PWD in the food insecurity/low-quality diet groups were significantly more likely than were those with food security/high-quality diets to have hemoglobin A1c of at least 7.0% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.85), A1c of at least 8.0% (aOR, 1.79), low HDL cholesterol (aOR, 1.69), and high triglycerides (aOR, 3.26).
PWD with food insecurity but a high-quality diet also were significantly more likely than were those with food security and a high quality diet to have A1c of at least 7.0% (aOR, 1.69), A1c of at least 8.0% (aOR, 1.83), and high triglycerides (aOR, 2.44). PWD with food security but a low-quality diet were significantly more likely than was the food security/high-quality diet group to have A1c of at least 7% (aOR, 1.55).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design, reliance on self-reports, and inability to distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, the researchers wrote.
However, the results were strengthened by the large, nationally representative sample and the inclusion of multiple clinical outcomes in the patient assessment, they said.
The results suggest that food insecurity had a significant impact on both glycemic control and cholesterol management independent of diet quality, the researchers noted. Based on these findings, health care providers treating PWD may wish to assess their patients’ food security status, and “interventions could address disparities in food security,” they concluded.
Food insecurity a growing problem
“With more communities being pushed into state of war, drought, and famine globally, it is important to track impact of food insecurity and low quality food on common medical conditions like diabetes in our vulnerable communities,” Romesh K. Khardori, MD, professor of medicine: endocrinology, and metabolism at Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, said in an interview.
Dr. Khardori, who was not involved in the study, said he was not surprised by the current study findings.
“Type of food, amount of food, and quality of food have been stressed in diabetes management for more than 100 years,” he said. “Organizations charged with recommendations, such as the ADA and American Dietetic Association, have regularly updated their recommendations,” he noted. “It was not surprising, therefore, to find food insecurity and low quality tied to poor glycemic control.”
The take-home message for clinicians is to consider the availability and quality of food that their patients are exposed to when evaluating barriers to proper glycemic control, Dr. Khardori emphasized.
However, additional research is needed to explore whether the prescription of a sufficient amount of good quality food would alleviate the adverse impact seen in the current study, he said.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. The researchers and Dr. Khardori had no financial conflicts to disclose.
People with diabetes who had a poor-quality diet and food insecurity were significantly more likely to have poor glycemic and cholesterol control than were those with a healthier diet and food security, based on data from a national study of more than 2,000 individuals.
The American Diabetes Association recommends a high-quality diet for people with diabetes (PWD) to achieve treatment goals; however, roughly 18% of PWD in the United States are food insecure and/or have a poor-quality diet, Sarah S. Casagrande, PhD, of DLH Corporation, Silver Spring, Md., and colleagues wrote in a poster presented at the annual scientific sessions of the ADA in New Orleans.
To examine the impact of food insecurity and diet quality on diabetes and lipid management, the researchers reviewed data from 2,075 adults with self-reported diabetes who completed the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys between 2013 and 2018.
Diet quality was divided into quartiles based on the 2015 Healthy Eating Index. Food insecurity was assessed using a standard 10-item questionnaire including questions about running out of food and not being able to afford more, reducing meal sizes, eating less or not at all, and going hungry because of lack of money for food.
The logistic regression analysis controlled for factors including sociodemographics, health care use, smoking, diabetes medications, blood pressure medication use, cholesterol medication use, and body mass index.
Overall, 17.6% of the participants were food insecure and had a low-quality diet, 14.2% were food insecure with a high-quality diet, 33.1% were food secure with a low-quality diet, and 35.2% were food secure with a high-quality diet.
PWD in the food insecure/low-quality diet group were significantly more likely to be younger, non-Hispanic black or Hispanic, and uninsured compared to those in the food secure/high-quality diet group (P < .001 for all).
When the researchers examined glycemic control, they found that PWD in the food insecurity/low-quality diet groups were significantly more likely than were those with food security/high-quality diets to have hemoglobin A1c of at least 7.0% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.85), A1c of at least 8.0% (aOR, 1.79), low HDL cholesterol (aOR, 1.69), and high triglycerides (aOR, 3.26).
PWD with food insecurity but a high-quality diet also were significantly more likely than were those with food security and a high quality diet to have A1c of at least 7.0% (aOR, 1.69), A1c of at least 8.0% (aOR, 1.83), and high triglycerides (aOR, 2.44). PWD with food security but a low-quality diet were significantly more likely than was the food security/high-quality diet group to have A1c of at least 7% (aOR, 1.55).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design, reliance on self-reports, and inability to distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, the researchers wrote.
However, the results were strengthened by the large, nationally representative sample and the inclusion of multiple clinical outcomes in the patient assessment, they said.
The results suggest that food insecurity had a significant impact on both glycemic control and cholesterol management independent of diet quality, the researchers noted. Based on these findings, health care providers treating PWD may wish to assess their patients’ food security status, and “interventions could address disparities in food security,” they concluded.
Food insecurity a growing problem
“With more communities being pushed into state of war, drought, and famine globally, it is important to track impact of food insecurity and low quality food on common medical conditions like diabetes in our vulnerable communities,” Romesh K. Khardori, MD, professor of medicine: endocrinology, and metabolism at Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, said in an interview.
Dr. Khardori, who was not involved in the study, said he was not surprised by the current study findings.
“Type of food, amount of food, and quality of food have been stressed in diabetes management for more than 100 years,” he said. “Organizations charged with recommendations, such as the ADA and American Dietetic Association, have regularly updated their recommendations,” he noted. “It was not surprising, therefore, to find food insecurity and low quality tied to poor glycemic control.”
The take-home message for clinicians is to consider the availability and quality of food that their patients are exposed to when evaluating barriers to proper glycemic control, Dr. Khardori emphasized.
However, additional research is needed to explore whether the prescription of a sufficient amount of good quality food would alleviate the adverse impact seen in the current study, he said.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. The researchers and Dr. Khardori had no financial conflicts to disclose.
People with diabetes who had a poor-quality diet and food insecurity were significantly more likely to have poor glycemic and cholesterol control than were those with a healthier diet and food security, based on data from a national study of more than 2,000 individuals.
The American Diabetes Association recommends a high-quality diet for people with diabetes (PWD) to achieve treatment goals; however, roughly 18% of PWD in the United States are food insecure and/or have a poor-quality diet, Sarah S. Casagrande, PhD, of DLH Corporation, Silver Spring, Md., and colleagues wrote in a poster presented at the annual scientific sessions of the ADA in New Orleans.
To examine the impact of food insecurity and diet quality on diabetes and lipid management, the researchers reviewed data from 2,075 adults with self-reported diabetes who completed the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys between 2013 and 2018.
Diet quality was divided into quartiles based on the 2015 Healthy Eating Index. Food insecurity was assessed using a standard 10-item questionnaire including questions about running out of food and not being able to afford more, reducing meal sizes, eating less or not at all, and going hungry because of lack of money for food.
The logistic regression analysis controlled for factors including sociodemographics, health care use, smoking, diabetes medications, blood pressure medication use, cholesterol medication use, and body mass index.
Overall, 17.6% of the participants were food insecure and had a low-quality diet, 14.2% were food insecure with a high-quality diet, 33.1% were food secure with a low-quality diet, and 35.2% were food secure with a high-quality diet.
PWD in the food insecure/low-quality diet group were significantly more likely to be younger, non-Hispanic black or Hispanic, and uninsured compared to those in the food secure/high-quality diet group (P < .001 for all).
When the researchers examined glycemic control, they found that PWD in the food insecurity/low-quality diet groups were significantly more likely than were those with food security/high-quality diets to have hemoglobin A1c of at least 7.0% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.85), A1c of at least 8.0% (aOR, 1.79), low HDL cholesterol (aOR, 1.69), and high triglycerides (aOR, 3.26).
PWD with food insecurity but a high-quality diet also were significantly more likely than were those with food security and a high quality diet to have A1c of at least 7.0% (aOR, 1.69), A1c of at least 8.0% (aOR, 1.83), and high triglycerides (aOR, 2.44). PWD with food security but a low-quality diet were significantly more likely than was the food security/high-quality diet group to have A1c of at least 7% (aOR, 1.55).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design, reliance on self-reports, and inability to distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, the researchers wrote.
However, the results were strengthened by the large, nationally representative sample and the inclusion of multiple clinical outcomes in the patient assessment, they said.
The results suggest that food insecurity had a significant impact on both glycemic control and cholesterol management independent of diet quality, the researchers noted. Based on these findings, health care providers treating PWD may wish to assess their patients’ food security status, and “interventions could address disparities in food security,” they concluded.
Food insecurity a growing problem
“With more communities being pushed into state of war, drought, and famine globally, it is important to track impact of food insecurity and low quality food on common medical conditions like diabetes in our vulnerable communities,” Romesh K. Khardori, MD, professor of medicine: endocrinology, and metabolism at Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, said in an interview.
Dr. Khardori, who was not involved in the study, said he was not surprised by the current study findings.
“Type of food, amount of food, and quality of food have been stressed in diabetes management for more than 100 years,” he said. “Organizations charged with recommendations, such as the ADA and American Dietetic Association, have regularly updated their recommendations,” he noted. “It was not surprising, therefore, to find food insecurity and low quality tied to poor glycemic control.”
The take-home message for clinicians is to consider the availability and quality of food that their patients are exposed to when evaluating barriers to proper glycemic control, Dr. Khardori emphasized.
However, additional research is needed to explore whether the prescription of a sufficient amount of good quality food would alleviate the adverse impact seen in the current study, he said.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. The researchers and Dr. Khardori had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ADA 2022
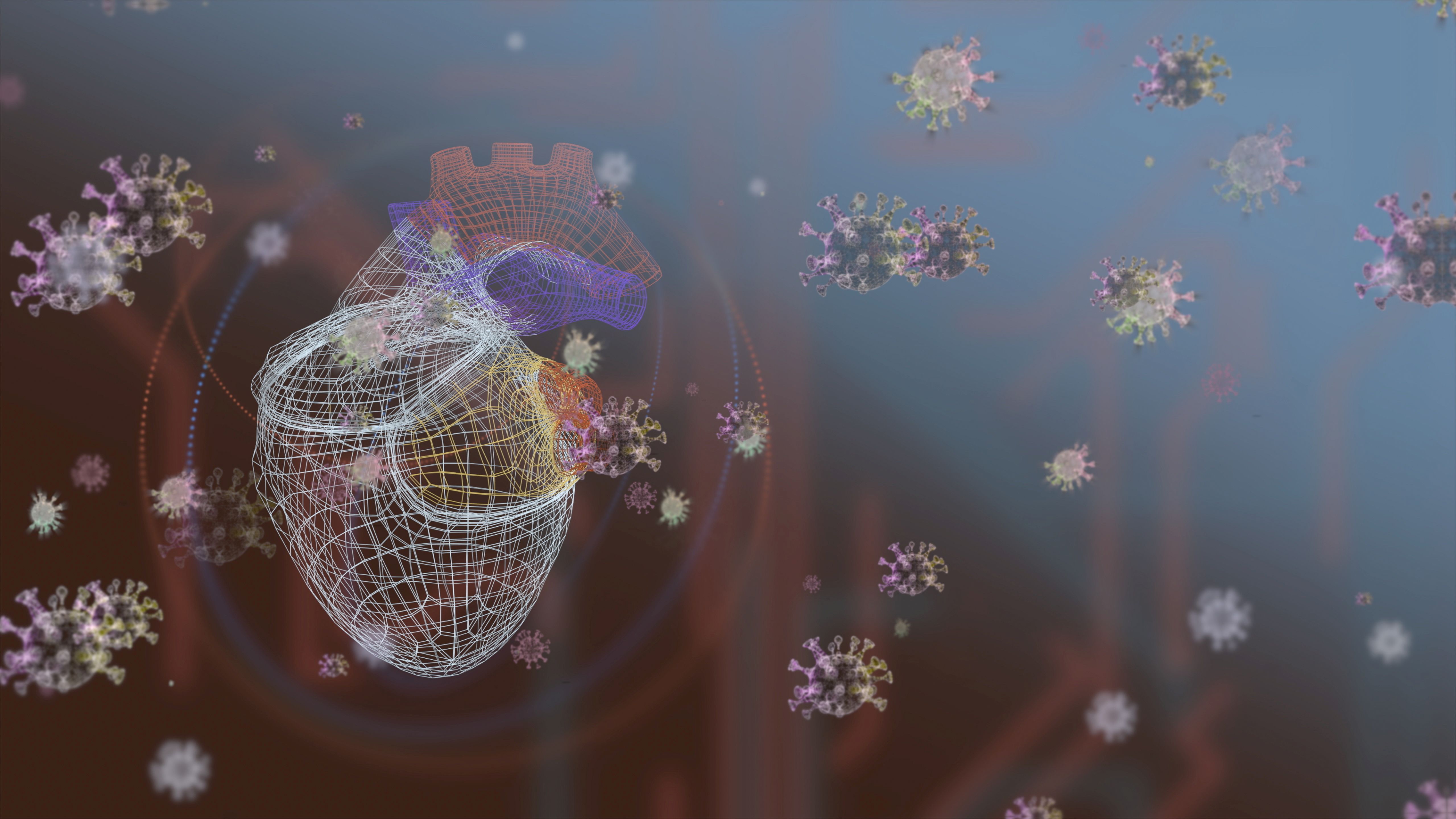
ACC/AHA issue clinical lexicon for complications of COVID-19
The American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association have jointly issued a comprehensive set of data standards to help clarify definitions of the cardiovascular (CV) and non-CV complications of COVID-19.
It’s the work of the ACC/AHA Task Force on Clinical Data Standards and has been endorsed by the Heart Failure Society of America and Society for Cardiac Angiography and Interventions.
There is increased importance to understanding the acute and long-term impact of COVID-19 on CV health, the writing group notes. Until now, however, there has not been “clarity or consensus” on definitions of CV conditions related to COVID-19, with different diagnostic terminologies being used for overlapping conditions, such as “myocardial injury,” “myocarditis,” “type Il myocardial infarction,” “stress cardiomyopathy,” and “inflammatory cardiomyopathy,” they point out.
“We, as a research community, did some things right and some things wrong surrounding the COVID pandemic,” Sandeep Das, MD, MPH, vice chair of the writing group, noted in an interview with this news organization.
“The things that we really did right is that everybody responded with enthusiasm, kind of all hands on deck with a massive crisis response, and that was fantastic,” Dr. Das said.
“However, because of the need to hurry, we didn’t structure and organize in the way that we typically would for something that was sort of a slow burn kind of problem rather than an emergency. One of the consequences of that was fragmentation of how things are collected, reported, et cetera, and that leads to confusion,” he added.
The report was published simultaneously June 23 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
A necessary but not glamorous project
The new data standards for COVID-19 will help standardize definitions and set the framework to capture and better understand how COVID-19 affects CV health.
“It wasn’t exactly a glamorous-type project but, at the same time, it’s super necessary to kind of get everybody on the same page and working together,” Dr. Das said.
Broad agreement on common vocabulary and definitions will help with efforts to pool or compare data from electronic health records, clinical registries, administrative datasets, and other databases, and determine whether these data apply to clinical practice and research endeavors, the writing group says.
They considered data elements relevant to the full range of care provided to COVID-19 patients in all care settings. Among the key items included in the document are:
- Case definitions for confirmed, probable, and suspected acute COVID-19, as well as postacute sequelae of COVID-19.
- Definitions for acute CV complications related to COVID-19, including acute myocardial injury, heart failure, shock, arrhythmia, thromboembolic complications, and .
- Data elements related to COVID-19 vaccination status, comorbidities, and preexisting CV conditions.
- Definitions for postacute CV sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection and long-term CV complications of COVID-19.
- Data elements for CV mortality during acute COVID-19.
- Data elements for non-CV complications to help document severity of illness and other competing diagnoses and complications that might affect CV outcomes.
- A list of symptoms and signs related to COVID-19 and CV complications.
- Data elements for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for COVID-19 and CV conditions.
- A discussion of advanced therapies, including , extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and end-of-life management strategies.
These data standards will be useful for researchers, registry developers, and clinicians, and they are proposed as a framework for ICD-10 code development of COVID-19–related CV conditions, the writing group says.
The standards are also of “great importance” to patients, clinicians, investigators, scientists, administrators, public health officials, policymakers, and payers, the group says.
Dr. Das said that, although there is no formal plan in place to update the document, he could see sections that might be refined.
“For example, there’s a nice long list of all the various variants, and unfortunately, I suspect that that is going to change and evolve over time,” Dr. Das told this news organization.
“We tried very hard not to include things like specifying specific treatments so we didn’t get proscriptive. We wanted to make it descriptive, so hopefully it will stand the test of time pretty well,” he added.
This research had no commercial funding. The writing group has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association have jointly issued a comprehensive set of data standards to help clarify definitions of the cardiovascular (CV) and non-CV complications of COVID-19.
It’s the work of the ACC/AHA Task Force on Clinical Data Standards and has been endorsed by the Heart Failure Society of America and Society for Cardiac Angiography and Interventions.
There is increased importance to understanding the acute and long-term impact of COVID-19 on CV health, the writing group notes. Until now, however, there has not been “clarity or consensus” on definitions of CV conditions related to COVID-19, with different diagnostic terminologies being used for overlapping conditions, such as “myocardial injury,” “myocarditis,” “type Il myocardial infarction,” “stress cardiomyopathy,” and “inflammatory cardiomyopathy,” they point out.
“We, as a research community, did some things right and some things wrong surrounding the COVID pandemic,” Sandeep Das, MD, MPH, vice chair of the writing group, noted in an interview with this news organization.
“The things that we really did right is that everybody responded with enthusiasm, kind of all hands on deck with a massive crisis response, and that was fantastic,” Dr. Das said.
“However, because of the need to hurry, we didn’t structure and organize in the way that we typically would for something that was sort of a slow burn kind of problem rather than an emergency. One of the consequences of that was fragmentation of how things are collected, reported, et cetera, and that leads to confusion,” he added.
The report was published simultaneously June 23 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
A necessary but not glamorous project
The new data standards for COVID-19 will help standardize definitions and set the framework to capture and better understand how COVID-19 affects CV health.
“It wasn’t exactly a glamorous-type project but, at the same time, it’s super necessary to kind of get everybody on the same page and working together,” Dr. Das said.
Broad agreement on common vocabulary and definitions will help with efforts to pool or compare data from electronic health records, clinical registries, administrative datasets, and other databases, and determine whether these data apply to clinical practice and research endeavors, the writing group says.
They considered data elements relevant to the full range of care provided to COVID-19 patients in all care settings. Among the key items included in the document are:
- Case definitions for confirmed, probable, and suspected acute COVID-19, as well as postacute sequelae of COVID-19.
- Definitions for acute CV complications related to COVID-19, including acute myocardial injury, heart failure, shock, arrhythmia, thromboembolic complications, and .
- Data elements related to COVID-19 vaccination status, comorbidities, and preexisting CV conditions.
- Definitions for postacute CV sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection and long-term CV complications of COVID-19.
- Data elements for CV mortality during acute COVID-19.
- Data elements for non-CV complications to help document severity of illness and other competing diagnoses and complications that might affect CV outcomes.
- A list of symptoms and signs related to COVID-19 and CV complications.
- Data elements for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for COVID-19 and CV conditions.
- A discussion of advanced therapies, including , extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and end-of-life management strategies.
These data standards will be useful for researchers, registry developers, and clinicians, and they are proposed as a framework for ICD-10 code development of COVID-19–related CV conditions, the writing group says.
The standards are also of “great importance” to patients, clinicians, investigators, scientists, administrators, public health officials, policymakers, and payers, the group says.
Dr. Das said that, although there is no formal plan in place to update the document, he could see sections that might be refined.
“For example, there’s a nice long list of all the various variants, and unfortunately, I suspect that that is going to change and evolve over time,” Dr. Das told this news organization.
“We tried very hard not to include things like specifying specific treatments so we didn’t get proscriptive. We wanted to make it descriptive, so hopefully it will stand the test of time pretty well,” he added.
This research had no commercial funding. The writing group has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association have jointly issued a comprehensive set of data standards to help clarify definitions of the cardiovascular (CV) and non-CV complications of COVID-19.
It’s the work of the ACC/AHA Task Force on Clinical Data Standards and has been endorsed by the Heart Failure Society of America and Society for Cardiac Angiography and Interventions.
There is increased importance to understanding the acute and long-term impact of COVID-19 on CV health, the writing group notes. Until now, however, there has not been “clarity or consensus” on definitions of CV conditions related to COVID-19, with different diagnostic terminologies being used for overlapping conditions, such as “myocardial injury,” “myocarditis,” “type Il myocardial infarction,” “stress cardiomyopathy,” and “inflammatory cardiomyopathy,” they point out.
“We, as a research community, did some things right and some things wrong surrounding the COVID pandemic,” Sandeep Das, MD, MPH, vice chair of the writing group, noted in an interview with this news organization.
“The things that we really did right is that everybody responded with enthusiasm, kind of all hands on deck with a massive crisis response, and that was fantastic,” Dr. Das said.
“However, because of the need to hurry, we didn’t structure and organize in the way that we typically would for something that was sort of a slow burn kind of problem rather than an emergency. One of the consequences of that was fragmentation of how things are collected, reported, et cetera, and that leads to confusion,” he added.
The report was published simultaneously June 23 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
A necessary but not glamorous project
The new data standards for COVID-19 will help standardize definitions and set the framework to capture and better understand how COVID-19 affects CV health.
“It wasn’t exactly a glamorous-type project but, at the same time, it’s super necessary to kind of get everybody on the same page and working together,” Dr. Das said.
Broad agreement on common vocabulary and definitions will help with efforts to pool or compare data from electronic health records, clinical registries, administrative datasets, and other databases, and determine whether these data apply to clinical practice and research endeavors, the writing group says.
They considered data elements relevant to the full range of care provided to COVID-19 patients in all care settings. Among the key items included in the document are:
- Case definitions for confirmed, probable, and suspected acute COVID-19, as well as postacute sequelae of COVID-19.
- Definitions for acute CV complications related to COVID-19, including acute myocardial injury, heart failure, shock, arrhythmia, thromboembolic complications, and .
- Data elements related to COVID-19 vaccination status, comorbidities, and preexisting CV conditions.
- Definitions for postacute CV sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection and long-term CV complications of COVID-19.
- Data elements for CV mortality during acute COVID-19.
- Data elements for non-CV complications to help document severity of illness and other competing diagnoses and complications that might affect CV outcomes.
- A list of symptoms and signs related to COVID-19 and CV complications.
- Data elements for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for COVID-19 and CV conditions.
- A discussion of advanced therapies, including , extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and end-of-life management strategies.
These data standards will be useful for researchers, registry developers, and clinicians, and they are proposed as a framework for ICD-10 code development of COVID-19–related CV conditions, the writing group says.
The standards are also of “great importance” to patients, clinicians, investigators, scientists, administrators, public health officials, policymakers, and payers, the group says.
Dr. Das said that, although there is no formal plan in place to update the document, he could see sections that might be refined.
“For example, there’s a nice long list of all the various variants, and unfortunately, I suspect that that is going to change and evolve over time,” Dr. Das told this news organization.
“We tried very hard not to include things like specifying specific treatments so we didn’t get proscriptive. We wanted to make it descriptive, so hopefully it will stand the test of time pretty well,” he added.
This research had no commercial funding. The writing group has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Simultaneous Cases of Carfilzomib-Induced Thrombotic Microangiopathy in 2 Patients With Multiple Myeloma
As a class of drugs, proteasome inhibitors are known to rarely cause drug-induced thrombotic microangiopathy (DITMA). In particular, carfilzomib is a second-generation, irreversible proteasome inhibitor approved for the treatment of relapsed, refractory multiple myeloma (MM) in combination with other therapeutic agents.1 Although generally well tolerated, carfilzomib has been associated with serious adverse events such as cardiovascular toxicity and DITMA.2-4 Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) is a life-threatening disorder characterized by thrombocytopenia, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, and end-organ damage.5 Its occurrence secondary to carfilzomib has been reported only rarely in clinical trials of MM, and the most effective management of the disorder as well as the concurrent risk factors that contribute to its development remain incompletely understood.6,7 As a result, given both the expanding use of carfilzomib in practice and the morbidity of TMA, descriptions of carfilzomib-induced TMA from the real-world setting continue to provide important contributions to our understanding of the disorder.
At our US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical center, 2 patients developed severe carfilzomib-induced TMA within days of one another. The presentation of simultaneous cases was highly unexpected and offered the unique opportunity to compare clinical features in real time. Here, we describe our 2 cases in detail, review their presentations and management in the context of the prior literature, and discuss potential insights gained into the disease.
Case Presentation
Case 1
A 78-year-old male patient was diagnosed with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance in 2012 that progressed to Revised International Staging System stage II IgG-κ MM in 2016 due to worsening anemia with a hemoglobin level < 10 g/dL (Table 1). He was treated initially with 8 cycles of first-line bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone, to which he achieved a partial response with > 50% reduction in serum M-protein. He then received 3 cycles of maintenance bortezomib until relapse, at which time he was switched to second-line therapy consisting of carfilzomib 20 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 and 56 mg/m2 on days 8, 9, 15, and 16 for cycle 1, followed by 56 mg/m2 on days 1, 2, 8, 9, 15, and 16 for subsequent cycles plus dexamethasone 20 mg twice weekly every 28 days.
After the patient received cycle 3, day 1 of carfilzomib, he developed subjective fevers, chills, and diarrhea. He missed his day 2 infusion and instead presented to the VA emergency department, where his vital signs were stable and laboratory tests were notable for the following levels: leukocytosis of20.3 K/µL (91.7% neutrophils), hemoglobin 12.4 g/dL (prior 13.5 g/dL), platelet count 171 K/µL, and creatinine 1.39 mg/dL (prior 1.13 g/dL). A chest X-ray demonstrated diffuse bilateral opacities concerning for edema vs infection, and he was started empirically on vancomycin, piperacillin-tazobactam, and azithromycin. His outpatient medications, which included acyclovir, aspirin, finasteride, oxybutynin, ranitidine, omega-3 fatty acids, fish oil, vitamin D, and senna, were continued as indicated.
On hospital day 2, the patient’s platelet count dropped to 81 K/µL and creatinine level rose to 1.78 mg/dL. He developed dark urine (urinalysis [UA] 3+ blood, 6-11 red blood cells per high power field [RBC/HPF]) and had laboratory tests suggestive of hemolysis, including lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) > 1,200 IU/L (reference range, 60-250 IU/L), haptoglobin < 30 mg/dL (reference range, 44-215 mg/dL), total bilirubin 3.2 mg/dL (reference range, 0.2-1.3 mg/dL; indirect bilirubin, 2.6 mg/dL), and a peripheral blood smear demonstrating moderate microangiopathy (Figure 1).
Workup for alternative causes of thrombocytopenia included a negative heparin-induced thrombocytopenia panel and a disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) panel showing elevated fibrinogen (515 mg/dL; reference range, 200-400 mg/dL) and mildly elevated international normalized ratio (INR) (1.3). Blood cultures were negative, and a 22-pathogen gastrointestinal polymerase chain reaction (PCR) panel failed to identify viral or bacterial pathogens, including Escherichia coli O157:H7. C3 (81 mg/dL; reference range, 90-180 mg/dL) and C4 (16 mg/dL; reference range, 16-47 mg/dL) complement levels were borderline to mildly reduced.
Based on this constellation of findings, a diagnosis of TMA was made, and the patient was started empirically on plasma exchange and pulse-dosed steroids. After 4 cycles of plasma exchange, the platelet count had normalized from its nadir of 29 K/µL. ADAMTS13 activity (98% enzyme activity) ruled out thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), and the patient continued to have anuric renal failure (creatinine, 8.62 mg/dL) necessitating the initiation of hemodialysis. Given persistent renal insufficiency, a diagnosis of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) was considered, and eculizumab 900 mg was administered on days 8 and 15 with stabilization of renal function. By the time of discharge on day 18, the patient’s creatinine level had decreased to 3.89 mg/dL, and platelet count was 403 K/µL. Creatinine normalized to 1.07 mg/dL by day 46.
Outpatient genetic testing through the BloodCenter of Wisconsin Diagnostic Laboratories was negative for mutations in the following genes associated with atypical HUS: CFH, CFI, MCP (CD46), THBD, CFB, C3, DGKE, ADAMTS13, C4BPA, C4BPB, LMNA, CFHR1, CFHR3, CFHR4, and CFHR5. The patient subsequently remained off all antimyeloma therapy for > 1 year until eventually starting third-line pomalidomide plus dexamethasone without reinitiation of proteasome inhibitor therapy.
Case 2
A 59-year-old male patient, diagnosed in 2013 with ISS stage I IgG-κ MM after presenting with compression fractures, completed 8 cycles of cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone before undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with complete response (Table 1). He subsequently received single-agent maintenance bortezomib until relapse nearly 2 years later, at which time he started second-line carfilzomib 20 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 and 27 mg/m2 on days 8, 9, 15, and 16 for cycle 1, followed by 27 mg/m2 on days 8, 9, 15, and 16 for cycles 2 to 8, lenalidomide 25 mg on days 1 to 21, and dexamethasone 40 mg weekly every 28 days. Serum free light chain levels normalized after 9 cycles, and he subsequently began maintenance carfilzomib 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 15 plus lenalidomide 10 mg on days 1 to 21 every 28 days.
On the morning before admission, the patient received C6D17 of maintenance carfilzomib, which had been delayed from day 15 because of the holiday. Later that evening, he developed nausea, vomiting, and fever of 101.3 °F. He presented to the VA emergency department and was tachycardic (108 beats per minute) and hypotensive (86/55 mm Hg). Laboratory tests were notable for hemoglobin level 9.9 g/dL (prior 11.6 g/dL), platelet count 270 K/µL, and creatinine level 1.86 mg/dL (prior 1.12 mg/dL). A respiratory viral panel was positive for influenza A, and antimicrobial agents were eventually broadened to piperacillin-tazobactam, azithromycin, and oseltamivir. His outpatient medications, which included acyclovir, zoledronic acid, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, aspirin, amlodipine, atorvastatin, omeprazole, zolpidem, calcium, vitamin D, loratadine, ascorbic acid, and prochlorperazine, were continued as indicated.
On hospital day 2, the patient’s platelet count declined from 211 to 57 K/µL. He developed tea-colored urine (UA 2+ blood, 0-2 RBC/HPF) and had laboratory tests suggestive of hemolysis, including LDH 910 IU/L (reference range, 60-250 IU/L), total bilirubin 3.3 mg/dL (reference range, 0.2-1.3 mg/dL; no direct or indirect available), and a peripheral blood smear demonstrating moderate microangiopathy. Although haptoglobin level was normal at this time (206 mg/dL; reference range, 44-215 mg/dL), it decreased to 42 mg/dL by the following day. Additional workup included a negative direct Coombs and a DIC panel showing elevated fibrinogen (596 mg/dL; reference range, 200-400 mg/dL) and mildly elevated INR (1.16). Blood cultures remained negative, and a 22-pathogen GI PCR panel identified no viral or bacterial pathogens, including E coli O157:H7. C3 (114 mg/dL; reference range, 90-180 mg/dL) and C4 (40 mg/dL; reference range, 16-47 mg/dL) complement levels were both normal.
Based on these findings, empiric treatment was started with plasma exchange and pulse-dosed steroids. The patient received 3 cycles of plasma exchange until the results of the ADAMTS13 activity ruled out TTP (63% enzyme activity). Over the next 6 days, his platelet count reached a nadir of 6 K/µL and creatinine level peaked at 10.36 mg/dL, necessitating the initiation of hemodialysis. Given severe renal insufficiency, a diagnosis of atypical HUS was again considered, and eculizumab 900 mg was administered on days 9 and 16 with stabilization of renal function. By the time of discharge on day 17, the patient’s creatinine level had decreased to 4.17 mg/dL and platelet count was 164 K/µL. Creatinine level normalized to 1.02 mg/dL by day 72.
Outpatient genetic testing through the BloodCenter of Wisconsin Diagnostic Laboratories was negative for gene mutations associated with atypical HUS. Approximately 1 month after discharge, the patient resumed maintenance lenalidomide alone without reinitiation of proteasome inhibitor therapy.
Discussion
In this case series, we describe the uncommon drug-related adverse event of TMA occurring in 2 patients with MM after receiving carfilzomib. Although the incidence of TMA disorders is low, reaching up to 2.8% in patients receiving carfilzomib plus cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone in the phase 2 CARDAMON trial, our experience suggests that a high index of suspicion for carfilzomib-induced TMA is warranted in the real-world setting.8 TMA syndromes, including TTP, HUS, and DITMA, are characterized by microvascular endothelial injury and thrombosis leading to thrombocytopenia and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia.5,9 Several drug culprits of DITMA are recognized, including quinine, gemcitabine, tacrolimus, and proteasome inhibitors (bortezomib, carfilzomib, ixazomib).10-12 In a real-world series of patients receiving proteasome inhibitor therapy, either carfilzomib (n=8) or bortezomib (n=3), common clinical features of DITMA included thrombocytopenia, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, gastrointestinal symptoms, and renal insufficiency with or without a need for hemodialysis.2 Although DITMA has been described primarily as an early event, its occurrence after 12 months of proteasome inhibitor therapy has also been reported, both in this series and elsewhere, thereby suggesting an ongoing risk for DITMA throughout the duration of carfilzomib treatment.2,13
The diagnosis of DITMA can be challenging given its nonspecific symptoms that overlap with other TMA syndromes. Previous studies have proposed that for a drug to be associated with DITMA, there should be: (1) evidence of clinical and/or pathologic findings of TMA; (2) exclusion of alternative causes of TMA; (3) no other new drug exposures other than the suspected culprit medication; and (4) a lack of recurrence of TMA in absence of the drug.10 In the case of patients with MM, other causes of TMA have also been described, including the underlying plasma cell disorder itself and stem cell transplantation.14 In the 2 cases we have described, these alternative causes were considered unlikely given that only 1 patient underwent transplantation remotely and neither had a previous history of TMA secondary to their disease. With respect to other TMA syndromes, ADAMTS13 levels > 10% and negative stool studies for E coli O157:H7 suggested against TTP or typical HUS, respectively. No other drug culprits were identified, and the close timing between the receipt of carfilzomib and symptom onset supported a causal relationship.
Because specific therapies are lacking, management of DITMA has traditionally included drug discontinuation and supportive care for end-organ injury.5 The terminal complement inhibitor, eculizumab, improves hematologic abnormalities and renal function in patients with atypical HUS but its use for treating patients with DITMA is not standard.15 Therefore, the decision to administer eculizumab to our 2 patients was driven by their severe renal insufficiency without improvement after plasma exchange, which suggested a phenotype similar to atypical HUS. After administration of eculizumab, renal function stabilized and then gradually improved over weeks to months, a time course similar to that described in cases of patients with DITMA secondary to other anticancer therapies treated with eculizumab.16 Although these results suggest a potential role for eculizumab in proteasome inhibitor–induced TMA, distinguishing the benefit of eculizumab over drug discontinuation alone remains challenging, and well-designed prospective investigations are needed.
The clustered occurrence of our 2 cases is unique from previous reports that describe carfilzomib-induced TMA as a sporadic event (Table 2).13,17-28 Both immune-mediated and direct toxic effects have been proposed as mechanisms of DITMA, and while our cases do not differentiate between these mechanisms, we considered whether a combined model of initiation, whereby patient or environmental risk factors modulate occurrence of the disease in conjunction with the inciting drug, could explain the clustered occurrence of cases. In this series, drug manufacturing was not a shared risk factor as each patient received carfilzomib from different lot numbers. Furthermore, other patients at our center received carfilzomib from the same batches without developing DITMA. We also considered the role of infection given that 1 patient was diagnosed with influenza A and both presented with nonspecific, viral-like symptoms during the winter season. Interestingly, concurrent viral infections have been reported in other cases of carfilzomib-induced DITMA as well and have also been discussed as a trigger of atypical HUS.20,29 Finally, genetic testing was negative for complement pathway mutations that might predispose to complement dysregulation.
The absence of complement mutations in our 2 patients differs from a recent series describing heterozygous CFHR3-CHFR1 deletions in association with carfilzomib-induced TMA.22 In that report, the authors hypothesized that carfilzomib decreases expression of complement factor H (CFH), a negative regulator of complement activation, thereby leading to complement dysregulation in patients who are genetically predisposed. In a second series, plasma from patients with DITMA secondary to carfilzomib induced the deposition of the complement complex, C5b-9, on endothelial cells in culture, suggesting activation of the complement pathway.30 The effective use of eculizumab would also point to a role for complement activation, and ongoing investigations should aim to identify the triggers and mechanisms of complement dysregulation in this setting, especially for patients like ours in whom genetic testing for complement pathway mutations is negative (Figure 2).
Conclusions
DITMA is a known risk of proteasome inhibitors and is listed as a safety warning in the prescribing information for bortezomib, carfilzomib, and ixazomib.12 Given the overall rarity of this adverse event, the simultaneous presentation of our 2 cases was unexpected and underscores the need for heightened awareness in clinical practice. In addition, while no underlying complement mutations were identified, eculizumab was used in both cases to successfully stabilize renal function. Further research investigating the efficacy of eculizumab and the role of complement activation in proteasome inhibitor–induced TMA will be valuable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the patients whose histories are reported in this manuscript as well as the physicians and staff who provided care during the hospitalizations and beyond. We also thank Oscar Silva, MD, PhD, for his assistance in reviewing and formatting the peripheral blood smear images.
1. McBride A, Klaus JO, Stockeri-Goldstein K. Carfilzomib: a second-generation proteasome inhibitor for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2015;72(5):353-360. doi:10.2146/ajhp130281
2. Yui JC, Van Keer J, Weiss BM, et al. Proteasome inhibitor associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Am J Hematol. 2016;91(9):E348-E352. doi:10.1002/ajh.24447
3. Dimopoulos MA, Roussou M, Gavriatopoulou M, et al. Cardiac and renal complications of carfilzomib in patients with multiple myeloma. Blood Adv. 2017;1(7):449-454. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2016003269
4. Chari A, Stewart AK, Russell SD, et al. Analysis of carfilzomib cardiovascular safety profile across relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma clinical trials. Blood Adv. 2018;2(13):1633-1644. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2017015545
5. George JN, Nester CM. Syndromes of thrombotic microangiopathy. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(7):654-666. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1312353
6. Dimopoulos MA, Moreau P, Palumbo A, et al. Carfilzomib and dexamethasone versus bortezomib and dexamethasone for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (ENDEAVOR): a randomised, phase 3, open-label, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(1):27-38. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00464-7
7. Dimopoulos M, Quach H, Mateos MV, et al. Carfilzomib, dexamethasone, and daratumumab versus carfilzomib and dexamethasone for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (CANDOR): results from a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2020;396(10245):186-197. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30734-0
8. Camilleri M, Cuadrado M, Phillips E, et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy in untreated myeloma patients receiving carfilzomib, cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone on the CARDAMON study. Br J Haematol. 2021;193(4):750-760. doi:10.1111/bjh.17377
9. Masias C, Vasu S, Cataland SR. None of the above: thrombotic microangiopathy beyond TTP and HUS. Blood. 2017;129(21):2857-2863. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-11-743104
10. Al-Nouri ZL, Reese JA, Terrell DR, Vesely SK, George JN. Drug-induced thrombotic microangiopathy: a systemic review of published reports. Blood. 2015;125(4):616-618. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-11-611335
11. Saleem R, Reese JA, George JN. Drug-induced thrombotic-microangiopathy: an updated systematic review, 2014-2018. Am J Hematol. 2018;93(9):E241-E243. doi:10.1002/ajh.25208
12 Nguyen MN, Nayernama A, Jones SC, Kanapuru B, Gormley N, Waldron PE. Proteasome inhibitor-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a review of cases reported to the FDA adverse event reporting system and published in the literature. Am J Hematol. 2020;95(9):E218-E222. doi:10.1002/ajh.25832
13. Haddadin M, Al-Sadawi M, Madanat S, et al. Late presentation of carfilzomib associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Am J Med Case Rep. 2019;7(10):240-243. doi:10.12691/ajmcr-7-10-5
14 Portuguese AJ, Gleber C, Passero Jr FC, Lipe B. A review of thrombotic microangiopathies in multiple myeloma. Leuk Res. 2019;85:106195. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2019.106195
15. Legendre CM, Licht C, Muus P, et al. Terminal complement inhibitor eculizumab in atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(23):2169-2181. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1208981
16. Olson SR, Lu E, Sulpizio E, Shatzel JJ, Rueda JF, DeLoughery TG. When to stop eculizumab in complement-mediated thrombotic microangiopathies. Am J Nephrol. 2018;48(2):96-107. doi:10.1159/000492033
17. Lodhi A, Kumar A, Saqlain MU, Suneja M. Thrombotic microangiopathy associated with proteasome inhibitors. Clin Kidney J. 2015;8(5):632-636. doi:10.1093/ckj/sfv059
18. Sullivan MR, Danilov AV, Lansigan F, Dunbar NM. Carfilzomib associated thrombotic microangiopathy initially treated with therapeutic plasma exchange. J Clin Apher., 2015;30(5):308-310. doi:10.1002/jca.21371
19. Qaqish I, Schlam IM, Chakkera HA, Fonseca R, Adamski J. Carfilzomib: a cause of drug associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Transfus Apher Sci. 2016;54(3):401-404. doi:10.1016/j.transci.2016.03.002
20. Chen Y, Ooi M, Lim SF, et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy during carfilzomib use: case series in Singapore. Blood Cancer J. 2016;6(7):e450. doi:10.1038/bcj.2016.62
21. Gosain R, Gill A, Fuqua J, et al. Gemcitabine and carfilzomib induced thrombotic microangiopathy: eculizumab as a life-saving treatment. Clin Case Rep. 2017;5(12):1926-1930. doi:10.1002/ccr3.1214
22. Portuguese AJ, Lipe B. Carfilzomib-induced aHUS responds to early eculizumab and may be associated with heterozygrous CFHR3-CFHR1 deletion. Blood Adv. 2018;2(23):3443-3446. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2018027532
23. Moliz C, Gutiérrez E, Cavero T, Redondo B, Praga M. Eculizumab as a treatment for atypical hemolytic syndrome secondary to carfilzomib. Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2019;39(1):86-88. doi:10.1016/j.nefro.2018.02.005
24. Jeyaraman P, Borah P, Singh A, et al., Thrombotic microangiopathy after carfilzomib in a very young myeloma patient. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2020;81:102400. doi:10.1016/j.bcmd.2019.102400
25. Bhutani D, Assal A, Mapara MY, Prinzing S, Lentzsch S. Case report: carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy with complement activation treated successfully with eculizumab. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20(4):e155-e157. doi:10.1016/j.clml.2020.01.016
26. Jindal N, Jandial A, Jain A, et al. Carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy: a case based review. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2020;S1658-3876(20)30118-7. doi:10.1016/j.hemonc.2020.07.001
27. Monteith BE, Venner CP, Reece DE, et al. Drug-induced thrombotic microangiopathy with concurrent proteasome inhibitor use in the treatment of multiple myeloma: a case series and review of the literature. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20(11):e791-e780. doi:10.1016/j.clml.2020.04.014
28. Rassner M, Baur R, Wäsch R, et al. Two cases of carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy successfully treated with eculizumab in multiple myeloma. BMC Nephrol. 2021;22(1):32. doi:10.1186/s12882-020-02226-5
29. Kavanagh D, Goodship THJ. Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, genetic basis, and clinical manifestations. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2011;2011:15-20. doi:10.1182/asheducation-2011.1.15
30. Blasco M, Martínez-Roca A, Rodríguez-Lobato LG, et al. Complement as the enabler of carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy. Br J Haematol. 2021;193(1):181-187. doi:10.1111/bjh.16796
As a class of drugs, proteasome inhibitors are known to rarely cause drug-induced thrombotic microangiopathy (DITMA). In particular, carfilzomib is a second-generation, irreversible proteasome inhibitor approved for the treatment of relapsed, refractory multiple myeloma (MM) in combination with other therapeutic agents.1 Although generally well tolerated, carfilzomib has been associated with serious adverse events such as cardiovascular toxicity and DITMA.2-4 Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) is a life-threatening disorder characterized by thrombocytopenia, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, and end-organ damage.5 Its occurrence secondary to carfilzomib has been reported only rarely in clinical trials of MM, and the most effective management of the disorder as well as the concurrent risk factors that contribute to its development remain incompletely understood.6,7 As a result, given both the expanding use of carfilzomib in practice and the morbidity of TMA, descriptions of carfilzomib-induced TMA from the real-world setting continue to provide important contributions to our understanding of the disorder.
At our US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical center, 2 patients developed severe carfilzomib-induced TMA within days of one another. The presentation of simultaneous cases was highly unexpected and offered the unique opportunity to compare clinical features in real time. Here, we describe our 2 cases in detail, review their presentations and management in the context of the prior literature, and discuss potential insights gained into the disease.
Case Presentation
Case 1
A 78-year-old male patient was diagnosed with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance in 2012 that progressed to Revised International Staging System stage II IgG-κ MM in 2016 due to worsening anemia with a hemoglobin level < 10 g/dL (Table 1). He was treated initially with 8 cycles of first-line bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone, to which he achieved a partial response with > 50% reduction in serum M-protein. He then received 3 cycles of maintenance bortezomib until relapse, at which time he was switched to second-line therapy consisting of carfilzomib 20 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 and 56 mg/m2 on days 8, 9, 15, and 16 for cycle 1, followed by 56 mg/m2 on days 1, 2, 8, 9, 15, and 16 for subsequent cycles plus dexamethasone 20 mg twice weekly every 28 days.
After the patient received cycle 3, day 1 of carfilzomib, he developed subjective fevers, chills, and diarrhea. He missed his day 2 infusion and instead presented to the VA emergency department, where his vital signs were stable and laboratory tests were notable for the following levels: leukocytosis of20.3 K/µL (91.7% neutrophils), hemoglobin 12.4 g/dL (prior 13.5 g/dL), platelet count 171 K/µL, and creatinine 1.39 mg/dL (prior 1.13 g/dL). A chest X-ray demonstrated diffuse bilateral opacities concerning for edema vs infection, and he was started empirically on vancomycin, piperacillin-tazobactam, and azithromycin. His outpatient medications, which included acyclovir, aspirin, finasteride, oxybutynin, ranitidine, omega-3 fatty acids, fish oil, vitamin D, and senna, were continued as indicated.
On hospital day 2, the patient’s platelet count dropped to 81 K/µL and creatinine level rose to 1.78 mg/dL. He developed dark urine (urinalysis [UA] 3+ blood, 6-11 red blood cells per high power field [RBC/HPF]) and had laboratory tests suggestive of hemolysis, including lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) > 1,200 IU/L (reference range, 60-250 IU/L), haptoglobin < 30 mg/dL (reference range, 44-215 mg/dL), total bilirubin 3.2 mg/dL (reference range, 0.2-1.3 mg/dL; indirect bilirubin, 2.6 mg/dL), and a peripheral blood smear demonstrating moderate microangiopathy (Figure 1).
Workup for alternative causes of thrombocytopenia included a negative heparin-induced thrombocytopenia panel and a disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) panel showing elevated fibrinogen (515 mg/dL; reference range, 200-400 mg/dL) and mildly elevated international normalized ratio (INR) (1.3). Blood cultures were negative, and a 22-pathogen gastrointestinal polymerase chain reaction (PCR) panel failed to identify viral or bacterial pathogens, including Escherichia coli O157:H7. C3 (81 mg/dL; reference range, 90-180 mg/dL) and C4 (16 mg/dL; reference range, 16-47 mg/dL) complement levels were borderline to mildly reduced.
Based on this constellation of findings, a diagnosis of TMA was made, and the patient was started empirically on plasma exchange and pulse-dosed steroids. After 4 cycles of plasma exchange, the platelet count had normalized from its nadir of 29 K/µL. ADAMTS13 activity (98% enzyme activity) ruled out thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), and the patient continued to have anuric renal failure (creatinine, 8.62 mg/dL) necessitating the initiation of hemodialysis. Given persistent renal insufficiency, a diagnosis of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) was considered, and eculizumab 900 mg was administered on days 8 and 15 with stabilization of renal function. By the time of discharge on day 18, the patient’s creatinine level had decreased to 3.89 mg/dL, and platelet count was 403 K/µL. Creatinine normalized to 1.07 mg/dL by day 46.
Outpatient genetic testing through the BloodCenter of Wisconsin Diagnostic Laboratories was negative for mutations in the following genes associated with atypical HUS: CFH, CFI, MCP (CD46), THBD, CFB, C3, DGKE, ADAMTS13, C4BPA, C4BPB, LMNA, CFHR1, CFHR3, CFHR4, and CFHR5. The patient subsequently remained off all antimyeloma therapy for > 1 year until eventually starting third-line pomalidomide plus dexamethasone without reinitiation of proteasome inhibitor therapy.
Case 2
A 59-year-old male patient, diagnosed in 2013 with ISS stage I IgG-κ MM after presenting with compression fractures, completed 8 cycles of cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone before undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with complete response (Table 1). He subsequently received single-agent maintenance bortezomib until relapse nearly 2 years later, at which time he started second-line carfilzomib 20 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 and 27 mg/m2 on days 8, 9, 15, and 16 for cycle 1, followed by 27 mg/m2 on days 8, 9, 15, and 16 for cycles 2 to 8, lenalidomide 25 mg on days 1 to 21, and dexamethasone 40 mg weekly every 28 days. Serum free light chain levels normalized after 9 cycles, and he subsequently began maintenance carfilzomib 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 15 plus lenalidomide 10 mg on days 1 to 21 every 28 days.
On the morning before admission, the patient received C6D17 of maintenance carfilzomib, which had been delayed from day 15 because of the holiday. Later that evening, he developed nausea, vomiting, and fever of 101.3 °F. He presented to the VA emergency department and was tachycardic (108 beats per minute) and hypotensive (86/55 mm Hg). Laboratory tests were notable for hemoglobin level 9.9 g/dL (prior 11.6 g/dL), platelet count 270 K/µL, and creatinine level 1.86 mg/dL (prior 1.12 mg/dL). A respiratory viral panel was positive for influenza A, and antimicrobial agents were eventually broadened to piperacillin-tazobactam, azithromycin, and oseltamivir. His outpatient medications, which included acyclovir, zoledronic acid, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, aspirin, amlodipine, atorvastatin, omeprazole, zolpidem, calcium, vitamin D, loratadine, ascorbic acid, and prochlorperazine, were continued as indicated.
On hospital day 2, the patient’s platelet count declined from 211 to 57 K/µL. He developed tea-colored urine (UA 2+ blood, 0-2 RBC/HPF) and had laboratory tests suggestive of hemolysis, including LDH 910 IU/L (reference range, 60-250 IU/L), total bilirubin 3.3 mg/dL (reference range, 0.2-1.3 mg/dL; no direct or indirect available), and a peripheral blood smear demonstrating moderate microangiopathy. Although haptoglobin level was normal at this time (206 mg/dL; reference range, 44-215 mg/dL), it decreased to 42 mg/dL by the following day. Additional workup included a negative direct Coombs and a DIC panel showing elevated fibrinogen (596 mg/dL; reference range, 200-400 mg/dL) and mildly elevated INR (1.16). Blood cultures remained negative, and a 22-pathogen GI PCR panel identified no viral or bacterial pathogens, including E coli O157:H7. C3 (114 mg/dL; reference range, 90-180 mg/dL) and C4 (40 mg/dL; reference range, 16-47 mg/dL) complement levels were both normal.
Based on these findings, empiric treatment was started with plasma exchange and pulse-dosed steroids. The patient received 3 cycles of plasma exchange until the results of the ADAMTS13 activity ruled out TTP (63% enzyme activity). Over the next 6 days, his platelet count reached a nadir of 6 K/µL and creatinine level peaked at 10.36 mg/dL, necessitating the initiation of hemodialysis. Given severe renal insufficiency, a diagnosis of atypical HUS was again considered, and eculizumab 900 mg was administered on days 9 and 16 with stabilization of renal function. By the time of discharge on day 17, the patient’s creatinine level had decreased to 4.17 mg/dL and platelet count was 164 K/µL. Creatinine level normalized to 1.02 mg/dL by day 72.
Outpatient genetic testing through the BloodCenter of Wisconsin Diagnostic Laboratories was negative for gene mutations associated with atypical HUS. Approximately 1 month after discharge, the patient resumed maintenance lenalidomide alone without reinitiation of proteasome inhibitor therapy.
Discussion
In this case series, we describe the uncommon drug-related adverse event of TMA occurring in 2 patients with MM after receiving carfilzomib. Although the incidence of TMA disorders is low, reaching up to 2.8% in patients receiving carfilzomib plus cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone in the phase 2 CARDAMON trial, our experience suggests that a high index of suspicion for carfilzomib-induced TMA is warranted in the real-world setting.8 TMA syndromes, including TTP, HUS, and DITMA, are characterized by microvascular endothelial injury and thrombosis leading to thrombocytopenia and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia.5,9 Several drug culprits of DITMA are recognized, including quinine, gemcitabine, tacrolimus, and proteasome inhibitors (bortezomib, carfilzomib, ixazomib).10-12 In a real-world series of patients receiving proteasome inhibitor therapy, either carfilzomib (n=8) or bortezomib (n=3), common clinical features of DITMA included thrombocytopenia, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, gastrointestinal symptoms, and renal insufficiency with or without a need for hemodialysis.2 Although DITMA has been described primarily as an early event, its occurrence after 12 months of proteasome inhibitor therapy has also been reported, both in this series and elsewhere, thereby suggesting an ongoing risk for DITMA throughout the duration of carfilzomib treatment.2,13
The diagnosis of DITMA can be challenging given its nonspecific symptoms that overlap with other TMA syndromes. Previous studies have proposed that for a drug to be associated with DITMA, there should be: (1) evidence of clinical and/or pathologic findings of TMA; (2) exclusion of alternative causes of TMA; (3) no other new drug exposures other than the suspected culprit medication; and (4) a lack of recurrence of TMA in absence of the drug.10 In the case of patients with MM, other causes of TMA have also been described, including the underlying plasma cell disorder itself and stem cell transplantation.14 In the 2 cases we have described, these alternative causes were considered unlikely given that only 1 patient underwent transplantation remotely and neither had a previous history of TMA secondary to their disease. With respect to other TMA syndromes, ADAMTS13 levels > 10% and negative stool studies for E coli O157:H7 suggested against TTP or typical HUS, respectively. No other drug culprits were identified, and the close timing between the receipt of carfilzomib and symptom onset supported a causal relationship.
Because specific therapies are lacking, management of DITMA has traditionally included drug discontinuation and supportive care for end-organ injury.5 The terminal complement inhibitor, eculizumab, improves hematologic abnormalities and renal function in patients with atypical HUS but its use for treating patients with DITMA is not standard.15 Therefore, the decision to administer eculizumab to our 2 patients was driven by their severe renal insufficiency without improvement after plasma exchange, which suggested a phenotype similar to atypical HUS. After administration of eculizumab, renal function stabilized and then gradually improved over weeks to months, a time course similar to that described in cases of patients with DITMA secondary to other anticancer therapies treated with eculizumab.16 Although these results suggest a potential role for eculizumab in proteasome inhibitor–induced TMA, distinguishing the benefit of eculizumab over drug discontinuation alone remains challenging, and well-designed prospective investigations are needed.
The clustered occurrence of our 2 cases is unique from previous reports that describe carfilzomib-induced TMA as a sporadic event (Table 2).13,17-28 Both immune-mediated and direct toxic effects have been proposed as mechanisms of DITMA, and while our cases do not differentiate between these mechanisms, we considered whether a combined model of initiation, whereby patient or environmental risk factors modulate occurrence of the disease in conjunction with the inciting drug, could explain the clustered occurrence of cases. In this series, drug manufacturing was not a shared risk factor as each patient received carfilzomib from different lot numbers. Furthermore, other patients at our center received carfilzomib from the same batches without developing DITMA. We also considered the role of infection given that 1 patient was diagnosed with influenza A and both presented with nonspecific, viral-like symptoms during the winter season. Interestingly, concurrent viral infections have been reported in other cases of carfilzomib-induced DITMA as well and have also been discussed as a trigger of atypical HUS.20,29 Finally, genetic testing was negative for complement pathway mutations that might predispose to complement dysregulation.
The absence of complement mutations in our 2 patients differs from a recent series describing heterozygous CFHR3-CHFR1 deletions in association with carfilzomib-induced TMA.22 In that report, the authors hypothesized that carfilzomib decreases expression of complement factor H (CFH), a negative regulator of complement activation, thereby leading to complement dysregulation in patients who are genetically predisposed. In a second series, plasma from patients with DITMA secondary to carfilzomib induced the deposition of the complement complex, C5b-9, on endothelial cells in culture, suggesting activation of the complement pathway.30 The effective use of eculizumab would also point to a role for complement activation, and ongoing investigations should aim to identify the triggers and mechanisms of complement dysregulation in this setting, especially for patients like ours in whom genetic testing for complement pathway mutations is negative (Figure 2).
Conclusions
DITMA is a known risk of proteasome inhibitors and is listed as a safety warning in the prescribing information for bortezomib, carfilzomib, and ixazomib.12 Given the overall rarity of this adverse event, the simultaneous presentation of our 2 cases was unexpected and underscores the need for heightened awareness in clinical practice. In addition, while no underlying complement mutations were identified, eculizumab was used in both cases to successfully stabilize renal function. Further research investigating the efficacy of eculizumab and the role of complement activation in proteasome inhibitor–induced TMA will be valuable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the patients whose histories are reported in this manuscript as well as the physicians and staff who provided care during the hospitalizations and beyond. We also thank Oscar Silva, MD, PhD, for his assistance in reviewing and formatting the peripheral blood smear images.
As a class of drugs, proteasome inhibitors are known to rarely cause drug-induced thrombotic microangiopathy (DITMA). In particular, carfilzomib is a second-generation, irreversible proteasome inhibitor approved for the treatment of relapsed, refractory multiple myeloma (MM) in combination with other therapeutic agents.1 Although generally well tolerated, carfilzomib has been associated with serious adverse events such as cardiovascular toxicity and DITMA.2-4 Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) is a life-threatening disorder characterized by thrombocytopenia, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, and end-organ damage.5 Its occurrence secondary to carfilzomib has been reported only rarely in clinical trials of MM, and the most effective management of the disorder as well as the concurrent risk factors that contribute to its development remain incompletely understood.6,7 As a result, given both the expanding use of carfilzomib in practice and the morbidity of TMA, descriptions of carfilzomib-induced TMA from the real-world setting continue to provide important contributions to our understanding of the disorder.
At our US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical center, 2 patients developed severe carfilzomib-induced TMA within days of one another. The presentation of simultaneous cases was highly unexpected and offered the unique opportunity to compare clinical features in real time. Here, we describe our 2 cases in detail, review their presentations and management in the context of the prior literature, and discuss potential insights gained into the disease.
Case Presentation
Case 1
A 78-year-old male patient was diagnosed with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance in 2012 that progressed to Revised International Staging System stage II IgG-κ MM in 2016 due to worsening anemia with a hemoglobin level < 10 g/dL (Table 1). He was treated initially with 8 cycles of first-line bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone, to which he achieved a partial response with > 50% reduction in serum M-protein. He then received 3 cycles of maintenance bortezomib until relapse, at which time he was switched to second-line therapy consisting of carfilzomib 20 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 and 56 mg/m2 on days 8, 9, 15, and 16 for cycle 1, followed by 56 mg/m2 on days 1, 2, 8, 9, 15, and 16 for subsequent cycles plus dexamethasone 20 mg twice weekly every 28 days.
After the patient received cycle 3, day 1 of carfilzomib, he developed subjective fevers, chills, and diarrhea. He missed his day 2 infusion and instead presented to the VA emergency department, where his vital signs were stable and laboratory tests were notable for the following levels: leukocytosis of20.3 K/µL (91.7% neutrophils), hemoglobin 12.4 g/dL (prior 13.5 g/dL), platelet count 171 K/µL, and creatinine 1.39 mg/dL (prior 1.13 g/dL). A chest X-ray demonstrated diffuse bilateral opacities concerning for edema vs infection, and he was started empirically on vancomycin, piperacillin-tazobactam, and azithromycin. His outpatient medications, which included acyclovir, aspirin, finasteride, oxybutynin, ranitidine, omega-3 fatty acids, fish oil, vitamin D, and senna, were continued as indicated.
On hospital day 2, the patient’s platelet count dropped to 81 K/µL and creatinine level rose to 1.78 mg/dL. He developed dark urine (urinalysis [UA] 3+ blood, 6-11 red blood cells per high power field [RBC/HPF]) and had laboratory tests suggestive of hemolysis, including lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) > 1,200 IU/L (reference range, 60-250 IU/L), haptoglobin < 30 mg/dL (reference range, 44-215 mg/dL), total bilirubin 3.2 mg/dL (reference range, 0.2-1.3 mg/dL; indirect bilirubin, 2.6 mg/dL), and a peripheral blood smear demonstrating moderate microangiopathy (Figure 1).
Workup for alternative causes of thrombocytopenia included a negative heparin-induced thrombocytopenia panel and a disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) panel showing elevated fibrinogen (515 mg/dL; reference range, 200-400 mg/dL) and mildly elevated international normalized ratio (INR) (1.3). Blood cultures were negative, and a 22-pathogen gastrointestinal polymerase chain reaction (PCR) panel failed to identify viral or bacterial pathogens, including Escherichia coli O157:H7. C3 (81 mg/dL; reference range, 90-180 mg/dL) and C4 (16 mg/dL; reference range, 16-47 mg/dL) complement levels were borderline to mildly reduced.
Based on this constellation of findings, a diagnosis of TMA was made, and the patient was started empirically on plasma exchange and pulse-dosed steroids. After 4 cycles of plasma exchange, the platelet count had normalized from its nadir of 29 K/µL. ADAMTS13 activity (98% enzyme activity) ruled out thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), and the patient continued to have anuric renal failure (creatinine, 8.62 mg/dL) necessitating the initiation of hemodialysis. Given persistent renal insufficiency, a diagnosis of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) was considered, and eculizumab 900 mg was administered on days 8 and 15 with stabilization of renal function. By the time of discharge on day 18, the patient’s creatinine level had decreased to 3.89 mg/dL, and platelet count was 403 K/µL. Creatinine normalized to 1.07 mg/dL by day 46.
Outpatient genetic testing through the BloodCenter of Wisconsin Diagnostic Laboratories was negative for mutations in the following genes associated with atypical HUS: CFH, CFI, MCP (CD46), THBD, CFB, C3, DGKE, ADAMTS13, C4BPA, C4BPB, LMNA, CFHR1, CFHR3, CFHR4, and CFHR5. The patient subsequently remained off all antimyeloma therapy for > 1 year until eventually starting third-line pomalidomide plus dexamethasone without reinitiation of proteasome inhibitor therapy.
Case 2
A 59-year-old male patient, diagnosed in 2013 with ISS stage I IgG-κ MM after presenting with compression fractures, completed 8 cycles of cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone before undergoing autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with complete response (Table 1). He subsequently received single-agent maintenance bortezomib until relapse nearly 2 years later, at which time he started second-line carfilzomib 20 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 and 27 mg/m2 on days 8, 9, 15, and 16 for cycle 1, followed by 27 mg/m2 on days 8, 9, 15, and 16 for cycles 2 to 8, lenalidomide 25 mg on days 1 to 21, and dexamethasone 40 mg weekly every 28 days. Serum free light chain levels normalized after 9 cycles, and he subsequently began maintenance carfilzomib 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 15 plus lenalidomide 10 mg on days 1 to 21 every 28 days.
On the morning before admission, the patient received C6D17 of maintenance carfilzomib, which had been delayed from day 15 because of the holiday. Later that evening, he developed nausea, vomiting, and fever of 101.3 °F. He presented to the VA emergency department and was tachycardic (108 beats per minute) and hypotensive (86/55 mm Hg). Laboratory tests were notable for hemoglobin level 9.9 g/dL (prior 11.6 g/dL), platelet count 270 K/µL, and creatinine level 1.86 mg/dL (prior 1.12 mg/dL). A respiratory viral panel was positive for influenza A, and antimicrobial agents were eventually broadened to piperacillin-tazobactam, azithromycin, and oseltamivir. His outpatient medications, which included acyclovir, zoledronic acid, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, aspirin, amlodipine, atorvastatin, omeprazole, zolpidem, calcium, vitamin D, loratadine, ascorbic acid, and prochlorperazine, were continued as indicated.
On hospital day 2, the patient’s platelet count declined from 211 to 57 K/µL. He developed tea-colored urine (UA 2+ blood, 0-2 RBC/HPF) and had laboratory tests suggestive of hemolysis, including LDH 910 IU/L (reference range, 60-250 IU/L), total bilirubin 3.3 mg/dL (reference range, 0.2-1.3 mg/dL; no direct or indirect available), and a peripheral blood smear demonstrating moderate microangiopathy. Although haptoglobin level was normal at this time (206 mg/dL; reference range, 44-215 mg/dL), it decreased to 42 mg/dL by the following day. Additional workup included a negative direct Coombs and a DIC panel showing elevated fibrinogen (596 mg/dL; reference range, 200-400 mg/dL) and mildly elevated INR (1.16). Blood cultures remained negative, and a 22-pathogen GI PCR panel identified no viral or bacterial pathogens, including E coli O157:H7. C3 (114 mg/dL; reference range, 90-180 mg/dL) and C4 (40 mg/dL; reference range, 16-47 mg/dL) complement levels were both normal.
Based on these findings, empiric treatment was started with plasma exchange and pulse-dosed steroids. The patient received 3 cycles of plasma exchange until the results of the ADAMTS13 activity ruled out TTP (63% enzyme activity). Over the next 6 days, his platelet count reached a nadir of 6 K/µL and creatinine level peaked at 10.36 mg/dL, necessitating the initiation of hemodialysis. Given severe renal insufficiency, a diagnosis of atypical HUS was again considered, and eculizumab 900 mg was administered on days 9 and 16 with stabilization of renal function. By the time of discharge on day 17, the patient’s creatinine level had decreased to 4.17 mg/dL and platelet count was 164 K/µL. Creatinine level normalized to 1.02 mg/dL by day 72.
Outpatient genetic testing through the BloodCenter of Wisconsin Diagnostic Laboratories was negative for gene mutations associated with atypical HUS. Approximately 1 month after discharge, the patient resumed maintenance lenalidomide alone without reinitiation of proteasome inhibitor therapy.
Discussion
In this case series, we describe the uncommon drug-related adverse event of TMA occurring in 2 patients with MM after receiving carfilzomib. Although the incidence of TMA disorders is low, reaching up to 2.8% in patients receiving carfilzomib plus cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone in the phase 2 CARDAMON trial, our experience suggests that a high index of suspicion for carfilzomib-induced TMA is warranted in the real-world setting.8 TMA syndromes, including TTP, HUS, and DITMA, are characterized by microvascular endothelial injury and thrombosis leading to thrombocytopenia and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia.5,9 Several drug culprits of DITMA are recognized, including quinine, gemcitabine, tacrolimus, and proteasome inhibitors (bortezomib, carfilzomib, ixazomib).10-12 In a real-world series of patients receiving proteasome inhibitor therapy, either carfilzomib (n=8) or bortezomib (n=3), common clinical features of DITMA included thrombocytopenia, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, gastrointestinal symptoms, and renal insufficiency with or without a need for hemodialysis.2 Although DITMA has been described primarily as an early event, its occurrence after 12 months of proteasome inhibitor therapy has also been reported, both in this series and elsewhere, thereby suggesting an ongoing risk for DITMA throughout the duration of carfilzomib treatment.2,13
The diagnosis of DITMA can be challenging given its nonspecific symptoms that overlap with other TMA syndromes. Previous studies have proposed that for a drug to be associated with DITMA, there should be: (1) evidence of clinical and/or pathologic findings of TMA; (2) exclusion of alternative causes of TMA; (3) no other new drug exposures other than the suspected culprit medication; and (4) a lack of recurrence of TMA in absence of the drug.10 In the case of patients with MM, other causes of TMA have also been described, including the underlying plasma cell disorder itself and stem cell transplantation.14 In the 2 cases we have described, these alternative causes were considered unlikely given that only 1 patient underwent transplantation remotely and neither had a previous history of TMA secondary to their disease. With respect to other TMA syndromes, ADAMTS13 levels > 10% and negative stool studies for E coli O157:H7 suggested against TTP or typical HUS, respectively. No other drug culprits were identified, and the close timing between the receipt of carfilzomib and symptom onset supported a causal relationship.
Because specific therapies are lacking, management of DITMA has traditionally included drug discontinuation and supportive care for end-organ injury.5 The terminal complement inhibitor, eculizumab, improves hematologic abnormalities and renal function in patients with atypical HUS but its use for treating patients with DITMA is not standard.15 Therefore, the decision to administer eculizumab to our 2 patients was driven by their severe renal insufficiency without improvement after plasma exchange, which suggested a phenotype similar to atypical HUS. After administration of eculizumab, renal function stabilized and then gradually improved over weeks to months, a time course similar to that described in cases of patients with DITMA secondary to other anticancer therapies treated with eculizumab.16 Although these results suggest a potential role for eculizumab in proteasome inhibitor–induced TMA, distinguishing the benefit of eculizumab over drug discontinuation alone remains challenging, and well-designed prospective investigations are needed.
The clustered occurrence of our 2 cases is unique from previous reports that describe carfilzomib-induced TMA as a sporadic event (Table 2).13,17-28 Both immune-mediated and direct toxic effects have been proposed as mechanisms of DITMA, and while our cases do not differentiate between these mechanisms, we considered whether a combined model of initiation, whereby patient or environmental risk factors modulate occurrence of the disease in conjunction with the inciting drug, could explain the clustered occurrence of cases. In this series, drug manufacturing was not a shared risk factor as each patient received carfilzomib from different lot numbers. Furthermore, other patients at our center received carfilzomib from the same batches without developing DITMA. We also considered the role of infection given that 1 patient was diagnosed with influenza A and both presented with nonspecific, viral-like symptoms during the winter season. Interestingly, concurrent viral infections have been reported in other cases of carfilzomib-induced DITMA as well and have also been discussed as a trigger of atypical HUS.20,29 Finally, genetic testing was negative for complement pathway mutations that might predispose to complement dysregulation.
The absence of complement mutations in our 2 patients differs from a recent series describing heterozygous CFHR3-CHFR1 deletions in association with carfilzomib-induced TMA.22 In that report, the authors hypothesized that carfilzomib decreases expression of complement factor H (CFH), a negative regulator of complement activation, thereby leading to complement dysregulation in patients who are genetically predisposed. In a second series, plasma from patients with DITMA secondary to carfilzomib induced the deposition of the complement complex, C5b-9, on endothelial cells in culture, suggesting activation of the complement pathway.30 The effective use of eculizumab would also point to a role for complement activation, and ongoing investigations should aim to identify the triggers and mechanisms of complement dysregulation in this setting, especially for patients like ours in whom genetic testing for complement pathway mutations is negative (Figure 2).
Conclusions
DITMA is a known risk of proteasome inhibitors and is listed as a safety warning in the prescribing information for bortezomib, carfilzomib, and ixazomib.12 Given the overall rarity of this adverse event, the simultaneous presentation of our 2 cases was unexpected and underscores the need for heightened awareness in clinical practice. In addition, while no underlying complement mutations were identified, eculizumab was used in both cases to successfully stabilize renal function. Further research investigating the efficacy of eculizumab and the role of complement activation in proteasome inhibitor–induced TMA will be valuable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the patients whose histories are reported in this manuscript as well as the physicians and staff who provided care during the hospitalizations and beyond. We also thank Oscar Silva, MD, PhD, for his assistance in reviewing and formatting the peripheral blood smear images.
1. McBride A, Klaus JO, Stockeri-Goldstein K. Carfilzomib: a second-generation proteasome inhibitor for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2015;72(5):353-360. doi:10.2146/ajhp130281
2. Yui JC, Van Keer J, Weiss BM, et al. Proteasome inhibitor associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Am J Hematol. 2016;91(9):E348-E352. doi:10.1002/ajh.24447
3. Dimopoulos MA, Roussou M, Gavriatopoulou M, et al. Cardiac and renal complications of carfilzomib in patients with multiple myeloma. Blood Adv. 2017;1(7):449-454. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2016003269
4. Chari A, Stewart AK, Russell SD, et al. Analysis of carfilzomib cardiovascular safety profile across relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma clinical trials. Blood Adv. 2018;2(13):1633-1644. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2017015545
5. George JN, Nester CM. Syndromes of thrombotic microangiopathy. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(7):654-666. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1312353
6. Dimopoulos MA, Moreau P, Palumbo A, et al. Carfilzomib and dexamethasone versus bortezomib and dexamethasone for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (ENDEAVOR): a randomised, phase 3, open-label, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(1):27-38. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00464-7
7. Dimopoulos M, Quach H, Mateos MV, et al. Carfilzomib, dexamethasone, and daratumumab versus carfilzomib and dexamethasone for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (CANDOR): results from a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2020;396(10245):186-197. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30734-0
8. Camilleri M, Cuadrado M, Phillips E, et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy in untreated myeloma patients receiving carfilzomib, cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone on the CARDAMON study. Br J Haematol. 2021;193(4):750-760. doi:10.1111/bjh.17377
9. Masias C, Vasu S, Cataland SR. None of the above: thrombotic microangiopathy beyond TTP and HUS. Blood. 2017;129(21):2857-2863. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-11-743104
10. Al-Nouri ZL, Reese JA, Terrell DR, Vesely SK, George JN. Drug-induced thrombotic microangiopathy: a systemic review of published reports. Blood. 2015;125(4):616-618. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-11-611335
11. Saleem R, Reese JA, George JN. Drug-induced thrombotic-microangiopathy: an updated systematic review, 2014-2018. Am J Hematol. 2018;93(9):E241-E243. doi:10.1002/ajh.25208
12 Nguyen MN, Nayernama A, Jones SC, Kanapuru B, Gormley N, Waldron PE. Proteasome inhibitor-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a review of cases reported to the FDA adverse event reporting system and published in the literature. Am J Hematol. 2020;95(9):E218-E222. doi:10.1002/ajh.25832
13. Haddadin M, Al-Sadawi M, Madanat S, et al. Late presentation of carfilzomib associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Am J Med Case Rep. 2019;7(10):240-243. doi:10.12691/ajmcr-7-10-5
14 Portuguese AJ, Gleber C, Passero Jr FC, Lipe B. A review of thrombotic microangiopathies in multiple myeloma. Leuk Res. 2019;85:106195. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2019.106195
15. Legendre CM, Licht C, Muus P, et al. Terminal complement inhibitor eculizumab in atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(23):2169-2181. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1208981
16. Olson SR, Lu E, Sulpizio E, Shatzel JJ, Rueda JF, DeLoughery TG. When to stop eculizumab in complement-mediated thrombotic microangiopathies. Am J Nephrol. 2018;48(2):96-107. doi:10.1159/000492033
17. Lodhi A, Kumar A, Saqlain MU, Suneja M. Thrombotic microangiopathy associated with proteasome inhibitors. Clin Kidney J. 2015;8(5):632-636. doi:10.1093/ckj/sfv059
18. Sullivan MR, Danilov AV, Lansigan F, Dunbar NM. Carfilzomib associated thrombotic microangiopathy initially treated with therapeutic plasma exchange. J Clin Apher., 2015;30(5):308-310. doi:10.1002/jca.21371
19. Qaqish I, Schlam IM, Chakkera HA, Fonseca R, Adamski J. Carfilzomib: a cause of drug associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Transfus Apher Sci. 2016;54(3):401-404. doi:10.1016/j.transci.2016.03.002
20. Chen Y, Ooi M, Lim SF, et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy during carfilzomib use: case series in Singapore. Blood Cancer J. 2016;6(7):e450. doi:10.1038/bcj.2016.62
21. Gosain R, Gill A, Fuqua J, et al. Gemcitabine and carfilzomib induced thrombotic microangiopathy: eculizumab as a life-saving treatment. Clin Case Rep. 2017;5(12):1926-1930. doi:10.1002/ccr3.1214
22. Portuguese AJ, Lipe B. Carfilzomib-induced aHUS responds to early eculizumab and may be associated with heterozygrous CFHR3-CFHR1 deletion. Blood Adv. 2018;2(23):3443-3446. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2018027532
23. Moliz C, Gutiérrez E, Cavero T, Redondo B, Praga M. Eculizumab as a treatment for atypical hemolytic syndrome secondary to carfilzomib. Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2019;39(1):86-88. doi:10.1016/j.nefro.2018.02.005
24. Jeyaraman P, Borah P, Singh A, et al., Thrombotic microangiopathy after carfilzomib in a very young myeloma patient. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2020;81:102400. doi:10.1016/j.bcmd.2019.102400
25. Bhutani D, Assal A, Mapara MY, Prinzing S, Lentzsch S. Case report: carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy with complement activation treated successfully with eculizumab. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20(4):e155-e157. doi:10.1016/j.clml.2020.01.016
26. Jindal N, Jandial A, Jain A, et al. Carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy: a case based review. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2020;S1658-3876(20)30118-7. doi:10.1016/j.hemonc.2020.07.001
27. Monteith BE, Venner CP, Reece DE, et al. Drug-induced thrombotic microangiopathy with concurrent proteasome inhibitor use in the treatment of multiple myeloma: a case series and review of the literature. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20(11):e791-e780. doi:10.1016/j.clml.2020.04.014
28. Rassner M, Baur R, Wäsch R, et al. Two cases of carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy successfully treated with eculizumab in multiple myeloma. BMC Nephrol. 2021;22(1):32. doi:10.1186/s12882-020-02226-5
29. Kavanagh D, Goodship THJ. Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, genetic basis, and clinical manifestations. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2011;2011:15-20. doi:10.1182/asheducation-2011.1.15
30. Blasco M, Martínez-Roca A, Rodríguez-Lobato LG, et al. Complement as the enabler of carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy. Br J Haematol. 2021;193(1):181-187. doi:10.1111/bjh.16796
1. McBride A, Klaus JO, Stockeri-Goldstein K. Carfilzomib: a second-generation proteasome inhibitor for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2015;72(5):353-360. doi:10.2146/ajhp130281
2. Yui JC, Van Keer J, Weiss BM, et al. Proteasome inhibitor associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Am J Hematol. 2016;91(9):E348-E352. doi:10.1002/ajh.24447
3. Dimopoulos MA, Roussou M, Gavriatopoulou M, et al. Cardiac and renal complications of carfilzomib in patients with multiple myeloma. Blood Adv. 2017;1(7):449-454. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2016003269
4. Chari A, Stewart AK, Russell SD, et al. Analysis of carfilzomib cardiovascular safety profile across relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma clinical trials. Blood Adv. 2018;2(13):1633-1644. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2017015545
5. George JN, Nester CM. Syndromes of thrombotic microangiopathy. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(7):654-666. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1312353
6. Dimopoulos MA, Moreau P, Palumbo A, et al. Carfilzomib and dexamethasone versus bortezomib and dexamethasone for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (ENDEAVOR): a randomised, phase 3, open-label, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(1):27-38. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00464-7
7. Dimopoulos M, Quach H, Mateos MV, et al. Carfilzomib, dexamethasone, and daratumumab versus carfilzomib and dexamethasone for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (CANDOR): results from a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2020;396(10245):186-197. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30734-0
8. Camilleri M, Cuadrado M, Phillips E, et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy in untreated myeloma patients receiving carfilzomib, cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone on the CARDAMON study. Br J Haematol. 2021;193(4):750-760. doi:10.1111/bjh.17377
9. Masias C, Vasu S, Cataland SR. None of the above: thrombotic microangiopathy beyond TTP and HUS. Blood. 2017;129(21):2857-2863. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-11-743104
10. Al-Nouri ZL, Reese JA, Terrell DR, Vesely SK, George JN. Drug-induced thrombotic microangiopathy: a systemic review of published reports. Blood. 2015;125(4):616-618. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-11-611335
11. Saleem R, Reese JA, George JN. Drug-induced thrombotic-microangiopathy: an updated systematic review, 2014-2018. Am J Hematol. 2018;93(9):E241-E243. doi:10.1002/ajh.25208
12 Nguyen MN, Nayernama A, Jones SC, Kanapuru B, Gormley N, Waldron PE. Proteasome inhibitor-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a review of cases reported to the FDA adverse event reporting system and published in the literature. Am J Hematol. 2020;95(9):E218-E222. doi:10.1002/ajh.25832
13. Haddadin M, Al-Sadawi M, Madanat S, et al. Late presentation of carfilzomib associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Am J Med Case Rep. 2019;7(10):240-243. doi:10.12691/ajmcr-7-10-5
14 Portuguese AJ, Gleber C, Passero Jr FC, Lipe B. A review of thrombotic microangiopathies in multiple myeloma. Leuk Res. 2019;85:106195. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2019.106195
15. Legendre CM, Licht C, Muus P, et al. Terminal complement inhibitor eculizumab in atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(23):2169-2181. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1208981
16. Olson SR, Lu E, Sulpizio E, Shatzel JJ, Rueda JF, DeLoughery TG. When to stop eculizumab in complement-mediated thrombotic microangiopathies. Am J Nephrol. 2018;48(2):96-107. doi:10.1159/000492033
17. Lodhi A, Kumar A, Saqlain MU, Suneja M. Thrombotic microangiopathy associated with proteasome inhibitors. Clin Kidney J. 2015;8(5):632-636. doi:10.1093/ckj/sfv059
18. Sullivan MR, Danilov AV, Lansigan F, Dunbar NM. Carfilzomib associated thrombotic microangiopathy initially treated with therapeutic plasma exchange. J Clin Apher., 2015;30(5):308-310. doi:10.1002/jca.21371
19. Qaqish I, Schlam IM, Chakkera HA, Fonseca R, Adamski J. Carfilzomib: a cause of drug associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Transfus Apher Sci. 2016;54(3):401-404. doi:10.1016/j.transci.2016.03.002
20. Chen Y, Ooi M, Lim SF, et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy during carfilzomib use: case series in Singapore. Blood Cancer J. 2016;6(7):e450. doi:10.1038/bcj.2016.62
21. Gosain R, Gill A, Fuqua J, et al. Gemcitabine and carfilzomib induced thrombotic microangiopathy: eculizumab as a life-saving treatment. Clin Case Rep. 2017;5(12):1926-1930. doi:10.1002/ccr3.1214
22. Portuguese AJ, Lipe B. Carfilzomib-induced aHUS responds to early eculizumab and may be associated with heterozygrous CFHR3-CFHR1 deletion. Blood Adv. 2018;2(23):3443-3446. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2018027532
23. Moliz C, Gutiérrez E, Cavero T, Redondo B, Praga M. Eculizumab as a treatment for atypical hemolytic syndrome secondary to carfilzomib. Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2019;39(1):86-88. doi:10.1016/j.nefro.2018.02.005
24. Jeyaraman P, Borah P, Singh A, et al., Thrombotic microangiopathy after carfilzomib in a very young myeloma patient. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2020;81:102400. doi:10.1016/j.bcmd.2019.102400
25. Bhutani D, Assal A, Mapara MY, Prinzing S, Lentzsch S. Case report: carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy with complement activation treated successfully with eculizumab. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20(4):e155-e157. doi:10.1016/j.clml.2020.01.016
26. Jindal N, Jandial A, Jain A, et al. Carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy: a case based review. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2020;S1658-3876(20)30118-7. doi:10.1016/j.hemonc.2020.07.001
27. Monteith BE, Venner CP, Reece DE, et al. Drug-induced thrombotic microangiopathy with concurrent proteasome inhibitor use in the treatment of multiple myeloma: a case series and review of the literature. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20(11):e791-e780. doi:10.1016/j.clml.2020.04.014
28. Rassner M, Baur R, Wäsch R, et al. Two cases of carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy successfully treated with eculizumab in multiple myeloma. BMC Nephrol. 2021;22(1):32. doi:10.1186/s12882-020-02226-5
29. Kavanagh D, Goodship THJ. Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, genetic basis, and clinical manifestations. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2011;2011:15-20. doi:10.1182/asheducation-2011.1.15
30. Blasco M, Martínez-Roca A, Rodríguez-Lobato LG, et al. Complement as the enabler of carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy. Br J Haematol. 2021;193(1):181-187. doi:10.1111/bjh.16796
Racial/ethnic disparities exacerbated maternal death rise during 2020 pandemic.
U.S. maternal deaths – those during pregnancy or within 42 days of pregnancy – increased substantially by 33.3% after March 2020 corresponding to the COVID-19 pandemic onset, according to new research published in JAMA Network Open.
Data from the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) revealed this rise in maternal deaths was higher than the 22% overall excess death estimate associated with the pandemic in 2020.
Increases were highest for Hispanic and non-Hispanic Black women, exacerbating already high rates of disparity in comparison with White women, wrote Marie E. Thoma, PhD, an associate professor at the University of Maryland, College Park, and Eugene R. Declercq, PhD, a professor at Boston University.
The authors noted that this spike in maternal deaths might be caused either by conditions directly related to COVID-19, such as respiratory or viral infections, or by conditions worsened by pandemic-associated health care disruptions including those for diabetes or cardiovascular disease.
The precise causes, however, could not be discerned from the data, the authors noted.
The NCHS reported an 18.4% increase in U.S. maternal mortality from 2019 to 2020. The relative increase was 44.4% among Hispanic, 25.7% among non-Hispanic Black, and 6.1% among non-Hispanic White women.
“The rise in maternal mortality among Hispanic women was unprecedented,” Dr. Thoma said in an interview. Given a 16.8% increase in overall U.S. mortality in 2020, largely attributed to the COVID-19 pandemic, the authors examined the pandemic’s role in [the higher] maternal death rates for 2020.
“Prior to this report, the NCHS released an e-report that there had been a rise in maternal mortality in 2020, but questions remained about the role of the pandemic in this rise that their report hadn’t addressed,” Dr. Thoma said in an interview “So we decided to look at the data further to assess whether the rise coincided with the pandemic and how this differed by race/ethnicity, whether there were changes in the causes of maternal death, and how often COVID-19 was listed as a contributory factor in those deaths.”
A total of 1,588 maternal deaths (18.8 per 100,000 live births) occurred before the pandemic versus 684 deaths (25.1 per 100,000 live births) during the 2020 phase of the pandemic, for a relative increase of 33.3%.
Direct obstetrical causes of death included diabetes, hypertensive and liver disorders, pregnancy-related infections, and obstetrical hemorrhage and embolism. Indirect causes comprised, among others, nonobstetrical infections and diseases of the circulatory and respiratory systems as well as mental and nervous disorders.
Relative increases in direct causes (27.7%) were mostly associated with diabetes (95.9%), hypertensive disorders (39.0%), and other specified pregnancy-related conditions (48.0%).
COVID-19 was commonly listed as a lethal condition along with other viral diseases (16 of 16 deaths and diseases of the respiratory system (11 of 19 deaths).
Late maternal mortality – defined as more than 42 days but less than 1 year after pregnancy – increased by 41%. “This was surprising as we might anticipate risk being higher during pregnancy given that pregnant women may be more susceptible, but we see that this rise was also found among people in the later postpartum period,” Dr. Thoma said.
Absolute and relative changes were highest for Hispanic women (8.9 per 100,000 live births and 74.2%, respectively) and non-Hispanic Black women (16.8 per 100,000 live births and 40.2%). In contrast, non-Hispanic White women saw increases of just 2.9 per 100,000 live births and 17.2%.
“Overall, we found the rise in maternal mortality in 2020 was concentrated after the start of pandemic, particularly for non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic women, and we saw a dramatic rise in respiratory-related conditions,” Dr. Thoma said.
In a comment, Steven Woolf, MD, MPH, director emeritus of the Center on Society and Health at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, said the findings are very consistent with his and others research showing dramatic increases in overall death rates from many causes during the pandemic, with these ranging from COVID-19 leading conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular and Alzheimer’s disease to less-studied causes such as drug overdoses and alcoholism caused by the stresses of the pandemic. Again, deaths were likely caused by both COVID-19 infections and disruptions in diagnosis and care.
“So a rise in maternal mortality would unfortunately also be expected, and these researchers have shown that,” he said in an interview. In addition, they have confirmed “the pattern of stark health disparities in the Hispanic and Black populations relative to the White. Our group has shown marked decreases in the life expectancies of the Black and Hispanic populations relative to the White population.”
While he might take issue with the study’s research methodology, Dr. Woolf said, “The work is useful partly because we need to work out the best research methods to do this kind of analysis because we really need to understand the effects on maternal mortality.”
He said sorting out the best way to do this type of research will be important for looking at excess deaths and maternal mortality following other events, for example, in the wake of the Supreme Court’s recent decision to reverse Roe v. Wade.
The authors acknowledged certain study limitations, including the large percentage of COVID-19 cases with a nonspecific underlying cause. According to Dr. Thoma and Dr. Declercq, that reflects a maternal death coding problem that needs to be addressed, as well as a partitioning of data. The latter resulted in small numbers for some categories, with rates suppressed for fewer than 16 deaths because of reduced reliability.
“We found that more specific information is often available on death certificates but is lost in the process of coding,” said Dr. Thoma. “We were able to reclassify many of these causes to a more specific cause that we attributed to be the primary cause of death.”
The authors said future studies of maternal death should examine the contribution of the pandemic to racial and ethnic disparities and should identify specific causes of maternal deaths overall and associated with COVID-19.
In earlier research, the authors previously warned of possible misclassifications of maternal deaths.
They found evidence of both underreporting and overreporting of deaths, with possible overreporting predominant, whereas accurate data are essential for measuring the effectiveness of maternal mortality reduction programs.
Dr. Thoma’s group will continue to monitor mortality trends with the release of 2021 data. “We hope we will see improvements in 2021 given greater access to vaccines, treatments, and fewer health care disruptions,” Dr. Thoma said. “It will be important to continue to stress the importance of COVID-19 vaccines for pregnant and postpartum people.”
This study had no external funding. The authors disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Woolf declared no conflicts of interest.
U.S. maternal deaths – those during pregnancy or within 42 days of pregnancy – increased substantially by 33.3% after March 2020 corresponding to the COVID-19 pandemic onset, according to new research published in JAMA Network Open.
Data from the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) revealed this rise in maternal deaths was higher than the 22% overall excess death estimate associated with the pandemic in 2020.
Increases were highest for Hispanic and non-Hispanic Black women, exacerbating already high rates of disparity in comparison with White women, wrote Marie E. Thoma, PhD, an associate professor at the University of Maryland, College Park, and Eugene R. Declercq, PhD, a professor at Boston University.
The authors noted that this spike in maternal deaths might be caused either by conditions directly related to COVID-19, such as respiratory or viral infections, or by conditions worsened by pandemic-associated health care disruptions including those for diabetes or cardiovascular disease.
The precise causes, however, could not be discerned from the data, the authors noted.
The NCHS reported an 18.4% increase in U.S. maternal mortality from 2019 to 2020. The relative increase was 44.4% among Hispanic, 25.7% among non-Hispanic Black, and 6.1% among non-Hispanic White women.
“The rise in maternal mortality among Hispanic women was unprecedented,” Dr. Thoma said in an interview. Given a 16.8% increase in overall U.S. mortality in 2020, largely attributed to the COVID-19 pandemic, the authors examined the pandemic’s role in [the higher] maternal death rates for 2020.
“Prior to this report, the NCHS released an e-report that there had been a rise in maternal mortality in 2020, but questions remained about the role of the pandemic in this rise that their report hadn’t addressed,” Dr. Thoma said in an interview “So we decided to look at the data further to assess whether the rise coincided with the pandemic and how this differed by race/ethnicity, whether there were changes in the causes of maternal death, and how often COVID-19 was listed as a contributory factor in those deaths.”
A total of 1,588 maternal deaths (18.8 per 100,000 live births) occurred before the pandemic versus 684 deaths (25.1 per 100,000 live births) during the 2020 phase of the pandemic, for a relative increase of 33.3%.
Direct obstetrical causes of death included diabetes, hypertensive and liver disorders, pregnancy-related infections, and obstetrical hemorrhage and embolism. Indirect causes comprised, among others, nonobstetrical infections and diseases of the circulatory and respiratory systems as well as mental and nervous disorders.
Relative increases in direct causes (27.7%) were mostly associated with diabetes (95.9%), hypertensive disorders (39.0%), and other specified pregnancy-related conditions (48.0%).
COVID-19 was commonly listed as a lethal condition along with other viral diseases (16 of 16 deaths and diseases of the respiratory system (11 of 19 deaths).
Late maternal mortality – defined as more than 42 days but less than 1 year after pregnancy – increased by 41%. “This was surprising as we might anticipate risk being higher during pregnancy given that pregnant women may be more susceptible, but we see that this rise was also found among people in the later postpartum period,” Dr. Thoma said.
Absolute and relative changes were highest for Hispanic women (8.9 per 100,000 live births and 74.2%, respectively) and non-Hispanic Black women (16.8 per 100,000 live births and 40.2%). In contrast, non-Hispanic White women saw increases of just 2.9 per 100,000 live births and 17.2%.
“Overall, we found the rise in maternal mortality in 2020 was concentrated after the start of pandemic, particularly for non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic women, and we saw a dramatic rise in respiratory-related conditions,” Dr. Thoma said.
In a comment, Steven Woolf, MD, MPH, director emeritus of the Center on Society and Health at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, said the findings are very consistent with his and others research showing dramatic increases in overall death rates from many causes during the pandemic, with these ranging from COVID-19 leading conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular and Alzheimer’s disease to less-studied causes such as drug overdoses and alcoholism caused by the stresses of the pandemic. Again, deaths were likely caused by both COVID-19 infections and disruptions in diagnosis and care.
“So a rise in maternal mortality would unfortunately also be expected, and these researchers have shown that,” he said in an interview. In addition, they have confirmed “the pattern of stark health disparities in the Hispanic and Black populations relative to the White. Our group has shown marked decreases in the life expectancies of the Black and Hispanic populations relative to the White population.”
While he might take issue with the study’s research methodology, Dr. Woolf said, “The work is useful partly because we need to work out the best research methods to do this kind of analysis because we really need to understand the effects on maternal mortality.”
He said sorting out the best way to do this type of research will be important for looking at excess deaths and maternal mortality following other events, for example, in the wake of the Supreme Court’s recent decision to reverse Roe v. Wade.
The authors acknowledged certain study limitations, including the large percentage of COVID-19 cases with a nonspecific underlying cause. According to Dr. Thoma and Dr. Declercq, that reflects a maternal death coding problem that needs to be addressed, as well as a partitioning of data. The latter resulted in small numbers for some categories, with rates suppressed for fewer than 16 deaths because of reduced reliability.
“We found that more specific information is often available on death certificates but is lost in the process of coding,” said Dr. Thoma. “We were able to reclassify many of these causes to a more specific cause that we attributed to be the primary cause of death.”
The authors said future studies of maternal death should examine the contribution of the pandemic to racial and ethnic disparities and should identify specific causes of maternal deaths overall and associated with COVID-19.
In earlier research, the authors previously warned of possible misclassifications of maternal deaths.
They found evidence of both underreporting and overreporting of deaths, with possible overreporting predominant, whereas accurate data are essential for measuring the effectiveness of maternal mortality reduction programs.
Dr. Thoma’s group will continue to monitor mortality trends with the release of 2021 data. “We hope we will see improvements in 2021 given greater access to vaccines, treatments, and fewer health care disruptions,” Dr. Thoma said. “It will be important to continue to stress the importance of COVID-19 vaccines for pregnant and postpartum people.”
This study had no external funding. The authors disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Woolf declared no conflicts of interest.
U.S. maternal deaths – those during pregnancy or within 42 days of pregnancy – increased substantially by 33.3% after March 2020 corresponding to the COVID-19 pandemic onset, according to new research published in JAMA Network Open.
Data from the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) revealed this rise in maternal deaths was higher than the 22% overall excess death estimate associated with the pandemic in 2020.
Increases were highest for Hispanic and non-Hispanic Black women, exacerbating already high rates of disparity in comparison with White women, wrote Marie E. Thoma, PhD, an associate professor at the University of Maryland, College Park, and Eugene R. Declercq, PhD, a professor at Boston University.
The authors noted that this spike in maternal deaths might be caused either by conditions directly related to COVID-19, such as respiratory or viral infections, or by conditions worsened by pandemic-associated health care disruptions including those for diabetes or cardiovascular disease.
The precise causes, however, could not be discerned from the data, the authors noted.
The NCHS reported an 18.4% increase in U.S. maternal mortality from 2019 to 2020. The relative increase was 44.4% among Hispanic, 25.7% among non-Hispanic Black, and 6.1% among non-Hispanic White women.
“The rise in maternal mortality among Hispanic women was unprecedented,” Dr. Thoma said in an interview. Given a 16.8% increase in overall U.S. mortality in 2020, largely attributed to the COVID-19 pandemic, the authors examined the pandemic’s role in [the higher] maternal death rates for 2020.
“Prior to this report, the NCHS released an e-report that there had been a rise in maternal mortality in 2020, but questions remained about the role of the pandemic in this rise that their report hadn’t addressed,” Dr. Thoma said in an interview “So we decided to look at the data further to assess whether the rise coincided with the pandemic and how this differed by race/ethnicity, whether there were changes in the causes of maternal death, and how often COVID-19 was listed as a contributory factor in those deaths.”
A total of 1,588 maternal deaths (18.8 per 100,000 live births) occurred before the pandemic versus 684 deaths (25.1 per 100,000 live births) during the 2020 phase of the pandemic, for a relative increase of 33.3%.
Direct obstetrical causes of death included diabetes, hypertensive and liver disorders, pregnancy-related infections, and obstetrical hemorrhage and embolism. Indirect causes comprised, among others, nonobstetrical infections and diseases of the circulatory and respiratory systems as well as mental and nervous disorders.
Relative increases in direct causes (27.7%) were mostly associated with diabetes (95.9%), hypertensive disorders (39.0%), and other specified pregnancy-related conditions (48.0%).
COVID-19 was commonly listed as a lethal condition along with other viral diseases (16 of 16 deaths and diseases of the respiratory system (11 of 19 deaths).
Late maternal mortality – defined as more than 42 days but less than 1 year after pregnancy – increased by 41%. “This was surprising as we might anticipate risk being higher during pregnancy given that pregnant women may be more susceptible, but we see that this rise was also found among people in the later postpartum period,” Dr. Thoma said.
Absolute and relative changes were highest for Hispanic women (8.9 per 100,000 live births and 74.2%, respectively) and non-Hispanic Black women (16.8 per 100,000 live births and 40.2%). In contrast, non-Hispanic White women saw increases of just 2.9 per 100,000 live births and 17.2%.
“Overall, we found the rise in maternal mortality in 2020 was concentrated after the start of pandemic, particularly for non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic women, and we saw a dramatic rise in respiratory-related conditions,” Dr. Thoma said.
In a comment, Steven Woolf, MD, MPH, director emeritus of the Center on Society and Health at Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, said the findings are very consistent with his and others research showing dramatic increases in overall death rates from many causes during the pandemic, with these ranging from COVID-19 leading conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular and Alzheimer’s disease to less-studied causes such as drug overdoses and alcoholism caused by the stresses of the pandemic. Again, deaths were likely caused by both COVID-19 infections and disruptions in diagnosis and care.
“So a rise in maternal mortality would unfortunately also be expected, and these researchers have shown that,” he said in an interview. In addition, they have confirmed “the pattern of stark health disparities in the Hispanic and Black populations relative to the White. Our group has shown marked decreases in the life expectancies of the Black and Hispanic populations relative to the White population.”
While he might take issue with the study’s research methodology, Dr. Woolf said, “The work is useful partly because we need to work out the best research methods to do this kind of analysis because we really need to understand the effects on maternal mortality.”
He said sorting out the best way to do this type of research will be important for looking at excess deaths and maternal mortality following other events, for example, in the wake of the Supreme Court’s recent decision to reverse Roe v. Wade.
The authors acknowledged certain study limitations, including the large percentage of COVID-19 cases with a nonspecific underlying cause. According to Dr. Thoma and Dr. Declercq, that reflects a maternal death coding problem that needs to be addressed, as well as a partitioning of data. The latter resulted in small numbers for some categories, with rates suppressed for fewer than 16 deaths because of reduced reliability.
“We found that more specific information is often available on death certificates but is lost in the process of coding,” said Dr. Thoma. “We were able to reclassify many of these causes to a more specific cause that we attributed to be the primary cause of death.”
The authors said future studies of maternal death should examine the contribution of the pandemic to racial and ethnic disparities and should identify specific causes of maternal deaths overall and associated with COVID-19.
In earlier research, the authors previously warned of possible misclassifications of maternal deaths.
They found evidence of both underreporting and overreporting of deaths, with possible overreporting predominant, whereas accurate data are essential for measuring the effectiveness of maternal mortality reduction programs.
Dr. Thoma’s group will continue to monitor mortality trends with the release of 2021 data. “We hope we will see improvements in 2021 given greater access to vaccines, treatments, and fewer health care disruptions,” Dr. Thoma said. “It will be important to continue to stress the importance of COVID-19 vaccines for pregnant and postpartum people.”
This study had no external funding. The authors disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Woolf declared no conflicts of interest.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Artificial intelligence colonoscopy system shows promise
A new artificial intelligence (AI) system can help expert endoscopists improve their colonoscopies, a new study indicates.
Endoscopists using the computer program SKOUT (Iterative Scopes) achieved a 27% better detection rate of adenomas per colonoscopy, compared with endoscopists working without computer assistance, said lead author Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, director of outcomes research in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at New York University.
The study showed that AI colonoscopy systems can work in a routine population of U.S. patients, Dr. Shaukat said in an interview.
“As gastroenterologists, we are very excited,” she said.
The study was published online in Gastroenterology and was presented at the annual Digestive Disease® Week.
Previous research has shown that experienced endoscopists miss many polyps. To improve their detection rate, multiple companies have used machine learning to develop algorithms to identify suspicious areas.
“Once the computer sees the polyp, it puts a bounding box around it,” said Dr. Shaukat. “It draws the attention of the endoscopist to it. It assists the endoscopist but doesn’t replace the endoscopist.”
The Food and Drug Administration has approved two such systems: EndoScreener (Wision AI) and GI Genius (Cosmo Pharmaceuticals).
The SKOUT algorithm was trained on 3,616 full-length colonoscopy procedure videos from multiple centers. In bench testing, it achieved a 93.5% polyp-level true positive rate and a 2.3% false positive rate.
Randomized trial pits AI against standard procedure
To see how well the system works in the clinic, Dr. Shaukat and colleagues recruited 22 U.S. board-certified gastroenterologists from five academic and community centers. The gastroenterologists all had a minimum adenoma detection rate of 25%, defined as the number of colonoscopies in which at least one adenoma is found, divided by the number of colonoscopies performed. All the gastroenterologists had performed a minimum of 1,000 colonoscopy procedures.
The researchers randomly assigned 682 patients to undergo colonoscopy with the SKOUT and 677 to undergo colonoscopy using the standard procedure. The patients were aged 40 years or older and were scheduled for either screening or surveillance.
The endoscopists who received computer assistance detected 1.05 adenomas per colonoscopy versus 0.83 for those who did not have computer assistance, a statistically significant difference.
The proportion of resections with clinically significant histology was 71.7% with standard colonoscopies versus 67.4% with computer-assisted colonoscopies. This fell within the 14% margin that the researchers had set to show noninferiority for the computer system.
“The important thing is not just detecting all polyps but the polyps we care about, which are adenomas, and doing so without increasing the false positive rate,” said Dr. Shaukat.
The adenoma detection rate was 43.9% for the standard procedure and 47.8% for the computer-assisted procedure. This difference was not statistically significant, but Dr. Shaukat argued that the adenoma detection rate is not the best measure of success, because endoscopists sometimes stop looking for polyps once they find one.
The overall sessile serrated lesion detection rate for the standard colonoscopies was 16.0% versus 12.6% for the computer-assisted colonoscopies, which also was not statistically significant.
Next steps
This study is important because it was a large, multicenter trial in the United States, said Omer Ahmad, BSc, MBBS, MRCP, a gastroenterologist and clinical researcher at University College London, who was not involved in the study. Most of the trials of AI have been in China or Europe. “It was very important just to see this replicated in the U.S. population.”
The average procedure time was 15.41 minutes for the standard colonoscopies versus 15.82 minutes for the computer-assisted colonoscopies, which was not statistically different.
“It is important to note that the studies so far suggest that false positives do not have a significant impact on workflow,” said Dr. Ahmad.
The next crucial step in evaluating AI colonoscopy will be to track the effects over the long term, said Dr. Shaukat.
“As these technologies get approved and we see them in practice, we need to see that it’s leading to some outcome, like reduced colon cancer,” she said.
That also may be necessary before payers in the United States are willing to pay the additional cost for this technology, she added.
In the meantime, Dr. Ahmad said computer assistance is improving his own colonoscopies.
“I have found the systems have spotted some polyps that I may have otherwise missed,” he said. “There is a false positive rate, but for me, it doesn’t distract from my workflow.”
He believes the systems will be particularly helpful in improving the performance of less-skilled endoscopists.
He is also looking forward to systems that can help complete the reports needed at the end of each colonoscopy. “Most of us dislike having to write a laborious report and having to code everything at the end of the procedure,” he said.
The study was funded by Iterative Scopes. Dr. Shaukat reported having received research funding to her institution for the current study from Iterative Scopes and consulting fees from Freenome and Medtronic. Dr. Ahmad reports receiving speaker fees from the Canadian Association of Gastroenterology/Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new artificial intelligence (AI) system can help expert endoscopists improve their colonoscopies, a new study indicates.
Endoscopists using the computer program SKOUT (Iterative Scopes) achieved a 27% better detection rate of adenomas per colonoscopy, compared with endoscopists working without computer assistance, said lead author Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, director of outcomes research in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at New York University.
The study showed that AI colonoscopy systems can work in a routine population of U.S. patients, Dr. Shaukat said in an interview.
“As gastroenterologists, we are very excited,” she said.
The study was published online in Gastroenterology and was presented at the annual Digestive Disease® Week.
Previous research has shown that experienced endoscopists miss many polyps. To improve their detection rate, multiple companies have used machine learning to develop algorithms to identify suspicious areas.
“Once the computer sees the polyp, it puts a bounding box around it,” said Dr. Shaukat. “It draws the attention of the endoscopist to it. It assists the endoscopist but doesn’t replace the endoscopist.”
The Food and Drug Administration has approved two such systems: EndoScreener (Wision AI) and GI Genius (Cosmo Pharmaceuticals).
The SKOUT algorithm was trained on 3,616 full-length colonoscopy procedure videos from multiple centers. In bench testing, it achieved a 93.5% polyp-level true positive rate and a 2.3% false positive rate.
Randomized trial pits AI against standard procedure
To see how well the system works in the clinic, Dr. Shaukat and colleagues recruited 22 U.S. board-certified gastroenterologists from five academic and community centers. The gastroenterologists all had a minimum adenoma detection rate of 25%, defined as the number of colonoscopies in which at least one adenoma is found, divided by the number of colonoscopies performed. All the gastroenterologists had performed a minimum of 1,000 colonoscopy procedures.
The researchers randomly assigned 682 patients to undergo colonoscopy with the SKOUT and 677 to undergo colonoscopy using the standard procedure. The patients were aged 40 years or older and were scheduled for either screening or surveillance.
The endoscopists who received computer assistance detected 1.05 adenomas per colonoscopy versus 0.83 for those who did not have computer assistance, a statistically significant difference.
The proportion of resections with clinically significant histology was 71.7% with standard colonoscopies versus 67.4% with computer-assisted colonoscopies. This fell within the 14% margin that the researchers had set to show noninferiority for the computer system.
“The important thing is not just detecting all polyps but the polyps we care about, which are adenomas, and doing so without increasing the false positive rate,” said Dr. Shaukat.
The adenoma detection rate was 43.9% for the standard procedure and 47.8% for the computer-assisted procedure. This difference was not statistically significant, but Dr. Shaukat argued that the adenoma detection rate is not the best measure of success, because endoscopists sometimes stop looking for polyps once they find one.
The overall sessile serrated lesion detection rate for the standard colonoscopies was 16.0% versus 12.6% for the computer-assisted colonoscopies, which also was not statistically significant.
Next steps
This study is important because it was a large, multicenter trial in the United States, said Omer Ahmad, BSc, MBBS, MRCP, a gastroenterologist and clinical researcher at University College London, who was not involved in the study. Most of the trials of AI have been in China or Europe. “It was very important just to see this replicated in the U.S. population.”
The average procedure time was 15.41 minutes for the standard colonoscopies versus 15.82 minutes for the computer-assisted colonoscopies, which was not statistically different.
“It is important to note that the studies so far suggest that false positives do not have a significant impact on workflow,” said Dr. Ahmad.
The next crucial step in evaluating AI colonoscopy will be to track the effects over the long term, said Dr. Shaukat.
“As these technologies get approved and we see them in practice, we need to see that it’s leading to some outcome, like reduced colon cancer,” she said.
That also may be necessary before payers in the United States are willing to pay the additional cost for this technology, she added.
In the meantime, Dr. Ahmad said computer assistance is improving his own colonoscopies.
“I have found the systems have spotted some polyps that I may have otherwise missed,” he said. “There is a false positive rate, but for me, it doesn’t distract from my workflow.”
He believes the systems will be particularly helpful in improving the performance of less-skilled endoscopists.
He is also looking forward to systems that can help complete the reports needed at the end of each colonoscopy. “Most of us dislike having to write a laborious report and having to code everything at the end of the procedure,” he said.
The study was funded by Iterative Scopes. Dr. Shaukat reported having received research funding to her institution for the current study from Iterative Scopes and consulting fees from Freenome and Medtronic. Dr. Ahmad reports receiving speaker fees from the Canadian Association of Gastroenterology/Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new artificial intelligence (AI) system can help expert endoscopists improve their colonoscopies, a new study indicates.
Endoscopists using the computer program SKOUT (Iterative Scopes) achieved a 27% better detection rate of adenomas per colonoscopy, compared with endoscopists working without computer assistance, said lead author Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, director of outcomes research in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at New York University.
The study showed that AI colonoscopy systems can work in a routine population of U.S. patients, Dr. Shaukat said in an interview.
“As gastroenterologists, we are very excited,” she said.
The study was published online in Gastroenterology and was presented at the annual Digestive Disease® Week.
Previous research has shown that experienced endoscopists miss many polyps. To improve their detection rate, multiple companies have used machine learning to develop algorithms to identify suspicious areas.
“Once the computer sees the polyp, it puts a bounding box around it,” said Dr. Shaukat. “It draws the attention of the endoscopist to it. It assists the endoscopist but doesn’t replace the endoscopist.”
The Food and Drug Administration has approved two such systems: EndoScreener (Wision AI) and GI Genius (Cosmo Pharmaceuticals).
The SKOUT algorithm was trained on 3,616 full-length colonoscopy procedure videos from multiple centers. In bench testing, it achieved a 93.5% polyp-level true positive rate and a 2.3% false positive rate.
Randomized trial pits AI against standard procedure
To see how well the system works in the clinic, Dr. Shaukat and colleagues recruited 22 U.S. board-certified gastroenterologists from five academic and community centers. The gastroenterologists all had a minimum adenoma detection rate of 25%, defined as the number of colonoscopies in which at least one adenoma is found, divided by the number of colonoscopies performed. All the gastroenterologists had performed a minimum of 1,000 colonoscopy procedures.
The researchers randomly assigned 682 patients to undergo colonoscopy with the SKOUT and 677 to undergo colonoscopy using the standard procedure. The patients were aged 40 years or older and were scheduled for either screening or surveillance.
The endoscopists who received computer assistance detected 1.05 adenomas per colonoscopy versus 0.83 for those who did not have computer assistance, a statistically significant difference.
The proportion of resections with clinically significant histology was 71.7% with standard colonoscopies versus 67.4% with computer-assisted colonoscopies. This fell within the 14% margin that the researchers had set to show noninferiority for the computer system.
“The important thing is not just detecting all polyps but the polyps we care about, which are adenomas, and doing so without increasing the false positive rate,” said Dr. Shaukat.
The adenoma detection rate was 43.9% for the standard procedure and 47.8% for the computer-assisted procedure. This difference was not statistically significant, but Dr. Shaukat argued that the adenoma detection rate is not the best measure of success, because endoscopists sometimes stop looking for polyps once they find one.
The overall sessile serrated lesion detection rate for the standard colonoscopies was 16.0% versus 12.6% for the computer-assisted colonoscopies, which also was not statistically significant.
Next steps
This study is important because it was a large, multicenter trial in the United States, said Omer Ahmad, BSc, MBBS, MRCP, a gastroenterologist and clinical researcher at University College London, who was not involved in the study. Most of the trials of AI have been in China or Europe. “It was very important just to see this replicated in the U.S. population.”
The average procedure time was 15.41 minutes for the standard colonoscopies versus 15.82 minutes for the computer-assisted colonoscopies, which was not statistically different.
“It is important to note that the studies so far suggest that false positives do not have a significant impact on workflow,” said Dr. Ahmad.
The next crucial step in evaluating AI colonoscopy will be to track the effects over the long term, said Dr. Shaukat.
“As these technologies get approved and we see them in practice, we need to see that it’s leading to some outcome, like reduced colon cancer,” she said.
That also may be necessary before payers in the United States are willing to pay the additional cost for this technology, she added.
In the meantime, Dr. Ahmad said computer assistance is improving his own colonoscopies.
“I have found the systems have spotted some polyps that I may have otherwise missed,” he said. “There is a false positive rate, but for me, it doesn’t distract from my workflow.”
He believes the systems will be particularly helpful in improving the performance of less-skilled endoscopists.
He is also looking forward to systems that can help complete the reports needed at the end of each colonoscopy. “Most of us dislike having to write a laborious report and having to code everything at the end of the procedure,” he said.
The study was funded by Iterative Scopes. Dr. Shaukat reported having received research funding to her institution for the current study from Iterative Scopes and consulting fees from Freenome and Medtronic. Dr. Ahmad reports receiving speaker fees from the Canadian Association of Gastroenterology/Medtronic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves liso-cel as second-line therapy for LBCL
This expanded indication is based on findings from the pivotal phase 3 TRANSFORM study, which showed significant and clinically meaningful improvements with CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor T-cell immunotherapy over salvage chemotherapy followed by high-dose chemotherapy plus autologous stem cell transplant. The latter course of treatment had been the standard of care for more than 2 decades.
Data from the global, randomized, multicenter TRANSFORM study, as reported in December 2021 at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, showed that second-line treatment with liso-cel in 92 patients with r/r LBCL within 12 months after first-line therapy, compared with 92 patient who received standard of care therapy, was associated with highly statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in event-free survival (10.1 vs. 2.3 months; hazard ratio, 0.349), complete response rate (66% vs. 39%), and progression-free survival (14.8 vs. 5.7 months; HR, 0.406).
A positive trend in overall survival was also observed (HR, 0.509 at median follow-up of 6.2 months). No new liso-cel safety signals were detected in the second-line setting.
Liso-cel was initially approved in February 2021 for the treatment of adults with LBCL, including diffuse LBCL not otherwise specified (including DLBCL arising from indolent lymphoma), high-grade B-cell lymphoma, primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, and follicular lymphoma grade 3B, who have:
- Refractory disease to first-line chemoimmunotherapy or relapse within 12 months of first-line chemoimmunotherapy.
- Refractory disease to first-line chemoimmunotherapy or relapse after first-line chemoimmunotherapy and are not eligible for hematopoietic stem cell transplant because of comorbidities or age.
Liso-cel is not indicated for the treatment of patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma.
In February 2022, the FDA granted Priority Review status for a Bristol-Myers Squibb supplemental Biologics License Application (sBLA), based on the TRANSFORM study data, to expand the indication to include use after the failure of first-line therapy.
The agent “now has the potential to be a new standard of care for patients after failure of first-line therapy, offering significantly improved outcomes beyond the current mainstay of care,” Anne Kerber, the BMS senior vice president of cell therapy development, said in a press release at that time.
The European Medicines Agency has also validated a type II variation application for extension of the indication for liso-cel in this setting. Validation of the application “confirms the submission is complete and begins the EMA’s centralized review procedure,” BMS announced in a June 20, 2022, press release.
Liso-cel, which has been available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy, includes a boxed warning regarding the risk for cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurologic toxicities.
The warning states that liso-cel should not be administered to patients with active infection or inflammatory disorders, and that severe or life-threatening CRS should be treated with tocilizumab with or without corticosteroids.
Patients should also be monitored for neurologic events after treatment with liso-cel, and supportive care and/or corticosteroids should be administered as needed.
This expanded indication is based on findings from the pivotal phase 3 TRANSFORM study, which showed significant and clinically meaningful improvements with CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor T-cell immunotherapy over salvage chemotherapy followed by high-dose chemotherapy plus autologous stem cell transplant. The latter course of treatment had been the standard of care for more than 2 decades.
Data from the global, randomized, multicenter TRANSFORM study, as reported in December 2021 at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, showed that second-line treatment with liso-cel in 92 patients with r/r LBCL within 12 months after first-line therapy, compared with 92 patient who received standard of care therapy, was associated with highly statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in event-free survival (10.1 vs. 2.3 months; hazard ratio, 0.349), complete response rate (66% vs. 39%), and progression-free survival (14.8 vs. 5.7 months; HR, 0.406).
A positive trend in overall survival was also observed (HR, 0.509 at median follow-up of 6.2 months). No new liso-cel safety signals were detected in the second-line setting.
Liso-cel was initially approved in February 2021 for the treatment of adults with LBCL, including diffuse LBCL not otherwise specified (including DLBCL arising from indolent lymphoma), high-grade B-cell lymphoma, primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, and follicular lymphoma grade 3B, who have:
- Refractory disease to first-line chemoimmunotherapy or relapse within 12 months of first-line chemoimmunotherapy.
- Refractory disease to first-line chemoimmunotherapy or relapse after first-line chemoimmunotherapy and are not eligible for hematopoietic stem cell transplant because of comorbidities or age.
Liso-cel is not indicated for the treatment of patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma.
In February 2022, the FDA granted Priority Review status for a Bristol-Myers Squibb supplemental Biologics License Application (sBLA), based on the TRANSFORM study data, to expand the indication to include use after the failure of first-line therapy.
The agent “now has the potential to be a new standard of care for patients after failure of first-line therapy, offering significantly improved outcomes beyond the current mainstay of care,” Anne Kerber, the BMS senior vice president of cell therapy development, said in a press release at that time.
The European Medicines Agency has also validated a type II variation application for extension of the indication for liso-cel in this setting. Validation of the application “confirms the submission is complete and begins the EMA’s centralized review procedure,” BMS announced in a June 20, 2022, press release.
Liso-cel, which has been available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy, includes a boxed warning regarding the risk for cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurologic toxicities.
The warning states that liso-cel should not be administered to patients with active infection or inflammatory disorders, and that severe or life-threatening CRS should be treated with tocilizumab with or without corticosteroids.
Patients should also be monitored for neurologic events after treatment with liso-cel, and supportive care and/or corticosteroids should be administered as needed.
This expanded indication is based on findings from the pivotal phase 3 TRANSFORM study, which showed significant and clinically meaningful improvements with CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor T-cell immunotherapy over salvage chemotherapy followed by high-dose chemotherapy plus autologous stem cell transplant. The latter course of treatment had been the standard of care for more than 2 decades.
Data from the global, randomized, multicenter TRANSFORM study, as reported in December 2021 at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, showed that second-line treatment with liso-cel in 92 patients with r/r LBCL within 12 months after first-line therapy, compared with 92 patient who received standard of care therapy, was associated with highly statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in event-free survival (10.1 vs. 2.3 months; hazard ratio, 0.349), complete response rate (66% vs. 39%), and progression-free survival (14.8 vs. 5.7 months; HR, 0.406).
A positive trend in overall survival was also observed (HR, 0.509 at median follow-up of 6.2 months). No new liso-cel safety signals were detected in the second-line setting.
Liso-cel was initially approved in February 2021 for the treatment of adults with LBCL, including diffuse LBCL not otherwise specified (including DLBCL arising from indolent lymphoma), high-grade B-cell lymphoma, primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, and follicular lymphoma grade 3B, who have:
- Refractory disease to first-line chemoimmunotherapy or relapse within 12 months of first-line chemoimmunotherapy.
- Refractory disease to first-line chemoimmunotherapy or relapse after first-line chemoimmunotherapy and are not eligible for hematopoietic stem cell transplant because of comorbidities or age.
Liso-cel is not indicated for the treatment of patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma.
In February 2022, the FDA granted Priority Review status for a Bristol-Myers Squibb supplemental Biologics License Application (sBLA), based on the TRANSFORM study data, to expand the indication to include use after the failure of first-line therapy.
The agent “now has the potential to be a new standard of care for patients after failure of first-line therapy, offering significantly improved outcomes beyond the current mainstay of care,” Anne Kerber, the BMS senior vice president of cell therapy development, said in a press release at that time.
The European Medicines Agency has also validated a type II variation application for extension of the indication for liso-cel in this setting. Validation of the application “confirms the submission is complete and begins the EMA’s centralized review procedure,” BMS announced in a June 20, 2022, press release.
Liso-cel, which has been available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy, includes a boxed warning regarding the risk for cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurologic toxicities.
The warning states that liso-cel should not be administered to patients with active infection or inflammatory disorders, and that severe or life-threatening CRS should be treated with tocilizumab with or without corticosteroids.
Patients should also be monitored for neurologic events after treatment with liso-cel, and supportive care and/or corticosteroids should be administered as needed.
$150K: Average industry payment to top 1% of oncologists
A small number of U.S. medical oncologists make more than $100,000 a year in general payments from drug companies, a new study shows.
These high-payment physicians represent just 1% of all U.S. medical oncologists, yet they account for 37% of industry payments. These oncologists often hold important leadership positions, draft treatment guidelines, and sit on journal editorial boards.
The findings highlight a risk for “perceived and real conflict of interest,” corresponding author Christopher Booth, MD, of Queen’s University Cancer Research Center, Kingston, Ont., said in an interview. “Because of the leadership positions they hold, the potential impact of this small group of physicians on oncology practice and policy may be substantial.”
The study was published online in JCO Oncology Practice.
‘We have a problem’
It’s no secret that many oncologists have financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies. They receive payments for research initiatives, but they also receive more general, personal payments in the form of honoraria, consultant fees, gifts, and reimbursement for travel and meals.
Prior studies have shown that these payments are typically modest, but a small subset of medical oncologists receive more than $100,000 annually. Dr. Booth and colleagues wanted to know more about the characteristics of these “high-payment” oncologists.
Using the national Open Payments database, the researchers identified a total of 139 medical oncologists who practice in the United States and who received $100,000 or more in general payments linked to cancer medications in 2018.
In U.S. dollars, the median payment was $154,613, and the total was $24.2 million.
The majority (95%) of high-payment oncologists were active in clinical work, 56% worked in an academic setting, 31% worked at National Cancer Institute–designated cancer centers, and 23% worked at National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) centers.
Many were based in California (17%), Texas (12%), Florida (10%), and New York (8%).
Most currently hold or have held hospital leadership positions (60%) or faculty appointments (72%) and 21% have held leadership positions in specialty associations in the past 5 years. Nearly one-quarter (24%) have served on journal editorial boards, and 10% have authored clinical practice guidelines in the past 5 years.
More specifically, three physicians authored NCCN guidelines, and two authored American Society of Clinical Oncology guidelines during 2016-2021; one guideline was published in 2018 when payments were made.
“Oncology specialty associations, guideline panels, and journal editorial boards should reconsider if it is appropriate for physicians with such large payments to hold these high-profile positions,” Dr. Booth said.
Following publication of the study, some oncologists took to Twitter with reactions, including Manni Mohyuddin, MD (@ManniMD1), from the Huntsman Cancer Institute, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, who wrote: “I recognize that some conflict of interest ‘may’ be unavoidable in order to run trials. But when greater than TWICE the average American household annual salary is taken in payments from industry by those in leadership/editorial roles, we have a problem.”
Weighing in on the results, ASCO CEO Clifford A. Hudis, MD, told this news organization that the “limitations of the study make it difficult to draw conclusions about the scope or potential impact of these payments on care.”
For example, he explained, some payments attributed to individuals may have been made directly to the physicians’ institutions or employers for sponsored research expenses.
Dr. Hudis also noted that the payments examined in the study were made in 2018, whereas the potentially relevant leadership positions could have been attained at a different time.
Furthermore, in 2020, an editorial appeared in Cancer, showing that errors in Open Payments are “fairly common,” Dr. Hudis said. It’s also unclear whether the reported financial relationships were appropriately disclosed and were managed at the time under relevant conflict of interest policies, he said.
“The question left unanswered by this study is whether or not these relationships influence patient care,” said Dr. Hudis. He noted that decisions about care should come from physicians and patients who are informed of the best available, unbiased, peer-reviewed, scientific evidence.
“The potential impact of financial conflicts of interest on this effort is an issue of concern, even if this study does not directly address it,” Dr. Hudis said.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Booth has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A complete list of author disclosures is available with the original article. Dr. Hudis has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A small number of U.S. medical oncologists make more than $100,000 a year in general payments from drug companies, a new study shows.
These high-payment physicians represent just 1% of all U.S. medical oncologists, yet they account for 37% of industry payments. These oncologists often hold important leadership positions, draft treatment guidelines, and sit on journal editorial boards.
The findings highlight a risk for “perceived and real conflict of interest,” corresponding author Christopher Booth, MD, of Queen’s University Cancer Research Center, Kingston, Ont., said in an interview. “Because of the leadership positions they hold, the potential impact of this small group of physicians on oncology practice and policy may be substantial.”
The study was published online in JCO Oncology Practice.
‘We have a problem’
It’s no secret that many oncologists have financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies. They receive payments for research initiatives, but they also receive more general, personal payments in the form of honoraria, consultant fees, gifts, and reimbursement for travel and meals.
Prior studies have shown that these payments are typically modest, but a small subset of medical oncologists receive more than $100,000 annually. Dr. Booth and colleagues wanted to know more about the characteristics of these “high-payment” oncologists.
Using the national Open Payments database, the researchers identified a total of 139 medical oncologists who practice in the United States and who received $100,000 or more in general payments linked to cancer medications in 2018.
In U.S. dollars, the median payment was $154,613, and the total was $24.2 million.
The majority (95%) of high-payment oncologists were active in clinical work, 56% worked in an academic setting, 31% worked at National Cancer Institute–designated cancer centers, and 23% worked at National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) centers.
Many were based in California (17%), Texas (12%), Florida (10%), and New York (8%).
Most currently hold or have held hospital leadership positions (60%) or faculty appointments (72%) and 21% have held leadership positions in specialty associations in the past 5 years. Nearly one-quarter (24%) have served on journal editorial boards, and 10% have authored clinical practice guidelines in the past 5 years.
More specifically, three physicians authored NCCN guidelines, and two authored American Society of Clinical Oncology guidelines during 2016-2021; one guideline was published in 2018 when payments were made.
“Oncology specialty associations, guideline panels, and journal editorial boards should reconsider if it is appropriate for physicians with such large payments to hold these high-profile positions,” Dr. Booth said.
Following publication of the study, some oncologists took to Twitter with reactions, including Manni Mohyuddin, MD (@ManniMD1), from the Huntsman Cancer Institute, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, who wrote: “I recognize that some conflict of interest ‘may’ be unavoidable in order to run trials. But when greater than TWICE the average American household annual salary is taken in payments from industry by those in leadership/editorial roles, we have a problem.”
Weighing in on the results, ASCO CEO Clifford A. Hudis, MD, told this news organization that the “limitations of the study make it difficult to draw conclusions about the scope or potential impact of these payments on care.”
For example, he explained, some payments attributed to individuals may have been made directly to the physicians’ institutions or employers for sponsored research expenses.
Dr. Hudis also noted that the payments examined in the study were made in 2018, whereas the potentially relevant leadership positions could have been attained at a different time.
Furthermore, in 2020, an editorial appeared in Cancer, showing that errors in Open Payments are “fairly common,” Dr. Hudis said. It’s also unclear whether the reported financial relationships were appropriately disclosed and were managed at the time under relevant conflict of interest policies, he said.
“The question left unanswered by this study is whether or not these relationships influence patient care,” said Dr. Hudis. He noted that decisions about care should come from physicians and patients who are informed of the best available, unbiased, peer-reviewed, scientific evidence.
“The potential impact of financial conflicts of interest on this effort is an issue of concern, even if this study does not directly address it,” Dr. Hudis said.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Booth has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A complete list of author disclosures is available with the original article. Dr. Hudis has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A small number of U.S. medical oncologists make more than $100,000 a year in general payments from drug companies, a new study shows.
These high-payment physicians represent just 1% of all U.S. medical oncologists, yet they account for 37% of industry payments. These oncologists often hold important leadership positions, draft treatment guidelines, and sit on journal editorial boards.
The findings highlight a risk for “perceived and real conflict of interest,” corresponding author Christopher Booth, MD, of Queen’s University Cancer Research Center, Kingston, Ont., said in an interview. “Because of the leadership positions they hold, the potential impact of this small group of physicians on oncology practice and policy may be substantial.”
The study was published online in JCO Oncology Practice.
‘We have a problem’
It’s no secret that many oncologists have financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies. They receive payments for research initiatives, but they also receive more general, personal payments in the form of honoraria, consultant fees, gifts, and reimbursement for travel and meals.
Prior studies have shown that these payments are typically modest, but a small subset of medical oncologists receive more than $100,000 annually. Dr. Booth and colleagues wanted to know more about the characteristics of these “high-payment” oncologists.
Using the national Open Payments database, the researchers identified a total of 139 medical oncologists who practice in the United States and who received $100,000 or more in general payments linked to cancer medications in 2018.
In U.S. dollars, the median payment was $154,613, and the total was $24.2 million.
The majority (95%) of high-payment oncologists were active in clinical work, 56% worked in an academic setting, 31% worked at National Cancer Institute–designated cancer centers, and 23% worked at National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) centers.
Many were based in California (17%), Texas (12%), Florida (10%), and New York (8%).
Most currently hold or have held hospital leadership positions (60%) or faculty appointments (72%) and 21% have held leadership positions in specialty associations in the past 5 years. Nearly one-quarter (24%) have served on journal editorial boards, and 10% have authored clinical practice guidelines in the past 5 years.
More specifically, three physicians authored NCCN guidelines, and two authored American Society of Clinical Oncology guidelines during 2016-2021; one guideline was published in 2018 when payments were made.
“Oncology specialty associations, guideline panels, and journal editorial boards should reconsider if it is appropriate for physicians with such large payments to hold these high-profile positions,” Dr. Booth said.
Following publication of the study, some oncologists took to Twitter with reactions, including Manni Mohyuddin, MD (@ManniMD1), from the Huntsman Cancer Institute, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, who wrote: “I recognize that some conflict of interest ‘may’ be unavoidable in order to run trials. But when greater than TWICE the average American household annual salary is taken in payments from industry by those in leadership/editorial roles, we have a problem.”
Weighing in on the results, ASCO CEO Clifford A. Hudis, MD, told this news organization that the “limitations of the study make it difficult to draw conclusions about the scope or potential impact of these payments on care.”
For example, he explained, some payments attributed to individuals may have been made directly to the physicians’ institutions or employers for sponsored research expenses.
Dr. Hudis also noted that the payments examined in the study were made in 2018, whereas the potentially relevant leadership positions could have been attained at a different time.
Furthermore, in 2020, an editorial appeared in Cancer, showing that errors in Open Payments are “fairly common,” Dr. Hudis said. It’s also unclear whether the reported financial relationships were appropriately disclosed and were managed at the time under relevant conflict of interest policies, he said.
“The question left unanswered by this study is whether or not these relationships influence patient care,” said Dr. Hudis. He noted that decisions about care should come from physicians and patients who are informed of the best available, unbiased, peer-reviewed, scientific evidence.
“The potential impact of financial conflicts of interest on this effort is an issue of concern, even if this study does not directly address it,” Dr. Hudis said.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Booth has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A complete list of author disclosures is available with the original article. Dr. Hudis has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JCO ONCOLOGY PRACTICE