User login
Pandemic may be limiting ED access for sexual assault
“In 2020, we hoped that the COVID pandemic would only last a few months. However, as it continued, we became increasingly concerned about limited health care access for survivors of sexual assault throughout the ongoing crisis,” study author Katherine A. Muldoon, PhD, MPH, a senior clinical research associate at the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute in Ontario, told this news organization.
“Unexpectedly, we found a 20%-25% increase in the number of survivors of sexual assault presenting for emergency care before the lockdown protocols were enacted,” she added. “After lockdown, the numbers dropped by 50%-60% and fluctuated throughout ... the pandemic.”
As they develop new lockdown protocols, public health officials and governments should incorporate warnings of the risks of violence and state that survivors should still present for urgent care when needed, said Dr. Muldoon. “COVID-19 lockdown protocols have limited access to health care for survivors worldwide, and barriers are likely greater in low-resource settings and those heavily affected by COVID-19.”
The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
Both sexes affected
The researchers analyzed linked health administrative data from 197 EDs in Ontario from January 2019 to September 2021. They used 10 bimonthly time periods to compare differences in the frequency and rates of ED visits for sexual assault in 2020-2021 (during the pandemic), compared with baseline prepandemic rates in 2019.
Sexual assault was defined by 27 ICD-10 procedure and diagnoses codes.
More than 14 million ED presentations occurred during the study period, including 10,523 for sexual assault. The median age was 23 years for female patients and 15 years for males. Most encounters (88.4%) were among females.
During the 2 months before the pandemic (Jan. 11 to Mar. 10, 2020), the rates of ED encounters for sexual assault among females were significantly higher than prepandemic levels (8.4 vs. 6.9 cases per 100,000; age-adjusted rate ratio [aRR], 1.22), whereas during the first 2 months of the pandemic (Mar. 11 to May 10, 2020), rates were significantly lower (4.2 vs. 8.3 cases per 100,000; aRR, 0.51).
Among males, rates were higher during the 2 months before the pandemic, but not significantly different, compared with prepandemic levels (1.2 vs. 1.0 cases per 100,000; aRR, 1.19). However, the rates decreased significantly during the first 2 months of the pandemic (0.5 vs. 1.2 cases per 100,000; aRR, 0.39).
For the 12 months starting July 11, 2020, rates were the same as in 2019. In the final time period (July 11 to Sept. 10, 2021), however, the rates were significantly higher than during prepandemic levels (1.5 vs. 1.1 cases per 100,000; aRR, 1.40).
Further analyses showed a similar pattern for all age groups, community sizes, and income quintiles. Rates were predominantly above prepandemic levels for the 2 months leading up to the pandemic and below expected levels from the beginning of the pandemic onward. However, from July 11 to Sept. 10, 2020 (during a trough in the summer, when sexual assaults are generally higher), and from May 11 to Sept. 10, 2021 (also during a trough and the summer), the rates returned to prepandemic levels.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has caused many changes to society and health care delivery and access,” the authors wrote. “We recommend that the decision-making regarding the management of the COVID-19 pandemic include antiviolence considerations to evaluate how policies and protocols affect the risk of violence and ensure that those who need health care can access services without concern.”
“Specialized and trauma-informed clinics are the best solution for encouraging survivors to come for urgent care following a sexual assault,” said Dr. Muldoon. “Clinicians should be prepared and trained to provide the best possible care for survivors of violence and ensure that getting care is not retraumatizing. Fostering conversations about the common experience of violence and destigmatizing those exposed to violence remain the most important ways to create safer spaces and societies.”
Dedicated care pathways
Commenting on the study, Samuel A. McLean, MD, MPH, director of the Institute for Trauma Recovery and professor of emergency medicine, psychiatry, and anesthesiology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said, “This important work documents a reduction in visits by sexual assault survivors for emergency care and forensic evidence collection during times of pandemic surge. It’s impossible to know for certain if this reduction in visits is entirely due to a reduction in sexual assaults, but a number of lines of circumstantial evidence make this unlikely.”
The results highlight the importance of ensuring that sexual assault care is maintained during surges in emergency care volume, added Dr. McLean, who was not involved with the current study. “This can be done via methods such as dedicated care pathways that avoid prolonged survivor wait times for care, and public health messaging that informs the public of the continued ready access to care during surges. Evidence, including data cited by the authors, suggests that these same care-seeking reductions are occurring in the United States and elsewhere.”
The study was supported by the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-term Care Applied Health Research Question Fund. Dr. Muldoon, study coauthors, and Dr. McLean report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“In 2020, we hoped that the COVID pandemic would only last a few months. However, as it continued, we became increasingly concerned about limited health care access for survivors of sexual assault throughout the ongoing crisis,” study author Katherine A. Muldoon, PhD, MPH, a senior clinical research associate at the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute in Ontario, told this news organization.
“Unexpectedly, we found a 20%-25% increase in the number of survivors of sexual assault presenting for emergency care before the lockdown protocols were enacted,” she added. “After lockdown, the numbers dropped by 50%-60% and fluctuated throughout ... the pandemic.”
As they develop new lockdown protocols, public health officials and governments should incorporate warnings of the risks of violence and state that survivors should still present for urgent care when needed, said Dr. Muldoon. “COVID-19 lockdown protocols have limited access to health care for survivors worldwide, and barriers are likely greater in low-resource settings and those heavily affected by COVID-19.”
The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
Both sexes affected
The researchers analyzed linked health administrative data from 197 EDs in Ontario from January 2019 to September 2021. They used 10 bimonthly time periods to compare differences in the frequency and rates of ED visits for sexual assault in 2020-2021 (during the pandemic), compared with baseline prepandemic rates in 2019.
Sexual assault was defined by 27 ICD-10 procedure and diagnoses codes.
More than 14 million ED presentations occurred during the study period, including 10,523 for sexual assault. The median age was 23 years for female patients and 15 years for males. Most encounters (88.4%) were among females.
During the 2 months before the pandemic (Jan. 11 to Mar. 10, 2020), the rates of ED encounters for sexual assault among females were significantly higher than prepandemic levels (8.4 vs. 6.9 cases per 100,000; age-adjusted rate ratio [aRR], 1.22), whereas during the first 2 months of the pandemic (Mar. 11 to May 10, 2020), rates were significantly lower (4.2 vs. 8.3 cases per 100,000; aRR, 0.51).
Among males, rates were higher during the 2 months before the pandemic, but not significantly different, compared with prepandemic levels (1.2 vs. 1.0 cases per 100,000; aRR, 1.19). However, the rates decreased significantly during the first 2 months of the pandemic (0.5 vs. 1.2 cases per 100,000; aRR, 0.39).
For the 12 months starting July 11, 2020, rates were the same as in 2019. In the final time period (July 11 to Sept. 10, 2021), however, the rates were significantly higher than during prepandemic levels (1.5 vs. 1.1 cases per 100,000; aRR, 1.40).
Further analyses showed a similar pattern for all age groups, community sizes, and income quintiles. Rates were predominantly above prepandemic levels for the 2 months leading up to the pandemic and below expected levels from the beginning of the pandemic onward. However, from July 11 to Sept. 10, 2020 (during a trough in the summer, when sexual assaults are generally higher), and from May 11 to Sept. 10, 2021 (also during a trough and the summer), the rates returned to prepandemic levels.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has caused many changes to society and health care delivery and access,” the authors wrote. “We recommend that the decision-making regarding the management of the COVID-19 pandemic include antiviolence considerations to evaluate how policies and protocols affect the risk of violence and ensure that those who need health care can access services without concern.”
“Specialized and trauma-informed clinics are the best solution for encouraging survivors to come for urgent care following a sexual assault,” said Dr. Muldoon. “Clinicians should be prepared and trained to provide the best possible care for survivors of violence and ensure that getting care is not retraumatizing. Fostering conversations about the common experience of violence and destigmatizing those exposed to violence remain the most important ways to create safer spaces and societies.”
Dedicated care pathways
Commenting on the study, Samuel A. McLean, MD, MPH, director of the Institute for Trauma Recovery and professor of emergency medicine, psychiatry, and anesthesiology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said, “This important work documents a reduction in visits by sexual assault survivors for emergency care and forensic evidence collection during times of pandemic surge. It’s impossible to know for certain if this reduction in visits is entirely due to a reduction in sexual assaults, but a number of lines of circumstantial evidence make this unlikely.”
The results highlight the importance of ensuring that sexual assault care is maintained during surges in emergency care volume, added Dr. McLean, who was not involved with the current study. “This can be done via methods such as dedicated care pathways that avoid prolonged survivor wait times for care, and public health messaging that informs the public of the continued ready access to care during surges. Evidence, including data cited by the authors, suggests that these same care-seeking reductions are occurring in the United States and elsewhere.”
The study was supported by the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-term Care Applied Health Research Question Fund. Dr. Muldoon, study coauthors, and Dr. McLean report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“In 2020, we hoped that the COVID pandemic would only last a few months. However, as it continued, we became increasingly concerned about limited health care access for survivors of sexual assault throughout the ongoing crisis,” study author Katherine A. Muldoon, PhD, MPH, a senior clinical research associate at the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute in Ontario, told this news organization.
“Unexpectedly, we found a 20%-25% increase in the number of survivors of sexual assault presenting for emergency care before the lockdown protocols were enacted,” she added. “After lockdown, the numbers dropped by 50%-60% and fluctuated throughout ... the pandemic.”
As they develop new lockdown protocols, public health officials and governments should incorporate warnings of the risks of violence and state that survivors should still present for urgent care when needed, said Dr. Muldoon. “COVID-19 lockdown protocols have limited access to health care for survivors worldwide, and barriers are likely greater in low-resource settings and those heavily affected by COVID-19.”
The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
Both sexes affected
The researchers analyzed linked health administrative data from 197 EDs in Ontario from January 2019 to September 2021. They used 10 bimonthly time periods to compare differences in the frequency and rates of ED visits for sexual assault in 2020-2021 (during the pandemic), compared with baseline prepandemic rates in 2019.
Sexual assault was defined by 27 ICD-10 procedure and diagnoses codes.
More than 14 million ED presentations occurred during the study period, including 10,523 for sexual assault. The median age was 23 years for female patients and 15 years for males. Most encounters (88.4%) were among females.
During the 2 months before the pandemic (Jan. 11 to Mar. 10, 2020), the rates of ED encounters for sexual assault among females were significantly higher than prepandemic levels (8.4 vs. 6.9 cases per 100,000; age-adjusted rate ratio [aRR], 1.22), whereas during the first 2 months of the pandemic (Mar. 11 to May 10, 2020), rates were significantly lower (4.2 vs. 8.3 cases per 100,000; aRR, 0.51).
Among males, rates were higher during the 2 months before the pandemic, but not significantly different, compared with prepandemic levels (1.2 vs. 1.0 cases per 100,000; aRR, 1.19). However, the rates decreased significantly during the first 2 months of the pandemic (0.5 vs. 1.2 cases per 100,000; aRR, 0.39).
For the 12 months starting July 11, 2020, rates were the same as in 2019. In the final time period (July 11 to Sept. 10, 2021), however, the rates were significantly higher than during prepandemic levels (1.5 vs. 1.1 cases per 100,000; aRR, 1.40).
Further analyses showed a similar pattern for all age groups, community sizes, and income quintiles. Rates were predominantly above prepandemic levels for the 2 months leading up to the pandemic and below expected levels from the beginning of the pandemic onward. However, from July 11 to Sept. 10, 2020 (during a trough in the summer, when sexual assaults are generally higher), and from May 11 to Sept. 10, 2021 (also during a trough and the summer), the rates returned to prepandemic levels.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has caused many changes to society and health care delivery and access,” the authors wrote. “We recommend that the decision-making regarding the management of the COVID-19 pandemic include antiviolence considerations to evaluate how policies and protocols affect the risk of violence and ensure that those who need health care can access services without concern.”
“Specialized and trauma-informed clinics are the best solution for encouraging survivors to come for urgent care following a sexual assault,” said Dr. Muldoon. “Clinicians should be prepared and trained to provide the best possible care for survivors of violence and ensure that getting care is not retraumatizing. Fostering conversations about the common experience of violence and destigmatizing those exposed to violence remain the most important ways to create safer spaces and societies.”
Dedicated care pathways
Commenting on the study, Samuel A. McLean, MD, MPH, director of the Institute for Trauma Recovery and professor of emergency medicine, psychiatry, and anesthesiology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said, “This important work documents a reduction in visits by sexual assault survivors for emergency care and forensic evidence collection during times of pandemic surge. It’s impossible to know for certain if this reduction in visits is entirely due to a reduction in sexual assaults, but a number of lines of circumstantial evidence make this unlikely.”
The results highlight the importance of ensuring that sexual assault care is maintained during surges in emergency care volume, added Dr. McLean, who was not involved with the current study. “This can be done via methods such as dedicated care pathways that avoid prolonged survivor wait times for care, and public health messaging that informs the public of the continued ready access to care during surges. Evidence, including data cited by the authors, suggests that these same care-seeking reductions are occurring in the United States and elsewhere.”
The study was supported by the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-term Care Applied Health Research Question Fund. Dr. Muldoon, study coauthors, and Dr. McLean report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Powering down cellphone use in middle schools
As vice principal of Pennsville Middle School in New Jersey, Adam J. Slusher knows he’s not always going to be Mr. Popularity.
Part of a vice principal’s job includes scheduling, enforcing policy, and discipline, so Dr. Slusher – who holds a doctorate in education from Wilmington University in Delaware – sometimes has to send emails or make phone calls that address unpleasant topics or unpopular new policies.
Or punishments.
But there was a much different reaction this past July, after he sent a message to the homes of Pennsville’s 450 students spanning grades 6 to 8. The email blast announced a new cellphone policy for the school. Starting in September, as he explained in the message – which also went out to the school’s 60 faculty and staff members – the use of cellphones by Pennsville students would be prohibited during school hours for any reason.
Phones, he emphasized, “are to be turned OFF” and stowed away in backpacks or handbags, not carried or tucked into back pockets.
The announcement of the new Away for the Day policy, which was decided upon by Dr. Slusher and Pennsville Principal Carolyn Carels, provoked a response different from those to his announcements on, say, test dates, emergency procedures, or new detention policies.
“It was one of the most popular emails I’ve ever sent,” chuckled Dr. Slusher, who has been an educator for 17 years. “We’ve gotten so many thanks from teachers for this.”
Ditto with the staff, who in conversations with Dr. Slusher and Ms. Carels, had reported on the rampant use of phones in the cafeteria and hallways – confirming what both of them had seen.
“They were telling us, ‘You’ve got to do something about the phones’ ” he recalled. “They were delighted that a clear policy was now going to be in place.”
The overwhelming majority of Pennsville parents have also supported the new policy, especially when presented with some of the sobering evidence about the extent of phone use among this population. One study Dr. Slusher cited in his email showed that the average middle school child is spending between 6 and 9 hours a day on screens.
“That’s like a full-time job,” he said.
The heavy cellphone use by kids – in school, out of school, anywhere and everywhere – was part of what prompted internal medicine doctor and filmmaker Delaney Ruston, MD, to create the “Away for the Day” initiative, which Pennsville has adopted.
She and collaborator Lisa Tabb were driven to do “Away for the Day” while working on Screenagers, their award-winning 2016 film examining the impact of social media, videos, and screen time on youngsters and their families that also offered tips for better navigating the digital world.
“Over 3 years of making the film, I was visiting schools all over the country,” Dr. Ruston said. “By the end, I was seeing devices all over the place, even in elementary schools. When I’d ask a student in the hall, ‘What’s the policy?’ they would shrug and say ‘I don’t know.’ When I got the same reaction from teachers – who in many cases were left to decide on their own, so that they had to be the bad guys – I realized there was a problem here.”
The result was what Dr. Ruston and Ms. Tabb describe on their website as a “movement,” designed to provide tools to parents, teachers, and administrators to help them make policies that put phones away during the school day.
The age of social centrality
As even a casual glance in the homeroom of every high school or college lecture hall will confirm, phone use is high in teenagers and young adults. But Dr. Ruston and Ms. Tabb decided to focus on middle schools.
“That’s the age where we know schools are facing the most challenges,” Dr. Ruston said. “This is also the age when social centrality becomes a major focus for youth. Thus, the pull to be on social media games, where their peers are, is incredibly enticing.”
A recent study in the journal JAMA Pediatrics found that middle schoolers who compulsively check social networks on their phones appear to have changes in areas of the brain linked to reward and punishment.
It was in middle schools, she concluded, “where effective policies on cellphones are most needed.”
As part of their research into the issue, she and ms. Tabb did a survey using email contacts collected by Dr. Ruston’s company, MyDoc Productions, during the making of the film, along with subscribers to her blog. In all, 1,200 parents – each of whom had at least one child in middle school at the time – were surveyed. The researchers found an interesting disconnect: Eighty-two percent of the parents surveyed did not want their children using phones in school. Yet 55% of middle schools allowed students to carry phones during the school day.
That survey was done in 2017. Since the COVID-19 pandemic, the use of cellphones by children, both in school and at home, has risen dramatically. A literature review of 46 studies, published in JAMA Pediatrics in November, found that average screen time among children and adolescents has increased by 52% – or 84 minutes a day – during the pandemic.
That trend has given many schools, including Pennsville, the drive to adopt an Away for the Day–type policy. As part of the program, Dr. Ruston’s website provides ammunition against the kinds of pushback they might expect to get. One of the most common is the idea that banning cellphone use among middle school children is a misguided, antitechnology measure.
“We’re not at all antitech,” Dr. Ruston asserts. Away for the Day, she explains, advocates the use of learning technologies in school that are monitored and supervised by teachers.
“The majority of students have access to learning devices in the school,” she said. “These have different kinds of blockers, making it harder for their kid to respond to their friend on TikTok when they’re supposed to be using technology for learning.”
Dr. Ruston estimates that about 10,000 middle schools are now using various pieces of the Away for the Day campaign, which includes videos, posters, fact sheets, and other materials. Other schools have adopted similar measures in the same spirit.
Predictable and calm? Not so much
When Katherine Holden was named principal of Oregon’s Talent Middle School in 2022, one of the first things she wanted to do was create some structure for the routines of students (and parents) who were frazzled after 2 years of remote learning, staggered schedules, and mask mandates.
“Predictable and calm,” she said, with a laugh. “I use those words every day.”
Achieving both is hard enough in a middle school without a pandemic – not to mention an epidemic of cellphone use. (Talent also endured a massive fire in 2020 that left many families homeless.)
For this school year, Ms. Holden is using a new and clearly articulated policy: “Devices are put away from the first bell to the last bell,” she said. “We want them to have a focus on other things. We want them to be socializing, interacting with their peers face to face, thinking about getting to class. We want them making eye contact, asking questions. Learning how to make a friend face to face. Those are important developmental social skills they should be practicing.”
Instead of scrolling through photos on Instagram, watching trending videos on TikTok, or texting their friends.
Like Dr. Slusher, she announced the new cellphone policy last summer, in a letter sent home to parents along with the list of school supplies their children would need.
“Students are welcome to use their cell phones and personal devices before entering the building prior to 8:30 a.m. and after exiting the school building at 3:10 p.m.,” she wrote. “However, during the school day students’ cellphones and personal devices need to be off and out of sight.
“I think parents generally understand the need for this,” Ms. Holden said. “They’ve watched their children getting distracted at home by these devices, so they have a sense of how a cellphone adds a layer of challenge to learning. And parents are aware of the unkind behavior that often happens online.”
As for the kids themselves? Safe to say the excitement that Dr. Slusher’s email got from Pennsville faculty, staff, and parents didn’t extend to students.
“They don’t like it all, to be honest,” he said. “But they understand it’s for their benefit. When we sold it to them at our beginning-of-the-year meeting, we presented our rationale. From the kids I speak to, I think the majority understand why we’re doing it.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
As vice principal of Pennsville Middle School in New Jersey, Adam J. Slusher knows he’s not always going to be Mr. Popularity.
Part of a vice principal’s job includes scheduling, enforcing policy, and discipline, so Dr. Slusher – who holds a doctorate in education from Wilmington University in Delaware – sometimes has to send emails or make phone calls that address unpleasant topics or unpopular new policies.
Or punishments.
But there was a much different reaction this past July, after he sent a message to the homes of Pennsville’s 450 students spanning grades 6 to 8. The email blast announced a new cellphone policy for the school. Starting in September, as he explained in the message – which also went out to the school’s 60 faculty and staff members – the use of cellphones by Pennsville students would be prohibited during school hours for any reason.
Phones, he emphasized, “are to be turned OFF” and stowed away in backpacks or handbags, not carried or tucked into back pockets.
The announcement of the new Away for the Day policy, which was decided upon by Dr. Slusher and Pennsville Principal Carolyn Carels, provoked a response different from those to his announcements on, say, test dates, emergency procedures, or new detention policies.
“It was one of the most popular emails I’ve ever sent,” chuckled Dr. Slusher, who has been an educator for 17 years. “We’ve gotten so many thanks from teachers for this.”
Ditto with the staff, who in conversations with Dr. Slusher and Ms. Carels, had reported on the rampant use of phones in the cafeteria and hallways – confirming what both of them had seen.
“They were telling us, ‘You’ve got to do something about the phones’ ” he recalled. “They were delighted that a clear policy was now going to be in place.”
The overwhelming majority of Pennsville parents have also supported the new policy, especially when presented with some of the sobering evidence about the extent of phone use among this population. One study Dr. Slusher cited in his email showed that the average middle school child is spending between 6 and 9 hours a day on screens.
“That’s like a full-time job,” he said.
The heavy cellphone use by kids – in school, out of school, anywhere and everywhere – was part of what prompted internal medicine doctor and filmmaker Delaney Ruston, MD, to create the “Away for the Day” initiative, which Pennsville has adopted.
She and collaborator Lisa Tabb were driven to do “Away for the Day” while working on Screenagers, their award-winning 2016 film examining the impact of social media, videos, and screen time on youngsters and their families that also offered tips for better navigating the digital world.
“Over 3 years of making the film, I was visiting schools all over the country,” Dr. Ruston said. “By the end, I was seeing devices all over the place, even in elementary schools. When I’d ask a student in the hall, ‘What’s the policy?’ they would shrug and say ‘I don’t know.’ When I got the same reaction from teachers – who in many cases were left to decide on their own, so that they had to be the bad guys – I realized there was a problem here.”
The result was what Dr. Ruston and Ms. Tabb describe on their website as a “movement,” designed to provide tools to parents, teachers, and administrators to help them make policies that put phones away during the school day.
The age of social centrality
As even a casual glance in the homeroom of every high school or college lecture hall will confirm, phone use is high in teenagers and young adults. But Dr. Ruston and Ms. Tabb decided to focus on middle schools.
“That’s the age where we know schools are facing the most challenges,” Dr. Ruston said. “This is also the age when social centrality becomes a major focus for youth. Thus, the pull to be on social media games, where their peers are, is incredibly enticing.”
A recent study in the journal JAMA Pediatrics found that middle schoolers who compulsively check social networks on their phones appear to have changes in areas of the brain linked to reward and punishment.
It was in middle schools, she concluded, “where effective policies on cellphones are most needed.”
As part of their research into the issue, she and ms. Tabb did a survey using email contacts collected by Dr. Ruston’s company, MyDoc Productions, during the making of the film, along with subscribers to her blog. In all, 1,200 parents – each of whom had at least one child in middle school at the time – were surveyed. The researchers found an interesting disconnect: Eighty-two percent of the parents surveyed did not want their children using phones in school. Yet 55% of middle schools allowed students to carry phones during the school day.
That survey was done in 2017. Since the COVID-19 pandemic, the use of cellphones by children, both in school and at home, has risen dramatically. A literature review of 46 studies, published in JAMA Pediatrics in November, found that average screen time among children and adolescents has increased by 52% – or 84 minutes a day – during the pandemic.
That trend has given many schools, including Pennsville, the drive to adopt an Away for the Day–type policy. As part of the program, Dr. Ruston’s website provides ammunition against the kinds of pushback they might expect to get. One of the most common is the idea that banning cellphone use among middle school children is a misguided, antitechnology measure.
“We’re not at all antitech,” Dr. Ruston asserts. Away for the Day, she explains, advocates the use of learning technologies in school that are monitored and supervised by teachers.
“The majority of students have access to learning devices in the school,” she said. “These have different kinds of blockers, making it harder for their kid to respond to their friend on TikTok when they’re supposed to be using technology for learning.”
Dr. Ruston estimates that about 10,000 middle schools are now using various pieces of the Away for the Day campaign, which includes videos, posters, fact sheets, and other materials. Other schools have adopted similar measures in the same spirit.
Predictable and calm? Not so much
When Katherine Holden was named principal of Oregon’s Talent Middle School in 2022, one of the first things she wanted to do was create some structure for the routines of students (and parents) who were frazzled after 2 years of remote learning, staggered schedules, and mask mandates.
“Predictable and calm,” she said, with a laugh. “I use those words every day.”
Achieving both is hard enough in a middle school without a pandemic – not to mention an epidemic of cellphone use. (Talent also endured a massive fire in 2020 that left many families homeless.)
For this school year, Ms. Holden is using a new and clearly articulated policy: “Devices are put away from the first bell to the last bell,” she said. “We want them to have a focus on other things. We want them to be socializing, interacting with their peers face to face, thinking about getting to class. We want them making eye contact, asking questions. Learning how to make a friend face to face. Those are important developmental social skills they should be practicing.”
Instead of scrolling through photos on Instagram, watching trending videos on TikTok, or texting their friends.
Like Dr. Slusher, she announced the new cellphone policy last summer, in a letter sent home to parents along with the list of school supplies their children would need.
“Students are welcome to use their cell phones and personal devices before entering the building prior to 8:30 a.m. and after exiting the school building at 3:10 p.m.,” she wrote. “However, during the school day students’ cellphones and personal devices need to be off and out of sight.
“I think parents generally understand the need for this,” Ms. Holden said. “They’ve watched their children getting distracted at home by these devices, so they have a sense of how a cellphone adds a layer of challenge to learning. And parents are aware of the unkind behavior that often happens online.”
As for the kids themselves? Safe to say the excitement that Dr. Slusher’s email got from Pennsville faculty, staff, and parents didn’t extend to students.
“They don’t like it all, to be honest,” he said. “But they understand it’s for their benefit. When we sold it to them at our beginning-of-the-year meeting, we presented our rationale. From the kids I speak to, I think the majority understand why we’re doing it.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
As vice principal of Pennsville Middle School in New Jersey, Adam J. Slusher knows he’s not always going to be Mr. Popularity.
Part of a vice principal’s job includes scheduling, enforcing policy, and discipline, so Dr. Slusher – who holds a doctorate in education from Wilmington University in Delaware – sometimes has to send emails or make phone calls that address unpleasant topics or unpopular new policies.
Or punishments.
But there was a much different reaction this past July, after he sent a message to the homes of Pennsville’s 450 students spanning grades 6 to 8. The email blast announced a new cellphone policy for the school. Starting in September, as he explained in the message – which also went out to the school’s 60 faculty and staff members – the use of cellphones by Pennsville students would be prohibited during school hours for any reason.
Phones, he emphasized, “are to be turned OFF” and stowed away in backpacks or handbags, not carried or tucked into back pockets.
The announcement of the new Away for the Day policy, which was decided upon by Dr. Slusher and Pennsville Principal Carolyn Carels, provoked a response different from those to his announcements on, say, test dates, emergency procedures, or new detention policies.
“It was one of the most popular emails I’ve ever sent,” chuckled Dr. Slusher, who has been an educator for 17 years. “We’ve gotten so many thanks from teachers for this.”
Ditto with the staff, who in conversations with Dr. Slusher and Ms. Carels, had reported on the rampant use of phones in the cafeteria and hallways – confirming what both of them had seen.
“They were telling us, ‘You’ve got to do something about the phones’ ” he recalled. “They were delighted that a clear policy was now going to be in place.”
The overwhelming majority of Pennsville parents have also supported the new policy, especially when presented with some of the sobering evidence about the extent of phone use among this population. One study Dr. Slusher cited in his email showed that the average middle school child is spending between 6 and 9 hours a day on screens.
“That’s like a full-time job,” he said.
The heavy cellphone use by kids – in school, out of school, anywhere and everywhere – was part of what prompted internal medicine doctor and filmmaker Delaney Ruston, MD, to create the “Away for the Day” initiative, which Pennsville has adopted.
She and collaborator Lisa Tabb were driven to do “Away for the Day” while working on Screenagers, their award-winning 2016 film examining the impact of social media, videos, and screen time on youngsters and their families that also offered tips for better navigating the digital world.
“Over 3 years of making the film, I was visiting schools all over the country,” Dr. Ruston said. “By the end, I was seeing devices all over the place, even in elementary schools. When I’d ask a student in the hall, ‘What’s the policy?’ they would shrug and say ‘I don’t know.’ When I got the same reaction from teachers – who in many cases were left to decide on their own, so that they had to be the bad guys – I realized there was a problem here.”
The result was what Dr. Ruston and Ms. Tabb describe on their website as a “movement,” designed to provide tools to parents, teachers, and administrators to help them make policies that put phones away during the school day.
The age of social centrality
As even a casual glance in the homeroom of every high school or college lecture hall will confirm, phone use is high in teenagers and young adults. But Dr. Ruston and Ms. Tabb decided to focus on middle schools.
“That’s the age where we know schools are facing the most challenges,” Dr. Ruston said. “This is also the age when social centrality becomes a major focus for youth. Thus, the pull to be on social media games, where their peers are, is incredibly enticing.”
A recent study in the journal JAMA Pediatrics found that middle schoolers who compulsively check social networks on their phones appear to have changes in areas of the brain linked to reward and punishment.
It was in middle schools, she concluded, “where effective policies on cellphones are most needed.”
As part of their research into the issue, she and ms. Tabb did a survey using email contacts collected by Dr. Ruston’s company, MyDoc Productions, during the making of the film, along with subscribers to her blog. In all, 1,200 parents – each of whom had at least one child in middle school at the time – were surveyed. The researchers found an interesting disconnect: Eighty-two percent of the parents surveyed did not want their children using phones in school. Yet 55% of middle schools allowed students to carry phones during the school day.
That survey was done in 2017. Since the COVID-19 pandemic, the use of cellphones by children, both in school and at home, has risen dramatically. A literature review of 46 studies, published in JAMA Pediatrics in November, found that average screen time among children and adolescents has increased by 52% – or 84 minutes a day – during the pandemic.
That trend has given many schools, including Pennsville, the drive to adopt an Away for the Day–type policy. As part of the program, Dr. Ruston’s website provides ammunition against the kinds of pushback they might expect to get. One of the most common is the idea that banning cellphone use among middle school children is a misguided, antitechnology measure.
“We’re not at all antitech,” Dr. Ruston asserts. Away for the Day, she explains, advocates the use of learning technologies in school that are monitored and supervised by teachers.
“The majority of students have access to learning devices in the school,” she said. “These have different kinds of blockers, making it harder for their kid to respond to their friend on TikTok when they’re supposed to be using technology for learning.”
Dr. Ruston estimates that about 10,000 middle schools are now using various pieces of the Away for the Day campaign, which includes videos, posters, fact sheets, and other materials. Other schools have adopted similar measures in the same spirit.
Predictable and calm? Not so much
When Katherine Holden was named principal of Oregon’s Talent Middle School in 2022, one of the first things she wanted to do was create some structure for the routines of students (and parents) who were frazzled after 2 years of remote learning, staggered schedules, and mask mandates.
“Predictable and calm,” she said, with a laugh. “I use those words every day.”
Achieving both is hard enough in a middle school without a pandemic – not to mention an epidemic of cellphone use. (Talent also endured a massive fire in 2020 that left many families homeless.)
For this school year, Ms. Holden is using a new and clearly articulated policy: “Devices are put away from the first bell to the last bell,” she said. “We want them to have a focus on other things. We want them to be socializing, interacting with their peers face to face, thinking about getting to class. We want them making eye contact, asking questions. Learning how to make a friend face to face. Those are important developmental social skills they should be practicing.”
Instead of scrolling through photos on Instagram, watching trending videos on TikTok, or texting their friends.
Like Dr. Slusher, she announced the new cellphone policy last summer, in a letter sent home to parents along with the list of school supplies their children would need.
“Students are welcome to use their cell phones and personal devices before entering the building prior to 8:30 a.m. and after exiting the school building at 3:10 p.m.,” she wrote. “However, during the school day students’ cellphones and personal devices need to be off and out of sight.
“I think parents generally understand the need for this,” Ms. Holden said. “They’ve watched their children getting distracted at home by these devices, so they have a sense of how a cellphone adds a layer of challenge to learning. And parents are aware of the unkind behavior that often happens online.”
As for the kids themselves? Safe to say the excitement that Dr. Slusher’s email got from Pennsville faculty, staff, and parents didn’t extend to students.
“They don’t like it all, to be honest,” he said. “But they understand it’s for their benefit. When we sold it to them at our beginning-of-the-year meeting, we presented our rationale. From the kids I speak to, I think the majority understand why we’re doing it.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Sleep complaints in major depression flag risk for other psychiatric disorders
Investigators studied 3-year incidence rates of psychiatric disorders in almost 3,000 patients experiencing an MDE. Results showed that having a history of difficulty falling asleep, early morning awakening, and hypersomnia increased risk for incident psychiatric disorders.
“The findings of this study suggest the potential value of including insomnia and hypersomnia in clinical assessments of all psychiatric disorders,” write the investigators, led by Bénédicte Barbotin, MD, Département de Psychiatrie et d’Addictologie, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Hôpital Bichat-Claude Bernard, France.
“Insomnia and hypersomnia symptoms may be prodromal transdiagnostic biomarkers and easily modifiable therapeutic targets for the prevention of psychiatric disorders,” they add.
The findings were published online recently in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Bidirectional association
The researchers note that sleep disturbance is “one of the most common symptoms” associated with major depressive disorder (MDD) and may be “both a consequence and a cause.”
Moreover, improving sleep disturbances for patients with an MDE “tends to improve depressive symptom and outcomes,” they add.
Although the possibility of a bidirectional association between MDEs and sleep disturbances “offers a new perspective that sleep complaints might be a predictive prodromal symptom,” the association of sleep complaints with the subsequent development of other psychiatric disorders in MDEs “remains poorly documented,” the investigators write.
The observation that sleep complaints are associated with psychiatric complications and adverse outcomes, such as suicidality and substance overdose, suggests that longitudinal studies “may help to better understand these relationships.”
To investigate these issues, the researchers examined three sleep complaints among patients with MDE: trouble falling asleep, early morning awakening, and hypersomnia. They adjusted for an array of variables, including antisocial personality disorders, use of sedatives or tranquilizers, sociodemographic characteristics, MDE severity, poverty, obesity, educational level, and stressful life events.
They also used a “bifactor latent variable approach” to “disentangle” a number of effects, including those shared by all psychiatric disorders; those specific to dimensions of psychopathology, such as internalizing dimension; and those specific to individual psychiatric disorders, such as dysthymia.
“To our knowledge, this is the most extensive prospective assessment [ever conducted] of associations between sleep complaints and incident psychiatric disorders,” the investigators write.
They drew on data from Waves 1 and 2 of the National Epidemiological Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions, a large nationally representative survey conducted in 2001-2002 (Wave 1) and 2004-2005 (Wave 2) by the National Institute on Alcoholism and Alcohol Abuse.
The analysis included 2,864 participants who experienced MDE in the year prior to Wave 1 and who completed interviews at both waves.
Researchers assessed past-year DSM-IV Axis I disorders and baseline sleep complaints at Wave 1, as well as incident DSM-IV Axis I disorders between the two waves – including substance use, mood, and anxiety disorders.
Screening needed?
Results showed a wide range of incidence rates for psychiatric disorders between Wave 1 and Wave 2, ranging from 2.7% for cannabis use to 8.2% for generalized anxiety disorder.
The lifetime prevalence of sleep complaints was higher among participants who developed a psychiatric disorder between the two waves than among those who did not have sleep complaints. The range (from lowest to highest percentage) is shown in the accompanying table.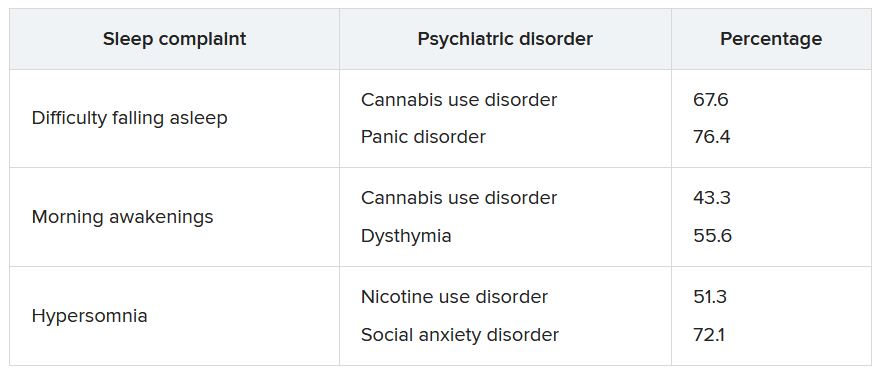
A higher number of sleep complaints was also associated with higher percentages of psychiatric disorders.
Hypersomnia, in particular, significantly increased the odds of having another psychiatric disorder. For patients with MDD who reported hypersomnia, the mean number of sleep disorders was significantly higher than for patients without hypersomnia (2.08 vs. 1.32; P < .001).
“This explains why hypersomnia appears more strongly associated with the incidence of psychiatric disorders,” the investigators write.
After adjusting for sociodemographic and clinical characteristics and antisocial personality disorder, the effects shared across all sleep complaints were “significantly associated with the incident general psychopathology factor, representing mechanisms that may lead to incidence of all psychiatric disorder in the model,” they add.
The researchers note that insomnia and hypersomnia can impair cognitive function, decision-making, problem-solving, and emotion processing networks, thereby increasing the onset of psychiatric disorders in vulnerable individuals.
Shared biological determinants, such as monoamine neurotransmitters that play a major role in depression, anxiety, substance use disorders, and the regulation of sleep stages, may also underlie both sleep disturbances and psychiatric disorders, they speculate.
“These results suggest the importance of systematically assessing insomnia and hypersomnia when evaluating psychiatric disorders and considering these symptoms as nonspecific prodromal or at-risk symptoms, also shared with suicidal behaviors,” the investigators write.
“In addition, since most individuals who developed a psychiatric disorder had at least one sleep complaint, all psychiatric disorders should be carefully screened among individuals with sleep complaints,” they add.
Transdiagnostic phenomenon
In a comment, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology at the University of Toronto, and head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit, noted that the study replicates previous observations that a bidirectional relationship exists between sleep disturbances and mental disorders and that there “seems to be a relationship between sleep disturbance and suicidality that is bidirectional.”
He added that he appreciated the fact that the investigators “took this knowledge one step further; and what they are saying is that within the syndrome of depression, it is the sleep disturbance that is predicting future problems.”
Dr. McIntyre, who is also chairman and executive director of the Brain and Cognitive Discover Foundation in Toronto, was not involved with the study.
The data suggest that, “conceptually, sleep disturbance is a transdiagnostic phenomenon that may also be the nexus when multiple comorbid mental disorders occur,” he said.
“If this is the case, clinically, there is an opportunity here to prevent incident mental disorders in persons with depression and sleep disturbance, prioritizing sleep management in any patient with a mood disorder,” Dr. McIntyre added.
He noted that “the testable hypothesis” is how this is occurring mechanistically.
“I would conjecture that it could be inflammation and/or insulin resistance that is part of sleep disturbance that could predispose and portend other mental illnesses – and likely other medical conditions too, such as obesity and diabetes,” he said.
The study received no specific funding from any funding agency, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. The investigators’ relevant financial relationships are listed in the original article. Dr. McIntyre has received research grant support from CIHR/GACD/National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Milken Institute; has received speaker/consultation fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Alkermes,Neumora Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sage, Biogen, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Bausch Health, Axsome, Novo Nordisk, Kris, Sanofi, Eisai, Intra-Cellular, NewBridge Pharmaceuticals, Viatris, AbbVie, and Atai Life Sciences; and is a CEO of Braxia Scientific Corp.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators studied 3-year incidence rates of psychiatric disorders in almost 3,000 patients experiencing an MDE. Results showed that having a history of difficulty falling asleep, early morning awakening, and hypersomnia increased risk for incident psychiatric disorders.
“The findings of this study suggest the potential value of including insomnia and hypersomnia in clinical assessments of all psychiatric disorders,” write the investigators, led by Bénédicte Barbotin, MD, Département de Psychiatrie et d’Addictologie, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Hôpital Bichat-Claude Bernard, France.
“Insomnia and hypersomnia symptoms may be prodromal transdiagnostic biomarkers and easily modifiable therapeutic targets for the prevention of psychiatric disorders,” they add.
The findings were published online recently in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Bidirectional association
The researchers note that sleep disturbance is “one of the most common symptoms” associated with major depressive disorder (MDD) and may be “both a consequence and a cause.”
Moreover, improving sleep disturbances for patients with an MDE “tends to improve depressive symptom and outcomes,” they add.
Although the possibility of a bidirectional association between MDEs and sleep disturbances “offers a new perspective that sleep complaints might be a predictive prodromal symptom,” the association of sleep complaints with the subsequent development of other psychiatric disorders in MDEs “remains poorly documented,” the investigators write.
The observation that sleep complaints are associated with psychiatric complications and adverse outcomes, such as suicidality and substance overdose, suggests that longitudinal studies “may help to better understand these relationships.”
To investigate these issues, the researchers examined three sleep complaints among patients with MDE: trouble falling asleep, early morning awakening, and hypersomnia. They adjusted for an array of variables, including antisocial personality disorders, use of sedatives or tranquilizers, sociodemographic characteristics, MDE severity, poverty, obesity, educational level, and stressful life events.
They also used a “bifactor latent variable approach” to “disentangle” a number of effects, including those shared by all psychiatric disorders; those specific to dimensions of psychopathology, such as internalizing dimension; and those specific to individual psychiatric disorders, such as dysthymia.
“To our knowledge, this is the most extensive prospective assessment [ever conducted] of associations between sleep complaints and incident psychiatric disorders,” the investigators write.
They drew on data from Waves 1 and 2 of the National Epidemiological Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions, a large nationally representative survey conducted in 2001-2002 (Wave 1) and 2004-2005 (Wave 2) by the National Institute on Alcoholism and Alcohol Abuse.
The analysis included 2,864 participants who experienced MDE in the year prior to Wave 1 and who completed interviews at both waves.
Researchers assessed past-year DSM-IV Axis I disorders and baseline sleep complaints at Wave 1, as well as incident DSM-IV Axis I disorders between the two waves – including substance use, mood, and anxiety disorders.
Screening needed?
Results showed a wide range of incidence rates for psychiatric disorders between Wave 1 and Wave 2, ranging from 2.7% for cannabis use to 8.2% for generalized anxiety disorder.
The lifetime prevalence of sleep complaints was higher among participants who developed a psychiatric disorder between the two waves than among those who did not have sleep complaints. The range (from lowest to highest percentage) is shown in the accompanying table.
A higher number of sleep complaints was also associated with higher percentages of psychiatric disorders.
Hypersomnia, in particular, significantly increased the odds of having another psychiatric disorder. For patients with MDD who reported hypersomnia, the mean number of sleep disorders was significantly higher than for patients without hypersomnia (2.08 vs. 1.32; P < .001).
“This explains why hypersomnia appears more strongly associated with the incidence of psychiatric disorders,” the investigators write.
After adjusting for sociodemographic and clinical characteristics and antisocial personality disorder, the effects shared across all sleep complaints were “significantly associated with the incident general psychopathology factor, representing mechanisms that may lead to incidence of all psychiatric disorder in the model,” they add.
The researchers note that insomnia and hypersomnia can impair cognitive function, decision-making, problem-solving, and emotion processing networks, thereby increasing the onset of psychiatric disorders in vulnerable individuals.
Shared biological determinants, such as monoamine neurotransmitters that play a major role in depression, anxiety, substance use disorders, and the regulation of sleep stages, may also underlie both sleep disturbances and psychiatric disorders, they speculate.
“These results suggest the importance of systematically assessing insomnia and hypersomnia when evaluating psychiatric disorders and considering these symptoms as nonspecific prodromal or at-risk symptoms, also shared with suicidal behaviors,” the investigators write.
“In addition, since most individuals who developed a psychiatric disorder had at least one sleep complaint, all psychiatric disorders should be carefully screened among individuals with sleep complaints,” they add.
Transdiagnostic phenomenon
In a comment, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology at the University of Toronto, and head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit, noted that the study replicates previous observations that a bidirectional relationship exists between sleep disturbances and mental disorders and that there “seems to be a relationship between sleep disturbance and suicidality that is bidirectional.”
He added that he appreciated the fact that the investigators “took this knowledge one step further; and what they are saying is that within the syndrome of depression, it is the sleep disturbance that is predicting future problems.”
Dr. McIntyre, who is also chairman and executive director of the Brain and Cognitive Discover Foundation in Toronto, was not involved with the study.
The data suggest that, “conceptually, sleep disturbance is a transdiagnostic phenomenon that may also be the nexus when multiple comorbid mental disorders occur,” he said.
“If this is the case, clinically, there is an opportunity here to prevent incident mental disorders in persons with depression and sleep disturbance, prioritizing sleep management in any patient with a mood disorder,” Dr. McIntyre added.
He noted that “the testable hypothesis” is how this is occurring mechanistically.
“I would conjecture that it could be inflammation and/or insulin resistance that is part of sleep disturbance that could predispose and portend other mental illnesses – and likely other medical conditions too, such as obesity and diabetes,” he said.
The study received no specific funding from any funding agency, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. The investigators’ relevant financial relationships are listed in the original article. Dr. McIntyre has received research grant support from CIHR/GACD/National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Milken Institute; has received speaker/consultation fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Alkermes,Neumora Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sage, Biogen, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Bausch Health, Axsome, Novo Nordisk, Kris, Sanofi, Eisai, Intra-Cellular, NewBridge Pharmaceuticals, Viatris, AbbVie, and Atai Life Sciences; and is a CEO of Braxia Scientific Corp.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators studied 3-year incidence rates of psychiatric disorders in almost 3,000 patients experiencing an MDE. Results showed that having a history of difficulty falling asleep, early morning awakening, and hypersomnia increased risk for incident psychiatric disorders.
“The findings of this study suggest the potential value of including insomnia and hypersomnia in clinical assessments of all psychiatric disorders,” write the investigators, led by Bénédicte Barbotin, MD, Département de Psychiatrie et d’Addictologie, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Hôpital Bichat-Claude Bernard, France.
“Insomnia and hypersomnia symptoms may be prodromal transdiagnostic biomarkers and easily modifiable therapeutic targets for the prevention of psychiatric disorders,” they add.
The findings were published online recently in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Bidirectional association
The researchers note that sleep disturbance is “one of the most common symptoms” associated with major depressive disorder (MDD) and may be “both a consequence and a cause.”
Moreover, improving sleep disturbances for patients with an MDE “tends to improve depressive symptom and outcomes,” they add.
Although the possibility of a bidirectional association between MDEs and sleep disturbances “offers a new perspective that sleep complaints might be a predictive prodromal symptom,” the association of sleep complaints with the subsequent development of other psychiatric disorders in MDEs “remains poorly documented,” the investigators write.
The observation that sleep complaints are associated with psychiatric complications and adverse outcomes, such as suicidality and substance overdose, suggests that longitudinal studies “may help to better understand these relationships.”
To investigate these issues, the researchers examined three sleep complaints among patients with MDE: trouble falling asleep, early morning awakening, and hypersomnia. They adjusted for an array of variables, including antisocial personality disorders, use of sedatives or tranquilizers, sociodemographic characteristics, MDE severity, poverty, obesity, educational level, and stressful life events.
They also used a “bifactor latent variable approach” to “disentangle” a number of effects, including those shared by all psychiatric disorders; those specific to dimensions of psychopathology, such as internalizing dimension; and those specific to individual psychiatric disorders, such as dysthymia.
“To our knowledge, this is the most extensive prospective assessment [ever conducted] of associations between sleep complaints and incident psychiatric disorders,” the investigators write.
They drew on data from Waves 1 and 2 of the National Epidemiological Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions, a large nationally representative survey conducted in 2001-2002 (Wave 1) and 2004-2005 (Wave 2) by the National Institute on Alcoholism and Alcohol Abuse.
The analysis included 2,864 participants who experienced MDE in the year prior to Wave 1 and who completed interviews at both waves.
Researchers assessed past-year DSM-IV Axis I disorders and baseline sleep complaints at Wave 1, as well as incident DSM-IV Axis I disorders between the two waves – including substance use, mood, and anxiety disorders.
Screening needed?
Results showed a wide range of incidence rates for psychiatric disorders between Wave 1 and Wave 2, ranging from 2.7% for cannabis use to 8.2% for generalized anxiety disorder.
The lifetime prevalence of sleep complaints was higher among participants who developed a psychiatric disorder between the two waves than among those who did not have sleep complaints. The range (from lowest to highest percentage) is shown in the accompanying table.
A higher number of sleep complaints was also associated with higher percentages of psychiatric disorders.
Hypersomnia, in particular, significantly increased the odds of having another psychiatric disorder. For patients with MDD who reported hypersomnia, the mean number of sleep disorders was significantly higher than for patients without hypersomnia (2.08 vs. 1.32; P < .001).
“This explains why hypersomnia appears more strongly associated with the incidence of psychiatric disorders,” the investigators write.
After adjusting for sociodemographic and clinical characteristics and antisocial personality disorder, the effects shared across all sleep complaints were “significantly associated with the incident general psychopathology factor, representing mechanisms that may lead to incidence of all psychiatric disorder in the model,” they add.
The researchers note that insomnia and hypersomnia can impair cognitive function, decision-making, problem-solving, and emotion processing networks, thereby increasing the onset of psychiatric disorders in vulnerable individuals.
Shared biological determinants, such as monoamine neurotransmitters that play a major role in depression, anxiety, substance use disorders, and the regulation of sleep stages, may also underlie both sleep disturbances and psychiatric disorders, they speculate.
“These results suggest the importance of systematically assessing insomnia and hypersomnia when evaluating psychiatric disorders and considering these symptoms as nonspecific prodromal or at-risk symptoms, also shared with suicidal behaviors,” the investigators write.
“In addition, since most individuals who developed a psychiatric disorder had at least one sleep complaint, all psychiatric disorders should be carefully screened among individuals with sleep complaints,” they add.
Transdiagnostic phenomenon
In a comment, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology at the University of Toronto, and head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit, noted that the study replicates previous observations that a bidirectional relationship exists between sleep disturbances and mental disorders and that there “seems to be a relationship between sleep disturbance and suicidality that is bidirectional.”
He added that he appreciated the fact that the investigators “took this knowledge one step further; and what they are saying is that within the syndrome of depression, it is the sleep disturbance that is predicting future problems.”
Dr. McIntyre, who is also chairman and executive director of the Brain and Cognitive Discover Foundation in Toronto, was not involved with the study.
The data suggest that, “conceptually, sleep disturbance is a transdiagnostic phenomenon that may also be the nexus when multiple comorbid mental disorders occur,” he said.
“If this is the case, clinically, there is an opportunity here to prevent incident mental disorders in persons with depression and sleep disturbance, prioritizing sleep management in any patient with a mood disorder,” Dr. McIntyre added.
He noted that “the testable hypothesis” is how this is occurring mechanistically.
“I would conjecture that it could be inflammation and/or insulin resistance that is part of sleep disturbance that could predispose and portend other mental illnesses – and likely other medical conditions too, such as obesity and diabetes,” he said.
The study received no specific funding from any funding agency, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. The investigators’ relevant financial relationships are listed in the original article. Dr. McIntyre has received research grant support from CIHR/GACD/National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Milken Institute; has received speaker/consultation fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Alkermes,Neumora Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sage, Biogen, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Bausch Health, Axsome, Novo Nordisk, Kris, Sanofi, Eisai, Intra-Cellular, NewBridge Pharmaceuticals, Viatris, AbbVie, and Atai Life Sciences; and is a CEO of Braxia Scientific Corp.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
Arkansas cardiologist pays $900K to settle false claims allegations
in violation of the False Claims Act.
As part of the settlement, Dr. Tauth will enter into an integrity agreement with the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, according to a news release from Henry Leventis, U.S. attorney for the Middle District of Tennessee.
“Health care fraud is a top priority of this office. We will aggressively pursue all those who are involved in fraud against government programs,” Mr. Leventis said.
Dr. Tauth formerly treated patients at National Park Medical Center (NPMC) in Hot Springs. The alleged false claims were submitted from September 2013 through August 2019.
The settlement with Dr. Tauth, aged 60, follows a November 2019 voluntary disclosure of the alleged false claims by Brentwood, Tenn.–based Lifepoint Health, which acquired NPMC and Hot Springs Cardiology Associates in November 2018.
NPMC and Hot Springs Cardiology entered into a settlement in October 2020 for the alleged violations and agreed to pay roughly $14.6 million, which includes over $9 million in restitution, according to the news release.
NPMC CEO Scott Smith said NPMC is “committed to maintaining high standards of integrity, legal compliance, and quality care for our patients. We regularly monitor our processes, procedures, and reporting and actively self-report concerns to regulators to ensure we are upholding these standards across our organization.”
“We are proud that our hospital took the appropriate steps to promptly self-report and finalize a settlement with the government for a swift resolution more than 2 years ago,” Mr. Smith said.
Dr. Tauth, however, maintains that the allegations made by NPMC are false.
“I am pleased to have reached a settlement agreement with the Department of Justice regarding allegations brought to them by my former employer, National Park Medical Center,” he said in a statement.
“The settlement agreement specifically states that it is not ‘an admission of liability’ by me, and I remain steadfast in my position that the allegations made by my former employer are false and without merit,” Dr. Tauth added.
He further stated that he has “chosen to enter into the settlement agreement because the legal process initiated by National Park’s allegations has been emotionally and financially damaging to me and my family in the extreme, and a settlement puts an end to the delays, uncertainties, inconveniences, and expenses of protracted litigation. Settlement is in the best interests of my family, my patients, and my medical practice.”
Dr. Tauth said he is “extremely grateful for the support I have received from my patients, medical staff, colleagues, friends, and family during this difficult time, and I look forward to providing high-quality cardiac care in the greater Hot Springs community for many years to come.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in violation of the False Claims Act.
As part of the settlement, Dr. Tauth will enter into an integrity agreement with the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, according to a news release from Henry Leventis, U.S. attorney for the Middle District of Tennessee.
“Health care fraud is a top priority of this office. We will aggressively pursue all those who are involved in fraud against government programs,” Mr. Leventis said.
Dr. Tauth formerly treated patients at National Park Medical Center (NPMC) in Hot Springs. The alleged false claims were submitted from September 2013 through August 2019.
The settlement with Dr. Tauth, aged 60, follows a November 2019 voluntary disclosure of the alleged false claims by Brentwood, Tenn.–based Lifepoint Health, which acquired NPMC and Hot Springs Cardiology Associates in November 2018.
NPMC and Hot Springs Cardiology entered into a settlement in October 2020 for the alleged violations and agreed to pay roughly $14.6 million, which includes over $9 million in restitution, according to the news release.
NPMC CEO Scott Smith said NPMC is “committed to maintaining high standards of integrity, legal compliance, and quality care for our patients. We regularly monitor our processes, procedures, and reporting and actively self-report concerns to regulators to ensure we are upholding these standards across our organization.”
“We are proud that our hospital took the appropriate steps to promptly self-report and finalize a settlement with the government for a swift resolution more than 2 years ago,” Mr. Smith said.
Dr. Tauth, however, maintains that the allegations made by NPMC are false.
“I am pleased to have reached a settlement agreement with the Department of Justice regarding allegations brought to them by my former employer, National Park Medical Center,” he said in a statement.
“The settlement agreement specifically states that it is not ‘an admission of liability’ by me, and I remain steadfast in my position that the allegations made by my former employer are false and without merit,” Dr. Tauth added.
He further stated that he has “chosen to enter into the settlement agreement because the legal process initiated by National Park’s allegations has been emotionally and financially damaging to me and my family in the extreme, and a settlement puts an end to the delays, uncertainties, inconveniences, and expenses of protracted litigation. Settlement is in the best interests of my family, my patients, and my medical practice.”
Dr. Tauth said he is “extremely grateful for the support I have received from my patients, medical staff, colleagues, friends, and family during this difficult time, and I look forward to providing high-quality cardiac care in the greater Hot Springs community for many years to come.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in violation of the False Claims Act.
As part of the settlement, Dr. Tauth will enter into an integrity agreement with the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, according to a news release from Henry Leventis, U.S. attorney for the Middle District of Tennessee.
“Health care fraud is a top priority of this office. We will aggressively pursue all those who are involved in fraud against government programs,” Mr. Leventis said.
Dr. Tauth formerly treated patients at National Park Medical Center (NPMC) in Hot Springs. The alleged false claims were submitted from September 2013 through August 2019.
The settlement with Dr. Tauth, aged 60, follows a November 2019 voluntary disclosure of the alleged false claims by Brentwood, Tenn.–based Lifepoint Health, which acquired NPMC and Hot Springs Cardiology Associates in November 2018.
NPMC and Hot Springs Cardiology entered into a settlement in October 2020 for the alleged violations and agreed to pay roughly $14.6 million, which includes over $9 million in restitution, according to the news release.
NPMC CEO Scott Smith said NPMC is “committed to maintaining high standards of integrity, legal compliance, and quality care for our patients. We regularly monitor our processes, procedures, and reporting and actively self-report concerns to regulators to ensure we are upholding these standards across our organization.”
“We are proud that our hospital took the appropriate steps to promptly self-report and finalize a settlement with the government for a swift resolution more than 2 years ago,” Mr. Smith said.
Dr. Tauth, however, maintains that the allegations made by NPMC are false.
“I am pleased to have reached a settlement agreement with the Department of Justice regarding allegations brought to them by my former employer, National Park Medical Center,” he said in a statement.
“The settlement agreement specifically states that it is not ‘an admission of liability’ by me, and I remain steadfast in my position that the allegations made by my former employer are false and without merit,” Dr. Tauth added.
He further stated that he has “chosen to enter into the settlement agreement because the legal process initiated by National Park’s allegations has been emotionally and financially damaging to me and my family in the extreme, and a settlement puts an end to the delays, uncertainties, inconveniences, and expenses of protracted litigation. Settlement is in the best interests of my family, my patients, and my medical practice.”
Dr. Tauth said he is “extremely grateful for the support I have received from my patients, medical staff, colleagues, friends, and family during this difficult time, and I look forward to providing high-quality cardiac care in the greater Hot Springs community for many years to come.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long COVID comes into focus, showing older patients fare worse
These findings help define long COVID, guiding providers and patients through the recovery process, Barak Mizrahi, MSc, of KI Research Institute, Kfar Malal, Israel, and colleagues reported.
“To provide efficient continuous treatment and prevent adverse events related to potential long term effects and delayed symptoms of COVID-19, determining the magnitude and severity of this phenomenon and distinguishing it from similar clinical manifestations that occur normally or following infections with other pathogens is essential,” the investigators wrote in The BMJ.
To this end, they conducted a retrospective, nationwide cohort study involving 1,913,234 people who took a polymerase chain reaction test for SARS-CoV-2 between March 1, 2020, and Oct. 1, 2021. They compared a range of long-term outcomes at different intervals post infection, and compared these trends across subgroups sorted by age, sex, and variant. Outcomes ranged broadly, including respiratory disorders, cough, arthralgia, weakness, hair loss, and others.
The investigators compared hazard ratios for each of these outcomes among patients who tested positive versus those who tested negative at three intervals after testing: 30-90 days, 30-180 days, and 180-360 days. Statistically significant differences in the risks of these outcomes between infected versus uninfected groups suggested that COVID was playing a role.
“The health outcomes that represent long COVID showed a significant increase in both early and late phases,” the investigators wrote. These outcomes included anosmia and dysgeusia, cognitive impairment, dyspnea, weakness, and palpitations. In contrast, chest pain, myalgia, arthralgia, cough, and dizziness were associated with patients who were in the early phase, but not the late phase of long COVID.
“Vaccinated patients with a breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection had a lower risk for dyspnea and similar risk for other outcomes compared with unvaccinated infected patients,” the investigators noted.
For the long COVID outcomes, plots of risk differences over time showed that symptoms tended to get milder or resolve within a few months to a year. Patients 41-60 years were most likely to be impacted by long COVID outcomes, and show least improvement at 1 year, compared with other age groups.
“We believe that these findings will shed light on what is ‘long COVID’, support patients and doctors, and facilitate better and more efficient care,” Mr. Mizrahi and coauthor Maytal Bivas-Benita, PhD said in a joint written comment. “Primary care physicians (and patients) will now more clearly understand what are the symptoms that might be related to COVID and for how long they might linger. This would help physicians monitor the patients efficiently, ease their patients’ concerns and navigate a more efficient disease management.”
They suggested that the findings should hold consistent for future variants, although they could not “rule out the possibility of the emergence of new and more severe variants which will be more virulent and cause a more severe illness.”
One “major limitation” of the study, according to Monica Verduzco-Gutierrez, MD, a physiatrist and professor and chair of rehabilitation medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, is the lack of data for fatigue and dysautonomia, which are “the major presentations” that she sees in her long COVID clinic.
“The authors of the article focus on the primary damage being related to the lungs, though we know this is a systemic disease beyond the respiratory system, with endothelial dysfunction and immune dysregulation,” Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez, who is also director of COVID recovery at the University of Texas Health Science Center, said in an interview.
Although it was reassuring to see that younger adults with long COVID trended toward improvement, she noted that patients 41-60 years “still had pretty significant symptoms” after 12 months.
“That [age group comprises] probably the majority of my patients that I’m seeing in the long COVID clinic,” Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez said. “If you look at the whole thing, it looks better, but then when you drill down to that age group where you’re seeing patients, then it’s not.”
Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez is so busy managing patients with long COVID that new appointments in her clinic are now delayed until May 31, so most patients will remain under the care of their primary care providers. She recommended that these physicians follow guidance from the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, who offer consensus statements based on clinical characteristics, with separate recommendations for pediatric patients.
Our understanding of long COVID will continue to improve, and with it, available recommendations, she predicted, but further advances will require persistent effort.
“I think no matter what this [study] shows us, more research is needed,” Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez said. “We can’t just forget about it, just because there is a population of people who get better. What about the ones who don’t?”
The investigators and Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez disclosed no conflicts of interest.
These findings help define long COVID, guiding providers and patients through the recovery process, Barak Mizrahi, MSc, of KI Research Institute, Kfar Malal, Israel, and colleagues reported.
“To provide efficient continuous treatment and prevent adverse events related to potential long term effects and delayed symptoms of COVID-19, determining the magnitude and severity of this phenomenon and distinguishing it from similar clinical manifestations that occur normally or following infections with other pathogens is essential,” the investigators wrote in The BMJ.
To this end, they conducted a retrospective, nationwide cohort study involving 1,913,234 people who took a polymerase chain reaction test for SARS-CoV-2 between March 1, 2020, and Oct. 1, 2021. They compared a range of long-term outcomes at different intervals post infection, and compared these trends across subgroups sorted by age, sex, and variant. Outcomes ranged broadly, including respiratory disorders, cough, arthralgia, weakness, hair loss, and others.
The investigators compared hazard ratios for each of these outcomes among patients who tested positive versus those who tested negative at three intervals after testing: 30-90 days, 30-180 days, and 180-360 days. Statistically significant differences in the risks of these outcomes between infected versus uninfected groups suggested that COVID was playing a role.
“The health outcomes that represent long COVID showed a significant increase in both early and late phases,” the investigators wrote. These outcomes included anosmia and dysgeusia, cognitive impairment, dyspnea, weakness, and palpitations. In contrast, chest pain, myalgia, arthralgia, cough, and dizziness were associated with patients who were in the early phase, but not the late phase of long COVID.
“Vaccinated patients with a breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection had a lower risk for dyspnea and similar risk for other outcomes compared with unvaccinated infected patients,” the investigators noted.
For the long COVID outcomes, plots of risk differences over time showed that symptoms tended to get milder or resolve within a few months to a year. Patients 41-60 years were most likely to be impacted by long COVID outcomes, and show least improvement at 1 year, compared with other age groups.
“We believe that these findings will shed light on what is ‘long COVID’, support patients and doctors, and facilitate better and more efficient care,” Mr. Mizrahi and coauthor Maytal Bivas-Benita, PhD said in a joint written comment. “Primary care physicians (and patients) will now more clearly understand what are the symptoms that might be related to COVID and for how long they might linger. This would help physicians monitor the patients efficiently, ease their patients’ concerns and navigate a more efficient disease management.”
They suggested that the findings should hold consistent for future variants, although they could not “rule out the possibility of the emergence of new and more severe variants which will be more virulent and cause a more severe illness.”
One “major limitation” of the study, according to Monica Verduzco-Gutierrez, MD, a physiatrist and professor and chair of rehabilitation medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, is the lack of data for fatigue and dysautonomia, which are “the major presentations” that she sees in her long COVID clinic.
“The authors of the article focus on the primary damage being related to the lungs, though we know this is a systemic disease beyond the respiratory system, with endothelial dysfunction and immune dysregulation,” Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez, who is also director of COVID recovery at the University of Texas Health Science Center, said in an interview.
Although it was reassuring to see that younger adults with long COVID trended toward improvement, she noted that patients 41-60 years “still had pretty significant symptoms” after 12 months.
“That [age group comprises] probably the majority of my patients that I’m seeing in the long COVID clinic,” Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez said. “If you look at the whole thing, it looks better, but then when you drill down to that age group where you’re seeing patients, then it’s not.”
Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez is so busy managing patients with long COVID that new appointments in her clinic are now delayed until May 31, so most patients will remain under the care of their primary care providers. She recommended that these physicians follow guidance from the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, who offer consensus statements based on clinical characteristics, with separate recommendations for pediatric patients.
Our understanding of long COVID will continue to improve, and with it, available recommendations, she predicted, but further advances will require persistent effort.
“I think no matter what this [study] shows us, more research is needed,” Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez said. “We can’t just forget about it, just because there is a population of people who get better. What about the ones who don’t?”
The investigators and Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez disclosed no conflicts of interest.
These findings help define long COVID, guiding providers and patients through the recovery process, Barak Mizrahi, MSc, of KI Research Institute, Kfar Malal, Israel, and colleagues reported.
“To provide efficient continuous treatment and prevent adverse events related to potential long term effects and delayed symptoms of COVID-19, determining the magnitude and severity of this phenomenon and distinguishing it from similar clinical manifestations that occur normally or following infections with other pathogens is essential,” the investigators wrote in The BMJ.
To this end, they conducted a retrospective, nationwide cohort study involving 1,913,234 people who took a polymerase chain reaction test for SARS-CoV-2 between March 1, 2020, and Oct. 1, 2021. They compared a range of long-term outcomes at different intervals post infection, and compared these trends across subgroups sorted by age, sex, and variant. Outcomes ranged broadly, including respiratory disorders, cough, arthralgia, weakness, hair loss, and others.
The investigators compared hazard ratios for each of these outcomes among patients who tested positive versus those who tested negative at three intervals after testing: 30-90 days, 30-180 days, and 180-360 days. Statistically significant differences in the risks of these outcomes between infected versus uninfected groups suggested that COVID was playing a role.
“The health outcomes that represent long COVID showed a significant increase in both early and late phases,” the investigators wrote. These outcomes included anosmia and dysgeusia, cognitive impairment, dyspnea, weakness, and palpitations. In contrast, chest pain, myalgia, arthralgia, cough, and dizziness were associated with patients who were in the early phase, but not the late phase of long COVID.
“Vaccinated patients with a breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection had a lower risk for dyspnea and similar risk for other outcomes compared with unvaccinated infected patients,” the investigators noted.
For the long COVID outcomes, plots of risk differences over time showed that symptoms tended to get milder or resolve within a few months to a year. Patients 41-60 years were most likely to be impacted by long COVID outcomes, and show least improvement at 1 year, compared with other age groups.
“We believe that these findings will shed light on what is ‘long COVID’, support patients and doctors, and facilitate better and more efficient care,” Mr. Mizrahi and coauthor Maytal Bivas-Benita, PhD said in a joint written comment. “Primary care physicians (and patients) will now more clearly understand what are the symptoms that might be related to COVID and for how long they might linger. This would help physicians monitor the patients efficiently, ease their patients’ concerns and navigate a more efficient disease management.”
They suggested that the findings should hold consistent for future variants, although they could not “rule out the possibility of the emergence of new and more severe variants which will be more virulent and cause a more severe illness.”
One “major limitation” of the study, according to Monica Verduzco-Gutierrez, MD, a physiatrist and professor and chair of rehabilitation medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, is the lack of data for fatigue and dysautonomia, which are “the major presentations” that she sees in her long COVID clinic.
“The authors of the article focus on the primary damage being related to the lungs, though we know this is a systemic disease beyond the respiratory system, with endothelial dysfunction and immune dysregulation,” Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez, who is also director of COVID recovery at the University of Texas Health Science Center, said in an interview.
Although it was reassuring to see that younger adults with long COVID trended toward improvement, she noted that patients 41-60 years “still had pretty significant symptoms” after 12 months.
“That [age group comprises] probably the majority of my patients that I’m seeing in the long COVID clinic,” Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez said. “If you look at the whole thing, it looks better, but then when you drill down to that age group where you’re seeing patients, then it’s not.”
Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez is so busy managing patients with long COVID that new appointments in her clinic are now delayed until May 31, so most patients will remain under the care of their primary care providers. She recommended that these physicians follow guidance from the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, who offer consensus statements based on clinical characteristics, with separate recommendations for pediatric patients.
Our understanding of long COVID will continue to improve, and with it, available recommendations, she predicted, but further advances will require persistent effort.
“I think no matter what this [study] shows us, more research is needed,” Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez said. “We can’t just forget about it, just because there is a population of people who get better. What about the ones who don’t?”
The investigators and Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM THE BMJ
Does EPA lower CV risk? REDUCE-IT revisited
The prescription product (Vascepa), consisting of a “highly purified” form of the omega-3 acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), was heralded in 2018 (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:11-22) as ushering in “the dawn of a new era” in cardiovascular disease (CVD) prevention that “should definitely change practice going forward,” according to REDUCE-IT’s lead author Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, formerly of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and now director of the Mount Sinai Heart Center in New York.
However, skeptics questioned why the results differed from most previous trials of fish oil that showed no benefit. Was it caused by the high dose of EPA: 4 g/daily versus 1 g daily in earlier trials with fish oil capsules? Was it the different formulation of purified EPA versus more common combinations of EPA plus docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)? Or, as suggested by Steven Nissen, MD, chief academic officer of Cleveland Clinic’s Heart and Vascular Institute and others, was it caused by the negative effects of the mineral oil placebo, given the significant increases in LDL cholesterol and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) seen in the control group?
‘Not all omega-3s created equal’
Dr. Bhatt recently said in an interview: “I think there’s confusion in the field. It’s a challenge when just one drug in a class looks good and everything else in that class looks bad. That in itself can breed some skepticism. Also, not everyone always embraces advances. Some people have other reasons to impugn datasets; for example, it could be because they are running competing trials with competing drugs.”
REDUCE-IT enrolled more than 8,000 patients at high CV risk despite statin treatment, and randomly assigned them to 2 g of EPA twice daily or the mineral oil placebo. Although the results showed a 25% reduction in the rate of CV events in the EPA group, there was also an increased risk of atrial fibrillation among those taking EPA after a median of 4.9 years follow-up.
Dr. Bhatt noted that Amarin, which manufactures Vascepa, is essentially a one-drug company, and its stock price is dependent on the product. When the trial results were released, he said, “there were people in the investor world that wanted the stock price to go up or wanted it to go down, and they were alternately hyping or disparaging the data in both cases, sometimes inappropriately and excessively, which created noise around the science.”
The fact is, he said, “not all omega-3 fatty acids are created equal. There are differences between supplements and prescription medicines, and within the prescription medicines, differences between pure EPA and the mixtures of EPA and DHA.”
Dr. Bhatt added that other trials also showed positive results. He pointed to the JELIS trial, published in 2007, which showed a 19% reduction in major adverse CV events with a 1.8-g daily EPA dose.
More recently, RESPECT-EPA was presented at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Heart Association. That study had methodological issues and was underpowered, but it did suggest a possible benefit of EPA in reducing CV events in patients with chronic coronary artery disease who were taking statins. “Looking at the totality of evidence, I think it’s quite clear there’s CV benefit,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Placebo effects?
Concerns about the mineral oil placebo cast doubt on that benefit. Table 4 of the supplement accompanying REDUCE-IT’s publication in the New England Journal of Medicine shows significant increases of non–HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, apolipoprotein B, and hsCRP in the control group.
Jane Armitage, MBBS, a professor of clinical trials and epidemiology, clinical trial service unit at Oxford University (England), said in an interview: “I was surprised by the backlash and at the time felt that it was unlikely that the mineral oil was the problem. But the size of benefit was still out of kilter.”
“Two further pieces of evidence have influenced my thoughts since then,” she said. One is the lack of effect of high doses of fish oils in the STRENGTH trial. STRENGTH tested 4 g of omega-3 oil containing a mixture of EPA and DHA and found no benefit in statin-treated, high-risk patients.
“The amount of EPA [was] substantially less than given in REDUCE-IT,” Armitage said, “but it seems to me that in a similar hypertriglyceridemic population, if the effect were due to the EPA, you would have seen some impact in STRENGTH – and none was seen.”
“The other piece of evidence is in a paper by Paul Ridker, MD, et al. on the changes in biomarkers during REDUCE-IT,” she said. “Several inflammatory biomarkers associated with atherosclerosis rose during the study among those allocated mineral oil, but remained largely unchanged in the EPA group. This is in contrast to what is seen with these biomarkers in other large trials, where no changes were seen in the placebo groups, and once again raises the possibility that the apparent benefits of EPA may be related to hazard from the mineral oil.”
Still room for benefit?
Based largely on the results of REDUCE-IT, Vascepa is currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration as an adjunctive therapy to lower the risk for CV events among adults with elevated triglyceride levels (≥ 150 mg/dL). Patients must also have either established CVD or diabetes and two or more additional CV risk factors and are advised to continue physical activity and maintain a healthy diet.
Dr. Nissen, the principal author of the STRENGTH trial, said in an interview, “REDUCE-IT is an outlier. Other trials of omega-3 fatty acids, some of them very large, showed no benefits, and a meta-analysis of nearly 78,000 patients showed no beneficial effects. In this context,” he said, “the large ‘benefit’ observed in REDUCE-IT doesn’t make any sense.”
Dr. Nissen noted that a secondary analysis of STRENGTH further showed that higher plasma EPA levels did not reduce CV outcomes. He also highlighted the elevated risk of atrial fibrillation with EPA. “We need to see another study comparing EPA to a neutral comparator such as corn oil, which had no significant effect on lipid or inflammatory biomarkers in STRENGTH,” he said. “Without such a trial, the results of REDUCE-IT cannot be accepted as definitive.”
Dr. Ridker, the lead author of the REDUCE-IT substudy that found biomarker changes with the mineral oil placebo, said in an interview: “Is it possible that EPA is an outstanding drug? Absolutely, and I continue to think it useful for our very high-risk, secondary-prevention patients when we are running out of options.”
“But,” said Dr. Ridker, who is a professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and director of the Center for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention at Brigham and Women’s, “the reality ... is that ongoing uncertainties need resolution.” Like Dr. Nissen, he thinks the best way to resolve these uncertainties is through a second trial using a fully neutral comparator. “I am hopeful that the U.S. National Institutes of Health will see fit to undertake such an endeavor, perhaps with support from industry partners.”
Although Dr. Armitage is no longer in clinical practice, when asked how she might use EPA, she said it might be reasonable for patients who meet the prescribing criteria and remain high risk after all other risk factors have been addressed. She added that, although EPA is approved in the United Kingdom, she doesn’t think it is being widely prescribed.
Salim S. Virani, MD, PhD, a professor in the Sections of Cardiology and Cardiovascular Research at Baylor College of Medicine who has published articles about REDUCE-IT and on the eligibility and cost of EPA in the Veterans Affairs system, said in an interview: “In my personal opinion, clinicians [should] first optimize diet and lifestyle and work on secondary causes, as they play a very big role in hypertriglyceridemia.” He also recommended optimizing LDL-C levels because of “consistent data showing that LDL [cholesterol] control leads to significant reduction in atherosclerotic CVD events.”
“Once these two steps are taken and triglycerides still remain elevated,” he said, “then adding EPA in patients with established atherosclerotic CVD or those with diabetes plus other CV risk factors may be a reasonable option to further lower residual atherosclerotic CVD risk.”
Clinical inertia?
Dr. Bhatt acknowledged that, despite the benefit of EPA in the context of REDUCE-IT, “a few issues stand in the way of prescribing, particularly in the U.S.”
Vascepa’s manufacturer Amarin lost a patent challenge in the United States, enabling the relatively early introduction of multiple generics. “They’ve lost interest in the U.S. because there are three generics.”
“The sad truth is, if there isn’t a drug rep saying, ‘hey, look at this new data,’ there’s clinical inertia,” said Dr. Bhatt. He believes that the lack of marketing will hurt awareness among physicians and “ultimately hurt patients because they won’t get the drug.”
Cost is also an issue, Dr. Bhatt affirmed. Vascepa has significant out-of-pocket costs for many patients, as do some of the generics. Currently, the branded product costs about $300 per month without insurance, according to drugs.com; prices for generics vary widely, running anywhere from $82 to $200 or more.
Despite these challenges, he noted that many guidelines around the world have already changed to reflect the data, including the American Diabetes Association and the U.S. National Lipid Association.
Will there be another trial of EPA with a neutral placebo? Dr. Bhatt believes it’s not going to happen. “The company that funded REDUCE-IT is struggling just to stay alive, and another investigator-funded trial like RESPECT EPA would probably be underpowered and not move the needle much.”
Dr. Virani agreed that while it would be best to test EPA against a fully inert placebo, “whether there is enough appetite to fund such a large trial remains a big question.”
Meanwhile, Dr. Bhatt said, “EPA is not for everybody, but for the high-risk patients who meet the stringent inclusion criteria of REDUCE-IT, I think clinicians should at least consider use of EPA in a way consistent with the U.S. FDA label, the Canadian label, and the label in parts of Europe where the drug is being introduced.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The prescription product (Vascepa), consisting of a “highly purified” form of the omega-3 acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), was heralded in 2018 (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:11-22) as ushering in “the dawn of a new era” in cardiovascular disease (CVD) prevention that “should definitely change practice going forward,” according to REDUCE-IT’s lead author Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, formerly of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and now director of the Mount Sinai Heart Center in New York.
However, skeptics questioned why the results differed from most previous trials of fish oil that showed no benefit. Was it caused by the high dose of EPA: 4 g/daily versus 1 g daily in earlier trials with fish oil capsules? Was it the different formulation of purified EPA versus more common combinations of EPA plus docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)? Or, as suggested by Steven Nissen, MD, chief academic officer of Cleveland Clinic’s Heart and Vascular Institute and others, was it caused by the negative effects of the mineral oil placebo, given the significant increases in LDL cholesterol and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) seen in the control group?
‘Not all omega-3s created equal’
Dr. Bhatt recently said in an interview: “I think there’s confusion in the field. It’s a challenge when just one drug in a class looks good and everything else in that class looks bad. That in itself can breed some skepticism. Also, not everyone always embraces advances. Some people have other reasons to impugn datasets; for example, it could be because they are running competing trials with competing drugs.”
REDUCE-IT enrolled more than 8,000 patients at high CV risk despite statin treatment, and randomly assigned them to 2 g of EPA twice daily or the mineral oil placebo. Although the results showed a 25% reduction in the rate of CV events in the EPA group, there was also an increased risk of atrial fibrillation among those taking EPA after a median of 4.9 years follow-up.
Dr. Bhatt noted that Amarin, which manufactures Vascepa, is essentially a one-drug company, and its stock price is dependent on the product. When the trial results were released, he said, “there were people in the investor world that wanted the stock price to go up or wanted it to go down, and they were alternately hyping or disparaging the data in both cases, sometimes inappropriately and excessively, which created noise around the science.”
The fact is, he said, “not all omega-3 fatty acids are created equal. There are differences between supplements and prescription medicines, and within the prescription medicines, differences between pure EPA and the mixtures of EPA and DHA.”
Dr. Bhatt added that other trials also showed positive results. He pointed to the JELIS trial, published in 2007, which showed a 19% reduction in major adverse CV events with a 1.8-g daily EPA dose.
More recently, RESPECT-EPA was presented at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Heart Association. That study had methodological issues and was underpowered, but it did suggest a possible benefit of EPA in reducing CV events in patients with chronic coronary artery disease who were taking statins. “Looking at the totality of evidence, I think it’s quite clear there’s CV benefit,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Placebo effects?
Concerns about the mineral oil placebo cast doubt on that benefit. Table 4 of the supplement accompanying REDUCE-IT’s publication in the New England Journal of Medicine shows significant increases of non–HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, apolipoprotein B, and hsCRP in the control group.
Jane Armitage, MBBS, a professor of clinical trials and epidemiology, clinical trial service unit at Oxford University (England), said in an interview: “I was surprised by the backlash and at the time felt that it was unlikely that the mineral oil was the problem. But the size of benefit was still out of kilter.”
“Two further pieces of evidence have influenced my thoughts since then,” she said. One is the lack of effect of high doses of fish oils in the STRENGTH trial. STRENGTH tested 4 g of omega-3 oil containing a mixture of EPA and DHA and found no benefit in statin-treated, high-risk patients.
“The amount of EPA [was] substantially less than given in REDUCE-IT,” Armitage said, “but it seems to me that in a similar hypertriglyceridemic population, if the effect were due to the EPA, you would have seen some impact in STRENGTH – and none was seen.”
“The other piece of evidence is in a paper by Paul Ridker, MD, et al. on the changes in biomarkers during REDUCE-IT,” she said. “Several inflammatory biomarkers associated with atherosclerosis rose during the study among those allocated mineral oil, but remained largely unchanged in the EPA group. This is in contrast to what is seen with these biomarkers in other large trials, where no changes were seen in the placebo groups, and once again raises the possibility that the apparent benefits of EPA may be related to hazard from the mineral oil.”
Still room for benefit?
Based largely on the results of REDUCE-IT, Vascepa is currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration as an adjunctive therapy to lower the risk for CV events among adults with elevated triglyceride levels (≥ 150 mg/dL). Patients must also have either established CVD or diabetes and two or more additional CV risk factors and are advised to continue physical activity and maintain a healthy diet.
Dr. Nissen, the principal author of the STRENGTH trial, said in an interview, “REDUCE-IT is an outlier. Other trials of omega-3 fatty acids, some of them very large, showed no benefits, and a meta-analysis of nearly 78,000 patients showed no beneficial effects. In this context,” he said, “the large ‘benefit’ observed in REDUCE-IT doesn’t make any sense.”
Dr. Nissen noted that a secondary analysis of STRENGTH further showed that higher plasma EPA levels did not reduce CV outcomes. He also highlighted the elevated risk of atrial fibrillation with EPA. “We need to see another study comparing EPA to a neutral comparator such as corn oil, which had no significant effect on lipid or inflammatory biomarkers in STRENGTH,” he said. “Without such a trial, the results of REDUCE-IT cannot be accepted as definitive.”
Dr. Ridker, the lead author of the REDUCE-IT substudy that found biomarker changes with the mineral oil placebo, said in an interview: “Is it possible that EPA is an outstanding drug? Absolutely, and I continue to think it useful for our very high-risk, secondary-prevention patients when we are running out of options.”
“But,” said Dr. Ridker, who is a professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and director of the Center for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention at Brigham and Women’s, “the reality ... is that ongoing uncertainties need resolution.” Like Dr. Nissen, he thinks the best way to resolve these uncertainties is through a second trial using a fully neutral comparator. “I am hopeful that the U.S. National Institutes of Health will see fit to undertake such an endeavor, perhaps with support from industry partners.”
Although Dr. Armitage is no longer in clinical practice, when asked how she might use EPA, she said it might be reasonable for patients who meet the prescribing criteria and remain high risk after all other risk factors have been addressed. She added that, although EPA is approved in the United Kingdom, she doesn’t think it is being widely prescribed.
Salim S. Virani, MD, PhD, a professor in the Sections of Cardiology and Cardiovascular Research at Baylor College of Medicine who has published articles about REDUCE-IT and on the eligibility and cost of EPA in the Veterans Affairs system, said in an interview: “In my personal opinion, clinicians [should] first optimize diet and lifestyle and work on secondary causes, as they play a very big role in hypertriglyceridemia.” He also recommended optimizing LDL-C levels because of “consistent data showing that LDL [cholesterol] control leads to significant reduction in atherosclerotic CVD events.”
“Once these two steps are taken and triglycerides still remain elevated,” he said, “then adding EPA in patients with established atherosclerotic CVD or those with diabetes plus other CV risk factors may be a reasonable option to further lower residual atherosclerotic CVD risk.”
Clinical inertia?
Dr. Bhatt acknowledged that, despite the benefit of EPA in the context of REDUCE-IT, “a few issues stand in the way of prescribing, particularly in the U.S.”
Vascepa’s manufacturer Amarin lost a patent challenge in the United States, enabling the relatively early introduction of multiple generics. “They’ve lost interest in the U.S. because there are three generics.”
“The sad truth is, if there isn’t a drug rep saying, ‘hey, look at this new data,’ there’s clinical inertia,” said Dr. Bhatt. He believes that the lack of marketing will hurt awareness among physicians and “ultimately hurt patients because they won’t get the drug.”
Cost is also an issue, Dr. Bhatt affirmed. Vascepa has significant out-of-pocket costs for many patients, as do some of the generics. Currently, the branded product costs about $300 per month without insurance, according to drugs.com; prices for generics vary widely, running anywhere from $82 to $200 or more.
Despite these challenges, he noted that many guidelines around the world have already changed to reflect the data, including the American Diabetes Association and the U.S. National Lipid Association.
Will there be another trial of EPA with a neutral placebo? Dr. Bhatt believes it’s not going to happen. “The company that funded REDUCE-IT is struggling just to stay alive, and another investigator-funded trial like RESPECT EPA would probably be underpowered and not move the needle much.”
Dr. Virani agreed that while it would be best to test EPA against a fully inert placebo, “whether there is enough appetite to fund such a large trial remains a big question.”
Meanwhile, Dr. Bhatt said, “EPA is not for everybody, but for the high-risk patients who meet the stringent inclusion criteria of REDUCE-IT, I think clinicians should at least consider use of EPA in a way consistent with the U.S. FDA label, the Canadian label, and the label in parts of Europe where the drug is being introduced.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The prescription product (Vascepa), consisting of a “highly purified” form of the omega-3 acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), was heralded in 2018 (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:11-22) as ushering in “the dawn of a new era” in cardiovascular disease (CVD) prevention that “should definitely change practice going forward,” according to REDUCE-IT’s lead author Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, formerly of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and now director of the Mount Sinai Heart Center in New York.
However, skeptics questioned why the results differed from most previous trials of fish oil that showed no benefit. Was it caused by the high dose of EPA: 4 g/daily versus 1 g daily in earlier trials with fish oil capsules? Was it the different formulation of purified EPA versus more common combinations of EPA plus docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)? Or, as suggested by Steven Nissen, MD, chief academic officer of Cleveland Clinic’s Heart and Vascular Institute and others, was it caused by the negative effects of the mineral oil placebo, given the significant increases in LDL cholesterol and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) seen in the control group?
‘Not all omega-3s created equal’
Dr. Bhatt recently said in an interview: “I think there’s confusion in the field. It’s a challenge when just one drug in a class looks good and everything else in that class looks bad. That in itself can breed some skepticism. Also, not everyone always embraces advances. Some people have other reasons to impugn datasets; for example, it could be because they are running competing trials with competing drugs.”
REDUCE-IT enrolled more than 8,000 patients at high CV risk despite statin treatment, and randomly assigned them to 2 g of EPA twice daily or the mineral oil placebo. Although the results showed a 25% reduction in the rate of CV events in the EPA group, there was also an increased risk of atrial fibrillation among those taking EPA after a median of 4.9 years follow-up.
Dr. Bhatt noted that Amarin, which manufactures Vascepa, is essentially a one-drug company, and its stock price is dependent on the product. When the trial results were released, he said, “there were people in the investor world that wanted the stock price to go up or wanted it to go down, and they were alternately hyping or disparaging the data in both cases, sometimes inappropriately and excessively, which created noise around the science.”
The fact is, he said, “not all omega-3 fatty acids are created equal. There are differences between supplements and prescription medicines, and within the prescription medicines, differences between pure EPA and the mixtures of EPA and DHA.”
Dr. Bhatt added that other trials also showed positive results. He pointed to the JELIS trial, published in 2007, which showed a 19% reduction in major adverse CV events with a 1.8-g daily EPA dose.
More recently, RESPECT-EPA was presented at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Heart Association. That study had methodological issues and was underpowered, but it did suggest a possible benefit of EPA in reducing CV events in patients with chronic coronary artery disease who were taking statins. “Looking at the totality of evidence, I think it’s quite clear there’s CV benefit,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Placebo effects?
Concerns about the mineral oil placebo cast doubt on that benefit. Table 4 of the supplement accompanying REDUCE-IT’s publication in the New England Journal of Medicine shows significant increases of non–HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, apolipoprotein B, and hsCRP in the control group.
Jane Armitage, MBBS, a professor of clinical trials and epidemiology, clinical trial service unit at Oxford University (England), said in an interview: “I was surprised by the backlash and at the time felt that it was unlikely that the mineral oil was the problem. But the size of benefit was still out of kilter.”
“Two further pieces of evidence have influenced my thoughts since then,” she said. One is the lack of effect of high doses of fish oils in the STRENGTH trial. STRENGTH tested 4 g of omega-3 oil containing a mixture of EPA and DHA and found no benefit in statin-treated, high-risk patients.
“The amount of EPA [was] substantially less than given in REDUCE-IT,” Armitage said, “but it seems to me that in a similar hypertriglyceridemic population, if the effect were due to the EPA, you would have seen some impact in STRENGTH – and none was seen.”
“The other piece of evidence is in a paper by Paul Ridker, MD, et al. on the changes in biomarkers during REDUCE-IT,” she said. “Several inflammatory biomarkers associated with atherosclerosis rose during the study among those allocated mineral oil, but remained largely unchanged in the EPA group. This is in contrast to what is seen with these biomarkers in other large trials, where no changes were seen in the placebo groups, and once again raises the possibility that the apparent benefits of EPA may be related to hazard from the mineral oil.”
Still room for benefit?
Based largely on the results of REDUCE-IT, Vascepa is currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration as an adjunctive therapy to lower the risk for CV events among adults with elevated triglyceride levels (≥ 150 mg/dL). Patients must also have either established CVD or diabetes and two or more additional CV risk factors and are advised to continue physical activity and maintain a healthy diet.
Dr. Nissen, the principal author of the STRENGTH trial, said in an interview, “REDUCE-IT is an outlier. Other trials of omega-3 fatty acids, some of them very large, showed no benefits, and a meta-analysis of nearly 78,000 patients showed no beneficial effects. In this context,” he said, “the large ‘benefit’ observed in REDUCE-IT doesn’t make any sense.”
Dr. Nissen noted that a secondary analysis of STRENGTH further showed that higher plasma EPA levels did not reduce CV outcomes. He also highlighted the elevated risk of atrial fibrillation with EPA. “We need to see another study comparing EPA to a neutral comparator such as corn oil, which had no significant effect on lipid or inflammatory biomarkers in STRENGTH,” he said. “Without such a trial, the results of REDUCE-IT cannot be accepted as definitive.”
Dr. Ridker, the lead author of the REDUCE-IT substudy that found biomarker changes with the mineral oil placebo, said in an interview: “Is it possible that EPA is an outstanding drug? Absolutely, and I continue to think it useful for our very high-risk, secondary-prevention patients when we are running out of options.”
“But,” said Dr. Ridker, who is a professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and director of the Center for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention at Brigham and Women’s, “the reality ... is that ongoing uncertainties need resolution.” Like Dr. Nissen, he thinks the best way to resolve these uncertainties is through a second trial using a fully neutral comparator. “I am hopeful that the U.S. National Institutes of Health will see fit to undertake such an endeavor, perhaps with support from industry partners.”
Although Dr. Armitage is no longer in clinical practice, when asked how she might use EPA, she said it might be reasonable for patients who meet the prescribing criteria and remain high risk after all other risk factors have been addressed. She added that, although EPA is approved in the United Kingdom, she doesn’t think it is being widely prescribed.
Salim S. Virani, MD, PhD, a professor in the Sections of Cardiology and Cardiovascular Research at Baylor College of Medicine who has published articles about REDUCE-IT and on the eligibility and cost of EPA in the Veterans Affairs system, said in an interview: “In my personal opinion, clinicians [should] first optimize diet and lifestyle and work on secondary causes, as they play a very big role in hypertriglyceridemia.” He also recommended optimizing LDL-C levels because of “consistent data showing that LDL [cholesterol] control leads to significant reduction in atherosclerotic CVD events.”
“Once these two steps are taken and triglycerides still remain elevated,” he said, “then adding EPA in patients with established atherosclerotic CVD or those with diabetes plus other CV risk factors may be a reasonable option to further lower residual atherosclerotic CVD risk.”
Clinical inertia?
Dr. Bhatt acknowledged that, despite the benefit of EPA in the context of REDUCE-IT, “a few issues stand in the way of prescribing, particularly in the U.S.”
Vascepa’s manufacturer Amarin lost a patent challenge in the United States, enabling the relatively early introduction of multiple generics. “They’ve lost interest in the U.S. because there are three generics.”
“The sad truth is, if there isn’t a drug rep saying, ‘hey, look at this new data,’ there’s clinical inertia,” said Dr. Bhatt. He believes that the lack of marketing will hurt awareness among physicians and “ultimately hurt patients because they won’t get the drug.”
Cost is also an issue, Dr. Bhatt affirmed. Vascepa has significant out-of-pocket costs for many patients, as do some of the generics. Currently, the branded product costs about $300 per month without insurance, according to drugs.com; prices for generics vary widely, running anywhere from $82 to $200 or more.
Despite these challenges, he noted that many guidelines around the world have already changed to reflect the data, including the American Diabetes Association and the U.S. National Lipid Association.
Will there be another trial of EPA with a neutral placebo? Dr. Bhatt believes it’s not going to happen. “The company that funded REDUCE-IT is struggling just to stay alive, and another investigator-funded trial like RESPECT EPA would probably be underpowered and not move the needle much.”
Dr. Virani agreed that while it would be best to test EPA against a fully inert placebo, “whether there is enough appetite to fund such a large trial remains a big question.”
Meanwhile, Dr. Bhatt said, “EPA is not for everybody, but for the high-risk patients who meet the stringent inclusion criteria of REDUCE-IT, I think clinicians should at least consider use of EPA in a way consistent with the U.S. FDA label, the Canadian label, and the label in parts of Europe where the drug is being introduced.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Early retirement and the terrible, horrible, no good, very bad cognitive decline
The ‘scheme’ in the name should have been a clue
Retirement. The shiny reward to a lifetime’s worth of working and saving. We’re all literally working to get there, some of us more to get there early, but current research reveals that early retirement isn’t the relaxing finish line we dream about, cognitively speaking.
Researchers at Binghamton (N.Y.) University set out to examine just how retirement plans affect cognitive performance. They started off with China’s New Rural Pension Scheme (scheme probably has a less negative connotation in Chinese), a plan that financially aids the growing rural retirement-age population in the country. Then they looked at data from the Chinese Health and Retirement Longitudinal Survey, which tests cognition with a focus on episodic memory and parts of intact mental status.
What they found was the opposite of what you would expect out of retirees with nothing but time on their hands.
The pension program, which had been in place for almost a decade, led to delayed recall, especially among women, supporting “the mental retirement hypothesis that decreased mental activity results in worsening cognitive skills,” the investigators said in a written statement.
There also was a drop in social engagement, with lower rates of volunteering and social interaction than people who didn’t receive the pension. Some behaviors, like regular alcohol consumption, did improve over the previous year, as did total health in general, but “the adverse effects of early retirement on mental and social engagement significantly outweigh the program’s protective effect on various health behaviors,” Plamen Nikolov, PhD, said about his research.
So if you’re looking to retire early, don’t skimp on the crosswords and the bingo nights. Stay busy in a good way. Your brain will thank you.
Indiana Jones and the First Smallpox Ancestor
Smallpox was, not that long ago, one of the most devastating diseases known to humanity, killing 300 million people in the 20th century alone. Eradicating it has to be one of medicine’s crowning achievements. Now it can only be found in museums, which is where it belongs.
Here’s the thing with smallpox though: For all it did to us, we know frustratingly little about where it came from. Until very recently, the best available genetic evidence placed its emergence in the 17th century, which clashes with historical data. You know what that means, right? It’s time to dig out the fedora and whip, cue the music, and dig into a recently published study spanning continents in search of the mythical smallpox origin story.
We pick up in 2020, when genetic evidence definitively showed smallpox in a Viking burial site, moving the disease’s emergence a thousand years earlier. Which is all well and good, but there’s solid visual evidence that Egyptian pharaohs were dying of smallpox, as their bodies show the signature scarring. Historians were pretty sure smallpox went back about 4,000 years, but there was no genetic material to prove it.
Since there aren’t any 4,000-year-old smallpox germs laying around, the researchers chose to attack the problem another way – by burning down a Venetian catacomb, er, conducting a analysis of historical smallpox genetics to find the virus’s origin. By analyzing the genomes of various strains at different periods of time, they were able to determine that the variola virus had a definitive common ancestor. Some of the genetic components in the Viking-age sample, for example, persisted until the 18th century.
Armed with this information, the scientists determined that the first smallpox ancestor emerged about 3,800 years ago. That’s very close to the historians’ estimate for the disease’s emergence. Proof at last of smallpox’s truly ancient origin. One might even say the researchers chose wisely.
The only hall of fame that really matters
LOTME loves the holiday season – the food, the gifts, the radio stations that play nothing but Christmas music – but for us the most wonderful time of the year comes just a bit later. No, it’s not our annual Golden Globes slap bet. Nope, not even the “excitement” of the College Football Playoff National Championship. It’s time for the National Inventors Hall of Fame to announce its latest inductees, and we could hardly sleep last night after putting cookies out for Thomas Edison. Fasten your seatbelts!
- Robert G. Bryant is a NASA chemist who developed Langley Research Center-Soluble Imide (yes, that’s the actual name) a polymer used as an insulation material for leads in implantable cardiac resynchronization therapy devices.
- Rory Cooper is a biomedical engineer who was paralyzed in a bicycle accident. His work has improved manual and electric wheelchairs and advanced the health, mobility, and social inclusion of people with disabilities and older adults. He is also the first NIHF inductee named Rory.
- Katalin Karikó, a biochemist, and Drew Weissman, an immunologist, “discovered how to enable messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) to enter cells without triggering the body’s immune system,” NIHF said, and that laid the foundation for the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines developed by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna. That, of course, led to the antivax movement, which has provided so much LOTME fodder over the years.
- Angela Hartley Brodie was a biochemist who discovered and developed a class of drugs called aromatase inhibitors, which can stop the production of hormones that fuel cancer cell growth and are used to treat breast cancer in 500,000 women worldwide each year.
We can’t mention all of the inductees for 2023 (our editor made that very clear), but we would like to offer a special shout-out to brothers Cyril (the first Cyril in the NIHF, by the way) and Louis Keller, who invented the world’s first compact loader, which eventually became the Bobcat skid-steer loader. Not really medical, you’re probably thinking, but we’re sure that someone, somewhere, at some time, used one to build a hospital, landscape a hospital, or clean up after the demolition of a hospital.
The ‘scheme’ in the name should have been a clue
Retirement. The shiny reward to a lifetime’s worth of working and saving. We’re all literally working to get there, some of us more to get there early, but current research reveals that early retirement isn’t the relaxing finish line we dream about, cognitively speaking.
Researchers at Binghamton (N.Y.) University set out to examine just how retirement plans affect cognitive performance. They started off with China’s New Rural Pension Scheme (scheme probably has a less negative connotation in Chinese), a plan that financially aids the growing rural retirement-age population in the country. Then they looked at data from the Chinese Health and Retirement Longitudinal Survey, which tests cognition with a focus on episodic memory and parts of intact mental status.
What they found was the opposite of what you would expect out of retirees with nothing but time on their hands.
The pension program, which had been in place for almost a decade, led to delayed recall, especially among women, supporting “the mental retirement hypothesis that decreased mental activity results in worsening cognitive skills,” the investigators said in a written statement.
There also was a drop in social engagement, with lower rates of volunteering and social interaction than people who didn’t receive the pension. Some behaviors, like regular alcohol consumption, did improve over the previous year, as did total health in general, but “the adverse effects of early retirement on mental and social engagement significantly outweigh the program’s protective effect on various health behaviors,” Plamen Nikolov, PhD, said about his research.
So if you’re looking to retire early, don’t skimp on the crosswords and the bingo nights. Stay busy in a good way. Your brain will thank you.
Indiana Jones and the First Smallpox Ancestor
Smallpox was, not that long ago, one of the most devastating diseases known to humanity, killing 300 million people in the 20th century alone. Eradicating it has to be one of medicine’s crowning achievements. Now it can only be found in museums, which is where it belongs.
Here’s the thing with smallpox though: For all it did to us, we know frustratingly little about where it came from. Until very recently, the best available genetic evidence placed its emergence in the 17th century, which clashes with historical data. You know what that means, right? It’s time to dig out the fedora and whip, cue the music, and dig into a recently published study spanning continents in search of the mythical smallpox origin story.
We pick up in 2020, when genetic evidence definitively showed smallpox in a Viking burial site, moving the disease’s emergence a thousand years earlier. Which is all well and good, but there’s solid visual evidence that Egyptian pharaohs were dying of smallpox, as their bodies show the signature scarring. Historians were pretty sure smallpox went back about 4,000 years, but there was no genetic material to prove it.
Since there aren’t any 4,000-year-old smallpox germs laying around, the researchers chose to attack the problem another way – by burning down a Venetian catacomb, er, conducting a analysis of historical smallpox genetics to find the virus’s origin. By analyzing the genomes of various strains at different periods of time, they were able to determine that the variola virus had a definitive common ancestor. Some of the genetic components in the Viking-age sample, for example, persisted until the 18th century.
Armed with this information, the scientists determined that the first smallpox ancestor emerged about 3,800 years ago. That’s very close to the historians’ estimate for the disease’s emergence. Proof at last of smallpox’s truly ancient origin. One might even say the researchers chose wisely.
The only hall of fame that really matters
LOTME loves the holiday season – the food, the gifts, the radio stations that play nothing but Christmas music – but for us the most wonderful time of the year comes just a bit later. No, it’s not our annual Golden Globes slap bet. Nope, not even the “excitement” of the College Football Playoff National Championship. It’s time for the National Inventors Hall of Fame to announce its latest inductees, and we could hardly sleep last night after putting cookies out for Thomas Edison. Fasten your seatbelts!
- Robert G. Bryant is a NASA chemist who developed Langley Research Center-Soluble Imide (yes, that’s the actual name) a polymer used as an insulation material for leads in implantable cardiac resynchronization therapy devices.
- Rory Cooper is a biomedical engineer who was paralyzed in a bicycle accident. His work has improved manual and electric wheelchairs and advanced the health, mobility, and social inclusion of people with disabilities and older adults. He is also the first NIHF inductee named Rory.
- Katalin Karikó, a biochemist, and Drew Weissman, an immunologist, “discovered how to enable messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) to enter cells without triggering the body’s immune system,” NIHF said, and that laid the foundation for the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines developed by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna. That, of course, led to the antivax movement, which has provided so much LOTME fodder over the years.
- Angela Hartley Brodie was a biochemist who discovered and developed a class of drugs called aromatase inhibitors, which can stop the production of hormones that fuel cancer cell growth and are used to treat breast cancer in 500,000 women worldwide each year.
We can’t mention all of the inductees for 2023 (our editor made that very clear), but we would like to offer a special shout-out to brothers Cyril (the first Cyril in the NIHF, by the way) and Louis Keller, who invented the world’s first compact loader, which eventually became the Bobcat skid-steer loader. Not really medical, you’re probably thinking, but we’re sure that someone, somewhere, at some time, used one to build a hospital, landscape a hospital, or clean up after the demolition of a hospital.
The ‘scheme’ in the name should have been a clue
Retirement. The shiny reward to a lifetime’s worth of working and saving. We’re all literally working to get there, some of us more to get there early, but current research reveals that early retirement isn’t the relaxing finish line we dream about, cognitively speaking.
Researchers at Binghamton (N.Y.) University set out to examine just how retirement plans affect cognitive performance. They started off with China’s New Rural Pension Scheme (scheme probably has a less negative connotation in Chinese), a plan that financially aids the growing rural retirement-age population in the country. Then they looked at data from the Chinese Health and Retirement Longitudinal Survey, which tests cognition with a focus on episodic memory and parts of intact mental status.
What they found was the opposite of what you would expect out of retirees with nothing but time on their hands.
The pension program, which had been in place for almost a decade, led to delayed recall, especially among women, supporting “the mental retirement hypothesis that decreased mental activity results in worsening cognitive skills,” the investigators said in a written statement.
There also was a drop in social engagement, with lower rates of volunteering and social interaction than people who didn’t receive the pension. Some behaviors, like regular alcohol consumption, did improve over the previous year, as did total health in general, but “the adverse effects of early retirement on mental and social engagement significantly outweigh the program’s protective effect on various health behaviors,” Plamen Nikolov, PhD, said about his research.
So if you’re looking to retire early, don’t skimp on the crosswords and the bingo nights. Stay busy in a good way. Your brain will thank you.
Indiana Jones and the First Smallpox Ancestor
Smallpox was, not that long ago, one of the most devastating diseases known to humanity, killing 300 million people in the 20th century alone. Eradicating it has to be one of medicine’s crowning achievements. Now it can only be found in museums, which is where it belongs.
Here’s the thing with smallpox though: For all it did to us, we know frustratingly little about where it came from. Until very recently, the best available genetic evidence placed its emergence in the 17th century, which clashes with historical data. You know what that means, right? It’s time to dig out the fedora and whip, cue the music, and dig into a recently published study spanning continents in search of the mythical smallpox origin story.
We pick up in 2020, when genetic evidence definitively showed smallpox in a Viking burial site, moving the disease’s emergence a thousand years earlier. Which is all well and good, but there’s solid visual evidence that Egyptian pharaohs were dying of smallpox, as their bodies show the signature scarring. Historians were pretty sure smallpox went back about 4,000 years, but there was no genetic material to prove it.
Since there aren’t any 4,000-year-old smallpox germs laying around, the researchers chose to attack the problem another way – by burning down a Venetian catacomb, er, conducting a analysis of historical smallpox genetics to find the virus’s origin. By analyzing the genomes of various strains at different periods of time, they were able to determine that the variola virus had a definitive common ancestor. Some of the genetic components in the Viking-age sample, for example, persisted until the 18th century.
Armed with this information, the scientists determined that the first smallpox ancestor emerged about 3,800 years ago. That’s very close to the historians’ estimate for the disease’s emergence. Proof at last of smallpox’s truly ancient origin. One might even say the researchers chose wisely.
The only hall of fame that really matters
LOTME loves the holiday season – the food, the gifts, the radio stations that play nothing but Christmas music – but for us the most wonderful time of the year comes just a bit later. No, it’s not our annual Golden Globes slap bet. Nope, not even the “excitement” of the College Football Playoff National Championship. It’s time for the National Inventors Hall of Fame to announce its latest inductees, and we could hardly sleep last night after putting cookies out for Thomas Edison. Fasten your seatbelts!
- Robert G. Bryant is a NASA chemist who developed Langley Research Center-Soluble Imide (yes, that’s the actual name) a polymer used as an insulation material for leads in implantable cardiac resynchronization therapy devices.
- Rory Cooper is a biomedical engineer who was paralyzed in a bicycle accident. His work has improved manual and electric wheelchairs and advanced the health, mobility, and social inclusion of people with disabilities and older adults. He is also the first NIHF inductee named Rory.
- Katalin Karikó, a biochemist, and Drew Weissman, an immunologist, “discovered how to enable messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) to enter cells without triggering the body’s immune system,” NIHF said, and that laid the foundation for the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines developed by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna. That, of course, led to the antivax movement, which has provided so much LOTME fodder over the years.
- Angela Hartley Brodie was a biochemist who discovered and developed a class of drugs called aromatase inhibitors, which can stop the production of hormones that fuel cancer cell growth and are used to treat breast cancer in 500,000 women worldwide each year.
We can’t mention all of the inductees for 2023 (our editor made that very clear), but we would like to offer a special shout-out to brothers Cyril (the first Cyril in the NIHF, by the way) and Louis Keller, who invented the world’s first compact loader, which eventually became the Bobcat skid-steer loader. Not really medical, you’re probably thinking, but we’re sure that someone, somewhere, at some time, used one to build a hospital, landscape a hospital, or clean up after the demolition of a hospital.
What to do when patients don’t listen
The term “nonadherent” has gradually replaced “noncompliant” in the physician lexicon as a nod to the evolving doctor-patient relationship. Noncompliance implies that a patient isn’t following their doctor’s orders. Adherence, on the other hand, is a measure of how closely your patient’s behavior matches the recommendations you’ve made. It’s a subtle difference but an important distinction in approaching care.
“Noncompliance is inherently negative feedback to the patient, whereas there’s a reason for nonadherence, and it’s usually external,” said Sharon Rabinovitz, MD, president of the Georgia Academy of Family Physicians.
Why won’t patients listen?
The reasons behind a patient’s nonadherence are multifaceted, but they are often driven by social determinants of health, such as transportation, poor health literacy, finances, and lack of access to pharmacies.
Other times, patients don’t want to take medicine, don’t prioritize their health, or they find the dietary and lifestyle modifications doctors suggest too hard to make or they struggle at losing weight, eating more healthfully, or cutting back on alcohol, for instance.
“When you come down to it, the big hindrance of it all is cost and the ability for the patient to be able to afford some of the things that we think they should be able to do,” said Teresa Lovins, MD, a physician in private practice Columbus, Ind., and a member of the board of directors of the American Academy of Family Physicians.
Another common deterrent to treatment is undesired side effects that a patient may not want to mention.
“For example, a lot of patients who are taking antidepressants have sexual dysfunction associated with those medications,” said Dr. Rabinovitz. “If you don’t ask the right questions, you’re not going to be able to fully assess the experience the patient is having and a reason why they might not take it [the medication].”
Much nonadherence is intentional and is based on experience, belief systems, and knowledge. For example, the American Medical Association finds that patients may not understand why they need a certain treatment (and therefore dismiss it), or they may be overloaded with multiple medications, fear dependency on a drug, have a mistrust of pharmaceutical companies or the medical system as a whole, or have symptoms of depression that make taking healthy actions more difficult. In addition, patients may be unable to afford their medication, or their lack of symptoms may lead them to believe they don’t really need the prescription, as occurs with disorders such as hypertension or high cholesterol.
“In my training, we did something called Balint training, where we would get together as a group with attendings and discuss cases that were difficult from a biopsychosocial perspective and consider all the factors in the patient perspective, including family dynamics, social systems, and economic realities,” said Russell Blackwelder, MD, director of geriatric education and associate professor of family medicine at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
“That training was, for me, very helpful for opening up and being more empathetic and really examining the patient’s point of view and everything that impacts them.”
Dr. Lovins agreed that it’s crucial to establish a good rapport and build mutual trust.
“If you don’t know the patient, you have a harder time asking the right questions to get to the meat of why they’re not taking their medicine or what they’re not doing to help their health,” she said. “It takes a little bit of trust on both parts to get to that question that really gets to the heart of why they’re not doing what you’re asking them to do.”
How to encourage adherence
Although there may not be a one-size-fits-all approach for achieving general adherence or adherence to a medication regimen, some methods may increase success.
Kenneth Zweig, MD, an internist at Northern Virginia Family Practice Associates, Alexandria, said that convincing patients to make one small change that they can sustain can get the ball rolling.
“I had one patient who was very overweight and had high blood pressure, high cholesterol, back pain, insomnia, and depression, who was also drinking three to four beers a night,” Dr. Zweig said. “After a long discussion, I challenged him to stop all alcohol for 1 week. At the end of the week, he noticed that he slept better, lost some weight, had lower blood pressure, and had more energy. Once he saw the benefits of this one change, he was motivated to improve other aspects of his health as well. He improved his diet, started exercising, and lost over 50 pounds. He has persisted with these lifestyle changes ever since.”
A team-based approach may also increase treatment understanding and adherence. In one older study, patients who were assigned to team-based care, including care by pharmacists, were significantly more adherent to medication regimens. Patients were more comfortable asking questions and raising concerns when they felt their treatment plan was a collaboration between several providers and themselves.
Dr. Lovins said to always approach the patient with a positive. “Say, what can we do together to make this work? What are your questions about this medication? And try and focus on the positive things that you can change instead of leaving the patient with a negative feeling or that you’re angry with them or that you’re unhappy with their choices. Patients respond better when they are treated as part of the team.”
Fear of judgment can also be a barrier to honesty between patients and their doctors. Shame creates a reluctance to admit nonadherence. Dr. Lovins said in an interview that it’s the physician’s responsibility to create a blame-free space for patients to speak openly about their struggles with treatment and reasons for nonadherence.
When should you redirect care?
Ultimately, the goal is good care and treatment of disease. However, if you and your patient are at an impasse and progress is stalling or failing, it may be appropriate to encourage the patient to seek care elsewhere.
“Just like any relationship, some physician-patient relationships are just not a good fit,” said Dr. Blackwelder. And this may be the reason why the patient is nonadherent — something between the two of you doesn’t click.
While there are ethical considerations for this decision, most medical boards have guidelines on how to go about it, Dr. Blackwelder said in an interview. “In the state of South Carolina, we have to be available to provide urgent coverage for at least 30 days and notify the patient in writing that they need to find somebody else and to help them find somebody else if we can.”
Just as with care, a clear conversation is the best practice if you’re proposing a potential shift away from a physician-patient relationship. You might say: We’re not making the kind of progress I’d like to see, and I’m wondering if you think working with another doctor may help you.
“The most important thing is being very honest and transparent with the patient that you’re concerned you’re not making the appropriate strides forward,” said Dr. Rabinovitz. Then you can ask, ‘Am I the right doctor to help you reach your goals? And if not, how can I help you get to where you need to be?’ ”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The term “nonadherent” has gradually replaced “noncompliant” in the physician lexicon as a nod to the evolving doctor-patient relationship. Noncompliance implies that a patient isn’t following their doctor’s orders. Adherence, on the other hand, is a measure of how closely your patient’s behavior matches the recommendations you’ve made. It’s a subtle difference but an important distinction in approaching care.
“Noncompliance is inherently negative feedback to the patient, whereas there’s a reason for nonadherence, and it’s usually external,” said Sharon Rabinovitz, MD, president of the Georgia Academy of Family Physicians.
Why won’t patients listen?
The reasons behind a patient’s nonadherence are multifaceted, but they are often driven by social determinants of health, such as transportation, poor health literacy, finances, and lack of access to pharmacies.
Other times, patients don’t want to take medicine, don’t prioritize their health, or they find the dietary and lifestyle modifications doctors suggest too hard to make or they struggle at losing weight, eating more healthfully, or cutting back on alcohol, for instance.
“When you come down to it, the big hindrance of it all is cost and the ability for the patient to be able to afford some of the things that we think they should be able to do,” said Teresa Lovins, MD, a physician in private practice Columbus, Ind., and a member of the board of directors of the American Academy of Family Physicians.
Another common deterrent to treatment is undesired side effects that a patient may not want to mention.
“For example, a lot of patients who are taking antidepressants have sexual dysfunction associated with those medications,” said Dr. Rabinovitz. “If you don’t ask the right questions, you’re not going to be able to fully assess the experience the patient is having and a reason why they might not take it [the medication].”
Much nonadherence is intentional and is based on experience, belief systems, and knowledge. For example, the American Medical Association finds that patients may not understand why they need a certain treatment (and therefore dismiss it), or they may be overloaded with multiple medications, fear dependency on a drug, have a mistrust of pharmaceutical companies or the medical system as a whole, or have symptoms of depression that make taking healthy actions more difficult. In addition, patients may be unable to afford their medication, or their lack of symptoms may lead them to believe they don’t really need the prescription, as occurs with disorders such as hypertension or high cholesterol.
“In my training, we did something called Balint training, where we would get together as a group with attendings and discuss cases that were difficult from a biopsychosocial perspective and consider all the factors in the patient perspective, including family dynamics, social systems, and economic realities,” said Russell Blackwelder, MD, director of geriatric education and associate professor of family medicine at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
“That training was, for me, very helpful for opening up and being more empathetic and really examining the patient’s point of view and everything that impacts them.”
Dr. Lovins agreed that it’s crucial to establish a good rapport and build mutual trust.
“If you don’t know the patient, you have a harder time asking the right questions to get to the meat of why they’re not taking their medicine or what they’re not doing to help their health,” she said. “It takes a little bit of trust on both parts to get to that question that really gets to the heart of why they’re not doing what you’re asking them to do.”
How to encourage adherence
Although there may not be a one-size-fits-all approach for achieving general adherence or adherence to a medication regimen, some methods may increase success.
Kenneth Zweig, MD, an internist at Northern Virginia Family Practice Associates, Alexandria, said that convincing patients to make one small change that they can sustain can get the ball rolling.
“I had one patient who was very overweight and had high blood pressure, high cholesterol, back pain, insomnia, and depression, who was also drinking three to four beers a night,” Dr. Zweig said. “After a long discussion, I challenged him to stop all alcohol for 1 week. At the end of the week, he noticed that he slept better, lost some weight, had lower blood pressure, and had more energy. Once he saw the benefits of this one change, he was motivated to improve other aspects of his health as well. He improved his diet, started exercising, and lost over 50 pounds. He has persisted with these lifestyle changes ever since.”
A team-based approach may also increase treatment understanding and adherence. In one older study, patients who were assigned to team-based care, including care by pharmacists, were significantly more adherent to medication regimens. Patients were more comfortable asking questions and raising concerns when they felt their treatment plan was a collaboration between several providers and themselves.
Dr. Lovins said to always approach the patient with a positive. “Say, what can we do together to make this work? What are your questions about this medication? And try and focus on the positive things that you can change instead of leaving the patient with a negative feeling or that you’re angry with them or that you’re unhappy with their choices. Patients respond better when they are treated as part of the team.”
Fear of judgment can also be a barrier to honesty between patients and their doctors. Shame creates a reluctance to admit nonadherence. Dr. Lovins said in an interview that it’s the physician’s responsibility to create a blame-free space for patients to speak openly about their struggles with treatment and reasons for nonadherence.
When should you redirect care?
Ultimately, the goal is good care and treatment of disease. However, if you and your patient are at an impasse and progress is stalling or failing, it may be appropriate to encourage the patient to seek care elsewhere.
“Just like any relationship, some physician-patient relationships are just not a good fit,” said Dr. Blackwelder. And this may be the reason why the patient is nonadherent — something between the two of you doesn’t click.
While there are ethical considerations for this decision, most medical boards have guidelines on how to go about it, Dr. Blackwelder said in an interview. “In the state of South Carolina, we have to be available to provide urgent coverage for at least 30 days and notify the patient in writing that they need to find somebody else and to help them find somebody else if we can.”
Just as with care, a clear conversation is the best practice if you’re proposing a potential shift away from a physician-patient relationship. You might say: We’re not making the kind of progress I’d like to see, and I’m wondering if you think working with another doctor may help you.
“The most important thing is being very honest and transparent with the patient that you’re concerned you’re not making the appropriate strides forward,” said Dr. Rabinovitz. Then you can ask, ‘Am I the right doctor to help you reach your goals? And if not, how can I help you get to where you need to be?’ ”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The term “nonadherent” has gradually replaced “noncompliant” in the physician lexicon as a nod to the evolving doctor-patient relationship. Noncompliance implies that a patient isn’t following their doctor’s orders. Adherence, on the other hand, is a measure of how closely your patient’s behavior matches the recommendations you’ve made. It’s a subtle difference but an important distinction in approaching care.
“Noncompliance is inherently negative feedback to the patient, whereas there’s a reason for nonadherence, and it’s usually external,” said Sharon Rabinovitz, MD, president of the Georgia Academy of Family Physicians.
Why won’t patients listen?
The reasons behind a patient’s nonadherence are multifaceted, but they are often driven by social determinants of health, such as transportation, poor health literacy, finances, and lack of access to pharmacies.
Other times, patients don’t want to take medicine, don’t prioritize their health, or they find the dietary and lifestyle modifications doctors suggest too hard to make or they struggle at losing weight, eating more healthfully, or cutting back on alcohol, for instance.
“When you come down to it, the big hindrance of it all is cost and the ability for the patient to be able to afford some of the things that we think they should be able to do,” said Teresa Lovins, MD, a physician in private practice Columbus, Ind., and a member of the board of directors of the American Academy of Family Physicians.
Another common deterrent to treatment is undesired side effects that a patient may not want to mention.
“For example, a lot of patients who are taking antidepressants have sexual dysfunction associated with those medications,” said Dr. Rabinovitz. “If you don’t ask the right questions, you’re not going to be able to fully assess the experience the patient is having and a reason why they might not take it [the medication].”
Much nonadherence is intentional and is based on experience, belief systems, and knowledge. For example, the American Medical Association finds that patients may not understand why they need a certain treatment (and therefore dismiss it), or they may be overloaded with multiple medications, fear dependency on a drug, have a mistrust of pharmaceutical companies or the medical system as a whole, or have symptoms of depression that make taking healthy actions more difficult. In addition, patients may be unable to afford their medication, or their lack of symptoms may lead them to believe they don’t really need the prescription, as occurs with disorders such as hypertension or high cholesterol.
“In my training, we did something called Balint training, where we would get together as a group with attendings and discuss cases that were difficult from a biopsychosocial perspective and consider all the factors in the patient perspective, including family dynamics, social systems, and economic realities,” said Russell Blackwelder, MD, director of geriatric education and associate professor of family medicine at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
“That training was, for me, very helpful for opening up and being more empathetic and really examining the patient’s point of view and everything that impacts them.”
Dr. Lovins agreed that it’s crucial to establish a good rapport and build mutual trust.
“If you don’t know the patient, you have a harder time asking the right questions to get to the meat of why they’re not taking their medicine or what they’re not doing to help their health,” she said. “It takes a little bit of trust on both parts to get to that question that really gets to the heart of why they’re not doing what you’re asking them to do.”
How to encourage adherence
Although there may not be a one-size-fits-all approach for achieving general adherence or adherence to a medication regimen, some methods may increase success.
Kenneth Zweig, MD, an internist at Northern Virginia Family Practice Associates, Alexandria, said that convincing patients to make one small change that they can sustain can get the ball rolling.
“I had one patient who was very overweight and had high blood pressure, high cholesterol, back pain, insomnia, and depression, who was also drinking three to four beers a night,” Dr. Zweig said. “After a long discussion, I challenged him to stop all alcohol for 1 week. At the end of the week, he noticed that he slept better, lost some weight, had lower blood pressure, and had more energy. Once he saw the benefits of this one change, he was motivated to improve other aspects of his health as well. He improved his diet, started exercising, and lost over 50 pounds. He has persisted with these lifestyle changes ever since.”
A team-based approach may also increase treatment understanding and adherence. In one older study, patients who were assigned to team-based care, including care by pharmacists, were significantly more adherent to medication regimens. Patients were more comfortable asking questions and raising concerns when they felt their treatment plan was a collaboration between several providers and themselves.
Dr. Lovins said to always approach the patient with a positive. “Say, what can we do together to make this work? What are your questions about this medication? And try and focus on the positive things that you can change instead of leaving the patient with a negative feeling or that you’re angry with them or that you’re unhappy with their choices. Patients respond better when they are treated as part of the team.”
Fear of judgment can also be a barrier to honesty between patients and their doctors. Shame creates a reluctance to admit nonadherence. Dr. Lovins said in an interview that it’s the physician’s responsibility to create a blame-free space for patients to speak openly about their struggles with treatment and reasons for nonadherence.
When should you redirect care?
Ultimately, the goal is good care and treatment of disease. However, if you and your patient are at an impasse and progress is stalling or failing, it may be appropriate to encourage the patient to seek care elsewhere.
“Just like any relationship, some physician-patient relationships are just not a good fit,” said Dr. Blackwelder. And this may be the reason why the patient is nonadherent — something between the two of you doesn’t click.
While there are ethical considerations for this decision, most medical boards have guidelines on how to go about it, Dr. Blackwelder said in an interview. “In the state of South Carolina, we have to be available to provide urgent coverage for at least 30 days and notify the patient in writing that they need to find somebody else and to help them find somebody else if we can.”
Just as with care, a clear conversation is the best practice if you’re proposing a potential shift away from a physician-patient relationship. You might say: We’re not making the kind of progress I’d like to see, and I’m wondering if you think working with another doctor may help you.
“The most important thing is being very honest and transparent with the patient that you’re concerned you’re not making the appropriate strides forward,” said Dr. Rabinovitz. Then you can ask, ‘Am I the right doctor to help you reach your goals? And if not, how can I help you get to where you need to be?’ ”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Telehealth parent-child interaction therapy improved behavior in children with developmental delay
The children received the therapy with their parents or caregivers, who were more likely to demonstrate positive parenting behaviors than parents in the control group, authors of the new research published in JAMA Pediatrics found.
Approximately 13% of children have some form of developmental delay (DD) and more than half of these children also have at least one mental health disorder, which makes behavior problems a common and ongoing challenge, Daniel M. Bagner, PhD, a psychologist at Florida International University, Miami, and colleagues wrote.
Clinic-based interventions such as parent-child interaction therapy (PCIT) have been effective for improving behavior in children with DD, the researchers said. PCIT involves in-session caregiver coaching using a 1-way mirror and a wireless earpiece worn by the caregiver.
Barriers to the use of PCIT, especially in marginalized and low-income communities, include transportation, clinician shortages, and stigma-related concerns about a clinic visit, the researchers wrote. Technology now allows for Internet-delivered PCIT to reach more children and families, but its effectiveness for children with DD has not been well studied.
In the new study, the researchers randomized 150 children with DD and externalizing behavior problems to up to 20 weeks of Internet-delivered parent-child interaction therapy (iPCIT) or to referral as usual (RAU, the control group). The children were randomized after completion of early intervention services within 3 months of their third birthday, and participated in the sessions with a parent or caregiver. Most of the participants were from economically disadvantaged households and underrepresented ethnic backgrounds.
The iPCIT intervention was conducted weekly with a remote therapist and lasted for 1-1.5 hours; approximately half of the families received the intervention in Spanish.
The primary outcome was rating on the Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL) and assessment of children and caregivers using the Dyadic Parent-Child Interaction Coding System, fourth edition (DPICS). Assessments occurred at baseline and at week 20 (post treatment), with follow ups at 6 and 12 months.
Scores on the CBCL in the iPCIT group decreased from a mean of 61.18 at baseline to 53.83 post intervention. Scores for the control group started at 64.05 and decreased to 59.49 post intervention. At 6-12 months, the scores for both groups remained stable.
Children who received iPCIT with their parent or caregiver also showed significantly lower levels of externalizing behavior problems, compared with the RAU controls post treatment, and at 6-month and 12-month follow-ups based on the Cohen d measure of standardized effect size for differences between groups.
Significantly more children in the iPCIT group showed clinically significant improvements in externalizing problems at post treatment, compared with the RAU group (74% vs. 42%; P < .001) and at 6 months’ follow-up (73% vs. 45%; P = .002). However, the differences from baseline were not significantly different between the two groups after 12 months, which suggests that the effects may wane over time, the researchers noted.
In addition, the rate of child compliance with parent commands, as measured by a cleanup task, approximately doubled by the 12-month follow-up among children in the iPCIT group versus an increase of approximately one-third in the RAU group.
For secondary outcome measures related to caregiver behaviors, the proportion of observed positive parenting behaviors increased in the iPCIT group during the course of the intervention (postintervention odds ratio, 1.10), and the proportion of controlling and critical behaviors decreased (postintervention OR, 1.40). Harsh and inconsistent discipline decreased in both groups based on self-reports, but the decrease was steeper in iPCIT families.
iPCIT did not have a greater impact than RAU in reducing caregiver stress. The researchers wrote that they were not surprised by the lack of stress reduction “given mixed findings on the impact of parenting interventions on stress in caregivers of children with DD.”
Data support iPCIT potential
Overall, the results support findings from previous studies of clinic-based PCIT for children with DD and previous studies of telehealth interventions for typically developing children, the researchers said.
“Moreover, iPCIT-treated children not only showed reductions in behavior problems, such as aggression, but demonstrated higher rates of following directions, which is especially important for children entering kindergarten,” they wrote.
The findings were limited by several factors including the narrow focus on the primary and secondary outcomes, the use of data from a single site in a single metropolitan area – which may limit generalizability – and the lack of comparison between iPCIT and a clinic-based PCIT control group, the researchers noted. The equipment in the current study was provided to families; therefore, differences in treatment response could not be attributed to differences in technology.
The study represents the first known randomized controlled trial to evaluate a telehealth parenting intervention for children with, according to the researchers. The results suggest that technology can be leveraged to help these patients, including those from ethnic minority families who may be underserved by clinic-based care in overcoming barriers to treatment such as transportation and availability of clinicians. Use of iPCIT could be a critical resource as young children with DD complete Part C services and enter the school system.
Practical pediatric takeaways
“This was a great study, well-designed and very important and helpful for pediatric providers,” Cathy Haut, DNP, CPNP-AC, CPNP-PC, a pediatric nurse practitioner in Rehoboth Beach, Del., said in an interview.
“Young children with developmental delay and/or mental and behavioral health disorders require early identification and intervention,” said Dr. Haut. However, obstacles to intervention include stigma or parental denial of the disorder, as well as more practical challenges related to transportation, time to access a clinic or office, potential long length of treatment, and cost.
“Despite availability of state programs for young children, follow up and continued services can be challenging to complete. Once the child outgrows the state program finding alternative therapy can be difficult with the current shortage of pediatric mental health providers,” Dr. Haut noted.
“I was surprised to see that this study treatment phase was completed prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, when telehealth was not as popular a mode for health care and was not utilized to the extent that it is now, especially for pediatric care,” said Dr. Haut. “I was not surprised at the results, as the traditional mode of PCIT includes therapy and training in a space that may not be as familiar to the child as their home environment, and would include live presence of the therapist/s, which may add to anxiety for both the parent and child.”
That almost half of the parents participating in the study had graduated from college and/or completed graduate degrees “may have contributed to some of the success of this study,” Dr. Haut noted.
Benefits and barriers
“The COVID-19 pandemic brought significant change to the frequency of use and overall success of telehealth services,” Dr. Haut said. “Additional provider education in aspects such as provider technique and the use of medical devices with improved specific health care technology assisted in advancing the experience and opportunity for successful telehealth visits. Telehealth therapy offers a cost-effective option for any pediatric patients and for providers, as the time and space commitment for the patient visit can be considerably less than live office visits.
“Unfortunately, there are still overall barriers that I have personally experienced with telehealth, including interruptions in connectivity, background noise, and lack of an available computer or tablet; and with the use of cell phones not always allowing full inclusion of the caregiver and child,” said Dr. Haut. Children with DD, behavioral problems, or other mental health disorders may pose challenges for parents to manage at home while simultaneously trying to fully focus on the therapy in an online setting.
Although the current study is encouraging, “larger studies focused on specific or individual pediatric mental health and/or behavioral disorders may offer more information for providers, and better document the success of telehealth delivery of services,” Dr. Haut said.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Bagner disclosed funding from the National Institutes of Health. He also disclosed personal fees from PCIT International to train clinicians in PCIT supported by a grant from the Florida Department of Children and Families outside the current study. Dr. Haut had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
The children received the therapy with their parents or caregivers, who were more likely to demonstrate positive parenting behaviors than parents in the control group, authors of the new research published in JAMA Pediatrics found.
Approximately 13% of children have some form of developmental delay (DD) and more than half of these children also have at least one mental health disorder, which makes behavior problems a common and ongoing challenge, Daniel M. Bagner, PhD, a psychologist at Florida International University, Miami, and colleagues wrote.
Clinic-based interventions such as parent-child interaction therapy (PCIT) have been effective for improving behavior in children with DD, the researchers said. PCIT involves in-session caregiver coaching using a 1-way mirror and a wireless earpiece worn by the caregiver.
Barriers to the use of PCIT, especially in marginalized and low-income communities, include transportation, clinician shortages, and stigma-related concerns about a clinic visit, the researchers wrote. Technology now allows for Internet-delivered PCIT to reach more children and families, but its effectiveness for children with DD has not been well studied.
In the new study, the researchers randomized 150 children with DD and externalizing behavior problems to up to 20 weeks of Internet-delivered parent-child interaction therapy (iPCIT) or to referral as usual (RAU, the control group). The children were randomized after completion of early intervention services within 3 months of their third birthday, and participated in the sessions with a parent or caregiver. Most of the participants were from economically disadvantaged households and underrepresented ethnic backgrounds.
The iPCIT intervention was conducted weekly with a remote therapist and lasted for 1-1.5 hours; approximately half of the families received the intervention in Spanish.
The primary outcome was rating on the Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL) and assessment of children and caregivers using the Dyadic Parent-Child Interaction Coding System, fourth edition (DPICS). Assessments occurred at baseline and at week 20 (post treatment), with follow ups at 6 and 12 months.
Scores on the CBCL in the iPCIT group decreased from a mean of 61.18 at baseline to 53.83 post intervention. Scores for the control group started at 64.05 and decreased to 59.49 post intervention. At 6-12 months, the scores for both groups remained stable.
Children who received iPCIT with their parent or caregiver also showed significantly lower levels of externalizing behavior problems, compared with the RAU controls post treatment, and at 6-month and 12-month follow-ups based on the Cohen d measure of standardized effect size for differences between groups.
Significantly more children in the iPCIT group showed clinically significant improvements in externalizing problems at post treatment, compared with the RAU group (74% vs. 42%; P < .001) and at 6 months’ follow-up (73% vs. 45%; P = .002). However, the differences from baseline were not significantly different between the two groups after 12 months, which suggests that the effects may wane over time, the researchers noted.
In addition, the rate of child compliance with parent commands, as measured by a cleanup task, approximately doubled by the 12-month follow-up among children in the iPCIT group versus an increase of approximately one-third in the RAU group.
For secondary outcome measures related to caregiver behaviors, the proportion of observed positive parenting behaviors increased in the iPCIT group during the course of the intervention (postintervention odds ratio, 1.10), and the proportion of controlling and critical behaviors decreased (postintervention OR, 1.40). Harsh and inconsistent discipline decreased in both groups based on self-reports, but the decrease was steeper in iPCIT families.
iPCIT did not have a greater impact than RAU in reducing caregiver stress. The researchers wrote that they were not surprised by the lack of stress reduction “given mixed findings on the impact of parenting interventions on stress in caregivers of children with DD.”
Data support iPCIT potential
Overall, the results support findings from previous studies of clinic-based PCIT for children with DD and previous studies of telehealth interventions for typically developing children, the researchers said.
“Moreover, iPCIT-treated children not only showed reductions in behavior problems, such as aggression, but demonstrated higher rates of following directions, which is especially important for children entering kindergarten,” they wrote.
The findings were limited by several factors including the narrow focus on the primary and secondary outcomes, the use of data from a single site in a single metropolitan area – which may limit generalizability – and the lack of comparison between iPCIT and a clinic-based PCIT control group, the researchers noted. The equipment in the current study was provided to families; therefore, differences in treatment response could not be attributed to differences in technology.
The study represents the first known randomized controlled trial to evaluate a telehealth parenting intervention for children with, according to the researchers. The results suggest that technology can be leveraged to help these patients, including those from ethnic minority families who may be underserved by clinic-based care in overcoming barriers to treatment such as transportation and availability of clinicians. Use of iPCIT could be a critical resource as young children with DD complete Part C services and enter the school system.
Practical pediatric takeaways
“This was a great study, well-designed and very important and helpful for pediatric providers,” Cathy Haut, DNP, CPNP-AC, CPNP-PC, a pediatric nurse practitioner in Rehoboth Beach, Del., said in an interview.
“Young children with developmental delay and/or mental and behavioral health disorders require early identification and intervention,” said Dr. Haut. However, obstacles to intervention include stigma or parental denial of the disorder, as well as more practical challenges related to transportation, time to access a clinic or office, potential long length of treatment, and cost.
“Despite availability of state programs for young children, follow up and continued services can be challenging to complete. Once the child outgrows the state program finding alternative therapy can be difficult with the current shortage of pediatric mental health providers,” Dr. Haut noted.
“I was surprised to see that this study treatment phase was completed prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, when telehealth was not as popular a mode for health care and was not utilized to the extent that it is now, especially for pediatric care,” said Dr. Haut. “I was not surprised at the results, as the traditional mode of PCIT includes therapy and training in a space that may not be as familiar to the child as their home environment, and would include live presence of the therapist/s, which may add to anxiety for both the parent and child.”
That almost half of the parents participating in the study had graduated from college and/or completed graduate degrees “may have contributed to some of the success of this study,” Dr. Haut noted.
Benefits and barriers
“The COVID-19 pandemic brought significant change to the frequency of use and overall success of telehealth services,” Dr. Haut said. “Additional provider education in aspects such as provider technique and the use of medical devices with improved specific health care technology assisted in advancing the experience and opportunity for successful telehealth visits. Telehealth therapy offers a cost-effective option for any pediatric patients and for providers, as the time and space commitment for the patient visit can be considerably less than live office visits.
“Unfortunately, there are still overall barriers that I have personally experienced with telehealth, including interruptions in connectivity, background noise, and lack of an available computer or tablet; and with the use of cell phones not always allowing full inclusion of the caregiver and child,” said Dr. Haut. Children with DD, behavioral problems, or other mental health disorders may pose challenges for parents to manage at home while simultaneously trying to fully focus on the therapy in an online setting.
Although the current study is encouraging, “larger studies focused on specific or individual pediatric mental health and/or behavioral disorders may offer more information for providers, and better document the success of telehealth delivery of services,” Dr. Haut said.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Bagner disclosed funding from the National Institutes of Health. He also disclosed personal fees from PCIT International to train clinicians in PCIT supported by a grant from the Florida Department of Children and Families outside the current study. Dr. Haut had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
The children received the therapy with their parents or caregivers, who were more likely to demonstrate positive parenting behaviors than parents in the control group, authors of the new research published in JAMA Pediatrics found.
Approximately 13% of children have some form of developmental delay (DD) and more than half of these children also have at least one mental health disorder, which makes behavior problems a common and ongoing challenge, Daniel M. Bagner, PhD, a psychologist at Florida International University, Miami, and colleagues wrote.
Clinic-based interventions such as parent-child interaction therapy (PCIT) have been effective for improving behavior in children with DD, the researchers said. PCIT involves in-session caregiver coaching using a 1-way mirror and a wireless earpiece worn by the caregiver.
Barriers to the use of PCIT, especially in marginalized and low-income communities, include transportation, clinician shortages, and stigma-related concerns about a clinic visit, the researchers wrote. Technology now allows for Internet-delivered PCIT to reach more children and families, but its effectiveness for children with DD has not been well studied.
In the new study, the researchers randomized 150 children with DD and externalizing behavior problems to up to 20 weeks of Internet-delivered parent-child interaction therapy (iPCIT) or to referral as usual (RAU, the control group). The children were randomized after completion of early intervention services within 3 months of their third birthday, and participated in the sessions with a parent or caregiver. Most of the participants were from economically disadvantaged households and underrepresented ethnic backgrounds.
The iPCIT intervention was conducted weekly with a remote therapist and lasted for 1-1.5 hours; approximately half of the families received the intervention in Spanish.
The primary outcome was rating on the Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL) and assessment of children and caregivers using the Dyadic Parent-Child Interaction Coding System, fourth edition (DPICS). Assessments occurred at baseline and at week 20 (post treatment), with follow ups at 6 and 12 months.
Scores on the CBCL in the iPCIT group decreased from a mean of 61.18 at baseline to 53.83 post intervention. Scores for the control group started at 64.05 and decreased to 59.49 post intervention. At 6-12 months, the scores for both groups remained stable.
Children who received iPCIT with their parent or caregiver also showed significantly lower levels of externalizing behavior problems, compared with the RAU controls post treatment, and at 6-month and 12-month follow-ups based on the Cohen d measure of standardized effect size for differences between groups.
Significantly more children in the iPCIT group showed clinically significant improvements in externalizing problems at post treatment, compared with the RAU group (74% vs. 42%; P < .001) and at 6 months’ follow-up (73% vs. 45%; P = .002). However, the differences from baseline were not significantly different between the two groups after 12 months, which suggests that the effects may wane over time, the researchers noted.
In addition, the rate of child compliance with parent commands, as measured by a cleanup task, approximately doubled by the 12-month follow-up among children in the iPCIT group versus an increase of approximately one-third in the RAU group.
For secondary outcome measures related to caregiver behaviors, the proportion of observed positive parenting behaviors increased in the iPCIT group during the course of the intervention (postintervention odds ratio, 1.10), and the proportion of controlling and critical behaviors decreased (postintervention OR, 1.40). Harsh and inconsistent discipline decreased in both groups based on self-reports, but the decrease was steeper in iPCIT families.
iPCIT did not have a greater impact than RAU in reducing caregiver stress. The researchers wrote that they were not surprised by the lack of stress reduction “given mixed findings on the impact of parenting interventions on stress in caregivers of children with DD.”
Data support iPCIT potential
Overall, the results support findings from previous studies of clinic-based PCIT for children with DD and previous studies of telehealth interventions for typically developing children, the researchers said.
“Moreover, iPCIT-treated children not only showed reductions in behavior problems, such as aggression, but demonstrated higher rates of following directions, which is especially important for children entering kindergarten,” they wrote.
The findings were limited by several factors including the narrow focus on the primary and secondary outcomes, the use of data from a single site in a single metropolitan area – which may limit generalizability – and the lack of comparison between iPCIT and a clinic-based PCIT control group, the researchers noted. The equipment in the current study was provided to families; therefore, differences in treatment response could not be attributed to differences in technology.
The study represents the first known randomized controlled trial to evaluate a telehealth parenting intervention for children with, according to the researchers. The results suggest that technology can be leveraged to help these patients, including those from ethnic minority families who may be underserved by clinic-based care in overcoming barriers to treatment such as transportation and availability of clinicians. Use of iPCIT could be a critical resource as young children with DD complete Part C services and enter the school system.
Practical pediatric takeaways
“This was a great study, well-designed and very important and helpful for pediatric providers,” Cathy Haut, DNP, CPNP-AC, CPNP-PC, a pediatric nurse practitioner in Rehoboth Beach, Del., said in an interview.
“Young children with developmental delay and/or mental and behavioral health disorders require early identification and intervention,” said Dr. Haut. However, obstacles to intervention include stigma or parental denial of the disorder, as well as more practical challenges related to transportation, time to access a clinic or office, potential long length of treatment, and cost.
“Despite availability of state programs for young children, follow up and continued services can be challenging to complete. Once the child outgrows the state program finding alternative therapy can be difficult with the current shortage of pediatric mental health providers,” Dr. Haut noted.
“I was surprised to see that this study treatment phase was completed prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, when telehealth was not as popular a mode for health care and was not utilized to the extent that it is now, especially for pediatric care,” said Dr. Haut. “I was not surprised at the results, as the traditional mode of PCIT includes therapy and training in a space that may not be as familiar to the child as their home environment, and would include live presence of the therapist/s, which may add to anxiety for both the parent and child.”
That almost half of the parents participating in the study had graduated from college and/or completed graduate degrees “may have contributed to some of the success of this study,” Dr. Haut noted.
Benefits and barriers
“The COVID-19 pandemic brought significant change to the frequency of use and overall success of telehealth services,” Dr. Haut said. “Additional provider education in aspects such as provider technique and the use of medical devices with improved specific health care technology assisted in advancing the experience and opportunity for successful telehealth visits. Telehealth therapy offers a cost-effective option for any pediatric patients and for providers, as the time and space commitment for the patient visit can be considerably less than live office visits.
“Unfortunately, there are still overall barriers that I have personally experienced with telehealth, including interruptions in connectivity, background noise, and lack of an available computer or tablet; and with the use of cell phones not always allowing full inclusion of the caregiver and child,” said Dr. Haut. Children with DD, behavioral problems, or other mental health disorders may pose challenges for parents to manage at home while simultaneously trying to fully focus on the therapy in an online setting.
Although the current study is encouraging, “larger studies focused on specific or individual pediatric mental health and/or behavioral disorders may offer more information for providers, and better document the success of telehealth delivery of services,” Dr. Haut said.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Bagner disclosed funding from the National Institutes of Health. He also disclosed personal fees from PCIT International to train clinicians in PCIT supported by a grant from the Florida Department of Children and Families outside the current study. Dr. Haut had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
New Omicron subvariant is ‘crazy infectious,’ COVID expert warns
“It’s crazy infectious,” said Paula Cannon, PhD, a virologist at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “All the things that have protected you for the past couple of years, I don’t think are going to protect you against this new crop of variants.”
XBB.1.5 is spreading quickly in the United States. It accounted for 27.6% of cases in the country in the week ending on Jan. 7, up from about 1% of cases at one point in December, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It’s especially prevalent in the Northeast, now accounting for more than 70% of the cases in that region.
It’s spreading across the globe, too. Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, technical lead of the World Health Organization, has called XBB.1.5 is “the most transmissible subvariant that has been detected yet.”
Ashish Jha, MD, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, tweeted a few days ago that the spread of XBB.1.5 is “stunning” but cautioned that it’s unclear if the symptoms of infection will be more severe than for previous variants.
“Whether we’ll have an XBB.1.5 wave (and if yes, how big) will depend on many factors including immunity of the population, people’s actions, etc.,” he tweeted.
He urged people to get up to date on their boosters, wear a snug-fitting mask, and avoid crowded indoor spaces. He noted that people who haven’t been infected recently or haven’t gotten the bivalent booster likely have little protection against infection.
The symptoms for XBB.1.5 appear to be the same as for other versions of COVID-19. However, it’s less common for people infected with XBB.1.5 to report losing their sense of taste and smell, USA Today reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
“It’s crazy infectious,” said Paula Cannon, PhD, a virologist at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “All the things that have protected you for the past couple of years, I don’t think are going to protect you against this new crop of variants.”
XBB.1.5 is spreading quickly in the United States. It accounted for 27.6% of cases in the country in the week ending on Jan. 7, up from about 1% of cases at one point in December, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It’s especially prevalent in the Northeast, now accounting for more than 70% of the cases in that region.
It’s spreading across the globe, too. Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, technical lead of the World Health Organization, has called XBB.1.5 is “the most transmissible subvariant that has been detected yet.”
Ashish Jha, MD, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, tweeted a few days ago that the spread of XBB.1.5 is “stunning” but cautioned that it’s unclear if the symptoms of infection will be more severe than for previous variants.
“Whether we’ll have an XBB.1.5 wave (and if yes, how big) will depend on many factors including immunity of the population, people’s actions, etc.,” he tweeted.
He urged people to get up to date on their boosters, wear a snug-fitting mask, and avoid crowded indoor spaces. He noted that people who haven’t been infected recently or haven’t gotten the bivalent booster likely have little protection against infection.
The symptoms for XBB.1.5 appear to be the same as for other versions of COVID-19. However, it’s less common for people infected with XBB.1.5 to report losing their sense of taste and smell, USA Today reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
“It’s crazy infectious,” said Paula Cannon, PhD, a virologist at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “All the things that have protected you for the past couple of years, I don’t think are going to protect you against this new crop of variants.”
XBB.1.5 is spreading quickly in the United States. It accounted for 27.6% of cases in the country in the week ending on Jan. 7, up from about 1% of cases at one point in December, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It’s especially prevalent in the Northeast, now accounting for more than 70% of the cases in that region.
It’s spreading across the globe, too. Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, technical lead of the World Health Organization, has called XBB.1.5 is “the most transmissible subvariant that has been detected yet.”
Ashish Jha, MD, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, tweeted a few days ago that the spread of XBB.1.5 is “stunning” but cautioned that it’s unclear if the symptoms of infection will be more severe than for previous variants.
“Whether we’ll have an XBB.1.5 wave (and if yes, how big) will depend on many factors including immunity of the population, people’s actions, etc.,” he tweeted.
He urged people to get up to date on their boosters, wear a snug-fitting mask, and avoid crowded indoor spaces. He noted that people who haven’t been infected recently or haven’t gotten the bivalent booster likely have little protection against infection.
The symptoms for XBB.1.5 appear to be the same as for other versions of COVID-19. However, it’s less common for people infected with XBB.1.5 to report losing their sense of taste and smell, USA Today reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.