User login
How to Advise Medical Students Interested in Dermatology: A Survey of Academic Dermatology Mentors
Dermatology remains one of the most competitive specialties in medicine. In 2022, there were 851 applicants (613 doctor of medicine seniors, 85 doctor of osteopathic medicine seniors) for 492 postgraduate year (PGY) 2 positions.1 During the 2022 application season, the average matched dermatology candidate had 7.2 research experiences; 20.9 abstracts, presentations, or publications; 11 volunteer experiences; and a US Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 2 Clinical Knowledge score of 257.1 With hopes of matching into such a competitive field, students often seek advice from academic dermatology mentors. Such advice may substantially differ based on each mentor and may or may not be evidence based.
We sought to analyze the range of advice given to medical students applying to dermatology residency programs via a survey to members of the Association of Professors of Dermatology (APD) with the intent to help applicants and mentors understand how letters of intent, letters of recommendation (LORs), and Electronic Residency Application Service (ERAS) supplemental applications are used by dermatology programs nationwide.
Methods
The study was reviewed by The Ohio State University institutional review board and was deemed exempt. A branching-logic survey with common questions from medical students while applying to dermatology residency programs (Table) was sent to all members of APD through the email listserve. Study data were collected and managed using REDCap electronic data capture tools hosted at The Ohio State University (Columbus, Ohio) to ensure data security.

The survey was distributed from August 28, 2022, to September 12, 2022. A total of 101 surveys were returned from 646 listserve members (15.6%). Given the branching-logic questions, differing numbers of responses were collected for each question. Descriptive statistics were utilized to analyze and report the results.
Results
Residency Program Number—Members of the APD were asked if they recommend students apply to a certain number of programs, and if so, how many programs. Of members who responded, 62.2% (61/98) either always (22.4% [22/98]) or sometimes (40.2% [39/97]) suggested students apply to a certain number of programs. When mentors made a recommendation, 54.1% (33/61) recommended applying to 59 or fewer programs, with only 9.8% (6/61) recommending students apply to 80 or more programs.
Gap Year—We queried mentors about their recommendations for a research gap year and asked which applicants should pursue this extra year. Our survey found that 74.5% of mentors (73/98) almost always (4.1% [4/98]) or sometimes (70.4% [69/98]) recommended a research gap year, most commonly for those applicants with a strong research interest (71.8% [51/71]). Other reasons mentors recommended a dedicated research year during medical school included low USMLE Step scores (50.7% [36/71]), low grades (45.1% [32/71]), little research (46.5% [33/71]), and no home program (43.7% [31/71]).
Internship Choices—Our survey results indicated that nearly two-thirds (63.3% [62/98]) of mentors did not give applicants a recommendation on type of internship (PGY-1). If a recommendation was given, academic dermatologists more commonly recommended an internal medicine preliminary year (29.6% [29/98]) over a transitional year (7.1% [7/98]).
Communication of Interest Via a Letter of Intent—We asked mentors if they recommended applicants send a letter of intent and conversely if receiving a letter of intent impacted their rank list. Nearly half (48.5% [47/97]) of mentors indicated they did not recommend sending a letter of intent, with only 15.5% (15/97) of mentors regularly recommending this practice. Additionally, 75.8% of mentors indicated that a letter of intent never (42.1% [40/95]) or rarely (33.7% [32/95]) impacted their rank list.
Rotation Choices—We queried mentors if they recommended students complete away rotations, and if so, how many rotations did they recommend. We found that 85.9% (85/99) of mentors recommended students complete an away rotation; 63.1% (53/84) of them recommended performing 2 away rotations, and 14.3% (12/84) of respondents recommended students complete 3 away rotations. More than a quarter of mentors (27.1% [23/85]) indicated their home medical schools limited the number of away rotations a medical student could complete in any 1 specialty, and 42.4% (36/85) of respondents were unsure if such a limitation existed.
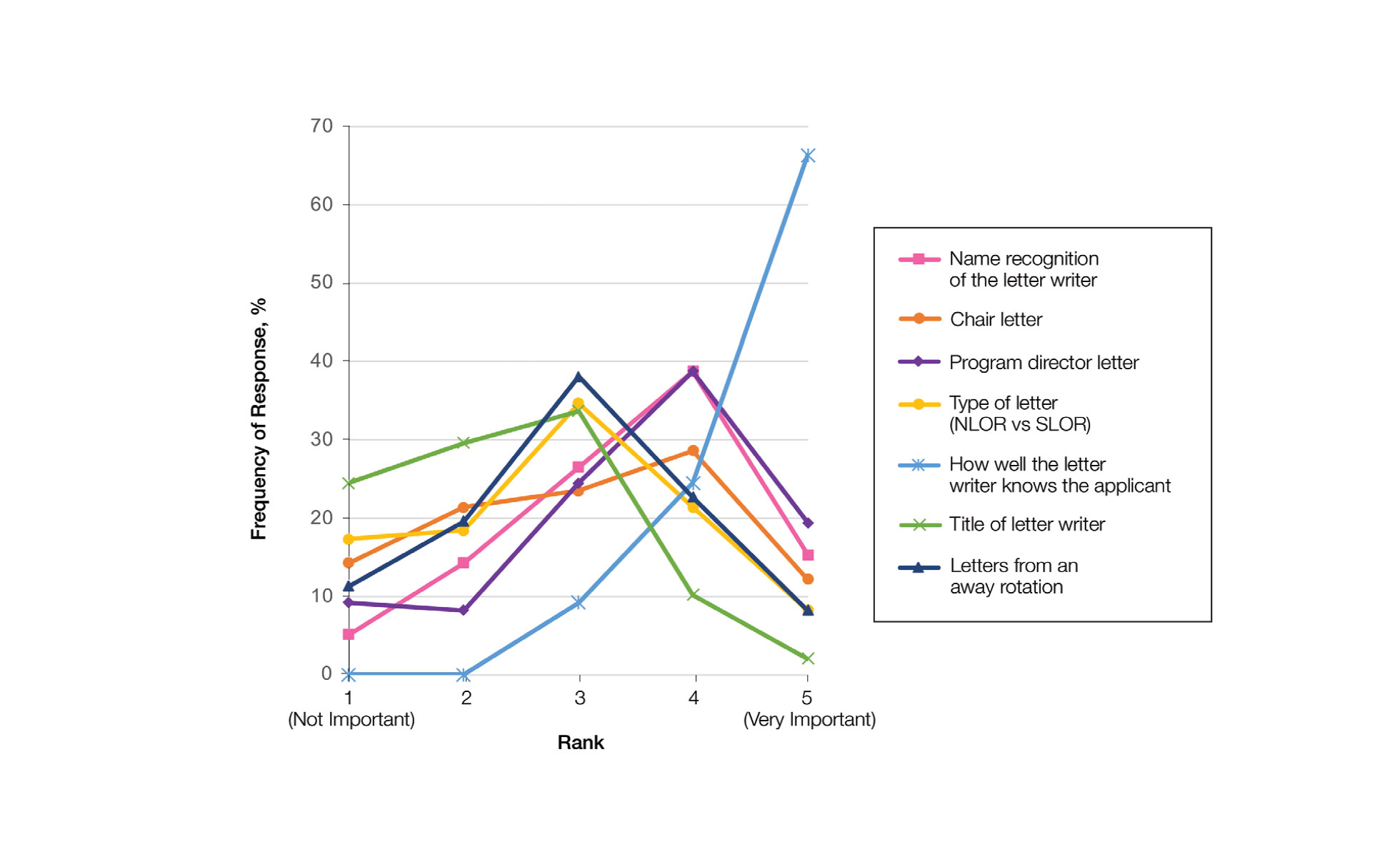
Letters of Recommendation—Our survey asked respondents to rank various factors on a 5-point scale (1=not important; 5=very important) when deciding who should write the students’ LORs. Mentors indicated that the most important factor for letter-writer selection was how well the letter writer knows the applicant, with 90.8% (89/98) of mentors rating the importance of this quality as a 4 or 5 (Figure). More than half of respondents rated the name recognition of the letter writer and program director letter as a 4 or 5 in importance (54.1% [53/98] and 58.2% [57/98], respectively). Type of letter (standardized vs nonstandardized), title of letter writer, letters from an away rotation, and chair letter scored lower, with fewer than half of mentors rating these as a 4 or 5 in importance.
Supplemental Application—When asked about the 2022 application cycle, respondents of our survey reported that the supplemental application was overall more important in deciding which applicants to interview vs which to rank highly. Prior experiences were important (ranked 4 or 5) for 58.8% (57/97) of respondents in choosing applicants to interview, and 49.4% (48/97) of respondents thought prior experiences were important for ranking. Similarly, 34.0% (33/97) of mentors indicated geographic preference was important (ranked 4 or 5) for interview compared with only 23.8% (23/97) for ranking. Finally, 57.7% (56/97) of our survey respondents denoted that program signals were important or very important in choosing which applicants to interview, while 32.0% (31/97) indicated that program signals were important in ranking applicants.
Comment
Residency Programs: Which Ones, and How Many?—The number of applications for dermatology residency programs has increased 33.9% from 2010 to 2019.2 The American Association of Medical Colleges Apply Smart data from 2013 to 2017 indicate that dermatology applicants arrive at a point of diminishing return between 37 and 62 applications, with variation within that range based on USMLE Step 1 score,3 and our data support this with nearly two-thirds of dermatology advisors recommending students apply within this range. Despite this data, dermatology residency applicants applied to more programs over the last decade (64.8 vs 77.0),2 likely to maximize their chance of matching.
Research Gap Years During Medical School—Prior research has shown that nearly half of faculty indicated that a research year during medical school can distinguish similar applicants, and close to 25% of applicants completed a research gap year.4,5 However, available data indicate that taking a research gap year has no effect on match rate or number of interview invites but does correlate with match rates at the highest ranked dermatology residency programs.6-8
Our data indicate that the most commonly recommended reason for a research gap year was an applicants’ strong interest in research. However, nearly half of dermatology mentors recommended research years during medical school for reasons other than an interest in research. As research gap years increase in popularity, future research is needed to confirm the consequence of this additional year and which applicants, if any, will benefit from such a year.
Preferences for Intern Year—Prior research suggests that dermatology residency program directors favor PGY-1 preliminary medicine internships because of the rigor of training.9,10 Our data continue to show a preference for internal medicine preliminary years over transitional years. However, given nearly two-thirds of dermatology mentors do not give applicants any recommendations on PGY-1 year, this preference may be fading.
Letters of Intent Not Recommended—Research in 2022 found that 78.8% of dermatology applicants sent a letter of intent communicating a plan to rank that program number 1, with nearly 13% sending such a letter to more than 1 program.11 With nearly half of mentors in our survey actively discouraging this process and more than 75% of mentors not utilizing this letter, the APD issued a brief statement on the 2022-2023 application cycle stating, “Post-interview communication of preference—including ‘letters of intent’ and thank you letters—should not be sent to programs. These types of communication are typically not used by residency programs in decision-making and lead to downstream pressures on applicants.”12
Away Rotations—Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, data demonstrated that nearly one-third of dermatology applicants (29%) matched at their home institution, and nearly one-fifth (18%) matched where they completed an away rotation.13 In-person away rotations were eliminated in 2020 and restricted to 1 away rotation in 2021. Restrictions regarding away rotations were removed in 2022. Our data indicate that dermatology mentors strongly supported an away rotation, with more than half of them recommending at least 2 away rotations.
Further research is needed to determine the effect numerous away rotations have on minimizing students’ exposure to other specialties outside their chosen field. Additionally, further studies are needed to determine the impact away rotations have on economically disadvantaged students, students without home programs, and students with families. In an effort to standardize the number of away rotations, the APD issued a statement for the 2023-2024 application cycle indicating that dermatology applicants should limit away rotations to 2 in-person electives. Students without a home dermatology program could consider completing up to 3 electives.14
Who Should Write LORs?—Research in 2014 demonstrated that LORs were very important in determining applicants to interview, with a strong preference for LORs from academic dermatologists and colleagues.15 Our data strongly indicated applicants should predominantly ask for letters from writers who know them well. The majority of mentors did not give value to the rank of the letter writer (eg, assistant professor, associate professor, professor), type of letter, chair letters, or letters from an away rotation. These data may help alleviate stress many students feel as they search for letter writers.
How is the Supplemental Application Used?—In 2022, the ERAS supplemental application was introduced, which allowed applicants to detail 5 meaningful experiences, describe impactful life challenges, and indicate preferences for geographic region. Dermatology residency applicants also were able to choose 3 residency programs to signal interest in that program. Our data found that the supplemental application was utilized predominantly to select applicants to interview, which is in line with the Association of American Medical Colleges’ and APD guidelines indicating that this tool is solely meant to assist with application review.16 Further research and data will hopefully inform approaches to best utilize the ERAS supplemental application data.
Limitations—Our data were limited by response rate and sample size, as only academic dermatologists belonging to the APD were queried. Additionally, we did not track personal information of the mentors, so more than 1 mentor may have responded from a single institution, making it possible that our data may not be broadly applicable to all institutions.
Conclusion
Although there is no algorithmic method of advising medical students who are interested in dermatology, our survey data help to describe the range of advice currently given to students, which can improve and guide future recommendations. Additionally, some of our data demonstrate a discrepancy between mentor advice and current medical student practice for the number of applications and use of a letter of intent. We hope our data will assist academic dermatology mentors in the provision of advice to mentees as well as inform organizations seeking to create standards and official recommendations regarding aspects of the application process.
- National Resident Matching Program. Results and Data: 2022 Main Residency Match. May 2022. Accessed February 21, 2023. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/2022-Main-Match-Results-and-Data_Final.pdf
- Secrest AM, Coman GC, Swink JM, et al. Limiting residency applications to dermatology benefits nearly everyone. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:30-32.
- Apply smart for residency. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed February 21, 2023. https://students-residents.aamc.org/apply-smart-residency
- Shamloul N, Grandhi R, Hossler E. Perceived importance of dermatology research fellowships. Presented at: Dermatology Teachers Exchange Group; October 3, 2020.
- Runge M, Jairath NK, Renati S, et al. Pursuit of a research year or dual degree by dermatology residency applicants: a cross-sectional study. Cutis. 2022;109:E12-E13.
- Costello CM, Harvey JA, Besch-Stokes JG, et al. The role of race and ethnicity in the dermatology applicant match process. J Natl Med Assoc. 2022;113:666-670.
- Costello CM, Harvey JA, Besch-Stokes JG, et al. The role research gap years play in a successful dermatology match. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:226-230.
- Ramachandran V, Nguyen HY, Dao H Jr. Does it match? analyzing self-reported online dermatology match data to charting outcomes in the Match. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26:13030/qt4604h1w4.
- Hopkins C, Jalali O, Guffey D, et al. A survey of dermatology residents and program directors assessing the transition to dermatology residency. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Center). 2021;34:59-62.
- Stratman EJ, Ness RM. Factors associated with successful matching to dermatology residency programs by reapplicants and other applicants who previously graduated from medical school. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:196-202.
- Brumfiel CM, Jefferson IS, Rinderknecht FA, et al. Current perspectives of and potential reforms to the dermatology residency application process: a nationwide survey of program directors and applicants. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:595-601.
- Association of Professors of Dermatology. Residency Program Directors Section. Updated Information Regarding the 2022-2023 Application Cycle. Updated October 18, 2022. Accessed February 24, 2023. https://www.dermatologyprofessors.org/files/APD%20statement%20on%202022-2023%20application%20cycle_updated%20Oct.pdf
- Narang J, Morgan F, Eversman A, et al. Trends in geographic and home program preferences in the dermatology residency match: a retrospective cohort analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:645-647.
- Association of Professors of Dermatology Residency Program Directors Section. Recommendations Regarding Away Electives. Updated December 14, 2022. Accessed February 24, 2022. https://www.dermatologyprofessors.org/files/APD%20recommendations%20on%20away%20rotations%202023-2024.pdf
- Kaffenberger BH, Kaffenberger JA, Zirwas MJ. Academic dermatologists’ views on the value of residency letters of recommendation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:395-396.
- Supplemental ERAS Application: Guide for Residency Program. Association of American Medical Colleges; June 2022.
Dermatology remains one of the most competitive specialties in medicine. In 2022, there were 851 applicants (613 doctor of medicine seniors, 85 doctor of osteopathic medicine seniors) for 492 postgraduate year (PGY) 2 positions.1 During the 2022 application season, the average matched dermatology candidate had 7.2 research experiences; 20.9 abstracts, presentations, or publications; 11 volunteer experiences; and a US Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 2 Clinical Knowledge score of 257.1 With hopes of matching into such a competitive field, students often seek advice from academic dermatology mentors. Such advice may substantially differ based on each mentor and may or may not be evidence based.
We sought to analyze the range of advice given to medical students applying to dermatology residency programs via a survey to members of the Association of Professors of Dermatology (APD) with the intent to help applicants and mentors understand how letters of intent, letters of recommendation (LORs), and Electronic Residency Application Service (ERAS) supplemental applications are used by dermatology programs nationwide.
Methods
The study was reviewed by The Ohio State University institutional review board and was deemed exempt. A branching-logic survey with common questions from medical students while applying to dermatology residency programs (Table) was sent to all members of APD through the email listserve. Study data were collected and managed using REDCap electronic data capture tools hosted at The Ohio State University (Columbus, Ohio) to ensure data security.

The survey was distributed from August 28, 2022, to September 12, 2022. A total of 101 surveys were returned from 646 listserve members (15.6%). Given the branching-logic questions, differing numbers of responses were collected for each question. Descriptive statistics were utilized to analyze and report the results.
Results
Residency Program Number—Members of the APD were asked if they recommend students apply to a certain number of programs, and if so, how many programs. Of members who responded, 62.2% (61/98) either always (22.4% [22/98]) or sometimes (40.2% [39/97]) suggested students apply to a certain number of programs. When mentors made a recommendation, 54.1% (33/61) recommended applying to 59 or fewer programs, with only 9.8% (6/61) recommending students apply to 80 or more programs.
Gap Year—We queried mentors about their recommendations for a research gap year and asked which applicants should pursue this extra year. Our survey found that 74.5% of mentors (73/98) almost always (4.1% [4/98]) or sometimes (70.4% [69/98]) recommended a research gap year, most commonly for those applicants with a strong research interest (71.8% [51/71]). Other reasons mentors recommended a dedicated research year during medical school included low USMLE Step scores (50.7% [36/71]), low grades (45.1% [32/71]), little research (46.5% [33/71]), and no home program (43.7% [31/71]).
Internship Choices—Our survey results indicated that nearly two-thirds (63.3% [62/98]) of mentors did not give applicants a recommendation on type of internship (PGY-1). If a recommendation was given, academic dermatologists more commonly recommended an internal medicine preliminary year (29.6% [29/98]) over a transitional year (7.1% [7/98]).
Communication of Interest Via a Letter of Intent—We asked mentors if they recommended applicants send a letter of intent and conversely if receiving a letter of intent impacted their rank list. Nearly half (48.5% [47/97]) of mentors indicated they did not recommend sending a letter of intent, with only 15.5% (15/97) of mentors regularly recommending this practice. Additionally, 75.8% of mentors indicated that a letter of intent never (42.1% [40/95]) or rarely (33.7% [32/95]) impacted their rank list.
Rotation Choices—We queried mentors if they recommended students complete away rotations, and if so, how many rotations did they recommend. We found that 85.9% (85/99) of mentors recommended students complete an away rotation; 63.1% (53/84) of them recommended performing 2 away rotations, and 14.3% (12/84) of respondents recommended students complete 3 away rotations. More than a quarter of mentors (27.1% [23/85]) indicated their home medical schools limited the number of away rotations a medical student could complete in any 1 specialty, and 42.4% (36/85) of respondents were unsure if such a limitation existed.
Letters of Recommendation—Our survey asked respondents to rank various factors on a 5-point scale (1=not important; 5=very important) when deciding who should write the students’ LORs. Mentors indicated that the most important factor for letter-writer selection was how well the letter writer knows the applicant, with 90.8% (89/98) of mentors rating the importance of this quality as a 4 or 5 (Figure). More than half of respondents rated the name recognition of the letter writer and program director letter as a 4 or 5 in importance (54.1% [53/98] and 58.2% [57/98], respectively). Type of letter (standardized vs nonstandardized), title of letter writer, letters from an away rotation, and chair letter scored lower, with fewer than half of mentors rating these as a 4 or 5 in importance.

Supplemental Application—When asked about the 2022 application cycle, respondents of our survey reported that the supplemental application was overall more important in deciding which applicants to interview vs which to rank highly. Prior experiences were important (ranked 4 or 5) for 58.8% (57/97) of respondents in choosing applicants to interview, and 49.4% (48/97) of respondents thought prior experiences were important for ranking. Similarly, 34.0% (33/97) of mentors indicated geographic preference was important (ranked 4 or 5) for interview compared with only 23.8% (23/97) for ranking. Finally, 57.7% (56/97) of our survey respondents denoted that program signals were important or very important in choosing which applicants to interview, while 32.0% (31/97) indicated that program signals were important in ranking applicants.
Comment
Residency Programs: Which Ones, and How Many?—The number of applications for dermatology residency programs has increased 33.9% from 2010 to 2019.2 The American Association of Medical Colleges Apply Smart data from 2013 to 2017 indicate that dermatology applicants arrive at a point of diminishing return between 37 and 62 applications, with variation within that range based on USMLE Step 1 score,3 and our data support this with nearly two-thirds of dermatology advisors recommending students apply within this range. Despite this data, dermatology residency applicants applied to more programs over the last decade (64.8 vs 77.0),2 likely to maximize their chance of matching.
Research Gap Years During Medical School—Prior research has shown that nearly half of faculty indicated that a research year during medical school can distinguish similar applicants, and close to 25% of applicants completed a research gap year.4,5 However, available data indicate that taking a research gap year has no effect on match rate or number of interview invites but does correlate with match rates at the highest ranked dermatology residency programs.6-8
Our data indicate that the most commonly recommended reason for a research gap year was an applicants’ strong interest in research. However, nearly half of dermatology mentors recommended research years during medical school for reasons other than an interest in research. As research gap years increase in popularity, future research is needed to confirm the consequence of this additional year and which applicants, if any, will benefit from such a year.
Preferences for Intern Year—Prior research suggests that dermatology residency program directors favor PGY-1 preliminary medicine internships because of the rigor of training.9,10 Our data continue to show a preference for internal medicine preliminary years over transitional years. However, given nearly two-thirds of dermatology mentors do not give applicants any recommendations on PGY-1 year, this preference may be fading.
Letters of Intent Not Recommended—Research in 2022 found that 78.8% of dermatology applicants sent a letter of intent communicating a plan to rank that program number 1, with nearly 13% sending such a letter to more than 1 program.11 With nearly half of mentors in our survey actively discouraging this process and more than 75% of mentors not utilizing this letter, the APD issued a brief statement on the 2022-2023 application cycle stating, “Post-interview communication of preference—including ‘letters of intent’ and thank you letters—should not be sent to programs. These types of communication are typically not used by residency programs in decision-making and lead to downstream pressures on applicants.”12
Away Rotations—Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, data demonstrated that nearly one-third of dermatology applicants (29%) matched at their home institution, and nearly one-fifth (18%) matched where they completed an away rotation.13 In-person away rotations were eliminated in 2020 and restricted to 1 away rotation in 2021. Restrictions regarding away rotations were removed in 2022. Our data indicate that dermatology mentors strongly supported an away rotation, with more than half of them recommending at least 2 away rotations.
Further research is needed to determine the effect numerous away rotations have on minimizing students’ exposure to other specialties outside their chosen field. Additionally, further studies are needed to determine the impact away rotations have on economically disadvantaged students, students without home programs, and students with families. In an effort to standardize the number of away rotations, the APD issued a statement for the 2023-2024 application cycle indicating that dermatology applicants should limit away rotations to 2 in-person electives. Students without a home dermatology program could consider completing up to 3 electives.14
Who Should Write LORs?—Research in 2014 demonstrated that LORs were very important in determining applicants to interview, with a strong preference for LORs from academic dermatologists and colleagues.15 Our data strongly indicated applicants should predominantly ask for letters from writers who know them well. The majority of mentors did not give value to the rank of the letter writer (eg, assistant professor, associate professor, professor), type of letter, chair letters, or letters from an away rotation. These data may help alleviate stress many students feel as they search for letter writers.
How is the Supplemental Application Used?—In 2022, the ERAS supplemental application was introduced, which allowed applicants to detail 5 meaningful experiences, describe impactful life challenges, and indicate preferences for geographic region. Dermatology residency applicants also were able to choose 3 residency programs to signal interest in that program. Our data found that the supplemental application was utilized predominantly to select applicants to interview, which is in line with the Association of American Medical Colleges’ and APD guidelines indicating that this tool is solely meant to assist with application review.16 Further research and data will hopefully inform approaches to best utilize the ERAS supplemental application data.
Limitations—Our data were limited by response rate and sample size, as only academic dermatologists belonging to the APD were queried. Additionally, we did not track personal information of the mentors, so more than 1 mentor may have responded from a single institution, making it possible that our data may not be broadly applicable to all institutions.
Conclusion
Although there is no algorithmic method of advising medical students who are interested in dermatology, our survey data help to describe the range of advice currently given to students, which can improve and guide future recommendations. Additionally, some of our data demonstrate a discrepancy between mentor advice and current medical student practice for the number of applications and use of a letter of intent. We hope our data will assist academic dermatology mentors in the provision of advice to mentees as well as inform organizations seeking to create standards and official recommendations regarding aspects of the application process.
Dermatology remains one of the most competitive specialties in medicine. In 2022, there were 851 applicants (613 doctor of medicine seniors, 85 doctor of osteopathic medicine seniors) for 492 postgraduate year (PGY) 2 positions.1 During the 2022 application season, the average matched dermatology candidate had 7.2 research experiences; 20.9 abstracts, presentations, or publications; 11 volunteer experiences; and a US Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 2 Clinical Knowledge score of 257.1 With hopes of matching into such a competitive field, students often seek advice from academic dermatology mentors. Such advice may substantially differ based on each mentor and may or may not be evidence based.
We sought to analyze the range of advice given to medical students applying to dermatology residency programs via a survey to members of the Association of Professors of Dermatology (APD) with the intent to help applicants and mentors understand how letters of intent, letters of recommendation (LORs), and Electronic Residency Application Service (ERAS) supplemental applications are used by dermatology programs nationwide.
Methods
The study was reviewed by The Ohio State University institutional review board and was deemed exempt. A branching-logic survey with common questions from medical students while applying to dermatology residency programs (Table) was sent to all members of APD through the email listserve. Study data were collected and managed using REDCap electronic data capture tools hosted at The Ohio State University (Columbus, Ohio) to ensure data security.

The survey was distributed from August 28, 2022, to September 12, 2022. A total of 101 surveys were returned from 646 listserve members (15.6%). Given the branching-logic questions, differing numbers of responses were collected for each question. Descriptive statistics were utilized to analyze and report the results.
Results
Residency Program Number—Members of the APD were asked if they recommend students apply to a certain number of programs, and if so, how many programs. Of members who responded, 62.2% (61/98) either always (22.4% [22/98]) or sometimes (40.2% [39/97]) suggested students apply to a certain number of programs. When mentors made a recommendation, 54.1% (33/61) recommended applying to 59 or fewer programs, with only 9.8% (6/61) recommending students apply to 80 or more programs.
Gap Year—We queried mentors about their recommendations for a research gap year and asked which applicants should pursue this extra year. Our survey found that 74.5% of mentors (73/98) almost always (4.1% [4/98]) or sometimes (70.4% [69/98]) recommended a research gap year, most commonly for those applicants with a strong research interest (71.8% [51/71]). Other reasons mentors recommended a dedicated research year during medical school included low USMLE Step scores (50.7% [36/71]), low grades (45.1% [32/71]), little research (46.5% [33/71]), and no home program (43.7% [31/71]).
Internship Choices—Our survey results indicated that nearly two-thirds (63.3% [62/98]) of mentors did not give applicants a recommendation on type of internship (PGY-1). If a recommendation was given, academic dermatologists more commonly recommended an internal medicine preliminary year (29.6% [29/98]) over a transitional year (7.1% [7/98]).
Communication of Interest Via a Letter of Intent—We asked mentors if they recommended applicants send a letter of intent and conversely if receiving a letter of intent impacted their rank list. Nearly half (48.5% [47/97]) of mentors indicated they did not recommend sending a letter of intent, with only 15.5% (15/97) of mentors regularly recommending this practice. Additionally, 75.8% of mentors indicated that a letter of intent never (42.1% [40/95]) or rarely (33.7% [32/95]) impacted their rank list.
Rotation Choices—We queried mentors if they recommended students complete away rotations, and if so, how many rotations did they recommend. We found that 85.9% (85/99) of mentors recommended students complete an away rotation; 63.1% (53/84) of them recommended performing 2 away rotations, and 14.3% (12/84) of respondents recommended students complete 3 away rotations. More than a quarter of mentors (27.1% [23/85]) indicated their home medical schools limited the number of away rotations a medical student could complete in any 1 specialty, and 42.4% (36/85) of respondents were unsure if such a limitation existed.
Letters of Recommendation—Our survey asked respondents to rank various factors on a 5-point scale (1=not important; 5=very important) when deciding who should write the students’ LORs. Mentors indicated that the most important factor for letter-writer selection was how well the letter writer knows the applicant, with 90.8% (89/98) of mentors rating the importance of this quality as a 4 or 5 (Figure). More than half of respondents rated the name recognition of the letter writer and program director letter as a 4 or 5 in importance (54.1% [53/98] and 58.2% [57/98], respectively). Type of letter (standardized vs nonstandardized), title of letter writer, letters from an away rotation, and chair letter scored lower, with fewer than half of mentors rating these as a 4 or 5 in importance.

Supplemental Application—When asked about the 2022 application cycle, respondents of our survey reported that the supplemental application was overall more important in deciding which applicants to interview vs which to rank highly. Prior experiences were important (ranked 4 or 5) for 58.8% (57/97) of respondents in choosing applicants to interview, and 49.4% (48/97) of respondents thought prior experiences were important for ranking. Similarly, 34.0% (33/97) of mentors indicated geographic preference was important (ranked 4 or 5) for interview compared with only 23.8% (23/97) for ranking. Finally, 57.7% (56/97) of our survey respondents denoted that program signals were important or very important in choosing which applicants to interview, while 32.0% (31/97) indicated that program signals were important in ranking applicants.
Comment
Residency Programs: Which Ones, and How Many?—The number of applications for dermatology residency programs has increased 33.9% from 2010 to 2019.2 The American Association of Medical Colleges Apply Smart data from 2013 to 2017 indicate that dermatology applicants arrive at a point of diminishing return between 37 and 62 applications, with variation within that range based on USMLE Step 1 score,3 and our data support this with nearly two-thirds of dermatology advisors recommending students apply within this range. Despite this data, dermatology residency applicants applied to more programs over the last decade (64.8 vs 77.0),2 likely to maximize their chance of matching.
Research Gap Years During Medical School—Prior research has shown that nearly half of faculty indicated that a research year during medical school can distinguish similar applicants, and close to 25% of applicants completed a research gap year.4,5 However, available data indicate that taking a research gap year has no effect on match rate or number of interview invites but does correlate with match rates at the highest ranked dermatology residency programs.6-8
Our data indicate that the most commonly recommended reason for a research gap year was an applicants’ strong interest in research. However, nearly half of dermatology mentors recommended research years during medical school for reasons other than an interest in research. As research gap years increase in popularity, future research is needed to confirm the consequence of this additional year and which applicants, if any, will benefit from such a year.
Preferences for Intern Year—Prior research suggests that dermatology residency program directors favor PGY-1 preliminary medicine internships because of the rigor of training.9,10 Our data continue to show a preference for internal medicine preliminary years over transitional years. However, given nearly two-thirds of dermatology mentors do not give applicants any recommendations on PGY-1 year, this preference may be fading.
Letters of Intent Not Recommended—Research in 2022 found that 78.8% of dermatology applicants sent a letter of intent communicating a plan to rank that program number 1, with nearly 13% sending such a letter to more than 1 program.11 With nearly half of mentors in our survey actively discouraging this process and more than 75% of mentors not utilizing this letter, the APD issued a brief statement on the 2022-2023 application cycle stating, “Post-interview communication of preference—including ‘letters of intent’ and thank you letters—should not be sent to programs. These types of communication are typically not used by residency programs in decision-making and lead to downstream pressures on applicants.”12
Away Rotations—Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, data demonstrated that nearly one-third of dermatology applicants (29%) matched at their home institution, and nearly one-fifth (18%) matched where they completed an away rotation.13 In-person away rotations were eliminated in 2020 and restricted to 1 away rotation in 2021. Restrictions regarding away rotations were removed in 2022. Our data indicate that dermatology mentors strongly supported an away rotation, with more than half of them recommending at least 2 away rotations.
Further research is needed to determine the effect numerous away rotations have on minimizing students’ exposure to other specialties outside their chosen field. Additionally, further studies are needed to determine the impact away rotations have on economically disadvantaged students, students without home programs, and students with families. In an effort to standardize the number of away rotations, the APD issued a statement for the 2023-2024 application cycle indicating that dermatology applicants should limit away rotations to 2 in-person electives. Students without a home dermatology program could consider completing up to 3 electives.14
Who Should Write LORs?—Research in 2014 demonstrated that LORs were very important in determining applicants to interview, with a strong preference for LORs from academic dermatologists and colleagues.15 Our data strongly indicated applicants should predominantly ask for letters from writers who know them well. The majority of mentors did not give value to the rank of the letter writer (eg, assistant professor, associate professor, professor), type of letter, chair letters, or letters from an away rotation. These data may help alleviate stress many students feel as they search for letter writers.
How is the Supplemental Application Used?—In 2022, the ERAS supplemental application was introduced, which allowed applicants to detail 5 meaningful experiences, describe impactful life challenges, and indicate preferences for geographic region. Dermatology residency applicants also were able to choose 3 residency programs to signal interest in that program. Our data found that the supplemental application was utilized predominantly to select applicants to interview, which is in line with the Association of American Medical Colleges’ and APD guidelines indicating that this tool is solely meant to assist with application review.16 Further research and data will hopefully inform approaches to best utilize the ERAS supplemental application data.
Limitations—Our data were limited by response rate and sample size, as only academic dermatologists belonging to the APD were queried. Additionally, we did not track personal information of the mentors, so more than 1 mentor may have responded from a single institution, making it possible that our data may not be broadly applicable to all institutions.
Conclusion
Although there is no algorithmic method of advising medical students who are interested in dermatology, our survey data help to describe the range of advice currently given to students, which can improve and guide future recommendations. Additionally, some of our data demonstrate a discrepancy between mentor advice and current medical student practice for the number of applications and use of a letter of intent. We hope our data will assist academic dermatology mentors in the provision of advice to mentees as well as inform organizations seeking to create standards and official recommendations regarding aspects of the application process.
- National Resident Matching Program. Results and Data: 2022 Main Residency Match. May 2022. Accessed February 21, 2023. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/2022-Main-Match-Results-and-Data_Final.pdf
- Secrest AM, Coman GC, Swink JM, et al. Limiting residency applications to dermatology benefits nearly everyone. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:30-32.
- Apply smart for residency. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed February 21, 2023. https://students-residents.aamc.org/apply-smart-residency
- Shamloul N, Grandhi R, Hossler E. Perceived importance of dermatology research fellowships. Presented at: Dermatology Teachers Exchange Group; October 3, 2020.
- Runge M, Jairath NK, Renati S, et al. Pursuit of a research year or dual degree by dermatology residency applicants: a cross-sectional study. Cutis. 2022;109:E12-E13.
- Costello CM, Harvey JA, Besch-Stokes JG, et al. The role of race and ethnicity in the dermatology applicant match process. J Natl Med Assoc. 2022;113:666-670.
- Costello CM, Harvey JA, Besch-Stokes JG, et al. The role research gap years play in a successful dermatology match. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:226-230.
- Ramachandran V, Nguyen HY, Dao H Jr. Does it match? analyzing self-reported online dermatology match data to charting outcomes in the Match. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26:13030/qt4604h1w4.
- Hopkins C, Jalali O, Guffey D, et al. A survey of dermatology residents and program directors assessing the transition to dermatology residency. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Center). 2021;34:59-62.
- Stratman EJ, Ness RM. Factors associated with successful matching to dermatology residency programs by reapplicants and other applicants who previously graduated from medical school. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:196-202.
- Brumfiel CM, Jefferson IS, Rinderknecht FA, et al. Current perspectives of and potential reforms to the dermatology residency application process: a nationwide survey of program directors and applicants. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:595-601.
- Association of Professors of Dermatology. Residency Program Directors Section. Updated Information Regarding the 2022-2023 Application Cycle. Updated October 18, 2022. Accessed February 24, 2023. https://www.dermatologyprofessors.org/files/APD%20statement%20on%202022-2023%20application%20cycle_updated%20Oct.pdf
- Narang J, Morgan F, Eversman A, et al. Trends in geographic and home program preferences in the dermatology residency match: a retrospective cohort analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:645-647.
- Association of Professors of Dermatology Residency Program Directors Section. Recommendations Regarding Away Electives. Updated December 14, 2022. Accessed February 24, 2022. https://www.dermatologyprofessors.org/files/APD%20recommendations%20on%20away%20rotations%202023-2024.pdf
- Kaffenberger BH, Kaffenberger JA, Zirwas MJ. Academic dermatologists’ views on the value of residency letters of recommendation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:395-396.
- Supplemental ERAS Application: Guide for Residency Program. Association of American Medical Colleges; June 2022.
- National Resident Matching Program. Results and Data: 2022 Main Residency Match. May 2022. Accessed February 21, 2023. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/2022-Main-Match-Results-and-Data_Final.pdf
- Secrest AM, Coman GC, Swink JM, et al. Limiting residency applications to dermatology benefits nearly everyone. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:30-32.
- Apply smart for residency. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed February 21, 2023. https://students-residents.aamc.org/apply-smart-residency
- Shamloul N, Grandhi R, Hossler E. Perceived importance of dermatology research fellowships. Presented at: Dermatology Teachers Exchange Group; October 3, 2020.
- Runge M, Jairath NK, Renati S, et al. Pursuit of a research year or dual degree by dermatology residency applicants: a cross-sectional study. Cutis. 2022;109:E12-E13.
- Costello CM, Harvey JA, Besch-Stokes JG, et al. The role of race and ethnicity in the dermatology applicant match process. J Natl Med Assoc. 2022;113:666-670.
- Costello CM, Harvey JA, Besch-Stokes JG, et al. The role research gap years play in a successful dermatology match. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:226-230.
- Ramachandran V, Nguyen HY, Dao H Jr. Does it match? analyzing self-reported online dermatology match data to charting outcomes in the Match. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26:13030/qt4604h1w4.
- Hopkins C, Jalali O, Guffey D, et al. A survey of dermatology residents and program directors assessing the transition to dermatology residency. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Center). 2021;34:59-62.
- Stratman EJ, Ness RM. Factors associated with successful matching to dermatology residency programs by reapplicants and other applicants who previously graduated from medical school. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:196-202.
- Brumfiel CM, Jefferson IS, Rinderknecht FA, et al. Current perspectives of and potential reforms to the dermatology residency application process: a nationwide survey of program directors and applicants. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:595-601.
- Association of Professors of Dermatology. Residency Program Directors Section. Updated Information Regarding the 2022-2023 Application Cycle. Updated October 18, 2022. Accessed February 24, 2023. https://www.dermatologyprofessors.org/files/APD%20statement%20on%202022-2023%20application%20cycle_updated%20Oct.pdf
- Narang J, Morgan F, Eversman A, et al. Trends in geographic and home program preferences in the dermatology residency match: a retrospective cohort analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:645-647.
- Association of Professors of Dermatology Residency Program Directors Section. Recommendations Regarding Away Electives. Updated December 14, 2022. Accessed February 24, 2022. https://www.dermatologyprofessors.org/files/APD%20recommendations%20on%20away%20rotations%202023-2024.pdf
- Kaffenberger BH, Kaffenberger JA, Zirwas MJ. Academic dermatologists’ views on the value of residency letters of recommendation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:395-396.
- Supplemental ERAS Application: Guide for Residency Program. Association of American Medical Colleges; June 2022.
Practice Points
- Dermatology mentors recommend students apply to 60 or fewer programs, with only a small percentage of faculty routinely recommending students apply to more than 80 programs.
- Dermatology mentors strongly recommend that students should not send a letter of intent to programs, as it rarely is used in the ranking process.
- Dermatology mentors encourage students to ask for letters of recommendation from writers who know them the best, irrespective of the letter writer’s rank or title. The type of letter (standardized vs nonstandardized), chair letter, or letters from an away rotation do not hold as much importance.
The Evidence Behind Topical Hair Loss Remedies on TikTok
Hair loss is an exceedingly common chief concern in outpatient dermatology clinics. An estimated 50% of males and females will experience androgenetic alopecia.1 Approximately 2% of new dermatology outpatient visits in the United States and the United Kingdom are for alopecia areata, the second most common type of hair loss.2 As access to dermatology appointments remains an issue with some studies citing wait times ranging from 2 to 25 days for a dermatologic consultation, the ease of accessibility of medical information on social media continues to grow,3 which leaves many of our patients turning to social media as a first-line source of information. As dermatology resident physicians, it is essential to be aware of popular dermatologic therapies on social media so that we may provide evidence-based opinions to our patients.
Remedies for Hair Loss on Social Media
Many trends on hair loss therapies found on TikTok focus on natural remedies that are produced by ingredients accessible to patients at home and over the counter, which may increase the appeal due to ease of treatment.
Rosemary Oil—The top trends in hair loss remedies I have come across are rosemary oil and rosemary water. Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) has been known to possess antimicrobial and antioxidant properties but also has shown enhancement of microcapillary perfusion, which could explain its role in the prevention of hair loss and aiding hair growth in a similar mechanism to minoxidil.4,5 Unlike many other natural hair loss remedies, there are randomized controlled trials that assess the efficacy of rosemary oil for the treatment of hair loss. In a 2015 study of 100 patients with androgenetic alopecia, there was no statistically significant difference in mean hair count measured by microphotographic assessment after 6 months of treatment in 2 groups treated with either minoxidil solution 2% or rosemary oil, and both groups experienced a significant increase in hair count at 6 months (P<.05) compared with baseline and 3 months.6 Additionally, essential oils, including a mixture of thyme, rosemary, lavender, and cedarwood oils for alopecia were superior to placebo carrier oils in a posttreatment photographic assessment of their efficacy.7
Rice Water—The use of rice water and rice bran extract is a common hair care practice in Asia. Rice bran extract preparations have been shown in vivo to increase the number of anagen hair follicles as well as the number of anagen-related molecules in the dermal papillae.8,9 However, there are limited clinical data to support the use of rice water for hair growth.10
Onion Juice—Sharquie and Al-Obaidi11 conducted a study comparing crude onion juice to tap water in 38 patients with alopecia areata. They found that onion juice produced hair regrowth in significantly more patients than tap water (P<.0001).11 The mechanism of crude onion juice in hair growth is unknown; however, the induction of irritant or allergic contact dermatitis to components in crude onion juice may stimulate antigenic competition.12
Garlic Gel—Garlic gel, which is in the genus Allium, produces organosulfur compounds that provide antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory benefits.12 Additionally, in a double-blind randomized controlled trial, garlic powder was shown to increase cutaneous capillary perfusion.5 One study in 40 patients with alopecia areata demonstrated garlic gel 5% added to betamethasone valerate cream 0.1% was statistically superior to betamethasone alone in stimulating terminal hair growth (P=.001).13
Limitations and Downsides to Hair Loss Remedies on Social Media
Social media continues to be a prominent source of medical information for our patients, but most sources of hair content on social media are not board-certified dermatologists. A recent review of alopecia-related content found only 4% and 10% of posts were created by medical professionals on Instagram and TikTok, respectively, making misinformation extremely likely.14 Natural hair loss remedies contrived by TikTok have little clinical evidence to support their claims. Few data are available that compare these treatments to gold-standard hair loss therapies. Additionally, while some of these agents may be beneficial, the lack of standardized dosing may counteract these benefits. For example, videos on rosemary water advise the viewer to boil fresh rosemary sprigs in water and apply the solution to the hair daily with a spray bottle or apply cloves of garlic directly to the scalp, as opposed to a measured and standardized percentage. Some preparations may even induce harm to patients. Over-the-counter oils with added fragrances and natural compounds in onion and garlic may cause contact dermatitis. Finally, by using these products, patients may delay consultation with a board-certified dermatologist, leading to delays in applying evidence-based therapies targeted to specific hair loss subtypes while also incurring unnecessary expenses for these preparations.
Final Thoughts
Hair loss affects a notable portion of the population and is a common chief concern in dermatology clinics. Misinformation on social media continues to grow in prevalence. It is important to be aware of the hair loss remedies that are commonly touted to patients online and the evidence behind them.
- Ho CH, Sood T, Zito PM. Androgenetic alopecia. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- McMichael AJ, Pearce DJ, Wasserman D, et al. Alopecia in the United States: outpatient utilization and common prescribing patterns. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57(2 suppl):S49-S51.
- Creadore A, Desai S, Li SJ, et al. Insurance acceptance, appointment wait time, and dermatologist access across practice types in the US. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:181-188. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.5173
- Bassino E, Gasparri F, Munaron L. Protective role of nutritional plants containing flavonoids in hair follicle disruption: a review. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:523. doi:10.3390/ijms21020523
- Ezekwe N, King M, Hollinger JC. The use of natural ingredients in the treatment of alopecias with an emphasis on central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia: a systematic review [published online August 1, 2020]. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13:23-27.
- Panahi Y, Taghizadeh M, Marzony ET, et al. Rosemary oil vs minoxidil 2% for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia: a randomized comparative trial. Skinmed. 2015;13:15-21.
- Hay IC, Jamieson M, Ormerod AD. Randomized trial of aromatherapy. successful treatment for alopecia areata. Arch Dermatol. 1998;134:1349-1352. doi:10.1001/archderm.134.11.1349
- Choi JS, Jeon MH, Moon WS, et al. In vivo hair growth-promoting effect of rice bran extract prepared by supercritical carbon dioxide fluid. Biol Pharm Bull. 2014;37:44-53. doi:10.1248/bpb.b13-00528
- Kim YM, Kwon SJ, Jang HJ, et al. Rice bran mineral extract increases the expression of anagen-related molecules in human dermal papilla through wnt/catenin pathway. Food Nutr Res. 2017;61:1412792. doi:10.1080/16546628.2017.1412792
- Hashemi K, Pham C, Sung C, et al. A systematic review: application of rice products for hair growth. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:177-185. doi:10.36849/jdd.6345
- Sharquie KE, Al-Obaidi HK. Onion juice (Allium cepa L.), a new topical treatment for alopecia areata. J Dermatol. 2002;29:343-346. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2002.tb00277.x
- Hosking AM, Juhasz M, Atanaskova Mesinkovska N. Complementary and alternative treatments for alopecia: a comprehensive review. Skin Appendage Disord. 2019;5:72-89. doi:10.1159/000492035
- Hajheydari Z, Jamshidi M, Akbari J, et al. Combination of topical garlic gel and betamethasone valerate cream in the treatment of localized alopecia areata: a double-blind randomized controlled study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2007;73:29-32. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.30648
- Laughter M, Anderson J, Kolla A, et al. An analysis of alopecia related content on Instagram and TikTok. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:1316-1321. doi:10.36849/JDD.6707
Hair loss is an exceedingly common chief concern in outpatient dermatology clinics. An estimated 50% of males and females will experience androgenetic alopecia.1 Approximately 2% of new dermatology outpatient visits in the United States and the United Kingdom are for alopecia areata, the second most common type of hair loss.2 As access to dermatology appointments remains an issue with some studies citing wait times ranging from 2 to 25 days for a dermatologic consultation, the ease of accessibility of medical information on social media continues to grow,3 which leaves many of our patients turning to social media as a first-line source of information. As dermatology resident physicians, it is essential to be aware of popular dermatologic therapies on social media so that we may provide evidence-based opinions to our patients.
Remedies for Hair Loss on Social Media
Many trends on hair loss therapies found on TikTok focus on natural remedies that are produced by ingredients accessible to patients at home and over the counter, which may increase the appeal due to ease of treatment.
Rosemary Oil—The top trends in hair loss remedies I have come across are rosemary oil and rosemary water. Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) has been known to possess antimicrobial and antioxidant properties but also has shown enhancement of microcapillary perfusion, which could explain its role in the prevention of hair loss and aiding hair growth in a similar mechanism to minoxidil.4,5 Unlike many other natural hair loss remedies, there are randomized controlled trials that assess the efficacy of rosemary oil for the treatment of hair loss. In a 2015 study of 100 patients with androgenetic alopecia, there was no statistically significant difference in mean hair count measured by microphotographic assessment after 6 months of treatment in 2 groups treated with either minoxidil solution 2% or rosemary oil, and both groups experienced a significant increase in hair count at 6 months (P<.05) compared with baseline and 3 months.6 Additionally, essential oils, including a mixture of thyme, rosemary, lavender, and cedarwood oils for alopecia were superior to placebo carrier oils in a posttreatment photographic assessment of their efficacy.7
Rice Water—The use of rice water and rice bran extract is a common hair care practice in Asia. Rice bran extract preparations have been shown in vivo to increase the number of anagen hair follicles as well as the number of anagen-related molecules in the dermal papillae.8,9 However, there are limited clinical data to support the use of rice water for hair growth.10
Onion Juice—Sharquie and Al-Obaidi11 conducted a study comparing crude onion juice to tap water in 38 patients with alopecia areata. They found that onion juice produced hair regrowth in significantly more patients than tap water (P<.0001).11 The mechanism of crude onion juice in hair growth is unknown; however, the induction of irritant or allergic contact dermatitis to components in crude onion juice may stimulate antigenic competition.12
Garlic Gel—Garlic gel, which is in the genus Allium, produces organosulfur compounds that provide antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory benefits.12 Additionally, in a double-blind randomized controlled trial, garlic powder was shown to increase cutaneous capillary perfusion.5 One study in 40 patients with alopecia areata demonstrated garlic gel 5% added to betamethasone valerate cream 0.1% was statistically superior to betamethasone alone in stimulating terminal hair growth (P=.001).13
Limitations and Downsides to Hair Loss Remedies on Social Media
Social media continues to be a prominent source of medical information for our patients, but most sources of hair content on social media are not board-certified dermatologists. A recent review of alopecia-related content found only 4% and 10% of posts were created by medical professionals on Instagram and TikTok, respectively, making misinformation extremely likely.14 Natural hair loss remedies contrived by TikTok have little clinical evidence to support their claims. Few data are available that compare these treatments to gold-standard hair loss therapies. Additionally, while some of these agents may be beneficial, the lack of standardized dosing may counteract these benefits. For example, videos on rosemary water advise the viewer to boil fresh rosemary sprigs in water and apply the solution to the hair daily with a spray bottle or apply cloves of garlic directly to the scalp, as opposed to a measured and standardized percentage. Some preparations may even induce harm to patients. Over-the-counter oils with added fragrances and natural compounds in onion and garlic may cause contact dermatitis. Finally, by using these products, patients may delay consultation with a board-certified dermatologist, leading to delays in applying evidence-based therapies targeted to specific hair loss subtypes while also incurring unnecessary expenses for these preparations.
Final Thoughts
Hair loss affects a notable portion of the population and is a common chief concern in dermatology clinics. Misinformation on social media continues to grow in prevalence. It is important to be aware of the hair loss remedies that are commonly touted to patients online and the evidence behind them.
Hair loss is an exceedingly common chief concern in outpatient dermatology clinics. An estimated 50% of males and females will experience androgenetic alopecia.1 Approximately 2% of new dermatology outpatient visits in the United States and the United Kingdom are for alopecia areata, the second most common type of hair loss.2 As access to dermatology appointments remains an issue with some studies citing wait times ranging from 2 to 25 days for a dermatologic consultation, the ease of accessibility of medical information on social media continues to grow,3 which leaves many of our patients turning to social media as a first-line source of information. As dermatology resident physicians, it is essential to be aware of popular dermatologic therapies on social media so that we may provide evidence-based opinions to our patients.
Remedies for Hair Loss on Social Media
Many trends on hair loss therapies found on TikTok focus on natural remedies that are produced by ingredients accessible to patients at home and over the counter, which may increase the appeal due to ease of treatment.
Rosemary Oil—The top trends in hair loss remedies I have come across are rosemary oil and rosemary water. Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) has been known to possess antimicrobial and antioxidant properties but also has shown enhancement of microcapillary perfusion, which could explain its role in the prevention of hair loss and aiding hair growth in a similar mechanism to minoxidil.4,5 Unlike many other natural hair loss remedies, there are randomized controlled trials that assess the efficacy of rosemary oil for the treatment of hair loss. In a 2015 study of 100 patients with androgenetic alopecia, there was no statistically significant difference in mean hair count measured by microphotographic assessment after 6 months of treatment in 2 groups treated with either minoxidil solution 2% or rosemary oil, and both groups experienced a significant increase in hair count at 6 months (P<.05) compared with baseline and 3 months.6 Additionally, essential oils, including a mixture of thyme, rosemary, lavender, and cedarwood oils for alopecia were superior to placebo carrier oils in a posttreatment photographic assessment of their efficacy.7
Rice Water—The use of rice water and rice bran extract is a common hair care practice in Asia. Rice bran extract preparations have been shown in vivo to increase the number of anagen hair follicles as well as the number of anagen-related molecules in the dermal papillae.8,9 However, there are limited clinical data to support the use of rice water for hair growth.10
Onion Juice—Sharquie and Al-Obaidi11 conducted a study comparing crude onion juice to tap water in 38 patients with alopecia areata. They found that onion juice produced hair regrowth in significantly more patients than tap water (P<.0001).11 The mechanism of crude onion juice in hair growth is unknown; however, the induction of irritant or allergic contact dermatitis to components in crude onion juice may stimulate antigenic competition.12
Garlic Gel—Garlic gel, which is in the genus Allium, produces organosulfur compounds that provide antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory benefits.12 Additionally, in a double-blind randomized controlled trial, garlic powder was shown to increase cutaneous capillary perfusion.5 One study in 40 patients with alopecia areata demonstrated garlic gel 5% added to betamethasone valerate cream 0.1% was statistically superior to betamethasone alone in stimulating terminal hair growth (P=.001).13
Limitations and Downsides to Hair Loss Remedies on Social Media
Social media continues to be a prominent source of medical information for our patients, but most sources of hair content on social media are not board-certified dermatologists. A recent review of alopecia-related content found only 4% and 10% of posts were created by medical professionals on Instagram and TikTok, respectively, making misinformation extremely likely.14 Natural hair loss remedies contrived by TikTok have little clinical evidence to support their claims. Few data are available that compare these treatments to gold-standard hair loss therapies. Additionally, while some of these agents may be beneficial, the lack of standardized dosing may counteract these benefits. For example, videos on rosemary water advise the viewer to boil fresh rosemary sprigs in water and apply the solution to the hair daily with a spray bottle or apply cloves of garlic directly to the scalp, as opposed to a measured and standardized percentage. Some preparations may even induce harm to patients. Over-the-counter oils with added fragrances and natural compounds in onion and garlic may cause contact dermatitis. Finally, by using these products, patients may delay consultation with a board-certified dermatologist, leading to delays in applying evidence-based therapies targeted to specific hair loss subtypes while also incurring unnecessary expenses for these preparations.
Final Thoughts
Hair loss affects a notable portion of the population and is a common chief concern in dermatology clinics. Misinformation on social media continues to grow in prevalence. It is important to be aware of the hair loss remedies that are commonly touted to patients online and the evidence behind them.
- Ho CH, Sood T, Zito PM. Androgenetic alopecia. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- McMichael AJ, Pearce DJ, Wasserman D, et al. Alopecia in the United States: outpatient utilization and common prescribing patterns. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57(2 suppl):S49-S51.
- Creadore A, Desai S, Li SJ, et al. Insurance acceptance, appointment wait time, and dermatologist access across practice types in the US. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:181-188. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.5173
- Bassino E, Gasparri F, Munaron L. Protective role of nutritional plants containing flavonoids in hair follicle disruption: a review. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:523. doi:10.3390/ijms21020523
- Ezekwe N, King M, Hollinger JC. The use of natural ingredients in the treatment of alopecias with an emphasis on central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia: a systematic review [published online August 1, 2020]. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13:23-27.
- Panahi Y, Taghizadeh M, Marzony ET, et al. Rosemary oil vs minoxidil 2% for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia: a randomized comparative trial. Skinmed. 2015;13:15-21.
- Hay IC, Jamieson M, Ormerod AD. Randomized trial of aromatherapy. successful treatment for alopecia areata. Arch Dermatol. 1998;134:1349-1352. doi:10.1001/archderm.134.11.1349
- Choi JS, Jeon MH, Moon WS, et al. In vivo hair growth-promoting effect of rice bran extract prepared by supercritical carbon dioxide fluid. Biol Pharm Bull. 2014;37:44-53. doi:10.1248/bpb.b13-00528
- Kim YM, Kwon SJ, Jang HJ, et al. Rice bran mineral extract increases the expression of anagen-related molecules in human dermal papilla through wnt/catenin pathway. Food Nutr Res. 2017;61:1412792. doi:10.1080/16546628.2017.1412792
- Hashemi K, Pham C, Sung C, et al. A systematic review: application of rice products for hair growth. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:177-185. doi:10.36849/jdd.6345
- Sharquie KE, Al-Obaidi HK. Onion juice (Allium cepa L.), a new topical treatment for alopecia areata. J Dermatol. 2002;29:343-346. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2002.tb00277.x
- Hosking AM, Juhasz M, Atanaskova Mesinkovska N. Complementary and alternative treatments for alopecia: a comprehensive review. Skin Appendage Disord. 2019;5:72-89. doi:10.1159/000492035
- Hajheydari Z, Jamshidi M, Akbari J, et al. Combination of topical garlic gel and betamethasone valerate cream in the treatment of localized alopecia areata: a double-blind randomized controlled study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2007;73:29-32. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.30648
- Laughter M, Anderson J, Kolla A, et al. An analysis of alopecia related content on Instagram and TikTok. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:1316-1321. doi:10.36849/JDD.6707
- Ho CH, Sood T, Zito PM. Androgenetic alopecia. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- McMichael AJ, Pearce DJ, Wasserman D, et al. Alopecia in the United States: outpatient utilization and common prescribing patterns. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57(2 suppl):S49-S51.
- Creadore A, Desai S, Li SJ, et al. Insurance acceptance, appointment wait time, and dermatologist access across practice types in the US. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:181-188. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.5173
- Bassino E, Gasparri F, Munaron L. Protective role of nutritional plants containing flavonoids in hair follicle disruption: a review. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:523. doi:10.3390/ijms21020523
- Ezekwe N, King M, Hollinger JC. The use of natural ingredients in the treatment of alopecias with an emphasis on central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia: a systematic review [published online August 1, 2020]. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13:23-27.
- Panahi Y, Taghizadeh M, Marzony ET, et al. Rosemary oil vs minoxidil 2% for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia: a randomized comparative trial. Skinmed. 2015;13:15-21.
- Hay IC, Jamieson M, Ormerod AD. Randomized trial of aromatherapy. successful treatment for alopecia areata. Arch Dermatol. 1998;134:1349-1352. doi:10.1001/archderm.134.11.1349
- Choi JS, Jeon MH, Moon WS, et al. In vivo hair growth-promoting effect of rice bran extract prepared by supercritical carbon dioxide fluid. Biol Pharm Bull. 2014;37:44-53. doi:10.1248/bpb.b13-00528
- Kim YM, Kwon SJ, Jang HJ, et al. Rice bran mineral extract increases the expression of anagen-related molecules in human dermal papilla through wnt/catenin pathway. Food Nutr Res. 2017;61:1412792. doi:10.1080/16546628.2017.1412792
- Hashemi K, Pham C, Sung C, et al. A systematic review: application of rice products for hair growth. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:177-185. doi:10.36849/jdd.6345
- Sharquie KE, Al-Obaidi HK. Onion juice (Allium cepa L.), a new topical treatment for alopecia areata. J Dermatol. 2002;29:343-346. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2002.tb00277.x
- Hosking AM, Juhasz M, Atanaskova Mesinkovska N. Complementary and alternative treatments for alopecia: a comprehensive review. Skin Appendage Disord. 2019;5:72-89. doi:10.1159/000492035
- Hajheydari Z, Jamshidi M, Akbari J, et al. Combination of topical garlic gel and betamethasone valerate cream in the treatment of localized alopecia areata: a double-blind randomized controlled study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2007;73:29-32. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.30648
- Laughter M, Anderson J, Kolla A, et al. An analysis of alopecia related content on Instagram and TikTok. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21:1316-1321. doi:10.36849/JDD.6707
Resident Pearl
- With terabytes of information at their fingertips, patients often turn to social media for hair loss advice. Many recommended therapies lack evidence-based research, and some may even be harmful to patients or delay time to efficacious treatments.
Co-occurring psychogenic nonepileptic seizures and possible true seizures
Psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) are a physical manifestation of a psychological disturbance. They are characterized by episodes of altered subjective experience and movements that can resemble epilepsy, syncope, or other paroxysmal disorders, but are not caused by neuronal hypersynchronization or other epileptic semiology.
Patients with PNES may present to multiple clinicians and hospitals for assessment. Access to outside hospital records can be limited, which can lead to redundant testing and increased health care costs and burden. Additionally, repeat presentations can increase stigmatization of the patient and delay or prevent appropriate therapeutic management, which might exacerbate a patient’s underlying psychiatric condition and could be dangerous in a patient with a co-occurring true seizure disorder. Though obtaining and reviewing external medical records can be cumbersome, doing so may prevent unnecessary testing, guide medical treatment, and strengthen the patient-doctor therapeutic alliance.
In this article, I discuss our treatment team’s management of a patient with PNES who, based on our careful review of records from previous hospitalizations, may have had a co-occurring true seizure disorder.
Case report
Ms. M, age 31, has a medical history of anxiety, depression, first-degree atrioventricular block, type 2 diabetes, and PNES. She presented to the ED with witnessed seizure activity at home.
According to collateral information, earlier that day Ms. M said she felt like she was seizing and began mumbling, but returned to baseline within a few minutes. Later, she demonstrated intermittent upper and lower extremity shaking for more than 1 hour. At one point, Ms. M appeared to be not breathing. However, upon initiation of chest compressions, she began gasping for air and immediately returned to baseline.
In the ED, Ms. M demonstrated multiple seizure-like episodes every 5 minutes, each lasting 5 to 10 seconds. These episodes were described as thrashing of the bilateral limbs and head crossing midline with eyes closed. No urinary incontinence or tongue biting was observed. Following each episode, Ms. M was unresponsive to verbal or tactile stimuli but intermittently opened her eyes. Laboratory test results were notable for an elevated serum lactate and positive for cannabinoids on urine drug screen.
Ms. M expressed frustration when told that her seizures were psychogenic. She was adamant that she had a true seizure disorder, demanded testing, and threatened to leave against medical advice without it. She said her brother had epilepsy, and thus she knew how seizures present. The interview was complicated by Ms. M’s mistrust and Cluster B personality disorder traits, such as splitting staff into “good and bad.” Ultimately, she was able to be reassured and did not leave the hospital.
Continue to: The treatment team...
The treatment team reviewed external records from 2 hospitals, Hospital A and Hospital B. These records showed well-documented inpatient and outpatient Psychiatry and Neurology diagnoses of PNES and other conversion disorders. Her medications included
Ms. M’s first lifetime documented seizure occurred in May 2020, when she woke up with tongue biting, extremity shaking (laterality was unclear), and urinary incontinence followed by fatigue. She did not go to the hospital after this first episode. In June 2020, she presented and was admitted to Hospital A after similar seizure-like activity. While admitted and monitored on continuous EEG (cEEG), she had numerous events consistent with a nonepileptic etiology without a postictal state. A brain MRI was unremarkable, and Ms. M was diagnosed with PNES.
She presented to Hospital B in October 2020 reporting seizure-like activity. Hospital B reviewed Hospital A’s brain MRI and found right temporal lobe cortical dysplasia that was not noted in Hospital A’s MRI read. Ms. M again underwent cEEG while at Hospital B and had 2 recorded nonepileptic events. Interestingly, the cEEG demonstrated
Ms. M documented 3 seizure-like events between October and December 2020. She documented activity with and without full-body convulsions, some with laterality, some with loss of consciousness, and some preceded by an aura of impending doom. Ms. M was referred to psychotherapy and instructed to continue topiramate 100 mg every 12 hours for seizure prophylaxis.
Ms. M presented to Hospital B again in March 2022 reporting seizure-like activity. A brain MRI found cortical dysplasia in the right temporal lobe, consistent with the MRI at Hospital A in June 2020. cEEG was also repeated at Hospital B and was unremarkable. Oxcarbazepine 300 mg every 12 hours was added to Ms. M’s medications.
Ultimately, based on an external record review, our team (at Hospital C) concluded Ms. M had a possible true seizure co-occurrence with PNES. To avoid redundant testing, we did not repeat imaging or cEEG. Instead, we increased the patient’s oxcarbazepine to 450 mg every 12 hours, for both its effectiveness in temporal seizures and its mood-stabilizing properties. Moreover, in collecting our own data to draw a conclusion by a thorough record review, we gained Ms. M’s trust and strengthened the therapeutic alliance. She was agreeable to forgo more testing and continue outpatient follow-up with our hospital’s Neurology team.
Take-home points
Although PNES and true seizure disorder may not frequently co-occur, this case highlights the importance of clinician due diligence when evaluating a potential psychogenic illness, both for patient safety and clinician liability. By trusting our patients and drawing our own data-based conclusions, we can cultivate a safer and more satisfactory patient-clinician experience in the context of psychosomatic disorders.
1. Bajestan SN, LaFrance WC Jr. Clinical approaches to psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Focus (Am Psychiatr Publ). 2016;14(4):422-431. doi:10.1176/appi.focus.20160020
2. Dickson JM, Dudhill H, Shewan J, et al. Cross-sectional study of the hospital management of adult patients with a suspected seizure (EPIC2). BMJ Open. 2017;7(7):e015696. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015696
3. Kutlubaev MA, Xu Y, Hackett ML, et al. Dual diagnosis of epilepsy and psychogenic nonepileptic seizures: systematic review and meta-analysis of frequency, correlates, and outcomes. Epilepsy Behav. 2018;89:70-78. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2018.10.010
Psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) are a physical manifestation of a psychological disturbance. They are characterized by episodes of altered subjective experience and movements that can resemble epilepsy, syncope, or other paroxysmal disorders, but are not caused by neuronal hypersynchronization or other epileptic semiology.
Patients with PNES may present to multiple clinicians and hospitals for assessment. Access to outside hospital records can be limited, which can lead to redundant testing and increased health care costs and burden. Additionally, repeat presentations can increase stigmatization of the patient and delay or prevent appropriate therapeutic management, which might exacerbate a patient’s underlying psychiatric condition and could be dangerous in a patient with a co-occurring true seizure disorder. Though obtaining and reviewing external medical records can be cumbersome, doing so may prevent unnecessary testing, guide medical treatment, and strengthen the patient-doctor therapeutic alliance.
In this article, I discuss our treatment team’s management of a patient with PNES who, based on our careful review of records from previous hospitalizations, may have had a co-occurring true seizure disorder.
Case report
Ms. M, age 31, has a medical history of anxiety, depression, first-degree atrioventricular block, type 2 diabetes, and PNES. She presented to the ED with witnessed seizure activity at home.
According to collateral information, earlier that day Ms. M said she felt like she was seizing and began mumbling, but returned to baseline within a few minutes. Later, she demonstrated intermittent upper and lower extremity shaking for more than 1 hour. At one point, Ms. M appeared to be not breathing. However, upon initiation of chest compressions, she began gasping for air and immediately returned to baseline.
In the ED, Ms. M demonstrated multiple seizure-like episodes every 5 minutes, each lasting 5 to 10 seconds. These episodes were described as thrashing of the bilateral limbs and head crossing midline with eyes closed. No urinary incontinence or tongue biting was observed. Following each episode, Ms. M was unresponsive to verbal or tactile stimuli but intermittently opened her eyes. Laboratory test results were notable for an elevated serum lactate and positive for cannabinoids on urine drug screen.
Ms. M expressed frustration when told that her seizures were psychogenic. She was adamant that she had a true seizure disorder, demanded testing, and threatened to leave against medical advice without it. She said her brother had epilepsy, and thus she knew how seizures present. The interview was complicated by Ms. M’s mistrust and Cluster B personality disorder traits, such as splitting staff into “good and bad.” Ultimately, she was able to be reassured and did not leave the hospital.
Continue to: The treatment team...
The treatment team reviewed external records from 2 hospitals, Hospital A and Hospital B. These records showed well-documented inpatient and outpatient Psychiatry and Neurology diagnoses of PNES and other conversion disorders. Her medications included
Ms. M’s first lifetime documented seizure occurred in May 2020, when she woke up with tongue biting, extremity shaking (laterality was unclear), and urinary incontinence followed by fatigue. She did not go to the hospital after this first episode. In June 2020, she presented and was admitted to Hospital A after similar seizure-like activity. While admitted and monitored on continuous EEG (cEEG), she had numerous events consistent with a nonepileptic etiology without a postictal state. A brain MRI was unremarkable, and Ms. M was diagnosed with PNES.
She presented to Hospital B in October 2020 reporting seizure-like activity. Hospital B reviewed Hospital A’s brain MRI and found right temporal lobe cortical dysplasia that was not noted in Hospital A’s MRI read. Ms. M again underwent cEEG while at Hospital B and had 2 recorded nonepileptic events. Interestingly, the cEEG demonstrated
Ms. M documented 3 seizure-like events between October and December 2020. She documented activity with and without full-body convulsions, some with laterality, some with loss of consciousness, and some preceded by an aura of impending doom. Ms. M was referred to psychotherapy and instructed to continue topiramate 100 mg every 12 hours for seizure prophylaxis.
Ms. M presented to Hospital B again in March 2022 reporting seizure-like activity. A brain MRI found cortical dysplasia in the right temporal lobe, consistent with the MRI at Hospital A in June 2020. cEEG was also repeated at Hospital B and was unremarkable. Oxcarbazepine 300 mg every 12 hours was added to Ms. M’s medications.
Ultimately, based on an external record review, our team (at Hospital C) concluded Ms. M had a possible true seizure co-occurrence with PNES. To avoid redundant testing, we did not repeat imaging or cEEG. Instead, we increased the patient’s oxcarbazepine to 450 mg every 12 hours, for both its effectiveness in temporal seizures and its mood-stabilizing properties. Moreover, in collecting our own data to draw a conclusion by a thorough record review, we gained Ms. M’s trust and strengthened the therapeutic alliance. She was agreeable to forgo more testing and continue outpatient follow-up with our hospital’s Neurology team.
Take-home points
Although PNES and true seizure disorder may not frequently co-occur, this case highlights the importance of clinician due diligence when evaluating a potential psychogenic illness, both for patient safety and clinician liability. By trusting our patients and drawing our own data-based conclusions, we can cultivate a safer and more satisfactory patient-clinician experience in the context of psychosomatic disorders.
Psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) are a physical manifestation of a psychological disturbance. They are characterized by episodes of altered subjective experience and movements that can resemble epilepsy, syncope, or other paroxysmal disorders, but are not caused by neuronal hypersynchronization or other epileptic semiology.
Patients with PNES may present to multiple clinicians and hospitals for assessment. Access to outside hospital records can be limited, which can lead to redundant testing and increased health care costs and burden. Additionally, repeat presentations can increase stigmatization of the patient and delay or prevent appropriate therapeutic management, which might exacerbate a patient’s underlying psychiatric condition and could be dangerous in a patient with a co-occurring true seizure disorder. Though obtaining and reviewing external medical records can be cumbersome, doing so may prevent unnecessary testing, guide medical treatment, and strengthen the patient-doctor therapeutic alliance.
In this article, I discuss our treatment team’s management of a patient with PNES who, based on our careful review of records from previous hospitalizations, may have had a co-occurring true seizure disorder.
Case report
Ms. M, age 31, has a medical history of anxiety, depression, first-degree atrioventricular block, type 2 diabetes, and PNES. She presented to the ED with witnessed seizure activity at home.
According to collateral information, earlier that day Ms. M said she felt like she was seizing and began mumbling, but returned to baseline within a few minutes. Later, she demonstrated intermittent upper and lower extremity shaking for more than 1 hour. At one point, Ms. M appeared to be not breathing. However, upon initiation of chest compressions, she began gasping for air and immediately returned to baseline.
In the ED, Ms. M demonstrated multiple seizure-like episodes every 5 minutes, each lasting 5 to 10 seconds. These episodes were described as thrashing of the bilateral limbs and head crossing midline with eyes closed. No urinary incontinence or tongue biting was observed. Following each episode, Ms. M was unresponsive to verbal or tactile stimuli but intermittently opened her eyes. Laboratory test results were notable for an elevated serum lactate and positive for cannabinoids on urine drug screen.
Ms. M expressed frustration when told that her seizures were psychogenic. She was adamant that she had a true seizure disorder, demanded testing, and threatened to leave against medical advice without it. She said her brother had epilepsy, and thus she knew how seizures present. The interview was complicated by Ms. M’s mistrust and Cluster B personality disorder traits, such as splitting staff into “good and bad.” Ultimately, she was able to be reassured and did not leave the hospital.
Continue to: The treatment team...
The treatment team reviewed external records from 2 hospitals, Hospital A and Hospital B. These records showed well-documented inpatient and outpatient Psychiatry and Neurology diagnoses of PNES and other conversion disorders. Her medications included
Ms. M’s first lifetime documented seizure occurred in May 2020, when she woke up with tongue biting, extremity shaking (laterality was unclear), and urinary incontinence followed by fatigue. She did not go to the hospital after this first episode. In June 2020, she presented and was admitted to Hospital A after similar seizure-like activity. While admitted and monitored on continuous EEG (cEEG), she had numerous events consistent with a nonepileptic etiology without a postictal state. A brain MRI was unremarkable, and Ms. M was diagnosed with PNES.
She presented to Hospital B in October 2020 reporting seizure-like activity. Hospital B reviewed Hospital A’s brain MRI and found right temporal lobe cortical dysplasia that was not noted in Hospital A’s MRI read. Ms. M again underwent cEEG while at Hospital B and had 2 recorded nonepileptic events. Interestingly, the cEEG demonstrated
Ms. M documented 3 seizure-like events between October and December 2020. She documented activity with and without full-body convulsions, some with laterality, some with loss of consciousness, and some preceded by an aura of impending doom. Ms. M was referred to psychotherapy and instructed to continue topiramate 100 mg every 12 hours for seizure prophylaxis.
Ms. M presented to Hospital B again in March 2022 reporting seizure-like activity. A brain MRI found cortical dysplasia in the right temporal lobe, consistent with the MRI at Hospital A in June 2020. cEEG was also repeated at Hospital B and was unremarkable. Oxcarbazepine 300 mg every 12 hours was added to Ms. M’s medications.
Ultimately, based on an external record review, our team (at Hospital C) concluded Ms. M had a possible true seizure co-occurrence with PNES. To avoid redundant testing, we did not repeat imaging or cEEG. Instead, we increased the patient’s oxcarbazepine to 450 mg every 12 hours, for both its effectiveness in temporal seizures and its mood-stabilizing properties. Moreover, in collecting our own data to draw a conclusion by a thorough record review, we gained Ms. M’s trust and strengthened the therapeutic alliance. She was agreeable to forgo more testing and continue outpatient follow-up with our hospital’s Neurology team.
Take-home points
Although PNES and true seizure disorder may not frequently co-occur, this case highlights the importance of clinician due diligence when evaluating a potential psychogenic illness, both for patient safety and clinician liability. By trusting our patients and drawing our own data-based conclusions, we can cultivate a safer and more satisfactory patient-clinician experience in the context of psychosomatic disorders.
1. Bajestan SN, LaFrance WC Jr. Clinical approaches to psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Focus (Am Psychiatr Publ). 2016;14(4):422-431. doi:10.1176/appi.focus.20160020
2. Dickson JM, Dudhill H, Shewan J, et al. Cross-sectional study of the hospital management of adult patients with a suspected seizure (EPIC2). BMJ Open. 2017;7(7):e015696. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015696
3. Kutlubaev MA, Xu Y, Hackett ML, et al. Dual diagnosis of epilepsy and psychogenic nonepileptic seizures: systematic review and meta-analysis of frequency, correlates, and outcomes. Epilepsy Behav. 2018;89:70-78. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2018.10.010
1. Bajestan SN, LaFrance WC Jr. Clinical approaches to psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Focus (Am Psychiatr Publ). 2016;14(4):422-431. doi:10.1176/appi.focus.20160020
2. Dickson JM, Dudhill H, Shewan J, et al. Cross-sectional study of the hospital management of adult patients with a suspected seizure (EPIC2). BMJ Open. 2017;7(7):e015696. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015696
3. Kutlubaev MA, Xu Y, Hackett ML, et al. Dual diagnosis of epilepsy and psychogenic nonepileptic seizures: systematic review and meta-analysis of frequency, correlates, and outcomes. Epilepsy Behav. 2018;89:70-78. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2018.10.010
Dermatology Articles in Preprint Servers: A Cross-sectional Study
To the Editor:
Preprint servers allow researchers to post manuscripts before publication in peer-reviewed journals. As of January 2022, 41 public preprint servers accepted medicine/science submissions.1 We sought to analyze characteristics of dermatology manuscripts in preprint servers and assess preprint publication policies in top dermatology journals.
Thirty-five biology/health sciences preprint servers1 were searched (March 3 to March 24, 2021) with keywords dermatology, skin, and cutaneous. Preprint server, preprint post date, location, metrics, journal, impact factor (IF), and journal publication date were recorded. Preprint policies of the top 20 dermatology journals—determined by impact factor of the journal (https://www.scimagojr.com/)—were reviewed. Two-tailed t tests and χ2 tests were performed (P<.05).
A total of 1420 articles were posted to 11 preprint servers between June 20, 2007, and February 15, 2021 (Table 1); 377 (27%) were published in peer-reviewed journals, with 350 (93%) of those published within 1 year of preprint post. Preprints were published in 203 journals with a mean IF of 6.2. Growth in preprint posts by year (2007-2020) was exponential (R2=0.78)(Figure). On average, preprints were viewed 424 times (Table 2), with published preprints viewed more often than unpublished preprints (596 vs 362 views)(P<.001). Only 23 of 786 (3%) preprints with comments enabled had feedback. Among the top 20 dermatology journals, 18 (90%) allowed preprints, 1 (5%) evaluated case by case, and 1 (5%) prohibited preprints.
Our study showed exponential growth in dermatology preprints, a low proportion published in peer-reviewed journals with high IFs, and a substantial number of page views for both published and unpublished preprints. Very few preprints had feedback. We found that most of the top 20 dermatology journals accept preprints. An analysis of 61 dermatology articles in medRxiv found only 51% (31/61) of articles were subsequently published.2 The low rate of publication may be due to the quality of preprints that do not meet criteria to be published following peer review.
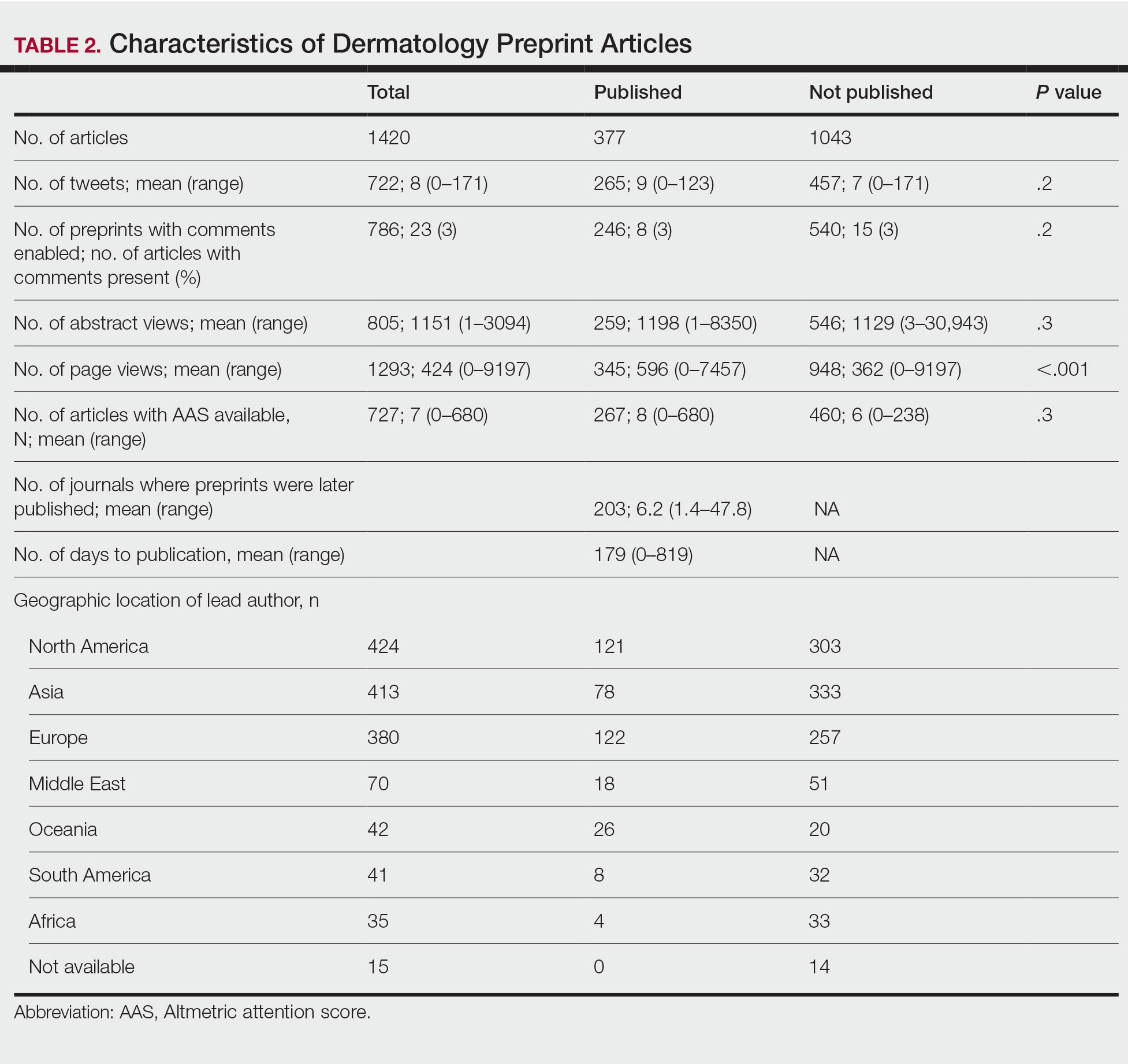
Preprint servers are fairly novel, with a majority launched within the last 5 years.1 The goal of preprints is to claim conception of an idea, solicit feedback prior to submission for peer review, and expedite research distribution.3 Because preprints are uploaded without peer review, manuscripts may lack quality and accuracy. An analysis of 57 of thelargest preprint servers found that few provided guidelines on authorship, image manipulation, or reporting of study limitations; however, most preprint servers do perform some screening.4 medRxiv requires full scientific research reports and absence of obscenity, plagiarism, and patient identifiers. In its first year, medRxiv rejected 34% of 176 submissios; reasons were not disclosed.5
The low rate of on-site comments suggests that preprint servers may not be effective for obtaining feedback to improve dermatology manuscripts prior to journal submission. Almost all of the top 20 dermatologyjournals accept preprints. Therefore, dermatologists may use these preprint servers to assert project ideas and disseminate research quickly and freely but may not receive constructive criticism.
Our study is subject to several limitations. Although our search was extensive, it is possible manuscripts were missed. Article metrics also were not available on all servers, and we could not account for accepted articles that were not yet indexed.
There has been a surge in posting of dermatology preprints in recent years. Preprints have not been peer reviewed, and data should be corroborated before incorporating new diagnostics or treatments into clinical practice. Utilization of preprint servers by dermatologists is increasing, but because the impact is still unknown, further studies on accuracy and reliability of preprints are warranted.
1. List of preprint servers: policies and practices across platforms. ASAPbio website. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://asapbio.org/preprint-servers
2. Jia JL, Hua VJ, Sarin KY. Journal attitudes and outcomes of preprints in dermatology. Br J Dermatol. 2021;185:230-232.
3. Chiarelli A, Johnson R, Richens E, et al. Accelerating scholarly communication: the transformative role of preprints. Copyright, Fair Use, Scholarly Communication, etc. 127. September 20, 2019. Accessed January 18, 2023. https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1128&context=scholcom
4. Malicki M, Jeroncic A, Riet GT, et al. Preprint servers’ policies, submission requirements, and transparency in reporting and research integrity recommendations. JAMA. 2020;324:1901-1903.
5. Krumholz HM, Bloom T, Sever R, et al. Submissions and downloads of preprints in the first year of medRxiv. JAMA. 2020;324:1903-1905.
To the Editor:
Preprint servers allow researchers to post manuscripts before publication in peer-reviewed journals. As of January 2022, 41 public preprint servers accepted medicine/science submissions.1 We sought to analyze characteristics of dermatology manuscripts in preprint servers and assess preprint publication policies in top dermatology journals.
Thirty-five biology/health sciences preprint servers1 were searched (March 3 to March 24, 2021) with keywords dermatology, skin, and cutaneous. Preprint server, preprint post date, location, metrics, journal, impact factor (IF), and journal publication date were recorded. Preprint policies of the top 20 dermatology journals—determined by impact factor of the journal (https://www.scimagojr.com/)—were reviewed. Two-tailed t tests and χ2 tests were performed (P<.05).

A total of 1420 articles were posted to 11 preprint servers between June 20, 2007, and February 15, 2021 (Table 1); 377 (27%) were published in peer-reviewed journals, with 350 (93%) of those published within 1 year of preprint post. Preprints were published in 203 journals with a mean IF of 6.2. Growth in preprint posts by year (2007-2020) was exponential (R2=0.78)(Figure). On average, preprints were viewed 424 times (Table 2), with published preprints viewed more often than unpublished preprints (596 vs 362 views)(P<.001). Only 23 of 786 (3%) preprints with comments enabled had feedback. Among the top 20 dermatology journals, 18 (90%) allowed preprints, 1 (5%) evaluated case by case, and 1 (5%) prohibited preprints.

Our study showed exponential growth in dermatology preprints, a low proportion published in peer-reviewed journals with high IFs, and a substantial number of page views for both published and unpublished preprints. Very few preprints had feedback. We found that most of the top 20 dermatology journals accept preprints. An analysis of 61 dermatology articles in medRxiv found only 51% (31/61) of articles were subsequently published.2 The low rate of publication may be due to the quality of preprints that do not meet criteria to be published following peer review.

Preprint servers are fairly novel, with a majority launched within the last 5 years.1 The goal of preprints is to claim conception of an idea, solicit feedback prior to submission for peer review, and expedite research distribution.3 Because preprints are uploaded without peer review, manuscripts may lack quality and accuracy. An analysis of 57 of thelargest preprint servers found that few provided guidelines on authorship, image manipulation, or reporting of study limitations; however, most preprint servers do perform some screening.4 medRxiv requires full scientific research reports and absence of obscenity, plagiarism, and patient identifiers. In its first year, medRxiv rejected 34% of 176 submissios; reasons were not disclosed.5
The low rate of on-site comments suggests that preprint servers may not be effective for obtaining feedback to improve dermatology manuscripts prior to journal submission. Almost all of the top 20 dermatologyjournals accept preprints. Therefore, dermatologists may use these preprint servers to assert project ideas and disseminate research quickly and freely but may not receive constructive criticism.
Our study is subject to several limitations. Although our search was extensive, it is possible manuscripts were missed. Article metrics also were not available on all servers, and we could not account for accepted articles that were not yet indexed.
There has been a surge in posting of dermatology preprints in recent years. Preprints have not been peer reviewed, and data should be corroborated before incorporating new diagnostics or treatments into clinical practice. Utilization of preprint servers by dermatologists is increasing, but because the impact is still unknown, further studies on accuracy and reliability of preprints are warranted.
To the Editor:
Preprint servers allow researchers to post manuscripts before publication in peer-reviewed journals. As of January 2022, 41 public preprint servers accepted medicine/science submissions.1 We sought to analyze characteristics of dermatology manuscripts in preprint servers and assess preprint publication policies in top dermatology journals.
Thirty-five biology/health sciences preprint servers1 were searched (March 3 to March 24, 2021) with keywords dermatology, skin, and cutaneous. Preprint server, preprint post date, location, metrics, journal, impact factor (IF), and journal publication date were recorded. Preprint policies of the top 20 dermatology journals—determined by impact factor of the journal (https://www.scimagojr.com/)—were reviewed. Two-tailed t tests and χ2 tests were performed (P<.05).

A total of 1420 articles were posted to 11 preprint servers between June 20, 2007, and February 15, 2021 (Table 1); 377 (27%) were published in peer-reviewed journals, with 350 (93%) of those published within 1 year of preprint post. Preprints were published in 203 journals with a mean IF of 6.2. Growth in preprint posts by year (2007-2020) was exponential (R2=0.78)(Figure). On average, preprints were viewed 424 times (Table 2), with published preprints viewed more often than unpublished preprints (596 vs 362 views)(P<.001). Only 23 of 786 (3%) preprints with comments enabled had feedback. Among the top 20 dermatology journals, 18 (90%) allowed preprints, 1 (5%) evaluated case by case, and 1 (5%) prohibited preprints.

Our study showed exponential growth in dermatology preprints, a low proportion published in peer-reviewed journals with high IFs, and a substantial number of page views for both published and unpublished preprints. Very few preprints had feedback. We found that most of the top 20 dermatology journals accept preprints. An analysis of 61 dermatology articles in medRxiv found only 51% (31/61) of articles were subsequently published.2 The low rate of publication may be due to the quality of preprints that do not meet criteria to be published following peer review.

Preprint servers are fairly novel, with a majority launched within the last 5 years.1 The goal of preprints is to claim conception of an idea, solicit feedback prior to submission for peer review, and expedite research distribution.3 Because preprints are uploaded without peer review, manuscripts may lack quality and accuracy. An analysis of 57 of thelargest preprint servers found that few provided guidelines on authorship, image manipulation, or reporting of study limitations; however, most preprint servers do perform some screening.4 medRxiv requires full scientific research reports and absence of obscenity, plagiarism, and patient identifiers. In its first year, medRxiv rejected 34% of 176 submissios; reasons were not disclosed.5
The low rate of on-site comments suggests that preprint servers may not be effective for obtaining feedback to improve dermatology manuscripts prior to journal submission. Almost all of the top 20 dermatologyjournals accept preprints. Therefore, dermatologists may use these preprint servers to assert project ideas and disseminate research quickly and freely but may not receive constructive criticism.
Our study is subject to several limitations. Although our search was extensive, it is possible manuscripts were missed. Article metrics also were not available on all servers, and we could not account for accepted articles that were not yet indexed.
There has been a surge in posting of dermatology preprints in recent years. Preprints have not been peer reviewed, and data should be corroborated before incorporating new diagnostics or treatments into clinical practice. Utilization of preprint servers by dermatologists is increasing, but because the impact is still unknown, further studies on accuracy and reliability of preprints are warranted.
1. List of preprint servers: policies and practices across platforms. ASAPbio website. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://asapbio.org/preprint-servers
2. Jia JL, Hua VJ, Sarin KY. Journal attitudes and outcomes of preprints in dermatology. Br J Dermatol. 2021;185:230-232.
3. Chiarelli A, Johnson R, Richens E, et al. Accelerating scholarly communication: the transformative role of preprints. Copyright, Fair Use, Scholarly Communication, etc. 127. September 20, 2019. Accessed January 18, 2023. https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1128&context=scholcom
4. Malicki M, Jeroncic A, Riet GT, et al. Preprint servers’ policies, submission requirements, and transparency in reporting and research integrity recommendations. JAMA. 2020;324:1901-1903.
5. Krumholz HM, Bloom T, Sever R, et al. Submissions and downloads of preprints in the first year of medRxiv. JAMA. 2020;324:1903-1905.
1. List of preprint servers: policies and practices across platforms. ASAPbio website. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://asapbio.org/preprint-servers
2. Jia JL, Hua VJ, Sarin KY. Journal attitudes and outcomes of preprints in dermatology. Br J Dermatol. 2021;185:230-232.
3. Chiarelli A, Johnson R, Richens E, et al. Accelerating scholarly communication: the transformative role of preprints. Copyright, Fair Use, Scholarly Communication, etc. 127. September 20, 2019. Accessed January 18, 2023. https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1128&context=scholcom
4. Malicki M, Jeroncic A, Riet GT, et al. Preprint servers’ policies, submission requirements, and transparency in reporting and research integrity recommendations. JAMA. 2020;324:1901-1903.
5. Krumholz HM, Bloom T, Sever R, et al. Submissions and downloads of preprints in the first year of medRxiv. JAMA. 2020;324:1903-1905.
PRACTICE POINTS
- Preprint servers allow researchers to post manuscripts before publication in peer-reviewed journals.
- The low rate of on-site comments suggests that preprint servers may not be effective for obtaining feedback to improve dermatology manuscripts prior to journal submission; therefore, dermatologists may use these servers to disseminate research quickly and freely but may not receive constructive criticism.
- Preprints have not been peer reviewed, and data should be corroborated before incorporating new diagnostics or treatments into clinical practice.
The Ins and Outs of Transferring Residency Programs
Transferring from one residency program to another is rare but not unheard of. According to the most recent Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education Data Resource Book, there were 1020 residents who transferred residency programs in the 2020-2021 academic year.1 With a total of 126,759 active residents in specialty programs, the percentage of transferring residents was less than 1%. The specialties with the highest number of transferring residents included psychiatry, general surgery, internal medicine, and family medicine. In dermatology programs, there were only 2 resident transfers during the 2019-2020 academic year and 6 transfers in the 2020-2021 academic year.1,2 A resident contemplating transferring training programs must carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages before undertaking the uncertain transfer process, but transferring residency programs can be achieved successfully with planning and luck.
Deciding to Transfer
The decision to transfer residency programs may be a difficult one that is wrought with anxiety. There are many reasons why a trainee may wish to pursue transferring training programs. A transfer to another geographic area may be necessary for personal or family reasons, such as to reunite with a spouse and children or to care for a sick family member. A resident may find their program to be a poor fit and may wish to train in a different educational environment. Occasionally, a program can lose its accreditation, and its residents will be tasked with finding a new position elsewhere. A trainee also may realize that the specialty they matched into initially does not align with their true passions. It is important for the potential transfer applicant to be levelheaded about their decision. Residency is a demanding period for every trainee; switching programs may not be the best solution for every problem and should only be considered if essential.
Transfer Timing
A trainee may have thoughts of leaving a program soon after starting residency or perhaps even before starting if their National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) Match result was a disappointment; however, there are certain rules related to transfer timing. The NRMP Match represents a binding commitment for both the applicant and program. If for any reason an applicant will not honor the binding commitment, the NRMP requires the applicant to initiate a waiver review, which can be requested for unanticipated serious and extreme hardship, change of specialty, or ineligibility. According to the NRMP rules and regulations, applicants cannot apply for, discuss, interview for, or accept a position in another program until a waiver has been granted.3 Waivers based on change of specialty must be requested by mid-January prior to the start of training, which means most applicants who match to positions that begin in the same year of the Match do not qualify for change of specialty waivers. However, those who matched to an advanced position and are doing a preliminary year position may consider this option if they have a change of heart during their internship. The NRMP may consider a 1-year deferral to delay training if mutually agreed upon by both the matched applicant and the program.3 The binding commitment is in place for the first 45 days of training, and applicants who resign within 45 days or a program that tries to solicit the transfer of a resident prior to that date could be in violation of the Match and can face consequences such as being barred from entering the matching process in future cycles. Of the 1020 transfers that occurred among residents in specialty programs during the 2020-2021 academic year, 354 (34.7%) occurred during the first year of the training program; 228 (22.4%) occurred during the second year; 389 (38.1%) occurred during the third year; and 49 (4.8%) occurred in the fourth, fifth, or sixth year of the program.1 Unlike other jobs/occupations in which one can simply give notice, in medical training even if a transfer position is accepted, the transition date between programs must be mutually agreed upon. Often, this may coincide with the start of the new academic year.
The Transfer Process
Transferring residency programs is a substantial undertaking. Unlike the Match, a trainee seeking to transfer programs does so without a standardized application system or structured support through the process; the transfer applicant must be prepared to navigate the transfer process on their own. The first step after making the decision to transfer is for the resident to meet with the program leadership (ie, program director[s], coordinator, designated official) at their home program to discuss the decision—a nerve-wracking but imperative first step. A receiving program may not favor an applicant secretly applying to a new program without the knowledge of their home program and often will require the home program’s blessing to proceed. The receiving program also would want to ensure the applicant is in good standing and not leaving due to misconduct. Once given the go-ahead, the process is largely in the hands of the applicant. The transfer applicant should identify locations or programs of interest and then take initiative to reach out to potential programs. FREIDA (Fellowship and Residency Electronic Interactive Database Access) is the American Medical Association’s residency and fellowship database that allows vacant position listings to be posted online.4 Additionally, the Association of American Medical Colleges’ FindAResident website is a year-round search tool designed to help find open residency and fellowship positions.5 Various specialties also may have program director listserves that communicate vacant positions. On occasion, there are spots in the main NRMP Match that are reserved positions (“R”). These are postgraduate year 2 positions in specialty programs that begin in the year of the Match and are reserved for physicians with prior graduate medical education; these also are known as “Physician Positions.”6 Ultimately, advertisements for vacancies may be few and far between, requiring the resident to send unsolicited emails with curriculum vitae attached to the program directors at programs of interest to inquire about any vacancies and hope for a favorable response. Even if the transfer applicant is qualified, luck that the right spot will be available at the right time may be the deciding factor in transferring programs.
The next step is interviewing for the position. There likely will be fewer candidates interviewing for an open spot but that does not make the process less competitive. The candidate should highlight their strengths and achievements and discuss why the new program would be a great fit both personally and professionally. Even if an applicant is seeking a transfer due to discontent with a prior program, it is best to act graciously and not speak poorly about another training program.
Prior to selection, the candidate may be asked to provide information such as diplomas, US Medical Licensing Examination Step and residency in-service training examination scores, and academic reviews from their current residency program. The interview process may take several weeks as the graduate medical education office often will need to officially approve of an applicant before a formal offer to transfer is extended.
Finally, once an offer is made and accepted, there still is a great amount of paperwork to complete before the transition. The applicant should stay on track with all off-boarding and on-boarding requirements, such as signing a contract, obtaining background checks, and applying for a new license to ensure the switch is not delayed.
Disadvantages of Transferring Programs
The transfer process is not easy to navigate and can be a source of stress for the applicant. It is natural to fear resentment from colleagues and co-residents. Although transferring programs might be in the best interest of the trainee, it may leave a large gap in the program that they are leaving, which can place a burden on the remaining residents.
There are many adjustments to be made after transferring programs. The transferring resident will again start from scratch, needing to learn the ropes and adapt to the growing pains of being at a new institution. This may require learning a completely new electronic medical record, adapting to a new culture, and in many cases stepping in as a senior resident without fully knowing the ins and outs of the program.
Advantages of Transferring Programs
Successfully transferring programs is something to celebrate. There may be great benefits to transferring to a program that is better suited to the trainee—either personally or professionally. Ameliorating the adversity that led to the decision to transfer such as reuniting a long-distance family or realizing one’s true passion can allow the resident to thrive as a trainee and maximize their potential. Transferring programs can give a resident a more well-rounded training experience, as different programs may have different strengths, patient populations, and practice settings. Working with different faculty members with varied niches and practice styles can create a more comprehensive residency experience.
Final Thoughts
Ultimately, transferring residency programs is not easy but also is not impossible. Successfully switching residency programs can be a rewarding experience providing greater well-being and fulfillment.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Data Resource Book, Academic Year 2021-2022. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/publicationsbooks/2021-2022_acgme__databook_document.pdf
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Data Resource Book, Academic Year 2020-2021. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/publicationsbooks/2020-2021_acgme_databook_document.pdf
- After the Match. National Resident Matching Program website. Accessed January 23, 2023. https://www.nrmp.org/fellowship-applicants/after-the-match/
- FREIDA vacant position listings. American Medical Association website. Accessed January 23, 2023. https://freida.ama-assn.org/vacant-position
- FindAResident. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed January 23, 2023. https://students-residents.aamc.org/findaresident/findaresident
- What are the types of program positions in the main residency match? National Resident Matching Program website. Published August 5, 2021. Accessed January 23, 2023. https://www.nrmp.org/help/item/what-types-of-programs-participate-in-the-main-residency-match/
Transferring from one residency program to another is rare but not unheard of. According to the most recent Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education Data Resource Book, there were 1020 residents who transferred residency programs in the 2020-2021 academic year.1 With a total of 126,759 active residents in specialty programs, the percentage of transferring residents was less than 1%. The specialties with the highest number of transferring residents included psychiatry, general surgery, internal medicine, and family medicine. In dermatology programs, there were only 2 resident transfers during the 2019-2020 academic year and 6 transfers in the 2020-2021 academic year.1,2 A resident contemplating transferring training programs must carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages before undertaking the uncertain transfer process, but transferring residency programs can be achieved successfully with planning and luck.
Deciding to Transfer
The decision to transfer residency programs may be a difficult one that is wrought with anxiety. There are many reasons why a trainee may wish to pursue transferring training programs. A transfer to another geographic area may be necessary for personal or family reasons, such as to reunite with a spouse and children or to care for a sick family member. A resident may find their program to be a poor fit and may wish to train in a different educational environment. Occasionally, a program can lose its accreditation, and its residents will be tasked with finding a new position elsewhere. A trainee also may realize that the specialty they matched into initially does not align with their true passions. It is important for the potential transfer applicant to be levelheaded about their decision. Residency is a demanding period for every trainee; switching programs may not be the best solution for every problem and should only be considered if essential.
Transfer Timing
A trainee may have thoughts of leaving a program soon after starting residency or perhaps even before starting if their National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) Match result was a disappointment; however, there are certain rules related to transfer timing. The NRMP Match represents a binding commitment for both the applicant and program. If for any reason an applicant will not honor the binding commitment, the NRMP requires the applicant to initiate a waiver review, which can be requested for unanticipated serious and extreme hardship, change of specialty, or ineligibility. According to the NRMP rules and regulations, applicants cannot apply for, discuss, interview for, or accept a position in another program until a waiver has been granted.3 Waivers based on change of specialty must be requested by mid-January prior to the start of training, which means most applicants who match to positions that begin in the same year of the Match do not qualify for change of specialty waivers. However, those who matched to an advanced position and are doing a preliminary year position may consider this option if they have a change of heart during their internship. The NRMP may consider a 1-year deferral to delay training if mutually agreed upon by both the matched applicant and the program.3 The binding commitment is in place for the first 45 days of training, and applicants who resign within 45 days or a program that tries to solicit the transfer of a resident prior to that date could be in violation of the Match and can face consequences such as being barred from entering the matching process in future cycles. Of the 1020 transfers that occurred among residents in specialty programs during the 2020-2021 academic year, 354 (34.7%) occurred during the first year of the training program; 228 (22.4%) occurred during the second year; 389 (38.1%) occurred during the third year; and 49 (4.8%) occurred in the fourth, fifth, or sixth year of the program.1 Unlike other jobs/occupations in which one can simply give notice, in medical training even if a transfer position is accepted, the transition date between programs must be mutually agreed upon. Often, this may coincide with the start of the new academic year.
The Transfer Process
Transferring residency programs is a substantial undertaking. Unlike the Match, a trainee seeking to transfer programs does so without a standardized application system or structured support through the process; the transfer applicant must be prepared to navigate the transfer process on their own. The first step after making the decision to transfer is for the resident to meet with the program leadership (ie, program director[s], coordinator, designated official) at their home program to discuss the decision—a nerve-wracking but imperative first step. A receiving program may not favor an applicant secretly applying to a new program without the knowledge of their home program and often will require the home program’s blessing to proceed. The receiving program also would want to ensure the applicant is in good standing and not leaving due to misconduct. Once given the go-ahead, the process is largely in the hands of the applicant. The transfer applicant should identify locations or programs of interest and then take initiative to reach out to potential programs. FREIDA (Fellowship and Residency Electronic Interactive Database Access) is the American Medical Association’s residency and fellowship database that allows vacant position listings to be posted online.4 Additionally, the Association of American Medical Colleges’ FindAResident website is a year-round search tool designed to help find open residency and fellowship positions.5 Various specialties also may have program director listserves that communicate vacant positions. On occasion, there are spots in the main NRMP Match that are reserved positions (“R”). These are postgraduate year 2 positions in specialty programs that begin in the year of the Match and are reserved for physicians with prior graduate medical education; these also are known as “Physician Positions.”6 Ultimately, advertisements for vacancies may be few and far between, requiring the resident to send unsolicited emails with curriculum vitae attached to the program directors at programs of interest to inquire about any vacancies and hope for a favorable response. Even if the transfer applicant is qualified, luck that the right spot will be available at the right time may be the deciding factor in transferring programs.
The next step is interviewing for the position. There likely will be fewer candidates interviewing for an open spot but that does not make the process less competitive. The candidate should highlight their strengths and achievements and discuss why the new program would be a great fit both personally and professionally. Even if an applicant is seeking a transfer due to discontent with a prior program, it is best to act graciously and not speak poorly about another training program.
Prior to selection, the candidate may be asked to provide information such as diplomas, US Medical Licensing Examination Step and residency in-service training examination scores, and academic reviews from their current residency program. The interview process may take several weeks as the graduate medical education office often will need to officially approve of an applicant before a formal offer to transfer is extended.
Finally, once an offer is made and accepted, there still is a great amount of paperwork to complete before the transition. The applicant should stay on track with all off-boarding and on-boarding requirements, such as signing a contract, obtaining background checks, and applying for a new license to ensure the switch is not delayed.
Disadvantages of Transferring Programs
The transfer process is not easy to navigate and can be a source of stress for the applicant. It is natural to fear resentment from colleagues and co-residents. Although transferring programs might be in the best interest of the trainee, it may leave a large gap in the program that they are leaving, which can place a burden on the remaining residents.
There are many adjustments to be made after transferring programs. The transferring resident will again start from scratch, needing to learn the ropes and adapt to the growing pains of being at a new institution. This may require learning a completely new electronic medical record, adapting to a new culture, and in many cases stepping in as a senior resident without fully knowing the ins and outs of the program.
Advantages of Transferring Programs
Successfully transferring programs is something to celebrate. There may be great benefits to transferring to a program that is better suited to the trainee—either personally or professionally. Ameliorating the adversity that led to the decision to transfer such as reuniting a long-distance family or realizing one’s true passion can allow the resident to thrive as a trainee and maximize their potential. Transferring programs can give a resident a more well-rounded training experience, as different programs may have different strengths, patient populations, and practice settings. Working with different faculty members with varied niches and practice styles can create a more comprehensive residency experience.
Final Thoughts
Ultimately, transferring residency programs is not easy but also is not impossible. Successfully switching residency programs can be a rewarding experience providing greater well-being and fulfillment.
Transferring from one residency program to another is rare but not unheard of. According to the most recent Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education Data Resource Book, there were 1020 residents who transferred residency programs in the 2020-2021 academic year.1 With a total of 126,759 active residents in specialty programs, the percentage of transferring residents was less than 1%. The specialties with the highest number of transferring residents included psychiatry, general surgery, internal medicine, and family medicine. In dermatology programs, there were only 2 resident transfers during the 2019-2020 academic year and 6 transfers in the 2020-2021 academic year.1,2 A resident contemplating transferring training programs must carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages before undertaking the uncertain transfer process, but transferring residency programs can be achieved successfully with planning and luck.
Deciding to Transfer
The decision to transfer residency programs may be a difficult one that is wrought with anxiety. There are many reasons why a trainee may wish to pursue transferring training programs. A transfer to another geographic area may be necessary for personal or family reasons, such as to reunite with a spouse and children or to care for a sick family member. A resident may find their program to be a poor fit and may wish to train in a different educational environment. Occasionally, a program can lose its accreditation, and its residents will be tasked with finding a new position elsewhere. A trainee also may realize that the specialty they matched into initially does not align with their true passions. It is important for the potential transfer applicant to be levelheaded about their decision. Residency is a demanding period for every trainee; switching programs may not be the best solution for every problem and should only be considered if essential.
Transfer Timing
A trainee may have thoughts of leaving a program soon after starting residency or perhaps even before starting if their National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) Match result was a disappointment; however, there are certain rules related to transfer timing. The NRMP Match represents a binding commitment for both the applicant and program. If for any reason an applicant will not honor the binding commitment, the NRMP requires the applicant to initiate a waiver review, which can be requested for unanticipated serious and extreme hardship, change of specialty, or ineligibility. According to the NRMP rules and regulations, applicants cannot apply for, discuss, interview for, or accept a position in another program until a waiver has been granted.3 Waivers based on change of specialty must be requested by mid-January prior to the start of training, which means most applicants who match to positions that begin in the same year of the Match do not qualify for change of specialty waivers. However, those who matched to an advanced position and are doing a preliminary year position may consider this option if they have a change of heart during their internship. The NRMP may consider a 1-year deferral to delay training if mutually agreed upon by both the matched applicant and the program.3 The binding commitment is in place for the first 45 days of training, and applicants who resign within 45 days or a program that tries to solicit the transfer of a resident prior to that date could be in violation of the Match and can face consequences such as being barred from entering the matching process in future cycles. Of the 1020 transfers that occurred among residents in specialty programs during the 2020-2021 academic year, 354 (34.7%) occurred during the first year of the training program; 228 (22.4%) occurred during the second year; 389 (38.1%) occurred during the third year; and 49 (4.8%) occurred in the fourth, fifth, or sixth year of the program.1 Unlike other jobs/occupations in which one can simply give notice, in medical training even if a transfer position is accepted, the transition date between programs must be mutually agreed upon. Often, this may coincide with the start of the new academic year.
The Transfer Process
Transferring residency programs is a substantial undertaking. Unlike the Match, a trainee seeking to transfer programs does so without a standardized application system or structured support through the process; the transfer applicant must be prepared to navigate the transfer process on their own. The first step after making the decision to transfer is for the resident to meet with the program leadership (ie, program director[s], coordinator, designated official) at their home program to discuss the decision—a nerve-wracking but imperative first step. A receiving program may not favor an applicant secretly applying to a new program without the knowledge of their home program and often will require the home program’s blessing to proceed. The receiving program also would want to ensure the applicant is in good standing and not leaving due to misconduct. Once given the go-ahead, the process is largely in the hands of the applicant. The transfer applicant should identify locations or programs of interest and then take initiative to reach out to potential programs. FREIDA (Fellowship and Residency Electronic Interactive Database Access) is the American Medical Association’s residency and fellowship database that allows vacant position listings to be posted online.4 Additionally, the Association of American Medical Colleges’ FindAResident website is a year-round search tool designed to help find open residency and fellowship positions.5 Various specialties also may have program director listserves that communicate vacant positions. On occasion, there are spots in the main NRMP Match that are reserved positions (“R”). These are postgraduate year 2 positions in specialty programs that begin in the year of the Match and are reserved for physicians with prior graduate medical education; these also are known as “Physician Positions.”6 Ultimately, advertisements for vacancies may be few and far between, requiring the resident to send unsolicited emails with curriculum vitae attached to the program directors at programs of interest to inquire about any vacancies and hope for a favorable response. Even if the transfer applicant is qualified, luck that the right spot will be available at the right time may be the deciding factor in transferring programs.
The next step is interviewing for the position. There likely will be fewer candidates interviewing for an open spot but that does not make the process less competitive. The candidate should highlight their strengths and achievements and discuss why the new program would be a great fit both personally and professionally. Even if an applicant is seeking a transfer due to discontent with a prior program, it is best to act graciously and not speak poorly about another training program.
Prior to selection, the candidate may be asked to provide information such as diplomas, US Medical Licensing Examination Step and residency in-service training examination scores, and academic reviews from their current residency program. The interview process may take several weeks as the graduate medical education office often will need to officially approve of an applicant before a formal offer to transfer is extended.
Finally, once an offer is made and accepted, there still is a great amount of paperwork to complete before the transition. The applicant should stay on track with all off-boarding and on-boarding requirements, such as signing a contract, obtaining background checks, and applying for a new license to ensure the switch is not delayed.
Disadvantages of Transferring Programs
The transfer process is not easy to navigate and can be a source of stress for the applicant. It is natural to fear resentment from colleagues and co-residents. Although transferring programs might be in the best interest of the trainee, it may leave a large gap in the program that they are leaving, which can place a burden on the remaining residents.
There are many adjustments to be made after transferring programs. The transferring resident will again start from scratch, needing to learn the ropes and adapt to the growing pains of being at a new institution. This may require learning a completely new electronic medical record, adapting to a new culture, and in many cases stepping in as a senior resident without fully knowing the ins and outs of the program.
Advantages of Transferring Programs
Successfully transferring programs is something to celebrate. There may be great benefits to transferring to a program that is better suited to the trainee—either personally or professionally. Ameliorating the adversity that led to the decision to transfer such as reuniting a long-distance family or realizing one’s true passion can allow the resident to thrive as a trainee and maximize their potential. Transferring programs can give a resident a more well-rounded training experience, as different programs may have different strengths, patient populations, and practice settings. Working with different faculty members with varied niches and practice styles can create a more comprehensive residency experience.
Final Thoughts
Ultimately, transferring residency programs is not easy but also is not impossible. Successfully switching residency programs can be a rewarding experience providing greater well-being and fulfillment.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Data Resource Book, Academic Year 2021-2022. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/publicationsbooks/2021-2022_acgme__databook_document.pdf
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Data Resource Book, Academic Year 2020-2021. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/publicationsbooks/2020-2021_acgme_databook_document.pdf
- After the Match. National Resident Matching Program website. Accessed January 23, 2023. https://www.nrmp.org/fellowship-applicants/after-the-match/
- FREIDA vacant position listings. American Medical Association website. Accessed January 23, 2023. https://freida.ama-assn.org/vacant-position
- FindAResident. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed January 23, 2023. https://students-residents.aamc.org/findaresident/findaresident
- What are the types of program positions in the main residency match? National Resident Matching Program website. Published August 5, 2021. Accessed January 23, 2023. https://www.nrmp.org/help/item/what-types-of-programs-participate-in-the-main-residency-match/
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Data Resource Book, Academic Year 2021-2022. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/publicationsbooks/2021-2022_acgme__databook_document.pdf
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Data Resource Book, Academic Year 2020-2021. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Accessed January 20, 2023. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/publicationsbooks/2020-2021_acgme_databook_document.pdf
- After the Match. National Resident Matching Program website. Accessed January 23, 2023. https://www.nrmp.org/fellowship-applicants/after-the-match/
- FREIDA vacant position listings. American Medical Association website. Accessed January 23, 2023. https://freida.ama-assn.org/vacant-position
- FindAResident. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed January 23, 2023. https://students-residents.aamc.org/findaresident/findaresident
- What are the types of program positions in the main residency match? National Resident Matching Program website. Published August 5, 2021. Accessed January 23, 2023. https://www.nrmp.org/help/item/what-types-of-programs-participate-in-the-main-residency-match/
RESIDENT PEARL
- Transferring residency programs is difficult but possible. The decision to transfer residencies may be anxiety producing, but with substantial motives, the rewards of transferring can be worthwhile.
Disability in medicine: My experience
What does a doctor look like? Throughout history, this concept has shifted due to societal norms and increased access to medical education. Today, the idea of a physician has expanded to incorporate a myriad of people; however, stigma still exists in medicine regarding mental illness and disability. I would like to share my personal journey through high school, college, medical school, and now residency, and how my identity and struggles have shaped me into the physician I am today. There are few conversations around disability—especially disability and mental health—in medicine, and through my own advocacy, I have met many students with disability who feel that medical school is unattainable. Additionally, I have met many medical students, residents, and pre-health advisors who are happy for the experience to learn more about a marginalized group in medicine. My hope in sharing my story is to offer a space for conversation about intersectionality within medical communities and how physicians and physicians in training can facilitate that change, regardless of their position or specialty. Additionally, I hope to shed light on the unique mental health needs of patients with disabilities and how mental health clinicians can address those needs.
Perceived weaknesses turned into strengths
“Why do you walk like that?” “What is that brace on your leg?” The early years of my childhood were marked by these questions and others like them. I was the kid with the limp, the kid with a brace on his leg, and the kid who disappeared multiple times a week for doctor’s appointments or physical therapy. I learned to deflect these questions or give nebulous answers about an accident or injury. The reality is that I was born with cerebral palsy (CP). My CP manifested as hemiparesis on the left side of my body. I was in aggressive physical therapy throughout childhood, received Botox injections for muscle spasticity, and underwent corrective surgery on my left leg to straighten my foot. In childhood, the diagnosis meant nothing more than 2 words that sounded like they belonged to superheroes in comic books. Even with supportive parents and family, I kept my disability a secret, much like the powers and abilities of my favorite superheroes.
However, like all great origin stories, what I once thought were weaknesses turned out to be strengths that pushed me through college, medical school, and now psychiatry residency. Living with a disability has shaped how I see the world and relate to my patients. My experience has helped me connect to my patients in ways others might not. These properties are important in any physician but vital in psychiatry, where many patients feel neglected or stigmatized; this is another reason there should be more doctors with disabilities in medicine. Unfortunately, systemic barriers are still in place that disincentivize those with a disability from pursuing careers in medicine. Stories like mine are important to inspire a reexamination of what a physician should be and how medicine, patients, and communities benefit from this change.
My experience through medical school
My path to psychiatry and residency was shaped by my early experience with the medical field and treatment. From the early days of my diagnosis at age 4, I was told that my brain was “wired differently” and that, because of this disruption in circuitry, I would have difficulty with physical activity. I grew to appreciate the intricacies of the brain and pathology to understand my body. With greater understanding came the existential realization that I would live with a disability for the rest of my life. Rather than dream of a future where I would be “normal,” I focused on adapting my life to my normal. An unfortunate reality of this normal was that no doctor would be able to relate to me, and my health care would focus on limitations rather than possibilities.
I focused on school as a distraction and slowly warmed to the idea of pursuing medicine as a career. The seed was planted years prior by the numerous doctors’ visits and procedures, and was cultivated by a desire to understand pathologies and offer treatment to patients from the perspective of a patient. When I applied to medical school, I did not know how to address my CP. Living as a person with CP was a core reason for my decision to pursue medicine, but I was afraid that a disclosure of disability would preclude any admission to medical school. Research into programs offered little guidance because most institutions only listed vague “physical expectations” of each student. There were times I doubted if I would be accepted anywhere. Many programs I reached out to about my situation seemed unenthusiastic about the prospect of a student with CP, and when I brought up my CP in interviews, the reaction was often of surprise and an admission that they had forgotten about “that part” of my application. Fortunately, I was accepted to medical school, but still struggled with the fear that one day I would be found out and not allowed to continue. No one in my class or school was like me, and a meeting with an Americans with Disabilities Act coordinator who asked me to reexamine the physical competencies of the school before advancing to clinical clerkships only further reinforced this fear. I decided to fly under the radar and not say anything about my disability to my attendings. I slowly worked my way through clerkships by making do with adapted ways to perform procedures and exams with additional practice and maneuvering at home. I found myself drawn to psychiatry because of the similarities I saw in the patients and myself. I empathized with how the patients struggled with chronic conditions that left them feeling separated from society and how they felt that their diagnosis was something they needed to hide. When medical school ended and I decided to pursue psychiatry, I wanted to share my story to inspire others with a disability to consider medicine as a career given their unique experiences. My experience thus far has been uplifting as my journey has echoed so many others.
A need for greater representation
Disability representation in medicine is needed more than ever. According to the CDC, >60 million adults in the United States (1 in 4) live with a disability.1 Although the physical health disparities are often discussed, there is less conversation surrounding mental health for individuals with disabilities. A 2018 study by Cree et al2 found that approximately 17.4 million adults with disabilities experienced frequent mental distress, defined as reporting ≥14 mentally unhealthy days in the past 30 days. Furthermore, compared to individuals without a disability, those with a disability are statistically more likely to have suicidal ideation, suicidal planning, and suicide attempts.3 One way to address this disparity is to recruit medical students with disabilities to become physicians with disabilities. Evidence suggests that physicians who are members of groups that are underrepresented in medicine are more likely to deliver care to underrepresented patients.4 However, medical schools and institutions have been slow to address the disparity. A 2019 survey found an estimated 4.6% of medical students responded “yes” when asked if they had a disability, with most students reporting a psychological or attention/hyperactive disorder.5 Existing barriers include restrictive language surrounding technical standards influenced by long-standing vestiges of what a physician should be.6
An opportunity to connect with patients
I now do not see myself as having a secret identity to hide. Although my CP does not give me any superpowers, it has given me the opportunity to connect with my patients and serve as an example of why medical school recruitment and admissions should expand. Psychiatrists have been on the forefront of change in medicine and can shift the perception of a physician. In doing so, we not only enrich our field but also the lives of our patients who may need it most.
1. Okoro CA, Hollis ND, Cyrus AC, et al. Prevalence of disabilities and health care access by disability status and type among adults—United States, 2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67(32):882-887.
2. Cree RA, Okoro CA, Zack MM, et al. Frequent mental distress among adults, by disability status, disability type, and selected characteristics—United States 2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(36):1238-1243.
3. Marlow NM, Xie Z, Tanner R, et al. Association between disability and suicide-related outcomes among US adults. Am J Prev Med. 2021;61(6):852-862.
4. Thurmond VB, Kirch DG. Impact of minority physicians on health care. South Med J. 1998;91(11):1009-1013.
5. Meeks LM, Case B, Herzer K, et al. Change in prevalence of disabilities and accommodation practices among US medical schools, 2016 vs 2019. JAMA. 2019;322(20):2022-2024.
6. Stauffer C, Case B, Moreland CJ, et al. Technical standards from newly established medical schools: a review of disability inclusive practices. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2022;9:23821205211072763.
What does a doctor look like? Throughout history, this concept has shifted due to societal norms and increased access to medical education. Today, the idea of a physician has expanded to incorporate a myriad of people; however, stigma still exists in medicine regarding mental illness and disability. I would like to share my personal journey through high school, college, medical school, and now residency, and how my identity and struggles have shaped me into the physician I am today. There are few conversations around disability—especially disability and mental health—in medicine, and through my own advocacy, I have met many students with disability who feel that medical school is unattainable. Additionally, I have met many medical students, residents, and pre-health advisors who are happy for the experience to learn more about a marginalized group in medicine. My hope in sharing my story is to offer a space for conversation about intersectionality within medical communities and how physicians and physicians in training can facilitate that change, regardless of their position or specialty. Additionally, I hope to shed light on the unique mental health needs of patients with disabilities and how mental health clinicians can address those needs.
Perceived weaknesses turned into strengths
“Why do you walk like that?” “What is that brace on your leg?” The early years of my childhood were marked by these questions and others like them. I was the kid with the limp, the kid with a brace on his leg, and the kid who disappeared multiple times a week for doctor’s appointments or physical therapy. I learned to deflect these questions or give nebulous answers about an accident or injury. The reality is that I was born with cerebral palsy (CP). My CP manifested as hemiparesis on the left side of my body. I was in aggressive physical therapy throughout childhood, received Botox injections for muscle spasticity, and underwent corrective surgery on my left leg to straighten my foot. In childhood, the diagnosis meant nothing more than 2 words that sounded like they belonged to superheroes in comic books. Even with supportive parents and family, I kept my disability a secret, much like the powers and abilities of my favorite superheroes.
However, like all great origin stories, what I once thought were weaknesses turned out to be strengths that pushed me through college, medical school, and now psychiatry residency. Living with a disability has shaped how I see the world and relate to my patients. My experience has helped me connect to my patients in ways others might not. These properties are important in any physician but vital in psychiatry, where many patients feel neglected or stigmatized; this is another reason there should be more doctors with disabilities in medicine. Unfortunately, systemic barriers are still in place that disincentivize those with a disability from pursuing careers in medicine. Stories like mine are important to inspire a reexamination of what a physician should be and how medicine, patients, and communities benefit from this change.
My experience through medical school
My path to psychiatry and residency was shaped by my early experience with the medical field and treatment. From the early days of my diagnosis at age 4, I was told that my brain was “wired differently” and that, because of this disruption in circuitry, I would have difficulty with physical activity. I grew to appreciate the intricacies of the brain and pathology to understand my body. With greater understanding came the existential realization that I would live with a disability for the rest of my life. Rather than dream of a future where I would be “normal,” I focused on adapting my life to my normal. An unfortunate reality of this normal was that no doctor would be able to relate to me, and my health care would focus on limitations rather than possibilities.
I focused on school as a distraction and slowly warmed to the idea of pursuing medicine as a career. The seed was planted years prior by the numerous doctors’ visits and procedures, and was cultivated by a desire to understand pathologies and offer treatment to patients from the perspective of a patient. When I applied to medical school, I did not know how to address my CP. Living as a person with CP was a core reason for my decision to pursue medicine, but I was afraid that a disclosure of disability would preclude any admission to medical school. Research into programs offered little guidance because most institutions only listed vague “physical expectations” of each student. There were times I doubted if I would be accepted anywhere. Many programs I reached out to about my situation seemed unenthusiastic about the prospect of a student with CP, and when I brought up my CP in interviews, the reaction was often of surprise and an admission that they had forgotten about “that part” of my application. Fortunately, I was accepted to medical school, but still struggled with the fear that one day I would be found out and not allowed to continue. No one in my class or school was like me, and a meeting with an Americans with Disabilities Act coordinator who asked me to reexamine the physical competencies of the school before advancing to clinical clerkships only further reinforced this fear. I decided to fly under the radar and not say anything about my disability to my attendings. I slowly worked my way through clerkships by making do with adapted ways to perform procedures and exams with additional practice and maneuvering at home. I found myself drawn to psychiatry because of the similarities I saw in the patients and myself. I empathized with how the patients struggled with chronic conditions that left them feeling separated from society and how they felt that their diagnosis was something they needed to hide. When medical school ended and I decided to pursue psychiatry, I wanted to share my story to inspire others with a disability to consider medicine as a career given their unique experiences. My experience thus far has been uplifting as my journey has echoed so many others.
A need for greater representation
Disability representation in medicine is needed more than ever. According to the CDC, >60 million adults in the United States (1 in 4) live with a disability.1 Although the physical health disparities are often discussed, there is less conversation surrounding mental health for individuals with disabilities. A 2018 study by Cree et al2 found that approximately 17.4 million adults with disabilities experienced frequent mental distress, defined as reporting ≥14 mentally unhealthy days in the past 30 days. Furthermore, compared to individuals without a disability, those with a disability are statistically more likely to have suicidal ideation, suicidal planning, and suicide attempts.3 One way to address this disparity is to recruit medical students with disabilities to become physicians with disabilities. Evidence suggests that physicians who are members of groups that are underrepresented in medicine are more likely to deliver care to underrepresented patients.4 However, medical schools and institutions have been slow to address the disparity. A 2019 survey found an estimated 4.6% of medical students responded “yes” when asked if they had a disability, with most students reporting a psychological or attention/hyperactive disorder.5 Existing barriers include restrictive language surrounding technical standards influenced by long-standing vestiges of what a physician should be.6
An opportunity to connect with patients
I now do not see myself as having a secret identity to hide. Although my CP does not give me any superpowers, it has given me the opportunity to connect with my patients and serve as an example of why medical school recruitment and admissions should expand. Psychiatrists have been on the forefront of change in medicine and can shift the perception of a physician. In doing so, we not only enrich our field but also the lives of our patients who may need it most.
What does a doctor look like? Throughout history, this concept has shifted due to societal norms and increased access to medical education. Today, the idea of a physician has expanded to incorporate a myriad of people; however, stigma still exists in medicine regarding mental illness and disability. I would like to share my personal journey through high school, college, medical school, and now residency, and how my identity and struggles have shaped me into the physician I am today. There are few conversations around disability—especially disability and mental health—in medicine, and through my own advocacy, I have met many students with disability who feel that medical school is unattainable. Additionally, I have met many medical students, residents, and pre-health advisors who are happy for the experience to learn more about a marginalized group in medicine. My hope in sharing my story is to offer a space for conversation about intersectionality within medical communities and how physicians and physicians in training can facilitate that change, regardless of their position or specialty. Additionally, I hope to shed light on the unique mental health needs of patients with disabilities and how mental health clinicians can address those needs.
Perceived weaknesses turned into strengths
“Why do you walk like that?” “What is that brace on your leg?” The early years of my childhood were marked by these questions and others like them. I was the kid with the limp, the kid with a brace on his leg, and the kid who disappeared multiple times a week for doctor’s appointments or physical therapy. I learned to deflect these questions or give nebulous answers about an accident or injury. The reality is that I was born with cerebral palsy (CP). My CP manifested as hemiparesis on the left side of my body. I was in aggressive physical therapy throughout childhood, received Botox injections for muscle spasticity, and underwent corrective surgery on my left leg to straighten my foot. In childhood, the diagnosis meant nothing more than 2 words that sounded like they belonged to superheroes in comic books. Even with supportive parents and family, I kept my disability a secret, much like the powers and abilities of my favorite superheroes.
However, like all great origin stories, what I once thought were weaknesses turned out to be strengths that pushed me through college, medical school, and now psychiatry residency. Living with a disability has shaped how I see the world and relate to my patients. My experience has helped me connect to my patients in ways others might not. These properties are important in any physician but vital in psychiatry, where many patients feel neglected or stigmatized; this is another reason there should be more doctors with disabilities in medicine. Unfortunately, systemic barriers are still in place that disincentivize those with a disability from pursuing careers in medicine. Stories like mine are important to inspire a reexamination of what a physician should be and how medicine, patients, and communities benefit from this change.
My experience through medical school
My path to psychiatry and residency was shaped by my early experience with the medical field and treatment. From the early days of my diagnosis at age 4, I was told that my brain was “wired differently” and that, because of this disruption in circuitry, I would have difficulty with physical activity. I grew to appreciate the intricacies of the brain and pathology to understand my body. With greater understanding came the existential realization that I would live with a disability for the rest of my life. Rather than dream of a future where I would be “normal,” I focused on adapting my life to my normal. An unfortunate reality of this normal was that no doctor would be able to relate to me, and my health care would focus on limitations rather than possibilities.
I focused on school as a distraction and slowly warmed to the idea of pursuing medicine as a career. The seed was planted years prior by the numerous doctors’ visits and procedures, and was cultivated by a desire to understand pathologies and offer treatment to patients from the perspective of a patient. When I applied to medical school, I did not know how to address my CP. Living as a person with CP was a core reason for my decision to pursue medicine, but I was afraid that a disclosure of disability would preclude any admission to medical school. Research into programs offered little guidance because most institutions only listed vague “physical expectations” of each student. There were times I doubted if I would be accepted anywhere. Many programs I reached out to about my situation seemed unenthusiastic about the prospect of a student with CP, and when I brought up my CP in interviews, the reaction was often of surprise and an admission that they had forgotten about “that part” of my application. Fortunately, I was accepted to medical school, but still struggled with the fear that one day I would be found out and not allowed to continue. No one in my class or school was like me, and a meeting with an Americans with Disabilities Act coordinator who asked me to reexamine the physical competencies of the school before advancing to clinical clerkships only further reinforced this fear. I decided to fly under the radar and not say anything about my disability to my attendings. I slowly worked my way through clerkships by making do with adapted ways to perform procedures and exams with additional practice and maneuvering at home. I found myself drawn to psychiatry because of the similarities I saw in the patients and myself. I empathized with how the patients struggled with chronic conditions that left them feeling separated from society and how they felt that their diagnosis was something they needed to hide. When medical school ended and I decided to pursue psychiatry, I wanted to share my story to inspire others with a disability to consider medicine as a career given their unique experiences. My experience thus far has been uplifting as my journey has echoed so many others.
A need for greater representation
Disability representation in medicine is needed more than ever. According to the CDC, >60 million adults in the United States (1 in 4) live with a disability.1 Although the physical health disparities are often discussed, there is less conversation surrounding mental health for individuals with disabilities. A 2018 study by Cree et al2 found that approximately 17.4 million adults with disabilities experienced frequent mental distress, defined as reporting ≥14 mentally unhealthy days in the past 30 days. Furthermore, compared to individuals without a disability, those with a disability are statistically more likely to have suicidal ideation, suicidal planning, and suicide attempts.3 One way to address this disparity is to recruit medical students with disabilities to become physicians with disabilities. Evidence suggests that physicians who are members of groups that are underrepresented in medicine are more likely to deliver care to underrepresented patients.4 However, medical schools and institutions have been slow to address the disparity. A 2019 survey found an estimated 4.6% of medical students responded “yes” when asked if they had a disability, with most students reporting a psychological or attention/hyperactive disorder.5 Existing barriers include restrictive language surrounding technical standards influenced by long-standing vestiges of what a physician should be.6
An opportunity to connect with patients
I now do not see myself as having a secret identity to hide. Although my CP does not give me any superpowers, it has given me the opportunity to connect with my patients and serve as an example of why medical school recruitment and admissions should expand. Psychiatrists have been on the forefront of change in medicine and can shift the perception of a physician. In doing so, we not only enrich our field but also the lives of our patients who may need it most.
1. Okoro CA, Hollis ND, Cyrus AC, et al. Prevalence of disabilities and health care access by disability status and type among adults—United States, 2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67(32):882-887.
2. Cree RA, Okoro CA, Zack MM, et al. Frequent mental distress among adults, by disability status, disability type, and selected characteristics—United States 2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(36):1238-1243.
3. Marlow NM, Xie Z, Tanner R, et al. Association between disability and suicide-related outcomes among US adults. Am J Prev Med. 2021;61(6):852-862.
4. Thurmond VB, Kirch DG. Impact of minority physicians on health care. South Med J. 1998;91(11):1009-1013.
5. Meeks LM, Case B, Herzer K, et al. Change in prevalence of disabilities and accommodation practices among US medical schools, 2016 vs 2019. JAMA. 2019;322(20):2022-2024.
6. Stauffer C, Case B, Moreland CJ, et al. Technical standards from newly established medical schools: a review of disability inclusive practices. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2022;9:23821205211072763.
1. Okoro CA, Hollis ND, Cyrus AC, et al. Prevalence of disabilities and health care access by disability status and type among adults—United States, 2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67(32):882-887.
2. Cree RA, Okoro CA, Zack MM, et al. Frequent mental distress among adults, by disability status, disability type, and selected characteristics—United States 2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(36):1238-1243.
3. Marlow NM, Xie Z, Tanner R, et al. Association between disability and suicide-related outcomes among US adults. Am J Prev Med. 2021;61(6):852-862.
4. Thurmond VB, Kirch DG. Impact of minority physicians on health care. South Med J. 1998;91(11):1009-1013.
5. Meeks LM, Case B, Herzer K, et al. Change in prevalence of disabilities and accommodation practices among US medical schools, 2016 vs 2019. JAMA. 2019;322(20):2022-2024.
6. Stauffer C, Case B, Moreland CJ, et al. Technical standards from newly established medical schools: a review of disability inclusive practices. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2022;9:23821205211072763.
Characteristics of Matched vs Nonmatched Dermatology Applicants
Dermatology residency continues to be one of the most competitive specialties, with a match rate of 84.7% for US allopathic seniors in the 2019-2020 academic year.1 In the 2019-2020 cycle, dermatology applicants were tied with plastic surgery for the highest median US Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 1 score compared with other specialties, which suggests that the top medical students are applying, yet only approximately 5 of 6 students are matching.
Factors that have been cited with successful dermatology matching include USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 Clinical Knowledge (CK) scores,2 research accomplishments,3 letters of recommendation,4 medical school performance, personal statement, grades in required clerkships, and volunteer/extracurricular experiences, among others.5
The National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) publishes data each year regarding different academic factors—USMLE scores; number of abstracts, presentations, and papers; work, volunteer, and research experiences—and compares the mean between matched and nonmatched applicants.1 However, the USMLE does not report any demographic information of the applicants and the implication it has for matching. Additionally, the number of couples participating in the couples match continues to increase each year. In the 2019-2020 cycle, 1224 couples participated in the couples match.1 However, NRMP reports only limited data regarding the couples match, and it is not specialty specific.
We aimed to determine the characteristics of matched vs nonmatched dermatology applicants. Secondarily, we aimed to determine any differences among demographics regarding matching rates, academic performance, and research publications. We also aimed to characterize the strategy and outcomes of applicants that couples matched.
Materials and Methods
The Mayo Clinic institutional review board deemed this study exempt. All applicants who applied to Mayo Clinic dermatology residency in Scottsdale, Arizona, during the 2018-2019 cycle were emailed an initial survey (N=475) before Match Day that obtained demographic information, geographic information, gap-year information, USMLE Step 1 score, publications, medical school grades, number of away rotations, and number of interviews. A follow-up survey gathering match data and couples matching data was sent to the applicants who completed the first survey on Match Day. The survey was repeated for the 2019-2020 cycle. In the second survey, Step 2 CK data were obtained. The survey was sent to 629 applicants who applied to Mayo Clinic dermatology residencies in Arizona, Minnesota, and Florida to include a broader group of applicants. For publications, applicants were asked to count only published or accepted manuscripts, not abstracts, posters, conference presentations, or submitted manuscripts. Applicants who did not respond to the second survey (match data) were not included in that part of the analysis. One survey was excluded because of implausible answers (eg, scores outside of range for USMLE Step scores).
Statistical Analysis—For statistical analyses, the applicants from both applications cycles were combined. Descriptive statistics were reported in the form of mean, median, or counts (percentages), as applicable. Means were compared using 2-sided t tests. Group comparisons were examined using χ2 tests for categorical variables. Statistical analyses were performed using the BlueSky Statistics version 6.30. P<.05 was considered significant.
Results
In 2019, a total of 149 applicants completed the initial survey (31.4% response rate), and 112 completed the follow-up survey (75.2% response rate). In 2020, a total of 142 applicants completed the initial survey (22.6% response rate), and 124 completed the follow-up survey (87.3% response rate). Combining the 2 years, after removing 1 survey with implausible answers, there were 290 respondents from the initial survey and 235 from the follow-up survey. The median (SD) age for the total applicants over both years was 27 (3.0) years, and 180 applicants were female (61.9%).
USMLE Scores—The median USMLE Step 1 score was 250, and scores ranged from 196 to 271. The median USMLE Step 2 CK score was 257, and scores ranged from 213 to 281. Higher USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK scores and more interviews were associated with higher match rates (Table 1). In addition, students with a dermatology program at their medical school were more likely to match than those without a home dermatology program.
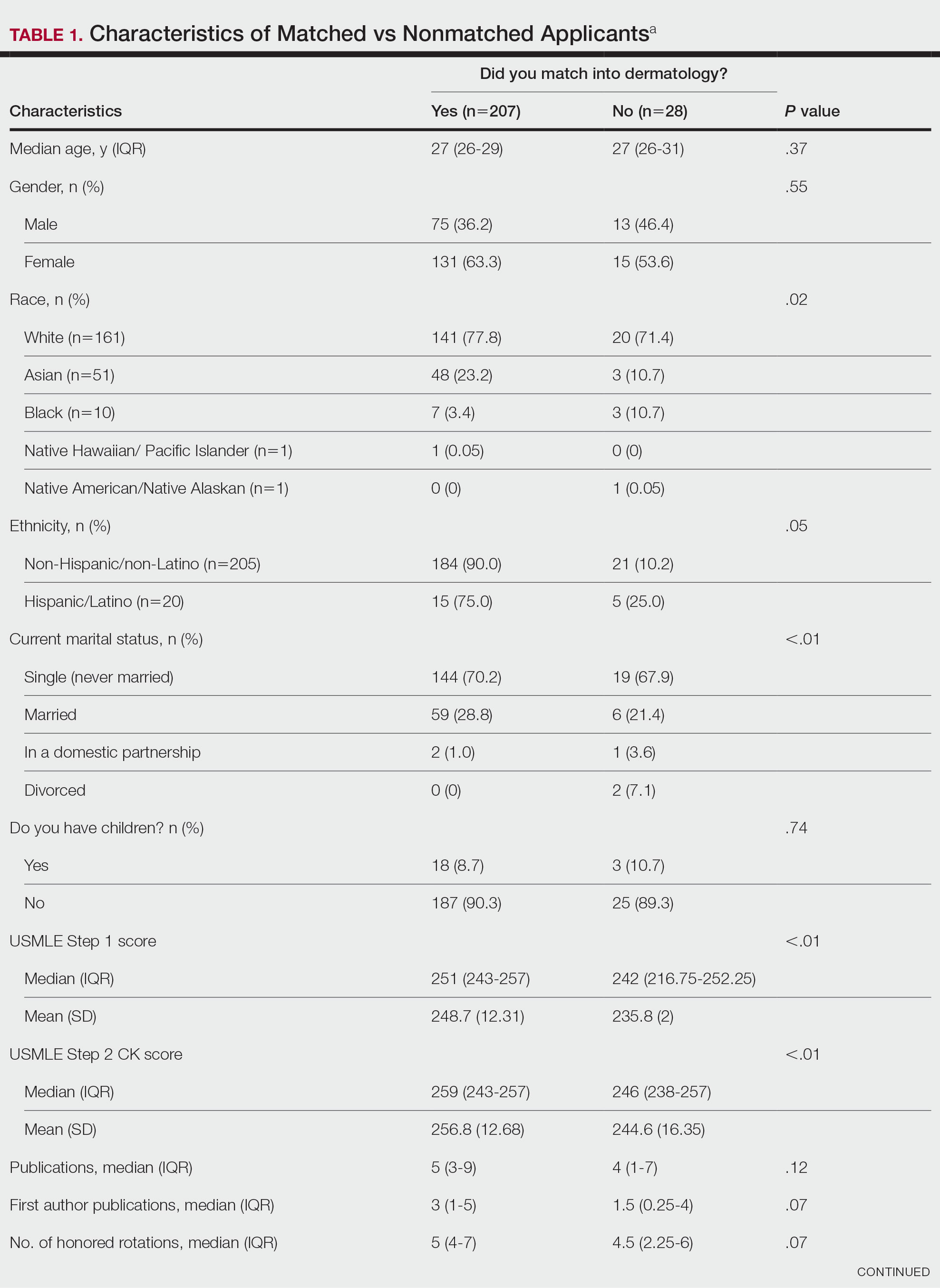
Gender Differences—There were 180 females and 110 males who completed the surveys. Males and females had similar match rates (85.2% vs 89.0%; P=.39)(Table 2).
Family Life—In comparing marital status, applicants who were divorced had a higher median age (38.5 years) compared with applicants who were single, married, or in a domestic partnership (all 27 years; P<.01). Differences are outlined in Table 3.
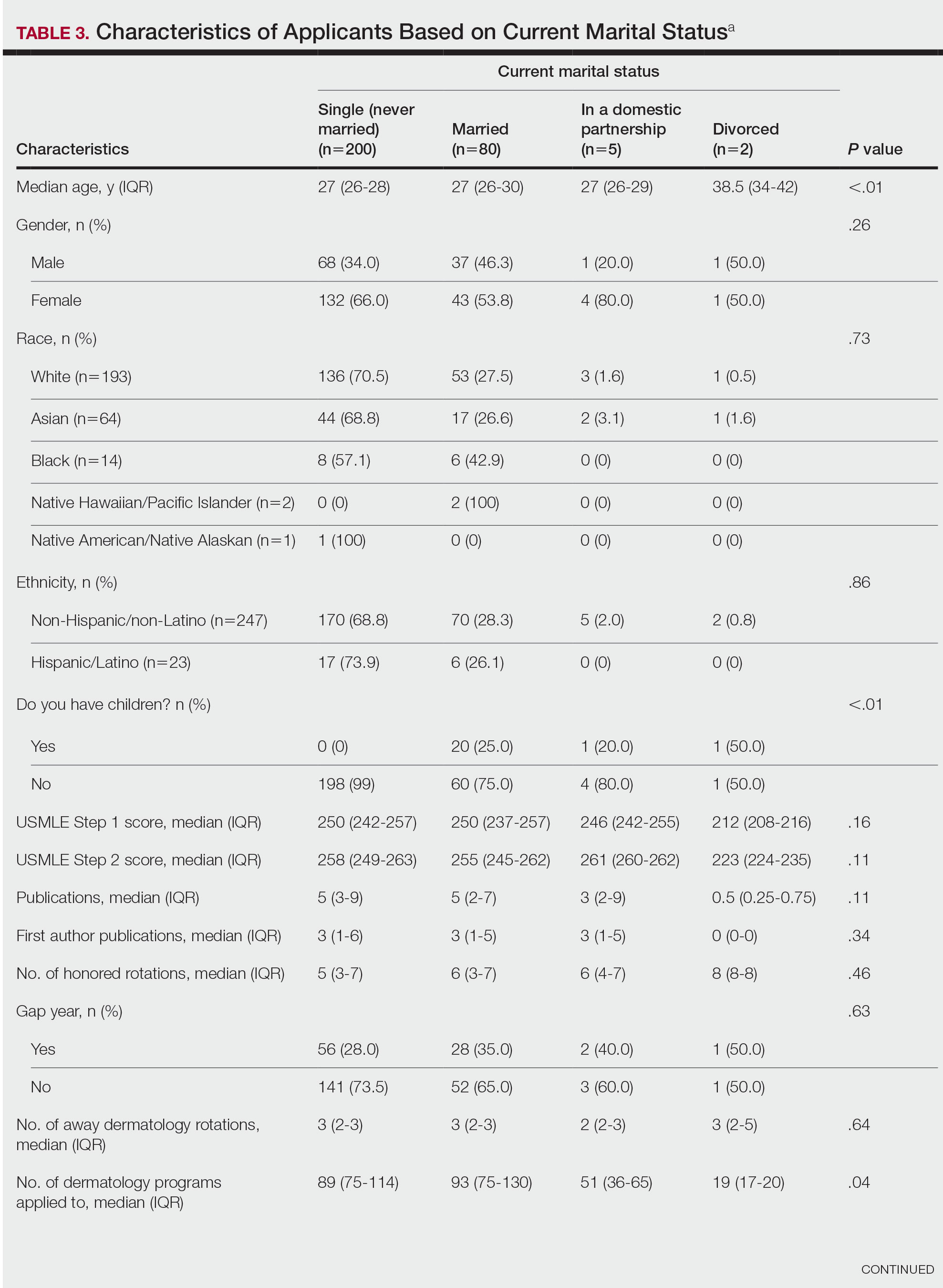
On average, applicants with children (n=27 [15 male, 12 female]; P=.13) were 3 years older than those without (30.5 vs 27; P<.01) and were more likely to be married (88.9% vs 21.5%; P<.01). Applicants with children had a mean USMLE Step 1 score of 241 compared to 251 for those without children (P=.02) and a mean USMLE Step 2 CK score of 246 compared to 258 for those without children (P<.01). Applicants with children had similar debt, number of publications, number of honored rotations, and match rates compared to applicants without children (Figure).
Couples Match—Seventeen individuals in our survey participated in the couples match (7.8%), and all 17 (100%) matched into dermatology. The mean age was 26.7 years, 12 applicants were female, 2 applicants were married, and 1 applicant had children. The mean number of interviews offered was 13.6, and the mean number of interviews attended was 11.3. This was higher than participants who were not couples matching (13.6 vs 9.8 [P=.02] and 11.3 vs 8.9 [P=.04], respectively). Applicants and their partners applied to programs and received interviews in a mean of 10 cities. Sixteen applicants reported that they contacted programs where their partner had interview offers. All participants’ rank lists included programs located in different cities than their partners’ ranked programs, and all but 1 participant ranked programs located in a different state than their partners’ ranked programs. Fifteen participants had options in their rank list for the applicant not to match, even if the partner would match. Similarly, 12 had the option for the applicant to match, even if the partner would not match. Fourteen (82.4%) matched at the same institution as their significant other. Three (17.6%) applicants matched to a program in a different state than the partner’s matched program. Two (11.8%) participants felt their relationship with their partner suffered because of the match, and 1 (5.9%) applicant was undetermined. One applicant described their relationship suffering from “unnecessary tension and anxiety” and noted “difficult conversations” about potentially matching into dermatology in a different location from their partner that could have been “devastating and not something [he or she] should have to choose.”
Comment
Factors for Matching in Dermatology—In our survey, we found the statistically significant factors of matching into dermatology included high USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK scores (P<.01), having a home dermatology program (P=.04), and attending a higher number of dermatology interviews (P<.01). These data are similar to NRMP results1; however, the higher likelihood of matching if the medical school has a home dermatology program has not been reported. This finding could be due to multiple factors such as students have less access to academic dermatologists for research projects, letters of recommendations, mentorship, and clinical rotations.
Gender and having children were factors that had no correlation with the match rate. There was a statistical difference of matching based on marital status (P<.01), but this is likely due to the low number of applicants in the divorced category. There were differences among demographics with USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK scores, which is a known factor in matching.1,2 Applicants with children had lower USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK scores compared to applicants without children. Females also had lower median USMLE Step 1 scores compared to males. This finding may serve as a reminder to programs when comparing USMLE Step examination scores that demographic factors may play a role. The race and ethnicity of applicants likely play a role. It has been reported that underrepresented minorities had lower match rates than White and Asian applicants in dermatology.6 There have been several published articles discussing the lack of diversity in dermatology, with a call to action.7-9
Factors for Couples Matching—The number of applicants participating in the couples match continues to increase yearly. The NMRP does publish data regarding “successful” couples matching but does not specify how many couples match together. There also is little published regarding advice for participation in the couples match. Although we had a limited number of couples that participated in the match, it is interesting to note they had similar strategies, including contacting programs at institutions that had offered interviews to their partners. This strategy may be effective, as dermatology programs offer interviews relatively late compared with other specialties.5 Additionally, this strategy may increase the number of interviews offered and received, as evidenced by the higher number of interviews offered compared with those who were not couples matching. Additionally, this survey highlights the sacrifice often needed by couples in the couples match as revealed by the inclusion of rank-list options in which the couples reside long distance or in which 1 partner does not match. This information may be helpful to applicants who are planning a strategy for the couples match in dermatology. Although this study does not encompass all dermatology applicants in the 2019-2020 cycle, we do believe it may be representative. The USMLE Step 1 scores in this study were similar to the published NRMP data.1,10 According to NRMP data from the 2019-2020 cycle, the mean USMLE Step 1 score was 248 for matched applicants and 239 for unmatched.1 The NRMP reported the mean USMLE Step 2 CK score for matched was 256 and 248 for unmatched, which also is similar to our data. The NRMP reported the mean number of programs ranked was 9.9 for matched and 4.5 for unmatched applicants.1 Again, our data were similar for number of dermatology interviews attended.
Limitations—There are limitations to this study. The main limitation is that the survey is from a single institution and had a limited number of respondents. Given the nature of the study, the accuracy of the data is dependent on the applicants’ honesty in self-reporting academic performance and other variables. There also may be a selection bias given the low response rate. The subanalyses—children and couples matching—were underpowered with the limited number of participants. Further studies that include multiple residency programs and multiple years could be helpful to provide more power and less risk of bias. We did not gather information such as the Medical Student Performance Evaluation letter, letters of recommendation, or personal statements, which do play an important role in the assessment of an applicant. However, because the applicants completed these surveys, and given these are largely blinded to applicants, we did not feel the applicants could accurately respond to those aspects of the application.
Conclusion
Our survey finds that factors associated with matching included a higher USMLE Step 1 score, having a home dermatology program, and a higher number of interviews offered and attended. Some demographics had varying USMLE Step 1 scores but similar match rates.
- National Resident Matching Program. Results and Data: 2020 Main Residency Match. National Resident Matching Program; May 2020. Accessed January 9, 2023. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/MM_Results_and-Data_2020-1.pdf
- Gauer JL, Jackson JB. The association of USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK scores with residency match specialty and location. Med Educ Online. 2017;22:1358579.
- Wang JV, Keller M. Pressure to publish for residency applicants in dermatology. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt56x1t7ww.
- Wang RF, Zhang M, Kaffenberger JA. Does the dermatology standardized letter of recommendation alter applicants’ chances of matching into residency. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:e139-e140.
- National Resident Matching Program, Data Release and Research Committee: results of the 2018 NRMP Program Director Survey. Accessed December 19, 2022. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/NRMP-2018-Program-Director-Survey-for-WWW.pdf
- Costello CM, Harvey JA, Besch-Stokes JG, et al. The role of race and ethnicity in the dermatology applicant match process. J Natl Med Assoc. 2022;113:666-670.
- Chen A, Shinkai K. Rethinking how we select dermatology applicants-turning the tide. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:259-260.
- Pandya AG, Alexis AF, Berger TG, et al. Increasing racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology: a call to action. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:584-587.
- Van Voorhees AS, Enos CW. Diversity in dermatology residency programs. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S46-S49.
- National Resident Matching Program. Charting outcomes in the match: U.S. allopathic seniors. Characteristics of U.S. allopathic seniors who matched to their preferred specialty in the 2018 main residency match. 2nd ed. Accessed December 19, 2022. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Charting-Outcomes-in-the-Match-2018_Seniors-1.pdf
Dermatology residency continues to be one of the most competitive specialties, with a match rate of 84.7% for US allopathic seniors in the 2019-2020 academic year.1 In the 2019-2020 cycle, dermatology applicants were tied with plastic surgery for the highest median US Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 1 score compared with other specialties, which suggests that the top medical students are applying, yet only approximately 5 of 6 students are matching.
Factors that have been cited with successful dermatology matching include USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 Clinical Knowledge (CK) scores,2 research accomplishments,3 letters of recommendation,4 medical school performance, personal statement, grades in required clerkships, and volunteer/extracurricular experiences, among others.5
The National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) publishes data each year regarding different academic factors—USMLE scores; number of abstracts, presentations, and papers; work, volunteer, and research experiences—and compares the mean between matched and nonmatched applicants.1 However, the USMLE does not report any demographic information of the applicants and the implication it has for matching. Additionally, the number of couples participating in the couples match continues to increase each year. In the 2019-2020 cycle, 1224 couples participated in the couples match.1 However, NRMP reports only limited data regarding the couples match, and it is not specialty specific.
We aimed to determine the characteristics of matched vs nonmatched dermatology applicants. Secondarily, we aimed to determine any differences among demographics regarding matching rates, academic performance, and research publications. We also aimed to characterize the strategy and outcomes of applicants that couples matched.
Materials and Methods
The Mayo Clinic institutional review board deemed this study exempt. All applicants who applied to Mayo Clinic dermatology residency in Scottsdale, Arizona, during the 2018-2019 cycle were emailed an initial survey (N=475) before Match Day that obtained demographic information, geographic information, gap-year information, USMLE Step 1 score, publications, medical school grades, number of away rotations, and number of interviews. A follow-up survey gathering match data and couples matching data was sent to the applicants who completed the first survey on Match Day. The survey was repeated for the 2019-2020 cycle. In the second survey, Step 2 CK data were obtained. The survey was sent to 629 applicants who applied to Mayo Clinic dermatology residencies in Arizona, Minnesota, and Florida to include a broader group of applicants. For publications, applicants were asked to count only published or accepted manuscripts, not abstracts, posters, conference presentations, or submitted manuscripts. Applicants who did not respond to the second survey (match data) were not included in that part of the analysis. One survey was excluded because of implausible answers (eg, scores outside of range for USMLE Step scores).
Statistical Analysis—For statistical analyses, the applicants from both applications cycles were combined. Descriptive statistics were reported in the form of mean, median, or counts (percentages), as applicable. Means were compared using 2-sided t tests. Group comparisons were examined using χ2 tests for categorical variables. Statistical analyses were performed using the BlueSky Statistics version 6.30. P<.05 was considered significant.
Results
In 2019, a total of 149 applicants completed the initial survey (31.4% response rate), and 112 completed the follow-up survey (75.2% response rate). In 2020, a total of 142 applicants completed the initial survey (22.6% response rate), and 124 completed the follow-up survey (87.3% response rate). Combining the 2 years, after removing 1 survey with implausible answers, there were 290 respondents from the initial survey and 235 from the follow-up survey. The median (SD) age for the total applicants over both years was 27 (3.0) years, and 180 applicants were female (61.9%).
USMLE Scores—The median USMLE Step 1 score was 250, and scores ranged from 196 to 271. The median USMLE Step 2 CK score was 257, and scores ranged from 213 to 281. Higher USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK scores and more interviews were associated with higher match rates (Table 1). In addition, students with a dermatology program at their medical school were more likely to match than those without a home dermatology program.


Gender Differences—There were 180 females and 110 males who completed the surveys. Males and females had similar match rates (85.2% vs 89.0%; P=.39)(Table 2).

Family Life—In comparing marital status, applicants who were divorced had a higher median age (38.5 years) compared with applicants who were single, married, or in a domestic partnership (all 27 years; P<.01). Differences are outlined in Table 3.


On average, applicants with children (n=27 [15 male, 12 female]; P=.13) were 3 years older than those without (30.5 vs 27; P<.01) and were more likely to be married (88.9% vs 21.5%; P<.01). Applicants with children had a mean USMLE Step 1 score of 241 compared to 251 for those without children (P=.02) and a mean USMLE Step 2 CK score of 246 compared to 258 for those without children (P<.01). Applicants with children had similar debt, number of publications, number of honored rotations, and match rates compared to applicants without children (Figure).

Couples Match—Seventeen individuals in our survey participated in the couples match (7.8%), and all 17 (100%) matched into dermatology. The mean age was 26.7 years, 12 applicants were female, 2 applicants were married, and 1 applicant had children. The mean number of interviews offered was 13.6, and the mean number of interviews attended was 11.3. This was higher than participants who were not couples matching (13.6 vs 9.8 [P=.02] and 11.3 vs 8.9 [P=.04], respectively). Applicants and their partners applied to programs and received interviews in a mean of 10 cities. Sixteen applicants reported that they contacted programs where their partner had interview offers. All participants’ rank lists included programs located in different cities than their partners’ ranked programs, and all but 1 participant ranked programs located in a different state than their partners’ ranked programs. Fifteen participants had options in their rank list for the applicant not to match, even if the partner would match. Similarly, 12 had the option for the applicant to match, even if the partner would not match. Fourteen (82.4%) matched at the same institution as their significant other. Three (17.6%) applicants matched to a program in a different state than the partner’s matched program. Two (11.8%) participants felt their relationship with their partner suffered because of the match, and 1 (5.9%) applicant was undetermined. One applicant described their relationship suffering from “unnecessary tension and anxiety” and noted “difficult conversations” about potentially matching into dermatology in a different location from their partner that could have been “devastating and not something [he or she] should have to choose.”
Comment
Factors for Matching in Dermatology—In our survey, we found the statistically significant factors of matching into dermatology included high USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK scores (P<.01), having a home dermatology program (P=.04), and attending a higher number of dermatology interviews (P<.01). These data are similar to NRMP results1; however, the higher likelihood of matching if the medical school has a home dermatology program has not been reported. This finding could be due to multiple factors such as students have less access to academic dermatologists for research projects, letters of recommendations, mentorship, and clinical rotations.
Gender and having children were factors that had no correlation with the match rate. There was a statistical difference of matching based on marital status (P<.01), but this is likely due to the low number of applicants in the divorced category. There were differences among demographics with USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK scores, which is a known factor in matching.1,2 Applicants with children had lower USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK scores compared to applicants without children. Females also had lower median USMLE Step 1 scores compared to males. This finding may serve as a reminder to programs when comparing USMLE Step examination scores that demographic factors may play a role. The race and ethnicity of applicants likely play a role. It has been reported that underrepresented minorities had lower match rates than White and Asian applicants in dermatology.6 There have been several published articles discussing the lack of diversity in dermatology, with a call to action.7-9
Factors for Couples Matching—The number of applicants participating in the couples match continues to increase yearly. The NMRP does publish data regarding “successful” couples matching but does not specify how many couples match together. There also is little published regarding advice for participation in the couples match. Although we had a limited number of couples that participated in the match, it is interesting to note they had similar strategies, including contacting programs at institutions that had offered interviews to their partners. This strategy may be effective, as dermatology programs offer interviews relatively late compared with other specialties.5 Additionally, this strategy may increase the number of interviews offered and received, as evidenced by the higher number of interviews offered compared with those who were not couples matching. Additionally, this survey highlights the sacrifice often needed by couples in the couples match as revealed by the inclusion of rank-list options in which the couples reside long distance or in which 1 partner does not match. This information may be helpful to applicants who are planning a strategy for the couples match in dermatology. Although this study does not encompass all dermatology applicants in the 2019-2020 cycle, we do believe it may be representative. The USMLE Step 1 scores in this study were similar to the published NRMP data.1,10 According to NRMP data from the 2019-2020 cycle, the mean USMLE Step 1 score was 248 for matched applicants and 239 for unmatched.1 The NRMP reported the mean USMLE Step 2 CK score for matched was 256 and 248 for unmatched, which also is similar to our data. The NRMP reported the mean number of programs ranked was 9.9 for matched and 4.5 for unmatched applicants.1 Again, our data were similar for number of dermatology interviews attended.
Limitations—There are limitations to this study. The main limitation is that the survey is from a single institution and had a limited number of respondents. Given the nature of the study, the accuracy of the data is dependent on the applicants’ honesty in self-reporting academic performance and other variables. There also may be a selection bias given the low response rate. The subanalyses—children and couples matching—were underpowered with the limited number of participants. Further studies that include multiple residency programs and multiple years could be helpful to provide more power and less risk of bias. We did not gather information such as the Medical Student Performance Evaluation letter, letters of recommendation, or personal statements, which do play an important role in the assessment of an applicant. However, because the applicants completed these surveys, and given these are largely blinded to applicants, we did not feel the applicants could accurately respond to those aspects of the application.
Conclusion
Our survey finds that factors associated with matching included a higher USMLE Step 1 score, having a home dermatology program, and a higher number of interviews offered and attended. Some demographics had varying USMLE Step 1 scores but similar match rates.
Dermatology residency continues to be one of the most competitive specialties, with a match rate of 84.7% for US allopathic seniors in the 2019-2020 academic year.1 In the 2019-2020 cycle, dermatology applicants were tied with plastic surgery for the highest median US Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 1 score compared with other specialties, which suggests that the top medical students are applying, yet only approximately 5 of 6 students are matching.
Factors that have been cited with successful dermatology matching include USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 Clinical Knowledge (CK) scores,2 research accomplishments,3 letters of recommendation,4 medical school performance, personal statement, grades in required clerkships, and volunteer/extracurricular experiences, among others.5
The National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) publishes data each year regarding different academic factors—USMLE scores; number of abstracts, presentations, and papers; work, volunteer, and research experiences—and compares the mean between matched and nonmatched applicants.1 However, the USMLE does not report any demographic information of the applicants and the implication it has for matching. Additionally, the number of couples participating in the couples match continues to increase each year. In the 2019-2020 cycle, 1224 couples participated in the couples match.1 However, NRMP reports only limited data regarding the couples match, and it is not specialty specific.
We aimed to determine the characteristics of matched vs nonmatched dermatology applicants. Secondarily, we aimed to determine any differences among demographics regarding matching rates, academic performance, and research publications. We also aimed to characterize the strategy and outcomes of applicants that couples matched.
Materials and Methods
The Mayo Clinic institutional review board deemed this study exempt. All applicants who applied to Mayo Clinic dermatology residency in Scottsdale, Arizona, during the 2018-2019 cycle were emailed an initial survey (N=475) before Match Day that obtained demographic information, geographic information, gap-year information, USMLE Step 1 score, publications, medical school grades, number of away rotations, and number of interviews. A follow-up survey gathering match data and couples matching data was sent to the applicants who completed the first survey on Match Day. The survey was repeated for the 2019-2020 cycle. In the second survey, Step 2 CK data were obtained. The survey was sent to 629 applicants who applied to Mayo Clinic dermatology residencies in Arizona, Minnesota, and Florida to include a broader group of applicants. For publications, applicants were asked to count only published or accepted manuscripts, not abstracts, posters, conference presentations, or submitted manuscripts. Applicants who did not respond to the second survey (match data) were not included in that part of the analysis. One survey was excluded because of implausible answers (eg, scores outside of range for USMLE Step scores).
Statistical Analysis—For statistical analyses, the applicants from both applications cycles were combined. Descriptive statistics were reported in the form of mean, median, or counts (percentages), as applicable. Means were compared using 2-sided t tests. Group comparisons were examined using χ2 tests for categorical variables. Statistical analyses were performed using the BlueSky Statistics version 6.30. P<.05 was considered significant.
Results
In 2019, a total of 149 applicants completed the initial survey (31.4% response rate), and 112 completed the follow-up survey (75.2% response rate). In 2020, a total of 142 applicants completed the initial survey (22.6% response rate), and 124 completed the follow-up survey (87.3% response rate). Combining the 2 years, after removing 1 survey with implausible answers, there were 290 respondents from the initial survey and 235 from the follow-up survey. The median (SD) age for the total applicants over both years was 27 (3.0) years, and 180 applicants were female (61.9%).
USMLE Scores—The median USMLE Step 1 score was 250, and scores ranged from 196 to 271. The median USMLE Step 2 CK score was 257, and scores ranged from 213 to 281. Higher USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK scores and more interviews were associated with higher match rates (Table 1). In addition, students with a dermatology program at their medical school were more likely to match than those without a home dermatology program.


Gender Differences—There were 180 females and 110 males who completed the surveys. Males and females had similar match rates (85.2% vs 89.0%; P=.39)(Table 2).

Family Life—In comparing marital status, applicants who were divorced had a higher median age (38.5 years) compared with applicants who were single, married, or in a domestic partnership (all 27 years; P<.01). Differences are outlined in Table 3.


On average, applicants with children (n=27 [15 male, 12 female]; P=.13) were 3 years older than those without (30.5 vs 27; P<.01) and were more likely to be married (88.9% vs 21.5%; P<.01). Applicants with children had a mean USMLE Step 1 score of 241 compared to 251 for those without children (P=.02) and a mean USMLE Step 2 CK score of 246 compared to 258 for those without children (P<.01). Applicants with children had similar debt, number of publications, number of honored rotations, and match rates compared to applicants without children (Figure).

Couples Match—Seventeen individuals in our survey participated in the couples match (7.8%), and all 17 (100%) matched into dermatology. The mean age was 26.7 years, 12 applicants were female, 2 applicants were married, and 1 applicant had children. The mean number of interviews offered was 13.6, and the mean number of interviews attended was 11.3. This was higher than participants who were not couples matching (13.6 vs 9.8 [P=.02] and 11.3 vs 8.9 [P=.04], respectively). Applicants and their partners applied to programs and received interviews in a mean of 10 cities. Sixteen applicants reported that they contacted programs where their partner had interview offers. All participants’ rank lists included programs located in different cities than their partners’ ranked programs, and all but 1 participant ranked programs located in a different state than their partners’ ranked programs. Fifteen participants had options in their rank list for the applicant not to match, even if the partner would match. Similarly, 12 had the option for the applicant to match, even if the partner would not match. Fourteen (82.4%) matched at the same institution as their significant other. Three (17.6%) applicants matched to a program in a different state than the partner’s matched program. Two (11.8%) participants felt their relationship with their partner suffered because of the match, and 1 (5.9%) applicant was undetermined. One applicant described their relationship suffering from “unnecessary tension and anxiety” and noted “difficult conversations” about potentially matching into dermatology in a different location from their partner that could have been “devastating and not something [he or she] should have to choose.”
Comment
Factors for Matching in Dermatology—In our survey, we found the statistically significant factors of matching into dermatology included high USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK scores (P<.01), having a home dermatology program (P=.04), and attending a higher number of dermatology interviews (P<.01). These data are similar to NRMP results1; however, the higher likelihood of matching if the medical school has a home dermatology program has not been reported. This finding could be due to multiple factors such as students have less access to academic dermatologists for research projects, letters of recommendations, mentorship, and clinical rotations.
Gender and having children were factors that had no correlation with the match rate. There was a statistical difference of matching based on marital status (P<.01), but this is likely due to the low number of applicants in the divorced category. There were differences among demographics with USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK scores, which is a known factor in matching.1,2 Applicants with children had lower USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK scores compared to applicants without children. Females also had lower median USMLE Step 1 scores compared to males. This finding may serve as a reminder to programs when comparing USMLE Step examination scores that demographic factors may play a role. The race and ethnicity of applicants likely play a role. It has been reported that underrepresented minorities had lower match rates than White and Asian applicants in dermatology.6 There have been several published articles discussing the lack of diversity in dermatology, with a call to action.7-9
Factors for Couples Matching—The number of applicants participating in the couples match continues to increase yearly. The NMRP does publish data regarding “successful” couples matching but does not specify how many couples match together. There also is little published regarding advice for participation in the couples match. Although we had a limited number of couples that participated in the match, it is interesting to note they had similar strategies, including contacting programs at institutions that had offered interviews to their partners. This strategy may be effective, as dermatology programs offer interviews relatively late compared with other specialties.5 Additionally, this strategy may increase the number of interviews offered and received, as evidenced by the higher number of interviews offered compared with those who were not couples matching. Additionally, this survey highlights the sacrifice often needed by couples in the couples match as revealed by the inclusion of rank-list options in which the couples reside long distance or in which 1 partner does not match. This information may be helpful to applicants who are planning a strategy for the couples match in dermatology. Although this study does not encompass all dermatology applicants in the 2019-2020 cycle, we do believe it may be representative. The USMLE Step 1 scores in this study were similar to the published NRMP data.1,10 According to NRMP data from the 2019-2020 cycle, the mean USMLE Step 1 score was 248 for matched applicants and 239 for unmatched.1 The NRMP reported the mean USMLE Step 2 CK score for matched was 256 and 248 for unmatched, which also is similar to our data. The NRMP reported the mean number of programs ranked was 9.9 for matched and 4.5 for unmatched applicants.1 Again, our data were similar for number of dermatology interviews attended.
Limitations—There are limitations to this study. The main limitation is that the survey is from a single institution and had a limited number of respondents. Given the nature of the study, the accuracy of the data is dependent on the applicants’ honesty in self-reporting academic performance and other variables. There also may be a selection bias given the low response rate. The subanalyses—children and couples matching—were underpowered with the limited number of participants. Further studies that include multiple residency programs and multiple years could be helpful to provide more power and less risk of bias. We did not gather information such as the Medical Student Performance Evaluation letter, letters of recommendation, or personal statements, which do play an important role in the assessment of an applicant. However, because the applicants completed these surveys, and given these are largely blinded to applicants, we did not feel the applicants could accurately respond to those aspects of the application.
Conclusion
Our survey finds that factors associated with matching included a higher USMLE Step 1 score, having a home dermatology program, and a higher number of interviews offered and attended. Some demographics had varying USMLE Step 1 scores but similar match rates.
- National Resident Matching Program. Results and Data: 2020 Main Residency Match. National Resident Matching Program; May 2020. Accessed January 9, 2023. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/MM_Results_and-Data_2020-1.pdf
- Gauer JL, Jackson JB. The association of USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK scores with residency match specialty and location. Med Educ Online. 2017;22:1358579.
- Wang JV, Keller M. Pressure to publish for residency applicants in dermatology. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt56x1t7ww.
- Wang RF, Zhang M, Kaffenberger JA. Does the dermatology standardized letter of recommendation alter applicants’ chances of matching into residency. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:e139-e140.
- National Resident Matching Program, Data Release and Research Committee: results of the 2018 NRMP Program Director Survey. Accessed December 19, 2022. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/NRMP-2018-Program-Director-Survey-for-WWW.pdf
- Costello CM, Harvey JA, Besch-Stokes JG, et al. The role of race and ethnicity in the dermatology applicant match process. J Natl Med Assoc. 2022;113:666-670.
- Chen A, Shinkai K. Rethinking how we select dermatology applicants-turning the tide. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:259-260.
- Pandya AG, Alexis AF, Berger TG, et al. Increasing racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology: a call to action. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:584-587.
- Van Voorhees AS, Enos CW. Diversity in dermatology residency programs. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S46-S49.
- National Resident Matching Program. Charting outcomes in the match: U.S. allopathic seniors. Characteristics of U.S. allopathic seniors who matched to their preferred specialty in the 2018 main residency match. 2nd ed. Accessed December 19, 2022. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Charting-Outcomes-in-the-Match-2018_Seniors-1.pdf
- National Resident Matching Program. Results and Data: 2020 Main Residency Match. National Resident Matching Program; May 2020. Accessed January 9, 2023. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/MM_Results_and-Data_2020-1.pdf
- Gauer JL, Jackson JB. The association of USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK scores with residency match specialty and location. Med Educ Online. 2017;22:1358579.
- Wang JV, Keller M. Pressure to publish for residency applicants in dermatology. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt56x1t7ww.
- Wang RF, Zhang M, Kaffenberger JA. Does the dermatology standardized letter of recommendation alter applicants’ chances of matching into residency. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:e139-e140.
- National Resident Matching Program, Data Release and Research Committee: results of the 2018 NRMP Program Director Survey. Accessed December 19, 2022. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/NRMP-2018-Program-Director-Survey-for-WWW.pdf
- Costello CM, Harvey JA, Besch-Stokes JG, et al. The role of race and ethnicity in the dermatology applicant match process. J Natl Med Assoc. 2022;113:666-670.
- Chen A, Shinkai K. Rethinking how we select dermatology applicants-turning the tide. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:259-260.
- Pandya AG, Alexis AF, Berger TG, et al. Increasing racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology: a call to action. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:584-587.
- Van Voorhees AS, Enos CW. Diversity in dermatology residency programs. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2017;18:S46-S49.
- National Resident Matching Program. Charting outcomes in the match: U.S. allopathic seniors. Characteristics of U.S. allopathic seniors who matched to their preferred specialty in the 2018 main residency match. 2nd ed. Accessed December 19, 2022. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Charting-Outcomes-in-the-Match-2018_Seniors-1.pdf
PRACTICE POINTS
- Dermatology residency continues to be one of the most competitive specialties, with a match rate of 84.7% in 2019.
- A high US Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 1 score and having a home dermatology program and a greater number of interviews may lead to higher likeliness of matching in dermatology.
- Most applicants (82.4%) applied to programs their partner had interviews at, suggesting this may be a helpful strategy.
Insights From the 2020-2021 Dermatology Residency Match
To the Editor:
Data from the program director survey of the National Resident Matching Program offer key insights into the 2021 dermatology application process.1,2 Examination of data from the 2020 (N=12) and 2021 (N=17) program director survey regarding interviewing applicants revealed that specialty-specific letters of recommendation (LORs), personal prior knowledge of an applicant, and personal statement increased in importance by 17%, 7.4%, and 17%, respectively, whereas away rotations within the department decreased in importance by 44.9% (Table).1,2 Interestingly, for ranking applicants, programs decreased their emphasis on specialty-specific LORs by 25.8% and away rotations within the department by 22.7% and increased emphasis on personal statements by 14.7% and personal prior knowledge of an applicant by 0.8% from 2020 to 2021 (Table).1,2 These findings align with the prior recommendation to limit away rotations; data are contradictory—when comparing factors for interviewing as compared to ranking applicants—for specialty-specific LORs.
We further compared data from the otolaryngology cycle, which implemented preference signaling by which an applicant can signal their interest in a particular residency program in the 2021 Match, to data from dermatology with no preference signaling. A 90% probability of matching is estimated to require approximately 8 or 9 interviews for dermatology or 12 interviews for otolaryngology for MD senior students in 2020.4 In prior dermatology application cycles, the most highly qualified candidates constituted 7% to 21% of all applicants but were estimated to receive half of all interviews, causing a maldistribution of interviews.5,6
For the 2021 otolaryngology match, the Society of University Otolaryngologists implemented a novel preference signaling system that allowed candidates to show interest in programs by sending 5 preferences, or tokens.7 Recent data reports from the otolaryngology cycle demonstrated at least a 2-fold increase in the rate of receiving an interview invitation for signaled programs compared to the closest nonsignaled program if applicants were provided an additional token.7 Regarding overall applicant competitiveness (ie, dividing participants into quartiles based on their competitiveness), the highest increase in the overall rate of interview invitations (3.5 [total invitations/total applications]) was demonstrated for fourth-quartile (ie, “lowest quartile”) applicants compared with the increase in the overall rate of interview invitations seen in other quartiles (first quartile, an increase of 2.3; second quartile, an increase of 2.6; and third quartile, an increase of 2.4).7 We look forward to seeing the impact of preference signaling on the results of the 2022 dermatology cycle.
Despite changes in the interviewing process to accommodate COVID-19 pandemic safety recommendations, the overall dermatology postgraduate year (PGY) 2 fill rate remained unchanged from 2018 (98.6%) to 2021 (98.7%). Zero PGY-1 positions and 5 PGY-2 positions were unfilled in the 2021 Main Residency Match compared to 1 unfilled PGY-1 position and 4 unfilled PGY-2 positions in 2018.8 The coordinated interview invitation release, holistic review of applications, increased number of rankings, and virtual interviews might have helped offset potential obstacles imparted by inability to complete away rotations, inability to obtain LORs, and conducting interviews virtually.5
A limitation of our analysis is the low response rate of program directors to National Resident Matching Program surveys.
These strategies—holistic application review and coordinated interview release—may be considered in future cycles given their convenience and negligible impact on the dermatology match rate. For example, virtual interviews relieve the financial and time burdens of in-person interviews—approximately $10,000 for each US senior applicant—thus potentially allowing for a more equitable matching process.3 Inversely, in-person interviews allow participants to effectively network and form more meaningful connections while obtaining a better understanding of facilities and surrounding locales. As such, the medical community should continue to come to a consensus on the optimal format to host interviews.
- Results of the 2021 NRMP Program Director Survey. National Resident Matching Program. August 2021. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/2021-PD-Survey-Report-for-WWW.pdf
- Results of the 2020 NRMP Program Director Survey. National Resident Matching Program. August 2020. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/2020-PD-Survey.pdf
- Rojek NW, Shinkai K, Fett N. Dermatology faculty and residents’ perspectives on the dermatology residency application process: a nationwide survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:157-159. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.01.00
- Charting Outcomes in the Match: Senior Students of U.S. MD Medical Schools. National Resident Matching Program. July 2020. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Charting-Outcomes-in-the-Match-2020_MD-Senior_final.pdf
- Thatiparthi A, Martin A, Liu J, et al. Preliminary outcomes of 2020-2021 dermatology residency application cycle and adverse effects of COVID-19. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:e263-e264. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.03.034
- Hammoud MM, Standiford T, Carmody JB. Potential implications of COVID-19 for the 2020-2021 residency application cycle. JAMA. 2020;324:29-30. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.8911
- Interview offer rate with/without ENTSignaling. Society of University Otolaryngologists. Updated July 19, 2022. Accessed December 12, 2022. https://opdo-hns.org/mpage/signaling-updates
- Results and Data: 2021 Main Residency Match. National Resident Matching Program. May 2021. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/MRM-Results_and-Data_2021.pdf
To the Editor:
Data from the program director survey of the National Resident Matching Program offer key insights into the 2021 dermatology application process.1,2 Examination of data from the 2020 (N=12) and 2021 (N=17) program director survey regarding interviewing applicants revealed that specialty-specific letters of recommendation (LORs), personal prior knowledge of an applicant, and personal statement increased in importance by 17%, 7.4%, and 17%, respectively, whereas away rotations within the department decreased in importance by 44.9% (Table).1,2 Interestingly, for ranking applicants, programs decreased their emphasis on specialty-specific LORs by 25.8% and away rotations within the department by 22.7% and increased emphasis on personal statements by 14.7% and personal prior knowledge of an applicant by 0.8% from 2020 to 2021 (Table).1,2 These findings align with the prior recommendation to limit away rotations; data are contradictory—when comparing factors for interviewing as compared to ranking applicants—for specialty-specific LORs.

We further compared data from the otolaryngology cycle, which implemented preference signaling by which an applicant can signal their interest in a particular residency program in the 2021 Match, to data from dermatology with no preference signaling. A 90% probability of matching is estimated to require approximately 8 or 9 interviews for dermatology or 12 interviews for otolaryngology for MD senior students in 2020.4 In prior dermatology application cycles, the most highly qualified candidates constituted 7% to 21% of all applicants but were estimated to receive half of all interviews, causing a maldistribution of interviews.5,6
For the 2021 otolaryngology match, the Society of University Otolaryngologists implemented a novel preference signaling system that allowed candidates to show interest in programs by sending 5 preferences, or tokens.7 Recent data reports from the otolaryngology cycle demonstrated at least a 2-fold increase in the rate of receiving an interview invitation for signaled programs compared to the closest nonsignaled program if applicants were provided an additional token.7 Regarding overall applicant competitiveness (ie, dividing participants into quartiles based on their competitiveness), the highest increase in the overall rate of interview invitations (3.5 [total invitations/total applications]) was demonstrated for fourth-quartile (ie, “lowest quartile”) applicants compared with the increase in the overall rate of interview invitations seen in other quartiles (first quartile, an increase of 2.3; second quartile, an increase of 2.6; and third quartile, an increase of 2.4).7 We look forward to seeing the impact of preference signaling on the results of the 2022 dermatology cycle.
Despite changes in the interviewing process to accommodate COVID-19 pandemic safety recommendations, the overall dermatology postgraduate year (PGY) 2 fill rate remained unchanged from 2018 (98.6%) to 2021 (98.7%). Zero PGY-1 positions and 5 PGY-2 positions were unfilled in the 2021 Main Residency Match compared to 1 unfilled PGY-1 position and 4 unfilled PGY-2 positions in 2018.8 The coordinated interview invitation release, holistic review of applications, increased number of rankings, and virtual interviews might have helped offset potential obstacles imparted by inability to complete away rotations, inability to obtain LORs, and conducting interviews virtually.5
A limitation of our analysis is the low response rate of program directors to National Resident Matching Program surveys.
These strategies—holistic application review and coordinated interview release—may be considered in future cycles given their convenience and negligible impact on the dermatology match rate. For example, virtual interviews relieve the financial and time burdens of in-person interviews—approximately $10,000 for each US senior applicant—thus potentially allowing for a more equitable matching process.3 Inversely, in-person interviews allow participants to effectively network and form more meaningful connections while obtaining a better understanding of facilities and surrounding locales. As such, the medical community should continue to come to a consensus on the optimal format to host interviews.
To the Editor:
Data from the program director survey of the National Resident Matching Program offer key insights into the 2021 dermatology application process.1,2 Examination of data from the 2020 (N=12) and 2021 (N=17) program director survey regarding interviewing applicants revealed that specialty-specific letters of recommendation (LORs), personal prior knowledge of an applicant, and personal statement increased in importance by 17%, 7.4%, and 17%, respectively, whereas away rotations within the department decreased in importance by 44.9% (Table).1,2 Interestingly, for ranking applicants, programs decreased their emphasis on specialty-specific LORs by 25.8% and away rotations within the department by 22.7% and increased emphasis on personal statements by 14.7% and personal prior knowledge of an applicant by 0.8% from 2020 to 2021 (Table).1,2 These findings align with the prior recommendation to limit away rotations; data are contradictory—when comparing factors for interviewing as compared to ranking applicants—for specialty-specific LORs.

We further compared data from the otolaryngology cycle, which implemented preference signaling by which an applicant can signal their interest in a particular residency program in the 2021 Match, to data from dermatology with no preference signaling. A 90% probability of matching is estimated to require approximately 8 or 9 interviews for dermatology or 12 interviews for otolaryngology for MD senior students in 2020.4 In prior dermatology application cycles, the most highly qualified candidates constituted 7% to 21% of all applicants but were estimated to receive half of all interviews, causing a maldistribution of interviews.5,6
For the 2021 otolaryngology match, the Society of University Otolaryngologists implemented a novel preference signaling system that allowed candidates to show interest in programs by sending 5 preferences, or tokens.7 Recent data reports from the otolaryngology cycle demonstrated at least a 2-fold increase in the rate of receiving an interview invitation for signaled programs compared to the closest nonsignaled program if applicants were provided an additional token.7 Regarding overall applicant competitiveness (ie, dividing participants into quartiles based on their competitiveness), the highest increase in the overall rate of interview invitations (3.5 [total invitations/total applications]) was demonstrated for fourth-quartile (ie, “lowest quartile”) applicants compared with the increase in the overall rate of interview invitations seen in other quartiles (first quartile, an increase of 2.3; second quartile, an increase of 2.6; and third quartile, an increase of 2.4).7 We look forward to seeing the impact of preference signaling on the results of the 2022 dermatology cycle.
Despite changes in the interviewing process to accommodate COVID-19 pandemic safety recommendations, the overall dermatology postgraduate year (PGY) 2 fill rate remained unchanged from 2018 (98.6%) to 2021 (98.7%). Zero PGY-1 positions and 5 PGY-2 positions were unfilled in the 2021 Main Residency Match compared to 1 unfilled PGY-1 position and 4 unfilled PGY-2 positions in 2018.8 The coordinated interview invitation release, holistic review of applications, increased number of rankings, and virtual interviews might have helped offset potential obstacles imparted by inability to complete away rotations, inability to obtain LORs, and conducting interviews virtually.5
A limitation of our analysis is the low response rate of program directors to National Resident Matching Program surveys.
These strategies—holistic application review and coordinated interview release—may be considered in future cycles given their convenience and negligible impact on the dermatology match rate. For example, virtual interviews relieve the financial and time burdens of in-person interviews—approximately $10,000 for each US senior applicant—thus potentially allowing for a more equitable matching process.3 Inversely, in-person interviews allow participants to effectively network and form more meaningful connections while obtaining a better understanding of facilities and surrounding locales. As such, the medical community should continue to come to a consensus on the optimal format to host interviews.
- Results of the 2021 NRMP Program Director Survey. National Resident Matching Program. August 2021. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/2021-PD-Survey-Report-for-WWW.pdf
- Results of the 2020 NRMP Program Director Survey. National Resident Matching Program. August 2020. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/2020-PD-Survey.pdf
- Rojek NW, Shinkai K, Fett N. Dermatology faculty and residents’ perspectives on the dermatology residency application process: a nationwide survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:157-159. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.01.00
- Charting Outcomes in the Match: Senior Students of U.S. MD Medical Schools. National Resident Matching Program. July 2020. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Charting-Outcomes-in-the-Match-2020_MD-Senior_final.pdf
- Thatiparthi A, Martin A, Liu J, et al. Preliminary outcomes of 2020-2021 dermatology residency application cycle and adverse effects of COVID-19. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:e263-e264. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.03.034
- Hammoud MM, Standiford T, Carmody JB. Potential implications of COVID-19 for the 2020-2021 residency application cycle. JAMA. 2020;324:29-30. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.8911
- Interview offer rate with/without ENTSignaling. Society of University Otolaryngologists. Updated July 19, 2022. Accessed December 12, 2022. https://opdo-hns.org/mpage/signaling-updates
- Results and Data: 2021 Main Residency Match. National Resident Matching Program. May 2021. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/MRM-Results_and-Data_2021.pdf
- Results of the 2021 NRMP Program Director Survey. National Resident Matching Program. August 2021. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/2021-PD-Survey-Report-for-WWW.pdf
- Results of the 2020 NRMP Program Director Survey. National Resident Matching Program. August 2020. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/2020-PD-Survey.pdf
- Rojek NW, Shinkai K, Fett N. Dermatology faculty and residents’ perspectives on the dermatology residency application process: a nationwide survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:157-159. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.01.00
- Charting Outcomes in the Match: Senior Students of U.S. MD Medical Schools. National Resident Matching Program. July 2020. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Charting-Outcomes-in-the-Match-2020_MD-Senior_final.pdf
- Thatiparthi A, Martin A, Liu J, et al. Preliminary outcomes of 2020-2021 dermatology residency application cycle and adverse effects of COVID-19. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:e263-e264. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.03.034
- Hammoud MM, Standiford T, Carmody JB. Potential implications of COVID-19 for the 2020-2021 residency application cycle. JAMA. 2020;324:29-30. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.8911
- Interview offer rate with/without ENTSignaling. Society of University Otolaryngologists. Updated July 19, 2022. Accessed December 12, 2022. https://opdo-hns.org/mpage/signaling-updates
- Results and Data: 2021 Main Residency Match. National Resident Matching Program. May 2021. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/MRM-Results_and-Data_2021.pdf
PRACTICE POINTS
- Although there have been numerous changes to the dermatology interview process due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the overall fill rate for postgraduate year 2 positions remained unchanged from 2018 (prepandemic) to 2021 (postpandemic).
- Strategies to accommodate new safety recommendations for interviews may reduce the financial burden (approximately $10,000 for each senior applicant) and time constraints on applicants. These strategies should be considered for implementation in future cycles.
Feedback and Education in Dermatology Residency
A dermatology resident has more education and experience than a medical student or intern but less than a fellow or attending physician. Because of this position, residents have a unique opportunity to provide feedback and education to those with less knowledge and experience as a teacher and also to provide feedback to their more senior colleagues about their teaching effectiveness while simultaneously learning from them. The reciprocal exchange of information—from patients and colleagues in clinic, co-residents or attendings in lectures, or in other environments such as pathology at the microscope or skills during simulation training sessions—is the cornerstone of medical education. Being able to give effective feedback while also learning to accept it is one of the most vital skills a resident can learn to thrive in medical education.
The importance of feedback cannot be understated. The art of medicine involves the scientific knowledge needed to treat disease, as well as the social ability to educate, comfort, and heal those afflicted. Mastering this art takes a lifetime. The direct imparting of knowledge from those more experienced to those learning occurs via feedback. In addition, the desire to better oneself leads to more satisfaction with work and improved performance.1 The ability to give and receive feedback is vital for the field of dermatology and medicine in general.
Types and Implementation of Feedback
Feedback comes in many forms and can be classified via different characteristics such as formal vs informal, written vs spoken, real time vs delayed, and single observer vs pooled data. Each style of feedback has positive and negative aspects, and a feedback provider will need to weigh the pros and cons when deciding the most appropriate one. Although there is no one correct way to provide feedback, the literature shows that some forms of feedback may be more effective and better received than others. This can depend on the context of what is being evaluated.
Many dermatology residencies employ formal scheduled feedback as part of their curricula, ensuring that residents will receive feedback at preset time intervals and providing residency directors with information to assess improvement and areas where more growth is needed. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education provides a reference for programs on how to give this formal standardized feedback in The Milestones Guidebook.2 This feedback is a minimum required amount, with a survey of residents showing preference for frequent informal feedback sessions in addition to standardized formal feedback.3 Another study showed that residents want feedback that is confidential, in person, shortly after experiences, and specific to their actions.4 Medical students also voiced a need for frequent, transparent, and actionable feedback during protected, predetermined, and communicated times.5 Clearly, learners appreciate spoken intentional feedback as opposed to the traditional formal model of feedback.
Finally, a study was performed analyzing how prior generations of physician educators view millennial trainees.6 Because most current dermatology residents were born between 1981 and 1996, this study seemed to pinpoint thoughts toward teaching current residents. The study found that although negative judgments such as millennial entitlement (P<.001), impoliteness (P<.001), oversensitivity (P<.001), and inferior work ethic (P<.001) reached significance, millennial ideals of social justice (P<.001) and savviness with technology (P<.001) also were notable. Overall, millennials were thought to be good colleagues (P<.001), were equally competent to more experienced clinicians (P<.001), and would lead medicine to a good future (P=.039).6
Identifying and Maximizing the Impact of Feedback
In addition to how and when to provide feedback, there are discrepancies between attending and resident perception of what is considered feedback. This disconnect can be seen in a study of 122 respondents (67 residents and 55 attendings) that showed 31% of attendings reported giving feedback daily, as opposed to only 9% of residents who reported receiving daily feedback.4 When feedback is to be performed, it may be important to specifically announce the process so that it can be properly acknowledged.7
Beach8 provided a systematic breakdown of clinical teaching to those who may be unfamiliar with the process. This method is divided into preclinic, in-clinic, and postclinic strategies to maximize learning. The author recommended establishing the objectives of the rotation from the teacher’s perspective and inquiring about the objectives of the learner. Both perspectives should inform the lessons to be learned; for example, if a medical student expresses specific interest in psoriasis (a well-established part of a medical student curriculum), all efforts should be placed on arranging for that student to see those specific patients. Beach8 also recommended providing resources and creating a positive supportive learning environment to better utilize precious clinic time and create investment in all learning parties. The author recommended matching trainees during clinic to competence-specific challenges in clinical practice where appropriate technical skill is needed. Appropriate autonomy also is promoted, as it requires higher levels of learning and knowledge consolidation. Group discussions can be facilitated by asking questions of increasing levels of difficulty as experience increases. Finally, postclinic feedback should be timely and constructive.8
One technique discussed by Beach8 is the “1-minute preceptor plus” approach. In this approach, the teacher wants to establish 5 “micro-skills” by first getting a commitment, then checking for supportive evidence of this initial plan, teaching a general principle, reinforcing what was properly performed, and correcting errors. The “plus” comes from trying to take that lesson and apply it to a broader concept. Although this concept is meant to be used in a time-limited setting, it can be expanded to larger conversations. A common example could be made when residents teach rotating medical students through direct observation and supervision during clinic. In this hypothetical situation, the resident and medical student see a patient with erythematous silver-scaled plaques on the elbows and knees. During the patient encounter, the student then inquires about any personal history of cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. After leaving the examination room, the medical student asserts the diagnosis is plaque psoriasis because of the physical examination findings and distribution of lesions. A discussion about the relationship between psoriasis and metabolic syndrome commences, emphasizing the pathophysiology of type 1 helper T-cell–mediated and type 17 helper T-cell–mediated inflammation with vascular damage and growth from inflammatory cytokines.9 The student subsequently is praised on inquiring about relevant comorbidities, and a relevant journal article is retrieved for the student’s future studies. Teaching points regarding the Koebner phenomenon, such as that it is not an instantaneous process and comes with a differential diagnosis, are then provided.
Situation-Behavior-Impact is another teaching method developed by the Center for Creative Leadership. In this technique, one will identify what specifically happened, how the learner responded, and what occurred because of the response.10 This technique is exemplified in the following mock conversation between an attending and their resident following a challenging patient situation: “When you walked into the room and asked the patient coming in for a follow-up appointment ‘What brings you in today?,’ they immediately tensed up and responded that you should already know and check your electronic medical record. This tension could be ameliorated by reviewing the patient’s medical record and addressing what they initially presented for, followed by inquiring if there are other skin problems they want to discuss afterwards.” By identifying the cause-and-effect relationship, helpful and unhelpful responses can be identified and ways to mitigate or continue behaviors can be brainstormed.
The Learning Process
Brodell et all11 outlined techniques to augment the education process that are specific to dermatology. They recommended learning general applicable concepts instead of contextless memorization, mnemonic devices to assist memory for associations and lists, and repetition and practice of learned material. For teaching, they divided techniques into Aristotelian or Socratic; Aristotelian teaching is the formal lecture style, whereas Socratic is conversation based. Both have a place in teaching—as fundamental knowledge grows via Aristotelian teaching, critical thinking can be enhanced via the Socratic method. The authors then outlined tips to create the most conducive learning environment for students.11
Feedback is a reciprocal process with information being given and received by both the teacher and the learner. This is paramount because perfecting the art of teaching is a career-long process and can only be achieved via correction of oversights and mistakes. A questionnaire-based study found that when critiquing the teacher, a combination of self-assessment with assessment from learners was effective in stimulating the greatest level of change in the teacher.12 This finding likely is because the educator was able to see the juxtaposition of how they think they performed with how students interpreted the same situation. Another survey-based study showed that of 68 attending physicians, 28 attendings saw utility in specialized feedback training; an additional 11 attendings agreed with online modules to improve their feedback skills. A recommendation that trainees receive training on the acceptance feedback also was proposed.13 Specialized training to give and receive feedback could be initiated for both attending and resident physicians to fully create an environment emphasizing improvement and teamwork.
Final Thoughts
The art of giving and receiving feedback is a deliberate process that develops with experience and training. Because residents are early in their medical career, being familiar with techniques such as those outlined in this article can enhance teaching and the reception of feedback. Residents are in a unique position, as residency itself is a time of dramatic learning and teaching. Providing feedback gives us a way to advance medicine and better ourselves by solidifying good habits and knowledge.
Acknowledgment—I thank Warren R. Heymann, MD (Camden, New Jersey), for assisting in the creation of this topic and reviewing this article.
- Crommelinck M, Anseel F. Understanding and encouraging feedback-seeking behavior: a literature review. Med Educ. 2013;47:232-241.
- Edgar L, McLean S, Hogan SO, et al. The Milestones Guidebook. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education; 2020. Accessed December 12, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/milestonesguidebook.pdf
- Wang JV, O’Connor M, McGuinn K, et al. Feedback practices in dermatology residency programs: building a culture for millennials. Clin Dermatol. 2019;37:282-283.
- Hajar T, Wanat KA, Fett N. Survey of resident physician and attending physician feedback perceptions: there is still work to be done. Dermatol Online J. 2020;25:13030/qt2sg354p6.
- Yoon J, Said JT, Thompson LL, et al. Medical student perceptions of assessment systems, subjectivity, and variability on introductory dermatology clerkships. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:232-330.
- Marka A, LeBoeuf MR, Vidal NY. Perspectives of dermatology faculty toward millennial trainees and colleagues: a national survey. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2021;5:65-71.
- Bernard AW, Kman NE, Khandelwal S. Feedback in the emergency medicine clerkship. West J Emerg Med. 2011;12:537-542.
- Beach RA. Strategies to maximise teaching in your next ambulatory clinic. Clin Teach. 2017;14:85-89.
- Takeshita J, Grewal S, Langan SM, et al. Psoriasis and comorbid diseases part I. epidemiology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:377-390.
- Olbricht SM. What makes feedback productive? Cutis. 2016;98:222-223.
- Brodell RT, Wile MZ, Chren M, et al. Learning and teaching in dermatology: a practitioner’s guide. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:946-952.
- Stalmeijer RE, Dolmans DHJM, Wolfhagen IHAP, et al. Combined student ratings and self-assessment provide useful feedback for clinical teachers. Adv in Health Sci Educ. 2010;15:315-328.
- Chelliah P, Srivastava D, Nijhawan RI. What makes giving feedback challenging? a survey of the Association of Professors of Dermatology (APD)[published online July 19, 2022]. Arch Dermatol Res. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02370-y
A dermatology resident has more education and experience than a medical student or intern but less than a fellow or attending physician. Because of this position, residents have a unique opportunity to provide feedback and education to those with less knowledge and experience as a teacher and also to provide feedback to their more senior colleagues about their teaching effectiveness while simultaneously learning from them. The reciprocal exchange of information—from patients and colleagues in clinic, co-residents or attendings in lectures, or in other environments such as pathology at the microscope or skills during simulation training sessions—is the cornerstone of medical education. Being able to give effective feedback while also learning to accept it is one of the most vital skills a resident can learn to thrive in medical education.
The importance of feedback cannot be understated. The art of medicine involves the scientific knowledge needed to treat disease, as well as the social ability to educate, comfort, and heal those afflicted. Mastering this art takes a lifetime. The direct imparting of knowledge from those more experienced to those learning occurs via feedback. In addition, the desire to better oneself leads to more satisfaction with work and improved performance.1 The ability to give and receive feedback is vital for the field of dermatology and medicine in general.
Types and Implementation of Feedback
Feedback comes in many forms and can be classified via different characteristics such as formal vs informal, written vs spoken, real time vs delayed, and single observer vs pooled data. Each style of feedback has positive and negative aspects, and a feedback provider will need to weigh the pros and cons when deciding the most appropriate one. Although there is no one correct way to provide feedback, the literature shows that some forms of feedback may be more effective and better received than others. This can depend on the context of what is being evaluated.
Many dermatology residencies employ formal scheduled feedback as part of their curricula, ensuring that residents will receive feedback at preset time intervals and providing residency directors with information to assess improvement and areas where more growth is needed. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education provides a reference for programs on how to give this formal standardized feedback in The Milestones Guidebook.2 This feedback is a minimum required amount, with a survey of residents showing preference for frequent informal feedback sessions in addition to standardized formal feedback.3 Another study showed that residents want feedback that is confidential, in person, shortly after experiences, and specific to their actions.4 Medical students also voiced a need for frequent, transparent, and actionable feedback during protected, predetermined, and communicated times.5 Clearly, learners appreciate spoken intentional feedback as opposed to the traditional formal model of feedback.
Finally, a study was performed analyzing how prior generations of physician educators view millennial trainees.6 Because most current dermatology residents were born between 1981 and 1996, this study seemed to pinpoint thoughts toward teaching current residents. The study found that although negative judgments such as millennial entitlement (P<.001), impoliteness (P<.001), oversensitivity (P<.001), and inferior work ethic (P<.001) reached significance, millennial ideals of social justice (P<.001) and savviness with technology (P<.001) also were notable. Overall, millennials were thought to be good colleagues (P<.001), were equally competent to more experienced clinicians (P<.001), and would lead medicine to a good future (P=.039).6
Identifying and Maximizing the Impact of Feedback
In addition to how and when to provide feedback, there are discrepancies between attending and resident perception of what is considered feedback. This disconnect can be seen in a study of 122 respondents (67 residents and 55 attendings) that showed 31% of attendings reported giving feedback daily, as opposed to only 9% of residents who reported receiving daily feedback.4 When feedback is to be performed, it may be important to specifically announce the process so that it can be properly acknowledged.7
Beach8 provided a systematic breakdown of clinical teaching to those who may be unfamiliar with the process. This method is divided into preclinic, in-clinic, and postclinic strategies to maximize learning. The author recommended establishing the objectives of the rotation from the teacher’s perspective and inquiring about the objectives of the learner. Both perspectives should inform the lessons to be learned; for example, if a medical student expresses specific interest in psoriasis (a well-established part of a medical student curriculum), all efforts should be placed on arranging for that student to see those specific patients. Beach8 also recommended providing resources and creating a positive supportive learning environment to better utilize precious clinic time and create investment in all learning parties. The author recommended matching trainees during clinic to competence-specific challenges in clinical practice where appropriate technical skill is needed. Appropriate autonomy also is promoted, as it requires higher levels of learning and knowledge consolidation. Group discussions can be facilitated by asking questions of increasing levels of difficulty as experience increases. Finally, postclinic feedback should be timely and constructive.8
One technique discussed by Beach8 is the “1-minute preceptor plus” approach. In this approach, the teacher wants to establish 5 “micro-skills” by first getting a commitment, then checking for supportive evidence of this initial plan, teaching a general principle, reinforcing what was properly performed, and correcting errors. The “plus” comes from trying to take that lesson and apply it to a broader concept. Although this concept is meant to be used in a time-limited setting, it can be expanded to larger conversations. A common example could be made when residents teach rotating medical students through direct observation and supervision during clinic. In this hypothetical situation, the resident and medical student see a patient with erythematous silver-scaled plaques on the elbows and knees. During the patient encounter, the student then inquires about any personal history of cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. After leaving the examination room, the medical student asserts the diagnosis is plaque psoriasis because of the physical examination findings and distribution of lesions. A discussion about the relationship between psoriasis and metabolic syndrome commences, emphasizing the pathophysiology of type 1 helper T-cell–mediated and type 17 helper T-cell–mediated inflammation with vascular damage and growth from inflammatory cytokines.9 The student subsequently is praised on inquiring about relevant comorbidities, and a relevant journal article is retrieved for the student’s future studies. Teaching points regarding the Koebner phenomenon, such as that it is not an instantaneous process and comes with a differential diagnosis, are then provided.
Situation-Behavior-Impact is another teaching method developed by the Center for Creative Leadership. In this technique, one will identify what specifically happened, how the learner responded, and what occurred because of the response.10 This technique is exemplified in the following mock conversation between an attending and their resident following a challenging patient situation: “When you walked into the room and asked the patient coming in for a follow-up appointment ‘What brings you in today?,’ they immediately tensed up and responded that you should already know and check your electronic medical record. This tension could be ameliorated by reviewing the patient’s medical record and addressing what they initially presented for, followed by inquiring if there are other skin problems they want to discuss afterwards.” By identifying the cause-and-effect relationship, helpful and unhelpful responses can be identified and ways to mitigate or continue behaviors can be brainstormed.
The Learning Process
Brodell et all11 outlined techniques to augment the education process that are specific to dermatology. They recommended learning general applicable concepts instead of contextless memorization, mnemonic devices to assist memory for associations and lists, and repetition and practice of learned material. For teaching, they divided techniques into Aristotelian or Socratic; Aristotelian teaching is the formal lecture style, whereas Socratic is conversation based. Both have a place in teaching—as fundamental knowledge grows via Aristotelian teaching, critical thinking can be enhanced via the Socratic method. The authors then outlined tips to create the most conducive learning environment for students.11
Feedback is a reciprocal process with information being given and received by both the teacher and the learner. This is paramount because perfecting the art of teaching is a career-long process and can only be achieved via correction of oversights and mistakes. A questionnaire-based study found that when critiquing the teacher, a combination of self-assessment with assessment from learners was effective in stimulating the greatest level of change in the teacher.12 This finding likely is because the educator was able to see the juxtaposition of how they think they performed with how students interpreted the same situation. Another survey-based study showed that of 68 attending physicians, 28 attendings saw utility in specialized feedback training; an additional 11 attendings agreed with online modules to improve their feedback skills. A recommendation that trainees receive training on the acceptance feedback also was proposed.13 Specialized training to give and receive feedback could be initiated for both attending and resident physicians to fully create an environment emphasizing improvement and teamwork.
Final Thoughts
The art of giving and receiving feedback is a deliberate process that develops with experience and training. Because residents are early in their medical career, being familiar with techniques such as those outlined in this article can enhance teaching and the reception of feedback. Residents are in a unique position, as residency itself is a time of dramatic learning and teaching. Providing feedback gives us a way to advance medicine and better ourselves by solidifying good habits and knowledge.
Acknowledgment—I thank Warren R. Heymann, MD (Camden, New Jersey), for assisting in the creation of this topic and reviewing this article.
A dermatology resident has more education and experience than a medical student or intern but less than a fellow or attending physician. Because of this position, residents have a unique opportunity to provide feedback and education to those with less knowledge and experience as a teacher and also to provide feedback to their more senior colleagues about their teaching effectiveness while simultaneously learning from them. The reciprocal exchange of information—from patients and colleagues in clinic, co-residents or attendings in lectures, or in other environments such as pathology at the microscope or skills during simulation training sessions—is the cornerstone of medical education. Being able to give effective feedback while also learning to accept it is one of the most vital skills a resident can learn to thrive in medical education.
The importance of feedback cannot be understated. The art of medicine involves the scientific knowledge needed to treat disease, as well as the social ability to educate, comfort, and heal those afflicted. Mastering this art takes a lifetime. The direct imparting of knowledge from those more experienced to those learning occurs via feedback. In addition, the desire to better oneself leads to more satisfaction with work and improved performance.1 The ability to give and receive feedback is vital for the field of dermatology and medicine in general.
Types and Implementation of Feedback
Feedback comes in many forms and can be classified via different characteristics such as formal vs informal, written vs spoken, real time vs delayed, and single observer vs pooled data. Each style of feedback has positive and negative aspects, and a feedback provider will need to weigh the pros and cons when deciding the most appropriate one. Although there is no one correct way to provide feedback, the literature shows that some forms of feedback may be more effective and better received than others. This can depend on the context of what is being evaluated.
Many dermatology residencies employ formal scheduled feedback as part of their curricula, ensuring that residents will receive feedback at preset time intervals and providing residency directors with information to assess improvement and areas where more growth is needed. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education provides a reference for programs on how to give this formal standardized feedback in The Milestones Guidebook.2 This feedback is a minimum required amount, with a survey of residents showing preference for frequent informal feedback sessions in addition to standardized formal feedback.3 Another study showed that residents want feedback that is confidential, in person, shortly after experiences, and specific to their actions.4 Medical students also voiced a need for frequent, transparent, and actionable feedback during protected, predetermined, and communicated times.5 Clearly, learners appreciate spoken intentional feedback as opposed to the traditional formal model of feedback.
Finally, a study was performed analyzing how prior generations of physician educators view millennial trainees.6 Because most current dermatology residents were born between 1981 and 1996, this study seemed to pinpoint thoughts toward teaching current residents. The study found that although negative judgments such as millennial entitlement (P<.001), impoliteness (P<.001), oversensitivity (P<.001), and inferior work ethic (P<.001) reached significance, millennial ideals of social justice (P<.001) and savviness with technology (P<.001) also were notable. Overall, millennials were thought to be good colleagues (P<.001), were equally competent to more experienced clinicians (P<.001), and would lead medicine to a good future (P=.039).6
Identifying and Maximizing the Impact of Feedback
In addition to how and when to provide feedback, there are discrepancies between attending and resident perception of what is considered feedback. This disconnect can be seen in a study of 122 respondents (67 residents and 55 attendings) that showed 31% of attendings reported giving feedback daily, as opposed to only 9% of residents who reported receiving daily feedback.4 When feedback is to be performed, it may be important to specifically announce the process so that it can be properly acknowledged.7
Beach8 provided a systematic breakdown of clinical teaching to those who may be unfamiliar with the process. This method is divided into preclinic, in-clinic, and postclinic strategies to maximize learning. The author recommended establishing the objectives of the rotation from the teacher’s perspective and inquiring about the objectives of the learner. Both perspectives should inform the lessons to be learned; for example, if a medical student expresses specific interest in psoriasis (a well-established part of a medical student curriculum), all efforts should be placed on arranging for that student to see those specific patients. Beach8 also recommended providing resources and creating a positive supportive learning environment to better utilize precious clinic time and create investment in all learning parties. The author recommended matching trainees during clinic to competence-specific challenges in clinical practice where appropriate technical skill is needed. Appropriate autonomy also is promoted, as it requires higher levels of learning and knowledge consolidation. Group discussions can be facilitated by asking questions of increasing levels of difficulty as experience increases. Finally, postclinic feedback should be timely and constructive.8
One technique discussed by Beach8 is the “1-minute preceptor plus” approach. In this approach, the teacher wants to establish 5 “micro-skills” by first getting a commitment, then checking for supportive evidence of this initial plan, teaching a general principle, reinforcing what was properly performed, and correcting errors. The “plus” comes from trying to take that lesson and apply it to a broader concept. Although this concept is meant to be used in a time-limited setting, it can be expanded to larger conversations. A common example could be made when residents teach rotating medical students through direct observation and supervision during clinic. In this hypothetical situation, the resident and medical student see a patient with erythematous silver-scaled plaques on the elbows and knees. During the patient encounter, the student then inquires about any personal history of cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. After leaving the examination room, the medical student asserts the diagnosis is plaque psoriasis because of the physical examination findings and distribution of lesions. A discussion about the relationship between psoriasis and metabolic syndrome commences, emphasizing the pathophysiology of type 1 helper T-cell–mediated and type 17 helper T-cell–mediated inflammation with vascular damage and growth from inflammatory cytokines.9 The student subsequently is praised on inquiring about relevant comorbidities, and a relevant journal article is retrieved for the student’s future studies. Teaching points regarding the Koebner phenomenon, such as that it is not an instantaneous process and comes with a differential diagnosis, are then provided.
Situation-Behavior-Impact is another teaching method developed by the Center for Creative Leadership. In this technique, one will identify what specifically happened, how the learner responded, and what occurred because of the response.10 This technique is exemplified in the following mock conversation between an attending and their resident following a challenging patient situation: “When you walked into the room and asked the patient coming in for a follow-up appointment ‘What brings you in today?,’ they immediately tensed up and responded that you should already know and check your electronic medical record. This tension could be ameliorated by reviewing the patient’s medical record and addressing what they initially presented for, followed by inquiring if there are other skin problems they want to discuss afterwards.” By identifying the cause-and-effect relationship, helpful and unhelpful responses can be identified and ways to mitigate or continue behaviors can be brainstormed.
The Learning Process
Brodell et all11 outlined techniques to augment the education process that are specific to dermatology. They recommended learning general applicable concepts instead of contextless memorization, mnemonic devices to assist memory for associations and lists, and repetition and practice of learned material. For teaching, they divided techniques into Aristotelian or Socratic; Aristotelian teaching is the formal lecture style, whereas Socratic is conversation based. Both have a place in teaching—as fundamental knowledge grows via Aristotelian teaching, critical thinking can be enhanced via the Socratic method. The authors then outlined tips to create the most conducive learning environment for students.11
Feedback is a reciprocal process with information being given and received by both the teacher and the learner. This is paramount because perfecting the art of teaching is a career-long process and can only be achieved via correction of oversights and mistakes. A questionnaire-based study found that when critiquing the teacher, a combination of self-assessment with assessment from learners was effective in stimulating the greatest level of change in the teacher.12 This finding likely is because the educator was able to see the juxtaposition of how they think they performed with how students interpreted the same situation. Another survey-based study showed that of 68 attending physicians, 28 attendings saw utility in specialized feedback training; an additional 11 attendings agreed with online modules to improve their feedback skills. A recommendation that trainees receive training on the acceptance feedback also was proposed.13 Specialized training to give and receive feedback could be initiated for both attending and resident physicians to fully create an environment emphasizing improvement and teamwork.
Final Thoughts
The art of giving and receiving feedback is a deliberate process that develops with experience and training. Because residents are early in their medical career, being familiar with techniques such as those outlined in this article can enhance teaching and the reception of feedback. Residents are in a unique position, as residency itself is a time of dramatic learning and teaching. Providing feedback gives us a way to advance medicine and better ourselves by solidifying good habits and knowledge.
Acknowledgment—I thank Warren R. Heymann, MD (Camden, New Jersey), for assisting in the creation of this topic and reviewing this article.
- Crommelinck M, Anseel F. Understanding and encouraging feedback-seeking behavior: a literature review. Med Educ. 2013;47:232-241.
- Edgar L, McLean S, Hogan SO, et al. The Milestones Guidebook. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education; 2020. Accessed December 12, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/milestonesguidebook.pdf
- Wang JV, O’Connor M, McGuinn K, et al. Feedback practices in dermatology residency programs: building a culture for millennials. Clin Dermatol. 2019;37:282-283.
- Hajar T, Wanat KA, Fett N. Survey of resident physician and attending physician feedback perceptions: there is still work to be done. Dermatol Online J. 2020;25:13030/qt2sg354p6.
- Yoon J, Said JT, Thompson LL, et al. Medical student perceptions of assessment systems, subjectivity, and variability on introductory dermatology clerkships. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:232-330.
- Marka A, LeBoeuf MR, Vidal NY. Perspectives of dermatology faculty toward millennial trainees and colleagues: a national survey. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2021;5:65-71.
- Bernard AW, Kman NE, Khandelwal S. Feedback in the emergency medicine clerkship. West J Emerg Med. 2011;12:537-542.
- Beach RA. Strategies to maximise teaching in your next ambulatory clinic. Clin Teach. 2017;14:85-89.
- Takeshita J, Grewal S, Langan SM, et al. Psoriasis and comorbid diseases part I. epidemiology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:377-390.
- Olbricht SM. What makes feedback productive? Cutis. 2016;98:222-223.
- Brodell RT, Wile MZ, Chren M, et al. Learning and teaching in dermatology: a practitioner’s guide. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:946-952.
- Stalmeijer RE, Dolmans DHJM, Wolfhagen IHAP, et al. Combined student ratings and self-assessment provide useful feedback for clinical teachers. Adv in Health Sci Educ. 2010;15:315-328.
- Chelliah P, Srivastava D, Nijhawan RI. What makes giving feedback challenging? a survey of the Association of Professors of Dermatology (APD)[published online July 19, 2022]. Arch Dermatol Res. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02370-y
- Crommelinck M, Anseel F. Understanding and encouraging feedback-seeking behavior: a literature review. Med Educ. 2013;47:232-241.
- Edgar L, McLean S, Hogan SO, et al. The Milestones Guidebook. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education; 2020. Accessed December 12, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/milestonesguidebook.pdf
- Wang JV, O’Connor M, McGuinn K, et al. Feedback practices in dermatology residency programs: building a culture for millennials. Clin Dermatol. 2019;37:282-283.
- Hajar T, Wanat KA, Fett N. Survey of resident physician and attending physician feedback perceptions: there is still work to be done. Dermatol Online J. 2020;25:13030/qt2sg354p6.
- Yoon J, Said JT, Thompson LL, et al. Medical student perceptions of assessment systems, subjectivity, and variability on introductory dermatology clerkships. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:232-330.
- Marka A, LeBoeuf MR, Vidal NY. Perspectives of dermatology faculty toward millennial trainees and colleagues: a national survey. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2021;5:65-71.
- Bernard AW, Kman NE, Khandelwal S. Feedback in the emergency medicine clerkship. West J Emerg Med. 2011;12:537-542.
- Beach RA. Strategies to maximise teaching in your next ambulatory clinic. Clin Teach. 2017;14:85-89.
- Takeshita J, Grewal S, Langan SM, et al. Psoriasis and comorbid diseases part I. epidemiology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:377-390.
- Olbricht SM. What makes feedback productive? Cutis. 2016;98:222-223.
- Brodell RT, Wile MZ, Chren M, et al. Learning and teaching in dermatology: a practitioner’s guide. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:946-952.
- Stalmeijer RE, Dolmans DHJM, Wolfhagen IHAP, et al. Combined student ratings and self-assessment provide useful feedback for clinical teachers. Adv in Health Sci Educ. 2010;15:315-328.
- Chelliah P, Srivastava D, Nijhawan RI. What makes giving feedback challenging? a survey of the Association of Professors of Dermatology (APD)[published online July 19, 2022]. Arch Dermatol Res. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02370-y
RESIDENT PEARLS
- Feedback between dermatology trainees and their educators should be provided in a private and constructive way soon after the observation was performed.
- One method to improve education and feedback in a residency program is a specialty course to improve giving and receiving feedback by both residents and attending physicians.
Rheumatology Match Day follows same pattern as previous years
Rheumatology joined six other Medicine specialties that filled more than 95% of fellowship positions in 2022.
The National Resident Matching Program in its 2022 Medicine and Pediatric Specialties Match reported that rheumatology filled 123 of 127 certified programs (96.9%) along with 265 certified positions (97.8%).
Matched applicants for adult rheumatology programs included 40 U.S. foreign applicants (15.1%), 123 MD graduates (46.4%), 66 foreign (24.9%), and 36 DO graduates (13.6%).
A total of 352 applicants showed a preference for this specialty, and 75% matched to the specialty. Another 23% did not match to any program.
2022 was the first year that NRMP combined medical specialties, pediatric specialties, and adolescent medicine fellowship matches into the “Medicine and Pediatric Specialties Match.”
“We engaged the leadership of both pediatrics and internal medicine organizations to work with the NRMP to brainstorm solutions and were successful in combining pediatrics and internal medicine into one fellowship match,” said Jill Fussell, MD, immediate past chair of the Council of Pediatric Subspecialties in a statement. “It was an incredibly rewarding experience to work across pediatrics and internal medicine on behalf of resident well-being to make this collaborative change happen.”
Similar to 2021, pediatric rheumatology didn’t do as well as adult programs, filling just 18 of 32 certified programs (56.3%) and 27 out of 43 certified positions (62.8%). More than 66% of the applicants represented MD graduates. Eight were foreign, and one was a DO graduate.
The 2022 match was the largest on record, comprising 39 subspecialties in internal medicine, pediatrics, addiction, and multidisciplinary specialties. A total of 3,361 programs filled 7,648 (87.7%) of 8,724 positions in 2022. Three specialties – cardiovascular disease, interventional pulmonology, and oncology – filled all their positions offered in the match.
In addition to rheumatology, six other specialties filled 95% or more of their positions. This included clinical cardiac electrophysiology, critical care medicine, endocrinology, gastroenterology, hematology/oncology, and pulmonary/critical care medicine. Allergy and immunology, which accepts applicants from either internal medicine or pediatrics, also filled more than 95% of positions offered.
Matched applicants will start fellowship training in July 2023.
Rheumatology joined six other Medicine specialties that filled more than 95% of fellowship positions in 2022.
The National Resident Matching Program in its 2022 Medicine and Pediatric Specialties Match reported that rheumatology filled 123 of 127 certified programs (96.9%) along with 265 certified positions (97.8%).
Matched applicants for adult rheumatology programs included 40 U.S. foreign applicants (15.1%), 123 MD graduates (46.4%), 66 foreign (24.9%), and 36 DO graduates (13.6%).
A total of 352 applicants showed a preference for this specialty, and 75% matched to the specialty. Another 23% did not match to any program.
2022 was the first year that NRMP combined medical specialties, pediatric specialties, and adolescent medicine fellowship matches into the “Medicine and Pediatric Specialties Match.”
“We engaged the leadership of both pediatrics and internal medicine organizations to work with the NRMP to brainstorm solutions and were successful in combining pediatrics and internal medicine into one fellowship match,” said Jill Fussell, MD, immediate past chair of the Council of Pediatric Subspecialties in a statement. “It was an incredibly rewarding experience to work across pediatrics and internal medicine on behalf of resident well-being to make this collaborative change happen.”
Similar to 2021, pediatric rheumatology didn’t do as well as adult programs, filling just 18 of 32 certified programs (56.3%) and 27 out of 43 certified positions (62.8%). More than 66% of the applicants represented MD graduates. Eight were foreign, and one was a DO graduate.
The 2022 match was the largest on record, comprising 39 subspecialties in internal medicine, pediatrics, addiction, and multidisciplinary specialties. A total of 3,361 programs filled 7,648 (87.7%) of 8,724 positions in 2022. Three specialties – cardiovascular disease, interventional pulmonology, and oncology – filled all their positions offered in the match.
In addition to rheumatology, six other specialties filled 95% or more of their positions. This included clinical cardiac electrophysiology, critical care medicine, endocrinology, gastroenterology, hematology/oncology, and pulmonary/critical care medicine. Allergy and immunology, which accepts applicants from either internal medicine or pediatrics, also filled more than 95% of positions offered.
Matched applicants will start fellowship training in July 2023.
Rheumatology joined six other Medicine specialties that filled more than 95% of fellowship positions in 2022.
The National Resident Matching Program in its 2022 Medicine and Pediatric Specialties Match reported that rheumatology filled 123 of 127 certified programs (96.9%) along with 265 certified positions (97.8%).
Matched applicants for adult rheumatology programs included 40 U.S. foreign applicants (15.1%), 123 MD graduates (46.4%), 66 foreign (24.9%), and 36 DO graduates (13.6%).
A total of 352 applicants showed a preference for this specialty, and 75% matched to the specialty. Another 23% did not match to any program.
2022 was the first year that NRMP combined medical specialties, pediatric specialties, and adolescent medicine fellowship matches into the “Medicine and Pediatric Specialties Match.”
“We engaged the leadership of both pediatrics and internal medicine organizations to work with the NRMP to brainstorm solutions and were successful in combining pediatrics and internal medicine into one fellowship match,” said Jill Fussell, MD, immediate past chair of the Council of Pediatric Subspecialties in a statement. “It was an incredibly rewarding experience to work across pediatrics and internal medicine on behalf of resident well-being to make this collaborative change happen.”
Similar to 2021, pediatric rheumatology didn’t do as well as adult programs, filling just 18 of 32 certified programs (56.3%) and 27 out of 43 certified positions (62.8%). More than 66% of the applicants represented MD graduates. Eight were foreign, and one was a DO graduate.
The 2022 match was the largest on record, comprising 39 subspecialties in internal medicine, pediatrics, addiction, and multidisciplinary specialties. A total of 3,361 programs filled 7,648 (87.7%) of 8,724 positions in 2022. Three specialties – cardiovascular disease, interventional pulmonology, and oncology – filled all their positions offered in the match.
In addition to rheumatology, six other specialties filled 95% or more of their positions. This included clinical cardiac electrophysiology, critical care medicine, endocrinology, gastroenterology, hematology/oncology, and pulmonary/critical care medicine. Allergy and immunology, which accepts applicants from either internal medicine or pediatrics, also filled more than 95% of positions offered.
Matched applicants will start fellowship training in July 2023.