User login
Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia: Cutaneous Associations in Women With Skin of Color
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) has been reported in association with lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP) and facial papules.1-3 Lichen planus pigmentosus is a variant of lichen planus that causes hyperpigmentation of the face, neck, and/or intertriginous areas that may be useful as a clinical indicator in the development of FFA.1 Facial papules in association with FFA are secondary to fibrosed vellus hairs.2,3 Currently, reports of concomitant FFA, LPP, and facial papules in women with skin of color are limited in the literature. This case series includes 5 women of color (Hispanic and black) who presented to our clinic with FFA and various cutaneous associations. A review of the current literature on cutaneous associations of FFA also is provided.
Case Reports
Patient 1
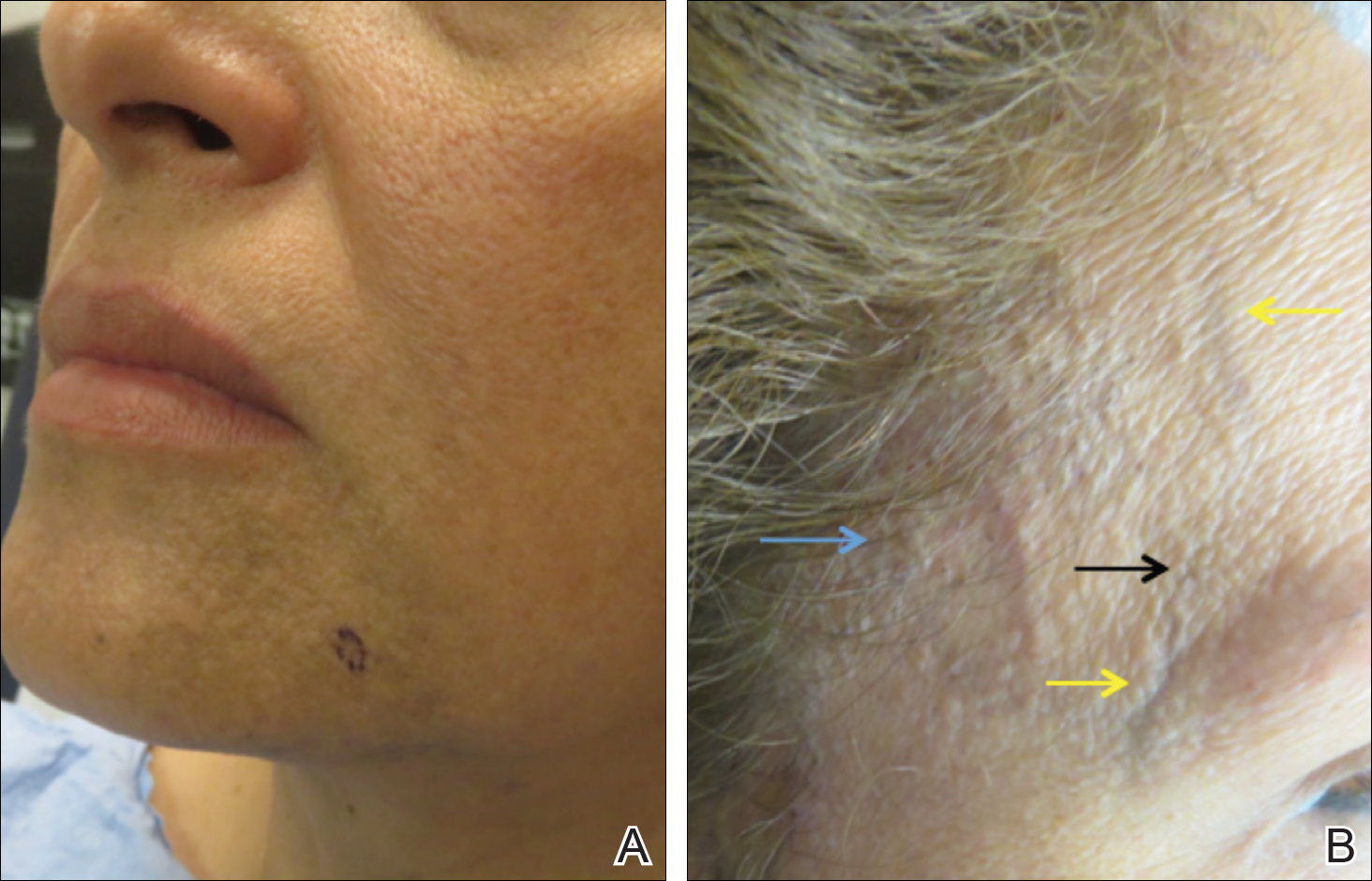
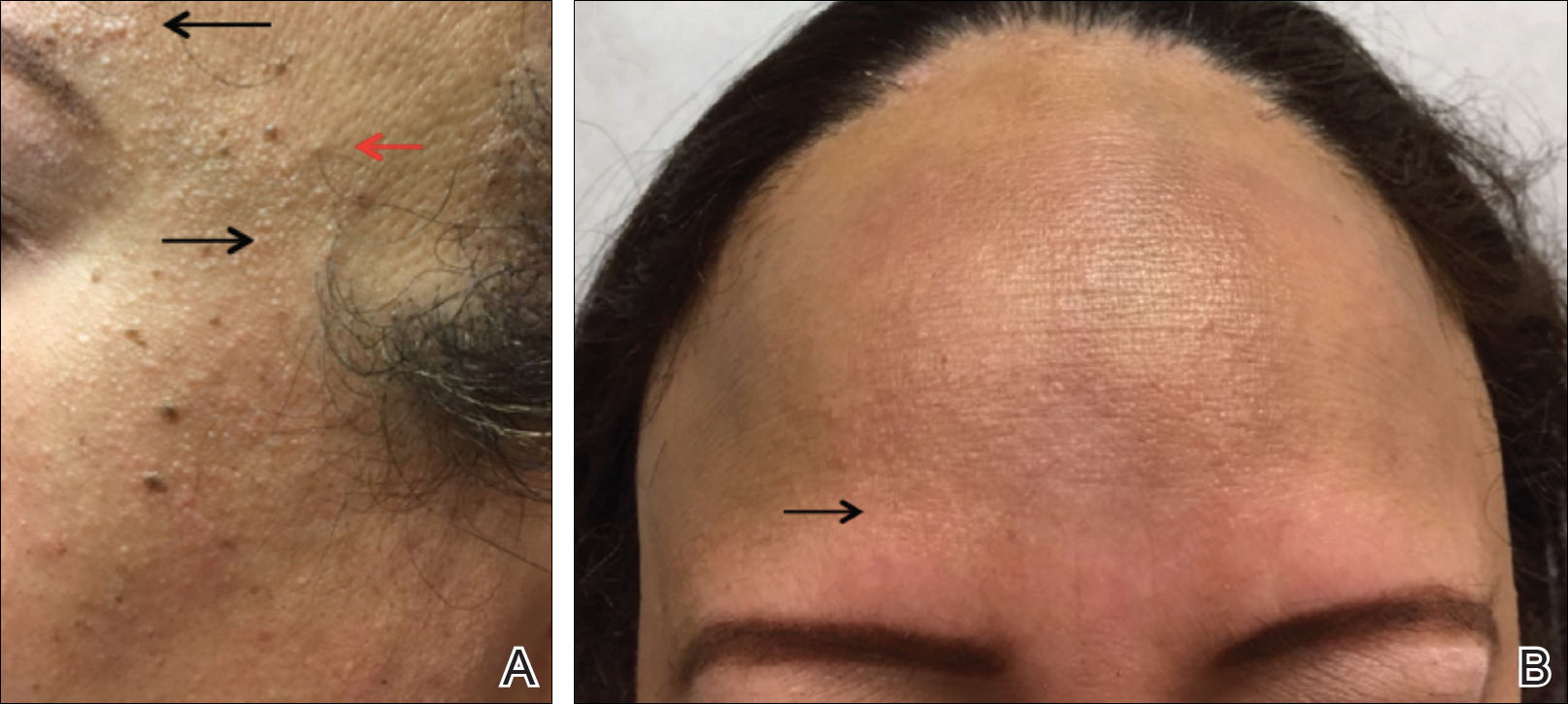
A 50-year-old Hispanic woman who was previously presumed to have melasma by an outside physician presented with pruritus of the scalp and eyebrows of 1 month’s duration. Physical examination revealed decreased frontal scalp hair density with perifollicular erythema and scale with thinning of the lateral eyebrows. Hyperpigmented coalesced macules (Figure 1A) and erythematous perifollicular papules were noted along the temples and on the perioral skin. Depressed forehead and temporal veins also were noted (Figure 1B). A biopsy of the scalp demonstrated perifollicular and perivascular lymphocytic inflammation and fibrosed hair follicles, and a biopsy of the perioral skin demonstrated perivascular lymphocytic inflammation with melanophages in the papillary dermis. A diagnosis of FFA with LPP was established with these biopsies.
Patient 2
A 61-year-old black woman presented with asymptomatic hair loss along the frontal hairline for an unknown duration. On physical examination the frontal scalp and lateral eyebrows demonstrated decreased hair density with loss of follicular ostia. Fine, flesh-colored, monomorphic papules were scattered along the forehead and temples, and ill-defined brown pigmentation was present along the forehead, temples, and cheeks. Biopsy of the frontal scalp demonstrated patchy lichenoid inflammation with decreased number of follicles with replacement by follicular scars, confirming the diagnosis of FFA.
Patient 3
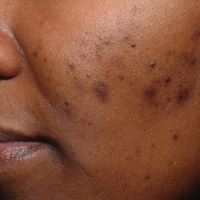
A 47-year-old Hispanic woman presented with hair loss of the frontal scalp and bilateral eyebrows with associated burning of 2 years’ duration. Physical examination demonstrated recession of the frontotemporal hairline with scattered lone hairs and thinning of the eyebrows. Innumerable flesh-colored papules were present on the forehead and temples (Figure 2A). Glabellar and eyebrow erythema was noted (Figure 2B). Biopsy of the frontal scalp demonstrated decreased terminal anagen hair follicles with perifollicular lymphoid infiltrate and fibrosis, consistent with a diagnosis of FFA. The patient was started on oral hydroxychloroquine 400 mg once daily, and 3 months later hyperpigmentation of the forehead and perioral skin was noted. The patient reported that she had facial hyperpigmentation prior to starting hydroxychloroquine and declined a biopsy.
Patient 4
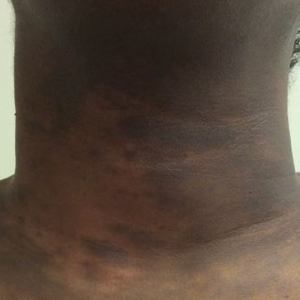
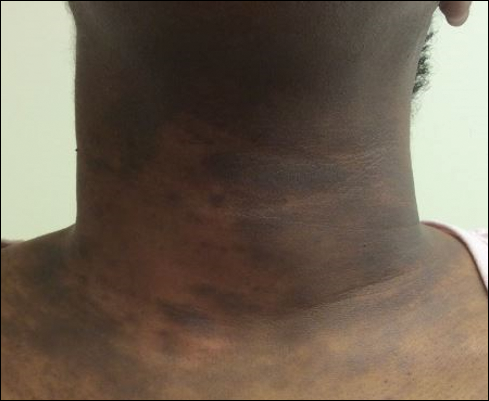
A 40-year-old black woman presented with brown pruritic macles of the face, neck, arms, and forearms of 4 years’ duration. She also reported hair loss on the frontal and occipital scalp, eyebrows, and arms. On physical examination, ill-defined brown macules and patches were noted on the neck (Figure 3), face, arms, and forearms. Decreased hair density was noted on the frontal and occipital scalp with follicular dropout and perifollicular hyperpigmentation. Biopsy of the scalp demonstrated perivascular lymphocytic inflammation with sparse anagen follicles and fibrous tracts, and biopsy of the neck revealed superficial perivascular inflammation with numerous melanophages in the upper dermis; these histopathologic findings were consistent with FFA and LPP, respectively.
Patient 5
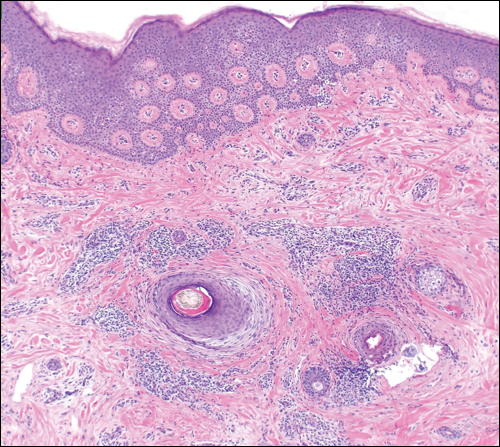
A 46-year-old black woman with history of hair loss presented with hyperpigmentation of the face and neck of 2 years’ duration. On physical examination decreased hair density of the frontal and vertex scalp and lateral eyebrows was noted. Flesh-colored papules were noted on the forehead and cheeks, and confluent dark brown patches were present on the temples and neck. Three punch biopsies were performed. Biopsy of the scalp revealed lymphocytic inflammation with surrounding fibroplasia with overlapping features of FFA and central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (Figure 4). Biopsy of the neck revealed vacuolar interface dermatitis. Additionally, biopsy of a facial papule revealed lichenoid inflammation involving a vellus hair follicle. Clinical and histopathological correlation confirmed the diagnosis of FFA with LPP and facial papules.
Comment
Current understanding of FFA as a progressive, lymphocytic, scarring alopecia has expanded in recent years. Clinical observation suggests that the incidence of FFA is increasing4; however more epidemiologic data are needed. Frontal fibrosing alopecia presents clinically with symmetrical frontotemporal hair loss with lone hairs. Trichoscopy reveals perifollicular hyperkeratosis, perifollicular erythema, and follicular plugging in 72%, 66%, and 44% of cases, respectively.5 In one study (N=242), patients were classified into 3 clinical patterns of FFA: pattern I (linear) showed bandlike loss of frontal hair with normal density directly behind the hairline; pattern II (diffuse) showed loss of density behind the frontal hairline; and pattern III (double line) showed a pseudo–“fringe sign” appearance. The majority of patients were classified as either pattern I or II, with pattern II predicting a poorer prognosis.6
rontal fibrosing alopecia is increasingly recognized in men, with prevalence as high as 5%.1 Facial hair involvement, particularly of the upper lip and sideburns, is an important consideration in men.7 Most studies suggest that 80% to 90% of affected women are postmenopausal,8 though a case series presented by Dlova1 identified 27% of affected women as postmenopausal. The coexistence of premature menopause and hysterectomy in FFA patients suggests a hormonal contribution, but this association is still poorly understood.8 Epidemiologic data on ethnicity in FFA are sparse but suggest that white individuals are more likely to be affected. Frontal fibrosing alopecia also may be misdiagnosed as traction alopecia in Hispanic and black patients.8
It is prudent for physicians to assess for and recognize clinical clues to severe forms of FFA. A 2014 multicenter review of 355 patients identified 3 clinical entities that predicted more severe forms of FFA: eyelash loss (madarosis), loss of body hair, and facial papules.8 Madarosis occurs due to perifollicular inflammation and fibrosis of eyelash hair follicles. Similarly, perifollicular inflammation of body hair was present in 24% of patients (N=86), most commonly of the axillary and pubic hair. Facial papules form due to facial vellus hair inflammation and fibrosis and were identified in 14% of patients (N=49).8 These clinical findings may allow providers to predict more extensive clinical involvement of FFA.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia and LPP occur concomitantly in up 54% of patients, more commonly in darker-skinned patients.1,9,10 Lichen planus pigmentosus frequently occurs on the face and neck, most commonly in a diffuse pattern, though reticulated and macular patterns also have been identified.11 In some patients, LPP precedes the development of FFA and may be useful as a herald sign1; therefore, it is important for dermatologists to evaluate for signs of FFA when evaluating those with LPP. Thorough evaluation in patients with skin of color also is important because FFA may be misdiagnosed as traction alopecia.
Additional cutaneous associations of FFA include eyebrow loss, glabellar red dots, and prominent frontal veins. Eyebrow loss occurs secondary to fibrosis of eyebrow hair follicles and has been found in 40% to 80% of patients with FFA; it is thought to be associated with milder forms of FFA.8 Glabellar red dots correlate with histopathologic lymphocytic inflammation of vellus hair follicles.12 Additionally, frontal vein prominence has been described in FFA and is thought to be secondary to atrophy in this scarring process, perhaps worsened by local steroid treatments.13 Mucocutaneous lichen planus, rosacea, thyroid disease, vitiligo, and other autoimmune disorders also have been reported in patients with FFA.14
Conclusion
Concomitant FFA, LPP, and facial papules have been rarely reported and exemplify the spectrum of cutaneous associations with FFA, particularly in individuals with skin of color. Clinical variants and associations of FFA are broad, including predictors of poorer prognosis such as eyelash loss and vellus hair involvement seen as facial papules. Lichen planus pigmentosus is well described in association with FFA and may serve as a herald sign that frontal hair loss should not be mistaken for traction alopecia in early stages. Eyebrow loss is thought to represent milder disease. It is important for dermatologists to be aware of these findings to understand the breadth of this disease and for appropriate evaluation and management of patients with FFA.
- Dlova NC. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and lichen planus pigmentosus: is there a link? Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:439-432.
- Donati A, Molina L, Doche I, et al. Facial papules in frontal fibrosing alopecia: evidence of vellus follicle involvement. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:1424-1427.
- Tan KT, Messenger AG. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: clinical presentations and prognosis. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:75-79.
- Rudnicka L, Rakowska A. The increasing incidence of frontal fibrosing alopecia. in search of triggering factors. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:1579-1580.
- Toledo-Pastrana T, Hernández MJ, Camacho Martínez FM. Perifollicular erythema as a trichoscopy sign of progression in frontal fibrosing alopecia. Int J Trichology. 2013;5:151-153.
- Moreno-Arrones OM, Saceda-Corralo D, Fonda-Pascual P, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: clinical and prognostic classification. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:1739-1745.
- Tolkachjov SN, Chaudhry HM, Camilleri MJ, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia among men: a clinicopathologic study of 7 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:683-690.e2.
- Vañó-Galván S, Molina-Ruiz AM, Serrano-Falcón C, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a multicenter review of 355 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:670-678.
- Berliner JG, McCalmont TH, Price VH, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and lichen planus pigmentosus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E26-E27.
- Rao R, Sarda A, Khanna R, et al. Coexistence of frontal fibrosing alopecia with lichen planus pigmentosus. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:622-624.
- Pirmez R, Duque-Estrada B, Donati A, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic features of lichen planus pigmentosus in 37 patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:1387-1390.
- Pirmez R, Donati A, Valente NS, et al. Glabellar red dots in frontal fibrosing alopecia: a further clinical sign of vellus follicle involvement. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:745-746.
- Vañó-Galván S, Rodrigues-Barata AR, Urech M, et al. Depression of the frontal veins: a new clinical sign of frontal fibrosing alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:1087-1088.
- Pindado-Ortega C, Saceda-Corralo D, Buendía-Castaño D, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and cutaneous comorbidities: a potential relationship with rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:596-597.e1.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) has been reported in association with lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP) and facial papules.1-3 Lichen planus pigmentosus is a variant of lichen planus that causes hyperpigmentation of the face, neck, and/or intertriginous areas that may be useful as a clinical indicator in the development of FFA.1 Facial papules in association with FFA are secondary to fibrosed vellus hairs.2,3 Currently, reports of concomitant FFA, LPP, and facial papules in women with skin of color are limited in the literature. This case series includes 5 women of color (Hispanic and black) who presented to our clinic with FFA and various cutaneous associations. A review of the current literature on cutaneous associations of FFA also is provided.
Case Reports
Patient 1
A 50-year-old Hispanic woman who was previously presumed to have melasma by an outside physician presented with pruritus of the scalp and eyebrows of 1 month’s duration. Physical examination revealed decreased frontal scalp hair density with perifollicular erythema and scale with thinning of the lateral eyebrows. Hyperpigmented coalesced macules (Figure 1A) and erythematous perifollicular papules were noted along the temples and on the perioral skin. Depressed forehead and temporal veins also were noted (Figure 1B). A biopsy of the scalp demonstrated perifollicular and perivascular lymphocytic inflammation and fibrosed hair follicles, and a biopsy of the perioral skin demonstrated perivascular lymphocytic inflammation with melanophages in the papillary dermis. A diagnosis of FFA with LPP was established with these biopsies.

Patient 2
A 61-year-old black woman presented with asymptomatic hair loss along the frontal hairline for an unknown duration. On physical examination the frontal scalp and lateral eyebrows demonstrated decreased hair density with loss of follicular ostia. Fine, flesh-colored, monomorphic papules were scattered along the forehead and temples, and ill-defined brown pigmentation was present along the forehead, temples, and cheeks. Biopsy of the frontal scalp demonstrated patchy lichenoid inflammation with decreased number of follicles with replacement by follicular scars, confirming the diagnosis of FFA.
Patient 3
A 47-year-old Hispanic woman presented with hair loss of the frontal scalp and bilateral eyebrows with associated burning of 2 years’ duration. Physical examination demonstrated recession of the frontotemporal hairline with scattered lone hairs and thinning of the eyebrows. Innumerable flesh-colored papules were present on the forehead and temples (Figure 2A). Glabellar and eyebrow erythema was noted (Figure 2B). Biopsy of the frontal scalp demonstrated decreased terminal anagen hair follicles with perifollicular lymphoid infiltrate and fibrosis, consistent with a diagnosis of FFA. The patient was started on oral hydroxychloroquine 400 mg once daily, and 3 months later hyperpigmentation of the forehead and perioral skin was noted. The patient reported that she had facial hyperpigmentation prior to starting hydroxychloroquine and declined a biopsy.

Patient 4
A 40-year-old black woman presented with brown pruritic macles of the face, neck, arms, and forearms of 4 years’ duration. She also reported hair loss on the frontal and occipital scalp, eyebrows, and arms. On physical examination, ill-defined brown macules and patches were noted on the neck (Figure 3), face, arms, and forearms. Decreased hair density was noted on the frontal and occipital scalp with follicular dropout and perifollicular hyperpigmentation. Biopsy of the scalp demonstrated perivascular lymphocytic inflammation with sparse anagen follicles and fibrous tracts, and biopsy of the neck revealed superficial perivascular inflammation with numerous melanophages in the upper dermis; these histopathologic findings were consistent with FFA and LPP, respectively.

Patient 5
A 46-year-old black woman with history of hair loss presented with hyperpigmentation of the face and neck of 2 years’ duration. On physical examination decreased hair density of the frontal and vertex scalp and lateral eyebrows was noted. Flesh-colored papules were noted on the forehead and cheeks, and confluent dark brown patches were present on the temples and neck. Three punch biopsies were performed. Biopsy of the scalp revealed lymphocytic inflammation with surrounding fibroplasia with overlapping features of FFA and central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (Figure 4). Biopsy of the neck revealed vacuolar interface dermatitis. Additionally, biopsy of a facial papule revealed lichenoid inflammation involving a vellus hair follicle. Clinical and histopathological correlation confirmed the diagnosis of FFA with LPP and facial papules.

Comment
Current understanding of FFA as a progressive, lymphocytic, scarring alopecia has expanded in recent years. Clinical observation suggests that the incidence of FFA is increasing4; however more epidemiologic data are needed. Frontal fibrosing alopecia presents clinically with symmetrical frontotemporal hair loss with lone hairs. Trichoscopy reveals perifollicular hyperkeratosis, perifollicular erythema, and follicular plugging in 72%, 66%, and 44% of cases, respectively.5 In one study (N=242), patients were classified into 3 clinical patterns of FFA: pattern I (linear) showed bandlike loss of frontal hair with normal density directly behind the hairline; pattern II (diffuse) showed loss of density behind the frontal hairline; and pattern III (double line) showed a pseudo–“fringe sign” appearance. The majority of patients were classified as either pattern I or II, with pattern II predicting a poorer prognosis.6
rontal fibrosing alopecia is increasingly recognized in men, with prevalence as high as 5%.1 Facial hair involvement, particularly of the upper lip and sideburns, is an important consideration in men.7 Most studies suggest that 80% to 90% of affected women are postmenopausal,8 though a case series presented by Dlova1 identified 27% of affected women as postmenopausal. The coexistence of premature menopause and hysterectomy in FFA patients suggests a hormonal contribution, but this association is still poorly understood.8 Epidemiologic data on ethnicity in FFA are sparse but suggest that white individuals are more likely to be affected. Frontal fibrosing alopecia also may be misdiagnosed as traction alopecia in Hispanic and black patients.8
It is prudent for physicians to assess for and recognize clinical clues to severe forms of FFA. A 2014 multicenter review of 355 patients identified 3 clinical entities that predicted more severe forms of FFA: eyelash loss (madarosis), loss of body hair, and facial papules.8 Madarosis occurs due to perifollicular inflammation and fibrosis of eyelash hair follicles. Similarly, perifollicular inflammation of body hair was present in 24% of patients (N=86), most commonly of the axillary and pubic hair. Facial papules form due to facial vellus hair inflammation and fibrosis and were identified in 14% of patients (N=49).8 These clinical findings may allow providers to predict more extensive clinical involvement of FFA.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia and LPP occur concomitantly in up 54% of patients, more commonly in darker-skinned patients.1,9,10 Lichen planus pigmentosus frequently occurs on the face and neck, most commonly in a diffuse pattern, though reticulated and macular patterns also have been identified.11 In some patients, LPP precedes the development of FFA and may be useful as a herald sign1; therefore, it is important for dermatologists to evaluate for signs of FFA when evaluating those with LPP. Thorough evaluation in patients with skin of color also is important because FFA may be misdiagnosed as traction alopecia.
Additional cutaneous associations of FFA include eyebrow loss, glabellar red dots, and prominent frontal veins. Eyebrow loss occurs secondary to fibrosis of eyebrow hair follicles and has been found in 40% to 80% of patients with FFA; it is thought to be associated with milder forms of FFA.8 Glabellar red dots correlate with histopathologic lymphocytic inflammation of vellus hair follicles.12 Additionally, frontal vein prominence has been described in FFA and is thought to be secondary to atrophy in this scarring process, perhaps worsened by local steroid treatments.13 Mucocutaneous lichen planus, rosacea, thyroid disease, vitiligo, and other autoimmune disorders also have been reported in patients with FFA.14
Conclusion
Concomitant FFA, LPP, and facial papules have been rarely reported and exemplify the spectrum of cutaneous associations with FFA, particularly in individuals with skin of color. Clinical variants and associations of FFA are broad, including predictors of poorer prognosis such as eyelash loss and vellus hair involvement seen as facial papules. Lichen planus pigmentosus is well described in association with FFA and may serve as a herald sign that frontal hair loss should not be mistaken for traction alopecia in early stages. Eyebrow loss is thought to represent milder disease. It is important for dermatologists to be aware of these findings to understand the breadth of this disease and for appropriate evaluation and management of patients with FFA.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) has been reported in association with lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP) and facial papules.1-3 Lichen planus pigmentosus is a variant of lichen planus that causes hyperpigmentation of the face, neck, and/or intertriginous areas that may be useful as a clinical indicator in the development of FFA.1 Facial papules in association with FFA are secondary to fibrosed vellus hairs.2,3 Currently, reports of concomitant FFA, LPP, and facial papules in women with skin of color are limited in the literature. This case series includes 5 women of color (Hispanic and black) who presented to our clinic with FFA and various cutaneous associations. A review of the current literature on cutaneous associations of FFA also is provided.
Case Reports
Patient 1
A 50-year-old Hispanic woman who was previously presumed to have melasma by an outside physician presented with pruritus of the scalp and eyebrows of 1 month’s duration. Physical examination revealed decreased frontal scalp hair density with perifollicular erythema and scale with thinning of the lateral eyebrows. Hyperpigmented coalesced macules (Figure 1A) and erythematous perifollicular papules were noted along the temples and on the perioral skin. Depressed forehead and temporal veins also were noted (Figure 1B). A biopsy of the scalp demonstrated perifollicular and perivascular lymphocytic inflammation and fibrosed hair follicles, and a biopsy of the perioral skin demonstrated perivascular lymphocytic inflammation with melanophages in the papillary dermis. A diagnosis of FFA with LPP was established with these biopsies.

Patient 2
A 61-year-old black woman presented with asymptomatic hair loss along the frontal hairline for an unknown duration. On physical examination the frontal scalp and lateral eyebrows demonstrated decreased hair density with loss of follicular ostia. Fine, flesh-colored, monomorphic papules were scattered along the forehead and temples, and ill-defined brown pigmentation was present along the forehead, temples, and cheeks. Biopsy of the frontal scalp demonstrated patchy lichenoid inflammation with decreased number of follicles with replacement by follicular scars, confirming the diagnosis of FFA.
Patient 3
A 47-year-old Hispanic woman presented with hair loss of the frontal scalp and bilateral eyebrows with associated burning of 2 years’ duration. Physical examination demonstrated recession of the frontotemporal hairline with scattered lone hairs and thinning of the eyebrows. Innumerable flesh-colored papules were present on the forehead and temples (Figure 2A). Glabellar and eyebrow erythema was noted (Figure 2B). Biopsy of the frontal scalp demonstrated decreased terminal anagen hair follicles with perifollicular lymphoid infiltrate and fibrosis, consistent with a diagnosis of FFA. The patient was started on oral hydroxychloroquine 400 mg once daily, and 3 months later hyperpigmentation of the forehead and perioral skin was noted. The patient reported that she had facial hyperpigmentation prior to starting hydroxychloroquine and declined a biopsy.

Patient 4
A 40-year-old black woman presented with brown pruritic macles of the face, neck, arms, and forearms of 4 years’ duration. She also reported hair loss on the frontal and occipital scalp, eyebrows, and arms. On physical examination, ill-defined brown macules and patches were noted on the neck (Figure 3), face, arms, and forearms. Decreased hair density was noted on the frontal and occipital scalp with follicular dropout and perifollicular hyperpigmentation. Biopsy of the scalp demonstrated perivascular lymphocytic inflammation with sparse anagen follicles and fibrous tracts, and biopsy of the neck revealed superficial perivascular inflammation with numerous melanophages in the upper dermis; these histopathologic findings were consistent with FFA and LPP, respectively.

Patient 5
A 46-year-old black woman with history of hair loss presented with hyperpigmentation of the face and neck of 2 years’ duration. On physical examination decreased hair density of the frontal and vertex scalp and lateral eyebrows was noted. Flesh-colored papules were noted on the forehead and cheeks, and confluent dark brown patches were present on the temples and neck. Three punch biopsies were performed. Biopsy of the scalp revealed lymphocytic inflammation with surrounding fibroplasia with overlapping features of FFA and central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (Figure 4). Biopsy of the neck revealed vacuolar interface dermatitis. Additionally, biopsy of a facial papule revealed lichenoid inflammation involving a vellus hair follicle. Clinical and histopathological correlation confirmed the diagnosis of FFA with LPP and facial papules.

Comment
Current understanding of FFA as a progressive, lymphocytic, scarring alopecia has expanded in recent years. Clinical observation suggests that the incidence of FFA is increasing4; however more epidemiologic data are needed. Frontal fibrosing alopecia presents clinically with symmetrical frontotemporal hair loss with lone hairs. Trichoscopy reveals perifollicular hyperkeratosis, perifollicular erythema, and follicular plugging in 72%, 66%, and 44% of cases, respectively.5 In one study (N=242), patients were classified into 3 clinical patterns of FFA: pattern I (linear) showed bandlike loss of frontal hair with normal density directly behind the hairline; pattern II (diffuse) showed loss of density behind the frontal hairline; and pattern III (double line) showed a pseudo–“fringe sign” appearance. The majority of patients were classified as either pattern I or II, with pattern II predicting a poorer prognosis.6
rontal fibrosing alopecia is increasingly recognized in men, with prevalence as high as 5%.1 Facial hair involvement, particularly of the upper lip and sideburns, is an important consideration in men.7 Most studies suggest that 80% to 90% of affected women are postmenopausal,8 though a case series presented by Dlova1 identified 27% of affected women as postmenopausal. The coexistence of premature menopause and hysterectomy in FFA patients suggests a hormonal contribution, but this association is still poorly understood.8 Epidemiologic data on ethnicity in FFA are sparse but suggest that white individuals are more likely to be affected. Frontal fibrosing alopecia also may be misdiagnosed as traction alopecia in Hispanic and black patients.8
It is prudent for physicians to assess for and recognize clinical clues to severe forms of FFA. A 2014 multicenter review of 355 patients identified 3 clinical entities that predicted more severe forms of FFA: eyelash loss (madarosis), loss of body hair, and facial papules.8 Madarosis occurs due to perifollicular inflammation and fibrosis of eyelash hair follicles. Similarly, perifollicular inflammation of body hair was present in 24% of patients (N=86), most commonly of the axillary and pubic hair. Facial papules form due to facial vellus hair inflammation and fibrosis and were identified in 14% of patients (N=49).8 These clinical findings may allow providers to predict more extensive clinical involvement of FFA.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia and LPP occur concomitantly in up 54% of patients, more commonly in darker-skinned patients.1,9,10 Lichen planus pigmentosus frequently occurs on the face and neck, most commonly in a diffuse pattern, though reticulated and macular patterns also have been identified.11 In some patients, LPP precedes the development of FFA and may be useful as a herald sign1; therefore, it is important for dermatologists to evaluate for signs of FFA when evaluating those with LPP. Thorough evaluation in patients with skin of color also is important because FFA may be misdiagnosed as traction alopecia.
Additional cutaneous associations of FFA include eyebrow loss, glabellar red dots, and prominent frontal veins. Eyebrow loss occurs secondary to fibrosis of eyebrow hair follicles and has been found in 40% to 80% of patients with FFA; it is thought to be associated with milder forms of FFA.8 Glabellar red dots correlate with histopathologic lymphocytic inflammation of vellus hair follicles.12 Additionally, frontal vein prominence has been described in FFA and is thought to be secondary to atrophy in this scarring process, perhaps worsened by local steroid treatments.13 Mucocutaneous lichen planus, rosacea, thyroid disease, vitiligo, and other autoimmune disorders also have been reported in patients with FFA.14
Conclusion
Concomitant FFA, LPP, and facial papules have been rarely reported and exemplify the spectrum of cutaneous associations with FFA, particularly in individuals with skin of color. Clinical variants and associations of FFA are broad, including predictors of poorer prognosis such as eyelash loss and vellus hair involvement seen as facial papules. Lichen planus pigmentosus is well described in association with FFA and may serve as a herald sign that frontal hair loss should not be mistaken for traction alopecia in early stages. Eyebrow loss is thought to represent milder disease. It is important for dermatologists to be aware of these findings to understand the breadth of this disease and for appropriate evaluation and management of patients with FFA.
- Dlova NC. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and lichen planus pigmentosus: is there a link? Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:439-432.
- Donati A, Molina L, Doche I, et al. Facial papules in frontal fibrosing alopecia: evidence of vellus follicle involvement. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:1424-1427.
- Tan KT, Messenger AG. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: clinical presentations and prognosis. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:75-79.
- Rudnicka L, Rakowska A. The increasing incidence of frontal fibrosing alopecia. in search of triggering factors. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:1579-1580.
- Toledo-Pastrana T, Hernández MJ, Camacho Martínez FM. Perifollicular erythema as a trichoscopy sign of progression in frontal fibrosing alopecia. Int J Trichology. 2013;5:151-153.
- Moreno-Arrones OM, Saceda-Corralo D, Fonda-Pascual P, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: clinical and prognostic classification. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:1739-1745.
- Tolkachjov SN, Chaudhry HM, Camilleri MJ, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia among men: a clinicopathologic study of 7 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:683-690.e2.
- Vañó-Galván S, Molina-Ruiz AM, Serrano-Falcón C, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a multicenter review of 355 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:670-678.
- Berliner JG, McCalmont TH, Price VH, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and lichen planus pigmentosus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E26-E27.
- Rao R, Sarda A, Khanna R, et al. Coexistence of frontal fibrosing alopecia with lichen planus pigmentosus. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:622-624.
- Pirmez R, Duque-Estrada B, Donati A, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic features of lichen planus pigmentosus in 37 patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:1387-1390.
- Pirmez R, Donati A, Valente NS, et al. Glabellar red dots in frontal fibrosing alopecia: a further clinical sign of vellus follicle involvement. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:745-746.
- Vañó-Galván S, Rodrigues-Barata AR, Urech M, et al. Depression of the frontal veins: a new clinical sign of frontal fibrosing alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:1087-1088.
- Pindado-Ortega C, Saceda-Corralo D, Buendía-Castaño D, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and cutaneous comorbidities: a potential relationship with rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:596-597.e1.
- Dlova NC. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and lichen planus pigmentosus: is there a link? Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:439-432.
- Donati A, Molina L, Doche I, et al. Facial papules in frontal fibrosing alopecia: evidence of vellus follicle involvement. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:1424-1427.
- Tan KT, Messenger AG. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: clinical presentations and prognosis. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:75-79.
- Rudnicka L, Rakowska A. The increasing incidence of frontal fibrosing alopecia. in search of triggering factors. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:1579-1580.
- Toledo-Pastrana T, Hernández MJ, Camacho Martínez FM. Perifollicular erythema as a trichoscopy sign of progression in frontal fibrosing alopecia. Int J Trichology. 2013;5:151-153.
- Moreno-Arrones OM, Saceda-Corralo D, Fonda-Pascual P, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: clinical and prognostic classification. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:1739-1745.
- Tolkachjov SN, Chaudhry HM, Camilleri MJ, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia among men: a clinicopathologic study of 7 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:683-690.e2.
- Vañó-Galván S, Molina-Ruiz AM, Serrano-Falcón C, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a multicenter review of 355 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:670-678.
- Berliner JG, McCalmont TH, Price VH, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and lichen planus pigmentosus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E26-E27.
- Rao R, Sarda A, Khanna R, et al. Coexistence of frontal fibrosing alopecia with lichen planus pigmentosus. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:622-624.
- Pirmez R, Duque-Estrada B, Donati A, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic features of lichen planus pigmentosus in 37 patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:1387-1390.
- Pirmez R, Donati A, Valente NS, et al. Glabellar red dots in frontal fibrosing alopecia: a further clinical sign of vellus follicle involvement. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:745-746.
- Vañó-Galván S, Rodrigues-Barata AR, Urech M, et al. Depression of the frontal veins: a new clinical sign of frontal fibrosing alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:1087-1088.
- Pindado-Ortega C, Saceda-Corralo D, Buendía-Castaño D, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and cutaneous comorbidities: a potential relationship with rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:596-597.e1.
Practice Points
- Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) is associated with lichen planus pigmentosus, especially in patients with skin of color.
- Patients with FFA should be evaluated for additional cutaneous features including facial papules, glabellar red dots, and depressed frontal veins.
Surgical Procedures for Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that has a social and psychosocial impact on patients with skin of color.1 It is characterized by recurrent abscesses, draining sinus tracts, and scarring in the intertriginous skin folds. The lesions are difficult to treat and present with considerable frustration for both patients and physicians. Although current treatment ladders can delay procedures and surgical intervention,1 some believe that surgery should be introduced earlier in HS management.2 In this article, we review current procedures for the management of HS, including cryoinsufflation, incision and drainage, deroofing, skin tissue–saving excision with electrosurgical peeling, and wide surgical excision, along with various closure techniques.
Cryoinsufflation
First described in 2014, cryoinsufflation is a novel method for treating sinus tracts.3 Lesions initially are identified on physical examination. Prior to the procedure, local anesthesia is administered to the lesion.3 A 21-gauge needle is mounted onto a cryosurgical unit and inserted into the opening of the sinus tract. Liquid nitrogen is sprayed into the tract for 5 seconds, followed by a 3-second pause; the process is repeated 3 times. Patients return for treatment sessions monthly until the tract is obliterated. This procedure was first performed on 2 patients with satisfactory results.3
Since the initial report, the investigators made 2 changes to refine the procedure.4 First, systemic antibiotics should be prescribed 2 months prior to the procedure to clear the sinus tracts of infection. Furthermore, a 21-gauge, olive-tipped cannula is recommended in lieu of a 21-gauge needle to mitigate the risk of adverse events such as air embolism.4
Incision and Drainage
Incision and drainage provides rapid pain relief for tense fluctuant abscesses, but recurrence is common and the procedure costs are high.5 For drainage, wide circumferential local anesthesia is administered followed by incision.6 Pus is eliminated using digital pressure or saline rinses.2 Following the elimination of pus, the wound may need gauze packing or placement of a wick for a few days.6 The general belief is that incision and drainage should be used, if necessary, to rapidly relieve the patient’s pain; however, other surgical options should be considered if the patient has had multiple incision and drainage procedures.7 Currently there are no randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on incision and drainage procedures in HS abscesses.
Deroofing
In 1959, Mullins et al8 first described the deroofing procedure, which was refined to preserve the floor of the sinus tract in the 1980s.9,10 Culp10 and Brown et al9 theorized that preservation of the exposed floor of the sinus tract allowed for the epithelial cells from sweat glands and hair follicle remnants to rapidly reepithelialize the wound. In 2010, van der Zee et al11 performed a prospective study of 88 deroofed lesions in which the investigators removed keratinous debris and epithelial remnants of the floor due to concern for recurrence in this area if the tissues remained. Only 17% (15/88) of the lesions recurred at a median follow-up of 34 months.11
In Hurley stage I or II HS, deroofing remains the primary procedure for persistent nodules and sinus tracts.2 The lesion is identified on physical examination and local anesthesia is administered, first to the area surrounding the lesion, then to the lesion itself.11 A blunt probe is used to identify openings and search for connecting fistulas. After defining the sinus tract, the roof and wings created by the incision are removed.11,12 The material on the floor of the tract is scraped away, and the wound is left to heal by secondary intention.11 In general, deroofed lesions heal with cosmetically acceptable scars. We have used this procedure in skin of color patients with good results and no difficulties with healing. Controlled trials with long-term follow-up are lacking in this population.
Skin Tissue–Saving Excision With Electrosurgical Peeling
Skin tissue–saving excision with electrosurgical peeling was first introduced in 2015.13 Blok et al14 described the procedure as a promising alternative to wide surgical excision for Hurley stage II or III HS. The procedure saves healthy tissue while completely removing lesional tissue, leading to rapid wound healing, excellent cosmesis, and a low risk of contractures2,14; however, recurrence rates are higher than those seen in wide surgical excision.15 There are no known RCTs with long-term follow-up for HS patients treated with skin tissue–saving excision with electrosurgical peeling.
The procedure typically is performed under general anesthesia.14 First, the sinus tract is palpated on physical examination and probed to delineate the extent of the tract. Next, the roof of the tract is incised electrosurgically with a wire loop tip coupled to an electrosurgical generator.14 Consecutive tangential excisions are made until the floor of the sinus tract is reached. The process of incising sinus tracts followed by tangential peeling off of tissue continues until the entire area is clear of lesional and fibrotic tissue. The wound margins are probed for the presence and subsequent removal of residual sinus tracts. Lastly, the electrosurgical generator is used to achieve hemostasis, steroids are injected to prevent the formation of hypergranulation tissue, and the wound is left to heal by secondary intention.14 Following intervention, recurrence rates appear to be similar to wide surgical excision.13,14
Wide Surgical Excision
Wide excision is a widely established technique consisting of surgical excision of a lesion plus an area of surrounding disease-free tissue such as subcutaneous fat or a lateral margin of intertriginous skin.15 Similar to other surgical techniques, wide excision is considered in cases of severe disease when pharmacologic management cannot remedy extensive fibrosis or architectural loss. It typically is performed in Hurley stage II and III HS, with pathology extending to involve deeper structures inaccessible to more superficial surgical methods.2 Prominent areas of use include gluteal, axillary, perineal, and perianal HS lesions on which conservative treatments have little effect and depend on wide excision to provide successful postoperative results.16 Although retrospective and prospective studies exist on wide excision in HS, there continues to be a dearth of RCTs. Based on the available literature, the primary motive for wide excision is lower recurrence rates (13% overall compared to 22% and 27% for local excision and deroofing, respectively) and longer asymptomatic periods compared to more local techniques.7,17 Wide excision combined with continued aggressive medical management and dietary modifications currently is an efficacious treatment in providing functional long-term results.6 These benefits, however, are not without their drawbacks, as the more extensive nature of wide surgical excision predisposes patients to larger wounds, surgery-induced infection, and prolonged recovery periods.6,15 If preoperative measurements are not wisely assessed, the excision also can extend to involve neurovascular bundles and other vital structures, contributing to greater postoperative morbidity.15 Ultrasonography provides useful anatomic information in HS, such as location and extent of fistulous tracts and fluid collections; these findings can assist in guiding the width and depth of the excision itself to ensure the entire area of HS involvement is removed.18 Published data revealed that 204 of 255 (80%) patients were markedly satisfied with postoperative outcomes of wide excision,19 which gives credence to the idea that although the complications of wide excision may not be as favorable, the long-lasting improvements in quality of life make wide surgical excision a suggested first-line treatment in all stages of HS.16,20
Closure Techniques
The best skin closure method following surgical excision is controversial and not well established in literature. Options include healing by secondary intention, primary (suture-based) closure, skin grafts, and skin flaps. Each of these methods has had moderate success in multiple observational studies, and the choice should be made based on individualized assessment of the patient’s HS lesion characteristics, ability to adhere to recovery protocols, and relevant demographics. A systematic review by Mehdizadeh et al17 provided the following recurrence rates for techniques utilized after wide excision: primary closure, 15%; flaps, 8%; and grafting, 6%. Despite conflicting evidence, allowing wounds to heal by secondary intention is best, based on the author’s experience (I.H.H.).
Secondary Intention
Healing by secondary intention refers to a wound that is intentionally left open to be filled in with granulation tissue and eventual epithelization over time rather than being approximated and closed via sutures or staples as in primary intention. It is a well-established option in wound management and results in a longer but more comfortable period of convalescence in postsurgical HS management.20 Patients can add regular moist wound dressings (eg, silastic foam dressing) to manage the wound at home and continue normal activities for most of the healing period; however, the recovery period can become excessively long and painful, and there is a high risk of formation of retractile scar bands at and around the healing site.12 Strict adherence to wound-healing protocols is paramount to minimizing unwanted complications.21 Secondary intention often is used after wide local excision and has been demonstrated to yield positive functional and aesthetic results in multiple studies, especially in the more severe Hurley stage II or III cases.21,22 It can be successfully employed after laser treatment and in surgical defects of all sizes with little to no contractures or reduced range of motion.6 Ultimately, the choice to heal via secondary intention should be made after thorough assessment of patient needs and with ample education to ensure compliance.
Primary Closure
Primary closure is the suture-mediated closing technique that is most often used in wound closure for lower-grade HS cases, especially smaller excisions. However, it is associated with potential complications. If HS lesions are not effectively excised, disease can then recur at the periphery of the excision and wound dehiscence can manifest more readily, especially as wound size increases.23 Consequently, primary closure is associated with the highest recurrence rates among closure techniques.17 Avoiding primary closure in active disease also is recommended due to the potential of burying residual foci of inflammation.6 Finally, primary closures lack skin coverage and thus often are not viable options in most perianal and genital lesions that require more extensive reconstruction. Retrospective case series and case reports exist on primary excision, but further study is needed.
Skin Grafts
Skin grafting is a technique of surgically transplanting a piece of healthy skin from one body site to another. Skin grafts typically are used when primary closure or skin flaps are not feasible (eg, in large wounds) and also when shorter time to wound closure is a greater concern in patient recovery.2,24 Additionally, skin grafts can be employed on large flat surfaces of the body, such as the buttocks or thighs, for timely wound closure when wound contraction is less effective or wound healing is slow via epithelization. Types of skin graft techniques include split-thickness skin graft (STSG), full-thickness skin graft, and recycled skin graft. All 3 types have demonstrated acceptable functional and aesthetic results in observational studies and case reports, and thus deciding which technique to use should include individualized assessment.2,25 The STSG has several advantages over the full-thickness skin graft, including hairlessness (ie, without hair follicles), ease of harvest, and a less complicated transfer to contaminated lesional areas such as those in HS.26 Additionally, STSGs allow for closure of even the largest wounds with minimal risk of serious infection. Split-thickness skin grafts are considered one of the most efficacious tools for axilla reconstruction; however, they require prolonged immobilization of the arm, result in sequelae in donor sites, and do not always prevent retractile scars.26 The recycled skin graft technique can be used to treat chronic gluteal HS, but reliability and outcomes have not been reported. Skin grafting after excision is associated with increased pain, immobilization, prolonged hospitalization, and longer healing times compared to skin flaps.19 In a systematic review of wound healing techniques following wide excision, grafting was shown to have the lowest recurrence rate (6%) compared to skin flaps (8%) and primary closure (15%).17 The absence of hair follicles and sweat glands in STSGs may be advantageous in HS because both hair follicles and sweat glands are thought to play more roles in the pathogenesis of HS.18,24 Most studies on skin grafts are limited to case reports.
Skin Flaps
Skin flaps are similar to skin grafts in that healthy skin is transplanted from one site to another; the difference is that flaps maintain an intact blood supply, whereas skin grafts depend on growth of new blood vessels.12,13 The primary advantage of skin flaps is that they provide the best quality of skin due to the thick tissue coverage, which is an important concern, especially in aesthetic scenarios. Additionally, they have been shown to provide shorter healing times than grafts, primary closure, and secondary healing, which can be especially important when functional disability is a concern in the postoperative period.26 However, their use should be limited due to several complications owing to their blood supply, as there is a high risk of ischemia to distant portions of flaps, which often can progress to necrosis and hemorrhage during the harvesting process.2 Thus, skin flaps are incredibly difficult to use in larger wounds and often require debulking due to their thickness. Additionally, skin flaps are definitive by nature, which can pose an issue if HS recurs locally. Skin flaps are recommended only when their use is mandatory, such as in the coverage of important anatomic structures (eg, exposed neurovascular bundles and large vessels).2 Advances have been made in flap construction, and now several types of flaps are employed in several body areas with differing indications and recommendations.2,21 As with skin grafts, most studies in the literature are case reports; therefore, further investigation is needed.
Combination Reconstructions
Combination reconstructions refer to the simultaneous use of multiple closure or healing techniques. By combining 2 or more methods, surgeons can utilize the advantages of each technique to provide an individualized approach that can substantially diminish wound surface area and accelerate wound healing.2 For example, with the starlike technique, 5 equilateral triangles bordering a foci of axillary disease are excised in addition to the central foci, and the edges of each triangle are then sutured together to create a final scar of considerably smaller size. The starlike technique allows the wound to be partially sutured while leaving the remaining area to heal by secondary intention.2 There are a small number of case series and prospective studies on combined reconstructions in HS but no RCTs.
Conclusion
- Smith MK, Nicholson CL, Parks-Miller A, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: an update on connecting the tracts. F1000Res. 2017;6:1272.
- Janse I, Bieniek A, Horvath B, et al. Surgical procedures in hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:97-109.
- Pagliarello C, Fabrizi G, Feliciani C, et al. Cryoinsufflation for Hurley stage II hidradenitis suppurativa: a useful treatment option when systemic therapies should be avoided. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:765-766.
- Pagliarello C, Fabrizi G, di Nuzzo S. Cryoinsufflation for hidradenitis suppurativa: technical refinement to prevent complications. Dermatol Surg. 2016;42:130-132.
- Ritz JP, Runkel N, Haier J, et al. Extent of surgery and recurrence rate of hidradenitis suppurativa. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1998;13:164-168.
- Danby FW, Hazen PG, Boer J. New and traditional surgical approaches to hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73(5, suppl 1):S62-S65.
- Ellis LZ. Hidradenitis suppurativa: surgical and other management techniques. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38:517-536.
- Mullins JF, McCash WB, Boudreau RF. Treatment of chronic hidradenitis suppurativa: surgical modification. Postgrad Med. 1959;26:805-808.
- Brown SC, Kazzazi N, Lord PH. Surgical treatment of perineal hidradenitis suppurativa with special reference to recognition of the perianal form. Br J Surg. 1986;73:978-980.
- Culp CE. Chronic hidradenitis suppurativa of the anal canal. a surgical skin disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 1983;26:669-676.
- van der Zee HH, Prens EP, Boer J. Deroofing: a tissue-saving surgical technique for the treatment of mild to moderate hidradenitis suppurativa lesions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:475-480.
- Lin CH, Chang KP, Huang SH. Deroofing: an effective method for treating chronic diffuse hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Surg. 2016;42:273-275.
- Blok JL, Boersma M, Terra JB, et al. Surgery under general anaes-thesia in severe hidradenitis suppurativa: a study of 363 primary operations in 113 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1590-1597.
- Blok JL, Spoo JR, Leeman FW, et al. Skin-Tissue-sparing Excision with Electrosurgical Peeling (STEEP): a surgical treatment option for severe hidradenitis suppurativa Hurley stage II/III. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:379-382.
- Saunte DML, Jemec GBE. Hidradenitis suppurativa: advances in diagnosis and treatment. JAMA. 2017;318:2019-2032.
- Maghsoudi H, Almasi H, Miri Bonjar MR. Men, main victims of hidradenitis suppurativa (a prospective cohort study). Int J Surg. 2018;50:6-10.
- Mehdizadeh A, Hazen PG, Bechara FG, et al. Recurrence of hidradenitis suppurativa after surgical management: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73(5, suppl 1):S70-S77.
- Wortsman X, Moreno C, Soto R, et al. Ultrasound in-depth characterization and staging of hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:1835-1842.
- Kofler L, Schweinzer K, Heister M, et al. Surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa: an analysis of postoperative outcome, cosmetic results and quality of life in 255 patients [published online February 17, 2018]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. doi:10.1111/jdv.14892.
- Dini V, Oranges T, Rotella L, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa and wound management. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2015;14:236-244.
- Humphries LS, Kueberuwa E, Beederman M, et al. Wide excision and healing by secondary intent for the surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa: a single-center experience. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;69:554-566.
- Wollina U, Langner D, Heinig B, et al. Comorbidities, treatment, and outcome in severe anogenital inverse acne (hidradenitis suppurativa): a 15-year single center report. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:109-115.
- Watson JD. Hidradenitis suppurativa—a clinical review. Br J Plast Surg. 1985;38:567-569.
- Sugio Y, Tomita K, Hosokawa K. Reconstruction after excision of hidradenitis suppurativa: are skin grafts better than flaps? Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2016;4:E1128.
- Burney RE. 35-year experience with surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. World J Surg. 2017;41:2723-2730.
- Nail-Barthelemy R, Stroumza N, Qassemyar Q, et al. Evaluation of the mobility of the shoulder and quality of life after perforator flaps for recalcitrant axillary hidradenitis [published online February 13, 2018]. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. pii:S0294-1260(18)30005-0. doi:10.1016/j.anplas.2018.01.003.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that has a social and psychosocial impact on patients with skin of color.1 It is characterized by recurrent abscesses, draining sinus tracts, and scarring in the intertriginous skin folds. The lesions are difficult to treat and present with considerable frustration for both patients and physicians. Although current treatment ladders can delay procedures and surgical intervention,1 some believe that surgery should be introduced earlier in HS management.2 In this article, we review current procedures for the management of HS, including cryoinsufflation, incision and drainage, deroofing, skin tissue–saving excision with electrosurgical peeling, and wide surgical excision, along with various closure techniques.
Cryoinsufflation
First described in 2014, cryoinsufflation is a novel method for treating sinus tracts.3 Lesions initially are identified on physical examination. Prior to the procedure, local anesthesia is administered to the lesion.3 A 21-gauge needle is mounted onto a cryosurgical unit and inserted into the opening of the sinus tract. Liquid nitrogen is sprayed into the tract for 5 seconds, followed by a 3-second pause; the process is repeated 3 times. Patients return for treatment sessions monthly until the tract is obliterated. This procedure was first performed on 2 patients with satisfactory results.3
Since the initial report, the investigators made 2 changes to refine the procedure.4 First, systemic antibiotics should be prescribed 2 months prior to the procedure to clear the sinus tracts of infection. Furthermore, a 21-gauge, olive-tipped cannula is recommended in lieu of a 21-gauge needle to mitigate the risk of adverse events such as air embolism.4
Incision and Drainage
Incision and drainage provides rapid pain relief for tense fluctuant abscesses, but recurrence is common and the procedure costs are high.5 For drainage, wide circumferential local anesthesia is administered followed by incision.6 Pus is eliminated using digital pressure or saline rinses.2 Following the elimination of pus, the wound may need gauze packing or placement of a wick for a few days.6 The general belief is that incision and drainage should be used, if necessary, to rapidly relieve the patient’s pain; however, other surgical options should be considered if the patient has had multiple incision and drainage procedures.7 Currently there are no randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on incision and drainage procedures in HS abscesses.
Deroofing
In 1959, Mullins et al8 first described the deroofing procedure, which was refined to preserve the floor of the sinus tract in the 1980s.9,10 Culp10 and Brown et al9 theorized that preservation of the exposed floor of the sinus tract allowed for the epithelial cells from sweat glands and hair follicle remnants to rapidly reepithelialize the wound. In 2010, van der Zee et al11 performed a prospective study of 88 deroofed lesions in which the investigators removed keratinous debris and epithelial remnants of the floor due to concern for recurrence in this area if the tissues remained. Only 17% (15/88) of the lesions recurred at a median follow-up of 34 months.11
In Hurley stage I or II HS, deroofing remains the primary procedure for persistent nodules and sinus tracts.2 The lesion is identified on physical examination and local anesthesia is administered, first to the area surrounding the lesion, then to the lesion itself.11 A blunt probe is used to identify openings and search for connecting fistulas. After defining the sinus tract, the roof and wings created by the incision are removed.11,12 The material on the floor of the tract is scraped away, and the wound is left to heal by secondary intention.11 In general, deroofed lesions heal with cosmetically acceptable scars. We have used this procedure in skin of color patients with good results and no difficulties with healing. Controlled trials with long-term follow-up are lacking in this population.
Skin Tissue–Saving Excision With Electrosurgical Peeling
Skin tissue–saving excision with electrosurgical peeling was first introduced in 2015.13 Blok et al14 described the procedure as a promising alternative to wide surgical excision for Hurley stage II or III HS. The procedure saves healthy tissue while completely removing lesional tissue, leading to rapid wound healing, excellent cosmesis, and a low risk of contractures2,14; however, recurrence rates are higher than those seen in wide surgical excision.15 There are no known RCTs with long-term follow-up for HS patients treated with skin tissue–saving excision with electrosurgical peeling.
The procedure typically is performed under general anesthesia.14 First, the sinus tract is palpated on physical examination and probed to delineate the extent of the tract. Next, the roof of the tract is incised electrosurgically with a wire loop tip coupled to an electrosurgical generator.14 Consecutive tangential excisions are made until the floor of the sinus tract is reached. The process of incising sinus tracts followed by tangential peeling off of tissue continues until the entire area is clear of lesional and fibrotic tissue. The wound margins are probed for the presence and subsequent removal of residual sinus tracts. Lastly, the electrosurgical generator is used to achieve hemostasis, steroids are injected to prevent the formation of hypergranulation tissue, and the wound is left to heal by secondary intention.14 Following intervention, recurrence rates appear to be similar to wide surgical excision.13,14
Wide Surgical Excision
Wide excision is a widely established technique consisting of surgical excision of a lesion plus an area of surrounding disease-free tissue such as subcutaneous fat or a lateral margin of intertriginous skin.15 Similar to other surgical techniques, wide excision is considered in cases of severe disease when pharmacologic management cannot remedy extensive fibrosis or architectural loss. It typically is performed in Hurley stage II and III HS, with pathology extending to involve deeper structures inaccessible to more superficial surgical methods.2 Prominent areas of use include gluteal, axillary, perineal, and perianal HS lesions on which conservative treatments have little effect and depend on wide excision to provide successful postoperative results.16 Although retrospective and prospective studies exist on wide excision in HS, there continues to be a dearth of RCTs. Based on the available literature, the primary motive for wide excision is lower recurrence rates (13% overall compared to 22% and 27% for local excision and deroofing, respectively) and longer asymptomatic periods compared to more local techniques.7,17 Wide excision combined with continued aggressive medical management and dietary modifications currently is an efficacious treatment in providing functional long-term results.6 These benefits, however, are not without their drawbacks, as the more extensive nature of wide surgical excision predisposes patients to larger wounds, surgery-induced infection, and prolonged recovery periods.6,15 If preoperative measurements are not wisely assessed, the excision also can extend to involve neurovascular bundles and other vital structures, contributing to greater postoperative morbidity.15 Ultrasonography provides useful anatomic information in HS, such as location and extent of fistulous tracts and fluid collections; these findings can assist in guiding the width and depth of the excision itself to ensure the entire area of HS involvement is removed.18 Published data revealed that 204 of 255 (80%) patients were markedly satisfied with postoperative outcomes of wide excision,19 which gives credence to the idea that although the complications of wide excision may not be as favorable, the long-lasting improvements in quality of life make wide surgical excision a suggested first-line treatment in all stages of HS.16,20
Closure Techniques
The best skin closure method following surgical excision is controversial and not well established in literature. Options include healing by secondary intention, primary (suture-based) closure, skin grafts, and skin flaps. Each of these methods has had moderate success in multiple observational studies, and the choice should be made based on individualized assessment of the patient’s HS lesion characteristics, ability to adhere to recovery protocols, and relevant demographics. A systematic review by Mehdizadeh et al17 provided the following recurrence rates for techniques utilized after wide excision: primary closure, 15%; flaps, 8%; and grafting, 6%. Despite conflicting evidence, allowing wounds to heal by secondary intention is best, based on the author’s experience (I.H.H.).
Secondary Intention
Healing by secondary intention refers to a wound that is intentionally left open to be filled in with granulation tissue and eventual epithelization over time rather than being approximated and closed via sutures or staples as in primary intention. It is a well-established option in wound management and results in a longer but more comfortable period of convalescence in postsurgical HS management.20 Patients can add regular moist wound dressings (eg, silastic foam dressing) to manage the wound at home and continue normal activities for most of the healing period; however, the recovery period can become excessively long and painful, and there is a high risk of formation of retractile scar bands at and around the healing site.12 Strict adherence to wound-healing protocols is paramount to minimizing unwanted complications.21 Secondary intention often is used after wide local excision and has been demonstrated to yield positive functional and aesthetic results in multiple studies, especially in the more severe Hurley stage II or III cases.21,22 It can be successfully employed after laser treatment and in surgical defects of all sizes with little to no contractures or reduced range of motion.6 Ultimately, the choice to heal via secondary intention should be made after thorough assessment of patient needs and with ample education to ensure compliance.
Primary Closure
Primary closure is the suture-mediated closing technique that is most often used in wound closure for lower-grade HS cases, especially smaller excisions. However, it is associated with potential complications. If HS lesions are not effectively excised, disease can then recur at the periphery of the excision and wound dehiscence can manifest more readily, especially as wound size increases.23 Consequently, primary closure is associated with the highest recurrence rates among closure techniques.17 Avoiding primary closure in active disease also is recommended due to the potential of burying residual foci of inflammation.6 Finally, primary closures lack skin coverage and thus often are not viable options in most perianal and genital lesions that require more extensive reconstruction. Retrospective case series and case reports exist on primary excision, but further study is needed.
Skin Grafts
Skin grafting is a technique of surgically transplanting a piece of healthy skin from one body site to another. Skin grafts typically are used when primary closure or skin flaps are not feasible (eg, in large wounds) and also when shorter time to wound closure is a greater concern in patient recovery.2,24 Additionally, skin grafts can be employed on large flat surfaces of the body, such as the buttocks or thighs, for timely wound closure when wound contraction is less effective or wound healing is slow via epithelization. Types of skin graft techniques include split-thickness skin graft (STSG), full-thickness skin graft, and recycled skin graft. All 3 types have demonstrated acceptable functional and aesthetic results in observational studies and case reports, and thus deciding which technique to use should include individualized assessment.2,25 The STSG has several advantages over the full-thickness skin graft, including hairlessness (ie, without hair follicles), ease of harvest, and a less complicated transfer to contaminated lesional areas such as those in HS.26 Additionally, STSGs allow for closure of even the largest wounds with minimal risk of serious infection. Split-thickness skin grafts are considered one of the most efficacious tools for axilla reconstruction; however, they require prolonged immobilization of the arm, result in sequelae in donor sites, and do not always prevent retractile scars.26 The recycled skin graft technique can be used to treat chronic gluteal HS, but reliability and outcomes have not been reported. Skin grafting after excision is associated with increased pain, immobilization, prolonged hospitalization, and longer healing times compared to skin flaps.19 In a systematic review of wound healing techniques following wide excision, grafting was shown to have the lowest recurrence rate (6%) compared to skin flaps (8%) and primary closure (15%).17 The absence of hair follicles and sweat glands in STSGs may be advantageous in HS because both hair follicles and sweat glands are thought to play more roles in the pathogenesis of HS.18,24 Most studies on skin grafts are limited to case reports.
Skin Flaps
Skin flaps are similar to skin grafts in that healthy skin is transplanted from one site to another; the difference is that flaps maintain an intact blood supply, whereas skin grafts depend on growth of new blood vessels.12,13 The primary advantage of skin flaps is that they provide the best quality of skin due to the thick tissue coverage, which is an important concern, especially in aesthetic scenarios. Additionally, they have been shown to provide shorter healing times than grafts, primary closure, and secondary healing, which can be especially important when functional disability is a concern in the postoperative period.26 However, their use should be limited due to several complications owing to their blood supply, as there is a high risk of ischemia to distant portions of flaps, which often can progress to necrosis and hemorrhage during the harvesting process.2 Thus, skin flaps are incredibly difficult to use in larger wounds and often require debulking due to their thickness. Additionally, skin flaps are definitive by nature, which can pose an issue if HS recurs locally. Skin flaps are recommended only when their use is mandatory, such as in the coverage of important anatomic structures (eg, exposed neurovascular bundles and large vessels).2 Advances have been made in flap construction, and now several types of flaps are employed in several body areas with differing indications and recommendations.2,21 As with skin grafts, most studies in the literature are case reports; therefore, further investigation is needed.
Combination Reconstructions
Combination reconstructions refer to the simultaneous use of multiple closure or healing techniques. By combining 2 or more methods, surgeons can utilize the advantages of each technique to provide an individualized approach that can substantially diminish wound surface area and accelerate wound healing.2 For example, with the starlike technique, 5 equilateral triangles bordering a foci of axillary disease are excised in addition to the central foci, and the edges of each triangle are then sutured together to create a final scar of considerably smaller size. The starlike technique allows the wound to be partially sutured while leaving the remaining area to heal by secondary intention.2 There are a small number of case series and prospective studies on combined reconstructions in HS but no RCTs.
Conclusion
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that has a social and psychosocial impact on patients with skin of color.1 It is characterized by recurrent abscesses, draining sinus tracts, and scarring in the intertriginous skin folds. The lesions are difficult to treat and present with considerable frustration for both patients and physicians. Although current treatment ladders can delay procedures and surgical intervention,1 some believe that surgery should be introduced earlier in HS management.2 In this article, we review current procedures for the management of HS, including cryoinsufflation, incision and drainage, deroofing, skin tissue–saving excision with electrosurgical peeling, and wide surgical excision, along with various closure techniques.
Cryoinsufflation
First described in 2014, cryoinsufflation is a novel method for treating sinus tracts.3 Lesions initially are identified on physical examination. Prior to the procedure, local anesthesia is administered to the lesion.3 A 21-gauge needle is mounted onto a cryosurgical unit and inserted into the opening of the sinus tract. Liquid nitrogen is sprayed into the tract for 5 seconds, followed by a 3-second pause; the process is repeated 3 times. Patients return for treatment sessions monthly until the tract is obliterated. This procedure was first performed on 2 patients with satisfactory results.3
Since the initial report, the investigators made 2 changes to refine the procedure.4 First, systemic antibiotics should be prescribed 2 months prior to the procedure to clear the sinus tracts of infection. Furthermore, a 21-gauge, olive-tipped cannula is recommended in lieu of a 21-gauge needle to mitigate the risk of adverse events such as air embolism.4
Incision and Drainage
Incision and drainage provides rapid pain relief for tense fluctuant abscesses, but recurrence is common and the procedure costs are high.5 For drainage, wide circumferential local anesthesia is administered followed by incision.6 Pus is eliminated using digital pressure or saline rinses.2 Following the elimination of pus, the wound may need gauze packing or placement of a wick for a few days.6 The general belief is that incision and drainage should be used, if necessary, to rapidly relieve the patient’s pain; however, other surgical options should be considered if the patient has had multiple incision and drainage procedures.7 Currently there are no randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on incision and drainage procedures in HS abscesses.
Deroofing
In 1959, Mullins et al8 first described the deroofing procedure, which was refined to preserve the floor of the sinus tract in the 1980s.9,10 Culp10 and Brown et al9 theorized that preservation of the exposed floor of the sinus tract allowed for the epithelial cells from sweat glands and hair follicle remnants to rapidly reepithelialize the wound. In 2010, van der Zee et al11 performed a prospective study of 88 deroofed lesions in which the investigators removed keratinous debris and epithelial remnants of the floor due to concern for recurrence in this area if the tissues remained. Only 17% (15/88) of the lesions recurred at a median follow-up of 34 months.11
In Hurley stage I or II HS, deroofing remains the primary procedure for persistent nodules and sinus tracts.2 The lesion is identified on physical examination and local anesthesia is administered, first to the area surrounding the lesion, then to the lesion itself.11 A blunt probe is used to identify openings and search for connecting fistulas. After defining the sinus tract, the roof and wings created by the incision are removed.11,12 The material on the floor of the tract is scraped away, and the wound is left to heal by secondary intention.11 In general, deroofed lesions heal with cosmetically acceptable scars. We have used this procedure in skin of color patients with good results and no difficulties with healing. Controlled trials with long-term follow-up are lacking in this population.
Skin Tissue–Saving Excision With Electrosurgical Peeling
Skin tissue–saving excision with electrosurgical peeling was first introduced in 2015.13 Blok et al14 described the procedure as a promising alternative to wide surgical excision for Hurley stage II or III HS. The procedure saves healthy tissue while completely removing lesional tissue, leading to rapid wound healing, excellent cosmesis, and a low risk of contractures2,14; however, recurrence rates are higher than those seen in wide surgical excision.15 There are no known RCTs with long-term follow-up for HS patients treated with skin tissue–saving excision with electrosurgical peeling.
The procedure typically is performed under general anesthesia.14 First, the sinus tract is palpated on physical examination and probed to delineate the extent of the tract. Next, the roof of the tract is incised electrosurgically with a wire loop tip coupled to an electrosurgical generator.14 Consecutive tangential excisions are made until the floor of the sinus tract is reached. The process of incising sinus tracts followed by tangential peeling off of tissue continues until the entire area is clear of lesional and fibrotic tissue. The wound margins are probed for the presence and subsequent removal of residual sinus tracts. Lastly, the electrosurgical generator is used to achieve hemostasis, steroids are injected to prevent the formation of hypergranulation tissue, and the wound is left to heal by secondary intention.14 Following intervention, recurrence rates appear to be similar to wide surgical excision.13,14
Wide Surgical Excision
Wide excision is a widely established technique consisting of surgical excision of a lesion plus an area of surrounding disease-free tissue such as subcutaneous fat or a lateral margin of intertriginous skin.15 Similar to other surgical techniques, wide excision is considered in cases of severe disease when pharmacologic management cannot remedy extensive fibrosis or architectural loss. It typically is performed in Hurley stage II and III HS, with pathology extending to involve deeper structures inaccessible to more superficial surgical methods.2 Prominent areas of use include gluteal, axillary, perineal, and perianal HS lesions on which conservative treatments have little effect and depend on wide excision to provide successful postoperative results.16 Although retrospective and prospective studies exist on wide excision in HS, there continues to be a dearth of RCTs. Based on the available literature, the primary motive for wide excision is lower recurrence rates (13% overall compared to 22% and 27% for local excision and deroofing, respectively) and longer asymptomatic periods compared to more local techniques.7,17 Wide excision combined with continued aggressive medical management and dietary modifications currently is an efficacious treatment in providing functional long-term results.6 These benefits, however, are not without their drawbacks, as the more extensive nature of wide surgical excision predisposes patients to larger wounds, surgery-induced infection, and prolonged recovery periods.6,15 If preoperative measurements are not wisely assessed, the excision also can extend to involve neurovascular bundles and other vital structures, contributing to greater postoperative morbidity.15 Ultrasonography provides useful anatomic information in HS, such as location and extent of fistulous tracts and fluid collections; these findings can assist in guiding the width and depth of the excision itself to ensure the entire area of HS involvement is removed.18 Published data revealed that 204 of 255 (80%) patients were markedly satisfied with postoperative outcomes of wide excision,19 which gives credence to the idea that although the complications of wide excision may not be as favorable, the long-lasting improvements in quality of life make wide surgical excision a suggested first-line treatment in all stages of HS.16,20
Closure Techniques
The best skin closure method following surgical excision is controversial and not well established in literature. Options include healing by secondary intention, primary (suture-based) closure, skin grafts, and skin flaps. Each of these methods has had moderate success in multiple observational studies, and the choice should be made based on individualized assessment of the patient’s HS lesion characteristics, ability to adhere to recovery protocols, and relevant demographics. A systematic review by Mehdizadeh et al17 provided the following recurrence rates for techniques utilized after wide excision: primary closure, 15%; flaps, 8%; and grafting, 6%. Despite conflicting evidence, allowing wounds to heal by secondary intention is best, based on the author’s experience (I.H.H.).
Secondary Intention
Healing by secondary intention refers to a wound that is intentionally left open to be filled in with granulation tissue and eventual epithelization over time rather than being approximated and closed via sutures or staples as in primary intention. It is a well-established option in wound management and results in a longer but more comfortable period of convalescence in postsurgical HS management.20 Patients can add regular moist wound dressings (eg, silastic foam dressing) to manage the wound at home and continue normal activities for most of the healing period; however, the recovery period can become excessively long and painful, and there is a high risk of formation of retractile scar bands at and around the healing site.12 Strict adherence to wound-healing protocols is paramount to minimizing unwanted complications.21 Secondary intention often is used after wide local excision and has been demonstrated to yield positive functional and aesthetic results in multiple studies, especially in the more severe Hurley stage II or III cases.21,22 It can be successfully employed after laser treatment and in surgical defects of all sizes with little to no contractures or reduced range of motion.6 Ultimately, the choice to heal via secondary intention should be made after thorough assessment of patient needs and with ample education to ensure compliance.
Primary Closure
Primary closure is the suture-mediated closing technique that is most often used in wound closure for lower-grade HS cases, especially smaller excisions. However, it is associated with potential complications. If HS lesions are not effectively excised, disease can then recur at the periphery of the excision and wound dehiscence can manifest more readily, especially as wound size increases.23 Consequently, primary closure is associated with the highest recurrence rates among closure techniques.17 Avoiding primary closure in active disease also is recommended due to the potential of burying residual foci of inflammation.6 Finally, primary closures lack skin coverage and thus often are not viable options in most perianal and genital lesions that require more extensive reconstruction. Retrospective case series and case reports exist on primary excision, but further study is needed.
Skin Grafts
Skin grafting is a technique of surgically transplanting a piece of healthy skin from one body site to another. Skin grafts typically are used when primary closure or skin flaps are not feasible (eg, in large wounds) and also when shorter time to wound closure is a greater concern in patient recovery.2,24 Additionally, skin grafts can be employed on large flat surfaces of the body, such as the buttocks or thighs, for timely wound closure when wound contraction is less effective or wound healing is slow via epithelization. Types of skin graft techniques include split-thickness skin graft (STSG), full-thickness skin graft, and recycled skin graft. All 3 types have demonstrated acceptable functional and aesthetic results in observational studies and case reports, and thus deciding which technique to use should include individualized assessment.2,25 The STSG has several advantages over the full-thickness skin graft, including hairlessness (ie, without hair follicles), ease of harvest, and a less complicated transfer to contaminated lesional areas such as those in HS.26 Additionally, STSGs allow for closure of even the largest wounds with minimal risk of serious infection. Split-thickness skin grafts are considered one of the most efficacious tools for axilla reconstruction; however, they require prolonged immobilization of the arm, result in sequelae in donor sites, and do not always prevent retractile scars.26 The recycled skin graft technique can be used to treat chronic gluteal HS, but reliability and outcomes have not been reported. Skin grafting after excision is associated with increased pain, immobilization, prolonged hospitalization, and longer healing times compared to skin flaps.19 In a systematic review of wound healing techniques following wide excision, grafting was shown to have the lowest recurrence rate (6%) compared to skin flaps (8%) and primary closure (15%).17 The absence of hair follicles and sweat glands in STSGs may be advantageous in HS because both hair follicles and sweat glands are thought to play more roles in the pathogenesis of HS.18,24 Most studies on skin grafts are limited to case reports.
Skin Flaps
Skin flaps are similar to skin grafts in that healthy skin is transplanted from one site to another; the difference is that flaps maintain an intact blood supply, whereas skin grafts depend on growth of new blood vessels.12,13 The primary advantage of skin flaps is that they provide the best quality of skin due to the thick tissue coverage, which is an important concern, especially in aesthetic scenarios. Additionally, they have been shown to provide shorter healing times than grafts, primary closure, and secondary healing, which can be especially important when functional disability is a concern in the postoperative period.26 However, their use should be limited due to several complications owing to their blood supply, as there is a high risk of ischemia to distant portions of flaps, which often can progress to necrosis and hemorrhage during the harvesting process.2 Thus, skin flaps are incredibly difficult to use in larger wounds and often require debulking due to their thickness. Additionally, skin flaps are definitive by nature, which can pose an issue if HS recurs locally. Skin flaps are recommended only when their use is mandatory, such as in the coverage of important anatomic structures (eg, exposed neurovascular bundles and large vessels).2 Advances have been made in flap construction, and now several types of flaps are employed in several body areas with differing indications and recommendations.2,21 As with skin grafts, most studies in the literature are case reports; therefore, further investigation is needed.
Combination Reconstructions
Combination reconstructions refer to the simultaneous use of multiple closure or healing techniques. By combining 2 or more methods, surgeons can utilize the advantages of each technique to provide an individualized approach that can substantially diminish wound surface area and accelerate wound healing.2 For example, with the starlike technique, 5 equilateral triangles bordering a foci of axillary disease are excised in addition to the central foci, and the edges of each triangle are then sutured together to create a final scar of considerably smaller size. The starlike technique allows the wound to be partially sutured while leaving the remaining area to heal by secondary intention.2 There are a small number of case series and prospective studies on combined reconstructions in HS but no RCTs.
Conclusion
- Smith MK, Nicholson CL, Parks-Miller A, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: an update on connecting the tracts. F1000Res. 2017;6:1272.
- Janse I, Bieniek A, Horvath B, et al. Surgical procedures in hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:97-109.
- Pagliarello C, Fabrizi G, Feliciani C, et al. Cryoinsufflation for Hurley stage II hidradenitis suppurativa: a useful treatment option when systemic therapies should be avoided. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:765-766.
- Pagliarello C, Fabrizi G, di Nuzzo S. Cryoinsufflation for hidradenitis suppurativa: technical refinement to prevent complications. Dermatol Surg. 2016;42:130-132.
- Ritz JP, Runkel N, Haier J, et al. Extent of surgery and recurrence rate of hidradenitis suppurativa. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1998;13:164-168.
- Danby FW, Hazen PG, Boer J. New and traditional surgical approaches to hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73(5, suppl 1):S62-S65.
- Ellis LZ. Hidradenitis suppurativa: surgical and other management techniques. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38:517-536.
- Mullins JF, McCash WB, Boudreau RF. Treatment of chronic hidradenitis suppurativa: surgical modification. Postgrad Med. 1959;26:805-808.
- Brown SC, Kazzazi N, Lord PH. Surgical treatment of perineal hidradenitis suppurativa with special reference to recognition of the perianal form. Br J Surg. 1986;73:978-980.
- Culp CE. Chronic hidradenitis suppurativa of the anal canal. a surgical skin disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 1983;26:669-676.
- van der Zee HH, Prens EP, Boer J. Deroofing: a tissue-saving surgical technique for the treatment of mild to moderate hidradenitis suppurativa lesions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:475-480.
- Lin CH, Chang KP, Huang SH. Deroofing: an effective method for treating chronic diffuse hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Surg. 2016;42:273-275.
- Blok JL, Boersma M, Terra JB, et al. Surgery under general anaes-thesia in severe hidradenitis suppurativa: a study of 363 primary operations in 113 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1590-1597.
- Blok JL, Spoo JR, Leeman FW, et al. Skin-Tissue-sparing Excision with Electrosurgical Peeling (STEEP): a surgical treatment option for severe hidradenitis suppurativa Hurley stage II/III. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:379-382.
- Saunte DML, Jemec GBE. Hidradenitis suppurativa: advances in diagnosis and treatment. JAMA. 2017;318:2019-2032.
- Maghsoudi H, Almasi H, Miri Bonjar MR. Men, main victims of hidradenitis suppurativa (a prospective cohort study). Int J Surg. 2018;50:6-10.
- Mehdizadeh A, Hazen PG, Bechara FG, et al. Recurrence of hidradenitis suppurativa after surgical management: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73(5, suppl 1):S70-S77.
- Wortsman X, Moreno C, Soto R, et al. Ultrasound in-depth characterization and staging of hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:1835-1842.
- Kofler L, Schweinzer K, Heister M, et al. Surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa: an analysis of postoperative outcome, cosmetic results and quality of life in 255 patients [published online February 17, 2018]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. doi:10.1111/jdv.14892.
- Dini V, Oranges T, Rotella L, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa and wound management. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2015;14:236-244.
- Humphries LS, Kueberuwa E, Beederman M, et al. Wide excision and healing by secondary intent for the surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa: a single-center experience. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;69:554-566.
- Wollina U, Langner D, Heinig B, et al. Comorbidities, treatment, and outcome in severe anogenital inverse acne (hidradenitis suppurativa): a 15-year single center report. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:109-115.
- Watson JD. Hidradenitis suppurativa—a clinical review. Br J Plast Surg. 1985;38:567-569.
- Sugio Y, Tomita K, Hosokawa K. Reconstruction after excision of hidradenitis suppurativa: are skin grafts better than flaps? Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2016;4:E1128.
- Burney RE. 35-year experience with surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. World J Surg. 2017;41:2723-2730.
- Nail-Barthelemy R, Stroumza N, Qassemyar Q, et al. Evaluation of the mobility of the shoulder and quality of life after perforator flaps for recalcitrant axillary hidradenitis [published online February 13, 2018]. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. pii:S0294-1260(18)30005-0. doi:10.1016/j.anplas.2018.01.003.
- Smith MK, Nicholson CL, Parks-Miller A, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: an update on connecting the tracts. F1000Res. 2017;6:1272.
- Janse I, Bieniek A, Horvath B, et al. Surgical procedures in hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:97-109.
- Pagliarello C, Fabrizi G, Feliciani C, et al. Cryoinsufflation for Hurley stage II hidradenitis suppurativa: a useful treatment option when systemic therapies should be avoided. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:765-766.
- Pagliarello C, Fabrizi G, di Nuzzo S. Cryoinsufflation for hidradenitis suppurativa: technical refinement to prevent complications. Dermatol Surg. 2016;42:130-132.
- Ritz JP, Runkel N, Haier J, et al. Extent of surgery and recurrence rate of hidradenitis suppurativa. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1998;13:164-168.
- Danby FW, Hazen PG, Boer J. New and traditional surgical approaches to hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73(5, suppl 1):S62-S65.
- Ellis LZ. Hidradenitis suppurativa: surgical and other management techniques. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38:517-536.
- Mullins JF, McCash WB, Boudreau RF. Treatment of chronic hidradenitis suppurativa: surgical modification. Postgrad Med. 1959;26:805-808.
- Brown SC, Kazzazi N, Lord PH. Surgical treatment of perineal hidradenitis suppurativa with special reference to recognition of the perianal form. Br J Surg. 1986;73:978-980.
- Culp CE. Chronic hidradenitis suppurativa of the anal canal. a surgical skin disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 1983;26:669-676.
- van der Zee HH, Prens EP, Boer J. Deroofing: a tissue-saving surgical technique for the treatment of mild to moderate hidradenitis suppurativa lesions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:475-480.
- Lin CH, Chang KP, Huang SH. Deroofing: an effective method for treating chronic diffuse hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Surg. 2016;42:273-275.
- Blok JL, Boersma M, Terra JB, et al. Surgery under general anaes-thesia in severe hidradenitis suppurativa: a study of 363 primary operations in 113 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1590-1597.
- Blok JL, Spoo JR, Leeman FW, et al. Skin-Tissue-sparing Excision with Electrosurgical Peeling (STEEP): a surgical treatment option for severe hidradenitis suppurativa Hurley stage II/III. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:379-382.
- Saunte DML, Jemec GBE. Hidradenitis suppurativa: advances in diagnosis and treatment. JAMA. 2017;318:2019-2032.
- Maghsoudi H, Almasi H, Miri Bonjar MR. Men, main victims of hidradenitis suppurativa (a prospective cohort study). Int J Surg. 2018;50:6-10.
- Mehdizadeh A, Hazen PG, Bechara FG, et al. Recurrence of hidradenitis suppurativa after surgical management: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73(5, suppl 1):S70-S77.
- Wortsman X, Moreno C, Soto R, et al. Ultrasound in-depth characterization and staging of hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:1835-1842.
- Kofler L, Schweinzer K, Heister M, et al. Surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa: an analysis of postoperative outcome, cosmetic results and quality of life in 255 patients [published online February 17, 2018]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. doi:10.1111/jdv.14892.
- Dini V, Oranges T, Rotella L, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa and wound management. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2015;14:236-244.
- Humphries LS, Kueberuwa E, Beederman M, et al. Wide excision and healing by secondary intent for the surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa: a single-center experience. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;69:554-566.
- Wollina U, Langner D, Heinig B, et al. Comorbidities, treatment, and outcome in severe anogenital inverse acne (hidradenitis suppurativa): a 15-year single center report. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:109-115.
- Watson JD. Hidradenitis suppurativa—a clinical review. Br J Plast Surg. 1985;38:567-569.
- Sugio Y, Tomita K, Hosokawa K. Reconstruction after excision of hidradenitis suppurativa: are skin grafts better than flaps? Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2016;4:E1128.
- Burney RE. 35-year experience with surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. World J Surg. 2017;41:2723-2730.
- Nail-Barthelemy R, Stroumza N, Qassemyar Q, et al. Evaluation of the mobility of the shoulder and quality of life after perforator flaps for recalcitrant axillary hidradenitis [published online February 13, 2018]. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. pii:S0294-1260(18)30005-0. doi:10.1016/j.anplas.2018.01.003.
Practice Points
- Surgical intervention currently is the only definitive treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa (HS).
- There is no consensus on the best surgical intervention for long-term outcomes in HS; rather, approach is based on clinical judgment dependent upon the location and severity of lesions.
- After wide excision, allow wounds to heal by secondary intention.
Melanoma in US Hispanics: Recommended Strategies to Reduce Disparities in Outcomes
Cutaneous melanoma is a considerable public health concern. In the United States, an estimated 87,110 cases were diagnosed in 2017, and more than 9000 deaths are expected as result of this disease in 2018.1 Early diagnosis of melanoma is associated with favorable survival rates (5-year overall survival rates for melanoma in situ and stage IA melanoma, 99% and 97%, respectively).2 In contrast, the prognosis for advanced-stage melanoma is poor, with a 5-year survival rate of 16% for patients with stage IV disease. Therefore, early detection is critical to reducing mortality in melanoma patients.3
The term Hispanic refers to a panethnic category primarily encompassing Mexican-Americans, Cubans, and Puerto Ricans, as well as individuals from the Caribbean and Central and South America. These populations are diverse in birth origin, primary language, acculturation, distinct ethnic traditions, education level, and occupation. Hispanics in the United States are heterogeneous in many dimensions related to health risks, health care use, and health outcomes.4 Genetic predisposition, lifestyle risks, and access to and use of health care services can shape melanoma diagnosis, treatment, and progression across Hispanic populations differently than in other populations.
In this review, the epidemiology and clinical presentation of melanoma in US Hispanics is summarized, and recommendations for a research agenda to advance understanding of this disease in the most rapidly growing segment of the US population is provided.
In the period from 2008 to 2012, the age-adjusted incidence of melanoma in US Hispanics (4.6 per 100,00 men and 4.2 per 100,00 women) was lower than in NHWs.5 Garnett et al5 reported a decline in melanoma incidence in US Hispanics between 2003 and 2012—an observation that stands in contrast to state-level studies in California and Florida, in which small but substantial increases in melanoma incidence among Hispanics were reported.6,7 The rising incidence of melanomas thicker than 1.5 mm at presentation among Hispanic men living in California is particularly worrisome.6 Discrepancies in incidence trends might reflect changes in incidence over time or differences in state-level registry reporting of melanoma.5
Despite a lower overall incidence of melanoma in US Hispanics, those who do develop the disease are 2.4 times more likely (age-adjusted odds ratio) to present with stage III disease (confidence interval, 1.89-3.05)8 and are 3.64 times more likely to develop distant metastases (confidence interval, 2.65-5.0) than NHWs.3,7,9-13 Disparities also exist in the diagnosis of childhood melanoma: Hispanic children and adolescents who have a diagnosis of melanoma are 3 times more likely to present with advanced disease than NHW counterparts.14 Survival analyses by age and stage show considerably lower survival among Hispanic patients compared to NHW patients with stage I and II disease. In part, worse survival outcomes among Hispanics are the result of the pattern of more advanced disease at presentation.8,14,15
Late presentation for evaluation of melanomas in Hispanics has been attributed to a number of variables, including a lack of skin cancer awareness and knowledge,9,16 a lower rate of self- and physician-performed skin examinations,10 differences in tumor biology,9 and socioeconomic forces.7,17
In a previous study investigating the relationship between neighborhood characteristics and tumor stage at melanoma diagnosis in Hispanic men in California, Texas, and Florida, several key findings emerged.17 First, residency in a census tract with a high density of immigrants (California, Texas) and a high composition of Hispanics (California, Florida) was an important predictor of a late-stage melanoma diagnosis in fully adjusted models. Additionally, the strength of association between measures of socioeconomic status (ie, poverty and education) and tumor stage at melanoma diagnosis was attenuated in multivariate models when enclaves and availability of primary care resources were taken into account. Hispanic melanoma cases in areas with a low density of primary care physicians had an increased likelihood of late-stage diagnosis in California and Texas. The probability of late-stage diagnosis was concentrated in specific regions along the United States–Mexico border, in south central California, and along the southeastern coast of Florida. Lastly, in Texas, Hispanic men aged 18 to 34 years and 35 to 49 years were at an increased risk of late-stage melanoma diagnosis compared to men 65 years and older.17
Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Melanoma in Hispanic Patients
Among Hispanics, white Hispanics comprise the majority of melanoma cases.5 Median age at diagnosis is younger in Hispanics compared to whites.5,6 Hispanic men typically are older (median age, 61 years) than Hispanic women (median age, 52 years) at diagnosis.5 Similar to what is seen in NHWs, young Hispanic women experience a higher melanoma incidence than young Hispanic men.5 Among older Hispanics, melanoma is more common in men.5,8
Melanomas located on the lower extremities and hips are more prevalent in Hispanics than in NHWs.5,8,18 Among Hispanics, there are age- and sex-based variations in the anatomic location of primary tumors: in Hispanic men, truncal tumors predominate, and in Hispanic women, tumors of the lower extremities are most common across all age groups.5 The incidence of melanomas located in the head and neck region increases with age for both Hispanic men and women.
For melanomas in which the histologic type is known, superficial spreading melanoma is the most common subtype among Hispanics.5,17,19 Acral lentiginous melanomas and nodular melanomas are more common among Hispanics than among NHWs.5,17,19
The observation that Hispanics with melanoma are more prone to lower-extremity tumors and nodular and acral lentiginous melanoma subtypes than NHWs suggests that UV exposure history may be of less importance in this population. Although numerous studies have explored melanoma risk factors in NHWs, there is a striking paucity of such studies in Hispanics. For example, there are conflicting data regarding the role of UV exposure in melanoma risk among Hispanics. Hu et al20 found that UV index and latitude correlated with melanoma risk in this population, whereas Eide et al21 found no association between UV exposure and melanoma incidence in Hispanics. A prospective study involving a multiethnic cohort (of whom 40 of the 107 participants were Hispanic) found no clear association between a history of sunburn and melanoma risk in Hispanics.18
Strategies for Reducing Disparities in Outcomes
Our knowledge of melanoma epidemiology in Hispanics derives mainly from secondary analyses of state-level and national cancer registry data sets.5-8,13-15,17,19,20 These administrative data sources often are limited by missing data (eg, tumor thickness, histologic subtype) or lack important patient-level information (eg, self-identified race and ethnicity, health insurance status). Additionally, the manner in which data are collected and integrated into research varies; for example, socioeconomic measures often are reported as either area-based or composite measures.
The host phenotypic characteristics of melanoma in NHWs are well understood, but the biological and environmental determinants of melanoma risk in Hispanics and other minorities are unknown. For example, fair complexion, red hair, blue eyes, increased freckling density, and the presence of numerous dysplastic and common melanocytic nevi indicate a propensity toward cutaneous melanoma.23,24 However, the relevance of such risk factors in Hispanics is unknown and has not been widely investigated in this patient population. Park et al18 found that a person’s sunburn susceptibility phenotype (defined as hair and eye color, ability to tan, and skin reaction to sunlight) was associated with an increased risk of melanoma among nonwhite, multiracial individuals. However, this study was limited by a small number of minority cases, which included only 40 Hispanic participants with melanoma.18 There is a need for rigorous observational studies to clearly define the phenotypic characteristics, sun-exposure behavior patterns, and genetic contributors to melanoma genesis in Hispanics.
The biologic determinants of postdiagnosis survival in Hispanics with melanoma are not well understood. It is unknown if genetic predisposition modifies melanoma risk in Hispanics. For example, the frequency of BRAF gene mutation or other driver mutations in US Hispanics has been understudied. It is important to know if mutation frequency patterns differ in Hispanics patients compared to NHWs because this knowledge could have considerable implications for treatment. Several recommendations should be considered to address these knowledge gaps. First, there is a need for development or enhancement of melanoma biorepositories, which should include tumor and nontumor specimens from a diverse sample of melanoma patients.
Conclusion
- American Cancer Society. Key statistics for melanoma skin cancer. www.cancer.org/cancer/melanoma-skin-cancer/about/key-statistics.html. Accessed January 13, 2018.
- Balch CM, Gershenwald JE, Soong S, et al. Final version of 2009 AJCC melanoma staging and classification. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:6199-6206.
- Katalinic A, Waldmann A, Weinstock MA, et al. Does skin cancer screening save lives? Cancer. 2012;118:5395-5402.
- Bergad LW, Klein HS. Hispanics in the United States: A Demographic, Social, and Economic History, 1980-2005. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 2010.
- Garnett E, Townsend J, Steele B, et al. Characteristics, rates, and trends of melanoma incidence among Hispanics in the USA. Cancer Causes Control. 2016;27:647-659.
- Pollitt RA, Clarke CA, Swetter SM, et al. The expanding melanoma burden in California Hispanics: importance of socioeconomic distribution, histologic subtype, and anatomic location. Cancer. 2011;117:152-161.
- Hu S, Parmet, Y, Allen G, et al. Disparity in melanoma: a trend analysis of melanoma incidence and stage at diagnosis among whites,Hispanics, and blacks in Florida. JAMA Dermatology. 2010;145:1369-1374.
- Cormier JN, Xing Y, Ding M, et al. Ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1907-1914.
- Pollitt RA, Swetter SM, Johnson TM, et al. Examining the pathways linking lower socioeconomic status and advanced melanoma. Cancer. 2012;118:4004-4013.
- Ortiz CA, Goodwin JS, Freeman JL. The effect of socioeconomic factors on incidence, stage at diagnosis and survival of cutaneous melanoma. Med Sci Monit. 2005;11:RA163-RA172.
- Singh SD, Ajani UA, Johnson CJ, et al. Association of cutaneous melanoma incidence with area-based socioeconomic indicators-United States, 2004-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5 suppl 1):S58-S68.
- Pollitt RA, Clarke CA, Shema SJ, et al. California Medicaid enrollment and melanoma stage at diagnosis: a population-based study. Am J Prev Med. 2008;35:7-13.
- Clairwood M, Ricketts J, Grant-Kels J, et al. Melanoma in skin of color in Connecticut: an analysis of melanoma incidence and stage at diagnosis in non-Hispanic blacks, non-Hispanic whites, and Hispanics. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:425-433.
- Hamilton EC, Nguyen HT, Chang YC, et al. Health disparities influence childhood melanoma stage at diagnosis and outcome. J Pediatr. 2016;175:182-187.
- Dawes SM, Tsai S, Gittleman H, et al. Racial disparities in melanoma survival. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:983-991.
- Imahiyerobo-Ip J, Ip I, Jamal S, et al. Skin cancer awareness in communities of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:198-200.
- Harvey VM, Enos CW, Chen JT, et al. The role of neighborhood characteristics in late stage melanoma diagnosis among Hispanic men in California, Texas, and Florida, 1996-2012 [published online June 18, 2017]. J Cancer Epidemiol. 2017;2017:8418904.
- Park SL, Le Marchand L, Wilkens LR, et al. Risk factors for malignant melanoma in white and non-white/non-African American populations: the multiethnic cohort. Cancer Prev Res. 2012;5:423-434.
- Wu XC, Eide MJ, King J, et al. Racial and ethnic variations in incidence and survival of cutaneous melanoma in the United States, 1999-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5 suppl 1):S26-S37.
- Hu S, Ma F, Collado-Mesa F, et al. UV radiation, latitude, and melanoma in US Hispanics and blacks. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:819-824.
- Eide MJ, Weinstock MA. Association of UV index, latitude, and melanoma incidence in nonwhite populations—US Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program, 1992 to 2001. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:477-481.
- Polite BN, Adams-Campbell LL, Brawley OW, et al. Charting the future of cancer health disparities research: a position statement from the American Association for Cancer Research, the American Cancer Society, the American Society of Clinical Oncology, and the National Cancer Institute. Cancer Res. 2017;77:4548-4555.
- Gandini S, Sera F, Cattaruzza MS, et al. Meta-analysis of risk factors for cutaneous melanoma: III. family history, actinic damage and phenotypic factors. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41:2040-2059.
- Chang YM, Newton-Bishop JA, Bishop DT, et al. A pooled analysis of melanocytic nevus phenotype and the risk of cutaneous melanoma at different latitudes. Int J Cancer. 2009;124:420-428.
- Palmer JR, Ambrosone CB, Olshan AF. A collaborative study of the etiology of breast cancer subtypes in African American women: the AMBER consortium. Cancer Causes Control. 2014;25:309-319.
- Rapkin BD, Weiss E, Lounsbury D, et al. Reducing disparities in cancer screening and prevention through community-based participatory research partnerships with local libraries: a comprehensive dynamic trial. Am J Community Psychol. 2017;60:145-159.
Cutaneous melanoma is a considerable public health concern. In the United States, an estimated 87,110 cases were diagnosed in 2017, and more than 9000 deaths are expected as result of this disease in 2018.1 Early diagnosis of melanoma is associated with favorable survival rates (5-year overall survival rates for melanoma in situ and stage IA melanoma, 99% and 97%, respectively).2 In contrast, the prognosis for advanced-stage melanoma is poor, with a 5-year survival rate of 16% for patients with stage IV disease. Therefore, early detection is critical to reducing mortality in melanoma patients.3
The term Hispanic refers to a panethnic category primarily encompassing Mexican-Americans, Cubans, and Puerto Ricans, as well as individuals from the Caribbean and Central and South America. These populations are diverse in birth origin, primary language, acculturation, distinct ethnic traditions, education level, and occupation. Hispanics in the United States are heterogeneous in many dimensions related to health risks, health care use, and health outcomes.4 Genetic predisposition, lifestyle risks, and access to and use of health care services can shape melanoma diagnosis, treatment, and progression across Hispanic populations differently than in other populations.
In this review, the epidemiology and clinical presentation of melanoma in US Hispanics is summarized, and recommendations for a research agenda to advance understanding of this disease in the most rapidly growing segment of the US population is provided.
In the period from 2008 to 2012, the age-adjusted incidence of melanoma in US Hispanics (4.6 per 100,00 men and 4.2 per 100,00 women) was lower than in NHWs.5 Garnett et al5 reported a decline in melanoma incidence in US Hispanics between 2003 and 2012—an observation that stands in contrast to state-level studies in California and Florida, in which small but substantial increases in melanoma incidence among Hispanics were reported.6,7 The rising incidence of melanomas thicker than 1.5 mm at presentation among Hispanic men living in California is particularly worrisome.6 Discrepancies in incidence trends might reflect changes in incidence over time or differences in state-level registry reporting of melanoma.5
Despite a lower overall incidence of melanoma in US Hispanics, those who do develop the disease are 2.4 times more likely (age-adjusted odds ratio) to present with stage III disease (confidence interval, 1.89-3.05)8 and are 3.64 times more likely to develop distant metastases (confidence interval, 2.65-5.0) than NHWs.3,7,9-13 Disparities also exist in the diagnosis of childhood melanoma: Hispanic children and adolescents who have a diagnosis of melanoma are 3 times more likely to present with advanced disease than NHW counterparts.14 Survival analyses by age and stage show considerably lower survival among Hispanic patients compared to NHW patients with stage I and II disease. In part, worse survival outcomes among Hispanics are the result of the pattern of more advanced disease at presentation.8,14,15
Late presentation for evaluation of melanomas in Hispanics has been attributed to a number of variables, including a lack of skin cancer awareness and knowledge,9,16 a lower rate of self- and physician-performed skin examinations,10 differences in tumor biology,9 and socioeconomic forces.7,17
In a previous study investigating the relationship between neighborhood characteristics and tumor stage at melanoma diagnosis in Hispanic men in California, Texas, and Florida, several key findings emerged.17 First, residency in a census tract with a high density of immigrants (California, Texas) and a high composition of Hispanics (California, Florida) was an important predictor of a late-stage melanoma diagnosis in fully adjusted models. Additionally, the strength of association between measures of socioeconomic status (ie, poverty and education) and tumor stage at melanoma diagnosis was attenuated in multivariate models when enclaves and availability of primary care resources were taken into account. Hispanic melanoma cases in areas with a low density of primary care physicians had an increased likelihood of late-stage diagnosis in California and Texas. The probability of late-stage diagnosis was concentrated in specific regions along the United States–Mexico border, in south central California, and along the southeastern coast of Florida. Lastly, in Texas, Hispanic men aged 18 to 34 years and 35 to 49 years were at an increased risk of late-stage melanoma diagnosis compared to men 65 years and older.17
Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Melanoma in Hispanic Patients
Among Hispanics, white Hispanics comprise the majority of melanoma cases.5 Median age at diagnosis is younger in Hispanics compared to whites.5,6 Hispanic men typically are older (median age, 61 years) than Hispanic women (median age, 52 years) at diagnosis.5 Similar to what is seen in NHWs, young Hispanic women experience a higher melanoma incidence than young Hispanic men.5 Among older Hispanics, melanoma is more common in men.5,8
Melanomas located on the lower extremities and hips are more prevalent in Hispanics than in NHWs.5,8,18 Among Hispanics, there are age- and sex-based variations in the anatomic location of primary tumors: in Hispanic men, truncal tumors predominate, and in Hispanic women, tumors of the lower extremities are most common across all age groups.5 The incidence of melanomas located in the head and neck region increases with age for both Hispanic men and women.
For melanomas in which the histologic type is known, superficial spreading melanoma is the most common subtype among Hispanics.5,17,19 Acral lentiginous melanomas and nodular melanomas are more common among Hispanics than among NHWs.5,17,19
The observation that Hispanics with melanoma are more prone to lower-extremity tumors and nodular and acral lentiginous melanoma subtypes than NHWs suggests that UV exposure history may be of less importance in this population. Although numerous studies have explored melanoma risk factors in NHWs, there is a striking paucity of such studies in Hispanics. For example, there are conflicting data regarding the role of UV exposure in melanoma risk among Hispanics. Hu et al20 found that UV index and latitude correlated with melanoma risk in this population, whereas Eide et al21 found no association between UV exposure and melanoma incidence in Hispanics. A prospective study involving a multiethnic cohort (of whom 40 of the 107 participants were Hispanic) found no clear association between a history of sunburn and melanoma risk in Hispanics.18
Strategies for Reducing Disparities in Outcomes
Our knowledge of melanoma epidemiology in Hispanics derives mainly from secondary analyses of state-level and national cancer registry data sets.5-8,13-15,17,19,20 These administrative data sources often are limited by missing data (eg, tumor thickness, histologic subtype) or lack important patient-level information (eg, self-identified race and ethnicity, health insurance status). Additionally, the manner in which data are collected and integrated into research varies; for example, socioeconomic measures often are reported as either area-based or composite measures.
The host phenotypic characteristics of melanoma in NHWs are well understood, but the biological and environmental determinants of melanoma risk in Hispanics and other minorities are unknown. For example, fair complexion, red hair, blue eyes, increased freckling density, and the presence of numerous dysplastic and common melanocytic nevi indicate a propensity toward cutaneous melanoma.23,24 However, the relevance of such risk factors in Hispanics is unknown and has not been widely investigated in this patient population. Park et al18 found that a person’s sunburn susceptibility phenotype (defined as hair and eye color, ability to tan, and skin reaction to sunlight) was associated with an increased risk of melanoma among nonwhite, multiracial individuals. However, this study was limited by a small number of minority cases, which included only 40 Hispanic participants with melanoma.18 There is a need for rigorous observational studies to clearly define the phenotypic characteristics, sun-exposure behavior patterns, and genetic contributors to melanoma genesis in Hispanics.
The biologic determinants of postdiagnosis survival in Hispanics with melanoma are not well understood. It is unknown if genetic predisposition modifies melanoma risk in Hispanics. For example, the frequency of BRAF gene mutation or other driver mutations in US Hispanics has been understudied. It is important to know if mutation frequency patterns differ in Hispanics patients compared to NHWs because this knowledge could have considerable implications for treatment. Several recommendations should be considered to address these knowledge gaps. First, there is a need for development or enhancement of melanoma biorepositories, which should include tumor and nontumor specimens from a diverse sample of melanoma patients.
Conclusion
Cutaneous melanoma is a considerable public health concern. In the United States, an estimated 87,110 cases were diagnosed in 2017, and more than 9000 deaths are expected as result of this disease in 2018.1 Early diagnosis of melanoma is associated with favorable survival rates (5-year overall survival rates for melanoma in situ and stage IA melanoma, 99% and 97%, respectively).2 In contrast, the prognosis for advanced-stage melanoma is poor, with a 5-year survival rate of 16% for patients with stage IV disease. Therefore, early detection is critical to reducing mortality in melanoma patients.3
The term Hispanic refers to a panethnic category primarily encompassing Mexican-Americans, Cubans, and Puerto Ricans, as well as individuals from the Caribbean and Central and South America. These populations are diverse in birth origin, primary language, acculturation, distinct ethnic traditions, education level, and occupation. Hispanics in the United States are heterogeneous in many dimensions related to health risks, health care use, and health outcomes.4 Genetic predisposition, lifestyle risks, and access to and use of health care services can shape melanoma diagnosis, treatment, and progression across Hispanic populations differently than in other populations.
In this review, the epidemiology and clinical presentation of melanoma in US Hispanics is summarized, and recommendations for a research agenda to advance understanding of this disease in the most rapidly growing segment of the US population is provided.
In the period from 2008 to 2012, the age-adjusted incidence of melanoma in US Hispanics (4.6 per 100,00 men and 4.2 per 100,00 women) was lower than in NHWs.5 Garnett et al5 reported a decline in melanoma incidence in US Hispanics between 2003 and 2012—an observation that stands in contrast to state-level studies in California and Florida, in which small but substantial increases in melanoma incidence among Hispanics were reported.6,7 The rising incidence of melanomas thicker than 1.5 mm at presentation among Hispanic men living in California is particularly worrisome.6 Discrepancies in incidence trends might reflect changes in incidence over time or differences in state-level registry reporting of melanoma.5
Despite a lower overall incidence of melanoma in US Hispanics, those who do develop the disease are 2.4 times more likely (age-adjusted odds ratio) to present with stage III disease (confidence interval, 1.89-3.05)8 and are 3.64 times more likely to develop distant metastases (confidence interval, 2.65-5.0) than NHWs.3,7,9-13 Disparities also exist in the diagnosis of childhood melanoma: Hispanic children and adolescents who have a diagnosis of melanoma are 3 times more likely to present with advanced disease than NHW counterparts.14 Survival analyses by age and stage show considerably lower survival among Hispanic patients compared to NHW patients with stage I and II disease. In part, worse survival outcomes among Hispanics are the result of the pattern of more advanced disease at presentation.8,14,15
Late presentation for evaluation of melanomas in Hispanics has been attributed to a number of variables, including a lack of skin cancer awareness and knowledge,9,16 a lower rate of self- and physician-performed skin examinations,10 differences in tumor biology,9 and socioeconomic forces.7,17
In a previous study investigating the relationship between neighborhood characteristics and tumor stage at melanoma diagnosis in Hispanic men in California, Texas, and Florida, several key findings emerged.17 First, residency in a census tract with a high density of immigrants (California, Texas) and a high composition of Hispanics (California, Florida) was an important predictor of a late-stage melanoma diagnosis in fully adjusted models. Additionally, the strength of association between measures of socioeconomic status (ie, poverty and education) and tumor stage at melanoma diagnosis was attenuated in multivariate models when enclaves and availability of primary care resources were taken into account. Hispanic melanoma cases in areas with a low density of primary care physicians had an increased likelihood of late-stage diagnosis in California and Texas. The probability of late-stage diagnosis was concentrated in specific regions along the United States–Mexico border, in south central California, and along the southeastern coast of Florida. Lastly, in Texas, Hispanic men aged 18 to 34 years and 35 to 49 years were at an increased risk of late-stage melanoma diagnosis compared to men 65 years and older.17
Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Melanoma in Hispanic Patients
Among Hispanics, white Hispanics comprise the majority of melanoma cases.5 Median age at diagnosis is younger in Hispanics compared to whites.5,6 Hispanic men typically are older (median age, 61 years) than Hispanic women (median age, 52 years) at diagnosis.5 Similar to what is seen in NHWs, young Hispanic women experience a higher melanoma incidence than young Hispanic men.5 Among older Hispanics, melanoma is more common in men.5,8
Melanomas located on the lower extremities and hips are more prevalent in Hispanics than in NHWs.5,8,18 Among Hispanics, there are age- and sex-based variations in the anatomic location of primary tumors: in Hispanic men, truncal tumors predominate, and in Hispanic women, tumors of the lower extremities are most common across all age groups.5 The incidence of melanomas located in the head and neck region increases with age for both Hispanic men and women.
For melanomas in which the histologic type is known, superficial spreading melanoma is the most common subtype among Hispanics.5,17,19 Acral lentiginous melanomas and nodular melanomas are more common among Hispanics than among NHWs.5,17,19
The observation that Hispanics with melanoma are more prone to lower-extremity tumors and nodular and acral lentiginous melanoma subtypes than NHWs suggests that UV exposure history may be of less importance in this population. Although numerous studies have explored melanoma risk factors in NHWs, there is a striking paucity of such studies in Hispanics. For example, there are conflicting data regarding the role of UV exposure in melanoma risk among Hispanics. Hu et al20 found that UV index and latitude correlated with melanoma risk in this population, whereas Eide et al21 found no association between UV exposure and melanoma incidence in Hispanics. A prospective study involving a multiethnic cohort (of whom 40 of the 107 participants were Hispanic) found no clear association between a history of sunburn and melanoma risk in Hispanics.18
Strategies for Reducing Disparities in Outcomes
Our knowledge of melanoma epidemiology in Hispanics derives mainly from secondary analyses of state-level and national cancer registry data sets.5-8,13-15,17,19,20 These administrative data sources often are limited by missing data (eg, tumor thickness, histologic subtype) or lack important patient-level information (eg, self-identified race and ethnicity, health insurance status). Additionally, the manner in which data are collected and integrated into research varies; for example, socioeconomic measures often are reported as either area-based or composite measures.
The host phenotypic characteristics of melanoma in NHWs are well understood, but the biological and environmental determinants of melanoma risk in Hispanics and other minorities are unknown. For example, fair complexion, red hair, blue eyes, increased freckling density, and the presence of numerous dysplastic and common melanocytic nevi indicate a propensity toward cutaneous melanoma.23,24 However, the relevance of such risk factors in Hispanics is unknown and has not been widely investigated in this patient population. Park et al18 found that a person’s sunburn susceptibility phenotype (defined as hair and eye color, ability to tan, and skin reaction to sunlight) was associated with an increased risk of melanoma among nonwhite, multiracial individuals. However, this study was limited by a small number of minority cases, which included only 40 Hispanic participants with melanoma.18 There is a need for rigorous observational studies to clearly define the phenotypic characteristics, sun-exposure behavior patterns, and genetic contributors to melanoma genesis in Hispanics.
The biologic determinants of postdiagnosis survival in Hispanics with melanoma are not well understood. It is unknown if genetic predisposition modifies melanoma risk in Hispanics. For example, the frequency of BRAF gene mutation or other driver mutations in US Hispanics has been understudied. It is important to know if mutation frequency patterns differ in Hispanics patients compared to NHWs because this knowledge could have considerable implications for treatment. Several recommendations should be considered to address these knowledge gaps. First, there is a need for development or enhancement of melanoma biorepositories, which should include tumor and nontumor specimens from a diverse sample of melanoma patients.
Conclusion
- American Cancer Society. Key statistics for melanoma skin cancer. www.cancer.org/cancer/melanoma-skin-cancer/about/key-statistics.html. Accessed January 13, 2018.
- Balch CM, Gershenwald JE, Soong S, et al. Final version of 2009 AJCC melanoma staging and classification. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:6199-6206.
- Katalinic A, Waldmann A, Weinstock MA, et al. Does skin cancer screening save lives? Cancer. 2012;118:5395-5402.
- Bergad LW, Klein HS. Hispanics in the United States: A Demographic, Social, and Economic History, 1980-2005. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 2010.
- Garnett E, Townsend J, Steele B, et al. Characteristics, rates, and trends of melanoma incidence among Hispanics in the USA. Cancer Causes Control. 2016;27:647-659.
- Pollitt RA, Clarke CA, Swetter SM, et al. The expanding melanoma burden in California Hispanics: importance of socioeconomic distribution, histologic subtype, and anatomic location. Cancer. 2011;117:152-161.
- Hu S, Parmet, Y, Allen G, et al. Disparity in melanoma: a trend analysis of melanoma incidence and stage at diagnosis among whites,Hispanics, and blacks in Florida. JAMA Dermatology. 2010;145:1369-1374.
- Cormier JN, Xing Y, Ding M, et al. Ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1907-1914.
- Pollitt RA, Swetter SM, Johnson TM, et al. Examining the pathways linking lower socioeconomic status and advanced melanoma. Cancer. 2012;118:4004-4013.
- Ortiz CA, Goodwin JS, Freeman JL. The effect of socioeconomic factors on incidence, stage at diagnosis and survival of cutaneous melanoma. Med Sci Monit. 2005;11:RA163-RA172.
- Singh SD, Ajani UA, Johnson CJ, et al. Association of cutaneous melanoma incidence with area-based socioeconomic indicators-United States, 2004-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5 suppl 1):S58-S68.
- Pollitt RA, Clarke CA, Shema SJ, et al. California Medicaid enrollment and melanoma stage at diagnosis: a population-based study. Am J Prev Med. 2008;35:7-13.
- Clairwood M, Ricketts J, Grant-Kels J, et al. Melanoma in skin of color in Connecticut: an analysis of melanoma incidence and stage at diagnosis in non-Hispanic blacks, non-Hispanic whites, and Hispanics. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:425-433.
- Hamilton EC, Nguyen HT, Chang YC, et al. Health disparities influence childhood melanoma stage at diagnosis and outcome. J Pediatr. 2016;175:182-187.
- Dawes SM, Tsai S, Gittleman H, et al. Racial disparities in melanoma survival. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:983-991.
- Imahiyerobo-Ip J, Ip I, Jamal S, et al. Skin cancer awareness in communities of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:198-200.
- Harvey VM, Enos CW, Chen JT, et al. The role of neighborhood characteristics in late stage melanoma diagnosis among Hispanic men in California, Texas, and Florida, 1996-2012 [published online June 18, 2017]. J Cancer Epidemiol. 2017;2017:8418904.
- Park SL, Le Marchand L, Wilkens LR, et al. Risk factors for malignant melanoma in white and non-white/non-African American populations: the multiethnic cohort. Cancer Prev Res. 2012;5:423-434.
- Wu XC, Eide MJ, King J, et al. Racial and ethnic variations in incidence and survival of cutaneous melanoma in the United States, 1999-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5 suppl 1):S26-S37.
- Hu S, Ma F, Collado-Mesa F, et al. UV radiation, latitude, and melanoma in US Hispanics and blacks. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:819-824.
- Eide MJ, Weinstock MA. Association of UV index, latitude, and melanoma incidence in nonwhite populations—US Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program, 1992 to 2001. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:477-481.
- Polite BN, Adams-Campbell LL, Brawley OW, et al. Charting the future of cancer health disparities research: a position statement from the American Association for Cancer Research, the American Cancer Society, the American Society of Clinical Oncology, and the National Cancer Institute. Cancer Res. 2017;77:4548-4555.
- Gandini S, Sera F, Cattaruzza MS, et al. Meta-analysis of risk factors for cutaneous melanoma: III. family history, actinic damage and phenotypic factors. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41:2040-2059.
- Chang YM, Newton-Bishop JA, Bishop DT, et al. A pooled analysis of melanocytic nevus phenotype and the risk of cutaneous melanoma at different latitudes. Int J Cancer. 2009;124:420-428.
- Palmer JR, Ambrosone CB, Olshan AF. A collaborative study of the etiology of breast cancer subtypes in African American women: the AMBER consortium. Cancer Causes Control. 2014;25:309-319.
- Rapkin BD, Weiss E, Lounsbury D, et al. Reducing disparities in cancer screening and prevention through community-based participatory research partnerships with local libraries: a comprehensive dynamic trial. Am J Community Psychol. 2017;60:145-159.
- American Cancer Society. Key statistics for melanoma skin cancer. www.cancer.org/cancer/melanoma-skin-cancer/about/key-statistics.html. Accessed January 13, 2018.
- Balch CM, Gershenwald JE, Soong S, et al. Final version of 2009 AJCC melanoma staging and classification. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:6199-6206.
- Katalinic A, Waldmann A, Weinstock MA, et al. Does skin cancer screening save lives? Cancer. 2012;118:5395-5402.
- Bergad LW, Klein HS. Hispanics in the United States: A Demographic, Social, and Economic History, 1980-2005. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 2010.
- Garnett E, Townsend J, Steele B, et al. Characteristics, rates, and trends of melanoma incidence among Hispanics in the USA. Cancer Causes Control. 2016;27:647-659.
- Pollitt RA, Clarke CA, Swetter SM, et al. The expanding melanoma burden in California Hispanics: importance of socioeconomic distribution, histologic subtype, and anatomic location. Cancer. 2011;117:152-161.
- Hu S, Parmet, Y, Allen G, et al. Disparity in melanoma: a trend analysis of melanoma incidence and stage at diagnosis among whites,Hispanics, and blacks in Florida. JAMA Dermatology. 2010;145:1369-1374.
- Cormier JN, Xing Y, Ding M, et al. Ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1907-1914.
- Pollitt RA, Swetter SM, Johnson TM, et al. Examining the pathways linking lower socioeconomic status and advanced melanoma. Cancer. 2012;118:4004-4013.
- Ortiz CA, Goodwin JS, Freeman JL. The effect of socioeconomic factors on incidence, stage at diagnosis and survival of cutaneous melanoma. Med Sci Monit. 2005;11:RA163-RA172.
- Singh SD, Ajani UA, Johnson CJ, et al. Association of cutaneous melanoma incidence with area-based socioeconomic indicators-United States, 2004-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5 suppl 1):S58-S68.
- Pollitt RA, Clarke CA, Shema SJ, et al. California Medicaid enrollment and melanoma stage at diagnosis: a population-based study. Am J Prev Med. 2008;35:7-13.
- Clairwood M, Ricketts J, Grant-Kels J, et al. Melanoma in skin of color in Connecticut: an analysis of melanoma incidence and stage at diagnosis in non-Hispanic blacks, non-Hispanic whites, and Hispanics. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:425-433.
- Hamilton EC, Nguyen HT, Chang YC, et al. Health disparities influence childhood melanoma stage at diagnosis and outcome. J Pediatr. 2016;175:182-187.
- Dawes SM, Tsai S, Gittleman H, et al. Racial disparities in melanoma survival. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:983-991.
- Imahiyerobo-Ip J, Ip I, Jamal S, et al. Skin cancer awareness in communities of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:198-200.
- Harvey VM, Enos CW, Chen JT, et al. The role of neighborhood characteristics in late stage melanoma diagnosis among Hispanic men in California, Texas, and Florida, 1996-2012 [published online June 18, 2017]. J Cancer Epidemiol. 2017;2017:8418904.
- Park SL, Le Marchand L, Wilkens LR, et al. Risk factors for malignant melanoma in white and non-white/non-African American populations: the multiethnic cohort. Cancer Prev Res. 2012;5:423-434.
- Wu XC, Eide MJ, King J, et al. Racial and ethnic variations in incidence and survival of cutaneous melanoma in the United States, 1999-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5 suppl 1):S26-S37.
- Hu S, Ma F, Collado-Mesa F, et al. UV radiation, latitude, and melanoma in US Hispanics and blacks. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:819-824.
- Eide MJ, Weinstock MA. Association of UV index, latitude, and melanoma incidence in nonwhite populations—US Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program, 1992 to 2001. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:477-481.
- Polite BN, Adams-Campbell LL, Brawley OW, et al. Charting the future of cancer health disparities research: a position statement from the American Association for Cancer Research, the American Cancer Society, the American Society of Clinical Oncology, and the National Cancer Institute. Cancer Res. 2017;77:4548-4555.
- Gandini S, Sera F, Cattaruzza MS, et al. Meta-analysis of risk factors for cutaneous melanoma: III. family history, actinic damage and phenotypic factors. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41:2040-2059.
- Chang YM, Newton-Bishop JA, Bishop DT, et al. A pooled analysis of melanocytic nevus phenotype and the risk of cutaneous melanoma at different latitudes. Int J Cancer. 2009;124:420-428.
- Palmer JR, Ambrosone CB, Olshan AF. A collaborative study of the etiology of breast cancer subtypes in African American women: the AMBER consortium. Cancer Causes Control. 2014;25:309-319.
- Rapkin BD, Weiss E, Lounsbury D, et al. Reducing disparities in cancer screening and prevention through community-based participatory research partnerships with local libraries: a comprehensive dynamic trial. Am J Community Psychol. 2017;60:145-159.
Practice Points
- Although the age-adjusted incidence of melanoma among US Hispanics is lower than among non-Hispanic whites, Hispanics with melanoma are more likely to present with stage III disease and have distant metastases.
- Late presentation of melanoma in Hispanics is not completely understood but may be attributed to socioeconomic factors, lack of skin cancer awareness and knowledge, lower rate of self- and physician-performed skin examinations, and differences in tumor biology, among other variables.
- Research is needed to address gaps in knowledge about the risk of melanoma and comparatively poor outcomes among Hispanics so interventional efforts for prevention, early detection, and treatment can be implemented.
No Sulfates, No Parabens, and the “No-Poo” Method: A New Patient Perspective on Common Shampoo Ingredients
Shampoo is a staple in hair grooming that is ever-evolving along with cultural trends. The global shampoo market is expected to reach an estimated value of $25.73 billion by 2019. A major driver of this upward trend in market growth is the increasing demand for natural and organic hair shampoos.1 Society today has a growing fixation on healthy living practices, and as of late, the ingredients in shampoos and other cosmetic products have become one of the latest targets in the health-consciousness craze. In the age of the Internet where information—and misinformation—is widely accessible and dispersed, the general public often strives to self-educate on specialized matters that are out of their expertise. As a result, individuals have developed an aversion to using certain shampoos out of fear that the ingredients, often referred to as “chemicals” by patients due to their complex names, are unnatural and therefore unhealthy.1,2 Product developers are working to meet the demand by reformulating shampoos with labels that indicate sulfate free or paraben free, despite the lack of proof that these formulations are an improvement over traditional approaches to hair health. Additionally, alternative methods of cleansing the hair and scalp, also known as the no-shampoo or “no-poo” method, have begun to gain popularity.2,3
It is essential that dermatologists acknowledge the concerns that their patients have about common shampoo ingredients to dispel the myths that may misinform patient decision-making. This article reviews the controversy surrounding the use of sulfates and parabens in shampoos as well as commonly used shampoo alternatives. Due to the increased prevalence of dry hair shafts in the skin of color population, especially black women, this group is particularly interested in products that will minimize breakage and dryness of the hair. To that end, this population has great interest in the removal of chemical ingredients that may cause damage to the hair shafts, despite the lack of data to support sulfates and paraben damage to hair shafts or scalp skin. Blogs and uninformed hairstylists may propagate these beliefs in a group of consumers who are desperate for new approaches to hair fragility and breakage.
Surfactants and Sulfates
The cleansing ability of a shampoo depends on the surface activity of its detergents. Surface-active ingredients, or surfactants, reduce the surface tension between water and dirt, thus facilitating the removal of environmental dirt from the hair and scalp,4 which is achieved by a molecular structure containing both a hydrophilic and a lipophilic group. Sebum and dirt are bound by the lipophilic ends of the surfactant, becoming the center of a micelle structure with the hydrophilic molecule ends pointing outward. Dirt particles become water soluble and are removed from the scalp and hair shaft upon rinsing with water.4
Surfactants are classified according to the electric charge of the hydrophilic polar group as either anionic, cationic, amphoteric (zwitterionic), or nonionic.5 Each possesses different hair conditioning and cleansing qualities, and multiple surfactants are used in shampoos in differing ratios to accommodate different hair types. In most shampoos, the base consists of anionic and amphoteric surfactants. Depending on individual product requirements, nonionic and cationic surfactants are used to either modify the effects of the surfactants or as conditioning agents.4,5
One subcategory of surfactants that receives much attention is the group of anionic surfactants known as sulfates. Sulfates, particularly sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), recently have developed a negative reputation as cosmetic ingredients, as reports from various unscientific sources have labeled them as hazardous to one’s health; SLS has been described as a skin and scalp irritant, has been linked to cataract formation, and has even been wrongly labeled as carcinogenic.6 The origins of some of these claims are not clear, though they likely arose from the misinterpretation of complex scientific studies that are easily accessible to laypeople. The link between SLS and ocular irritation or cataract formation is a good illustration of this unsubstantiated fear. A study by Green et al7 showed that corneal exposure to extremely high concentrations of SLS following physical or chemical damage to the eye can result in a slowed healing process. The results of this study have since been wrongly quoted to state that SLS-containing products lead to blindness or severe corneal damage.8 A different study tested for possible ocular irritation in vivo by submerging the lens of an eye into a 20% SLS solution, which accurately approximates the concentration of SLS in rinse-off consumer products.9 However, to achieve ocular irritation, the eyes of laboratory animals were exposed to SLS constantly for 14 days, which would not occur in practical use.9 Similarly, a third study achieved cataract formation in a laboratory only by immersing the lens of an eye into a highly concentrated solution of SLS.10 Such studies are not appropriate representations of how SLS-containing products are used by consumers and have unfortunately been vulnerable to misinterpretation by the general public.
There is no known study that has shown SLS to be carcinogenic. One possible origin of this idea may be from the wrongful interpretation of studies that used SLS as a vehicle substance to test agents that were deemed to be carcinogenic.11 Another possible source of the idea that SLS is carcinogenic comes from its association with 1,4-dioxane, a by-product of the synthesis of certain sulfates such as sodium laureth sulfate due to a process known as ethoxylation.6,12 Although SLS does not undergo this process in its formation and is not linked to 1,4-dioxane, there is potential for cross-contamination of SLS with 1,4-dioxane, which cannot be overlooked. 1,4-Dioxane is classified as “possibly carcinogenic to humans (Group 2B)” by the International Agency for Research on Cancer,13 but screening of SLS for this substance prior to its use in commercial products is standard.
Sulfates are inexpensive detergents that are responsible for lather formation in shampoos as well as in many household cleaning agents.5 Sulfates, similar to all anionic surfactants, are characterized by a negatively charged hydrophilic polar group. The best-known and most commonly used anionic surfactants are sulfated fatty alcohols, alkyl sulfates, and their polyethoxylated analogues alkyl ether sulfates.5,6 Sodium lauryl sulfate (also known as sodium laurilsulfate or sodium dodecyl sulfate) is the most common of them all, found in shampoo and conditioner formulations. Ammonium lauryl sulfate and sodium laureth sulfate are other sulfates commonly used in shampoos and household cleansing products. Sodium lauryl sulfate is a nonvolatile, water-soluble compound. Its partition coefficient (P0), a measure of a substance’s hydrophilic or lipophilic nature, is low at 1.6, making it a rather hydrophilic substance.6 Hydrophilic substances tend to have low bioaccumulation profiles in the body. Additionally, SLS is readily biodegradable. It can be derived from both synthetic and naturally occurring sources; for example, palm kernel oil, petrolatum, and coconut oil are all sources of lauric acid, the starting ingredient used to synthesize SLS. Sodium lauryl sulfate is created by reacting lauryl alcohol with sulfur trioxide gas, followed by neutralization with sodium carbonate (also a naturally occurring compound).6 Sodium lauryl sulfate and other sulfate-containing shampoos widely replaced the usage of traditional soaps formulated from animal or vegetable fats, as these latter formations created a film of insoluble calcium salts on the hair strands upon contact with water, resulting in tangled, dull-appearing hair.5 Additionally, sulfates were preferred to the alkaline pH of traditional soap, which can be harsh on hair strands and cause irritation of the skin and mucous membranes.14 Because they are highly water soluble, sulfates enable the formulation of clear shampoos. They exhibit remarkable cleaning properties and lather formation.5,14
Because sulfates are potent surfactants, they can remove dirt and debris as well as naturally produced healthy oils from the hair and scalp. As a result, sulfates can leave the hair feeling dry and stripped of moisture.4,5 Sulfates are used as the primary detergents in the formulation of deep-cleaning shampoos, which are designed for people who accumulate a heavy buildup of dirt, sebum, and debris from frequent use of styling products. Due to their potent detergency, these shampoos typically are not used on a daily basis but rather at longer intervals.15 A downside to sulfates is that they can have cosmetically unpleasant properties, which can be compensated for by including appropriate softening additives in shampoo formulations.4 A number of anionic surfactants such as olefin sulfonate, alkyl sulfosuccinate, acyl peptides, and alkyl ether carboxylates are well tolerated by the skin and are used together with other anionic and amphoteric surfactants to optimize shampoo properties. Alternatively, sulfate-free shampoos are cleansers compounded by the removal of the anionic group and switched for surfactants with less detergency.4,5
Preservatives and Parabens
Parabens refer to a group of esters of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid commonly used as preservatives in foods, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics whose widespread use dates back to 1923.16 Concerns over the presence of parabens in shampoos and other cosmetics have been raised by patients for their reputed estrogenic and antiandrogenic effects and suspected involvement in carcinogenesis via endocrine modulation.16,17 In in vitro studies done on yeast assays, parabens have shown weak estrogenic activity that increases in proportion to both the length and increased branching of the alkyl side chains in the paraben’s molecular structure.18 They are 10,000-fold less potent than 17β-estradiol. In in vivo animal studies, parabens show weak estrogenic activity and are 100,000-fold less potent than 17β-estradiol.18 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, a common metabolite, showed no estrogenic activity when tested both in vitro and in vivo.19 Some concerning research has implicated a link between parabens used in underarm cosmetics, such as deodorants and antiperspirants, and breast cancer16; however, the studies have been conflicting, and there is simply not enough data to assert that parabens cause breast cancer.
The Cosmetic Ingredient Review expert panel first reviewed parabens in 1984 and concluded that “methylparaben, ethylparaben, propylparaben, and butylparaben are safe as cosmetic ingredients in the present practices of use.”20 They extended this statement to include isopropylparaben and isobutylparaben in a later review.21 In 2005, the Scientific Committee on Consumer Products (now known as the Scientific Committee for Consumer Safety) in Europe stated that methylparaben and ethylparaben can be used at levels up to 0.4% in products.22 This decision was reached due to reports of decreased sperm counts and testosterone levels in male juvenile rats exposed to these parabens; however, these reults were not successfully replicated in larger studies.16,22 In 2010, the Scientific Committee for Consumer Safety revisited its stance on parabens, and they then revised their recommendations to say that concentrations of propylparaben and butylparaben should not exceed concentrations of 0.19%, based on “the conservative choice for the calculation of the [Margin-of-Safety] of butyl- and propylparaben.”23 However, in 2011 the use of propylparaben and butylparaben was banned in Denmark for cosmetic products used in children 3 years or younger,16 and the European Commission subsequently amended their directive in 2014, banning isopropylparaben, isobutylparaben, phenylparaben, benzylparaben, and pentylparaben due to lack of data available to evaluate the human risk of these products.24
Contrary to the trends in Europe, there currently are no regulations against the use of parabens in shampoos or other cosmetics in the United States. The American Cancer Society found that there is no evidence to suggest that the current levels of parabens in cosmetic products (eg, antiperspirants) increase one’s risk of breast cancer.25 Parabens are readily absorbed into the body both transdermally and through ingestion but also are believed to be rapidly transformed into harmless and nonspecific metabolites; they are readily metabolized by the liver and excreted in urine, and there is no measured accumulation in tissues.17
Parabens continue to be the most widely used preservatives in personal care products, usually in conjunction with other preservatives. Parabens are good biocides; short-chain esters (eg, methylparabens, ethylparabens) are effective against gram-positive bacteria and are weakly effective against gram-negative bacteria. Long-chain paraben esters (eg, propylparabens, butylparabens) are effective against mold and yeast. The addition of other preservatives creates a broad spectrum of antimicrobial defense in consumer products. Other preservatives include formaldehyde releasers or phenoxyethanol, as well as chelating agents such as EDTA, which improve the stability of these cosmetic products when exposed to air.16 Parabens are naturally occurring substances found in foods such as blueberries, barley, strawberries, yeast, olives, and grapes. As a colorless, odorless, and inexpensive substance, their use has been heavily favored in cosmetic and food products.16
Shampoo Alternatives and the No-Poo Method
Although research has not demonstrated any long-term danger to using shampoo, certain chemicals found in shampoos have the potential to irritate the scalp. Commonly cited allergens in shampoos include cocamidopropyl betaine, propylene glycol, vitamin E (tocopherol), parabens, and benzophenones.5 Additionally, the rising use of formaldehyde-releasing preservatives and isothiazolinones due to mounting pressures to move away from parabens has led to an increase in cases of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD).16 However, the irritability (rather than allergenicity) of these substances often is established during patch testing, a method of detecting delayed-type allergic reactions, which is important to note because patch testing requires a substance to be exposed to the skin for 24 to 48 hours, whereas exposure to shampoo ingredients may last a matter of minutes at most and occur in lesser concentrations because the ingredients are diluted by water in the rinsing process. Given these differences, it is unlikely that a patient would develop a true allergic response from regular shampoo use. Nevertheless, in patients who are already sensitized, exposure could conceivably trigger ACD, and patients must be cognizant of the composition of their shampoos.16
The no-poo method refers to the avoidance of commercial shampoo products when cleansing the hair and scalp and encompasses different methods of cleansing the hair, such as the use of household items (eg, baking soda, apple cider vinegar [ACV]), the use of conditioners to wash the hair (also known as conditioner-only washing or co-washing), treating the scalp with tea tree oil, or simply rinsing the hair with water. Proponents of the no-poo method believe that abstaining from shampoo use leads to healthier hair, retained natural oils, and less exposure to supposedly dangerous chemicals such as parabens or sulfates.2,3,26-28 However, there are no known studies in the literature that assess or support the hypotheses of the no-poo method.
Baking Soda and ACV
Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) is a substance commonly found in the average household. It has been used in toothpaste formulas and cosmetic products and is known for its acid-neutralizing properties. Baking soda has been shown to have some antifungal and viricidal properties through an unknown mechanism of action.28 It has gained popularity for its use as a means of reducing the appearance of excessive greasiness of the hair shafts. Users also have reported that when washing their hair with baking soda, they are able to achieve a clean scalp and hair that feels soft to the touch.2,3,26,27,29 Despite these reports, users must beware of using baking soda without adequately diluting it with water. Baking soda is a known alkaline irritant.26,30 With a pH of 9, baking soda causes the cuticle layer of the hair fiber to open, increasing the capacity for water absorption. Water penetrates the scales that open, breaking the hydrogen bonds of the keratin molecule.31 Keratin is a spiral helical molecule that keeps its shape due to hydrogen, disulfide, and ionic bonds, as well as Van der Waals force.30 Hydrolysis of these bonds due to exposure to baking soda lowers the elasticity of the hair and increases the negative electrical net charge of the hair fiber surface, which leads to increased friction between fibers, cuticle damage, hair fragility, and fiber breakage.32,33
Apple cider vinegar is an apple-derived acetic acid solution with a pH ranging from 3.1 to 5.28 The pH range of ACV is considered to be ideal for hair by no-poo proponents, as it is similar to the natural pH of the scalp. Its acidic properties are responsible for its antimicrobial abilities, particularly its effectiveness against gram-negative bacteria.30 The acetic acid of ACV can partially interrupt oil interfaces, which contributes to its mild ability to remove product residue and scalp buildup from the hair shaft; the acetic acid also tightens the cuticles on hair fibers.33 Apple cider vinegar is used as a means of cleansing the hair and scalp by no-poo proponents2,3,26; other uses for ACV include using it as a rinse following washing and/or conditioning of the hair or as a means of preserving color in color-treated hair. There also is evidence that ACV may have antifungal properties.28 However, consumers must be aware that if it is not diluted in water, ACV may be too caustic for direct application to the hair and may lead to damage; it can be irritating to eyes, mucus membranes, and acutely inflamed skin. Also, vinegar rinses used on processed or chemically damaged hair may lead to increased hair fragility.2,3
Hair fibers have a pH of 3.67, while the scalp has a pH between 4.5 and 6.2. This slightly acidic film acts as a barrier to viruses, bacteria, and other potential contaminants.33 Studies have shown that the pH of skin increases in proportion to the pH of the cleanser used.34 Therefore, due to the naturally acidic pH of the scalp, acid-balanced shampoos generally are recommended. Shampoos should not have a pH higher than 5.5, as hair shafts can swell due to alkalinization, which can be prevented by pH balancing the shampoo through the addition of an acidic substance (eg, glycolic acid, citric acid) to lower the pH down to approximately 5.5. Apple cider vinegar often is used for this purpose. However, one study revealed that 82% of shampoos already have an acidic pH.34
Conditioner-Only Washing (Co-washing)
Conditioner-only washing, or co-washing, is a widely practiced method of hair grooming. It is popular among individuals who find that commercial shampoos strip too much of the natural hair oils away, leaving the hair rough or unmanageable. Co-washing is not harmful to the hair; however, the molecular structure and function of a conditioner and that of a shampoo are very different.5,35,36 Conditioners are not formulated to remove dirt and buildup in the hair but rather to add substances to the hair, and thus cannot provide extensive cleansing of the hair and scalp; therefore, it is inappropriate to use co-washing as a replacement for shampooing. Quaternary conditioning agents are an exception because they contain amphoteric detergents comprised of both anionic and cationic groups, which allow them both the ability to remove dirt and sebum with its anionic group, typically found in shampoos, as well as the ability to coat and condition the hair due to the high affinity of the cationic group for the negatively charged hair fibers.36,37 Amphoteric detergents are commonly found in 2-in-1 conditioning cleansers, among other ingredients, such as hydrolyzed animal proteins that temporarily plug surface defects on the hair fiber, and dimethicone, a synthetic oil that creates a thin film over the hair shaft, increasing shine and manageability. Of note, these conditioning shampoos are ideal for individuals with minimal product buildup on the hair and scalp and are not adequate scalp cleansers for individuals who either wash their hair infrequently or who regularly use hairstyling products.36,37
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is an essential oil extracted from the Melaleuca alternifolia plant of the Myrtaceae family. It is native to the coast of northeastern Australia. A holy grail of natural cosmetics, tea tree oil is widely known for its antiviral, antifungal, and antiseptic properties.38 Although not used as a stand-alone cleanser, it is often added to a number of cosmetic products, including shampoos and co-washes. Although deemed safe for topical use, it has been shown to be quite toxic when ingested. Symptoms of ingestion include nausea, vomiting, hallucinations, and coma. The common concern with tea tree oil is its ability to cause ACD. In particular, it is believed that the oxidation products of tea tree oil are allergenic rather than the tea tree oil itself. The evaluation of tea tree oil as a potential contact allergen has been quite difficult; it consists of more than 100 distinct compounds and is often mislabeled, or does not meet the guidelines of the International Organization for Standardization. Nonetheless, the prevalence of ACD due to tea tree oil is low (approximately 1.4%). Despite its low prevalence, tea tree oil should remain in the differential as an ACD-inducing agent. Patch testing with the patient’s supply of tea tree oil is advised when possible.38
Conclusion
It is customary that the ingredients used in shampoos undergo periodic testing and monitoring to assure the safety of their use. Although it is encouraging that patients are proactive in their efforts to stay abreast of the literature, it is still important that cosmetic scientists, dermatologists, and other experts remain at the forefront of educating the public about these substances. Not doing so can result in the propagation of misinformation and unnecessary fears, which can lead to the adaptation of unhygienic or even unsafe hair care practices. As dermatologists, we must ensure that patients are educated about the benefits and hazards of off-label use of household ingredients to the extent that evidence-based medicine permits. Patients must be informed that not all synthetic substances are harmful, and likewise not all naturally occurring substances are safe.
- The global shampoo market 2014-2019 trends, forecast, and opportunity analysis [press release]. New York, NY: Reportlinker; May 21, 2015.
- Is the ‘no shampoo’ trend healthy or harmful? Mercola website. Published January 16, 2016. Accessed December 8, 2017.
- Feltman R. The science (or lack thereof) behind the ‘no-poo’ hair trend. Washington Post. March 10, 2016. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/speaking-of-science/wp/2016/03/10/the-science-or-lack-thereof-behind-the-no-poo-hair-trend/?utm_term=.9a61edf3fd5a. Accessed December 11, 2017.
- Bouillon C. Shampoos. Clin Dermatol. 1996;14:113-121.
- Trueb RM. Shampoos: ingredients, efficacy, and adverse effects. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2007;5:356-365.
- Bondi CA, Marks JL, Wroblewski LB, et al. Human and environmental toxicity of sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS): evidence for safe use in household cleaning products. Environ Health Insights. 2015;9:27-32.
- Green K, Johnson RE, Chapman JM, et al. Preservative effects on the healing rate of rabbit corneal epithelium. Lens Eye Toxic Res. 1989;6:37-41.
- Sodium lauryl sulphate. Healthy Choices website. http://www.healthychoices.co.uk/sls.html. Accessed December 8, 2017.
- Tekbas¸ ÖF, Uysal Y, Og˘ur R, et al. Non-irritant baby shampoos may cause cataract development. TSK Koruyucu Hekimlik Bülteni. 2008;1:1-6.
- Cater KC, Harbell JW. Prediction of eye irritation potential of surfactant-based rinse-off personal care formulations by the bovine corneal opacity and permeability (BCOP) assay. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2006;25:217-233.
- Birt DF, Lawson TA, Julius AD, et al. Inhibition by dietary selenium of colon cancer induced in the rat by bis(2-oxopropyl) nitrosamine. Cancer Res. 1982;42:4455-4459.
- Rastogi SC. Headspace analysis of 1,4-dioxane in products containing polyethoxylated surfactants by GC-MS. Chromatographia. 1990;29:441-445.
- 1,4-Dioxane. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 1999;71, pt 2:589-602.
- Trueb RM. Dermocosmetic aspects of hair and scalp. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2005;10:289-292.
- D’Souza P, Rathi SK. Shampoo and conditioners: what a dermatologist should know? Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:248-254.
- Sasseville D, Alfalah M, Lacroix JP. “Parabenoia” debunked, or “who’s afraid of parabens?” Dermatitis. 2015;26:254-259.
- Krowka JF, Loretz L, Geis PA, et al. Preserving the facts on parabens: an overview of these important tools of the trade. Cosmetics & Toiletries. http://www.cosmeticsandtoiletries.com/research/chemistry/Preserving-the-Facts-on-Parabens-An-Overview-of-These-Important-Tools-of-the Trade-425784294.html. Published June 1, 2017. Accessed December 20, 2017.
- Routledge EJ, Parker J, Odum J, et al. Some alkyl hydroxy benzoate preservatives (parabens) are estrogenic. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1998;153:12Y19.
- Hossaini A, Larsen JJ, Larsen JC. Lack of oestrogenic effects of food preservatives (parabens) in uterotrophic assays. Food Chem Toxicol. 2000;38:319-323.
- Cosmetic Ingredient Review. Final report on the safety assessment of methylparaben, ethylparaben, propylparaben and butylparaben. J Am Coll Toxicol. 1984;3:147-209.
- Cosmetic Ingredient Review. Final report on the safety assessment of isobutylparaben and isopropylparaben. J Am Coll Toxicol. 1995;14:364-372.
- Scientific Committee on Consumer Products. Extended Opinion on the Safety Evaluation of Parabens. European Commission website. https://ec.europa.eu/health/ph_risk/committees/04_sccp/docs/sccp_o_019.pdf. Published January 28, 2005. Accessed December 20, 2017.
- Scientific Committee on Consumer Products. Opinion on Parabens. European Commission website. http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/sccs_o_041.pdf. Revised March 22, 2011. Accessed December 20, 2017.
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) No 258/2014 of 9 April 2014 amending Annexes II and V to Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council on cosmetic products. EUR-Lex website. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=uriserv:OJ.L_.2014.107.01.0005.01.ENG. Accessed December 20, 2017.
- American Cancer Society. Antiperspirants and breast cancer risk. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/cancer-causes/antiperspirants-and-breast-cancer-risk.html#references. Revised October 14, 2014. Accessed January 2, 2018.
- MacMillan A. Cutting back on shampoo? 15 things you should know. Health. February 25, 2014. http://www.health.com/health/gallery/0,,20788089,00.html#should-you-go-no-poo--1. Accessed December 10, 2017.
- The ‘no poo’ method. https://www.nopoomethod.com/. Accessed December 10, 2017.
- Fong, D, Gaulin C, Le M, et al. Effectiveness of alternative antimicrobial agents for disinfection of hard surfaces. National Collaborating Centre for Environmental Health website. http://www.ncceh.ca/sites/default/files/Alternative_Antimicrobial_Agents_Aug_2014.pdf. Published August 2014. Accessed December 10, 2017.
- Is baking soda too harsh for natural hair? Black Girl With Long Hair website. http://blackgirllonghair.com/2012/02/is-baking-soda-too-harsh-for-hair/2/. Published February 5, 2012. Accessed December 12, 2017.
- O’Lenick T. Anionic/cationic complexes in hair care. J Cosmet Sci. 2011;62:209-228.
- Gavazzoni Dias MF, de Almeida AM, Cecato PM, et al. The shampoo pH can affect the hair: myth or reality? Int J Trichology. 2014;6:95-99.
- Goodman H. The acid mantle of the skin surface. Ind Med Surg. 1958;27:105-108.
- Korting HC, Kober M, Mueller M, et al. Influence of repeated washings with soap and synthetic detergents on pH and resident flora of the skin of forehead and forearm. results of a cross-over trial in health probationers. Acta Derm Venereol. 1987;67:41-47.
- Tarun J, Susan J, Suria J, et al. Evaluation of pH of bathing soaps and shampoos for skin and hair care. Indian J Dermatol. 2014;59:442-444.
- Corbett JF. The chemistry of hair-care products. J Soc Dyers Colour. 1976;92:285-303.
- McMichael AJ, Hordinsky M. Hair Diseases: Medical, Surgical, and Cosmetic Treatments. New York, NY: Taylor & Francis; 2008:59-72.
- Allardice A, Gummo G. Hair conditioning: quaternary ammonium compounds on various hair types. Cosmet Toiletries. 1993;108:107-109.
- Larson D, Jacob SE. Tea tree oil. Dermatitis. 2012;23:48-49.
Shampoo is a staple in hair grooming that is ever-evolving along with cultural trends. The global shampoo market is expected to reach an estimated value of $25.73 billion by 2019. A major driver of this upward trend in market growth is the increasing demand for natural and organic hair shampoos.1 Society today has a growing fixation on healthy living practices, and as of late, the ingredients in shampoos and other cosmetic products have become one of the latest targets in the health-consciousness craze. In the age of the Internet where information—and misinformation—is widely accessible and dispersed, the general public often strives to self-educate on specialized matters that are out of their expertise. As a result, individuals have developed an aversion to using certain shampoos out of fear that the ingredients, often referred to as “chemicals” by patients due to their complex names, are unnatural and therefore unhealthy.1,2 Product developers are working to meet the demand by reformulating shampoos with labels that indicate sulfate free or paraben free, despite the lack of proof that these formulations are an improvement over traditional approaches to hair health. Additionally, alternative methods of cleansing the hair and scalp, also known as the no-shampoo or “no-poo” method, have begun to gain popularity.2,3
It is essential that dermatologists acknowledge the concerns that their patients have about common shampoo ingredients to dispel the myths that may misinform patient decision-making. This article reviews the controversy surrounding the use of sulfates and parabens in shampoos as well as commonly used shampoo alternatives. Due to the increased prevalence of dry hair shafts in the skin of color population, especially black women, this group is particularly interested in products that will minimize breakage and dryness of the hair. To that end, this population has great interest in the removal of chemical ingredients that may cause damage to the hair shafts, despite the lack of data to support sulfates and paraben damage to hair shafts or scalp skin. Blogs and uninformed hairstylists may propagate these beliefs in a group of consumers who are desperate for new approaches to hair fragility and breakage.
Surfactants and Sulfates
The cleansing ability of a shampoo depends on the surface activity of its detergents. Surface-active ingredients, or surfactants, reduce the surface tension between water and dirt, thus facilitating the removal of environmental dirt from the hair and scalp,4 which is achieved by a molecular structure containing both a hydrophilic and a lipophilic group. Sebum and dirt are bound by the lipophilic ends of the surfactant, becoming the center of a micelle structure with the hydrophilic molecule ends pointing outward. Dirt particles become water soluble and are removed from the scalp and hair shaft upon rinsing with water.4
Surfactants are classified according to the electric charge of the hydrophilic polar group as either anionic, cationic, amphoteric (zwitterionic), or nonionic.5 Each possesses different hair conditioning and cleansing qualities, and multiple surfactants are used in shampoos in differing ratios to accommodate different hair types. In most shampoos, the base consists of anionic and amphoteric surfactants. Depending on individual product requirements, nonionic and cationic surfactants are used to either modify the effects of the surfactants or as conditioning agents.4,5
One subcategory of surfactants that receives much attention is the group of anionic surfactants known as sulfates. Sulfates, particularly sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), recently have developed a negative reputation as cosmetic ingredients, as reports from various unscientific sources have labeled them as hazardous to one’s health; SLS has been described as a skin and scalp irritant, has been linked to cataract formation, and has even been wrongly labeled as carcinogenic.6 The origins of some of these claims are not clear, though they likely arose from the misinterpretation of complex scientific studies that are easily accessible to laypeople. The link between SLS and ocular irritation or cataract formation is a good illustration of this unsubstantiated fear. A study by Green et al7 showed that corneal exposure to extremely high concentrations of SLS following physical or chemical damage to the eye can result in a slowed healing process. The results of this study have since been wrongly quoted to state that SLS-containing products lead to blindness or severe corneal damage.8 A different study tested for possible ocular irritation in vivo by submerging the lens of an eye into a 20% SLS solution, which accurately approximates the concentration of SLS in rinse-off consumer products.9 However, to achieve ocular irritation, the eyes of laboratory animals were exposed to SLS constantly for 14 days, which would not occur in practical use.9 Similarly, a third study achieved cataract formation in a laboratory only by immersing the lens of an eye into a highly concentrated solution of SLS.10 Such studies are not appropriate representations of how SLS-containing products are used by consumers and have unfortunately been vulnerable to misinterpretation by the general public.
There is no known study that has shown SLS to be carcinogenic. One possible origin of this idea may be from the wrongful interpretation of studies that used SLS as a vehicle substance to test agents that were deemed to be carcinogenic.11 Another possible source of the idea that SLS is carcinogenic comes from its association with 1,4-dioxane, a by-product of the synthesis of certain sulfates such as sodium laureth sulfate due to a process known as ethoxylation.6,12 Although SLS does not undergo this process in its formation and is not linked to 1,4-dioxane, there is potential for cross-contamination of SLS with 1,4-dioxane, which cannot be overlooked. 1,4-Dioxane is classified as “possibly carcinogenic to humans (Group 2B)” by the International Agency for Research on Cancer,13 but screening of SLS for this substance prior to its use in commercial products is standard.
Sulfates are inexpensive detergents that are responsible for lather formation in shampoos as well as in many household cleaning agents.5 Sulfates, similar to all anionic surfactants, are characterized by a negatively charged hydrophilic polar group. The best-known and most commonly used anionic surfactants are sulfated fatty alcohols, alkyl sulfates, and their polyethoxylated analogues alkyl ether sulfates.5,6 Sodium lauryl sulfate (also known as sodium laurilsulfate or sodium dodecyl sulfate) is the most common of them all, found in shampoo and conditioner formulations. Ammonium lauryl sulfate and sodium laureth sulfate are other sulfates commonly used in shampoos and household cleansing products. Sodium lauryl sulfate is a nonvolatile, water-soluble compound. Its partition coefficient (P0), a measure of a substance’s hydrophilic or lipophilic nature, is low at 1.6, making it a rather hydrophilic substance.6 Hydrophilic substances tend to have low bioaccumulation profiles in the body. Additionally, SLS is readily biodegradable. It can be derived from both synthetic and naturally occurring sources; for example, palm kernel oil, petrolatum, and coconut oil are all sources of lauric acid, the starting ingredient used to synthesize SLS. Sodium lauryl sulfate is created by reacting lauryl alcohol with sulfur trioxide gas, followed by neutralization with sodium carbonate (also a naturally occurring compound).6 Sodium lauryl sulfate and other sulfate-containing shampoos widely replaced the usage of traditional soaps formulated from animal or vegetable fats, as these latter formations created a film of insoluble calcium salts on the hair strands upon contact with water, resulting in tangled, dull-appearing hair.5 Additionally, sulfates were preferred to the alkaline pH of traditional soap, which can be harsh on hair strands and cause irritation of the skin and mucous membranes.14 Because they are highly water soluble, sulfates enable the formulation of clear shampoos. They exhibit remarkable cleaning properties and lather formation.5,14
Because sulfates are potent surfactants, they can remove dirt and debris as well as naturally produced healthy oils from the hair and scalp. As a result, sulfates can leave the hair feeling dry and stripped of moisture.4,5 Sulfates are used as the primary detergents in the formulation of deep-cleaning shampoos, which are designed for people who accumulate a heavy buildup of dirt, sebum, and debris from frequent use of styling products. Due to their potent detergency, these shampoos typically are not used on a daily basis but rather at longer intervals.15 A downside to sulfates is that they can have cosmetically unpleasant properties, which can be compensated for by including appropriate softening additives in shampoo formulations.4 A number of anionic surfactants such as olefin sulfonate, alkyl sulfosuccinate, acyl peptides, and alkyl ether carboxylates are well tolerated by the skin and are used together with other anionic and amphoteric surfactants to optimize shampoo properties. Alternatively, sulfate-free shampoos are cleansers compounded by the removal of the anionic group and switched for surfactants with less detergency.4,5
Preservatives and Parabens
Parabens refer to a group of esters of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid commonly used as preservatives in foods, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics whose widespread use dates back to 1923.16 Concerns over the presence of parabens in shampoos and other cosmetics have been raised by patients for their reputed estrogenic and antiandrogenic effects and suspected involvement in carcinogenesis via endocrine modulation.16,17 In in vitro studies done on yeast assays, parabens have shown weak estrogenic activity that increases in proportion to both the length and increased branching of the alkyl side chains in the paraben’s molecular structure.18 They are 10,000-fold less potent than 17β-estradiol. In in vivo animal studies, parabens show weak estrogenic activity and are 100,000-fold less potent than 17β-estradiol.18 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, a common metabolite, showed no estrogenic activity when tested both in vitro and in vivo.19 Some concerning research has implicated a link between parabens used in underarm cosmetics, such as deodorants and antiperspirants, and breast cancer16; however, the studies have been conflicting, and there is simply not enough data to assert that parabens cause breast cancer.
The Cosmetic Ingredient Review expert panel first reviewed parabens in 1984 and concluded that “methylparaben, ethylparaben, propylparaben, and butylparaben are safe as cosmetic ingredients in the present practices of use.”20 They extended this statement to include isopropylparaben and isobutylparaben in a later review.21 In 2005, the Scientific Committee on Consumer Products (now known as the Scientific Committee for Consumer Safety) in Europe stated that methylparaben and ethylparaben can be used at levels up to 0.4% in products.22 This decision was reached due to reports of decreased sperm counts and testosterone levels in male juvenile rats exposed to these parabens; however, these reults were not successfully replicated in larger studies.16,22 In 2010, the Scientific Committee for Consumer Safety revisited its stance on parabens, and they then revised their recommendations to say that concentrations of propylparaben and butylparaben should not exceed concentrations of 0.19%, based on “the conservative choice for the calculation of the [Margin-of-Safety] of butyl- and propylparaben.”23 However, in 2011 the use of propylparaben and butylparaben was banned in Denmark for cosmetic products used in children 3 years or younger,16 and the European Commission subsequently amended their directive in 2014, banning isopropylparaben, isobutylparaben, phenylparaben, benzylparaben, and pentylparaben due to lack of data available to evaluate the human risk of these products.24
Contrary to the trends in Europe, there currently are no regulations against the use of parabens in shampoos or other cosmetics in the United States. The American Cancer Society found that there is no evidence to suggest that the current levels of parabens in cosmetic products (eg, antiperspirants) increase one’s risk of breast cancer.25 Parabens are readily absorbed into the body both transdermally and through ingestion but also are believed to be rapidly transformed into harmless and nonspecific metabolites; they are readily metabolized by the liver and excreted in urine, and there is no measured accumulation in tissues.17
Parabens continue to be the most widely used preservatives in personal care products, usually in conjunction with other preservatives. Parabens are good biocides; short-chain esters (eg, methylparabens, ethylparabens) are effective against gram-positive bacteria and are weakly effective against gram-negative bacteria. Long-chain paraben esters (eg, propylparabens, butylparabens) are effective against mold and yeast. The addition of other preservatives creates a broad spectrum of antimicrobial defense in consumer products. Other preservatives include formaldehyde releasers or phenoxyethanol, as well as chelating agents such as EDTA, which improve the stability of these cosmetic products when exposed to air.16 Parabens are naturally occurring substances found in foods such as blueberries, barley, strawberries, yeast, olives, and grapes. As a colorless, odorless, and inexpensive substance, their use has been heavily favored in cosmetic and food products.16
Shampoo Alternatives and the No-Poo Method
Although research has not demonstrated any long-term danger to using shampoo, certain chemicals found in shampoos have the potential to irritate the scalp. Commonly cited allergens in shampoos include cocamidopropyl betaine, propylene glycol, vitamin E (tocopherol), parabens, and benzophenones.5 Additionally, the rising use of formaldehyde-releasing preservatives and isothiazolinones due to mounting pressures to move away from parabens has led to an increase in cases of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD).16 However, the irritability (rather than allergenicity) of these substances often is established during patch testing, a method of detecting delayed-type allergic reactions, which is important to note because patch testing requires a substance to be exposed to the skin for 24 to 48 hours, whereas exposure to shampoo ingredients may last a matter of minutes at most and occur in lesser concentrations because the ingredients are diluted by water in the rinsing process. Given these differences, it is unlikely that a patient would develop a true allergic response from regular shampoo use. Nevertheless, in patients who are already sensitized, exposure could conceivably trigger ACD, and patients must be cognizant of the composition of their shampoos.16
The no-poo method refers to the avoidance of commercial shampoo products when cleansing the hair and scalp and encompasses different methods of cleansing the hair, such as the use of household items (eg, baking soda, apple cider vinegar [ACV]), the use of conditioners to wash the hair (also known as conditioner-only washing or co-washing), treating the scalp with tea tree oil, or simply rinsing the hair with water. Proponents of the no-poo method believe that abstaining from shampoo use leads to healthier hair, retained natural oils, and less exposure to supposedly dangerous chemicals such as parabens or sulfates.2,3,26-28 However, there are no known studies in the literature that assess or support the hypotheses of the no-poo method.
Baking Soda and ACV
Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) is a substance commonly found in the average household. It has been used in toothpaste formulas and cosmetic products and is known for its acid-neutralizing properties. Baking soda has been shown to have some antifungal and viricidal properties through an unknown mechanism of action.28 It has gained popularity for its use as a means of reducing the appearance of excessive greasiness of the hair shafts. Users also have reported that when washing their hair with baking soda, they are able to achieve a clean scalp and hair that feels soft to the touch.2,3,26,27,29 Despite these reports, users must beware of using baking soda without adequately diluting it with water. Baking soda is a known alkaline irritant.26,30 With a pH of 9, baking soda causes the cuticle layer of the hair fiber to open, increasing the capacity for water absorption. Water penetrates the scales that open, breaking the hydrogen bonds of the keratin molecule.31 Keratin is a spiral helical molecule that keeps its shape due to hydrogen, disulfide, and ionic bonds, as well as Van der Waals force.30 Hydrolysis of these bonds due to exposure to baking soda lowers the elasticity of the hair and increases the negative electrical net charge of the hair fiber surface, which leads to increased friction between fibers, cuticle damage, hair fragility, and fiber breakage.32,33
Apple cider vinegar is an apple-derived acetic acid solution with a pH ranging from 3.1 to 5.28 The pH range of ACV is considered to be ideal for hair by no-poo proponents, as it is similar to the natural pH of the scalp. Its acidic properties are responsible for its antimicrobial abilities, particularly its effectiveness against gram-negative bacteria.30 The acetic acid of ACV can partially interrupt oil interfaces, which contributes to its mild ability to remove product residue and scalp buildup from the hair shaft; the acetic acid also tightens the cuticles on hair fibers.33 Apple cider vinegar is used as a means of cleansing the hair and scalp by no-poo proponents2,3,26; other uses for ACV include using it as a rinse following washing and/or conditioning of the hair or as a means of preserving color in color-treated hair. There also is evidence that ACV may have antifungal properties.28 However, consumers must be aware that if it is not diluted in water, ACV may be too caustic for direct application to the hair and may lead to damage; it can be irritating to eyes, mucus membranes, and acutely inflamed skin. Also, vinegar rinses used on processed or chemically damaged hair may lead to increased hair fragility.2,3
Hair fibers have a pH of 3.67, while the scalp has a pH between 4.5 and 6.2. This slightly acidic film acts as a barrier to viruses, bacteria, and other potential contaminants.33 Studies have shown that the pH of skin increases in proportion to the pH of the cleanser used.34 Therefore, due to the naturally acidic pH of the scalp, acid-balanced shampoos generally are recommended. Shampoos should not have a pH higher than 5.5, as hair shafts can swell due to alkalinization, which can be prevented by pH balancing the shampoo through the addition of an acidic substance (eg, glycolic acid, citric acid) to lower the pH down to approximately 5.5. Apple cider vinegar often is used for this purpose. However, one study revealed that 82% of shampoos already have an acidic pH.34
Conditioner-Only Washing (Co-washing)
Conditioner-only washing, or co-washing, is a widely practiced method of hair grooming. It is popular among individuals who find that commercial shampoos strip too much of the natural hair oils away, leaving the hair rough or unmanageable. Co-washing is not harmful to the hair; however, the molecular structure and function of a conditioner and that of a shampoo are very different.5,35,36 Conditioners are not formulated to remove dirt and buildup in the hair but rather to add substances to the hair, and thus cannot provide extensive cleansing of the hair and scalp; therefore, it is inappropriate to use co-washing as a replacement for shampooing. Quaternary conditioning agents are an exception because they contain amphoteric detergents comprised of both anionic and cationic groups, which allow them both the ability to remove dirt and sebum with its anionic group, typically found in shampoos, as well as the ability to coat and condition the hair due to the high affinity of the cationic group for the negatively charged hair fibers.36,37 Amphoteric detergents are commonly found in 2-in-1 conditioning cleansers, among other ingredients, such as hydrolyzed animal proteins that temporarily plug surface defects on the hair fiber, and dimethicone, a synthetic oil that creates a thin film over the hair shaft, increasing shine and manageability. Of note, these conditioning shampoos are ideal for individuals with minimal product buildup on the hair and scalp and are not adequate scalp cleansers for individuals who either wash their hair infrequently or who regularly use hairstyling products.36,37
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is an essential oil extracted from the Melaleuca alternifolia plant of the Myrtaceae family. It is native to the coast of northeastern Australia. A holy grail of natural cosmetics, tea tree oil is widely known for its antiviral, antifungal, and antiseptic properties.38 Although not used as a stand-alone cleanser, it is often added to a number of cosmetic products, including shampoos and co-washes. Although deemed safe for topical use, it has been shown to be quite toxic when ingested. Symptoms of ingestion include nausea, vomiting, hallucinations, and coma. The common concern with tea tree oil is its ability to cause ACD. In particular, it is believed that the oxidation products of tea tree oil are allergenic rather than the tea tree oil itself. The evaluation of tea tree oil as a potential contact allergen has been quite difficult; it consists of more than 100 distinct compounds and is often mislabeled, or does not meet the guidelines of the International Organization for Standardization. Nonetheless, the prevalence of ACD due to tea tree oil is low (approximately 1.4%). Despite its low prevalence, tea tree oil should remain in the differential as an ACD-inducing agent. Patch testing with the patient’s supply of tea tree oil is advised when possible.38
Conclusion
It is customary that the ingredients used in shampoos undergo periodic testing and monitoring to assure the safety of their use. Although it is encouraging that patients are proactive in their efforts to stay abreast of the literature, it is still important that cosmetic scientists, dermatologists, and other experts remain at the forefront of educating the public about these substances. Not doing so can result in the propagation of misinformation and unnecessary fears, which can lead to the adaptation of unhygienic or even unsafe hair care practices. As dermatologists, we must ensure that patients are educated about the benefits and hazards of off-label use of household ingredients to the extent that evidence-based medicine permits. Patients must be informed that not all synthetic substances are harmful, and likewise not all naturally occurring substances are safe.
Shampoo is a staple in hair grooming that is ever-evolving along with cultural trends. The global shampoo market is expected to reach an estimated value of $25.73 billion by 2019. A major driver of this upward trend in market growth is the increasing demand for natural and organic hair shampoos.1 Society today has a growing fixation on healthy living practices, and as of late, the ingredients in shampoos and other cosmetic products have become one of the latest targets in the health-consciousness craze. In the age of the Internet where information—and misinformation—is widely accessible and dispersed, the general public often strives to self-educate on specialized matters that are out of their expertise. As a result, individuals have developed an aversion to using certain shampoos out of fear that the ingredients, often referred to as “chemicals” by patients due to their complex names, are unnatural and therefore unhealthy.1,2 Product developers are working to meet the demand by reformulating shampoos with labels that indicate sulfate free or paraben free, despite the lack of proof that these formulations are an improvement over traditional approaches to hair health. Additionally, alternative methods of cleansing the hair and scalp, also known as the no-shampoo or “no-poo” method, have begun to gain popularity.2,3
It is essential that dermatologists acknowledge the concerns that their patients have about common shampoo ingredients to dispel the myths that may misinform patient decision-making. This article reviews the controversy surrounding the use of sulfates and parabens in shampoos as well as commonly used shampoo alternatives. Due to the increased prevalence of dry hair shafts in the skin of color population, especially black women, this group is particularly interested in products that will minimize breakage and dryness of the hair. To that end, this population has great interest in the removal of chemical ingredients that may cause damage to the hair shafts, despite the lack of data to support sulfates and paraben damage to hair shafts or scalp skin. Blogs and uninformed hairstylists may propagate these beliefs in a group of consumers who are desperate for new approaches to hair fragility and breakage.
Surfactants and Sulfates
The cleansing ability of a shampoo depends on the surface activity of its detergents. Surface-active ingredients, or surfactants, reduce the surface tension between water and dirt, thus facilitating the removal of environmental dirt from the hair and scalp,4 which is achieved by a molecular structure containing both a hydrophilic and a lipophilic group. Sebum and dirt are bound by the lipophilic ends of the surfactant, becoming the center of a micelle structure with the hydrophilic molecule ends pointing outward. Dirt particles become water soluble and are removed from the scalp and hair shaft upon rinsing with water.4
Surfactants are classified according to the electric charge of the hydrophilic polar group as either anionic, cationic, amphoteric (zwitterionic), or nonionic.5 Each possesses different hair conditioning and cleansing qualities, and multiple surfactants are used in shampoos in differing ratios to accommodate different hair types. In most shampoos, the base consists of anionic and amphoteric surfactants. Depending on individual product requirements, nonionic and cationic surfactants are used to either modify the effects of the surfactants or as conditioning agents.4,5
One subcategory of surfactants that receives much attention is the group of anionic surfactants known as sulfates. Sulfates, particularly sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), recently have developed a negative reputation as cosmetic ingredients, as reports from various unscientific sources have labeled them as hazardous to one’s health; SLS has been described as a skin and scalp irritant, has been linked to cataract formation, and has even been wrongly labeled as carcinogenic.6 The origins of some of these claims are not clear, though they likely arose from the misinterpretation of complex scientific studies that are easily accessible to laypeople. The link between SLS and ocular irritation or cataract formation is a good illustration of this unsubstantiated fear. A study by Green et al7 showed that corneal exposure to extremely high concentrations of SLS following physical or chemical damage to the eye can result in a slowed healing process. The results of this study have since been wrongly quoted to state that SLS-containing products lead to blindness or severe corneal damage.8 A different study tested for possible ocular irritation in vivo by submerging the lens of an eye into a 20% SLS solution, which accurately approximates the concentration of SLS in rinse-off consumer products.9 However, to achieve ocular irritation, the eyes of laboratory animals were exposed to SLS constantly for 14 days, which would not occur in practical use.9 Similarly, a third study achieved cataract formation in a laboratory only by immersing the lens of an eye into a highly concentrated solution of SLS.10 Such studies are not appropriate representations of how SLS-containing products are used by consumers and have unfortunately been vulnerable to misinterpretation by the general public.
There is no known study that has shown SLS to be carcinogenic. One possible origin of this idea may be from the wrongful interpretation of studies that used SLS as a vehicle substance to test agents that were deemed to be carcinogenic.11 Another possible source of the idea that SLS is carcinogenic comes from its association with 1,4-dioxane, a by-product of the synthesis of certain sulfates such as sodium laureth sulfate due to a process known as ethoxylation.6,12 Although SLS does not undergo this process in its formation and is not linked to 1,4-dioxane, there is potential for cross-contamination of SLS with 1,4-dioxane, which cannot be overlooked. 1,4-Dioxane is classified as “possibly carcinogenic to humans (Group 2B)” by the International Agency for Research on Cancer,13 but screening of SLS for this substance prior to its use in commercial products is standard.
Sulfates are inexpensive detergents that are responsible for lather formation in shampoos as well as in many household cleaning agents.5 Sulfates, similar to all anionic surfactants, are characterized by a negatively charged hydrophilic polar group. The best-known and most commonly used anionic surfactants are sulfated fatty alcohols, alkyl sulfates, and their polyethoxylated analogues alkyl ether sulfates.5,6 Sodium lauryl sulfate (also known as sodium laurilsulfate or sodium dodecyl sulfate) is the most common of them all, found in shampoo and conditioner formulations. Ammonium lauryl sulfate and sodium laureth sulfate are other sulfates commonly used in shampoos and household cleansing products. Sodium lauryl sulfate is a nonvolatile, water-soluble compound. Its partition coefficient (P0), a measure of a substance’s hydrophilic or lipophilic nature, is low at 1.6, making it a rather hydrophilic substance.6 Hydrophilic substances tend to have low bioaccumulation profiles in the body. Additionally, SLS is readily biodegradable. It can be derived from both synthetic and naturally occurring sources; for example, palm kernel oil, petrolatum, and coconut oil are all sources of lauric acid, the starting ingredient used to synthesize SLS. Sodium lauryl sulfate is created by reacting lauryl alcohol with sulfur trioxide gas, followed by neutralization with sodium carbonate (also a naturally occurring compound).6 Sodium lauryl sulfate and other sulfate-containing shampoos widely replaced the usage of traditional soaps formulated from animal or vegetable fats, as these latter formations created a film of insoluble calcium salts on the hair strands upon contact with water, resulting in tangled, dull-appearing hair.5 Additionally, sulfates were preferred to the alkaline pH of traditional soap, which can be harsh on hair strands and cause irritation of the skin and mucous membranes.14 Because they are highly water soluble, sulfates enable the formulation of clear shampoos. They exhibit remarkable cleaning properties and lather formation.5,14
Because sulfates are potent surfactants, they can remove dirt and debris as well as naturally produced healthy oils from the hair and scalp. As a result, sulfates can leave the hair feeling dry and stripped of moisture.4,5 Sulfates are used as the primary detergents in the formulation of deep-cleaning shampoos, which are designed for people who accumulate a heavy buildup of dirt, sebum, and debris from frequent use of styling products. Due to their potent detergency, these shampoos typically are not used on a daily basis but rather at longer intervals.15 A downside to sulfates is that they can have cosmetically unpleasant properties, which can be compensated for by including appropriate softening additives in shampoo formulations.4 A number of anionic surfactants such as olefin sulfonate, alkyl sulfosuccinate, acyl peptides, and alkyl ether carboxylates are well tolerated by the skin and are used together with other anionic and amphoteric surfactants to optimize shampoo properties. Alternatively, sulfate-free shampoos are cleansers compounded by the removal of the anionic group and switched for surfactants with less detergency.4,5
Preservatives and Parabens
Parabens refer to a group of esters of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid commonly used as preservatives in foods, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics whose widespread use dates back to 1923.16 Concerns over the presence of parabens in shampoos and other cosmetics have been raised by patients for their reputed estrogenic and antiandrogenic effects and suspected involvement in carcinogenesis via endocrine modulation.16,17 In in vitro studies done on yeast assays, parabens have shown weak estrogenic activity that increases in proportion to both the length and increased branching of the alkyl side chains in the paraben’s molecular structure.18 They are 10,000-fold less potent than 17β-estradiol. In in vivo animal studies, parabens show weak estrogenic activity and are 100,000-fold less potent than 17β-estradiol.18 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, a common metabolite, showed no estrogenic activity when tested both in vitro and in vivo.19 Some concerning research has implicated a link between parabens used in underarm cosmetics, such as deodorants and antiperspirants, and breast cancer16; however, the studies have been conflicting, and there is simply not enough data to assert that parabens cause breast cancer.
The Cosmetic Ingredient Review expert panel first reviewed parabens in 1984 and concluded that “methylparaben, ethylparaben, propylparaben, and butylparaben are safe as cosmetic ingredients in the present practices of use.”20 They extended this statement to include isopropylparaben and isobutylparaben in a later review.21 In 2005, the Scientific Committee on Consumer Products (now known as the Scientific Committee for Consumer Safety) in Europe stated that methylparaben and ethylparaben can be used at levels up to 0.4% in products.22 This decision was reached due to reports of decreased sperm counts and testosterone levels in male juvenile rats exposed to these parabens; however, these reults were not successfully replicated in larger studies.16,22 In 2010, the Scientific Committee for Consumer Safety revisited its stance on parabens, and they then revised their recommendations to say that concentrations of propylparaben and butylparaben should not exceed concentrations of 0.19%, based on “the conservative choice for the calculation of the [Margin-of-Safety] of butyl- and propylparaben.”23 However, in 2011 the use of propylparaben and butylparaben was banned in Denmark for cosmetic products used in children 3 years or younger,16 and the European Commission subsequently amended their directive in 2014, banning isopropylparaben, isobutylparaben, phenylparaben, benzylparaben, and pentylparaben due to lack of data available to evaluate the human risk of these products.24
Contrary to the trends in Europe, there currently are no regulations against the use of parabens in shampoos or other cosmetics in the United States. The American Cancer Society found that there is no evidence to suggest that the current levels of parabens in cosmetic products (eg, antiperspirants) increase one’s risk of breast cancer.25 Parabens are readily absorbed into the body both transdermally and through ingestion but also are believed to be rapidly transformed into harmless and nonspecific metabolites; they are readily metabolized by the liver and excreted in urine, and there is no measured accumulation in tissues.17
Parabens continue to be the most widely used preservatives in personal care products, usually in conjunction with other preservatives. Parabens are good biocides; short-chain esters (eg, methylparabens, ethylparabens) are effective against gram-positive bacteria and are weakly effective against gram-negative bacteria. Long-chain paraben esters (eg, propylparabens, butylparabens) are effective against mold and yeast. The addition of other preservatives creates a broad spectrum of antimicrobial defense in consumer products. Other preservatives include formaldehyde releasers or phenoxyethanol, as well as chelating agents such as EDTA, which improve the stability of these cosmetic products when exposed to air.16 Parabens are naturally occurring substances found in foods such as blueberries, barley, strawberries, yeast, olives, and grapes. As a colorless, odorless, and inexpensive substance, their use has been heavily favored in cosmetic and food products.16
Shampoo Alternatives and the No-Poo Method
Although research has not demonstrated any long-term danger to using shampoo, certain chemicals found in shampoos have the potential to irritate the scalp. Commonly cited allergens in shampoos include cocamidopropyl betaine, propylene glycol, vitamin E (tocopherol), parabens, and benzophenones.5 Additionally, the rising use of formaldehyde-releasing preservatives and isothiazolinones due to mounting pressures to move away from parabens has led to an increase in cases of allergic contact dermatitis (ACD).16 However, the irritability (rather than allergenicity) of these substances often is established during patch testing, a method of detecting delayed-type allergic reactions, which is important to note because patch testing requires a substance to be exposed to the skin for 24 to 48 hours, whereas exposure to shampoo ingredients may last a matter of minutes at most and occur in lesser concentrations because the ingredients are diluted by water in the rinsing process. Given these differences, it is unlikely that a patient would develop a true allergic response from regular shampoo use. Nevertheless, in patients who are already sensitized, exposure could conceivably trigger ACD, and patients must be cognizant of the composition of their shampoos.16
The no-poo method refers to the avoidance of commercial shampoo products when cleansing the hair and scalp and encompasses different methods of cleansing the hair, such as the use of household items (eg, baking soda, apple cider vinegar [ACV]), the use of conditioners to wash the hair (also known as conditioner-only washing or co-washing), treating the scalp with tea tree oil, or simply rinsing the hair with water. Proponents of the no-poo method believe that abstaining from shampoo use leads to healthier hair, retained natural oils, and less exposure to supposedly dangerous chemicals such as parabens or sulfates.2,3,26-28 However, there are no known studies in the literature that assess or support the hypotheses of the no-poo method.
Baking Soda and ACV
Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) is a substance commonly found in the average household. It has been used in toothpaste formulas and cosmetic products and is known for its acid-neutralizing properties. Baking soda has been shown to have some antifungal and viricidal properties through an unknown mechanism of action.28 It has gained popularity for its use as a means of reducing the appearance of excessive greasiness of the hair shafts. Users also have reported that when washing their hair with baking soda, they are able to achieve a clean scalp and hair that feels soft to the touch.2,3,26,27,29 Despite these reports, users must beware of using baking soda without adequately diluting it with water. Baking soda is a known alkaline irritant.26,30 With a pH of 9, baking soda causes the cuticle layer of the hair fiber to open, increasing the capacity for water absorption. Water penetrates the scales that open, breaking the hydrogen bonds of the keratin molecule.31 Keratin is a spiral helical molecule that keeps its shape due to hydrogen, disulfide, and ionic bonds, as well as Van der Waals force.30 Hydrolysis of these bonds due to exposure to baking soda lowers the elasticity of the hair and increases the negative electrical net charge of the hair fiber surface, which leads to increased friction between fibers, cuticle damage, hair fragility, and fiber breakage.32,33
Apple cider vinegar is an apple-derived acetic acid solution with a pH ranging from 3.1 to 5.28 The pH range of ACV is considered to be ideal for hair by no-poo proponents, as it is similar to the natural pH of the scalp. Its acidic properties are responsible for its antimicrobial abilities, particularly its effectiveness against gram-negative bacteria.30 The acetic acid of ACV can partially interrupt oil interfaces, which contributes to its mild ability to remove product residue and scalp buildup from the hair shaft; the acetic acid also tightens the cuticles on hair fibers.33 Apple cider vinegar is used as a means of cleansing the hair and scalp by no-poo proponents2,3,26; other uses for ACV include using it as a rinse following washing and/or conditioning of the hair or as a means of preserving color in color-treated hair. There also is evidence that ACV may have antifungal properties.28 However, consumers must be aware that if it is not diluted in water, ACV may be too caustic for direct application to the hair and may lead to damage; it can be irritating to eyes, mucus membranes, and acutely inflamed skin. Also, vinegar rinses used on processed or chemically damaged hair may lead to increased hair fragility.2,3
Hair fibers have a pH of 3.67, while the scalp has a pH between 4.5 and 6.2. This slightly acidic film acts as a barrier to viruses, bacteria, and other potential contaminants.33 Studies have shown that the pH of skin increases in proportion to the pH of the cleanser used.34 Therefore, due to the naturally acidic pH of the scalp, acid-balanced shampoos generally are recommended. Shampoos should not have a pH higher than 5.5, as hair shafts can swell due to alkalinization, which can be prevented by pH balancing the shampoo through the addition of an acidic substance (eg, glycolic acid, citric acid) to lower the pH down to approximately 5.5. Apple cider vinegar often is used for this purpose. However, one study revealed that 82% of shampoos already have an acidic pH.34
Conditioner-Only Washing (Co-washing)
Conditioner-only washing, or co-washing, is a widely practiced method of hair grooming. It is popular among individuals who find that commercial shampoos strip too much of the natural hair oils away, leaving the hair rough or unmanageable. Co-washing is not harmful to the hair; however, the molecular structure and function of a conditioner and that of a shampoo are very different.5,35,36 Conditioners are not formulated to remove dirt and buildup in the hair but rather to add substances to the hair, and thus cannot provide extensive cleansing of the hair and scalp; therefore, it is inappropriate to use co-washing as a replacement for shampooing. Quaternary conditioning agents are an exception because they contain amphoteric detergents comprised of both anionic and cationic groups, which allow them both the ability to remove dirt and sebum with its anionic group, typically found in shampoos, as well as the ability to coat and condition the hair due to the high affinity of the cationic group for the negatively charged hair fibers.36,37 Amphoteric detergents are commonly found in 2-in-1 conditioning cleansers, among other ingredients, such as hydrolyzed animal proteins that temporarily plug surface defects on the hair fiber, and dimethicone, a synthetic oil that creates a thin film over the hair shaft, increasing shine and manageability. Of note, these conditioning shampoos are ideal for individuals with minimal product buildup on the hair and scalp and are not adequate scalp cleansers for individuals who either wash their hair infrequently or who regularly use hairstyling products.36,37
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is an essential oil extracted from the Melaleuca alternifolia plant of the Myrtaceae family. It is native to the coast of northeastern Australia. A holy grail of natural cosmetics, tea tree oil is widely known for its antiviral, antifungal, and antiseptic properties.38 Although not used as a stand-alone cleanser, it is often added to a number of cosmetic products, including shampoos and co-washes. Although deemed safe for topical use, it has been shown to be quite toxic when ingested. Symptoms of ingestion include nausea, vomiting, hallucinations, and coma. The common concern with tea tree oil is its ability to cause ACD. In particular, it is believed that the oxidation products of tea tree oil are allergenic rather than the tea tree oil itself. The evaluation of tea tree oil as a potential contact allergen has been quite difficult; it consists of more than 100 distinct compounds and is often mislabeled, or does not meet the guidelines of the International Organization for Standardization. Nonetheless, the prevalence of ACD due to tea tree oil is low (approximately 1.4%). Despite its low prevalence, tea tree oil should remain in the differential as an ACD-inducing agent. Patch testing with the patient’s supply of tea tree oil is advised when possible.38
Conclusion
It is customary that the ingredients used in shampoos undergo periodic testing and monitoring to assure the safety of their use. Although it is encouraging that patients are proactive in their efforts to stay abreast of the literature, it is still important that cosmetic scientists, dermatologists, and other experts remain at the forefront of educating the public about these substances. Not doing so can result in the propagation of misinformation and unnecessary fears, which can lead to the adaptation of unhygienic or even unsafe hair care practices. As dermatologists, we must ensure that patients are educated about the benefits and hazards of off-label use of household ingredients to the extent that evidence-based medicine permits. Patients must be informed that not all synthetic substances are harmful, and likewise not all naturally occurring substances are safe.
- The global shampoo market 2014-2019 trends, forecast, and opportunity analysis [press release]. New York, NY: Reportlinker; May 21, 2015.
- Is the ‘no shampoo’ trend healthy or harmful? Mercola website. Published January 16, 2016. Accessed December 8, 2017.
- Feltman R. The science (or lack thereof) behind the ‘no-poo’ hair trend. Washington Post. March 10, 2016. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/speaking-of-science/wp/2016/03/10/the-science-or-lack-thereof-behind-the-no-poo-hair-trend/?utm_term=.9a61edf3fd5a. Accessed December 11, 2017.
- Bouillon C. Shampoos. Clin Dermatol. 1996;14:113-121.
- Trueb RM. Shampoos: ingredients, efficacy, and adverse effects. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2007;5:356-365.
- Bondi CA, Marks JL, Wroblewski LB, et al. Human and environmental toxicity of sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS): evidence for safe use in household cleaning products. Environ Health Insights. 2015;9:27-32.
- Green K, Johnson RE, Chapman JM, et al. Preservative effects on the healing rate of rabbit corneal epithelium. Lens Eye Toxic Res. 1989;6:37-41.
- Sodium lauryl sulphate. Healthy Choices website. http://www.healthychoices.co.uk/sls.html. Accessed December 8, 2017.
- Tekbas¸ ÖF, Uysal Y, Og˘ur R, et al. Non-irritant baby shampoos may cause cataract development. TSK Koruyucu Hekimlik Bülteni. 2008;1:1-6.
- Cater KC, Harbell JW. Prediction of eye irritation potential of surfactant-based rinse-off personal care formulations by the bovine corneal opacity and permeability (BCOP) assay. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2006;25:217-233.
- Birt DF, Lawson TA, Julius AD, et al. Inhibition by dietary selenium of colon cancer induced in the rat by bis(2-oxopropyl) nitrosamine. Cancer Res. 1982;42:4455-4459.
- Rastogi SC. Headspace analysis of 1,4-dioxane in products containing polyethoxylated surfactants by GC-MS. Chromatographia. 1990;29:441-445.
- 1,4-Dioxane. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 1999;71, pt 2:589-602.
- Trueb RM. Dermocosmetic aspects of hair and scalp. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2005;10:289-292.
- D’Souza P, Rathi SK. Shampoo and conditioners: what a dermatologist should know? Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:248-254.
- Sasseville D, Alfalah M, Lacroix JP. “Parabenoia” debunked, or “who’s afraid of parabens?” Dermatitis. 2015;26:254-259.
- Krowka JF, Loretz L, Geis PA, et al. Preserving the facts on parabens: an overview of these important tools of the trade. Cosmetics & Toiletries. http://www.cosmeticsandtoiletries.com/research/chemistry/Preserving-the-Facts-on-Parabens-An-Overview-of-These-Important-Tools-of-the Trade-425784294.html. Published June 1, 2017. Accessed December 20, 2017.
- Routledge EJ, Parker J, Odum J, et al. Some alkyl hydroxy benzoate preservatives (parabens) are estrogenic. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1998;153:12Y19.
- Hossaini A, Larsen JJ, Larsen JC. Lack of oestrogenic effects of food preservatives (parabens) in uterotrophic assays. Food Chem Toxicol. 2000;38:319-323.
- Cosmetic Ingredient Review. Final report on the safety assessment of methylparaben, ethylparaben, propylparaben and butylparaben. J Am Coll Toxicol. 1984;3:147-209.
- Cosmetic Ingredient Review. Final report on the safety assessment of isobutylparaben and isopropylparaben. J Am Coll Toxicol. 1995;14:364-372.
- Scientific Committee on Consumer Products. Extended Opinion on the Safety Evaluation of Parabens. European Commission website. https://ec.europa.eu/health/ph_risk/committees/04_sccp/docs/sccp_o_019.pdf. Published January 28, 2005. Accessed December 20, 2017.
- Scientific Committee on Consumer Products. Opinion on Parabens. European Commission website. http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/sccs_o_041.pdf. Revised March 22, 2011. Accessed December 20, 2017.
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) No 258/2014 of 9 April 2014 amending Annexes II and V to Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council on cosmetic products. EUR-Lex website. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=uriserv:OJ.L_.2014.107.01.0005.01.ENG. Accessed December 20, 2017.
- American Cancer Society. Antiperspirants and breast cancer risk. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/cancer-causes/antiperspirants-and-breast-cancer-risk.html#references. Revised October 14, 2014. Accessed January 2, 2018.
- MacMillan A. Cutting back on shampoo? 15 things you should know. Health. February 25, 2014. http://www.health.com/health/gallery/0,,20788089,00.html#should-you-go-no-poo--1. Accessed December 10, 2017.
- The ‘no poo’ method. https://www.nopoomethod.com/. Accessed December 10, 2017.
- Fong, D, Gaulin C, Le M, et al. Effectiveness of alternative antimicrobial agents for disinfection of hard surfaces. National Collaborating Centre for Environmental Health website. http://www.ncceh.ca/sites/default/files/Alternative_Antimicrobial_Agents_Aug_2014.pdf. Published August 2014. Accessed December 10, 2017.
- Is baking soda too harsh for natural hair? Black Girl With Long Hair website. http://blackgirllonghair.com/2012/02/is-baking-soda-too-harsh-for-hair/2/. Published February 5, 2012. Accessed December 12, 2017.
- O’Lenick T. Anionic/cationic complexes in hair care. J Cosmet Sci. 2011;62:209-228.
- Gavazzoni Dias MF, de Almeida AM, Cecato PM, et al. The shampoo pH can affect the hair: myth or reality? Int J Trichology. 2014;6:95-99.
- Goodman H. The acid mantle of the skin surface. Ind Med Surg. 1958;27:105-108.
- Korting HC, Kober M, Mueller M, et al. Influence of repeated washings with soap and synthetic detergents on pH and resident flora of the skin of forehead and forearm. results of a cross-over trial in health probationers. Acta Derm Venereol. 1987;67:41-47.
- Tarun J, Susan J, Suria J, et al. Evaluation of pH of bathing soaps and shampoos for skin and hair care. Indian J Dermatol. 2014;59:442-444.
- Corbett JF. The chemistry of hair-care products. J Soc Dyers Colour. 1976;92:285-303.
- McMichael AJ, Hordinsky M. Hair Diseases: Medical, Surgical, and Cosmetic Treatments. New York, NY: Taylor & Francis; 2008:59-72.
- Allardice A, Gummo G. Hair conditioning: quaternary ammonium compounds on various hair types. Cosmet Toiletries. 1993;108:107-109.
- Larson D, Jacob SE. Tea tree oil. Dermatitis. 2012;23:48-49.
- The global shampoo market 2014-2019 trends, forecast, and opportunity analysis [press release]. New York, NY: Reportlinker; May 21, 2015.
- Is the ‘no shampoo’ trend healthy or harmful? Mercola website. Published January 16, 2016. Accessed December 8, 2017.
- Feltman R. The science (or lack thereof) behind the ‘no-poo’ hair trend. Washington Post. March 10, 2016. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/speaking-of-science/wp/2016/03/10/the-science-or-lack-thereof-behind-the-no-poo-hair-trend/?utm_term=.9a61edf3fd5a. Accessed December 11, 2017.
- Bouillon C. Shampoos. Clin Dermatol. 1996;14:113-121.
- Trueb RM. Shampoos: ingredients, efficacy, and adverse effects. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2007;5:356-365.
- Bondi CA, Marks JL, Wroblewski LB, et al. Human and environmental toxicity of sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS): evidence for safe use in household cleaning products. Environ Health Insights. 2015;9:27-32.
- Green K, Johnson RE, Chapman JM, et al. Preservative effects on the healing rate of rabbit corneal epithelium. Lens Eye Toxic Res. 1989;6:37-41.
- Sodium lauryl sulphate. Healthy Choices website. http://www.healthychoices.co.uk/sls.html. Accessed December 8, 2017.
- Tekbas¸ ÖF, Uysal Y, Og˘ur R, et al. Non-irritant baby shampoos may cause cataract development. TSK Koruyucu Hekimlik Bülteni. 2008;1:1-6.
- Cater KC, Harbell JW. Prediction of eye irritation potential of surfactant-based rinse-off personal care formulations by the bovine corneal opacity and permeability (BCOP) assay. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2006;25:217-233.
- Birt DF, Lawson TA, Julius AD, et al. Inhibition by dietary selenium of colon cancer induced in the rat by bis(2-oxopropyl) nitrosamine. Cancer Res. 1982;42:4455-4459.
- Rastogi SC. Headspace analysis of 1,4-dioxane in products containing polyethoxylated surfactants by GC-MS. Chromatographia. 1990;29:441-445.
- 1,4-Dioxane. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 1999;71, pt 2:589-602.
- Trueb RM. Dermocosmetic aspects of hair and scalp. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2005;10:289-292.
- D’Souza P, Rathi SK. Shampoo and conditioners: what a dermatologist should know? Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:248-254.
- Sasseville D, Alfalah M, Lacroix JP. “Parabenoia” debunked, or “who’s afraid of parabens?” Dermatitis. 2015;26:254-259.
- Krowka JF, Loretz L, Geis PA, et al. Preserving the facts on parabens: an overview of these important tools of the trade. Cosmetics & Toiletries. http://www.cosmeticsandtoiletries.com/research/chemistry/Preserving-the-Facts-on-Parabens-An-Overview-of-These-Important-Tools-of-the Trade-425784294.html. Published June 1, 2017. Accessed December 20, 2017.
- Routledge EJ, Parker J, Odum J, et al. Some alkyl hydroxy benzoate preservatives (parabens) are estrogenic. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1998;153:12Y19.
- Hossaini A, Larsen JJ, Larsen JC. Lack of oestrogenic effects of food preservatives (parabens) in uterotrophic assays. Food Chem Toxicol. 2000;38:319-323.
- Cosmetic Ingredient Review. Final report on the safety assessment of methylparaben, ethylparaben, propylparaben and butylparaben. J Am Coll Toxicol. 1984;3:147-209.
- Cosmetic Ingredient Review. Final report on the safety assessment of isobutylparaben and isopropylparaben. J Am Coll Toxicol. 1995;14:364-372.
- Scientific Committee on Consumer Products. Extended Opinion on the Safety Evaluation of Parabens. European Commission website. https://ec.europa.eu/health/ph_risk/committees/04_sccp/docs/sccp_o_019.pdf. Published January 28, 2005. Accessed December 20, 2017.
- Scientific Committee on Consumer Products. Opinion on Parabens. European Commission website. http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/sccs_o_041.pdf. Revised March 22, 2011. Accessed December 20, 2017.
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) No 258/2014 of 9 April 2014 amending Annexes II and V to Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council on cosmetic products. EUR-Lex website. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=uriserv:OJ.L_.2014.107.01.0005.01.ENG. Accessed December 20, 2017.
- American Cancer Society. Antiperspirants and breast cancer risk. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/cancer-causes/antiperspirants-and-breast-cancer-risk.html#references. Revised October 14, 2014. Accessed January 2, 2018.
- MacMillan A. Cutting back on shampoo? 15 things you should know. Health. February 25, 2014. http://www.health.com/health/gallery/0,,20788089,00.html#should-you-go-no-poo--1. Accessed December 10, 2017.
- The ‘no poo’ method. https://www.nopoomethod.com/. Accessed December 10, 2017.
- Fong, D, Gaulin C, Le M, et al. Effectiveness of alternative antimicrobial agents for disinfection of hard surfaces. National Collaborating Centre for Environmental Health website. http://www.ncceh.ca/sites/default/files/Alternative_Antimicrobial_Agents_Aug_2014.pdf. Published August 2014. Accessed December 10, 2017.
- Is baking soda too harsh for natural hair? Black Girl With Long Hair website. http://blackgirllonghair.com/2012/02/is-baking-soda-too-harsh-for-hair/2/. Published February 5, 2012. Accessed December 12, 2017.
- O’Lenick T. Anionic/cationic complexes in hair care. J Cosmet Sci. 2011;62:209-228.
- Gavazzoni Dias MF, de Almeida AM, Cecato PM, et al. The shampoo pH can affect the hair: myth or reality? Int J Trichology. 2014;6:95-99.
- Goodman H. The acid mantle of the skin surface. Ind Med Surg. 1958;27:105-108.
- Korting HC, Kober M, Mueller M, et al. Influence of repeated washings with soap and synthetic detergents on pH and resident flora of the skin of forehead and forearm. results of a cross-over trial in health probationers. Acta Derm Venereol. 1987;67:41-47.
- Tarun J, Susan J, Suria J, et al. Evaluation of pH of bathing soaps and shampoos for skin and hair care. Indian J Dermatol. 2014;59:442-444.
- Corbett JF. The chemistry of hair-care products. J Soc Dyers Colour. 1976;92:285-303.
- McMichael AJ, Hordinsky M. Hair Diseases: Medical, Surgical, and Cosmetic Treatments. New York, NY: Taylor & Francis; 2008:59-72.
- Allardice A, Gummo G. Hair conditioning: quaternary ammonium compounds on various hair types. Cosmet Toiletries. 1993;108:107-109.
- Larson D, Jacob SE. Tea tree oil. Dermatitis. 2012;23:48-49.
Practice Points
- The ingredients in shampoos and other cosmetic products have become scrutinized by the general public and the Internet has contributed to misinformation about certain shampoos.
- Dermatologists must be prepared to acknowledge the concerns that their patients have about common shampoo ingredients to dispel the myths that may misinform patient decision-making.
- This article reviews the controversy surrounding the use of sulfates and parabens in shampoos, as well as commonly used shampoo alternatives, often called the “no-poo” method.
Approach to Treatment of Medical and Cosmetic Facial Concerns in Skin of Color Patients
The approach to the treatment of common skin disorders and cosmetic concerns in patients with skin of color (SOC) requires the clinician to understand the biological differences, nuances, and special considerations that are unique to patients with darker skin types.1-3 This article addresses 4 common facial concerns in SOC patients—acne, rosacea, facial hyperpigmentation, and cosmetic enhancement—and provides treatment recommendations and management pearls to assist the clinician with optimal outcomes for SOC patients.
Acne in SOC Patients
Acne vulgaris is one of the most common conditions that dermatologists treat and is estimated to affect 40 to 50 million individuals in the United States.1 Many of these acne patients are individuals with SOC.2-4 A study of 2835 females (aged 10–70 years) conducted in 4 different cities—Los Angeles, California; London, United Kingdom; Akita, Japan; and Rome, Italy—demonstrated acne prevalence of 37% in blacks, 32% in Hispanics, 30% in Asians, 24% in whites, and 23% in Continental Indians.5 Blacks, Hispanics, and Continental Indians demonstrated equal prevalence with comedonal and inflammatory acne. Asians displayed more inflammatory acne lesions than comedones. In contrast, whites demonstrated more comedones than inflammatory acne. Dyspigmentation, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), and atrophic scars were more common in black and Hispanic females than other ethnicities.5 This study illustrated that acne-induced PIH is a common sequela in SOC patients and is the main reason they seek treatment.6,7
The pathogenesis of acne is the same in all racial and ethnic groups: (1) follicular hyperkeratinization and the formation of a microcomedone caused by abnormal desquamation of the keratinocytes within the sebaceous follicle, (2) production of sebum by circulating androgens, (3) proliferation of Propionibacterium acnes, and (4) inflammation. Subclinical inflammation is present throughout all stages of acne, including normal-appearing skin, inflammatory lesions, comedones, and scarring, and may contribute to PIH in acne patients with SOC (Figure 1).8 A thorough history should be obtained from acne patients, including answers to the following questions7:
- What skin and hair care products do you use?
- Do you use sunscreen daily?
- What cosmetic products or makeup do you use?
- Do you use any ethnic skin care products, including skin lightening creams?
- Do you have a history of keloids?

It is important to ask these questions to assess if the SOC patient has developed pomade acne,9 acne cosmetica,10 or a potential risk of skin irritation from the use of skin care practices. It is best to take total control of the patient’s skin care regimen and discontinue use of toners, astringents, witch hazel, exfoliants, and rubbing alcohol, which may lead to skin dryness and irritation, particularly when combined with topical acne medications.
Treatment
Treatment of acne in SOC patients is similar to generally recommended treatments, with special considerations. Consider the following key points when treating acne in SOC patients:
- Treat acne early and aggressively to prevent or minimize subsequent PIH and acne scarring.
- Balance aggressive treatment with nonirritating topical skin care.
- Most importantly, target PIH in addition to acne and choose a regimen that limits skin irritation that might exacerbate existing PIH.7
Develop a maintenance program to control future breakouts. Topical agents can be used as monotherapy or in fixed combinations and may include benzoyl peroxide, antibiotics, dapsone, azelaic acid (AZA), and retinoids. Similar to white patients, topical retinoids remain a first-line treatment for acne in patients with SOC.11,12
Tolerability must be managed in SOC acne patients. Therapeutic maneuvers that can be instituted should include a discussion on using gentle skin care, initiating therapy with a retinoid applied every other night starting with a low concentration and gradually titrating up, and applying a moisturizer before or after applying acne medication. Oral therapies consist of antibiotics (doxycycline, minocycline), retinoids (isotretinoin), and hormonal modulators (oral contraceptives, spironolactone). Isotretinoin, recommended for patients with nodulocystic acne, may play a possible role in treating acne-induced PIH.13
Two common procedural therapies for acne include comedone extraction and intralesional corticosteroid injection. A 6- to 8-week course of a topical retinoid prior to comedonal extraction may facilitate the procedure and is recommended in SOC patients to help reduce cutaneous trauma and PIH.11 Inflammatory acne lesions can be treated with intralesional injection of triamcinolone acetonide 2.5 or 5.0 mg/mL, which usually reduces inflammation within 2 to 5 days.11
Treatment of acne-induced PIH includes sun protection, topical and oral medications, chemical peels, lasers, and energy devices. Treatment of hypertrophic scarring and keloids involves intralesional injection of triamcinolone acetonide 20, 30, or 40 mg/mL every 4 weeks until the lesion is flat.11
Superficial chemical peels can be used to treat acne and PIH in SOC patients,14 such as salicylic acid (20%–30%), glycolic acid (20%–70%), trichloroacetic acid (15%–30%), and Jessner peels.
Acne Scarring
Surgical approaches to acne scarring in patients with SOC include elliptical excision, punch excision, punch elevation, punch autografting, dermal grafting, dermal planning, subcutaneous incision (subcision), dermabrasion, microneedling, fillers, and laser skin resurfacing. The treatment of choice depends on the size, type, and depth of the scar and the clinician’s preference.
Lasers
Fractional photothermolysis has emerged as a treatment option for acne scars in SOC patients. This procedure produces microscopic columns of thermal injury in the epidermis and dermis, sparing the surrounding tissue and minimizing downtime and adverse events. Because fractional photothermolysis does not target melanin and produces limited epidermal injury, darker Fitzpatrick skin types (IV–VI) can be safely and effectively treated with this procedure.15
Rosacea in SOC Patients
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects the vasculature and pilosebaceous units of the face. It commonly is seen in Fitzpatrick skin types I and II; however, rosacea can occur in all skin types (Figure 2). Triggers include emotional stress, extreme environmental temperatures, hot and spicy foods, red wine or alcohol, and topical irritants or allergens found in common cosmetic products.16
Data suggest that 4% of rosacea patients in the United States are of African, Latino, or Asian descent.11 National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey data revealed that of 31.5 million rosacea visits, 2% of patients were black, 2.3% were Asian or Pacific Islander, and 3.9% were Hispanic or Latino. In a 5-year longitudinal study of 2587 rosacea patients enrolled in Medicaid in North Carolina who were prescribed at least 1 topical treatment for rosacea, 16.27% were black and 10% were of a race other than white.17
Although the pathogenesis of rosacea is unclear, hypotheses include immune system abnormalities, neurogenic dysregulation, presence of microorganisms (eg, Demodex folliculorum), UV damage, and skin barrier dysfunction.18
The 4 major subtypes of rosacea are erythematotelangiectatic, papulopustular, phymatous, and ocular rosacea.16 Interestingly, rosacea in SOC patients may present with hypopigmentation surrounding the borders of the facial erythema. For phymatous rosacea, isotretinoin may reduce incipient rhinophyma but must be carefully monitored and pregnancy must be excluded. Surgical or laser therapy may be indicated to recontour the nose if severe.
There are several skin conditions that can present with facial erythema in patients with SOC, including seborrheic dermatitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and contact dermatitis. It is important to note that the detection of facial erythema in darker skin types may be difficult; therefore, laboratory evaluation (antinuclear antibodies), patch testing, and skin biopsy should be considered if the clinical diagnosis is unclear.
Treatment
Treatment of rosacea in SOC patients does not differ from other racial groups. Common strategies include gentle skin care, sun protection (sun protection factor 30+), and barrier repair creams. Topical agents include metronidazole, AZA, sodium sulfacetamide/sulfur, ivermectin, and retinoids.16 Oral treatments include antibiotics in the tetracycline family (eg, subantimicrobial dose doxycycline) and isotretinoin.16 Persistent erythema associated with rosacea can be treated with brimonidine19 and oxymetazoline.20 Vascular lasers and intense pulsed light may be used to address the vascular components of rosacea21; however, the latter is not recommended in Fitzpatrick skin types IV through VI.
Facial Hyperpigmentation in SOC Patients
Hyperpigmentation disorders can be divided into conditions that affect Fitzpatrick skin types I through III and IV though VI. Mottled hyperpigmentation (photodamage) and solar lentigines occur in patients with lighter skin types as compared to melasma, PIH, and age-related (UV-induced) hyperpigmentation, which occur more commonly in patients with darker skin types. Facial hyperpigmentation is a common concern in SOC patients. In a survey of cosmetic concerns of 100 women with SOC, hyperpigmentation or dark spots (86%) and blotchy uneven skin (80%) were the top concerns.22 In addition, facial hyperpigmentation has been shown to negatively impact quality of life.23
Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation occurs from a pathophysiological response to inflammation, cutaneous irritation or injury, and subsequent melanocyte lability. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is a common presenting concern in patients with SOC and is seen as a result of many inflammatory skin disorders (eg, acne, eczema) and dermatologic procedures (eg, adverse reaction to electrodesiccation, microdermabrasion, chemical peels, laser surgery).24
Melasma is an acquired idiopathic disorder of hyperpigmentation and often referred to as the mask of pregnancy (Figure 3). It occurs on sun-exposed areas of skin, mainly in women with Fitzpatrick skin types III through V. Associated factors or triggers include pregnancy, hormonal treatments, exposure to UV radiation, and medications.25 Hereditary factors play a role in more than 40% of cases.26
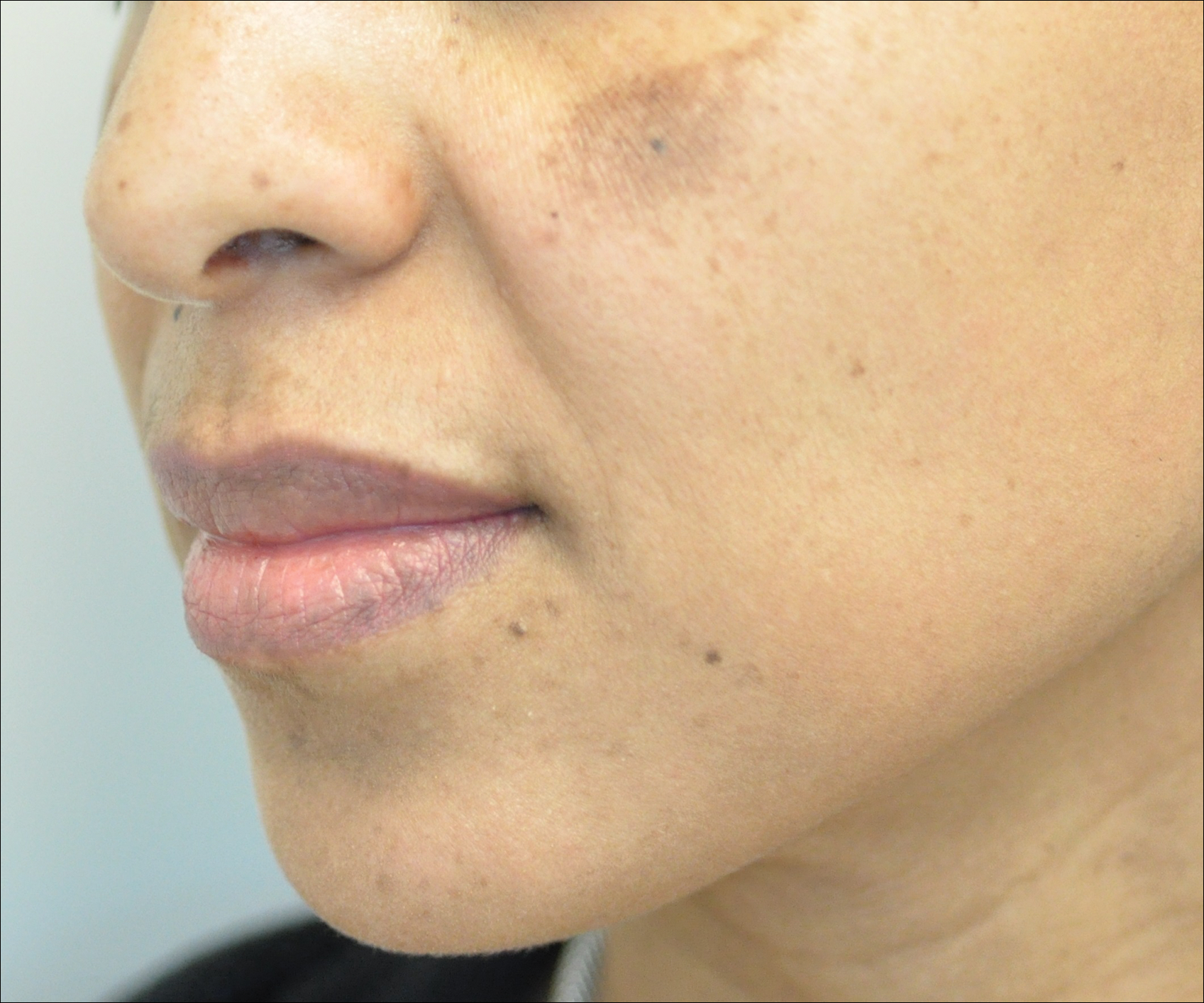
Other not-so-common facial dyschromias include contact dermatitis, acanthosis nigricans, exogenous ochronosis, lichen planus pigmentosus (associated with frontal fibrosing alopecia),27 drug-induced hyperpigmentation (associated with minocycline or diltiazem),28,29 and UV-induced (age-related) hyperpigmentation.
Treatment
The treatment of hyperpigmentation should provide the following: (1) protection from sun exposure; (2) inhibition of tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for the conversion of tyrosine to melanin; (3) inhibition of melanosome transfer from the melanocyte to the keratinocyte; (4) removal of melanin from the epidermis through exfoliation; and (5) destruction or disruption of melanin in the dermis.30 Therapies for facial hyperpigmentation are listed in Table 1.

Topical therapies include prescription medications and nonprescription cosmeceuticals. Prescription medications include hydroquinone (HQ), topical retinoids, and AZA. Hydroquinone, a tyrosinase inhibitor, is the gold standard for skin lightening and often is used as a first-line therapy. It is used as a monotherapy (HQ 4%) or as a fixed combination with tretinoin 0.05% and fluocinolone 0.01%.31 Use caution with HQ in high concentrations (6% and higher) and low concentrations (2% [over-the-counter strength]) used long-term due to the potential risk of exogenous ochronosis.
Topical retinoids have been shown to be effective therapeutic agents for melasma and PIH. Tretinoin,32 tazarotene,33 and adapalene34 all have demonstrated efficacy for acne and acne-induced PIH in SOC patients. Patients must be monitored for the development of retinoid dermatitis and worsening of hyperpigmentation.
Azelaic acid is a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid obtained from cultures of Malassezia furfur. Azelaic acid inhibits tyrosinase activity, DNA synthesis, and mitochondrial enzymes, thus blocking direct cytotoxic effects toward melanocytes. Azelaic acid is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for acne in a 20% cream formulation and rosacea in 15% gel and foam formulations, and it is used off label for melasma and PIH.35
Oral tranexamic acid is currently used as a hemostatic agent due to its ability to inhibit the plasminogen-plasmin pathway. In melasma, it blocks the interaction between melanocytes and keratinocytes in the epidermis and modulates the vascular component of melasma in the dermis. In an open-label study, 561 Asian melasma patients were treated with oral tranexamic acid 250 mg twice daily for 4 months. Results demonstrated improvement in 90% of patients, and 7.1% reported adverse effects (eg, abdominal bloating and pain, nausea, vomiting, headache, tinnitus, numbness, menstrual irregularities).36 Coagulation screening should be monitored monthly, and any patient with a history of clotting abnormalities should be excluded from off-label treatment with oral tranexamic acid.
Nonprescription cosmeceuticals are available over-the-counter or are office dispensed.37 For optimal results, cosmeceutical agents for skin lightening are used in combination. Most of these combinations are HQ free and have additive benefits such as a multimodal skin lightening agent containing key ingredients that correct and prevent skin pigmentation via several pathways affecting melanogenesis.38 It is an excellent alternative to HQ for mottled and diffuse UV-induced hyperpigmentation and can be used for maintenance therapy in patients with melasma.
Photoprotection is an essential component of therapy for melasma and PIH, but there is a paucity of data on the benefits for SOC patients. Halder et al39 performed a randomized prospective study of 89 black and Hispanic patients who applied sunscreen with a sun protection factor of 30 or 60 daily for 8 weeks. Clinical grading, triplicate L*A*B chromameter, and clinical photography were taken at baseline and weeks 4 and 8. The results demonstrated skin lightening in both black and Hispanic patients and support the use of sunscreen in the prevention and management of dyschromia in SOC patients.39 Visible light also may play a role in melasma development, and thus use of sunscreens or makeup containing iron oxides are recommended.40
Procedural treatments for facial hyperpigmentation include microdermabrasion, chemical peels, lasers, energy-based devices, and microneedling. There are many types and formulations of chemical peeling agents available; however, superficial and medium-depth chemical peels are recommended for SOC patients (Table 2). Deep chemical peels are not recommended for SOC patients due to the potential increased risk for PIH and scarring.

Cosmetic Enhancement in SOC Patients
Cosmetic procedures are gaining popularity in the SOC population and account for more than 20% of cosmetic procedures in the United States.41 Facial cosmetic concerns in SOC include dyschromia, benign growths (dermatosis papulosa nigra), hyperkinetic facial lines, volume loss, and skin laxity.42 Key principles to consider when treating SOC patients are the impact of ethnicity on aging and facial structure, the patient’s desired cosmetic outcome, tissue reaction to anticipated treatments, and the patient’s expectations for recommended therapies.
Aging in SOC Patients
Skin aging can be classified as intrinsic aging or extrinsic aging. Intrinsic aging is genetic and involves subsurface changes such as volume loss, muscle atrophy, and resorption of bony structure. Extrinsic aging (or photoaging) involves surface changes of the epidermis/dermis and manifests as mottled pigmentation, textural changes, and fine wrinkling. Due to the photoprotection of melanin (black skin=SPF 13.4), skin aging in SOC patients is delayed by 10 to 20 years.43 In addition, SOC patients have more reactive collagen and can benefit from noninvasive cosmetic procedures such as fillers and skin-tightening procedures.42
Cosmetic Treatments and Procedures
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (benign growths of skin that have a genetic predisposition)44 occur mainly on the face but can involve the entire body. Treatment modalities include electrodesiccation, cryotherapy, scissor excision, and laser surgery.45
Treatment of hyperkinetic facial lines with botulinum toxin type A is a safe and effective procedure in patients with SOC. Grimes and Shabazz46 performed a 4-month, randomized, double-blind study that evaluated the treatment of glabellar lines in women with Fitzpatrick skin types V and VI. The results demonstrated that the duration of effects was the same in the patients who received either 20 or 30 U of botulinum toxin type A.46 Dynamic rhytides (furrows and frown/scowl lines arising from laughing, frowning, or smiling) can be treated safely in patients with SOC using botulinum toxin type A off label for relaxation of the upper and lower hyperkinetic muscles that result in these unwanted signs of aging. Botulinum toxin type A often is used for etched-in crow’s-feet, which rarely are evident in SOC patients.47 Facial shaping also can be accomplished by injecting botulinum toxin type A in combination with soft-tissue dermal fillers.47
Although black individuals do not experience perioral rhytides at the frequency of white individuals, they experience a variety of other cosmetic issues related to skin sagging and sinking. Currently available hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers have been shown to be safe in patients with Fitzpatrick skin types IV through VI.48 Two studies evaluated fillers in patients with SOC, specifically HA49 and calcium hydroxylapatite,50 focused on treatment of the nasolabial folds and the potential risk for dyspigmentation and keloidal scarring. Taylor et al49 noted that the risk of hyperpigmentation was 6% to 9% for large- and small-particle HA, respectively, and was associated with the serial or multiple puncture injection technique. No hypertrophic or keloidal scarring occurred in both studies.49,50
Facial contouring applications with fillers include glabellar lines, temples, nasal bridge, tear troughs, malar and submalar areas, nasolabial folds, radial lines, lips, marionette lines, mental crease, and chin. Hyaluronic acid fillers also can be used for lip enhancement.47 Although white women are looking to increase the size of their lips, black women are seeking augmentation to restore their lip size to that of their youth. Black individuals do not experience the same frequency of perioral rhytides as white patients, but they experience a variety of other issues related to skin sagging and sinking. Unlike white women, enhancement of the vermilion border rarely is performed in black women due to development of rhytides, predominantly in the body of the lip below the vermilion border in response to volume loss in the upper lip while the lower lip usually maintains its same appearance.47
Facial enhancement utilizing poly-L-lactic acid can be used safely in SOC patients.51 Poly-L-lactic acid microparticles induce collagen formation, leading to dermal thickening over 3 to 6 months; however, multiple sessions are required to achieve optimal aesthetic results.
Patients with more reactive collagen can benefit from noninvasive cosmetic procedures such as skin-tightening procedures.52 Radiofrequency and microfocused ultrasound are cosmetic procedures used to provide skin tightening and facial lifting. They are safe and effective treatments for patients with Fitzpatrick skin types IV to VI.53 Histologically, there is less thinning of collagen bundles and elastic tissue in ethnic skin. Due to stimulation of collagen by these procedures, most SOC patients will experience a more enhanced response, requiring fewer treatment sessions than white individuals.
Conclusion
Medical and aesthetic facial concerns in SOC patients vary and can be a source of emotional and psychological distress that can negatively impact quality of life. The approach to the treatment of SOC patients should be a balance between tolerability and efficacy, considering the potential risk for PIH.
- White GM. Recent findings in the epidemiologic evidence, classification, and subtypes of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39(2 pt 3):S34-S37.
- Halder RM, Grimes PE, McLaurin CL, et al. Incidence of common dermatoses in a predominantly black dermatologic practice. Cutis. 1983;32:388, 390.
- Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
- Davis SA, Narahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Perkins AC, Cheng CE, Hillebrand GG, et al. Comparison of the epidemiology of acne vulgaris among Caucasians, Asian, Continental Indian and African American women. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:1054-1060.
- Taylor SC, Cook-Bolden F, Rahman Z, et al. Acne vulgaris in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl):S98-S106.
- Davis EC, Callender VD. A review of acne in ethnic skin: pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and management strategies. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010;3:24-38.
- Halder RM, Holmes YC, Bridgeman-Shah S, et al. A clinicohistologic study of acne vulgaris in black females (abstract). J Invest Dermatol. 1996;106:888.
- Plewig G, Fulton JE, Kligman AM. Pomade acne. Arch Dermatol. 1970;101:580-584.
- Kligman AM, Mills OH. Acne cosmetica. Arch Dermatol. 1972;106:893-897.
- Halder RM, Brooks HL, Callender VD. Acne in ethnic skin. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:609-615.
- Callender VD. Acne in ethnic skin: special considerations for therapy. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:184-195.
- Winhoven SM. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in an Asian patient. a dramatic response to oral isotretinoin (13-cis-retinoic acid). Br J Med. 2005;152:368-403.
- Sarkar R, Bansal S, Garg VK. Chemical peels for melasma in dark-skinned patients. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2012;5:247-253.
- Alexis AF, Coley MK, Nijhawan RI, et al. Nonablative fractional laser resurfacing for acne scarring in patients with Fitzpatrick skin phototypes IV-VI. Dermatol Surg. 2016;42:392-402.
- Culp B, Scheinfeld N. Rosacea: a review. P T. 2009;34:38-45.
- Al-Dabagh A, Davis SA, McMichael AJ, et al. Rosacea in skin of color: not a rare diagnosis. Dermatol Online J. 2014:20. pii:13030/qt1mv9r0ss.
- Del Rosso JQ. Advances in understanding and managing rosacea: part 1: connecting the dots between pathophysiological mechanisms and common clinical features of rosacea with emphasis on vascular changes and facial erythema. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012;5:16-25.
- Jackson JM, Knuckles M, Minni JP, et al. The role of brimonidine tartrate gel in the treatment of rosacea. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;23:529-538.
- Patel NU, Shukla S, Zaki J, et al. Oxymetazoline hydrochloride cream for facial erythema associated with rosacea. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2017;10:104954.
- Weinkle AP, Doktor V, Emer J. Update on the management of rosacea. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;8:159-177.
- Grimes PE. Skin and hair cosmetic issues in women of color. Dermatol Clin. 2000;19:659-665.
- Taylor A, Pawaskar M, Taylor SL, et al. Prevalence of pigmentary disorders and their impact on quality of life: a prospective cohort study. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2008;7:164-168.
- Davis EC, Callender VD. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: a review of the epidemiology, clinical features, and treatment options in skin of color. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010;3:20-31.
- Grimes PE. Melasma: etiologic and therapeutic considerations. Arch Dermatol. 1995;131:1453-1457.
- Handel AC, Miot LD, Miot HA. Melasma: a clinical and epidemiological review. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:771-782.
- Callender VD, Reid SD, Obayan O, et al. Diagnostic clues to frontal fibrosing alopecia in patients of African descent. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2016;9:45-51.
- Narang T, Sawatkar GU, Kumaran MS, et al. Minocycline for recurrent and/or chronic erythema nodosum leprosum. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1026-1028.
- Boyer M, Katta R, Markus R. Diltiazem-induced photodistributed hyperpigmentation. Dermatol Online J. 2003;9:10.
- Pandya AG, Guevara IL. Disorders of hyperpigmentation. Dermatol Clin. 2000;18:91-98.
- Taylor SC, Torok H, Jones T, et al. Efficacy and safety of a new triple-combination agent for the treatment of facial melasma. Cutis. 2003;72:67-72.
- Bulengo-Ransby SM. Topical tretinoin (retinoic acid) therapy for hyperpigmented lesions caused by inflammation of the skin in black patients. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1438-1443.
- Grimes P, Callender V. Tazarotene cream for postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and acne vulgaris in darker skin: a double-blind, randomized, vehicle-controlled study. Cutis. 2006;77:45-50.
- Jacyk WK. Adapalene in the treatment of African patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2001;15(suppl 3):37-42.
- Kircik LH. Efficacy and safety of azelaic acid (AzA) gel 15% in the treatment of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and acne: a 16-week, baseline-controlled study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2011;10:586-590.
- Lee HC, Thng TG, Goh CL. Oral tranexamic acid (TA) in the treatment of melasma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:385-392.
- Kindred C, Okereke U, Callender VD. Skin-lightening agents: an overview of prescription, office-dispensed, and over-the-counter products. Cosmet Dermatol. 2013;26:18-26.
- Makino ET, Kadoya K, Sigler ML, et al. Development and clinical assessment of a comprehensive product for pigmentation control in multiple ethnic populations. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:1562-1570.
- Halder R, Rodney I, Munhutu M, et al. Evaluation and effectiveness of a photoprotection composition (sunscreen) on subjects of skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72(suppl 1):AB215.
- Castanedo-Cazares JP, Hernandez-Blanco D, Carlos-Ortega B, et al. Near-visible light and UV photoprotection in the treatment of melasma: a double-blind randomized trial. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2014;30:35-42.
- American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. 2016 Cosmetic Surgery National Data Bank Statistics. https://www.surgery.org/sites/default/files/ASAPS-Stats2016.pdf. Accessed November 15, 2017.
- Burgess CM. Soft tissue augmentation in skin of color: market growth, available fillers and successful techniques. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:51-55.
- Davis EC, Callender VD. Aesthetic dermatology for aging ethnic skin. Dermatol Surg. 2011;37:901-917.
- Grimes PE, Arora S, Minus HR, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra. Cutis. 1983;32:385-386.
- Lupo M. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: treatment options. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:29-30.
- Grimes PE, Shabazz D. A four-month randomized, double-blind evaluation of the efficacy of botulinum toxin type A for the treatment of glabellar lines in women with skin types V and VI. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35:429-435.
- Burgess CM, Awosika O. Ethnic and gender considerations in the use of facial injectables: African-American patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;136(5 suppl):28S-31S.
- Taylor SC, Kelly AP, Lim HW, et al, eds. Taylor and Kelly’s Dermatology for Skin of Color. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2016.
- Taylor SC, Burgess CM, Callender VD. Safety of nonanimal stabilized hyaluronic acid dermal fillers in patients with skin of color: a randomized, evaluator-blinded comparative trial. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35(suppl 2):1653-1660.
- Marmur ES, Taylor SC, Grimes PE, et al. Six-month safety results of calcium hydroxylapatite for treatment of nasolabial folds in Fitzpatrick skin types IV to VI. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35(suppl 2):1641-1645.
- Hamilton TK, Burgess CM. Consideration for the use of injectable poly-L-lactic acid in people of color. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:451-456.
- Fabi SG, Goldman MP. Retrospective evaluation of micro-focused ultrasound for lifting and tightening of the face and neck. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:569-575.
- Harris MO, Sundaram HA. Safety of microfocused ultrasound with visualization in patients with Fitzpatrick skin phototypes III to VI. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2015;17:355-357.
The approach to the treatment of common skin disorders and cosmetic concerns in patients with skin of color (SOC) requires the clinician to understand the biological differences, nuances, and special considerations that are unique to patients with darker skin types.1-3 This article addresses 4 common facial concerns in SOC patients—acne, rosacea, facial hyperpigmentation, and cosmetic enhancement—and provides treatment recommendations and management pearls to assist the clinician with optimal outcomes for SOC patients.
Acne in SOC Patients
Acne vulgaris is one of the most common conditions that dermatologists treat and is estimated to affect 40 to 50 million individuals in the United States.1 Many of these acne patients are individuals with SOC.2-4 A study of 2835 females (aged 10–70 years) conducted in 4 different cities—Los Angeles, California; London, United Kingdom; Akita, Japan; and Rome, Italy—demonstrated acne prevalence of 37% in blacks, 32% in Hispanics, 30% in Asians, 24% in whites, and 23% in Continental Indians.5 Blacks, Hispanics, and Continental Indians demonstrated equal prevalence with comedonal and inflammatory acne. Asians displayed more inflammatory acne lesions than comedones. In contrast, whites demonstrated more comedones than inflammatory acne. Dyspigmentation, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), and atrophic scars were more common in black and Hispanic females than other ethnicities.5 This study illustrated that acne-induced PIH is a common sequela in SOC patients and is the main reason they seek treatment.6,7
The pathogenesis of acne is the same in all racial and ethnic groups: (1) follicular hyperkeratinization and the formation of a microcomedone caused by abnormal desquamation of the keratinocytes within the sebaceous follicle, (2) production of sebum by circulating androgens, (3) proliferation of Propionibacterium acnes, and (4) inflammation. Subclinical inflammation is present throughout all stages of acne, including normal-appearing skin, inflammatory lesions, comedones, and scarring, and may contribute to PIH in acne patients with SOC (Figure 1).8 A thorough history should be obtained from acne patients, including answers to the following questions7:
- What skin and hair care products do you use?
- Do you use sunscreen daily?
- What cosmetic products or makeup do you use?
- Do you use any ethnic skin care products, including skin lightening creams?
- Do you have a history of keloids?

It is important to ask these questions to assess if the SOC patient has developed pomade acne,9 acne cosmetica,10 or a potential risk of skin irritation from the use of skin care practices. It is best to take total control of the patient’s skin care regimen and discontinue use of toners, astringents, witch hazel, exfoliants, and rubbing alcohol, which may lead to skin dryness and irritation, particularly when combined with topical acne medications.
Treatment
Treatment of acne in SOC patients is similar to generally recommended treatments, with special considerations. Consider the following key points when treating acne in SOC patients:
- Treat acne early and aggressively to prevent or minimize subsequent PIH and acne scarring.
- Balance aggressive treatment with nonirritating topical skin care.
- Most importantly, target PIH in addition to acne and choose a regimen that limits skin irritation that might exacerbate existing PIH.7
Develop a maintenance program to control future breakouts. Topical agents can be used as monotherapy or in fixed combinations and may include benzoyl peroxide, antibiotics, dapsone, azelaic acid (AZA), and retinoids. Similar to white patients, topical retinoids remain a first-line treatment for acne in patients with SOC.11,12
Tolerability must be managed in SOC acne patients. Therapeutic maneuvers that can be instituted should include a discussion on using gentle skin care, initiating therapy with a retinoid applied every other night starting with a low concentration and gradually titrating up, and applying a moisturizer before or after applying acne medication. Oral therapies consist of antibiotics (doxycycline, minocycline), retinoids (isotretinoin), and hormonal modulators (oral contraceptives, spironolactone). Isotretinoin, recommended for patients with nodulocystic acne, may play a possible role in treating acne-induced PIH.13
Two common procedural therapies for acne include comedone extraction and intralesional corticosteroid injection. A 6- to 8-week course of a topical retinoid prior to comedonal extraction may facilitate the procedure and is recommended in SOC patients to help reduce cutaneous trauma and PIH.11 Inflammatory acne lesions can be treated with intralesional injection of triamcinolone acetonide 2.5 or 5.0 mg/mL, which usually reduces inflammation within 2 to 5 days.11
Treatment of acne-induced PIH includes sun protection, topical and oral medications, chemical peels, lasers, and energy devices. Treatment of hypertrophic scarring and keloids involves intralesional injection of triamcinolone acetonide 20, 30, or 40 mg/mL every 4 weeks until the lesion is flat.11
Superficial chemical peels can be used to treat acne and PIH in SOC patients,14 such as salicylic acid (20%–30%), glycolic acid (20%–70%), trichloroacetic acid (15%–30%), and Jessner peels.
Acne Scarring
Surgical approaches to acne scarring in patients with SOC include elliptical excision, punch excision, punch elevation, punch autografting, dermal grafting, dermal planning, subcutaneous incision (subcision), dermabrasion, microneedling, fillers, and laser skin resurfacing. The treatment of choice depends on the size, type, and depth of the scar and the clinician’s preference.
Lasers
Fractional photothermolysis has emerged as a treatment option for acne scars in SOC patients. This procedure produces microscopic columns of thermal injury in the epidermis and dermis, sparing the surrounding tissue and minimizing downtime and adverse events. Because fractional photothermolysis does not target melanin and produces limited epidermal injury, darker Fitzpatrick skin types (IV–VI) can be safely and effectively treated with this procedure.15
Rosacea in SOC Patients
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects the vasculature and pilosebaceous units of the face. It commonly is seen in Fitzpatrick skin types I and II; however, rosacea can occur in all skin types (Figure 2). Triggers include emotional stress, extreme environmental temperatures, hot and spicy foods, red wine or alcohol, and topical irritants or allergens found in common cosmetic products.16

Data suggest that 4% of rosacea patients in the United States are of African, Latino, or Asian descent.11 National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey data revealed that of 31.5 million rosacea visits, 2% of patients were black, 2.3% were Asian or Pacific Islander, and 3.9% were Hispanic or Latino. In a 5-year longitudinal study of 2587 rosacea patients enrolled in Medicaid in North Carolina who were prescribed at least 1 topical treatment for rosacea, 16.27% were black and 10% were of a race other than white.17
Although the pathogenesis of rosacea is unclear, hypotheses include immune system abnormalities, neurogenic dysregulation, presence of microorganisms (eg, Demodex folliculorum), UV damage, and skin barrier dysfunction.18
The 4 major subtypes of rosacea are erythematotelangiectatic, papulopustular, phymatous, and ocular rosacea.16 Interestingly, rosacea in SOC patients may present with hypopigmentation surrounding the borders of the facial erythema. For phymatous rosacea, isotretinoin may reduce incipient rhinophyma but must be carefully monitored and pregnancy must be excluded. Surgical or laser therapy may be indicated to recontour the nose if severe.
There are several skin conditions that can present with facial erythema in patients with SOC, including seborrheic dermatitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and contact dermatitis. It is important to note that the detection of facial erythema in darker skin types may be difficult; therefore, laboratory evaluation (antinuclear antibodies), patch testing, and skin biopsy should be considered if the clinical diagnosis is unclear.
Treatment
Treatment of rosacea in SOC patients does not differ from other racial groups. Common strategies include gentle skin care, sun protection (sun protection factor 30+), and barrier repair creams. Topical agents include metronidazole, AZA, sodium sulfacetamide/sulfur, ivermectin, and retinoids.16 Oral treatments include antibiotics in the tetracycline family (eg, subantimicrobial dose doxycycline) and isotretinoin.16 Persistent erythema associated with rosacea can be treated with brimonidine19 and oxymetazoline.20 Vascular lasers and intense pulsed light may be used to address the vascular components of rosacea21; however, the latter is not recommended in Fitzpatrick skin types IV through VI.
Facial Hyperpigmentation in SOC Patients
Hyperpigmentation disorders can be divided into conditions that affect Fitzpatrick skin types I through III and IV though VI. Mottled hyperpigmentation (photodamage) and solar lentigines occur in patients with lighter skin types as compared to melasma, PIH, and age-related (UV-induced) hyperpigmentation, which occur more commonly in patients with darker skin types. Facial hyperpigmentation is a common concern in SOC patients. In a survey of cosmetic concerns of 100 women with SOC, hyperpigmentation or dark spots (86%) and blotchy uneven skin (80%) were the top concerns.22 In addition, facial hyperpigmentation has been shown to negatively impact quality of life.23
Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation occurs from a pathophysiological response to inflammation, cutaneous irritation or injury, and subsequent melanocyte lability. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is a common presenting concern in patients with SOC and is seen as a result of many inflammatory skin disorders (eg, acne, eczema) and dermatologic procedures (eg, adverse reaction to electrodesiccation, microdermabrasion, chemical peels, laser surgery).24
Melasma is an acquired idiopathic disorder of hyperpigmentation and often referred to as the mask of pregnancy (Figure 3). It occurs on sun-exposed areas of skin, mainly in women with Fitzpatrick skin types III through V. Associated factors or triggers include pregnancy, hormonal treatments, exposure to UV radiation, and medications.25 Hereditary factors play a role in more than 40% of cases.26

Other not-so-common facial dyschromias include contact dermatitis, acanthosis nigricans, exogenous ochronosis, lichen planus pigmentosus (associated with frontal fibrosing alopecia),27 drug-induced hyperpigmentation (associated with minocycline or diltiazem),28,29 and UV-induced (age-related) hyperpigmentation.
Treatment
The treatment of hyperpigmentation should provide the following: (1) protection from sun exposure; (2) inhibition of tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for the conversion of tyrosine to melanin; (3) inhibition of melanosome transfer from the melanocyte to the keratinocyte; (4) removal of melanin from the epidermis through exfoliation; and (5) destruction or disruption of melanin in the dermis.30 Therapies for facial hyperpigmentation are listed in Table 1.

Topical therapies include prescription medications and nonprescription cosmeceuticals. Prescription medications include hydroquinone (HQ), topical retinoids, and AZA. Hydroquinone, a tyrosinase inhibitor, is the gold standard for skin lightening and often is used as a first-line therapy. It is used as a monotherapy (HQ 4%) or as a fixed combination with tretinoin 0.05% and fluocinolone 0.01%.31 Use caution with HQ in high concentrations (6% and higher) and low concentrations (2% [over-the-counter strength]) used long-term due to the potential risk of exogenous ochronosis.
Topical retinoids have been shown to be effective therapeutic agents for melasma and PIH. Tretinoin,32 tazarotene,33 and adapalene34 all have demonstrated efficacy for acne and acne-induced PIH in SOC patients. Patients must be monitored for the development of retinoid dermatitis and worsening of hyperpigmentation.
Azelaic acid is a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid obtained from cultures of Malassezia furfur. Azelaic acid inhibits tyrosinase activity, DNA synthesis, and mitochondrial enzymes, thus blocking direct cytotoxic effects toward melanocytes. Azelaic acid is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for acne in a 20% cream formulation and rosacea in 15% gel and foam formulations, and it is used off label for melasma and PIH.35
Oral tranexamic acid is currently used as a hemostatic agent due to its ability to inhibit the plasminogen-plasmin pathway. In melasma, it blocks the interaction between melanocytes and keratinocytes in the epidermis and modulates the vascular component of melasma in the dermis. In an open-label study, 561 Asian melasma patients were treated with oral tranexamic acid 250 mg twice daily for 4 months. Results demonstrated improvement in 90% of patients, and 7.1% reported adverse effects (eg, abdominal bloating and pain, nausea, vomiting, headache, tinnitus, numbness, menstrual irregularities).36 Coagulation screening should be monitored monthly, and any patient with a history of clotting abnormalities should be excluded from off-label treatment with oral tranexamic acid.
Nonprescription cosmeceuticals are available over-the-counter or are office dispensed.37 For optimal results, cosmeceutical agents for skin lightening are used in combination. Most of these combinations are HQ free and have additive benefits such as a multimodal skin lightening agent containing key ingredients that correct and prevent skin pigmentation via several pathways affecting melanogenesis.38 It is an excellent alternative to HQ for mottled and diffuse UV-induced hyperpigmentation and can be used for maintenance therapy in patients with melasma.
Photoprotection is an essential component of therapy for melasma and PIH, but there is a paucity of data on the benefits for SOC patients. Halder et al39 performed a randomized prospective study of 89 black and Hispanic patients who applied sunscreen with a sun protection factor of 30 or 60 daily for 8 weeks. Clinical grading, triplicate L*A*B chromameter, and clinical photography were taken at baseline and weeks 4 and 8. The results demonstrated skin lightening in both black and Hispanic patients and support the use of sunscreen in the prevention and management of dyschromia in SOC patients.39 Visible light also may play a role in melasma development, and thus use of sunscreens or makeup containing iron oxides are recommended.40
Procedural treatments for facial hyperpigmentation include microdermabrasion, chemical peels, lasers, energy-based devices, and microneedling. There are many types and formulations of chemical peeling agents available; however, superficial and medium-depth chemical peels are recommended for SOC patients (Table 2). Deep chemical peels are not recommended for SOC patients due to the potential increased risk for PIH and scarring.

Cosmetic Enhancement in SOC Patients
Cosmetic procedures are gaining popularity in the SOC population and account for more than 20% of cosmetic procedures in the United States.41 Facial cosmetic concerns in SOC include dyschromia, benign growths (dermatosis papulosa nigra), hyperkinetic facial lines, volume loss, and skin laxity.42 Key principles to consider when treating SOC patients are the impact of ethnicity on aging and facial structure, the patient’s desired cosmetic outcome, tissue reaction to anticipated treatments, and the patient’s expectations for recommended therapies.
Aging in SOC Patients
Skin aging can be classified as intrinsic aging or extrinsic aging. Intrinsic aging is genetic and involves subsurface changes such as volume loss, muscle atrophy, and resorption of bony structure. Extrinsic aging (or photoaging) involves surface changes of the epidermis/dermis and manifests as mottled pigmentation, textural changes, and fine wrinkling. Due to the photoprotection of melanin (black skin=SPF 13.4), skin aging in SOC patients is delayed by 10 to 20 years.43 In addition, SOC patients have more reactive collagen and can benefit from noninvasive cosmetic procedures such as fillers and skin-tightening procedures.42
Cosmetic Treatments and Procedures
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (benign growths of skin that have a genetic predisposition)44 occur mainly on the face but can involve the entire body. Treatment modalities include electrodesiccation, cryotherapy, scissor excision, and laser surgery.45
Treatment of hyperkinetic facial lines with botulinum toxin type A is a safe and effective procedure in patients with SOC. Grimes and Shabazz46 performed a 4-month, randomized, double-blind study that evaluated the treatment of glabellar lines in women with Fitzpatrick skin types V and VI. The results demonstrated that the duration of effects was the same in the patients who received either 20 or 30 U of botulinum toxin type A.46 Dynamic rhytides (furrows and frown/scowl lines arising from laughing, frowning, or smiling) can be treated safely in patients with SOC using botulinum toxin type A off label for relaxation of the upper and lower hyperkinetic muscles that result in these unwanted signs of aging. Botulinum toxin type A often is used for etched-in crow’s-feet, which rarely are evident in SOC patients.47 Facial shaping also can be accomplished by injecting botulinum toxin type A in combination with soft-tissue dermal fillers.47
Although black individuals do not experience perioral rhytides at the frequency of white individuals, they experience a variety of other cosmetic issues related to skin sagging and sinking. Currently available hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers have been shown to be safe in patients with Fitzpatrick skin types IV through VI.48 Two studies evaluated fillers in patients with SOC, specifically HA49 and calcium hydroxylapatite,50 focused on treatment of the nasolabial folds and the potential risk for dyspigmentation and keloidal scarring. Taylor et al49 noted that the risk of hyperpigmentation was 6% to 9% for large- and small-particle HA, respectively, and was associated with the serial or multiple puncture injection technique. No hypertrophic or keloidal scarring occurred in both studies.49,50
Facial contouring applications with fillers include glabellar lines, temples, nasal bridge, tear troughs, malar and submalar areas, nasolabial folds, radial lines, lips, marionette lines, mental crease, and chin. Hyaluronic acid fillers also can be used for lip enhancement.47 Although white women are looking to increase the size of their lips, black women are seeking augmentation to restore their lip size to that of their youth. Black individuals do not experience the same frequency of perioral rhytides as white patients, but they experience a variety of other issues related to skin sagging and sinking. Unlike white women, enhancement of the vermilion border rarely is performed in black women due to development of rhytides, predominantly in the body of the lip below the vermilion border in response to volume loss in the upper lip while the lower lip usually maintains its same appearance.47
Facial enhancement utilizing poly-L-lactic acid can be used safely in SOC patients.51 Poly-L-lactic acid microparticles induce collagen formation, leading to dermal thickening over 3 to 6 months; however, multiple sessions are required to achieve optimal aesthetic results.
Patients with more reactive collagen can benefit from noninvasive cosmetic procedures such as skin-tightening procedures.52 Radiofrequency and microfocused ultrasound are cosmetic procedures used to provide skin tightening and facial lifting. They are safe and effective treatments for patients with Fitzpatrick skin types IV to VI.53 Histologically, there is less thinning of collagen bundles and elastic tissue in ethnic skin. Due to stimulation of collagen by these procedures, most SOC patients will experience a more enhanced response, requiring fewer treatment sessions than white individuals.
Conclusion
Medical and aesthetic facial concerns in SOC patients vary and can be a source of emotional and psychological distress that can negatively impact quality of life. The approach to the treatment of SOC patients should be a balance between tolerability and efficacy, considering the potential risk for PIH.
The approach to the treatment of common skin disorders and cosmetic concerns in patients with skin of color (SOC) requires the clinician to understand the biological differences, nuances, and special considerations that are unique to patients with darker skin types.1-3 This article addresses 4 common facial concerns in SOC patients—acne, rosacea, facial hyperpigmentation, and cosmetic enhancement—and provides treatment recommendations and management pearls to assist the clinician with optimal outcomes for SOC patients.
Acne in SOC Patients
Acne vulgaris is one of the most common conditions that dermatologists treat and is estimated to affect 40 to 50 million individuals in the United States.1 Many of these acne patients are individuals with SOC.2-4 A study of 2835 females (aged 10–70 years) conducted in 4 different cities—Los Angeles, California; London, United Kingdom; Akita, Japan; and Rome, Italy—demonstrated acne prevalence of 37% in blacks, 32% in Hispanics, 30% in Asians, 24% in whites, and 23% in Continental Indians.5 Blacks, Hispanics, and Continental Indians demonstrated equal prevalence with comedonal and inflammatory acne. Asians displayed more inflammatory acne lesions than comedones. In contrast, whites demonstrated more comedones than inflammatory acne. Dyspigmentation, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), and atrophic scars were more common in black and Hispanic females than other ethnicities.5 This study illustrated that acne-induced PIH is a common sequela in SOC patients and is the main reason they seek treatment.6,7
The pathogenesis of acne is the same in all racial and ethnic groups: (1) follicular hyperkeratinization and the formation of a microcomedone caused by abnormal desquamation of the keratinocytes within the sebaceous follicle, (2) production of sebum by circulating androgens, (3) proliferation of Propionibacterium acnes, and (4) inflammation. Subclinical inflammation is present throughout all stages of acne, including normal-appearing skin, inflammatory lesions, comedones, and scarring, and may contribute to PIH in acne patients with SOC (Figure 1).8 A thorough history should be obtained from acne patients, including answers to the following questions7:
- What skin and hair care products do you use?
- Do you use sunscreen daily?
- What cosmetic products or makeup do you use?
- Do you use any ethnic skin care products, including skin lightening creams?
- Do you have a history of keloids?

It is important to ask these questions to assess if the SOC patient has developed pomade acne,9 acne cosmetica,10 or a potential risk of skin irritation from the use of skin care practices. It is best to take total control of the patient’s skin care regimen and discontinue use of toners, astringents, witch hazel, exfoliants, and rubbing alcohol, which may lead to skin dryness and irritation, particularly when combined with topical acne medications.
Treatment
Treatment of acne in SOC patients is similar to generally recommended treatments, with special considerations. Consider the following key points when treating acne in SOC patients:
- Treat acne early and aggressively to prevent or minimize subsequent PIH and acne scarring.
- Balance aggressive treatment with nonirritating topical skin care.
- Most importantly, target PIH in addition to acne and choose a regimen that limits skin irritation that might exacerbate existing PIH.7
Develop a maintenance program to control future breakouts. Topical agents can be used as monotherapy or in fixed combinations and may include benzoyl peroxide, antibiotics, dapsone, azelaic acid (AZA), and retinoids. Similar to white patients, topical retinoids remain a first-line treatment for acne in patients with SOC.11,12
Tolerability must be managed in SOC acne patients. Therapeutic maneuvers that can be instituted should include a discussion on using gentle skin care, initiating therapy with a retinoid applied every other night starting with a low concentration and gradually titrating up, and applying a moisturizer before or after applying acne medication. Oral therapies consist of antibiotics (doxycycline, minocycline), retinoids (isotretinoin), and hormonal modulators (oral contraceptives, spironolactone). Isotretinoin, recommended for patients with nodulocystic acne, may play a possible role in treating acne-induced PIH.13
Two common procedural therapies for acne include comedone extraction and intralesional corticosteroid injection. A 6- to 8-week course of a topical retinoid prior to comedonal extraction may facilitate the procedure and is recommended in SOC patients to help reduce cutaneous trauma and PIH.11 Inflammatory acne lesions can be treated with intralesional injection of triamcinolone acetonide 2.5 or 5.0 mg/mL, which usually reduces inflammation within 2 to 5 days.11
Treatment of acne-induced PIH includes sun protection, topical and oral medications, chemical peels, lasers, and energy devices. Treatment of hypertrophic scarring and keloids involves intralesional injection of triamcinolone acetonide 20, 30, or 40 mg/mL every 4 weeks until the lesion is flat.11
Superficial chemical peels can be used to treat acne and PIH in SOC patients,14 such as salicylic acid (20%–30%), glycolic acid (20%–70%), trichloroacetic acid (15%–30%), and Jessner peels.
Acne Scarring
Surgical approaches to acne scarring in patients with SOC include elliptical excision, punch excision, punch elevation, punch autografting, dermal grafting, dermal planning, subcutaneous incision (subcision), dermabrasion, microneedling, fillers, and laser skin resurfacing. The treatment of choice depends on the size, type, and depth of the scar and the clinician’s preference.
Lasers
Fractional photothermolysis has emerged as a treatment option for acne scars in SOC patients. This procedure produces microscopic columns of thermal injury in the epidermis and dermis, sparing the surrounding tissue and minimizing downtime and adverse events. Because fractional photothermolysis does not target melanin and produces limited epidermal injury, darker Fitzpatrick skin types (IV–VI) can be safely and effectively treated with this procedure.15
Rosacea in SOC Patients
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects the vasculature and pilosebaceous units of the face. It commonly is seen in Fitzpatrick skin types I and II; however, rosacea can occur in all skin types (Figure 2). Triggers include emotional stress, extreme environmental temperatures, hot and spicy foods, red wine or alcohol, and topical irritants or allergens found in common cosmetic products.16

Data suggest that 4% of rosacea patients in the United States are of African, Latino, or Asian descent.11 National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey data revealed that of 31.5 million rosacea visits, 2% of patients were black, 2.3% were Asian or Pacific Islander, and 3.9% were Hispanic or Latino. In a 5-year longitudinal study of 2587 rosacea patients enrolled in Medicaid in North Carolina who were prescribed at least 1 topical treatment for rosacea, 16.27% were black and 10% were of a race other than white.17
Although the pathogenesis of rosacea is unclear, hypotheses include immune system abnormalities, neurogenic dysregulation, presence of microorganisms (eg, Demodex folliculorum), UV damage, and skin barrier dysfunction.18
The 4 major subtypes of rosacea are erythematotelangiectatic, papulopustular, phymatous, and ocular rosacea.16 Interestingly, rosacea in SOC patients may present with hypopigmentation surrounding the borders of the facial erythema. For phymatous rosacea, isotretinoin may reduce incipient rhinophyma but must be carefully monitored and pregnancy must be excluded. Surgical or laser therapy may be indicated to recontour the nose if severe.
There are several skin conditions that can present with facial erythema in patients with SOC, including seborrheic dermatitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and contact dermatitis. It is important to note that the detection of facial erythema in darker skin types may be difficult; therefore, laboratory evaluation (antinuclear antibodies), patch testing, and skin biopsy should be considered if the clinical diagnosis is unclear.
Treatment
Treatment of rosacea in SOC patients does not differ from other racial groups. Common strategies include gentle skin care, sun protection (sun protection factor 30+), and barrier repair creams. Topical agents include metronidazole, AZA, sodium sulfacetamide/sulfur, ivermectin, and retinoids.16 Oral treatments include antibiotics in the tetracycline family (eg, subantimicrobial dose doxycycline) and isotretinoin.16 Persistent erythema associated with rosacea can be treated with brimonidine19 and oxymetazoline.20 Vascular lasers and intense pulsed light may be used to address the vascular components of rosacea21; however, the latter is not recommended in Fitzpatrick skin types IV through VI.
Facial Hyperpigmentation in SOC Patients
Hyperpigmentation disorders can be divided into conditions that affect Fitzpatrick skin types I through III and IV though VI. Mottled hyperpigmentation (photodamage) and solar lentigines occur in patients with lighter skin types as compared to melasma, PIH, and age-related (UV-induced) hyperpigmentation, which occur more commonly in patients with darker skin types. Facial hyperpigmentation is a common concern in SOC patients. In a survey of cosmetic concerns of 100 women with SOC, hyperpigmentation or dark spots (86%) and blotchy uneven skin (80%) were the top concerns.22 In addition, facial hyperpigmentation has been shown to negatively impact quality of life.23
Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation occurs from a pathophysiological response to inflammation, cutaneous irritation or injury, and subsequent melanocyte lability. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is a common presenting concern in patients with SOC and is seen as a result of many inflammatory skin disorders (eg, acne, eczema) and dermatologic procedures (eg, adverse reaction to electrodesiccation, microdermabrasion, chemical peels, laser surgery).24
Melasma is an acquired idiopathic disorder of hyperpigmentation and often referred to as the mask of pregnancy (Figure 3). It occurs on sun-exposed areas of skin, mainly in women with Fitzpatrick skin types III through V. Associated factors or triggers include pregnancy, hormonal treatments, exposure to UV radiation, and medications.25 Hereditary factors play a role in more than 40% of cases.26

Other not-so-common facial dyschromias include contact dermatitis, acanthosis nigricans, exogenous ochronosis, lichen planus pigmentosus (associated with frontal fibrosing alopecia),27 drug-induced hyperpigmentation (associated with minocycline or diltiazem),28,29 and UV-induced (age-related) hyperpigmentation.
Treatment
The treatment of hyperpigmentation should provide the following: (1) protection from sun exposure; (2) inhibition of tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for the conversion of tyrosine to melanin; (3) inhibition of melanosome transfer from the melanocyte to the keratinocyte; (4) removal of melanin from the epidermis through exfoliation; and (5) destruction or disruption of melanin in the dermis.30 Therapies for facial hyperpigmentation are listed in Table 1.

Topical therapies include prescription medications and nonprescription cosmeceuticals. Prescription medications include hydroquinone (HQ), topical retinoids, and AZA. Hydroquinone, a tyrosinase inhibitor, is the gold standard for skin lightening and often is used as a first-line therapy. It is used as a monotherapy (HQ 4%) or as a fixed combination with tretinoin 0.05% and fluocinolone 0.01%.31 Use caution with HQ in high concentrations (6% and higher) and low concentrations (2% [over-the-counter strength]) used long-term due to the potential risk of exogenous ochronosis.
Topical retinoids have been shown to be effective therapeutic agents for melasma and PIH. Tretinoin,32 tazarotene,33 and adapalene34 all have demonstrated efficacy for acne and acne-induced PIH in SOC patients. Patients must be monitored for the development of retinoid dermatitis and worsening of hyperpigmentation.
Azelaic acid is a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid obtained from cultures of Malassezia furfur. Azelaic acid inhibits tyrosinase activity, DNA synthesis, and mitochondrial enzymes, thus blocking direct cytotoxic effects toward melanocytes. Azelaic acid is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for acne in a 20% cream formulation and rosacea in 15% gel and foam formulations, and it is used off label for melasma and PIH.35
Oral tranexamic acid is currently used as a hemostatic agent due to its ability to inhibit the plasminogen-plasmin pathway. In melasma, it blocks the interaction between melanocytes and keratinocytes in the epidermis and modulates the vascular component of melasma in the dermis. In an open-label study, 561 Asian melasma patients were treated with oral tranexamic acid 250 mg twice daily for 4 months. Results demonstrated improvement in 90% of patients, and 7.1% reported adverse effects (eg, abdominal bloating and pain, nausea, vomiting, headache, tinnitus, numbness, menstrual irregularities).36 Coagulation screening should be monitored monthly, and any patient with a history of clotting abnormalities should be excluded from off-label treatment with oral tranexamic acid.
Nonprescription cosmeceuticals are available over-the-counter or are office dispensed.37 For optimal results, cosmeceutical agents for skin lightening are used in combination. Most of these combinations are HQ free and have additive benefits such as a multimodal skin lightening agent containing key ingredients that correct and prevent skin pigmentation via several pathways affecting melanogenesis.38 It is an excellent alternative to HQ for mottled and diffuse UV-induced hyperpigmentation and can be used for maintenance therapy in patients with melasma.
Photoprotection is an essential component of therapy for melasma and PIH, but there is a paucity of data on the benefits for SOC patients. Halder et al39 performed a randomized prospective study of 89 black and Hispanic patients who applied sunscreen with a sun protection factor of 30 or 60 daily for 8 weeks. Clinical grading, triplicate L*A*B chromameter, and clinical photography were taken at baseline and weeks 4 and 8. The results demonstrated skin lightening in both black and Hispanic patients and support the use of sunscreen in the prevention and management of dyschromia in SOC patients.39 Visible light also may play a role in melasma development, and thus use of sunscreens or makeup containing iron oxides are recommended.40
Procedural treatments for facial hyperpigmentation include microdermabrasion, chemical peels, lasers, energy-based devices, and microneedling. There are many types and formulations of chemical peeling agents available; however, superficial and medium-depth chemical peels are recommended for SOC patients (Table 2). Deep chemical peels are not recommended for SOC patients due to the potential increased risk for PIH and scarring.

Cosmetic Enhancement in SOC Patients
Cosmetic procedures are gaining popularity in the SOC population and account for more than 20% of cosmetic procedures in the United States.41 Facial cosmetic concerns in SOC include dyschromia, benign growths (dermatosis papulosa nigra), hyperkinetic facial lines, volume loss, and skin laxity.42 Key principles to consider when treating SOC patients are the impact of ethnicity on aging and facial structure, the patient’s desired cosmetic outcome, tissue reaction to anticipated treatments, and the patient’s expectations for recommended therapies.
Aging in SOC Patients
Skin aging can be classified as intrinsic aging or extrinsic aging. Intrinsic aging is genetic and involves subsurface changes such as volume loss, muscle atrophy, and resorption of bony structure. Extrinsic aging (or photoaging) involves surface changes of the epidermis/dermis and manifests as mottled pigmentation, textural changes, and fine wrinkling. Due to the photoprotection of melanin (black skin=SPF 13.4), skin aging in SOC patients is delayed by 10 to 20 years.43 In addition, SOC patients have more reactive collagen and can benefit from noninvasive cosmetic procedures such as fillers and skin-tightening procedures.42
Cosmetic Treatments and Procedures
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (benign growths of skin that have a genetic predisposition)44 occur mainly on the face but can involve the entire body. Treatment modalities include electrodesiccation, cryotherapy, scissor excision, and laser surgery.45
Treatment of hyperkinetic facial lines with botulinum toxin type A is a safe and effective procedure in patients with SOC. Grimes and Shabazz46 performed a 4-month, randomized, double-blind study that evaluated the treatment of glabellar lines in women with Fitzpatrick skin types V and VI. The results demonstrated that the duration of effects was the same in the patients who received either 20 or 30 U of botulinum toxin type A.46 Dynamic rhytides (furrows and frown/scowl lines arising from laughing, frowning, or smiling) can be treated safely in patients with SOC using botulinum toxin type A off label for relaxation of the upper and lower hyperkinetic muscles that result in these unwanted signs of aging. Botulinum toxin type A often is used for etched-in crow’s-feet, which rarely are evident in SOC patients.47 Facial shaping also can be accomplished by injecting botulinum toxin type A in combination with soft-tissue dermal fillers.47
Although black individuals do not experience perioral rhytides at the frequency of white individuals, they experience a variety of other cosmetic issues related to skin sagging and sinking. Currently available hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers have been shown to be safe in patients with Fitzpatrick skin types IV through VI.48 Two studies evaluated fillers in patients with SOC, specifically HA49 and calcium hydroxylapatite,50 focused on treatment of the nasolabial folds and the potential risk for dyspigmentation and keloidal scarring. Taylor et al49 noted that the risk of hyperpigmentation was 6% to 9% for large- and small-particle HA, respectively, and was associated with the serial or multiple puncture injection technique. No hypertrophic or keloidal scarring occurred in both studies.49,50
Facial contouring applications with fillers include glabellar lines, temples, nasal bridge, tear troughs, malar and submalar areas, nasolabial folds, radial lines, lips, marionette lines, mental crease, and chin. Hyaluronic acid fillers also can be used for lip enhancement.47 Although white women are looking to increase the size of their lips, black women are seeking augmentation to restore their lip size to that of their youth. Black individuals do not experience the same frequency of perioral rhytides as white patients, but they experience a variety of other issues related to skin sagging and sinking. Unlike white women, enhancement of the vermilion border rarely is performed in black women due to development of rhytides, predominantly in the body of the lip below the vermilion border in response to volume loss in the upper lip while the lower lip usually maintains its same appearance.47
Facial enhancement utilizing poly-L-lactic acid can be used safely in SOC patients.51 Poly-L-lactic acid microparticles induce collagen formation, leading to dermal thickening over 3 to 6 months; however, multiple sessions are required to achieve optimal aesthetic results.
Patients with more reactive collagen can benefit from noninvasive cosmetic procedures such as skin-tightening procedures.52 Radiofrequency and microfocused ultrasound are cosmetic procedures used to provide skin tightening and facial lifting. They are safe and effective treatments for patients with Fitzpatrick skin types IV to VI.53 Histologically, there is less thinning of collagen bundles and elastic tissue in ethnic skin. Due to stimulation of collagen by these procedures, most SOC patients will experience a more enhanced response, requiring fewer treatment sessions than white individuals.
Conclusion
Medical and aesthetic facial concerns in SOC patients vary and can be a source of emotional and psychological distress that can negatively impact quality of life. The approach to the treatment of SOC patients should be a balance between tolerability and efficacy, considering the potential risk for PIH.
- White GM. Recent findings in the epidemiologic evidence, classification, and subtypes of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39(2 pt 3):S34-S37.
- Halder RM, Grimes PE, McLaurin CL, et al. Incidence of common dermatoses in a predominantly black dermatologic practice. Cutis. 1983;32:388, 390.
- Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
- Davis SA, Narahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Perkins AC, Cheng CE, Hillebrand GG, et al. Comparison of the epidemiology of acne vulgaris among Caucasians, Asian, Continental Indian and African American women. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:1054-1060.
- Taylor SC, Cook-Bolden F, Rahman Z, et al. Acne vulgaris in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl):S98-S106.
- Davis EC, Callender VD. A review of acne in ethnic skin: pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and management strategies. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010;3:24-38.
- Halder RM, Holmes YC, Bridgeman-Shah S, et al. A clinicohistologic study of acne vulgaris in black females (abstract). J Invest Dermatol. 1996;106:888.
- Plewig G, Fulton JE, Kligman AM. Pomade acne. Arch Dermatol. 1970;101:580-584.
- Kligman AM, Mills OH. Acne cosmetica. Arch Dermatol. 1972;106:893-897.
- Halder RM, Brooks HL, Callender VD. Acne in ethnic skin. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:609-615.
- Callender VD. Acne in ethnic skin: special considerations for therapy. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:184-195.
- Winhoven SM. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in an Asian patient. a dramatic response to oral isotretinoin (13-cis-retinoic acid). Br J Med. 2005;152:368-403.
- Sarkar R, Bansal S, Garg VK. Chemical peels for melasma in dark-skinned patients. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2012;5:247-253.
- Alexis AF, Coley MK, Nijhawan RI, et al. Nonablative fractional laser resurfacing for acne scarring in patients with Fitzpatrick skin phototypes IV-VI. Dermatol Surg. 2016;42:392-402.
- Culp B, Scheinfeld N. Rosacea: a review. P T. 2009;34:38-45.
- Al-Dabagh A, Davis SA, McMichael AJ, et al. Rosacea in skin of color: not a rare diagnosis. Dermatol Online J. 2014:20. pii:13030/qt1mv9r0ss.
- Del Rosso JQ. Advances in understanding and managing rosacea: part 1: connecting the dots between pathophysiological mechanisms and common clinical features of rosacea with emphasis on vascular changes and facial erythema. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012;5:16-25.
- Jackson JM, Knuckles M, Minni JP, et al. The role of brimonidine tartrate gel in the treatment of rosacea. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;23:529-538.
- Patel NU, Shukla S, Zaki J, et al. Oxymetazoline hydrochloride cream for facial erythema associated with rosacea. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2017;10:104954.
- Weinkle AP, Doktor V, Emer J. Update on the management of rosacea. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;8:159-177.
- Grimes PE. Skin and hair cosmetic issues in women of color. Dermatol Clin. 2000;19:659-665.
- Taylor A, Pawaskar M, Taylor SL, et al. Prevalence of pigmentary disorders and their impact on quality of life: a prospective cohort study. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2008;7:164-168.
- Davis EC, Callender VD. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: a review of the epidemiology, clinical features, and treatment options in skin of color. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010;3:20-31.
- Grimes PE. Melasma: etiologic and therapeutic considerations. Arch Dermatol. 1995;131:1453-1457.
- Handel AC, Miot LD, Miot HA. Melasma: a clinical and epidemiological review. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:771-782.
- Callender VD, Reid SD, Obayan O, et al. Diagnostic clues to frontal fibrosing alopecia in patients of African descent. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2016;9:45-51.
- Narang T, Sawatkar GU, Kumaran MS, et al. Minocycline for recurrent and/or chronic erythema nodosum leprosum. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1026-1028.
- Boyer M, Katta R, Markus R. Diltiazem-induced photodistributed hyperpigmentation. Dermatol Online J. 2003;9:10.
- Pandya AG, Guevara IL. Disorders of hyperpigmentation. Dermatol Clin. 2000;18:91-98.
- Taylor SC, Torok H, Jones T, et al. Efficacy and safety of a new triple-combination agent for the treatment of facial melasma. Cutis. 2003;72:67-72.
- Bulengo-Ransby SM. Topical tretinoin (retinoic acid) therapy for hyperpigmented lesions caused by inflammation of the skin in black patients. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1438-1443.
- Grimes P, Callender V. Tazarotene cream for postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and acne vulgaris in darker skin: a double-blind, randomized, vehicle-controlled study. Cutis. 2006;77:45-50.
- Jacyk WK. Adapalene in the treatment of African patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2001;15(suppl 3):37-42.
- Kircik LH. Efficacy and safety of azelaic acid (AzA) gel 15% in the treatment of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and acne: a 16-week, baseline-controlled study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2011;10:586-590.
- Lee HC, Thng TG, Goh CL. Oral tranexamic acid (TA) in the treatment of melasma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:385-392.
- Kindred C, Okereke U, Callender VD. Skin-lightening agents: an overview of prescription, office-dispensed, and over-the-counter products. Cosmet Dermatol. 2013;26:18-26.
- Makino ET, Kadoya K, Sigler ML, et al. Development and clinical assessment of a comprehensive product for pigmentation control in multiple ethnic populations. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:1562-1570.
- Halder R, Rodney I, Munhutu M, et al. Evaluation and effectiveness of a photoprotection composition (sunscreen) on subjects of skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72(suppl 1):AB215.
- Castanedo-Cazares JP, Hernandez-Blanco D, Carlos-Ortega B, et al. Near-visible light and UV photoprotection in the treatment of melasma: a double-blind randomized trial. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2014;30:35-42.
- American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. 2016 Cosmetic Surgery National Data Bank Statistics. https://www.surgery.org/sites/default/files/ASAPS-Stats2016.pdf. Accessed November 15, 2017.
- Burgess CM. Soft tissue augmentation in skin of color: market growth, available fillers and successful techniques. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:51-55.
- Davis EC, Callender VD. Aesthetic dermatology for aging ethnic skin. Dermatol Surg. 2011;37:901-917.
- Grimes PE, Arora S, Minus HR, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra. Cutis. 1983;32:385-386.
- Lupo M. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: treatment options. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:29-30.
- Grimes PE, Shabazz D. A four-month randomized, double-blind evaluation of the efficacy of botulinum toxin type A for the treatment of glabellar lines in women with skin types V and VI. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35:429-435.
- Burgess CM, Awosika O. Ethnic and gender considerations in the use of facial injectables: African-American patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;136(5 suppl):28S-31S.
- Taylor SC, Kelly AP, Lim HW, et al, eds. Taylor and Kelly’s Dermatology for Skin of Color. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2016.
- Taylor SC, Burgess CM, Callender VD. Safety of nonanimal stabilized hyaluronic acid dermal fillers in patients with skin of color: a randomized, evaluator-blinded comparative trial. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35(suppl 2):1653-1660.
- Marmur ES, Taylor SC, Grimes PE, et al. Six-month safety results of calcium hydroxylapatite for treatment of nasolabial folds in Fitzpatrick skin types IV to VI. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35(suppl 2):1641-1645.
- Hamilton TK, Burgess CM. Consideration for the use of injectable poly-L-lactic acid in people of color. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:451-456.
- Fabi SG, Goldman MP. Retrospective evaluation of micro-focused ultrasound for lifting and tightening of the face and neck. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:569-575.
- Harris MO, Sundaram HA. Safety of microfocused ultrasound with visualization in patients with Fitzpatrick skin phototypes III to VI. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2015;17:355-357.
- White GM. Recent findings in the epidemiologic evidence, classification, and subtypes of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39(2 pt 3):S34-S37.
- Halder RM, Grimes PE, McLaurin CL, et al. Incidence of common dermatoses in a predominantly black dermatologic practice. Cutis. 1983;32:388, 390.
- Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
- Davis SA, Narahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Perkins AC, Cheng CE, Hillebrand GG, et al. Comparison of the epidemiology of acne vulgaris among Caucasians, Asian, Continental Indian and African American women. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:1054-1060.
- Taylor SC, Cook-Bolden F, Rahman Z, et al. Acne vulgaris in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl):S98-S106.
- Davis EC, Callender VD. A review of acne in ethnic skin: pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and management strategies. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010;3:24-38.
- Halder RM, Holmes YC, Bridgeman-Shah S, et al. A clinicohistologic study of acne vulgaris in black females (abstract). J Invest Dermatol. 1996;106:888.
- Plewig G, Fulton JE, Kligman AM. Pomade acne. Arch Dermatol. 1970;101:580-584.
- Kligman AM, Mills OH. Acne cosmetica. Arch Dermatol. 1972;106:893-897.
- Halder RM, Brooks HL, Callender VD. Acne in ethnic skin. Dermatol Clin. 2003;21:609-615.
- Callender VD. Acne in ethnic skin: special considerations for therapy. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:184-195.
- Winhoven SM. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in an Asian patient. a dramatic response to oral isotretinoin (13-cis-retinoic acid). Br J Med. 2005;152:368-403.
- Sarkar R, Bansal S, Garg VK. Chemical peels for melasma in dark-skinned patients. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2012;5:247-253.
- Alexis AF, Coley MK, Nijhawan RI, et al. Nonablative fractional laser resurfacing for acne scarring in patients with Fitzpatrick skin phototypes IV-VI. Dermatol Surg. 2016;42:392-402.
- Culp B, Scheinfeld N. Rosacea: a review. P T. 2009;34:38-45.
- Al-Dabagh A, Davis SA, McMichael AJ, et al. Rosacea in skin of color: not a rare diagnosis. Dermatol Online J. 2014:20. pii:13030/qt1mv9r0ss.
- Del Rosso JQ. Advances in understanding and managing rosacea: part 1: connecting the dots between pathophysiological mechanisms and common clinical features of rosacea with emphasis on vascular changes and facial erythema. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012;5:16-25.
- Jackson JM, Knuckles M, Minni JP, et al. The role of brimonidine tartrate gel in the treatment of rosacea. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;23:529-538.
- Patel NU, Shukla S, Zaki J, et al. Oxymetazoline hydrochloride cream for facial erythema associated with rosacea. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2017;10:104954.
- Weinkle AP, Doktor V, Emer J. Update on the management of rosacea. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;8:159-177.
- Grimes PE. Skin and hair cosmetic issues in women of color. Dermatol Clin. 2000;19:659-665.
- Taylor A, Pawaskar M, Taylor SL, et al. Prevalence of pigmentary disorders and their impact on quality of life: a prospective cohort study. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2008;7:164-168.
- Davis EC, Callender VD. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: a review of the epidemiology, clinical features, and treatment options in skin of color. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010;3:20-31.
- Grimes PE. Melasma: etiologic and therapeutic considerations. Arch Dermatol. 1995;131:1453-1457.
- Handel AC, Miot LD, Miot HA. Melasma: a clinical and epidemiological review. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:771-782.
- Callender VD, Reid SD, Obayan O, et al. Diagnostic clues to frontal fibrosing alopecia in patients of African descent. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2016;9:45-51.
- Narang T, Sawatkar GU, Kumaran MS, et al. Minocycline for recurrent and/or chronic erythema nodosum leprosum. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1026-1028.
- Boyer M, Katta R, Markus R. Diltiazem-induced photodistributed hyperpigmentation. Dermatol Online J. 2003;9:10.
- Pandya AG, Guevara IL. Disorders of hyperpigmentation. Dermatol Clin. 2000;18:91-98.
- Taylor SC, Torok H, Jones T, et al. Efficacy and safety of a new triple-combination agent for the treatment of facial melasma. Cutis. 2003;72:67-72.
- Bulengo-Ransby SM. Topical tretinoin (retinoic acid) therapy for hyperpigmented lesions caused by inflammation of the skin in black patients. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1438-1443.
- Grimes P, Callender V. Tazarotene cream for postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and acne vulgaris in darker skin: a double-blind, randomized, vehicle-controlled study. Cutis. 2006;77:45-50.
- Jacyk WK. Adapalene in the treatment of African patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2001;15(suppl 3):37-42.
- Kircik LH. Efficacy and safety of azelaic acid (AzA) gel 15% in the treatment of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and acne: a 16-week, baseline-controlled study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2011;10:586-590.
- Lee HC, Thng TG, Goh CL. Oral tranexamic acid (TA) in the treatment of melasma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:385-392.
- Kindred C, Okereke U, Callender VD. Skin-lightening agents: an overview of prescription, office-dispensed, and over-the-counter products. Cosmet Dermatol. 2013;26:18-26.
- Makino ET, Kadoya K, Sigler ML, et al. Development and clinical assessment of a comprehensive product for pigmentation control in multiple ethnic populations. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:1562-1570.
- Halder R, Rodney I, Munhutu M, et al. Evaluation and effectiveness of a photoprotection composition (sunscreen) on subjects of skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72(suppl 1):AB215.
- Castanedo-Cazares JP, Hernandez-Blanco D, Carlos-Ortega B, et al. Near-visible light and UV photoprotection in the treatment of melasma: a double-blind randomized trial. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2014;30:35-42.
- American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. 2016 Cosmetic Surgery National Data Bank Statistics. https://www.surgery.org/sites/default/files/ASAPS-Stats2016.pdf. Accessed November 15, 2017.
- Burgess CM. Soft tissue augmentation in skin of color: market growth, available fillers and successful techniques. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:51-55.
- Davis EC, Callender VD. Aesthetic dermatology for aging ethnic skin. Dermatol Surg. 2011;37:901-917.
- Grimes PE, Arora S, Minus HR, et al. Dermatosis papulosa nigra. Cutis. 1983;32:385-386.
- Lupo M. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: treatment options. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:29-30.
- Grimes PE, Shabazz D. A four-month randomized, double-blind evaluation of the efficacy of botulinum toxin type A for the treatment of glabellar lines in women with skin types V and VI. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35:429-435.
- Burgess CM, Awosika O. Ethnic and gender considerations in the use of facial injectables: African-American patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;136(5 suppl):28S-31S.
- Taylor SC, Kelly AP, Lim HW, et al, eds. Taylor and Kelly’s Dermatology for Skin of Color. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2016.
- Taylor SC, Burgess CM, Callender VD. Safety of nonanimal stabilized hyaluronic acid dermal fillers in patients with skin of color: a randomized, evaluator-blinded comparative trial. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35(suppl 2):1653-1660.
- Marmur ES, Taylor SC, Grimes PE, et al. Six-month safety results of calcium hydroxylapatite for treatment of nasolabial folds in Fitzpatrick skin types IV to VI. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35(suppl 2):1641-1645.
- Hamilton TK, Burgess CM. Consideration for the use of injectable poly-L-lactic acid in people of color. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:451-456.
- Fabi SG, Goldman MP. Retrospective evaluation of micro-focused ultrasound for lifting and tightening of the face and neck. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:569-575.
- Harris MO, Sundaram HA. Safety of microfocused ultrasound with visualization in patients with Fitzpatrick skin phototypes III to VI. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2015;17:355-357.
Practice Points
- Treat acne in skin of color (SOC) patients early and aggressively to prevent or minimize subsequent postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) and acne scarring.
- Vascular lasers and intense pulsed light may be used to address the vascular components of rosacea; however, the latter is not recommended in Fitzpatrick skin types IV to VI.
- Hydroquinone is the gold standard for skin lightening and is often used as a first-line therapy for melasma and PIH.
- Photoprotection is an essential component of therapy for hyperpigmented skin disorders.
- Cosmetic procedures are gaining popularity in the SOC population. When treating SOC patients, consider the impact of ethnicity on aging and facial structure, the patient's desired cosmetic outcome, tissue reaction to anticipated treatments, and the patient's expectations for recommended therapies.
Assessing the Effectiveness of Knowledge-Based Interventions in Increasing Skin Cancer Awareness, Knowledge, and Protective Behaviors in Skin of Color Populations
Malignant melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma account for approximately 40% of all neoplasms among the white population in the United States. Skin cancer is the most common malignancy in the United States.1 However, despite this occurrence, there are limited data regarding skin cancer in individuals with skin of color (SOC). The 5-year survival rates for melanoma are 58.2% for black individuals, 69.7% for Hispanics, and 70.9% for Asians compared to 79.8% for white individuals in the United States.2 Even though SOC populations have lower incidences of skin cancer—melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma—they exhibit higher death rates.3-7 Nonetheless, no specific guidelines exist to address sun exposure and safety habits in SOC populations.6,8 Furthermore, current demographics suggest that by the year 2050, approximately half of the US population will be nonwhite.4 Paradoxically, despite having increased sun protection from greater amounts of melanin in their skin, black individuals are more likely to present with advanced-stage melanoma (eg, stage III/IV) compared to white individuals.8-12 Furthermore, those of nonwhite populations are more likely to present with more advanced stages of acral lentiginous melanomas than white individuals.13,14 Hispanics also face an increasing incidence of more invasive acral lentiginous melanomas.15 Overall, SOC patients have the poorest skin cancer prognosis, and the data suggest that the reason for this paradox is delayed diagnosis.1
Although skin cancer is largely a preventable condition, the literature suggests that lack of awareness of melanoma among ethnic minorities is one of the main reasons for their poor skin cancer prognosis.16 This lack of awareness decreases the likelihood that an SOC patient would be alert to early detection of cancerous changes.17 Because educating at-risk SOC populations is key to decreasing skin cancer risk, this study focused on determining the efficacy of major knowledge-based interventions conducted to date.1 Overall, we sought to answer the question, do knowledge-based interventions increase skin cancer awareness, knowledge, and protective behavior among people of color?
Methods
For this review, the Cochrane method of analysis was used to conduct a thorough search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE (1994-2016), as well as a search of CINAHL (1997-2016), PsycINFO (1999-2016), and Web of Science (1965-2016), using a combination of more than 100 search terms including but not limited to skin cancer, skin of color, intervention, and ethnic skin. The search yielded a total of 52 articles (Figure). Following review, only 8 articles met inclusion criteria, which were as follows: (1) study was related to skin cancer in SOC patients, which included an intervention to increase skin cancer awareness and knowledge; (2) study included adult participants or adolescents aged 12 to 18 years; (3) study was written in English; and (4) study was published in a peer-reviewed journal. Of the remaining 8 articles, 4 were excluded due to the following criteria: (1) study failed to provide both preintervention and postintervention data, (2) study failed to provide quantitative data, and (3) study included participants who worked as health care professionals or ancillary staff. As a result, a total of 4 articles were analyzed and discussed in this review (Table).
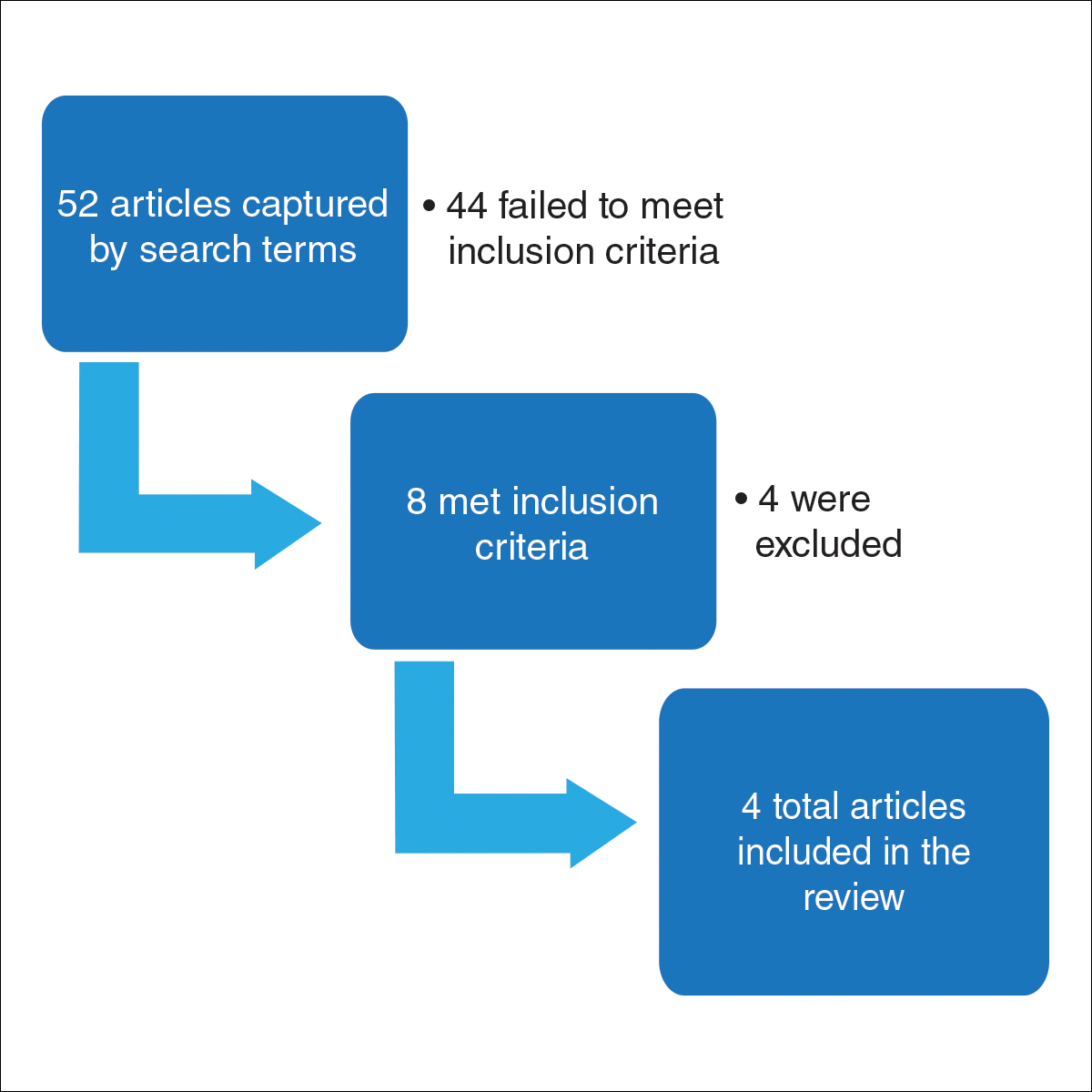
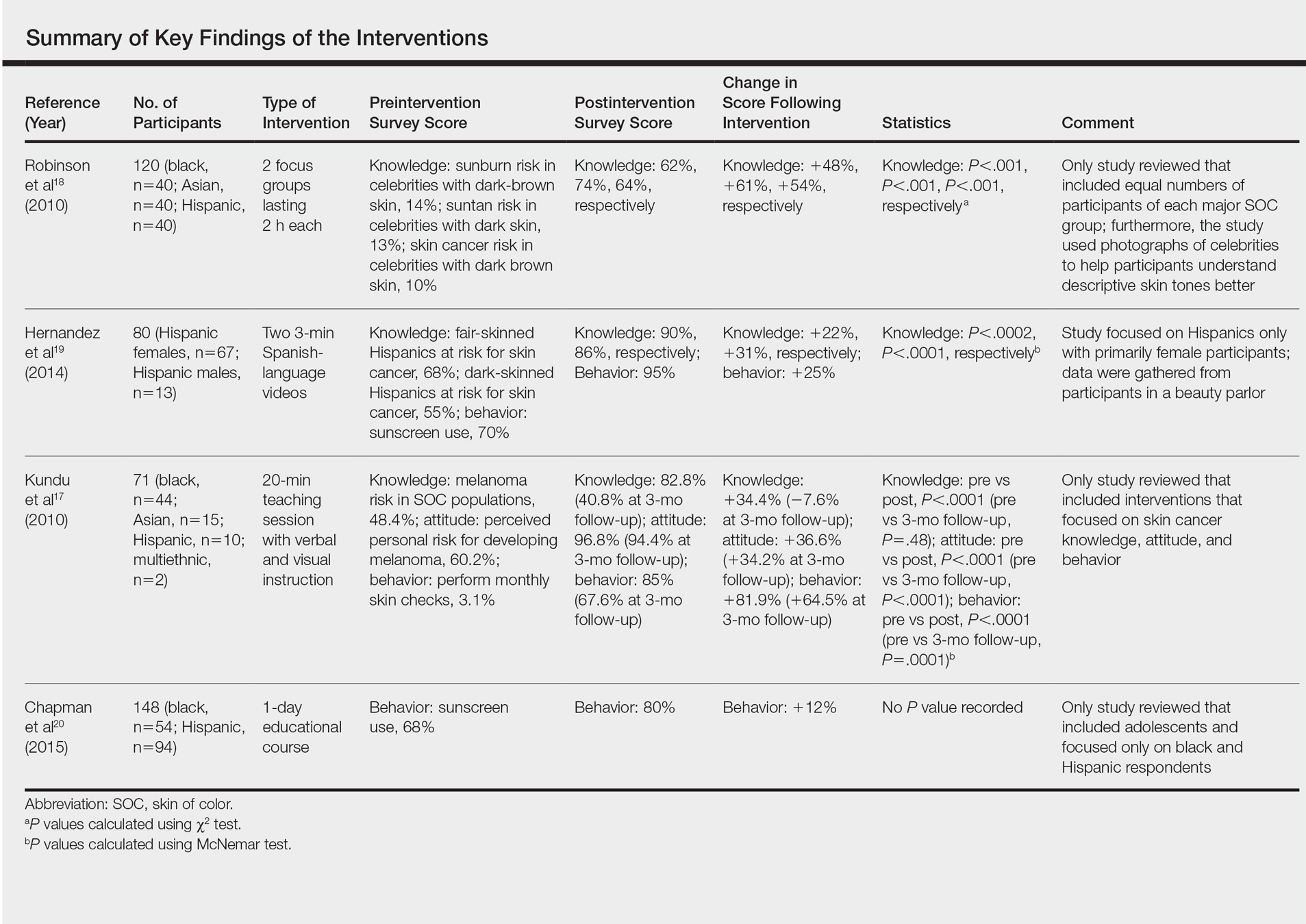
Results
Robinson et al18 conducted 12 focus groups with 120 total participants (40 black, 40 Asian, and 40 Hispanic patients). Participants engaged in a 2-hour tape-recorded focus group with a moderator guide on melanoma and skin cancer. Furthermore, they also were asked to assess skin cancer risk in 5 celebrities with different skin tones. The statistically significant preintervention results of the study (χ2=4.6, P<.001) were as follows: only 2%, 4%, and 14% correctly reported that celebrities with a very fair skin type, a fair skin type, and very dark skin type, respectively, could get sunburn, compared to 75%, 76%, and 62% post-intervention. Additionally, prior to intervention, 14% of the study population believed that dark brown skin type could get sunburn compared to 62% of the same group postintervention. This study demonstrated that the intervention helped SOC patients better identify their ability to get sunburn and identify their skin cancer risk.18
Hernandez et al19 used a video-based intervention in a Hispanic community, which was in contrast to the multiracial focus group intervention conducted by Robinson et al.18 Eighty Hispanic individuals were recruited from beauty salons to participate in the study. Participants watched two 3-minute videos in Spanish and completed a preintervention and postintervention survey. The first video emphasized the photoaging benefits of sun protection, while the second focused on skin cancer prevention. Preintervention surveys indicated that only 54 (68%) participants believed that fair-skinned Hispanics were at risk for skin cancer, which improved to 72 (90%) participants postintervention. Furthermore, initially only 44 (55%) participants thought those with darker skin types could develop skin cancer, but this number increased to 69 (86%) postintervention. For both questions regarding fair and dark skin, the agreement proportion was significantly different between the preeducation and posteducation videos (P<.0002 for the fair skin question and P<.0001 for the dark skin question). This study greatly increased awareness of skin cancer risk among Hispanics,19 similar to the Robinson et al18 study.
In contrast to 2-hour focus groups or 3-minute video–based interventions, a study by Kundu et al17 employed a 20-minute educational class-based intervention with both verbal and visual instruction. This study assessed the efficacy of an educational tutorial on improving awareness and early detection of melanoma in SOC individuals. Photographs were used to help participants recognize the ABCDEs of melanoma and to show examples of acral lentiginous melanomas in white individuals. A total of 71 participants completed a preintervention questionnaire, participated in a 20-minute class, and completed a postintervention questionnaire immediately after and 3 months following the class. The study population included 44 black, 15 Asian, 10 Hispanic, and 2 multiethnic participants. Knowledge that melanoma is a skin cancer increased from 83.9% to 100% immediately postintervention (P=.0001) and 97.2% at 3 months postintervention (P=.0075). Additionally, knowledge that people of color are at risk for melanoma increased from 48.4% preintervention to 82.8% immediately postintervention (P<.0001). However, only 40.8% of participants retained this knowledge at 3 months postintervention. Because only 1 participant reported a family history of skin cancer, the authors hypothesized that the reason for this loss of knowledge was that most participants were not personally affected by friends or family members with melanoma. A future study with an appropriate control group would be needed to support this claim. This study shed light on the potential of class-based interventions to increase both awareness and knowledge of skin cancer in SOC populations.17
A study by Chapman et al20 examined the effects of a sun protection educational program on increasing awareness of skin cancer in Hispanic and black middle school students in southern Los Angeles, California. It was the only study we reviewed that focused primarily on adolescents. Furthermore, it included the largest sample size (N=148) analyzed here. Students were given a preintervention questionnaire to evaluate their awareness of skin cancer and current sun-protection practices. Based on these results, the investigators devised a set of learning goals and incorporated them into an educational pamphlet. The intervention, called “Skin Teaching Day,” was a 1-day program discussing skin cancer and the importance of sun protection. Prior to the intervention, 68% of participants reported that they used sunscreen. Three months after completing the program, 80% of participants reported sunscreen use, an increase of 12% prior to the intervention. The results of this study demonstrated the unique effectiveness and potential of pamphlets in increasing sunscreen use.20
Comment
Overall, various methods of interventions such as focus groups, videos, pamphlets, and lectures improved knowledge of skin cancer risk and sun-protection behaviors in SOC populations. Furthermore, the unique differences of each study provided important insights into the successful design of an intervention.
An important characteristic of the Robinson et al18 study was the addition of photographs, which allowed participants not only to visualize different skin tones but also provided them with the opportunity to relate themselves to the photographs; by doing so, participants could effectively pick out the skin tone that best suited them. Written SOC scales are limited to mere descriptions and thus make it more difficult for participants to accurately identify the tone that best fits them. Kundu et al17 used photographs to teach skin self-examination and ABCDEs for detection of melanoma. Additionally, both studies used photographs to demonstrate examples of skin cancer.17,18 Recent evidence suggests the use of visuals can be efficacious for improving skin cancer knowledge and awareness; a study in 16 SOC kidney transplant recipients found that the addition of photographs of squamous cell carcinoma in various skin tones to a sun-protection educational pamphlet was more effective than the original pamphlet without photographs.21
In contrast to the Robinson et al18 study and Hernandez et al19 study, the Kundu et al17 study showed photographs of acral lentiginous melanomas in white patients rather than SOC patients. However, SOC populations may be less likely to relate to or identify skin changes in skin types that are different from their own. This technique was still beneficial, as acral lentiginous melanoma is the most common type of melanoma in SOC populations. Another benefit of the study was that it was the only study reviewed that included a follow-up postintervention questionnaire. Such data is useful, as it demonstrates how muchinformation is retained by participants and may be more likely to predict compliance with skin cancer protective behaviors.17
The Hernandez et al19 study is unique in that it was the only one to include an educational intervention entirely in Spanish, which is important to consider, as language may be a hindrance to participants’ understanding in the other studies, particularly Hispanics, possibly leading to a lack of information retention regarding sun-protective behaviors. Furthermore, it also was the only study to utilize videos as a method for interventions. The 3-minute videos demonstrated that interventions could be efficient as compared to the 2-hour in-class intervention used by Robinson et al18 and the 20-minute intervention used by Kundu et al.17 Additionally, videos also could be more cost-effective, as incentives for large focus groups would no longer be needed. Furthermore, in the Hernandez et al19 study, there was minimal to no disruption in the participants’ daily routine, as the participants were getting cosmetic services while watching the videos, perhaps allowing them to be more attentive. In contrast, both the Robinson et al18 and Kundu et al17 studies required time out from the participants’ daily schedules. In addition, these studies were notably longer than the Hernandez et al19 study. The 8-hour intervention in the Chapman et al20 study also may not be feasible for the general population because of its excessive length. However, the intervention was successful among the adolescent participants, which suggested that shorter durations are effective in the adult population and longer interventions may be more appropriate for adolescents because they benefit from peer activity.
Despite the success of the educational interventions as outlined in the 4 studies described here, a major epidemiologic flaw is that these interventions included only a small percentage of the target population. The largest total number of adults surveyed and undergoing an intervention in any of the populations was only 120.17 By failing to reach a substantial proportion of the population at risk, the number of preventable deaths likely will not decrease. The authors believe a larger-scale intervention would provide meaningful change. Australia’s SunSmart campaign to increase skin cancer awareness in the Australian population is an example of one such large-scale national intervention. The campaign focused on massive television advertisements in the summer to educate participants about the dangers of skin cancer and the importance of protective behaviors. Telephone surveys conducted from 1987 to 2011 demonstrated that more exposure to the advertisements in the SunSmart campaign meant that individuals were more likely to use sunscreen and avoid sun exposure.22 In the United States, a similar intervention would be of great benefit in educating SOC populations regarding skin cancer risk. Additionally, dermatology residents need to be adequately trained to educate patients of color about the risk for skin cancer, as survey data indicated more than 80% of Australian dermatologists desired more SOC teaching during their training and 50% indicated that they would have time to learn it during their training if offered.23 Furthermore, one study suggested that future interventions must include primary-, secondary-, and tertiary-prevention methods to effectively reduce skin cancer risk among patients of color.24 Primary prevention involves sun avoidance, secondary prevention involves detecting cancerous lesions, and tertiary prevention involves undergoing treatment of skin malignancies. However, increased knowledge does not necessarily mean increased preventative action will be employed (eg, sunscreen use, wearing sun-protective clothing and sunglasses, avoiding tanning beds and excessive sun exposure). Additional studies that demonstrate a notable increase in sun-protective behaviors related to increased knowledge are needed.
Because retention of skin cancer knowledge decreased in several postintervention surveys, there also is a dire need for continuing skin cancer education in patients of color, which may be accomplished through a combination effort of television advertisement campaigns, pamphlets, social media, community health departments, or even community members. For example, a pilot program found that Hispanic lay health workers who are educated about skin cancer may serve as a bridge between medical providers and the Hispanic community by encouraging individuals in this population to get regular skin examinations from a physician.25 Overall, there are currently gaps in the understanding and treatment of skin cancer in people of color.26 Identifying the advantages and disadvantages of all relevant skin cancer interventions conducted in the SOC population will hopefully guide future studies to help close these gaps by allowing others to design the best possible intervention. By doing so, researchers can generate an intervention that is precise, well-informed, and effective in decreasing mortality rates from skin cancer among SOC populations.
Conclusion
All of the studies reviewed demonstrated that instructional and educational interventions are promising methods for improving either knowledge, awareness, or safe skin practices and sun-protective behaviors in SOC populations to differing degrees (Table). Although each of the 4 interventions employed their own methods, they all increased 1 or more of the 3 aforementioned concepts—knowledge, awareness, or safe skin practices and sun-protective behaviors—when comparing postsurvey to presurvey data. However, the critically important message derived from this research is that there is a tremendous need for a substantial large-scale educational intervention to increase knowledge regarding skin cancer in SOC populations.
- Agbai ON, Buster K, Sanchez M, et al. Skin cancer and photoprotection in people of color: a review and recommendations for physicians and the public. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:748-762.
- Cormier JN, Xing Y, Ding M, et al. Ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1907-1914.
- Gloster HM Jr, Neal K. Skin cancer in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:741-760.
- Dawes SM, Tsai S, Gittleman H, et al. Racial disparities in melanoma survival. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:983-991.
- Byrd KM, Wilson DC, Hoyler SS, et al. Advanced presentation of melanoma in African Americans. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:21-24.
- Hu S, Parmet Y, Allen G, et al. Disparity in melanoma: a trend analysis of melanoma incidence and stage at diagnosis among whites, Hispanics, and blacks in Florida. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:1369-1374.
- Wu XC, Eide MJ, King J, et al. Racial and ethnic variations in incidence and survival of cutaneous melanoma in the United States, 1999-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5, suppl 1):S26-S37.
- Byrd-Miles K, Toombs EL, Peck GL. Skin cancer in individuals of African, Asian, Latin-American, and American-Indian descent: differences in incidence, clinical presentation, and survival compared to Caucasians. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:10-16.
- Hu S, Soza-Vento RM, Parker DF, et al. Comparison of stage at diagnosis of melanoma among Hispanic, black, and white patients in Miami-Dade County, Florida. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:704-708.
- Hu S, Parker DF, Thomas AG, et al. Advanced presentation of melanoma in African Americans: the Miami-Dade County experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;5:1031-1032.
- Bellows CF, Belafsky P, Fortgang IS, et al. Melanoma in African-Americans: trends in biological behavior and clinical characteristics over two decades. J Surg Oncol. 2001;78:10-16.
- Pritchett EN, Doyle A, Shaver CM, et al. Nonmelanoma skin cancer in nonwhite organ transplant recipients. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:1348-1353.
- Shin S, Palis BE, Phillips JL, et al. Cutaneous melanoma in Asian-Americans. J Surg Oncol. 2009;99:114-118.
- Stubblefield J, Kelly B. Melanoma in non-caucasian populations. Surg Clin North Am. 2014;94:1115-1126.
- Bradford PT, Goldstein AM, McMaster ML, et al. Acral lentiginous melanoma: incidence and survival patterns in the United States, 1986-2005. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:427-434.
- Pichon LC, Corral I, Landrine H, et al. Perceived skin cancer risk and sunscreen use among African American adults. J Health Psychol. 2010;15:1181-1189.
- Kundu RV, Kamaria M, Ortiz S, et al. Effectiveness of a knowledge-based intervention for melanoma among those with ethnic skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:777-784.
- Robinson JK, Joshi KM, Ortiz S, et al. Melanoma knowledge, perception, and awareness in ethnic minorities in Chicago: recommendations regarding education. Psychooncology. 2010;20:313-320.
- Hernandez C, Wang S, Abraham I, et al. Evaluation of educational videos to increase skin cancer risk awareness and sun safe behaviors among adult Hispanics. J Cancer Educ. 2014;29:563-569.
- Chapman LW, Ochoa A, Tenconi F, et al. Dermatologic health literacy in underserved communities: a case report of south Los Angeles middle schools. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21. pii:13030/qt8671p40n.
- Yanina G, Gaber R, Clayman ML, et al. Sun protection education for diverse audiences: need for skin cancer pictures. J Cancer Educ. 2015;30:187-189.
- Dobbinson SJ, Volkov A, Wakefield MA. Continued impact of sunsmart advertising on youth and adults’ behaviors. Am J Prev Med. 2015;49:20-28.
- Rodrigues MA, Ross AL, Gilmore S, et al. Australian dermatologists’ perspective on skin of colour: results of a national survey [published online December 9, 2016]. Australas J Dermatol. doi:10.1111/ajd.12556.
- Jacobsen A, Galvan A, Lachapelle CC, et al. Defining the need for skin cancer prevention education in uninsured, minority, and immigrant communities. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:1342-1347.
- Hernandez C, Kim H, Mauleon G, et al. A pilot program in collaboration with community centers to increase awareness and participation in skin cancer screening among Latinos in Chicago. J Cancer Educ. 2013;28:342-345.
- Kailas A, Solomon JA, Mostow EN, et al. Gaps in the understanding and treatment of skin cancer in people of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:144-149.
Malignant melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma account for approximately 40% of all neoplasms among the white population in the United States. Skin cancer is the most common malignancy in the United States.1 However, despite this occurrence, there are limited data regarding skin cancer in individuals with skin of color (SOC). The 5-year survival rates for melanoma are 58.2% for black individuals, 69.7% for Hispanics, and 70.9% for Asians compared to 79.8% for white individuals in the United States.2 Even though SOC populations have lower incidences of skin cancer—melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma—they exhibit higher death rates.3-7 Nonetheless, no specific guidelines exist to address sun exposure and safety habits in SOC populations.6,8 Furthermore, current demographics suggest that by the year 2050, approximately half of the US population will be nonwhite.4 Paradoxically, despite having increased sun protection from greater amounts of melanin in their skin, black individuals are more likely to present with advanced-stage melanoma (eg, stage III/IV) compared to white individuals.8-12 Furthermore, those of nonwhite populations are more likely to present with more advanced stages of acral lentiginous melanomas than white individuals.13,14 Hispanics also face an increasing incidence of more invasive acral lentiginous melanomas.15 Overall, SOC patients have the poorest skin cancer prognosis, and the data suggest that the reason for this paradox is delayed diagnosis.1
Although skin cancer is largely a preventable condition, the literature suggests that lack of awareness of melanoma among ethnic minorities is one of the main reasons for their poor skin cancer prognosis.16 This lack of awareness decreases the likelihood that an SOC patient would be alert to early detection of cancerous changes.17 Because educating at-risk SOC populations is key to decreasing skin cancer risk, this study focused on determining the efficacy of major knowledge-based interventions conducted to date.1 Overall, we sought to answer the question, do knowledge-based interventions increase skin cancer awareness, knowledge, and protective behavior among people of color?
Methods
For this review, the Cochrane method of analysis was used to conduct a thorough search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE (1994-2016), as well as a search of CINAHL (1997-2016), PsycINFO (1999-2016), and Web of Science (1965-2016), using a combination of more than 100 search terms including but not limited to skin cancer, skin of color, intervention, and ethnic skin. The search yielded a total of 52 articles (Figure). Following review, only 8 articles met inclusion criteria, which were as follows: (1) study was related to skin cancer in SOC patients, which included an intervention to increase skin cancer awareness and knowledge; (2) study included adult participants or adolescents aged 12 to 18 years; (3) study was written in English; and (4) study was published in a peer-reviewed journal. Of the remaining 8 articles, 4 were excluded due to the following criteria: (1) study failed to provide both preintervention and postintervention data, (2) study failed to provide quantitative data, and (3) study included participants who worked as health care professionals or ancillary staff. As a result, a total of 4 articles were analyzed and discussed in this review (Table).


Results
Robinson et al18 conducted 12 focus groups with 120 total participants (40 black, 40 Asian, and 40 Hispanic patients). Participants engaged in a 2-hour tape-recorded focus group with a moderator guide on melanoma and skin cancer. Furthermore, they also were asked to assess skin cancer risk in 5 celebrities with different skin tones. The statistically significant preintervention results of the study (χ2=4.6, P<.001) were as follows: only 2%, 4%, and 14% correctly reported that celebrities with a very fair skin type, a fair skin type, and very dark skin type, respectively, could get sunburn, compared to 75%, 76%, and 62% post-intervention. Additionally, prior to intervention, 14% of the study population believed that dark brown skin type could get sunburn compared to 62% of the same group postintervention. This study demonstrated that the intervention helped SOC patients better identify their ability to get sunburn and identify their skin cancer risk.18
Hernandez et al19 used a video-based intervention in a Hispanic community, which was in contrast to the multiracial focus group intervention conducted by Robinson et al.18 Eighty Hispanic individuals were recruited from beauty salons to participate in the study. Participants watched two 3-minute videos in Spanish and completed a preintervention and postintervention survey. The first video emphasized the photoaging benefits of sun protection, while the second focused on skin cancer prevention. Preintervention surveys indicated that only 54 (68%) participants believed that fair-skinned Hispanics were at risk for skin cancer, which improved to 72 (90%) participants postintervention. Furthermore, initially only 44 (55%) participants thought those with darker skin types could develop skin cancer, but this number increased to 69 (86%) postintervention. For both questions regarding fair and dark skin, the agreement proportion was significantly different between the preeducation and posteducation videos (P<.0002 for the fair skin question and P<.0001 for the dark skin question). This study greatly increased awareness of skin cancer risk among Hispanics,19 similar to the Robinson et al18 study.
In contrast to 2-hour focus groups or 3-minute video–based interventions, a study by Kundu et al17 employed a 20-minute educational class-based intervention with both verbal and visual instruction. This study assessed the efficacy of an educational tutorial on improving awareness and early detection of melanoma in SOC individuals. Photographs were used to help participants recognize the ABCDEs of melanoma and to show examples of acral lentiginous melanomas in white individuals. A total of 71 participants completed a preintervention questionnaire, participated in a 20-minute class, and completed a postintervention questionnaire immediately after and 3 months following the class. The study population included 44 black, 15 Asian, 10 Hispanic, and 2 multiethnic participants. Knowledge that melanoma is a skin cancer increased from 83.9% to 100% immediately postintervention (P=.0001) and 97.2% at 3 months postintervention (P=.0075). Additionally, knowledge that people of color are at risk for melanoma increased from 48.4% preintervention to 82.8% immediately postintervention (P<.0001). However, only 40.8% of participants retained this knowledge at 3 months postintervention. Because only 1 participant reported a family history of skin cancer, the authors hypothesized that the reason for this loss of knowledge was that most participants were not personally affected by friends or family members with melanoma. A future study with an appropriate control group would be needed to support this claim. This study shed light on the potential of class-based interventions to increase both awareness and knowledge of skin cancer in SOC populations.17
A study by Chapman et al20 examined the effects of a sun protection educational program on increasing awareness of skin cancer in Hispanic and black middle school students in southern Los Angeles, California. It was the only study we reviewed that focused primarily on adolescents. Furthermore, it included the largest sample size (N=148) analyzed here. Students were given a preintervention questionnaire to evaluate their awareness of skin cancer and current sun-protection practices. Based on these results, the investigators devised a set of learning goals and incorporated them into an educational pamphlet. The intervention, called “Skin Teaching Day,” was a 1-day program discussing skin cancer and the importance of sun protection. Prior to the intervention, 68% of participants reported that they used sunscreen. Three months after completing the program, 80% of participants reported sunscreen use, an increase of 12% prior to the intervention. The results of this study demonstrated the unique effectiveness and potential of pamphlets in increasing sunscreen use.20
Comment
Overall, various methods of interventions such as focus groups, videos, pamphlets, and lectures improved knowledge of skin cancer risk and sun-protection behaviors in SOC populations. Furthermore, the unique differences of each study provided important insights into the successful design of an intervention.
An important characteristic of the Robinson et al18 study was the addition of photographs, which allowed participants not only to visualize different skin tones but also provided them with the opportunity to relate themselves to the photographs; by doing so, participants could effectively pick out the skin tone that best suited them. Written SOC scales are limited to mere descriptions and thus make it more difficult for participants to accurately identify the tone that best fits them. Kundu et al17 used photographs to teach skin self-examination and ABCDEs for detection of melanoma. Additionally, both studies used photographs to demonstrate examples of skin cancer.17,18 Recent evidence suggests the use of visuals can be efficacious for improving skin cancer knowledge and awareness; a study in 16 SOC kidney transplant recipients found that the addition of photographs of squamous cell carcinoma in various skin tones to a sun-protection educational pamphlet was more effective than the original pamphlet without photographs.21
In contrast to the Robinson et al18 study and Hernandez et al19 study, the Kundu et al17 study showed photographs of acral lentiginous melanomas in white patients rather than SOC patients. However, SOC populations may be less likely to relate to or identify skin changes in skin types that are different from their own. This technique was still beneficial, as acral lentiginous melanoma is the most common type of melanoma in SOC populations. Another benefit of the study was that it was the only study reviewed that included a follow-up postintervention questionnaire. Such data is useful, as it demonstrates how muchinformation is retained by participants and may be more likely to predict compliance with skin cancer protective behaviors.17
The Hernandez et al19 study is unique in that it was the only one to include an educational intervention entirely in Spanish, which is important to consider, as language may be a hindrance to participants’ understanding in the other studies, particularly Hispanics, possibly leading to a lack of information retention regarding sun-protective behaviors. Furthermore, it also was the only study to utilize videos as a method for interventions. The 3-minute videos demonstrated that interventions could be efficient as compared to the 2-hour in-class intervention used by Robinson et al18 and the 20-minute intervention used by Kundu et al.17 Additionally, videos also could be more cost-effective, as incentives for large focus groups would no longer be needed. Furthermore, in the Hernandez et al19 study, there was minimal to no disruption in the participants’ daily routine, as the participants were getting cosmetic services while watching the videos, perhaps allowing them to be more attentive. In contrast, both the Robinson et al18 and Kundu et al17 studies required time out from the participants’ daily schedules. In addition, these studies were notably longer than the Hernandez et al19 study. The 8-hour intervention in the Chapman et al20 study also may not be feasible for the general population because of its excessive length. However, the intervention was successful among the adolescent participants, which suggested that shorter durations are effective in the adult population and longer interventions may be more appropriate for adolescents because they benefit from peer activity.
Despite the success of the educational interventions as outlined in the 4 studies described here, a major epidemiologic flaw is that these interventions included only a small percentage of the target population. The largest total number of adults surveyed and undergoing an intervention in any of the populations was only 120.17 By failing to reach a substantial proportion of the population at risk, the number of preventable deaths likely will not decrease. The authors believe a larger-scale intervention would provide meaningful change. Australia’s SunSmart campaign to increase skin cancer awareness in the Australian population is an example of one such large-scale national intervention. The campaign focused on massive television advertisements in the summer to educate participants about the dangers of skin cancer and the importance of protective behaviors. Telephone surveys conducted from 1987 to 2011 demonstrated that more exposure to the advertisements in the SunSmart campaign meant that individuals were more likely to use sunscreen and avoid sun exposure.22 In the United States, a similar intervention would be of great benefit in educating SOC populations regarding skin cancer risk. Additionally, dermatology residents need to be adequately trained to educate patients of color about the risk for skin cancer, as survey data indicated more than 80% of Australian dermatologists desired more SOC teaching during their training and 50% indicated that they would have time to learn it during their training if offered.23 Furthermore, one study suggested that future interventions must include primary-, secondary-, and tertiary-prevention methods to effectively reduce skin cancer risk among patients of color.24 Primary prevention involves sun avoidance, secondary prevention involves detecting cancerous lesions, and tertiary prevention involves undergoing treatment of skin malignancies. However, increased knowledge does not necessarily mean increased preventative action will be employed (eg, sunscreen use, wearing sun-protective clothing and sunglasses, avoiding tanning beds and excessive sun exposure). Additional studies that demonstrate a notable increase in sun-protective behaviors related to increased knowledge are needed.
Because retention of skin cancer knowledge decreased in several postintervention surveys, there also is a dire need for continuing skin cancer education in patients of color, which may be accomplished through a combination effort of television advertisement campaigns, pamphlets, social media, community health departments, or even community members. For example, a pilot program found that Hispanic lay health workers who are educated about skin cancer may serve as a bridge between medical providers and the Hispanic community by encouraging individuals in this population to get regular skin examinations from a physician.25 Overall, there are currently gaps in the understanding and treatment of skin cancer in people of color.26 Identifying the advantages and disadvantages of all relevant skin cancer interventions conducted in the SOC population will hopefully guide future studies to help close these gaps by allowing others to design the best possible intervention. By doing so, researchers can generate an intervention that is precise, well-informed, and effective in decreasing mortality rates from skin cancer among SOC populations.
Conclusion
All of the studies reviewed demonstrated that instructional and educational interventions are promising methods for improving either knowledge, awareness, or safe skin practices and sun-protective behaviors in SOC populations to differing degrees (Table). Although each of the 4 interventions employed their own methods, they all increased 1 or more of the 3 aforementioned concepts—knowledge, awareness, or safe skin practices and sun-protective behaviors—when comparing postsurvey to presurvey data. However, the critically important message derived from this research is that there is a tremendous need for a substantial large-scale educational intervention to increase knowledge regarding skin cancer in SOC populations.
Malignant melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma account for approximately 40% of all neoplasms among the white population in the United States. Skin cancer is the most common malignancy in the United States.1 However, despite this occurrence, there are limited data regarding skin cancer in individuals with skin of color (SOC). The 5-year survival rates for melanoma are 58.2% for black individuals, 69.7% for Hispanics, and 70.9% for Asians compared to 79.8% for white individuals in the United States.2 Even though SOC populations have lower incidences of skin cancer—melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma—they exhibit higher death rates.3-7 Nonetheless, no specific guidelines exist to address sun exposure and safety habits in SOC populations.6,8 Furthermore, current demographics suggest that by the year 2050, approximately half of the US population will be nonwhite.4 Paradoxically, despite having increased sun protection from greater amounts of melanin in their skin, black individuals are more likely to present with advanced-stage melanoma (eg, stage III/IV) compared to white individuals.8-12 Furthermore, those of nonwhite populations are more likely to present with more advanced stages of acral lentiginous melanomas than white individuals.13,14 Hispanics also face an increasing incidence of more invasive acral lentiginous melanomas.15 Overall, SOC patients have the poorest skin cancer prognosis, and the data suggest that the reason for this paradox is delayed diagnosis.1
Although skin cancer is largely a preventable condition, the literature suggests that lack of awareness of melanoma among ethnic minorities is one of the main reasons for their poor skin cancer prognosis.16 This lack of awareness decreases the likelihood that an SOC patient would be alert to early detection of cancerous changes.17 Because educating at-risk SOC populations is key to decreasing skin cancer risk, this study focused on determining the efficacy of major knowledge-based interventions conducted to date.1 Overall, we sought to answer the question, do knowledge-based interventions increase skin cancer awareness, knowledge, and protective behavior among people of color?
Methods
For this review, the Cochrane method of analysis was used to conduct a thorough search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE (1994-2016), as well as a search of CINAHL (1997-2016), PsycINFO (1999-2016), and Web of Science (1965-2016), using a combination of more than 100 search terms including but not limited to skin cancer, skin of color, intervention, and ethnic skin. The search yielded a total of 52 articles (Figure). Following review, only 8 articles met inclusion criteria, which were as follows: (1) study was related to skin cancer in SOC patients, which included an intervention to increase skin cancer awareness and knowledge; (2) study included adult participants or adolescents aged 12 to 18 years; (3) study was written in English; and (4) study was published in a peer-reviewed journal. Of the remaining 8 articles, 4 were excluded due to the following criteria: (1) study failed to provide both preintervention and postintervention data, (2) study failed to provide quantitative data, and (3) study included participants who worked as health care professionals or ancillary staff. As a result, a total of 4 articles were analyzed and discussed in this review (Table).


Results
Robinson et al18 conducted 12 focus groups with 120 total participants (40 black, 40 Asian, and 40 Hispanic patients). Participants engaged in a 2-hour tape-recorded focus group with a moderator guide on melanoma and skin cancer. Furthermore, they also were asked to assess skin cancer risk in 5 celebrities with different skin tones. The statistically significant preintervention results of the study (χ2=4.6, P<.001) were as follows: only 2%, 4%, and 14% correctly reported that celebrities with a very fair skin type, a fair skin type, and very dark skin type, respectively, could get sunburn, compared to 75%, 76%, and 62% post-intervention. Additionally, prior to intervention, 14% of the study population believed that dark brown skin type could get sunburn compared to 62% of the same group postintervention. This study demonstrated that the intervention helped SOC patients better identify their ability to get sunburn and identify their skin cancer risk.18
Hernandez et al19 used a video-based intervention in a Hispanic community, which was in contrast to the multiracial focus group intervention conducted by Robinson et al.18 Eighty Hispanic individuals were recruited from beauty salons to participate in the study. Participants watched two 3-minute videos in Spanish and completed a preintervention and postintervention survey. The first video emphasized the photoaging benefits of sun protection, while the second focused on skin cancer prevention. Preintervention surveys indicated that only 54 (68%) participants believed that fair-skinned Hispanics were at risk for skin cancer, which improved to 72 (90%) participants postintervention. Furthermore, initially only 44 (55%) participants thought those with darker skin types could develop skin cancer, but this number increased to 69 (86%) postintervention. For both questions regarding fair and dark skin, the agreement proportion was significantly different between the preeducation and posteducation videos (P<.0002 for the fair skin question and P<.0001 for the dark skin question). This study greatly increased awareness of skin cancer risk among Hispanics,19 similar to the Robinson et al18 study.
In contrast to 2-hour focus groups or 3-minute video–based interventions, a study by Kundu et al17 employed a 20-minute educational class-based intervention with both verbal and visual instruction. This study assessed the efficacy of an educational tutorial on improving awareness and early detection of melanoma in SOC individuals. Photographs were used to help participants recognize the ABCDEs of melanoma and to show examples of acral lentiginous melanomas in white individuals. A total of 71 participants completed a preintervention questionnaire, participated in a 20-minute class, and completed a postintervention questionnaire immediately after and 3 months following the class. The study population included 44 black, 15 Asian, 10 Hispanic, and 2 multiethnic participants. Knowledge that melanoma is a skin cancer increased from 83.9% to 100% immediately postintervention (P=.0001) and 97.2% at 3 months postintervention (P=.0075). Additionally, knowledge that people of color are at risk for melanoma increased from 48.4% preintervention to 82.8% immediately postintervention (P<.0001). However, only 40.8% of participants retained this knowledge at 3 months postintervention. Because only 1 participant reported a family history of skin cancer, the authors hypothesized that the reason for this loss of knowledge was that most participants were not personally affected by friends or family members with melanoma. A future study with an appropriate control group would be needed to support this claim. This study shed light on the potential of class-based interventions to increase both awareness and knowledge of skin cancer in SOC populations.17
A study by Chapman et al20 examined the effects of a sun protection educational program on increasing awareness of skin cancer in Hispanic and black middle school students in southern Los Angeles, California. It was the only study we reviewed that focused primarily on adolescents. Furthermore, it included the largest sample size (N=148) analyzed here. Students were given a preintervention questionnaire to evaluate their awareness of skin cancer and current sun-protection practices. Based on these results, the investigators devised a set of learning goals and incorporated them into an educational pamphlet. The intervention, called “Skin Teaching Day,” was a 1-day program discussing skin cancer and the importance of sun protection. Prior to the intervention, 68% of participants reported that they used sunscreen. Three months after completing the program, 80% of participants reported sunscreen use, an increase of 12% prior to the intervention. The results of this study demonstrated the unique effectiveness and potential of pamphlets in increasing sunscreen use.20
Comment
Overall, various methods of interventions such as focus groups, videos, pamphlets, and lectures improved knowledge of skin cancer risk and sun-protection behaviors in SOC populations. Furthermore, the unique differences of each study provided important insights into the successful design of an intervention.
An important characteristic of the Robinson et al18 study was the addition of photographs, which allowed participants not only to visualize different skin tones but also provided them with the opportunity to relate themselves to the photographs; by doing so, participants could effectively pick out the skin tone that best suited them. Written SOC scales are limited to mere descriptions and thus make it more difficult for participants to accurately identify the tone that best fits them. Kundu et al17 used photographs to teach skin self-examination and ABCDEs for detection of melanoma. Additionally, both studies used photographs to demonstrate examples of skin cancer.17,18 Recent evidence suggests the use of visuals can be efficacious for improving skin cancer knowledge and awareness; a study in 16 SOC kidney transplant recipients found that the addition of photographs of squamous cell carcinoma in various skin tones to a sun-protection educational pamphlet was more effective than the original pamphlet without photographs.21
In contrast to the Robinson et al18 study and Hernandez et al19 study, the Kundu et al17 study showed photographs of acral lentiginous melanomas in white patients rather than SOC patients. However, SOC populations may be less likely to relate to or identify skin changes in skin types that are different from their own. This technique was still beneficial, as acral lentiginous melanoma is the most common type of melanoma in SOC populations. Another benefit of the study was that it was the only study reviewed that included a follow-up postintervention questionnaire. Such data is useful, as it demonstrates how muchinformation is retained by participants and may be more likely to predict compliance with skin cancer protective behaviors.17
The Hernandez et al19 study is unique in that it was the only one to include an educational intervention entirely in Spanish, which is important to consider, as language may be a hindrance to participants’ understanding in the other studies, particularly Hispanics, possibly leading to a lack of information retention regarding sun-protective behaviors. Furthermore, it also was the only study to utilize videos as a method for interventions. The 3-minute videos demonstrated that interventions could be efficient as compared to the 2-hour in-class intervention used by Robinson et al18 and the 20-minute intervention used by Kundu et al.17 Additionally, videos also could be more cost-effective, as incentives for large focus groups would no longer be needed. Furthermore, in the Hernandez et al19 study, there was minimal to no disruption in the participants’ daily routine, as the participants were getting cosmetic services while watching the videos, perhaps allowing them to be more attentive. In contrast, both the Robinson et al18 and Kundu et al17 studies required time out from the participants’ daily schedules. In addition, these studies were notably longer than the Hernandez et al19 study. The 8-hour intervention in the Chapman et al20 study also may not be feasible for the general population because of its excessive length. However, the intervention was successful among the adolescent participants, which suggested that shorter durations are effective in the adult population and longer interventions may be more appropriate for adolescents because they benefit from peer activity.
Despite the success of the educational interventions as outlined in the 4 studies described here, a major epidemiologic flaw is that these interventions included only a small percentage of the target population. The largest total number of adults surveyed and undergoing an intervention in any of the populations was only 120.17 By failing to reach a substantial proportion of the population at risk, the number of preventable deaths likely will not decrease. The authors believe a larger-scale intervention would provide meaningful change. Australia’s SunSmart campaign to increase skin cancer awareness in the Australian population is an example of one such large-scale national intervention. The campaign focused on massive television advertisements in the summer to educate participants about the dangers of skin cancer and the importance of protective behaviors. Telephone surveys conducted from 1987 to 2011 demonstrated that more exposure to the advertisements in the SunSmart campaign meant that individuals were more likely to use sunscreen and avoid sun exposure.22 In the United States, a similar intervention would be of great benefit in educating SOC populations regarding skin cancer risk. Additionally, dermatology residents need to be adequately trained to educate patients of color about the risk for skin cancer, as survey data indicated more than 80% of Australian dermatologists desired more SOC teaching during their training and 50% indicated that they would have time to learn it during their training if offered.23 Furthermore, one study suggested that future interventions must include primary-, secondary-, and tertiary-prevention methods to effectively reduce skin cancer risk among patients of color.24 Primary prevention involves sun avoidance, secondary prevention involves detecting cancerous lesions, and tertiary prevention involves undergoing treatment of skin malignancies. However, increased knowledge does not necessarily mean increased preventative action will be employed (eg, sunscreen use, wearing sun-protective clothing and sunglasses, avoiding tanning beds and excessive sun exposure). Additional studies that demonstrate a notable increase in sun-protective behaviors related to increased knowledge are needed.
Because retention of skin cancer knowledge decreased in several postintervention surveys, there also is a dire need for continuing skin cancer education in patients of color, which may be accomplished through a combination effort of television advertisement campaigns, pamphlets, social media, community health departments, or even community members. For example, a pilot program found that Hispanic lay health workers who are educated about skin cancer may serve as a bridge between medical providers and the Hispanic community by encouraging individuals in this population to get regular skin examinations from a physician.25 Overall, there are currently gaps in the understanding and treatment of skin cancer in people of color.26 Identifying the advantages and disadvantages of all relevant skin cancer interventions conducted in the SOC population will hopefully guide future studies to help close these gaps by allowing others to design the best possible intervention. By doing so, researchers can generate an intervention that is precise, well-informed, and effective in decreasing mortality rates from skin cancer among SOC populations.
Conclusion
All of the studies reviewed demonstrated that instructional and educational interventions are promising methods for improving either knowledge, awareness, or safe skin practices and sun-protective behaviors in SOC populations to differing degrees (Table). Although each of the 4 interventions employed their own methods, they all increased 1 or more of the 3 aforementioned concepts—knowledge, awareness, or safe skin practices and sun-protective behaviors—when comparing postsurvey to presurvey data. However, the critically important message derived from this research is that there is a tremendous need for a substantial large-scale educational intervention to increase knowledge regarding skin cancer in SOC populations.
- Agbai ON, Buster K, Sanchez M, et al. Skin cancer and photoprotection in people of color: a review and recommendations for physicians and the public. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:748-762.
- Cormier JN, Xing Y, Ding M, et al. Ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1907-1914.
- Gloster HM Jr, Neal K. Skin cancer in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:741-760.
- Dawes SM, Tsai S, Gittleman H, et al. Racial disparities in melanoma survival. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:983-991.
- Byrd KM, Wilson DC, Hoyler SS, et al. Advanced presentation of melanoma in African Americans. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:21-24.
- Hu S, Parmet Y, Allen G, et al. Disparity in melanoma: a trend analysis of melanoma incidence and stage at diagnosis among whites, Hispanics, and blacks in Florida. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:1369-1374.
- Wu XC, Eide MJ, King J, et al. Racial and ethnic variations in incidence and survival of cutaneous melanoma in the United States, 1999-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5, suppl 1):S26-S37.
- Byrd-Miles K, Toombs EL, Peck GL. Skin cancer in individuals of African, Asian, Latin-American, and American-Indian descent: differences in incidence, clinical presentation, and survival compared to Caucasians. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:10-16.
- Hu S, Soza-Vento RM, Parker DF, et al. Comparison of stage at diagnosis of melanoma among Hispanic, black, and white patients in Miami-Dade County, Florida. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:704-708.
- Hu S, Parker DF, Thomas AG, et al. Advanced presentation of melanoma in African Americans: the Miami-Dade County experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;5:1031-1032.
- Bellows CF, Belafsky P, Fortgang IS, et al. Melanoma in African-Americans: trends in biological behavior and clinical characteristics over two decades. J Surg Oncol. 2001;78:10-16.
- Pritchett EN, Doyle A, Shaver CM, et al. Nonmelanoma skin cancer in nonwhite organ transplant recipients. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:1348-1353.
- Shin S, Palis BE, Phillips JL, et al. Cutaneous melanoma in Asian-Americans. J Surg Oncol. 2009;99:114-118.
- Stubblefield J, Kelly B. Melanoma in non-caucasian populations. Surg Clin North Am. 2014;94:1115-1126.
- Bradford PT, Goldstein AM, McMaster ML, et al. Acral lentiginous melanoma: incidence and survival patterns in the United States, 1986-2005. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:427-434.
- Pichon LC, Corral I, Landrine H, et al. Perceived skin cancer risk and sunscreen use among African American adults. J Health Psychol. 2010;15:1181-1189.
- Kundu RV, Kamaria M, Ortiz S, et al. Effectiveness of a knowledge-based intervention for melanoma among those with ethnic skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:777-784.
- Robinson JK, Joshi KM, Ortiz S, et al. Melanoma knowledge, perception, and awareness in ethnic minorities in Chicago: recommendations regarding education. Psychooncology. 2010;20:313-320.
- Hernandez C, Wang S, Abraham I, et al. Evaluation of educational videos to increase skin cancer risk awareness and sun safe behaviors among adult Hispanics. J Cancer Educ. 2014;29:563-569.
- Chapman LW, Ochoa A, Tenconi F, et al. Dermatologic health literacy in underserved communities: a case report of south Los Angeles middle schools. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21. pii:13030/qt8671p40n.
- Yanina G, Gaber R, Clayman ML, et al. Sun protection education for diverse audiences: need for skin cancer pictures. J Cancer Educ. 2015;30:187-189.
- Dobbinson SJ, Volkov A, Wakefield MA. Continued impact of sunsmart advertising on youth and adults’ behaviors. Am J Prev Med. 2015;49:20-28.
- Rodrigues MA, Ross AL, Gilmore S, et al. Australian dermatologists’ perspective on skin of colour: results of a national survey [published online December 9, 2016]. Australas J Dermatol. doi:10.1111/ajd.12556.
- Jacobsen A, Galvan A, Lachapelle CC, et al. Defining the need for skin cancer prevention education in uninsured, minority, and immigrant communities. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:1342-1347.
- Hernandez C, Kim H, Mauleon G, et al. A pilot program in collaboration with community centers to increase awareness and participation in skin cancer screening among Latinos in Chicago. J Cancer Educ. 2013;28:342-345.
- Kailas A, Solomon JA, Mostow EN, et al. Gaps in the understanding and treatment of skin cancer in people of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:144-149.
- Agbai ON, Buster K, Sanchez M, et al. Skin cancer and photoprotection in people of color: a review and recommendations for physicians and the public. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:748-762.
- Cormier JN, Xing Y, Ding M, et al. Ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1907-1914.
- Gloster HM Jr, Neal K. Skin cancer in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:741-760.
- Dawes SM, Tsai S, Gittleman H, et al. Racial disparities in melanoma survival. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:983-991.
- Byrd KM, Wilson DC, Hoyler SS, et al. Advanced presentation of melanoma in African Americans. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:21-24.
- Hu S, Parmet Y, Allen G, et al. Disparity in melanoma: a trend analysis of melanoma incidence and stage at diagnosis among whites, Hispanics, and blacks in Florida. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:1369-1374.
- Wu XC, Eide MJ, King J, et al. Racial and ethnic variations in incidence and survival of cutaneous melanoma in the United States, 1999-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5, suppl 1):S26-S37.
- Byrd-Miles K, Toombs EL, Peck GL. Skin cancer in individuals of African, Asian, Latin-American, and American-Indian descent: differences in incidence, clinical presentation, and survival compared to Caucasians. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:10-16.
- Hu S, Soza-Vento RM, Parker DF, et al. Comparison of stage at diagnosis of melanoma among Hispanic, black, and white patients in Miami-Dade County, Florida. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:704-708.
- Hu S, Parker DF, Thomas AG, et al. Advanced presentation of melanoma in African Americans: the Miami-Dade County experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;5:1031-1032.
- Bellows CF, Belafsky P, Fortgang IS, et al. Melanoma in African-Americans: trends in biological behavior and clinical characteristics over two decades. J Surg Oncol. 2001;78:10-16.
- Pritchett EN, Doyle A, Shaver CM, et al. Nonmelanoma skin cancer in nonwhite organ transplant recipients. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:1348-1353.
- Shin S, Palis BE, Phillips JL, et al. Cutaneous melanoma in Asian-Americans. J Surg Oncol. 2009;99:114-118.
- Stubblefield J, Kelly B. Melanoma in non-caucasian populations. Surg Clin North Am. 2014;94:1115-1126.
- Bradford PT, Goldstein AM, McMaster ML, et al. Acral lentiginous melanoma: incidence and survival patterns in the United States, 1986-2005. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:427-434.
- Pichon LC, Corral I, Landrine H, et al. Perceived skin cancer risk and sunscreen use among African American adults. J Health Psychol. 2010;15:1181-1189.
- Kundu RV, Kamaria M, Ortiz S, et al. Effectiveness of a knowledge-based intervention for melanoma among those with ethnic skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:777-784.
- Robinson JK, Joshi KM, Ortiz S, et al. Melanoma knowledge, perception, and awareness in ethnic minorities in Chicago: recommendations regarding education. Psychooncology. 2010;20:313-320.
- Hernandez C, Wang S, Abraham I, et al. Evaluation of educational videos to increase skin cancer risk awareness and sun safe behaviors among adult Hispanics. J Cancer Educ. 2014;29:563-569.
- Chapman LW, Ochoa A, Tenconi F, et al. Dermatologic health literacy in underserved communities: a case report of south Los Angeles middle schools. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21. pii:13030/qt8671p40n.
- Yanina G, Gaber R, Clayman ML, et al. Sun protection education for diverse audiences: need for skin cancer pictures. J Cancer Educ. 2015;30:187-189.
- Dobbinson SJ, Volkov A, Wakefield MA. Continued impact of sunsmart advertising on youth and adults’ behaviors. Am J Prev Med. 2015;49:20-28.
- Rodrigues MA, Ross AL, Gilmore S, et al. Australian dermatologists’ perspective on skin of colour: results of a national survey [published online December 9, 2016]. Australas J Dermatol. doi:10.1111/ajd.12556.
- Jacobsen A, Galvan A, Lachapelle CC, et al. Defining the need for skin cancer prevention education in uninsured, minority, and immigrant communities. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:1342-1347.
- Hernandez C, Kim H, Mauleon G, et al. A pilot program in collaboration with community centers to increase awareness and participation in skin cancer screening among Latinos in Chicago. J Cancer Educ. 2013;28:342-345.
- Kailas A, Solomon JA, Mostow EN, et al. Gaps in the understanding and treatment of skin cancer in people of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:144-149.
Practice Points
- Patients of color should be informed that they are at risk for skin cancer including melanoma.
- Patients of color should be taught to identify suspicious skin lesions including the ABCDEs of melanoma.
- Patients of color should be instructed to perform self-body skin examinations, especially of the palms and soles, for any evolving skin lesions. Patients should be instructed on the importance of visiting a physician for an evolving or suspicious mole or lesion.
Hair and Scalp Disorders in Adult and Pediatric Patients With Skin of Color
One of the most common concerns among black patients is hair- and scalp-related disease. As increasing numbers of black patients opt to see dermatologists, it is imperative that all dermatologists be adequately trained to address the concerns of this patient population. When patients ask for help with common skin diseases of the hair and scalp, there are details that must be included in diagnosis, treatment, and hair care recommendations to reach goals for excellence in patient care. Herein, we provide must-know information to effectively approach this patient population.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
A study utilizing data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey from 1993 to 2009 revealed seborrheic dermatitis (SD) as the second most common diagnosis for black patients who visit a dermatologist.1 Prevalence data from a population of 1408 white, black, and Chinese patients from the United States and China revealed scalp flaking in 81% to 95% of black patients, 66% to 82% in white patients, and 30% to 42% in Chinese patients.2 Seborrheic dermatitis has a notable prevalence in black women and often is considered normal by patients. It can be exacerbated by infrequent shampooing (ranging from once per month or longer in between shampoos) and the inappropriate use of hair oils and pomades; it also has been associated with hair breakage, lichen simplex chronicus, and folliculitis. Seborrheic dermatitis must be distinguished from other disorders including sarcoidosis, psoriasis, discoid lupus erythematosus, tinea capitis, and lichen simplex chronicus.
Although there is a paucity of literature on the treatment of SD in black patients, components of treatment are similar to those recommended for other populations. Black women are advised to carefully utilize antidandruff shampoos containing zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, or tar to avoid hair shaft damage and dryness. Ketoconazole shampoo rarely is recommended and may be more appropriately used in men and boys, as hair fragility is less of a concern for them. The shampoo should be applied directly to the scalp rather than the hair shafts to minimize dryness, with no particular elongated contact time needed for these medicated shampoos to be effective. Because conditioners can wash off the active ingredients in therapeutic shampoos, antidandruff conditioners are recommended. Potent or ultrapotent topical corticosteroids applied to the scalp 3 to 4 times weekly initially will control the symptoms of itching as well as scaling, and mid-potency topical corticosteroid oil may be used at weekly intervals.
Hairline and facial involvement of SD often co-occurs, and low-potency topical steroids may be applied to the affected areas twice daily for 3 to 4 weeks, which may be repeated for flares. Topical calcineurin inhibitors or antifungal creams such as ketoconazole or econazole may then provide effective control. Encouraging patients to increase shampooing to once weekly or every 2 weeks and discontinue use of scalp pomades and oils also is recommended. Patients must know that an itchy scaly scalp represents a treatable disorder.
Acquired Trichorrhexis Nodosa
Hair fragility and breakage is common and multifactorial in black patients. Hair shaft breakage can occur on the vertex scalp in central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA), with random localized breakage due to scratching in SD. Heat, hair colorants, and chemical relaxers may result in diffuse damage and breakage.3 Sodium-, potassium-, and guanine hydroxide–containing chemical relaxers change the physical properties of the hair by rearranging disulfide bonds. They remove the monomolecular layer of fatty acids covalently bound to the cuticle that help prevent penetration of water into the hair shaft. Additionally, chemical relaxers weaken the hair shaft and decrease tensile strength.
Unlike hair relaxers, colorants are less likely to lead to catastrophic hair breakage after a single use and require frequent use, which leads to cumulative damage. Thermal straightening is another cause of hair-shaft weakening in black patients.4,5 Flat irons and curling irons can cause substantially more damage than blow-dryers due to the amount of heat generated. Flat irons may reach a high temperature of 230ºC (450ºF) as compared to 100°C (210°F) for a blow-dryer. Even the simple act of combing the hair can cause hair breakage, as demonstrated in African volunteers whose hair remained short in contrast to white and Asian volunteers, despite the fact that they had not cut their hair for 1 or more years.6,7 These volunteers had many hair strand knots that led to breakage during combing and hair grooming.6
There is no known prevalence data for acquired trichorrhexis nodosa, though a study of 30 white and black women demonstrated that broken hairs were significantly increased in black women (P=.0001).8 Another study by Hall et al9 of 103 black women showed that 55% of the women reported breakage of hair shafts with normal styling. Khumalo et al6 investigated hair shaft fragility and reported no trichothiodystrophy; the authors concluded that the cause of the hair fragility likely was physical trauma or an undiscovered structural abnormality. Franbourg et al10 examined the structure of hair fibers in white, Asian, and black patients and found no differences, but microfractures were only present in black patients and were determined to be the cause of hair breakage. These studies underscore the need for specific questioning of the patient on hair care including combing, washing, drying, and using products and chemicals.
The approach to the treatment of hair breakage involves correcting underlying abnormalities (eg, iron deficiency, hypothyroidism, nutritional deficiencies). Patients should “give their hair a rest” by discontinuing use of heat, colorants, and chemical relaxers. For patients who are unable to comply, advising them to stop these processes for 6 to 12 months will allow for repair of the hair shaft. To minimize damage from colorants, recommend semipermanent, demipermanent, or temporary dyes. Patients should be counseled to stop bleaching their hair or using permanent colorants. The use of heat protectant products on the hair before styling as well as layering moisturizing regimens starting with a moisturizing shampoo followed by a leave-in, dimethicone-containing conditioner marketed for dry damaged hair is suggested. Dimethicone thinly coats the hair shaft to restore hydrophobicity, smoothes cuticular scales, decreases frizz, and protects the hair from damage. Use of a 2-in-1 shampoo and conditioner containing anionic surfactants and wide-toothed, smooth (no jagged edges in the grooves) combs along with rare brushing are recommended. The hair may be worn in its natural state, but straightening with heat should be avoided. Air drying the hair can minimize breakage, but if thermal styling is necessary, patients should turn the temperature setting of the flat or curling iron down. Protective hair care practices may include placing a loosely sewn-in hair weave that will allow for good hair care, wearing loose braids, or using a wig. Serial trimming of the hair every 6 to 8 weeks is recommended. Improvement may take time, and patients should be advised of this timeline to prevent frustration.
Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is characterized by papules and pustules located on the occipital scalp and/or the nape of the neck, which may result in keloidal papules and plaques. The etiology is unknown, but ingrown hairs, genetics, trauma, infection, inflammation, and androgen hormones have been proposed to play a role.11 Although AKN may occur in black women, it is primarily a disorder in black men. The diagnosis is made based primarily on clinical findings, and a history of short haircuts may support the diagnosis. Treatment is tailored to the severity of the disease (Table 1). Avoidance of short haircuts and irritation from shirt collars may be helpful. Patients should be advised that the condition is controllable but not curable.
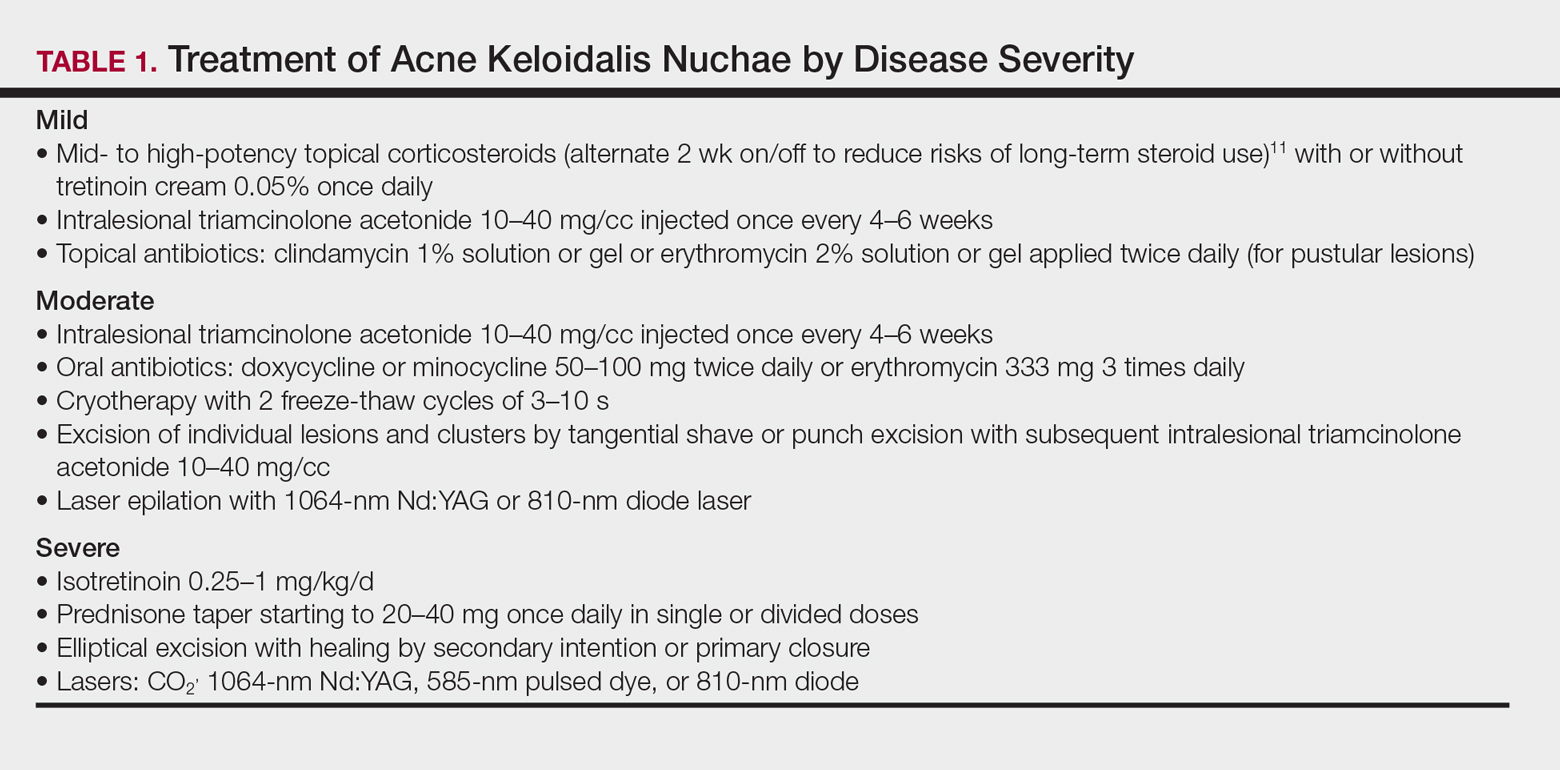
Pseudofolliculitis Barbae
Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB) is characterized by papules and pustules in the beard region that may result in postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, keloidal scar formation, and/or linear scarring. The coarse curled hairs characteristic of black men penetrate the follicle before exiting the skin and penetrate the skin after exiting the follicle, resulting in inflammation. Shaving methods and genetics also may contribute to the development of PFB. As with AKN, diagnosis is made clinically and does not require a skin biopsy. Important components of the patient’s history that should be obtained are hair removal practices and the use of over-the-counter products (eg, shave [pre and post] moisturizers, exfoliants, shaving creams or gels, keratin-softening agents containing α- or β-hydroxy acids). A bacterial culture may be appropriate if a notable pustular component is present. The patient should be advised to discontinue shaving if possible, which may require a physician’s letter explaining the necessity to the patient’s employer. Pseudofolliculitis barbae often can be prevented or lessened with the right hair removal strategy. Because there is not one optimal hair removal strategy that suits every patient, encourage the patient to experiment with different hair removal techniques, from depilatories to electric shavers, foil-guard razors, and multiple-blade razors. Preshave hydration and postshave moisturiza-tion also should be encouraged.12 Benzoyl peroxide–containing shave gels and cleansers, as well as moisturizers containing glycolic, salicylic, and phytic acids, may minimize ingrown hairs, papules, and inflammation.
Other useful topical agents include eflornithine hydrochloride to decrease hair growth, retinoids to soften hair fibers, mild topical steroids to reduce inflammation, and/or topical erythromycin or clindamycin if pustules are present.13 Oral antibiotics such as doxycycline, minocycline, or erythromycin can be added for more severe cases of inflammation or infection. Procedural interventions include laser hair removal to prevent PFB and intralesional triamcinolone 10 to 40 mg/cc every 4 to 6 weeks, with the total volume depending on the size and number of lesions.
Alopecia
Alopecia is the sixth most common diagnosis seen in black patients visiting a dermatologist.14 The physician’s response to the patient’s chief concern of hair loss is key to building a relationship of confidence and trust. Trivializing the concern or dismissing it will undermine the physician-patient relationship. A survey by Gathers and Mahan15 revealed that 68% of patients thought that physicians did not understand their hair.
Hair loss negatively impacts quality of life, and a study of 50 black South African women with alopecia demonstrated a notable disease burden. Factors with the highest impact were those related to self-image, relationships, and interactions with others.16
It is not unusual for black women to have multiple types of alopecia identified in one biopsy specimen. Wohltmann and Sperling17 demonstrated 2 or more different types of alopecia in more than 10% of biopsy specimens of alopecia, including CCCA, androgenetic alopecia, end-stage traction alopecia, telogen effluvium, and tinea capitis. A complete history, physical examination, and appropriate procedures (eg, hair pull test, dermatoscopic examination and scalp biopsy) likely will yield an accurate diagnosis. Table 2 highlights important questions that should be asked about the patient’s history.
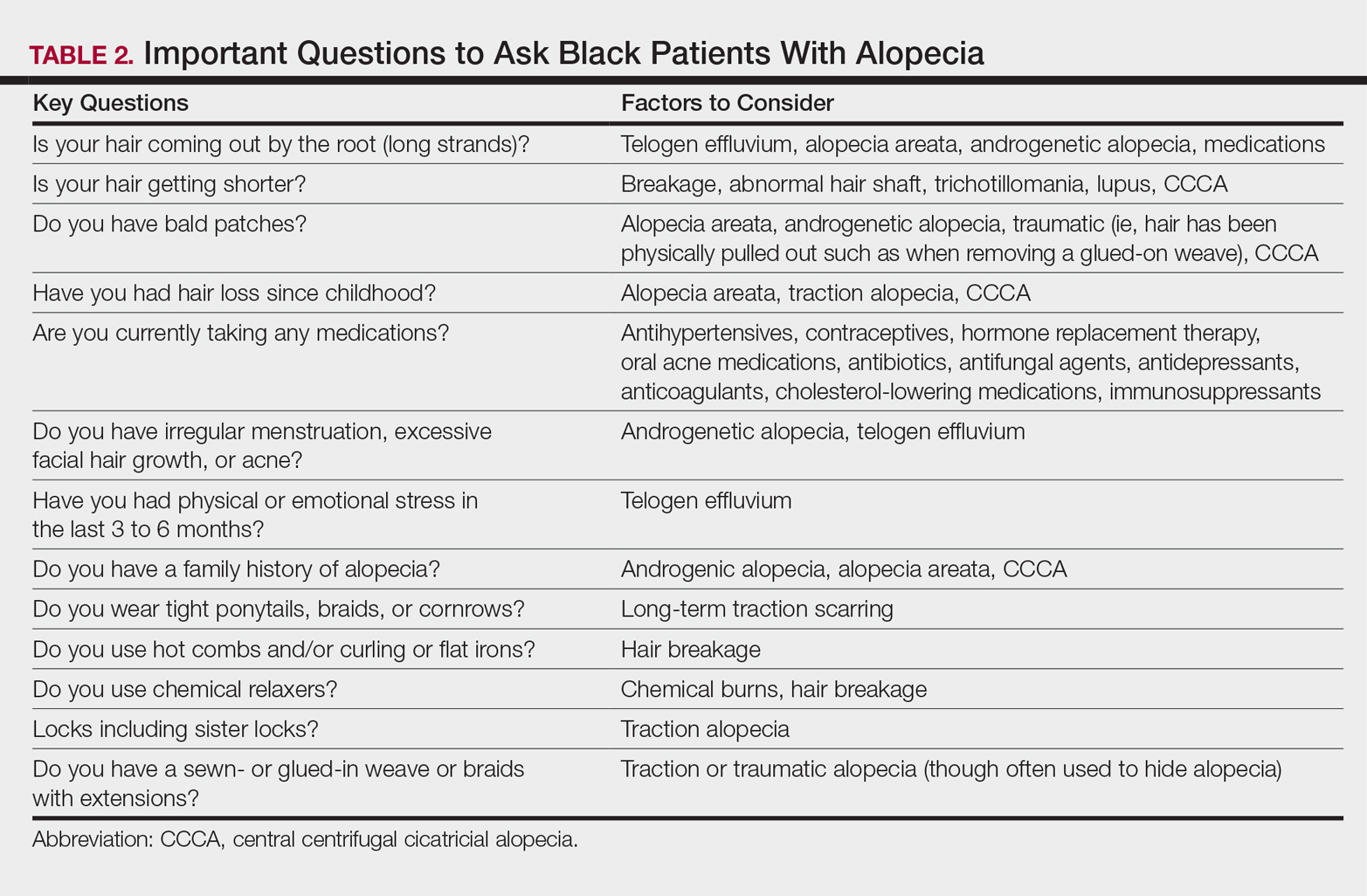
Physical examination of the scalp including dermatoscopic examination and a hair pull test as well as an evaluation of other hair-bearing areas may suggest a diagnosis that can be confirmed with a scalp biopsy.18,19 Selection of a biopsy site at the periphery of the alopecic area that includes hair and consultation with a dermatopathologist familiar with features of CCCA, traction, and traumatic alopecia are important for making an accurate diagnosis.
Tinea Capitis in Black Pediatric Patients
Tinea capitis, a fungal infection of the scalp and hair, is one of the most common issues in children with skin of color. Clinical presentation may include widely distributed scaling, annular scaly plaques, annular patches of alopecia studded with black dots (broken hairs), and/or annular inflammatory plaques. Although scalp hyperkeratosis often is a hallmark of pediatric tinea capitis, it is not diagnostic. The differential diagnosis of pediatric scalp hyperkeratosis/scaling includes tinea capitis, SD, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and sebopsoriasis.20,21 Clues to accurate diagnosis of tinea capitis may be found by examination of the adult who combs the child’s hair, as erythematous annular scaly plaques representing tinea corporis may be observed on the forearms or thighs. Although the thighs are a seemingly unusual location, the frequent practice of the child sitting on the floor between the legs of the adult during hairstyling provides a point of contact for the transmission of tinea from the child’s scalp to the thighs or forearms of the adult. Once tinea capitis is clinically suspected, the diagnosis is confirmed by a fungal culture. Adequate sampling is obtained by clipping hairs in an area of scaling for submission and vigorously rubbing the area of black dots or hyperkeratosis with a cotton swab.
Hubbard22 shed light on the decision to treat tinea capitis empirically or await the culture results. One hundred consecutive children (98 were black) presented with the constellation of scalp alopecia, scaling, pruritus, and occipital lymphadenopathy. Sixty-eight of those children had positive fungal cultures, and of them, 60 had both occipital lymphadenopathy and scaling and 55 had both occipital lymphadenopathy and alopecia.22 Thus, occipital lymphadenopathy in conjunction with alopecia and/or scaling is predictive of tinea capitis in this population and suggests that the initiation of treatment prior to confirmative culture results is appropriate.
The mainstay of treatment for tinea capitis is griseofulvin, but it is often underdosed and not continued for an adequate period of time to ensure clearance of the infection. Griseofulvin microsize (125 mg/5 mL) at the dosage of 20 to 25 mg/kg once daily for 8 to 12 weeks is recommended instead of a lower-dosed 4- to 6-week course.23,24
Options for treating a child with residual disease include increasing and/or extending the griseofulvin dosage, encouraging ingestion of fatty foods to enhance absorption, dividing the dosage of griseofulvin from once daily to twice daily, changing therapy to oral terbinafine due to resistance to griseofulvin, examining siblings as a source of reinfection, and reviewing the positive fungal culture report to distinguish Trichophyton tonsurans versus Microsporum canis as the causative agent and adjust treatment accordingly. Although griseofulvin is the first-line treatment for M canis, terbinafine, which is approved for children 4 years and older for tineacapitis, is most efficacious for T tonsurans.25 Treatment with terbinafine is weight based and should extend for 2 to 4 weeksfor T tonsurans and 8 to 12 weeks for M canis.
Antifungal shampoos may help reduce household spread of tinea and decrease transmissible fungal spores, but they may cause hair dryness and breakage.26,27 Antifungal shampoos can be applied directly onto the scalp for a 5- to 10-minute contact time and rinsed, and then the hair should be shampooed with a moisturizing shampoo followed by a moisturizing conditioner. Hair conditioners may decrease household spread of tinea capitis and should be used by the patient and other members of the household.28 Infection control may be enhanced by advising parents to dispose of hair pomades and washing hair accessories, combs, and brushes in hot soapy water, preferably in the dishwasher.
Hair Growth
The inability of the hair of black children to grow long is a common concern for parents of toddlers and preschool-aged children. Although the hair does grow, it grows more slowly than hair in white children (0.259 vs 0.330 mm per day), and it is likely to break faster than it is growing in black versus white children (146.6 vs 13.13 total broken hairs).8 Reassurance that the hair is indeed growing and that the length will increase as the child matures is important. Avoidance of hairstyles that promote traction and use of hair extensions, as well as use of moisturizing shampoos and conditioners, may minimize breakage and support the growth of healthy hair.
Conclusion
Hair- and scalp-related disease in black adults and children is commonly encountered in dermatology practice. It is important to understand the intrinsic characteristics of facial and scalp hair as well as hair care practices in this patient population that differ from those of white and Asian populations, such as frequency of shampooing, products, and styling. Familiarity with these differences may aid in effective diagnosis, treatment, and hair care recommendations in patients with these conditions.
- Davis SA, Naarahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Hickman JG, Cardin C, Dawson TL, et al. Dandruff, part I: scalp disease prevalence in Caucasians, African Americans, and Chinese and the effects of shampoo frequency on scalp health. Poster presented at: 60th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology; February 22-27, 2002; New Orleans, LA.
- Swee W, Klontz KC, Lambert LA. A nationwide outbreak of alopecia associated with the use of a hair-relaxing formulation. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1104-1108.
- Nicholson AG, Harland CC, Bull RH, et al. Chemically induced cosmetic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1993;128:537-541.
- Detwiler SP, Carson JL, Woosley JT, et al. Bubble hair. case caused by an overheating hair dryer and reproducibility in normal hair with heat. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30:54-60.
- Khumalo NP, Dawber RP, Ferguson DJ. Apparent fragility of African hair is unrelated to the cystine-rich protein distribution: a cytochemical electron microscopic study. Exp Dermatol. 2005;14:311-314.
- Robbins C. Hair breakage during combing. I. pathways of breakage. J Cosmet Sci. 2006;57:233-243.
- Lewallen R, Francis S, Fisher B, et al. Hair care practices and structural evaluation of scalp and hair shaft parameter in African American and Caucasian women. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2015;14:216-223.
- Hall RR, Francis S, Whitt-Glover M, et al. Hair care practices as a barrier to physical activity in African American women. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:310-314.
- Franbourg A, Hallegot P, Baltenneck F, et al. Current research on ethnic hair. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48(6 suppl):S115-S119.
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489.
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38(suppl 1):24-27.
- Kundu RV, Patterson S. Dermatologic conditions in skin of color: part II. disorders occurring predominately in skin of color. Am Fam Physician. 2013;87:859-865.
- Davis SA, Naarahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Gathers RC, Mahan MG. African American women, hair care and health barriers. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:26-29.
- Dlova NC, Fabbrocini G, Lauro C, et al. Quality of life in South African black women with alopecia: a pilot study. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:875-881.
- Wohltmann WE, Sperling L. Histopathologic diagnosis of multifactorial alopecia. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:483-491.
- McDonald KA, Shelley AJ, Colantonio S, et al. Hair pull test: evidence-based update and revision of guidelines. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:472-477.
- Miteva M, Tosti A. Dermatoscopic features of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:443-444.
- Coley MK, Bhanusali DG, Silverberg JI, et al. Scalp hyperkeratosis and alopecia in children of color. J Drugs Dermatol. 2011;10:511-516.
- Silverberg NB. Scalp hyperkeratosis in children with skin of color: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Cutis. 2015;95:199-204, 207.
- Hubbard TW. The predictive value of symptoms in diagnosing childhood tinea capitis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1999;153:1150-1153.
- Kakourou T, Uksal U; European Society for Pediatric Dermatology. Guidelines for the management of tinea capitis in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:226-228.
- Sethi A, Antanya R. Systemic antifungal therapy for cutaneous infections in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006;25:643-644.
- Gupta AK. Drummond-Main C. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing particular doses of griseofulvin and terbinafine for the treatment of tinea capitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:1-6.
- Greer DL. Successful treatment of tinea capitis with 2% ketoconazole shampoo. Int J Dermatol 2000;39:302-304.
- Sharma V, Silverberg NB, Howard R, et al. Do hair care practices affect the acquisition of tinea capitis? a case-control study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2001;155:818-821.
- Greer DL. Successful treatment of tinea capitis with 2% ketoconazole shampoo. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:302-304.
One of the most common concerns among black patients is hair- and scalp-related disease. As increasing numbers of black patients opt to see dermatologists, it is imperative that all dermatologists be adequately trained to address the concerns of this patient population. When patients ask for help with common skin diseases of the hair and scalp, there are details that must be included in diagnosis, treatment, and hair care recommendations to reach goals for excellence in patient care. Herein, we provide must-know information to effectively approach this patient population.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
A study utilizing data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey from 1993 to 2009 revealed seborrheic dermatitis (SD) as the second most common diagnosis for black patients who visit a dermatologist.1 Prevalence data from a population of 1408 white, black, and Chinese patients from the United States and China revealed scalp flaking in 81% to 95% of black patients, 66% to 82% in white patients, and 30% to 42% in Chinese patients.2 Seborrheic dermatitis has a notable prevalence in black women and often is considered normal by patients. It can be exacerbated by infrequent shampooing (ranging from once per month or longer in between shampoos) and the inappropriate use of hair oils and pomades; it also has been associated with hair breakage, lichen simplex chronicus, and folliculitis. Seborrheic dermatitis must be distinguished from other disorders including sarcoidosis, psoriasis, discoid lupus erythematosus, tinea capitis, and lichen simplex chronicus.
Although there is a paucity of literature on the treatment of SD in black patients, components of treatment are similar to those recommended for other populations. Black women are advised to carefully utilize antidandruff shampoos containing zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, or tar to avoid hair shaft damage and dryness. Ketoconazole shampoo rarely is recommended and may be more appropriately used in men and boys, as hair fragility is less of a concern for them. The shampoo should be applied directly to the scalp rather than the hair shafts to minimize dryness, with no particular elongated contact time needed for these medicated shampoos to be effective. Because conditioners can wash off the active ingredients in therapeutic shampoos, antidandruff conditioners are recommended. Potent or ultrapotent topical corticosteroids applied to the scalp 3 to 4 times weekly initially will control the symptoms of itching as well as scaling, and mid-potency topical corticosteroid oil may be used at weekly intervals.
Hairline and facial involvement of SD often co-occurs, and low-potency topical steroids may be applied to the affected areas twice daily for 3 to 4 weeks, which may be repeated for flares. Topical calcineurin inhibitors or antifungal creams such as ketoconazole or econazole may then provide effective control. Encouraging patients to increase shampooing to once weekly or every 2 weeks and discontinue use of scalp pomades and oils also is recommended. Patients must know that an itchy scaly scalp represents a treatable disorder.
Acquired Trichorrhexis Nodosa
Hair fragility and breakage is common and multifactorial in black patients. Hair shaft breakage can occur on the vertex scalp in central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA), with random localized breakage due to scratching in SD. Heat, hair colorants, and chemical relaxers may result in diffuse damage and breakage.3 Sodium-, potassium-, and guanine hydroxide–containing chemical relaxers change the physical properties of the hair by rearranging disulfide bonds. They remove the monomolecular layer of fatty acids covalently bound to the cuticle that help prevent penetration of water into the hair shaft. Additionally, chemical relaxers weaken the hair shaft and decrease tensile strength.
Unlike hair relaxers, colorants are less likely to lead to catastrophic hair breakage after a single use and require frequent use, which leads to cumulative damage. Thermal straightening is another cause of hair-shaft weakening in black patients.4,5 Flat irons and curling irons can cause substantially more damage than blow-dryers due to the amount of heat generated. Flat irons may reach a high temperature of 230ºC (450ºF) as compared to 100°C (210°F) for a blow-dryer. Even the simple act of combing the hair can cause hair breakage, as demonstrated in African volunteers whose hair remained short in contrast to white and Asian volunteers, despite the fact that they had not cut their hair for 1 or more years.6,7 These volunteers had many hair strand knots that led to breakage during combing and hair grooming.6
There is no known prevalence data for acquired trichorrhexis nodosa, though a study of 30 white and black women demonstrated that broken hairs were significantly increased in black women (P=.0001).8 Another study by Hall et al9 of 103 black women showed that 55% of the women reported breakage of hair shafts with normal styling. Khumalo et al6 investigated hair shaft fragility and reported no trichothiodystrophy; the authors concluded that the cause of the hair fragility likely was physical trauma or an undiscovered structural abnormality. Franbourg et al10 examined the structure of hair fibers in white, Asian, and black patients and found no differences, but microfractures were only present in black patients and were determined to be the cause of hair breakage. These studies underscore the need for specific questioning of the patient on hair care including combing, washing, drying, and using products and chemicals.
The approach to the treatment of hair breakage involves correcting underlying abnormalities (eg, iron deficiency, hypothyroidism, nutritional deficiencies). Patients should “give their hair a rest” by discontinuing use of heat, colorants, and chemical relaxers. For patients who are unable to comply, advising them to stop these processes for 6 to 12 months will allow for repair of the hair shaft. To minimize damage from colorants, recommend semipermanent, demipermanent, or temporary dyes. Patients should be counseled to stop bleaching their hair or using permanent colorants. The use of heat protectant products on the hair before styling as well as layering moisturizing regimens starting with a moisturizing shampoo followed by a leave-in, dimethicone-containing conditioner marketed for dry damaged hair is suggested. Dimethicone thinly coats the hair shaft to restore hydrophobicity, smoothes cuticular scales, decreases frizz, and protects the hair from damage. Use of a 2-in-1 shampoo and conditioner containing anionic surfactants and wide-toothed, smooth (no jagged edges in the grooves) combs along with rare brushing are recommended. The hair may be worn in its natural state, but straightening with heat should be avoided. Air drying the hair can minimize breakage, but if thermal styling is necessary, patients should turn the temperature setting of the flat or curling iron down. Protective hair care practices may include placing a loosely sewn-in hair weave that will allow for good hair care, wearing loose braids, or using a wig. Serial trimming of the hair every 6 to 8 weeks is recommended. Improvement may take time, and patients should be advised of this timeline to prevent frustration.
Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is characterized by papules and pustules located on the occipital scalp and/or the nape of the neck, which may result in keloidal papules and plaques. The etiology is unknown, but ingrown hairs, genetics, trauma, infection, inflammation, and androgen hormones have been proposed to play a role.11 Although AKN may occur in black women, it is primarily a disorder in black men. The diagnosis is made based primarily on clinical findings, and a history of short haircuts may support the diagnosis. Treatment is tailored to the severity of the disease (Table 1). Avoidance of short haircuts and irritation from shirt collars may be helpful. Patients should be advised that the condition is controllable but not curable.

Pseudofolliculitis Barbae
Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB) is characterized by papules and pustules in the beard region that may result in postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, keloidal scar formation, and/or linear scarring. The coarse curled hairs characteristic of black men penetrate the follicle before exiting the skin and penetrate the skin after exiting the follicle, resulting in inflammation. Shaving methods and genetics also may contribute to the development of PFB. As with AKN, diagnosis is made clinically and does not require a skin biopsy. Important components of the patient’s history that should be obtained are hair removal practices and the use of over-the-counter products (eg, shave [pre and post] moisturizers, exfoliants, shaving creams or gels, keratin-softening agents containing α- or β-hydroxy acids). A bacterial culture may be appropriate if a notable pustular component is present. The patient should be advised to discontinue shaving if possible, which may require a physician’s letter explaining the necessity to the patient’s employer. Pseudofolliculitis barbae often can be prevented or lessened with the right hair removal strategy. Because there is not one optimal hair removal strategy that suits every patient, encourage the patient to experiment with different hair removal techniques, from depilatories to electric shavers, foil-guard razors, and multiple-blade razors. Preshave hydration and postshave moisturiza-tion also should be encouraged.12 Benzoyl peroxide–containing shave gels and cleansers, as well as moisturizers containing glycolic, salicylic, and phytic acids, may minimize ingrown hairs, papules, and inflammation.
Other useful topical agents include eflornithine hydrochloride to decrease hair growth, retinoids to soften hair fibers, mild topical steroids to reduce inflammation, and/or topical erythromycin or clindamycin if pustules are present.13 Oral antibiotics such as doxycycline, minocycline, or erythromycin can be added for more severe cases of inflammation or infection. Procedural interventions include laser hair removal to prevent PFB and intralesional triamcinolone 10 to 40 mg/cc every 4 to 6 weeks, with the total volume depending on the size and number of lesions.
Alopecia
Alopecia is the sixth most common diagnosis seen in black patients visiting a dermatologist.14 The physician’s response to the patient’s chief concern of hair loss is key to building a relationship of confidence and trust. Trivializing the concern or dismissing it will undermine the physician-patient relationship. A survey by Gathers and Mahan15 revealed that 68% of patients thought that physicians did not understand their hair.
Hair loss negatively impacts quality of life, and a study of 50 black South African women with alopecia demonstrated a notable disease burden. Factors with the highest impact were those related to self-image, relationships, and interactions with others.16
It is not unusual for black women to have multiple types of alopecia identified in one biopsy specimen. Wohltmann and Sperling17 demonstrated 2 or more different types of alopecia in more than 10% of biopsy specimens of alopecia, including CCCA, androgenetic alopecia, end-stage traction alopecia, telogen effluvium, and tinea capitis. A complete history, physical examination, and appropriate procedures (eg, hair pull test, dermatoscopic examination and scalp biopsy) likely will yield an accurate diagnosis. Table 2 highlights important questions that should be asked about the patient’s history.

Physical examination of the scalp including dermatoscopic examination and a hair pull test as well as an evaluation of other hair-bearing areas may suggest a diagnosis that can be confirmed with a scalp biopsy.18,19 Selection of a biopsy site at the periphery of the alopecic area that includes hair and consultation with a dermatopathologist familiar with features of CCCA, traction, and traumatic alopecia are important for making an accurate diagnosis.
Tinea Capitis in Black Pediatric Patients
Tinea capitis, a fungal infection of the scalp and hair, is one of the most common issues in children with skin of color. Clinical presentation may include widely distributed scaling, annular scaly plaques, annular patches of alopecia studded with black dots (broken hairs), and/or annular inflammatory plaques. Although scalp hyperkeratosis often is a hallmark of pediatric tinea capitis, it is not diagnostic. The differential diagnosis of pediatric scalp hyperkeratosis/scaling includes tinea capitis, SD, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and sebopsoriasis.20,21 Clues to accurate diagnosis of tinea capitis may be found by examination of the adult who combs the child’s hair, as erythematous annular scaly plaques representing tinea corporis may be observed on the forearms or thighs. Although the thighs are a seemingly unusual location, the frequent practice of the child sitting on the floor between the legs of the adult during hairstyling provides a point of contact for the transmission of tinea from the child’s scalp to the thighs or forearms of the adult. Once tinea capitis is clinically suspected, the diagnosis is confirmed by a fungal culture. Adequate sampling is obtained by clipping hairs in an area of scaling for submission and vigorously rubbing the area of black dots or hyperkeratosis with a cotton swab.
Hubbard22 shed light on the decision to treat tinea capitis empirically or await the culture results. One hundred consecutive children (98 were black) presented with the constellation of scalp alopecia, scaling, pruritus, and occipital lymphadenopathy. Sixty-eight of those children had positive fungal cultures, and of them, 60 had both occipital lymphadenopathy and scaling and 55 had both occipital lymphadenopathy and alopecia.22 Thus, occipital lymphadenopathy in conjunction with alopecia and/or scaling is predictive of tinea capitis in this population and suggests that the initiation of treatment prior to confirmative culture results is appropriate.
The mainstay of treatment for tinea capitis is griseofulvin, but it is often underdosed and not continued for an adequate period of time to ensure clearance of the infection. Griseofulvin microsize (125 mg/5 mL) at the dosage of 20 to 25 mg/kg once daily for 8 to 12 weeks is recommended instead of a lower-dosed 4- to 6-week course.23,24
Options for treating a child with residual disease include increasing and/or extending the griseofulvin dosage, encouraging ingestion of fatty foods to enhance absorption, dividing the dosage of griseofulvin from once daily to twice daily, changing therapy to oral terbinafine due to resistance to griseofulvin, examining siblings as a source of reinfection, and reviewing the positive fungal culture report to distinguish Trichophyton tonsurans versus Microsporum canis as the causative agent and adjust treatment accordingly. Although griseofulvin is the first-line treatment for M canis, terbinafine, which is approved for children 4 years and older for tineacapitis, is most efficacious for T tonsurans.25 Treatment with terbinafine is weight based and should extend for 2 to 4 weeksfor T tonsurans and 8 to 12 weeks for M canis.
Antifungal shampoos may help reduce household spread of tinea and decrease transmissible fungal spores, but they may cause hair dryness and breakage.26,27 Antifungal shampoos can be applied directly onto the scalp for a 5- to 10-minute contact time and rinsed, and then the hair should be shampooed with a moisturizing shampoo followed by a moisturizing conditioner. Hair conditioners may decrease household spread of tinea capitis and should be used by the patient and other members of the household.28 Infection control may be enhanced by advising parents to dispose of hair pomades and washing hair accessories, combs, and brushes in hot soapy water, preferably in the dishwasher.
Hair Growth
The inability of the hair of black children to grow long is a common concern for parents of toddlers and preschool-aged children. Although the hair does grow, it grows more slowly than hair in white children (0.259 vs 0.330 mm per day), and it is likely to break faster than it is growing in black versus white children (146.6 vs 13.13 total broken hairs).8 Reassurance that the hair is indeed growing and that the length will increase as the child matures is important. Avoidance of hairstyles that promote traction and use of hair extensions, as well as use of moisturizing shampoos and conditioners, may minimize breakage and support the growth of healthy hair.
Conclusion
Hair- and scalp-related disease in black adults and children is commonly encountered in dermatology practice. It is important to understand the intrinsic characteristics of facial and scalp hair as well as hair care practices in this patient population that differ from those of white and Asian populations, such as frequency of shampooing, products, and styling. Familiarity with these differences may aid in effective diagnosis, treatment, and hair care recommendations in patients with these conditions.
One of the most common concerns among black patients is hair- and scalp-related disease. As increasing numbers of black patients opt to see dermatologists, it is imperative that all dermatologists be adequately trained to address the concerns of this patient population. When patients ask for help with common skin diseases of the hair and scalp, there are details that must be included in diagnosis, treatment, and hair care recommendations to reach goals for excellence in patient care. Herein, we provide must-know information to effectively approach this patient population.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
A study utilizing data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey from 1993 to 2009 revealed seborrheic dermatitis (SD) as the second most common diagnosis for black patients who visit a dermatologist.1 Prevalence data from a population of 1408 white, black, and Chinese patients from the United States and China revealed scalp flaking in 81% to 95% of black patients, 66% to 82% in white patients, and 30% to 42% in Chinese patients.2 Seborrheic dermatitis has a notable prevalence in black women and often is considered normal by patients. It can be exacerbated by infrequent shampooing (ranging from once per month or longer in between shampoos) and the inappropriate use of hair oils and pomades; it also has been associated with hair breakage, lichen simplex chronicus, and folliculitis. Seborrheic dermatitis must be distinguished from other disorders including sarcoidosis, psoriasis, discoid lupus erythematosus, tinea capitis, and lichen simplex chronicus.
Although there is a paucity of literature on the treatment of SD in black patients, components of treatment are similar to those recommended for other populations. Black women are advised to carefully utilize antidandruff shampoos containing zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, or tar to avoid hair shaft damage and dryness. Ketoconazole shampoo rarely is recommended and may be more appropriately used in men and boys, as hair fragility is less of a concern for them. The shampoo should be applied directly to the scalp rather than the hair shafts to minimize dryness, with no particular elongated contact time needed for these medicated shampoos to be effective. Because conditioners can wash off the active ingredients in therapeutic shampoos, antidandruff conditioners are recommended. Potent or ultrapotent topical corticosteroids applied to the scalp 3 to 4 times weekly initially will control the symptoms of itching as well as scaling, and mid-potency topical corticosteroid oil may be used at weekly intervals.
Hairline and facial involvement of SD often co-occurs, and low-potency topical steroids may be applied to the affected areas twice daily for 3 to 4 weeks, which may be repeated for flares. Topical calcineurin inhibitors or antifungal creams such as ketoconazole or econazole may then provide effective control. Encouraging patients to increase shampooing to once weekly or every 2 weeks and discontinue use of scalp pomades and oils also is recommended. Patients must know that an itchy scaly scalp represents a treatable disorder.
Acquired Trichorrhexis Nodosa
Hair fragility and breakage is common and multifactorial in black patients. Hair shaft breakage can occur on the vertex scalp in central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA), with random localized breakage due to scratching in SD. Heat, hair colorants, and chemical relaxers may result in diffuse damage and breakage.3 Sodium-, potassium-, and guanine hydroxide–containing chemical relaxers change the physical properties of the hair by rearranging disulfide bonds. They remove the monomolecular layer of fatty acids covalently bound to the cuticle that help prevent penetration of water into the hair shaft. Additionally, chemical relaxers weaken the hair shaft and decrease tensile strength.
Unlike hair relaxers, colorants are less likely to lead to catastrophic hair breakage after a single use and require frequent use, which leads to cumulative damage. Thermal straightening is another cause of hair-shaft weakening in black patients.4,5 Flat irons and curling irons can cause substantially more damage than blow-dryers due to the amount of heat generated. Flat irons may reach a high temperature of 230ºC (450ºF) as compared to 100°C (210°F) for a blow-dryer. Even the simple act of combing the hair can cause hair breakage, as demonstrated in African volunteers whose hair remained short in contrast to white and Asian volunteers, despite the fact that they had not cut their hair for 1 or more years.6,7 These volunteers had many hair strand knots that led to breakage during combing and hair grooming.6
There is no known prevalence data for acquired trichorrhexis nodosa, though a study of 30 white and black women demonstrated that broken hairs were significantly increased in black women (P=.0001).8 Another study by Hall et al9 of 103 black women showed that 55% of the women reported breakage of hair shafts with normal styling. Khumalo et al6 investigated hair shaft fragility and reported no trichothiodystrophy; the authors concluded that the cause of the hair fragility likely was physical trauma or an undiscovered structural abnormality. Franbourg et al10 examined the structure of hair fibers in white, Asian, and black patients and found no differences, but microfractures were only present in black patients and were determined to be the cause of hair breakage. These studies underscore the need for specific questioning of the patient on hair care including combing, washing, drying, and using products and chemicals.
The approach to the treatment of hair breakage involves correcting underlying abnormalities (eg, iron deficiency, hypothyroidism, nutritional deficiencies). Patients should “give their hair a rest” by discontinuing use of heat, colorants, and chemical relaxers. For patients who are unable to comply, advising them to stop these processes for 6 to 12 months will allow for repair of the hair shaft. To minimize damage from colorants, recommend semipermanent, demipermanent, or temporary dyes. Patients should be counseled to stop bleaching their hair or using permanent colorants. The use of heat protectant products on the hair before styling as well as layering moisturizing regimens starting with a moisturizing shampoo followed by a leave-in, dimethicone-containing conditioner marketed for dry damaged hair is suggested. Dimethicone thinly coats the hair shaft to restore hydrophobicity, smoothes cuticular scales, decreases frizz, and protects the hair from damage. Use of a 2-in-1 shampoo and conditioner containing anionic surfactants and wide-toothed, smooth (no jagged edges in the grooves) combs along with rare brushing are recommended. The hair may be worn in its natural state, but straightening with heat should be avoided. Air drying the hair can minimize breakage, but if thermal styling is necessary, patients should turn the temperature setting of the flat or curling iron down. Protective hair care practices may include placing a loosely sewn-in hair weave that will allow for good hair care, wearing loose braids, or using a wig. Serial trimming of the hair every 6 to 8 weeks is recommended. Improvement may take time, and patients should be advised of this timeline to prevent frustration.
Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is characterized by papules and pustules located on the occipital scalp and/or the nape of the neck, which may result in keloidal papules and plaques. The etiology is unknown, but ingrown hairs, genetics, trauma, infection, inflammation, and androgen hormones have been proposed to play a role.11 Although AKN may occur in black women, it is primarily a disorder in black men. The diagnosis is made based primarily on clinical findings, and a history of short haircuts may support the diagnosis. Treatment is tailored to the severity of the disease (Table 1). Avoidance of short haircuts and irritation from shirt collars may be helpful. Patients should be advised that the condition is controllable but not curable.

Pseudofolliculitis Barbae
Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB) is characterized by papules and pustules in the beard region that may result in postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, keloidal scar formation, and/or linear scarring. The coarse curled hairs characteristic of black men penetrate the follicle before exiting the skin and penetrate the skin after exiting the follicle, resulting in inflammation. Shaving methods and genetics also may contribute to the development of PFB. As with AKN, diagnosis is made clinically and does not require a skin biopsy. Important components of the patient’s history that should be obtained are hair removal practices and the use of over-the-counter products (eg, shave [pre and post] moisturizers, exfoliants, shaving creams or gels, keratin-softening agents containing α- or β-hydroxy acids). A bacterial culture may be appropriate if a notable pustular component is present. The patient should be advised to discontinue shaving if possible, which may require a physician’s letter explaining the necessity to the patient’s employer. Pseudofolliculitis barbae often can be prevented or lessened with the right hair removal strategy. Because there is not one optimal hair removal strategy that suits every patient, encourage the patient to experiment with different hair removal techniques, from depilatories to electric shavers, foil-guard razors, and multiple-blade razors. Preshave hydration and postshave moisturiza-tion also should be encouraged.12 Benzoyl peroxide–containing shave gels and cleansers, as well as moisturizers containing glycolic, salicylic, and phytic acids, may minimize ingrown hairs, papules, and inflammation.
Other useful topical agents include eflornithine hydrochloride to decrease hair growth, retinoids to soften hair fibers, mild topical steroids to reduce inflammation, and/or topical erythromycin or clindamycin if pustules are present.13 Oral antibiotics such as doxycycline, minocycline, or erythromycin can be added for more severe cases of inflammation or infection. Procedural interventions include laser hair removal to prevent PFB and intralesional triamcinolone 10 to 40 mg/cc every 4 to 6 weeks, with the total volume depending on the size and number of lesions.
Alopecia
Alopecia is the sixth most common diagnosis seen in black patients visiting a dermatologist.14 The physician’s response to the patient’s chief concern of hair loss is key to building a relationship of confidence and trust. Trivializing the concern or dismissing it will undermine the physician-patient relationship. A survey by Gathers and Mahan15 revealed that 68% of patients thought that physicians did not understand their hair.
Hair loss negatively impacts quality of life, and a study of 50 black South African women with alopecia demonstrated a notable disease burden. Factors with the highest impact were those related to self-image, relationships, and interactions with others.16
It is not unusual for black women to have multiple types of alopecia identified in one biopsy specimen. Wohltmann and Sperling17 demonstrated 2 or more different types of alopecia in more than 10% of biopsy specimens of alopecia, including CCCA, androgenetic alopecia, end-stage traction alopecia, telogen effluvium, and tinea capitis. A complete history, physical examination, and appropriate procedures (eg, hair pull test, dermatoscopic examination and scalp biopsy) likely will yield an accurate diagnosis. Table 2 highlights important questions that should be asked about the patient’s history.

Physical examination of the scalp including dermatoscopic examination and a hair pull test as well as an evaluation of other hair-bearing areas may suggest a diagnosis that can be confirmed with a scalp biopsy.18,19 Selection of a biopsy site at the periphery of the alopecic area that includes hair and consultation with a dermatopathologist familiar with features of CCCA, traction, and traumatic alopecia are important for making an accurate diagnosis.
Tinea Capitis in Black Pediatric Patients
Tinea capitis, a fungal infection of the scalp and hair, is one of the most common issues in children with skin of color. Clinical presentation may include widely distributed scaling, annular scaly plaques, annular patches of alopecia studded with black dots (broken hairs), and/or annular inflammatory plaques. Although scalp hyperkeratosis often is a hallmark of pediatric tinea capitis, it is not diagnostic. The differential diagnosis of pediatric scalp hyperkeratosis/scaling includes tinea capitis, SD, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and sebopsoriasis.20,21 Clues to accurate diagnosis of tinea capitis may be found by examination of the adult who combs the child’s hair, as erythematous annular scaly plaques representing tinea corporis may be observed on the forearms or thighs. Although the thighs are a seemingly unusual location, the frequent practice of the child sitting on the floor between the legs of the adult during hairstyling provides a point of contact for the transmission of tinea from the child’s scalp to the thighs or forearms of the adult. Once tinea capitis is clinically suspected, the diagnosis is confirmed by a fungal culture. Adequate sampling is obtained by clipping hairs in an area of scaling for submission and vigorously rubbing the area of black dots or hyperkeratosis with a cotton swab.
Hubbard22 shed light on the decision to treat tinea capitis empirically or await the culture results. One hundred consecutive children (98 were black) presented with the constellation of scalp alopecia, scaling, pruritus, and occipital lymphadenopathy. Sixty-eight of those children had positive fungal cultures, and of them, 60 had both occipital lymphadenopathy and scaling and 55 had both occipital lymphadenopathy and alopecia.22 Thus, occipital lymphadenopathy in conjunction with alopecia and/or scaling is predictive of tinea capitis in this population and suggests that the initiation of treatment prior to confirmative culture results is appropriate.
The mainstay of treatment for tinea capitis is griseofulvin, but it is often underdosed and not continued for an adequate period of time to ensure clearance of the infection. Griseofulvin microsize (125 mg/5 mL) at the dosage of 20 to 25 mg/kg once daily for 8 to 12 weeks is recommended instead of a lower-dosed 4- to 6-week course.23,24
Options for treating a child with residual disease include increasing and/or extending the griseofulvin dosage, encouraging ingestion of fatty foods to enhance absorption, dividing the dosage of griseofulvin from once daily to twice daily, changing therapy to oral terbinafine due to resistance to griseofulvin, examining siblings as a source of reinfection, and reviewing the positive fungal culture report to distinguish Trichophyton tonsurans versus Microsporum canis as the causative agent and adjust treatment accordingly. Although griseofulvin is the first-line treatment for M canis, terbinafine, which is approved for children 4 years and older for tineacapitis, is most efficacious for T tonsurans.25 Treatment with terbinafine is weight based and should extend for 2 to 4 weeksfor T tonsurans and 8 to 12 weeks for M canis.
Antifungal shampoos may help reduce household spread of tinea and decrease transmissible fungal spores, but they may cause hair dryness and breakage.26,27 Antifungal shampoos can be applied directly onto the scalp for a 5- to 10-minute contact time and rinsed, and then the hair should be shampooed with a moisturizing shampoo followed by a moisturizing conditioner. Hair conditioners may decrease household spread of tinea capitis and should be used by the patient and other members of the household.28 Infection control may be enhanced by advising parents to dispose of hair pomades and washing hair accessories, combs, and brushes in hot soapy water, preferably in the dishwasher.
Hair Growth
The inability of the hair of black children to grow long is a common concern for parents of toddlers and preschool-aged children. Although the hair does grow, it grows more slowly than hair in white children (0.259 vs 0.330 mm per day), and it is likely to break faster than it is growing in black versus white children (146.6 vs 13.13 total broken hairs).8 Reassurance that the hair is indeed growing and that the length will increase as the child matures is important. Avoidance of hairstyles that promote traction and use of hair extensions, as well as use of moisturizing shampoos and conditioners, may minimize breakage and support the growth of healthy hair.
Conclusion
Hair- and scalp-related disease in black adults and children is commonly encountered in dermatology practice. It is important to understand the intrinsic characteristics of facial and scalp hair as well as hair care practices in this patient population that differ from those of white and Asian populations, such as frequency of shampooing, products, and styling. Familiarity with these differences may aid in effective diagnosis, treatment, and hair care recommendations in patients with these conditions.
- Davis SA, Naarahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Hickman JG, Cardin C, Dawson TL, et al. Dandruff, part I: scalp disease prevalence in Caucasians, African Americans, and Chinese and the effects of shampoo frequency on scalp health. Poster presented at: 60th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology; February 22-27, 2002; New Orleans, LA.
- Swee W, Klontz KC, Lambert LA. A nationwide outbreak of alopecia associated with the use of a hair-relaxing formulation. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1104-1108.
- Nicholson AG, Harland CC, Bull RH, et al. Chemically induced cosmetic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1993;128:537-541.
- Detwiler SP, Carson JL, Woosley JT, et al. Bubble hair. case caused by an overheating hair dryer and reproducibility in normal hair with heat. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30:54-60.
- Khumalo NP, Dawber RP, Ferguson DJ. Apparent fragility of African hair is unrelated to the cystine-rich protein distribution: a cytochemical electron microscopic study. Exp Dermatol. 2005;14:311-314.
- Robbins C. Hair breakage during combing. I. pathways of breakage. J Cosmet Sci. 2006;57:233-243.
- Lewallen R, Francis S, Fisher B, et al. Hair care practices and structural evaluation of scalp and hair shaft parameter in African American and Caucasian women. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2015;14:216-223.
- Hall RR, Francis S, Whitt-Glover M, et al. Hair care practices as a barrier to physical activity in African American women. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:310-314.
- Franbourg A, Hallegot P, Baltenneck F, et al. Current research on ethnic hair. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48(6 suppl):S115-S119.
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489.
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38(suppl 1):24-27.
- Kundu RV, Patterson S. Dermatologic conditions in skin of color: part II. disorders occurring predominately in skin of color. Am Fam Physician. 2013;87:859-865.
- Davis SA, Naarahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Gathers RC, Mahan MG. African American women, hair care and health barriers. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:26-29.
- Dlova NC, Fabbrocini G, Lauro C, et al. Quality of life in South African black women with alopecia: a pilot study. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:875-881.
- Wohltmann WE, Sperling L. Histopathologic diagnosis of multifactorial alopecia. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:483-491.
- McDonald KA, Shelley AJ, Colantonio S, et al. Hair pull test: evidence-based update and revision of guidelines. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:472-477.
- Miteva M, Tosti A. Dermatoscopic features of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:443-444.
- Coley MK, Bhanusali DG, Silverberg JI, et al. Scalp hyperkeratosis and alopecia in children of color. J Drugs Dermatol. 2011;10:511-516.
- Silverberg NB. Scalp hyperkeratosis in children with skin of color: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Cutis. 2015;95:199-204, 207.
- Hubbard TW. The predictive value of symptoms in diagnosing childhood tinea capitis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1999;153:1150-1153.
- Kakourou T, Uksal U; European Society for Pediatric Dermatology. Guidelines for the management of tinea capitis in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:226-228.
- Sethi A, Antanya R. Systemic antifungal therapy for cutaneous infections in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006;25:643-644.
- Gupta AK. Drummond-Main C. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing particular doses of griseofulvin and terbinafine for the treatment of tinea capitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:1-6.
- Greer DL. Successful treatment of tinea capitis with 2% ketoconazole shampoo. Int J Dermatol 2000;39:302-304.
- Sharma V, Silverberg NB, Howard R, et al. Do hair care practices affect the acquisition of tinea capitis? a case-control study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2001;155:818-821.
- Greer DL. Successful treatment of tinea capitis with 2% ketoconazole shampoo. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:302-304.
- Davis SA, Naarahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Hickman JG, Cardin C, Dawson TL, et al. Dandruff, part I: scalp disease prevalence in Caucasians, African Americans, and Chinese and the effects of shampoo frequency on scalp health. Poster presented at: 60th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology; February 22-27, 2002; New Orleans, LA.
- Swee W, Klontz KC, Lambert LA. A nationwide outbreak of alopecia associated with the use of a hair-relaxing formulation. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1104-1108.
- Nicholson AG, Harland CC, Bull RH, et al. Chemically induced cosmetic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1993;128:537-541.
- Detwiler SP, Carson JL, Woosley JT, et al. Bubble hair. case caused by an overheating hair dryer and reproducibility in normal hair with heat. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30:54-60.
- Khumalo NP, Dawber RP, Ferguson DJ. Apparent fragility of African hair is unrelated to the cystine-rich protein distribution: a cytochemical electron microscopic study. Exp Dermatol. 2005;14:311-314.
- Robbins C. Hair breakage during combing. I. pathways of breakage. J Cosmet Sci. 2006;57:233-243.
- Lewallen R, Francis S, Fisher B, et al. Hair care practices and structural evaluation of scalp and hair shaft parameter in African American and Caucasian women. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2015;14:216-223.
- Hall RR, Francis S, Whitt-Glover M, et al. Hair care practices as a barrier to physical activity in African American women. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:310-314.
- Franbourg A, Hallegot P, Baltenneck F, et al. Current research on ethnic hair. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48(6 suppl):S115-S119.
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489.
- Gray J, McMichael AJ. Pseudofolliculitis barbae: understanding the condition and the role of facial grooming. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2016;38(suppl 1):24-27.
- Kundu RV, Patterson S. Dermatologic conditions in skin of color: part II. disorders occurring predominately in skin of color. Am Fam Physician. 2013;87:859-865.
- Davis SA, Naarahari S, Feldman SR, et al. Top dermatologic conditions in patients of color: an analysis of nationally representative data. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:466-473.
- Gathers RC, Mahan MG. African American women, hair care and health barriers. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:26-29.
- Dlova NC, Fabbrocini G, Lauro C, et al. Quality of life in South African black women with alopecia: a pilot study. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:875-881.
- Wohltmann WE, Sperling L. Histopathologic diagnosis of multifactorial alopecia. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:483-491.
- McDonald KA, Shelley AJ, Colantonio S, et al. Hair pull test: evidence-based update and revision of guidelines. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:472-477.
- Miteva M, Tosti A. Dermatoscopic features of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:443-444.
- Coley MK, Bhanusali DG, Silverberg JI, et al. Scalp hyperkeratosis and alopecia in children of color. J Drugs Dermatol. 2011;10:511-516.
- Silverberg NB. Scalp hyperkeratosis in children with skin of color: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Cutis. 2015;95:199-204, 207.
- Hubbard TW. The predictive value of symptoms in diagnosing childhood tinea capitis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1999;153:1150-1153.
- Kakourou T, Uksal U; European Society for Pediatric Dermatology. Guidelines for the management of tinea capitis in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:226-228.
- Sethi A, Antanya R. Systemic antifungal therapy for cutaneous infections in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006;25:643-644.
- Gupta AK. Drummond-Main C. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing particular doses of griseofulvin and terbinafine for the treatment of tinea capitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:1-6.
- Greer DL. Successful treatment of tinea capitis with 2% ketoconazole shampoo. Int J Dermatol 2000;39:302-304.
- Sharma V, Silverberg NB, Howard R, et al. Do hair care practices affect the acquisition of tinea capitis? a case-control study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2001;155:818-821.
- Greer DL. Successful treatment of tinea capitis with 2% ketoconazole shampoo. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:302-304.
Practice Points
- Instruct patients with acquired trichorrhexis nodosa to discontinue use of heat, colorants, and chemical relaxers on their hair.
- Create a contract with your seborrheic dermatitis patients to have them shampoo at least weekly or every 2 weeks.
- For children with treated tinea capitis that has not completely resolved, increase or extend the griseofulvin dosage, encourage ingestion of fatty foods to enhance absorption, and divide dosage of griseofulvin from once to twice daily.
- Selection of a biopsy site at the periphery of an alopecic area that includes hair and hair follicles and evaluation by a dermatopathologist familiar with the features of central centrifugal cicatricial, traction, and traumatic alopecias will ensure an accurate diagnosis of alopecia.
Diversity in Dermatology: A Society Devoted to Skin of Color
The US Census Bureau predicts that more than half of the country’s population will identify as a race other than non-Hispanic white by the year 2044.In 2014, the US population was 62.2% non-Hispanic white, and the projected figure for 2060 is 43.6%.1 However, most physicians currently are informed by research that is generalized from a study population of primarily white males.2 Disparities also exist among the physician population where black individuals and Latinos are underrepresented.3 These differences have inspired dermatologists to develop methods to address the need for parity among patients with skin of color. Both ethnic skin centers and the Skin of Color Society (SOCS) have been established since the turn of the millennium to improve disparities and prepare for the future. The efforts and impact of SOCS are widening since its inception and chronicle one approach to broadening the scope of the specialty of dermatology.
Established in 2004 by dermatologist Susan C. Taylor, MD (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania), SOCS provides educational support to health care providers, the media, the legislature, third parties (eg, insurance organizations), and the general public on dermatologic health for patients with skin of color. The society is organized into committees that represent the multifaceted aspects of the organization. It also stimulates and endorses an increase in scientific knowledge through basic science and clinical, surgical, and cosmetic research.4
Scientific, research, mentorship, professional development, national and international outreach, patient education, and technology and media committees within SOCS, as well as a newly formed diversity in action task force, uphold the mission of the society. The scientific committee, one of the organization’s major committees, plans the annual symposium. The annual symposium, which immediately precedes the Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, acts as a central educational symposium for dermatologists (both domestic and international), residents, students, and other scientists to present data on unique properties, statistics, and diseases associated with individuals with ethnic skin. New research, perspectives, and interests are shared with an audience of physicians, research fellows, residents, and students who are also the presenters of topics relevant to skin of color such as cutaneous T-cell lymphomas/mycosis fungoides in black individuals, central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA), pigmentary disorders in Brazilians, and many others. There is an emphasis on allowing learners to present their research in a comfortable and constructive setting, and these shorter talks are interspersed with experts who deliver cutting-edge lectures in their specialty area.4
Each year during the SOCS symposium, the SOCS Research Award is endowed to a dermatology resident, fellow, or young dermatologist within the first 8 years of postgraduate training. The research committee oversees the selection of the SOCS Research Award. Prior recipients of the award have explored topics such as genetic causes of keloid formation or CCCA, epigenetic changes in ethnic skin during skin aging, and development of a vitiligo-specific quality-of-life scale.4
Another key mission of SOCS is to foster the growth of younger dermatologists interested in skin of color via mentorships; SOCS has a mentorship committee dedicated to engaging in this effort. Dermatology residents or young dermatologists who are within 3 years of finishing residency can work with a SOCS-approved mentor to develop knowledge, skills, and networking in the skin of color realm. Research is encouraged, and 3 to 4 professional development meetings (both in person or online) help set objectives. The professional development committee also coordinates efforts to offer young dermatologists opportunities to work with experienced mentors and further partnerships with existing members.4
The national and international outreach committee acts as a liaison between organizations abroad and those based in the United States. The patient education committee strives to improve public knowledge about dermatologic diseases that affect individuals with skin of color. Ethnic patients often have poor access to medical information, and sometimes adequate medical information does not exist in the current searchable medical literature. The SOCS website (http://skinofcolorsociety.org/) offers an entire section on dermatology education with succinct, patient-friendly prose on diseases such as acne in skin of color, CCCA, eczema, melanoma, melasma, sun protection, tinea capitis, and more; the website also includes educational videos, blogs, and a central location for useful links to other dermatology organizations that may be of interest to both members and patients who use the site. Maintenance of the website and the SOCS media day fall under the purview of the technology and media committee. There have been 2 media days thus far that have given voice to sun safety and skin cancer in individuals with skin of color as well as hair health and cosmetic treatments for patients with pigmented skin. The content for the media days is provided by SOCS experts to national magazine editors and beauty bloggers to raise awareness about these issues and get the message to the public.4
The diversity in action task force is a new committee that is tasked with addressing training for individuals of diverse ethnicities and backgrounds for health care careers at every level, ranging from middle school to dermatology residency. Resources to help those applying to medical school and current medical students interested in dermatology as well as those applying for dermatology residency are being developed for students at all stages of their academic careers. The middle school to undergraduate educational levels will encompass general guidelines for success; the medical school level will focus on students taking the appropriate steps to enter dermatology residency. The task force also will act as a liaison through existing student groups, such as the Student National Medical Association, Minority Association of Premedical Students, Latino Medical Student Association, Dermatology Interest Group Association, and more to reach learners at critical stages in their academic development.4The society plays an important role in the educational process for dermatologists at all levels. Although this organization is critical in increasing knowledge of treatment of individuals with skin of color in research, clinical practice, and the public domain, the hope is that SOCS will continue to reach new members of the dermatology community. As a group that embraces the onus to improve skin of color education, the members of SOCS know that there is still much to do to increase awareness among the public as well as dermatology residents and dermatologists practicing in geographical regions that are not ethnically diverse. There are many reasons that both cultural competence and knowledge of skin of color in dermatology will be important as the United States becomes increasingly diverse, and SOCS is at the forefront of this effort. Looking to the future, the goals of SOCS really are the goals of dermatology, which are to continue to deliver the best care to all patients and to continue to improve our specialty with new techniques and medications for all patients who need care.
- Colby SL, Jennifer JO. Projections of the Size and Composition of the U.S. Population: 2014 to 2060. Washington, DC: US Census Bureau; 2014.
- Oh SS, Galanter J, Thakur N, et al. Diversity in clinical and biomedical research: a promise yet to be fulfilled. PLoS Med. 2015;12:e1001918.
- Castillo-Page L. Diversity in the physician workforce facts & figures 2010. Washington, DC: Association of American Medical Colleges; 2010. https://www.aamc.org/download/432976/data/factsandfigures2010.pdf. Accessed April 12, 2017.
- Our committees. Skin of Color Society website. http://skinofcolorsociety.org/about-socs/our-committees/. Accessed April 19, 2017.
The US Census Bureau predicts that more than half of the country’s population will identify as a race other than non-Hispanic white by the year 2044.In 2014, the US population was 62.2% non-Hispanic white, and the projected figure for 2060 is 43.6%.1 However, most physicians currently are informed by research that is generalized from a study population of primarily white males.2 Disparities also exist among the physician population where black individuals and Latinos are underrepresented.3 These differences have inspired dermatologists to develop methods to address the need for parity among patients with skin of color. Both ethnic skin centers and the Skin of Color Society (SOCS) have been established since the turn of the millennium to improve disparities and prepare for the future. The efforts and impact of SOCS are widening since its inception and chronicle one approach to broadening the scope of the specialty of dermatology.
Established in 2004 by dermatologist Susan C. Taylor, MD (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania), SOCS provides educational support to health care providers, the media, the legislature, third parties (eg, insurance organizations), and the general public on dermatologic health for patients with skin of color. The society is organized into committees that represent the multifaceted aspects of the organization. It also stimulates and endorses an increase in scientific knowledge through basic science and clinical, surgical, and cosmetic research.4
Scientific, research, mentorship, professional development, national and international outreach, patient education, and technology and media committees within SOCS, as well as a newly formed diversity in action task force, uphold the mission of the society. The scientific committee, one of the organization’s major committees, plans the annual symposium. The annual symposium, which immediately precedes the Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, acts as a central educational symposium for dermatologists (both domestic and international), residents, students, and other scientists to present data on unique properties, statistics, and diseases associated with individuals with ethnic skin. New research, perspectives, and interests are shared with an audience of physicians, research fellows, residents, and students who are also the presenters of topics relevant to skin of color such as cutaneous T-cell lymphomas/mycosis fungoides in black individuals, central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA), pigmentary disorders in Brazilians, and many others. There is an emphasis on allowing learners to present their research in a comfortable and constructive setting, and these shorter talks are interspersed with experts who deliver cutting-edge lectures in their specialty area.4
Each year during the SOCS symposium, the SOCS Research Award is endowed to a dermatology resident, fellow, or young dermatologist within the first 8 years of postgraduate training. The research committee oversees the selection of the SOCS Research Award. Prior recipients of the award have explored topics such as genetic causes of keloid formation or CCCA, epigenetic changes in ethnic skin during skin aging, and development of a vitiligo-specific quality-of-life scale.4
Another key mission of SOCS is to foster the growth of younger dermatologists interested in skin of color via mentorships; SOCS has a mentorship committee dedicated to engaging in this effort. Dermatology residents or young dermatologists who are within 3 years of finishing residency can work with a SOCS-approved mentor to develop knowledge, skills, and networking in the skin of color realm. Research is encouraged, and 3 to 4 professional development meetings (both in person or online) help set objectives. The professional development committee also coordinates efforts to offer young dermatologists opportunities to work with experienced mentors and further partnerships with existing members.4
The national and international outreach committee acts as a liaison between organizations abroad and those based in the United States. The patient education committee strives to improve public knowledge about dermatologic diseases that affect individuals with skin of color. Ethnic patients often have poor access to medical information, and sometimes adequate medical information does not exist in the current searchable medical literature. The SOCS website (http://skinofcolorsociety.org/) offers an entire section on dermatology education with succinct, patient-friendly prose on diseases such as acne in skin of color, CCCA, eczema, melanoma, melasma, sun protection, tinea capitis, and more; the website also includes educational videos, blogs, and a central location for useful links to other dermatology organizations that may be of interest to both members and patients who use the site. Maintenance of the website and the SOCS media day fall under the purview of the technology and media committee. There have been 2 media days thus far that have given voice to sun safety and skin cancer in individuals with skin of color as well as hair health and cosmetic treatments for patients with pigmented skin. The content for the media days is provided by SOCS experts to national magazine editors and beauty bloggers to raise awareness about these issues and get the message to the public.4
The diversity in action task force is a new committee that is tasked with addressing training for individuals of diverse ethnicities and backgrounds for health care careers at every level, ranging from middle school to dermatology residency. Resources to help those applying to medical school and current medical students interested in dermatology as well as those applying for dermatology residency are being developed for students at all stages of their academic careers. The middle school to undergraduate educational levels will encompass general guidelines for success; the medical school level will focus on students taking the appropriate steps to enter dermatology residency. The task force also will act as a liaison through existing student groups, such as the Student National Medical Association, Minority Association of Premedical Students, Latino Medical Student Association, Dermatology Interest Group Association, and more to reach learners at critical stages in their academic development.4The society plays an important role in the educational process for dermatologists at all levels. Although this organization is critical in increasing knowledge of treatment of individuals with skin of color in research, clinical practice, and the public domain, the hope is that SOCS will continue to reach new members of the dermatology community. As a group that embraces the onus to improve skin of color education, the members of SOCS know that there is still much to do to increase awareness among the public as well as dermatology residents and dermatologists practicing in geographical regions that are not ethnically diverse. There are many reasons that both cultural competence and knowledge of skin of color in dermatology will be important as the United States becomes increasingly diverse, and SOCS is at the forefront of this effort. Looking to the future, the goals of SOCS really are the goals of dermatology, which are to continue to deliver the best care to all patients and to continue to improve our specialty with new techniques and medications for all patients who need care.
The US Census Bureau predicts that more than half of the country’s population will identify as a race other than non-Hispanic white by the year 2044.In 2014, the US population was 62.2% non-Hispanic white, and the projected figure for 2060 is 43.6%.1 However, most physicians currently are informed by research that is generalized from a study population of primarily white males.2 Disparities also exist among the physician population where black individuals and Latinos are underrepresented.3 These differences have inspired dermatologists to develop methods to address the need for parity among patients with skin of color. Both ethnic skin centers and the Skin of Color Society (SOCS) have been established since the turn of the millennium to improve disparities and prepare for the future. The efforts and impact of SOCS are widening since its inception and chronicle one approach to broadening the scope of the specialty of dermatology.
Established in 2004 by dermatologist Susan C. Taylor, MD (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania), SOCS provides educational support to health care providers, the media, the legislature, third parties (eg, insurance organizations), and the general public on dermatologic health for patients with skin of color. The society is organized into committees that represent the multifaceted aspects of the organization. It also stimulates and endorses an increase in scientific knowledge through basic science and clinical, surgical, and cosmetic research.4
Scientific, research, mentorship, professional development, national and international outreach, patient education, and technology and media committees within SOCS, as well as a newly formed diversity in action task force, uphold the mission of the society. The scientific committee, one of the organization’s major committees, plans the annual symposium. The annual symposium, which immediately precedes the Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, acts as a central educational symposium for dermatologists (both domestic and international), residents, students, and other scientists to present data on unique properties, statistics, and diseases associated with individuals with ethnic skin. New research, perspectives, and interests are shared with an audience of physicians, research fellows, residents, and students who are also the presenters of topics relevant to skin of color such as cutaneous T-cell lymphomas/mycosis fungoides in black individuals, central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA), pigmentary disorders in Brazilians, and many others. There is an emphasis on allowing learners to present their research in a comfortable and constructive setting, and these shorter talks are interspersed with experts who deliver cutting-edge lectures in their specialty area.4
Each year during the SOCS symposium, the SOCS Research Award is endowed to a dermatology resident, fellow, or young dermatologist within the first 8 years of postgraduate training. The research committee oversees the selection of the SOCS Research Award. Prior recipients of the award have explored topics such as genetic causes of keloid formation or CCCA, epigenetic changes in ethnic skin during skin aging, and development of a vitiligo-specific quality-of-life scale.4
Another key mission of SOCS is to foster the growth of younger dermatologists interested in skin of color via mentorships; SOCS has a mentorship committee dedicated to engaging in this effort. Dermatology residents or young dermatologists who are within 3 years of finishing residency can work with a SOCS-approved mentor to develop knowledge, skills, and networking in the skin of color realm. Research is encouraged, and 3 to 4 professional development meetings (both in person or online) help set objectives. The professional development committee also coordinates efforts to offer young dermatologists opportunities to work with experienced mentors and further partnerships with existing members.4
The national and international outreach committee acts as a liaison between organizations abroad and those based in the United States. The patient education committee strives to improve public knowledge about dermatologic diseases that affect individuals with skin of color. Ethnic patients often have poor access to medical information, and sometimes adequate medical information does not exist in the current searchable medical literature. The SOCS website (http://skinofcolorsociety.org/) offers an entire section on dermatology education with succinct, patient-friendly prose on diseases such as acne in skin of color, CCCA, eczema, melanoma, melasma, sun protection, tinea capitis, and more; the website also includes educational videos, blogs, and a central location for useful links to other dermatology organizations that may be of interest to both members and patients who use the site. Maintenance of the website and the SOCS media day fall under the purview of the technology and media committee. There have been 2 media days thus far that have given voice to sun safety and skin cancer in individuals with skin of color as well as hair health and cosmetic treatments for patients with pigmented skin. The content for the media days is provided by SOCS experts to national magazine editors and beauty bloggers to raise awareness about these issues and get the message to the public.4
The diversity in action task force is a new committee that is tasked with addressing training for individuals of diverse ethnicities and backgrounds for health care careers at every level, ranging from middle school to dermatology residency. Resources to help those applying to medical school and current medical students interested in dermatology as well as those applying for dermatology residency are being developed for students at all stages of their academic careers. The middle school to undergraduate educational levels will encompass general guidelines for success; the medical school level will focus on students taking the appropriate steps to enter dermatology residency. The task force also will act as a liaison through existing student groups, such as the Student National Medical Association, Minority Association of Premedical Students, Latino Medical Student Association, Dermatology Interest Group Association, and more to reach learners at critical stages in their academic development.4The society plays an important role in the educational process for dermatologists at all levels. Although this organization is critical in increasing knowledge of treatment of individuals with skin of color in research, clinical practice, and the public domain, the hope is that SOCS will continue to reach new members of the dermatology community. As a group that embraces the onus to improve skin of color education, the members of SOCS know that there is still much to do to increase awareness among the public as well as dermatology residents and dermatologists practicing in geographical regions that are not ethnically diverse. There are many reasons that both cultural competence and knowledge of skin of color in dermatology will be important as the United States becomes increasingly diverse, and SOCS is at the forefront of this effort. Looking to the future, the goals of SOCS really are the goals of dermatology, which are to continue to deliver the best care to all patients and to continue to improve our specialty with new techniques and medications for all patients who need care.
- Colby SL, Jennifer JO. Projections of the Size and Composition of the U.S. Population: 2014 to 2060. Washington, DC: US Census Bureau; 2014.
- Oh SS, Galanter J, Thakur N, et al. Diversity in clinical and biomedical research: a promise yet to be fulfilled. PLoS Med. 2015;12:e1001918.
- Castillo-Page L. Diversity in the physician workforce facts & figures 2010. Washington, DC: Association of American Medical Colleges; 2010. https://www.aamc.org/download/432976/data/factsandfigures2010.pdf. Accessed April 12, 2017.
- Our committees. Skin of Color Society website. http://skinofcolorsociety.org/about-socs/our-committees/. Accessed April 19, 2017.
- Colby SL, Jennifer JO. Projections of the Size and Composition of the U.S. Population: 2014 to 2060. Washington, DC: US Census Bureau; 2014.
- Oh SS, Galanter J, Thakur N, et al. Diversity in clinical and biomedical research: a promise yet to be fulfilled. PLoS Med. 2015;12:e1001918.
- Castillo-Page L. Diversity in the physician workforce facts & figures 2010. Washington, DC: Association of American Medical Colleges; 2010. https://www.aamc.org/download/432976/data/factsandfigures2010.pdf. Accessed April 12, 2017.
- Our committees. Skin of Color Society website. http://skinofcolorsociety.org/about-socs/our-committees/. Accessed April 19, 2017.
Practice Points
- The mission of the Skin of Color Society (SOCS) is to improve education of young dermatologists relevant to skin of color patients.
- Educational resources on many different diseases important to patients with skin of color are available to patients and providers on the SOCS website.
A Primer to Natural Hair Care Practices in Black Patients
The phenomenon of natural (nonchemically treated) hair in individuals of African and Afro-Caribbean descent is sweeping across the United States. The ideals of beauty among this patient population have shifted from a relaxed, straightened, noncurly look to a more natural curly and/or kinky appearance. The discussion on natural hair versus straight hair has been brought to the mainstream by films such as Good Hair (2009). Furthermore, major hair care companies have increased their marketing of natural hair products to address the needs of these patients.
Popular traumatic hair care practices such as chemical relaxation and thermal straightening may lead to hair damage. Although the role of hair care practices in various scalp and hair disorders is ambiguous, traumatic practices commonly are performed by patients who are diagnosed with dermatologic conditions such as scarring alopecia.1 Alopecia is the fourth most common dermatologic diagnosis in black patients.2 Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia is the most common form of scarring alopecia in this patient population3 and has been associated with traumatic hair care practices. As a result, many patients have switched to natural hairstyles that are less traumatic and damaging, often due to recommendations by dermatologists.
As the US population continues to become more diverse, dermatologists will be faced with many questions regarding hair disease and natural hair care in patients with skin of color. A basic understanding of hair care practices among black individuals is important to aid in the diagnosis and treatment of hair shaft and scalp disorders.4 When patients switch to natural hairstyles, are dermatologists prepared to answer questions that may arise during this process? This article will familiarize dermatologists with basic hair care terminology and general recommendations they can make to black patients who are transitioning to natural hairstyles.
Characteristics of Hair in the Skin of Color Population
A basic understanding of the structural properties of hair is fundamental. Human hair is categorized into 3 groups: Asian, Caucasian, and African.5 African hair typically is curly and, depending on the degree of the curl, is more susceptible to damage due to increased mechanical fragility. It also has a tendency to form knots and fissures along the hair shaft, which causes additional fracturing with simple manipulation. African hair grows more slowly than Asian and Caucasian hair, which can be discouraging to patients. It also has a lower water concentration and does not become coated with sebum as naturally as straightened hair.5 A simplified explanation of these characteristics can help patients understand how to proceed in managing and styling their natural hair.
As physicians, it is important for us to treat any underlying conditions related to the hair and scalp in black patients. Common dermatologic conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis, lupus, folliculitis, and alopecia can affect patients’ hair health. In addition to traumatic hair care practices, inflammation secondary to bacterial infections can contribute to the onset of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia.6 Therefore, a detailed history and physical examination are needed to evaluate the etiology of associated symptoms. Treatment of these associated symptoms will aid in the overall care of patients.
Transitioning to Natural Hairstyles
Following evaluation and treatment of any hair or scalp conditions, how can dermatologists help black patients transition to natural hairstyles? The term transition refers to the process of switching from a chemically relaxed or thermally straightened hairstyle to a natural hairstyle. Dermatologists must understand the common terminology used to describe natural hair practices in this patient population.
There are several methods patients can use to transition from chemically treated hairstyles to natural hairstyles. Patients may consider the option of the “big chop,” or cutting off all chemically treated hair. This option typically leaves women with very short hairstyles down to the new growth, or hair that has grown since the last chemical relaxer. Other commonly used methods during the transition phase include protective styling (eg, braids, weaves, extensions) or simply growing out the chemically treated hair.
Protective styling methods such as braids, weaves, and extensions allow hair to be easily styled while the chemically treated hair grows out over time.7 Typically, protective styles may be worn for weeks to months, allowing hair growth without hair breakage and shedding. Hair weaving is a practice that incorporates artificial (synthetic) or human hair into one’s natural scalp hair.8 There are various techniques to extend hair including clip-in extensions, hair bonding and fusion with adhesives, sewing hair into braided hair, or the application of single strands of hair into a cap made of nylon mesh known as a lace front. Braided styles, weaves, and hair extensions cannot be washed as often as natural hair, but it is important to remind patients to replenish moisture as often as possible. Moisturizing or greasing the exposed scalp and proximal hair shafts can assist with water retention. It is imperative to inform patients that overuse of tight braids and glues for weaves and extensions may further damage the hair and scalp. Some of the natural ingredients commonly used in moisturizers include olive oil, jojoba oil, coconut oil, castor oil, and glycerin. These products can commonly cause pomade acne, which should be recognized and treated by dermatologists. Furthermore, long weaves and extensions can put excess weight on natural hair causing breakage. To prevent breakage, wearing an updo (a hairstyle in which the hair is pulled upward) can reduce the heavy strain on the hair.
Dermatologists should remind patients who wish to grow out chemically treated hair to frequently moisturize the hair and scalp as well as to avoid trauma to prevent hair breakage. As the natural hair grows out, the patient will experience varying hair textures from the natural curly hair to the previously processed straightened hair; as a result, the hair may tangle and become damaged. Manual detangling and detangling conditioners can help prevent damage. Patients should be advised to detangle the hair in sections first with the fingers, then with a wide-tooth comb working retrograde from the hair end to the roots.
Frequent hair trimming, ranging from every 4 to 6 weeks to every 2 to 4 months, should be recommended to patients who are experiencing breakage or wish to prevent damage. Trimming damaged hair can relieve excess weight on the natural hair and remove split ends, which promotes hair growth. Braiding and other lengthening techniques can prevent the hair from curling upon itself or tangling, causing less kinking and thereby decreasing the need for trimming.7 Wearing bonnets, using satin pillowcases, and wearing protective hairstyles while sleeping also can decrease hair breakage and hair loss. A commonly used hairstyle to protect the hair while sleeping is called “pineappling,” which is used to preserve and protect curls. This technique is described as gathering the hair in a high but loose ponytail at the top of the head. For patients with straightened hair, wrapping the hair underneath a bonnet or satin scarf while sleeping can prevent damage.
Managing Natural Hairstyles
An important factor in the management of natural hairstyles is the retention of hair moisture, as there is less water content in African hair compared to other hair types.5 Overuse of heat and harsh shampoos can strip moisture from the hair. Similar to patients with atopic dermatitis who should restore and maintain the skin barrier to prevent transepidermal water loss, it is important to remind patients with natural hairstyles to avoid using products and styling practices that may further deplete water content in the hair. Moisture is crucial to healthy hair.
A common culprit in shampoos that leads to hair dryness is sodium lauryl sulfate/sodium laureth sulfate, a detergent/surfactant used as a foaming agent. Sodium lauryl sulfate is a potent degreaser that binds dirt and excess product on the hair and scalp. It also dissolves oil in the hair, causing additional dryness and breakage.
Patients with natural hairstyles commonly use sulfate-free shampoos to prevent stripping the hair of its moisture and natural oils. Another method used to prevent hair dryness is co-washing, or washing the hair with a conditioner. Co-washing can effectively cleanse the hair while maintaining moisture. The use of cationic ingredients in conditioners aids in sealing moisture within the hair shaft. Hair consists of the negatively charged protein keratin, which binds to cationic surfactants in conditioners.9 The hydrophobic ends of the surfactant prevent the substance from being rinsed out and act to restore the hair barrier.
Silicone is another important ingredient in hair care products. In patients with natural hair, there are varying views on the use of products containing silicone. Silicones are added to products designed to coat the hair, adding shine, retaining moisture, and providing thermal protection. Silicones are used to provide “slip.” Slip is a term that is commonly used among patients with natural hair to describe how slippery a product is and how easily the product will help comb or detangle the hair. There are 2 basic types of silicones: water insoluble and water soluble. Water-insoluble silicones traditionally build up on the hair and require surfactant-containing shampoos to becompletely removed. Residue buildup on the hair weighs the hair down and causes damage. In contrast, water-soluble silicones do not build up and typically do not cause damage.
Silicones with the prefixes PEG- or PPG- typically are water soluble and will not build up on the hair. Dimethicone copolyol and lauryl methicone copolyol are other water-soluble silicones. In general, water-soluble silicones provide moisturizing properties without leaving residue. Other silicones such as amodimethicone and cyclomethicone are not water soluble but have properties that prevent buildup.
It is common practice for patients with natural hairstyles to avoid using water-insoluble silicones. As dermatologists, we can recommend silicone-free conditioners or conditioners containing water-soluble silicones to prevent hair dehydration and subsequent breakage. It may be advantageous to have patients try various products to determine which ones work best for their hair.
More Resources for Patients
Dermatologists have extensive knowledge of the pathophysiology of skin, hair, and nail diseases; however, despite our vast knowledge, we also need to recognize our limits. In addition to increasing your own knowledge of natural hair care practices to help your patients, it is important to recommend that your patients search for additional resources to aid in their transition to natural hairstyles. Natural hairstylists can be great resources for patients to help with hair management. In the current digital age, there also are thousands of blogs and social media forums dedicated to the topic of natural hair care. Advising patients to consult natural hair care resources can be beneficial, but as hair specialists, it also is important for us to dispel any false information that our patients may receive. As physicians, it is essential not only to manage patients who present to our offices with conditions resulting from damaging hair practices but also to help prevent such conditions from occurring. Although there may not be an overwhelming amount of evidence-based medical research to guide our decisions, we also can learn from the thousands of patients who have articulated their stories and experiences. Through observing and listening to our patients, we can incorporate this new knowledge in the management of our patients.
1. Shah SK, Alexis AF. Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia: retrospective chart review. J Cutan Med Surg. 2010;14:212-222.
2. Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
3. Uhlenhake EE, Mehregan DM. Prospective histologic examinations in patients who practice traumatic hairstyling [published online ahead of print March 3, 2013]. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:1506-1512.
4. Roseborough IE, McMichael AJ. Hair care practices in African-American patients. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009;28:103-108.
5. Kelly AP, Taylor S, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2009.
6. Kyei A, Bergfeld WF, Piliang M, et al. Medical and environmental risk factors for the development of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia: a population study [published online ahead of print April 11, 2011]. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:909-914.
7. Walton N, Carter ET. Better Than Good Hair: The Curly Girl Guide to Healthy, Gorgeous Natural Hair! New York, NY: Amistad; 2013.
8. Quinn CR, Quinn TM, Kelly AP. Hair care practices in African American women. Cutis. 2003;72:280-282, 285-289.
9. Cruz CF, Fernandes MM, Gomes AC, et al. Keratins and lipids in ethnic hair [published online ahead of print January 24, 2013]. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2013;35:244-249.
The phenomenon of natural (nonchemically treated) hair in individuals of African and Afro-Caribbean descent is sweeping across the United States. The ideals of beauty among this patient population have shifted from a relaxed, straightened, noncurly look to a more natural curly and/or kinky appearance. The discussion on natural hair versus straight hair has been brought to the mainstream by films such as Good Hair (2009). Furthermore, major hair care companies have increased their marketing of natural hair products to address the needs of these patients.
Popular traumatic hair care practices such as chemical relaxation and thermal straightening may lead to hair damage. Although the role of hair care practices in various scalp and hair disorders is ambiguous, traumatic practices commonly are performed by patients who are diagnosed with dermatologic conditions such as scarring alopecia.1 Alopecia is the fourth most common dermatologic diagnosis in black patients.2 Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia is the most common form of scarring alopecia in this patient population3 and has been associated with traumatic hair care practices. As a result, many patients have switched to natural hairstyles that are less traumatic and damaging, often due to recommendations by dermatologists.
As the US population continues to become more diverse, dermatologists will be faced with many questions regarding hair disease and natural hair care in patients with skin of color. A basic understanding of hair care practices among black individuals is important to aid in the diagnosis and treatment of hair shaft and scalp disorders.4 When patients switch to natural hairstyles, are dermatologists prepared to answer questions that may arise during this process? This article will familiarize dermatologists with basic hair care terminology and general recommendations they can make to black patients who are transitioning to natural hairstyles.
Characteristics of Hair in the Skin of Color Population
A basic understanding of the structural properties of hair is fundamental. Human hair is categorized into 3 groups: Asian, Caucasian, and African.5 African hair typically is curly and, depending on the degree of the curl, is more susceptible to damage due to increased mechanical fragility. It also has a tendency to form knots and fissures along the hair shaft, which causes additional fracturing with simple manipulation. African hair grows more slowly than Asian and Caucasian hair, which can be discouraging to patients. It also has a lower water concentration and does not become coated with sebum as naturally as straightened hair.5 A simplified explanation of these characteristics can help patients understand how to proceed in managing and styling their natural hair.
As physicians, it is important for us to treat any underlying conditions related to the hair and scalp in black patients. Common dermatologic conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis, lupus, folliculitis, and alopecia can affect patients’ hair health. In addition to traumatic hair care practices, inflammation secondary to bacterial infections can contribute to the onset of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia.6 Therefore, a detailed history and physical examination are needed to evaluate the etiology of associated symptoms. Treatment of these associated symptoms will aid in the overall care of patients.
Transitioning to Natural Hairstyles
Following evaluation and treatment of any hair or scalp conditions, how can dermatologists help black patients transition to natural hairstyles? The term transition refers to the process of switching from a chemically relaxed or thermally straightened hairstyle to a natural hairstyle. Dermatologists must understand the common terminology used to describe natural hair practices in this patient population.
There are several methods patients can use to transition from chemically treated hairstyles to natural hairstyles. Patients may consider the option of the “big chop,” or cutting off all chemically treated hair. This option typically leaves women with very short hairstyles down to the new growth, or hair that has grown since the last chemical relaxer. Other commonly used methods during the transition phase include protective styling (eg, braids, weaves, extensions) or simply growing out the chemically treated hair.
Protective styling methods such as braids, weaves, and extensions allow hair to be easily styled while the chemically treated hair grows out over time.7 Typically, protective styles may be worn for weeks to months, allowing hair growth without hair breakage and shedding. Hair weaving is a practice that incorporates artificial (synthetic) or human hair into one’s natural scalp hair.8 There are various techniques to extend hair including clip-in extensions, hair bonding and fusion with adhesives, sewing hair into braided hair, or the application of single strands of hair into a cap made of nylon mesh known as a lace front. Braided styles, weaves, and hair extensions cannot be washed as often as natural hair, but it is important to remind patients to replenish moisture as often as possible. Moisturizing or greasing the exposed scalp and proximal hair shafts can assist with water retention. It is imperative to inform patients that overuse of tight braids and glues for weaves and extensions may further damage the hair and scalp. Some of the natural ingredients commonly used in moisturizers include olive oil, jojoba oil, coconut oil, castor oil, and glycerin. These products can commonly cause pomade acne, which should be recognized and treated by dermatologists. Furthermore, long weaves and extensions can put excess weight on natural hair causing breakage. To prevent breakage, wearing an updo (a hairstyle in which the hair is pulled upward) can reduce the heavy strain on the hair.
Dermatologists should remind patients who wish to grow out chemically treated hair to frequently moisturize the hair and scalp as well as to avoid trauma to prevent hair breakage. As the natural hair grows out, the patient will experience varying hair textures from the natural curly hair to the previously processed straightened hair; as a result, the hair may tangle and become damaged. Manual detangling and detangling conditioners can help prevent damage. Patients should be advised to detangle the hair in sections first with the fingers, then with a wide-tooth comb working retrograde from the hair end to the roots.
Frequent hair trimming, ranging from every 4 to 6 weeks to every 2 to 4 months, should be recommended to patients who are experiencing breakage or wish to prevent damage. Trimming damaged hair can relieve excess weight on the natural hair and remove split ends, which promotes hair growth. Braiding and other lengthening techniques can prevent the hair from curling upon itself or tangling, causing less kinking and thereby decreasing the need for trimming.7 Wearing bonnets, using satin pillowcases, and wearing protective hairstyles while sleeping also can decrease hair breakage and hair loss. A commonly used hairstyle to protect the hair while sleeping is called “pineappling,” which is used to preserve and protect curls. This technique is described as gathering the hair in a high but loose ponytail at the top of the head. For patients with straightened hair, wrapping the hair underneath a bonnet or satin scarf while sleeping can prevent damage.
Managing Natural Hairstyles
An important factor in the management of natural hairstyles is the retention of hair moisture, as there is less water content in African hair compared to other hair types.5 Overuse of heat and harsh shampoos can strip moisture from the hair. Similar to patients with atopic dermatitis who should restore and maintain the skin barrier to prevent transepidermal water loss, it is important to remind patients with natural hairstyles to avoid using products and styling practices that may further deplete water content in the hair. Moisture is crucial to healthy hair.
A common culprit in shampoos that leads to hair dryness is sodium lauryl sulfate/sodium laureth sulfate, a detergent/surfactant used as a foaming agent. Sodium lauryl sulfate is a potent degreaser that binds dirt and excess product on the hair and scalp. It also dissolves oil in the hair, causing additional dryness and breakage.
Patients with natural hairstyles commonly use sulfate-free shampoos to prevent stripping the hair of its moisture and natural oils. Another method used to prevent hair dryness is co-washing, or washing the hair with a conditioner. Co-washing can effectively cleanse the hair while maintaining moisture. The use of cationic ingredients in conditioners aids in sealing moisture within the hair shaft. Hair consists of the negatively charged protein keratin, which binds to cationic surfactants in conditioners.9 The hydrophobic ends of the surfactant prevent the substance from being rinsed out and act to restore the hair barrier.
Silicone is another important ingredient in hair care products. In patients with natural hair, there are varying views on the use of products containing silicone. Silicones are added to products designed to coat the hair, adding shine, retaining moisture, and providing thermal protection. Silicones are used to provide “slip.” Slip is a term that is commonly used among patients with natural hair to describe how slippery a product is and how easily the product will help comb or detangle the hair. There are 2 basic types of silicones: water insoluble and water soluble. Water-insoluble silicones traditionally build up on the hair and require surfactant-containing shampoos to becompletely removed. Residue buildup on the hair weighs the hair down and causes damage. In contrast, water-soluble silicones do not build up and typically do not cause damage.
Silicones with the prefixes PEG- or PPG- typically are water soluble and will not build up on the hair. Dimethicone copolyol and lauryl methicone copolyol are other water-soluble silicones. In general, water-soluble silicones provide moisturizing properties without leaving residue. Other silicones such as amodimethicone and cyclomethicone are not water soluble but have properties that prevent buildup.
It is common practice for patients with natural hairstyles to avoid using water-insoluble silicones. As dermatologists, we can recommend silicone-free conditioners or conditioners containing water-soluble silicones to prevent hair dehydration and subsequent breakage. It may be advantageous to have patients try various products to determine which ones work best for their hair.
More Resources for Patients
Dermatologists have extensive knowledge of the pathophysiology of skin, hair, and nail diseases; however, despite our vast knowledge, we also need to recognize our limits. In addition to increasing your own knowledge of natural hair care practices to help your patients, it is important to recommend that your patients search for additional resources to aid in their transition to natural hairstyles. Natural hairstylists can be great resources for patients to help with hair management. In the current digital age, there also are thousands of blogs and social media forums dedicated to the topic of natural hair care. Advising patients to consult natural hair care resources can be beneficial, but as hair specialists, it also is important for us to dispel any false information that our patients may receive. As physicians, it is essential not only to manage patients who present to our offices with conditions resulting from damaging hair practices but also to help prevent such conditions from occurring. Although there may not be an overwhelming amount of evidence-based medical research to guide our decisions, we also can learn from the thousands of patients who have articulated their stories and experiences. Through observing and listening to our patients, we can incorporate this new knowledge in the management of our patients.
The phenomenon of natural (nonchemically treated) hair in individuals of African and Afro-Caribbean descent is sweeping across the United States. The ideals of beauty among this patient population have shifted from a relaxed, straightened, noncurly look to a more natural curly and/or kinky appearance. The discussion on natural hair versus straight hair has been brought to the mainstream by films such as Good Hair (2009). Furthermore, major hair care companies have increased their marketing of natural hair products to address the needs of these patients.
Popular traumatic hair care practices such as chemical relaxation and thermal straightening may lead to hair damage. Although the role of hair care practices in various scalp and hair disorders is ambiguous, traumatic practices commonly are performed by patients who are diagnosed with dermatologic conditions such as scarring alopecia.1 Alopecia is the fourth most common dermatologic diagnosis in black patients.2 Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia is the most common form of scarring alopecia in this patient population3 and has been associated with traumatic hair care practices. As a result, many patients have switched to natural hairstyles that are less traumatic and damaging, often due to recommendations by dermatologists.
As the US population continues to become more diverse, dermatologists will be faced with many questions regarding hair disease and natural hair care in patients with skin of color. A basic understanding of hair care practices among black individuals is important to aid in the diagnosis and treatment of hair shaft and scalp disorders.4 When patients switch to natural hairstyles, are dermatologists prepared to answer questions that may arise during this process? This article will familiarize dermatologists with basic hair care terminology and general recommendations they can make to black patients who are transitioning to natural hairstyles.
Characteristics of Hair in the Skin of Color Population
A basic understanding of the structural properties of hair is fundamental. Human hair is categorized into 3 groups: Asian, Caucasian, and African.5 African hair typically is curly and, depending on the degree of the curl, is more susceptible to damage due to increased mechanical fragility. It also has a tendency to form knots and fissures along the hair shaft, which causes additional fracturing with simple manipulation. African hair grows more slowly than Asian and Caucasian hair, which can be discouraging to patients. It also has a lower water concentration and does not become coated with sebum as naturally as straightened hair.5 A simplified explanation of these characteristics can help patients understand how to proceed in managing and styling their natural hair.
As physicians, it is important for us to treat any underlying conditions related to the hair and scalp in black patients. Common dermatologic conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis, lupus, folliculitis, and alopecia can affect patients’ hair health. In addition to traumatic hair care practices, inflammation secondary to bacterial infections can contribute to the onset of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia.6 Therefore, a detailed history and physical examination are needed to evaluate the etiology of associated symptoms. Treatment of these associated symptoms will aid in the overall care of patients.
Transitioning to Natural Hairstyles
Following evaluation and treatment of any hair or scalp conditions, how can dermatologists help black patients transition to natural hairstyles? The term transition refers to the process of switching from a chemically relaxed or thermally straightened hairstyle to a natural hairstyle. Dermatologists must understand the common terminology used to describe natural hair practices in this patient population.
There are several methods patients can use to transition from chemically treated hairstyles to natural hairstyles. Patients may consider the option of the “big chop,” or cutting off all chemically treated hair. This option typically leaves women with very short hairstyles down to the new growth, or hair that has grown since the last chemical relaxer. Other commonly used methods during the transition phase include protective styling (eg, braids, weaves, extensions) or simply growing out the chemically treated hair.
Protective styling methods such as braids, weaves, and extensions allow hair to be easily styled while the chemically treated hair grows out over time.7 Typically, protective styles may be worn for weeks to months, allowing hair growth without hair breakage and shedding. Hair weaving is a practice that incorporates artificial (synthetic) or human hair into one’s natural scalp hair.8 There are various techniques to extend hair including clip-in extensions, hair bonding and fusion with adhesives, sewing hair into braided hair, or the application of single strands of hair into a cap made of nylon mesh known as a lace front. Braided styles, weaves, and hair extensions cannot be washed as often as natural hair, but it is important to remind patients to replenish moisture as often as possible. Moisturizing or greasing the exposed scalp and proximal hair shafts can assist with water retention. It is imperative to inform patients that overuse of tight braids and glues for weaves and extensions may further damage the hair and scalp. Some of the natural ingredients commonly used in moisturizers include olive oil, jojoba oil, coconut oil, castor oil, and glycerin. These products can commonly cause pomade acne, which should be recognized and treated by dermatologists. Furthermore, long weaves and extensions can put excess weight on natural hair causing breakage. To prevent breakage, wearing an updo (a hairstyle in which the hair is pulled upward) can reduce the heavy strain on the hair.
Dermatologists should remind patients who wish to grow out chemically treated hair to frequently moisturize the hair and scalp as well as to avoid trauma to prevent hair breakage. As the natural hair grows out, the patient will experience varying hair textures from the natural curly hair to the previously processed straightened hair; as a result, the hair may tangle and become damaged. Manual detangling and detangling conditioners can help prevent damage. Patients should be advised to detangle the hair in sections first with the fingers, then with a wide-tooth comb working retrograde from the hair end to the roots.
Frequent hair trimming, ranging from every 4 to 6 weeks to every 2 to 4 months, should be recommended to patients who are experiencing breakage or wish to prevent damage. Trimming damaged hair can relieve excess weight on the natural hair and remove split ends, which promotes hair growth. Braiding and other lengthening techniques can prevent the hair from curling upon itself or tangling, causing less kinking and thereby decreasing the need for trimming.7 Wearing bonnets, using satin pillowcases, and wearing protective hairstyles while sleeping also can decrease hair breakage and hair loss. A commonly used hairstyle to protect the hair while sleeping is called “pineappling,” which is used to preserve and protect curls. This technique is described as gathering the hair in a high but loose ponytail at the top of the head. For patients with straightened hair, wrapping the hair underneath a bonnet or satin scarf while sleeping can prevent damage.
Managing Natural Hairstyles
An important factor in the management of natural hairstyles is the retention of hair moisture, as there is less water content in African hair compared to other hair types.5 Overuse of heat and harsh shampoos can strip moisture from the hair. Similar to patients with atopic dermatitis who should restore and maintain the skin barrier to prevent transepidermal water loss, it is important to remind patients with natural hairstyles to avoid using products and styling practices that may further deplete water content in the hair. Moisture is crucial to healthy hair.
A common culprit in shampoos that leads to hair dryness is sodium lauryl sulfate/sodium laureth sulfate, a detergent/surfactant used as a foaming agent. Sodium lauryl sulfate is a potent degreaser that binds dirt and excess product on the hair and scalp. It also dissolves oil in the hair, causing additional dryness and breakage.
Patients with natural hairstyles commonly use sulfate-free shampoos to prevent stripping the hair of its moisture and natural oils. Another method used to prevent hair dryness is co-washing, or washing the hair with a conditioner. Co-washing can effectively cleanse the hair while maintaining moisture. The use of cationic ingredients in conditioners aids in sealing moisture within the hair shaft. Hair consists of the negatively charged protein keratin, which binds to cationic surfactants in conditioners.9 The hydrophobic ends of the surfactant prevent the substance from being rinsed out and act to restore the hair barrier.
Silicone is another important ingredient in hair care products. In patients with natural hair, there are varying views on the use of products containing silicone. Silicones are added to products designed to coat the hair, adding shine, retaining moisture, and providing thermal protection. Silicones are used to provide “slip.” Slip is a term that is commonly used among patients with natural hair to describe how slippery a product is and how easily the product will help comb or detangle the hair. There are 2 basic types of silicones: water insoluble and water soluble. Water-insoluble silicones traditionally build up on the hair and require surfactant-containing shampoos to becompletely removed. Residue buildup on the hair weighs the hair down and causes damage. In contrast, water-soluble silicones do not build up and typically do not cause damage.
Silicones with the prefixes PEG- or PPG- typically are water soluble and will not build up on the hair. Dimethicone copolyol and lauryl methicone copolyol are other water-soluble silicones. In general, water-soluble silicones provide moisturizing properties without leaving residue. Other silicones such as amodimethicone and cyclomethicone are not water soluble but have properties that prevent buildup.
It is common practice for patients with natural hairstyles to avoid using water-insoluble silicones. As dermatologists, we can recommend silicone-free conditioners or conditioners containing water-soluble silicones to prevent hair dehydration and subsequent breakage. It may be advantageous to have patients try various products to determine which ones work best for their hair.
More Resources for Patients
Dermatologists have extensive knowledge of the pathophysiology of skin, hair, and nail diseases; however, despite our vast knowledge, we also need to recognize our limits. In addition to increasing your own knowledge of natural hair care practices to help your patients, it is important to recommend that your patients search for additional resources to aid in their transition to natural hairstyles. Natural hairstylists can be great resources for patients to help with hair management. In the current digital age, there also are thousands of blogs and social media forums dedicated to the topic of natural hair care. Advising patients to consult natural hair care resources can be beneficial, but as hair specialists, it also is important for us to dispel any false information that our patients may receive. As physicians, it is essential not only to manage patients who present to our offices with conditions resulting from damaging hair practices but also to help prevent such conditions from occurring. Although there may not be an overwhelming amount of evidence-based medical research to guide our decisions, we also can learn from the thousands of patients who have articulated their stories and experiences. Through observing and listening to our patients, we can incorporate this new knowledge in the management of our patients.
1. Shah SK, Alexis AF. Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia: retrospective chart review. J Cutan Med Surg. 2010;14:212-222.
2. Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
3. Uhlenhake EE, Mehregan DM. Prospective histologic examinations in patients who practice traumatic hairstyling [published online ahead of print March 3, 2013]. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:1506-1512.
4. Roseborough IE, McMichael AJ. Hair care practices in African-American patients. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009;28:103-108.
5. Kelly AP, Taylor S, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2009.
6. Kyei A, Bergfeld WF, Piliang M, et al. Medical and environmental risk factors for the development of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia: a population study [published online ahead of print April 11, 2011]. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:909-914.
7. Walton N, Carter ET. Better Than Good Hair: The Curly Girl Guide to Healthy, Gorgeous Natural Hair! New York, NY: Amistad; 2013.
8. Quinn CR, Quinn TM, Kelly AP. Hair care practices in African American women. Cutis. 2003;72:280-282, 285-289.
9. Cruz CF, Fernandes MM, Gomes AC, et al. Keratins and lipids in ethnic hair [published online ahead of print January 24, 2013]. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2013;35:244-249.
1. Shah SK, Alexis AF. Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia: retrospective chart review. J Cutan Med Surg. 2010;14:212-222.
2. Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
3. Uhlenhake EE, Mehregan DM. Prospective histologic examinations in patients who practice traumatic hairstyling [published online ahead of print March 3, 2013]. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:1506-1512.
4. Roseborough IE, McMichael AJ. Hair care practices in African-American patients. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009;28:103-108.
5. Kelly AP, Taylor S, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2009.
6. Kyei A, Bergfeld WF, Piliang M, et al. Medical and environmental risk factors for the development of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia: a population study [published online ahead of print April 11, 2011]. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:909-914.
7. Walton N, Carter ET. Better Than Good Hair: The Curly Girl Guide to Healthy, Gorgeous Natural Hair! New York, NY: Amistad; 2013.
8. Quinn CR, Quinn TM, Kelly AP. Hair care practices in African American women. Cutis. 2003;72:280-282, 285-289.
9. Cruz CF, Fernandes MM, Gomes AC, et al. Keratins and lipids in ethnic hair [published online ahead of print January 24, 2013]. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2013;35:244-249.
Practice Points
- Many scalp and hair diseases in patients of African and Afro-Caribbean descent result from traumatic hairstyling practices and poor management. Proper care of these patients requires an understanding of hair variances and styling techniques across ethnicities.
- The use of protective hairstyles and adequate trimming can aid black patients in the transition to healthier natural hair.
- The use of natural oils for scalp health and the avoidance of products containing chemicals that remove moisture from the hair are helpful in maintaining healthy natural hair.