User login
What are your treatment options when isotretinoin fails?
INDIANAPOLIS – – which is known to increase the drug’s bioavailability, advises James R. Treat, MD, a pediatric dermatologist at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“We see lots of teenagers who are on a restrictive diet,” which is “certainly one reason they could be failing isotretinoin,” Dr. Treat said at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Often, patients say that they have been referred to him because they had no response to 20 mg or 30 mg per day of isotretinoin. But after a dose escalation to 60 mg per day, their acne worsened.
If the patient’s acne is worsening with a cystic flare, “tripling the dose of isotretinoin is not something that you should do,” Dr. Treat said. “You should lower the dose and consider adding steroids.” For evidence-based recommendations on managing acne fulminans, he recommended an article published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2017.
Skin picking is another common reason for failure of isotretinoin, as well as with other acne therapies. These patients may have associated anxiety, which “might be a contraindication or at least something to consider before you put them on isotretinoin,” he noted.
In his experience, off-label use of N-acetylcysteine, an antioxidant and cysteine prodrug, has been “extremely effective” for patients with excoriation disorder. In a randomized trial of adults 18-60 years of age, 47% patients who took 1,200-3,000 mg per day doses of N-acetylcysteine for 12 weeks reported that their skin picking was much or very much improved, compared to 19% of those who took placebo (P = .03). The authors wrote that N-acetylcysteine “increases extracellular levels of glutamate in the nucleus accumbens,” and that these results support the hypothesis that “pharmacologic manipulation of the glutamate system may target core symptoms of compulsive behaviors.”
The tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha blocker adalimumab is a reasonable option for patients with severe cystic inflammatory acne who fail isotretinoin, Dr. Treat said. In one published case, clinicians administered adalimumab 40 mg every other week for a 16-year-old male patient who received isotretinoin for moderate acne vulgaris, which caused sudden development of acne fulminans and incapacitating acute sacroiliitis with bilateral hip arthritis. Inflammatory lesions started to clear in 1 month and comedones improved by 3 months of treatment. Adalimumab was discontinued after 1 year and the patient remained clear.
“There are now multiple reports as well as some case series showing TNF-alpha agents causing clearance of acne,” said Dr. Treat, who directs the hospital’s pediatric dermatology fellowship program. A literature review of adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab for treatment-resistant acne found that all agents had similar efficacy after 3-6 months of therapy. “We see this in our GI population, where TNF-alpha agents are helping their acne also,” he said. “We just have to augment it with some topical medications.”
Certain medications can drive the development of acne, including phenytoin, phenobarbital, lithium, MEK inhibitors, EGFR inhibitors, systemic steroids, and unopposed progesterone contraceptives. Some genetic conditions also predispose patients to acne, including mutations in the NCSTN gene and trisomy 13.
Dr. Treat discussed one of his patients with severe acne who had trisomy 13. The patient failed 12 months of doxycycline and amoxicillin in combination with a topical retinoid. He also failed low- and high-dose isotretinoin in combination with prednisone, as well as oral dapsone at a dose of 1 mg/kg per day for 3 months. He was started on adalimumab, but that was stopped after he flared. The patient is now maintained on ustekinumab monthly at a dose of 45 mg.
“I’ve only had a few patients where isotretinoin truly has failed,” Dr. Treat said. He described one patient with severe acne who had a hidradenitis-like appearance in his axilla and groin. “I treated with isotretinoin very gingerly in the beginning, [but] he flared significantly. I had given him concomitant steroids from the very beginning and transitioned to multiple different therapies – all of which failed.”
Next, Dr. Treat tried a course of systemic dapsone, and the patient responded nicely. “As an anti-inflammatory agent, dapsone is very reasonable” to consider, he said. “It’s something to add to your armamentarium.”
Dr. Treat disclosed that he is a consultant for Palvella and Regeneron. He has ownership interests in Matinas Biopharma Holdings, Axsome, Sorrento, and Amarin.
INDIANAPOLIS – – which is known to increase the drug’s bioavailability, advises James R. Treat, MD, a pediatric dermatologist at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“We see lots of teenagers who are on a restrictive diet,” which is “certainly one reason they could be failing isotretinoin,” Dr. Treat said at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Often, patients say that they have been referred to him because they had no response to 20 mg or 30 mg per day of isotretinoin. But after a dose escalation to 60 mg per day, their acne worsened.
If the patient’s acne is worsening with a cystic flare, “tripling the dose of isotretinoin is not something that you should do,” Dr. Treat said. “You should lower the dose and consider adding steroids.” For evidence-based recommendations on managing acne fulminans, he recommended an article published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2017.
Skin picking is another common reason for failure of isotretinoin, as well as with other acne therapies. These patients may have associated anxiety, which “might be a contraindication or at least something to consider before you put them on isotretinoin,” he noted.
In his experience, off-label use of N-acetylcysteine, an antioxidant and cysteine prodrug, has been “extremely effective” for patients with excoriation disorder. In a randomized trial of adults 18-60 years of age, 47% patients who took 1,200-3,000 mg per day doses of N-acetylcysteine for 12 weeks reported that their skin picking was much or very much improved, compared to 19% of those who took placebo (P = .03). The authors wrote that N-acetylcysteine “increases extracellular levels of glutamate in the nucleus accumbens,” and that these results support the hypothesis that “pharmacologic manipulation of the glutamate system may target core symptoms of compulsive behaviors.”
The tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha blocker adalimumab is a reasonable option for patients with severe cystic inflammatory acne who fail isotretinoin, Dr. Treat said. In one published case, clinicians administered adalimumab 40 mg every other week for a 16-year-old male patient who received isotretinoin for moderate acne vulgaris, which caused sudden development of acne fulminans and incapacitating acute sacroiliitis with bilateral hip arthritis. Inflammatory lesions started to clear in 1 month and comedones improved by 3 months of treatment. Adalimumab was discontinued after 1 year and the patient remained clear.
“There are now multiple reports as well as some case series showing TNF-alpha agents causing clearance of acne,” said Dr. Treat, who directs the hospital’s pediatric dermatology fellowship program. A literature review of adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab for treatment-resistant acne found that all agents had similar efficacy after 3-6 months of therapy. “We see this in our GI population, where TNF-alpha agents are helping their acne also,” he said. “We just have to augment it with some topical medications.”
Certain medications can drive the development of acne, including phenytoin, phenobarbital, lithium, MEK inhibitors, EGFR inhibitors, systemic steroids, and unopposed progesterone contraceptives. Some genetic conditions also predispose patients to acne, including mutations in the NCSTN gene and trisomy 13.
Dr. Treat discussed one of his patients with severe acne who had trisomy 13. The patient failed 12 months of doxycycline and amoxicillin in combination with a topical retinoid. He also failed low- and high-dose isotretinoin in combination with prednisone, as well as oral dapsone at a dose of 1 mg/kg per day for 3 months. He was started on adalimumab, but that was stopped after he flared. The patient is now maintained on ustekinumab monthly at a dose of 45 mg.
“I’ve only had a few patients where isotretinoin truly has failed,” Dr. Treat said. He described one patient with severe acne who had a hidradenitis-like appearance in his axilla and groin. “I treated with isotretinoin very gingerly in the beginning, [but] he flared significantly. I had given him concomitant steroids from the very beginning and transitioned to multiple different therapies – all of which failed.”
Next, Dr. Treat tried a course of systemic dapsone, and the patient responded nicely. “As an anti-inflammatory agent, dapsone is very reasonable” to consider, he said. “It’s something to add to your armamentarium.”
Dr. Treat disclosed that he is a consultant for Palvella and Regeneron. He has ownership interests in Matinas Biopharma Holdings, Axsome, Sorrento, and Amarin.
INDIANAPOLIS – – which is known to increase the drug’s bioavailability, advises James R. Treat, MD, a pediatric dermatologist at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“We see lots of teenagers who are on a restrictive diet,” which is “certainly one reason they could be failing isotretinoin,” Dr. Treat said at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Often, patients say that they have been referred to him because they had no response to 20 mg or 30 mg per day of isotretinoin. But after a dose escalation to 60 mg per day, their acne worsened.
If the patient’s acne is worsening with a cystic flare, “tripling the dose of isotretinoin is not something that you should do,” Dr. Treat said. “You should lower the dose and consider adding steroids.” For evidence-based recommendations on managing acne fulminans, he recommended an article published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2017.
Skin picking is another common reason for failure of isotretinoin, as well as with other acne therapies. These patients may have associated anxiety, which “might be a contraindication or at least something to consider before you put them on isotretinoin,” he noted.
In his experience, off-label use of N-acetylcysteine, an antioxidant and cysteine prodrug, has been “extremely effective” for patients with excoriation disorder. In a randomized trial of adults 18-60 years of age, 47% patients who took 1,200-3,000 mg per day doses of N-acetylcysteine for 12 weeks reported that their skin picking was much or very much improved, compared to 19% of those who took placebo (P = .03). The authors wrote that N-acetylcysteine “increases extracellular levels of glutamate in the nucleus accumbens,” and that these results support the hypothesis that “pharmacologic manipulation of the glutamate system may target core symptoms of compulsive behaviors.”
The tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha blocker adalimumab is a reasonable option for patients with severe cystic inflammatory acne who fail isotretinoin, Dr. Treat said. In one published case, clinicians administered adalimumab 40 mg every other week for a 16-year-old male patient who received isotretinoin for moderate acne vulgaris, which caused sudden development of acne fulminans and incapacitating acute sacroiliitis with bilateral hip arthritis. Inflammatory lesions started to clear in 1 month and comedones improved by 3 months of treatment. Adalimumab was discontinued after 1 year and the patient remained clear.
“There are now multiple reports as well as some case series showing TNF-alpha agents causing clearance of acne,” said Dr. Treat, who directs the hospital’s pediatric dermatology fellowship program. A literature review of adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab for treatment-resistant acne found that all agents had similar efficacy after 3-6 months of therapy. “We see this in our GI population, where TNF-alpha agents are helping their acne also,” he said. “We just have to augment it with some topical medications.”
Certain medications can drive the development of acne, including phenytoin, phenobarbital, lithium, MEK inhibitors, EGFR inhibitors, systemic steroids, and unopposed progesterone contraceptives. Some genetic conditions also predispose patients to acne, including mutations in the NCSTN gene and trisomy 13.
Dr. Treat discussed one of his patients with severe acne who had trisomy 13. The patient failed 12 months of doxycycline and amoxicillin in combination with a topical retinoid. He also failed low- and high-dose isotretinoin in combination with prednisone, as well as oral dapsone at a dose of 1 mg/kg per day for 3 months. He was started on adalimumab, but that was stopped after he flared. The patient is now maintained on ustekinumab monthly at a dose of 45 mg.
“I’ve only had a few patients where isotretinoin truly has failed,” Dr. Treat said. He described one patient with severe acne who had a hidradenitis-like appearance in his axilla and groin. “I treated with isotretinoin very gingerly in the beginning, [but] he flared significantly. I had given him concomitant steroids from the very beginning and transitioned to multiple different therapies – all of which failed.”
Next, Dr. Treat tried a course of systemic dapsone, and the patient responded nicely. “As an anti-inflammatory agent, dapsone is very reasonable” to consider, he said. “It’s something to add to your armamentarium.”
Dr. Treat disclosed that he is a consultant for Palvella and Regeneron. He has ownership interests in Matinas Biopharma Holdings, Axsome, Sorrento, and Amarin.
AT SPD 2022
Study eyes characteristics of pediatric patients with hidradenitis suppurativa
INDIANAPOLIS – in a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In addition, 44% presented with scarring, which suggests that HS may be underdiagnosed in this patient population. Those are the key findings from the study, a single-center retrospective chart review presented by Stephanie Sanchez during a poster session at the meeting.

“There is limited research on HS within the pediatric population,” said Ms. Sanchez, a fourth-year medical student at Boston University. “It’s not very well defined or characterized.” The “unusually high number of pediatric patients with HS” at Boston Medical Center provided “a unique opportunity to study this topic.”
Working with her mentor, Lisa Shen, MD, associate medical director of pediatric dermatology at Boston University, Ms. Sanchez and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 303 patients aged 4-18 years who were diagnosed with HS at Boston Medical Center from 2012 to 2021. Boston Medical Center is the largest safety net hospital in New England. All data points and outcome measures were collected within 6 months of the patient’s HS diagnosis date.
Of the 303 patients with HS, 84% were female and 16% were male. Complete information about race was available in 286 patients. Of these, 65% were Black/African American, 11% were White, and the rest were from other racial groups. The mean age at symptom onset was 13 years, while the mean age at diagnosis was 15 years, and the mean delay to diagnosis was 2 years. A family history of HS was reported in 36% of patients.
The most common clinical features in these HS patients were pain/tenderness (90%), pustules/papules (65%), discharge/drainage (62%), and deep-seated nodules (51%). Scarring was present in 44% of patients at the time of diagnosis. The three most common sites of involvement were the axillary area (79%), the pubic area (36%), and the inguinal folds/inner thighs (34%).
Obesity was the most common comorbidity at the time of diagnosis, with 64% of patients affected. The next most common comorbidities were acne vulgaris (36%), acanthosis nigricans (25%), depression (18%), being overweight (17%), polycystic ovary syndrome (16%) and anxiety (13%). None had type 1 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Referring to the large population of underserved minority patients at Boston Medical Center, Dr. Shen noted, “we have to make sure not to underestimate the prevalence of obesity in this population as they get older. We need to start from a younger age to incorporate multidisciplinary care such as weight management, nutrition, and working with our pediatric surgery colleagues in trying to tackle [HS] because there is data to suggest that the earlier we intervene, the better outcomes they have. That makes sense.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the findings, said that the study “highlights the impressive and concerning gap and delays in diagnosis, not too dissimilar to what the literature shows in adult HS patients, which unfortunately has tremendous ramifications, both physically and emotionally/psychosocially.”
While this single-center study identified potential risk factors, such as obesity and self-identifying as Black, he said, “it is important to note that this condition does not discriminate and therefore it is important not to miss the cases that don’t follow the textbook nor stigmatize this condition as one that only impacts certain demographics.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is a speaker for companies including, Regeneron, Sanofi, AbbVie, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
INDIANAPOLIS – in a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In addition, 44% presented with scarring, which suggests that HS may be underdiagnosed in this patient population. Those are the key findings from the study, a single-center retrospective chart review presented by Stephanie Sanchez during a poster session at the meeting.

“There is limited research on HS within the pediatric population,” said Ms. Sanchez, a fourth-year medical student at Boston University. “It’s not very well defined or characterized.” The “unusually high number of pediatric patients with HS” at Boston Medical Center provided “a unique opportunity to study this topic.”
Working with her mentor, Lisa Shen, MD, associate medical director of pediatric dermatology at Boston University, Ms. Sanchez and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 303 patients aged 4-18 years who were diagnosed with HS at Boston Medical Center from 2012 to 2021. Boston Medical Center is the largest safety net hospital in New England. All data points and outcome measures were collected within 6 months of the patient’s HS diagnosis date.
Of the 303 patients with HS, 84% were female and 16% were male. Complete information about race was available in 286 patients. Of these, 65% were Black/African American, 11% were White, and the rest were from other racial groups. The mean age at symptom onset was 13 years, while the mean age at diagnosis was 15 years, and the mean delay to diagnosis was 2 years. A family history of HS was reported in 36% of patients.
The most common clinical features in these HS patients were pain/tenderness (90%), pustules/papules (65%), discharge/drainage (62%), and deep-seated nodules (51%). Scarring was present in 44% of patients at the time of diagnosis. The three most common sites of involvement were the axillary area (79%), the pubic area (36%), and the inguinal folds/inner thighs (34%).
Obesity was the most common comorbidity at the time of diagnosis, with 64% of patients affected. The next most common comorbidities were acne vulgaris (36%), acanthosis nigricans (25%), depression (18%), being overweight (17%), polycystic ovary syndrome (16%) and anxiety (13%). None had type 1 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Referring to the large population of underserved minority patients at Boston Medical Center, Dr. Shen noted, “we have to make sure not to underestimate the prevalence of obesity in this population as they get older. We need to start from a younger age to incorporate multidisciplinary care such as weight management, nutrition, and working with our pediatric surgery colleagues in trying to tackle [HS] because there is data to suggest that the earlier we intervene, the better outcomes they have. That makes sense.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the findings, said that the study “highlights the impressive and concerning gap and delays in diagnosis, not too dissimilar to what the literature shows in adult HS patients, which unfortunately has tremendous ramifications, both physically and emotionally/psychosocially.”
While this single-center study identified potential risk factors, such as obesity and self-identifying as Black, he said, “it is important to note that this condition does not discriminate and therefore it is important not to miss the cases that don’t follow the textbook nor stigmatize this condition as one that only impacts certain demographics.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is a speaker for companies including, Regeneron, Sanofi, AbbVie, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
INDIANAPOLIS – in a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In addition, 44% presented with scarring, which suggests that HS may be underdiagnosed in this patient population. Those are the key findings from the study, a single-center retrospective chart review presented by Stephanie Sanchez during a poster session at the meeting.

“There is limited research on HS within the pediatric population,” said Ms. Sanchez, a fourth-year medical student at Boston University. “It’s not very well defined or characterized.” The “unusually high number of pediatric patients with HS” at Boston Medical Center provided “a unique opportunity to study this topic.”
Working with her mentor, Lisa Shen, MD, associate medical director of pediatric dermatology at Boston University, Ms. Sanchez and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 303 patients aged 4-18 years who were diagnosed with HS at Boston Medical Center from 2012 to 2021. Boston Medical Center is the largest safety net hospital in New England. All data points and outcome measures were collected within 6 months of the patient’s HS diagnosis date.
Of the 303 patients with HS, 84% were female and 16% were male. Complete information about race was available in 286 patients. Of these, 65% were Black/African American, 11% were White, and the rest were from other racial groups. The mean age at symptom onset was 13 years, while the mean age at diagnosis was 15 years, and the mean delay to diagnosis was 2 years. A family history of HS was reported in 36% of patients.
The most common clinical features in these HS patients were pain/tenderness (90%), pustules/papules (65%), discharge/drainage (62%), and deep-seated nodules (51%). Scarring was present in 44% of patients at the time of diagnosis. The three most common sites of involvement were the axillary area (79%), the pubic area (36%), and the inguinal folds/inner thighs (34%).
Obesity was the most common comorbidity at the time of diagnosis, with 64% of patients affected. The next most common comorbidities were acne vulgaris (36%), acanthosis nigricans (25%), depression (18%), being overweight (17%), polycystic ovary syndrome (16%) and anxiety (13%). None had type 1 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Referring to the large population of underserved minority patients at Boston Medical Center, Dr. Shen noted, “we have to make sure not to underestimate the prevalence of obesity in this population as they get older. We need to start from a younger age to incorporate multidisciplinary care such as weight management, nutrition, and working with our pediatric surgery colleagues in trying to tackle [HS] because there is data to suggest that the earlier we intervene, the better outcomes they have. That makes sense.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the findings, said that the study “highlights the impressive and concerning gap and delays in diagnosis, not too dissimilar to what the literature shows in adult HS patients, which unfortunately has tremendous ramifications, both physically and emotionally/psychosocially.”
While this single-center study identified potential risk factors, such as obesity and self-identifying as Black, he said, “it is important to note that this condition does not discriminate and therefore it is important not to miss the cases that don’t follow the textbook nor stigmatize this condition as one that only impacts certain demographics.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is a speaker for companies including, Regeneron, Sanofi, AbbVie, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
AT SPD 2022
Telemedicine and Home Pregnancy Testing for iPLEDGE: A Survey of Clinician Perspectives
To the Editor:
In response to the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic, iPLEDGE announced that they would accept results from home pregnancy tests and explicitly permit telemedicine.1 Given the financial and logistical burdens associated with iPLEDGE, these changes have the potential to increase access.2 However, it is unclear whether these modifications will be allowed to continue. We sought to evaluate clinician perspectives on the role of telemedicine and home pregnancy testing for iPLEDGE.
After piloting among several clinicians, a 13-question survey was distributed using the Qualtrics platform to members of the American Acne & Rosacea Society between April 14, 2021, and June 14, 2021. This survey consisted of items addressing provider practices and perspectives on telemedicine and home pregnancy testing for patients taking isotretinoin (eTable). Respondents were asked whether they think telemedicine and home pregnancy testing have improved access to care and whether they would like to continue these practices going forward. In addition, participants were asked about their concerns with home pregnancy testing and how comfortable they feel with home pregnancy testing for various contraceptive strategies (abstinence, condoms, combined oral contraceptives, and long-acting reversible contraception). This study was deemed exempt (category 2) by the University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania) institutional review board (Protocol #844549).

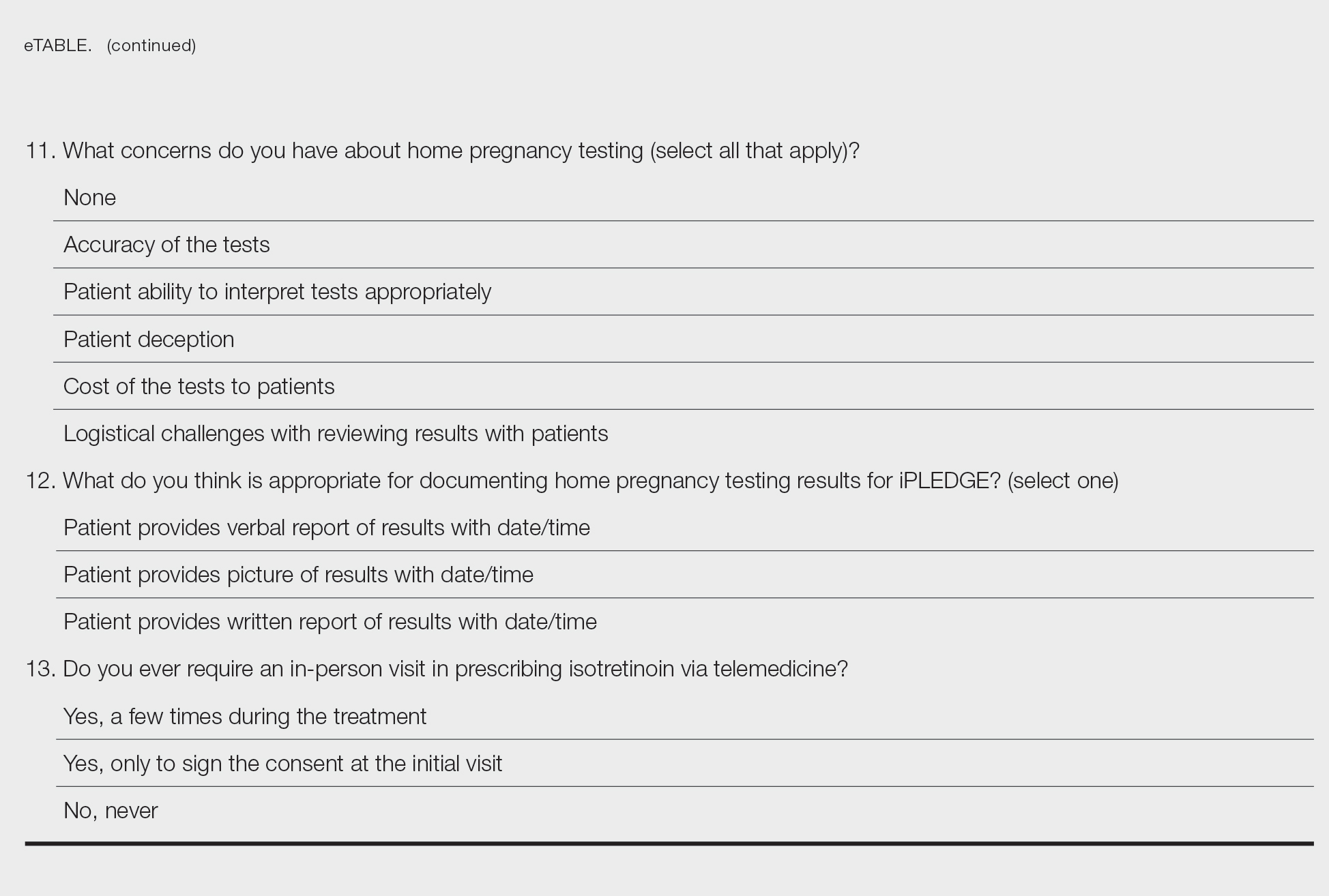
Among 70 clinicians who completed the survey (response rate, 6.4%), 33 (47.1%) practiced in an academic setting. At the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, clinicians reported using telemedicine for a median of 90% (IQR=50%–100%) of their patients on isotretinoin, and 57 respondents (81.4%) reported having patients use a home pregnancy test for iPLEDGE (Table 1). More than 75% (55/70) agreed that they would like to continue to use telemedicine for patients on isotretinoin, and more than 75% (54/70) agreed that they would like to continue using home pregnancy testing for patients outside the setting of the COVID-19 pandemic. More than 75% (54/70) agreed that telemedicine has increased access for their patients, and more than 70% (52/70) agreed that home pregnancy testing has increased access (Table 2). Clinicians agreed that they would be comfortable using home pregnancy testing for patients choosing long-acting reversible contraception (63/70 [90.0%]), combined oral contraceptives (61/69 [88.4%]), condoms (47/70 [67.1%]), or abstinence (48/70 [68.6%])(Table 3).
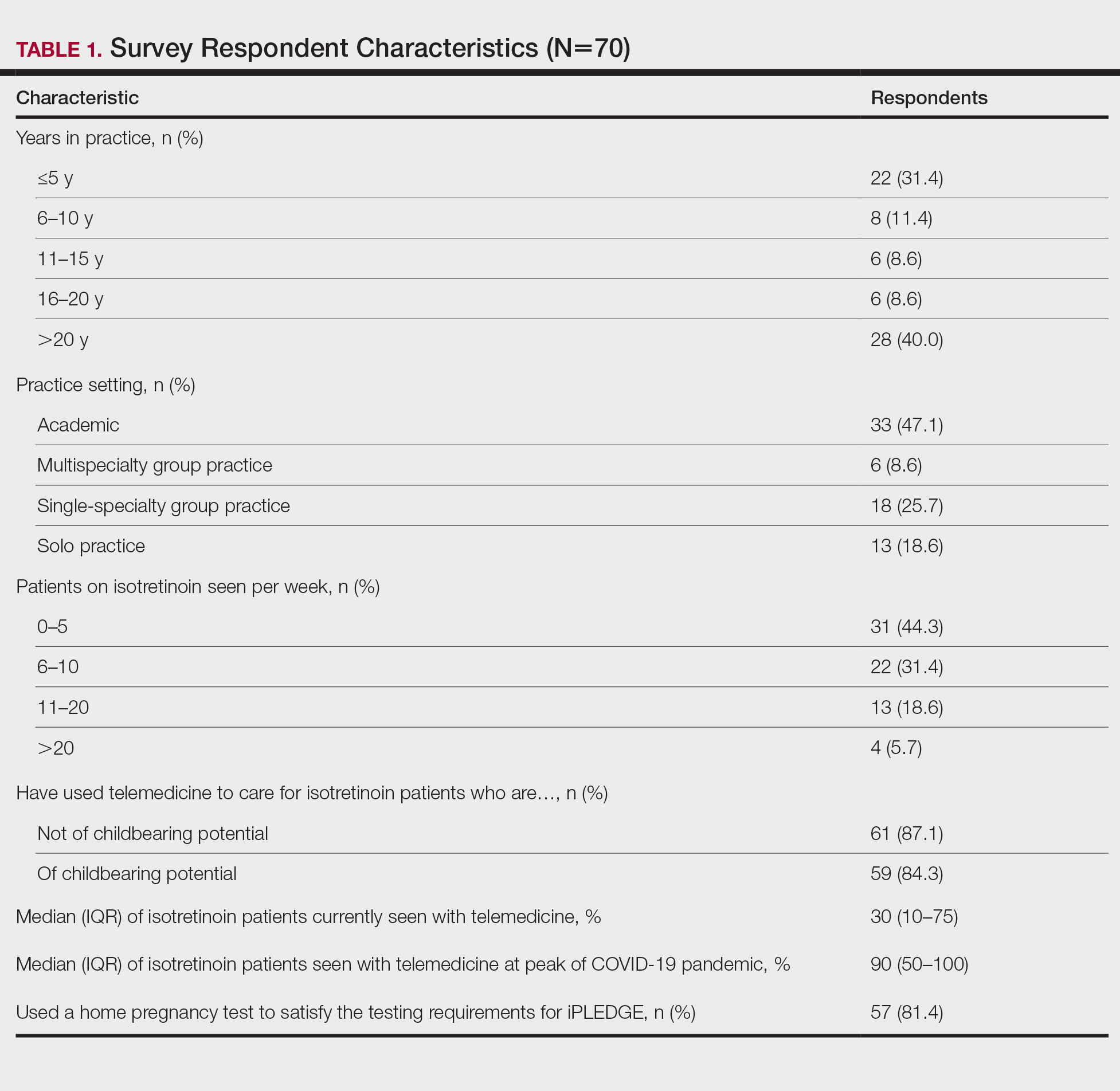
The most common concerns about home pregnancy testing were patient deception (39/70 [55.7%]), logistical challenges with reviewing results (19/70 [27.1%]), accuracy of the tests (19/70 [27.1%]), and patient ability to interpret tests appropriately (18/70 [25.7%]). To document testing results, 50 respondents (73.5%) would require a picture of results, 4 (5.9%) would accept a written report from the patient, and 14 (20.6%) would accept a verbal report from the patient (Table 2).
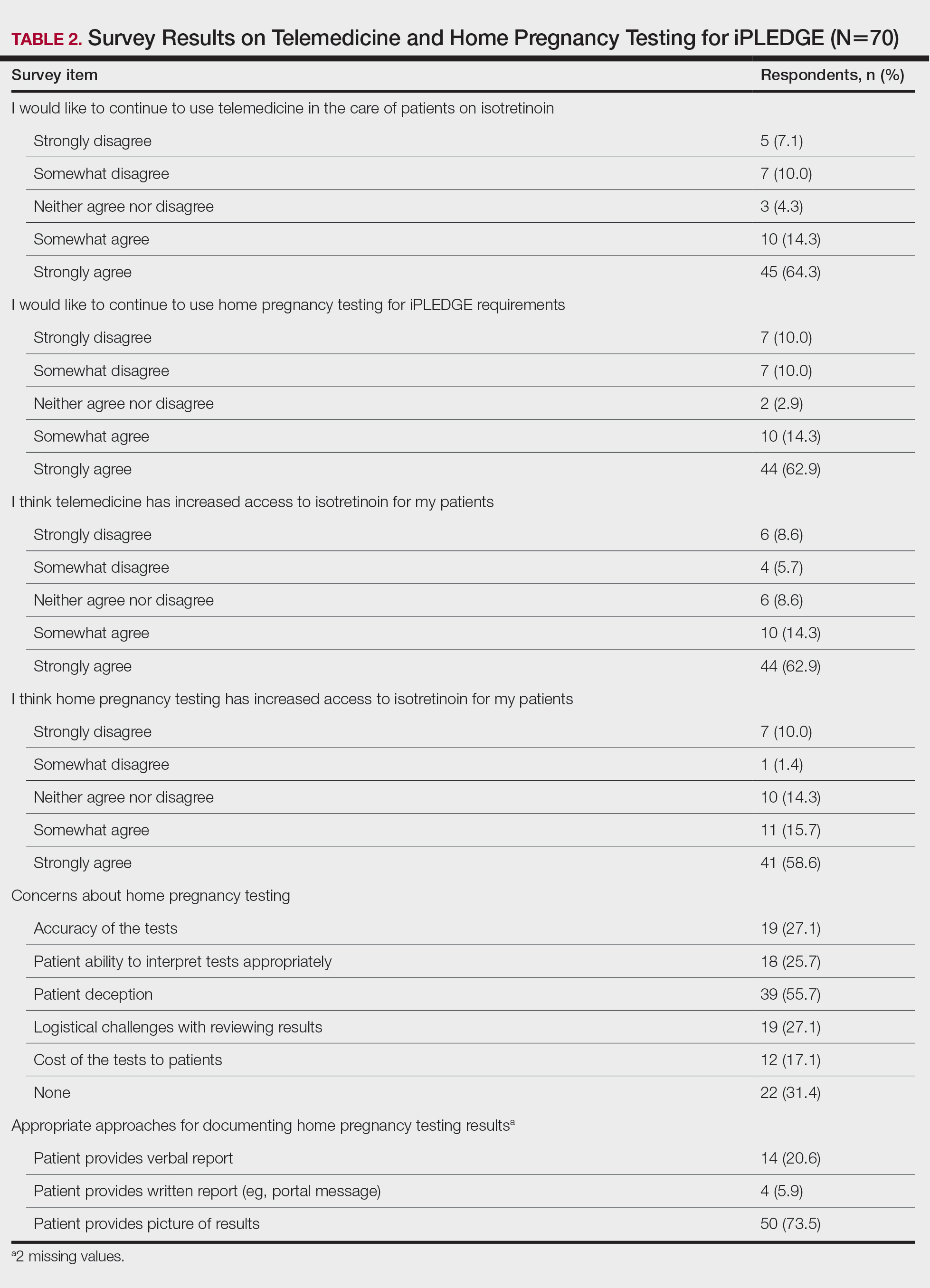
In this survey, clinicians expressed interest in continuing to use telemedicine and home pregnancy testing to care for patients with acne treated with isotretinoin. More than 75% agreed that these changes have increased access, which is notable, as several studies have identified that female and minority patients may face iPLEDGE-associated access barriers.3,4 Continuing to allow home pregnancy testing and explicitly permitting telemedicine can enable clinicians to provide patient-centered care.2
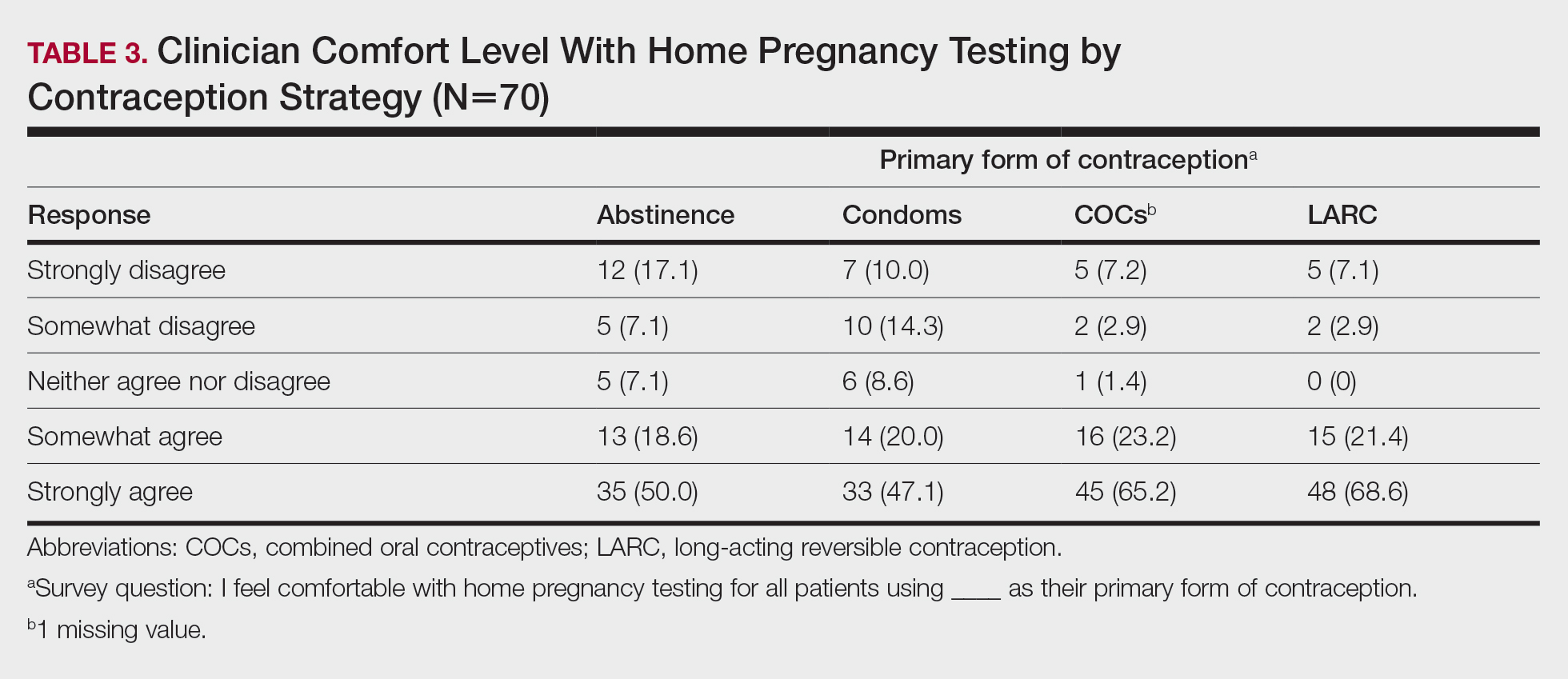
Although clinicians felt comfortable with a variety of contraceptive strategies, particularly those with high reported effectiveness,5 there were concerns about deception and interpretation of test results. Future studies are needed to identify optimal workflows for home pregnancy testing and whether patients should be required to provide a photograph of the results.
This survey study is limited by the possibility of sampling and response bias due to the low response rate. Although the use of national listservs was employed to maximize the generalizability of the results, given the response rate, future studies are needed to evaluate whether these findings generalize to other settings. In addition, given iPLEDGE-associated access barriers, further research is needed to examine how changes such as telemedicine and home pregnancy testing influence both access to isotretinoin and pregnancy prevention.
Acknowledgments—We would like to thank Stacey Moore (Montclair, New Jersey) and the American Acne & Rosacea Society for their help distributing the survey.
- Kane S, Admani S. COVID-19 pandemic leading to the accelerated development of a virtual health model for isotretinoin. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2021;13:54-57.
- Barbieri JS, Frieden IJ, Nagler AR. Isotretinoin, patient safety, and patient-centered care-time to reform iPLEDGE. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:21-22.
- Barbieri JS, Shin DB, Wang S, et al. Association of race/ethnicity and sex with differences in health care use and treatment for acne. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:312-319.
- Charrow A, Xia FD, Lu J, et al. Differences in isotretinoin start, interruption, and early termination across race and sex in the iPLEDGE era. PloS One. 2019;14:E0210445.
- Barbieri JS, Roe AH, Mostaghimi A. Simplifying contraception requirements for iPLEDGE: a decision analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:104-108.
To the Editor:
In response to the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic, iPLEDGE announced that they would accept results from home pregnancy tests and explicitly permit telemedicine.1 Given the financial and logistical burdens associated with iPLEDGE, these changes have the potential to increase access.2 However, it is unclear whether these modifications will be allowed to continue. We sought to evaluate clinician perspectives on the role of telemedicine and home pregnancy testing for iPLEDGE.
After piloting among several clinicians, a 13-question survey was distributed using the Qualtrics platform to members of the American Acne & Rosacea Society between April 14, 2021, and June 14, 2021. This survey consisted of items addressing provider practices and perspectives on telemedicine and home pregnancy testing for patients taking isotretinoin (eTable). Respondents were asked whether they think telemedicine and home pregnancy testing have improved access to care and whether they would like to continue these practices going forward. In addition, participants were asked about their concerns with home pregnancy testing and how comfortable they feel with home pregnancy testing for various contraceptive strategies (abstinence, condoms, combined oral contraceptives, and long-acting reversible contraception). This study was deemed exempt (category 2) by the University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania) institutional review board (Protocol #844549).


Among 70 clinicians who completed the survey (response rate, 6.4%), 33 (47.1%) practiced in an academic setting. At the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, clinicians reported using telemedicine for a median of 90% (IQR=50%–100%) of their patients on isotretinoin, and 57 respondents (81.4%) reported having patients use a home pregnancy test for iPLEDGE (Table 1). More than 75% (55/70) agreed that they would like to continue to use telemedicine for patients on isotretinoin, and more than 75% (54/70) agreed that they would like to continue using home pregnancy testing for patients outside the setting of the COVID-19 pandemic. More than 75% (54/70) agreed that telemedicine has increased access for their patients, and more than 70% (52/70) agreed that home pregnancy testing has increased access (Table 2). Clinicians agreed that they would be comfortable using home pregnancy testing for patients choosing long-acting reversible contraception (63/70 [90.0%]), combined oral contraceptives (61/69 [88.4%]), condoms (47/70 [67.1%]), or abstinence (48/70 [68.6%])(Table 3).

The most common concerns about home pregnancy testing were patient deception (39/70 [55.7%]), logistical challenges with reviewing results (19/70 [27.1%]), accuracy of the tests (19/70 [27.1%]), and patient ability to interpret tests appropriately (18/70 [25.7%]). To document testing results, 50 respondents (73.5%) would require a picture of results, 4 (5.9%) would accept a written report from the patient, and 14 (20.6%) would accept a verbal report from the patient (Table 2).

In this survey, clinicians expressed interest in continuing to use telemedicine and home pregnancy testing to care for patients with acne treated with isotretinoin. More than 75% agreed that these changes have increased access, which is notable, as several studies have identified that female and minority patients may face iPLEDGE-associated access barriers.3,4 Continuing to allow home pregnancy testing and explicitly permitting telemedicine can enable clinicians to provide patient-centered care.2

Although clinicians felt comfortable with a variety of contraceptive strategies, particularly those with high reported effectiveness,5 there were concerns about deception and interpretation of test results. Future studies are needed to identify optimal workflows for home pregnancy testing and whether patients should be required to provide a photograph of the results.
This survey study is limited by the possibility of sampling and response bias due to the low response rate. Although the use of national listservs was employed to maximize the generalizability of the results, given the response rate, future studies are needed to evaluate whether these findings generalize to other settings. In addition, given iPLEDGE-associated access barriers, further research is needed to examine how changes such as telemedicine and home pregnancy testing influence both access to isotretinoin and pregnancy prevention.
Acknowledgments—We would like to thank Stacey Moore (Montclair, New Jersey) and the American Acne & Rosacea Society for their help distributing the survey.
To the Editor:
In response to the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic, iPLEDGE announced that they would accept results from home pregnancy tests and explicitly permit telemedicine.1 Given the financial and logistical burdens associated with iPLEDGE, these changes have the potential to increase access.2 However, it is unclear whether these modifications will be allowed to continue. We sought to evaluate clinician perspectives on the role of telemedicine and home pregnancy testing for iPLEDGE.
After piloting among several clinicians, a 13-question survey was distributed using the Qualtrics platform to members of the American Acne & Rosacea Society between April 14, 2021, and June 14, 2021. This survey consisted of items addressing provider practices and perspectives on telemedicine and home pregnancy testing for patients taking isotretinoin (eTable). Respondents were asked whether they think telemedicine and home pregnancy testing have improved access to care and whether they would like to continue these practices going forward. In addition, participants were asked about their concerns with home pregnancy testing and how comfortable they feel with home pregnancy testing for various contraceptive strategies (abstinence, condoms, combined oral contraceptives, and long-acting reversible contraception). This study was deemed exempt (category 2) by the University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania) institutional review board (Protocol #844549).


Among 70 clinicians who completed the survey (response rate, 6.4%), 33 (47.1%) practiced in an academic setting. At the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, clinicians reported using telemedicine for a median of 90% (IQR=50%–100%) of their patients on isotretinoin, and 57 respondents (81.4%) reported having patients use a home pregnancy test for iPLEDGE (Table 1). More than 75% (55/70) agreed that they would like to continue to use telemedicine for patients on isotretinoin, and more than 75% (54/70) agreed that they would like to continue using home pregnancy testing for patients outside the setting of the COVID-19 pandemic. More than 75% (54/70) agreed that telemedicine has increased access for their patients, and more than 70% (52/70) agreed that home pregnancy testing has increased access (Table 2). Clinicians agreed that they would be comfortable using home pregnancy testing for patients choosing long-acting reversible contraception (63/70 [90.0%]), combined oral contraceptives (61/69 [88.4%]), condoms (47/70 [67.1%]), or abstinence (48/70 [68.6%])(Table 3).

The most common concerns about home pregnancy testing were patient deception (39/70 [55.7%]), logistical challenges with reviewing results (19/70 [27.1%]), accuracy of the tests (19/70 [27.1%]), and patient ability to interpret tests appropriately (18/70 [25.7%]). To document testing results, 50 respondents (73.5%) would require a picture of results, 4 (5.9%) would accept a written report from the patient, and 14 (20.6%) would accept a verbal report from the patient (Table 2).

In this survey, clinicians expressed interest in continuing to use telemedicine and home pregnancy testing to care for patients with acne treated with isotretinoin. More than 75% agreed that these changes have increased access, which is notable, as several studies have identified that female and minority patients may face iPLEDGE-associated access barriers.3,4 Continuing to allow home pregnancy testing and explicitly permitting telemedicine can enable clinicians to provide patient-centered care.2

Although clinicians felt comfortable with a variety of contraceptive strategies, particularly those with high reported effectiveness,5 there were concerns about deception and interpretation of test results. Future studies are needed to identify optimal workflows for home pregnancy testing and whether patients should be required to provide a photograph of the results.
This survey study is limited by the possibility of sampling and response bias due to the low response rate. Although the use of national listservs was employed to maximize the generalizability of the results, given the response rate, future studies are needed to evaluate whether these findings generalize to other settings. In addition, given iPLEDGE-associated access barriers, further research is needed to examine how changes such as telemedicine and home pregnancy testing influence both access to isotretinoin and pregnancy prevention.
Acknowledgments—We would like to thank Stacey Moore (Montclair, New Jersey) and the American Acne & Rosacea Society for their help distributing the survey.
- Kane S, Admani S. COVID-19 pandemic leading to the accelerated development of a virtual health model for isotretinoin. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2021;13:54-57.
- Barbieri JS, Frieden IJ, Nagler AR. Isotretinoin, patient safety, and patient-centered care-time to reform iPLEDGE. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:21-22.
- Barbieri JS, Shin DB, Wang S, et al. Association of race/ethnicity and sex with differences in health care use and treatment for acne. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:312-319.
- Charrow A, Xia FD, Lu J, et al. Differences in isotretinoin start, interruption, and early termination across race and sex in the iPLEDGE era. PloS One. 2019;14:E0210445.
- Barbieri JS, Roe AH, Mostaghimi A. Simplifying contraception requirements for iPLEDGE: a decision analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:104-108.
- Kane S, Admani S. COVID-19 pandemic leading to the accelerated development of a virtual health model for isotretinoin. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc. 2021;13:54-57.
- Barbieri JS, Frieden IJ, Nagler AR. Isotretinoin, patient safety, and patient-centered care-time to reform iPLEDGE. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:21-22.
- Barbieri JS, Shin DB, Wang S, et al. Association of race/ethnicity and sex with differences in health care use and treatment for acne. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:312-319.
- Charrow A, Xia FD, Lu J, et al. Differences in isotretinoin start, interruption, and early termination across race and sex in the iPLEDGE era. PloS One. 2019;14:E0210445.
- Barbieri JS, Roe AH, Mostaghimi A. Simplifying contraception requirements for iPLEDGE: a decision analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:104-108.
PRACTICE POINTS
- The majority of clinicians report that the use of telemedicine and home pregnancy testing for iPLEDGE has improved access to care and that they would like to continue these practices.
- Continuing to allow home pregnancy testing and explicitly permitting telemedicine can enable clinicians to provide patient-centered care for patients treated with isotretinoin.
What’s Diet Got to Do With It? Basic and Clinical Science Behind Diet and Acne
The current understanding of the pathogenesis of acne includes altered keratinization, follicular obstruction, overproduction of sebum, and microbial colonization ( Cutibacterium acnes ) of the pilosebaceous unit resulting in perifollicular inflammation. 1 A deeper dive into the hormonal and molecular drivers of acne have implicated insulin, insulinlike growth factor 1 (IGF-1), corticotropin-releasing hormone, the phosphoinositide 3 -kinase/Akt pathway, mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, and the nuclear factor κ B pathway. 2-4 A Western diet comprised of high glycemic index foods, carbohydrates, and dairy enhances the production of insulin and IGF-1. A downstream effect of excess insulin and IGF-1 is overactivity of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1), a major promoter of cellular growth and proliferation that primarily is regulated through nutrient availability. 5 This article will review our understanding of the impact of the Western diet on acne pathogenesis and highlight the existing evidence behind the contributions of the mTORC1 pathway in this process. Although quality randomized controlled trials analyzing these effects are limited, dermatologists should understand the existing evidence supporting the potential impacts of diet on acne.
The Western Diet
Glycemic Index—To assess the impact of a high glycemic index diet on acne, Kwon et al6 evaluated 32 patients with mild to moderate acne and placed them on a low or high glycemic index diet for 10 weeks. The low glycemic index diet group was found to have a 70% reduction in the mean number of inflammatory acne lesions from baseline (P<.05), while the high glycemic index diet group had no significant reduction. Noninflammatory lesion counts remained statistically unchanged.6 Smith et al7 studied 43 male patients with acne on either a low glycemic index diet or a self-directed high glycemic diet that was carbohydrate dense. The low glycemic index group showed greater improvement in lesion count as well as improved insulin sensitivity at 12 weeks. Specifically, the mean lesion count (SEM) decreased by 23.5 (3.9) in the low glycemic index group and by only 12.0 (3.5) in the control group (P=.03).7 Observational studies also have supported this hypothesis. After adjustment, an analysis of 24,452 participants in the NutriNet-Santé cohort found significant associations between current acne and the consumption of sugary beverages (adjusted OR, 1.18; 95% CI, 1.01-1.38) and the consumption of fatty and sugary products (adjusted OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.09-2.16).8 A Cochrane review that included only 2 studies (Kwon et al6 and Smith et al7) did not find evidence to suggest a low glycemic index diet for noninflammatory lesion count reduction but did note possible benefit for a reduction in inflammatory and total lesion counts; however, Kwon et al6 had incomplete data.9
Dairy—A large retrospective study including 47,355 nurses noted the frequency of milk intake was significantly associated with increased prevalence of acne in adolescence (prevalence ratio, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.03-1.44; P=.002).10 A 2019 meta-analysis further suggested a significant relationship between acne and milk in highest vs lowest intake groups (OR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.31-1.66) with no significant heterogeneity between the studies (I2=23.6%, P=.24 for heterogeneity), as well as a positive relationship between the highest vs lowest intake of low-fat milk (OR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.10-1.43) and skim milk (OR, 1.82; 95% CI, 1.34-2.47). In this meta-analysis, yogurt and cheese consumption were not significantly associated with acne (OR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.73-1.11).11 One non–evidence-based explanation for this may be that fermented dairy products have different biological actions. Pasteurized milk allows microRNAs that directly activate mTORC1 to persist, whereas the bacteria present in the fermentation process may augment this.12 A separate meta-analysis from 2018 did find that yogurt consumption was positively associated with acne (OR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.05-1.77; P=.022), highlighting the need for larger, more rigorous studies on this topic.13
Insulin and IGF-1—As reviewed above, acne has been considered a disease of Western society, with the Western diet at the center of this association.14 A typical Western diet consists of high glycemic index foods, carbohydrates, and dairy, all of which enhance the production of insulin and IGF-1. Insulin levels increase secondary to high blood glucose and to a lesser degree by protein intake.15 Insulinlike growth factor 1 production is most influenced by age and peaks during puberty; however, high protein diets also increase liver IGF-1 production and release.16 When present in excess, insulin can function as a growth factor. Insulin exerts its anabolic effects through the IGF-1 pathway; however, insulin and IGF-1 are produced in response to different signals.17 Endocrine production of IGF-1 represents 70% of blood levels, peaks at puberty, and rapidly declines in the third decade of life.18 Insulin is produced by the pancreas, and levels correspond to lifestyle and genetically induced insulin resistance.19
Adolescents have elevated levels of IGF-1 as a major driver of puberty-associated growth.20 Despite the natural decrease in IGF-1 following puberty, acne persists in many patients and can even develop for the first time in adulthood in a subset of patients. A study of 40 acne patients and 20 controls found that patients with acne who consumed a high glycemic–load diet was significantly higher than the number of controls consuming a similar diet (P=.008). Additionally, significantly higher levels of mean (SD) serum IGF-1 on quantitative sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in acne patients vs controls (543.2 [174.7] ng/mL vs 316.9 [95.7] ng/mL; P<.001) was identified, and these levels correlated significantly with high glycemic–load diet consumption.21 In another study, Kartal et al22 found that basal and fasting insulin levels and homeostasis model assessment scores evaluating for insulin resistance were significantly higher in 36 women compared with 24 age/sex-matched controls (P<.05). This finding remained significant even after excluding women with hyperandrogenemia (P<.05).22
Highlighting the importance of IGF-1 in the pathogenesis of acne, patients with genetic disorders characterized by IGF-1 deficiency, such as Laron syndrome, do not develop acne despite having a functional androgen receptor. Treatment with IGF-1 in these patients induces acne, further supporting the role of IGF-1 in the pathogenesis of this condition.23
The mTORC1 Pathway
Comprised of mTOR in addition to other proteins, mTORC1 is a nutrient-sensitive regulator of cellular growth, proliferation, lipid synthesis, and protein translation.5 Increased activity of mTORC1 has been described in diabetes, neurodegenerative disease, and cancer,14,24 while decreased activity may promote longevity.25 Regulation of mTORC1 occurs through several mechanisms. Growth factors such as insulin and IGF-1 promote mTORC1 activation through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Several amino acids—specifically branched chain amino acids such as alanine, arginine, asparagine, glutamine, histidine, leucine, methionine, serine, threonine, and valine—also can activate mTORC1 independently.26 Excess glucose leads to decreased adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase and increased activity of mTORC1, which occurs separately from insulin or IGF-1.27 Starvation blocks mTORC1 via increased adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase and starvation-induced hypoxia.26,28 To activate mTORC1, both the IGF-1 or insulin signal and amino acid excess must be present.29 Although not studied in acne, altering the dietary protein content in obese mice has been shown to perturb the mTORC1 pathway, leading to pathologic changes in the mTORC1-autophagy signaling axis, increased amino acid release into the blood, and an acute elevation in mTORC1 signaling.30
Another major regulator of mTORC1 is Forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1), which is a transcription factor that regulates mTORC1 through sestrin 3.31,32 Sestrin 3 is a stress-induced protein that helps regulate blood glucose and promote insulin sensitivity.33 When FOXO1 is translocated to the cell nucleus, it upregulates the expression of sestrin 3, resulting in mTORC1 inhibition.31,32 Insulin, IGF-1, and nutrient excess lead to FOXO1 translocation to the cell cytoplasm where it can no longer mitigate mTORC1 activity, while the fasted state leads to translocation to the nucleus.34 A single study evaluated the association between FOXO1, mTORC1, a high glycemic–load diet, and acne development. Immunohistochemical detection of mTORC1 assessed by digital image analysis revealed significantly greater expression in inflamed pilosebaceous units found in acne patients (P<.001). Immunohistochemical cytoplasmic expression of FOXO1 and mTOR (used as a proxy for mTORC1) was significantly higher in patients on a high glycemic–load diet (P=.021 and P=.009, respectively) as well as in patients with more severe forms of acne (P=.005 and P=.015, respectively) and elevated IGF-1 levels (P=.004 and P=.003, respectively).21
mTORC1 contributes to the proliferation of keratinocytes and excess sebum production, both independently and through androgen-mediated processes.35-40 Insulinlike growth factor 1 binding the IGF-1 receptor leads to proliferation of keratinocytes lining the sebaceous gland and hair follicle in vivo.35 In mice with epidermis-specific deletion of mTOR, keratinocyte proliferation was decreased and hair follicles were diminished both in number and development. Genetic loss of mTOR in the epidermis led to attenuated signaling pathways of mTORC1 and mTORC2.36
Androgen function is augmented by mTORC1, FOXO1, and IGF-1 through several mechanisms, which may partially explain the hormonal relationship to acne. Androgens increase IGF-1 within the hair follicle.37 In prostate cancer cells, IGF-1 then facilitates movement of FOXO1 to the cytoplasm, preventing it from blocking mTORC1. This effective inactivation of FOXO1 thus further augments the impact of androgens by both allowing unchecked mTORC1 pathway activity and increasing translocation of the androgen receptor (AR) to the nucleus where it exerts its effects.38 Interestingly, genetic polymorphisms of the AR have been shown to cause variable affinity of FOXO1 for the AR; specifically, shorter CAG (cytosine, adenine, guanine) repeat length may lead to decreased FOXO1 binding and is associated with an increased risk for acne.41-43 In addition to its effects on the hair follicle, IGF-1 stimulates production of testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone as well as activates 5α-reductase, leading to higher dihydrotestosterone levels, which activate the AR with higher affinity than testosterone.44 In some tissues, androgens help regulate the mTORC1 pathway through positive feedback loops.45,46 At this time, we do not know if this occurs in the pathogenesis of acne.
Isotretinoin is the treatment of choice for refractory acne. It has been hypothesized that isotretinoin induces sebocyte apoptosis via the upregulation of FOXO transcription factors and p53.47 Elevated levels of nuclear FOXO1 have been found in the sebaceous glands of patients following initiation of treatment with isotretinoin and are hypothesized to play a major role in the drug’s effectiveness. Specifically, biopsies from 14 acne patients before and after 6 weeks of isotretinoin therapy were analyzed with immunohistochemical staining and found to have a significantly improved nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio of nonphosphorylated FOXO1 (P<.001).47
Practical Recommendations
Given the available evidence, it is important for dermatologists to address dietary recommendations in acne patients. Although large randomized controlled trials on diet and acne severity are challenging to conduct in this population, the existing literature suggests that patients should avoid high glycemic index simple sugars and processed grains, and patients should focus on eating more complex carbohydrates in the form of legumes, vegetables, fruits, and tubers.6-8 With regard to dairy, milk (especially skim) has been associated with increased risks for acne.11,13 Fermented dairy products may have less impact on acne severity and include cheese, yogurt (unsweetened to keep glycemic index low), and sour cream.12
- Zaenglein AL. Acne vulgaris. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. Elsevier; 2017:588-603.
- Ganceviciene R, Graziene V, Fimmel S, et al. Involvement of the corticotropin-releasing hormone system in the pathogenesis of acne vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:345-352.
- Kang S, Cho S, Chung JH, et al. Inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation mediated by activated transcription factors nuclear factor-kappaB and activator protein-1 in inflammatory acne lesions in vivo. Am J Pathol. 2005;166:1691-1699.
- Cong TX, Hao D, Wen X, et al. From pathogenesis of acne vulgaris to anti-acne agents. Arch Dermatol Res. 2019;311:337-349.
- Pópulo H, Lopes JM, Soares P. The mTOR signalling pathway in human cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:1886-1918.
- Kwon HH, Yoon JY, Hong JS, et al. Clinical and histological effect of a low glycaemic load diet in treatment of acne vulgaris in Korean patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012;92:241-246.
- Smith RN, Mann NJ, Braue A, et al. A low-glycemic-load diet improves symptoms in acne vulgaris patients: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:107-115.
- Penso L, Touvier M, Deschasaux M, et al. Association between adult acne and dietary behaviors: findings from the NutriNet-Santé prospective cohort study. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:854-862.
- Cao H, Yang G, Wang Y, et al. Complementary therapies for acne vulgaris. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;1:CD009436.
- Adebamowo CA, Spiegelman D, Danby FW, et al. High school dietary dairy intake and teenage acne. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:207-214.
- Aghasi M, Golzarand M, Shab-Bidar S, et al. Dairy intake and acne development: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Clin Nutr. 2019;38:1067-1075.
- Melnik BC, Schmitz G. Pasteurized non-fermented cow’s milk but not fermented milk is a promoter of mTORC1-driven aging and increased mortality. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;67:101270.
- Juhl CR, Bergholdt HKM, Miller IM, et al. Dairy intake and acne vulgaris: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 78,529 children, adolescents, and young adults. Nutrients. 2018;10:1049. doi:10.3390/nu10081049
- Melnik BC. Linking diet to acne metabolomics, inflammation, and comedogenesis: an update. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;8:371-388.
- Smart CEM, King BR, Lopez PE. Insulin dosing for fat and protein: is it time? Diabetes Care. 2020;43:13-15.
- Wan X, Wang S, Xu J, et al. Dietary protein-induced hepatic IGF-1 secretion mediated by PPARγ activation. PLoS One. 2017;12:E0173174.
- Bedinger DH, Adams SH. Metabolic, anabolic, and mitogenic insulin responses: a tissue-specific perspective for insulin receptor activators. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015;415:143-156.
- Gubbi S, Quipildor GF, Barzilai N, et al. 40 YEARS of IGF1: IGF1: the Jekyll and Hyde of the aging brain. J Mol Endocrinol. 2018;61:T171-T185.
- Kolb H, Kempf K, Röhling M, et al. Insulin: too much of a good thing is bad. BMC Med. 2020;18:224.
- Wood CL, Lane LC, Cheetham T. Puberty: normal physiology (brief overview). Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;33:101265.
- Agamia NF, Abdallah DM, Sorour O, et al. Skin expression of mammalian target of rapamycin and forkhead box transcription factor O1, and serum insulin-like growth factor-1 in patients with acne vulgaris and their relationship with diet. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:1299-1307.
- Kartal D, Yildiz H, Ertas R, et al. Association between isolated female acne and insulin resistance: a prospective study. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2016;151:353-357.
- Ben-Amitai D, Laron Z. Effect of insulin-like growth factor-1 deficiency or administration on the occurrence of acne. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:950-954.
- Kim LC, Cook RS, Chen J. mTORC1 and mTORC2 in cancer and the tumor microenvironment. Oncogene. 2017;36:2191-2201.
- Weichhart T. mTOR as regulator of lifespan, aging, and cellular senescence: a mini-review. Gerontology. 2018;64:127-134.
- Melick CH, Jewell JL. Regulation of mTORC1 by upstream stimuli. Genes. 2020;11:989. doi:10.3390/genes11090989
- Li M, Zhang CS, Feng JW, et al. Aldolase is a sensor for both low and high glucose, linking to AMPK and mTORC1. Cell Res. 2021;31:478-481.
- Yan T, Zhang J, Tang D, et al. Hypoxia regulates mTORC1-mediated keratinocyte motility and migration via the AMPK pathway. PLoS One. 2017;12:E0169155.
- Dennis MD, Baum JI, Kimball SR, et al. Mechanisms involved in the coordinate regulation of mTORC1 by insulin and amino acids. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:8287-8296.
- Choi BSY, Daniel N, Houde VP, et al. Feeding diversified protein sources exacerbates hepatic insulin resistance via increased gut microbial branched-chain fatty acids and mTORC1 signaling in obese mice. Nat Commun. 2021;12:3377.
- Chen CC, Jeon SM, Bhaskar PT, et al. FoxOs inhibit mTORC1 and activate Akt by inducing the expression of Sestrin3 and Rictor. Dev Cell. 2010;18:592-604.
- Chen Y, Huang T, Yu Z, et al. The functions and roles of sestrins in regulating human diseases. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022;27:2.
- Tao R, Xiong X, Liangpunsakul S, et al. Sestrin 3 protein enhances hepatic insulin sensitivity by direct activation of the mTORC2-Akt signaling. Diabetes. 2015;64:1211-1223.
- Gross DN, Wan M, Birnbaum MJ. The role of FOXO in the regulation of metabolism. Curr Diab Rep. 2009;9:208-214.
- Gilhar A, Ish-Shalom S, Pillar T, et al. Effect of anti–insulin-like growth factor 1 on epidermal proliferation of human skin transplanted onto nude mice treated with growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1994;134:229-232.
- Ding X, Bloch W, Iden S, et al. mTORC1 and mTORC2 regulate skin morphogenesis and epidermal barrier formation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13226.
- Inui S, Itami S. Androgen actions on the human hair follicle: perspectives. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22:168-171.
- Fan W, Yanase T, Morinaga H, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1/insulin signaling activates androgen signaling through direct interactions of Foxo1 with androgen receptor. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:7329-7338.
- Alestas T, Ganceviciene R, Fimmel S, et al. Enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of leukotriene B4 and prostaglandin E2 are active in sebaceous glands. J Mol Med. 2006;84:75-87.
- Smith TM, Gilliland K, Clawson GA, et al. IGF-1 induces SREBP-1 expression and lipogenesis in SEB-1 sebocytes via activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:1286-1293.
- Furtado GV, Yang J, Wu D, et al. FOXO1 controls protein synthesis and transcript abundance of mutant polyglutamine proteins, preventing protein aggregation. Hum Mol Genet. 2021;30:996-1005.
- Melnik BC. Isotretinoin and FoxO1: a scientific hypothesis. Dermatoendocrinol. 2011;3:141-165.
- Heng AHS, Say YH, Sio YY, et al. Gene variants associated with acne vulgaris presentation and severity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med Genomics. 2021;14:103.
- Li J, Al-Azzawi F. Mechanism of androgen receptor action. Maturitas. 2009;63:142-148.
- Zhao Y, Tindall DJ, Huang H. Modulation of androgen receptor by FOXA1 and FOXO1 factors in prostate cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2014;10:614-619.
- Hamdi MM, Mutungi G. Dihydrotestosterone stimulates amino acid uptake and the expression of LAT2 in mouse skeletal muscle fibres through an ERK1/2-dependent mechanism. J Physiol. 2011;589(pt 14):3623-3640.
- Agamia NF, Hussein OM, Abdelmaksoud RE, et al. Effect of oral isotretinoin on the nucleocytoplasmic distribution of FoxO1 and FoxO3 proteins in sebaceous glands of patients with acne vulgaris. Exp Dermatol. 2018;27:1344-1351.
- Kolovou GD, Watts GF, Mikhailidis DP, et al. Postprandial hypertriglyceridaemia revisited in the era of non-fasting lipid profile testing: a 2019 expert panel statement, main text. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2019;17:498-514.
- Svoboda SA, Shields BE. Cutaneous manifestations of nutritional excess: pathophysiologic effects of hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia on the skin. Cutis. 2021;107:74-78.
- González-González JG, Mancillas-Adame LG, Fernández-Reyes M, et al. Androgenetic alopecia and insulin resistance in young men. Clin Endocrinol . 2009;71:494-499.
- Livadas S, Anagnostis P, Bosdou JK, et al. Polycystic ovary syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a state-of-the-art review. World J Diabetes. 2022;13:5-26.
The current understanding of the pathogenesis of acne includes altered keratinization, follicular obstruction, overproduction of sebum, and microbial colonization ( Cutibacterium acnes ) of the pilosebaceous unit resulting in perifollicular inflammation. 1 A deeper dive into the hormonal and molecular drivers of acne have implicated insulin, insulinlike growth factor 1 (IGF-1), corticotropin-releasing hormone, the phosphoinositide 3 -kinase/Akt pathway, mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, and the nuclear factor κ B pathway. 2-4 A Western diet comprised of high glycemic index foods, carbohydrates, and dairy enhances the production of insulin and IGF-1. A downstream effect of excess insulin and IGF-1 is overactivity of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1), a major promoter of cellular growth and proliferation that primarily is regulated through nutrient availability. 5 This article will review our understanding of the impact of the Western diet on acne pathogenesis and highlight the existing evidence behind the contributions of the mTORC1 pathway in this process. Although quality randomized controlled trials analyzing these effects are limited, dermatologists should understand the existing evidence supporting the potential impacts of diet on acne.
The Western Diet
Glycemic Index—To assess the impact of a high glycemic index diet on acne, Kwon et al6 evaluated 32 patients with mild to moderate acne and placed them on a low or high glycemic index diet for 10 weeks. The low glycemic index diet group was found to have a 70% reduction in the mean number of inflammatory acne lesions from baseline (P<.05), while the high glycemic index diet group had no significant reduction. Noninflammatory lesion counts remained statistically unchanged.6 Smith et al7 studied 43 male patients with acne on either a low glycemic index diet or a self-directed high glycemic diet that was carbohydrate dense. The low glycemic index group showed greater improvement in lesion count as well as improved insulin sensitivity at 12 weeks. Specifically, the mean lesion count (SEM) decreased by 23.5 (3.9) in the low glycemic index group and by only 12.0 (3.5) in the control group (P=.03).7 Observational studies also have supported this hypothesis. After adjustment, an analysis of 24,452 participants in the NutriNet-Santé cohort found significant associations between current acne and the consumption of sugary beverages (adjusted OR, 1.18; 95% CI, 1.01-1.38) and the consumption of fatty and sugary products (adjusted OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.09-2.16).8 A Cochrane review that included only 2 studies (Kwon et al6 and Smith et al7) did not find evidence to suggest a low glycemic index diet for noninflammatory lesion count reduction but did note possible benefit for a reduction in inflammatory and total lesion counts; however, Kwon et al6 had incomplete data.9
Dairy—A large retrospective study including 47,355 nurses noted the frequency of milk intake was significantly associated with increased prevalence of acne in adolescence (prevalence ratio, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.03-1.44; P=.002).10 A 2019 meta-analysis further suggested a significant relationship between acne and milk in highest vs lowest intake groups (OR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.31-1.66) with no significant heterogeneity between the studies (I2=23.6%, P=.24 for heterogeneity), as well as a positive relationship between the highest vs lowest intake of low-fat milk (OR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.10-1.43) and skim milk (OR, 1.82; 95% CI, 1.34-2.47). In this meta-analysis, yogurt and cheese consumption were not significantly associated with acne (OR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.73-1.11).11 One non–evidence-based explanation for this may be that fermented dairy products have different biological actions. Pasteurized milk allows microRNAs that directly activate mTORC1 to persist, whereas the bacteria present in the fermentation process may augment this.12 A separate meta-analysis from 2018 did find that yogurt consumption was positively associated with acne (OR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.05-1.77; P=.022), highlighting the need for larger, more rigorous studies on this topic.13
Insulin and IGF-1—As reviewed above, acne has been considered a disease of Western society, with the Western diet at the center of this association.14 A typical Western diet consists of high glycemic index foods, carbohydrates, and dairy, all of which enhance the production of insulin and IGF-1. Insulin levels increase secondary to high blood glucose and to a lesser degree by protein intake.15 Insulinlike growth factor 1 production is most influenced by age and peaks during puberty; however, high protein diets also increase liver IGF-1 production and release.16 When present in excess, insulin can function as a growth factor. Insulin exerts its anabolic effects through the IGF-1 pathway; however, insulin and IGF-1 are produced in response to different signals.17 Endocrine production of IGF-1 represents 70% of blood levels, peaks at puberty, and rapidly declines in the third decade of life.18 Insulin is produced by the pancreas, and levels correspond to lifestyle and genetically induced insulin resistance.19
Adolescents have elevated levels of IGF-1 as a major driver of puberty-associated growth.20 Despite the natural decrease in IGF-1 following puberty, acne persists in many patients and can even develop for the first time in adulthood in a subset of patients. A study of 40 acne patients and 20 controls found that patients with acne who consumed a high glycemic–load diet was significantly higher than the number of controls consuming a similar diet (P=.008). Additionally, significantly higher levels of mean (SD) serum IGF-1 on quantitative sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in acne patients vs controls (543.2 [174.7] ng/mL vs 316.9 [95.7] ng/mL; P<.001) was identified, and these levels correlated significantly with high glycemic–load diet consumption.21 In another study, Kartal et al22 found that basal and fasting insulin levels and homeostasis model assessment scores evaluating for insulin resistance were significantly higher in 36 women compared with 24 age/sex-matched controls (P<.05). This finding remained significant even after excluding women with hyperandrogenemia (P<.05).22
Highlighting the importance of IGF-1 in the pathogenesis of acne, patients with genetic disorders characterized by IGF-1 deficiency, such as Laron syndrome, do not develop acne despite having a functional androgen receptor. Treatment with IGF-1 in these patients induces acne, further supporting the role of IGF-1 in the pathogenesis of this condition.23
The mTORC1 Pathway
Comprised of mTOR in addition to other proteins, mTORC1 is a nutrient-sensitive regulator of cellular growth, proliferation, lipid synthesis, and protein translation.5 Increased activity of mTORC1 has been described in diabetes, neurodegenerative disease, and cancer,14,24 while decreased activity may promote longevity.25 Regulation of mTORC1 occurs through several mechanisms. Growth factors such as insulin and IGF-1 promote mTORC1 activation through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Several amino acids—specifically branched chain amino acids such as alanine, arginine, asparagine, glutamine, histidine, leucine, methionine, serine, threonine, and valine—also can activate mTORC1 independently.26 Excess glucose leads to decreased adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase and increased activity of mTORC1, which occurs separately from insulin or IGF-1.27 Starvation blocks mTORC1 via increased adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase and starvation-induced hypoxia.26,28 To activate mTORC1, both the IGF-1 or insulin signal and amino acid excess must be present.29 Although not studied in acne, altering the dietary protein content in obese mice has been shown to perturb the mTORC1 pathway, leading to pathologic changes in the mTORC1-autophagy signaling axis, increased amino acid release into the blood, and an acute elevation in mTORC1 signaling.30
Another major regulator of mTORC1 is Forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1), which is a transcription factor that regulates mTORC1 through sestrin 3.31,32 Sestrin 3 is a stress-induced protein that helps regulate blood glucose and promote insulin sensitivity.33 When FOXO1 is translocated to the cell nucleus, it upregulates the expression of sestrin 3, resulting in mTORC1 inhibition.31,32 Insulin, IGF-1, and nutrient excess lead to FOXO1 translocation to the cell cytoplasm where it can no longer mitigate mTORC1 activity, while the fasted state leads to translocation to the nucleus.34 A single study evaluated the association between FOXO1, mTORC1, a high glycemic–load diet, and acne development. Immunohistochemical detection of mTORC1 assessed by digital image analysis revealed significantly greater expression in inflamed pilosebaceous units found in acne patients (P<.001). Immunohistochemical cytoplasmic expression of FOXO1 and mTOR (used as a proxy for mTORC1) was significantly higher in patients on a high glycemic–load diet (P=.021 and P=.009, respectively) as well as in patients with more severe forms of acne (P=.005 and P=.015, respectively) and elevated IGF-1 levels (P=.004 and P=.003, respectively).21
mTORC1 contributes to the proliferation of keratinocytes and excess sebum production, both independently and through androgen-mediated processes.35-40 Insulinlike growth factor 1 binding the IGF-1 receptor leads to proliferation of keratinocytes lining the sebaceous gland and hair follicle in vivo.35 In mice with epidermis-specific deletion of mTOR, keratinocyte proliferation was decreased and hair follicles were diminished both in number and development. Genetic loss of mTOR in the epidermis led to attenuated signaling pathways of mTORC1 and mTORC2.36
Androgen function is augmented by mTORC1, FOXO1, and IGF-1 through several mechanisms, which may partially explain the hormonal relationship to acne. Androgens increase IGF-1 within the hair follicle.37 In prostate cancer cells, IGF-1 then facilitates movement of FOXO1 to the cytoplasm, preventing it from blocking mTORC1. This effective inactivation of FOXO1 thus further augments the impact of androgens by both allowing unchecked mTORC1 pathway activity and increasing translocation of the androgen receptor (AR) to the nucleus where it exerts its effects.38 Interestingly, genetic polymorphisms of the AR have been shown to cause variable affinity of FOXO1 for the AR; specifically, shorter CAG (cytosine, adenine, guanine) repeat length may lead to decreased FOXO1 binding and is associated with an increased risk for acne.41-43 In addition to its effects on the hair follicle, IGF-1 stimulates production of testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone as well as activates 5α-reductase, leading to higher dihydrotestosterone levels, which activate the AR with higher affinity than testosterone.44 In some tissues, androgens help regulate the mTORC1 pathway through positive feedback loops.45,46 At this time, we do not know if this occurs in the pathogenesis of acne.
Isotretinoin is the treatment of choice for refractory acne. It has been hypothesized that isotretinoin induces sebocyte apoptosis via the upregulation of FOXO transcription factors and p53.47 Elevated levels of nuclear FOXO1 have been found in the sebaceous glands of patients following initiation of treatment with isotretinoin and are hypothesized to play a major role in the drug’s effectiveness. Specifically, biopsies from 14 acne patients before and after 6 weeks of isotretinoin therapy were analyzed with immunohistochemical staining and found to have a significantly improved nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio of nonphosphorylated FOXO1 (P<.001).47
Practical Recommendations
Given the available evidence, it is important for dermatologists to address dietary recommendations in acne patients. Although large randomized controlled trials on diet and acne severity are challenging to conduct in this population, the existing literature suggests that patients should avoid high glycemic index simple sugars and processed grains, and patients should focus on eating more complex carbohydrates in the form of legumes, vegetables, fruits, and tubers.6-8 With regard to dairy, milk (especially skim) has been associated with increased risks for acne.11,13 Fermented dairy products may have less impact on acne severity and include cheese, yogurt (unsweetened to keep glycemic index low), and sour cream.12
The current understanding of the pathogenesis of acne includes altered keratinization, follicular obstruction, overproduction of sebum, and microbial colonization ( Cutibacterium acnes ) of the pilosebaceous unit resulting in perifollicular inflammation. 1 A deeper dive into the hormonal and molecular drivers of acne have implicated insulin, insulinlike growth factor 1 (IGF-1), corticotropin-releasing hormone, the phosphoinositide 3 -kinase/Akt pathway, mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, and the nuclear factor κ B pathway. 2-4 A Western diet comprised of high glycemic index foods, carbohydrates, and dairy enhances the production of insulin and IGF-1. A downstream effect of excess insulin and IGF-1 is overactivity of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1), a major promoter of cellular growth and proliferation that primarily is regulated through nutrient availability. 5 This article will review our understanding of the impact of the Western diet on acne pathogenesis and highlight the existing evidence behind the contributions of the mTORC1 pathway in this process. Although quality randomized controlled trials analyzing these effects are limited, dermatologists should understand the existing evidence supporting the potential impacts of diet on acne.
The Western Diet
Glycemic Index—To assess the impact of a high glycemic index diet on acne, Kwon et al6 evaluated 32 patients with mild to moderate acne and placed them on a low or high glycemic index diet for 10 weeks. The low glycemic index diet group was found to have a 70% reduction in the mean number of inflammatory acne lesions from baseline (P<.05), while the high glycemic index diet group had no significant reduction. Noninflammatory lesion counts remained statistically unchanged.6 Smith et al7 studied 43 male patients with acne on either a low glycemic index diet or a self-directed high glycemic diet that was carbohydrate dense. The low glycemic index group showed greater improvement in lesion count as well as improved insulin sensitivity at 12 weeks. Specifically, the mean lesion count (SEM) decreased by 23.5 (3.9) in the low glycemic index group and by only 12.0 (3.5) in the control group (P=.03).7 Observational studies also have supported this hypothesis. After adjustment, an analysis of 24,452 participants in the NutriNet-Santé cohort found significant associations between current acne and the consumption of sugary beverages (adjusted OR, 1.18; 95% CI, 1.01-1.38) and the consumption of fatty and sugary products (adjusted OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.09-2.16).8 A Cochrane review that included only 2 studies (Kwon et al6 and Smith et al7) did not find evidence to suggest a low glycemic index diet for noninflammatory lesion count reduction but did note possible benefit for a reduction in inflammatory and total lesion counts; however, Kwon et al6 had incomplete data.9
Dairy—A large retrospective study including 47,355 nurses noted the frequency of milk intake was significantly associated with increased prevalence of acne in adolescence (prevalence ratio, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.03-1.44; P=.002).10 A 2019 meta-analysis further suggested a significant relationship between acne and milk in highest vs lowest intake groups (OR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.31-1.66) with no significant heterogeneity between the studies (I2=23.6%, P=.24 for heterogeneity), as well as a positive relationship between the highest vs lowest intake of low-fat milk (OR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.10-1.43) and skim milk (OR, 1.82; 95% CI, 1.34-2.47). In this meta-analysis, yogurt and cheese consumption were not significantly associated with acne (OR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.73-1.11).11 One non–evidence-based explanation for this may be that fermented dairy products have different biological actions. Pasteurized milk allows microRNAs that directly activate mTORC1 to persist, whereas the bacteria present in the fermentation process may augment this.12 A separate meta-analysis from 2018 did find that yogurt consumption was positively associated with acne (OR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.05-1.77; P=.022), highlighting the need for larger, more rigorous studies on this topic.13
Insulin and IGF-1—As reviewed above, acne has been considered a disease of Western society, with the Western diet at the center of this association.14 A typical Western diet consists of high glycemic index foods, carbohydrates, and dairy, all of which enhance the production of insulin and IGF-1. Insulin levels increase secondary to high blood glucose and to a lesser degree by protein intake.15 Insulinlike growth factor 1 production is most influenced by age and peaks during puberty; however, high protein diets also increase liver IGF-1 production and release.16 When present in excess, insulin can function as a growth factor. Insulin exerts its anabolic effects through the IGF-1 pathway; however, insulin and IGF-1 are produced in response to different signals.17 Endocrine production of IGF-1 represents 70% of blood levels, peaks at puberty, and rapidly declines in the third decade of life.18 Insulin is produced by the pancreas, and levels correspond to lifestyle and genetically induced insulin resistance.19
Adolescents have elevated levels of IGF-1 as a major driver of puberty-associated growth.20 Despite the natural decrease in IGF-1 following puberty, acne persists in many patients and can even develop for the first time in adulthood in a subset of patients. A study of 40 acne patients and 20 controls found that patients with acne who consumed a high glycemic–load diet was significantly higher than the number of controls consuming a similar diet (P=.008). Additionally, significantly higher levels of mean (SD) serum IGF-1 on quantitative sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in acne patients vs controls (543.2 [174.7] ng/mL vs 316.9 [95.7] ng/mL; P<.001) was identified, and these levels correlated significantly with high glycemic–load diet consumption.21 In another study, Kartal et al22 found that basal and fasting insulin levels and homeostasis model assessment scores evaluating for insulin resistance were significantly higher in 36 women compared with 24 age/sex-matched controls (P<.05). This finding remained significant even after excluding women with hyperandrogenemia (P<.05).22
Highlighting the importance of IGF-1 in the pathogenesis of acne, patients with genetic disorders characterized by IGF-1 deficiency, such as Laron syndrome, do not develop acne despite having a functional androgen receptor. Treatment with IGF-1 in these patients induces acne, further supporting the role of IGF-1 in the pathogenesis of this condition.23
The mTORC1 Pathway
Comprised of mTOR in addition to other proteins, mTORC1 is a nutrient-sensitive regulator of cellular growth, proliferation, lipid synthesis, and protein translation.5 Increased activity of mTORC1 has been described in diabetes, neurodegenerative disease, and cancer,14,24 while decreased activity may promote longevity.25 Regulation of mTORC1 occurs through several mechanisms. Growth factors such as insulin and IGF-1 promote mTORC1 activation through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Several amino acids—specifically branched chain amino acids such as alanine, arginine, asparagine, glutamine, histidine, leucine, methionine, serine, threonine, and valine—also can activate mTORC1 independently.26 Excess glucose leads to decreased adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase and increased activity of mTORC1, which occurs separately from insulin or IGF-1.27 Starvation blocks mTORC1 via increased adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase and starvation-induced hypoxia.26,28 To activate mTORC1, both the IGF-1 or insulin signal and amino acid excess must be present.29 Although not studied in acne, altering the dietary protein content in obese mice has been shown to perturb the mTORC1 pathway, leading to pathologic changes in the mTORC1-autophagy signaling axis, increased amino acid release into the blood, and an acute elevation in mTORC1 signaling.30
Another major regulator of mTORC1 is Forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1), which is a transcription factor that regulates mTORC1 through sestrin 3.31,32 Sestrin 3 is a stress-induced protein that helps regulate blood glucose and promote insulin sensitivity.33 When FOXO1 is translocated to the cell nucleus, it upregulates the expression of sestrin 3, resulting in mTORC1 inhibition.31,32 Insulin, IGF-1, and nutrient excess lead to FOXO1 translocation to the cell cytoplasm where it can no longer mitigate mTORC1 activity, while the fasted state leads to translocation to the nucleus.34 A single study evaluated the association between FOXO1, mTORC1, a high glycemic–load diet, and acne development. Immunohistochemical detection of mTORC1 assessed by digital image analysis revealed significantly greater expression in inflamed pilosebaceous units found in acne patients (P<.001). Immunohistochemical cytoplasmic expression of FOXO1 and mTOR (used as a proxy for mTORC1) was significantly higher in patients on a high glycemic–load diet (P=.021 and P=.009, respectively) as well as in patients with more severe forms of acne (P=.005 and P=.015, respectively) and elevated IGF-1 levels (P=.004 and P=.003, respectively).21
mTORC1 contributes to the proliferation of keratinocytes and excess sebum production, both independently and through androgen-mediated processes.35-40 Insulinlike growth factor 1 binding the IGF-1 receptor leads to proliferation of keratinocytes lining the sebaceous gland and hair follicle in vivo.35 In mice with epidermis-specific deletion of mTOR, keratinocyte proliferation was decreased and hair follicles were diminished both in number and development. Genetic loss of mTOR in the epidermis led to attenuated signaling pathways of mTORC1 and mTORC2.36
Androgen function is augmented by mTORC1, FOXO1, and IGF-1 through several mechanisms, which may partially explain the hormonal relationship to acne. Androgens increase IGF-1 within the hair follicle.37 In prostate cancer cells, IGF-1 then facilitates movement of FOXO1 to the cytoplasm, preventing it from blocking mTORC1. This effective inactivation of FOXO1 thus further augments the impact of androgens by both allowing unchecked mTORC1 pathway activity and increasing translocation of the androgen receptor (AR) to the nucleus where it exerts its effects.38 Interestingly, genetic polymorphisms of the AR have been shown to cause variable affinity of FOXO1 for the AR; specifically, shorter CAG (cytosine, adenine, guanine) repeat length may lead to decreased FOXO1 binding and is associated with an increased risk for acne.41-43 In addition to its effects on the hair follicle, IGF-1 stimulates production of testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone as well as activates 5α-reductase, leading to higher dihydrotestosterone levels, which activate the AR with higher affinity than testosterone.44 In some tissues, androgens help regulate the mTORC1 pathway through positive feedback loops.45,46 At this time, we do not know if this occurs in the pathogenesis of acne.
Isotretinoin is the treatment of choice for refractory acne. It has been hypothesized that isotretinoin induces sebocyte apoptosis via the upregulation of FOXO transcription factors and p53.47 Elevated levels of nuclear FOXO1 have been found in the sebaceous glands of patients following initiation of treatment with isotretinoin and are hypothesized to play a major role in the drug’s effectiveness. Specifically, biopsies from 14 acne patients before and after 6 weeks of isotretinoin therapy were analyzed with immunohistochemical staining and found to have a significantly improved nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio of nonphosphorylated FOXO1 (P<.001).47
Practical Recommendations
Given the available evidence, it is important for dermatologists to address dietary recommendations in acne patients. Although large randomized controlled trials on diet and acne severity are challenging to conduct in this population, the existing literature suggests that patients should avoid high glycemic index simple sugars and processed grains, and patients should focus on eating more complex carbohydrates in the form of legumes, vegetables, fruits, and tubers.6-8 With regard to dairy, milk (especially skim) has been associated with increased risks for acne.11,13 Fermented dairy products may have less impact on acne severity and include cheese, yogurt (unsweetened to keep glycemic index low), and sour cream.12
- Zaenglein AL. Acne vulgaris. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. Elsevier; 2017:588-603.
- Ganceviciene R, Graziene V, Fimmel S, et al. Involvement of the corticotropin-releasing hormone system in the pathogenesis of acne vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:345-352.
- Kang S, Cho S, Chung JH, et al. Inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation mediated by activated transcription factors nuclear factor-kappaB and activator protein-1 in inflammatory acne lesions in vivo. Am J Pathol. 2005;166:1691-1699.
- Cong TX, Hao D, Wen X, et al. From pathogenesis of acne vulgaris to anti-acne agents. Arch Dermatol Res. 2019;311:337-349.
- Pópulo H, Lopes JM, Soares P. The mTOR signalling pathway in human cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:1886-1918.
- Kwon HH, Yoon JY, Hong JS, et al. Clinical and histological effect of a low glycaemic load diet in treatment of acne vulgaris in Korean patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012;92:241-246.
- Smith RN, Mann NJ, Braue A, et al. A low-glycemic-load diet improves symptoms in acne vulgaris patients: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:107-115.
- Penso L, Touvier M, Deschasaux M, et al. Association between adult acne and dietary behaviors: findings from the NutriNet-Santé prospective cohort study. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:854-862.
- Cao H, Yang G, Wang Y, et al. Complementary therapies for acne vulgaris. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;1:CD009436.
- Adebamowo CA, Spiegelman D, Danby FW, et al. High school dietary dairy intake and teenage acne. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:207-214.
- Aghasi M, Golzarand M, Shab-Bidar S, et al. Dairy intake and acne development: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Clin Nutr. 2019;38:1067-1075.
- Melnik BC, Schmitz G. Pasteurized non-fermented cow’s milk but not fermented milk is a promoter of mTORC1-driven aging and increased mortality. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;67:101270.
- Juhl CR, Bergholdt HKM, Miller IM, et al. Dairy intake and acne vulgaris: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 78,529 children, adolescents, and young adults. Nutrients. 2018;10:1049. doi:10.3390/nu10081049
- Melnik BC. Linking diet to acne metabolomics, inflammation, and comedogenesis: an update. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;8:371-388.
- Smart CEM, King BR, Lopez PE. Insulin dosing for fat and protein: is it time? Diabetes Care. 2020;43:13-15.
- Wan X, Wang S, Xu J, et al. Dietary protein-induced hepatic IGF-1 secretion mediated by PPARγ activation. PLoS One. 2017;12:E0173174.
- Bedinger DH, Adams SH. Metabolic, anabolic, and mitogenic insulin responses: a tissue-specific perspective for insulin receptor activators. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015;415:143-156.
- Gubbi S, Quipildor GF, Barzilai N, et al. 40 YEARS of IGF1: IGF1: the Jekyll and Hyde of the aging brain. J Mol Endocrinol. 2018;61:T171-T185.
- Kolb H, Kempf K, Röhling M, et al. Insulin: too much of a good thing is bad. BMC Med. 2020;18:224.
- Wood CL, Lane LC, Cheetham T. Puberty: normal physiology (brief overview). Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;33:101265.
- Agamia NF, Abdallah DM, Sorour O, et al. Skin expression of mammalian target of rapamycin and forkhead box transcription factor O1, and serum insulin-like growth factor-1 in patients with acne vulgaris and their relationship with diet. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:1299-1307.
- Kartal D, Yildiz H, Ertas R, et al. Association between isolated female acne and insulin resistance: a prospective study. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2016;151:353-357.
- Ben-Amitai D, Laron Z. Effect of insulin-like growth factor-1 deficiency or administration on the occurrence of acne. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:950-954.
- Kim LC, Cook RS, Chen J. mTORC1 and mTORC2 in cancer and the tumor microenvironment. Oncogene. 2017;36:2191-2201.
- Weichhart T. mTOR as regulator of lifespan, aging, and cellular senescence: a mini-review. Gerontology. 2018;64:127-134.
- Melick CH, Jewell JL. Regulation of mTORC1 by upstream stimuli. Genes. 2020;11:989. doi:10.3390/genes11090989
- Li M, Zhang CS, Feng JW, et al. Aldolase is a sensor for both low and high glucose, linking to AMPK and mTORC1. Cell Res. 2021;31:478-481.
- Yan T, Zhang J, Tang D, et al. Hypoxia regulates mTORC1-mediated keratinocyte motility and migration via the AMPK pathway. PLoS One. 2017;12:E0169155.
- Dennis MD, Baum JI, Kimball SR, et al. Mechanisms involved in the coordinate regulation of mTORC1 by insulin and amino acids. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:8287-8296.
- Choi BSY, Daniel N, Houde VP, et al. Feeding diversified protein sources exacerbates hepatic insulin resistance via increased gut microbial branched-chain fatty acids and mTORC1 signaling in obese mice. Nat Commun. 2021;12:3377.
- Chen CC, Jeon SM, Bhaskar PT, et al. FoxOs inhibit mTORC1 and activate Akt by inducing the expression of Sestrin3 and Rictor. Dev Cell. 2010;18:592-604.
- Chen Y, Huang T, Yu Z, et al. The functions and roles of sestrins in regulating human diseases. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022;27:2.
- Tao R, Xiong X, Liangpunsakul S, et al. Sestrin 3 protein enhances hepatic insulin sensitivity by direct activation of the mTORC2-Akt signaling. Diabetes. 2015;64:1211-1223.
- Gross DN, Wan M, Birnbaum MJ. The role of FOXO in the regulation of metabolism. Curr Diab Rep. 2009;9:208-214.
- Gilhar A, Ish-Shalom S, Pillar T, et al. Effect of anti–insulin-like growth factor 1 on epidermal proliferation of human skin transplanted onto nude mice treated with growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1994;134:229-232.
- Ding X, Bloch W, Iden S, et al. mTORC1 and mTORC2 regulate skin morphogenesis and epidermal barrier formation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13226.
- Inui S, Itami S. Androgen actions on the human hair follicle: perspectives. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22:168-171.
- Fan W, Yanase T, Morinaga H, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1/insulin signaling activates androgen signaling through direct interactions of Foxo1 with androgen receptor. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:7329-7338.
- Alestas T, Ganceviciene R, Fimmel S, et al. Enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of leukotriene B4 and prostaglandin E2 are active in sebaceous glands. J Mol Med. 2006;84:75-87.
- Smith TM, Gilliland K, Clawson GA, et al. IGF-1 induces SREBP-1 expression and lipogenesis in SEB-1 sebocytes via activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:1286-1293.
- Furtado GV, Yang J, Wu D, et al. FOXO1 controls protein synthesis and transcript abundance of mutant polyglutamine proteins, preventing protein aggregation. Hum Mol Genet. 2021;30:996-1005.
- Melnik BC. Isotretinoin and FoxO1: a scientific hypothesis. Dermatoendocrinol. 2011;3:141-165.
- Heng AHS, Say YH, Sio YY, et al. Gene variants associated with acne vulgaris presentation and severity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med Genomics. 2021;14:103.
- Li J, Al-Azzawi F. Mechanism of androgen receptor action. Maturitas. 2009;63:142-148.
- Zhao Y, Tindall DJ, Huang H. Modulation of androgen receptor by FOXA1 and FOXO1 factors in prostate cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2014;10:614-619.
- Hamdi MM, Mutungi G. Dihydrotestosterone stimulates amino acid uptake and the expression of LAT2 in mouse skeletal muscle fibres through an ERK1/2-dependent mechanism. J Physiol. 2011;589(pt 14):3623-3640.
- Agamia NF, Hussein OM, Abdelmaksoud RE, et al. Effect of oral isotretinoin on the nucleocytoplasmic distribution of FoxO1 and FoxO3 proteins in sebaceous glands of patients with acne vulgaris. Exp Dermatol. 2018;27:1344-1351.
- Kolovou GD, Watts GF, Mikhailidis DP, et al. Postprandial hypertriglyceridaemia revisited in the era of non-fasting lipid profile testing: a 2019 expert panel statement, main text. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2019;17:498-514.
- Svoboda SA, Shields BE. Cutaneous manifestations of nutritional excess: pathophysiologic effects of hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia on the skin. Cutis. 2021;107:74-78.
- González-González JG, Mancillas-Adame LG, Fernández-Reyes M, et al. Androgenetic alopecia and insulin resistance in young men. Clin Endocrinol . 2009;71:494-499.
- Livadas S, Anagnostis P, Bosdou JK, et al. Polycystic ovary syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a state-of-the-art review. World J Diabetes. 2022;13:5-26.
- Zaenglein AL. Acne vulgaris. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. Elsevier; 2017:588-603.
- Ganceviciene R, Graziene V, Fimmel S, et al. Involvement of the corticotropin-releasing hormone system in the pathogenesis of acne vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:345-352.
- Kang S, Cho S, Chung JH, et al. Inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation mediated by activated transcription factors nuclear factor-kappaB and activator protein-1 in inflammatory acne lesions in vivo. Am J Pathol. 2005;166:1691-1699.
- Cong TX, Hao D, Wen X, et al. From pathogenesis of acne vulgaris to anti-acne agents. Arch Dermatol Res. 2019;311:337-349.
- Pópulo H, Lopes JM, Soares P. The mTOR signalling pathway in human cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:1886-1918.
- Kwon HH, Yoon JY, Hong JS, et al. Clinical and histological effect of a low glycaemic load diet in treatment of acne vulgaris in Korean patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012;92:241-246.
- Smith RN, Mann NJ, Braue A, et al. A low-glycemic-load diet improves symptoms in acne vulgaris patients: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:107-115.
- Penso L, Touvier M, Deschasaux M, et al. Association between adult acne and dietary behaviors: findings from the NutriNet-Santé prospective cohort study. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:854-862.
- Cao H, Yang G, Wang Y, et al. Complementary therapies for acne vulgaris. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;1:CD009436.
- Adebamowo CA, Spiegelman D, Danby FW, et al. High school dietary dairy intake and teenage acne. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:207-214.
- Aghasi M, Golzarand M, Shab-Bidar S, et al. Dairy intake and acne development: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Clin Nutr. 2019;38:1067-1075.
- Melnik BC, Schmitz G. Pasteurized non-fermented cow’s milk but not fermented milk is a promoter of mTORC1-driven aging and increased mortality. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;67:101270.
- Juhl CR, Bergholdt HKM, Miller IM, et al. Dairy intake and acne vulgaris: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 78,529 children, adolescents, and young adults. Nutrients. 2018;10:1049. doi:10.3390/nu10081049
- Melnik BC. Linking diet to acne metabolomics, inflammation, and comedogenesis: an update. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2015;8:371-388.
- Smart CEM, King BR, Lopez PE. Insulin dosing for fat and protein: is it time? Diabetes Care. 2020;43:13-15.
- Wan X, Wang S, Xu J, et al. Dietary protein-induced hepatic IGF-1 secretion mediated by PPARγ activation. PLoS One. 2017;12:E0173174.
- Bedinger DH, Adams SH. Metabolic, anabolic, and mitogenic insulin responses: a tissue-specific perspective for insulin receptor activators. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015;415:143-156.
- Gubbi S, Quipildor GF, Barzilai N, et al. 40 YEARS of IGF1: IGF1: the Jekyll and Hyde of the aging brain. J Mol Endocrinol. 2018;61:T171-T185.
- Kolb H, Kempf K, Röhling M, et al. Insulin: too much of a good thing is bad. BMC Med. 2020;18:224.
- Wood CL, Lane LC, Cheetham T. Puberty: normal physiology (brief overview). Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;33:101265.
- Agamia NF, Abdallah DM, Sorour O, et al. Skin expression of mammalian target of rapamycin and forkhead box transcription factor O1, and serum insulin-like growth factor-1 in patients with acne vulgaris and their relationship with diet. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:1299-1307.
- Kartal D, Yildiz H, Ertas R, et al. Association between isolated female acne and insulin resistance: a prospective study. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2016;151:353-357.
- Ben-Amitai D, Laron Z. Effect of insulin-like growth factor-1 deficiency or administration on the occurrence of acne. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:950-954.
- Kim LC, Cook RS, Chen J. mTORC1 and mTORC2 in cancer and the tumor microenvironment. Oncogene. 2017;36:2191-2201.
- Weichhart T. mTOR as regulator of lifespan, aging, and cellular senescence: a mini-review. Gerontology. 2018;64:127-134.
- Melick CH, Jewell JL. Regulation of mTORC1 by upstream stimuli. Genes. 2020;11:989. doi:10.3390/genes11090989
- Li M, Zhang CS, Feng JW, et al. Aldolase is a sensor for both low and high glucose, linking to AMPK and mTORC1. Cell Res. 2021;31:478-481.
- Yan T, Zhang J, Tang D, et al. Hypoxia regulates mTORC1-mediated keratinocyte motility and migration via the AMPK pathway. PLoS One. 2017;12:E0169155.
- Dennis MD, Baum JI, Kimball SR, et al. Mechanisms involved in the coordinate regulation of mTORC1 by insulin and amino acids. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:8287-8296.
- Choi BSY, Daniel N, Houde VP, et al. Feeding diversified protein sources exacerbates hepatic insulin resistance via increased gut microbial branched-chain fatty acids and mTORC1 signaling in obese mice. Nat Commun. 2021;12:3377.
- Chen CC, Jeon SM, Bhaskar PT, et al. FoxOs inhibit mTORC1 and activate Akt by inducing the expression of Sestrin3 and Rictor. Dev Cell. 2010;18:592-604.
- Chen Y, Huang T, Yu Z, et al. The functions and roles of sestrins in regulating human diseases. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022;27:2.
- Tao R, Xiong X, Liangpunsakul S, et al. Sestrin 3 protein enhances hepatic insulin sensitivity by direct activation of the mTORC2-Akt signaling. Diabetes. 2015;64:1211-1223.
- Gross DN, Wan M, Birnbaum MJ. The role of FOXO in the regulation of metabolism. Curr Diab Rep. 2009;9:208-214.
- Gilhar A, Ish-Shalom S, Pillar T, et al. Effect of anti–insulin-like growth factor 1 on epidermal proliferation of human skin transplanted onto nude mice treated with growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1994;134:229-232.
- Ding X, Bloch W, Iden S, et al. mTORC1 and mTORC2 regulate skin morphogenesis and epidermal barrier formation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13226.
- Inui S, Itami S. Androgen actions on the human hair follicle: perspectives. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22:168-171.
- Fan W, Yanase T, Morinaga H, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1/insulin signaling activates androgen signaling through direct interactions of Foxo1 with androgen receptor. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:7329-7338.
- Alestas T, Ganceviciene R, Fimmel S, et al. Enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of leukotriene B4 and prostaglandin E2 are active in sebaceous glands. J Mol Med. 2006;84:75-87.
- Smith TM, Gilliland K, Clawson GA, et al. IGF-1 induces SREBP-1 expression and lipogenesis in SEB-1 sebocytes via activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:1286-1293.
- Furtado GV, Yang J, Wu D, et al. FOXO1 controls protein synthesis and transcript abundance of mutant polyglutamine proteins, preventing protein aggregation. Hum Mol Genet. 2021;30:996-1005.
- Melnik BC. Isotretinoin and FoxO1: a scientific hypothesis. Dermatoendocrinol. 2011;3:141-165.
- Heng AHS, Say YH, Sio YY, et al. Gene variants associated with acne vulgaris presentation and severity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med Genomics. 2021;14:103.
- Li J, Al-Azzawi F. Mechanism of androgen receptor action. Maturitas. 2009;63:142-148.
- Zhao Y, Tindall DJ, Huang H. Modulation of androgen receptor by FOXA1 and FOXO1 factors in prostate cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2014;10:614-619.
- Hamdi MM, Mutungi G. Dihydrotestosterone stimulates amino acid uptake and the expression of LAT2 in mouse skeletal muscle fibres through an ERK1/2-dependent mechanism. J Physiol. 2011;589(pt 14):3623-3640.
- Agamia NF, Hussein OM, Abdelmaksoud RE, et al. Effect of oral isotretinoin on the nucleocytoplasmic distribution of FoxO1 and FoxO3 proteins in sebaceous glands of patients with acne vulgaris. Exp Dermatol. 2018;27:1344-1351.
- Kolovou GD, Watts GF, Mikhailidis DP, et al. Postprandial hypertriglyceridaemia revisited in the era of non-fasting lipid profile testing: a 2019 expert panel statement, main text. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2019;17:498-514.
- Svoboda SA, Shields BE. Cutaneous manifestations of nutritional excess: pathophysiologic effects of hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia on the skin. Cutis. 2021;107:74-78.
- González-González JG, Mancillas-Adame LG, Fernández-Reyes M, et al. Androgenetic alopecia and insulin resistance in young men. Clin Endocrinol . 2009;71:494-499.
- Livadas S, Anagnostis P, Bosdou JK, et al. Polycystic ovary syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a state-of-the-art review. World J Diabetes. 2022;13:5-26.
Practice Points
- Patients are frequently interested in the role that diet plays in acne, and dermatologists should be aware of the current evidence to answer these questions effectively.
- One of the primary pathways in acne pathogenesis, mTORC1 (mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1), is partially regulated by nutrient availability, insulin, and insulinlike growth factor 1.
- Dietary recommendations for acne based on available evidence may include a low glycemic index diet and avoidance of certain dairy products.
- Insulin resistance may underlie the pathogenesis of acne in a subset of patients, and assessing insulin resistance in acne patients should be considered.
Adapting to Changes in Acne Management: Take One Step at a Time
After most dermatology residents graduate from their programs, they go out into practice and will often carry with them what they learned from their teachers, especially clinicians. Everyone else in their dermatology residency programs approaches disease management and the use of different therapies in the same way, right?
It does not take very long before these same dermatology residents realize that things are different in real-world clinical practice in many ways. Most clinicians develop a range of fairly predictable patterns in how they approach and treat common skin disorders such as acne, rosacea, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis/eczema, and seborrheic dermatitis. These patterns often include what testing is performed at baseline and at follow-up.
Recently, I have been giving thought to how clinicians—myself included—change their approaches to management of specific skin diseases over time, especially as new information and therapies emerge. Are we fast adopters, or are we slow adopters? How much evidence do we need to see before we consider adjusting our approach? Is the needle moving too fast or not fast enough?
I would like to use an example that relates to acne treatment, especially as this is one of the most common skin disorders encountered in outpatient dermatologic practice. Despite lack of US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for use in acne, oral spironolactone commonly is used in females, especially adults, with acne vulgaris and has a long history as an acceptable approach in dermatology.1 Because spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic, one question that commonly arises is: Do we monitor serum potassium levels at baseline and periodically during treatment with spironolactone? There has never been a definitive consensus on which approach to take. However, there has been evidence to suggest that such monitoring is not necessary in young healthy women due to a negligible risk for clinically relevant hyperkalemia.2,3
In fact, the suggestion that there is a very low risk for clinically significant hyperkalemia in healthy young women treated with spironolactone is accurate based on population-based studies. Nevertheless, the clinician is faced with confirming the patient is in fact healthy rather than assuming this is the case due to her “young” age. In addition, it is important to exclude potential drug-drug interactions that can increase the risk for hyperkalemia when coadministered with spironolactone and also to exclude an unknown underlying decrease in renal function.1 At the end of the day, I support the continued research that is being done to evaluate questions that can challenge the recycled dogma on how we manage patients, and I do not fault those who follow what they believe to be new cogent evidence. However, in the case of oral spironolactone use, I also could never fault a clinician for monitoring renal function and electrolytes including serum potassium levels in a female patient treated for acne, especially with a drug that has the known potential to cause hyperkalemia in certain clinical situations and is not FDA approved for the indication of acne (ie, the guidance that accompanies the level of investigation needed for such FDA approval is missing). The clinical judgment of the clinician who is responsible for the individual patient trumps the results from population-based studies completed thus far. Ultimately, it is the responsibility of that clinician to assure the safety of their patient in a manner that they are comfortable with.
It takes time to make changes in our approaches to patient management, and in the majority of cases, that is rightfully so. There are several potential limitations to how certain data are collected, and a reasonable verification of results over time is what tends to change behavior patterns. Ultimately, the common goal is to do what is in the best interest of our patients. No one can argue successfully against that.
- Kim GK, Del Rosso JQ. Oral spironolactone in post-teenage female patients with acne vulgaris: practical considerations for the clinician based on current data and clinical experience. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012;5:37-50.
- Plovanich M, Weng QY, Arash Mostaghimi A. Low usefulness of potassium monitoring among healthy young women taking spironolactone for acne. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:941-944.
- Barbieri JS, Margolis DJ, Mostaghimi A. Temporal trends and clinician variability in potassium monitoring of healthy young women treated for acne with spironolactone. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:296-300.
After most dermatology residents graduate from their programs, they go out into practice and will often carry with them what they learned from their teachers, especially clinicians. Everyone else in their dermatology residency programs approaches disease management and the use of different therapies in the same way, right?
It does not take very long before these same dermatology residents realize that things are different in real-world clinical practice in many ways. Most clinicians develop a range of fairly predictable patterns in how they approach and treat common skin disorders such as acne, rosacea, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis/eczema, and seborrheic dermatitis. These patterns often include what testing is performed at baseline and at follow-up.
Recently, I have been giving thought to how clinicians—myself included—change their approaches to management of specific skin diseases over time, especially as new information and therapies emerge. Are we fast adopters, or are we slow adopters? How much evidence do we need to see before we consider adjusting our approach? Is the needle moving too fast or not fast enough?
I would like to use an example that relates to acne treatment, especially as this is one of the most common skin disorders encountered in outpatient dermatologic practice. Despite lack of US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for use in acne, oral spironolactone commonly is used in females, especially adults, with acne vulgaris and has a long history as an acceptable approach in dermatology.1 Because spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic, one question that commonly arises is: Do we monitor serum potassium levels at baseline and periodically during treatment with spironolactone? There has never been a definitive consensus on which approach to take. However, there has been evidence to suggest that such monitoring is not necessary in young healthy women due to a negligible risk for clinically relevant hyperkalemia.2,3
In fact, the suggestion that there is a very low risk for clinically significant hyperkalemia in healthy young women treated with spironolactone is accurate based on population-based studies. Nevertheless, the clinician is faced with confirming the patient is in fact healthy rather than assuming this is the case due to her “young” age. In addition, it is important to exclude potential drug-drug interactions that can increase the risk for hyperkalemia when coadministered with spironolactone and also to exclude an unknown underlying decrease in renal function.1 At the end of the day, I support the continued research that is being done to evaluate questions that can challenge the recycled dogma on how we manage patients, and I do not fault those who follow what they believe to be new cogent evidence. However, in the case of oral spironolactone use, I also could never fault a clinician for monitoring renal function and electrolytes including serum potassium levels in a female patient treated for acne, especially with a drug that has the known potential to cause hyperkalemia in certain clinical situations and is not FDA approved for the indication of acne (ie, the guidance that accompanies the level of investigation needed for such FDA approval is missing). The clinical judgment of the clinician who is responsible for the individual patient trumps the results from population-based studies completed thus far. Ultimately, it is the responsibility of that clinician to assure the safety of their patient in a manner that they are comfortable with.
It takes time to make changes in our approaches to patient management, and in the majority of cases, that is rightfully so. There are several potential limitations to how certain data are collected, and a reasonable verification of results over time is what tends to change behavior patterns. Ultimately, the common goal is to do what is in the best interest of our patients. No one can argue successfully against that.
After most dermatology residents graduate from their programs, they go out into practice and will often carry with them what they learned from their teachers, especially clinicians. Everyone else in their dermatology residency programs approaches disease management and the use of different therapies in the same way, right?
It does not take very long before these same dermatology residents realize that things are different in real-world clinical practice in many ways. Most clinicians develop a range of fairly predictable patterns in how they approach and treat common skin disorders such as acne, rosacea, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis/eczema, and seborrheic dermatitis. These patterns often include what testing is performed at baseline and at follow-up.
Recently, I have been giving thought to how clinicians—myself included—change their approaches to management of specific skin diseases over time, especially as new information and therapies emerge. Are we fast adopters, or are we slow adopters? How much evidence do we need to see before we consider adjusting our approach? Is the needle moving too fast or not fast enough?
I would like to use an example that relates to acne treatment, especially as this is one of the most common skin disorders encountered in outpatient dermatologic practice. Despite lack of US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for use in acne, oral spironolactone commonly is used in females, especially adults, with acne vulgaris and has a long history as an acceptable approach in dermatology.1 Because spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic, one question that commonly arises is: Do we monitor serum potassium levels at baseline and periodically during treatment with spironolactone? There has never been a definitive consensus on which approach to take. However, there has been evidence to suggest that such monitoring is not necessary in young healthy women due to a negligible risk for clinically relevant hyperkalemia.2,3
In fact, the suggestion that there is a very low risk for clinically significant hyperkalemia in healthy young women treated with spironolactone is accurate based on population-based studies. Nevertheless, the clinician is faced with confirming the patient is in fact healthy rather than assuming this is the case due to her “young” age. In addition, it is important to exclude potential drug-drug interactions that can increase the risk for hyperkalemia when coadministered with spironolactone and also to exclude an unknown underlying decrease in renal function.1 At the end of the day, I support the continued research that is being done to evaluate questions that can challenge the recycled dogma on how we manage patients, and I do not fault those who follow what they believe to be new cogent evidence. However, in the case of oral spironolactone use, I also could never fault a clinician for monitoring renal function and electrolytes including serum potassium levels in a female patient treated for acne, especially with a drug that has the known potential to cause hyperkalemia in certain clinical situations and is not FDA approved for the indication of acne (ie, the guidance that accompanies the level of investigation needed for such FDA approval is missing). The clinical judgment of the clinician who is responsible for the individual patient trumps the results from population-based studies completed thus far. Ultimately, it is the responsibility of that clinician to assure the safety of their patient in a manner that they are comfortable with.
It takes time to make changes in our approaches to patient management, and in the majority of cases, that is rightfully so. There are several potential limitations to how certain data are collected, and a reasonable verification of results over time is what tends to change behavior patterns. Ultimately, the common goal is to do what is in the best interest of our patients. No one can argue successfully against that.
- Kim GK, Del Rosso JQ. Oral spironolactone in post-teenage female patients with acne vulgaris: practical considerations for the clinician based on current data and clinical experience. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012;5:37-50.
- Plovanich M, Weng QY, Arash Mostaghimi A. Low usefulness of potassium monitoring among healthy young women taking spironolactone for acne. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:941-944.
- Barbieri JS, Margolis DJ, Mostaghimi A. Temporal trends and clinician variability in potassium monitoring of healthy young women treated for acne with spironolactone. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:296-300.
- Kim GK, Del Rosso JQ. Oral spironolactone in post-teenage female patients with acne vulgaris: practical considerations for the clinician based on current data and clinical experience. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012;5:37-50.
- Plovanich M, Weng QY, Arash Mostaghimi A. Low usefulness of potassium monitoring among healthy young women taking spironolactone for acne. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:941-944.
- Barbieri JS, Margolis DJ, Mostaghimi A. Temporal trends and clinician variability in potassium monitoring of healthy young women treated for acne with spironolactone. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:296-300.
Administrative Burden of iPLEDGE Deters Isotretinoin Prescriptions: Results From a Survey of Dermatologists
Isotretinoin is the most effective treatment of recalcitrant acne, but because of its teratogenicity and potential association with psychiatric adverse effects, it has been heavily regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) through the iPLEDGE program since 2006.1,2 To manage the risk of teratogenicity associated with isotretinoin, various pregnancy prevention programs have been developed, but none of these programs have demonstrated a zero fetal exposure rate. The FDA reported 122 isotretinoin-exposed pregnancies during the first year iPLEDGE was implemented, which was a slight increase from the 120 pregnancies reported the year after the implementation of the System to Manage Accutane-Related Teratogenicity program, iPLEDGE’s predecessor.3 The iPLEDGE program requires registration of all wholesalers distributing isotretinoin, all health care providers prescribing isotretinoin, all pharmacies dispensing isotretinoin, and all female and male patients prescribed isotretinoin to create a verifiable link that only enables patients who have met all criteria to pick up their prescriptions. For patients of reproductive potential, there are additional qualification criteria and monthly requirements; before receiving their prescription every month, patients of reproductive potential must undergo a urine or serum pregnancy test with negative results, and patients must be counseled by prescribers regarding the risks of the drug and verify they are using 2 methods of contraception (or practicing abstinence) each month before completing online questions that test their understanding of the drug’s side effects and their chosen methods of contraception.4 These requirements place burdens on both patients and prescribers. Studies have shown that in the 2 years after the implementation of iPLEDGE, there was a 29% decrease in isotretinoin prescriptions.1-3
We conducted a survey study to see if clinicians chose not to prescribe isotretinoin to appropriate candidates specifically because of the administrative burden of iPLEDGE. Secondarily, we investigated the medications these clinicians would prescribe instead of isotretinoin.
Methods
In March 2020, we administered an anonymous online survey consisting of 12 multiple-choice questions to verified board-certified dermatologists in the United States using a social media group. The University of Rochester’s (Rochester, New York) institutional review board determined that our protocol met criteria for exemption (IRB STUDY00004693).
Statistical Analysis—Primary analyses used Pearson χ2 tests to identify significant differences among respondent groups, practice settings, age of respondents, and time spent registering patients for iPLEDGE.
Results
Survey results from 510 respondents are summarized in the Table.
Burden of iPLEDGE—Of the respondents, 336 (65.9%) were frequent prescribers of isotretinoin, 166 (32.5%) were infrequent prescribers, and 8 (1.6%) were never prescribers. Significantly more isotretinoin prescribers estimated that their offices spend 16 to 30 minutes registering a new isotretinoin patient with the iPLEDGE program (289 [57.6%]) compared with 0 to 15 minutes (140 [27.9%]), 31 to 45 minutes (57 [11.3%]), and morethan 45 minutes (16 [3.2%])(χ23=22.09, P<.0001). Furthermore, 150 dermatologists reported sometimes not prescribing, and 2 reported never prescribing isotretinoin because of the burden of iPLEDGE.
Systemic Agents Prescribed Instead of Isotretinoin—Of the respondents, 73.0% (n=111) prescribed spironolactone to female patients and 88.8% (n=135) prescribed oral antibiotics to male patients instead of isotretinoin. Spironolactone typically is not prescribed to male patients with acne because of its feminizing side effects, such as gynecomastia.5 According to the American Academy of Dermatology guidelines on acne, systemic antibiotic usage should be limited to the shortest possible duration (ie, less than 3–4 months) because of potential bacterial resistance and reported associations with inflammatory bowel disease, Clostridium difficile infection, and candidiasis.6,7
Prescriber Demographics—The frequency of not prescribing isotretinoin did not vary by practice setting (χ 24=6.44, P=.1689) but did vary by age of the dermatologist (χ23=15.57, P=.0014). Dermatologists younger than 46 years were more likely (Figure) to report not prescribing isotretinoin because of the administrative burden of iPLEDGE. We speculate that this is because younger dermatologists are less established in their practices and therefore may have less support to complete registration without interruption of clinic workflow.
Comment
The results of our survey suggest that the administrative burden of iPLEDGE may be compelling prescribers to refrain from prescribing isotretinoin therapy to appropriate candidates when it would otherwise be the drug of choice.
Recent Changes to iPLEDGE—The FDA recently approved a modification to the iPLEDGE Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program based on the advocacy efforts from the American Academy of Dermatology. Starting December 13, 2021, the 3 patient risk categories were consolidated into 2 gender-neutral categories: patients who can get pregnant and patients who cannot get pregnant.8 The iPLEDGE website was transitioned to a new system, and all iPLEDGE REMS users had to update their iPLEDGE accounts. After the implementation of the modified program, user access issues arose, leading to delayed treatment when patients, providers, and pharmacists were all locked out of the online system; users also experienced long hold times with the call center.8 This change highlights the ongoing critical need for a streamlined program that increases patient access to isotretinoin while maintaining safety.
Study Limitations—The main limitation of this study was the inability to calculate a true response rate to our survey. We distributed the survey via social media to maintain anonymity of the respondents. We could not track how many saw the link to compare with the number of respondents. Therefore, the only way we could calculate a response rate was with the total number of members in the group, which fluctuated around 4000 at the time we administered the survey. We calculated that we would need at least 351 responses to have a 5% margin of error at 95% confidence for our results to be generalizable and significant. We ultimately received 510 responses, which gave us a 4.05% margin of error at 95% confidence and an estimated 12.7% response rate. Since some members of the group are not active and did not see the survey link, our true response rate was likely higher. Therefore, we concluded that the survey was successful, and our significant responses were representative of US dermatologists.
Suggestions to Improve iPLEDGE Process—Our survey study should facilitate further discussions on the importance of simplifying iPLEDGE. One suggestion for improving iPLEDGE is to remove the initial registration month so care is not delayed. Currently, a patient who can get pregnant must be on 2 forms of contraception for 30 days after they register as a patient before they are eligible to fill their prescription.4 This process is unnecessarily long and arduous and could be eliminated as long as the patient has already been on an effective form of contraception and has a negative pregnancy test on the day of registration. The need to repeat contraception comprehension questions monthly is redundant and also could be removed. Another suggestion is to remove the category of patients who cannot become pregnant from the system entirely. Isotretinoin does not appear to be associated with adverse psychiatric effects as shown through the systematic review and meta-analysis of numerous studies.9 If anything, the treatment of acne with isotretinoin appears to mitigate depressive symptoms. The iPLEDGE program does not manage this largely debunked idea. Because the program’s sole goal is to manage the risk of isotretinoin’s teratogenicity, the category of those who cannot become pregnant should not be included.
Conclusion
This survey highlights the burdens of iPLEDGE for dermatologists and the need for a more streamlined risk management program. The burden was felt equally among all practice types but especially by younger dermatologists (<46 years). This time-consuming program is deterring some dermatologists from prescribing isotretinoin and ultimately limiting patient access to an effective medication.
Acknowledgment—The authors thank all of the responding clinicians who provided insight into the impact of iPLEDGE on their isotretinoin prescribing patterns.
- Prevost N, English JC. Isotretinoin: update on controversial issues. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2013;26:290-293.
- Tkachenko E, Singer S, Sharma P, et al. US Food and Drug Administration reports of pregnancy and pregnancy-related adverse events associated with isotretinoin. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1175-1179.
- Shin J, Cheetham TC, Wong L, et al. The impact of the IPLEDGE program on isotretinoin fetal exposure in an integrated health care system. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:1117-1125.
- iPLEDGE Program. About iPLEDGE. Accessed June 13, 2022. https://ipledgeprogram.com/#Main/AboutiPledge
- Marson JW, Baldwin HE. An overview of acne therapy, part 2: hormonal therapy and isotretinoin. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:195-203.
- Margolis DJ, Fanelli M, Hoffstad O, et al. Potential association between the oral tetracycline class of antimicrobials used to treat acne and inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:2610-2616.
- Zaenglein AL, Pathy AL, Schlosser BJ, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:945-973.e33.
- iPLEDGE Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS). Updated January 14, 2022. Accessed June 13, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/ipledge-risk-evaluation-and-mitigation-strategy-rems
- Huang YC, Cheng YC. Isotretinoin treatment for acne and risk of depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:1068-1076.e9.
Isotretinoin is the most effective treatment of recalcitrant acne, but because of its teratogenicity and potential association with psychiatric adverse effects, it has been heavily regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) through the iPLEDGE program since 2006.1,2 To manage the risk of teratogenicity associated with isotretinoin, various pregnancy prevention programs have been developed, but none of these programs have demonstrated a zero fetal exposure rate. The FDA reported 122 isotretinoin-exposed pregnancies during the first year iPLEDGE was implemented, which was a slight increase from the 120 pregnancies reported the year after the implementation of the System to Manage Accutane-Related Teratogenicity program, iPLEDGE’s predecessor.3 The iPLEDGE program requires registration of all wholesalers distributing isotretinoin, all health care providers prescribing isotretinoin, all pharmacies dispensing isotretinoin, and all female and male patients prescribed isotretinoin to create a verifiable link that only enables patients who have met all criteria to pick up their prescriptions. For patients of reproductive potential, there are additional qualification criteria and monthly requirements; before receiving their prescription every month, patients of reproductive potential must undergo a urine or serum pregnancy test with negative results, and patients must be counseled by prescribers regarding the risks of the drug and verify they are using 2 methods of contraception (or practicing abstinence) each month before completing online questions that test their understanding of the drug’s side effects and their chosen methods of contraception.4 These requirements place burdens on both patients and prescribers. Studies have shown that in the 2 years after the implementation of iPLEDGE, there was a 29% decrease in isotretinoin prescriptions.1-3
We conducted a survey study to see if clinicians chose not to prescribe isotretinoin to appropriate candidates specifically because of the administrative burden of iPLEDGE. Secondarily, we investigated the medications these clinicians would prescribe instead of isotretinoin.
Methods
In March 2020, we administered an anonymous online survey consisting of 12 multiple-choice questions to verified board-certified dermatologists in the United States using a social media group. The University of Rochester’s (Rochester, New York) institutional review board determined that our protocol met criteria for exemption (IRB STUDY00004693).
Statistical Analysis—Primary analyses used Pearson χ2 tests to identify significant differences among respondent groups, practice settings, age of respondents, and time spent registering patients for iPLEDGE.
Results
Survey results from 510 respondents are summarized in the Table.

Burden of iPLEDGE—Of the respondents, 336 (65.9%) were frequent prescribers of isotretinoin, 166 (32.5%) were infrequent prescribers, and 8 (1.6%) were never prescribers. Significantly more isotretinoin prescribers estimated that their offices spend 16 to 30 minutes registering a new isotretinoin patient with the iPLEDGE program (289 [57.6%]) compared with 0 to 15 minutes (140 [27.9%]), 31 to 45 minutes (57 [11.3%]), and morethan 45 minutes (16 [3.2%])(χ23=22.09, P<.0001). Furthermore, 150 dermatologists reported sometimes not prescribing, and 2 reported never prescribing isotretinoin because of the burden of iPLEDGE.
Systemic Agents Prescribed Instead of Isotretinoin—Of the respondents, 73.0% (n=111) prescribed spironolactone to female patients and 88.8% (n=135) prescribed oral antibiotics to male patients instead of isotretinoin. Spironolactone typically is not prescribed to male patients with acne because of its feminizing side effects, such as gynecomastia.5 According to the American Academy of Dermatology guidelines on acne, systemic antibiotic usage should be limited to the shortest possible duration (ie, less than 3–4 months) because of potential bacterial resistance and reported associations with inflammatory bowel disease, Clostridium difficile infection, and candidiasis.6,7
Prescriber Demographics—The frequency of not prescribing isotretinoin did not vary by practice setting (χ 24=6.44, P=.1689) but did vary by age of the dermatologist (χ23=15.57, P=.0014). Dermatologists younger than 46 years were more likely (Figure) to report not prescribing isotretinoin because of the administrative burden of iPLEDGE. We speculate that this is because younger dermatologists are less established in their practices and therefore may have less support to complete registration without interruption of clinic workflow.

Comment
The results of our survey suggest that the administrative burden of iPLEDGE may be compelling prescribers to refrain from prescribing isotretinoin therapy to appropriate candidates when it would otherwise be the drug of choice.
Recent Changes to iPLEDGE—The FDA recently approved a modification to the iPLEDGE Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program based on the advocacy efforts from the American Academy of Dermatology. Starting December 13, 2021, the 3 patient risk categories were consolidated into 2 gender-neutral categories: patients who can get pregnant and patients who cannot get pregnant.8 The iPLEDGE website was transitioned to a new system, and all iPLEDGE REMS users had to update their iPLEDGE accounts. After the implementation of the modified program, user access issues arose, leading to delayed treatment when patients, providers, and pharmacists were all locked out of the online system; users also experienced long hold times with the call center.8 This change highlights the ongoing critical need for a streamlined program that increases patient access to isotretinoin while maintaining safety.
Study Limitations—The main limitation of this study was the inability to calculate a true response rate to our survey. We distributed the survey via social media to maintain anonymity of the respondents. We could not track how many saw the link to compare with the number of respondents. Therefore, the only way we could calculate a response rate was with the total number of members in the group, which fluctuated around 4000 at the time we administered the survey. We calculated that we would need at least 351 responses to have a 5% margin of error at 95% confidence for our results to be generalizable and significant. We ultimately received 510 responses, which gave us a 4.05% margin of error at 95% confidence and an estimated 12.7% response rate. Since some members of the group are not active and did not see the survey link, our true response rate was likely higher. Therefore, we concluded that the survey was successful, and our significant responses were representative of US dermatologists.
Suggestions to Improve iPLEDGE Process—Our survey study should facilitate further discussions on the importance of simplifying iPLEDGE. One suggestion for improving iPLEDGE is to remove the initial registration month so care is not delayed. Currently, a patient who can get pregnant must be on 2 forms of contraception for 30 days after they register as a patient before they are eligible to fill their prescription.4 This process is unnecessarily long and arduous and could be eliminated as long as the patient has already been on an effective form of contraception and has a negative pregnancy test on the day of registration. The need to repeat contraception comprehension questions monthly is redundant and also could be removed. Another suggestion is to remove the category of patients who cannot become pregnant from the system entirely. Isotretinoin does not appear to be associated with adverse psychiatric effects as shown through the systematic review and meta-analysis of numerous studies.9 If anything, the treatment of acne with isotretinoin appears to mitigate depressive symptoms. The iPLEDGE program does not manage this largely debunked idea. Because the program’s sole goal is to manage the risk of isotretinoin’s teratogenicity, the category of those who cannot become pregnant should not be included.
Conclusion
This survey highlights the burdens of iPLEDGE for dermatologists and the need for a more streamlined risk management program. The burden was felt equally among all practice types but especially by younger dermatologists (<46 years). This time-consuming program is deterring some dermatologists from prescribing isotretinoin and ultimately limiting patient access to an effective medication.
Acknowledgment—The authors thank all of the responding clinicians who provided insight into the impact of iPLEDGE on their isotretinoin prescribing patterns.
Isotretinoin is the most effective treatment of recalcitrant acne, but because of its teratogenicity and potential association with psychiatric adverse effects, it has been heavily regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) through the iPLEDGE program since 2006.1,2 To manage the risk of teratogenicity associated with isotretinoin, various pregnancy prevention programs have been developed, but none of these programs have demonstrated a zero fetal exposure rate. The FDA reported 122 isotretinoin-exposed pregnancies during the first year iPLEDGE was implemented, which was a slight increase from the 120 pregnancies reported the year after the implementation of the System to Manage Accutane-Related Teratogenicity program, iPLEDGE’s predecessor.3 The iPLEDGE program requires registration of all wholesalers distributing isotretinoin, all health care providers prescribing isotretinoin, all pharmacies dispensing isotretinoin, and all female and male patients prescribed isotretinoin to create a verifiable link that only enables patients who have met all criteria to pick up their prescriptions. For patients of reproductive potential, there are additional qualification criteria and monthly requirements; before receiving their prescription every month, patients of reproductive potential must undergo a urine or serum pregnancy test with negative results, and patients must be counseled by prescribers regarding the risks of the drug and verify they are using 2 methods of contraception (or practicing abstinence) each month before completing online questions that test their understanding of the drug’s side effects and their chosen methods of contraception.4 These requirements place burdens on both patients and prescribers. Studies have shown that in the 2 years after the implementation of iPLEDGE, there was a 29% decrease in isotretinoin prescriptions.1-3
We conducted a survey study to see if clinicians chose not to prescribe isotretinoin to appropriate candidates specifically because of the administrative burden of iPLEDGE. Secondarily, we investigated the medications these clinicians would prescribe instead of isotretinoin.
Methods
In March 2020, we administered an anonymous online survey consisting of 12 multiple-choice questions to verified board-certified dermatologists in the United States using a social media group. The University of Rochester’s (Rochester, New York) institutional review board determined that our protocol met criteria for exemption (IRB STUDY00004693).
Statistical Analysis—Primary analyses used Pearson χ2 tests to identify significant differences among respondent groups, practice settings, age of respondents, and time spent registering patients for iPLEDGE.
Results
Survey results from 510 respondents are summarized in the Table.

Burden of iPLEDGE—Of the respondents, 336 (65.9%) were frequent prescribers of isotretinoin, 166 (32.5%) were infrequent prescribers, and 8 (1.6%) were never prescribers. Significantly more isotretinoin prescribers estimated that their offices spend 16 to 30 minutes registering a new isotretinoin patient with the iPLEDGE program (289 [57.6%]) compared with 0 to 15 minutes (140 [27.9%]), 31 to 45 minutes (57 [11.3%]), and morethan 45 minutes (16 [3.2%])(χ23=22.09, P<.0001). Furthermore, 150 dermatologists reported sometimes not prescribing, and 2 reported never prescribing isotretinoin because of the burden of iPLEDGE.
Systemic Agents Prescribed Instead of Isotretinoin—Of the respondents, 73.0% (n=111) prescribed spironolactone to female patients and 88.8% (n=135) prescribed oral antibiotics to male patients instead of isotretinoin. Spironolactone typically is not prescribed to male patients with acne because of its feminizing side effects, such as gynecomastia.5 According to the American Academy of Dermatology guidelines on acne, systemic antibiotic usage should be limited to the shortest possible duration (ie, less than 3–4 months) because of potential bacterial resistance and reported associations with inflammatory bowel disease, Clostridium difficile infection, and candidiasis.6,7
Prescriber Demographics—The frequency of not prescribing isotretinoin did not vary by practice setting (χ 24=6.44, P=.1689) but did vary by age of the dermatologist (χ23=15.57, P=.0014). Dermatologists younger than 46 years were more likely (Figure) to report not prescribing isotretinoin because of the administrative burden of iPLEDGE. We speculate that this is because younger dermatologists are less established in their practices and therefore may have less support to complete registration without interruption of clinic workflow.

Comment
The results of our survey suggest that the administrative burden of iPLEDGE may be compelling prescribers to refrain from prescribing isotretinoin therapy to appropriate candidates when it would otherwise be the drug of choice.
Recent Changes to iPLEDGE—The FDA recently approved a modification to the iPLEDGE Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program based on the advocacy efforts from the American Academy of Dermatology. Starting December 13, 2021, the 3 patient risk categories were consolidated into 2 gender-neutral categories: patients who can get pregnant and patients who cannot get pregnant.8 The iPLEDGE website was transitioned to a new system, and all iPLEDGE REMS users had to update their iPLEDGE accounts. After the implementation of the modified program, user access issues arose, leading to delayed treatment when patients, providers, and pharmacists were all locked out of the online system; users also experienced long hold times with the call center.8 This change highlights the ongoing critical need for a streamlined program that increases patient access to isotretinoin while maintaining safety.
Study Limitations—The main limitation of this study was the inability to calculate a true response rate to our survey. We distributed the survey via social media to maintain anonymity of the respondents. We could not track how many saw the link to compare with the number of respondents. Therefore, the only way we could calculate a response rate was with the total number of members in the group, which fluctuated around 4000 at the time we administered the survey. We calculated that we would need at least 351 responses to have a 5% margin of error at 95% confidence for our results to be generalizable and significant. We ultimately received 510 responses, which gave us a 4.05% margin of error at 95% confidence and an estimated 12.7% response rate. Since some members of the group are not active and did not see the survey link, our true response rate was likely higher. Therefore, we concluded that the survey was successful, and our significant responses were representative of US dermatologists.
Suggestions to Improve iPLEDGE Process—Our survey study should facilitate further discussions on the importance of simplifying iPLEDGE. One suggestion for improving iPLEDGE is to remove the initial registration month so care is not delayed. Currently, a patient who can get pregnant must be on 2 forms of contraception for 30 days after they register as a patient before they are eligible to fill their prescription.4 This process is unnecessarily long and arduous and could be eliminated as long as the patient has already been on an effective form of contraception and has a negative pregnancy test on the day of registration. The need to repeat contraception comprehension questions monthly is redundant and also could be removed. Another suggestion is to remove the category of patients who cannot become pregnant from the system entirely. Isotretinoin does not appear to be associated with adverse psychiatric effects as shown through the systematic review and meta-analysis of numerous studies.9 If anything, the treatment of acne with isotretinoin appears to mitigate depressive symptoms. The iPLEDGE program does not manage this largely debunked idea. Because the program’s sole goal is to manage the risk of isotretinoin’s teratogenicity, the category of those who cannot become pregnant should not be included.
Conclusion
This survey highlights the burdens of iPLEDGE for dermatologists and the need for a more streamlined risk management program. The burden was felt equally among all practice types but especially by younger dermatologists (<46 years). This time-consuming program is deterring some dermatologists from prescribing isotretinoin and ultimately limiting patient access to an effective medication.
Acknowledgment—The authors thank all of the responding clinicians who provided insight into the impact of iPLEDGE on their isotretinoin prescribing patterns.
- Prevost N, English JC. Isotretinoin: update on controversial issues. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2013;26:290-293.
- Tkachenko E, Singer S, Sharma P, et al. US Food and Drug Administration reports of pregnancy and pregnancy-related adverse events associated with isotretinoin. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1175-1179.
- Shin J, Cheetham TC, Wong L, et al. The impact of the IPLEDGE program on isotretinoin fetal exposure in an integrated health care system. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:1117-1125.
- iPLEDGE Program. About iPLEDGE. Accessed June 13, 2022. https://ipledgeprogram.com/#Main/AboutiPledge
- Marson JW, Baldwin HE. An overview of acne therapy, part 2: hormonal therapy and isotretinoin. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:195-203.
- Margolis DJ, Fanelli M, Hoffstad O, et al. Potential association between the oral tetracycline class of antimicrobials used to treat acne and inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:2610-2616.
- Zaenglein AL, Pathy AL, Schlosser BJ, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:945-973.e33.
- iPLEDGE Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS). Updated January 14, 2022. Accessed June 13, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/ipledge-risk-evaluation-and-mitigation-strategy-rems
- Huang YC, Cheng YC. Isotretinoin treatment for acne and risk of depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:1068-1076.e9.
- Prevost N, English JC. Isotretinoin: update on controversial issues. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2013;26:290-293.
- Tkachenko E, Singer S, Sharma P, et al. US Food and Drug Administration reports of pregnancy and pregnancy-related adverse events associated with isotretinoin. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1175-1179.
- Shin J, Cheetham TC, Wong L, et al. The impact of the IPLEDGE program on isotretinoin fetal exposure in an integrated health care system. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:1117-1125.
- iPLEDGE Program. About iPLEDGE. Accessed June 13, 2022. https://ipledgeprogram.com/#Main/AboutiPledge
- Marson JW, Baldwin HE. An overview of acne therapy, part 2: hormonal therapy and isotretinoin. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:195-203.
- Margolis DJ, Fanelli M, Hoffstad O, et al. Potential association between the oral tetracycline class of antimicrobials used to treat acne and inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:2610-2616.
- Zaenglein AL, Pathy AL, Schlosser BJ, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:945-973.e33.
- iPLEDGE Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS). Updated January 14, 2022. Accessed June 13, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/ipledge-risk-evaluation-and-mitigation-strategy-rems
- Huang YC, Cheng YC. Isotretinoin treatment for acne and risk of depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:1068-1076.e9.
Practice Points
- Of clinicians who regularly prescribe isotretinoin, approximately 30% have at times chosen not to prescribe isotretinoin to patients with severe acne because of the burden of the iPLEDGE program.
- The US Food and Drug Administration should consider further streamlining the iPLEDGE program, as it is causing physician burden and therefore suboptimal treatment plans for patients.
Can dietary tweaks improve some skin diseases?
Since 1950, the terms “diet and skin” in the medical literature have markedly increased, said Vivian Shi, MD associate professor of dermatology at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, who talked about nutritional approaches for select skin diseases at MedscapeLive’s Women’s and Pediatric Dermatology Seminar.
Myths abound, but some associations of diet with skin diseases hold water, and she said.
Acne
What’s known, Dr. Shi said, is that the prevalence of acne is substantially lower in non-Westernized countries, and that diets in those countries generally have a low glycemic load, which decreases IGF-1 insulinlike growth factor 1 (IGF-1) concentrations, an accepted risk factor for acne. The Western diet also includes the hormonal effects of cow’s milk products.
Whey protein, which is popular as a supplement, isn’t good for acne, Dr. Shi said. It takes a couple of hours to digest, while casein protein digests more slowly, over 5-7 hours. If casein protein isn’t acceptable, good alternatives to whey protein are hemp seed, plant protein blends (peas, seeds, berries), egg white, brown rice isolate, and soy isolate protein.
Dairy products increase IGF-1 levels, hormonal mediators that can make acne worse. In addition, industrial cow’s milk can contain anabolic steroids and growth factor, leading to sebogenesis, Dr. Shi said. As for the type of milk, skim milk tends to be the most acnegenic and associated with the highest blood levels of IGF-1.
Supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids and gamma-linolenic acid improved mild to moderate acne in a double-blind, controlled study. Researchers randomized 45 patients with mild to moderate acne to an omega-3 fatty acid group (2,000 mg of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid), a gamma-linolenic acid group (borage oil with 400 mg gamma-linolenic acid) or a control group. After 10 weeks in both treatment groups, there was a significant reduction in inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions.
Those with acne are more likely to be deficient in Vitamin D, research suggests. Researchers also found that among those who had vitamin D deficiency, supplementing with 1,000 IU daily for 2 months reduced inflammatory lesions by 35% after 8 weeks, compared with a 6% reduction in the control group.
Other research has found that those with a low serum zinc level had more severe acne and that 30-200 mg of zinc orally for 2-4 months reduced inflammatory acne. However, Dr. Shi cautioned that those taking zinc for more than 2 months also need a copper supplement, as zinc reduces the amount of copper absorbed by the body.
Dr. Shi’s “do’s” diet list for acne patients is a follows: Paleolithic and Mediterranean diets, omega-3 fatty acids, gamma-linolenic acids, Vitamin D, zinc, tubers, legumes, vegetables, fruits, and fish.
Unknowns, she said, include chocolate, caffeine, green tea, and high salt.
Hidradenitis suppurativa
Patents with HS who follow a Mediterranean diet most closely have less severe disease, research has found. In this study, those patients with HS with the lowest adherence had a Sartorius HS score of 59.38, while those who followed it the most closely had a score of 39 (of 80).
In another study, patients with HS reported the following foods as exacerbating HS: sweets, bread/pasta/rice, dairy, and high-fat foods. Alleviating foods included vegetables, fruit, chicken, and fish.
Dr. Shi’s dietary recommendations for patients with HS: Follow a Mediterranean diet, avoid high fat foods and highly processed foods, and focus on eating more vegetables, fresh fruit, corn-based cereal, white meat, and fish.
A retrospective study of patients with Hurley stage 1 and 2 found that oral zinc gluconate, 90 mg a day, combined with 2% topical triclosan twice a day, resulted in significantly decreased HS scores and nodules and improved quality of life after 3 months. Expect vitamin D deficiency, she added.
Lastly, Dr. Shi recommended, if necessary, “weight loss to reduce the inflammatory burden.”
Rosacea
Dietary triggers for rosacea are thought to include high-fat foods, dairy foods, spicy foods, hot drinks, cinnamon, and vanilla.
A population-based case-control study in China, which evaluated 1,347 rosacea patients and 1,290 healthy controls, found that a high intake of fatty foods positively correlated with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea (ETR) and phymatous rosacea. High-frequency dairy intake negatively correlated with ETR and papulopustular rosacea, which was a surprise, she said. And in this study, no significant correlations were found between sweets, coffee, and spicy foods. That goes against the traditional thinking, she said, but this was a Chinese cohort and their diet is probably vastly different than those in the United States.
Other rosacea triggers, Dr. Shi said, are niacin-containing foods such as turkey, chicken breast, crustaceans, dried Shiitake mushrooms, peanuts, tuna, and liver, as well as cold drinks, and formalin-containing foods (fish, squid, tofu, wet noodles).
As the field of nutrigenics – how genes affect how the body responds to food – evolves, more answers about the impact of diet on these diseases will be forthcoming, Dr. Shi said.
In an interactive panel discussion, she was asked if she talks about diet with all her patients with acne, rosacea, and HS, or just those not responding to traditional therapy.
“I think it’s an important conversation to have,” Dr. Shi responded. “When I’m done with the medication [instructions], I say: ‘There is something else you can do to augment what I just told you.’ ” That’s when she explains the dietary information. She also has a handout on diet and routinely refers patients for dietary counseling.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Shi disclosed consulting, investigative and research funding from several sources, but not directly related to the content of her talk.
Since 1950, the terms “diet and skin” in the medical literature have markedly increased, said Vivian Shi, MD associate professor of dermatology at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, who talked about nutritional approaches for select skin diseases at MedscapeLive’s Women’s and Pediatric Dermatology Seminar.
Myths abound, but some associations of diet with skin diseases hold water, and she said.
Acne
What’s known, Dr. Shi said, is that the prevalence of acne is substantially lower in non-Westernized countries, and that diets in those countries generally have a low glycemic load, which decreases IGF-1 insulinlike growth factor 1 (IGF-1) concentrations, an accepted risk factor for acne. The Western diet also includes the hormonal effects of cow’s milk products.
Whey protein, which is popular as a supplement, isn’t good for acne, Dr. Shi said. It takes a couple of hours to digest, while casein protein digests more slowly, over 5-7 hours. If casein protein isn’t acceptable, good alternatives to whey protein are hemp seed, plant protein blends (peas, seeds, berries), egg white, brown rice isolate, and soy isolate protein.
Dairy products increase IGF-1 levels, hormonal mediators that can make acne worse. In addition, industrial cow’s milk can contain anabolic steroids and growth factor, leading to sebogenesis, Dr. Shi said. As for the type of milk, skim milk tends to be the most acnegenic and associated with the highest blood levels of IGF-1.
Supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids and gamma-linolenic acid improved mild to moderate acne in a double-blind, controlled study. Researchers randomized 45 patients with mild to moderate acne to an omega-3 fatty acid group (2,000 mg of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid), a gamma-linolenic acid group (borage oil with 400 mg gamma-linolenic acid) or a control group. After 10 weeks in both treatment groups, there was a significant reduction in inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions.
Those with acne are more likely to be deficient in Vitamin D, research suggests. Researchers also found that among those who had vitamin D deficiency, supplementing with 1,000 IU daily for 2 months reduced inflammatory lesions by 35% after 8 weeks, compared with a 6% reduction in the control group.
Other research has found that those with a low serum zinc level had more severe acne and that 30-200 mg of zinc orally for 2-4 months reduced inflammatory acne. However, Dr. Shi cautioned that those taking zinc for more than 2 months also need a copper supplement, as zinc reduces the amount of copper absorbed by the body.
Dr. Shi’s “do’s” diet list for acne patients is a follows: Paleolithic and Mediterranean diets, omega-3 fatty acids, gamma-linolenic acids, Vitamin D, zinc, tubers, legumes, vegetables, fruits, and fish.
Unknowns, she said, include chocolate, caffeine, green tea, and high salt.
Hidradenitis suppurativa
Patents with HS who follow a Mediterranean diet most closely have less severe disease, research has found. In this study, those patients with HS with the lowest adherence had a Sartorius HS score of 59.38, while those who followed it the most closely had a score of 39 (of 80).
In another study, patients with HS reported the following foods as exacerbating HS: sweets, bread/pasta/rice, dairy, and high-fat foods. Alleviating foods included vegetables, fruit, chicken, and fish.
Dr. Shi’s dietary recommendations for patients with HS: Follow a Mediterranean diet, avoid high fat foods and highly processed foods, and focus on eating more vegetables, fresh fruit, corn-based cereal, white meat, and fish.
A retrospective study of patients with Hurley stage 1 and 2 found that oral zinc gluconate, 90 mg a day, combined with 2% topical triclosan twice a day, resulted in significantly decreased HS scores and nodules and improved quality of life after 3 months. Expect vitamin D deficiency, she added.
Lastly, Dr. Shi recommended, if necessary, “weight loss to reduce the inflammatory burden.”
Rosacea
Dietary triggers for rosacea are thought to include high-fat foods, dairy foods, spicy foods, hot drinks, cinnamon, and vanilla.
A population-based case-control study in China, which evaluated 1,347 rosacea patients and 1,290 healthy controls, found that a high intake of fatty foods positively correlated with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea (ETR) and phymatous rosacea. High-frequency dairy intake negatively correlated with ETR and papulopustular rosacea, which was a surprise, she said. And in this study, no significant correlations were found between sweets, coffee, and spicy foods. That goes against the traditional thinking, she said, but this was a Chinese cohort and their diet is probably vastly different than those in the United States.
Other rosacea triggers, Dr. Shi said, are niacin-containing foods such as turkey, chicken breast, crustaceans, dried Shiitake mushrooms, peanuts, tuna, and liver, as well as cold drinks, and formalin-containing foods (fish, squid, tofu, wet noodles).
As the field of nutrigenics – how genes affect how the body responds to food – evolves, more answers about the impact of diet on these diseases will be forthcoming, Dr. Shi said.
In an interactive panel discussion, she was asked if she talks about diet with all her patients with acne, rosacea, and HS, or just those not responding to traditional therapy.
“I think it’s an important conversation to have,” Dr. Shi responded. “When I’m done with the medication [instructions], I say: ‘There is something else you can do to augment what I just told you.’ ” That’s when she explains the dietary information. She also has a handout on diet and routinely refers patients for dietary counseling.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Shi disclosed consulting, investigative and research funding from several sources, but not directly related to the content of her talk.
Since 1950, the terms “diet and skin” in the medical literature have markedly increased, said Vivian Shi, MD associate professor of dermatology at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, who talked about nutritional approaches for select skin diseases at MedscapeLive’s Women’s and Pediatric Dermatology Seminar.
Myths abound, but some associations of diet with skin diseases hold water, and she said.
Acne
What’s known, Dr. Shi said, is that the prevalence of acne is substantially lower in non-Westernized countries, and that diets in those countries generally have a low glycemic load, which decreases IGF-1 insulinlike growth factor 1 (IGF-1) concentrations, an accepted risk factor for acne. The Western diet also includes the hormonal effects of cow’s milk products.
Whey protein, which is popular as a supplement, isn’t good for acne, Dr. Shi said. It takes a couple of hours to digest, while casein protein digests more slowly, over 5-7 hours. If casein protein isn’t acceptable, good alternatives to whey protein are hemp seed, plant protein blends (peas, seeds, berries), egg white, brown rice isolate, and soy isolate protein.
Dairy products increase IGF-1 levels, hormonal mediators that can make acne worse. In addition, industrial cow’s milk can contain anabolic steroids and growth factor, leading to sebogenesis, Dr. Shi said. As for the type of milk, skim milk tends to be the most acnegenic and associated with the highest blood levels of IGF-1.
Supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids and gamma-linolenic acid improved mild to moderate acne in a double-blind, controlled study. Researchers randomized 45 patients with mild to moderate acne to an omega-3 fatty acid group (2,000 mg of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid), a gamma-linolenic acid group (borage oil with 400 mg gamma-linolenic acid) or a control group. After 10 weeks in both treatment groups, there was a significant reduction in inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions.
Those with acne are more likely to be deficient in Vitamin D, research suggests. Researchers also found that among those who had vitamin D deficiency, supplementing with 1,000 IU daily for 2 months reduced inflammatory lesions by 35% after 8 weeks, compared with a 6% reduction in the control group.
Other research has found that those with a low serum zinc level had more severe acne and that 30-200 mg of zinc orally for 2-4 months reduced inflammatory acne. However, Dr. Shi cautioned that those taking zinc for more than 2 months also need a copper supplement, as zinc reduces the amount of copper absorbed by the body.
Dr. Shi’s “do’s” diet list for acne patients is a follows: Paleolithic and Mediterranean diets, omega-3 fatty acids, gamma-linolenic acids, Vitamin D, zinc, tubers, legumes, vegetables, fruits, and fish.
Unknowns, she said, include chocolate, caffeine, green tea, and high salt.
Hidradenitis suppurativa
Patents with HS who follow a Mediterranean diet most closely have less severe disease, research has found. In this study, those patients with HS with the lowest adherence had a Sartorius HS score of 59.38, while those who followed it the most closely had a score of 39 (of 80).
In another study, patients with HS reported the following foods as exacerbating HS: sweets, bread/pasta/rice, dairy, and high-fat foods. Alleviating foods included vegetables, fruit, chicken, and fish.
Dr. Shi’s dietary recommendations for patients with HS: Follow a Mediterranean diet, avoid high fat foods and highly processed foods, and focus on eating more vegetables, fresh fruit, corn-based cereal, white meat, and fish.
A retrospective study of patients with Hurley stage 1 and 2 found that oral zinc gluconate, 90 mg a day, combined with 2% topical triclosan twice a day, resulted in significantly decreased HS scores and nodules and improved quality of life after 3 months. Expect vitamin D deficiency, she added.
Lastly, Dr. Shi recommended, if necessary, “weight loss to reduce the inflammatory burden.”
Rosacea
Dietary triggers for rosacea are thought to include high-fat foods, dairy foods, spicy foods, hot drinks, cinnamon, and vanilla.
A population-based case-control study in China, which evaluated 1,347 rosacea patients and 1,290 healthy controls, found that a high intake of fatty foods positively correlated with erythematotelangiectatic rosacea (ETR) and phymatous rosacea. High-frequency dairy intake negatively correlated with ETR and papulopustular rosacea, which was a surprise, she said. And in this study, no significant correlations were found between sweets, coffee, and spicy foods. That goes against the traditional thinking, she said, but this was a Chinese cohort and their diet is probably vastly different than those in the United States.
Other rosacea triggers, Dr. Shi said, are niacin-containing foods such as turkey, chicken breast, crustaceans, dried Shiitake mushrooms, peanuts, tuna, and liver, as well as cold drinks, and formalin-containing foods (fish, squid, tofu, wet noodles).
As the field of nutrigenics – how genes affect how the body responds to food – evolves, more answers about the impact of diet on these diseases will be forthcoming, Dr. Shi said.
In an interactive panel discussion, she was asked if she talks about diet with all her patients with acne, rosacea, and HS, or just those not responding to traditional therapy.
“I think it’s an important conversation to have,” Dr. Shi responded. “When I’m done with the medication [instructions], I say: ‘There is something else you can do to augment what I just told you.’ ” That’s when she explains the dietary information. She also has a handout on diet and routinely refers patients for dietary counseling.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Shi disclosed consulting, investigative and research funding from several sources, but not directly related to the content of her talk.
FROM MEDSCAPELIVE WOMEN’S & PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Alabama cites Roe decision in call to ban transgender health care
Alabama urged a federal court on June 28 to drop its block on the state’s ban on gender-affirming care for transgender youth, citing the Supreme Court’s recent decision to overturn Roe v. Wade.
Alabama Attorney General Steve Marshall said the high court ruled that abortion isn’t protected under the 14th Amendment because it’s not “deeply rooted” in the nation’s history, which he noted could be said about access to gender-affirming care as well, according to Axios.
“No one – adult or child – has a right to transitioning treatments that is deeply rooted in our Nation’s history and tradition,” he wrote in a court document.
“The State can thus regulate or prohibit those interventions for children, even if an adult wants the drugs for his child,” he wrote.
In May, a federal judge blocked part of Alabama’s Senate Bill 184, which makes it a felony for someone to “engage in or cause” certain types of medical care for transgender youths. The law, which was put in place in April, allows for criminal prosecution against doctors, parents, guardians, and anyone else who provides care to a minor. The penalties could result in up to 10 years in prison and up to $15,000 in fines.
At that time, U.S. District Judge Liles Burke issued an injunction to stop Alabama from enforcing the law and allow challenges, including one filed by the Department of Justice. Mr. Burke said the state provided “no credible evidence to show that transitioning medications are ‘experimental.’ ”
“While Defendants offer some evidence that transitioning medications pose certain risks, the uncontradicted record evidence is that at least twenty-two major medical associations in the United States endorse transitioning medications as well-established, evidence-based treatments for gender dysphoria in minors,” he wrote in the ruling.
Medical organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Psychological Association, and American Medical Association have urged governors to oppose legislation this year that would restrict gender-affirming medical care, saying that such laws could have negative effects on the mental health of transgender youths.
But on June 28, Mr. Marshall focused on the Constitution and what he believes the recent overturn of Roe implies.
“Just as the parental relationship does not unlock a Due Process right allowing parents to obtain medical marijuana or abortions for their children, neither does it unlock a right to transitioning treatments,” he wrote.
“The Constitution reserves to the State – not courts or medical interest groups – the authority to determine that these sterilizing interventions are too dangerous for minors,” he said.
Since the Supreme Court overturned Roe, people have expressed concerns that lawsuits could now target several rights that are protected under the 14th Amendment, including same-sex relationships, marriage equality, and access to contraceptives.
Justice Clarence Thomas, who wrote a concurring opinion to the majority decision, said the Supreme Court, “in future cases” should reconsider “substantive due process precedents” under previous landmark cases such as Griswold v. Connecticut, Lawrence v. Texas, and Obergefell v. Hodges.
At the same time, Justice Brett Kavanaugh, who also wrote a concurring opinion, said the decision to overturn Roe was only focused on abortion, saying it “does not mean the overruling of those precedents, and does not threaten or cast doubt on those precedents.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Alabama urged a federal court on June 28 to drop its block on the state’s ban on gender-affirming care for transgender youth, citing the Supreme Court’s recent decision to overturn Roe v. Wade.
Alabama Attorney General Steve Marshall said the high court ruled that abortion isn’t protected under the 14th Amendment because it’s not “deeply rooted” in the nation’s history, which he noted could be said about access to gender-affirming care as well, according to Axios.
“No one – adult or child – has a right to transitioning treatments that is deeply rooted in our Nation’s history and tradition,” he wrote in a court document.
“The State can thus regulate or prohibit those interventions for children, even if an adult wants the drugs for his child,” he wrote.
In May, a federal judge blocked part of Alabama’s Senate Bill 184, which makes it a felony for someone to “engage in or cause” certain types of medical care for transgender youths. The law, which was put in place in April, allows for criminal prosecution against doctors, parents, guardians, and anyone else who provides care to a minor. The penalties could result in up to 10 years in prison and up to $15,000 in fines.
At that time, U.S. District Judge Liles Burke issued an injunction to stop Alabama from enforcing the law and allow challenges, including one filed by the Department of Justice. Mr. Burke said the state provided “no credible evidence to show that transitioning medications are ‘experimental.’ ”
“While Defendants offer some evidence that transitioning medications pose certain risks, the uncontradicted record evidence is that at least twenty-two major medical associations in the United States endorse transitioning medications as well-established, evidence-based treatments for gender dysphoria in minors,” he wrote in the ruling.
Medical organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Psychological Association, and American Medical Association have urged governors to oppose legislation this year that would restrict gender-affirming medical care, saying that such laws could have negative effects on the mental health of transgender youths.
But on June 28, Mr. Marshall focused on the Constitution and what he believes the recent overturn of Roe implies.
“Just as the parental relationship does not unlock a Due Process right allowing parents to obtain medical marijuana or abortions for their children, neither does it unlock a right to transitioning treatments,” he wrote.
“The Constitution reserves to the State – not courts or medical interest groups – the authority to determine that these sterilizing interventions are too dangerous for minors,” he said.
Since the Supreme Court overturned Roe, people have expressed concerns that lawsuits could now target several rights that are protected under the 14th Amendment, including same-sex relationships, marriage equality, and access to contraceptives.
Justice Clarence Thomas, who wrote a concurring opinion to the majority decision, said the Supreme Court, “in future cases” should reconsider “substantive due process precedents” under previous landmark cases such as Griswold v. Connecticut, Lawrence v. Texas, and Obergefell v. Hodges.
At the same time, Justice Brett Kavanaugh, who also wrote a concurring opinion, said the decision to overturn Roe was only focused on abortion, saying it “does not mean the overruling of those precedents, and does not threaten or cast doubt on those precedents.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Alabama urged a federal court on June 28 to drop its block on the state’s ban on gender-affirming care for transgender youth, citing the Supreme Court’s recent decision to overturn Roe v. Wade.
Alabama Attorney General Steve Marshall said the high court ruled that abortion isn’t protected under the 14th Amendment because it’s not “deeply rooted” in the nation’s history, which he noted could be said about access to gender-affirming care as well, according to Axios.
“No one – adult or child – has a right to transitioning treatments that is deeply rooted in our Nation’s history and tradition,” he wrote in a court document.
“The State can thus regulate or prohibit those interventions for children, even if an adult wants the drugs for his child,” he wrote.
In May, a federal judge blocked part of Alabama’s Senate Bill 184, which makes it a felony for someone to “engage in or cause” certain types of medical care for transgender youths. The law, which was put in place in April, allows for criminal prosecution against doctors, parents, guardians, and anyone else who provides care to a minor. The penalties could result in up to 10 years in prison and up to $15,000 in fines.
At that time, U.S. District Judge Liles Burke issued an injunction to stop Alabama from enforcing the law and allow challenges, including one filed by the Department of Justice. Mr. Burke said the state provided “no credible evidence to show that transitioning medications are ‘experimental.’ ”
“While Defendants offer some evidence that transitioning medications pose certain risks, the uncontradicted record evidence is that at least twenty-two major medical associations in the United States endorse transitioning medications as well-established, evidence-based treatments for gender dysphoria in minors,” he wrote in the ruling.
Medical organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Psychological Association, and American Medical Association have urged governors to oppose legislation this year that would restrict gender-affirming medical care, saying that such laws could have negative effects on the mental health of transgender youths.
But on June 28, Mr. Marshall focused on the Constitution and what he believes the recent overturn of Roe implies.
“Just as the parental relationship does not unlock a Due Process right allowing parents to obtain medical marijuana or abortions for their children, neither does it unlock a right to transitioning treatments,” he wrote.
“The Constitution reserves to the State – not courts or medical interest groups – the authority to determine that these sterilizing interventions are too dangerous for minors,” he said.
Since the Supreme Court overturned Roe, people have expressed concerns that lawsuits could now target several rights that are protected under the 14th Amendment, including same-sex relationships, marriage equality, and access to contraceptives.
Justice Clarence Thomas, who wrote a concurring opinion to the majority decision, said the Supreme Court, “in future cases” should reconsider “substantive due process precedents” under previous landmark cases such as Griswold v. Connecticut, Lawrence v. Texas, and Obergefell v. Hodges.
At the same time, Justice Brett Kavanaugh, who also wrote a concurring opinion, said the decision to overturn Roe was only focused on abortion, saying it “does not mean the overruling of those precedents, and does not threaten or cast doubt on those precedents.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Study provides consensus on lab monitoring during isotretinoin therapy
For generally ideally within a month prior to the start of treatment, and a second time at peak dose.
Other tests such as complete blood cell counts and basic metabolic panels as well as specific laboratory tests such as LDL and HDL cholesterol should not be routinely monitored.
Those are key conclusions from a Delphi consensus study that included 22 acne experts from five continents and was published in JAMA Dermatology.
“Our results apply findings from recent literature and are in accordance with recent studies that have recommended against excessive laboratory monitoring,” senior corresponding author Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPA, MPH, and coauthors wrote. “For instance, several studies in both teenagers and adults have shown that routine complete blood cell count laboratory tests are unnecessary without suspicion of an underlying abnormality and that rare abnormalities, if present, either resolved or remained stable without clinical impact on treatment. Likewise, liver function tests and lipid panels ordered at baseline and after 2 months of therapy were deemed sufficient if the clinical context and results do not suggest potential abnormalities.”
The authors also noted that, while published acne management guidelines exist, such as the American Academy of Dermatology work group guidelines and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guideline, “the specific recommendations surrounding laboratory monitoring frequency are nonstandardized and often nonspecific.”
To establish a consensus for isotretinoin laboratory monitoring, Dr. Mostaghimi, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues used a Delphi process to administer four rounds of electronic surveys to 22 board-certified dermatologists between 2021 and 2022. The primary outcome measured was whether participants could reach consensus on key isotretinoin lab monitoring parameters. Responses that failed to reach a threshold of 70% indicated no consensus.
The surveyed dermatologists had been in practice for a mean of 23.7 years, 54.5% were female, 54.5% practiced in an academic setting, and 63.9% were based in North America. They reached consensus for checking ALT within a month prior to initiation (89.5%) and at peak dose (89.5%), but not checking monthly (76.2%) or after completing treatment (73.7%). They also reached consensus on checking triglycerides within a month prior to initiation (89.5%) and at peak dose (78.9%) but not to check monthly (84.2%) or after completing treatment (73.7%).
Meanwhile, consensus was achieved for not checking complete blood cell count or basic metabolic panel parameters at any point during isotretinoin treatment (all > 70%), as well as not checking gamma-glutamyl transferase (78.9%), bilirubin (81.0%), albumin (72.7%), total protein (72.7%), LDL cholesterol (73.7%), HDL cholesterol (73.7%), or C-reactive protein (77.3%).
“Additional research is required to determine best practices for laboratory measures that did not reach consensus,” the authors wrote. The study results “are intended to guide appropriate clinical decision-making,” they added. “Although our recommendations cannot replace clinical judgment based on the unique circumstances of individual patients, we believe they provide a framework for management of a typical, otherwise healthy patient being treated with isotretinoin for acne. More routine monitoring, or reduced monitoring, should be considered on a case-by-case basis accounting for the unique medical history, circumstances, and baseline abnormalities, if present, of each patient.”
“Practicing dermatologists, including myself, routinely check blood laboratory values during isotretinoin treatment,” said Lawrence J. Green, MD, clinical professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study. “Even though just a small number of U.S.-based and international acne researchers were involved in this Delphi consensus statement, this article still makes us practicing clinicians feel more comfortable in checking fewer lab chemistries and also less frequently checking labs when we use isotretinoin.
“That said, I don’t think most of us are ready, because of legal reasons, to do that infrequent monitoring” during isotretinoin therapy, Dr. Green added. “I think most dermatologists do not routinely perform CBCs anymore, but we still feel obligated to check triglycerides and liver function more frequently” than recommended in the new study.
Dr. Mostaghimi reported receiving grants and personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Eli Lilly, personal fees and licensing from Concert, personal fees from Bioniz, holds equity and advisory board membership from Hims & Hers and Figure 1, personal fees from Digital Diagnostics, and personal fees from AbbVie outside the submitted work. Other authors reported serving as an adviser, a speaker consultant, investigator, and/or board member, or having received honoraria from different pharmaceutical companies; several authors had no disclosures. Dr. Green disclosed that he is a speaker, consultant, or investigator for numerous pharmaceutical companies.
For generally ideally within a month prior to the start of treatment, and a second time at peak dose.
Other tests such as complete blood cell counts and basic metabolic panels as well as specific laboratory tests such as LDL and HDL cholesterol should not be routinely monitored.
Those are key conclusions from a Delphi consensus study that included 22 acne experts from five continents and was published in JAMA Dermatology.
“Our results apply findings from recent literature and are in accordance with recent studies that have recommended against excessive laboratory monitoring,” senior corresponding author Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPA, MPH, and coauthors wrote. “For instance, several studies in both teenagers and adults have shown that routine complete blood cell count laboratory tests are unnecessary without suspicion of an underlying abnormality and that rare abnormalities, if present, either resolved or remained stable without clinical impact on treatment. Likewise, liver function tests and lipid panels ordered at baseline and after 2 months of therapy were deemed sufficient if the clinical context and results do not suggest potential abnormalities.”
The authors also noted that, while published acne management guidelines exist, such as the American Academy of Dermatology work group guidelines and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guideline, “the specific recommendations surrounding laboratory monitoring frequency are nonstandardized and often nonspecific.”
To establish a consensus for isotretinoin laboratory monitoring, Dr. Mostaghimi, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues used a Delphi process to administer four rounds of electronic surveys to 22 board-certified dermatologists between 2021 and 2022. The primary outcome measured was whether participants could reach consensus on key isotretinoin lab monitoring parameters. Responses that failed to reach a threshold of 70% indicated no consensus.
The surveyed dermatologists had been in practice for a mean of 23.7 years, 54.5% were female, 54.5% practiced in an academic setting, and 63.9% were based in North America. They reached consensus for checking ALT within a month prior to initiation (89.5%) and at peak dose (89.5%), but not checking monthly (76.2%) or after completing treatment (73.7%). They also reached consensus on checking triglycerides within a month prior to initiation (89.5%) and at peak dose (78.9%) but not to check monthly (84.2%) or after completing treatment (73.7%).
Meanwhile, consensus was achieved for not checking complete blood cell count or basic metabolic panel parameters at any point during isotretinoin treatment (all > 70%), as well as not checking gamma-glutamyl transferase (78.9%), bilirubin (81.0%), albumin (72.7%), total protein (72.7%), LDL cholesterol (73.7%), HDL cholesterol (73.7%), or C-reactive protein (77.3%).
“Additional research is required to determine best practices for laboratory measures that did not reach consensus,” the authors wrote. The study results “are intended to guide appropriate clinical decision-making,” they added. “Although our recommendations cannot replace clinical judgment based on the unique circumstances of individual patients, we believe they provide a framework for management of a typical, otherwise healthy patient being treated with isotretinoin for acne. More routine monitoring, or reduced monitoring, should be considered on a case-by-case basis accounting for the unique medical history, circumstances, and baseline abnormalities, if present, of each patient.”
“Practicing dermatologists, including myself, routinely check blood laboratory values during isotretinoin treatment,” said Lawrence J. Green, MD, clinical professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study. “Even though just a small number of U.S.-based and international acne researchers were involved in this Delphi consensus statement, this article still makes us practicing clinicians feel more comfortable in checking fewer lab chemistries and also less frequently checking labs when we use isotretinoin.
“That said, I don’t think most of us are ready, because of legal reasons, to do that infrequent monitoring” during isotretinoin therapy, Dr. Green added. “I think most dermatologists do not routinely perform CBCs anymore, but we still feel obligated to check triglycerides and liver function more frequently” than recommended in the new study.
Dr. Mostaghimi reported receiving grants and personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Eli Lilly, personal fees and licensing from Concert, personal fees from Bioniz, holds equity and advisory board membership from Hims & Hers and Figure 1, personal fees from Digital Diagnostics, and personal fees from AbbVie outside the submitted work. Other authors reported serving as an adviser, a speaker consultant, investigator, and/or board member, or having received honoraria from different pharmaceutical companies; several authors had no disclosures. Dr. Green disclosed that he is a speaker, consultant, or investigator for numerous pharmaceutical companies.
For generally ideally within a month prior to the start of treatment, and a second time at peak dose.
Other tests such as complete blood cell counts and basic metabolic panels as well as specific laboratory tests such as LDL and HDL cholesterol should not be routinely monitored.
Those are key conclusions from a Delphi consensus study that included 22 acne experts from five continents and was published in JAMA Dermatology.
“Our results apply findings from recent literature and are in accordance with recent studies that have recommended against excessive laboratory monitoring,” senior corresponding author Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPA, MPH, and coauthors wrote. “For instance, several studies in both teenagers and adults have shown that routine complete blood cell count laboratory tests are unnecessary without suspicion of an underlying abnormality and that rare abnormalities, if present, either resolved or remained stable without clinical impact on treatment. Likewise, liver function tests and lipid panels ordered at baseline and after 2 months of therapy were deemed sufficient if the clinical context and results do not suggest potential abnormalities.”
The authors also noted that, while published acne management guidelines exist, such as the American Academy of Dermatology work group guidelines and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guideline, “the specific recommendations surrounding laboratory monitoring frequency are nonstandardized and often nonspecific.”
To establish a consensus for isotretinoin laboratory monitoring, Dr. Mostaghimi, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and colleagues used a Delphi process to administer four rounds of electronic surveys to 22 board-certified dermatologists between 2021 and 2022. The primary outcome measured was whether participants could reach consensus on key isotretinoin lab monitoring parameters. Responses that failed to reach a threshold of 70% indicated no consensus.
The surveyed dermatologists had been in practice for a mean of 23.7 years, 54.5% were female, 54.5% practiced in an academic setting, and 63.9% were based in North America. They reached consensus for checking ALT within a month prior to initiation (89.5%) and at peak dose (89.5%), but not checking monthly (76.2%) or after completing treatment (73.7%). They also reached consensus on checking triglycerides within a month prior to initiation (89.5%) and at peak dose (78.9%) but not to check monthly (84.2%) or after completing treatment (73.7%).
Meanwhile, consensus was achieved for not checking complete blood cell count or basic metabolic panel parameters at any point during isotretinoin treatment (all > 70%), as well as not checking gamma-glutamyl transferase (78.9%), bilirubin (81.0%), albumin (72.7%), total protein (72.7%), LDL cholesterol (73.7%), HDL cholesterol (73.7%), or C-reactive protein (77.3%).
“Additional research is required to determine best practices for laboratory measures that did not reach consensus,” the authors wrote. The study results “are intended to guide appropriate clinical decision-making,” they added. “Although our recommendations cannot replace clinical judgment based on the unique circumstances of individual patients, we believe they provide a framework for management of a typical, otherwise healthy patient being treated with isotretinoin for acne. More routine monitoring, or reduced monitoring, should be considered on a case-by-case basis accounting for the unique medical history, circumstances, and baseline abnormalities, if present, of each patient.”
“Practicing dermatologists, including myself, routinely check blood laboratory values during isotretinoin treatment,” said Lawrence J. Green, MD, clinical professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study. “Even though just a small number of U.S.-based and international acne researchers were involved in this Delphi consensus statement, this article still makes us practicing clinicians feel more comfortable in checking fewer lab chemistries and also less frequently checking labs when we use isotretinoin.
“That said, I don’t think most of us are ready, because of legal reasons, to do that infrequent monitoring” during isotretinoin therapy, Dr. Green added. “I think most dermatologists do not routinely perform CBCs anymore, but we still feel obligated to check triglycerides and liver function more frequently” than recommended in the new study.
Dr. Mostaghimi reported receiving grants and personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Eli Lilly, personal fees and licensing from Concert, personal fees from Bioniz, holds equity and advisory board membership from Hims & Hers and Figure 1, personal fees from Digital Diagnostics, and personal fees from AbbVie outside the submitted work. Other authors reported serving as an adviser, a speaker consultant, investigator, and/or board member, or having received honoraria from different pharmaceutical companies; several authors had no disclosures. Dr. Green disclosed that he is a speaker, consultant, or investigator for numerous pharmaceutical companies.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Cutaneous Body Image: How the Mental Health Benefits of Treating Dermatologic Disease Support Military Readiness in Service Members
According to the US Department of Defense, the term readiness refers to the ability to recruit, train, deploy, and sustain military forces that will be ready to “fight tonight” and succeed in combat. Readiness is a top priority for military medicine, which functions to diagnose, treat, and rehabilitate service members so that they can return to the fight. This central concept drives programs across the military—from operational training events to the establishment of medical and dental standards. Readiness is tracked and scrutinized constantly, and although it is a shared responsibility, efforts to increase and sustain readiness often fall on support staff and military medical providers.
In recent years, there has been a greater awareness of the negative effects of mental illness, low morale, and suicidality on military readiness. In 2013, suicide accounted for 28.1% of all deaths that occurred in the US Armed Forces.1 Put frankly, suicide was one of the leading causes of death among military members.
The most recent Marine Corps Order regarding the Marine Corps Suicide Prevention Program stated that “suicidal behaviors are a barrier to readiness that have lasting effects on Marines and Service Members attached to Marine Commands. . .Families, and the Marine Corps.” It goes on to say that “[e]ffective suicide prevention requires coordinated efforts within a prevention framework dedicated to promoting mental, physical, spiritual, and social fitness. . .[and] mitigating stressors that interfere with mission readiness.”2 This statement supports the notion that preventing suicide is not just about treating mental illness; it also involves maximizing physical, spiritual, and social fitness. Although it is well established that various mental health disorders are associated with an increased risk for suicide, it is worth noting that, in one study, only half of individuals who died by suicide had a mental health disorder diagnosed prior to their death.3 These statistics translate to the military. The 2015 Department of Defense Suicide Event Report noted that only 28% of service members who died by suicide and 22% of members with attempted suicide had been documented as having sought mental health care and disclosed their potential for self-harm prior to the event.1,4 In 2018, a study published by Ursano et al5 showed that 36.3% of US soldiers with a documented suicide attempt (N=9650) had no prior mental health diagnoses.
Expanding the scope to include mental health issues in general, only 29% of service members who reported experiencing a mental health problem actually sought mental health care in that same period. Overall, approximately 40% of service members with a reported perceived need for mental health care actually sought care over their entire course of service time,1 which raises concern for a large population of undiagnosed and undertreated mental illnesses across the military. In response to these statistics, Reger et al3 posited that it is “essential that suicide prevention efforts move outside the silo of mental health.” The authors went on to challenge health care providers across all specialties and civilians alike to take responsibility in understanding, recognizing, and mitigating risk factors for suicide in the general population.3 Although treating a service member’s acne or offering to stand duty for a service member who has been under a great deal of stress in their personal life may appear to be indirect ways of reducing suicide in the US military, they actually may be the most critical means of prevention in a culture that emphasizes resilience and self-reliance, where seeking help for mental health struggles could be perceived as weakness.1
In this review article, we discuss the concept of cutaneous body image (CBI) and its associated outcomes on health, satisfaction, and quality of life in military service members. We then examine the intersections between common dermatologic conditions, CBI, and mental health and explore the ability and role of the military dermatologist to serve as a positive influence on military readiness.
What is cutaneous body image?
Cutaneous body image is “the individual’s mental perception of his or her skin and its appendages (ie, hair, nails).”6 It is measured objectively using the Cutaneous Body Image Scale, a questionnaire that includes 7 items related to the overall satisfaction with the appearance of skin, color of skin, skin of the face, complexion of the face, hair, fingernails, and toenails. Each question is rated using a 10-point Likert scale (0=not at all; 10=very markedly).6
Some degree of CBI dissatisfaction is expected and has been shown in the general population at large; for example, more than 56% of women older than 30 years report some degree of dissatisfaction with their skin. Similarly, data from the American Society of Plastic Surgeons showed that while 10.9 million cosmetic procedures were performed in 2006, 9.1 million of them involved minimally invasive procedures such as botulinum toxin type A injections with the purpose of skin rejuvenation and improvement of facial appearance.7 However, lower than average CBI can contribute to considerable psychosocial morbidity. Dissatisfaction with CBI is associated with self-consciousness, feelings of inferiority, and social exclusion. These symptoms can be grouped into a construct called interpersonal sensitivity (IS). A 2013 study by Gupta and Gupta6 investigated the relationship between CBI, IS, and suicidal ideation among 312 consenting nonclinical participants in Canada. The study found that greater dissatisfaction with an individual’s CBI correlated to increased IS and increased rates of suicidal ideation and intentional self-injury.6
Cutaneous body image is particularly relevant to dermatologists, as many common dermatoses can cause cosmetically disfiguring skin conditions; for example, acne and rosacea have the propensity to cause notable disfigurement to the facial unit. Other common conditions such as atopic dermatitis or psoriasis can flare with stress and thereby throw patients into a vicious cycle of physical and psychosocial stress caused by social stigma, cosmetic disfigurement, and reduced CBI, in turn leading to worsening of the disease at hand. Dermatologists need to be aware that common dermatoses can impact a patient’s mental health via poor CBI.8 Similarly, dermatologists may be empowered by the awareness that treating common dermatoses, especially those associated with poor cosmesis, have 2-fold benefits—on the skin condition itself and on the patient’s mental health.
How are common dermatoses associated with mental health?
Acne—Acne is one of the most common skin diseases, so much so that in many cases acne has become an accepted and expected part of adolescence and young adulthood. Studies estimate that 85% of the US population aged 12 to 25 years have acne.9 For some adults, acne persists even longer, with 1% to 5% of adults reporting to have active lesions at 40 years of age.10 Acne is a multifactorial skin disease of the pilosebaceous unit that results in the development of inflammatory papules, pustules, and cysts. These lesions are most common on the face but can extend to other areas of the body, such as the chest and back.11 Although the active lesions can be painful and disfiguring, if left untreated, acne may lead to permanent disfigurement and scarring, which can have long-lasting psychosocial impacts.
Individuals with acne have an increased likelihood of self-consciousness, social isolation, depression, and suicidal ideation. This relationship has been well established for decades. In the 1990s, a small study reported that 7 of 16 (43.8%) cases of completed suicide in dermatology patients were in patients with acne.12 In a recent meta-analysis including 2,276,798 participants across 5 separate studies, researchers found that suicide was positively associated with acne, carrying an odds ratio of 1.50 (95% CI, 1.09-2.06).13
Rosacea—Rosacea is a common chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by facial erythema, telangiectasia, phymatous changes, papules, pustules, and ocular irritation. The estimated worldwide prevalence is 5.5%.14 In addition to discomfort and irritation of the skin and eyes, rosacea often carries a higher risk of psychological and psychosocial distress due to its potentially disfiguring nature. Rosacea patients are at greater risk for having anxiety disorders and depression,15 and a 2018 study by Alinia et al16 showed that there is a direct relationship between rosacea severity and the actual level of depression.Although disease improvement certainly leads to improvements in quality of life and psychosocial status, Alinia et al16 noted that depression often is associated with poor treatment adherence due to poor motivation and hopelessness. It is critical that dermatologists are aware of these associations and maintain close follow-up with patients, even when the condition is not life-threatening, such as rosacea.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa—Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the pilosebaceous unit that is characterized by the development of painful, malodorous, draining abscesses, fistulas, sinus tracts, and scars in sensitive areas such as the axillae, breasts, groin, and perineum.17 In severe cases, surgery may be required to excise affected areas. Compared to other cutaneous disease, HS is considered one of the most life-impacting disorders.18 The physical symptoms themselves often are debilitating, and patients often report considerable psychosocial and psychological impairment with decreased quality of life. Major depression frequently is noted, with 1 in 4 adults with HS also being depressed. In a large cross-sectional analysis of 38,140 adults and 1162 pediatric patients with HS, Wright et al17 reported the prevalence of depression among adults with HS as 30.0% compared to 16.9% in healthy controls. In children, the prevalence of depression was 11.7% compared to 4.1% in the general population.17 Similarly, 1 out of every 5 patients with HS experiences anxiety.18
In the military population, HS often can be duty limiting. The disease requires constant attention to wound care and frequent medical visits. For many service members operating in field training or combat environments, opportunities for and access to showers and basic hygiene is limited. Uniforms and additional necessary combat gear often are thick and occlusive. Taken as a whole, these factors may contribute to worsening of the disease and in severe cases are simply not conducive to the successful management of the condition. However, given the most commonly involved body areas and the nature of the disease, many service members with HS may feel embarrassed to disclose their condition. In uniform, the disease is not easily visible, and for unaware persons, the frequency of medical visits and limited duty status may seem unnecessary. This perception of a service member’s lack of productivity due to an unseen disease may further add to the psychosocial stress they experience.
The treatments for acne, rosacea, and HS are outlined in the eTable.11,19 Also noted are specific considerations when managing an active-duty service member due to various operational duty restrictions and constraints.
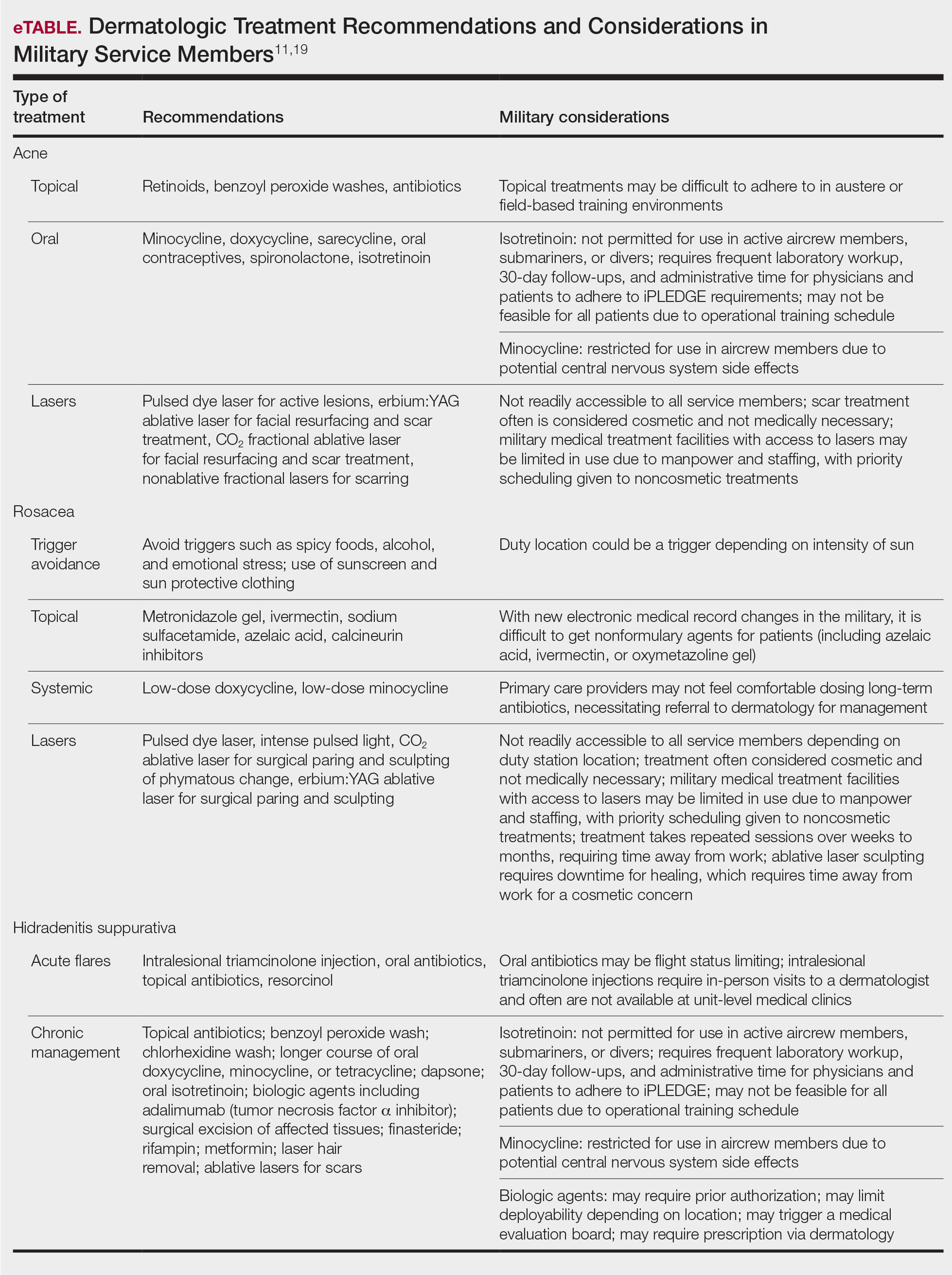
Final Thoughts
Maintaining readiness in the military is essential to the ability to not only “fight tonight” but also to win tonight in whatever operational or combat mission a service member may be. Although many factors impact readiness, the rates of suicide within the armed forces cannot be ignored. Suicide not only eliminates the readiness of the deceased service member but has lasting ripple effects on the overall readiness of their unit and command at large. Most suicides in the military occur in personnel with no prior documented mental health diagnoses or treatment. Therefore, it is the responsibility of all service members to recognize and mitigate stressors and risk factors that may lead to mental health distress and suicidality. In the medical corps, this translates to a responsibility of all medical specialists to recognize and understand unique risk factors for suicidality and to do as much as they can to reduce these risks. For military dermatologists and for civilian physicians treating military service members, it is imperative to predict and understand the relationship between common dermatoses; reduced satisfaction with CBI; and increased risk for mental health illness, self-harm, and suicide. Military dermatologists, as well as other specialists, may be limited in the care they are able to provide due to manpower, staffing, demand, and institutional guidelines; however, to better serve those who serve in a holistic manner, consideration must be given to rethink what is “medically essential” and “cosmetic” and leverage the available skills, techniques, and equipment to increase the readiness of the force.

- Ghahramanlou-Holloway M, LaCroix JM, Koss K, et al. Outpatient mental health treatment utilization and military career impact in the United States Marine Corps. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15:828. doi:10.3390/ijerph15040828
- Ottignon DA. Marine Corps Suicide Prevention System (MCSPS). Marine Corps Order 1720.2A. 2021. Headquarters United States Marine Corps. Published August 2, 2021. Accessed May 25, 2022. https://www.marines.mil/Portals/1/Publications/MCO%201720.2A.pdf?ver=QPxZ_qMS-X-d037B65N9Tg%3d%3d
- Reger MA, Smolenski DJ, Carter SP. Suicide prevention in the US Army: a mission for more than mental health clinicians. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75:991-992. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.2042
- Pruitt LD, Smolenski DJ, Bush NE, et al. Department of Defense Suicide Event Report Calendar Year 2015 Annual Report. National Center for Telehealth & Technology (T2); 2016. Accessed May 20, 2022. https://health.mil/Military-Health-Topics/Centers-of-Excellence/Psychological-Health-Center-of-Excellence/Department-of-Defense-Suicide-Event-Report
- Ursano RJ, Kessler RC, Naifeh JA, et al. Risk factors associated with attempted suicide among US Army soldiers without a history of mental health diagnosis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75:1022-1032. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.2069
- Gupta MA, Gupta AK. Cutaneous body image dissatisfaction and suicidal ideation: mediation by interpersonal sensitivity. J Psychosom Res. 2013;75:55-59. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychores.2013.01.015
- Gupta MA, Gupta AK. Evaluation of cutaneous body image dissatisfaction in the dermatology patient. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:72-79. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2011.11.010
- Hinkley SB, Holub SC, Menter A. The validity of cutaneous body image as a construct and as a mediator of the relationship between cutaneous disease and mental health. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020;10:203-211. doi:10.1007/s13555-020-00351-5
- Stamu-O’Brien C, Jafferany M, Carniciu S, et al. Psychodermatology of acne: psychological aspects and effects of acne vulgaris. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:1080-1083. doi:10.1111/jocd.13765
- Sood S, Jafferany M, Vinaya Kumar S. Depression, psychiatric comorbidities, and psychosocial implications associated with acne vulgaris. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19:3177-3182. doi:10.1111/jocd.13753
- Brahe C, Peters K. Fighting acne for the fighting forces. Cutis. 2020;106:18-20, 22. doi:10.12788/cutis.0057
- Cotterill JA, Cunliffe WJ. Suicide in dermatological patients. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:246-250.
- Xu S, Zhu Y, Hu H, et al. The analysis of acne increasing suicide risk. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:E26035. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000026035
- Chen M, Deng Z, Huang Y, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of anxiety and depression in rosacea patients: a cross-sectional study in China [published online June 16, 2021]. Front Psychiatry. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2021.659171
- Incel Uysal P, Akdogan N, Hayran Y, et al. Rosacea associated with increased risk of generalized anxiety disorder: a case-control study of prevalence and risk of anxiety in patients with rosacea. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94:704-709. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2019.03.002
- Alinia H, Cardwell LA, Tuchayi SM, et al. Screening for depression in rosacea patients. Cutis. 2018;102:36-38.
- Wright S, Strunk A, Garg A. Prevalence of depression among children, adolescents, and adults with hidradenitis suppurativa [published online June 16, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.843
- Misitzis A, Goldust M, Jafferany M, et al. Psychiatric comorbidities in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13541. doi:10.1111/dth.13541
- Bolognia J, Schaffer J, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017.
According to the US Department of Defense, the term readiness refers to the ability to recruit, train, deploy, and sustain military forces that will be ready to “fight tonight” and succeed in combat. Readiness is a top priority for military medicine, which functions to diagnose, treat, and rehabilitate service members so that they can return to the fight. This central concept drives programs across the military—from operational training events to the establishment of medical and dental standards. Readiness is tracked and scrutinized constantly, and although it is a shared responsibility, efforts to increase and sustain readiness often fall on support staff and military medical providers.
In recent years, there has been a greater awareness of the negative effects of mental illness, low morale, and suicidality on military readiness. In 2013, suicide accounted for 28.1% of all deaths that occurred in the US Armed Forces.1 Put frankly, suicide was one of the leading causes of death among military members.
The most recent Marine Corps Order regarding the Marine Corps Suicide Prevention Program stated that “suicidal behaviors are a barrier to readiness that have lasting effects on Marines and Service Members attached to Marine Commands. . .Families, and the Marine Corps.” It goes on to say that “[e]ffective suicide prevention requires coordinated efforts within a prevention framework dedicated to promoting mental, physical, spiritual, and social fitness. . .[and] mitigating stressors that interfere with mission readiness.”2 This statement supports the notion that preventing suicide is not just about treating mental illness; it also involves maximizing physical, spiritual, and social fitness. Although it is well established that various mental health disorders are associated with an increased risk for suicide, it is worth noting that, in one study, only half of individuals who died by suicide had a mental health disorder diagnosed prior to their death.3 These statistics translate to the military. The 2015 Department of Defense Suicide Event Report noted that only 28% of service members who died by suicide and 22% of members with attempted suicide had been documented as having sought mental health care and disclosed their potential for self-harm prior to the event.1,4 In 2018, a study published by Ursano et al5 showed that 36.3% of US soldiers with a documented suicide attempt (N=9650) had no prior mental health diagnoses.
Expanding the scope to include mental health issues in general, only 29% of service members who reported experiencing a mental health problem actually sought mental health care in that same period. Overall, approximately 40% of service members with a reported perceived need for mental health care actually sought care over their entire course of service time,1 which raises concern for a large population of undiagnosed and undertreated mental illnesses across the military. In response to these statistics, Reger et al3 posited that it is “essential that suicide prevention efforts move outside the silo of mental health.” The authors went on to challenge health care providers across all specialties and civilians alike to take responsibility in understanding, recognizing, and mitigating risk factors for suicide in the general population.3 Although treating a service member’s acne or offering to stand duty for a service member who has been under a great deal of stress in their personal life may appear to be indirect ways of reducing suicide in the US military, they actually may be the most critical means of prevention in a culture that emphasizes resilience and self-reliance, where seeking help for mental health struggles could be perceived as weakness.1
In this review article, we discuss the concept of cutaneous body image (CBI) and its associated outcomes on health, satisfaction, and quality of life in military service members. We then examine the intersections between common dermatologic conditions, CBI, and mental health and explore the ability and role of the military dermatologist to serve as a positive influence on military readiness.
What is cutaneous body image?
Cutaneous body image is “the individual’s mental perception of his or her skin and its appendages (ie, hair, nails).”6 It is measured objectively using the Cutaneous Body Image Scale, a questionnaire that includes 7 items related to the overall satisfaction with the appearance of skin, color of skin, skin of the face, complexion of the face, hair, fingernails, and toenails. Each question is rated using a 10-point Likert scale (0=not at all; 10=very markedly).6
Some degree of CBI dissatisfaction is expected and has been shown in the general population at large; for example, more than 56% of women older than 30 years report some degree of dissatisfaction with their skin. Similarly, data from the American Society of Plastic Surgeons showed that while 10.9 million cosmetic procedures were performed in 2006, 9.1 million of them involved minimally invasive procedures such as botulinum toxin type A injections with the purpose of skin rejuvenation and improvement of facial appearance.7 However, lower than average CBI can contribute to considerable psychosocial morbidity. Dissatisfaction with CBI is associated with self-consciousness, feelings of inferiority, and social exclusion. These symptoms can be grouped into a construct called interpersonal sensitivity (IS). A 2013 study by Gupta and Gupta6 investigated the relationship between CBI, IS, and suicidal ideation among 312 consenting nonclinical participants in Canada. The study found that greater dissatisfaction with an individual’s CBI correlated to increased IS and increased rates of suicidal ideation and intentional self-injury.6
Cutaneous body image is particularly relevant to dermatologists, as many common dermatoses can cause cosmetically disfiguring skin conditions; for example, acne and rosacea have the propensity to cause notable disfigurement to the facial unit. Other common conditions such as atopic dermatitis or psoriasis can flare with stress and thereby throw patients into a vicious cycle of physical and psychosocial stress caused by social stigma, cosmetic disfigurement, and reduced CBI, in turn leading to worsening of the disease at hand. Dermatologists need to be aware that common dermatoses can impact a patient’s mental health via poor CBI.8 Similarly, dermatologists may be empowered by the awareness that treating common dermatoses, especially those associated with poor cosmesis, have 2-fold benefits—on the skin condition itself and on the patient’s mental health.
How are common dermatoses associated with mental health?
Acne—Acne is one of the most common skin diseases, so much so that in many cases acne has become an accepted and expected part of adolescence and young adulthood. Studies estimate that 85% of the US population aged 12 to 25 years have acne.9 For some adults, acne persists even longer, with 1% to 5% of adults reporting to have active lesions at 40 years of age.10 Acne is a multifactorial skin disease of the pilosebaceous unit that results in the development of inflammatory papules, pustules, and cysts. These lesions are most common on the face but can extend to other areas of the body, such as the chest and back.11 Although the active lesions can be painful and disfiguring, if left untreated, acne may lead to permanent disfigurement and scarring, which can have long-lasting psychosocial impacts.
Individuals with acne have an increased likelihood of self-consciousness, social isolation, depression, and suicidal ideation. This relationship has been well established for decades. In the 1990s, a small study reported that 7 of 16 (43.8%) cases of completed suicide in dermatology patients were in patients with acne.12 In a recent meta-analysis including 2,276,798 participants across 5 separate studies, researchers found that suicide was positively associated with acne, carrying an odds ratio of 1.50 (95% CI, 1.09-2.06).13
Rosacea—Rosacea is a common chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by facial erythema, telangiectasia, phymatous changes, papules, pustules, and ocular irritation. The estimated worldwide prevalence is 5.5%.14 In addition to discomfort and irritation of the skin and eyes, rosacea often carries a higher risk of psychological and psychosocial distress due to its potentially disfiguring nature. Rosacea patients are at greater risk for having anxiety disorders and depression,15 and a 2018 study by Alinia et al16 showed that there is a direct relationship between rosacea severity and the actual level of depression.Although disease improvement certainly leads to improvements in quality of life and psychosocial status, Alinia et al16 noted that depression often is associated with poor treatment adherence due to poor motivation and hopelessness. It is critical that dermatologists are aware of these associations and maintain close follow-up with patients, even when the condition is not life-threatening, such as rosacea.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa—Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the pilosebaceous unit that is characterized by the development of painful, malodorous, draining abscesses, fistulas, sinus tracts, and scars in sensitive areas such as the axillae, breasts, groin, and perineum.17 In severe cases, surgery may be required to excise affected areas. Compared to other cutaneous disease, HS is considered one of the most life-impacting disorders.18 The physical symptoms themselves often are debilitating, and patients often report considerable psychosocial and psychological impairment with decreased quality of life. Major depression frequently is noted, with 1 in 4 adults with HS also being depressed. In a large cross-sectional analysis of 38,140 adults and 1162 pediatric patients with HS, Wright et al17 reported the prevalence of depression among adults with HS as 30.0% compared to 16.9% in healthy controls. In children, the prevalence of depression was 11.7% compared to 4.1% in the general population.17 Similarly, 1 out of every 5 patients with HS experiences anxiety.18
In the military population, HS often can be duty limiting. The disease requires constant attention to wound care and frequent medical visits. For many service members operating in field training or combat environments, opportunities for and access to showers and basic hygiene is limited. Uniforms and additional necessary combat gear often are thick and occlusive. Taken as a whole, these factors may contribute to worsening of the disease and in severe cases are simply not conducive to the successful management of the condition. However, given the most commonly involved body areas and the nature of the disease, many service members with HS may feel embarrassed to disclose their condition. In uniform, the disease is not easily visible, and for unaware persons, the frequency of medical visits and limited duty status may seem unnecessary. This perception of a service member’s lack of productivity due to an unseen disease may further add to the psychosocial stress they experience.
The treatments for acne, rosacea, and HS are outlined in the eTable.11,19 Also noted are specific considerations when managing an active-duty service member due to various operational duty restrictions and constraints.

Final Thoughts
Maintaining readiness in the military is essential to the ability to not only “fight tonight” but also to win tonight in whatever operational or combat mission a service member may be. Although many factors impact readiness, the rates of suicide within the armed forces cannot be ignored. Suicide not only eliminates the readiness of the deceased service member but has lasting ripple effects on the overall readiness of their unit and command at large. Most suicides in the military occur in personnel with no prior documented mental health diagnoses or treatment. Therefore, it is the responsibility of all service members to recognize and mitigate stressors and risk factors that may lead to mental health distress and suicidality. In the medical corps, this translates to a responsibility of all medical specialists to recognize and understand unique risk factors for suicidality and to do as much as they can to reduce these risks. For military dermatologists and for civilian physicians treating military service members, it is imperative to predict and understand the relationship between common dermatoses; reduced satisfaction with CBI; and increased risk for mental health illness, self-harm, and suicide. Military dermatologists, as well as other specialists, may be limited in the care they are able to provide due to manpower, staffing, demand, and institutional guidelines; however, to better serve those who serve in a holistic manner, consideration must be given to rethink what is “medically essential” and “cosmetic” and leverage the available skills, techniques, and equipment to increase the readiness of the force.

According to the US Department of Defense, the term readiness refers to the ability to recruit, train, deploy, and sustain military forces that will be ready to “fight tonight” and succeed in combat. Readiness is a top priority for military medicine, which functions to diagnose, treat, and rehabilitate service members so that they can return to the fight. This central concept drives programs across the military—from operational training events to the establishment of medical and dental standards. Readiness is tracked and scrutinized constantly, and although it is a shared responsibility, efforts to increase and sustain readiness often fall on support staff and military medical providers.
In recent years, there has been a greater awareness of the negative effects of mental illness, low morale, and suicidality on military readiness. In 2013, suicide accounted for 28.1% of all deaths that occurred in the US Armed Forces.1 Put frankly, suicide was one of the leading causes of death among military members.
The most recent Marine Corps Order regarding the Marine Corps Suicide Prevention Program stated that “suicidal behaviors are a barrier to readiness that have lasting effects on Marines and Service Members attached to Marine Commands. . .Families, and the Marine Corps.” It goes on to say that “[e]ffective suicide prevention requires coordinated efforts within a prevention framework dedicated to promoting mental, physical, spiritual, and social fitness. . .[and] mitigating stressors that interfere with mission readiness.”2 This statement supports the notion that preventing suicide is not just about treating mental illness; it also involves maximizing physical, spiritual, and social fitness. Although it is well established that various mental health disorders are associated with an increased risk for suicide, it is worth noting that, in one study, only half of individuals who died by suicide had a mental health disorder diagnosed prior to their death.3 These statistics translate to the military. The 2015 Department of Defense Suicide Event Report noted that only 28% of service members who died by suicide and 22% of members with attempted suicide had been documented as having sought mental health care and disclosed their potential for self-harm prior to the event.1,4 In 2018, a study published by Ursano et al5 showed that 36.3% of US soldiers with a documented suicide attempt (N=9650) had no prior mental health diagnoses.
Expanding the scope to include mental health issues in general, only 29% of service members who reported experiencing a mental health problem actually sought mental health care in that same period. Overall, approximately 40% of service members with a reported perceived need for mental health care actually sought care over their entire course of service time,1 which raises concern for a large population of undiagnosed and undertreated mental illnesses across the military. In response to these statistics, Reger et al3 posited that it is “essential that suicide prevention efforts move outside the silo of mental health.” The authors went on to challenge health care providers across all specialties and civilians alike to take responsibility in understanding, recognizing, and mitigating risk factors for suicide in the general population.3 Although treating a service member’s acne or offering to stand duty for a service member who has been under a great deal of stress in their personal life may appear to be indirect ways of reducing suicide in the US military, they actually may be the most critical means of prevention in a culture that emphasizes resilience and self-reliance, where seeking help for mental health struggles could be perceived as weakness.1
In this review article, we discuss the concept of cutaneous body image (CBI) and its associated outcomes on health, satisfaction, and quality of life in military service members. We then examine the intersections between common dermatologic conditions, CBI, and mental health and explore the ability and role of the military dermatologist to serve as a positive influence on military readiness.
What is cutaneous body image?
Cutaneous body image is “the individual’s mental perception of his or her skin and its appendages (ie, hair, nails).”6 It is measured objectively using the Cutaneous Body Image Scale, a questionnaire that includes 7 items related to the overall satisfaction with the appearance of skin, color of skin, skin of the face, complexion of the face, hair, fingernails, and toenails. Each question is rated using a 10-point Likert scale (0=not at all; 10=very markedly).6
Some degree of CBI dissatisfaction is expected and has been shown in the general population at large; for example, more than 56% of women older than 30 years report some degree of dissatisfaction with their skin. Similarly, data from the American Society of Plastic Surgeons showed that while 10.9 million cosmetic procedures were performed in 2006, 9.1 million of them involved minimally invasive procedures such as botulinum toxin type A injections with the purpose of skin rejuvenation and improvement of facial appearance.7 However, lower than average CBI can contribute to considerable psychosocial morbidity. Dissatisfaction with CBI is associated with self-consciousness, feelings of inferiority, and social exclusion. These symptoms can be grouped into a construct called interpersonal sensitivity (IS). A 2013 study by Gupta and Gupta6 investigated the relationship between CBI, IS, and suicidal ideation among 312 consenting nonclinical participants in Canada. The study found that greater dissatisfaction with an individual’s CBI correlated to increased IS and increased rates of suicidal ideation and intentional self-injury.6
Cutaneous body image is particularly relevant to dermatologists, as many common dermatoses can cause cosmetically disfiguring skin conditions; for example, acne and rosacea have the propensity to cause notable disfigurement to the facial unit. Other common conditions such as atopic dermatitis or psoriasis can flare with stress and thereby throw patients into a vicious cycle of physical and psychosocial stress caused by social stigma, cosmetic disfigurement, and reduced CBI, in turn leading to worsening of the disease at hand. Dermatologists need to be aware that common dermatoses can impact a patient’s mental health via poor CBI.8 Similarly, dermatologists may be empowered by the awareness that treating common dermatoses, especially those associated with poor cosmesis, have 2-fold benefits—on the skin condition itself and on the patient’s mental health.
How are common dermatoses associated with mental health?
Acne—Acne is one of the most common skin diseases, so much so that in many cases acne has become an accepted and expected part of adolescence and young adulthood. Studies estimate that 85% of the US population aged 12 to 25 years have acne.9 For some adults, acne persists even longer, with 1% to 5% of adults reporting to have active lesions at 40 years of age.10 Acne is a multifactorial skin disease of the pilosebaceous unit that results in the development of inflammatory papules, pustules, and cysts. These lesions are most common on the face but can extend to other areas of the body, such as the chest and back.11 Although the active lesions can be painful and disfiguring, if left untreated, acne may lead to permanent disfigurement and scarring, which can have long-lasting psychosocial impacts.
Individuals with acne have an increased likelihood of self-consciousness, social isolation, depression, and suicidal ideation. This relationship has been well established for decades. In the 1990s, a small study reported that 7 of 16 (43.8%) cases of completed suicide in dermatology patients were in patients with acne.12 In a recent meta-analysis including 2,276,798 participants across 5 separate studies, researchers found that suicide was positively associated with acne, carrying an odds ratio of 1.50 (95% CI, 1.09-2.06).13
Rosacea—Rosacea is a common chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by facial erythema, telangiectasia, phymatous changes, papules, pustules, and ocular irritation. The estimated worldwide prevalence is 5.5%.14 In addition to discomfort and irritation of the skin and eyes, rosacea often carries a higher risk of psychological and psychosocial distress due to its potentially disfiguring nature. Rosacea patients are at greater risk for having anxiety disorders and depression,15 and a 2018 study by Alinia et al16 showed that there is a direct relationship between rosacea severity and the actual level of depression.Although disease improvement certainly leads to improvements in quality of life and psychosocial status, Alinia et al16 noted that depression often is associated with poor treatment adherence due to poor motivation and hopelessness. It is critical that dermatologists are aware of these associations and maintain close follow-up with patients, even when the condition is not life-threatening, such as rosacea.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa—Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the pilosebaceous unit that is characterized by the development of painful, malodorous, draining abscesses, fistulas, sinus tracts, and scars in sensitive areas such as the axillae, breasts, groin, and perineum.17 In severe cases, surgery may be required to excise affected areas. Compared to other cutaneous disease, HS is considered one of the most life-impacting disorders.18 The physical symptoms themselves often are debilitating, and patients often report considerable psychosocial and psychological impairment with decreased quality of life. Major depression frequently is noted, with 1 in 4 adults with HS also being depressed. In a large cross-sectional analysis of 38,140 adults and 1162 pediatric patients with HS, Wright et al17 reported the prevalence of depression among adults with HS as 30.0% compared to 16.9% in healthy controls. In children, the prevalence of depression was 11.7% compared to 4.1% in the general population.17 Similarly, 1 out of every 5 patients with HS experiences anxiety.18
In the military population, HS often can be duty limiting. The disease requires constant attention to wound care and frequent medical visits. For many service members operating in field training or combat environments, opportunities for and access to showers and basic hygiene is limited. Uniforms and additional necessary combat gear often are thick and occlusive. Taken as a whole, these factors may contribute to worsening of the disease and in severe cases are simply not conducive to the successful management of the condition. However, given the most commonly involved body areas and the nature of the disease, many service members with HS may feel embarrassed to disclose their condition. In uniform, the disease is not easily visible, and for unaware persons, the frequency of medical visits and limited duty status may seem unnecessary. This perception of a service member’s lack of productivity due to an unseen disease may further add to the psychosocial stress they experience.
The treatments for acne, rosacea, and HS are outlined in the eTable.11,19 Also noted are specific considerations when managing an active-duty service member due to various operational duty restrictions and constraints.

Final Thoughts
Maintaining readiness in the military is essential to the ability to not only “fight tonight” but also to win tonight in whatever operational or combat mission a service member may be. Although many factors impact readiness, the rates of suicide within the armed forces cannot be ignored. Suicide not only eliminates the readiness of the deceased service member but has lasting ripple effects on the overall readiness of their unit and command at large. Most suicides in the military occur in personnel with no prior documented mental health diagnoses or treatment. Therefore, it is the responsibility of all service members to recognize and mitigate stressors and risk factors that may lead to mental health distress and suicidality. In the medical corps, this translates to a responsibility of all medical specialists to recognize and understand unique risk factors for suicidality and to do as much as they can to reduce these risks. For military dermatologists and for civilian physicians treating military service members, it is imperative to predict and understand the relationship between common dermatoses; reduced satisfaction with CBI; and increased risk for mental health illness, self-harm, and suicide. Military dermatologists, as well as other specialists, may be limited in the care they are able to provide due to manpower, staffing, demand, and institutional guidelines; however, to better serve those who serve in a holistic manner, consideration must be given to rethink what is “medically essential” and “cosmetic” and leverage the available skills, techniques, and equipment to increase the readiness of the force.

- Ghahramanlou-Holloway M, LaCroix JM, Koss K, et al. Outpatient mental health treatment utilization and military career impact in the United States Marine Corps. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15:828. doi:10.3390/ijerph15040828
- Ottignon DA. Marine Corps Suicide Prevention System (MCSPS). Marine Corps Order 1720.2A. 2021. Headquarters United States Marine Corps. Published August 2, 2021. Accessed May 25, 2022. https://www.marines.mil/Portals/1/Publications/MCO%201720.2A.pdf?ver=QPxZ_qMS-X-d037B65N9Tg%3d%3d
- Reger MA, Smolenski DJ, Carter SP. Suicide prevention in the US Army: a mission for more than mental health clinicians. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75:991-992. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.2042
- Pruitt LD, Smolenski DJ, Bush NE, et al. Department of Defense Suicide Event Report Calendar Year 2015 Annual Report. National Center for Telehealth & Technology (T2); 2016. Accessed May 20, 2022. https://health.mil/Military-Health-Topics/Centers-of-Excellence/Psychological-Health-Center-of-Excellence/Department-of-Defense-Suicide-Event-Report
- Ursano RJ, Kessler RC, Naifeh JA, et al. Risk factors associated with attempted suicide among US Army soldiers without a history of mental health diagnosis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75:1022-1032. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.2069
- Gupta MA, Gupta AK. Cutaneous body image dissatisfaction and suicidal ideation: mediation by interpersonal sensitivity. J Psychosom Res. 2013;75:55-59. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychores.2013.01.015
- Gupta MA, Gupta AK. Evaluation of cutaneous body image dissatisfaction in the dermatology patient. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:72-79. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2011.11.010
- Hinkley SB, Holub SC, Menter A. The validity of cutaneous body image as a construct and as a mediator of the relationship between cutaneous disease and mental health. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020;10:203-211. doi:10.1007/s13555-020-00351-5
- Stamu-O’Brien C, Jafferany M, Carniciu S, et al. Psychodermatology of acne: psychological aspects and effects of acne vulgaris. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:1080-1083. doi:10.1111/jocd.13765
- Sood S, Jafferany M, Vinaya Kumar S. Depression, psychiatric comorbidities, and psychosocial implications associated with acne vulgaris. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19:3177-3182. doi:10.1111/jocd.13753
- Brahe C, Peters K. Fighting acne for the fighting forces. Cutis. 2020;106:18-20, 22. doi:10.12788/cutis.0057
- Cotterill JA, Cunliffe WJ. Suicide in dermatological patients. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:246-250.
- Xu S, Zhu Y, Hu H, et al. The analysis of acne increasing suicide risk. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:E26035. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000026035
- Chen M, Deng Z, Huang Y, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of anxiety and depression in rosacea patients: a cross-sectional study in China [published online June 16, 2021]. Front Psychiatry. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2021.659171
- Incel Uysal P, Akdogan N, Hayran Y, et al. Rosacea associated with increased risk of generalized anxiety disorder: a case-control study of prevalence and risk of anxiety in patients with rosacea. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94:704-709. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2019.03.002
- Alinia H, Cardwell LA, Tuchayi SM, et al. Screening for depression in rosacea patients. Cutis. 2018;102:36-38.
- Wright S, Strunk A, Garg A. Prevalence of depression among children, adolescents, and adults with hidradenitis suppurativa [published online June 16, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.843
- Misitzis A, Goldust M, Jafferany M, et al. Psychiatric comorbidities in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13541. doi:10.1111/dth.13541
- Bolognia J, Schaffer J, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017.
- Ghahramanlou-Holloway M, LaCroix JM, Koss K, et al. Outpatient mental health treatment utilization and military career impact in the United States Marine Corps. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15:828. doi:10.3390/ijerph15040828
- Ottignon DA. Marine Corps Suicide Prevention System (MCSPS). Marine Corps Order 1720.2A. 2021. Headquarters United States Marine Corps. Published August 2, 2021. Accessed May 25, 2022. https://www.marines.mil/Portals/1/Publications/MCO%201720.2A.pdf?ver=QPxZ_qMS-X-d037B65N9Tg%3d%3d
- Reger MA, Smolenski DJ, Carter SP. Suicide prevention in the US Army: a mission for more than mental health clinicians. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75:991-992. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.2042
- Pruitt LD, Smolenski DJ, Bush NE, et al. Department of Defense Suicide Event Report Calendar Year 2015 Annual Report. National Center for Telehealth & Technology (T2); 2016. Accessed May 20, 2022. https://health.mil/Military-Health-Topics/Centers-of-Excellence/Psychological-Health-Center-of-Excellence/Department-of-Defense-Suicide-Event-Report
- Ursano RJ, Kessler RC, Naifeh JA, et al. Risk factors associated with attempted suicide among US Army soldiers without a history of mental health diagnosis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75:1022-1032. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.2069
- Gupta MA, Gupta AK. Cutaneous body image dissatisfaction and suicidal ideation: mediation by interpersonal sensitivity. J Psychosom Res. 2013;75:55-59. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychores.2013.01.015
- Gupta MA, Gupta AK. Evaluation of cutaneous body image dissatisfaction in the dermatology patient. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:72-79. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2011.11.010
- Hinkley SB, Holub SC, Menter A. The validity of cutaneous body image as a construct and as a mediator of the relationship between cutaneous disease and mental health. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020;10:203-211. doi:10.1007/s13555-020-00351-5
- Stamu-O’Brien C, Jafferany M, Carniciu S, et al. Psychodermatology of acne: psychological aspects and effects of acne vulgaris. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:1080-1083. doi:10.1111/jocd.13765
- Sood S, Jafferany M, Vinaya Kumar S. Depression, psychiatric comorbidities, and psychosocial implications associated with acne vulgaris. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19:3177-3182. doi:10.1111/jocd.13753
- Brahe C, Peters K. Fighting acne for the fighting forces. Cutis. 2020;106:18-20, 22. doi:10.12788/cutis.0057
- Cotterill JA, Cunliffe WJ. Suicide in dermatological patients. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:246-250.
- Xu S, Zhu Y, Hu H, et al. The analysis of acne increasing suicide risk. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:E26035. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000026035
- Chen M, Deng Z, Huang Y, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of anxiety and depression in rosacea patients: a cross-sectional study in China [published online June 16, 2021]. Front Psychiatry. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2021.659171
- Incel Uysal P, Akdogan N, Hayran Y, et al. Rosacea associated with increased risk of generalized anxiety disorder: a case-control study of prevalence and risk of anxiety in patients with rosacea. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94:704-709. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2019.03.002
- Alinia H, Cardwell LA, Tuchayi SM, et al. Screening for depression in rosacea patients. Cutis. 2018;102:36-38.
- Wright S, Strunk A, Garg A. Prevalence of depression among children, adolescents, and adults with hidradenitis suppurativa [published online June 16, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.843
- Misitzis A, Goldust M, Jafferany M, et al. Psychiatric comorbidities in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13541. doi:10.1111/dth.13541
- Bolognia J, Schaffer J, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2017.
Practice Points
- The term readiness refers to the ability to recruit, train, deploy, and sustain military forces that are ready to “fight tonight” and succeed in combat.
- Maintaining readiness requires a holistic approach, as it is directly affected by physical and mental health outcomes.
- Cutaneous body image (CBI) refers to an individual’s mental perception of the condition of their hair, nails, and skin. Positive CBI is related to increased quality of life, while negative CBI, which often is associated with dermatologic disease, is associated with poorer health outcomes and even self-injury.
- Treatment of dermatologic disease in the context of active-duty military members can positively influence CBI, which may in turn increase service members’ quality of life and overall military readiness.