User login
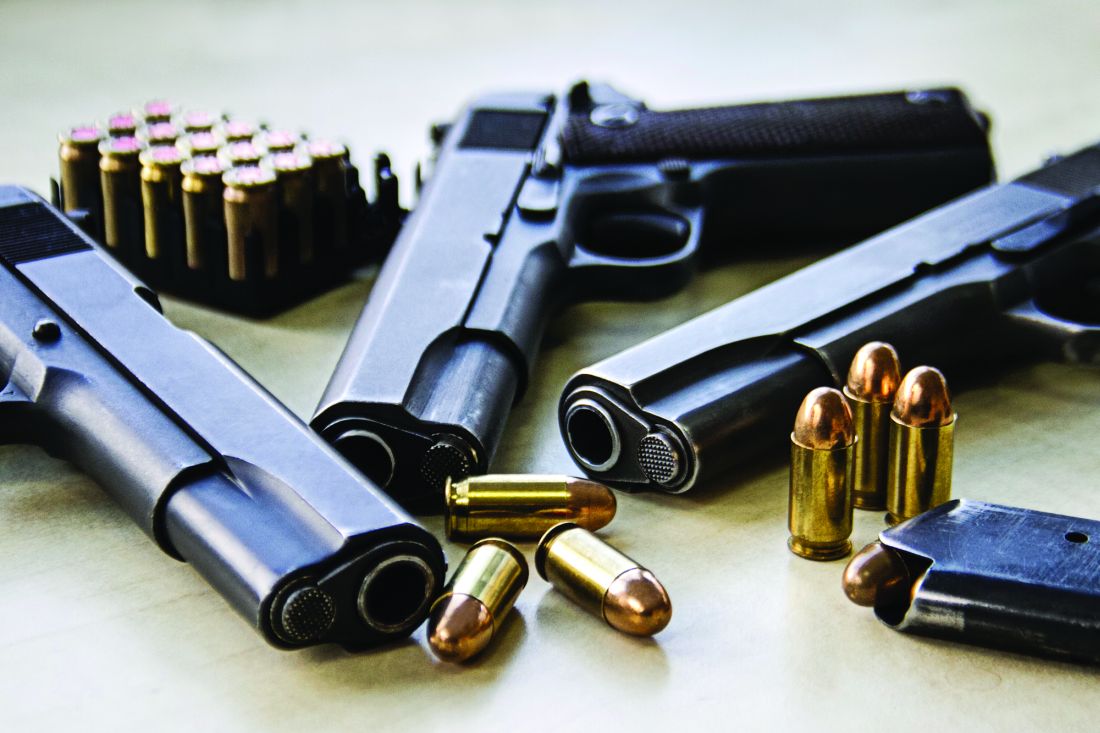
Surge in firearm sales tied to COVID-19 fears, uncertainty presents risks
Use gentle assumptions and focus on home access to elicit positive answers.
In the wake of the 2012 shooting at Sandy Hook Elementary, in Newtown, Conn., after 20 children and seven adults were murdered, American gun sales surged on fears of new restrictions.
In the ensuing months, 20 more children and 40 more adults died from unintentional shootings believed to be tied to that surge in gun purchases.1 More recently, American gun sales surged in response to the COVID-19 pandemic with heated legal battles brewing over whether gun sales are essential.2,3 The results of this surge in sales are yet to fully manifest, but I would like to discuss several risks.
The public health risks of firearm access are well established: Nearly every measure of harm, from suicide to negligent injury and death to homicide to shootings of police, increase along with access to firearms.4 That firearms in the home are associated with greater likelihoods of suicide, negligent injury and death, and intrafamilial homicide has been recognized for decades as has the substantially heightened risk in the immediate period after a firearm is brought into the home.5,6 Defensive gun use is rare despite this being the nominal reason for firearm ownership among many.7 Even prior to recent events, there had been concerns of increased unsafe carrying and handling of firearms.8 It seems reasonable to expect such trends not to be diminished by recent events.
Added to this are several stressors, which one can reasonably expect to be associated with increased risks for unsafe use. There are new, broad social stressors from fear and uncertainty about COVID-19. Unemployment rates have skyrocketed, clinical care has been disrupted, and basic necessities have become scant. Children are home from school, unable to play with friends and unable to access mental health services as easily as before; risks of negligent and suicidal injuries and death may ensue. Couples and families are isolated in homes together for longer periods and with fewer avenues for relief; previously peaceful homes may see conflicts increase and homes with abuse have now trapped victims with their assailants. Social isolation is difficult for any person and may be even more traumatic for people with underlying vulnerabilities, including mental illness. The risks of being isolated in a home – struggling with worsening symptoms – with ready access to a firearm are self-evident.
- Consider reassessing for firearm access. Patients may be in new homes, or there may be new firearms in their homes. Use gentle assumptions and focus on home access over personal access to elicit the most true, positive answers, for example: “I understand there have been a lot of changes recently; how many guns are in the home now?”
- Reinforce safer storage practices. Simple measures, such as storing ammunition separately and using trigger locks or safes, can make a substantial difference in injury risks.
- Do not forget aging clients; suicide risk increases with age, and there may be substantial risks among the geriatric population for suicide and murder-suicide. If using telepsychiatry, realize that the abuser might be in the home or within earshot of any clinical encounter, and this might put the client at heightened risk, during and after telesessions.
- Highlight access to local and national resources, including the Disaster Distress Hotline (800-985-5990) and the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline (800-273-TALK). Promote both numbers, and note that some people may be more comfortable reaching out for help for “distress” than for “suicide.”
References
1. Levine PB and McKnight R. Science. 2017 Dec 8;358(6368):1324-8.
2. Levin D. “Coronavirus and firearms: Are gun shops essential businesses?” The New York Times. 2020 Mar 25.
3. Robertson L. “Neither hurricanes nor 9/11 caused as big a surge in gun sales as coronavirus.” Miami Herald. 2020 Mar 25.
4. Moyer MW. Scientific American. 2017 Oct;317(4):54-63.
5. Kellermann AL et al. J Trauma. 1998 Aug;45(2):263-7.
6. Wintemute GJ et al. New Engl J Med. 1999 Nov 18;341(21):1583-9.
7. Firearm Justifiable Homicides and Non-Fatal Self-Defense Gun Use: An Analysis of Federal Bureau of Investigation and National Crime Victimization Survey Data. Washington: Violence Policy Center; 2019 Jul.
8. Towers S et al. bioRxiv. 2019 Apr 18;613687.
Dr. Rozel is the medical director of resolve Crisis Services at UPMC Western Psychiatric Hospital and president of the American Association for Emergency Psychiatry. He also is associate professor of psychiatry and an adjunct professor of law at the University of Pittsburgh. He has no conflicts of interest but has worked for a gun dealer to teach sales staff how to recognize people in crisis (rather than sell a gun).
Use gentle assumptions and focus on home access to elicit positive answers.
Use gentle assumptions and focus on home access to elicit positive answers.
In the wake of the 2012 shooting at Sandy Hook Elementary, in Newtown, Conn., after 20 children and seven adults were murdered, American gun sales surged on fears of new restrictions.
In the ensuing months, 20 more children and 40 more adults died from unintentional shootings believed to be tied to that surge in gun purchases.1 More recently, American gun sales surged in response to the COVID-19 pandemic with heated legal battles brewing over whether gun sales are essential.2,3 The results of this surge in sales are yet to fully manifest, but I would like to discuss several risks.
The public health risks of firearm access are well established: Nearly every measure of harm, from suicide to negligent injury and death to homicide to shootings of police, increase along with access to firearms.4 That firearms in the home are associated with greater likelihoods of suicide, negligent injury and death, and intrafamilial homicide has been recognized for decades as has the substantially heightened risk in the immediate period after a firearm is brought into the home.5,6 Defensive gun use is rare despite this being the nominal reason for firearm ownership among many.7 Even prior to recent events, there had been concerns of increased unsafe carrying and handling of firearms.8 It seems reasonable to expect such trends not to be diminished by recent events.
Added to this are several stressors, which one can reasonably expect to be associated with increased risks for unsafe use. There are new, broad social stressors from fear and uncertainty about COVID-19. Unemployment rates have skyrocketed, clinical care has been disrupted, and basic necessities have become scant. Children are home from school, unable to play with friends and unable to access mental health services as easily as before; risks of negligent and suicidal injuries and death may ensue. Couples and families are isolated in homes together for longer periods and with fewer avenues for relief; previously peaceful homes may see conflicts increase and homes with abuse have now trapped victims with their assailants. Social isolation is difficult for any person and may be even more traumatic for people with underlying vulnerabilities, including mental illness. The risks of being isolated in a home – struggling with worsening symptoms – with ready access to a firearm are self-evident.
- Consider reassessing for firearm access. Patients may be in new homes, or there may be new firearms in their homes. Use gentle assumptions and focus on home access over personal access to elicit the most true, positive answers, for example: “I understand there have been a lot of changes recently; how many guns are in the home now?”
- Reinforce safer storage practices. Simple measures, such as storing ammunition separately and using trigger locks or safes, can make a substantial difference in injury risks.
- Do not forget aging clients; suicide risk increases with age, and there may be substantial risks among the geriatric population for suicide and murder-suicide. If using telepsychiatry, realize that the abuser might be in the home or within earshot of any clinical encounter, and this might put the client at heightened risk, during and after telesessions.
- Highlight access to local and national resources, including the Disaster Distress Hotline (800-985-5990) and the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline (800-273-TALK). Promote both numbers, and note that some people may be more comfortable reaching out for help for “distress” than for “suicide.”
References
1. Levine PB and McKnight R. Science. 2017 Dec 8;358(6368):1324-8.
2. Levin D. “Coronavirus and firearms: Are gun shops essential businesses?” The New York Times. 2020 Mar 25.
3. Robertson L. “Neither hurricanes nor 9/11 caused as big a surge in gun sales as coronavirus.” Miami Herald. 2020 Mar 25.
4. Moyer MW. Scientific American. 2017 Oct;317(4):54-63.
5. Kellermann AL et al. J Trauma. 1998 Aug;45(2):263-7.
6. Wintemute GJ et al. New Engl J Med. 1999 Nov 18;341(21):1583-9.
7. Firearm Justifiable Homicides and Non-Fatal Self-Defense Gun Use: An Analysis of Federal Bureau of Investigation and National Crime Victimization Survey Data. Washington: Violence Policy Center; 2019 Jul.
8. Towers S et al. bioRxiv. 2019 Apr 18;613687.
Dr. Rozel is the medical director of resolve Crisis Services at UPMC Western Psychiatric Hospital and president of the American Association for Emergency Psychiatry. He also is associate professor of psychiatry and an adjunct professor of law at the University of Pittsburgh. He has no conflicts of interest but has worked for a gun dealer to teach sales staff how to recognize people in crisis (rather than sell a gun).
In the wake of the 2012 shooting at Sandy Hook Elementary, in Newtown, Conn., after 20 children and seven adults were murdered, American gun sales surged on fears of new restrictions.
In the ensuing months, 20 more children and 40 more adults died from unintentional shootings believed to be tied to that surge in gun purchases.1 More recently, American gun sales surged in response to the COVID-19 pandemic with heated legal battles brewing over whether gun sales are essential.2,3 The results of this surge in sales are yet to fully manifest, but I would like to discuss several risks.
The public health risks of firearm access are well established: Nearly every measure of harm, from suicide to negligent injury and death to homicide to shootings of police, increase along with access to firearms.4 That firearms in the home are associated with greater likelihoods of suicide, negligent injury and death, and intrafamilial homicide has been recognized for decades as has the substantially heightened risk in the immediate period after a firearm is brought into the home.5,6 Defensive gun use is rare despite this being the nominal reason for firearm ownership among many.7 Even prior to recent events, there had been concerns of increased unsafe carrying and handling of firearms.8 It seems reasonable to expect such trends not to be diminished by recent events.
Added to this are several stressors, which one can reasonably expect to be associated with increased risks for unsafe use. There are new, broad social stressors from fear and uncertainty about COVID-19. Unemployment rates have skyrocketed, clinical care has been disrupted, and basic necessities have become scant. Children are home from school, unable to play with friends and unable to access mental health services as easily as before; risks of negligent and suicidal injuries and death may ensue. Couples and families are isolated in homes together for longer periods and with fewer avenues for relief; previously peaceful homes may see conflicts increase and homes with abuse have now trapped victims with their assailants. Social isolation is difficult for any person and may be even more traumatic for people with underlying vulnerabilities, including mental illness. The risks of being isolated in a home – struggling with worsening symptoms – with ready access to a firearm are self-evident.
- Consider reassessing for firearm access. Patients may be in new homes, or there may be new firearms in their homes. Use gentle assumptions and focus on home access over personal access to elicit the most true, positive answers, for example: “I understand there have been a lot of changes recently; how many guns are in the home now?”
- Reinforce safer storage practices. Simple measures, such as storing ammunition separately and using trigger locks or safes, can make a substantial difference in injury risks.
- Do not forget aging clients; suicide risk increases with age, and there may be substantial risks among the geriatric population for suicide and murder-suicide. If using telepsychiatry, realize that the abuser might be in the home or within earshot of any clinical encounter, and this might put the client at heightened risk, during and after telesessions.
- Highlight access to local and national resources, including the Disaster Distress Hotline (800-985-5990) and the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline (800-273-TALK). Promote both numbers, and note that some people may be more comfortable reaching out for help for “distress” than for “suicide.”
References
1. Levine PB and McKnight R. Science. 2017 Dec 8;358(6368):1324-8.
2. Levin D. “Coronavirus and firearms: Are gun shops essential businesses?” The New York Times. 2020 Mar 25.
3. Robertson L. “Neither hurricanes nor 9/11 caused as big a surge in gun sales as coronavirus.” Miami Herald. 2020 Mar 25.
4. Moyer MW. Scientific American. 2017 Oct;317(4):54-63.
5. Kellermann AL et al. J Trauma. 1998 Aug;45(2):263-7.
6. Wintemute GJ et al. New Engl J Med. 1999 Nov 18;341(21):1583-9.
7. Firearm Justifiable Homicides and Non-Fatal Self-Defense Gun Use: An Analysis of Federal Bureau of Investigation and National Crime Victimization Survey Data. Washington: Violence Policy Center; 2019 Jul.
8. Towers S et al. bioRxiv. 2019 Apr 18;613687.
Dr. Rozel is the medical director of resolve Crisis Services at UPMC Western Psychiatric Hospital and president of the American Association for Emergency Psychiatry. He also is associate professor of psychiatry and an adjunct professor of law at the University of Pittsburgh. He has no conflicts of interest but has worked for a gun dealer to teach sales staff how to recognize people in crisis (rather than sell a gun).
What Happens When COVID-19 Breaks Out on a Nuclear Aircraft Carrier?
Updated April 2, 2020.
The commander of a US Navy aircraft carrier in the midst of a COVID-19 outbreak was swiftly fired by Acting Secretary of the Navy Thomas Modly following media coverage of the plight of more than 200 COVID-19 positive sailors on the USS Theodore Roosevelt.
In a statement released April 2, Modly announced the removal of Capt. Brett Crozier for writing a memo that was later leaked to the San Francisco Chronicle newspaper. According to Acting Secretary Modly, the memo was sent “outside the chain of command” and his action “made his Sailors, their families, and many in the public believe that his letter was the only reason help from our larger Navy family was forthcoming, which was hardly the case.”
On Monday, March 30, Capt. Crozier, commanding officer of the nuclear aircraft carrier USS Theodore Roosevelt, sent an urgent request for assistance to senior Navy officials: “[I]n combat we are willing to take certain risks that are not acceptable in peacetime. However, we are not at war, and therefore cannot allow a single Sailor to perish as a result of this pandemic unnecessarily. Decisive action is required now in order to comply with CDC and NAVADMIN 083/20 guidance and prevent tragic outcomes.”
Even as a number of cruise ships with ill and dying passengers were—are—waiting to be allowed to dock in Florida and elsewhere, the USS Theodore Roosevelt was also dealing with a COVID-19 outbreak onboard—and awaiting permission to let the crew of more than 4,000 on shore so they could quarantine safely.
Crozier pointed to “lessons learned” from the Diamond Princess—the only comparable situation at the time. He quoted from the abstract to an epidemiological research study: An index case on board the cruise ship was reported in late January; a month later, 619 of 3,700 passengers and crew had tested positive. Without any interventions, the abstract noted, between January 21st and February 19th an estimated 2,920 of the passengers would have been infected. Isolation and quarantine, it concluded, prevented 2,307 cases. Further, an early evacuation would have been associated with 76 infected persons.
The Diamond Princess, Crozier wrote, was able to more effectively isolate people due to a higher percentage of individual and compartmentalized accommodations. However, due to a warship’s “inherent limitations of space,” his crew could not comply with orders to practice social distancing. “With the exceptions of a handful of senior officer staterooms,” he wrote, “none of the berthing onboard a warship is appropriate for quarantine or isolation.” He also pointed to other obstacles: shared bathrooms, shared sleeping quarters, group mealtimes, and ladders and other surfaces touched and possibly contaminated as crew move around the ship.
Moreover, Crozier wrote, “The spread of the disease is ongoing and accelerating.” By Tuesday March 31st, nearly 1,300 sailors had been tested, and hundreds were testing negative, but 243 sailors had tested positive and 87 more were showing symptoms, according to the latest reports. So far, none are showing serious symptoms.
“If we do not act now, we are failing to take care of our most trusted asset—our sailors,” Capt Crozier wrote. At first, no one seemed to be listening, but after the Chronicle broke the story and it began circulating in the media—things changed. “I heard about the letter from Capt. Crozier [Tuesday] morning,” said Acting Secretary Modly in an interview with the Chronicle. “I know that our command organization has been aware of this for about 24 hours and we have been working actually the last 7 days to move those sailors off the ship and get them into accommodations in Guam. The problem is that Guam doesn’t have enough beds right now and we’re having to talk to the government there to see if we can get some hotel space, create tent-type facilities.”
He noted that the situation for the USS Theodore Roosevelt is “a little bit different and unique” in that it has aircraft and armaments on it, fire hazards, and “we have to run a nuclear power plant.” Crozier had proposed that approximately 10% of the crew remain on board to take care of the duties such as tending to the nuclear reactor.
As of April 1, the Navy plans to remove some 2,700 sailors to the hotel rooms government officials on Guam have secured for them. Secretary Modly made no mention of the care or treatment of infected sailors in his April 2nd statement, but offered this reassurance: "You can offer comfort to your fellow citizens who are struggling and fearful here at home by standing the watch, and working your way through this pandemic with courage and optimism and set the example for the nation. We have an obligation to ensure you have everything you need as fast as we can get it there, and you have my commitment that we will not let you down."
Updated April 2, 2020.
The commander of a US Navy aircraft carrier in the midst of a COVID-19 outbreak was swiftly fired by Acting Secretary of the Navy Thomas Modly following media coverage of the plight of more than 200 COVID-19 positive sailors on the USS Theodore Roosevelt.
In a statement released April 2, Modly announced the removal of Capt. Brett Crozier for writing a memo that was later leaked to the San Francisco Chronicle newspaper. According to Acting Secretary Modly, the memo was sent “outside the chain of command” and his action “made his Sailors, their families, and many in the public believe that his letter was the only reason help from our larger Navy family was forthcoming, which was hardly the case.”
On Monday, March 30, Capt. Crozier, commanding officer of the nuclear aircraft carrier USS Theodore Roosevelt, sent an urgent request for assistance to senior Navy officials: “[I]n combat we are willing to take certain risks that are not acceptable in peacetime. However, we are not at war, and therefore cannot allow a single Sailor to perish as a result of this pandemic unnecessarily. Decisive action is required now in order to comply with CDC and NAVADMIN 083/20 guidance and prevent tragic outcomes.”
Even as a number of cruise ships with ill and dying passengers were—are—waiting to be allowed to dock in Florida and elsewhere, the USS Theodore Roosevelt was also dealing with a COVID-19 outbreak onboard—and awaiting permission to let the crew of more than 4,000 on shore so they could quarantine safely.
Crozier pointed to “lessons learned” from the Diamond Princess—the only comparable situation at the time. He quoted from the abstract to an epidemiological research study: An index case on board the cruise ship was reported in late January; a month later, 619 of 3,700 passengers and crew had tested positive. Without any interventions, the abstract noted, between January 21st and February 19th an estimated 2,920 of the passengers would have been infected. Isolation and quarantine, it concluded, prevented 2,307 cases. Further, an early evacuation would have been associated with 76 infected persons.
The Diamond Princess, Crozier wrote, was able to more effectively isolate people due to a higher percentage of individual and compartmentalized accommodations. However, due to a warship’s “inherent limitations of space,” his crew could not comply with orders to practice social distancing. “With the exceptions of a handful of senior officer staterooms,” he wrote, “none of the berthing onboard a warship is appropriate for quarantine or isolation.” He also pointed to other obstacles: shared bathrooms, shared sleeping quarters, group mealtimes, and ladders and other surfaces touched and possibly contaminated as crew move around the ship.
Moreover, Crozier wrote, “The spread of the disease is ongoing and accelerating.” By Tuesday March 31st, nearly 1,300 sailors had been tested, and hundreds were testing negative, but 243 sailors had tested positive and 87 more were showing symptoms, according to the latest reports. So far, none are showing serious symptoms.
“If we do not act now, we are failing to take care of our most trusted asset—our sailors,” Capt Crozier wrote. At first, no one seemed to be listening, but after the Chronicle broke the story and it began circulating in the media—things changed. “I heard about the letter from Capt. Crozier [Tuesday] morning,” said Acting Secretary Modly in an interview with the Chronicle. “I know that our command organization has been aware of this for about 24 hours and we have been working actually the last 7 days to move those sailors off the ship and get them into accommodations in Guam. The problem is that Guam doesn’t have enough beds right now and we’re having to talk to the government there to see if we can get some hotel space, create tent-type facilities.”
He noted that the situation for the USS Theodore Roosevelt is “a little bit different and unique” in that it has aircraft and armaments on it, fire hazards, and “we have to run a nuclear power plant.” Crozier had proposed that approximately 10% of the crew remain on board to take care of the duties such as tending to the nuclear reactor.
As of April 1, the Navy plans to remove some 2,700 sailors to the hotel rooms government officials on Guam have secured for them. Secretary Modly made no mention of the care or treatment of infected sailors in his April 2nd statement, but offered this reassurance: "You can offer comfort to your fellow citizens who are struggling and fearful here at home by standing the watch, and working your way through this pandemic with courage and optimism and set the example for the nation. We have an obligation to ensure you have everything you need as fast as we can get it there, and you have my commitment that we will not let you down."
Updated April 2, 2020.
The commander of a US Navy aircraft carrier in the midst of a COVID-19 outbreak was swiftly fired by Acting Secretary of the Navy Thomas Modly following media coverage of the plight of more than 200 COVID-19 positive sailors on the USS Theodore Roosevelt.
In a statement released April 2, Modly announced the removal of Capt. Brett Crozier for writing a memo that was later leaked to the San Francisco Chronicle newspaper. According to Acting Secretary Modly, the memo was sent “outside the chain of command” and his action “made his Sailors, their families, and many in the public believe that his letter was the only reason help from our larger Navy family was forthcoming, which was hardly the case.”
On Monday, March 30, Capt. Crozier, commanding officer of the nuclear aircraft carrier USS Theodore Roosevelt, sent an urgent request for assistance to senior Navy officials: “[I]n combat we are willing to take certain risks that are not acceptable in peacetime. However, we are not at war, and therefore cannot allow a single Sailor to perish as a result of this pandemic unnecessarily. Decisive action is required now in order to comply with CDC and NAVADMIN 083/20 guidance and prevent tragic outcomes.”
Even as a number of cruise ships with ill and dying passengers were—are—waiting to be allowed to dock in Florida and elsewhere, the USS Theodore Roosevelt was also dealing with a COVID-19 outbreak onboard—and awaiting permission to let the crew of more than 4,000 on shore so they could quarantine safely.
Crozier pointed to “lessons learned” from the Diamond Princess—the only comparable situation at the time. He quoted from the abstract to an epidemiological research study: An index case on board the cruise ship was reported in late January; a month later, 619 of 3,700 passengers and crew had tested positive. Without any interventions, the abstract noted, between January 21st and February 19th an estimated 2,920 of the passengers would have been infected. Isolation and quarantine, it concluded, prevented 2,307 cases. Further, an early evacuation would have been associated with 76 infected persons.
The Diamond Princess, Crozier wrote, was able to more effectively isolate people due to a higher percentage of individual and compartmentalized accommodations. However, due to a warship’s “inherent limitations of space,” his crew could not comply with orders to practice social distancing. “With the exceptions of a handful of senior officer staterooms,” he wrote, “none of the berthing onboard a warship is appropriate for quarantine or isolation.” He also pointed to other obstacles: shared bathrooms, shared sleeping quarters, group mealtimes, and ladders and other surfaces touched and possibly contaminated as crew move around the ship.
Moreover, Crozier wrote, “The spread of the disease is ongoing and accelerating.” By Tuesday March 31st, nearly 1,300 sailors had been tested, and hundreds were testing negative, but 243 sailors had tested positive and 87 more were showing symptoms, according to the latest reports. So far, none are showing serious symptoms.
“If we do not act now, we are failing to take care of our most trusted asset—our sailors,” Capt Crozier wrote. At first, no one seemed to be listening, but after the Chronicle broke the story and it began circulating in the media—things changed. “I heard about the letter from Capt. Crozier [Tuesday] morning,” said Acting Secretary Modly in an interview with the Chronicle. “I know that our command organization has been aware of this for about 24 hours and we have been working actually the last 7 days to move those sailors off the ship and get them into accommodations in Guam. The problem is that Guam doesn’t have enough beds right now and we’re having to talk to the government there to see if we can get some hotel space, create tent-type facilities.”
He noted that the situation for the USS Theodore Roosevelt is “a little bit different and unique” in that it has aircraft and armaments on it, fire hazards, and “we have to run a nuclear power plant.” Crozier had proposed that approximately 10% of the crew remain on board to take care of the duties such as tending to the nuclear reactor.
As of April 1, the Navy plans to remove some 2,700 sailors to the hotel rooms government officials on Guam have secured for them. Secretary Modly made no mention of the care or treatment of infected sailors in his April 2nd statement, but offered this reassurance: "You can offer comfort to your fellow citizens who are struggling and fearful here at home by standing the watch, and working your way through this pandemic with courage and optimism and set the example for the nation. We have an obligation to ensure you have everything you need as fast as we can get it there, and you have my commitment that we will not let you down."
Comorbidities more common in hospitalized COVID-19 patients
Greater prevalence of underlying health conditions such as diabetes and chronic lung disease was seen among nearly 7,200 Americans hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
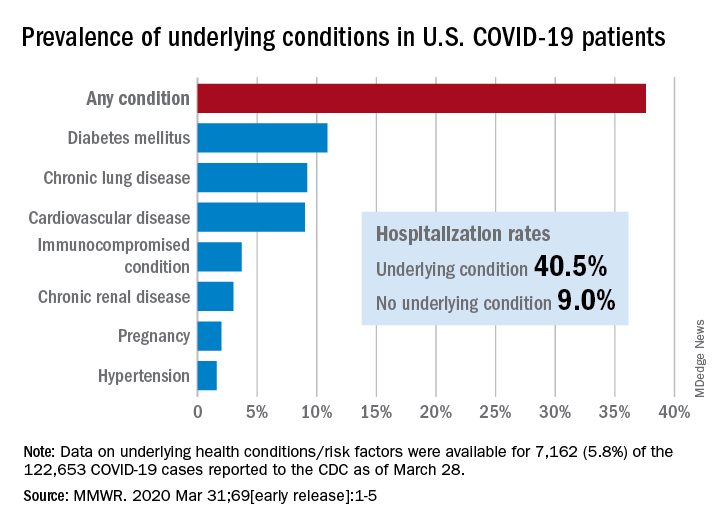
Of the 122,653 laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 cases reported to the CDC as of March 28, the COVID-19 Response Team had access to data on the presence or absence of underlying health conditions and other recognized risk factors for severe outcomes from respiratory infections for 7,162 (5.8%) patients.
“Among these patients, higher percentages of patients with underlying conditions were admitted to the hospital and to an ICU than patients without reported underlying conditions. These results are consistent with findings from China and Italy,” Katherine Fleming-Dutra, MD, and associates said in the MMWR.
Individuals with underlying health conditions/risk factors made up 37.6% of all COVID-19 patients in the study but represented a majority of ICU (78%) and non-ICU (71%) hospital admissions. In contrast, 73% of COVID-19 patients who were not hospitalized had no underlying conditions, Dr. Fleming-Dutra and the CDC COVID-19 Response Team reported.
With a prevalence of 10.9%, diabetes mellitus was the most common condition reported among all COVID-19 patients, followed by chronic lung disease (9.2%) and cardiovascular disease (9.0%), the investigators said.
Another look at the data shows that 40.5% of those with underlying conditions were hospitalized, compared with 9.0% of the 4,470 COVID-19 patients without any risk factors.
“Strategies to protect all persons and especially those with underlying health conditions, including social distancing and handwashing, should be implemented by all communities and all persons to help slow the spread of COVID-19,” the response team wrote.
SOURCE: Fleming-Dutra K et al. MMWR. 2020 Mar 31;69 (early release):1-5.
Greater prevalence of underlying health conditions such as diabetes and chronic lung disease was seen among nearly 7,200 Americans hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Of the 122,653 laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 cases reported to the CDC as of March 28, the COVID-19 Response Team had access to data on the presence or absence of underlying health conditions and other recognized risk factors for severe outcomes from respiratory infections for 7,162 (5.8%) patients.
“Among these patients, higher percentages of patients with underlying conditions were admitted to the hospital and to an ICU than patients without reported underlying conditions. These results are consistent with findings from China and Italy,” Katherine Fleming-Dutra, MD, and associates said in the MMWR.
Individuals with underlying health conditions/risk factors made up 37.6% of all COVID-19 patients in the study but represented a majority of ICU (78%) and non-ICU (71%) hospital admissions. In contrast, 73% of COVID-19 patients who were not hospitalized had no underlying conditions, Dr. Fleming-Dutra and the CDC COVID-19 Response Team reported.
With a prevalence of 10.9%, diabetes mellitus was the most common condition reported among all COVID-19 patients, followed by chronic lung disease (9.2%) and cardiovascular disease (9.0%), the investigators said.
Another look at the data shows that 40.5% of those with underlying conditions were hospitalized, compared with 9.0% of the 4,470 COVID-19 patients without any risk factors.
“Strategies to protect all persons and especially those with underlying health conditions, including social distancing and handwashing, should be implemented by all communities and all persons to help slow the spread of COVID-19,” the response team wrote.
SOURCE: Fleming-Dutra K et al. MMWR. 2020 Mar 31;69 (early release):1-5.
Greater prevalence of underlying health conditions such as diabetes and chronic lung disease was seen among nearly 7,200 Americans hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Of the 122,653 laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 cases reported to the CDC as of March 28, the COVID-19 Response Team had access to data on the presence or absence of underlying health conditions and other recognized risk factors for severe outcomes from respiratory infections for 7,162 (5.8%) patients.
“Among these patients, higher percentages of patients with underlying conditions were admitted to the hospital and to an ICU than patients without reported underlying conditions. These results are consistent with findings from China and Italy,” Katherine Fleming-Dutra, MD, and associates said in the MMWR.
Individuals with underlying health conditions/risk factors made up 37.6% of all COVID-19 patients in the study but represented a majority of ICU (78%) and non-ICU (71%) hospital admissions. In contrast, 73% of COVID-19 patients who were not hospitalized had no underlying conditions, Dr. Fleming-Dutra and the CDC COVID-19 Response Team reported.
With a prevalence of 10.9%, diabetes mellitus was the most common condition reported among all COVID-19 patients, followed by chronic lung disease (9.2%) and cardiovascular disease (9.0%), the investigators said.
Another look at the data shows that 40.5% of those with underlying conditions were hospitalized, compared with 9.0% of the 4,470 COVID-19 patients without any risk factors.
“Strategies to protect all persons and especially those with underlying health conditions, including social distancing and handwashing, should be implemented by all communities and all persons to help slow the spread of COVID-19,” the response team wrote.
SOURCE: Fleming-Dutra K et al. MMWR. 2020 Mar 31;69 (early release):1-5.
FROM MMWR
SARS serum neutralizing antibodies may inform the treatment of COVID-19
The immune responses of specific antibodies were maintained in more than 90% of recovered SARS-CoV patients for 2 years, raising the likelihood that the similarly behaving SARS-CoV-2 might provoke the same response, according to an online communication published in the Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection.
The authors cited a cohort study of convalescent SARS-CoV patients (56 cases, from the Beijing hospital of the Armed Forces Police, China) that showed that specific IgG antibodies and neutralizing antibodies were highly correlated, peaking at month 4 after the onset of disease and decreasing gradually thereafter.
This and other studies suggest that the immune responses of specific antibodies were maintained in more than 90% of recovered SARS-CoV patients for 2 years, according to the authors.
However, of particular concern is the fact that only 11.8% of patients acquire specific SARS-CoV Abs in the early period after recovery at day 7, not reaching 100% until day 90, which highlights the importance of the detection of antibody titers for convalescent COVID-19 patients, according to the authors. “Otherwise, these patients with low titers of antibodies may not be efficient for the clearance of SARS-CoV-2.”
The authors also cited a recent study that showed how neutralizing antibody from a convalescent SARS patient could block the SARS-CoV-2 from entering into target cells in vitro, and suggested that previous experimental SARS-CoV vaccines and neutralizing antibodies could provide novel preventive and therapeutic options for COVID-19.
“These experiences from SARS-CoV are expected to have some implications for the treatment, management and surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 patients,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE: Lin Q et al. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2020 Mar 25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.015.
The immune responses of specific antibodies were maintained in more than 90% of recovered SARS-CoV patients for 2 years, raising the likelihood that the similarly behaving SARS-CoV-2 might provoke the same response, according to an online communication published in the Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection.
The authors cited a cohort study of convalescent SARS-CoV patients (56 cases, from the Beijing hospital of the Armed Forces Police, China) that showed that specific IgG antibodies and neutralizing antibodies were highly correlated, peaking at month 4 after the onset of disease and decreasing gradually thereafter.
This and other studies suggest that the immune responses of specific antibodies were maintained in more than 90% of recovered SARS-CoV patients for 2 years, according to the authors.
However, of particular concern is the fact that only 11.8% of patients acquire specific SARS-CoV Abs in the early period after recovery at day 7, not reaching 100% until day 90, which highlights the importance of the detection of antibody titers for convalescent COVID-19 patients, according to the authors. “Otherwise, these patients with low titers of antibodies may not be efficient for the clearance of SARS-CoV-2.”
The authors also cited a recent study that showed how neutralizing antibody from a convalescent SARS patient could block the SARS-CoV-2 from entering into target cells in vitro, and suggested that previous experimental SARS-CoV vaccines and neutralizing antibodies could provide novel preventive and therapeutic options for COVID-19.
“These experiences from SARS-CoV are expected to have some implications for the treatment, management and surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 patients,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE: Lin Q et al. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2020 Mar 25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.015.
The immune responses of specific antibodies were maintained in more than 90% of recovered SARS-CoV patients for 2 years, raising the likelihood that the similarly behaving SARS-CoV-2 might provoke the same response, according to an online communication published in the Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection.
The authors cited a cohort study of convalescent SARS-CoV patients (56 cases, from the Beijing hospital of the Armed Forces Police, China) that showed that specific IgG antibodies and neutralizing antibodies were highly correlated, peaking at month 4 after the onset of disease and decreasing gradually thereafter.
This and other studies suggest that the immune responses of specific antibodies were maintained in more than 90% of recovered SARS-CoV patients for 2 years, according to the authors.
However, of particular concern is the fact that only 11.8% of patients acquire specific SARS-CoV Abs in the early period after recovery at day 7, not reaching 100% until day 90, which highlights the importance of the detection of antibody titers for convalescent COVID-19 patients, according to the authors. “Otherwise, these patients with low titers of antibodies may not be efficient for the clearance of SARS-CoV-2.”
The authors also cited a recent study that showed how neutralizing antibody from a convalescent SARS patient could block the SARS-CoV-2 from entering into target cells in vitro, and suggested that previous experimental SARS-CoV vaccines and neutralizing antibodies could provide novel preventive and therapeutic options for COVID-19.
“These experiences from SARS-CoV are expected to have some implications for the treatment, management and surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 patients,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE: Lin Q et al. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2020 Mar 25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.015.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF MICROBIOLOGY, IMMUNOLOGY AND INFECTION
COVID-19: More hydroxychloroquine data from France, more questions
A controversial study led by Didier Raoult, MD, PhD, on the combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in patients with COVID-19 was published March 20. The latest results from the same Marseille team, which involve 80 patients, were reported on March 27.
The investigators report a significant reduction in the viral load (83% patients had negative results on quantitative polymerase chain reaction testing at day 7, and 93% had negative results on day 8). There was a “clinical improvement compared to the natural progression.” One death occurred, and three patients were transferred to intensive care units.
If the data seem encouraging, the lack of a control arm in the study leaves clinicians perplexed, however.
Benjamin Davido, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Raymond-Poincaré Hospital in Garches, Paris, spoke in an interview about the implications of these new results.
What do you think about the new results presented by Prof. Raoult’s team? Do they confirm the effectiveness of hydroxychloroquine?
These results are complementary [to the original results] but don’t offer any new information or new statistical evidence. They are absolutely superimposable and say overall that, between 5 and 7 days [of treatment], very few patients shed the virus. But that is not the question that everyone is asking.
Even if we don’t necessarily have to conduct a randomized study, we should at least compare the treatment, either against another therapy – which could be hydroxychloroquine monotherapy, or just standard of care. It needed an authentic control arm.
To recruit 80 patients so quickly, the researchers probably took people with essentially ambulatory forms of the disease (there was a call for screening in the south of France) – therefore, by definition, less severe cases.
But to describe such a population of patients as going home and saying, “There were very few hospitalizations and it is going well,” does not in any way prove that the treatment reduces hospitalizations.
The argument for not having a control arm in this study was that it would be unethical. What do you think?
I agree with this argument when it comes to patients presenting with risk factors or who are starting to develop pneumonia.
But I don’t think this is the case at the beginning of the illness. Of course, you don’t want to wait to have severe disease or for the patient to be in intensive care to start treatment. In these cases, it is indeed very difficult to find a control arm.
In the ongoing Discovery trial, which involves more than 3,000 patients in Europe, including 800 in France, the patients have severe disease, and there are five treatment arms. Moreover, hydroxychloroquine is given without azithromycin. What do you think of this?
I think it’s a mistake. It will not answer the question of the effectiveness of hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19, especially as they’re not studying azithromycin in a situation where the compound seems necessary for the effectiveness of the treatment.
In addition, Discovery reinforces the notion of studying Kaletra [lopinavir/ritonavir, AbbVie] again, while Chinese researchers have shown that it does not work, the argument being that Kaletra was given too late (N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282). Therefore, if we make the same mistakes from a methodological point of view, we will end up with negative results.
What should have been done in the Marseille study?
The question is: Are there more or fewer hospitalizations when we treat a homogeneous population straight away?
The answer could be very clear, as a control already exists! They are the patients that flow into our hospitals every day – ironically, these 80 patients [in the latest results, presented March 27] could be among the 80% who had a form similar to nasopharyngitis and resolved.
In this illness, we know that there are 80% spontaneous recoveries and 20% so-called severe forms. Therefore, with 80 patients, we are very underpowered. The cohort is too small for a disease in which 80% of the evolution is benign.
It would take 1,000 patients, and then, even without a control arm, we would have an answer.
On March 26, Didier Raoult’s team also announced having already treated 700 patients with hydroxychloroquine, with only one death. Therefore, if this cohort increases significantly in Marseille and we see that, on the map, there are fewer issues with patient flow and saturation in Marseille and that there are fewer patients in intensive care, you will have to wonder about the effect of hydroxychloroquine.
We will find out very quickly. If it really works, and they treat all the patients presenting at Timone Hospital, we will soon have the answer. It will be a real-life study.
What are the other studies on hydroxychloroquine that could give us answers?
There was a Chinese study that did not show a difference in effectiveness between hydroxychloroquine and placebo, but that was, again, conducted in only around 20 patients (J Zhejiang Univ (Med Sci). 2020. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2020.03.03). This cohort is too small and tells us nothing; it cannot show anything. We must wait for the results of larger trials being conducted in China.
It surprises me that, today, we still do not have Italian data on the use of chloroquine-type drugs ... perhaps because they have a care pathway that means there is no outpatient treatment and that they arrive already with severe disease. The Italian recommendations nevertheless indicate the use of hydroxychloroquine.
I also wonder about the lack of studies of cohorts where, in retrospect, we could have followed people previously treated with hydroxychloroquine for chronic diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, etc.). Or we could identify all those patients on the health insurance system who had prescriptions.
That is how we discovered the AIDS epidemic in San Francisco: There was an increase in the number of prescriptions for trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim) that corresponded to a population subtype (homosexual), and we realized that it was for a disease that resembled pneumocystosis. We discovered that via the drug!
If hydroxychloroquine is effective, it is enough to look at people who took it before the epidemic and see how they fared. And there, we do not need a control arm. This could give us some direction. The March 26 decree of the new Véran Law states that community pharmacies can dispense to patients with a previous prescription, so we can find these individuals.
Do you think that the lack of, or difficulty in setting up, studies on hydroxychloroquine in France is linked to decisions that are more political than scientific?
Perhaps the contaminated blood scandal still casts a shadow in France, and there is a great deal of anxiety over the fact that we are already in a crisis, and we do not want a second one. I can understand that.
However, just a week ago, access to this drug (and others with market approval that have been on the market for several years) was blocked in hospital central pharmacies, while we are the medical specialists with the authorization! It was unacceptable.
It was sorted out 48 hours ago: hydroxychloroquine is now available in the hospital, and to my knowledge, we no longer have a problem obtaining it.
It took time to alleviate doubts over the major health risks with this drug. [Officials] seemed almost like amateurs in their hesitation; I think they lacked foresight. We have forgotten that the treatment advocated by Prof. Didier Raoult is not chloroquine but rather hydroxychloroquine, and we know that the adverse effects are less [with hydroxychloroquine] than with chloroquine.
You yourself have treated patients with chloroquine, despite the risk for toxicity highlighted by some.
Initially, when we first started treating patients, we thought of chloroquine because we did not have data on hydroxychloroquine, only Chinese data with chloroquine. We therefore prescribed chloroquine several days before prescribing hydroxychloroquine.
The question of the toxicity of chloroquine was not unjustified, but I think we took far too much time to decide on the toxicity of hydroxychloroquine. Is [the latter] political? I don’t know. It was widely publicized, which amazes me for a drug that is already available.
On the other hand, everyone was talking at the same time about the toxicity of NSAIDs. ... One has the impression it was to create a diversion. I think there were double standards at play and a scapegoat was needed to gain some time and ask questions.
What is sure is that it is probably not for financial reasons, as hydroxychloroquine costs nothing. That’s to say there were probably pharmaceutical issues at stake for possible competitors of hydroxychloroquine; I do not want to get into this debate, and it doesn’t matter, as long as we have an answer.
Today, the only thing we have advanced on is the “safety” of hydroxychloroquine, the low risk to the general population. ... On the other hand, we have still not made any progress on the evidence of efficacy, compared with other treatments.
Personally, I really believe in hydroxychloroquine. It would nevertheless be a shame to think we had found the fountain of youth and realize, in 4 weeks, that we have the same number of deaths. That is the problem. I hope that we will soon have solid data so we do not waste time focusing solely on hydroxychloroquine.
What are the other avenues of research that grab your attention?
The Discovery trial will probably give an answer on remdesivir [GS-5734, Gilead], which is a direct antiviral and could be interesting. But there are other studies being conducted currently in China.
There is also favipiravir [T-705, Avigan, Toyama Chemical], which is an anti-influenza drug used in Japan, which could explain, in part, the control of the epidemic in that country. There are effects in vitro on coronavirus. But it is not at all studied in France at the moment. Therefore, we should not focus exclusively on hydroxychloroquine; we must keep a close eye on other molecules, in particular the “old” drugs, like this antiviral.
The study was supported by the Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire (IHU) Méditerranée Infection, the National Research Agency, under the Investissements d’avenir program, Région Provence Alpes Côte d’Azur, and European funding FEDER PRIMI. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A controversial study led by Didier Raoult, MD, PhD, on the combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in patients with COVID-19 was published March 20. The latest results from the same Marseille team, which involve 80 patients, were reported on March 27.
The investigators report a significant reduction in the viral load (83% patients had negative results on quantitative polymerase chain reaction testing at day 7, and 93% had negative results on day 8). There was a “clinical improvement compared to the natural progression.” One death occurred, and three patients were transferred to intensive care units.
If the data seem encouraging, the lack of a control arm in the study leaves clinicians perplexed, however.
Benjamin Davido, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Raymond-Poincaré Hospital in Garches, Paris, spoke in an interview about the implications of these new results.
What do you think about the new results presented by Prof. Raoult’s team? Do they confirm the effectiveness of hydroxychloroquine?
These results are complementary [to the original results] but don’t offer any new information or new statistical evidence. They are absolutely superimposable and say overall that, between 5 and 7 days [of treatment], very few patients shed the virus. But that is not the question that everyone is asking.
Even if we don’t necessarily have to conduct a randomized study, we should at least compare the treatment, either against another therapy – which could be hydroxychloroquine monotherapy, or just standard of care. It needed an authentic control arm.
To recruit 80 patients so quickly, the researchers probably took people with essentially ambulatory forms of the disease (there was a call for screening in the south of France) – therefore, by definition, less severe cases.
But to describe such a population of patients as going home and saying, “There were very few hospitalizations and it is going well,” does not in any way prove that the treatment reduces hospitalizations.
The argument for not having a control arm in this study was that it would be unethical. What do you think?
I agree with this argument when it comes to patients presenting with risk factors or who are starting to develop pneumonia.
But I don’t think this is the case at the beginning of the illness. Of course, you don’t want to wait to have severe disease or for the patient to be in intensive care to start treatment. In these cases, it is indeed very difficult to find a control arm.
In the ongoing Discovery trial, which involves more than 3,000 patients in Europe, including 800 in France, the patients have severe disease, and there are five treatment arms. Moreover, hydroxychloroquine is given without azithromycin. What do you think of this?
I think it’s a mistake. It will not answer the question of the effectiveness of hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19, especially as they’re not studying azithromycin in a situation where the compound seems necessary for the effectiveness of the treatment.
In addition, Discovery reinforces the notion of studying Kaletra [lopinavir/ritonavir, AbbVie] again, while Chinese researchers have shown that it does not work, the argument being that Kaletra was given too late (N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282). Therefore, if we make the same mistakes from a methodological point of view, we will end up with negative results.
What should have been done in the Marseille study?
The question is: Are there more or fewer hospitalizations when we treat a homogeneous population straight away?
The answer could be very clear, as a control already exists! They are the patients that flow into our hospitals every day – ironically, these 80 patients [in the latest results, presented March 27] could be among the 80% who had a form similar to nasopharyngitis and resolved.
In this illness, we know that there are 80% spontaneous recoveries and 20% so-called severe forms. Therefore, with 80 patients, we are very underpowered. The cohort is too small for a disease in which 80% of the evolution is benign.
It would take 1,000 patients, and then, even without a control arm, we would have an answer.
On March 26, Didier Raoult’s team also announced having already treated 700 patients with hydroxychloroquine, with only one death. Therefore, if this cohort increases significantly in Marseille and we see that, on the map, there are fewer issues with patient flow and saturation in Marseille and that there are fewer patients in intensive care, you will have to wonder about the effect of hydroxychloroquine.
We will find out very quickly. If it really works, and they treat all the patients presenting at Timone Hospital, we will soon have the answer. It will be a real-life study.
What are the other studies on hydroxychloroquine that could give us answers?
There was a Chinese study that did not show a difference in effectiveness between hydroxychloroquine and placebo, but that was, again, conducted in only around 20 patients (J Zhejiang Univ (Med Sci). 2020. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2020.03.03). This cohort is too small and tells us nothing; it cannot show anything. We must wait for the results of larger trials being conducted in China.
It surprises me that, today, we still do not have Italian data on the use of chloroquine-type drugs ... perhaps because they have a care pathway that means there is no outpatient treatment and that they arrive already with severe disease. The Italian recommendations nevertheless indicate the use of hydroxychloroquine.
I also wonder about the lack of studies of cohorts where, in retrospect, we could have followed people previously treated with hydroxychloroquine for chronic diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, etc.). Or we could identify all those patients on the health insurance system who had prescriptions.
That is how we discovered the AIDS epidemic in San Francisco: There was an increase in the number of prescriptions for trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim) that corresponded to a population subtype (homosexual), and we realized that it was for a disease that resembled pneumocystosis. We discovered that via the drug!
If hydroxychloroquine is effective, it is enough to look at people who took it before the epidemic and see how they fared. And there, we do not need a control arm. This could give us some direction. The March 26 decree of the new Véran Law states that community pharmacies can dispense to patients with a previous prescription, so we can find these individuals.
Do you think that the lack of, or difficulty in setting up, studies on hydroxychloroquine in France is linked to decisions that are more political than scientific?
Perhaps the contaminated blood scandal still casts a shadow in France, and there is a great deal of anxiety over the fact that we are already in a crisis, and we do not want a second one. I can understand that.
However, just a week ago, access to this drug (and others with market approval that have been on the market for several years) was blocked in hospital central pharmacies, while we are the medical specialists with the authorization! It was unacceptable.
It was sorted out 48 hours ago: hydroxychloroquine is now available in the hospital, and to my knowledge, we no longer have a problem obtaining it.
It took time to alleviate doubts over the major health risks with this drug. [Officials] seemed almost like amateurs in their hesitation; I think they lacked foresight. We have forgotten that the treatment advocated by Prof. Didier Raoult is not chloroquine but rather hydroxychloroquine, and we know that the adverse effects are less [with hydroxychloroquine] than with chloroquine.
You yourself have treated patients with chloroquine, despite the risk for toxicity highlighted by some.
Initially, when we first started treating patients, we thought of chloroquine because we did not have data on hydroxychloroquine, only Chinese data with chloroquine. We therefore prescribed chloroquine several days before prescribing hydroxychloroquine.
The question of the toxicity of chloroquine was not unjustified, but I think we took far too much time to decide on the toxicity of hydroxychloroquine. Is [the latter] political? I don’t know. It was widely publicized, which amazes me for a drug that is already available.
On the other hand, everyone was talking at the same time about the toxicity of NSAIDs. ... One has the impression it was to create a diversion. I think there were double standards at play and a scapegoat was needed to gain some time and ask questions.
What is sure is that it is probably not for financial reasons, as hydroxychloroquine costs nothing. That’s to say there were probably pharmaceutical issues at stake for possible competitors of hydroxychloroquine; I do not want to get into this debate, and it doesn’t matter, as long as we have an answer.
Today, the only thing we have advanced on is the “safety” of hydroxychloroquine, the low risk to the general population. ... On the other hand, we have still not made any progress on the evidence of efficacy, compared with other treatments.
Personally, I really believe in hydroxychloroquine. It would nevertheless be a shame to think we had found the fountain of youth and realize, in 4 weeks, that we have the same number of deaths. That is the problem. I hope that we will soon have solid data so we do not waste time focusing solely on hydroxychloroquine.
What are the other avenues of research that grab your attention?
The Discovery trial will probably give an answer on remdesivir [GS-5734, Gilead], which is a direct antiviral and could be interesting. But there are other studies being conducted currently in China.
There is also favipiravir [T-705, Avigan, Toyama Chemical], which is an anti-influenza drug used in Japan, which could explain, in part, the control of the epidemic in that country. There are effects in vitro on coronavirus. But it is not at all studied in France at the moment. Therefore, we should not focus exclusively on hydroxychloroquine; we must keep a close eye on other molecules, in particular the “old” drugs, like this antiviral.
The study was supported by the Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire (IHU) Méditerranée Infection, the National Research Agency, under the Investissements d’avenir program, Région Provence Alpes Côte d’Azur, and European funding FEDER PRIMI. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A controversial study led by Didier Raoult, MD, PhD, on the combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in patients with COVID-19 was published March 20. The latest results from the same Marseille team, which involve 80 patients, were reported on March 27.
The investigators report a significant reduction in the viral load (83% patients had negative results on quantitative polymerase chain reaction testing at day 7, and 93% had negative results on day 8). There was a “clinical improvement compared to the natural progression.” One death occurred, and three patients were transferred to intensive care units.
If the data seem encouraging, the lack of a control arm in the study leaves clinicians perplexed, however.
Benjamin Davido, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Raymond-Poincaré Hospital in Garches, Paris, spoke in an interview about the implications of these new results.
What do you think about the new results presented by Prof. Raoult’s team? Do they confirm the effectiveness of hydroxychloroquine?
These results are complementary [to the original results] but don’t offer any new information or new statistical evidence. They are absolutely superimposable and say overall that, between 5 and 7 days [of treatment], very few patients shed the virus. But that is not the question that everyone is asking.
Even if we don’t necessarily have to conduct a randomized study, we should at least compare the treatment, either against another therapy – which could be hydroxychloroquine monotherapy, or just standard of care. It needed an authentic control arm.
To recruit 80 patients so quickly, the researchers probably took people with essentially ambulatory forms of the disease (there was a call for screening in the south of France) – therefore, by definition, less severe cases.
But to describe such a population of patients as going home and saying, “There were very few hospitalizations and it is going well,” does not in any way prove that the treatment reduces hospitalizations.
The argument for not having a control arm in this study was that it would be unethical. What do you think?
I agree with this argument when it comes to patients presenting with risk factors or who are starting to develop pneumonia.
But I don’t think this is the case at the beginning of the illness. Of course, you don’t want to wait to have severe disease or for the patient to be in intensive care to start treatment. In these cases, it is indeed very difficult to find a control arm.
In the ongoing Discovery trial, which involves more than 3,000 patients in Europe, including 800 in France, the patients have severe disease, and there are five treatment arms. Moreover, hydroxychloroquine is given without azithromycin. What do you think of this?
I think it’s a mistake. It will not answer the question of the effectiveness of hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19, especially as they’re not studying azithromycin in a situation where the compound seems necessary for the effectiveness of the treatment.
In addition, Discovery reinforces the notion of studying Kaletra [lopinavir/ritonavir, AbbVie] again, while Chinese researchers have shown that it does not work, the argument being that Kaletra was given too late (N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282). Therefore, if we make the same mistakes from a methodological point of view, we will end up with negative results.
What should have been done in the Marseille study?
The question is: Are there more or fewer hospitalizations when we treat a homogeneous population straight away?
The answer could be very clear, as a control already exists! They are the patients that flow into our hospitals every day – ironically, these 80 patients [in the latest results, presented March 27] could be among the 80% who had a form similar to nasopharyngitis and resolved.
In this illness, we know that there are 80% spontaneous recoveries and 20% so-called severe forms. Therefore, with 80 patients, we are very underpowered. The cohort is too small for a disease in which 80% of the evolution is benign.
It would take 1,000 patients, and then, even without a control arm, we would have an answer.
On March 26, Didier Raoult’s team also announced having already treated 700 patients with hydroxychloroquine, with only one death. Therefore, if this cohort increases significantly in Marseille and we see that, on the map, there are fewer issues with patient flow and saturation in Marseille and that there are fewer patients in intensive care, you will have to wonder about the effect of hydroxychloroquine.
We will find out very quickly. If it really works, and they treat all the patients presenting at Timone Hospital, we will soon have the answer. It will be a real-life study.
What are the other studies on hydroxychloroquine that could give us answers?
There was a Chinese study that did not show a difference in effectiveness between hydroxychloroquine and placebo, but that was, again, conducted in only around 20 patients (J Zhejiang Univ (Med Sci). 2020. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2020.03.03). This cohort is too small and tells us nothing; it cannot show anything. We must wait for the results of larger trials being conducted in China.
It surprises me that, today, we still do not have Italian data on the use of chloroquine-type drugs ... perhaps because they have a care pathway that means there is no outpatient treatment and that they arrive already with severe disease. The Italian recommendations nevertheless indicate the use of hydroxychloroquine.
I also wonder about the lack of studies of cohorts where, in retrospect, we could have followed people previously treated with hydroxychloroquine for chronic diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, etc.). Or we could identify all those patients on the health insurance system who had prescriptions.
That is how we discovered the AIDS epidemic in San Francisco: There was an increase in the number of prescriptions for trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim) that corresponded to a population subtype (homosexual), and we realized that it was for a disease that resembled pneumocystosis. We discovered that via the drug!
If hydroxychloroquine is effective, it is enough to look at people who took it before the epidemic and see how they fared. And there, we do not need a control arm. This could give us some direction. The March 26 decree of the new Véran Law states that community pharmacies can dispense to patients with a previous prescription, so we can find these individuals.
Do you think that the lack of, or difficulty in setting up, studies on hydroxychloroquine in France is linked to decisions that are more political than scientific?
Perhaps the contaminated blood scandal still casts a shadow in France, and there is a great deal of anxiety over the fact that we are already in a crisis, and we do not want a second one. I can understand that.
However, just a week ago, access to this drug (and others with market approval that have been on the market for several years) was blocked in hospital central pharmacies, while we are the medical specialists with the authorization! It was unacceptable.
It was sorted out 48 hours ago: hydroxychloroquine is now available in the hospital, and to my knowledge, we no longer have a problem obtaining it.
It took time to alleviate doubts over the major health risks with this drug. [Officials] seemed almost like amateurs in their hesitation; I think they lacked foresight. We have forgotten that the treatment advocated by Prof. Didier Raoult is not chloroquine but rather hydroxychloroquine, and we know that the adverse effects are less [with hydroxychloroquine] than with chloroquine.
You yourself have treated patients with chloroquine, despite the risk for toxicity highlighted by some.
Initially, when we first started treating patients, we thought of chloroquine because we did not have data on hydroxychloroquine, only Chinese data with chloroquine. We therefore prescribed chloroquine several days before prescribing hydroxychloroquine.
The question of the toxicity of chloroquine was not unjustified, but I think we took far too much time to decide on the toxicity of hydroxychloroquine. Is [the latter] political? I don’t know. It was widely publicized, which amazes me for a drug that is already available.
On the other hand, everyone was talking at the same time about the toxicity of NSAIDs. ... One has the impression it was to create a diversion. I think there were double standards at play and a scapegoat was needed to gain some time and ask questions.
What is sure is that it is probably not for financial reasons, as hydroxychloroquine costs nothing. That’s to say there were probably pharmaceutical issues at stake for possible competitors of hydroxychloroquine; I do not want to get into this debate, and it doesn’t matter, as long as we have an answer.
Today, the only thing we have advanced on is the “safety” of hydroxychloroquine, the low risk to the general population. ... On the other hand, we have still not made any progress on the evidence of efficacy, compared with other treatments.
Personally, I really believe in hydroxychloroquine. It would nevertheless be a shame to think we had found the fountain of youth and realize, in 4 weeks, that we have the same number of deaths. That is the problem. I hope that we will soon have solid data so we do not waste time focusing solely on hydroxychloroquine.
What are the other avenues of research that grab your attention?
The Discovery trial will probably give an answer on remdesivir [GS-5734, Gilead], which is a direct antiviral and could be interesting. But there are other studies being conducted currently in China.
There is also favipiravir [T-705, Avigan, Toyama Chemical], which is an anti-influenza drug used in Japan, which could explain, in part, the control of the epidemic in that country. There are effects in vitro on coronavirus. But it is not at all studied in France at the moment. Therefore, we should not focus exclusively on hydroxychloroquine; we must keep a close eye on other molecules, in particular the “old” drugs, like this antiviral.
The study was supported by the Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire (IHU) Méditerranée Infection, the National Research Agency, under the Investissements d’avenir program, Région Provence Alpes Côte d’Azur, and European funding FEDER PRIMI. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Case fatality rate for COVID-19 near 1.4%, increases with age
The risk for death from COVID-19 is 1.38% overall, according to a new study. However, the fatality rate rises with age, from well below 1% among children aged 9 years or younger to nearly 8% for seniors aged 80 years or older, the latest statistics show.
“These early estimates give an indication of the fatality ratio across the spectrum of COVID-19 disease and show a strong age gradient in risk of death,” Robert Verity, PhD, of University College London, and colleagues, wrote in a study published online in the Lancet Infectious Diseases.
Among those infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, the risk for hospitalization also increases with age. Specifically, 11.8% of people in their 60s require admission, as do 16.6% of people in their 70s and 18.4% for those in their 80s or older.
The case fatality estimates are based on data regarding individual patients who died from COVID-19 in Hubei, China, through Feb. 8, as well as those who died in Hong Kong, Macau, and 37 countries outside China through Feb. 25.
“It is clear from the data that have emerged from China that case fatality ratio increases substantially with age. Our results suggest a very low fatality ratio in those under the age of 20 years. As there are very few cases in this age group, it remains unclear whether this reflects a low risk of death or a difference in susceptibility, although early results indicate young people are not at lower risk of infection than adults,” Dr. Verity and colleagues wrote.
The authors emphasized that serologic testing of adolescents and children will be vital to understanding how individuals younger than 20 years may be driving viral transmission.
In an accompanying editorial Shigui Ruan, PhD, of the department of mathematics at the University of Miami in Coral Gables, Fla., wrote that early detection, diagnosis, isolation, and treatment, as practiced in China, may help to prevent more deaths
“Even though the fatality rate is low for younger people, it is very clear that any suggestion of COVID-19 being just like influenza is false: Even for those aged 20-29 years, once infected with SARS-CoV-2, the mortality rate is 33 times higher than that from seasonal influenza,” he noted.
Dr. Ruan, who uses applied mathematics to model disease transmission, noted that otherwise healthy people stand a good chance – approximately 95% – of surviving COVID-19, but the odds of survival for people with comorbidities will be “considerably decreased.”
Time to death or discharge
Dr. Verity and colleagues first used data on deaths of 24 patients in mainland China and on 165 persons who recovered from infection outside of China to estimate the time between onset of symptoms and either death or discharge from the hospital. They estimated that the mean duration from symptom onset to death is 17.8 days, and the mean duration to discharge is 24.7 days.
They then estimated age-stratified case fatality ratios among all clinically diagnosed and laboratory-confirmed cases in mainland China to the end of the study period (70,117 cases).
The estimated crude case fatality ratio, adjusted for censoring, was 3.67%. With further adjustment for demographic characteristics and under-ascertainment, the authors’ best estimate of a case fatality ratio in China is 1.38%.
The following figure shows adjusted fatality infection rates by age group.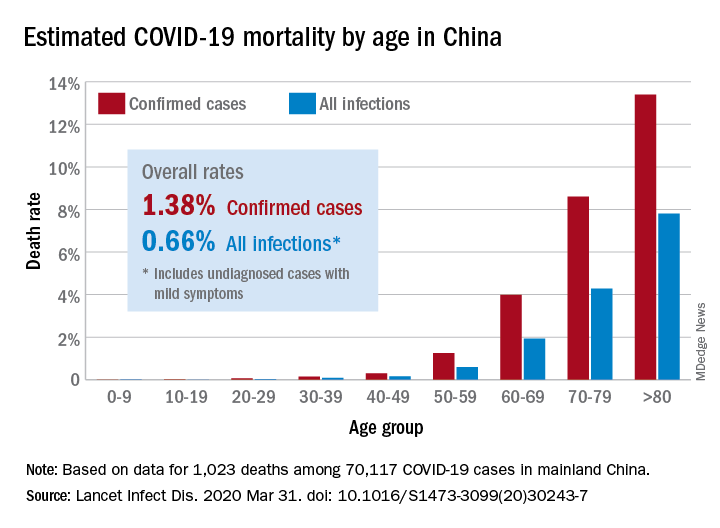
The investigators noted that the case fatality estimate is lower than the estimates for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) outbreaks, both caused by coronaviruses, but “is substantially higher than estimates from the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic.”
Earlier reports suggested that the overall fatality rate in China through Feb. 11 was 2.3%. The rate in Hubei province, which is believed to be where the infection started, was 2.9%.
Hospitalizations rise with age
The investigators also estimated the proportion of infected patients who require hospitalization. Their estimation was based on data from a subset of cases reported in mainland China. The hospitalization estimates range from zero among the youngest patients to 18% among the oldest.
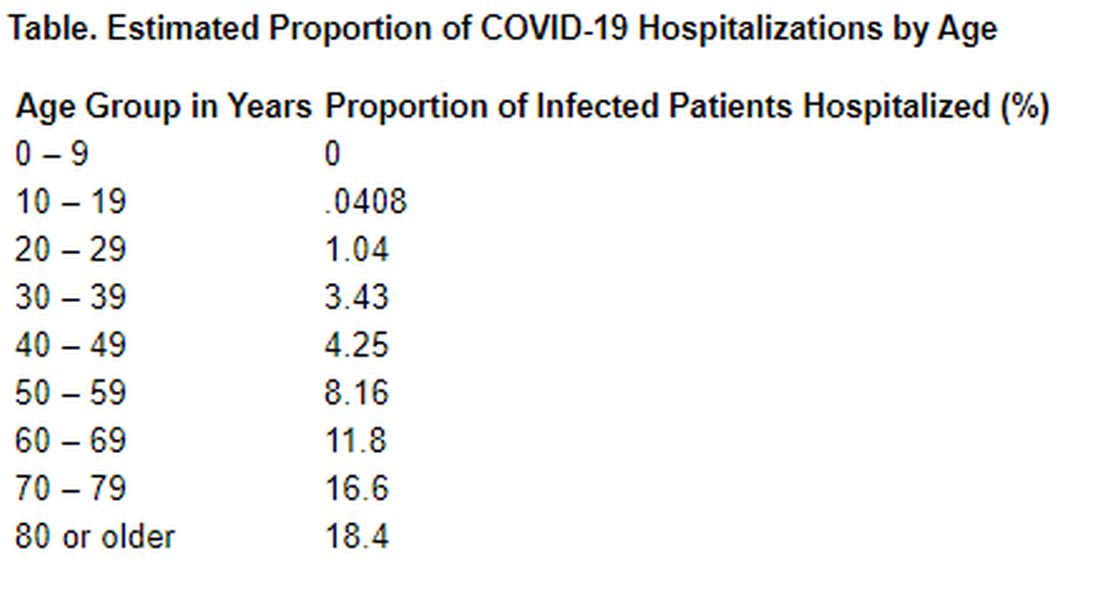
“Although China has succeeded in containing the disease spread for 2 months, such containment is unlikely to be achievable in most countries. Thus, much of the world will experience very large community epidemics of COVID-19 over the coming weeks and months. Our estimates of the underlying infection fatality ratio of this virus will inform assessments of health effects likely to be experienced in different countries, and thus decisions around appropriate mitigation policies to be adopted,” Dr. Verity and colleagues concluded.
In his editorial, Dr. Ruan agreed with that assessment. “Although China seems to be out of the woods now, many other countries are facing tremendous pressure from the COVID-19 pandemic,” he wrote. “The strategies of early detection, early diagnosis, early isolation, and early treatment that were practiced in China are likely to be not only useful in controlling the outbreak but also contribute to decreasing the case fatality ratio of the disease.”
The study was supported by the UK Medical Research Council. Dr. Verity and Dr. Ruan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk for death from COVID-19 is 1.38% overall, according to a new study. However, the fatality rate rises with age, from well below 1% among children aged 9 years or younger to nearly 8% for seniors aged 80 years or older, the latest statistics show.
“These early estimates give an indication of the fatality ratio across the spectrum of COVID-19 disease and show a strong age gradient in risk of death,” Robert Verity, PhD, of University College London, and colleagues, wrote in a study published online in the Lancet Infectious Diseases.
Among those infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, the risk for hospitalization also increases with age. Specifically, 11.8% of people in their 60s require admission, as do 16.6% of people in their 70s and 18.4% for those in their 80s or older.
The case fatality estimates are based on data regarding individual patients who died from COVID-19 in Hubei, China, through Feb. 8, as well as those who died in Hong Kong, Macau, and 37 countries outside China through Feb. 25.
“It is clear from the data that have emerged from China that case fatality ratio increases substantially with age. Our results suggest a very low fatality ratio in those under the age of 20 years. As there are very few cases in this age group, it remains unclear whether this reflects a low risk of death or a difference in susceptibility, although early results indicate young people are not at lower risk of infection than adults,” Dr. Verity and colleagues wrote.
The authors emphasized that serologic testing of adolescents and children will be vital to understanding how individuals younger than 20 years may be driving viral transmission.
In an accompanying editorial Shigui Ruan, PhD, of the department of mathematics at the University of Miami in Coral Gables, Fla., wrote that early detection, diagnosis, isolation, and treatment, as practiced in China, may help to prevent more deaths
“Even though the fatality rate is low for younger people, it is very clear that any suggestion of COVID-19 being just like influenza is false: Even for those aged 20-29 years, once infected with SARS-CoV-2, the mortality rate is 33 times higher than that from seasonal influenza,” he noted.
Dr. Ruan, who uses applied mathematics to model disease transmission, noted that otherwise healthy people stand a good chance – approximately 95% – of surviving COVID-19, but the odds of survival for people with comorbidities will be “considerably decreased.”
Time to death or discharge
Dr. Verity and colleagues first used data on deaths of 24 patients in mainland China and on 165 persons who recovered from infection outside of China to estimate the time between onset of symptoms and either death or discharge from the hospital. They estimated that the mean duration from symptom onset to death is 17.8 days, and the mean duration to discharge is 24.7 days.
They then estimated age-stratified case fatality ratios among all clinically diagnosed and laboratory-confirmed cases in mainland China to the end of the study period (70,117 cases).
The estimated crude case fatality ratio, adjusted for censoring, was 3.67%. With further adjustment for demographic characteristics and under-ascertainment, the authors’ best estimate of a case fatality ratio in China is 1.38%.
The following figure shows adjusted fatality infection rates by age group.
The investigators noted that the case fatality estimate is lower than the estimates for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) outbreaks, both caused by coronaviruses, but “is substantially higher than estimates from the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic.”
Earlier reports suggested that the overall fatality rate in China through Feb. 11 was 2.3%. The rate in Hubei province, which is believed to be where the infection started, was 2.9%.
Hospitalizations rise with age
The investigators also estimated the proportion of infected patients who require hospitalization. Their estimation was based on data from a subset of cases reported in mainland China. The hospitalization estimates range from zero among the youngest patients to 18% among the oldest.

“Although China has succeeded in containing the disease spread for 2 months, such containment is unlikely to be achievable in most countries. Thus, much of the world will experience very large community epidemics of COVID-19 over the coming weeks and months. Our estimates of the underlying infection fatality ratio of this virus will inform assessments of health effects likely to be experienced in different countries, and thus decisions around appropriate mitigation policies to be adopted,” Dr. Verity and colleagues concluded.
In his editorial, Dr. Ruan agreed with that assessment. “Although China seems to be out of the woods now, many other countries are facing tremendous pressure from the COVID-19 pandemic,” he wrote. “The strategies of early detection, early diagnosis, early isolation, and early treatment that were practiced in China are likely to be not only useful in controlling the outbreak but also contribute to decreasing the case fatality ratio of the disease.”
The study was supported by the UK Medical Research Council. Dr. Verity and Dr. Ruan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk for death from COVID-19 is 1.38% overall, according to a new study. However, the fatality rate rises with age, from well below 1% among children aged 9 years or younger to nearly 8% for seniors aged 80 years or older, the latest statistics show.
“These early estimates give an indication of the fatality ratio across the spectrum of COVID-19 disease and show a strong age gradient in risk of death,” Robert Verity, PhD, of University College London, and colleagues, wrote in a study published online in the Lancet Infectious Diseases.
Among those infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, the risk for hospitalization also increases with age. Specifically, 11.8% of people in their 60s require admission, as do 16.6% of people in their 70s and 18.4% for those in their 80s or older.
The case fatality estimates are based on data regarding individual patients who died from COVID-19 in Hubei, China, through Feb. 8, as well as those who died in Hong Kong, Macau, and 37 countries outside China through Feb. 25.
“It is clear from the data that have emerged from China that case fatality ratio increases substantially with age. Our results suggest a very low fatality ratio in those under the age of 20 years. As there are very few cases in this age group, it remains unclear whether this reflects a low risk of death or a difference in susceptibility, although early results indicate young people are not at lower risk of infection than adults,” Dr. Verity and colleagues wrote.
The authors emphasized that serologic testing of adolescents and children will be vital to understanding how individuals younger than 20 years may be driving viral transmission.
In an accompanying editorial Shigui Ruan, PhD, of the department of mathematics at the University of Miami in Coral Gables, Fla., wrote that early detection, diagnosis, isolation, and treatment, as practiced in China, may help to prevent more deaths
“Even though the fatality rate is low for younger people, it is very clear that any suggestion of COVID-19 being just like influenza is false: Even for those aged 20-29 years, once infected with SARS-CoV-2, the mortality rate is 33 times higher than that from seasonal influenza,” he noted.
Dr. Ruan, who uses applied mathematics to model disease transmission, noted that otherwise healthy people stand a good chance – approximately 95% – of surviving COVID-19, but the odds of survival for people with comorbidities will be “considerably decreased.”
Time to death or discharge
Dr. Verity and colleagues first used data on deaths of 24 patients in mainland China and on 165 persons who recovered from infection outside of China to estimate the time between onset of symptoms and either death or discharge from the hospital. They estimated that the mean duration from symptom onset to death is 17.8 days, and the mean duration to discharge is 24.7 days.
They then estimated age-stratified case fatality ratios among all clinically diagnosed and laboratory-confirmed cases in mainland China to the end of the study period (70,117 cases).
The estimated crude case fatality ratio, adjusted for censoring, was 3.67%. With further adjustment for demographic characteristics and under-ascertainment, the authors’ best estimate of a case fatality ratio in China is 1.38%.
The following figure shows adjusted fatality infection rates by age group.
The investigators noted that the case fatality estimate is lower than the estimates for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) outbreaks, both caused by coronaviruses, but “is substantially higher than estimates from the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic.”
Earlier reports suggested that the overall fatality rate in China through Feb. 11 was 2.3%. The rate in Hubei province, which is believed to be where the infection started, was 2.9%.
Hospitalizations rise with age
The investigators also estimated the proportion of infected patients who require hospitalization. Their estimation was based on data from a subset of cases reported in mainland China. The hospitalization estimates range from zero among the youngest patients to 18% among the oldest.

“Although China has succeeded in containing the disease spread for 2 months, such containment is unlikely to be achievable in most countries. Thus, much of the world will experience very large community epidemics of COVID-19 over the coming weeks and months. Our estimates of the underlying infection fatality ratio of this virus will inform assessments of health effects likely to be experienced in different countries, and thus decisions around appropriate mitigation policies to be adopted,” Dr. Verity and colleagues concluded.
In his editorial, Dr. Ruan agreed with that assessment. “Although China seems to be out of the woods now, many other countries are facing tremendous pressure from the COVID-19 pandemic,” he wrote. “The strategies of early detection, early diagnosis, early isolation, and early treatment that were practiced in China are likely to be not only useful in controlling the outbreak but also contribute to decreasing the case fatality ratio of the disease.”
The study was supported by the UK Medical Research Council. Dr. Verity and Dr. Ruan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19: Adjusting practice in acute leukemia care
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic poses significant risks to leukemia patients and their providers, impacting every aspect of care from diagnosis through therapy, according to an editorial letter published online in Leukemia Research.
One key concern to be considered is the risk of missed or delayed diagnosis due to the pandemic conditions. An estimated 50%-75% of patients with acute leukemia are febrile at diagnosis and this puts them at high risk of a misdiagnosis of COVID-19 upon initial evaluation. As with other oncological conditions (primary mediastinal lymphoma or lung cancer, for example), which often present with a cough with or without fever, their symptoms “are likely to be considered trivial after a negative SARS-CoV-2 test,” with patients then being sent home without further assessment. In a rapidly progressing disease such as acute leukemia, this could lead to critical delays in therapeutic intervention.
The authors, from the Service and Central Laboratory of Hematology, Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, also discussed the problems that might occur with regard to most standard forms of therapy. In particular, they addressed potential impacts of the pandemic on chemotherapy, bone marrow transplantation, maintenance treatments, supportive measures, and targeted therapies.
Of particular concern, “most patients may suffer from postponed chemotherapy, due to a shortage of isolation beds and blood products or the wish to avoid immunosuppressive treatments,” the authors noted, warning that “delay in chemotherapy initiation may negatively affect prognosis, [particularly in patients under age 60] with favorable- or intermediate-risk disease.”
With regard to stem cell transplantation, the authors detail the many potential difficulties with regard to procedures involving both donors and recipients, and warn that in some cases, delay in transplant could result in the reappearance of a significant minimal residual disease, which has a well-established negative impact on survival.
The authors also noted that blood product shortages have already begun in most affected countries, and how, in response, transfusion societies have called for conservative transfusion policies in strict adherence to evidence-based guidelines for patient’s blood management.
“COVID-19 will result in numerous casualties. Acute leukemia patients are at a higher risk of severe complications,” the authors stated. In particular, physicians should especially be aware of how treatment for acute leukemia may have “interactions with other drugs used to treat SARS-CoV-2–related infections/complications such as antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and various other drugs that prolong QTc or impact targeted-therapy pharmacokinetics,” they concluded.
The authors reported that they received no government or private funding for this research, and that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Gavillet M et al. Leuk. Res. 2020. doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2020.106353.
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic poses significant risks to leukemia patients and their providers, impacting every aspect of care from diagnosis through therapy, according to an editorial letter published online in Leukemia Research.
One key concern to be considered is the risk of missed or delayed diagnosis due to the pandemic conditions. An estimated 50%-75% of patients with acute leukemia are febrile at diagnosis and this puts them at high risk of a misdiagnosis of COVID-19 upon initial evaluation. As with other oncological conditions (primary mediastinal lymphoma or lung cancer, for example), which often present with a cough with or without fever, their symptoms “are likely to be considered trivial after a negative SARS-CoV-2 test,” with patients then being sent home without further assessment. In a rapidly progressing disease such as acute leukemia, this could lead to critical delays in therapeutic intervention.
The authors, from the Service and Central Laboratory of Hematology, Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, also discussed the problems that might occur with regard to most standard forms of therapy. In particular, they addressed potential impacts of the pandemic on chemotherapy, bone marrow transplantation, maintenance treatments, supportive measures, and targeted therapies.
Of particular concern, “most patients may suffer from postponed chemotherapy, due to a shortage of isolation beds and blood products or the wish to avoid immunosuppressive treatments,” the authors noted, warning that “delay in chemotherapy initiation may negatively affect prognosis, [particularly in patients under age 60] with favorable- or intermediate-risk disease.”
With regard to stem cell transplantation, the authors detail the many potential difficulties with regard to procedures involving both donors and recipients, and warn that in some cases, delay in transplant could result in the reappearance of a significant minimal residual disease, which has a well-established negative impact on survival.
The authors also noted that blood product shortages have already begun in most affected countries, and how, in response, transfusion societies have called for conservative transfusion policies in strict adherence to evidence-based guidelines for patient’s blood management.
“COVID-19 will result in numerous casualties. Acute leukemia patients are at a higher risk of severe complications,” the authors stated. In particular, physicians should especially be aware of how treatment for acute leukemia may have “interactions with other drugs used to treat SARS-CoV-2–related infections/complications such as antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and various other drugs that prolong QTc or impact targeted-therapy pharmacokinetics,” they concluded.
The authors reported that they received no government or private funding for this research, and that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Gavillet M et al. Leuk. Res. 2020. doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2020.106353.
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic poses significant risks to leukemia patients and their providers, impacting every aspect of care from diagnosis through therapy, according to an editorial letter published online in Leukemia Research.
One key concern to be considered is the risk of missed or delayed diagnosis due to the pandemic conditions. An estimated 50%-75% of patients with acute leukemia are febrile at diagnosis and this puts them at high risk of a misdiagnosis of COVID-19 upon initial evaluation. As with other oncological conditions (primary mediastinal lymphoma or lung cancer, for example), which often present with a cough with or without fever, their symptoms “are likely to be considered trivial after a negative SARS-CoV-2 test,” with patients then being sent home without further assessment. In a rapidly progressing disease such as acute leukemia, this could lead to critical delays in therapeutic intervention.
The authors, from the Service and Central Laboratory of Hematology, Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, also discussed the problems that might occur with regard to most standard forms of therapy. In particular, they addressed potential impacts of the pandemic on chemotherapy, bone marrow transplantation, maintenance treatments, supportive measures, and targeted therapies.
Of particular concern, “most patients may suffer from postponed chemotherapy, due to a shortage of isolation beds and blood products or the wish to avoid immunosuppressive treatments,” the authors noted, warning that “delay in chemotherapy initiation may negatively affect prognosis, [particularly in patients under age 60] with favorable- or intermediate-risk disease.”
With regard to stem cell transplantation, the authors detail the many potential difficulties with regard to procedures involving both donors and recipients, and warn that in some cases, delay in transplant could result in the reappearance of a significant minimal residual disease, which has a well-established negative impact on survival.
The authors also noted that blood product shortages have already begun in most affected countries, and how, in response, transfusion societies have called for conservative transfusion policies in strict adherence to evidence-based guidelines for patient’s blood management.
“COVID-19 will result in numerous casualties. Acute leukemia patients are at a higher risk of severe complications,” the authors stated. In particular, physicians should especially be aware of how treatment for acute leukemia may have “interactions with other drugs used to treat SARS-CoV-2–related infections/complications such as antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and various other drugs that prolong QTc or impact targeted-therapy pharmacokinetics,” they concluded.
The authors reported that they received no government or private funding for this research, and that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Gavillet M et al. Leuk. Res. 2020. doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2020.106353.
FROM LEUKEMIA RESEARCH
Maintaining cancer care in the face of COVID-19
Medical oncologist Anne Chiang, MD, PhD, is scrambling to maintain cancer care in New Haven, Connecticut, while COVID-19 advances unrelentingly. As deputy chief medical officer of the Smilow Cancer Network, the largest cancer care delivery system in Connecticut and Rhode Island, she has no illusions about dodging what’s unfolding just 2 hours down the road in New York City.
“They’re trying their best to continue active cancer treatment but it’s getting harder,” she says of her colleagues in the thick of the pandemic. “We have to be prepared for it here.”
In anticipation of what’s coming, her team has just emptied the top three floors of the Smilow Cancer Hospital, moving 60 patients by ambulance and other medical transport to a different hospital nearby.
The move frees the Smilow Cancer hospital’s negative-pressure wards for the anticipated wave of COVID-19 patients. It will keep the virus sealed off from the rest of the hospital. But in other locations it’s harder to shield patients with cancer from the infection.
Around the state, Smilow Cancer Network’s affiliated hospitals are already treating a growing number of COVID-19 patients, especially at Greenwich Hospital, right on the border with New York state.
To protect patients with cancer, who are among the most vulnerable to the virus, oncologists are embracing telemedicine to allow most patients to stay home.
“We’re really concentrating on decreasing the risk to these patients, with a widespread massive-scale conversion to telehealth,” said Chiang. “This is something that, in the space of about a week, has transformed the care of our patients — it’s a really amazing transformation.”
If anything good comes out of the COVID-19 pandemic, it will be this global adoption of virtual healthcare.
Across the US border in Canada, the medical director of Toronto’s Princess Margaret Cancer Centre is directing a similar transformation.
“We have converted probably about 70% to 80% of our clinic visits to virtual visits,” says radiation oncologist Mary Gospodarowicz, MD.
“We have three priorities: number one, to keep our patients safe; number two, to keep our staff safe, because if staff are sick we won’t be treating anybody; and number three, to treat as many patients with cancer as possible.”
Gospodarowicz woke up last week to a local headline about a woman whose mastectomy had been canceled “because of the coronavirus.” The story exposed the many layers of the COVID-19 crisis. “A lot of hospitals have canceled elective surgeries,” she acknowledged. “For patients who have treatment or surgery deferred, we have a database and we’ll make sure we look after those patients eventually. We have a priority system, so low-risk prostate cancer, very low-risk breast cancer patients are waiting. All the urgent head and neck, breast, and other higher priority surgeries are still being done, but it just depends how it goes. The situation changes every day.”
It’s similar in Los Angeles, at the University of Southern California, says Elizabeth David, MD, a cardiothoracic surgeon with Keck Medicine.
“For thoracic, we just had a conference call with about 30 surgeons around the country going through really nitty-gritty specifics to help with our decision making about what could wait without detriment to the patient – hopefully – and what should be done now,” she told Medscape Medical News.
“There are some hospitals where they are not doing anything but life and death emergency operations, whereas we are still doing our emergent cancer operations in our institution, but we all know – and patients know – that could change from one day to the next. They may think they’re having surgery tomorrow but may get a call saying we can’t do it,” David said.
Many of David’s patients have non–small cell lung cancer, putting them at particular risk with a pulmonary infection like COVID-19. For now, she says delivery of postsurgical chemotherapy and radiotherapy has not been impacted in her area, but her videoconference discussions with patients are much longer – and harder – these days.
“I’ve been in practice a while now and I’ve had numerous conversations with patients this week that I never trained for, and I’ve never known anyone else who has. It’s really hard as a provider to know what to say,” she said.
In cardiothoracic surgery, David said guidance on clinical decision making is coming from the American College of Surgeons, Society of Thoracic Surgery, and American Association of Thoracic Surgeons. Yet, she says each patient is being assessed – and reassessed – individually.
“You have to balance the risk of delaying the intervention with supply issues, hospital exposure issues, the danger to the patient of being in the hospital environment – there’s just so many factors. We’re spending so much time talking through cases, and a lot of times we’re talking about cases we already talked about, but we’re just making sure that based on today’s numbers we should still be moving forward,” she commented.
In Connecticut, Chiang said treatment decisions are also mostly on a case-by-case basis at the moment, although more standardized guidelines are being worked out.
“Our disease teams have been really proactive in terms of offering alternative solutions to patients, creative ways to basically keep them out of the hospital and also reduce the immunosuppressive regimens that we give them,” she said.
Examples include offering endocrine therapy to patients who can’t get breast cancer surgery, or offering alternative drug regimens and dosing schedules. “At this point we haven’t needed to ration actual treatment – patients are continuing to get active therapy if that’s appropriate – it’s more about how can we protect them,” she said. “It’s a complex puzzle of moving pieces.”
In Toronto, Gospodarowicz says newly published medical and radiation oncology guidelines from France are the backbone of her hospital’s policy discussions about treating cancer and protecting patients from COVID-19.
While patients’ concerns are understandable, she says even in the current hot spots of infection, it’s encouraging to know that cancer patients are not being forgotten.
“I recently had email communication with a radiation oncologist in Brescia, one of the worst-affected areas in Italy, and he told me the radiotherapy department has been 60% to 70% capacity, so they still treat 70% these patients, just taking precautions and separating the COVID-positive and negative ones. When we read the stats it looks horrible, but life still goes on and people are still being treated,” she said.
Although telemedicine offers meaningful solutions to the COVID-19 crisis in North America, it may not be possible in other parts of the world.
Web consultations were only just approved in Brazil this week. “We are still discussing how to make it official and reimbursed,” says Rachel Riechelmann, MD, head of clinical oncology at AC Camargo Cancer Center in São Paulo.
To minimize infection risk for patients, Riechelmann says her hospital is doing the following: postponing surgeries in cases where there is good evidence of neoadjuvant treatment, such as total neoadjuvant therapy for rectal cancer; avoiding adjuvant chemo for stage 2 colon cancer; moving to hypofractionated radiotherapy if possible; adopting watchful waiting in grade 1 nonfunctional neuroendocrine tumors; and postponing follow-up visits.
“We do our best,” she wrote in an email. “We keep treating cancer if treatment cannot wait.”
Riechelmann’s center has just launched a trial of hydroxychloroquine and tocilizumab therapy in patients with cancer who have severe COVID-19 and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Meanwhile in New Haven, Chiang says for patients with cancer who are infected with COVID-19, her team is also prognosticating about the fair allocation of limited resources such as ventilators.
“If it ever gets to the point where somebody has to choose between a cancer patient and a noncancer patient in providing life support, it’s really important that people understand that cancer patients are doing very well nowadays and even with a diagnosis of cancer they can potentially live for many years, so that shouldn’t necessarily be a decision-point,” she emphasized.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medical oncologist Anne Chiang, MD, PhD, is scrambling to maintain cancer care in New Haven, Connecticut, while COVID-19 advances unrelentingly. As deputy chief medical officer of the Smilow Cancer Network, the largest cancer care delivery system in Connecticut and Rhode Island, she has no illusions about dodging what’s unfolding just 2 hours down the road in New York City.
“They’re trying their best to continue active cancer treatment but it’s getting harder,” she says of her colleagues in the thick of the pandemic. “We have to be prepared for it here.”
In anticipation of what’s coming, her team has just emptied the top three floors of the Smilow Cancer Hospital, moving 60 patients by ambulance and other medical transport to a different hospital nearby.
The move frees the Smilow Cancer hospital’s negative-pressure wards for the anticipated wave of COVID-19 patients. It will keep the virus sealed off from the rest of the hospital. But in other locations it’s harder to shield patients with cancer from the infection.
Around the state, Smilow Cancer Network’s affiliated hospitals are already treating a growing number of COVID-19 patients, especially at Greenwich Hospital, right on the border with New York state.
To protect patients with cancer, who are among the most vulnerable to the virus, oncologists are embracing telemedicine to allow most patients to stay home.
“We’re really concentrating on decreasing the risk to these patients, with a widespread massive-scale conversion to telehealth,” said Chiang. “This is something that, in the space of about a week, has transformed the care of our patients — it’s a really amazing transformation.”
If anything good comes out of the COVID-19 pandemic, it will be this global adoption of virtual healthcare.
Across the US border in Canada, the medical director of Toronto’s Princess Margaret Cancer Centre is directing a similar transformation.
“We have converted probably about 70% to 80% of our clinic visits to virtual visits,” says radiation oncologist Mary Gospodarowicz, MD.
“We have three priorities: number one, to keep our patients safe; number two, to keep our staff safe, because if staff are sick we won’t be treating anybody; and number three, to treat as many patients with cancer as possible.”
Gospodarowicz woke up last week to a local headline about a woman whose mastectomy had been canceled “because of the coronavirus.” The story exposed the many layers of the COVID-19 crisis. “A lot of hospitals have canceled elective surgeries,” she acknowledged. “For patients who have treatment or surgery deferred, we have a database and we’ll make sure we look after those patients eventually. We have a priority system, so low-risk prostate cancer, very low-risk breast cancer patients are waiting. All the urgent head and neck, breast, and other higher priority surgeries are still being done, but it just depends how it goes. The situation changes every day.”
It’s similar in Los Angeles, at the University of Southern California, says Elizabeth David, MD, a cardiothoracic surgeon with Keck Medicine.
“For thoracic, we just had a conference call with about 30 surgeons around the country going through really nitty-gritty specifics to help with our decision making about what could wait without detriment to the patient – hopefully – and what should be done now,” she told Medscape Medical News.
“There are some hospitals where they are not doing anything but life and death emergency operations, whereas we are still doing our emergent cancer operations in our institution, but we all know – and patients know – that could change from one day to the next. They may think they’re having surgery tomorrow but may get a call saying we can’t do it,” David said.
Many of David’s patients have non–small cell lung cancer, putting them at particular risk with a pulmonary infection like COVID-19. For now, she says delivery of postsurgical chemotherapy and radiotherapy has not been impacted in her area, but her videoconference discussions with patients are much longer – and harder – these days.
“I’ve been in practice a while now and I’ve had numerous conversations with patients this week that I never trained for, and I’ve never known anyone else who has. It’s really hard as a provider to know what to say,” she said.
In cardiothoracic surgery, David said guidance on clinical decision making is coming from the American College of Surgeons, Society of Thoracic Surgery, and American Association of Thoracic Surgeons. Yet, she says each patient is being assessed – and reassessed – individually.
“You have to balance the risk of delaying the intervention with supply issues, hospital exposure issues, the danger to the patient of being in the hospital environment – there’s just so many factors. We’re spending so much time talking through cases, and a lot of times we’re talking about cases we already talked about, but we’re just making sure that based on today’s numbers we should still be moving forward,” she commented.
In Connecticut, Chiang said treatment decisions are also mostly on a case-by-case basis at the moment, although more standardized guidelines are being worked out.
“Our disease teams have been really proactive in terms of offering alternative solutions to patients, creative ways to basically keep them out of the hospital and also reduce the immunosuppressive regimens that we give them,” she said.
Examples include offering endocrine therapy to patients who can’t get breast cancer surgery, or offering alternative drug regimens and dosing schedules. “At this point we haven’t needed to ration actual treatment – patients are continuing to get active therapy if that’s appropriate – it’s more about how can we protect them,” she said. “It’s a complex puzzle of moving pieces.”
In Toronto, Gospodarowicz says newly published medical and radiation oncology guidelines from France are the backbone of her hospital’s policy discussions about treating cancer and protecting patients from COVID-19.
While patients’ concerns are understandable, she says even in the current hot spots of infection, it’s encouraging to know that cancer patients are not being forgotten.
“I recently had email communication with a radiation oncologist in Brescia, one of the worst-affected areas in Italy, and he told me the radiotherapy department has been 60% to 70% capacity, so they still treat 70% these patients, just taking precautions and separating the COVID-positive and negative ones. When we read the stats it looks horrible, but life still goes on and people are still being treated,” she said.
Although telemedicine offers meaningful solutions to the COVID-19 crisis in North America, it may not be possible in other parts of the world.
Web consultations were only just approved in Brazil this week. “We are still discussing how to make it official and reimbursed,” says Rachel Riechelmann, MD, head of clinical oncology at AC Camargo Cancer Center in São Paulo.
To minimize infection risk for patients, Riechelmann says her hospital is doing the following: postponing surgeries in cases where there is good evidence of neoadjuvant treatment, such as total neoadjuvant therapy for rectal cancer; avoiding adjuvant chemo for stage 2 colon cancer; moving to hypofractionated radiotherapy if possible; adopting watchful waiting in grade 1 nonfunctional neuroendocrine tumors; and postponing follow-up visits.
“We do our best,” she wrote in an email. “We keep treating cancer if treatment cannot wait.”
Riechelmann’s center has just launched a trial of hydroxychloroquine and tocilizumab therapy in patients with cancer who have severe COVID-19 and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Meanwhile in New Haven, Chiang says for patients with cancer who are infected with COVID-19, her team is also prognosticating about the fair allocation of limited resources such as ventilators.
“If it ever gets to the point where somebody has to choose between a cancer patient and a noncancer patient in providing life support, it’s really important that people understand that cancer patients are doing very well nowadays and even with a diagnosis of cancer they can potentially live for many years, so that shouldn’t necessarily be a decision-point,” she emphasized.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medical oncologist Anne Chiang, MD, PhD, is scrambling to maintain cancer care in New Haven, Connecticut, while COVID-19 advances unrelentingly. As deputy chief medical officer of the Smilow Cancer Network, the largest cancer care delivery system in Connecticut and Rhode Island, she has no illusions about dodging what’s unfolding just 2 hours down the road in New York City.
“They’re trying their best to continue active cancer treatment but it’s getting harder,” she says of her colleagues in the thick of the pandemic. “We have to be prepared for it here.”
In anticipation of what’s coming, her team has just emptied the top three floors of the Smilow Cancer Hospital, moving 60 patients by ambulance and other medical transport to a different hospital nearby.
The move frees the Smilow Cancer hospital’s negative-pressure wards for the anticipated wave of COVID-19 patients. It will keep the virus sealed off from the rest of the hospital. But in other locations it’s harder to shield patients with cancer from the infection.
Around the state, Smilow Cancer Network’s affiliated hospitals are already treating a growing number of COVID-19 patients, especially at Greenwich Hospital, right on the border with New York state.
To protect patients with cancer, who are among the most vulnerable to the virus, oncologists are embracing telemedicine to allow most patients to stay home.
“We’re really concentrating on decreasing the risk to these patients, with a widespread massive-scale conversion to telehealth,” said Chiang. “This is something that, in the space of about a week, has transformed the care of our patients — it’s a really amazing transformation.”
If anything good comes out of the COVID-19 pandemic, it will be this global adoption of virtual healthcare.
Across the US border in Canada, the medical director of Toronto’s Princess Margaret Cancer Centre is directing a similar transformation.
“We have converted probably about 70% to 80% of our clinic visits to virtual visits,” says radiation oncologist Mary Gospodarowicz, MD.
“We have three priorities: number one, to keep our patients safe; number two, to keep our staff safe, because if staff are sick we won’t be treating anybody; and number three, to treat as many patients with cancer as possible.”
Gospodarowicz woke up last week to a local headline about a woman whose mastectomy had been canceled “because of the coronavirus.” The story exposed the many layers of the COVID-19 crisis. “A lot of hospitals have canceled elective surgeries,” she acknowledged. “For patients who have treatment or surgery deferred, we have a database and we’ll make sure we look after those patients eventually. We have a priority system, so low-risk prostate cancer, very low-risk breast cancer patients are waiting. All the urgent head and neck, breast, and other higher priority surgeries are still being done, but it just depends how it goes. The situation changes every day.”
It’s similar in Los Angeles, at the University of Southern California, says Elizabeth David, MD, a cardiothoracic surgeon with Keck Medicine.
“For thoracic, we just had a conference call with about 30 surgeons around the country going through really nitty-gritty specifics to help with our decision making about what could wait without detriment to the patient – hopefully – and what should be done now,” she told Medscape Medical News.
“There are some hospitals where they are not doing anything but life and death emergency operations, whereas we are still doing our emergent cancer operations in our institution, but we all know – and patients know – that could change from one day to the next. They may think they’re having surgery tomorrow but may get a call saying we can’t do it,” David said.
Many of David’s patients have non–small cell lung cancer, putting them at particular risk with a pulmonary infection like COVID-19. For now, she says delivery of postsurgical chemotherapy and radiotherapy has not been impacted in her area, but her videoconference discussions with patients are much longer – and harder – these days.
“I’ve been in practice a while now and I’ve had numerous conversations with patients this week that I never trained for, and I’ve never known anyone else who has. It’s really hard as a provider to know what to say,” she said.
In cardiothoracic surgery, David said guidance on clinical decision making is coming from the American College of Surgeons, Society of Thoracic Surgery, and American Association of Thoracic Surgeons. Yet, she says each patient is being assessed – and reassessed – individually.
“You have to balance the risk of delaying the intervention with supply issues, hospital exposure issues, the danger to the patient of being in the hospital environment – there’s just so many factors. We’re spending so much time talking through cases, and a lot of times we’re talking about cases we already talked about, but we’re just making sure that based on today’s numbers we should still be moving forward,” she commented.
In Connecticut, Chiang said treatment decisions are also mostly on a case-by-case basis at the moment, although more standardized guidelines are being worked out.
“Our disease teams have been really proactive in terms of offering alternative solutions to patients, creative ways to basically keep them out of the hospital and also reduce the immunosuppressive regimens that we give them,” she said.
Examples include offering endocrine therapy to patients who can’t get breast cancer surgery, or offering alternative drug regimens and dosing schedules. “At this point we haven’t needed to ration actual treatment – patients are continuing to get active therapy if that’s appropriate – it’s more about how can we protect them,” she said. “It’s a complex puzzle of moving pieces.”
In Toronto, Gospodarowicz says newly published medical and radiation oncology guidelines from France are the backbone of her hospital’s policy discussions about treating cancer and protecting patients from COVID-19.
While patients’ concerns are understandable, she says even in the current hot spots of infection, it’s encouraging to know that cancer patients are not being forgotten.
“I recently had email communication with a radiation oncologist in Brescia, one of the worst-affected areas in Italy, and he told me the radiotherapy department has been 60% to 70% capacity, so they still treat 70% these patients, just taking precautions and separating the COVID-positive and negative ones. When we read the stats it looks horrible, but life still goes on and people are still being treated,” she said.
Although telemedicine offers meaningful solutions to the COVID-19 crisis in North America, it may not be possible in other parts of the world.
Web consultations were only just approved in Brazil this week. “We are still discussing how to make it official and reimbursed,” says Rachel Riechelmann, MD, head of clinical oncology at AC Camargo Cancer Center in São Paulo.
To minimize infection risk for patients, Riechelmann says her hospital is doing the following: postponing surgeries in cases where there is good evidence of neoadjuvant treatment, such as total neoadjuvant therapy for rectal cancer; avoiding adjuvant chemo for stage 2 colon cancer; moving to hypofractionated radiotherapy if possible; adopting watchful waiting in grade 1 nonfunctional neuroendocrine tumors; and postponing follow-up visits.
“We do our best,” she wrote in an email. “We keep treating cancer if treatment cannot wait.”
Riechelmann’s center has just launched a trial of hydroxychloroquine and tocilizumab therapy in patients with cancer who have severe COVID-19 and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Meanwhile in New Haven, Chiang says for patients with cancer who are infected with COVID-19, her team is also prognosticating about the fair allocation of limited resources such as ventilators.
“If it ever gets to the point where somebody has to choose between a cancer patient and a noncancer patient in providing life support, it’s really important that people understand that cancer patients are doing very well nowadays and even with a diagnosis of cancer they can potentially live for many years, so that shouldn’t necessarily be a decision-point,” she emphasized.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Predictors of bacteremia in children hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia
Children with bacteremia had longer lengths of stay
Clinical question: Are blood cultures warranted in specific subsets of children hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP)?
Background: Guidelines from the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommend obtaining blood cultures in children hospitalized with moderate to severe community-acquired pneumonia. This group of authors recently published a study showing the prevalence of bacteremia of 2.5% in a cohort of generally healthy children hospitalized with CAP who had blood cultures obtained, with only 0.4% harboring a pathogen not susceptible to penicillin. They found low yield for blood cultures in children hospitalized with CAP.
Study design: Retrospective Cohort Study.
Setting: Pediatric Health Information System Plus (PHIS+) database (six institutions).
Synopsis: Secondary analysis of prior study of children aged 3 months to 18 years hospitalized with CAP between 2007 to 2011. For the secondary analysis only children in whom a blood culture was obtained on the initial or second day of hospitalization were studied. CAP was defined by a primary ICD-9 discharge diagnosis code for pneumonia or a primary ICD-9 discharge diagnosis code for pleural effusion with a secondary diagnosis code for pneumonia. Children transferred into the study institution and children with complex chronic conditions were excluded from the study. The primary outcome was the presence of bacteremia based on pathogen detection in the initial blood culture. Bacteria were labeled as pathogens or contaminants.
A total of 7,509 children were included in the initial study. Of them, 2,568 (34.2%) had a blood culture obtained on the initial or second day of hospitalization; 65 (2.5%) of the children with blood cultures obtained on admission had bacteremia. The most common penicillin-susceptible blood pathogen isolated was Streptococcus pneumoniae (n = 47). Eleven children (0.4%) had bacteremia with a pathogen not susceptible to penicillin. Children with bacteremia had a higher median admission white blood cell (WBC) count than did those without bacteremia (17.5 × 103 cells per mcL vs. 12.4 × 103 cells per mcL; P < .01) and definite radiographic pneumonia on admission chest radiograph (P < .01). C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate were also higher in children with bacteremia but were only obtained in 35% and 15% of patients, respectively. Children with bacteremia had a higher prevalence of complicated pneumonia on admission (P = .06) than did children without bacteremia. Children with bacteremia had longer lengths of stay (4 days vs. 2 days; P < .01) and were more likely to be admitted to an ICU (P < .01) than were children without bacteremia.
This study is limited by its sample because all of the patients were cared for at tertiary care hospitals. It is also limited by its timing; the PHIS+ data set spans the introduction of the 13-valent pneumococcal vaccine, and so the current prevalence of bacteremia in CAP may be lower than that found in the study.
Bottom line: The prevalence of bacteremia was low among a cohort of generally healthy children hospitalized with CAP, and no features strongly predicted the presence of bacteremia. The authors recommend that blood cultures in children with CAP should be limited to patients admitted to the ICU.
Citation: Lipsett SC et al. Predictors of Bacteremia in Children Hospitalized With Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Hosp Pediatr. 2019 Oct;9(10):770-8.
Dr. Kumar is a pediatric hospitalist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. She is a clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and serves as the Pediatrics Editor for The Hospitalist.
Children with bacteremia had longer lengths of stay
Children with bacteremia had longer lengths of stay
Clinical question: Are blood cultures warranted in specific subsets of children hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP)?
Background: Guidelines from the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommend obtaining blood cultures in children hospitalized with moderate to severe community-acquired pneumonia. This group of authors recently published a study showing the prevalence of bacteremia of 2.5% in a cohort of generally healthy children hospitalized with CAP who had blood cultures obtained, with only 0.4% harboring a pathogen not susceptible to penicillin. They found low yield for blood cultures in children hospitalized with CAP.
Study design: Retrospective Cohort Study.
Setting: Pediatric Health Information System Plus (PHIS+) database (six institutions).
Synopsis: Secondary analysis of prior study of children aged 3 months to 18 years hospitalized with CAP between 2007 to 2011. For the secondary analysis only children in whom a blood culture was obtained on the initial or second day of hospitalization were studied. CAP was defined by a primary ICD-9 discharge diagnosis code for pneumonia or a primary ICD-9 discharge diagnosis code for pleural effusion with a secondary diagnosis code for pneumonia. Children transferred into the study institution and children with complex chronic conditions were excluded from the study. The primary outcome was the presence of bacteremia based on pathogen detection in the initial blood culture. Bacteria were labeled as pathogens or contaminants.
A total of 7,509 children were included in the initial study. Of them, 2,568 (34.2%) had a blood culture obtained on the initial or second day of hospitalization; 65 (2.5%) of the children with blood cultures obtained on admission had bacteremia. The most common penicillin-susceptible blood pathogen isolated was Streptococcus pneumoniae (n = 47). Eleven children (0.4%) had bacteremia with a pathogen not susceptible to penicillin. Children with bacteremia had a higher median admission white blood cell (WBC) count than did those without bacteremia (17.5 × 103 cells per mcL vs. 12.4 × 103 cells per mcL; P < .01) and definite radiographic pneumonia on admission chest radiograph (P < .01). C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate were also higher in children with bacteremia but were only obtained in 35% and 15% of patients, respectively. Children with bacteremia had a higher prevalence of complicated pneumonia on admission (P = .06) than did children without bacteremia. Children with bacteremia had longer lengths of stay (4 days vs. 2 days; P < .01) and were more likely to be admitted to an ICU (P < .01) than were children without bacteremia.
This study is limited by its sample because all of the patients were cared for at tertiary care hospitals. It is also limited by its timing; the PHIS+ data set spans the introduction of the 13-valent pneumococcal vaccine, and so the current prevalence of bacteremia in CAP may be lower than that found in the study.
Bottom line: The prevalence of bacteremia was low among a cohort of generally healthy children hospitalized with CAP, and no features strongly predicted the presence of bacteremia. The authors recommend that blood cultures in children with CAP should be limited to patients admitted to the ICU.
Citation: Lipsett SC et al. Predictors of Bacteremia in Children Hospitalized With Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Hosp Pediatr. 2019 Oct;9(10):770-8.
Dr. Kumar is a pediatric hospitalist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. She is a clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and serves as the Pediatrics Editor for The Hospitalist.
Clinical question: Are blood cultures warranted in specific subsets of children hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP)?
Background: Guidelines from the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommend obtaining blood cultures in children hospitalized with moderate to severe community-acquired pneumonia. This group of authors recently published a study showing the prevalence of bacteremia of 2.5% in a cohort of generally healthy children hospitalized with CAP who had blood cultures obtained, with only 0.4% harboring a pathogen not susceptible to penicillin. They found low yield for blood cultures in children hospitalized with CAP.
Study design: Retrospective Cohort Study.
Setting: Pediatric Health Information System Plus (PHIS+) database (six institutions).
Synopsis: Secondary analysis of prior study of children aged 3 months to 18 years hospitalized with CAP between 2007 to 2011. For the secondary analysis only children in whom a blood culture was obtained on the initial or second day of hospitalization were studied. CAP was defined by a primary ICD-9 discharge diagnosis code for pneumonia or a primary ICD-9 discharge diagnosis code for pleural effusion with a secondary diagnosis code for pneumonia. Children transferred into the study institution and children with complex chronic conditions were excluded from the study. The primary outcome was the presence of bacteremia based on pathogen detection in the initial blood culture. Bacteria were labeled as pathogens or contaminants.
A total of 7,509 children were included in the initial study. Of them, 2,568 (34.2%) had a blood culture obtained on the initial or second day of hospitalization; 65 (2.5%) of the children with blood cultures obtained on admission had bacteremia. The most common penicillin-susceptible blood pathogen isolated was Streptococcus pneumoniae (n = 47). Eleven children (0.4%) had bacteremia with a pathogen not susceptible to penicillin. Children with bacteremia had a higher median admission white blood cell (WBC) count than did those without bacteremia (17.5 × 103 cells per mcL vs. 12.4 × 103 cells per mcL; P < .01) and definite radiographic pneumonia on admission chest radiograph (P < .01). C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate were also higher in children with bacteremia but were only obtained in 35% and 15% of patients, respectively. Children with bacteremia had a higher prevalence of complicated pneumonia on admission (P = .06) than did children without bacteremia. Children with bacteremia had longer lengths of stay (4 days vs. 2 days; P < .01) and were more likely to be admitted to an ICU (P < .01) than were children without bacteremia.
This study is limited by its sample because all of the patients were cared for at tertiary care hospitals. It is also limited by its timing; the PHIS+ data set spans the introduction of the 13-valent pneumococcal vaccine, and so the current prevalence of bacteremia in CAP may be lower than that found in the study.
Bottom line: The prevalence of bacteremia was low among a cohort of generally healthy children hospitalized with CAP, and no features strongly predicted the presence of bacteremia. The authors recommend that blood cultures in children with CAP should be limited to patients admitted to the ICU.
Citation: Lipsett SC et al. Predictors of Bacteremia in Children Hospitalized With Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Hosp Pediatr. 2019 Oct;9(10):770-8.
Dr. Kumar is a pediatric hospitalist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. She is a clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and serves as the Pediatrics Editor for The Hospitalist.
Top 10 must-dos in ICU in COVID-19 include prone ventilation
As the first international guidelines on the management of critically ill patients with COVID-19 are understandably comprehensive, one expert involved in their development highlights the essential recommendations and explains the rationale behind prone ventilation.
A panel of 39 experts from 12 countries from across the globe developed the 50 recommendations within four domains, under the auspices of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign. They are issued by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM), and will subsequently be published in the journal Intensive Care Medicine.
A central aspect of the guidance is what works, and what does not, in treating critically ill patients with COVID-19 in intensive care.
Ten of the recommendations cover potential pharmacotherapies, most of which have only weak or no evidence of benefit, as discussed in a recent perspective on Medscape. All 50 recommendations, along with the associated level of evidence, are detailed in table 2 in the paper.
There is also an algorithm for the management of patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19 (figure 2) and a summary of clinical practice recommendations (figure 3).
In an editorial in the Journal of the American Medical Association issued just days after these new guidelines, Francois Lamontagne, MD, MSc, and Derek C. Angus, MD, MPH, say they “represent an excellent first step toward optimal, evidence-informed care for patients with COVID-19.” Lamontagne is from Universitaire de Sherbrooke, Canada, and Angus is from University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pennsylvania, and is an associate editor with JAMA.
Dealing With Tide of COVID-19 Patients, Protecting Healthcare Workers
Editor in chief of Intensive Care Medicine Giuseppe Citerio, MD, from University of Milano-Bicocca, Monza, Italy, said: “COVID-19 cases are rising rapidly worldwide, and so we are increasingly seeing that intensive care units [ICUs] have difficulty in dealing with the tide of patients.”
“We need more resource in ICUs, and quickly. This means more ventilators and more trained personnel. In the meantime, this guidance aims to rationalize our approach and to avoid unproven strategies,” he explains in a press release from ESICM.
“This is the first guidance to lay out what works and what doesn’t in treating coronavirus-infected patients in intensive care. It’s based on decades of research on acute respiratory infection being applied to COVID-19 patients,” added ESICM President-Elect Maurizio Cecconi, MD, from Humanitas University, Milan, Italy.
“At the same time as caring for patients, we need to make sure that health workers are following procedures which will allow themselves to be protected against infection,” he stressed.
“We must protect them, they are in the frontline. We cannot allow our healthcare workers to be at risk. On top of that, if they get infected they could also spread the disease further.”
Top-10 Recommendations
While all 50 recommendations are key to the successful management of COVID-19 patients, busy clinicians on the frontline need to zone in on those indispensable practical recommendations that they should implement immediately.
Medscape Medical News therefore asked lead author Waleed Alhazzani, MD, MSc, from the Division of Critical Care, McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada, to give his personal top 10, the first three of which are focused on limiting the spread of infection.
1. For healthcare workers performing aerosol-generating procedures1 on patients with COVID-19 in the ICU, we recommend using fitted respirator masks (N95 respirators, FFP2, or equivalent), as compared to surgical/medical masks, in addition to other personal protective equipment (eg, gloves, gown, and eye protection such as a face shield or safety goggles.
2. We recommend performing aerosol-generating procedures on ICU patients with COVID-19 in a negative-pressure room.
3. For healthcare workers providing usual care for nonventilated COVID-19 patients, we suggest using surgical/medical masks, as compared to respirator masks in addition to other personal protective equipment.
4. For healthcare workers performing endotracheal intubation on patients with COVID-19, we suggest using video guided laryngoscopy, over direct laryngoscopy, if available.
5. We recommend endotracheal intubation in patients with COVID-19, performed by healthcare workers experienced with airway management, to minimize the number of attempts and risk of transmission.
6. For intubated and mechanically ventilated adults with suspicion of COVID-19, we suggest obtaining endotracheal aspirates, over bronchial wash or bronchoalveolar lavage samples.
7. For adults with COVID-19 and acute hypoxemic respiratory failure, we suggest using high-flow nasal cannula [HFNC] over noninvasive positive pressure ventilation [NIPPV].
8. For adults with COVID-19 receiving NIPPV or HFNC, we recommend close monitoring for worsening of respiratory status and early intubation in a controlled setting if worsening occurs.
9. For mechanically ventilated adults with COVID-19 and moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome [ARDS], we suggest prone ventilation for 12 to 16 hours over no prone ventilation.
10. For mechanically ventilated adults with COVID-19 and respiratory failure (without ARDS), we don’t recommend routine use of systemic corticosteroids.
1 This includes endotracheal intubation, bronchoscopy, open suctioning, administration of nebulized treatment, manual ventilation before intubation, physical proning of the patient, disconnecting the patient from the ventilator, noninvasive positive pressure ventilation, tracheostomy, and cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
These choices are in broad agreement with those selected by Jason T. Poston, MD, University of Chicago, Illinois, and colleagues in their synopsis of these guidelines, published online March 26 in JAMA, although they also highlight another recommendation on infection control:
- For healthcare workers who are performing non-aerosol-generating procedures on mechanically ventilated (closed circuit) patients with COVID-19, we suggest using surgical/medical masks, as opposed to respirator masks, in addition to other personal protective equipment.
Importance of Prone Ventilation, Perhaps for Many Days
One recommendation singled out by both Alhazzani and coauthors, and Poston and colleagues, relates to prone ventilation for 12 to 16 hours in adults with moderate to severe ARDS receiving mechanical ventilation.
Michelle N. Gong, MD, MS, chief of critical care medicine at Montefiore Medical Center, New York City, also highlighted this practice in a live-stream interview with JAMA editor in chief Howard Bauchner, MD.
She explained that, in her institution, they have been “very aggressive about proning these patients as early as possible, but unlike some of the past ARDS patients…they tend to require many, many days of proning in order to get a response”.
Gong added that patients “may improve very rapidly when they are proned, but when we supinate them, they lose [the improvement] and then they get proned for upwards of 10 days or more, if need be.”
Alhazzani told Medscape Medical News that prone ventilation “is a simple intervention that requires training of healthcare providers but can be applied in most contexts.”
He explained that the recommendation “is driven by indirect evidence from ARDS,” not specifically those in COVID-19, with recent studies having shown that COVID-19 “can affect lung bases and may cause significant atelectasis and reduced lung compliance in the context of ARDS.”
“Prone ventilation has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with moderate to severe ARDS. Therefore, we issued a suggestion for clinicians to consider prone ventilation in this population.”
‘Impressively Thorough’ Recommendations, With Some Caveats
In their JAMA editorial, Lamontagne and Angus describe the recommendations as “impressively thorough and expansive.”
They note that they address resource scarcity, which “is likely to be a critical issue in low- and middle-income countries experiencing any reasonably large number of cases and in high-income countries experiencing a surge in the demand for critical care.”
The authors say, however, that a “weakness” of the guidelines is that they make recommendations for interventions that “lack supporting evidence.”
Consequently, “when prioritizing scarce resources, clinicians and healthcare systems will have to choose among options that have limited evidence to support them.”
“In future iterations of the guidelines, there should be more detailed recommendations for how clinicians should prioritize scarce resources, or include more recommendations against the use of unproven therapies.”
“The tasks ahead for the dissemination and uptake of optimal critical care are herculean,” Lamontagne and Angus say.
They include “a need to generate more robust evidence, consider carefully the application of that evidence across a wide variety of clinical circumstances, and generate supporting materials to ensure effective implementation of the guideline recommendations,” they conclude.
ESICM recommendations coauthor Yaseen Arabi is the principal investigator on a clinical trial for lopinavir/ritonavir and interferon in Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) and he was a nonpaid consultant on antiviral active for MERS- coronavirus (CoV) for Gilead Sciences and SAB Biotherapeutics. He is an investigator on REMAP-CAP trial and is a Board Members of the International Severe Acute Respiratory and Emerging Infection Consortium (ISARIC). Coauthor Eddy Fan declared receiving consultancy fees from ALung Technologies and MC3 Cardiopulmonary. Coauthor Maurizio Cecconi declared consultancy work with Edwards Lifesciences, Directed Systems, and Cheetah Medical.
JAMA Clinical Guidelines Synopsis coauthor Poston declares receiving honoraria for the CHEST Critical Care Board Review Course.
Editorialist Lamontagne reported receiving grants from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), Fonds de recherche du Québec-Santé, and the Lotte & John Hecht Foundation, unrelated to this work. Editorialist Angus participated in the development of Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for sepsis, but had no role in the creation of the current COVID-19 guidelines, nor the decision to create these guidelines.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As the first international guidelines on the management of critically ill patients with COVID-19 are understandably comprehensive, one expert involved in their development highlights the essential recommendations and explains the rationale behind prone ventilation.
A panel of 39 experts from 12 countries from across the globe developed the 50 recommendations within four domains, under the auspices of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign. They are issued by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM), and will subsequently be published in the journal Intensive Care Medicine.
A central aspect of the guidance is what works, and what does not, in treating critically ill patients with COVID-19 in intensive care.
Ten of the recommendations cover potential pharmacotherapies, most of which have only weak or no evidence of benefit, as discussed in a recent perspective on Medscape. All 50 recommendations, along with the associated level of evidence, are detailed in table 2 in the paper.
There is also an algorithm for the management of patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19 (figure 2) and a summary of clinical practice recommendations (figure 3).
In an editorial in the Journal of the American Medical Association issued just days after these new guidelines, Francois Lamontagne, MD, MSc, and Derek C. Angus, MD, MPH, say they “represent an excellent first step toward optimal, evidence-informed care for patients with COVID-19.” Lamontagne is from Universitaire de Sherbrooke, Canada, and Angus is from University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pennsylvania, and is an associate editor with JAMA.
Dealing With Tide of COVID-19 Patients, Protecting Healthcare Workers
Editor in chief of Intensive Care Medicine Giuseppe Citerio, MD, from University of Milano-Bicocca, Monza, Italy, said: “COVID-19 cases are rising rapidly worldwide, and so we are increasingly seeing that intensive care units [ICUs] have difficulty in dealing with the tide of patients.”
“We need more resource in ICUs, and quickly. This means more ventilators and more trained personnel. In the meantime, this guidance aims to rationalize our approach and to avoid unproven strategies,” he explains in a press release from ESICM.
“This is the first guidance to lay out what works and what doesn’t in treating coronavirus-infected patients in intensive care. It’s based on decades of research on acute respiratory infection being applied to COVID-19 patients,” added ESICM President-Elect Maurizio Cecconi, MD, from Humanitas University, Milan, Italy.
“At the same time as caring for patients, we need to make sure that health workers are following procedures which will allow themselves to be protected against infection,” he stressed.
“We must protect them, they are in the frontline. We cannot allow our healthcare workers to be at risk. On top of that, if they get infected they could also spread the disease further.”
Top-10 Recommendations
While all 50 recommendations are key to the successful management of COVID-19 patients, busy clinicians on the frontline need to zone in on those indispensable practical recommendations that they should implement immediately.
Medscape Medical News therefore asked lead author Waleed Alhazzani, MD, MSc, from the Division of Critical Care, McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada, to give his personal top 10, the first three of which are focused on limiting the spread of infection.
1. For healthcare workers performing aerosol-generating procedures1 on patients with COVID-19 in the ICU, we recommend using fitted respirator masks (N95 respirators, FFP2, or equivalent), as compared to surgical/medical masks, in addition to other personal protective equipment (eg, gloves, gown, and eye protection such as a face shield or safety goggles.
2. We recommend performing aerosol-generating procedures on ICU patients with COVID-19 in a negative-pressure room.
3. For healthcare workers providing usual care for nonventilated COVID-19 patients, we suggest using surgical/medical masks, as compared to respirator masks in addition to other personal protective equipment.
4. For healthcare workers performing endotracheal intubation on patients with COVID-19, we suggest using video guided laryngoscopy, over direct laryngoscopy, if available.
5. We recommend endotracheal intubation in patients with COVID-19, performed by healthcare workers experienced with airway management, to minimize the number of attempts and risk of transmission.
6. For intubated and mechanically ventilated adults with suspicion of COVID-19, we suggest obtaining endotracheal aspirates, over bronchial wash or bronchoalveolar lavage samples.
7. For adults with COVID-19 and acute hypoxemic respiratory failure, we suggest using high-flow nasal cannula [HFNC] over noninvasive positive pressure ventilation [NIPPV].
8. For adults with COVID-19 receiving NIPPV or HFNC, we recommend close monitoring for worsening of respiratory status and early intubation in a controlled setting if worsening occurs.
9. For mechanically ventilated adults with COVID-19 and moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome [ARDS], we suggest prone ventilation for 12 to 16 hours over no prone ventilation.
10. For mechanically ventilated adults with COVID-19 and respiratory failure (without ARDS), we don’t recommend routine use of systemic corticosteroids.
1 This includes endotracheal intubation, bronchoscopy, open suctioning, administration of nebulized treatment, manual ventilation before intubation, physical proning of the patient, disconnecting the patient from the ventilator, noninvasive positive pressure ventilation, tracheostomy, and cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
These choices are in broad agreement with those selected by Jason T. Poston, MD, University of Chicago, Illinois, and colleagues in their synopsis of these guidelines, published online March 26 in JAMA, although they also highlight another recommendation on infection control:
- For healthcare workers who are performing non-aerosol-generating procedures on mechanically ventilated (closed circuit) patients with COVID-19, we suggest using surgical/medical masks, as opposed to respirator masks, in addition to other personal protective equipment.
Importance of Prone Ventilation, Perhaps for Many Days
One recommendation singled out by both Alhazzani and coauthors, and Poston and colleagues, relates to prone ventilation for 12 to 16 hours in adults with moderate to severe ARDS receiving mechanical ventilation.
Michelle N. Gong, MD, MS, chief of critical care medicine at Montefiore Medical Center, New York City, also highlighted this practice in a live-stream interview with JAMA editor in chief Howard Bauchner, MD.
She explained that, in her institution, they have been “very aggressive about proning these patients as early as possible, but unlike some of the past ARDS patients…they tend to require many, many days of proning in order to get a response”.
Gong added that patients “may improve very rapidly when they are proned, but when we supinate them, they lose [the improvement] and then they get proned for upwards of 10 days or more, if need be.”
Alhazzani told Medscape Medical News that prone ventilation “is a simple intervention that requires training of healthcare providers but can be applied in most contexts.”
He explained that the recommendation “is driven by indirect evidence from ARDS,” not specifically those in COVID-19, with recent studies having shown that COVID-19 “can affect lung bases and may cause significant atelectasis and reduced lung compliance in the context of ARDS.”
“Prone ventilation has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with moderate to severe ARDS. Therefore, we issued a suggestion for clinicians to consider prone ventilation in this population.”
‘Impressively Thorough’ Recommendations, With Some Caveats
In their JAMA editorial, Lamontagne and Angus describe the recommendations as “impressively thorough and expansive.”
They note that they address resource scarcity, which “is likely to be a critical issue in low- and middle-income countries experiencing any reasonably large number of cases and in high-income countries experiencing a surge in the demand for critical care.”
The authors say, however, that a “weakness” of the guidelines is that they make recommendations for interventions that “lack supporting evidence.”
Consequently, “when prioritizing scarce resources, clinicians and healthcare systems will have to choose among options that have limited evidence to support them.”
“In future iterations of the guidelines, there should be more detailed recommendations for how clinicians should prioritize scarce resources, or include more recommendations against the use of unproven therapies.”
“The tasks ahead for the dissemination and uptake of optimal critical care are herculean,” Lamontagne and Angus say.
They include “a need to generate more robust evidence, consider carefully the application of that evidence across a wide variety of clinical circumstances, and generate supporting materials to ensure effective implementation of the guideline recommendations,” they conclude.
ESICM recommendations coauthor Yaseen Arabi is the principal investigator on a clinical trial for lopinavir/ritonavir and interferon in Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) and he was a nonpaid consultant on antiviral active for MERS- coronavirus (CoV) for Gilead Sciences and SAB Biotherapeutics. He is an investigator on REMAP-CAP trial and is a Board Members of the International Severe Acute Respiratory and Emerging Infection Consortium (ISARIC). Coauthor Eddy Fan declared receiving consultancy fees from ALung Technologies and MC3 Cardiopulmonary. Coauthor Maurizio Cecconi declared consultancy work with Edwards Lifesciences, Directed Systems, and Cheetah Medical.
JAMA Clinical Guidelines Synopsis coauthor Poston declares receiving honoraria for the CHEST Critical Care Board Review Course.
Editorialist Lamontagne reported receiving grants from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), Fonds de recherche du Québec-Santé, and the Lotte & John Hecht Foundation, unrelated to this work. Editorialist Angus participated in the development of Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for sepsis, but had no role in the creation of the current COVID-19 guidelines, nor the decision to create these guidelines.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As the first international guidelines on the management of critically ill patients with COVID-19 are understandably comprehensive, one expert involved in their development highlights the essential recommendations and explains the rationale behind prone ventilation.
A panel of 39 experts from 12 countries from across the globe developed the 50 recommendations within four domains, under the auspices of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign. They are issued by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM), and will subsequently be published in the journal Intensive Care Medicine.
A central aspect of the guidance is what works, and what does not, in treating critically ill patients with COVID-19 in intensive care.
Ten of the recommendations cover potential pharmacotherapies, most of which have only weak or no evidence of benefit, as discussed in a recent perspective on Medscape. All 50 recommendations, along with the associated level of evidence, are detailed in table 2 in the paper.
There is also an algorithm for the management of patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19 (figure 2) and a summary of clinical practice recommendations (figure 3).
In an editorial in the Journal of the American Medical Association issued just days after these new guidelines, Francois Lamontagne, MD, MSc, and Derek C. Angus, MD, MPH, say they “represent an excellent first step toward optimal, evidence-informed care for patients with COVID-19.” Lamontagne is from Universitaire de Sherbrooke, Canada, and Angus is from University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pennsylvania, and is an associate editor with JAMA.
Dealing With Tide of COVID-19 Patients, Protecting Healthcare Workers
Editor in chief of Intensive Care Medicine Giuseppe Citerio, MD, from University of Milano-Bicocca, Monza, Italy, said: “COVID-19 cases are rising rapidly worldwide, and so we are increasingly seeing that intensive care units [ICUs] have difficulty in dealing with the tide of patients.”
“We need more resource in ICUs, and quickly. This means more ventilators and more trained personnel. In the meantime, this guidance aims to rationalize our approach and to avoid unproven strategies,” he explains in a press release from ESICM.
“This is the first guidance to lay out what works and what doesn’t in treating coronavirus-infected patients in intensive care. It’s based on decades of research on acute respiratory infection being applied to COVID-19 patients,” added ESICM President-Elect Maurizio Cecconi, MD, from Humanitas University, Milan, Italy.
“At the same time as caring for patients, we need to make sure that health workers are following procedures which will allow themselves to be protected against infection,” he stressed.
“We must protect them, they are in the frontline. We cannot allow our healthcare workers to be at risk. On top of that, if they get infected they could also spread the disease further.”
Top-10 Recommendations
While all 50 recommendations are key to the successful management of COVID-19 patients, busy clinicians on the frontline need to zone in on those indispensable practical recommendations that they should implement immediately.
Medscape Medical News therefore asked lead author Waleed Alhazzani, MD, MSc, from the Division of Critical Care, McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada, to give his personal top 10, the first three of which are focused on limiting the spread of infection.
1. For healthcare workers performing aerosol-generating procedures1 on patients with COVID-19 in the ICU, we recommend using fitted respirator masks (N95 respirators, FFP2, or equivalent), as compared to surgical/medical masks, in addition to other personal protective equipment (eg, gloves, gown, and eye protection such as a face shield or safety goggles.
2. We recommend performing aerosol-generating procedures on ICU patients with COVID-19 in a negative-pressure room.
3. For healthcare workers providing usual care for nonventilated COVID-19 patients, we suggest using surgical/medical masks, as compared to respirator masks in addition to other personal protective equipment.
4. For healthcare workers performing endotracheal intubation on patients with COVID-19, we suggest using video guided laryngoscopy, over direct laryngoscopy, if available.
5. We recommend endotracheal intubation in patients with COVID-19, performed by healthcare workers experienced with airway management, to minimize the number of attempts and risk of transmission.
6. For intubated and mechanically ventilated adults with suspicion of COVID-19, we suggest obtaining endotracheal aspirates, over bronchial wash or bronchoalveolar lavage samples.
7. For adults with COVID-19 and acute hypoxemic respiratory failure, we suggest using high-flow nasal cannula [HFNC] over noninvasive positive pressure ventilation [NIPPV].
8. For adults with COVID-19 receiving NIPPV or HFNC, we recommend close monitoring for worsening of respiratory status and early intubation in a controlled setting if worsening occurs.
9. For mechanically ventilated adults with COVID-19 and moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome [ARDS], we suggest prone ventilation for 12 to 16 hours over no prone ventilation.
10. For mechanically ventilated adults with COVID-19 and respiratory failure (without ARDS), we don’t recommend routine use of systemic corticosteroids.
1 This includes endotracheal intubation, bronchoscopy, open suctioning, administration of nebulized treatment, manual ventilation before intubation, physical proning of the patient, disconnecting the patient from the ventilator, noninvasive positive pressure ventilation, tracheostomy, and cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
These choices are in broad agreement with those selected by Jason T. Poston, MD, University of Chicago, Illinois, and colleagues in their synopsis of these guidelines, published online March 26 in JAMA, although they also highlight another recommendation on infection control:
- For healthcare workers who are performing non-aerosol-generating procedures on mechanically ventilated (closed circuit) patients with COVID-19, we suggest using surgical/medical masks, as opposed to respirator masks, in addition to other personal protective equipment.
Importance of Prone Ventilation, Perhaps for Many Days
One recommendation singled out by both Alhazzani and coauthors, and Poston and colleagues, relates to prone ventilation for 12 to 16 hours in adults with moderate to severe ARDS receiving mechanical ventilation.
Michelle N. Gong, MD, MS, chief of critical care medicine at Montefiore Medical Center, New York City, also highlighted this practice in a live-stream interview with JAMA editor in chief Howard Bauchner, MD.
She explained that, in her institution, they have been “very aggressive about proning these patients as early as possible, but unlike some of the past ARDS patients…they tend to require many, many days of proning in order to get a response”.
Gong added that patients “may improve very rapidly when they are proned, but when we supinate them, they lose [the improvement] and then they get proned for upwards of 10 days or more, if need be.”
Alhazzani told Medscape Medical News that prone ventilation “is a simple intervention that requires training of healthcare providers but can be applied in most contexts.”
He explained that the recommendation “is driven by indirect evidence from ARDS,” not specifically those in COVID-19, with recent studies having shown that COVID-19 “can affect lung bases and may cause significant atelectasis and reduced lung compliance in the context of ARDS.”
“Prone ventilation has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with moderate to severe ARDS. Therefore, we issued a suggestion for clinicians to consider prone ventilation in this population.”
‘Impressively Thorough’ Recommendations, With Some Caveats
In their JAMA editorial, Lamontagne and Angus describe the recommendations as “impressively thorough and expansive.”
They note that they address resource scarcity, which “is likely to be a critical issue in low- and middle-income countries experiencing any reasonably large number of cases and in high-income countries experiencing a surge in the demand for critical care.”
The authors say, however, that a “weakness” of the guidelines is that they make recommendations for interventions that “lack supporting evidence.”
Consequently, “when prioritizing scarce resources, clinicians and healthcare systems will have to choose among options that have limited evidence to support them.”
“In future iterations of the guidelines, there should be more detailed recommendations for how clinicians should prioritize scarce resources, or include more recommendations against the use of unproven therapies.”
“The tasks ahead for the dissemination and uptake of optimal critical care are herculean,” Lamontagne and Angus say.
They include “a need to generate more robust evidence, consider carefully the application of that evidence across a wide variety of clinical circumstances, and generate supporting materials to ensure effective implementation of the guideline recommendations,” they conclude.
ESICM recommendations coauthor Yaseen Arabi is the principal investigator on a clinical trial for lopinavir/ritonavir and interferon in Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) and he was a nonpaid consultant on antiviral active for MERS- coronavirus (CoV) for Gilead Sciences and SAB Biotherapeutics. He is an investigator on REMAP-CAP trial and is a Board Members of the International Severe Acute Respiratory and Emerging Infection Consortium (ISARIC). Coauthor Eddy Fan declared receiving consultancy fees from ALung Technologies and MC3 Cardiopulmonary. Coauthor Maurizio Cecconi declared consultancy work with Edwards Lifesciences, Directed Systems, and Cheetah Medical.
JAMA Clinical Guidelines Synopsis coauthor Poston declares receiving honoraria for the CHEST Critical Care Board Review Course.
Editorialist Lamontagne reported receiving grants from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), Fonds de recherche du Québec-Santé, and the Lotte & John Hecht Foundation, unrelated to this work. Editorialist Angus participated in the development of Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for sepsis, but had no role in the creation of the current COVID-19 guidelines, nor the decision to create these guidelines.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.