User login
Doxy PEP does not lower risk of STIs in cisgender women
The benefits of doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP) in preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in men and transgender women do not appear to extend to cisgender women, who have disproportionately high rates of infection in many regions.
“This was the first trial to evaluate doxycycline PEP for cisgender women,” said first author Jenell Stewart, DO, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, in discussing the findings at a press conference at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
“Unfortunately, our primary outcome was not statistically significant – we did not see a reduction in STIs among cisgender women, which is in stark contrast to [reported effects] among cisgender men and transgender women,” she said.
The findings are from a study of 449 nonpregnant cisgender women (mean age, 24 years) in Kenya who had been taking daily oral HIV preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for a median of about 7 months.
The women were randomly assigned to receive either Doxy PEP 200 mg, to be taken within 72 hours of sex (n = 224), or standard care, which included quarterly screening and treatment of STIs (n = 225).
Of the women, 36.7% reported transactional sex at enrollment; their baseline prevalence of STIs was 17.9%, including 14.1% with chlamydia, 3.8% gonorrhea, and 0.4% syphilis. There were no differences between the study groups.
In surveys, 78% of the women reported adherence to the use of Doxy PEP; they took the prophylaxis at least as many days as they had sex.
Nevertheless, there was no significant difference in the incidence of STIs, reported over 1 year, at quarterly visits that included genital STI testing, between groups, with 50 patients in the Doxy PEP group and 59 in the standard screening group developing STIs (relative risk, 0.88; P = .51).
Of the infections, 85 were chlamydia, including 35 in the Doxy PEP group and 50 with standard of care, while 31 were gonorrhea, including 19 in the Doxy PEP group and 12 with standard of care; 8 had both infections, and there was 1 syphilis infection.
The results were consistent across subanalyses of patients grouped according to STI, who became pregnant (n = 80), or sorted by other factors including age, contraceptive use, transactional sex, and STI at baseline.
None of the women developed HIV, and there were no serious events associated with the Doxy PEP treatment.
Cisgender women bear ‘highest burden’ of STIs
The findings are disappointing in light of the higher rates of STIs among cisgender women, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reporting that women also disproportionately bear the long-term consequences of STIs.
“For example, each year, untreated sexually transmitted diseases cause infertility in at least 20,000 women in the United States, and a pregnant woman is highly likely to pass syphilis unto her unborn baby if left untested or untreated,” the CDC reports.
The STI rates are particularly high for women taking HIV PrEP in regions like East Africa, where rates of STIs among cisgender women in many cases are higher than rates for men taking PrEP in high income countries, Dr. Stewart said.
Previous studies of Doxy PEP in men and transgender women taking HIV PrEP, including new research presented at CROI, have shown highly encouraging reductions in STIs, at rates of up to approximately 80% for chlamydia and syphilis.
Adherence, anatomy, resistance
The key theories for the lack of a prevention of infections in cisgender women surround the issues of resistances, as well as anatomy and adherence, said Dr. Stewart.
In terms of bacterial resistances, while initial testing in a limited number of samples the study found no evidence of markers of resistance for chlamydia, all of the gonorrhea samples did show tetracycline-resistant N gonorrhea at baseline and follow-up in both groups.
Regarding anatomic differences, doxycycline may not prevent STIs in endocervical tissue among cisgender women, Dr. Stewart noted. Women are known to be at higher risk of infection because the lining of the vagina is thinner than the skin of the penis, allowing for easier penetration of bacteria and viruses.
The study was designed to optimize adherence to Doxy PEP. Measures included monitoring with weekly text message surveys, in which the women reported a high rate of adherence.
The overall retention rate in the study was high; as many as 97% of the quarterly follow-up visits were completed, including 95% in the Doxy PEP group and 98% of the standard care group. The response rate for the weekly surveys was 81%.
Of note, women reported the use of the treatment to be “imperfect,” suggesting social problems, such as biases toward the use of the prophylaxis.
The results underscore the need for ongoing efforts to make sure no groups of patients are left behind as interventions advance, Dr. Stewart said.
“The burden of STIs on cisgender women is large and growing,” she concluded. “STI prevention interventions are needed.”
Commenting on the study, Renee A. Heffron, PhD, MPH, said the findings “are somewhat surprising because results from trials in other populations have been positive.
“But cisgender women are exposed through the cervix, and this tissue is different from rectal or urethral tissue,” Dr. Heffron, a professor at the department of medicine and director of the Center for AIDS Research at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, told this news organization.
Further findings from the research should help shed light on key issues of adherence and drug concentration levels in cervical tissue, she added.
“For cisgender women, these data are the first and the beginning of understanding whether this is a viable strategy,” Dr. Heffron said.
“We have more to learn to better understand the results from the trial main outcomes, and if there are tweaks to this strategy that would improve efficacy.”
The authors and Dr. Heffron have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The benefits of doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP) in preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in men and transgender women do not appear to extend to cisgender women, who have disproportionately high rates of infection in many regions.
“This was the first trial to evaluate doxycycline PEP for cisgender women,” said first author Jenell Stewart, DO, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, in discussing the findings at a press conference at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
“Unfortunately, our primary outcome was not statistically significant – we did not see a reduction in STIs among cisgender women, which is in stark contrast to [reported effects] among cisgender men and transgender women,” she said.
The findings are from a study of 449 nonpregnant cisgender women (mean age, 24 years) in Kenya who had been taking daily oral HIV preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for a median of about 7 months.
The women were randomly assigned to receive either Doxy PEP 200 mg, to be taken within 72 hours of sex (n = 224), or standard care, which included quarterly screening and treatment of STIs (n = 225).
Of the women, 36.7% reported transactional sex at enrollment; their baseline prevalence of STIs was 17.9%, including 14.1% with chlamydia, 3.8% gonorrhea, and 0.4% syphilis. There were no differences between the study groups.
In surveys, 78% of the women reported adherence to the use of Doxy PEP; they took the prophylaxis at least as many days as they had sex.
Nevertheless, there was no significant difference in the incidence of STIs, reported over 1 year, at quarterly visits that included genital STI testing, between groups, with 50 patients in the Doxy PEP group and 59 in the standard screening group developing STIs (relative risk, 0.88; P = .51).
Of the infections, 85 were chlamydia, including 35 in the Doxy PEP group and 50 with standard of care, while 31 were gonorrhea, including 19 in the Doxy PEP group and 12 with standard of care; 8 had both infections, and there was 1 syphilis infection.
The results were consistent across subanalyses of patients grouped according to STI, who became pregnant (n = 80), or sorted by other factors including age, contraceptive use, transactional sex, and STI at baseline.
None of the women developed HIV, and there were no serious events associated with the Doxy PEP treatment.
Cisgender women bear ‘highest burden’ of STIs
The findings are disappointing in light of the higher rates of STIs among cisgender women, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reporting that women also disproportionately bear the long-term consequences of STIs.
“For example, each year, untreated sexually transmitted diseases cause infertility in at least 20,000 women in the United States, and a pregnant woman is highly likely to pass syphilis unto her unborn baby if left untested or untreated,” the CDC reports.
The STI rates are particularly high for women taking HIV PrEP in regions like East Africa, where rates of STIs among cisgender women in many cases are higher than rates for men taking PrEP in high income countries, Dr. Stewart said.
Previous studies of Doxy PEP in men and transgender women taking HIV PrEP, including new research presented at CROI, have shown highly encouraging reductions in STIs, at rates of up to approximately 80% for chlamydia and syphilis.
Adherence, anatomy, resistance
The key theories for the lack of a prevention of infections in cisgender women surround the issues of resistances, as well as anatomy and adherence, said Dr. Stewart.
In terms of bacterial resistances, while initial testing in a limited number of samples the study found no evidence of markers of resistance for chlamydia, all of the gonorrhea samples did show tetracycline-resistant N gonorrhea at baseline and follow-up in both groups.
Regarding anatomic differences, doxycycline may not prevent STIs in endocervical tissue among cisgender women, Dr. Stewart noted. Women are known to be at higher risk of infection because the lining of the vagina is thinner than the skin of the penis, allowing for easier penetration of bacteria and viruses.
The study was designed to optimize adherence to Doxy PEP. Measures included monitoring with weekly text message surveys, in which the women reported a high rate of adherence.
The overall retention rate in the study was high; as many as 97% of the quarterly follow-up visits were completed, including 95% in the Doxy PEP group and 98% of the standard care group. The response rate for the weekly surveys was 81%.
Of note, women reported the use of the treatment to be “imperfect,” suggesting social problems, such as biases toward the use of the prophylaxis.
The results underscore the need for ongoing efforts to make sure no groups of patients are left behind as interventions advance, Dr. Stewart said.
“The burden of STIs on cisgender women is large and growing,” she concluded. “STI prevention interventions are needed.”
Commenting on the study, Renee A. Heffron, PhD, MPH, said the findings “are somewhat surprising because results from trials in other populations have been positive.
“But cisgender women are exposed through the cervix, and this tissue is different from rectal or urethral tissue,” Dr. Heffron, a professor at the department of medicine and director of the Center for AIDS Research at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, told this news organization.
Further findings from the research should help shed light on key issues of adherence and drug concentration levels in cervical tissue, she added.
“For cisgender women, these data are the first and the beginning of understanding whether this is a viable strategy,” Dr. Heffron said.
“We have more to learn to better understand the results from the trial main outcomes, and if there are tweaks to this strategy that would improve efficacy.”
The authors and Dr. Heffron have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The benefits of doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP) in preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in men and transgender women do not appear to extend to cisgender women, who have disproportionately high rates of infection in many regions.
“This was the first trial to evaluate doxycycline PEP for cisgender women,” said first author Jenell Stewart, DO, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, in discussing the findings at a press conference at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
“Unfortunately, our primary outcome was not statistically significant – we did not see a reduction in STIs among cisgender women, which is in stark contrast to [reported effects] among cisgender men and transgender women,” she said.
The findings are from a study of 449 nonpregnant cisgender women (mean age, 24 years) in Kenya who had been taking daily oral HIV preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for a median of about 7 months.
The women were randomly assigned to receive either Doxy PEP 200 mg, to be taken within 72 hours of sex (n = 224), or standard care, which included quarterly screening and treatment of STIs (n = 225).
Of the women, 36.7% reported transactional sex at enrollment; their baseline prevalence of STIs was 17.9%, including 14.1% with chlamydia, 3.8% gonorrhea, and 0.4% syphilis. There were no differences between the study groups.
In surveys, 78% of the women reported adherence to the use of Doxy PEP; they took the prophylaxis at least as many days as they had sex.
Nevertheless, there was no significant difference in the incidence of STIs, reported over 1 year, at quarterly visits that included genital STI testing, between groups, with 50 patients in the Doxy PEP group and 59 in the standard screening group developing STIs (relative risk, 0.88; P = .51).
Of the infections, 85 were chlamydia, including 35 in the Doxy PEP group and 50 with standard of care, while 31 were gonorrhea, including 19 in the Doxy PEP group and 12 with standard of care; 8 had both infections, and there was 1 syphilis infection.
The results were consistent across subanalyses of patients grouped according to STI, who became pregnant (n = 80), or sorted by other factors including age, contraceptive use, transactional sex, and STI at baseline.
None of the women developed HIV, and there were no serious events associated with the Doxy PEP treatment.
Cisgender women bear ‘highest burden’ of STIs
The findings are disappointing in light of the higher rates of STIs among cisgender women, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reporting that women also disproportionately bear the long-term consequences of STIs.
“For example, each year, untreated sexually transmitted diseases cause infertility in at least 20,000 women in the United States, and a pregnant woman is highly likely to pass syphilis unto her unborn baby if left untested or untreated,” the CDC reports.
The STI rates are particularly high for women taking HIV PrEP in regions like East Africa, where rates of STIs among cisgender women in many cases are higher than rates for men taking PrEP in high income countries, Dr. Stewart said.
Previous studies of Doxy PEP in men and transgender women taking HIV PrEP, including new research presented at CROI, have shown highly encouraging reductions in STIs, at rates of up to approximately 80% for chlamydia and syphilis.
Adherence, anatomy, resistance
The key theories for the lack of a prevention of infections in cisgender women surround the issues of resistances, as well as anatomy and adherence, said Dr. Stewart.
In terms of bacterial resistances, while initial testing in a limited number of samples the study found no evidence of markers of resistance for chlamydia, all of the gonorrhea samples did show tetracycline-resistant N gonorrhea at baseline and follow-up in both groups.
Regarding anatomic differences, doxycycline may not prevent STIs in endocervical tissue among cisgender women, Dr. Stewart noted. Women are known to be at higher risk of infection because the lining of the vagina is thinner than the skin of the penis, allowing for easier penetration of bacteria and viruses.
The study was designed to optimize adherence to Doxy PEP. Measures included monitoring with weekly text message surveys, in which the women reported a high rate of adherence.
The overall retention rate in the study was high; as many as 97% of the quarterly follow-up visits were completed, including 95% in the Doxy PEP group and 98% of the standard care group. The response rate for the weekly surveys was 81%.
Of note, women reported the use of the treatment to be “imperfect,” suggesting social problems, such as biases toward the use of the prophylaxis.
The results underscore the need for ongoing efforts to make sure no groups of patients are left behind as interventions advance, Dr. Stewart said.
“The burden of STIs on cisgender women is large and growing,” she concluded. “STI prevention interventions are needed.”
Commenting on the study, Renee A. Heffron, PhD, MPH, said the findings “are somewhat surprising because results from trials in other populations have been positive.
“But cisgender women are exposed through the cervix, and this tissue is different from rectal or urethral tissue,” Dr. Heffron, a professor at the department of medicine and director of the Center for AIDS Research at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, told this news organization.
Further findings from the research should help shed light on key issues of adherence and drug concentration levels in cervical tissue, she added.
“For cisgender women, these data are the first and the beginning of understanding whether this is a viable strategy,” Dr. Heffron said.
“We have more to learn to better understand the results from the trial main outcomes, and if there are tweaks to this strategy that would improve efficacy.”
The authors and Dr. Heffron have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CROI 2023
Prone positioning curbs need for intubation in nonintubated COVID-19 patients
as indicated by data from a new meta-analysis of more than 2,000 individuals.
The use of prone positioning for nonintubated patients (so-called “awake prone positioning”) has been common since the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic. Prone positioning is more comfortable for patients, and it entails no additional cost. Also, awake prone positioning is less labor intensive than prone positioning for intubated patients, said Jie Li, PhD, in a presentation at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
However, data on the specific benefits of prone positioning are lacking and contradictory, said Dr. Li, a respiratory care specialist at Rush University, Chicago.
Dr. Li and colleagues from a multinational research group found that outcomes were improved for patients who were treated with awake prone positioning – notably, fewer treatment failures at day 28 – but a pair of subsequent studies by other researchers showed contradictory outcomes.
For more definitive evidence, Dr. Li and colleagues conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of 11 randomized, controlled trials and one unpublished study of awake prone positioning for patients with COVID-19. The studies were published between Jan. 1, 2020, and July 1, 2022, and included a total of 2,886 adult patients.
The primary outcome was the reported cumulative risk of intubation among nonintubated COVID-19 patients. Secondary outcomes included mortality, the need for escalating respiratory support, length of hospital length of stay, ICU admission, and adverse events.
Overall, awake prone positioning significantly reduced the intubation risk among nonintubated patients compared to standard care (risk ratio, 0.85).
A further subgroup analysis showed a significant reduction in risk for intubation among patients supported by high-flow nasal cannula or noninvasive ventilation (RR, 0.83).
However, no additional reduction in intubation risk occurred among patients who received conventional oxygen therapy (RR, 1.02).
Mortality rates were similar for patients who underwent awake prone positioning and those who underwent supine positioning (RR, 0.96), as was the need for additional respiratory support (RR, 1.03). The length of hospital stay, ICU admission, and adverse events were similar between the patients who underwent prone positioning and those who underwent supine positioning.
The findings were limited by several factors. There was a potential for confounding by disease severity, which may have increased the use of respiratory support devices, Li said in her presentation.
“Another factor we should not ignore is the daily duration of prone positioning,” said Dr. Li. More research is needed to identify which factors play the greatest roles in treatment success.
The current study was important in that it evaluated the current evidence of awake prone positioning, “particularly to identify the patients who benefit most from this treatment, in order to guide clinical practice,” Dr. Li said in an interview.
“Since early in the pandemic, awake prone positioning has been broadly utilized to treat patients with COVID-19,” she said. “In 2021, we published a multinational randomized controlled trial with over 1,100 patients enrolled and reported lower treatment failure. However, no significant differences of treatment failure were reported in several subsequent multicenter randomized, controlled trials published after our study.”
Dr. Li said she was not surprised by the findings, which reflect those of her team’s previously published meta-analysis. “The increased number of patients helps confirm our previous finding, even with the inclusion of several recently published randomized controlled trials,” she said.
For clinicians, “the current evidence supports the use of awake prone positioning for patients with COVID-19, particularly those who require advanced respiratory support from high-flow nasal cannula or noninvasive ventilation,” Dr. Li said.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Li has relationships with AARC, Heyer, Aeorgen, the Rice Foundation, and Fisher & Paykel Healthcare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
as indicated by data from a new meta-analysis of more than 2,000 individuals.
The use of prone positioning for nonintubated patients (so-called “awake prone positioning”) has been common since the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic. Prone positioning is more comfortable for patients, and it entails no additional cost. Also, awake prone positioning is less labor intensive than prone positioning for intubated patients, said Jie Li, PhD, in a presentation at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
However, data on the specific benefits of prone positioning are lacking and contradictory, said Dr. Li, a respiratory care specialist at Rush University, Chicago.
Dr. Li and colleagues from a multinational research group found that outcomes were improved for patients who were treated with awake prone positioning – notably, fewer treatment failures at day 28 – but a pair of subsequent studies by other researchers showed contradictory outcomes.
For more definitive evidence, Dr. Li and colleagues conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of 11 randomized, controlled trials and one unpublished study of awake prone positioning for patients with COVID-19. The studies were published between Jan. 1, 2020, and July 1, 2022, and included a total of 2,886 adult patients.
The primary outcome was the reported cumulative risk of intubation among nonintubated COVID-19 patients. Secondary outcomes included mortality, the need for escalating respiratory support, length of hospital length of stay, ICU admission, and adverse events.
Overall, awake prone positioning significantly reduced the intubation risk among nonintubated patients compared to standard care (risk ratio, 0.85).
A further subgroup analysis showed a significant reduction in risk for intubation among patients supported by high-flow nasal cannula or noninvasive ventilation (RR, 0.83).
However, no additional reduction in intubation risk occurred among patients who received conventional oxygen therapy (RR, 1.02).
Mortality rates were similar for patients who underwent awake prone positioning and those who underwent supine positioning (RR, 0.96), as was the need for additional respiratory support (RR, 1.03). The length of hospital stay, ICU admission, and adverse events were similar between the patients who underwent prone positioning and those who underwent supine positioning.
The findings were limited by several factors. There was a potential for confounding by disease severity, which may have increased the use of respiratory support devices, Li said in her presentation.
“Another factor we should not ignore is the daily duration of prone positioning,” said Dr. Li. More research is needed to identify which factors play the greatest roles in treatment success.
The current study was important in that it evaluated the current evidence of awake prone positioning, “particularly to identify the patients who benefit most from this treatment, in order to guide clinical practice,” Dr. Li said in an interview.
“Since early in the pandemic, awake prone positioning has been broadly utilized to treat patients with COVID-19,” she said. “In 2021, we published a multinational randomized controlled trial with over 1,100 patients enrolled and reported lower treatment failure. However, no significant differences of treatment failure were reported in several subsequent multicenter randomized, controlled trials published after our study.”
Dr. Li said she was not surprised by the findings, which reflect those of her team’s previously published meta-analysis. “The increased number of patients helps confirm our previous finding, even with the inclusion of several recently published randomized controlled trials,” she said.
For clinicians, “the current evidence supports the use of awake prone positioning for patients with COVID-19, particularly those who require advanced respiratory support from high-flow nasal cannula or noninvasive ventilation,” Dr. Li said.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Li has relationships with AARC, Heyer, Aeorgen, the Rice Foundation, and Fisher & Paykel Healthcare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
as indicated by data from a new meta-analysis of more than 2,000 individuals.
The use of prone positioning for nonintubated patients (so-called “awake prone positioning”) has been common since the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic. Prone positioning is more comfortable for patients, and it entails no additional cost. Also, awake prone positioning is less labor intensive than prone positioning for intubated patients, said Jie Li, PhD, in a presentation at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
However, data on the specific benefits of prone positioning are lacking and contradictory, said Dr. Li, a respiratory care specialist at Rush University, Chicago.
Dr. Li and colleagues from a multinational research group found that outcomes were improved for patients who were treated with awake prone positioning – notably, fewer treatment failures at day 28 – but a pair of subsequent studies by other researchers showed contradictory outcomes.
For more definitive evidence, Dr. Li and colleagues conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of 11 randomized, controlled trials and one unpublished study of awake prone positioning for patients with COVID-19. The studies were published between Jan. 1, 2020, and July 1, 2022, and included a total of 2,886 adult patients.
The primary outcome was the reported cumulative risk of intubation among nonintubated COVID-19 patients. Secondary outcomes included mortality, the need for escalating respiratory support, length of hospital length of stay, ICU admission, and adverse events.
Overall, awake prone positioning significantly reduced the intubation risk among nonintubated patients compared to standard care (risk ratio, 0.85).
A further subgroup analysis showed a significant reduction in risk for intubation among patients supported by high-flow nasal cannula or noninvasive ventilation (RR, 0.83).
However, no additional reduction in intubation risk occurred among patients who received conventional oxygen therapy (RR, 1.02).
Mortality rates were similar for patients who underwent awake prone positioning and those who underwent supine positioning (RR, 0.96), as was the need for additional respiratory support (RR, 1.03). The length of hospital stay, ICU admission, and adverse events were similar between the patients who underwent prone positioning and those who underwent supine positioning.
The findings were limited by several factors. There was a potential for confounding by disease severity, which may have increased the use of respiratory support devices, Li said in her presentation.
“Another factor we should not ignore is the daily duration of prone positioning,” said Dr. Li. More research is needed to identify which factors play the greatest roles in treatment success.
The current study was important in that it evaluated the current evidence of awake prone positioning, “particularly to identify the patients who benefit most from this treatment, in order to guide clinical practice,” Dr. Li said in an interview.
“Since early in the pandemic, awake prone positioning has been broadly utilized to treat patients with COVID-19,” she said. “In 2021, we published a multinational randomized controlled trial with over 1,100 patients enrolled and reported lower treatment failure. However, no significant differences of treatment failure were reported in several subsequent multicenter randomized, controlled trials published after our study.”
Dr. Li said she was not surprised by the findings, which reflect those of her team’s previously published meta-analysis. “The increased number of patients helps confirm our previous finding, even with the inclusion of several recently published randomized controlled trials,” she said.
For clinicians, “the current evidence supports the use of awake prone positioning for patients with COVID-19, particularly those who require advanced respiratory support from high-flow nasal cannula or noninvasive ventilation,” Dr. Li said.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Li has relationships with AARC, Heyer, Aeorgen, the Rice Foundation, and Fisher & Paykel Healthcare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SCCM 2023
FDA broadens warning on potentially contaminated eye products
The announcement released Wednesday adds to a previous warning issued earlier this month for EzriCare Artificial Tears or Delsam Pharma’s Artificial Tears because of potential bacterial contamination. All three products are manufactured by the same company, Global Pharma Healthcare, based in Tamilnadu, India.
The FDA has faulted the company for multiple violations, including “lack of appropriate microbial testing” and “lack of proper controls concerning tamper-evident packaging,” and has banned imports to the United States.
The updated warning from the FDA did not give additional information about the over-the-counter eye ointment beyond potential bacterial contamination.
On Feb. 1, the CDC issued an alert about an outbreak of a drug-resistant strain of bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, linked to artificial tear products. To date, 58 patients across 13 states have been identified, and the most commonly reported artificial tear brand was EzriCare Artificial Tears. Five patients had permanent vision loss, and one patient died.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The announcement released Wednesday adds to a previous warning issued earlier this month for EzriCare Artificial Tears or Delsam Pharma’s Artificial Tears because of potential bacterial contamination. All three products are manufactured by the same company, Global Pharma Healthcare, based in Tamilnadu, India.
The FDA has faulted the company for multiple violations, including “lack of appropriate microbial testing” and “lack of proper controls concerning tamper-evident packaging,” and has banned imports to the United States.
The updated warning from the FDA did not give additional information about the over-the-counter eye ointment beyond potential bacterial contamination.
On Feb. 1, the CDC issued an alert about an outbreak of a drug-resistant strain of bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, linked to artificial tear products. To date, 58 patients across 13 states have been identified, and the most commonly reported artificial tear brand was EzriCare Artificial Tears. Five patients had permanent vision loss, and one patient died.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The announcement released Wednesday adds to a previous warning issued earlier this month for EzriCare Artificial Tears or Delsam Pharma’s Artificial Tears because of potential bacterial contamination. All three products are manufactured by the same company, Global Pharma Healthcare, based in Tamilnadu, India.
The FDA has faulted the company for multiple violations, including “lack of appropriate microbial testing” and “lack of proper controls concerning tamper-evident packaging,” and has banned imports to the United States.
The updated warning from the FDA did not give additional information about the over-the-counter eye ointment beyond potential bacterial contamination.
On Feb. 1, the CDC issued an alert about an outbreak of a drug-resistant strain of bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, linked to artificial tear products. To date, 58 patients across 13 states have been identified, and the most commonly reported artificial tear brand was EzriCare Artificial Tears. Five patients had permanent vision loss, and one patient died.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Meningococcal vaccine shows benefit in STI prevention
The latest study to show high efficacy of doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP) in preventing sexually transmitted infections among men who have sex with men (MSM) adds a new twist, showing – for the first time – reductions in gonorrhea among those receiving the meningococcal B vaccine.
said first author Jean-Michel Molina, MD, PhD, in presenting the findings at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections.
In addition, “two doses of the meningococcal B vaccine reduced the incidence of a first episode of gonorrhea by roughly 50% among men who have sex with men,” said Dr. Molina, a professor of infectious diseases at the University of Paris, and head of the Infectious Diseases Department at the Saint-Louis and Lariboisière Hospitals, Paris.
Whereas the advent of PrEP has been associated with significant reductions in HIV transmission, rates of STIs have conversely been on the rise among MSM, specifically among those receiving PrEP.
Post-exposure prophylaxis with Doxy PEP has been shown to reduce the incidence of chlamydia and syphilis by approximately 70%; however, effects on prevention of gonorrhea have been less clear.
Meningococcal B vaccination has, meanwhile, shown intriguing reductions of gonorrhea incidence of as much as 26%-46% in some observational studies.
Therefore, Dr. Molina and colleagues decided to further investigate Doxy PEP as well as the meningococcal B vaccine in prevention of STIs.
For the ANRS 174 DOXYVAC trial, they enrolled 546 MSM in the open-label, multicenter study between January 2021 and July 2022.
The men were randomly assigned to one of 4 groups: doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP: 200 mg; n = 332), no Doxy PEP (n = 170), two shots of meningococcal B vaccine (4CMenB vaccine; n = 257), or no 4CMenB vaccine (n = 245).
All participants were assigned to their groups within 72 hours of condomless sex.
The men, who had a median age of 39, had a median time of PrEP use of 42 months, a history of an STI in the past year, and their median number of sexual partners in the past 3 months was 10.
Their characteristics were well-balanced across the treatment groups. After discontinuations of 54 patients across the groups, the final analysis included 502 participants.
With a median follow-up of 9 months, the intent-to-treat analysis showed 13 subjects had a first episode of chlamydia or syphilis in the Doxy PEP group, versus 49 subjects infected in the no Doxy PEP arm, for an incidence of 5.6 versus 35.4 per 100 person-years, respectively (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.16; P < .0001).
Infection specifically with chlamydia occurred among 21 men with no Doxy PEP versus 5 receiving Dox PEP (19.3 vs. 2.1 per 100 person-years, respectively; HR, 0.11; P < .0001).
And infection with syphilis occurred in 18 men receiving no Doxy PEP versus 8 receiving the treatment (16.3 vs. 3.4 per 100 person-years, respectively; HR, 0.21; P < .001).
The corresponding rates for gonorrhea infection were an incidence 41.3 versus 20.5 per 100 person-years, in the no Doxy PEP versus Doxy PEP arms, respectively (adjusted HR, 0.49; P = .001), and 29.4 versus 16.8 per 100 person-years for Mycoplasma genitalium infection (aHR, 0.55; P = .015).
Throughout the study, about 80% of patients in the Doxy PEP group reported using the prophylaxis treatment after their most recent sexual intercourse, with subjects reporting taking a median of seven pills per month.
In the vaccine/no vaccine comparisons, 32 subjects in the no meningococcal vaccine group were infected with a first gonorrhea infection, compared with 17 in the vaccine group, representing an incidence of 19.7 versus 9.8 per 100 person-years, respectively (adjusted HR, 0.49; P = .016), which Dr. Molina called “highly significant.”
An analysis of the cumulative incidence of gonorrhea infection with the meningococcal vaccine showed rates in the no vaccine versus vaccine groups of 30.4 versus 20.1 per 100 person-years, respectively; however, statistical significance was not reached (aHR, 0.66; P = .052).
Importantly, there were no significant interactions in the results between those receiving Doxy PEP or the 4CMenB vaccine group, and there were no significant differences in drug-related serious adverse events between the groups.
Dr. Molina noted that the meningococcal B vaccine is known to contain key antigens that are shared between meningitis and gonorrhea, which could explain the benefits.
Although chlamydia and syphilis thus far appear to remain susceptible to Doxy PEP, resistances with gonorrhea remain a concern, hence the ability of the vaccine to provide some protection could be an added bonus.
“We know that [gonorrhea] is able to very quickly develop resistances to any antibiotics, so that was why we wanted to look beyond the antibiotic prophylaxis,” said Dr. Molina.
Among questions to explore looking ahead is the potential longevity of protection with the vaccine.
“We don’t know at this point how long the protection with the vaccine could last, or if [people] may need booster injections, for instance, but the literature suggests benefits for at least a year,” Dr. Molina said. “We are still monitoring the patients in the study to see what happens.”
He added that combination of the interventions may be of benefit.
“In the future, we think we may need to combine these approaches if we want to meet the WHO/UNAIDS targets to reduce the incidence of HIV and STIs by 90% by 2030.”
Commenting on the study, CROI vice-chair Landon Myer, MD, PhD, noted that “gonorrhea develops resistance quickly and can be hard to treat or prophylaxis, so the vaccine finding, which was hinted at by previous observational data, is really important.”
He agrees that “the duration of protective efficacy – a big thing in vaccines – is unknown.”
“Still, this is really significant,” Dr. Myer stressed. “An efficacious vaccine against a stubborn sexually transmitted infection.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The latest study to show high efficacy of doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP) in preventing sexually transmitted infections among men who have sex with men (MSM) adds a new twist, showing – for the first time – reductions in gonorrhea among those receiving the meningococcal B vaccine.
said first author Jean-Michel Molina, MD, PhD, in presenting the findings at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections.
In addition, “two doses of the meningococcal B vaccine reduced the incidence of a first episode of gonorrhea by roughly 50% among men who have sex with men,” said Dr. Molina, a professor of infectious diseases at the University of Paris, and head of the Infectious Diseases Department at the Saint-Louis and Lariboisière Hospitals, Paris.
Whereas the advent of PrEP has been associated with significant reductions in HIV transmission, rates of STIs have conversely been on the rise among MSM, specifically among those receiving PrEP.
Post-exposure prophylaxis with Doxy PEP has been shown to reduce the incidence of chlamydia and syphilis by approximately 70%; however, effects on prevention of gonorrhea have been less clear.
Meningococcal B vaccination has, meanwhile, shown intriguing reductions of gonorrhea incidence of as much as 26%-46% in some observational studies.
Therefore, Dr. Molina and colleagues decided to further investigate Doxy PEP as well as the meningococcal B vaccine in prevention of STIs.
For the ANRS 174 DOXYVAC trial, they enrolled 546 MSM in the open-label, multicenter study between January 2021 and July 2022.
The men were randomly assigned to one of 4 groups: doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP: 200 mg; n = 332), no Doxy PEP (n = 170), two shots of meningococcal B vaccine (4CMenB vaccine; n = 257), or no 4CMenB vaccine (n = 245).
All participants were assigned to their groups within 72 hours of condomless sex.
The men, who had a median age of 39, had a median time of PrEP use of 42 months, a history of an STI in the past year, and their median number of sexual partners in the past 3 months was 10.
Their characteristics were well-balanced across the treatment groups. After discontinuations of 54 patients across the groups, the final analysis included 502 participants.
With a median follow-up of 9 months, the intent-to-treat analysis showed 13 subjects had a first episode of chlamydia or syphilis in the Doxy PEP group, versus 49 subjects infected in the no Doxy PEP arm, for an incidence of 5.6 versus 35.4 per 100 person-years, respectively (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.16; P < .0001).
Infection specifically with chlamydia occurred among 21 men with no Doxy PEP versus 5 receiving Dox PEP (19.3 vs. 2.1 per 100 person-years, respectively; HR, 0.11; P < .0001).
And infection with syphilis occurred in 18 men receiving no Doxy PEP versus 8 receiving the treatment (16.3 vs. 3.4 per 100 person-years, respectively; HR, 0.21; P < .001).
The corresponding rates for gonorrhea infection were an incidence 41.3 versus 20.5 per 100 person-years, in the no Doxy PEP versus Doxy PEP arms, respectively (adjusted HR, 0.49; P = .001), and 29.4 versus 16.8 per 100 person-years for Mycoplasma genitalium infection (aHR, 0.55; P = .015).
Throughout the study, about 80% of patients in the Doxy PEP group reported using the prophylaxis treatment after their most recent sexual intercourse, with subjects reporting taking a median of seven pills per month.
In the vaccine/no vaccine comparisons, 32 subjects in the no meningococcal vaccine group were infected with a first gonorrhea infection, compared with 17 in the vaccine group, representing an incidence of 19.7 versus 9.8 per 100 person-years, respectively (adjusted HR, 0.49; P = .016), which Dr. Molina called “highly significant.”
An analysis of the cumulative incidence of gonorrhea infection with the meningococcal vaccine showed rates in the no vaccine versus vaccine groups of 30.4 versus 20.1 per 100 person-years, respectively; however, statistical significance was not reached (aHR, 0.66; P = .052).
Importantly, there were no significant interactions in the results between those receiving Doxy PEP or the 4CMenB vaccine group, and there were no significant differences in drug-related serious adverse events between the groups.
Dr. Molina noted that the meningococcal B vaccine is known to contain key antigens that are shared between meningitis and gonorrhea, which could explain the benefits.
Although chlamydia and syphilis thus far appear to remain susceptible to Doxy PEP, resistances with gonorrhea remain a concern, hence the ability of the vaccine to provide some protection could be an added bonus.
“We know that [gonorrhea] is able to very quickly develop resistances to any antibiotics, so that was why we wanted to look beyond the antibiotic prophylaxis,” said Dr. Molina.
Among questions to explore looking ahead is the potential longevity of protection with the vaccine.
“We don’t know at this point how long the protection with the vaccine could last, or if [people] may need booster injections, for instance, but the literature suggests benefits for at least a year,” Dr. Molina said. “We are still monitoring the patients in the study to see what happens.”
He added that combination of the interventions may be of benefit.
“In the future, we think we may need to combine these approaches if we want to meet the WHO/UNAIDS targets to reduce the incidence of HIV and STIs by 90% by 2030.”
Commenting on the study, CROI vice-chair Landon Myer, MD, PhD, noted that “gonorrhea develops resistance quickly and can be hard to treat or prophylaxis, so the vaccine finding, which was hinted at by previous observational data, is really important.”
He agrees that “the duration of protective efficacy – a big thing in vaccines – is unknown.”
“Still, this is really significant,” Dr. Myer stressed. “An efficacious vaccine against a stubborn sexually transmitted infection.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The latest study to show high efficacy of doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP) in preventing sexually transmitted infections among men who have sex with men (MSM) adds a new twist, showing – for the first time – reductions in gonorrhea among those receiving the meningococcal B vaccine.
said first author Jean-Michel Molina, MD, PhD, in presenting the findings at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections.
In addition, “two doses of the meningococcal B vaccine reduced the incidence of a first episode of gonorrhea by roughly 50% among men who have sex with men,” said Dr. Molina, a professor of infectious diseases at the University of Paris, and head of the Infectious Diseases Department at the Saint-Louis and Lariboisière Hospitals, Paris.
Whereas the advent of PrEP has been associated with significant reductions in HIV transmission, rates of STIs have conversely been on the rise among MSM, specifically among those receiving PrEP.
Post-exposure prophylaxis with Doxy PEP has been shown to reduce the incidence of chlamydia and syphilis by approximately 70%; however, effects on prevention of gonorrhea have been less clear.
Meningococcal B vaccination has, meanwhile, shown intriguing reductions of gonorrhea incidence of as much as 26%-46% in some observational studies.
Therefore, Dr. Molina and colleagues decided to further investigate Doxy PEP as well as the meningococcal B vaccine in prevention of STIs.
For the ANRS 174 DOXYVAC trial, they enrolled 546 MSM in the open-label, multicenter study between January 2021 and July 2022.
The men were randomly assigned to one of 4 groups: doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP: 200 mg; n = 332), no Doxy PEP (n = 170), two shots of meningococcal B vaccine (4CMenB vaccine; n = 257), or no 4CMenB vaccine (n = 245).
All participants were assigned to their groups within 72 hours of condomless sex.
The men, who had a median age of 39, had a median time of PrEP use of 42 months, a history of an STI in the past year, and their median number of sexual partners in the past 3 months was 10.
Their characteristics were well-balanced across the treatment groups. After discontinuations of 54 patients across the groups, the final analysis included 502 participants.
With a median follow-up of 9 months, the intent-to-treat analysis showed 13 subjects had a first episode of chlamydia or syphilis in the Doxy PEP group, versus 49 subjects infected in the no Doxy PEP arm, for an incidence of 5.6 versus 35.4 per 100 person-years, respectively (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.16; P < .0001).
Infection specifically with chlamydia occurred among 21 men with no Doxy PEP versus 5 receiving Dox PEP (19.3 vs. 2.1 per 100 person-years, respectively; HR, 0.11; P < .0001).
And infection with syphilis occurred in 18 men receiving no Doxy PEP versus 8 receiving the treatment (16.3 vs. 3.4 per 100 person-years, respectively; HR, 0.21; P < .001).
The corresponding rates for gonorrhea infection were an incidence 41.3 versus 20.5 per 100 person-years, in the no Doxy PEP versus Doxy PEP arms, respectively (adjusted HR, 0.49; P = .001), and 29.4 versus 16.8 per 100 person-years for Mycoplasma genitalium infection (aHR, 0.55; P = .015).
Throughout the study, about 80% of patients in the Doxy PEP group reported using the prophylaxis treatment after their most recent sexual intercourse, with subjects reporting taking a median of seven pills per month.
In the vaccine/no vaccine comparisons, 32 subjects in the no meningococcal vaccine group were infected with a first gonorrhea infection, compared with 17 in the vaccine group, representing an incidence of 19.7 versus 9.8 per 100 person-years, respectively (adjusted HR, 0.49; P = .016), which Dr. Molina called “highly significant.”
An analysis of the cumulative incidence of gonorrhea infection with the meningococcal vaccine showed rates in the no vaccine versus vaccine groups of 30.4 versus 20.1 per 100 person-years, respectively; however, statistical significance was not reached (aHR, 0.66; P = .052).
Importantly, there were no significant interactions in the results between those receiving Doxy PEP or the 4CMenB vaccine group, and there were no significant differences in drug-related serious adverse events between the groups.
Dr. Molina noted that the meningococcal B vaccine is known to contain key antigens that are shared between meningitis and gonorrhea, which could explain the benefits.
Although chlamydia and syphilis thus far appear to remain susceptible to Doxy PEP, resistances with gonorrhea remain a concern, hence the ability of the vaccine to provide some protection could be an added bonus.
“We know that [gonorrhea] is able to very quickly develop resistances to any antibiotics, so that was why we wanted to look beyond the antibiotic prophylaxis,” said Dr. Molina.
Among questions to explore looking ahead is the potential longevity of protection with the vaccine.
“We don’t know at this point how long the protection with the vaccine could last, or if [people] may need booster injections, for instance, but the literature suggests benefits for at least a year,” Dr. Molina said. “We are still monitoring the patients in the study to see what happens.”
He added that combination of the interventions may be of benefit.
“In the future, we think we may need to combine these approaches if we want to meet the WHO/UNAIDS targets to reduce the incidence of HIV and STIs by 90% by 2030.”
Commenting on the study, CROI vice-chair Landon Myer, MD, PhD, noted that “gonorrhea develops resistance quickly and can be hard to treat or prophylaxis, so the vaccine finding, which was hinted at by previous observational data, is really important.”
He agrees that “the duration of protective efficacy – a big thing in vaccines – is unknown.”
“Still, this is really significant,” Dr. Myer stressed. “An efficacious vaccine against a stubborn sexually transmitted infection.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CROI 2023
Ticking Time: Spreading Awareness About African Tick-Bite Fever
To the Editor:
One of the more common tick-borne infections seen in travelers returning from sub-Saharan Africa is caused by Rickettsia africae, which is the etiologic agent of African tick-bite fever (ATBF), the most common tick-borne bacterial zoonosis.1 There are 2 known tick vectors of disease: Amblyomma variegatum, found in sub-Saharan Africa and the West Indies, and Amblyomma hebraeum, found specifically in southern Africa.2,3
Unlike other disease-carrying ticks that passively wait on vegetation to be picked up by a host, A hebraeum uniquely attract other nearby ticks to the host. Studies have shown that male ticks feeding on a nonhuman host (usually cattle) can emit an aggression-attachment pheromone that attracts other ticks to the host. The presence of the pheromone allows unfed ticks to actively discriminate between hosts on which these parasites have fed successfully (ie, suitable hosts) and those on which they have not.4
The aggressive hunting nature of A hebraeum explains the clinical presentation of multiple eschars and why large groups of exposed travelers—such as soldiers, leisure safari tourists, game hunters, and foreign-aid workers—are affected.2
Another southern African spotted fever group, Rickettsia conorii is the causative agent of Mediterranean spotted fever (MSF). Ticks carrying R conorii exhibit a much less aggressive hunting stylethan A hebraeum; consequently, infected patients present with a single eschar site.5
Rickettsia africae is estimated to have very high prevalence (95.2%) in Amblyomma ticks and a fairly high prevalence (approximately 4.0% to 8.6%) in travelers coming from rural southern Africa,6,7 with an incubation period of 5 to 10 days after inoculation by an infected tick.8 Signs include fever, a generalized maculopapular or papulovesicular rash, and regional lymphadenopathy; symptoms include fatigue, headache, and myalgia.
The inoculation eschar—single or multiple—commonly presents on the legs and is accompanied by tender lymphadenopathy of draining nodes1,8 More severe findings, such as myocarditis and subacute neuropathy, have been reported in elderly patients.9
A 77-year-old man presented with a pruritic maculopapular and papulovesicular rash distributed over the upper and lower extremities of 3 weeks’ duration. The patient reported having been on a 12-day mission trip to Limpopo, South Africa, where he was constructing and installing safe toilets to replace dangerous toilet pits. He believed he had been bitten by 2 ticks, after which he noted a dark purple and black patch on the left lower leg by the third day of the trip. He developed a sudden persistent pruritic rash, first on the lower extremities and then spreading to the upper extremities. The patient was seen by an American physician in South Africa who gave him a 7-day course of oral doxycycline monohydrate 100 mg twice daily. He then returned to the United States.
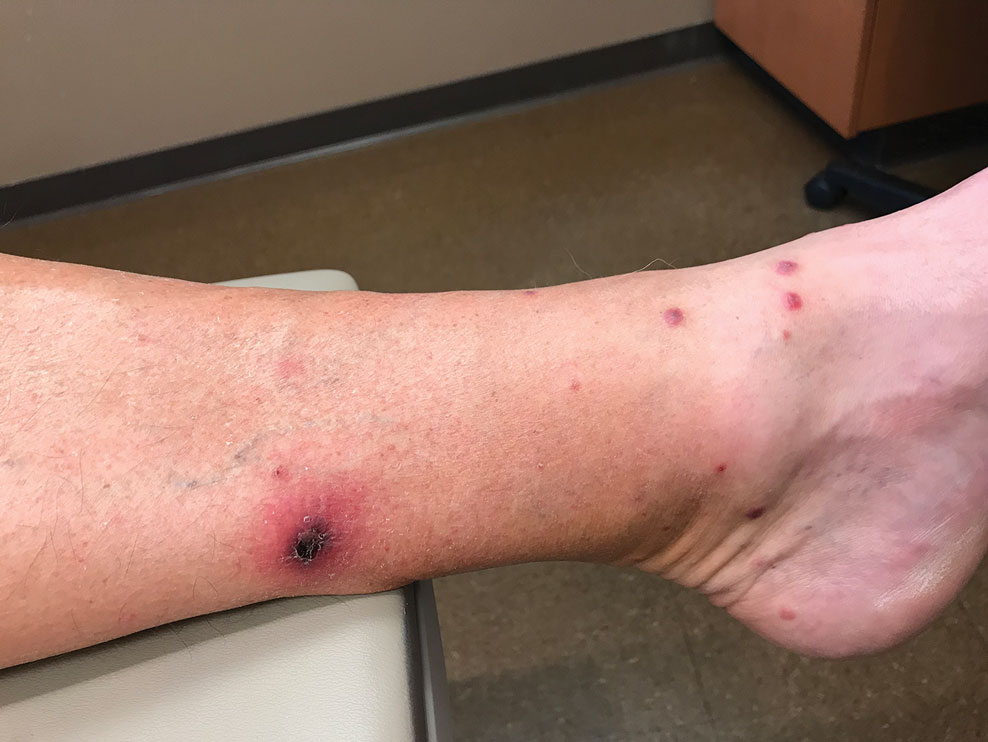
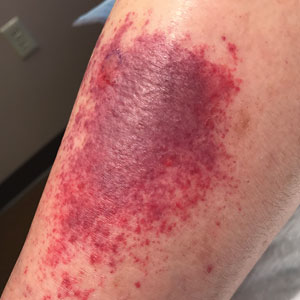
Sixteen days after being bitten by the ticks, the patient was examined in our dermatology office. Physical examination revealed an erythematous plaque with a central eschar over the medial aspect of the left leg (Figure 1) and multiple 3- to 6-mm, erythematous, dome-shaped papules scattered over the dorsal aspects of the feet and ankles (Figure 2). The examination was otherwise normal. Blood was drawn the same day for laboratory analysis; no abnormalities of platelets, red blood cells, or white blood cells were found. Results of a chemistry panel and liver enzyme tests were within reference range.
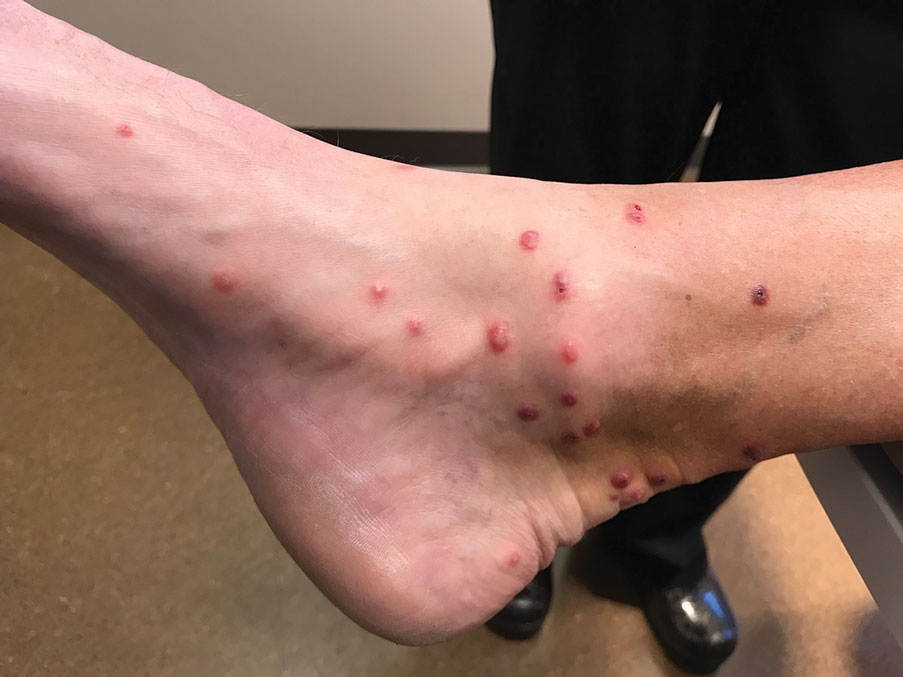
Skin biopsies were taken to elucidate the underlying pathology. Although an arthropod assault was suspected, there also was concern for deep vessel vasculitis because of the presence of considerable petechiae and purpura (Figure 3). Histologically, leukocytoclasia was seen in deep dermal blood vessels. A mild eosinophilic spongiosis with a mixed dermal infiltrate was identified—strengthening our suspicion of an arthropod assault. Bacterial cultures for aerobes and anaerobes using material taken from the right shin showed no growth.
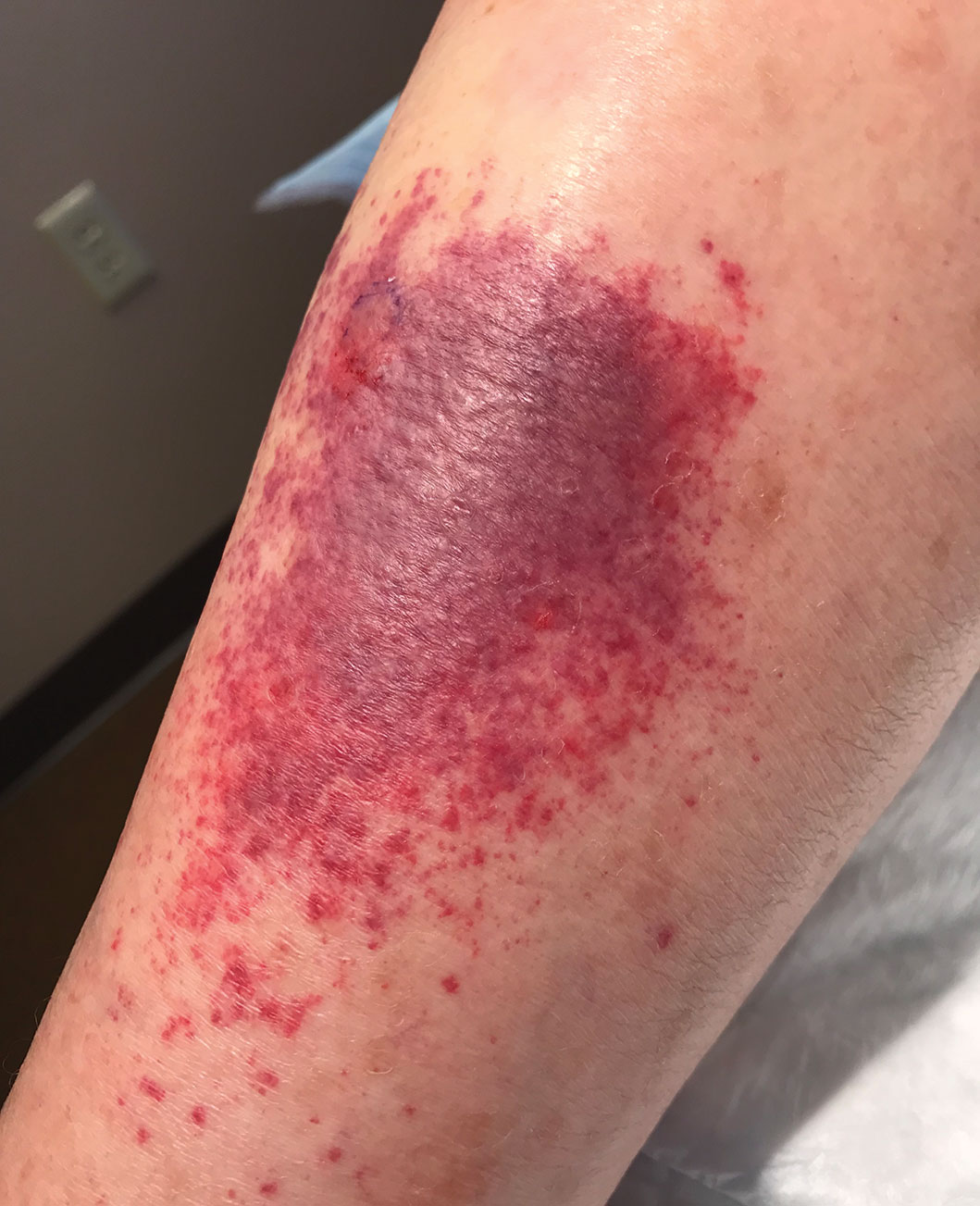
Ten days after the initial biopsies, serum specimens were drawn and swabs of eschar were collected and sent to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for further testing. Serum was tested by immunofluorescence assay (IFA) for spotted fever group IgG to detect Rocky Mountain spotted fever and ATBF antibodies; both tests were negative. Swab material from eschar was tested again by IFA for spotted fever group IgG (Rocky Mountain spotted fever) and antibodies to ATBF and with bacterial culture isolation and nucleic acid amplification; the culture and amplification came back positive for R africae.
Because the specialized tests confirmed infection with R africae, the patient was given triamcinolone cream 0.1% to apply twice daily to the pruritic lesions for as long as 4 weeks; an additional 14-day course of oral doxycycline monohydrate (100 mg twice daily) was given. At follow-up, the lesions had fully resolved without evident scarring.
Various diagnostic techniques can detect R africae. Bacterial culture and the polymerase chain reaction are specific and therefore diagnostic. In addition, the diagnosis of rickettsiosis can be made with serology testing, in which disease-specific antibodies are detected by indirect IFA using disease-specific antigens.
Antigens from R rickettsii (the agent of Rocky Mountain spotted fever), R conorii (Mediterranean spotted fever), and R africae (ATBF) are commercially available for making the diagnosis of rickettsiosis. However, antigens from R conorii exhibit cross-reactivity with R africae, which can confound the diagnosis.1,10 Serologic IFA tests have been shown to be less sensitive, especially when performed after antibacterial treatment has started.
In a study, 17 of 65 (26%) ATBF-confirmed patients were seronegative (acute and convalescent-phase sera) against R africae; 14 had received doxycycline during the first week of clinical signs. The current hypothesis is that R africae is highly sensitive to doxycycline and that early exposure to the drug prevented development of detectable titers of reactive antibodies, thus producing a negative serology test.11
Furthermore, it has been shown that seroconversion of IgG and IgM antibodies in R africae–infected sera is delayed compared to what is observed with R conorii–infected sera. Typically, seroconversion of R conorii–infected sera can be detected within 2 weeks; seroconversion in R africae–infected sera can take 4 weeks or longer.11
Our patient had a confirmed case of ATBF secondary to R africae infection, which was evident from tissue culture isolation and polymerase chain reaction analysis of swab material obtained from eschar sites, both of which yielded a positive result for R africae. The traveler’s negative serologic status might be due to his early exposure to doxycycline or to the 4-week delay in R africae seroconversion; his serum was collected only 3 weeks after the tick bites.
Clinical signs also aid in making the diagnosis of ATBF and distinguishing R conorii from R africae infection. Because of the aggressive hunting nature of the tick carrying R africae, they are associated with multiple eschars and tend to affect groups of multiple people, especially in rural areas.4,5 In contrast, ticks carrying R conorii yield a single eschar due to their passive style of infecting a host and because they favor a single host within urban areas.5 Both infections exhibit a maculopapular or papulovesicular rash and are accompanied by fatigue, headache, and myalgia, though ATBF tends to present with a milder rash than MSF.
Infection with either R conorii or R africae responds to tetracyclines, quinolones, and macrolides.10,12
African tick-bite fever is becoming more common, which should encourage clinicians to become familiar with the disease. Less than 2 decades ago, ATBF virtually was unknown outside of Zimbabwe, Botswana, Tanzania, Zambia, and Kenya, where it is endemic. However, after the abolition of apartheid in the 1990s, international tourism in southern Africa increased 6-fold.13 African tick-bite fever is now one of the most common rickettsial infections in Africa.7 In addition to diagnosing ATBF and managing infected patients, clinicians can help prevent ATBF in individuals who travel to endemic areas by recommending commercial topical insect repellents containing at least 19.5% N,N-diethyl-meta-toluamide (DEET).14
- Parola P, Paddock CD, Socolovschi C, et al. Update on tick-borne rickettsioses around the world: a geographic approach. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013;26:657-702. doi:10.1128/CMR.00032-13
- Jensenius M, Fournier P-E, Vene S, et al; Norwegian African Tick Bite Fever Study Group. African tick bite fever in travelers to rural sub-equatorial Africa. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36:1411-1417. doi:10.1086/375083
- Parola P, Jourdan J, Raoult D. Tick-borne infection caused by Rickettsia africae in the West Indies. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1391-1392. doi:10.1056/NEJM199805073381918
- Norval RA, Andrew HR, Yunker CE. Pheromone-mediation of host-selection in bont ticks (Amblyomma hebraeum Koch). Science. 1989;243:364-365. doi:10.1126/science.2911745
- Parola P, Raoult D. Ticks and tickborne bacterial diseases in humans: an emerging infectious threat. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:897-928. doi:10.1086/319347
- Kelly PJ, Mason PR. Transmission of a spotted fever group rickettsia by Amblyomma hebraeum (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1991;28:598-600. doi:10.1093/jmedent/28.5.598
- Maina AN, Jiang J, Omulo SA, et al. High prevalence of Rickettsia africae variants in Amblyomma variegatum ticks from domestic mammals in rural Western Kenya: implications for human health. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014;14:693-702. doi:10.1089/vbz.2014.1578
- Jensenius M, Fournier P-E, Kelly P, et al. African tick bite fever. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003;3:557-564. doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(03)00739-4
- Roch N, Epaulard O, Pelloux I, et al. African tick bite fever in elderly patients: 8 cases in French tourists returning from South Africa. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:E28-E35. doi:10.1086/589868
- Palau L, Pankey GA. Mediterranean spotted fever in travelers from the United States. J Travel Med. 1997;4:179-182. doi:10.1111/j.1708-8305.1997.tb00816.x
- Fournier P-E, Jensenius M, Laferl H, et al. Kinetics of antibody responses in Rickettsia africae and Rickettsia conorii infections. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002;9:324-328. doi:10.1128/cdli.9.2.324-328.2002
- Brouqui P, Bacellar F, Baranton G, et al; ; . Guidelines for the diagnosis of tick-borne bacterial diseases in Europe. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004;10:1108-1132. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2004.01019.x
- Rolain JM, Jensenius M, Raoult D. Rickettsial infections—a threat to travelers? Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2004;17:433-437. doi:10.1097/00001432-200410000-00008
- Jensenius M, Pretorius AM, Clarke F, et al. Repellent efficacy of four commercial DEET lotions against Amblyomma hebraeum (Acari: Ixodidae), the principal vector of Rickettsia africae in southern Africa. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2005;99:708-711. doi:10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.01.006
To the Editor:
One of the more common tick-borne infections seen in travelers returning from sub-Saharan Africa is caused by Rickettsia africae, which is the etiologic agent of African tick-bite fever (ATBF), the most common tick-borne bacterial zoonosis.1 There are 2 known tick vectors of disease: Amblyomma variegatum, found in sub-Saharan Africa and the West Indies, and Amblyomma hebraeum, found specifically in southern Africa.2,3
Unlike other disease-carrying ticks that passively wait on vegetation to be picked up by a host, A hebraeum uniquely attract other nearby ticks to the host. Studies have shown that male ticks feeding on a nonhuman host (usually cattle) can emit an aggression-attachment pheromone that attracts other ticks to the host. The presence of the pheromone allows unfed ticks to actively discriminate between hosts on which these parasites have fed successfully (ie, suitable hosts) and those on which they have not.4
The aggressive hunting nature of A hebraeum explains the clinical presentation of multiple eschars and why large groups of exposed travelers—such as soldiers, leisure safari tourists, game hunters, and foreign-aid workers—are affected.2
Another southern African spotted fever group, Rickettsia conorii is the causative agent of Mediterranean spotted fever (MSF). Ticks carrying R conorii exhibit a much less aggressive hunting stylethan A hebraeum; consequently, infected patients present with a single eschar site.5
Rickettsia africae is estimated to have very high prevalence (95.2%) in Amblyomma ticks and a fairly high prevalence (approximately 4.0% to 8.6%) in travelers coming from rural southern Africa,6,7 with an incubation period of 5 to 10 days after inoculation by an infected tick.8 Signs include fever, a generalized maculopapular or papulovesicular rash, and regional lymphadenopathy; symptoms include fatigue, headache, and myalgia.
The inoculation eschar—single or multiple—commonly presents on the legs and is accompanied by tender lymphadenopathy of draining nodes1,8 More severe findings, such as myocarditis and subacute neuropathy, have been reported in elderly patients.9
A 77-year-old man presented with a pruritic maculopapular and papulovesicular rash distributed over the upper and lower extremities of 3 weeks’ duration. The patient reported having been on a 12-day mission trip to Limpopo, South Africa, where he was constructing and installing safe toilets to replace dangerous toilet pits. He believed he had been bitten by 2 ticks, after which he noted a dark purple and black patch on the left lower leg by the third day of the trip. He developed a sudden persistent pruritic rash, first on the lower extremities and then spreading to the upper extremities. The patient was seen by an American physician in South Africa who gave him a 7-day course of oral doxycycline monohydrate 100 mg twice daily. He then returned to the United States.

Sixteen days after being bitten by the ticks, the patient was examined in our dermatology office. Physical examination revealed an erythematous plaque with a central eschar over the medial aspect of the left leg (Figure 1) and multiple 3- to 6-mm, erythematous, dome-shaped papules scattered over the dorsal aspects of the feet and ankles (Figure 2). The examination was otherwise normal. Blood was drawn the same day for laboratory analysis; no abnormalities of platelets, red blood cells, or white blood cells were found. Results of a chemistry panel and liver enzyme tests were within reference range.

Skin biopsies were taken to elucidate the underlying pathology. Although an arthropod assault was suspected, there also was concern for deep vessel vasculitis because of the presence of considerable petechiae and purpura (Figure 3). Histologically, leukocytoclasia was seen in deep dermal blood vessels. A mild eosinophilic spongiosis with a mixed dermal infiltrate was identified—strengthening our suspicion of an arthropod assault. Bacterial cultures for aerobes and anaerobes using material taken from the right shin showed no growth.

Ten days after the initial biopsies, serum specimens were drawn and swabs of eschar were collected and sent to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for further testing. Serum was tested by immunofluorescence assay (IFA) for spotted fever group IgG to detect Rocky Mountain spotted fever and ATBF antibodies; both tests were negative. Swab material from eschar was tested again by IFA for spotted fever group IgG (Rocky Mountain spotted fever) and antibodies to ATBF and with bacterial culture isolation and nucleic acid amplification; the culture and amplification came back positive for R africae.
Because the specialized tests confirmed infection with R africae, the patient was given triamcinolone cream 0.1% to apply twice daily to the pruritic lesions for as long as 4 weeks; an additional 14-day course of oral doxycycline monohydrate (100 mg twice daily) was given. At follow-up, the lesions had fully resolved without evident scarring.
Various diagnostic techniques can detect R africae. Bacterial culture and the polymerase chain reaction are specific and therefore diagnostic. In addition, the diagnosis of rickettsiosis can be made with serology testing, in which disease-specific antibodies are detected by indirect IFA using disease-specific antigens.
Antigens from R rickettsii (the agent of Rocky Mountain spotted fever), R conorii (Mediterranean spotted fever), and R africae (ATBF) are commercially available for making the diagnosis of rickettsiosis. However, antigens from R conorii exhibit cross-reactivity with R africae, which can confound the diagnosis.1,10 Serologic IFA tests have been shown to be less sensitive, especially when performed after antibacterial treatment has started.
In a study, 17 of 65 (26%) ATBF-confirmed patients were seronegative (acute and convalescent-phase sera) against R africae; 14 had received doxycycline during the first week of clinical signs. The current hypothesis is that R africae is highly sensitive to doxycycline and that early exposure to the drug prevented development of detectable titers of reactive antibodies, thus producing a negative serology test.11
Furthermore, it has been shown that seroconversion of IgG and IgM antibodies in R africae–infected sera is delayed compared to what is observed with R conorii–infected sera. Typically, seroconversion of R conorii–infected sera can be detected within 2 weeks; seroconversion in R africae–infected sera can take 4 weeks or longer.11
Our patient had a confirmed case of ATBF secondary to R africae infection, which was evident from tissue culture isolation and polymerase chain reaction analysis of swab material obtained from eschar sites, both of which yielded a positive result for R africae. The traveler’s negative serologic status might be due to his early exposure to doxycycline or to the 4-week delay in R africae seroconversion; his serum was collected only 3 weeks after the tick bites.
Clinical signs also aid in making the diagnosis of ATBF and distinguishing R conorii from R africae infection. Because of the aggressive hunting nature of the tick carrying R africae, they are associated with multiple eschars and tend to affect groups of multiple people, especially in rural areas.4,5 In contrast, ticks carrying R conorii yield a single eschar due to their passive style of infecting a host and because they favor a single host within urban areas.5 Both infections exhibit a maculopapular or papulovesicular rash and are accompanied by fatigue, headache, and myalgia, though ATBF tends to present with a milder rash than MSF.
Infection with either R conorii or R africae responds to tetracyclines, quinolones, and macrolides.10,12
African tick-bite fever is becoming more common, which should encourage clinicians to become familiar with the disease. Less than 2 decades ago, ATBF virtually was unknown outside of Zimbabwe, Botswana, Tanzania, Zambia, and Kenya, where it is endemic. However, after the abolition of apartheid in the 1990s, international tourism in southern Africa increased 6-fold.13 African tick-bite fever is now one of the most common rickettsial infections in Africa.7 In addition to diagnosing ATBF and managing infected patients, clinicians can help prevent ATBF in individuals who travel to endemic areas by recommending commercial topical insect repellents containing at least 19.5% N,N-diethyl-meta-toluamide (DEET).14
To the Editor:
One of the more common tick-borne infections seen in travelers returning from sub-Saharan Africa is caused by Rickettsia africae, which is the etiologic agent of African tick-bite fever (ATBF), the most common tick-borne bacterial zoonosis.1 There are 2 known tick vectors of disease: Amblyomma variegatum, found in sub-Saharan Africa and the West Indies, and Amblyomma hebraeum, found specifically in southern Africa.2,3
Unlike other disease-carrying ticks that passively wait on vegetation to be picked up by a host, A hebraeum uniquely attract other nearby ticks to the host. Studies have shown that male ticks feeding on a nonhuman host (usually cattle) can emit an aggression-attachment pheromone that attracts other ticks to the host. The presence of the pheromone allows unfed ticks to actively discriminate between hosts on which these parasites have fed successfully (ie, suitable hosts) and those on which they have not.4
The aggressive hunting nature of A hebraeum explains the clinical presentation of multiple eschars and why large groups of exposed travelers—such as soldiers, leisure safari tourists, game hunters, and foreign-aid workers—are affected.2
Another southern African spotted fever group, Rickettsia conorii is the causative agent of Mediterranean spotted fever (MSF). Ticks carrying R conorii exhibit a much less aggressive hunting stylethan A hebraeum; consequently, infected patients present with a single eschar site.5
Rickettsia africae is estimated to have very high prevalence (95.2%) in Amblyomma ticks and a fairly high prevalence (approximately 4.0% to 8.6%) in travelers coming from rural southern Africa,6,7 with an incubation period of 5 to 10 days after inoculation by an infected tick.8 Signs include fever, a generalized maculopapular or papulovesicular rash, and regional lymphadenopathy; symptoms include fatigue, headache, and myalgia.
The inoculation eschar—single or multiple—commonly presents on the legs and is accompanied by tender lymphadenopathy of draining nodes1,8 More severe findings, such as myocarditis and subacute neuropathy, have been reported in elderly patients.9
A 77-year-old man presented with a pruritic maculopapular and papulovesicular rash distributed over the upper and lower extremities of 3 weeks’ duration. The patient reported having been on a 12-day mission trip to Limpopo, South Africa, where he was constructing and installing safe toilets to replace dangerous toilet pits. He believed he had been bitten by 2 ticks, after which he noted a dark purple and black patch on the left lower leg by the third day of the trip. He developed a sudden persistent pruritic rash, first on the lower extremities and then spreading to the upper extremities. The patient was seen by an American physician in South Africa who gave him a 7-day course of oral doxycycline monohydrate 100 mg twice daily. He then returned to the United States.

Sixteen days after being bitten by the ticks, the patient was examined in our dermatology office. Physical examination revealed an erythematous plaque with a central eschar over the medial aspect of the left leg (Figure 1) and multiple 3- to 6-mm, erythematous, dome-shaped papules scattered over the dorsal aspects of the feet and ankles (Figure 2). The examination was otherwise normal. Blood was drawn the same day for laboratory analysis; no abnormalities of platelets, red blood cells, or white blood cells were found. Results of a chemistry panel and liver enzyme tests were within reference range.

Skin biopsies were taken to elucidate the underlying pathology. Although an arthropod assault was suspected, there also was concern for deep vessel vasculitis because of the presence of considerable petechiae and purpura (Figure 3). Histologically, leukocytoclasia was seen in deep dermal blood vessels. A mild eosinophilic spongiosis with a mixed dermal infiltrate was identified—strengthening our suspicion of an arthropod assault. Bacterial cultures for aerobes and anaerobes using material taken from the right shin showed no growth.

Ten days after the initial biopsies, serum specimens were drawn and swabs of eschar were collected and sent to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for further testing. Serum was tested by immunofluorescence assay (IFA) for spotted fever group IgG to detect Rocky Mountain spotted fever and ATBF antibodies; both tests were negative. Swab material from eschar was tested again by IFA for spotted fever group IgG (Rocky Mountain spotted fever) and antibodies to ATBF and with bacterial culture isolation and nucleic acid amplification; the culture and amplification came back positive for R africae.
Because the specialized tests confirmed infection with R africae, the patient was given triamcinolone cream 0.1% to apply twice daily to the pruritic lesions for as long as 4 weeks; an additional 14-day course of oral doxycycline monohydrate (100 mg twice daily) was given. At follow-up, the lesions had fully resolved without evident scarring.
Various diagnostic techniques can detect R africae. Bacterial culture and the polymerase chain reaction are specific and therefore diagnostic. In addition, the diagnosis of rickettsiosis can be made with serology testing, in which disease-specific antibodies are detected by indirect IFA using disease-specific antigens.
Antigens from R rickettsii (the agent of Rocky Mountain spotted fever), R conorii (Mediterranean spotted fever), and R africae (ATBF) are commercially available for making the diagnosis of rickettsiosis. However, antigens from R conorii exhibit cross-reactivity with R africae, which can confound the diagnosis.1,10 Serologic IFA tests have been shown to be less sensitive, especially when performed after antibacterial treatment has started.
In a study, 17 of 65 (26%) ATBF-confirmed patients were seronegative (acute and convalescent-phase sera) against R africae; 14 had received doxycycline during the first week of clinical signs. The current hypothesis is that R africae is highly sensitive to doxycycline and that early exposure to the drug prevented development of detectable titers of reactive antibodies, thus producing a negative serology test.11
Furthermore, it has been shown that seroconversion of IgG and IgM antibodies in R africae–infected sera is delayed compared to what is observed with R conorii–infected sera. Typically, seroconversion of R conorii–infected sera can be detected within 2 weeks; seroconversion in R africae–infected sera can take 4 weeks or longer.11
Our patient had a confirmed case of ATBF secondary to R africae infection, which was evident from tissue culture isolation and polymerase chain reaction analysis of swab material obtained from eschar sites, both of which yielded a positive result for R africae. The traveler’s negative serologic status might be due to his early exposure to doxycycline or to the 4-week delay in R africae seroconversion; his serum was collected only 3 weeks after the tick bites.
Clinical signs also aid in making the diagnosis of ATBF and distinguishing R conorii from R africae infection. Because of the aggressive hunting nature of the tick carrying R africae, they are associated with multiple eschars and tend to affect groups of multiple people, especially in rural areas.4,5 In contrast, ticks carrying R conorii yield a single eschar due to their passive style of infecting a host and because they favor a single host within urban areas.5 Both infections exhibit a maculopapular or papulovesicular rash and are accompanied by fatigue, headache, and myalgia, though ATBF tends to present with a milder rash than MSF.
Infection with either R conorii or R africae responds to tetracyclines, quinolones, and macrolides.10,12
African tick-bite fever is becoming more common, which should encourage clinicians to become familiar with the disease. Less than 2 decades ago, ATBF virtually was unknown outside of Zimbabwe, Botswana, Tanzania, Zambia, and Kenya, where it is endemic. However, after the abolition of apartheid in the 1990s, international tourism in southern Africa increased 6-fold.13 African tick-bite fever is now one of the most common rickettsial infections in Africa.7 In addition to diagnosing ATBF and managing infected patients, clinicians can help prevent ATBF in individuals who travel to endemic areas by recommending commercial topical insect repellents containing at least 19.5% N,N-diethyl-meta-toluamide (DEET).14
- Parola P, Paddock CD, Socolovschi C, et al. Update on tick-borne rickettsioses around the world: a geographic approach. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013;26:657-702. doi:10.1128/CMR.00032-13
- Jensenius M, Fournier P-E, Vene S, et al; Norwegian African Tick Bite Fever Study Group. African tick bite fever in travelers to rural sub-equatorial Africa. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36:1411-1417. doi:10.1086/375083
- Parola P, Jourdan J, Raoult D. Tick-borne infection caused by Rickettsia africae in the West Indies. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1391-1392. doi:10.1056/NEJM199805073381918
- Norval RA, Andrew HR, Yunker CE. Pheromone-mediation of host-selection in bont ticks (Amblyomma hebraeum Koch). Science. 1989;243:364-365. doi:10.1126/science.2911745
- Parola P, Raoult D. Ticks and tickborne bacterial diseases in humans: an emerging infectious threat. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:897-928. doi:10.1086/319347
- Kelly PJ, Mason PR. Transmission of a spotted fever group rickettsia by Amblyomma hebraeum (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1991;28:598-600. doi:10.1093/jmedent/28.5.598
- Maina AN, Jiang J, Omulo SA, et al. High prevalence of Rickettsia africae variants in Amblyomma variegatum ticks from domestic mammals in rural Western Kenya: implications for human health. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014;14:693-702. doi:10.1089/vbz.2014.1578
- Jensenius M, Fournier P-E, Kelly P, et al. African tick bite fever. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003;3:557-564. doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(03)00739-4
- Roch N, Epaulard O, Pelloux I, et al. African tick bite fever in elderly patients: 8 cases in French tourists returning from South Africa. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:E28-E35. doi:10.1086/589868
- Palau L, Pankey GA. Mediterranean spotted fever in travelers from the United States. J Travel Med. 1997;4:179-182. doi:10.1111/j.1708-8305.1997.tb00816.x
- Fournier P-E, Jensenius M, Laferl H, et al. Kinetics of antibody responses in Rickettsia africae and Rickettsia conorii infections. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002;9:324-328. doi:10.1128/cdli.9.2.324-328.2002
- Brouqui P, Bacellar F, Baranton G, et al; ; . Guidelines for the diagnosis of tick-borne bacterial diseases in Europe. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004;10:1108-1132. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2004.01019.x
- Rolain JM, Jensenius M, Raoult D. Rickettsial infections—a threat to travelers? Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2004;17:433-437. doi:10.1097/00001432-200410000-00008
- Jensenius M, Pretorius AM, Clarke F, et al. Repellent efficacy of four commercial DEET lotions against Amblyomma hebraeum (Acari: Ixodidae), the principal vector of Rickettsia africae in southern Africa. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2005;99:708-711. doi:10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.01.006
- Parola P, Paddock CD, Socolovschi C, et al. Update on tick-borne rickettsioses around the world: a geographic approach. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013;26:657-702. doi:10.1128/CMR.00032-13
- Jensenius M, Fournier P-E, Vene S, et al; Norwegian African Tick Bite Fever Study Group. African tick bite fever in travelers to rural sub-equatorial Africa. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36:1411-1417. doi:10.1086/375083
- Parola P, Jourdan J, Raoult D. Tick-borne infection caused by Rickettsia africae in the West Indies. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1391-1392. doi:10.1056/NEJM199805073381918
- Norval RA, Andrew HR, Yunker CE. Pheromone-mediation of host-selection in bont ticks (Amblyomma hebraeum Koch). Science. 1989;243:364-365. doi:10.1126/science.2911745
- Parola P, Raoult D. Ticks and tickborne bacterial diseases in humans: an emerging infectious threat. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:897-928. doi:10.1086/319347
- Kelly PJ, Mason PR. Transmission of a spotted fever group rickettsia by Amblyomma hebraeum (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1991;28:598-600. doi:10.1093/jmedent/28.5.598
- Maina AN, Jiang J, Omulo SA, et al. High prevalence of Rickettsia africae variants in Amblyomma variegatum ticks from domestic mammals in rural Western Kenya: implications for human health. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014;14:693-702. doi:10.1089/vbz.2014.1578
- Jensenius M, Fournier P-E, Kelly P, et al. African tick bite fever. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003;3:557-564. doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(03)00739-4
- Roch N, Epaulard O, Pelloux I, et al. African tick bite fever in elderly patients: 8 cases in French tourists returning from South Africa. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:E28-E35. doi:10.1086/589868
- Palau L, Pankey GA. Mediterranean spotted fever in travelers from the United States. J Travel Med. 1997;4:179-182. doi:10.1111/j.1708-8305.1997.tb00816.x
- Fournier P-E, Jensenius M, Laferl H, et al. Kinetics of antibody responses in Rickettsia africae and Rickettsia conorii infections. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002;9:324-328. doi:10.1128/cdli.9.2.324-328.2002
- Brouqui P, Bacellar F, Baranton G, et al; ; . Guidelines for the diagnosis of tick-borne bacterial diseases in Europe. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004;10:1108-1132. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2004.01019.x
- Rolain JM, Jensenius M, Raoult D. Rickettsial infections—a threat to travelers? Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2004;17:433-437. doi:10.1097/00001432-200410000-00008
- Jensenius M, Pretorius AM, Clarke F, et al. Repellent efficacy of four commercial DEET lotions against Amblyomma hebraeum (Acari: Ixodidae), the principal vector of Rickettsia africae in southern Africa. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2005;99:708-711. doi:10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.01.006
PRACTICE POINTS
- African tick-bite fever (ATBF) is one of the more common tick-borne bacterial zoonoses and should be considered in patients presenting with multiple eschar sites who have had exposure to rural areas of southern Africa in the preceding 2 weeks.
- Ticks carrying Rickettsia africae are unique, given their ability to actively be attracted to and hunt their nonhuman hosts via an aggression-attachment pheromone.
- Laboratory diagnosis of ATBF can be challenging due to the high cross-reactivity of Helvetica Neue LT StdR africae with Helvetica Neue LT StdRickettsia conorii in serologic testing and the delay in seroconversion in Helvetica Neue LT StdR africae infection.
COVID vs. flu: Which is deadlier?
a new study shows.
People who were hospitalized with Omicron COVID-19 infections were 54% more likely to die, compared with people who were hospitalized with the flu, Swiss researchers found.
The results of the study continue to debunk an earlier belief from the start of the pandemic that the flu was the more dangerous of the two respiratory viruses. The researchers noted that the deadliness of COVID-19, compared with flu, persisted “despite virus evolution and improved management strategies.”
The study was published in JAMA Network Open and included 5,212 patients in Switzerland hospitalized with COVID-19 or the flu. All the COVID patients were infected with the Omicron variant and hospitalized between Jan. 15, 2022, and March 15, 2022. Flu data included cases from January 2018 to March 15, 2022.
Overall, 7% of COVID-19 patients died, compared with 4.4% of flu patients. Researchers noted that the death rate for hospitalized COVID patients had declined since their previous study, which was conducted during the first COVID wave in the first half of 2020. At that time, the death rate of hospitalized COVID patients was 12.8%.
Since then, 98% of the Swiss population has been vaccinated. “Vaccination still plays a significant role regarding the main outcome,” the authors concluded, since a secondary analysis in this most recent study showed that unvaccinated COVID patients were twice as likely to die, compared with flu patients.
“Our results demonstrate that COVID-19 still cannot simply be compared with influenza,” they wrote.
While the death rate among COVID patients was significantly higher, there was no difference in the rate that COVID or flu patients were admitted to the ICU, which was around 8%.
A limitation of the study was that all the COVID cases did not have laboratory testing to confirm the Omicron variant. However, the study authors noted that Omicron accounted for at least 95% of cases during the time the patients were hospitalized. The authors were confident that their results were not biased by the potential for other variants being included in the data.
Four coauthors reported receiving grants and personal fees from various sources.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
a new study shows.
People who were hospitalized with Omicron COVID-19 infections were 54% more likely to die, compared with people who were hospitalized with the flu, Swiss researchers found.
The results of the study continue to debunk an earlier belief from the start of the pandemic that the flu was the more dangerous of the two respiratory viruses. The researchers noted that the deadliness of COVID-19, compared with flu, persisted “despite virus evolution and improved management strategies.”
The study was published in JAMA Network Open and included 5,212 patients in Switzerland hospitalized with COVID-19 or the flu. All the COVID patients were infected with the Omicron variant and hospitalized between Jan. 15, 2022, and March 15, 2022. Flu data included cases from January 2018 to March 15, 2022.
Overall, 7% of COVID-19 patients died, compared with 4.4% of flu patients. Researchers noted that the death rate for hospitalized COVID patients had declined since their previous study, which was conducted during the first COVID wave in the first half of 2020. At that time, the death rate of hospitalized COVID patients was 12.8%.
Since then, 98% of the Swiss population has been vaccinated. “Vaccination still plays a significant role regarding the main outcome,” the authors concluded, since a secondary analysis in this most recent study showed that unvaccinated COVID patients were twice as likely to die, compared with flu patients.
“Our results demonstrate that COVID-19 still cannot simply be compared with influenza,” they wrote.
While the death rate among COVID patients was significantly higher, there was no difference in the rate that COVID or flu patients were admitted to the ICU, which was around 8%.
A limitation of the study was that all the COVID cases did not have laboratory testing to confirm the Omicron variant. However, the study authors noted that Omicron accounted for at least 95% of cases during the time the patients were hospitalized. The authors were confident that their results were not biased by the potential for other variants being included in the data.
Four coauthors reported receiving grants and personal fees from various sources.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
a new study shows.
People who were hospitalized with Omicron COVID-19 infections were 54% more likely to die, compared with people who were hospitalized with the flu, Swiss researchers found.
The results of the study continue to debunk an earlier belief from the start of the pandemic that the flu was the more dangerous of the two respiratory viruses. The researchers noted that the deadliness of COVID-19, compared with flu, persisted “despite virus evolution and improved management strategies.”
The study was published in JAMA Network Open and included 5,212 patients in Switzerland hospitalized with COVID-19 or the flu. All the COVID patients were infected with the Omicron variant and hospitalized between Jan. 15, 2022, and March 15, 2022. Flu data included cases from January 2018 to March 15, 2022.
Overall, 7% of COVID-19 patients died, compared with 4.4% of flu patients. Researchers noted that the death rate for hospitalized COVID patients had declined since their previous study, which was conducted during the first COVID wave in the first half of 2020. At that time, the death rate of hospitalized COVID patients was 12.8%.
Since then, 98% of the Swiss population has been vaccinated. “Vaccination still plays a significant role regarding the main outcome,” the authors concluded, since a secondary analysis in this most recent study showed that unvaccinated COVID patients were twice as likely to die, compared with flu patients.
“Our results demonstrate that COVID-19 still cannot simply be compared with influenza,” they wrote.
While the death rate among COVID patients was significantly higher, there was no difference in the rate that COVID or flu patients were admitted to the ICU, which was around 8%.
A limitation of the study was that all the COVID cases did not have laboratory testing to confirm the Omicron variant. However, the study authors noted that Omicron accounted for at least 95% of cases during the time the patients were hospitalized. The authors were confident that their results were not biased by the potential for other variants being included in the data.
Four coauthors reported receiving grants and personal fees from various sources.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Zika virus still calls for preparedness and vaccine development
Warming U.S. temperatures, the resumption of travel, and new knowledge about Zika’s long-term effects on children signal that Zika prevention and vaccine development should be on public health officials’, doctors’, and communities’ radar, even when community infection is not occurring.
“Although we haven’t seen confirmed Zika virus circulation in the continental United States or its territories for several years, it’s still something that we are closely monitoring, particularly as we move into the summer months,” Erin Staples, MD, PhD, medical epidemiologist at the Arboviral Diseases Branch of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Fort Collins, Colo., told this news organization.
“This is because cases are still being reported in other countries, particularly in South America. Travel to these places is increasing following the pandemic, leaving more potential for individuals who might have acquired the infection to come back and restart community transmission.”
How Zika might reemerge
The Aedes aegypti mosquito is the vector by which Zika spreads, and “during the COVID pandemic, these mosquitoes moved further north in the United States, into southern California, and were identified as far north as Washington, D.C.,” said Neil Silverman, MD, professor of clinical obstetrics and gynecology and director of the Infections in Pregnancy Program at UCLA Medical Center in Los Angeles.
“On a population level, Americans have essentially no immunity to Zika from prior infection, and there is no vaccine yet approved. If individuals infected with Zika came into a U.S. region where the Aedes aegypti mosquito was present, that population could be very susceptible to infection spread and even another outbreak. This would be a confluence of bad circumstances, but that’s exactly what infectious disease specialists continue to be watchful about, especially because Zika is so dangerous for fetuses,” said Dr. Silverman.
How the public can prepare
The CDC recommends that pregnant women or women who plan to become pregnant avoid traveling to regions where there are currently outbreaks of Zika, but this is not the only way that individuals can protect themselves.
“The message we want to deliver to people is that in the United States, people are at risk for several mosquito-borne diseases every summer beyond just Zika,” Dr. Staples said. “It’s really important that people are instructed to make a habit of wearing EPA [U.S. Environmental Protection Agency)–registered insect repellents when they go outside. Right now, that is the single best tool that we have to prevent mosquito-borne diseases in the U.S.
“From a community standpoint, there are several emerging mosquito control methods that are being evaluated right now, such as genetic modification and irradiation of mosquitoes. These methods are aimed at producing sterile mosquitoes that are released into the wild to mate with the local mosquito population, which will render them infertile. This leads, over time, to suppression of the overall Aedes aegypti mosquito population – the main vector of Zika transmission,” said Dr. Staples.
Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, professor of medicine and associate chief of the division of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, encourages her patients to wear mosquito repellent but cautioned that “there’s no antiviral that you can take for Zika. Until we have a vaccine, the key to controlling/preventing Zika is controlling the mosquitoes that spread the virus.”
Vaccines
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) is currently investigating a variety of Zika vaccines, including a DNA-based vaccine, (phase 2), a purified inactivated virus vaccine (phase 1), live attenuated vaccines (phase 2), and mRNA vaccines (phase 2).
“I’m most excited about mRNA vaccines because they help patients produce a lot of proteins. The protein from a typical protein-adjuvant vaccine will break down, and patients can only raise an immune response to whatever proteins are left. On the other hand, mRNA vaccines provide the body [with] a recipe to make the protein from the pathogen in high amounts, so that a strong immune response can be raised for protection,” noted Dr. Gandhi.
Moderna’s mRNA-1893 vaccine was recently studied in a randomized, observer-blind, controlled, phase 1 trial among 120 adults in the United States and Puerto Rico, the results of which were published online in The Lancet. “The vaccine was found to be generally well tolerated with no serious adverse events considered related to vaccine. Furthermore, the vaccine was able to generate a potent immune response that was capable of neutralizing the virus in vitro,” said Brett Leav, MD, executive director of clinical development for public health vaccines at Moderna.
“Our mRNA platform technology ... can be very helpful against emerging pandemic threats, as we saw in response to COVID-19. What is unique in our approach is that if the genetic sequence of the virus is known, we can quickly generate vaccines to test for their capability to generate a functional immune response. In the case of the mRNA-1893 trial, the vaccine was developed with antigens that were present in the strain of virus circulating in 2016, but we could easily match whatever strain reemerges,” said Dr. Leav.
A phase 2 trial to confirm the dose of mRNA-1893 in a larger study population is underway.
Although it’s been demonstrated that Moderna’s mRNA vaccine is safe and effective, moving from a phase 2 to a phase 3 study presents a challenge, given the fact that currently, the disease burden from Zika is low. If an outbreak were to occur in the future, these mRNA vaccines could potentially be given emergency approval, as occurred during the COVID pandemic, according to Dr. Silverman.
If approved, provisionally or through a traditional route, the vaccine would “accelerate the ability to tamp down any further outbreaks, because vaccine-based immunity could be made available to a large portion of the population who were pregnant or planning a pregnancy, not just in the U.S. but also in these endemic areas,” said Dr. Silverman.
Takeaways from the last Zika outbreak
Practical steps such as mosquito eradication and development of vaccines are not the only takeaway from the recent Zika epidemics inside and outside the United States. A clearer picture of the short- and long-term stakes of the disease has emerged.
According to the CDC, most people who become infected with Zika experience only mild symptoms, such as fever, rash, headache, and muscle pain, but babies conceived by mothers infected with Zika are at risk for stillbirth, miscarriage, and microcephaly and other brain defects.
Although a pregnant woman who tests positive for Zika is in a very high-risk situation, “data show that only about 30% of mothers with Zika have a baby with birth defects. If a pregnant woman contracted Zika, what would happen is we would just do very close screening by ultrasound of the fetus. If microcephaly in utero or fetal brain defects were observed, then a mother would be counseled on her options,” said Dr. Gandhi.
Dr. Silverman noted that “new data on children who were exposed in utero and had normal exams, including head measurements when they were born, have raised concerns. In recently published long-term follow-up studies, even when children born to mothers infected with Zika during pregnancy had normal head growth at least 3 years after birth, they were still at risk for neurodevelopmental delay and behavioral disorders, including impact on coordination and executive function.
“This is another good reason to keep the potential risks of Zika active in the public’s consciousness and in public health planning.”
Dr. Silverman, Dr. Gandhi, and Dr. Staples have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Leav is an employee of Moderna and owns stock in the company.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Warming U.S. temperatures, the resumption of travel, and new knowledge about Zika’s long-term effects on children signal that Zika prevention and vaccine development should be on public health officials’, doctors’, and communities’ radar, even when community infection is not occurring.
“Although we haven’t seen confirmed Zika virus circulation in the continental United States or its territories for several years, it’s still something that we are closely monitoring, particularly as we move into the summer months,” Erin Staples, MD, PhD, medical epidemiologist at the Arboviral Diseases Branch of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Fort Collins, Colo., told this news organization.
“This is because cases are still being reported in other countries, particularly in South America. Travel to these places is increasing following the pandemic, leaving more potential for individuals who might have acquired the infection to come back and restart community transmission.”
How Zika might reemerge
The Aedes aegypti mosquito is the vector by which Zika spreads, and “during the COVID pandemic, these mosquitoes moved further north in the United States, into southern California, and were identified as far north as Washington, D.C.,” said Neil Silverman, MD, professor of clinical obstetrics and gynecology and director of the Infections in Pregnancy Program at UCLA Medical Center in Los Angeles.
“On a population level, Americans have essentially no immunity to Zika from prior infection, and there is no vaccine yet approved. If individuals infected with Zika came into a U.S. region where the Aedes aegypti mosquito was present, that population could be very susceptible to infection spread and even another outbreak. This would be a confluence of bad circumstances, but that’s exactly what infectious disease specialists continue to be watchful about, especially because Zika is so dangerous for fetuses,” said Dr. Silverman.
How the public can prepare
The CDC recommends that pregnant women or women who plan to become pregnant avoid traveling to regions where there are currently outbreaks of Zika, but this is not the only way that individuals can protect themselves.
“The message we want to deliver to people is that in the United States, people are at risk for several mosquito-borne diseases every summer beyond just Zika,” Dr. Staples said. “It’s really important that people are instructed to make a habit of wearing EPA [U.S. Environmental Protection Agency)–registered insect repellents when they go outside. Right now, that is the single best tool that we have to prevent mosquito-borne diseases in the U.S.
“From a community standpoint, there are several emerging mosquito control methods that are being evaluated right now, such as genetic modification and irradiation of mosquitoes. These methods are aimed at producing sterile mosquitoes that are released into the wild to mate with the local mosquito population, which will render them infertile. This leads, over time, to suppression of the overall Aedes aegypti mosquito population – the main vector of Zika transmission,” said Dr. Staples.
Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, professor of medicine and associate chief of the division of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, encourages her patients to wear mosquito repellent but cautioned that “there’s no antiviral that you can take for Zika. Until we have a vaccine, the key to controlling/preventing Zika is controlling the mosquitoes that spread the virus.”
Vaccines
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) is currently investigating a variety of Zika vaccines, including a DNA-based vaccine, (phase 2), a purified inactivated virus vaccine (phase 1), live attenuated vaccines (phase 2), and mRNA vaccines (phase 2).
“I’m most excited about mRNA vaccines because they help patients produce a lot of proteins. The protein from a typical protein-adjuvant vaccine will break down, and patients can only raise an immune response to whatever proteins are left. On the other hand, mRNA vaccines provide the body [with] a recipe to make the protein from the pathogen in high amounts, so that a strong immune response can be raised for protection,” noted Dr. Gandhi.
Moderna’s mRNA-1893 vaccine was recently studied in a randomized, observer-blind, controlled, phase 1 trial among 120 adults in the United States and Puerto Rico, the results of which were published online in The Lancet. “The vaccine was found to be generally well tolerated with no serious adverse events considered related to vaccine. Furthermore, the vaccine was able to generate a potent immune response that was capable of neutralizing the virus in vitro,” said Brett Leav, MD, executive director of clinical development for public health vaccines at Moderna.
“Our mRNA platform technology ... can be very helpful against emerging pandemic threats, as we saw in response to COVID-19. What is unique in our approach is that if the genetic sequence of the virus is known, we can quickly generate vaccines to test for their capability to generate a functional immune response. In the case of the mRNA-1893 trial, the vaccine was developed with antigens that were present in the strain of virus circulating in 2016, but we could easily match whatever strain reemerges,” said Dr. Leav.
A phase 2 trial to confirm the dose of mRNA-1893 in a larger study population is underway.
Although it’s been demonstrated that Moderna’s mRNA vaccine is safe and effective, moving from a phase 2 to a phase 3 study presents a challenge, given the fact that currently, the disease burden from Zika is low. If an outbreak were to occur in the future, these mRNA vaccines could potentially be given emergency approval, as occurred during the COVID pandemic, according to Dr. Silverman.
If approved, provisionally or through a traditional route, the vaccine would “accelerate the ability to tamp down any further outbreaks, because vaccine-based immunity could be made available to a large portion of the population who were pregnant or planning a pregnancy, not just in the U.S. but also in these endemic areas,” said Dr. Silverman.
Takeaways from the last Zika outbreak
Practical steps such as mosquito eradication and development of vaccines are not the only takeaway from the recent Zika epidemics inside and outside the United States. A clearer picture of the short- and long-term stakes of the disease has emerged.
According to the CDC, most people who become infected with Zika experience only mild symptoms, such as fever, rash, headache, and muscle pain, but babies conceived by mothers infected with Zika are at risk for stillbirth, miscarriage, and microcephaly and other brain defects.
Although a pregnant woman who tests positive for Zika is in a very high-risk situation, “data show that only about 30% of mothers with Zika have a baby with birth defects. If a pregnant woman contracted Zika, what would happen is we would just do very close screening by ultrasound of the fetus. If microcephaly in utero or fetal brain defects were observed, then a mother would be counseled on her options,” said Dr. Gandhi.
Dr. Silverman noted that “new data on children who were exposed in utero and had normal exams, including head measurements when they were born, have raised concerns. In recently published long-term follow-up studies, even when children born to mothers infected with Zika during pregnancy had normal head growth at least 3 years after birth, they were still at risk for neurodevelopmental delay and behavioral disorders, including impact on coordination and executive function.
“This is another good reason to keep the potential risks of Zika active in the public’s consciousness and in public health planning.”
Dr. Silverman, Dr. Gandhi, and Dr. Staples have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Leav is an employee of Moderna and owns stock in the company.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Warming U.S. temperatures, the resumption of travel, and new knowledge about Zika’s long-term effects on children signal that Zika prevention and vaccine development should be on public health officials’, doctors’, and communities’ radar, even when community infection is not occurring.
“Although we haven’t seen confirmed Zika virus circulation in the continental United States or its territories for several years, it’s still something that we are closely monitoring, particularly as we move into the summer months,” Erin Staples, MD, PhD, medical epidemiologist at the Arboviral Diseases Branch of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Fort Collins, Colo., told this news organization.
“This is because cases are still being reported in other countries, particularly in South America. Travel to these places is increasing following the pandemic, leaving more potential for individuals who might have acquired the infection to come back and restart community transmission.”
How Zika might reemerge
The Aedes aegypti mosquito is the vector by which Zika spreads, and “during the COVID pandemic, these mosquitoes moved further north in the United States, into southern California, and were identified as far north as Washington, D.C.,” said Neil Silverman, MD, professor of clinical obstetrics and gynecology and director of the Infections in Pregnancy Program at UCLA Medical Center in Los Angeles.
“On a population level, Americans have essentially no immunity to Zika from prior infection, and there is no vaccine yet approved. If individuals infected with Zika came into a U.S. region where the Aedes aegypti mosquito was present, that population could be very susceptible to infection spread and even another outbreak. This would be a confluence of bad circumstances, but that’s exactly what infectious disease specialists continue to be watchful about, especially because Zika is so dangerous for fetuses,” said Dr. Silverman.
How the public can prepare
The CDC recommends that pregnant women or women who plan to become pregnant avoid traveling to regions where there are currently outbreaks of Zika, but this is not the only way that individuals can protect themselves.
“The message we want to deliver to people is that in the United States, people are at risk for several mosquito-borne diseases every summer beyond just Zika,” Dr. Staples said. “It’s really important that people are instructed to make a habit of wearing EPA [U.S. Environmental Protection Agency)–registered insect repellents when they go outside. Right now, that is the single best tool that we have to prevent mosquito-borne diseases in the U.S.
“From a community standpoint, there are several emerging mosquito control methods that are being evaluated right now, such as genetic modification and irradiation of mosquitoes. These methods are aimed at producing sterile mosquitoes that are released into the wild to mate with the local mosquito population, which will render them infertile. This leads, over time, to suppression of the overall Aedes aegypti mosquito population – the main vector of Zika transmission,” said Dr. Staples.
Monica Gandhi, MD, MPH, professor of medicine and associate chief of the division of HIV, infectious diseases, and global medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, encourages her patients to wear mosquito repellent but cautioned that “there’s no antiviral that you can take for Zika. Until we have a vaccine, the key to controlling/preventing Zika is controlling the mosquitoes that spread the virus.”
Vaccines
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) is currently investigating a variety of Zika vaccines, including a DNA-based vaccine, (phase 2), a purified inactivated virus vaccine (phase 1), live attenuated vaccines (phase 2), and mRNA vaccines (phase 2).
“I’m most excited about mRNA vaccines because they help patients produce a lot of proteins. The protein from a typical protein-adjuvant vaccine will break down, and patients can only raise an immune response to whatever proteins are left. On the other hand, mRNA vaccines provide the body [with] a recipe to make the protein from the pathogen in high amounts, so that a strong immune response can be raised for protection,” noted Dr. Gandhi.
Moderna’s mRNA-1893 vaccine was recently studied in a randomized, observer-blind, controlled, phase 1 trial among 120 adults in the United States and Puerto Rico, the results of which were published online in The Lancet. “The vaccine was found to be generally well tolerated with no serious adverse events considered related to vaccine. Furthermore, the vaccine was able to generate a potent immune response that was capable of neutralizing the virus in vitro,” said Brett Leav, MD, executive director of clinical development for public health vaccines at Moderna.
“Our mRNA platform technology ... can be very helpful against emerging pandemic threats, as we saw in response to COVID-19. What is unique in our approach is that if the genetic sequence of the virus is known, we can quickly generate vaccines to test for their capability to generate a functional immune response. In the case of the mRNA-1893 trial, the vaccine was developed with antigens that were present in the strain of virus circulating in 2016, but we could easily match whatever strain reemerges,” said Dr. Leav.
A phase 2 trial to confirm the dose of mRNA-1893 in a larger study population is underway.
Although it’s been demonstrated that Moderna’s mRNA vaccine is safe and effective, moving from a phase 2 to a phase 3 study presents a challenge, given the fact that currently, the disease burden from Zika is low. If an outbreak were to occur in the future, these mRNA vaccines could potentially be given emergency approval, as occurred during the COVID pandemic, according to Dr. Silverman.
If approved, provisionally or through a traditional route, the vaccine would “accelerate the ability to tamp down any further outbreaks, because vaccine-based immunity could be made available to a large portion of the population who were pregnant or planning a pregnancy, not just in the U.S. but also in these endemic areas,” said Dr. Silverman.
Takeaways from the last Zika outbreak
Practical steps such as mosquito eradication and development of vaccines are not the only takeaway from the recent Zika epidemics inside and outside the United States. A clearer picture of the short- and long-term stakes of the disease has emerged.
According to the CDC, most people who become infected with Zika experience only mild symptoms, such as fever, rash, headache, and muscle pain, but babies conceived by mothers infected with Zika are at risk for stillbirth, miscarriage, and microcephaly and other brain defects.
Although a pregnant woman who tests positive for Zika is in a very high-risk situation, “data show that only about 30% of mothers with Zika have a baby with birth defects. If a pregnant woman contracted Zika, what would happen is we would just do very close screening by ultrasound of the fetus. If microcephaly in utero or fetal brain defects were observed, then a mother would be counseled on her options,” said Dr. Gandhi.
Dr. Silverman noted that “new data on children who were exposed in utero and had normal exams, including head measurements when they were born, have raised concerns. In recently published long-term follow-up studies, even when children born to mothers infected with Zika during pregnancy had normal head growth at least 3 years after birth, they were still at risk for neurodevelopmental delay and behavioral disorders, including impact on coordination and executive function.
“This is another good reason to keep the potential risks of Zika active in the public’s consciousness and in public health planning.”
Dr. Silverman, Dr. Gandhi, and Dr. Staples have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Leav is an employee of Moderna and owns stock in the company.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Maternal infection in pregnancy ups risk for childhood leukemia?
Children born to mothers who had urinary or genital tract infections during pregnancy appear to have an increased risk for childhood leukemia, said researchers reporting a Danish registry analysis that may point to preventive strategies for the disease.
The research was published online in JAMA Network Open.
The team studied more than 2.2 million children born in Denmark over more than 3 decades, linking their records across multiple national registries to examine both later cancer risk and maternal infection rates.
They found that, overall, at least one maternal infection during pregnancy was associated with a 35% increased risk for leukemia in the children, rising to 65% for urinary tract infections, and 142% for genital infections.
“The findings of this large population-based cohort study suggest that maternal urinary and genital tract infections during pregnancy are associated with a higher risk of childhood leukemia in offspring,” said lead author Jian-Rong He, DPhil, division of birth cohort study, Guangzhou (China) Women and Children’s Medical Center.
However, he added, “the associated absolute risk remained small given the rarity” of the disease. In absolute terms, the risk difference between exposed and unexposed children was 1.8 cases per 100,000 person-years for any infection, 3.4 cases per 100,000 person-years for urinary traction infection, and 7.1 cases per 100,000 person-years for genital tract infection.
Maternal infections during pregnancy may be associated with chromosomal and immunologic alterations in the fetus, the authors speculated.
“Given that little is known about the etiology of childhood leukemia,” these results “suggest an important direction for research on the etiology of childhood leukemia as well as development of potential preventive measures,” they wrote.
In many countries, pregnant women are tested for urinary tract infection and bacterial vaginosis, and treated with antibiotics in antenatal care, as these infections are linked to adverse perinatal outcomes, they pointed out.
Study details
The team conducted a large population-based study that included all live births in Denmark between 1978 and 2015.
After exclusions, they gathered information on 2,222,797 children, linking data from several national registries, including the Danish Medical Birth Register, the Danish National Patient Registry, and the Danish National Cancer Registry, to identify cases of childhood cancers and maternal infection during pregnancy.
The results were then validated by comparing them with those in 2.6 million live births in Sweden between 1988 and 2014, for whom similar data were available through linkage with several Swedish registries.
The Danish cohort was followed up for a mean of 12 years per person, yielding a total of 27 million person-years. Just over half (51.3%) were boys.
Cancer was diagnosed in 4,362 children before 15 years of age, of whom 1,307 had leukemia (1,050 had acute lymphocytic leukemia), 1,267 had a brain tumor, 224 had lymphoma, and 1,564 had other cancers.
At least one infection during pregnancy was diagnosed in 81,717 mothers (3.7%). Urinary tract infections were the most common (in 1.7% of women), followed by genital tract infection (in 0.7%), digestive system infection (in 0.5%), and respiratory tract infection (in 0.3%).
Women with any infection during pregnancy were more likely to be younger and primiparous than were women who did not have infections, and they were also more likely to have fewer years of education, higher prepregnancy BMI, diabetes, and to smoke during early pregnancy.
Preterm delivery and low-birth-weight infants were also more common in women with infections during pregnancy.
Cox proportional hazards regression models revealed that, after adjustment for confounders, any maternal infection was associated with a hazard ratio of childhood leukemia of 1.35.
Further analysis revealed that the association was driven by genital tract infection, at a hazard ratio for childhood leukemia of 2.42, and urinary tract infection, at a hazard ratio 1.65.
Moreover, children born to women who had a sexually transmitted infection during pregnancy had a hazard ratio for developing leukemia of 3.13 compared with unexposed children.
There were no associations between other maternal infections and childhood leukemia.
The patterns of association between maternal infections and childhood leukemia were similar when looking at disease subtypes, as well as in the Swedish validation cohort, they added.
When interpreting the results, the researchers caution that, as data on maternal infection were drawn from hospital data, “milder infections and those not diagnosed or treated in specialized health care facilities were not captured.”
“Also, some infections could be captured because the mother sought care for other, more serious conditions, which might bias the association of maternal infections and childhood leukemia.”
The study was supported by grants from the China Scholarship Council–University of Oxford; National Natural Science Foundation of China; Danish Council for Independent Research; Nordic Cancer Union; Novo Nordisk Fonden; and the Swedish Council for Working Life and Social Research. Dr He reported receiving a PhD scholarship from the China Scholarship Council during the conduct of the study. Several other coauthors have disclosures; the full list can be found with the original article.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Children born to mothers who had urinary or genital tract infections during pregnancy appear to have an increased risk for childhood leukemia, said researchers reporting a Danish registry analysis that may point to preventive strategies for the disease.
The research was published online in JAMA Network Open.
The team studied more than 2.2 million children born in Denmark over more than 3 decades, linking their records across multiple national registries to examine both later cancer risk and maternal infection rates.
They found that, overall, at least one maternal infection during pregnancy was associated with a 35% increased risk for leukemia in the children, rising to 65% for urinary tract infections, and 142% for genital infections.
“The findings of this large population-based cohort study suggest that maternal urinary and genital tract infections during pregnancy are associated with a higher risk of childhood leukemia in offspring,” said lead author Jian-Rong He, DPhil, division of birth cohort study, Guangzhou (China) Women and Children’s Medical Center.
However, he added, “the associated absolute risk remained small given the rarity” of the disease. In absolute terms, the risk difference between exposed and unexposed children was 1.8 cases per 100,000 person-years for any infection, 3.4 cases per 100,000 person-years for urinary traction infection, and 7.1 cases per 100,000 person-years for genital tract infection.
Maternal infections during pregnancy may be associated with chromosomal and immunologic alterations in the fetus, the authors speculated.
“Given that little is known about the etiology of childhood leukemia,” these results “suggest an important direction for research on the etiology of childhood leukemia as well as development of potential preventive measures,” they wrote.
In many countries, pregnant women are tested for urinary tract infection and bacterial vaginosis, and treated with antibiotics in antenatal care, as these infections are linked to adverse perinatal outcomes, they pointed out.
Study details
The team conducted a large population-based study that included all live births in Denmark between 1978 and 2015.
After exclusions, they gathered information on 2,222,797 children, linking data from several national registries, including the Danish Medical Birth Register, the Danish National Patient Registry, and the Danish National Cancer Registry, to identify cases of childhood cancers and maternal infection during pregnancy.
The results were then validated by comparing them with those in 2.6 million live births in Sweden between 1988 and 2014, for whom similar data were available through linkage with several Swedish registries.
The Danish cohort was followed up for a mean of 12 years per person, yielding a total of 27 million person-years. Just over half (51.3%) were boys.
Cancer was diagnosed in 4,362 children before 15 years of age, of whom 1,307 had leukemia (1,050 had acute lymphocytic leukemia), 1,267 had a brain tumor, 224 had lymphoma, and 1,564 had other cancers.
At least one infection during pregnancy was diagnosed in 81,717 mothers (3.7%). Urinary tract infections were the most common (in 1.7% of women), followed by genital tract infection (in 0.7%), digestive system infection (in 0.5%), and respiratory tract infection (in 0.3%).
Women with any infection during pregnancy were more likely to be younger and primiparous than were women who did not have infections, and they were also more likely to have fewer years of education, higher prepregnancy BMI, diabetes, and to smoke during early pregnancy.
Preterm delivery and low-birth-weight infants were also more common in women with infections during pregnancy.
Cox proportional hazards regression models revealed that, after adjustment for confounders, any maternal infection was associated with a hazard ratio of childhood leukemia of 1.35.
Further analysis revealed that the association was driven by genital tract infection, at a hazard ratio for childhood leukemia of 2.42, and urinary tract infection, at a hazard ratio 1.65.
Moreover, children born to women who had a sexually transmitted infection during pregnancy had a hazard ratio for developing leukemia of 3.13 compared with unexposed children.
There were no associations between other maternal infections and childhood leukemia.
The patterns of association between maternal infections and childhood leukemia were similar when looking at disease subtypes, as well as in the Swedish validation cohort, they added.
When interpreting the results, the researchers caution that, as data on maternal infection were drawn from hospital data, “milder infections and those not diagnosed or treated in specialized health care facilities were not captured.”
“Also, some infections could be captured because the mother sought care for other, more serious conditions, which might bias the association of maternal infections and childhood leukemia.”
The study was supported by grants from the China Scholarship Council–University of Oxford; National Natural Science Foundation of China; Danish Council for Independent Research; Nordic Cancer Union; Novo Nordisk Fonden; and the Swedish Council for Working Life and Social Research. Dr He reported receiving a PhD scholarship from the China Scholarship Council during the conduct of the study. Several other coauthors have disclosures; the full list can be found with the original article.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Children born to mothers who had urinary or genital tract infections during pregnancy appear to have an increased risk for childhood leukemia, said researchers reporting a Danish registry analysis that may point to preventive strategies for the disease.
The research was published online in JAMA Network Open.
The team studied more than 2.2 million children born in Denmark over more than 3 decades, linking their records across multiple national registries to examine both later cancer risk and maternal infection rates.
They found that, overall, at least one maternal infection during pregnancy was associated with a 35% increased risk for leukemia in the children, rising to 65% for urinary tract infections, and 142% for genital infections.
“The findings of this large population-based cohort study suggest that maternal urinary and genital tract infections during pregnancy are associated with a higher risk of childhood leukemia in offspring,” said lead author Jian-Rong He, DPhil, division of birth cohort study, Guangzhou (China) Women and Children’s Medical Center.
However, he added, “the associated absolute risk remained small given the rarity” of the disease. In absolute terms, the risk difference between exposed and unexposed children was 1.8 cases per 100,000 person-years for any infection, 3.4 cases per 100,000 person-years for urinary traction infection, and 7.1 cases per 100,000 person-years for genital tract infection.
Maternal infections during pregnancy may be associated with chromosomal and immunologic alterations in the fetus, the authors speculated.
“Given that little is known about the etiology of childhood leukemia,” these results “suggest an important direction for research on the etiology of childhood leukemia as well as development of potential preventive measures,” they wrote.
In many countries, pregnant women are tested for urinary tract infection and bacterial vaginosis, and treated with antibiotics in antenatal care, as these infections are linked to adverse perinatal outcomes, they pointed out.
Study details
The team conducted a large population-based study that included all live births in Denmark between 1978 and 2015.
After exclusions, they gathered information on 2,222,797 children, linking data from several national registries, including the Danish Medical Birth Register, the Danish National Patient Registry, and the Danish National Cancer Registry, to identify cases of childhood cancers and maternal infection during pregnancy.
The results were then validated by comparing them with those in 2.6 million live births in Sweden between 1988 and 2014, for whom similar data were available through linkage with several Swedish registries.
The Danish cohort was followed up for a mean of 12 years per person, yielding a total of 27 million person-years. Just over half (51.3%) were boys.
Cancer was diagnosed in 4,362 children before 15 years of age, of whom 1,307 had leukemia (1,050 had acute lymphocytic leukemia), 1,267 had a brain tumor, 224 had lymphoma, and 1,564 had other cancers.
At least one infection during pregnancy was diagnosed in 81,717 mothers (3.7%). Urinary tract infections were the most common (in 1.7% of women), followed by genital tract infection (in 0.7%), digestive system infection (in 0.5%), and respiratory tract infection (in 0.3%).
Women with any infection during pregnancy were more likely to be younger and primiparous than were women who did not have infections, and they were also more likely to have fewer years of education, higher prepregnancy BMI, diabetes, and to smoke during early pregnancy.
Preterm delivery and low-birth-weight infants were also more common in women with infections during pregnancy.
Cox proportional hazards regression models revealed that, after adjustment for confounders, any maternal infection was associated with a hazard ratio of childhood leukemia of 1.35.
Further analysis revealed that the association was driven by genital tract infection, at a hazard ratio for childhood leukemia of 2.42, and urinary tract infection, at a hazard ratio 1.65.
Moreover, children born to women who had a sexually transmitted infection during pregnancy had a hazard ratio for developing leukemia of 3.13 compared with unexposed children.
There were no associations between other maternal infections and childhood leukemia.
The patterns of association between maternal infections and childhood leukemia were similar when looking at disease subtypes, as well as in the Swedish validation cohort, they added.
When interpreting the results, the researchers caution that, as data on maternal infection were drawn from hospital data, “milder infections and those not diagnosed or treated in specialized health care facilities were not captured.”
“Also, some infections could be captured because the mother sought care for other, more serious conditions, which might bias the association of maternal infections and childhood leukemia.”
The study was supported by grants from the China Scholarship Council–University of Oxford; National Natural Science Foundation of China; Danish Council for Independent Research; Nordic Cancer Union; Novo Nordisk Fonden; and the Swedish Council for Working Life and Social Research. Dr He reported receiving a PhD scholarship from the China Scholarship Council during the conduct of the study. Several other coauthors have disclosures; the full list can be found with the original article.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Eight-week TB treatment strategy shows potential
A strategy for the
“We found that if we use the strategy of a bedaquiline-linezolid five-drug regimen for 8 weeks and then followed patients for 96 weeks, [the regimen] was noninferior, clinically, to the standard regimen in terms of the number of people alive, free of TB disease, and not on treatment,” said lead author Nicholas Paton, MD, of the National University of Singapore, in a press conference held during the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
“The total time on treatment was reduced by half – instead of 160 days, it was 85 days for the total duration.”
Commenting on the study, which was published concurrently in the New England Journal of Medicine, Richard E. Chaisson, MD, noted that, although more needs to be understood, the high number of responses is nevertheless encouraging.
“Clinicians will not feel comfortable with the short regimens at this point, but it is remarkable that so many patients did well with shorter treatments,” Dr. Chaisson, who is a professor of medicine, epidemiology, and international health and director of the Johns Hopkins University Center for Tuberculosis Research, Baltimore, said in an interview.
Importantly, the study should help push forward “future studies [that] will stratify patients according to their likelihood of responding to shorter treatments,” he said.
The current global standard for TB treatment, practiced for 4 decades, has been a 6-month rifampin-based regimen. Although the regimen performs well, curing more than 95% of cases in clinical trials, in real-world practice, the prolonged duration can be problematic, with issues of nonadherence and loss of patients to follow-up.
Previous research has shown that shorter regimens have potential, with some studies showing as many as 85% of patients cured with 3- and 4-month regimens, and some promising 2-month regimens showing efficacy specifically for those with smear-negative TB.
These efforts suggest that “the current 6-month regimen may lead to overtreatment in the majority of persons in order to prevent relapse in a minority of persons,” the authors asserted.
TRUNCATE-TB
To investigate a suitable shorter-term alternative, the authors conducted the phase 2-3, prospective, open-label TRUNCATE-TB trial, in which 674 patients with rifampin-susceptible pulmonary TB were enrolled at 18 sites in Asia and Africa.
The patients were randomly assigned to receive either the standard treatment regimen (rifampin and isoniazid for 24 weeks with pyrazinamide and ethambutol for the first 8 weeks; n = 181), or one of four novel five-drug regimens to be administered over 8 weeks, along with extended treatment for persistent clinical disease of up to 12 weeks, if needed, and a plan for retreatment in the case of relapse (n = 493).
Two of the regimens were dropped because of logistic criteria; the two remaining shorter-course groups included in the study involved either high-dose rifampin plus linezolid or bedaquiline plus linezolid, each combined with isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol.
Of the patients, 62% were male, and four withdrew or were lost to follow-up by the end of the study at a final follow-up at week 96.
Among patients assigned to the 8-week regimens, 80% stopped at exactly 8 weeks, while 9% wound up having extended treatment to 10 weeks and 3% were extended to 12 weeks.
For the primary endpoint, a composite of death, ongoing treatment, or active disease at week 96, the rate was lowest in the standard 24-week therapy group, occurring in 7 of 181 patients (3.9%), compared with 21 of 184 patients (11.4%) in the rifampin plus linezolid group (adjusted difference, 7.4 percentage points, which did not meet noninferiority criterion), and 11 of 189 (5.8%) in the group in the bedaquiline plus linezolid group (adjusted difference, 0.8 percentage points, meeting noninferiority criterion).
The mean total duration of treatment through week 96 in the standard treatment group was 180 days versus 106 days in the rifampin–linezolid group, and 85 days in the bedaquiline-linezolid group.
The results were consistent across multiple subgroups defined according to baseline characteristics, including some that could be linked to severe disease and a high risk for relapse.
In terms of safety, there were no significant differences between the groups in terms of grade 3 or 4 adverse events.
Of note, only two patients (1.1%) in the bedaquiline plus linezolid group acquired a resistance, which Dr. Paton said was “encouraging,” because of concerns about resistance to that drug.
‘Unfavorable’ composite also evaluated
In an updated analysis of the study that Dr. Paton presented at the meeting, the authors looked at a revised “unfavorable” primary outcome – a composite including treatment failure, relapse, death, or nonattendance at week 96 without evidence of prior disease clearance.
The rate remained lowest in the standard 24-week therapy group (3.9%) versus 25% in the rifampin plus linezolid group, and 13.8% in the bedaquiline plus linezolid group.
Though the lower rate with the standard treatment was expected, Dr. Paton said the results nevertheless hold promise, at least for some patients, for successful treatment with the 8-week bedaquiline plus linezolid strategy.
“What the trial has told us is that even with that 13.8% relapse rate, we can manage patients within this strategy and people can do fine at the end, because with some simple clinical biomarkers, we can pick the people who may have a high chance of achieving a cure.”
Dr. Chaisson expressed concern over the higher unfavorable rates, but said the results help pave the way for refining a workable-shorter term strategy.
“TRUNCATE-TB did find that most patients could be successfully treated in 2 months with the novel regimen of bedaquiline plus linezolid, but the failure rate was still unacceptably high,” he said.
“This regimen will not be widely adapted at this point, but additional analyses may identify subsets of patients who will do well with shorter regimens, and future studies will stratify patients according to their likelihood of responding to shorter treatments.”
The authors of an accompanying editorial further commented that the benefits of a shorter treatment strategy could very well outweigh possible shortcomings.
“Treatment algorithms such as that used in the TRUNCATE-TB trial are fundamental to tuberculosis control,” wrote Véronique Dartois, PhD, Center for Discovery and Innovation, Nutley, N.J., and Eric J. Rubin, MD, PhD, the editor-in-chief of NEJM. “Although implementing them could be a challenge, any added burden might be offset by reduced costs, better adherence, and increased patient satisfaction. Thus, for tuberculosis, a strategy might be more than just a regimen.”
The good news, as summed up by CROI vice-chair Landon Myer, MD, PhD, in the press conference, is that “we’re moving closer and closer to the holy grail of a short, efficacious regimen for TB treatment. We’re getting there slowly, but we’re getting there.”
The study received grant funding from the Singapore National Medical Research Council; a grant from the Department of Health and Social Care; the Foreign, Commonwealth, and Development Office; the Medical Research Council; and Wellcome Trust; as well as a grant from the UK Research and Innovation Medical Research Council. Dr. Dartois reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Chaisson had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A strategy for the
“We found that if we use the strategy of a bedaquiline-linezolid five-drug regimen for 8 weeks and then followed patients for 96 weeks, [the regimen] was noninferior, clinically, to the standard regimen in terms of the number of people alive, free of TB disease, and not on treatment,” said lead author Nicholas Paton, MD, of the National University of Singapore, in a press conference held during the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
“The total time on treatment was reduced by half – instead of 160 days, it was 85 days for the total duration.”
Commenting on the study, which was published concurrently in the New England Journal of Medicine, Richard E. Chaisson, MD, noted that, although more needs to be understood, the high number of responses is nevertheless encouraging.
“Clinicians will not feel comfortable with the short regimens at this point, but it is remarkable that so many patients did well with shorter treatments,” Dr. Chaisson, who is a professor of medicine, epidemiology, and international health and director of the Johns Hopkins University Center for Tuberculosis Research, Baltimore, said in an interview.
Importantly, the study should help push forward “future studies [that] will stratify patients according to their likelihood of responding to shorter treatments,” he said.
The current global standard for TB treatment, practiced for 4 decades, has been a 6-month rifampin-based regimen. Although the regimen performs well, curing more than 95% of cases in clinical trials, in real-world practice, the prolonged duration can be problematic, with issues of nonadherence and loss of patients to follow-up.
Previous research has shown that shorter regimens have potential, with some studies showing as many as 85% of patients cured with 3- and 4-month regimens, and some promising 2-month regimens showing efficacy specifically for those with smear-negative TB.
These efforts suggest that “the current 6-month regimen may lead to overtreatment in the majority of persons in order to prevent relapse in a minority of persons,” the authors asserted.
TRUNCATE-TB
To investigate a suitable shorter-term alternative, the authors conducted the phase 2-3, prospective, open-label TRUNCATE-TB trial, in which 674 patients with rifampin-susceptible pulmonary TB were enrolled at 18 sites in Asia and Africa.
The patients were randomly assigned to receive either the standard treatment regimen (rifampin and isoniazid for 24 weeks with pyrazinamide and ethambutol for the first 8 weeks; n = 181), or one of four novel five-drug regimens to be administered over 8 weeks, along with extended treatment for persistent clinical disease of up to 12 weeks, if needed, and a plan for retreatment in the case of relapse (n = 493).
Two of the regimens were dropped because of logistic criteria; the two remaining shorter-course groups included in the study involved either high-dose rifampin plus linezolid or bedaquiline plus linezolid, each combined with isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol.
Of the patients, 62% were male, and four withdrew or were lost to follow-up by the end of the study at a final follow-up at week 96.
Among patients assigned to the 8-week regimens, 80% stopped at exactly 8 weeks, while 9% wound up having extended treatment to 10 weeks and 3% were extended to 12 weeks.
For the primary endpoint, a composite of death, ongoing treatment, or active disease at week 96, the rate was lowest in the standard 24-week therapy group, occurring in 7 of 181 patients (3.9%), compared with 21 of 184 patients (11.4%) in the rifampin plus linezolid group (adjusted difference, 7.4 percentage points, which did not meet noninferiority criterion), and 11 of 189 (5.8%) in the group in the bedaquiline plus linezolid group (adjusted difference, 0.8 percentage points, meeting noninferiority criterion).
The mean total duration of treatment through week 96 in the standard treatment group was 180 days versus 106 days in the rifampin–linezolid group, and 85 days in the bedaquiline-linezolid group.
The results were consistent across multiple subgroups defined according to baseline characteristics, including some that could be linked to severe disease and a high risk for relapse.
In terms of safety, there were no significant differences between the groups in terms of grade 3 or 4 adverse events.
Of note, only two patients (1.1%) in the bedaquiline plus linezolid group acquired a resistance, which Dr. Paton said was “encouraging,” because of concerns about resistance to that drug.
‘Unfavorable’ composite also evaluated
In an updated analysis of the study that Dr. Paton presented at the meeting, the authors looked at a revised “unfavorable” primary outcome – a composite including treatment failure, relapse, death, or nonattendance at week 96 without evidence of prior disease clearance.
The rate remained lowest in the standard 24-week therapy group (3.9%) versus 25% in the rifampin plus linezolid group, and 13.8% in the bedaquiline plus linezolid group.
Though the lower rate with the standard treatment was expected, Dr. Paton said the results nevertheless hold promise, at least for some patients, for successful treatment with the 8-week bedaquiline plus linezolid strategy.
“What the trial has told us is that even with that 13.8% relapse rate, we can manage patients within this strategy and people can do fine at the end, because with some simple clinical biomarkers, we can pick the people who may have a high chance of achieving a cure.”
Dr. Chaisson expressed concern over the higher unfavorable rates, but said the results help pave the way for refining a workable-shorter term strategy.
“TRUNCATE-TB did find that most patients could be successfully treated in 2 months with the novel regimen of bedaquiline plus linezolid, but the failure rate was still unacceptably high,” he said.
“This regimen will not be widely adapted at this point, but additional analyses may identify subsets of patients who will do well with shorter regimens, and future studies will stratify patients according to their likelihood of responding to shorter treatments.”
The authors of an accompanying editorial further commented that the benefits of a shorter treatment strategy could very well outweigh possible shortcomings.
“Treatment algorithms such as that used in the TRUNCATE-TB trial are fundamental to tuberculosis control,” wrote Véronique Dartois, PhD, Center for Discovery and Innovation, Nutley, N.J., and Eric J. Rubin, MD, PhD, the editor-in-chief of NEJM. “Although implementing them could be a challenge, any added burden might be offset by reduced costs, better adherence, and increased patient satisfaction. Thus, for tuberculosis, a strategy might be more than just a regimen.”
The good news, as summed up by CROI vice-chair Landon Myer, MD, PhD, in the press conference, is that “we’re moving closer and closer to the holy grail of a short, efficacious regimen for TB treatment. We’re getting there slowly, but we’re getting there.”
The study received grant funding from the Singapore National Medical Research Council; a grant from the Department of Health and Social Care; the Foreign, Commonwealth, and Development Office; the Medical Research Council; and Wellcome Trust; as well as a grant from the UK Research and Innovation Medical Research Council. Dr. Dartois reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Chaisson had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A strategy for the
“We found that if we use the strategy of a bedaquiline-linezolid five-drug regimen for 8 weeks and then followed patients for 96 weeks, [the regimen] was noninferior, clinically, to the standard regimen in terms of the number of people alive, free of TB disease, and not on treatment,” said lead author Nicholas Paton, MD, of the National University of Singapore, in a press conference held during the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
“The total time on treatment was reduced by half – instead of 160 days, it was 85 days for the total duration.”
Commenting on the study, which was published concurrently in the New England Journal of Medicine, Richard E. Chaisson, MD, noted that, although more needs to be understood, the high number of responses is nevertheless encouraging.
“Clinicians will not feel comfortable with the short regimens at this point, but it is remarkable that so many patients did well with shorter treatments,” Dr. Chaisson, who is a professor of medicine, epidemiology, and international health and director of the Johns Hopkins University Center for Tuberculosis Research, Baltimore, said in an interview.
Importantly, the study should help push forward “future studies [that] will stratify patients according to their likelihood of responding to shorter treatments,” he said.
The current global standard for TB treatment, practiced for 4 decades, has been a 6-month rifampin-based regimen. Although the regimen performs well, curing more than 95% of cases in clinical trials, in real-world practice, the prolonged duration can be problematic, with issues of nonadherence and loss of patients to follow-up.
Previous research has shown that shorter regimens have potential, with some studies showing as many as 85% of patients cured with 3- and 4-month regimens, and some promising 2-month regimens showing efficacy specifically for those with smear-negative TB.
These efforts suggest that “the current 6-month regimen may lead to overtreatment in the majority of persons in order to prevent relapse in a minority of persons,” the authors asserted.
TRUNCATE-TB
To investigate a suitable shorter-term alternative, the authors conducted the phase 2-3, prospective, open-label TRUNCATE-TB trial, in which 674 patients with rifampin-susceptible pulmonary TB were enrolled at 18 sites in Asia and Africa.
The patients were randomly assigned to receive either the standard treatment regimen (rifampin and isoniazid for 24 weeks with pyrazinamide and ethambutol for the first 8 weeks; n = 181), or one of four novel five-drug regimens to be administered over 8 weeks, along with extended treatment for persistent clinical disease of up to 12 weeks, if needed, and a plan for retreatment in the case of relapse (n = 493).
Two of the regimens were dropped because of logistic criteria; the two remaining shorter-course groups included in the study involved either high-dose rifampin plus linezolid or bedaquiline plus linezolid, each combined with isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol.
Of the patients, 62% were male, and four withdrew or were lost to follow-up by the end of the study at a final follow-up at week 96.
Among patients assigned to the 8-week regimens, 80% stopped at exactly 8 weeks, while 9% wound up having extended treatment to 10 weeks and 3% were extended to 12 weeks.
For the primary endpoint, a composite of death, ongoing treatment, or active disease at week 96, the rate was lowest in the standard 24-week therapy group, occurring in 7 of 181 patients (3.9%), compared with 21 of 184 patients (11.4%) in the rifampin plus linezolid group (adjusted difference, 7.4 percentage points, which did not meet noninferiority criterion), and 11 of 189 (5.8%) in the group in the bedaquiline plus linezolid group (adjusted difference, 0.8 percentage points, meeting noninferiority criterion).
The mean total duration of treatment through week 96 in the standard treatment group was 180 days versus 106 days in the rifampin–linezolid group, and 85 days in the bedaquiline-linezolid group.
The results were consistent across multiple subgroups defined according to baseline characteristics, including some that could be linked to severe disease and a high risk for relapse.
In terms of safety, there were no significant differences between the groups in terms of grade 3 or 4 adverse events.
Of note, only two patients (1.1%) in the bedaquiline plus linezolid group acquired a resistance, which Dr. Paton said was “encouraging,” because of concerns about resistance to that drug.
‘Unfavorable’ composite also evaluated
In an updated analysis of the study that Dr. Paton presented at the meeting, the authors looked at a revised “unfavorable” primary outcome – a composite including treatment failure, relapse, death, or nonattendance at week 96 without evidence of prior disease clearance.
The rate remained lowest in the standard 24-week therapy group (3.9%) versus 25% in the rifampin plus linezolid group, and 13.8% in the bedaquiline plus linezolid group.
Though the lower rate with the standard treatment was expected, Dr. Paton said the results nevertheless hold promise, at least for some patients, for successful treatment with the 8-week bedaquiline plus linezolid strategy.
“What the trial has told us is that even with that 13.8% relapse rate, we can manage patients within this strategy and people can do fine at the end, because with some simple clinical biomarkers, we can pick the people who may have a high chance of achieving a cure.”
Dr. Chaisson expressed concern over the higher unfavorable rates, but said the results help pave the way for refining a workable-shorter term strategy.
“TRUNCATE-TB did find that most patients could be successfully treated in 2 months with the novel regimen of bedaquiline plus linezolid, but the failure rate was still unacceptably high,” he said.
“This regimen will not be widely adapted at this point, but additional analyses may identify subsets of patients who will do well with shorter regimens, and future studies will stratify patients according to their likelihood of responding to shorter treatments.”
The authors of an accompanying editorial further commented that the benefits of a shorter treatment strategy could very well outweigh possible shortcomings.
“Treatment algorithms such as that used in the TRUNCATE-TB trial are fundamental to tuberculosis control,” wrote Véronique Dartois, PhD, Center for Discovery and Innovation, Nutley, N.J., and Eric J. Rubin, MD, PhD, the editor-in-chief of NEJM. “Although implementing them could be a challenge, any added burden might be offset by reduced costs, better adherence, and increased patient satisfaction. Thus, for tuberculosis, a strategy might be more than just a regimen.”
The good news, as summed up by CROI vice-chair Landon Myer, MD, PhD, in the press conference, is that “we’re moving closer and closer to the holy grail of a short, efficacious regimen for TB treatment. We’re getting there slowly, but we’re getting there.”
The study received grant funding from the Singapore National Medical Research Council; a grant from the Department of Health and Social Care; the Foreign, Commonwealth, and Development Office; the Medical Research Council; and Wellcome Trust; as well as a grant from the UK Research and Innovation Medical Research Council. Dr. Dartois reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Chaisson had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CROI 2023
COVID infection provides immunity equal to vaccination: Study
People who’ve been infected with COVID reduced their chances of hospitalization and death by 88% over 10 months compared to somebody who hasn’t been infected, according to the study, published in The Lancet.
The natural immunity provided by infection was “at least as high, if not higher” than the immunity provided by two doses of Moderna or Pfizer mRNA vaccines against the ancestral, Alpha, Delta, and Omicron BA.1 variants, the researchers reported.
But protection against the BA.1 subvariant of Omicron was not as high – 36% at 10 months after infection, wrote the research team from the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington.
They examined 65 studies from 19 countries through Sept. 31, 2022. They did not study data about infection from Omicron XBB and its sub-lineages. People who had immunity from both infection and vaccination, known as hybrid immunity, were not studied.
The findings don’t mean people should skip the vaccines and get COVID on purpose, one of the researchers told NBC News.
“The problem of saying ‘I’m gonna get infected to get immunity’ is you might be one of those people that end up in the hospital or die,” said Christopher Murray, MD, DPhil, director of the IHME. “Why would you take the risk when you can get immunity through vaccination quite safely?”
The findings could help people figure out the most effective time to get vaccinated or boosted and guide officials in setting policies on workplace vaccine mandates and rules for high-occupancy indoor settings, the researchers concluded.
This was the largest meta-analysis of immunity following infection to date, NBC News reports.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
People who’ve been infected with COVID reduced their chances of hospitalization and death by 88% over 10 months compared to somebody who hasn’t been infected, according to the study, published in The Lancet.
The natural immunity provided by infection was “at least as high, if not higher” than the immunity provided by two doses of Moderna or Pfizer mRNA vaccines against the ancestral, Alpha, Delta, and Omicron BA.1 variants, the researchers reported.
But protection against the BA.1 subvariant of Omicron was not as high – 36% at 10 months after infection, wrote the research team from the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington.
They examined 65 studies from 19 countries through Sept. 31, 2022. They did not study data about infection from Omicron XBB and its sub-lineages. People who had immunity from both infection and vaccination, known as hybrid immunity, were not studied.
The findings don’t mean people should skip the vaccines and get COVID on purpose, one of the researchers told NBC News.
“The problem of saying ‘I’m gonna get infected to get immunity’ is you might be one of those people that end up in the hospital or die,” said Christopher Murray, MD, DPhil, director of the IHME. “Why would you take the risk when you can get immunity through vaccination quite safely?”
The findings could help people figure out the most effective time to get vaccinated or boosted and guide officials in setting policies on workplace vaccine mandates and rules for high-occupancy indoor settings, the researchers concluded.
This was the largest meta-analysis of immunity following infection to date, NBC News reports.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
People who’ve been infected with COVID reduced their chances of hospitalization and death by 88% over 10 months compared to somebody who hasn’t been infected, according to the study, published in The Lancet.
The natural immunity provided by infection was “at least as high, if not higher” than the immunity provided by two doses of Moderna or Pfizer mRNA vaccines against the ancestral, Alpha, Delta, and Omicron BA.1 variants, the researchers reported.
But protection against the BA.1 subvariant of Omicron was not as high – 36% at 10 months after infection, wrote the research team from the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington.
They examined 65 studies from 19 countries through Sept. 31, 2022. They did not study data about infection from Omicron XBB and its sub-lineages. People who had immunity from both infection and vaccination, known as hybrid immunity, were not studied.
The findings don’t mean people should skip the vaccines and get COVID on purpose, one of the researchers told NBC News.
“The problem of saying ‘I’m gonna get infected to get immunity’ is you might be one of those people that end up in the hospital or die,” said Christopher Murray, MD, DPhil, director of the IHME. “Why would you take the risk when you can get immunity through vaccination quite safely?”
The findings could help people figure out the most effective time to get vaccinated or boosted and guide officials in setting policies on workplace vaccine mandates and rules for high-occupancy indoor settings, the researchers concluded.
This was the largest meta-analysis of immunity following infection to date, NBC News reports.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM THE LANCET