User login
For MD-IQ use only
Low-Dose Oral Minoxidil: Expert Consensus Provide Guidance for Treating Hair Loss
. With large randomized, controlled trials lacking, the guidelines authors and other dermatologists said the paper provides practical pointers that should increase clinicians’ confidence in prescribing LDOM for hair loss.
Comfort and Confidence
Benjamin N. Ungar, MD, director of the Alopecia Center of Excellence at Mount Sinai Icahn School of Medicine, New York City, said he hopes that the guidelines will “make dermatologists in practice more comfortable with the use of low-dose oral minoxidil to treat different kinds of hair loss, and therefore, more patients will benefit.” He was not an author of the paper, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology on November 20, but was asked to comment.
Members of the multidisciplinary Low-Dose Oral Minoxidil Initiation steering committee recruited dermatologists with hair loss expertise from 12 countries. Using a modified four-round Delphi process that required at least 70% agreement, the group of 43 dermatologists crafted 76 consensus statements. “Notably,” said Co-senior author Jennifer Fu, MD, director of the Hair Disorders Clinic at the University of California, San Francisco, “27 items achieved at least 90% consensus after the first two rounds, indicating broad agreement in expert practice.”
Indications for LDOM
At least 90% of experts concurred regarding the appropriateness of LDOM use for androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and age-related thinning and in cases where topical minoxidil proves ineffective or problematic. Additional situations in which LDOM might provide direct benefit involve follicular miniaturization, such as alopecia areata, or hair cycle disruption, such as chemotherapy. The authors also recommended considering LDOM over topical minoxidil when the latter is more expensive and when patients desire enhanced hypertrichosis.
Contraindications and Precautions
Before prescribing LDOM, the authors wrote, clinicians may consult with primary care or cardiology when contraindications (cardiovascular issues, pregnancy/nursing, and potential drug interactions) or precautions (history of tachycardia or arrhythmia, hypotension, or impaired kidney function) exist. Patients with precautions may require blood pressure monitoring, as well as monitoring for adverse effects of treatment. The panel also suggested the latter for all patients at the time of LDOM initiation and dose escalation. The authors advised against routine baseline laboratory and EKG testing in cases without relevant precautions.
Dosing Considerations
Along with systemic adverse event risk and baseline hair loss severity, key dosing considerations include patient age, sex, and whether patients desire hypertrichosis. Consensus on daily doses for adolescent females and males begins at 0.625 mg and 1.25 mg, respectively, and ranges up to 2.5 mg for adolescent females vs 5 mg for adult females and adolescent and adult males.
Presently, said Ungar, many dermatologists — including some who prescribe LDOM — remain uncomfortable even with very low doses, perhaps because of an invalid perception of cardiovascular safety issues including potential hypotension and pericardial effusions. However, recently published data include a review published November 7 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, which showed no significant effect of LDOM on blood pressure. And in a September Journal of Drugs in Dermatology article the authors found no impact on pericardial effusions in a 100-patient cohort.
Some dermatologists worry about the impact hypertrichosis may have on patients, Ungar added. Although incidence estimates range from 15% to 30%, he said, more than half of his patients experience hypertrichosis. “However, most continue treatment because the beneficial effects outweigh the effect of hypertrichosis.”
Practical Roadmap
Adam Friedman, MD, who was not involved with the publication, applauds its inclusion of pragmatic clinical guidance, which he said consensus papers often lack. “This paper sets a great roadmap for working low-dose oral minoxidil into your clinical practice, Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said in an interview.
Rather than limiting LDOM use to AGA, he said, the paper is most helpful in showing the spectrum of disease states for which the expert panel prescribes LDOM. “We use it as adjunctive therapy for many other things, both scarring and nonscarring hair loss,” he added.
In appropriate clinical contexts, the authors wrote, clinicians may consider combining LDOM with spironolactone or beta-blockers. Friedman said that in his hands, combining LDOM with a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor (5ARI) is “absolutely outstanding.” Minoxidil increases blood flow to the scalp, he explained, while 5ARIs prevent production of dihydrotestosterone, which miniaturizes hair.
Fu said, “We hope these consensus outcomes will be helpful to dermatology colleagues as they consider using LDOM to treat hair loss in their adult and adolescent patient populations. We anticipate that these guidelines will be updated as additional evidence-based data emerges and are encouraged that we are already seeing new publications on this topic.”
Important areas for future research, she noted, include pediatric use of LDOM, the comparative efficacy of topical vs oral minoxidil, the safety of oral minoxidil for patients with a history of allergic contact dermatitis to topical minoxidil, and the use of other off-label forms of minoxidil, such as compounded oral minoxidil and sublingual minoxidil.
The study was funded by the University of California, San Francisco, Department of Dermatology Medical Student Summer Research Fellowship Program. Fu reported personal fees from Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Company, and Sun Pharma outside of the study. The full list of author disclosures can be found in the paper. Ungar and Friedman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
. With large randomized, controlled trials lacking, the guidelines authors and other dermatologists said the paper provides practical pointers that should increase clinicians’ confidence in prescribing LDOM for hair loss.
Comfort and Confidence
Benjamin N. Ungar, MD, director of the Alopecia Center of Excellence at Mount Sinai Icahn School of Medicine, New York City, said he hopes that the guidelines will “make dermatologists in practice more comfortable with the use of low-dose oral minoxidil to treat different kinds of hair loss, and therefore, more patients will benefit.” He was not an author of the paper, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology on November 20, but was asked to comment.
Members of the multidisciplinary Low-Dose Oral Minoxidil Initiation steering committee recruited dermatologists with hair loss expertise from 12 countries. Using a modified four-round Delphi process that required at least 70% agreement, the group of 43 dermatologists crafted 76 consensus statements. “Notably,” said Co-senior author Jennifer Fu, MD, director of the Hair Disorders Clinic at the University of California, San Francisco, “27 items achieved at least 90% consensus after the first two rounds, indicating broad agreement in expert practice.”
Indications for LDOM
At least 90% of experts concurred regarding the appropriateness of LDOM use for androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and age-related thinning and in cases where topical minoxidil proves ineffective or problematic. Additional situations in which LDOM might provide direct benefit involve follicular miniaturization, such as alopecia areata, or hair cycle disruption, such as chemotherapy. The authors also recommended considering LDOM over topical minoxidil when the latter is more expensive and when patients desire enhanced hypertrichosis.
Contraindications and Precautions
Before prescribing LDOM, the authors wrote, clinicians may consult with primary care or cardiology when contraindications (cardiovascular issues, pregnancy/nursing, and potential drug interactions) or precautions (history of tachycardia or arrhythmia, hypotension, or impaired kidney function) exist. Patients with precautions may require blood pressure monitoring, as well as monitoring for adverse effects of treatment. The panel also suggested the latter for all patients at the time of LDOM initiation and dose escalation. The authors advised against routine baseline laboratory and EKG testing in cases without relevant precautions.
Dosing Considerations
Along with systemic adverse event risk and baseline hair loss severity, key dosing considerations include patient age, sex, and whether patients desire hypertrichosis. Consensus on daily doses for adolescent females and males begins at 0.625 mg and 1.25 mg, respectively, and ranges up to 2.5 mg for adolescent females vs 5 mg for adult females and adolescent and adult males.
Presently, said Ungar, many dermatologists — including some who prescribe LDOM — remain uncomfortable even with very low doses, perhaps because of an invalid perception of cardiovascular safety issues including potential hypotension and pericardial effusions. However, recently published data include a review published November 7 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, which showed no significant effect of LDOM on blood pressure. And in a September Journal of Drugs in Dermatology article the authors found no impact on pericardial effusions in a 100-patient cohort.
Some dermatologists worry about the impact hypertrichosis may have on patients, Ungar added. Although incidence estimates range from 15% to 30%, he said, more than half of his patients experience hypertrichosis. “However, most continue treatment because the beneficial effects outweigh the effect of hypertrichosis.”
Practical Roadmap
Adam Friedman, MD, who was not involved with the publication, applauds its inclusion of pragmatic clinical guidance, which he said consensus papers often lack. “This paper sets a great roadmap for working low-dose oral minoxidil into your clinical practice, Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said in an interview.
Rather than limiting LDOM use to AGA, he said, the paper is most helpful in showing the spectrum of disease states for which the expert panel prescribes LDOM. “We use it as adjunctive therapy for many other things, both scarring and nonscarring hair loss,” he added.
In appropriate clinical contexts, the authors wrote, clinicians may consider combining LDOM with spironolactone or beta-blockers. Friedman said that in his hands, combining LDOM with a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor (5ARI) is “absolutely outstanding.” Minoxidil increases blood flow to the scalp, he explained, while 5ARIs prevent production of dihydrotestosterone, which miniaturizes hair.
Fu said, “We hope these consensus outcomes will be helpful to dermatology colleagues as they consider using LDOM to treat hair loss in their adult and adolescent patient populations. We anticipate that these guidelines will be updated as additional evidence-based data emerges and are encouraged that we are already seeing new publications on this topic.”
Important areas for future research, she noted, include pediatric use of LDOM, the comparative efficacy of topical vs oral minoxidil, the safety of oral minoxidil for patients with a history of allergic contact dermatitis to topical minoxidil, and the use of other off-label forms of minoxidil, such as compounded oral minoxidil and sublingual minoxidil.
The study was funded by the University of California, San Francisco, Department of Dermatology Medical Student Summer Research Fellowship Program. Fu reported personal fees from Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Company, and Sun Pharma outside of the study. The full list of author disclosures can be found in the paper. Ungar and Friedman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
. With large randomized, controlled trials lacking, the guidelines authors and other dermatologists said the paper provides practical pointers that should increase clinicians’ confidence in prescribing LDOM for hair loss.
Comfort and Confidence
Benjamin N. Ungar, MD, director of the Alopecia Center of Excellence at Mount Sinai Icahn School of Medicine, New York City, said he hopes that the guidelines will “make dermatologists in practice more comfortable with the use of low-dose oral minoxidil to treat different kinds of hair loss, and therefore, more patients will benefit.” He was not an author of the paper, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology on November 20, but was asked to comment.
Members of the multidisciplinary Low-Dose Oral Minoxidil Initiation steering committee recruited dermatologists with hair loss expertise from 12 countries. Using a modified four-round Delphi process that required at least 70% agreement, the group of 43 dermatologists crafted 76 consensus statements. “Notably,” said Co-senior author Jennifer Fu, MD, director of the Hair Disorders Clinic at the University of California, San Francisco, “27 items achieved at least 90% consensus after the first two rounds, indicating broad agreement in expert practice.”
Indications for LDOM
At least 90% of experts concurred regarding the appropriateness of LDOM use for androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and age-related thinning and in cases where topical minoxidil proves ineffective or problematic. Additional situations in which LDOM might provide direct benefit involve follicular miniaturization, such as alopecia areata, or hair cycle disruption, such as chemotherapy. The authors also recommended considering LDOM over topical minoxidil when the latter is more expensive and when patients desire enhanced hypertrichosis.
Contraindications and Precautions
Before prescribing LDOM, the authors wrote, clinicians may consult with primary care or cardiology when contraindications (cardiovascular issues, pregnancy/nursing, and potential drug interactions) or precautions (history of tachycardia or arrhythmia, hypotension, or impaired kidney function) exist. Patients with precautions may require blood pressure monitoring, as well as monitoring for adverse effects of treatment. The panel also suggested the latter for all patients at the time of LDOM initiation and dose escalation. The authors advised against routine baseline laboratory and EKG testing in cases without relevant precautions.
Dosing Considerations
Along with systemic adverse event risk and baseline hair loss severity, key dosing considerations include patient age, sex, and whether patients desire hypertrichosis. Consensus on daily doses for adolescent females and males begins at 0.625 mg and 1.25 mg, respectively, and ranges up to 2.5 mg for adolescent females vs 5 mg for adult females and adolescent and adult males.
Presently, said Ungar, many dermatologists — including some who prescribe LDOM — remain uncomfortable even with very low doses, perhaps because of an invalid perception of cardiovascular safety issues including potential hypotension and pericardial effusions. However, recently published data include a review published November 7 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, which showed no significant effect of LDOM on blood pressure. And in a September Journal of Drugs in Dermatology article the authors found no impact on pericardial effusions in a 100-patient cohort.
Some dermatologists worry about the impact hypertrichosis may have on patients, Ungar added. Although incidence estimates range from 15% to 30%, he said, more than half of his patients experience hypertrichosis. “However, most continue treatment because the beneficial effects outweigh the effect of hypertrichosis.”
Practical Roadmap
Adam Friedman, MD, who was not involved with the publication, applauds its inclusion of pragmatic clinical guidance, which he said consensus papers often lack. “This paper sets a great roadmap for working low-dose oral minoxidil into your clinical practice, Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said in an interview.
Rather than limiting LDOM use to AGA, he said, the paper is most helpful in showing the spectrum of disease states for which the expert panel prescribes LDOM. “We use it as adjunctive therapy for many other things, both scarring and nonscarring hair loss,” he added.
In appropriate clinical contexts, the authors wrote, clinicians may consider combining LDOM with spironolactone or beta-blockers. Friedman said that in his hands, combining LDOM with a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor (5ARI) is “absolutely outstanding.” Minoxidil increases blood flow to the scalp, he explained, while 5ARIs prevent production of dihydrotestosterone, which miniaturizes hair.
Fu said, “We hope these consensus outcomes will be helpful to dermatology colleagues as they consider using LDOM to treat hair loss in their adult and adolescent patient populations. We anticipate that these guidelines will be updated as additional evidence-based data emerges and are encouraged that we are already seeing new publications on this topic.”
Important areas for future research, she noted, include pediatric use of LDOM, the comparative efficacy of topical vs oral minoxidil, the safety of oral minoxidil for patients with a history of allergic contact dermatitis to topical minoxidil, and the use of other off-label forms of minoxidil, such as compounded oral minoxidil and sublingual minoxidil.
The study was funded by the University of California, San Francisco, Department of Dermatology Medical Student Summer Research Fellowship Program. Fu reported personal fees from Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Company, and Sun Pharma outside of the study. The full list of author disclosures can be found in the paper. Ungar and Friedman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
NCCN Expands Cancer Genetic Risk Assessment Guidelines
Additional cancer types were included in the title and content for both guidelines. Prostate cancer was added to Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Breast, Ovarian, Pancreatic, and Prostate, and endometrial and gastric cancer were added to Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Colorectal, Endometrial, and Gastric.
For these cancers, the expanded guidelines include information on when genetic testing is recommended and what type of testing may be best. These guidelines also detail the hereditary conditions and genetic mutations associated with elevated cancer risk and include appropriate “next steps” for individuals who have them, which may involve increased screening or prevention surgeries.
“These updates include the spectrum of genes associated with genetic syndromes, the range of risk associated with each pathogenic variant, the improvements in screening and prevention strategies, the role of genetic data to inform cancer treatment, and the expansion of the role of genetic counseling as this field moves forward,” Mary B. Daly, MD, PhD, with Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, said in a news release. Daly chaired the panel that updated the breast, ovarian, pancreatic, and prostate cancer guidelines.
Oncologists should, for instance, ask patients about their family and personal history of cancer and known germline variants at time of initial diagnosis. With prostate cancer, if patients meet criteria for germline testing, multigene testing should include a host of variants, including BRCA1, BRCA2, ATM, PALB2, CHEK2, HOXB13, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2.
The updated guidelines on genetic risk assessment of colorectal, endometrial, and gastric cancer include new recommendations to consider for hereditary cancer screening in patients with newly diagnosed endometrial cancer, for evaluating and managing CDH1-associated gastric cancer risk, and for managing gastric cancer risk in patients with APC pathogenic variants.
For CDH1-associated gastric cancer, for instance, the guidelines recommend carriers be referred to institutions with expertise in managing risks for cancer associated with CDH1, “given the still limited understanding and rarity of this syndrome.”
“These expanded guidelines reflect the recommendations from leading experts on genetic testing based on the latest scientific research across the cancer spectrum, consolidated into two convenient resources,” said NCCN CEO Crystal S. Denlinger, MD, with Fox Chase Cancer Center, in a news release.
“This information is critical for guiding shared decision-making between health care providers and their patients, enhancing screening practices as appropriate, and potentially choosing options for prevention and targeted treatment choices. Genetic testing guidelines enable us to better care for people with cancer and their family members,” Denlinger added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Additional cancer types were included in the title and content for both guidelines. Prostate cancer was added to Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Breast, Ovarian, Pancreatic, and Prostate, and endometrial and gastric cancer were added to Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Colorectal, Endometrial, and Gastric.
For these cancers, the expanded guidelines include information on when genetic testing is recommended and what type of testing may be best. These guidelines also detail the hereditary conditions and genetic mutations associated with elevated cancer risk and include appropriate “next steps” for individuals who have them, which may involve increased screening or prevention surgeries.
“These updates include the spectrum of genes associated with genetic syndromes, the range of risk associated with each pathogenic variant, the improvements in screening and prevention strategies, the role of genetic data to inform cancer treatment, and the expansion of the role of genetic counseling as this field moves forward,” Mary B. Daly, MD, PhD, with Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, said in a news release. Daly chaired the panel that updated the breast, ovarian, pancreatic, and prostate cancer guidelines.
Oncologists should, for instance, ask patients about their family and personal history of cancer and known germline variants at time of initial diagnosis. With prostate cancer, if patients meet criteria for germline testing, multigene testing should include a host of variants, including BRCA1, BRCA2, ATM, PALB2, CHEK2, HOXB13, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2.
The updated guidelines on genetic risk assessment of colorectal, endometrial, and gastric cancer include new recommendations to consider for hereditary cancer screening in patients with newly diagnosed endometrial cancer, for evaluating and managing CDH1-associated gastric cancer risk, and for managing gastric cancer risk in patients with APC pathogenic variants.
For CDH1-associated gastric cancer, for instance, the guidelines recommend carriers be referred to institutions with expertise in managing risks for cancer associated with CDH1, “given the still limited understanding and rarity of this syndrome.”
“These expanded guidelines reflect the recommendations from leading experts on genetic testing based on the latest scientific research across the cancer spectrum, consolidated into two convenient resources,” said NCCN CEO Crystal S. Denlinger, MD, with Fox Chase Cancer Center, in a news release.
“This information is critical for guiding shared decision-making between health care providers and their patients, enhancing screening practices as appropriate, and potentially choosing options for prevention and targeted treatment choices. Genetic testing guidelines enable us to better care for people with cancer and their family members,” Denlinger added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Additional cancer types were included in the title and content for both guidelines. Prostate cancer was added to Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Breast, Ovarian, Pancreatic, and Prostate, and endometrial and gastric cancer were added to Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Colorectal, Endometrial, and Gastric.
For these cancers, the expanded guidelines include information on when genetic testing is recommended and what type of testing may be best. These guidelines also detail the hereditary conditions and genetic mutations associated with elevated cancer risk and include appropriate “next steps” for individuals who have them, which may involve increased screening or prevention surgeries.
“These updates include the spectrum of genes associated with genetic syndromes, the range of risk associated with each pathogenic variant, the improvements in screening and prevention strategies, the role of genetic data to inform cancer treatment, and the expansion of the role of genetic counseling as this field moves forward,” Mary B. Daly, MD, PhD, with Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, said in a news release. Daly chaired the panel that updated the breast, ovarian, pancreatic, and prostate cancer guidelines.
Oncologists should, for instance, ask patients about their family and personal history of cancer and known germline variants at time of initial diagnosis. With prostate cancer, if patients meet criteria for germline testing, multigene testing should include a host of variants, including BRCA1, BRCA2, ATM, PALB2, CHEK2, HOXB13, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2.
The updated guidelines on genetic risk assessment of colorectal, endometrial, and gastric cancer include new recommendations to consider for hereditary cancer screening in patients with newly diagnosed endometrial cancer, for evaluating and managing CDH1-associated gastric cancer risk, and for managing gastric cancer risk in patients with APC pathogenic variants.
For CDH1-associated gastric cancer, for instance, the guidelines recommend carriers be referred to institutions with expertise in managing risks for cancer associated with CDH1, “given the still limited understanding and rarity of this syndrome.”
“These expanded guidelines reflect the recommendations from leading experts on genetic testing based on the latest scientific research across the cancer spectrum, consolidated into two convenient resources,” said NCCN CEO Crystal S. Denlinger, MD, with Fox Chase Cancer Center, in a news release.
“This information is critical for guiding shared decision-making between health care providers and their patients, enhancing screening practices as appropriate, and potentially choosing options for prevention and targeted treatment choices. Genetic testing guidelines enable us to better care for people with cancer and their family members,” Denlinger added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is Pancreatic Cancer Really Rising in Young People?
TOPLINE:
Given the stable mortality rates in this population, the increase in incidence likely reflects previously undetected cases instead of a true rise in new cases, researchers say.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data from several registries have indicated that the incidence of pancreatic cancer among younger individuals, particularly women, is on the rise in the United States and worldwide.
- In a new analysis, researchers wanted to see if the observed increase in pancreatic cancer incidence among young Americans represented a true rise in cancer occurrence or indicated greater diagnostic scrutiny. If pancreatic cancer incidence is really increasing, “incidence and mortality would be expected to increase concurrently, as would early- and late-stage diagnoses,” the researchers explained.
- The researchers collected data on pancreatic cancer incidence, histology, and stage distribution for individuals aged 15-39 years from US Cancer Statistics, a database covering almost the entire US population from 2001 to 2020. Pancreatic cancer mortality data from the same timeframe came from the National Vital Statistics System.
- The researchers looked at four histologic categories: Adenocarcinoma, the dominant pancreatic cancer histology, as well as more rare subtypes — endocrine and solid pseudopapillary — and “other” category. Researchers also categorized stage-specific incidence as early stage (in situ or localized) or late stage (regional or distant).
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence of pancreatic cancer increased 2.1-fold in young women (incidence, 3.3-6.9 per million) and 1.6-fold in young men (incidence, 3.9-6.2 per million) between 2001 and 2019. However, mortality rates remained stable for women (1.5 deaths per million; annual percent change [AAPC], −0.5%; 95% CI, –1.4% to 0.5%) and men (2.5 deaths per million; AAPC, –0.1%; 95% CI, –0.8% to 0.6%) over this period.
- Looking at cancer subtypes, the increase in incidence was largely caused by early-stage endocrine cancer and solid pseudopapillary neoplasms in women, not adenocarcinoma (which remained stable over the study period).
- Looking at cancer stage, most of the increase in incidence came from detection of smaller tumors (< 2 cm) and early-stage cancer, which rose from 0.6 to 3.7 per million in women and from 0.4 to 2.2 per million in men. The authors also found no statistically significant change in the incidence of late-stage cancer in women or men.
- Rates of surgical treatment for pancreatic cancer increased, more than tripling among women (from 1.5 to 4.7 per million) and more than doubling among men (from 1.1 to 2.3 per million).
IN PRACTICE:
“Pancreatic cancer now can be another cancer subject to overdiagnosis: The detection of disease not destined to cause symptoms or death,” the authors concluded. “Although the observed changes in incidence are small, overdiagnosis is especially concerning for pancreatic cancer, as pancreatic surgery has substantial risk for morbidity (in particular, pancreatic fistulas) and mortality.”
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Vishal R. Patel, MD, MPH, and corresponding author H. Gilbert Welch, MD, MPH, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, was published online on November 19 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by the lack of data on the method of cancer detection, which may have affected the interpretation of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
Disclosure forms are available with the article online.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Given the stable mortality rates in this population, the increase in incidence likely reflects previously undetected cases instead of a true rise in new cases, researchers say.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data from several registries have indicated that the incidence of pancreatic cancer among younger individuals, particularly women, is on the rise in the United States and worldwide.
- In a new analysis, researchers wanted to see if the observed increase in pancreatic cancer incidence among young Americans represented a true rise in cancer occurrence or indicated greater diagnostic scrutiny. If pancreatic cancer incidence is really increasing, “incidence and mortality would be expected to increase concurrently, as would early- and late-stage diagnoses,” the researchers explained.
- The researchers collected data on pancreatic cancer incidence, histology, and stage distribution for individuals aged 15-39 years from US Cancer Statistics, a database covering almost the entire US population from 2001 to 2020. Pancreatic cancer mortality data from the same timeframe came from the National Vital Statistics System.
- The researchers looked at four histologic categories: Adenocarcinoma, the dominant pancreatic cancer histology, as well as more rare subtypes — endocrine and solid pseudopapillary — and “other” category. Researchers also categorized stage-specific incidence as early stage (in situ or localized) or late stage (regional or distant).
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence of pancreatic cancer increased 2.1-fold in young women (incidence, 3.3-6.9 per million) and 1.6-fold in young men (incidence, 3.9-6.2 per million) between 2001 and 2019. However, mortality rates remained stable for women (1.5 deaths per million; annual percent change [AAPC], −0.5%; 95% CI, –1.4% to 0.5%) and men (2.5 deaths per million; AAPC, –0.1%; 95% CI, –0.8% to 0.6%) over this period.
- Looking at cancer subtypes, the increase in incidence was largely caused by early-stage endocrine cancer and solid pseudopapillary neoplasms in women, not adenocarcinoma (which remained stable over the study period).
- Looking at cancer stage, most of the increase in incidence came from detection of smaller tumors (< 2 cm) and early-stage cancer, which rose from 0.6 to 3.7 per million in women and from 0.4 to 2.2 per million in men. The authors also found no statistically significant change in the incidence of late-stage cancer in women or men.
- Rates of surgical treatment for pancreatic cancer increased, more than tripling among women (from 1.5 to 4.7 per million) and more than doubling among men (from 1.1 to 2.3 per million).
IN PRACTICE:
“Pancreatic cancer now can be another cancer subject to overdiagnosis: The detection of disease not destined to cause symptoms or death,” the authors concluded. “Although the observed changes in incidence are small, overdiagnosis is especially concerning for pancreatic cancer, as pancreatic surgery has substantial risk for morbidity (in particular, pancreatic fistulas) and mortality.”
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Vishal R. Patel, MD, MPH, and corresponding author H. Gilbert Welch, MD, MPH, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, was published online on November 19 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by the lack of data on the method of cancer detection, which may have affected the interpretation of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
Disclosure forms are available with the article online.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Given the stable mortality rates in this population, the increase in incidence likely reflects previously undetected cases instead of a true rise in new cases, researchers say.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data from several registries have indicated that the incidence of pancreatic cancer among younger individuals, particularly women, is on the rise in the United States and worldwide.
- In a new analysis, researchers wanted to see if the observed increase in pancreatic cancer incidence among young Americans represented a true rise in cancer occurrence or indicated greater diagnostic scrutiny. If pancreatic cancer incidence is really increasing, “incidence and mortality would be expected to increase concurrently, as would early- and late-stage diagnoses,” the researchers explained.
- The researchers collected data on pancreatic cancer incidence, histology, and stage distribution for individuals aged 15-39 years from US Cancer Statistics, a database covering almost the entire US population from 2001 to 2020. Pancreatic cancer mortality data from the same timeframe came from the National Vital Statistics System.
- The researchers looked at four histologic categories: Adenocarcinoma, the dominant pancreatic cancer histology, as well as more rare subtypes — endocrine and solid pseudopapillary — and “other” category. Researchers also categorized stage-specific incidence as early stage (in situ or localized) or late stage (regional or distant).
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence of pancreatic cancer increased 2.1-fold in young women (incidence, 3.3-6.9 per million) and 1.6-fold in young men (incidence, 3.9-6.2 per million) between 2001 and 2019. However, mortality rates remained stable for women (1.5 deaths per million; annual percent change [AAPC], −0.5%; 95% CI, –1.4% to 0.5%) and men (2.5 deaths per million; AAPC, –0.1%; 95% CI, –0.8% to 0.6%) over this period.
- Looking at cancer subtypes, the increase in incidence was largely caused by early-stage endocrine cancer and solid pseudopapillary neoplasms in women, not adenocarcinoma (which remained stable over the study period).
- Looking at cancer stage, most of the increase in incidence came from detection of smaller tumors (< 2 cm) and early-stage cancer, which rose from 0.6 to 3.7 per million in women and from 0.4 to 2.2 per million in men. The authors also found no statistically significant change in the incidence of late-stage cancer in women or men.
- Rates of surgical treatment for pancreatic cancer increased, more than tripling among women (from 1.5 to 4.7 per million) and more than doubling among men (from 1.1 to 2.3 per million).
IN PRACTICE:
“Pancreatic cancer now can be another cancer subject to overdiagnosis: The detection of disease not destined to cause symptoms or death,” the authors concluded. “Although the observed changes in incidence are small, overdiagnosis is especially concerning for pancreatic cancer, as pancreatic surgery has substantial risk for morbidity (in particular, pancreatic fistulas) and mortality.”
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Vishal R. Patel, MD, MPH, and corresponding author H. Gilbert Welch, MD, MPH, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, was published online on November 19 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by the lack of data on the method of cancer detection, which may have affected the interpretation of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
Disclosure forms are available with the article online.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A Group Approach to Clinical Research Mentorship at a Veterans Affairs Medical Center
A Group Approach to Clinical Research Mentorship at a Veterans Affairs Medical Center
Supporting meaningful research that has a positive impact on the health and quality of life of veterans is a priority of the US Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development.1 For nearly a century, VA researchers have been conducting high quality studies. To continue this trajectory, it is imperative to attract, train, and retain exceptional investigators while nurturing their development throughout their careers.2
Mentorship is defined as guidance provided by an experienced and trusted party to another (usually junior) individual with the intent of helping the person succeed. It benefits the mentee, mentor, and their institutions.3 Mentorship is crucial for personal and professional development as well as productivity, which may help reduce clinician burnout.4-7 Conversely, a lack of mentorship could have negative effects on work satisfaction and stagnate career progression.8
Mentorship is vital for developing and advancing a VA investigator’s research agenda. Funding, grant writing, and research design were among the most discussed topics in a large comprehensive mentorship program for academic faculty.9 However, there are several known barriers to effective research mentorship; among them include a lack of resources, time constraints, and competing clinical priorities.10,11
Finding time for effective one-on-one research mentoring is difficult within the time constraints of clinical duties; a group mentorship model may help overcome this barrier. Group mentorship can aid in personal and professional development because no single mentor can effectively meet every mentoring need of an individual.12 Group mentorship also allows for the exchange of ideas among individuals with different backgrounds and the ability to utilize the strengths of each member of the group. For example, a member may have methodological expertise, while another may be skilled in grantsmanship. A team of mentors may be more beneficial for both the mentors (eg, establish a more manageable workload) and the mentee (eg, gains a broader perspective of expertise) when compared to having a single mentor.3
Peer mentorship within the group setting may also yield additional benefits. For example, having a supportive peer group may help reduce stress levels and burnout, while also improving overall well-being.3,13 Formal mentorship programs do not frequently discuss concerns such as work-life balance, so including peers as mentors may help fill this void.9 Peer mentorship has also been found to be beneficial in providing mentees with pooled resources and shared learning.12,13 This article describes the components, benefits, impacts, and challenges of a group research mentorship program for VA clinicians interested in conducting VA-relevant research.
Program Description
The VA Clinical Research Mentorship Program was initiated at the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System (VAAAHS) in October 2015 by the Chief of Medicine to assist VA clinician investigators with developing and submitting VA clinical science and health services research grant applications. The program offers group and one-on-one consultation services through the expertise of 2 experienced investigators/faculty mentors who also serve as program directors, each of whom devote about 3 to 5 hours per month to activities associated with the mentorship program (eg, attending the meeting, reviewing materials sent by mentees, and one-on-one discussions with mentees).
The program also fostered peer-led mentorship. This encourages all attendees to provide feedback during group sessions and communication by mentees outside the group sessions. An experienced project manager serves as program coordinator and contributes about 4 hours per month for activities such as attending, scheduling, and sending reminders for each meeting, distributing handouts, reviewing materials, and answering mentee’s questions via email. A statistician and additional research staff (ie, an epidemiologist and research assistant) do not attend the recurring meetings, but are available for offline consultation as needed. The program runs on a 12-month cycle with regular meetings occurring twice monthly during the 9-month academic period. Resources to support the program, primarily program director(s) and project coordinator effort, are provided by the Chief of Medicine and through the VAAAHS affiliated VA Health Systems Research (formerly Health Services Research & Development) Center of Innovation.
Invitations for new mentees are sent annually. Mentees expressing interest in the program outside of its annual recruitment period are evaluated for inclusion on a rolling basis. Recruitment begins with the program coordinator sending email notifications to all VAAAHS Medicine Service faculty, section chiefs, and division chiefs at the VAAAHS academic affiliate. Recipients are encouraged to distribute the announcement to eligible applicants and refer them to the application materials for entry consideration into the program. The application consists of the applicant’s curriculum vitae and a 1-page summary that includes a description of their research area of interest, how it is relevant to the VA, in addition to an idea for a research study, its potential significance, and proposed methodology. Applicant materials are reviewed by the program coordinator and program directors. The applicants are evaluated using a simple scoring approach that focuses on the applicant’s research area and agenda, past research training, past research productivity, potential for obtaining VA funding, and whether they have sufficient research time.
Program eligibility initially required being a physician with ≥ 1/8 VA appointment from the Medicine Service. However, clinicians with clinical appointments from other VA services are also accepted for participation as needed. Applicants must have previous research experience and have a career goal to obtain external funding for conducting and publishing original research. Those who have previously served as a principal investigator on a funded VA grant proposal are not eligible as new applicants but can remain in the program as peer mentors. The number of annual applicants varies and ranges from 1 to 11; on average, about 90% of applicants receive invitations to join the program.
Sessions
The program holds recurring meetings twice monthly for 1 hour during the 9-month academic year. However, program directors are available year-round, and mentees are encouraged to communicate questions or concerns via email during nonacademic months. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, all meetings were held in-person. However, the group pivoted to virtual meetings and continues to utilize this format. The dedicated program coordinator is responsible for coordinating meetings and distributing meeting materials.
Each session is informal, flexible, and supportive. Attendance is not enforced, and mentees are allowed to join meetings as their schedules permit; however, program directors and program coordinator attend each meeting. In advance of each session, the program coordinator sends out a call for agenda items to all active members invited to discuss any research related items. Each mentee presents their ideas to lead the discussion for their portion of the meeting with no defined format required.
A variety of topics are covered including, but not limited to: (1) grant-specific concerns (eg, questions related to specific aim pages, grantsmanship, postsubmission comments from reviewers, or postaward logistics); (2) research procedures (eg, questions related to methodological practices or institutional review board concerns); (3) manuscript or presentation preparation; and (4) careerrelated issues. The program coordinator distributes handouts prior to meetings and mentees may record their presentations. These handouts may include, but are not limited to, specific aims pages, analytical plans, grant solicitations, and PowerPoint presentations. If a resource that can benefit the entire group is mentioned during the meeting, the program coordinator is responsible for distribution.
The program follows a group facilitated discussion format. Program directors facilitate each meeting, but input is encouraged from all attendees. This model allows for mentees to learn from the faculty mentors as well as peer mentees in a simultaneous and efficient fashion. Group discussions foster collective problem solving, peer support, and resource sharing that would not be possible through individualized mentorship. Participants have access to varied expertise during each session which reduces the need to seek specialized help elsewhere. Participants are also encouraged to contact the program directors or research staff for consultation as needed. Some one-on-one consultations have transitioned to a more sustained and ongoing mentorship relationship between a program director and mentee, but most are often brief email exchanges or a single meeting.
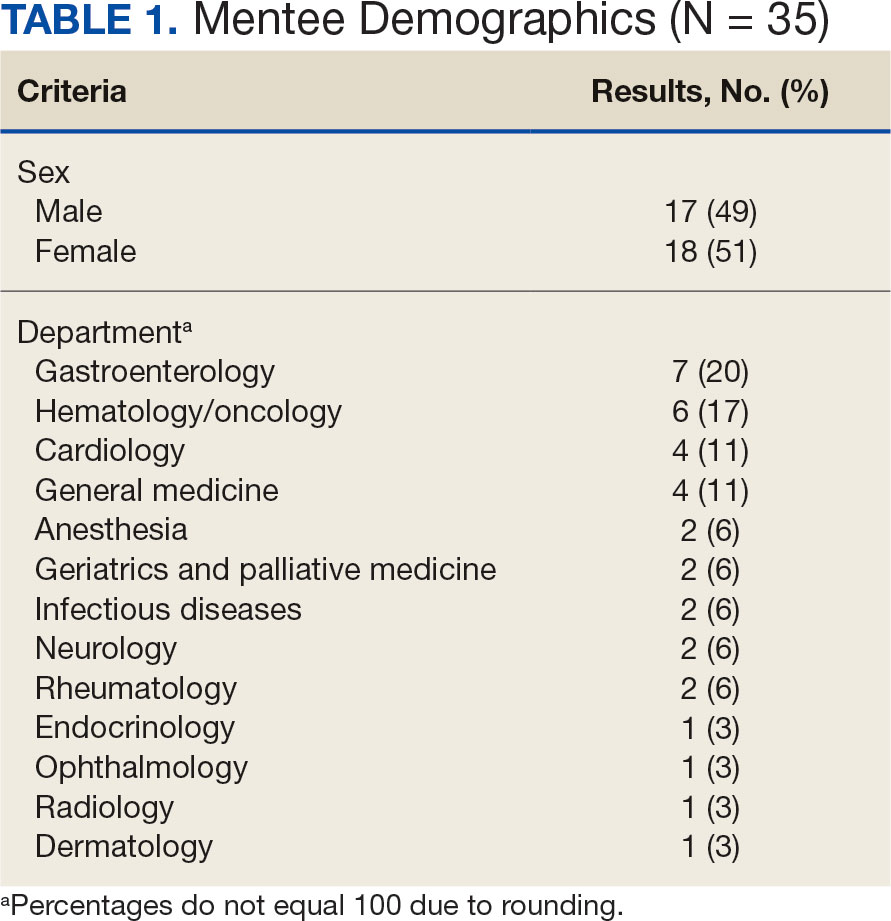
Participants
Since its inception in 2015, 35 clinicians have enrolled in the program. The mentees are equally distributed by sex and practice in a variety of disciplines including gastroenterology, hematology/oncology, cardiology, and general medicine (Table 1). Mentees have submitted 33 grant proposals addressing a variety of health care issues to a diverse group of federal and nonfederal funding agencies (Table 2). As of May 15, 2024, 19 (58%) of the submitted applications have been funded.

Many factors contribute to a successfully funded grant application, and several mentees report that participating in the mentorship program was helpful. For example, a mentee became the first lead investigator for a VA Cooperative Studies Program funded at VAAAHS. The VA Cooperative Studies Program, a division of the Office of Research and Development, plans and conducts large multicenter clinical trials and epidemiological studies within the VA via a vast network of clinician investigators, statisticians, and other key research experts.14
Several program mentees have also received VA Clinical Science Research and Development Career Development Awards. The VA Career Development program supports investigators during their early research careers with a goal of retaining talented researchers committed to improving the health and care of veterans.15
Survey Responses
Mentee productivity and updates are tracked through direct mentee input, as requested by the program coordinator. Since 2022, participants could complete an end-of-year survey based on an assessment tool used in a VAAAHS nonresearch mentorship program.16 The survey, distributed to mentees and program directors, requests feedback on logistics (eg, if the meeting was a good use of time and barriers to attendance); perceptions of effectiveness (eg, ability to discuss agenda items, helpfulness with setting and reaching research goals, and quality of mentors’ feedback); and the impact of the mentoring program on work satisfaction and clinician burnout. Respondents are also encouraged to leave open-ended qualitative feedback.
To date the survey has elicited 19 responses. Seventeen (89%) indicated that they agree or strongly agree the meetings were an effective use of their time and 11 (58%) indicated that they were able to discuss all or most of the items they wanted to during the meeting. Sixteen respondents (84%) agreed the program helped them set and achieve their research goals and 14 respondents (74%) agreed the feedback they received during the meeting was specific, actionable, and focused on how to improve their research agenda. Seventeen respondents (89%) agreed the program increased their work satisfaction, while 13 respondents (68%) felt the program reduced levels of clinician burnout.
As attendance was not mandatory, the survey asked participants how often they attended meetings during the past year. Responses were mixed: 4 (21%) respondents attended regularly (12 to 16 times per year) and 8 (42%) attended most sessions (8 to 11 times per year). Noted barriers to attendance included conflicts with patient care activities and conflicts with other high priority meetings.
Mentees also provided qualitive feedback regarding the program. They highlighted the supportive environment, valuable expertise of the mentors, and usefulness of obtaining tailored feedback from the group. “This group is an amazing resource to anyone developing a research career,” a mentee noted, adding that the program directors “fostered an incredibly supportive group where research ideas and methodology can be explored in a nonthreatening and creative environment.”
Conclusions
This mentorship program aims to help aspiring VA clinician investigators develop and submit competitive research grant applications. The addition of the program to the existing robust research environments at VAAAHS and its academic affiliate appears to have contributed to this success, with 58% of applications submitted by program mentees receiving funding.
In addition to funding success, we also found that most participants have a favorable impression of the program. Of the participants who responded to the program evaluation survey, nearly all indicated the program was an effective use of their time. The program also appeared to increase work satisfaction and reduce levels of clinician burnout. Barriers to attendance were also noted, with the most frequent being scheduling conflicts.
This program’s format includes facilitated group discussion as well as peer mentorship. This collaborative structure allows for an efficient and rich learning experience. Feedback from multiple perspectives encourages natural networking and relationship building. Incorporating the collective wisdom of the faculty mentors and peer mentees is beneficial; it not only empowers the mentees but also enriches the experience for the mentors. This program can serve as a model for other VA facilities—or non-VA academic medical centers—to enhance their research programs.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Strategic priorities for VA research. Published March 10, 2021. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/strategic_priorities.cfm
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. About the Office of Research & Development. Published November 11, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/default.cfm
- Chopra V, Vaughn V, Saint S. The Mentoring Guide: Helping Mentors and Mentees Succeed. Michigan Publishing Services; 2019.
- Gilster SD, Accorinti KL. Mentoring program yields staff satisfaction. Mentoring through the exchange of information across all organizational levels can help administrators retain valuable staff. Provider. 1999;25(10):99-100.
- Ramanan RA, Phillips RS, Davis RB, Silen W, Reede JY. Mentoring in medicine: keys to satisfaction. Am J Med. 2002;112(4):336-341. doi:10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01032-x
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. Mentoring in academic medicine: a systematic review. JAMA. 2006;296(9):1103-1115. doi:10.1001/jama.296.9.1103
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. A systematic review of qualitative research on the meaning and characteristics of mentoring in academic medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(1):72-78. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1165-8
- Jackson VA, Palepu A, Szalacha L, Caswell C, Carr PL, Inui T. “Having the right chemistry”: a qualitative study of mentoring in academic medicine. Acad Med. 2003;78(3):328-334. doi:10.1097/00001888-200303000-00020
- Feldman MD, Arean PA, Marshall SJ, Lovett M, O’Sullivan P. Does mentoring matter: results from a survey of faculty mentees at a large health sciences university. Med Educ Online. 2010;15:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063. doi:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063
- Leary JC, Schainker EG, Leyenaar JK. The unwritten rules of mentorship: facilitators of and barriers to effective mentorship in pediatric hospital medicine. Hosp Pediatr. 2016;6(4):219-225. doi:10.1542/hpeds.2015-0108
- Rustgi AK, Hecht GA. Mentorship in academic medicine. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(3):789-792. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.024
- DeCastro R, Sambuco D, Ubel PA, Stewart A, Jagsi R. Mentor networks in academic medicine: moving beyond a dyadic conception of mentoring for junior faculty researchers. Acad Med. 2013;88(4):488-496. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e318285d302
- McDaugall M, Beattie RS. Peer mentoring at work: the nature and outcomes of non-hierarchical developmental relationships. Management Learning. 2016;28(4):423-437. doi:10.1177/1350507697284003
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rsearch and Development. VA Cooperative Studies Program (CSP). Updated July 2019. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.vacsp.research.va.gov
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Career development program for biomedical laboratory and clinical science R&D services. Published April 17, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/services/shared_docs/career_dev.cfm
- Houchens N, Kuhn L, Ratz D, Su G, Saint S. Committed to success: a structured mentoring program for clinically-oriented physicians. Mayo Clin Pro Innov Qual Outcomes. 2024;8(4):356-363. doi:10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2024.05.002
Supporting meaningful research that has a positive impact on the health and quality of life of veterans is a priority of the US Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development.1 For nearly a century, VA researchers have been conducting high quality studies. To continue this trajectory, it is imperative to attract, train, and retain exceptional investigators while nurturing their development throughout their careers.2
Mentorship is defined as guidance provided by an experienced and trusted party to another (usually junior) individual with the intent of helping the person succeed. It benefits the mentee, mentor, and their institutions.3 Mentorship is crucial for personal and professional development as well as productivity, which may help reduce clinician burnout.4-7 Conversely, a lack of mentorship could have negative effects on work satisfaction and stagnate career progression.8
Mentorship is vital for developing and advancing a VA investigator’s research agenda. Funding, grant writing, and research design were among the most discussed topics in a large comprehensive mentorship program for academic faculty.9 However, there are several known barriers to effective research mentorship; among them include a lack of resources, time constraints, and competing clinical priorities.10,11
Finding time for effective one-on-one research mentoring is difficult within the time constraints of clinical duties; a group mentorship model may help overcome this barrier. Group mentorship can aid in personal and professional development because no single mentor can effectively meet every mentoring need of an individual.12 Group mentorship also allows for the exchange of ideas among individuals with different backgrounds and the ability to utilize the strengths of each member of the group. For example, a member may have methodological expertise, while another may be skilled in grantsmanship. A team of mentors may be more beneficial for both the mentors (eg, establish a more manageable workload) and the mentee (eg, gains a broader perspective of expertise) when compared to having a single mentor.3
Peer mentorship within the group setting may also yield additional benefits. For example, having a supportive peer group may help reduce stress levels and burnout, while also improving overall well-being.3,13 Formal mentorship programs do not frequently discuss concerns such as work-life balance, so including peers as mentors may help fill this void.9 Peer mentorship has also been found to be beneficial in providing mentees with pooled resources and shared learning.12,13 This article describes the components, benefits, impacts, and challenges of a group research mentorship program for VA clinicians interested in conducting VA-relevant research.
Program Description
The VA Clinical Research Mentorship Program was initiated at the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System (VAAAHS) in October 2015 by the Chief of Medicine to assist VA clinician investigators with developing and submitting VA clinical science and health services research grant applications. The program offers group and one-on-one consultation services through the expertise of 2 experienced investigators/faculty mentors who also serve as program directors, each of whom devote about 3 to 5 hours per month to activities associated with the mentorship program (eg, attending the meeting, reviewing materials sent by mentees, and one-on-one discussions with mentees).
The program also fostered peer-led mentorship. This encourages all attendees to provide feedback during group sessions and communication by mentees outside the group sessions. An experienced project manager serves as program coordinator and contributes about 4 hours per month for activities such as attending, scheduling, and sending reminders for each meeting, distributing handouts, reviewing materials, and answering mentee’s questions via email. A statistician and additional research staff (ie, an epidemiologist and research assistant) do not attend the recurring meetings, but are available for offline consultation as needed. The program runs on a 12-month cycle with regular meetings occurring twice monthly during the 9-month academic period. Resources to support the program, primarily program director(s) and project coordinator effort, are provided by the Chief of Medicine and through the VAAAHS affiliated VA Health Systems Research (formerly Health Services Research & Development) Center of Innovation.
Invitations for new mentees are sent annually. Mentees expressing interest in the program outside of its annual recruitment period are evaluated for inclusion on a rolling basis. Recruitment begins with the program coordinator sending email notifications to all VAAAHS Medicine Service faculty, section chiefs, and division chiefs at the VAAAHS academic affiliate. Recipients are encouraged to distribute the announcement to eligible applicants and refer them to the application materials for entry consideration into the program. The application consists of the applicant’s curriculum vitae and a 1-page summary that includes a description of their research area of interest, how it is relevant to the VA, in addition to an idea for a research study, its potential significance, and proposed methodology. Applicant materials are reviewed by the program coordinator and program directors. The applicants are evaluated using a simple scoring approach that focuses on the applicant’s research area and agenda, past research training, past research productivity, potential for obtaining VA funding, and whether they have sufficient research time.
Program eligibility initially required being a physician with ≥ 1/8 VA appointment from the Medicine Service. However, clinicians with clinical appointments from other VA services are also accepted for participation as needed. Applicants must have previous research experience and have a career goal to obtain external funding for conducting and publishing original research. Those who have previously served as a principal investigator on a funded VA grant proposal are not eligible as new applicants but can remain in the program as peer mentors. The number of annual applicants varies and ranges from 1 to 11; on average, about 90% of applicants receive invitations to join the program.
Sessions
The program holds recurring meetings twice monthly for 1 hour during the 9-month academic year. However, program directors are available year-round, and mentees are encouraged to communicate questions or concerns via email during nonacademic months. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, all meetings were held in-person. However, the group pivoted to virtual meetings and continues to utilize this format. The dedicated program coordinator is responsible for coordinating meetings and distributing meeting materials.
Each session is informal, flexible, and supportive. Attendance is not enforced, and mentees are allowed to join meetings as their schedules permit; however, program directors and program coordinator attend each meeting. In advance of each session, the program coordinator sends out a call for agenda items to all active members invited to discuss any research related items. Each mentee presents their ideas to lead the discussion for their portion of the meeting with no defined format required.
A variety of topics are covered including, but not limited to: (1) grant-specific concerns (eg, questions related to specific aim pages, grantsmanship, postsubmission comments from reviewers, or postaward logistics); (2) research procedures (eg, questions related to methodological practices or institutional review board concerns); (3) manuscript or presentation preparation; and (4) careerrelated issues. The program coordinator distributes handouts prior to meetings and mentees may record their presentations. These handouts may include, but are not limited to, specific aims pages, analytical plans, grant solicitations, and PowerPoint presentations. If a resource that can benefit the entire group is mentioned during the meeting, the program coordinator is responsible for distribution.
The program follows a group facilitated discussion format. Program directors facilitate each meeting, but input is encouraged from all attendees. This model allows for mentees to learn from the faculty mentors as well as peer mentees in a simultaneous and efficient fashion. Group discussions foster collective problem solving, peer support, and resource sharing that would not be possible through individualized mentorship. Participants have access to varied expertise during each session which reduces the need to seek specialized help elsewhere. Participants are also encouraged to contact the program directors or research staff for consultation as needed. Some one-on-one consultations have transitioned to a more sustained and ongoing mentorship relationship between a program director and mentee, but most are often brief email exchanges or a single meeting.

Participants
Since its inception in 2015, 35 clinicians have enrolled in the program. The mentees are equally distributed by sex and practice in a variety of disciplines including gastroenterology, hematology/oncology, cardiology, and general medicine (Table 1). Mentees have submitted 33 grant proposals addressing a variety of health care issues to a diverse group of federal and nonfederal funding agencies (Table 2). As of May 15, 2024, 19 (58%) of the submitted applications have been funded.

Many factors contribute to a successfully funded grant application, and several mentees report that participating in the mentorship program was helpful. For example, a mentee became the first lead investigator for a VA Cooperative Studies Program funded at VAAAHS. The VA Cooperative Studies Program, a division of the Office of Research and Development, plans and conducts large multicenter clinical trials and epidemiological studies within the VA via a vast network of clinician investigators, statisticians, and other key research experts.14
Several program mentees have also received VA Clinical Science Research and Development Career Development Awards. The VA Career Development program supports investigators during their early research careers with a goal of retaining talented researchers committed to improving the health and care of veterans.15
Survey Responses
Mentee productivity and updates are tracked through direct mentee input, as requested by the program coordinator. Since 2022, participants could complete an end-of-year survey based on an assessment tool used in a VAAAHS nonresearch mentorship program.16 The survey, distributed to mentees and program directors, requests feedback on logistics (eg, if the meeting was a good use of time and barriers to attendance); perceptions of effectiveness (eg, ability to discuss agenda items, helpfulness with setting and reaching research goals, and quality of mentors’ feedback); and the impact of the mentoring program on work satisfaction and clinician burnout. Respondents are also encouraged to leave open-ended qualitative feedback.
To date the survey has elicited 19 responses. Seventeen (89%) indicated that they agree or strongly agree the meetings were an effective use of their time and 11 (58%) indicated that they were able to discuss all or most of the items they wanted to during the meeting. Sixteen respondents (84%) agreed the program helped them set and achieve their research goals and 14 respondents (74%) agreed the feedback they received during the meeting was specific, actionable, and focused on how to improve their research agenda. Seventeen respondents (89%) agreed the program increased their work satisfaction, while 13 respondents (68%) felt the program reduced levels of clinician burnout.
As attendance was not mandatory, the survey asked participants how often they attended meetings during the past year. Responses were mixed: 4 (21%) respondents attended regularly (12 to 16 times per year) and 8 (42%) attended most sessions (8 to 11 times per year). Noted barriers to attendance included conflicts with patient care activities and conflicts with other high priority meetings.
Mentees also provided qualitive feedback regarding the program. They highlighted the supportive environment, valuable expertise of the mentors, and usefulness of obtaining tailored feedback from the group. “This group is an amazing resource to anyone developing a research career,” a mentee noted, adding that the program directors “fostered an incredibly supportive group where research ideas and methodology can be explored in a nonthreatening and creative environment.”
Conclusions
This mentorship program aims to help aspiring VA clinician investigators develop and submit competitive research grant applications. The addition of the program to the existing robust research environments at VAAAHS and its academic affiliate appears to have contributed to this success, with 58% of applications submitted by program mentees receiving funding.
In addition to funding success, we also found that most participants have a favorable impression of the program. Of the participants who responded to the program evaluation survey, nearly all indicated the program was an effective use of their time. The program also appeared to increase work satisfaction and reduce levels of clinician burnout. Barriers to attendance were also noted, with the most frequent being scheduling conflicts.
This program’s format includes facilitated group discussion as well as peer mentorship. This collaborative structure allows for an efficient and rich learning experience. Feedback from multiple perspectives encourages natural networking and relationship building. Incorporating the collective wisdom of the faculty mentors and peer mentees is beneficial; it not only empowers the mentees but also enriches the experience for the mentors. This program can serve as a model for other VA facilities—or non-VA academic medical centers—to enhance their research programs.
Supporting meaningful research that has a positive impact on the health and quality of life of veterans is a priority of the US Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development.1 For nearly a century, VA researchers have been conducting high quality studies. To continue this trajectory, it is imperative to attract, train, and retain exceptional investigators while nurturing their development throughout their careers.2
Mentorship is defined as guidance provided by an experienced and trusted party to another (usually junior) individual with the intent of helping the person succeed. It benefits the mentee, mentor, and their institutions.3 Mentorship is crucial for personal and professional development as well as productivity, which may help reduce clinician burnout.4-7 Conversely, a lack of mentorship could have negative effects on work satisfaction and stagnate career progression.8
Mentorship is vital for developing and advancing a VA investigator’s research agenda. Funding, grant writing, and research design were among the most discussed topics in a large comprehensive mentorship program for academic faculty.9 However, there are several known barriers to effective research mentorship; among them include a lack of resources, time constraints, and competing clinical priorities.10,11
Finding time for effective one-on-one research mentoring is difficult within the time constraints of clinical duties; a group mentorship model may help overcome this barrier. Group mentorship can aid in personal and professional development because no single mentor can effectively meet every mentoring need of an individual.12 Group mentorship also allows for the exchange of ideas among individuals with different backgrounds and the ability to utilize the strengths of each member of the group. For example, a member may have methodological expertise, while another may be skilled in grantsmanship. A team of mentors may be more beneficial for both the mentors (eg, establish a more manageable workload) and the mentee (eg, gains a broader perspective of expertise) when compared to having a single mentor.3
Peer mentorship within the group setting may also yield additional benefits. For example, having a supportive peer group may help reduce stress levels and burnout, while also improving overall well-being.3,13 Formal mentorship programs do not frequently discuss concerns such as work-life balance, so including peers as mentors may help fill this void.9 Peer mentorship has also been found to be beneficial in providing mentees with pooled resources and shared learning.12,13 This article describes the components, benefits, impacts, and challenges of a group research mentorship program for VA clinicians interested in conducting VA-relevant research.
Program Description
The VA Clinical Research Mentorship Program was initiated at the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System (VAAAHS) in October 2015 by the Chief of Medicine to assist VA clinician investigators with developing and submitting VA clinical science and health services research grant applications. The program offers group and one-on-one consultation services through the expertise of 2 experienced investigators/faculty mentors who also serve as program directors, each of whom devote about 3 to 5 hours per month to activities associated with the mentorship program (eg, attending the meeting, reviewing materials sent by mentees, and one-on-one discussions with mentees).
The program also fostered peer-led mentorship. This encourages all attendees to provide feedback during group sessions and communication by mentees outside the group sessions. An experienced project manager serves as program coordinator and contributes about 4 hours per month for activities such as attending, scheduling, and sending reminders for each meeting, distributing handouts, reviewing materials, and answering mentee’s questions via email. A statistician and additional research staff (ie, an epidemiologist and research assistant) do not attend the recurring meetings, but are available for offline consultation as needed. The program runs on a 12-month cycle with regular meetings occurring twice monthly during the 9-month academic period. Resources to support the program, primarily program director(s) and project coordinator effort, are provided by the Chief of Medicine and through the VAAAHS affiliated VA Health Systems Research (formerly Health Services Research & Development) Center of Innovation.
Invitations for new mentees are sent annually. Mentees expressing interest in the program outside of its annual recruitment period are evaluated for inclusion on a rolling basis. Recruitment begins with the program coordinator sending email notifications to all VAAAHS Medicine Service faculty, section chiefs, and division chiefs at the VAAAHS academic affiliate. Recipients are encouraged to distribute the announcement to eligible applicants and refer them to the application materials for entry consideration into the program. The application consists of the applicant’s curriculum vitae and a 1-page summary that includes a description of their research area of interest, how it is relevant to the VA, in addition to an idea for a research study, its potential significance, and proposed methodology. Applicant materials are reviewed by the program coordinator and program directors. The applicants are evaluated using a simple scoring approach that focuses on the applicant’s research area and agenda, past research training, past research productivity, potential for obtaining VA funding, and whether they have sufficient research time.
Program eligibility initially required being a physician with ≥ 1/8 VA appointment from the Medicine Service. However, clinicians with clinical appointments from other VA services are also accepted for participation as needed. Applicants must have previous research experience and have a career goal to obtain external funding for conducting and publishing original research. Those who have previously served as a principal investigator on a funded VA grant proposal are not eligible as new applicants but can remain in the program as peer mentors. The number of annual applicants varies and ranges from 1 to 11; on average, about 90% of applicants receive invitations to join the program.
Sessions
The program holds recurring meetings twice monthly for 1 hour during the 9-month academic year. However, program directors are available year-round, and mentees are encouraged to communicate questions or concerns via email during nonacademic months. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, all meetings were held in-person. However, the group pivoted to virtual meetings and continues to utilize this format. The dedicated program coordinator is responsible for coordinating meetings and distributing meeting materials.
Each session is informal, flexible, and supportive. Attendance is not enforced, and mentees are allowed to join meetings as their schedules permit; however, program directors and program coordinator attend each meeting. In advance of each session, the program coordinator sends out a call for agenda items to all active members invited to discuss any research related items. Each mentee presents their ideas to lead the discussion for their portion of the meeting with no defined format required.
A variety of topics are covered including, but not limited to: (1) grant-specific concerns (eg, questions related to specific aim pages, grantsmanship, postsubmission comments from reviewers, or postaward logistics); (2) research procedures (eg, questions related to methodological practices or institutional review board concerns); (3) manuscript or presentation preparation; and (4) careerrelated issues. The program coordinator distributes handouts prior to meetings and mentees may record their presentations. These handouts may include, but are not limited to, specific aims pages, analytical plans, grant solicitations, and PowerPoint presentations. If a resource that can benefit the entire group is mentioned during the meeting, the program coordinator is responsible for distribution.
The program follows a group facilitated discussion format. Program directors facilitate each meeting, but input is encouraged from all attendees. This model allows for mentees to learn from the faculty mentors as well as peer mentees in a simultaneous and efficient fashion. Group discussions foster collective problem solving, peer support, and resource sharing that would not be possible through individualized mentorship. Participants have access to varied expertise during each session which reduces the need to seek specialized help elsewhere. Participants are also encouraged to contact the program directors or research staff for consultation as needed. Some one-on-one consultations have transitioned to a more sustained and ongoing mentorship relationship between a program director and mentee, but most are often brief email exchanges or a single meeting.

Participants
Since its inception in 2015, 35 clinicians have enrolled in the program. The mentees are equally distributed by sex and practice in a variety of disciplines including gastroenterology, hematology/oncology, cardiology, and general medicine (Table 1). Mentees have submitted 33 grant proposals addressing a variety of health care issues to a diverse group of federal and nonfederal funding agencies (Table 2). As of May 15, 2024, 19 (58%) of the submitted applications have been funded.

Many factors contribute to a successfully funded grant application, and several mentees report that participating in the mentorship program was helpful. For example, a mentee became the first lead investigator for a VA Cooperative Studies Program funded at VAAAHS. The VA Cooperative Studies Program, a division of the Office of Research and Development, plans and conducts large multicenter clinical trials and epidemiological studies within the VA via a vast network of clinician investigators, statisticians, and other key research experts.14
Several program mentees have also received VA Clinical Science Research and Development Career Development Awards. The VA Career Development program supports investigators during their early research careers with a goal of retaining talented researchers committed to improving the health and care of veterans.15
Survey Responses
Mentee productivity and updates are tracked through direct mentee input, as requested by the program coordinator. Since 2022, participants could complete an end-of-year survey based on an assessment tool used in a VAAAHS nonresearch mentorship program.16 The survey, distributed to mentees and program directors, requests feedback on logistics (eg, if the meeting was a good use of time and barriers to attendance); perceptions of effectiveness (eg, ability to discuss agenda items, helpfulness with setting and reaching research goals, and quality of mentors’ feedback); and the impact of the mentoring program on work satisfaction and clinician burnout. Respondents are also encouraged to leave open-ended qualitative feedback.
To date the survey has elicited 19 responses. Seventeen (89%) indicated that they agree or strongly agree the meetings were an effective use of their time and 11 (58%) indicated that they were able to discuss all or most of the items they wanted to during the meeting. Sixteen respondents (84%) agreed the program helped them set and achieve their research goals and 14 respondents (74%) agreed the feedback they received during the meeting was specific, actionable, and focused on how to improve their research agenda. Seventeen respondents (89%) agreed the program increased their work satisfaction, while 13 respondents (68%) felt the program reduced levels of clinician burnout.
As attendance was not mandatory, the survey asked participants how often they attended meetings during the past year. Responses were mixed: 4 (21%) respondents attended regularly (12 to 16 times per year) and 8 (42%) attended most sessions (8 to 11 times per year). Noted barriers to attendance included conflicts with patient care activities and conflicts with other high priority meetings.
Mentees also provided qualitive feedback regarding the program. They highlighted the supportive environment, valuable expertise of the mentors, and usefulness of obtaining tailored feedback from the group. “This group is an amazing resource to anyone developing a research career,” a mentee noted, adding that the program directors “fostered an incredibly supportive group where research ideas and methodology can be explored in a nonthreatening and creative environment.”
Conclusions
This mentorship program aims to help aspiring VA clinician investigators develop and submit competitive research grant applications. The addition of the program to the existing robust research environments at VAAAHS and its academic affiliate appears to have contributed to this success, with 58% of applications submitted by program mentees receiving funding.
In addition to funding success, we also found that most participants have a favorable impression of the program. Of the participants who responded to the program evaluation survey, nearly all indicated the program was an effective use of their time. The program also appeared to increase work satisfaction and reduce levels of clinician burnout. Barriers to attendance were also noted, with the most frequent being scheduling conflicts.
This program’s format includes facilitated group discussion as well as peer mentorship. This collaborative structure allows for an efficient and rich learning experience. Feedback from multiple perspectives encourages natural networking and relationship building. Incorporating the collective wisdom of the faculty mentors and peer mentees is beneficial; it not only empowers the mentees but also enriches the experience for the mentors. This program can serve as a model for other VA facilities—or non-VA academic medical centers—to enhance their research programs.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Strategic priorities for VA research. Published March 10, 2021. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/strategic_priorities.cfm
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. About the Office of Research & Development. Published November 11, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/default.cfm
- Chopra V, Vaughn V, Saint S. The Mentoring Guide: Helping Mentors and Mentees Succeed. Michigan Publishing Services; 2019.
- Gilster SD, Accorinti KL. Mentoring program yields staff satisfaction. Mentoring through the exchange of information across all organizational levels can help administrators retain valuable staff. Provider. 1999;25(10):99-100.
- Ramanan RA, Phillips RS, Davis RB, Silen W, Reede JY. Mentoring in medicine: keys to satisfaction. Am J Med. 2002;112(4):336-341. doi:10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01032-x
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. Mentoring in academic medicine: a systematic review. JAMA. 2006;296(9):1103-1115. doi:10.1001/jama.296.9.1103
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. A systematic review of qualitative research on the meaning and characteristics of mentoring in academic medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(1):72-78. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1165-8
- Jackson VA, Palepu A, Szalacha L, Caswell C, Carr PL, Inui T. “Having the right chemistry”: a qualitative study of mentoring in academic medicine. Acad Med. 2003;78(3):328-334. doi:10.1097/00001888-200303000-00020
- Feldman MD, Arean PA, Marshall SJ, Lovett M, O’Sullivan P. Does mentoring matter: results from a survey of faculty mentees at a large health sciences university. Med Educ Online. 2010;15:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063. doi:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063
- Leary JC, Schainker EG, Leyenaar JK. The unwritten rules of mentorship: facilitators of and barriers to effective mentorship in pediatric hospital medicine. Hosp Pediatr. 2016;6(4):219-225. doi:10.1542/hpeds.2015-0108
- Rustgi AK, Hecht GA. Mentorship in academic medicine. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(3):789-792. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.024
- DeCastro R, Sambuco D, Ubel PA, Stewart A, Jagsi R. Mentor networks in academic medicine: moving beyond a dyadic conception of mentoring for junior faculty researchers. Acad Med. 2013;88(4):488-496. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e318285d302
- McDaugall M, Beattie RS. Peer mentoring at work: the nature and outcomes of non-hierarchical developmental relationships. Management Learning. 2016;28(4):423-437. doi:10.1177/1350507697284003
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rsearch and Development. VA Cooperative Studies Program (CSP). Updated July 2019. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.vacsp.research.va.gov
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Career development program for biomedical laboratory and clinical science R&D services. Published April 17, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/services/shared_docs/career_dev.cfm
- Houchens N, Kuhn L, Ratz D, Su G, Saint S. Committed to success: a structured mentoring program for clinically-oriented physicians. Mayo Clin Pro Innov Qual Outcomes. 2024;8(4):356-363. doi:10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2024.05.002
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Strategic priorities for VA research. Published March 10, 2021. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/strategic_priorities.cfm
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. About the Office of Research & Development. Published November 11, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/default.cfm
- Chopra V, Vaughn V, Saint S. The Mentoring Guide: Helping Mentors and Mentees Succeed. Michigan Publishing Services; 2019.
- Gilster SD, Accorinti KL. Mentoring program yields staff satisfaction. Mentoring through the exchange of information across all organizational levels can help administrators retain valuable staff. Provider. 1999;25(10):99-100.
- Ramanan RA, Phillips RS, Davis RB, Silen W, Reede JY. Mentoring in medicine: keys to satisfaction. Am J Med. 2002;112(4):336-341. doi:10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01032-x
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. Mentoring in academic medicine: a systematic review. JAMA. 2006;296(9):1103-1115. doi:10.1001/jama.296.9.1103
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. A systematic review of qualitative research on the meaning and characteristics of mentoring in academic medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(1):72-78. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1165-8
- Jackson VA, Palepu A, Szalacha L, Caswell C, Carr PL, Inui T. “Having the right chemistry”: a qualitative study of mentoring in academic medicine. Acad Med. 2003;78(3):328-334. doi:10.1097/00001888-200303000-00020
- Feldman MD, Arean PA, Marshall SJ, Lovett M, O’Sullivan P. Does mentoring matter: results from a survey of faculty mentees at a large health sciences university. Med Educ Online. 2010;15:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063. doi:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063
- Leary JC, Schainker EG, Leyenaar JK. The unwritten rules of mentorship: facilitators of and barriers to effective mentorship in pediatric hospital medicine. Hosp Pediatr. 2016;6(4):219-225. doi:10.1542/hpeds.2015-0108
- Rustgi AK, Hecht GA. Mentorship in academic medicine. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(3):789-792. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.024
- DeCastro R, Sambuco D, Ubel PA, Stewart A, Jagsi R. Mentor networks in academic medicine: moving beyond a dyadic conception of mentoring for junior faculty researchers. Acad Med. 2013;88(4):488-496. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e318285d302
- McDaugall M, Beattie RS. Peer mentoring at work: the nature and outcomes of non-hierarchical developmental relationships. Management Learning. 2016;28(4):423-437. doi:10.1177/1350507697284003
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rsearch and Development. VA Cooperative Studies Program (CSP). Updated July 2019. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.vacsp.research.va.gov
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Career development program for biomedical laboratory and clinical science R&D services. Published April 17, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/services/shared_docs/career_dev.cfm
- Houchens N, Kuhn L, Ratz D, Su G, Saint S. Committed to success: a structured mentoring program for clinically-oriented physicians. Mayo Clin Pro Innov Qual Outcomes. 2024;8(4):356-363. doi:10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2024.05.002
A Group Approach to Clinical Research Mentorship at a Veterans Affairs Medical Center
A Group Approach to Clinical Research Mentorship at a Veterans Affairs Medical Center
Financial Empowerment Journey
Dear Friends,
One of the challenges I faced during training was managing my life outside of work. Many astute trainees started their financial empowerment journey early. However, I was too overwhelmed with what I did not know (the financial world) and just avoided it. Over the last year, I finally decided to embrace my lack of knowledge and find the support of experts, just as we would in medicine. A lot of questions from my journey translated into several articles in the “Finance” section of The New Gastroenterologist, so I encourage those who need guidance on embarking on their financial journeys to explore that section!
In the “In Focus” section, Dr. Patrick Chang, Dr. Supisara Tintara, and Dr. Jennifer Phan – all from the University of Southern California – review diagnostic modalities to assess gastroesophageal reflux disease with an emphasis on medical, endoscopic, and surgical managements.
With the rise in metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), patient education is starting in the primary care and gastroenterologist’s office. Dr. Newsha Nikzad, medical student Daniel Huynh, and Dr. Nikki Duong share their approach to ask effectively about and communicate lifestyle modifications, with examples of using sensitive language and prompts to help guide patients, in the “Short Clinical Review” section.
The “Finance” section highlights the ins and outs of a physician mortgage loan and additional information for first time home buyers, reviewed by John G. Kelley II, a physician mortgage specialist and vice president of mortgage lending at Arvest Bank.
Lastly, in the “Early Career” section, Dr. Neil Gupta shares his experiences of transitioning from academic medicine to building a private practice group. He reflects on lessons learned from the first year after establishing his practice.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]) or Danielle Kiefer ([email protected]), managing editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: The first proton pump inhibitor was omeprazole, discovered 45 years ago in 1979 in Sweden, and clinically available in the United States only 36 years ago in 1988.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University in St. Louis
Dear Friends,
One of the challenges I faced during training was managing my life outside of work. Many astute trainees started their financial empowerment journey early. However, I was too overwhelmed with what I did not know (the financial world) and just avoided it. Over the last year, I finally decided to embrace my lack of knowledge and find the support of experts, just as we would in medicine. A lot of questions from my journey translated into several articles in the “Finance” section of The New Gastroenterologist, so I encourage those who need guidance on embarking on their financial journeys to explore that section!
In the “In Focus” section, Dr. Patrick Chang, Dr. Supisara Tintara, and Dr. Jennifer Phan – all from the University of Southern California – review diagnostic modalities to assess gastroesophageal reflux disease with an emphasis on medical, endoscopic, and surgical managements.
With the rise in metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), patient education is starting in the primary care and gastroenterologist’s office. Dr. Newsha Nikzad, medical student Daniel Huynh, and Dr. Nikki Duong share their approach to ask effectively about and communicate lifestyle modifications, with examples of using sensitive language and prompts to help guide patients, in the “Short Clinical Review” section.
The “Finance” section highlights the ins and outs of a physician mortgage loan and additional information for first time home buyers, reviewed by John G. Kelley II, a physician mortgage specialist and vice president of mortgage lending at Arvest Bank.
Lastly, in the “Early Career” section, Dr. Neil Gupta shares his experiences of transitioning from academic medicine to building a private practice group. He reflects on lessons learned from the first year after establishing his practice.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]) or Danielle Kiefer ([email protected]), managing editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: The first proton pump inhibitor was omeprazole, discovered 45 years ago in 1979 in Sweden, and clinically available in the United States only 36 years ago in 1988.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University in St. Louis
Dear Friends,
One of the challenges I faced during training was managing my life outside of work. Many astute trainees started their financial empowerment journey early. However, I was too overwhelmed with what I did not know (the financial world) and just avoided it. Over the last year, I finally decided to embrace my lack of knowledge and find the support of experts, just as we would in medicine. A lot of questions from my journey translated into several articles in the “Finance” section of The New Gastroenterologist, so I encourage those who need guidance on embarking on their financial journeys to explore that section!
In the “In Focus” section, Dr. Patrick Chang, Dr. Supisara Tintara, and Dr. Jennifer Phan – all from the University of Southern California – review diagnostic modalities to assess gastroesophageal reflux disease with an emphasis on medical, endoscopic, and surgical managements.
With the rise in metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), patient education is starting in the primary care and gastroenterologist’s office. Dr. Newsha Nikzad, medical student Daniel Huynh, and Dr. Nikki Duong share their approach to ask effectively about and communicate lifestyle modifications, with examples of using sensitive language and prompts to help guide patients, in the “Short Clinical Review” section.
The “Finance” section highlights the ins and outs of a physician mortgage loan and additional information for first time home buyers, reviewed by John G. Kelley II, a physician mortgage specialist and vice president of mortgage lending at Arvest Bank.
Lastly, in the “Early Career” section, Dr. Neil Gupta shares his experiences of transitioning from academic medicine to building a private practice group. He reflects on lessons learned from the first year after establishing his practice.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]) or Danielle Kiefer ([email protected]), managing editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: The first proton pump inhibitor was omeprazole, discovered 45 years ago in 1979 in Sweden, and clinically available in the United States only 36 years ago in 1988.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University in St. Louis
Post COVID-19, Long-term Risk for Autoimmune, Autoinflammatory Skin Disorders Increased, Study Finds
In addition, the authors reported that COVID-19 vaccination appears to reduce these risks.
The study was published in JAMA Dermatology.
‘Compelling Evidence’
“This well-executed study by Heo et al provides compelling evidence to support an association between COVID-19 infection and the development of subsequent autoimmune and autoinflammatory skin diseases,” wrote authors led by Lisa M. Arkin, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health in Madison, in an accompanying editorial.
Using databases from Korea’s National Health Insurance Service and the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, investigators led by Yeon-Woo Heo, MD, a dermatology resident at Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Republic of Korea, compared 3.1 million people who had COVID-19 with 3.8 million controls, all with at least 180 days’ follow-up through December 31, 2022.
At a mean follow-up of 287 days in both cohorts, authors found significantly elevated risks for AA and vitiligo (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.11 for both), AT (aHR, 1.24), Behçet disease (aHR, 1.45), and BP (aHR, 1.62) in the post–COVID-19 cohort. The infection also raised the risk for other conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus (aHR, 1.14) and Crohn’s disease (aHR, 1.35).
In subgroup analyses, demographic factors were associated with diverse effects: COVID-19 infection was associated with significantly higher odds of developing AA (for both men and women), vitiligo (men), Behçet disease (men and women), Crohn’s disease (men), ulcerative colitis (men), rheumatoid arthritis (men and women), systemic lupus erythematosus (men), ankylosing spondylitis (men), AT (women), and BP (women) than controls.
Those aged under 40 years were more likely to develop AA, primary cicatricial alopecia, Behçet disease, and ulcerative colitis, while those aged 40 years or older were more likely to develop AA, AT, vitiligo, Behçet disease, Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren’s syndrome, ankylosing spondylitis, and BP.
Additionally, severe COVID-19 requiring intensive care unit admission was associated with a significantly increased risk for autoimmune diseases, including AA, psoriasis, BP, and sarcoidosis. By timeframe, risks for AA, AT, and psoriasis were significantly higher during the initial Delta-dominant period.
Vaccination Effect
Moreover, vaccinated individuals were less likely to develop AA, AT, psoriasis, Behçet disease, and various nondermatologic conditions than were those who were unvaccinated. This finding, wrote Heo and colleagues, “may provide evidence to support the hypothesis that COVID-19 vaccines can help prevent autoimmune diseases.”
“That’s the part we all need to take into our offices tomorrow,” said Brett King, MD, PhD, a Fairfield, Connecticut–based dermatologist in private practice. He was not involved with the study but was asked to comment.
Overall, King said, the study carries two main messages. “The first is that COVID-19 infection increases the likelihood of developing an autoimmune or autoinflammatory disease in a large population.” The second and very important message is that being vaccinated against COVID-19 provides protection against developing an autoimmune or autoinflammatory disease.
“My concern is that the popular media highlights the first part,” said King, “and everybody who develops alopecia areata, vitiligo, or sarcoidosis blames COVID-19. That’s not what this work says.”
The foregoing distinction is especially important during the fall and winter, he added, when people getting influenza vaccines are routinely offered COVID-19 vaccines. “Many patients have said, ‘I got the COVID vaccine and developed alopecia areata 6 months later.’ Nearly everybody who has developed a new or worsening health condition in the last almost 5 years has had the perfect fall guy — the COVID vaccine or infection.”
With virtually all patients asking if they should get an updated COVID-19 vaccine or booster, he added, many report having heard that such vaccines cause AA, vitiligo, or other diseases. “To anchor these conversations in real data and not just anecdotes from a blog or Facebook is very useful,” said King, “and now we have very good data saying that the COVID vaccine is protective against these disorders.”
George Han, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at the Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York, applauds investigators’ use of a large, robust database but suggests interpreting results cautiously. He was not involved with the study but was asked to comment.
“You could do a large, well-done study,” Han said, “but it could still not necessarily be generalizable. These autoimmune conditions they’re looking at have clear ethnic and racial biases.” Heo and colleagues acknowledged shortcomings including their study population’s monomorphic nature.
Additional issues that limit the study’s impact, said Han, include the difficulty of conceptualizing a 10%-20% increase in conditions that at baseline are rare. And many of the findings reflected natural patterns, he said. For instance, BP more commonly affects older people, COVID-19 notwithstanding.
Han said that for him, the study’s main value going forward is helping to explain a rash of worsening inflammatory skin disease that many dermatologists saw early in the pandemic. “We would regularly see patients who were well controlled with, for example, psoriasis or eczema. But after COVID-19 infection or a vaccine (usually mRNA-type), in some cases they would come in flaring badly.” This happened at least a dozen times during the first year of post-shutdown appointments, he said.
“We’ve seen patients who have flared multiple times — they get the booster, then flare again,” Han added. Similar patterns occurred with pyoderma gangrenosum and other inflammatory skin diseases, he said.
Given the modest effect sizes of the associations reported in the Korean study, Arkin and colleagues wrote in their JAMA Dermatology editorial that surveillance for autoimmune disease is probably not warranted without new examination findings or symptoms. “For certain,” King said, “we should not go hunting for things that aren’t obviously there.”
Rather, Arkin and colleagues wrote, the higher autoimmunity rates seen among the unvaccinated, as well as during the Delta phase (when patients were sicker and hospitalizations were more likely) and in patients requiring intensive care, suggest that “interventions that reduce disease severity could also potentially reduce long-term risk of subsequent autoimmune sequelae.”
Future research addressing whether people with preexisting autoimmune conditions are at greater risk for flares or developing new autoimmune diseases following COVID-19 infection “would help to frame an evidence-based approach for patients with autoimmune disorders who develop COVID-19 infection, including the role for antiviral treatments,” they added.
The study was supported by grants from the Research Program of the Korea Medical Institute, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Han and King reported no relevant financial relationships. Arkin disclosed receiving research grants to her institution from Amgen and Eli Lilly, personal fees from Sanofi/Regeneron for consulting, and personal consulting fees from Merck outside the submitted work. Another author reported personal consulting fees from Dexcel Pharma and Honeydew outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In addition, the authors reported that COVID-19 vaccination appears to reduce these risks.
The study was published in JAMA Dermatology.
‘Compelling Evidence’
“This well-executed study by Heo et al provides compelling evidence to support an association between COVID-19 infection and the development of subsequent autoimmune and autoinflammatory skin diseases,” wrote authors led by Lisa M. Arkin, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health in Madison, in an accompanying editorial.
Using databases from Korea’s National Health Insurance Service and the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, investigators led by Yeon-Woo Heo, MD, a dermatology resident at Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Republic of Korea, compared 3.1 million people who had COVID-19 with 3.8 million controls, all with at least 180 days’ follow-up through December 31, 2022.
At a mean follow-up of 287 days in both cohorts, authors found significantly elevated risks for AA and vitiligo (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.11 for both), AT (aHR, 1.24), Behçet disease (aHR, 1.45), and BP (aHR, 1.62) in the post–COVID-19 cohort. The infection also raised the risk for other conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus (aHR, 1.14) and Crohn’s disease (aHR, 1.35).
In subgroup analyses, demographic factors were associated with diverse effects: COVID-19 infection was associated with significantly higher odds of developing AA (for both men and women), vitiligo (men), Behçet disease (men and women), Crohn’s disease (men), ulcerative colitis (men), rheumatoid arthritis (men and women), systemic lupus erythematosus (men), ankylosing spondylitis (men), AT (women), and BP (women) than controls.
Those aged under 40 years were more likely to develop AA, primary cicatricial alopecia, Behçet disease, and ulcerative colitis, while those aged 40 years or older were more likely to develop AA, AT, vitiligo, Behçet disease, Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren’s syndrome, ankylosing spondylitis, and BP.
Additionally, severe COVID-19 requiring intensive care unit admission was associated with a significantly increased risk for autoimmune diseases, including AA, psoriasis, BP, and sarcoidosis. By timeframe, risks for AA, AT, and psoriasis were significantly higher during the initial Delta-dominant period.
Vaccination Effect
Moreover, vaccinated individuals were less likely to develop AA, AT, psoriasis, Behçet disease, and various nondermatologic conditions than were those who were unvaccinated. This finding, wrote Heo and colleagues, “may provide evidence to support the hypothesis that COVID-19 vaccines can help prevent autoimmune diseases.”
“That’s the part we all need to take into our offices tomorrow,” said Brett King, MD, PhD, a Fairfield, Connecticut–based dermatologist in private practice. He was not involved with the study but was asked to comment.
Overall, King said, the study carries two main messages. “The first is that COVID-19 infection increases the likelihood of developing an autoimmune or autoinflammatory disease in a large population.” The second and very important message is that being vaccinated against COVID-19 provides protection against developing an autoimmune or autoinflammatory disease.
“My concern is that the popular media highlights the first part,” said King, “and everybody who develops alopecia areata, vitiligo, or sarcoidosis blames COVID-19. That’s not what this work says.”
The foregoing distinction is especially important during the fall and winter, he added, when people getting influenza vaccines are routinely offered COVID-19 vaccines. “Many patients have said, ‘I got the COVID vaccine and developed alopecia areata 6 months later.’ Nearly everybody who has developed a new or worsening health condition in the last almost 5 years has had the perfect fall guy — the COVID vaccine or infection.”
With virtually all patients asking if they should get an updated COVID-19 vaccine or booster, he added, many report having heard that such vaccines cause AA, vitiligo, or other diseases. “To anchor these conversations in real data and not just anecdotes from a blog or Facebook is very useful,” said King, “and now we have very good data saying that the COVID vaccine is protective against these disorders.”
George Han, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at the Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York, applauds investigators’ use of a large, robust database but suggests interpreting results cautiously. He was not involved with the study but was asked to comment.
“You could do a large, well-done study,” Han said, “but it could still not necessarily be generalizable. These autoimmune conditions they’re looking at have clear ethnic and racial biases.” Heo and colleagues acknowledged shortcomings including their study population’s monomorphic nature.
Additional issues that limit the study’s impact, said Han, include the difficulty of conceptualizing a 10%-20% increase in conditions that at baseline are rare. And many of the findings reflected natural patterns, he said. For instance, BP more commonly affects older people, COVID-19 notwithstanding.
Han said that for him, the study’s main value going forward is helping to explain a rash of worsening inflammatory skin disease that many dermatologists saw early in the pandemic. “We would regularly see patients who were well controlled with, for example, psoriasis or eczema. But after COVID-19 infection or a vaccine (usually mRNA-type), in some cases they would come in flaring badly.” This happened at least a dozen times during the first year of post-shutdown appointments, he said.
“We’ve seen patients who have flared multiple times — they get the booster, then flare again,” Han added. Similar patterns occurred with pyoderma gangrenosum and other inflammatory skin diseases, he said.
Given the modest effect sizes of the associations reported in the Korean study, Arkin and colleagues wrote in their JAMA Dermatology editorial that surveillance for autoimmune disease is probably not warranted without new examination findings or symptoms. “For certain,” King said, “we should not go hunting for things that aren’t obviously there.”
Rather, Arkin and colleagues wrote, the higher autoimmunity rates seen among the unvaccinated, as well as during the Delta phase (when patients were sicker and hospitalizations were more likely) and in patients requiring intensive care, suggest that “interventions that reduce disease severity could also potentially reduce long-term risk of subsequent autoimmune sequelae.”
Future research addressing whether people with preexisting autoimmune conditions are at greater risk for flares or developing new autoimmune diseases following COVID-19 infection “would help to frame an evidence-based approach for patients with autoimmune disorders who develop COVID-19 infection, including the role for antiviral treatments,” they added.
The study was supported by grants from the Research Program of the Korea Medical Institute, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Han and King reported no relevant financial relationships. Arkin disclosed receiving research grants to her institution from Amgen and Eli Lilly, personal fees from Sanofi/Regeneron for consulting, and personal consulting fees from Merck outside the submitted work. Another author reported personal consulting fees from Dexcel Pharma and Honeydew outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In addition, the authors reported that COVID-19 vaccination appears to reduce these risks.
The study was published in JAMA Dermatology.
‘Compelling Evidence’
“This well-executed study by Heo et al provides compelling evidence to support an association between COVID-19 infection and the development of subsequent autoimmune and autoinflammatory skin diseases,” wrote authors led by Lisa M. Arkin, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health in Madison, in an accompanying editorial.
Using databases from Korea’s National Health Insurance Service and the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, investigators led by Yeon-Woo Heo, MD, a dermatology resident at Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Republic of Korea, compared 3.1 million people who had COVID-19 with 3.8 million controls, all with at least 180 days’ follow-up through December 31, 2022.
At a mean follow-up of 287 days in both cohorts, authors found significantly elevated risks for AA and vitiligo (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.11 for both), AT (aHR, 1.24), Behçet disease (aHR, 1.45), and BP (aHR, 1.62) in the post–COVID-19 cohort. The infection also raised the risk for other conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus (aHR, 1.14) and Crohn’s disease (aHR, 1.35).
In subgroup analyses, demographic factors were associated with diverse effects: COVID-19 infection was associated with significantly higher odds of developing AA (for both men and women), vitiligo (men), Behçet disease (men and women), Crohn’s disease (men), ulcerative colitis (men), rheumatoid arthritis (men and women), systemic lupus erythematosus (men), ankylosing spondylitis (men), AT (women), and BP (women) than controls.
Those aged under 40 years were more likely to develop AA, primary cicatricial alopecia, Behçet disease, and ulcerative colitis, while those aged 40 years or older were more likely to develop AA, AT, vitiligo, Behçet disease, Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren’s syndrome, ankylosing spondylitis, and BP.
Additionally, severe COVID-19 requiring intensive care unit admission was associated with a significantly increased risk for autoimmune diseases, including AA, psoriasis, BP, and sarcoidosis. By timeframe, risks for AA, AT, and psoriasis were significantly higher during the initial Delta-dominant period.
Vaccination Effect
Moreover, vaccinated individuals were less likely to develop AA, AT, psoriasis, Behçet disease, and various nondermatologic conditions than were those who were unvaccinated. This finding, wrote Heo and colleagues, “may provide evidence to support the hypothesis that COVID-19 vaccines can help prevent autoimmune diseases.”
“That’s the part we all need to take into our offices tomorrow,” said Brett King, MD, PhD, a Fairfield, Connecticut–based dermatologist in private practice. He was not involved with the study but was asked to comment.
Overall, King said, the study carries two main messages. “The first is that COVID-19 infection increases the likelihood of developing an autoimmune or autoinflammatory disease in a large population.” The second and very important message is that being vaccinated against COVID-19 provides protection against developing an autoimmune or autoinflammatory disease.
“My concern is that the popular media highlights the first part,” said King, “and everybody who develops alopecia areata, vitiligo, or sarcoidosis blames COVID-19. That’s not what this work says.”
The foregoing distinction is especially important during the fall and winter, he added, when people getting influenza vaccines are routinely offered COVID-19 vaccines. “Many patients have said, ‘I got the COVID vaccine and developed alopecia areata 6 months later.’ Nearly everybody who has developed a new or worsening health condition in the last almost 5 years has had the perfect fall guy — the COVID vaccine or infection.”
With virtually all patients asking if they should get an updated COVID-19 vaccine or booster, he added, many report having heard that such vaccines cause AA, vitiligo, or other diseases. “To anchor these conversations in real data and not just anecdotes from a blog or Facebook is very useful,” said King, “and now we have very good data saying that the COVID vaccine is protective against these disorders.”
George Han, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at the Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York, applauds investigators’ use of a large, robust database but suggests interpreting results cautiously. He was not involved with the study but was asked to comment.
“You could do a large, well-done study,” Han said, “but it could still not necessarily be generalizable. These autoimmune conditions they’re looking at have clear ethnic and racial biases.” Heo and colleagues acknowledged shortcomings including their study population’s monomorphic nature.
Additional issues that limit the study’s impact, said Han, include the difficulty of conceptualizing a 10%-20% increase in conditions that at baseline are rare. And many of the findings reflected natural patterns, he said. For instance, BP more commonly affects older people, COVID-19 notwithstanding.
Han said that for him, the study’s main value going forward is helping to explain a rash of worsening inflammatory skin disease that many dermatologists saw early in the pandemic. “We would regularly see patients who were well controlled with, for example, psoriasis or eczema. But after COVID-19 infection or a vaccine (usually mRNA-type), in some cases they would come in flaring badly.” This happened at least a dozen times during the first year of post-shutdown appointments, he said.
“We’ve seen patients who have flared multiple times — they get the booster, then flare again,” Han added. Similar patterns occurred with pyoderma gangrenosum and other inflammatory skin diseases, he said.
Given the modest effect sizes of the associations reported in the Korean study, Arkin and colleagues wrote in their JAMA Dermatology editorial that surveillance for autoimmune disease is probably not warranted without new examination findings or symptoms. “For certain,” King said, “we should not go hunting for things that aren’t obviously there.”
Rather, Arkin and colleagues wrote, the higher autoimmunity rates seen among the unvaccinated, as well as during the Delta phase (when patients were sicker and hospitalizations were more likely) and in patients requiring intensive care, suggest that “interventions that reduce disease severity could also potentially reduce long-term risk of subsequent autoimmune sequelae.”
Future research addressing whether people with preexisting autoimmune conditions are at greater risk for flares or developing new autoimmune diseases following COVID-19 infection “would help to frame an evidence-based approach for patients with autoimmune disorders who develop COVID-19 infection, including the role for antiviral treatments,” they added.
The study was supported by grants from the Research Program of the Korea Medical Institute, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Han and King reported no relevant financial relationships. Arkin disclosed receiving research grants to her institution from Amgen and Eli Lilly, personal fees from Sanofi/Regeneron for consulting, and personal consulting fees from Merck outside the submitted work. Another author reported personal consulting fees from Dexcel Pharma and Honeydew outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Dupilumab Beneficial When Antihistamines Fall Short for Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
based on data from 151 individuals.
“Approximately 50% of patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria do not respond to antihistamines,” said Thomas B. Casale, MD, professor of internal medicine at the University of South Florida, Tampa, in an interview. Omalizumab, the only biologic approved for this condition, is not effective in all patients, and additional treatment options are needed, added Casale, the lead author who presented the new data, at the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (ACAAI) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting.
Dupilumab (Dupixent), a fully human monoclonal antibody that targets the interleukin (IL)–4 and IL-13 pathways, is currently approved in the United States for the treatment of several allergy and dermatology indications, including atopic dermatitis, severe asthma exacerbations, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, and prurigo nodularis.
In the study, known as LIBERTY-CSU CUPID Study C, researchers randomized 74 patients with CSU aged 6 years or older to add-on dupilumab subcutaneously every 2 weeks and 77 to placebo. (Patients were omalizumab-naive and had symptomatic CSU, despite treatment with up to four times the approved dose of standard-of-care H1-antihistamines.) Dupilumab doses were 300 mg for adults and adolescents weighing ≥ 60 kg or 200 mg for adolescents weighing < 60 kg and children weighing ≥ 30 kg.
The primary outcomes were Itch Severity Score over 7 days (ISS7; range, 0-21) and Urticaria Activity Score over 7 days (UAS7; range, 0-42).
Over the 24-week study period, patients in the dupilumab group showed significantly greater change from baseline than those in the placebo group on both measures, with least squares mean changes of 8.6 vs 6.1 for ISS7 and 15.9 vs 11.2 for UAS7 (P = .02 for both).
In addition, at 24 weeks, significantly more patients in the dupilumab group than in the placebo group achieved well-controlled disease based on a UAS of 6 or lower (41% vs 23%; P = .005). Significantly more dupilumab-treated patients also achieved a complete response (defined as a UAS of 0), compared with placebo-treated patients (30% vs 18%; P = .02).
Overall rates of treatment-emergent adverse events were 53% for both groups, and safety data were mainly consistent with dupilumab’s known safety profile, the researchers wrote.
The findings were not surprising, as a previous related study, LIBERTY-CSU CUPID Study A, showed that dupilumab was effective for CSU, Casale told this news organization. “This replicate study confirms the previous study and provides evidence for regulatory approval.”
If approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), “dupilumab will provide another therapeutic option for patients with chronic urticaria unresponsive to antihistamines,” Casale commented.
No new safety signals occurred, and the ability to self-administer the medication at home provides an advantage for patients, he added. As for additional research, “analysis of patient characteristics and potential biomarkers that would predict responsiveness is needed.”
More Research Needed to Fine-Tune Management
An unmet need persists for patients with CSU whose disease is not adequately controlled by higher-dose H1-antihistamines, Robert G. Micheletti, MD, associate professor of dermatology and medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview. “It is important not only to identify effective add-on therapies for these patients but also to generate data to support insurance coverage and drug access,” said Micheletti, who was not involved in the study.
Also referring to the similar findings reported in the LIBERTY-CSU CUPID Study A, Micheletti said, “as in the earlier study, the results demonstrate significantly reduced itch and urticaria in treated patients compared to placebo.”
“While many providers currently prescribe dupilumab off-label for refractory CSU, FDA approval would improve access to the drug for patients who need it and provide an alternative for patients who may not be good candidates for omalizumab,” he added. However, more research is needed to define optimal management of patients with CSU with inadequate response to omalizumab.
“The LIBERTY-CSU CUPID Study B showed a small improvement in itch severity and urticaria activity among such patients receiving dupilumab,” he noted. “Future work should aim to identify biomarkers and other features predictive of response to various therapies.”
Study B involved patients with CSU who were uncontrolled on standard-of-care antihistamines and refractory or intolerant to omalizumab, according to Regeneron.
On November 15, after the ACAAI meeting had ended, the company announced that the FDA had accepted the resubmission of an application for approval of dupilumab for the treatment of CSU in adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years or older not adequately controlled with H1-antihistamines.
The study was supported and sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Casale disclosed serving as a consultant for ALK, ARS Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bryn Pharma, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Genentech, GSK, Jasper, Novartis, Regeneron, and Sanofi and as a speaker for Genentech and Regeneron. Micheletti had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
based on data from 151 individuals.
“Approximately 50% of patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria do not respond to antihistamines,” said Thomas B. Casale, MD, professor of internal medicine at the University of South Florida, Tampa, in an interview. Omalizumab, the only biologic approved for this condition, is not effective in all patients, and additional treatment options are needed, added Casale, the lead author who presented the new data, at the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (ACAAI) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting.
Dupilumab (Dupixent), a fully human monoclonal antibody that targets the interleukin (IL)–4 and IL-13 pathways, is currently approved in the United States for the treatment of several allergy and dermatology indications, including atopic dermatitis, severe asthma exacerbations, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, and prurigo nodularis.
In the study, known as LIBERTY-CSU CUPID Study C, researchers randomized 74 patients with CSU aged 6 years or older to add-on dupilumab subcutaneously every 2 weeks and 77 to placebo. (Patients were omalizumab-naive and had symptomatic CSU, despite treatment with up to four times the approved dose of standard-of-care H1-antihistamines.) Dupilumab doses were 300 mg for adults and adolescents weighing ≥ 60 kg or 200 mg for adolescents weighing < 60 kg and children weighing ≥ 30 kg.
The primary outcomes were Itch Severity Score over 7 days (ISS7; range, 0-21) and Urticaria Activity Score over 7 days (UAS7; range, 0-42).
Over the 24-week study period, patients in the dupilumab group showed significantly greater change from baseline than those in the placebo group on both measures, with least squares mean changes of 8.6 vs 6.1 for ISS7 and 15.9 vs 11.2 for UAS7 (P = .02 for both).
In addition, at 24 weeks, significantly more patients in the dupilumab group than in the placebo group achieved well-controlled disease based on a UAS of 6 or lower (41% vs 23%; P = .005). Significantly more dupilumab-treated patients also achieved a complete response (defined as a UAS of 0), compared with placebo-treated patients (30% vs 18%; P = .02).
Overall rates of treatment-emergent adverse events were 53% for both groups, and safety data were mainly consistent with dupilumab’s known safety profile, the researchers wrote.
The findings were not surprising, as a previous related study, LIBERTY-CSU CUPID Study A, showed that dupilumab was effective for CSU, Casale told this news organization. “This replicate study confirms the previous study and provides evidence for regulatory approval.”
If approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), “dupilumab will provide another therapeutic option for patients with chronic urticaria unresponsive to antihistamines,” Casale commented.
No new safety signals occurred, and the ability to self-administer the medication at home provides an advantage for patients, he added. As for additional research, “analysis of patient characteristics and potential biomarkers that would predict responsiveness is needed.”
More Research Needed to Fine-Tune Management
An unmet need persists for patients with CSU whose disease is not adequately controlled by higher-dose H1-antihistamines, Robert G. Micheletti, MD, associate professor of dermatology and medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview. “It is important not only to identify effective add-on therapies for these patients but also to generate data to support insurance coverage and drug access,” said Micheletti, who was not involved in the study.
Also referring to the similar findings reported in the LIBERTY-CSU CUPID Study A, Micheletti said, “as in the earlier study, the results demonstrate significantly reduced itch and urticaria in treated patients compared to placebo.”
“While many providers currently prescribe dupilumab off-label for refractory CSU, FDA approval would improve access to the drug for patients who need it and provide an alternative for patients who may not be good candidates for omalizumab,” he added. However, more research is needed to define optimal management of patients with CSU with inadequate response to omalizumab.
“The LIBERTY-CSU CUPID Study B showed a small improvement in itch severity and urticaria activity among such patients receiving dupilumab,” he noted. “Future work should aim to identify biomarkers and other features predictive of response to various therapies.”
Study B involved patients with CSU who were uncontrolled on standard-of-care antihistamines and refractory or intolerant to omalizumab, according to Regeneron.
On November 15, after the ACAAI meeting had ended, the company announced that the FDA had accepted the resubmission of an application for approval of dupilumab for the treatment of CSU in adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years or older not adequately controlled with H1-antihistamines.
The study was supported and sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Casale disclosed serving as a consultant for ALK, ARS Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bryn Pharma, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Genentech, GSK, Jasper, Novartis, Regeneron, and Sanofi and as a speaker for Genentech and Regeneron. Micheletti had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
based on data from 151 individuals.
“Approximately 50% of patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria do not respond to antihistamines,” said Thomas B. Casale, MD, professor of internal medicine at the University of South Florida, Tampa, in an interview. Omalizumab, the only biologic approved for this condition, is not effective in all patients, and additional treatment options are needed, added Casale, the lead author who presented the new data, at the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (ACAAI) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting.
Dupilumab (Dupixent), a fully human monoclonal antibody that targets the interleukin (IL)–4 and IL-13 pathways, is currently approved in the United States for the treatment of several allergy and dermatology indications, including atopic dermatitis, severe asthma exacerbations, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, and prurigo nodularis.
In the study, known as LIBERTY-CSU CUPID Study C, researchers randomized 74 patients with CSU aged 6 years or older to add-on dupilumab subcutaneously every 2 weeks and 77 to placebo. (Patients were omalizumab-naive and had symptomatic CSU, despite treatment with up to four times the approved dose of standard-of-care H1-antihistamines.) Dupilumab doses were 300 mg for adults and adolescents weighing ≥ 60 kg or 200 mg for adolescents weighing < 60 kg and children weighing ≥ 30 kg.
The primary outcomes were Itch Severity Score over 7 days (ISS7; range, 0-21) and Urticaria Activity Score over 7 days (UAS7; range, 0-42).
Over the 24-week study period, patients in the dupilumab group showed significantly greater change from baseline than those in the placebo group on both measures, with least squares mean changes of 8.6 vs 6.1 for ISS7 and 15.9 vs 11.2 for UAS7 (P = .02 for both).
In addition, at 24 weeks, significantly more patients in the dupilumab group than in the placebo group achieved well-controlled disease based on a UAS of 6 or lower (41% vs 23%; P = .005). Significantly more dupilumab-treated patients also achieved a complete response (defined as a UAS of 0), compared with placebo-treated patients (30% vs 18%; P = .02).
Overall rates of treatment-emergent adverse events were 53% for both groups, and safety data were mainly consistent with dupilumab’s known safety profile, the researchers wrote.
The findings were not surprising, as a previous related study, LIBERTY-CSU CUPID Study A, showed that dupilumab was effective for CSU, Casale told this news organization. “This replicate study confirms the previous study and provides evidence for regulatory approval.”
If approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), “dupilumab will provide another therapeutic option for patients with chronic urticaria unresponsive to antihistamines,” Casale commented.
No new safety signals occurred, and the ability to self-administer the medication at home provides an advantage for patients, he added. As for additional research, “analysis of patient characteristics and potential biomarkers that would predict responsiveness is needed.”
More Research Needed to Fine-Tune Management
An unmet need persists for patients with CSU whose disease is not adequately controlled by higher-dose H1-antihistamines, Robert G. Micheletti, MD, associate professor of dermatology and medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview. “It is important not only to identify effective add-on therapies for these patients but also to generate data to support insurance coverage and drug access,” said Micheletti, who was not involved in the study.
Also referring to the similar findings reported in the LIBERTY-CSU CUPID Study A, Micheletti said, “as in the earlier study, the results demonstrate significantly reduced itch and urticaria in treated patients compared to placebo.”
“While many providers currently prescribe dupilumab off-label for refractory CSU, FDA approval would improve access to the drug for patients who need it and provide an alternative for patients who may not be good candidates for omalizumab,” he added. However, more research is needed to define optimal management of patients with CSU with inadequate response to omalizumab.
“The LIBERTY-CSU CUPID Study B showed a small improvement in itch severity and urticaria activity among such patients receiving dupilumab,” he noted. “Future work should aim to identify biomarkers and other features predictive of response to various therapies.”
Study B involved patients with CSU who were uncontrolled on standard-of-care antihistamines and refractory or intolerant to omalizumab, according to Regeneron.
On November 15, after the ACAAI meeting had ended, the company announced that the FDA had accepted the resubmission of an application for approval of dupilumab for the treatment of CSU in adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years or older not adequately controlled with H1-antihistamines.
The study was supported and sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Casale disclosed serving as a consultant for ALK, ARS Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bryn Pharma, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Genentech, GSK, Jasper, Novartis, Regeneron, and Sanofi and as a speaker for Genentech and Regeneron. Micheletti had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACAAI 2024
The Veteran’s Canon Under Fire
The Veteran’s Canon Under Fire
As Veterans Day approaches, stores and restaurants will offer discounts and free meals to veterans. Children will write thank you letters, and citizens nationwide will raise flags to honor and thank veterans. We can never repay those who lost their life, health, or livelihood in defense of the nation. Since the American Revolution, and in gratitude for that incalculable debt, the US government, on behalf of the American public, has seen fit to grant a host of benefits and services to those who wore the uniform.2,3 Among the best known are health care, burial services, compensation and pensions, home loans, and the GI Bill.
Less recognized yet arguably essential for the fair and consistent provision of these entitlements is a legal principle: the veteran’s canon. A canon is a system of rules or maxims used to interpret legal instruments, such as statutes. They are not rules but serve as a “principle that guides the interpretation of the text.”4 Since I am not a lawyer, I will undoubtedly oversimplify this legal principle, but I hope to get enough right to explain why the veteran’s canon should matter to federal health care professionals.
At its core, the veteran’s canon means that when the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) and a veteran have a legal dispute about VA benefits, the courts will give deference to the veteran. Underscoring that any ambiguity in the statute is resolved in the veteran’s favor, the canon is known in legal circles as the Gardner deference. This is a reference to a 1994 case in which a Korean War veteran underwent surgery in a VA facility for a herniated disc he alleged caused pain and weakness in his left lower extremity.5 Gardner argued that federal statutes 38 USC § 1151 underlying corresponding VA regulation 38 CFR § 3.358(c)(3) granted disability benefits to veterans injured during VA treatment. The VA denied the disability claim, contending the regulation restricted compensation to veterans whose injury was the fault of the VA; thus, the disability had to have been the result of negligent treatment or an unforeseen therapeutic accident.5
The case wound its way through various appeals boards and courts until the Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) ruled that the statute’s context left no ambiguity, and that any care provided under VA auspices was covered under the statute. What is important for this column is that the justices opined that had ambiguity been present, it would have legally necessitated, “applying the rule that interpretive doubt is to be resolved in the veteran’s favor.”5 In Gardner’s case, the courts reaffirmed nearly 80 years of judicial precedent upholding the veteran’s canon.
Thirty years later, Rudisill v McDonough again questioned the veteran’s canon.6 Educational benefits, namely the GI Bill, were the issue in this case. Rudisill served during 3 different periods in the US Army, totaling 8 years. Two educational programs overlapped during Rudisill’s tenure in the military: the Montgomery GI Bill and Post-9/11 Veterans Educational Assistance Act. Rudisill had used a portion of his Montgomery benefits to fund his undergraduate education and now wished to use the more extensive Post-9/11 assistance to finance his graduate degree. Rudisill and the VA disagreed about when his combined benefits would be capped, either at 36 or 48 months. After working its way through appeals courts, SCOTUS was again called upon for judgment.
The justices found that Rudisill qualified under both programs and could use them in any order he wished up to the cap. The majority found no ambiguity in the statute; however, if interpretation was required, the majority of justices indicated that the veteran’s canon would have supported Rudisill. While this sounds like good news for veterans, 2 justices authored a dissenting opinion that questioned the constitutional grounding of the veteran’s canon, noting that the “canon appears to have developed almost by accident.”6 The minority opinion suggested that when the veteran’s canon allocates resources to pay for specific veteran benefits, other interests and groups are deprived of those same resources, resulting in potential inequity.7
The potential ethical import and clinical impact of striking down the veteran’s canon is serious. It is especially concerning given that in a recent case, the SCOTUS ruling struck down another legal interpretation that also benefited the VA and ultimately veterans: the Chevron deference.8 This precedent held that when a legal dispute arises about the meaning of a specific federal agency regulation or policy, the courts should defer to the federal agency’s presumably superior understanding of the matter. The principle places the locus of decision-making with the subject-matter experts of the respective agency rather than the courts.
Ironically, given the legislative purposes of both interpretive principles, their overturning would likely introduce much more uncertainty, variation, and unpredictability in cases involving veteran benefits. This is bad news for both veterans and the VA. Veterans might not prevail as often in court when they have a reasonable claim, leading to more aggressive challenges. In response, the VA would have a heavier and more costly burden of administrative proof to defend sound decisions.9 Recently, the VA has tried to reduce the backlog of claims. The inability to have legal recourse to Chevron or Gardener could result in even more delay in adjudicating veterans’ claims that enable them to access benefits and services, already an object of congressional pressure.10
Courts will continue to debate the issue with another judicial test of the canon on the current SCOTUS docket (Bufkin v McDonough).11 The veteran’s canon was put in place to equalize the power differential between the VA and the veteran: in administrative language, to make it more likely than not that the veteran would prevail when regulations were ambiguous. There are many legal and political rationales for veteran’s canon, including enabling veterans to file claims for service-connected illnesses. The veteran’s cannon helped Vietnam War-era veterans receive VA care while researchers were still studying the sequela of Agent Orange exposure. 12 The legislative purpose of the veteran’s canon is the same as that of all VA benefits and services commemorated on Veterans Day. As expressed by SCOTUS justices in the wake of World War II, the benefit statutes should be “liberally construed for the benefit of those who left private life to serve their country in its hour of greatest need.”13
- Henderson v Shinseki, 562 US. 428, 440-441 (2011).
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Veteran Outreach Office. The difference between Veterans Day and Memorial Day. October 30, 2023. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://news.va.gov/125549/difference-between-veterans-day-memorial-day/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA history summary. Updated August 6, 2024. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://department.va.gov/history/history-overview
- Cornell Law School, Legal Information Institute. Canons of construction. Updated March 2022. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://www.law.cornell.edu/wex/canons_of_construction
- Brown v Gardner, 513 US 115 (1994).
- Rudisill v McDonough, 601 US __ (2024).
- Hoover J. Justices will decide if vets are getting the ‘benefit of the doubt’. National Law Journal. April 30, 2024. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://www.law.com/nationallawjournal/2024/04/30/justices-will-decide-if-vets-are-getting-the-benefit-of-the-doubt/
- Relentless, Inc. v Department of Commerce Docket # 22-219, January 17, 2024.
- Kime P. Two veterans will argue to Supreme Court that VA disability claims aren’t getting, ‘benefit of the doubt’. Military. com. October 15, 2024. Accessed October 21, 2024. https:// www.military.com/daily-news/2024/10/15/supreme-court-hears-case-questioning-vas-commitment-favoring-veterans-benefits-decisions.html
- Rehagen J. SCOTUS’s chevron deference ruling: how it could hurt veterans and the VA. Veteran.com. Updated July 9, 2024. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://veteran.com/scotus-chevron-deference-impact-va-veteran/
- Hersey LF. Lawmakers urge VA to reduce backlog, wait times on veterans claims for benefits. Stars & Stripes. June 27, 2024. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://www.stripes.com/veterans/2024-06-27/veterans-benefits-claims-backlog-pact-act-14315042.html
- Harper CJ. Give veterans the benefit of the doubt: Chevron, Auer, and the veteran’s canon. Harvard J Law Public Policy. 2019; 42(3):931-969. https://journals.law.harvard.edu/jlpp/wp-content/uploads/sites/90/2019/06/42_3-Full-Issue.pdf
- Fishgold v Sullivan Drydock & Repair Corp, 328 US 275, 285 (1946).
As Veterans Day approaches, stores and restaurants will offer discounts and free meals to veterans. Children will write thank you letters, and citizens nationwide will raise flags to honor and thank veterans. We can never repay those who lost their life, health, or livelihood in defense of the nation. Since the American Revolution, and in gratitude for that incalculable debt, the US government, on behalf of the American public, has seen fit to grant a host of benefits and services to those who wore the uniform.2,3 Among the best known are health care, burial services, compensation and pensions, home loans, and the GI Bill.
Less recognized yet arguably essential for the fair and consistent provision of these entitlements is a legal principle: the veteran’s canon. A canon is a system of rules or maxims used to interpret legal instruments, such as statutes. They are not rules but serve as a “principle that guides the interpretation of the text.”4 Since I am not a lawyer, I will undoubtedly oversimplify this legal principle, but I hope to get enough right to explain why the veteran’s canon should matter to federal health care professionals.
At its core, the veteran’s canon means that when the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) and a veteran have a legal dispute about VA benefits, the courts will give deference to the veteran. Underscoring that any ambiguity in the statute is resolved in the veteran’s favor, the canon is known in legal circles as the Gardner deference. This is a reference to a 1994 case in which a Korean War veteran underwent surgery in a VA facility for a herniated disc he alleged caused pain and weakness in his left lower extremity.5 Gardner argued that federal statutes 38 USC § 1151 underlying corresponding VA regulation 38 CFR § 3.358(c)(3) granted disability benefits to veterans injured during VA treatment. The VA denied the disability claim, contending the regulation restricted compensation to veterans whose injury was the fault of the VA; thus, the disability had to have been the result of negligent treatment or an unforeseen therapeutic accident.5
The case wound its way through various appeals boards and courts until the Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) ruled that the statute’s context left no ambiguity, and that any care provided under VA auspices was covered under the statute. What is important for this column is that the justices opined that had ambiguity been present, it would have legally necessitated, “applying the rule that interpretive doubt is to be resolved in the veteran’s favor.”5 In Gardner’s case, the courts reaffirmed nearly 80 years of judicial precedent upholding the veteran’s canon.
Thirty years later, Rudisill v McDonough again questioned the veteran’s canon.6 Educational benefits, namely the GI Bill, were the issue in this case. Rudisill served during 3 different periods in the US Army, totaling 8 years. Two educational programs overlapped during Rudisill’s tenure in the military: the Montgomery GI Bill and Post-9/11 Veterans Educational Assistance Act. Rudisill had used a portion of his Montgomery benefits to fund his undergraduate education and now wished to use the more extensive Post-9/11 assistance to finance his graduate degree. Rudisill and the VA disagreed about when his combined benefits would be capped, either at 36 or 48 months. After working its way through appeals courts, SCOTUS was again called upon for judgment.
The justices found that Rudisill qualified under both programs and could use them in any order he wished up to the cap. The majority found no ambiguity in the statute; however, if interpretation was required, the majority of justices indicated that the veteran’s canon would have supported Rudisill. While this sounds like good news for veterans, 2 justices authored a dissenting opinion that questioned the constitutional grounding of the veteran’s canon, noting that the “canon appears to have developed almost by accident.”6 The minority opinion suggested that when the veteran’s canon allocates resources to pay for specific veteran benefits, other interests and groups are deprived of those same resources, resulting in potential inequity.7
The potential ethical import and clinical impact of striking down the veteran’s canon is serious. It is especially concerning given that in a recent case, the SCOTUS ruling struck down another legal interpretation that also benefited the VA and ultimately veterans: the Chevron deference.8 This precedent held that when a legal dispute arises about the meaning of a specific federal agency regulation or policy, the courts should defer to the federal agency’s presumably superior understanding of the matter. The principle places the locus of decision-making with the subject-matter experts of the respective agency rather than the courts.
Ironically, given the legislative purposes of both interpretive principles, their overturning would likely introduce much more uncertainty, variation, and unpredictability in cases involving veteran benefits. This is bad news for both veterans and the VA. Veterans might not prevail as often in court when they have a reasonable claim, leading to more aggressive challenges. In response, the VA would have a heavier and more costly burden of administrative proof to defend sound decisions.9 Recently, the VA has tried to reduce the backlog of claims. The inability to have legal recourse to Chevron or Gardener could result in even more delay in adjudicating veterans’ claims that enable them to access benefits and services, already an object of congressional pressure.10
Courts will continue to debate the issue with another judicial test of the canon on the current SCOTUS docket (Bufkin v McDonough).11 The veteran’s canon was put in place to equalize the power differential between the VA and the veteran: in administrative language, to make it more likely than not that the veteran would prevail when regulations were ambiguous. There are many legal and political rationales for veteran’s canon, including enabling veterans to file claims for service-connected illnesses. The veteran’s cannon helped Vietnam War-era veterans receive VA care while researchers were still studying the sequela of Agent Orange exposure. 12 The legislative purpose of the veteran’s canon is the same as that of all VA benefits and services commemorated on Veterans Day. As expressed by SCOTUS justices in the wake of World War II, the benefit statutes should be “liberally construed for the benefit of those who left private life to serve their country in its hour of greatest need.”13
As Veterans Day approaches, stores and restaurants will offer discounts and free meals to veterans. Children will write thank you letters, and citizens nationwide will raise flags to honor and thank veterans. We can never repay those who lost their life, health, or livelihood in defense of the nation. Since the American Revolution, and in gratitude for that incalculable debt, the US government, on behalf of the American public, has seen fit to grant a host of benefits and services to those who wore the uniform.2,3 Among the best known are health care, burial services, compensation and pensions, home loans, and the GI Bill.
Less recognized yet arguably essential for the fair and consistent provision of these entitlements is a legal principle: the veteran’s canon. A canon is a system of rules or maxims used to interpret legal instruments, such as statutes. They are not rules but serve as a “principle that guides the interpretation of the text.”4 Since I am not a lawyer, I will undoubtedly oversimplify this legal principle, but I hope to get enough right to explain why the veteran’s canon should matter to federal health care professionals.
At its core, the veteran’s canon means that when the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) and a veteran have a legal dispute about VA benefits, the courts will give deference to the veteran. Underscoring that any ambiguity in the statute is resolved in the veteran’s favor, the canon is known in legal circles as the Gardner deference. This is a reference to a 1994 case in which a Korean War veteran underwent surgery in a VA facility for a herniated disc he alleged caused pain and weakness in his left lower extremity.5 Gardner argued that federal statutes 38 USC § 1151 underlying corresponding VA regulation 38 CFR § 3.358(c)(3) granted disability benefits to veterans injured during VA treatment. The VA denied the disability claim, contending the regulation restricted compensation to veterans whose injury was the fault of the VA; thus, the disability had to have been the result of negligent treatment or an unforeseen therapeutic accident.5
The case wound its way through various appeals boards and courts until the Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) ruled that the statute’s context left no ambiguity, and that any care provided under VA auspices was covered under the statute. What is important for this column is that the justices opined that had ambiguity been present, it would have legally necessitated, “applying the rule that interpretive doubt is to be resolved in the veteran’s favor.”5 In Gardner’s case, the courts reaffirmed nearly 80 years of judicial precedent upholding the veteran’s canon.
Thirty years later, Rudisill v McDonough again questioned the veteran’s canon.6 Educational benefits, namely the GI Bill, were the issue in this case. Rudisill served during 3 different periods in the US Army, totaling 8 years. Two educational programs overlapped during Rudisill’s tenure in the military: the Montgomery GI Bill and Post-9/11 Veterans Educational Assistance Act. Rudisill had used a portion of his Montgomery benefits to fund his undergraduate education and now wished to use the more extensive Post-9/11 assistance to finance his graduate degree. Rudisill and the VA disagreed about when his combined benefits would be capped, either at 36 or 48 months. After working its way through appeals courts, SCOTUS was again called upon for judgment.
The justices found that Rudisill qualified under both programs and could use them in any order he wished up to the cap. The majority found no ambiguity in the statute; however, if interpretation was required, the majority of justices indicated that the veteran’s canon would have supported Rudisill. While this sounds like good news for veterans, 2 justices authored a dissenting opinion that questioned the constitutional grounding of the veteran’s canon, noting that the “canon appears to have developed almost by accident.”6 The minority opinion suggested that when the veteran’s canon allocates resources to pay for specific veteran benefits, other interests and groups are deprived of those same resources, resulting in potential inequity.7
The potential ethical import and clinical impact of striking down the veteran’s canon is serious. It is especially concerning given that in a recent case, the SCOTUS ruling struck down another legal interpretation that also benefited the VA and ultimately veterans: the Chevron deference.8 This precedent held that when a legal dispute arises about the meaning of a specific federal agency regulation or policy, the courts should defer to the federal agency’s presumably superior understanding of the matter. The principle places the locus of decision-making with the subject-matter experts of the respective agency rather than the courts.
Ironically, given the legislative purposes of both interpretive principles, their overturning would likely introduce much more uncertainty, variation, and unpredictability in cases involving veteran benefits. This is bad news for both veterans and the VA. Veterans might not prevail as often in court when they have a reasonable claim, leading to more aggressive challenges. In response, the VA would have a heavier and more costly burden of administrative proof to defend sound decisions.9 Recently, the VA has tried to reduce the backlog of claims. The inability to have legal recourse to Chevron or Gardener could result in even more delay in adjudicating veterans’ claims that enable them to access benefits and services, already an object of congressional pressure.10
Courts will continue to debate the issue with another judicial test of the canon on the current SCOTUS docket (Bufkin v McDonough).11 The veteran’s canon was put in place to equalize the power differential between the VA and the veteran: in administrative language, to make it more likely than not that the veteran would prevail when regulations were ambiguous. There are many legal and political rationales for veteran’s canon, including enabling veterans to file claims for service-connected illnesses. The veteran’s cannon helped Vietnam War-era veterans receive VA care while researchers were still studying the sequela of Agent Orange exposure. 12 The legislative purpose of the veteran’s canon is the same as that of all VA benefits and services commemorated on Veterans Day. As expressed by SCOTUS justices in the wake of World War II, the benefit statutes should be “liberally construed for the benefit of those who left private life to serve their country in its hour of greatest need.”13
- Henderson v Shinseki, 562 US. 428, 440-441 (2011).
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Veteran Outreach Office. The difference between Veterans Day and Memorial Day. October 30, 2023. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://news.va.gov/125549/difference-between-veterans-day-memorial-day/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA history summary. Updated August 6, 2024. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://department.va.gov/history/history-overview
- Cornell Law School, Legal Information Institute. Canons of construction. Updated March 2022. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://www.law.cornell.edu/wex/canons_of_construction
- Brown v Gardner, 513 US 115 (1994).
- Rudisill v McDonough, 601 US __ (2024).
- Hoover J. Justices will decide if vets are getting the ‘benefit of the doubt’. National Law Journal. April 30, 2024. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://www.law.com/nationallawjournal/2024/04/30/justices-will-decide-if-vets-are-getting-the-benefit-of-the-doubt/
- Relentless, Inc. v Department of Commerce Docket # 22-219, January 17, 2024.
- Kime P. Two veterans will argue to Supreme Court that VA disability claims aren’t getting, ‘benefit of the doubt’. Military. com. October 15, 2024. Accessed October 21, 2024. https:// www.military.com/daily-news/2024/10/15/supreme-court-hears-case-questioning-vas-commitment-favoring-veterans-benefits-decisions.html
- Rehagen J. SCOTUS’s chevron deference ruling: how it could hurt veterans and the VA. Veteran.com. Updated July 9, 2024. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://veteran.com/scotus-chevron-deference-impact-va-veteran/
- Hersey LF. Lawmakers urge VA to reduce backlog, wait times on veterans claims for benefits. Stars & Stripes. June 27, 2024. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://www.stripes.com/veterans/2024-06-27/veterans-benefits-claims-backlog-pact-act-14315042.html
- Harper CJ. Give veterans the benefit of the doubt: Chevron, Auer, and the veteran’s canon. Harvard J Law Public Policy. 2019; 42(3):931-969. https://journals.law.harvard.edu/jlpp/wp-content/uploads/sites/90/2019/06/42_3-Full-Issue.pdf
- Fishgold v Sullivan Drydock & Repair Corp, 328 US 275, 285 (1946).
- Henderson v Shinseki, 562 US. 428, 440-441 (2011).
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Veteran Outreach Office. The difference between Veterans Day and Memorial Day. October 30, 2023. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://news.va.gov/125549/difference-between-veterans-day-memorial-day/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA history summary. Updated August 6, 2024. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://department.va.gov/history/history-overview
- Cornell Law School, Legal Information Institute. Canons of construction. Updated March 2022. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://www.law.cornell.edu/wex/canons_of_construction
- Brown v Gardner, 513 US 115 (1994).
- Rudisill v McDonough, 601 US __ (2024).
- Hoover J. Justices will decide if vets are getting the ‘benefit of the doubt’. National Law Journal. April 30, 2024. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://www.law.com/nationallawjournal/2024/04/30/justices-will-decide-if-vets-are-getting-the-benefit-of-the-doubt/
- Relentless, Inc. v Department of Commerce Docket # 22-219, January 17, 2024.
- Kime P. Two veterans will argue to Supreme Court that VA disability claims aren’t getting, ‘benefit of the doubt’. Military. com. October 15, 2024. Accessed October 21, 2024. https:// www.military.com/daily-news/2024/10/15/supreme-court-hears-case-questioning-vas-commitment-favoring-veterans-benefits-decisions.html
- Rehagen J. SCOTUS’s chevron deference ruling: how it could hurt veterans and the VA. Veteran.com. Updated July 9, 2024. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://veteran.com/scotus-chevron-deference-impact-va-veteran/
- Hersey LF. Lawmakers urge VA to reduce backlog, wait times on veterans claims for benefits. Stars & Stripes. June 27, 2024. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://www.stripes.com/veterans/2024-06-27/veterans-benefits-claims-backlog-pact-act-14315042.html
- Harper CJ. Give veterans the benefit of the doubt: Chevron, Auer, and the veteran’s canon. Harvard J Law Public Policy. 2019; 42(3):931-969. https://journals.law.harvard.edu/jlpp/wp-content/uploads/sites/90/2019/06/42_3-Full-Issue.pdf
- Fishgold v Sullivan Drydock & Repair Corp, 328 US 275, 285 (1946).
The Veteran’s Canon Under Fire
The Veteran’s Canon Under Fire
Navigating the Physician Mortgage Loan
Navigating the path to homeownership can be particularly challenging for physicians, who often face a unique set of financial circumstances. With substantial student loan debt, limited savings, and a delayed peak earning potential, traditional mortgage options may seem out of reach.
Enter physician mortgage loans—specialized financing designed specifically for medical professionals. These loans offer tailored solutions that address the common barriers faced by doctors, making it easier for them to achieve their homeownership goals. In this article, we’ll
What Is a Physician Mortgage Loan?
A physician mortgage loan, also known as a ‘doctor loan,’ is a specialized mortgage product designed for a specific group of qualifying medical professionals. These loans are particularly attractive to new doctors who may have substantial student loan debt, limited savings, and an income that is expected to increase significantly over time. As unique portfolio loans, physician mortgage products can vary considerably between lending institutions. However, a common feature is that they typically require little to no down payment and do not require private mortgage insurance (PMI).
Beyond the common features, loan options and qualifying parameters can vary significantly from one institution to another. Therefore, it’s important to start gathering information as early as possible, giving you ample time to evaluate which institution and loan option best meet your needs.
How Do I Know if I Am Eligible for a Physician Mortgage Loan?
Physician loans are typically offered to MDs, DOs, DDSs, DMDs, and ODs, though some institutions expand this list to include DPMs, PAs, CRNAs, NPs, PharmDs, and DVMs. Additionally, most of these loan products are available to residents, fellows, and attending or practicing physicians.
How Do I Know What Physician Mortgage Loan Is Best for Me?
When selecting the optimal physician loan option for your home purchase, consider several important metrics:
- Duration of Stay: Consider how long you expect to live in the home. If you’re in a lengthy residency or fellowship program, or if you plan to move for a new job soon after, a 30-year fixed-rate loan might not be ideal. Instead, evaluate loan options that match your anticipated duration of stay. For example, a 5-year or 7-year ARM (adjustable rate mortgage) could offer a lower interest rate and reduced monthly payments for the initial fixed period, which aligns with your shorter-term stay. This can result in substantial savings if you do not plan to stay in the home for the full term of a traditional mortgage.
- Underwriting Guidelines: Each lender has different underwriting standards and qualifying criteria, so it’s essential to understand these differences. For instance, some lenders may have higher minimum credit score requirements or stricter debt-to-income (DTI) ratio limits. Others might require a larger down payment or have different rules regarding student loan payments and closing costs. Flexibility in these guidelines can impact your ability to qualify for a loan and the terms you receive. For example, some lenders may allow you to include student loan payments at a lower percentage of your income, which could improve your DTI ratio and help you secure a better loan offer.
- Closing Timing: The timing of your home closing relative to your job start date can be crucial, especially if you’re relocating. Some lenders permit closing up to 60-90 days before your job begins, while others offer up to 120 days. If you need to relocate your family before starting your new position, having the ability to close earlier can provide you with more flexibility in finding and moving into a home. This additional time can ease the transition and allow you to settle in before your new job starts.
Given the wide range of options and standards, it’s important to strategically identify which factors are most meaningful to you. Beyond interest rates, consider the overall cost of the loan, the flexibility of terms, and how well the loan aligns with your financial goals and career plans. For example, if you value lower monthly payments over a longer period or need to accommodate significant student loan debt, ensure that the loan program you choose aligns with these priorities.
What Attributes Should I Look for in My Loan Officer?
When interviewing multiple loan officers for your upcoming loan needs, it’s essential to use the right metrics—beyond just the interest rate—to determine the best fit for your situation. Some critical factors to consider include the loan officer’s experience working with physicians, that person’s availability and responsiveness, and the potential for building a long-term relationship.
As in most professions, experience is paramount—it’s something that cannot be taught or simply read in a training manual. Physicians, especially those in training or just stepping into an attending role, often have unique financial situations. This makes it crucial to work with a loan officer who has extensive experience serving physician clients. An experienced loan officer will better understand how to customize a loan solution that aligns with your specific needs, resulting in a much more tailored and meaningful mortgage. There is no one-size-fits-all mortgage. You are unique, and your loan officer should be crafting a mortgage solution that reflects your individuality and financial circumstances.
In my opinion, availability and responsiveness are among the most critical attributes your chosen loan officer should possess. Interestingly, this factor doesn’t directly influence the ‘cost’ of your loan but can significantly impact your experience. As a physician with a demanding schedule, it’s unrealistic to expect that all communication will take place strictly during business hours—this is true for any consumer. Pay close attention to how promptly loan officers respond during your initial interactions, and evaluate how thoroughly they explain loan terms, out-of-pocket costs, and the overall loan process. Your loan officer should be your trusted guide as you navigate through the complexities of the loan process, so setting yourself up for success starts with choosing someone who meets your expectations in this regard.
It’s crucial to build a good rapport with the loan officer you choose, as this likely won’t be the last mortgage or financial need you encounter in your lifetime. Establishing a personal connection with your loan officer fosters a level of trust that is invaluable. Whether you’re considering refinancing your current mortgage or exploring additional loan products for other financial needs, having a trusted advisor you can rely on as a financial resource is immensely beneficial as you progress in your career. A strong, long-standing relationship with a loan officer ensures you receive reliable and sound financial advice tailored to your unique needs.
Additional Things to Consider if You Are a First-Time Home Buyer
Interview multiple lenders and make those conversations about more than just interest rates. This approach will help you gauge their knowledge of physician mortgage loans while allowing you to assess who might be the best fit for you in terms of compatibility. Relying solely on an email blast to inquire about rates could easily lead you to a subpar lender and result in an unfavorable experience.
Don’t be afraid to ask a lot of questions! As a first-time home buyer, it’s natural to feel a bit overwhelmed by the process—it can seem daunting if you’ve never been through it before. That’s why it’s crucial to ask any questions that come to mind and to work with a lender who is willing to take the time to answer them while educating you throughout the home-buying journey. With a trusted guide and the right education, the process will feel far less overwhelming, leading to a smoother and more positive experience from start to finish.
In conclusion, choosing the right lender for a physician mortgage loan is a crucial step in securing your financial future and achieving homeownership. By thoroughly evaluating interest rates, down payment requirements, loan terms, and other key metrics, you can find a lender that offers competitive rates and favorable terms tailored to your unique needs. Consider factors such as customer service, closing costs, and the lender’s experience with physician loans to ensure a smooth and supportive mortgage process. By taking the time to compare options and select the best fit for your financial situation, you can confidently move forward in your home-buying journey and set the stage for a successful and fulfilling homeownership experience.
Mr. Kelley is vice president of mortgage lending and a physician mortgage specialist at Arvest Bank in Overland Park, Kansas.
Navigating the path to homeownership can be particularly challenging for physicians, who often face a unique set of financial circumstances. With substantial student loan debt, limited savings, and a delayed peak earning potential, traditional mortgage options may seem out of reach.
Enter physician mortgage loans—specialized financing designed specifically for medical professionals. These loans offer tailored solutions that address the common barriers faced by doctors, making it easier for them to achieve their homeownership goals. In this article, we’ll
What Is a Physician Mortgage Loan?
A physician mortgage loan, also known as a ‘doctor loan,’ is a specialized mortgage product designed for a specific group of qualifying medical professionals. These loans are particularly attractive to new doctors who may have substantial student loan debt, limited savings, and an income that is expected to increase significantly over time. As unique portfolio loans, physician mortgage products can vary considerably between lending institutions. However, a common feature is that they typically require little to no down payment and do not require private mortgage insurance (PMI).
Beyond the common features, loan options and qualifying parameters can vary significantly from one institution to another. Therefore, it’s important to start gathering information as early as possible, giving you ample time to evaluate which institution and loan option best meet your needs.
How Do I Know if I Am Eligible for a Physician Mortgage Loan?
Physician loans are typically offered to MDs, DOs, DDSs, DMDs, and ODs, though some institutions expand this list to include DPMs, PAs, CRNAs, NPs, PharmDs, and DVMs. Additionally, most of these loan products are available to residents, fellows, and attending or practicing physicians.
How Do I Know What Physician Mortgage Loan Is Best for Me?
When selecting the optimal physician loan option for your home purchase, consider several important metrics:
- Duration of Stay: Consider how long you expect to live in the home. If you’re in a lengthy residency or fellowship program, or if you plan to move for a new job soon after, a 30-year fixed-rate loan might not be ideal. Instead, evaluate loan options that match your anticipated duration of stay. For example, a 5-year or 7-year ARM (adjustable rate mortgage) could offer a lower interest rate and reduced monthly payments for the initial fixed period, which aligns with your shorter-term stay. This can result in substantial savings if you do not plan to stay in the home for the full term of a traditional mortgage.
- Underwriting Guidelines: Each lender has different underwriting standards and qualifying criteria, so it’s essential to understand these differences. For instance, some lenders may have higher minimum credit score requirements or stricter debt-to-income (DTI) ratio limits. Others might require a larger down payment or have different rules regarding student loan payments and closing costs. Flexibility in these guidelines can impact your ability to qualify for a loan and the terms you receive. For example, some lenders may allow you to include student loan payments at a lower percentage of your income, which could improve your DTI ratio and help you secure a better loan offer.
- Closing Timing: The timing of your home closing relative to your job start date can be crucial, especially if you’re relocating. Some lenders permit closing up to 60-90 days before your job begins, while others offer up to 120 days. If you need to relocate your family before starting your new position, having the ability to close earlier can provide you with more flexibility in finding and moving into a home. This additional time can ease the transition and allow you to settle in before your new job starts.
Given the wide range of options and standards, it’s important to strategically identify which factors are most meaningful to you. Beyond interest rates, consider the overall cost of the loan, the flexibility of terms, and how well the loan aligns with your financial goals and career plans. For example, if you value lower monthly payments over a longer period or need to accommodate significant student loan debt, ensure that the loan program you choose aligns with these priorities.
What Attributes Should I Look for in My Loan Officer?
When interviewing multiple loan officers for your upcoming loan needs, it’s essential to use the right metrics—beyond just the interest rate—to determine the best fit for your situation. Some critical factors to consider include the loan officer’s experience working with physicians, that person’s availability and responsiveness, and the potential for building a long-term relationship.
As in most professions, experience is paramount—it’s something that cannot be taught or simply read in a training manual. Physicians, especially those in training or just stepping into an attending role, often have unique financial situations. This makes it crucial to work with a loan officer who has extensive experience serving physician clients. An experienced loan officer will better understand how to customize a loan solution that aligns with your specific needs, resulting in a much more tailored and meaningful mortgage. There is no one-size-fits-all mortgage. You are unique, and your loan officer should be crafting a mortgage solution that reflects your individuality and financial circumstances.
In my opinion, availability and responsiveness are among the most critical attributes your chosen loan officer should possess. Interestingly, this factor doesn’t directly influence the ‘cost’ of your loan but can significantly impact your experience. As a physician with a demanding schedule, it’s unrealistic to expect that all communication will take place strictly during business hours—this is true for any consumer. Pay close attention to how promptly loan officers respond during your initial interactions, and evaluate how thoroughly they explain loan terms, out-of-pocket costs, and the overall loan process. Your loan officer should be your trusted guide as you navigate through the complexities of the loan process, so setting yourself up for success starts with choosing someone who meets your expectations in this regard.
It’s crucial to build a good rapport with the loan officer you choose, as this likely won’t be the last mortgage or financial need you encounter in your lifetime. Establishing a personal connection with your loan officer fosters a level of trust that is invaluable. Whether you’re considering refinancing your current mortgage or exploring additional loan products for other financial needs, having a trusted advisor you can rely on as a financial resource is immensely beneficial as you progress in your career. A strong, long-standing relationship with a loan officer ensures you receive reliable and sound financial advice tailored to your unique needs.
Additional Things to Consider if You Are a First-Time Home Buyer
Interview multiple lenders and make those conversations about more than just interest rates. This approach will help you gauge their knowledge of physician mortgage loans while allowing you to assess who might be the best fit for you in terms of compatibility. Relying solely on an email blast to inquire about rates could easily lead you to a subpar lender and result in an unfavorable experience.
Don’t be afraid to ask a lot of questions! As a first-time home buyer, it’s natural to feel a bit overwhelmed by the process—it can seem daunting if you’ve never been through it before. That’s why it’s crucial to ask any questions that come to mind and to work with a lender who is willing to take the time to answer them while educating you throughout the home-buying journey. With a trusted guide and the right education, the process will feel far less overwhelming, leading to a smoother and more positive experience from start to finish.
In conclusion, choosing the right lender for a physician mortgage loan is a crucial step in securing your financial future and achieving homeownership. By thoroughly evaluating interest rates, down payment requirements, loan terms, and other key metrics, you can find a lender that offers competitive rates and favorable terms tailored to your unique needs. Consider factors such as customer service, closing costs, and the lender’s experience with physician loans to ensure a smooth and supportive mortgage process. By taking the time to compare options and select the best fit for your financial situation, you can confidently move forward in your home-buying journey and set the stage for a successful and fulfilling homeownership experience.
Mr. Kelley is vice president of mortgage lending and a physician mortgage specialist at Arvest Bank in Overland Park, Kansas.
Navigating the path to homeownership can be particularly challenging for physicians, who often face a unique set of financial circumstances. With substantial student loan debt, limited savings, and a delayed peak earning potential, traditional mortgage options may seem out of reach.
Enter physician mortgage loans—specialized financing designed specifically for medical professionals. These loans offer tailored solutions that address the common barriers faced by doctors, making it easier for them to achieve their homeownership goals. In this article, we’ll
What Is a Physician Mortgage Loan?
A physician mortgage loan, also known as a ‘doctor loan,’ is a specialized mortgage product designed for a specific group of qualifying medical professionals. These loans are particularly attractive to new doctors who may have substantial student loan debt, limited savings, and an income that is expected to increase significantly over time. As unique portfolio loans, physician mortgage products can vary considerably between lending institutions. However, a common feature is that they typically require little to no down payment and do not require private mortgage insurance (PMI).
Beyond the common features, loan options and qualifying parameters can vary significantly from one institution to another. Therefore, it’s important to start gathering information as early as possible, giving you ample time to evaluate which institution and loan option best meet your needs.
How Do I Know if I Am Eligible for a Physician Mortgage Loan?
Physician loans are typically offered to MDs, DOs, DDSs, DMDs, and ODs, though some institutions expand this list to include DPMs, PAs, CRNAs, NPs, PharmDs, and DVMs. Additionally, most of these loan products are available to residents, fellows, and attending or practicing physicians.
How Do I Know What Physician Mortgage Loan Is Best for Me?
When selecting the optimal physician loan option for your home purchase, consider several important metrics:
- Duration of Stay: Consider how long you expect to live in the home. If you’re in a lengthy residency or fellowship program, or if you plan to move for a new job soon after, a 30-year fixed-rate loan might not be ideal. Instead, evaluate loan options that match your anticipated duration of stay. For example, a 5-year or 7-year ARM (adjustable rate mortgage) could offer a lower interest rate and reduced monthly payments for the initial fixed period, which aligns with your shorter-term stay. This can result in substantial savings if you do not plan to stay in the home for the full term of a traditional mortgage.
- Underwriting Guidelines: Each lender has different underwriting standards and qualifying criteria, so it’s essential to understand these differences. For instance, some lenders may have higher minimum credit score requirements or stricter debt-to-income (DTI) ratio limits. Others might require a larger down payment or have different rules regarding student loan payments and closing costs. Flexibility in these guidelines can impact your ability to qualify for a loan and the terms you receive. For example, some lenders may allow you to include student loan payments at a lower percentage of your income, which could improve your DTI ratio and help you secure a better loan offer.
- Closing Timing: The timing of your home closing relative to your job start date can be crucial, especially if you’re relocating. Some lenders permit closing up to 60-90 days before your job begins, while others offer up to 120 days. If you need to relocate your family before starting your new position, having the ability to close earlier can provide you with more flexibility in finding and moving into a home. This additional time can ease the transition and allow you to settle in before your new job starts.
Given the wide range of options and standards, it’s important to strategically identify which factors are most meaningful to you. Beyond interest rates, consider the overall cost of the loan, the flexibility of terms, and how well the loan aligns with your financial goals and career plans. For example, if you value lower monthly payments over a longer period or need to accommodate significant student loan debt, ensure that the loan program you choose aligns with these priorities.
What Attributes Should I Look for in My Loan Officer?
When interviewing multiple loan officers for your upcoming loan needs, it’s essential to use the right metrics—beyond just the interest rate—to determine the best fit for your situation. Some critical factors to consider include the loan officer’s experience working with physicians, that person’s availability and responsiveness, and the potential for building a long-term relationship.
As in most professions, experience is paramount—it’s something that cannot be taught or simply read in a training manual. Physicians, especially those in training or just stepping into an attending role, often have unique financial situations. This makes it crucial to work with a loan officer who has extensive experience serving physician clients. An experienced loan officer will better understand how to customize a loan solution that aligns with your specific needs, resulting in a much more tailored and meaningful mortgage. There is no one-size-fits-all mortgage. You are unique, and your loan officer should be crafting a mortgage solution that reflects your individuality and financial circumstances.
In my opinion, availability and responsiveness are among the most critical attributes your chosen loan officer should possess. Interestingly, this factor doesn’t directly influence the ‘cost’ of your loan but can significantly impact your experience. As a physician with a demanding schedule, it’s unrealistic to expect that all communication will take place strictly during business hours—this is true for any consumer. Pay close attention to how promptly loan officers respond during your initial interactions, and evaluate how thoroughly they explain loan terms, out-of-pocket costs, and the overall loan process. Your loan officer should be your trusted guide as you navigate through the complexities of the loan process, so setting yourself up for success starts with choosing someone who meets your expectations in this regard.
It’s crucial to build a good rapport with the loan officer you choose, as this likely won’t be the last mortgage or financial need you encounter in your lifetime. Establishing a personal connection with your loan officer fosters a level of trust that is invaluable. Whether you’re considering refinancing your current mortgage or exploring additional loan products for other financial needs, having a trusted advisor you can rely on as a financial resource is immensely beneficial as you progress in your career. A strong, long-standing relationship with a loan officer ensures you receive reliable and sound financial advice tailored to your unique needs.
Additional Things to Consider if You Are a First-Time Home Buyer
Interview multiple lenders and make those conversations about more than just interest rates. This approach will help you gauge their knowledge of physician mortgage loans while allowing you to assess who might be the best fit for you in terms of compatibility. Relying solely on an email blast to inquire about rates could easily lead you to a subpar lender and result in an unfavorable experience.
Don’t be afraid to ask a lot of questions! As a first-time home buyer, it’s natural to feel a bit overwhelmed by the process—it can seem daunting if you’ve never been through it before. That’s why it’s crucial to ask any questions that come to mind and to work with a lender who is willing to take the time to answer them while educating you throughout the home-buying journey. With a trusted guide and the right education, the process will feel far less overwhelming, leading to a smoother and more positive experience from start to finish.
In conclusion, choosing the right lender for a physician mortgage loan is a crucial step in securing your financial future and achieving homeownership. By thoroughly evaluating interest rates, down payment requirements, loan terms, and other key metrics, you can find a lender that offers competitive rates and favorable terms tailored to your unique needs. Consider factors such as customer service, closing costs, and the lender’s experience with physician loans to ensure a smooth and supportive mortgage process. By taking the time to compare options and select the best fit for your financial situation, you can confidently move forward in your home-buying journey and set the stage for a successful and fulfilling homeownership experience.
Mr. Kelley is vice president of mortgage lending and a physician mortgage specialist at Arvest Bank in Overland Park, Kansas.
Comparing Patient Care Models at a Local Free Clinic vs an Insurance- Based University Medical Center
Comparing Patient Care Models at a Local Free Clinic vs an Insurance- Based University Medical Center
Approximately 25% of Americans have at least one skin condition, and 20% are estimated to develop skin cancer during their lifetime.1,2 However, 40% of the US population lives in areas underserved by dermatologists. 3 The severity and mortality of skin cancers such as melanoma and mycosis fungoides have been positively associated with minoritized race, lack of health insurance, and unstable housing status.4-6 Patients who receive health care at free clinics often are of a racial or ethnic minoritized social group, are uninsured, and/or lack stable housing; this underserved group also includes recent immigrants to the United States who have limited English proficiency (LEP).7 Only 25% of free clinics offer specialty care services such as dermatology.7,8
Of the 42 free clinics and Federally Qualified Health Centers in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, the Birmingham Free Clinic (BFC) is one of the few that offers specialty care services including dermatology.9 Founded in 1994, the BFC serves as a safety net for Pittsburgh’s medically underserved population, offering primary and acute care, medication access, and social services. From January 2020 to May 2022, the BFC offered 27 dermatology clinics that provided approximately 100 people with comprehensive care including full-body skin examinations, dermatologic diagnoses and treatments, minor procedures, and dermatopathology services.
In this study, we compared the BFC dermatology patient care model with that of the dermatology department at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC), an insurance-based tertiary referral health care system in western Pennsylvania. By analyzing the demographics, dermatologic diagnoses, and management strategies of both the BFC and UPMC, we gained an understanding of how these patient care models differ and how they can be improved to care for diverse patient populations.
Methods
A retrospective chart review of dermatology patients seen in person at the BFC and UPMC during the period from January 2020 to May 2022 was performed. The UPMC group included patients seen by 3 general dermatologists (including A.J.J.) at matched time points. Data were collected from patients’ first in-person visit during the study period. Variables of interest included patient age, sex, race, ethnicity, primary language, zip code, health insurance status, distance to clinic (estimated using Google Maps to calculate the shortest driving distance from the patient’s zip code to the clinic), history of skin cancer, dermatologic diagnoses, and management strategies. These variables were not collected for patients who cancelled or noshowed their first in-person appointments. All patient charts and notes corresponding to the date and visit of interest were accessed through the electronic medical record (EMR). Patient data were de-identified and stored in a password-protected spreadsheet. Comparisons between the BFC and UPMC patient populations were performed using X2 tests of independence, Fisher exact tests, and Mann-Whitney U tests via SPSS software (IBM). Statistical significance was set at P<.05.
Results
Patient Characteristics—Our analysis included 76 initial appointments at the BFC and 322 at UPMC (Table 1). The mean age for patients at the BFC and UPMC was 39.6 years and 47.8 years, respectively (P=.001). Males accounted for 39 (51.3%) and 112 (34.8%) of BFC and UPMC patients, respectively (P=.008); 2 (0.6%) patients from UPMC were transgender. Of the BFC and UPMC patients, 44.7% (34/76) and 0.9% (3/322) were Hispanic, respectively (P<.001). With regard to race, 52.6% (40/76) of BFC patients were White, 19.7% (15/76) were Black, 6.6% (5/76) were Asian/Pacific Islander (Chinese, 1.3% [1/76]; other Asian, 5.3% [4/76]), and 21.1% (16/76) were American Indian/other/unspecified (American Indian, 1.3% [1/76]; other, 13.2% [10/76]; unspecified, 6.6% [5/76]). At UPMC, 61.2% (197/322) of patients were White, 28.0% (90/322) were Black, 5.3% (17/322) were Asian/Pacific Islander (Chinese, 1.2% [4/322]; Indian [Asian], 1.9% [6/322]; Japanese, 0.3% [1/322]; other Asian, 1.6% [5/322]; other Asian/American Indian, 0.3% [1/322]), and 5.6% (18/322) were American Indian/other/ unspecified (American Indian, 0.3% [1/322]; other, 0.3% [1/322]; unspecified, 5.0% [16/322]). Overall, the BFC patient population was more ethnically and racially diverse than that of UPMC (P<.001).
Forty-six percent (35/76) of BFC patients and 4.3% (14/322) of UPMC patients had LEP (P<.001). Primary languages among BFC patients were 53.9% (41/76) English, 40.8% (31/76) Spanish, and 5.2% (4/76) other/ unspecified (Chinese, 1.3% [1/76]; Indonesian, 2.6% [2/76]; unspecified, 1.3% [1/76]). Primary languages among UPMC patients were 95.7% (308/322) English and 4.3% (14/322) other/unspecified (Chinese, 0.6% [2/322]; Nepali, 0.6% [2/322]; Pali, 0.3% [1/322]; Russian, 0.3% [1/322]; unspecified, 2.5% [8/322]). There were notable differences in insurance status at the BFC vs UPMC (P<.001), with more UPMC patients having private insurance (52.8% [170/322] vs 11.8% [9/76]) and more BFC patients being uninsured (52.8% [51/76] vs 1.9% [6/322]). There was no significant difference in distance to clinic between the 2 groups (P=.183). More UPMC patients had a history of skin cancer (P=.003). More patients at the BFC were no-shows for their appointments (P<.001), and UPMC patients more frequently canceled their appointments (P<.001).
Dermatologic Diagnoses—The most commonly diagnosed dermatologic conditions at the BFC were dermatitis (23.7% [18/76]), neoplasm of uncertain behavior (15.8% [12/76]), alopecia (11.8% [9/76]), and acne (10.5% [8/76]) (Table 2). The most commonly diagnosed conditions at UPMC were nevi (26.4% [85/322]), dermatitis (22.7% [73/322]), seborrheic keratosis (21.7% [70/322]), and skin cancer screening (21.4% [70/322]). Neoplasm of uncertain behavior was more common in BFC vs UPMC patients (P=.040), while UPMC patients were more frequently diagnosed with nevi (P<.001), seborrheic keratosis (P<.001), and skin cancer screening (P<.001). There was no significant difference between the incidence of skin cancer diagnoses in the BFC (1.3% [1/76]) and UPMC (0.6% [2/76]) patient populations (P=.471). Among the biopsied neoplasms, there was also no significant difference in malignant (BFC, 50.0% [5/10]; UPMC, 32.0% [8/25]) and benign (BFC, 50.0% [5/10]; UPMC, 36.0% [9/25]) neoplasms diagnosed at each clinic (P=.444).
Management Strategies—Systemic antibiotics were more frequently prescribed (P<.001) and laboratory testing/ imaging were more frequently ordered (P=.005) at the BFC vs UPMC (Table 3). Patients at the BFC also more frequently required emergency insurance (P=.036). Patients at UPMC were more frequently recommended sunscreen (P=.003) and received education about skin cancer signs by review of the ABCDEs of melanoma (P<.001), sun-protective behaviors (P=.001), and skin examination frequency (P<.001). Notes in the EMR for UPMC patients more frequently specified patient followup instructions (P<.001).
Comment
As of 2020, the city of Pittsburgh had an estimated population of nearly 303,000 based on US Census data.10 Its population is predominantly White (62.7%) followed by Black/African American (22.8%) and Asian (6.5%); 5.9% identify as 2 or more races. Approximately 3.8% identify as Hispanic or Latino. More than 11% of the Pittsburgh population aged 5 years and older speaks a language other than English as their primary language, including Spanish (2.3%), other Indo-European languages (3.9%), and Asian and Pacific Island languages (3.5%).11 More than 5% of the Pittsburgh population does not have health insurance.12
The BFC is located in Pittsburgh’s South Side area, while one of UPMC’s primary dermatology clinics is located in the Oakland district; however, most patients who seek care at these clinics live outside these areas. Our study results indicated that the BFC and UPMC serve distinct groups of people within the Pittsburgh population. The BFC patient population was younger with a higher percentage of patients who were male, Hispanic, racially diverse, and with LEP compared with the UPMC patient population. In this clinical setting, the BFC health care team engages with people from diverse backgrounds and requires greater interpreter and medical support services.
The BFC largely is supported by volunteers, UPMC, grants, and philanthropy. Dermatology clinics are staffed by paid and volunteer team members. Paid team members include 1 nurse and 1 access lead who operates the front desk and registration. Volunteer team members include 1 board-certified dermatologist from UPMC (A.J.J.), or an affiliate clinic and 1 or 2 of each of the following: UPMC dermatology residents, medical or undergraduate students from the University of Pittsburgh, AmeriCorps national service members, and student or community medical interpreters. The onsite pharmacy is run by volunteer faculty, resident, and student pharmacists from the University of Pittsburgh. Dermatology clinics are half-day clinics that occur monthly. Volunteers for each clinic are recruited approximately 1 month in advance.
Dermatology patients at the BFC are referred from the BFC general medicine clinic and nearby Federally Qualified Health Center s for simple to complex medical and surgical dermatologic skin conditions. Each BFC dermatology clinic schedules an average of 7 patients per clinic and places other patients on a wait-list unless more urgent triage is needed. Patients are notified when they are scheduled via phone or text message, and they receive a reminder call or text 1 or 2 days prior to their appointment that also asks them to confirm attendance. Patients with LEP are called with an interpreter and also may receive text reminders that can be translated using Google Translate. Patients are instructed to notify the BFC if they need to cancel or reschedule their appointment. At the end of each visit, patients are given an after-visit summary that lists follow-up instructions, medications prescribed during the visit, and upcoming appointments. The BFC offers bus tickets to help patients get to their appointments. In rare cases, the BFC may pay for a car service to drive patients to and from the clinic.
Dermatology clinics at UPMC use scheduling and self-scheduling systems through which patients can make appointments at a location of their choice with any available board-certified dermatologist or physician assistant. Patients receive a reminder phone call 3 days prior to their appointment instructing them to call the office if they are unable to keep their appointment. Patients signed up for the online portal also receive a reminder message and an option to confirm or cancel their appointment. Patients with cell phone numbers in the UPMC system receive a text message approximately 2 days prior to their appointment that allows them to preregister and pay their copayment in advance. They receive another text 20 minutes prior to their appointment with an option for contactless check-in. At the conclusion of their visit, patients can schedule a follow-up appointment and receive a printed copy of their after-visit summary that provides information about follow-up instructions, prescribed medications, and upcoming visits. They may alternatively access this summary via the online patient portal. Patients are not provided transportation to UPMC clinics, but they are offered parking validation.
Among the most common dermatologic diagnoses for each group, BFC patients presented for treatment of more acute dermatologic conditions, while UPMC patients presented for more benign and preventive-care conditions. This difference may be attributable to the BFC’s referral and triage system, wherein patients with more urgent problems are given scheduling priority. This patient care model contrasts with UPMC’s scheduling process in which no known formal triage system is utilized. Interestingly, there was no difference in skin cancer incidence despite a higher percentage of preventive skin cancer screenings at UPMC.
Patients at the BFC more often required emergency insurance for surgical interventions, which is consistent with the higher percentage of uninsured individuals in this population. Patients at UPMC more frequently were recommended sunscreen and were educated about skin cancer, sun protection, and skin examination, in part due to this group’s more extensive history of skin cancer and frequent presentation for skin cancer screenings. At the same time, educational materials for skin care at both the BFC and UPMC are populated into the EMR in English, whereas materials in other languages are less readily available.
Our retrospective study had several limitations. Demographic information that relied on clinic-dependent intake questionnaires may be limited due to variable intake processes and patients opting out of self-reporting. By comparing patient populations between 2 clinics, confounding variables such as location and hours of operation may impact the patient demographics recorded at the BFC vs UPMC. Resources and staff availability may affect the management strategies and follow-up care offered by each clinic. Our study period also was unique in that COVID-19 may have affected resources, staffing, scheduling, and logistics at both clinics.
Based on the aforementioned differences between the BFC and UPMC patient characteristics, care models should be strategically designed to support the needs of diverse populations. The BFC patient care model appropriately focuses on communication skills with patients with LEP by using interpreter services. Providing more skin care education and follow-up instructions in patients’ primary languages will help them develop a better understanding of their skin conditions. Another key asset of the BFC patient care model is its provision of social services such as transportation and insurance assistance.
To improve the UPMC patient care model, providing patients with bus tickets and car services may potentially reduce appointment cancellations. Using interpreter services to call and text appointment reminders, as well as interpreter resources to facilitate patient visits and patient instructions, also can mitigate language barriers for patients with LEP. Implementing a triage system into the UPMC scheduling system may help patients with more urgent skin conditions to be seen in a timely manner.
Other investigators have analyzed costs of care and proven the value of dermatologic services at free clinics to guide allocation of supplies and resources, demonstrating an area for future investigation at the BFC.13 A cost analysis of care provided at the BFC compared to UPMC could inform us about the value of the BFC’s services.
Conclusion
The dermatology clinics at the BFC and UPMC have distinct demographics, diagnoses, and management strategies to provide an inclusive patient care model. The services provided by both clinics are necessary to ensure that people in Pittsburgh have access to dermatologic care regardless of social barriers (eg, lack of health insurance, LEP). To achieve greater accessibility and health equity, dermatologic care at the BFC and UPMC can be improved by strengthening communication with people with LEP, providing skin care education, and offering social and scheduling services.
- Lim HW, Collins SAB, Resneck JS, et al. The burden of skin disease in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:958-972.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.12.043
- American Academy of Dermatology. Skin cancer. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://www.aad.org/media/stats-skin-cancer
- Suneja T, Smith ED, Chen GJ, et al. Waiting times to see a dermatologist are perceived as too long by dermatologists: implications for the dermatology workforce. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1303-1307. doi:10.1001/archderm.137.10.1303
- Grossberg AL, Carranza D, Lamp K, et al. Dermatologic care in the homeless and underserved populations: observations from the Venice Family Clinic. Cutis. 2012;89:25-32.
- Amini A, Rusthoven CG, Waxweiler TV, et al. Association of health insurance with outcomes in adults ages 18 to 64 years with melanoma in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:309-316. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.09.054
- Su C, Nguyen KA, Bai HX, et al. Racial disparity in mycosis fungoides: an analysis of 4495 cases from the US National Cancer Database. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:497-502.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad .2017.04.1137
- Darnell JS. Free clinics in the United States: a nationwide survey. Arch Intern Med. 2010;170:946-953. doi:10.1001/archinternmed .2010.107
- Madray V, Ginjupalli S, Hashmi O, et al. Access to dermatology services at free medical clinics: a nationwide cross-sectional survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:245-246. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.011
- Pennsylvania free and income-based clinics. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://www.freeclinics.com/sta/pennsylvania
- United States Census Bureau. Decennial census. P1: race. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://data.census.gov/table/DECENNIALPL2020.P1?g=160XX00US4261000
- United States Census Bureau. American community survey. S1601: language spoken at home. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://data.census.gov/table/ACSST5Y2020S1601?g=160XX00US4261000
- United States Census Bureau. S2701: selected characteristics of health insurance coverage in the United States. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://data.census.gov/table/ACSST5Y2020.S2701?g=160XX00US4261000
- Lin CP, Loy S, Boothe WD, et al. Value of Dermatology Nights at a student-run free clinic. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2020;34:260-261. doi:10.1080/08998280.2020.1834771
Approximately 25% of Americans have at least one skin condition, and 20% are estimated to develop skin cancer during their lifetime.1,2 However, 40% of the US population lives in areas underserved by dermatologists. 3 The severity and mortality of skin cancers such as melanoma and mycosis fungoides have been positively associated with minoritized race, lack of health insurance, and unstable housing status.4-6 Patients who receive health care at free clinics often are of a racial or ethnic minoritized social group, are uninsured, and/or lack stable housing; this underserved group also includes recent immigrants to the United States who have limited English proficiency (LEP).7 Only 25% of free clinics offer specialty care services such as dermatology.7,8
Of the 42 free clinics and Federally Qualified Health Centers in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, the Birmingham Free Clinic (BFC) is one of the few that offers specialty care services including dermatology.9 Founded in 1994, the BFC serves as a safety net for Pittsburgh’s medically underserved population, offering primary and acute care, medication access, and social services. From January 2020 to May 2022, the BFC offered 27 dermatology clinics that provided approximately 100 people with comprehensive care including full-body skin examinations, dermatologic diagnoses and treatments, minor procedures, and dermatopathology services.
In this study, we compared the BFC dermatology patient care model with that of the dermatology department at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC), an insurance-based tertiary referral health care system in western Pennsylvania. By analyzing the demographics, dermatologic diagnoses, and management strategies of both the BFC and UPMC, we gained an understanding of how these patient care models differ and how they can be improved to care for diverse patient populations.
Methods
A retrospective chart review of dermatology patients seen in person at the BFC and UPMC during the period from January 2020 to May 2022 was performed. The UPMC group included patients seen by 3 general dermatologists (including A.J.J.) at matched time points. Data were collected from patients’ first in-person visit during the study period. Variables of interest included patient age, sex, race, ethnicity, primary language, zip code, health insurance status, distance to clinic (estimated using Google Maps to calculate the shortest driving distance from the patient’s zip code to the clinic), history of skin cancer, dermatologic diagnoses, and management strategies. These variables were not collected for patients who cancelled or noshowed their first in-person appointments. All patient charts and notes corresponding to the date and visit of interest were accessed through the electronic medical record (EMR). Patient data were de-identified and stored in a password-protected spreadsheet. Comparisons between the BFC and UPMC patient populations were performed using X2 tests of independence, Fisher exact tests, and Mann-Whitney U tests via SPSS software (IBM). Statistical significance was set at P<.05.
Results
Patient Characteristics—Our analysis included 76 initial appointments at the BFC and 322 at UPMC (Table 1). The mean age for patients at the BFC and UPMC was 39.6 years and 47.8 years, respectively (P=.001). Males accounted for 39 (51.3%) and 112 (34.8%) of BFC and UPMC patients, respectively (P=.008); 2 (0.6%) patients from UPMC were transgender. Of the BFC and UPMC patients, 44.7% (34/76) and 0.9% (3/322) were Hispanic, respectively (P<.001). With regard to race, 52.6% (40/76) of BFC patients were White, 19.7% (15/76) were Black, 6.6% (5/76) were Asian/Pacific Islander (Chinese, 1.3% [1/76]; other Asian, 5.3% [4/76]), and 21.1% (16/76) were American Indian/other/unspecified (American Indian, 1.3% [1/76]; other, 13.2% [10/76]; unspecified, 6.6% [5/76]). At UPMC, 61.2% (197/322) of patients were White, 28.0% (90/322) were Black, 5.3% (17/322) were Asian/Pacific Islander (Chinese, 1.2% [4/322]; Indian [Asian], 1.9% [6/322]; Japanese, 0.3% [1/322]; other Asian, 1.6% [5/322]; other Asian/American Indian, 0.3% [1/322]), and 5.6% (18/322) were American Indian/other/ unspecified (American Indian, 0.3% [1/322]; other, 0.3% [1/322]; unspecified, 5.0% [16/322]). Overall, the BFC patient population was more ethnically and racially diverse than that of UPMC (P<.001).
Forty-six percent (35/76) of BFC patients and 4.3% (14/322) of UPMC patients had LEP (P<.001). Primary languages among BFC patients were 53.9% (41/76) English, 40.8% (31/76) Spanish, and 5.2% (4/76) other/ unspecified (Chinese, 1.3% [1/76]; Indonesian, 2.6% [2/76]; unspecified, 1.3% [1/76]). Primary languages among UPMC patients were 95.7% (308/322) English and 4.3% (14/322) other/unspecified (Chinese, 0.6% [2/322]; Nepali, 0.6% [2/322]; Pali, 0.3% [1/322]; Russian, 0.3% [1/322]; unspecified, 2.5% [8/322]). There were notable differences in insurance status at the BFC vs UPMC (P<.001), with more UPMC patients having private insurance (52.8% [170/322] vs 11.8% [9/76]) and more BFC patients being uninsured (52.8% [51/76] vs 1.9% [6/322]). There was no significant difference in distance to clinic between the 2 groups (P=.183). More UPMC patients had a history of skin cancer (P=.003). More patients at the BFC were no-shows for their appointments (P<.001), and UPMC patients more frequently canceled their appointments (P<.001).
Dermatologic Diagnoses—The most commonly diagnosed dermatologic conditions at the BFC were dermatitis (23.7% [18/76]), neoplasm of uncertain behavior (15.8% [12/76]), alopecia (11.8% [9/76]), and acne (10.5% [8/76]) (Table 2). The most commonly diagnosed conditions at UPMC were nevi (26.4% [85/322]), dermatitis (22.7% [73/322]), seborrheic keratosis (21.7% [70/322]), and skin cancer screening (21.4% [70/322]). Neoplasm of uncertain behavior was more common in BFC vs UPMC patients (P=.040), while UPMC patients were more frequently diagnosed with nevi (P<.001), seborrheic keratosis (P<.001), and skin cancer screening (P<.001). There was no significant difference between the incidence of skin cancer diagnoses in the BFC (1.3% [1/76]) and UPMC (0.6% [2/76]) patient populations (P=.471). Among the biopsied neoplasms, there was also no significant difference in malignant (BFC, 50.0% [5/10]; UPMC, 32.0% [8/25]) and benign (BFC, 50.0% [5/10]; UPMC, 36.0% [9/25]) neoplasms diagnosed at each clinic (P=.444).
Management Strategies—Systemic antibiotics were more frequently prescribed (P<.001) and laboratory testing/ imaging were more frequently ordered (P=.005) at the BFC vs UPMC (Table 3). Patients at the BFC also more frequently required emergency insurance (P=.036). Patients at UPMC were more frequently recommended sunscreen (P=.003) and received education about skin cancer signs by review of the ABCDEs of melanoma (P<.001), sun-protective behaviors (P=.001), and skin examination frequency (P<.001). Notes in the EMR for UPMC patients more frequently specified patient followup instructions (P<.001).
Comment
As of 2020, the city of Pittsburgh had an estimated population of nearly 303,000 based on US Census data.10 Its population is predominantly White (62.7%) followed by Black/African American (22.8%) and Asian (6.5%); 5.9% identify as 2 or more races. Approximately 3.8% identify as Hispanic or Latino. More than 11% of the Pittsburgh population aged 5 years and older speaks a language other than English as their primary language, including Spanish (2.3%), other Indo-European languages (3.9%), and Asian and Pacific Island languages (3.5%).11 More than 5% of the Pittsburgh population does not have health insurance.12
The BFC is located in Pittsburgh’s South Side area, while one of UPMC’s primary dermatology clinics is located in the Oakland district; however, most patients who seek care at these clinics live outside these areas. Our study results indicated that the BFC and UPMC serve distinct groups of people within the Pittsburgh population. The BFC patient population was younger with a higher percentage of patients who were male, Hispanic, racially diverse, and with LEP compared with the UPMC patient population. In this clinical setting, the BFC health care team engages with people from diverse backgrounds and requires greater interpreter and medical support services.
The BFC largely is supported by volunteers, UPMC, grants, and philanthropy. Dermatology clinics are staffed by paid and volunteer team members. Paid team members include 1 nurse and 1 access lead who operates the front desk and registration. Volunteer team members include 1 board-certified dermatologist from UPMC (A.J.J.), or an affiliate clinic and 1 or 2 of each of the following: UPMC dermatology residents, medical or undergraduate students from the University of Pittsburgh, AmeriCorps national service members, and student or community medical interpreters. The onsite pharmacy is run by volunteer faculty, resident, and student pharmacists from the University of Pittsburgh. Dermatology clinics are half-day clinics that occur monthly. Volunteers for each clinic are recruited approximately 1 month in advance.
Dermatology patients at the BFC are referred from the BFC general medicine clinic and nearby Federally Qualified Health Center s for simple to complex medical and surgical dermatologic skin conditions. Each BFC dermatology clinic schedules an average of 7 patients per clinic and places other patients on a wait-list unless more urgent triage is needed. Patients are notified when they are scheduled via phone or text message, and they receive a reminder call or text 1 or 2 days prior to their appointment that also asks them to confirm attendance. Patients with LEP are called with an interpreter and also may receive text reminders that can be translated using Google Translate. Patients are instructed to notify the BFC if they need to cancel or reschedule their appointment. At the end of each visit, patients are given an after-visit summary that lists follow-up instructions, medications prescribed during the visit, and upcoming appointments. The BFC offers bus tickets to help patients get to their appointments. In rare cases, the BFC may pay for a car service to drive patients to and from the clinic.
Dermatology clinics at UPMC use scheduling and self-scheduling systems through which patients can make appointments at a location of their choice with any available board-certified dermatologist or physician assistant. Patients receive a reminder phone call 3 days prior to their appointment instructing them to call the office if they are unable to keep their appointment. Patients signed up for the online portal also receive a reminder message and an option to confirm or cancel their appointment. Patients with cell phone numbers in the UPMC system receive a text message approximately 2 days prior to their appointment that allows them to preregister and pay their copayment in advance. They receive another text 20 minutes prior to their appointment with an option for contactless check-in. At the conclusion of their visit, patients can schedule a follow-up appointment and receive a printed copy of their after-visit summary that provides information about follow-up instructions, prescribed medications, and upcoming visits. They may alternatively access this summary via the online patient portal. Patients are not provided transportation to UPMC clinics, but they are offered parking validation.
Among the most common dermatologic diagnoses for each group, BFC patients presented for treatment of more acute dermatologic conditions, while UPMC patients presented for more benign and preventive-care conditions. This difference may be attributable to the BFC’s referral and triage system, wherein patients with more urgent problems are given scheduling priority. This patient care model contrasts with UPMC’s scheduling process in which no known formal triage system is utilized. Interestingly, there was no difference in skin cancer incidence despite a higher percentage of preventive skin cancer screenings at UPMC.
Patients at the BFC more often required emergency insurance for surgical interventions, which is consistent with the higher percentage of uninsured individuals in this population. Patients at UPMC more frequently were recommended sunscreen and were educated about skin cancer, sun protection, and skin examination, in part due to this group’s more extensive history of skin cancer and frequent presentation for skin cancer screenings. At the same time, educational materials for skin care at both the BFC and UPMC are populated into the EMR in English, whereas materials in other languages are less readily available.
Our retrospective study had several limitations. Demographic information that relied on clinic-dependent intake questionnaires may be limited due to variable intake processes and patients opting out of self-reporting. By comparing patient populations between 2 clinics, confounding variables such as location and hours of operation may impact the patient demographics recorded at the BFC vs UPMC. Resources and staff availability may affect the management strategies and follow-up care offered by each clinic. Our study period also was unique in that COVID-19 may have affected resources, staffing, scheduling, and logistics at both clinics.
Based on the aforementioned differences between the BFC and UPMC patient characteristics, care models should be strategically designed to support the needs of diverse populations. The BFC patient care model appropriately focuses on communication skills with patients with LEP by using interpreter services. Providing more skin care education and follow-up instructions in patients’ primary languages will help them develop a better understanding of their skin conditions. Another key asset of the BFC patient care model is its provision of social services such as transportation and insurance assistance.
To improve the UPMC patient care model, providing patients with bus tickets and car services may potentially reduce appointment cancellations. Using interpreter services to call and text appointment reminders, as well as interpreter resources to facilitate patient visits and patient instructions, also can mitigate language barriers for patients with LEP. Implementing a triage system into the UPMC scheduling system may help patients with more urgent skin conditions to be seen in a timely manner.
Other investigators have analyzed costs of care and proven the value of dermatologic services at free clinics to guide allocation of supplies and resources, demonstrating an area for future investigation at the BFC.13 A cost analysis of care provided at the BFC compared to UPMC could inform us about the value of the BFC’s services.
Conclusion
The dermatology clinics at the BFC and UPMC have distinct demographics, diagnoses, and management strategies to provide an inclusive patient care model. The services provided by both clinics are necessary to ensure that people in Pittsburgh have access to dermatologic care regardless of social barriers (eg, lack of health insurance, LEP). To achieve greater accessibility and health equity, dermatologic care at the BFC and UPMC can be improved by strengthening communication with people with LEP, providing skin care education, and offering social and scheduling services.
Approximately 25% of Americans have at least one skin condition, and 20% are estimated to develop skin cancer during their lifetime.1,2 However, 40% of the US population lives in areas underserved by dermatologists. 3 The severity and mortality of skin cancers such as melanoma and mycosis fungoides have been positively associated with minoritized race, lack of health insurance, and unstable housing status.4-6 Patients who receive health care at free clinics often are of a racial or ethnic minoritized social group, are uninsured, and/or lack stable housing; this underserved group also includes recent immigrants to the United States who have limited English proficiency (LEP).7 Only 25% of free clinics offer specialty care services such as dermatology.7,8
Of the 42 free clinics and Federally Qualified Health Centers in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, the Birmingham Free Clinic (BFC) is one of the few that offers specialty care services including dermatology.9 Founded in 1994, the BFC serves as a safety net for Pittsburgh’s medically underserved population, offering primary and acute care, medication access, and social services. From January 2020 to May 2022, the BFC offered 27 dermatology clinics that provided approximately 100 people with comprehensive care including full-body skin examinations, dermatologic diagnoses and treatments, minor procedures, and dermatopathology services.
In this study, we compared the BFC dermatology patient care model with that of the dermatology department at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC), an insurance-based tertiary referral health care system in western Pennsylvania. By analyzing the demographics, dermatologic diagnoses, and management strategies of both the BFC and UPMC, we gained an understanding of how these patient care models differ and how they can be improved to care for diverse patient populations.
Methods
A retrospective chart review of dermatology patients seen in person at the BFC and UPMC during the period from January 2020 to May 2022 was performed. The UPMC group included patients seen by 3 general dermatologists (including A.J.J.) at matched time points. Data were collected from patients’ first in-person visit during the study period. Variables of interest included patient age, sex, race, ethnicity, primary language, zip code, health insurance status, distance to clinic (estimated using Google Maps to calculate the shortest driving distance from the patient’s zip code to the clinic), history of skin cancer, dermatologic diagnoses, and management strategies. These variables were not collected for patients who cancelled or noshowed their first in-person appointments. All patient charts and notes corresponding to the date and visit of interest were accessed through the electronic medical record (EMR). Patient data were de-identified and stored in a password-protected spreadsheet. Comparisons between the BFC and UPMC patient populations were performed using X2 tests of independence, Fisher exact tests, and Mann-Whitney U tests via SPSS software (IBM). Statistical significance was set at P<.05.
Results
Patient Characteristics—Our analysis included 76 initial appointments at the BFC and 322 at UPMC (Table 1). The mean age for patients at the BFC and UPMC was 39.6 years and 47.8 years, respectively (P=.001). Males accounted for 39 (51.3%) and 112 (34.8%) of BFC and UPMC patients, respectively (P=.008); 2 (0.6%) patients from UPMC were transgender. Of the BFC and UPMC patients, 44.7% (34/76) and 0.9% (3/322) were Hispanic, respectively (P<.001). With regard to race, 52.6% (40/76) of BFC patients were White, 19.7% (15/76) were Black, 6.6% (5/76) were Asian/Pacific Islander (Chinese, 1.3% [1/76]; other Asian, 5.3% [4/76]), and 21.1% (16/76) were American Indian/other/unspecified (American Indian, 1.3% [1/76]; other, 13.2% [10/76]; unspecified, 6.6% [5/76]). At UPMC, 61.2% (197/322) of patients were White, 28.0% (90/322) were Black, 5.3% (17/322) were Asian/Pacific Islander (Chinese, 1.2% [4/322]; Indian [Asian], 1.9% [6/322]; Japanese, 0.3% [1/322]; other Asian, 1.6% [5/322]; other Asian/American Indian, 0.3% [1/322]), and 5.6% (18/322) were American Indian/other/ unspecified (American Indian, 0.3% [1/322]; other, 0.3% [1/322]; unspecified, 5.0% [16/322]). Overall, the BFC patient population was more ethnically and racially diverse than that of UPMC (P<.001).
Forty-six percent (35/76) of BFC patients and 4.3% (14/322) of UPMC patients had LEP (P<.001). Primary languages among BFC patients were 53.9% (41/76) English, 40.8% (31/76) Spanish, and 5.2% (4/76) other/ unspecified (Chinese, 1.3% [1/76]; Indonesian, 2.6% [2/76]; unspecified, 1.3% [1/76]). Primary languages among UPMC patients were 95.7% (308/322) English and 4.3% (14/322) other/unspecified (Chinese, 0.6% [2/322]; Nepali, 0.6% [2/322]; Pali, 0.3% [1/322]; Russian, 0.3% [1/322]; unspecified, 2.5% [8/322]). There were notable differences in insurance status at the BFC vs UPMC (P<.001), with more UPMC patients having private insurance (52.8% [170/322] vs 11.8% [9/76]) and more BFC patients being uninsured (52.8% [51/76] vs 1.9% [6/322]). There was no significant difference in distance to clinic between the 2 groups (P=.183). More UPMC patients had a history of skin cancer (P=.003). More patients at the BFC were no-shows for their appointments (P<.001), and UPMC patients more frequently canceled their appointments (P<.001).
Dermatologic Diagnoses—The most commonly diagnosed dermatologic conditions at the BFC were dermatitis (23.7% [18/76]), neoplasm of uncertain behavior (15.8% [12/76]), alopecia (11.8% [9/76]), and acne (10.5% [8/76]) (Table 2). The most commonly diagnosed conditions at UPMC were nevi (26.4% [85/322]), dermatitis (22.7% [73/322]), seborrheic keratosis (21.7% [70/322]), and skin cancer screening (21.4% [70/322]). Neoplasm of uncertain behavior was more common in BFC vs UPMC patients (P=.040), while UPMC patients were more frequently diagnosed with nevi (P<.001), seborrheic keratosis (P<.001), and skin cancer screening (P<.001). There was no significant difference between the incidence of skin cancer diagnoses in the BFC (1.3% [1/76]) and UPMC (0.6% [2/76]) patient populations (P=.471). Among the biopsied neoplasms, there was also no significant difference in malignant (BFC, 50.0% [5/10]; UPMC, 32.0% [8/25]) and benign (BFC, 50.0% [5/10]; UPMC, 36.0% [9/25]) neoplasms diagnosed at each clinic (P=.444).
Management Strategies—Systemic antibiotics were more frequently prescribed (P<.001) and laboratory testing/ imaging were more frequently ordered (P=.005) at the BFC vs UPMC (Table 3). Patients at the BFC also more frequently required emergency insurance (P=.036). Patients at UPMC were more frequently recommended sunscreen (P=.003) and received education about skin cancer signs by review of the ABCDEs of melanoma (P<.001), sun-protective behaviors (P=.001), and skin examination frequency (P<.001). Notes in the EMR for UPMC patients more frequently specified patient followup instructions (P<.001).
Comment
As of 2020, the city of Pittsburgh had an estimated population of nearly 303,000 based on US Census data.10 Its population is predominantly White (62.7%) followed by Black/African American (22.8%) and Asian (6.5%); 5.9% identify as 2 or more races. Approximately 3.8% identify as Hispanic or Latino. More than 11% of the Pittsburgh population aged 5 years and older speaks a language other than English as their primary language, including Spanish (2.3%), other Indo-European languages (3.9%), and Asian and Pacific Island languages (3.5%).11 More than 5% of the Pittsburgh population does not have health insurance.12
The BFC is located in Pittsburgh’s South Side area, while one of UPMC’s primary dermatology clinics is located in the Oakland district; however, most patients who seek care at these clinics live outside these areas. Our study results indicated that the BFC and UPMC serve distinct groups of people within the Pittsburgh population. The BFC patient population was younger with a higher percentage of patients who were male, Hispanic, racially diverse, and with LEP compared with the UPMC patient population. In this clinical setting, the BFC health care team engages with people from diverse backgrounds and requires greater interpreter and medical support services.
The BFC largely is supported by volunteers, UPMC, grants, and philanthropy. Dermatology clinics are staffed by paid and volunteer team members. Paid team members include 1 nurse and 1 access lead who operates the front desk and registration. Volunteer team members include 1 board-certified dermatologist from UPMC (A.J.J.), or an affiliate clinic and 1 or 2 of each of the following: UPMC dermatology residents, medical or undergraduate students from the University of Pittsburgh, AmeriCorps national service members, and student or community medical interpreters. The onsite pharmacy is run by volunteer faculty, resident, and student pharmacists from the University of Pittsburgh. Dermatology clinics are half-day clinics that occur monthly. Volunteers for each clinic are recruited approximately 1 month in advance.
Dermatology patients at the BFC are referred from the BFC general medicine clinic and nearby Federally Qualified Health Center s for simple to complex medical and surgical dermatologic skin conditions. Each BFC dermatology clinic schedules an average of 7 patients per clinic and places other patients on a wait-list unless more urgent triage is needed. Patients are notified when they are scheduled via phone or text message, and they receive a reminder call or text 1 or 2 days prior to their appointment that also asks them to confirm attendance. Patients with LEP are called with an interpreter and also may receive text reminders that can be translated using Google Translate. Patients are instructed to notify the BFC if they need to cancel or reschedule their appointment. At the end of each visit, patients are given an after-visit summary that lists follow-up instructions, medications prescribed during the visit, and upcoming appointments. The BFC offers bus tickets to help patients get to their appointments. In rare cases, the BFC may pay for a car service to drive patients to and from the clinic.
Dermatology clinics at UPMC use scheduling and self-scheduling systems through which patients can make appointments at a location of their choice with any available board-certified dermatologist or physician assistant. Patients receive a reminder phone call 3 days prior to their appointment instructing them to call the office if they are unable to keep their appointment. Patients signed up for the online portal also receive a reminder message and an option to confirm or cancel their appointment. Patients with cell phone numbers in the UPMC system receive a text message approximately 2 days prior to their appointment that allows them to preregister and pay their copayment in advance. They receive another text 20 minutes prior to their appointment with an option for contactless check-in. At the conclusion of their visit, patients can schedule a follow-up appointment and receive a printed copy of their after-visit summary that provides information about follow-up instructions, prescribed medications, and upcoming visits. They may alternatively access this summary via the online patient portal. Patients are not provided transportation to UPMC clinics, but they are offered parking validation.
Among the most common dermatologic diagnoses for each group, BFC patients presented for treatment of more acute dermatologic conditions, while UPMC patients presented for more benign and preventive-care conditions. This difference may be attributable to the BFC’s referral and triage system, wherein patients with more urgent problems are given scheduling priority. This patient care model contrasts with UPMC’s scheduling process in which no known formal triage system is utilized. Interestingly, there was no difference in skin cancer incidence despite a higher percentage of preventive skin cancer screenings at UPMC.
Patients at the BFC more often required emergency insurance for surgical interventions, which is consistent with the higher percentage of uninsured individuals in this population. Patients at UPMC more frequently were recommended sunscreen and were educated about skin cancer, sun protection, and skin examination, in part due to this group’s more extensive history of skin cancer and frequent presentation for skin cancer screenings. At the same time, educational materials for skin care at both the BFC and UPMC are populated into the EMR in English, whereas materials in other languages are less readily available.
Our retrospective study had several limitations. Demographic information that relied on clinic-dependent intake questionnaires may be limited due to variable intake processes and patients opting out of self-reporting. By comparing patient populations between 2 clinics, confounding variables such as location and hours of operation may impact the patient demographics recorded at the BFC vs UPMC. Resources and staff availability may affect the management strategies and follow-up care offered by each clinic. Our study period also was unique in that COVID-19 may have affected resources, staffing, scheduling, and logistics at both clinics.
Based on the aforementioned differences between the BFC and UPMC patient characteristics, care models should be strategically designed to support the needs of diverse populations. The BFC patient care model appropriately focuses on communication skills with patients with LEP by using interpreter services. Providing more skin care education and follow-up instructions in patients’ primary languages will help them develop a better understanding of their skin conditions. Another key asset of the BFC patient care model is its provision of social services such as transportation and insurance assistance.
To improve the UPMC patient care model, providing patients with bus tickets and car services may potentially reduce appointment cancellations. Using interpreter services to call and text appointment reminders, as well as interpreter resources to facilitate patient visits and patient instructions, also can mitigate language barriers for patients with LEP. Implementing a triage system into the UPMC scheduling system may help patients with more urgent skin conditions to be seen in a timely manner.
Other investigators have analyzed costs of care and proven the value of dermatologic services at free clinics to guide allocation of supplies and resources, demonstrating an area for future investigation at the BFC.13 A cost analysis of care provided at the BFC compared to UPMC could inform us about the value of the BFC’s services.
Conclusion
The dermatology clinics at the BFC and UPMC have distinct demographics, diagnoses, and management strategies to provide an inclusive patient care model. The services provided by both clinics are necessary to ensure that people in Pittsburgh have access to dermatologic care regardless of social barriers (eg, lack of health insurance, LEP). To achieve greater accessibility and health equity, dermatologic care at the BFC and UPMC can be improved by strengthening communication with people with LEP, providing skin care education, and offering social and scheduling services.
- Lim HW, Collins SAB, Resneck JS, et al. The burden of skin disease in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:958-972.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.12.043
- American Academy of Dermatology. Skin cancer. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://www.aad.org/media/stats-skin-cancer
- Suneja T, Smith ED, Chen GJ, et al. Waiting times to see a dermatologist are perceived as too long by dermatologists: implications for the dermatology workforce. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1303-1307. doi:10.1001/archderm.137.10.1303
- Grossberg AL, Carranza D, Lamp K, et al. Dermatologic care in the homeless and underserved populations: observations from the Venice Family Clinic. Cutis. 2012;89:25-32.
- Amini A, Rusthoven CG, Waxweiler TV, et al. Association of health insurance with outcomes in adults ages 18 to 64 years with melanoma in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:309-316. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.09.054
- Su C, Nguyen KA, Bai HX, et al. Racial disparity in mycosis fungoides: an analysis of 4495 cases from the US National Cancer Database. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:497-502.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad .2017.04.1137
- Darnell JS. Free clinics in the United States: a nationwide survey. Arch Intern Med. 2010;170:946-953. doi:10.1001/archinternmed .2010.107
- Madray V, Ginjupalli S, Hashmi O, et al. Access to dermatology services at free medical clinics: a nationwide cross-sectional survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:245-246. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.011
- Pennsylvania free and income-based clinics. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://www.freeclinics.com/sta/pennsylvania
- United States Census Bureau. Decennial census. P1: race. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://data.census.gov/table/DECENNIALPL2020.P1?g=160XX00US4261000
- United States Census Bureau. American community survey. S1601: language spoken at home. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://data.census.gov/table/ACSST5Y2020S1601?g=160XX00US4261000
- United States Census Bureau. S2701: selected characteristics of health insurance coverage in the United States. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://data.census.gov/table/ACSST5Y2020.S2701?g=160XX00US4261000
- Lin CP, Loy S, Boothe WD, et al. Value of Dermatology Nights at a student-run free clinic. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2020;34:260-261. doi:10.1080/08998280.2020.1834771
- Lim HW, Collins SAB, Resneck JS, et al. The burden of skin disease in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:958-972.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.12.043
- American Academy of Dermatology. Skin cancer. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://www.aad.org/media/stats-skin-cancer
- Suneja T, Smith ED, Chen GJ, et al. Waiting times to see a dermatologist are perceived as too long by dermatologists: implications for the dermatology workforce. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1303-1307. doi:10.1001/archderm.137.10.1303
- Grossberg AL, Carranza D, Lamp K, et al. Dermatologic care in the homeless and underserved populations: observations from the Venice Family Clinic. Cutis. 2012;89:25-32.
- Amini A, Rusthoven CG, Waxweiler TV, et al. Association of health insurance with outcomes in adults ages 18 to 64 years with melanoma in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:309-316. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.09.054
- Su C, Nguyen KA, Bai HX, et al. Racial disparity in mycosis fungoides: an analysis of 4495 cases from the US National Cancer Database. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:497-502.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad .2017.04.1137
- Darnell JS. Free clinics in the United States: a nationwide survey. Arch Intern Med. 2010;170:946-953. doi:10.1001/archinternmed .2010.107
- Madray V, Ginjupalli S, Hashmi O, et al. Access to dermatology services at free medical clinics: a nationwide cross-sectional survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:245-246. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.011
- Pennsylvania free and income-based clinics. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://www.freeclinics.com/sta/pennsylvania
- United States Census Bureau. Decennial census. P1: race. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://data.census.gov/table/DECENNIALPL2020.P1?g=160XX00US4261000
- United States Census Bureau. American community survey. S1601: language spoken at home. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://data.census.gov/table/ACSST5Y2020S1601?g=160XX00US4261000
- United States Census Bureau. S2701: selected characteristics of health insurance coverage in the United States. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://data.census.gov/table/ACSST5Y2020.S2701?g=160XX00US4261000
- Lin CP, Loy S, Boothe WD, et al. Value of Dermatology Nights at a student-run free clinic. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2020;34:260-261. doi:10.1080/08998280.2020.1834771
Comparing Patient Care Models at a Local Free Clinic vs an Insurance- Based University Medical Center
Comparing Patient Care Models at a Local Free Clinic vs an Insurance- Based University Medical Center
PRACTICE POINTS
- Both free clinics and insurance-based health care systems serve dermatology patients with diverse characteristics, necessitating inclusive health care models.
- Dermatologic care can be improved at both free and insurance-based clinics by strengthening communication with individuals with limited English proficiency, providing skin care education, and offering social and scheduling services such as transportation, insurance assistance, and triage.