User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
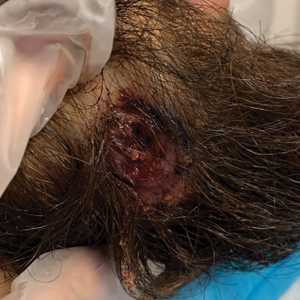
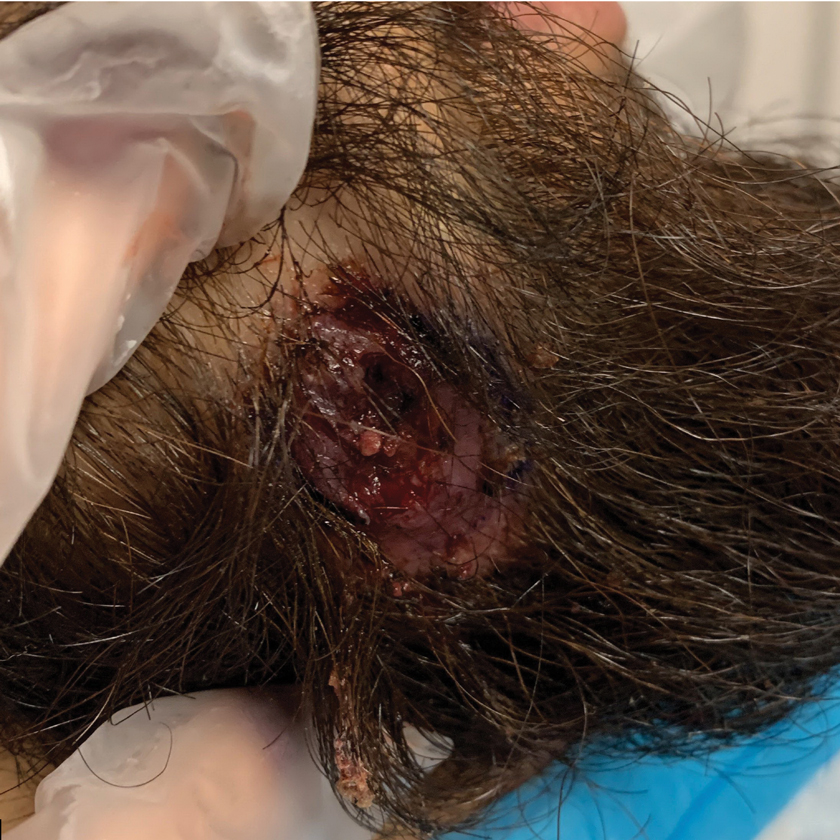
Nonhealing Ulcer in a Patient With Crohn Disease
The Diagnosis: Mycobacterium abscessus Infection
Upon further testing, cultures were positive for Mycobacterium abscessus. Our patient was referred to infectious disease for co-management, and his treatment plan consisted of intravenous amikacin 885 mg 3 times weekly, intravenous imipenem 1 g twice daily, azithromycin 500 mg/d, and omadacycline 150 mg/d for at least 3 months. Magnetic resonance imaging findings were consistent with a combination of cellulitis and osteomyelitis, and our patient was referred to plastic surgery for debridement. He subsequently was lost to follow-up.
Mycobacterium abscessus is classified as both a nontuberculous and rapidly growing mycobacterium. Mycobacterium abscessus recently has emerged as a pathogen of increasing public health concern, especially due to its high rate of antibiotic resistance.1-5 It is highly prevalent in the environment, and infection has been reported from a wide variety of environmental sources.6-8 Immunocompromised individuals, such as our patient, undergoing anti–tumor necrosis factor therapy are at increased risk for infection from all Mycobacterium species.9-11 Recognizing these infections quickly is a priority for patient care, as M abscessus can lead to disseminated infection and high mortality rates.1
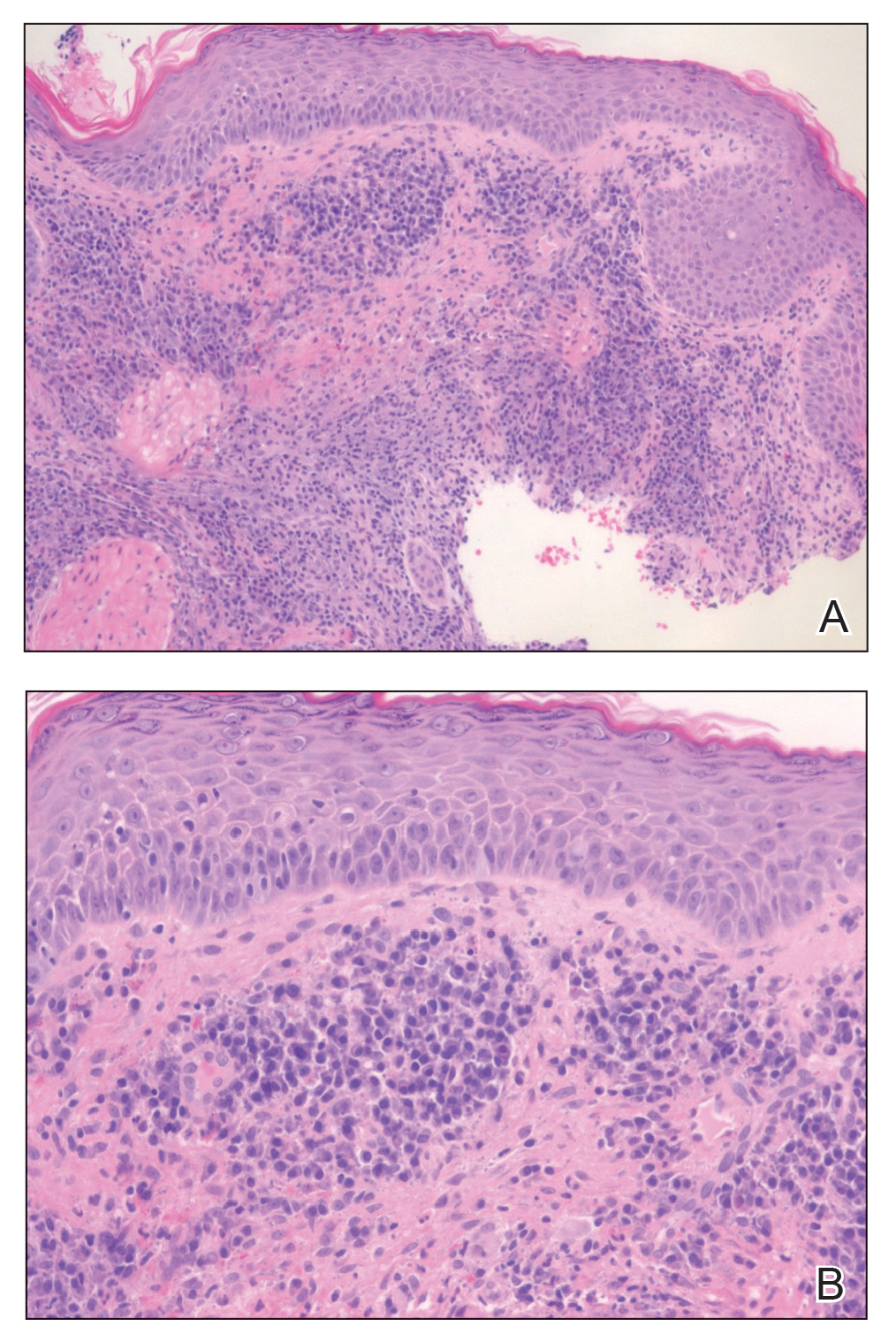
Histopathology of M abscessus consists of granulomatous inflammation with mixed granulomas12; however, these findings are not always appreciable, and staining does not always reveal visible organisms. In our patient, histopathology revealed patchy plasmalymphocytic infiltrates of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, which are signs of generalized inflammation (Figure). Therefore, cultures positive for M abscessus are the gold standard for diagnosis and established the diagnosis in this case.
The differential diagnoses for our patient’s ulceration included squamous cell carcinoma, pyoderma gangrenosum, aseptic abscess ulcer, and pyodermatitispyostomatitis vegetans. Immunosuppressive therapy is a risk factor for squamous cell carcinoma13,14; however, ulcerated squamous cell carcinoma typically presents with prominent everted edges with a necrotic tumor base.15 Biopsy reveals cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, large nuclei, and variable keratin pearls.16 Pyoderma gangrenosum is an inflammatory skin condition associated with Crohn disease and often is a diagnosis of exclusion characterized by neutrophilic infiltrates on biopsy.17-19 Aseptic abscess ulcers are characterized by neutrophil-filled lesions that respond to corticosteroids but not antibiotics.20 Pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans is a rare skin manifestation of inflammatory bowel disease associated with a pustular eruption of the skin and/or mouth. Histopathology reveals pustules within or below the epidermis with many eosinophils or neutrophils. Granulomas do not occur as in M abscessus.21
Treatment of M abscessus infection requires the coadministration of several antibiotics across multiple classes to ensure complete disease resolution. High rates of antibiotic resistance are characterized by at least partial resistance to almost every antibiotic; clarithromycin has near-complete efficacy, but resistant strains have started to emerge. Amikacin and cefoxitin are other antibiotics that have reported a resistance rate of less than 50%, but they are only effective 90% and 70% of the time, respectively.1,22 The antibiotic omadacycline, which is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat acute bacterial skin and soft-tissue infections, also may have utility in treating M abscessus infections.23,24 Finally, phage therapy may offer a potential mode of treatment for this bacterium and was used to treat pulmonary infection in a patient with cystic fibrosis.25 Despite these newer innovations, the current standard of care involves clarithromycin or azithromycin in combination with a parenteral antibiotic such as cefoxitin, amikacin, or imipenem for at least 4 months.1
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367-416.
- Jeong SH, Kim SY, Huh HJ, et al. Mycobacteriological characteristics and treatment outcomes in extrapulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus complex infections. Int J Infect Dis. 2017;60:49-56.
- Strnad L, Winthrop KL. Treatment of Mycobacterium abscessus complex. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;39:362-376.
- Cardenas DD, Yasmin T, Ahmed S. A rare insidious case of skin and soft tissue infection due to Mycobacterium abscessus: a case report. Cureus. 2022;14:E25725.
- Gonzalez-Santiago TM, Drage LA. Nontuberculous mycobacteria: skin and soft tissue infections. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:563-577.
- Dickison P, Howard V, O’Kane G, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection following penetrations through wetsuits. Australas J Dermatol. 2019;60:57-59.
- Choi H, Kim YI, Na CH, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus skin infection associated with shaving activity in a 75-year-old man. Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2018;22:204.
- Costa-Silva M, Cesar A, Gomes NP, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection in a spa worker. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2018;27:159-161.
- Besada E. Rapid growing mycobacteria and TNF-α blockers: case report of a fatal lung infection with Mycobacterium abscessus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011;29:705-707.
- Mufti AH, Toye BW, Mckendry RR, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection after use of tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor therapy: case report and review of infectious complications associated with tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor use. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005;53:233-238.
- Lee SK, Kim SY, Kim EY, et al. Mycobacterial infections in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor antagonists in South Korea. Lung. 2013;191:565-571.
- Rodríguez G, Ortegón M, Camargo D, et al. Iatrogenic Mycobacterium abscessus infection: histopathology of 71 patients. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:214-218.
- Firnhaber JM. Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma. Am Fam Physician. 2012;86:161-168.
- Walker HS, Hardwicke J. Non-melanoma skin cancer. Surgery (Oxford). 2022;40:39-45.
- Browse NL. The skin. In: Browse NL, ed. An Introduction to the Symptoms and Signs of Surgical Disease. 3rd ed. London Arnold Publications; 2001:66-69.
- Weedon D. Squamous cell carcinoma. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 3rd ed. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010;691-700.
- Powell F, Schroeter A, Su W, et al. Pyoderma gangrenosum: a review of 86 patients. QJM Int J Med. 1985;55:173-186.
- Brunsting LA, Goeckerman WH, O’Leary PA. Pyoderma (ecthyma) gangrenosum: clinical and experimental observations in five cases occurring in adults. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:743-768.
- Maverakis E, Ma C, Shinkai K, et al. Diagnostic criteria of ulcerative pyoderma gangrenosum: a Delphi consensus of international experts. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:461-466.
- André MFJ, Piette JC, Kémény JL, et al. Aseptic abscesses: a study of 30 patients with or without inflammatory bowel disease and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007;86:145. doi:10.1097/md.0b013e18064f9f3
- Femiano F, Lanza A, Buonaiuto C, et al. Pyostomatitis vegetans: a review of the literature. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2009;14:E114-E117.
- Kasperbauer SH, De Groote MA. The treatment of rapidly growing mycobacterial infections. Clin Chest Med. 2015;36:67-78.
- Duah M, Beshay M. Omadacycline in first-line combination therapy for pulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus infection: a case series. Int J Infect Dis. 2022;122:953-956.
- Minhas R, Sharma S, Kundu S. Utilizing the promise of omadacycline in a resistant, non-tubercular mycobacterial pulmonary infection. Cureus. 2019;11:E5112.
- Dedrick RM, Guerrero-Bustamante CA, Garlena RA, et al. Engineered bacteriophages for treatment of a patient with a disseminated drug-resistant Mycobacterium abscessus. Nat Med. 2019;25:730-733.
The Diagnosis: Mycobacterium abscessus Infection
Upon further testing, cultures were positive for Mycobacterium abscessus. Our patient was referred to infectious disease for co-management, and his treatment plan consisted of intravenous amikacin 885 mg 3 times weekly, intravenous imipenem 1 g twice daily, azithromycin 500 mg/d, and omadacycline 150 mg/d for at least 3 months. Magnetic resonance imaging findings were consistent with a combination of cellulitis and osteomyelitis, and our patient was referred to plastic surgery for debridement. He subsequently was lost to follow-up.
Mycobacterium abscessus is classified as both a nontuberculous and rapidly growing mycobacterium. Mycobacterium abscessus recently has emerged as a pathogen of increasing public health concern, especially due to its high rate of antibiotic resistance.1-5 It is highly prevalent in the environment, and infection has been reported from a wide variety of environmental sources.6-8 Immunocompromised individuals, such as our patient, undergoing anti–tumor necrosis factor therapy are at increased risk for infection from all Mycobacterium species.9-11 Recognizing these infections quickly is a priority for patient care, as M abscessus can lead to disseminated infection and high mortality rates.1
Histopathology of M abscessus consists of granulomatous inflammation with mixed granulomas12; however, these findings are not always appreciable, and staining does not always reveal visible organisms. In our patient, histopathology revealed patchy plasmalymphocytic infiltrates of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, which are signs of generalized inflammation (Figure). Therefore, cultures positive for M abscessus are the gold standard for diagnosis and established the diagnosis in this case.

The differential diagnoses for our patient’s ulceration included squamous cell carcinoma, pyoderma gangrenosum, aseptic abscess ulcer, and pyodermatitispyostomatitis vegetans. Immunosuppressive therapy is a risk factor for squamous cell carcinoma13,14; however, ulcerated squamous cell carcinoma typically presents with prominent everted edges with a necrotic tumor base.15 Biopsy reveals cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, large nuclei, and variable keratin pearls.16 Pyoderma gangrenosum is an inflammatory skin condition associated with Crohn disease and often is a diagnosis of exclusion characterized by neutrophilic infiltrates on biopsy.17-19 Aseptic abscess ulcers are characterized by neutrophil-filled lesions that respond to corticosteroids but not antibiotics.20 Pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans is a rare skin manifestation of inflammatory bowel disease associated with a pustular eruption of the skin and/or mouth. Histopathology reveals pustules within or below the epidermis with many eosinophils or neutrophils. Granulomas do not occur as in M abscessus.21
Treatment of M abscessus infection requires the coadministration of several antibiotics across multiple classes to ensure complete disease resolution. High rates of antibiotic resistance are characterized by at least partial resistance to almost every antibiotic; clarithromycin has near-complete efficacy, but resistant strains have started to emerge. Amikacin and cefoxitin are other antibiotics that have reported a resistance rate of less than 50%, but they are only effective 90% and 70% of the time, respectively.1,22 The antibiotic omadacycline, which is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat acute bacterial skin and soft-tissue infections, also may have utility in treating M abscessus infections.23,24 Finally, phage therapy may offer a potential mode of treatment for this bacterium and was used to treat pulmonary infection in a patient with cystic fibrosis.25 Despite these newer innovations, the current standard of care involves clarithromycin or azithromycin in combination with a parenteral antibiotic such as cefoxitin, amikacin, or imipenem for at least 4 months.1
The Diagnosis: Mycobacterium abscessus Infection
Upon further testing, cultures were positive for Mycobacterium abscessus. Our patient was referred to infectious disease for co-management, and his treatment plan consisted of intravenous amikacin 885 mg 3 times weekly, intravenous imipenem 1 g twice daily, azithromycin 500 mg/d, and omadacycline 150 mg/d for at least 3 months. Magnetic resonance imaging findings were consistent with a combination of cellulitis and osteomyelitis, and our patient was referred to plastic surgery for debridement. He subsequently was lost to follow-up.
Mycobacterium abscessus is classified as both a nontuberculous and rapidly growing mycobacterium. Mycobacterium abscessus recently has emerged as a pathogen of increasing public health concern, especially due to its high rate of antibiotic resistance.1-5 It is highly prevalent in the environment, and infection has been reported from a wide variety of environmental sources.6-8 Immunocompromised individuals, such as our patient, undergoing anti–tumor necrosis factor therapy are at increased risk for infection from all Mycobacterium species.9-11 Recognizing these infections quickly is a priority for patient care, as M abscessus can lead to disseminated infection and high mortality rates.1
Histopathology of M abscessus consists of granulomatous inflammation with mixed granulomas12; however, these findings are not always appreciable, and staining does not always reveal visible organisms. In our patient, histopathology revealed patchy plasmalymphocytic infiltrates of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, which are signs of generalized inflammation (Figure). Therefore, cultures positive for M abscessus are the gold standard for diagnosis and established the diagnosis in this case.

The differential diagnoses for our patient’s ulceration included squamous cell carcinoma, pyoderma gangrenosum, aseptic abscess ulcer, and pyodermatitispyostomatitis vegetans. Immunosuppressive therapy is a risk factor for squamous cell carcinoma13,14; however, ulcerated squamous cell carcinoma typically presents with prominent everted edges with a necrotic tumor base.15 Biopsy reveals cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, large nuclei, and variable keratin pearls.16 Pyoderma gangrenosum is an inflammatory skin condition associated with Crohn disease and often is a diagnosis of exclusion characterized by neutrophilic infiltrates on biopsy.17-19 Aseptic abscess ulcers are characterized by neutrophil-filled lesions that respond to corticosteroids but not antibiotics.20 Pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans is a rare skin manifestation of inflammatory bowel disease associated with a pustular eruption of the skin and/or mouth. Histopathology reveals pustules within or below the epidermis with many eosinophils or neutrophils. Granulomas do not occur as in M abscessus.21
Treatment of M abscessus infection requires the coadministration of several antibiotics across multiple classes to ensure complete disease resolution. High rates of antibiotic resistance are characterized by at least partial resistance to almost every antibiotic; clarithromycin has near-complete efficacy, but resistant strains have started to emerge. Amikacin and cefoxitin are other antibiotics that have reported a resistance rate of less than 50%, but they are only effective 90% and 70% of the time, respectively.1,22 The antibiotic omadacycline, which is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat acute bacterial skin and soft-tissue infections, also may have utility in treating M abscessus infections.23,24 Finally, phage therapy may offer a potential mode of treatment for this bacterium and was used to treat pulmonary infection in a patient with cystic fibrosis.25 Despite these newer innovations, the current standard of care involves clarithromycin or azithromycin in combination with a parenteral antibiotic such as cefoxitin, amikacin, or imipenem for at least 4 months.1
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367-416.
- Jeong SH, Kim SY, Huh HJ, et al. Mycobacteriological characteristics and treatment outcomes in extrapulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus complex infections. Int J Infect Dis. 2017;60:49-56.
- Strnad L, Winthrop KL. Treatment of Mycobacterium abscessus complex. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;39:362-376.
- Cardenas DD, Yasmin T, Ahmed S. A rare insidious case of skin and soft tissue infection due to Mycobacterium abscessus: a case report. Cureus. 2022;14:E25725.
- Gonzalez-Santiago TM, Drage LA. Nontuberculous mycobacteria: skin and soft tissue infections. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:563-577.
- Dickison P, Howard V, O’Kane G, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection following penetrations through wetsuits. Australas J Dermatol. 2019;60:57-59.
- Choi H, Kim YI, Na CH, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus skin infection associated with shaving activity in a 75-year-old man. Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2018;22:204.
- Costa-Silva M, Cesar A, Gomes NP, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection in a spa worker. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2018;27:159-161.
- Besada E. Rapid growing mycobacteria and TNF-α blockers: case report of a fatal lung infection with Mycobacterium abscessus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011;29:705-707.
- Mufti AH, Toye BW, Mckendry RR, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection after use of tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor therapy: case report and review of infectious complications associated with tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor use. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005;53:233-238.
- Lee SK, Kim SY, Kim EY, et al. Mycobacterial infections in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor antagonists in South Korea. Lung. 2013;191:565-571.
- Rodríguez G, Ortegón M, Camargo D, et al. Iatrogenic Mycobacterium abscessus infection: histopathology of 71 patients. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:214-218.
- Firnhaber JM. Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma. Am Fam Physician. 2012;86:161-168.
- Walker HS, Hardwicke J. Non-melanoma skin cancer. Surgery (Oxford). 2022;40:39-45.
- Browse NL. The skin. In: Browse NL, ed. An Introduction to the Symptoms and Signs of Surgical Disease. 3rd ed. London Arnold Publications; 2001:66-69.
- Weedon D. Squamous cell carcinoma. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 3rd ed. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010;691-700.
- Powell F, Schroeter A, Su W, et al. Pyoderma gangrenosum: a review of 86 patients. QJM Int J Med. 1985;55:173-186.
- Brunsting LA, Goeckerman WH, O’Leary PA. Pyoderma (ecthyma) gangrenosum: clinical and experimental observations in five cases occurring in adults. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:743-768.
- Maverakis E, Ma C, Shinkai K, et al. Diagnostic criteria of ulcerative pyoderma gangrenosum: a Delphi consensus of international experts. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:461-466.
- André MFJ, Piette JC, Kémény JL, et al. Aseptic abscesses: a study of 30 patients with or without inflammatory bowel disease and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007;86:145. doi:10.1097/md.0b013e18064f9f3
- Femiano F, Lanza A, Buonaiuto C, et al. Pyostomatitis vegetans: a review of the literature. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2009;14:E114-E117.
- Kasperbauer SH, De Groote MA. The treatment of rapidly growing mycobacterial infections. Clin Chest Med. 2015;36:67-78.
- Duah M, Beshay M. Omadacycline in first-line combination therapy for pulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus infection: a case series. Int J Infect Dis. 2022;122:953-956.
- Minhas R, Sharma S, Kundu S. Utilizing the promise of omadacycline in a resistant, non-tubercular mycobacterial pulmonary infection. Cureus. 2019;11:E5112.
- Dedrick RM, Guerrero-Bustamante CA, Garlena RA, et al. Engineered bacteriophages for treatment of a patient with a disseminated drug-resistant Mycobacterium abscessus. Nat Med. 2019;25:730-733.
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367-416.
- Jeong SH, Kim SY, Huh HJ, et al. Mycobacteriological characteristics and treatment outcomes in extrapulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus complex infections. Int J Infect Dis. 2017;60:49-56.
- Strnad L, Winthrop KL. Treatment of Mycobacterium abscessus complex. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;39:362-376.
- Cardenas DD, Yasmin T, Ahmed S. A rare insidious case of skin and soft tissue infection due to Mycobacterium abscessus: a case report. Cureus. 2022;14:E25725.
- Gonzalez-Santiago TM, Drage LA. Nontuberculous mycobacteria: skin and soft tissue infections. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:563-577.
- Dickison P, Howard V, O’Kane G, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection following penetrations through wetsuits. Australas J Dermatol. 2019;60:57-59.
- Choi H, Kim YI, Na CH, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus skin infection associated with shaving activity in a 75-year-old man. Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2018;22:204.
- Costa-Silva M, Cesar A, Gomes NP, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection in a spa worker. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2018;27:159-161.
- Besada E. Rapid growing mycobacteria and TNF-α blockers: case report of a fatal lung infection with Mycobacterium abscessus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011;29:705-707.
- Mufti AH, Toye BW, Mckendry RR, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection after use of tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor therapy: case report and review of infectious complications associated with tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor use. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005;53:233-238.
- Lee SK, Kim SY, Kim EY, et al. Mycobacterial infections in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor antagonists in South Korea. Lung. 2013;191:565-571.
- Rodríguez G, Ortegón M, Camargo D, et al. Iatrogenic Mycobacterium abscessus infection: histopathology of 71 patients. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:214-218.
- Firnhaber JM. Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma. Am Fam Physician. 2012;86:161-168.
- Walker HS, Hardwicke J. Non-melanoma skin cancer. Surgery (Oxford). 2022;40:39-45.
- Browse NL. The skin. In: Browse NL, ed. An Introduction to the Symptoms and Signs of Surgical Disease. 3rd ed. London Arnold Publications; 2001:66-69.
- Weedon D. Squamous cell carcinoma. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 3rd ed. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010;691-700.
- Powell F, Schroeter A, Su W, et al. Pyoderma gangrenosum: a review of 86 patients. QJM Int J Med. 1985;55:173-186.
- Brunsting LA, Goeckerman WH, O’Leary PA. Pyoderma (ecthyma) gangrenosum: clinical and experimental observations in five cases occurring in adults. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:743-768.
- Maverakis E, Ma C, Shinkai K, et al. Diagnostic criteria of ulcerative pyoderma gangrenosum: a Delphi consensus of international experts. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:461-466.
- André MFJ, Piette JC, Kémény JL, et al. Aseptic abscesses: a study of 30 patients with or without inflammatory bowel disease and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007;86:145. doi:10.1097/md.0b013e18064f9f3
- Femiano F, Lanza A, Buonaiuto C, et al. Pyostomatitis vegetans: a review of the literature. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2009;14:E114-E117.
- Kasperbauer SH, De Groote MA. The treatment of rapidly growing mycobacterial infections. Clin Chest Med. 2015;36:67-78.
- Duah M, Beshay M. Omadacycline in first-line combination therapy for pulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus infection: a case series. Int J Infect Dis. 2022;122:953-956.
- Minhas R, Sharma S, Kundu S. Utilizing the promise of omadacycline in a resistant, non-tubercular mycobacterial pulmonary infection. Cureus. 2019;11:E5112.
- Dedrick RM, Guerrero-Bustamante CA, Garlena RA, et al. Engineered bacteriophages for treatment of a patient with a disseminated drug-resistant Mycobacterium abscessus. Nat Med. 2019;25:730-733.
A 24-year-old man presented to our dermatology clinic with a painful lesion on the right buccal cheek of 4 months’ duration that had not changed in size or appearance. He had a history of Crohn disease that was being treated with 6-mercaptopurine and infliximab. He underwent jaw surgery 7 years prior for correction of an underbite, followed by subsequent surgery to remove the hardware 1 year after the initial procedure. He experienced recurring skin abscesses following the initial jaw surgery roughly once a year that were treated with bedside incision and drainage procedures in the emergency department followed by trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole with complete resolution; however, treatment with mupirocin ointment 2%, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and azithromycin did not provide symptomatic relief or resolution for the current lesion. Physical examination revealed a 4-cm ulceration with actively draining serosanguineous discharge. Two punch biopsies were performed; 48-hour bacterial and fungal cultures, as well as Giemsa, acid-fast bacilli, and periodic acid–Schiff staining were negative.
Intravenous formulation of secukinumab gets FDA approval
The Food and Drug Administration has approved an intravenous (IV) formulation of secukinumab (Cosentyx) for the treatment of adults with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA).
Secukinumab is the only treatment approved in an IV formulation that specifically targets and blocks interleukin-17A and the only non–tumor necrosis factor alpha IV option available to treat the three indications of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA, according to a press release from the drug’s manufacturer, Novartis.
The approval marks the first new IV treatment in 6 years for these three conditions. The drug was first approved in 2015 and up to now has been available only as a subcutaneous injection.
The new formulation is also approved for secukinumab’s other indications of plaque psoriasis in people aged 6 years or older, children aged 2 years or older with PsA, and enthesitis-related arthritis in patients aged 4 years or older.
“A significant portion of the millions of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA patients in the United States require treatment through IV infusions for a variety of reasons, including not being comfortable with self-injections or simply preferring to have treatments administered in their health care provider’s office,” Philip J. Mease, MD, clinical professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, and director of rheumatology research at the Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, said in the press release. “The approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation is an important milestone for patients because it expands the treatment options available to them with a different mechanism of action than existing biologic IV therapies, along with the comfort and familiarity of an established treatment.”
This IV formulation is administered monthly in a 30-minute, weight-based dosing regimen. This new option will become available before the end of the year, Novartis said.
“With this approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation, along with the subcutaneous formulation, we can broaden the use of Cosentyx to help more patients manage their condition with a medicine backed by more than a decade of clinical research and 8 years of real-world experience,” said Christy Siegel, vice president and head of immunology, Novartis U.S.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved an intravenous (IV) formulation of secukinumab (Cosentyx) for the treatment of adults with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA).
Secukinumab is the only treatment approved in an IV formulation that specifically targets and blocks interleukin-17A and the only non–tumor necrosis factor alpha IV option available to treat the three indications of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA, according to a press release from the drug’s manufacturer, Novartis.
The approval marks the first new IV treatment in 6 years for these three conditions. The drug was first approved in 2015 and up to now has been available only as a subcutaneous injection.
The new formulation is also approved for secukinumab’s other indications of plaque psoriasis in people aged 6 years or older, children aged 2 years or older with PsA, and enthesitis-related arthritis in patients aged 4 years or older.
“A significant portion of the millions of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA patients in the United States require treatment through IV infusions for a variety of reasons, including not being comfortable with self-injections or simply preferring to have treatments administered in their health care provider’s office,” Philip J. Mease, MD, clinical professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, and director of rheumatology research at the Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, said in the press release. “The approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation is an important milestone for patients because it expands the treatment options available to them with a different mechanism of action than existing biologic IV therapies, along with the comfort and familiarity of an established treatment.”
This IV formulation is administered monthly in a 30-minute, weight-based dosing regimen. This new option will become available before the end of the year, Novartis said.
“With this approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation, along with the subcutaneous formulation, we can broaden the use of Cosentyx to help more patients manage their condition with a medicine backed by more than a decade of clinical research and 8 years of real-world experience,” said Christy Siegel, vice president and head of immunology, Novartis U.S.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved an intravenous (IV) formulation of secukinumab (Cosentyx) for the treatment of adults with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA).
Secukinumab is the only treatment approved in an IV formulation that specifically targets and blocks interleukin-17A and the only non–tumor necrosis factor alpha IV option available to treat the three indications of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA, according to a press release from the drug’s manufacturer, Novartis.
The approval marks the first new IV treatment in 6 years for these three conditions. The drug was first approved in 2015 and up to now has been available only as a subcutaneous injection.
The new formulation is also approved for secukinumab’s other indications of plaque psoriasis in people aged 6 years or older, children aged 2 years or older with PsA, and enthesitis-related arthritis in patients aged 4 years or older.
“A significant portion of the millions of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA patients in the United States require treatment through IV infusions for a variety of reasons, including not being comfortable with self-injections or simply preferring to have treatments administered in their health care provider’s office,” Philip J. Mease, MD, clinical professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, and director of rheumatology research at the Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, said in the press release. “The approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation is an important milestone for patients because it expands the treatment options available to them with a different mechanism of action than existing biologic IV therapies, along with the comfort and familiarity of an established treatment.”
This IV formulation is administered monthly in a 30-minute, weight-based dosing regimen. This new option will become available before the end of the year, Novartis said.
“With this approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation, along with the subcutaneous formulation, we can broaden the use of Cosentyx to help more patients manage their condition with a medicine backed by more than a decade of clinical research and 8 years of real-world experience,” said Christy Siegel, vice president and head of immunology, Novartis U.S.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More evidence shows COVID-19’s link to risk for autoimmune disease
TOPLINE:
Research from South Korea provides additional evidence for the connection between COVID-19 and an increased risk for autoimmune conditions post infection.
METHODOLOGY:
- In this retrospective study, researchers identified 354,527 individuals diagnosed with COVID-19 via polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing from Oct. 8, 2020, to Dec. 31, 2021.
- Researchers compared the COVID-19 group with 6,134,940 healthy individuals who had no evidence of COVID-19 to quantify the risk for autoimmune and autoinflammatory connective tissue disorders.
- Patients were followed until diagnosis, death, or end of study period (Dec. 31, 2021).
TAKEAWAY:
- Risks for alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis, Crohn’s disease, and sarcoidosis were higher in the COVID-19 group.
- Patients with more severe COVID-19 (admitted to the ICU) were at greater risk for many autoimmune conditions, including alopecia totalis, psoriasis, vitiligo, and vasculitis.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results emphasize the need to focus on managing not only the acute stages of COVID-19 itself but also autoimmune diseases as complications of COVID-19,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Sung Ha Lim, MD, of Yonsei University, Wonju, South Korea, was the first author of the study, published in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was retrospective and was composed almost exclusively of individuals from a single ethnicity. The study could have included individuals with COVID-19 in the control group who did not undergo PCR testing. The analysis did not include detailed information on each patient, including genetic information, that could have contributed to autoimmune disease risk.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by a fund from the research program of the Korea Medical Institute and by grants from the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, the Korean Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the National Research Foundation of Korea. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Research from South Korea provides additional evidence for the connection between COVID-19 and an increased risk for autoimmune conditions post infection.
METHODOLOGY:
- In this retrospective study, researchers identified 354,527 individuals diagnosed with COVID-19 via polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing from Oct. 8, 2020, to Dec. 31, 2021.
- Researchers compared the COVID-19 group with 6,134,940 healthy individuals who had no evidence of COVID-19 to quantify the risk for autoimmune and autoinflammatory connective tissue disorders.
- Patients were followed until diagnosis, death, or end of study period (Dec. 31, 2021).
TAKEAWAY:
- Risks for alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis, Crohn’s disease, and sarcoidosis were higher in the COVID-19 group.
- Patients with more severe COVID-19 (admitted to the ICU) were at greater risk for many autoimmune conditions, including alopecia totalis, psoriasis, vitiligo, and vasculitis.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results emphasize the need to focus on managing not only the acute stages of COVID-19 itself but also autoimmune diseases as complications of COVID-19,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Sung Ha Lim, MD, of Yonsei University, Wonju, South Korea, was the first author of the study, published in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was retrospective and was composed almost exclusively of individuals from a single ethnicity. The study could have included individuals with COVID-19 in the control group who did not undergo PCR testing. The analysis did not include detailed information on each patient, including genetic information, that could have contributed to autoimmune disease risk.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by a fund from the research program of the Korea Medical Institute and by grants from the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, the Korean Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the National Research Foundation of Korea. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Research from South Korea provides additional evidence for the connection between COVID-19 and an increased risk for autoimmune conditions post infection.
METHODOLOGY:
- In this retrospective study, researchers identified 354,527 individuals diagnosed with COVID-19 via polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing from Oct. 8, 2020, to Dec. 31, 2021.
- Researchers compared the COVID-19 group with 6,134,940 healthy individuals who had no evidence of COVID-19 to quantify the risk for autoimmune and autoinflammatory connective tissue disorders.
- Patients were followed until diagnosis, death, or end of study period (Dec. 31, 2021).
TAKEAWAY:
- Risks for alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis, Crohn’s disease, and sarcoidosis were higher in the COVID-19 group.
- Patients with more severe COVID-19 (admitted to the ICU) were at greater risk for many autoimmune conditions, including alopecia totalis, psoriasis, vitiligo, and vasculitis.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results emphasize the need to focus on managing not only the acute stages of COVID-19 itself but also autoimmune diseases as complications of COVID-19,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Sung Ha Lim, MD, of Yonsei University, Wonju, South Korea, was the first author of the study, published in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was retrospective and was composed almost exclusively of individuals from a single ethnicity. The study could have included individuals with COVID-19 in the control group who did not undergo PCR testing. The analysis did not include detailed information on each patient, including genetic information, that could have contributed to autoimmune disease risk.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by a fund from the research program of the Korea Medical Institute and by grants from the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, the Korean Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the National Research Foundation of Korea. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Choosing which biologic to prescribe for psoriasis
CARLSBAD, CALIF. –
“When you look at the list of options it can be confusing to many clinicians in deciding which one to choose,” April W. Armstrong, MD, MPH, professor and chief of dermatology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said at the annual symposium of the California Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery.
One approach is to consider how the biologics compare in short- and long-term efficacy. “Several different meta-analyses of biologics have been conducted,” which include some head-to head studies, Dr. Armstrong said. “In terms of efficacy, [biologics] are similar at the population level,” she said.
In a meta-analysis of 71 randomized, controlled trials through July 2020, Dr. Armstrong and colleagues found that in the short-term, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 response rates at 10-16 weeks from baseline were highest for ixekizumab (72.9%), risankizumab (72.5%), and brodalumab (72%). These PASI 90 responses were significantly higher than among patients on guselkumab (65%), secukinumab (65%), infliximab (56.8%), certolizumab (400 mg: 49.6%; 200 mg: 42.2%), ustekinumab (90 mg: 47.9%; weight-based: 45.7%; 45 mg: 44.6%), adalimumab (43%), tildrakizumab (200 mg: 39.7%; 100 mg: 37.2%), etanercept (18.0%), apremilast (12.4%), and dimethyl fumarate (12.2%).
In a more recent meta-analysis, Dr. Armstrong and coauthors used area under the curve (AUC) analyses to compare the cumulative clinical benefits of biologics over 1 year. They found that the placebo-adjusted normalized maximum AUC for a PASI 100 response was greatest for ixekizumab (0.436), risankizumab (0.423), and brodalumab (0.378), followed by guselkumab (0.358), secukinumab (0.324), ustekinumab (0.201), adalimumab (0.183), and etanercept (0.087).
In Dr. Armstrong’s opinion, the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, and certolizumab “have served their purpose for plaque psoriasis over time, but these days I would probably choose either an IL [interleukin]-17 inhibitor or an IL-23 inhibitor first,” she said. Still, TNF inhibitors “are certainly good for psoriatic arthritis, and certolizumab is appropriate for patients who are pregnant or breastfeeding,” she said. “Avoid them in patients with demyelinating disease and in those with hepatitis B. They are not preferred in patients with latent TB or advanced CHF.”
Dr. Armstrong said that there are robust efficacy data for the IL-17 inhibitors ixekizumab, secukinumab, and brodalumab in psoriasis and in the peripheral and axial forms of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). “Avoid using them in patients with a personal history of inflammatory bowel disease,” she advised.
Low rates of oral candidiasis have been reported in the literature, “but this has not been issue with our approved IL-17 inhibitors so far,” she said.
The IL-23 inhibitors guselkumab, risankizumab, tildrakizumab, and ustekinumab have robust data for psoriasis efficacy, she said, and three – guselkumab, risankizumab, and ustekinumab – are also approved for PsA. “These agents have the advantage of fewer injections, and the evidence [of efficacy] for IL-23 inhibitors continues to evolve, such as in patients with psoriatic arthritis involving the spine,” Dr. Armstrong said.
She also shared how she deals with patients who fail to respond to biologics. “Do you switch drugs, or do you dose escalate?” she asked. “In most cases, the strategy for dose escalation is to shorten the interval between the injections so the dosing is delivered more frequently.” In a case of primary failure, which Dr. Armstrong defined as a patient who has never responded optimally to a biologic, consider revisiting the diagnosis. “Maybe it’s cutaneous T-cell lymphoma or some other condition, because our current IL-17 and IL-23 medications work extremely well,” she said. “So, if you have a patient who is not responding at all, I would question the diagnosis and consider a biopsy.”
She generally waits about 6 months before switching a patient to another biologic, “to see if they’re one of the late bloomers who may catch up in efficacy,” she explained. “Switching the class of biologic is another consideration.”
If a patient had responded to the biologic for a long time and then lost response – known as secondary failure – Dr. Armstrong considers dose escalation or a switch to another agent within the same class “if it helps to address comorbidities such as PsA,” she said. “You can also try across-class switching.”
Dr. Armstrong disclosed ties with AbbVie, Arcutis, ASLAN, Beiersdorf, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Dermira, Dermavant, EPI, Galderma, InCyte, Janssen, Leo, Lilly, Meiji, Modmed, Nimbus, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Parexel, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Suna, UCB, and Ventyx.
CARLSBAD, CALIF. –
“When you look at the list of options it can be confusing to many clinicians in deciding which one to choose,” April W. Armstrong, MD, MPH, professor and chief of dermatology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said at the annual symposium of the California Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery.
One approach is to consider how the biologics compare in short- and long-term efficacy. “Several different meta-analyses of biologics have been conducted,” which include some head-to head studies, Dr. Armstrong said. “In terms of efficacy, [biologics] are similar at the population level,” she said.
In a meta-analysis of 71 randomized, controlled trials through July 2020, Dr. Armstrong and colleagues found that in the short-term, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 response rates at 10-16 weeks from baseline were highest for ixekizumab (72.9%), risankizumab (72.5%), and brodalumab (72%). These PASI 90 responses were significantly higher than among patients on guselkumab (65%), secukinumab (65%), infliximab (56.8%), certolizumab (400 mg: 49.6%; 200 mg: 42.2%), ustekinumab (90 mg: 47.9%; weight-based: 45.7%; 45 mg: 44.6%), adalimumab (43%), tildrakizumab (200 mg: 39.7%; 100 mg: 37.2%), etanercept (18.0%), apremilast (12.4%), and dimethyl fumarate (12.2%).
In a more recent meta-analysis, Dr. Armstrong and coauthors used area under the curve (AUC) analyses to compare the cumulative clinical benefits of biologics over 1 year. They found that the placebo-adjusted normalized maximum AUC for a PASI 100 response was greatest for ixekizumab (0.436), risankizumab (0.423), and brodalumab (0.378), followed by guselkumab (0.358), secukinumab (0.324), ustekinumab (0.201), adalimumab (0.183), and etanercept (0.087).
In Dr. Armstrong’s opinion, the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, and certolizumab “have served their purpose for plaque psoriasis over time, but these days I would probably choose either an IL [interleukin]-17 inhibitor or an IL-23 inhibitor first,” she said. Still, TNF inhibitors “are certainly good for psoriatic arthritis, and certolizumab is appropriate for patients who are pregnant or breastfeeding,” she said. “Avoid them in patients with demyelinating disease and in those with hepatitis B. They are not preferred in patients with latent TB or advanced CHF.”
Dr. Armstrong said that there are robust efficacy data for the IL-17 inhibitors ixekizumab, secukinumab, and brodalumab in psoriasis and in the peripheral and axial forms of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). “Avoid using them in patients with a personal history of inflammatory bowel disease,” she advised.
Low rates of oral candidiasis have been reported in the literature, “but this has not been issue with our approved IL-17 inhibitors so far,” she said.
The IL-23 inhibitors guselkumab, risankizumab, tildrakizumab, and ustekinumab have robust data for psoriasis efficacy, she said, and three – guselkumab, risankizumab, and ustekinumab – are also approved for PsA. “These agents have the advantage of fewer injections, and the evidence [of efficacy] for IL-23 inhibitors continues to evolve, such as in patients with psoriatic arthritis involving the spine,” Dr. Armstrong said.
She also shared how she deals with patients who fail to respond to biologics. “Do you switch drugs, or do you dose escalate?” she asked. “In most cases, the strategy for dose escalation is to shorten the interval between the injections so the dosing is delivered more frequently.” In a case of primary failure, which Dr. Armstrong defined as a patient who has never responded optimally to a biologic, consider revisiting the diagnosis. “Maybe it’s cutaneous T-cell lymphoma or some other condition, because our current IL-17 and IL-23 medications work extremely well,” she said. “So, if you have a patient who is not responding at all, I would question the diagnosis and consider a biopsy.”
She generally waits about 6 months before switching a patient to another biologic, “to see if they’re one of the late bloomers who may catch up in efficacy,” she explained. “Switching the class of biologic is another consideration.”
If a patient had responded to the biologic for a long time and then lost response – known as secondary failure – Dr. Armstrong considers dose escalation or a switch to another agent within the same class “if it helps to address comorbidities such as PsA,” she said. “You can also try across-class switching.”
Dr. Armstrong disclosed ties with AbbVie, Arcutis, ASLAN, Beiersdorf, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Dermira, Dermavant, EPI, Galderma, InCyte, Janssen, Leo, Lilly, Meiji, Modmed, Nimbus, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Parexel, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Suna, UCB, and Ventyx.
CARLSBAD, CALIF. –
“When you look at the list of options it can be confusing to many clinicians in deciding which one to choose,” April W. Armstrong, MD, MPH, professor and chief of dermatology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said at the annual symposium of the California Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery.
One approach is to consider how the biologics compare in short- and long-term efficacy. “Several different meta-analyses of biologics have been conducted,” which include some head-to head studies, Dr. Armstrong said. “In terms of efficacy, [biologics] are similar at the population level,” she said.
In a meta-analysis of 71 randomized, controlled trials through July 2020, Dr. Armstrong and colleagues found that in the short-term, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 response rates at 10-16 weeks from baseline were highest for ixekizumab (72.9%), risankizumab (72.5%), and brodalumab (72%). These PASI 90 responses were significantly higher than among patients on guselkumab (65%), secukinumab (65%), infliximab (56.8%), certolizumab (400 mg: 49.6%; 200 mg: 42.2%), ustekinumab (90 mg: 47.9%; weight-based: 45.7%; 45 mg: 44.6%), adalimumab (43%), tildrakizumab (200 mg: 39.7%; 100 mg: 37.2%), etanercept (18.0%), apremilast (12.4%), and dimethyl fumarate (12.2%).
In a more recent meta-analysis, Dr. Armstrong and coauthors used area under the curve (AUC) analyses to compare the cumulative clinical benefits of biologics over 1 year. They found that the placebo-adjusted normalized maximum AUC for a PASI 100 response was greatest for ixekizumab (0.436), risankizumab (0.423), and brodalumab (0.378), followed by guselkumab (0.358), secukinumab (0.324), ustekinumab (0.201), adalimumab (0.183), and etanercept (0.087).
In Dr. Armstrong’s opinion, the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, and certolizumab “have served their purpose for plaque psoriasis over time, but these days I would probably choose either an IL [interleukin]-17 inhibitor or an IL-23 inhibitor first,” she said. Still, TNF inhibitors “are certainly good for psoriatic arthritis, and certolizumab is appropriate for patients who are pregnant or breastfeeding,” she said. “Avoid them in patients with demyelinating disease and in those with hepatitis B. They are not preferred in patients with latent TB or advanced CHF.”
Dr. Armstrong said that there are robust efficacy data for the IL-17 inhibitors ixekizumab, secukinumab, and brodalumab in psoriasis and in the peripheral and axial forms of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). “Avoid using them in patients with a personal history of inflammatory bowel disease,” she advised.
Low rates of oral candidiasis have been reported in the literature, “but this has not been issue with our approved IL-17 inhibitors so far,” she said.
The IL-23 inhibitors guselkumab, risankizumab, tildrakizumab, and ustekinumab have robust data for psoriasis efficacy, she said, and three – guselkumab, risankizumab, and ustekinumab – are also approved for PsA. “These agents have the advantage of fewer injections, and the evidence [of efficacy] for IL-23 inhibitors continues to evolve, such as in patients with psoriatic arthritis involving the spine,” Dr. Armstrong said.
She also shared how she deals with patients who fail to respond to biologics. “Do you switch drugs, or do you dose escalate?” she asked. “In most cases, the strategy for dose escalation is to shorten the interval between the injections so the dosing is delivered more frequently.” In a case of primary failure, which Dr. Armstrong defined as a patient who has never responded optimally to a biologic, consider revisiting the diagnosis. “Maybe it’s cutaneous T-cell lymphoma or some other condition, because our current IL-17 and IL-23 medications work extremely well,” she said. “So, if you have a patient who is not responding at all, I would question the diagnosis and consider a biopsy.”
She generally waits about 6 months before switching a patient to another biologic, “to see if they’re one of the late bloomers who may catch up in efficacy,” she explained. “Switching the class of biologic is another consideration.”
If a patient had responded to the biologic for a long time and then lost response – known as secondary failure – Dr. Armstrong considers dose escalation or a switch to another agent within the same class “if it helps to address comorbidities such as PsA,” she said. “You can also try across-class switching.”
Dr. Armstrong disclosed ties with AbbVie, Arcutis, ASLAN, Beiersdorf, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Dermira, Dermavant, EPI, Galderma, InCyte, Janssen, Leo, Lilly, Meiji, Modmed, Nimbus, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Parexel, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Suna, UCB, and Ventyx.
AT CALDERM 2023
FDA approves topical roflumilast for psoriasis in children aged 6-11
On Oct. 6, the This marks an expanded indication for the drug, which was first approved for the same indication in July, 2022, for individuals aged 12 and older.
Roflumilast cream 0.3% is a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor approved for once-daily topical treatment of mild, moderate, and severe plaque psoriasis. According to a press release from the manufacturer, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, approval of the expanded indication is based on data from a 4-week Maximal Usage Systemic Exposure (MUSE) study in children ages 6-11 years with plaque psoriasis. It stated that pharmacokinetic, safety, tolerability, and efficacy data from this study were “generally consistent” with data from the DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2 pivotal phase 3 trials in adults.
According to the press release, a future FDA review is planned for the results from a second MUSE study in children ages 2-5 years, as well as data from an ongoing open-label extension study evaluating the long-term safety of roflumilast cream in individuals with plaque psoriasis aged 2 years and older. The company markets topical roflumilast as Zoryve.
On Oct. 6, the This marks an expanded indication for the drug, which was first approved for the same indication in July, 2022, for individuals aged 12 and older.
Roflumilast cream 0.3% is a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor approved for once-daily topical treatment of mild, moderate, and severe plaque psoriasis. According to a press release from the manufacturer, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, approval of the expanded indication is based on data from a 4-week Maximal Usage Systemic Exposure (MUSE) study in children ages 6-11 years with plaque psoriasis. It stated that pharmacokinetic, safety, tolerability, and efficacy data from this study were “generally consistent” with data from the DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2 pivotal phase 3 trials in adults.
According to the press release, a future FDA review is planned for the results from a second MUSE study in children ages 2-5 years, as well as data from an ongoing open-label extension study evaluating the long-term safety of roflumilast cream in individuals with plaque psoriasis aged 2 years and older. The company markets topical roflumilast as Zoryve.
On Oct. 6, the This marks an expanded indication for the drug, which was first approved for the same indication in July, 2022, for individuals aged 12 and older.
Roflumilast cream 0.3% is a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor approved for once-daily topical treatment of mild, moderate, and severe plaque psoriasis. According to a press release from the manufacturer, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, approval of the expanded indication is based on data from a 4-week Maximal Usage Systemic Exposure (MUSE) study in children ages 6-11 years with plaque psoriasis. It stated that pharmacokinetic, safety, tolerability, and efficacy data from this study were “generally consistent” with data from the DERMIS-1 and DERMIS-2 pivotal phase 3 trials in adults.
According to the press release, a future FDA review is planned for the results from a second MUSE study in children ages 2-5 years, as well as data from an ongoing open-label extension study evaluating the long-term safety of roflumilast cream in individuals with plaque psoriasis aged 2 years and older. The company markets topical roflumilast as Zoryve.
FDA approves ninth Humira biosimilar, with interchangeability
The Food and Drug Administration has granted an interchangeability designation to adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), according to an announcement from Pfizer.
This is the second adalimumab biosimilar granted interchangeability. The first, adalimumab-adbm (Cyltezo), became available in July.
Biosimilars introduce market competition that can help lower drug prices. Adalimumab-afzb is one of nine approved biosimilars for Humira, and the last to launch in 2023.
Adalimumab-afzb is indicated for:
- Adults with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis in patients 2 years of age and older.
- Adults with psoriatic arthritis.
- Adults with ankylosing spondylitis.
- Crohn’s disease in adults and children 6 years of age and older.
- Adults with ulcerative colitis.
- Adults with plaque psoriasis.
- Adults with hidradenitis suppurativa.
- Adults with noninfectious intermediate and posterior uveitis and panuveitis.
“With this designation, Abrilada is now both biosimilar to and interchangeable with Humira, reinforcing confidence among physicians and pharmacists that there is no decrease in effectiveness or increase in safety risk associated with switching between Abrilada and the reference product,” Roy Fleischmann, MD, clinical professor of medicine, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, said in Pfizer’s statement.
An interchangeability designation allows pharmacists to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician (according to state law). To achieve this designation, Pfizer submitted data from a phase 3 study led by Dr. Fleischmann that evaluated adalimumab-afzb in patients with RA. Patients who were switched three times between the biosimilar and the reference product had outcomes similar to those of patients continuously treated with the reference product.
Adalimumab-afzb will be available later in October at a 5% discount from Humira’s price. Later this year, the drug will launch at a second price, a 60% discount from Humira.
Full prescribing information for adalimumab-afzb is available here.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted an interchangeability designation to adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), according to an announcement from Pfizer.
This is the second adalimumab biosimilar granted interchangeability. The first, adalimumab-adbm (Cyltezo), became available in July.
Biosimilars introduce market competition that can help lower drug prices. Adalimumab-afzb is one of nine approved biosimilars for Humira, and the last to launch in 2023.
Adalimumab-afzb is indicated for:
- Adults with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis in patients 2 years of age and older.
- Adults with psoriatic arthritis.
- Adults with ankylosing spondylitis.
- Crohn’s disease in adults and children 6 years of age and older.
- Adults with ulcerative colitis.
- Adults with plaque psoriasis.
- Adults with hidradenitis suppurativa.
- Adults with noninfectious intermediate and posterior uveitis and panuveitis.
“With this designation, Abrilada is now both biosimilar to and interchangeable with Humira, reinforcing confidence among physicians and pharmacists that there is no decrease in effectiveness or increase in safety risk associated with switching between Abrilada and the reference product,” Roy Fleischmann, MD, clinical professor of medicine, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, said in Pfizer’s statement.
An interchangeability designation allows pharmacists to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician (according to state law). To achieve this designation, Pfizer submitted data from a phase 3 study led by Dr. Fleischmann that evaluated adalimumab-afzb in patients with RA. Patients who were switched three times between the biosimilar and the reference product had outcomes similar to those of patients continuously treated with the reference product.
Adalimumab-afzb will be available later in October at a 5% discount from Humira’s price. Later this year, the drug will launch at a second price, a 60% discount from Humira.
Full prescribing information for adalimumab-afzb is available here.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted an interchangeability designation to adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), according to an announcement from Pfizer.
This is the second adalimumab biosimilar granted interchangeability. The first, adalimumab-adbm (Cyltezo), became available in July.
Biosimilars introduce market competition that can help lower drug prices. Adalimumab-afzb is one of nine approved biosimilars for Humira, and the last to launch in 2023.
Adalimumab-afzb is indicated for:
- Adults with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis in patients 2 years of age and older.
- Adults with psoriatic arthritis.
- Adults with ankylosing spondylitis.
- Crohn’s disease in adults and children 6 years of age and older.
- Adults with ulcerative colitis.
- Adults with plaque psoriasis.
- Adults with hidradenitis suppurativa.
- Adults with noninfectious intermediate and posterior uveitis and panuveitis.
“With this designation, Abrilada is now both biosimilar to and interchangeable with Humira, reinforcing confidence among physicians and pharmacists that there is no decrease in effectiveness or increase in safety risk associated with switching between Abrilada and the reference product,” Roy Fleischmann, MD, clinical professor of medicine, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, said in Pfizer’s statement.
An interchangeability designation allows pharmacists to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician (according to state law). To achieve this designation, Pfizer submitted data from a phase 3 study led by Dr. Fleischmann that evaluated adalimumab-afzb in patients with RA. Patients who were switched three times between the biosimilar and the reference product had outcomes similar to those of patients continuously treated with the reference product.
Adalimumab-afzb will be available later in October at a 5% discount from Humira’s price. Later this year, the drug will launch at a second price, a 60% discount from Humira.
Full prescribing information for adalimumab-afzb is available here.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Training more doctors should be our first priority, says ethicist
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Recently, the Supreme Court of the United States struck down the use of affirmative action in admissions to colleges, universities, medical schools, and nursing schools. This has led to an enormous amount of worry and concern, particularly in medical school admissions in the world I’m in, where people start to say that diversity matters. Diversity is important.
I know many deans of medical schools immediately sent out messages of reassurance to their students, saying New York University or Stanford or Harvard or Minnesota or Case Western is still deeply concerned about diversity, and we’re going to do what we can to preserve attention to diversity.
I’ve served on admissions at a number of schools over the years for med school. I understand – and have been told – that diversity is important, and according to the Supreme Court, not explicitly by race. There are obviously many variables to take into account when trying to keep diversity at the forefront of admissions.
At the schools I’ve been at, including Columbia, NYU, University of Pittsburgh, University of Minnesota, and University of Pennsylvania, there are plenty of qualified students. Happily, we’ve always been engaged in some effort to try and whittle down the class to the size that we can manage and accept, and many qualified students don’t get admitted.
The first order of business for me is not to worry about how to maintain diversity. It’s to recognize that we need more doctors, nurses, and mental health care providers. I will, in a second, say a few words about diversity and where it fits into admissions, but I want to make the point clearly that what we should be doing is trying to expand the pool of students who are going to become doctors, nurses, mental health care providers, and social workers.
There are too many early retirements. We don’t have the person power we need to manage the health care challenges of an aging population. Let’s not get lost in arguing about what characteristics ought to get you into the finest medical schools. Let’s realize that we have to expand the number of schools we have.
We better be working pretty hard to expand our physician assistant programs, to make sure that we give full authority to qualified dentists and nurses who can help deliver some clinical care. We need more folks. That’s really where the battle ought to be: How do we get that done and how do we get it done quickly, not arguing about who’s in, who’s out, and why.
That said, diversity to me has never meant just race. I’m always interested in gender orientation, disability, and geographic input. Sometimes in decisions that you’re looking at, when I have students in front of me, they tell me they play a musical instrument or about the obstacles they had to overcome to get to medical school. Some of them will say they were involved in 4-H and did rodeo in high school or junior high school, which makes them a diverse potential student with characteristics that maybe some others don’t bring.
I’m not against diversity. I think having a rich set of experiences in any class – medicine, nursing, whatever it’s going to be – is beneficial to the students. They learn from each other. It is sometimes said that it’s also good for patients. I’m a little less excited about that, because I think our training goal should be to make every medical student and nursing student qualified to treat anybody.
I don’t think that, just because you’re Latinx or gay, that’s going to make a gay patient feel better. I think we should teach our students how to give care to everybody that they encounter. They shouldn’t have to match up characteristics to feel like they’re going to get quality care. That isn’t the right reason.
When you have a diverse set of providers, they can call that out and be on the alert for it, and that’s very important.
I also believe that we should think widely and broadly about diversity. Maybe race is out, but certainly other experiences related to income, background, struggle that got you to the point where you’re applying to medical school, motivation, the kinds of experiences you might have had caring for an elderly person, dealing with a disability or learning disability, and trying to overcome, let’s say, going to school in a poor area with not such a wonderful school, really help in terms of forming professionalism, empathy, and a caring point of view.
To me, the main goal is to expand our workforce. The secondary goal is to stay diverse, because we get better providers when we do so.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Recently, the Supreme Court of the United States struck down the use of affirmative action in admissions to colleges, universities, medical schools, and nursing schools. This has led to an enormous amount of worry and concern, particularly in medical school admissions in the world I’m in, where people start to say that diversity matters. Diversity is important.
I know many deans of medical schools immediately sent out messages of reassurance to their students, saying New York University or Stanford or Harvard or Minnesota or Case Western is still deeply concerned about diversity, and we’re going to do what we can to preserve attention to diversity.
I’ve served on admissions at a number of schools over the years for med school. I understand – and have been told – that diversity is important, and according to the Supreme Court, not explicitly by race. There are obviously many variables to take into account when trying to keep diversity at the forefront of admissions.
At the schools I’ve been at, including Columbia, NYU, University of Pittsburgh, University of Minnesota, and University of Pennsylvania, there are plenty of qualified students. Happily, we’ve always been engaged in some effort to try and whittle down the class to the size that we can manage and accept, and many qualified students don’t get admitted.
The first order of business for me is not to worry about how to maintain diversity. It’s to recognize that we need more doctors, nurses, and mental health care providers. I will, in a second, say a few words about diversity and where it fits into admissions, but I want to make the point clearly that what we should be doing is trying to expand the pool of students who are going to become doctors, nurses, mental health care providers, and social workers.
There are too many early retirements. We don’t have the person power we need to manage the health care challenges of an aging population. Let’s not get lost in arguing about what characteristics ought to get you into the finest medical schools. Let’s realize that we have to expand the number of schools we have.
We better be working pretty hard to expand our physician assistant programs, to make sure that we give full authority to qualified dentists and nurses who can help deliver some clinical care. We need more folks. That’s really where the battle ought to be: How do we get that done and how do we get it done quickly, not arguing about who’s in, who’s out, and why.
That said, diversity to me has never meant just race. I’m always interested in gender orientation, disability, and geographic input. Sometimes in decisions that you’re looking at, when I have students in front of me, they tell me they play a musical instrument or about the obstacles they had to overcome to get to medical school. Some of them will say they were involved in 4-H and did rodeo in high school or junior high school, which makes them a diverse potential student with characteristics that maybe some others don’t bring.
I’m not against diversity. I think having a rich set of experiences in any class – medicine, nursing, whatever it’s going to be – is beneficial to the students. They learn from each other. It is sometimes said that it’s also good for patients. I’m a little less excited about that, because I think our training goal should be to make every medical student and nursing student qualified to treat anybody.
I don’t think that, just because you’re Latinx or gay, that’s going to make a gay patient feel better. I think we should teach our students how to give care to everybody that they encounter. They shouldn’t have to match up characteristics to feel like they’re going to get quality care. That isn’t the right reason.
When you have a diverse set of providers, they can call that out and be on the alert for it, and that’s very important.
I also believe that we should think widely and broadly about diversity. Maybe race is out, but certainly other experiences related to income, background, struggle that got you to the point where you’re applying to medical school, motivation, the kinds of experiences you might have had caring for an elderly person, dealing with a disability or learning disability, and trying to overcome, let’s say, going to school in a poor area with not such a wonderful school, really help in terms of forming professionalism, empathy, and a caring point of view.
To me, the main goal is to expand our workforce. The secondary goal is to stay diverse, because we get better providers when we do so.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Recently, the Supreme Court of the United States struck down the use of affirmative action in admissions to colleges, universities, medical schools, and nursing schools. This has led to an enormous amount of worry and concern, particularly in medical school admissions in the world I’m in, where people start to say that diversity matters. Diversity is important.
I know many deans of medical schools immediately sent out messages of reassurance to their students, saying New York University or Stanford or Harvard or Minnesota or Case Western is still deeply concerned about diversity, and we’re going to do what we can to preserve attention to diversity.
I’ve served on admissions at a number of schools over the years for med school. I understand – and have been told – that diversity is important, and according to the Supreme Court, not explicitly by race. There are obviously many variables to take into account when trying to keep diversity at the forefront of admissions.
At the schools I’ve been at, including Columbia, NYU, University of Pittsburgh, University of Minnesota, and University of Pennsylvania, there are plenty of qualified students. Happily, we’ve always been engaged in some effort to try and whittle down the class to the size that we can manage and accept, and many qualified students don’t get admitted.
The first order of business for me is not to worry about how to maintain diversity. It’s to recognize that we need more doctors, nurses, and mental health care providers. I will, in a second, say a few words about diversity and where it fits into admissions, but I want to make the point clearly that what we should be doing is trying to expand the pool of students who are going to become doctors, nurses, mental health care providers, and social workers.
There are too many early retirements. We don’t have the person power we need to manage the health care challenges of an aging population. Let’s not get lost in arguing about what characteristics ought to get you into the finest medical schools. Let’s realize that we have to expand the number of schools we have.
We better be working pretty hard to expand our physician assistant programs, to make sure that we give full authority to qualified dentists and nurses who can help deliver some clinical care. We need more folks. That’s really where the battle ought to be: How do we get that done and how do we get it done quickly, not arguing about who’s in, who’s out, and why.
That said, diversity to me has never meant just race. I’m always interested in gender orientation, disability, and geographic input. Sometimes in decisions that you’re looking at, when I have students in front of me, they tell me they play a musical instrument or about the obstacles they had to overcome to get to medical school. Some of them will say they were involved in 4-H and did rodeo in high school or junior high school, which makes them a diverse potential student with characteristics that maybe some others don’t bring.
I’m not against diversity. I think having a rich set of experiences in any class – medicine, nursing, whatever it’s going to be – is beneficial to the students. They learn from each other. It is sometimes said that it’s also good for patients. I’m a little less excited about that, because I think our training goal should be to make every medical student and nursing student qualified to treat anybody.
I don’t think that, just because you’re Latinx or gay, that’s going to make a gay patient feel better. I think we should teach our students how to give care to everybody that they encounter. They shouldn’t have to match up characteristics to feel like they’re going to get quality care. That isn’t the right reason.
When you have a diverse set of providers, they can call that out and be on the alert for it, and that’s very important.
I also believe that we should think widely and broadly about diversity. Maybe race is out, but certainly other experiences related to income, background, struggle that got you to the point where you’re applying to medical school, motivation, the kinds of experiences you might have had caring for an elderly person, dealing with a disability or learning disability, and trying to overcome, let’s say, going to school in a poor area with not such a wonderful school, really help in terms of forming professionalism, empathy, and a caring point of view.
To me, the main goal is to expand our workforce. The secondary goal is to stay diverse, because we get better providers when we do so.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
From scrubs to screens: Growing your patient base with social media
With physicians under increasing pressure to see more patients in shorter office visits, developing a social media presence may offer valuable opportunities to connect with patients, explain procedures, combat misinformation, talk through a published article, and even share a joke or meme.
But there are caveats for doctors posting on social media platforms. This news organization spoke to four doctors who successfully use social media.
Use social media for the right reasons
While you’re under no obligation to build a social media presence, if you’re going to do it, be sure your intentions are solid, said Don S. Dizon, MD, professor of medicine and professor of surgery at Brown University, Providence, R.I. Dr. Dizon, as @DoctorDon, has 44,700 TikTok followers and uses the platform to answer cancer-related questions.
“It should be your altruism that motivates you to post,” said Dr. Dizon, who is also associate director of community outreach and engagement at the Legorreta Cancer Center in Providence, R.I., and director of medical oncology at Rhode Island Hospital. “What we can do for society at large is to provide our input into issues, add informed opinions where there’s controversy, and address misinformation.”
If you don’t know where to start, consider seeking a digital mentor to talk through your options.
“You may never meet this person, but you should choose them if you like their style, their content, their delivery, and their perspective,” Dr. Dizon said. “Find another doctor out there on social media whom you feel you can emulate. Take your time, too. Soon enough, you’ll develop your own style and your own online persona.”
Post clear, accurate information
If you want to be lighthearted on social media, that’s your choice. But Jennifer Trachtenberg, a pediatrician with nearly 7,000 Instagram followers in New York who posts as @askdrjen, prefers to offer vaccine scheduling tips, alert parents about COVID-19 rates, and offer advice on cold and flu prevention.
“Right now, I’m mainly doing this to educate patients and make them aware of topics that I think are important and that I see my patients needing more information on,” she said. “We have to be clear: People take what we say seriously. So, while it’s important to be relatable, it’s even more important to share evidence-based information.”
Many patients get their information on social media
While patients once came to the doctor armed with information sourced via “Doctor Google,” today, just as many patients use social media to learn about their condition or the medications they’re taking.
Unfortunately, a recent Ohio State University, Columbus, study found that the majority of gynecologic cancer advice on TikTok, for example, was either misleading or inaccurate.
“This misinformation should be a motivator for physicians to explore the social media space,” Dr. Dizon said. “Our voices need to be on there.”
Break down barriers – and make connections
Mike Natter, MD, an endocrinologist in New York, has type 1 diabetes. This informs his work – and his life – and he’s passionate about sharing it with his 117,000 followers as @mike.natter on Instagram.
“A lot of type 1s follow me, so there’s an advocacy component to what I do,” he said. “I enjoy being able to raise awareness and keep people up to date on the newest research and treatment.”
But that’s not all: Dr. Natter is also an artist who went to art school before he went to medical school, and his account is rife with his cartoons and illustrations about everything from valvular disease to diabetic ketoacidosis.
“I found that I was drawing a lot of my notes in medical school,” he said. “When I drew my notes, I did quite well, and I think that using art and illustration is a great tool. It breaks down barriers and makes health information all the more accessible to everyone.”
Share your expertise as a doctor – and a person
As a mom and pediatrician, Krupa Playforth, MD, who practices in Vienna, Va., knows that what she posts carries weight. So, whether she’s writing about backpack safety tips, choking hazards, or separation anxiety, her followers can rest assured that she’s posting responsibly.
“Pediatricians often underestimate how smart parents are,” said Dr. Playforth, who has three kids, ages 8, 5, and 2, and has 137,000 followers on @thepediatricianmom, her Instagram account. “Their anxiety comes from an understandable place, which is why I see my role as that of a parent and pediatrician who can translate the knowledge pediatricians have into something parents can understand.”
Dr. Playforth, who jumped on social media during COVID-19 and experienced a positive response in her local community, said being on social media is imperative if you’re a pediatrician.
“This is the future of pediatric medicine in particular,” she said. “A lot of pediatricians don’t want to embrace social media, but I think that’s a mistake. After all, while parents think pediatricians have all the answers, when we think of our own children, most doctors are like other parents – we can’t think objectively about our kids. It’s helpful for me to share that and to help parents feel less alone.”
If you’re not yet using social media to the best of your physician abilities, you might take a shot at becoming widely recognizable. Pick a preferred platform, answer common patient questions, dispel medical myths, provide pertinent information, and let your personality shine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With physicians under increasing pressure to see more patients in shorter office visits, developing a social media presence may offer valuable opportunities to connect with patients, explain procedures, combat misinformation, talk through a published article, and even share a joke or meme.
But there are caveats for doctors posting on social media platforms. This news organization spoke to four doctors who successfully use social media.
Use social media for the right reasons
While you’re under no obligation to build a social media presence, if you’re going to do it, be sure your intentions are solid, said Don S. Dizon, MD, professor of medicine and professor of surgery at Brown University, Providence, R.I. Dr. Dizon, as @DoctorDon, has 44,700 TikTok followers and uses the platform to answer cancer-related questions.
“It should be your altruism that motivates you to post,” said Dr. Dizon, who is also associate director of community outreach and engagement at the Legorreta Cancer Center in Providence, R.I., and director of medical oncology at Rhode Island Hospital. “What we can do for society at large is to provide our input into issues, add informed opinions where there’s controversy, and address misinformation.”
If you don’t know where to start, consider seeking a digital mentor to talk through your options.
“You may never meet this person, but you should choose them if you like their style, their content, their delivery, and their perspective,” Dr. Dizon said. “Find another doctor out there on social media whom you feel you can emulate. Take your time, too. Soon enough, you’ll develop your own style and your own online persona.”
Post clear, accurate information
If you want to be lighthearted on social media, that’s your choice. But Jennifer Trachtenberg, a pediatrician with nearly 7,000 Instagram followers in New York who posts as @askdrjen, prefers to offer vaccine scheduling tips, alert parents about COVID-19 rates, and offer advice on cold and flu prevention.
“Right now, I’m mainly doing this to educate patients and make them aware of topics that I think are important and that I see my patients needing more information on,” she said. “We have to be clear: People take what we say seriously. So, while it’s important to be relatable, it’s even more important to share evidence-based information.”
Many patients get their information on social media
While patients once came to the doctor armed with information sourced via “Doctor Google,” today, just as many patients use social media to learn about their condition or the medications they’re taking.
Unfortunately, a recent Ohio State University, Columbus, study found that the majority of gynecologic cancer advice on TikTok, for example, was either misleading or inaccurate.
“This misinformation should be a motivator for physicians to explore the social media space,” Dr. Dizon said. “Our voices need to be on there.”
Break down barriers – and make connections
Mike Natter, MD, an endocrinologist in New York, has type 1 diabetes. This informs his work – and his life – and he’s passionate about sharing it with his 117,000 followers as @mike.natter on Instagram.
“A lot of type 1s follow me, so there’s an advocacy component to what I do,” he said. “I enjoy being able to raise awareness and keep people up to date on the newest research and treatment.”
But that’s not all: Dr. Natter is also an artist who went to art school before he went to medical school, and his account is rife with his cartoons and illustrations about everything from valvular disease to diabetic ketoacidosis.
“I found that I was drawing a lot of my notes in medical school,” he said. “When I drew my notes, I did quite well, and I think that using art and illustration is a great tool. It breaks down barriers and makes health information all the more accessible to everyone.”
Share your expertise as a doctor – and a person
As a mom and pediatrician, Krupa Playforth, MD, who practices in Vienna, Va., knows that what she posts carries weight. So, whether she’s writing about backpack safety tips, choking hazards, or separation anxiety, her followers can rest assured that she’s posting responsibly.
“Pediatricians often underestimate how smart parents are,” said Dr. Playforth, who has three kids, ages 8, 5, and 2, and has 137,000 followers on @thepediatricianmom, her Instagram account. “Their anxiety comes from an understandable place, which is why I see my role as that of a parent and pediatrician who can translate the knowledge pediatricians have into something parents can understand.”
Dr. Playforth, who jumped on social media during COVID-19 and experienced a positive response in her local community, said being on social media is imperative if you’re a pediatrician.
“This is the future of pediatric medicine in particular,” she said. “A lot of pediatricians don’t want to embrace social media, but I think that’s a mistake. After all, while parents think pediatricians have all the answers, when we think of our own children, most doctors are like other parents – we can’t think objectively about our kids. It’s helpful for me to share that and to help parents feel less alone.”
If you’re not yet using social media to the best of your physician abilities, you might take a shot at becoming widely recognizable. Pick a preferred platform, answer common patient questions, dispel medical myths, provide pertinent information, and let your personality shine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With physicians under increasing pressure to see more patients in shorter office visits, developing a social media presence may offer valuable opportunities to connect with patients, explain procedures, combat misinformation, talk through a published article, and even share a joke or meme.
But there are caveats for doctors posting on social media platforms. This news organization spoke to four doctors who successfully use social media.
Use social media for the right reasons
While you’re under no obligation to build a social media presence, if you’re going to do it, be sure your intentions are solid, said Don S. Dizon, MD, professor of medicine and professor of surgery at Brown University, Providence, R.I. Dr. Dizon, as @DoctorDon, has 44,700 TikTok followers and uses the platform to answer cancer-related questions.
“It should be your altruism that motivates you to post,” said Dr. Dizon, who is also associate director of community outreach and engagement at the Legorreta Cancer Center in Providence, R.I., and director of medical oncology at Rhode Island Hospital. “What we can do for society at large is to provide our input into issues, add informed opinions where there’s controversy, and address misinformation.”
If you don’t know where to start, consider seeking a digital mentor to talk through your options.
“You may never meet this person, but you should choose them if you like their style, their content, their delivery, and their perspective,” Dr. Dizon said. “Find another doctor out there on social media whom you feel you can emulate. Take your time, too. Soon enough, you’ll develop your own style and your own online persona.”
Post clear, accurate information
If you want to be lighthearted on social media, that’s your choice. But Jennifer Trachtenberg, a pediatrician with nearly 7,000 Instagram followers in New York who posts as @askdrjen, prefers to offer vaccine scheduling tips, alert parents about COVID-19 rates, and offer advice on cold and flu prevention.
“Right now, I’m mainly doing this to educate patients and make them aware of topics that I think are important and that I see my patients needing more information on,” she said. “We have to be clear: People take what we say seriously. So, while it’s important to be relatable, it’s even more important to share evidence-based information.”
Many patients get their information on social media
While patients once came to the doctor armed with information sourced via “Doctor Google,” today, just as many patients use social media to learn about their condition or the medications they’re taking.
Unfortunately, a recent Ohio State University, Columbus, study found that the majority of gynecologic cancer advice on TikTok, for example, was either misleading or inaccurate.
“This misinformation should be a motivator for physicians to explore the social media space,” Dr. Dizon said. “Our voices need to be on there.”
Break down barriers – and make connections
Mike Natter, MD, an endocrinologist in New York, has type 1 diabetes. This informs his work – and his life – and he’s passionate about sharing it with his 117,000 followers as @mike.natter on Instagram.
“A lot of type 1s follow me, so there’s an advocacy component to what I do,” he said. “I enjoy being able to raise awareness and keep people up to date on the newest research and treatment.”
But that’s not all: Dr. Natter is also an artist who went to art school before he went to medical school, and his account is rife with his cartoons and illustrations about everything from valvular disease to diabetic ketoacidosis.
“I found that I was drawing a lot of my notes in medical school,” he said. “When I drew my notes, I did quite well, and I think that using art and illustration is a great tool. It breaks down barriers and makes health information all the more accessible to everyone.”
Share your expertise as a doctor – and a person
As a mom and pediatrician, Krupa Playforth, MD, who practices in Vienna, Va., knows that what she posts carries weight. So, whether she’s writing about backpack safety tips, choking hazards, or separation anxiety, her followers can rest assured that she’s posting responsibly.
“Pediatricians often underestimate how smart parents are,” said Dr. Playforth, who has three kids, ages 8, 5, and 2, and has 137,000 followers on @thepediatricianmom, her Instagram account. “Their anxiety comes from an understandable place, which is why I see my role as that of a parent and pediatrician who can translate the knowledge pediatricians have into something parents can understand.”
Dr. Playforth, who jumped on social media during COVID-19 and experienced a positive response in her local community, said being on social media is imperative if you’re a pediatrician.
“This is the future of pediatric medicine in particular,” she said. “A lot of pediatricians don’t want to embrace social media, but I think that’s a mistake. After all, while parents think pediatricians have all the answers, when we think of our own children, most doctors are like other parents – we can’t think objectively about our kids. It’s helpful for me to share that and to help parents feel less alone.”
If you’re not yet using social media to the best of your physician abilities, you might take a shot at becoming widely recognizable. Pick a preferred platform, answer common patient questions, dispel medical myths, provide pertinent information, and let your personality shine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Spironolactone safe, effective option for women with hidradenitis suppurativa
CARLSBAD, CALIF. –
Those are the key findings from a single-center retrospective study that Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, and colleagues presented during a poster session at the annual symposium of the California Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery.
In an interview after the meeting, Dr. Hsiao, a dermatologist who directs the hidradenitis suppurativa clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said that hormones are thought to play a role in HS pathogenesis given the typical HS symptom onset around puberty and fluctuations in disease activity with menses (typically premenstrual flares) and pregnancy. “Spironolactone, an anti-androgenic agent, is used to treat HS in women; however, there is a paucity of data on the efficacy of spironolactone for HS and whether certain patient characteristics may influence treatment response,” she told this news organization. “This study is unique in that we contribute to existing literature regarding spironolactone efficacy in HS and we also investigate whether the presence of menstrual HS flares or polycystic ovarian syndrome influences the likelihood of response to spironolactone.”
For the analysis, Dr. Hsiao and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 53 adult women with HS who were prescribed spironolactone and who received care at USC’s HS clinic between January 2015 and December 2021. They collected data on demographics, comorbidities, HS medications, treatment response at 3 and 6 months, as well as adverse events. They also evaluated physician-assessed response to treatment when available.
The mean age of patients was 31 years, 37% were White, 30.4% were Black, 21.7% were Hispanic, 6.5% were Asian, and the remainder were biracial. The mean age at HS diagnosis was 25.1 years and the three most common comorbidities were acne (50.9%), obesity (45.3%), and anemia (37.7%). As for menstrual history, 56.6% had perimenstrual HS flares and 37.7% had irregular menstrual cycles. The top three classes of concomitant medications were antibiotics (58.5%), oral contraceptives (50.9%), and other birth control methods (18.9%).
The mean spironolactone dose was 104 mg/day; 84.1% of the women experienced improvement of HS 3 months after starting the drug, while 81.8% had improvement of their HS 6 months after starting the drug. The researchers also found that 56.6% of women had documented perimenstrual HS flares and 7.5% had PCOS.
“Spironolactone is often thought of as a helpful medication to consider if a patient reports having HS flares around menses or features of PCOS,” Dr. Hsiao said. However, she added, “our study found that there was no statistically significant difference in the response to spironolactone based on the presence of premenstrual flares or concomitant PCOS.” She said that spironolactone may be used as an adjunct therapeutic option in patients with more severe disease in addition to other medical and surgical therapies for HS. “Combining different treatment options that target different pathophysiologic factors is usually required to achieve adequate disease control in HS,” she said.
Dr. Hsiao acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its single-center design and small sample size. “A confounding variable is that some patients were on other medications in addition to spironolactone, which may have influenced treatment outcomes,” she noted. “Larger prospective studies are needed to identify optimal dosing for spironolactone therapy in HS as well as predictors of treatment response.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, said that with only one FDA-approved systemic medication for the management of HS (adalimumab), “we off-label bandits must be creative to curtail the incredibly painful impact this chronic, destructive inflammatory disease can have on our patients.”
“The evidence supporting our approaches, whether it be antibiotics, immunomodulators, or in this case, antihormonal therapies, is limited, so more data is always welcome,” said Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study. “One very interesting point raised by the authors, one I share with my trainees frequently from my own experience, is that regardless of menstrual cycle abnormalities, spironolactone can be impactful. This is important to remember, in that overt signs of hormonal influences is not a requisite for the use or effectiveness of antihormonal therapy.”
Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of board of directors for the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation. She has also served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, UCB, as a speaker for AbbVie, and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte. Dr. Friedman reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
CARLSBAD, CALIF. –
Those are the key findings from a single-center retrospective study that Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, and colleagues presented during a poster session at the annual symposium of the California Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery.
In an interview after the meeting, Dr. Hsiao, a dermatologist who directs the hidradenitis suppurativa clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said that hormones are thought to play a role in HS pathogenesis given the typical HS symptom onset around puberty and fluctuations in disease activity with menses (typically premenstrual flares) and pregnancy. “Spironolactone, an anti-androgenic agent, is used to treat HS in women; however, there is a paucity of data on the efficacy of spironolactone for HS and whether certain patient characteristics may influence treatment response,” she told this news organization. “This study is unique in that we contribute to existing literature regarding spironolactone efficacy in HS and we also investigate whether the presence of menstrual HS flares or polycystic ovarian syndrome influences the likelihood of response to spironolactone.”
For the analysis, Dr. Hsiao and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 53 adult women with HS who were prescribed spironolactone and who received care at USC’s HS clinic between January 2015 and December 2021. They collected data on demographics, comorbidities, HS medications, treatment response at 3 and 6 months, as well as adverse events. They also evaluated physician-assessed response to treatment when available.
The mean age of patients was 31 years, 37% were White, 30.4% were Black, 21.7% were Hispanic, 6.5% were Asian, and the remainder were biracial. The mean age at HS diagnosis was 25.1 years and the three most common comorbidities were acne (50.9%), obesity (45.3%), and anemia (37.7%). As for menstrual history, 56.6% had perimenstrual HS flares and 37.7% had irregular menstrual cycles. The top three classes of concomitant medications were antibiotics (58.5%), oral contraceptives (50.9%), and other birth control methods (18.9%).
The mean spironolactone dose was 104 mg/day; 84.1% of the women experienced improvement of HS 3 months after starting the drug, while 81.8% had improvement of their HS 6 months after starting the drug. The researchers also found that 56.6% of women had documented perimenstrual HS flares and 7.5% had PCOS.
“Spironolactone is often thought of as a helpful medication to consider if a patient reports having HS flares around menses or features of PCOS,” Dr. Hsiao said. However, she added, “our study found that there was no statistically significant difference in the response to spironolactone based on the presence of premenstrual flares or concomitant PCOS.” She said that spironolactone may be used as an adjunct therapeutic option in patients with more severe disease in addition to other medical and surgical therapies for HS. “Combining different treatment options that target different pathophysiologic factors is usually required to achieve adequate disease control in HS,” she said.
Dr. Hsiao acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its single-center design and small sample size. “A confounding variable is that some patients were on other medications in addition to spironolactone, which may have influenced treatment outcomes,” she noted. “Larger prospective studies are needed to identify optimal dosing for spironolactone therapy in HS as well as predictors of treatment response.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, said that with only one FDA-approved systemic medication for the management of HS (adalimumab), “we off-label bandits must be creative to curtail the incredibly painful impact this chronic, destructive inflammatory disease can have on our patients.”
“The evidence supporting our approaches, whether it be antibiotics, immunomodulators, or in this case, antihormonal therapies, is limited, so more data is always welcome,” said Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study. “One very interesting point raised by the authors, one I share with my trainees frequently from my own experience, is that regardless of menstrual cycle abnormalities, spironolactone can be impactful. This is important to remember, in that overt signs of hormonal influences is not a requisite for the use or effectiveness of antihormonal therapy.”
Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of board of directors for the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation. She has also served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, UCB, as a speaker for AbbVie, and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte. Dr. Friedman reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
CARLSBAD, CALIF. –
Those are the key findings from a single-center retrospective study that Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, and colleagues presented during a poster session at the annual symposium of the California Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery.
In an interview after the meeting, Dr. Hsiao, a dermatologist who directs the hidradenitis suppurativa clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said that hormones are thought to play a role in HS pathogenesis given the typical HS symptom onset around puberty and fluctuations in disease activity with menses (typically premenstrual flares) and pregnancy. “Spironolactone, an anti-androgenic agent, is used to treat HS in women; however, there is a paucity of data on the efficacy of spironolactone for HS and whether certain patient characteristics may influence treatment response,” she told this news organization. “This study is unique in that we contribute to existing literature regarding spironolactone efficacy in HS and we also investigate whether the presence of menstrual HS flares or polycystic ovarian syndrome influences the likelihood of response to spironolactone.”
For the analysis, Dr. Hsiao and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 53 adult women with HS who were prescribed spironolactone and who received care at USC’s HS clinic between January 2015 and December 2021. They collected data on demographics, comorbidities, HS medications, treatment response at 3 and 6 months, as well as adverse events. They also evaluated physician-assessed response to treatment when available.
The mean age of patients was 31 years, 37% were White, 30.4% were Black, 21.7% were Hispanic, 6.5% were Asian, and the remainder were biracial. The mean age at HS diagnosis was 25.1 years and the three most common comorbidities were acne (50.9%), obesity (45.3%), and anemia (37.7%). As for menstrual history, 56.6% had perimenstrual HS flares and 37.7% had irregular menstrual cycles. The top three classes of concomitant medications were antibiotics (58.5%), oral contraceptives (50.9%), and other birth control methods (18.9%).
The mean spironolactone dose was 104 mg/day; 84.1% of the women experienced improvement of HS 3 months after starting the drug, while 81.8% had improvement of their HS 6 months after starting the drug. The researchers also found that 56.6% of women had documented perimenstrual HS flares and 7.5% had PCOS.
“Spironolactone is often thought of as a helpful medication to consider if a patient reports having HS flares around menses or features of PCOS,” Dr. Hsiao said. However, she added, “our study found that there was no statistically significant difference in the response to spironolactone based on the presence of premenstrual flares or concomitant PCOS.” She said that spironolactone may be used as an adjunct therapeutic option in patients with more severe disease in addition to other medical and surgical therapies for HS. “Combining different treatment options that target different pathophysiologic factors is usually required to achieve adequate disease control in HS,” she said.
Dr. Hsiao acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its single-center design and small sample size. “A confounding variable is that some patients were on other medications in addition to spironolactone, which may have influenced treatment outcomes,” she noted. “Larger prospective studies are needed to identify optimal dosing for spironolactone therapy in HS as well as predictors of treatment response.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, said that with only one FDA-approved systemic medication for the management of HS (adalimumab), “we off-label bandits must be creative to curtail the incredibly painful impact this chronic, destructive inflammatory disease can have on our patients.”
“The evidence supporting our approaches, whether it be antibiotics, immunomodulators, or in this case, antihormonal therapies, is limited, so more data is always welcome,” said Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study. “One very interesting point raised by the authors, one I share with my trainees frequently from my own experience, is that regardless of menstrual cycle abnormalities, spironolactone can be impactful. This is important to remember, in that overt signs of hormonal influences is not a requisite for the use or effectiveness of antihormonal therapy.”
Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of board of directors for the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation. She has also served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, UCB, as a speaker for AbbVie, and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte. Dr. Friedman reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
AT CALDERM 2023
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
THE COMPARISON
A An 11-year-old Hispanic boy with allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) on the abdomen. The geometric nature of the eruption and proximity to the belt buckle were highly suggestive of ACD to nickel; patch testing was not needed.
B A Black woman with ACD on the neck. A punch biopsy demonstrated spongiotic dermatitis that was typical of ACD. The diagnosis was supported by the patient’s history of dermatitis that developed after new products were applied to the hair. The patient declined patch testing.
C A Hispanic man with ACD on hair-bearing areas on the face where hair dye was used. The patient’s history of dermatitis following the application of hair dye was highly suggestive of ACD; patch testing confirmed the allergen was paraphenylenediamine (PPD).
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is an inflammatory condition of the skin caused by an immunologic response to one or more identifiable allergens. A delayed-type immune response (type IV hypersensitivity reaction) occurs after the skin is reexposed to an offending allergen.1 Severe pruritus is the main symptom of ACD in the early stages, accompanied by erythema, vesicles, and scaling in a distinct pattern corresponding to the allergen’s contact with the skin.2 Delayed widespread dermatitis after exposure to an allergen—a phenomenon known as autoeczematization (id reaction)—also may occur.3
The gold-standard diagnostic tool for ACD is patch testing, in which the patient is re-exposed to the suspected contact allergen(s) and observed for the development of dermatitis.4 However, ACD can be diagnosed with a detailed patient history including occupation, hobbies, personal care practices, and possible triggers with subsequent rashes. Thorough clinical examination of the skin is paramount. Indicators of possible ACD include dermatitis that persists despite use of appropriate treatment, an unexplained flare of previously quiescent dermatitis, and a diagnosis of dermatitis without a clear cause.1
Hairdressers, health care workers, and metal workers are at higher risk for ACD.5 Occupational ACD has notable socioeconomic implications, as it can result in frequent sick days, inability to perform tasks at work, and in some cases job loss.6
Patients with atopic dermatitis have impaired barrier function of the skin, permitting the entrance of allergens and subsequent sensitization.7 Allergic contact dermatitis is a challenge to manage, as complete avoidance of the allergen may not be possible.8
The underrepresentation of patients with skin of color (SOC) in educational materials as well as socioeconomic health disparities may contribute to the lower rates of diagnosis, patch testing, and treatment of ACD in this patient population.
Epidemiology
An ACD prevalence of 15.2% was reported in a study of 793 Danish patients who underwent skin prick and patch testing.9 Alinaghi et al10 conducted a meta-analysis of 20,107 patients across 28 studies who were patch tested to determine the prevalence of ACD in the general population. The researchers concluded that 20.1% (95% CI, 16.8%- 23.7%) of the general population experienced ACD. They analyzed 22 studies to determine the prevalence of ACD based on specific geographic area including 18,709 individuals from Europe with a prevalence of 19.5% (95% CI, 15.8%-23.4%), 1639 individuals from North America with a prevalence of 20.6% (95% CI, 9.2%-35.2%), and 2 studies from China (no other studies from Asia found) with a prevalence of 20.6% (95% CI, 17.4%-23.9%). Researchers did not find data from studies conducted in Africa or South America.10
The current available epidemiologic data on ACD are not representative of SOC populations. DeLeo et al11 looked at patch test reaction patterns in association with race and ethnicity in a large sample size (N=19,457); 17,803 (92.9%) of these patients were White and only 1360 (7.1%) were Black. Large-scale, inclusive studies are needed, which can only be achieved with increased suspicion for ACD and increased access to patch testing.
Allergic contact dermatitis is more common in women, with nickel being the most frequently identified allergen (Figure, A).10 Personal care products often are linked to ACD (Figure, B). An analysis of data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group revealed that the top 5 personal care product allergens were methylisothiazolinone (a preservative), fragrance mix I, balsam of Peru, quaternium-15 (a preservative), and paraphenylenediamine (PPD)(a common component of hair dye) (Figure, C).12
There is a paucity of epidemiologic data among various ethnic groups; however, a few studies have suggested that there is no difference in the frequency rates of positive patch test results in Black vs White populations.11,13,14 One study of patch test results from 114 Black patients and 877 White patients at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation in Ohio demonstrated a similar allergy frequency of 43.0% and 43.6%, respectively.13 However, there were differences in the types of allergen sensitization. Black patients had higher positive patch test rates for PPD than White patients (10.6% vs 4.5%). Black men had a higher frequency of sensitivity to PPD (21.2% vs 4.2%) and imidazolidinyl urea (a formaldehyde-releasing preservative) (9.1% vs 2.6%) compared to White men.13
Ethnicity and cultural practices influence epidemiologic patterns of ACD. Darker hair dyes used in Black patients14 and deeply pigmented PPD dye found in henna tattoos used in Indian and Black patients15 may lead to increased sensitization to PPD. Allergic contact dermatitis due to formaldehyde is more common in White patients, possibly due to more frequent use of formaldehyde-containing moisturizers, shampoos, and creams.15
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
In patients with SOC, the clinical features of ACD vary, posing a diagnostic challenge. Hyperpigmentation, lichenification, and induration are more likely to be seen than the papules, vesicles, and erythematous dermatitis often described in lighter skin tones or acute ACD. Erythema can be difficult to assess on darker skin and may appear violaceous or very faint pink.16
Worth noting
A high index of suspicion is necessary when interpreting patch tests in patients with SOC, as patch test kits use a reading plate with graduated intensities of erythema, papulation, and vesicular reactions to determine the likelihood of ACD. The potential contact allergens are placed on the skin on day 1 and covered. Then, on day 3 the allergens are removed. The skin is clinically evaluated using visual assessment and skin palpation. The reactions are graded as negative, irritant reaction, equivocal, weak positive, strong positive, or extreme reaction at around days 3 and 5 to capture both early and delayed reactions.17 A patch test may be positive even if obvious signs of erythema are not appreciated as expected.
Adjusting the lighting in the examination room, including side lighting, or using a blue background can be helpful in identifying erythema in darker skin tones.15,16,18 Palpation of the skin also is useful, as even slight texture changes and induration are indicators of a possible skin reaction to the test allergen.15
Health disparity highlight
Clinical photographs of ACD and patch test results in patients with SOC are not commonplace in the literature. Positive patch test results in patients with darker skin tones vary from those of patients with lighter skin tones, and if the clinician reading the patch test result is not familiar with the findings in darker skin tones, the diagnosis may be delayed or missed.15
Furthermore, Scott et al15 highlighted that many dermatology residency training programs have a paucity of SOC education in their curriculum. This lack of representation may contribute to the diagnostic challenges encountered by health care providers.
Timely access to health care and education as well as economic stability are essential for the successful management of patients with ACD. Some individuals with SOC have been disproportionately affected by social determinants of health. Rodriguez-Homs et al19 demonstrated that the distance needed to travel to a clinic and the poverty rate of the county the patient lives in play a role in referral to a clinician specializing in contact dermatitis.
A retrospective registry review of 2310 patients undergoing patch testing at the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston revealed that 2.5% were Black, 5.5% were Latinx, 8.3% were Asian, and the remaining 83.7% were White.20 Qian et al21 also looked at patch testing patterns among various sociodemographic groups (N=1,107,530) and found that 69% of patients were White and 59% were female. Rates of patch testing among patients who were Black, lesser educated, male, lower income, and younger (children aged 0–12 years) were significantly lower than for other groups when ACD was suspected (P<.0001).21 The lower rates of patch testing in patients with SOC may be due to low suspicion of diagnosis, low referral rates due to limited medical insurance, and financial instability, as well as other socioeconomic factors.20
Tamazian et al16 reviewed pediatric populations at 13 US centers and found that Black children received patch testing less frequently than White and Hispanic children. Another review of pediatric patch testing in patients with SOC found that a less comprehensive panel of allergens was used in this population.22
The key to resolution of ACD is removal of the offending antigen, and if patients are not being tested, then they risk having a prolonged and complicated course of ACD with a poor prognosis. Patients with SOC also experience greater negative psychosocial impact due to ACD disease burden.21,23
The lower rates of patch testing in Black patients cannot solely be attributed to difficulty diagnosing ACD in darker skin tones; it is likely due to the impact of social determinants of health. Alleviating health disparities will improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
- Mowad CM, Anderson B, Scheinman P, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: patient diagnosis and evaluation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74: 1029-1040. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.02.1139
- Usatine RP, Riojas M. Diagnosis and management of contact dermatitis. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82:249-255.
- Bertoli MJ, Schwartz RA, Janniger CK. Autoeczematization: a strange id reaction of the skin. Cutis. 2021;108:163-166. doi:10.12788/cutis.0342
- Johansen JD, Bonefeld CM, Schwensen JFB, et al. Novel insights into contact dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;149:1162-1171. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2022.02.002
- Karagounis TK, Cohen DE. Occupational hand dermatitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2023;23:201-212. doi:10.1007/s11882-023-01070-5
- Cvetkovski RS, Rothman KJ, Olsen J, et al. Relation between diagnoses on severity, sick leave and loss of job among patients with occupational hand eczema. Br J Dermatol. 2005;152:93-98. doi:10.1111/j .1365-2133.2005.06415.x
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0340-7
- Brites GS, Ferreira I, Sebastião AI, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: from pathophysiology to development of new preventive strategies. Pharmacol Res. 2020;162:105282. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105282
- Nielsen NH, Menne T. The relationship between IgE‐mediated and cell‐mediated hypersensitivities in an unselected Danish population: the Glostrup Allergy Study, Denmark. Br J Dermatol. 1996;134:669-672. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1996.tb06967.x
- Alinaghi F, Bennike NH, Egeberg A, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:77-85. doi:10.1111/cod.13119
- DeLeo VA, Alexis A, Warshaw EM, et al. The association of race/ethnicity and patch test results: North American Contact Dermatitis Group, 1998- 2006. Dermatitis. 2016;27:288-292. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000220
- Warshaw EM, Schlarbaum JP, Silverberg JI, et al. Contact dermatitis to personal care products is increasing (but different!) in males and females: North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 1996-2016. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1446-1455. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.10.003
- Dickel H, Taylor JS, Evey P, et al. Comparison of patch test results with a standard series among white and black racial groups. Am J Contact Dermatol. 2001;12:77-82. doi:10.1053/ajcd.2001.20110
- DeLeo VA, Taylor SC, Belsito DV, et al. The effect of race and ethnicity on patch test results. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl):S107-S112. doi:10.1067/mjd.2002.120792
- Scott I, Atwater AR, Reeder M. Update on contact dermatitis and patch testing in patients with skin of color. Cutis. 2021;108:10-12. doi:10.12788/cutis.0292
- Tamazian S, Oboite M, Treat JR. Patch testing in skin of color: a brief report. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38:952-953. doi:10.1111/pde.14578
- Litchman G, Nair PA, Atwater AR, et al. Contact dermatitis. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated February 9, 2023. Accessed September 25, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459230/
- Alexis AF, Callender VD, Baldwin HE, et al. Global epidemiology and clinical spectrum of rosacea, highlighting skin of color: review and clinical practice experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1722-1729. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.08.049
- Rodriguez-Homs LG, Liu B, Green CL, et al. Duration of dermatitis before patch test appointment is associated with distance to clinic and county poverty rate. Dermatitis. 2020;31:259-264. doi:10.1097 /DER.0000000000000581
- Foschi CM, Tam I, Schalock PC, et al. Patch testing results in skin of color: a retrospective review from the Massachusetts General Hospital contact dermatitis clinic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:452-454. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.09.022
- Qian MF, Li S, Honari G, et al. Sociodemographic disparities in patch testing for commercially insured patients with dermatitis: a retrospective analysis of administrative claims data. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1411-1413. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.08.041
- Young K, Collis RW, Sheinbein D, et al. Retrospective review of pediatric patch testing results in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:953-954. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.11.031
- Kadyk DL, Hall S, Belsito DV. Quality of life of patients with allergic contact dermatitis: an exploratory analysis by gender, ethnicity, age, and occupation. Dermatitis. 2004;15:117-124.
THE COMPARISON
A An 11-year-old Hispanic boy with allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) on the abdomen. The geometric nature of the eruption and proximity to the belt buckle were highly suggestive of ACD to nickel; patch testing was not needed.
B A Black woman with ACD on the neck. A punch biopsy demonstrated spongiotic dermatitis that was typical of ACD. The diagnosis was supported by the patient’s history of dermatitis that developed after new products were applied to the hair. The patient declined patch testing.
C A Hispanic man with ACD on hair-bearing areas on the face where hair dye was used. The patient’s history of dermatitis following the application of hair dye was highly suggestive of ACD; patch testing confirmed the allergen was paraphenylenediamine (PPD).

Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is an inflammatory condition of the skin caused by an immunologic response to one or more identifiable allergens. A delayed-type immune response (type IV hypersensitivity reaction) occurs after the skin is reexposed to an offending allergen.1 Severe pruritus is the main symptom of ACD in the early stages, accompanied by erythema, vesicles, and scaling in a distinct pattern corresponding to the allergen’s contact with the skin.2 Delayed widespread dermatitis after exposure to an allergen—a phenomenon known as autoeczematization (id reaction)—also may occur.3
The gold-standard diagnostic tool for ACD is patch testing, in which the patient is re-exposed to the suspected contact allergen(s) and observed for the development of dermatitis.4 However, ACD can be diagnosed with a detailed patient history including occupation, hobbies, personal care practices, and possible triggers with subsequent rashes. Thorough clinical examination of the skin is paramount. Indicators of possible ACD include dermatitis that persists despite use of appropriate treatment, an unexplained flare of previously quiescent dermatitis, and a diagnosis of dermatitis without a clear cause.1
Hairdressers, health care workers, and metal workers are at higher risk for ACD.5 Occupational ACD has notable socioeconomic implications, as it can result in frequent sick days, inability to perform tasks at work, and in some cases job loss.6
Patients with atopic dermatitis have impaired barrier function of the skin, permitting the entrance of allergens and subsequent sensitization.7 Allergic contact dermatitis is a challenge to manage, as complete avoidance of the allergen may not be possible.8
The underrepresentation of patients with skin of color (SOC) in educational materials as well as socioeconomic health disparities may contribute to the lower rates of diagnosis, patch testing, and treatment of ACD in this patient population.
Epidemiology
An ACD prevalence of 15.2% was reported in a study of 793 Danish patients who underwent skin prick and patch testing.9 Alinaghi et al10 conducted a meta-analysis of 20,107 patients across 28 studies who were patch tested to determine the prevalence of ACD in the general population. The researchers concluded that 20.1% (95% CI, 16.8%- 23.7%) of the general population experienced ACD. They analyzed 22 studies to determine the prevalence of ACD based on specific geographic area including 18,709 individuals from Europe with a prevalence of 19.5% (95% CI, 15.8%-23.4%), 1639 individuals from North America with a prevalence of 20.6% (95% CI, 9.2%-35.2%), and 2 studies from China (no other studies from Asia found) with a prevalence of 20.6% (95% CI, 17.4%-23.9%). Researchers did not find data from studies conducted in Africa or South America.10
The current available epidemiologic data on ACD are not representative of SOC populations. DeLeo et al11 looked at patch test reaction patterns in association with race and ethnicity in a large sample size (N=19,457); 17,803 (92.9%) of these patients were White and only 1360 (7.1%) were Black. Large-scale, inclusive studies are needed, which can only be achieved with increased suspicion for ACD and increased access to patch testing.
Allergic contact dermatitis is more common in women, with nickel being the most frequently identified allergen (Figure, A).10 Personal care products often are linked to ACD (Figure, B). An analysis of data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group revealed that the top 5 personal care product allergens were methylisothiazolinone (a preservative), fragrance mix I, balsam of Peru, quaternium-15 (a preservative), and paraphenylenediamine (PPD)(a common component of hair dye) (Figure, C).12
There is a paucity of epidemiologic data among various ethnic groups; however, a few studies have suggested that there is no difference in the frequency rates of positive patch test results in Black vs White populations.11,13,14 One study of patch test results from 114 Black patients and 877 White patients at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation in Ohio demonstrated a similar allergy frequency of 43.0% and 43.6%, respectively.13 However, there were differences in the types of allergen sensitization. Black patients had higher positive patch test rates for PPD than White patients (10.6% vs 4.5%). Black men had a higher frequency of sensitivity to PPD (21.2% vs 4.2%) and imidazolidinyl urea (a formaldehyde-releasing preservative) (9.1% vs 2.6%) compared to White men.13
Ethnicity and cultural practices influence epidemiologic patterns of ACD. Darker hair dyes used in Black patients14 and deeply pigmented PPD dye found in henna tattoos used in Indian and Black patients15 may lead to increased sensitization to PPD. Allergic contact dermatitis due to formaldehyde is more common in White patients, possibly due to more frequent use of formaldehyde-containing moisturizers, shampoos, and creams.15
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
In patients with SOC, the clinical features of ACD vary, posing a diagnostic challenge. Hyperpigmentation, lichenification, and induration are more likely to be seen than the papules, vesicles, and erythematous dermatitis often described in lighter skin tones or acute ACD. Erythema can be difficult to assess on darker skin and may appear violaceous or very faint pink.16
Worth noting
A high index of suspicion is necessary when interpreting patch tests in patients with SOC, as patch test kits use a reading plate with graduated intensities of erythema, papulation, and vesicular reactions to determine the likelihood of ACD. The potential contact allergens are placed on the skin on day 1 and covered. Then, on day 3 the allergens are removed. The skin is clinically evaluated using visual assessment and skin palpation. The reactions are graded as negative, irritant reaction, equivocal, weak positive, strong positive, or extreme reaction at around days 3 and 5 to capture both early and delayed reactions.17 A patch test may be positive even if obvious signs of erythema are not appreciated as expected.
Adjusting the lighting in the examination room, including side lighting, or using a blue background can be helpful in identifying erythema in darker skin tones.15,16,18 Palpation of the skin also is useful, as even slight texture changes and induration are indicators of a possible skin reaction to the test allergen.15
Health disparity highlight
Clinical photographs of ACD and patch test results in patients with SOC are not commonplace in the literature. Positive patch test results in patients with darker skin tones vary from those of patients with lighter skin tones, and if the clinician reading the patch test result is not familiar with the findings in darker skin tones, the diagnosis may be delayed or missed.15
Furthermore, Scott et al15 highlighted that many dermatology residency training programs have a paucity of SOC education in their curriculum. This lack of representation may contribute to the diagnostic challenges encountered by health care providers.
Timely access to health care and education as well as economic stability are essential for the successful management of patients with ACD. Some individuals with SOC have been disproportionately affected by social determinants of health. Rodriguez-Homs et al19 demonstrated that the distance needed to travel to a clinic and the poverty rate of the county the patient lives in play a role in referral to a clinician specializing in contact dermatitis.
A retrospective registry review of 2310 patients undergoing patch testing at the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston revealed that 2.5% were Black, 5.5% were Latinx, 8.3% were Asian, and the remaining 83.7% were White.20 Qian et al21 also looked at patch testing patterns among various sociodemographic groups (N=1,107,530) and found that 69% of patients were White and 59% were female. Rates of patch testing among patients who were Black, lesser educated, male, lower income, and younger (children aged 0–12 years) were significantly lower than for other groups when ACD was suspected (P<.0001).21 The lower rates of patch testing in patients with SOC may be due to low suspicion of diagnosis, low referral rates due to limited medical insurance, and financial instability, as well as other socioeconomic factors.20
Tamazian et al16 reviewed pediatric populations at 13 US centers and found that Black children received patch testing less frequently than White and Hispanic children. Another review of pediatric patch testing in patients with SOC found that a less comprehensive panel of allergens was used in this population.22
The key to resolution of ACD is removal of the offending antigen, and if patients are not being tested, then they risk having a prolonged and complicated course of ACD with a poor prognosis. Patients with SOC also experience greater negative psychosocial impact due to ACD disease burden.21,23
The lower rates of patch testing in Black patients cannot solely be attributed to difficulty diagnosing ACD in darker skin tones; it is likely due to the impact of social determinants of health. Alleviating health disparities will improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
THE COMPARISON
A An 11-year-old Hispanic boy with allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) on the abdomen. The geometric nature of the eruption and proximity to the belt buckle were highly suggestive of ACD to nickel; patch testing was not needed.
B A Black woman with ACD on the neck. A punch biopsy demonstrated spongiotic dermatitis that was typical of ACD. The diagnosis was supported by the patient’s history of dermatitis that developed after new products were applied to the hair. The patient declined patch testing.
C A Hispanic man with ACD on hair-bearing areas on the face where hair dye was used. The patient’s history of dermatitis following the application of hair dye was highly suggestive of ACD; patch testing confirmed the allergen was paraphenylenediamine (PPD).

Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is an inflammatory condition of the skin caused by an immunologic response to one or more identifiable allergens. A delayed-type immune response (type IV hypersensitivity reaction) occurs after the skin is reexposed to an offending allergen.1 Severe pruritus is the main symptom of ACD in the early stages, accompanied by erythema, vesicles, and scaling in a distinct pattern corresponding to the allergen’s contact with the skin.2 Delayed widespread dermatitis after exposure to an allergen—a phenomenon known as autoeczematization (id reaction)—also may occur.3
The gold-standard diagnostic tool for ACD is patch testing, in which the patient is re-exposed to the suspected contact allergen(s) and observed for the development of dermatitis.4 However, ACD can be diagnosed with a detailed patient history including occupation, hobbies, personal care practices, and possible triggers with subsequent rashes. Thorough clinical examination of the skin is paramount. Indicators of possible ACD include dermatitis that persists despite use of appropriate treatment, an unexplained flare of previously quiescent dermatitis, and a diagnosis of dermatitis without a clear cause.1
Hairdressers, health care workers, and metal workers are at higher risk for ACD.5 Occupational ACD has notable socioeconomic implications, as it can result in frequent sick days, inability to perform tasks at work, and in some cases job loss.6
Patients with atopic dermatitis have impaired barrier function of the skin, permitting the entrance of allergens and subsequent sensitization.7 Allergic contact dermatitis is a challenge to manage, as complete avoidance of the allergen may not be possible.8
The underrepresentation of patients with skin of color (SOC) in educational materials as well as socioeconomic health disparities may contribute to the lower rates of diagnosis, patch testing, and treatment of ACD in this patient population.
Epidemiology
An ACD prevalence of 15.2% was reported in a study of 793 Danish patients who underwent skin prick and patch testing.9 Alinaghi et al10 conducted a meta-analysis of 20,107 patients across 28 studies who were patch tested to determine the prevalence of ACD in the general population. The researchers concluded that 20.1% (95% CI, 16.8%- 23.7%) of the general population experienced ACD. They analyzed 22 studies to determine the prevalence of ACD based on specific geographic area including 18,709 individuals from Europe with a prevalence of 19.5% (95% CI, 15.8%-23.4%), 1639 individuals from North America with a prevalence of 20.6% (95% CI, 9.2%-35.2%), and 2 studies from China (no other studies from Asia found) with a prevalence of 20.6% (95% CI, 17.4%-23.9%). Researchers did not find data from studies conducted in Africa or South America.10
The current available epidemiologic data on ACD are not representative of SOC populations. DeLeo et al11 looked at patch test reaction patterns in association with race and ethnicity in a large sample size (N=19,457); 17,803 (92.9%) of these patients were White and only 1360 (7.1%) were Black. Large-scale, inclusive studies are needed, which can only be achieved with increased suspicion for ACD and increased access to patch testing.
Allergic contact dermatitis is more common in women, with nickel being the most frequently identified allergen (Figure, A).10 Personal care products often are linked to ACD (Figure, B). An analysis of data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group revealed that the top 5 personal care product allergens were methylisothiazolinone (a preservative), fragrance mix I, balsam of Peru, quaternium-15 (a preservative), and paraphenylenediamine (PPD)(a common component of hair dye) (Figure, C).12
There is a paucity of epidemiologic data among various ethnic groups; however, a few studies have suggested that there is no difference in the frequency rates of positive patch test results in Black vs White populations.11,13,14 One study of patch test results from 114 Black patients and 877 White patients at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation in Ohio demonstrated a similar allergy frequency of 43.0% and 43.6%, respectively.13 However, there were differences in the types of allergen sensitization. Black patients had higher positive patch test rates for PPD than White patients (10.6% vs 4.5%). Black men had a higher frequency of sensitivity to PPD (21.2% vs 4.2%) and imidazolidinyl urea (a formaldehyde-releasing preservative) (9.1% vs 2.6%) compared to White men.13
Ethnicity and cultural practices influence epidemiologic patterns of ACD. Darker hair dyes used in Black patients14 and deeply pigmented PPD dye found in henna tattoos used in Indian and Black patients15 may lead to increased sensitization to PPD. Allergic contact dermatitis due to formaldehyde is more common in White patients, possibly due to more frequent use of formaldehyde-containing moisturizers, shampoos, and creams.15
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
In patients with SOC, the clinical features of ACD vary, posing a diagnostic challenge. Hyperpigmentation, lichenification, and induration are more likely to be seen than the papules, vesicles, and erythematous dermatitis often described in lighter skin tones or acute ACD. Erythema can be difficult to assess on darker skin and may appear violaceous or very faint pink.16
Worth noting
A high index of suspicion is necessary when interpreting patch tests in patients with SOC, as patch test kits use a reading plate with graduated intensities of erythema, papulation, and vesicular reactions to determine the likelihood of ACD. The potential contact allergens are placed on the skin on day 1 and covered. Then, on day 3 the allergens are removed. The skin is clinically evaluated using visual assessment and skin palpation. The reactions are graded as negative, irritant reaction, equivocal, weak positive, strong positive, or extreme reaction at around days 3 and 5 to capture both early and delayed reactions.17 A patch test may be positive even if obvious signs of erythema are not appreciated as expected.
Adjusting the lighting in the examination room, including side lighting, or using a blue background can be helpful in identifying erythema in darker skin tones.15,16,18 Palpation of the skin also is useful, as even slight texture changes and induration are indicators of a possible skin reaction to the test allergen.15
Health disparity highlight
Clinical photographs of ACD and patch test results in patients with SOC are not commonplace in the literature. Positive patch test results in patients with darker skin tones vary from those of patients with lighter skin tones, and if the clinician reading the patch test result is not familiar with the findings in darker skin tones, the diagnosis may be delayed or missed.15
Furthermore, Scott et al15 highlighted that many dermatology residency training programs have a paucity of SOC education in their curriculum. This lack of representation may contribute to the diagnostic challenges encountered by health care providers.
Timely access to health care and education as well as economic stability are essential for the successful management of patients with ACD. Some individuals with SOC have been disproportionately affected by social determinants of health. Rodriguez-Homs et al19 demonstrated that the distance needed to travel to a clinic and the poverty rate of the county the patient lives in play a role in referral to a clinician specializing in contact dermatitis.
A retrospective registry review of 2310 patients undergoing patch testing at the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston revealed that 2.5% were Black, 5.5% were Latinx, 8.3% were Asian, and the remaining 83.7% were White.20 Qian et al21 also looked at patch testing patterns among various sociodemographic groups (N=1,107,530) and found that 69% of patients were White and 59% were female. Rates of patch testing among patients who were Black, lesser educated, male, lower income, and younger (children aged 0–12 years) were significantly lower than for other groups when ACD was suspected (P<.0001).21 The lower rates of patch testing in patients with SOC may be due to low suspicion of diagnosis, low referral rates due to limited medical insurance, and financial instability, as well as other socioeconomic factors.20
Tamazian et al16 reviewed pediatric populations at 13 US centers and found that Black children received patch testing less frequently than White and Hispanic children. Another review of pediatric patch testing in patients with SOC found that a less comprehensive panel of allergens was used in this population.22
The key to resolution of ACD is removal of the offending antigen, and if patients are not being tested, then they risk having a prolonged and complicated course of ACD with a poor prognosis. Patients with SOC also experience greater negative psychosocial impact due to ACD disease burden.21,23
The lower rates of patch testing in Black patients cannot solely be attributed to difficulty diagnosing ACD in darker skin tones; it is likely due to the impact of social determinants of health. Alleviating health disparities will improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
- Mowad CM, Anderson B, Scheinman P, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: patient diagnosis and evaluation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74: 1029-1040. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.02.1139
- Usatine RP, Riojas M. Diagnosis and management of contact dermatitis. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82:249-255.
- Bertoli MJ, Schwartz RA, Janniger CK. Autoeczematization: a strange id reaction of the skin. Cutis. 2021;108:163-166. doi:10.12788/cutis.0342
- Johansen JD, Bonefeld CM, Schwensen JFB, et al. Novel insights into contact dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;149:1162-1171. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2022.02.002
- Karagounis TK, Cohen DE. Occupational hand dermatitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2023;23:201-212. doi:10.1007/s11882-023-01070-5
- Cvetkovski RS, Rothman KJ, Olsen J, et al. Relation between diagnoses on severity, sick leave and loss of job among patients with occupational hand eczema. Br J Dermatol. 2005;152:93-98. doi:10.1111/j .1365-2133.2005.06415.x
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0340-7
- Brites GS, Ferreira I, Sebastião AI, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: from pathophysiology to development of new preventive strategies. Pharmacol Res. 2020;162:105282. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105282
- Nielsen NH, Menne T. The relationship between IgE‐mediated and cell‐mediated hypersensitivities in an unselected Danish population: the Glostrup Allergy Study, Denmark. Br J Dermatol. 1996;134:669-672. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1996.tb06967.x
- Alinaghi F, Bennike NH, Egeberg A, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:77-85. doi:10.1111/cod.13119
- DeLeo VA, Alexis A, Warshaw EM, et al. The association of race/ethnicity and patch test results: North American Contact Dermatitis Group, 1998- 2006. Dermatitis. 2016;27:288-292. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000220
- Warshaw EM, Schlarbaum JP, Silverberg JI, et al. Contact dermatitis to personal care products is increasing (but different!) in males and females: North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 1996-2016. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1446-1455. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.10.003
- Dickel H, Taylor JS, Evey P, et al. Comparison of patch test results with a standard series among white and black racial groups. Am J Contact Dermatol. 2001;12:77-82. doi:10.1053/ajcd.2001.20110
- DeLeo VA, Taylor SC, Belsito DV, et al. The effect of race and ethnicity on patch test results. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl):S107-S112. doi:10.1067/mjd.2002.120792
- Scott I, Atwater AR, Reeder M. Update on contact dermatitis and patch testing in patients with skin of color. Cutis. 2021;108:10-12. doi:10.12788/cutis.0292
- Tamazian S, Oboite M, Treat JR. Patch testing in skin of color: a brief report. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38:952-953. doi:10.1111/pde.14578
- Litchman G, Nair PA, Atwater AR, et al. Contact dermatitis. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated February 9, 2023. Accessed September 25, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459230/
- Alexis AF, Callender VD, Baldwin HE, et al. Global epidemiology and clinical spectrum of rosacea, highlighting skin of color: review and clinical practice experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1722-1729. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.08.049
- Rodriguez-Homs LG, Liu B, Green CL, et al. Duration of dermatitis before patch test appointment is associated with distance to clinic and county poverty rate. Dermatitis. 2020;31:259-264. doi:10.1097 /DER.0000000000000581
- Foschi CM, Tam I, Schalock PC, et al. Patch testing results in skin of color: a retrospective review from the Massachusetts General Hospital contact dermatitis clinic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:452-454. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.09.022
- Qian MF, Li S, Honari G, et al. Sociodemographic disparities in patch testing for commercially insured patients with dermatitis: a retrospective analysis of administrative claims data. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1411-1413. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.08.041
- Young K, Collis RW, Sheinbein D, et al. Retrospective review of pediatric patch testing results in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:953-954. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.11.031
- Kadyk DL, Hall S, Belsito DV. Quality of life of patients with allergic contact dermatitis: an exploratory analysis by gender, ethnicity, age, and occupation. Dermatitis. 2004;15:117-124.
- Mowad CM, Anderson B, Scheinman P, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: patient diagnosis and evaluation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74: 1029-1040. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.02.1139
- Usatine RP, Riojas M. Diagnosis and management of contact dermatitis. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82:249-255.
- Bertoli MJ, Schwartz RA, Janniger CK. Autoeczematization: a strange id reaction of the skin. Cutis. 2021;108:163-166. doi:10.12788/cutis.0342
- Johansen JD, Bonefeld CM, Schwensen JFB, et al. Novel insights into contact dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;149:1162-1171. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2022.02.002
- Karagounis TK, Cohen DE. Occupational hand dermatitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2023;23:201-212. doi:10.1007/s11882-023-01070-5
- Cvetkovski RS, Rothman KJ, Olsen J, et al. Relation between diagnoses on severity, sick leave and loss of job among patients with occupational hand eczema. Br J Dermatol. 2005;152:93-98. doi:10.1111/j .1365-2133.2005.06415.x
- Owen JL, Vakharia PP, Silverberg JI. The role and diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:293-302. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0340-7
- Brites GS, Ferreira I, Sebastião AI, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: from pathophysiology to development of new preventive strategies. Pharmacol Res. 2020;162:105282. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105282
- Nielsen NH, Menne T. The relationship between IgE‐mediated and cell‐mediated hypersensitivities in an unselected Danish population: the Glostrup Allergy Study, Denmark. Br J Dermatol. 1996;134:669-672. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1996.tb06967.x
- Alinaghi F, Bennike NH, Egeberg A, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:77-85. doi:10.1111/cod.13119
- DeLeo VA, Alexis A, Warshaw EM, et al. The association of race/ethnicity and patch test results: North American Contact Dermatitis Group, 1998- 2006. Dermatitis. 2016;27:288-292. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000220
- Warshaw EM, Schlarbaum JP, Silverberg JI, et al. Contact dermatitis to personal care products is increasing (but different!) in males and females: North American Contact Dermatitis Group data, 1996-2016. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:1446-1455. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.10.003
- Dickel H, Taylor JS, Evey P, et al. Comparison of patch test results with a standard series among white and black racial groups. Am J Contact Dermatol. 2001;12:77-82. doi:10.1053/ajcd.2001.20110
- DeLeo VA, Taylor SC, Belsito DV, et al. The effect of race and ethnicity on patch test results. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2 suppl):S107-S112. doi:10.1067/mjd.2002.120792
- Scott I, Atwater AR, Reeder M. Update on contact dermatitis and patch testing in patients with skin of color. Cutis. 2021;108:10-12. doi:10.12788/cutis.0292
- Tamazian S, Oboite M, Treat JR. Patch testing in skin of color: a brief report. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38:952-953. doi:10.1111/pde.14578
- Litchman G, Nair PA, Atwater AR, et al. Contact dermatitis. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated February 9, 2023. Accessed September 25, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459230/
- Alexis AF, Callender VD, Baldwin HE, et al. Global epidemiology and clinical spectrum of rosacea, highlighting skin of color: review and clinical practice experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1722-1729. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.08.049
- Rodriguez-Homs LG, Liu B, Green CL, et al. Duration of dermatitis before patch test appointment is associated with distance to clinic and county poverty rate. Dermatitis. 2020;31:259-264. doi:10.1097 /DER.0000000000000581
- Foschi CM, Tam I, Schalock PC, et al. Patch testing results in skin of color: a retrospective review from the Massachusetts General Hospital contact dermatitis clinic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:452-454. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.09.022
- Qian MF, Li S, Honari G, et al. Sociodemographic disparities in patch testing for commercially insured patients with dermatitis: a retrospective analysis of administrative claims data. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:1411-1413. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.08.041
- Young K, Collis RW, Sheinbein D, et al. Retrospective review of pediatric patch testing results in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:953-954. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2022.11.031
- Kadyk DL, Hall S, Belsito DV. Quality of life of patients with allergic contact dermatitis: an exploratory analysis by gender, ethnicity, age, and occupation. Dermatitis. 2004;15:117-124.