User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
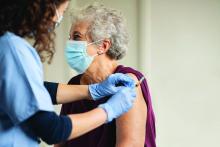
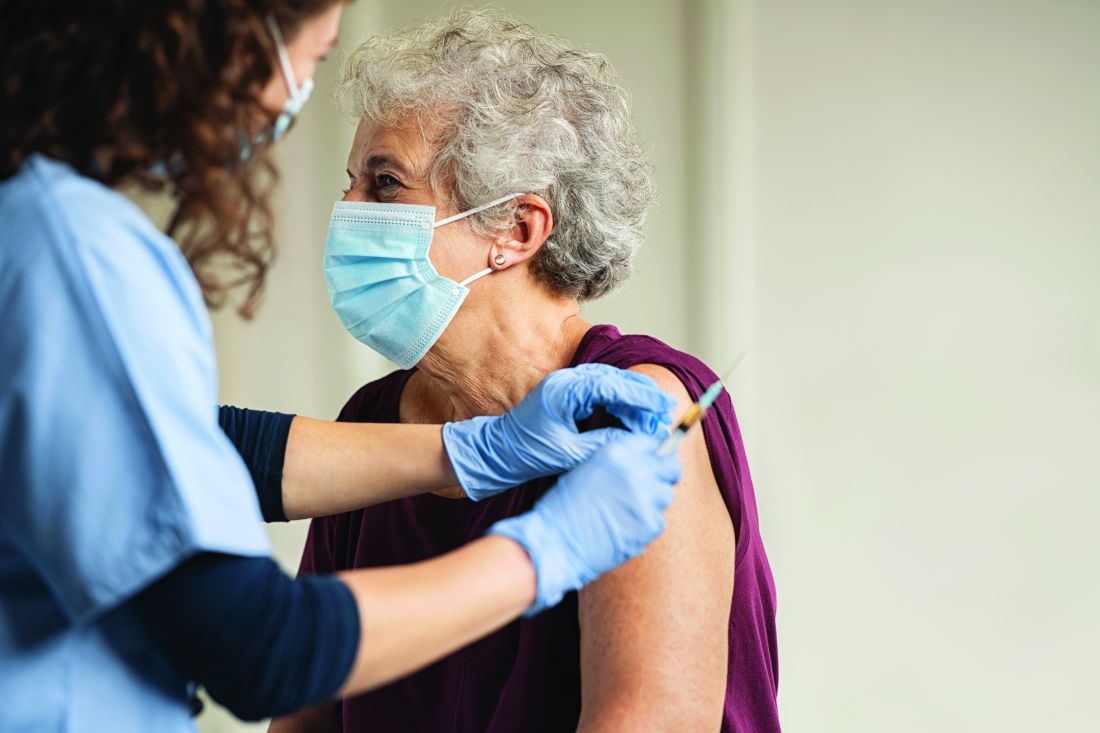
Cardiologist positive for Omicron after London conference
Elad Maor, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Sheba Medical Centre near Tel Aviv, posted on Twitter on Nov. 30: “What a mess! Came back from a conference in London. With a mask and 3 Pfizer vaccines I managed to get Omicron.”
Dr. Maor traveled to London on November 19 to attend the PCR London Valves 2021 conference held at the ExCeL Centre Nov. 21-23. He stayed four nights at a hotel in north London and took public transport to and from the ExCeL Centre in East London each day of the meeting. He returned to Israel on the evening of Nov. 23.
Dr. Maor, 45, who has received three doses of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine, had two PCR tests in the United Kingdom – on November 20 and 21 in line with travel requirements – and another PCR test upon arriving back in Israel in the early hours of Nov. 24. All three tests were negative.
He began experiencing symptoms within days and tested positive on Nov. 27. His symptoms have been mild so far, and he said he was feeling “better” at the time of his tweet on Nov. 30.
Dr. Maor believes he was infected during his trip to London. “The only reasonable explanation is that I got infected on the last day of the meeting – maybe at the airport, maybe at the meeting,” he told The Guardian newspaper.
Although his wife accompanied him to London, neither she nor any of his 3 children have experienced symptoms or tested positive for COVID-19. But Dr. Maor believes he has passed the infection to a 69-year-old colleague in Israel who has since tested positive for the Omicron variant. The colleague, who has also received three vaccine doses, is understood to have mild symptoms at present.
The case suggests that the Omicron variant of COVID-19 may have been circulating in the United Kingdom earlier than previously thought.
Implications for in-person conferences
It will also inevitably lead to questions about the safety of face-to-face conferences, which are only just starting to get underway again.
The PCR Valves 2021 meeting had more than 1,250 on-site attendees as well as 2,400 or more joining online, according to figures on its website. Dr. Maor said he did not have any issues with the conference organizers, who required proof of vaccination before entry. But he posted a photograph on his Twitter account of a crowded auditorium with many delegates not wearing masks.
The conference subsequently posted an announcement on its website alerting delegates that one of the attendees had tested positive for COVID-19 after returning to their home country. It reads: “Since the reported case comes less than a week after the end of PCR London Valves, we want to inform you so that you may decide the best course of action, for yourself, if any.” It does not mention that the case was the Omicron variant.
Patrick Jolly, strategic and market development director of the conference, commented: “As you may imagine, the health, safety and well-being of everyone who visited PCR London Valves was our number-one priority. All protocols mandated by the U.K. government were put in place. Anyone entering the congress center had to present a valid health pass and were requested to wear a mask. Hydro-alcoholic gel and masks were made readily available for all participants and disposal bins for used protective equipment were provided.”
Mr. Jolly also noted: “To date – more than 9 days after the end of PCR London Valves – we have had no report of any other case of participants testing positive who attended PCR London Valves.”
He said the EuroPCR organization believes that medical conferences are safe to be held in person.
“With the above sanitary requirements and protocols, and no complacency in their enforcement, we believe strongly that medical conferences can take place, as the benefits of in-person medical conferences are obvious for the concerned medical communities,” Mr. Jolly added.
But what about other meetings happening imminently and planning in-person attendance?
Eileen Murray, executive director of the American Epilepsy Society (AES), whose annual 5-day meeting starts today at Chicago’s McCormick Place Convention Center, said in an interview that the health, safety, and well-being of everyone attending is a priority.
“Vaccinations are required, with no exceptions, to anyone attending the in-person event,” Ms. Murray said. “AES is using the CLEAR HealthPass to verify identity and vaccination status for our attendees. No one who cannot verify identity and vaccination requirement will be permitted to attend the in-person event.”
She noted that masks will also be required except in limited circumstances when actively eating or drinking, or for a faculty member when actively presenting at a lecture or panel. “Anyone not adhering to the mask policy will be asked to leave the meeting and will be denied readmission to the meeting with no refund,” she said.
“These guidelines were developed in accordance with the latest public health guidance and AES will continue to follow that guidance as any updates are made with the emergence of the Omicron variant,” Ms. Murray added.
Also commenting on this issue, a spokesperson for the American Heart Association, which has its large annual international stroke meeting planned for in-person attendance in New Orleans in February, said: “As we have throughout the pandemic, the American Heart Association is closely monitoring conditions and following the guidance of the CDC as well as state and local health departments related to all in-person meetings.”
“Our upcoming International Stroke Conference, February 9-11, is planned as an in-person and digital experience which allows us the ultimate flexibility to address changing pandemic conditions. The health, safety, and well-being of our volunteers, members, and attendees from around the world remains our number-one priority,” the AHA spokesperson added.
But some COVID-19 experts are taking a more cautious view.
Rowland Kao, PhD, an expert in infectious disease dynamics at the University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom, expressed concern about such large in-person conferences.
“We know that the Omicron variant appears to be spreading rapidly, with a recent preprint also telling us that the reinfection rate appears to be higher in South Africa. Should this be borne out, then the evidence would support that our reliance on a combination of vaccine-induced and natural immunity may be compromised by the Omicron variant,” he commented.
“We already know that extended contact indoors provides an additional risk, and so large meetings of this type have the potential to create extended risks. Until we know the extent to which Omicron causes severe illness, we should be extra cautious about these high-risk settings,” Dr. Kao commented.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Elad Maor, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Sheba Medical Centre near Tel Aviv, posted on Twitter on Nov. 30: “What a mess! Came back from a conference in London. With a mask and 3 Pfizer vaccines I managed to get Omicron.”
Dr. Maor traveled to London on November 19 to attend the PCR London Valves 2021 conference held at the ExCeL Centre Nov. 21-23. He stayed four nights at a hotel in north London and took public transport to and from the ExCeL Centre in East London each day of the meeting. He returned to Israel on the evening of Nov. 23.
Dr. Maor, 45, who has received three doses of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine, had two PCR tests in the United Kingdom – on November 20 and 21 in line with travel requirements – and another PCR test upon arriving back in Israel in the early hours of Nov. 24. All three tests were negative.
He began experiencing symptoms within days and tested positive on Nov. 27. His symptoms have been mild so far, and he said he was feeling “better” at the time of his tweet on Nov. 30.
Dr. Maor believes he was infected during his trip to London. “The only reasonable explanation is that I got infected on the last day of the meeting – maybe at the airport, maybe at the meeting,” he told The Guardian newspaper.
Although his wife accompanied him to London, neither she nor any of his 3 children have experienced symptoms or tested positive for COVID-19. But Dr. Maor believes he has passed the infection to a 69-year-old colleague in Israel who has since tested positive for the Omicron variant. The colleague, who has also received three vaccine doses, is understood to have mild symptoms at present.
The case suggests that the Omicron variant of COVID-19 may have been circulating in the United Kingdom earlier than previously thought.
Implications for in-person conferences
It will also inevitably lead to questions about the safety of face-to-face conferences, which are only just starting to get underway again.
The PCR Valves 2021 meeting had more than 1,250 on-site attendees as well as 2,400 or more joining online, according to figures on its website. Dr. Maor said he did not have any issues with the conference organizers, who required proof of vaccination before entry. But he posted a photograph on his Twitter account of a crowded auditorium with many delegates not wearing masks.
The conference subsequently posted an announcement on its website alerting delegates that one of the attendees had tested positive for COVID-19 after returning to their home country. It reads: “Since the reported case comes less than a week after the end of PCR London Valves, we want to inform you so that you may decide the best course of action, for yourself, if any.” It does not mention that the case was the Omicron variant.
Patrick Jolly, strategic and market development director of the conference, commented: “As you may imagine, the health, safety and well-being of everyone who visited PCR London Valves was our number-one priority. All protocols mandated by the U.K. government were put in place. Anyone entering the congress center had to present a valid health pass and were requested to wear a mask. Hydro-alcoholic gel and masks were made readily available for all participants and disposal bins for used protective equipment were provided.”
Mr. Jolly also noted: “To date – more than 9 days after the end of PCR London Valves – we have had no report of any other case of participants testing positive who attended PCR London Valves.”
He said the EuroPCR organization believes that medical conferences are safe to be held in person.
“With the above sanitary requirements and protocols, and no complacency in their enforcement, we believe strongly that medical conferences can take place, as the benefits of in-person medical conferences are obvious for the concerned medical communities,” Mr. Jolly added.
But what about other meetings happening imminently and planning in-person attendance?
Eileen Murray, executive director of the American Epilepsy Society (AES), whose annual 5-day meeting starts today at Chicago’s McCormick Place Convention Center, said in an interview that the health, safety, and well-being of everyone attending is a priority.
“Vaccinations are required, with no exceptions, to anyone attending the in-person event,” Ms. Murray said. “AES is using the CLEAR HealthPass to verify identity and vaccination status for our attendees. No one who cannot verify identity and vaccination requirement will be permitted to attend the in-person event.”
She noted that masks will also be required except in limited circumstances when actively eating or drinking, or for a faculty member when actively presenting at a lecture or panel. “Anyone not adhering to the mask policy will be asked to leave the meeting and will be denied readmission to the meeting with no refund,” she said.
“These guidelines were developed in accordance with the latest public health guidance and AES will continue to follow that guidance as any updates are made with the emergence of the Omicron variant,” Ms. Murray added.
Also commenting on this issue, a spokesperson for the American Heart Association, which has its large annual international stroke meeting planned for in-person attendance in New Orleans in February, said: “As we have throughout the pandemic, the American Heart Association is closely monitoring conditions and following the guidance of the CDC as well as state and local health departments related to all in-person meetings.”
“Our upcoming International Stroke Conference, February 9-11, is planned as an in-person and digital experience which allows us the ultimate flexibility to address changing pandemic conditions. The health, safety, and well-being of our volunteers, members, and attendees from around the world remains our number-one priority,” the AHA spokesperson added.
But some COVID-19 experts are taking a more cautious view.
Rowland Kao, PhD, an expert in infectious disease dynamics at the University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom, expressed concern about such large in-person conferences.
“We know that the Omicron variant appears to be spreading rapidly, with a recent preprint also telling us that the reinfection rate appears to be higher in South Africa. Should this be borne out, then the evidence would support that our reliance on a combination of vaccine-induced and natural immunity may be compromised by the Omicron variant,” he commented.
“We already know that extended contact indoors provides an additional risk, and so large meetings of this type have the potential to create extended risks. Until we know the extent to which Omicron causes severe illness, we should be extra cautious about these high-risk settings,” Dr. Kao commented.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Elad Maor, MD, an interventional cardiologist at Sheba Medical Centre near Tel Aviv, posted on Twitter on Nov. 30: “What a mess! Came back from a conference in London. With a mask and 3 Pfizer vaccines I managed to get Omicron.”
Dr. Maor traveled to London on November 19 to attend the PCR London Valves 2021 conference held at the ExCeL Centre Nov. 21-23. He stayed four nights at a hotel in north London and took public transport to and from the ExCeL Centre in East London each day of the meeting. He returned to Israel on the evening of Nov. 23.
Dr. Maor, 45, who has received three doses of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine, had two PCR tests in the United Kingdom – on November 20 and 21 in line with travel requirements – and another PCR test upon arriving back in Israel in the early hours of Nov. 24. All three tests were negative.
He began experiencing symptoms within days and tested positive on Nov. 27. His symptoms have been mild so far, and he said he was feeling “better” at the time of his tweet on Nov. 30.
Dr. Maor believes he was infected during his trip to London. “The only reasonable explanation is that I got infected on the last day of the meeting – maybe at the airport, maybe at the meeting,” he told The Guardian newspaper.
Although his wife accompanied him to London, neither she nor any of his 3 children have experienced symptoms or tested positive for COVID-19. But Dr. Maor believes he has passed the infection to a 69-year-old colleague in Israel who has since tested positive for the Omicron variant. The colleague, who has also received three vaccine doses, is understood to have mild symptoms at present.
The case suggests that the Omicron variant of COVID-19 may have been circulating in the United Kingdom earlier than previously thought.
Implications for in-person conferences
It will also inevitably lead to questions about the safety of face-to-face conferences, which are only just starting to get underway again.
The PCR Valves 2021 meeting had more than 1,250 on-site attendees as well as 2,400 or more joining online, according to figures on its website. Dr. Maor said he did not have any issues with the conference organizers, who required proof of vaccination before entry. But he posted a photograph on his Twitter account of a crowded auditorium with many delegates not wearing masks.
The conference subsequently posted an announcement on its website alerting delegates that one of the attendees had tested positive for COVID-19 after returning to their home country. It reads: “Since the reported case comes less than a week after the end of PCR London Valves, we want to inform you so that you may decide the best course of action, for yourself, if any.” It does not mention that the case was the Omicron variant.
Patrick Jolly, strategic and market development director of the conference, commented: “As you may imagine, the health, safety and well-being of everyone who visited PCR London Valves was our number-one priority. All protocols mandated by the U.K. government were put in place. Anyone entering the congress center had to present a valid health pass and were requested to wear a mask. Hydro-alcoholic gel and masks were made readily available for all participants and disposal bins for used protective equipment were provided.”
Mr. Jolly also noted: “To date – more than 9 days after the end of PCR London Valves – we have had no report of any other case of participants testing positive who attended PCR London Valves.”
He said the EuroPCR organization believes that medical conferences are safe to be held in person.
“With the above sanitary requirements and protocols, and no complacency in their enforcement, we believe strongly that medical conferences can take place, as the benefits of in-person medical conferences are obvious for the concerned medical communities,” Mr. Jolly added.
But what about other meetings happening imminently and planning in-person attendance?
Eileen Murray, executive director of the American Epilepsy Society (AES), whose annual 5-day meeting starts today at Chicago’s McCormick Place Convention Center, said in an interview that the health, safety, and well-being of everyone attending is a priority.
“Vaccinations are required, with no exceptions, to anyone attending the in-person event,” Ms. Murray said. “AES is using the CLEAR HealthPass to verify identity and vaccination status for our attendees. No one who cannot verify identity and vaccination requirement will be permitted to attend the in-person event.”
She noted that masks will also be required except in limited circumstances when actively eating or drinking, or for a faculty member when actively presenting at a lecture or panel. “Anyone not adhering to the mask policy will be asked to leave the meeting and will be denied readmission to the meeting with no refund,” she said.
“These guidelines were developed in accordance with the latest public health guidance and AES will continue to follow that guidance as any updates are made with the emergence of the Omicron variant,” Ms. Murray added.
Also commenting on this issue, a spokesperson for the American Heart Association, which has its large annual international stroke meeting planned for in-person attendance in New Orleans in February, said: “As we have throughout the pandemic, the American Heart Association is closely monitoring conditions and following the guidance of the CDC as well as state and local health departments related to all in-person meetings.”
“Our upcoming International Stroke Conference, February 9-11, is planned as an in-person and digital experience which allows us the ultimate flexibility to address changing pandemic conditions. The health, safety, and well-being of our volunteers, members, and attendees from around the world remains our number-one priority,” the AHA spokesperson added.
But some COVID-19 experts are taking a more cautious view.
Rowland Kao, PhD, an expert in infectious disease dynamics at the University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom, expressed concern about such large in-person conferences.
“We know that the Omicron variant appears to be spreading rapidly, with a recent preprint also telling us that the reinfection rate appears to be higher in South Africa. Should this be borne out, then the evidence would support that our reliance on a combination of vaccine-induced and natural immunity may be compromised by the Omicron variant,” he commented.
“We already know that extended contact indoors provides an additional risk, and so large meetings of this type have the potential to create extended risks. Until we know the extent to which Omicron causes severe illness, we should be extra cautious about these high-risk settings,” Dr. Kao commented.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Baked milk immunotherapy may help children with cow’s milk allergy
, new research suggests.
The small, ongoing clinical trial has enabled some participants – all of whom reacted to less than a tablespoon of baked milk at baseline – to begin incorporating baked milk products into everyday diets and to eat in restaurants with less fear of allergic reactions, reported study author Jennifer Dantzer, MD, MHS, assistant professor of pediatrics in the division of pediatric allergy, immunology, and rheumatology at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
Cow’s milk is the most common food allergy in young children, and “for many, it’s a constant stressor that’s always there,” Dr. Dantzer said in an interview. “For a lot of families, this impacts where they eat out, if they eat out, and sometimes where they vacation, or a lot of the social activities they do.
“This was a unique group of kids with a very severe milk phenotype who were reactive to teeny doses and may not have qualified or done well with other types of oral immunotherapy,” she added. “Using a modified allergen – baked milk – seems to work. But for now, we think this is something that still needs further research before it’s ready for a clinical setting.”
The study, for which 24-month unblinded results are being tallied, was recently published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology .
About 2%-3% of preschool-age children are affected by cow’s milk allergy. Children often outgrow it, but for about 20% of children, it persists into adolescence and adulthood. The only current management approaches are avoidance and emergency medications to treat reactions.
But for those with severe milk allergy who react to even trace amounts of milk in any form, the now-routine clinical practice of introducing baked milk isn’t an option, Dr. Dantzer said. The new trial stood out from prior research by using lower starting doses and a more gradual dose escalation of extensively heated milk to determine if oral immunotherapy could be safer but still effective.
Dr. Dantzer and her team randomly assigned 30 participants (aged 3-18 years) into two blinded groups. For 12 months, one group received baked milk oral immunotherapy (BMOIT), and the other a placebo consisting of tapioca flour. At baseline, for all participants, the milk skin prick test wheal diameter was ≥ 3 mm, and the cow’s milk immunoglobulin E (IgE) level was > 5 kU/L. All the children experienced positive dose-limiting reactions to < 1 tablespoon of baked milk protein but could tolerate at least 3 mg on initial dose escalation.
Measured doses of baked milk and placebo powders were supplied to participants for all doses consumed at home. Participants were given instructions on how to prepare it in cupcake or muffin batter. Over 12 months, doses were gradually increased to a maximum cumulative dose of 4,044 mg baked milk protein, or approximately a half tablespoon.
Researchers collected blood samples for immune studies, and participants or their parents completed quality-of-life questionnaires that asked about food anxiety, social and dietary limitations, emotional impact, risk for accidental ingestion, and allergen avoidance.
Fourteen of 15 participants (93%) in the BMOIT group reached the goal-maintenance dose of 2,000 mg of baked milk protein (about a quarter tablespoon). Of those who completed the 12-month challenge, 11 of 14 (79%) in the BMOIT group tolerated 4,000 mg of baked milk protein, compared to none in the placebo group.
“We anticipated that by starting with really small amounts, we would be able to build up the amount of baked milk these kids could tolerate,” Dr. Dantzer said. “We were very pleased by how many could reach the maximal dose at the end of the first year. Once we get the results of the second year, that will provide a lot of additional detail about how this translates into unheated milk amounts they can tolerate and introduce into their diet at home.”
No significant changes were found in IgE levels over time in either study group. Most in the BMOIT group reported improvement in at least one quality-of-life domain, while more in the placebo group reported improvements in only the emotional impact domain.
Adverse events such as gastrointestinal side effects occurred in both groups of participants, but the vast majority of events were mild, Dr. Dantzer said. Fewer than 1% of dosing-related reactions were severe. Four participants required epinephrine.
“This highlights how this needs to be done by someone comfortable and trained, and not by a family at home on their own,” Dr. Dantzer said. “But potentially in the future, this concept of using a modified allergen could be applied to more kids with milk allergy.”
A Montreal-based pediatric allergy specialist who was not involved in the study said the results weren’t surprising. “We’ve known for a good while that the allergenic proteins found in certain foods, or caused by milk in this context, are influenced by the way in which food is processed,” said Christine McCusker, MD, associate professor of pediatrics and director of the division of pediatric allergy, immunology, and dermatology at Montreal Children’s Hospital at McGill University Health Center.
But “having this relatively definitive data that supports what you’re suggesting to patients is obviously the way to optimize your management,” Dr. McCusker said in an interview. “These types of studies are important steps, especially in this age of increased food allergies where many of these things can be dealt with in very young children before their immune systems are fixed.”
Dr. Dantzer and Dr. McCusker agreed that the small size of the study was a limitation, though “waiting for more participants means you don’t always get information out there in a timely manner,” Dr. McCusker said.
She said additional research should focus on preidentifying which children may be prone to severe, lasting food allergies. “If you have a milk allergy that will stay with you the rest of your life and we could maybe modify that outcome with early, targeted intervention, that would be the nirvana of the field,” Dr. McCusker said.
Dr. Dantzer said her research “showed us that oral immunotherapy is an option, but not a perfect option.
“We still need to keep working on other alternatives that can be even safer and potentially work better,” she added.
The study was supported by the Myra Reinhard Family Foundation. Dr. Dantzer and Dr. McCusker report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
The small, ongoing clinical trial has enabled some participants – all of whom reacted to less than a tablespoon of baked milk at baseline – to begin incorporating baked milk products into everyday diets and to eat in restaurants with less fear of allergic reactions, reported study author Jennifer Dantzer, MD, MHS, assistant professor of pediatrics in the division of pediatric allergy, immunology, and rheumatology at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
Cow’s milk is the most common food allergy in young children, and “for many, it’s a constant stressor that’s always there,” Dr. Dantzer said in an interview. “For a lot of families, this impacts where they eat out, if they eat out, and sometimes where they vacation, or a lot of the social activities they do.
“This was a unique group of kids with a very severe milk phenotype who were reactive to teeny doses and may not have qualified or done well with other types of oral immunotherapy,” she added. “Using a modified allergen – baked milk – seems to work. But for now, we think this is something that still needs further research before it’s ready for a clinical setting.”
The study, for which 24-month unblinded results are being tallied, was recently published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology .
About 2%-3% of preschool-age children are affected by cow’s milk allergy. Children often outgrow it, but for about 20% of children, it persists into adolescence and adulthood. The only current management approaches are avoidance and emergency medications to treat reactions.
But for those with severe milk allergy who react to even trace amounts of milk in any form, the now-routine clinical practice of introducing baked milk isn’t an option, Dr. Dantzer said. The new trial stood out from prior research by using lower starting doses and a more gradual dose escalation of extensively heated milk to determine if oral immunotherapy could be safer but still effective.
Dr. Dantzer and her team randomly assigned 30 participants (aged 3-18 years) into two blinded groups. For 12 months, one group received baked milk oral immunotherapy (BMOIT), and the other a placebo consisting of tapioca flour. At baseline, for all participants, the milk skin prick test wheal diameter was ≥ 3 mm, and the cow’s milk immunoglobulin E (IgE) level was > 5 kU/L. All the children experienced positive dose-limiting reactions to < 1 tablespoon of baked milk protein but could tolerate at least 3 mg on initial dose escalation.
Measured doses of baked milk and placebo powders were supplied to participants for all doses consumed at home. Participants were given instructions on how to prepare it in cupcake or muffin batter. Over 12 months, doses were gradually increased to a maximum cumulative dose of 4,044 mg baked milk protein, or approximately a half tablespoon.
Researchers collected blood samples for immune studies, and participants or their parents completed quality-of-life questionnaires that asked about food anxiety, social and dietary limitations, emotional impact, risk for accidental ingestion, and allergen avoidance.
Fourteen of 15 participants (93%) in the BMOIT group reached the goal-maintenance dose of 2,000 mg of baked milk protein (about a quarter tablespoon). Of those who completed the 12-month challenge, 11 of 14 (79%) in the BMOIT group tolerated 4,000 mg of baked milk protein, compared to none in the placebo group.
“We anticipated that by starting with really small amounts, we would be able to build up the amount of baked milk these kids could tolerate,” Dr. Dantzer said. “We were very pleased by how many could reach the maximal dose at the end of the first year. Once we get the results of the second year, that will provide a lot of additional detail about how this translates into unheated milk amounts they can tolerate and introduce into their diet at home.”
No significant changes were found in IgE levels over time in either study group. Most in the BMOIT group reported improvement in at least one quality-of-life domain, while more in the placebo group reported improvements in only the emotional impact domain.
Adverse events such as gastrointestinal side effects occurred in both groups of participants, but the vast majority of events were mild, Dr. Dantzer said. Fewer than 1% of dosing-related reactions were severe. Four participants required epinephrine.
“This highlights how this needs to be done by someone comfortable and trained, and not by a family at home on their own,” Dr. Dantzer said. “But potentially in the future, this concept of using a modified allergen could be applied to more kids with milk allergy.”
A Montreal-based pediatric allergy specialist who was not involved in the study said the results weren’t surprising. “We’ve known for a good while that the allergenic proteins found in certain foods, or caused by milk in this context, are influenced by the way in which food is processed,” said Christine McCusker, MD, associate professor of pediatrics and director of the division of pediatric allergy, immunology, and dermatology at Montreal Children’s Hospital at McGill University Health Center.
But “having this relatively definitive data that supports what you’re suggesting to patients is obviously the way to optimize your management,” Dr. McCusker said in an interview. “These types of studies are important steps, especially in this age of increased food allergies where many of these things can be dealt with in very young children before their immune systems are fixed.”
Dr. Dantzer and Dr. McCusker agreed that the small size of the study was a limitation, though “waiting for more participants means you don’t always get information out there in a timely manner,” Dr. McCusker said.
She said additional research should focus on preidentifying which children may be prone to severe, lasting food allergies. “If you have a milk allergy that will stay with you the rest of your life and we could maybe modify that outcome with early, targeted intervention, that would be the nirvana of the field,” Dr. McCusker said.
Dr. Dantzer said her research “showed us that oral immunotherapy is an option, but not a perfect option.
“We still need to keep working on other alternatives that can be even safer and potentially work better,” she added.
The study was supported by the Myra Reinhard Family Foundation. Dr. Dantzer and Dr. McCusker report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
The small, ongoing clinical trial has enabled some participants – all of whom reacted to less than a tablespoon of baked milk at baseline – to begin incorporating baked milk products into everyday diets and to eat in restaurants with less fear of allergic reactions, reported study author Jennifer Dantzer, MD, MHS, assistant professor of pediatrics in the division of pediatric allergy, immunology, and rheumatology at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
Cow’s milk is the most common food allergy in young children, and “for many, it’s a constant stressor that’s always there,” Dr. Dantzer said in an interview. “For a lot of families, this impacts where they eat out, if they eat out, and sometimes where they vacation, or a lot of the social activities they do.
“This was a unique group of kids with a very severe milk phenotype who were reactive to teeny doses and may not have qualified or done well with other types of oral immunotherapy,” she added. “Using a modified allergen – baked milk – seems to work. But for now, we think this is something that still needs further research before it’s ready for a clinical setting.”
The study, for which 24-month unblinded results are being tallied, was recently published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology .
About 2%-3% of preschool-age children are affected by cow’s milk allergy. Children often outgrow it, but for about 20% of children, it persists into adolescence and adulthood. The only current management approaches are avoidance and emergency medications to treat reactions.
But for those with severe milk allergy who react to even trace amounts of milk in any form, the now-routine clinical practice of introducing baked milk isn’t an option, Dr. Dantzer said. The new trial stood out from prior research by using lower starting doses and a more gradual dose escalation of extensively heated milk to determine if oral immunotherapy could be safer but still effective.
Dr. Dantzer and her team randomly assigned 30 participants (aged 3-18 years) into two blinded groups. For 12 months, one group received baked milk oral immunotherapy (BMOIT), and the other a placebo consisting of tapioca flour. At baseline, for all participants, the milk skin prick test wheal diameter was ≥ 3 mm, and the cow’s milk immunoglobulin E (IgE) level was > 5 kU/L. All the children experienced positive dose-limiting reactions to < 1 tablespoon of baked milk protein but could tolerate at least 3 mg on initial dose escalation.
Measured doses of baked milk and placebo powders were supplied to participants for all doses consumed at home. Participants were given instructions on how to prepare it in cupcake or muffin batter. Over 12 months, doses were gradually increased to a maximum cumulative dose of 4,044 mg baked milk protein, or approximately a half tablespoon.
Researchers collected blood samples for immune studies, and participants or their parents completed quality-of-life questionnaires that asked about food anxiety, social and dietary limitations, emotional impact, risk for accidental ingestion, and allergen avoidance.
Fourteen of 15 participants (93%) in the BMOIT group reached the goal-maintenance dose of 2,000 mg of baked milk protein (about a quarter tablespoon). Of those who completed the 12-month challenge, 11 of 14 (79%) in the BMOIT group tolerated 4,000 mg of baked milk protein, compared to none in the placebo group.
“We anticipated that by starting with really small amounts, we would be able to build up the amount of baked milk these kids could tolerate,” Dr. Dantzer said. “We were very pleased by how many could reach the maximal dose at the end of the first year. Once we get the results of the second year, that will provide a lot of additional detail about how this translates into unheated milk amounts they can tolerate and introduce into their diet at home.”
No significant changes were found in IgE levels over time in either study group. Most in the BMOIT group reported improvement in at least one quality-of-life domain, while more in the placebo group reported improvements in only the emotional impact domain.
Adverse events such as gastrointestinal side effects occurred in both groups of participants, but the vast majority of events were mild, Dr. Dantzer said. Fewer than 1% of dosing-related reactions were severe. Four participants required epinephrine.
“This highlights how this needs to be done by someone comfortable and trained, and not by a family at home on their own,” Dr. Dantzer said. “But potentially in the future, this concept of using a modified allergen could be applied to more kids with milk allergy.”
A Montreal-based pediatric allergy specialist who was not involved in the study said the results weren’t surprising. “We’ve known for a good while that the allergenic proteins found in certain foods, or caused by milk in this context, are influenced by the way in which food is processed,” said Christine McCusker, MD, associate professor of pediatrics and director of the division of pediatric allergy, immunology, and dermatology at Montreal Children’s Hospital at McGill University Health Center.
But “having this relatively definitive data that supports what you’re suggesting to patients is obviously the way to optimize your management,” Dr. McCusker said in an interview. “These types of studies are important steps, especially in this age of increased food allergies where many of these things can be dealt with in very young children before their immune systems are fixed.”
Dr. Dantzer and Dr. McCusker agreed that the small size of the study was a limitation, though “waiting for more participants means you don’t always get information out there in a timely manner,” Dr. McCusker said.
She said additional research should focus on preidentifying which children may be prone to severe, lasting food allergies. “If you have a milk allergy that will stay with you the rest of your life and we could maybe modify that outcome with early, targeted intervention, that would be the nirvana of the field,” Dr. McCusker said.
Dr. Dantzer said her research “showed us that oral immunotherapy is an option, but not a perfect option.
“We still need to keep working on other alternatives that can be even safer and potentially work better,” she added.
The study was supported by the Myra Reinhard Family Foundation. Dr. Dantzer and Dr. McCusker report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Finding healthcare ‘soul-destroying,’ some turn to online sex work
In March 2021, Prime Minister Boris Johnson proposed a 1% pay rise for National Health Service (NHS) workers in the United Kingdom — a move many deemed inadequate after a full year of fighting the COVID-19 pandemic. The next day, James Cowe, a 23-year-old healthcare assistant who had been working in dementia care for 6 years, decided to create a profile on the content subscription site OnlyFans.
The London-based site allows subscribers, or “fans,” to request content, making its name distributing nude pictures, videos, and other sexually explicit content. It garnered mainstream attention in 2020 when housebound individuals and even celebrities began using it to generate income. Back in August, OnlyFans released a statement stating that it would ban “sexually explicit” content beginning in October. Days later, the company recanted the statement after uproar from creators.
“Because of the one-percent pay rise, I’ve started OnlyFans and I’m making more money in three days than I make in a month at work,” Mr. Cowe said in a now-deleted TikTok post. “Sorry Boris, but I’m done with healthcare and now I’m an online whore.”
Mr. Cowe earned the equivalent of a year’s salary from his healthcare assistant job in his first 22 days on OnlyFans.
Stories like his have multiplied during the pandemic, at a time when healthcare professionals have been particularly overworked and particularly essential. Meanwhile, the pandemic has exacerbated challenges for many sex workers across the globe.
“[There have been] many, many reports over history that transactional sex is used as a sort of emergency livelihood strategy in all kinds of emergencies,” says Joanne Csete, PhD, associate professor of population and family health at Columbia University, New York, “and I suppose this is an emergency in that sense, like any other.”
The relationship between sex work and healthcare
A 2015 study by Leeds University found that 70% of sex workers in the United Kingdom previously worked in healthcare, charities, or education and that more than a third held university degrees.
The relationship between sex workers and healthcare workers has historically been disconnected. Sex workers are at higher risk of experiencing violence, sexually transmitted infections, and substance abuse and mental health problems than the general population, as noted by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. But according to the UN Population Fund, 63% of sex workers will not seek health services alone because they are distrustful and fearful of healthcare workers. A 2014 study by UNAIDS found that stigmatization also makes sex workers less likely to seek assistance from social services.
“I think it’s almost universally hard for sex workers to get respectful healthcare without judgment, and in some cases actual hostility, because of the stigma of their work,” Dr. Csete says. “Health workers are not always trained to see sex work as anything but either a criminal act or an immoral act.”
In August 2021, U.K. medical students called for the British Medical Association to protect students from being penalized by or expelled from their universities for engaging in sex work. BMA Medical Students Committee chair Becky Bates cited high medical school fees and a lack of financial support as motivations for student sex workers. She told this news organization that sex work often allows for flexible hours that might make it easier for students to balance the demands of medical school than other part-time jobs would.
At the annual BMA conference in September, two thirds of the association’s doctors voted in favor of the motion, while others criticized it as potential encouragement for students to get involved in sex work. “The motion isn’t about the morality of sex work,” Ms. Bates said. “[It’s] about the fact that it’s happening and what we can do to support students.”
Healthcare workers on OnlyFans
The rising pressures placed on individuals in the health field have coincided with the rise of online platforms that host pornographic content. During the pandemic, professionals worn down by their healthcare work have embraced sites like OnlyFans as lower-risk, lower-stress, and potentially higher-paying additions or alternatives.
“It’s quite exploitative to work for such low pay in harsh conditions,” Mr. Cowe told this news organizaation of his experience as a dementia care assistant. “It’s soul-destroying. You feel like, ‘It doesn’t matter how many hours I work, it doesn’t matter what I do, I’m still going to be in this same financial position.’ ”
Mr. Cowe earned the equivalent of a year’s salary from his healthcare assistant job in his first 22 days on OnlyFans. Within 8 months, he had earned £150,000, or approximately $205,000.
As an emergency medical services (EMS) worker in New York City, 23-year-old Lauren Kwei lifted obese bariatric patients, administered cardiopulmonary resuscitation to unresponsive recipients, and transported elderly patients and children with terminal illnesses to hospice. She earned $25 an hour, which she says was insufficient for life in one of the world’s most expensive cities. So, in addition to her paramedic work, Ms. Kwei posted photos and videos on OnlyFans to help pay for rent and groceries during the pandemic.
Ms. Kwei started her OnlyFans as a means of paying for necessities like rent and groceries, which her wage as an emergency medical services worker couldn’t cover entirely.
In December 2020, Ms. Kwei got a call from a New York Post reporter who informed her he was writing an article outing her OnlyFans side gig. Ms. Kwei immediately deleted her account on the site for fear of being penalized by her employer, SeniorCare.
“Leave her alone,” U.S. Representative Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez wrote on Twitter in response to the New York Post article. “The actual scandalous headline here is ‘Medics in the United States need two jobs to survive.’ ”
The article quoted an anonymous male paramedic who said Ms. Kwei should have been “pulling extra shifts, instead of pulling off [her] clothes” to earn more money. Ms. Kwei says such advice fails to acknowledge the intensity of the job. “Why would I pick up overtime shifts doing manual labor,” she says, “when I could be doing [OnlyFans] from the comfort of my own home?”
The future of the healthcare/sex work relationship
Ms. Kwei is young enough to receive health insurance through her parents, and Mr. Cowe has access to free healthcare through the NHS. But many sex workers — particularly full-service sex workers, who carry out their work in person — have limited access to services such as healthcare and unemployment benefits. Pandemic restrictions have concurrently driven full-service sex work further underground and therefore deepened the health and safety risks associated with its criminalization.
As health workers become increasingly involved in sex work, advocates in both fields are pushing for healthcare systems to involve sex workers.
“Just as we would do with supporting any group, it’s about understanding any specific barriers or specific problems that they’re encountering, and understanding what they think would help, and working together on that solution,” Ms. Bates says of supporting medical students who engage in sex work.
Tlaleng Mofokeng, MD, UN Special Rapporteur on the right to health, says it is crucial for healthcare organizations to partner with sex worker organizations when it comes to planning the resourcing and budgeting of the public health system in order to meet sex workers’ needs. “While we wait for national policy to change and while we wait for decriminalization,” she says, “tangible things can be done to ensure the provision of equitable services that are aligned with the respect of [sex workers’] rights and the restoration of their dignity.”
Today, healthcare professionals can expect to work with classmates, colleagues, and patients who are involved in sex work and who do not fit the socioeconomic stereotypes associated with sex workers. The number of medical students and healthcare workers engaging in sex work is likely to continue to rise as these individuals struggle to find financial and emotional support within the health sector. Ultimately, many health workers and sex workers share a common goal: to be involved in healthcare systems that respect their work and meet their basic needs.
Mr. Cowe doubts he will ever return to the healthcare industry, owing in part to the stigma against sex workers. “I would feel quite unwelcome,” he says. “[The publicity I received] probably made it not possible for me to go back, but even so, I wouldn’t have a desire to because I was just so burnt out in the end.”
Ms. Kwei is taking a break from her EMS work because of the emotional and financial toll it took, but she plans to return in the future. In the meantime, she is back on OnlyFans and advocating for higher wages for EMS workers as a member of the Emergency Medical Services Public Advocacy Council (EMSPAC). “In order to be a good paramedic, my mental health needs to be on point,” she says. “Hopefully down the line, when I decide to pick up EMS [work] again, I can find a job that pays me enough.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In March 2021, Prime Minister Boris Johnson proposed a 1% pay rise for National Health Service (NHS) workers in the United Kingdom — a move many deemed inadequate after a full year of fighting the COVID-19 pandemic. The next day, James Cowe, a 23-year-old healthcare assistant who had been working in dementia care for 6 years, decided to create a profile on the content subscription site OnlyFans.
The London-based site allows subscribers, or “fans,” to request content, making its name distributing nude pictures, videos, and other sexually explicit content. It garnered mainstream attention in 2020 when housebound individuals and even celebrities began using it to generate income. Back in August, OnlyFans released a statement stating that it would ban “sexually explicit” content beginning in October. Days later, the company recanted the statement after uproar from creators.
“Because of the one-percent pay rise, I’ve started OnlyFans and I’m making more money in three days than I make in a month at work,” Mr. Cowe said in a now-deleted TikTok post. “Sorry Boris, but I’m done with healthcare and now I’m an online whore.”
Mr. Cowe earned the equivalent of a year’s salary from his healthcare assistant job in his first 22 days on OnlyFans.
Stories like his have multiplied during the pandemic, at a time when healthcare professionals have been particularly overworked and particularly essential. Meanwhile, the pandemic has exacerbated challenges for many sex workers across the globe.
“[There have been] many, many reports over history that transactional sex is used as a sort of emergency livelihood strategy in all kinds of emergencies,” says Joanne Csete, PhD, associate professor of population and family health at Columbia University, New York, “and I suppose this is an emergency in that sense, like any other.”
The relationship between sex work and healthcare
A 2015 study by Leeds University found that 70% of sex workers in the United Kingdom previously worked in healthcare, charities, or education and that more than a third held university degrees.
The relationship between sex workers and healthcare workers has historically been disconnected. Sex workers are at higher risk of experiencing violence, sexually transmitted infections, and substance abuse and mental health problems than the general population, as noted by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. But according to the UN Population Fund, 63% of sex workers will not seek health services alone because they are distrustful and fearful of healthcare workers. A 2014 study by UNAIDS found that stigmatization also makes sex workers less likely to seek assistance from social services.
“I think it’s almost universally hard for sex workers to get respectful healthcare without judgment, and in some cases actual hostility, because of the stigma of their work,” Dr. Csete says. “Health workers are not always trained to see sex work as anything but either a criminal act or an immoral act.”
In August 2021, U.K. medical students called for the British Medical Association to protect students from being penalized by or expelled from their universities for engaging in sex work. BMA Medical Students Committee chair Becky Bates cited high medical school fees and a lack of financial support as motivations for student sex workers. She told this news organization that sex work often allows for flexible hours that might make it easier for students to balance the demands of medical school than other part-time jobs would.
At the annual BMA conference in September, two thirds of the association’s doctors voted in favor of the motion, while others criticized it as potential encouragement for students to get involved in sex work. “The motion isn’t about the morality of sex work,” Ms. Bates said. “[It’s] about the fact that it’s happening and what we can do to support students.”
Healthcare workers on OnlyFans
The rising pressures placed on individuals in the health field have coincided with the rise of online platforms that host pornographic content. During the pandemic, professionals worn down by their healthcare work have embraced sites like OnlyFans as lower-risk, lower-stress, and potentially higher-paying additions or alternatives.
“It’s quite exploitative to work for such low pay in harsh conditions,” Mr. Cowe told this news organizaation of his experience as a dementia care assistant. “It’s soul-destroying. You feel like, ‘It doesn’t matter how many hours I work, it doesn’t matter what I do, I’m still going to be in this same financial position.’ ”
Mr. Cowe earned the equivalent of a year’s salary from his healthcare assistant job in his first 22 days on OnlyFans. Within 8 months, he had earned £150,000, or approximately $205,000.
As an emergency medical services (EMS) worker in New York City, 23-year-old Lauren Kwei lifted obese bariatric patients, administered cardiopulmonary resuscitation to unresponsive recipients, and transported elderly patients and children with terminal illnesses to hospice. She earned $25 an hour, which she says was insufficient for life in one of the world’s most expensive cities. So, in addition to her paramedic work, Ms. Kwei posted photos and videos on OnlyFans to help pay for rent and groceries during the pandemic.
Ms. Kwei started her OnlyFans as a means of paying for necessities like rent and groceries, which her wage as an emergency medical services worker couldn’t cover entirely.
In December 2020, Ms. Kwei got a call from a New York Post reporter who informed her he was writing an article outing her OnlyFans side gig. Ms. Kwei immediately deleted her account on the site for fear of being penalized by her employer, SeniorCare.
“Leave her alone,” U.S. Representative Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez wrote on Twitter in response to the New York Post article. “The actual scandalous headline here is ‘Medics in the United States need two jobs to survive.’ ”
The article quoted an anonymous male paramedic who said Ms. Kwei should have been “pulling extra shifts, instead of pulling off [her] clothes” to earn more money. Ms. Kwei says such advice fails to acknowledge the intensity of the job. “Why would I pick up overtime shifts doing manual labor,” she says, “when I could be doing [OnlyFans] from the comfort of my own home?”
The future of the healthcare/sex work relationship
Ms. Kwei is young enough to receive health insurance through her parents, and Mr. Cowe has access to free healthcare through the NHS. But many sex workers — particularly full-service sex workers, who carry out their work in person — have limited access to services such as healthcare and unemployment benefits. Pandemic restrictions have concurrently driven full-service sex work further underground and therefore deepened the health and safety risks associated with its criminalization.
As health workers become increasingly involved in sex work, advocates in both fields are pushing for healthcare systems to involve sex workers.
“Just as we would do with supporting any group, it’s about understanding any specific barriers or specific problems that they’re encountering, and understanding what they think would help, and working together on that solution,” Ms. Bates says of supporting medical students who engage in sex work.
Tlaleng Mofokeng, MD, UN Special Rapporteur on the right to health, says it is crucial for healthcare organizations to partner with sex worker organizations when it comes to planning the resourcing and budgeting of the public health system in order to meet sex workers’ needs. “While we wait for national policy to change and while we wait for decriminalization,” she says, “tangible things can be done to ensure the provision of equitable services that are aligned with the respect of [sex workers’] rights and the restoration of their dignity.”
Today, healthcare professionals can expect to work with classmates, colleagues, and patients who are involved in sex work and who do not fit the socioeconomic stereotypes associated with sex workers. The number of medical students and healthcare workers engaging in sex work is likely to continue to rise as these individuals struggle to find financial and emotional support within the health sector. Ultimately, many health workers and sex workers share a common goal: to be involved in healthcare systems that respect their work and meet their basic needs.
Mr. Cowe doubts he will ever return to the healthcare industry, owing in part to the stigma against sex workers. “I would feel quite unwelcome,” he says. “[The publicity I received] probably made it not possible for me to go back, but even so, I wouldn’t have a desire to because I was just so burnt out in the end.”
Ms. Kwei is taking a break from her EMS work because of the emotional and financial toll it took, but she plans to return in the future. In the meantime, she is back on OnlyFans and advocating for higher wages for EMS workers as a member of the Emergency Medical Services Public Advocacy Council (EMSPAC). “In order to be a good paramedic, my mental health needs to be on point,” she says. “Hopefully down the line, when I decide to pick up EMS [work] again, I can find a job that pays me enough.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In March 2021, Prime Minister Boris Johnson proposed a 1% pay rise for National Health Service (NHS) workers in the United Kingdom — a move many deemed inadequate after a full year of fighting the COVID-19 pandemic. The next day, James Cowe, a 23-year-old healthcare assistant who had been working in dementia care for 6 years, decided to create a profile on the content subscription site OnlyFans.
The London-based site allows subscribers, or “fans,” to request content, making its name distributing nude pictures, videos, and other sexually explicit content. It garnered mainstream attention in 2020 when housebound individuals and even celebrities began using it to generate income. Back in August, OnlyFans released a statement stating that it would ban “sexually explicit” content beginning in October. Days later, the company recanted the statement after uproar from creators.
“Because of the one-percent pay rise, I’ve started OnlyFans and I’m making more money in three days than I make in a month at work,” Mr. Cowe said in a now-deleted TikTok post. “Sorry Boris, but I’m done with healthcare and now I’m an online whore.”
Mr. Cowe earned the equivalent of a year’s salary from his healthcare assistant job in his first 22 days on OnlyFans.
Stories like his have multiplied during the pandemic, at a time when healthcare professionals have been particularly overworked and particularly essential. Meanwhile, the pandemic has exacerbated challenges for many sex workers across the globe.
“[There have been] many, many reports over history that transactional sex is used as a sort of emergency livelihood strategy in all kinds of emergencies,” says Joanne Csete, PhD, associate professor of population and family health at Columbia University, New York, “and I suppose this is an emergency in that sense, like any other.”
The relationship between sex work and healthcare
A 2015 study by Leeds University found that 70% of sex workers in the United Kingdom previously worked in healthcare, charities, or education and that more than a third held university degrees.
The relationship between sex workers and healthcare workers has historically been disconnected. Sex workers are at higher risk of experiencing violence, sexually transmitted infections, and substance abuse and mental health problems than the general population, as noted by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. But according to the UN Population Fund, 63% of sex workers will not seek health services alone because they are distrustful and fearful of healthcare workers. A 2014 study by UNAIDS found that stigmatization also makes sex workers less likely to seek assistance from social services.
“I think it’s almost universally hard for sex workers to get respectful healthcare without judgment, and in some cases actual hostility, because of the stigma of their work,” Dr. Csete says. “Health workers are not always trained to see sex work as anything but either a criminal act or an immoral act.”
In August 2021, U.K. medical students called for the British Medical Association to protect students from being penalized by or expelled from their universities for engaging in sex work. BMA Medical Students Committee chair Becky Bates cited high medical school fees and a lack of financial support as motivations for student sex workers. She told this news organization that sex work often allows for flexible hours that might make it easier for students to balance the demands of medical school than other part-time jobs would.
At the annual BMA conference in September, two thirds of the association’s doctors voted in favor of the motion, while others criticized it as potential encouragement for students to get involved in sex work. “The motion isn’t about the morality of sex work,” Ms. Bates said. “[It’s] about the fact that it’s happening and what we can do to support students.”
Healthcare workers on OnlyFans
The rising pressures placed on individuals in the health field have coincided with the rise of online platforms that host pornographic content. During the pandemic, professionals worn down by their healthcare work have embraced sites like OnlyFans as lower-risk, lower-stress, and potentially higher-paying additions or alternatives.
“It’s quite exploitative to work for such low pay in harsh conditions,” Mr. Cowe told this news organizaation of his experience as a dementia care assistant. “It’s soul-destroying. You feel like, ‘It doesn’t matter how many hours I work, it doesn’t matter what I do, I’m still going to be in this same financial position.’ ”
Mr. Cowe earned the equivalent of a year’s salary from his healthcare assistant job in his first 22 days on OnlyFans. Within 8 months, he had earned £150,000, or approximately $205,000.
As an emergency medical services (EMS) worker in New York City, 23-year-old Lauren Kwei lifted obese bariatric patients, administered cardiopulmonary resuscitation to unresponsive recipients, and transported elderly patients and children with terminal illnesses to hospice. She earned $25 an hour, which she says was insufficient for life in one of the world’s most expensive cities. So, in addition to her paramedic work, Ms. Kwei posted photos and videos on OnlyFans to help pay for rent and groceries during the pandemic.
Ms. Kwei started her OnlyFans as a means of paying for necessities like rent and groceries, which her wage as an emergency medical services worker couldn’t cover entirely.
In December 2020, Ms. Kwei got a call from a New York Post reporter who informed her he was writing an article outing her OnlyFans side gig. Ms. Kwei immediately deleted her account on the site for fear of being penalized by her employer, SeniorCare.
“Leave her alone,” U.S. Representative Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez wrote on Twitter in response to the New York Post article. “The actual scandalous headline here is ‘Medics in the United States need two jobs to survive.’ ”
The article quoted an anonymous male paramedic who said Ms. Kwei should have been “pulling extra shifts, instead of pulling off [her] clothes” to earn more money. Ms. Kwei says such advice fails to acknowledge the intensity of the job. “Why would I pick up overtime shifts doing manual labor,” she says, “when I could be doing [OnlyFans] from the comfort of my own home?”
The future of the healthcare/sex work relationship
Ms. Kwei is young enough to receive health insurance through her parents, and Mr. Cowe has access to free healthcare through the NHS. But many sex workers — particularly full-service sex workers, who carry out their work in person — have limited access to services such as healthcare and unemployment benefits. Pandemic restrictions have concurrently driven full-service sex work further underground and therefore deepened the health and safety risks associated with its criminalization.
As health workers become increasingly involved in sex work, advocates in both fields are pushing for healthcare systems to involve sex workers.
“Just as we would do with supporting any group, it’s about understanding any specific barriers or specific problems that they’re encountering, and understanding what they think would help, and working together on that solution,” Ms. Bates says of supporting medical students who engage in sex work.
Tlaleng Mofokeng, MD, UN Special Rapporteur on the right to health, says it is crucial for healthcare organizations to partner with sex worker organizations when it comes to planning the resourcing and budgeting of the public health system in order to meet sex workers’ needs. “While we wait for national policy to change and while we wait for decriminalization,” she says, “tangible things can be done to ensure the provision of equitable services that are aligned with the respect of [sex workers’] rights and the restoration of their dignity.”
Today, healthcare professionals can expect to work with classmates, colleagues, and patients who are involved in sex work and who do not fit the socioeconomic stereotypes associated with sex workers. The number of medical students and healthcare workers engaging in sex work is likely to continue to rise as these individuals struggle to find financial and emotional support within the health sector. Ultimately, many health workers and sex workers share a common goal: to be involved in healthcare systems that respect their work and meet their basic needs.
Mr. Cowe doubts he will ever return to the healthcare industry, owing in part to the stigma against sex workers. “I would feel quite unwelcome,” he says. “[The publicity I received] probably made it not possible for me to go back, but even so, I wouldn’t have a desire to because I was just so burnt out in the end.”
Ms. Kwei is taking a break from her EMS work because of the emotional and financial toll it took, but she plans to return in the future. In the meantime, she is back on OnlyFans and advocating for higher wages for EMS workers as a member of the Emergency Medical Services Public Advocacy Council (EMSPAC). “In order to be a good paramedic, my mental health needs to be on point,” she says. “Hopefully down the line, when I decide to pick up EMS [work] again, I can find a job that pays me enough.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitals refused to give patients ivermectin. Lockdowns and political pressure followed.
Officials of another Montana hospital accused public officials of threatening and harassing their health care workers for refusing to treat a politically connected COVID-19 patient with that antiparasitic drug or hydroxychloroquine, another drug unauthorized by the Food and Drug Administration to treat COVID.
And in neighboring Idaho, a medical resident said police had to be called to a hospital after a COVID patient’s relative verbally abused her and threatened physical violence because she would not prescribe ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine, “drugs that are not beneficial in the treatment of COVID-19,” she wrote.
These three conflicts, which occurred from September to November, underline the pressure on health care workers to provide unauthorized COVID treatments, particularly in parts of the country where vaccination rates are low, government skepticism is high, and conservative leaders have championed the treatments.
“You’re going to have this from time to time, but it’s not the norm,” said Rich Rasmussen, president and CEO of the Montana Hospital Association. “The vast majority of patients are completely compliant and have good, robust conversations with their medical care team. But you’re going to have these outliers.”
Even before the pandemic, the health care and social assistance industry — which includes residential care facilities and child daycare, among other services — led all U.S. industries in nonfatal workplace violence, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. COVID has made the problem worse, leading to hospital security upgrades, staff training, and calls for increased federal regulation.
Ivermectin and other unauthorized covid treatments have become a major source of dispute in recent months. Lawsuits over hospitals’ refusals to provide ivermectin to patients have been filed in Texas, Florida, Illinois, and elsewhere. The ivermectin harassment extends beyond U.S. borders to providers and public health officials worldwide, in such countries as Australia, Brazil, and the United Kingdom. Even so, reports of threats of violence and harassment like those recently seen in the Northern Rocky Mountains region have been relatively rare.
Ivermectin is approved to treat parasites in animals, and low doses of the drug are approved to treat worms, head lice, and certain skin conditions in humans. But the FDA has not authorized the drug to treat COVID. The agency says that clinical trials are ongoing but that the current data does not show it is an effective COVID treatment and taking higher-than-approved levels can lead to overdose.
Likewise, hydroxychloroquine can cause serious health problems and the drug does not help speed recovery or decrease the chance of dying of COVID, according to the FDA.
In Missoula, Montana, the Community Medical Center was placed on lockdown, and police were called on Nov. 17 after a woman reportedly threatened violence over how her relative was being treated, according to a Police Department statement. Nobody was arrested.
“The family member was upset the patient was not treated with ivermectin,” Lt. Eddie McLean said Nov. 30.
Hospital spokesperson Megan Condra confirmed Dec. 1 that the patient’s relative demanded ivermectin, but she said the patient was not there for COVID, though she declined to disclose the patient’s medical issue. The main entrance of the hospital was locked to control who entered the building, Ms. Condra added, but the hospital’s formal lockdown procedures were not implemented.
The scare was reminiscent of one that happened in Idaho in September. Dr. Ashley Carvalho, who is completing her medical residency training in Boise, wrote in an op-ed in the Idaho Capital Sun that she was verbally abused and threatened with both physical violence and a lawsuit by a patient’s relative after she refused to prescribe ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine.
“My patient was struggling to breathe, but the family refused to allow me to provide care,” Dr. Carvalho wrote. “A call to the police was the only solution.”
An 82-year-old woman who was active in Montana Republican politics was admitted to St. Peter’s Health, the hospital in Helena, with COVID in October. According to a November report by a special counsel appointed by state lawmakers, a family friend contacted Chief Deputy Attorney General Kris Hansen, a former Republican state senator, with multiple complaints: Hospital officials had not delivered a power-of-attorney document left by relatives for the patient to sign, she was denied her preferred medical treatment, she was cut off from her family, and the family worried hospital officials might prevent her from leaving. The patient later died.
That complaint led to the involvement of Republican Attorney General Austin Knudsen, who texted a lobbyist for the Montana Hospital Association who is also on St. Peter’s board of directors. An image of the exchange was included in the report.
“I’m about to send law enforcement in and file unlawful restraint charges,” Mr. Knudsen wrote to Mark Taylor, who responded that he would make inquiries.
“This has been going on since yesterday and I was hoping the hospital would do the right thing. But my patience is wearing thin,” the attorney general added.
A Montana Highway Patrol trooper was sent to the hospital to take the statement of the patient’s family members. Ms. Hansen also participated in a conference call with multiple health care providers in which she talked about the “legal ramifications” of withholding documents and the patient’s preferred treatment, which included ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine.
Public Service Commissioner Jennifer Fielder, a former Republican state senator, left a three-minute voicemail on a hospital line saying the patient’s friends in the Senate would not be too happy to learn of the care St. Peter’s was providing, according to the special counsel’s report.
Ms. Fielder and the patient’s daughter also cited a “right to try” law that Montana legislators passed in 2015 that allows terminally ill patients to seek experimental treatments. But a legal analysis written for the Montana Medical Association says that while the law does not require a provider to prescribe a particular medication if a patient demands it, it could give a provider legal immunity if the provider decides to prescribe the treatment, according to the Montana State News Bureau.
The report did not offer any conclusions or allegations of wrongdoing.
Hospital officials said before and after the report’s release that their health care providers were threatened and harassed when they refused to administer certain treatments for COVID.
“We stand by our assertion that the involvement of public officials in clinical care is inappropriate; that individuals leveraged their official positions in an attempt to influence clinical care; and that some of the exchanges that took place were threatening or harassing,” spokesperson Katie Gallagher said in a statement.
“Further, we reviewed all medical and legal records related to this patient’s care and verified that our teams provided care in accordance with clinical best practice, hospital policy, and patient rights,” Ms. Gallagher added.
The attorney general’s office did not respond to a request for comment but told the Montana Free Press in a statement that nobody at the state agency threatened anyone.
Mr. Rasmussen, the head of the Montana Hospital Association, said St. Peter’s officials have not reached out to the group for assistance. He downplayed the attorney general’s intervention in Helena, saying it often happens that people who know medical leaders or trustees will advocate on behalf of a relative or friend.
“Is this situation different? Certainly, because it’s from the attorney general,” Mr. Rasmussen said. “But I think the AG was responding to a constituent. Others would reach out to whoever they know on the hospital board.”
He added that hospitals have procedures in place that allow family members of patients to take their complaints to a supervisor or other hospital leader without resorting to threats.
Hospitals in the region that have watched the allegations of threats and harassment unfold declined to comment on their procedures to handle such conflicts.
“We respect the independent medical judgment of our providers who practice medicine consistent with approved, authorized treatment and recognized clinical standards,” said Bozeman Health spokesperson Lauren Brendel.
Tanner Gooch, a spokesperson for SCL Health Montana, which operates hospitals in Billings, Butte, and Miles City, said SCL does not endorse ivermectin or other COVID treatments that haven’t been approved by the FDA but doesn’t ban them, either.
“Ultimately, the treatment decisions are at the discretion of the provider,” Mr. Gooch said. “To our knowledge, no COVID-19 patients have been treated with ivermectin at our hospitals.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Officials of another Montana hospital accused public officials of threatening and harassing their health care workers for refusing to treat a politically connected COVID-19 patient with that antiparasitic drug or hydroxychloroquine, another drug unauthorized by the Food and Drug Administration to treat COVID.
And in neighboring Idaho, a medical resident said police had to be called to a hospital after a COVID patient’s relative verbally abused her and threatened physical violence because she would not prescribe ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine, “drugs that are not beneficial in the treatment of COVID-19,” she wrote.
These three conflicts, which occurred from September to November, underline the pressure on health care workers to provide unauthorized COVID treatments, particularly in parts of the country where vaccination rates are low, government skepticism is high, and conservative leaders have championed the treatments.
“You’re going to have this from time to time, but it’s not the norm,” said Rich Rasmussen, president and CEO of the Montana Hospital Association. “The vast majority of patients are completely compliant and have good, robust conversations with their medical care team. But you’re going to have these outliers.”
Even before the pandemic, the health care and social assistance industry — which includes residential care facilities and child daycare, among other services — led all U.S. industries in nonfatal workplace violence, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. COVID has made the problem worse, leading to hospital security upgrades, staff training, and calls for increased federal regulation.
Ivermectin and other unauthorized covid treatments have become a major source of dispute in recent months. Lawsuits over hospitals’ refusals to provide ivermectin to patients have been filed in Texas, Florida, Illinois, and elsewhere. The ivermectin harassment extends beyond U.S. borders to providers and public health officials worldwide, in such countries as Australia, Brazil, and the United Kingdom. Even so, reports of threats of violence and harassment like those recently seen in the Northern Rocky Mountains region have been relatively rare.
Ivermectin is approved to treat parasites in animals, and low doses of the drug are approved to treat worms, head lice, and certain skin conditions in humans. But the FDA has not authorized the drug to treat COVID. The agency says that clinical trials are ongoing but that the current data does not show it is an effective COVID treatment and taking higher-than-approved levels can lead to overdose.
Likewise, hydroxychloroquine can cause serious health problems and the drug does not help speed recovery or decrease the chance of dying of COVID, according to the FDA.
In Missoula, Montana, the Community Medical Center was placed on lockdown, and police were called on Nov. 17 after a woman reportedly threatened violence over how her relative was being treated, according to a Police Department statement. Nobody was arrested.
“The family member was upset the patient was not treated with ivermectin,” Lt. Eddie McLean said Nov. 30.
Hospital spokesperson Megan Condra confirmed Dec. 1 that the patient’s relative demanded ivermectin, but she said the patient was not there for COVID, though she declined to disclose the patient’s medical issue. The main entrance of the hospital was locked to control who entered the building, Ms. Condra added, but the hospital’s formal lockdown procedures were not implemented.
The scare was reminiscent of one that happened in Idaho in September. Dr. Ashley Carvalho, who is completing her medical residency training in Boise, wrote in an op-ed in the Idaho Capital Sun that she was verbally abused and threatened with both physical violence and a lawsuit by a patient’s relative after she refused to prescribe ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine.
“My patient was struggling to breathe, but the family refused to allow me to provide care,” Dr. Carvalho wrote. “A call to the police was the only solution.”
An 82-year-old woman who was active in Montana Republican politics was admitted to St. Peter’s Health, the hospital in Helena, with COVID in October. According to a November report by a special counsel appointed by state lawmakers, a family friend contacted Chief Deputy Attorney General Kris Hansen, a former Republican state senator, with multiple complaints: Hospital officials had not delivered a power-of-attorney document left by relatives for the patient to sign, she was denied her preferred medical treatment, she was cut off from her family, and the family worried hospital officials might prevent her from leaving. The patient later died.
That complaint led to the involvement of Republican Attorney General Austin Knudsen, who texted a lobbyist for the Montana Hospital Association who is also on St. Peter’s board of directors. An image of the exchange was included in the report.
“I’m about to send law enforcement in and file unlawful restraint charges,” Mr. Knudsen wrote to Mark Taylor, who responded that he would make inquiries.
“This has been going on since yesterday and I was hoping the hospital would do the right thing. But my patience is wearing thin,” the attorney general added.
A Montana Highway Patrol trooper was sent to the hospital to take the statement of the patient’s family members. Ms. Hansen also participated in a conference call with multiple health care providers in which she talked about the “legal ramifications” of withholding documents and the patient’s preferred treatment, which included ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine.
Public Service Commissioner Jennifer Fielder, a former Republican state senator, left a three-minute voicemail on a hospital line saying the patient’s friends in the Senate would not be too happy to learn of the care St. Peter’s was providing, according to the special counsel’s report.
Ms. Fielder and the patient’s daughter also cited a “right to try” law that Montana legislators passed in 2015 that allows terminally ill patients to seek experimental treatments. But a legal analysis written for the Montana Medical Association says that while the law does not require a provider to prescribe a particular medication if a patient demands it, it could give a provider legal immunity if the provider decides to prescribe the treatment, according to the Montana State News Bureau.
The report did not offer any conclusions or allegations of wrongdoing.
Hospital officials said before and after the report’s release that their health care providers were threatened and harassed when they refused to administer certain treatments for COVID.
“We stand by our assertion that the involvement of public officials in clinical care is inappropriate; that individuals leveraged their official positions in an attempt to influence clinical care; and that some of the exchanges that took place were threatening or harassing,” spokesperson Katie Gallagher said in a statement.
“Further, we reviewed all medical and legal records related to this patient’s care and verified that our teams provided care in accordance with clinical best practice, hospital policy, and patient rights,” Ms. Gallagher added.
The attorney general’s office did not respond to a request for comment but told the Montana Free Press in a statement that nobody at the state agency threatened anyone.
Mr. Rasmussen, the head of the Montana Hospital Association, said St. Peter’s officials have not reached out to the group for assistance. He downplayed the attorney general’s intervention in Helena, saying it often happens that people who know medical leaders or trustees will advocate on behalf of a relative or friend.
“Is this situation different? Certainly, because it’s from the attorney general,” Mr. Rasmussen said. “But I think the AG was responding to a constituent. Others would reach out to whoever they know on the hospital board.”
He added that hospitals have procedures in place that allow family members of patients to take their complaints to a supervisor or other hospital leader without resorting to threats.
Hospitals in the region that have watched the allegations of threats and harassment unfold declined to comment on their procedures to handle such conflicts.
“We respect the independent medical judgment of our providers who practice medicine consistent with approved, authorized treatment and recognized clinical standards,” said Bozeman Health spokesperson Lauren Brendel.
Tanner Gooch, a spokesperson for SCL Health Montana, which operates hospitals in Billings, Butte, and Miles City, said SCL does not endorse ivermectin or other COVID treatments that haven’t been approved by the FDA but doesn’t ban them, either.
“Ultimately, the treatment decisions are at the discretion of the provider,” Mr. Gooch said. “To our knowledge, no COVID-19 patients have been treated with ivermectin at our hospitals.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Officials of another Montana hospital accused public officials of threatening and harassing their health care workers for refusing to treat a politically connected COVID-19 patient with that antiparasitic drug or hydroxychloroquine, another drug unauthorized by the Food and Drug Administration to treat COVID.
And in neighboring Idaho, a medical resident said police had to be called to a hospital after a COVID patient’s relative verbally abused her and threatened physical violence because she would not prescribe ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine, “drugs that are not beneficial in the treatment of COVID-19,” she wrote.
These three conflicts, which occurred from September to November, underline the pressure on health care workers to provide unauthorized COVID treatments, particularly in parts of the country where vaccination rates are low, government skepticism is high, and conservative leaders have championed the treatments.
“You’re going to have this from time to time, but it’s not the norm,” said Rich Rasmussen, president and CEO of the Montana Hospital Association. “The vast majority of patients are completely compliant and have good, robust conversations with their medical care team. But you’re going to have these outliers.”
Even before the pandemic, the health care and social assistance industry — which includes residential care facilities and child daycare, among other services — led all U.S. industries in nonfatal workplace violence, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. COVID has made the problem worse, leading to hospital security upgrades, staff training, and calls for increased federal regulation.
Ivermectin and other unauthorized covid treatments have become a major source of dispute in recent months. Lawsuits over hospitals’ refusals to provide ivermectin to patients have been filed in Texas, Florida, Illinois, and elsewhere. The ivermectin harassment extends beyond U.S. borders to providers and public health officials worldwide, in such countries as Australia, Brazil, and the United Kingdom. Even so, reports of threats of violence and harassment like those recently seen in the Northern Rocky Mountains region have been relatively rare.
Ivermectin is approved to treat parasites in animals, and low doses of the drug are approved to treat worms, head lice, and certain skin conditions in humans. But the FDA has not authorized the drug to treat COVID. The agency says that clinical trials are ongoing but that the current data does not show it is an effective COVID treatment and taking higher-than-approved levels can lead to overdose.
Likewise, hydroxychloroquine can cause serious health problems and the drug does not help speed recovery or decrease the chance of dying of COVID, according to the FDA.
In Missoula, Montana, the Community Medical Center was placed on lockdown, and police were called on Nov. 17 after a woman reportedly threatened violence over how her relative was being treated, according to a Police Department statement. Nobody was arrested.
“The family member was upset the patient was not treated with ivermectin,” Lt. Eddie McLean said Nov. 30.
Hospital spokesperson Megan Condra confirmed Dec. 1 that the patient’s relative demanded ivermectin, but she said the patient was not there for COVID, though she declined to disclose the patient’s medical issue. The main entrance of the hospital was locked to control who entered the building, Ms. Condra added, but the hospital’s formal lockdown procedures were not implemented.
The scare was reminiscent of one that happened in Idaho in September. Dr. Ashley Carvalho, who is completing her medical residency training in Boise, wrote in an op-ed in the Idaho Capital Sun that she was verbally abused and threatened with both physical violence and a lawsuit by a patient’s relative after she refused to prescribe ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine.
“My patient was struggling to breathe, but the family refused to allow me to provide care,” Dr. Carvalho wrote. “A call to the police was the only solution.”
An 82-year-old woman who was active in Montana Republican politics was admitted to St. Peter’s Health, the hospital in Helena, with COVID in October. According to a November report by a special counsel appointed by state lawmakers, a family friend contacted Chief Deputy Attorney General Kris Hansen, a former Republican state senator, with multiple complaints: Hospital officials had not delivered a power-of-attorney document left by relatives for the patient to sign, she was denied her preferred medical treatment, she was cut off from her family, and the family worried hospital officials might prevent her from leaving. The patient later died.
That complaint led to the involvement of Republican Attorney General Austin Knudsen, who texted a lobbyist for the Montana Hospital Association who is also on St. Peter’s board of directors. An image of the exchange was included in the report.
“I’m about to send law enforcement in and file unlawful restraint charges,” Mr. Knudsen wrote to Mark Taylor, who responded that he would make inquiries.
“This has been going on since yesterday and I was hoping the hospital would do the right thing. But my patience is wearing thin,” the attorney general added.
A Montana Highway Patrol trooper was sent to the hospital to take the statement of the patient’s family members. Ms. Hansen also participated in a conference call with multiple health care providers in which she talked about the “legal ramifications” of withholding documents and the patient’s preferred treatment, which included ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine.
Public Service Commissioner Jennifer Fielder, a former Republican state senator, left a three-minute voicemail on a hospital line saying the patient’s friends in the Senate would not be too happy to learn of the care St. Peter’s was providing, according to the special counsel’s report.
Ms. Fielder and the patient’s daughter also cited a “right to try” law that Montana legislators passed in 2015 that allows terminally ill patients to seek experimental treatments. But a legal analysis written for the Montana Medical Association says that while the law does not require a provider to prescribe a particular medication if a patient demands it, it could give a provider legal immunity if the provider decides to prescribe the treatment, according to the Montana State News Bureau.
The report did not offer any conclusions or allegations of wrongdoing.
Hospital officials said before and after the report’s release that their health care providers were threatened and harassed when they refused to administer certain treatments for COVID.
“We stand by our assertion that the involvement of public officials in clinical care is inappropriate; that individuals leveraged their official positions in an attempt to influence clinical care; and that some of the exchanges that took place were threatening or harassing,” spokesperson Katie Gallagher said in a statement.
“Further, we reviewed all medical and legal records related to this patient’s care and verified that our teams provided care in accordance with clinical best practice, hospital policy, and patient rights,” Ms. Gallagher added.
The attorney general’s office did not respond to a request for comment but told the Montana Free Press in a statement that nobody at the state agency threatened anyone.
Mr. Rasmussen, the head of the Montana Hospital Association, said St. Peter’s officials have not reached out to the group for assistance. He downplayed the attorney general’s intervention in Helena, saying it often happens that people who know medical leaders or trustees will advocate on behalf of a relative or friend.
“Is this situation different? Certainly, because it’s from the attorney general,” Mr. Rasmussen said. “But I think the AG was responding to a constituent. Others would reach out to whoever they know on the hospital board.”
He added that hospitals have procedures in place that allow family members of patients to take their complaints to a supervisor or other hospital leader without resorting to threats.
Hospitals in the region that have watched the allegations of threats and harassment unfold declined to comment on their procedures to handle such conflicts.
“We respect the independent medical judgment of our providers who practice medicine consistent with approved, authorized treatment and recognized clinical standards,” said Bozeman Health spokesperson Lauren Brendel.
Tanner Gooch, a spokesperson for SCL Health Montana, which operates hospitals in Billings, Butte, and Miles City, said SCL does not endorse ivermectin or other COVID treatments that haven’t been approved by the FDA but doesn’t ban them, either.
“Ultimately, the treatment decisions are at the discretion of the provider,” Mr. Gooch said. “To our knowledge, no COVID-19 patients have been treated with ivermectin at our hospitals.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Guselkumab’s efficacy, safety confirmed in patients with psoriatic arthritis and prior TNFi exposure
A new study has established guselkumab (Tremfya) as both a safe and effective treatment option for psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in patients who had previously responded poorly to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFis).
“While the positive guselkumab benefit-risk profile observed through week 24 was maintained through 1 year, real-world evidence will further inform long-term guselkumab persistence in TNFi-inadequate response patients,” writes Laura C. Coates, MBChB, PhD, of the University of Oxford (England), and her coauthors. The study was published in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Previous studies indicated that the anti–interleukin-23p19 monoclonal antibody improved outcomes in patients with PsA, even after 1 year, but some uncertainty remained regarding the surprisingly similar level of effectiveness in biologic-naive and TNFi-treated patients. Guselkumab is approved for treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy and adults with active psoriatic arthritis.
Clarity on guselkumab’s effectiveness in certain patients
“In previous studies that cemented guselkumab as a treatment option for PsA, what was odd was that the results were pretty comparable,” Eric M. Ruderman, MD, professor of medicine and associate chief for clinical affairs in the division of rheumatology at Northwestern University in Chicago, Illinois, said in an interview. “We didn’t really have a sense of how well it worked in patients who had failed other biologics, which is where you might expect a drug with a new mechanism to be used when it comes into a particular disease category.
“Not surprisingly, in this study, the overall response rate was a little less than the response rate in the other two trials,” said Dr. Ruderman, who was not involved in the study. “You can’t really compare across studies, but it does fit with what we might expect: People who’ve previously failed a TNF inhibitor might be a little less likely to respond to guselkumab, compared to someone who hasn’t seen a TNF inhibitor.”
When asked about potential follow-up studies, Dr. Ruderman noted that “the missing piece of the puzzle is that we still really have no way to compare this to other biologics. The next step would be to ask, in a single trial, what happens if you give some people TNF inhibitors and some people guselkumab? Just to try to give us context. Is this equivalent? Is it less effective? More effective? Where does it fit? Without that information, rheumatologists may struggle to figure out who is the right person for this drug and how often should they use it.”
Study details
To assess the efficacy and safety of guselkumab in patients who had previously taken TNFis but stopped because of inefficacy or intolerance, the researchers launched a randomized, double-blind study called COSMOS at 84 European sites from March 2019 to November 2020. The study’s 285 patients – 52% of whom were women, with an average overall age of 49 – were assigned to two groups: guselkumab (n = 189) or placebo (n = 96). A total of 88% of all patients had used one TNFi prior; 12% had used two.
The guselkumab group received 100-mg injections at week 0, week 4, and then every 8 weeks through week 44; the placebo group received injections at weeks 0, 4, 12, and 20, followed by 100 mg of guselkumab at weeks 24, 28, 36, and 44. Patients with less than 5% improvement from baseline in both tender and swollen joint counts at week 16 qualified for early escape to “initiate or increase the dose of one permitted concomitant medication up to the maximum allowed dose at the physician’s discretion.” Ultimately, 88% of patients in the guselkumab arm and 83% of the placebo arm completed the study.
At 24 weeks, more than 44% of the guselkumab group achieved a 20% or greater improvement in American College of Rheumatology criteria (ACR20), compared with just under 20% of the placebo group, a difference of nearly 25% (95% confidence interval, 14.1%-35.2%; multiplicity-adjusted P < .001). At 48 weeks, nearly 58% of the guselkumab group had achieved ACR20; of the 51 patients in the placebo arm who started taking guselkumab at week 24, 55% achieved ACR20 by week 48.
Through 24 weeks, 80 patients in the guselkumab group (42%) and 46 patients in the placebo group (48%) experienced adverse events; only 3.7% and 3.1% developed serious adverse events, respectively. The most common adverse events in the guselkumab group at that point included nasopharyngitis (5%) and upper respiratory tract infection (4%), which occurred at a similar frequency (5% and 3%) in the placebo group.
The authors acknowledge their study’s limitations, including imbalances in baseline characteristics such as gender and weight, as well as the COSMOS study being restricted to European patients and thus potentially limiting diversity. In addition, while the COVID-19 pandemic may have increased major protocol deviations near the end of the study, the authors note that “most were related to timing of study visits and did not impact efficacy.”
The study was funded by Janssen, and six authors reported being employees of the company. The authors also acknowledge numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving consulting fees and research grants from various pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen. Dr. Ruderman is a consultant for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Janssen and served on the data safety monitoring committee for two other phase 3 guselkumab trials.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study has established guselkumab (Tremfya) as both a safe and effective treatment option for psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in patients who had previously responded poorly to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFis).
“While the positive guselkumab benefit-risk profile observed through week 24 was maintained through 1 year, real-world evidence will further inform long-term guselkumab persistence in TNFi-inadequate response patients,” writes Laura C. Coates, MBChB, PhD, of the University of Oxford (England), and her coauthors. The study was published in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Previous studies indicated that the anti–interleukin-23p19 monoclonal antibody improved outcomes in patients with PsA, even after 1 year, but some uncertainty remained regarding the surprisingly similar level of effectiveness in biologic-naive and TNFi-treated patients. Guselkumab is approved for treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy and adults with active psoriatic arthritis.
Clarity on guselkumab’s effectiveness in certain patients
“In previous studies that cemented guselkumab as a treatment option for PsA, what was odd was that the results were pretty comparable,” Eric M. Ruderman, MD, professor of medicine and associate chief for clinical affairs in the division of rheumatology at Northwestern University in Chicago, Illinois, said in an interview. “We didn’t really have a sense of how well it worked in patients who had failed other biologics, which is where you might expect a drug with a new mechanism to be used when it comes into a particular disease category.
“Not surprisingly, in this study, the overall response rate was a little less than the response rate in the other two trials,” said Dr. Ruderman, who was not involved in the study. “You can’t really compare across studies, but it does fit with what we might expect: People who’ve previously failed a TNF inhibitor might be a little less likely to respond to guselkumab, compared to someone who hasn’t seen a TNF inhibitor.”
When asked about potential follow-up studies, Dr. Ruderman noted that “the missing piece of the puzzle is that we still really have no way to compare this to other biologics. The next step would be to ask, in a single trial, what happens if you give some people TNF inhibitors and some people guselkumab? Just to try to give us context. Is this equivalent? Is it less effective? More effective? Where does it fit? Without that information, rheumatologists may struggle to figure out who is the right person for this drug and how often should they use it.”
Study details
To assess the efficacy and safety of guselkumab in patients who had previously taken TNFis but stopped because of inefficacy or intolerance, the researchers launched a randomized, double-blind study called COSMOS at 84 European sites from March 2019 to November 2020. The study’s 285 patients – 52% of whom were women, with an average overall age of 49 – were assigned to two groups: guselkumab (n = 189) or placebo (n = 96). A total of 88% of all patients had used one TNFi prior; 12% had used two.
The guselkumab group received 100-mg injections at week 0, week 4, and then every 8 weeks through week 44; the placebo group received injections at weeks 0, 4, 12, and 20, followed by 100 mg of guselkumab at weeks 24, 28, 36, and 44. Patients with less than 5% improvement from baseline in both tender and swollen joint counts at week 16 qualified for early escape to “initiate or increase the dose of one permitted concomitant medication up to the maximum allowed dose at the physician’s discretion.” Ultimately, 88% of patients in the guselkumab arm and 83% of the placebo arm completed the study.
At 24 weeks, more than 44% of the guselkumab group achieved a 20% or greater improvement in American College of Rheumatology criteria (ACR20), compared with just under 20% of the placebo group, a difference of nearly 25% (95% confidence interval, 14.1%-35.2%; multiplicity-adjusted P < .001). At 48 weeks, nearly 58% of the guselkumab group had achieved ACR20; of the 51 patients in the placebo arm who started taking guselkumab at week 24, 55% achieved ACR20 by week 48.
Through 24 weeks, 80 patients in the guselkumab group (42%) and 46 patients in the placebo group (48%) experienced adverse events; only 3.7% and 3.1% developed serious adverse events, respectively. The most common adverse events in the guselkumab group at that point included nasopharyngitis (5%) and upper respiratory tract infection (4%), which occurred at a similar frequency (5% and 3%) in the placebo group.
The authors acknowledge their study’s limitations, including imbalances in baseline characteristics such as gender and weight, as well as the COSMOS study being restricted to European patients and thus potentially limiting diversity. In addition, while the COVID-19 pandemic may have increased major protocol deviations near the end of the study, the authors note that “most were related to timing of study visits and did not impact efficacy.”
The study was funded by Janssen, and six authors reported being employees of the company. The authors also acknowledge numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving consulting fees and research grants from various pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen. Dr. Ruderman is a consultant for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Janssen and served on the data safety monitoring committee for two other phase 3 guselkumab trials.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study has established guselkumab (Tremfya) as both a safe and effective treatment option for psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in patients who had previously responded poorly to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFis).
“While the positive guselkumab benefit-risk profile observed through week 24 was maintained through 1 year, real-world evidence will further inform long-term guselkumab persistence in TNFi-inadequate response patients,” writes Laura C. Coates, MBChB, PhD, of the University of Oxford (England), and her coauthors. The study was published in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Previous studies indicated that the anti–interleukin-23p19 monoclonal antibody improved outcomes in patients with PsA, even after 1 year, but some uncertainty remained regarding the surprisingly similar level of effectiveness in biologic-naive and TNFi-treated patients. Guselkumab is approved for treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy and adults with active psoriatic arthritis.
Clarity on guselkumab’s effectiveness in certain patients
“In previous studies that cemented guselkumab as a treatment option for PsA, what was odd was that the results were pretty comparable,” Eric M. Ruderman, MD, professor of medicine and associate chief for clinical affairs in the division of rheumatology at Northwestern University in Chicago, Illinois, said in an interview. “We didn’t really have a sense of how well it worked in patients who had failed other biologics, which is where you might expect a drug with a new mechanism to be used when it comes into a particular disease category.
“Not surprisingly, in this study, the overall response rate was a little less than the response rate in the other two trials,” said Dr. Ruderman, who was not involved in the study. “You can’t really compare across studies, but it does fit with what we might expect: People who’ve previously failed a TNF inhibitor might be a little less likely to respond to guselkumab, compared to someone who hasn’t seen a TNF inhibitor.”
When asked about potential follow-up studies, Dr. Ruderman noted that “the missing piece of the puzzle is that we still really have no way to compare this to other biologics. The next step would be to ask, in a single trial, what happens if you give some people TNF inhibitors and some people guselkumab? Just to try to give us context. Is this equivalent? Is it less effective? More effective? Where does it fit? Without that information, rheumatologists may struggle to figure out who is the right person for this drug and how often should they use it.”
Study details
To assess the efficacy and safety of guselkumab in patients who had previously taken TNFis but stopped because of inefficacy or intolerance, the researchers launched a randomized, double-blind study called COSMOS at 84 European sites from March 2019 to November 2020. The study’s 285 patients – 52% of whom were women, with an average overall age of 49 – were assigned to two groups: guselkumab (n = 189) or placebo (n = 96). A total of 88% of all patients had used one TNFi prior; 12% had used two.
The guselkumab group received 100-mg injections at week 0, week 4, and then every 8 weeks through week 44; the placebo group received injections at weeks 0, 4, 12, and 20, followed by 100 mg of guselkumab at weeks 24, 28, 36, and 44. Patients with less than 5% improvement from baseline in both tender and swollen joint counts at week 16 qualified for early escape to “initiate or increase the dose of one permitted concomitant medication up to the maximum allowed dose at the physician’s discretion.” Ultimately, 88% of patients in the guselkumab arm and 83% of the placebo arm completed the study.
At 24 weeks, more than 44% of the guselkumab group achieved a 20% or greater improvement in American College of Rheumatology criteria (ACR20), compared with just under 20% of the placebo group, a difference of nearly 25% (95% confidence interval, 14.1%-35.2%; multiplicity-adjusted P < .001). At 48 weeks, nearly 58% of the guselkumab group had achieved ACR20; of the 51 patients in the placebo arm who started taking guselkumab at week 24, 55% achieved ACR20 by week 48.
Through 24 weeks, 80 patients in the guselkumab group (42%) and 46 patients in the placebo group (48%) experienced adverse events; only 3.7% and 3.1% developed serious adverse events, respectively. The most common adverse events in the guselkumab group at that point included nasopharyngitis (5%) and upper respiratory tract infection (4%), which occurred at a similar frequency (5% and 3%) in the placebo group.
The authors acknowledge their study’s limitations, including imbalances in baseline characteristics such as gender and weight, as well as the COSMOS study being restricted to European patients and thus potentially limiting diversity. In addition, while the COVID-19 pandemic may have increased major protocol deviations near the end of the study, the authors note that “most were related to timing of study visits and did not impact efficacy.”
The study was funded by Janssen, and six authors reported being employees of the company. The authors also acknowledge numerous potential conflicts of interest, including receiving consulting fees and research grants from various pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen. Dr. Ruderman is a consultant for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Janssen and served on the data safety monitoring committee for two other phase 3 guselkumab trials.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES
No serious CV risks for elderly after Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine
A French population-based study provides further evidence that the BNT162b2 Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 vaccine does not increase the short-term risk for serious cardiovascular adverse events in older people.
The study showed no increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, or pulmonary embolism (PE) following vaccination in adults aged 75 years or older in the 14 days following vaccination.
“These findings regarding the BNT162b2 vaccine’s short-term cardiovascular safety profile in older people are reassuring. They should be taken into account by doctors when considering implementing a third dose of the vaccine in older people,” Marie Joelle Jabagi, PharmD, PhD, with the French National Agency for Medicines and Health Products Safety, Saint-Denis, France, said in an interview.
The study was published as a research letter online Nov. 22 in JAMA.
The Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine was the first SARS-CoV-2 vaccine authorized in France and has been widely used in older people. The phase 3 trials of the vaccine showed no increase in cardiovascular events, but older people were underrepresented in the trials.
As of April 30, 2021, nearly 3.9 million French adults aged 75 or older had received at least one dose of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine and 3.2 million had received two doses.
Using the French National Health Data System linked to the national COVID-19 vaccination database, Dr. Jabagi and her colleagues identified all unvaccinated or vaccinated adults aged 75 and older who were hospitalized between Dec. 15, 2020, and April 30, 2021, for acute MI, hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, or PE.
During the 4.5-month study period, 11,113 elderly were hospitalized for acute MI, 17,014 for ischemic stroke, 4,804 for hemorrhagic stroke, and 7,221 for PE. Of these, 58.6%, 54.0%, 42.7%, and 55.3%, respectively, had received at least one dose of vaccine.
In the 14 days following receipt of either dose, no significant increased risk was found for any outcome, the investigators report.
The relative incidence (RI) for MI after the first and second dose was 0.97 (95% CI, 0.88-1.06) and 1.04 (95% CI, 0.93-1.16), respectively.
For ischemic stroke, the RI was 0.90 after the first dose (95% CI, 0.84-0.98) and 0.92 (95% CI, 0.84-1.02) after the second; for hemorrhagic stroke, the RI was 0.90 (95% CI, 0.78-1.04) and 0.97 (95% CI, 0.81-1.15), respectively.
For PE, the RI was 0.85 (95% CI, 0.75-0.96) after the first dose and 1.10 (95% CI, 0.95-1.26) after the second dose.
There was also no significant increase for any of the cardiovascular events when the exposure risk window was subdivided into 1 to 7 days and 8 to 14 days.
“Evaluating the short-term risk of hospitalization for severe cardiovascular events after the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in older people was a priority, especially after signals for hypertension and cardiovascular, thromboembolic, and hemorrhagic events have been issued from spontaneous notification data,” Dr. Jabagi said in an interview.
“The results of this nationwide study provide further solid evidence regarding the lack of increase of serious cardiovascular adverse events in older people in the 14 days following both doses of the vaccine,” Dr. Jabagi said.
The French study supports a recent U.S. study of more than 6 million people demonstrating that serious health risks were no more common in the first 3 weeks after Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna COVID-19 vaccination compared with 22 to 42 days later.
As previously reported by this news organization, mRNA vaccination was not associated with greater risks for Guillain-Barré syndrome, myocarditis/pericarditis, stroke, or 20 other serious outcomes.
The current study had no specific funding. Dr. Jabagi and colleagues have declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A French population-based study provides further evidence that the BNT162b2 Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 vaccine does not increase the short-term risk for serious cardiovascular adverse events in older people.
The study showed no increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, or pulmonary embolism (PE) following vaccination in adults aged 75 years or older in the 14 days following vaccination.
“These findings regarding the BNT162b2 vaccine’s short-term cardiovascular safety profile in older people are reassuring. They should be taken into account by doctors when considering implementing a third dose of the vaccine in older people,” Marie Joelle Jabagi, PharmD, PhD, with the French National Agency for Medicines and Health Products Safety, Saint-Denis, France, said in an interview.
The study was published as a research letter online Nov. 22 in JAMA.
The Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine was the first SARS-CoV-2 vaccine authorized in France and has been widely used in older people. The phase 3 trials of the vaccine showed no increase in cardiovascular events, but older people were underrepresented in the trials.
As of April 30, 2021, nearly 3.9 million French adults aged 75 or older had received at least one dose of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine and 3.2 million had received two doses.
Using the French National Health Data System linked to the national COVID-19 vaccination database, Dr. Jabagi and her colleagues identified all unvaccinated or vaccinated adults aged 75 and older who were hospitalized between Dec. 15, 2020, and April 30, 2021, for acute MI, hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, or PE.
During the 4.5-month study period, 11,113 elderly were hospitalized for acute MI, 17,014 for ischemic stroke, 4,804 for hemorrhagic stroke, and 7,221 for PE. Of these, 58.6%, 54.0%, 42.7%, and 55.3%, respectively, had received at least one dose of vaccine.
In the 14 days following receipt of either dose, no significant increased risk was found for any outcome, the investigators report.
The relative incidence (RI) for MI after the first and second dose was 0.97 (95% CI, 0.88-1.06) and 1.04 (95% CI, 0.93-1.16), respectively.
For ischemic stroke, the RI was 0.90 after the first dose (95% CI, 0.84-0.98) and 0.92 (95% CI, 0.84-1.02) after the second; for hemorrhagic stroke, the RI was 0.90 (95% CI, 0.78-1.04) and 0.97 (95% CI, 0.81-1.15), respectively.
For PE, the RI was 0.85 (95% CI, 0.75-0.96) after the first dose and 1.10 (95% CI, 0.95-1.26) after the second dose.
There was also no significant increase for any of the cardiovascular events when the exposure risk window was subdivided into 1 to 7 days and 8 to 14 days.
“Evaluating the short-term risk of hospitalization for severe cardiovascular events after the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in older people was a priority, especially after signals for hypertension and cardiovascular, thromboembolic, and hemorrhagic events have been issued from spontaneous notification data,” Dr. Jabagi said in an interview.
“The results of this nationwide study provide further solid evidence regarding the lack of increase of serious cardiovascular adverse events in older people in the 14 days following both doses of the vaccine,” Dr. Jabagi said.
The French study supports a recent U.S. study of more than 6 million people demonstrating that serious health risks were no more common in the first 3 weeks after Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna COVID-19 vaccination compared with 22 to 42 days later.
As previously reported by this news organization, mRNA vaccination was not associated with greater risks for Guillain-Barré syndrome, myocarditis/pericarditis, stroke, or 20 other serious outcomes.
The current study had no specific funding. Dr. Jabagi and colleagues have declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A French population-based study provides further evidence that the BNT162b2 Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 vaccine does not increase the short-term risk for serious cardiovascular adverse events in older people.
The study showed no increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, or pulmonary embolism (PE) following vaccination in adults aged 75 years or older in the 14 days following vaccination.
“These findings regarding the BNT162b2 vaccine’s short-term cardiovascular safety profile in older people are reassuring. They should be taken into account by doctors when considering implementing a third dose of the vaccine in older people,” Marie Joelle Jabagi, PharmD, PhD, with the French National Agency for Medicines and Health Products Safety, Saint-Denis, France, said in an interview.
The study was published as a research letter online Nov. 22 in JAMA.
The Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine was the first SARS-CoV-2 vaccine authorized in France and has been widely used in older people. The phase 3 trials of the vaccine showed no increase in cardiovascular events, but older people were underrepresented in the trials.
As of April 30, 2021, nearly 3.9 million French adults aged 75 or older had received at least one dose of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine and 3.2 million had received two doses.
Using the French National Health Data System linked to the national COVID-19 vaccination database, Dr. Jabagi and her colleagues identified all unvaccinated or vaccinated adults aged 75 and older who were hospitalized between Dec. 15, 2020, and April 30, 2021, for acute MI, hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, or PE.
During the 4.5-month study period, 11,113 elderly were hospitalized for acute MI, 17,014 for ischemic stroke, 4,804 for hemorrhagic stroke, and 7,221 for PE. Of these, 58.6%, 54.0%, 42.7%, and 55.3%, respectively, had received at least one dose of vaccine.
In the 14 days following receipt of either dose, no significant increased risk was found for any outcome, the investigators report.
The relative incidence (RI) for MI after the first and second dose was 0.97 (95% CI, 0.88-1.06) and 1.04 (95% CI, 0.93-1.16), respectively.
For ischemic stroke, the RI was 0.90 after the first dose (95% CI, 0.84-0.98) and 0.92 (95% CI, 0.84-1.02) after the second; for hemorrhagic stroke, the RI was 0.90 (95% CI, 0.78-1.04) and 0.97 (95% CI, 0.81-1.15), respectively.
For PE, the RI was 0.85 (95% CI, 0.75-0.96) after the first dose and 1.10 (95% CI, 0.95-1.26) after the second dose.
There was also no significant increase for any of the cardiovascular events when the exposure risk window was subdivided into 1 to 7 days and 8 to 14 days.
“Evaluating the short-term risk of hospitalization for severe cardiovascular events after the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in older people was a priority, especially after signals for hypertension and cardiovascular, thromboembolic, and hemorrhagic events have been issued from spontaneous notification data,” Dr. Jabagi said in an interview.
“The results of this nationwide study provide further solid evidence regarding the lack of increase of serious cardiovascular adverse events in older people in the 14 days following both doses of the vaccine,” Dr. Jabagi said.
The French study supports a recent U.S. study of more than 6 million people demonstrating that serious health risks were no more common in the first 3 weeks after Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna COVID-19 vaccination compared with 22 to 42 days later.
As previously reported by this news organization, mRNA vaccination was not associated with greater risks for Guillain-Barré syndrome, myocarditis/pericarditis, stroke, or 20 other serious outcomes.
The current study had no specific funding. Dr. Jabagi and colleagues have declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 antibody drug likely works against Omicron, companies say
The companies said Dec. 2 that they tested the drug, called sotrovimab, against individual mutations found in the Omicron variant, according to The Wall Street Journal. The preliminary findings haven’t yet been peer-reviewed, and the drug will need to be tested against the whole spike protein on the virus to confirm results.
GlaxoSmithKline and Vir have previously tested sotrovimab against mutations on other variants, the newspaper reported. When the Omicron variant was identified, the companies looked at earlier research to find the tests they had done against mutations that are also found in Omicron.
Sotrovimab targets a spot on the spike protein that is found in other coronaviruses and is thought to be less likely to mutate, according to the newspaper. Omicron has at least two mutations that overlap with the drug’s target site, but researchers at the companies don’t think the mutations will affect the treatment’s ability to bind to the spike protein.
GlaxoSmithKline expects to see results from testing the drug against the full mutated spike protein in the next 2 to 3 weeks, the Journal reported.
Sotrovimab has been authorized in about a dozen countries, including the United States, which paid about $1 billion for hundreds of thousands of doses.
Other companies have also been testing their antibody treatments against the Omicron variant.
Regeneron announced Nov. 30 that its drug could be less effective, and it said further analyses will determine how much less effective by using the actual Omicron genetic sequence, according to Reuters.
Outside scientists have also said the antibody drug from Eli Lilly & Co. isn’t as effective against Omicron. The company told Reuters that it is still testing the treatment against the variant.
Another experimental antibody therapy developed by Adagio Therapeutics appears to work well against the new variant, the Journal reported, but the treatment is in late-stage clinical trials and isn’t yet authorized.
Antiviral drugs could also help prevent hospitalization and may be less vulnerable to new variants because they target a different part of the virus, the newspaper reported. Merck and Pfizer have developed antiviral pills, which still require FDA approval.
In addition, Gilead believes its approved IV therapy, called remdesivir, will continue to be effective against the variant, Reuters reported.
The FDA said Nov. 30 that it is looking at the effect that authorized COVID-19 vaccines can have on Omicron and expects to have more information in coming weeks, Reuters reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The companies said Dec. 2 that they tested the drug, called sotrovimab, against individual mutations found in the Omicron variant, according to The Wall Street Journal. The preliminary findings haven’t yet been peer-reviewed, and the drug will need to be tested against the whole spike protein on the virus to confirm results.
GlaxoSmithKline and Vir have previously tested sotrovimab against mutations on other variants, the newspaper reported. When the Omicron variant was identified, the companies looked at earlier research to find the tests they had done against mutations that are also found in Omicron.
Sotrovimab targets a spot on the spike protein that is found in other coronaviruses and is thought to be less likely to mutate, according to the newspaper. Omicron has at least two mutations that overlap with the drug’s target site, but researchers at the companies don’t think the mutations will affect the treatment’s ability to bind to the spike protein.
GlaxoSmithKline expects to see results from testing the drug against the full mutated spike protein in the next 2 to 3 weeks, the Journal reported.
Sotrovimab has been authorized in about a dozen countries, including the United States, which paid about $1 billion for hundreds of thousands of doses.
Other companies have also been testing their antibody treatments against the Omicron variant.
Regeneron announced Nov. 30 that its drug could be less effective, and it said further analyses will determine how much less effective by using the actual Omicron genetic sequence, according to Reuters.
Outside scientists have also said the antibody drug from Eli Lilly & Co. isn’t as effective against Omicron. The company told Reuters that it is still testing the treatment against the variant.
Another experimental antibody therapy developed by Adagio Therapeutics appears to work well against the new variant, the Journal reported, but the treatment is in late-stage clinical trials and isn’t yet authorized.
Antiviral drugs could also help prevent hospitalization and may be less vulnerable to new variants because they target a different part of the virus, the newspaper reported. Merck and Pfizer have developed antiviral pills, which still require FDA approval.
In addition, Gilead believes its approved IV therapy, called remdesivir, will continue to be effective against the variant, Reuters reported.
The FDA said Nov. 30 that it is looking at the effect that authorized COVID-19 vaccines can have on Omicron and expects to have more information in coming weeks, Reuters reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The companies said Dec. 2 that they tested the drug, called sotrovimab, against individual mutations found in the Omicron variant, according to The Wall Street Journal. The preliminary findings haven’t yet been peer-reviewed, and the drug will need to be tested against the whole spike protein on the virus to confirm results.
GlaxoSmithKline and Vir have previously tested sotrovimab against mutations on other variants, the newspaper reported. When the Omicron variant was identified, the companies looked at earlier research to find the tests they had done against mutations that are also found in Omicron.
Sotrovimab targets a spot on the spike protein that is found in other coronaviruses and is thought to be less likely to mutate, according to the newspaper. Omicron has at least two mutations that overlap with the drug’s target site, but researchers at the companies don’t think the mutations will affect the treatment’s ability to bind to the spike protein.
GlaxoSmithKline expects to see results from testing the drug against the full mutated spike protein in the next 2 to 3 weeks, the Journal reported.
Sotrovimab has been authorized in about a dozen countries, including the United States, which paid about $1 billion for hundreds of thousands of doses.
Other companies have also been testing their antibody treatments against the Omicron variant.
Regeneron announced Nov. 30 that its drug could be less effective, and it said further analyses will determine how much less effective by using the actual Omicron genetic sequence, according to Reuters.
Outside scientists have also said the antibody drug from Eli Lilly & Co. isn’t as effective against Omicron. The company told Reuters that it is still testing the treatment against the variant.
Another experimental antibody therapy developed by Adagio Therapeutics appears to work well against the new variant, the Journal reported, but the treatment is in late-stage clinical trials and isn’t yet authorized.
Antiviral drugs could also help prevent hospitalization and may be less vulnerable to new variants because they target a different part of the virus, the newspaper reported. Merck and Pfizer have developed antiviral pills, which still require FDA approval.
In addition, Gilead believes its approved IV therapy, called remdesivir, will continue to be effective against the variant, Reuters reported.
The FDA said Nov. 30 that it is looking at the effect that authorized COVID-19 vaccines can have on Omicron and expects to have more information in coming weeks, Reuters reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
DRESS Syndrome Due to Cefdinir Mimicking Superinfected Eczema in a Pediatric Patient
To the Editor:
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome, or drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome, is a serious and potentially fatal multiorgan drug hypersensitivity reaction. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome shares many clinical features with viral exanthems and may be difficult to diagnose in the setting of atopic dermatitis (AD) in which children may have baseline eosinophilia from an atopic diathesis. The cutaneous exanthema also may be variable in presentation, further complicating diagnosis.1,2
A 3-year-old boy with AD since infancy and a history of anaphylaxis to peanuts presented to the emergency department with reported fever, rash, sore throat, and decreased oral intake. Ten days prior, the patient was treated for cellulitis of the left foot with a 7-day course of cefdinir with complete resolution of symptoms. Four days prior to admission, the patient started developing “bumps” on the face and fevers. He was seen at an outside facility, where a rapid test for Streptococcus was negative, and the patient was treated with ibuprofen and fluids for a presumed viral exanthem. The rash subsequently spread to involve the trunk and extremities. On the day of admission, the patient had a positive rapid test for Streptococcus and was referred to the emergency department with concern for superinfected eczema and eczema herpeticum. The patient recently traveled to Puerto Rico, where he had contact with an aunt with active herpes zoster but no other sick contacts. The patient’s immunizations were reported to be up-to-date.
Physical examination revealed the patient was afebrile but irritable and had erythematous crusted papules and patches on the face, arms, and legs, as well as erythematous dry patches on the chest, abdomen, and back (Figure). There were no conjunctival erythematous or oral erosions. The patient was admitted to the hospital for presumed superinfected AD and possible eczema herpeticum. He was started on intravenous clindamycin and acyclovir.

The following day, the patient had new facial edema and fever (temperature, 102.8 °F [39.36 °C]) in addition to palpable mobile cervical, axillary, and inguinal lymphadenopathy. He also was noted to have notably worsening eosinophilia from 1288 (14%) to 2570 (29.2%) cells/µL (reference range, 0%–5%) and new-onset transaminitis. Herpes and varicella-zoster direct fluorescent antibody tests, culture, and serum polymerase chain reaction were all negative, and acyclovir was discontinued. Repeat laboratory tests 12 hours later showed a continued uptrend in transaminitis. Serologies for acute and chronic cytomegalovirus; Epstein-Barr virus; and hepatitis A, B, and C were all nonreactive. The patient was started on intravenous methylprednisolone 1 mg/kg daily for suspected DRESS syndrome likely due to cefdinir.
The patient’s eosinophilia completely resolved (from approximately 2600 to 100 cells/µL) after 1 dose of steroids, and his transaminitis trended down over the next few days. He remained afebrile for the remainder of his admission, and his facial swelling and rash continued to improve. Bacterial culture from the skin grew oxacillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus and group A Streptococcus pyogenes. A blood culture was negative. The patient was discharged home to complete a 10-day course of clindamycin and was given topical steroids for the eczema. He continued on oral prednisolone 1 mg/kg daily for 10 days, after which the dose was tapered down for a total 1-month course of systemic corticosteroids. At 1-month follow-up after completing the course of steroids, he was doing well with normal hepatic enzyme levels and no recurrence of fever, facial edema, or rash. He continues to be followed for management of the AD.
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome is a serious systemic adverse drug reaction, with high morbidity and even mortality, estimated at 10% in the adult population, though more specific pediatric mortality data are not available.1,2 The exact pathogenesis of DRESS syndrome has not been elucidated. Certain human leukocyte antigen class I alleles are predisposed to the development of DRESS syndrome, but there has not been a human leukocyte antigen subtype identified with beta-lactam–associated DRESS syndrome. Some studies have demonstrated a reactivation of human herpesvirus 6, human herpesvirus 7, and Epstein-Barr virus.3 One study involving 40 patients with DRESS syndrome identified viremia in 76% (29/38) of patients and identified CD8+ T-cell populations directed toward viral epitopes.3 Finally, DRESS syndrome may be related to the slow detoxification and elimination of intermediary products of offending medications that serve as an immunogenic stimulus for the inflammatory cascade.2
In adults, DRESS syndrome was first identified in association with phenytoin, but more recently other drugs have been identified, including other aromatic anticonvulsants (ie, lamotrigine, phenobarbital, carbamazepine), allopurinol, sulfonamides, antiretrovirals (particularly abacavir), and minocycline.2 In a 3-year pediatric prospective study, 11 cases of DRESS syndrome were identified: 4 cases due to lamotrigine, and 3 caused by penicillins.4 The trigger in our patient’s case was the beta-lactam, third-generation cephalosporin cefdinir, and his symptoms developed within 6 days of starting the medication. Many articles report that beta-lactams are a rare cause of DRESS syndrome, with only a handful of cases reported.1,5,6
The diagnosis of DRESS syndrome often can be delayed, as children present acutely febrile and toxic appearing. Unlike many adverse drug reactions, DRESS syndrome does not show rapid resolution with withdrawal of the causative agent, further complicating the diagnosis. The typical onset of DRESS syndrome generally ranges from 2 to 6 weeks after the initiation of the offending drug; however, faster onset of symptoms, similar to our case, has been noted in antibiotic-triggered cases. In the prospective pediatric series by Sasidharanpillai et al,4 the average time to onset among 3 antibiotic-triggered DRESS cases was 5.8 days vs 23.9 days among the 4 cases of lamotrigine-associated DRESS syndrome.
Our patient demonstrated the classic features of DRESS syndrome, including fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, facial edema, peripheral eosinophilia, atypical lymphocytosis, and hepatitis. Based on the proposed RegiSCAR scoring system, our patient was classified as a “definite” case of DRESS syndrome.1,7 Other hematologic findings in DRESS syndrome may include thrombocytopenia and anemia. The liver is the most commonly affected internal organ in DRESS syndrome, with pneumonitis, carditis, and nephritis reported less frequently.1 The pattern of liver injury in our patient was mixed (hepatocellular and cholestatic), the second most common pattern in patients with DRESS syndrome (the cholestatic pattern is most common).8
The exanthem of DRESS syndrome can vary in morphology, with up to 7% of patients reported to have eczemalike lesions in the multinational prospective RegiSCAR study.1 Other entities in the differential diagnosis for our patient included Kawasaki disease, where conjunctivitis and strawberry tongue are classically present, as well as erythrodermic AD, where internal organ involvement is not common.2 Our patient’s exanthem initially was considered to be a flare of AD with superimposed bacterial infection and possible eczema herpeticum. Although bacterial cultures did grow Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, viral studies were all negative, and this alone would not have explained the facial edema, rapidly rising eosinophil count, and transaminitis. The dramatic drop in his eosinophil count and decrease in hepatic enzymes after 1 dose of intravenous methylprednisolone also supported the diagnosis of DRESS syndrome.
Treatment recommendations remain largely anecdotal. Early systemic steroids generally are accepted as the first line of therapy, with a slow taper. Although the average required duration of systemic steroids in 1 series of adults was reported at 50.1 days,9 the duration was shorter (21–35 days) in a series of pediatric patients.4 Our patient’s clinical symptoms and laboratory values normalized after completing a 1-month steroid taper. Other therapies have been tried for recalcitrant cases, including intravenous immunoglobulin, plasmapheresis, rituximab, and valganciclovir.2
Early clinical recognition of the signs and symptoms of DRESS syndrome in the setting of a new medication can decrease morbidity and mortality. Although DRESS syndrome in pediatric patients presents with many similar clinical features as in adults, it may be a greater diagnostic challenge. As in adult cases, timely administration of systemic corticosteroids and tapering based on clinical signs and symptoms can lead to resolution of the hypersensitivity syndrome.
- Kardaun SH, Sekula P, Valeyrie-Allanore L, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): an original multisystem adverse drug reaction. results from the prospective RegiSCAR study. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:1071-1080.
- Fernando SL. Drug-reaction eosinophilia and systemic symptoms and drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Australas J Dermatol. 2014;55:15-23.
- Picard D, Janela B, Descamps V, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): a multiorgan antiviral T cell response. Sci Transl Med. 2010;2:46ra62.
- Sasidharanpillai S, Sabitha S, Riyaz N, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms in children: a prospective study. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:E162-E165.
- Aouam K, Chaabane A, Toumi A, et al. Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) probably induced by cefotaxime: a report of two cases. Clin Med Res. 2012;10:32-35.
- Guleria VS, Dhillon M, Gill S, et al. Ceftriaxone induced drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms. J Res Pharm Pract. 2014;3:72-74.
- Kardaun SH, Sidoroff A, Valeyrie-Allanore L, et al. Variability in the clinical pattern of cutaneous side-effects of drugs with systemic symptoms: does a DRESS syndrome really exist? Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:609-611.
- Lin IC, Yang HC, Strong C, et al. Liver injury in patients with DRESS: a clinical study of 72 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:984-991.
- Ang CC, Wang YS, Yoosuff EL, et al. Retrospective analysis of drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome: a study of 27 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:219-227.
To the Editor:
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome, or drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome, is a serious and potentially fatal multiorgan drug hypersensitivity reaction. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome shares many clinical features with viral exanthems and may be difficult to diagnose in the setting of atopic dermatitis (AD) in which children may have baseline eosinophilia from an atopic diathesis. The cutaneous exanthema also may be variable in presentation, further complicating diagnosis.1,2
A 3-year-old boy with AD since infancy and a history of anaphylaxis to peanuts presented to the emergency department with reported fever, rash, sore throat, and decreased oral intake. Ten days prior, the patient was treated for cellulitis of the left foot with a 7-day course of cefdinir with complete resolution of symptoms. Four days prior to admission, the patient started developing “bumps” on the face and fevers. He was seen at an outside facility, where a rapid test for Streptococcus was negative, and the patient was treated with ibuprofen and fluids for a presumed viral exanthem. The rash subsequently spread to involve the trunk and extremities. On the day of admission, the patient had a positive rapid test for Streptococcus and was referred to the emergency department with concern for superinfected eczema and eczema herpeticum. The patient recently traveled to Puerto Rico, where he had contact with an aunt with active herpes zoster but no other sick contacts. The patient’s immunizations were reported to be up-to-date.
Physical examination revealed the patient was afebrile but irritable and had erythematous crusted papules and patches on the face, arms, and legs, as well as erythematous dry patches on the chest, abdomen, and back (Figure). There were no conjunctival erythematous or oral erosions. The patient was admitted to the hospital for presumed superinfected AD and possible eczema herpeticum. He was started on intravenous clindamycin and acyclovir.

The following day, the patient had new facial edema and fever (temperature, 102.8 °F [39.36 °C]) in addition to palpable mobile cervical, axillary, and inguinal lymphadenopathy. He also was noted to have notably worsening eosinophilia from 1288 (14%) to 2570 (29.2%) cells/µL (reference range, 0%–5%) and new-onset transaminitis. Herpes and varicella-zoster direct fluorescent antibody tests, culture, and serum polymerase chain reaction were all negative, and acyclovir was discontinued. Repeat laboratory tests 12 hours later showed a continued uptrend in transaminitis. Serologies for acute and chronic cytomegalovirus; Epstein-Barr virus; and hepatitis A, B, and C were all nonreactive. The patient was started on intravenous methylprednisolone 1 mg/kg daily for suspected DRESS syndrome likely due to cefdinir.
The patient’s eosinophilia completely resolved (from approximately 2600 to 100 cells/µL) after 1 dose of steroids, and his transaminitis trended down over the next few days. He remained afebrile for the remainder of his admission, and his facial swelling and rash continued to improve. Bacterial culture from the skin grew oxacillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus and group A Streptococcus pyogenes. A blood culture was negative. The patient was discharged home to complete a 10-day course of clindamycin and was given topical steroids for the eczema. He continued on oral prednisolone 1 mg/kg daily for 10 days, after which the dose was tapered down for a total 1-month course of systemic corticosteroids. At 1-month follow-up after completing the course of steroids, he was doing well with normal hepatic enzyme levels and no recurrence of fever, facial edema, or rash. He continues to be followed for management of the AD.
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome is a serious systemic adverse drug reaction, with high morbidity and even mortality, estimated at 10% in the adult population, though more specific pediatric mortality data are not available.1,2 The exact pathogenesis of DRESS syndrome has not been elucidated. Certain human leukocyte antigen class I alleles are predisposed to the development of DRESS syndrome, but there has not been a human leukocyte antigen subtype identified with beta-lactam–associated DRESS syndrome. Some studies have demonstrated a reactivation of human herpesvirus 6, human herpesvirus 7, and Epstein-Barr virus.3 One study involving 40 patients with DRESS syndrome identified viremia in 76% (29/38) of patients and identified CD8+ T-cell populations directed toward viral epitopes.3 Finally, DRESS syndrome may be related to the slow detoxification and elimination of intermediary products of offending medications that serve as an immunogenic stimulus for the inflammatory cascade.2
In adults, DRESS syndrome was first identified in association with phenytoin, but more recently other drugs have been identified, including other aromatic anticonvulsants (ie, lamotrigine, phenobarbital, carbamazepine), allopurinol, sulfonamides, antiretrovirals (particularly abacavir), and minocycline.2 In a 3-year pediatric prospective study, 11 cases of DRESS syndrome were identified: 4 cases due to lamotrigine, and 3 caused by penicillins.4 The trigger in our patient’s case was the beta-lactam, third-generation cephalosporin cefdinir, and his symptoms developed within 6 days of starting the medication. Many articles report that beta-lactams are a rare cause of DRESS syndrome, with only a handful of cases reported.1,5,6
The diagnosis of DRESS syndrome often can be delayed, as children present acutely febrile and toxic appearing. Unlike many adverse drug reactions, DRESS syndrome does not show rapid resolution with withdrawal of the causative agent, further complicating the diagnosis. The typical onset of DRESS syndrome generally ranges from 2 to 6 weeks after the initiation of the offending drug; however, faster onset of symptoms, similar to our case, has been noted in antibiotic-triggered cases. In the prospective pediatric series by Sasidharanpillai et al,4 the average time to onset among 3 antibiotic-triggered DRESS cases was 5.8 days vs 23.9 days among the 4 cases of lamotrigine-associated DRESS syndrome.
Our patient demonstrated the classic features of DRESS syndrome, including fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, facial edema, peripheral eosinophilia, atypical lymphocytosis, and hepatitis. Based on the proposed RegiSCAR scoring system, our patient was classified as a “definite” case of DRESS syndrome.1,7 Other hematologic findings in DRESS syndrome may include thrombocytopenia and anemia. The liver is the most commonly affected internal organ in DRESS syndrome, with pneumonitis, carditis, and nephritis reported less frequently.1 The pattern of liver injury in our patient was mixed (hepatocellular and cholestatic), the second most common pattern in patients with DRESS syndrome (the cholestatic pattern is most common).8
The exanthem of DRESS syndrome can vary in morphology, with up to 7% of patients reported to have eczemalike lesions in the multinational prospective RegiSCAR study.1 Other entities in the differential diagnosis for our patient included Kawasaki disease, where conjunctivitis and strawberry tongue are classically present, as well as erythrodermic AD, where internal organ involvement is not common.2 Our patient’s exanthem initially was considered to be a flare of AD with superimposed bacterial infection and possible eczema herpeticum. Although bacterial cultures did grow Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, viral studies were all negative, and this alone would not have explained the facial edema, rapidly rising eosinophil count, and transaminitis. The dramatic drop in his eosinophil count and decrease in hepatic enzymes after 1 dose of intravenous methylprednisolone also supported the diagnosis of DRESS syndrome.
Treatment recommendations remain largely anecdotal. Early systemic steroids generally are accepted as the first line of therapy, with a slow taper. Although the average required duration of systemic steroids in 1 series of adults was reported at 50.1 days,9 the duration was shorter (21–35 days) in a series of pediatric patients.4 Our patient’s clinical symptoms and laboratory values normalized after completing a 1-month steroid taper. Other therapies have been tried for recalcitrant cases, including intravenous immunoglobulin, plasmapheresis, rituximab, and valganciclovir.2
Early clinical recognition of the signs and symptoms of DRESS syndrome in the setting of a new medication can decrease morbidity and mortality. Although DRESS syndrome in pediatric patients presents with many similar clinical features as in adults, it may be a greater diagnostic challenge. As in adult cases, timely administration of systemic corticosteroids and tapering based on clinical signs and symptoms can lead to resolution of the hypersensitivity syndrome.
To the Editor:
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome, or drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome, is a serious and potentially fatal multiorgan drug hypersensitivity reaction. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome shares many clinical features with viral exanthems and may be difficult to diagnose in the setting of atopic dermatitis (AD) in which children may have baseline eosinophilia from an atopic diathesis. The cutaneous exanthema also may be variable in presentation, further complicating diagnosis.1,2
A 3-year-old boy with AD since infancy and a history of anaphylaxis to peanuts presented to the emergency department with reported fever, rash, sore throat, and decreased oral intake. Ten days prior, the patient was treated for cellulitis of the left foot with a 7-day course of cefdinir with complete resolution of symptoms. Four days prior to admission, the patient started developing “bumps” on the face and fevers. He was seen at an outside facility, where a rapid test for Streptococcus was negative, and the patient was treated with ibuprofen and fluids for a presumed viral exanthem. The rash subsequently spread to involve the trunk and extremities. On the day of admission, the patient had a positive rapid test for Streptococcus and was referred to the emergency department with concern for superinfected eczema and eczema herpeticum. The patient recently traveled to Puerto Rico, where he had contact with an aunt with active herpes zoster but no other sick contacts. The patient’s immunizations were reported to be up-to-date.
Physical examination revealed the patient was afebrile but irritable and had erythematous crusted papules and patches on the face, arms, and legs, as well as erythematous dry patches on the chest, abdomen, and back (Figure). There were no conjunctival erythematous or oral erosions. The patient was admitted to the hospital for presumed superinfected AD and possible eczema herpeticum. He was started on intravenous clindamycin and acyclovir.

The following day, the patient had new facial edema and fever (temperature, 102.8 °F [39.36 °C]) in addition to palpable mobile cervical, axillary, and inguinal lymphadenopathy. He also was noted to have notably worsening eosinophilia from 1288 (14%) to 2570 (29.2%) cells/µL (reference range, 0%–5%) and new-onset transaminitis. Herpes and varicella-zoster direct fluorescent antibody tests, culture, and serum polymerase chain reaction were all negative, and acyclovir was discontinued. Repeat laboratory tests 12 hours later showed a continued uptrend in transaminitis. Serologies for acute and chronic cytomegalovirus; Epstein-Barr virus; and hepatitis A, B, and C were all nonreactive. The patient was started on intravenous methylprednisolone 1 mg/kg daily for suspected DRESS syndrome likely due to cefdinir.
The patient’s eosinophilia completely resolved (from approximately 2600 to 100 cells/µL) after 1 dose of steroids, and his transaminitis trended down over the next few days. He remained afebrile for the remainder of his admission, and his facial swelling and rash continued to improve. Bacterial culture from the skin grew oxacillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus and group A Streptococcus pyogenes. A blood culture was negative. The patient was discharged home to complete a 10-day course of clindamycin and was given topical steroids for the eczema. He continued on oral prednisolone 1 mg/kg daily for 10 days, after which the dose was tapered down for a total 1-month course of systemic corticosteroids. At 1-month follow-up after completing the course of steroids, he was doing well with normal hepatic enzyme levels and no recurrence of fever, facial edema, or rash. He continues to be followed for management of the AD.
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome is a serious systemic adverse drug reaction, with high morbidity and even mortality, estimated at 10% in the adult population, though more specific pediatric mortality data are not available.1,2 The exact pathogenesis of DRESS syndrome has not been elucidated. Certain human leukocyte antigen class I alleles are predisposed to the development of DRESS syndrome, but there has not been a human leukocyte antigen subtype identified with beta-lactam–associated DRESS syndrome. Some studies have demonstrated a reactivation of human herpesvirus 6, human herpesvirus 7, and Epstein-Barr virus.3 One study involving 40 patients with DRESS syndrome identified viremia in 76% (29/38) of patients and identified CD8+ T-cell populations directed toward viral epitopes.3 Finally, DRESS syndrome may be related to the slow detoxification and elimination of intermediary products of offending medications that serve as an immunogenic stimulus for the inflammatory cascade.2
In adults, DRESS syndrome was first identified in association with phenytoin, but more recently other drugs have been identified, including other aromatic anticonvulsants (ie, lamotrigine, phenobarbital, carbamazepine), allopurinol, sulfonamides, antiretrovirals (particularly abacavir), and minocycline.2 In a 3-year pediatric prospective study, 11 cases of DRESS syndrome were identified: 4 cases due to lamotrigine, and 3 caused by penicillins.4 The trigger in our patient’s case was the beta-lactam, third-generation cephalosporin cefdinir, and his symptoms developed within 6 days of starting the medication. Many articles report that beta-lactams are a rare cause of DRESS syndrome, with only a handful of cases reported.1,5,6
The diagnosis of DRESS syndrome often can be delayed, as children present acutely febrile and toxic appearing. Unlike many adverse drug reactions, DRESS syndrome does not show rapid resolution with withdrawal of the causative agent, further complicating the diagnosis. The typical onset of DRESS syndrome generally ranges from 2 to 6 weeks after the initiation of the offending drug; however, faster onset of symptoms, similar to our case, has been noted in antibiotic-triggered cases. In the prospective pediatric series by Sasidharanpillai et al,4 the average time to onset among 3 antibiotic-triggered DRESS cases was 5.8 days vs 23.9 days among the 4 cases of lamotrigine-associated DRESS syndrome.
Our patient demonstrated the classic features of DRESS syndrome, including fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, facial edema, peripheral eosinophilia, atypical lymphocytosis, and hepatitis. Based on the proposed RegiSCAR scoring system, our patient was classified as a “definite” case of DRESS syndrome.1,7 Other hematologic findings in DRESS syndrome may include thrombocytopenia and anemia. The liver is the most commonly affected internal organ in DRESS syndrome, with pneumonitis, carditis, and nephritis reported less frequently.1 The pattern of liver injury in our patient was mixed (hepatocellular and cholestatic), the second most common pattern in patients with DRESS syndrome (the cholestatic pattern is most common).8
The exanthem of DRESS syndrome can vary in morphology, with up to 7% of patients reported to have eczemalike lesions in the multinational prospective RegiSCAR study.1 Other entities in the differential diagnosis for our patient included Kawasaki disease, where conjunctivitis and strawberry tongue are classically present, as well as erythrodermic AD, where internal organ involvement is not common.2 Our patient’s exanthem initially was considered to be a flare of AD with superimposed bacterial infection and possible eczema herpeticum. Although bacterial cultures did grow Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, viral studies were all negative, and this alone would not have explained the facial edema, rapidly rising eosinophil count, and transaminitis. The dramatic drop in his eosinophil count and decrease in hepatic enzymes after 1 dose of intravenous methylprednisolone also supported the diagnosis of DRESS syndrome.
Treatment recommendations remain largely anecdotal. Early systemic steroids generally are accepted as the first line of therapy, with a slow taper. Although the average required duration of systemic steroids in 1 series of adults was reported at 50.1 days,9 the duration was shorter (21–35 days) in a series of pediatric patients.4 Our patient’s clinical symptoms and laboratory values normalized after completing a 1-month steroid taper. Other therapies have been tried for recalcitrant cases, including intravenous immunoglobulin, plasmapheresis, rituximab, and valganciclovir.2
Early clinical recognition of the signs and symptoms of DRESS syndrome in the setting of a new medication can decrease morbidity and mortality. Although DRESS syndrome in pediatric patients presents with many similar clinical features as in adults, it may be a greater diagnostic challenge. As in adult cases, timely administration of systemic corticosteroids and tapering based on clinical signs and symptoms can lead to resolution of the hypersensitivity syndrome.
- Kardaun SH, Sekula P, Valeyrie-Allanore L, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): an original multisystem adverse drug reaction. results from the prospective RegiSCAR study. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:1071-1080.
- Fernando SL. Drug-reaction eosinophilia and systemic symptoms and drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Australas J Dermatol. 2014;55:15-23.
- Picard D, Janela B, Descamps V, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): a multiorgan antiviral T cell response. Sci Transl Med. 2010;2:46ra62.
- Sasidharanpillai S, Sabitha S, Riyaz N, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms in children: a prospective study. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:E162-E165.
- Aouam K, Chaabane A, Toumi A, et al. Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) probably induced by cefotaxime: a report of two cases. Clin Med Res. 2012;10:32-35.
- Guleria VS, Dhillon M, Gill S, et al. Ceftriaxone induced drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms. J Res Pharm Pract. 2014;3:72-74.
- Kardaun SH, Sidoroff A, Valeyrie-Allanore L, et al. Variability in the clinical pattern of cutaneous side-effects of drugs with systemic symptoms: does a DRESS syndrome really exist? Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:609-611.
- Lin IC, Yang HC, Strong C, et al. Liver injury in patients with DRESS: a clinical study of 72 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:984-991.
- Ang CC, Wang YS, Yoosuff EL, et al. Retrospective analysis of drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome: a study of 27 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:219-227.
- Kardaun SH, Sekula P, Valeyrie-Allanore L, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): an original multisystem adverse drug reaction. results from the prospective RegiSCAR study. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:1071-1080.
- Fernando SL. Drug-reaction eosinophilia and systemic symptoms and drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Australas J Dermatol. 2014;55:15-23.
- Picard D, Janela B, Descamps V, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): a multiorgan antiviral T cell response. Sci Transl Med. 2010;2:46ra62.
- Sasidharanpillai S, Sabitha S, Riyaz N, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms in children: a prospective study. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:E162-E165.
- Aouam K, Chaabane A, Toumi A, et al. Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) probably induced by cefotaxime: a report of two cases. Clin Med Res. 2012;10:32-35.
- Guleria VS, Dhillon M, Gill S, et al. Ceftriaxone induced drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms. J Res Pharm Pract. 2014;3:72-74.
- Kardaun SH, Sidoroff A, Valeyrie-Allanore L, et al. Variability in the clinical pattern of cutaneous side-effects of drugs with systemic symptoms: does a DRESS syndrome really exist? Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:609-611.
- Lin IC, Yang HC, Strong C, et al. Liver injury in patients with DRESS: a clinical study of 72 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:984-991.
- Ang CC, Wang YS, Yoosuff EL, et al. Retrospective analysis of drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome: a study of 27 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:219-227.
Practice Points
- Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome shares many clinical features with viral exanthems and may be difficult to diagnose in the setting of atopic dermatitis in which children may have baseline eosinophilia from an atopic diathesis.
- Early clinical recognition of the signs and symptoms of DRESS syndrome in the setting of a new medication can decrease morbidity and mortality.
Ten changes that could keep clinicians in the workforce in a pandemic
Indeed, a recent poll of 1,000 health care workers conducted Sept. 2-8 by Morning Consult, showed that 18% of medical workers polled quit their jobs during the pandemic. Additionally, 31% said they had at least thought about leaving their work.
“As physicians, educators, peers and friends of COVID-19 responders, we are gravely concerned about our colleagues’ exhaustion, burnout, and disillusionment,” wrote lead author Eileen Barrett, MD, and coauthors of the new action plan, which was published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
The 10-point, one-page checklist includes providing “practical support in the areas that clinicians identify as causing emotional stress or moral injury,” such as managing anger and grief when patients have chosen not to be vaccinated or confronting misinformation.
“Those are the things that are making people’s mental health worse” psychiatrist Jessi Gold, MD, MS, said in an interview. “I don’t think I’ve seen that mentioned other places.”
Among the other action items are:
- Reduce administrative tasks that are not “mission critical,” such as mandatory training that has no evidence of improving patient outcomes and meetings that could be skipped.
- Offer free and confidential resources to support clinicians’ mental health, such as easy access to crisis hotlines and peer support groups.
- Maintain transparency about personal protective equipment and contingency plans when there are shortages to restore trust.
- Encourage clinicians to use vacation time; leaders should model this.
- Implement suicide prevention strategies, including wellness check-ins for clinicians in hard-hit areas.
The action plan was based on the authors’ own experiences and the stories of colleagues and information in literature. It includes 10 changes health care leaders could make to help retain providers who may be on the brink of leaving their jobs or leaving medicine
Action items intended to be easily achievable, low cost
Dr. Barrett, who is a hospitalist in Albuquerque, said the goal was to present easily achievable and low-cost action items that clinicians and health care leaders could use as a starting point when change seems insurmountable and evidence on what works is slow to come.
She said one of the things that spurred her to coauthor the list was becoming aware of other clinicians’ “secret shame” in thinking about leaving medicine.
“Maybe a person who is not being listened to could take this journal article and say ‘we don’t know where to start. It looks like we can start here,’ ” said Dr. Barrett, who is also an associate professor in the division of hospital medicine, department of internal medicine, at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque.
She noted that some of the good ideas floated around did not make the list, because they required daunting budget commitments and too much time to put into place.
Numerous other proposed solutions were of the wrong tone, according to Dr. Barrett.
“It’s not just about a hug or a piece of pizza,” she said.
Dr. Gold, who is an assistant professor at Washington University, St. Louis, and specializes in the mental health of health care workers, noted that, even though the list was pared to 10 action items, it is still hard for health care organizations to prioritize mental health.
“Many hospitals are still struggling with the active bleed of the pandemic and financially recovering,” she said. “If you’re dealing with a full ER and people are still dying of COVID and you don’t have the resources to support them, it’s really hard to then find magic money to deal with mental health. I’d love for that to be true.”
Every organization, however, can start with removing questions about mental and physical health diagnoses from credentialing and employment applications, which is one of the items on the list, she said.
“It’s the lowest-bar thing that you can fix for making people in crisis not fear getting help,” she said. That change must come on a state-by-state and individual hospital level.
Favorable reactions to list
Dr. Barrett, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News, said the reactions to the checklist have been “overwhelmingly favorable and appreciative.”
Eric J. Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape Medical News, tweeted about this list: “For COVID-19, more than ever before, it’s vital to keep clinicians in the U.S. health care workforce. These are 10 steps that will help.” The tweet was retweeted more than 100 times.
Lotte Dyrbye, MD, MHPE, a primary care physician and codirector of the program on physician well-being at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., said in an interview that managing the anger around patients who choose to be unvaccinated is critical and something that has gotten little notice since the vaccines became available.
“Physicians and nurses are working extremely hard and seeing a lot of suffering and are taking care of patients very sick with COVID-19, knowing they had access to the vaccine. That is causing anger and frustration. We haven’t prepared health care workers to deal with that,” she said.
Outside expert: Not all items may be easy to implement
Dr. Dyrbye said that, though she found adding time to address COVID misinformation questions in appointments is very important, it may be wishful thinking.
The authors suggested training other members of the care team to answer those questions to free up time, but she said, for patients who have been swayed by misinformation, hearing information from someone other than the physician they have a relationship with won’t be convincing.
According to Dr. Dyrbye, the items on the list are not easy to implement, but the action plan is worthwhile to consider adopting as a multipronged approach.
“Most of these things are hard and we need to be in it for the long run,” she said.
The need is clear for efforts to address the mental health of not just experienced clinicians but those in training as well, she noted.
Related research
A study that was also recently published in the Annals of Internal Medicine suggested that making a few simple changes can help improve the mental health of residents. The research, which included nearly 17,000 first-year residents who started training between 2007 and 2019, addressed indicators of mental health in light of interventions such as limiting residents’ work hours and providing more services.
The investigators found that, though depression remains high among residents, depressive symptoms among first-year residents dropped 24.4% from 2007 to 2019 in parallel with four main factors: an increase in mental health services; restrictions on work hours for residents; more sleep hours; and higher-quality feedback from faculty.
Dr. Barrett said she hopes her colleagues and health care workers everywhere will find some solace in seeing that the new checklist she coauthored was published in a prominent journal.
The message Dr. Barrett said she hopes they see is: “Someone is validating it is not in their head. They are validating we can do better. They are validating that we must.”
Dr. Barrett and coauthors had no conflicts of interest. Dr. Gold and Dr. Dyrbye also disclosed having no relevant financial relationships.
Indeed, a recent poll of 1,000 health care workers conducted Sept. 2-8 by Morning Consult, showed that 18% of medical workers polled quit their jobs during the pandemic. Additionally, 31% said they had at least thought about leaving their work.
“As physicians, educators, peers and friends of COVID-19 responders, we are gravely concerned about our colleagues’ exhaustion, burnout, and disillusionment,” wrote lead author Eileen Barrett, MD, and coauthors of the new action plan, which was published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
The 10-point, one-page checklist includes providing “practical support in the areas that clinicians identify as causing emotional stress or moral injury,” such as managing anger and grief when patients have chosen not to be vaccinated or confronting misinformation.
“Those are the things that are making people’s mental health worse” psychiatrist Jessi Gold, MD, MS, said in an interview. “I don’t think I’ve seen that mentioned other places.”
Among the other action items are:
- Reduce administrative tasks that are not “mission critical,” such as mandatory training that has no evidence of improving patient outcomes and meetings that could be skipped.
- Offer free and confidential resources to support clinicians’ mental health, such as easy access to crisis hotlines and peer support groups.
- Maintain transparency about personal protective equipment and contingency plans when there are shortages to restore trust.
- Encourage clinicians to use vacation time; leaders should model this.
- Implement suicide prevention strategies, including wellness check-ins for clinicians in hard-hit areas.
The action plan was based on the authors’ own experiences and the stories of colleagues and information in literature. It includes 10 changes health care leaders could make to help retain providers who may be on the brink of leaving their jobs or leaving medicine
Action items intended to be easily achievable, low cost
Dr. Barrett, who is a hospitalist in Albuquerque, said the goal was to present easily achievable and low-cost action items that clinicians and health care leaders could use as a starting point when change seems insurmountable and evidence on what works is slow to come.
She said one of the things that spurred her to coauthor the list was becoming aware of other clinicians’ “secret shame” in thinking about leaving medicine.
“Maybe a person who is not being listened to could take this journal article and say ‘we don’t know where to start. It looks like we can start here,’ ” said Dr. Barrett, who is also an associate professor in the division of hospital medicine, department of internal medicine, at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque.
She noted that some of the good ideas floated around did not make the list, because they required daunting budget commitments and too much time to put into place.
Numerous other proposed solutions were of the wrong tone, according to Dr. Barrett.
“It’s not just about a hug or a piece of pizza,” she said.
Dr. Gold, who is an assistant professor at Washington University, St. Louis, and specializes in the mental health of health care workers, noted that, even though the list was pared to 10 action items, it is still hard for health care organizations to prioritize mental health.
“Many hospitals are still struggling with the active bleed of the pandemic and financially recovering,” she said. “If you’re dealing with a full ER and people are still dying of COVID and you don’t have the resources to support them, it’s really hard to then find magic money to deal with mental health. I’d love for that to be true.”
Every organization, however, can start with removing questions about mental and physical health diagnoses from credentialing and employment applications, which is one of the items on the list, she said.
“It’s the lowest-bar thing that you can fix for making people in crisis not fear getting help,” she said. That change must come on a state-by-state and individual hospital level.
Favorable reactions to list
Dr. Barrett, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News, said the reactions to the checklist have been “overwhelmingly favorable and appreciative.”
Eric J. Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape Medical News, tweeted about this list: “For COVID-19, more than ever before, it’s vital to keep clinicians in the U.S. health care workforce. These are 10 steps that will help.” The tweet was retweeted more than 100 times.
Lotte Dyrbye, MD, MHPE, a primary care physician and codirector of the program on physician well-being at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., said in an interview that managing the anger around patients who choose to be unvaccinated is critical and something that has gotten little notice since the vaccines became available.
“Physicians and nurses are working extremely hard and seeing a lot of suffering and are taking care of patients very sick with COVID-19, knowing they had access to the vaccine. That is causing anger and frustration. We haven’t prepared health care workers to deal with that,” she said.
Outside expert: Not all items may be easy to implement
Dr. Dyrbye said that, though she found adding time to address COVID misinformation questions in appointments is very important, it may be wishful thinking.
The authors suggested training other members of the care team to answer those questions to free up time, but she said, for patients who have been swayed by misinformation, hearing information from someone other than the physician they have a relationship with won’t be convincing.
According to Dr. Dyrbye, the items on the list are not easy to implement, but the action plan is worthwhile to consider adopting as a multipronged approach.
“Most of these things are hard and we need to be in it for the long run,” she said.
The need is clear for efforts to address the mental health of not just experienced clinicians but those in training as well, she noted.
Related research
A study that was also recently published in the Annals of Internal Medicine suggested that making a few simple changes can help improve the mental health of residents. The research, which included nearly 17,000 first-year residents who started training between 2007 and 2019, addressed indicators of mental health in light of interventions such as limiting residents’ work hours and providing more services.
The investigators found that, though depression remains high among residents, depressive symptoms among first-year residents dropped 24.4% from 2007 to 2019 in parallel with four main factors: an increase in mental health services; restrictions on work hours for residents; more sleep hours; and higher-quality feedback from faculty.
Dr. Barrett said she hopes her colleagues and health care workers everywhere will find some solace in seeing that the new checklist she coauthored was published in a prominent journal.
The message Dr. Barrett said she hopes they see is: “Someone is validating it is not in their head. They are validating we can do better. They are validating that we must.”
Dr. Barrett and coauthors had no conflicts of interest. Dr. Gold and Dr. Dyrbye also disclosed having no relevant financial relationships.
Indeed, a recent poll of 1,000 health care workers conducted Sept. 2-8 by Morning Consult, showed that 18% of medical workers polled quit their jobs during the pandemic. Additionally, 31% said they had at least thought about leaving their work.
“As physicians, educators, peers and friends of COVID-19 responders, we are gravely concerned about our colleagues’ exhaustion, burnout, and disillusionment,” wrote lead author Eileen Barrett, MD, and coauthors of the new action plan, which was published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
The 10-point, one-page checklist includes providing “practical support in the areas that clinicians identify as causing emotional stress or moral injury,” such as managing anger and grief when patients have chosen not to be vaccinated or confronting misinformation.
“Those are the things that are making people’s mental health worse” psychiatrist Jessi Gold, MD, MS, said in an interview. “I don’t think I’ve seen that mentioned other places.”
Among the other action items are:
- Reduce administrative tasks that are not “mission critical,” such as mandatory training that has no evidence of improving patient outcomes and meetings that could be skipped.
- Offer free and confidential resources to support clinicians’ mental health, such as easy access to crisis hotlines and peer support groups.
- Maintain transparency about personal protective equipment and contingency plans when there are shortages to restore trust.
- Encourage clinicians to use vacation time; leaders should model this.
- Implement suicide prevention strategies, including wellness check-ins for clinicians in hard-hit areas.
The action plan was based on the authors’ own experiences and the stories of colleagues and information in literature. It includes 10 changes health care leaders could make to help retain providers who may be on the brink of leaving their jobs or leaving medicine
Action items intended to be easily achievable, low cost
Dr. Barrett, who is a hospitalist in Albuquerque, said the goal was to present easily achievable and low-cost action items that clinicians and health care leaders could use as a starting point when change seems insurmountable and evidence on what works is slow to come.
She said one of the things that spurred her to coauthor the list was becoming aware of other clinicians’ “secret shame” in thinking about leaving medicine.
“Maybe a person who is not being listened to could take this journal article and say ‘we don’t know where to start. It looks like we can start here,’ ” said Dr. Barrett, who is also an associate professor in the division of hospital medicine, department of internal medicine, at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque.
She noted that some of the good ideas floated around did not make the list, because they required daunting budget commitments and too much time to put into place.
Numerous other proposed solutions were of the wrong tone, according to Dr. Barrett.
“It’s not just about a hug or a piece of pizza,” she said.
Dr. Gold, who is an assistant professor at Washington University, St. Louis, and specializes in the mental health of health care workers, noted that, even though the list was pared to 10 action items, it is still hard for health care organizations to prioritize mental health.
“Many hospitals are still struggling with the active bleed of the pandemic and financially recovering,” she said. “If you’re dealing with a full ER and people are still dying of COVID and you don’t have the resources to support them, it’s really hard to then find magic money to deal with mental health. I’d love for that to be true.”
Every organization, however, can start with removing questions about mental and physical health diagnoses from credentialing and employment applications, which is one of the items on the list, she said.
“It’s the lowest-bar thing that you can fix for making people in crisis not fear getting help,” she said. That change must come on a state-by-state and individual hospital level.
Favorable reactions to list
Dr. Barrett, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News, said the reactions to the checklist have been “overwhelmingly favorable and appreciative.”
Eric J. Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape Medical News, tweeted about this list: “For COVID-19, more than ever before, it’s vital to keep clinicians in the U.S. health care workforce. These are 10 steps that will help.” The tweet was retweeted more than 100 times.
Lotte Dyrbye, MD, MHPE, a primary care physician and codirector of the program on physician well-being at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., said in an interview that managing the anger around patients who choose to be unvaccinated is critical and something that has gotten little notice since the vaccines became available.
“Physicians and nurses are working extremely hard and seeing a lot of suffering and are taking care of patients very sick with COVID-19, knowing they had access to the vaccine. That is causing anger and frustration. We haven’t prepared health care workers to deal with that,” she said.
Outside expert: Not all items may be easy to implement
Dr. Dyrbye said that, though she found adding time to address COVID misinformation questions in appointments is very important, it may be wishful thinking.
The authors suggested training other members of the care team to answer those questions to free up time, but she said, for patients who have been swayed by misinformation, hearing information from someone other than the physician they have a relationship with won’t be convincing.
According to Dr. Dyrbye, the items on the list are not easy to implement, but the action plan is worthwhile to consider adopting as a multipronged approach.
“Most of these things are hard and we need to be in it for the long run,” she said.
The need is clear for efforts to address the mental health of not just experienced clinicians but those in training as well, she noted.
Related research
A study that was also recently published in the Annals of Internal Medicine suggested that making a few simple changes can help improve the mental health of residents. The research, which included nearly 17,000 first-year residents who started training between 2007 and 2019, addressed indicators of mental health in light of interventions such as limiting residents’ work hours and providing more services.
The investigators found that, though depression remains high among residents, depressive symptoms among first-year residents dropped 24.4% from 2007 to 2019 in parallel with four main factors: an increase in mental health services; restrictions on work hours for residents; more sleep hours; and higher-quality feedback from faculty.
Dr. Barrett said she hopes her colleagues and health care workers everywhere will find some solace in seeing that the new checklist she coauthored was published in a prominent journal.
The message Dr. Barrett said she hopes they see is: “Someone is validating it is not in their head. They are validating we can do better. They are validating that we must.”
Dr. Barrett and coauthors had no conflicts of interest. Dr. Gold and Dr. Dyrbye also disclosed having no relevant financial relationships.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Second U.S. COVID-19 case caused by Omicron found
A second U.S. case of COVID-19 caused by the Omicron variant has been picked up by genetic testing in Minnesota.
The man, from Hennepin County, Minn., fell ill on Nov. 22 after attending the Anime NYC 2021 conference at the Javits Center in New York City a few days before. He sought testing on Nov. 24. His symptoms have resolved, according to a press release on the case from the Minnesota Department of Health. The man was fully vaccinated, the department said.
He was advised to isolate from others, but it’s unclear if he had contact with anyone else before he learning he was infected.
“This news is concerning, but it is not a surprise,” said Governor Tim Walz in a news release. “We know that this virus is highly infectious and moves quickly throughout the world. Minnesotans know what to do to keep each other safe now — get the vaccine, get tested, wear a mask indoors, and get a booster. Together, we can fight this virus and help keep Minnesotans safe,”
The first case of COVID-19 caused by Omicron was detected Dec. 1 in California. That case was in a traveler who had recently returned from South Africa.
This breaking news story will be updated.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A second U.S. case of COVID-19 caused by the Omicron variant has been picked up by genetic testing in Minnesota.
The man, from Hennepin County, Minn., fell ill on Nov. 22 after attending the Anime NYC 2021 conference at the Javits Center in New York City a few days before. He sought testing on Nov. 24. His symptoms have resolved, according to a press release on the case from the Minnesota Department of Health. The man was fully vaccinated, the department said.
He was advised to isolate from others, but it’s unclear if he had contact with anyone else before he learning he was infected.
“This news is concerning, but it is not a surprise,” said Governor Tim Walz in a news release. “We know that this virus is highly infectious and moves quickly throughout the world. Minnesotans know what to do to keep each other safe now — get the vaccine, get tested, wear a mask indoors, and get a booster. Together, we can fight this virus and help keep Minnesotans safe,”
The first case of COVID-19 caused by Omicron was detected Dec. 1 in California. That case was in a traveler who had recently returned from South Africa.
This breaking news story will be updated.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A second U.S. case of COVID-19 caused by the Omicron variant has been picked up by genetic testing in Minnesota.
The man, from Hennepin County, Minn., fell ill on Nov. 22 after attending the Anime NYC 2021 conference at the Javits Center in New York City a few days before. He sought testing on Nov. 24. His symptoms have resolved, according to a press release on the case from the Minnesota Department of Health. The man was fully vaccinated, the department said.
He was advised to isolate from others, but it’s unclear if he had contact with anyone else before he learning he was infected.
“This news is concerning, but it is not a surprise,” said Governor Tim Walz in a news release. “We know that this virus is highly infectious and moves quickly throughout the world. Minnesotans know what to do to keep each other safe now — get the vaccine, get tested, wear a mask indoors, and get a booster. Together, we can fight this virus and help keep Minnesotans safe,”
The first case of COVID-19 caused by Omicron was detected Dec. 1 in California. That case was in a traveler who had recently returned from South Africa.
This breaking news story will be updated.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.