User login
The Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management® is an independent, peer-reviewed journal offering evidence-based, practical information for improving the quality, safety, and value of health care.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Children and COVID: A look back as the fourth year begins
With 3 years of the COVID-19 experience now past, it’s safe to say that SARS-CoV-2 changed American society in ways that could not have been predicted when the first U.S. cases were reported in January of 2020.
Who would have guessed back then that not one but two vaccines would be developed, approved, and widely distributed before the end of the year? Or that those vaccines would be rejected by large segments of the population on ideological grounds? Could anyone have predicted in early 2020 that schools in 21 states would be forbidden by law to require COVID-19 vaccination in students?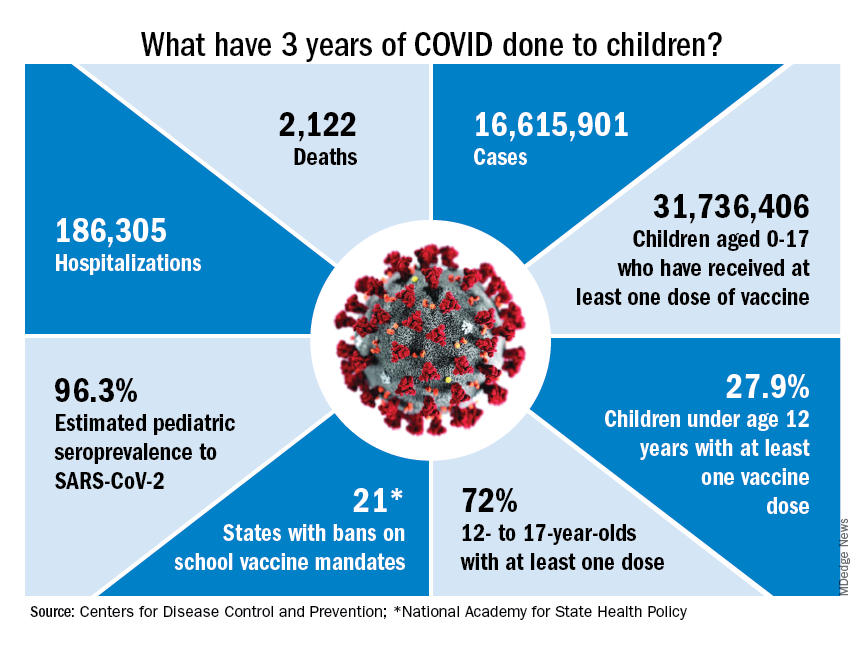
Vaccination is generally considered to be an activity of childhood, but that practice has been turned upside down with COVID-19. Among Americans aged 65 years and older, 95% have received at least one dose of vaccine, versus 27.9% of children younger than 12 years old, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The vaccine situation for children mirrors that of the population as a whole. The oldest children have the highest vaccination rates, and the rates decline along with age: 72.0% of those aged 12-17 years have received at least one dose, compared with 39.8% of 5- to 11-year-olds, 10.5% of 2- to 4-year-olds, and 8.0% of children under age 2, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The youngest children were, of course, the last ones to be eligible for the vaccine, but their uptake has been much slower since emergency use was authorized in June of 2022. In the nearly 9 months since then, 9.5% of children aged 4 and under have received at least one dose, versus 66% of children aged 12-15 years in the first 9 months (May 2021 to March 2022).
Altogether, a total of 31.7 million, or 43%, of all children under age 18 had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of March 8, 2023, according to the most recent CDC data.
Incidence: Counting COVID
Vaccination and other prevention efforts have tried to stem the tide, but what has COVID actually done to children since the Trump administration declared a nationwide emergency on March 13, 2020?
- 16.6 million cases.
- 186,035 new hospital admissions.
- 2,122 deaths.
Even the proportion of total COVID cases in children, 17.2%, is less than might be expected, given their relatively undervaccinated status.
Seroprevalence estimates seem to support the undercounting of pediatric cases. A survey of commercial laboratories working with the CDC put the seroprevalance of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in children at 96.3% as of late 2022, based on tests of almost 27,000 specimens performed over an 8-week period from mid-October to mid-December. That would put the number of infected children at 65.7 million children.
Since Omicron
There has not been another major COVID-19 surge since the winter of 2021-2022, when the weekly rate of new cases reached 1,900 per 100,000 population in children aged 16-17 years in early January 2022 – the highest seen among children of any of the CDC’s age groups (0-4, 5-11, 12-15, 16-17) during the entire pandemic. Since the Omicron surge, the highest weekly rate was 221 per 100,000 during the week of May 15-21, again in 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC reports.
The widely anticipated surge of COVID in the fall and winter of 2022 and 2023 – the so-called “tripledemic” involving influenza and respiratory syncytial virus – did not occur, possibly because so many Americans were vaccinated or previously infected, experts suggested. New-case rates, emergency room visits, and hospitalizations in children have continued to drop as winter comes to a close, CDC data show.
With 3 years of the COVID-19 experience now past, it’s safe to say that SARS-CoV-2 changed American society in ways that could not have been predicted when the first U.S. cases were reported in January of 2020.
Who would have guessed back then that not one but two vaccines would be developed, approved, and widely distributed before the end of the year? Or that those vaccines would be rejected by large segments of the population on ideological grounds? Could anyone have predicted in early 2020 that schools in 21 states would be forbidden by law to require COVID-19 vaccination in students?
Vaccination is generally considered to be an activity of childhood, but that practice has been turned upside down with COVID-19. Among Americans aged 65 years and older, 95% have received at least one dose of vaccine, versus 27.9% of children younger than 12 years old, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The vaccine situation for children mirrors that of the population as a whole. The oldest children have the highest vaccination rates, and the rates decline along with age: 72.0% of those aged 12-17 years have received at least one dose, compared with 39.8% of 5- to 11-year-olds, 10.5% of 2- to 4-year-olds, and 8.0% of children under age 2, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The youngest children were, of course, the last ones to be eligible for the vaccine, but their uptake has been much slower since emergency use was authorized in June of 2022. In the nearly 9 months since then, 9.5% of children aged 4 and under have received at least one dose, versus 66% of children aged 12-15 years in the first 9 months (May 2021 to March 2022).
Altogether, a total of 31.7 million, or 43%, of all children under age 18 had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of March 8, 2023, according to the most recent CDC data.
Incidence: Counting COVID
Vaccination and other prevention efforts have tried to stem the tide, but what has COVID actually done to children since the Trump administration declared a nationwide emergency on March 13, 2020?
- 16.6 million cases.
- 186,035 new hospital admissions.
- 2,122 deaths.
Even the proportion of total COVID cases in children, 17.2%, is less than might be expected, given their relatively undervaccinated status.
Seroprevalence estimates seem to support the undercounting of pediatric cases. A survey of commercial laboratories working with the CDC put the seroprevalance of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in children at 96.3% as of late 2022, based on tests of almost 27,000 specimens performed over an 8-week period from mid-October to mid-December. That would put the number of infected children at 65.7 million children.
Since Omicron
There has not been another major COVID-19 surge since the winter of 2021-2022, when the weekly rate of new cases reached 1,900 per 100,000 population in children aged 16-17 years in early January 2022 – the highest seen among children of any of the CDC’s age groups (0-4, 5-11, 12-15, 16-17) during the entire pandemic. Since the Omicron surge, the highest weekly rate was 221 per 100,000 during the week of May 15-21, again in 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC reports.
The widely anticipated surge of COVID in the fall and winter of 2022 and 2023 – the so-called “tripledemic” involving influenza and respiratory syncytial virus – did not occur, possibly because so many Americans were vaccinated or previously infected, experts suggested. New-case rates, emergency room visits, and hospitalizations in children have continued to drop as winter comes to a close, CDC data show.
With 3 years of the COVID-19 experience now past, it’s safe to say that SARS-CoV-2 changed American society in ways that could not have been predicted when the first U.S. cases were reported in January of 2020.
Who would have guessed back then that not one but two vaccines would be developed, approved, and widely distributed before the end of the year? Or that those vaccines would be rejected by large segments of the population on ideological grounds? Could anyone have predicted in early 2020 that schools in 21 states would be forbidden by law to require COVID-19 vaccination in students?
Vaccination is generally considered to be an activity of childhood, but that practice has been turned upside down with COVID-19. Among Americans aged 65 years and older, 95% have received at least one dose of vaccine, versus 27.9% of children younger than 12 years old, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The vaccine situation for children mirrors that of the population as a whole. The oldest children have the highest vaccination rates, and the rates decline along with age: 72.0% of those aged 12-17 years have received at least one dose, compared with 39.8% of 5- to 11-year-olds, 10.5% of 2- to 4-year-olds, and 8.0% of children under age 2, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The youngest children were, of course, the last ones to be eligible for the vaccine, but their uptake has been much slower since emergency use was authorized in June of 2022. In the nearly 9 months since then, 9.5% of children aged 4 and under have received at least one dose, versus 66% of children aged 12-15 years in the first 9 months (May 2021 to March 2022).
Altogether, a total of 31.7 million, or 43%, of all children under age 18 had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of March 8, 2023, according to the most recent CDC data.
Incidence: Counting COVID
Vaccination and other prevention efforts have tried to stem the tide, but what has COVID actually done to children since the Trump administration declared a nationwide emergency on March 13, 2020?
- 16.6 million cases.
- 186,035 new hospital admissions.
- 2,122 deaths.
Even the proportion of total COVID cases in children, 17.2%, is less than might be expected, given their relatively undervaccinated status.
Seroprevalence estimates seem to support the undercounting of pediatric cases. A survey of commercial laboratories working with the CDC put the seroprevalance of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in children at 96.3% as of late 2022, based on tests of almost 27,000 specimens performed over an 8-week period from mid-October to mid-December. That would put the number of infected children at 65.7 million children.
Since Omicron
There has not been another major COVID-19 surge since the winter of 2021-2022, when the weekly rate of new cases reached 1,900 per 100,000 population in children aged 16-17 years in early January 2022 – the highest seen among children of any of the CDC’s age groups (0-4, 5-11, 12-15, 16-17) during the entire pandemic. Since the Omicron surge, the highest weekly rate was 221 per 100,000 during the week of May 15-21, again in 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC reports.
The widely anticipated surge of COVID in the fall and winter of 2022 and 2023 – the so-called “tripledemic” involving influenza and respiratory syncytial virus – did not occur, possibly because so many Americans were vaccinated or previously infected, experts suggested. New-case rates, emergency room visits, and hospitalizations in children have continued to drop as winter comes to a close, CDC data show.
Strong support for CBT as first-line treatment for insomnia in seniors
NEW ORLEANS –
“The lack of awareness among clinicians who take care of older adults that CBT for insomnia (CBT-I) is an effective treatment for insomnia is an issue,” Rajesh R. Tampi, MD, professor and chairman of the department of psychiatry, Creighton University, Omaha, Neb., told this news organization.
Dr. Tampi was among the speakers during a session as part of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting addressing the complex challenges of treating insomnia in older patients, who tend to have higher rates of insomnia than their younger counterparts.
The prevalence of insomnia in older adults is estimated to be 20%-40%, and medication is frequently the first treatment choice, a less than ideal approach, said Dr. Tampi.
“Prescribing sedatives and hypnotics, which can cause severe adverse effects, without a thorough assessment that includes comorbidities that may be causing the insomnia” is among the biggest mistakes clinicians make in the treatment of insomnia in older patients, Dr. Tampi said in an interview.
“It’s our duty as providers to first take a good assessment, talk about polymorbidity, and try to address those conditions, and judiciously use medications in conjunction with at least components of CBT-I,” he said.
Long-term safety, efficacy unclear
About one-third of older adults take at least one form of pharmacological treatment for insomnia symptoms, said Ebony Dix, MD, assistant professor of psychiatry at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., in a separate talk during the session. This, despite the low-risk profile of CBT and recommendations from various medical societies that CBT should be tried first.
Dr. Dix noted that medications approved for insomnia by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, including melatonin receptor agonists, heterocyclics, and dual orexin receptor antagonists (DORAs), can play an important role in the short-term management of insomnia, but their long-term effects are unknown.
“Pharmacotherapeutic agents may be effective in the short term, but there is a lack of sufficient, statistically significant data to support the long-term safety and efficacy of any [sleep] medication, especially in aging adults, due to the impact of hypnotic drugs on sleep architecture, the impact of aging on pharmacokinetics, as well as polypharmacy and drug-to-drug interactions,” Dr. Dix said. She noted that clinical trials of insomnia drugs rarely include geriatric patients.
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommends CBT-I as first-line treatment for insomnia, with the key benefit being its exemplary safety profile, said Shilpa Srinivasan, MD, a professor of clinical psychiatry at the University of South Carolina, Columbia, who also presented during the session.
“The biggest [attribute] of CBT-I management strategies is the low risk of side effects,” she said. “How many medications can we say that about?”
The CBT-I intervention includes a focus on key components of lifestyle and mental health issues to improve sleep. These include the following:
- Strictly restricting sleep hours for bedtime and arising (with napping discouraged).
- Control of stimulus to disrupt falling asleep.
- Cognitive therapy to identify and replace maladaptive beliefs.
- Control of sleep hygiene for optimal sleep.
- Relaxation training.
Keys to success
Dr. Srinivasan noted one recent study of CBT-I among patients aged 60 and older with insomnia and depression. The 156 participants randomized to receive weekly 120-minute CBT-I sessions over 2 months were significantly less likely to develop new or recurrent major depression versus their counterparts randomized to receive sleep education (hazard ratio, 0.51; P = .02).
However, CBT-I is more labor intensive than medication and requires provider training and motivation, and commitment on the part of the patient, to be successful.
“We really need to ensure that even when patients are receiving pharmacologic interventions for insomnia that we provide psychoeducation. At the end of the day, some of these nonpharmacologic components can make or break the success of pharmacotherapy,” said Dr. Srinivasan.
Whether using CBT-I alone or in combination with pharmacotherapy, the intervention does not necessarily have to include all components to be beneficial, she said.
“I think one of the challenges in incorporating CBT-I is the misconception that it is an all-or-nothing approach wherein every modality must be utilized,” she said. “While multicomponent CBT-I has been shown to be effective, the individual components can be incorporated into patient encounters in a stepped approach.”
Informing patients that they have options other than medications and involving them in decision-making is key, she added.
“In the case of insomnia, this is particularly relevant because of the physical and emotional distress that it causes,” Dr. Srinivasan said. “Patients often seek over-the-counter medications or other nonprescribed agents to try to obtain relief even before seeking treatment in a health care setting. There is less awareness about evidence-based and effective nonpharmacologic treatments such as CBT-I.”
Dr. Tampi, Dr. Dix, and Dr. Srinivasan have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS –
“The lack of awareness among clinicians who take care of older adults that CBT for insomnia (CBT-I) is an effective treatment for insomnia is an issue,” Rajesh R. Tampi, MD, professor and chairman of the department of psychiatry, Creighton University, Omaha, Neb., told this news organization.
Dr. Tampi was among the speakers during a session as part of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting addressing the complex challenges of treating insomnia in older patients, who tend to have higher rates of insomnia than their younger counterparts.
The prevalence of insomnia in older adults is estimated to be 20%-40%, and medication is frequently the first treatment choice, a less than ideal approach, said Dr. Tampi.
“Prescribing sedatives and hypnotics, which can cause severe adverse effects, without a thorough assessment that includes comorbidities that may be causing the insomnia” is among the biggest mistakes clinicians make in the treatment of insomnia in older patients, Dr. Tampi said in an interview.
“It’s our duty as providers to first take a good assessment, talk about polymorbidity, and try to address those conditions, and judiciously use medications in conjunction with at least components of CBT-I,” he said.
Long-term safety, efficacy unclear
About one-third of older adults take at least one form of pharmacological treatment for insomnia symptoms, said Ebony Dix, MD, assistant professor of psychiatry at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., in a separate talk during the session. This, despite the low-risk profile of CBT and recommendations from various medical societies that CBT should be tried first.
Dr. Dix noted that medications approved for insomnia by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, including melatonin receptor agonists, heterocyclics, and dual orexin receptor antagonists (DORAs), can play an important role in the short-term management of insomnia, but their long-term effects are unknown.
“Pharmacotherapeutic agents may be effective in the short term, but there is a lack of sufficient, statistically significant data to support the long-term safety and efficacy of any [sleep] medication, especially in aging adults, due to the impact of hypnotic drugs on sleep architecture, the impact of aging on pharmacokinetics, as well as polypharmacy and drug-to-drug interactions,” Dr. Dix said. She noted that clinical trials of insomnia drugs rarely include geriatric patients.
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommends CBT-I as first-line treatment for insomnia, with the key benefit being its exemplary safety profile, said Shilpa Srinivasan, MD, a professor of clinical psychiatry at the University of South Carolina, Columbia, who also presented during the session.
“The biggest [attribute] of CBT-I management strategies is the low risk of side effects,” she said. “How many medications can we say that about?”
The CBT-I intervention includes a focus on key components of lifestyle and mental health issues to improve sleep. These include the following:
- Strictly restricting sleep hours for bedtime and arising (with napping discouraged).
- Control of stimulus to disrupt falling asleep.
- Cognitive therapy to identify and replace maladaptive beliefs.
- Control of sleep hygiene for optimal sleep.
- Relaxation training.
Keys to success
Dr. Srinivasan noted one recent study of CBT-I among patients aged 60 and older with insomnia and depression. The 156 participants randomized to receive weekly 120-minute CBT-I sessions over 2 months were significantly less likely to develop new or recurrent major depression versus their counterparts randomized to receive sleep education (hazard ratio, 0.51; P = .02).
However, CBT-I is more labor intensive than medication and requires provider training and motivation, and commitment on the part of the patient, to be successful.
“We really need to ensure that even when patients are receiving pharmacologic interventions for insomnia that we provide psychoeducation. At the end of the day, some of these nonpharmacologic components can make or break the success of pharmacotherapy,” said Dr. Srinivasan.
Whether using CBT-I alone or in combination with pharmacotherapy, the intervention does not necessarily have to include all components to be beneficial, she said.
“I think one of the challenges in incorporating CBT-I is the misconception that it is an all-or-nothing approach wherein every modality must be utilized,” she said. “While multicomponent CBT-I has been shown to be effective, the individual components can be incorporated into patient encounters in a stepped approach.”
Informing patients that they have options other than medications and involving them in decision-making is key, she added.
“In the case of insomnia, this is particularly relevant because of the physical and emotional distress that it causes,” Dr. Srinivasan said. “Patients often seek over-the-counter medications or other nonprescribed agents to try to obtain relief even before seeking treatment in a health care setting. There is less awareness about evidence-based and effective nonpharmacologic treatments such as CBT-I.”
Dr. Tampi, Dr. Dix, and Dr. Srinivasan have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS –
“The lack of awareness among clinicians who take care of older adults that CBT for insomnia (CBT-I) is an effective treatment for insomnia is an issue,” Rajesh R. Tampi, MD, professor and chairman of the department of psychiatry, Creighton University, Omaha, Neb., told this news organization.
Dr. Tampi was among the speakers during a session as part of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting addressing the complex challenges of treating insomnia in older patients, who tend to have higher rates of insomnia than their younger counterparts.
The prevalence of insomnia in older adults is estimated to be 20%-40%, and medication is frequently the first treatment choice, a less than ideal approach, said Dr. Tampi.
“Prescribing sedatives and hypnotics, which can cause severe adverse effects, without a thorough assessment that includes comorbidities that may be causing the insomnia” is among the biggest mistakes clinicians make in the treatment of insomnia in older patients, Dr. Tampi said in an interview.
“It’s our duty as providers to first take a good assessment, talk about polymorbidity, and try to address those conditions, and judiciously use medications in conjunction with at least components of CBT-I,” he said.
Long-term safety, efficacy unclear
About one-third of older adults take at least one form of pharmacological treatment for insomnia symptoms, said Ebony Dix, MD, assistant professor of psychiatry at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., in a separate talk during the session. This, despite the low-risk profile of CBT and recommendations from various medical societies that CBT should be tried first.
Dr. Dix noted that medications approved for insomnia by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, including melatonin receptor agonists, heterocyclics, and dual orexin receptor antagonists (DORAs), can play an important role in the short-term management of insomnia, but their long-term effects are unknown.
“Pharmacotherapeutic agents may be effective in the short term, but there is a lack of sufficient, statistically significant data to support the long-term safety and efficacy of any [sleep] medication, especially in aging adults, due to the impact of hypnotic drugs on sleep architecture, the impact of aging on pharmacokinetics, as well as polypharmacy and drug-to-drug interactions,” Dr. Dix said. She noted that clinical trials of insomnia drugs rarely include geriatric patients.
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommends CBT-I as first-line treatment for insomnia, with the key benefit being its exemplary safety profile, said Shilpa Srinivasan, MD, a professor of clinical psychiatry at the University of South Carolina, Columbia, who also presented during the session.
“The biggest [attribute] of CBT-I management strategies is the low risk of side effects,” she said. “How many medications can we say that about?”
The CBT-I intervention includes a focus on key components of lifestyle and mental health issues to improve sleep. These include the following:
- Strictly restricting sleep hours for bedtime and arising (with napping discouraged).
- Control of stimulus to disrupt falling asleep.
- Cognitive therapy to identify and replace maladaptive beliefs.
- Control of sleep hygiene for optimal sleep.
- Relaxation training.
Keys to success
Dr. Srinivasan noted one recent study of CBT-I among patients aged 60 and older with insomnia and depression. The 156 participants randomized to receive weekly 120-minute CBT-I sessions over 2 months were significantly less likely to develop new or recurrent major depression versus their counterparts randomized to receive sleep education (hazard ratio, 0.51; P = .02).
However, CBT-I is more labor intensive than medication and requires provider training and motivation, and commitment on the part of the patient, to be successful.
“We really need to ensure that even when patients are receiving pharmacologic interventions for insomnia that we provide psychoeducation. At the end of the day, some of these nonpharmacologic components can make or break the success of pharmacotherapy,” said Dr. Srinivasan.
Whether using CBT-I alone or in combination with pharmacotherapy, the intervention does not necessarily have to include all components to be beneficial, she said.
“I think one of the challenges in incorporating CBT-I is the misconception that it is an all-or-nothing approach wherein every modality must be utilized,” she said. “While multicomponent CBT-I has been shown to be effective, the individual components can be incorporated into patient encounters in a stepped approach.”
Informing patients that they have options other than medications and involving them in decision-making is key, she added.
“In the case of insomnia, this is particularly relevant because of the physical and emotional distress that it causes,” Dr. Srinivasan said. “Patients often seek over-the-counter medications or other nonprescribed agents to try to obtain relief even before seeking treatment in a health care setting. There is less awareness about evidence-based and effective nonpharmacologic treatments such as CBT-I.”
Dr. Tampi, Dr. Dix, and Dr. Srinivasan have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAGP 2023
New data on IV ketamine for resistant depression in the elderly
NEW ORLEANS –
“These were patients with depression who had not responded even to intensive therapies or procedures, and we found that after a 6-week ketamine infusion regimen, there was no difference in the response to the treatment between the treatment-resistant geriatric and nongeriatric patients,” study investigator Jonathan Kim, of Emory University, Atlanta, the first author of one of two studies presented as part of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting, said in an interview.
The findings are important because research on the effects of IV ketamine have not been well documented in geriatric patients, who have high rates of depression and TRD.
“There is a lack of data on IV ketamine in older adults with treatment-resistant depression, and there are some safety and tolerability concerns which may lead some older adults and their clinicians to be reluctant to pursue IV ketamine treatment,” study coinvestigator Hanadi Ajam Oughli, MD, a health sciences assistant clinical professor in the department of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, told this news organization.
Nasal vs. IV administration
Ketamine has traditionally been used as an anesthetic that blocks N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptors, Dr. Oughli and colleagues note.
In the treatment of TRD, an infusion of 0.5 mg/kg is typically administered over 40 minutes, producing a rapid antidepressant response. Recent research shows the drug reduces suicidality and improves mood and quality of life.
A more recent intranasal formulation of ketamine, esketamine, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for TRD in 2019, and some experts questioned its path to approval. In addition, the drug’s high cost and poor bioavailability in comparison with IV ketamine remains an issue, said Dr. Oughli.
In the previous TRANSFORM-3 study, a placebo-controlled randomized trial, there was no difference between esketamine, used in conjunction with an antidepressant, and placebo for geriatric patients.
To better understand the effects of IV ketamine in this patient population, Mr. Kim’s team conducted a retrospective chart review of 91 older patients with TRD who received IV ketamine treatment between October 2016 and August 2022.
Patients were divided into two groups – those older than 60 years (n = 36; 44% women; mean age, 68.86) and those younger than 60 (n = 55; 49% women; mean age, 41.05). Participants in each age group received six ketamine infusions over 6 weeks.
Results showed that with regard to depression severity, as assessed using Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II) scores, 27.8% of patients in the geriatric group had a 50% or greater improvement, vs. 25.4% of those younger than 60.
The average BDI-II scores represented a significant improvement for both groups (P < .01), and the difference in scores between the groups was not statistically significant (P = .973).
“It is important to note that our study was conducted in a real-world clinical setting with a treatment-resistant population; other clinical studies may not have such sick patients in their trials. Additional studies are therefore warranted to establish further treatment guidelines in this area,” Mr. Kim said.
Open-label trial results
In the second study, Dr. Oughli and colleagues evaluated additional key outcomes in geriatric patients treated with IV ketamine as part of a larger open-label late-life trial on TRD.
The secondary analysis of the trial focused on 23 patients (mean age, 71.5 years) who had been initially treated with twice-a-week IV ketamine for 4 weeks.
After the first 4 weeks, patients who had experienced a partial response received an additional 4 weeks of once-weekly IV ketamine.
Overall, 48% of participants achieved a response, and 24% achieved remission of depressive symptoms following the first 4 weeks of twice-weekly treatment. This effect was maintained during the continuation phase of the study.
These findings are consistent with research in younger adults and demonstrate that twice-weekly infusions yield a more sustained antidepressant response than once-weekly infusions, the authors note.
The analysis also showed important increases in psychological well-being scores on the Scale for Suicidal Ideation, improved sleep quality as measured by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, and overall psychological well-being as shown on the NIH Toolbox Positive Affect on happiness/contentment and the NIH Toolbox General Life Satisfaction scales.
In a previous analysis, published in The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, the researchers also evaluated cognitive function using the NIH Cognitive Battery, which showed that geriatric patients with TRD had significant improvements in a composite of executive functioning and fluid cognition during the 4-week acute treatment period of twice-weekly IV ketamine infusions (Cohen’s d = 0.61) and that those improvements were sustained in the continuation phase of once-weekly infusions for 4 more weeks.
Those results are consistent with ketamine’s known potential procognitive effects in TRD, due to a putative antidepressant mechanism that rescues prefrontal circuit dysfunction through synaptogenesis, the researchers note.
Dr. Oughli said that in both analyses, patients tolerated ketamine well, and there were no serious adverse events.
“Adverse events, including hypertension, dissociated effects, and cravings, were rare and did not prevent the continued use of IV ketamine by older adults. We were able to use clonidine to help manage blood pressure changes seen during the infusions,” she noted.
“These findings are very promising and will need to be confirmed and extended in a larger randomized controlled trial.”
Unsettling for some older patients
George T. Grossberg, MD, director, geriatric psychiatry, Saint Louis University, noted that in his experience, IV ketamine treatment can be unsettling for some older geriatric patients, such as those in their 80s.
“Particularly with some of my older patients, the kind of psychotomimetic properties of ketamine and the out-of-body experiences [with the initial treatment] can be frightening,” he said. “They may be willing to try, but I’ve had more than one patient quit after one treatment because they became so frightened.”
However, the dire nature of TRD and failure to respond to multiple medications and combinations and other strategies may prompt patients to try ketamine as a measure with at least some potential, he noted.
“But there is a high bar for acceptance, especially on the part of older adults and their families, more than for younger people,” he said.
The investigators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Grossberg has received consulting fees from Acadia, Avanir, Biogen, BioXcel, Genentech, Karuna, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Roche, and Takeda.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS –
“These were patients with depression who had not responded even to intensive therapies or procedures, and we found that after a 6-week ketamine infusion regimen, there was no difference in the response to the treatment between the treatment-resistant geriatric and nongeriatric patients,” study investigator Jonathan Kim, of Emory University, Atlanta, the first author of one of two studies presented as part of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting, said in an interview.
The findings are important because research on the effects of IV ketamine have not been well documented in geriatric patients, who have high rates of depression and TRD.
“There is a lack of data on IV ketamine in older adults with treatment-resistant depression, and there are some safety and tolerability concerns which may lead some older adults and their clinicians to be reluctant to pursue IV ketamine treatment,” study coinvestigator Hanadi Ajam Oughli, MD, a health sciences assistant clinical professor in the department of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, told this news organization.
Nasal vs. IV administration
Ketamine has traditionally been used as an anesthetic that blocks N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptors, Dr. Oughli and colleagues note.
In the treatment of TRD, an infusion of 0.5 mg/kg is typically administered over 40 minutes, producing a rapid antidepressant response. Recent research shows the drug reduces suicidality and improves mood and quality of life.
A more recent intranasal formulation of ketamine, esketamine, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for TRD in 2019, and some experts questioned its path to approval. In addition, the drug’s high cost and poor bioavailability in comparison with IV ketamine remains an issue, said Dr. Oughli.
In the previous TRANSFORM-3 study, a placebo-controlled randomized trial, there was no difference between esketamine, used in conjunction with an antidepressant, and placebo for geriatric patients.
To better understand the effects of IV ketamine in this patient population, Mr. Kim’s team conducted a retrospective chart review of 91 older patients with TRD who received IV ketamine treatment between October 2016 and August 2022.
Patients were divided into two groups – those older than 60 years (n = 36; 44% women; mean age, 68.86) and those younger than 60 (n = 55; 49% women; mean age, 41.05). Participants in each age group received six ketamine infusions over 6 weeks.
Results showed that with regard to depression severity, as assessed using Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II) scores, 27.8% of patients in the geriatric group had a 50% or greater improvement, vs. 25.4% of those younger than 60.
The average BDI-II scores represented a significant improvement for both groups (P < .01), and the difference in scores between the groups was not statistically significant (P = .973).
“It is important to note that our study was conducted in a real-world clinical setting with a treatment-resistant population; other clinical studies may not have such sick patients in their trials. Additional studies are therefore warranted to establish further treatment guidelines in this area,” Mr. Kim said.
Open-label trial results
In the second study, Dr. Oughli and colleagues evaluated additional key outcomes in geriatric patients treated with IV ketamine as part of a larger open-label late-life trial on TRD.
The secondary analysis of the trial focused on 23 patients (mean age, 71.5 years) who had been initially treated with twice-a-week IV ketamine for 4 weeks.
After the first 4 weeks, patients who had experienced a partial response received an additional 4 weeks of once-weekly IV ketamine.
Overall, 48% of participants achieved a response, and 24% achieved remission of depressive symptoms following the first 4 weeks of twice-weekly treatment. This effect was maintained during the continuation phase of the study.
These findings are consistent with research in younger adults and demonstrate that twice-weekly infusions yield a more sustained antidepressant response than once-weekly infusions, the authors note.
The analysis also showed important increases in psychological well-being scores on the Scale for Suicidal Ideation, improved sleep quality as measured by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, and overall psychological well-being as shown on the NIH Toolbox Positive Affect on happiness/contentment and the NIH Toolbox General Life Satisfaction scales.
In a previous analysis, published in The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, the researchers also evaluated cognitive function using the NIH Cognitive Battery, which showed that geriatric patients with TRD had significant improvements in a composite of executive functioning and fluid cognition during the 4-week acute treatment period of twice-weekly IV ketamine infusions (Cohen’s d = 0.61) and that those improvements were sustained in the continuation phase of once-weekly infusions for 4 more weeks.
Those results are consistent with ketamine’s known potential procognitive effects in TRD, due to a putative antidepressant mechanism that rescues prefrontal circuit dysfunction through synaptogenesis, the researchers note.
Dr. Oughli said that in both analyses, patients tolerated ketamine well, and there were no serious adverse events.
“Adverse events, including hypertension, dissociated effects, and cravings, were rare and did not prevent the continued use of IV ketamine by older adults. We were able to use clonidine to help manage blood pressure changes seen during the infusions,” she noted.
“These findings are very promising and will need to be confirmed and extended in a larger randomized controlled trial.”
Unsettling for some older patients
George T. Grossberg, MD, director, geriatric psychiatry, Saint Louis University, noted that in his experience, IV ketamine treatment can be unsettling for some older geriatric patients, such as those in their 80s.
“Particularly with some of my older patients, the kind of psychotomimetic properties of ketamine and the out-of-body experiences [with the initial treatment] can be frightening,” he said. “They may be willing to try, but I’ve had more than one patient quit after one treatment because they became so frightened.”
However, the dire nature of TRD and failure to respond to multiple medications and combinations and other strategies may prompt patients to try ketamine as a measure with at least some potential, he noted.
“But there is a high bar for acceptance, especially on the part of older adults and their families, more than for younger people,” he said.
The investigators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Grossberg has received consulting fees from Acadia, Avanir, Biogen, BioXcel, Genentech, Karuna, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Roche, and Takeda.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS –
“These were patients with depression who had not responded even to intensive therapies or procedures, and we found that after a 6-week ketamine infusion regimen, there was no difference in the response to the treatment between the treatment-resistant geriatric and nongeriatric patients,” study investigator Jonathan Kim, of Emory University, Atlanta, the first author of one of two studies presented as part of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting, said in an interview.
The findings are important because research on the effects of IV ketamine have not been well documented in geriatric patients, who have high rates of depression and TRD.
“There is a lack of data on IV ketamine in older adults with treatment-resistant depression, and there are some safety and tolerability concerns which may lead some older adults and their clinicians to be reluctant to pursue IV ketamine treatment,” study coinvestigator Hanadi Ajam Oughli, MD, a health sciences assistant clinical professor in the department of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, told this news organization.
Nasal vs. IV administration
Ketamine has traditionally been used as an anesthetic that blocks N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptors, Dr. Oughli and colleagues note.
In the treatment of TRD, an infusion of 0.5 mg/kg is typically administered over 40 minutes, producing a rapid antidepressant response. Recent research shows the drug reduces suicidality and improves mood and quality of life.
A more recent intranasal formulation of ketamine, esketamine, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for TRD in 2019, and some experts questioned its path to approval. In addition, the drug’s high cost and poor bioavailability in comparison with IV ketamine remains an issue, said Dr. Oughli.
In the previous TRANSFORM-3 study, a placebo-controlled randomized trial, there was no difference between esketamine, used in conjunction with an antidepressant, and placebo for geriatric patients.
To better understand the effects of IV ketamine in this patient population, Mr. Kim’s team conducted a retrospective chart review of 91 older patients with TRD who received IV ketamine treatment between October 2016 and August 2022.
Patients were divided into two groups – those older than 60 years (n = 36; 44% women; mean age, 68.86) and those younger than 60 (n = 55; 49% women; mean age, 41.05). Participants in each age group received six ketamine infusions over 6 weeks.
Results showed that with regard to depression severity, as assessed using Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II) scores, 27.8% of patients in the geriatric group had a 50% or greater improvement, vs. 25.4% of those younger than 60.
The average BDI-II scores represented a significant improvement for both groups (P < .01), and the difference in scores between the groups was not statistically significant (P = .973).
“It is important to note that our study was conducted in a real-world clinical setting with a treatment-resistant population; other clinical studies may not have such sick patients in their trials. Additional studies are therefore warranted to establish further treatment guidelines in this area,” Mr. Kim said.
Open-label trial results
In the second study, Dr. Oughli and colleagues evaluated additional key outcomes in geriatric patients treated with IV ketamine as part of a larger open-label late-life trial on TRD.
The secondary analysis of the trial focused on 23 patients (mean age, 71.5 years) who had been initially treated with twice-a-week IV ketamine for 4 weeks.
After the first 4 weeks, patients who had experienced a partial response received an additional 4 weeks of once-weekly IV ketamine.
Overall, 48% of participants achieved a response, and 24% achieved remission of depressive symptoms following the first 4 weeks of twice-weekly treatment. This effect was maintained during the continuation phase of the study.
These findings are consistent with research in younger adults and demonstrate that twice-weekly infusions yield a more sustained antidepressant response than once-weekly infusions, the authors note.
The analysis also showed important increases in psychological well-being scores on the Scale for Suicidal Ideation, improved sleep quality as measured by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, and overall psychological well-being as shown on the NIH Toolbox Positive Affect on happiness/contentment and the NIH Toolbox General Life Satisfaction scales.
In a previous analysis, published in The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, the researchers also evaluated cognitive function using the NIH Cognitive Battery, which showed that geriatric patients with TRD had significant improvements in a composite of executive functioning and fluid cognition during the 4-week acute treatment period of twice-weekly IV ketamine infusions (Cohen’s d = 0.61) and that those improvements were sustained in the continuation phase of once-weekly infusions for 4 more weeks.
Those results are consistent with ketamine’s known potential procognitive effects in TRD, due to a putative antidepressant mechanism that rescues prefrontal circuit dysfunction through synaptogenesis, the researchers note.
Dr. Oughli said that in both analyses, patients tolerated ketamine well, and there were no serious adverse events.
“Adverse events, including hypertension, dissociated effects, and cravings, were rare and did not prevent the continued use of IV ketamine by older adults. We were able to use clonidine to help manage blood pressure changes seen during the infusions,” she noted.
“These findings are very promising and will need to be confirmed and extended in a larger randomized controlled trial.”
Unsettling for some older patients
George T. Grossberg, MD, director, geriatric psychiatry, Saint Louis University, noted that in his experience, IV ketamine treatment can be unsettling for some older geriatric patients, such as those in their 80s.
“Particularly with some of my older patients, the kind of psychotomimetic properties of ketamine and the out-of-body experiences [with the initial treatment] can be frightening,” he said. “They may be willing to try, but I’ve had more than one patient quit after one treatment because they became so frightened.”
However, the dire nature of TRD and failure to respond to multiple medications and combinations and other strategies may prompt patients to try ketamine as a measure with at least some potential, he noted.
“But there is a high bar for acceptance, especially on the part of older adults and their families, more than for younger people,” he said.
The investigators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Grossberg has received consulting fees from Acadia, Avanir, Biogen, BioXcel, Genentech, Karuna, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Roche, and Takeda.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAGP 2023
COVID raises risk for long-term GI complications
, a large new study indicates.
The researchers estimate that, so far, SARS-CoV-2 infections have contributed to more than 6 million new cases of GI disorders in the United States and 42 million new cases worldwide.
The diagnoses more common among patients who’ve had COVID ranged from stomach upset to acute pancreatitis, say the researchers, led by Evan Xu, a data analyst at the Clinical Epidemiology Center, Research and Development Service, VA St. Louis Health Care System.
Signs and symptoms of GI problems, such as constipation and diarrhea, also were more common among patients who had had the virus, the study found.
“Altogether, our results show that people with SARS-CoV-2 infection are at increased risk of gastrointestinal disorders in the post-acute phase of COVID-19,” the researchers write. “Post-COVID care should involve attention to gastrointestinal health and disease.”
The results were published online in Nature Communications.
Disease risks jump
The researchers used data from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs national health care databases to identify 154,068 people with confirmed COVID-19 from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 15, 2021. They used statistical modeling to compare those patients with 5.6 million patients with similar characteristics who had not been infected during the same period and an historical control group of 5.9 million patients from March 1, 2018, to Dec. 31, 2019, before the virus began to spread across the globe.
The study included hospitalized and nonhospitalized COVID patients. The majority of the study population was male, but the study included almost 1.2 million female patients.
Compared with control persons, post-COVID patients’ increased risk of a GI diagnosis and the excess disease burden at 1 year, respectively, were as follows.
- 102% for cholangitis; 0.22 per 1,000 persons
- 62% for peptic ulcer disease; 1.57 per 1,000 persons
- 54% for irritable bowel syndrome; 0.44 per 1,000 persons
- 47% for acute gastritis; 0.47 per 1,000 persons
- 46% for acute pancreatitis; 0.6 per 1,000 persons
- 36% for functional dyspepsia; 0.63 per 1,000 persons
- 35% for gastroesophageal reflux disease; 15.5 per 1,000 persons
Patients who’d had the virus were also at higher risk for GI symptoms than their COVID-free peers. Their risk was 60% higher for constipation, 58% for diarrhea, 52% for vomiting, 46% for bloating, and 44% for abdominal pain, the investigators found.
The risk of developing GI symptoms increased with COVID-19 severity and was highest for those who received intensive care because of the virus, the researchers note.
Subgroup analyses found that the risks of composite gastrointestinal outcome were evident in all subgroups based on age, race, sex, obesity, smoking, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension, the authors write.
Disease burden rises
The increased numbers of GI patients with prior SARS-CoV-2 infection are altering the burden on the health care system, senior author Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a clinical epidemiologist at Washington University, St. Louis, said in an interview.
The shift may be pronounced in primary care, where GI concerns should be seen as a trigger for questions about prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, Dr. Al-Aly said.
Patients may encounter longer wait times at GI clinics or may give up on trying to schedule appointments if waits become too long, he said. They may also present to emergency departments if they can’t get an outpatient appointment, he added.
Simon C. Mathews, MD, assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology, Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization that he’s seeing increased wait times since COVID emerged.
“We know that the pandemic impacted patients’ ability and willingness to seek GI care. There continues to be a long backlog for patients who are only now getting reconnected to care. As a result, our clinics are busier than ever, and our wait times for appointments are unfortunately longer than we would like,” said Dr. Mathews, who was not involved in the research.
Abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation continue to be among the most common symptoms Dr. Mathews sees in clinic, he said.
Kyle Staller, MD, a Massachusetts General Brigham gastroenterologist, said in an interview that it’s important to distinguish symptoms from eventual diagnoses, which lag behind.
“Are patients attributing their symptoms to COVID, or is COVID itself creating a background of inflammation or changes in the nerves that are making these symptoms more common? My suspicion is a little bit of both,” said Dr. Staller, who is director of the Gastrointestinal Motility Laboratory at Mass General, Boston.
Although his clinic is seeing patients with the GI signs and symptoms listed in the article, “we’re not seeing as much of some of the diagnoses, like peptic ulcer disease and pancreatitis,” he said. “I wonder if those may be related to some of the consequences of being critically ill in general, rather than COVID specifically. Those diagnoses I would be more skeptical about.”
Duration of symptoms unclear
It’s hard to tell patients how long their GI symptoms might last after COVID, given the relatively short time researchers have had to study the virus, said Dr. Staller, who was not involved in the research.
The symptoms he’s seeing in patients after COVID mimic those of postinfectious IBS, which literature says could last for months or years, Dr. Staller said. “But they should improve over time,” he added.
Senior author Dr. Al-Aly agreed that the duration of post-COVID GI symptoms is unclear.
“What I can tell you is that even people who got SARS-CoV-2 infection from March 2020 are still coming back for GI problems,” he said.
Unlike other symptoms of long COVID, such as brain fog, gastroenterologists fortunately know how to treat the GI disorders that evolve from SARS-CoV-2 infection, said Dr. Al-Aly, who has studied the long-term effects of the virus on the brain, kidneys, heart, and other organs.
All health care providers “need to be thinking about COVID as a risk factor for all these diseases” and should ask patients about SARS-CoV-2 infection when they take their histories, he said.
The authors, Dr. Staller, and Dr. Mathews report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a large new study indicates.
The researchers estimate that, so far, SARS-CoV-2 infections have contributed to more than 6 million new cases of GI disorders in the United States and 42 million new cases worldwide.
The diagnoses more common among patients who’ve had COVID ranged from stomach upset to acute pancreatitis, say the researchers, led by Evan Xu, a data analyst at the Clinical Epidemiology Center, Research and Development Service, VA St. Louis Health Care System.
Signs and symptoms of GI problems, such as constipation and diarrhea, also were more common among patients who had had the virus, the study found.
“Altogether, our results show that people with SARS-CoV-2 infection are at increased risk of gastrointestinal disorders in the post-acute phase of COVID-19,” the researchers write. “Post-COVID care should involve attention to gastrointestinal health and disease.”
The results were published online in Nature Communications.
Disease risks jump
The researchers used data from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs national health care databases to identify 154,068 people with confirmed COVID-19 from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 15, 2021. They used statistical modeling to compare those patients with 5.6 million patients with similar characteristics who had not been infected during the same period and an historical control group of 5.9 million patients from March 1, 2018, to Dec. 31, 2019, before the virus began to spread across the globe.
The study included hospitalized and nonhospitalized COVID patients. The majority of the study population was male, but the study included almost 1.2 million female patients.
Compared with control persons, post-COVID patients’ increased risk of a GI diagnosis and the excess disease burden at 1 year, respectively, were as follows.
- 102% for cholangitis; 0.22 per 1,000 persons
- 62% for peptic ulcer disease; 1.57 per 1,000 persons
- 54% for irritable bowel syndrome; 0.44 per 1,000 persons
- 47% for acute gastritis; 0.47 per 1,000 persons
- 46% for acute pancreatitis; 0.6 per 1,000 persons
- 36% for functional dyspepsia; 0.63 per 1,000 persons
- 35% for gastroesophageal reflux disease; 15.5 per 1,000 persons
Patients who’d had the virus were also at higher risk for GI symptoms than their COVID-free peers. Their risk was 60% higher for constipation, 58% for diarrhea, 52% for vomiting, 46% for bloating, and 44% for abdominal pain, the investigators found.
The risk of developing GI symptoms increased with COVID-19 severity and was highest for those who received intensive care because of the virus, the researchers note.
Subgroup analyses found that the risks of composite gastrointestinal outcome were evident in all subgroups based on age, race, sex, obesity, smoking, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension, the authors write.
Disease burden rises
The increased numbers of GI patients with prior SARS-CoV-2 infection are altering the burden on the health care system, senior author Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a clinical epidemiologist at Washington University, St. Louis, said in an interview.
The shift may be pronounced in primary care, where GI concerns should be seen as a trigger for questions about prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, Dr. Al-Aly said.
Patients may encounter longer wait times at GI clinics or may give up on trying to schedule appointments if waits become too long, he said. They may also present to emergency departments if they can’t get an outpatient appointment, he added.
Simon C. Mathews, MD, assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology, Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization that he’s seeing increased wait times since COVID emerged.
“We know that the pandemic impacted patients’ ability and willingness to seek GI care. There continues to be a long backlog for patients who are only now getting reconnected to care. As a result, our clinics are busier than ever, and our wait times for appointments are unfortunately longer than we would like,” said Dr. Mathews, who was not involved in the research.
Abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation continue to be among the most common symptoms Dr. Mathews sees in clinic, he said.
Kyle Staller, MD, a Massachusetts General Brigham gastroenterologist, said in an interview that it’s important to distinguish symptoms from eventual diagnoses, which lag behind.
“Are patients attributing their symptoms to COVID, or is COVID itself creating a background of inflammation or changes in the nerves that are making these symptoms more common? My suspicion is a little bit of both,” said Dr. Staller, who is director of the Gastrointestinal Motility Laboratory at Mass General, Boston.
Although his clinic is seeing patients with the GI signs and symptoms listed in the article, “we’re not seeing as much of some of the diagnoses, like peptic ulcer disease and pancreatitis,” he said. “I wonder if those may be related to some of the consequences of being critically ill in general, rather than COVID specifically. Those diagnoses I would be more skeptical about.”
Duration of symptoms unclear
It’s hard to tell patients how long their GI symptoms might last after COVID, given the relatively short time researchers have had to study the virus, said Dr. Staller, who was not involved in the research.
The symptoms he’s seeing in patients after COVID mimic those of postinfectious IBS, which literature says could last for months or years, Dr. Staller said. “But they should improve over time,” he added.
Senior author Dr. Al-Aly agreed that the duration of post-COVID GI symptoms is unclear.
“What I can tell you is that even people who got SARS-CoV-2 infection from March 2020 are still coming back for GI problems,” he said.
Unlike other symptoms of long COVID, such as brain fog, gastroenterologists fortunately know how to treat the GI disorders that evolve from SARS-CoV-2 infection, said Dr. Al-Aly, who has studied the long-term effects of the virus on the brain, kidneys, heart, and other organs.
All health care providers “need to be thinking about COVID as a risk factor for all these diseases” and should ask patients about SARS-CoV-2 infection when they take their histories, he said.
The authors, Dr. Staller, and Dr. Mathews report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a large new study indicates.
The researchers estimate that, so far, SARS-CoV-2 infections have contributed to more than 6 million new cases of GI disorders in the United States and 42 million new cases worldwide.
The diagnoses more common among patients who’ve had COVID ranged from stomach upset to acute pancreatitis, say the researchers, led by Evan Xu, a data analyst at the Clinical Epidemiology Center, Research and Development Service, VA St. Louis Health Care System.
Signs and symptoms of GI problems, such as constipation and diarrhea, also were more common among patients who had had the virus, the study found.
“Altogether, our results show that people with SARS-CoV-2 infection are at increased risk of gastrointestinal disorders in the post-acute phase of COVID-19,” the researchers write. “Post-COVID care should involve attention to gastrointestinal health and disease.”
The results were published online in Nature Communications.
Disease risks jump
The researchers used data from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs national health care databases to identify 154,068 people with confirmed COVID-19 from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 15, 2021. They used statistical modeling to compare those patients with 5.6 million patients with similar characteristics who had not been infected during the same period and an historical control group of 5.9 million patients from March 1, 2018, to Dec. 31, 2019, before the virus began to spread across the globe.
The study included hospitalized and nonhospitalized COVID patients. The majority of the study population was male, but the study included almost 1.2 million female patients.
Compared with control persons, post-COVID patients’ increased risk of a GI diagnosis and the excess disease burden at 1 year, respectively, were as follows.
- 102% for cholangitis; 0.22 per 1,000 persons
- 62% for peptic ulcer disease; 1.57 per 1,000 persons
- 54% for irritable bowel syndrome; 0.44 per 1,000 persons
- 47% for acute gastritis; 0.47 per 1,000 persons
- 46% for acute pancreatitis; 0.6 per 1,000 persons
- 36% for functional dyspepsia; 0.63 per 1,000 persons
- 35% for gastroesophageal reflux disease; 15.5 per 1,000 persons
Patients who’d had the virus were also at higher risk for GI symptoms than their COVID-free peers. Their risk was 60% higher for constipation, 58% for diarrhea, 52% for vomiting, 46% for bloating, and 44% for abdominal pain, the investigators found.
The risk of developing GI symptoms increased with COVID-19 severity and was highest for those who received intensive care because of the virus, the researchers note.
Subgroup analyses found that the risks of composite gastrointestinal outcome were evident in all subgroups based on age, race, sex, obesity, smoking, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension, the authors write.
Disease burden rises
The increased numbers of GI patients with prior SARS-CoV-2 infection are altering the burden on the health care system, senior author Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a clinical epidemiologist at Washington University, St. Louis, said in an interview.
The shift may be pronounced in primary care, where GI concerns should be seen as a trigger for questions about prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, Dr. Al-Aly said.
Patients may encounter longer wait times at GI clinics or may give up on trying to schedule appointments if waits become too long, he said. They may also present to emergency departments if they can’t get an outpatient appointment, he added.
Simon C. Mathews, MD, assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology, Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization that he’s seeing increased wait times since COVID emerged.
“We know that the pandemic impacted patients’ ability and willingness to seek GI care. There continues to be a long backlog for patients who are only now getting reconnected to care. As a result, our clinics are busier than ever, and our wait times for appointments are unfortunately longer than we would like,” said Dr. Mathews, who was not involved in the research.
Abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation continue to be among the most common symptoms Dr. Mathews sees in clinic, he said.
Kyle Staller, MD, a Massachusetts General Brigham gastroenterologist, said in an interview that it’s important to distinguish symptoms from eventual diagnoses, which lag behind.
“Are patients attributing their symptoms to COVID, or is COVID itself creating a background of inflammation or changes in the nerves that are making these symptoms more common? My suspicion is a little bit of both,” said Dr. Staller, who is director of the Gastrointestinal Motility Laboratory at Mass General, Boston.
Although his clinic is seeing patients with the GI signs and symptoms listed in the article, “we’re not seeing as much of some of the diagnoses, like peptic ulcer disease and pancreatitis,” he said. “I wonder if those may be related to some of the consequences of being critically ill in general, rather than COVID specifically. Those diagnoses I would be more skeptical about.”
Duration of symptoms unclear
It’s hard to tell patients how long their GI symptoms might last after COVID, given the relatively short time researchers have had to study the virus, said Dr. Staller, who was not involved in the research.
The symptoms he’s seeing in patients after COVID mimic those of postinfectious IBS, which literature says could last for months or years, Dr. Staller said. “But they should improve over time,” he added.
Senior author Dr. Al-Aly agreed that the duration of post-COVID GI symptoms is unclear.
“What I can tell you is that even people who got SARS-CoV-2 infection from March 2020 are still coming back for GI problems,” he said.
Unlike other symptoms of long COVID, such as brain fog, gastroenterologists fortunately know how to treat the GI disorders that evolve from SARS-CoV-2 infection, said Dr. Al-Aly, who has studied the long-term effects of the virus on the brain, kidneys, heart, and other organs.
All health care providers “need to be thinking about COVID as a risk factor for all these diseases” and should ask patients about SARS-CoV-2 infection when they take their histories, he said.
The authors, Dr. Staller, and Dr. Mathews report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE COMMUNICATIONS
Add-on antipsychotic beats switching meds in older adults with resistant depression
NEW ORLEANS –
“We found that adding aripiprazole led to higher rates of depression remission and greater improvements in psychological well-being – which means how positive and satisfied patients felt – and this is good news,” study investigator Eric J. Lenze, MD, of the department of psychiatry, Washington University, St. Louis, said in a press statement.
“However, even that approach helped only about 30% of people in the study with treatment-resistant depression, underscoring the need to find and develop more effective treatments that can help more people,” he added.
The findings were presented here as part of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting, and published concurrently in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Need for safe treatment options
Treatment-resistant depression is common in older patients, but switching medications or adding other agents can be challenging. With higher rates of comorbidity and polypharmacy, treatment decisions in this patient population are more complex compared with those involving younger patients.
To compare the benefits of augmentation vs. drug-switching strategies, the researchers conducted a multicenter, two-step trial involving 619 patients with an average baseline age of 69 who had failed to respond to two courses of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Patients were randomly assigned to one of three groups. These included augmentation of existing antidepressant medication with either aripiprazole (n = 211) or the dopamine and norepinephrine–reuptake inhibitor bupropion (Wellbutrin, Zyban) (n = 206), or to taper off of their current antidepressant and switch to bupropion (n = 202).
After 10 weeks, patients’ psychological well-being was assessed via the National Institutes of Health Toolbox Positive Affect and General Life Satisfaction subscales. The researchers found patients in the aripiprazole and bupropion add-on groups improved by 4.83 points and 4.33 points, respectively. The bupropion switch group had a change of 2.04 points.
The difference between the aripiprazole augmentation group and the switch to bupropion group was significant (difference 2.79 points; P = .014). Other between-group differences were not significantly different.
Remission rates were similar in the aripiprazole and bupropion groups at 28.9% and 28.2%, respectively. The remission rate in the bupropion switch group was 19.3%.
The study results showed patients who received adjunctive bupropion had the highest fall rate at 0.55 falls per patient, vs. 0.33 falls per patient in the aripiprazole group, suggesting that among the three treatment options, adjunctive aripiprazole may be the best choice because of its superior efficacy and lower fall risk.
A total of 248 patients enrolled in the study showed no improvement and were further randomly assigned to receive adjunctive lithium (n = 127) or switch from current therapy to nortriptyline (n = 121).
Well-being scores in the lithium group improved by 3.17 points and 2.18 points in the nortriptyline group. Remission occurred in 18.9% of patients in the lithium group and 21.5% in the nortriptyline group. Fall rates were similar among the two groups.
Overall, “this large, randomized study demonstrated that adding aripiprazole was a superior option for older adults with treatment-resistant depression,” Dr. Lenze told this news organization.
“Since neither lithium nor nortriptyline were promising against treatment-resistant depression in older adults, those medications are unlikely to be helpful in most cases,” he added.
Practice changing?
In an accompanying editorial, Gemma Lewis, PhD, and Glyn Lewis, PhD, division of psychiatry, University of College London, noted the findings “support aripiprazole augmentation as a strategy for treatment-resistant depression in older persons, largely because of the lower risk of falls than with bupropion augmentation.”
However, “in clinical practice, [it] would be important to tailor treatment in light of potential adverse effects and the preferences of the patient,” they added.
Akathisia, for instance, is a common side effect of aripiprazole, shown in one recent trial to affect 11% of the patients. In addition, weight gain, though typically lower than seen with other antipsychotics, is a consideration with aripiprazole.
With respect to fall risk, they noted that bupropion was largely used in relatively high doses of 300 mg and 450 mg, despite some recent research showing little clinical benefit from increasing antidepressant doses above minimum recommendations.
“It is possible that smaller doses of bupropion than those used in the current trial would retain effectiveness while minimizing adverse effects such as falls,” the editorialists noted.
Commenting on the study, Jennifer R. Gatchel, MD, PhD, assistant psychiatrist at Massachusetts General Hospital/McLean Hospital and assistant professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said the findings have high clinical significance in the treatment of geriatric depression.
“These results are of great impact for clinicians managing older adults with treatment-resistant depression. They provide some of the first evidence of safety and efficacy of augmentation with aripiprazole as a strategy in clinical management of older adults who fail to initially respond to treatment,” said Dr. Gatchel, who was not associated with this research.
“Of particular significance, efficacy here is based on patient-centered outcomes and psychological well-being as a primary effectiveness outcome, which could translate into strengthened physician-patient alliance.”
While adjunctive aripiprazole is not necessarily a first-line strategy when older adults fail to respond to antidepressants, there is a lack of data on the risks and benefits of any other antipsychotic medications, she noted.
“Thus, this is evidence that will impact clinical practice and hopefully contribute to reduced societal burden of depression in older adults and the morbidity and mortality associated with it,” Dr. Gatchel said.
The study received support from a Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) Award (TRD-1511-33321). Dr. Lenze received additional support from the Taylor Family Institute for Innovative Psychiatric Research at Washington University School of Medicine, as well as the Washington University Institute of Clinical and Translational Sciences grant (UL1TR002345) from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Gatchel reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS –
“We found that adding aripiprazole led to higher rates of depression remission and greater improvements in psychological well-being – which means how positive and satisfied patients felt – and this is good news,” study investigator Eric J. Lenze, MD, of the department of psychiatry, Washington University, St. Louis, said in a press statement.
“However, even that approach helped only about 30% of people in the study with treatment-resistant depression, underscoring the need to find and develop more effective treatments that can help more people,” he added.
The findings were presented here as part of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting, and published concurrently in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Need for safe treatment options
Treatment-resistant depression is common in older patients, but switching medications or adding other agents can be challenging. With higher rates of comorbidity and polypharmacy, treatment decisions in this patient population are more complex compared with those involving younger patients.
To compare the benefits of augmentation vs. drug-switching strategies, the researchers conducted a multicenter, two-step trial involving 619 patients with an average baseline age of 69 who had failed to respond to two courses of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Patients were randomly assigned to one of three groups. These included augmentation of existing antidepressant medication with either aripiprazole (n = 211) or the dopamine and norepinephrine–reuptake inhibitor bupropion (Wellbutrin, Zyban) (n = 206), or to taper off of their current antidepressant and switch to bupropion (n = 202).
After 10 weeks, patients’ psychological well-being was assessed via the National Institutes of Health Toolbox Positive Affect and General Life Satisfaction subscales. The researchers found patients in the aripiprazole and bupropion add-on groups improved by 4.83 points and 4.33 points, respectively. The bupropion switch group had a change of 2.04 points.
The difference between the aripiprazole augmentation group and the switch to bupropion group was significant (difference 2.79 points; P = .014). Other between-group differences were not significantly different.
Remission rates were similar in the aripiprazole and bupropion groups at 28.9% and 28.2%, respectively. The remission rate in the bupropion switch group was 19.3%.
The study results showed patients who received adjunctive bupropion had the highest fall rate at 0.55 falls per patient, vs. 0.33 falls per patient in the aripiprazole group, suggesting that among the three treatment options, adjunctive aripiprazole may be the best choice because of its superior efficacy and lower fall risk.
A total of 248 patients enrolled in the study showed no improvement and were further randomly assigned to receive adjunctive lithium (n = 127) or switch from current therapy to nortriptyline (n = 121).
Well-being scores in the lithium group improved by 3.17 points and 2.18 points in the nortriptyline group. Remission occurred in 18.9% of patients in the lithium group and 21.5% in the nortriptyline group. Fall rates were similar among the two groups.
Overall, “this large, randomized study demonstrated that adding aripiprazole was a superior option for older adults with treatment-resistant depression,” Dr. Lenze told this news organization.
“Since neither lithium nor nortriptyline were promising against treatment-resistant depression in older adults, those medications are unlikely to be helpful in most cases,” he added.
Practice changing?
In an accompanying editorial, Gemma Lewis, PhD, and Glyn Lewis, PhD, division of psychiatry, University of College London, noted the findings “support aripiprazole augmentation as a strategy for treatment-resistant depression in older persons, largely because of the lower risk of falls than with bupropion augmentation.”
However, “in clinical practice, [it] would be important to tailor treatment in light of potential adverse effects and the preferences of the patient,” they added.
Akathisia, for instance, is a common side effect of aripiprazole, shown in one recent trial to affect 11% of the patients. In addition, weight gain, though typically lower than seen with other antipsychotics, is a consideration with aripiprazole.
With respect to fall risk, they noted that bupropion was largely used in relatively high doses of 300 mg and 450 mg, despite some recent research showing little clinical benefit from increasing antidepressant doses above minimum recommendations.
“It is possible that smaller doses of bupropion than those used in the current trial would retain effectiveness while minimizing adverse effects such as falls,” the editorialists noted.
Commenting on the study, Jennifer R. Gatchel, MD, PhD, assistant psychiatrist at Massachusetts General Hospital/McLean Hospital and assistant professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said the findings have high clinical significance in the treatment of geriatric depression.
“These results are of great impact for clinicians managing older adults with treatment-resistant depression. They provide some of the first evidence of safety and efficacy of augmentation with aripiprazole as a strategy in clinical management of older adults who fail to initially respond to treatment,” said Dr. Gatchel, who was not associated with this research.
“Of particular significance, efficacy here is based on patient-centered outcomes and psychological well-being as a primary effectiveness outcome, which could translate into strengthened physician-patient alliance.”
While adjunctive aripiprazole is not necessarily a first-line strategy when older adults fail to respond to antidepressants, there is a lack of data on the risks and benefits of any other antipsychotic medications, she noted.
“Thus, this is evidence that will impact clinical practice and hopefully contribute to reduced societal burden of depression in older adults and the morbidity and mortality associated with it,” Dr. Gatchel said.
The study received support from a Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) Award (TRD-1511-33321). Dr. Lenze received additional support from the Taylor Family Institute for Innovative Psychiatric Research at Washington University School of Medicine, as well as the Washington University Institute of Clinical and Translational Sciences grant (UL1TR002345) from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Gatchel reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS –
“We found that adding aripiprazole led to higher rates of depression remission and greater improvements in psychological well-being – which means how positive and satisfied patients felt – and this is good news,” study investigator Eric J. Lenze, MD, of the department of psychiatry, Washington University, St. Louis, said in a press statement.
“However, even that approach helped only about 30% of people in the study with treatment-resistant depression, underscoring the need to find and develop more effective treatments that can help more people,” he added.
The findings were presented here as part of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry annual meeting, and published concurrently in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Need for safe treatment options
Treatment-resistant depression is common in older patients, but switching medications or adding other agents can be challenging. With higher rates of comorbidity and polypharmacy, treatment decisions in this patient population are more complex compared with those involving younger patients.
To compare the benefits of augmentation vs. drug-switching strategies, the researchers conducted a multicenter, two-step trial involving 619 patients with an average baseline age of 69 who had failed to respond to two courses of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Patients were randomly assigned to one of three groups. These included augmentation of existing antidepressant medication with either aripiprazole (n = 211) or the dopamine and norepinephrine–reuptake inhibitor bupropion (Wellbutrin, Zyban) (n = 206), or to taper off of their current antidepressant and switch to bupropion (n = 202).
After 10 weeks, patients’ psychological well-being was assessed via the National Institutes of Health Toolbox Positive Affect and General Life Satisfaction subscales. The researchers found patients in the aripiprazole and bupropion add-on groups improved by 4.83 points and 4.33 points, respectively. The bupropion switch group had a change of 2.04 points.
The difference between the aripiprazole augmentation group and the switch to bupropion group was significant (difference 2.79 points; P = .014). Other between-group differences were not significantly different.
Remission rates were similar in the aripiprazole and bupropion groups at 28.9% and 28.2%, respectively. The remission rate in the bupropion switch group was 19.3%.
The study results showed patients who received adjunctive bupropion had the highest fall rate at 0.55 falls per patient, vs. 0.33 falls per patient in the aripiprazole group, suggesting that among the three treatment options, adjunctive aripiprazole may be the best choice because of its superior efficacy and lower fall risk.
A total of 248 patients enrolled in the study showed no improvement and were further randomly assigned to receive adjunctive lithium (n = 127) or switch from current therapy to nortriptyline (n = 121).
Well-being scores in the lithium group improved by 3.17 points and 2.18 points in the nortriptyline group. Remission occurred in 18.9% of patients in the lithium group and 21.5% in the nortriptyline group. Fall rates were similar among the two groups.
Overall, “this large, randomized study demonstrated that adding aripiprazole was a superior option for older adults with treatment-resistant depression,” Dr. Lenze told this news organization.
“Since neither lithium nor nortriptyline were promising against treatment-resistant depression in older adults, those medications are unlikely to be helpful in most cases,” he added.
Practice changing?
In an accompanying editorial, Gemma Lewis, PhD, and Glyn Lewis, PhD, division of psychiatry, University of College London, noted the findings “support aripiprazole augmentation as a strategy for treatment-resistant depression in older persons, largely because of the lower risk of falls than with bupropion augmentation.”
However, “in clinical practice, [it] would be important to tailor treatment in light of potential adverse effects and the preferences of the patient,” they added.
Akathisia, for instance, is a common side effect of aripiprazole, shown in one recent trial to affect 11% of the patients. In addition, weight gain, though typically lower than seen with other antipsychotics, is a consideration with aripiprazole.
With respect to fall risk, they noted that bupropion was largely used in relatively high doses of 300 mg and 450 mg, despite some recent research showing little clinical benefit from increasing antidepressant doses above minimum recommendations.
“It is possible that smaller doses of bupropion than those used in the current trial would retain effectiveness while minimizing adverse effects such as falls,” the editorialists noted.
Commenting on the study, Jennifer R. Gatchel, MD, PhD, assistant psychiatrist at Massachusetts General Hospital/McLean Hospital and assistant professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said the findings have high clinical significance in the treatment of geriatric depression.
“These results are of great impact for clinicians managing older adults with treatment-resistant depression. They provide some of the first evidence of safety and efficacy of augmentation with aripiprazole as a strategy in clinical management of older adults who fail to initially respond to treatment,” said Dr. Gatchel, who was not associated with this research.
“Of particular significance, efficacy here is based on patient-centered outcomes and psychological well-being as a primary effectiveness outcome, which could translate into strengthened physician-patient alliance.”
While adjunctive aripiprazole is not necessarily a first-line strategy when older adults fail to respond to antidepressants, there is a lack of data on the risks and benefits of any other antipsychotic medications, she noted.
“Thus, this is evidence that will impact clinical practice and hopefully contribute to reduced societal burden of depression in older adults and the morbidity and mortality associated with it,” Dr. Gatchel said.
The study received support from a Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) Award (TRD-1511-33321). Dr. Lenze received additional support from the Taylor Family Institute for Innovative Psychiatric Research at Washington University School of Medicine, as well as the Washington University Institute of Clinical and Translational Sciences grant (UL1TR002345) from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Gatchel reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAGP 2023
Factors linked with increased VTE risk in COVID outpatients
Though VTE risk is well studied and significant in those hospitalized with COVID, little is known about the risk in the outpatient setting, said the authors of the new research published online in JAMA Network Open.
The study was conducted at two integrated health care delivery systems in northern and southern California. Data were gathered from the Kaiser Permanente Virtual Data Warehouse and electronic health records.
Nearly 400,000 patients studied
Researchers, led by Margaret Fang, MD, with the division of hospital medicine, University of California, San Francisco, identified 398,530 outpatients with COVID-19 from Jan. 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2021.
VTE risk was low overall for ambulatory COVID patients.
“It is a reassuring study,” Dr. Fang said in an interview.
The researchers found that the risk is highest in the first 30 days after COVID-19 diagnosis (unadjusted rate, 0.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.67 per 100 person-years vs. 0.09; 95% CI, 0.08-0.11 per 100 person-years after 30 days).
Factors linked with high VTE risk
They also found that several factors were linked with a higher risk of blood clots in the study population, including being at least 55 years old; being male; having a history of blood clots or thrombophilia; and a body mass index (BMI) of at least 30 kg/m2.
The authors write, “These findings may help identify subsets of patients with COVID-19 who could benefit from VTE preventive strategies and more intensive short-term surveillance.”
Are routine anticoagulants justified?
Previously, randomized clinical trials have found that hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19 may benefit from therapeutically dosed heparin anticoagulants but that therapeutic anticoagulation had no net benefit – and perhaps could even harm – patients who were critically ill with COVID.
“[M]uch less is known about the optimal thromboprophylaxis strategy for people with milder presentations of COVID-19 who do not require hospitalization,” they write.
Mild COVID VTE risk similar to general population
The authors note that rates of blood clots linked with COVID-19 are not much higher than the average blood clot rate in the general population, which is about 0.1-0.2 per 100 person-years.
Therefore, the results don’t justify routine administration of anticoagulation given the costs, inconvenience, and bleeding risks, they acknowledge.
Dr. Fang told this publication that it’s hard to know what to tell patients, given the overall low VTE risk. She said their study wasn’t designed to advise when to give prophylaxis.
Physicians should inform patients of their higher risk
“We should tell our patients who fall into these risk categories that blood clot is a concern after the development of COVID, especially in those first 30 days. And some people might benefit from increased surveillance,” Dr. Fang said.
”I think this study would support ongoing studies that look at whether selected patients benefit from VTE prophylaxis, for example low-dose anticoagulants,” she said.
Dr. Fang said the subgroup factors they found increased risk of blood clots for all patients, not just COVID-19 patients. It’s not clear why factors such as being male may increase blood clot risk, though that is consistent with previous literature, but higher risk with higher BMI might be related to a combination of inflammation or decreased mobility, she said.
Unanswered questions
Robert H. Hopkins Jr., MD, says the study helps answer a couple of important questions – that the VTE risk in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients is low and when and for which patients risk may be highest.
However, there are several unanswered questions that argue against routine initiation of anticoagulants, notes the professor of internal medicine and pediatrics chief, division of general internal medicine, at University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock.
One is the change in the COVID variant landscape.
“We do not know whether rates of VTE are same or lower or higher with current circulating variants,” Dr. Hopkins said.
The authors acknowledge this as a limitation. Study data predate Omicron and subvariants, which appear to lower clinical severity, so it’s unclear whether VTE risk is different in this Omicron era.
Dr. Hopkins added another unknown: “We do not know whether vaccination affects rates of VTE in ambulatory breakthrough infection.”
Dr. Hopkins and the authors also note the lack of a control group in the study, to better compare risk.
Coauthor Dr. Prasad reports consultant fees from EpiExcellence LLC outside the submitted work. Coauthor Dr. Go reports grants paid to the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, from CSL Behring, Novartis, Bristol Meyers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance, and Janssen outside the submitted work.
The research was funded through Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
Dr. Hopkins reports no relevant financial relationships.
Though VTE risk is well studied and significant in those hospitalized with COVID, little is known about the risk in the outpatient setting, said the authors of the new research published online in JAMA Network Open.
The study was conducted at two integrated health care delivery systems in northern and southern California. Data were gathered from the Kaiser Permanente Virtual Data Warehouse and electronic health records.
Nearly 400,000 patients studied
Researchers, led by Margaret Fang, MD, with the division of hospital medicine, University of California, San Francisco, identified 398,530 outpatients with COVID-19 from Jan. 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2021.
VTE risk was low overall for ambulatory COVID patients.
“It is a reassuring study,” Dr. Fang said in an interview.
The researchers found that the risk is highest in the first 30 days after COVID-19 diagnosis (unadjusted rate, 0.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.67 per 100 person-years vs. 0.09; 95% CI, 0.08-0.11 per 100 person-years after 30 days).
Factors linked with high VTE risk
They also found that several factors were linked with a higher risk of blood clots in the study population, including being at least 55 years old; being male; having a history of blood clots or thrombophilia; and a body mass index (BMI) of at least 30 kg/m2.
The authors write, “These findings may help identify subsets of patients with COVID-19 who could benefit from VTE preventive strategies and more intensive short-term surveillance.”
Are routine anticoagulants justified?
Previously, randomized clinical trials have found that hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19 may benefit from therapeutically dosed heparin anticoagulants but that therapeutic anticoagulation had no net benefit – and perhaps could even harm – patients who were critically ill with COVID.
“[M]uch less is known about the optimal thromboprophylaxis strategy for people with milder presentations of COVID-19 who do not require hospitalization,” they write.
Mild COVID VTE risk similar to general population
The authors note that rates of blood clots linked with COVID-19 are not much higher than the average blood clot rate in the general population, which is about 0.1-0.2 per 100 person-years.
Therefore, the results don’t justify routine administration of anticoagulation given the costs, inconvenience, and bleeding risks, they acknowledge.
Dr. Fang told this publication that it’s hard to know what to tell patients, given the overall low VTE risk. She said their study wasn’t designed to advise when to give prophylaxis.
Physicians should inform patients of their higher risk
“We should tell our patients who fall into these risk categories that blood clot is a concern after the development of COVID, especially in those first 30 days. And some people might benefit from increased surveillance,” Dr. Fang said.
”I think this study would support ongoing studies that look at whether selected patients benefit from VTE prophylaxis, for example low-dose anticoagulants,” she said.
Dr. Fang said the subgroup factors they found increased risk of blood clots for all patients, not just COVID-19 patients. It’s not clear why factors such as being male may increase blood clot risk, though that is consistent with previous literature, but higher risk with higher BMI might be related to a combination of inflammation or decreased mobility, she said.
Unanswered questions
Robert H. Hopkins Jr., MD, says the study helps answer a couple of important questions – that the VTE risk in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients is low and when and for which patients risk may be highest.
However, there are several unanswered questions that argue against routine initiation of anticoagulants, notes the professor of internal medicine and pediatrics chief, division of general internal medicine, at University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock.
One is the change in the COVID variant landscape.
“We do not know whether rates of VTE are same or lower or higher with current circulating variants,” Dr. Hopkins said.
The authors acknowledge this as a limitation. Study data predate Omicron and subvariants, which appear to lower clinical severity, so it’s unclear whether VTE risk is different in this Omicron era.
Dr. Hopkins added another unknown: “We do not know whether vaccination affects rates of VTE in ambulatory breakthrough infection.”
Dr. Hopkins and the authors also note the lack of a control group in the study, to better compare risk.
Coauthor Dr. Prasad reports consultant fees from EpiExcellence LLC outside the submitted work. Coauthor Dr. Go reports grants paid to the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, from CSL Behring, Novartis, Bristol Meyers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance, and Janssen outside the submitted work.
The research was funded through Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
Dr. Hopkins reports no relevant financial relationships.
Though VTE risk is well studied and significant in those hospitalized with COVID, little is known about the risk in the outpatient setting, said the authors of the new research published online in JAMA Network Open.
The study was conducted at two integrated health care delivery systems in northern and southern California. Data were gathered from the Kaiser Permanente Virtual Data Warehouse and electronic health records.
Nearly 400,000 patients studied
Researchers, led by Margaret Fang, MD, with the division of hospital medicine, University of California, San Francisco, identified 398,530 outpatients with COVID-19 from Jan. 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2021.
VTE risk was low overall for ambulatory COVID patients.
“It is a reassuring study,” Dr. Fang said in an interview.
The researchers found that the risk is highest in the first 30 days after COVID-19 diagnosis (unadjusted rate, 0.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.67 per 100 person-years vs. 0.09; 95% CI, 0.08-0.11 per 100 person-years after 30 days).
Factors linked with high VTE risk
They also found that several factors were linked with a higher risk of blood clots in the study population, including being at least 55 years old; being male; having a history of blood clots or thrombophilia; and a body mass index (BMI) of at least 30 kg/m2.
The authors write, “These findings may help identify subsets of patients with COVID-19 who could benefit from VTE preventive strategies and more intensive short-term surveillance.”
Are routine anticoagulants justified?
Previously, randomized clinical trials have found that hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19 may benefit from therapeutically dosed heparin anticoagulants but that therapeutic anticoagulation had no net benefit – and perhaps could even harm – patients who were critically ill with COVID.
“[M]uch less is known about the optimal thromboprophylaxis strategy for people with milder presentations of COVID-19 who do not require hospitalization,” they write.
Mild COVID VTE risk similar to general population
The authors note that rates of blood clots linked with COVID-19 are not much higher than the average blood clot rate in the general population, which is about 0.1-0.2 per 100 person-years.
Therefore, the results don’t justify routine administration of anticoagulation given the costs, inconvenience, and bleeding risks, they acknowledge.
Dr. Fang told this publication that it’s hard to know what to tell patients, given the overall low VTE risk. She said their study wasn’t designed to advise when to give prophylaxis.
Physicians should inform patients of their higher risk
“We should tell our patients who fall into these risk categories that blood clot is a concern after the development of COVID, especially in those first 30 days. And some people might benefit from increased surveillance,” Dr. Fang said.
”I think this study would support ongoing studies that look at whether selected patients benefit from VTE prophylaxis, for example low-dose anticoagulants,” she said.
Dr. Fang said the subgroup factors they found increased risk of blood clots for all patients, not just COVID-19 patients. It’s not clear why factors such as being male may increase blood clot risk, though that is consistent with previous literature, but higher risk with higher BMI might be related to a combination of inflammation or decreased mobility, she said.
Unanswered questions
Robert H. Hopkins Jr., MD, says the study helps answer a couple of important questions – that the VTE risk in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients is low and when and for which patients risk may be highest.
However, there are several unanswered questions that argue against routine initiation of anticoagulants, notes the professor of internal medicine and pediatrics chief, division of general internal medicine, at University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock.
One is the change in the COVID variant landscape.
“We do not know whether rates of VTE are same or lower or higher with current circulating variants,” Dr. Hopkins said.
The authors acknowledge this as a limitation. Study data predate Omicron and subvariants, which appear to lower clinical severity, so it’s unclear whether VTE risk is different in this Omicron era.
Dr. Hopkins added another unknown: “We do not know whether vaccination affects rates of VTE in ambulatory breakthrough infection.”
Dr. Hopkins and the authors also note the lack of a control group in the study, to better compare risk.
Coauthor Dr. Prasad reports consultant fees from EpiExcellence LLC outside the submitted work. Coauthor Dr. Go reports grants paid to the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, from CSL Behring, Novartis, Bristol Meyers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance, and Janssen outside the submitted work.
The research was funded through Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
Dr. Hopkins reports no relevant financial relationships.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Can particles in dairy and beef cause cancer and MS?
In Western diets, dairy and beef are ubiquitous: Milk goes with coffee, melted cheese with pizza, and chili with rice. But what if dairy products and beef contained a new kind of pathogen that could infect you as a child and trigger cancer or multiple sclerosis (MS) 40-70 years later?
However, in two joint statements, the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR) and the Max Rubner Institute (MRI) have rejected such theories.
In 2008, Harald zur Hausen, MD, DSc, received the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his discovery that human papillomaviruses cause cervical cancer. His starting point was the observation that sexually abstinent women, such as nuns, rarely develop this cancer. So it was possible to draw the conclusion that pathogens are transmitted during sexual intercourse, explain Dr. zur Hausen and his wife Ethel-Michele de Villiers, PhD, both of DKFZ Heidelberg.
Papillomaviruses, as well as human herpes and Epstein-Barr viruses (EBV), polyomaviruses, and retroviruses, cause cancer in a direct way: by inserting their genes into the DNA of human cells. With a latency of a few years to a few decades, the proteins formed through expression stimulate malignant growth by altering the regulating host gene.
Acid radicals
However, viruses – just like bacteria and parasites – can also indirectly trigger cancer. One mechanism for this triggering is the disruption of immune defenses, as shown by the sometimes drastically increased tumor incidence with AIDS or with immunosuppressants after transplants. Chronic inflammation is a second mechanism that generates acid radicals and thereby causes random mutations in replicating cells. Examples include stomach cancer caused by Helicobacter pylori and liver cancer caused by Schistosoma, liver fluke, and hepatitis B and C viruses.
According to Dr. de Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen, there are good reasons to believe that other pathogens could cause chronic inflammation and thereby lead to cancer. Epidemiologic data suggest that dairy and meat products from European cows (Bos taurus) are a potential source. This is because colon cancer and breast cancer commonly occur in places where these foods are heavily consumed (that is, in North America, Argentina, Europe, and Australia). In contrast, the rate is low in India, where cows are revered as holy animals. Also noteworthy is that women with a lactose intolerance rarely develop breast cancer.
Viral progeny
In fact, the researchers found single-stranded DNA rings that originated in viruses, which they named bovine meat and milk factors (BMMF), in the intestines of patients with colon cancer. They reported, “This new class of pathogen deserves, in our opinion at least, to become the focus of cancer development and further chronic diseases.” They also detected elevated levels of acid radicals in these areas (that is, oxidative stress), which is typical for chronic inflammation.
The researchers assume that infants, whose immune system is not yet fully matured, ingest the BMMF as soon as they have dairy. Therefore, there is no need for adults to avoid dairy or beef because everyone is infected anyway, said Dr. zur Hausen.
‘Breast milk is healthy’
Dr. De Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen outlined more evidence of cancer-triggering pathogens. Mothers who have breastfed are less likely, especially after multiple pregnancies, to develop tumors in various organs or to have MS and type 2 diabetes. The authors attribute the protective effect to oligosaccharides in breast milk, which begin to be formed midway through the pregnancy. They bind to lectin receptors and, in so doing, mask the terminal molecule onto which the viruses need to dock. As a result, their port of entry into the cells is blocked.
The oligosaccharides also protect the baby against life-threatening infections by blocking access by rotaviruses and noroviruses. In this way, especially if breastfeeding lasts a long time – around 1 year – the period of incomplete immunocompetence is bridged.
Colon cancer
To date, it has been assumed that around 20% of all cancerous diseases globally are caused by infections, said the researchers. But if the suspected BMMF cases are included, this figure rises to 50%, even to around 80%, for colon cancer. If the suspicion is confirmed, the consequences for prevention and therapy would be significant.
The voice of a Nobel prize winner undoubtedly carries weight, but at the time, Dr. zur Hausen still had to convince a host of skeptics with his discovery that a viral infection is a major cause of cervical cancer. Nonetheless, some indicators suggest that he and his wife have found a dead end this time.
Institutional skepticism
When his working group made the results public in February 2019, the DKFZ felt the need to give an all-clear signal in response to alarmed press reports. There is no reason to see dairy and meat consumption as something negative. Similarly, in their first joint statement, the BfR and the MRI judged the data to be insufficient and called for further studies. Multiple research teams began to focus on BMMF as a result. In what foods can they be found? Are they more common in patients with cancer than in healthy people? Are they infectious? Do they cause inflammation and cancer?
The findings presented in a second statement by the BfR and MRI at the end of November 2022 contradicted the claims made by the DKFZ scientists across the board. In no way do BMMF represent new pathogens. They are variants of already known DNA sequences. In addition, they are present in numerous animal-based and plant-based foods, including pork, fish, fruit, vegetables, and nuts.
BMMF do not possess the ability to infect human cells, the institutes said. The proof that they are damaging to one’s health was also absent. It is true that the incidence of intestinal tumors correlates positively with the consumption of red and processed meat – which in no way signifies causality – but dairy products are linked to a reduced risk. On the other hand, breast cancer cannot be associated with the consumption of beef or dairy.
Therefore, both institutes recommend continuing to use these products as supplementary diet for infants because of their micronutrients. They further stated that the products are safe for people of all ages.
Association with MS?
Unperturbed, Dr. de Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen went one step further in their current article. They posited that MS is also associated with the consumption of dairy products and beef. Here too geographic distribution prompted the idea to look for BMMF in the brain lesions of patients with MS. The researchers isolated ring-shaped DNA molecules that proved to be closely related to BMMF from dairy and cattle blood. “The result was electrifying for us.”
However, there are several other factors to consider, such as vitamin D3 deficiency. This is because the incidence of MS decreases the further you travel from the poles toward the equator (that is, as solar radiation increases). Also, EBV clearly plays a role because patients with MS display increased titers of EBV antibodies. One study also showed that people in Antarctica excreted reactivated EBV in their saliva during winter and that vitamin D3 stopped the viral secretion.
Under these conditions, the researchers hypothesized that MS is caused by a double infection of brain cells by EBV and BMMF. EBV is reactivated by a lack of vitamin D3, and the BMMF multiply and are eventually converted into proteins. A focal immunoreaction causes the Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes to malfunction, which leads to the destruction of the myelin sheaths around the nerve fibers.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
In Western diets, dairy and beef are ubiquitous: Milk goes with coffee, melted cheese with pizza, and chili with rice. But what if dairy products and beef contained a new kind of pathogen that could infect you as a child and trigger cancer or multiple sclerosis (MS) 40-70 years later?
However, in two joint statements, the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR) and the Max Rubner Institute (MRI) have rejected such theories.
In 2008, Harald zur Hausen, MD, DSc, received the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his discovery that human papillomaviruses cause cervical cancer. His starting point was the observation that sexually abstinent women, such as nuns, rarely develop this cancer. So it was possible to draw the conclusion that pathogens are transmitted during sexual intercourse, explain Dr. zur Hausen and his wife Ethel-Michele de Villiers, PhD, both of DKFZ Heidelberg.
Papillomaviruses, as well as human herpes and Epstein-Barr viruses (EBV), polyomaviruses, and retroviruses, cause cancer in a direct way: by inserting their genes into the DNA of human cells. With a latency of a few years to a few decades, the proteins formed through expression stimulate malignant growth by altering the regulating host gene.
Acid radicals
However, viruses – just like bacteria and parasites – can also indirectly trigger cancer. One mechanism for this triggering is the disruption of immune defenses, as shown by the sometimes drastically increased tumor incidence with AIDS or with immunosuppressants after transplants. Chronic inflammation is a second mechanism that generates acid radicals and thereby causes random mutations in replicating cells. Examples include stomach cancer caused by Helicobacter pylori and liver cancer caused by Schistosoma, liver fluke, and hepatitis B and C viruses.
According to Dr. de Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen, there are good reasons to believe that other pathogens could cause chronic inflammation and thereby lead to cancer. Epidemiologic data suggest that dairy and meat products from European cows (Bos taurus) are a potential source. This is because colon cancer and breast cancer commonly occur in places where these foods are heavily consumed (that is, in North America, Argentina, Europe, and Australia). In contrast, the rate is low in India, where cows are revered as holy animals. Also noteworthy is that women with a lactose intolerance rarely develop breast cancer.
Viral progeny
In fact, the researchers found single-stranded DNA rings that originated in viruses, which they named bovine meat and milk factors (BMMF), in the intestines of patients with colon cancer. They reported, “This new class of pathogen deserves, in our opinion at least, to become the focus of cancer development and further chronic diseases.” They also detected elevated levels of acid radicals in these areas (that is, oxidative stress), which is typical for chronic inflammation.
The researchers assume that infants, whose immune system is not yet fully matured, ingest the BMMF as soon as they have dairy. Therefore, there is no need for adults to avoid dairy or beef because everyone is infected anyway, said Dr. zur Hausen.
‘Breast milk is healthy’
Dr. De Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen outlined more evidence of cancer-triggering pathogens. Mothers who have breastfed are less likely, especially after multiple pregnancies, to develop tumors in various organs or to have MS and type 2 diabetes. The authors attribute the protective effect to oligosaccharides in breast milk, which begin to be formed midway through the pregnancy. They bind to lectin receptors and, in so doing, mask the terminal molecule onto which the viruses need to dock. As a result, their port of entry into the cells is blocked.
The oligosaccharides also protect the baby against life-threatening infections by blocking access by rotaviruses and noroviruses. In this way, especially if breastfeeding lasts a long time – around 1 year – the period of incomplete immunocompetence is bridged.
Colon cancer
To date, it has been assumed that around 20% of all cancerous diseases globally are caused by infections, said the researchers. But if the suspected BMMF cases are included, this figure rises to 50%, even to around 80%, for colon cancer. If the suspicion is confirmed, the consequences for prevention and therapy would be significant.
The voice of a Nobel prize winner undoubtedly carries weight, but at the time, Dr. zur Hausen still had to convince a host of skeptics with his discovery that a viral infection is a major cause of cervical cancer. Nonetheless, some indicators suggest that he and his wife have found a dead end this time.
Institutional skepticism
When his working group made the results public in February 2019, the DKFZ felt the need to give an all-clear signal in response to alarmed press reports. There is no reason to see dairy and meat consumption as something negative. Similarly, in their first joint statement, the BfR and the MRI judged the data to be insufficient and called for further studies. Multiple research teams began to focus on BMMF as a result. In what foods can they be found? Are they more common in patients with cancer than in healthy people? Are they infectious? Do they cause inflammation and cancer?
The findings presented in a second statement by the BfR and MRI at the end of November 2022 contradicted the claims made by the DKFZ scientists across the board. In no way do BMMF represent new pathogens. They are variants of already known DNA sequences. In addition, they are present in numerous animal-based and plant-based foods, including pork, fish, fruit, vegetables, and nuts.
BMMF do not possess the ability to infect human cells, the institutes said. The proof that they are damaging to one’s health was also absent. It is true that the incidence of intestinal tumors correlates positively with the consumption of red and processed meat – which in no way signifies causality – but dairy products are linked to a reduced risk. On the other hand, breast cancer cannot be associated with the consumption of beef or dairy.
Therefore, both institutes recommend continuing to use these products as supplementary diet for infants because of their micronutrients. They further stated that the products are safe for people of all ages.
Association with MS?
Unperturbed, Dr. de Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen went one step further in their current article. They posited that MS is also associated with the consumption of dairy products and beef. Here too geographic distribution prompted the idea to look for BMMF in the brain lesions of patients with MS. The researchers isolated ring-shaped DNA molecules that proved to be closely related to BMMF from dairy and cattle blood. “The result was electrifying for us.”
However, there are several other factors to consider, such as vitamin D3 deficiency. This is because the incidence of MS decreases the further you travel from the poles toward the equator (that is, as solar radiation increases). Also, EBV clearly plays a role because patients with MS display increased titers of EBV antibodies. One study also showed that people in Antarctica excreted reactivated EBV in their saliva during winter and that vitamin D3 stopped the viral secretion.
Under these conditions, the researchers hypothesized that MS is caused by a double infection of brain cells by EBV and BMMF. EBV is reactivated by a lack of vitamin D3, and the BMMF multiply and are eventually converted into proteins. A focal immunoreaction causes the Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes to malfunction, which leads to the destruction of the myelin sheaths around the nerve fibers.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
In Western diets, dairy and beef are ubiquitous: Milk goes with coffee, melted cheese with pizza, and chili with rice. But what if dairy products and beef contained a new kind of pathogen that could infect you as a child and trigger cancer or multiple sclerosis (MS) 40-70 years later?
However, in two joint statements, the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR) and the Max Rubner Institute (MRI) have rejected such theories.
In 2008, Harald zur Hausen, MD, DSc, received the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his discovery that human papillomaviruses cause cervical cancer. His starting point was the observation that sexually abstinent women, such as nuns, rarely develop this cancer. So it was possible to draw the conclusion that pathogens are transmitted during sexual intercourse, explain Dr. zur Hausen and his wife Ethel-Michele de Villiers, PhD, both of DKFZ Heidelberg.
Papillomaviruses, as well as human herpes and Epstein-Barr viruses (EBV), polyomaviruses, and retroviruses, cause cancer in a direct way: by inserting their genes into the DNA of human cells. With a latency of a few years to a few decades, the proteins formed through expression stimulate malignant growth by altering the regulating host gene.
Acid radicals
However, viruses – just like bacteria and parasites – can also indirectly trigger cancer. One mechanism for this triggering is the disruption of immune defenses, as shown by the sometimes drastically increased tumor incidence with AIDS or with immunosuppressants after transplants. Chronic inflammation is a second mechanism that generates acid radicals and thereby causes random mutations in replicating cells. Examples include stomach cancer caused by Helicobacter pylori and liver cancer caused by Schistosoma, liver fluke, and hepatitis B and C viruses.
According to Dr. de Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen, there are good reasons to believe that other pathogens could cause chronic inflammation and thereby lead to cancer. Epidemiologic data suggest that dairy and meat products from European cows (Bos taurus) are a potential source. This is because colon cancer and breast cancer commonly occur in places where these foods are heavily consumed (that is, in North America, Argentina, Europe, and Australia). In contrast, the rate is low in India, where cows are revered as holy animals. Also noteworthy is that women with a lactose intolerance rarely develop breast cancer.
Viral progeny
In fact, the researchers found single-stranded DNA rings that originated in viruses, which they named bovine meat and milk factors (BMMF), in the intestines of patients with colon cancer. They reported, “This new class of pathogen deserves, in our opinion at least, to become the focus of cancer development and further chronic diseases.” They also detected elevated levels of acid radicals in these areas (that is, oxidative stress), which is typical for chronic inflammation.
The researchers assume that infants, whose immune system is not yet fully matured, ingest the BMMF as soon as they have dairy. Therefore, there is no need for adults to avoid dairy or beef because everyone is infected anyway, said Dr. zur Hausen.
‘Breast milk is healthy’
Dr. De Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen outlined more evidence of cancer-triggering pathogens. Mothers who have breastfed are less likely, especially after multiple pregnancies, to develop tumors in various organs or to have MS and type 2 diabetes. The authors attribute the protective effect to oligosaccharides in breast milk, which begin to be formed midway through the pregnancy. They bind to lectin receptors and, in so doing, mask the terminal molecule onto which the viruses need to dock. As a result, their port of entry into the cells is blocked.
The oligosaccharides also protect the baby against life-threatening infections by blocking access by rotaviruses and noroviruses. In this way, especially if breastfeeding lasts a long time – around 1 year – the period of incomplete immunocompetence is bridged.
Colon cancer
To date, it has been assumed that around 20% of all cancerous diseases globally are caused by infections, said the researchers. But if the suspected BMMF cases are included, this figure rises to 50%, even to around 80%, for colon cancer. If the suspicion is confirmed, the consequences for prevention and therapy would be significant.
The voice of a Nobel prize winner undoubtedly carries weight, but at the time, Dr. zur Hausen still had to convince a host of skeptics with his discovery that a viral infection is a major cause of cervical cancer. Nonetheless, some indicators suggest that he and his wife have found a dead end this time.
Institutional skepticism
When his working group made the results public in February 2019, the DKFZ felt the need to give an all-clear signal in response to alarmed press reports. There is no reason to see dairy and meat consumption as something negative. Similarly, in their first joint statement, the BfR and the MRI judged the data to be insufficient and called for further studies. Multiple research teams began to focus on BMMF as a result. In what foods can they be found? Are they more common in patients with cancer than in healthy people? Are they infectious? Do they cause inflammation and cancer?
The findings presented in a second statement by the BfR and MRI at the end of November 2022 contradicted the claims made by the DKFZ scientists across the board. In no way do BMMF represent new pathogens. They are variants of already known DNA sequences. In addition, they are present in numerous animal-based and plant-based foods, including pork, fish, fruit, vegetables, and nuts.
BMMF do not possess the ability to infect human cells, the institutes said. The proof that they are damaging to one’s health was also absent. It is true that the incidence of intestinal tumors correlates positively with the consumption of red and processed meat – which in no way signifies causality – but dairy products are linked to a reduced risk. On the other hand, breast cancer cannot be associated with the consumption of beef or dairy.
Therefore, both institutes recommend continuing to use these products as supplementary diet for infants because of their micronutrients. They further stated that the products are safe for people of all ages.
Association with MS?
Unperturbed, Dr. de Villiers and Dr. zur Hausen went one step further in their current article. They posited that MS is also associated with the consumption of dairy products and beef. Here too geographic distribution prompted the idea to look for BMMF in the brain lesions of patients with MS. The researchers isolated ring-shaped DNA molecules that proved to be closely related to BMMF from dairy and cattle blood. “The result was electrifying for us.”
However, there are several other factors to consider, such as vitamin D3 deficiency. This is because the incidence of MS decreases the further you travel from the poles toward the equator (that is, as solar radiation increases). Also, EBV clearly plays a role because patients with MS display increased titers of EBV antibodies. One study also showed that people in Antarctica excreted reactivated EBV in their saliva during winter and that vitamin D3 stopped the viral secretion.
Under these conditions, the researchers hypothesized that MS is caused by a double infection of brain cells by EBV and BMMF. EBV is reactivated by a lack of vitamin D3, and the BMMF multiply and are eventually converted into proteins. A focal immunoreaction causes the Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes to malfunction, which leads to the destruction of the myelin sheaths around the nerve fibers.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Two diets tied to lower Alzheimer’s pathology at autopsy
In a cohort of deceased older adults, those who had adhered to the Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) and Mediterranean diets for nearly a decade before death had less global Alzheimer’s disease–related pathology, primarily less beta-amyloid, at autopsy.
Those who most closely followed these diets had almost 40% lower odds of having an Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis at death. The findings offer one mechanism by which healthy diets protect cognition.
“While our research doesn’t prove that a healthy diet resulted in fewer brain deposits of amyloid plaques ... we know there is a relationship, and following the MIND and Mediterranean diets may be one way that people can improve their brain health and protect cognition as they age,” study investigator Puja Agarwal, PhD, of RUSH University Medical Center in Chicago, said in a statement.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Green leafy veggies key
The MIND diet was pioneered by the late Martha Clare Morris, ScD, a Rush nutritional epidemiologist, who died of cancer in 2020 at age 64.
Although similar, the Mediterranean diet recommends vegetables, fruit, and three or more servings of fish per week, whereas the MIND diet prioritizes green leafy vegetables, such as spinach, kale, and collard greens, along with other vegetables. The MIND diet also prioritizes berries over other fruit and recommends one or more servings of fish per week. Both diets recommend small amounts of wine.
The current study focused on 581 older adults who died while participating in the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP). All participants agreed to undergo annual clinical evaluations and brain autopsy after death.
Participants completed annual food frequency questionnaires beginning at a mean age of 84. The mean age at death was 91. Mean follow-up was 6.8 years.
Around the time of death, 224 participants (39%) had a diagnosis of clinical dementia, and 383 participants (66%) had a pathologic Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis at time of death.
The researchers used a series of regression analyses to investigate the MIND and Mediterranean diets and dietary components associated with Alzheimer’s disease pathology. They controlled for age at death, sex, education, APO-epsilon 4 status, and total calories.
Overall, both diets were significantly associated with lower global Alzheimer’s disease pathology (MIND: beta = –0.022, P = .034; and Mediterranean: beta = –0.007, P = .039) – specifically, with less beta-amyloid (MIND: beta = –0.068, P = .050; and Mediterranean: beta = –0.040, P = .004).
The findings persisted when the analysis was further adjusted for physical activity, smoking, and vascular disease burden and when participants with mild cognitive impairment or dementia at the baseline dietary assessment were excluded.
Individuals who most closely followed the Mediterranean diet had average beta-amyloid load similar to being 18 years younger than peers with the lowest adherence. And those who most closely followed the MIND diet had average beta-amyloid amounts similar to being 12 years younger than those with the lowest adherence.
A MIND diet score 1 point higher corresponded to typical plaque deposition of participants who are 4.25 years younger in age.
Regarding individual dietary components, those who ate seven or more servings of green leafy vegetables weekly had less global Alzheimer’s disease pathology than peers who ate one or fewer (beta = –0.115, P = .0038). Those who ate seven or more servings per week had plaque amounts in their brains corresponding to being almost 19 years younger in comparison with those who ate the fewest servings per week.
“Our finding that eating more green leafy vegetables is in itself associated with fewer signs of Alzheimer’s disease in the brain is intriguing enough for people to consider adding more of these vegetables to their diet,” Dr. Agarwal said in the news release.
Previous data from the MAP cohort showed that adherence to the MIND diet can improve memory and thinking skills of older adults, even in the presence of Alzheimer’s disease pathology.
Novel study, intriguing results
Heather Snyder, PhD, vice president of medical and scientific relations with the Alzheimer’s Association, noted that a number of studies have linked overall nutrition – especially a balanced diet low in saturated fats and sugar and high in vegetables – with brain health, including cognition, as one ages.
This new study “takes what we know about the link between nutrition and risk for cognitive decline a step further by looking at the specific brain changes that occur in Alzheimer’s disease. The study found an association of certain nutrition behaviors with less of these Alzheimer’s brain changes,” said Dr. Snyder, who was not involved in the study.
“This is intriguing, and more research is needed to test via an intervention if healthy dietary behaviors can modify the presence of Alzheimer’s brain changes and reduce risk of cognitive decline.”
The Alzheimer’s Association is leading a 2-year clinical trial known as US POINTER to study how targeting known dementia risk factors in combination may reduce risk of cognitive decline in older adults. The MIND diet is being used in US POINTER.
“But while we work to find an exact ‘recipe’ for risk reduction, it’s important to eat a heart-healthy diet that incorporates nutrients that our bodies and brains need to be at their best,” Dr. Snyder said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Agarwal and Dr. Snyder have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a cohort of deceased older adults, those who had adhered to the Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) and Mediterranean diets for nearly a decade before death had less global Alzheimer’s disease–related pathology, primarily less beta-amyloid, at autopsy.
Those who most closely followed these diets had almost 40% lower odds of having an Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis at death. The findings offer one mechanism by which healthy diets protect cognition.
“While our research doesn’t prove that a healthy diet resulted in fewer brain deposits of amyloid plaques ... we know there is a relationship, and following the MIND and Mediterranean diets may be one way that people can improve their brain health and protect cognition as they age,” study investigator Puja Agarwal, PhD, of RUSH University Medical Center in Chicago, said in a statement.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Green leafy veggies key
The MIND diet was pioneered by the late Martha Clare Morris, ScD, a Rush nutritional epidemiologist, who died of cancer in 2020 at age 64.
Although similar, the Mediterranean diet recommends vegetables, fruit, and three or more servings of fish per week, whereas the MIND diet prioritizes green leafy vegetables, such as spinach, kale, and collard greens, along with other vegetables. The MIND diet also prioritizes berries over other fruit and recommends one or more servings of fish per week. Both diets recommend small amounts of wine.
The current study focused on 581 older adults who died while participating in the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP). All participants agreed to undergo annual clinical evaluations and brain autopsy after death.
Participants completed annual food frequency questionnaires beginning at a mean age of 84. The mean age at death was 91. Mean follow-up was 6.8 years.
Around the time of death, 224 participants (39%) had a diagnosis of clinical dementia, and 383 participants (66%) had a pathologic Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis at time of death.
The researchers used a series of regression analyses to investigate the MIND and Mediterranean diets and dietary components associated with Alzheimer’s disease pathology. They controlled for age at death, sex, education, APO-epsilon 4 status, and total calories.
Overall, both diets were significantly associated with lower global Alzheimer’s disease pathology (MIND: beta = –0.022, P = .034; and Mediterranean: beta = –0.007, P = .039) – specifically, with less beta-amyloid (MIND: beta = –0.068, P = .050; and Mediterranean: beta = –0.040, P = .004).
The findings persisted when the analysis was further adjusted for physical activity, smoking, and vascular disease burden and when participants with mild cognitive impairment or dementia at the baseline dietary assessment were excluded.
Individuals who most closely followed the Mediterranean diet had average beta-amyloid load similar to being 18 years younger than peers with the lowest adherence. And those who most closely followed the MIND diet had average beta-amyloid amounts similar to being 12 years younger than those with the lowest adherence.
A MIND diet score 1 point higher corresponded to typical plaque deposition of participants who are 4.25 years younger in age.
Regarding individual dietary components, those who ate seven or more servings of green leafy vegetables weekly had less global Alzheimer’s disease pathology than peers who ate one or fewer (beta = –0.115, P = .0038). Those who ate seven or more servings per week had plaque amounts in their brains corresponding to being almost 19 years younger in comparison with those who ate the fewest servings per week.
“Our finding that eating more green leafy vegetables is in itself associated with fewer signs of Alzheimer’s disease in the brain is intriguing enough for people to consider adding more of these vegetables to their diet,” Dr. Agarwal said in the news release.
Previous data from the MAP cohort showed that adherence to the MIND diet can improve memory and thinking skills of older adults, even in the presence of Alzheimer’s disease pathology.
Novel study, intriguing results
Heather Snyder, PhD, vice president of medical and scientific relations with the Alzheimer’s Association, noted that a number of studies have linked overall nutrition – especially a balanced diet low in saturated fats and sugar and high in vegetables – with brain health, including cognition, as one ages.
This new study “takes what we know about the link between nutrition and risk for cognitive decline a step further by looking at the specific brain changes that occur in Alzheimer’s disease. The study found an association of certain nutrition behaviors with less of these Alzheimer’s brain changes,” said Dr. Snyder, who was not involved in the study.
“This is intriguing, and more research is needed to test via an intervention if healthy dietary behaviors can modify the presence of Alzheimer’s brain changes and reduce risk of cognitive decline.”
The Alzheimer’s Association is leading a 2-year clinical trial known as US POINTER to study how targeting known dementia risk factors in combination may reduce risk of cognitive decline in older adults. The MIND diet is being used in US POINTER.
“But while we work to find an exact ‘recipe’ for risk reduction, it’s important to eat a heart-healthy diet that incorporates nutrients that our bodies and brains need to be at their best,” Dr. Snyder said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Agarwal and Dr. Snyder have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a cohort of deceased older adults, those who had adhered to the Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) and Mediterranean diets for nearly a decade before death had less global Alzheimer’s disease–related pathology, primarily less beta-amyloid, at autopsy.
Those who most closely followed these diets had almost 40% lower odds of having an Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis at death. The findings offer one mechanism by which healthy diets protect cognition.
“While our research doesn’t prove that a healthy diet resulted in fewer brain deposits of amyloid plaques ... we know there is a relationship, and following the MIND and Mediterranean diets may be one way that people can improve their brain health and protect cognition as they age,” study investigator Puja Agarwal, PhD, of RUSH University Medical Center in Chicago, said in a statement.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Green leafy veggies key
The MIND diet was pioneered by the late Martha Clare Morris, ScD, a Rush nutritional epidemiologist, who died of cancer in 2020 at age 64.
Although similar, the Mediterranean diet recommends vegetables, fruit, and three or more servings of fish per week, whereas the MIND diet prioritizes green leafy vegetables, such as spinach, kale, and collard greens, along with other vegetables. The MIND diet also prioritizes berries over other fruit and recommends one or more servings of fish per week. Both diets recommend small amounts of wine.
The current study focused on 581 older adults who died while participating in the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP). All participants agreed to undergo annual clinical evaluations and brain autopsy after death.
Participants completed annual food frequency questionnaires beginning at a mean age of 84. The mean age at death was 91. Mean follow-up was 6.8 years.
Around the time of death, 224 participants (39%) had a diagnosis of clinical dementia, and 383 participants (66%) had a pathologic Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis at time of death.
The researchers used a series of regression analyses to investigate the MIND and Mediterranean diets and dietary components associated with Alzheimer’s disease pathology. They controlled for age at death, sex, education, APO-epsilon 4 status, and total calories.
Overall, both diets were significantly associated with lower global Alzheimer’s disease pathology (MIND: beta = –0.022, P = .034; and Mediterranean: beta = –0.007, P = .039) – specifically, with less beta-amyloid (MIND: beta = –0.068, P = .050; and Mediterranean: beta = –0.040, P = .004).
The findings persisted when the analysis was further adjusted for physical activity, smoking, and vascular disease burden and when participants with mild cognitive impairment or dementia at the baseline dietary assessment were excluded.
Individuals who most closely followed the Mediterranean diet had average beta-amyloid load similar to being 18 years younger than peers with the lowest adherence. And those who most closely followed the MIND diet had average beta-amyloid amounts similar to being 12 years younger than those with the lowest adherence.
A MIND diet score 1 point higher corresponded to typical plaque deposition of participants who are 4.25 years younger in age.
Regarding individual dietary components, those who ate seven or more servings of green leafy vegetables weekly had less global Alzheimer’s disease pathology than peers who ate one or fewer (beta = –0.115, P = .0038). Those who ate seven or more servings per week had plaque amounts in their brains corresponding to being almost 19 years younger in comparison with those who ate the fewest servings per week.
“Our finding that eating more green leafy vegetables is in itself associated with fewer signs of Alzheimer’s disease in the brain is intriguing enough for people to consider adding more of these vegetables to their diet,” Dr. Agarwal said in the news release.
Previous data from the MAP cohort showed that adherence to the MIND diet can improve memory and thinking skills of older adults, even in the presence of Alzheimer’s disease pathology.
Novel study, intriguing results
Heather Snyder, PhD, vice president of medical and scientific relations with the Alzheimer’s Association, noted that a number of studies have linked overall nutrition – especially a balanced diet low in saturated fats and sugar and high in vegetables – with brain health, including cognition, as one ages.
This new study “takes what we know about the link between nutrition and risk for cognitive decline a step further by looking at the specific brain changes that occur in Alzheimer’s disease. The study found an association of certain nutrition behaviors with less of these Alzheimer’s brain changes,” said Dr. Snyder, who was not involved in the study.
“This is intriguing, and more research is needed to test via an intervention if healthy dietary behaviors can modify the presence of Alzheimer’s brain changes and reduce risk of cognitive decline.”
The Alzheimer’s Association is leading a 2-year clinical trial known as US POINTER to study how targeting known dementia risk factors in combination may reduce risk of cognitive decline in older adults. The MIND diet is being used in US POINTER.
“But while we work to find an exact ‘recipe’ for risk reduction, it’s important to eat a heart-healthy diet that incorporates nutrients that our bodies and brains need to be at their best,” Dr. Snyder said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Agarwal and Dr. Snyder have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Digital rectal exam fails as screening tool for prostate cancer
, say investigators reporting the PROBASE study.
The study compared risk-adapted screening measures in men who had prostate-specific antigen (PSA) measured at age 45 with those who had PSA measurements plus DRE at age 50.
The results show that as a solitary screening tool, 99% of DREs did not raise suspicion for prostate cancer, and among the 57 cases where DRE did raise suspicion, only three men were found to have cancer, all of which were low-grade, reported Agne Krilaviciute, PhD, from the German Cancer Research Center in Heidelberg, and colleagues.
“We also see that the cancer detection rate by PSA is four times higher compared to the DRE detection. Around 18% of the tumors are located in the part of the prostate where DRE cannot detect them,” she said in an oral presentation at the European Association of Urology Congress.
The investigators found that the majority of prostate cancers that occurred in this relatively young population were International Society of Urological Pathology grade 1 (Gleason score 3 + 3 = 6) or grade 2 (Gleason 3 + 4 = 7). DRE yields positive results in only about 12% of cases of ISUP grade 1 or 2, they noted.
“We conclude that DRE as a solitary screening test does not lead to a significant PCa [prostate cancer] detection rate in young men,” Dr. Krilaviciute said.
Falling by the wayside
The study adds to the growing body of evidence that DRE may not be especially helpful as either a screening tool or when used in active surveillance of men with prostate cancer.
An international consensus panel found that DRE could be safely skipped for active surveillance when MRI and other more accurate and objective measures, such as biomarkers, are available.
A prostate cancer expert who was not involved in the PROBASE study told this news organization that when he was in medical school, it would have been considered a serious lapse of practice not to perform a DRE, but that things have changed considerably over the past several years.
“We have PSA now, we have technology with MRI, and the yield of digital rectal examination is very low,” commented Julio Pow-Sang, MD, chief of the genitourinary oncology program at Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla.
“Empirically, it’s very rare to find positive cancer through rectal exam in this day and age of PSA,” he said, adding that the examination itself is highly subjective, with varying results depending on the skills of the particular examiner.
“I think that in time, with good studies like this, digital rectal exam specifically for prostate cancer is going to slowly fade away,” Dr. Pow-Sang said.
PROBASE results
PROBASE was a randomized screening study enrolling men at age 45 to test a risk-adapted screening strategy using a baseline PSA value with the additional offer of DRE in a large subcohort of participants.
The study was conducted in Germany, and the authors note that the “German statutory early detection program recommends DRE as a stand-alone screening test starting annually at age 45.”
The PROBASE investigators enrolled 46,495 men from February 2014 through December 2019.
Among the first 23,194 men enrolled, 6,537 underwent DRE at enrollment without a study PSA test.
In this group, 6,480 DREs (99%) were not suspicious for cancer, and 57 (1%) were. Of those with suspected prostate cancer, 37 underwent biopsy and 20 did not. Of those biopsied, only two were found to have prostate cancer. This translated into a cancer detection rate of 0.03% for DRE.
After a median of 6.6 years of follow-up, only one additional case of ISUP grade 2 prostate cancer was detected among the 6,357 men who had DREs at enrollment, translating into a prostate cancer detection rate of .05%.
The investigators also looked at men who suspicious DRE findings at baseline. They assumed that a DRE-detectable tumor at age 45 would still be manifest 5 years later and should be detectable with PSA at age 50. Of the 57 men with initially suspicious findings, 11 returned for PSA screening but refused biopsy, and of this group only one had an elevated PSA level. He then underwent biopsy, but the findings were negative.
Of those who underwent biopsy on the basis of DRE, 16 had prostatitis, 14 had benign prostatic hyperplasia, 1 had high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, 1 had atypical small acinar proliferation, and 3 had equivocal findings.
In total, the investigators found 24 tumors among men screened with DRE. Of these, 3 occurred in men with results deemed suspicious and 21 were in men with unsuspicious digital exams. All of the tumors were ISUP grade 1, 2, or 3 tumors.
Among 245 men who had biopsies for a PSA level equal to or higher than 3 ng/mL, primarily Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) 3-5 tumors, DRE findings at the time of biopsy were unsuspicious in about 82% of cases, Dr. Krilaviciute said.
“We also used MRI data to determine what proportion of tumors would be potentially detectable by DRE. We estimated that around 18% of tumors are located in the upper part of the prostate, which is not detectable by DRE,” she said. “Even excluding those tumors, still the DRE detection rate is low in palpable tumors.”
Although DRE performed better in higher-grade tumors, 80% of the tumors in the PROBASE participants were ISUP grade 1 or 2 and were likely to be undetected by DRE, she added.
“In Germany, the recommendations for the screening still include 45-year-olds to go with annual DRE. The PROBASE trial allowed us to evaluate for the first time what was the diagnostic performance for DRE at such a young age, and we see that 99% of men undergoing DRE have no suspicious findings, and among the 1% of suspicious findings having cancers extremely unlikely,” she said.
The study was supported by Deutsche Krebshilfe (German Cancer Aid). Dr. Krilaviciute and Dr. Pow-Sang reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, say investigators reporting the PROBASE study.
The study compared risk-adapted screening measures in men who had prostate-specific antigen (PSA) measured at age 45 with those who had PSA measurements plus DRE at age 50.
The results show that as a solitary screening tool, 99% of DREs did not raise suspicion for prostate cancer, and among the 57 cases where DRE did raise suspicion, only three men were found to have cancer, all of which were low-grade, reported Agne Krilaviciute, PhD, from the German Cancer Research Center in Heidelberg, and colleagues.
“We also see that the cancer detection rate by PSA is four times higher compared to the DRE detection. Around 18% of the tumors are located in the part of the prostate where DRE cannot detect them,” she said in an oral presentation at the European Association of Urology Congress.
The investigators found that the majority of prostate cancers that occurred in this relatively young population were International Society of Urological Pathology grade 1 (Gleason score 3 + 3 = 6) or grade 2 (Gleason 3 + 4 = 7). DRE yields positive results in only about 12% of cases of ISUP grade 1 or 2, they noted.
“We conclude that DRE as a solitary screening test does not lead to a significant PCa [prostate cancer] detection rate in young men,” Dr. Krilaviciute said.
Falling by the wayside
The study adds to the growing body of evidence that DRE may not be especially helpful as either a screening tool or when used in active surveillance of men with prostate cancer.
An international consensus panel found that DRE could be safely skipped for active surveillance when MRI and other more accurate and objective measures, such as biomarkers, are available.
A prostate cancer expert who was not involved in the PROBASE study told this news organization that when he was in medical school, it would have been considered a serious lapse of practice not to perform a DRE, but that things have changed considerably over the past several years.
“We have PSA now, we have technology with MRI, and the yield of digital rectal examination is very low,” commented Julio Pow-Sang, MD, chief of the genitourinary oncology program at Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla.
“Empirically, it’s very rare to find positive cancer through rectal exam in this day and age of PSA,” he said, adding that the examination itself is highly subjective, with varying results depending on the skills of the particular examiner.
“I think that in time, with good studies like this, digital rectal exam specifically for prostate cancer is going to slowly fade away,” Dr. Pow-Sang said.
PROBASE results
PROBASE was a randomized screening study enrolling men at age 45 to test a risk-adapted screening strategy using a baseline PSA value with the additional offer of DRE in a large subcohort of participants.
The study was conducted in Germany, and the authors note that the “German statutory early detection program recommends DRE as a stand-alone screening test starting annually at age 45.”
The PROBASE investigators enrolled 46,495 men from February 2014 through December 2019.
Among the first 23,194 men enrolled, 6,537 underwent DRE at enrollment without a study PSA test.
In this group, 6,480 DREs (99%) were not suspicious for cancer, and 57 (1%) were. Of those with suspected prostate cancer, 37 underwent biopsy and 20 did not. Of those biopsied, only two were found to have prostate cancer. This translated into a cancer detection rate of 0.03% for DRE.
After a median of 6.6 years of follow-up, only one additional case of ISUP grade 2 prostate cancer was detected among the 6,357 men who had DREs at enrollment, translating into a prostate cancer detection rate of .05%.
The investigators also looked at men who suspicious DRE findings at baseline. They assumed that a DRE-detectable tumor at age 45 would still be manifest 5 years later and should be detectable with PSA at age 50. Of the 57 men with initially suspicious findings, 11 returned for PSA screening but refused biopsy, and of this group only one had an elevated PSA level. He then underwent biopsy, but the findings were negative.
Of those who underwent biopsy on the basis of DRE, 16 had prostatitis, 14 had benign prostatic hyperplasia, 1 had high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, 1 had atypical small acinar proliferation, and 3 had equivocal findings.
In total, the investigators found 24 tumors among men screened with DRE. Of these, 3 occurred in men with results deemed suspicious and 21 were in men with unsuspicious digital exams. All of the tumors were ISUP grade 1, 2, or 3 tumors.
Among 245 men who had biopsies for a PSA level equal to or higher than 3 ng/mL, primarily Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) 3-5 tumors, DRE findings at the time of biopsy were unsuspicious in about 82% of cases, Dr. Krilaviciute said.
“We also used MRI data to determine what proportion of tumors would be potentially detectable by DRE. We estimated that around 18% of tumors are located in the upper part of the prostate, which is not detectable by DRE,” she said. “Even excluding those tumors, still the DRE detection rate is low in palpable tumors.”
Although DRE performed better in higher-grade tumors, 80% of the tumors in the PROBASE participants were ISUP grade 1 or 2 and were likely to be undetected by DRE, she added.
“In Germany, the recommendations for the screening still include 45-year-olds to go with annual DRE. The PROBASE trial allowed us to evaluate for the first time what was the diagnostic performance for DRE at such a young age, and we see that 99% of men undergoing DRE have no suspicious findings, and among the 1% of suspicious findings having cancers extremely unlikely,” she said.
The study was supported by Deutsche Krebshilfe (German Cancer Aid). Dr. Krilaviciute and Dr. Pow-Sang reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, say investigators reporting the PROBASE study.
The study compared risk-adapted screening measures in men who had prostate-specific antigen (PSA) measured at age 45 with those who had PSA measurements plus DRE at age 50.
The results show that as a solitary screening tool, 99% of DREs did not raise suspicion for prostate cancer, and among the 57 cases where DRE did raise suspicion, only three men were found to have cancer, all of which were low-grade, reported Agne Krilaviciute, PhD, from the German Cancer Research Center in Heidelberg, and colleagues.
“We also see that the cancer detection rate by PSA is four times higher compared to the DRE detection. Around 18% of the tumors are located in the part of the prostate where DRE cannot detect them,” she said in an oral presentation at the European Association of Urology Congress.
The investigators found that the majority of prostate cancers that occurred in this relatively young population were International Society of Urological Pathology grade 1 (Gleason score 3 + 3 = 6) or grade 2 (Gleason 3 + 4 = 7). DRE yields positive results in only about 12% of cases of ISUP grade 1 or 2, they noted.
“We conclude that DRE as a solitary screening test does not lead to a significant PCa [prostate cancer] detection rate in young men,” Dr. Krilaviciute said.
Falling by the wayside
The study adds to the growing body of evidence that DRE may not be especially helpful as either a screening tool or when used in active surveillance of men with prostate cancer.
An international consensus panel found that DRE could be safely skipped for active surveillance when MRI and other more accurate and objective measures, such as biomarkers, are available.
A prostate cancer expert who was not involved in the PROBASE study told this news organization that when he was in medical school, it would have been considered a serious lapse of practice not to perform a DRE, but that things have changed considerably over the past several years.
“We have PSA now, we have technology with MRI, and the yield of digital rectal examination is very low,” commented Julio Pow-Sang, MD, chief of the genitourinary oncology program at Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla.
“Empirically, it’s very rare to find positive cancer through rectal exam in this day and age of PSA,” he said, adding that the examination itself is highly subjective, with varying results depending on the skills of the particular examiner.
“I think that in time, with good studies like this, digital rectal exam specifically for prostate cancer is going to slowly fade away,” Dr. Pow-Sang said.
PROBASE results
PROBASE was a randomized screening study enrolling men at age 45 to test a risk-adapted screening strategy using a baseline PSA value with the additional offer of DRE in a large subcohort of participants.
The study was conducted in Germany, and the authors note that the “German statutory early detection program recommends DRE as a stand-alone screening test starting annually at age 45.”
The PROBASE investigators enrolled 46,495 men from February 2014 through December 2019.
Among the first 23,194 men enrolled, 6,537 underwent DRE at enrollment without a study PSA test.
In this group, 6,480 DREs (99%) were not suspicious for cancer, and 57 (1%) were. Of those with suspected prostate cancer, 37 underwent biopsy and 20 did not. Of those biopsied, only two were found to have prostate cancer. This translated into a cancer detection rate of 0.03% for DRE.
After a median of 6.6 years of follow-up, only one additional case of ISUP grade 2 prostate cancer was detected among the 6,357 men who had DREs at enrollment, translating into a prostate cancer detection rate of .05%.
The investigators also looked at men who suspicious DRE findings at baseline. They assumed that a DRE-detectable tumor at age 45 would still be manifest 5 years later and should be detectable with PSA at age 50. Of the 57 men with initially suspicious findings, 11 returned for PSA screening but refused biopsy, and of this group only one had an elevated PSA level. He then underwent biopsy, but the findings were negative.
Of those who underwent biopsy on the basis of DRE, 16 had prostatitis, 14 had benign prostatic hyperplasia, 1 had high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, 1 had atypical small acinar proliferation, and 3 had equivocal findings.
In total, the investigators found 24 tumors among men screened with DRE. Of these, 3 occurred in men with results deemed suspicious and 21 were in men with unsuspicious digital exams. All of the tumors were ISUP grade 1, 2, or 3 tumors.
Among 245 men who had biopsies for a PSA level equal to or higher than 3 ng/mL, primarily Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) 3-5 tumors, DRE findings at the time of biopsy were unsuspicious in about 82% of cases, Dr. Krilaviciute said.
“We also used MRI data to determine what proportion of tumors would be potentially detectable by DRE. We estimated that around 18% of tumors are located in the upper part of the prostate, which is not detectable by DRE,” she said. “Even excluding those tumors, still the DRE detection rate is low in palpable tumors.”
Although DRE performed better in higher-grade tumors, 80% of the tumors in the PROBASE participants were ISUP grade 1 or 2 and were likely to be undetected by DRE, she added.
“In Germany, the recommendations for the screening still include 45-year-olds to go with annual DRE. The PROBASE trial allowed us to evaluate for the first time what was the diagnostic performance for DRE at such a young age, and we see that 99% of men undergoing DRE have no suspicious findings, and among the 1% of suspicious findings having cancers extremely unlikely,” she said.
The study was supported by Deutsche Krebshilfe (German Cancer Aid). Dr. Krilaviciute and Dr. Pow-Sang reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EAU 2023
Urine test predicts future bladder cancer 12 years before symptoms
an international team of researchers claims.
The test, if validated in further studies, has the potential to serve as a cancer screening tool for individuals at elevated risk for bladder cancer due to genetics, smoking, or from environmental exposures to known carcinogens, and it could help to reduce the frequency of unnecessary cystoscopies, say urologists who were not involved in the research.
The test involved was performed using a next-generation sequencing assay (UroAmp, Convergent Genomics, based in San Francisco) that identifies mutations in 60 genes associated with bladder cancer. New research reported at the annual congress of the European Association of Urology described the screening model that focused on 10 key genes covered in the assay.
In training and validation cohorts, the urinary comprehensive genomic profiling test accurately predicted future bladder cancer in 66% of patient urine samples, including some that had been collected more than a decade prior to being tested, reported Florence Le Calvez-Kelm, PhD, MSc, from the International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, France.
“Our results provide first evidence from a population-based cohort study of preclinical urothelial cancer detection with urinary comprehensive genomic profiling,” she told the meeting.
The results were consistent both in individuals with known risk factors for bladder cancer who were undergoing cystoscopy and in those with no evidence of disease, she said.
“Research of this nature is very encouraging, as it shows that our ability to identify molecular alterations in liquid biopsies such as urine that might indicate cancer is constantly improving,” commented Joost Boormans, MD, PhD, a urologist at the Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, Netherlands, and a member of the EAU Scientific Congress Office.
“While we do need to develop more accurate diagnostics, it’s unlikely that we’ll have a mass screening program for bladder cancer in the near future,” he continued. “Where a urine test for genetic mutations could show its value is in reducing cystoscopies and scans in bladder cancer patients who are being monitored for recurrence, as well as those referred for blood in their urine. A simple urine test would be far easier for patients to undergo than invasive procedures or scans, as well as being less costly for health services.”
Dr. Le Calvez-Kelm and colleagues had previously shown that promoter mutations in the gene encoding for the enzyme telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) identified in urine were “promising noninvasive biomarkers” for early detection of bladder cancer.
They found that TERT mutations in urine could predict which patients were likely to develop urothelial cancer with 48% sensitivity and 100% specificity.
In the study presented at EAU23, they hypothesized that uCGP of DNA in urine could offer enhanced sensitivity for early detection of urothelial cancer.
They first used the 60-gene assay to create a training set using urine samples from 46 patients with de novo urothelial cancer, 40 with recurrent cancer, and 140 healthy controls.
They then tested the model in two validation cohorts. The first validation cohort consisted of samples from 22 patients with de novo cancer, 48 with recurrent urothelial cancer, and 96 controls from a case-control study conducted at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and Ohio State University, Columbus.
The second validation cohort included 29 patients from the prospective Golestan Cohort Study who subsequently developed urothelial cancer, with 98 controls.
In all, 10 genes were identified as optimal for inclusion in a screening model, which was trained to an overall sensitivity of 88% and a 97% sensitivity for high-grade tumors, with a specificity of 94%.
In the MGH/OSU validation cohort the sensitivity of the models was 71%, and the specificity was 94%. In the Golestan cohort, the sensitivity was 66%, with a specificity of 94%. This compared favorably with the performance of the TERT-only screening model, which, as noted before, had a sensitivity of 48%, albeit with 100% specificity.
“Interestingly, when we broke down the analysis according to the lag time between urine collection and diagnosis, sensitivity increased as the time to diagnosis decreased, so the closer we got to the diagnosis, the higher was the sensitivity,” Dr. Le Calvez-Kelm said.
When the analysis was limited to urothelial cancers diagnosed within 7 years of sample collection, the sensitivity for detecting preclinical cancer improved to 86%, compared with 57% for a test of TERT promoter mutations alone.
Among the patients in the Golestan cohort, uCGP-predicted positive results were associated with a more than eightfold higher risk for worse cancer-free survival, compared with uCGP-predicted negatives (hazard ratio 8.5, P < .0001).
“Of course, further studies are needed to validate this finding and to assess the clinical utility in other longitudinal cohorts,” Dr. Le Calvez-Kelm concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
an international team of researchers claims.
The test, if validated in further studies, has the potential to serve as a cancer screening tool for individuals at elevated risk for bladder cancer due to genetics, smoking, or from environmental exposures to known carcinogens, and it could help to reduce the frequency of unnecessary cystoscopies, say urologists who were not involved in the research.
The test involved was performed using a next-generation sequencing assay (UroAmp, Convergent Genomics, based in San Francisco) that identifies mutations in 60 genes associated with bladder cancer. New research reported at the annual congress of the European Association of Urology described the screening model that focused on 10 key genes covered in the assay.
In training and validation cohorts, the urinary comprehensive genomic profiling test accurately predicted future bladder cancer in 66% of patient urine samples, including some that had been collected more than a decade prior to being tested, reported Florence Le Calvez-Kelm, PhD, MSc, from the International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, France.
“Our results provide first evidence from a population-based cohort study of preclinical urothelial cancer detection with urinary comprehensive genomic profiling,” she told the meeting.
The results were consistent both in individuals with known risk factors for bladder cancer who were undergoing cystoscopy and in those with no evidence of disease, she said.
“Research of this nature is very encouraging, as it shows that our ability to identify molecular alterations in liquid biopsies such as urine that might indicate cancer is constantly improving,” commented Joost Boormans, MD, PhD, a urologist at the Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, Netherlands, and a member of the EAU Scientific Congress Office.
“While we do need to develop more accurate diagnostics, it’s unlikely that we’ll have a mass screening program for bladder cancer in the near future,” he continued. “Where a urine test for genetic mutations could show its value is in reducing cystoscopies and scans in bladder cancer patients who are being monitored for recurrence, as well as those referred for blood in their urine. A simple urine test would be far easier for patients to undergo than invasive procedures or scans, as well as being less costly for health services.”
Dr. Le Calvez-Kelm and colleagues had previously shown that promoter mutations in the gene encoding for the enzyme telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) identified in urine were “promising noninvasive biomarkers” for early detection of bladder cancer.
They found that TERT mutations in urine could predict which patients were likely to develop urothelial cancer with 48% sensitivity and 100% specificity.
In the study presented at EAU23, they hypothesized that uCGP of DNA in urine could offer enhanced sensitivity for early detection of urothelial cancer.
They first used the 60-gene assay to create a training set using urine samples from 46 patients with de novo urothelial cancer, 40 with recurrent cancer, and 140 healthy controls.
They then tested the model in two validation cohorts. The first validation cohort consisted of samples from 22 patients with de novo cancer, 48 with recurrent urothelial cancer, and 96 controls from a case-control study conducted at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and Ohio State University, Columbus.
The second validation cohort included 29 patients from the prospective Golestan Cohort Study who subsequently developed urothelial cancer, with 98 controls.
In all, 10 genes were identified as optimal for inclusion in a screening model, which was trained to an overall sensitivity of 88% and a 97% sensitivity for high-grade tumors, with a specificity of 94%.
In the MGH/OSU validation cohort the sensitivity of the models was 71%, and the specificity was 94%. In the Golestan cohort, the sensitivity was 66%, with a specificity of 94%. This compared favorably with the performance of the TERT-only screening model, which, as noted before, had a sensitivity of 48%, albeit with 100% specificity.
“Interestingly, when we broke down the analysis according to the lag time between urine collection and diagnosis, sensitivity increased as the time to diagnosis decreased, so the closer we got to the diagnosis, the higher was the sensitivity,” Dr. Le Calvez-Kelm said.
When the analysis was limited to urothelial cancers diagnosed within 7 years of sample collection, the sensitivity for detecting preclinical cancer improved to 86%, compared with 57% for a test of TERT promoter mutations alone.
Among the patients in the Golestan cohort, uCGP-predicted positive results were associated with a more than eightfold higher risk for worse cancer-free survival, compared with uCGP-predicted negatives (hazard ratio 8.5, P < .0001).
“Of course, further studies are needed to validate this finding and to assess the clinical utility in other longitudinal cohorts,” Dr. Le Calvez-Kelm concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
an international team of researchers claims.
The test, if validated in further studies, has the potential to serve as a cancer screening tool for individuals at elevated risk for bladder cancer due to genetics, smoking, or from environmental exposures to known carcinogens, and it could help to reduce the frequency of unnecessary cystoscopies, say urologists who were not involved in the research.
The test involved was performed using a next-generation sequencing assay (UroAmp, Convergent Genomics, based in San Francisco) that identifies mutations in 60 genes associated with bladder cancer. New research reported at the annual congress of the European Association of Urology described the screening model that focused on 10 key genes covered in the assay.
In training and validation cohorts, the urinary comprehensive genomic profiling test accurately predicted future bladder cancer in 66% of patient urine samples, including some that had been collected more than a decade prior to being tested, reported Florence Le Calvez-Kelm, PhD, MSc, from the International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, France.
“Our results provide first evidence from a population-based cohort study of preclinical urothelial cancer detection with urinary comprehensive genomic profiling,” she told the meeting.
The results were consistent both in individuals with known risk factors for bladder cancer who were undergoing cystoscopy and in those with no evidence of disease, she said.
“Research of this nature is very encouraging, as it shows that our ability to identify molecular alterations in liquid biopsies such as urine that might indicate cancer is constantly improving,” commented Joost Boormans, MD, PhD, a urologist at the Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, Netherlands, and a member of the EAU Scientific Congress Office.
“While we do need to develop more accurate diagnostics, it’s unlikely that we’ll have a mass screening program for bladder cancer in the near future,” he continued. “Where a urine test for genetic mutations could show its value is in reducing cystoscopies and scans in bladder cancer patients who are being monitored for recurrence, as well as those referred for blood in their urine. A simple urine test would be far easier for patients to undergo than invasive procedures or scans, as well as being less costly for health services.”
Dr. Le Calvez-Kelm and colleagues had previously shown that promoter mutations in the gene encoding for the enzyme telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) identified in urine were “promising noninvasive biomarkers” for early detection of bladder cancer.
They found that TERT mutations in urine could predict which patients were likely to develop urothelial cancer with 48% sensitivity and 100% specificity.
In the study presented at EAU23, they hypothesized that uCGP of DNA in urine could offer enhanced sensitivity for early detection of urothelial cancer.
They first used the 60-gene assay to create a training set using urine samples from 46 patients with de novo urothelial cancer, 40 with recurrent cancer, and 140 healthy controls.
They then tested the model in two validation cohorts. The first validation cohort consisted of samples from 22 patients with de novo cancer, 48 with recurrent urothelial cancer, and 96 controls from a case-control study conducted at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and Ohio State University, Columbus.
The second validation cohort included 29 patients from the prospective Golestan Cohort Study who subsequently developed urothelial cancer, with 98 controls.
In all, 10 genes were identified as optimal for inclusion in a screening model, which was trained to an overall sensitivity of 88% and a 97% sensitivity for high-grade tumors, with a specificity of 94%.
In the MGH/OSU validation cohort the sensitivity of the models was 71%, and the specificity was 94%. In the Golestan cohort, the sensitivity was 66%, with a specificity of 94%. This compared favorably with the performance of the TERT-only screening model, which, as noted before, had a sensitivity of 48%, albeit with 100% specificity.
“Interestingly, when we broke down the analysis according to the lag time between urine collection and diagnosis, sensitivity increased as the time to diagnosis decreased, so the closer we got to the diagnosis, the higher was the sensitivity,” Dr. Le Calvez-Kelm said.
When the analysis was limited to urothelial cancers diagnosed within 7 years of sample collection, the sensitivity for detecting preclinical cancer improved to 86%, compared with 57% for a test of TERT promoter mutations alone.
Among the patients in the Golestan cohort, uCGP-predicted positive results were associated with a more than eightfold higher risk for worse cancer-free survival, compared with uCGP-predicted negatives (hazard ratio 8.5, P < .0001).
“Of course, further studies are needed to validate this finding and to assess the clinical utility in other longitudinal cohorts,” Dr. Le Calvez-Kelm concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EAU23





