User login
Strong support to provide DAA therapy to all patients with HCV
, a large, real-world analysis finds.
Improved outcomes were seen among patients without cirrhosis, those with compensated cirrhosis, and those with existing liver decompensation, the authors noted.
The findings highlight a “substantial need to provide DAA therapy to all patients with HCV, regardless of disease stage or financial status,” wrote Mindie Nguyen, MD, of Stanford University Medical Center, Palo Alto, Calif., and coinvestigators.
“Additional national efforts are needed to reach and treat U.S. population groups that are underinsured or not insured, incarcerated and otherwise marginalized, such as users of illicit drugs, who are also at higher risk of disease complication and reinfection,” they said.
The study was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
CHC and its complications are associated with high rates of illness and death. However, large-scale data on long-term liver and nonliver effects of DAA treatment are limited.
For their study, Dr. Nguyen and colleagues analyzed administrative claims data from 2010 to 2021 for 245,596 adults with CHC, of whom 40,654 had received one or more DAA therapies (without interferon) and 204,942 had not received treatment.
DAA-treated patients were slightly older than their untreated peers (mean age, 59.9 years, vs. 58.5 years) and were more likely to be male (62% vs. 58%) and White (59% vs. 57%), and to have diabetes (26% vs. 25%) and cirrhosis (44% vs. 29%).
For liver outcomes, DAA therapy was associated with a lower incidence of decompensation (28.2 vs. 40.8 per 1,000 person-years; P < .001) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in compensated cirrhosis (20.1 vs. 41.8; P < .001).
For nonliver outcomes, DAA treatment was associated with a lower incidence of diabetes (30.2 vs. 37.2 per 1,000 person-years; P < .001) and chronic kidney disease (31.1 vs. 34.1; P < .001).
The all-cause mortality rate per 1,000 person-years was 36.5 in the DAA-treated group, vs. 64.7 in the untreated group (P < .001).
In multivariable regression analysis, DAA treatment was independently associated with a significant decrease in the risk for HCC (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.73), decompensation (aHR, 0.36), diabetes (aHR, 0.74), chronic kidney disease (aHR, 0.81), cardiovascular disease (aHR, 0.90), nonliver cancer (aHR, 0.89), and mortality (aHR, 0.43).
The 57% lower mortality rate observed among DAA-treated vs. untreated patients aligns with a large French study of adults with CHC.
“Because HCV treatment with a DAA regimen is well tolerated for nearly all patients, we believe these findings provide further support for universal HCV treatment coverage for all patients affected by HCV,” Dr. Nguyen and colleagues wrote.
The strengths of this study are its large sample of DAA-treated and untreated patients from diverse racial and ethnic groups from across the United States and from diverse practice settings (not just tertiary centers).
One limitation is that the study cohort included only patients covered by private insurance; therefore, the findings may not be generalizable to individuals who are underinsured or not insured. Miscoding and misclassification are also possible with large claims databases.
Support for the study was provided by Stanford University and the Stanford Center for Population Health Sciences. Dr. Nguyen has received institutional grants and advisory board fees from Gilead Sciences outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a large, real-world analysis finds.
Improved outcomes were seen among patients without cirrhosis, those with compensated cirrhosis, and those with existing liver decompensation, the authors noted.
The findings highlight a “substantial need to provide DAA therapy to all patients with HCV, regardless of disease stage or financial status,” wrote Mindie Nguyen, MD, of Stanford University Medical Center, Palo Alto, Calif., and coinvestigators.
“Additional national efforts are needed to reach and treat U.S. population groups that are underinsured or not insured, incarcerated and otherwise marginalized, such as users of illicit drugs, who are also at higher risk of disease complication and reinfection,” they said.
The study was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
CHC and its complications are associated with high rates of illness and death. However, large-scale data on long-term liver and nonliver effects of DAA treatment are limited.
For their study, Dr. Nguyen and colleagues analyzed administrative claims data from 2010 to 2021 for 245,596 adults with CHC, of whom 40,654 had received one or more DAA therapies (without interferon) and 204,942 had not received treatment.
DAA-treated patients were slightly older than their untreated peers (mean age, 59.9 years, vs. 58.5 years) and were more likely to be male (62% vs. 58%) and White (59% vs. 57%), and to have diabetes (26% vs. 25%) and cirrhosis (44% vs. 29%).
For liver outcomes, DAA therapy was associated with a lower incidence of decompensation (28.2 vs. 40.8 per 1,000 person-years; P < .001) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in compensated cirrhosis (20.1 vs. 41.8; P < .001).
For nonliver outcomes, DAA treatment was associated with a lower incidence of diabetes (30.2 vs. 37.2 per 1,000 person-years; P < .001) and chronic kidney disease (31.1 vs. 34.1; P < .001).
The all-cause mortality rate per 1,000 person-years was 36.5 in the DAA-treated group, vs. 64.7 in the untreated group (P < .001).
In multivariable regression analysis, DAA treatment was independently associated with a significant decrease in the risk for HCC (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.73), decompensation (aHR, 0.36), diabetes (aHR, 0.74), chronic kidney disease (aHR, 0.81), cardiovascular disease (aHR, 0.90), nonliver cancer (aHR, 0.89), and mortality (aHR, 0.43).
The 57% lower mortality rate observed among DAA-treated vs. untreated patients aligns with a large French study of adults with CHC.
“Because HCV treatment with a DAA regimen is well tolerated for nearly all patients, we believe these findings provide further support for universal HCV treatment coverage for all patients affected by HCV,” Dr. Nguyen and colleagues wrote.
The strengths of this study are its large sample of DAA-treated and untreated patients from diverse racial and ethnic groups from across the United States and from diverse practice settings (not just tertiary centers).
One limitation is that the study cohort included only patients covered by private insurance; therefore, the findings may not be generalizable to individuals who are underinsured or not insured. Miscoding and misclassification are also possible with large claims databases.
Support for the study was provided by Stanford University and the Stanford Center for Population Health Sciences. Dr. Nguyen has received institutional grants and advisory board fees from Gilead Sciences outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a large, real-world analysis finds.
Improved outcomes were seen among patients without cirrhosis, those with compensated cirrhosis, and those with existing liver decompensation, the authors noted.
The findings highlight a “substantial need to provide DAA therapy to all patients with HCV, regardless of disease stage or financial status,” wrote Mindie Nguyen, MD, of Stanford University Medical Center, Palo Alto, Calif., and coinvestigators.
“Additional national efforts are needed to reach and treat U.S. population groups that are underinsured or not insured, incarcerated and otherwise marginalized, such as users of illicit drugs, who are also at higher risk of disease complication and reinfection,” they said.
The study was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
CHC and its complications are associated with high rates of illness and death. However, large-scale data on long-term liver and nonliver effects of DAA treatment are limited.
For their study, Dr. Nguyen and colleagues analyzed administrative claims data from 2010 to 2021 for 245,596 adults with CHC, of whom 40,654 had received one or more DAA therapies (without interferon) and 204,942 had not received treatment.
DAA-treated patients were slightly older than their untreated peers (mean age, 59.9 years, vs. 58.5 years) and were more likely to be male (62% vs. 58%) and White (59% vs. 57%), and to have diabetes (26% vs. 25%) and cirrhosis (44% vs. 29%).
For liver outcomes, DAA therapy was associated with a lower incidence of decompensation (28.2 vs. 40.8 per 1,000 person-years; P < .001) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in compensated cirrhosis (20.1 vs. 41.8; P < .001).
For nonliver outcomes, DAA treatment was associated with a lower incidence of diabetes (30.2 vs. 37.2 per 1,000 person-years; P < .001) and chronic kidney disease (31.1 vs. 34.1; P < .001).
The all-cause mortality rate per 1,000 person-years was 36.5 in the DAA-treated group, vs. 64.7 in the untreated group (P < .001).
In multivariable regression analysis, DAA treatment was independently associated with a significant decrease in the risk for HCC (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.73), decompensation (aHR, 0.36), diabetes (aHR, 0.74), chronic kidney disease (aHR, 0.81), cardiovascular disease (aHR, 0.90), nonliver cancer (aHR, 0.89), and mortality (aHR, 0.43).
The 57% lower mortality rate observed among DAA-treated vs. untreated patients aligns with a large French study of adults with CHC.
“Because HCV treatment with a DAA regimen is well tolerated for nearly all patients, we believe these findings provide further support for universal HCV treatment coverage for all patients affected by HCV,” Dr. Nguyen and colleagues wrote.
The strengths of this study are its large sample of DAA-treated and untreated patients from diverse racial and ethnic groups from across the United States and from diverse practice settings (not just tertiary centers).
One limitation is that the study cohort included only patients covered by private insurance; therefore, the findings may not be generalizable to individuals who are underinsured or not insured. Miscoding and misclassification are also possible with large claims databases.
Support for the study was provided by Stanford University and the Stanford Center for Population Health Sciences. Dr. Nguyen has received institutional grants and advisory board fees from Gilead Sciences outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE
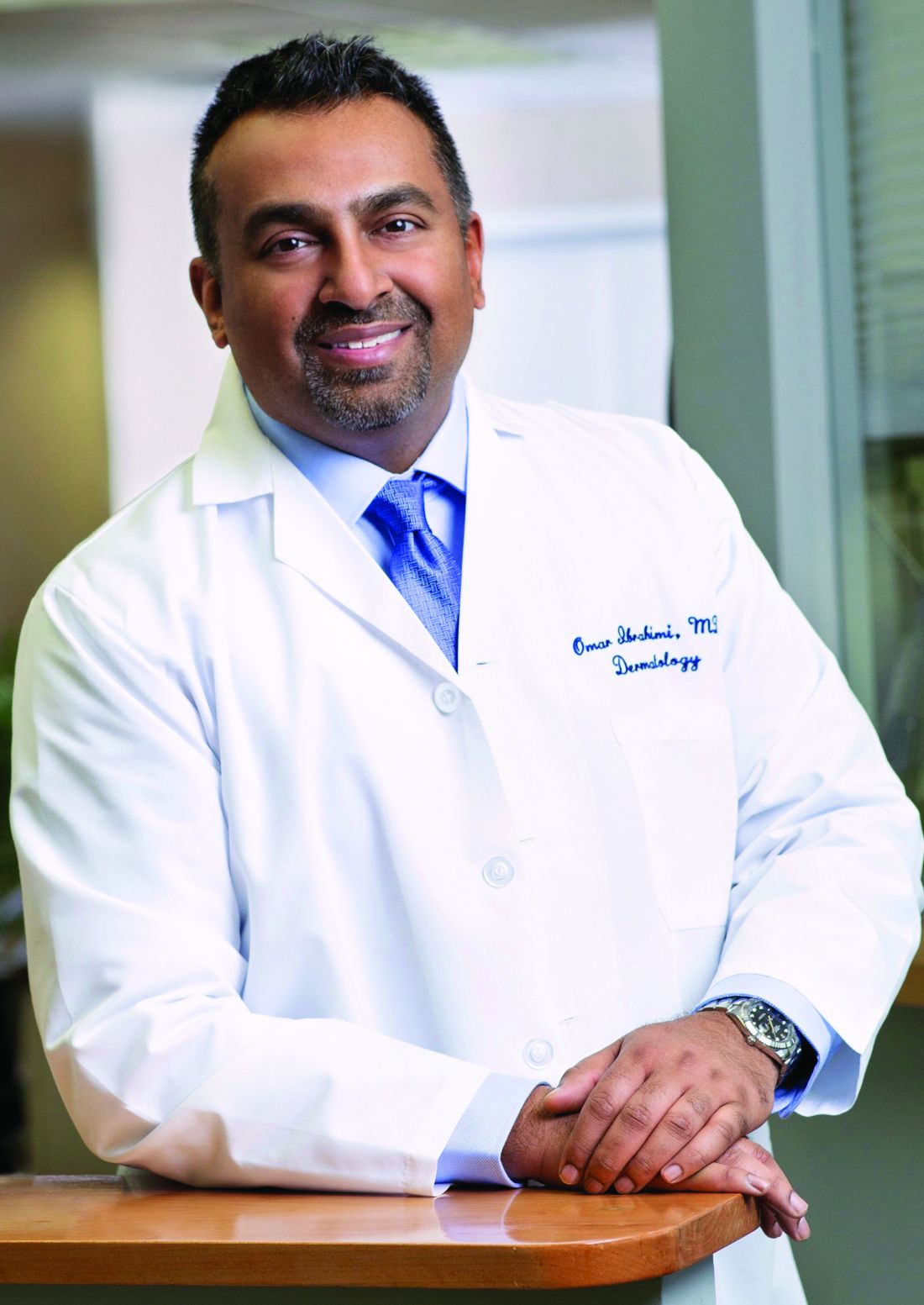
Picosecond lasers for tattoo removal could benefit from enhancements, expert says
SAN DIEGO – When picosecond lasers hit the market about 10 years ago, they became a game-changer for tattoo removal, boasting the delivery of energy that is about threefold faster than with nanosecond lasers.
However, picosecond lasers are far from perfect even in the hands of the most experienced clinicians, according to Omar A. Ibrahimi, MD, PhD, medical director of the Connecticut Skin Institute, Stamford. “They have been very difficult to build from an engineering perspective,” he said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium. It took a long time for these lasers to come to the market, and they are still fairly expensive and require a lot of maintenance, he noted. In addition, “they are also not quite as ‘picosecond’ as they need to be. I think there is definitely room to improve, but this is the gold standard.”
Today, . Tattoo ink particles average about 0.1 mcm in size, and the thermal relaxation size works out to be less than 10 nanoseconds, with shorter pulses better at capturing the ink particles that are smaller than average.
Black is the most common tattoo color dermatologists treat. “For that, you can typically use a 1064, which has the highest absorption, but you can also use many of the other wavelengths,” he said. “Other colors are less common, followed by red, for which you would use a 532-nm wavelength.”
Dr. Ibrahimi underscored the importance of setting realistic expectations during consults with patients seeking options for tattoo removal. Even with picosecond laser technology, many treatments are typically required and “a good patient consultation is key to setting proper expectations,” he said. “If you promise someone results in 4 to 5 treatments like many of the device companies will say you can achieve, you’re going to have a large group of patients who are disappointed.”
The clinical endpoint to strive for during tattoo removal is whitening of the ink, which typically fades about 20 minutes after treatment. That whitening corresponds to cavitation, or the production of gas vacuoles in the cells that were holding the ink. This discovery led to a technique intended to enhance tattoo removal. In 2012, R. Rox Anderson, MD, director of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and colleagues published results of a study that compared a single Q-switched laser treatment pass with four treatment passes separated by 20 minutes. After treating 18 tattoos in 12 adults, they found that the technique, known as the “R20” method, was more effective than a single-pass treatment (P < .01).
“Subsequent to this, there has been conflicting data on whether this is truly effective or not,” said Dr. Ibrahimi, who is also on the board of directors for the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery and the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “Most of us agree that one additional pass would be helpful, but when you’re doing this in the private practice setting, it’s often challenging because patients aren’t necessarily willing to pay more for more than just one pass for their tattoo removal.”
Another recent advance is use of a topical square silicone patch infused with perfluorodecalin (PFD) for use during tattoo removal, which has been shown to reduce epidermal whitening. The patch contains a fluorocarbon “that is very good at dissolving gas, and it is already widely used in medicine,” he said. When applied, “it almost instantaneously takes the whitening away; you don’t have to wait the 20 minutes to do your second pass.”
A different technology designed to speed up tattoo removal is the Resonic Rapid Acoustic Pulse device (marketed as Resonic, from Allergan Aesthetics), which is cleared by the FDA for use as an accessory to the 1064 nm Q-switched laser for black tattoo removal in patients with skin types I-III. “This uses acoustic pulses of sound waves; they’re rapid and powerful,” Dr. Ibrahimi said. “They can clear those cavitation bubbles much like the PFD patches do. It’s also thought that they further disperse the tattoo ink particles by supplementing the laser energy as well. It is also purported to alter the body’s healing response, or immune response, which is important in tattoo clearing.”
Dr. Ibrahimi disclosed that he is a member of the Advisory Board for Accure Acne, AbbVie (which owns Allergan), Cutera, Lutronic, Blueberry Therapeutics, Cytrellis, and Quthero. He also holds stock in many device and pharmaceutical companies.
SAN DIEGO – When picosecond lasers hit the market about 10 years ago, they became a game-changer for tattoo removal, boasting the delivery of energy that is about threefold faster than with nanosecond lasers.
However, picosecond lasers are far from perfect even in the hands of the most experienced clinicians, according to Omar A. Ibrahimi, MD, PhD, medical director of the Connecticut Skin Institute, Stamford. “They have been very difficult to build from an engineering perspective,” he said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium. It took a long time for these lasers to come to the market, and they are still fairly expensive and require a lot of maintenance, he noted. In addition, “they are also not quite as ‘picosecond’ as they need to be. I think there is definitely room to improve, but this is the gold standard.”
Today, . Tattoo ink particles average about 0.1 mcm in size, and the thermal relaxation size works out to be less than 10 nanoseconds, with shorter pulses better at capturing the ink particles that are smaller than average.
Black is the most common tattoo color dermatologists treat. “For that, you can typically use a 1064, which has the highest absorption, but you can also use many of the other wavelengths,” he said. “Other colors are less common, followed by red, for which you would use a 532-nm wavelength.”
Dr. Ibrahimi underscored the importance of setting realistic expectations during consults with patients seeking options for tattoo removal. Even with picosecond laser technology, many treatments are typically required and “a good patient consultation is key to setting proper expectations,” he said. “If you promise someone results in 4 to 5 treatments like many of the device companies will say you can achieve, you’re going to have a large group of patients who are disappointed.”
The clinical endpoint to strive for during tattoo removal is whitening of the ink, which typically fades about 20 minutes after treatment. That whitening corresponds to cavitation, or the production of gas vacuoles in the cells that were holding the ink. This discovery led to a technique intended to enhance tattoo removal. In 2012, R. Rox Anderson, MD, director of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and colleagues published results of a study that compared a single Q-switched laser treatment pass with four treatment passes separated by 20 minutes. After treating 18 tattoos in 12 adults, they found that the technique, known as the “R20” method, was more effective than a single-pass treatment (P < .01).
“Subsequent to this, there has been conflicting data on whether this is truly effective or not,” said Dr. Ibrahimi, who is also on the board of directors for the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery and the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “Most of us agree that one additional pass would be helpful, but when you’re doing this in the private practice setting, it’s often challenging because patients aren’t necessarily willing to pay more for more than just one pass for their tattoo removal.”
Another recent advance is use of a topical square silicone patch infused with perfluorodecalin (PFD) for use during tattoo removal, which has been shown to reduce epidermal whitening. The patch contains a fluorocarbon “that is very good at dissolving gas, and it is already widely used in medicine,” he said. When applied, “it almost instantaneously takes the whitening away; you don’t have to wait the 20 minutes to do your second pass.”
A different technology designed to speed up tattoo removal is the Resonic Rapid Acoustic Pulse device (marketed as Resonic, from Allergan Aesthetics), which is cleared by the FDA for use as an accessory to the 1064 nm Q-switched laser for black tattoo removal in patients with skin types I-III. “This uses acoustic pulses of sound waves; they’re rapid and powerful,” Dr. Ibrahimi said. “They can clear those cavitation bubbles much like the PFD patches do. It’s also thought that they further disperse the tattoo ink particles by supplementing the laser energy as well. It is also purported to alter the body’s healing response, or immune response, which is important in tattoo clearing.”
Dr. Ibrahimi disclosed that he is a member of the Advisory Board for Accure Acne, AbbVie (which owns Allergan), Cutera, Lutronic, Blueberry Therapeutics, Cytrellis, and Quthero. He also holds stock in many device and pharmaceutical companies.
SAN DIEGO – When picosecond lasers hit the market about 10 years ago, they became a game-changer for tattoo removal, boasting the delivery of energy that is about threefold faster than with nanosecond lasers.
However, picosecond lasers are far from perfect even in the hands of the most experienced clinicians, according to Omar A. Ibrahimi, MD, PhD, medical director of the Connecticut Skin Institute, Stamford. “They have been very difficult to build from an engineering perspective,” he said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium. It took a long time for these lasers to come to the market, and they are still fairly expensive and require a lot of maintenance, he noted. In addition, “they are also not quite as ‘picosecond’ as they need to be. I think there is definitely room to improve, but this is the gold standard.”
Today, . Tattoo ink particles average about 0.1 mcm in size, and the thermal relaxation size works out to be less than 10 nanoseconds, with shorter pulses better at capturing the ink particles that are smaller than average.
Black is the most common tattoo color dermatologists treat. “For that, you can typically use a 1064, which has the highest absorption, but you can also use many of the other wavelengths,” he said. “Other colors are less common, followed by red, for which you would use a 532-nm wavelength.”
Dr. Ibrahimi underscored the importance of setting realistic expectations during consults with patients seeking options for tattoo removal. Even with picosecond laser technology, many treatments are typically required and “a good patient consultation is key to setting proper expectations,” he said. “If you promise someone results in 4 to 5 treatments like many of the device companies will say you can achieve, you’re going to have a large group of patients who are disappointed.”
The clinical endpoint to strive for during tattoo removal is whitening of the ink, which typically fades about 20 minutes after treatment. That whitening corresponds to cavitation, or the production of gas vacuoles in the cells that were holding the ink. This discovery led to a technique intended to enhance tattoo removal. In 2012, R. Rox Anderson, MD, director of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and colleagues published results of a study that compared a single Q-switched laser treatment pass with four treatment passes separated by 20 minutes. After treating 18 tattoos in 12 adults, they found that the technique, known as the “R20” method, was more effective than a single-pass treatment (P < .01).
“Subsequent to this, there has been conflicting data on whether this is truly effective or not,” said Dr. Ibrahimi, who is also on the board of directors for the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery and the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “Most of us agree that one additional pass would be helpful, but when you’re doing this in the private practice setting, it’s often challenging because patients aren’t necessarily willing to pay more for more than just one pass for their tattoo removal.”
Another recent advance is use of a topical square silicone patch infused with perfluorodecalin (PFD) for use during tattoo removal, which has been shown to reduce epidermal whitening. The patch contains a fluorocarbon “that is very good at dissolving gas, and it is already widely used in medicine,” he said. When applied, “it almost instantaneously takes the whitening away; you don’t have to wait the 20 minutes to do your second pass.”
A different technology designed to speed up tattoo removal is the Resonic Rapid Acoustic Pulse device (marketed as Resonic, from Allergan Aesthetics), which is cleared by the FDA for use as an accessory to the 1064 nm Q-switched laser for black tattoo removal in patients with skin types I-III. “This uses acoustic pulses of sound waves; they’re rapid and powerful,” Dr. Ibrahimi said. “They can clear those cavitation bubbles much like the PFD patches do. It’s also thought that they further disperse the tattoo ink particles by supplementing the laser energy as well. It is also purported to alter the body’s healing response, or immune response, which is important in tattoo clearing.”
Dr. Ibrahimi disclosed that he is a member of the Advisory Board for Accure Acne, AbbVie (which owns Allergan), Cutera, Lutronic, Blueberry Therapeutics, Cytrellis, and Quthero. He also holds stock in many device and pharmaceutical companies.
AT MOAS 2022
FDA OKs Tdap shot in pregnancy to protect newborns from pertussis
The Food and Drug Administration has approved another Tdap vaccine option for use during pregnancy to protect newborns from whooping cough.
The agency on Jan. 9 licensed Adacel (Sanofi Pasteur) for immunization during the third trimester to prevent pertussis in infants younger than 2 months old.
The FDA in October approved a different Tdap vaccine, Boostrix (GlaxoSmithKline), for this indication. Boostrix was the first vaccine specifically approved to prevent a disease in newborns whose mothers receive the vaccine while pregnant.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that women receive a dose of Tdap vaccine during each pregnancy, preferably during gestational weeks 27-36 – and ideally toward the earlier end of that window – to help protect babies from whooping cough, the respiratory tract infection caused by Bordetella pertussis.
Providing a Tdap vaccine – tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis vaccine, adsorbed – in the third trimester confers passive immunity to the baby, according to the CDC. It also reduces the likelihood that the mother will get pertussis and pass it on to the infant.
One study found that providing Tdap vaccination during gestational weeks 27-36 was 85% more effective at preventing pertussis in infants younger than 2 months old, compared with providing Tdap vaccination to mothers in the hospital postpartum.
“On average, about 1,000 infants are hospitalized and typically between 5 and 15 infants die each year in the United States due to pertussis,” according to a CDC reference page. “Most of these deaths are among infants who are too young to be protected by the childhood pertussis vaccine series that starts when infants are 2 months old.”
The Food and Drug Administration has approved another Tdap vaccine option for use during pregnancy to protect newborns from whooping cough.
The agency on Jan. 9 licensed Adacel (Sanofi Pasteur) for immunization during the third trimester to prevent pertussis in infants younger than 2 months old.
The FDA in October approved a different Tdap vaccine, Boostrix (GlaxoSmithKline), for this indication. Boostrix was the first vaccine specifically approved to prevent a disease in newborns whose mothers receive the vaccine while pregnant.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that women receive a dose of Tdap vaccine during each pregnancy, preferably during gestational weeks 27-36 – and ideally toward the earlier end of that window – to help protect babies from whooping cough, the respiratory tract infection caused by Bordetella pertussis.
Providing a Tdap vaccine – tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis vaccine, adsorbed – in the third trimester confers passive immunity to the baby, according to the CDC. It also reduces the likelihood that the mother will get pertussis and pass it on to the infant.
One study found that providing Tdap vaccination during gestational weeks 27-36 was 85% more effective at preventing pertussis in infants younger than 2 months old, compared with providing Tdap vaccination to mothers in the hospital postpartum.
“On average, about 1,000 infants are hospitalized and typically between 5 and 15 infants die each year in the United States due to pertussis,” according to a CDC reference page. “Most of these deaths are among infants who are too young to be protected by the childhood pertussis vaccine series that starts when infants are 2 months old.”
The Food and Drug Administration has approved another Tdap vaccine option for use during pregnancy to protect newborns from whooping cough.
The agency on Jan. 9 licensed Adacel (Sanofi Pasteur) for immunization during the third trimester to prevent pertussis in infants younger than 2 months old.
The FDA in October approved a different Tdap vaccine, Boostrix (GlaxoSmithKline), for this indication. Boostrix was the first vaccine specifically approved to prevent a disease in newborns whose mothers receive the vaccine while pregnant.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that women receive a dose of Tdap vaccine during each pregnancy, preferably during gestational weeks 27-36 – and ideally toward the earlier end of that window – to help protect babies from whooping cough, the respiratory tract infection caused by Bordetella pertussis.
Providing a Tdap vaccine – tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis vaccine, adsorbed – in the third trimester confers passive immunity to the baby, according to the CDC. It also reduces the likelihood that the mother will get pertussis and pass it on to the infant.
One study found that providing Tdap vaccination during gestational weeks 27-36 was 85% more effective at preventing pertussis in infants younger than 2 months old, compared with providing Tdap vaccination to mothers in the hospital postpartum.
“On average, about 1,000 infants are hospitalized and typically between 5 and 15 infants die each year in the United States due to pertussis,” according to a CDC reference page. “Most of these deaths are among infants who are too young to be protected by the childhood pertussis vaccine series that starts when infants are 2 months old.”
Early retirement and the terrible, horrible, no good, very bad cognitive decline
The ‘scheme’ in the name should have been a clue
Retirement. The shiny reward to a lifetime’s worth of working and saving. We’re all literally working to get there, some of us more to get there early, but current research reveals that early retirement isn’t the relaxing finish line we dream about, cognitively speaking.
Researchers at Binghamton (N.Y.) University set out to examine just how retirement plans affect cognitive performance. They started off with China’s New Rural Pension Scheme (scheme probably has a less negative connotation in Chinese), a plan that financially aids the growing rural retirement-age population in the country. Then they looked at data from the Chinese Health and Retirement Longitudinal Survey, which tests cognition with a focus on episodic memory and parts of intact mental status.
What they found was the opposite of what you would expect out of retirees with nothing but time on their hands.
The pension program, which had been in place for almost a decade, led to delayed recall, especially among women, supporting “the mental retirement hypothesis that decreased mental activity results in worsening cognitive skills,” the investigators said in a written statement.
There also was a drop in social engagement, with lower rates of volunteering and social interaction than people who didn’t receive the pension. Some behaviors, like regular alcohol consumption, did improve over the previous year, as did total health in general, but “the adverse effects of early retirement on mental and social engagement significantly outweigh the program’s protective effect on various health behaviors,” Plamen Nikolov, PhD, said about his research.
So if you’re looking to retire early, don’t skimp on the crosswords and the bingo nights. Stay busy in a good way. Your brain will thank you.
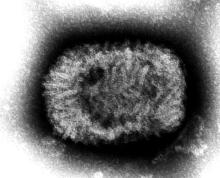
Indiana Jones and the First Smallpox Ancestor
Smallpox was, not that long ago, one of the most devastating diseases known to humanity, killing 300 million people in the 20th century alone. Eradicating it has to be one of medicine’s crowning achievements. Now it can only be found in museums, which is where it belongs.
Here’s the thing with smallpox though: For all it did to us, we know frustratingly little about where it came from. Until very recently, the best available genetic evidence placed its emergence in the 17th century, which clashes with historical data. You know what that means, right? It’s time to dig out the fedora and whip, cue the music, and dig into a recently published study spanning continents in search of the mythical smallpox origin story.
We pick up in 2020, when genetic evidence definitively showed smallpox in a Viking burial site, moving the disease’s emergence a thousand years earlier. Which is all well and good, but there’s solid visual evidence that Egyptian pharaohs were dying of smallpox, as their bodies show the signature scarring. Historians were pretty sure smallpox went back about 4,000 years, but there was no genetic material to prove it.
Since there aren’t any 4,000-year-old smallpox germs laying around, the researchers chose to attack the problem another way – by burning down a Venetian catacomb, er, conducting a analysis of historical smallpox genetics to find the virus’s origin. By analyzing the genomes of various strains at different periods of time, they were able to determine that the variola virus had a definitive common ancestor. Some of the genetic components in the Viking-age sample, for example, persisted until the 18th century.
Armed with this information, the scientists determined that the first smallpox ancestor emerged about 3,800 years ago. That’s very close to the historians’ estimate for the disease’s emergence. Proof at last of smallpox’s truly ancient origin. One might even say the researchers chose wisely.
The only hall of fame that really matters
LOTME loves the holiday season – the food, the gifts, the radio stations that play nothing but Christmas music – but for us the most wonderful time of the year comes just a bit later. No, it’s not our annual Golden Globes slap bet. Nope, not even the “excitement” of the College Football Playoff National Championship. It’s time for the National Inventors Hall of Fame to announce its latest inductees, and we could hardly sleep last night after putting cookies out for Thomas Edison. Fasten your seatbelts!
- Robert G. Bryant is a NASA chemist who developed Langley Research Center-Soluble Imide (yes, that’s the actual name) a polymer used as an insulation material for leads in implantable cardiac resynchronization therapy devices.
- Rory Cooper is a biomedical engineer who was paralyzed in a bicycle accident. His work has improved manual and electric wheelchairs and advanced the health, mobility, and social inclusion of people with disabilities and older adults. He is also the first NIHF inductee named Rory.
- Katalin Karikó, a biochemist, and Drew Weissman, an immunologist, “discovered how to enable messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) to enter cells without triggering the body’s immune system,” NIHF said, and that laid the foundation for the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines developed by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna. That, of course, led to the antivax movement, which has provided so much LOTME fodder over the years.
- Angela Hartley Brodie was a biochemist who discovered and developed a class of drugs called aromatase inhibitors, which can stop the production of hormones that fuel cancer cell growth and are used to treat breast cancer in 500,000 women worldwide each year.
We can’t mention all of the inductees for 2023 (our editor made that very clear), but we would like to offer a special shout-out to brothers Cyril (the first Cyril in the NIHF, by the way) and Louis Keller, who invented the world’s first compact loader, which eventually became the Bobcat skid-steer loader. Not really medical, you’re probably thinking, but we’re sure that someone, somewhere, at some time, used one to build a hospital, landscape a hospital, or clean up after the demolition of a hospital.
The ‘scheme’ in the name should have been a clue
Retirement. The shiny reward to a lifetime’s worth of working and saving. We’re all literally working to get there, some of us more to get there early, but current research reveals that early retirement isn’t the relaxing finish line we dream about, cognitively speaking.
Researchers at Binghamton (N.Y.) University set out to examine just how retirement plans affect cognitive performance. They started off with China’s New Rural Pension Scheme (scheme probably has a less negative connotation in Chinese), a plan that financially aids the growing rural retirement-age population in the country. Then they looked at data from the Chinese Health and Retirement Longitudinal Survey, which tests cognition with a focus on episodic memory and parts of intact mental status.
What they found was the opposite of what you would expect out of retirees with nothing but time on their hands.
The pension program, which had been in place for almost a decade, led to delayed recall, especially among women, supporting “the mental retirement hypothesis that decreased mental activity results in worsening cognitive skills,” the investigators said in a written statement.
There also was a drop in social engagement, with lower rates of volunteering and social interaction than people who didn’t receive the pension. Some behaviors, like regular alcohol consumption, did improve over the previous year, as did total health in general, but “the adverse effects of early retirement on mental and social engagement significantly outweigh the program’s protective effect on various health behaviors,” Plamen Nikolov, PhD, said about his research.
So if you’re looking to retire early, don’t skimp on the crosswords and the bingo nights. Stay busy in a good way. Your brain will thank you.
Indiana Jones and the First Smallpox Ancestor
Smallpox was, not that long ago, one of the most devastating diseases known to humanity, killing 300 million people in the 20th century alone. Eradicating it has to be one of medicine’s crowning achievements. Now it can only be found in museums, which is where it belongs.
Here’s the thing with smallpox though: For all it did to us, we know frustratingly little about where it came from. Until very recently, the best available genetic evidence placed its emergence in the 17th century, which clashes with historical data. You know what that means, right? It’s time to dig out the fedora and whip, cue the music, and dig into a recently published study spanning continents in search of the mythical smallpox origin story.
We pick up in 2020, when genetic evidence definitively showed smallpox in a Viking burial site, moving the disease’s emergence a thousand years earlier. Which is all well and good, but there’s solid visual evidence that Egyptian pharaohs were dying of smallpox, as their bodies show the signature scarring. Historians were pretty sure smallpox went back about 4,000 years, but there was no genetic material to prove it.
Since there aren’t any 4,000-year-old smallpox germs laying around, the researchers chose to attack the problem another way – by burning down a Venetian catacomb, er, conducting a analysis of historical smallpox genetics to find the virus’s origin. By analyzing the genomes of various strains at different periods of time, they were able to determine that the variola virus had a definitive common ancestor. Some of the genetic components in the Viking-age sample, for example, persisted until the 18th century.
Armed with this information, the scientists determined that the first smallpox ancestor emerged about 3,800 years ago. That’s very close to the historians’ estimate for the disease’s emergence. Proof at last of smallpox’s truly ancient origin. One might even say the researchers chose wisely.
The only hall of fame that really matters
LOTME loves the holiday season – the food, the gifts, the radio stations that play nothing but Christmas music – but for us the most wonderful time of the year comes just a bit later. No, it’s not our annual Golden Globes slap bet. Nope, not even the “excitement” of the College Football Playoff National Championship. It’s time for the National Inventors Hall of Fame to announce its latest inductees, and we could hardly sleep last night after putting cookies out for Thomas Edison. Fasten your seatbelts!
- Robert G. Bryant is a NASA chemist who developed Langley Research Center-Soluble Imide (yes, that’s the actual name) a polymer used as an insulation material for leads in implantable cardiac resynchronization therapy devices.
- Rory Cooper is a biomedical engineer who was paralyzed in a bicycle accident. His work has improved manual and electric wheelchairs and advanced the health, mobility, and social inclusion of people with disabilities and older adults. He is also the first NIHF inductee named Rory.
- Katalin Karikó, a biochemist, and Drew Weissman, an immunologist, “discovered how to enable messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) to enter cells without triggering the body’s immune system,” NIHF said, and that laid the foundation for the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines developed by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna. That, of course, led to the antivax movement, which has provided so much LOTME fodder over the years.
- Angela Hartley Brodie was a biochemist who discovered and developed a class of drugs called aromatase inhibitors, which can stop the production of hormones that fuel cancer cell growth and are used to treat breast cancer in 500,000 women worldwide each year.
We can’t mention all of the inductees for 2023 (our editor made that very clear), but we would like to offer a special shout-out to brothers Cyril (the first Cyril in the NIHF, by the way) and Louis Keller, who invented the world’s first compact loader, which eventually became the Bobcat skid-steer loader. Not really medical, you’re probably thinking, but we’re sure that someone, somewhere, at some time, used one to build a hospital, landscape a hospital, or clean up after the demolition of a hospital.
The ‘scheme’ in the name should have been a clue
Retirement. The shiny reward to a lifetime’s worth of working and saving. We’re all literally working to get there, some of us more to get there early, but current research reveals that early retirement isn’t the relaxing finish line we dream about, cognitively speaking.
Researchers at Binghamton (N.Y.) University set out to examine just how retirement plans affect cognitive performance. They started off with China’s New Rural Pension Scheme (scheme probably has a less negative connotation in Chinese), a plan that financially aids the growing rural retirement-age population in the country. Then they looked at data from the Chinese Health and Retirement Longitudinal Survey, which tests cognition with a focus on episodic memory and parts of intact mental status.
What they found was the opposite of what you would expect out of retirees with nothing but time on their hands.
The pension program, which had been in place for almost a decade, led to delayed recall, especially among women, supporting “the mental retirement hypothesis that decreased mental activity results in worsening cognitive skills,” the investigators said in a written statement.
There also was a drop in social engagement, with lower rates of volunteering and social interaction than people who didn’t receive the pension. Some behaviors, like regular alcohol consumption, did improve over the previous year, as did total health in general, but “the adverse effects of early retirement on mental and social engagement significantly outweigh the program’s protective effect on various health behaviors,” Plamen Nikolov, PhD, said about his research.
So if you’re looking to retire early, don’t skimp on the crosswords and the bingo nights. Stay busy in a good way. Your brain will thank you.
Indiana Jones and the First Smallpox Ancestor
Smallpox was, not that long ago, one of the most devastating diseases known to humanity, killing 300 million people in the 20th century alone. Eradicating it has to be one of medicine’s crowning achievements. Now it can only be found in museums, which is where it belongs.
Here’s the thing with smallpox though: For all it did to us, we know frustratingly little about where it came from. Until very recently, the best available genetic evidence placed its emergence in the 17th century, which clashes with historical data. You know what that means, right? It’s time to dig out the fedora and whip, cue the music, and dig into a recently published study spanning continents in search of the mythical smallpox origin story.
We pick up in 2020, when genetic evidence definitively showed smallpox in a Viking burial site, moving the disease’s emergence a thousand years earlier. Which is all well and good, but there’s solid visual evidence that Egyptian pharaohs were dying of smallpox, as their bodies show the signature scarring. Historians were pretty sure smallpox went back about 4,000 years, but there was no genetic material to prove it.
Since there aren’t any 4,000-year-old smallpox germs laying around, the researchers chose to attack the problem another way – by burning down a Venetian catacomb, er, conducting a analysis of historical smallpox genetics to find the virus’s origin. By analyzing the genomes of various strains at different periods of time, they were able to determine that the variola virus had a definitive common ancestor. Some of the genetic components in the Viking-age sample, for example, persisted until the 18th century.
Armed with this information, the scientists determined that the first smallpox ancestor emerged about 3,800 years ago. That’s very close to the historians’ estimate for the disease’s emergence. Proof at last of smallpox’s truly ancient origin. One might even say the researchers chose wisely.
The only hall of fame that really matters
LOTME loves the holiday season – the food, the gifts, the radio stations that play nothing but Christmas music – but for us the most wonderful time of the year comes just a bit later. No, it’s not our annual Golden Globes slap bet. Nope, not even the “excitement” of the College Football Playoff National Championship. It’s time for the National Inventors Hall of Fame to announce its latest inductees, and we could hardly sleep last night after putting cookies out for Thomas Edison. Fasten your seatbelts!
- Robert G. Bryant is a NASA chemist who developed Langley Research Center-Soluble Imide (yes, that’s the actual name) a polymer used as an insulation material for leads in implantable cardiac resynchronization therapy devices.
- Rory Cooper is a biomedical engineer who was paralyzed in a bicycle accident. His work has improved manual and electric wheelchairs and advanced the health, mobility, and social inclusion of people with disabilities and older adults. He is also the first NIHF inductee named Rory.
- Katalin Karikó, a biochemist, and Drew Weissman, an immunologist, “discovered how to enable messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) to enter cells without triggering the body’s immune system,” NIHF said, and that laid the foundation for the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines developed by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna. That, of course, led to the antivax movement, which has provided so much LOTME fodder over the years.
- Angela Hartley Brodie was a biochemist who discovered and developed a class of drugs called aromatase inhibitors, which can stop the production of hormones that fuel cancer cell growth and are used to treat breast cancer in 500,000 women worldwide each year.
We can’t mention all of the inductees for 2023 (our editor made that very clear), but we would like to offer a special shout-out to brothers Cyril (the first Cyril in the NIHF, by the way) and Louis Keller, who invented the world’s first compact loader, which eventually became the Bobcat skid-steer loader. Not really medical, you’re probably thinking, but we’re sure that someone, somewhere, at some time, used one to build a hospital, landscape a hospital, or clean up after the demolition of a hospital.
35 years in service to you, our community of reproductive health care clinicians
The mission of OBG
OBG
We wish all our readers a wonderful New Year and the best health possible for our patients.
Arnold P. Advincula, MD
I serve on the executive board that oversees the Fellowships in Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery (FMIGS), and in January 2023 will transition into the role of President. I bring to this leadership role nearly 25 years of surgical experience, both as a clinician educator and inventor. My goal during the next 2 years will be to move toward subspecialty recognition of Complex Gynecology.
Linda D. Bradley, MD
My passion is diagnostic and operative hysteroscopy, simple procedures that can both evaluate and treat intrauterine pathology. Recently, I was thrilled to coauthor an article on office hysteroscopy for Obstetrics & Gynecology (September 2022). I will have a chapter on operative hysteroscopy in the 2023 edition of TeLinde’s Textbook of Gynecology, and I am an author for the topic Office and Operative Hysteroscopy in UpToDate. Locally, I am known as the “foodie gynecologist”—I travel, take cooking classes, and I have more cookbooks than gynecology textbooks. Since Covid, I have embraced biking and just completed a riverboat biking cruise from Salamanca, Spain, to Lisbon, Portugal.
Amy L. Garcia, MD
I am fellowship trained as a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon (MIGS) and have had a private surgical practice since 2005. I am involved with The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), AAGL, and international surgical education for office hysteroscopy and related practice management. I am passionate about working with start-up companies in the gynecologic medical device arena and innovation in gynecologic surgery.
Steven R. Goldstein, MD, NCMP, CCD
I just completed my term as President of the International Menopause Society. This culminated in the society’s 18th World Congress in Lisbon, attended by over 1,700 health care providers from 76 countries. I delivered the Pieter van Keep Memorial Lecture, named for one of the society’s founders who died prematurely of pancreatic cancer. I was further honored by receiving the society’s Distinguished Service Award. I am very proud to have previously received the NAMS Thomas B. Clarkson award for Outstanding Clinical and Basic Science Research in Menopause. I also have one foot in the gynecologic ultrasound world and was given the Joseph H. Holmes Pioneer Award and was the 2023 recipient of the William J. Fry Memorial Lecture Award, both from the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine, having written the second book ever on vaginal ultrasonography.
On a personal level, I love to play golf (in spite of my foot drop and 14 orthopedic surgeries). My season tickets show some diversity—the New York City Ballet and St. John’s basketball.
Cheryl B. Iglesia, MD
I am the 49th president of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons, the 5th woman to hold this position, and the first of Filipino-American descent. I recognize that it is only through extraordinary mentorship and support from other giants in gynecology, like Drs. Andrew Kaunitz (fellow OBG
PS—In the spirit of continually learning, I want to add the Argentine tango to my dancing repertoire and go on an African safari; both are on my bucket list as the pandemic eases.
Andrew M. Kaunitz, MD, NCMP
Since starting with the University of Florida College of Medicine-Jacksonville in 1984, I have enjoyed caring for patients, training residents and medical students, and being involved with publications and research. My areas of focus are menopause, contraception, gyn ultrasound and evaluation/management of women with abnormal uterine bleeding. In 2020, I received the North American Menopause Society/Leon Speroff Outstanding Educator Award. In 2021, I received the ACOG Distinguished Service Award. I enjoy spending time with my family, neighborhood bicycling, and searching for sharks’ teeth at the beach.
Barbara Levy, MD
I have been privileged to serve on the OBG
Continue to: David G. Mutch, MD...
David G. Mutch, MD
I am ending my 6-year term as Chair of the National Cancer Institute’s (NCI) gynecologic cancer steering committee. That is the committee that vets all NCI-sponsored clinical trials in gynecologic oncology. I am on the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) Cancer committee, Co-Chair of the American Joint Committee on Cancer gyn staging committee and on the Reproductive Scientist Development Program selection committee. I also am completing my term as Chair of the Foundation for Women’s Cancer; this is the C3, charitable arm, of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology. We have distributed more than $3.5 million to young investigators to help start their research careers in gynecologic oncology.
Errol R. Norwitz, MD, PhD, MBA
I am a physician-scientist with subspecialty training in high-risk obstetrics (maternal-fetal medicine). I was born and raised in Cape Town, South Africa, and I have trained/practiced in 5 countries on 3 continents. My research interests include the pathophysiology, prediction, prevention, and management of pregnancy complications, primarily preterm birth and preeclampsia. I am a member of the Board of Scientific Counselors of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. I am currently President & CEO of Newton-Wellesley Hospital, a comprehensive community-based academic medical center and a member of the Mass General Brigham health care system in Boston, Massachusetts.
Jaimey Pauli, MD
I am the Division Chief and Professor of Maternal-Fetal Medicine (MFM) at the Penn State College of Medicine and Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center. I had exceptional mentoring throughout my medical career, particularly by a former member of the Editorial Board, Dr. John T. Repke. One of the biggest perks of my job is that our division provides full-scope MFM care. While I often serve as the more traditional MFM consultant and academic educator, I also provide longitudinal prenatal care and deliver many of my own patients, often through subsequent pregnancies. Serving as a member of the Editorial Board combines my passion for clinical obstetrical care with my talents (as a former English major) of reading, writing, and editing. I believe that the work we do provides accessible, evidence-based, and practical guidance for our colleagues so they can provide excellence in obstetrical care.
JoAnn Pinkerton, MD, NCMP
I am a Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology and Division Chief of Midlife Health at the University of Virginia (UVA) Health. Passionate about menopause, I am an executive director emeritus of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS) and past-President of NAMS (2008-2009). Within the past few years, I have served as an expert advisor for the recent ACOG Clinical Practice Guidelines on Osteoporosis, the NAMS Position Statements on Hormone Therapy and Osteoporosis, and the Global Consensus on Menopause and Androgen Therapy. I received the 2022 South Atlantic Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Lifetime Achievement Award for my expertise and work in menopause and the NAMS 2020 Ann Voda Community Service Award for my biannual community educational symposiums. I remain active in research, currently the lead and UVA principal investigator for the Oasis 2 multicenter clinical trial, which is testing a neurokinin receptor antagonist as a nonhormone therapy for the relief of hot flashes. Serving on the OBG
Joseph S. Sanfilippo, MD, MBA
I feel honored and privileged to have received the Golden Apple Teaching Award from the Universityof Pittsburgh School of Medicine. I am also fortunate to be the recipient of the Faculty Educator of the Month Award for resident teaching. I have been named Top Doctor 20 years in a row. My current academic activities include, since 2007, Program Director for Reproductive Endocrinology & Infertility Fellowship at the University of Pittsburgh and Chair of the Mentor-Mentee Program at University of Pittsburgh Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences. I am Guest Editor for the medical malpractice section of the journal Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology. Recently, I completed a patient-focused book, “Experts Guide to Fertility,” which will be published in May 2023 by J Hopkins University Publisher and is designed for patients going through infertility treatment. Regarding outside events, I enjoy climbing steep hills and riding far and wide on my “electric bike.” Highly recommend it!
James Simon, MD, CCD, IF, NCMP
It’s been an honor serving on the OBG
I asked our distinguished Board of Editors to identify the most important changes that they believe will occur over the next 5 years, influencing the practice of obstetrics and gynecology. Their expert predictions are summarized below.
Arnold Advincula, MD
As one of the world’s most experienced gynecologic robotic surgeons, the role of this technology will become even more refined over the next 2-5 years with the introduction of sophisticated image guidance, “smart molecules,” and artificial intelligence. All of this will transform both the patient and surgeon experience as well as impact how we train future surgeons.
Linda Bradley, MD
My hope is that a partnership with industry and hysteroscopy thought leaders will enable new developments/technology in performing hysteroscopic sterilization. Conquering the tubal ostia for sterilization in an office setting would profoundly improve contraceptive options for women. Conquering the tubal ostia is the last frontier in gynecology.
Amy Garcia, MD
I predict that new technologies will allow for a significant increase in the number of gynecologists who perform in-office hysteroscopy and that a paradigm shift will occur to replace blind biopsy with hysteroscopy-directed biopsy and evaluation of the uterine cavity.
Steven Goldstein, MD, NCMP, CCD
Among the most important changes in the next 5 years, in my opinion, will be in the arenas of precision medicine, genetic advancement, and artificial intelligence. In addition, unfortunately, there will be an even greater movement toward guidelines utilizing algorithms and clinical pathways. I leave you with the following quote:
“Neither evidence nor clinical judgement alone is sufficient. Evidence without judgement can be applied by a technician. Judgement without evidence can be applied by a friend. But the integration of evidence and judgement is what the healthcare provider does in order to dispense the best clinical care.” —Hertzel Gerstein, MD
Cheryl Iglesia, MD
Technology related to minimally invasive surgery will continue to change our practice, and I predict that surgery will be more centralized to high volume practices. Reimbursements for these procedures may remain a hot button issue, however. The materials used for pelvic reconstruction will be derived from autologous stem cells and advancements made in regenerative medicine.
Andrew Kaunitz, MD, NCMP
As use of contraceptive implants and intrauterine devices continues to grow, I anticipate the incidence of unintended pregnancies will continue to decline. As the novel gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonists combined with estrogen-progestin add-back grow in use, I anticipate this will provide our patients with more nonsurgical options for managing abnormal uterine bleeding, including that associated with uterine fibroids.
Barbara Levy, MD
Quality will be redefined by patient-defined outcome measures that assess what matters to the people we serve. Real-world evidence will be incorporated to support those measures and provide data on patient outcomes in populations not studied in the randomized controlled trials on which we have created guidelines. This will help to refine guidelines and support more equitable and accessible care.
David Mutch, MD
Over the next 5 years, our expanding insights into the molecular biology of cancer will lead to targeted therapies that will yield better responses with less toxicity.
Errol R. Norwitz, MD, PhD, MBA
In the near future we will use predictive AI algorithms to: 1) identify patients at risk of adverse pregnancy events; 2) stratify patients into high-, average-, and low-risk; and 3) design a personalized obstetric care journey for each patient based on their individualized risk stratification with a view to improving safety and quality outcome metrics, addressing health care disparity, and lowering the cost of care.
Jaimey Pauli, MD
I predict (and fervently hope) that breakthroughs will occur in the prevention of two of the most devastating diseases to affect obstetric patients and their families—preterm birth and preeclampsia.
JoAnn Pinkerton, MD, NCMP
New nonhormone management therapies will be available to treat hot flashes and the genitourinary syndrome of menopause. These treatments will be especially welcomed by patients who cannot or choose not to take hormone therapy. We should not allow new technology to overshadow the patient. We must remember to treat the patient with the condition, not just the disease. Consider what is important to the individual woman, her quality of life, and her ability to function, and keep that in mind when deciding what therapy to suggest.
Joseph S. Sanfilippo, MD, MBA
Artificial intelligence will change the way we educate and provide patient care. Three-dimensional perspectives will cross a number of horizons, some of which include:
- advances in assisted reproductive technology (IVF), offering the next level of “in vitro maturation” of oocytes for patients heretofore unable to conceive. They can progress to having a baby with decreased ovarian reserve or in association with “life after cancer.”
- biogenic engineering and bioinformatics will allow correction of genetic defects in embryos prior to implantation
- the surgical arena will incorporate direct robotic initiated procedures and bring robotic surgery to the next level
- with regard to medical education, at all levels, virtual reality, computer-generated 3-dimensional imaging will provide innovative tools.
James Simon, MD, CCD, IF, NCMP
Medicine’s near-term future portends the realization of truly personalized medicine based upon one’s genetic predisposition to disease, and intentional genetic manipulation to mitigate it. Such advances are here already, simply pending regulatory and ethical approval. My concern going forward is that such individualization, and an algorithm-driven decision-making process will result in taking the personal out of personalized medicine. We humans are more than the collected downstream impact of our genes. In our quest for advances, let’s not forget the balance between nature (our genes) and nurture (environment). The risk of forgetting this aphorism, like the electronic health record, gives me heartburn, or worse, burnout!
The mission of OBG
OBG
We wish all our readers a wonderful New Year and the best health possible for our patients.
Arnold P. Advincula, MD
I serve on the executive board that oversees the Fellowships in Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery (FMIGS), and in January 2023 will transition into the role of President. I bring to this leadership role nearly 25 years of surgical experience, both as a clinician educator and inventor. My goal during the next 2 years will be to move toward subspecialty recognition of Complex Gynecology.
Linda D. Bradley, MD
My passion is diagnostic and operative hysteroscopy, simple procedures that can both evaluate and treat intrauterine pathology. Recently, I was thrilled to coauthor an article on office hysteroscopy for Obstetrics & Gynecology (September 2022). I will have a chapter on operative hysteroscopy in the 2023 edition of TeLinde’s Textbook of Gynecology, and I am an author for the topic Office and Operative Hysteroscopy in UpToDate. Locally, I am known as the “foodie gynecologist”—I travel, take cooking classes, and I have more cookbooks than gynecology textbooks. Since Covid, I have embraced biking and just completed a riverboat biking cruise from Salamanca, Spain, to Lisbon, Portugal.
Amy L. Garcia, MD
I am fellowship trained as a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon (MIGS) and have had a private surgical practice since 2005. I am involved with The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), AAGL, and international surgical education for office hysteroscopy and related practice management. I am passionate about working with start-up companies in the gynecologic medical device arena and innovation in gynecologic surgery.
Steven R. Goldstein, MD, NCMP, CCD
I just completed my term as President of the International Menopause Society. This culminated in the society’s 18th World Congress in Lisbon, attended by over 1,700 health care providers from 76 countries. I delivered the Pieter van Keep Memorial Lecture, named for one of the society’s founders who died prematurely of pancreatic cancer. I was further honored by receiving the society’s Distinguished Service Award. I am very proud to have previously received the NAMS Thomas B. Clarkson award for Outstanding Clinical and Basic Science Research in Menopause. I also have one foot in the gynecologic ultrasound world and was given the Joseph H. Holmes Pioneer Award and was the 2023 recipient of the William J. Fry Memorial Lecture Award, both from the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine, having written the second book ever on vaginal ultrasonography.
On a personal level, I love to play golf (in spite of my foot drop and 14 orthopedic surgeries). My season tickets show some diversity—the New York City Ballet and St. John’s basketball.
Cheryl B. Iglesia, MD
I am the 49th president of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons, the 5th woman to hold this position, and the first of Filipino-American descent. I recognize that it is only through extraordinary mentorship and support from other giants in gynecology, like Drs. Andrew Kaunitz (fellow OBG
PS—In the spirit of continually learning, I want to add the Argentine tango to my dancing repertoire and go on an African safari; both are on my bucket list as the pandemic eases.
Andrew M. Kaunitz, MD, NCMP
Since starting with the University of Florida College of Medicine-Jacksonville in 1984, I have enjoyed caring for patients, training residents and medical students, and being involved with publications and research. My areas of focus are menopause, contraception, gyn ultrasound and evaluation/management of women with abnormal uterine bleeding. In 2020, I received the North American Menopause Society/Leon Speroff Outstanding Educator Award. In 2021, I received the ACOG Distinguished Service Award. I enjoy spending time with my family, neighborhood bicycling, and searching for sharks’ teeth at the beach.
Barbara Levy, MD
I have been privileged to serve on the OBG
Continue to: David G. Mutch, MD...
David G. Mutch, MD
I am ending my 6-year term as Chair of the National Cancer Institute’s (NCI) gynecologic cancer steering committee. That is the committee that vets all NCI-sponsored clinical trials in gynecologic oncology. I am on the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) Cancer committee, Co-Chair of the American Joint Committee on Cancer gyn staging committee and on the Reproductive Scientist Development Program selection committee. I also am completing my term as Chair of the Foundation for Women’s Cancer; this is the C3, charitable arm, of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology. We have distributed more than $3.5 million to young investigators to help start their research careers in gynecologic oncology.
Errol R. Norwitz, MD, PhD, MBA
I am a physician-scientist with subspecialty training in high-risk obstetrics (maternal-fetal medicine). I was born and raised in Cape Town, South Africa, and I have trained/practiced in 5 countries on 3 continents. My research interests include the pathophysiology, prediction, prevention, and management of pregnancy complications, primarily preterm birth and preeclampsia. I am a member of the Board of Scientific Counselors of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. I am currently President & CEO of Newton-Wellesley Hospital, a comprehensive community-based academic medical center and a member of the Mass General Brigham health care system in Boston, Massachusetts.
Jaimey Pauli, MD
I am the Division Chief and Professor of Maternal-Fetal Medicine (MFM) at the Penn State College of Medicine and Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center. I had exceptional mentoring throughout my medical career, particularly by a former member of the Editorial Board, Dr. John T. Repke. One of the biggest perks of my job is that our division provides full-scope MFM care. While I often serve as the more traditional MFM consultant and academic educator, I also provide longitudinal prenatal care and deliver many of my own patients, often through subsequent pregnancies. Serving as a member of the Editorial Board combines my passion for clinical obstetrical care with my talents (as a former English major) of reading, writing, and editing. I believe that the work we do provides accessible, evidence-based, and practical guidance for our colleagues so they can provide excellence in obstetrical care.
JoAnn Pinkerton, MD, NCMP
I am a Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology and Division Chief of Midlife Health at the University of Virginia (UVA) Health. Passionate about menopause, I am an executive director emeritus of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS) and past-President of NAMS (2008-2009). Within the past few years, I have served as an expert advisor for the recent ACOG Clinical Practice Guidelines on Osteoporosis, the NAMS Position Statements on Hormone Therapy and Osteoporosis, and the Global Consensus on Menopause and Androgen Therapy. I received the 2022 South Atlantic Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Lifetime Achievement Award for my expertise and work in menopause and the NAMS 2020 Ann Voda Community Service Award for my biannual community educational symposiums. I remain active in research, currently the lead and UVA principal investigator for the Oasis 2 multicenter clinical trial, which is testing a neurokinin receptor antagonist as a nonhormone therapy for the relief of hot flashes. Serving on the OBG
Joseph S. Sanfilippo, MD, MBA
I feel honored and privileged to have received the Golden Apple Teaching Award from the Universityof Pittsburgh School of Medicine. I am also fortunate to be the recipient of the Faculty Educator of the Month Award for resident teaching. I have been named Top Doctor 20 years in a row. My current academic activities include, since 2007, Program Director for Reproductive Endocrinology & Infertility Fellowship at the University of Pittsburgh and Chair of the Mentor-Mentee Program at University of Pittsburgh Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences. I am Guest Editor for the medical malpractice section of the journal Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology. Recently, I completed a patient-focused book, “Experts Guide to Fertility,” which will be published in May 2023 by J Hopkins University Publisher and is designed for patients going through infertility treatment. Regarding outside events, I enjoy climbing steep hills and riding far and wide on my “electric bike.” Highly recommend it!
James Simon, MD, CCD, IF, NCMP
It’s been an honor serving on the OBG
I asked our distinguished Board of Editors to identify the most important changes that they believe will occur over the next 5 years, influencing the practice of obstetrics and gynecology. Their expert predictions are summarized below.
Arnold Advincula, MD
As one of the world’s most experienced gynecologic robotic surgeons, the role of this technology will become even more refined over the next 2-5 years with the introduction of sophisticated image guidance, “smart molecules,” and artificial intelligence. All of this will transform both the patient and surgeon experience as well as impact how we train future surgeons.
Linda Bradley, MD
My hope is that a partnership with industry and hysteroscopy thought leaders will enable new developments/technology in performing hysteroscopic sterilization. Conquering the tubal ostia for sterilization in an office setting would profoundly improve contraceptive options for women. Conquering the tubal ostia is the last frontier in gynecology.
Amy Garcia, MD
I predict that new technologies will allow for a significant increase in the number of gynecologists who perform in-office hysteroscopy and that a paradigm shift will occur to replace blind biopsy with hysteroscopy-directed biopsy and evaluation of the uterine cavity.
Steven Goldstein, MD, NCMP, CCD
Among the most important changes in the next 5 years, in my opinion, will be in the arenas of precision medicine, genetic advancement, and artificial intelligence. In addition, unfortunately, there will be an even greater movement toward guidelines utilizing algorithms and clinical pathways. I leave you with the following quote:
“Neither evidence nor clinical judgement alone is sufficient. Evidence without judgement can be applied by a technician. Judgement without evidence can be applied by a friend. But the integration of evidence and judgement is what the healthcare provider does in order to dispense the best clinical care.” —Hertzel Gerstein, MD
Cheryl Iglesia, MD
Technology related to minimally invasive surgery will continue to change our practice, and I predict that surgery will be more centralized to high volume practices. Reimbursements for these procedures may remain a hot button issue, however. The materials used for pelvic reconstruction will be derived from autologous stem cells and advancements made in regenerative medicine.
Andrew Kaunitz, MD, NCMP
As use of contraceptive implants and intrauterine devices continues to grow, I anticipate the incidence of unintended pregnancies will continue to decline. As the novel gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonists combined with estrogen-progestin add-back grow in use, I anticipate this will provide our patients with more nonsurgical options for managing abnormal uterine bleeding, including that associated with uterine fibroids.
Barbara Levy, MD
Quality will be redefined by patient-defined outcome measures that assess what matters to the people we serve. Real-world evidence will be incorporated to support those measures and provide data on patient outcomes in populations not studied in the randomized controlled trials on which we have created guidelines. This will help to refine guidelines and support more equitable and accessible care.
David Mutch, MD
Over the next 5 years, our expanding insights into the molecular biology of cancer will lead to targeted therapies that will yield better responses with less toxicity.
Errol R. Norwitz, MD, PhD, MBA
In the near future we will use predictive AI algorithms to: 1) identify patients at risk of adverse pregnancy events; 2) stratify patients into high-, average-, and low-risk; and 3) design a personalized obstetric care journey for each patient based on their individualized risk stratification with a view to improving safety and quality outcome metrics, addressing health care disparity, and lowering the cost of care.
Jaimey Pauli, MD
I predict (and fervently hope) that breakthroughs will occur in the prevention of two of the most devastating diseases to affect obstetric patients and their families—preterm birth and preeclampsia.
JoAnn Pinkerton, MD, NCMP
New nonhormone management therapies will be available to treat hot flashes and the genitourinary syndrome of menopause. These treatments will be especially welcomed by patients who cannot or choose not to take hormone therapy. We should not allow new technology to overshadow the patient. We must remember to treat the patient with the condition, not just the disease. Consider what is important to the individual woman, her quality of life, and her ability to function, and keep that in mind when deciding what therapy to suggest.
Joseph S. Sanfilippo, MD, MBA
Artificial intelligence will change the way we educate and provide patient care. Three-dimensional perspectives will cross a number of horizons, some of which include:
- advances in assisted reproductive technology (IVF), offering the next level of “in vitro maturation” of oocytes for patients heretofore unable to conceive. They can progress to having a baby with decreased ovarian reserve or in association with “life after cancer.”
- biogenic engineering and bioinformatics will allow correction of genetic defects in embryos prior to implantation
- the surgical arena will incorporate direct robotic initiated procedures and bring robotic surgery to the next level
- with regard to medical education, at all levels, virtual reality, computer-generated 3-dimensional imaging will provide innovative tools.
James Simon, MD, CCD, IF, NCMP
Medicine’s near-term future portends the realization of truly personalized medicine based upon one’s genetic predisposition to disease, and intentional genetic manipulation to mitigate it. Such advances are here already, simply pending regulatory and ethical approval. My concern going forward is that such individualization, and an algorithm-driven decision-making process will result in taking the personal out of personalized medicine. We humans are more than the collected downstream impact of our genes. In our quest for advances, let’s not forget the balance between nature (our genes) and nurture (environment). The risk of forgetting this aphorism, like the electronic health record, gives me heartburn, or worse, burnout!
The mission of OBG
OBG
We wish all our readers a wonderful New Year and the best health possible for our patients.
Arnold P. Advincula, MD
I serve on the executive board that oversees the Fellowships in Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery (FMIGS), and in January 2023 will transition into the role of President. I bring to this leadership role nearly 25 years of surgical experience, both as a clinician educator and inventor. My goal during the next 2 years will be to move toward subspecialty recognition of Complex Gynecology.
Linda D. Bradley, MD
My passion is diagnostic and operative hysteroscopy, simple procedures that can both evaluate and treat intrauterine pathology. Recently, I was thrilled to coauthor an article on office hysteroscopy for Obstetrics & Gynecology (September 2022). I will have a chapter on operative hysteroscopy in the 2023 edition of TeLinde’s Textbook of Gynecology, and I am an author for the topic Office and Operative Hysteroscopy in UpToDate. Locally, I am known as the “foodie gynecologist”—I travel, take cooking classes, and I have more cookbooks than gynecology textbooks. Since Covid, I have embraced biking and just completed a riverboat biking cruise from Salamanca, Spain, to Lisbon, Portugal.
Amy L. Garcia, MD
I am fellowship trained as a minimally invasive gynecologic surgeon (MIGS) and have had a private surgical practice since 2005. I am involved with The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), AAGL, and international surgical education for office hysteroscopy and related practice management. I am passionate about working with start-up companies in the gynecologic medical device arena and innovation in gynecologic surgery.
Steven R. Goldstein, MD, NCMP, CCD
I just completed my term as President of the International Menopause Society. This culminated in the society’s 18th World Congress in Lisbon, attended by over 1,700 health care providers from 76 countries. I delivered the Pieter van Keep Memorial Lecture, named for one of the society’s founders who died prematurely of pancreatic cancer. I was further honored by receiving the society’s Distinguished Service Award. I am very proud to have previously received the NAMS Thomas B. Clarkson award for Outstanding Clinical and Basic Science Research in Menopause. I also have one foot in the gynecologic ultrasound world and was given the Joseph H. Holmes Pioneer Award and was the 2023 recipient of the William J. Fry Memorial Lecture Award, both from the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine, having written the second book ever on vaginal ultrasonography.
On a personal level, I love to play golf (in spite of my foot drop and 14 orthopedic surgeries). My season tickets show some diversity—the New York City Ballet and St. John’s basketball.
Cheryl B. Iglesia, MD
I am the 49th president of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons, the 5th woman to hold this position, and the first of Filipino-American descent. I recognize that it is only through extraordinary mentorship and support from other giants in gynecology, like Drs. Andrew Kaunitz (fellow OBG
PS—In the spirit of continually learning, I want to add the Argentine tango to my dancing repertoire and go on an African safari; both are on my bucket list as the pandemic eases.
Andrew M. Kaunitz, MD, NCMP
Since starting with the University of Florida College of Medicine-Jacksonville in 1984, I have enjoyed caring for patients, training residents and medical students, and being involved with publications and research. My areas of focus are menopause, contraception, gyn ultrasound and evaluation/management of women with abnormal uterine bleeding. In 2020, I received the North American Menopause Society/Leon Speroff Outstanding Educator Award. In 2021, I received the ACOG Distinguished Service Award. I enjoy spending time with my family, neighborhood bicycling, and searching for sharks’ teeth at the beach.
Barbara Levy, MD
I have been privileged to serve on the OBG
Continue to: David G. Mutch, MD...
David G. Mutch, MD
I am ending my 6-year term as Chair of the National Cancer Institute’s (NCI) gynecologic cancer steering committee. That is the committee that vets all NCI-sponsored clinical trials in gynecologic oncology. I am on the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) Cancer committee, Co-Chair of the American Joint Committee on Cancer gyn staging committee and on the Reproductive Scientist Development Program selection committee. I also am completing my term as Chair of the Foundation for Women’s Cancer; this is the C3, charitable arm, of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology. We have distributed more than $3.5 million to young investigators to help start their research careers in gynecologic oncology.
Errol R. Norwitz, MD, PhD, MBA
I am a physician-scientist with subspecialty training in high-risk obstetrics (maternal-fetal medicine). I was born and raised in Cape Town, South Africa, and I have trained/practiced in 5 countries on 3 continents. My research interests include the pathophysiology, prediction, prevention, and management of pregnancy complications, primarily preterm birth and preeclampsia. I am a member of the Board of Scientific Counselors of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. I am currently President & CEO of Newton-Wellesley Hospital, a comprehensive community-based academic medical center and a member of the Mass General Brigham health care system in Boston, Massachusetts.
Jaimey Pauli, MD
I am the Division Chief and Professor of Maternal-Fetal Medicine (MFM) at the Penn State College of Medicine and Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center. I had exceptional mentoring throughout my medical career, particularly by a former member of the Editorial Board, Dr. John T. Repke. One of the biggest perks of my job is that our division provides full-scope MFM care. While I often serve as the more traditional MFM consultant and academic educator, I also provide longitudinal prenatal care and deliver many of my own patients, often through subsequent pregnancies. Serving as a member of the Editorial Board combines my passion for clinical obstetrical care with my talents (as a former English major) of reading, writing, and editing. I believe that the work we do provides accessible, evidence-based, and practical guidance for our colleagues so they can provide excellence in obstetrical care.
JoAnn Pinkerton, MD, NCMP
I am a Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology and Division Chief of Midlife Health at the University of Virginia (UVA) Health. Passionate about menopause, I am an executive director emeritus of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS) and past-President of NAMS (2008-2009). Within the past few years, I have served as an expert advisor for the recent ACOG Clinical Practice Guidelines on Osteoporosis, the NAMS Position Statements on Hormone Therapy and Osteoporosis, and the Global Consensus on Menopause and Androgen Therapy. I received the 2022 South Atlantic Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Lifetime Achievement Award for my expertise and work in menopause and the NAMS 2020 Ann Voda Community Service Award for my biannual community educational symposiums. I remain active in research, currently the lead and UVA principal investigator for the Oasis 2 multicenter clinical trial, which is testing a neurokinin receptor antagonist as a nonhormone therapy for the relief of hot flashes. Serving on the OBG
Joseph S. Sanfilippo, MD, MBA
I feel honored and privileged to have received the Golden Apple Teaching Award from the Universityof Pittsburgh School of Medicine. I am also fortunate to be the recipient of the Faculty Educator of the Month Award for resident teaching. I have been named Top Doctor 20 years in a row. My current academic activities include, since 2007, Program Director for Reproductive Endocrinology & Infertility Fellowship at the University of Pittsburgh and Chair of the Mentor-Mentee Program at University of Pittsburgh Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences. I am Guest Editor for the medical malpractice section of the journal Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology. Recently, I completed a patient-focused book, “Experts Guide to Fertility,” which will be published in May 2023 by J Hopkins University Publisher and is designed for patients going through infertility treatment. Regarding outside events, I enjoy climbing steep hills and riding far and wide on my “electric bike.” Highly recommend it!
James Simon, MD, CCD, IF, NCMP
It’s been an honor serving on the OBG
I asked our distinguished Board of Editors to identify the most important changes that they believe will occur over the next 5 years, influencing the practice of obstetrics and gynecology. Their expert predictions are summarized below.
Arnold Advincula, MD
As one of the world’s most experienced gynecologic robotic surgeons, the role of this technology will become even more refined over the next 2-5 years with the introduction of sophisticated image guidance, “smart molecules,” and artificial intelligence. All of this will transform both the patient and surgeon experience as well as impact how we train future surgeons.
Linda Bradley, MD
My hope is that a partnership with industry and hysteroscopy thought leaders will enable new developments/technology in performing hysteroscopic sterilization. Conquering the tubal ostia for sterilization in an office setting would profoundly improve contraceptive options for women. Conquering the tubal ostia is the last frontier in gynecology.
Amy Garcia, MD
I predict that new technologies will allow for a significant increase in the number of gynecologists who perform in-office hysteroscopy and that a paradigm shift will occur to replace blind biopsy with hysteroscopy-directed biopsy and evaluation of the uterine cavity.
Steven Goldstein, MD, NCMP, CCD
Among the most important changes in the next 5 years, in my opinion, will be in the arenas of precision medicine, genetic advancement, and artificial intelligence. In addition, unfortunately, there will be an even greater movement toward guidelines utilizing algorithms and clinical pathways. I leave you with the following quote:
“Neither evidence nor clinical judgement alone is sufficient. Evidence without judgement can be applied by a technician. Judgement without evidence can be applied by a friend. But the integration of evidence and judgement is what the healthcare provider does in order to dispense the best clinical care.” —Hertzel Gerstein, MD
Cheryl Iglesia, MD
Technology related to minimally invasive surgery will continue to change our practice, and I predict that surgery will be more centralized to high volume practices. Reimbursements for these procedures may remain a hot button issue, however. The materials used for pelvic reconstruction will be derived from autologous stem cells and advancements made in regenerative medicine.
Andrew Kaunitz, MD, NCMP
As use of contraceptive implants and intrauterine devices continues to grow, I anticipate the incidence of unintended pregnancies will continue to decline. As the novel gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonists combined with estrogen-progestin add-back grow in use, I anticipate this will provide our patients with more nonsurgical options for managing abnormal uterine bleeding, including that associated with uterine fibroids.
Barbara Levy, MD
Quality will be redefined by patient-defined outcome measures that assess what matters to the people we serve. Real-world evidence will be incorporated to support those measures and provide data on patient outcomes in populations not studied in the randomized controlled trials on which we have created guidelines. This will help to refine guidelines and support more equitable and accessible care.
David Mutch, MD
Over the next 5 years, our expanding insights into the molecular biology of cancer will lead to targeted therapies that will yield better responses with less toxicity.
Errol R. Norwitz, MD, PhD, MBA
In the near future we will use predictive AI algorithms to: 1) identify patients at risk of adverse pregnancy events; 2) stratify patients into high-, average-, and low-risk; and 3) design a personalized obstetric care journey for each patient based on their individualized risk stratification with a view to improving safety and quality outcome metrics, addressing health care disparity, and lowering the cost of care.
Jaimey Pauli, MD
I predict (and fervently hope) that breakthroughs will occur in the prevention of two of the most devastating diseases to affect obstetric patients and their families—preterm birth and preeclampsia.
JoAnn Pinkerton, MD, NCMP
New nonhormone management therapies will be available to treat hot flashes and the genitourinary syndrome of menopause. These treatments will be especially welcomed by patients who cannot or choose not to take hormone therapy. We should not allow new technology to overshadow the patient. We must remember to treat the patient with the condition, not just the disease. Consider what is important to the individual woman, her quality of life, and her ability to function, and keep that in mind when deciding what therapy to suggest.
Joseph S. Sanfilippo, MD, MBA
Artificial intelligence will change the way we educate and provide patient care. Three-dimensional perspectives will cross a number of horizons, some of which include:
- advances in assisted reproductive technology (IVF), offering the next level of “in vitro maturation” of oocytes for patients heretofore unable to conceive. They can progress to having a baby with decreased ovarian reserve or in association with “life after cancer.”
- biogenic engineering and bioinformatics will allow correction of genetic defects in embryos prior to implantation
- the surgical arena will incorporate direct robotic initiated procedures and bring robotic surgery to the next level
- with regard to medical education, at all levels, virtual reality, computer-generated 3-dimensional imaging will provide innovative tools.
James Simon, MD, CCD, IF, NCMP
Medicine’s near-term future portends the realization of truly personalized medicine based upon one’s genetic predisposition to disease, and intentional genetic manipulation to mitigate it. Such advances are here already, simply pending regulatory and ethical approval. My concern going forward is that such individualization, and an algorithm-driven decision-making process will result in taking the personal out of personalized medicine. We humans are more than the collected downstream impact of our genes. In our quest for advances, let’s not forget the balance between nature (our genes) and nurture (environment). The risk of forgetting this aphorism, like the electronic health record, gives me heartburn, or worse, burnout!
Marriage rates declining for Canadian adolescent mothers?
The decline in marriage rates in Canada is sharper among adolescent mothers, new data suggest.
An analysis of data from the Canadian Vital Statistics – Birth Database indicates that marriages declined by 80.5% among mothers younger than 18 years between 1989 and 2018.
“This study documents a decrease in marriage prevalence among mothers aged <18, 18-19, 20-24, and 25-49 years and suggests a larger relative decline in prevalence in younger mothers, especially those below age 18,” wrote study author Andrée-Anne Fafard St-Germain, PhD, a postdoctoral trainee at the University of Toronto, and colleagues.
The study was published online in the Canadian Journal of Public Health.
A general decline
The researchers estimated marriage rates among mothers in the four age groups mentioned above. They compared marriage rates in each group during the periods 1989-1990 and 2017-2018. The study included records of 10,399,250 mothers. In all, 1,118,630 records were used to identify socioeconomic and geographic patterns.
The researchers found an expected decline in marriage rates between 1989 and 2018, but the decline was steeper among younger women. Marriage rates decreased by 13.6% among women aged 25-49 years (16.0% relative decline), 29.3% among those aged 20-24 years (47.3% relative decline), 14.3% among those aged 18-19 years (60.2% relative decline), and 6.7% among those under 18 (80.5% relative decline).
Compared with Canadian-born mothers, foreign-born mothers were more likely to be married in all age groups (adjusted odds ratios [aORs], 5.18-6.36). Residence in rural locales or small towns was also associated with greater probability of marriage (aOR, 1.27-1.32).
Compared with women in the prairie provinces, those in Ontario were more likely to be married (aOR, 1.23-1.41), while the rate was lower in Quebec (aOR, 0.27-0.70), the Atlantic Provinces (aOR, 0.49-0.65), and the territories (aOR, 0.26-0.49). The researchers found no statistically significant association between neighborhood income quintiles and marriage rates in those younger than 18. They found a greater likelihood of marriage for mothers aged 18-19 years and those aged 20-24 years who resided in neighborhoods in higher income quintiles.
Human rights concern
Commenting on the study, Alissa Koski, PhD, assistant professor of epidemiology, biostatistics, and occupational health at McGill University, said, “Nearly all research on child marriage has focused on countries in South Asia and Africa. The authors acknowledge that child marriage remains legal across Canada. This draws attention to a domestic human rights concern that is largely unacknowledged.”
Overall, the study confirms trends that have been noted in Canada and have been studied by sociologists, Dr. Koski added. Traditional marriage rates have been declining for decades, while common-law marriages have been increasing. The mean age at the time of marriage increased from 30.0 years in 2016 to 30.7 years in 2020, according to Statistics Canada.
The study is limited by its failure to account for common-law marriages, which represent 98% of child marriages, said Dr. Koski. “The percentage of mothers in all age groups who were in legal or common-law marriage is almost certainly much higher than reported in this paper. However, because common-law unions are more common among younger people, the percentage of mothers in younger age groups, including those under 18, may be underestimated to a greater extent.”
The authors’ conclusion that the decline in marriages was larger among mothers younger than 18 years is not supported by the data in the article, said Dr. Koski. “That conclusion seems to overlook the fact that the absolute decline was lowest among those below age 18. The percentage decline in marriage was highest among mothers under 18, but this is at least in part because the percentage was so low to begin with. If we look instead at the absolute decline in marriage, it was lowest among mothers under age 18.”
The authors also suggest that the change in socioeconomic conditions associated with marriage may be different among mothers younger than 18 years, compared with mothers aged 18-19 years or 20-24 years. Higher socioeconomic status, as reflected in higher maternal neighborhood income quintiles, was associated with marriage among older adolescent mothers but not among mothers younger than 18 years. The socioeconomic distinction between married mothers younger than 18 years and older mothers could contribute to differences in the health advantages of marriage over time, the authors wrote.
But this conclusion as well is an “inappropriate interpretation ... not supported by the data,” said Dr. Koski. She noted that births to mothers younger than 18 years are rare in Canada, and births to married mothers in that age group are even rarer. That factor could have led the study to be underpowered in this group and yielded odds ratios that are not statistically significant. “The data are consistent with either an increase or a decrease in the odds of marriage. The data were too sparse to measure accurately,” said Dr. Koski.
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research Foundation. Dr. Fafard St-Germain and Dr. Koski reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The decline in marriage rates in Canada is sharper among adolescent mothers, new data suggest.
An analysis of data from the Canadian Vital Statistics – Birth Database indicates that marriages declined by 80.5% among mothers younger than 18 years between 1989 and 2018.
“This study documents a decrease in marriage prevalence among mothers aged <18, 18-19, 20-24, and 25-49 years and suggests a larger relative decline in prevalence in younger mothers, especially those below age 18,” wrote study author Andrée-Anne Fafard St-Germain, PhD, a postdoctoral trainee at the University of Toronto, and colleagues.
The study was published online in the Canadian Journal of Public Health.
A general decline
The researchers estimated marriage rates among mothers in the four age groups mentioned above. They compared marriage rates in each group during the periods 1989-1990 and 2017-2018. The study included records of 10,399,250 mothers. In all, 1,118,630 records were used to identify socioeconomic and geographic patterns.
The researchers found an expected decline in marriage rates between 1989 and 2018, but the decline was steeper among younger women. Marriage rates decreased by 13.6% among women aged 25-49 years (16.0% relative decline), 29.3% among those aged 20-24 years (47.3% relative decline), 14.3% among those aged 18-19 years (60.2% relative decline), and 6.7% among those under 18 (80.5% relative decline).
Compared with Canadian-born mothers, foreign-born mothers were more likely to be married in all age groups (adjusted odds ratios [aORs], 5.18-6.36). Residence in rural locales or small towns was also associated with greater probability of marriage (aOR, 1.27-1.32).
Compared with women in the prairie provinces, those in Ontario were more likely to be married (aOR, 1.23-1.41), while the rate was lower in Quebec (aOR, 0.27-0.70), the Atlantic Provinces (aOR, 0.49-0.65), and the territories (aOR, 0.26-0.49). The researchers found no statistically significant association between neighborhood income quintiles and marriage rates in those younger than 18. They found a greater likelihood of marriage for mothers aged 18-19 years and those aged 20-24 years who resided in neighborhoods in higher income quintiles.
Human rights concern
Commenting on the study, Alissa Koski, PhD, assistant professor of epidemiology, biostatistics, and occupational health at McGill University, said, “Nearly all research on child marriage has focused on countries in South Asia and Africa. The authors acknowledge that child marriage remains legal across Canada. This draws attention to a domestic human rights concern that is largely unacknowledged.”
Overall, the study confirms trends that have been noted in Canada and have been studied by sociologists, Dr. Koski added. Traditional marriage rates have been declining for decades, while common-law marriages have been increasing. The mean age at the time of marriage increased from 30.0 years in 2016 to 30.7 years in 2020, according to Statistics Canada.
The study is limited by its failure to account for common-law marriages, which represent 98% of child marriages, said Dr. Koski. “The percentage of mothers in all age groups who were in legal or common-law marriage is almost certainly much higher than reported in this paper. However, because common-law unions are more common among younger people, the percentage of mothers in younger age groups, including those under 18, may be underestimated to a greater extent.”
The authors’ conclusion that the decline in marriages was larger among mothers younger than 18 years is not supported by the data in the article, said Dr. Koski. “That conclusion seems to overlook the fact that the absolute decline was lowest among those below age 18. The percentage decline in marriage was highest among mothers under 18, but this is at least in part because the percentage was so low to begin with. If we look instead at the absolute decline in marriage, it was lowest among mothers under age 18.”
The authors also suggest that the change in socioeconomic conditions associated with marriage may be different among mothers younger than 18 years, compared with mothers aged 18-19 years or 20-24 years. Higher socioeconomic status, as reflected in higher maternal neighborhood income quintiles, was associated with marriage among older adolescent mothers but not among mothers younger than 18 years. The socioeconomic distinction between married mothers younger than 18 years and older mothers could contribute to differences in the health advantages of marriage over time, the authors wrote.
But this conclusion as well is an “inappropriate interpretation ... not supported by the data,” said Dr. Koski. She noted that births to mothers younger than 18 years are rare in Canada, and births to married mothers in that age group are even rarer. That factor could have led the study to be underpowered in this group and yielded odds ratios that are not statistically significant. “The data are consistent with either an increase or a decrease in the odds of marriage. The data were too sparse to measure accurately,” said Dr. Koski.
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research Foundation. Dr. Fafard St-Germain and Dr. Koski reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The decline in marriage rates in Canada is sharper among adolescent mothers, new data suggest.
An analysis of data from the Canadian Vital Statistics – Birth Database indicates that marriages declined by 80.5% among mothers younger than 18 years between 1989 and 2018.
“This study documents a decrease in marriage prevalence among mothers aged <18, 18-19, 20-24, and 25-49 years and suggests a larger relative decline in prevalence in younger mothers, especially those below age 18,” wrote study author Andrée-Anne Fafard St-Germain, PhD, a postdoctoral trainee at the University of Toronto, and colleagues.
The study was published online in the Canadian Journal of Public Health.
A general decline
The researchers estimated marriage rates among mothers in the four age groups mentioned above. They compared marriage rates in each group during the periods 1989-1990 and 2017-2018. The study included records of 10,399,250 mothers. In all, 1,118,630 records were used to identify socioeconomic and geographic patterns.
The researchers found an expected decline in marriage rates between 1989 and 2018, but the decline was steeper among younger women. Marriage rates decreased by 13.6% among women aged 25-49 years (16.0% relative decline), 29.3% among those aged 20-24 years (47.3% relative decline), 14.3% among those aged 18-19 years (60.2% relative decline), and 6.7% among those under 18 (80.5% relative decline).
Compared with Canadian-born mothers, foreign-born mothers were more likely to be married in all age groups (adjusted odds ratios [aORs], 5.18-6.36). Residence in rural locales or small towns was also associated with greater probability of marriage (aOR, 1.27-1.32).
Compared with women in the prairie provinces, those in Ontario were more likely to be married (aOR, 1.23-1.41), while the rate was lower in Quebec (aOR, 0.27-0.70), the Atlantic Provinces (aOR, 0.49-0.65), and the territories (aOR, 0.26-0.49). The researchers found no statistically significant association between neighborhood income quintiles and marriage rates in those younger than 18. They found a greater likelihood of marriage for mothers aged 18-19 years and those aged 20-24 years who resided in neighborhoods in higher income quintiles.
Human rights concern
Commenting on the study, Alissa Koski, PhD, assistant professor of epidemiology, biostatistics, and occupational health at McGill University, said, “Nearly all research on child marriage has focused on countries in South Asia and Africa. The authors acknowledge that child marriage remains legal across Canada. This draws attention to a domestic human rights concern that is largely unacknowledged.”
Overall, the study confirms trends that have been noted in Canada and have been studied by sociologists, Dr. Koski added. Traditional marriage rates have been declining for decades, while common-law marriages have been increasing. The mean age at the time of marriage increased from 30.0 years in 2016 to 30.7 years in 2020, according to Statistics Canada.
The study is limited by its failure to account for common-law marriages, which represent 98% of child marriages, said Dr. Koski. “The percentage of mothers in all age groups who were in legal or common-law marriage is almost certainly much higher than reported in this paper. However, because common-law unions are more common among younger people, the percentage of mothers in younger age groups, including those under 18, may be underestimated to a greater extent.”
The authors’ conclusion that the decline in marriages was larger among mothers younger than 18 years is not supported by the data in the article, said Dr. Koski. “That conclusion seems to overlook the fact that the absolute decline was lowest among those below age 18. The percentage decline in marriage was highest among mothers under 18, but this is at least in part because the percentage was so low to begin with. If we look instead at the absolute decline in marriage, it was lowest among mothers under age 18.”
The authors also suggest that the change in socioeconomic conditions associated with marriage may be different among mothers younger than 18 years, compared with mothers aged 18-19 years or 20-24 years. Higher socioeconomic status, as reflected in higher maternal neighborhood income quintiles, was associated with marriage among older adolescent mothers but not among mothers younger than 18 years. The socioeconomic distinction between married mothers younger than 18 years and older mothers could contribute to differences in the health advantages of marriage over time, the authors wrote.
But this conclusion as well is an “inappropriate interpretation ... not supported by the data,” said Dr. Koski. She noted that births to mothers younger than 18 years are rare in Canada, and births to married mothers in that age group are even rarer. That factor could have led the study to be underpowered in this group and yielded odds ratios that are not statistically significant. “The data are consistent with either an increase or a decrease in the odds of marriage. The data were too sparse to measure accurately,” said Dr. Koski.
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research Foundation. Dr. Fafard St-Germain and Dr. Koski reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE CANADIAN JOURNAL OF PUBLIC HEALTH
Fair access crucial for new diabetes/kidney disease drugs, say guidelines
The 2022 guideline update released by the KDIGO organization for managing people with diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD) highlighted the safety and expanded, evidence-based role for agents from three drug classes: the SGLT2 inhibitors, the GLP-1 receptor agonists, and the nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists.
But this key take-away from the guideline also underscored the challenges for ensuring fair and affordable access among US patients to these practice-changing medications.
The impact of widespread adoption of these three drug classes into routine US management of people with diabetes and CKD “will be determined by how effective the health care system and its patients and clinicians are at overcoming individual and structural barriers,” write Milda Saunders, MD, and Neda Laiteerapong, MD, in an editorial that accompanied the publication of a synopsis of the 2022 guideline update in Annals of Internal Medicine.
The synopsis is an 11-page distillation of the full 128-page guideline released by the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) organization in 2022.
The recommendations in the 2022 guideline update “are exciting for their potential to change the natural history of CKD and diabetes, but their effect could be highly limited by barriers at multiple levels,” write Dr. Saunders and Dr. Laiteerapong, two internal medicine physicians at the University of Chicago.
“Without equitable implementation of the KDIGO 2022 guidelines there is a potential that clinical practice variation will increase and widen health inequities for minoritized people with CKD and diabetes,” they warn.
Generics to the rescue
One potentially effective, and likely imminent, way to level the prescribing field for patients with CKD and diabetes is for agents from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, glucagonlike peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, and nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist classes to become available in generic formulations.
That should lower prices and thereby boost wider access and will likely occur fairly soon for at least two of the three drug classes, Dr. Laiteerapong predicts.
Some GLP-1 receptor agonists have already escaped patent exclusivity or will do so in 2023, she notes, including the anticipated ability of one drugmaker to start U.S. marketing of generic liraglutide by the end of 2023.
However, whether that manufacturer, Teva, proceeds with generic liraglutide “is a big question,” Dr. Laiteerapong said in an interview. She cited Teva’s history of failing to introduce a generic formulation of exenatide onto the U.S. market even though it has had a green light to do so since 2017.
The only nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist now on the market is finerenone (Kerendia), which will not go off patent for several more years, but for some branded SGLT2 inhibitors, U.S. patents will expire in 2025. In addition, remogliflozin is an SGLT2 inhibitor that “may have already lost patent exclusivity,” noted Dr. Laiteerapong, although it has also never received U.S. marketing approval.
Dr. Laiteerapong expressed optimism that the overall trajectory of access is on the rise. “Many people have type 2 diabetes, and these drugs are in demand,” she noted. She also pointed to progress recently made on insulin affordability. “Things will get better as long as people advocate and argue for equity,” she maintained.
Incentivize formulary listings
Dr. Laiteerapong cited other approaches that could boost access to these medications, such as “creating incentives for pharmaceutical companies to ensure that [these drugs] are on formularies” of large, government-affiliated U.S. health insurance programs, such as Medicare Advantage plans, Medicare Part D, state Medicaid plans, and coverage through U.S. Veterans Affairs and the Tricare health insurance plans available to active members of the US military.
The editorial she coauthored with Dr. Saunders also calls for future collaborations among various medical societies to create “a more unified and streamlined set of recommendations” that benefits patients with diabetes, CKD, and multiple other chronic conditions.
“Over the last decade, we have seen more societies willing to present cooperative guidelines, as well as a surge in research on patients who live with multiple chronic conditions. There is momentum that will allow these different societies to work together,” Dr. Laiteerapong said.
Dr. Laiteerapong and Dr. Saunders have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The 2022 guideline update released by the KDIGO organization for managing people with diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD) highlighted the safety and expanded, evidence-based role for agents from three drug classes: the SGLT2 inhibitors, the GLP-1 receptor agonists, and the nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists.
But this key take-away from the guideline also underscored the challenges for ensuring fair and affordable access among US patients to these practice-changing medications.
The impact of widespread adoption of these three drug classes into routine US management of people with diabetes and CKD “will be determined by how effective the health care system and its patients and clinicians are at overcoming individual and structural barriers,” write Milda Saunders, MD, and Neda Laiteerapong, MD, in an editorial that accompanied the publication of a synopsis of the 2022 guideline update in Annals of Internal Medicine.
The synopsis is an 11-page distillation of the full 128-page guideline released by the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) organization in 2022.
The recommendations in the 2022 guideline update “are exciting for their potential to change the natural history of CKD and diabetes, but their effect could be highly limited by barriers at multiple levels,” write Dr. Saunders and Dr. Laiteerapong, two internal medicine physicians at the University of Chicago.
“Without equitable implementation of the KDIGO 2022 guidelines there is a potential that clinical practice variation will increase and widen health inequities for minoritized people with CKD and diabetes,” they warn.
Generics to the rescue
One potentially effective, and likely imminent, way to level the prescribing field for patients with CKD and diabetes is for agents from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, glucagonlike peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, and nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist classes to become available in generic formulations.
That should lower prices and thereby boost wider access and will likely occur fairly soon for at least two of the three drug classes, Dr. Laiteerapong predicts.
Some GLP-1 receptor agonists have already escaped patent exclusivity or will do so in 2023, she notes, including the anticipated ability of one drugmaker to start U.S. marketing of generic liraglutide by the end of 2023.
However, whether that manufacturer, Teva, proceeds with generic liraglutide “is a big question,” Dr. Laiteerapong said in an interview. She cited Teva’s history of failing to introduce a generic formulation of exenatide onto the U.S. market even though it has had a green light to do so since 2017.
The only nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist now on the market is finerenone (Kerendia), which will not go off patent for several more years, but for some branded SGLT2 inhibitors, U.S. patents will expire in 2025. In addition, remogliflozin is an SGLT2 inhibitor that “may have already lost patent exclusivity,” noted Dr. Laiteerapong, although it has also never received U.S. marketing approval.
Dr. Laiteerapong expressed optimism that the overall trajectory of access is on the rise. “Many people have type 2 diabetes, and these drugs are in demand,” she noted. She also pointed to progress recently made on insulin affordability. “Things will get better as long as people advocate and argue for equity,” she maintained.
Incentivize formulary listings
Dr. Laiteerapong cited other approaches that could boost access to these medications, such as “creating incentives for pharmaceutical companies to ensure that [these drugs] are on formularies” of large, government-affiliated U.S. health insurance programs, such as Medicare Advantage plans, Medicare Part D, state Medicaid plans, and coverage through U.S. Veterans Affairs and the Tricare health insurance plans available to active members of the US military.
The editorial she coauthored with Dr. Saunders also calls for future collaborations among various medical societies to create “a more unified and streamlined set of recommendations” that benefits patients with diabetes, CKD, and multiple other chronic conditions.
“Over the last decade, we have seen more societies willing to present cooperative guidelines, as well as a surge in research on patients who live with multiple chronic conditions. There is momentum that will allow these different societies to work together,” Dr. Laiteerapong said.
Dr. Laiteerapong and Dr. Saunders have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The 2022 guideline update released by the KDIGO organization for managing people with diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD) highlighted the safety and expanded, evidence-based role for agents from three drug classes: the SGLT2 inhibitors, the GLP-1 receptor agonists, and the nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists.
But this key take-away from the guideline also underscored the challenges for ensuring fair and affordable access among US patients to these practice-changing medications.
The impact of widespread adoption of these three drug classes into routine US management of people with diabetes and CKD “will be determined by how effective the health care system and its patients and clinicians are at overcoming individual and structural barriers,” write Milda Saunders, MD, and Neda Laiteerapong, MD, in an editorial that accompanied the publication of a synopsis of the 2022 guideline update in Annals of Internal Medicine.
The synopsis is an 11-page distillation of the full 128-page guideline released by the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) organization in 2022.
The recommendations in the 2022 guideline update “are exciting for their potential to change the natural history of CKD and diabetes, but their effect could be highly limited by barriers at multiple levels,” write Dr. Saunders and Dr. Laiteerapong, two internal medicine physicians at the University of Chicago.
“Without equitable implementation of the KDIGO 2022 guidelines there is a potential that clinical practice variation will increase and widen health inequities for minoritized people with CKD and diabetes,” they warn.
Generics to the rescue
One potentially effective, and likely imminent, way to level the prescribing field for patients with CKD and diabetes is for agents from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, glucagonlike peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, and nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist classes to become available in generic formulations.
That should lower prices and thereby boost wider access and will likely occur fairly soon for at least two of the three drug classes, Dr. Laiteerapong predicts.
Some GLP-1 receptor agonists have already escaped patent exclusivity or will do so in 2023, she notes, including the anticipated ability of one drugmaker to start U.S. marketing of generic liraglutide by the end of 2023.
However, whether that manufacturer, Teva, proceeds with generic liraglutide “is a big question,” Dr. Laiteerapong said in an interview. She cited Teva’s history of failing to introduce a generic formulation of exenatide onto the U.S. market even though it has had a green light to do so since 2017.
The only nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist now on the market is finerenone (Kerendia), which will not go off patent for several more years, but for some branded SGLT2 inhibitors, U.S. patents will expire in 2025. In addition, remogliflozin is an SGLT2 inhibitor that “may have already lost patent exclusivity,” noted Dr. Laiteerapong, although it has also never received U.S. marketing approval.
Dr. Laiteerapong expressed optimism that the overall trajectory of access is on the rise. “Many people have type 2 diabetes, and these drugs are in demand,” she noted. She also pointed to progress recently made on insulin affordability. “Things will get better as long as people advocate and argue for equity,” she maintained.
Incentivize formulary listings
Dr. Laiteerapong cited other approaches that could boost access to these medications, such as “creating incentives for pharmaceutical companies to ensure that [these drugs] are on formularies” of large, government-affiliated U.S. health insurance programs, such as Medicare Advantage plans, Medicare Part D, state Medicaid plans, and coverage through U.S. Veterans Affairs and the Tricare health insurance plans available to active members of the US military.
The editorial she coauthored with Dr. Saunders also calls for future collaborations among various medical societies to create “a more unified and streamlined set of recommendations” that benefits patients with diabetes, CKD, and multiple other chronic conditions.
“Over the last decade, we have seen more societies willing to present cooperative guidelines, as well as a surge in research on patients who live with multiple chronic conditions. There is momentum that will allow these different societies to work together,” Dr. Laiteerapong said.
Dr. Laiteerapong and Dr. Saunders have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
PPI use in type 2 diabetes links with cardiovascular events
Among people with type 2 diabetes who self-reported regularly using a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) events as well as all-cause death was significantly increased in a study of more than 19,000 people with type 2 diabetes in a prospective U.K. database.
During median follow-up of about 11 years, regular use of a PPI by people with type 2 diabetes was significantly linked with a 27% relative increase in the incidence of coronary artery disease, compared with nonuse of a PPI, after full adjustment for potential confounding variables.
The results also show PPI use was significantly linked after full adjustment with a 34% relative increase in MI, a 35% relative increase in heart failure, and a 30% relative increase in all-cause death, say a team of Chinese researchers in a recent report in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
PPIs are a medication class widely used in both over-the-counter and prescription formulations to reduce acid production in the stomach and to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease and other acid-related disorders. The PPI class includes such widely used agents as esomeprazole (Nexium), lansoprazole (Prevacid), and omeprazole (Prilosec).
The analyses in this report, which used data collected in the UK Biobank, are “rigorous,” and the findings of “a modest elevation of CVD risk are consistent with a growing number of observational studies in populations with and without diabetes,” commented Mary R. Rooney, PhD, an epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, who focuses on diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
Prior observational reports
For example, a report from a prospective, observational study of more than 4300 U.S. residents published in 2021 that Dr. Rooney coauthored documented that cumulative PPI exposure for more than 5 years was significantly linked with a twofold increase in the rate of CVD events, compared with people who did not use a PPI. (This analysis did not examine a possible effect of diabetes status.)
And in a separate prospective, observational study of more than 1,000 Australians with type 2 diabetes, initiation of PPI treatment was significantly linked with a 3.6-fold increased incidence of CVD events, compared with PPI nonuse.
However, Dr. Rooney cautioned that the role of PPI use in raising CVD events “is still an unresolved question. It is too soon to tell if PPI use in people with diabetes should trigger additional caution.” Findings are needed from prospective, randomized trials to determine more definitively whether PPIs play a causal role in the incidence of CVD events, she said in an interview.
U.S. practice often results in unwarranted prolongation of PPI treatment, said the authors of an editorial that accompanied the 2021 report by Dr. Rooney and coauthors.
Long-term PPI use threatens harm
“The practice of initiating stress ulcer prophylaxis [by administering a PPI] in critical care is common,” wrote the authors of the 2021 editorial, Nitin Malik, MD, and William S. Weintraub, MD. “Although it is data driven and well intentioned, the possibility of causing harm – if it is continued on a long-term basis after resolution of the acute illness – is palpable.”
The new analyses using UK Biobank data included 19,229 adults with type 2 diabetes and no preexisting coronary artery disease, MI, heart failure, or stroke. The cohort included 15,954 people (83%) who did not report using a PPI and 3,275 who currently used PPIs regularly. Study limitations include self-report as the only verification of PPI use and lack of information on type of PPI, dose size, or use duration.
The findings remained consistent in several sensitivity analyses, including a propensity score–matched analysis and after further adjustment for use of histamine2 receptor antagonists, a drug class with indications similar to those for PPIs.
The authors of the report speculated that mechanisms that might link PPI use and increased CVD and mortality risk could include changes to the gut microbiota and possible interactions between PPIs and antiplatelet agents.
The study received no commercial funding. The authors and Dr. Rooney disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among people with type 2 diabetes who self-reported regularly using a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) events as well as all-cause death was significantly increased in a study of more than 19,000 people with type 2 diabetes in a prospective U.K. database.
During median follow-up of about 11 years, regular use of a PPI by people with type 2 diabetes was significantly linked with a 27% relative increase in the incidence of coronary artery disease, compared with nonuse of a PPI, after full adjustment for potential confounding variables.
The results also show PPI use was significantly linked after full adjustment with a 34% relative increase in MI, a 35% relative increase in heart failure, and a 30% relative increase in all-cause death, say a team of Chinese researchers in a recent report in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
PPIs are a medication class widely used in both over-the-counter and prescription formulations to reduce acid production in the stomach and to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease and other acid-related disorders. The PPI class includes such widely used agents as esomeprazole (Nexium), lansoprazole (Prevacid), and omeprazole (Prilosec).
The analyses in this report, which used data collected in the UK Biobank, are “rigorous,” and the findings of “a modest elevation of CVD risk are consistent with a growing number of observational studies in populations with and without diabetes,” commented Mary R. Rooney, PhD, an epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, who focuses on diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
Prior observational reports
For example, a report from a prospective, observational study of more than 4300 U.S. residents published in 2021 that Dr. Rooney coauthored documented that cumulative PPI exposure for more than 5 years was significantly linked with a twofold increase in the rate of CVD events, compared with people who did not use a PPI. (This analysis did not examine a possible effect of diabetes status.)
And in a separate prospective, observational study of more than 1,000 Australians with type 2 diabetes, initiation of PPI treatment was significantly linked with a 3.6-fold increased incidence of CVD events, compared with PPI nonuse.
However, Dr. Rooney cautioned that the role of PPI use in raising CVD events “is still an unresolved question. It is too soon to tell if PPI use in people with diabetes should trigger additional caution.” Findings are needed from prospective, randomized trials to determine more definitively whether PPIs play a causal role in the incidence of CVD events, she said in an interview.
U.S. practice often results in unwarranted prolongation of PPI treatment, said the authors of an editorial that accompanied the 2021 report by Dr. Rooney and coauthors.
Long-term PPI use threatens harm
“The practice of initiating stress ulcer prophylaxis [by administering a PPI] in critical care is common,” wrote the authors of the 2021 editorial, Nitin Malik, MD, and William S. Weintraub, MD. “Although it is data driven and well intentioned, the possibility of causing harm – if it is continued on a long-term basis after resolution of the acute illness – is palpable.”
The new analyses using UK Biobank data included 19,229 adults with type 2 diabetes and no preexisting coronary artery disease, MI, heart failure, or stroke. The cohort included 15,954 people (83%) who did not report using a PPI and 3,275 who currently used PPIs regularly. Study limitations include self-report as the only verification of PPI use and lack of information on type of PPI, dose size, or use duration.
The findings remained consistent in several sensitivity analyses, including a propensity score–matched analysis and after further adjustment for use of histamine2 receptor antagonists, a drug class with indications similar to those for PPIs.
The authors of the report speculated that mechanisms that might link PPI use and increased CVD and mortality risk could include changes to the gut microbiota and possible interactions between PPIs and antiplatelet agents.
The study received no commercial funding. The authors and Dr. Rooney disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among people with type 2 diabetes who self-reported regularly using a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) events as well as all-cause death was significantly increased in a study of more than 19,000 people with type 2 diabetes in a prospective U.K. database.
During median follow-up of about 11 years, regular use of a PPI by people with type 2 diabetes was significantly linked with a 27% relative increase in the incidence of coronary artery disease, compared with nonuse of a PPI, after full adjustment for potential confounding variables.
The results also show PPI use was significantly linked after full adjustment with a 34% relative increase in MI, a 35% relative increase in heart failure, and a 30% relative increase in all-cause death, say a team of Chinese researchers in a recent report in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
PPIs are a medication class widely used in both over-the-counter and prescription formulations to reduce acid production in the stomach and to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease and other acid-related disorders. The PPI class includes such widely used agents as esomeprazole (Nexium), lansoprazole (Prevacid), and omeprazole (Prilosec).
The analyses in this report, which used data collected in the UK Biobank, are “rigorous,” and the findings of “a modest elevation of CVD risk are consistent with a growing number of observational studies in populations with and without diabetes,” commented Mary R. Rooney, PhD, an epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, who focuses on diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
Prior observational reports
For example, a report from a prospective, observational study of more than 4300 U.S. residents published in 2021 that Dr. Rooney coauthored documented that cumulative PPI exposure for more than 5 years was significantly linked with a twofold increase in the rate of CVD events, compared with people who did not use a PPI. (This analysis did not examine a possible effect of diabetes status.)
And in a separate prospective, observational study of more than 1,000 Australians with type 2 diabetes, initiation of PPI treatment was significantly linked with a 3.6-fold increased incidence of CVD events, compared with PPI nonuse.
However, Dr. Rooney cautioned that the role of PPI use in raising CVD events “is still an unresolved question. It is too soon to tell if PPI use in people with diabetes should trigger additional caution.” Findings are needed from prospective, randomized trials to determine more definitively whether PPIs play a causal role in the incidence of CVD events, she said in an interview.
U.S. practice often results in unwarranted prolongation of PPI treatment, said the authors of an editorial that accompanied the 2021 report by Dr. Rooney and coauthors.
Long-term PPI use threatens harm
“The practice of initiating stress ulcer prophylaxis [by administering a PPI] in critical care is common,” wrote the authors of the 2021 editorial, Nitin Malik, MD, and William S. Weintraub, MD. “Although it is data driven and well intentioned, the possibility of causing harm – if it is continued on a long-term basis after resolution of the acute illness – is palpable.”
The new analyses using UK Biobank data included 19,229 adults with type 2 diabetes and no preexisting coronary artery disease, MI, heart failure, or stroke. The cohort included 15,954 people (83%) who did not report using a PPI and 3,275 who currently used PPIs regularly. Study limitations include self-report as the only verification of PPI use and lack of information on type of PPI, dose size, or use duration.
The findings remained consistent in several sensitivity analyses, including a propensity score–matched analysis and after further adjustment for use of histamine2 receptor antagonists, a drug class with indications similar to those for PPIs.
The authors of the report speculated that mechanisms that might link PPI use and increased CVD and mortality risk could include changes to the gut microbiota and possible interactions between PPIs and antiplatelet agents.
The study received no commercial funding. The authors and Dr. Rooney disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGY AND METABOLISM
Frail ADHF patients benefit more from early rehab
Patients with acute decompensated heart failure who were frail at baseline improved more with targeted, early physical rehabilitation than those who were prefrail, a new analysis of the REHAB-HF study suggests.
“The robust response to the intervention by frail patients exceeded our expectations,” Gordon R. Reeves, MD, PT, of Novant Health Heart and Vascular Institute, Charlotte, N.C., told this news organization. “The effect size from improvement in physical function among frail patients was very large, with at least four times the minimal meaningful improvement, based on the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB).”
Furthermore, the interaction between baseline frailty status and treatment in REHAB-HF was such that a 2.6-fold larger improvement in SPPB was seen among frail versus prefrail patients.
However, Dr. Reeves noted, “We need to further evaluate safety and efficacy as it relates to adverse clinical events. Specifically, we observed a numerically higher number of deaths with the REHAB-HF intervention, which warrants further investigation before the intervention is implemented in clinical practice.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Interpret with caution
Dr. Reeves and colleagues conducted a prespecified secondary analysis of the previously published Therapy in Older Acute Heart Failure Patients (REHAB-HF) trial, a multicenter, randomized controlled trial that showed that a 3-month early, transitional, tailored, multidomain physical rehabilitation intervention improved physical function and quality of life (QoL), compared with usual care. The secondary analysis aimed to evaluate whether baseline frailty altered the benefits of the intervention or was associated with risk of adverse outcomes.
According to Dr. Reeves, REHAB-HF differs from more traditional cardiac rehab programs in several ways.
- The intervention targets patients with acute HF, including HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). Medicare policy limits standard cardiac rehabilitation in HF to long-term patients with HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) only who have been stabilized for 6 weeks or longer after a recent hospitalization.
- It addresses multiple physical function domains, including balance, mobility, functional strength, and endurance. Standard cardiac rehab is primarily focused on endurance training, which can result in injuries and falls if deficits in balance, mobility, and strength are not addressed first.
- It is delivered one to one rather than in a group setting and primarily by physical therapists who are experts in the rehabilitation of medically complex patients.
- It is transitional, beginning in the hospital, then moving to the outpatient setting, then to home and includes a home assessment.
For the analysis, the Fried phenotype model was used to assess baseline frailty across five domains: unintentional weight loss during the past year; self-reported exhaustion; grip strength; slowness, as assessed by gait speed; and low physical activity, as assessed by the Short Form-12 Physical Composite Score.
At the baseline visit, patients were categorized as frail if they met three or more of these criteria. They were categorized as prefrail if they met one or two criteria and as nonfrail if they met none of the criteria. Because of the small number of nonfrail participants, the analysis included only frail and prefrail participants.
The analysis included 337 participants (mean age, 72; 54%, women; 50%, Black). At baseline, 57% were frail, and 43% were prefrail.
A significant interaction was seen between baseline frailty and the intervention for the primary trial endpoint of overall SPPB score, with a 2.6-fold larger improvement in SPPB among frail (2.1) versus prefrail (0.8) patients.
Trends favored a larger intervention effect size, with significant improvement among frail versus prefrail participants for 6-minute walk distance, QoL, and the geriatric depression score.
“However, we must interpret these findings with caution,” the authors write. “The REHAB-HF trial was not adequately powered to determine the effect of the intervention on clinical events.” This plus the number of deaths “underscore the need for additional research, including prospective clinical trials, investigating the effect of physical function interventions on clinical events among frail patients with HF.”
To address this need, the researchers recently launched a larger clinical trial, called REHAB-HFpEF, which is powered to assess the impact of the intervention on clinical events, according to Dr. Reeves. “As the name implies,” he said, “this trial is focused on older patients recently hospitalized with HFpEF, who, [compared with HFrEF] also showed a more robust response to the intervention, with worse physical function and very high prevalence of frailty near the time of hospital discharge.”
‘Never too old or sick to benefit’
Jonathan H. Whiteson, MD, vice chair of clinical operations and medical director of cardiac and pulmonary rehabilitation at NYU Langone Health’s Rusk Rehabilitation, said, “We have seen in clinical practice and in other (non–heart failure) clinical areas that frail older patients do improve proportionally more than younger and less frail patients with rehabilitation programs. Encouragingly, this very much supports the practice that patients are never too old or too sick to benefit from an individualized multidisciplinary rehabilitation program.”
However, he noted, “patients had to be independent with basic activities of daily living to be included in the study,” so many frail, elderly patients with heart failure who are not independent were not included in the study. It also wasn’t clear whether patients who received postacute care at a rehab facility before going home were included in the trial.
Furthermore, he said, outcomes over 1 to 5 years are needed to understand the long-term impact of the intervention.
On the other hand, he added, the fact that about half of participants were Black and were women is a “tremendous strength.”
“Repeating this study in population groups at high risk for frailty with different diagnoses, such as chronic lung diseases, interstitial lung diseases, chronic kidney disease, and rheumatologic disorders will further support the value of rehabilitation in improving patient health, function, quality of life, and reducing rehospitalizations and health care costs,” Dr. Whiteson concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the National Key R&D program. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with acute decompensated heart failure who were frail at baseline improved more with targeted, early physical rehabilitation than those who were prefrail, a new analysis of the REHAB-HF study suggests.
“The robust response to the intervention by frail patients exceeded our expectations,” Gordon R. Reeves, MD, PT, of Novant Health Heart and Vascular Institute, Charlotte, N.C., told this news organization. “The effect size from improvement in physical function among frail patients was very large, with at least four times the minimal meaningful improvement, based on the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB).”
Furthermore, the interaction between baseline frailty status and treatment in REHAB-HF was such that a 2.6-fold larger improvement in SPPB was seen among frail versus prefrail patients.
However, Dr. Reeves noted, “We need to further evaluate safety and efficacy as it relates to adverse clinical events. Specifically, we observed a numerically higher number of deaths with the REHAB-HF intervention, which warrants further investigation before the intervention is implemented in clinical practice.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Interpret with caution
Dr. Reeves and colleagues conducted a prespecified secondary analysis of the previously published Therapy in Older Acute Heart Failure Patients (REHAB-HF) trial, a multicenter, randomized controlled trial that showed that a 3-month early, transitional, tailored, multidomain physical rehabilitation intervention improved physical function and quality of life (QoL), compared with usual care. The secondary analysis aimed to evaluate whether baseline frailty altered the benefits of the intervention or was associated with risk of adverse outcomes.
According to Dr. Reeves, REHAB-HF differs from more traditional cardiac rehab programs in several ways.
- The intervention targets patients with acute HF, including HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). Medicare policy limits standard cardiac rehabilitation in HF to long-term patients with HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) only who have been stabilized for 6 weeks or longer after a recent hospitalization.
- It addresses multiple physical function domains, including balance, mobility, functional strength, and endurance. Standard cardiac rehab is primarily focused on endurance training, which can result in injuries and falls if deficits in balance, mobility, and strength are not addressed first.
- It is delivered one to one rather than in a group setting and primarily by physical therapists who are experts in the rehabilitation of medically complex patients.
- It is transitional, beginning in the hospital, then moving to the outpatient setting, then to home and includes a home assessment.
For the analysis, the Fried phenotype model was used to assess baseline frailty across five domains: unintentional weight loss during the past year; self-reported exhaustion; grip strength; slowness, as assessed by gait speed; and low physical activity, as assessed by the Short Form-12 Physical Composite Score.
At the baseline visit, patients were categorized as frail if they met three or more of these criteria. They were categorized as prefrail if they met one or two criteria and as nonfrail if they met none of the criteria. Because of the small number of nonfrail participants, the analysis included only frail and prefrail participants.
The analysis included 337 participants (mean age, 72; 54%, women; 50%, Black). At baseline, 57% were frail, and 43% were prefrail.
A significant interaction was seen between baseline frailty and the intervention for the primary trial endpoint of overall SPPB score, with a 2.6-fold larger improvement in SPPB among frail (2.1) versus prefrail (0.8) patients.
Trends favored a larger intervention effect size, with significant improvement among frail versus prefrail participants for 6-minute walk distance, QoL, and the geriatric depression score.
“However, we must interpret these findings with caution,” the authors write. “The REHAB-HF trial was not adequately powered to determine the effect of the intervention on clinical events.” This plus the number of deaths “underscore the need for additional research, including prospective clinical trials, investigating the effect of physical function interventions on clinical events among frail patients with HF.”
To address this need, the researchers recently launched a larger clinical trial, called REHAB-HFpEF, which is powered to assess the impact of the intervention on clinical events, according to Dr. Reeves. “As the name implies,” he said, “this trial is focused on older patients recently hospitalized with HFpEF, who, [compared with HFrEF] also showed a more robust response to the intervention, with worse physical function and very high prevalence of frailty near the time of hospital discharge.”
‘Never too old or sick to benefit’
Jonathan H. Whiteson, MD, vice chair of clinical operations and medical director of cardiac and pulmonary rehabilitation at NYU Langone Health’s Rusk Rehabilitation, said, “We have seen in clinical practice and in other (non–heart failure) clinical areas that frail older patients do improve proportionally more than younger and less frail patients with rehabilitation programs. Encouragingly, this very much supports the practice that patients are never too old or too sick to benefit from an individualized multidisciplinary rehabilitation program.”
However, he noted, “patients had to be independent with basic activities of daily living to be included in the study,” so many frail, elderly patients with heart failure who are not independent were not included in the study. It also wasn’t clear whether patients who received postacute care at a rehab facility before going home were included in the trial.
Furthermore, he said, outcomes over 1 to 5 years are needed to understand the long-term impact of the intervention.
On the other hand, he added, the fact that about half of participants were Black and were women is a “tremendous strength.”
“Repeating this study in population groups at high risk for frailty with different diagnoses, such as chronic lung diseases, interstitial lung diseases, chronic kidney disease, and rheumatologic disorders will further support the value of rehabilitation in improving patient health, function, quality of life, and reducing rehospitalizations and health care costs,” Dr. Whiteson concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the National Key R&D program. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with acute decompensated heart failure who were frail at baseline improved more with targeted, early physical rehabilitation than those who were prefrail, a new analysis of the REHAB-HF study suggests.
“The robust response to the intervention by frail patients exceeded our expectations,” Gordon R. Reeves, MD, PT, of Novant Health Heart and Vascular Institute, Charlotte, N.C., told this news organization. “The effect size from improvement in physical function among frail patients was very large, with at least four times the minimal meaningful improvement, based on the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB).”
Furthermore, the interaction between baseline frailty status and treatment in REHAB-HF was such that a 2.6-fold larger improvement in SPPB was seen among frail versus prefrail patients.
However, Dr. Reeves noted, “We need to further evaluate safety and efficacy as it relates to adverse clinical events. Specifically, we observed a numerically higher number of deaths with the REHAB-HF intervention, which warrants further investigation before the intervention is implemented in clinical practice.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Interpret with caution
Dr. Reeves and colleagues conducted a prespecified secondary analysis of the previously published Therapy in Older Acute Heart Failure Patients (REHAB-HF) trial, a multicenter, randomized controlled trial that showed that a 3-month early, transitional, tailored, multidomain physical rehabilitation intervention improved physical function and quality of life (QoL), compared with usual care. The secondary analysis aimed to evaluate whether baseline frailty altered the benefits of the intervention or was associated with risk of adverse outcomes.
According to Dr. Reeves, REHAB-HF differs from more traditional cardiac rehab programs in several ways.
- The intervention targets patients with acute HF, including HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). Medicare policy limits standard cardiac rehabilitation in HF to long-term patients with HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) only who have been stabilized for 6 weeks or longer after a recent hospitalization.
- It addresses multiple physical function domains, including balance, mobility, functional strength, and endurance. Standard cardiac rehab is primarily focused on endurance training, which can result in injuries and falls if deficits in balance, mobility, and strength are not addressed first.
- It is delivered one to one rather than in a group setting and primarily by physical therapists who are experts in the rehabilitation of medically complex patients.
- It is transitional, beginning in the hospital, then moving to the outpatient setting, then to home and includes a home assessment.
For the analysis, the Fried phenotype model was used to assess baseline frailty across five domains: unintentional weight loss during the past year; self-reported exhaustion; grip strength; slowness, as assessed by gait speed; and low physical activity, as assessed by the Short Form-12 Physical Composite Score.
At the baseline visit, patients were categorized as frail if they met three or more of these criteria. They were categorized as prefrail if they met one or two criteria and as nonfrail if they met none of the criteria. Because of the small number of nonfrail participants, the analysis included only frail and prefrail participants.
The analysis included 337 participants (mean age, 72; 54%, women; 50%, Black). At baseline, 57% were frail, and 43% were prefrail.
A significant interaction was seen between baseline frailty and the intervention for the primary trial endpoint of overall SPPB score, with a 2.6-fold larger improvement in SPPB among frail (2.1) versus prefrail (0.8) patients.
Trends favored a larger intervention effect size, with significant improvement among frail versus prefrail participants for 6-minute walk distance, QoL, and the geriatric depression score.
“However, we must interpret these findings with caution,” the authors write. “The REHAB-HF trial was not adequately powered to determine the effect of the intervention on clinical events.” This plus the number of deaths “underscore the need for additional research, including prospective clinical trials, investigating the effect of physical function interventions on clinical events among frail patients with HF.”
To address this need, the researchers recently launched a larger clinical trial, called REHAB-HFpEF, which is powered to assess the impact of the intervention on clinical events, according to Dr. Reeves. “As the name implies,” he said, “this trial is focused on older patients recently hospitalized with HFpEF, who, [compared with HFrEF] also showed a more robust response to the intervention, with worse physical function and very high prevalence of frailty near the time of hospital discharge.”
‘Never too old or sick to benefit’
Jonathan H. Whiteson, MD, vice chair of clinical operations and medical director of cardiac and pulmonary rehabilitation at NYU Langone Health’s Rusk Rehabilitation, said, “We have seen in clinical practice and in other (non–heart failure) clinical areas that frail older patients do improve proportionally more than younger and less frail patients with rehabilitation programs. Encouragingly, this very much supports the practice that patients are never too old or too sick to benefit from an individualized multidisciplinary rehabilitation program.”
However, he noted, “patients had to be independent with basic activities of daily living to be included in the study,” so many frail, elderly patients with heart failure who are not independent were not included in the study. It also wasn’t clear whether patients who received postacute care at a rehab facility before going home were included in the trial.
Furthermore, he said, outcomes over 1 to 5 years are needed to understand the long-term impact of the intervention.
On the other hand, he added, the fact that about half of participants were Black and were women is a “tremendous strength.”
“Repeating this study in population groups at high risk for frailty with different diagnoses, such as chronic lung diseases, interstitial lung diseases, chronic kidney disease, and rheumatologic disorders will further support the value of rehabilitation in improving patient health, function, quality of life, and reducing rehospitalizations and health care costs,” Dr. Whiteson concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the National Key R&D program. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Patients Make Unexpected Medical Choices
Due to advances in medicine, people are living longer with the aid of increased options for life-prolonging treatments. These treatment options may improve the quantity but not necessarily the quality of life.1
Kidney failure can be treated with renal replacement therapy (dialysis or renal transplantation) or supportive care.2 In 2017, the global prevalence of kidney failure was about 5.3 to 9.7 million.3 In the United States, about 500,000 patients are receiving maintenance dialysis for end-stage renal disease (ESRD), and about 1 in 4 will stop dialysis before death, coupled with hospice enrollment.4 ESRD is 2 times more prevalent among veterans than in nonveterans, which can be due in part to high rates of comorbid predisposing conditions, such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and advanced age, among others.5 The decision to discontinue dialysis and receive hospice care tends to be more difficult than choosing to withhold or forego dialysis.6
A study conducted among patients who were taken off hemodialysis before death reported that the 2 most common reasons for the withdrawal were acute medical complications and frailty.7 A retrospective study among patients with ESRD receiving hemodialysis highlighted the underutilization of hospice care in this patient population.8 The study also found that those patients who were aged > 75 years, had poor functional status, and had dialysis-related complications, such as sepsis and anemia, were more likely to elect withdrawal of hemodialysis. There was no difference in overall survival or quality of life among patients who were aged ≥ 75 years with multiple comorbidities and functional impairment who elected conservative management vs those who started dialysis.8 Long-term continuous dialysis has been associated with a lower quality of life, increased dependence on others, and a variety of symptoms, such as pain, nausea, insomnia, anxiety, or depression.9
Conservative Care vs Medical Paternalism
In the United States, it is unusual for patients with ESRD to choose conservative care, and supportive services are less available for those who do compared with patients with ESRD in Europe, Asia, Australia, and Canada.10 A study looking at a small number of US nephrologists has shown they may have limited experience in caring for patients who forego dialysis and they are not comfortable offering conservative management over dialysis.10 Another small study from Sweden also showed that many nephrologists do not feel prepared for end-of-life care and conversations.11
Patients often rely on knowledgeable recommendations from medical experts. However, medical paternalism occurs when a physician makes decisions deemed to be in the patient’s best interest but are against the patient’s wishes or when the patient is unable to give their consent.12 Hard paternalism occurs when the patient is competent to make their own medical decisions, while soft paternalism occurs when a patient is not competent to make their own medical decisions.13
Patient autonomy is widely recognized as an ethical principle in medicine. It recognizes patients as well-informed decision makers who may act without excessive influence to make intentional determinations on their own behalf.14 Autonomy can be exercised at any point during the health care process.12 Although ethical and legal guidelines encourage physicians to recommend appropriate treatment, medical opinion cannot overrule the wishes of a competent patient who refuses treatment.12
Case Presentation
Mr. S presented to the emergency department at a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical center with abdominal pain from recurrent pancreatitis. The patient aged > 65 years had a history of depression, ESRD, and was receiving hemodialysis. A computed tomography scan revealed a new pancreatic mass, and he was referred to the palliative care (PC) department nurse practitioner (NP) for a goals-of-care discussion. PC was informed to assist with hospice care initiation: The patient elected a do-not-resuscitate (DNR) code status and hospice care.
At the consultation, Mr. S stated that he had decided to forego life-prolonging treatments, including hemodialysis, and declined further evaluation for his pancreatic mass. He shared a good understanding of concerns for malignancy with his mass but did not wish to pursue further diagnostics as he knew his life expectancy was very limited without dialysis. He had been dependent on hemodialysis for the past 10 years. He had briefly received hospice care 5 years before but changed his mind and decided to pursue standard care, including life-prolonging dialysis treatments. He reported no depression, suicidal ideation, or intentions of hastening his death. He stated that he was just physically tired from his ongoing dialysis, recurrent hospitalizations, and being repeatedly subjected to diagnostic tests. Mr. S added that he had discussed his plan with his family, including his son and sister-in-law who is married to his brother. Mr. S previously identified his brother as his surrogate decision maker.
Mr. S shared that his brother had sustained a traumatic brain injury and was now unable to engage in a meaningful conversation. He shared that his family supported his decision. He also recognized that with his debility, he would need inpatient hospice care. On finding out that Mr. S’s brother was no longer able to act as the surrogate decision maker, the PC NP asked whether he wanted her to contact his son to share the outcome of their visit. The patient declined, adding that he had discussed his care plans with his family and did not feel that his health care team needed to have additional discussions with them.
Mr. S also reported chronic, recurrent right upper quadrant pain. He was prescribed oxycodone 10 mg every 4 hours as needed; however, it did little to control his pain. He also reported generalized pruritus, a complication of his renal failure.
After 1 week, Mr. S was transferred to the inpatient hospice unit. At that time, he allowed the hospice team to contact his son for medical updates and identified him as the primary point of contact for the hospice team if the need arose to reach his family. Due to the restrictions imposed by the pandemic, Mr. S had virtual video visits with his family. Mr. S developed intermittent confusion and worsening fatigue over time. His son was informed of his deteriorating condition and visited his father. Mr. S died peacefully 2 days later with his family present.
Multidisciplinary Inputs on the Case
Medicine. In discussing the case with medicine, the PC NP was informed that the goals the patient had for his care, which included stopping dialysis, having a DNR code status and pursuing hospice care, along with the patient’s pain symptoms prompted the PC consultation. The resident also shared concerns about the patient’s refusal to have his surrogate decision maker and family contacted regarding his decisions for his care.
Palliative care. After meeting with the patient and assisting in identifying goals for care, the PC NP recommended initiation of hospice care in the hospital while the patient awaited transfer to the inpatient hospice unit. The PC NP also recommended a psychiatric evaluation to rule out untreated depression that might influence the patient’s decision making. A follow-up visit with nephrology was also recommended. Optimal management of his distressing physical symptoms was recommended, including prescribing hydromorphone instead of oxycodone for his pain and starting a topical emollient for pruritus.
Nephrology. The patient’s electronic health records (EHR) showed that he informed nephrology of his desire to pursue hospice care and that he decided against further dialysis, including as-needed dialysis for comfort. The records also indicated that the patient understood the consequences of discontinuing dialysis.
Psychiatry. The patient’s EHR also showed that during his psychiatric visits, Mr. S reported he had no thoughts of suicide, and it was against his spiritual beliefs. He said he made his own medical decisions and expressed that his health care team should not attempt to change his mind. He also said he understood that stopping dialysis could lead to early death. He stated he had a close relationship with his family and discussed his medical decisions with them. He was tearful at times when he talked about his family. Mr. S shared his frustration about repeatedly being asked the same questions on succeeding visits.
After evaluation, psychiatry diagnosed Mr. S with mood disorder with depressive features and he was prescribed methylphenidate 5 mg daily and sertraline 25 mg daily. They also recommended continuing to offer dialysis in a supportive manner since the patient had changed his mind about hospice in the past. However, psychiatry followed the patient daily for 5 days and concluded that his medical decisions were not clouded by mood symptoms.
Discussion
Patients who are aged > 65 years and on dialysis are more likely to experience higher rates of hospitalization, intensive care unit admission, procedures, and death in the hospital compared with patients who have cancer or heart failure. They also use hospice services less.15 Often this is not consistent with a patient’s wishes but may occur due to limited discussion of goals, values, and preferences between physician and patient.15 Many nephrologists do not engage in these conversations for fear of upsetting patients, their perceived lack of skill in prognostication and discussing the topic, or the lack of time to have the conversation.15 It is important to have an honest and open communication with patients that allows them to be fully informed as they make their medical decisions and exercise their autonomy.
Medicare hospice guidelines also are used to help determine hospice appropriateness among veterans in the VA. Medicare requires enrollees to discontinue disease-modifying treatment for the medical condition leading to their hospice diagnosis, which can result in late hospice referrals and shorter hospice stays.16 Even though hospice referrals for patients with ESRD have increased over time, they are still happening close to the time of death, and patients’ health care utilization near the end of life remains unchanged.16 According to Medicare, patients qualify for hospice care if they are terminally ill (defined as having a life expectancy of ≤ 6 months), choose comfort care over curative care for their terminal illness, and sign a statement electing hospice care over treatments for their terminal illness.17 A DNR order is not a condition for hospice admission.18
The VA defines hospice care as comfort care provided to patients with a terminal condition, a life expectancy of ≤ 6 months, and who are no longer seeking treatment other than those that are palliative.19 Based on his ESRD, Mr. S was qualified for hospice care, and his goals for care were consistent with the hospice philosophy. Most families of patients who elected to withdraw dialysis reported a good death, using the criteria of the duration of dying, discomfort, and psychosocial circumstances.20
Role of HCPs
Health care practitioners (HCPs) are expected to help patients understand the risks and benefits of their choices and its alternative, align patients’ goals with those risks and benefits, and assist patients in making choices that promote their goals and autonomy.21 Family members are often not involved in medical decision making when patients have the capacity to make their own decisions.22 Patients will also have to give permission for protected health information to be shared with their family members.22 On the other hand, families have been shown to provide valuable emotional support to patients and are considered second patients themselves in the sense that they can be impacted by patients’ clinical situation.22 Families may also need care, time, and attention from HCPs.22
Mr. S was found capable of making his own decisions, and part of that decision was that his family not to be present for the goals-of-care discussion. He added that he would discuss the care decisions with his family. At the time of registering for VA health care services, Mr. S had provided his health care team with his brother and sister-in-law’s emergency contact information as well as named his brother surrogate decision maker. As Mr. S’s condition was expected to rapidly decline wthout dialysis, the HCPs would be able to notify family members once his condition changed, including death.
Neuroplasticity changes can contribute to chronic pain that may also lead to depression.23 Chronic pain and depression may involve the same brain structures, neurotransmitters, and signaling pathway.23 Factors leading to chronic pain and depression include decreased availability of monoamine neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine in the central nervous system, decreased brain-derived neurotrophic factor, inflammatory response, and increased glutamate activity.23 Depression and hopelessness have been associated with the desire to hasten death among patients with a terminal illness.24 Worse mental health has been associated with the desire to hasten death among patients who are older and functionally impaired.25 It was important to optimize Mr. S’s treatment for pain and depression to ensure that these factors were not influencing his medical decisions.
With increasing recognition of the need to improve quality of life, health care utilization, and provide care consistent with patients’ goals in nephrology, the concept of renal PC is emerging but remains limited.26 The need to improve supportive care or PC for patients starting on dialysis for ESRD is high as these patients tend to be older (aged > 75 years), have high rates of cardiovascular comorbidities, can have coexisting cognitive impairment and functional debility, and have an adjusted mortality rate of up to 32.5% within 1 year of starting dialysis.26 Some ways to enhance renal PC programs include incorporating PC skill development and training within nephrology fellowships, educating patients with chronic and ESRD about PC and options for medical management without dialysis, and increasing the collaboration between nephrology and PC.26
Outcomes and Implications
Respect for the ethical principle of autonomy is paramount in health care. Patients should be able to give informed consent for treatment decisions without undue influence from their HCPs and should be able to withdraw that consent at any point during treatment. Factors that may influence patients’ ability to make medical decisions should be considered, including untreated or poorly treated symptoms. The involvement of PC helps optimize symptom management, provide support, and assist in goals-of-care discussions. Advanced practice PC nurses can offer other members of the health care team additional information and support in end-of-life care. Family involvement should be encouraged even for patients who can make their own medical decisions for emotional support and to assist families in what could be a traumatic event, such as the loss of a loved one.
The desire to pursue a comfort-focused approach to terminal illness and stop disease-modifying treatments are criteria for hospice care. An interdisciplinary approach to end-of-life care is beneficial, and every specialty should be equipped to engage in honest communication and skillful prognostication. These conversations should start early in the course of a terminal illness. Multiple factors contribute to poor clinical outcomes among patients with ESRD even with renal replacement therapy, such as dialysis. There is a need to improve PC training in the field of nephrology.
Conclusions
Mr. S was able to choose to withdraw potentially life-prolonging treatments with the support of his family and HCPs. He was able to continue receiving high-quality care and treatment in accordance with his wishes and goals for his care. The provision of interdisciplinary care that focused on supporting him allowed for his peaceful and comfortable death.
1. Carr D, Luth EA. Well-being at the end of life. Annu Rev Sociol. 2019;45:515-534. doi:10.1146/annurev-soc-073018-022524
2. Teno JM, Gozalo P, Trivedi AN, et al. Site of death, place of care, and health care transitions among US Medicare beneficiaries, 2000-2015. JAMA. 2018;320(3):264-271. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.8981
3. Himmelfarb J, Vanholder R, Mehrotra R, Tonelli M. The current and future landscape of dialysis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16(10):573-585. doi:10.1038/s41581-020-0315-4
4. Richards CA, Hebert PL, Liu CF, et al. Association of family ratings of quality of end-of-life care with stopping dialysis treatment and receipt of hospice services. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(10):e1913115. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.13115
5. Fischer MJ, Kourany WM, Sovern K, Forrester K, Griffin C, Lightner N, Loftus S, Murphy K, Roth G, Palevsky PM, Crowley ST. Development, implementation and user experience of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) dialysis dashboard. BMC Nephrol. 2020 Apr 16;21(1):136. doi:10.1186/s12882-020-01798-6
6. Schwarze ML, Schueller K, Jhagroo RA. Hospice use and end-of-life care for patients with end-stage renal disease: too little, too late. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(6):799-801.doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.1078
7. Chen JC, Thorsteinsdottir B, Vaughan LE, et al. End of life, withdrawal, and palliative care utilization among patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis therapy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;13(8):1172-1179. doi:10.2215/CJN.00590118
8. Chen HC, Wu CY, Hsieh HY, He JS, Hwang SJ, Hsieh HM. Predictors and assessment of hospice use for end-stage renal disease patients in Taiwan. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;19(1):85. doi:10.3390/ijerph19010085
9. Rak A, Raina R, Suh TT, et al. Palliative care for patients with end-stage renal disease: approach to treatment that aims to improve quality of life and relieve suffering for patients (and families) with chronic illnesses. Clin Kidney J. 2017;10(1):68-73. doi.10.1093/ckj/sfw10510. Wong SPY, Boyapati S, Engelberg RA, Thorsteinsdottir B, Taylor JS, O’Hare AM. Experiences of US nephrologists in the delivery of conservative care to patients with advanced kidney disease: a national qualitative study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020;75(2):167-176. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.07.006
11. Axelsson L, Benzein E, Lindberg J, Persson C. End-of-life and palliative care of patients on maintenance hemodialysis treatment: a focus group study. BMC Palliat Care. 2019;18(1):89. doi:10.1186/s12904-019-0481-y
12. Tweeddale MG. Grasping the nettle—what to do when patients withdraw their consent for treatment: (a clinical perspective on the case of Ms B). J Med Ethics. 2002;28(4):236-237. doi:10.1136/jme.28.4.236
13. Lynøe N, Engström I, Juth N. How to reveal disguised paternalism: version 2.0. BMC Med Ethics. 2021;22(1):170. doi:10.1186/s12910-021-00739-8
14. Murgic L, Hébert PC, Sovic S, Pavlekovic G. Paternalism and autonomy: views of patients and providers in a transitional (post-communist) country. BMC Med Ethics. 2015;16(1):65. doi:10.1186/s12910-015-0059-z
15. Mandel EI, Bernacki RE, Block SD. Serious illness conversations in ESRD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12(5):854-863. doi:10.2215/CJN.05760516
16. Wachterman MW, Hailpern SM, Keating NL, Kurella Tamura M, O’Hare AM. Association between hospice length of stay, health care utilization, and Medicare costs at the end of life among patients who received maintenance hemodialysis. JAMA Int Med. 2018;178(6):792-799. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.0256
17. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Hospice care. Accessed April 2, 2022. https://www.medicare.gov/coverage/hospice-care
18. National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization. Ethical behavior and consumer rights. Standards of Practice for Hospice Programs Professional Development and Resource Series. Accessed December 6, 2022. https://www.nhpco.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Standards_Hospice_2018.pdf
19. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Geriatrics and extended care. Updated October 5, 2022. Accessed August 29, 2022. https://www.va.gov/geriatrics/pages/Hospice_Care.asp
20. Cohen LM, McCue JD, Germain M, Kjellstrand CM. Dialysis discontinuation. A ‘good’ death? Arch Intern Med. 1995;155(1):42-47.
21. Ubel PA, Scherr KA, Fagerlin A. Autonomy: What’s shared decision making have to do with it? Am J Bioeth. 2018;18(2):W11-W12.doi:10.1080/15265161.2017.1409844
22. Laryionava, K, Pfeil TA, Dietrich M. et al. The second patient? Family members of cancer patients and their role in end-of-life decision making. BMC Palliat Care. 2018;17(1):29. doi:10.1186/s12904-018-0288-2
23. Sheng J, Liu S, Wang Y, Cui R, Zhang X. The link between depression and chronic pain: neural mechanisms in the brain. Neural Plast. 2017;2017:9724371. doi:10.1155/2017/9724371
24. Breitbart W, Rosenfeld B, Pessin H, et al. Depression, hopelessness, and desire for hastened death in terminally ill patients with cancer. JAMA. 2000;284(22):2907-2911. doi:10.1001/jama.284.22.2907
25. Sullivan M, Ormel J, Kempen GIJM, Tymstra T. Beliefs concerning death, dying, and hastening death among older, functionally impaired Dutch adults: a one-year longitudinal study. J Am Gec Soc. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1998.tb04541.x26. Gelfand SL, Schell J, Eneanya ND. Palliative care in nephrology: the work and the workforce. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2020;27(4):350-355.e1. doi:10.1053/j.ackd.2020.02.007
Due to advances in medicine, people are living longer with the aid of increased options for life-prolonging treatments. These treatment options may improve the quantity but not necessarily the quality of life.1
Kidney failure can be treated with renal replacement therapy (dialysis or renal transplantation) or supportive care.2 In 2017, the global prevalence of kidney failure was about 5.3 to 9.7 million.3 In the United States, about 500,000 patients are receiving maintenance dialysis for end-stage renal disease (ESRD), and about 1 in 4 will stop dialysis before death, coupled with hospice enrollment.4 ESRD is 2 times more prevalent among veterans than in nonveterans, which can be due in part to high rates of comorbid predisposing conditions, such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and advanced age, among others.5 The decision to discontinue dialysis and receive hospice care tends to be more difficult than choosing to withhold or forego dialysis.6
A study conducted among patients who were taken off hemodialysis before death reported that the 2 most common reasons for the withdrawal were acute medical complications and frailty.7 A retrospective study among patients with ESRD receiving hemodialysis highlighted the underutilization of hospice care in this patient population.8 The study also found that those patients who were aged > 75 years, had poor functional status, and had dialysis-related complications, such as sepsis and anemia, were more likely to elect withdrawal of hemodialysis. There was no difference in overall survival or quality of life among patients who were aged ≥ 75 years with multiple comorbidities and functional impairment who elected conservative management vs those who started dialysis.8 Long-term continuous dialysis has been associated with a lower quality of life, increased dependence on others, and a variety of symptoms, such as pain, nausea, insomnia, anxiety, or depression.9
Conservative Care vs Medical Paternalism
In the United States, it is unusual for patients with ESRD to choose conservative care, and supportive services are less available for those who do compared with patients with ESRD in Europe, Asia, Australia, and Canada.10 A study looking at a small number of US nephrologists has shown they may have limited experience in caring for patients who forego dialysis and they are not comfortable offering conservative management over dialysis.10 Another small study from Sweden also showed that many nephrologists do not feel prepared for end-of-life care and conversations.11
Patients often rely on knowledgeable recommendations from medical experts. However, medical paternalism occurs when a physician makes decisions deemed to be in the patient’s best interest but are against the patient’s wishes or when the patient is unable to give their consent.12 Hard paternalism occurs when the patient is competent to make their own medical decisions, while soft paternalism occurs when a patient is not competent to make their own medical decisions.13
Patient autonomy is widely recognized as an ethical principle in medicine. It recognizes patients as well-informed decision makers who may act without excessive influence to make intentional determinations on their own behalf.14 Autonomy can be exercised at any point during the health care process.12 Although ethical and legal guidelines encourage physicians to recommend appropriate treatment, medical opinion cannot overrule the wishes of a competent patient who refuses treatment.12
Case Presentation
Mr. S presented to the emergency department at a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical center with abdominal pain from recurrent pancreatitis. The patient aged > 65 years had a history of depression, ESRD, and was receiving hemodialysis. A computed tomography scan revealed a new pancreatic mass, and he was referred to the palliative care (PC) department nurse practitioner (NP) for a goals-of-care discussion. PC was informed to assist with hospice care initiation: The patient elected a do-not-resuscitate (DNR) code status and hospice care.
At the consultation, Mr. S stated that he had decided to forego life-prolonging treatments, including hemodialysis, and declined further evaluation for his pancreatic mass. He shared a good understanding of concerns for malignancy with his mass but did not wish to pursue further diagnostics as he knew his life expectancy was very limited without dialysis. He had been dependent on hemodialysis for the past 10 years. He had briefly received hospice care 5 years before but changed his mind and decided to pursue standard care, including life-prolonging dialysis treatments. He reported no depression, suicidal ideation, or intentions of hastening his death. He stated that he was just physically tired from his ongoing dialysis, recurrent hospitalizations, and being repeatedly subjected to diagnostic tests. Mr. S added that he had discussed his plan with his family, including his son and sister-in-law who is married to his brother. Mr. S previously identified his brother as his surrogate decision maker.
Mr. S shared that his brother had sustained a traumatic brain injury and was now unable to engage in a meaningful conversation. He shared that his family supported his decision. He also recognized that with his debility, he would need inpatient hospice care. On finding out that Mr. S’s brother was no longer able to act as the surrogate decision maker, the PC NP asked whether he wanted her to contact his son to share the outcome of their visit. The patient declined, adding that he had discussed his care plans with his family and did not feel that his health care team needed to have additional discussions with them.
Mr. S also reported chronic, recurrent right upper quadrant pain. He was prescribed oxycodone 10 mg every 4 hours as needed; however, it did little to control his pain. He also reported generalized pruritus, a complication of his renal failure.
After 1 week, Mr. S was transferred to the inpatient hospice unit. At that time, he allowed the hospice team to contact his son for medical updates and identified him as the primary point of contact for the hospice team if the need arose to reach his family. Due to the restrictions imposed by the pandemic, Mr. S had virtual video visits with his family. Mr. S developed intermittent confusion and worsening fatigue over time. His son was informed of his deteriorating condition and visited his father. Mr. S died peacefully 2 days later with his family present.
Multidisciplinary Inputs on the Case
Medicine. In discussing the case with medicine, the PC NP was informed that the goals the patient had for his care, which included stopping dialysis, having a DNR code status and pursuing hospice care, along with the patient’s pain symptoms prompted the PC consultation. The resident also shared concerns about the patient’s refusal to have his surrogate decision maker and family contacted regarding his decisions for his care.
Palliative care. After meeting with the patient and assisting in identifying goals for care, the PC NP recommended initiation of hospice care in the hospital while the patient awaited transfer to the inpatient hospice unit. The PC NP also recommended a psychiatric evaluation to rule out untreated depression that might influence the patient’s decision making. A follow-up visit with nephrology was also recommended. Optimal management of his distressing physical symptoms was recommended, including prescribing hydromorphone instead of oxycodone for his pain and starting a topical emollient for pruritus.
Nephrology. The patient’s electronic health records (EHR) showed that he informed nephrology of his desire to pursue hospice care and that he decided against further dialysis, including as-needed dialysis for comfort. The records also indicated that the patient understood the consequences of discontinuing dialysis.
Psychiatry. The patient’s EHR also showed that during his psychiatric visits, Mr. S reported he had no thoughts of suicide, and it was against his spiritual beliefs. He said he made his own medical decisions and expressed that his health care team should not attempt to change his mind. He also said he understood that stopping dialysis could lead to early death. He stated he had a close relationship with his family and discussed his medical decisions with them. He was tearful at times when he talked about his family. Mr. S shared his frustration about repeatedly being asked the same questions on succeeding visits.
After evaluation, psychiatry diagnosed Mr. S with mood disorder with depressive features and he was prescribed methylphenidate 5 mg daily and sertraline 25 mg daily. They also recommended continuing to offer dialysis in a supportive manner since the patient had changed his mind about hospice in the past. However, psychiatry followed the patient daily for 5 days and concluded that his medical decisions were not clouded by mood symptoms.
Discussion
Patients who are aged > 65 years and on dialysis are more likely to experience higher rates of hospitalization, intensive care unit admission, procedures, and death in the hospital compared with patients who have cancer or heart failure. They also use hospice services less.15 Often this is not consistent with a patient’s wishes but may occur due to limited discussion of goals, values, and preferences between physician and patient.15 Many nephrologists do not engage in these conversations for fear of upsetting patients, their perceived lack of skill in prognostication and discussing the topic, or the lack of time to have the conversation.15 It is important to have an honest and open communication with patients that allows them to be fully informed as they make their medical decisions and exercise their autonomy.
Medicare hospice guidelines also are used to help determine hospice appropriateness among veterans in the VA. Medicare requires enrollees to discontinue disease-modifying treatment for the medical condition leading to their hospice diagnosis, which can result in late hospice referrals and shorter hospice stays.16 Even though hospice referrals for patients with ESRD have increased over time, they are still happening close to the time of death, and patients’ health care utilization near the end of life remains unchanged.16 According to Medicare, patients qualify for hospice care if they are terminally ill (defined as having a life expectancy of ≤ 6 months), choose comfort care over curative care for their terminal illness, and sign a statement electing hospice care over treatments for their terminal illness.17 A DNR order is not a condition for hospice admission.18
The VA defines hospice care as comfort care provided to patients with a terminal condition, a life expectancy of ≤ 6 months, and who are no longer seeking treatment other than those that are palliative.19 Based on his ESRD, Mr. S was qualified for hospice care, and his goals for care were consistent with the hospice philosophy. Most families of patients who elected to withdraw dialysis reported a good death, using the criteria of the duration of dying, discomfort, and psychosocial circumstances.20
Role of HCPs
Health care practitioners (HCPs) are expected to help patients understand the risks and benefits of their choices and its alternative, align patients’ goals with those risks and benefits, and assist patients in making choices that promote their goals and autonomy.21 Family members are often not involved in medical decision making when patients have the capacity to make their own decisions.22 Patients will also have to give permission for protected health information to be shared with their family members.22 On the other hand, families have been shown to provide valuable emotional support to patients and are considered second patients themselves in the sense that they can be impacted by patients’ clinical situation.22 Families may also need care, time, and attention from HCPs.22
Mr. S was found capable of making his own decisions, and part of that decision was that his family not to be present for the goals-of-care discussion. He added that he would discuss the care decisions with his family. At the time of registering for VA health care services, Mr. S had provided his health care team with his brother and sister-in-law’s emergency contact information as well as named his brother surrogate decision maker. As Mr. S’s condition was expected to rapidly decline wthout dialysis, the HCPs would be able to notify family members once his condition changed, including death.
Neuroplasticity changes can contribute to chronic pain that may also lead to depression.23 Chronic pain and depression may involve the same brain structures, neurotransmitters, and signaling pathway.23 Factors leading to chronic pain and depression include decreased availability of monoamine neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine in the central nervous system, decreased brain-derived neurotrophic factor, inflammatory response, and increased glutamate activity.23 Depression and hopelessness have been associated with the desire to hasten death among patients with a terminal illness.24 Worse mental health has been associated with the desire to hasten death among patients who are older and functionally impaired.25 It was important to optimize Mr. S’s treatment for pain and depression to ensure that these factors were not influencing his medical decisions.
With increasing recognition of the need to improve quality of life, health care utilization, and provide care consistent with patients’ goals in nephrology, the concept of renal PC is emerging but remains limited.26 The need to improve supportive care or PC for patients starting on dialysis for ESRD is high as these patients tend to be older (aged > 75 years), have high rates of cardiovascular comorbidities, can have coexisting cognitive impairment and functional debility, and have an adjusted mortality rate of up to 32.5% within 1 year of starting dialysis.26 Some ways to enhance renal PC programs include incorporating PC skill development and training within nephrology fellowships, educating patients with chronic and ESRD about PC and options for medical management without dialysis, and increasing the collaboration between nephrology and PC.26
Outcomes and Implications
Respect for the ethical principle of autonomy is paramount in health care. Patients should be able to give informed consent for treatment decisions without undue influence from their HCPs and should be able to withdraw that consent at any point during treatment. Factors that may influence patients’ ability to make medical decisions should be considered, including untreated or poorly treated symptoms. The involvement of PC helps optimize symptom management, provide support, and assist in goals-of-care discussions. Advanced practice PC nurses can offer other members of the health care team additional information and support in end-of-life care. Family involvement should be encouraged even for patients who can make their own medical decisions for emotional support and to assist families in what could be a traumatic event, such as the loss of a loved one.
The desire to pursue a comfort-focused approach to terminal illness and stop disease-modifying treatments are criteria for hospice care. An interdisciplinary approach to end-of-life care is beneficial, and every specialty should be equipped to engage in honest communication and skillful prognostication. These conversations should start early in the course of a terminal illness. Multiple factors contribute to poor clinical outcomes among patients with ESRD even with renal replacement therapy, such as dialysis. There is a need to improve PC training in the field of nephrology.
Conclusions
Mr. S was able to choose to withdraw potentially life-prolonging treatments with the support of his family and HCPs. He was able to continue receiving high-quality care and treatment in accordance with his wishes and goals for his care. The provision of interdisciplinary care that focused on supporting him allowed for his peaceful and comfortable death.
Due to advances in medicine, people are living longer with the aid of increased options for life-prolonging treatments. These treatment options may improve the quantity but not necessarily the quality of life.1
Kidney failure can be treated with renal replacement therapy (dialysis or renal transplantation) or supportive care.2 In 2017, the global prevalence of kidney failure was about 5.3 to 9.7 million.3 In the United States, about 500,000 patients are receiving maintenance dialysis for end-stage renal disease (ESRD), and about 1 in 4 will stop dialysis before death, coupled with hospice enrollment.4 ESRD is 2 times more prevalent among veterans than in nonveterans, which can be due in part to high rates of comorbid predisposing conditions, such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and advanced age, among others.5 The decision to discontinue dialysis and receive hospice care tends to be more difficult than choosing to withhold or forego dialysis.6
A study conducted among patients who were taken off hemodialysis before death reported that the 2 most common reasons for the withdrawal were acute medical complications and frailty.7 A retrospective study among patients with ESRD receiving hemodialysis highlighted the underutilization of hospice care in this patient population.8 The study also found that those patients who were aged > 75 years, had poor functional status, and had dialysis-related complications, such as sepsis and anemia, were more likely to elect withdrawal of hemodialysis. There was no difference in overall survival or quality of life among patients who were aged ≥ 75 years with multiple comorbidities and functional impairment who elected conservative management vs those who started dialysis.8 Long-term continuous dialysis has been associated with a lower quality of life, increased dependence on others, and a variety of symptoms, such as pain, nausea, insomnia, anxiety, or depression.9
Conservative Care vs Medical Paternalism
In the United States, it is unusual for patients with ESRD to choose conservative care, and supportive services are less available for those who do compared with patients with ESRD in Europe, Asia, Australia, and Canada.10 A study looking at a small number of US nephrologists has shown they may have limited experience in caring for patients who forego dialysis and they are not comfortable offering conservative management over dialysis.10 Another small study from Sweden also showed that many nephrologists do not feel prepared for end-of-life care and conversations.11
Patients often rely on knowledgeable recommendations from medical experts. However, medical paternalism occurs when a physician makes decisions deemed to be in the patient’s best interest but are against the patient’s wishes or when the patient is unable to give their consent.12 Hard paternalism occurs when the patient is competent to make their own medical decisions, while soft paternalism occurs when a patient is not competent to make their own medical decisions.13
Patient autonomy is widely recognized as an ethical principle in medicine. It recognizes patients as well-informed decision makers who may act without excessive influence to make intentional determinations on their own behalf.14 Autonomy can be exercised at any point during the health care process.12 Although ethical and legal guidelines encourage physicians to recommend appropriate treatment, medical opinion cannot overrule the wishes of a competent patient who refuses treatment.12
Case Presentation
Mr. S presented to the emergency department at a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical center with abdominal pain from recurrent pancreatitis. The patient aged > 65 years had a history of depression, ESRD, and was receiving hemodialysis. A computed tomography scan revealed a new pancreatic mass, and he was referred to the palliative care (PC) department nurse practitioner (NP) for a goals-of-care discussion. PC was informed to assist with hospice care initiation: The patient elected a do-not-resuscitate (DNR) code status and hospice care.
At the consultation, Mr. S stated that he had decided to forego life-prolonging treatments, including hemodialysis, and declined further evaluation for his pancreatic mass. He shared a good understanding of concerns for malignancy with his mass but did not wish to pursue further diagnostics as he knew his life expectancy was very limited without dialysis. He had been dependent on hemodialysis for the past 10 years. He had briefly received hospice care 5 years before but changed his mind and decided to pursue standard care, including life-prolonging dialysis treatments. He reported no depression, suicidal ideation, or intentions of hastening his death. He stated that he was just physically tired from his ongoing dialysis, recurrent hospitalizations, and being repeatedly subjected to diagnostic tests. Mr. S added that he had discussed his plan with his family, including his son and sister-in-law who is married to his brother. Mr. S previously identified his brother as his surrogate decision maker.
Mr. S shared that his brother had sustained a traumatic brain injury and was now unable to engage in a meaningful conversation. He shared that his family supported his decision. He also recognized that with his debility, he would need inpatient hospice care. On finding out that Mr. S’s brother was no longer able to act as the surrogate decision maker, the PC NP asked whether he wanted her to contact his son to share the outcome of their visit. The patient declined, adding that he had discussed his care plans with his family and did not feel that his health care team needed to have additional discussions with them.
Mr. S also reported chronic, recurrent right upper quadrant pain. He was prescribed oxycodone 10 mg every 4 hours as needed; however, it did little to control his pain. He also reported generalized pruritus, a complication of his renal failure.
After 1 week, Mr. S was transferred to the inpatient hospice unit. At that time, he allowed the hospice team to contact his son for medical updates and identified him as the primary point of contact for the hospice team if the need arose to reach his family. Due to the restrictions imposed by the pandemic, Mr. S had virtual video visits with his family. Mr. S developed intermittent confusion and worsening fatigue over time. His son was informed of his deteriorating condition and visited his father. Mr. S died peacefully 2 days later with his family present.
Multidisciplinary Inputs on the Case
Medicine. In discussing the case with medicine, the PC NP was informed that the goals the patient had for his care, which included stopping dialysis, having a DNR code status and pursuing hospice care, along with the patient’s pain symptoms prompted the PC consultation. The resident also shared concerns about the patient’s refusal to have his surrogate decision maker and family contacted regarding his decisions for his care.
Palliative care. After meeting with the patient and assisting in identifying goals for care, the PC NP recommended initiation of hospice care in the hospital while the patient awaited transfer to the inpatient hospice unit. The PC NP also recommended a psychiatric evaluation to rule out untreated depression that might influence the patient’s decision making. A follow-up visit with nephrology was also recommended. Optimal management of his distressing physical symptoms was recommended, including prescribing hydromorphone instead of oxycodone for his pain and starting a topical emollient for pruritus.
Nephrology. The patient’s electronic health records (EHR) showed that he informed nephrology of his desire to pursue hospice care and that he decided against further dialysis, including as-needed dialysis for comfort. The records also indicated that the patient understood the consequences of discontinuing dialysis.
Psychiatry. The patient’s EHR also showed that during his psychiatric visits, Mr. S reported he had no thoughts of suicide, and it was against his spiritual beliefs. He said he made his own medical decisions and expressed that his health care team should not attempt to change his mind. He also said he understood that stopping dialysis could lead to early death. He stated he had a close relationship with his family and discussed his medical decisions with them. He was tearful at times when he talked about his family. Mr. S shared his frustration about repeatedly being asked the same questions on succeeding visits.
After evaluation, psychiatry diagnosed Mr. S with mood disorder with depressive features and he was prescribed methylphenidate 5 mg daily and sertraline 25 mg daily. They also recommended continuing to offer dialysis in a supportive manner since the patient had changed his mind about hospice in the past. However, psychiatry followed the patient daily for 5 days and concluded that his medical decisions were not clouded by mood symptoms.
Discussion
Patients who are aged > 65 years and on dialysis are more likely to experience higher rates of hospitalization, intensive care unit admission, procedures, and death in the hospital compared with patients who have cancer or heart failure. They also use hospice services less.15 Often this is not consistent with a patient’s wishes but may occur due to limited discussion of goals, values, and preferences between physician and patient.15 Many nephrologists do not engage in these conversations for fear of upsetting patients, their perceived lack of skill in prognostication and discussing the topic, or the lack of time to have the conversation.15 It is important to have an honest and open communication with patients that allows them to be fully informed as they make their medical decisions and exercise their autonomy.
Medicare hospice guidelines also are used to help determine hospice appropriateness among veterans in the VA. Medicare requires enrollees to discontinue disease-modifying treatment for the medical condition leading to their hospice diagnosis, which can result in late hospice referrals and shorter hospice stays.16 Even though hospice referrals for patients with ESRD have increased over time, they are still happening close to the time of death, and patients’ health care utilization near the end of life remains unchanged.16 According to Medicare, patients qualify for hospice care if they are terminally ill (defined as having a life expectancy of ≤ 6 months), choose comfort care over curative care for their terminal illness, and sign a statement electing hospice care over treatments for their terminal illness.17 A DNR order is not a condition for hospice admission.18
The VA defines hospice care as comfort care provided to patients with a terminal condition, a life expectancy of ≤ 6 months, and who are no longer seeking treatment other than those that are palliative.19 Based on his ESRD, Mr. S was qualified for hospice care, and his goals for care were consistent with the hospice philosophy. Most families of patients who elected to withdraw dialysis reported a good death, using the criteria of the duration of dying, discomfort, and psychosocial circumstances.20
Role of HCPs
Health care practitioners (HCPs) are expected to help patients understand the risks and benefits of their choices and its alternative, align patients’ goals with those risks and benefits, and assist patients in making choices that promote their goals and autonomy.21 Family members are often not involved in medical decision making when patients have the capacity to make their own decisions.22 Patients will also have to give permission for protected health information to be shared with their family members.22 On the other hand, families have been shown to provide valuable emotional support to patients and are considered second patients themselves in the sense that they can be impacted by patients’ clinical situation.22 Families may also need care, time, and attention from HCPs.22
Mr. S was found capable of making his own decisions, and part of that decision was that his family not to be present for the goals-of-care discussion. He added that he would discuss the care decisions with his family. At the time of registering for VA health care services, Mr. S had provided his health care team with his brother and sister-in-law’s emergency contact information as well as named his brother surrogate decision maker. As Mr. S’s condition was expected to rapidly decline wthout dialysis, the HCPs would be able to notify family members once his condition changed, including death.
Neuroplasticity changes can contribute to chronic pain that may also lead to depression.23 Chronic pain and depression may involve the same brain structures, neurotransmitters, and signaling pathway.23 Factors leading to chronic pain and depression include decreased availability of monoamine neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine in the central nervous system, decreased brain-derived neurotrophic factor, inflammatory response, and increased glutamate activity.23 Depression and hopelessness have been associated with the desire to hasten death among patients with a terminal illness.24 Worse mental health has been associated with the desire to hasten death among patients who are older and functionally impaired.25 It was important to optimize Mr. S’s treatment for pain and depression to ensure that these factors were not influencing his medical decisions.
With increasing recognition of the need to improve quality of life, health care utilization, and provide care consistent with patients’ goals in nephrology, the concept of renal PC is emerging but remains limited.26 The need to improve supportive care or PC for patients starting on dialysis for ESRD is high as these patients tend to be older (aged > 75 years), have high rates of cardiovascular comorbidities, can have coexisting cognitive impairment and functional debility, and have an adjusted mortality rate of up to 32.5% within 1 year of starting dialysis.26 Some ways to enhance renal PC programs include incorporating PC skill development and training within nephrology fellowships, educating patients with chronic and ESRD about PC and options for medical management without dialysis, and increasing the collaboration between nephrology and PC.26
Outcomes and Implications
Respect for the ethical principle of autonomy is paramount in health care. Patients should be able to give informed consent for treatment decisions without undue influence from their HCPs and should be able to withdraw that consent at any point during treatment. Factors that may influence patients’ ability to make medical decisions should be considered, including untreated or poorly treated symptoms. The involvement of PC helps optimize symptom management, provide support, and assist in goals-of-care discussions. Advanced practice PC nurses can offer other members of the health care team additional information and support in end-of-life care. Family involvement should be encouraged even for patients who can make their own medical decisions for emotional support and to assist families in what could be a traumatic event, such as the loss of a loved one.
The desire to pursue a comfort-focused approach to terminal illness and stop disease-modifying treatments are criteria for hospice care. An interdisciplinary approach to end-of-life care is beneficial, and every specialty should be equipped to engage in honest communication and skillful prognostication. These conversations should start early in the course of a terminal illness. Multiple factors contribute to poor clinical outcomes among patients with ESRD even with renal replacement therapy, such as dialysis. There is a need to improve PC training in the field of nephrology.
Conclusions
Mr. S was able to choose to withdraw potentially life-prolonging treatments with the support of his family and HCPs. He was able to continue receiving high-quality care and treatment in accordance with his wishes and goals for his care. The provision of interdisciplinary care that focused on supporting him allowed for his peaceful and comfortable death.
1. Carr D, Luth EA. Well-being at the end of life. Annu Rev Sociol. 2019;45:515-534. doi:10.1146/annurev-soc-073018-022524
2. Teno JM, Gozalo P, Trivedi AN, et al. Site of death, place of care, and health care transitions among US Medicare beneficiaries, 2000-2015. JAMA. 2018;320(3):264-271. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.8981
3. Himmelfarb J, Vanholder R, Mehrotra R, Tonelli M. The current and future landscape of dialysis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16(10):573-585. doi:10.1038/s41581-020-0315-4
4. Richards CA, Hebert PL, Liu CF, et al. Association of family ratings of quality of end-of-life care with stopping dialysis treatment and receipt of hospice services. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(10):e1913115. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.13115
5. Fischer MJ, Kourany WM, Sovern K, Forrester K, Griffin C, Lightner N, Loftus S, Murphy K, Roth G, Palevsky PM, Crowley ST. Development, implementation and user experience of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) dialysis dashboard. BMC Nephrol. 2020 Apr 16;21(1):136. doi:10.1186/s12882-020-01798-6
6. Schwarze ML, Schueller K, Jhagroo RA. Hospice use and end-of-life care for patients with end-stage renal disease: too little, too late. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(6):799-801.doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.1078
7. Chen JC, Thorsteinsdottir B, Vaughan LE, et al. End of life, withdrawal, and palliative care utilization among patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis therapy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;13(8):1172-1179. doi:10.2215/CJN.00590118
8. Chen HC, Wu CY, Hsieh HY, He JS, Hwang SJ, Hsieh HM. Predictors and assessment of hospice use for end-stage renal disease patients in Taiwan. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;19(1):85. doi:10.3390/ijerph19010085
9. Rak A, Raina R, Suh TT, et al. Palliative care for patients with end-stage renal disease: approach to treatment that aims to improve quality of life and relieve suffering for patients (and families) with chronic illnesses. Clin Kidney J. 2017;10(1):68-73. doi.10.1093/ckj/sfw10510. Wong SPY, Boyapati S, Engelberg RA, Thorsteinsdottir B, Taylor JS, O’Hare AM. Experiences of US nephrologists in the delivery of conservative care to patients with advanced kidney disease: a national qualitative study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020;75(2):167-176. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.07.006
11. Axelsson L, Benzein E, Lindberg J, Persson C. End-of-life and palliative care of patients on maintenance hemodialysis treatment: a focus group study. BMC Palliat Care. 2019;18(1):89. doi:10.1186/s12904-019-0481-y
12. Tweeddale MG. Grasping the nettle—what to do when patients withdraw their consent for treatment: (a clinical perspective on the case of Ms B). J Med Ethics. 2002;28(4):236-237. doi:10.1136/jme.28.4.236
13. Lynøe N, Engström I, Juth N. How to reveal disguised paternalism: version 2.0. BMC Med Ethics. 2021;22(1):170. doi:10.1186/s12910-021-00739-8
14. Murgic L, Hébert PC, Sovic S, Pavlekovic G. Paternalism and autonomy: views of patients and providers in a transitional (post-communist) country. BMC Med Ethics. 2015;16(1):65. doi:10.1186/s12910-015-0059-z
15. Mandel EI, Bernacki RE, Block SD. Serious illness conversations in ESRD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12(5):854-863. doi:10.2215/CJN.05760516
16. Wachterman MW, Hailpern SM, Keating NL, Kurella Tamura M, O’Hare AM. Association between hospice length of stay, health care utilization, and Medicare costs at the end of life among patients who received maintenance hemodialysis. JAMA Int Med. 2018;178(6):792-799. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.0256
17. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Hospice care. Accessed April 2, 2022. https://www.medicare.gov/coverage/hospice-care
18. National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization. Ethical behavior and consumer rights. Standards of Practice for Hospice Programs Professional Development and Resource Series. Accessed December 6, 2022. https://www.nhpco.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Standards_Hospice_2018.pdf
19. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Geriatrics and extended care. Updated October 5, 2022. Accessed August 29, 2022. https://www.va.gov/geriatrics/pages/Hospice_Care.asp
20. Cohen LM, McCue JD, Germain M, Kjellstrand CM. Dialysis discontinuation. A ‘good’ death? Arch Intern Med. 1995;155(1):42-47.
21. Ubel PA, Scherr KA, Fagerlin A. Autonomy: What’s shared decision making have to do with it? Am J Bioeth. 2018;18(2):W11-W12.doi:10.1080/15265161.2017.1409844
22. Laryionava, K, Pfeil TA, Dietrich M. et al. The second patient? Family members of cancer patients and their role in end-of-life decision making. BMC Palliat Care. 2018;17(1):29. doi:10.1186/s12904-018-0288-2
23. Sheng J, Liu S, Wang Y, Cui R, Zhang X. The link between depression and chronic pain: neural mechanisms in the brain. Neural Plast. 2017;2017:9724371. doi:10.1155/2017/9724371
24. Breitbart W, Rosenfeld B, Pessin H, et al. Depression, hopelessness, and desire for hastened death in terminally ill patients with cancer. JAMA. 2000;284(22):2907-2911. doi:10.1001/jama.284.22.2907
25. Sullivan M, Ormel J, Kempen GIJM, Tymstra T. Beliefs concerning death, dying, and hastening death among older, functionally impaired Dutch adults: a one-year longitudinal study. J Am Gec Soc. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1998.tb04541.x26. Gelfand SL, Schell J, Eneanya ND. Palliative care in nephrology: the work and the workforce. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2020;27(4):350-355.e1. doi:10.1053/j.ackd.2020.02.007
1. Carr D, Luth EA. Well-being at the end of life. Annu Rev Sociol. 2019;45:515-534. doi:10.1146/annurev-soc-073018-022524
2. Teno JM, Gozalo P, Trivedi AN, et al. Site of death, place of care, and health care transitions among US Medicare beneficiaries, 2000-2015. JAMA. 2018;320(3):264-271. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.8981
3. Himmelfarb J, Vanholder R, Mehrotra R, Tonelli M. The current and future landscape of dialysis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16(10):573-585. doi:10.1038/s41581-020-0315-4
4. Richards CA, Hebert PL, Liu CF, et al. Association of family ratings of quality of end-of-life care with stopping dialysis treatment and receipt of hospice services. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(10):e1913115. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.13115
5. Fischer MJ, Kourany WM, Sovern K, Forrester K, Griffin C, Lightner N, Loftus S, Murphy K, Roth G, Palevsky PM, Crowley ST. Development, implementation and user experience of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) dialysis dashboard. BMC Nephrol. 2020 Apr 16;21(1):136. doi:10.1186/s12882-020-01798-6
6. Schwarze ML, Schueller K, Jhagroo RA. Hospice use and end-of-life care for patients with end-stage renal disease: too little, too late. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(6):799-801.doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.1078
7. Chen JC, Thorsteinsdottir B, Vaughan LE, et al. End of life, withdrawal, and palliative care utilization among patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis therapy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;13(8):1172-1179. doi:10.2215/CJN.00590118
8. Chen HC, Wu CY, Hsieh HY, He JS, Hwang SJ, Hsieh HM. Predictors and assessment of hospice use for end-stage renal disease patients in Taiwan. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;19(1):85. doi:10.3390/ijerph19010085
9. Rak A, Raina R, Suh TT, et al. Palliative care for patients with end-stage renal disease: approach to treatment that aims to improve quality of life and relieve suffering for patients (and families) with chronic illnesses. Clin Kidney J. 2017;10(1):68-73. doi.10.1093/ckj/sfw10510. Wong SPY, Boyapati S, Engelberg RA, Thorsteinsdottir B, Taylor JS, O’Hare AM. Experiences of US nephrologists in the delivery of conservative care to patients with advanced kidney disease: a national qualitative study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020;75(2):167-176. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.07.006
11. Axelsson L, Benzein E, Lindberg J, Persson C. End-of-life and palliative care of patients on maintenance hemodialysis treatment: a focus group study. BMC Palliat Care. 2019;18(1):89. doi:10.1186/s12904-019-0481-y
12. Tweeddale MG. Grasping the nettle—what to do when patients withdraw their consent for treatment: (a clinical perspective on the case of Ms B). J Med Ethics. 2002;28(4):236-237. doi:10.1136/jme.28.4.236
13. Lynøe N, Engström I, Juth N. How to reveal disguised paternalism: version 2.0. BMC Med Ethics. 2021;22(1):170. doi:10.1186/s12910-021-00739-8
14. Murgic L, Hébert PC, Sovic S, Pavlekovic G. Paternalism and autonomy: views of patients and providers in a transitional (post-communist) country. BMC Med Ethics. 2015;16(1):65. doi:10.1186/s12910-015-0059-z
15. Mandel EI, Bernacki RE, Block SD. Serious illness conversations in ESRD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12(5):854-863. doi:10.2215/CJN.05760516
16. Wachterman MW, Hailpern SM, Keating NL, Kurella Tamura M, O’Hare AM. Association between hospice length of stay, health care utilization, and Medicare costs at the end of life among patients who received maintenance hemodialysis. JAMA Int Med. 2018;178(6):792-799. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.0256
17. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Hospice care. Accessed April 2, 2022. https://www.medicare.gov/coverage/hospice-care
18. National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization. Ethical behavior and consumer rights. Standards of Practice for Hospice Programs Professional Development and Resource Series. Accessed December 6, 2022. https://www.nhpco.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Standards_Hospice_2018.pdf
19. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Geriatrics and extended care. Updated October 5, 2022. Accessed August 29, 2022. https://www.va.gov/geriatrics/pages/Hospice_Care.asp
20. Cohen LM, McCue JD, Germain M, Kjellstrand CM. Dialysis discontinuation. A ‘good’ death? Arch Intern Med. 1995;155(1):42-47.
21. Ubel PA, Scherr KA, Fagerlin A. Autonomy: What’s shared decision making have to do with it? Am J Bioeth. 2018;18(2):W11-W12.doi:10.1080/15265161.2017.1409844
22. Laryionava, K, Pfeil TA, Dietrich M. et al. The second patient? Family members of cancer patients and their role in end-of-life decision making. BMC Palliat Care. 2018;17(1):29. doi:10.1186/s12904-018-0288-2
23. Sheng J, Liu S, Wang Y, Cui R, Zhang X. The link between depression and chronic pain: neural mechanisms in the brain. Neural Plast. 2017;2017:9724371. doi:10.1155/2017/9724371
24. Breitbart W, Rosenfeld B, Pessin H, et al. Depression, hopelessness, and desire for hastened death in terminally ill patients with cancer. JAMA. 2000;284(22):2907-2911. doi:10.1001/jama.284.22.2907
25. Sullivan M, Ormel J, Kempen GIJM, Tymstra T. Beliefs concerning death, dying, and hastening death among older, functionally impaired Dutch adults: a one-year longitudinal study. J Am Gec Soc. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1998.tb04541.x26. Gelfand SL, Schell J, Eneanya ND. Palliative care in nephrology: the work and the workforce. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2020;27(4):350-355.e1. doi:10.1053/j.ackd.2020.02.007