User login
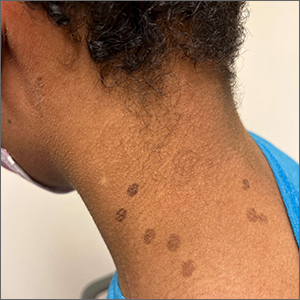
Teen with hyperpigmented skin lesions
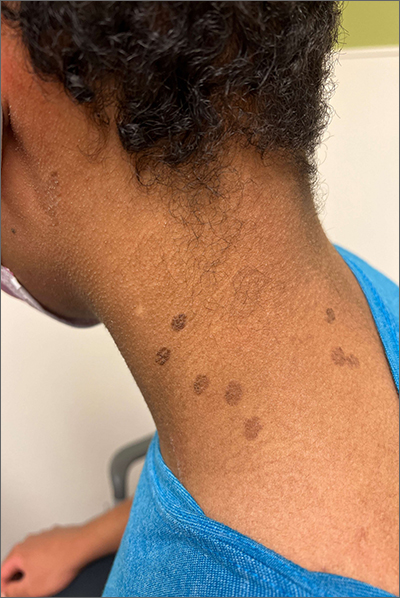
These hyperpigmented lesions with fine scale on the outer edges are characteristic of pityriasis versicolor, also known as tinea versicolor. These macules (or patches) are commonly found on the trunk, proximal extremities, or neck. The lesions can be hypopigmented (pityriasis versicolor alba), hyperpigmented (pityriasis versicolor nigra), or erythematous (pityriasis versicolor rubra).1 It is common to see hyperpigmentation in people with darker skin tones, as was the case with this patient. Pityriasis versicolor is often asymptomatic, but patients may describe mild to moderate pruritis.
Pityriasis versicolor is a common fungal infection of the superficial layers of the dermis caused by Malassezia furfur.2 Impaired immunity and excessive sweating are risk factors for pityriasis versicolor; other risk factors include having a family member with tinea versicolor and living in a hot, humid region.1 Adolescents and young adults are most often affected.1
An evoked scale sign is a helpful tool to confirm the diagnosis clinically.3 Scale will appear when you stretch the affected skin with your thumb and index finger (or you scrape the area with a scalpel blade).3 If there is doubt about the diagnosis, use a potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation; a positive test will reveal the classic “spaghetti and meatballs” pattern.1
Selenium sulfide 2.5%, zinc pyrithione 1%, and ketoconazole 2% shampoo are effective topical treatments. The shampoo is applied full strength to the affected skin daily for 5 to 10 minutes before it’s washed off. This can be done for 1 to 4 weeks, with longer treatment courses resulting in higher cure rates. Systemic therapy is reserved for patients with widespread infection or those who do not respond to topical treatment.4 It’s important to advise patients that the restoration of normal skin pigmentation can takes months.
This patient was treated with ketoconazole 2% shampoo for 3 weeks. A complete return of skin color was achieved 6 months after completion of therapy.
Image courtesy of Judy Jasser, MD. Text courtesy of Judy Jasser, MD, Department of Pediatrics, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Crespo-Erchiga, V, Florencio, VD. Malassezia yeasts and pityriasis versicolor. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2006;19:139-147. doi: 10.1097/01.qco.0000216624.21069.61
2. Gupta, AK, Bluhm R, Summerbell R. Pityriasis versicolor. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2002;16:19-33. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-3083.2002.00378.x
3. Han, A, Calcara DA, Stoecker WV, et al. Evoked scale sign of tinea versicolor. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:1078. doi: 10.1001/archdermatol.2009.203
4. Renati S, Cukras A, Bigby M. Pityriasis versicolor. BMJ. 2015;350:h1394. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h1394

These hyperpigmented lesions with fine scale on the outer edges are characteristic of pityriasis versicolor, also known as tinea versicolor. These macules (or patches) are commonly found on the trunk, proximal extremities, or neck. The lesions can be hypopigmented (pityriasis versicolor alba), hyperpigmented (pityriasis versicolor nigra), or erythematous (pityriasis versicolor rubra).1 It is common to see hyperpigmentation in people with darker skin tones, as was the case with this patient. Pityriasis versicolor is often asymptomatic, but patients may describe mild to moderate pruritis.
Pityriasis versicolor is a common fungal infection of the superficial layers of the dermis caused by Malassezia furfur.2 Impaired immunity and excessive sweating are risk factors for pityriasis versicolor; other risk factors include having a family member with tinea versicolor and living in a hot, humid region.1 Adolescents and young adults are most often affected.1
An evoked scale sign is a helpful tool to confirm the diagnosis clinically.3 Scale will appear when you stretch the affected skin with your thumb and index finger (or you scrape the area with a scalpel blade).3 If there is doubt about the diagnosis, use a potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation; a positive test will reveal the classic “spaghetti and meatballs” pattern.1
Selenium sulfide 2.5%, zinc pyrithione 1%, and ketoconazole 2% shampoo are effective topical treatments. The shampoo is applied full strength to the affected skin daily for 5 to 10 minutes before it’s washed off. This can be done for 1 to 4 weeks, with longer treatment courses resulting in higher cure rates. Systemic therapy is reserved for patients with widespread infection or those who do not respond to topical treatment.4 It’s important to advise patients that the restoration of normal skin pigmentation can takes months.
This patient was treated with ketoconazole 2% shampoo for 3 weeks. A complete return of skin color was achieved 6 months after completion of therapy.
Image courtesy of Judy Jasser, MD. Text courtesy of Judy Jasser, MD, Department of Pediatrics, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.

These hyperpigmented lesions with fine scale on the outer edges are characteristic of pityriasis versicolor, also known as tinea versicolor. These macules (or patches) are commonly found on the trunk, proximal extremities, or neck. The lesions can be hypopigmented (pityriasis versicolor alba), hyperpigmented (pityriasis versicolor nigra), or erythematous (pityriasis versicolor rubra).1 It is common to see hyperpigmentation in people with darker skin tones, as was the case with this patient. Pityriasis versicolor is often asymptomatic, but patients may describe mild to moderate pruritis.
Pityriasis versicolor is a common fungal infection of the superficial layers of the dermis caused by Malassezia furfur.2 Impaired immunity and excessive sweating are risk factors for pityriasis versicolor; other risk factors include having a family member with tinea versicolor and living in a hot, humid region.1 Adolescents and young adults are most often affected.1
An evoked scale sign is a helpful tool to confirm the diagnosis clinically.3 Scale will appear when you stretch the affected skin with your thumb and index finger (or you scrape the area with a scalpel blade).3 If there is doubt about the diagnosis, use a potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation; a positive test will reveal the classic “spaghetti and meatballs” pattern.1
Selenium sulfide 2.5%, zinc pyrithione 1%, and ketoconazole 2% shampoo are effective topical treatments. The shampoo is applied full strength to the affected skin daily for 5 to 10 minutes before it’s washed off. This can be done for 1 to 4 weeks, with longer treatment courses resulting in higher cure rates. Systemic therapy is reserved for patients with widespread infection or those who do not respond to topical treatment.4 It’s important to advise patients that the restoration of normal skin pigmentation can takes months.
This patient was treated with ketoconazole 2% shampoo for 3 weeks. A complete return of skin color was achieved 6 months after completion of therapy.
Image courtesy of Judy Jasser, MD. Text courtesy of Judy Jasser, MD, Department of Pediatrics, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Crespo-Erchiga, V, Florencio, VD. Malassezia yeasts and pityriasis versicolor. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2006;19:139-147. doi: 10.1097/01.qco.0000216624.21069.61
2. Gupta, AK, Bluhm R, Summerbell R. Pityriasis versicolor. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2002;16:19-33. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-3083.2002.00378.x
3. Han, A, Calcara DA, Stoecker WV, et al. Evoked scale sign of tinea versicolor. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:1078. doi: 10.1001/archdermatol.2009.203
4. Renati S, Cukras A, Bigby M. Pityriasis versicolor. BMJ. 2015;350:h1394. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h1394
1. Crespo-Erchiga, V, Florencio, VD. Malassezia yeasts and pityriasis versicolor. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2006;19:139-147. doi: 10.1097/01.qco.0000216624.21069.61
2. Gupta, AK, Bluhm R, Summerbell R. Pityriasis versicolor. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2002;16:19-33. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-3083.2002.00378.x
3. Han, A, Calcara DA, Stoecker WV, et al. Evoked scale sign of tinea versicolor. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:1078. doi: 10.1001/archdermatol.2009.203
4. Renati S, Cukras A, Bigby M. Pityriasis versicolor. BMJ. 2015;350:h1394. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h1394
Immune dysregulation may drive long-term postpartum depression
Postpartum depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder that persist 2-3 years after birth are associated with a dysregulated immune system that is characterized by increased inflammatory signaling, according to investigators.
These findings suggest that mental health screening for women who have given birth should continue beyond the first year post partum, reported lead author Jennifer M. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
“Delayed postpartum depression, also known as late-onset postpartum depression, can affect women up to 18 months after delivery,” the investigators wrote in the American Journal of Reproductive Immunology. “It can appear even later in some women, depending on the hormonal changes that occur after having a baby (for example, timing of weaning). However, the majority of research on maternal mental health focuses on the first year post birth, leaving a gap in research beyond 12 months post partum.”
To address this gap, the investigators enrolled 33 women who were 2-3 years post partum. Participants completed self-guided questionnaires on PTSD, depression, and anxiety, and provided blood samples for gene expression analysis.
Sixteen of the 33 women had clinically significant mood disturbances. and significantly reduced activation of genes associated with viral response.
“The results provide preliminary evidence of a mechanism (e.g., immune dysregulation) that might be contributing to mood disorders and bring us closer to the goal of identifying targetable biomarkers for mood disorders,” Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara said in a written comment. “This work highlights the need for standardized and continual depression and anxiety screening in ob.gyn. and primary care settings that extends beyond the 6-week maternal visit and possibly beyond the first postpartum year.”
Findings draw skepticism
“The authors argue that mothers need to be screened for depression/anxiety longer than the first year post partum, and this is true, but it has nothing to do with their findings,” said Jennifer L. Payne, MD, an expert in reproductive psychiatry at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
In a written comment, she explained that the cross-sectional design makes it impossible to know whether the mood disturbances were linked with delivery at all.
“It is unclear if the depression/anxiety symptoms began after delivery or not,” Dr. Payne said. “In addition, it is unclear if the findings are causative or a result of depression/anxiety symptoms (the authors admit this in the limitations section). It is likely that the findings are not specific or even related to having delivered a child, but rather reflect a more general process related to depression/anxiety outside of the postpartum time period.”
Only prospective studies can answer these questions, she said.
Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara agreed that further research is needed.
“Our findings are exciting, but still need to be replicated in larger samples with diverse women in order to make sure they generalize,” she said. “More work is needed to understand why inflammation plays a role in postpartum mental illness for some women and not others.”
The study was supported by a Cedars-Sinai Precision Health Grant, the Cousins Center for Psychoneuroimmunology, University of California, Los Angeles, and the National Institute of Mental Health. The investigators and Dr. Payne disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Postpartum depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder that persist 2-3 years after birth are associated with a dysregulated immune system that is characterized by increased inflammatory signaling, according to investigators.
These findings suggest that mental health screening for women who have given birth should continue beyond the first year post partum, reported lead author Jennifer M. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
“Delayed postpartum depression, also known as late-onset postpartum depression, can affect women up to 18 months after delivery,” the investigators wrote in the American Journal of Reproductive Immunology. “It can appear even later in some women, depending on the hormonal changes that occur after having a baby (for example, timing of weaning). However, the majority of research on maternal mental health focuses on the first year post birth, leaving a gap in research beyond 12 months post partum.”
To address this gap, the investigators enrolled 33 women who were 2-3 years post partum. Participants completed self-guided questionnaires on PTSD, depression, and anxiety, and provided blood samples for gene expression analysis.
Sixteen of the 33 women had clinically significant mood disturbances. and significantly reduced activation of genes associated with viral response.
“The results provide preliminary evidence of a mechanism (e.g., immune dysregulation) that might be contributing to mood disorders and bring us closer to the goal of identifying targetable biomarkers for mood disorders,” Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara said in a written comment. “This work highlights the need for standardized and continual depression and anxiety screening in ob.gyn. and primary care settings that extends beyond the 6-week maternal visit and possibly beyond the first postpartum year.”
Findings draw skepticism
“The authors argue that mothers need to be screened for depression/anxiety longer than the first year post partum, and this is true, but it has nothing to do with their findings,” said Jennifer L. Payne, MD, an expert in reproductive psychiatry at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
In a written comment, she explained that the cross-sectional design makes it impossible to know whether the mood disturbances were linked with delivery at all.
“It is unclear if the depression/anxiety symptoms began after delivery or not,” Dr. Payne said. “In addition, it is unclear if the findings are causative or a result of depression/anxiety symptoms (the authors admit this in the limitations section). It is likely that the findings are not specific or even related to having delivered a child, but rather reflect a more general process related to depression/anxiety outside of the postpartum time period.”
Only prospective studies can answer these questions, she said.
Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara agreed that further research is needed.
“Our findings are exciting, but still need to be replicated in larger samples with diverse women in order to make sure they generalize,” she said. “More work is needed to understand why inflammation plays a role in postpartum mental illness for some women and not others.”
The study was supported by a Cedars-Sinai Precision Health Grant, the Cousins Center for Psychoneuroimmunology, University of California, Los Angeles, and the National Institute of Mental Health. The investigators and Dr. Payne disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Postpartum depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder that persist 2-3 years after birth are associated with a dysregulated immune system that is characterized by increased inflammatory signaling, according to investigators.
These findings suggest that mental health screening for women who have given birth should continue beyond the first year post partum, reported lead author Jennifer M. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
“Delayed postpartum depression, also known as late-onset postpartum depression, can affect women up to 18 months after delivery,” the investigators wrote in the American Journal of Reproductive Immunology. “It can appear even later in some women, depending on the hormonal changes that occur after having a baby (for example, timing of weaning). However, the majority of research on maternal mental health focuses on the first year post birth, leaving a gap in research beyond 12 months post partum.”
To address this gap, the investigators enrolled 33 women who were 2-3 years post partum. Participants completed self-guided questionnaires on PTSD, depression, and anxiety, and provided blood samples for gene expression analysis.
Sixteen of the 33 women had clinically significant mood disturbances. and significantly reduced activation of genes associated with viral response.
“The results provide preliminary evidence of a mechanism (e.g., immune dysregulation) that might be contributing to mood disorders and bring us closer to the goal of identifying targetable biomarkers for mood disorders,” Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara said in a written comment. “This work highlights the need for standardized and continual depression and anxiety screening in ob.gyn. and primary care settings that extends beyond the 6-week maternal visit and possibly beyond the first postpartum year.”
Findings draw skepticism
“The authors argue that mothers need to be screened for depression/anxiety longer than the first year post partum, and this is true, but it has nothing to do with their findings,” said Jennifer L. Payne, MD, an expert in reproductive psychiatry at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
In a written comment, she explained that the cross-sectional design makes it impossible to know whether the mood disturbances were linked with delivery at all.
“It is unclear if the depression/anxiety symptoms began after delivery or not,” Dr. Payne said. “In addition, it is unclear if the findings are causative or a result of depression/anxiety symptoms (the authors admit this in the limitations section). It is likely that the findings are not specific or even related to having delivered a child, but rather reflect a more general process related to depression/anxiety outside of the postpartum time period.”
Only prospective studies can answer these questions, she said.
Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara agreed that further research is needed.
“Our findings are exciting, but still need to be replicated in larger samples with diverse women in order to make sure they generalize,” she said. “More work is needed to understand why inflammation plays a role in postpartum mental illness for some women and not others.”
The study was supported by a Cedars-Sinai Precision Health Grant, the Cousins Center for Psychoneuroimmunology, University of California, Los Angeles, and the National Institute of Mental Health. The investigators and Dr. Payne disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF REPRODUCTIVE IMMUNOLOGY
‘Striking’ rate of mental health comorbidities in epilepsy
NASHVILLE, TENN. – , new research reveals.
“We hope these results inspire epileptologists and neurologists to both recognize and screen for suicide ideation and behaviors in their adolescent patients,” said study investigator Hadley Greenwood, a third-year medical student at New York University.
The new data should also encourage providers “to become more comfortable” providing support to patients, “be that by increasing their familiarity with prescribing different antidepressants or by being well versed in how to connect patients to resources within their community,” said Mr. Greenwood.
The findings were presented here at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society.
Little research
Previous studies have reported on the prevalence of suicidality as well as depression and anxiety among adults with epilepsy. “We wanted to look at adolescents because there’s much less in the literature out there about psychiatric comorbidity, and specifically suicidality, in this population,” said Mr. Greenwood.
Researchers used data from the Human Epilepsy Project, a study that collected data from 34 sites in the United States, Canada, Europe, and Australia from 2012 to 2017.
From a cohort of more than 400 participants, researchers identified 67 patients aged 11-17 years who were enrolled within 4 months of starting treatment for focal epilepsy.
Participants completed the Columbia–Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) at enrollment and at follow-ups over 36 months. The C-SSRS measures suicidal ideation and severity, said Mr. Greenwood.
“It’s scaled from passive suicide ideation, such as thoughts of ‘I wish I were dead’ without active intent, all the way up to active suicidal ideation with a plan and intent.”
Researchers were able to distinguish individuals with passive suicide ideation from those with more serious intentions, said Mr. Greenwood. They used medical records to evaluate the prevalence of suicidal ideation and behavior.
The investigators found that more than one in five (20.9%) teens endorsed any lifetime suicide ideation. This, said Mr. Greenwood, is “roughly equivalent” to the prevalence reported earlier in the adult cohort of the Human Epilepsy Project (21.6%).
‘Striking’ rate
The fact that one in five adolescents had any lifetime suicide ideation is “definitely a striking number,” said Mr. Greenwood.
Researchers found that 15% of patients experienced active suicide ideation, 7.5% exhibited preparatory or suicidal behaviors, and 3% had made a prior suicide attempt.
All of these percentages increased at 3 years: Thirty-one percent for suicide ideation; 25% for active suicide behavior, 15% for preparatory or suicide behaviors, and 5% for prior suicide attempt.
The fact that nearly one in three adolescents endorsed suicide ideation at 3 years is another “striking” finding, said Mr. Greenwood.
Of the 53 adolescents who had never had suicide ideation at the time of enrollment, 7 endorsed new-onset suicide ideation in the follow-up period. Five of 14 who had had suicide ideation at some point prior to enrollment continued to endorse it.
“The value of the study is identifying the prevalence and identifying the significant number of adolescents with epilepsy who are endorsing either suicide ideation or suicidal behaviors,” said Mr. Greenwood.
The researchers found that among younger teens (aged 11–14 years) rates of suicide ideation were higher than among their older counterparts (aged 15–17 years).
The study does not shed light on the biological connection between epilepsy and suicidality, but Mr. Greenwood noted that prior research has suggested a bidirectional relationship.
“Depression and other psychiatric comorbidities might exist prior to epileptic activity and actually predispose to epileptic activity.”
Mr. Greenwood noted that suicide ideation has “spiked” recently across the general population, and so it’s difficult to compare the prevalence in her study with “today’s prevalence.”
However, other research generally shows that the suicide ideation rate in the general adolescent population is much lower than in teens with epilepsy.
Unique aspects of the current study are that it reports suicide ideation and behaviors at around the time of an epilepsy diagnosis and documents how suicidality progresses or resolves over time, said Mr. Greenwood.
Underdiagnosed, undertreated
Commenting on the research, Elizabeth Donner, MD, director of the comprehensive epilepsy program, Hospital for Sick Children, and associate professor, department of pediatrics, University of Toronto, said a “key point” from the study is that the suicidality rate among teens with epilepsy exceeds that of children not living with epilepsy.
“We are significantly underdiagnosing and undertreating the mental health comorbidities in epilepsy,” said Dr. Donner. “Epilepsy is a brain disease and so are mental health disorders, so it shouldn’t come as any surprise that they coexist in individuals with epilepsy.”
The new results contribute to what is already known about the significant mortality rates among persons with epilepsy, said Dr. Donner. She referred to a 2018 study that showed that people with epilepsy were 3.5 times more likely to die by suicide.
Other research has shown that people with epilepsy are 10 times more likely to die by drowning, mostly in the bathtub, said Dr. Donner.
“You would think that we’re educating these people about risks related to their epilepsy, but either the messages don’t get through, or they don’t know how to keep themselves safe,” she said.
“This needs to be seen in a bigger picture, and the bigger picture is we need to recognize comorbid mental health issues; we need to address them once recognized; and then we need to counsel and support people to live safely with their epilepsy.
The study received funding from the Epilepsy Study Consortium, Finding a Cure for Epilepsy and Seizures (FACES) and other related foundations, UCB, Pfizer, Eisai, Lundbeck, and Sunovion. Mr. Greenwood and Dr. Donner report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NASHVILLE, TENN. – , new research reveals.
“We hope these results inspire epileptologists and neurologists to both recognize and screen for suicide ideation and behaviors in their adolescent patients,” said study investigator Hadley Greenwood, a third-year medical student at New York University.
The new data should also encourage providers “to become more comfortable” providing support to patients, “be that by increasing their familiarity with prescribing different antidepressants or by being well versed in how to connect patients to resources within their community,” said Mr. Greenwood.
The findings were presented here at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society.
Little research
Previous studies have reported on the prevalence of suicidality as well as depression and anxiety among adults with epilepsy. “We wanted to look at adolescents because there’s much less in the literature out there about psychiatric comorbidity, and specifically suicidality, in this population,” said Mr. Greenwood.
Researchers used data from the Human Epilepsy Project, a study that collected data from 34 sites in the United States, Canada, Europe, and Australia from 2012 to 2017.
From a cohort of more than 400 participants, researchers identified 67 patients aged 11-17 years who were enrolled within 4 months of starting treatment for focal epilepsy.
Participants completed the Columbia–Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) at enrollment and at follow-ups over 36 months. The C-SSRS measures suicidal ideation and severity, said Mr. Greenwood.
“It’s scaled from passive suicide ideation, such as thoughts of ‘I wish I were dead’ without active intent, all the way up to active suicidal ideation with a plan and intent.”
Researchers were able to distinguish individuals with passive suicide ideation from those with more serious intentions, said Mr. Greenwood. They used medical records to evaluate the prevalence of suicidal ideation and behavior.
The investigators found that more than one in five (20.9%) teens endorsed any lifetime suicide ideation. This, said Mr. Greenwood, is “roughly equivalent” to the prevalence reported earlier in the adult cohort of the Human Epilepsy Project (21.6%).
‘Striking’ rate
The fact that one in five adolescents had any lifetime suicide ideation is “definitely a striking number,” said Mr. Greenwood.
Researchers found that 15% of patients experienced active suicide ideation, 7.5% exhibited preparatory or suicidal behaviors, and 3% had made a prior suicide attempt.
All of these percentages increased at 3 years: Thirty-one percent for suicide ideation; 25% for active suicide behavior, 15% for preparatory or suicide behaviors, and 5% for prior suicide attempt.
The fact that nearly one in three adolescents endorsed suicide ideation at 3 years is another “striking” finding, said Mr. Greenwood.
Of the 53 adolescents who had never had suicide ideation at the time of enrollment, 7 endorsed new-onset suicide ideation in the follow-up period. Five of 14 who had had suicide ideation at some point prior to enrollment continued to endorse it.
“The value of the study is identifying the prevalence and identifying the significant number of adolescents with epilepsy who are endorsing either suicide ideation or suicidal behaviors,” said Mr. Greenwood.
The researchers found that among younger teens (aged 11–14 years) rates of suicide ideation were higher than among their older counterparts (aged 15–17 years).
The study does not shed light on the biological connection between epilepsy and suicidality, but Mr. Greenwood noted that prior research has suggested a bidirectional relationship.
“Depression and other psychiatric comorbidities might exist prior to epileptic activity and actually predispose to epileptic activity.”
Mr. Greenwood noted that suicide ideation has “spiked” recently across the general population, and so it’s difficult to compare the prevalence in her study with “today’s prevalence.”
However, other research generally shows that the suicide ideation rate in the general adolescent population is much lower than in teens with epilepsy.
Unique aspects of the current study are that it reports suicide ideation and behaviors at around the time of an epilepsy diagnosis and documents how suicidality progresses or resolves over time, said Mr. Greenwood.
Underdiagnosed, undertreated
Commenting on the research, Elizabeth Donner, MD, director of the comprehensive epilepsy program, Hospital for Sick Children, and associate professor, department of pediatrics, University of Toronto, said a “key point” from the study is that the suicidality rate among teens with epilepsy exceeds that of children not living with epilepsy.
“We are significantly underdiagnosing and undertreating the mental health comorbidities in epilepsy,” said Dr. Donner. “Epilepsy is a brain disease and so are mental health disorders, so it shouldn’t come as any surprise that they coexist in individuals with epilepsy.”
The new results contribute to what is already known about the significant mortality rates among persons with epilepsy, said Dr. Donner. She referred to a 2018 study that showed that people with epilepsy were 3.5 times more likely to die by suicide.
Other research has shown that people with epilepsy are 10 times more likely to die by drowning, mostly in the bathtub, said Dr. Donner.
“You would think that we’re educating these people about risks related to their epilepsy, but either the messages don’t get through, or they don’t know how to keep themselves safe,” she said.
“This needs to be seen in a bigger picture, and the bigger picture is we need to recognize comorbid mental health issues; we need to address them once recognized; and then we need to counsel and support people to live safely with their epilepsy.
The study received funding from the Epilepsy Study Consortium, Finding a Cure for Epilepsy and Seizures (FACES) and other related foundations, UCB, Pfizer, Eisai, Lundbeck, and Sunovion. Mr. Greenwood and Dr. Donner report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NASHVILLE, TENN. – , new research reveals.
“We hope these results inspire epileptologists and neurologists to both recognize and screen for suicide ideation and behaviors in their adolescent patients,” said study investigator Hadley Greenwood, a third-year medical student at New York University.
The new data should also encourage providers “to become more comfortable” providing support to patients, “be that by increasing their familiarity with prescribing different antidepressants or by being well versed in how to connect patients to resources within their community,” said Mr. Greenwood.
The findings were presented here at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society.
Little research
Previous studies have reported on the prevalence of suicidality as well as depression and anxiety among adults with epilepsy. “We wanted to look at adolescents because there’s much less in the literature out there about psychiatric comorbidity, and specifically suicidality, in this population,” said Mr. Greenwood.
Researchers used data from the Human Epilepsy Project, a study that collected data from 34 sites in the United States, Canada, Europe, and Australia from 2012 to 2017.
From a cohort of more than 400 participants, researchers identified 67 patients aged 11-17 years who were enrolled within 4 months of starting treatment for focal epilepsy.
Participants completed the Columbia–Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) at enrollment and at follow-ups over 36 months. The C-SSRS measures suicidal ideation and severity, said Mr. Greenwood.
“It’s scaled from passive suicide ideation, such as thoughts of ‘I wish I were dead’ without active intent, all the way up to active suicidal ideation with a plan and intent.”
Researchers were able to distinguish individuals with passive suicide ideation from those with more serious intentions, said Mr. Greenwood. They used medical records to evaluate the prevalence of suicidal ideation and behavior.
The investigators found that more than one in five (20.9%) teens endorsed any lifetime suicide ideation. This, said Mr. Greenwood, is “roughly equivalent” to the prevalence reported earlier in the adult cohort of the Human Epilepsy Project (21.6%).
‘Striking’ rate
The fact that one in five adolescents had any lifetime suicide ideation is “definitely a striking number,” said Mr. Greenwood.
Researchers found that 15% of patients experienced active suicide ideation, 7.5% exhibited preparatory or suicidal behaviors, and 3% had made a prior suicide attempt.
All of these percentages increased at 3 years: Thirty-one percent for suicide ideation; 25% for active suicide behavior, 15% for preparatory or suicide behaviors, and 5% for prior suicide attempt.
The fact that nearly one in three adolescents endorsed suicide ideation at 3 years is another “striking” finding, said Mr. Greenwood.
Of the 53 adolescents who had never had suicide ideation at the time of enrollment, 7 endorsed new-onset suicide ideation in the follow-up period. Five of 14 who had had suicide ideation at some point prior to enrollment continued to endorse it.
“The value of the study is identifying the prevalence and identifying the significant number of adolescents with epilepsy who are endorsing either suicide ideation or suicidal behaviors,” said Mr. Greenwood.
The researchers found that among younger teens (aged 11–14 years) rates of suicide ideation were higher than among their older counterparts (aged 15–17 years).
The study does not shed light on the biological connection between epilepsy and suicidality, but Mr. Greenwood noted that prior research has suggested a bidirectional relationship.
“Depression and other psychiatric comorbidities might exist prior to epileptic activity and actually predispose to epileptic activity.”
Mr. Greenwood noted that suicide ideation has “spiked” recently across the general population, and so it’s difficult to compare the prevalence in her study with “today’s prevalence.”
However, other research generally shows that the suicide ideation rate in the general adolescent population is much lower than in teens with epilepsy.
Unique aspects of the current study are that it reports suicide ideation and behaviors at around the time of an epilepsy diagnosis and documents how suicidality progresses or resolves over time, said Mr. Greenwood.
Underdiagnosed, undertreated
Commenting on the research, Elizabeth Donner, MD, director of the comprehensive epilepsy program, Hospital for Sick Children, and associate professor, department of pediatrics, University of Toronto, said a “key point” from the study is that the suicidality rate among teens with epilepsy exceeds that of children not living with epilepsy.
“We are significantly underdiagnosing and undertreating the mental health comorbidities in epilepsy,” said Dr. Donner. “Epilepsy is a brain disease and so are mental health disorders, so it shouldn’t come as any surprise that they coexist in individuals with epilepsy.”
The new results contribute to what is already known about the significant mortality rates among persons with epilepsy, said Dr. Donner. She referred to a 2018 study that showed that people with epilepsy were 3.5 times more likely to die by suicide.
Other research has shown that people with epilepsy are 10 times more likely to die by drowning, mostly in the bathtub, said Dr. Donner.
“You would think that we’re educating these people about risks related to their epilepsy, but either the messages don’t get through, or they don’t know how to keep themselves safe,” she said.
“This needs to be seen in a bigger picture, and the bigger picture is we need to recognize comorbid mental health issues; we need to address them once recognized; and then we need to counsel and support people to live safely with their epilepsy.
The study received funding from the Epilepsy Study Consortium, Finding a Cure for Epilepsy and Seizures (FACES) and other related foundations, UCB, Pfizer, Eisai, Lundbeck, and Sunovion. Mr. Greenwood and Dr. Donner report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AES 2022
Significant racial disparities persist in status epilepticus
NASHVILLE, Tenn. – Investigators found that among Black patients with status epilepticus, the hospitalization rate was twice that of their White counterparts. Other findings reveal age and income disparities.
“The results suggest that racial minorities, those with a lower income, and the elderly are an appropriate target to improve health outcomes and reduce health inequality,” said Gabriela Tantillo Sepúlveda, MD, assistant professor of neurology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society.
An examination of outcomes
Status epilepticus is associated with high rates of morbidity and mortality. Disparities in epilepsy care have previously been described, but little attention has been paid to the contribution of disparities to status epilepticus care and associated outcomes.
Researchers used 2010-2019 data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, a database covering a cross-section of hospitalizations in 48 states and the District of Columbia. From relevant diagnostic codes, they calculated status epilepticus prevalence as the rate per 10,000 hospitalizations and stratified this by demographics.
Over the study period, investigators identified 486,861 status epilepticus hospitalizations, most (71.3%) at urban teaching hospitals.
Status epilepticus prevalence was highest for non-Hispanic Black patients, at 27.3, followed by non-Hispanic others, at 16.1, Hispanic patients, at 15.8, and non-Hispanic-White patients, at 13.7 (P < .01).
The finding that Black patients had double the rate as White patients was “definitely surprising,” said Dr. Tantillo Sepúlveda.
Research over the past 20 years revealed similar disparities related to status epilepticus, “so it’s upsetting that these disparities have persisted. Unfortunately, we still have a lot of work to do to reduce health inequalities,” she said.
The investigators found that the prevalence of status epilepticus was higher in the lowest-income quartile, compared with the highest (18.7 vs. 14; P < .01).
Need for physician advocacy
Unlike previous studies, this research assessed various interventions in different age groups and showed that the likelihood of intubation, tracheostomy, gastrostomy, and in-hospital mortality increased with age.
For example, compared with the reference group (patients aged 18-39 years), the odds of intubation were 1.22 (95% confidence interval, 1.16-1.27) for those aged 40-59 years and 1.48 (95% CI, 1.42-1.54) for those aged 60-79. Those aged 80 and older were most likely to be intubated, at an odds ratio of 1.5 (95% CI, 1.43-1.58).
Elderly patients were most likely to undergo tracheostomy (OR, 2.0; 95% CI, 1.75-2.27), gastrostomy (OR, 3.37; 95% CI, 2.97-3.83), and to experience in-hospital mortality (OR, 6.51; 95% CI, 5.95-7.13), compared with the youngest patients.
These intervention rates also varied by racial/ethnic groups. Minority populations, particularly Black people, had higher odds of tracheostomy and gastrostomy, compared with non-Hispanic White persons.
The odds of undergoing electroencephalography monitoring progressively rose as income level increased (OR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.34-1.62) for the highest income quartile versus the lowest quartile. The odds of undergoing EEG monitoring were also higher at urban teaching hospitals than at rural hospitals.
Tackling these disparities in this patient population include increasing resources, personnel, and health education aimed at minorities, low-income patients, and the elderly, said Dr. Tantillo Sepúlveda. She added that more research is needed “to determine the most effective ways of accomplishing this goal.”
The medical community can help reduce disparities, said Dr. Tantillo Sepúlveda, by working to improve health literacy, to reduce stigma associated with seizures, and to increase awareness of seizure risk factors.
They can also work to expand access to outpatient neurology clinics, epilepsy monitoring units, and epilepsy surgery. “Ethnic and racial minorities are less likely to receive epilepsy surgery for temporal lobe epilepsy, which has been shown to improve quality of life and reduce seizure burden,” Dr. Tantillo Sepúlveda noted.
Across-the-board problem
Commenting on the research, Daniel Lowenstein, MD, professor of neurology, University of California, San Francisco, said the findings aren’t at all surprising. “It’s yet another piece of evidence on what has now become a rather voluminous literature that documents the very significant disparities that exist in our health care system,” said Dr. Lowenstein. “There’s just a huge literature on ‘name your disease and you’ll see the disparities.’ ”
Disparities exist, for example, in diagnosing breast cancer and prostate cancer, in the treatment of stroke and in related outcomes, and there is a well-documented “big disparity” in the approach to pain control among patients presenting at the emergency department, said Dr. Lowenstein.
However, he doesn’t know how disparities in epilepsy and specifically in status epilepticus, compared with disparities regarding other diseases and disorders. He noted that in the case of epilepsy, the situation is likely exacerbated by the stigma associated with that disease.
Dr. Lowenstein agreed that clinicians should play a role in reversing disparities. “We as physicians have a responsibility to be a voice for change in our health care system.”
The study was supported by the Center of Excellence for health equity, training, and research at the Baylor College of Medicine. Dr. Tantillo Sepúlveda and Dr. Lowenstein report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NASHVILLE, Tenn. – Investigators found that among Black patients with status epilepticus, the hospitalization rate was twice that of their White counterparts. Other findings reveal age and income disparities.
“The results suggest that racial minorities, those with a lower income, and the elderly are an appropriate target to improve health outcomes and reduce health inequality,” said Gabriela Tantillo Sepúlveda, MD, assistant professor of neurology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society.
An examination of outcomes
Status epilepticus is associated with high rates of morbidity and mortality. Disparities in epilepsy care have previously been described, but little attention has been paid to the contribution of disparities to status epilepticus care and associated outcomes.
Researchers used 2010-2019 data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, a database covering a cross-section of hospitalizations in 48 states and the District of Columbia. From relevant diagnostic codes, they calculated status epilepticus prevalence as the rate per 10,000 hospitalizations and stratified this by demographics.
Over the study period, investigators identified 486,861 status epilepticus hospitalizations, most (71.3%) at urban teaching hospitals.
Status epilepticus prevalence was highest for non-Hispanic Black patients, at 27.3, followed by non-Hispanic others, at 16.1, Hispanic patients, at 15.8, and non-Hispanic-White patients, at 13.7 (P < .01).
The finding that Black patients had double the rate as White patients was “definitely surprising,” said Dr. Tantillo Sepúlveda.
Research over the past 20 years revealed similar disparities related to status epilepticus, “so it’s upsetting that these disparities have persisted. Unfortunately, we still have a lot of work to do to reduce health inequalities,” she said.
The investigators found that the prevalence of status epilepticus was higher in the lowest-income quartile, compared with the highest (18.7 vs. 14; P < .01).
Need for physician advocacy
Unlike previous studies, this research assessed various interventions in different age groups and showed that the likelihood of intubation, tracheostomy, gastrostomy, and in-hospital mortality increased with age.
For example, compared with the reference group (patients aged 18-39 years), the odds of intubation were 1.22 (95% confidence interval, 1.16-1.27) for those aged 40-59 years and 1.48 (95% CI, 1.42-1.54) for those aged 60-79. Those aged 80 and older were most likely to be intubated, at an odds ratio of 1.5 (95% CI, 1.43-1.58).
Elderly patients were most likely to undergo tracheostomy (OR, 2.0; 95% CI, 1.75-2.27), gastrostomy (OR, 3.37; 95% CI, 2.97-3.83), and to experience in-hospital mortality (OR, 6.51; 95% CI, 5.95-7.13), compared with the youngest patients.
These intervention rates also varied by racial/ethnic groups. Minority populations, particularly Black people, had higher odds of tracheostomy and gastrostomy, compared with non-Hispanic White persons.
The odds of undergoing electroencephalography monitoring progressively rose as income level increased (OR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.34-1.62) for the highest income quartile versus the lowest quartile. The odds of undergoing EEG monitoring were also higher at urban teaching hospitals than at rural hospitals.
Tackling these disparities in this patient population include increasing resources, personnel, and health education aimed at minorities, low-income patients, and the elderly, said Dr. Tantillo Sepúlveda. She added that more research is needed “to determine the most effective ways of accomplishing this goal.”
The medical community can help reduce disparities, said Dr. Tantillo Sepúlveda, by working to improve health literacy, to reduce stigma associated with seizures, and to increase awareness of seizure risk factors.
They can also work to expand access to outpatient neurology clinics, epilepsy monitoring units, and epilepsy surgery. “Ethnic and racial minorities are less likely to receive epilepsy surgery for temporal lobe epilepsy, which has been shown to improve quality of life and reduce seizure burden,” Dr. Tantillo Sepúlveda noted.
Across-the-board problem
Commenting on the research, Daniel Lowenstein, MD, professor of neurology, University of California, San Francisco, said the findings aren’t at all surprising. “It’s yet another piece of evidence on what has now become a rather voluminous literature that documents the very significant disparities that exist in our health care system,” said Dr. Lowenstein. “There’s just a huge literature on ‘name your disease and you’ll see the disparities.’ ”
Disparities exist, for example, in diagnosing breast cancer and prostate cancer, in the treatment of stroke and in related outcomes, and there is a well-documented “big disparity” in the approach to pain control among patients presenting at the emergency department, said Dr. Lowenstein.
However, he doesn’t know how disparities in epilepsy and specifically in status epilepticus, compared with disparities regarding other diseases and disorders. He noted that in the case of epilepsy, the situation is likely exacerbated by the stigma associated with that disease.
Dr. Lowenstein agreed that clinicians should play a role in reversing disparities. “We as physicians have a responsibility to be a voice for change in our health care system.”
The study was supported by the Center of Excellence for health equity, training, and research at the Baylor College of Medicine. Dr. Tantillo Sepúlveda and Dr. Lowenstein report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NASHVILLE, Tenn. – Investigators found that among Black patients with status epilepticus, the hospitalization rate was twice that of their White counterparts. Other findings reveal age and income disparities.
“The results suggest that racial minorities, those with a lower income, and the elderly are an appropriate target to improve health outcomes and reduce health inequality,” said Gabriela Tantillo Sepúlveda, MD, assistant professor of neurology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society.
An examination of outcomes
Status epilepticus is associated with high rates of morbidity and mortality. Disparities in epilepsy care have previously been described, but little attention has been paid to the contribution of disparities to status epilepticus care and associated outcomes.
Researchers used 2010-2019 data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, a database covering a cross-section of hospitalizations in 48 states and the District of Columbia. From relevant diagnostic codes, they calculated status epilepticus prevalence as the rate per 10,000 hospitalizations and stratified this by demographics.
Over the study period, investigators identified 486,861 status epilepticus hospitalizations, most (71.3%) at urban teaching hospitals.
Status epilepticus prevalence was highest for non-Hispanic Black patients, at 27.3, followed by non-Hispanic others, at 16.1, Hispanic patients, at 15.8, and non-Hispanic-White patients, at 13.7 (P < .01).
The finding that Black patients had double the rate as White patients was “definitely surprising,” said Dr. Tantillo Sepúlveda.
Research over the past 20 years revealed similar disparities related to status epilepticus, “so it’s upsetting that these disparities have persisted. Unfortunately, we still have a lot of work to do to reduce health inequalities,” she said.
The investigators found that the prevalence of status epilepticus was higher in the lowest-income quartile, compared with the highest (18.7 vs. 14; P < .01).
Need for physician advocacy
Unlike previous studies, this research assessed various interventions in different age groups and showed that the likelihood of intubation, tracheostomy, gastrostomy, and in-hospital mortality increased with age.
For example, compared with the reference group (patients aged 18-39 years), the odds of intubation were 1.22 (95% confidence interval, 1.16-1.27) for those aged 40-59 years and 1.48 (95% CI, 1.42-1.54) for those aged 60-79. Those aged 80 and older were most likely to be intubated, at an odds ratio of 1.5 (95% CI, 1.43-1.58).
Elderly patients were most likely to undergo tracheostomy (OR, 2.0; 95% CI, 1.75-2.27), gastrostomy (OR, 3.37; 95% CI, 2.97-3.83), and to experience in-hospital mortality (OR, 6.51; 95% CI, 5.95-7.13), compared with the youngest patients.
These intervention rates also varied by racial/ethnic groups. Minority populations, particularly Black people, had higher odds of tracheostomy and gastrostomy, compared with non-Hispanic White persons.
The odds of undergoing electroencephalography monitoring progressively rose as income level increased (OR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.34-1.62) for the highest income quartile versus the lowest quartile. The odds of undergoing EEG monitoring were also higher at urban teaching hospitals than at rural hospitals.
Tackling these disparities in this patient population include increasing resources, personnel, and health education aimed at minorities, low-income patients, and the elderly, said Dr. Tantillo Sepúlveda. She added that more research is needed “to determine the most effective ways of accomplishing this goal.”
The medical community can help reduce disparities, said Dr. Tantillo Sepúlveda, by working to improve health literacy, to reduce stigma associated with seizures, and to increase awareness of seizure risk factors.
They can also work to expand access to outpatient neurology clinics, epilepsy monitoring units, and epilepsy surgery. “Ethnic and racial minorities are less likely to receive epilepsy surgery for temporal lobe epilepsy, which has been shown to improve quality of life and reduce seizure burden,” Dr. Tantillo Sepúlveda noted.
Across-the-board problem
Commenting on the research, Daniel Lowenstein, MD, professor of neurology, University of California, San Francisco, said the findings aren’t at all surprising. “It’s yet another piece of evidence on what has now become a rather voluminous literature that documents the very significant disparities that exist in our health care system,” said Dr. Lowenstein. “There’s just a huge literature on ‘name your disease and you’ll see the disparities.’ ”
Disparities exist, for example, in diagnosing breast cancer and prostate cancer, in the treatment of stroke and in related outcomes, and there is a well-documented “big disparity” in the approach to pain control among patients presenting at the emergency department, said Dr. Lowenstein.
However, he doesn’t know how disparities in epilepsy and specifically in status epilepticus, compared with disparities regarding other diseases and disorders. He noted that in the case of epilepsy, the situation is likely exacerbated by the stigma associated with that disease.
Dr. Lowenstein agreed that clinicians should play a role in reversing disparities. “We as physicians have a responsibility to be a voice for change in our health care system.”
The study was supported by the Center of Excellence for health equity, training, and research at the Baylor College of Medicine. Dr. Tantillo Sepúlveda and Dr. Lowenstein report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AES 2022
Bempedoic acid cuts CV risk in the statin-intolerant: CLEAR top-line results
The randomized, placebo-controlled CLEAR Outcomes trial has shown a significant reduction in risk for a composite cardiovascular (CV) endpoint among its patients treated with the lipid-lowering agent bempedoic acid (Nexletol), the drug’s owner, Esperion, announced today.
The trial marks the first time an ATP-citrate lyase inhibitor has shown significant and “clinically meaningful” benefit for patients not adequately managed with standard lipid-modifying agents, Esperion president and CEO Sheldon Koenig said in a press release.
The brief statement provided only top-line results, without P values or other evidence of the magnitude of benefit in the active-therapy group. The company expects to present more complete results “at a key medical conference in the first quarter of 2023.”
CLEAR Outcomes had entered 14,014 patients with a history of or at high risk for CV disease events, elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels, and demonstrated intolerance to at least two statins.
They were randomly assigned to bempedoic acid 180 mg once daily or placebo and followed for the primary endpoint of CV death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or coronary revascularization. The trial, conducted in 32 countries, launched in December 2016.
Bempedoic acid is currently approved for adults with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease on maximally tolerated statins who require additional LDL-C lowering, the company states.
Concomitant use of bempedoic acid with simvastatin or pravastatin, the press release says, may lead to increased statin concentrations and risk for “simvastatin- or pravastatin-related myopathy.” Therefore, “use with greater than 20 mg of simvastatin or 40 mg of pravastatin should be avoided.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The randomized, placebo-controlled CLEAR Outcomes trial has shown a significant reduction in risk for a composite cardiovascular (CV) endpoint among its patients treated with the lipid-lowering agent bempedoic acid (Nexletol), the drug’s owner, Esperion, announced today.
The trial marks the first time an ATP-citrate lyase inhibitor has shown significant and “clinically meaningful” benefit for patients not adequately managed with standard lipid-modifying agents, Esperion president and CEO Sheldon Koenig said in a press release.
The brief statement provided only top-line results, without P values or other evidence of the magnitude of benefit in the active-therapy group. The company expects to present more complete results “at a key medical conference in the first quarter of 2023.”
CLEAR Outcomes had entered 14,014 patients with a history of or at high risk for CV disease events, elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels, and demonstrated intolerance to at least two statins.
They were randomly assigned to bempedoic acid 180 mg once daily or placebo and followed for the primary endpoint of CV death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or coronary revascularization. The trial, conducted in 32 countries, launched in December 2016.
Bempedoic acid is currently approved for adults with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease on maximally tolerated statins who require additional LDL-C lowering, the company states.
Concomitant use of bempedoic acid with simvastatin or pravastatin, the press release says, may lead to increased statin concentrations and risk for “simvastatin- or pravastatin-related myopathy.” Therefore, “use with greater than 20 mg of simvastatin or 40 mg of pravastatin should be avoided.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The randomized, placebo-controlled CLEAR Outcomes trial has shown a significant reduction in risk for a composite cardiovascular (CV) endpoint among its patients treated with the lipid-lowering agent bempedoic acid (Nexletol), the drug’s owner, Esperion, announced today.
The trial marks the first time an ATP-citrate lyase inhibitor has shown significant and “clinically meaningful” benefit for patients not adequately managed with standard lipid-modifying agents, Esperion president and CEO Sheldon Koenig said in a press release.
The brief statement provided only top-line results, without P values or other evidence of the magnitude of benefit in the active-therapy group. The company expects to present more complete results “at a key medical conference in the first quarter of 2023.”
CLEAR Outcomes had entered 14,014 patients with a history of or at high risk for CV disease events, elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels, and demonstrated intolerance to at least two statins.
They were randomly assigned to bempedoic acid 180 mg once daily or placebo and followed for the primary endpoint of CV death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or coronary revascularization. The trial, conducted in 32 countries, launched in December 2016.
Bempedoic acid is currently approved for adults with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease on maximally tolerated statins who require additional LDL-C lowering, the company states.
Concomitant use of bempedoic acid with simvastatin or pravastatin, the press release says, may lead to increased statin concentrations and risk for “simvastatin- or pravastatin-related myopathy.” Therefore, “use with greater than 20 mg of simvastatin or 40 mg of pravastatin should be avoided.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Getting testosterone online is easy. Solid advice, not so much
When a secret shopper used telemedicine to request testosterone supplements, options were plentiful but good advice was scarce. As researchers showed, companies offered testosterone replacement therapy to the prospective buyer even though his stated T level was much higher than the cut-off for low testosterone levels.
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) delivery of testosterone or medications for erectile dysfunction has become routine. The many benefits of wide access include convenience and the ability to discuss sensitive topics in a safe environment. But as the new findings indicate, a lack of adherence to solid medical advice – such as guidance from the Endocrine Society and the American Urological Association – may be putting some people at risk for potentially harmful outcomes.
The Endocrine Society and the AUA state that only people with true testosterone deficiency should receive a T boost. Both groups discourage men who are planning to become parents in the near future from taking supplemental testosterone because of possible harms to their fertility.
“When guidelines are not being followed, there’s always the potential that we might not get the best outcomes for patients,” said Joshua A. Halpern, MD, a urologist at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, who led the study, which was published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
To conduct the research, the secret shopper approached seven different DTC testosterone websites with the same story for each: He was a 34-year-old man with low energy and libido who hoped to become a father soon. The customer noted that he had a testosterone level of 675 ng/dL, well above the 300 ng/dL the AUA considers low.
Despite these red flags – the normal T levels, the parenthood aspirations – representatives of almost every platform moved the shopper along toward receiving additional testosterone, with no attention to the possible harms to fertility. Only one platform declined to offer the testosterone because the shopper’s T levels were sufficient. In the other cases the secret shopper did not go forward with obtaining the medication, which would have required a prescription.
“Our goal with this study was to achieve a better understanding of what patients are experiencing and what’s out there,” Dr. Halpern said. While this study focused on cisgender patients, Dr. Halpern noted that it’s also important to understand the experiences of transgender patients who seek DTC hormonal therapy.
The research could help keep DTC companies more honest, according to Jesse N. Mills, MD, a urologist and men’s health specialist at the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved in the work. DTC platforms are financially incentivized to dispense medications regardless of need, unlike a traditional doctor who generally has no personal financial stake in a prescription.
“We need to keep the heat on DTC platforms,” Dr. Mills said, calling the article a “punchback” against the current DTC model for testosterone products. Dr. Mills said he is not opposed to telemedicine or DTC practices in general, adding that UCLA made a successful pivot to telemedicine during the pandemic.
“You can set up a lot of good care through video visits,” Dr. Mills said, as long as the system is ethical.
Dr. Halpern and Dr. Mills reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When a secret shopper used telemedicine to request testosterone supplements, options were plentiful but good advice was scarce. As researchers showed, companies offered testosterone replacement therapy to the prospective buyer even though his stated T level was much higher than the cut-off for low testosterone levels.
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) delivery of testosterone or medications for erectile dysfunction has become routine. The many benefits of wide access include convenience and the ability to discuss sensitive topics in a safe environment. But as the new findings indicate, a lack of adherence to solid medical advice – such as guidance from the Endocrine Society and the American Urological Association – may be putting some people at risk for potentially harmful outcomes.
The Endocrine Society and the AUA state that only people with true testosterone deficiency should receive a T boost. Both groups discourage men who are planning to become parents in the near future from taking supplemental testosterone because of possible harms to their fertility.
“When guidelines are not being followed, there’s always the potential that we might not get the best outcomes for patients,” said Joshua A. Halpern, MD, a urologist at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, who led the study, which was published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
To conduct the research, the secret shopper approached seven different DTC testosterone websites with the same story for each: He was a 34-year-old man with low energy and libido who hoped to become a father soon. The customer noted that he had a testosterone level of 675 ng/dL, well above the 300 ng/dL the AUA considers low.
Despite these red flags – the normal T levels, the parenthood aspirations – representatives of almost every platform moved the shopper along toward receiving additional testosterone, with no attention to the possible harms to fertility. Only one platform declined to offer the testosterone because the shopper’s T levels were sufficient. In the other cases the secret shopper did not go forward with obtaining the medication, which would have required a prescription.
“Our goal with this study was to achieve a better understanding of what patients are experiencing and what’s out there,” Dr. Halpern said. While this study focused on cisgender patients, Dr. Halpern noted that it’s also important to understand the experiences of transgender patients who seek DTC hormonal therapy.
The research could help keep DTC companies more honest, according to Jesse N. Mills, MD, a urologist and men’s health specialist at the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved in the work. DTC platforms are financially incentivized to dispense medications regardless of need, unlike a traditional doctor who generally has no personal financial stake in a prescription.
“We need to keep the heat on DTC platforms,” Dr. Mills said, calling the article a “punchback” against the current DTC model for testosterone products. Dr. Mills said he is not opposed to telemedicine or DTC practices in general, adding that UCLA made a successful pivot to telemedicine during the pandemic.
“You can set up a lot of good care through video visits,” Dr. Mills said, as long as the system is ethical.
Dr. Halpern and Dr. Mills reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When a secret shopper used telemedicine to request testosterone supplements, options were plentiful but good advice was scarce. As researchers showed, companies offered testosterone replacement therapy to the prospective buyer even though his stated T level was much higher than the cut-off for low testosterone levels.
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) delivery of testosterone or medications for erectile dysfunction has become routine. The many benefits of wide access include convenience and the ability to discuss sensitive topics in a safe environment. But as the new findings indicate, a lack of adherence to solid medical advice – such as guidance from the Endocrine Society and the American Urological Association – may be putting some people at risk for potentially harmful outcomes.
The Endocrine Society and the AUA state that only people with true testosterone deficiency should receive a T boost. Both groups discourage men who are planning to become parents in the near future from taking supplemental testosterone because of possible harms to their fertility.
“When guidelines are not being followed, there’s always the potential that we might not get the best outcomes for patients,” said Joshua A. Halpern, MD, a urologist at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, who led the study, which was published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
To conduct the research, the secret shopper approached seven different DTC testosterone websites with the same story for each: He was a 34-year-old man with low energy and libido who hoped to become a father soon. The customer noted that he had a testosterone level of 675 ng/dL, well above the 300 ng/dL the AUA considers low.
Despite these red flags – the normal T levels, the parenthood aspirations – representatives of almost every platform moved the shopper along toward receiving additional testosterone, with no attention to the possible harms to fertility. Only one platform declined to offer the testosterone because the shopper’s T levels were sufficient. In the other cases the secret shopper did not go forward with obtaining the medication, which would have required a prescription.
“Our goal with this study was to achieve a better understanding of what patients are experiencing and what’s out there,” Dr. Halpern said. While this study focused on cisgender patients, Dr. Halpern noted that it’s also important to understand the experiences of transgender patients who seek DTC hormonal therapy.
The research could help keep DTC companies more honest, according to Jesse N. Mills, MD, a urologist and men’s health specialist at the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved in the work. DTC platforms are financially incentivized to dispense medications regardless of need, unlike a traditional doctor who generally has no personal financial stake in a prescription.
“We need to keep the heat on DTC platforms,” Dr. Mills said, calling the article a “punchback” against the current DTC model for testosterone products. Dr. Mills said he is not opposed to telemedicine or DTC practices in general, adding that UCLA made a successful pivot to telemedicine during the pandemic.
“You can set up a lot of good care through video visits,” Dr. Mills said, as long as the system is ethical.
Dr. Halpern and Dr. Mills reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MCL: Ibrutinib could become the ‘new standard’
First-line patients fared well on ibrutinib, a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, according to the findings.
“Based on the results so far ... at least for the majority of patients, ibrutinib early will become the new standard,” said study lead author Martin Dreyling, MD, associate professor of medicine at Ludwig Maximilian University (LMU) Munich. Dr. Dreyling spoke in a news briefing and at a separate presentation at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. “It might well be that specific subsets of patients may benefit from autologous transplant.”
MCL is a rare form of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma that strikes cells in the mantle zone of lymph nodes. It is usually diagnosed in older men and often presents at an advanced stage. Multiple available treatments include rituximab/bendamustine, CAR-T cell therapy, stem cell transplants, and Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ibrutinib is approved by the Food and Drug Administration only for refractory/relapsed cases, however.
Dr. Dreyling was a pioneer in confirming benefit from stem-cell transplants for MCL. “However,” he said, “no one likes autologous transplant because it also has side effects.”
For the new open-label study, Dr. Dreyling and colleagues in the European MCL Network in 2016 began recruiting patients with newly diagnosed, advanced stage II-IV MCL. The patients were younger than 65.
The subjects were randomly assigned to three trial arms: Standard treatment (high-dose cytarabine followed by autologous stem cell transplant and rituximab maintenance, n = 288), the standard treatment plus ibrutinib (n = 292), and ibrutinib without stem cell transplant (n = 290). The median age was 57, and 76% of patients were male.
The primary endpoint was failure-free survival at 31 months. Standard therapy was not superior to the ibrutinib without transplant group (72% vs. 86%, respectively, P = .9979). However, standard therapy with ibrutinib was superior to the standard therapy group (88% vs. 72%, respectively, P = .0008). The researchers haven’t finished their analysis of standard therapy with ibrutinib vs. ibrutinib without transplant.
Subjects in the standard therapy plus ibrutinib arm had more grade 3-5 adverse events than did the standard therapy and ibrutinib without transplant groups: Neutropenia, 44%, 17%, and 23%, respectively; leukopenia, 4%, 2%, and 2%; febrile neutropenia, 6%, 3%, and 3%; infections and infestations, 25%, 13%, and 19%; and cardiac disorders, 3%, 1%, 4%. P values were not provided.
In an interview, Ohio State University hematologist Narendranath Epperla, MD, MS, who was not involved in the study, said that this research reflects efforts to understand how novel agents such as ibrutinib and cellular therapies fit into MCL treatment. “We are trying to incorporate them in the frontline setting with either chemo backbone or with other targeted agents to improve outcomes and minimize toxicity. We are also trying to understand in whom auto-HCT can be precluded.”
The results of the new study appear promising, Dr. Epperla said, but he questioned the primary endpoint (failure-free survival instead of progress-free survival) and the short duration of the trial.
“I would like to see how the patients with high-risk features such as TP53 mutation, complex cytogenetics, and blastoid/pleomorphic variants did on the three arms,” Dr. Epperla said. “And I would like to see longer follow-up data before adapting this – [addition] of ibrutinib to the chemotherapy backbone without auto-HCT – into clinical practice.”
What’s next? Dr. Dreyling said that upcoming data will provide further insight into ibrutinib vs. stem-cell transplantation. And “within the next half year or so,” he said, “there will be a next generation of studies challenging chemotherapy overall in mantle cell lymphoma and substituting targeted treatment, hopefully achieving much better tolerability.”
Funding information was not provided. Dr. Dreyling disclosed ties with Lilly/Loxo, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Amgen, Roche, Janssen, Gilead/Kite, BMS/Celgene, Bayer, Abbvie, and Beigene. The other study authors reported various disclosures. Dr. Epperla disclosed a relationship with Pharmacyclics.
First-line patients fared well on ibrutinib, a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, according to the findings.
“Based on the results so far ... at least for the majority of patients, ibrutinib early will become the new standard,” said study lead author Martin Dreyling, MD, associate professor of medicine at Ludwig Maximilian University (LMU) Munich. Dr. Dreyling spoke in a news briefing and at a separate presentation at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. “It might well be that specific subsets of patients may benefit from autologous transplant.”
MCL is a rare form of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma that strikes cells in the mantle zone of lymph nodes. It is usually diagnosed in older men and often presents at an advanced stage. Multiple available treatments include rituximab/bendamustine, CAR-T cell therapy, stem cell transplants, and Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ibrutinib is approved by the Food and Drug Administration only for refractory/relapsed cases, however.
Dr. Dreyling was a pioneer in confirming benefit from stem-cell transplants for MCL. “However,” he said, “no one likes autologous transplant because it also has side effects.”
For the new open-label study, Dr. Dreyling and colleagues in the European MCL Network in 2016 began recruiting patients with newly diagnosed, advanced stage II-IV MCL. The patients were younger than 65.
The subjects were randomly assigned to three trial arms: Standard treatment (high-dose cytarabine followed by autologous stem cell transplant and rituximab maintenance, n = 288), the standard treatment plus ibrutinib (n = 292), and ibrutinib without stem cell transplant (n = 290). The median age was 57, and 76% of patients were male.
The primary endpoint was failure-free survival at 31 months. Standard therapy was not superior to the ibrutinib without transplant group (72% vs. 86%, respectively, P = .9979). However, standard therapy with ibrutinib was superior to the standard therapy group (88% vs. 72%, respectively, P = .0008). The researchers haven’t finished their analysis of standard therapy with ibrutinib vs. ibrutinib without transplant.
Subjects in the standard therapy plus ibrutinib arm had more grade 3-5 adverse events than did the standard therapy and ibrutinib without transplant groups: Neutropenia, 44%, 17%, and 23%, respectively; leukopenia, 4%, 2%, and 2%; febrile neutropenia, 6%, 3%, and 3%; infections and infestations, 25%, 13%, and 19%; and cardiac disorders, 3%, 1%, 4%. P values were not provided.
In an interview, Ohio State University hematologist Narendranath Epperla, MD, MS, who was not involved in the study, said that this research reflects efforts to understand how novel agents such as ibrutinib and cellular therapies fit into MCL treatment. “We are trying to incorporate them in the frontline setting with either chemo backbone or with other targeted agents to improve outcomes and minimize toxicity. We are also trying to understand in whom auto-HCT can be precluded.”
The results of the new study appear promising, Dr. Epperla said, but he questioned the primary endpoint (failure-free survival instead of progress-free survival) and the short duration of the trial.
“I would like to see how the patients with high-risk features such as TP53 mutation, complex cytogenetics, and blastoid/pleomorphic variants did on the three arms,” Dr. Epperla said. “And I would like to see longer follow-up data before adapting this – [addition] of ibrutinib to the chemotherapy backbone without auto-HCT – into clinical practice.”
What’s next? Dr. Dreyling said that upcoming data will provide further insight into ibrutinib vs. stem-cell transplantation. And “within the next half year or so,” he said, “there will be a next generation of studies challenging chemotherapy overall in mantle cell lymphoma and substituting targeted treatment, hopefully achieving much better tolerability.”
Funding information was not provided. Dr. Dreyling disclosed ties with Lilly/Loxo, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Amgen, Roche, Janssen, Gilead/Kite, BMS/Celgene, Bayer, Abbvie, and Beigene. The other study authors reported various disclosures. Dr. Epperla disclosed a relationship with Pharmacyclics.
First-line patients fared well on ibrutinib, a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, according to the findings.
“Based on the results so far ... at least for the majority of patients, ibrutinib early will become the new standard,” said study lead author Martin Dreyling, MD, associate professor of medicine at Ludwig Maximilian University (LMU) Munich. Dr. Dreyling spoke in a news briefing and at a separate presentation at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. “It might well be that specific subsets of patients may benefit from autologous transplant.”
MCL is a rare form of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma that strikes cells in the mantle zone of lymph nodes. It is usually diagnosed in older men and often presents at an advanced stage. Multiple available treatments include rituximab/bendamustine, CAR-T cell therapy, stem cell transplants, and Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ibrutinib is approved by the Food and Drug Administration only for refractory/relapsed cases, however.
Dr. Dreyling was a pioneer in confirming benefit from stem-cell transplants for MCL. “However,” he said, “no one likes autologous transplant because it also has side effects.”
For the new open-label study, Dr. Dreyling and colleagues in the European MCL Network in 2016 began recruiting patients with newly diagnosed, advanced stage II-IV MCL. The patients were younger than 65.
The subjects were randomly assigned to three trial arms: Standard treatment (high-dose cytarabine followed by autologous stem cell transplant and rituximab maintenance, n = 288), the standard treatment plus ibrutinib (n = 292), and ibrutinib without stem cell transplant (n = 290). The median age was 57, and 76% of patients were male.
The primary endpoint was failure-free survival at 31 months. Standard therapy was not superior to the ibrutinib without transplant group (72% vs. 86%, respectively, P = .9979). However, standard therapy with ibrutinib was superior to the standard therapy group (88% vs. 72%, respectively, P = .0008). The researchers haven’t finished their analysis of standard therapy with ibrutinib vs. ibrutinib without transplant.
Subjects in the standard therapy plus ibrutinib arm had more grade 3-5 adverse events than did the standard therapy and ibrutinib without transplant groups: Neutropenia, 44%, 17%, and 23%, respectively; leukopenia, 4%, 2%, and 2%; febrile neutropenia, 6%, 3%, and 3%; infections and infestations, 25%, 13%, and 19%; and cardiac disorders, 3%, 1%, 4%. P values were not provided.
In an interview, Ohio State University hematologist Narendranath Epperla, MD, MS, who was not involved in the study, said that this research reflects efforts to understand how novel agents such as ibrutinib and cellular therapies fit into MCL treatment. “We are trying to incorporate them in the frontline setting with either chemo backbone or with other targeted agents to improve outcomes and minimize toxicity. We are also trying to understand in whom auto-HCT can be precluded.”
The results of the new study appear promising, Dr. Epperla said, but he questioned the primary endpoint (failure-free survival instead of progress-free survival) and the short duration of the trial.
“I would like to see how the patients with high-risk features such as TP53 mutation, complex cytogenetics, and blastoid/pleomorphic variants did on the three arms,” Dr. Epperla said. “And I would like to see longer follow-up data before adapting this – [addition] of ibrutinib to the chemotherapy backbone without auto-HCT – into clinical practice.”
What’s next? Dr. Dreyling said that upcoming data will provide further insight into ibrutinib vs. stem-cell transplantation. And “within the next half year or so,” he said, “there will be a next generation of studies challenging chemotherapy overall in mantle cell lymphoma and substituting targeted treatment, hopefully achieving much better tolerability.”
Funding information was not provided. Dr. Dreyling disclosed ties with Lilly/Loxo, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Amgen, Roche, Janssen, Gilead/Kite, BMS/Celgene, Bayer, Abbvie, and Beigene. The other study authors reported various disclosures. Dr. Epperla disclosed a relationship with Pharmacyclics.
AT ASH 2022
A bold national plan to eliminate HCV by 2050
WASHINGTON – “We don’t get to use the ‘eliminate’ word all that often with a disease that’s taking thousands or tens of thousands – or worldwide, hundreds of thousands – of lives every year, but we have that opportunity with hepatitis C.”
So said Francis S. Collins, MD, PhD, special projects advisor to the Executive Office of the President of the United States, and former director of the National Institutes of Health, speaking at a special session outlining ambitious goals for a national plan to eliminate hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections by the year 2050.
The session was held at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
A public health crisis
Dr. Collins labeled HCV a public health crisis, citing statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that show that the rate of reported acute HCV infection cases increased 400% between 2010 and 2020, with the highest rates among young adults aged 20-39 years.
In addition, an estimated 2.4 million people in the United States are living with chronic HCV infections, but as many as 40% of these people are unaware of their infection, despite broad recommendations for the screening of all adults aged 18 years and older, he said.
“Our goal is to try to do something to change this,” Dr. Collins said. He noted that for the past 8 years we have had highly effective oral agents that don’t just treat the disease but cure it – 95%-97% of the time, with only 8-12 weeks of oral therapy and relatively few side effects.
“A wonderful story, one of the most exciting stories that’s come out of biomedical research in the last couple of decades,” he said.
Yet Dr. Collins also acknowledged that the task of developing a national plan is daunting, despite that pharmaceutical triumph.
National pharmacy claims data show that the number of persons treated for HCV with direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs) in the United States declined from a high of 164,247 in 2015 to 83,740 in 2020.
Furthermore, CDC data from 2019 and 2020 show that, of persons with a diagnosis of HCV infection, only 23% of those on Medicaid, 28% of those on Medicare, and 35% of those with private insurance were treated for their infections.
“We have a huge gap here between the ability to know you have the disease and to get treatment, and we don’t see the numbers here for the uninsured, or people in prisons, but they’re probably much worse,” he said.
Obstacles abound, as do ways to overcome them
Current barriers to treatment include the aforementioned lack of awareness of infection, a “clunky” two-step diagnosis requiring an antibody test followed by an RNA or core antigen test necessitating three visits often separated by several weeks, and the high cost of treatment (around $90,000 per patient).
In addition, insurers commonly require proof that patients remain sober for extended periods, insist that treatment monitoring be performed by specialists only, and often approve treatment only for those patients who have documented evidence of liver damage.
“Does that make sense to you?” Dr. Collins asked. “You’ve got a cure for a liver disease, and you have to wait and show that the liver’s been damaged before you receive it? That just doesn’t fit,” he said.
Dr. Collins also pointed out that we’re dealing with hard-to-reach populations (underserved, uninsured, justice-involved), and people who are in tough times. “Anything that you put in the way as a barrier is going to make this worse in terms of its ability to be implemented,” he said.
To demonstrate how a coordinated HCV-elimination program could work, Dr. Collins pointed to a Medicaid cohort study in Louisiana conducted from July 2019 through December 2021, in which 8,867 patients started on therapy, 7,763 (88%) completed therapy, and 5,882 (66%) returned for testing. Of those tested, 5,285 (90%) had sustained virologic responses.
Another model of a hepatitis C elimination program was provided by the Veterans Health Administration. They received funding for an effort for all veterans, and in the space of 7 years were able to reach out even to some of their difficult-to-reach populations and achieve high diagnosis and treatment rates in a way that could be a model for what we would want to do across the nation, Dr. Collins noted.
Doing the math
Also at the session, Jagpreet Chhatwal, PhD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Institute for Technology Assessment and associate professor of radiology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, described outcomes projected by a mathematical simulation model of the HCV epidemic that he and his colleagues developed.
The HEP-SIM (Hepatitis C Disease Burden Simulation) model evaluates HCV prevalence trends, the number needed to screen and treat to eliminate HCV, HCV-associated clinical outcomes, the cost of an elimination program, and the cost savings that could be realized from preventing long-term complications.
The model seeks to determine whether the upfront costs of a national HCV elimination program could be offset by savings down the road. Specifically, it assumes that within the next 5 years 1.31 million individuals would be diagnosed with HCV and projects that within that time frame 1.52 million would need to be treated to meet HCV elimination goals.
The model shows that, compared with the status quo, a concerted campaign of screening and treatment would prevent more than 10,000 HCV-related deaths by 2030, and 91,000 deaths by 2050.
A coordinated screening program is also projected to prevent 17,000 cases of hepatocellular carcinoma by 2030 and 108,000 cases by 2050, as well as avert 29,000 cases of decompensated cirrhosis by 2030 and 93,000 such cases by 2050.
The cost savings associated with an HCV elimination plan would also be substantial, Dr. Chhatwal said.
According to the model, over the next decade the cumulative costs associated with HCV would decline by $14.2 billion, compared with the status quo. Nearly 80% of those savings ($11.2 billion) would be in Medicare and Medicaid.
The total projected savings from 2024 through 2050 – in disease management, testing, treatment, and pragmatic costs – are estimated at $59.3 billion, Dr. Chhatwal said.
“This is unprecedented,” he said.
Getting it done
Rachael L. Fleurence, PhD, MSc, a health economist currently serving as a senior advisor in the Executive Office of the President, summarized efforts to build a national HCV elimination program with input from federal health care agencies, state health leaders, patients, advocacy groups, drug manufacturers, and insurers.
She noted that a large component and focus of the program will be working on diagnostic test development but also accelerating bringing tests into the United States that are currently unavailable here. “These include point-of-care RNA diagnostic tests, as well as core antigen laboratory tests,” she said.
The program will be designed to offer broad access to curative anti-HCV drugs through a national subscription model that would make DAAs available to Medicaid recipients, justice-involved populations, the uninsured, and American Indians and Alaskan Natives who receive care through the Indian Health Service.
“On the Medicare and commercial insurance fronts, we’re still exploring different approaches, including potentially a co-pay assistance for Medicare beneficiaries, as well as working with commercial insurers to reduce barriers to access,” she said.
The program would also involve screening strategies extending to more settings, especially for high-risk populations, expanding the number of providers allowed to screen and treat HCV infections through telehealth, ensuring incentives for providers, and increasing the number of community health workers and case workers to improve linkage to care.
The next steps for the program would include funding to support the NIH’s RADx diagnostics program to accelerate access to testing, planning for the subscription model for DAA purchase, and launching pilot programs with the CDC, the Health Resources and Services Administration, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, and the Indian Health Service.
A call to action
Dr. Collins ended this portion of the program with an exhortation to AASLD members to do their part.
“We need your help,” Dr. Collins said. “This is a bold initiative, but it’s an opportunity. It’s even a responsibility. If we can actually succeed at this kind of outreach and save lives, and at the same time save money, how can we not do that?”
Dr. Collins, Dr. Chhatwal, and Dr. Fleurence each reported having no financial conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON – “We don’t get to use the ‘eliminate’ word all that often with a disease that’s taking thousands or tens of thousands – or worldwide, hundreds of thousands – of lives every year, but we have that opportunity with hepatitis C.”
So said Francis S. Collins, MD, PhD, special projects advisor to the Executive Office of the President of the United States, and former director of the National Institutes of Health, speaking at a special session outlining ambitious goals for a national plan to eliminate hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections by the year 2050.
The session was held at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
A public health crisis
Dr. Collins labeled HCV a public health crisis, citing statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that show that the rate of reported acute HCV infection cases increased 400% between 2010 and 2020, with the highest rates among young adults aged 20-39 years.
In addition, an estimated 2.4 million people in the United States are living with chronic HCV infections, but as many as 40% of these people are unaware of their infection, despite broad recommendations for the screening of all adults aged 18 years and older, he said.
“Our goal is to try to do something to change this,” Dr. Collins said. He noted that for the past 8 years we have had highly effective oral agents that don’t just treat the disease but cure it – 95%-97% of the time, with only 8-12 weeks of oral therapy and relatively few side effects.
“A wonderful story, one of the most exciting stories that’s come out of biomedical research in the last couple of decades,” he said.
Yet Dr. Collins also acknowledged that the task of developing a national plan is daunting, despite that pharmaceutical triumph.
National pharmacy claims data show that the number of persons treated for HCV with direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs) in the United States declined from a high of 164,247 in 2015 to 83,740 in 2020.
Furthermore, CDC data from 2019 and 2020 show that, of persons with a diagnosis of HCV infection, only 23% of those on Medicaid, 28% of those on Medicare, and 35% of those with private insurance were treated for their infections.
“We have a huge gap here between the ability to know you have the disease and to get treatment, and we don’t see the numbers here for the uninsured, or people in prisons, but they’re probably much worse,” he said.
Obstacles abound, as do ways to overcome them
Current barriers to treatment include the aforementioned lack of awareness of infection, a “clunky” two-step diagnosis requiring an antibody test followed by an RNA or core antigen test necessitating three visits often separated by several weeks, and the high cost of treatment (around $90,000 per patient).
In addition, insurers commonly require proof that patients remain sober for extended periods, insist that treatment monitoring be performed by specialists only, and often approve treatment only for those patients who have documented evidence of liver damage.
“Does that make sense to you?” Dr. Collins asked. “You’ve got a cure for a liver disease, and you have to wait and show that the liver’s been damaged before you receive it? That just doesn’t fit,” he said.
Dr. Collins also pointed out that we’re dealing with hard-to-reach populations (underserved, uninsured, justice-involved), and people who are in tough times. “Anything that you put in the way as a barrier is going to make this worse in terms of its ability to be implemented,” he said.
To demonstrate how a coordinated HCV-elimination program could work, Dr. Collins pointed to a Medicaid cohort study in Louisiana conducted from July 2019 through December 2021, in which 8,867 patients started on therapy, 7,763 (88%) completed therapy, and 5,882 (66%) returned for testing. Of those tested, 5,285 (90%) had sustained virologic responses.
Another model of a hepatitis C elimination program was provided by the Veterans Health Administration. They received funding for an effort for all veterans, and in the space of 7 years were able to reach out even to some of their difficult-to-reach populations and achieve high diagnosis and treatment rates in a way that could be a model for what we would want to do across the nation, Dr. Collins noted.
Doing the math
Also at the session, Jagpreet Chhatwal, PhD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Institute for Technology Assessment and associate professor of radiology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, described outcomes projected by a mathematical simulation model of the HCV epidemic that he and his colleagues developed.
The HEP-SIM (Hepatitis C Disease Burden Simulation) model evaluates HCV prevalence trends, the number needed to screen and treat to eliminate HCV, HCV-associated clinical outcomes, the cost of an elimination program, and the cost savings that could be realized from preventing long-term complications.
The model seeks to determine whether the upfront costs of a national HCV elimination program could be offset by savings down the road. Specifically, it assumes that within the next 5 years 1.31 million individuals would be diagnosed with HCV and projects that within that time frame 1.52 million would need to be treated to meet HCV elimination goals.
The model shows that, compared with the status quo, a concerted campaign of screening and treatment would prevent more than 10,000 HCV-related deaths by 2030, and 91,000 deaths by 2050.
A coordinated screening program is also projected to prevent 17,000 cases of hepatocellular carcinoma by 2030 and 108,000 cases by 2050, as well as avert 29,000 cases of decompensated cirrhosis by 2030 and 93,000 such cases by 2050.
The cost savings associated with an HCV elimination plan would also be substantial, Dr. Chhatwal said.
According to the model, over the next decade the cumulative costs associated with HCV would decline by $14.2 billion, compared with the status quo. Nearly 80% of those savings ($11.2 billion) would be in Medicare and Medicaid.
The total projected savings from 2024 through 2050 – in disease management, testing, treatment, and pragmatic costs – are estimated at $59.3 billion, Dr. Chhatwal said.
“This is unprecedented,” he said.
Getting it done
Rachael L. Fleurence, PhD, MSc, a health economist currently serving as a senior advisor in the Executive Office of the President, summarized efforts to build a national HCV elimination program with input from federal health care agencies, state health leaders, patients, advocacy groups, drug manufacturers, and insurers.
She noted that a large component and focus of the program will be working on diagnostic test development but also accelerating bringing tests into the United States that are currently unavailable here. “These include point-of-care RNA diagnostic tests, as well as core antigen laboratory tests,” she said.
The program will be designed to offer broad access to curative anti-HCV drugs through a national subscription model that would make DAAs available to Medicaid recipients, justice-involved populations, the uninsured, and American Indians and Alaskan Natives who receive care through the Indian Health Service.
“On the Medicare and commercial insurance fronts, we’re still exploring different approaches, including potentially a co-pay assistance for Medicare beneficiaries, as well as working with commercial insurers to reduce barriers to access,” she said.
The program would also involve screening strategies extending to more settings, especially for high-risk populations, expanding the number of providers allowed to screen and treat HCV infections through telehealth, ensuring incentives for providers, and increasing the number of community health workers and case workers to improve linkage to care.
The next steps for the program would include funding to support the NIH’s RADx diagnostics program to accelerate access to testing, planning for the subscription model for DAA purchase, and launching pilot programs with the CDC, the Health Resources and Services Administration, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, and the Indian Health Service.
A call to action
Dr. Collins ended this portion of the program with an exhortation to AASLD members to do their part.
“We need your help,” Dr. Collins said. “This is a bold initiative, but it’s an opportunity. It’s even a responsibility. If we can actually succeed at this kind of outreach and save lives, and at the same time save money, how can we not do that?”
Dr. Collins, Dr. Chhatwal, and Dr. Fleurence each reported having no financial conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON – “We don’t get to use the ‘eliminate’ word all that often with a disease that’s taking thousands or tens of thousands – or worldwide, hundreds of thousands – of lives every year, but we have that opportunity with hepatitis C.”
So said Francis S. Collins, MD, PhD, special projects advisor to the Executive Office of the President of the United States, and former director of the National Institutes of Health, speaking at a special session outlining ambitious goals for a national plan to eliminate hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections by the year 2050.
The session was held at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
A public health crisis
Dr. Collins labeled HCV a public health crisis, citing statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that show that the rate of reported acute HCV infection cases increased 400% between 2010 and 2020, with the highest rates among young adults aged 20-39 years.
In addition, an estimated 2.4 million people in the United States are living with chronic HCV infections, but as many as 40% of these people are unaware of their infection, despite broad recommendations for the screening of all adults aged 18 years and older, he said.
“Our goal is to try to do something to change this,” Dr. Collins said. He noted that for the past 8 years we have had highly effective oral agents that don’t just treat the disease but cure it – 95%-97% of the time, with only 8-12 weeks of oral therapy and relatively few side effects.
“A wonderful story, one of the most exciting stories that’s come out of biomedical research in the last couple of decades,” he said.
Yet Dr. Collins also acknowledged that the task of developing a national plan is daunting, despite that pharmaceutical triumph.
National pharmacy claims data show that the number of persons treated for HCV with direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs) in the United States declined from a high of 164,247 in 2015 to 83,740 in 2020.
Furthermore, CDC data from 2019 and 2020 show that, of persons with a diagnosis of HCV infection, only 23% of those on Medicaid, 28% of those on Medicare, and 35% of those with private insurance were treated for their infections.
“We have a huge gap here between the ability to know you have the disease and to get treatment, and we don’t see the numbers here for the uninsured, or people in prisons, but they’re probably much worse,” he said.
Obstacles abound, as do ways to overcome them
Current barriers to treatment include the aforementioned lack of awareness of infection, a “clunky” two-step diagnosis requiring an antibody test followed by an RNA or core antigen test necessitating three visits often separated by several weeks, and the high cost of treatment (around $90,000 per patient).
In addition, insurers commonly require proof that patients remain sober for extended periods, insist that treatment monitoring be performed by specialists only, and often approve treatment only for those patients who have documented evidence of liver damage.
“Does that make sense to you?” Dr. Collins asked. “You’ve got a cure for a liver disease, and you have to wait and show that the liver’s been damaged before you receive it? That just doesn’t fit,” he said.
Dr. Collins also pointed out that we’re dealing with hard-to-reach populations (underserved, uninsured, justice-involved), and people who are in tough times. “Anything that you put in the way as a barrier is going to make this worse in terms of its ability to be implemented,” he said.
To demonstrate how a coordinated HCV-elimination program could work, Dr. Collins pointed to a Medicaid cohort study in Louisiana conducted from July 2019 through December 2021, in which 8,867 patients started on therapy, 7,763 (88%) completed therapy, and 5,882 (66%) returned for testing. Of those tested, 5,285 (90%) had sustained virologic responses.
Another model of a hepatitis C elimination program was provided by the Veterans Health Administration. They received funding for an effort for all veterans, and in the space of 7 years were able to reach out even to some of their difficult-to-reach populations and achieve high diagnosis and treatment rates in a way that could be a model for what we would want to do across the nation, Dr. Collins noted.
Doing the math
Also at the session, Jagpreet Chhatwal, PhD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Institute for Technology Assessment and associate professor of radiology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, described outcomes projected by a mathematical simulation model of the HCV epidemic that he and his colleagues developed.
The HEP-SIM (Hepatitis C Disease Burden Simulation) model evaluates HCV prevalence trends, the number needed to screen and treat to eliminate HCV, HCV-associated clinical outcomes, the cost of an elimination program, and the cost savings that could be realized from preventing long-term complications.
The model seeks to determine whether the upfront costs of a national HCV elimination program could be offset by savings down the road. Specifically, it assumes that within the next 5 years 1.31 million individuals would be diagnosed with HCV and projects that within that time frame 1.52 million would need to be treated to meet HCV elimination goals.
The model shows that, compared with the status quo, a concerted campaign of screening and treatment would prevent more than 10,000 HCV-related deaths by 2030, and 91,000 deaths by 2050.
A coordinated screening program is also projected to prevent 17,000 cases of hepatocellular carcinoma by 2030 and 108,000 cases by 2050, as well as avert 29,000 cases of decompensated cirrhosis by 2030 and 93,000 such cases by 2050.
The cost savings associated with an HCV elimination plan would also be substantial, Dr. Chhatwal said.
According to the model, over the next decade the cumulative costs associated with HCV would decline by $14.2 billion, compared with the status quo. Nearly 80% of those savings ($11.2 billion) would be in Medicare and Medicaid.
The total projected savings from 2024 through 2050 – in disease management, testing, treatment, and pragmatic costs – are estimated at $59.3 billion, Dr. Chhatwal said.
“This is unprecedented,” he said.
Getting it done
Rachael L. Fleurence, PhD, MSc, a health economist currently serving as a senior advisor in the Executive Office of the President, summarized efforts to build a national HCV elimination program with input from federal health care agencies, state health leaders, patients, advocacy groups, drug manufacturers, and insurers.
She noted that a large component and focus of the program will be working on diagnostic test development but also accelerating bringing tests into the United States that are currently unavailable here. “These include point-of-care RNA diagnostic tests, as well as core antigen laboratory tests,” she said.
The program will be designed to offer broad access to curative anti-HCV drugs through a national subscription model that would make DAAs available to Medicaid recipients, justice-involved populations, the uninsured, and American Indians and Alaskan Natives who receive care through the Indian Health Service.
“On the Medicare and commercial insurance fronts, we’re still exploring different approaches, including potentially a co-pay assistance for Medicare beneficiaries, as well as working with commercial insurers to reduce barriers to access,” she said.
The program would also involve screening strategies extending to more settings, especially for high-risk populations, expanding the number of providers allowed to screen and treat HCV infections through telehealth, ensuring incentives for providers, and increasing the number of community health workers and case workers to improve linkage to care.
The next steps for the program would include funding to support the NIH’s RADx diagnostics program to accelerate access to testing, planning for the subscription model for DAA purchase, and launching pilot programs with the CDC, the Health Resources and Services Administration, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, and the Indian Health Service.
A call to action
Dr. Collins ended this portion of the program with an exhortation to AASLD members to do their part.
“We need your help,” Dr. Collins said. “This is a bold initiative, but it’s an opportunity. It’s even a responsibility. If we can actually succeed at this kind of outreach and save lives, and at the same time save money, how can we not do that?”
Dr. Collins, Dr. Chhatwal, and Dr. Fleurence each reported having no financial conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT THE LIVER MEETING
Hospital financial decisions play a role in the critical shortage of pediatric beds for RSV patients
The dire shortage of pediatric hospital beds plaguing the nation in the fall of 2022 is a byproduct of financial decisions made by hospitals over the past decade, as they shuttered children’s wards, which often operate in the red, and expanded the number of beds available for more profitable endeavors like joint replacements and cancer care.
To cope with the flood of young patients sickened by a sweeping convergence of nasty bugs – especially respiratory syncytial virus, influenza, and coronavirus – medical centers nationwide have deployed triage tents, delayed elective surgeries, and transferred critically ill children out of state.
A major factor in the bed shortage is a years-long trend among hospitals of eliminating pediatric units, which tend to be less profitable than adult units, said Mark Wietecha, MS, MBA, CEO of the Children’s Hospital Association. Hospitals optimize revenue by striving to keep their beds 100% full – and filled with patients whose conditions command generous insurance reimbursements.
“It really has to do with dollars,” said Scott Krugman, MD, MS, vice chair of pediatrics at the Herman and Walter Samuelson Children’s Hospital at Sinai in Baltimore. “Hospitals rely on high-volume, high-reimbursement procedures from good payers to make money. There’s no incentive for hospitals to provide money-losing services.”
The number of pediatric inpatient units in hospitals fell 19% from 2008 to 2018, according to a study published in 2021 in the journal Pediatrics. Just this year, hospitals have closed pediatric units in Boston and Springfield, Mass.; Richmond, Va.; and Tulsa, Okla.
The current surge in dangerous respiratory illnesses among children is yet another example of how COVID-19 has upended the health care system. The lockdowns and isolation that marked the first years of the pandemic left kids largely unexposed – and still vulnerable – to viruses other than COVID for two winters, and doctors are now essentially treating multiple years’ worth of respiratory ailments.
The pandemic also accelerated changes in the health care industry that have left many communities with fewer hospital beds available for children who are acutely ill, along with fewer doctors and nurses to care for them.
When intensive care units were flooded with older COVID patients in 2020, some hospitals began using children’s beds to treat adults. Many of those pediatric beds haven’t been restored, said Daniel Rauch, MD, chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics’ committee on hospital care.
In addition, the relentless pace of the pandemic has spurred more than 230,000 health care providers – including doctors, nurses, and physician assistants – to quit. Before the pandemic, about 10% of nurses left their jobs every year; the rate has risen to about 20%, Dr. Wietecha said. He estimates that pediatric hospitals are unable to maintain as many as 10% of their beds because of staffing shortages.
“There is just not enough space for all the kids who need beds,” said Megan Ranney, MD, MPH, who works in several emergency departments in Providence, R.I., including Hasbro Children’s Hospital. The number of children seeking emergency care in recent weeks was 25% higher than the hospital’s previous record.
“We have doctors who are cleaning beds so we can get children into them faster,” said Dr. Ranney, a deputy dean at Brown University’s School of Public Health.
There’s not great money in treating kids. About 40% of U.S. children are covered by Medicaid, a joint federal-state program for low-income patients and people with disabilities. Base Medicaid rates are typically more than 20% below those paid by Medicare, the government insurance program for older adults, and are even lower when compared with private insurance. While specialty care for a range of common adult procedures, from knee and hip replacements to heart surgeries and cancer treatments, generates major profits for medical centers, hospitals complain they typically lose money on inpatient pediatric care.
When Tufts Children’s Hospital closed 41 pediatric beds this summer, hospital officials assured residents that young patients could receive care at nearby Boston Children’s Hospital. Now, Boston Children’s is delaying some elective surgeries to make room for kids who are acutely ill.
Dr. Rauch noted that children’s hospitals, which specialize in treating rare and serious conditions such as pediatric cancer, cystic fibrosis, and heart defects, simply aren’t designed to handle this season’s crush of kids acutely ill with respiratory bugs.
Even before the autumn’s viral trifecta, pediatric units were straining to absorb rising numbers of young people in acute mental distress. Stories abound of children in mental crises being marooned for weeks in emergency departments while awaiting transfer to a pediatric psychiatric unit. On a good day, Dr. Ranney said, 20% of pediatric emergency room beds at Hasbro Children’s Hospital are occupied by children experiencing mental health issues.
In hopes of adding pediatric capacity, the American Academy of Pediatrics joined the Children’s Hospital Association last month in calling on the White House to declare a national emergency due to child respiratory infections and provide additional resources to help cover the costs of care. The Biden administration has said that the flexibility hospital systems and providers have been given during the pandemic to sidestep certain staffing requirements also applies to RSV and flu.
Doernbecher Children’s Hospital at Oregon Health & Science University has shifted to “crisis standards of care,” enabling intensive care nurses to treat more patients than they’re usually assigned. Hospitals in Atlanta, Pittsburgh, and Aurora, Colorado, meanwhile, have resorted to treating young patients in overflow tents in parking lots.
Alex Kon, MD, a pediatric critical care physician at Community Medical Center in Missoula, Mont., said providers there have made plans to care for older kids in the adult intensive care unit, and to divert ambulances to other facilities when necessary. With only three pediatric ICUs in the state, that means young patients may be flown as far as Seattle or Spokane, Wash., or Idaho.
Hollis Lillard took her 1-year-old son, Calder, to an Army hospital in Northern Virginia last month after he experienced several days of fever, coughing, and labored breathing. They spent 7 anguished hours in the emergency room before the hospital found an open bed and transferred them by ambulance to Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Maryland.
With proper therapy and instructions for home care, Calder’s virus was readily treatable: He recovered after he was given oxygen and treated with steroids, which fight inflammation, and albuterol, which counteracts bronchospasms. He was discharged the next day.
Although hospitalizations for RSV are falling, rates remain well above the norm for this time of year. And hospitals may not get much relief.
People can be infected with RSV more than once a year, and Dr. Krugman worries about a resurgence in the months to come. Because of the coronavirus, which competes with other viruses, “the usual seasonal pattern of viruses has gone out the window,” he said.
Like RSV, influenza arrived early this season. Both viruses usually peak around January. Three strains of flu are circulating and have caused an estimated 8.7 million illnesses, 78,000 hospitalizations, and 4,500 deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Dr. Krugman doubts the health care industry will learn any quick lessons from the current crisis. “Unless there is a radical change in how we pay for pediatric hospital care,” Dr. Krugman said, “the bed shortage is only going to get worse.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
The dire shortage of pediatric hospital beds plaguing the nation in the fall of 2022 is a byproduct of financial decisions made by hospitals over the past decade, as they shuttered children’s wards, which often operate in the red, and expanded the number of beds available for more profitable endeavors like joint replacements and cancer care.
To cope with the flood of young patients sickened by a sweeping convergence of nasty bugs – especially respiratory syncytial virus, influenza, and coronavirus – medical centers nationwide have deployed triage tents, delayed elective surgeries, and transferred critically ill children out of state.
A major factor in the bed shortage is a years-long trend among hospitals of eliminating pediatric units, which tend to be less profitable than adult units, said Mark Wietecha, MS, MBA, CEO of the Children’s Hospital Association. Hospitals optimize revenue by striving to keep their beds 100% full – and filled with patients whose conditions command generous insurance reimbursements.
“It really has to do with dollars,” said Scott Krugman, MD, MS, vice chair of pediatrics at the Herman and Walter Samuelson Children’s Hospital at Sinai in Baltimore. “Hospitals rely on high-volume, high-reimbursement procedures from good payers to make money. There’s no incentive for hospitals to provide money-losing services.”
The number of pediatric inpatient units in hospitals fell 19% from 2008 to 2018, according to a study published in 2021 in the journal Pediatrics. Just this year, hospitals have closed pediatric units in Boston and Springfield, Mass.; Richmond, Va.; and Tulsa, Okla.
The current surge in dangerous respiratory illnesses among children is yet another example of how COVID-19 has upended the health care system. The lockdowns and isolation that marked the first years of the pandemic left kids largely unexposed – and still vulnerable – to viruses other than COVID for two winters, and doctors are now essentially treating multiple years’ worth of respiratory ailments.
The pandemic also accelerated changes in the health care industry that have left many communities with fewer hospital beds available for children who are acutely ill, along with fewer doctors and nurses to care for them.
When intensive care units were flooded with older COVID patients in 2020, some hospitals began using children’s beds to treat adults. Many of those pediatric beds haven’t been restored, said Daniel Rauch, MD, chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics’ committee on hospital care.
In addition, the relentless pace of the pandemic has spurred more than 230,000 health care providers – including doctors, nurses, and physician assistants – to quit. Before the pandemic, about 10% of nurses left their jobs every year; the rate has risen to about 20%, Dr. Wietecha said. He estimates that pediatric hospitals are unable to maintain as many as 10% of their beds because of staffing shortages.
“There is just not enough space for all the kids who need beds,” said Megan Ranney, MD, MPH, who works in several emergency departments in Providence, R.I., including Hasbro Children’s Hospital. The number of children seeking emergency care in recent weeks was 25% higher than the hospital’s previous record.
“We have doctors who are cleaning beds so we can get children into them faster,” said Dr. Ranney, a deputy dean at Brown University’s School of Public Health.
There’s not great money in treating kids. About 40% of U.S. children are covered by Medicaid, a joint federal-state program for low-income patients and people with disabilities. Base Medicaid rates are typically more than 20% below those paid by Medicare, the government insurance program for older adults, and are even lower when compared with private insurance. While specialty care for a range of common adult procedures, from knee and hip replacements to heart surgeries and cancer treatments, generates major profits for medical centers, hospitals complain they typically lose money on inpatient pediatric care.
When Tufts Children’s Hospital closed 41 pediatric beds this summer, hospital officials assured residents that young patients could receive care at nearby Boston Children’s Hospital. Now, Boston Children’s is delaying some elective surgeries to make room for kids who are acutely ill.
Dr. Rauch noted that children’s hospitals, which specialize in treating rare and serious conditions such as pediatric cancer, cystic fibrosis, and heart defects, simply aren’t designed to handle this season’s crush of kids acutely ill with respiratory bugs.
Even before the autumn’s viral trifecta, pediatric units were straining to absorb rising numbers of young people in acute mental distress. Stories abound of children in mental crises being marooned for weeks in emergency departments while awaiting transfer to a pediatric psychiatric unit. On a good day, Dr. Ranney said, 20% of pediatric emergency room beds at Hasbro Children’s Hospital are occupied by children experiencing mental health issues.
In hopes of adding pediatric capacity, the American Academy of Pediatrics joined the Children’s Hospital Association last month in calling on the White House to declare a national emergency due to child respiratory infections and provide additional resources to help cover the costs of care. The Biden administration has said that the flexibility hospital systems and providers have been given during the pandemic to sidestep certain staffing requirements also applies to RSV and flu.
Doernbecher Children’s Hospital at Oregon Health & Science University has shifted to “crisis standards of care,” enabling intensive care nurses to treat more patients than they’re usually assigned. Hospitals in Atlanta, Pittsburgh, and Aurora, Colorado, meanwhile, have resorted to treating young patients in overflow tents in parking lots.
Alex Kon, MD, a pediatric critical care physician at Community Medical Center in Missoula, Mont., said providers there have made plans to care for older kids in the adult intensive care unit, and to divert ambulances to other facilities when necessary. With only three pediatric ICUs in the state, that means young patients may be flown as far as Seattle or Spokane, Wash., or Idaho.
Hollis Lillard took her 1-year-old son, Calder, to an Army hospital in Northern Virginia last month after he experienced several days of fever, coughing, and labored breathing. They spent 7 anguished hours in the emergency room before the hospital found an open bed and transferred them by ambulance to Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Maryland.
With proper therapy and instructions for home care, Calder’s virus was readily treatable: He recovered after he was given oxygen and treated with steroids, which fight inflammation, and albuterol, which counteracts bronchospasms. He was discharged the next day.
Although hospitalizations for RSV are falling, rates remain well above the norm for this time of year. And hospitals may not get much relief.
People can be infected with RSV more than once a year, and Dr. Krugman worries about a resurgence in the months to come. Because of the coronavirus, which competes with other viruses, “the usual seasonal pattern of viruses has gone out the window,” he said.
Like RSV, influenza arrived early this season. Both viruses usually peak around January. Three strains of flu are circulating and have caused an estimated 8.7 million illnesses, 78,000 hospitalizations, and 4,500 deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Dr. Krugman doubts the health care industry will learn any quick lessons from the current crisis. “Unless there is a radical change in how we pay for pediatric hospital care,” Dr. Krugman said, “the bed shortage is only going to get worse.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
The dire shortage of pediatric hospital beds plaguing the nation in the fall of 2022 is a byproduct of financial decisions made by hospitals over the past decade, as they shuttered children’s wards, which often operate in the red, and expanded the number of beds available for more profitable endeavors like joint replacements and cancer care.
To cope with the flood of young patients sickened by a sweeping convergence of nasty bugs – especially respiratory syncytial virus, influenza, and coronavirus – medical centers nationwide have deployed triage tents, delayed elective surgeries, and transferred critically ill children out of state.
A major factor in the bed shortage is a years-long trend among hospitals of eliminating pediatric units, which tend to be less profitable than adult units, said Mark Wietecha, MS, MBA, CEO of the Children’s Hospital Association. Hospitals optimize revenue by striving to keep their beds 100% full – and filled with patients whose conditions command generous insurance reimbursements.
“It really has to do with dollars,” said Scott Krugman, MD, MS, vice chair of pediatrics at the Herman and Walter Samuelson Children’s Hospital at Sinai in Baltimore. “Hospitals rely on high-volume, high-reimbursement procedures from good payers to make money. There’s no incentive for hospitals to provide money-losing services.”
The number of pediatric inpatient units in hospitals fell 19% from 2008 to 2018, according to a study published in 2021 in the journal Pediatrics. Just this year, hospitals have closed pediatric units in Boston and Springfield, Mass.; Richmond, Va.; and Tulsa, Okla.
The current surge in dangerous respiratory illnesses among children is yet another example of how COVID-19 has upended the health care system. The lockdowns and isolation that marked the first years of the pandemic left kids largely unexposed – and still vulnerable – to viruses other than COVID for two winters, and doctors are now essentially treating multiple years’ worth of respiratory ailments.
The pandemic also accelerated changes in the health care industry that have left many communities with fewer hospital beds available for children who are acutely ill, along with fewer doctors and nurses to care for them.
When intensive care units were flooded with older COVID patients in 2020, some hospitals began using children’s beds to treat adults. Many of those pediatric beds haven’t been restored, said Daniel Rauch, MD, chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics’ committee on hospital care.
In addition, the relentless pace of the pandemic has spurred more than 230,000 health care providers – including doctors, nurses, and physician assistants – to quit. Before the pandemic, about 10% of nurses left their jobs every year; the rate has risen to about 20%, Dr. Wietecha said. He estimates that pediatric hospitals are unable to maintain as many as 10% of their beds because of staffing shortages.
“There is just not enough space for all the kids who need beds,” said Megan Ranney, MD, MPH, who works in several emergency departments in Providence, R.I., including Hasbro Children’s Hospital. The number of children seeking emergency care in recent weeks was 25% higher than the hospital’s previous record.
“We have doctors who are cleaning beds so we can get children into them faster,” said Dr. Ranney, a deputy dean at Brown University’s School of Public Health.
There’s not great money in treating kids. About 40% of U.S. children are covered by Medicaid, a joint federal-state program for low-income patients and people with disabilities. Base Medicaid rates are typically more than 20% below those paid by Medicare, the government insurance program for older adults, and are even lower when compared with private insurance. While specialty care for a range of common adult procedures, from knee and hip replacements to heart surgeries and cancer treatments, generates major profits for medical centers, hospitals complain they typically lose money on inpatient pediatric care.
When Tufts Children’s Hospital closed 41 pediatric beds this summer, hospital officials assured residents that young patients could receive care at nearby Boston Children’s Hospital. Now, Boston Children’s is delaying some elective surgeries to make room for kids who are acutely ill.
Dr. Rauch noted that children’s hospitals, which specialize in treating rare and serious conditions such as pediatric cancer, cystic fibrosis, and heart defects, simply aren’t designed to handle this season’s crush of kids acutely ill with respiratory bugs.
Even before the autumn’s viral trifecta, pediatric units were straining to absorb rising numbers of young people in acute mental distress. Stories abound of children in mental crises being marooned for weeks in emergency departments while awaiting transfer to a pediatric psychiatric unit. On a good day, Dr. Ranney said, 20% of pediatric emergency room beds at Hasbro Children’s Hospital are occupied by children experiencing mental health issues.
In hopes of adding pediatric capacity, the American Academy of Pediatrics joined the Children’s Hospital Association last month in calling on the White House to declare a national emergency due to child respiratory infections and provide additional resources to help cover the costs of care. The Biden administration has said that the flexibility hospital systems and providers have been given during the pandemic to sidestep certain staffing requirements also applies to RSV and flu.
Doernbecher Children’s Hospital at Oregon Health & Science University has shifted to “crisis standards of care,” enabling intensive care nurses to treat more patients than they’re usually assigned. Hospitals in Atlanta, Pittsburgh, and Aurora, Colorado, meanwhile, have resorted to treating young patients in overflow tents in parking lots.
Alex Kon, MD, a pediatric critical care physician at Community Medical Center in Missoula, Mont., said providers there have made plans to care for older kids in the adult intensive care unit, and to divert ambulances to other facilities when necessary. With only three pediatric ICUs in the state, that means young patients may be flown as far as Seattle or Spokane, Wash., or Idaho.
Hollis Lillard took her 1-year-old son, Calder, to an Army hospital in Northern Virginia last month after he experienced several days of fever, coughing, and labored breathing. They spent 7 anguished hours in the emergency room before the hospital found an open bed and transferred them by ambulance to Walter Reed National Military Medical Center in Maryland.
With proper therapy and instructions for home care, Calder’s virus was readily treatable: He recovered after he was given oxygen and treated with steroids, which fight inflammation, and albuterol, which counteracts bronchospasms. He was discharged the next day.
Although hospitalizations for RSV are falling, rates remain well above the norm for this time of year. And hospitals may not get much relief.
People can be infected with RSV more than once a year, and Dr. Krugman worries about a resurgence in the months to come. Because of the coronavirus, which competes with other viruses, “the usual seasonal pattern of viruses has gone out the window,” he said.
Like RSV, influenza arrived early this season. Both viruses usually peak around January. Three strains of flu are circulating and have caused an estimated 8.7 million illnesses, 78,000 hospitalizations, and 4,500 deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Dr. Krugman doubts the health care industry will learn any quick lessons from the current crisis. “Unless there is a radical change in how we pay for pediatric hospital care,” Dr. Krugman said, “the bed shortage is only going to get worse.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
What in medicine is “permissible but not edifying”?
Morality is often talked about in binary terms, black and white, right or wrong. That is how children 4-8 years old first conceive of it. Moral development progresses alongside motor, language, and social skills, but pediatricians typically do not screen for it or chart it. In adolescence, the ability for abstract thought develops and, once susceptibility to peer pressure lessens, nuances begin to shade the binary model. Honor codes become possible by the college years; scandals at colleges and military academies demonstrate that some 18- to 22-year-old young adults still lack that maturity. Lawrence Kohlberg, PhD, in the 1950s proposed a six-stage model of moral development and indicated that some people never achieve the upper stages.
Recently, neuroimaging research has demonstrated that the prefrontal cortex is still developing up to 25 years of age. Those data have ramifications for obtaining truly informed consent for medical procedures. Arbitrarily, driver’s licenses are issued at 16 years of age, the right to vote comes at age 18, and the purchase of alcohol allowed at age 21. Consent for medical care varies by state and by procedure. Treatment for general medical care, pregnancy, sexually transmitted infections, and mental health problems often have different age requirements. In some states, a 14-year-old can give consent for treatment of depression or pregnancy but cannot get a tattoo.
The rules for firearms are also complex and vary by state. Perhaps more important is the determination of medical, psychological, moral, and criminal conditions for which guns should be removed from someone’s access. Some states have created formalized red flag laws to accomplish this. Other states have informal procedures used by police and social workers rather than involving medical personnel. Recent gun-related tragedies at a St. Louis high school near me and at a Colorado Springs bar demonstrate deficiencies in the red flag approach, with multiple fatal consequences.
Some moral issues do not neatly fit the binary approach. There are many concerns that are better described by a paradigm that “all things are permissible but not everything is edifying.” Take as a model of this the consumption of alcohol. The risks of an occasional single drink are very small for most people. For some, one drink leads to binges of alcoholism. Others drink and drive. Over the centuries, various groups in various localities have counseled temperance. Some personally avoid alcohol to avoid leading others astray.
The United States from 1920 to 1933 carried out the national social experiment Prohibition that outlawed intoxicating beverages. Ultimately, the organized crime of black market alcohol production, distribution, and consumption was found to be worse than the disease. Alcohol use was again legalized. That is understandable. Still, I doubt Carrie Nation ever thought that the sponsorship of most major sporting events would rely heavily on beer and liquor companies. Legalization and promotion are two distinct acts.
A federal prohibition of marijuana since the 1950s similarly produced crime from drug dealing. It also induced many otherwise law-abiding citizens to be scofflaws. (I think the 55 mph national speed limit under President Nixon created greater numbers of scofflaws.) In my state recreational marijuana became legal as I write this column. But is that good? Wise? Edifying?
State lotteries were created partly to reduce the negative effects of the numbers games funding organized crime. That rationale is understandable, but why are states promoting the games with commercials and billion dollar payouts?
I find the “permissible but not edifying” paradigm helpful in many areas of medical ethics. The ethical concerns typically then fall into one of four categories: Slippery slope, bright lines, overuse, and conscientiously opting out. All are subspecies of the theme of going too far.
Oregon’s Death with Dignity Act was enacted 25 years ago. Nine other states now allow some form of medically assisted death. Most states prohibit it. As is now the case for abortion, medical care is typically legislated at the state level to reflect local values. Canada goes beyond assisted suicide and in the vast majority of cases employs active euthanasia with a physician pushing lethal drugs intravenously. That action is forbidden in the United States. Currently, euthanasia is involved in 10,000 deaths per year in Canada. A terminal illness is no longer needed; that requirement was ruled unconstitutional. By March 2023, intractable mental health problems will be eligible for the euthanasia cure in Canada. I have long considered myself a navigator of ethical slippery slopes because that is where the suffering people are. Canada has gone too far down this particular slope for my skill set.
Dr. Powell is a retired pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. Email him at [email protected].
Morality is often talked about in binary terms, black and white, right or wrong. That is how children 4-8 years old first conceive of it. Moral development progresses alongside motor, language, and social skills, but pediatricians typically do not screen for it or chart it. In adolescence, the ability for abstract thought develops and, once susceptibility to peer pressure lessens, nuances begin to shade the binary model. Honor codes become possible by the college years; scandals at colleges and military academies demonstrate that some 18- to 22-year-old young adults still lack that maturity. Lawrence Kohlberg, PhD, in the 1950s proposed a six-stage model of moral development and indicated that some people never achieve the upper stages.
Recently, neuroimaging research has demonstrated that the prefrontal cortex is still developing up to 25 years of age. Those data have ramifications for obtaining truly informed consent for medical procedures. Arbitrarily, driver’s licenses are issued at 16 years of age, the right to vote comes at age 18, and the purchase of alcohol allowed at age 21. Consent for medical care varies by state and by procedure. Treatment for general medical care, pregnancy, sexually transmitted infections, and mental health problems often have different age requirements. In some states, a 14-year-old can give consent for treatment of depression or pregnancy but cannot get a tattoo.
The rules for firearms are also complex and vary by state. Perhaps more important is the determination of medical, psychological, moral, and criminal conditions for which guns should be removed from someone’s access. Some states have created formalized red flag laws to accomplish this. Other states have informal procedures used by police and social workers rather than involving medical personnel. Recent gun-related tragedies at a St. Louis high school near me and at a Colorado Springs bar demonstrate deficiencies in the red flag approach, with multiple fatal consequences.
Some moral issues do not neatly fit the binary approach. There are many concerns that are better described by a paradigm that “all things are permissible but not everything is edifying.” Take as a model of this the consumption of alcohol. The risks of an occasional single drink are very small for most people. For some, one drink leads to binges of alcoholism. Others drink and drive. Over the centuries, various groups in various localities have counseled temperance. Some personally avoid alcohol to avoid leading others astray.
The United States from 1920 to 1933 carried out the national social experiment Prohibition that outlawed intoxicating beverages. Ultimately, the organized crime of black market alcohol production, distribution, and consumption was found to be worse than the disease. Alcohol use was again legalized. That is understandable. Still, I doubt Carrie Nation ever thought that the sponsorship of most major sporting events would rely heavily on beer and liquor companies. Legalization and promotion are two distinct acts.
A federal prohibition of marijuana since the 1950s similarly produced crime from drug dealing. It also induced many otherwise law-abiding citizens to be scofflaws. (I think the 55 mph national speed limit under President Nixon created greater numbers of scofflaws.) In my state recreational marijuana became legal as I write this column. But is that good? Wise? Edifying?
State lotteries were created partly to reduce the negative effects of the numbers games funding organized crime. That rationale is understandable, but why are states promoting the games with commercials and billion dollar payouts?
I find the “permissible but not edifying” paradigm helpful in many areas of medical ethics. The ethical concerns typically then fall into one of four categories: Slippery slope, bright lines, overuse, and conscientiously opting out. All are subspecies of the theme of going too far.
Oregon’s Death with Dignity Act was enacted 25 years ago. Nine other states now allow some form of medically assisted death. Most states prohibit it. As is now the case for abortion, medical care is typically legislated at the state level to reflect local values. Canada goes beyond assisted suicide and in the vast majority of cases employs active euthanasia with a physician pushing lethal drugs intravenously. That action is forbidden in the United States. Currently, euthanasia is involved in 10,000 deaths per year in Canada. A terminal illness is no longer needed; that requirement was ruled unconstitutional. By March 2023, intractable mental health problems will be eligible for the euthanasia cure in Canada. I have long considered myself a navigator of ethical slippery slopes because that is where the suffering people are. Canada has gone too far down this particular slope for my skill set.
Dr. Powell is a retired pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. Email him at [email protected].
Morality is often talked about in binary terms, black and white, right or wrong. That is how children 4-8 years old first conceive of it. Moral development progresses alongside motor, language, and social skills, but pediatricians typically do not screen for it or chart it. In adolescence, the ability for abstract thought develops and, once susceptibility to peer pressure lessens, nuances begin to shade the binary model. Honor codes become possible by the college years; scandals at colleges and military academies demonstrate that some 18- to 22-year-old young adults still lack that maturity. Lawrence Kohlberg, PhD, in the 1950s proposed a six-stage model of moral development and indicated that some people never achieve the upper stages.
Recently, neuroimaging research has demonstrated that the prefrontal cortex is still developing up to 25 years of age. Those data have ramifications for obtaining truly informed consent for medical procedures. Arbitrarily, driver’s licenses are issued at 16 years of age, the right to vote comes at age 18, and the purchase of alcohol allowed at age 21. Consent for medical care varies by state and by procedure. Treatment for general medical care, pregnancy, sexually transmitted infections, and mental health problems often have different age requirements. In some states, a 14-year-old can give consent for treatment of depression or pregnancy but cannot get a tattoo.
The rules for firearms are also complex and vary by state. Perhaps more important is the determination of medical, psychological, moral, and criminal conditions for which guns should be removed from someone’s access. Some states have created formalized red flag laws to accomplish this. Other states have informal procedures used by police and social workers rather than involving medical personnel. Recent gun-related tragedies at a St. Louis high school near me and at a Colorado Springs bar demonstrate deficiencies in the red flag approach, with multiple fatal consequences.
Some moral issues do not neatly fit the binary approach. There are many concerns that are better described by a paradigm that “all things are permissible but not everything is edifying.” Take as a model of this the consumption of alcohol. The risks of an occasional single drink are very small for most people. For some, one drink leads to binges of alcoholism. Others drink and drive. Over the centuries, various groups in various localities have counseled temperance. Some personally avoid alcohol to avoid leading others astray.
The United States from 1920 to 1933 carried out the national social experiment Prohibition that outlawed intoxicating beverages. Ultimately, the organized crime of black market alcohol production, distribution, and consumption was found to be worse than the disease. Alcohol use was again legalized. That is understandable. Still, I doubt Carrie Nation ever thought that the sponsorship of most major sporting events would rely heavily on beer and liquor companies. Legalization and promotion are two distinct acts.
A federal prohibition of marijuana since the 1950s similarly produced crime from drug dealing. It also induced many otherwise law-abiding citizens to be scofflaws. (I think the 55 mph national speed limit under President Nixon created greater numbers of scofflaws.) In my state recreational marijuana became legal as I write this column. But is that good? Wise? Edifying?
State lotteries were created partly to reduce the negative effects of the numbers games funding organized crime. That rationale is understandable, but why are states promoting the games with commercials and billion dollar payouts?
I find the “permissible but not edifying” paradigm helpful in many areas of medical ethics. The ethical concerns typically then fall into one of four categories: Slippery slope, bright lines, overuse, and conscientiously opting out. All are subspecies of the theme of going too far.
Oregon’s Death with Dignity Act was enacted 25 years ago. Nine other states now allow some form of medically assisted death. Most states prohibit it. As is now the case for abortion, medical care is typically legislated at the state level to reflect local values. Canada goes beyond assisted suicide and in the vast majority of cases employs active euthanasia with a physician pushing lethal drugs intravenously. That action is forbidden in the United States. Currently, euthanasia is involved in 10,000 deaths per year in Canada. A terminal illness is no longer needed; that requirement was ruled unconstitutional. By March 2023, intractable mental health problems will be eligible for the euthanasia cure in Canada. I have long considered myself a navigator of ethical slippery slopes because that is where the suffering people are. Canada has gone too far down this particular slope for my skill set.
Dr. Powell is a retired pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. Email him at [email protected].