User login
Asthma management: How the guidelines compare
CASE
Erica S*, age 22, has intermittent asthma and presents to your clinic to discuss refills of her albuterol inhaler. Two years ago, she was hospitalized for a severe asthma exacerbation because she was unable to afford medications. Since then, her asthma has generally been well controlled, and she needs to use albuterol only 1 or 2 times per month. Ms. S says she has no morning chest tightness or nocturnal coughing, but she does experience increased wheezing and shortness of breath with activity.
What would you recommend? Would your recommendation differ if she had persistent asthma?
* The patient’s name has been changed to protect her identity .
As of 2020, more than 20 million adults and 4 million children younger than 18 years of age in the United States were living with asthma.1 In 2019 alone, there were more than 1.8 million asthma-related emergency department visits for adults, and more than 790,000 asthma-related emergency department visits for children. Asthma caused more than 4000 deaths in the United States in 2020.1 Given the scale of the burden of asthma, it is not surprising that approximately 60% of all asthma visits occur in primary care settings,2 making it essential that primary care physicians stay abreast of recent developments in asthma diagnosis and management.
Since 1991, the major guidance on best practices for asthma management in the United States has been provided by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)’s National Asthma Education and Prevention Program (NAEPP). Its last major update on asthma was released in 2007 as the Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma (EPR-3).3 Since that time, there has been significant progress in our understanding of asthma as a complex spectrum of phenotypes, which has advanced our knowledge of pathophysiology and helped refine treatment. In contrast to the NAEPP, the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) has published annual updates on asthma management incorporating up-to-date information.4 In response to the continuously evolving body of knowledge on asthma, the NAEPP Coordinating Committee Expert Panel Working Group published the 2020 Focused Updates to the Asthma Management Guidelines.5
Given the vast resources available on asthma, our purpose in this article is not to provide a comprehensive review of the stepwise approach to asthma management, but instead to summarize the major points presented in the 2020 Focused Updates and how these compare and contrast with the latest guidance from GINA.
A heterogeneous disease
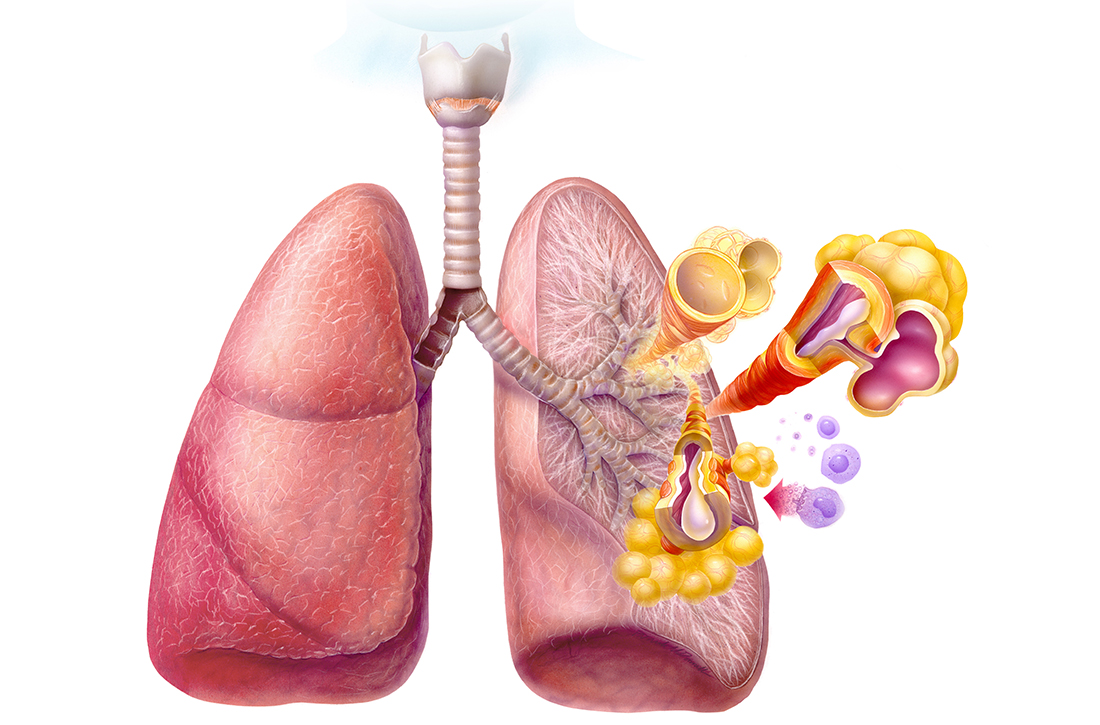
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by both variable symptoms and airflow limitation that change over time, often in response to external triggers such as exercise, allergens, and viral respiratory infections. Common symptoms include wheezing, cough, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. Despite the common symptomatology, asthma is a heterogeneous disease with several recognizable phenotypes including allergic, nonallergic, and asthma with persistent airflow limitation.
Continue to: The airflow limitation...
The airflow limitation in asthma occurs through both airway hyperresponsiveness to external stimuli and chronic airway inflammation. Airway constriction is regulated by nerves to the smooth muscles of the airway. Beta-2 nerve receptors have long been the target of asthma therapy with both short-acting beta-2 agonists (SABAs) as rescue treatment and long-acting beta-2 agonists (LABAs) as maintenance therapy.3,4 However, there is increasing evidence that cholinergic nerves also have a role in airway regulation in asthma, and long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMAs) have recently shown benefit as add-on therapy in some types of asthma.4-6 Inhaled corticosteroids (ICSs) have long held an important role in reducing airway inflammation, especially in the setting of allergic or eosinophilic inflammation.3-5
Spirometry is essential to asthma Dx—but what about FeNO?
The mainstay of asthma diagnosis is confirming both a history of variable respiratory symptoms and variable expiratory airflow limitation exhibited by spirometry. Obstruction is defined as a reduced forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) and as a decreased ratio of FEV1 over forced vital capacity (FVC) based on predicted values. An increase of at least 12% in FEV1 post bronchodilator use indicates asthma for adolescents and adults.
More recently, studies have examined the role of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) in the diagnosis of asthma. The 2020 Focused Updates report states that FeNO may be useful when the diagnosis of asthma is uncertain using initial history, physical exam, and spirometry findings, or when spirometry cannot be performed reliably.5 Levels of FeNO > 50 ppb make eosinophilic inflammation and treatment response to an ICS more likely. FeNO levels < 25 ppb make inflammatory asthma less likely and should prompt a search for an alternate diagnosis.5 For patients with FeNO of 25 to 50 ppb, more detailed clinical context is needed. In contrast, the 2022 GINA updates conclude that FeNO is not yet an established diagnostic tool for asthma.4
Management
When to start and adjust an ICS
ICSs continue to be the primary controller treatment for patients with asthma. However, the NAEPP and GINA have provided different guidance on how to initiate step therapy (TABLE3-5). NAEPP focuses on severity classification, while GINA recommends treatment initiation based on presenting symptoms. Since both guidelines recommend early follow-up and adjustment of therapy according to level of control, this difference becomes less apparent in ongoing care.
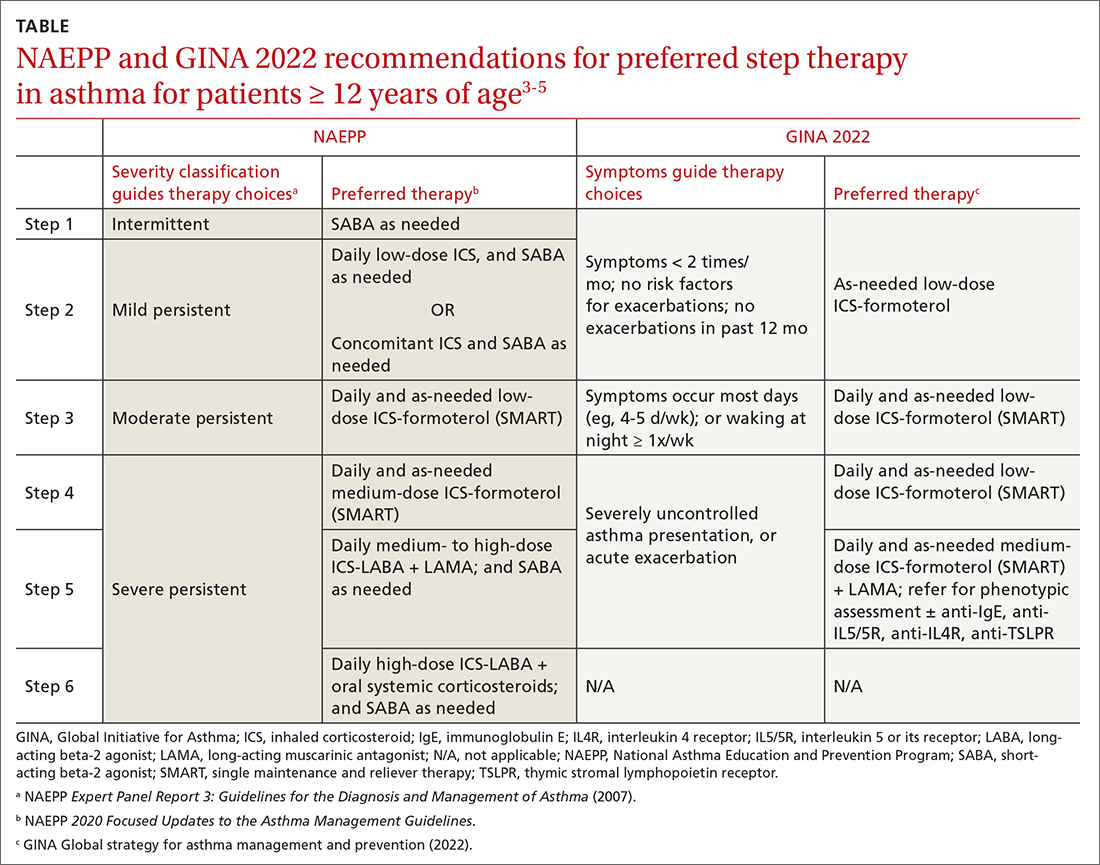
A more fundamental difference is seen in the recommended therapies for each step (TABLE3-5). Whereas the 2020 Focused Updates prefers a SABA as needed in step 1, GINA favors a low-dose combination of ICS-formoterol as needed. The GINA recommendation is driven by supportive evidence for early initiation of low-dose ICS in any patient with asthma for greater improvement in lung function. This also addresses concerns that overuse of as-needed SABAs may increase the risk for severe exacerbations. Evidence also indicates that the risk for asthma-related death and urgent asthma-related health care increases when a patient takes a SABA as needed as monotherapy compared with ICS therapy, even with good symptom control.7,8
Continue to: Dosing of an ICS
Dosing of an ICS is based on step therapy regardless of the guideline used and is given at a total daily amount—low, medium, and high—for each age group. When initiating an ICS, consider differences between available treatment options (eg, cost, administration technique, likely patient adherence, patient preferences) and employ shared decision-making strategies. Dosing may need to be limited depending on the commercially available product, especially when used in combination with a LABA. However, as GINA emphasizes, a low-dose ICS provides the most clinical benefit. A high-dose ICS is needed by very few patients and is associated with greater risk for local and systemic adverse effects, such as adrenal suppression. With these considerations, both guidelines recommend using the lowest effective ICS dose and stepping up and down according to the patient’s comfort level.
Give an ICS time to work. Although an ICS can begin to reduce inflammation within days of initiation, the full benefit may be evident only after 2 to 3 months.4 Once the patient’s asthma is well controlled for 3 months, stepping down the dose can be considered and approached carefully. Complete cessation of ICSs is associated with significantly higher risk for exacerbations. Therefore, a general recommendation is to step down an ICS by 50% or reduce ICS-LABA from twice-daily administration to once daily. Risk for exacerbation after step-down therapy is heightened if the patient has a history of exacerbation or an emergency department visit in the past 12 months, a low baseline FEV1, or a loss of control during a dose reduction (ie, airway hyperresponsiveness and sputum eosinophilia).
Weigh the utility of FeNO measurement. The 2020 Focused Updates also recommend considering FeNO measurement to guide treatment choice and monitoring, although this is based on overall low certainty of evidence.5 GINA affirms the mixed evidence for FeNO, stating that while a few studies have shown significantly reduced exacerbations among children, adolescents, and pregnant women with FeNO-guided treatment, other studies have shown no significant difference in exacerbations.4,9-15 At this time, the role for FeNO in asthma management remains inconclusive, and access to it is limited across primary care settings.
When assessing response to ICS therapy (and before stepping up therapy), consider patient adherence, inhaler technique, whether allergen exposure is persistent, and possible comorbidities. Inhaler technique can be especially challenging, as each inhaler varies in appearance and operation. Employ patient education strategies (eg, videos, demonstration, teach-back methods). If stepping up therapy is indicated, adding a LABA is recommended over increasing the ICS dose. Since asthma is variable, stepping up therapy can be tried and reassessed in 2 to 3 months.
SMART is preferred
Single maintenance and reliever therapy (SMART) with ICS-formoterol, used as needed, is the preferred therapy for steps 3 and 4 in both GINA recommendations and the 2020 Focused Updates (TABLE3-5). GINA also prefers SMART for step 5. The recommended SMART combination that has been studied contains budesonide (or beclomethasone, not available in combination in the United States) for the ICS and formoterol for the LABA in a single inhaler that is used both daily for control and as needed for rescue therapy.
Continue to: Other ICS-formoterol...
Other ICS-formoterol or ICS-LABA combinations can be considered for controller therapy, especially those described in the NAEPP and GINA alternative step therapy recommendations. However, SMART has been more effective than other combinations in reducing exacerbations and provides similar or better levels of control at lower average ICS doses (compared with ICS-LABA with SABA or ICS with SABA) for adolescent and adult patients.3,4 As patients use greater amounts of ICS-formoterol during episodes of increased symptoms, this additional ICS may augment the anti-inflammatory effects. SMART may also improve adherence, especially among those who confuse multiple inhalers.
SMART is also recommended for use in children. Specifically, from the 2020 Focused Updates, any patient ≥ 4 years of age with a severe exacerbation in the past year is a good SMART candidate. Also consider SMART before higher-dose ICS-LABA and SABA as needed. Additional benefits in this younger patient population are fewer medical visits or less systemic corticosteroid use with improved control and quality of life.
Caveats. Patients who have a difficult time recognizing symptoms may not be good candidates for SMART, due to the potential for taking higher or lower ICS doses than necessary.
SMART specifically refers to formoterol combinations that produce bronchodilation within 1 to 3 minutes.16 For example, the SMART strategy is not recommended for patients using ICS-salmeterol as controller therapy.
Although guideline supported, SMART options are not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for use as reliever therapy.
Continue to: With the single combination...
With the single combination inhaler, consider the dosing limits of formoterol. The maximum daily amount of formoterol for adolescents and adults is 54 μg (12 puffs) delivered with the budesonide-formoterol metered dose inhaler. When using SMART as reliever therapy, the low-dose ICS-formoterol recommendation remains. However, depending on insurance coverage, a 1-month supply of ICS-formoterol may not be sufficient for additional reliever therapy use.
The role of LAMAs as add-on therapy
Bronchiolar smooth muscle tone is mediated by complex mechanisms that include cholinergic stimulation at muscarinic (M3) receptors.17 LAMAs, a mainstay in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are likely to be effective in reducing asthma exacerbations and the need for oral steroids. When patients have not achieved control at step 4 of asthma therapy, both the 2020 Focused Updates and GINA now recommend considering a LAMA (eg, tiotropium) as add-on therapy for patients > 12 years of age already taking medium-dose ICS-LABA for modest improvements in lung function and reductions in severe exacerbations. GINA recommendations also now include a LAMA as add-on treatment for those ages 6 to 11 years, as some evidence supports the use in school-aged children.18 It is important to note that LAMAs should not replace a LABA for treatment, as the ICS-LABA combination is likely more effective than ICS-LAMA.
Addressing asthma-COPD overlap
Asthma and COPD are frequently and frustratingly intertwined without clear demarcation. This tends to occur as patients age and chronic lung changes appear from longstanding asthma. However, it is important to distinguish between these conditions, because there are clearly delineated treatments for each that can improve outcomes.
The priority in addressing asthma-COPD overlap (ACO) is to evaluate symptoms and determine if asthma or COPD is predominant.19 This includes establishing patient age at which symptoms began, variation and triggers of symptoms, and history of exposures to smoke/environmental respiratory toxins. Age 40 years is often used as the tipping point at which symptom onset favors a diagnosis of COPD. Serial spirometry may also be used to evaluate lung function over time and persistence of disease. If a firm diagnosis is evasive, consider a referral to a pulmonary specialist for further testing.
Choosing to use an ICS or LAMA depends on which underlying disorder is more likely. While early COPD management includes LAMA + LABA, the addition of an ICS is reserved for more severe disease. High-dose ICSs, particularly fluticasone, should be limited in COPD due to an increased risk for pneumonia. For asthma or ACO, the addition of an ICS is critical and prioritized to reduce airway inflammation and risk for exacerbations and death. While a LAMA is likely useful earlier in ACO, it is not used until step 5 of asthma therapy. Given the complexities of ACO treatment, further research is needed to provide adequate guidance.
CASE
For Ms. S, you would be wise to use an ICS-formoterol combination for as-needed symptom relief. If symptoms were more persistent, you could consider recommending the ICS-formoterol inhaler as SMART therapy, with regular doses taken twice daily and extra doses taken as needed.
CORRESPONDENCE
Tanner Nissly, DO, University of Minnesota School of Medicine, Department of Family Medicine and Community Health, 2426 West Broadway Avenue, Minneapolis, MN 55411; [email protected]
1. CDC. Most recent national asthma data. Accessed October 24, 2022. www.cdc.gov/asthma/most_recent_national_asthma_data.htm
2. Akinbami LJ, Santo L, Williams S, et al. Characteristics of asthma visits to physician offices in the United States: 2012–2015 National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey. Natl Health Stat Report. 2019;128:1-20.
3. NHLBI. National Asthma Education and Prevention Program expert panel report 3: guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma. NIH Publication 07-4051. 2007. Accessed October 24, 2022. www.nhlbi.nih.gov/sites/default/files/media/docs/EPR-3_Asthma_Full_Report_2007.pdf
4. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. 2022. Accessed October 24, 2022. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/GINA-Main-Report-2022-FINAL-22-07-01-WMS.pdf
5. NHLBI. 2020 Focused updates to the asthma management guidelines. Accessed October 24, 2022. www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/all-publications-and-resources/2020-focused-updates-asthma-management-guidelines
6. Lazarus SC, Krishnan JA, King TS, et al. Mometasone or tiotropium in mild asthma with a low sputum eosinophil level. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2009-2019. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1814917
7. Suissa S, Ernst P, Benayoun S, et al. Low-dose inhaled corticosteroids and the prevention of death from asthma. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:332-336. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200008033430504
8. Suissa S, Ernst P, Kezouh A. Regular use of inhaled corticosteroids and the long term prevention of hospitalisation for asthma. Thorax. 2002;57:880-884. doi: 10.1136/thorax.57.10.880
9. Szefler SJ, Mitchell H, Sorkness CA, et al. Management of asthma based on exhaled nitric oxide in addition to guideline-based treatment for inner-city adolescents and young adults: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2008;372:1065-1072. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61448-8
10. Calhoun WJ, Ameredes BT, King TS, et al. Comparison of physician-, biomarker-, and symptom-based strategies for adjustment of inhaled corticosteroid therapy in adults with asthma: the BASALT randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2012;308:987-997. doi: 10.1001/2012.jama.10893
11. Garg Y, Kakria N, Katoch CDS, et al. Exhaled nitric oxide as a guiding tool for bronchial asthma: a randomised controlled trial. Med J Armed Forces India. 2020;76:17-22. doi: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2018.02.001
12. Honkoop PJ, Loijmans RJ, Termeer EH, et al. Symptom- and fraction of exhaled nitric oxide-driven strategies for asthma control: a cluster-randomized trial in primary care. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;135:682-8.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.07.016
13. Peirsman EJ, Carvelli TJ, Hage PY, et al. Exhaled nitric oxide in childhood allergic asthma management: a randomised controlled trial. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2014;49:624-631. doi: 10.1002/ppul.22873
14. Powell H, Murphy VE, Taylor DR, et al. Management of asthma in pregnancy guided by measurement of fraction of exhaled nitric oxide: a double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2011;378:983-990. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60971-9
15. Shaw DE, Berry MA, Thomas M, et al. The use of exhaled nitric oxide to guide asthma management: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176:231-237. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200610-1427OC
16. Stam J, Souren M, Zweers P. The onset of action of formoterol, a new beta 2 adrenoceptor agonist. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1993;31:23-26.
17. Evgenov OV, Liang Y, Jiang Y, et al. Pulmonary pharmacology and inhaled anesthetics. In: Gropper MA, Miller RD, Evgenov O, et al, eds. Miller’s Anesthesia. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2020:540-571.
18. Rodrigo GJ, Neffen H. Efficacy and safety of tiotropium in school-age children with moderate-to-severe symptomatic asthma: a systematic review. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2017;28:573-578. doi: 10.1111/pai.12759
19. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Asthma, COPD, and asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS). 2015. Accessed October 24, 2022. https://goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/GOLD_ACOS_2015.pdf
CASE
Erica S*, age 22, has intermittent asthma and presents to your clinic to discuss refills of her albuterol inhaler. Two years ago, she was hospitalized for a severe asthma exacerbation because she was unable to afford medications. Since then, her asthma has generally been well controlled, and she needs to use albuterol only 1 or 2 times per month. Ms. S says she has no morning chest tightness or nocturnal coughing, but she does experience increased wheezing and shortness of breath with activity.
What would you recommend? Would your recommendation differ if she had persistent asthma?
* The patient’s name has been changed to protect her identity .
As of 2020, more than 20 million adults and 4 million children younger than 18 years of age in the United States were living with asthma.1 In 2019 alone, there were more than 1.8 million asthma-related emergency department visits for adults, and more than 790,000 asthma-related emergency department visits for children. Asthma caused more than 4000 deaths in the United States in 2020.1 Given the scale of the burden of asthma, it is not surprising that approximately 60% of all asthma visits occur in primary care settings,2 making it essential that primary care physicians stay abreast of recent developments in asthma diagnosis and management.
Since 1991, the major guidance on best practices for asthma management in the United States has been provided by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)’s National Asthma Education and Prevention Program (NAEPP). Its last major update on asthma was released in 2007 as the Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma (EPR-3).3 Since that time, there has been significant progress in our understanding of asthma as a complex spectrum of phenotypes, which has advanced our knowledge of pathophysiology and helped refine treatment. In contrast to the NAEPP, the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) has published annual updates on asthma management incorporating up-to-date information.4 In response to the continuously evolving body of knowledge on asthma, the NAEPP Coordinating Committee Expert Panel Working Group published the 2020 Focused Updates to the Asthma Management Guidelines.5
Given the vast resources available on asthma, our purpose in this article is not to provide a comprehensive review of the stepwise approach to asthma management, but instead to summarize the major points presented in the 2020 Focused Updates and how these compare and contrast with the latest guidance from GINA.
A heterogeneous disease
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by both variable symptoms and airflow limitation that change over time, often in response to external triggers such as exercise, allergens, and viral respiratory infections. Common symptoms include wheezing, cough, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. Despite the common symptomatology, asthma is a heterogeneous disease with several recognizable phenotypes including allergic, nonallergic, and asthma with persistent airflow limitation.
Continue to: The airflow limitation...
The airflow limitation in asthma occurs through both airway hyperresponsiveness to external stimuli and chronic airway inflammation. Airway constriction is regulated by nerves to the smooth muscles of the airway. Beta-2 nerve receptors have long been the target of asthma therapy with both short-acting beta-2 agonists (SABAs) as rescue treatment and long-acting beta-2 agonists (LABAs) as maintenance therapy.3,4 However, there is increasing evidence that cholinergic nerves also have a role in airway regulation in asthma, and long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMAs) have recently shown benefit as add-on therapy in some types of asthma.4-6 Inhaled corticosteroids (ICSs) have long held an important role in reducing airway inflammation, especially in the setting of allergic or eosinophilic inflammation.3-5
Spirometry is essential to asthma Dx—but what about FeNO?
The mainstay of asthma diagnosis is confirming both a history of variable respiratory symptoms and variable expiratory airflow limitation exhibited by spirometry. Obstruction is defined as a reduced forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) and as a decreased ratio of FEV1 over forced vital capacity (FVC) based on predicted values. An increase of at least 12% in FEV1 post bronchodilator use indicates asthma for adolescents and adults.
More recently, studies have examined the role of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) in the diagnosis of asthma. The 2020 Focused Updates report states that FeNO may be useful when the diagnosis of asthma is uncertain using initial history, physical exam, and spirometry findings, or when spirometry cannot be performed reliably.5 Levels of FeNO > 50 ppb make eosinophilic inflammation and treatment response to an ICS more likely. FeNO levels < 25 ppb make inflammatory asthma less likely and should prompt a search for an alternate diagnosis.5 For patients with FeNO of 25 to 50 ppb, more detailed clinical context is needed. In contrast, the 2022 GINA updates conclude that FeNO is not yet an established diagnostic tool for asthma.4
Management
When to start and adjust an ICS
ICSs continue to be the primary controller treatment for patients with asthma. However, the NAEPP and GINA have provided different guidance on how to initiate step therapy (TABLE3-5). NAEPP focuses on severity classification, while GINA recommends treatment initiation based on presenting symptoms. Since both guidelines recommend early follow-up and adjustment of therapy according to level of control, this difference becomes less apparent in ongoing care.

A more fundamental difference is seen in the recommended therapies for each step (TABLE3-5). Whereas the 2020 Focused Updates prefers a SABA as needed in step 1, GINA favors a low-dose combination of ICS-formoterol as needed. The GINA recommendation is driven by supportive evidence for early initiation of low-dose ICS in any patient with asthma for greater improvement in lung function. This also addresses concerns that overuse of as-needed SABAs may increase the risk for severe exacerbations. Evidence also indicates that the risk for asthma-related death and urgent asthma-related health care increases when a patient takes a SABA as needed as monotherapy compared with ICS therapy, even with good symptom control.7,8
Continue to: Dosing of an ICS
Dosing of an ICS is based on step therapy regardless of the guideline used and is given at a total daily amount—low, medium, and high—for each age group. When initiating an ICS, consider differences between available treatment options (eg, cost, administration technique, likely patient adherence, patient preferences) and employ shared decision-making strategies. Dosing may need to be limited depending on the commercially available product, especially when used in combination with a LABA. However, as GINA emphasizes, a low-dose ICS provides the most clinical benefit. A high-dose ICS is needed by very few patients and is associated with greater risk for local and systemic adverse effects, such as adrenal suppression. With these considerations, both guidelines recommend using the lowest effective ICS dose and stepping up and down according to the patient’s comfort level.
Give an ICS time to work. Although an ICS can begin to reduce inflammation within days of initiation, the full benefit may be evident only after 2 to 3 months.4 Once the patient’s asthma is well controlled for 3 months, stepping down the dose can be considered and approached carefully. Complete cessation of ICSs is associated with significantly higher risk for exacerbations. Therefore, a general recommendation is to step down an ICS by 50% or reduce ICS-LABA from twice-daily administration to once daily. Risk for exacerbation after step-down therapy is heightened if the patient has a history of exacerbation or an emergency department visit in the past 12 months, a low baseline FEV1, or a loss of control during a dose reduction (ie, airway hyperresponsiveness and sputum eosinophilia).
Weigh the utility of FeNO measurement. The 2020 Focused Updates also recommend considering FeNO measurement to guide treatment choice and monitoring, although this is based on overall low certainty of evidence.5 GINA affirms the mixed evidence for FeNO, stating that while a few studies have shown significantly reduced exacerbations among children, adolescents, and pregnant women with FeNO-guided treatment, other studies have shown no significant difference in exacerbations.4,9-15 At this time, the role for FeNO in asthma management remains inconclusive, and access to it is limited across primary care settings.
When assessing response to ICS therapy (and before stepping up therapy), consider patient adherence, inhaler technique, whether allergen exposure is persistent, and possible comorbidities. Inhaler technique can be especially challenging, as each inhaler varies in appearance and operation. Employ patient education strategies (eg, videos, demonstration, teach-back methods). If stepping up therapy is indicated, adding a LABA is recommended over increasing the ICS dose. Since asthma is variable, stepping up therapy can be tried and reassessed in 2 to 3 months.
SMART is preferred
Single maintenance and reliever therapy (SMART) with ICS-formoterol, used as needed, is the preferred therapy for steps 3 and 4 in both GINA recommendations and the 2020 Focused Updates (TABLE3-5). GINA also prefers SMART for step 5. The recommended SMART combination that has been studied contains budesonide (or beclomethasone, not available in combination in the United States) for the ICS and formoterol for the LABA in a single inhaler that is used both daily for control and as needed for rescue therapy.
Continue to: Other ICS-formoterol...
Other ICS-formoterol or ICS-LABA combinations can be considered for controller therapy, especially those described in the NAEPP and GINA alternative step therapy recommendations. However, SMART has been more effective than other combinations in reducing exacerbations and provides similar or better levels of control at lower average ICS doses (compared with ICS-LABA with SABA or ICS with SABA) for adolescent and adult patients.3,4 As patients use greater amounts of ICS-formoterol during episodes of increased symptoms, this additional ICS may augment the anti-inflammatory effects. SMART may also improve adherence, especially among those who confuse multiple inhalers.
SMART is also recommended for use in children. Specifically, from the 2020 Focused Updates, any patient ≥ 4 years of age with a severe exacerbation in the past year is a good SMART candidate. Also consider SMART before higher-dose ICS-LABA and SABA as needed. Additional benefits in this younger patient population are fewer medical visits or less systemic corticosteroid use with improved control and quality of life.
Caveats. Patients who have a difficult time recognizing symptoms may not be good candidates for SMART, due to the potential for taking higher or lower ICS doses than necessary.
SMART specifically refers to formoterol combinations that produce bronchodilation within 1 to 3 minutes.16 For example, the SMART strategy is not recommended for patients using ICS-salmeterol as controller therapy.
Although guideline supported, SMART options are not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for use as reliever therapy.
Continue to: With the single combination...
With the single combination inhaler, consider the dosing limits of formoterol. The maximum daily amount of formoterol for adolescents and adults is 54 μg (12 puffs) delivered with the budesonide-formoterol metered dose inhaler. When using SMART as reliever therapy, the low-dose ICS-formoterol recommendation remains. However, depending on insurance coverage, a 1-month supply of ICS-formoterol may not be sufficient for additional reliever therapy use.
The role of LAMAs as add-on therapy
Bronchiolar smooth muscle tone is mediated by complex mechanisms that include cholinergic stimulation at muscarinic (M3) receptors.17 LAMAs, a mainstay in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are likely to be effective in reducing asthma exacerbations and the need for oral steroids. When patients have not achieved control at step 4 of asthma therapy, both the 2020 Focused Updates and GINA now recommend considering a LAMA (eg, tiotropium) as add-on therapy for patients > 12 years of age already taking medium-dose ICS-LABA for modest improvements in lung function and reductions in severe exacerbations. GINA recommendations also now include a LAMA as add-on treatment for those ages 6 to 11 years, as some evidence supports the use in school-aged children.18 It is important to note that LAMAs should not replace a LABA for treatment, as the ICS-LABA combination is likely more effective than ICS-LAMA.
Addressing asthma-COPD overlap
Asthma and COPD are frequently and frustratingly intertwined without clear demarcation. This tends to occur as patients age and chronic lung changes appear from longstanding asthma. However, it is important to distinguish between these conditions, because there are clearly delineated treatments for each that can improve outcomes.
The priority in addressing asthma-COPD overlap (ACO) is to evaluate symptoms and determine if asthma or COPD is predominant.19 This includes establishing patient age at which symptoms began, variation and triggers of symptoms, and history of exposures to smoke/environmental respiratory toxins. Age 40 years is often used as the tipping point at which symptom onset favors a diagnosis of COPD. Serial spirometry may also be used to evaluate lung function over time and persistence of disease. If a firm diagnosis is evasive, consider a referral to a pulmonary specialist for further testing.
Choosing to use an ICS or LAMA depends on which underlying disorder is more likely. While early COPD management includes LAMA + LABA, the addition of an ICS is reserved for more severe disease. High-dose ICSs, particularly fluticasone, should be limited in COPD due to an increased risk for pneumonia. For asthma or ACO, the addition of an ICS is critical and prioritized to reduce airway inflammation and risk for exacerbations and death. While a LAMA is likely useful earlier in ACO, it is not used until step 5 of asthma therapy. Given the complexities of ACO treatment, further research is needed to provide adequate guidance.
CASE
For Ms. S, you would be wise to use an ICS-formoterol combination for as-needed symptom relief. If symptoms were more persistent, you could consider recommending the ICS-formoterol inhaler as SMART therapy, with regular doses taken twice daily and extra doses taken as needed.
CORRESPONDENCE
Tanner Nissly, DO, University of Minnesota School of Medicine, Department of Family Medicine and Community Health, 2426 West Broadway Avenue, Minneapolis, MN 55411; [email protected]
CASE
Erica S*, age 22, has intermittent asthma and presents to your clinic to discuss refills of her albuterol inhaler. Two years ago, she was hospitalized for a severe asthma exacerbation because she was unable to afford medications. Since then, her asthma has generally been well controlled, and she needs to use albuterol only 1 or 2 times per month. Ms. S says she has no morning chest tightness or nocturnal coughing, but she does experience increased wheezing and shortness of breath with activity.
What would you recommend? Would your recommendation differ if she had persistent asthma?
* The patient’s name has been changed to protect her identity .
As of 2020, more than 20 million adults and 4 million children younger than 18 years of age in the United States were living with asthma.1 In 2019 alone, there were more than 1.8 million asthma-related emergency department visits for adults, and more than 790,000 asthma-related emergency department visits for children. Asthma caused more than 4000 deaths in the United States in 2020.1 Given the scale of the burden of asthma, it is not surprising that approximately 60% of all asthma visits occur in primary care settings,2 making it essential that primary care physicians stay abreast of recent developments in asthma diagnosis and management.
Since 1991, the major guidance on best practices for asthma management in the United States has been provided by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)’s National Asthma Education and Prevention Program (NAEPP). Its last major update on asthma was released in 2007 as the Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma (EPR-3).3 Since that time, there has been significant progress in our understanding of asthma as a complex spectrum of phenotypes, which has advanced our knowledge of pathophysiology and helped refine treatment. In contrast to the NAEPP, the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) has published annual updates on asthma management incorporating up-to-date information.4 In response to the continuously evolving body of knowledge on asthma, the NAEPP Coordinating Committee Expert Panel Working Group published the 2020 Focused Updates to the Asthma Management Guidelines.5
Given the vast resources available on asthma, our purpose in this article is not to provide a comprehensive review of the stepwise approach to asthma management, but instead to summarize the major points presented in the 2020 Focused Updates and how these compare and contrast with the latest guidance from GINA.
A heterogeneous disease
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by both variable symptoms and airflow limitation that change over time, often in response to external triggers such as exercise, allergens, and viral respiratory infections. Common symptoms include wheezing, cough, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. Despite the common symptomatology, asthma is a heterogeneous disease with several recognizable phenotypes including allergic, nonallergic, and asthma with persistent airflow limitation.
Continue to: The airflow limitation...
The airflow limitation in asthma occurs through both airway hyperresponsiveness to external stimuli and chronic airway inflammation. Airway constriction is regulated by nerves to the smooth muscles of the airway. Beta-2 nerve receptors have long been the target of asthma therapy with both short-acting beta-2 agonists (SABAs) as rescue treatment and long-acting beta-2 agonists (LABAs) as maintenance therapy.3,4 However, there is increasing evidence that cholinergic nerves also have a role in airway regulation in asthma, and long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMAs) have recently shown benefit as add-on therapy in some types of asthma.4-6 Inhaled corticosteroids (ICSs) have long held an important role in reducing airway inflammation, especially in the setting of allergic or eosinophilic inflammation.3-5
Spirometry is essential to asthma Dx—but what about FeNO?
The mainstay of asthma diagnosis is confirming both a history of variable respiratory symptoms and variable expiratory airflow limitation exhibited by spirometry. Obstruction is defined as a reduced forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) and as a decreased ratio of FEV1 over forced vital capacity (FVC) based on predicted values. An increase of at least 12% in FEV1 post bronchodilator use indicates asthma for adolescents and adults.
More recently, studies have examined the role of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) in the diagnosis of asthma. The 2020 Focused Updates report states that FeNO may be useful when the diagnosis of asthma is uncertain using initial history, physical exam, and spirometry findings, or when spirometry cannot be performed reliably.5 Levels of FeNO > 50 ppb make eosinophilic inflammation and treatment response to an ICS more likely. FeNO levels < 25 ppb make inflammatory asthma less likely and should prompt a search for an alternate diagnosis.5 For patients with FeNO of 25 to 50 ppb, more detailed clinical context is needed. In contrast, the 2022 GINA updates conclude that FeNO is not yet an established diagnostic tool for asthma.4
Management
When to start and adjust an ICS
ICSs continue to be the primary controller treatment for patients with asthma. However, the NAEPP and GINA have provided different guidance on how to initiate step therapy (TABLE3-5). NAEPP focuses on severity classification, while GINA recommends treatment initiation based on presenting symptoms. Since both guidelines recommend early follow-up and adjustment of therapy according to level of control, this difference becomes less apparent in ongoing care.

A more fundamental difference is seen in the recommended therapies for each step (TABLE3-5). Whereas the 2020 Focused Updates prefers a SABA as needed in step 1, GINA favors a low-dose combination of ICS-formoterol as needed. The GINA recommendation is driven by supportive evidence for early initiation of low-dose ICS in any patient with asthma for greater improvement in lung function. This also addresses concerns that overuse of as-needed SABAs may increase the risk for severe exacerbations. Evidence also indicates that the risk for asthma-related death and urgent asthma-related health care increases when a patient takes a SABA as needed as monotherapy compared with ICS therapy, even with good symptom control.7,8
Continue to: Dosing of an ICS
Dosing of an ICS is based on step therapy regardless of the guideline used and is given at a total daily amount—low, medium, and high—for each age group. When initiating an ICS, consider differences between available treatment options (eg, cost, administration technique, likely patient adherence, patient preferences) and employ shared decision-making strategies. Dosing may need to be limited depending on the commercially available product, especially when used in combination with a LABA. However, as GINA emphasizes, a low-dose ICS provides the most clinical benefit. A high-dose ICS is needed by very few patients and is associated with greater risk for local and systemic adverse effects, such as adrenal suppression. With these considerations, both guidelines recommend using the lowest effective ICS dose and stepping up and down according to the patient’s comfort level.
Give an ICS time to work. Although an ICS can begin to reduce inflammation within days of initiation, the full benefit may be evident only after 2 to 3 months.4 Once the patient’s asthma is well controlled for 3 months, stepping down the dose can be considered and approached carefully. Complete cessation of ICSs is associated with significantly higher risk for exacerbations. Therefore, a general recommendation is to step down an ICS by 50% or reduce ICS-LABA from twice-daily administration to once daily. Risk for exacerbation after step-down therapy is heightened if the patient has a history of exacerbation or an emergency department visit in the past 12 months, a low baseline FEV1, or a loss of control during a dose reduction (ie, airway hyperresponsiveness and sputum eosinophilia).
Weigh the utility of FeNO measurement. The 2020 Focused Updates also recommend considering FeNO measurement to guide treatment choice and monitoring, although this is based on overall low certainty of evidence.5 GINA affirms the mixed evidence for FeNO, stating that while a few studies have shown significantly reduced exacerbations among children, adolescents, and pregnant women with FeNO-guided treatment, other studies have shown no significant difference in exacerbations.4,9-15 At this time, the role for FeNO in asthma management remains inconclusive, and access to it is limited across primary care settings.
When assessing response to ICS therapy (and before stepping up therapy), consider patient adherence, inhaler technique, whether allergen exposure is persistent, and possible comorbidities. Inhaler technique can be especially challenging, as each inhaler varies in appearance and operation. Employ patient education strategies (eg, videos, demonstration, teach-back methods). If stepping up therapy is indicated, adding a LABA is recommended over increasing the ICS dose. Since asthma is variable, stepping up therapy can be tried and reassessed in 2 to 3 months.
SMART is preferred
Single maintenance and reliever therapy (SMART) with ICS-formoterol, used as needed, is the preferred therapy for steps 3 and 4 in both GINA recommendations and the 2020 Focused Updates (TABLE3-5). GINA also prefers SMART for step 5. The recommended SMART combination that has been studied contains budesonide (or beclomethasone, not available in combination in the United States) for the ICS and formoterol for the LABA in a single inhaler that is used both daily for control and as needed for rescue therapy.
Continue to: Other ICS-formoterol...
Other ICS-formoterol or ICS-LABA combinations can be considered for controller therapy, especially those described in the NAEPP and GINA alternative step therapy recommendations. However, SMART has been more effective than other combinations in reducing exacerbations and provides similar or better levels of control at lower average ICS doses (compared with ICS-LABA with SABA or ICS with SABA) for adolescent and adult patients.3,4 As patients use greater amounts of ICS-formoterol during episodes of increased symptoms, this additional ICS may augment the anti-inflammatory effects. SMART may also improve adherence, especially among those who confuse multiple inhalers.
SMART is also recommended for use in children. Specifically, from the 2020 Focused Updates, any patient ≥ 4 years of age with a severe exacerbation in the past year is a good SMART candidate. Also consider SMART before higher-dose ICS-LABA and SABA as needed. Additional benefits in this younger patient population are fewer medical visits or less systemic corticosteroid use with improved control and quality of life.
Caveats. Patients who have a difficult time recognizing symptoms may not be good candidates for SMART, due to the potential for taking higher or lower ICS doses than necessary.
SMART specifically refers to formoterol combinations that produce bronchodilation within 1 to 3 minutes.16 For example, the SMART strategy is not recommended for patients using ICS-salmeterol as controller therapy.
Although guideline supported, SMART options are not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for use as reliever therapy.
Continue to: With the single combination...
With the single combination inhaler, consider the dosing limits of formoterol. The maximum daily amount of formoterol for adolescents and adults is 54 μg (12 puffs) delivered with the budesonide-formoterol metered dose inhaler. When using SMART as reliever therapy, the low-dose ICS-formoterol recommendation remains. However, depending on insurance coverage, a 1-month supply of ICS-formoterol may not be sufficient for additional reliever therapy use.
The role of LAMAs as add-on therapy
Bronchiolar smooth muscle tone is mediated by complex mechanisms that include cholinergic stimulation at muscarinic (M3) receptors.17 LAMAs, a mainstay in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are likely to be effective in reducing asthma exacerbations and the need for oral steroids. When patients have not achieved control at step 4 of asthma therapy, both the 2020 Focused Updates and GINA now recommend considering a LAMA (eg, tiotropium) as add-on therapy for patients > 12 years of age already taking medium-dose ICS-LABA for modest improvements in lung function and reductions in severe exacerbations. GINA recommendations also now include a LAMA as add-on treatment for those ages 6 to 11 years, as some evidence supports the use in school-aged children.18 It is important to note that LAMAs should not replace a LABA for treatment, as the ICS-LABA combination is likely more effective than ICS-LAMA.
Addressing asthma-COPD overlap
Asthma and COPD are frequently and frustratingly intertwined without clear demarcation. This tends to occur as patients age and chronic lung changes appear from longstanding asthma. However, it is important to distinguish between these conditions, because there are clearly delineated treatments for each that can improve outcomes.
The priority in addressing asthma-COPD overlap (ACO) is to evaluate symptoms and determine if asthma or COPD is predominant.19 This includes establishing patient age at which symptoms began, variation and triggers of symptoms, and history of exposures to smoke/environmental respiratory toxins. Age 40 years is often used as the tipping point at which symptom onset favors a diagnosis of COPD. Serial spirometry may also be used to evaluate lung function over time and persistence of disease. If a firm diagnosis is evasive, consider a referral to a pulmonary specialist for further testing.
Choosing to use an ICS or LAMA depends on which underlying disorder is more likely. While early COPD management includes LAMA + LABA, the addition of an ICS is reserved for more severe disease. High-dose ICSs, particularly fluticasone, should be limited in COPD due to an increased risk for pneumonia. For asthma or ACO, the addition of an ICS is critical and prioritized to reduce airway inflammation and risk for exacerbations and death. While a LAMA is likely useful earlier in ACO, it is not used until step 5 of asthma therapy. Given the complexities of ACO treatment, further research is needed to provide adequate guidance.
CASE
For Ms. S, you would be wise to use an ICS-formoterol combination for as-needed symptom relief. If symptoms were more persistent, you could consider recommending the ICS-formoterol inhaler as SMART therapy, with regular doses taken twice daily and extra doses taken as needed.
CORRESPONDENCE
Tanner Nissly, DO, University of Minnesota School of Medicine, Department of Family Medicine and Community Health, 2426 West Broadway Avenue, Minneapolis, MN 55411; [email protected]
1. CDC. Most recent national asthma data. Accessed October 24, 2022. www.cdc.gov/asthma/most_recent_national_asthma_data.htm
2. Akinbami LJ, Santo L, Williams S, et al. Characteristics of asthma visits to physician offices in the United States: 2012–2015 National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey. Natl Health Stat Report. 2019;128:1-20.
3. NHLBI. National Asthma Education and Prevention Program expert panel report 3: guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma. NIH Publication 07-4051. 2007. Accessed October 24, 2022. www.nhlbi.nih.gov/sites/default/files/media/docs/EPR-3_Asthma_Full_Report_2007.pdf
4. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. 2022. Accessed October 24, 2022. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/GINA-Main-Report-2022-FINAL-22-07-01-WMS.pdf
5. NHLBI. 2020 Focused updates to the asthma management guidelines. Accessed October 24, 2022. www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/all-publications-and-resources/2020-focused-updates-asthma-management-guidelines
6. Lazarus SC, Krishnan JA, King TS, et al. Mometasone or tiotropium in mild asthma with a low sputum eosinophil level. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2009-2019. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1814917
7. Suissa S, Ernst P, Benayoun S, et al. Low-dose inhaled corticosteroids and the prevention of death from asthma. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:332-336. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200008033430504
8. Suissa S, Ernst P, Kezouh A. Regular use of inhaled corticosteroids and the long term prevention of hospitalisation for asthma. Thorax. 2002;57:880-884. doi: 10.1136/thorax.57.10.880
9. Szefler SJ, Mitchell H, Sorkness CA, et al. Management of asthma based on exhaled nitric oxide in addition to guideline-based treatment for inner-city adolescents and young adults: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2008;372:1065-1072. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61448-8
10. Calhoun WJ, Ameredes BT, King TS, et al. Comparison of physician-, biomarker-, and symptom-based strategies for adjustment of inhaled corticosteroid therapy in adults with asthma: the BASALT randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2012;308:987-997. doi: 10.1001/2012.jama.10893
11. Garg Y, Kakria N, Katoch CDS, et al. Exhaled nitric oxide as a guiding tool for bronchial asthma: a randomised controlled trial. Med J Armed Forces India. 2020;76:17-22. doi: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2018.02.001
12. Honkoop PJ, Loijmans RJ, Termeer EH, et al. Symptom- and fraction of exhaled nitric oxide-driven strategies for asthma control: a cluster-randomized trial in primary care. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;135:682-8.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.07.016
13. Peirsman EJ, Carvelli TJ, Hage PY, et al. Exhaled nitric oxide in childhood allergic asthma management: a randomised controlled trial. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2014;49:624-631. doi: 10.1002/ppul.22873
14. Powell H, Murphy VE, Taylor DR, et al. Management of asthma in pregnancy guided by measurement of fraction of exhaled nitric oxide: a double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2011;378:983-990. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60971-9
15. Shaw DE, Berry MA, Thomas M, et al. The use of exhaled nitric oxide to guide asthma management: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176:231-237. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200610-1427OC
16. Stam J, Souren M, Zweers P. The onset of action of formoterol, a new beta 2 adrenoceptor agonist. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1993;31:23-26.
17. Evgenov OV, Liang Y, Jiang Y, et al. Pulmonary pharmacology and inhaled anesthetics. In: Gropper MA, Miller RD, Evgenov O, et al, eds. Miller’s Anesthesia. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2020:540-571.
18. Rodrigo GJ, Neffen H. Efficacy and safety of tiotropium in school-age children with moderate-to-severe symptomatic asthma: a systematic review. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2017;28:573-578. doi: 10.1111/pai.12759
19. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Asthma, COPD, and asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS). 2015. Accessed October 24, 2022. https://goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/GOLD_ACOS_2015.pdf
1. CDC. Most recent national asthma data. Accessed October 24, 2022. www.cdc.gov/asthma/most_recent_national_asthma_data.htm
2. Akinbami LJ, Santo L, Williams S, et al. Characteristics of asthma visits to physician offices in the United States: 2012–2015 National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey. Natl Health Stat Report. 2019;128:1-20.
3. NHLBI. National Asthma Education and Prevention Program expert panel report 3: guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma. NIH Publication 07-4051. 2007. Accessed October 24, 2022. www.nhlbi.nih.gov/sites/default/files/media/docs/EPR-3_Asthma_Full_Report_2007.pdf
4. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. 2022. Accessed October 24, 2022. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/GINA-Main-Report-2022-FINAL-22-07-01-WMS.pdf
5. NHLBI. 2020 Focused updates to the asthma management guidelines. Accessed October 24, 2022. www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/all-publications-and-resources/2020-focused-updates-asthma-management-guidelines
6. Lazarus SC, Krishnan JA, King TS, et al. Mometasone or tiotropium in mild asthma with a low sputum eosinophil level. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2009-2019. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1814917
7. Suissa S, Ernst P, Benayoun S, et al. Low-dose inhaled corticosteroids and the prevention of death from asthma. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:332-336. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200008033430504
8. Suissa S, Ernst P, Kezouh A. Regular use of inhaled corticosteroids and the long term prevention of hospitalisation for asthma. Thorax. 2002;57:880-884. doi: 10.1136/thorax.57.10.880
9. Szefler SJ, Mitchell H, Sorkness CA, et al. Management of asthma based on exhaled nitric oxide in addition to guideline-based treatment for inner-city adolescents and young adults: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2008;372:1065-1072. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61448-8
10. Calhoun WJ, Ameredes BT, King TS, et al. Comparison of physician-, biomarker-, and symptom-based strategies for adjustment of inhaled corticosteroid therapy in adults with asthma: the BASALT randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2012;308:987-997. doi: 10.1001/2012.jama.10893
11. Garg Y, Kakria N, Katoch CDS, et al. Exhaled nitric oxide as a guiding tool for bronchial asthma: a randomised controlled trial. Med J Armed Forces India. 2020;76:17-22. doi: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2018.02.001
12. Honkoop PJ, Loijmans RJ, Termeer EH, et al. Symptom- and fraction of exhaled nitric oxide-driven strategies for asthma control: a cluster-randomized trial in primary care. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;135:682-8.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.07.016
13. Peirsman EJ, Carvelli TJ, Hage PY, et al. Exhaled nitric oxide in childhood allergic asthma management: a randomised controlled trial. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2014;49:624-631. doi: 10.1002/ppul.22873
14. Powell H, Murphy VE, Taylor DR, et al. Management of asthma in pregnancy guided by measurement of fraction of exhaled nitric oxide: a double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2011;378:983-990. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60971-9
15. Shaw DE, Berry MA, Thomas M, et al. The use of exhaled nitric oxide to guide asthma management: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176:231-237. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200610-1427OC
16. Stam J, Souren M, Zweers P. The onset of action of formoterol, a new beta 2 adrenoceptor agonist. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1993;31:23-26.
17. Evgenov OV, Liang Y, Jiang Y, et al. Pulmonary pharmacology and inhaled anesthetics. In: Gropper MA, Miller RD, Evgenov O, et al, eds. Miller’s Anesthesia. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2020:540-571.
18. Rodrigo GJ, Neffen H. Efficacy and safety of tiotropium in school-age children with moderate-to-severe symptomatic asthma: a systematic review. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2017;28:573-578. doi: 10.1111/pai.12759
19. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Asthma, COPD, and asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS). 2015. Accessed October 24, 2022. https://goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/GOLD_ACOS_2015.pdf
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
› Consider early initiation of intermittent inhaled corticosteroid (ICS)- formoterol over a short-acting beta-2 agonist for reliever therapy. A
› Start prescribing single maintenance and reliever therapy (SMART) with ICS-formoterol to reduce exacerbation rates and simplify application. A
› Consider FeNO assessment when the diagnosis of asthma remains unclear despite history and spirometry findings. B
› Consider adding a longacting antimuscarinic agent to a medium- or high-dose ICS-LABA (long-acting beta-2 agonist) combination in uncontrolled asthma. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Top 10 unproven infertility tests and treatments
In 2019, a New York Times opinion piece titled, “The Big IVF Add-On Racket – This is no way to treat patients desperate for a baby”1 alleged exploitation of infertility patients based on a Fertility and Sterility article, “Do à la carte menus serve infertility patients? The ethics and regulation of in vitro fertility add-ons.”2 The desperation of infertility patients combined with their financial burden, caused by inconsistent insurance coverage, has resulted in a perfect storm of frustration and overzealous recommendations for a successful outcome. Since the inception of in vitro fertilization (IVF) itself, infertility patients have been subjected to many unproven tests and procedures that enter the mainstream of care before unequivocal efficacy and safety have been shown.
From ovarian stimulation with intrauterine insemination (IUI) or IVF along with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), assisted hatching, and preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A), a multitude of options with varying success can overwhelm fertility patients as they walk the tightrope of wanting “the kitchen sink” of treatment while experiencing sticker shock. This month’s article examines the top 10 infertility add-ons that have yet to be shown to improve pregnancy outcomes.
1. Blood testing: Prolactin and FSH
In a woman with ovulatory monthly menstrual cycles, a serum prolactin level provides no elucidation of the cause of infertility. If obtained following ovulation, prolactin can often be physiologically elevated, thereby compelling a repeat blood level, which is ideally performed during the early proliferative phase. False elevations of prolactin can be caused by an early morning blood sample, eating, and stress – which may result from worry caused by having to repeat the unnecessary initial blood test!
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) was a first-line hormone test to assess for ovarian age. For nearly 15 years now, FSH has been replaced by anti-Müllerian hormone as a more reliable and earlier test for diminished ovarian reserve. However, FSH is still the hormone test of choice to diagnose primary ovarian insufficiency. Note that the use of ovarian age testing in a woman without infertility can result in both unnecessary patient anxiety and additional testing.
2. Endometrial scratch
The concept was understandable, that is, induce endometrial trauma by a biopsy or “scratch,” that results in an inflammatory and immunologic response to increase implantation. Endometrial sampling was recommended to be performed during the month prior to the embryo transfer cycle. While the procedure is brief, the pain response of women varies from minimal to severe. Unfortunately, a randomized controlled trial of over 1,300 patients did not show any improvement in the IVF live birth rate from the scratch procedure.3
3. Diagnostic laparoscopy
In years past, a diagnosis of unexplained infertility was not accepted until a laparoscopy was performed that revealed a normal pelvis. This approach subjected many women to an unindicated and a potentially risky surgery that has not shown benefit. The American Society for Reproductive Medicine’s ReproductiveFacts.org website states: “Routine diagnostic laparoscopy should not be performed unless there is a suspicion of pelvic pathology based on clinical history, an abnormal pelvic exam, or abnormalities identified with less invasive testing. In patients with a normal hysterosalpingogram or the presence of a unilaterally patent tube, diagnostic laparoscopy typically will not change the initial recommendation for treatment.”
4. Prescribing clomiphene citrate without IUI
Ovulation dysfunction is found in 40% of female factors for fertility. Provided testing reveals a reasonably normal sperm analysis and hysterosalpingogram, ovulation induction medication with ultrasound monitoring along with an hCG trigger is appropriate. In women who ovulate with unexplained infertility and/or mild male factor, the use of clomiphene citrate or letrozole with timed intercourse is often prescribed, particularly in clinics when IUI preparation is not available. Unfortunately, without including IUI, the use of oral ovarian stimulation has been shown by good evidence to be no more effective than natural cycle attempts at conception.4
5. Thrombophilia testing
Recurrent miscarriage, defined by the spontaneous loss of two or more pregnancies (often during the first trimester but may include up to 20 weeks estimated gestational age), has remained an ill-defined problem that lacks a consensus on the most optimal evaluation and treatment. In 2006, an international consensus statement provided guidance on laboratory testing for antiphospholipid syndrome limited to lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin IgG and IgM, and IgG and IgM anti–beta2-glycoprotein I assays.5 ASRM does not recommend additional thrombophilia tests as they are unproven causative factors of recurrent miscarriage.
6. Screening hysteroscopy
A standard infertility evaluation includes ovulation testing, assessment of fallopian tube patency, and a sperm analysis. In a subfertile women with a normal ultrasound or hysterosalpingogram in the basic fertility work‐up, a Cochrane data review concluded there is no definitive evidence for improved outcome with a screening hysteroscopy prior to IUI or IVF.6,7 Two large trials included in the Cochrane review, confirmed similar live birth rates whether or not hysteroscopy was performed before IVF. There may value in screening patients with recurrent implantation failure.
7. PGT-A for all
As the efficacy of the first generation of embryo preimplantation genetic testing, i.e., FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) was disproven, so has the same result been determined for PGT-A, specifically in women younger than 35.8 In an elegant randomized prospective trial, Munne and colleagues showed no improvement in the ongoing pregnancy rate (OPR) of study patients of all ages who were enrolled with the intention to treat. However, a subanalysis of patients aged 35-40 who completed the protocol did show an improved OPR and lower miscarriage rate per embryo transfer. While there is no evidence to support improved outcomes with the universal application of PGT-A, there may be some benefit in women older than 35 as well as in certain individual patient circumstances.
8. ICSI for nonmale factor infertility; assisted hatching
In an effort to reduce the risk of fertilization failure, programs have broadened the use of ICSI to nonmale factor infertility. While it has been used in PGT to reduce the risk of DNA contamination, particularly in PGT-M (monogenic disorder) and PGT-SR (structural rearrangement) cases, ICSI has not been shown to improve outcomes when there is a normal sperm analysis.9 During IVF embryo development, assisted hatching involves the thinning and/or opening of the zona pellucida either by chemical, mechanical, or laser means around the embryo before transfer with the intention of facilitating implantation. The routine use of assisted hatching is not recommended based on the lack of increase in live birth rates and because it may increase multiple pregnancy and monozygotic twinning rates.10
9. Acupuncture
Four meta-analyses showed no evidence of the overall benefit of acupuncture for improving live birth rates regardless of whether acupuncture was performed around the time of oocyte retrieval or around the day of embryo transfer. Consequently, acupuncture cannot be recommended routinely to improve IVF outcomes.11
10. Immunologic tests/treatments
Given the “foreign” genetic nature of a fetus, attempts to suppress the maternal immunologic response to sustain the pregnancy have been made for decades, especially for recurrent miscarriage and recurrent implantation failure with IVF. Testing has included natural killer (NK) cells, human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotypes, and cytokines. While NK cells can be examined by endometrial biopsy, levels fluctuate based on the cycle phase, and no correlation between peripheral blood testing and uterine NK cell levels has been shown. Further, no consensus has been reached on reliable normal reference ranges in uterine NK cells.12
Several treatments have been proposed to somehow modulate the immune system during the implantation process thereby improving implantation and live birth, including lipid emulsion (intralipid) infusion, intravenous immunoglobulin, leukocyte immunization therapy, tacrolimus, anti–tumor necrosis factor agents, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis cited low-quality studies and did not recommend the use of any of these immune treatments.13 Further, immunomodulation has many known side effects, some of which are serious (including hepatosplenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, renal failure, thromboembolism, and anaphylactic reactions). Excluding women with autoimmune disease, taking glucocorticoids or other immune treatments to improve fertility has not been proven.13
Conclusion
To quote the New York Times opinion piece, “IVF remains an under-regulated arena, and entrepreneurial doctors and pharmaceutical and life science companies are eager to find new ways to cash in on a growing global market that is projected to be as large as $40 billion by 2024.” While this bold statement compels a huge “Ouch!”, it reminds us of our obligation to provide evidence-based medicine and to include emotional and financial harm to our oath of Primum non nocere.
References
1. The News York Times. 2019 Dec 12. Opinion.
2. Wilkinson J et al. Fertil Steril. 2019;112(6):973-7.
3. Lensen S et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 24;380(4):325-34.
4. Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Fertil Steril. 2020;113(2):305-22.
5. Miyakis S et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(2):295-306.
6. Kamath MS et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Apr 16;4(4):CD012856.
7. Bosteels J et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jan 31;(1):CD009461.
8. Munne S et al. Fertil Steril. 2019;112(6):1071-9.
9. Practice Committees of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine and the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology. Fertil Steril. 2020;114(2):239-45.
10. Lacey L et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. March 7 2021;3:2199.
11. Coyle ME et al. Acupunct Med. 2021;39(1):20-9.
12. Von Woon E et al. Hum Reprod Update. 2022;30;28(4):548-82.
13. Achilli C et al. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(6):1089-100.
In 2019, a New York Times opinion piece titled, “The Big IVF Add-On Racket – This is no way to treat patients desperate for a baby”1 alleged exploitation of infertility patients based on a Fertility and Sterility article, “Do à la carte menus serve infertility patients? The ethics and regulation of in vitro fertility add-ons.”2 The desperation of infertility patients combined with their financial burden, caused by inconsistent insurance coverage, has resulted in a perfect storm of frustration and overzealous recommendations for a successful outcome. Since the inception of in vitro fertilization (IVF) itself, infertility patients have been subjected to many unproven tests and procedures that enter the mainstream of care before unequivocal efficacy and safety have been shown.
From ovarian stimulation with intrauterine insemination (IUI) or IVF along with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), assisted hatching, and preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A), a multitude of options with varying success can overwhelm fertility patients as they walk the tightrope of wanting “the kitchen sink” of treatment while experiencing sticker shock. This month’s article examines the top 10 infertility add-ons that have yet to be shown to improve pregnancy outcomes.
1. Blood testing: Prolactin and FSH
In a woman with ovulatory monthly menstrual cycles, a serum prolactin level provides no elucidation of the cause of infertility. If obtained following ovulation, prolactin can often be physiologically elevated, thereby compelling a repeat blood level, which is ideally performed during the early proliferative phase. False elevations of prolactin can be caused by an early morning blood sample, eating, and stress – which may result from worry caused by having to repeat the unnecessary initial blood test!
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) was a first-line hormone test to assess for ovarian age. For nearly 15 years now, FSH has been replaced by anti-Müllerian hormone as a more reliable and earlier test for diminished ovarian reserve. However, FSH is still the hormone test of choice to diagnose primary ovarian insufficiency. Note that the use of ovarian age testing in a woman without infertility can result in both unnecessary patient anxiety and additional testing.
2. Endometrial scratch
The concept was understandable, that is, induce endometrial trauma by a biopsy or “scratch,” that results in an inflammatory and immunologic response to increase implantation. Endometrial sampling was recommended to be performed during the month prior to the embryo transfer cycle. While the procedure is brief, the pain response of women varies from minimal to severe. Unfortunately, a randomized controlled trial of over 1,300 patients did not show any improvement in the IVF live birth rate from the scratch procedure.3
3. Diagnostic laparoscopy
In years past, a diagnosis of unexplained infertility was not accepted until a laparoscopy was performed that revealed a normal pelvis. This approach subjected many women to an unindicated and a potentially risky surgery that has not shown benefit. The American Society for Reproductive Medicine’s ReproductiveFacts.org website states: “Routine diagnostic laparoscopy should not be performed unless there is a suspicion of pelvic pathology based on clinical history, an abnormal pelvic exam, or abnormalities identified with less invasive testing. In patients with a normal hysterosalpingogram or the presence of a unilaterally patent tube, diagnostic laparoscopy typically will not change the initial recommendation for treatment.”
4. Prescribing clomiphene citrate without IUI
Ovulation dysfunction is found in 40% of female factors for fertility. Provided testing reveals a reasonably normal sperm analysis and hysterosalpingogram, ovulation induction medication with ultrasound monitoring along with an hCG trigger is appropriate. In women who ovulate with unexplained infertility and/or mild male factor, the use of clomiphene citrate or letrozole with timed intercourse is often prescribed, particularly in clinics when IUI preparation is not available. Unfortunately, without including IUI, the use of oral ovarian stimulation has been shown by good evidence to be no more effective than natural cycle attempts at conception.4
5. Thrombophilia testing
Recurrent miscarriage, defined by the spontaneous loss of two or more pregnancies (often during the first trimester but may include up to 20 weeks estimated gestational age), has remained an ill-defined problem that lacks a consensus on the most optimal evaluation and treatment. In 2006, an international consensus statement provided guidance on laboratory testing for antiphospholipid syndrome limited to lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin IgG and IgM, and IgG and IgM anti–beta2-glycoprotein I assays.5 ASRM does not recommend additional thrombophilia tests as they are unproven causative factors of recurrent miscarriage.
6. Screening hysteroscopy
A standard infertility evaluation includes ovulation testing, assessment of fallopian tube patency, and a sperm analysis. In a subfertile women with a normal ultrasound or hysterosalpingogram in the basic fertility work‐up, a Cochrane data review concluded there is no definitive evidence for improved outcome with a screening hysteroscopy prior to IUI or IVF.6,7 Two large trials included in the Cochrane review, confirmed similar live birth rates whether or not hysteroscopy was performed before IVF. There may value in screening patients with recurrent implantation failure.
7. PGT-A for all
As the efficacy of the first generation of embryo preimplantation genetic testing, i.e., FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) was disproven, so has the same result been determined for PGT-A, specifically in women younger than 35.8 In an elegant randomized prospective trial, Munne and colleagues showed no improvement in the ongoing pregnancy rate (OPR) of study patients of all ages who were enrolled with the intention to treat. However, a subanalysis of patients aged 35-40 who completed the protocol did show an improved OPR and lower miscarriage rate per embryo transfer. While there is no evidence to support improved outcomes with the universal application of PGT-A, there may be some benefit in women older than 35 as well as in certain individual patient circumstances.
8. ICSI for nonmale factor infertility; assisted hatching
In an effort to reduce the risk of fertilization failure, programs have broadened the use of ICSI to nonmale factor infertility. While it has been used in PGT to reduce the risk of DNA contamination, particularly in PGT-M (monogenic disorder) and PGT-SR (structural rearrangement) cases, ICSI has not been shown to improve outcomes when there is a normal sperm analysis.9 During IVF embryo development, assisted hatching involves the thinning and/or opening of the zona pellucida either by chemical, mechanical, or laser means around the embryo before transfer with the intention of facilitating implantation. The routine use of assisted hatching is not recommended based on the lack of increase in live birth rates and because it may increase multiple pregnancy and monozygotic twinning rates.10
9. Acupuncture
Four meta-analyses showed no evidence of the overall benefit of acupuncture for improving live birth rates regardless of whether acupuncture was performed around the time of oocyte retrieval or around the day of embryo transfer. Consequently, acupuncture cannot be recommended routinely to improve IVF outcomes.11
10. Immunologic tests/treatments
Given the “foreign” genetic nature of a fetus, attempts to suppress the maternal immunologic response to sustain the pregnancy have been made for decades, especially for recurrent miscarriage and recurrent implantation failure with IVF. Testing has included natural killer (NK) cells, human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotypes, and cytokines. While NK cells can be examined by endometrial biopsy, levels fluctuate based on the cycle phase, and no correlation between peripheral blood testing and uterine NK cell levels has been shown. Further, no consensus has been reached on reliable normal reference ranges in uterine NK cells.12
Several treatments have been proposed to somehow modulate the immune system during the implantation process thereby improving implantation and live birth, including lipid emulsion (intralipid) infusion, intravenous immunoglobulin, leukocyte immunization therapy, tacrolimus, anti–tumor necrosis factor agents, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis cited low-quality studies and did not recommend the use of any of these immune treatments.13 Further, immunomodulation has many known side effects, some of which are serious (including hepatosplenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, renal failure, thromboembolism, and anaphylactic reactions). Excluding women with autoimmune disease, taking glucocorticoids or other immune treatments to improve fertility has not been proven.13
Conclusion
To quote the New York Times opinion piece, “IVF remains an under-regulated arena, and entrepreneurial doctors and pharmaceutical and life science companies are eager to find new ways to cash in on a growing global market that is projected to be as large as $40 billion by 2024.” While this bold statement compels a huge “Ouch!”, it reminds us of our obligation to provide evidence-based medicine and to include emotional and financial harm to our oath of Primum non nocere.
References
1. The News York Times. 2019 Dec 12. Opinion.
2. Wilkinson J et al. Fertil Steril. 2019;112(6):973-7.
3. Lensen S et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 24;380(4):325-34.
4. Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Fertil Steril. 2020;113(2):305-22.
5. Miyakis S et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(2):295-306.
6. Kamath MS et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Apr 16;4(4):CD012856.
7. Bosteels J et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jan 31;(1):CD009461.
8. Munne S et al. Fertil Steril. 2019;112(6):1071-9.
9. Practice Committees of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine and the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology. Fertil Steril. 2020;114(2):239-45.
10. Lacey L et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. March 7 2021;3:2199.
11. Coyle ME et al. Acupunct Med. 2021;39(1):20-9.
12. Von Woon E et al. Hum Reprod Update. 2022;30;28(4):548-82.
13. Achilli C et al. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(6):1089-100.
In 2019, a New York Times opinion piece titled, “The Big IVF Add-On Racket – This is no way to treat patients desperate for a baby”1 alleged exploitation of infertility patients based on a Fertility and Sterility article, “Do à la carte menus serve infertility patients? The ethics and regulation of in vitro fertility add-ons.”2 The desperation of infertility patients combined with their financial burden, caused by inconsistent insurance coverage, has resulted in a perfect storm of frustration and overzealous recommendations for a successful outcome. Since the inception of in vitro fertilization (IVF) itself, infertility patients have been subjected to many unproven tests and procedures that enter the mainstream of care before unequivocal efficacy and safety have been shown.
From ovarian stimulation with intrauterine insemination (IUI) or IVF along with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), assisted hatching, and preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A), a multitude of options with varying success can overwhelm fertility patients as they walk the tightrope of wanting “the kitchen sink” of treatment while experiencing sticker shock. This month’s article examines the top 10 infertility add-ons that have yet to be shown to improve pregnancy outcomes.
1. Blood testing: Prolactin and FSH
In a woman with ovulatory monthly menstrual cycles, a serum prolactin level provides no elucidation of the cause of infertility. If obtained following ovulation, prolactin can often be physiologically elevated, thereby compelling a repeat blood level, which is ideally performed during the early proliferative phase. False elevations of prolactin can be caused by an early morning blood sample, eating, and stress – which may result from worry caused by having to repeat the unnecessary initial blood test!
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) was a first-line hormone test to assess for ovarian age. For nearly 15 years now, FSH has been replaced by anti-Müllerian hormone as a more reliable and earlier test for diminished ovarian reserve. However, FSH is still the hormone test of choice to diagnose primary ovarian insufficiency. Note that the use of ovarian age testing in a woman without infertility can result in both unnecessary patient anxiety and additional testing.
2. Endometrial scratch
The concept was understandable, that is, induce endometrial trauma by a biopsy or “scratch,” that results in an inflammatory and immunologic response to increase implantation. Endometrial sampling was recommended to be performed during the month prior to the embryo transfer cycle. While the procedure is brief, the pain response of women varies from minimal to severe. Unfortunately, a randomized controlled trial of over 1,300 patients did not show any improvement in the IVF live birth rate from the scratch procedure.3
3. Diagnostic laparoscopy
In years past, a diagnosis of unexplained infertility was not accepted until a laparoscopy was performed that revealed a normal pelvis. This approach subjected many women to an unindicated and a potentially risky surgery that has not shown benefit. The American Society for Reproductive Medicine’s ReproductiveFacts.org website states: “Routine diagnostic laparoscopy should not be performed unless there is a suspicion of pelvic pathology based on clinical history, an abnormal pelvic exam, or abnormalities identified with less invasive testing. In patients with a normal hysterosalpingogram or the presence of a unilaterally patent tube, diagnostic laparoscopy typically will not change the initial recommendation for treatment.”
4. Prescribing clomiphene citrate without IUI
Ovulation dysfunction is found in 40% of female factors for fertility. Provided testing reveals a reasonably normal sperm analysis and hysterosalpingogram, ovulation induction medication with ultrasound monitoring along with an hCG trigger is appropriate. In women who ovulate with unexplained infertility and/or mild male factor, the use of clomiphene citrate or letrozole with timed intercourse is often prescribed, particularly in clinics when IUI preparation is not available. Unfortunately, without including IUI, the use of oral ovarian stimulation has been shown by good evidence to be no more effective than natural cycle attempts at conception.4
5. Thrombophilia testing
Recurrent miscarriage, defined by the spontaneous loss of two or more pregnancies (often during the first trimester but may include up to 20 weeks estimated gestational age), has remained an ill-defined problem that lacks a consensus on the most optimal evaluation and treatment. In 2006, an international consensus statement provided guidance on laboratory testing for antiphospholipid syndrome limited to lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin IgG and IgM, and IgG and IgM anti–beta2-glycoprotein I assays.5 ASRM does not recommend additional thrombophilia tests as they are unproven causative factors of recurrent miscarriage.
6. Screening hysteroscopy
A standard infertility evaluation includes ovulation testing, assessment of fallopian tube patency, and a sperm analysis. In a subfertile women with a normal ultrasound or hysterosalpingogram in the basic fertility work‐up, a Cochrane data review concluded there is no definitive evidence for improved outcome with a screening hysteroscopy prior to IUI or IVF.6,7 Two large trials included in the Cochrane review, confirmed similar live birth rates whether or not hysteroscopy was performed before IVF. There may value in screening patients with recurrent implantation failure.
7. PGT-A for all
As the efficacy of the first generation of embryo preimplantation genetic testing, i.e., FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) was disproven, so has the same result been determined for PGT-A, specifically in women younger than 35.8 In an elegant randomized prospective trial, Munne and colleagues showed no improvement in the ongoing pregnancy rate (OPR) of study patients of all ages who were enrolled with the intention to treat. However, a subanalysis of patients aged 35-40 who completed the protocol did show an improved OPR and lower miscarriage rate per embryo transfer. While there is no evidence to support improved outcomes with the universal application of PGT-A, there may be some benefit in women older than 35 as well as in certain individual patient circumstances.
8. ICSI for nonmale factor infertility; assisted hatching
In an effort to reduce the risk of fertilization failure, programs have broadened the use of ICSI to nonmale factor infertility. While it has been used in PGT to reduce the risk of DNA contamination, particularly in PGT-M (monogenic disorder) and PGT-SR (structural rearrangement) cases, ICSI has not been shown to improve outcomes when there is a normal sperm analysis.9 During IVF embryo development, assisted hatching involves the thinning and/or opening of the zona pellucida either by chemical, mechanical, or laser means around the embryo before transfer with the intention of facilitating implantation. The routine use of assisted hatching is not recommended based on the lack of increase in live birth rates and because it may increase multiple pregnancy and monozygotic twinning rates.10
9. Acupuncture
Four meta-analyses showed no evidence of the overall benefit of acupuncture for improving live birth rates regardless of whether acupuncture was performed around the time of oocyte retrieval or around the day of embryo transfer. Consequently, acupuncture cannot be recommended routinely to improve IVF outcomes.11
10. Immunologic tests/treatments
Given the “foreign” genetic nature of a fetus, attempts to suppress the maternal immunologic response to sustain the pregnancy have been made for decades, especially for recurrent miscarriage and recurrent implantation failure with IVF. Testing has included natural killer (NK) cells, human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotypes, and cytokines. While NK cells can be examined by endometrial biopsy, levels fluctuate based on the cycle phase, and no correlation between peripheral blood testing and uterine NK cell levels has been shown. Further, no consensus has been reached on reliable normal reference ranges in uterine NK cells.12
Several treatments have been proposed to somehow modulate the immune system during the implantation process thereby improving implantation and live birth, including lipid emulsion (intralipid) infusion, intravenous immunoglobulin, leukocyte immunization therapy, tacrolimus, anti–tumor necrosis factor agents, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis cited low-quality studies and did not recommend the use of any of these immune treatments.13 Further, immunomodulation has many known side effects, some of which are serious (including hepatosplenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, renal failure, thromboembolism, and anaphylactic reactions). Excluding women with autoimmune disease, taking glucocorticoids or other immune treatments to improve fertility has not been proven.13
Conclusion
To quote the New York Times opinion piece, “IVF remains an under-regulated arena, and entrepreneurial doctors and pharmaceutical and life science companies are eager to find new ways to cash in on a growing global market that is projected to be as large as $40 billion by 2024.” While this bold statement compels a huge “Ouch!”, it reminds us of our obligation to provide evidence-based medicine and to include emotional and financial harm to our oath of Primum non nocere.
References
1. The News York Times. 2019 Dec 12. Opinion.
2. Wilkinson J et al. Fertil Steril. 2019;112(6):973-7.
3. Lensen S et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 24;380(4):325-34.
4. Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Fertil Steril. 2020;113(2):305-22.
5. Miyakis S et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(2):295-306.
6. Kamath MS et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Apr 16;4(4):CD012856.
7. Bosteels J et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jan 31;(1):CD009461.
8. Munne S et al. Fertil Steril. 2019;112(6):1071-9.
9. Practice Committees of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine and the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology. Fertil Steril. 2020;114(2):239-45.
10. Lacey L et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. March 7 2021;3:2199.
11. Coyle ME et al. Acupunct Med. 2021;39(1):20-9.
12. Von Woon E et al. Hum Reprod Update. 2022;30;28(4):548-82.
13. Achilli C et al. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(6):1089-100.
Mortality after acute stroke worsened by accompanying acute AFib
The study covered in this summary was published on ResearchSquare.com as a preprint and has not yet been peer-reviewed.
Key takeaway
Why this matters
- A comprehensive understanding of the relationship between acute AF and risk for acute ischemic stroke and prognosis will help improve management and treatment of patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Study design
- The retrospective study included patients with acute ischemic stroke within the prior 24 hours; 12-lead electrocardiogram in the emergency department; and hospitalization and treatment at the hospital stroke center.
- The cohort of 706 patients admitted to a single center in Shanghai, China, from December 2019 to December 2021, included 142 with episodes of acute AF and 564 without such episodes.
- Patients with acute ischemic stroke and acute AF – including AF of new onset, paroxysmal, persistent, or permanent with symptoms such as palpitations or dizziness attributed to rapid ventricular rates – were identified.
- Neurological deficits were assessed using the 7-day National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale/Score (NIHSS). Patients with a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 were considered to have moderate to severe stroke.
- Associations between acute AF onset and the severity of early neurological deficits were assessed and related to all-cause mortality within 30 days of the stroke.
Key results
- Patients with acute AF were older than those without acute AF (80.3 years vs. 71.0 years; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS scores averaged 16.09 for the stroke patients with acute AF and 8.65 for those without acute AF (P < .001).
- Significantly more patients with acute AF than without acute AF had a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 (45.1% vs. 14.4%; P < .001).
- More patients with than without acute AF underwent transcatheter thrombectomy (44.4% vs. 24.5%; P < .001) or received thrombolytic therapy (31.6% vs. 19.7%; P = .005).
- Patients aged 73 years or older showed baseline NIHSS score and acute AF as independent risk factors for early neurological deficits in stroke patients admitted to the emergency department.
- Mortality at 30 days was significantly higher in patients with acute AF than in those without acute AF (30.3% vs. 10.1%; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS had an adjusted odds ratio for 30-day mortality of 1.18 (95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.22; P < .001).
- Other independent predictors included acute AF (1.87 [95% CI, 1.09-3.19; P = .022]) and age 73 or older (2.00 [95% CI, 1.18-3.37; P = .01]).
Limitations
- The study was retrospective and didn’t have access to some potentially relevant data, such as duration of AF.
- The single-center study with limited generalizability does not necessarily represent the broad population of stroke patients in China or elsewhere.
Disclosures
- This study was supported by the Cardiovascular Multidisciplinary Integrated Research Fund and Construction of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission.
- The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
This is a summary of a preprint research study, “Acute Atrial Fibrillation During Onset of Stroke Indicates Higher Probability of Post-Stroke Death Outcomes,” written by Yongxia Li, from the Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital, and colleagues, on ResearchSquare.com. This study has not yet been peer reviewed. The full text of the study can be found on ResearchSquare.com.A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study covered in this summary was published on ResearchSquare.com as a preprint and has not yet been peer-reviewed.
Key takeaway
Why this matters
- A comprehensive understanding of the relationship between acute AF and risk for acute ischemic stroke and prognosis will help improve management and treatment of patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Study design
- The retrospective study included patients with acute ischemic stroke within the prior 24 hours; 12-lead electrocardiogram in the emergency department; and hospitalization and treatment at the hospital stroke center.
- The cohort of 706 patients admitted to a single center in Shanghai, China, from December 2019 to December 2021, included 142 with episodes of acute AF and 564 without such episodes.
- Patients with acute ischemic stroke and acute AF – including AF of new onset, paroxysmal, persistent, or permanent with symptoms such as palpitations or dizziness attributed to rapid ventricular rates – were identified.
- Neurological deficits were assessed using the 7-day National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale/Score (NIHSS). Patients with a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 were considered to have moderate to severe stroke.
- Associations between acute AF onset and the severity of early neurological deficits were assessed and related to all-cause mortality within 30 days of the stroke.
Key results
- Patients with acute AF were older than those without acute AF (80.3 years vs. 71.0 years; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS scores averaged 16.09 for the stroke patients with acute AF and 8.65 for those without acute AF (P < .001).
- Significantly more patients with acute AF than without acute AF had a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 (45.1% vs. 14.4%; P < .001).
- More patients with than without acute AF underwent transcatheter thrombectomy (44.4% vs. 24.5%; P < .001) or received thrombolytic therapy (31.6% vs. 19.7%; P = .005).
- Patients aged 73 years or older showed baseline NIHSS score and acute AF as independent risk factors for early neurological deficits in stroke patients admitted to the emergency department.
- Mortality at 30 days was significantly higher in patients with acute AF than in those without acute AF (30.3% vs. 10.1%; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS had an adjusted odds ratio for 30-day mortality of 1.18 (95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.22; P < .001).
- Other independent predictors included acute AF (1.87 [95% CI, 1.09-3.19; P = .022]) and age 73 or older (2.00 [95% CI, 1.18-3.37; P = .01]).
Limitations
- The study was retrospective and didn’t have access to some potentially relevant data, such as duration of AF.
- The single-center study with limited generalizability does not necessarily represent the broad population of stroke patients in China or elsewhere.
Disclosures
- This study was supported by the Cardiovascular Multidisciplinary Integrated Research Fund and Construction of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission.
- The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
This is a summary of a preprint research study, “Acute Atrial Fibrillation During Onset of Stroke Indicates Higher Probability of Post-Stroke Death Outcomes,” written by Yongxia Li, from the Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital, and colleagues, on ResearchSquare.com. This study has not yet been peer reviewed. The full text of the study can be found on ResearchSquare.com.A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study covered in this summary was published on ResearchSquare.com as a preprint and has not yet been peer-reviewed.
Key takeaway
Why this matters
- A comprehensive understanding of the relationship between acute AF and risk for acute ischemic stroke and prognosis will help improve management and treatment of patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Study design
- The retrospective study included patients with acute ischemic stroke within the prior 24 hours; 12-lead electrocardiogram in the emergency department; and hospitalization and treatment at the hospital stroke center.
- The cohort of 706 patients admitted to a single center in Shanghai, China, from December 2019 to December 2021, included 142 with episodes of acute AF and 564 without such episodes.
- Patients with acute ischemic stroke and acute AF – including AF of new onset, paroxysmal, persistent, or permanent with symptoms such as palpitations or dizziness attributed to rapid ventricular rates – were identified.
- Neurological deficits were assessed using the 7-day National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale/Score (NIHSS). Patients with a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 were considered to have moderate to severe stroke.
- Associations between acute AF onset and the severity of early neurological deficits were assessed and related to all-cause mortality within 30 days of the stroke.
Key results
- Patients with acute AF were older than those without acute AF (80.3 years vs. 71.0 years; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS scores averaged 16.09 for the stroke patients with acute AF and 8.65 for those without acute AF (P < .001).
- Significantly more patients with acute AF than without acute AF had a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 (45.1% vs. 14.4%; P < .001).
- More patients with than without acute AF underwent transcatheter thrombectomy (44.4% vs. 24.5%; P < .001) or received thrombolytic therapy (31.6% vs. 19.7%; P = .005).
- Patients aged 73 years or older showed baseline NIHSS score and acute AF as independent risk factors for early neurological deficits in stroke patients admitted to the emergency department.
- Mortality at 30 days was significantly higher in patients with acute AF than in those without acute AF (30.3% vs. 10.1%; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS had an adjusted odds ratio for 30-day mortality of 1.18 (95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.22; P < .001).
- Other independent predictors included acute AF (1.87 [95% CI, 1.09-3.19; P = .022]) and age 73 or older (2.00 [95% CI, 1.18-3.37; P = .01]).
Limitations
- The study was retrospective and didn’t have access to some potentially relevant data, such as duration of AF.
- The single-center study with limited generalizability does not necessarily represent the broad population of stroke patients in China or elsewhere.
Disclosures
- This study was supported by the Cardiovascular Multidisciplinary Integrated Research Fund and Construction of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission.
- The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
This is a summary of a preprint research study, “Acute Atrial Fibrillation During Onset of Stroke Indicates Higher Probability of Post-Stroke Death Outcomes,” written by Yongxia Li, from the Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital, and colleagues, on ResearchSquare.com. This study has not yet been peer reviewed. The full text of the study can be found on ResearchSquare.com.A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Add tezepelumab to SCIT to improve cat allergy symptoms?
according to results of a phase 1/2 clinical trial.
“One year of allergen immunotherapy [AIT] combined with tezepelumab was significantly more effective than SCIT alone in reducing the nasal response to allergen challenge both at the end of treatment and one year after stopping treatment,” lead study author Jonathan Corren, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and his colleagues wrote in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
“This persistent improvement in clinical response was paralleled by reductions in nasal transcripts for multiple immunologic pathways, including mast cell activation.”
The study was cited in a news release from the National Institutes of Health that said that the approach may work in a similar way with other allergens.
The Food and Drug Administration recently approved tezepelumab for the treatment of severe asthma in people aged 12 years and older. Tezelumab, a monoclonal antibody, works by blocking the cytokine thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP).
“Cells that cover the surface of organs like the skin and intestines or that line the inside of the nose and lungs rapidly secrete TSLP in response to signals of potential danger,” according to the NIH news release. “In allergic disease, TSLP helps initiate an overreactive immune response to otherwise harmless substances like cat dander, provoking airway inflammation that leads to the symptoms of allergic rhinitis.”
Testing an enhanced strategy
The double-blind CATNIP trial was conducted by Dr. Corren and colleagues at nine sites in the United States. The trial included patients aged 18-65 years who’d had moderate to severe cat-induced allergic rhinitis for at least 2 years from 2015 to 2019.
The researchers excluded patients with recurrent acute or chronic sinusitis. They excluded patients who had undergone SCIT with cat allergen within the past 10 years or seasonal or perennial allergen sensitivity during nasal challenges. They also excluded persons with a history of persistent asthma.
In the parallel-design study, 121 participants were randomly allocated into four groups: 32 patients were treated with intravenous tezepelumab plus cat SCIT, 31 received the allergy shots alone, 30 received tezepelumab alone, and 28 received placebo alone for 52 weeks, followed by 52 weeks of observation.
Participants received SCIT (10,000 bioequivalent allergy units per milliliter) or matched placebo via subcutaneous injections weekly in increasing doses for around 12 weeks, followed by monthly maintenance injections (4,000 BAU or maximum tolerated dose) until week 48.
They received tezepelumab (700 mg IV) or matched placebo 1-3 days prior to the SCIT or placebo SCIT injections once every 4 weeks through week 24, then before or on the same day as the SCIT or placebo injections through week 48.
Measures of effectiveness
Participants were also given nasal allergy challenges – one spritz of a nasal spray containing cat allergen extract in each nostril at screening, baseline, and weeks 26, 52, 78, and 104. The researchers recorded participants’ total nasal symptom score (TNSS) and peak nasal inspiratory flow at 5, 15, 30, and 60 minutes after being sprayed and hourly for up to 6 hours post challenge. Blood and nasal cell samples were also collected.
The research team performed skin prick tests using serial dilutions of cat extract and an intradermal skin test (IDST) using the concentration of allergen that produced an early response of at least 15 mm at baseline. They measured early-phase responses for the both tests at 15 minutes and late-phase response to the IDST at 6 hours.
They measured serum levels of cat dander–specific IgE, IgG4, and total IgE using fluoroenzyme immunoassay. They measured serum interleukin-5 and IL-13 using high-sensitivity single-molecule digital immunoassay and performed nasal brushing using a 3-mm cytology brush 6 hours after a nasal allergy challenge. They performed whole-genome transcriptional profiling on the extracted RNA.
Combination therapy worked better and longer
The combined therapy worked better while being administered. Although the allergy shots alone stopped working after they were discontinued, the combination continued to benefit participants 1 year after that therapy ended.
At week 52, statistically significant reductions in TNSS induced by nasal allergy challenges occurred in patients receiving tezepelumab plus SCIT compared with patients receiving SCIT alone.
At week 104, 1 year after treatment ended, the primary endpoint TNSS was not significantly different in the tezepelumab-plus-SCIT group than in the SCIT-alone group, but TNSS peak 0–1 hour was significantly lower in the combination treatment group than in the SCIT-alone group.
In analysis of gene expression from nasal epithelial samples, participants who had been treated with the combination but not with either therapy by itself showed persistent modulation of the nasal immunologic environment, including diminished mast cell function. This was explained in large part by decreased transcription of the gene TPSAB1 (tryptase). Tryptase protein in nasal fluid was also decreased in the combination group, compared with the SCIT-alone group.
Adverse and serious adverse events, including infections and infestations as well as respiratory, thoracic, mediastinal, gastrointestinal, immune system, and nervous system disorders, did not differ significantly between treatment groups.
Four independent experts welcome the results
Patricia Lynne Lugar, MD, associate professor of medicine in the division of pulmonology, allergy, and critical care medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C., found the results, especially the 1-year posttreatment response durability, surprising.
“AIT is a very effective treatment that often provides prolonged symptom improvement and is ‘curative’ in many cases,” she said in an interview. “If further studies show that tezepelumab offers long-term results, more patients might opt for combination therapy.
“A significant strength of the study is its evaluation of responses of the combination therapy on cellular output and gene expression,” Dr. Lugar added. “The mechanism by which AIT modulates the allergic response is largely understood. Tezepelumab may augment this modulation to alter the Th2 response upon exposure to the allergens.”
Will payors cover the prohibitively costly biologic?
Scott Frank, MD, associate professor in the department of family medicine and community health at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, called the study well designed and rigorous.
“The practicality of the approach may be limited by the need for intravenous administration of tezepelumab in addition to the traditional allergy shot,” he noted by email, “and the cost of this therapeutic approach is not addressed.”
Christopher Brooks, MD, clinical assistant professor of allergy and immunology in the department of otolaryngology at Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, also pointed out the drug’s cost.
“Tezepelumab is currently an expensive biologic, so it remains to be seen whether patients and payors will be willing to pay for this add-on medication when AIT by itself still remains very effective,” he said by email.
“AIT is most effective when given for 5 years, so it also remains to be seen whether the results and conclusions of this study would still hold true if done for the typical 5-year treatment period,” he added.
Stokes Peebles, MD, professor of medicine in the division of allergy, pulmonary, and critical care medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., called the study “very well designed by a highly respected group of investigators using well-matched study populations.
“Tezepelumab has been shown to work in asthma, and there is no reason to think it would not work in allergic rhinitis,” he said in an interview.
“However, while the results of the combined therapy were statistically significant, their clinical significance was not clear. Patients do not care about statistical significance. They want to know whether a drug will be clinically significant,” he added.
Many people avoid cat allergy symptoms by avoiding cats and, in some cases, by avoiding people who live with cats, he said. Medical therapy, usually involving nasal corticosteroids and antihistamines, helps most people avoid cat allergy symptoms.
“Patients with bad allergies who have not done well with SCIT may consider adding tezepelumab, but it incurs a major cost. If medical therapy doesn’t work, allergy shots are available at roughly $3,000 per year. Adding tezepelumab costs around $40,000 more per year,” he explained. “Does the slight clinical benefit justify the greatly increased cost?”
The authors and uninvolved experts recommend further related research.
The research was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. AstraZeneca and Amgen donated the drug used in the study. Dr. Corren reported financial relationships with AstraZeneca, and one coauthor reported relevant financial relationships with Amgen and other pharmaceutical companies. The remaining coauthors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to results of a phase 1/2 clinical trial.
“One year of allergen immunotherapy [AIT] combined with tezepelumab was significantly more effective than SCIT alone in reducing the nasal response to allergen challenge both at the end of treatment and one year after stopping treatment,” lead study author Jonathan Corren, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and his colleagues wrote in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
“This persistent improvement in clinical response was paralleled by reductions in nasal transcripts for multiple immunologic pathways, including mast cell activation.”
The study was cited in a news release from the National Institutes of Health that said that the approach may work in a similar way with other allergens.
The Food and Drug Administration recently approved tezepelumab for the treatment of severe asthma in people aged 12 years and older. Tezelumab, a monoclonal antibody, works by blocking the cytokine thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP).
“Cells that cover the surface of organs like the skin and intestines or that line the inside of the nose and lungs rapidly secrete TSLP in response to signals of potential danger,” according to the NIH news release. “In allergic disease, TSLP helps initiate an overreactive immune response to otherwise harmless substances like cat dander, provoking airway inflammation that leads to the symptoms of allergic rhinitis.”
Testing an enhanced strategy
The double-blind CATNIP trial was conducted by Dr. Corren and colleagues at nine sites in the United States. The trial included patients aged 18-65 years who’d had moderate to severe cat-induced allergic rhinitis for at least 2 years from 2015 to 2019.
The researchers excluded patients with recurrent acute or chronic sinusitis. They excluded patients who had undergone SCIT with cat allergen within the past 10 years or seasonal or perennial allergen sensitivity during nasal challenges. They also excluded persons with a history of persistent asthma.
In the parallel-design study, 121 participants were randomly allocated into four groups: 32 patients were treated with intravenous tezepelumab plus cat SCIT, 31 received the allergy shots alone, 30 received tezepelumab alone, and 28 received placebo alone for 52 weeks, followed by 52 weeks of observation.
Participants received SCIT (10,000 bioequivalent allergy units per milliliter) or matched placebo via subcutaneous injections weekly in increasing doses for around 12 weeks, followed by monthly maintenance injections (4,000 BAU or maximum tolerated dose) until week 48.
They received tezepelumab (700 mg IV) or matched placebo 1-3 days prior to the SCIT or placebo SCIT injections once every 4 weeks through week 24, then before or on the same day as the SCIT or placebo injections through week 48.
Measures of effectiveness
Participants were also given nasal allergy challenges – one spritz of a nasal spray containing cat allergen extract in each nostril at screening, baseline, and weeks 26, 52, 78, and 104. The researchers recorded participants’ total nasal symptom score (TNSS) and peak nasal inspiratory flow at 5, 15, 30, and 60 minutes after being sprayed and hourly for up to 6 hours post challenge. Blood and nasal cell samples were also collected.
The research team performed skin prick tests using serial dilutions of cat extract and an intradermal skin test (IDST) using the concentration of allergen that produced an early response of at least 15 mm at baseline. They measured early-phase responses for the both tests at 15 minutes and late-phase response to the IDST at 6 hours.
They measured serum levels of cat dander–specific IgE, IgG4, and total IgE using fluoroenzyme immunoassay. They measured serum interleukin-5 and IL-13 using high-sensitivity single-molecule digital immunoassay and performed nasal brushing using a 3-mm cytology brush 6 hours after a nasal allergy challenge. They performed whole-genome transcriptional profiling on the extracted RNA.
Combination therapy worked better and longer
The combined therapy worked better while being administered. Although the allergy shots alone stopped working after they were discontinued, the combination continued to benefit participants 1 year after that therapy ended.
At week 52, statistically significant reductions in TNSS induced by nasal allergy challenges occurred in patients receiving tezepelumab plus SCIT compared with patients receiving SCIT alone.
At week 104, 1 year after treatment ended, the primary endpoint TNSS was not significantly different in the tezepelumab-plus-SCIT group than in the SCIT-alone group, but TNSS peak 0–1 hour was significantly lower in the combination treatment group than in the SCIT-alone group.
In analysis of gene expression from nasal epithelial samples, participants who had been treated with the combination but not with either therapy by itself showed persistent modulation of the nasal immunologic environment, including diminished mast cell function. This was explained in large part by decreased transcription of the gene TPSAB1 (tryptase). Tryptase protein in nasal fluid was also decreased in the combination group, compared with the SCIT-alone group.
Adverse and serious adverse events, including infections and infestations as well as respiratory, thoracic, mediastinal, gastrointestinal, immune system, and nervous system disorders, did not differ significantly between treatment groups.
Four independent experts welcome the results
Patricia Lynne Lugar, MD, associate professor of medicine in the division of pulmonology, allergy, and critical care medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C., found the results, especially the 1-year posttreatment response durability, surprising.
“AIT is a very effective treatment that often provides prolonged symptom improvement and is ‘curative’ in many cases,” she said in an interview. “If further studies show that tezepelumab offers long-term results, more patients might opt for combination therapy.
“A significant strength of the study is its evaluation of responses of the combination therapy on cellular output and gene expression,” Dr. Lugar added. “The mechanism by which AIT modulates the allergic response is largely understood. Tezepelumab may augment this modulation to alter the Th2 response upon exposure to the allergens.”
Will payors cover the prohibitively costly biologic?
Scott Frank, MD, associate professor in the department of family medicine and community health at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, called the study well designed and rigorous.
“The practicality of the approach may be limited by the need for intravenous administration of tezepelumab in addition to the traditional allergy shot,” he noted by email, “and the cost of this therapeutic approach is not addressed.”
Christopher Brooks, MD, clinical assistant professor of allergy and immunology in the department of otolaryngology at Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, also pointed out the drug’s cost.
“Tezepelumab is currently an expensive biologic, so it remains to be seen whether patients and payors will be willing to pay for this add-on medication when AIT by itself still remains very effective,” he said by email.
“AIT is most effective when given for 5 years, so it also remains to be seen whether the results and conclusions of this study would still hold true if done for the typical 5-year treatment period,” he added.
Stokes Peebles, MD, professor of medicine in the division of allergy, pulmonary, and critical care medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., called the study “very well designed by a highly respected group of investigators using well-matched study populations.
“Tezepelumab has been shown to work in asthma, and there is no reason to think it would not work in allergic rhinitis,” he said in an interview.
“However, while the results of the combined therapy were statistically significant, their clinical significance was not clear. Patients do not care about statistical significance. They want to know whether a drug will be clinically significant,” he added.
Many people avoid cat allergy symptoms by avoiding cats and, in some cases, by avoiding people who live with cats, he said. Medical therapy, usually involving nasal corticosteroids and antihistamines, helps most people avoid cat allergy symptoms.
“Patients with bad allergies who have not done well with SCIT may consider adding tezepelumab, but it incurs a major cost. If medical therapy doesn’t work, allergy shots are available at roughly $3,000 per year. Adding tezepelumab costs around $40,000 more per year,” he explained. “Does the slight clinical benefit justify the greatly increased cost?”
The authors and uninvolved experts recommend further related research.
The research was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. AstraZeneca and Amgen donated the drug used in the study. Dr. Corren reported financial relationships with AstraZeneca, and one coauthor reported relevant financial relationships with Amgen and other pharmaceutical companies. The remaining coauthors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to results of a phase 1/2 clinical trial.
“One year of allergen immunotherapy [AIT] combined with tezepelumab was significantly more effective than SCIT alone in reducing the nasal response to allergen challenge both at the end of treatment and one year after stopping treatment,” lead study author Jonathan Corren, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and his colleagues wrote in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
“This persistent improvement in clinical response was paralleled by reductions in nasal transcripts for multiple immunologic pathways, including mast cell activation.”
The study was cited in a news release from the National Institutes of Health that said that the approach may work in a similar way with other allergens.
The Food and Drug Administration recently approved tezepelumab for the treatment of severe asthma in people aged 12 years and older. Tezelumab, a monoclonal antibody, works by blocking the cytokine thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP).
“Cells that cover the surface of organs like the skin and intestines or that line the inside of the nose and lungs rapidly secrete TSLP in response to signals of potential danger,” according to the NIH news release. “In allergic disease, TSLP helps initiate an overreactive immune response to otherwise harmless substances like cat dander, provoking airway inflammation that leads to the symptoms of allergic rhinitis.”
Testing an enhanced strategy
The double-blind CATNIP trial was conducted by Dr. Corren and colleagues at nine sites in the United States. The trial included patients aged 18-65 years who’d had moderate to severe cat-induced allergic rhinitis for at least 2 years from 2015 to 2019.
The researchers excluded patients with recurrent acute or chronic sinusitis. They excluded patients who had undergone SCIT with cat allergen within the past 10 years or seasonal or perennial allergen sensitivity during nasal challenges. They also excluded persons with a history of persistent asthma.
In the parallel-design study, 121 participants were randomly allocated into four groups: 32 patients were treated with intravenous tezepelumab plus cat SCIT, 31 received the allergy shots alone, 30 received tezepelumab alone, and 28 received placebo alone for 52 weeks, followed by 52 weeks of observation.
Participants received SCIT (10,000 bioequivalent allergy units per milliliter) or matched placebo via subcutaneous injections weekly in increasing doses for around 12 weeks, followed by monthly maintenance injections (4,000 BAU or maximum tolerated dose) until week 48.
They received tezepelumab (700 mg IV) or matched placebo 1-3 days prior to the SCIT or placebo SCIT injections once every 4 weeks through week 24, then before or on the same day as the SCIT or placebo injections through week 48.
Measures of effectiveness
Participants were also given nasal allergy challenges – one spritz of a nasal spray containing cat allergen extract in each nostril at screening, baseline, and weeks 26, 52, 78, and 104. The researchers recorded participants’ total nasal symptom score (TNSS) and peak nasal inspiratory flow at 5, 15, 30, and 60 minutes after being sprayed and hourly for up to 6 hours post challenge. Blood and nasal cell samples were also collected.
The research team performed skin prick tests using serial dilutions of cat extract and an intradermal skin test (IDST) using the concentration of allergen that produced an early response of at least 15 mm at baseline. They measured early-phase responses for the both tests at 15 minutes and late-phase response to the IDST at 6 hours.
They measured serum levels of cat dander–specific IgE, IgG4, and total IgE using fluoroenzyme immunoassay. They measured serum interleukin-5 and IL-13 using high-sensitivity single-molecule digital immunoassay and performed nasal brushing using a 3-mm cytology brush 6 hours after a nasal allergy challenge. They performed whole-genome transcriptional profiling on the extracted RNA.
Combination therapy worked better and longer
The combined therapy worked better while being administered. Although the allergy shots alone stopped working after they were discontinued, the combination continued to benefit participants 1 year after that therapy ended.
At week 52, statistically significant reductions in TNSS induced by nasal allergy challenges occurred in patients receiving tezepelumab plus SCIT compared with patients receiving SCIT alone.
At week 104, 1 year after treatment ended, the primary endpoint TNSS was not significantly different in the tezepelumab-plus-SCIT group than in the SCIT-alone group, but TNSS peak 0–1 hour was significantly lower in the combination treatment group than in the SCIT-alone group.
In analysis of gene expression from nasal epithelial samples, participants who had been treated with the combination but not with either therapy by itself showed persistent modulation of the nasal immunologic environment, including diminished mast cell function. This was explained in large part by decreased transcription of the gene TPSAB1 (tryptase). Tryptase protein in nasal fluid was also decreased in the combination group, compared with the SCIT-alone group.
Adverse and serious adverse events, including infections and infestations as well as respiratory, thoracic, mediastinal, gastrointestinal, immune system, and nervous system disorders, did not differ significantly between treatment groups.
Four independent experts welcome the results
Patricia Lynne Lugar, MD, associate professor of medicine in the division of pulmonology, allergy, and critical care medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C., found the results, especially the 1-year posttreatment response durability, surprising.
“AIT is a very effective treatment that often provides prolonged symptom improvement and is ‘curative’ in many cases,” she said in an interview. “If further studies show that tezepelumab offers long-term results, more patients might opt for combination therapy.
“A significant strength of the study is its evaluation of responses of the combination therapy on cellular output and gene expression,” Dr. Lugar added. “The mechanism by which AIT modulates the allergic response is largely understood. Tezepelumab may augment this modulation to alter the Th2 response upon exposure to the allergens.”
Will payors cover the prohibitively costly biologic?
Scott Frank, MD, associate professor in the department of family medicine and community health at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, called the study well designed and rigorous.
“The practicality of the approach may be limited by the need for intravenous administration of tezepelumab in addition to the traditional allergy shot,” he noted by email, “and the cost of this therapeutic approach is not addressed.”
Christopher Brooks, MD, clinical assistant professor of allergy and immunology in the department of otolaryngology at Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, also pointed out the drug’s cost.
“Tezepelumab is currently an expensive biologic, so it remains to be seen whether patients and payors will be willing to pay for this add-on medication when AIT by itself still remains very effective,” he said by email.
“AIT is most effective when given for 5 years, so it also remains to be seen whether the results and conclusions of this study would still hold true if done for the typical 5-year treatment period,” he added.
Stokes Peebles, MD, professor of medicine in the division of allergy, pulmonary, and critical care medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., called the study “very well designed by a highly respected group of investigators using well-matched study populations.
“Tezepelumab has been shown to work in asthma, and there is no reason to think it would not work in allergic rhinitis,” he said in an interview.
“However, while the results of the combined therapy were statistically significant, their clinical significance was not clear. Patients do not care about statistical significance. They want to know whether a drug will be clinically significant,” he added.
Many people avoid cat allergy symptoms by avoiding cats and, in some cases, by avoiding people who live with cats, he said. Medical therapy, usually involving nasal corticosteroids and antihistamines, helps most people avoid cat allergy symptoms.
“Patients with bad allergies who have not done well with SCIT may consider adding tezepelumab, but it incurs a major cost. If medical therapy doesn’t work, allergy shots are available at roughly $3,000 per year. Adding tezepelumab costs around $40,000 more per year,” he explained. “Does the slight clinical benefit justify the greatly increased cost?”
The authors and uninvolved experts recommend further related research.
The research was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. AstraZeneca and Amgen donated the drug used in the study. Dr. Corren reported financial relationships with AstraZeneca, and one coauthor reported relevant financial relationships with Amgen and other pharmaceutical companies. The remaining coauthors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
Fentanyl vaccine a potential ‘game changer’ for opioid crisis
Texas-based researchers have developed a vaccine that blocks the euphoric effects of fentanyl, a potent synthetic opioid that is increasingly involved in opioid overdose deaths in the United States.
In studies in male and female mice, the vaccine generated significant and long-lasting levels of anti-fentanyl antibodies that were highly effective at reducing the antinociceptive, behavioral, and physiological effects of the drug.
“Thus, the individual will not feel the euphoric effects and can ‘get back on the wagon’ to sobriety,” lead investigator Colin Haile, MD, PhD, with University of Houston and founding member of the UH Drug Discovery Institute, said in a news release. The study was published online in the journal Pharmaceutics.
“The anti-fentanyl antibodies were specific to fentanyl and a fentanyl derivative and did not cross-react with other opioids, such as morphine. That means a vaccinated person would still be able to be treated for pain relief with other opioids,” said Dr. Haile.
The vaccine did not cause any adverse effects in the immunized mice. The research team plans to start manufacturing clinical-grade vaccine in the coming months with clinical trials in humans planned soon.
If proven safe and effective in clinical testing, the vaccine could have major implications for the nation’s opioid epidemic by becoming a relapse prevention agent for people trying to quit using opioids, the researchers note.
The United States in 2021 recorded more than 107,000 drug overdose deaths – a record high, according to federal health officials – and fentanyl was involved in most of these deaths.
Senior author Therese Kosten, PhD, director of the UH Developmental, Cognitive & Behavioral Neuroscience program, calls the new fentanyl vaccine a potential “game changer.”
“Fentanyl use and overdose is a particular treatment challenge that is not adequately addressed with current medications because of its pharmacodynamics, and managing acute overdose with the short-acting naloxone [Narcan] is not appropriately effective as multiple doses of naloxone are often needed to reverse fentanyl’s fatal effects,” said Dr. Kosten.
Funding for the study was provided by the Department of Defense through the Alcohol and Substance Abuse Disorders Program managed by RTI International’s Pharmacotherapies for Alcohol and Substance Use Disorders Alliance, which has funded Dr. Haile’s lab for several years to develop the anti-fentanyl vaccine. The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest. A provisional patent has been submitted by the University of Houston on behalf of four of the investigators containing technology related to the fentanyl vaccine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Texas-based researchers have developed a vaccine that blocks the euphoric effects of fentanyl, a potent synthetic opioid that is increasingly involved in opioid overdose deaths in the United States.
In studies in male and female mice, the vaccine generated significant and long-lasting levels of anti-fentanyl antibodies that were highly effective at reducing the antinociceptive, behavioral, and physiological effects of the drug.
“Thus, the individual will not feel the euphoric effects and can ‘get back on the wagon’ to sobriety,” lead investigator Colin Haile, MD, PhD, with University of Houston and founding member of the UH Drug Discovery Institute, said in a news release. The study was published online in the journal Pharmaceutics.
“The anti-fentanyl antibodies were specific to fentanyl and a fentanyl derivative and did not cross-react with other opioids, such as morphine. That means a vaccinated person would still be able to be treated for pain relief with other opioids,” said Dr. Haile.
The vaccine did not cause any adverse effects in the immunized mice. The research team plans to start manufacturing clinical-grade vaccine in the coming months with clinical trials in humans planned soon.
If proven safe and effective in clinical testing, the vaccine could have major implications for the nation’s opioid epidemic by becoming a relapse prevention agent for people trying to quit using opioids, the researchers note.
The United States in 2021 recorded more than 107,000 drug overdose deaths – a record high, according to federal health officials – and fentanyl was involved in most of these deaths.
Senior author Therese Kosten, PhD, director of the UH Developmental, Cognitive & Behavioral Neuroscience program, calls the new fentanyl vaccine a potential “game changer.”
“Fentanyl use and overdose is a particular treatment challenge that is not adequately addressed with current medications because of its pharmacodynamics, and managing acute overdose with the short-acting naloxone [Narcan] is not appropriately effective as multiple doses of naloxone are often needed to reverse fentanyl’s fatal effects,” said Dr. Kosten.
Funding for the study was provided by the Department of Defense through the Alcohol and Substance Abuse Disorders Program managed by RTI International’s Pharmacotherapies for Alcohol and Substance Use Disorders Alliance, which has funded Dr. Haile’s lab for several years to develop the anti-fentanyl vaccine. The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest. A provisional patent has been submitted by the University of Houston on behalf of four of the investigators containing technology related to the fentanyl vaccine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Texas-based researchers have developed a vaccine that blocks the euphoric effects of fentanyl, a potent synthetic opioid that is increasingly involved in opioid overdose deaths in the United States.
In studies in male and female mice, the vaccine generated significant and long-lasting levels of anti-fentanyl antibodies that were highly effective at reducing the antinociceptive, behavioral, and physiological effects of the drug.
“Thus, the individual will not feel the euphoric effects and can ‘get back on the wagon’ to sobriety,” lead investigator Colin Haile, MD, PhD, with University of Houston and founding member of the UH Drug Discovery Institute, said in a news release. The study was published online in the journal Pharmaceutics.
“The anti-fentanyl antibodies were specific to fentanyl and a fentanyl derivative and did not cross-react with other opioids, such as morphine. That means a vaccinated person would still be able to be treated for pain relief with other opioids,” said Dr. Haile.
The vaccine did not cause any adverse effects in the immunized mice. The research team plans to start manufacturing clinical-grade vaccine in the coming months with clinical trials in humans planned soon.
If proven safe and effective in clinical testing, the vaccine could have major implications for the nation’s opioid epidemic by becoming a relapse prevention agent for people trying to quit using opioids, the researchers note.
The United States in 2021 recorded more than 107,000 drug overdose deaths – a record high, according to federal health officials – and fentanyl was involved in most of these deaths.
Senior author Therese Kosten, PhD, director of the UH Developmental, Cognitive & Behavioral Neuroscience program, calls the new fentanyl vaccine a potential “game changer.”
“Fentanyl use and overdose is a particular treatment challenge that is not adequately addressed with current medications because of its pharmacodynamics, and managing acute overdose with the short-acting naloxone [Narcan] is not appropriately effective as multiple doses of naloxone are often needed to reverse fentanyl’s fatal effects,” said Dr. Kosten.
Funding for the study was provided by the Department of Defense through the Alcohol and Substance Abuse Disorders Program managed by RTI International’s Pharmacotherapies for Alcohol and Substance Use Disorders Alliance, which has funded Dr. Haile’s lab for several years to develop the anti-fentanyl vaccine. The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest. A provisional patent has been submitted by the University of Houston on behalf of four of the investigators containing technology related to the fentanyl vaccine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PHARMACEUTICS
Major life stressors ‘strongly predictive’ of long COVID symptoms
new research suggests.
Major life stressors in the year after hospital discharge for COVID-19 are “strongly predictive of a lot of the important outcomes that people may face after COVID,” lead investigator Jennifer A. Frontera, MD, a professor in the department of neurology at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
These outcomes include depression, brain fog, fatigue, trouble sleeping, and other long COVID symptoms.
The findings were published online in the Journal of the Neurological Sciences.
Major stressful events common
Dr. Frontera and the NYU Neurology COVID-19 study team evaluated 451 adults who survived a COVID hospital stay. Of these, 383 completed a 6-month follow-up, 242 completed a 12-month follow-up, and 174 completed follow-up at both time points.
Within 1 year of discharge, 77 (17%) patients died and 51% suffered a major stressful life event.
In multivariable analyses, major life stressors – including financial insecurity, food insecurity, death of a close contact, and new disability – were strong independent predictors of disability, trouble with activities of daily living, depression, fatigue, sleep problems, and prolonged post-acute COVID symptoms. The adjusted odds ratios for these outcomes ranged from 2.5 to 20.8.
The research also confirmed the contribution of traditional risk factors for long COVID symptoms, as shown in past studies. These include older age, poor pre-COVID functional status, and more severe initial COVID-19 infection.
Long-term sequelae of COVID are increasingly recognized as major public health issues.
It has been estimated that roughly 16 million U.S. adults aged 18-65 years ave long COVID, with the often debilitating symptoms keeping up to 4 million out of work.
Holistic approach
Dr. Frontera said it’s important to realize that “sleep, fatigue, anxiety, depression, even cognition are so interwoven with each other that anything that impacts any one of them could have repercussions on the other.”
She added that it “certainly makes sense that there is an interplay or even a bidirectional relationship between the stressors that people face and how well they can recover after COVID.”
Therapies that lessen the trauma of the most stress-inducing life events need to be a central part of treatment for long COVID, with more research needed to validate the best approaches, Dr. Frontera said.
She also noted that social services or case management resources may be able to help address at least some of the stressors that individuals are under – and it is important to refer them to these resources. Referral to mental health services is also important.
“I think it’s really important to take a holistic approach and try to deal with whatever the problem may be,” said Dr. Frontera.
“I’m a neurologist, but as part of my evaluation, I really need to address if there are life stressors or mental health issues that may be impacting this person’s function,” she added.
The study had no commercial funding. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Major life stressors in the year after hospital discharge for COVID-19 are “strongly predictive of a lot of the important outcomes that people may face after COVID,” lead investigator Jennifer A. Frontera, MD, a professor in the department of neurology at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
These outcomes include depression, brain fog, fatigue, trouble sleeping, and other long COVID symptoms.
The findings were published online in the Journal of the Neurological Sciences.
Major stressful events common
Dr. Frontera and the NYU Neurology COVID-19 study team evaluated 451 adults who survived a COVID hospital stay. Of these, 383 completed a 6-month follow-up, 242 completed a 12-month follow-up, and 174 completed follow-up at both time points.
Within 1 year of discharge, 77 (17%) patients died and 51% suffered a major stressful life event.
In multivariable analyses, major life stressors – including financial insecurity, food insecurity, death of a close contact, and new disability – were strong independent predictors of disability, trouble with activities of daily living, depression, fatigue, sleep problems, and prolonged post-acute COVID symptoms. The adjusted odds ratios for these outcomes ranged from 2.5 to 20.8.
The research also confirmed the contribution of traditional risk factors for long COVID symptoms, as shown in past studies. These include older age, poor pre-COVID functional status, and more severe initial COVID-19 infection.
Long-term sequelae of COVID are increasingly recognized as major public health issues.
It has been estimated that roughly 16 million U.S. adults aged 18-65 years ave long COVID, with the often debilitating symptoms keeping up to 4 million out of work.
Holistic approach
Dr. Frontera said it’s important to realize that “sleep, fatigue, anxiety, depression, even cognition are so interwoven with each other that anything that impacts any one of them could have repercussions on the other.”
She added that it “certainly makes sense that there is an interplay or even a bidirectional relationship between the stressors that people face and how well they can recover after COVID.”
Therapies that lessen the trauma of the most stress-inducing life events need to be a central part of treatment for long COVID, with more research needed to validate the best approaches, Dr. Frontera said.
She also noted that social services or case management resources may be able to help address at least some of the stressors that individuals are under – and it is important to refer them to these resources. Referral to mental health services is also important.
“I think it’s really important to take a holistic approach and try to deal with whatever the problem may be,” said Dr. Frontera.
“I’m a neurologist, but as part of my evaluation, I really need to address if there are life stressors or mental health issues that may be impacting this person’s function,” she added.
The study had no commercial funding. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Major life stressors in the year after hospital discharge for COVID-19 are “strongly predictive of a lot of the important outcomes that people may face after COVID,” lead investigator Jennifer A. Frontera, MD, a professor in the department of neurology at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
These outcomes include depression, brain fog, fatigue, trouble sleeping, and other long COVID symptoms.
The findings were published online in the Journal of the Neurological Sciences.
Major stressful events common
Dr. Frontera and the NYU Neurology COVID-19 study team evaluated 451 adults who survived a COVID hospital stay. Of these, 383 completed a 6-month follow-up, 242 completed a 12-month follow-up, and 174 completed follow-up at both time points.
Within 1 year of discharge, 77 (17%) patients died and 51% suffered a major stressful life event.
In multivariable analyses, major life stressors – including financial insecurity, food insecurity, death of a close contact, and new disability – were strong independent predictors of disability, trouble with activities of daily living, depression, fatigue, sleep problems, and prolonged post-acute COVID symptoms. The adjusted odds ratios for these outcomes ranged from 2.5 to 20.8.
The research also confirmed the contribution of traditional risk factors for long COVID symptoms, as shown in past studies. These include older age, poor pre-COVID functional status, and more severe initial COVID-19 infection.
Long-term sequelae of COVID are increasingly recognized as major public health issues.
It has been estimated that roughly 16 million U.S. adults aged 18-65 years ave long COVID, with the often debilitating symptoms keeping up to 4 million out of work.
Holistic approach
Dr. Frontera said it’s important to realize that “sleep, fatigue, anxiety, depression, even cognition are so interwoven with each other that anything that impacts any one of them could have repercussions on the other.”
She added that it “certainly makes sense that there is an interplay or even a bidirectional relationship between the stressors that people face and how well they can recover after COVID.”
Therapies that lessen the trauma of the most stress-inducing life events need to be a central part of treatment for long COVID, with more research needed to validate the best approaches, Dr. Frontera said.
She also noted that social services or case management resources may be able to help address at least some of the stressors that individuals are under – and it is important to refer them to these resources. Referral to mental health services is also important.
“I think it’s really important to take a holistic approach and try to deal with whatever the problem may be,” said Dr. Frontera.
“I’m a neurologist, but as part of my evaluation, I really need to address if there are life stressors or mental health issues that may be impacting this person’s function,” she added.
The study had no commercial funding. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE NEUROLOGICAL SCIENCES
Why your professional persona may be considered unprofessional
On one of the first days of medical school, Adaira Landry, MD, applied her favorite dark shade of lipstick and headed to her orientation. She was eager to learn about program expectations and connect with fellow aspiring physicians. But when Dr. Landry got there, one of her brand-new peers turned to her and asked, “Why do you wear your lipstick like an angry Black woman?”
“Imagine hearing that,” Dr. Landry, now an emergency medical physician in Boston, says. “It was so hurtful.”
So, what is a “standard-issue doctor” expected to look like? Physicians manage their appearances in myriad ways: through clothes, accessories, hair style, makeup; through a social media presence or lack thereof; in the rhythms and nuances of their interactions with patients and colleagues. These things add up to a professional “persona” – the Latin word for “mask,” or the face on display for the world to see.
While the health care field itself is diversifying, its guidelines for professionalism appear slower to change, often excluding or frowning upon expressions of individual personality or identity.
“Medicine is run primarily by men. It’s an objective truth,” Dr. Landry says. “Currently and historically, the standard of professionalism, especially in the physical sense, was set by them. As we increase diversity and welcome people bringing their authentic self to work, the prior definitions of professionalism are obviously in need of change.”
Split social media personalities
In August 2020, the Journal of Vascular Surgery published a study on the “prevalence of unprofessional social media content among young vascular surgeons.” The content that was deemed “unprofessional” included opinions on political issues like abortion and gun control. Photos of physicians holding alcoholic drinks or wearing “inappropriate/offensive attire,” including underwear, “provocative Halloween costumes,” and “bikinis/swimwear” were also censured. Six men and one woman worked on the study, and three of the male researchers took on the task of seeking out the “unprofessional” photos on social media. The resulting paper was reviewed by an all-male editorial board.
The study sparked immediate backlash and prompted hundreds of health care professionals to post photos of themselves in bathing suits with the hashtag “#medbikini.” The journal then retracted the study and issued an apology on Twitter, recognizing “errors in the design of the study with regards to conscious and unconscious bias.”
The researchers’ original definition of professionalism suggests that physicians should manage their personae even outside of work hours. “I think medicine in general is a very conservative and hierarchical field of study and of work, to say the least,” says Sarah Fraser, MD, a family medicine physician in Nova Scotia, Canada. “There’s this view that we have to have completely separate personal and professional lives, like church and state.”
The #medbikini controversy inspired Dr. Fraser to write an op-ed for the British Medical Journal blog about the flaws of requiring physicians to keep their personal and professional selves separate. The piece referenced Robert Louis Stevenson’s 1886 Gothic novella “The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde,” in which the respected scientist Dr. Jekyll creates an alter ego so he can express his evil urges without experiencing guilt, punishment, or loss of livelihood. Dr. Fraser likened this story to the pressure physicians feel to shrink or split themselves to squeeze into a narrow definition of professionalism.
But Dr. Landry points out that some elements of expression seen as unprofessional cannot be entirely separated from a physician’s fundamental identity. “For Black women, our daily behaviors and forms of expression that are deemed ‘unprofessional’ are much more subtle than being able to wear a bikini on social media,” she says. “The way we wear our hair, the tone of our voice, the color of our lipstick, the way we wear scrub caps are parts of us that are called into question.”
Keeping up appearances
The stereotype of what a doctor should look like starts to shape physicians’ professional personae in medical school. When Jennifer Caputo-Seidler, MD, started medical school in 2008, the dress code requirements for male students were simple: pants, a button-down shirt, a tie. But then there were the rules for women: Hair should be tied back. Minimal makeup. No flashy jewelry. Nothing without sleeves. Neutral colors. High necklines. Low hemlines. “The message I got was that we need to dress like the men in order to be taken seriously and to be seen as professional,” says Dr. Caputo-Seidler, now an assistant professor of medicine at the University of South Florida, Tampa, “and so that’s what I did.”
A 2018 analysis of 78 “draw-a-scientist” studies found that children have overwhelmingly associated scientific fields with men for the last 50 years. Overall, children drew 73% of scientists as men. The drawings grew more gender diverse over time, but even as more women entered scientific fields, both boys and girls continued to draw significantly more male than female scientists.
Not everyone at Dr. Caputo-Seidler’s medical school adhered to the environment’s gendered expectations. One resident she worked with often wore voluminous hairstyles, lipstick, and high heels. Dr. Caputo-Seidler overheard her peers as they gossiped behind the resident’s back, ridiculing the way she looked.
“She was good at her job,” Dr. Caputo-Seidler says. “She knew her patients. She had things down. She was, by all measures, very competent. But when people saw her dressing outside the norm and being forward with her femininity, there was definitely a lot of chatter about it.”
While expectations for a conservative appearance may disproportionately affect women, and particularly women of color, they also affect men who deviate from the norm. “As an LGBTQ+ person working as a ‘professional,’ I have countless stories and moments where I had my professionalism questioned,” Blair Peters, MD, a plastic surgeon and assistant professor at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, wrote on Twitter. “Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to have colored hair? Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to have a visible tattoo? Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to wear bright colors and patterns?”
Dr. Fraser remembers a fellow medical student who had full-sleeve tattoos on both of his arms. A preceptor made a comment about it to Dr. Fraser, and then instructed the student to cover up his tattoos. “I think that there are scenarios when having tattoos or having different-colored hair or expressing your individual personality could help you even better bond with your patients,” Dr. Fraser says, “especially if you’re, for example, working with youth.”
Unmasking health care
Beyond the facets of dress codes and social media posts, the issue of professional personae speaks to the deeper issue of inclusion in medicine. As the field grows increasingly diverse, health care institutions and those they serve may need to expand their definitions of professionalism to include more truthful expressions of who contemporary health care professionals are as people.
Dr. Fraser suggests that the benefits of physicians embracing self-expression – rather than assimilating to an outdated model of professionalism – extend beyond the individual.
“Whether it comes to what you choose to wear to the clinic on a day-to-day basis, or what you choose to share on a social media account, as long as it’s not harming others, then I think that it’s a positive thing to be able to be yourself and express yourself,” she says. “I feel like doctors are expected to have a different personality when we’re at the clinic, and usually it’s more conservative or objective or aloof. But I think that by being open about who we are, we’ll actually help build a trusting relationship with both patients and society.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On one of the first days of medical school, Adaira Landry, MD, applied her favorite dark shade of lipstick and headed to her orientation. She was eager to learn about program expectations and connect with fellow aspiring physicians. But when Dr. Landry got there, one of her brand-new peers turned to her and asked, “Why do you wear your lipstick like an angry Black woman?”
“Imagine hearing that,” Dr. Landry, now an emergency medical physician in Boston, says. “It was so hurtful.”
So, what is a “standard-issue doctor” expected to look like? Physicians manage their appearances in myriad ways: through clothes, accessories, hair style, makeup; through a social media presence or lack thereof; in the rhythms and nuances of their interactions with patients and colleagues. These things add up to a professional “persona” – the Latin word for “mask,” or the face on display for the world to see.
While the health care field itself is diversifying, its guidelines for professionalism appear slower to change, often excluding or frowning upon expressions of individual personality or identity.
“Medicine is run primarily by men. It’s an objective truth,” Dr. Landry says. “Currently and historically, the standard of professionalism, especially in the physical sense, was set by them. As we increase diversity and welcome people bringing their authentic self to work, the prior definitions of professionalism are obviously in need of change.”
Split social media personalities
In August 2020, the Journal of Vascular Surgery published a study on the “prevalence of unprofessional social media content among young vascular surgeons.” The content that was deemed “unprofessional” included opinions on political issues like abortion and gun control. Photos of physicians holding alcoholic drinks or wearing “inappropriate/offensive attire,” including underwear, “provocative Halloween costumes,” and “bikinis/swimwear” were also censured. Six men and one woman worked on the study, and three of the male researchers took on the task of seeking out the “unprofessional” photos on social media. The resulting paper was reviewed by an all-male editorial board.
The study sparked immediate backlash and prompted hundreds of health care professionals to post photos of themselves in bathing suits with the hashtag “#medbikini.” The journal then retracted the study and issued an apology on Twitter, recognizing “errors in the design of the study with regards to conscious and unconscious bias.”
The researchers’ original definition of professionalism suggests that physicians should manage their personae even outside of work hours. “I think medicine in general is a very conservative and hierarchical field of study and of work, to say the least,” says Sarah Fraser, MD, a family medicine physician in Nova Scotia, Canada. “There’s this view that we have to have completely separate personal and professional lives, like church and state.”
The #medbikini controversy inspired Dr. Fraser to write an op-ed for the British Medical Journal blog about the flaws of requiring physicians to keep their personal and professional selves separate. The piece referenced Robert Louis Stevenson’s 1886 Gothic novella “The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde,” in which the respected scientist Dr. Jekyll creates an alter ego so he can express his evil urges without experiencing guilt, punishment, or loss of livelihood. Dr. Fraser likened this story to the pressure physicians feel to shrink or split themselves to squeeze into a narrow definition of professionalism.
But Dr. Landry points out that some elements of expression seen as unprofessional cannot be entirely separated from a physician’s fundamental identity. “For Black women, our daily behaviors and forms of expression that are deemed ‘unprofessional’ are much more subtle than being able to wear a bikini on social media,” she says. “The way we wear our hair, the tone of our voice, the color of our lipstick, the way we wear scrub caps are parts of us that are called into question.”
Keeping up appearances
The stereotype of what a doctor should look like starts to shape physicians’ professional personae in medical school. When Jennifer Caputo-Seidler, MD, started medical school in 2008, the dress code requirements for male students were simple: pants, a button-down shirt, a tie. But then there were the rules for women: Hair should be tied back. Minimal makeup. No flashy jewelry. Nothing without sleeves. Neutral colors. High necklines. Low hemlines. “The message I got was that we need to dress like the men in order to be taken seriously and to be seen as professional,” says Dr. Caputo-Seidler, now an assistant professor of medicine at the University of South Florida, Tampa, “and so that’s what I did.”
A 2018 analysis of 78 “draw-a-scientist” studies found that children have overwhelmingly associated scientific fields with men for the last 50 years. Overall, children drew 73% of scientists as men. The drawings grew more gender diverse over time, but even as more women entered scientific fields, both boys and girls continued to draw significantly more male than female scientists.
Not everyone at Dr. Caputo-Seidler’s medical school adhered to the environment’s gendered expectations. One resident she worked with often wore voluminous hairstyles, lipstick, and high heels. Dr. Caputo-Seidler overheard her peers as they gossiped behind the resident’s back, ridiculing the way she looked.
“She was good at her job,” Dr. Caputo-Seidler says. “She knew her patients. She had things down. She was, by all measures, very competent. But when people saw her dressing outside the norm and being forward with her femininity, there was definitely a lot of chatter about it.”
While expectations for a conservative appearance may disproportionately affect women, and particularly women of color, they also affect men who deviate from the norm. “As an LGBTQ+ person working as a ‘professional,’ I have countless stories and moments where I had my professionalism questioned,” Blair Peters, MD, a plastic surgeon and assistant professor at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, wrote on Twitter. “Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to have colored hair? Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to have a visible tattoo? Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to wear bright colors and patterns?”
Dr. Fraser remembers a fellow medical student who had full-sleeve tattoos on both of his arms. A preceptor made a comment about it to Dr. Fraser, and then instructed the student to cover up his tattoos. “I think that there are scenarios when having tattoos or having different-colored hair or expressing your individual personality could help you even better bond with your patients,” Dr. Fraser says, “especially if you’re, for example, working with youth.”
Unmasking health care
Beyond the facets of dress codes and social media posts, the issue of professional personae speaks to the deeper issue of inclusion in medicine. As the field grows increasingly diverse, health care institutions and those they serve may need to expand their definitions of professionalism to include more truthful expressions of who contemporary health care professionals are as people.
Dr. Fraser suggests that the benefits of physicians embracing self-expression – rather than assimilating to an outdated model of professionalism – extend beyond the individual.
“Whether it comes to what you choose to wear to the clinic on a day-to-day basis, or what you choose to share on a social media account, as long as it’s not harming others, then I think that it’s a positive thing to be able to be yourself and express yourself,” she says. “I feel like doctors are expected to have a different personality when we’re at the clinic, and usually it’s more conservative or objective or aloof. But I think that by being open about who we are, we’ll actually help build a trusting relationship with both patients and society.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On one of the first days of medical school, Adaira Landry, MD, applied her favorite dark shade of lipstick and headed to her orientation. She was eager to learn about program expectations and connect with fellow aspiring physicians. But when Dr. Landry got there, one of her brand-new peers turned to her and asked, “Why do you wear your lipstick like an angry Black woman?”
“Imagine hearing that,” Dr. Landry, now an emergency medical physician in Boston, says. “It was so hurtful.”
So, what is a “standard-issue doctor” expected to look like? Physicians manage their appearances in myriad ways: through clothes, accessories, hair style, makeup; through a social media presence or lack thereof; in the rhythms and nuances of their interactions with patients and colleagues. These things add up to a professional “persona” – the Latin word for “mask,” or the face on display for the world to see.
While the health care field itself is diversifying, its guidelines for professionalism appear slower to change, often excluding or frowning upon expressions of individual personality or identity.
“Medicine is run primarily by men. It’s an objective truth,” Dr. Landry says. “Currently and historically, the standard of professionalism, especially in the physical sense, was set by them. As we increase diversity and welcome people bringing their authentic self to work, the prior definitions of professionalism are obviously in need of change.”
Split social media personalities
In August 2020, the Journal of Vascular Surgery published a study on the “prevalence of unprofessional social media content among young vascular surgeons.” The content that was deemed “unprofessional” included opinions on political issues like abortion and gun control. Photos of physicians holding alcoholic drinks or wearing “inappropriate/offensive attire,” including underwear, “provocative Halloween costumes,” and “bikinis/swimwear” were also censured. Six men and one woman worked on the study, and three of the male researchers took on the task of seeking out the “unprofessional” photos on social media. The resulting paper was reviewed by an all-male editorial board.
The study sparked immediate backlash and prompted hundreds of health care professionals to post photos of themselves in bathing suits with the hashtag “#medbikini.” The journal then retracted the study and issued an apology on Twitter, recognizing “errors in the design of the study with regards to conscious and unconscious bias.”
The researchers’ original definition of professionalism suggests that physicians should manage their personae even outside of work hours. “I think medicine in general is a very conservative and hierarchical field of study and of work, to say the least,” says Sarah Fraser, MD, a family medicine physician in Nova Scotia, Canada. “There’s this view that we have to have completely separate personal and professional lives, like church and state.”
The #medbikini controversy inspired Dr. Fraser to write an op-ed for the British Medical Journal blog about the flaws of requiring physicians to keep their personal and professional selves separate. The piece referenced Robert Louis Stevenson’s 1886 Gothic novella “The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde,” in which the respected scientist Dr. Jekyll creates an alter ego so he can express his evil urges without experiencing guilt, punishment, or loss of livelihood. Dr. Fraser likened this story to the pressure physicians feel to shrink or split themselves to squeeze into a narrow definition of professionalism.
But Dr. Landry points out that some elements of expression seen as unprofessional cannot be entirely separated from a physician’s fundamental identity. “For Black women, our daily behaviors and forms of expression that are deemed ‘unprofessional’ are much more subtle than being able to wear a bikini on social media,” she says. “The way we wear our hair, the tone of our voice, the color of our lipstick, the way we wear scrub caps are parts of us that are called into question.”
Keeping up appearances
The stereotype of what a doctor should look like starts to shape physicians’ professional personae in medical school. When Jennifer Caputo-Seidler, MD, started medical school in 2008, the dress code requirements for male students were simple: pants, a button-down shirt, a tie. But then there were the rules for women: Hair should be tied back. Minimal makeup. No flashy jewelry. Nothing without sleeves. Neutral colors. High necklines. Low hemlines. “The message I got was that we need to dress like the men in order to be taken seriously and to be seen as professional,” says Dr. Caputo-Seidler, now an assistant professor of medicine at the University of South Florida, Tampa, “and so that’s what I did.”
A 2018 analysis of 78 “draw-a-scientist” studies found that children have overwhelmingly associated scientific fields with men for the last 50 years. Overall, children drew 73% of scientists as men. The drawings grew more gender diverse over time, but even as more women entered scientific fields, both boys and girls continued to draw significantly more male than female scientists.
Not everyone at Dr. Caputo-Seidler’s medical school adhered to the environment’s gendered expectations. One resident she worked with often wore voluminous hairstyles, lipstick, and high heels. Dr. Caputo-Seidler overheard her peers as they gossiped behind the resident’s back, ridiculing the way she looked.
“She was good at her job,” Dr. Caputo-Seidler says. “She knew her patients. She had things down. She was, by all measures, very competent. But when people saw her dressing outside the norm and being forward with her femininity, there was definitely a lot of chatter about it.”
While expectations for a conservative appearance may disproportionately affect women, and particularly women of color, they also affect men who deviate from the norm. “As an LGBTQ+ person working as a ‘professional,’ I have countless stories and moments where I had my professionalism questioned,” Blair Peters, MD, a plastic surgeon and assistant professor at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, wrote on Twitter. “Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to have colored hair? Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to have a visible tattoo? Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to wear bright colors and patterns?”
Dr. Fraser remembers a fellow medical student who had full-sleeve tattoos on both of his arms. A preceptor made a comment about it to Dr. Fraser, and then instructed the student to cover up his tattoos. “I think that there are scenarios when having tattoos or having different-colored hair or expressing your individual personality could help you even better bond with your patients,” Dr. Fraser says, “especially if you’re, for example, working with youth.”
Unmasking health care
Beyond the facets of dress codes and social media posts, the issue of professional personae speaks to the deeper issue of inclusion in medicine. As the field grows increasingly diverse, health care institutions and those they serve may need to expand their definitions of professionalism to include more truthful expressions of who contemporary health care professionals are as people.
Dr. Fraser suggests that the benefits of physicians embracing self-expression – rather than assimilating to an outdated model of professionalism – extend beyond the individual.
“Whether it comes to what you choose to wear to the clinic on a day-to-day basis, or what you choose to share on a social media account, as long as it’s not harming others, then I think that it’s a positive thing to be able to be yourself and express yourself,” she says. “I feel like doctors are expected to have a different personality when we’re at the clinic, and usually it’s more conservative or objective or aloof. But I think that by being open about who we are, we’ll actually help build a trusting relationship with both patients and society.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Experts explain the ‘perfect storm’ of rampant RSV and flu
Headlines over the past few weeks are ringing the alarm about earlier and more serious influenza (flu) and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) outbreaks compared with previous years. Add COVID-19 to the mix and you have a dangerous mash of viruses that have many experts calling for caution and searching for explanations.
RSV and the flu “are certainly getting more attention, and they’re getting more attention for two reasons,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
“The first is that they’re both extraordinarily early. The second is that they’re both out there spreading very, very rapidly,” he told this news organization.
RSV usually follows a seasonal pattern with cases peaking in January and February. Both viruses tend to hit different regions of the country at different times, and that’s not the case in 2022.
“This is particularly striking for RSV, which usually doesn’t affect the entire country simultaneously,” Dr. Schaffner said.
“Yes, RSV is causing many more hospitalizations and earlier than any previously recorded season in the U.S.,” according to figures from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on RSV hospitalizations, said Kevin Messacar, MD, PhD, associate professor at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora.
Although there could be some increase in diagnoses because of increased awareness, the jump in RSV and flu cases “is a real phenomenon for multiple reasons,” said Peter Chin-Hong, MD, professor in the division of infectious diseases at the University of California, San Francisco.
With fewer COVID-related restrictions, people are moving around more. Also, during fall and winter, people tend to gather indoors. Colder temperatures and lower humidity contribute as well, Dr. Chin-Hong said, because “the droplets are just simply lighter.
“I think those are all factors,” he told this news organization.
Paul Auwaerter, MD, agreed that there are likely multiple causes for the unusual timing and severity of RSV and flu this year.
“Change in behaviors is a leading cause,” said the clinical director for the division of infectious diseases at the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. More people returning to the workplace and children going to school without masks are examples, he added.
Less exposure to these three viruses also means there was less immune boosting among existing populations, he said. This can lead to “larger susceptible populations, especially infants and younger children, due to the relative absence of circulating virus in past years.”
A leading theory
Are we paying a price now for people following the edicts from officials to mask up, stand apart, and take other personal and public health precautions during the COVID-19 pandemic?
It’s possible, but that may not be the whole story.
“When it comes to RSV, I think that theory of isolation, social distancing, mask wearing, and not attending schools is a very valid one,” Dr. Schaffner said. “That’s everybody’s favorite [reason].”
He said he is confident that the jump in RSV cases is being driven by previous COVID public health protections. However, he’s “a little more cautious about influenza, in part because influenza is so variable.
“Like people in influenza say, if you’ve seen one influenza season, you’ve seen one influenza season,” Dr. Schaffner said.
“There’s a lot of debate,” he added. “Nobody can say definitively whether the immune deficit or debt is a consequence of not being stimulated and restimulated by the influenza virus over the past two seasons.”
‘A perfect storm’
“Now you kind of have the perfect storm,” Dr. Chin-Hong said. “It’s not a good situation for COVID with the variants that are emerging. For influenza, not having seen a lot of influenza the last 2 years, we’re probably more susceptible to getting infected.”
RSV cases rose during summer 2021, but now the weather is colder, and people are interacting more closely. “And it’s very, very transmissible,” he said.
Dr. Chin-Hong also predicted that “even though we don’t have a lot of COVID now, COVID will probably pick up.”
The rise in RSV was unexpected by some experts. “This early influenza is also a bit of a surprise and may be influenced by the fact that lots of us are going back and seeing each other again close-to-close, face-to-face in many enclosed environments,” Dr. Schaffner said.
He estimated the 2022-2023 flu season started 4-6 weeks early “and it’s taken off like a rocket. It started in the Southeast, quickly went to the Southwest and up the East Coast. Now it’s moving dramatically through the Midwest and will continue. It’s quite sure to hit the West Coast if it isn’t there already.”
A phenomenon by any other name
Some are calling the situation an “immunity debt,” while others dub it an “immunity pause” or an “immunity deficit.” Many physicians and immunologists have taken to social media to push back on the term “immunity debt,” saying it’s a mischaracterization that is being used to vilify COVID precautions, such as masking, social distancing, and other protective measures taken during the pandemic.
“I prefer the term ‘immunity gap’ ... which is more established in the epidemiology literature, especially given the politicization of the term ‘immunity debt’ by folks recently,” Dr. Messacar said.
“To me, the immunity gap is a scientific observation, not a political argument,” he added.
In a July 2022 publication in The Lancet, Dr. Messacar and his colleagues stated that “decreased exposure to endemic viruses created an immunity gap – a group of susceptible individuals who avoided infection and therefore lack pathogen-specific immunity to protect against future infection. Decreases in childhood vaccinations with pandemic disruptions to health care delivery contribute to this immunity gap for vaccine-preventable diseases, such as influenza,measles, and polio.”
The researchers noted that because of isolation during the pandemic, older children and newborns are being exposed to RSV for the first time. Returning to birthday parties, playing with friends, and going to school without masks means “children are being exposed to RSV, and that’s likely the reason that RSV is moving early and very, very substantially through this now expanded pool of susceptible children,” Dr. Schaffner said.
How likely are coinfections?
With peaks in RSV, flu, and COVID-19 cases each predicted in the coming months, how likely is it that someone could get sick with more than one infection at the same time?
Early in the pandemic, coinfection with COVID and the flu was reported in people at some centers on the West Coast, Dr. Auwaerter said. Now, however, “the unpredictable nature of the Omicron subvariants and the potential for further change, along with the never-before-seen significant lessening of influenza over 2 years, leave little for predictability.
“I do think it is less likely, given the extent of immunity now to SARS-CoV-2 in the population,” Dr. Auwaerter said.
“I most worry about viral coinfections ... in people with suppressed immune systems if we have high community rates of the SARS-CoV-2 and influenza circulating this fall and winter,” he added.
Studies during the pandemic suggest that coinfection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus and another respiratory virus were either rare or nonexistent.
Dr. Schaffner said these findings align with his experience at Vanderbilt University, which is part of a CDC-sponsored network that tracks laboratory-confirmed RSV, flu, and COVID cases among people in the hospital. “Coinfections are, at least to date, very unusual.”
There needs to be an asterisk next to that, Dr. Schaffner added. “Looking back over the last 2 years, we’ve had very little influenza, and we’ve had curtailed RSV seasons. So there hasn’t been a whole lot of opportunity for dual infections to occur.
“So this year may be more revelatory as we go forward,” he said.
Future concerns
The future is uncertain, Dr. Messacar and colleagues wrote in The Lancet: “Crucially, the patterns of these returning viral outbreaks have been heterogeneous across locations, populations, and pathogens, making predictions and preparations challenging.”
Dr. Chin-Hong used a horse race analogy to illustrate the situation now and going forward. RSV is the front-running horse, and influenza is running behind but trying to catch up. “And then COVID is the dark horse. It’s trailing the race right now – but all these variants are giving the horse extra supplements.
“And the COVID horse is probably going to be very competitive with the front-runner,” he said.
“We’re just at the beginning of the race right now,” Dr. Chin-Hong said, “so that’s why we’re worried that these three [viruses] will be even more pronounced come later in the year.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Headlines over the past few weeks are ringing the alarm about earlier and more serious influenza (flu) and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) outbreaks compared with previous years. Add COVID-19 to the mix and you have a dangerous mash of viruses that have many experts calling for caution and searching for explanations.
RSV and the flu “are certainly getting more attention, and they’re getting more attention for two reasons,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
“The first is that they’re both extraordinarily early. The second is that they’re both out there spreading very, very rapidly,” he told this news organization.
RSV usually follows a seasonal pattern with cases peaking in January and February. Both viruses tend to hit different regions of the country at different times, and that’s not the case in 2022.
“This is particularly striking for RSV, which usually doesn’t affect the entire country simultaneously,” Dr. Schaffner said.
“Yes, RSV is causing many more hospitalizations and earlier than any previously recorded season in the U.S.,” according to figures from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on RSV hospitalizations, said Kevin Messacar, MD, PhD, associate professor at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora.
Although there could be some increase in diagnoses because of increased awareness, the jump in RSV and flu cases “is a real phenomenon for multiple reasons,” said Peter Chin-Hong, MD, professor in the division of infectious diseases at the University of California, San Francisco.
With fewer COVID-related restrictions, people are moving around more. Also, during fall and winter, people tend to gather indoors. Colder temperatures and lower humidity contribute as well, Dr. Chin-Hong said, because “the droplets are just simply lighter.
“I think those are all factors,” he told this news organization.
Paul Auwaerter, MD, agreed that there are likely multiple causes for the unusual timing and severity of RSV and flu this year.
“Change in behaviors is a leading cause,” said the clinical director for the division of infectious diseases at the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. More people returning to the workplace and children going to school without masks are examples, he added.
Less exposure to these three viruses also means there was less immune boosting among existing populations, he said. This can lead to “larger susceptible populations, especially infants and younger children, due to the relative absence of circulating virus in past years.”
A leading theory
Are we paying a price now for people following the edicts from officials to mask up, stand apart, and take other personal and public health precautions during the COVID-19 pandemic?
It’s possible, but that may not be the whole story.
“When it comes to RSV, I think that theory of isolation, social distancing, mask wearing, and not attending schools is a very valid one,” Dr. Schaffner said. “That’s everybody’s favorite [reason].”
He said he is confident that the jump in RSV cases is being driven by previous COVID public health protections. However, he’s “a little more cautious about influenza, in part because influenza is so variable.
“Like people in influenza say, if you’ve seen one influenza season, you’ve seen one influenza season,” Dr. Schaffner said.
“There’s a lot of debate,” he added. “Nobody can say definitively whether the immune deficit or debt is a consequence of not being stimulated and restimulated by the influenza virus over the past two seasons.”
‘A perfect storm’
“Now you kind of have the perfect storm,” Dr. Chin-Hong said. “It’s not a good situation for COVID with the variants that are emerging. For influenza, not having seen a lot of influenza the last 2 years, we’re probably more susceptible to getting infected.”
RSV cases rose during summer 2021, but now the weather is colder, and people are interacting more closely. “And it’s very, very transmissible,” he said.
Dr. Chin-Hong also predicted that “even though we don’t have a lot of COVID now, COVID will probably pick up.”
The rise in RSV was unexpected by some experts. “This early influenza is also a bit of a surprise and may be influenced by the fact that lots of us are going back and seeing each other again close-to-close, face-to-face in many enclosed environments,” Dr. Schaffner said.
He estimated the 2022-2023 flu season started 4-6 weeks early “and it’s taken off like a rocket. It started in the Southeast, quickly went to the Southwest and up the East Coast. Now it’s moving dramatically through the Midwest and will continue. It’s quite sure to hit the West Coast if it isn’t there already.”
A phenomenon by any other name
Some are calling the situation an “immunity debt,” while others dub it an “immunity pause” or an “immunity deficit.” Many physicians and immunologists have taken to social media to push back on the term “immunity debt,” saying it’s a mischaracterization that is being used to vilify COVID precautions, such as masking, social distancing, and other protective measures taken during the pandemic.
“I prefer the term ‘immunity gap’ ... which is more established in the epidemiology literature, especially given the politicization of the term ‘immunity debt’ by folks recently,” Dr. Messacar said.
“To me, the immunity gap is a scientific observation, not a political argument,” he added.
In a July 2022 publication in The Lancet, Dr. Messacar and his colleagues stated that “decreased exposure to endemic viruses created an immunity gap – a group of susceptible individuals who avoided infection and therefore lack pathogen-specific immunity to protect against future infection. Decreases in childhood vaccinations with pandemic disruptions to health care delivery contribute to this immunity gap for vaccine-preventable diseases, such as influenza,measles, and polio.”
The researchers noted that because of isolation during the pandemic, older children and newborns are being exposed to RSV for the first time. Returning to birthday parties, playing with friends, and going to school without masks means “children are being exposed to RSV, and that’s likely the reason that RSV is moving early and very, very substantially through this now expanded pool of susceptible children,” Dr. Schaffner said.
How likely are coinfections?
With peaks in RSV, flu, and COVID-19 cases each predicted in the coming months, how likely is it that someone could get sick with more than one infection at the same time?
Early in the pandemic, coinfection with COVID and the flu was reported in people at some centers on the West Coast, Dr. Auwaerter said. Now, however, “the unpredictable nature of the Omicron subvariants and the potential for further change, along with the never-before-seen significant lessening of influenza over 2 years, leave little for predictability.
“I do think it is less likely, given the extent of immunity now to SARS-CoV-2 in the population,” Dr. Auwaerter said.
“I most worry about viral coinfections ... in people with suppressed immune systems if we have high community rates of the SARS-CoV-2 and influenza circulating this fall and winter,” he added.
Studies during the pandemic suggest that coinfection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus and another respiratory virus were either rare or nonexistent.
Dr. Schaffner said these findings align with his experience at Vanderbilt University, which is part of a CDC-sponsored network that tracks laboratory-confirmed RSV, flu, and COVID cases among people in the hospital. “Coinfections are, at least to date, very unusual.”
There needs to be an asterisk next to that, Dr. Schaffner added. “Looking back over the last 2 years, we’ve had very little influenza, and we’ve had curtailed RSV seasons. So there hasn’t been a whole lot of opportunity for dual infections to occur.
“So this year may be more revelatory as we go forward,” he said.
Future concerns
The future is uncertain, Dr. Messacar and colleagues wrote in The Lancet: “Crucially, the patterns of these returning viral outbreaks have been heterogeneous across locations, populations, and pathogens, making predictions and preparations challenging.”
Dr. Chin-Hong used a horse race analogy to illustrate the situation now and going forward. RSV is the front-running horse, and influenza is running behind but trying to catch up. “And then COVID is the dark horse. It’s trailing the race right now – but all these variants are giving the horse extra supplements.
“And the COVID horse is probably going to be very competitive with the front-runner,” he said.
“We’re just at the beginning of the race right now,” Dr. Chin-Hong said, “so that’s why we’re worried that these three [viruses] will be even more pronounced come later in the year.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Headlines over the past few weeks are ringing the alarm about earlier and more serious influenza (flu) and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) outbreaks compared with previous years. Add COVID-19 to the mix and you have a dangerous mash of viruses that have many experts calling for caution and searching for explanations.
RSV and the flu “are certainly getting more attention, and they’re getting more attention for two reasons,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
“The first is that they’re both extraordinarily early. The second is that they’re both out there spreading very, very rapidly,” he told this news organization.
RSV usually follows a seasonal pattern with cases peaking in January and February. Both viruses tend to hit different regions of the country at different times, and that’s not the case in 2022.
“This is particularly striking for RSV, which usually doesn’t affect the entire country simultaneously,” Dr. Schaffner said.
“Yes, RSV is causing many more hospitalizations and earlier than any previously recorded season in the U.S.,” according to figures from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on RSV hospitalizations, said Kevin Messacar, MD, PhD, associate professor at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora.
Although there could be some increase in diagnoses because of increased awareness, the jump in RSV and flu cases “is a real phenomenon for multiple reasons,” said Peter Chin-Hong, MD, professor in the division of infectious diseases at the University of California, San Francisco.
With fewer COVID-related restrictions, people are moving around more. Also, during fall and winter, people tend to gather indoors. Colder temperatures and lower humidity contribute as well, Dr. Chin-Hong said, because “the droplets are just simply lighter.
“I think those are all factors,” he told this news organization.
Paul Auwaerter, MD, agreed that there are likely multiple causes for the unusual timing and severity of RSV and flu this year.
“Change in behaviors is a leading cause,” said the clinical director for the division of infectious diseases at the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. More people returning to the workplace and children going to school without masks are examples, he added.
Less exposure to these three viruses also means there was less immune boosting among existing populations, he said. This can lead to “larger susceptible populations, especially infants and younger children, due to the relative absence of circulating virus in past years.”
A leading theory
Are we paying a price now for people following the edicts from officials to mask up, stand apart, and take other personal and public health precautions during the COVID-19 pandemic?
It’s possible, but that may not be the whole story.
“When it comes to RSV, I think that theory of isolation, social distancing, mask wearing, and not attending schools is a very valid one,” Dr. Schaffner said. “That’s everybody’s favorite [reason].”
He said he is confident that the jump in RSV cases is being driven by previous COVID public health protections. However, he’s “a little more cautious about influenza, in part because influenza is so variable.
“Like people in influenza say, if you’ve seen one influenza season, you’ve seen one influenza season,” Dr. Schaffner said.
“There’s a lot of debate,” he added. “Nobody can say definitively whether the immune deficit or debt is a consequence of not being stimulated and restimulated by the influenza virus over the past two seasons.”
‘A perfect storm’
“Now you kind of have the perfect storm,” Dr. Chin-Hong said. “It’s not a good situation for COVID with the variants that are emerging. For influenza, not having seen a lot of influenza the last 2 years, we’re probably more susceptible to getting infected.”
RSV cases rose during summer 2021, but now the weather is colder, and people are interacting more closely. “And it’s very, very transmissible,” he said.
Dr. Chin-Hong also predicted that “even though we don’t have a lot of COVID now, COVID will probably pick up.”
The rise in RSV was unexpected by some experts. “This early influenza is also a bit of a surprise and may be influenced by the fact that lots of us are going back and seeing each other again close-to-close, face-to-face in many enclosed environments,” Dr. Schaffner said.
He estimated the 2022-2023 flu season started 4-6 weeks early “and it’s taken off like a rocket. It started in the Southeast, quickly went to the Southwest and up the East Coast. Now it’s moving dramatically through the Midwest and will continue. It’s quite sure to hit the West Coast if it isn’t there already.”
A phenomenon by any other name
Some are calling the situation an “immunity debt,” while others dub it an “immunity pause” or an “immunity deficit.” Many physicians and immunologists have taken to social media to push back on the term “immunity debt,” saying it’s a mischaracterization that is being used to vilify COVID precautions, such as masking, social distancing, and other protective measures taken during the pandemic.
“I prefer the term ‘immunity gap’ ... which is more established in the epidemiology literature, especially given the politicization of the term ‘immunity debt’ by folks recently,” Dr. Messacar said.
“To me, the immunity gap is a scientific observation, not a political argument,” he added.
In a July 2022 publication in The Lancet, Dr. Messacar and his colleagues stated that “decreased exposure to endemic viruses created an immunity gap – a group of susceptible individuals who avoided infection and therefore lack pathogen-specific immunity to protect against future infection. Decreases in childhood vaccinations with pandemic disruptions to health care delivery contribute to this immunity gap for vaccine-preventable diseases, such as influenza,measles, and polio.”
The researchers noted that because of isolation during the pandemic, older children and newborns are being exposed to RSV for the first time. Returning to birthday parties, playing with friends, and going to school without masks means “children are being exposed to RSV, and that’s likely the reason that RSV is moving early and very, very substantially through this now expanded pool of susceptible children,” Dr. Schaffner said.
How likely are coinfections?
With peaks in RSV, flu, and COVID-19 cases each predicted in the coming months, how likely is it that someone could get sick with more than one infection at the same time?
Early in the pandemic, coinfection with COVID and the flu was reported in people at some centers on the West Coast, Dr. Auwaerter said. Now, however, “the unpredictable nature of the Omicron subvariants and the potential for further change, along with the never-before-seen significant lessening of influenza over 2 years, leave little for predictability.
“I do think it is less likely, given the extent of immunity now to SARS-CoV-2 in the population,” Dr. Auwaerter said.
“I most worry about viral coinfections ... in people with suppressed immune systems if we have high community rates of the SARS-CoV-2 and influenza circulating this fall and winter,” he added.
Studies during the pandemic suggest that coinfection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus and another respiratory virus were either rare or nonexistent.
Dr. Schaffner said these findings align with his experience at Vanderbilt University, which is part of a CDC-sponsored network that tracks laboratory-confirmed RSV, flu, and COVID cases among people in the hospital. “Coinfections are, at least to date, very unusual.”
There needs to be an asterisk next to that, Dr. Schaffner added. “Looking back over the last 2 years, we’ve had very little influenza, and we’ve had curtailed RSV seasons. So there hasn’t been a whole lot of opportunity for dual infections to occur.
“So this year may be more revelatory as we go forward,” he said.
Future concerns
The future is uncertain, Dr. Messacar and colleagues wrote in The Lancet: “Crucially, the patterns of these returning viral outbreaks have been heterogeneous across locations, populations, and pathogens, making predictions and preparations challenging.”
Dr. Chin-Hong used a horse race analogy to illustrate the situation now and going forward. RSV is the front-running horse, and influenza is running behind but trying to catch up. “And then COVID is the dark horse. It’s trailing the race right now – but all these variants are giving the horse extra supplements.
“And the COVID horse is probably going to be very competitive with the front-runner,” he said.
“We’re just at the beginning of the race right now,” Dr. Chin-Hong said, “so that’s why we’re worried that these three [viruses] will be even more pronounced come later in the year.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
IRONMAN galvanizes case for IV iron repletion in heart failure
CHICAGO – Another major study appears to back the use of intravenous iron repletion in patients with heart failure (HF) and iron deficiency, strengthening largely consistent evidence, researchers say, that the treatment may improve symptoms and prevent some HF-related hospital admissions.
To be sure, the IRONMAN trial, which compared intravenous iron versus usual care in such patients – most with reduced ejection fraction and not hospitalized – failed to show a benefit for its primary endpoint. The 18% reduction in risk for HF hospitalization or cardiovascular (CV) death seen in the trial, however encouraging, can only be called a trend (P = .07).
But the intervention showed signs of benefit for some secondary endpoints, including quality of life scores, and hinted at such an effect on HF hospitalization. Risk for the latter endpoint dropped 20% (P = .085) over a median follow-up of 2.7 years.
The findings “build upon the other data we have that correcting iron deficiency can help improve well-being, and particularly reduce the risk of hospitalization, in a broad range of [HF] patients,” said Paul Kalra, MD, of the University of Glasgow and Portsmouth (England) Hospitals University NHS Trust.
The tested regimen “was well tolerated with no safety concerns” and offers “reassurance about the long-term safety” of the intravenous iron it used, ferric derisomaltose (MonoFerric), in patients with HF, Dr. Kalra said at a media briefing on the trial.
The remarks preceded his formal presentation of IRONMAN at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. Dr. Kalra is also lead author on the trial’s publication in The Lancet.
IRONMAN strengthens the base of evidence supporting intravenous iron in HF with iron deficiency, especially chronic HF in outpatients, Dr. Kalra and others said. It also supports efficacy for a form of intravenous iron not previously tested in a major HF trial.
Still, “the totality of data are now supporting intravenous iron per se,” regardless of the iron agent used, said Dr. Kalra. But ferric derisomaltose may have dosing advantages, he observed, “and we’ve now got these long-term safety data.”
The strongest prior support for intravenous iron in HF came from hospitalized patients who received it as ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject) and were followed only 12 months. That was in the AFFIRM-AHF trial, published 2 years ago, which also missed its primary endpoint – the same one used in IRONMAN. Some outcomes in the two trials were similar.
The risk for HF hospitalization or CV death for intravenous iron therapy, compared with usual care, in AFFIRM-AHF fell 21% (P = .059), missing significance but apparently driven by a 26% drop in risk for HF readmissions (P = .013). But neither that trial nor IRONMAN suggested a benefit for CV mortality on its own.
The COVID effect
In IRONMAN, Dr. Kalra said, usual care could include oral iron supplementation, which 17% of patients in the control group received. That could potentially have kept the intravenous iron group from making a better showing for the primary endpoint, he proposed.
And some iron doses and other treatments were missed by a substantial number of patients in both groups who entered the trial after the United Kingdom’s national lockdown in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, he observed. “Patients were not able to come into hospitals for research visits, or in fact when they were able, may not have wanted to.”
So, the group conducted a “prespecified” sensitivity analysis that excluded the 9% of patients enrolled by the end of March 2020, about the time of the first lockdown, and followed the remainder for another 6 months.
In that analysis, risk for HF hospitalization or CV death declined 24% in the intravenous iron group, a marginal but significant result (P = .047) that was dominated by an improvement in HF hospitalizations.
Effects on guidelines
The intravenous iron recommendations in the European HF guidelines refer only to ferric carboxymaltose without mentioning other forms, such as ferric derisomaltose, “but this is now a class effect given the similarities between AFFIRM-AHF and IRONMAN,” said Gregory D. Lewis, MD, Mass General Brigham, Boston, invited discussant for Dr. Kalra’s presentation at the AHA session.
“In the United States, we relegate IV iron to improvement in functional capacity as a comorbidity of heart failure. Perhaps this role will expand,” added Dr. Lewis, who is medical director of his center’s heart transplant program.
He also wondered aloud whether the purported clinical benefits of intravenous iron in HF patients with iron deficiency, not as yet supported by a significant primary-endpoint showing in one of the major trials, currently justify expansion of its use in practice.
“With the benefits of IV iron on exercise capacity and quality of life, and the safety of administering high doses of IV iron,” potentially reducing HF polypharmacy, he noted, “should we be considering IV iron more commonly for utilization in our patients even if we find that heart failure hospitalizations and mortality are only modestly improved?”
IRONMAN “asked whether there’s benefit to IV iron in the longer term,” Kiran Musunuru, MD, PhD, MPH, University of Pennsylvania,Philadelphia, observed at the media briefing. As the trial was reported, “that does in fact, seem to be the case,” said Dr. Musunuru, who was not involved in IRONMAN.
Therefore, he said, “this study reinforces the message that we should be routinely monitoring our heart failure patients for iron deficiency and supplementing them as needed.”
A commentary linked to the IRONMAN publication agreed. The trial “increases the evidence base for the treatment of iron deficiency with intravenous iron supplementation,” wrote the editorialists, led by Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College Hospital and School of Cardiovascular Sciences, London.
Patients with acute or chronic HF, iron deficiency, and reduced or mildly reduced ejection fractions “should be offered treatment with intravenous iron to reduce their risk of hospital admission for heart failure,” they concluded.
Mostly reduced-EF outpatients
The open-label, blinded-endpoint IRONMAN trial, conducted at 70 centers in the United Kingdom, entered adults with HF, ejection fractions 45% or lower within the previous 2 years, and iron deficiency defined as transferrin saturation less than 20% or serum ferritin levels below 100 mcg/L, the report states. They were either hospitalized for HF, had such a hospitalization within the past 6 months, or were outpatients with elevated natriuretic peptide levels; the third category accounted for two thirds of the trial population.
Of the 1,137 randomized patients, 569 were assigned to receive intravenous ferric derisomaltose at weight- and hemoglobin-adjusted dosages; 568 went to the usual-care group.
Those receiving intravenous iron visited the trial clinic 4 weeks later and then every 4 months. At those visits, they received a round of ferric derisomaltose if their ferritin levels were below 100 mcg/L, or 400 mcg/L or lower if transferrin saturation was below 25%, the published report states.
Mean scores on the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire improved by a marginally significant 3.33 points (P = .050) at 4 months in the intravenous iron group. The gain receded to a nonsignificant 2.57 points by 20 months (P = .23).
In COVID-related sensitivity analysis, the intravenous iron group showed a significant benefit for the primary endpoint and a trend for improved HF hospitalizations.
- HF hospitalization or CV death: RR, 0.76 (95% confidence interval, 0.58-1.00; P = .047)
- HF hospitalization: RR 0.76 (95% CI, 0.56-1.03; P = .077)
Fewer patients in the intravenous iron group experienced serious cardiac adverse events, 36% compared with 43% in for those on usual care, P = .016.
The recently updated European Society of Cardiology guidelines for HF made it a class 1 recommendation to assess iron status in every patient, Kalra observed. “It doesn›t specify how frequently, but I think we should be thinking about every 4-6 months.”
Dr. Kalra disclosed receiving research grants from Pharmacosmos; and consulting or lecturing for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacosmos, Servier, and Vifor Pharma. Dr. Musunuru disclosed significant ownership interest in Verve Therapeutics and Variant Bio. Dr. Lewis disclosed relationships with NXT, American Regent, and RIVUS; and receiving research grants from Cytokinetics and Amgen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Another major study appears to back the use of intravenous iron repletion in patients with heart failure (HF) and iron deficiency, strengthening largely consistent evidence, researchers say, that the treatment may improve symptoms and prevent some HF-related hospital admissions.
To be sure, the IRONMAN trial, which compared intravenous iron versus usual care in such patients – most with reduced ejection fraction and not hospitalized – failed to show a benefit for its primary endpoint. The 18% reduction in risk for HF hospitalization or cardiovascular (CV) death seen in the trial, however encouraging, can only be called a trend (P = .07).
But the intervention showed signs of benefit for some secondary endpoints, including quality of life scores, and hinted at such an effect on HF hospitalization. Risk for the latter endpoint dropped 20% (P = .085) over a median follow-up of 2.7 years.
The findings “build upon the other data we have that correcting iron deficiency can help improve well-being, and particularly reduce the risk of hospitalization, in a broad range of [HF] patients,” said Paul Kalra, MD, of the University of Glasgow and Portsmouth (England) Hospitals University NHS Trust.
The tested regimen “was well tolerated with no safety concerns” and offers “reassurance about the long-term safety” of the intravenous iron it used, ferric derisomaltose (MonoFerric), in patients with HF, Dr. Kalra said at a media briefing on the trial.
The remarks preceded his formal presentation of IRONMAN at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. Dr. Kalra is also lead author on the trial’s publication in The Lancet.
IRONMAN strengthens the base of evidence supporting intravenous iron in HF with iron deficiency, especially chronic HF in outpatients, Dr. Kalra and others said. It also supports efficacy for a form of intravenous iron not previously tested in a major HF trial.
Still, “the totality of data are now supporting intravenous iron per se,” regardless of the iron agent used, said Dr. Kalra. But ferric derisomaltose may have dosing advantages, he observed, “and we’ve now got these long-term safety data.”
The strongest prior support for intravenous iron in HF came from hospitalized patients who received it as ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject) and were followed only 12 months. That was in the AFFIRM-AHF trial, published 2 years ago, which also missed its primary endpoint – the same one used in IRONMAN. Some outcomes in the two trials were similar.
The risk for HF hospitalization or CV death for intravenous iron therapy, compared with usual care, in AFFIRM-AHF fell 21% (P = .059), missing significance but apparently driven by a 26% drop in risk for HF readmissions (P = .013). But neither that trial nor IRONMAN suggested a benefit for CV mortality on its own.
The COVID effect
In IRONMAN, Dr. Kalra said, usual care could include oral iron supplementation, which 17% of patients in the control group received. That could potentially have kept the intravenous iron group from making a better showing for the primary endpoint, he proposed.
And some iron doses and other treatments were missed by a substantial number of patients in both groups who entered the trial after the United Kingdom’s national lockdown in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, he observed. “Patients were not able to come into hospitals for research visits, or in fact when they were able, may not have wanted to.”
So, the group conducted a “prespecified” sensitivity analysis that excluded the 9% of patients enrolled by the end of March 2020, about the time of the first lockdown, and followed the remainder for another 6 months.
In that analysis, risk for HF hospitalization or CV death declined 24% in the intravenous iron group, a marginal but significant result (P = .047) that was dominated by an improvement in HF hospitalizations.
Effects on guidelines
The intravenous iron recommendations in the European HF guidelines refer only to ferric carboxymaltose without mentioning other forms, such as ferric derisomaltose, “but this is now a class effect given the similarities between AFFIRM-AHF and IRONMAN,” said Gregory D. Lewis, MD, Mass General Brigham, Boston, invited discussant for Dr. Kalra’s presentation at the AHA session.
“In the United States, we relegate IV iron to improvement in functional capacity as a comorbidity of heart failure. Perhaps this role will expand,” added Dr. Lewis, who is medical director of his center’s heart transplant program.
He also wondered aloud whether the purported clinical benefits of intravenous iron in HF patients with iron deficiency, not as yet supported by a significant primary-endpoint showing in one of the major trials, currently justify expansion of its use in practice.
“With the benefits of IV iron on exercise capacity and quality of life, and the safety of administering high doses of IV iron,” potentially reducing HF polypharmacy, he noted, “should we be considering IV iron more commonly for utilization in our patients even if we find that heart failure hospitalizations and mortality are only modestly improved?”
IRONMAN “asked whether there’s benefit to IV iron in the longer term,” Kiran Musunuru, MD, PhD, MPH, University of Pennsylvania,Philadelphia, observed at the media briefing. As the trial was reported, “that does in fact, seem to be the case,” said Dr. Musunuru, who was not involved in IRONMAN.
Therefore, he said, “this study reinforces the message that we should be routinely monitoring our heart failure patients for iron deficiency and supplementing them as needed.”
A commentary linked to the IRONMAN publication agreed. The trial “increases the evidence base for the treatment of iron deficiency with intravenous iron supplementation,” wrote the editorialists, led by Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College Hospital and School of Cardiovascular Sciences, London.
Patients with acute or chronic HF, iron deficiency, and reduced or mildly reduced ejection fractions “should be offered treatment with intravenous iron to reduce their risk of hospital admission for heart failure,” they concluded.
Mostly reduced-EF outpatients
The open-label, blinded-endpoint IRONMAN trial, conducted at 70 centers in the United Kingdom, entered adults with HF, ejection fractions 45% or lower within the previous 2 years, and iron deficiency defined as transferrin saturation less than 20% or serum ferritin levels below 100 mcg/L, the report states. They were either hospitalized for HF, had such a hospitalization within the past 6 months, or were outpatients with elevated natriuretic peptide levels; the third category accounted for two thirds of the trial population.
Of the 1,137 randomized patients, 569 were assigned to receive intravenous ferric derisomaltose at weight- and hemoglobin-adjusted dosages; 568 went to the usual-care group.
Those receiving intravenous iron visited the trial clinic 4 weeks later and then every 4 months. At those visits, they received a round of ferric derisomaltose if their ferritin levels were below 100 mcg/L, or 400 mcg/L or lower if transferrin saturation was below 25%, the published report states.
Mean scores on the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire improved by a marginally significant 3.33 points (P = .050) at 4 months in the intravenous iron group. The gain receded to a nonsignificant 2.57 points by 20 months (P = .23).
In COVID-related sensitivity analysis, the intravenous iron group showed a significant benefit for the primary endpoint and a trend for improved HF hospitalizations.
- HF hospitalization or CV death: RR, 0.76 (95% confidence interval, 0.58-1.00; P = .047)
- HF hospitalization: RR 0.76 (95% CI, 0.56-1.03; P = .077)
Fewer patients in the intravenous iron group experienced serious cardiac adverse events, 36% compared with 43% in for those on usual care, P = .016.
The recently updated European Society of Cardiology guidelines for HF made it a class 1 recommendation to assess iron status in every patient, Kalra observed. “It doesn›t specify how frequently, but I think we should be thinking about every 4-6 months.”
Dr. Kalra disclosed receiving research grants from Pharmacosmos; and consulting or lecturing for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacosmos, Servier, and Vifor Pharma. Dr. Musunuru disclosed significant ownership interest in Verve Therapeutics and Variant Bio. Dr. Lewis disclosed relationships with NXT, American Regent, and RIVUS; and receiving research grants from Cytokinetics and Amgen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Another major study appears to back the use of intravenous iron repletion in patients with heart failure (HF) and iron deficiency, strengthening largely consistent evidence, researchers say, that the treatment may improve symptoms and prevent some HF-related hospital admissions.
To be sure, the IRONMAN trial, which compared intravenous iron versus usual care in such patients – most with reduced ejection fraction and not hospitalized – failed to show a benefit for its primary endpoint. The 18% reduction in risk for HF hospitalization or cardiovascular (CV) death seen in the trial, however encouraging, can only be called a trend (P = .07).
But the intervention showed signs of benefit for some secondary endpoints, including quality of life scores, and hinted at such an effect on HF hospitalization. Risk for the latter endpoint dropped 20% (P = .085) over a median follow-up of 2.7 years.
The findings “build upon the other data we have that correcting iron deficiency can help improve well-being, and particularly reduce the risk of hospitalization, in a broad range of [HF] patients,” said Paul Kalra, MD, of the University of Glasgow and Portsmouth (England) Hospitals University NHS Trust.
The tested regimen “was well tolerated with no safety concerns” and offers “reassurance about the long-term safety” of the intravenous iron it used, ferric derisomaltose (MonoFerric), in patients with HF, Dr. Kalra said at a media briefing on the trial.
The remarks preceded his formal presentation of IRONMAN at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. Dr. Kalra is also lead author on the trial’s publication in The Lancet.
IRONMAN strengthens the base of evidence supporting intravenous iron in HF with iron deficiency, especially chronic HF in outpatients, Dr. Kalra and others said. It also supports efficacy for a form of intravenous iron not previously tested in a major HF trial.
Still, “the totality of data are now supporting intravenous iron per se,” regardless of the iron agent used, said Dr. Kalra. But ferric derisomaltose may have dosing advantages, he observed, “and we’ve now got these long-term safety data.”
The strongest prior support for intravenous iron in HF came from hospitalized patients who received it as ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject) and were followed only 12 months. That was in the AFFIRM-AHF trial, published 2 years ago, which also missed its primary endpoint – the same one used in IRONMAN. Some outcomes in the two trials were similar.
The risk for HF hospitalization or CV death for intravenous iron therapy, compared with usual care, in AFFIRM-AHF fell 21% (P = .059), missing significance but apparently driven by a 26% drop in risk for HF readmissions (P = .013). But neither that trial nor IRONMAN suggested a benefit for CV mortality on its own.
The COVID effect
In IRONMAN, Dr. Kalra said, usual care could include oral iron supplementation, which 17% of patients in the control group received. That could potentially have kept the intravenous iron group from making a better showing for the primary endpoint, he proposed.
And some iron doses and other treatments were missed by a substantial number of patients in both groups who entered the trial after the United Kingdom’s national lockdown in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, he observed. “Patients were not able to come into hospitals for research visits, or in fact when they were able, may not have wanted to.”
So, the group conducted a “prespecified” sensitivity analysis that excluded the 9% of patients enrolled by the end of March 2020, about the time of the first lockdown, and followed the remainder for another 6 months.
In that analysis, risk for HF hospitalization or CV death declined 24% in the intravenous iron group, a marginal but significant result (P = .047) that was dominated by an improvement in HF hospitalizations.
Effects on guidelines
The intravenous iron recommendations in the European HF guidelines refer only to ferric carboxymaltose without mentioning other forms, such as ferric derisomaltose, “but this is now a class effect given the similarities between AFFIRM-AHF and IRONMAN,” said Gregory D. Lewis, MD, Mass General Brigham, Boston, invited discussant for Dr. Kalra’s presentation at the AHA session.
“In the United States, we relegate IV iron to improvement in functional capacity as a comorbidity of heart failure. Perhaps this role will expand,” added Dr. Lewis, who is medical director of his center’s heart transplant program.
He also wondered aloud whether the purported clinical benefits of intravenous iron in HF patients with iron deficiency, not as yet supported by a significant primary-endpoint showing in one of the major trials, currently justify expansion of its use in practice.
“With the benefits of IV iron on exercise capacity and quality of life, and the safety of administering high doses of IV iron,” potentially reducing HF polypharmacy, he noted, “should we be considering IV iron more commonly for utilization in our patients even if we find that heart failure hospitalizations and mortality are only modestly improved?”
IRONMAN “asked whether there’s benefit to IV iron in the longer term,” Kiran Musunuru, MD, PhD, MPH, University of Pennsylvania,Philadelphia, observed at the media briefing. As the trial was reported, “that does in fact, seem to be the case,” said Dr. Musunuru, who was not involved in IRONMAN.
Therefore, he said, “this study reinforces the message that we should be routinely monitoring our heart failure patients for iron deficiency and supplementing them as needed.”
A commentary linked to the IRONMAN publication agreed. The trial “increases the evidence base for the treatment of iron deficiency with intravenous iron supplementation,” wrote the editorialists, led by Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College Hospital and School of Cardiovascular Sciences, London.
Patients with acute or chronic HF, iron deficiency, and reduced or mildly reduced ejection fractions “should be offered treatment with intravenous iron to reduce their risk of hospital admission for heart failure,” they concluded.
Mostly reduced-EF outpatients
The open-label, blinded-endpoint IRONMAN trial, conducted at 70 centers in the United Kingdom, entered adults with HF, ejection fractions 45% or lower within the previous 2 years, and iron deficiency defined as transferrin saturation less than 20% or serum ferritin levels below 100 mcg/L, the report states. They were either hospitalized for HF, had such a hospitalization within the past 6 months, or were outpatients with elevated natriuretic peptide levels; the third category accounted for two thirds of the trial population.
Of the 1,137 randomized patients, 569 were assigned to receive intravenous ferric derisomaltose at weight- and hemoglobin-adjusted dosages; 568 went to the usual-care group.
Those receiving intravenous iron visited the trial clinic 4 weeks later and then every 4 months. At those visits, they received a round of ferric derisomaltose if their ferritin levels were below 100 mcg/L, or 400 mcg/L or lower if transferrin saturation was below 25%, the published report states.
Mean scores on the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire improved by a marginally significant 3.33 points (P = .050) at 4 months in the intravenous iron group. The gain receded to a nonsignificant 2.57 points by 20 months (P = .23).
In COVID-related sensitivity analysis, the intravenous iron group showed a significant benefit for the primary endpoint and a trend for improved HF hospitalizations.
- HF hospitalization or CV death: RR, 0.76 (95% confidence interval, 0.58-1.00; P = .047)
- HF hospitalization: RR 0.76 (95% CI, 0.56-1.03; P = .077)
Fewer patients in the intravenous iron group experienced serious cardiac adverse events, 36% compared with 43% in for those on usual care, P = .016.
The recently updated European Society of Cardiology guidelines for HF made it a class 1 recommendation to assess iron status in every patient, Kalra observed. “It doesn›t specify how frequently, but I think we should be thinking about every 4-6 months.”
Dr. Kalra disclosed receiving research grants from Pharmacosmos; and consulting or lecturing for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacosmos, Servier, and Vifor Pharma. Dr. Musunuru disclosed significant ownership interest in Verve Therapeutics and Variant Bio. Dr. Lewis disclosed relationships with NXT, American Regent, and RIVUS; and receiving research grants from Cytokinetics and Amgen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AHA 2022
Laser pioneer reflects on the future of robots in dermatology
In the opinion of R. Rox Anderson, MD, it’s only a matter of time before true robots make further inroads in dermatology.
“We humans just can’t do everything perfectly,” Dr. Anderson, a dermatologist who directs the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “We have limited speed and special accuracy and are not good at repetitive tasks. We can’t see in the UV or infrared, and we’re qualitative, not quantitative. ... We’re good at high-level visual assessment.”
During a presentation at the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center, he distinguished between robotics and true robots. A prime example of robotics in medicine is the Da Vinci Surgical System in which a human user “is controlling every movement of this device with capabilities that humans don’t have, such as fine movement and high magnification of imaging,” said Dr. Anderson, who conceived and developed many of the nonscarring laser treatments now widely used in dermatology. “In the military, we have drone aircraft. The pilot is perhaps thousands of miles away; it’s still run by a human being in every way.”
By contrast, true robots are devices in which a human being programs the rules for action but the action itself is not exactly predictable. Artificial intelligence enables robots to perform certain tasks. “If you look at an Amazon warehouse, there’s barely anyone there; robots are packing and unpacking the shelves,” Dr. Anderson said.
Currently, he said, one true robot exists in dermatology: the Food and Drug Administration–cleared ARTAS Robotic Hair Restoration System, which precisely dissects follicular units from the donor area and eliminates the potential for human error. The device “extracts single follicular units from the occipital scalp and makes them available to the surgeon to do an artistic human job of implanting them in the frontal scalp,” Dr. Anderson said.
He predicts that a Mohs surgery robot with image-guided laser ablation would “launch a sea change in the whole field of surgical oncology, and I believe we are in a good position to do it. Everything for this is now sitting on the shelf and it’s unbelievable to me that a company hasn’t accomplished it yet.”
He would also like to see a true laser robot for surgery of tumors that would enable clinicians to download an app for their existing laser instead of having to buy a new device. Currently, “it takes about a half second to make a good optical coherence tomography image of basal cell carcinoma,” he said. “That image could be used for real-time robotic human control of, say, a laser to extirpate the tumor.”
Dr. Anderson’s “wish list” of applications for treatment with a robotic fractional laser includes those that target the sweat glands, sebaceous glands, nerves, inflammatory cells, white hair, blood vessels, lymphatics, hair, tumors, nevi, cysts, and surface contour. “It might be possible to have one software-programmable laser robot for many different applications in dermatology,” he added.
Dr. Anderson reported having received research funding and/or consulting fees from numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
In the opinion of R. Rox Anderson, MD, it’s only a matter of time before true robots make further inroads in dermatology.
“We humans just can’t do everything perfectly,” Dr. Anderson, a dermatologist who directs the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “We have limited speed and special accuracy and are not good at repetitive tasks. We can’t see in the UV or infrared, and we’re qualitative, not quantitative. ... We’re good at high-level visual assessment.”
During a presentation at the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center, he distinguished between robotics and true robots. A prime example of robotics in medicine is the Da Vinci Surgical System in which a human user “is controlling every movement of this device with capabilities that humans don’t have, such as fine movement and high magnification of imaging,” said Dr. Anderson, who conceived and developed many of the nonscarring laser treatments now widely used in dermatology. “In the military, we have drone aircraft. The pilot is perhaps thousands of miles away; it’s still run by a human being in every way.”
By contrast, true robots are devices in which a human being programs the rules for action but the action itself is not exactly predictable. Artificial intelligence enables robots to perform certain tasks. “If you look at an Amazon warehouse, there’s barely anyone there; robots are packing and unpacking the shelves,” Dr. Anderson said.
Currently, he said, one true robot exists in dermatology: the Food and Drug Administration–cleared ARTAS Robotic Hair Restoration System, which precisely dissects follicular units from the donor area and eliminates the potential for human error. The device “extracts single follicular units from the occipital scalp and makes them available to the surgeon to do an artistic human job of implanting them in the frontal scalp,” Dr. Anderson said.
He predicts that a Mohs surgery robot with image-guided laser ablation would “launch a sea change in the whole field of surgical oncology, and I believe we are in a good position to do it. Everything for this is now sitting on the shelf and it’s unbelievable to me that a company hasn’t accomplished it yet.”
He would also like to see a true laser robot for surgery of tumors that would enable clinicians to download an app for their existing laser instead of having to buy a new device. Currently, “it takes about a half second to make a good optical coherence tomography image of basal cell carcinoma,” he said. “That image could be used for real-time robotic human control of, say, a laser to extirpate the tumor.”
Dr. Anderson’s “wish list” of applications for treatment with a robotic fractional laser includes those that target the sweat glands, sebaceous glands, nerves, inflammatory cells, white hair, blood vessels, lymphatics, hair, tumors, nevi, cysts, and surface contour. “It might be possible to have one software-programmable laser robot for many different applications in dermatology,” he added.
Dr. Anderson reported having received research funding and/or consulting fees from numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
In the opinion of R. Rox Anderson, MD, it’s only a matter of time before true robots make further inroads in dermatology.
“We humans just can’t do everything perfectly,” Dr. Anderson, a dermatologist who directs the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “We have limited speed and special accuracy and are not good at repetitive tasks. We can’t see in the UV or infrared, and we’re qualitative, not quantitative. ... We’re good at high-level visual assessment.”
During a presentation at the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center, he distinguished between robotics and true robots. A prime example of robotics in medicine is the Da Vinci Surgical System in which a human user “is controlling every movement of this device with capabilities that humans don’t have, such as fine movement and high magnification of imaging,” said Dr. Anderson, who conceived and developed many of the nonscarring laser treatments now widely used in dermatology. “In the military, we have drone aircraft. The pilot is perhaps thousands of miles away; it’s still run by a human being in every way.”
By contrast, true robots are devices in which a human being programs the rules for action but the action itself is not exactly predictable. Artificial intelligence enables robots to perform certain tasks. “If you look at an Amazon warehouse, there’s barely anyone there; robots are packing and unpacking the shelves,” Dr. Anderson said.
Currently, he said, one true robot exists in dermatology: the Food and Drug Administration–cleared ARTAS Robotic Hair Restoration System, which precisely dissects follicular units from the donor area and eliminates the potential for human error. The device “extracts single follicular units from the occipital scalp and makes them available to the surgeon to do an artistic human job of implanting them in the frontal scalp,” Dr. Anderson said.
He predicts that a Mohs surgery robot with image-guided laser ablation would “launch a sea change in the whole field of surgical oncology, and I believe we are in a good position to do it. Everything for this is now sitting on the shelf and it’s unbelievable to me that a company hasn’t accomplished it yet.”
He would also like to see a true laser robot for surgery of tumors that would enable clinicians to download an app for their existing laser instead of having to buy a new device. Currently, “it takes about a half second to make a good optical coherence tomography image of basal cell carcinoma,” he said. “That image could be used for real-time robotic human control of, say, a laser to extirpate the tumor.”
Dr. Anderson’s “wish list” of applications for treatment with a robotic fractional laser includes those that target the sweat glands, sebaceous glands, nerves, inflammatory cells, white hair, blood vessels, lymphatics, hair, tumors, nevi, cysts, and surface contour. “It might be possible to have one software-programmable laser robot for many different applications in dermatology,” he added.
Dr. Anderson reported having received research funding and/or consulting fees from numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE