User login
Policy in Clinical Practice: Hospital Price Transparency
CLINICAL SCENARIO
A 59-year-old man is observed in the hospital for substernal chest pain initially concerning for angina. Serial troponin testing is negative, and based on additional history of intermittent dysphagia, an elective upper endoscopy is recommended after discharge. The patient does not have health insurance and expresses anxiety about the cost of endoscopy. He asks how he could compare the costs at different hospitals. How do federal price transparency rules assist the hospitalist in addressing this patient’s question?
BACKGROUND AND HISTORY
Healthcare costs continue to rise in the United States despite mounting concerns about wasteful spending and unaffordability.1 One contributor is a lack of price transparency.2 In theory, price transparency allows individuals to shop for services, spurring competition and lower prices. However, healthcare prices have historically been opaque to both physicians and patients; unlike other licensed professionals who provide clients estimates for their work (eg, lawyers, electricians), physicians are rarely able to offer patients real-time insight or guidance about costs, which most patients discover only when the bill arrives. The situation is particularly problematic for patients who bear higher out-of-pocket costs, such as the uninsured or those with high-deductible health plans.3
Decades of work to improve healthcare price transparency have unfortunately borne little fruit. Multiple states and organizations have attempted to disseminate price information on comparison websites.4 These efforts only modestly reduced some prices, with benefits confined to elective, single-episode, commodifiable services such as magnetic resonance imaging scans.5 The Affordable Care Act required hospitals to publish standard charges, also called a chargemaster (Table).6 However, chargemaster fees are notoriously inflated and inaccessible at the point of service, undercutting transparency.

POLICY IN CLINICAL PRACTICE
Beginning January 2021, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) required all hospitals to publish negotiated prices—including payor-specific negotiated charges—for 300 “shoppable services” (Table).6 The list must include 70 common CMS-specified services, such as a basic metabolic panel, upper endoscopy, and prostate biopsy, as well as another 230 services that each hospital determines relevant to its patient population.
In circumstances where hospitals have negotiated different prices for a service, they must list each third-party payor and their payor-specific charge. The information must be prominently displayed, accessible without requiring the patient to enter personal information, and provided in a machine-readable file. CMS may impose a $300 daily penalty on hospitals failing to comply with the policy. Of note, the policy does not apply to clinics or ambulatory surgery centers.
As more hospitals share data, this policy will directly benefit both patients and physicians. It can benefit patients with the time, foresight, and ability to search for the lowest price for shoppable services. Other patients may also benefit indirectly, to the extent that insurers and other purchasers apply this information to negotiate lower and more uniform prices. Decreased price variation may also encourage hospitals to compete on quality to distinguish the value of their services. Hospitalists could benefit through the ability to directly help patients locate price information.
Despite these potential benefits, the policy has limitations. Price information about shoppable services is most useful for discharge planning, and other solutions are needed to address transparency before and during unplanned admissions. Patients who prioritize continuity with a hospital or physician may be less price sensitive, particularly for more complex services. Patients with commercial insurance may be shielded from cost considerations and personal incentives to comparison shop. Interpreting hospitals’ estimates remains difficult, as it can be unclear if professional fees are included or if certain prices are offered to outpatients.7 Price information is not accompanied by corresponding quality data. Additionally, price transparency may also fail to lower prices in heavily concentrated payor or provider markets, and it remains unknown whether some providers may actually raise prices after learning about higher rates negotiated by competitors.8,9
Another issue is hospital participation. Early evidence suggests that most hospitals have not complied with the letter or spirit of the regulation.
Despite its limitations, this policy represents a meaningful advance for healthcare competition and patient empowerment. Additionally, it signals federal willingness to address the lack of price transparency as a source of widespread patient and clinician frustration—a commitment that will be needed to sustain this policy and implement additional measures in the future.
COMMENTARY AND RECOMMENDATIONS
CMS could consider five steps to augment the policy and maximize transparency and value for patients.
First, CMS could consider increasing daily nonparticipation penalties. Hospitals, particularly those in areas with less competition, have less incentive to participate given meager current penalties. Because the magnitude needed to compel action remains unknown, CMS could gradually escalate penalties over time until there is broader participation across hospitals.
Second, policymakers could aggregate price information centrally, organize the data around patients’ clinical scenarios, and advertise its availability. Currently, this information is scattered and time-consuming for hospitalists and patients to gather for decision-making. Additionally, CMS could encourage the development of third-party tools that aggregate and analyze machine-readable price data or require that prices be posted at the point of service.
Third, CMS could revise the policy to include quality as well as price information. Price alone does not offer a full enough picture of what consumers can expect from hospitals for shoppable services. Pairing price and quality information is better aligned to addressing costs in the context of value, rather than cost-cutting for its own purposes.
Fourth, over time, CMS could expand the list of services and sites required to report (eg, clinics and ambulatory surgical centers as well as hospitals).
Fifth, CMS rule-makers could set reporting standards and contextualize price information in common clinical scenarios. Patients may have difficulty shopping for complex healthcare services without understanding how they apply in different clinical situations. Decision-making would also be aided by reporting standards—for instance, for how prices are displayed and whether they include certain fees (eg, professional fees, pathology studies).
WHAT SHOULD I TELL MY PATIENT?
Hospitalists planning follow-up care should inform patients that price information is increasingly available and encourage them to search on the internet or contact hospital billing offices to request information (eg, discounted cash prices and minimum negotiated charges) before obtaining elective services after discharge. Hospitalists can also encourage patients to discuss shoppable services with their primary care physicians to understand the clinical context and make high-value decisions. Hospitalists who wish to build communication skills discussing costs with patients can increasingly find resources for these conversations and request that prices be displayed in the electronic health record for this purpose.13,14 As conversations occur, hospitalists should seek to understand other factors, such as convenience and continuity relationships, that might influence choices.
CONCLUSIONS
Starting in 2021, CMS policy requires that hospitals report prices for services such as the endoscopy recommended for the patient in the scenario. Though the policy gives patients new hope for greater transparency and better prices, additional steps are needed to help patients and hospitalists achieve these benefits.
1. Shrank WH, Rogstad TL, Parekh N. Waste in the US health care system: estimated costs and potential for savings. JAMA. 2019;322(15):1501-1509. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.13978
2. Wetzell S. Transparency: a needed step towards health care affordability. American Health Policy Institute. March 2014. Accessed August 26, 2021. https://www.americanhealthpolicy.org/Content/documents/resources/Transparency%20Study%201%20-%20The%20Need%20for%20Health%20Care%20Transparency.pdf
3. Mehrotra A, Dean KM, Sinaiko AD, Sood N. Americans support price shopping for health care, but few actually seek out price information. Health Aff (Millwood). 2017;36(8):1392-1400. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2016.1471
4. Kullgren JT, Duey KA, Werner RM. A census of state health care price transparency websites. JAMA. 2013;309(23):2437-2438. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.6557
5. Brown ZY. Equilibrium effects of health care price information. Rev Econ Stat. 2019;101(4):699-712. https://doi.org/10.1162/rest_a_00765
6. Medicare and Medicaid Programs: CY 2020 hospital outpatient PPS policy changes and payment rates and ambulatory surgical center payment system policy changes and payment rates. Price transparency requirements for hospitals to make standard charges public. 45 CFR §180.20 (2019).
7. Kurani N, Ramirez G, Hudman J, Cox C, Kamal R. Early results from federal price transparency rule show difficulty in estimating the cost of care. Peterson-Kaiser Family Foundation. April 9, 2021. Accessed August 26, 2021. https://www.healthsystemtracker.org/brief/early-results-from-federal-price-transparency-rule-show-difficultly-in-estimating-the-cost-of-care/
8. Miller BJ, Mandelberg MC, Griffith NC, Ehrenfeld JM. Price transparency: empowering patient choice and promoting provider competition. J Med Syst. 2020;44(4):80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-020-01553-2
9. Glied S. Price transparency–promise and peril. JAMA. 2021;325(15):1496-1497. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.4640
10. Haque W, Ahmadzada M, Allahrakha H, Haque E, Hsiehchen D. Transparency, accessibility, and variability of US hospital price data. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(5):e2110109. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10109
11. Henderson M, Mouslim MC. Low compliance from big hospitals on CMS’s hospital price transparency rule. Health Affairs Blog. March 16, 2021. Accessed August 26, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1377/hblog20210311.899634
12. McGinty T, Wilde Mathews A, Evans M. Hospitals hide pricing data from search results. The Wall Street Journal. March 22, 2021. Accessed August 26, 2021. https://www.wsj.com/articles/hospitals-hide-pricing-data-from-search-results-11616405402
13. Dine CJ, Masi D, Smith CD. Tools to help overcome barriers to cost-of-care conversations. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170(9 suppl):S36-S38. https://doi.org/10.7326/M19-0778
14. Miller BJ, Slota JM, Ehrenfeld JM. Redefining the physician’s role in cost-conscious care: the potential role of the electronic health record. JAMA. 2019;322(8):721-722. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.9114
CLINICAL SCENARIO
A 59-year-old man is observed in the hospital for substernal chest pain initially concerning for angina. Serial troponin testing is negative, and based on additional history of intermittent dysphagia, an elective upper endoscopy is recommended after discharge. The patient does not have health insurance and expresses anxiety about the cost of endoscopy. He asks how he could compare the costs at different hospitals. How do federal price transparency rules assist the hospitalist in addressing this patient’s question?
BACKGROUND AND HISTORY
Healthcare costs continue to rise in the United States despite mounting concerns about wasteful spending and unaffordability.1 One contributor is a lack of price transparency.2 In theory, price transparency allows individuals to shop for services, spurring competition and lower prices. However, healthcare prices have historically been opaque to both physicians and patients; unlike other licensed professionals who provide clients estimates for their work (eg, lawyers, electricians), physicians are rarely able to offer patients real-time insight or guidance about costs, which most patients discover only when the bill arrives. The situation is particularly problematic for patients who bear higher out-of-pocket costs, such as the uninsured or those with high-deductible health plans.3
Decades of work to improve healthcare price transparency have unfortunately borne little fruit. Multiple states and organizations have attempted to disseminate price information on comparison websites.4 These efforts only modestly reduced some prices, with benefits confined to elective, single-episode, commodifiable services such as magnetic resonance imaging scans.5 The Affordable Care Act required hospitals to publish standard charges, also called a chargemaster (Table).6 However, chargemaster fees are notoriously inflated and inaccessible at the point of service, undercutting transparency.

POLICY IN CLINICAL PRACTICE
Beginning January 2021, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) required all hospitals to publish negotiated prices—including payor-specific negotiated charges—for 300 “shoppable services” (Table).6 The list must include 70 common CMS-specified services, such as a basic metabolic panel, upper endoscopy, and prostate biopsy, as well as another 230 services that each hospital determines relevant to its patient population.
In circumstances where hospitals have negotiated different prices for a service, they must list each third-party payor and their payor-specific charge. The information must be prominently displayed, accessible without requiring the patient to enter personal information, and provided in a machine-readable file. CMS may impose a $300 daily penalty on hospitals failing to comply with the policy. Of note, the policy does not apply to clinics or ambulatory surgery centers.
As more hospitals share data, this policy will directly benefit both patients and physicians. It can benefit patients with the time, foresight, and ability to search for the lowest price for shoppable services. Other patients may also benefit indirectly, to the extent that insurers and other purchasers apply this information to negotiate lower and more uniform prices. Decreased price variation may also encourage hospitals to compete on quality to distinguish the value of their services. Hospitalists could benefit through the ability to directly help patients locate price information.
Despite these potential benefits, the policy has limitations. Price information about shoppable services is most useful for discharge planning, and other solutions are needed to address transparency before and during unplanned admissions. Patients who prioritize continuity with a hospital or physician may be less price sensitive, particularly for more complex services. Patients with commercial insurance may be shielded from cost considerations and personal incentives to comparison shop. Interpreting hospitals’ estimates remains difficult, as it can be unclear if professional fees are included or if certain prices are offered to outpatients.7 Price information is not accompanied by corresponding quality data. Additionally, price transparency may also fail to lower prices in heavily concentrated payor or provider markets, and it remains unknown whether some providers may actually raise prices after learning about higher rates negotiated by competitors.8,9
Another issue is hospital participation. Early evidence suggests that most hospitals have not complied with the letter or spirit of the regulation.
Despite its limitations, this policy represents a meaningful advance for healthcare competition and patient empowerment. Additionally, it signals federal willingness to address the lack of price transparency as a source of widespread patient and clinician frustration—a commitment that will be needed to sustain this policy and implement additional measures in the future.
COMMENTARY AND RECOMMENDATIONS
CMS could consider five steps to augment the policy and maximize transparency and value for patients.
First, CMS could consider increasing daily nonparticipation penalties. Hospitals, particularly those in areas with less competition, have less incentive to participate given meager current penalties. Because the magnitude needed to compel action remains unknown, CMS could gradually escalate penalties over time until there is broader participation across hospitals.
Second, policymakers could aggregate price information centrally, organize the data around patients’ clinical scenarios, and advertise its availability. Currently, this information is scattered and time-consuming for hospitalists and patients to gather for decision-making. Additionally, CMS could encourage the development of third-party tools that aggregate and analyze machine-readable price data or require that prices be posted at the point of service.
Third, CMS could revise the policy to include quality as well as price information. Price alone does not offer a full enough picture of what consumers can expect from hospitals for shoppable services. Pairing price and quality information is better aligned to addressing costs in the context of value, rather than cost-cutting for its own purposes.
Fourth, over time, CMS could expand the list of services and sites required to report (eg, clinics and ambulatory surgical centers as well as hospitals).
Fifth, CMS rule-makers could set reporting standards and contextualize price information in common clinical scenarios. Patients may have difficulty shopping for complex healthcare services without understanding how they apply in different clinical situations. Decision-making would also be aided by reporting standards—for instance, for how prices are displayed and whether they include certain fees (eg, professional fees, pathology studies).
WHAT SHOULD I TELL MY PATIENT?
Hospitalists planning follow-up care should inform patients that price information is increasingly available and encourage them to search on the internet or contact hospital billing offices to request information (eg, discounted cash prices and minimum negotiated charges) before obtaining elective services after discharge. Hospitalists can also encourage patients to discuss shoppable services with their primary care physicians to understand the clinical context and make high-value decisions. Hospitalists who wish to build communication skills discussing costs with patients can increasingly find resources for these conversations and request that prices be displayed in the electronic health record for this purpose.13,14 As conversations occur, hospitalists should seek to understand other factors, such as convenience and continuity relationships, that might influence choices.
CONCLUSIONS
Starting in 2021, CMS policy requires that hospitals report prices for services such as the endoscopy recommended for the patient in the scenario. Though the policy gives patients new hope for greater transparency and better prices, additional steps are needed to help patients and hospitalists achieve these benefits.
CLINICAL SCENARIO
A 59-year-old man is observed in the hospital for substernal chest pain initially concerning for angina. Serial troponin testing is negative, and based on additional history of intermittent dysphagia, an elective upper endoscopy is recommended after discharge. The patient does not have health insurance and expresses anxiety about the cost of endoscopy. He asks how he could compare the costs at different hospitals. How do federal price transparency rules assist the hospitalist in addressing this patient’s question?
BACKGROUND AND HISTORY
Healthcare costs continue to rise in the United States despite mounting concerns about wasteful spending and unaffordability.1 One contributor is a lack of price transparency.2 In theory, price transparency allows individuals to shop for services, spurring competition and lower prices. However, healthcare prices have historically been opaque to both physicians and patients; unlike other licensed professionals who provide clients estimates for their work (eg, lawyers, electricians), physicians are rarely able to offer patients real-time insight or guidance about costs, which most patients discover only when the bill arrives. The situation is particularly problematic for patients who bear higher out-of-pocket costs, such as the uninsured or those with high-deductible health plans.3
Decades of work to improve healthcare price transparency have unfortunately borne little fruit. Multiple states and organizations have attempted to disseminate price information on comparison websites.4 These efforts only modestly reduced some prices, with benefits confined to elective, single-episode, commodifiable services such as magnetic resonance imaging scans.5 The Affordable Care Act required hospitals to publish standard charges, also called a chargemaster (Table).6 However, chargemaster fees are notoriously inflated and inaccessible at the point of service, undercutting transparency.

POLICY IN CLINICAL PRACTICE
Beginning January 2021, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) required all hospitals to publish negotiated prices—including payor-specific negotiated charges—for 300 “shoppable services” (Table).6 The list must include 70 common CMS-specified services, such as a basic metabolic panel, upper endoscopy, and prostate biopsy, as well as another 230 services that each hospital determines relevant to its patient population.
In circumstances where hospitals have negotiated different prices for a service, they must list each third-party payor and their payor-specific charge. The information must be prominently displayed, accessible without requiring the patient to enter personal information, and provided in a machine-readable file. CMS may impose a $300 daily penalty on hospitals failing to comply with the policy. Of note, the policy does not apply to clinics or ambulatory surgery centers.
As more hospitals share data, this policy will directly benefit both patients and physicians. It can benefit patients with the time, foresight, and ability to search for the lowest price for shoppable services. Other patients may also benefit indirectly, to the extent that insurers and other purchasers apply this information to negotiate lower and more uniform prices. Decreased price variation may also encourage hospitals to compete on quality to distinguish the value of their services. Hospitalists could benefit through the ability to directly help patients locate price information.
Despite these potential benefits, the policy has limitations. Price information about shoppable services is most useful for discharge planning, and other solutions are needed to address transparency before and during unplanned admissions. Patients who prioritize continuity with a hospital or physician may be less price sensitive, particularly for more complex services. Patients with commercial insurance may be shielded from cost considerations and personal incentives to comparison shop. Interpreting hospitals’ estimates remains difficult, as it can be unclear if professional fees are included or if certain prices are offered to outpatients.7 Price information is not accompanied by corresponding quality data. Additionally, price transparency may also fail to lower prices in heavily concentrated payor or provider markets, and it remains unknown whether some providers may actually raise prices after learning about higher rates negotiated by competitors.8,9
Another issue is hospital participation. Early evidence suggests that most hospitals have not complied with the letter or spirit of the regulation.
Despite its limitations, this policy represents a meaningful advance for healthcare competition and patient empowerment. Additionally, it signals federal willingness to address the lack of price transparency as a source of widespread patient and clinician frustration—a commitment that will be needed to sustain this policy and implement additional measures in the future.
COMMENTARY AND RECOMMENDATIONS
CMS could consider five steps to augment the policy and maximize transparency and value for patients.
First, CMS could consider increasing daily nonparticipation penalties. Hospitals, particularly those in areas with less competition, have less incentive to participate given meager current penalties. Because the magnitude needed to compel action remains unknown, CMS could gradually escalate penalties over time until there is broader participation across hospitals.
Second, policymakers could aggregate price information centrally, organize the data around patients’ clinical scenarios, and advertise its availability. Currently, this information is scattered and time-consuming for hospitalists and patients to gather for decision-making. Additionally, CMS could encourage the development of third-party tools that aggregate and analyze machine-readable price data or require that prices be posted at the point of service.
Third, CMS could revise the policy to include quality as well as price information. Price alone does not offer a full enough picture of what consumers can expect from hospitals for shoppable services. Pairing price and quality information is better aligned to addressing costs in the context of value, rather than cost-cutting for its own purposes.
Fourth, over time, CMS could expand the list of services and sites required to report (eg, clinics and ambulatory surgical centers as well as hospitals).
Fifth, CMS rule-makers could set reporting standards and contextualize price information in common clinical scenarios. Patients may have difficulty shopping for complex healthcare services without understanding how they apply in different clinical situations. Decision-making would also be aided by reporting standards—for instance, for how prices are displayed and whether they include certain fees (eg, professional fees, pathology studies).
WHAT SHOULD I TELL MY PATIENT?
Hospitalists planning follow-up care should inform patients that price information is increasingly available and encourage them to search on the internet or contact hospital billing offices to request information (eg, discounted cash prices and minimum negotiated charges) before obtaining elective services after discharge. Hospitalists can also encourage patients to discuss shoppable services with their primary care physicians to understand the clinical context and make high-value decisions. Hospitalists who wish to build communication skills discussing costs with patients can increasingly find resources for these conversations and request that prices be displayed in the electronic health record for this purpose.13,14 As conversations occur, hospitalists should seek to understand other factors, such as convenience and continuity relationships, that might influence choices.
CONCLUSIONS
Starting in 2021, CMS policy requires that hospitals report prices for services such as the endoscopy recommended for the patient in the scenario. Though the policy gives patients new hope for greater transparency and better prices, additional steps are needed to help patients and hospitalists achieve these benefits.
1. Shrank WH, Rogstad TL, Parekh N. Waste in the US health care system: estimated costs and potential for savings. JAMA. 2019;322(15):1501-1509. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.13978
2. Wetzell S. Transparency: a needed step towards health care affordability. American Health Policy Institute. March 2014. Accessed August 26, 2021. https://www.americanhealthpolicy.org/Content/documents/resources/Transparency%20Study%201%20-%20The%20Need%20for%20Health%20Care%20Transparency.pdf
3. Mehrotra A, Dean KM, Sinaiko AD, Sood N. Americans support price shopping for health care, but few actually seek out price information. Health Aff (Millwood). 2017;36(8):1392-1400. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2016.1471
4. Kullgren JT, Duey KA, Werner RM. A census of state health care price transparency websites. JAMA. 2013;309(23):2437-2438. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.6557
5. Brown ZY. Equilibrium effects of health care price information. Rev Econ Stat. 2019;101(4):699-712. https://doi.org/10.1162/rest_a_00765
6. Medicare and Medicaid Programs: CY 2020 hospital outpatient PPS policy changes and payment rates and ambulatory surgical center payment system policy changes and payment rates. Price transparency requirements for hospitals to make standard charges public. 45 CFR §180.20 (2019).
7. Kurani N, Ramirez G, Hudman J, Cox C, Kamal R. Early results from federal price transparency rule show difficulty in estimating the cost of care. Peterson-Kaiser Family Foundation. April 9, 2021. Accessed August 26, 2021. https://www.healthsystemtracker.org/brief/early-results-from-federal-price-transparency-rule-show-difficultly-in-estimating-the-cost-of-care/
8. Miller BJ, Mandelberg MC, Griffith NC, Ehrenfeld JM. Price transparency: empowering patient choice and promoting provider competition. J Med Syst. 2020;44(4):80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-020-01553-2
9. Glied S. Price transparency–promise and peril. JAMA. 2021;325(15):1496-1497. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.4640
10. Haque W, Ahmadzada M, Allahrakha H, Haque E, Hsiehchen D. Transparency, accessibility, and variability of US hospital price data. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(5):e2110109. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10109
11. Henderson M, Mouslim MC. Low compliance from big hospitals on CMS’s hospital price transparency rule. Health Affairs Blog. March 16, 2021. Accessed August 26, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1377/hblog20210311.899634
12. McGinty T, Wilde Mathews A, Evans M. Hospitals hide pricing data from search results. The Wall Street Journal. March 22, 2021. Accessed August 26, 2021. https://www.wsj.com/articles/hospitals-hide-pricing-data-from-search-results-11616405402
13. Dine CJ, Masi D, Smith CD. Tools to help overcome barriers to cost-of-care conversations. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170(9 suppl):S36-S38. https://doi.org/10.7326/M19-0778
14. Miller BJ, Slota JM, Ehrenfeld JM. Redefining the physician’s role in cost-conscious care: the potential role of the electronic health record. JAMA. 2019;322(8):721-722. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.9114
1. Shrank WH, Rogstad TL, Parekh N. Waste in the US health care system: estimated costs and potential for savings. JAMA. 2019;322(15):1501-1509. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.13978
2. Wetzell S. Transparency: a needed step towards health care affordability. American Health Policy Institute. March 2014. Accessed August 26, 2021. https://www.americanhealthpolicy.org/Content/documents/resources/Transparency%20Study%201%20-%20The%20Need%20for%20Health%20Care%20Transparency.pdf
3. Mehrotra A, Dean KM, Sinaiko AD, Sood N. Americans support price shopping for health care, but few actually seek out price information. Health Aff (Millwood). 2017;36(8):1392-1400. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2016.1471
4. Kullgren JT, Duey KA, Werner RM. A census of state health care price transparency websites. JAMA. 2013;309(23):2437-2438. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.6557
5. Brown ZY. Equilibrium effects of health care price information. Rev Econ Stat. 2019;101(4):699-712. https://doi.org/10.1162/rest_a_00765
6. Medicare and Medicaid Programs: CY 2020 hospital outpatient PPS policy changes and payment rates and ambulatory surgical center payment system policy changes and payment rates. Price transparency requirements for hospitals to make standard charges public. 45 CFR §180.20 (2019).
7. Kurani N, Ramirez G, Hudman J, Cox C, Kamal R. Early results from federal price transparency rule show difficulty in estimating the cost of care. Peterson-Kaiser Family Foundation. April 9, 2021. Accessed August 26, 2021. https://www.healthsystemtracker.org/brief/early-results-from-federal-price-transparency-rule-show-difficultly-in-estimating-the-cost-of-care/
8. Miller BJ, Mandelberg MC, Griffith NC, Ehrenfeld JM. Price transparency: empowering patient choice and promoting provider competition. J Med Syst. 2020;44(4):80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-020-01553-2
9. Glied S. Price transparency–promise and peril. JAMA. 2021;325(15):1496-1497. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.4640
10. Haque W, Ahmadzada M, Allahrakha H, Haque E, Hsiehchen D. Transparency, accessibility, and variability of US hospital price data. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(5):e2110109. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10109
11. Henderson M, Mouslim MC. Low compliance from big hospitals on CMS’s hospital price transparency rule. Health Affairs Blog. March 16, 2021. Accessed August 26, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1377/hblog20210311.899634
12. McGinty T, Wilde Mathews A, Evans M. Hospitals hide pricing data from search results. The Wall Street Journal. March 22, 2021. Accessed August 26, 2021. https://www.wsj.com/articles/hospitals-hide-pricing-data-from-search-results-11616405402
13. Dine CJ, Masi D, Smith CD. Tools to help overcome barriers to cost-of-care conversations. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170(9 suppl):S36-S38. https://doi.org/10.7326/M19-0778
14. Miller BJ, Slota JM, Ehrenfeld JM. Redefining the physician’s role in cost-conscious care: the potential role of the electronic health record. JAMA. 2019;322(8):721-722. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.9114
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine
Evaluation and Medical Management of the Pediatric Patient With Orbital Cellulitis/Abscess: A Systematic Review
Orbital cellulitis/abscess (OCA) is a potential complication of sinusitis. If not treated promptly, it can result in vision loss, intracranial infection, or cavernous sinus thrombosis.1,2 In 1970, Chandler et al3 classified orbital complications of acute sinusitis into five groups: inflammatory edema (group 1); orbital cellulitis (group 2); subperiosteal abscess (SPA) (group 3); orbital abscess (group 4); and cavernous sinus thrombosis (group 5). Group 1, or preseptal cellulitis, is significantly different from groups 2, 3, and 4, collectively referred to as OCA, which affect the actual orbital content.
Children with OCA are generally hospitalized so they can be treated with intravenous antibiotics. While orbital abscesses (group 4) are typically treated surgically, successful medical management has been reported for cases of orbital cellulitis and SPA (groups 2 and 3).4,5 No widely accepted guidelines exist for the evaluation and medical management of OCA, resulting in significant variation in care.6 The purpose of this systematic review is to summarize existing evidence guiding the medical management of OCA regarding laboratory testing, imaging, and microbiology. This review does not address surgical considerations.
METHODS
The review protocol has been registered in the PROSPERO International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/index.asp; identifier: CRD42020158463), and the review was reported according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.7
Search Strategy
A systematic search of the literature was designed and conducted by a medical librarian (ES), with input from the research team (AB, SM). The search strategy included Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms and keywords related to orbital or subperiosteal cellulitis/abscess and children; see Appendix Table 1 for the complete search strategy. Searches were conducted in MEDLINE (Ovid), Web of Science Core Collection, Scopus, CINAHL (EBSCO), and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) using advanced search techniques relative to each database. Searches were last conducted on February 9, 2021.
Eligibility Criteria
The study designs (retrospective and prospective) included in the search were limited to randomized clinical trials, cohort studies, case-control studies, and case series with participants <18 years of age. Case reports describing fewer than 5 patients and literature reviews were excluded. Studies including a combination of adult and pediatric patients were included if pediatric outcomes were reported separately. Only studies available in English were included.
Outcome Measures
The outcome measures were determined a priori based on three clinical questions:
- Q1. What is the role of inflammatory markers—white blood cell (WBC) count, C-reactive protein (CRP), and fever—in distinguishing between the following: preseptal cellulitis (group 1) and OCA (groups 2, 3, and 4); orbital cellulitis (group 2) and abscess (groups 3 and 4); and patients who do and do not require surgery?
- Q2. What is the role of imaging in the evaluation of OCA?
- Q3. What is the microbiology of OCA over the past 2 decades? What is the prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)?
Screening
Two review authors (AB, SM) performed both the title/abstract and full-text screen, independently applying the eligibility criteria. Disagreements were discussed, and conflicts were resolved with input from a third reviewer author (ES). Duplications were removed. When two studies had overlapping patient data, the study with fewer data points was excluded.
Data Extraction and Synthesis
All studies included after the full-text screen were divided based on the clinical question they answered (Q1, Q2, Q3 above). Some studies reported outcomes pertinent to more than one question. Two review authors were assigned to each clinical question. They independently reviewed each article and extracted the pertinent data into question-specific extraction sheets. Articles assigned to Q2 were reviewed by two pediatric neuroradiologists. For each study, the following details were extracted: authors, location, year, study type, study period, population, and number and ages of participants. Details that were question-specific included: (Q1) values and/or percentages for inflammatory markers; (Q2) reasons for imaging or type of imaging; and (Q3) participants managed surgically and culture results. The data were then synthesized in table and/or narrative format. For Q3, the organisms identified from intraoperative and blood cultures in each study were mathematically combined. When possible, prevalence was calculated using the number of patients with at least one pathogen recovered as the denominator. If this number was not available, the number of patients who underwent surgery was used as the denominator.
Quality Assessment
No randomized controlled trials were identified. More than 90% of the studies identified and included were retrospective descriptive studies. By the nature of the case series design, the study quality was felt to be poor, with high risk of bias. The Joanna Briggs Institute Critical Appraisal tools for systematic reviews were used to appraise each individual study included (Appendix Table 2).8 The Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE) criteria were used in rating the quality of evidence for each question.9
RESULTS
A summary of the search strategy and study selection is provided in the Figure (PRISMA flow diagram). The initial search identified 3007 studies. After duplicates were removed and general eligibility criteria applied, 94 articles remained. Question-specific eligibility criteria, discussed in the following sections, were then applied, resulting in 63 articles included in the review.
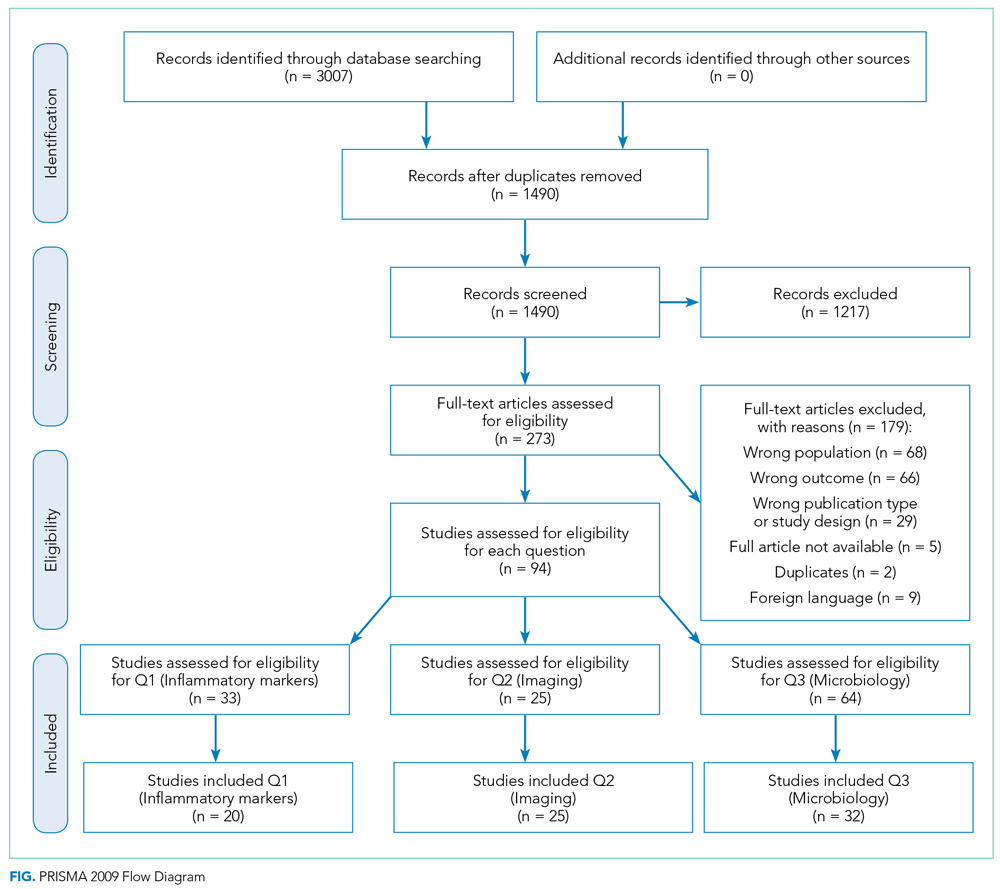
Q1: Are Inflammatory Markers, Including Fever, WBC, and CRP, Useful in Distinguishing Preseptal Cellulitis (group 1) From OCA (Groups 2, 3, and 4); Orbital Cellulitis (group 2) From Abscess (Groups 3 and 4); or Identifying Patients Who Require Surgical Intervention?
Fever and elevation of the WBC count and CRP have been used to assess the severity of certain pediatric infections10,11 and therefore may be helpful in distinguishing severity of illness in OCA. Studies included in this section provided numerical values for at least one of the following: WBC count, CRP, or percentage of patients with fever for at least one type of orbital infection. Included studies had at least five patients per group.
Thirty-three articles were screened for the inflammatory marker section. Thirteen were excluded for the following reasons: no numbers reported for inflammatory markers (n = 6); group 1 and groups 2, 3, and 4 results combined (n = 6); fewer than five patients with orbital cellulitis included (n = 1). Twenty studies were included: 18 case series and 2 retrospective cohorts. Appendix Table 3 summarizes the data from studies included. Based on GRADE criteria, the body of evidence included in this section is of low quality.9
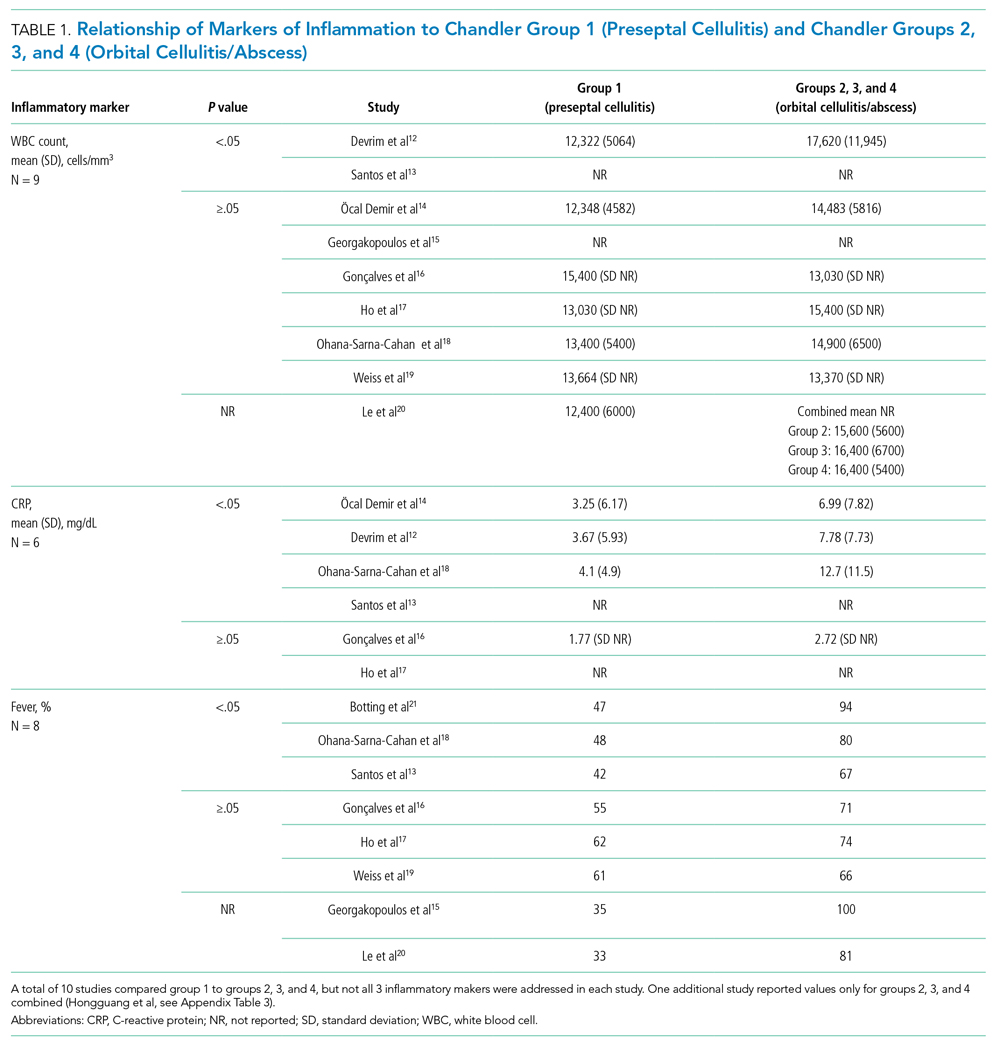
Distinguishing Between Preseptal and OCA
Eleven studies were included in this section (Table 1). WBC count was significantly higher in patients with groups 2, 3, and 4 than group 1 in two studies (Devrim et al,12P < .01; Santos et al,13P = .025). CRP was significantly higher in patients with groups 2, 3, and 4 than group 1 in four studies (Öcal Demir et al,14P = .02; Devrim et al,12P < .01; Ohana-Sarna-Cahan et al,18P < .001; Santos et al,13P < .001). Patients with groups 2, 3, and 4 had a significantly higher fever rate in three studies (Botting et al,21P < .001; Ohana-Sarna-Cahan et al,18P = .0001; Santos et al,13 P = .029).
Distinguishing Between Orbital Cellulitis and Abscess
Seven studies were included in this section (Appendix Table 3). One study showed significantly higher WBC count in group 3 than group 2 (P = .004), although results were reported as percentage of patients above a cutoff number calculated to distinguish between cellulitis and abscess (Appendix Table 3).22 CRP was not significantly different between group 2 and groups 3 and 4. One study found a significantly higher fever rate in patients with group 3 compared to patients with group 2 (P < .001).22
Identifying Patients Requiring Surgery
Six studies were included in this section (Appendix Table 3). One study found a significantly higher WBC count in patients treated surgically (Tabarino et al,24P < .05). Patients treated surgically had a significantly higher CRP in two studies (Cohen et al,25P = .02; Friling et al,26 P = .04). Fever was inconsistently reported in the studies, with some using mean presenting temperatures and some using rates of fever. One study found a significantly higher mean presenting temperature in patients treated surgically (P = .027), but the difference between the two groups was 0.7 °C.23
Summary
Most studies found no significant difference in WBC count, CRP, or fever between preseptal and OCA, cellulitis and abscess, or patients receiving medical and surgical interventions.
Q2: What Is the Role of Imaging in Evaluation of OCA?
Twenty-five articles were selected for the imaging section review. All the included studies were retrospective descriptive studies. Quantitative data extraction and analysis of these studies could not be performed because of their heterogeneous methodologies and lack of objective data. Therefore, the information gleaned from these studies is summarized in narrative format. Per GRADE criteria, the body of evidence included in this section is of low quality.
Who Needs Imaging?
Proptosis, ophthalmoplegia, decreased vision, and pain with eye movements are widely agreed-upon indications for imaging evaluation.21,27,28 Because of concern for radiation exposure in pediatric patients, some authors suggested that computed tomography (CT) should only be obtained if patients fail to respond to medical therapy or if surgery is being considered.17,29,30 However, Rudloe et al31 found that half of the patients with group 3 or higher disease on CT did not have proptosis, ophthalmoplegia, or pain with extraocular movement. In addition, evaluation of young children with acute periorbital swelling can be difficult, so a lower threshold for imaging is likely warranted in these younger patients.
What Type of Imaging Should Be Obtained?
The American College of Radiology 2018 Appropriateness Criteria (ACR criteria) for orbital imaging state that orbital CT is usually indicated for patients with suspected Chandler groups 2, 3, and 4 infections.32 CT with contrast is useful for evaluating the extent of orbital infection and size of the abscess and for delineating the adjacent osseous anatomy, which is essential for cases in which surgical intervention is planned.20,21,26,27,30,31,33,34 Distinguishing abscess from cellulitis on CT sometimes can be challenging; therefore, serial clinical examinations and, occasionally, surgical exploration may be required.35,36
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is helpful for evaluating intracranial complications (eg, epidural abscess),27,37 but it is limited for evaluating the osseous components of the paranasal sinuses. Although one study suggested that rapid MRI is comparable to contrast CT for differentiating group 1 infections from groups 2, 3, and 4 infections, it provided limited assessment of other complications.38 With no definitive studies comparing CT with MRI for orbital infections, adherence to the ACR criteria is recommended.
Orbital ultrasound is limited by its small field of view and artifact produced by the surrounding bony interface, both of which can obscure posterior intraorbital pathologies.29,39,40 Plain radiographs are not helpful for evaluating OCA due to limited soft-tissue contrast.41
When Should Repeat Imaging Be Obtained?
Children with group 3 OCA have been successfully managed medically in a carefully monitored setting.42 Repeat CT imaging is sometimes useful in these patients, particularly if the clinical examination is difficult.42-44 However, improvement in CT findings may lag behind clinical improvement.39
Summary
Per ACR criteria, orbital CT with contrast is recommended to evaluate patients with suspected Chandler groups 2, 3, and 4 OCA. MRI is reserved for evaluating intracranial complications.
Q3: What Is the Microbiology of OCA? What Is the MRSA Prevalence?
Knowledge of the microbiology of OCA is essential for the appropriate selection of empiric antibiotics. Because fewer children with groups 2 and 3 OCA undergo surgery, intraoperative cultures often are not available to guide antibiotic selection.45 As a result, significant variation exists in antibiotic prescribing.6
Studies discussing the microbiology of OCA were included only if they were published in the past 2 decades (2000-2020) and were excluded if the study period was before 1990, as microbiology changes over time and new vaccines are introduced. To be included, the majority of cultures reported had to be intraoperative (orbital or sinus) specimens. Studies reporting only nasal, conjunctival, or other surface cultures were excluded. When studies included patients with group 1 OCA, only microbiology data for groups 2, 3, and 4 OCA were extracted. The pattern of resistance for S aureus was not always explicitly reported; however, when non-MRSA active antibiotics were used, methicillin-susceptible S aureus was assumed.
A total of 63 studies were screened for the microbiology section; 32 were excluded for the following reasons: published before 2000 or study period before 1990 (n = 18), reported surface cultures or culture site not clearly stated (n = 4), microbiology mixed between preseptal and orbital (n = 6), wrong study type (n = 2), and study group overlaps with a different article included (n = 2). Of the 32 studies included, 3 were prospective observational, 4 were retrospective cohort, and 25 were case series. Based on GRADE criteria, the body of evidence included in this section is of low quality.42
Appendix Table 4 summarizes the microbiologic data from the studies included. In the group of children that had a positive culture (orbital, sinus, or blood), the most commonly recovered organisms reported were S aureus (median, 22%; range, 0%-100%), Streptococcus anginosus group (median, 16%; range, 0%-100%), group A Streptococcus (median, 12%; range, 0%-80%), and Streptococcus pneumoniae (median, 8%; range, 0%-100%). Streptococcus as a group had a median prevalence of 57%, ranging from 0% to 100%. MRSA prevalence had a median of 3% (interquartile range [IQR], 0%-13%). Median prevalence of polymicrobial cultures was 20%, and median prevalence of anaerobic organisms was 14% (Table 2). Orbital and sinus cultures had the highest yield, with an average return of an organism of 72% (median, 75%; IQR, 64%-84%).

Microbiology was compared between studies completed in the United States and in other countries (Table 2). Based on median prevalence across studies, both S anginosus group and MRSA were more prevalent in the United States than internationally (28% vs 0% and 11% vs 0%, respectively). No clear trend in MRSA prevalence was evident over the 2 decades; however, the studies included were heterogeneous and did not have the power to detect such a trend.
Two reports suggest a difference of MRSA prevalence by patient age. Hsu et al46 found that three of eight MRSA infections were in infants age <1 year, which accounted for 50% (3/6) of infants included in the study. Miller et al47 reported MRSA in 4 of 9 (44%) infants with OCA. Age <1 year may be associated with increased frequency of MRSA infection in OCA.
Summary
Blood cultures have low yield. The most common organisms recovered from OCA are Streptococcus species (most commonly S anginosus group, group A Streptococcus, and pneumococcus) and S aureus. Polymicrobial infections including anaerobes are common. MRSA prevalence is low globally but varies significantly among geographic areas.
DISCUSSION
Our systematic review of the literature for the medical management of OCA revealed predominantly descriptive studies and only a limited number of comparison-based studies, likely reflecting the rarity of advanced forms of OCA. Given the lack of high-quality evidence and the level of heterogeneity among studies, the conclusions that can be drawn are limited.
Distinguishing between disease severity and OCA requiring surgical intervention remains challenging. Although studies in our review suggest a trend toward markers of inflammation (fever, elevated WBC count and CRP) being more common in more severe presentations, the results were mixed, and studies were low quality and underpowered to detect meaningful differences. For example, most studies do not define what constitutes a fever in their cohort. Our review suggests that markers of inflammation cannot be used to distinguish between Chandler groups or to identify patients requiring surgery. Of note, the presence of fever and elevated inflammatory markers may have influenced the decision to obtain imaging or to proceed to surgery, thereby also potentially biasing these clinical indicators toward predictors for more severe disease. Decisions regarding surgery should therefore be based on the entire clinical picture, including response to appropriate antibiotics.
We found a lack of high-quality evidence regarding the role of imaging in OCA, and the studies reviewed were heterogeneous. Recommendations for imaging therefore remain at the level of expert opinion (ACR criteria). CT imaging is the first-line modality for imaging in suspected OCA given the limitations of alternative imaging modalities, but the sensitivity and specificity of CT imaging remain unknown for diagnosis of orbital abscesses.
Our review of the published microbiology confirmed that Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species are the most common pathogens identified in OCA. Prevalence across the different studies varied greatly. Owing to the significant heterogeneity in studies, calculation of pooled prevalence was not possible. By using the number of positive cultures as our denominator (or total surgeries if number of positive cultures was unavailable), we likely overestimated the prevalence of S aureus. S aureus is generally recognized as a pyogenic pathogen, more likely to be associated with abscess formation.48 Therefore, culture results obtained predominantly from abscesses likely result in an overestimate of S aureus in OCA (groups 2, 3, and 4). Regardless, MRSA prevalence was generally low, both nationally and internationally. The MRSA results from the study by McKinley at el49 (Texas) was a notable outlier in the United States, with MRSA prevalence as high as 44% compared with the median prevalence of 3% (IQR, 0-13), highlighting the importance of local resistance patterns when choosing empiric antibiotics.
Limitations to the microbiology review included significant heterogeneity in both the types of cultures included and the reporting of results. Although we excluded studies that reported only surface culture results or did not specify culture type, we did include studies that had surface culture results combined with intraoperative culture results, making it impossible to separate the two. Since most of the cultures included in combined results reported organisms based on intraoperative cultures, we felt they provided valuable information that should be included. In most studies, blood cultures were not obtained in all participants, so the yield of blood cultures is likely an overestimate, as blood cultures are more likely to be obtained in higher-acuity patients.
CONCLUSION
Although the available evidence regarding the medical management of OCA remains low quality, certain limited conclusions can be drawn, as presented in this review. Further high-quality studies are needed to better inform the medical management of OCA.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Dr Kyle Pronko for his help with data extraction for the imaging section.
1. Reynolds D.J, Kodsi SR, Rubin SE, Rodgers IR. Intracranial infection associated with preseptal and orbital cellulitis in the pediatric patient. J AAPOS. 2003;7(6):413-417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaapos.2003.09.013
2. Chaudhry IA, Shamsi FA, Elzaridi E, et al. Outcome of treated orbital cellulitis in a tertiary eye care center in the Middle East. Ophthalmology. 2007;114(2):345-354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2006.07.059
3. Chandler JR, Langenbrunner DJ, Stevens ER. Pathogenesis of orbital complications in acute sinusitis. Laryngoscope. 1970;1414-1428. https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-197009000-00007
4. Wong SJ, Levi J. Management of pediatric orbital cellulitis: a systematic review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2018;110:123-129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2018.05.006
5. Liao JC, Harris GJ. Subperiosteal abscess of the orbit: evolving pathogens and the therapeutic protocol. Ophthalmology. 2015;122(3):639-647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.09.009
6. Markham JL, Hall M, Bettenhausen JL, Myers AL, Puls HT, McColloh RJ. Variation in care and clinical outcomes in children hospitalized with orbital cellulitis. Hosp Pediatr. 2018;8(1):28-35. https://doi.org/10.1542/hpeds.2017-0040
7. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
8. Munn Z, Barker TH, Moola S, et al. Methodological quality of case series studies: an introduction to the JBI critical appraisal tool. JBI Evid Synth. 2020;18(10):2127-2133. https://doi.org/10.11124/JBISRIR-D-19-00099
9. Balshem H, Helfand M, Schünemann HJ, et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(4):401-406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.07.015
10. Dean P, Florin TA. Factors associated with pneumonia severity in children: a systematic review. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2018;7(4):323-334. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpids/piy046
11. Hofer N, Zacharias E, Müller W, Resch B. An update on the use of C-reactive protein in early-onset neonatal sepsis: current insights and new tasks. Neonatology. 2012;102(1):25-36. https://doi.org/10.1159/000336629
12. Devrim I, Kanra G, Kara A, et al. Preseptal and orbital cellulitis: 15-year experience with sulbactam ampicillin treatment. Turk J Pediatr. 2008;50(3):214-218.
13. Santos JC, Pinto S, Ferreira S, Maia C, Alves S, da Silva V. Pediatric preseptal and orbital cellulitis: a 10-year experience. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;120:82-88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.02.003
14. Öcal Demir S , Çagan E, Kepenekli Kadayifci E, et al. Clinical features and outcome of preseptal and orbital cellulitis in hospitalized children: four years experience. Medeni Med J. 2017;32(1):7-13. https://doi.org/10.5222/MMJ.2017.007
15. Georgakopoulos CD, Eliopoulou MI, Stasinos S, Exarchou A, Pharmakakis N, Varvarigou A. Periorbital and orbitaln cellulitis: a 10-year review of hospitalized children. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2010;20(6):1066-1072. https://doi.org/10.1177/112067211002000607
16. Gonçalves R, Menezes C, Machado R, Ribeiro I, Lemos JA. Periorbital cellulitis in children: analysis of outcome of intravenous antibiotic therapy. Orbit. 2016;34(4):175-180. https://doi.org/10.1080/01676830.2016.1176205
17. Ho CF, Huang YC, Wang CJ, Chiu CH, Lin TY. Clinical analysis of computed tomography-staged orbital cellulitis in children. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2017;40(6):518-524.
18. Ohana-Sarna-Cahan L, Hurvitz N, Gross I, Cohen A, Hashavya S. Factors associated with increased risk of pediatric orbital cellulitis—who should be scanned? Pediatr Emerg Care. Published online ahead of print March 19, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000002083
19. Weiss A, Friendly D, Eglin K, Chang M, Gold B. Bacterial periorbital and orbital cellulitis in childhood. Ophthalmology. 1983;90(3):195-203. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0161-6420(83)34573-5
20. Le TD, Liu ES, Adatia FA, Buncic JR Blaser S. The effect of adding orbital computed tomography findings to the Chandler criteria for classifying pediatric orbital cellulitis in predicting which patients will require surgical intervention. J AAPOS. 2014;18(3):271-277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaapos.2014.01.015
21. Botting AM, McIntosh D, Mahadevan M. Paediatric pre- and post-septal peri-orbital infections are different diseases. A retrospective review of 262 cases. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2008;72(3):377-383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2007.11.013
22. Huang SF, Lee TJ, Lee YS, Chen CC, Chin SC, Wang NC. Acute rhinosinusitis-related orbital infection in pediatric patients: a retrospective analysis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2011;120(3):185-190. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348941112000307
23. Ryan JT, Preciado A, Bauman N, et al. Management of pediatric orbital cellulitis in patients with radiographic findings of subperiosteal abscess. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;140(6):907-911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2009.02.014
24. Tabarino F, Elmaleh-Bergès M, Quesnel S, Lorrot M, Van Den Abbeele T, Teissier N. Subperiosteal orbital abscess: volumetric criteria for surgical drainage. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015;79(2):131-135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2014.11.021
25. Cohen N, Erisson S, Anafy A, et al. Clinicians need to consider surgery when presented with some markers for severe paediatric orbital cellulitis. Acta Paediatr. 2020;109(6):1269-1270. https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.15125
26. Friling R, Garty BZ, Kornreich L, et al. Medical and surgical management of orbital cellulitis in children. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2014;56(4):253-258. https://doi.org/10.1515/folmed-2015-0004
27. Gavriel H, Yeheskeli E, Aviram E, Yehoshua L, Eviatar E. Dimension of subperiosteal orbital abscess as an indication for surgical management in children. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011;145(5):823-827. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599811416559
28. Mathew AV, Craig E, Al-Mahmoud R, et al. Paediatric post-septal and pre-septal cellulitis: 10 years’ experience at a tertiary-level children’s hospital. Br J Radiol. 2014;87(1033):20130503. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20130503
29. Goodwin WJ Jr, Weinshall M, Chandler JR. The role of high resolution computerized tomography and standardized ultrasound in the evaluation of orbital cellulitis. Laryngoscope. 1982;92(7 pt 1):729-731.
30. Bilaniuk LT, Zimmerman RA. Computer‐assisted tomography: sinus lesions with orbital involvement. Head Neck Surg. 1980;2(4):293-301. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.2890020407
31. Rudloe TF, Harper MB, Prabhu SP, Rahbar R, Vanderveen D, Kimia AA. Acute periorbital infections: who needs emergent imaging? Pediatrics. 2010;125(4):e719-e726. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-1709
32. Kennedy TA, Corey AS, Policeni B, et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® orbits vision and visual loss. J Am Coll Radiol. 2018;15(5S):S116-S131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2018.03.023
33. De Silva M, Lam V, Broadfoot J. C.T. findings of orbital inflammation in children. Australas Radiol. 1987;31(3):241-245. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1673.1987.tb01822.x
34. Hirsch M, Lifshitz T. Computerized tomography in the diagnosis and treatment of orbital cellulitis. Pediatr Radiol. 1988;18(4):302-305. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02388996
35. Andrews TM, Myer CM 3rd. The role of computed tomography in the diagnosis of subperiosteal abscess of the orbit. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1992;31(1):37-43. https://doi.org/10.1177/000992289203100108
36. Clary RA, Cunningham MJ, Eavey RD. Orbital complications of acute sinusitis: comparison of computed tomography scan and surgical findings. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1992;101(7):598-600. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348949210100710
37. Arjmand EM, LuskRP, Muntz HR. Pediatric sinusitis and subperiosteal orbital abscess formation: diagnosis and treatment. Otolaryngol Neck Surg. 1993;109(5):886.894. https://doi.org/10.1177/019459989310900518
38. Jain SF, Ishihara R, Wheelock L, et al. Feasibility of rapid magnetic resonance imaging (rMRI) for the emergency evaluation of suspected pediatric orbital cellulitis. J AAPOS. 2020;24(5):289.e1-289.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaapos.2020.05.018
39. Harris GJ. Subperiosteal abscess of the orbit: computed tomography and the clinical course. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996;12:1-8. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002341-199603000-00001
40. Kaplan DM, Briscoe D, Gatot A, Niv A, Leiberman A, Fliss DM. The use of standardized orbital ultrasound in the diagnosis of sinus induced infections of the orbit in children: a preliminary report. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1999;48(2):155-162. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-5876(99)00023-3
41. Towbin R, Han BK, Kaufman RA, Burke M. Postseptal cellulitis: CT in diagnosis and management. Radiology. 1986;158(3):735-737. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.158.3.3945747
42. Starkey CR, Steele RW. Medical management of orbital cellulitis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20(10):1002-1005. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006454-200110000-00017
43. Brown CL, Graham SM, Griffin MC, et al. Pediatric medial subperiosteal orbital abscess: medical management where possible. Am J Rhinol. 2004;18(5):321-327.
44. Cossack MT, Herretes SP, Cham A, Sniegowski MC, Lyon DB. Radiographic course of medically managed pediatric orbital subperiosteal abscesses. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2018;55(6):387-392. https://doi.org/10.3928/01913913-20180802-02
45. Zhao EE, Koochakzadeh S, Nguyen SA, et al. Orbital complications of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis in the pediatric population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;135:110078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110078
46. Hsu J, Treister AD, Ralay Ranaivo H, Rowley AH, Rahmani B. Microbiology of pediatric orbital cellulitis and trends in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus cases. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2019;58(10):1056-1062. https://doi.org/10.1177/0009922819864587
47. Miller A, Castanes M, Yen M, Coats D, Yen K. Infantile orbital cellulitis. Ophthalmology. 2008;115(3):594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2007.10.011
48. Dajani AS, Garcia RE, Wolinsky E. Etiology of cervical lymphadenitis in children. N Engl J Med. 1963;268:1329-1333. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM196306132682403
49. McKinley SH, Yen MT, Miller AM, Yen KG. Microbiology of pediatric orbital cellulitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007;144(4):497-501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2007.04.049
Orbital cellulitis/abscess (OCA) is a potential complication of sinusitis. If not treated promptly, it can result in vision loss, intracranial infection, or cavernous sinus thrombosis.1,2 In 1970, Chandler et al3 classified orbital complications of acute sinusitis into five groups: inflammatory edema (group 1); orbital cellulitis (group 2); subperiosteal abscess (SPA) (group 3); orbital abscess (group 4); and cavernous sinus thrombosis (group 5). Group 1, or preseptal cellulitis, is significantly different from groups 2, 3, and 4, collectively referred to as OCA, which affect the actual orbital content.
Children with OCA are generally hospitalized so they can be treated with intravenous antibiotics. While orbital abscesses (group 4) are typically treated surgically, successful medical management has been reported for cases of orbital cellulitis and SPA (groups 2 and 3).4,5 No widely accepted guidelines exist for the evaluation and medical management of OCA, resulting in significant variation in care.6 The purpose of this systematic review is to summarize existing evidence guiding the medical management of OCA regarding laboratory testing, imaging, and microbiology. This review does not address surgical considerations.
METHODS
The review protocol has been registered in the PROSPERO International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/index.asp; identifier: CRD42020158463), and the review was reported according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.7
Search Strategy
A systematic search of the literature was designed and conducted by a medical librarian (ES), with input from the research team (AB, SM). The search strategy included Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms and keywords related to orbital or subperiosteal cellulitis/abscess and children; see Appendix Table 1 for the complete search strategy. Searches were conducted in MEDLINE (Ovid), Web of Science Core Collection, Scopus, CINAHL (EBSCO), and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) using advanced search techniques relative to each database. Searches were last conducted on February 9, 2021.
Eligibility Criteria
The study designs (retrospective and prospective) included in the search were limited to randomized clinical trials, cohort studies, case-control studies, and case series with participants <18 years of age. Case reports describing fewer than 5 patients and literature reviews were excluded. Studies including a combination of adult and pediatric patients were included if pediatric outcomes were reported separately. Only studies available in English were included.
Outcome Measures
The outcome measures were determined a priori based on three clinical questions:
- Q1. What is the role of inflammatory markers—white blood cell (WBC) count, C-reactive protein (CRP), and fever—in distinguishing between the following: preseptal cellulitis (group 1) and OCA (groups 2, 3, and 4); orbital cellulitis (group 2) and abscess (groups 3 and 4); and patients who do and do not require surgery?
- Q2. What is the role of imaging in the evaluation of OCA?
- Q3. What is the microbiology of OCA over the past 2 decades? What is the prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)?
Screening
Two review authors (AB, SM) performed both the title/abstract and full-text screen, independently applying the eligibility criteria. Disagreements were discussed, and conflicts were resolved with input from a third reviewer author (ES). Duplications were removed. When two studies had overlapping patient data, the study with fewer data points was excluded.
Data Extraction and Synthesis
All studies included after the full-text screen were divided based on the clinical question they answered (Q1, Q2, Q3 above). Some studies reported outcomes pertinent to more than one question. Two review authors were assigned to each clinical question. They independently reviewed each article and extracted the pertinent data into question-specific extraction sheets. Articles assigned to Q2 were reviewed by two pediatric neuroradiologists. For each study, the following details were extracted: authors, location, year, study type, study period, population, and number and ages of participants. Details that were question-specific included: (Q1) values and/or percentages for inflammatory markers; (Q2) reasons for imaging or type of imaging; and (Q3) participants managed surgically and culture results. The data were then synthesized in table and/or narrative format. For Q3, the organisms identified from intraoperative and blood cultures in each study were mathematically combined. When possible, prevalence was calculated using the number of patients with at least one pathogen recovered as the denominator. If this number was not available, the number of patients who underwent surgery was used as the denominator.
Quality Assessment
No randomized controlled trials were identified. More than 90% of the studies identified and included were retrospective descriptive studies. By the nature of the case series design, the study quality was felt to be poor, with high risk of bias. The Joanna Briggs Institute Critical Appraisal tools for systematic reviews were used to appraise each individual study included (Appendix Table 2).8 The Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE) criteria were used in rating the quality of evidence for each question.9
RESULTS
A summary of the search strategy and study selection is provided in the Figure (PRISMA flow diagram). The initial search identified 3007 studies. After duplicates were removed and general eligibility criteria applied, 94 articles remained. Question-specific eligibility criteria, discussed in the following sections, were then applied, resulting in 63 articles included in the review.

Q1: Are Inflammatory Markers, Including Fever, WBC, and CRP, Useful in Distinguishing Preseptal Cellulitis (group 1) From OCA (Groups 2, 3, and 4); Orbital Cellulitis (group 2) From Abscess (Groups 3 and 4); or Identifying Patients Who Require Surgical Intervention?
Fever and elevation of the WBC count and CRP have been used to assess the severity of certain pediatric infections10,11 and therefore may be helpful in distinguishing severity of illness in OCA. Studies included in this section provided numerical values for at least one of the following: WBC count, CRP, or percentage of patients with fever for at least one type of orbital infection. Included studies had at least five patients per group.
Thirty-three articles were screened for the inflammatory marker section. Thirteen were excluded for the following reasons: no numbers reported for inflammatory markers (n = 6); group 1 and groups 2, 3, and 4 results combined (n = 6); fewer than five patients with orbital cellulitis included (n = 1). Twenty studies were included: 18 case series and 2 retrospective cohorts. Appendix Table 3 summarizes the data from studies included. Based on GRADE criteria, the body of evidence included in this section is of low quality.9
Distinguishing Between Preseptal and OCA
Eleven studies were included in this section (Table 1). WBC count was significantly higher in patients with groups 2, 3, and 4 than group 1 in two studies (Devrim et al,12P < .01; Santos et al,13P = .025). CRP was significantly higher in patients with groups 2, 3, and 4 than group 1 in four studies (Öcal Demir et al,14P = .02; Devrim et al,12P < .01; Ohana-Sarna-Cahan et al,18P < .001; Santos et al,13P < .001). Patients with groups 2, 3, and 4 had a significantly higher fever rate in three studies (Botting et al,21P < .001; Ohana-Sarna-Cahan et al,18P = .0001; Santos et al,13 P = .029).

Distinguishing Between Orbital Cellulitis and Abscess
Seven studies were included in this section (Appendix Table 3). One study showed significantly higher WBC count in group 3 than group 2 (P = .004), although results were reported as percentage of patients above a cutoff number calculated to distinguish between cellulitis and abscess (Appendix Table 3).22 CRP was not significantly different between group 2 and groups 3 and 4. One study found a significantly higher fever rate in patients with group 3 compared to patients with group 2 (P < .001).22
Identifying Patients Requiring Surgery
Six studies were included in this section (Appendix Table 3). One study found a significantly higher WBC count in patients treated surgically (Tabarino et al,24P < .05). Patients treated surgically had a significantly higher CRP in two studies (Cohen et al,25P = .02; Friling et al,26 P = .04). Fever was inconsistently reported in the studies, with some using mean presenting temperatures and some using rates of fever. One study found a significantly higher mean presenting temperature in patients treated surgically (P = .027), but the difference between the two groups was 0.7 °C.23
Summary
Most studies found no significant difference in WBC count, CRP, or fever between preseptal and OCA, cellulitis and abscess, or patients receiving medical and surgical interventions.
Q2: What Is the Role of Imaging in Evaluation of OCA?
Twenty-five articles were selected for the imaging section review. All the included studies were retrospective descriptive studies. Quantitative data extraction and analysis of these studies could not be performed because of their heterogeneous methodologies and lack of objective data. Therefore, the information gleaned from these studies is summarized in narrative format. Per GRADE criteria, the body of evidence included in this section is of low quality.
Who Needs Imaging?
Proptosis, ophthalmoplegia, decreased vision, and pain with eye movements are widely agreed-upon indications for imaging evaluation.21,27,28 Because of concern for radiation exposure in pediatric patients, some authors suggested that computed tomography (CT) should only be obtained if patients fail to respond to medical therapy or if surgery is being considered.17,29,30 However, Rudloe et al31 found that half of the patients with group 3 or higher disease on CT did not have proptosis, ophthalmoplegia, or pain with extraocular movement. In addition, evaluation of young children with acute periorbital swelling can be difficult, so a lower threshold for imaging is likely warranted in these younger patients.
What Type of Imaging Should Be Obtained?
The American College of Radiology 2018 Appropriateness Criteria (ACR criteria) for orbital imaging state that orbital CT is usually indicated for patients with suspected Chandler groups 2, 3, and 4 infections.32 CT with contrast is useful for evaluating the extent of orbital infection and size of the abscess and for delineating the adjacent osseous anatomy, which is essential for cases in which surgical intervention is planned.20,21,26,27,30,31,33,34 Distinguishing abscess from cellulitis on CT sometimes can be challenging; therefore, serial clinical examinations and, occasionally, surgical exploration may be required.35,36
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is helpful for evaluating intracranial complications (eg, epidural abscess),27,37 but it is limited for evaluating the osseous components of the paranasal sinuses. Although one study suggested that rapid MRI is comparable to contrast CT for differentiating group 1 infections from groups 2, 3, and 4 infections, it provided limited assessment of other complications.38 With no definitive studies comparing CT with MRI for orbital infections, adherence to the ACR criteria is recommended.
Orbital ultrasound is limited by its small field of view and artifact produced by the surrounding bony interface, both of which can obscure posterior intraorbital pathologies.29,39,40 Plain radiographs are not helpful for evaluating OCA due to limited soft-tissue contrast.41
When Should Repeat Imaging Be Obtained?
Children with group 3 OCA have been successfully managed medically in a carefully monitored setting.42 Repeat CT imaging is sometimes useful in these patients, particularly if the clinical examination is difficult.42-44 However, improvement in CT findings may lag behind clinical improvement.39
Summary
Per ACR criteria, orbital CT with contrast is recommended to evaluate patients with suspected Chandler groups 2, 3, and 4 OCA. MRI is reserved for evaluating intracranial complications.
Q3: What Is the Microbiology of OCA? What Is the MRSA Prevalence?
Knowledge of the microbiology of OCA is essential for the appropriate selection of empiric antibiotics. Because fewer children with groups 2 and 3 OCA undergo surgery, intraoperative cultures often are not available to guide antibiotic selection.45 As a result, significant variation exists in antibiotic prescribing.6
Studies discussing the microbiology of OCA were included only if they were published in the past 2 decades (2000-2020) and were excluded if the study period was before 1990, as microbiology changes over time and new vaccines are introduced. To be included, the majority of cultures reported had to be intraoperative (orbital or sinus) specimens. Studies reporting only nasal, conjunctival, or other surface cultures were excluded. When studies included patients with group 1 OCA, only microbiology data for groups 2, 3, and 4 OCA were extracted. The pattern of resistance for S aureus was not always explicitly reported; however, when non-MRSA active antibiotics were used, methicillin-susceptible S aureus was assumed.
A total of 63 studies were screened for the microbiology section; 32 were excluded for the following reasons: published before 2000 or study period before 1990 (n = 18), reported surface cultures or culture site not clearly stated (n = 4), microbiology mixed between preseptal and orbital (n = 6), wrong study type (n = 2), and study group overlaps with a different article included (n = 2). Of the 32 studies included, 3 were prospective observational, 4 were retrospective cohort, and 25 were case series. Based on GRADE criteria, the body of evidence included in this section is of low quality.42
Appendix Table 4 summarizes the microbiologic data from the studies included. In the group of children that had a positive culture (orbital, sinus, or blood), the most commonly recovered organisms reported were S aureus (median, 22%; range, 0%-100%), Streptococcus anginosus group (median, 16%; range, 0%-100%), group A Streptococcus (median, 12%; range, 0%-80%), and Streptococcus pneumoniae (median, 8%; range, 0%-100%). Streptococcus as a group had a median prevalence of 57%, ranging from 0% to 100%. MRSA prevalence had a median of 3% (interquartile range [IQR], 0%-13%). Median prevalence of polymicrobial cultures was 20%, and median prevalence of anaerobic organisms was 14% (Table 2). Orbital and sinus cultures had the highest yield, with an average return of an organism of 72% (median, 75%; IQR, 64%-84%).

Microbiology was compared between studies completed in the United States and in other countries (Table 2). Based on median prevalence across studies, both S anginosus group and MRSA were more prevalent in the United States than internationally (28% vs 0% and 11% vs 0%, respectively). No clear trend in MRSA prevalence was evident over the 2 decades; however, the studies included were heterogeneous and did not have the power to detect such a trend.
Two reports suggest a difference of MRSA prevalence by patient age. Hsu et al46 found that three of eight MRSA infections were in infants age <1 year, which accounted for 50% (3/6) of infants included in the study. Miller et al47 reported MRSA in 4 of 9 (44%) infants with OCA. Age <1 year may be associated with increased frequency of MRSA infection in OCA.
Summary
Blood cultures have low yield. The most common organisms recovered from OCA are Streptococcus species (most commonly S anginosus group, group A Streptococcus, and pneumococcus) and S aureus. Polymicrobial infections including anaerobes are common. MRSA prevalence is low globally but varies significantly among geographic areas.
DISCUSSION
Our systematic review of the literature for the medical management of OCA revealed predominantly descriptive studies and only a limited number of comparison-based studies, likely reflecting the rarity of advanced forms of OCA. Given the lack of high-quality evidence and the level of heterogeneity among studies, the conclusions that can be drawn are limited.
Distinguishing between disease severity and OCA requiring surgical intervention remains challenging. Although studies in our review suggest a trend toward markers of inflammation (fever, elevated WBC count and CRP) being more common in more severe presentations, the results were mixed, and studies were low quality and underpowered to detect meaningful differences. For example, most studies do not define what constitutes a fever in their cohort. Our review suggests that markers of inflammation cannot be used to distinguish between Chandler groups or to identify patients requiring surgery. Of note, the presence of fever and elevated inflammatory markers may have influenced the decision to obtain imaging or to proceed to surgery, thereby also potentially biasing these clinical indicators toward predictors for more severe disease. Decisions regarding surgery should therefore be based on the entire clinical picture, including response to appropriate antibiotics.
We found a lack of high-quality evidence regarding the role of imaging in OCA, and the studies reviewed were heterogeneous. Recommendations for imaging therefore remain at the level of expert opinion (ACR criteria). CT imaging is the first-line modality for imaging in suspected OCA given the limitations of alternative imaging modalities, but the sensitivity and specificity of CT imaging remain unknown for diagnosis of orbital abscesses.
Our review of the published microbiology confirmed that Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species are the most common pathogens identified in OCA. Prevalence across the different studies varied greatly. Owing to the significant heterogeneity in studies, calculation of pooled prevalence was not possible. By using the number of positive cultures as our denominator (or total surgeries if number of positive cultures was unavailable), we likely overestimated the prevalence of S aureus. S aureus is generally recognized as a pyogenic pathogen, more likely to be associated with abscess formation.48 Therefore, culture results obtained predominantly from abscesses likely result in an overestimate of S aureus in OCA (groups 2, 3, and 4). Regardless, MRSA prevalence was generally low, both nationally and internationally. The MRSA results from the study by McKinley at el49 (Texas) was a notable outlier in the United States, with MRSA prevalence as high as 44% compared with the median prevalence of 3% (IQR, 0-13), highlighting the importance of local resistance patterns when choosing empiric antibiotics.
Limitations to the microbiology review included significant heterogeneity in both the types of cultures included and the reporting of results. Although we excluded studies that reported only surface culture results or did not specify culture type, we did include studies that had surface culture results combined with intraoperative culture results, making it impossible to separate the two. Since most of the cultures included in combined results reported organisms based on intraoperative cultures, we felt they provided valuable information that should be included. In most studies, blood cultures were not obtained in all participants, so the yield of blood cultures is likely an overestimate, as blood cultures are more likely to be obtained in higher-acuity patients.
CONCLUSION
Although the available evidence regarding the medical management of OCA remains low quality, certain limited conclusions can be drawn, as presented in this review. Further high-quality studies are needed to better inform the medical management of OCA.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Dr Kyle Pronko for his help with data extraction for the imaging section.
Orbital cellulitis/abscess (OCA) is a potential complication of sinusitis. If not treated promptly, it can result in vision loss, intracranial infection, or cavernous sinus thrombosis.1,2 In 1970, Chandler et al3 classified orbital complications of acute sinusitis into five groups: inflammatory edema (group 1); orbital cellulitis (group 2); subperiosteal abscess (SPA) (group 3); orbital abscess (group 4); and cavernous sinus thrombosis (group 5). Group 1, or preseptal cellulitis, is significantly different from groups 2, 3, and 4, collectively referred to as OCA, which affect the actual orbital content.
Children with OCA are generally hospitalized so they can be treated with intravenous antibiotics. While orbital abscesses (group 4) are typically treated surgically, successful medical management has been reported for cases of orbital cellulitis and SPA (groups 2 and 3).4,5 No widely accepted guidelines exist for the evaluation and medical management of OCA, resulting in significant variation in care.6 The purpose of this systematic review is to summarize existing evidence guiding the medical management of OCA regarding laboratory testing, imaging, and microbiology. This review does not address surgical considerations.
METHODS
The review protocol has been registered in the PROSPERO International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/index.asp; identifier: CRD42020158463), and the review was reported according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.7
Search Strategy
A systematic search of the literature was designed and conducted by a medical librarian (ES), with input from the research team (AB, SM). The search strategy included Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms and keywords related to orbital or subperiosteal cellulitis/abscess and children; see Appendix Table 1 for the complete search strategy. Searches were conducted in MEDLINE (Ovid), Web of Science Core Collection, Scopus, CINAHL (EBSCO), and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) using advanced search techniques relative to each database. Searches were last conducted on February 9, 2021.
Eligibility Criteria
The study designs (retrospective and prospective) included in the search were limited to randomized clinical trials, cohort studies, case-control studies, and case series with participants <18 years of age. Case reports describing fewer than 5 patients and literature reviews were excluded. Studies including a combination of adult and pediatric patients were included if pediatric outcomes were reported separately. Only studies available in English were included.
Outcome Measures
The outcome measures were determined a priori based on three clinical questions:
- Q1. What is the role of inflammatory markers—white blood cell (WBC) count, C-reactive protein (CRP), and fever—in distinguishing between the following: preseptal cellulitis (group 1) and OCA (groups 2, 3, and 4); orbital cellulitis (group 2) and abscess (groups 3 and 4); and patients who do and do not require surgery?
- Q2. What is the role of imaging in the evaluation of OCA?
- Q3. What is the microbiology of OCA over the past 2 decades? What is the prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)?
Screening
Two review authors (AB, SM) performed both the title/abstract and full-text screen, independently applying the eligibility criteria. Disagreements were discussed, and conflicts were resolved with input from a third reviewer author (ES). Duplications were removed. When two studies had overlapping patient data, the study with fewer data points was excluded.
Data Extraction and Synthesis
All studies included after the full-text screen were divided based on the clinical question they answered (Q1, Q2, Q3 above). Some studies reported outcomes pertinent to more than one question. Two review authors were assigned to each clinical question. They independently reviewed each article and extracted the pertinent data into question-specific extraction sheets. Articles assigned to Q2 were reviewed by two pediatric neuroradiologists. For each study, the following details were extracted: authors, location, year, study type, study period, population, and number and ages of participants. Details that were question-specific included: (Q1) values and/or percentages for inflammatory markers; (Q2) reasons for imaging or type of imaging; and (Q3) participants managed surgically and culture results. The data were then synthesized in table and/or narrative format. For Q3, the organisms identified from intraoperative and blood cultures in each study were mathematically combined. When possible, prevalence was calculated using the number of patients with at least one pathogen recovered as the denominator. If this number was not available, the number of patients who underwent surgery was used as the denominator.
Quality Assessment
No randomized controlled trials were identified. More than 90% of the studies identified and included were retrospective descriptive studies. By the nature of the case series design, the study quality was felt to be poor, with high risk of bias. The Joanna Briggs Institute Critical Appraisal tools for systematic reviews were used to appraise each individual study included (Appendix Table 2).8 The Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE) criteria were used in rating the quality of evidence for each question.9
RESULTS
A summary of the search strategy and study selection is provided in the Figure (PRISMA flow diagram). The initial search identified 3007 studies. After duplicates were removed and general eligibility criteria applied, 94 articles remained. Question-specific eligibility criteria, discussed in the following sections, were then applied, resulting in 63 articles included in the review.

Q1: Are Inflammatory Markers, Including Fever, WBC, and CRP, Useful in Distinguishing Preseptal Cellulitis (group 1) From OCA (Groups 2, 3, and 4); Orbital Cellulitis (group 2) From Abscess (Groups 3 and 4); or Identifying Patients Who Require Surgical Intervention?
Fever and elevation of the WBC count and CRP have been used to assess the severity of certain pediatric infections10,11 and therefore may be helpful in distinguishing severity of illness in OCA. Studies included in this section provided numerical values for at least one of the following: WBC count, CRP, or percentage of patients with fever for at least one type of orbital infection. Included studies had at least five patients per group.
Thirty-three articles were screened for the inflammatory marker section. Thirteen were excluded for the following reasons: no numbers reported for inflammatory markers (n = 6); group 1 and groups 2, 3, and 4 results combined (n = 6); fewer than five patients with orbital cellulitis included (n = 1). Twenty studies were included: 18 case series and 2 retrospective cohorts. Appendix Table 3 summarizes the data from studies included. Based on GRADE criteria, the body of evidence included in this section is of low quality.9
Distinguishing Between Preseptal and OCA
Eleven studies were included in this section (Table 1). WBC count was significantly higher in patients with groups 2, 3, and 4 than group 1 in two studies (Devrim et al,12P < .01; Santos et al,13P = .025). CRP was significantly higher in patients with groups 2, 3, and 4 than group 1 in four studies (Öcal Demir et al,14P = .02; Devrim et al,12P < .01; Ohana-Sarna-Cahan et al,18P < .001; Santos et al,13P < .001). Patients with groups 2, 3, and 4 had a significantly higher fever rate in three studies (Botting et al,21P < .001; Ohana-Sarna-Cahan et al,18P = .0001; Santos et al,13 P = .029).

Distinguishing Between Orbital Cellulitis and Abscess
Seven studies were included in this section (Appendix Table 3). One study showed significantly higher WBC count in group 3 than group 2 (P = .004), although results were reported as percentage of patients above a cutoff number calculated to distinguish between cellulitis and abscess (Appendix Table 3).22 CRP was not significantly different between group 2 and groups 3 and 4. One study found a significantly higher fever rate in patients with group 3 compared to patients with group 2 (P < .001).22
Identifying Patients Requiring Surgery
Six studies were included in this section (Appendix Table 3). One study found a significantly higher WBC count in patients treated surgically (Tabarino et al,24P < .05). Patients treated surgically had a significantly higher CRP in two studies (Cohen et al,25P = .02; Friling et al,26 P = .04). Fever was inconsistently reported in the studies, with some using mean presenting temperatures and some using rates of fever. One study found a significantly higher mean presenting temperature in patients treated surgically (P = .027), but the difference between the two groups was 0.7 °C.23
Summary
Most studies found no significant difference in WBC count, CRP, or fever between preseptal and OCA, cellulitis and abscess, or patients receiving medical and surgical interventions.
Q2: What Is the Role of Imaging in Evaluation of OCA?
Twenty-five articles were selected for the imaging section review. All the included studies were retrospective descriptive studies. Quantitative data extraction and analysis of these studies could not be performed because of their heterogeneous methodologies and lack of objective data. Therefore, the information gleaned from these studies is summarized in narrative format. Per GRADE criteria, the body of evidence included in this section is of low quality.
Who Needs Imaging?
Proptosis, ophthalmoplegia, decreased vision, and pain with eye movements are widely agreed-upon indications for imaging evaluation.21,27,28 Because of concern for radiation exposure in pediatric patients, some authors suggested that computed tomography (CT) should only be obtained if patients fail to respond to medical therapy or if surgery is being considered.17,29,30 However, Rudloe et al31 found that half of the patients with group 3 or higher disease on CT did not have proptosis, ophthalmoplegia, or pain with extraocular movement. In addition, evaluation of young children with acute periorbital swelling can be difficult, so a lower threshold for imaging is likely warranted in these younger patients.
What Type of Imaging Should Be Obtained?
The American College of Radiology 2018 Appropriateness Criteria (ACR criteria) for orbital imaging state that orbital CT is usually indicated for patients with suspected Chandler groups 2, 3, and 4 infections.32 CT with contrast is useful for evaluating the extent of orbital infection and size of the abscess and for delineating the adjacent osseous anatomy, which is essential for cases in which surgical intervention is planned.20,21,26,27,30,31,33,34 Distinguishing abscess from cellulitis on CT sometimes can be challenging; therefore, serial clinical examinations and, occasionally, surgical exploration may be required.35,36
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is helpful for evaluating intracranial complications (eg, epidural abscess),27,37 but it is limited for evaluating the osseous components of the paranasal sinuses. Although one study suggested that rapid MRI is comparable to contrast CT for differentiating group 1 infections from groups 2, 3, and 4 infections, it provided limited assessment of other complications.38 With no definitive studies comparing CT with MRI for orbital infections, adherence to the ACR criteria is recommended.
Orbital ultrasound is limited by its small field of view and artifact produced by the surrounding bony interface, both of which can obscure posterior intraorbital pathologies.29,39,40 Plain radiographs are not helpful for evaluating OCA due to limited soft-tissue contrast.41
When Should Repeat Imaging Be Obtained?
Children with group 3 OCA have been successfully managed medically in a carefully monitored setting.42 Repeat CT imaging is sometimes useful in these patients, particularly if the clinical examination is difficult.42-44 However, improvement in CT findings may lag behind clinical improvement.39
Summary
Per ACR criteria, orbital CT with contrast is recommended to evaluate patients with suspected Chandler groups 2, 3, and 4 OCA. MRI is reserved for evaluating intracranial complications.
Q3: What Is the Microbiology of OCA? What Is the MRSA Prevalence?
Knowledge of the microbiology of OCA is essential for the appropriate selection of empiric antibiotics. Because fewer children with groups 2 and 3 OCA undergo surgery, intraoperative cultures often are not available to guide antibiotic selection.45 As a result, significant variation exists in antibiotic prescribing.6
Studies discussing the microbiology of OCA were included only if they were published in the past 2 decades (2000-2020) and were excluded if the study period was before 1990, as microbiology changes over time and new vaccines are introduced. To be included, the majority of cultures reported had to be intraoperative (orbital or sinus) specimens. Studies reporting only nasal, conjunctival, or other surface cultures were excluded. When studies included patients with group 1 OCA, only microbiology data for groups 2, 3, and 4 OCA were extracted. The pattern of resistance for S aureus was not always explicitly reported; however, when non-MRSA active antibiotics were used, methicillin-susceptible S aureus was assumed.
A total of 63 studies were screened for the microbiology section; 32 were excluded for the following reasons: published before 2000 or study period before 1990 (n = 18), reported surface cultures or culture site not clearly stated (n = 4), microbiology mixed between preseptal and orbital (n = 6), wrong study type (n = 2), and study group overlaps with a different article included (n = 2). Of the 32 studies included, 3 were prospective observational, 4 were retrospective cohort, and 25 were case series. Based on GRADE criteria, the body of evidence included in this section is of low quality.42
Appendix Table 4 summarizes the microbiologic data from the studies included. In the group of children that had a positive culture (orbital, sinus, or blood), the most commonly recovered organisms reported were S aureus (median, 22%; range, 0%-100%), Streptococcus anginosus group (median, 16%; range, 0%-100%), group A Streptococcus (median, 12%; range, 0%-80%), and Streptococcus pneumoniae (median, 8%; range, 0%-100%). Streptococcus as a group had a median prevalence of 57%, ranging from 0% to 100%. MRSA prevalence had a median of 3% (interquartile range [IQR], 0%-13%). Median prevalence of polymicrobial cultures was 20%, and median prevalence of anaerobic organisms was 14% (Table 2). Orbital and sinus cultures had the highest yield, with an average return of an organism of 72% (median, 75%; IQR, 64%-84%).

Microbiology was compared between studies completed in the United States and in other countries (Table 2). Based on median prevalence across studies, both S anginosus group and MRSA were more prevalent in the United States than internationally (28% vs 0% and 11% vs 0%, respectively). No clear trend in MRSA prevalence was evident over the 2 decades; however, the studies included were heterogeneous and did not have the power to detect such a trend.
Two reports suggest a difference of MRSA prevalence by patient age. Hsu et al46 found that three of eight MRSA infections were in infants age <1 year, which accounted for 50% (3/6) of infants included in the study. Miller et al47 reported MRSA in 4 of 9 (44%) infants with OCA. Age <1 year may be associated with increased frequency of MRSA infection in OCA.
Summary
Blood cultures have low yield. The most common organisms recovered from OCA are Streptococcus species (most commonly S anginosus group, group A Streptococcus, and pneumococcus) and S aureus. Polymicrobial infections including anaerobes are common. MRSA prevalence is low globally but varies significantly among geographic areas.
DISCUSSION
Our systematic review of the literature for the medical management of OCA revealed predominantly descriptive studies and only a limited number of comparison-based studies, likely reflecting the rarity of advanced forms of OCA. Given the lack of high-quality evidence and the level of heterogeneity among studies, the conclusions that can be drawn are limited.
Distinguishing between disease severity and OCA requiring surgical intervention remains challenging. Although studies in our review suggest a trend toward markers of inflammation (fever, elevated WBC count and CRP) being more common in more severe presentations, the results were mixed, and studies were low quality and underpowered to detect meaningful differences. For example, most studies do not define what constitutes a fever in their cohort. Our review suggests that markers of inflammation cannot be used to distinguish between Chandler groups or to identify patients requiring surgery. Of note, the presence of fever and elevated inflammatory markers may have influenced the decision to obtain imaging or to proceed to surgery, thereby also potentially biasing these clinical indicators toward predictors for more severe disease. Decisions regarding surgery should therefore be based on the entire clinical picture, including response to appropriate antibiotics.
We found a lack of high-quality evidence regarding the role of imaging in OCA, and the studies reviewed were heterogeneous. Recommendations for imaging therefore remain at the level of expert opinion (ACR criteria). CT imaging is the first-line modality for imaging in suspected OCA given the limitations of alternative imaging modalities, but the sensitivity and specificity of CT imaging remain unknown for diagnosis of orbital abscesses.
Our review of the published microbiology confirmed that Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species are the most common pathogens identified in OCA. Prevalence across the different studies varied greatly. Owing to the significant heterogeneity in studies, calculation of pooled prevalence was not possible. By using the number of positive cultures as our denominator (or total surgeries if number of positive cultures was unavailable), we likely overestimated the prevalence of S aureus. S aureus is generally recognized as a pyogenic pathogen, more likely to be associated with abscess formation.48 Therefore, culture results obtained predominantly from abscesses likely result in an overestimate of S aureus in OCA (groups 2, 3, and 4). Regardless, MRSA prevalence was generally low, both nationally and internationally. The MRSA results from the study by McKinley at el49 (Texas) was a notable outlier in the United States, with MRSA prevalence as high as 44% compared with the median prevalence of 3% (IQR, 0-13), highlighting the importance of local resistance patterns when choosing empiric antibiotics.
Limitations to the microbiology review included significant heterogeneity in both the types of cultures included and the reporting of results. Although we excluded studies that reported only surface culture results or did not specify culture type, we did include studies that had surface culture results combined with intraoperative culture results, making it impossible to separate the two. Since most of the cultures included in combined results reported organisms based on intraoperative cultures, we felt they provided valuable information that should be included. In most studies, blood cultures were not obtained in all participants, so the yield of blood cultures is likely an overestimate, as blood cultures are more likely to be obtained in higher-acuity patients.
CONCLUSION
Although the available evidence regarding the medical management of OCA remains low quality, certain limited conclusions can be drawn, as presented in this review. Further high-quality studies are needed to better inform the medical management of OCA.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Dr Kyle Pronko for his help with data extraction for the imaging section.
1. Reynolds D.J, Kodsi SR, Rubin SE, Rodgers IR. Intracranial infection associated with preseptal and orbital cellulitis in the pediatric patient. J AAPOS. 2003;7(6):413-417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaapos.2003.09.013
2. Chaudhry IA, Shamsi FA, Elzaridi E, et al. Outcome of treated orbital cellulitis in a tertiary eye care center in the Middle East. Ophthalmology. 2007;114(2):345-354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2006.07.059
3. Chandler JR, Langenbrunner DJ, Stevens ER. Pathogenesis of orbital complications in acute sinusitis. Laryngoscope. 1970;1414-1428. https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-197009000-00007
4. Wong SJ, Levi J. Management of pediatric orbital cellulitis: a systematic review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2018;110:123-129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2018.05.006
5. Liao JC, Harris GJ. Subperiosteal abscess of the orbit: evolving pathogens and the therapeutic protocol. Ophthalmology. 2015;122(3):639-647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.09.009
6. Markham JL, Hall M, Bettenhausen JL, Myers AL, Puls HT, McColloh RJ. Variation in care and clinical outcomes in children hospitalized with orbital cellulitis. Hosp Pediatr. 2018;8(1):28-35. https://doi.org/10.1542/hpeds.2017-0040
7. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
8. Munn Z, Barker TH, Moola S, et al. Methodological quality of case series studies: an introduction to the JBI critical appraisal tool. JBI Evid Synth. 2020;18(10):2127-2133. https://doi.org/10.11124/JBISRIR-D-19-00099
9. Balshem H, Helfand M, Schünemann HJ, et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(4):401-406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.07.015
10. Dean P, Florin TA. Factors associated with pneumonia severity in children: a systematic review. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2018;7(4):323-334. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpids/piy046
11. Hofer N, Zacharias E, Müller W, Resch B. An update on the use of C-reactive protein in early-onset neonatal sepsis: current insights and new tasks. Neonatology. 2012;102(1):25-36. https://doi.org/10.1159/000336629
12. Devrim I, Kanra G, Kara A, et al. Preseptal and orbital cellulitis: 15-year experience with sulbactam ampicillin treatment. Turk J Pediatr. 2008;50(3):214-218.
13. Santos JC, Pinto S, Ferreira S, Maia C, Alves S, da Silva V. Pediatric preseptal and orbital cellulitis: a 10-year experience. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;120:82-88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.02.003
14. Öcal Demir S , Çagan E, Kepenekli Kadayifci E, et al. Clinical features and outcome of preseptal and orbital cellulitis in hospitalized children: four years experience. Medeni Med J. 2017;32(1):7-13. https://doi.org/10.5222/MMJ.2017.007
15. Georgakopoulos CD, Eliopoulou MI, Stasinos S, Exarchou A, Pharmakakis N, Varvarigou A. Periorbital and orbitaln cellulitis: a 10-year review of hospitalized children. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2010;20(6):1066-1072. https://doi.org/10.1177/112067211002000607
16. Gonçalves R, Menezes C, Machado R, Ribeiro I, Lemos JA. Periorbital cellulitis in children: analysis of outcome of intravenous antibiotic therapy. Orbit. 2016;34(4):175-180. https://doi.org/10.1080/01676830.2016.1176205
17. Ho CF, Huang YC, Wang CJ, Chiu CH, Lin TY. Clinical analysis of computed tomography-staged orbital cellulitis in children. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2017;40(6):518-524.
18. Ohana-Sarna-Cahan L, Hurvitz N, Gross I, Cohen A, Hashavya S. Factors associated with increased risk of pediatric orbital cellulitis—who should be scanned? Pediatr Emerg Care. Published online ahead of print March 19, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000002083
19. Weiss A, Friendly D, Eglin K, Chang M, Gold B. Bacterial periorbital and orbital cellulitis in childhood. Ophthalmology. 1983;90(3):195-203. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0161-6420(83)34573-5
20. Le TD, Liu ES, Adatia FA, Buncic JR Blaser S. The effect of adding orbital computed tomography findings to the Chandler criteria for classifying pediatric orbital cellulitis in predicting which patients will require surgical intervention. J AAPOS. 2014;18(3):271-277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaapos.2014.01.015
21. Botting AM, McIntosh D, Mahadevan M. Paediatric pre- and post-septal peri-orbital infections are different diseases. A retrospective review of 262 cases. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2008;72(3):377-383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2007.11.013
22. Huang SF, Lee TJ, Lee YS, Chen CC, Chin SC, Wang NC. Acute rhinosinusitis-related orbital infection in pediatric patients: a retrospective analysis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2011;120(3):185-190. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348941112000307
23. Ryan JT, Preciado A, Bauman N, et al. Management of pediatric orbital cellulitis in patients with radiographic findings of subperiosteal abscess. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;140(6):907-911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2009.02.014
24. Tabarino F, Elmaleh-Bergès M, Quesnel S, Lorrot M, Van Den Abbeele T, Teissier N. Subperiosteal orbital abscess: volumetric criteria for surgical drainage. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015;79(2):131-135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2014.11.021
25. Cohen N, Erisson S, Anafy A, et al. Clinicians need to consider surgery when presented with some markers for severe paediatric orbital cellulitis. Acta Paediatr. 2020;109(6):1269-1270. https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.15125
26. Friling R, Garty BZ, Kornreich L, et al. Medical and surgical management of orbital cellulitis in children. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2014;56(4):253-258. https://doi.org/10.1515/folmed-2015-0004
27. Gavriel H, Yeheskeli E, Aviram E, Yehoshua L, Eviatar E. Dimension of subperiosteal orbital abscess as an indication for surgical management in children. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011;145(5):823-827. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599811416559
28. Mathew AV, Craig E, Al-Mahmoud R, et al. Paediatric post-septal and pre-septal cellulitis: 10 years’ experience at a tertiary-level children’s hospital. Br J Radiol. 2014;87(1033):20130503. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20130503
29. Goodwin WJ Jr, Weinshall M, Chandler JR. The role of high resolution computerized tomography and standardized ultrasound in the evaluation of orbital cellulitis. Laryngoscope. 1982;92(7 pt 1):729-731.
30. Bilaniuk LT, Zimmerman RA. Computer‐assisted tomography: sinus lesions with orbital involvement. Head Neck Surg. 1980;2(4):293-301. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.2890020407
31. Rudloe TF, Harper MB, Prabhu SP, Rahbar R, Vanderveen D, Kimia AA. Acute periorbital infections: who needs emergent imaging? Pediatrics. 2010;125(4):e719-e726. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-1709
32. Kennedy TA, Corey AS, Policeni B, et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® orbits vision and visual loss. J Am Coll Radiol. 2018;15(5S):S116-S131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2018.03.023
33. De Silva M, Lam V, Broadfoot J. C.T. findings of orbital inflammation in children. Australas Radiol. 1987;31(3):241-245. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1673.1987.tb01822.x
34. Hirsch M, Lifshitz T. Computerized tomography in the diagnosis and treatment of orbital cellulitis. Pediatr Radiol. 1988;18(4):302-305. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02388996
35. Andrews TM, Myer CM 3rd. The role of computed tomography in the diagnosis of subperiosteal abscess of the orbit. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1992;31(1):37-43. https://doi.org/10.1177/000992289203100108
36. Clary RA, Cunningham MJ, Eavey RD. Orbital complications of acute sinusitis: comparison of computed tomography scan and surgical findings. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1992;101(7):598-600. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348949210100710
37. Arjmand EM, LuskRP, Muntz HR. Pediatric sinusitis and subperiosteal orbital abscess formation: diagnosis and treatment. Otolaryngol Neck Surg. 1993;109(5):886.894. https://doi.org/10.1177/019459989310900518
38. Jain SF, Ishihara R, Wheelock L, et al. Feasibility of rapid magnetic resonance imaging (rMRI) for the emergency evaluation of suspected pediatric orbital cellulitis. J AAPOS. 2020;24(5):289.e1-289.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaapos.2020.05.018
39. Harris GJ. Subperiosteal abscess of the orbit: computed tomography and the clinical course. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996;12:1-8. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002341-199603000-00001
40. Kaplan DM, Briscoe D, Gatot A, Niv A, Leiberman A, Fliss DM. The use of standardized orbital ultrasound in the diagnosis of sinus induced infections of the orbit in children: a preliminary report. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1999;48(2):155-162. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-5876(99)00023-3
41. Towbin R, Han BK, Kaufman RA, Burke M. Postseptal cellulitis: CT in diagnosis and management. Radiology. 1986;158(3):735-737. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.158.3.3945747
42. Starkey CR, Steele RW. Medical management of orbital cellulitis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20(10):1002-1005. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006454-200110000-00017
43. Brown CL, Graham SM, Griffin MC, et al. Pediatric medial subperiosteal orbital abscess: medical management where possible. Am J Rhinol. 2004;18(5):321-327.
44. Cossack MT, Herretes SP, Cham A, Sniegowski MC, Lyon DB. Radiographic course of medically managed pediatric orbital subperiosteal abscesses. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2018;55(6):387-392. https://doi.org/10.3928/01913913-20180802-02
45. Zhao EE, Koochakzadeh S, Nguyen SA, et al. Orbital complications of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis in the pediatric population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;135:110078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110078
46. Hsu J, Treister AD, Ralay Ranaivo H, Rowley AH, Rahmani B. Microbiology of pediatric orbital cellulitis and trends in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus cases. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2019;58(10):1056-1062. https://doi.org/10.1177/0009922819864587
47. Miller A, Castanes M, Yen M, Coats D, Yen K. Infantile orbital cellulitis. Ophthalmology. 2008;115(3):594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2007.10.011
48. Dajani AS, Garcia RE, Wolinsky E. Etiology of cervical lymphadenitis in children. N Engl J Med. 1963;268:1329-1333. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM196306132682403
49. McKinley SH, Yen MT, Miller AM, Yen KG. Microbiology of pediatric orbital cellulitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007;144(4):497-501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2007.04.049
1. Reynolds D.J, Kodsi SR, Rubin SE, Rodgers IR. Intracranial infection associated with preseptal and orbital cellulitis in the pediatric patient. J AAPOS. 2003;7(6):413-417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaapos.2003.09.013
2. Chaudhry IA, Shamsi FA, Elzaridi E, et al. Outcome of treated orbital cellulitis in a tertiary eye care center in the Middle East. Ophthalmology. 2007;114(2):345-354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2006.07.059
3. Chandler JR, Langenbrunner DJ, Stevens ER. Pathogenesis of orbital complications in acute sinusitis. Laryngoscope. 1970;1414-1428. https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-197009000-00007
4. Wong SJ, Levi J. Management of pediatric orbital cellulitis: a systematic review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2018;110:123-129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2018.05.006
5. Liao JC, Harris GJ. Subperiosteal abscess of the orbit: evolving pathogens and the therapeutic protocol. Ophthalmology. 2015;122(3):639-647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.09.009
6. Markham JL, Hall M, Bettenhausen JL, Myers AL, Puls HT, McColloh RJ. Variation in care and clinical outcomes in children hospitalized with orbital cellulitis. Hosp Pediatr. 2018;8(1):28-35. https://doi.org/10.1542/hpeds.2017-0040
7. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
8. Munn Z, Barker TH, Moola S, et al. Methodological quality of case series studies: an introduction to the JBI critical appraisal tool. JBI Evid Synth. 2020;18(10):2127-2133. https://doi.org/10.11124/JBISRIR-D-19-00099
9. Balshem H, Helfand M, Schünemann HJ, et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(4):401-406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.07.015
10. Dean P, Florin TA. Factors associated with pneumonia severity in children: a systematic review. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2018;7(4):323-334. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpids/piy046
11. Hofer N, Zacharias E, Müller W, Resch B. An update on the use of C-reactive protein in early-onset neonatal sepsis: current insights and new tasks. Neonatology. 2012;102(1):25-36. https://doi.org/10.1159/000336629
12. Devrim I, Kanra G, Kara A, et al. Preseptal and orbital cellulitis: 15-year experience with sulbactam ampicillin treatment. Turk J Pediatr. 2008;50(3):214-218.
13. Santos JC, Pinto S, Ferreira S, Maia C, Alves S, da Silva V. Pediatric preseptal and orbital cellulitis: a 10-year experience. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;120:82-88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.02.003
14. Öcal Demir S , Çagan E, Kepenekli Kadayifci E, et al. Clinical features and outcome of preseptal and orbital cellulitis in hospitalized children: four years experience. Medeni Med J. 2017;32(1):7-13. https://doi.org/10.5222/MMJ.2017.007
15. Georgakopoulos CD, Eliopoulou MI, Stasinos S, Exarchou A, Pharmakakis N, Varvarigou A. Periorbital and orbitaln cellulitis: a 10-year review of hospitalized children. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2010;20(6):1066-1072. https://doi.org/10.1177/112067211002000607
16. Gonçalves R, Menezes C, Machado R, Ribeiro I, Lemos JA. Periorbital cellulitis in children: analysis of outcome of intravenous antibiotic therapy. Orbit. 2016;34(4):175-180. https://doi.org/10.1080/01676830.2016.1176205
17. Ho CF, Huang YC, Wang CJ, Chiu CH, Lin TY. Clinical analysis of computed tomography-staged orbital cellulitis in children. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2017;40(6):518-524.
18. Ohana-Sarna-Cahan L, Hurvitz N, Gross I, Cohen A, Hashavya S. Factors associated with increased risk of pediatric orbital cellulitis—who should be scanned? Pediatr Emerg Care. Published online ahead of print March 19, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000002083
19. Weiss A, Friendly D, Eglin K, Chang M, Gold B. Bacterial periorbital and orbital cellulitis in childhood. Ophthalmology. 1983;90(3):195-203. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0161-6420(83)34573-5
20. Le TD, Liu ES, Adatia FA, Buncic JR Blaser S. The effect of adding orbital computed tomography findings to the Chandler criteria for classifying pediatric orbital cellulitis in predicting which patients will require surgical intervention. J AAPOS. 2014;18(3):271-277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaapos.2014.01.015
21. Botting AM, McIntosh D, Mahadevan M. Paediatric pre- and post-septal peri-orbital infections are different diseases. A retrospective review of 262 cases. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2008;72(3):377-383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2007.11.013
22. Huang SF, Lee TJ, Lee YS, Chen CC, Chin SC, Wang NC. Acute rhinosinusitis-related orbital infection in pediatric patients: a retrospective analysis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2011;120(3):185-190. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348941112000307
23. Ryan JT, Preciado A, Bauman N, et al. Management of pediatric orbital cellulitis in patients with radiographic findings of subperiosteal abscess. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;140(6):907-911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2009.02.014
24. Tabarino F, Elmaleh-Bergès M, Quesnel S, Lorrot M, Van Den Abbeele T, Teissier N. Subperiosteal orbital abscess: volumetric criteria for surgical drainage. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015;79(2):131-135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2014.11.021
25. Cohen N, Erisson S, Anafy A, et al. Clinicians need to consider surgery when presented with some markers for severe paediatric orbital cellulitis. Acta Paediatr. 2020;109(6):1269-1270. https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.15125
26. Friling R, Garty BZ, Kornreich L, et al. Medical and surgical management of orbital cellulitis in children. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2014;56(4):253-258. https://doi.org/10.1515/folmed-2015-0004
27. Gavriel H, Yeheskeli E, Aviram E, Yehoshua L, Eviatar E. Dimension of subperiosteal orbital abscess as an indication for surgical management in children. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011;145(5):823-827. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599811416559
28. Mathew AV, Craig E, Al-Mahmoud R, et al. Paediatric post-septal and pre-septal cellulitis: 10 years’ experience at a tertiary-level children’s hospital. Br J Radiol. 2014;87(1033):20130503. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20130503
29. Goodwin WJ Jr, Weinshall M, Chandler JR. The role of high resolution computerized tomography and standardized ultrasound in the evaluation of orbital cellulitis. Laryngoscope. 1982;92(7 pt 1):729-731.
30. Bilaniuk LT, Zimmerman RA. Computer‐assisted tomography: sinus lesions with orbital involvement. Head Neck Surg. 1980;2(4):293-301. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.2890020407
31. Rudloe TF, Harper MB, Prabhu SP, Rahbar R, Vanderveen D, Kimia AA. Acute periorbital infections: who needs emergent imaging? Pediatrics. 2010;125(4):e719-e726. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-1709
32. Kennedy TA, Corey AS, Policeni B, et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® orbits vision and visual loss. J Am Coll Radiol. 2018;15(5S):S116-S131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2018.03.023
33. De Silva M, Lam V, Broadfoot J. C.T. findings of orbital inflammation in children. Australas Radiol. 1987;31(3):241-245. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1673.1987.tb01822.x
34. Hirsch M, Lifshitz T. Computerized tomography in the diagnosis and treatment of orbital cellulitis. Pediatr Radiol. 1988;18(4):302-305. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02388996
35. Andrews TM, Myer CM 3rd. The role of computed tomography in the diagnosis of subperiosteal abscess of the orbit. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1992;31(1):37-43. https://doi.org/10.1177/000992289203100108
36. Clary RA, Cunningham MJ, Eavey RD. Orbital complications of acute sinusitis: comparison of computed tomography scan and surgical findings. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1992;101(7):598-600. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348949210100710
37. Arjmand EM, LuskRP, Muntz HR. Pediatric sinusitis and subperiosteal orbital abscess formation: diagnosis and treatment. Otolaryngol Neck Surg. 1993;109(5):886.894. https://doi.org/10.1177/019459989310900518
38. Jain SF, Ishihara R, Wheelock L, et al. Feasibility of rapid magnetic resonance imaging (rMRI) for the emergency evaluation of suspected pediatric orbital cellulitis. J AAPOS. 2020;24(5):289.e1-289.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaapos.2020.05.018
39. Harris GJ. Subperiosteal abscess of the orbit: computed tomography and the clinical course. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996;12:1-8. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002341-199603000-00001
40. Kaplan DM, Briscoe D, Gatot A, Niv A, Leiberman A, Fliss DM. The use of standardized orbital ultrasound in the diagnosis of sinus induced infections of the orbit in children: a preliminary report. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1999;48(2):155-162. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-5876(99)00023-3
41. Towbin R, Han BK, Kaufman RA, Burke M. Postseptal cellulitis: CT in diagnosis and management. Radiology. 1986;158(3):735-737. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.158.3.3945747
42. Starkey CR, Steele RW. Medical management of orbital cellulitis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20(10):1002-1005. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006454-200110000-00017
43. Brown CL, Graham SM, Griffin MC, et al. Pediatric medial subperiosteal orbital abscess: medical management where possible. Am J Rhinol. 2004;18(5):321-327.
44. Cossack MT, Herretes SP, Cham A, Sniegowski MC, Lyon DB. Radiographic course of medically managed pediatric orbital subperiosteal abscesses. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2018;55(6):387-392. https://doi.org/10.3928/01913913-20180802-02
45. Zhao EE, Koochakzadeh S, Nguyen SA, et al. Orbital complications of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis in the pediatric population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;135:110078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110078
46. Hsu J, Treister AD, Ralay Ranaivo H, Rowley AH, Rahmani B. Microbiology of pediatric orbital cellulitis and trends in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus cases. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2019;58(10):1056-1062. https://doi.org/10.1177/0009922819864587
47. Miller A, Castanes M, Yen M, Coats D, Yen K. Infantile orbital cellulitis. Ophthalmology. 2008;115(3):594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2007.10.011
48. Dajani AS, Garcia RE, Wolinsky E. Etiology of cervical lymphadenitis in children. N Engl J Med. 1963;268:1329-1333. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM196306132682403
49. McKinley SH, Yen MT, Miller AM, Yen KG. Microbiology of pediatric orbital cellulitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007;144(4):497-501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2007.04.049
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine
Methodologic Progress Note: A Clinician’s Guide to Logistic Regression
The ability to read and correctly interpret research is an essential skill, but most hospitalists—and physicians in general—do not receive formal training in biostatistics during their medical education.1-3 In addition to straightforward statistical tests that compare a single exposure and outcome, researchers commonly use statistical models to identify and quantify complex relationships among many exposures (eg, demographics, clinical characteristics, interventions, or other variables) and an outcome. Understanding statistical models can be challenging. Still, it is important to recognize the advantages and limitations of statistical models, how to interpret their results, and the potential implications of findings on current clinical practice.
In the article “Rates and Characteristics of Medical Malpractice Claims Against Hospitalists” published in the July 2021 issue of the Journal of Hospital Medicine, Schaffer et al4 used the Comparative Benchmarking System database, which is maintained by a malpractice insurer, to characterize malpractice claims against hospitalists. The authors used multiple logistic regression models to understand the relationship among clinical factors and indemnity payments. In this Progress Note, we describe situations in which logistic regression is the proper statistical method to analyze a data set, explain results from logistic regression analyses, and equip readers with skills to critically appraise conclusions drawn from these models.
Choosing an Appropriate Statistical Model
Statistical models often are used to describe the relationship among one or more exposure variables (ie, independent variables) and an outcome (ie, dependent variable). These models allow researchers to evaluate the effects of multiple exposure variables simultaneously, which in turn allows them to “isolate” the effect of each variable; in other words, models facilitate an understanding of the relationship between each exposure variable and the outcome, adjusted for (ie, independent of) the other exposure variables in the model.
Several statistical models can be used to quantify relationships within the data, but each type of model has certain assumptions that must be satisfied. Two important assumptions include characteristics of the outcome (eg, the type and distribution) and the nature of the relationships among the outcome and independent variables (eg, linear vs nonlinear). Simple linear regression, one of the most basic statistical models used in research,5 assumes that (a) the outcome is continuous (ie, any numeric value is possible) and normally distributed (ie, its histogram is a bell-shaped curve) and (b) the relationship between the independent variable and the outcome is linear (ie, follows a straight line). If an investigator wanted to understand how weight is related to height, a simple linear regression could be used to develop a mathematical equation that tells us how the outcome (weight) generally increases as the independent variable (height) increases.
Often, the outcome in a study is not a continuous variable but a simple success/failure variable (ie, dichotomous variable that can be one of two possible values). Schaffer et al4 examined the binary outcome of whether a malpractice claim case would end in an indemnity payment or no payment. Linear regression models are not equipped to handle dichotomous outcomes. Instead, we need to use a different statistical model: logistic regression. In logistic regression, the probability (p) of a defined outcome event is estimated by creating a regression model.
The Logistic Model
A probability (p) is a measure of how likely an event (eg, a malpractice claim ends in an indemnity payment or not) is to occur. It is always between 0 (ie, the event will definitely not occur) and 1 (ie, the event will definitely occur). A p of 0.5 means there is a 50/50 chance that the event will occur (ie, equivalent to a coin flip). Because p is a probability, we need to make sure it is always between 0 and 1. If we were to try to model p with a linear regression, the model would assume that p could extend beyond 0 and 1. What can we do?
Applying a transformation is a commonly used tool in statistics to make data work better within statistical models.6 In this case, we will transform the variable p. In logistic regression, we model the probability of experiencing the outcome through a transformation called a logit. The logit represents the natural logarithm (ln) of the ratio of the probability of experiencing the outcome (p) vs the probability of not experiencing the outcome (1 – p), with the ratio being the odds of the event occurring.
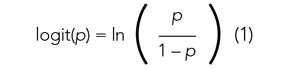
This transformation works well for dichotomous outcomes because the logit transformation approximates a straight line as long as p is not too large or too small (between 0.05 and 0.95).
If we are performing a logistic regression with only one independent variable (x) and want to understand the relationship between this variable (x) and the probability of an outcome event (p), then our model is the equation of a line. The equation for the base model of logistic regression with one independent variable (x) is
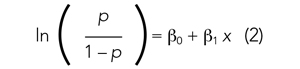
where β0 is the y-intercept and β1 is the slope of the line. Equation (2) is identical to the algebraic equation y = mx + b for a line, just rearranged slightly. In this algebraic equation, m is the slope (the same as β1) and b is the y-intercept (the same as β0). We will see that β0 and β1 are estimated (ie, assigned numeric values) from the data collected to help us understand how x and
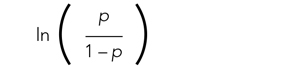
are related and are the basis for estimating odds ratios.
We can build more complex models using multivariable logistic regression by adding more independent variables to the right side of equation (2). Essentially, this is what S
There are two notable techniques used frequently with multivariable logistic regression models. The first involves choosing which independent variables to include in the model. One way to select variables for multivariable models is defining them a priori, that is deciding which variables are clinically or conceptually associated with the outcome before looking at the data. With this approach, we can test specific hypotheses about the relationships between the independent variables and the outcome. Another common approach is to look at the data and identify the variables that vary significantly between the two outcome groups. Schaffer et al4 used an a priori approach to define variables in their multivariable model (ie, “variables for inclusion into the multivariable model were determined a priori”).
A second technique is the evaluation of collinearity, which helps us understand whether the i
Understanding the Results of the Logistic Model
Fitting the model is the process by which statistical software (eg, SAS, Stata, R, SPSS) estimates the relationships among independent variables in the model and the outcome within a specific dataset. In equation (2), this essentially means that the software will evaluate the data and provide us with the best estimates for β0 (the y-intercept) and β1 (the slope) that describe the relationship between the variable x and
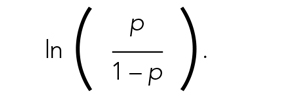
Modeling can be iterative, and part of the process may include removing variables from the model that are not significantly associated with the outcome to create a simpler solution, a process known as model reduction. The results from models describe the independent association between a specific characteristic and the outcome, meaning that the relationship has been adjusted for all the other characteristics in the model.
The relationships among the independent variables and outcome are most often represented as an odds ratio (OR), which quantifies the strength of the association between two variables and is directly calculated from the β values in the model. As the name suggests, an OR is a ratio of odds. But what are odds? Simply, the odds of an outcome (such as mortality) is the probability of experiencing the event divided by the probability of not experiencing that event; in other words, it is the ratio:

The concept of odds is often unfamiliar, so it can be helpful to consider the definition in the context of games of chance. For example, in horse race betting, the outcome of interest is that a horse will lose a race. Imagine that the probability of a horse losing a race is 0.8 and the probability of winning is 0.2. The odds of losing are
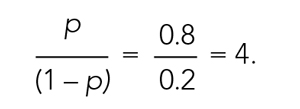
These odds usually are listed as 4-to-1, meaning that out of 5 races (ie, 4 + 1) the horse is expected to lose 4 times and win once. When odds are listed this way, we can easily calculate the associated probability by recognizing that the total number of expected races is the sum of two numbers (probability of losing: 4 races out of 5, or 0.80 vs probability of winning: 1 race out of 5, or 0.20).
In medical research, the OR typically represents the odds for one group of patients (A) compared with the odds for another group of patients (B) experiencing an outcome. If the odds of the outcome are the same for group A and group B, then OR = 1.0, meaning that the probability of the outcome is the same between the two groups. If the patients in group A have greater odds of experiencing the outcome compared with group B patients (and a greater probability of the outcome), then the OR will be >1. If the opposite is true, then the OR will be <1.
Schaffer et al4 estimated that the OR of an indemnity payment in malpractice cases involving errors in clinical judgment as a contributing factor was 5.01 (95% CI, 3.37-7.45). This means that malpractice cases involving errors in clinical judgement had a 5.01 times greater odds of indemnity payment compared with those without these errors after adjusting for all other variables in the model (eg, age, severity). Note that the 95% CI does not include 1.0. This indicates that the OR is statistically >1, and we can conclude that there is a significant relationship between errors in clinical judgment and payment that is unlikely to be attributed to chance alone.
In logistic regression for categorical independent variables, all categories are compared with a reference group within that variable, with the reference group serving as the denominator of the OR. The authors4 did not incorporate continuous independent variables in their multivariable logistic regression model. However, if the authors examined length of hospitalization as a contributing factor in indemnity payments, for example, the OR would represent a 1-unit increase in this variable (eg, 1-day increase in length of stay).
Conclusion
Logistic regression describes the relationships in data and is an important statistical model across many types of research. This Progress Note emphasizes the importance of weighing the advantages and limitations of logistic regression, provides a common approach to data transformation, and guides the correct interpretation of logistic regression model results.
1. Windish DM, Huot SJ, Green ML. Medicine residents’ understanding of the biostatistics and results in the medical literature. JAMA. 2007;298(9):1010. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.298.9.1010
2. MacDougall M, Cameron HS, Maxwell SRJ. Medical graduate views on statistical learning needs for clinical practice: a comprehensive survey. BMC Med Educ. 2019;20(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-019-1842-1
3. Montori VM. Progress in evidence-based medicine. JAMA. 2008;300(15):1814-1816. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.300.15.1814
4. Schaffer AC, Yu-Moe CW, Babayan A, Wachter RM, Einbinder JS. Rates and characteristics of medical malpractice claims against hospitalists. J Hosp Med. 2021;16(7):390-396. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3557
5. Lane DM, Scott D, Hebl M, Guerra R, Osherson D, Zimmer H. Introducton to Statistics. Accessed April 13, 2021. https://onlinestatbook.com/Online_Statistics_Education.pdf
6. Marill KA. Advanced statistics: linear regression, part II: multiple linear regression. Acad Emerg Med Off J Soc Acad Emerg Med. 2004;11(1):94-102. https://doi.org/10.1197/j.aem.2003.09.006
The ability to read and correctly interpret research is an essential skill, but most hospitalists—and physicians in general—do not receive formal training in biostatistics during their medical education.1-3 In addition to straightforward statistical tests that compare a single exposure and outcome, researchers commonly use statistical models to identify and quantify complex relationships among many exposures (eg, demographics, clinical characteristics, interventions, or other variables) and an outcome. Understanding statistical models can be challenging. Still, it is important to recognize the advantages and limitations of statistical models, how to interpret their results, and the potential implications of findings on current clinical practice.
In the article “Rates and Characteristics of Medical Malpractice Claims Against Hospitalists” published in the July 2021 issue of the Journal of Hospital Medicine, Schaffer et al4 used the Comparative Benchmarking System database, which is maintained by a malpractice insurer, to characterize malpractice claims against hospitalists. The authors used multiple logistic regression models to understand the relationship among clinical factors and indemnity payments. In this Progress Note, we describe situations in which logistic regression is the proper statistical method to analyze a data set, explain results from logistic regression analyses, and equip readers with skills to critically appraise conclusions drawn from these models.
Choosing an Appropriate Statistical Model
Statistical models often are used to describe the relationship among one or more exposure variables (ie, independent variables) and an outcome (ie, dependent variable). These models allow researchers to evaluate the effects of multiple exposure variables simultaneously, which in turn allows them to “isolate” the effect of each variable; in other words, models facilitate an understanding of the relationship between each exposure variable and the outcome, adjusted for (ie, independent of) the other exposure variables in the model.
Several statistical models can be used to quantify relationships within the data, but each type of model has certain assumptions that must be satisfied. Two important assumptions include characteristics of the outcome (eg, the type and distribution) and the nature of the relationships among the outcome and independent variables (eg, linear vs nonlinear). Simple linear regression, one of the most basic statistical models used in research,5 assumes that (a) the outcome is continuous (ie, any numeric value is possible) and normally distributed (ie, its histogram is a bell-shaped curve) and (b) the relationship between the independent variable and the outcome is linear (ie, follows a straight line). If an investigator wanted to understand how weight is related to height, a simple linear regression could be used to develop a mathematical equation that tells us how the outcome (weight) generally increases as the independent variable (height) increases.
Often, the outcome in a study is not a continuous variable but a simple success/failure variable (ie, dichotomous variable that can be one of two possible values). Schaffer et al4 examined the binary outcome of whether a malpractice claim case would end in an indemnity payment or no payment. Linear regression models are not equipped to handle dichotomous outcomes. Instead, we need to use a different statistical model: logistic regression. In logistic regression, the probability (p) of a defined outcome event is estimated by creating a regression model.
The Logistic Model
A probability (p) is a measure of how likely an event (eg, a malpractice claim ends in an indemnity payment or not) is to occur. It is always between 0 (ie, the event will definitely not occur) and 1 (ie, the event will definitely occur). A p of 0.5 means there is a 50/50 chance that the event will occur (ie, equivalent to a coin flip). Because p is a probability, we need to make sure it is always between 0 and 1. If we were to try to model p with a linear regression, the model would assume that p could extend beyond 0 and 1. What can we do?
Applying a transformation is a commonly used tool in statistics to make data work better within statistical models.6 In this case, we will transform the variable p. In logistic regression, we model the probability of experiencing the outcome through a transformation called a logit. The logit represents the natural logarithm (ln) of the ratio of the probability of experiencing the outcome (p) vs the probability of not experiencing the outcome (1 – p), with the ratio being the odds of the event occurring.
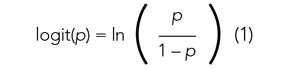
This transformation works well for dichotomous outcomes because the logit transformation approximates a straight line as long as p is not too large or too small (between 0.05 and 0.95).
If we are performing a logistic regression with only one independent variable (x) and want to understand the relationship between this variable (x) and the probability of an outcome event (p), then our model is the equation of a line. The equation for the base model of logistic regression with one independent variable (x) is
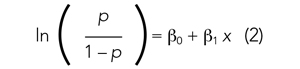
where β0 is the y-intercept and β1 is the slope of the line. Equation (2) is identical to the algebraic equation y = mx + b for a line, just rearranged slightly. In this algebraic equation, m is the slope (the same as β1) and b is the y-intercept (the same as β0). We will see that β0 and β1 are estimated (ie, assigned numeric values) from the data collected to help us understand how x and
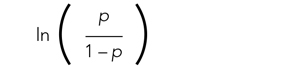
are related and are the basis for estimating odds ratios.
We can build more complex models using multivariable logistic regression by adding more independent variables to the right side of equation (2). Essentially, this is what S
There are two notable techniques used frequently with multivariable logistic regression models. The first involves choosing which independent variables to include in the model. One way to select variables for multivariable models is defining them a priori, that is deciding which variables are clinically or conceptually associated with the outcome before looking at the data. With this approach, we can test specific hypotheses about the relationships between the independent variables and the outcome. Another common approach is to look at the data and identify the variables that vary significantly between the two outcome groups. Schaffer et al4 used an a priori approach to define variables in their multivariable model (ie, “variables for inclusion into the multivariable model were determined a priori”).
A second technique is the evaluation of collinearity, which helps us understand whether the i
Understanding the Results of the Logistic Model
Fitting the model is the process by which statistical software (eg, SAS, Stata, R, SPSS) estimates the relationships among independent variables in the model and the outcome within a specific dataset. In equation (2), this essentially means that the software will evaluate the data and provide us with the best estimates for β0 (the y-intercept) and β1 (the slope) that describe the relationship between the variable x and
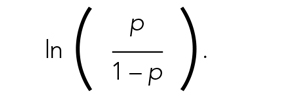
Modeling can be iterative, and part of the process may include removing variables from the model that are not significantly associated with the outcome to create a simpler solution, a process known as model reduction. The results from models describe the independent association between a specific characteristic and the outcome, meaning that the relationship has been adjusted for all the other characteristics in the model.
The relationships among the independent variables and outcome are most often represented as an odds ratio (OR), which quantifies the strength of the association between two variables and is directly calculated from the β values in the model. As the name suggests, an OR is a ratio of odds. But what are odds? Simply, the odds of an outcome (such as mortality) is the probability of experiencing the event divided by the probability of not experiencing that event; in other words, it is the ratio:

The concept of odds is often unfamiliar, so it can be helpful to consider the definition in the context of games of chance. For example, in horse race betting, the outcome of interest is that a horse will lose a race. Imagine that the probability of a horse losing a race is 0.8 and the probability of winning is 0.2. The odds of losing are
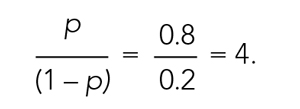
These odds usually are listed as 4-to-1, meaning that out of 5 races (ie, 4 + 1) the horse is expected to lose 4 times and win once. When odds are listed this way, we can easily calculate the associated probability by recognizing that the total number of expected races is the sum of two numbers (probability of losing: 4 races out of 5, or 0.80 vs probability of winning: 1 race out of 5, or 0.20).
In medical research, the OR typically represents the odds for one group of patients (A) compared with the odds for another group of patients (B) experiencing an outcome. If the odds of the outcome are the same for group A and group B, then OR = 1.0, meaning that the probability of the outcome is the same between the two groups. If the patients in group A have greater odds of experiencing the outcome compared with group B patients (and a greater probability of the outcome), then the OR will be >1. If the opposite is true, then the OR will be <1.
Schaffer et al4 estimated that the OR of an indemnity payment in malpractice cases involving errors in clinical judgment as a contributing factor was 5.01 (95% CI, 3.37-7.45). This means that malpractice cases involving errors in clinical judgement had a 5.01 times greater odds of indemnity payment compared with those without these errors after adjusting for all other variables in the model (eg, age, severity). Note that the 95% CI does not include 1.0. This indicates that the OR is statistically >1, and we can conclude that there is a significant relationship between errors in clinical judgment and payment that is unlikely to be attributed to chance alone.
In logistic regression for categorical independent variables, all categories are compared with a reference group within that variable, with the reference group serving as the denominator of the OR. The authors4 did not incorporate continuous independent variables in their multivariable logistic regression model. However, if the authors examined length of hospitalization as a contributing factor in indemnity payments, for example, the OR would represent a 1-unit increase in this variable (eg, 1-day increase in length of stay).
Conclusion
Logistic regression describes the relationships in data and is an important statistical model across many types of research. This Progress Note emphasizes the importance of weighing the advantages and limitations of logistic regression, provides a common approach to data transformation, and guides the correct interpretation of logistic regression model results.
The ability to read and correctly interpret research is an essential skill, but most hospitalists—and physicians in general—do not receive formal training in biostatistics during their medical education.1-3 In addition to straightforward statistical tests that compare a single exposure and outcome, researchers commonly use statistical models to identify and quantify complex relationships among many exposures (eg, demographics, clinical characteristics, interventions, or other variables) and an outcome. Understanding statistical models can be challenging. Still, it is important to recognize the advantages and limitations of statistical models, how to interpret their results, and the potential implications of findings on current clinical practice.
In the article “Rates and Characteristics of Medical Malpractice Claims Against Hospitalists” published in the July 2021 issue of the Journal of Hospital Medicine, Schaffer et al4 used the Comparative Benchmarking System database, which is maintained by a malpractice insurer, to characterize malpractice claims against hospitalists. The authors used multiple logistic regression models to understand the relationship among clinical factors and indemnity payments. In this Progress Note, we describe situations in which logistic regression is the proper statistical method to analyze a data set, explain results from logistic regression analyses, and equip readers with skills to critically appraise conclusions drawn from these models.
Choosing an Appropriate Statistical Model
Statistical models often are used to describe the relationship among one or more exposure variables (ie, independent variables) and an outcome (ie, dependent variable). These models allow researchers to evaluate the effects of multiple exposure variables simultaneously, which in turn allows them to “isolate” the effect of each variable; in other words, models facilitate an understanding of the relationship between each exposure variable and the outcome, adjusted for (ie, independent of) the other exposure variables in the model.
Several statistical models can be used to quantify relationships within the data, but each type of model has certain assumptions that must be satisfied. Two important assumptions include characteristics of the outcome (eg, the type and distribution) and the nature of the relationships among the outcome and independent variables (eg, linear vs nonlinear). Simple linear regression, one of the most basic statistical models used in research,5 assumes that (a) the outcome is continuous (ie, any numeric value is possible) and normally distributed (ie, its histogram is a bell-shaped curve) and (b) the relationship between the independent variable and the outcome is linear (ie, follows a straight line). If an investigator wanted to understand how weight is related to height, a simple linear regression could be used to develop a mathematical equation that tells us how the outcome (weight) generally increases as the independent variable (height) increases.
Often, the outcome in a study is not a continuous variable but a simple success/failure variable (ie, dichotomous variable that can be one of two possible values). Schaffer et al4 examined the binary outcome of whether a malpractice claim case would end in an indemnity payment or no payment. Linear regression models are not equipped to handle dichotomous outcomes. Instead, we need to use a different statistical model: logistic regression. In logistic regression, the probability (p) of a defined outcome event is estimated by creating a regression model.
The Logistic Model
A probability (p) is a measure of how likely an event (eg, a malpractice claim ends in an indemnity payment or not) is to occur. It is always between 0 (ie, the event will definitely not occur) and 1 (ie, the event will definitely occur). A p of 0.5 means there is a 50/50 chance that the event will occur (ie, equivalent to a coin flip). Because p is a probability, we need to make sure it is always between 0 and 1. If we were to try to model p with a linear regression, the model would assume that p could extend beyond 0 and 1. What can we do?
Applying a transformation is a commonly used tool in statistics to make data work better within statistical models.6 In this case, we will transform the variable p. In logistic regression, we model the probability of experiencing the outcome through a transformation called a logit. The logit represents the natural logarithm (ln) of the ratio of the probability of experiencing the outcome (p) vs the probability of not experiencing the outcome (1 – p), with the ratio being the odds of the event occurring.
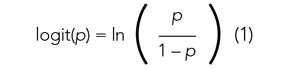
This transformation works well for dichotomous outcomes because the logit transformation approximates a straight line as long as p is not too large or too small (between 0.05 and 0.95).
If we are performing a logistic regression with only one independent variable (x) and want to understand the relationship between this variable (x) and the probability of an outcome event (p), then our model is the equation of a line. The equation for the base model of logistic regression with one independent variable (x) is
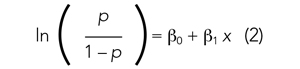
where β0 is the y-intercept and β1 is the slope of the line. Equation (2) is identical to the algebraic equation y = mx + b for a line, just rearranged slightly. In this algebraic equation, m is the slope (the same as β1) and b is the y-intercept (the same as β0). We will see that β0 and β1 are estimated (ie, assigned numeric values) from the data collected to help us understand how x and
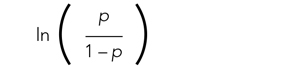
are related and are the basis for estimating odds ratios.
We can build more complex models using multivariable logistic regression by adding more independent variables to the right side of equation (2). Essentially, this is what S
There are two notable techniques used frequently with multivariable logistic regression models. The first involves choosing which independent variables to include in the model. One way to select variables for multivariable models is defining them a priori, that is deciding which variables are clinically or conceptually associated with the outcome before looking at the data. With this approach, we can test specific hypotheses about the relationships between the independent variables and the outcome. Another common approach is to look at the data and identify the variables that vary significantly between the two outcome groups. Schaffer et al4 used an a priori approach to define variables in their multivariable model (ie, “variables for inclusion into the multivariable model were determined a priori”).
A second technique is the evaluation of collinearity, which helps us understand whether the i
Understanding the Results of the Logistic Model
Fitting the model is the process by which statistical software (eg, SAS, Stata, R, SPSS) estimates the relationships among independent variables in the model and the outcome within a specific dataset. In equation (2), this essentially means that the software will evaluate the data and provide us with the best estimates for β0 (the y-intercept) and β1 (the slope) that describe the relationship between the variable x and
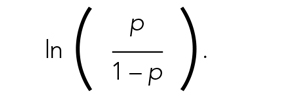
Modeling can be iterative, and part of the process may include removing variables from the model that are not significantly associated with the outcome to create a simpler solution, a process known as model reduction. The results from models describe the independent association between a specific characteristic and the outcome, meaning that the relationship has been adjusted for all the other characteristics in the model.
The relationships among the independent variables and outcome are most often represented as an odds ratio (OR), which quantifies the strength of the association between two variables and is directly calculated from the β values in the model. As the name suggests, an OR is a ratio of odds. But what are odds? Simply, the odds of an outcome (such as mortality) is the probability of experiencing the event divided by the probability of not experiencing that event; in other words, it is the ratio:

The concept of odds is often unfamiliar, so it can be helpful to consider the definition in the context of games of chance. For example, in horse race betting, the outcome of interest is that a horse will lose a race. Imagine that the probability of a horse losing a race is 0.8 and the probability of winning is 0.2. The odds of losing are
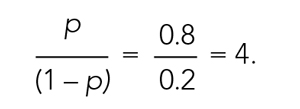
These odds usually are listed as 4-to-1, meaning that out of 5 races (ie, 4 + 1) the horse is expected to lose 4 times and win once. When odds are listed this way, we can easily calculate the associated probability by recognizing that the total number of expected races is the sum of two numbers (probability of losing: 4 races out of 5, or 0.80 vs probability of winning: 1 race out of 5, or 0.20).
In medical research, the OR typically represents the odds for one group of patients (A) compared with the odds for another group of patients (B) experiencing an outcome. If the odds of the outcome are the same for group A and group B, then OR = 1.0, meaning that the probability of the outcome is the same between the two groups. If the patients in group A have greater odds of experiencing the outcome compared with group B patients (and a greater probability of the outcome), then the OR will be >1. If the opposite is true, then the OR will be <1.
Schaffer et al4 estimated that the OR of an indemnity payment in malpractice cases involving errors in clinical judgment as a contributing factor was 5.01 (95% CI, 3.37-7.45). This means that malpractice cases involving errors in clinical judgement had a 5.01 times greater odds of indemnity payment compared with those without these errors after adjusting for all other variables in the model (eg, age, severity). Note that the 95% CI does not include 1.0. This indicates that the OR is statistically >1, and we can conclude that there is a significant relationship between errors in clinical judgment and payment that is unlikely to be attributed to chance alone.
In logistic regression for categorical independent variables, all categories are compared with a reference group within that variable, with the reference group serving as the denominator of the OR. The authors4 did not incorporate continuous independent variables in their multivariable logistic regression model. However, if the authors examined length of hospitalization as a contributing factor in indemnity payments, for example, the OR would represent a 1-unit increase in this variable (eg, 1-day increase in length of stay).
Conclusion
Logistic regression describes the relationships in data and is an important statistical model across many types of research. This Progress Note emphasizes the importance of weighing the advantages and limitations of logistic regression, provides a common approach to data transformation, and guides the correct interpretation of logistic regression model results.
1. Windish DM, Huot SJ, Green ML. Medicine residents’ understanding of the biostatistics and results in the medical literature. JAMA. 2007;298(9):1010. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.298.9.1010
2. MacDougall M, Cameron HS, Maxwell SRJ. Medical graduate views on statistical learning needs for clinical practice: a comprehensive survey. BMC Med Educ. 2019;20(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-019-1842-1
3. Montori VM. Progress in evidence-based medicine. JAMA. 2008;300(15):1814-1816. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.300.15.1814
4. Schaffer AC, Yu-Moe CW, Babayan A, Wachter RM, Einbinder JS. Rates and characteristics of medical malpractice claims against hospitalists. J Hosp Med. 2021;16(7):390-396. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3557
5. Lane DM, Scott D, Hebl M, Guerra R, Osherson D, Zimmer H. Introducton to Statistics. Accessed April 13, 2021. https://onlinestatbook.com/Online_Statistics_Education.pdf
6. Marill KA. Advanced statistics: linear regression, part II: multiple linear regression. Acad Emerg Med Off J Soc Acad Emerg Med. 2004;11(1):94-102. https://doi.org/10.1197/j.aem.2003.09.006
1. Windish DM, Huot SJ, Green ML. Medicine residents’ understanding of the biostatistics and results in the medical literature. JAMA. 2007;298(9):1010. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.298.9.1010
2. MacDougall M, Cameron HS, Maxwell SRJ. Medical graduate views on statistical learning needs for clinical practice: a comprehensive survey. BMC Med Educ. 2019;20(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-019-1842-1
3. Montori VM. Progress in evidence-based medicine. JAMA. 2008;300(15):1814-1816. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.300.15.1814
4. Schaffer AC, Yu-Moe CW, Babayan A, Wachter RM, Einbinder JS. Rates and characteristics of medical malpractice claims against hospitalists. J Hosp Med. 2021;16(7):390-396. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3557
5. Lane DM, Scott D, Hebl M, Guerra R, Osherson D, Zimmer H. Introducton to Statistics. Accessed April 13, 2021. https://onlinestatbook.com/Online_Statistics_Education.pdf
6. Marill KA. Advanced statistics: linear regression, part II: multiple linear regression. Acad Emerg Med Off J Soc Acad Emerg Med. 2004;11(1):94-102. https://doi.org/10.1197/j.aem.2003.09.006
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine
Clinical Progress Note: Intravenous Human Albumin in Patients With Cirrhosis
The burden of chronic liver disease (CLD) in the United States is growing, and it is currently the fourth leading cause of death in adults aged 45 to 64 years.1 From 2012 to 2016, there were 538,720 hospitalizations in the United States for patients with cirrhosis, with almost a quarter having at least one cirrhosis-related complication. Inpatient hospitalizations for cirrhosis contribute to healthcare resource utilization, with a mean cost per CLD-related hospitalization of $16,271, and the presence of cirrhosis results in higher mortality and cost burden.1
In hospitalized patients with decompensated cirrhosis with ascites, intravenous human albumin (HA) infusion has been utilized for decades for a variety of indications. Current guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) and the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) recommends the use of albumin for the prevention of paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction (PICD) for the prevention of kidney injury in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) and for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatorenal syndrome (HRS).2,3 There have been several major trials in recent years studying the use of HA for other indications in patients with cirrhosis, and the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) updated their guidelines in 2020 to recommend HA administration in resuscitation of critically ill patients with liver failure with hypoalbuminemia.4This Clinical Progress Note addresses the use of albumin in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis, focusing on current indications and discussing potential uses published after the 2018 EASL guidelines. We conducted a literature search via the PubMed database. The authors began by using the Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) terms albumins/administration AND dosage; organization AND administration; adverse effects; and therapeutic use combined with liver cirrhosis as a MeSH major topic, which yielded 107 English-language articles published in the previous 10 years, and MeSH major topics of albumins and liver cirrhosis, which yielded 461 English-language articles, with 178 published in the previous 10 years. The search results were reviewed for applicability to albumin strategies for patients with cirrhosis.
CURRENT EVIDENCE-BASED INDICATIONS FOR USE OF ALBUMIN IN PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOSIS
There are three widely accepted and evidence-based indications for HA infusion in patients with cirrhosis, considered standard of care (Table).
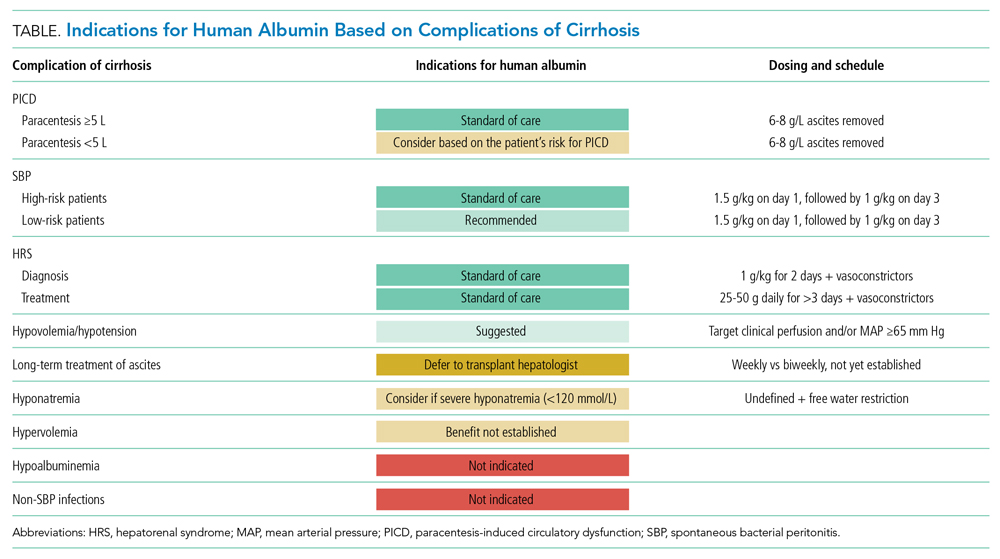
Prevention of PICD
Therapeutic large-volume paracentesis (LVP) leads to a rise in plasma renin activity (PRA) centrally through several mechanisms and is not impacted by the rate of ascites removal.5 LVP relieves abdominal pressure, increasing venous return to the heart and cardiac output, and the corresponding drop in systemic vascular resistance with splanchnic vasodilation decreases effective circulating volume and activates the renin-angiotensin system. This PRA activation and circulatory dysfunction are associated with reaccumulating ascites, renal impairment, hypervolemic hyponatremia, and increased mortality.6 A large meta-analysis of 17 trials with 1225 patients found that HA infusion improves outcomes and reduces mortality for patients undergoing LVP (odds ratio [OR], 0.64; 95% CI, 0.41-0.98), reduces the risk of PICD more than other volume expanders tested, and lowers the incidence of hyponatremia.6 More recently, in 2017, Kütting et al7 analyzed 21 trials with 1277 patients and did not observe a significant mortality benefit for HA after LVP (OR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.55-1.11). However, negative outcomes such as rise in PRA (OR, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.29-0.97) and hyponatremia (OR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.42-0.94) were prevented. Guidelines recommend HA after LVP ≥5 L to prevent PICD, with a replacement volume of 6 to 8 g of albumin per liter of ascitic fluid removed.2,3 Some patients may be at higher risk for PICD with less ascites removed, and the AASLD supports the use of HA to prevent PICD after smaller-volume paracentesis in patients who are already hypotensive (systolic blood pressure <90 mm Hg) or hyponatremic (<130 mmol/L), or have acute kidney injury.3
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis is diagnosed by paracentesis, defined as ascitic neutrophil count ≥250 cells/µL with or without bacterascites (positive bacteriological culture). Bacterascites may be a precursor to the development of SBP, with the fluid neutrophil count of ≥250 determining the need for SBP treatment.2 SBP can lead to circulatory dysfunction, hepatic encephalopathy, and HRS. Treating SBP with HA in addition to antibiotics reduces the risk of kidney injury compared with antibiotics alone (OR for kidney injury with antibiotics alone, 4.6; 95% CI, 1.3-16.1) and also reduces the risk of death (OR for mortality with antibiotics alone, 4.5; 95% CI, 1.0-20.9).8 The AASLD recommends albumin in addition to antibiotics in SBP to prevent HRS and acute kidney injury, and high-risk patients who already have kidney dysfunction (creatinine >1 mg/dL) or jaundice (total bilirubin >5 mg/dL) are more likely to benefit from albumin. The treatment schedule is 25% HA at 1.5 g/kg on day 1 and 1 g/kg on day 3.3 The EASL recommends administering HA to all patients with cirrhosis with SBP regardless of renal or liver indices. They acknowledge, however, that the incidence of SBP-associated acute kidney injury will be low in patients without severe hepatic disease or baseline renal impairment.2
Hepatorenal Syndrome
Albumin combined with vasoconstrictors is effective in treating HRS with a response rate of 20% to 80% (average, 50%).3 Vasoactive medications can include combination midodrine and octreotide or norepinephrine (or terlipressin outside of the United States). In patients with suspected HRS, the recommended dosing of 25% HA is 1 g/kg (to a maximum of 100 g of albumin) on day 1 and then 40 to 50 g daily for at least 3 days after the diagnosis is confirmed.3 The optimal duration of therapy beyond 3 days of combined therapy with midodrine, albumin, and octreotide is not established. Terlipressin treatment is recommended for a maximum of 14 days in cases of partial response or nonresponse in renal recovery.2
INDICATIONS FOR ALBUMIN WITHOUT CLEAR EVIDENCE OF EFFICACY
Hypoalbuminemia
Albumin administration to raise serum albumin levels in hospitalized patients has been a common practice. However, new evidence suggests that treating hypoalbuminemia with infusion of HA in hospitalized patients with decompensated cirrhosis does not protect patients from risk and causes harm. The Albumin To prevenT Infection in chronic liveR (ATTIRE) trial, published in 2021, randomly assigned 777 patients across 35 centers in the United Kingdom to receive daily 20% HA to target a serum albumin level of 3.0 g/dL vs standard care, including HA for established indications.2,3 The primary end point was a composite of infection, kidney dysfunction, and death within 3 to 15 days of initiating treatment. There were no differences in the primary end point; secondary end points of death at 28 days, 3 months, or 6 months; or duration of hospitalization. The treatment group received 10 times more albumin than the control group and reported more adverse events, including pulmonary edema.9
Long-Term Treatment in Patients With Ascites
The human Albumin for the treatmeNt of aScites in patients With hEpatic ciRrhosis (ANSWER) trial, published in 2018, found improved 18-month survival in patients with cirrhosis and ascites treated with diuretics who received long-term albumin. This was an open-label trial of 431 patients at 33 sites in Italy, and the treatment arm received weekly infusions of 40 g of 20% HA. They observed a 38% reduction in mortality hazard ratio and half the number of hospital days annually.10 Based on these data and those from a 2006 Italian study with similar design and results, the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF) strongly recommends long-term albumin treatment in patients with cirrhosis with ascites.11 The lead author on the ANSWER trial also authored the AISF statement, although this recommendation has not been adopted by the EASL or the AASLD.
Conversely, the Midodrine and Albumin for CirrHoTic patients (MACHT) trial, also published in 2018, randomly assigned 173 patients with ascites awaiting liver transplant to receive 40 g of HA every 15 days and midodrine in addition to standard care vs placebo. MACHT found no difference in mortality or complications at 1 year.12
Long-term albumin therapy as a preventive measure may be a disease modifier, taking advantage of the pleiotropic effects of albumin, though the differing conclusions from ANSWER and MACHT necessitate additional trials. The ongoing PRECIOSA study in Spain is assessing dosage and schedule for this therapy.13
Augmenting Diuresis
Loop diuretics are highly protein-bound, and, with hypoalbuminemia, there is less effective drug delivered to the site of action. One clinical approach is to augment diuretics with concomitant HA infusion. This approach is not supported by strong evidence or guidelines.
Hyponatremia
In a retrospective cohort study of 2435 hospitalized patients with cirrhosis, 1126 of whom had hyponatremia, those patients with sodium <130 mmol/L who received HA were more likely to have resolution of hyponatremia to >135 mmol/L. This was associated with improved 30-day survival.14 From this observational data, the AASLD supports the use of albumin combined with extreme fluid restriction (<1000 mL/d) for patients with severe hyponatremia (<120 mmol/L).3
Non-SBP Infections
A 2019 meta-analysis found no evidence of a benefit of HA for bacterial infections other than SBP. However, only three trials encompassing 407 patients met the inclusion criteria.15
NEW GUIDELINE-SUGGESTED USE FOR ALBUMIN IN PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOSIS
SCCM Guideline Update: Hypoalbuminemia and Hypotension
The 2020 SCCM Guidelines for the Management of Adult Acute and Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure in the ICU “suggest using albumin for resuscitation of patients [with liver failure] over other fluids, especially when serum albumin is low (<3 g/dL).” Acute-on-chronic liver failure is decompensation of cirrhosis combined with organ dysfunction (eg, coagulopathy, encephalopathy, kidney injury), a scenario that is frequently encountered by hospitalists outside of intensive care settings. In hypotensive patients with cirrhosis, the SCCM recommends administering albumin to a target mean arterial pressure of 65 mm Hg or otherwise adequate perfusion. This new recommendation is conditional, based on expert consensus, and derives from low-quality evidence, with acknowledgement that “costs may be prohibitive.”4
While the ATTIRE study demonstrated no benefit in treating hypoalbuminemia with infusion of HA in hospitalized patients with decompensated cirrhosis, the 2020 SCCM guidelines, released prior to the publication of the ATTIRE study, focused on more acutely ill patients. In the ATTIRE study, only 2% to 3% of the study population was in an intensive care unit.4,9 The use of albumin infusion in the critically ill, hypoalbuminemic, hypotensive patient is not well studied, and the SCCM acknowledges the lack of supportive evidence for this practice in their guideline statement.
CONCLUSION
The three cardinal clinical indications for human albumin in patients with cirrhosis—prevention of PICD after LVP, in SBP, and for HRS—remain supported by the literature and guidelines, with the most recent guidance adding more nuance in patient selection based on individual risk (Table). With the publication of several large-scale studies in the past few years and a 2021 update to the AASLD guidance statement, clinicians have more evidence to guide their use of HA in patients with cirrhosis. In particular, the practice of treating isolated hypoalbuminemia with HA is no longer supported by the best evidence and is potentially harmful. A professional society recommendation to preferentially use albumin as a resuscitation fluid in hypoalbuminemia was made without the benefit of the results of the 2021 ATTIRE trial. On the horizon, additional results from ongoing and upcoming studies exploring concepts of effective albumin concentration and the pleiotropic properties of HA will impact the use of this therapy in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis.
1. Hirode G, Saab S, Wong RJ. Trends in the burden of chronic liver disease among hospitalized US adults. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(4):e201997. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.1997
2. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2018;69(2):406-460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.024
3. Biggins SW, Angeli P, Garcia-Tsao G, et al. Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and hepatorenal syndrome: 2021 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2021;74(2):1014-1048. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.31884
4. Nanchal R, Subramanian R, Karvellas CJ, et al. Guidelines for the management of adult acute and acute-on-chronic liver failure in the ICU: cardiovascular, endocrine, hematologic, pulmonary, and renal considerations. Crit Care Med. 2020;48(3):e173-e191. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000004192
5. Elsabaawy MM, Abdelhamid SR, Alsebaey A, et al. The impact of paracentesis flow rate in patients with liver cirrhosis on the development of paracentesis induced circulatory dysfunction. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2015;21(4):365-371. https://doi.org/10.3350/cmh.2015.21.4.365
6. Bernardi M, Caraceni P, Navickis RJ, Wilkes MM. Albumin infusion in patients undergoing large-volume paracentesis: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Hepatology. 2012;55(4):1172-1181. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.24786
7. Kütting F, Schubert J, Franklin J, et al. Insufficient evidence of benefit regarding mortality due to albumin substitution in HCC-free cirrhotic patients undergoing large volume paracentesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;32(2):327-338. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.13421
8. Sort P, Navasa M, Arroyo V, et al. Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(6):403-409. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199908053410603
9. China L, Freemantle N, Forrest E, et al. A randomized trial of albumin infusions in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(9):808-817. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2022166
10. Caraceni P, Riggio O, Angeli P, et al. Long-term albumin administration in decompensated cirrhosis (ANSWER): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10138):2417-2429. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30840-7
11. Caraceni P, Angeli P, Prati D, et al. AISF-SIMTI position paper on the appropriate use of albumin in patients with liver cirrhosis: a 2020 update. Blood Transfus. 2021;19(1):9-13. https://doi.org/10.2450/2020.0414-20
12. Solà E, Solé C, Simón-Talero M, et al. Midodrine and albumin for prevention of complications in patients with cirrhosis awaiting liver transplantation. A randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Hepatol. 2018;69(6):1250-1259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.08.006
13. Fernández J, Clària J, Amorós A, et al. Effects of albumin treatment on systemic and portal hemodynamics and systemic inflammation in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2019;157(1):149-162. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2019.03.021
14. Bajaj JS, Tandon P, O’Leary JG, et al. The impact of albumin use on resolution of hyponatremia in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113(9):1339. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41395-018-0119-3
15. Leão GS, Neto GJ, Jotz RdF, de Mattos AA, de Mattos ÂZ. Albumin for cirrhotic patients with extraperitoneal infections: a meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;34(12):2071-2076. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.14791
The burden of chronic liver disease (CLD) in the United States is growing, and it is currently the fourth leading cause of death in adults aged 45 to 64 years.1 From 2012 to 2016, there were 538,720 hospitalizations in the United States for patients with cirrhosis, with almost a quarter having at least one cirrhosis-related complication. Inpatient hospitalizations for cirrhosis contribute to healthcare resource utilization, with a mean cost per CLD-related hospitalization of $16,271, and the presence of cirrhosis results in higher mortality and cost burden.1
In hospitalized patients with decompensated cirrhosis with ascites, intravenous human albumin (HA) infusion has been utilized for decades for a variety of indications. Current guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) and the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) recommends the use of albumin for the prevention of paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction (PICD) for the prevention of kidney injury in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) and for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatorenal syndrome (HRS).2,3 There have been several major trials in recent years studying the use of HA for other indications in patients with cirrhosis, and the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) updated their guidelines in 2020 to recommend HA administration in resuscitation of critically ill patients with liver failure with hypoalbuminemia.4This Clinical Progress Note addresses the use of albumin in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis, focusing on current indications and discussing potential uses published after the 2018 EASL guidelines. We conducted a literature search via the PubMed database. The authors began by using the Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) terms albumins/administration AND dosage; organization AND administration; adverse effects; and therapeutic use combined with liver cirrhosis as a MeSH major topic, which yielded 107 English-language articles published in the previous 10 years, and MeSH major topics of albumins and liver cirrhosis, which yielded 461 English-language articles, with 178 published in the previous 10 years. The search results were reviewed for applicability to albumin strategies for patients with cirrhosis.
CURRENT EVIDENCE-BASED INDICATIONS FOR USE OF ALBUMIN IN PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOSIS
There are three widely accepted and evidence-based indications for HA infusion in patients with cirrhosis, considered standard of care (Table).

Prevention of PICD
Therapeutic large-volume paracentesis (LVP) leads to a rise in plasma renin activity (PRA) centrally through several mechanisms and is not impacted by the rate of ascites removal.5 LVP relieves abdominal pressure, increasing venous return to the heart and cardiac output, and the corresponding drop in systemic vascular resistance with splanchnic vasodilation decreases effective circulating volume and activates the renin-angiotensin system. This PRA activation and circulatory dysfunction are associated with reaccumulating ascites, renal impairment, hypervolemic hyponatremia, and increased mortality.6 A large meta-analysis of 17 trials with 1225 patients found that HA infusion improves outcomes and reduces mortality for patients undergoing LVP (odds ratio [OR], 0.64; 95% CI, 0.41-0.98), reduces the risk of PICD more than other volume expanders tested, and lowers the incidence of hyponatremia.6 More recently, in 2017, Kütting et al7 analyzed 21 trials with 1277 patients and did not observe a significant mortality benefit for HA after LVP (OR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.55-1.11). However, negative outcomes such as rise in PRA (OR, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.29-0.97) and hyponatremia (OR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.42-0.94) were prevented. Guidelines recommend HA after LVP ≥5 L to prevent PICD, with a replacement volume of 6 to 8 g of albumin per liter of ascitic fluid removed.2,3 Some patients may be at higher risk for PICD with less ascites removed, and the AASLD supports the use of HA to prevent PICD after smaller-volume paracentesis in patients who are already hypotensive (systolic blood pressure <90 mm Hg) or hyponatremic (<130 mmol/L), or have acute kidney injury.3
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis is diagnosed by paracentesis, defined as ascitic neutrophil count ≥250 cells/µL with or without bacterascites (positive bacteriological culture). Bacterascites may be a precursor to the development of SBP, with the fluid neutrophil count of ≥250 determining the need for SBP treatment.2 SBP can lead to circulatory dysfunction, hepatic encephalopathy, and HRS. Treating SBP with HA in addition to antibiotics reduces the risk of kidney injury compared with antibiotics alone (OR for kidney injury with antibiotics alone, 4.6; 95% CI, 1.3-16.1) and also reduces the risk of death (OR for mortality with antibiotics alone, 4.5; 95% CI, 1.0-20.9).8 The AASLD recommends albumin in addition to antibiotics in SBP to prevent HRS and acute kidney injury, and high-risk patients who already have kidney dysfunction (creatinine >1 mg/dL) or jaundice (total bilirubin >5 mg/dL) are more likely to benefit from albumin. The treatment schedule is 25% HA at 1.5 g/kg on day 1 and 1 g/kg on day 3.3 The EASL recommends administering HA to all patients with cirrhosis with SBP regardless of renal or liver indices. They acknowledge, however, that the incidence of SBP-associated acute kidney injury will be low in patients without severe hepatic disease or baseline renal impairment.2
Hepatorenal Syndrome
Albumin combined with vasoconstrictors is effective in treating HRS with a response rate of 20% to 80% (average, 50%).3 Vasoactive medications can include combination midodrine and octreotide or norepinephrine (or terlipressin outside of the United States). In patients with suspected HRS, the recommended dosing of 25% HA is 1 g/kg (to a maximum of 100 g of albumin) on day 1 and then 40 to 50 g daily for at least 3 days after the diagnosis is confirmed.3 The optimal duration of therapy beyond 3 days of combined therapy with midodrine, albumin, and octreotide is not established. Terlipressin treatment is recommended for a maximum of 14 days in cases of partial response or nonresponse in renal recovery.2
INDICATIONS FOR ALBUMIN WITHOUT CLEAR EVIDENCE OF EFFICACY
Hypoalbuminemia
Albumin administration to raise serum albumin levels in hospitalized patients has been a common practice. However, new evidence suggests that treating hypoalbuminemia with infusion of HA in hospitalized patients with decompensated cirrhosis does not protect patients from risk and causes harm. The Albumin To prevenT Infection in chronic liveR (ATTIRE) trial, published in 2021, randomly assigned 777 patients across 35 centers in the United Kingdom to receive daily 20% HA to target a serum albumin level of 3.0 g/dL vs standard care, including HA for established indications.2,3 The primary end point was a composite of infection, kidney dysfunction, and death within 3 to 15 days of initiating treatment. There were no differences in the primary end point; secondary end points of death at 28 days, 3 months, or 6 months; or duration of hospitalization. The treatment group received 10 times more albumin than the control group and reported more adverse events, including pulmonary edema.9
Long-Term Treatment in Patients With Ascites
The human Albumin for the treatmeNt of aScites in patients With hEpatic ciRrhosis (ANSWER) trial, published in 2018, found improved 18-month survival in patients with cirrhosis and ascites treated with diuretics who received long-term albumin. This was an open-label trial of 431 patients at 33 sites in Italy, and the treatment arm received weekly infusions of 40 g of 20% HA. They observed a 38% reduction in mortality hazard ratio and half the number of hospital days annually.10 Based on these data and those from a 2006 Italian study with similar design and results, the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF) strongly recommends long-term albumin treatment in patients with cirrhosis with ascites.11 The lead author on the ANSWER trial also authored the AISF statement, although this recommendation has not been adopted by the EASL or the AASLD.
Conversely, the Midodrine and Albumin for CirrHoTic patients (MACHT) trial, also published in 2018, randomly assigned 173 patients with ascites awaiting liver transplant to receive 40 g of HA every 15 days and midodrine in addition to standard care vs placebo. MACHT found no difference in mortality or complications at 1 year.12
Long-term albumin therapy as a preventive measure may be a disease modifier, taking advantage of the pleiotropic effects of albumin, though the differing conclusions from ANSWER and MACHT necessitate additional trials. The ongoing PRECIOSA study in Spain is assessing dosage and schedule for this therapy.13
Augmenting Diuresis
Loop diuretics are highly protein-bound, and, with hypoalbuminemia, there is less effective drug delivered to the site of action. One clinical approach is to augment diuretics with concomitant HA infusion. This approach is not supported by strong evidence or guidelines.
Hyponatremia
In a retrospective cohort study of 2435 hospitalized patients with cirrhosis, 1126 of whom had hyponatremia, those patients with sodium <130 mmol/L who received HA were more likely to have resolution of hyponatremia to >135 mmol/L. This was associated with improved 30-day survival.14 From this observational data, the AASLD supports the use of albumin combined with extreme fluid restriction (<1000 mL/d) for patients with severe hyponatremia (<120 mmol/L).3
Non-SBP Infections
A 2019 meta-analysis found no evidence of a benefit of HA for bacterial infections other than SBP. However, only three trials encompassing 407 patients met the inclusion criteria.15
NEW GUIDELINE-SUGGESTED USE FOR ALBUMIN IN PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOSIS
SCCM Guideline Update: Hypoalbuminemia and Hypotension
The 2020 SCCM Guidelines for the Management of Adult Acute and Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure in the ICU “suggest using albumin for resuscitation of patients [with liver failure] over other fluids, especially when serum albumin is low (<3 g/dL).” Acute-on-chronic liver failure is decompensation of cirrhosis combined with organ dysfunction (eg, coagulopathy, encephalopathy, kidney injury), a scenario that is frequently encountered by hospitalists outside of intensive care settings. In hypotensive patients with cirrhosis, the SCCM recommends administering albumin to a target mean arterial pressure of 65 mm Hg or otherwise adequate perfusion. This new recommendation is conditional, based on expert consensus, and derives from low-quality evidence, with acknowledgement that “costs may be prohibitive.”4
While the ATTIRE study demonstrated no benefit in treating hypoalbuminemia with infusion of HA in hospitalized patients with decompensated cirrhosis, the 2020 SCCM guidelines, released prior to the publication of the ATTIRE study, focused on more acutely ill patients. In the ATTIRE study, only 2% to 3% of the study population was in an intensive care unit.4,9 The use of albumin infusion in the critically ill, hypoalbuminemic, hypotensive patient is not well studied, and the SCCM acknowledges the lack of supportive evidence for this practice in their guideline statement.
CONCLUSION
The three cardinal clinical indications for human albumin in patients with cirrhosis—prevention of PICD after LVP, in SBP, and for HRS—remain supported by the literature and guidelines, with the most recent guidance adding more nuance in patient selection based on individual risk (Table). With the publication of several large-scale studies in the past few years and a 2021 update to the AASLD guidance statement, clinicians have more evidence to guide their use of HA in patients with cirrhosis. In particular, the practice of treating isolated hypoalbuminemia with HA is no longer supported by the best evidence and is potentially harmful. A professional society recommendation to preferentially use albumin as a resuscitation fluid in hypoalbuminemia was made without the benefit of the results of the 2021 ATTIRE trial. On the horizon, additional results from ongoing and upcoming studies exploring concepts of effective albumin concentration and the pleiotropic properties of HA will impact the use of this therapy in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis.
The burden of chronic liver disease (CLD) in the United States is growing, and it is currently the fourth leading cause of death in adults aged 45 to 64 years.1 From 2012 to 2016, there were 538,720 hospitalizations in the United States for patients with cirrhosis, with almost a quarter having at least one cirrhosis-related complication. Inpatient hospitalizations for cirrhosis contribute to healthcare resource utilization, with a mean cost per CLD-related hospitalization of $16,271, and the presence of cirrhosis results in higher mortality and cost burden.1
In hospitalized patients with decompensated cirrhosis with ascites, intravenous human albumin (HA) infusion has been utilized for decades for a variety of indications. Current guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) and the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) recommends the use of albumin for the prevention of paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction (PICD) for the prevention of kidney injury in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) and for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatorenal syndrome (HRS).2,3 There have been several major trials in recent years studying the use of HA for other indications in patients with cirrhosis, and the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) updated their guidelines in 2020 to recommend HA administration in resuscitation of critically ill patients with liver failure with hypoalbuminemia.4This Clinical Progress Note addresses the use of albumin in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis, focusing on current indications and discussing potential uses published after the 2018 EASL guidelines. We conducted a literature search via the PubMed database. The authors began by using the Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) terms albumins/administration AND dosage; organization AND administration; adverse effects; and therapeutic use combined with liver cirrhosis as a MeSH major topic, which yielded 107 English-language articles published in the previous 10 years, and MeSH major topics of albumins and liver cirrhosis, which yielded 461 English-language articles, with 178 published in the previous 10 years. The search results were reviewed for applicability to albumin strategies for patients with cirrhosis.
CURRENT EVIDENCE-BASED INDICATIONS FOR USE OF ALBUMIN IN PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOSIS
There are three widely accepted and evidence-based indications for HA infusion in patients with cirrhosis, considered standard of care (Table).

Prevention of PICD
Therapeutic large-volume paracentesis (LVP) leads to a rise in plasma renin activity (PRA) centrally through several mechanisms and is not impacted by the rate of ascites removal.5 LVP relieves abdominal pressure, increasing venous return to the heart and cardiac output, and the corresponding drop in systemic vascular resistance with splanchnic vasodilation decreases effective circulating volume and activates the renin-angiotensin system. This PRA activation and circulatory dysfunction are associated with reaccumulating ascites, renal impairment, hypervolemic hyponatremia, and increased mortality.6 A large meta-analysis of 17 trials with 1225 patients found that HA infusion improves outcomes and reduces mortality for patients undergoing LVP (odds ratio [OR], 0.64; 95% CI, 0.41-0.98), reduces the risk of PICD more than other volume expanders tested, and lowers the incidence of hyponatremia.6 More recently, in 2017, Kütting et al7 analyzed 21 trials with 1277 patients and did not observe a significant mortality benefit for HA after LVP (OR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.55-1.11). However, negative outcomes such as rise in PRA (OR, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.29-0.97) and hyponatremia (OR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.42-0.94) were prevented. Guidelines recommend HA after LVP ≥5 L to prevent PICD, with a replacement volume of 6 to 8 g of albumin per liter of ascitic fluid removed.2,3 Some patients may be at higher risk for PICD with less ascites removed, and the AASLD supports the use of HA to prevent PICD after smaller-volume paracentesis in patients who are already hypotensive (systolic blood pressure <90 mm Hg) or hyponatremic (<130 mmol/L), or have acute kidney injury.3
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis is diagnosed by paracentesis, defined as ascitic neutrophil count ≥250 cells/µL with or without bacterascites (positive bacteriological culture). Bacterascites may be a precursor to the development of SBP, with the fluid neutrophil count of ≥250 determining the need for SBP treatment.2 SBP can lead to circulatory dysfunction, hepatic encephalopathy, and HRS. Treating SBP with HA in addition to antibiotics reduces the risk of kidney injury compared with antibiotics alone (OR for kidney injury with antibiotics alone, 4.6; 95% CI, 1.3-16.1) and also reduces the risk of death (OR for mortality with antibiotics alone, 4.5; 95% CI, 1.0-20.9).8 The AASLD recommends albumin in addition to antibiotics in SBP to prevent HRS and acute kidney injury, and high-risk patients who already have kidney dysfunction (creatinine >1 mg/dL) or jaundice (total bilirubin >5 mg/dL) are more likely to benefit from albumin. The treatment schedule is 25% HA at 1.5 g/kg on day 1 and 1 g/kg on day 3.3 The EASL recommends administering HA to all patients with cirrhosis with SBP regardless of renal or liver indices. They acknowledge, however, that the incidence of SBP-associated acute kidney injury will be low in patients without severe hepatic disease or baseline renal impairment.2
Hepatorenal Syndrome
Albumin combined with vasoconstrictors is effective in treating HRS with a response rate of 20% to 80% (average, 50%).3 Vasoactive medications can include combination midodrine and octreotide or norepinephrine (or terlipressin outside of the United States). In patients with suspected HRS, the recommended dosing of 25% HA is 1 g/kg (to a maximum of 100 g of albumin) on day 1 and then 40 to 50 g daily for at least 3 days after the diagnosis is confirmed.3 The optimal duration of therapy beyond 3 days of combined therapy with midodrine, albumin, and octreotide is not established. Terlipressin treatment is recommended for a maximum of 14 days in cases of partial response or nonresponse in renal recovery.2
INDICATIONS FOR ALBUMIN WITHOUT CLEAR EVIDENCE OF EFFICACY
Hypoalbuminemia
Albumin administration to raise serum albumin levels in hospitalized patients has been a common practice. However, new evidence suggests that treating hypoalbuminemia with infusion of HA in hospitalized patients with decompensated cirrhosis does not protect patients from risk and causes harm. The Albumin To prevenT Infection in chronic liveR (ATTIRE) trial, published in 2021, randomly assigned 777 patients across 35 centers in the United Kingdom to receive daily 20% HA to target a serum albumin level of 3.0 g/dL vs standard care, including HA for established indications.2,3 The primary end point was a composite of infection, kidney dysfunction, and death within 3 to 15 days of initiating treatment. There were no differences in the primary end point; secondary end points of death at 28 days, 3 months, or 6 months; or duration of hospitalization. The treatment group received 10 times more albumin than the control group and reported more adverse events, including pulmonary edema.9
Long-Term Treatment in Patients With Ascites
The human Albumin for the treatmeNt of aScites in patients With hEpatic ciRrhosis (ANSWER) trial, published in 2018, found improved 18-month survival in patients with cirrhosis and ascites treated with diuretics who received long-term albumin. This was an open-label trial of 431 patients at 33 sites in Italy, and the treatment arm received weekly infusions of 40 g of 20% HA. They observed a 38% reduction in mortality hazard ratio and half the number of hospital days annually.10 Based on these data and those from a 2006 Italian study with similar design and results, the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF) strongly recommends long-term albumin treatment in patients with cirrhosis with ascites.11 The lead author on the ANSWER trial also authored the AISF statement, although this recommendation has not been adopted by the EASL or the AASLD.
Conversely, the Midodrine and Albumin for CirrHoTic patients (MACHT) trial, also published in 2018, randomly assigned 173 patients with ascites awaiting liver transplant to receive 40 g of HA every 15 days and midodrine in addition to standard care vs placebo. MACHT found no difference in mortality or complications at 1 year.12
Long-term albumin therapy as a preventive measure may be a disease modifier, taking advantage of the pleiotropic effects of albumin, though the differing conclusions from ANSWER and MACHT necessitate additional trials. The ongoing PRECIOSA study in Spain is assessing dosage and schedule for this therapy.13
Augmenting Diuresis
Loop diuretics are highly protein-bound, and, with hypoalbuminemia, there is less effective drug delivered to the site of action. One clinical approach is to augment diuretics with concomitant HA infusion. This approach is not supported by strong evidence or guidelines.
Hyponatremia
In a retrospective cohort study of 2435 hospitalized patients with cirrhosis, 1126 of whom had hyponatremia, those patients with sodium <130 mmol/L who received HA were more likely to have resolution of hyponatremia to >135 mmol/L. This was associated with improved 30-day survival.14 From this observational data, the AASLD supports the use of albumin combined with extreme fluid restriction (<1000 mL/d) for patients with severe hyponatremia (<120 mmol/L).3
Non-SBP Infections
A 2019 meta-analysis found no evidence of a benefit of HA for bacterial infections other than SBP. However, only three trials encompassing 407 patients met the inclusion criteria.15
NEW GUIDELINE-SUGGESTED USE FOR ALBUMIN IN PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOSIS
SCCM Guideline Update: Hypoalbuminemia and Hypotension
The 2020 SCCM Guidelines for the Management of Adult Acute and Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure in the ICU “suggest using albumin for resuscitation of patients [with liver failure] over other fluids, especially when serum albumin is low (<3 g/dL).” Acute-on-chronic liver failure is decompensation of cirrhosis combined with organ dysfunction (eg, coagulopathy, encephalopathy, kidney injury), a scenario that is frequently encountered by hospitalists outside of intensive care settings. In hypotensive patients with cirrhosis, the SCCM recommends administering albumin to a target mean arterial pressure of 65 mm Hg or otherwise adequate perfusion. This new recommendation is conditional, based on expert consensus, and derives from low-quality evidence, with acknowledgement that “costs may be prohibitive.”4
While the ATTIRE study demonstrated no benefit in treating hypoalbuminemia with infusion of HA in hospitalized patients with decompensated cirrhosis, the 2020 SCCM guidelines, released prior to the publication of the ATTIRE study, focused on more acutely ill patients. In the ATTIRE study, only 2% to 3% of the study population was in an intensive care unit.4,9 The use of albumin infusion in the critically ill, hypoalbuminemic, hypotensive patient is not well studied, and the SCCM acknowledges the lack of supportive evidence for this practice in their guideline statement.
CONCLUSION
The three cardinal clinical indications for human albumin in patients with cirrhosis—prevention of PICD after LVP, in SBP, and for HRS—remain supported by the literature and guidelines, with the most recent guidance adding more nuance in patient selection based on individual risk (Table). With the publication of several large-scale studies in the past few years and a 2021 update to the AASLD guidance statement, clinicians have more evidence to guide their use of HA in patients with cirrhosis. In particular, the practice of treating isolated hypoalbuminemia with HA is no longer supported by the best evidence and is potentially harmful. A professional society recommendation to preferentially use albumin as a resuscitation fluid in hypoalbuminemia was made without the benefit of the results of the 2021 ATTIRE trial. On the horizon, additional results from ongoing and upcoming studies exploring concepts of effective albumin concentration and the pleiotropic properties of HA will impact the use of this therapy in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis.
1. Hirode G, Saab S, Wong RJ. Trends in the burden of chronic liver disease among hospitalized US adults. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(4):e201997. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.1997
2. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2018;69(2):406-460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.024
3. Biggins SW, Angeli P, Garcia-Tsao G, et al. Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and hepatorenal syndrome: 2021 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2021;74(2):1014-1048. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.31884
4. Nanchal R, Subramanian R, Karvellas CJ, et al. Guidelines for the management of adult acute and acute-on-chronic liver failure in the ICU: cardiovascular, endocrine, hematologic, pulmonary, and renal considerations. Crit Care Med. 2020;48(3):e173-e191. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000004192
5. Elsabaawy MM, Abdelhamid SR, Alsebaey A, et al. The impact of paracentesis flow rate in patients with liver cirrhosis on the development of paracentesis induced circulatory dysfunction. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2015;21(4):365-371. https://doi.org/10.3350/cmh.2015.21.4.365
6. Bernardi M, Caraceni P, Navickis RJ, Wilkes MM. Albumin infusion in patients undergoing large-volume paracentesis: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Hepatology. 2012;55(4):1172-1181. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.24786
7. Kütting F, Schubert J, Franklin J, et al. Insufficient evidence of benefit regarding mortality due to albumin substitution in HCC-free cirrhotic patients undergoing large volume paracentesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;32(2):327-338. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.13421
8. Sort P, Navasa M, Arroyo V, et al. Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(6):403-409. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199908053410603
9. China L, Freemantle N, Forrest E, et al. A randomized trial of albumin infusions in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(9):808-817. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2022166
10. Caraceni P, Riggio O, Angeli P, et al. Long-term albumin administration in decompensated cirrhosis (ANSWER): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10138):2417-2429. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30840-7
11. Caraceni P, Angeli P, Prati D, et al. AISF-SIMTI position paper on the appropriate use of albumin in patients with liver cirrhosis: a 2020 update. Blood Transfus. 2021;19(1):9-13. https://doi.org/10.2450/2020.0414-20
12. Solà E, Solé C, Simón-Talero M, et al. Midodrine and albumin for prevention of complications in patients with cirrhosis awaiting liver transplantation. A randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Hepatol. 2018;69(6):1250-1259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.08.006
13. Fernández J, Clària J, Amorós A, et al. Effects of albumin treatment on systemic and portal hemodynamics and systemic inflammation in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2019;157(1):149-162. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2019.03.021
14. Bajaj JS, Tandon P, O’Leary JG, et al. The impact of albumin use on resolution of hyponatremia in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113(9):1339. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41395-018-0119-3
15. Leão GS, Neto GJ, Jotz RdF, de Mattos AA, de Mattos ÂZ. Albumin for cirrhotic patients with extraperitoneal infections: a meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;34(12):2071-2076. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.14791
1. Hirode G, Saab S, Wong RJ. Trends in the burden of chronic liver disease among hospitalized US adults. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(4):e201997. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.1997
2. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2018;69(2):406-460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.024
3. Biggins SW, Angeli P, Garcia-Tsao G, et al. Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and hepatorenal syndrome: 2021 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2021;74(2):1014-1048. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.31884
4. Nanchal R, Subramanian R, Karvellas CJ, et al. Guidelines for the management of adult acute and acute-on-chronic liver failure in the ICU: cardiovascular, endocrine, hematologic, pulmonary, and renal considerations. Crit Care Med. 2020;48(3):e173-e191. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000004192
5. Elsabaawy MM, Abdelhamid SR, Alsebaey A, et al. The impact of paracentesis flow rate in patients with liver cirrhosis on the development of paracentesis induced circulatory dysfunction. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2015;21(4):365-371. https://doi.org/10.3350/cmh.2015.21.4.365
6. Bernardi M, Caraceni P, Navickis RJ, Wilkes MM. Albumin infusion in patients undergoing large-volume paracentesis: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Hepatology. 2012;55(4):1172-1181. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.24786
7. Kütting F, Schubert J, Franklin J, et al. Insufficient evidence of benefit regarding mortality due to albumin substitution in HCC-free cirrhotic patients undergoing large volume paracentesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;32(2):327-338. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.13421
8. Sort P, Navasa M, Arroyo V, et al. Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(6):403-409. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199908053410603
9. China L, Freemantle N, Forrest E, et al. A randomized trial of albumin infusions in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(9):808-817. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2022166
10. Caraceni P, Riggio O, Angeli P, et al. Long-term albumin administration in decompensated cirrhosis (ANSWER): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10138):2417-2429. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30840-7
11. Caraceni P, Angeli P, Prati D, et al. AISF-SIMTI position paper on the appropriate use of albumin in patients with liver cirrhosis: a 2020 update. Blood Transfus. 2021;19(1):9-13. https://doi.org/10.2450/2020.0414-20
12. Solà E, Solé C, Simón-Talero M, et al. Midodrine and albumin for prevention of complications in patients with cirrhosis awaiting liver transplantation. A randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Hepatol. 2018;69(6):1250-1259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.08.006
13. Fernández J, Clària J, Amorós A, et al. Effects of albumin treatment on systemic and portal hemodynamics and systemic inflammation in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2019;157(1):149-162. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2019.03.021
14. Bajaj JS, Tandon P, O’Leary JG, et al. The impact of albumin use on resolution of hyponatremia in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113(9):1339. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41395-018-0119-3
15. Leão GS, Neto GJ, Jotz RdF, de Mattos AA, de Mattos ÂZ. Albumin for cirrhotic patients with extraperitoneal infections: a meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;34(12):2071-2076. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.14791
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine
Deficits in Identification of Goals and Goal-Concordant Care After Sepsis Hospitalization
Identifying and supporting patients’ care goals through shared decision-making was named the highest priority in the Improving Hospital Outcomes through Patient Engagement (i-HOPE) study.1 Ensuring that seriously ill patients’ goals for their future care are understood and honored is particularly important for patients hospitalized with conditions known to be associated with high near-term mortality or functional disability, such as sepsis. It is increasingly recognized that a hospital admission for sepsis is associated with poor outcomes, including high rates of readmission and postdischarge mortality,2-5 yet little is known about the assessment, status, and stability of patient care goals after discharge for sepsis. Using a cohort of high-risk sepsis survivors enrolled in a clinical trial, we aimed to determine how frequently care goals were documented, describe patterns in care goals, and evaluate how frequently care goals changed over 90 days after sepsis discharge. We also used expert reviewers to assess care delivered in the 90 days after hospitalization and determine the proportion of patients who received goal-concordant care.6,7
METHODS
Design, Setting, Participants
We conducted a secondary analysis using data from the Improving Morbidity During Post-Acute Care Transitions for Sepsis (IMPACTS) study,8 a pragmatic randomized trial evaluating the effectiveness of a multicomponent transition program to reduce mortality and rehospitalization after sepsis among patients enrolled from three hospitals between January 2019 and March 2020 (NCT03865602). The study intervention emphasized preference-sensitive care for patients but did not specifically require documentation of care goals in the electronic health record (EHR).
Data Collection
Clinical and outcomes data were collected from the EHR and enterprise data warehouse. We included data collected as part of routine care at IMPACTS trial enrollment (ie, age at admission, gender, race, marital status, coexisting conditions) and during index hospitalization (ie, organ failures, hospital length of stay, discharge disposition). The Charlson Comorbidity Index score was calculated from diagnosis codes captured during both inpatient and outpatient healthcare encounters in the 12 months prior to trial enrollment. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Adult Sepsis Event definitions9 were applied to measure organ failures.
Two palliative care physicians, three internal medicine physicians, and one critical care clinician retrospectively reviewed the EHR of study patients to: (1) identify whether patient care goals were documented in a standardized care alignment tool at discharge or in the subsequent 90 days; (2) categorize each patient’s care goals as focused on longevity, function, or comfort6 using either standardized documentation or unstructured information from the EHR; and (3) determine whether care goals changed over the first 90 days after discharge. Reviewers also classified care received over the 90-day postdischarge period as focused on longevity, function, or comfort. A random sample of 75 cases was selected for double review by a palliative care reviewer to assess interrater agreement in these assessments. Reviewers indicated whether the goal changed and, if so, what the new goal was. The data collection form is provided in the Appendix. The study was approved by the Atrium Health Institutional Review Board.
Outcomes
The primary outcome was the proportion of cases with care goals documented in the standardized care alignment tool, an EHR-embedded tool prompting questions about goals for future health states, including choices among longevity-, function-, and comfort-focused goals. A secondary outcome was the proportion of cases for which a goal could be determined using all information available in the EHR, such as family meeting notes, discharge summaries, and inpatient or outpatient visit notes. We also measured the proportion of patients who received goal-concordant care, defined as agreement between reviewers’ categorizations of patients’ goals and the primary focus of the care delivered, using a well-defined approach.6 In this approach, reviewers first categorized the care delivered during the 90 days after hospital discharge as focused on longevity, function, or comfort using clinical documentation in each patient’s medical record. To enhance transparency of this decision process, reviewers indicated which specific treatments (eg, new medications, hospital admission, hospice enrollment) supported their categorization. Reviewers then separately categorized the patient’s primary goal over the same period. Reviewer training emphasized that classifications of goals and care delivered should be independent. Patients were considered to have received goal-concordant care if the category of care delivered matched the category of the primary care goal. For patients with changing goals, care delivered was compared with the most recent documented goal.
Analyses
We characterized distributions of care goals and care delivered and reported rates of goal-concordant care overall and by care goals. We calculated weighted kappa statistics to assess interrater reliability. We conducted a multivariable logistic regression analysis in the full cohort to evaluate the association of standardized care goal documentation in the EHR with the dependent outcome of goal-concordant care, adjusting for other risk factors (ie, gender, race, marital status, coexisting chronic conditions, organ failures, and hospital length of stay).
RESULTS
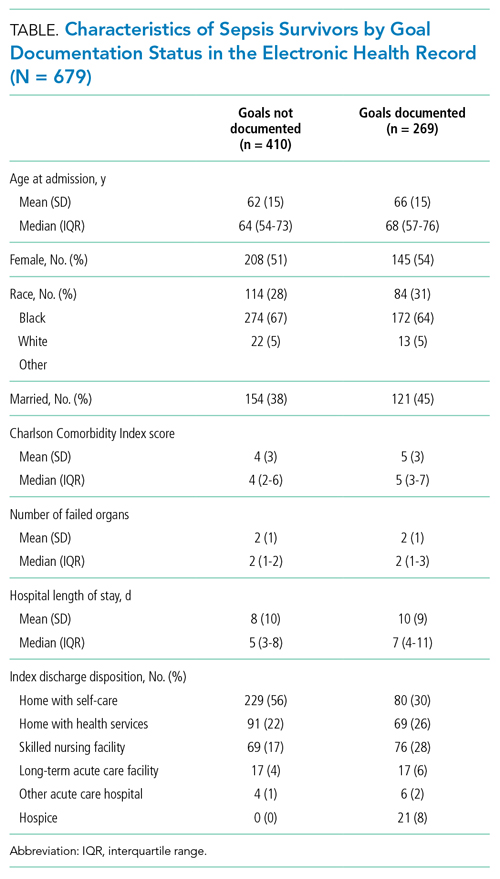
Characterization of Sepsis Survivors’ Goals
The Figure shows patterns of goal documentation and goal-concordant care in the study cohort. Care goals for sepsis survivors were documented in the standardized EHR care alignment tool at discharge for 130 (19%) patients. When reviewers used all information available in the EHR to categorize goals (73% interrater agreement; interrater reliability by weighted κ, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.58-0.83), reviewers were able to categorize patients’ goals in 269 (40%) cases. Among those categorized, goals were classified as prioritizing longevity in 95 (35%), function in 141 (52%), and comfort in 33 (12%) cases.
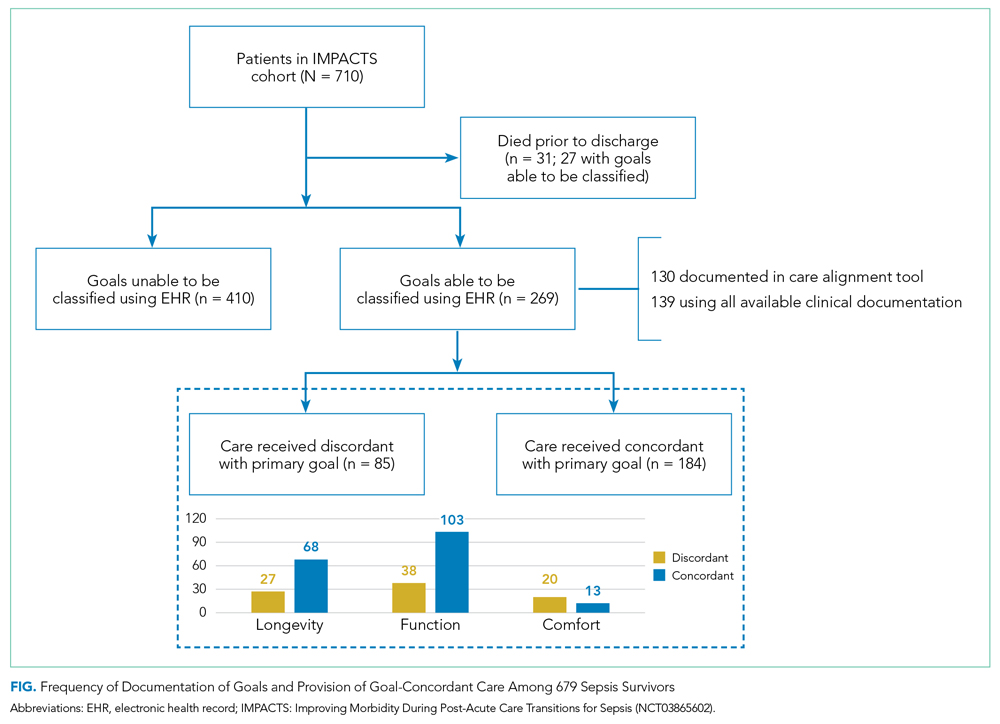
Goals changed over the 90-day observation period for 41 (6%) patients. Of patients whose goals changed, 15 (37%) initially had a goal focused on longevity, 24 (59%) had a goal focused on function, and 2 (5%) had a goal focused on comfort. Of goals that changed, the most frequent new goal was comfort, which was documented in 33 (80%) patients.
Characterization of Goal-Concordant Care
Interrater reliability was moderate for reviewer-based determination of care delivered (73% interrater agreement; weighted κ, 0.60; 95% CI, 0.43-0.78). Reviewers categorized care delivered as focused on longevity in 374 (55%), function in 290 (43%), and comfort in 13 (2%) patients, with <1% unable to be determined. Care elements most frequently cited for longevity-focused classification included intensive care unit (ICU) stay (39%) and new medications for nonsymptom benefit (29%). Care elements most frequently cited for function-focused classification included new medications for nonsymptom benefit (50%) and new medication for symptom benefit (41%). Care elements most frequently cited for comfort-focused classification included hospice enrollment (50%) and new medications for symptom benefit (48%). The rate of goal-concordant care was 68% among those with care goals determined and 27% when cases with unknown goals were classified as not concordant. Concordance was highest among those with longevity-focused (72%) and function-focused (73%) care goals compared with comfort-focused (39%) care goals (P < .01). Adjusting for other potential risk factors, completion of the standardized EHR care alignment tool was associated with higher odds of receiving goal-concordant care (OR, 3.6; 95% CI, 2.4-5.5).
DISCUSSION
Our study identified deficits in the current delivery of goal-concordant care in the first 90 days after sepsis hospitalization. First, goals were only documented in the standardized EHR care alignment tool in one-fifth of cases. Otherwise, information about goals, values, and treatment preferences of sepsis patients was documented idiosyncratically in progress notes, which may not be apparent to clinicians involved in patients’ future care. Lack of clinician attention to documenting the goals of sepsis patients post discharge may reflect suboptimal awareness of the lasting health consequences of sepsis, including persistently elevated risk of mortality up to 2 years following the index hospitalization.2-5 Second, even when goals could be classified by reviewers, the focus of care delivered did not match patients’ goals in nearly one-third of cases.
Our findings inspire several considerations for postsepsis care during hospitalization or in the peridischarge period. First, efforts should focus on increasing assessment and documentation of sepsis survivors’ goals—this might begin with enhanced education about the lasting health consequences after sepsis and communication skills training. Importantly, sepsis survivors’ goals were relatively stable over 90 days after discharge, suggesting that hospitalization for sepsis represents an important opportunity to assess and document patients’ goals. Improving documentation of care goals explicitly in a standardized EHR tool may be an important target for quality-improvement initiatives, as this practice was associated with higher odds of receiving goal-concordant care in our cohort. Second, our findings that one-third of patients received care that was not consistent with their goals is worrisome. Concordance was lowest among comfort-focused care goals, suggesting that some of the high rates of healthcare utilization after sepsis may be unwanted.10-12 For example, ICU stay and new medication for nonsymptom benefit were commonly cited as indications of longevity-focused care among patients with comfort-focused goals. Thus, improving the alignment between sepsis survivors’ goals and subsequent care received is an important target from both a patient-centered and value perspective. Consistent with the recommendations of the i-HOPE study,1 future interventions designed to improve posthospitalization care of sepsis patients should aim to capture goal-concordant care as a patient-centered outcome, if possible.
Our examination of goals and goal-concordant care after sepsis hospitalization advances the goal of enhancing understanding of survivorship in this population.4 Strengths of this study include the large, real-world sample and use of expert palliative care physicians conducting granular EHR review to assess goal-concordant care. Our utilization of this methodology to evaluate goal-concordant care provides information to refine efforts toward developing reliable measures of this important outcome—for example, interrater reliability was similar among reviewers in our study compared with studies assessing goal-concordant care using similar methodology.13
Limitations include potential generalizability challenges for goal and goal-concordant care assessments in other health systems with different EHR platforms or local documentation practices, although deficits in EHR documentation of care goals have been reported in other settings.14,15 We double-reviewed a sample of cases to evaluate interrater reliability, but double-review of all cases with a discussion and adjudication approach may have increased the number of goals that could ultimately be classified. However, this might overestimate the number of goals that are identifiable in real-world practice by a treating clinician. Finally, reviewers may have been challenged to select one goal when two or more competing goals existed. Future refinements of goal-concordant care measurement will need to define methods for handling tradeoffs and prioritization associated with competing goals.
CONCLUSION
The hospitalization and peridischarge periods represent an important opportunity to address deficits in the documentation of goals and provision of goal-concordant care for sepsis survivors. Doing so may improve patient-centered care and reduce the high rates of healthcare utilization after sepsis.
1. Harrison JD, Archuleta M, Avitia E, et al. Developing a patient- and family-centered research agenda for hospital medicine: the Improving Hospital Outcomes through Patient Engagement (i-HOPE) study. J Hosp Med. 2020;15(6):331-337. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3386
2. Courtright KR, Jordan L, Murtaugh CM, et al. Risk factors for long-term mortality and patterns of end-of-life care among Medicare sepsis survivors discharged to home health care. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 ;3(2):e200038. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.0038
3. Prescott HC, Angus DC. Enhancing recovery from sepsis: a review. JAMA. 2018;319(1):62-75. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.17687
4. Prescott HC, Iwashyna TJ, Blackwood B, et al. Understanding and enhancing sepsis survivorship. Priorities for research and practice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200(8):972-981. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201812-2383CP
5. Prescott HC, Osterholzer JJ, Langa KM, Angus DC, Iwashyna TJ. Late mortality after sepsis: propensity matched cohort study. BMJ. 2016;353:i2375. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i2375
6. Halpern SD. Goal-concordant care - searching for the Holy Grail. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(17):1603-1606. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp1908153
7. Ernecoff NC, Wessell KL, Bennett AV, Hanson LC. Measuring goal-concordant care in palliative care research. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2021;62(3):e305-e314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2021.02.030
8. Kowalkowski M, Chou SH, McWilliams A, et al. Structured, proactive care coordination versus usual care for Improving Morbidity during Post-Acute Care Transitions for Sepsis (IMPACTS): a pragmatic, randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2019;20(1):660. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-019-3792-7
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hospital Toolkit for Adult Sepsis Surveillance. March 2018. Accessed September 20, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/sepsis/pdfs/Sepsis-Surveillance-Toolkit-Mar-2018_508.pdf
10. Liu V, Lei X, Prescott HC, Kipnis P, Iwashyna TJ, Escobar GJ. Hospital readmission and healthcare utilization following sepsis in community settings. J Hosp Med. 2014;9(8):502-507. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2197
11. DeMerle KM, Vincent BM, Iwashyna TJ, Prescott HC. Increased healthcare facility use in veterans surviving sepsis hospitalization. J Crit Care. 2017;42:59-64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2017.06.026
12. Shankar-Hari M, Saha R, Wilson J, et al. Rate and risk factors for rehospitalisation in sepsis survivors: systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(4):619-636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-019-05908-3
13. Turnbull AE, Sahetya SK, Colantuoni E, Kweku J, Nikooie R, Curtis JR. Inter-rater agreement of intensivists evaluating the goal concordance of preference-sensitive ICU interventions. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2018;56(3):406-413.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2018.06.003
14. Wilson CJ, Newman J, Tapper S, et al. Multiple locations of advance care planning documentation in an electronic health record: are they easy to find? J Palliat Med. 2013;16(9):1089-1094. https://doi.org/10.1089/jpm.2012.0472
15. Buck K, Detering KM, Pollard A, et al. Concordance between self-reported completion of advance care planning documentation and availability of documentation in Australian health and residential aged care services. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2019;58(2):264-274. https://.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2019.04.026
Identifying and supporting patients’ care goals through shared decision-making was named the highest priority in the Improving Hospital Outcomes through Patient Engagement (i-HOPE) study.1 Ensuring that seriously ill patients’ goals for their future care are understood and honored is particularly important for patients hospitalized with conditions known to be associated with high near-term mortality or functional disability, such as sepsis. It is increasingly recognized that a hospital admission for sepsis is associated with poor outcomes, including high rates of readmission and postdischarge mortality,2-5 yet little is known about the assessment, status, and stability of patient care goals after discharge for sepsis. Using a cohort of high-risk sepsis survivors enrolled in a clinical trial, we aimed to determine how frequently care goals were documented, describe patterns in care goals, and evaluate how frequently care goals changed over 90 days after sepsis discharge. We also used expert reviewers to assess care delivered in the 90 days after hospitalization and determine the proportion of patients who received goal-concordant care.6,7
METHODS
Design, Setting, Participants
We conducted a secondary analysis using data from the Improving Morbidity During Post-Acute Care Transitions for Sepsis (IMPACTS) study,8 a pragmatic randomized trial evaluating the effectiveness of a multicomponent transition program to reduce mortality and rehospitalization after sepsis among patients enrolled from three hospitals between January 2019 and March 2020 (NCT03865602). The study intervention emphasized preference-sensitive care for patients but did not specifically require documentation of care goals in the electronic health record (EHR).
Data Collection
Clinical and outcomes data were collected from the EHR and enterprise data warehouse. We included data collected as part of routine care at IMPACTS trial enrollment (ie, age at admission, gender, race, marital status, coexisting conditions) and during index hospitalization (ie, organ failures, hospital length of stay, discharge disposition). The Charlson Comorbidity Index score was calculated from diagnosis codes captured during both inpatient and outpatient healthcare encounters in the 12 months prior to trial enrollment. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Adult Sepsis Event definitions9 were applied to measure organ failures.
Two palliative care physicians, three internal medicine physicians, and one critical care clinician retrospectively reviewed the EHR of study patients to: (1) identify whether patient care goals were documented in a standardized care alignment tool at discharge or in the subsequent 90 days; (2) categorize each patient’s care goals as focused on longevity, function, or comfort6 using either standardized documentation or unstructured information from the EHR; and (3) determine whether care goals changed over the first 90 days after discharge. Reviewers also classified care received over the 90-day postdischarge period as focused on longevity, function, or comfort. A random sample of 75 cases was selected for double review by a palliative care reviewer to assess interrater agreement in these assessments. Reviewers indicated whether the goal changed and, if so, what the new goal was. The data collection form is provided in the Appendix. The study was approved by the Atrium Health Institutional Review Board.
Outcomes
The primary outcome was the proportion of cases with care goals documented in the standardized care alignment tool, an EHR-embedded tool prompting questions about goals for future health states, including choices among longevity-, function-, and comfort-focused goals. A secondary outcome was the proportion of cases for which a goal could be determined using all information available in the EHR, such as family meeting notes, discharge summaries, and inpatient or outpatient visit notes. We also measured the proportion of patients who received goal-concordant care, defined as agreement between reviewers’ categorizations of patients’ goals and the primary focus of the care delivered, using a well-defined approach.6 In this approach, reviewers first categorized the care delivered during the 90 days after hospital discharge as focused on longevity, function, or comfort using clinical documentation in each patient’s medical record. To enhance transparency of this decision process, reviewers indicated which specific treatments (eg, new medications, hospital admission, hospice enrollment) supported their categorization. Reviewers then separately categorized the patient’s primary goal over the same period. Reviewer training emphasized that classifications of goals and care delivered should be independent. Patients were considered to have received goal-concordant care if the category of care delivered matched the category of the primary care goal. For patients with changing goals, care delivered was compared with the most recent documented goal.
Analyses
We characterized distributions of care goals and care delivered and reported rates of goal-concordant care overall and by care goals. We calculated weighted kappa statistics to assess interrater reliability. We conducted a multivariable logistic regression analysis in the full cohort to evaluate the association of standardized care goal documentation in the EHR with the dependent outcome of goal-concordant care, adjusting for other risk factors (ie, gender, race, marital status, coexisting chronic conditions, organ failures, and hospital length of stay).
RESULTS

Characterization of Sepsis Survivors’ Goals
The Figure shows patterns of goal documentation and goal-concordant care in the study cohort. Care goals for sepsis survivors were documented in the standardized EHR care alignment tool at discharge for 130 (19%) patients. When reviewers used all information available in the EHR to categorize goals (73% interrater agreement; interrater reliability by weighted κ, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.58-0.83), reviewers were able to categorize patients’ goals in 269 (40%) cases. Among those categorized, goals were classified as prioritizing longevity in 95 (35%), function in 141 (52%), and comfort in 33 (12%) cases.

Goals changed over the 90-day observation period for 41 (6%) patients. Of patients whose goals changed, 15 (37%) initially had a goal focused on longevity, 24 (59%) had a goal focused on function, and 2 (5%) had a goal focused on comfort. Of goals that changed, the most frequent new goal was comfort, which was documented in 33 (80%) patients.
Characterization of Goal-Concordant Care
Interrater reliability was moderate for reviewer-based determination of care delivered (73% interrater agreement; weighted κ, 0.60; 95% CI, 0.43-0.78). Reviewers categorized care delivered as focused on longevity in 374 (55%), function in 290 (43%), and comfort in 13 (2%) patients, with <1% unable to be determined. Care elements most frequently cited for longevity-focused classification included intensive care unit (ICU) stay (39%) and new medications for nonsymptom benefit (29%). Care elements most frequently cited for function-focused classification included new medications for nonsymptom benefit (50%) and new medication for symptom benefit (41%). Care elements most frequently cited for comfort-focused classification included hospice enrollment (50%) and new medications for symptom benefit (48%). The rate of goal-concordant care was 68% among those with care goals determined and 27% when cases with unknown goals were classified as not concordant. Concordance was highest among those with longevity-focused (72%) and function-focused (73%) care goals compared with comfort-focused (39%) care goals (P < .01). Adjusting for other potential risk factors, completion of the standardized EHR care alignment tool was associated with higher odds of receiving goal-concordant care (OR, 3.6; 95% CI, 2.4-5.5).
DISCUSSION
Our study identified deficits in the current delivery of goal-concordant care in the first 90 days after sepsis hospitalization. First, goals were only documented in the standardized EHR care alignment tool in one-fifth of cases. Otherwise, information about goals, values, and treatment preferences of sepsis patients was documented idiosyncratically in progress notes, which may not be apparent to clinicians involved in patients’ future care. Lack of clinician attention to documenting the goals of sepsis patients post discharge may reflect suboptimal awareness of the lasting health consequences of sepsis, including persistently elevated risk of mortality up to 2 years following the index hospitalization.2-5 Second, even when goals could be classified by reviewers, the focus of care delivered did not match patients’ goals in nearly one-third of cases.
Our findings inspire several considerations for postsepsis care during hospitalization or in the peridischarge period. First, efforts should focus on increasing assessment and documentation of sepsis survivors’ goals—this might begin with enhanced education about the lasting health consequences after sepsis and communication skills training. Importantly, sepsis survivors’ goals were relatively stable over 90 days after discharge, suggesting that hospitalization for sepsis represents an important opportunity to assess and document patients’ goals. Improving documentation of care goals explicitly in a standardized EHR tool may be an important target for quality-improvement initiatives, as this practice was associated with higher odds of receiving goal-concordant care in our cohort. Second, our findings that one-third of patients received care that was not consistent with their goals is worrisome. Concordance was lowest among comfort-focused care goals, suggesting that some of the high rates of healthcare utilization after sepsis may be unwanted.10-12 For example, ICU stay and new medication for nonsymptom benefit were commonly cited as indications of longevity-focused care among patients with comfort-focused goals. Thus, improving the alignment between sepsis survivors’ goals and subsequent care received is an important target from both a patient-centered and value perspective. Consistent with the recommendations of the i-HOPE study,1 future interventions designed to improve posthospitalization care of sepsis patients should aim to capture goal-concordant care as a patient-centered outcome, if possible.
Our examination of goals and goal-concordant care after sepsis hospitalization advances the goal of enhancing understanding of survivorship in this population.4 Strengths of this study include the large, real-world sample and use of expert palliative care physicians conducting granular EHR review to assess goal-concordant care. Our utilization of this methodology to evaluate goal-concordant care provides information to refine efforts toward developing reliable measures of this important outcome—for example, interrater reliability was similar among reviewers in our study compared with studies assessing goal-concordant care using similar methodology.13
Limitations include potential generalizability challenges for goal and goal-concordant care assessments in other health systems with different EHR platforms or local documentation practices, although deficits in EHR documentation of care goals have been reported in other settings.14,15 We double-reviewed a sample of cases to evaluate interrater reliability, but double-review of all cases with a discussion and adjudication approach may have increased the number of goals that could ultimately be classified. However, this might overestimate the number of goals that are identifiable in real-world practice by a treating clinician. Finally, reviewers may have been challenged to select one goal when two or more competing goals existed. Future refinements of goal-concordant care measurement will need to define methods for handling tradeoffs and prioritization associated with competing goals.
CONCLUSION
The hospitalization and peridischarge periods represent an important opportunity to address deficits in the documentation of goals and provision of goal-concordant care for sepsis survivors. Doing so may improve patient-centered care and reduce the high rates of healthcare utilization after sepsis.
Identifying and supporting patients’ care goals through shared decision-making was named the highest priority in the Improving Hospital Outcomes through Patient Engagement (i-HOPE) study.1 Ensuring that seriously ill patients’ goals for their future care are understood and honored is particularly important for patients hospitalized with conditions known to be associated with high near-term mortality or functional disability, such as sepsis. It is increasingly recognized that a hospital admission for sepsis is associated with poor outcomes, including high rates of readmission and postdischarge mortality,2-5 yet little is known about the assessment, status, and stability of patient care goals after discharge for sepsis. Using a cohort of high-risk sepsis survivors enrolled in a clinical trial, we aimed to determine how frequently care goals were documented, describe patterns in care goals, and evaluate how frequently care goals changed over 90 days after sepsis discharge. We also used expert reviewers to assess care delivered in the 90 days after hospitalization and determine the proportion of patients who received goal-concordant care.6,7
METHODS
Design, Setting, Participants
We conducted a secondary analysis using data from the Improving Morbidity During Post-Acute Care Transitions for Sepsis (IMPACTS) study,8 a pragmatic randomized trial evaluating the effectiveness of a multicomponent transition program to reduce mortality and rehospitalization after sepsis among patients enrolled from three hospitals between January 2019 and March 2020 (NCT03865602). The study intervention emphasized preference-sensitive care for patients but did not specifically require documentation of care goals in the electronic health record (EHR).
Data Collection
Clinical and outcomes data were collected from the EHR and enterprise data warehouse. We included data collected as part of routine care at IMPACTS trial enrollment (ie, age at admission, gender, race, marital status, coexisting conditions) and during index hospitalization (ie, organ failures, hospital length of stay, discharge disposition). The Charlson Comorbidity Index score was calculated from diagnosis codes captured during both inpatient and outpatient healthcare encounters in the 12 months prior to trial enrollment. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Adult Sepsis Event definitions9 were applied to measure organ failures.
Two palliative care physicians, three internal medicine physicians, and one critical care clinician retrospectively reviewed the EHR of study patients to: (1) identify whether patient care goals were documented in a standardized care alignment tool at discharge or in the subsequent 90 days; (2) categorize each patient’s care goals as focused on longevity, function, or comfort6 using either standardized documentation or unstructured information from the EHR; and (3) determine whether care goals changed over the first 90 days after discharge. Reviewers also classified care received over the 90-day postdischarge period as focused on longevity, function, or comfort. A random sample of 75 cases was selected for double review by a palliative care reviewer to assess interrater agreement in these assessments. Reviewers indicated whether the goal changed and, if so, what the new goal was. The data collection form is provided in the Appendix. The study was approved by the Atrium Health Institutional Review Board.
Outcomes
The primary outcome was the proportion of cases with care goals documented in the standardized care alignment tool, an EHR-embedded tool prompting questions about goals for future health states, including choices among longevity-, function-, and comfort-focused goals. A secondary outcome was the proportion of cases for which a goal could be determined using all information available in the EHR, such as family meeting notes, discharge summaries, and inpatient or outpatient visit notes. We also measured the proportion of patients who received goal-concordant care, defined as agreement between reviewers’ categorizations of patients’ goals and the primary focus of the care delivered, using a well-defined approach.6 In this approach, reviewers first categorized the care delivered during the 90 days after hospital discharge as focused on longevity, function, or comfort using clinical documentation in each patient’s medical record. To enhance transparency of this decision process, reviewers indicated which specific treatments (eg, new medications, hospital admission, hospice enrollment) supported their categorization. Reviewers then separately categorized the patient’s primary goal over the same period. Reviewer training emphasized that classifications of goals and care delivered should be independent. Patients were considered to have received goal-concordant care if the category of care delivered matched the category of the primary care goal. For patients with changing goals, care delivered was compared with the most recent documented goal.
Analyses
We characterized distributions of care goals and care delivered and reported rates of goal-concordant care overall and by care goals. We calculated weighted kappa statistics to assess interrater reliability. We conducted a multivariable logistic regression analysis in the full cohort to evaluate the association of standardized care goal documentation in the EHR with the dependent outcome of goal-concordant care, adjusting for other risk factors (ie, gender, race, marital status, coexisting chronic conditions, organ failures, and hospital length of stay).
RESULTS

Characterization of Sepsis Survivors’ Goals
The Figure shows patterns of goal documentation and goal-concordant care in the study cohort. Care goals for sepsis survivors were documented in the standardized EHR care alignment tool at discharge for 130 (19%) patients. When reviewers used all information available in the EHR to categorize goals (73% interrater agreement; interrater reliability by weighted κ, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.58-0.83), reviewers were able to categorize patients’ goals in 269 (40%) cases. Among those categorized, goals were classified as prioritizing longevity in 95 (35%), function in 141 (52%), and comfort in 33 (12%) cases.

Goals changed over the 90-day observation period for 41 (6%) patients. Of patients whose goals changed, 15 (37%) initially had a goal focused on longevity, 24 (59%) had a goal focused on function, and 2 (5%) had a goal focused on comfort. Of goals that changed, the most frequent new goal was comfort, which was documented in 33 (80%) patients.
Characterization of Goal-Concordant Care
Interrater reliability was moderate for reviewer-based determination of care delivered (73% interrater agreement; weighted κ, 0.60; 95% CI, 0.43-0.78). Reviewers categorized care delivered as focused on longevity in 374 (55%), function in 290 (43%), and comfort in 13 (2%) patients, with <1% unable to be determined. Care elements most frequently cited for longevity-focused classification included intensive care unit (ICU) stay (39%) and new medications for nonsymptom benefit (29%). Care elements most frequently cited for function-focused classification included new medications for nonsymptom benefit (50%) and new medication for symptom benefit (41%). Care elements most frequently cited for comfort-focused classification included hospice enrollment (50%) and new medications for symptom benefit (48%). The rate of goal-concordant care was 68% among those with care goals determined and 27% when cases with unknown goals were classified as not concordant. Concordance was highest among those with longevity-focused (72%) and function-focused (73%) care goals compared with comfort-focused (39%) care goals (P < .01). Adjusting for other potential risk factors, completion of the standardized EHR care alignment tool was associated with higher odds of receiving goal-concordant care (OR, 3.6; 95% CI, 2.4-5.5).
DISCUSSION
Our study identified deficits in the current delivery of goal-concordant care in the first 90 days after sepsis hospitalization. First, goals were only documented in the standardized EHR care alignment tool in one-fifth of cases. Otherwise, information about goals, values, and treatment preferences of sepsis patients was documented idiosyncratically in progress notes, which may not be apparent to clinicians involved in patients’ future care. Lack of clinician attention to documenting the goals of sepsis patients post discharge may reflect suboptimal awareness of the lasting health consequences of sepsis, including persistently elevated risk of mortality up to 2 years following the index hospitalization.2-5 Second, even when goals could be classified by reviewers, the focus of care delivered did not match patients’ goals in nearly one-third of cases.
Our findings inspire several considerations for postsepsis care during hospitalization or in the peridischarge period. First, efforts should focus on increasing assessment and documentation of sepsis survivors’ goals—this might begin with enhanced education about the lasting health consequences after sepsis and communication skills training. Importantly, sepsis survivors’ goals were relatively stable over 90 days after discharge, suggesting that hospitalization for sepsis represents an important opportunity to assess and document patients’ goals. Improving documentation of care goals explicitly in a standardized EHR tool may be an important target for quality-improvement initiatives, as this practice was associated with higher odds of receiving goal-concordant care in our cohort. Second, our findings that one-third of patients received care that was not consistent with their goals is worrisome. Concordance was lowest among comfort-focused care goals, suggesting that some of the high rates of healthcare utilization after sepsis may be unwanted.10-12 For example, ICU stay and new medication for nonsymptom benefit were commonly cited as indications of longevity-focused care among patients with comfort-focused goals. Thus, improving the alignment between sepsis survivors’ goals and subsequent care received is an important target from both a patient-centered and value perspective. Consistent with the recommendations of the i-HOPE study,1 future interventions designed to improve posthospitalization care of sepsis patients should aim to capture goal-concordant care as a patient-centered outcome, if possible.
Our examination of goals and goal-concordant care after sepsis hospitalization advances the goal of enhancing understanding of survivorship in this population.4 Strengths of this study include the large, real-world sample and use of expert palliative care physicians conducting granular EHR review to assess goal-concordant care. Our utilization of this methodology to evaluate goal-concordant care provides information to refine efforts toward developing reliable measures of this important outcome—for example, interrater reliability was similar among reviewers in our study compared with studies assessing goal-concordant care using similar methodology.13
Limitations include potential generalizability challenges for goal and goal-concordant care assessments in other health systems with different EHR platforms or local documentation practices, although deficits in EHR documentation of care goals have been reported in other settings.14,15 We double-reviewed a sample of cases to evaluate interrater reliability, but double-review of all cases with a discussion and adjudication approach may have increased the number of goals that could ultimately be classified. However, this might overestimate the number of goals that are identifiable in real-world practice by a treating clinician. Finally, reviewers may have been challenged to select one goal when two or more competing goals existed. Future refinements of goal-concordant care measurement will need to define methods for handling tradeoffs and prioritization associated with competing goals.
CONCLUSION
The hospitalization and peridischarge periods represent an important opportunity to address deficits in the documentation of goals and provision of goal-concordant care for sepsis survivors. Doing so may improve patient-centered care and reduce the high rates of healthcare utilization after sepsis.
1. Harrison JD, Archuleta M, Avitia E, et al. Developing a patient- and family-centered research agenda for hospital medicine: the Improving Hospital Outcomes through Patient Engagement (i-HOPE) study. J Hosp Med. 2020;15(6):331-337. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3386
2. Courtright KR, Jordan L, Murtaugh CM, et al. Risk factors for long-term mortality and patterns of end-of-life care among Medicare sepsis survivors discharged to home health care. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 ;3(2):e200038. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.0038
3. Prescott HC, Angus DC. Enhancing recovery from sepsis: a review. JAMA. 2018;319(1):62-75. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.17687
4. Prescott HC, Iwashyna TJ, Blackwood B, et al. Understanding and enhancing sepsis survivorship. Priorities for research and practice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200(8):972-981. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201812-2383CP
5. Prescott HC, Osterholzer JJ, Langa KM, Angus DC, Iwashyna TJ. Late mortality after sepsis: propensity matched cohort study. BMJ. 2016;353:i2375. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i2375
6. Halpern SD. Goal-concordant care - searching for the Holy Grail. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(17):1603-1606. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp1908153
7. Ernecoff NC, Wessell KL, Bennett AV, Hanson LC. Measuring goal-concordant care in palliative care research. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2021;62(3):e305-e314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2021.02.030
8. Kowalkowski M, Chou SH, McWilliams A, et al. Structured, proactive care coordination versus usual care for Improving Morbidity during Post-Acute Care Transitions for Sepsis (IMPACTS): a pragmatic, randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2019;20(1):660. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-019-3792-7
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hospital Toolkit for Adult Sepsis Surveillance. March 2018. Accessed September 20, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/sepsis/pdfs/Sepsis-Surveillance-Toolkit-Mar-2018_508.pdf
10. Liu V, Lei X, Prescott HC, Kipnis P, Iwashyna TJ, Escobar GJ. Hospital readmission and healthcare utilization following sepsis in community settings. J Hosp Med. 2014;9(8):502-507. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2197
11. DeMerle KM, Vincent BM, Iwashyna TJ, Prescott HC. Increased healthcare facility use in veterans surviving sepsis hospitalization. J Crit Care. 2017;42:59-64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2017.06.026
12. Shankar-Hari M, Saha R, Wilson J, et al. Rate and risk factors for rehospitalisation in sepsis survivors: systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(4):619-636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-019-05908-3
13. Turnbull AE, Sahetya SK, Colantuoni E, Kweku J, Nikooie R, Curtis JR. Inter-rater agreement of intensivists evaluating the goal concordance of preference-sensitive ICU interventions. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2018;56(3):406-413.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2018.06.003
14. Wilson CJ, Newman J, Tapper S, et al. Multiple locations of advance care planning documentation in an electronic health record: are they easy to find? J Palliat Med. 2013;16(9):1089-1094. https://doi.org/10.1089/jpm.2012.0472
15. Buck K, Detering KM, Pollard A, et al. Concordance between self-reported completion of advance care planning documentation and availability of documentation in Australian health and residential aged care services. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2019;58(2):264-274. https://.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2019.04.026
1. Harrison JD, Archuleta M, Avitia E, et al. Developing a patient- and family-centered research agenda for hospital medicine: the Improving Hospital Outcomes through Patient Engagement (i-HOPE) study. J Hosp Med. 2020;15(6):331-337. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3386
2. Courtright KR, Jordan L, Murtaugh CM, et al. Risk factors for long-term mortality and patterns of end-of-life care among Medicare sepsis survivors discharged to home health care. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 ;3(2):e200038. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.0038
3. Prescott HC, Angus DC. Enhancing recovery from sepsis: a review. JAMA. 2018;319(1):62-75. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.17687
4. Prescott HC, Iwashyna TJ, Blackwood B, et al. Understanding and enhancing sepsis survivorship. Priorities for research and practice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200(8):972-981. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201812-2383CP
5. Prescott HC, Osterholzer JJ, Langa KM, Angus DC, Iwashyna TJ. Late mortality after sepsis: propensity matched cohort study. BMJ. 2016;353:i2375. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i2375
6. Halpern SD. Goal-concordant care - searching for the Holy Grail. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(17):1603-1606. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp1908153
7. Ernecoff NC, Wessell KL, Bennett AV, Hanson LC. Measuring goal-concordant care in palliative care research. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2021;62(3):e305-e314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2021.02.030
8. Kowalkowski M, Chou SH, McWilliams A, et al. Structured, proactive care coordination versus usual care for Improving Morbidity during Post-Acute Care Transitions for Sepsis (IMPACTS): a pragmatic, randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2019;20(1):660. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-019-3792-7
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hospital Toolkit for Adult Sepsis Surveillance. March 2018. Accessed September 20, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/sepsis/pdfs/Sepsis-Surveillance-Toolkit-Mar-2018_508.pdf
10. Liu V, Lei X, Prescott HC, Kipnis P, Iwashyna TJ, Escobar GJ. Hospital readmission and healthcare utilization following sepsis in community settings. J Hosp Med. 2014;9(8):502-507. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2197
11. DeMerle KM, Vincent BM, Iwashyna TJ, Prescott HC. Increased healthcare facility use in veterans surviving sepsis hospitalization. J Crit Care. 2017;42:59-64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2017.06.026
12. Shankar-Hari M, Saha R, Wilson J, et al. Rate and risk factors for rehospitalisation in sepsis survivors: systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(4):619-636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-019-05908-3
13. Turnbull AE, Sahetya SK, Colantuoni E, Kweku J, Nikooie R, Curtis JR. Inter-rater agreement of intensivists evaluating the goal concordance of preference-sensitive ICU interventions. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2018;56(3):406-413.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2018.06.003
14. Wilson CJ, Newman J, Tapper S, et al. Multiple locations of advance care planning documentation in an electronic health record: are they easy to find? J Palliat Med. 2013;16(9):1089-1094. https://doi.org/10.1089/jpm.2012.0472
15. Buck K, Detering KM, Pollard A, et al. Concordance between self-reported completion of advance care planning documentation and availability of documentation in Australian health and residential aged care services. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2019;58(2):264-274. https://.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2019.04.026
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine
Traditional Medicare Spending on Inpatient Episodes as Hospitalizations Decline
The rate of inpatient admissions among adults aged 65 years and older has decreased by approximately 25% since 2000.1,2 This long-term trend raises important questions about inpatient-related spending in the traditional Medicare program for hospitals and providers who treat beneficiaries after a hospitalization. As traditional Medicare’s most expensive sector (accounting for 21% of all Medicare spending3), reducing hospitalizations is often championed as an opportunity to moderate Medicare spending growth.
Medicare’s ability to achieve significant savings from declining inpatient use may be tempered by a shift toward more expensive hospitalizations. If marginal hospitalizations among healthier beneficiaries are avoided, then the remaining inpatient users may be sicker and have greater spending per hospitalization and greater need for follow-up services. This study examines trends in Medicare spending related to episodes initiated by an inpatient stay because of its importance to overall Medicare spending and the implications for several Medicare value-based payment initiatives. In care models seeking to contain spending at a population level, such as accountable care organizations and managed care plans, reducing inpatient use and associated services may have the largest impact in curbing overall spending growth per beneficiary. Other models focused on spending at an episode level, including bundled payment initiatives, may face challenges if inpatient episodes become more expensive over time.
As Medicare shifts toward value-based payments, hospitalists and other hospital leaders are often involved in redesigning care delivery models for the hospital or accountable care organization (eg, through readmission reduction initiatives, post–acute care coordination, and bundled-care delivery programs). Not all savings strategies rely on providers to change how services are delivered; Medicare can modify payment rates, such as Affordable Care Act provisions that slowed how quickly Medicare payment rates increased.4 For clinicians to navigate the shift toward new payment models, it is important to recognize how each of these elements—declining hospital admissions, spending per inpatient episode, and payment rates—affect spending trends for inpatient services and associated care. Previous articles on overall Medicare inpatient spending have examined inpatient stays alone5 or focused mainly on spending per episode6,7 without quantifying how these elements contributed to overall episode-related Medicare spending per beneficiary. This article addresses this gap by demonstrating how inpatient-related spending trends reflect each component.
This study examined trends in Medicare’s spending on inpatient episodes during the years 2009 to 2017. We described changes in the volume and spending on inpatient-initiated episodes across several dimensions, including beneficiary-level and hospitalization-level factors. We examined whether declines in spending associated with fewer inpatient-initiated episodes have been offset by increased spending per episode and how spending would have differed without changes in Medicare payment rates.
Episode Definition
We constructed an episode measure that captured traditional Medicare spending for 30 days prior to hospital admission, hospitalization duration, and 90 days following hospital discharge (additional details in the Appendix).
Any acute hospitalization triggered a new episode, with one exception: if a beneficiary was discharged and readmitted within 90 days for the same diagnosis-related group (DRG), then the readmission did not trigger a new episode. The spending for that readmission was attributed to the prior hospital stay. In effect, the annual number of episodes is equivalent to the annual number of hospital admissions minus subsequent rehospitalizations for the same DRG. Neither observation stays nor hospitalizations in inpatient rehabilitation, psychiatric, or long-term facilities were considered acute hospital admissions.
We assigned claims from noninpatient sectors to an episode based on whether the claim start date fell within the episode window. All traditional Medicare sectors were measured, including outpatient services, physician claims, post–acute care services, and Medicare Part D prescription drug events.
Our analysis aimed to measure all spending related to inpatient episodes without double-counting spending for overlapping episodes. If episodes overlapped, then spending for overlapping days was weighted to be evenly divided across episodes.
Outcome Measures
The study’s main outcomes summarized episode trends across the entire traditional Medicare population, including beneficiaries without an episode, in annual mean number of episodes per beneficiary and annual mean episode-related spending per beneficiary. The denominator of these measures is person-years, or total number of beneficiary months with Medicare Part A and B coverage divided by 12. The annual mean number of episodes per beneficiary is the total number of episodes initiated in a calendar year divided by person-years. The annual mean episode-related spending per beneficiary is the total amount of spending attributed to episodes divided by person-years. We also measured annual mean spending per episode, or total amount of spending attributed to episodes divided by the total number of episodes.
Medicare annually updates each sector’s payment rates for several factors, including inflation. We constructed an index for each sector to adjust for these annual payment rate changes. We also accounted for sequestration measures in effect since April 2013 that reduced Medicare payments to all sectors by 2%. We report our spending measures twice, with and without adjusting for changes in payment rates. Adjusted numbers reflect payment rates in effect in 2015.
Analysis Approach
We present annual trends on changes in the number of inpatient episodes per beneficiary, mean episode-related spending per beneficiary, and mean spending per episode. To quantify how changes in episode-related spending per beneficiary reflect changes in the number of episodes per beneficiary vs changes in spending per episode, we modified an approach implemented by Rosen and colleagues.8
To better understand which beneficiaries have declining inpatient use, we performed stratified analyses describing changes in the number of episodes per beneficiary between 2009 and 2017, spending per episode, and total episode-related spending per beneficiary. We report these measures for several subpopulations defined by age, sex, race, dual-eligible status, and whether the beneficiary used long-term nursing home services during the episode’s calendar year. Descriptive statistics also detail how these measures changed between 2009 and 2017 for episodes stratified by characteristics of the index hospital stay: planned vs unplanned, medical vs surgical, and any use of intensive care unit (ICU) or coronary care unit services. We also stratify study measures by whether an episode included any use of post–acute care services (skilled nursing facility, home health, or inpatient rehabilitation facility use). Finally, we aggregate the episodes into major diagnostic categories (MDCs) based on the index hospital stay’s DRG to report study outcomes by condition. Because of a shift in coding hospitalizations for pneumonia as sepsis,9,10 we exclude these two diseases from their respective MDCs and analyze them jointly as a unique category.
RESULTS
Changes in Number of Inpatient Episodes and Related Spending
From 2009 to 2017, the number of inpatient episodes per 1000 traditional Medicare beneficiaries declined from 326 to 267 (Table 1), or a relative decline of 18.2% (Figure 1). The total volume of inpatient episodes declined by only 13.4%, from 10.2 million to 8.8 million, reflecting that the size of the traditional Medicare population grew during these years. Over the same years, mean payment-rate–adjusted spending per episode increased 11.4% from $20,891 to $23,273.

When considering overall episode-related spending, the large decline in the volume of episodes outweighed increased spending per episode: the mean amount of episode-related Medicare spending per beneficiary decreased 8.9% from $6810 to $6206 (Table 1), or a net change of $604 (Figure 2). This net change reflects decreased spending due to fewer episodes per beneficiary ($1239 reduction in episode-related spending) offset by increased spending per episode (translating to a $776 increase in episode-related spending per beneficiary).
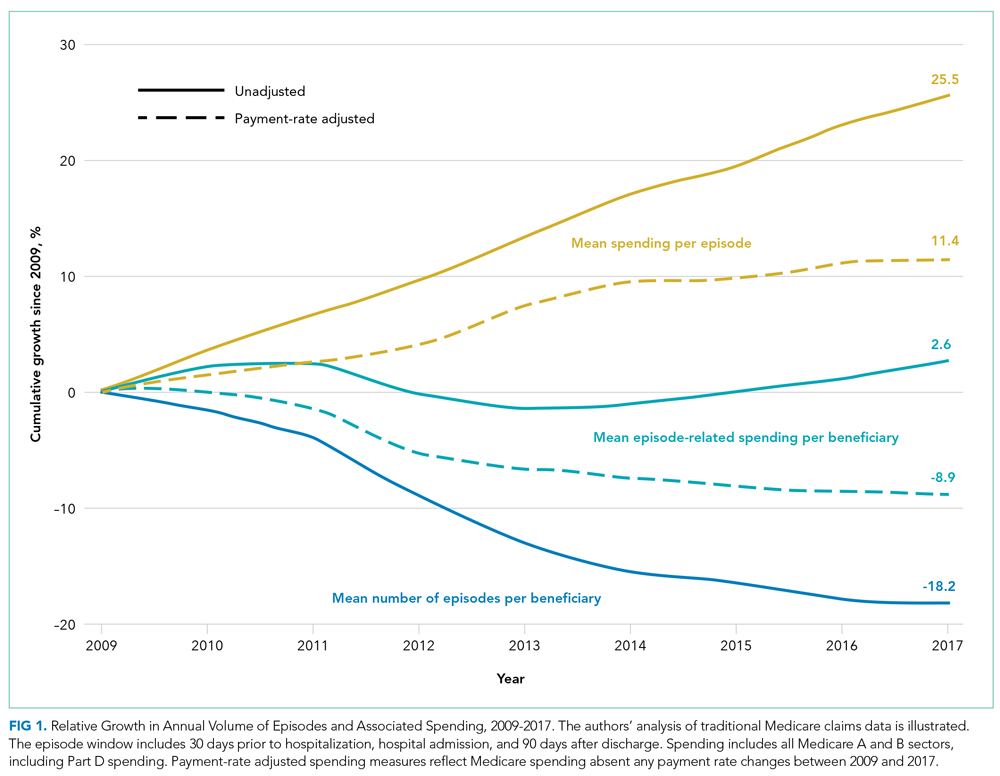
When these estimates are calculated separately for the inpatient sector and all other sectors, the inpatient sector experienced small increases in spending associated with greater spending per episode ($304) compared with noninpatient sectors ($472). Accordingly, the inpatient sector had a larger net decline in episode-related spending per beneficiary ($420) than noninpatient sectors ($184) after taking into account declining episode volume.
As expected, episode-related spending increased more when measures were not adjusted for annual payment rate increases. Without such adjustment, mean spending per episode increased 25.5%, and episode-related spending per beneficiary was nearly flat (2.6% between 2009 and 2017 [Figure 1]). The decline in unadjusted spending associated with fewer episodes ($1138) was offset by the spending increase associated with higher spending per episode ($1592) (Figure 2).
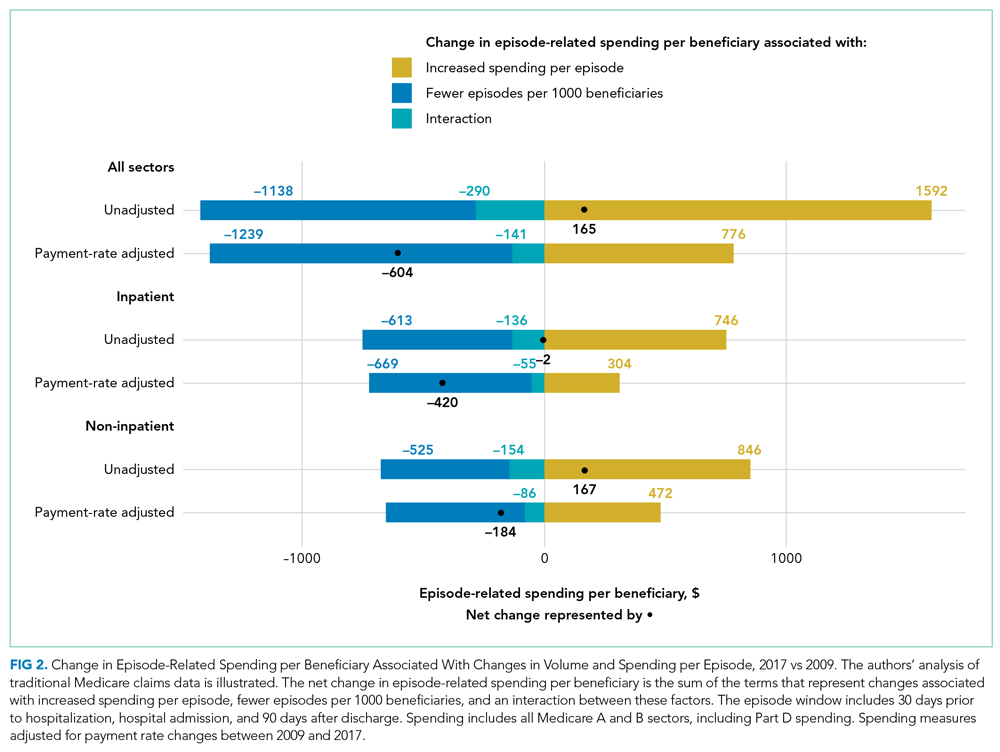
Analyses Stratified by Beneficiary Characteristics
Every population examined had declines in the number of inpatient episodes, even beneficiaries with more frequent inpatient use (Table 2). Among Medicare beneficiaries aged 85 years and older, the mean number of episodes per 1000 beneficiaries declined by 12.7%, from 524 to 457. Populations with less frequent inpatient use often experienced larger relative declines in number of episodes than populations with more frequent inpatient use. For example, the mean number of episodes per 1000 beneficiaries decreased by 17.7% for beneficiaries without nursing home use (306 to 252), as compared with an 8.1% decline for beneficiaries with nursing home use (from 888 to 816). In contrast, populations with less frequent inpatient use had larger relative increases in spending per episode with adjustment for payment rate changes. For example, spending per episode increased by 13.1% for beneficiaries aged 65 to 74 years ($20,904 to $23,644), but only by 8.6% for beneficiaries 85 years and older ($20,384 to $22,138).

Analyses Stratified by Service Use Characteristics
Some types of inpatient episodes had larger declines in the number of episodes, including episodes with planned admissions for the index hospital stay (28.8% decline from 68 to 48 episodes per 1000 beneficiaries) and episodes without post–acute care use (23.9% decline from 169 to 129 episodes per 1000 beneficiaries) (Appendix Table). In contrast, declines in the number of episodes were similar for index hospital admissions that did or did not involve ICU use (17.8% and 18.3% reduction in mean number of episodes per 1000 beneficiaries, respectively) or that included a surgical procedure or not (17.1% versus 18.6%, respectively). Several types of inpatient episodes had larger increases in spending per episode, such as a 15.1% increase for planned admissions and a 13.2% increase for hospitalizations without ICU use.
According to diagnosis information for an episode’s index hospital stay, inpatient episodes related to conditions affecting the circulatory system had the largest decline in mean number of episodes, decreasing by 31.8% from 78 to 53 episodes per 1000 beneficiaries (Appendix Table). Episodes for other diseases had much smaller declines in volume. Admissions for diagnoses of pneumonia or sepsis had notable increases in the volume of episodes, increasing by 20.7% from 25 to 30 admissions per 1000 beneficiaries.
DISCUSSION
Medicare spending per beneficiary on inpatient episodes, including services provided pre- and post hospitalization, declined by 8.9% from 2009 to 2017 after adjusting for payment rate changes. This decline reflects two components. First, the number of episodes per 1000 beneficiaries declined by 18.2%. Although the extent of this decrease varied across populations, every group examined had declines in inpatient use. In particular, hospitalizations for conditions affecting the circulatory system, such as heart attacks and cardiac procedures, decreased. Second, as inpatient volume declined, spending per episode increased by 11.4% to an average of $23,273 in 2017. This increase in spending per episode offset how much overall Medicare spending on episode-related care declined.
Medicare is increasingly challenging hospitals to demonstrate the value of inpatient services and associated treatment, which requires hospital leaders to recognize how their facilities’ spending trends relate to these national patterns. Understanding how much national episode-related spending has decreased over time with declining inpatient volume can help an accountable care organization evaluate whether it is feasible to achieve significant savings by reducing hospitalizations. Bundled payment providers focused on managing spending per episode can benefit from identifying which types of hospitalizations have increased spending per episode, especially for certain diagnoses.
These results also highlight the continued importance of a perennial factor in Medicare spending: payment rates. If Medicare payment rates had not increased over our study period, Medicare spending per inpatient episode would have increased by only 11%. Actual Medicare spending per episode increased by 25%, demonstrating that over half of the relative increase in spending per episode reflected increases in Medicare’s payment rates.
Increased spending per episode, even after adjustment for payment rate changes, suggests that services provided during an episode have increased in intensity or shifted toward higher-cost treatments.
When interpreting these trends, several points are notable. The underlying health of the Medicare population may contribute to declining inpatient use but is difficult to quantify. The observed decline in cardiac-related hospitalizations is consistent with evidence that the impact of ischemic heart disease, the leading source of disease or injury in the US population, has dramatically declined over recent decades15 and that the Medicare program has experienced large declines in overall spending and use related to cardiac conditions.16-18
Other potential factors include a shift toward hospitals treating Medicare beneficiaries as outpatients during an observation stay instead of admitting them as inpatients. Observation stays have increased as traditional Medicare implemented measures to penalize readmissions and limit payments for short inpatient stays.19-21 Even so, the increase in observation stays would have to be at least three times as large as described in other work to fully substitute for the decrease in inpatient stays: between the years 2007 and 2018, the number of observation stays per 1000 beneficiaries increased by only 26 stays, whereas the number of hospitalizations per 1000 beneficiaries decreased by 83 hospitalizations.20
Outpatient services may also broaden treatment availability in alternative settings or enable beneficiaries to avoid inpatient treatment with appropriate preventative care.22-27 These considerations are even more relevant as the COVID-19 pandemic spurred reduced admissions and shifted acute services outside of hospitals.28,29 Some services, such as elective surgeries, have probably shifted from an inpatient to an outpatient setting, which would be consistent with our finding that there are larger relative declines in planned hospitalizations. Although this analysis does not capture spending for outpatient services that are not linked to an inpatient admission, prior work demonstrates that annual growth in total Medicare spending per beneficiary (episode related or not) has recently declined for the inpatient sector but increased for outpatient and physician sectors.30 By offering other outpatient services, hospitals may be able to recoup some declining inpatient revenues. However, outpatient services are reimbursed at a lower rate than inpatient services, suggesting these trends may create financial pressure for hospitals.
There are several limitations to our analysis. First, our analysis is not designed to uncover the reason for the shift away from inpatient services nor to analyze how it has affected beneficiaries’ overall quality of care.
CONCLUSION
Over an 8-year period, Medicare spending per beneficiary on inpatient episodes, including all services immediately preceding and following hospitalizations, declined by 8.9% after taking into account payment rate increases. This broad shift away from inpatient services among all Medicare beneficiaries suggests policymakers should aim for payment policies that balance financial sustainability for hospitals and associated facilities with more efficient use of inpatient and related services.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Sunita Thapa, Lucas Stewart, Christine Lai, and Liliana Podczerwinski for contributions in data analysis and manuscript preparation.
1. Sun R, Karaca Z, Wong HS. Trends in hospital inpatient stays by age and payer, 2000-2015: Statistical Brief #235. In: Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2006.
2. HCUP Fast Stats - trends in inpatient stays. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP). April 2021. Accessed August 29, 2021. www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/faststats/national/inpatienttrends.jsp
3. The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. Section 1: National health care and Medicare spending. In: A Data Book: Health Care Spending and the Medicare Program. June 2018. Accessed August 13, 2021. http://www.medpac.gov/docs/default-source/data-book/jun18_databooksec1_sec.pdf
4. Buntin MB, Graves JA. How the ACA dented the cost curve. Health Aff (Millwood). 2020;39(3):403-412. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2019.01478
5. Krumholz HM, Nuti SV, Downing NS, Normand SLT, Wang Y. Mortality, hospitalizations, and expenditures for the Medicare population aged 65 years or older, 1999-2013. JAMA. 2015;314(4):355-365. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.8035
6. Chen LM, Norton EC, Banerjee M, Regenbogen SE, Cain-Nielsen AH, Birkmeyer JD. Spending on care after surgery driven by choice of care settings instead of intensity of services. Health Aff (Millwood). 2017;36(1):83-90. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2016.0668
7. Ibrahim AM, Nuliyalu U, Lawton EJ, et al. Evaluation of US hospital episode spending for acute inpatient conditions after the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(11):e2023926. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.23926
8. Rosen A, Aizcorbe A, Ryu AJ, Nestoriak N, Cutler DM, Chernew ME. Policy makers will need a way to update bundled payments that reflects highly skewed spending growth of various care episodes. Health Aff (Millwood). 2013;32(5):944-951. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2012.1246
9. Lindenauer PK, Lagu T, Shieh MS, Pekow PS, Rothberg MB. Association of diagnostic coding with trends in hospitalizations and mortality of patients with pneumonia, 2003-2009. JAMA. 2012;307(13):1405-1413. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2012.384
10. Buntin MB, Lai C, Podczerwinski L, Poon S, Wallis C. Changing diagnosis patterns are increasing Medicare spending for inpatient hospital services. The Commonwealth Fund. April 28, 2021. Accessed August 13, 2021. https://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/2021/apr/changing-diagnosis-patterns-are-increasing-medicare-spending-inpatient
11. The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. Hospital inpatient and outpatient services. In: Report to the Congress: Medicare Payment Policy. . March 2018. Accessed August 13, 2021. http://www.medpac.gov/docs/default-source/reports/mar18_medpac_ch3_sec.pdf?sfvrsn=0
12. Ody C, Msall L, Dafny LS, Grabowski DC, Cutler DM. Decreases In readmissions credited to Medicare’s program to reduce hospital readmissions have been overstated. Health Aff (Millwood). 2019;38(1):36-43. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2018.05178
13. Dharmarajan K, Qin L, Lin Z, et al. Declining admission rates and thirty-day readmission rates positively associated even though patients grew sicker over time. Health Aff (Millwood). 2016;35(7):1294-1302. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2015.1614
14. Sjoding MW, Prescott HC, Wunsch H, Iwashyna TJ, Cooke CR. Longitudinal changes in ICU admissions among elderly patients in the United States. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(7):1353-1360. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000001664
15. Murray CJ, Atkinson C, Bhalla K, et al. The state of US health, 1990-2010: burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors. JAMA. 2013;310(6):591-608. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.13805
16. Cutler DM, Ghosh K, Messer KL, Raghunathan TE, Stewart ST, Rosen AB. Explaining the slowdown in medical spending growth among the elderly, 1999-2012. Health Aff (Millwood). 2019;38(2):222-229. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2018.05372
17. Ward MJ, Kripalani S, Zhu Y, et al. Incidence of emergency department visits for ST-elevation myocardial infarction in a recent six-year period in the United States. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115(2):167-170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.10.020
18. Keohane LM, Gambrel RJ, Freed SS, Stevenson D, Buntin MB. Understanding trends in Medicare spending, 2007-2014. Health Serv Res. 2018;53(5):3507-3527. https://doi.org/10.1111/1475-6773.12845
19. Nuckols TK, Fingar KR, Barrett M, Steiner CA, Stocks C, Owens PL. The shifting landscape in utilization of inpatient, observation, and emergency department services across payers. J Hosp Med. 2017;12(6):443-446. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.2751
20. Poon SJ, Wallis CJ, Lai P, Podczerwinski L, Buntin MB. Medicare two-midnight rule accelerated shift to observation stays. Health Affairs. In press.
21. Sheehy AM, Kaiksow F, Powell WR, et al. The Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program and observation hospitalizations. J Hosp Med. 2021;16(7):409-411. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3634
22. Culler SD, Parchman ML, Przybylski M. Factors related to potentially preventable hospitalizations among the elderly. Med Care. 1998;36(6):804-817. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005650-199806000-00004
23. Kozak LJ, Hall MJ, Owings MF. Trends in avoidable hospitalizations, 1980-1998. Health Aff (Millwood). 2001;20(2):225-232. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.20.2.225
24. Ouslander JG, Lamb G, Perloe M, et al. Potentially avoidable hospitalizations of nursing home residents: frequency, causes, and costs. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;58(4):627-635. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.02768.x
25. Konetzka RT, Karon SL, Potter DEB. Users of Medicaid home and community-based services are especially vulnerable to costly avoidable hospital admissions. Health Aff (Millwood). 2012;31(6):1167-1175. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2011.0902
26. Nyweide DJ, Anthony DL, Bynum JPW, et al. Continuity of care and the risk of preventable hospitalization in older adults. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173(20):1879-1885. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.10059
27. Auerbach AD, Kripalani S, Vasilevskis EE, et al. Preventability and causes of readmissions in a national cohort of general medicine patients. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(4):484-493. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.7863
28. Birkmeyer JD, Barnato A, Birkmeyer N, Bessler R, Skinner J. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on hospital admissions in the United States. Health Aff (Millwood). 2020;39(11):2010-2017. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2020.00980
29. Nundy S, Patel KK. Hospital-at-home to support COVID-19 surge—time to bring down the walls? JAMA Health Forum. 2020;1(5):e200504. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamahealthforum.2020.0504
30. Keohane LM, Stevenson DG, Freed S, Thapa S, Stewart L, Buntin MB. Trends in Medicare fee-for-service spending growth for dual-eligible beneficiaries, 2007–15. Health Aff (Millwood). 2018;37(8):1265-1273. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2018.0143
31. Freed M, Biniek JF, Damico A, Neuman T. Medicare Advantage in 2021: enrollment update and key trends. June 21, 2021. Accessed August 13, 2021. https://www.kff.org/medicare/issue-brief/medicare-advantage-in-2021-enrollment-update-and-key-trends/
32. Li Q, Rahman M, Gozalo P, Keohane LM, Gold MR, Trivedi AN. Regional variations: the use of hospitals, home health, and skilled nursing in traditional Medicare and Medicare Advantage. Health Aff (Millwood). 2018;37(8):1274-1281. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2018.0147
The rate of inpatient admissions among adults aged 65 years and older has decreased by approximately 25% since 2000.1,2 This long-term trend raises important questions about inpatient-related spending in the traditional Medicare program for hospitals and providers who treat beneficiaries after a hospitalization. As traditional Medicare’s most expensive sector (accounting for 21% of all Medicare spending3), reducing hospitalizations is often championed as an opportunity to moderate Medicare spending growth.
Medicare’s ability to achieve significant savings from declining inpatient use may be tempered by a shift toward more expensive hospitalizations. If marginal hospitalizations among healthier beneficiaries are avoided, then the remaining inpatient users may be sicker and have greater spending per hospitalization and greater need for follow-up services. This study examines trends in Medicare spending related to episodes initiated by an inpatient stay because of its importance to overall Medicare spending and the implications for several Medicare value-based payment initiatives. In care models seeking to contain spending at a population level, such as accountable care organizations and managed care plans, reducing inpatient use and associated services may have the largest impact in curbing overall spending growth per beneficiary. Other models focused on spending at an episode level, including bundled payment initiatives, may face challenges if inpatient episodes become more expensive over time.
As Medicare shifts toward value-based payments, hospitalists and other hospital leaders are often involved in redesigning care delivery models for the hospital or accountable care organization (eg, through readmission reduction initiatives, post–acute care coordination, and bundled-care delivery programs). Not all savings strategies rely on providers to change how services are delivered; Medicare can modify payment rates, such as Affordable Care Act provisions that slowed how quickly Medicare payment rates increased.4 For clinicians to navigate the shift toward new payment models, it is important to recognize how each of these elements—declining hospital admissions, spending per inpatient episode, and payment rates—affect spending trends for inpatient services and associated care. Previous articles on overall Medicare inpatient spending have examined inpatient stays alone5 or focused mainly on spending per episode6,7 without quantifying how these elements contributed to overall episode-related Medicare spending per beneficiary. This article addresses this gap by demonstrating how inpatient-related spending trends reflect each component.
This study examined trends in Medicare’s spending on inpatient episodes during the years 2009 to 2017. We described changes in the volume and spending on inpatient-initiated episodes across several dimensions, including beneficiary-level and hospitalization-level factors. We examined whether declines in spending associated with fewer inpatient-initiated episodes have been offset by increased spending per episode and how spending would have differed without changes in Medicare payment rates.
Episode Definition
We constructed an episode measure that captured traditional Medicare spending for 30 days prior to hospital admission, hospitalization duration, and 90 days following hospital discharge (additional details in the Appendix).
Any acute hospitalization triggered a new episode, with one exception: if a beneficiary was discharged and readmitted within 90 days for the same diagnosis-related group (DRG), then the readmission did not trigger a new episode. The spending for that readmission was attributed to the prior hospital stay. In effect, the annual number of episodes is equivalent to the annual number of hospital admissions minus subsequent rehospitalizations for the same DRG. Neither observation stays nor hospitalizations in inpatient rehabilitation, psychiatric, or long-term facilities were considered acute hospital admissions.
We assigned claims from noninpatient sectors to an episode based on whether the claim start date fell within the episode window. All traditional Medicare sectors were measured, including outpatient services, physician claims, post–acute care services, and Medicare Part D prescription drug events.
Our analysis aimed to measure all spending related to inpatient episodes without double-counting spending for overlapping episodes. If episodes overlapped, then spending for overlapping days was weighted to be evenly divided across episodes.
Outcome Measures
The study’s main outcomes summarized episode trends across the entire traditional Medicare population, including beneficiaries without an episode, in annual mean number of episodes per beneficiary and annual mean episode-related spending per beneficiary. The denominator of these measures is person-years, or total number of beneficiary months with Medicare Part A and B coverage divided by 12. The annual mean number of episodes per beneficiary is the total number of episodes initiated in a calendar year divided by person-years. The annual mean episode-related spending per beneficiary is the total amount of spending attributed to episodes divided by person-years. We also measured annual mean spending per episode, or total amount of spending attributed to episodes divided by the total number of episodes.
Medicare annually updates each sector’s payment rates for several factors, including inflation. We constructed an index for each sector to adjust for these annual payment rate changes. We also accounted for sequestration measures in effect since April 2013 that reduced Medicare payments to all sectors by 2%. We report our spending measures twice, with and without adjusting for changes in payment rates. Adjusted numbers reflect payment rates in effect in 2015.
Analysis Approach
We present annual trends on changes in the number of inpatient episodes per beneficiary, mean episode-related spending per beneficiary, and mean spending per episode. To quantify how changes in episode-related spending per beneficiary reflect changes in the number of episodes per beneficiary vs changes in spending per episode, we modified an approach implemented by Rosen and colleagues.8
To better understand which beneficiaries have declining inpatient use, we performed stratified analyses describing changes in the number of episodes per beneficiary between 2009 and 2017, spending per episode, and total episode-related spending per beneficiary. We report these measures for several subpopulations defined by age, sex, race, dual-eligible status, and whether the beneficiary used long-term nursing home services during the episode’s calendar year. Descriptive statistics also detail how these measures changed between 2009 and 2017 for episodes stratified by characteristics of the index hospital stay: planned vs unplanned, medical vs surgical, and any use of intensive care unit (ICU) or coronary care unit services. We also stratify study measures by whether an episode included any use of post–acute care services (skilled nursing facility, home health, or inpatient rehabilitation facility use). Finally, we aggregate the episodes into major diagnostic categories (MDCs) based on the index hospital stay’s DRG to report study outcomes by condition. Because of a shift in coding hospitalizations for pneumonia as sepsis,9,10 we exclude these two diseases from their respective MDCs and analyze them jointly as a unique category.
RESULTS
Changes in Number of Inpatient Episodes and Related Spending
From 2009 to 2017, the number of inpatient episodes per 1000 traditional Medicare beneficiaries declined from 326 to 267 (Table 1), or a relative decline of 18.2% (Figure 1). The total volume of inpatient episodes declined by only 13.4%, from 10.2 million to 8.8 million, reflecting that the size of the traditional Medicare population grew during these years. Over the same years, mean payment-rate–adjusted spending per episode increased 11.4% from $20,891 to $23,273.

When considering overall episode-related spending, the large decline in the volume of episodes outweighed increased spending per episode: the mean amount of episode-related Medicare spending per beneficiary decreased 8.9% from $6810 to $6206 (Table 1), or a net change of $604 (Figure 2). This net change reflects decreased spending due to fewer episodes per beneficiary ($1239 reduction in episode-related spending) offset by increased spending per episode (translating to a $776 increase in episode-related spending per beneficiary).

When these estimates are calculated separately for the inpatient sector and all other sectors, the inpatient sector experienced small increases in spending associated with greater spending per episode ($304) compared with noninpatient sectors ($472). Accordingly, the inpatient sector had a larger net decline in episode-related spending per beneficiary ($420) than noninpatient sectors ($184) after taking into account declining episode volume.
As expected, episode-related spending increased more when measures were not adjusted for annual payment rate increases. Without such adjustment, mean spending per episode increased 25.5%, and episode-related spending per beneficiary was nearly flat (2.6% between 2009 and 2017 [Figure 1]). The decline in unadjusted spending associated with fewer episodes ($1138) was offset by the spending increase associated with higher spending per episode ($1592) (Figure 2).

Analyses Stratified by Beneficiary Characteristics
Every population examined had declines in the number of inpatient episodes, even beneficiaries with more frequent inpatient use (Table 2). Among Medicare beneficiaries aged 85 years and older, the mean number of episodes per 1000 beneficiaries declined by 12.7%, from 524 to 457. Populations with less frequent inpatient use often experienced larger relative declines in number of episodes than populations with more frequent inpatient use. For example, the mean number of episodes per 1000 beneficiaries decreased by 17.7% for beneficiaries without nursing home use (306 to 252), as compared with an 8.1% decline for beneficiaries with nursing home use (from 888 to 816). In contrast, populations with less frequent inpatient use had larger relative increases in spending per episode with adjustment for payment rate changes. For example, spending per episode increased by 13.1% for beneficiaries aged 65 to 74 years ($20,904 to $23,644), but only by 8.6% for beneficiaries 85 years and older ($20,384 to $22,138).

Analyses Stratified by Service Use Characteristics
Some types of inpatient episodes had larger declines in the number of episodes, including episodes with planned admissions for the index hospital stay (28.8% decline from 68 to 48 episodes per 1000 beneficiaries) and episodes without post–acute care use (23.9% decline from 169 to 129 episodes per 1000 beneficiaries) (Appendix Table). In contrast, declines in the number of episodes were similar for index hospital admissions that did or did not involve ICU use (17.8% and 18.3% reduction in mean number of episodes per 1000 beneficiaries, respectively) or that included a surgical procedure or not (17.1% versus 18.6%, respectively). Several types of inpatient episodes had larger increases in spending per episode, such as a 15.1% increase for planned admissions and a 13.2% increase for hospitalizations without ICU use.
According to diagnosis information for an episode’s index hospital stay, inpatient episodes related to conditions affecting the circulatory system had the largest decline in mean number of episodes, decreasing by 31.8% from 78 to 53 episodes per 1000 beneficiaries (Appendix Table). Episodes for other diseases had much smaller declines in volume. Admissions for diagnoses of pneumonia or sepsis had notable increases in the volume of episodes, increasing by 20.7% from 25 to 30 admissions per 1000 beneficiaries.
DISCUSSION
Medicare spending per beneficiary on inpatient episodes, including services provided pre- and post hospitalization, declined by 8.9% from 2009 to 2017 after adjusting for payment rate changes. This decline reflects two components. First, the number of episodes per 1000 beneficiaries declined by 18.2%. Although the extent of this decrease varied across populations, every group examined had declines in inpatient use. In particular, hospitalizations for conditions affecting the circulatory system, such as heart attacks and cardiac procedures, decreased. Second, as inpatient volume declined, spending per episode increased by 11.4% to an average of $23,273 in 2017. This increase in spending per episode offset how much overall Medicare spending on episode-related care declined.
Medicare is increasingly challenging hospitals to demonstrate the value of inpatient services and associated treatment, which requires hospital leaders to recognize how their facilities’ spending trends relate to these national patterns. Understanding how much national episode-related spending has decreased over time with declining inpatient volume can help an accountable care organization evaluate whether it is feasible to achieve significant savings by reducing hospitalizations. Bundled payment providers focused on managing spending per episode can benefit from identifying which types of hospitalizations have increased spending per episode, especially for certain diagnoses.
These results also highlight the continued importance of a perennial factor in Medicare spending: payment rates. If Medicare payment rates had not increased over our study period, Medicare spending per inpatient episode would have increased by only 11%. Actual Medicare spending per episode increased by 25%, demonstrating that over half of the relative increase in spending per episode reflected increases in Medicare’s payment rates.
Increased spending per episode, even after adjustment for payment rate changes, suggests that services provided during an episode have increased in intensity or shifted toward higher-cost treatments.
When interpreting these trends, several points are notable. The underlying health of the Medicare population may contribute to declining inpatient use but is difficult to quantify. The observed decline in cardiac-related hospitalizations is consistent with evidence that the impact of ischemic heart disease, the leading source of disease or injury in the US population, has dramatically declined over recent decades15 and that the Medicare program has experienced large declines in overall spending and use related to cardiac conditions.16-18
Other potential factors include a shift toward hospitals treating Medicare beneficiaries as outpatients during an observation stay instead of admitting them as inpatients. Observation stays have increased as traditional Medicare implemented measures to penalize readmissions and limit payments for short inpatient stays.19-21 Even so, the increase in observation stays would have to be at least three times as large as described in other work to fully substitute for the decrease in inpatient stays: between the years 2007 and 2018, the number of observation stays per 1000 beneficiaries increased by only 26 stays, whereas the number of hospitalizations per 1000 beneficiaries decreased by 83 hospitalizations.20
Outpatient services may also broaden treatment availability in alternative settings or enable beneficiaries to avoid inpatient treatment with appropriate preventative care.22-27 These considerations are even more relevant as the COVID-19 pandemic spurred reduced admissions and shifted acute services outside of hospitals.28,29 Some services, such as elective surgeries, have probably shifted from an inpatient to an outpatient setting, which would be consistent with our finding that there are larger relative declines in planned hospitalizations. Although this analysis does not capture spending for outpatient services that are not linked to an inpatient admission, prior work demonstrates that annual growth in total Medicare spending per beneficiary (episode related or not) has recently declined for the inpatient sector but increased for outpatient and physician sectors.30 By offering other outpatient services, hospitals may be able to recoup some declining inpatient revenues. However, outpatient services are reimbursed at a lower rate than inpatient services, suggesting these trends may create financial pressure for hospitals.
There are several limitations to our analysis. First, our analysis is not designed to uncover the reason for the shift away from inpatient services nor to analyze how it has affected beneficiaries’ overall quality of care.
CONCLUSION
Over an 8-year period, Medicare spending per beneficiary on inpatient episodes, including all services immediately preceding and following hospitalizations, declined by 8.9% after taking into account payment rate increases. This broad shift away from inpatient services among all Medicare beneficiaries suggests policymakers should aim for payment policies that balance financial sustainability for hospitals and associated facilities with more efficient use of inpatient and related services.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Sunita Thapa, Lucas Stewart, Christine Lai, and Liliana Podczerwinski for contributions in data analysis and manuscript preparation.
The rate of inpatient admissions among adults aged 65 years and older has decreased by approximately 25% since 2000.1,2 This long-term trend raises important questions about inpatient-related spending in the traditional Medicare program for hospitals and providers who treat beneficiaries after a hospitalization. As traditional Medicare’s most expensive sector (accounting for 21% of all Medicare spending3), reducing hospitalizations is often championed as an opportunity to moderate Medicare spending growth.
Medicare’s ability to achieve significant savings from declining inpatient use may be tempered by a shift toward more expensive hospitalizations. If marginal hospitalizations among healthier beneficiaries are avoided, then the remaining inpatient users may be sicker and have greater spending per hospitalization and greater need for follow-up services. This study examines trends in Medicare spending related to episodes initiated by an inpatient stay because of its importance to overall Medicare spending and the implications for several Medicare value-based payment initiatives. In care models seeking to contain spending at a population level, such as accountable care organizations and managed care plans, reducing inpatient use and associated services may have the largest impact in curbing overall spending growth per beneficiary. Other models focused on spending at an episode level, including bundled payment initiatives, may face challenges if inpatient episodes become more expensive over time.
As Medicare shifts toward value-based payments, hospitalists and other hospital leaders are often involved in redesigning care delivery models for the hospital or accountable care organization (eg, through readmission reduction initiatives, post–acute care coordination, and bundled-care delivery programs). Not all savings strategies rely on providers to change how services are delivered; Medicare can modify payment rates, such as Affordable Care Act provisions that slowed how quickly Medicare payment rates increased.4 For clinicians to navigate the shift toward new payment models, it is important to recognize how each of these elements—declining hospital admissions, spending per inpatient episode, and payment rates—affect spending trends for inpatient services and associated care. Previous articles on overall Medicare inpatient spending have examined inpatient stays alone5 or focused mainly on spending per episode6,7 without quantifying how these elements contributed to overall episode-related Medicare spending per beneficiary. This article addresses this gap by demonstrating how inpatient-related spending trends reflect each component.
This study examined trends in Medicare’s spending on inpatient episodes during the years 2009 to 2017. We described changes in the volume and spending on inpatient-initiated episodes across several dimensions, including beneficiary-level and hospitalization-level factors. We examined whether declines in spending associated with fewer inpatient-initiated episodes have been offset by increased spending per episode and how spending would have differed without changes in Medicare payment rates.
Episode Definition
We constructed an episode measure that captured traditional Medicare spending for 30 days prior to hospital admission, hospitalization duration, and 90 days following hospital discharge (additional details in the Appendix).
Any acute hospitalization triggered a new episode, with one exception: if a beneficiary was discharged and readmitted within 90 days for the same diagnosis-related group (DRG), then the readmission did not trigger a new episode. The spending for that readmission was attributed to the prior hospital stay. In effect, the annual number of episodes is equivalent to the annual number of hospital admissions minus subsequent rehospitalizations for the same DRG. Neither observation stays nor hospitalizations in inpatient rehabilitation, psychiatric, or long-term facilities were considered acute hospital admissions.
We assigned claims from noninpatient sectors to an episode based on whether the claim start date fell within the episode window. All traditional Medicare sectors were measured, including outpatient services, physician claims, post–acute care services, and Medicare Part D prescription drug events.
Our analysis aimed to measure all spending related to inpatient episodes without double-counting spending for overlapping episodes. If episodes overlapped, then spending for overlapping days was weighted to be evenly divided across episodes.
Outcome Measures
The study’s main outcomes summarized episode trends across the entire traditional Medicare population, including beneficiaries without an episode, in annual mean number of episodes per beneficiary and annual mean episode-related spending per beneficiary. The denominator of these measures is person-years, or total number of beneficiary months with Medicare Part A and B coverage divided by 12. The annual mean number of episodes per beneficiary is the total number of episodes initiated in a calendar year divided by person-years. The annual mean episode-related spending per beneficiary is the total amount of spending attributed to episodes divided by person-years. We also measured annual mean spending per episode, or total amount of spending attributed to episodes divided by the total number of episodes.
Medicare annually updates each sector’s payment rates for several factors, including inflation. We constructed an index for each sector to adjust for these annual payment rate changes. We also accounted for sequestration measures in effect since April 2013 that reduced Medicare payments to all sectors by 2%. We report our spending measures twice, with and without adjusting for changes in payment rates. Adjusted numbers reflect payment rates in effect in 2015.
Analysis Approach
We present annual trends on changes in the number of inpatient episodes per beneficiary, mean episode-related spending per beneficiary, and mean spending per episode. To quantify how changes in episode-related spending per beneficiary reflect changes in the number of episodes per beneficiary vs changes in spending per episode, we modified an approach implemented by Rosen and colleagues.8
To better understand which beneficiaries have declining inpatient use, we performed stratified analyses describing changes in the number of episodes per beneficiary between 2009 and 2017, spending per episode, and total episode-related spending per beneficiary. We report these measures for several subpopulations defined by age, sex, race, dual-eligible status, and whether the beneficiary used long-term nursing home services during the episode’s calendar year. Descriptive statistics also detail how these measures changed between 2009 and 2017 for episodes stratified by characteristics of the index hospital stay: planned vs unplanned, medical vs surgical, and any use of intensive care unit (ICU) or coronary care unit services. We also stratify study measures by whether an episode included any use of post–acute care services (skilled nursing facility, home health, or inpatient rehabilitation facility use). Finally, we aggregate the episodes into major diagnostic categories (MDCs) based on the index hospital stay’s DRG to report study outcomes by condition. Because of a shift in coding hospitalizations for pneumonia as sepsis,9,10 we exclude these two diseases from their respective MDCs and analyze them jointly as a unique category.
RESULTS
Changes in Number of Inpatient Episodes and Related Spending
From 2009 to 2017, the number of inpatient episodes per 1000 traditional Medicare beneficiaries declined from 326 to 267 (Table 1), or a relative decline of 18.2% (Figure 1). The total volume of inpatient episodes declined by only 13.4%, from 10.2 million to 8.8 million, reflecting that the size of the traditional Medicare population grew during these years. Over the same years, mean payment-rate–adjusted spending per episode increased 11.4% from $20,891 to $23,273.

When considering overall episode-related spending, the large decline in the volume of episodes outweighed increased spending per episode: the mean amount of episode-related Medicare spending per beneficiary decreased 8.9% from $6810 to $6206 (Table 1), or a net change of $604 (Figure 2). This net change reflects decreased spending due to fewer episodes per beneficiary ($1239 reduction in episode-related spending) offset by increased spending per episode (translating to a $776 increase in episode-related spending per beneficiary).

When these estimates are calculated separately for the inpatient sector and all other sectors, the inpatient sector experienced small increases in spending associated with greater spending per episode ($304) compared with noninpatient sectors ($472). Accordingly, the inpatient sector had a larger net decline in episode-related spending per beneficiary ($420) than noninpatient sectors ($184) after taking into account declining episode volume.
As expected, episode-related spending increased more when measures were not adjusted for annual payment rate increases. Without such adjustment, mean spending per episode increased 25.5%, and episode-related spending per beneficiary was nearly flat (2.6% between 2009 and 2017 [Figure 1]). The decline in unadjusted spending associated with fewer episodes ($1138) was offset by the spending increase associated with higher spending per episode ($1592) (Figure 2).

Analyses Stratified by Beneficiary Characteristics
Every population examined had declines in the number of inpatient episodes, even beneficiaries with more frequent inpatient use (Table 2). Among Medicare beneficiaries aged 85 years and older, the mean number of episodes per 1000 beneficiaries declined by 12.7%, from 524 to 457. Populations with less frequent inpatient use often experienced larger relative declines in number of episodes than populations with more frequent inpatient use. For example, the mean number of episodes per 1000 beneficiaries decreased by 17.7% for beneficiaries without nursing home use (306 to 252), as compared with an 8.1% decline for beneficiaries with nursing home use (from 888 to 816). In contrast, populations with less frequent inpatient use had larger relative increases in spending per episode with adjustment for payment rate changes. For example, spending per episode increased by 13.1% for beneficiaries aged 65 to 74 years ($20,904 to $23,644), but only by 8.6% for beneficiaries 85 years and older ($20,384 to $22,138).

Analyses Stratified by Service Use Characteristics
Some types of inpatient episodes had larger declines in the number of episodes, including episodes with planned admissions for the index hospital stay (28.8% decline from 68 to 48 episodes per 1000 beneficiaries) and episodes without post–acute care use (23.9% decline from 169 to 129 episodes per 1000 beneficiaries) (Appendix Table). In contrast, declines in the number of episodes were similar for index hospital admissions that did or did not involve ICU use (17.8% and 18.3% reduction in mean number of episodes per 1000 beneficiaries, respectively) or that included a surgical procedure or not (17.1% versus 18.6%, respectively). Several types of inpatient episodes had larger increases in spending per episode, such as a 15.1% increase for planned admissions and a 13.2% increase for hospitalizations without ICU use.
According to diagnosis information for an episode’s index hospital stay, inpatient episodes related to conditions affecting the circulatory system had the largest decline in mean number of episodes, decreasing by 31.8% from 78 to 53 episodes per 1000 beneficiaries (Appendix Table). Episodes for other diseases had much smaller declines in volume. Admissions for diagnoses of pneumonia or sepsis had notable increases in the volume of episodes, increasing by 20.7% from 25 to 30 admissions per 1000 beneficiaries.
DISCUSSION
Medicare spending per beneficiary on inpatient episodes, including services provided pre- and post hospitalization, declined by 8.9% from 2009 to 2017 after adjusting for payment rate changes. This decline reflects two components. First, the number of episodes per 1000 beneficiaries declined by 18.2%. Although the extent of this decrease varied across populations, every group examined had declines in inpatient use. In particular, hospitalizations for conditions affecting the circulatory system, such as heart attacks and cardiac procedures, decreased. Second, as inpatient volume declined, spending per episode increased by 11.4% to an average of $23,273 in 2017. This increase in spending per episode offset how much overall Medicare spending on episode-related care declined.
Medicare is increasingly challenging hospitals to demonstrate the value of inpatient services and associated treatment, which requires hospital leaders to recognize how their facilities’ spending trends relate to these national patterns. Understanding how much national episode-related spending has decreased over time with declining inpatient volume can help an accountable care organization evaluate whether it is feasible to achieve significant savings by reducing hospitalizations. Bundled payment providers focused on managing spending per episode can benefit from identifying which types of hospitalizations have increased spending per episode, especially for certain diagnoses.
These results also highlight the continued importance of a perennial factor in Medicare spending: payment rates. If Medicare payment rates had not increased over our study period, Medicare spending per inpatient episode would have increased by only 11%. Actual Medicare spending per episode increased by 25%, demonstrating that over half of the relative increase in spending per episode reflected increases in Medicare’s payment rates.
Increased spending per episode, even after adjustment for payment rate changes, suggests that services provided during an episode have increased in intensity or shifted toward higher-cost treatments.
When interpreting these trends, several points are notable. The underlying health of the Medicare population may contribute to declining inpatient use but is difficult to quantify. The observed decline in cardiac-related hospitalizations is consistent with evidence that the impact of ischemic heart disease, the leading source of disease or injury in the US population, has dramatically declined over recent decades15 and that the Medicare program has experienced large declines in overall spending and use related to cardiac conditions.16-18
Other potential factors include a shift toward hospitals treating Medicare beneficiaries as outpatients during an observation stay instead of admitting them as inpatients. Observation stays have increased as traditional Medicare implemented measures to penalize readmissions and limit payments for short inpatient stays.19-21 Even so, the increase in observation stays would have to be at least three times as large as described in other work to fully substitute for the decrease in inpatient stays: between the years 2007 and 2018, the number of observation stays per 1000 beneficiaries increased by only 26 stays, whereas the number of hospitalizations per 1000 beneficiaries decreased by 83 hospitalizations.20
Outpatient services may also broaden treatment availability in alternative settings or enable beneficiaries to avoid inpatient treatment with appropriate preventative care.22-27 These considerations are even more relevant as the COVID-19 pandemic spurred reduced admissions and shifted acute services outside of hospitals.28,29 Some services, such as elective surgeries, have probably shifted from an inpatient to an outpatient setting, which would be consistent with our finding that there are larger relative declines in planned hospitalizations. Although this analysis does not capture spending for outpatient services that are not linked to an inpatient admission, prior work demonstrates that annual growth in total Medicare spending per beneficiary (episode related or not) has recently declined for the inpatient sector but increased for outpatient and physician sectors.30 By offering other outpatient services, hospitals may be able to recoup some declining inpatient revenues. However, outpatient services are reimbursed at a lower rate than inpatient services, suggesting these trends may create financial pressure for hospitals.
There are several limitations to our analysis. First, our analysis is not designed to uncover the reason for the shift away from inpatient services nor to analyze how it has affected beneficiaries’ overall quality of care.
CONCLUSION
Over an 8-year period, Medicare spending per beneficiary on inpatient episodes, including all services immediately preceding and following hospitalizations, declined by 8.9% after taking into account payment rate increases. This broad shift away from inpatient services among all Medicare beneficiaries suggests policymakers should aim for payment policies that balance financial sustainability for hospitals and associated facilities with more efficient use of inpatient and related services.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Sunita Thapa, Lucas Stewart, Christine Lai, and Liliana Podczerwinski for contributions in data analysis and manuscript preparation.
1. Sun R, Karaca Z, Wong HS. Trends in hospital inpatient stays by age and payer, 2000-2015: Statistical Brief #235. In: Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2006.
2. HCUP Fast Stats - trends in inpatient stays. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP). April 2021. Accessed August 29, 2021. www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/faststats/national/inpatienttrends.jsp
3. The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. Section 1: National health care and Medicare spending. In: A Data Book: Health Care Spending and the Medicare Program. June 2018. Accessed August 13, 2021. http://www.medpac.gov/docs/default-source/data-book/jun18_databooksec1_sec.pdf
4. Buntin MB, Graves JA. How the ACA dented the cost curve. Health Aff (Millwood). 2020;39(3):403-412. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2019.01478
5. Krumholz HM, Nuti SV, Downing NS, Normand SLT, Wang Y. Mortality, hospitalizations, and expenditures for the Medicare population aged 65 years or older, 1999-2013. JAMA. 2015;314(4):355-365. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.8035
6. Chen LM, Norton EC, Banerjee M, Regenbogen SE, Cain-Nielsen AH, Birkmeyer JD. Spending on care after surgery driven by choice of care settings instead of intensity of services. Health Aff (Millwood). 2017;36(1):83-90. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2016.0668
7. Ibrahim AM, Nuliyalu U, Lawton EJ, et al. Evaluation of US hospital episode spending for acute inpatient conditions after the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(11):e2023926. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.23926
8. Rosen A, Aizcorbe A, Ryu AJ, Nestoriak N, Cutler DM, Chernew ME. Policy makers will need a way to update bundled payments that reflects highly skewed spending growth of various care episodes. Health Aff (Millwood). 2013;32(5):944-951. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2012.1246
9. Lindenauer PK, Lagu T, Shieh MS, Pekow PS, Rothberg MB. Association of diagnostic coding with trends in hospitalizations and mortality of patients with pneumonia, 2003-2009. JAMA. 2012;307(13):1405-1413. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2012.384
10. Buntin MB, Lai C, Podczerwinski L, Poon S, Wallis C. Changing diagnosis patterns are increasing Medicare spending for inpatient hospital services. The Commonwealth Fund. April 28, 2021. Accessed August 13, 2021. https://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/2021/apr/changing-diagnosis-patterns-are-increasing-medicare-spending-inpatient
11. The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. Hospital inpatient and outpatient services. In: Report to the Congress: Medicare Payment Policy. . March 2018. Accessed August 13, 2021. http://www.medpac.gov/docs/default-source/reports/mar18_medpac_ch3_sec.pdf?sfvrsn=0
12. Ody C, Msall L, Dafny LS, Grabowski DC, Cutler DM. Decreases In readmissions credited to Medicare’s program to reduce hospital readmissions have been overstated. Health Aff (Millwood). 2019;38(1):36-43. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2018.05178
13. Dharmarajan K, Qin L, Lin Z, et al. Declining admission rates and thirty-day readmission rates positively associated even though patients grew sicker over time. Health Aff (Millwood). 2016;35(7):1294-1302. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2015.1614
14. Sjoding MW, Prescott HC, Wunsch H, Iwashyna TJ, Cooke CR. Longitudinal changes in ICU admissions among elderly patients in the United States. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(7):1353-1360. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000001664
15. Murray CJ, Atkinson C, Bhalla K, et al. The state of US health, 1990-2010: burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors. JAMA. 2013;310(6):591-608. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.13805
16. Cutler DM, Ghosh K, Messer KL, Raghunathan TE, Stewart ST, Rosen AB. Explaining the slowdown in medical spending growth among the elderly, 1999-2012. Health Aff (Millwood). 2019;38(2):222-229. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2018.05372
17. Ward MJ, Kripalani S, Zhu Y, et al. Incidence of emergency department visits for ST-elevation myocardial infarction in a recent six-year period in the United States. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115(2):167-170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.10.020
18. Keohane LM, Gambrel RJ, Freed SS, Stevenson D, Buntin MB. Understanding trends in Medicare spending, 2007-2014. Health Serv Res. 2018;53(5):3507-3527. https://doi.org/10.1111/1475-6773.12845
19. Nuckols TK, Fingar KR, Barrett M, Steiner CA, Stocks C, Owens PL. The shifting landscape in utilization of inpatient, observation, and emergency department services across payers. J Hosp Med. 2017;12(6):443-446. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.2751
20. Poon SJ, Wallis CJ, Lai P, Podczerwinski L, Buntin MB. Medicare two-midnight rule accelerated shift to observation stays. Health Affairs. In press.
21. Sheehy AM, Kaiksow F, Powell WR, et al. The Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program and observation hospitalizations. J Hosp Med. 2021;16(7):409-411. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3634
22. Culler SD, Parchman ML, Przybylski M. Factors related to potentially preventable hospitalizations among the elderly. Med Care. 1998;36(6):804-817. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005650-199806000-00004
23. Kozak LJ, Hall MJ, Owings MF. Trends in avoidable hospitalizations, 1980-1998. Health Aff (Millwood). 2001;20(2):225-232. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.20.2.225
24. Ouslander JG, Lamb G, Perloe M, et al. Potentially avoidable hospitalizations of nursing home residents: frequency, causes, and costs. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;58(4):627-635. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.02768.x
25. Konetzka RT, Karon SL, Potter DEB. Users of Medicaid home and community-based services are especially vulnerable to costly avoidable hospital admissions. Health Aff (Millwood). 2012;31(6):1167-1175. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2011.0902
26. Nyweide DJ, Anthony DL, Bynum JPW, et al. Continuity of care and the risk of preventable hospitalization in older adults. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173(20):1879-1885. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.10059
27. Auerbach AD, Kripalani S, Vasilevskis EE, et al. Preventability and causes of readmissions in a national cohort of general medicine patients. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(4):484-493. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.7863
28. Birkmeyer JD, Barnato A, Birkmeyer N, Bessler R, Skinner J. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on hospital admissions in the United States. Health Aff (Millwood). 2020;39(11):2010-2017. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2020.00980
29. Nundy S, Patel KK. Hospital-at-home to support COVID-19 surge—time to bring down the walls? JAMA Health Forum. 2020;1(5):e200504. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamahealthforum.2020.0504
30. Keohane LM, Stevenson DG, Freed S, Thapa S, Stewart L, Buntin MB. Trends in Medicare fee-for-service spending growth for dual-eligible beneficiaries, 2007–15. Health Aff (Millwood). 2018;37(8):1265-1273. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2018.0143
31. Freed M, Biniek JF, Damico A, Neuman T. Medicare Advantage in 2021: enrollment update and key trends. June 21, 2021. Accessed August 13, 2021. https://www.kff.org/medicare/issue-brief/medicare-advantage-in-2021-enrollment-update-and-key-trends/
32. Li Q, Rahman M, Gozalo P, Keohane LM, Gold MR, Trivedi AN. Regional variations: the use of hospitals, home health, and skilled nursing in traditional Medicare and Medicare Advantage. Health Aff (Millwood). 2018;37(8):1274-1281. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2018.0147
1. Sun R, Karaca Z, Wong HS. Trends in hospital inpatient stays by age and payer, 2000-2015: Statistical Brief #235. In: Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2006.
2. HCUP Fast Stats - trends in inpatient stays. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP). April 2021. Accessed August 29, 2021. www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/faststats/national/inpatienttrends.jsp
3. The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. Section 1: National health care and Medicare spending. In: A Data Book: Health Care Spending and the Medicare Program. June 2018. Accessed August 13, 2021. http://www.medpac.gov/docs/default-source/data-book/jun18_databooksec1_sec.pdf
4. Buntin MB, Graves JA. How the ACA dented the cost curve. Health Aff (Millwood). 2020;39(3):403-412. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2019.01478
5. Krumholz HM, Nuti SV, Downing NS, Normand SLT, Wang Y. Mortality, hospitalizations, and expenditures for the Medicare population aged 65 years or older, 1999-2013. JAMA. 2015;314(4):355-365. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.8035
6. Chen LM, Norton EC, Banerjee M, Regenbogen SE, Cain-Nielsen AH, Birkmeyer JD. Spending on care after surgery driven by choice of care settings instead of intensity of services. Health Aff (Millwood). 2017;36(1):83-90. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2016.0668
7. Ibrahim AM, Nuliyalu U, Lawton EJ, et al. Evaluation of US hospital episode spending for acute inpatient conditions after the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(11):e2023926. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.23926
8. Rosen A, Aizcorbe A, Ryu AJ, Nestoriak N, Cutler DM, Chernew ME. Policy makers will need a way to update bundled payments that reflects highly skewed spending growth of various care episodes. Health Aff (Millwood). 2013;32(5):944-951. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2012.1246
9. Lindenauer PK, Lagu T, Shieh MS, Pekow PS, Rothberg MB. Association of diagnostic coding with trends in hospitalizations and mortality of patients with pneumonia, 2003-2009. JAMA. 2012;307(13):1405-1413. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2012.384
10. Buntin MB, Lai C, Podczerwinski L, Poon S, Wallis C. Changing diagnosis patterns are increasing Medicare spending for inpatient hospital services. The Commonwealth Fund. April 28, 2021. Accessed August 13, 2021. https://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/2021/apr/changing-diagnosis-patterns-are-increasing-medicare-spending-inpatient
11. The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. Hospital inpatient and outpatient services. In: Report to the Congress: Medicare Payment Policy. . March 2018. Accessed August 13, 2021. http://www.medpac.gov/docs/default-source/reports/mar18_medpac_ch3_sec.pdf?sfvrsn=0
12. Ody C, Msall L, Dafny LS, Grabowski DC, Cutler DM. Decreases In readmissions credited to Medicare’s program to reduce hospital readmissions have been overstated. Health Aff (Millwood). 2019;38(1):36-43. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2018.05178
13. Dharmarajan K, Qin L, Lin Z, et al. Declining admission rates and thirty-day readmission rates positively associated even though patients grew sicker over time. Health Aff (Millwood). 2016;35(7):1294-1302. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2015.1614
14. Sjoding MW, Prescott HC, Wunsch H, Iwashyna TJ, Cooke CR. Longitudinal changes in ICU admissions among elderly patients in the United States. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(7):1353-1360. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000001664
15. Murray CJ, Atkinson C, Bhalla K, et al. The state of US health, 1990-2010: burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors. JAMA. 2013;310(6):591-608. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.13805
16. Cutler DM, Ghosh K, Messer KL, Raghunathan TE, Stewart ST, Rosen AB. Explaining the slowdown in medical spending growth among the elderly, 1999-2012. Health Aff (Millwood). 2019;38(2):222-229. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2018.05372
17. Ward MJ, Kripalani S, Zhu Y, et al. Incidence of emergency department visits for ST-elevation myocardial infarction in a recent six-year period in the United States. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115(2):167-170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.10.020
18. Keohane LM, Gambrel RJ, Freed SS, Stevenson D, Buntin MB. Understanding trends in Medicare spending, 2007-2014. Health Serv Res. 2018;53(5):3507-3527. https://doi.org/10.1111/1475-6773.12845
19. Nuckols TK, Fingar KR, Barrett M, Steiner CA, Stocks C, Owens PL. The shifting landscape in utilization of inpatient, observation, and emergency department services across payers. J Hosp Med. 2017;12(6):443-446. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.2751
20. Poon SJ, Wallis CJ, Lai P, Podczerwinski L, Buntin MB. Medicare two-midnight rule accelerated shift to observation stays. Health Affairs. In press.
21. Sheehy AM, Kaiksow F, Powell WR, et al. The Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program and observation hospitalizations. J Hosp Med. 2021;16(7):409-411. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3634
22. Culler SD, Parchman ML, Przybylski M. Factors related to potentially preventable hospitalizations among the elderly. Med Care. 1998;36(6):804-817. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005650-199806000-00004
23. Kozak LJ, Hall MJ, Owings MF. Trends in avoidable hospitalizations, 1980-1998. Health Aff (Millwood). 2001;20(2):225-232. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.20.2.225
24. Ouslander JG, Lamb G, Perloe M, et al. Potentially avoidable hospitalizations of nursing home residents: frequency, causes, and costs. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;58(4):627-635. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.02768.x
25. Konetzka RT, Karon SL, Potter DEB. Users of Medicaid home and community-based services are especially vulnerable to costly avoidable hospital admissions. Health Aff (Millwood). 2012;31(6):1167-1175. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2011.0902
26. Nyweide DJ, Anthony DL, Bynum JPW, et al. Continuity of care and the risk of preventable hospitalization in older adults. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173(20):1879-1885. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.10059
27. Auerbach AD, Kripalani S, Vasilevskis EE, et al. Preventability and causes of readmissions in a national cohort of general medicine patients. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(4):484-493. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.7863
28. Birkmeyer JD, Barnato A, Birkmeyer N, Bessler R, Skinner J. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on hospital admissions in the United States. Health Aff (Millwood). 2020;39(11):2010-2017. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2020.00980
29. Nundy S, Patel KK. Hospital-at-home to support COVID-19 surge—time to bring down the walls? JAMA Health Forum. 2020;1(5):e200504. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamahealthforum.2020.0504
30. Keohane LM, Stevenson DG, Freed S, Thapa S, Stewart L, Buntin MB. Trends in Medicare fee-for-service spending growth for dual-eligible beneficiaries, 2007–15. Health Aff (Millwood). 2018;37(8):1265-1273. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2018.0143
31. Freed M, Biniek JF, Damico A, Neuman T. Medicare Advantage in 2021: enrollment update and key trends. June 21, 2021. Accessed August 13, 2021. https://www.kff.org/medicare/issue-brief/medicare-advantage-in-2021-enrollment-update-and-key-trends/
32. Li Q, Rahman M, Gozalo P, Keohane LM, Gold MR, Trivedi AN. Regional variations: the use of hospitals, home health, and skilled nursing in traditional Medicare and Medicare Advantage. Health Aff (Millwood). 2018;37(8):1274-1281. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2018.0147
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine
Preterm delivery raises lifetime hypertension risk
Women who had a preterm delivery were at least 1.6 times as likely to develop hypertension over the next decade as those who had full-term deliveries, based on data from a national cohort study of more than 2 million women.
Pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia and other hypertensive disorders of pregnancy have been associated with chronic hypertension as well as with preterm delivery, but the independent role of preterm delivery in chronic hypertension risk remains unclear, Casey Crump, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues wrote. “A better understanding of the long-term hypertension risks associated with preterm delivery is needed to improve risk stratification, clinical monitoring, and CVD [cardiovascular disease] prevention in women.”
In a study published in JAMA Cardiology, the researchers reviewed data from 2,195,989 women with 4,308,286 singleton deliveries in Sweden from Jan. 1, 1973, to Dec. 31, 2015. Women with preexisting hypertension before their first pregnancy were excluded. Pregnancy duration was based on maternal reports of the last menstrual period for patients in the 1970s, and based on ultrasound estimates in the 1980s and beyond. Pregnancy duration was divided into six groups in terms of completed weeks of gestation: extremely preterm (22-27 weeks), moderately preterm (28-33 weeks), late preterm (34-36 weeks), early term (37-38 weeks), full term (39-41 weeks), and post term (≥42 weeks). Full-term delivery was used as the reference, and the three preterm groups were combined for summaries of preterm delivery (less than 37 weeks).
Overall, women who delivered at less than 37 weeks’ gestation had a 1.6-fold increased risk of hypertension (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.67) within the next 10 years, compared with women who delivered full term after controlling for preeclampsia, other hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, and maternal factors.
When further stratified by pregnancy duration, the aHRs for extremely preterm, moderately preterm, late preterm, and early term, compared with full-term deliveries were 2.23, 1.85, 1.55, and 1.26, respectively, in the first decade after delivery. Each additional week of pregnancy was associated with a mean 7% reduction in hypertension risk (a HR, 0.93).
The increased hypertension risk following preterm delivery (less than 37 weeks) persisted at 10-19 years, 20-29 years, and 30-43 years, with aHRs of 1.40, 1.20, and 1.12, respectively. Early-term delivery at 37-38 weeks also carried an increased risk of long-term hypertension compared with full-term delivery, with aHRs of 1.12 and 1.06 at 20-29 years and 30-43 years, respectively.
“Cosibling analyses suggested that these findings were only partially explained by familial (genetic and/or early-life environmental) factors that are shared determinants of both preterm delivery and hypertension,” the researchers noted. The findings suggest that preterm delivery itself may contribute to or affect the pathophysiology that leads to cardiovascular disease, they added, hypothesizing that endothelial dysfunction caused by preterm delivery may cause functional impairments in the microvasculature.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of detailed records to verify hypertension and the use of data from a single country, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large study population, the use of highly complete prenatal and birth records to minimize selection bias, and the long-term follow-up.
The results are consistent with those from previous studies, and support the recognition of preterm delivery as a lifetime risk factor for hypertension, but future studies should focus on racial and ethnic subgroups already at increased risk for both preterm delivery and hypertension, they added.
“Additional follow-up will be needed to examine these associations in older adulthood when hypertension increasingly and disproportionately affects women,” they concluded.
Data highlight the need for patient and provider education
“This study furthers our knowledge regarding long-term complications associated with the frequent pregnancy complication of preterm delivery,” Stephen S. Crane, MD, an ob.gyn. and maternal-fetal medicine specialist in private practice in Orlando, said in an interview. “Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death and often goes unrecognized in women. There are shared risk factors among women and men for developing CVD, the most common being hypertension. However, women have the unique risk factor of pregnancy and its attendant complications including preeclampsia, glucose intolerance, and preterm delivery. Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy often lead to indicated premature delivery, and are associated with development of chronic hypertension and subsequent CVD. However, prior data suggest that preterm delivery itself is a risk factor for developing chronic hypertension later in life.
“The current study, which evaluates one of the most complete population data sets with up to 43 years of follow-up, is the first to assess for familial determinants by cosibling analysis, and supports preterm delivery as an independent risk factor for the development of hypertension,” he said. The study results illustrate that this risk is longstanding, and that recurrent preterm birth further increases the risk of developing hypertension.
Dr. Crane said he was not surprised by the study findings, given that inflammatory processes have been linked to the development of hypertension and CVD. “Similarly, inflammatory processes have been implicated in the pathophysiology of preterm labor and inflammatory cytokines may also play a role in normal term labor. Therefore, it is not surprising that preterm delivery would be a marker for the risk of development of hypertension, as both may be responses to underlying inflammatory processes. Identification of these underlying inflammatory processes and methods for prevention will be critical if we are to decrease both the incidence of preterm birth and CVD.
“As prenatal care may be the only medical care women obtain, it is important to take this opportunity to educate patients regarding their long-term risks of developing hypertension and the need for long-term follow up. Interventions that may help reduce the risk for recurrent preterm birth and long-term risks for developing hypertension and CVD include weight loss, increased activity, and smoking cessation; the resources to achieve these goals need to be shared with patients,” he said.
“Knowledge deficits both on the part of the provider and patient may be a significant barrier to intervention that may be overcome with improved education,” said Dr. Crane. “Care providers need education regarding the long-term risks associated with a history of preterm delivery in order to better educate their patients regarding both prevention of recurrent preterm birth and the development of hypertension and CVD.” However, socioeconomic status, education level, and the inability to obtain further health care remain common barriers to intervention for many women.
“Additional research is needed to identify the causes of inflammatory processes leading to preterm delivery and risks for hypertension and CVD,” said Dr. Crane. “Only after the causes are identified can treatments be sought to successfully treat these conditions.”
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute at the National Institutes of Health; the Swedish Research Council; the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation; and an Avtal om Läkarutbildning och Forskning (Agreement on Medical Training and Research) (ALF) project grant from Region Skåne/Lund University. Neither the researchers nor Dr. Crane had any financial conflicts to disclose.
Women who had a preterm delivery were at least 1.6 times as likely to develop hypertension over the next decade as those who had full-term deliveries, based on data from a national cohort study of more than 2 million women.
Pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia and other hypertensive disorders of pregnancy have been associated with chronic hypertension as well as with preterm delivery, but the independent role of preterm delivery in chronic hypertension risk remains unclear, Casey Crump, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues wrote. “A better understanding of the long-term hypertension risks associated with preterm delivery is needed to improve risk stratification, clinical monitoring, and CVD [cardiovascular disease] prevention in women.”
In a study published in JAMA Cardiology, the researchers reviewed data from 2,195,989 women with 4,308,286 singleton deliveries in Sweden from Jan. 1, 1973, to Dec. 31, 2015. Women with preexisting hypertension before their first pregnancy were excluded. Pregnancy duration was based on maternal reports of the last menstrual period for patients in the 1970s, and based on ultrasound estimates in the 1980s and beyond. Pregnancy duration was divided into six groups in terms of completed weeks of gestation: extremely preterm (22-27 weeks), moderately preterm (28-33 weeks), late preterm (34-36 weeks), early term (37-38 weeks), full term (39-41 weeks), and post term (≥42 weeks). Full-term delivery was used as the reference, and the three preterm groups were combined for summaries of preterm delivery (less than 37 weeks).
Overall, women who delivered at less than 37 weeks’ gestation had a 1.6-fold increased risk of hypertension (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.67) within the next 10 years, compared with women who delivered full term after controlling for preeclampsia, other hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, and maternal factors.
When further stratified by pregnancy duration, the aHRs for extremely preterm, moderately preterm, late preterm, and early term, compared with full-term deliveries were 2.23, 1.85, 1.55, and 1.26, respectively, in the first decade after delivery. Each additional week of pregnancy was associated with a mean 7% reduction in hypertension risk (a HR, 0.93).
The increased hypertension risk following preterm delivery (less than 37 weeks) persisted at 10-19 years, 20-29 years, and 30-43 years, with aHRs of 1.40, 1.20, and 1.12, respectively. Early-term delivery at 37-38 weeks also carried an increased risk of long-term hypertension compared with full-term delivery, with aHRs of 1.12 and 1.06 at 20-29 years and 30-43 years, respectively.
“Cosibling analyses suggested that these findings were only partially explained by familial (genetic and/or early-life environmental) factors that are shared determinants of both preterm delivery and hypertension,” the researchers noted. The findings suggest that preterm delivery itself may contribute to or affect the pathophysiology that leads to cardiovascular disease, they added, hypothesizing that endothelial dysfunction caused by preterm delivery may cause functional impairments in the microvasculature.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of detailed records to verify hypertension and the use of data from a single country, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large study population, the use of highly complete prenatal and birth records to minimize selection bias, and the long-term follow-up.
The results are consistent with those from previous studies, and support the recognition of preterm delivery as a lifetime risk factor for hypertension, but future studies should focus on racial and ethnic subgroups already at increased risk for both preterm delivery and hypertension, they added.
“Additional follow-up will be needed to examine these associations in older adulthood when hypertension increasingly and disproportionately affects women,” they concluded.
Data highlight the need for patient and provider education
“This study furthers our knowledge regarding long-term complications associated with the frequent pregnancy complication of preterm delivery,” Stephen S. Crane, MD, an ob.gyn. and maternal-fetal medicine specialist in private practice in Orlando, said in an interview. “Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death and often goes unrecognized in women. There are shared risk factors among women and men for developing CVD, the most common being hypertension. However, women have the unique risk factor of pregnancy and its attendant complications including preeclampsia, glucose intolerance, and preterm delivery. Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy often lead to indicated premature delivery, and are associated with development of chronic hypertension and subsequent CVD. However, prior data suggest that preterm delivery itself is a risk factor for developing chronic hypertension later in life.
“The current study, which evaluates one of the most complete population data sets with up to 43 years of follow-up, is the first to assess for familial determinants by cosibling analysis, and supports preterm delivery as an independent risk factor for the development of hypertension,” he said. The study results illustrate that this risk is longstanding, and that recurrent preterm birth further increases the risk of developing hypertension.
Dr. Crane said he was not surprised by the study findings, given that inflammatory processes have been linked to the development of hypertension and CVD. “Similarly, inflammatory processes have been implicated in the pathophysiology of preterm labor and inflammatory cytokines may also play a role in normal term labor. Therefore, it is not surprising that preterm delivery would be a marker for the risk of development of hypertension, as both may be responses to underlying inflammatory processes. Identification of these underlying inflammatory processes and methods for prevention will be critical if we are to decrease both the incidence of preterm birth and CVD.
“As prenatal care may be the only medical care women obtain, it is important to take this opportunity to educate patients regarding their long-term risks of developing hypertension and the need for long-term follow up. Interventions that may help reduce the risk for recurrent preterm birth and long-term risks for developing hypertension and CVD include weight loss, increased activity, and smoking cessation; the resources to achieve these goals need to be shared with patients,” he said.
“Knowledge deficits both on the part of the provider and patient may be a significant barrier to intervention that may be overcome with improved education,” said Dr. Crane. “Care providers need education regarding the long-term risks associated with a history of preterm delivery in order to better educate their patients regarding both prevention of recurrent preterm birth and the development of hypertension and CVD.” However, socioeconomic status, education level, and the inability to obtain further health care remain common barriers to intervention for many women.
“Additional research is needed to identify the causes of inflammatory processes leading to preterm delivery and risks for hypertension and CVD,” said Dr. Crane. “Only after the causes are identified can treatments be sought to successfully treat these conditions.”
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute at the National Institutes of Health; the Swedish Research Council; the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation; and an Avtal om Läkarutbildning och Forskning (Agreement on Medical Training and Research) (ALF) project grant from Region Skåne/Lund University. Neither the researchers nor Dr. Crane had any financial conflicts to disclose.
Women who had a preterm delivery were at least 1.6 times as likely to develop hypertension over the next decade as those who had full-term deliveries, based on data from a national cohort study of more than 2 million women.
Pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia and other hypertensive disorders of pregnancy have been associated with chronic hypertension as well as with preterm delivery, but the independent role of preterm delivery in chronic hypertension risk remains unclear, Casey Crump, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues wrote. “A better understanding of the long-term hypertension risks associated with preterm delivery is needed to improve risk stratification, clinical monitoring, and CVD [cardiovascular disease] prevention in women.”
In a study published in JAMA Cardiology, the researchers reviewed data from 2,195,989 women with 4,308,286 singleton deliveries in Sweden from Jan. 1, 1973, to Dec. 31, 2015. Women with preexisting hypertension before their first pregnancy were excluded. Pregnancy duration was based on maternal reports of the last menstrual period for patients in the 1970s, and based on ultrasound estimates in the 1980s and beyond. Pregnancy duration was divided into six groups in terms of completed weeks of gestation: extremely preterm (22-27 weeks), moderately preterm (28-33 weeks), late preterm (34-36 weeks), early term (37-38 weeks), full term (39-41 weeks), and post term (≥42 weeks). Full-term delivery was used as the reference, and the three preterm groups were combined for summaries of preterm delivery (less than 37 weeks).
Overall, women who delivered at less than 37 weeks’ gestation had a 1.6-fold increased risk of hypertension (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.67) within the next 10 years, compared with women who delivered full term after controlling for preeclampsia, other hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, and maternal factors.
When further stratified by pregnancy duration, the aHRs for extremely preterm, moderately preterm, late preterm, and early term, compared with full-term deliveries were 2.23, 1.85, 1.55, and 1.26, respectively, in the first decade after delivery. Each additional week of pregnancy was associated with a mean 7% reduction in hypertension risk (a HR, 0.93).
The increased hypertension risk following preterm delivery (less than 37 weeks) persisted at 10-19 years, 20-29 years, and 30-43 years, with aHRs of 1.40, 1.20, and 1.12, respectively. Early-term delivery at 37-38 weeks also carried an increased risk of long-term hypertension compared with full-term delivery, with aHRs of 1.12 and 1.06 at 20-29 years and 30-43 years, respectively.
“Cosibling analyses suggested that these findings were only partially explained by familial (genetic and/or early-life environmental) factors that are shared determinants of both preterm delivery and hypertension,” the researchers noted. The findings suggest that preterm delivery itself may contribute to or affect the pathophysiology that leads to cardiovascular disease, they added, hypothesizing that endothelial dysfunction caused by preterm delivery may cause functional impairments in the microvasculature.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of detailed records to verify hypertension and the use of data from a single country, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large study population, the use of highly complete prenatal and birth records to minimize selection bias, and the long-term follow-up.
The results are consistent with those from previous studies, and support the recognition of preterm delivery as a lifetime risk factor for hypertension, but future studies should focus on racial and ethnic subgroups already at increased risk for both preterm delivery and hypertension, they added.
“Additional follow-up will be needed to examine these associations in older adulthood when hypertension increasingly and disproportionately affects women,” they concluded.
Data highlight the need for patient and provider education
“This study furthers our knowledge regarding long-term complications associated with the frequent pregnancy complication of preterm delivery,” Stephen S. Crane, MD, an ob.gyn. and maternal-fetal medicine specialist in private practice in Orlando, said in an interview. “Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death and often goes unrecognized in women. There are shared risk factors among women and men for developing CVD, the most common being hypertension. However, women have the unique risk factor of pregnancy and its attendant complications including preeclampsia, glucose intolerance, and preterm delivery. Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy often lead to indicated premature delivery, and are associated with development of chronic hypertension and subsequent CVD. However, prior data suggest that preterm delivery itself is a risk factor for developing chronic hypertension later in life.
“The current study, which evaluates one of the most complete population data sets with up to 43 years of follow-up, is the first to assess for familial determinants by cosibling analysis, and supports preterm delivery as an independent risk factor for the development of hypertension,” he said. The study results illustrate that this risk is longstanding, and that recurrent preterm birth further increases the risk of developing hypertension.
Dr. Crane said he was not surprised by the study findings, given that inflammatory processes have been linked to the development of hypertension and CVD. “Similarly, inflammatory processes have been implicated in the pathophysiology of preterm labor and inflammatory cytokines may also play a role in normal term labor. Therefore, it is not surprising that preterm delivery would be a marker for the risk of development of hypertension, as both may be responses to underlying inflammatory processes. Identification of these underlying inflammatory processes and methods for prevention will be critical if we are to decrease both the incidence of preterm birth and CVD.
“As prenatal care may be the only medical care women obtain, it is important to take this opportunity to educate patients regarding their long-term risks of developing hypertension and the need for long-term follow up. Interventions that may help reduce the risk for recurrent preterm birth and long-term risks for developing hypertension and CVD include weight loss, increased activity, and smoking cessation; the resources to achieve these goals need to be shared with patients,” he said.
“Knowledge deficits both on the part of the provider and patient may be a significant barrier to intervention that may be overcome with improved education,” said Dr. Crane. “Care providers need education regarding the long-term risks associated with a history of preterm delivery in order to better educate their patients regarding both prevention of recurrent preterm birth and the development of hypertension and CVD.” However, socioeconomic status, education level, and the inability to obtain further health care remain common barriers to intervention for many women.
“Additional research is needed to identify the causes of inflammatory processes leading to preterm delivery and risks for hypertension and CVD,” said Dr. Crane. “Only after the causes are identified can treatments be sought to successfully treat these conditions.”
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute at the National Institutes of Health; the Swedish Research Council; the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation; and an Avtal om Läkarutbildning och Forskning (Agreement on Medical Training and Research) (ALF) project grant from Region Skåne/Lund University. Neither the researchers nor Dr. Crane had any financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM JAMA CARDIOLOGY
Early mortality falls in advanced ovarian cancer with neoadjuvant chemo
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Cancer centers with a high use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with advanced-stage epithelial ovarian cancer show similar improvements in median overall survival and larger declines in short-term mortality than in centers with low use of this treatment. This is according to a study published in JAMA Oncology, suggesting that neoadjuvant chemotherapy may be a suitable first-line treatment approach for many patients with advanced-stage ovarian cancer.
“There is considerable variation in practice. Some centers administer neoadjuvant chemotherapy to 75% of patients with advanced ovarian cancers, others use the approach very infrequently,” said Alexander Melamed, MD, MPH, of Columbia University, New York.
“I hope that those clinicians who have been worried about the negative impacts of too frequent administration of neoadjuvant chemotherapy may be reassured by this study and may come to use this good treatment more often.”
Research has shown that, compared with primary cytoreductive surgery, the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy has similar long-term survival and improved perioperative outcomes in patients with ovarian cancer. While the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy has increased, many experts continue to recommend upfront surgery as the preferred treatment for these patients.
“In part, these recommendations are based on flawed interpretations of real-world data. Specifically, many observational studies have concluded that upfront surgery results in better survival than neoadjuvant chemotherapy, based on study designs that ignored the fact that patients who receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the real word are sicker and have more extensive cancer than those who receive upfront surgery,” Dr. Melamed said.
In this difference-in-differences comparative effectiveness analysis, researchers asked if the difference in adoption of neoadjuvant chemotherapy by U.S. cancer centers for advanced-stage epithelial ovarian cancer was associated with differences in median overall survival and 1-year all-cause mortality.
“By assessing how this divergence in practice impacted patient outcomes we were able to infer how frequent use of neoadjuvant impacts survival in ovarian cancer patients. This study design allowed us to sidestep the problem of selection bias that has plagued many other observational studies in this space,” Dr. Melamed explained.
This observational study included 39,299 women with stage IIIC and IV epithelial ovarian cancer, diagnosed between 2004 and 2015 who were followed to the end of 2018, and treated at one of 664 cancer programs. Patients treated in programs that increased neoadjuvant chemotherapy administration had greater improvements in 1-year mortality (difference-in-differences, −2.1%; 95% confidence interval, −3.7 to −0.5) and equivalent gains in median overall survival (difference-in-differences, 0.9 months; 95% CI, −1.9 to 3.7 months), compared with those treated in programs that used the treatment infrequently.
“For a long time, experts have suggested that the apparent discordance between randomized controlled trials and real-world studies that compare neoadjuvant chemotherapy to upfront surgery for ovarian cancer might mean that the randomized trials are not applicable to real-world practice. What is significant about our findings, is that, when more appropriate study methods are used to analyze the real-world data, the apparent contradiction between real-world and randomized studies is resolved.
“We found that, just as one would guess based on the findings of randomized trials, patients treated in the centers that increased the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy did not have any decrement in long-term survival, but that short-term mortality did improve more in these centers than in centers that administered neoadjuvant chemotherapy rarely,” she said.
Dr. Melamed said that the findings should “spur a reappraisal” of what clinicians consider the default treatment for women with stage IIIC and IV ovarian cancer.
Taken together with randomized controlled trials, “the evidence may be at a point where it is now time to consider neoadjuvant chemotherapy as the default approach to patients with bulky carcinomatosis, and that primary surgery may be a reasonable alternative for a select group of healthy, young patients with low-volume metastasis.
“Other factors like the route of adjuvant chemotherapy may also need to be considered. However, I believe the belief that aggressive primary debulking is beneficial for most women with advanced ovarian cancer is outdated,” Dr. Melamed said.
No relevant conflicts of interest were reported for this research.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Cancer centers with a high use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with advanced-stage epithelial ovarian cancer show similar improvements in median overall survival and larger declines in short-term mortality than in centers with low use of this treatment. This is according to a study published in JAMA Oncology, suggesting that neoadjuvant chemotherapy may be a suitable first-line treatment approach for many patients with advanced-stage ovarian cancer.
“There is considerable variation in practice. Some centers administer neoadjuvant chemotherapy to 75% of patients with advanced ovarian cancers, others use the approach very infrequently,” said Alexander Melamed, MD, MPH, of Columbia University, New York.
“I hope that those clinicians who have been worried about the negative impacts of too frequent administration of neoadjuvant chemotherapy may be reassured by this study and may come to use this good treatment more often.”
Research has shown that, compared with primary cytoreductive surgery, the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy has similar long-term survival and improved perioperative outcomes in patients with ovarian cancer. While the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy has increased, many experts continue to recommend upfront surgery as the preferred treatment for these patients.
“In part, these recommendations are based on flawed interpretations of real-world data. Specifically, many observational studies have concluded that upfront surgery results in better survival than neoadjuvant chemotherapy, based on study designs that ignored the fact that patients who receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the real word are sicker and have more extensive cancer than those who receive upfront surgery,” Dr. Melamed said.
In this difference-in-differences comparative effectiveness analysis, researchers asked if the difference in adoption of neoadjuvant chemotherapy by U.S. cancer centers for advanced-stage epithelial ovarian cancer was associated with differences in median overall survival and 1-year all-cause mortality.
“By assessing how this divergence in practice impacted patient outcomes we were able to infer how frequent use of neoadjuvant impacts survival in ovarian cancer patients. This study design allowed us to sidestep the problem of selection bias that has plagued many other observational studies in this space,” Dr. Melamed explained.
This observational study included 39,299 women with stage IIIC and IV epithelial ovarian cancer, diagnosed between 2004 and 2015 who were followed to the end of 2018, and treated at one of 664 cancer programs. Patients treated in programs that increased neoadjuvant chemotherapy administration had greater improvements in 1-year mortality (difference-in-differences, −2.1%; 95% confidence interval, −3.7 to −0.5) and equivalent gains in median overall survival (difference-in-differences, 0.9 months; 95% CI, −1.9 to 3.7 months), compared with those treated in programs that used the treatment infrequently.
“For a long time, experts have suggested that the apparent discordance between randomized controlled trials and real-world studies that compare neoadjuvant chemotherapy to upfront surgery for ovarian cancer might mean that the randomized trials are not applicable to real-world practice. What is significant about our findings, is that, when more appropriate study methods are used to analyze the real-world data, the apparent contradiction between real-world and randomized studies is resolved.
“We found that, just as one would guess based on the findings of randomized trials, patients treated in the centers that increased the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy did not have any decrement in long-term survival, but that short-term mortality did improve more in these centers than in centers that administered neoadjuvant chemotherapy rarely,” she said.
Dr. Melamed said that the findings should “spur a reappraisal” of what clinicians consider the default treatment for women with stage IIIC and IV ovarian cancer.
Taken together with randomized controlled trials, “the evidence may be at a point where it is now time to consider neoadjuvant chemotherapy as the default approach to patients with bulky carcinomatosis, and that primary surgery may be a reasonable alternative for a select group of healthy, young patients with low-volume metastasis.
“Other factors like the route of adjuvant chemotherapy may also need to be considered. However, I believe the belief that aggressive primary debulking is beneficial for most women with advanced ovarian cancer is outdated,” Dr. Melamed said.
No relevant conflicts of interest were reported for this research.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Cancer centers with a high use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with advanced-stage epithelial ovarian cancer show similar improvements in median overall survival and larger declines in short-term mortality than in centers with low use of this treatment. This is according to a study published in JAMA Oncology, suggesting that neoadjuvant chemotherapy may be a suitable first-line treatment approach for many patients with advanced-stage ovarian cancer.
“There is considerable variation in practice. Some centers administer neoadjuvant chemotherapy to 75% of patients with advanced ovarian cancers, others use the approach very infrequently,” said Alexander Melamed, MD, MPH, of Columbia University, New York.
“I hope that those clinicians who have been worried about the negative impacts of too frequent administration of neoadjuvant chemotherapy may be reassured by this study and may come to use this good treatment more often.”
Research has shown that, compared with primary cytoreductive surgery, the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy has similar long-term survival and improved perioperative outcomes in patients with ovarian cancer. While the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy has increased, many experts continue to recommend upfront surgery as the preferred treatment for these patients.
“In part, these recommendations are based on flawed interpretations of real-world data. Specifically, many observational studies have concluded that upfront surgery results in better survival than neoadjuvant chemotherapy, based on study designs that ignored the fact that patients who receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the real word are sicker and have more extensive cancer than those who receive upfront surgery,” Dr. Melamed said.
In this difference-in-differences comparative effectiveness analysis, researchers asked if the difference in adoption of neoadjuvant chemotherapy by U.S. cancer centers for advanced-stage epithelial ovarian cancer was associated with differences in median overall survival and 1-year all-cause mortality.
“By assessing how this divergence in practice impacted patient outcomes we were able to infer how frequent use of neoadjuvant impacts survival in ovarian cancer patients. This study design allowed us to sidestep the problem of selection bias that has plagued many other observational studies in this space,” Dr. Melamed explained.
This observational study included 39,299 women with stage IIIC and IV epithelial ovarian cancer, diagnosed between 2004 and 2015 who were followed to the end of 2018, and treated at one of 664 cancer programs. Patients treated in programs that increased neoadjuvant chemotherapy administration had greater improvements in 1-year mortality (difference-in-differences, −2.1%; 95% confidence interval, −3.7 to −0.5) and equivalent gains in median overall survival (difference-in-differences, 0.9 months; 95% CI, −1.9 to 3.7 months), compared with those treated in programs that used the treatment infrequently.
“For a long time, experts have suggested that the apparent discordance between randomized controlled trials and real-world studies that compare neoadjuvant chemotherapy to upfront surgery for ovarian cancer might mean that the randomized trials are not applicable to real-world practice. What is significant about our findings, is that, when more appropriate study methods are used to analyze the real-world data, the apparent contradiction between real-world and randomized studies is resolved.
“We found that, just as one would guess based on the findings of randomized trials, patients treated in the centers that increased the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy did not have any decrement in long-term survival, but that short-term mortality did improve more in these centers than in centers that administered neoadjuvant chemotherapy rarely,” she said.
Dr. Melamed said that the findings should “spur a reappraisal” of what clinicians consider the default treatment for women with stage IIIC and IV ovarian cancer.
Taken together with randomized controlled trials, “the evidence may be at a point where it is now time to consider neoadjuvant chemotherapy as the default approach to patients with bulky carcinomatosis, and that primary surgery may be a reasonable alternative for a select group of healthy, young patients with low-volume metastasis.
“Other factors like the route of adjuvant chemotherapy may also need to be considered. However, I believe the belief that aggressive primary debulking is beneficial for most women with advanced ovarian cancer is outdated,” Dr. Melamed said.
No relevant conflicts of interest were reported for this research.
FDA approves combo pill for severe, acute pain
enough to require an opioid analgesic and for which alternative treatments fail to provide adequate pain relief.
Celecoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug and tramadol is an opioid agonist. Seglentis contains 56 mg of celecoxib and 44 mg of tramadol.
“The unique co-crystal formulation of Seglentis provides effective pain relief via a multimodal approach,” Craig A. Sponseller, MD, chief medical officer of Kowa Pharmaceuticals America, said in a news release.
Esteve Pharmaceuticals has entered into an agreement with Kowa Pharmaceuticals America to commercialize the pain medicine in the United States, with a launch planned for early 2022.
“Seglentis uses four different and complementary mechanisms of analgesia and offers healthcare providers an important option to treat acute pain in adults that is severe enough to require opioid treatment and for which alternative treatments are inadequate,” Dr. Sponseller said.
Because of the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse with opioids, even at recommended doses, the FDA will require a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) for Seglentis.
The label states that the drug should be initiated as two tablets every 12 hours as needed and should be prescribed for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals.
Patients should be monitored for respiratory depression, especially within the first 24 to 72 hours of initiating therapy with Seglentis.
Prescribers should discuss naloxone (Narcan) with patients and consider prescribing the opioid antagonist naloxone based on the patient’s risk factors for overdose.
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article was first published on Medscape.com.
enough to require an opioid analgesic and for which alternative treatments fail to provide adequate pain relief.
Celecoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug and tramadol is an opioid agonist. Seglentis contains 56 mg of celecoxib and 44 mg of tramadol.
“The unique co-crystal formulation of Seglentis provides effective pain relief via a multimodal approach,” Craig A. Sponseller, MD, chief medical officer of Kowa Pharmaceuticals America, said in a news release.
Esteve Pharmaceuticals has entered into an agreement with Kowa Pharmaceuticals America to commercialize the pain medicine in the United States, with a launch planned for early 2022.
“Seglentis uses four different and complementary mechanisms of analgesia and offers healthcare providers an important option to treat acute pain in adults that is severe enough to require opioid treatment and for which alternative treatments are inadequate,” Dr. Sponseller said.
Because of the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse with opioids, even at recommended doses, the FDA will require a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) for Seglentis.
The label states that the drug should be initiated as two tablets every 12 hours as needed and should be prescribed for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals.
Patients should be monitored for respiratory depression, especially within the first 24 to 72 hours of initiating therapy with Seglentis.
Prescribers should discuss naloxone (Narcan) with patients and consider prescribing the opioid antagonist naloxone based on the patient’s risk factors for overdose.
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article was first published on Medscape.com.
enough to require an opioid analgesic and for which alternative treatments fail to provide adequate pain relief.
Celecoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug and tramadol is an opioid agonist. Seglentis contains 56 mg of celecoxib and 44 mg of tramadol.
“The unique co-crystal formulation of Seglentis provides effective pain relief via a multimodal approach,” Craig A. Sponseller, MD, chief medical officer of Kowa Pharmaceuticals America, said in a news release.
Esteve Pharmaceuticals has entered into an agreement with Kowa Pharmaceuticals America to commercialize the pain medicine in the United States, with a launch planned for early 2022.
“Seglentis uses four different and complementary mechanisms of analgesia and offers healthcare providers an important option to treat acute pain in adults that is severe enough to require opioid treatment and for which alternative treatments are inadequate,” Dr. Sponseller said.
Because of the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse with opioids, even at recommended doses, the FDA will require a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) for Seglentis.
The label states that the drug should be initiated as two tablets every 12 hours as needed and should be prescribed for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals.
Patients should be monitored for respiratory depression, especially within the first 24 to 72 hours of initiating therapy with Seglentis.
Prescribers should discuss naloxone (Narcan) with patients and consider prescribing the opioid antagonist naloxone based on the patient’s risk factors for overdose.
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article was first published on Medscape.com.
Donafenib shows potential as first-line treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
“An improvement in the pharmacotherapy of advanced HCC remains a clinical need,” wrote Feng Bi, MD, of Sichuan University, in Chengdu, China, and colleagues.
Liver cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide, with HCC representing 90% of liver malignancies. HCC most commonly occurs in people with liver disease, particularly in those with chronic hepatitis B and C and although rare, HCC is the ninth leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States. Most patients are diagnosed at the advanced stage with a median survival of 6-8 months. Sorafenib, the standard first-line therapy for advanced HCC, has demonstrated the median OS of 10.7 to 14.7 months. No other monotherapy has shown a significant improvement in OS, compared with sorafenib. Donafenib has shown favorable efficacy and safety in phase 1 studies.
This phase 2-3 trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of first-line donafenib, compared with sorafenib, in 668 Chinese patients with advanced HCC. Patients were randomly assigned to receive twice-daily oral donafenib 0.2 g or sorafenib 0.4 g until intolerable toxicity or disease progression. The primary end point was OS, tested for noninferiority and superiority.
Compared with sorafenib, donafenib significantly prolonged OS, 10.3 and 12.1 months, respectively, (hazard ratio, 95% confidence interval, 0.699-0.988; 0.83; P = .0245), and the superiority criteria for OS were met. Donafenib also presented improved safety and tolerability. Common drug-related adverse events, such as hand-foot skin reactions and diarrhea, and drug-related grade 3 or higher adverse events, occurred in fewer patients receiving donafenib than sorafenib, (38% vs. 50%; P = .0018). The authors noted that this lower frequency in adverse events with donafenib “contributed to improved patient adherence and decreased levels of drug interruption and discontinuation.”
Donafenib is a novel, oral, small-molecule, multikinase inhibitor that suppresses tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor receptors and platelet-derived growth factor receptors, and Raf kinases. It is a derivative of sorafenib and in June 2021, it was approved in China as a treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma for patients who have not received systemic treatment. It is not yet available in the United States.
“This pivotal head-to-head comparison study is the first to demonstrate noninferiority and superiority of a monotherapy, donafenib, with statistically significant extension in OS over sorafenib for first-line treatment of advanced HCC,” the authors wrote. “Compared with international trials, patients in this study presented with more severe baseline disease states, further emphasizing the positive response observed with donafenib.”
Another study, published in the same issue of the Journal of Clinical Oncology, compared tremelimumab and durvalumab as monotherapies and in combination for patients with unresectable HCC, found that use a single priming dose of tremelimumab combined with durvalumab showed the best benefit-risk profile.
“An improvement in the pharmacotherapy of advanced HCC remains a clinical need,” wrote Feng Bi, MD, of Sichuan University, in Chengdu, China, and colleagues.
Liver cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide, with HCC representing 90% of liver malignancies. HCC most commonly occurs in people with liver disease, particularly in those with chronic hepatitis B and C and although rare, HCC is the ninth leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States. Most patients are diagnosed at the advanced stage with a median survival of 6-8 months. Sorafenib, the standard first-line therapy for advanced HCC, has demonstrated the median OS of 10.7 to 14.7 months. No other monotherapy has shown a significant improvement in OS, compared with sorafenib. Donafenib has shown favorable efficacy and safety in phase 1 studies.
This phase 2-3 trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of first-line donafenib, compared with sorafenib, in 668 Chinese patients with advanced HCC. Patients were randomly assigned to receive twice-daily oral donafenib 0.2 g or sorafenib 0.4 g until intolerable toxicity or disease progression. The primary end point was OS, tested for noninferiority and superiority.
Compared with sorafenib, donafenib significantly prolonged OS, 10.3 and 12.1 months, respectively, (hazard ratio, 95% confidence interval, 0.699-0.988; 0.83; P = .0245), and the superiority criteria for OS were met. Donafenib also presented improved safety and tolerability. Common drug-related adverse events, such as hand-foot skin reactions and diarrhea, and drug-related grade 3 or higher adverse events, occurred in fewer patients receiving donafenib than sorafenib, (38% vs. 50%; P = .0018). The authors noted that this lower frequency in adverse events with donafenib “contributed to improved patient adherence and decreased levels of drug interruption and discontinuation.”
Donafenib is a novel, oral, small-molecule, multikinase inhibitor that suppresses tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor receptors and platelet-derived growth factor receptors, and Raf kinases. It is a derivative of sorafenib and in June 2021, it was approved in China as a treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma for patients who have not received systemic treatment. It is not yet available in the United States.
“This pivotal head-to-head comparison study is the first to demonstrate noninferiority and superiority of a monotherapy, donafenib, with statistically significant extension in OS over sorafenib for first-line treatment of advanced HCC,” the authors wrote. “Compared with international trials, patients in this study presented with more severe baseline disease states, further emphasizing the positive response observed with donafenib.”
Another study, published in the same issue of the Journal of Clinical Oncology, compared tremelimumab and durvalumab as monotherapies and in combination for patients with unresectable HCC, found that use a single priming dose of tremelimumab combined with durvalumab showed the best benefit-risk profile.
“An improvement in the pharmacotherapy of advanced HCC remains a clinical need,” wrote Feng Bi, MD, of Sichuan University, in Chengdu, China, and colleagues.
Liver cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide, with HCC representing 90% of liver malignancies. HCC most commonly occurs in people with liver disease, particularly in those with chronic hepatitis B and C and although rare, HCC is the ninth leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States. Most patients are diagnosed at the advanced stage with a median survival of 6-8 months. Sorafenib, the standard first-line therapy for advanced HCC, has demonstrated the median OS of 10.7 to 14.7 months. No other monotherapy has shown a significant improvement in OS, compared with sorafenib. Donafenib has shown favorable efficacy and safety in phase 1 studies.
This phase 2-3 trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of first-line donafenib, compared with sorafenib, in 668 Chinese patients with advanced HCC. Patients were randomly assigned to receive twice-daily oral donafenib 0.2 g or sorafenib 0.4 g until intolerable toxicity or disease progression. The primary end point was OS, tested for noninferiority and superiority.
Compared with sorafenib, donafenib significantly prolonged OS, 10.3 and 12.1 months, respectively, (hazard ratio, 95% confidence interval, 0.699-0.988; 0.83; P = .0245), and the superiority criteria for OS were met. Donafenib also presented improved safety and tolerability. Common drug-related adverse events, such as hand-foot skin reactions and diarrhea, and drug-related grade 3 or higher adverse events, occurred in fewer patients receiving donafenib than sorafenib, (38% vs. 50%; P = .0018). The authors noted that this lower frequency in adverse events with donafenib “contributed to improved patient adherence and decreased levels of drug interruption and discontinuation.”
Donafenib is a novel, oral, small-molecule, multikinase inhibitor that suppresses tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor receptors and platelet-derived growth factor receptors, and Raf kinases. It is a derivative of sorafenib and in June 2021, it was approved in China as a treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma for patients who have not received systemic treatment. It is not yet available in the United States.
“This pivotal head-to-head comparison study is the first to demonstrate noninferiority and superiority of a monotherapy, donafenib, with statistically significant extension in OS over sorafenib for first-line treatment of advanced HCC,” the authors wrote. “Compared with international trials, patients in this study presented with more severe baseline disease states, further emphasizing the positive response observed with donafenib.”
Another study, published in the same issue of the Journal of Clinical Oncology, compared tremelimumab and durvalumab as monotherapies and in combination for patients with unresectable HCC, found that use a single priming dose of tremelimumab combined with durvalumab showed the best benefit-risk profile.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY

