User login
HR-positive breast cancer: Entinostat fails phase 3 trial
Key clinical point: Adding entinostat to exemestane does not improve survival in aromatase inhibitor (AI)-resistant advanced hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative breast cancer.
Major finding: There were no differences between the entinostat and placebo groups in median progression-free survival (3.3 months vs. 3.1 months; P = 0.30) and median overall survival (23.4 months vs. 21.7 months; P = 0.94). The most common grade 3-4 adverse events in the entinostat group were neutropenia (20%) and hypophosphatemia (14%).
Study details: This was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 E2112 study of 608 patients with AI-resistant, HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer, randomly assigned to entinostat plus exemestane or placebo plus exemestane.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported receiving consulting/advisory/speaker fees, research funding, accommodation/travel/expenses, and royalties from and/or stock ownership and/or other relationship in companies or patents owned/filed.
Source: Connoly RM et al. J Clin Oncol. 2021 Aug 6 (in press). doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.00944.
Key clinical point: Adding entinostat to exemestane does not improve survival in aromatase inhibitor (AI)-resistant advanced hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative breast cancer.
Major finding: There were no differences between the entinostat and placebo groups in median progression-free survival (3.3 months vs. 3.1 months; P = 0.30) and median overall survival (23.4 months vs. 21.7 months; P = 0.94). The most common grade 3-4 adverse events in the entinostat group were neutropenia (20%) and hypophosphatemia (14%).
Study details: This was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 E2112 study of 608 patients with AI-resistant, HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer, randomly assigned to entinostat plus exemestane or placebo plus exemestane.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported receiving consulting/advisory/speaker fees, research funding, accommodation/travel/expenses, and royalties from and/or stock ownership and/or other relationship in companies or patents owned/filed.
Source: Connoly RM et al. J Clin Oncol. 2021 Aug 6 (in press). doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.00944.
Key clinical point: Adding entinostat to exemestane does not improve survival in aromatase inhibitor (AI)-resistant advanced hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative breast cancer.
Major finding: There were no differences between the entinostat and placebo groups in median progression-free survival (3.3 months vs. 3.1 months; P = 0.30) and median overall survival (23.4 months vs. 21.7 months; P = 0.94). The most common grade 3-4 adverse events in the entinostat group were neutropenia (20%) and hypophosphatemia (14%).
Study details: This was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 E2112 study of 608 patients with AI-resistant, HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer, randomly assigned to entinostat plus exemestane or placebo plus exemestane.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported receiving consulting/advisory/speaker fees, research funding, accommodation/travel/expenses, and royalties from and/or stock ownership and/or other relationship in companies or patents owned/filed.
Source: Connoly RM et al. J Clin Oncol. 2021 Aug 6 (in press). doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.00944.
Breast cancer: 10-year treatment extension with aromatase inhibitors yields no benefit
Key clinical point: A 10-year vs 7-year treatment with aromatase inhibitors (anastrozole) in patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive breast cancer does not yield survival benefit but increases the risk for bone fracture.
Major finding: Anastrozole treatment for 10 years vs. 7 years was not associated with a significant difference in disease-free survival (P = 0.90). The risk of clinical bone fracture was higher with 10-year treatment (hazard ratio, 1.35; 95% confidence interval, 1.00-1.84).
Study details: The phase 3 Secondary Adjuvant Long Term Study With Arimidex (SALSA) trial studied 3,484 postmenopausal women with HR-positive breast cancer who had received anastrozole for 5 years and were randomly assigned to therapy extension by 2 years (for a total of 7 years) or 5 years (for a total of 10 years).
Disclosures: This study was supported by AstraZeneca and the Austrian Breast and Colorectal Cancer Study Group. The authors received grants, honoraria, personal/lecture/advisory/consulting/speaker fees, and/or travel/accommodation/expenses outside this work.
Source: Gnant M et al. New Engl J Med. 2021;385:395-405. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2104162.
Key clinical point: A 10-year vs 7-year treatment with aromatase inhibitors (anastrozole) in patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive breast cancer does not yield survival benefit but increases the risk for bone fracture.
Major finding: Anastrozole treatment for 10 years vs. 7 years was not associated with a significant difference in disease-free survival (P = 0.90). The risk of clinical bone fracture was higher with 10-year treatment (hazard ratio, 1.35; 95% confidence interval, 1.00-1.84).
Study details: The phase 3 Secondary Adjuvant Long Term Study With Arimidex (SALSA) trial studied 3,484 postmenopausal women with HR-positive breast cancer who had received anastrozole for 5 years and were randomly assigned to therapy extension by 2 years (for a total of 7 years) or 5 years (for a total of 10 years).
Disclosures: This study was supported by AstraZeneca and the Austrian Breast and Colorectal Cancer Study Group. The authors received grants, honoraria, personal/lecture/advisory/consulting/speaker fees, and/or travel/accommodation/expenses outside this work.
Source: Gnant M et al. New Engl J Med. 2021;385:395-405. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2104162.
Key clinical point: A 10-year vs 7-year treatment with aromatase inhibitors (anastrozole) in patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive breast cancer does not yield survival benefit but increases the risk for bone fracture.
Major finding: Anastrozole treatment for 10 years vs. 7 years was not associated with a significant difference in disease-free survival (P = 0.90). The risk of clinical bone fracture was higher with 10-year treatment (hazard ratio, 1.35; 95% confidence interval, 1.00-1.84).
Study details: The phase 3 Secondary Adjuvant Long Term Study With Arimidex (SALSA) trial studied 3,484 postmenopausal women with HR-positive breast cancer who had received anastrozole for 5 years and were randomly assigned to therapy extension by 2 years (for a total of 7 years) or 5 years (for a total of 10 years).
Disclosures: This study was supported by AstraZeneca and the Austrian Breast and Colorectal Cancer Study Group. The authors received grants, honoraria, personal/lecture/advisory/consulting/speaker fees, and/or travel/accommodation/expenses outside this work.
Source: Gnant M et al. New Engl J Med. 2021;385:395-405. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2104162.
Neuropsychiatry affects pediatric OCD treatment
Treatment of pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) has evolved in recent years, with more attention given to some of the neuropsychiatric underpinnings of the condition and how they can affect treatment response.
At the Focus on Neuropsychiatry 2021 meeting, Jeffrey Strawn, MD, outlined some of the neuropsychiatry affecting disease and potential mechanisms to help control obsessions and behaviors, and how they may fit with some therapeutic regimens.
Dr. Strawn discussed the psychological construct of cognitive control, which can provide patients an “out” from the cycle of obsession/fear/worry and compulsion/avoidance. In the face of distress, compulsion and avoidance lead to relief, which reinforces the obsession/fear/worry; this in turn leads to more distress.
“We have an escape door for this circuit” in the form of cognitive control, said Dr. Strawn, who is an associate professor of pediatrics at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
Cognitive control is linked to insight, which can in turn increase adaptive behaviors that help the patient resist the compulsion. Patients won’t eliminate distress, but they can be helped to make it more tolerable. Therapists can then help them move toward goal-directed thoughts and behaviors. Cognitive control is associated with several neural networks, but Dr. Strawn focused on two: the frontoparietal network, associated with top-down regulation; and the cingular-opercular network. Both of these are engaged during cognitive control processes, and play a role inhibitory control and error monitoring.
Dr. Strawn discussed a recent study that explored the neurofunctional basis of treatment. It compared the effects of a stress management therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in children and adults with OCD at 6 and 12 weeks. The study found similar symptom reductions in both adults and adolescents in both intervention groups.
Before initiating treatment, the researchers conducted functional MRI scans of participants while conducting an incentive flanker task, which reveals brain activity in response to cognitive control and reward processing.
A larger therapeutic response was found in the CBT group among patients who had a larger pretreatment activation within the right temporal lobe and rostral anterior cingulate cortex during cognitive control, as well as those with more activation within the medial prefrontal, orbitofrontal, lateral prefrontal, and amygdala regions during reward processing. On the other hand, within the stress management therapy group, treatment responses were better among those who had lower pretreatment activation among overlapping regions.
“There was a difference in terms of the neurofunctional predictors of treatment response. One of the key regions is the medial prefrontal cortex as well as the rostral anterior cingulate,” said Dr. Strawn, at the meeting presented by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
On the neuropharmacology side, numerous medications have been approved for OCD. Dr. Strawn highlighted some studies to illustrate general OCD treatment concepts. That included the 2004 Pediatric OCD Treatment Study, which was one of the only trials to compare placebo with an SSRI, CBT, and the combination of SSRI and CBT. It showed the best results with combination therapy, and the difference appeared early in the treatment course.
That study had aggressive dosing, which led to some issues with sertraline tolerability. Dr. Strawn showed results of a study at his institution which showed that the drug levels of pediatric patients treated with sertraline depended on CYP2C19 metabolism, which affects overall exposure and peak dose concentration. In pediatric populations, some SSRIs clear more slowly and can have high peak concentrations. SSRIs have more side effects than serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors in both anxiety disorders and OCD. A key difference between the two is that SSRI treatment is associated with greater frequency of activation, which is difficult to define, but includes restlessness and agitation and insomnia in the beginning stages of treatment.
SSRIs also lead to improvement early in the course of treatment, which was shown in a meta-analysis of nine trials. However, the same study showed that clomipramine is associated with a faster and greater magnitude of improvement, compared with SSRIs, even when the latter are dosed aggressively.
Clomipramine is a potent inhibitor of both serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake. It is recommended to monitor clomipramine levels in pediatric OCD patients, and Dr. Strawn suggested that monitoring should include both the parent drug and its primary metabolite, norclomipramine. At a given dose, there can be a great deal of variation in drug level. The clomipramine/norclomipramine ratio can provide information about the patient’s metabolic state, as well as drug adherence.
Dr. Strawn noted that peak levels occur around 1-3 hours after the dose, “and we really do want at least a 12-hour trough level.” EKGs should be performed at baseline and after any titration of clomipramine dose.
He also discussed pediatric OCD patients with OCD and tics. About one-third of Tourette syndrome patients experience OCD at some point. Tics often improve, whereas OCD more often persists. Tics that co-occur with OCD are associated with a lesser response to SSRI treatment, but not CBT treatment. Similarly, patients with hoarding tendencies are about one-third less likely to respond to SSRIs, CBT, or combination therapy.
Dr. Strawn discussed the concept of accommodation, in which family members cope with a patient’s behavior by altering routines to minimize distress and impairment. This may take the form of facilitating rituals, providing reassurance about a patient’s fears, acquiescing to demands, reducing the child’s day-to-day responsibilities, or helping the child complete tasks. Such actions are well intentioned, but they undermine cognitive control, negatively reinforce symptom engagement, and are associated with functional impairment. Reassurance is the most important behavior, occurring in more than half of patients, and it’s measurable. Parental involvement with rituals is also a concern. “This is associated with higher levels of child OCD severity, as well as parental psychopathology, and lower family cohesion. So
New developments in neurobiology and neuropsychology have changed the view of exposure. The old model emphasized the child’s fear rating as an index of corrective learning. The idea was that habituation would decrease anxiety and distress from future exposures. The new model revolves around inhibitory learning theory, which focuses on the variability of distress and aims to increase tolerance of distress. Another goal is to develop new, non-threat associations.
Finally, Dr. Strawn pointed out predictors of poor outcomes in pediatric OCD, including factors such as compulsion severity, oppositional behavior, frequent handwashing, functional impairment, lack of insight, externalizing symptoms, and possibly hoarding. Problematic family characteristics include higher levels of accommodation, parental anxiety, low family cohesion, and high levels of conflict. “The last three really represent a very concerning triad of family behaviors that may necessitate specific family work in order to facilitate the recovery of the pediatric patient,” Dr. Strawn said.
During the question-and-answer session after the talk, Dr. Strawn was asked whether there might be an inflammatory component to OCD, and whether pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcus (PANDAS) might be a prodromal condition. He noted that some studies have shown a relationship, but results have been mixed, with lots of heterogeneity within the studied populations. To be suspicious that a patient had OCD resulting from PANDAS would require a high threshold, including an acute onset of symptoms. “This is a situation also where I would tend to involve consultation with some other specialties, including neurology. And obviously there would be follow-up in terms of the general workup,” he said.
Dr. Strawn has received research funding from Allergan, Otsuka, and Myriad Genetics. He has consulted for Myriad Genetics, and is a speaker for CMEology and the Neuroscience Education Institute.
Treatment of pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) has evolved in recent years, with more attention given to some of the neuropsychiatric underpinnings of the condition and how they can affect treatment response.
At the Focus on Neuropsychiatry 2021 meeting, Jeffrey Strawn, MD, outlined some of the neuropsychiatry affecting disease and potential mechanisms to help control obsessions and behaviors, and how they may fit with some therapeutic regimens.
Dr. Strawn discussed the psychological construct of cognitive control, which can provide patients an “out” from the cycle of obsession/fear/worry and compulsion/avoidance. In the face of distress, compulsion and avoidance lead to relief, which reinforces the obsession/fear/worry; this in turn leads to more distress.
“We have an escape door for this circuit” in the form of cognitive control, said Dr. Strawn, who is an associate professor of pediatrics at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
Cognitive control is linked to insight, which can in turn increase adaptive behaviors that help the patient resist the compulsion. Patients won’t eliminate distress, but they can be helped to make it more tolerable. Therapists can then help them move toward goal-directed thoughts and behaviors. Cognitive control is associated with several neural networks, but Dr. Strawn focused on two: the frontoparietal network, associated with top-down regulation; and the cingular-opercular network. Both of these are engaged during cognitive control processes, and play a role inhibitory control and error monitoring.
Dr. Strawn discussed a recent study that explored the neurofunctional basis of treatment. It compared the effects of a stress management therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in children and adults with OCD at 6 and 12 weeks. The study found similar symptom reductions in both adults and adolescents in both intervention groups.
Before initiating treatment, the researchers conducted functional MRI scans of participants while conducting an incentive flanker task, which reveals brain activity in response to cognitive control and reward processing.
A larger therapeutic response was found in the CBT group among patients who had a larger pretreatment activation within the right temporal lobe and rostral anterior cingulate cortex during cognitive control, as well as those with more activation within the medial prefrontal, orbitofrontal, lateral prefrontal, and amygdala regions during reward processing. On the other hand, within the stress management therapy group, treatment responses were better among those who had lower pretreatment activation among overlapping regions.
“There was a difference in terms of the neurofunctional predictors of treatment response. One of the key regions is the medial prefrontal cortex as well as the rostral anterior cingulate,” said Dr. Strawn, at the meeting presented by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
On the neuropharmacology side, numerous medications have been approved for OCD. Dr. Strawn highlighted some studies to illustrate general OCD treatment concepts. That included the 2004 Pediatric OCD Treatment Study, which was one of the only trials to compare placebo with an SSRI, CBT, and the combination of SSRI and CBT. It showed the best results with combination therapy, and the difference appeared early in the treatment course.
That study had aggressive dosing, which led to some issues with sertraline tolerability. Dr. Strawn showed results of a study at his institution which showed that the drug levels of pediatric patients treated with sertraline depended on CYP2C19 metabolism, which affects overall exposure and peak dose concentration. In pediatric populations, some SSRIs clear more slowly and can have high peak concentrations. SSRIs have more side effects than serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors in both anxiety disorders and OCD. A key difference between the two is that SSRI treatment is associated with greater frequency of activation, which is difficult to define, but includes restlessness and agitation and insomnia in the beginning stages of treatment.
SSRIs also lead to improvement early in the course of treatment, which was shown in a meta-analysis of nine trials. However, the same study showed that clomipramine is associated with a faster and greater magnitude of improvement, compared with SSRIs, even when the latter are dosed aggressively.
Clomipramine is a potent inhibitor of both serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake. It is recommended to monitor clomipramine levels in pediatric OCD patients, and Dr. Strawn suggested that monitoring should include both the parent drug and its primary metabolite, norclomipramine. At a given dose, there can be a great deal of variation in drug level. The clomipramine/norclomipramine ratio can provide information about the patient’s metabolic state, as well as drug adherence.
Dr. Strawn noted that peak levels occur around 1-3 hours after the dose, “and we really do want at least a 12-hour trough level.” EKGs should be performed at baseline and after any titration of clomipramine dose.
He also discussed pediatric OCD patients with OCD and tics. About one-third of Tourette syndrome patients experience OCD at some point. Tics often improve, whereas OCD more often persists. Tics that co-occur with OCD are associated with a lesser response to SSRI treatment, but not CBT treatment. Similarly, patients with hoarding tendencies are about one-third less likely to respond to SSRIs, CBT, or combination therapy.
Dr. Strawn discussed the concept of accommodation, in which family members cope with a patient’s behavior by altering routines to minimize distress and impairment. This may take the form of facilitating rituals, providing reassurance about a patient’s fears, acquiescing to demands, reducing the child’s day-to-day responsibilities, or helping the child complete tasks. Such actions are well intentioned, but they undermine cognitive control, negatively reinforce symptom engagement, and are associated with functional impairment. Reassurance is the most important behavior, occurring in more than half of patients, and it’s measurable. Parental involvement with rituals is also a concern. “This is associated with higher levels of child OCD severity, as well as parental psychopathology, and lower family cohesion. So
New developments in neurobiology and neuropsychology have changed the view of exposure. The old model emphasized the child’s fear rating as an index of corrective learning. The idea was that habituation would decrease anxiety and distress from future exposures. The new model revolves around inhibitory learning theory, which focuses on the variability of distress and aims to increase tolerance of distress. Another goal is to develop new, non-threat associations.
Finally, Dr. Strawn pointed out predictors of poor outcomes in pediatric OCD, including factors such as compulsion severity, oppositional behavior, frequent handwashing, functional impairment, lack of insight, externalizing symptoms, and possibly hoarding. Problematic family characteristics include higher levels of accommodation, parental anxiety, low family cohesion, and high levels of conflict. “The last three really represent a very concerning triad of family behaviors that may necessitate specific family work in order to facilitate the recovery of the pediatric patient,” Dr. Strawn said.
During the question-and-answer session after the talk, Dr. Strawn was asked whether there might be an inflammatory component to OCD, and whether pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcus (PANDAS) might be a prodromal condition. He noted that some studies have shown a relationship, but results have been mixed, with lots of heterogeneity within the studied populations. To be suspicious that a patient had OCD resulting from PANDAS would require a high threshold, including an acute onset of symptoms. “This is a situation also where I would tend to involve consultation with some other specialties, including neurology. And obviously there would be follow-up in terms of the general workup,” he said.
Dr. Strawn has received research funding from Allergan, Otsuka, and Myriad Genetics. He has consulted for Myriad Genetics, and is a speaker for CMEology and the Neuroscience Education Institute.
Treatment of pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) has evolved in recent years, with more attention given to some of the neuropsychiatric underpinnings of the condition and how they can affect treatment response.
At the Focus on Neuropsychiatry 2021 meeting, Jeffrey Strawn, MD, outlined some of the neuropsychiatry affecting disease and potential mechanisms to help control obsessions and behaviors, and how they may fit with some therapeutic regimens.
Dr. Strawn discussed the psychological construct of cognitive control, which can provide patients an “out” from the cycle of obsession/fear/worry and compulsion/avoidance. In the face of distress, compulsion and avoidance lead to relief, which reinforces the obsession/fear/worry; this in turn leads to more distress.
“We have an escape door for this circuit” in the form of cognitive control, said Dr. Strawn, who is an associate professor of pediatrics at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
Cognitive control is linked to insight, which can in turn increase adaptive behaviors that help the patient resist the compulsion. Patients won’t eliminate distress, but they can be helped to make it more tolerable. Therapists can then help them move toward goal-directed thoughts and behaviors. Cognitive control is associated with several neural networks, but Dr. Strawn focused on two: the frontoparietal network, associated with top-down regulation; and the cingular-opercular network. Both of these are engaged during cognitive control processes, and play a role inhibitory control and error monitoring.
Dr. Strawn discussed a recent study that explored the neurofunctional basis of treatment. It compared the effects of a stress management therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in children and adults with OCD at 6 and 12 weeks. The study found similar symptom reductions in both adults and adolescents in both intervention groups.
Before initiating treatment, the researchers conducted functional MRI scans of participants while conducting an incentive flanker task, which reveals brain activity in response to cognitive control and reward processing.
A larger therapeutic response was found in the CBT group among patients who had a larger pretreatment activation within the right temporal lobe and rostral anterior cingulate cortex during cognitive control, as well as those with more activation within the medial prefrontal, orbitofrontal, lateral prefrontal, and amygdala regions during reward processing. On the other hand, within the stress management therapy group, treatment responses were better among those who had lower pretreatment activation among overlapping regions.
“There was a difference in terms of the neurofunctional predictors of treatment response. One of the key regions is the medial prefrontal cortex as well as the rostral anterior cingulate,” said Dr. Strawn, at the meeting presented by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
On the neuropharmacology side, numerous medications have been approved for OCD. Dr. Strawn highlighted some studies to illustrate general OCD treatment concepts. That included the 2004 Pediatric OCD Treatment Study, which was one of the only trials to compare placebo with an SSRI, CBT, and the combination of SSRI and CBT. It showed the best results with combination therapy, and the difference appeared early in the treatment course.
That study had aggressive dosing, which led to some issues with sertraline tolerability. Dr. Strawn showed results of a study at his institution which showed that the drug levels of pediatric patients treated with sertraline depended on CYP2C19 metabolism, which affects overall exposure and peak dose concentration. In pediatric populations, some SSRIs clear more slowly and can have high peak concentrations. SSRIs have more side effects than serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors in both anxiety disorders and OCD. A key difference between the two is that SSRI treatment is associated with greater frequency of activation, which is difficult to define, but includes restlessness and agitation and insomnia in the beginning stages of treatment.
SSRIs also lead to improvement early in the course of treatment, which was shown in a meta-analysis of nine trials. However, the same study showed that clomipramine is associated with a faster and greater magnitude of improvement, compared with SSRIs, even when the latter are dosed aggressively.
Clomipramine is a potent inhibitor of both serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake. It is recommended to monitor clomipramine levels in pediatric OCD patients, and Dr. Strawn suggested that monitoring should include both the parent drug and its primary metabolite, norclomipramine. At a given dose, there can be a great deal of variation in drug level. The clomipramine/norclomipramine ratio can provide information about the patient’s metabolic state, as well as drug adherence.
Dr. Strawn noted that peak levels occur around 1-3 hours after the dose, “and we really do want at least a 12-hour trough level.” EKGs should be performed at baseline and after any titration of clomipramine dose.
He also discussed pediatric OCD patients with OCD and tics. About one-third of Tourette syndrome patients experience OCD at some point. Tics often improve, whereas OCD more often persists. Tics that co-occur with OCD are associated with a lesser response to SSRI treatment, but not CBT treatment. Similarly, patients with hoarding tendencies are about one-third less likely to respond to SSRIs, CBT, or combination therapy.
Dr. Strawn discussed the concept of accommodation, in which family members cope with a patient’s behavior by altering routines to minimize distress and impairment. This may take the form of facilitating rituals, providing reassurance about a patient’s fears, acquiescing to demands, reducing the child’s day-to-day responsibilities, or helping the child complete tasks. Such actions are well intentioned, but they undermine cognitive control, negatively reinforce symptom engagement, and are associated with functional impairment. Reassurance is the most important behavior, occurring in more than half of patients, and it’s measurable. Parental involvement with rituals is also a concern. “This is associated with higher levels of child OCD severity, as well as parental psychopathology, and lower family cohesion. So
New developments in neurobiology and neuropsychology have changed the view of exposure. The old model emphasized the child’s fear rating as an index of corrective learning. The idea was that habituation would decrease anxiety and distress from future exposures. The new model revolves around inhibitory learning theory, which focuses on the variability of distress and aims to increase tolerance of distress. Another goal is to develop new, non-threat associations.
Finally, Dr. Strawn pointed out predictors of poor outcomes in pediatric OCD, including factors such as compulsion severity, oppositional behavior, frequent handwashing, functional impairment, lack of insight, externalizing symptoms, and possibly hoarding. Problematic family characteristics include higher levels of accommodation, parental anxiety, low family cohesion, and high levels of conflict. “The last three really represent a very concerning triad of family behaviors that may necessitate specific family work in order to facilitate the recovery of the pediatric patient,” Dr. Strawn said.
During the question-and-answer session after the talk, Dr. Strawn was asked whether there might be an inflammatory component to OCD, and whether pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcus (PANDAS) might be a prodromal condition. He noted that some studies have shown a relationship, but results have been mixed, with lots of heterogeneity within the studied populations. To be suspicious that a patient had OCD resulting from PANDAS would require a high threshold, including an acute onset of symptoms. “This is a situation also where I would tend to involve consultation with some other specialties, including neurology. And obviously there would be follow-up in terms of the general workup,” he said.
Dr. Strawn has received research funding from Allergan, Otsuka, and Myriad Genetics. He has consulted for Myriad Genetics, and is a speaker for CMEology and the Neuroscience Education Institute.
FROM FOCUS ON NEUROPSYCHIATRY 2021
EDs saw more benzodiazepine overdoses, but fewer patients overall, in 2020
In a year when emergency department visits dropped by almost 18%, visits for benzodiazepine overdoses did the opposite, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
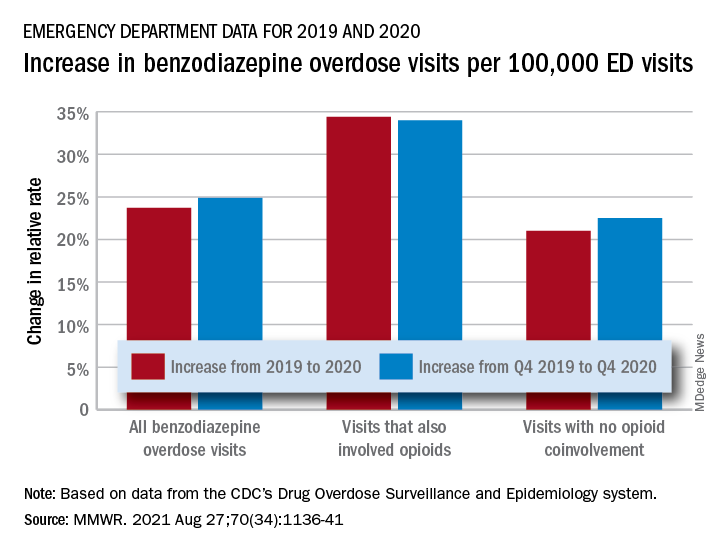
The actual increase in the number of overdose visits for benzodiazepine overdoses was quite small – from 15,547 in 2019 to 15,830 in 2020 (1.8%) – but the 11 million fewer ED visits magnified its effect, Stephen Liu, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The rate of benzodiazepine overdose visits to all visits increased by 23.7% from 2019 (24.22 per 100,000 ED visits) to 2020 (29.97 per 100,000), with the larger share going to those involving opioids, which were up by 34.4%, compared with overdose visits not involving opioids (21.0%), the investigators said, based on data reported by 32 states and the District of Columbia to the CDC’s Drug Overdose Surveillance and Epidemiology system. All of the rate changes are statistically significant.
The number of overdose visits without opioid coinvolvement actually dropped, from 2019 (12,276) to 2020 (12,218), but not by enough to offset the decline in total visits, noted Dr. Liu, of the CDC’s National Center for Injury Prevention and Control and associates.
The number of deaths from benzodiazepine overdose, on the other hand, did not drop in 2020. Those data, coming from 23 states participating in the CDC’s State Unintentional Drug Overdose Reporting System, were available only for the first half of the year.
In those 6 months, The first quarter of 2020 also showed an increase, but exact numbers were not provided in the report. Overdose deaths rose by 22% for prescription forms of benzodiazepine and 520% for illicit forms in Q2 of 2020, compared with 2019, the researchers said.
Almost all of the benzodiazepine deaths (93%) in the first half of 2020 also involved opioids, mostly in the form of illicitly manufactured fentanyls (67% of all deaths). Between Q2 of 2019 and Q2 of 2020, involvement of illicit fentanyls in benzodiazepine overdose deaths increased from almost 57% to 71%, Dr. Liu and associates reported.
“Despite progress in reducing coprescribing [of opioids and benzodiazepines] before 2019, this study suggests a reversal in the decline in benzodiazepine deaths from 2017 to 2019, driven in part by increasing involvement of [illicitly manufactured fentanyls] in benzodiazepine deaths and influxes of illicit benzodiazepines,” they wrote.
In a year when emergency department visits dropped by almost 18%, visits for benzodiazepine overdoses did the opposite, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The actual increase in the number of overdose visits for benzodiazepine overdoses was quite small – from 15,547 in 2019 to 15,830 in 2020 (1.8%) – but the 11 million fewer ED visits magnified its effect, Stephen Liu, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The rate of benzodiazepine overdose visits to all visits increased by 23.7% from 2019 (24.22 per 100,000 ED visits) to 2020 (29.97 per 100,000), with the larger share going to those involving opioids, which were up by 34.4%, compared with overdose visits not involving opioids (21.0%), the investigators said, based on data reported by 32 states and the District of Columbia to the CDC’s Drug Overdose Surveillance and Epidemiology system. All of the rate changes are statistically significant.
The number of overdose visits without opioid coinvolvement actually dropped, from 2019 (12,276) to 2020 (12,218), but not by enough to offset the decline in total visits, noted Dr. Liu, of the CDC’s National Center for Injury Prevention and Control and associates.
The number of deaths from benzodiazepine overdose, on the other hand, did not drop in 2020. Those data, coming from 23 states participating in the CDC’s State Unintentional Drug Overdose Reporting System, were available only for the first half of the year.
In those 6 months, The first quarter of 2020 also showed an increase, but exact numbers were not provided in the report. Overdose deaths rose by 22% for prescription forms of benzodiazepine and 520% for illicit forms in Q2 of 2020, compared with 2019, the researchers said.
Almost all of the benzodiazepine deaths (93%) in the first half of 2020 also involved opioids, mostly in the form of illicitly manufactured fentanyls (67% of all deaths). Between Q2 of 2019 and Q2 of 2020, involvement of illicit fentanyls in benzodiazepine overdose deaths increased from almost 57% to 71%, Dr. Liu and associates reported.
“Despite progress in reducing coprescribing [of opioids and benzodiazepines] before 2019, this study suggests a reversal in the decline in benzodiazepine deaths from 2017 to 2019, driven in part by increasing involvement of [illicitly manufactured fentanyls] in benzodiazepine deaths and influxes of illicit benzodiazepines,” they wrote.
In a year when emergency department visits dropped by almost 18%, visits for benzodiazepine overdoses did the opposite, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The actual increase in the number of overdose visits for benzodiazepine overdoses was quite small – from 15,547 in 2019 to 15,830 in 2020 (1.8%) – but the 11 million fewer ED visits magnified its effect, Stephen Liu, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The rate of benzodiazepine overdose visits to all visits increased by 23.7% from 2019 (24.22 per 100,000 ED visits) to 2020 (29.97 per 100,000), with the larger share going to those involving opioids, which were up by 34.4%, compared with overdose visits not involving opioids (21.0%), the investigators said, based on data reported by 32 states and the District of Columbia to the CDC’s Drug Overdose Surveillance and Epidemiology system. All of the rate changes are statistically significant.
The number of overdose visits without opioid coinvolvement actually dropped, from 2019 (12,276) to 2020 (12,218), but not by enough to offset the decline in total visits, noted Dr. Liu, of the CDC’s National Center for Injury Prevention and Control and associates.
The number of deaths from benzodiazepine overdose, on the other hand, did not drop in 2020. Those data, coming from 23 states participating in the CDC’s State Unintentional Drug Overdose Reporting System, were available only for the first half of the year.
In those 6 months, The first quarter of 2020 also showed an increase, but exact numbers were not provided in the report. Overdose deaths rose by 22% for prescription forms of benzodiazepine and 520% for illicit forms in Q2 of 2020, compared with 2019, the researchers said.
Almost all of the benzodiazepine deaths (93%) in the first half of 2020 also involved opioids, mostly in the form of illicitly manufactured fentanyls (67% of all deaths). Between Q2 of 2019 and Q2 of 2020, involvement of illicit fentanyls in benzodiazepine overdose deaths increased from almost 57% to 71%, Dr. Liu and associates reported.
“Despite progress in reducing coprescribing [of opioids and benzodiazepines] before 2019, this study suggests a reversal in the decline in benzodiazepine deaths from 2017 to 2019, driven in part by increasing involvement of [illicitly manufactured fentanyls] in benzodiazepine deaths and influxes of illicit benzodiazepines,” they wrote.
FROM MMWR
Reassuring data on long-term outcomes among kids with MIS-C
Most children who develop multisystemic inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) after infection with SARS-CoV-2 recover relatively quickly and without significant sequelae, according to a research letter published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
“The results of this research letter offer some reassurance as has been the case with other longitudinal reports, that children with MIS-C largely recover from the illness with minimal sequelae,” said Kanwal M. Farooqi, MD, a pediatric cardiologist from Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
“This is despite the severity of the initial clinical presentation, which can be quite significant with signs of systemic inflammation, hypotension, and need for ICU-level care,” continued Dr. Farooqi, who was not involved in the study.
Given that little is known about the medium- and long-term effects of MIS-C following infection with COVID-19, Patrick Davies, MRCPCH, Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust, and colleagues reviewed data from one of the earliest multicenter national cohorts of children in the United Kingdom. The cohort included children admitted to the hospital prior to May 10, 2020, and the analysis was based on data from 68 of 76 (89%) patients of the initial surviving cohort. Information regarding critical care readmissions and outpatient follow-up visits up to April 1, 2021 (1-year post admission), was included in the analysis.
Overall laboratory results appeared normal for most children at 50 days post admission, including neutrophils, platelets, ferritin, creatinine, and alanine transaminase. Just 3% (2/65 test results) of children showed elevated levels of C-reactive protein, 3% (2/59 test results) for D-dimer, and 2% (1/60 test results) for troponin.
Based on echocardiographic data, 14 of the 19 patients who presented with aneurysms had resolution. Nine of 10 patients who presented with “bright” coronary arteries had resolution and only one progressed to having unresolved coronary artery aneurysms with the latest follow-up at 86 days post admission. All of the 38 patients who presented with impaired function without aneurysm had recovered by day 74.
Of the six patients with ongoing echocardiographic abnormalities, all had aneurysmal changes noted on echocardiograms performed between 86 and 336 days post admission. The authors were surprised to find that troponin levels in this group were lower when compared with others in the cohort (0.06 ng/mL [interquartile range, 0.02-0.418 ng/mL] vs. 0.157 ng/mL [0.033-0.81 ng/mL]; P = .02).
These six patients ranged in age from 0 to 13 years (median age, 8.75 years); five were Afro Caribbean boys and one was a White girl.
The researchers acknowledged that, despite coming from a nationwide data set, the interpretation of this data is limited given the small size of the cohort and the lack of standardized follow-up protocol available at the time.
When asked how this data might inform follow-up guidance for children post COVID infection, Dr. Farooqi said, “although it appears from the data that we have seen in the last few months that the patients recover relatively quickly from MIS-C, I believe it is reasonable to evaluate them at 6-month intervals for the second year until we have more information regarding longer-term outcomes.”
The study authors and Dr. Farooqi disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most children who develop multisystemic inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) after infection with SARS-CoV-2 recover relatively quickly and without significant sequelae, according to a research letter published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
“The results of this research letter offer some reassurance as has been the case with other longitudinal reports, that children with MIS-C largely recover from the illness with minimal sequelae,” said Kanwal M. Farooqi, MD, a pediatric cardiologist from Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
“This is despite the severity of the initial clinical presentation, which can be quite significant with signs of systemic inflammation, hypotension, and need for ICU-level care,” continued Dr. Farooqi, who was not involved in the study.
Given that little is known about the medium- and long-term effects of MIS-C following infection with COVID-19, Patrick Davies, MRCPCH, Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust, and colleagues reviewed data from one of the earliest multicenter national cohorts of children in the United Kingdom. The cohort included children admitted to the hospital prior to May 10, 2020, and the analysis was based on data from 68 of 76 (89%) patients of the initial surviving cohort. Information regarding critical care readmissions and outpatient follow-up visits up to April 1, 2021 (1-year post admission), was included in the analysis.
Overall laboratory results appeared normal for most children at 50 days post admission, including neutrophils, platelets, ferritin, creatinine, and alanine transaminase. Just 3% (2/65 test results) of children showed elevated levels of C-reactive protein, 3% (2/59 test results) for D-dimer, and 2% (1/60 test results) for troponin.
Based on echocardiographic data, 14 of the 19 patients who presented with aneurysms had resolution. Nine of 10 patients who presented with “bright” coronary arteries had resolution and only one progressed to having unresolved coronary artery aneurysms with the latest follow-up at 86 days post admission. All of the 38 patients who presented with impaired function without aneurysm had recovered by day 74.
Of the six patients with ongoing echocardiographic abnormalities, all had aneurysmal changes noted on echocardiograms performed between 86 and 336 days post admission. The authors were surprised to find that troponin levels in this group were lower when compared with others in the cohort (0.06 ng/mL [interquartile range, 0.02-0.418 ng/mL] vs. 0.157 ng/mL [0.033-0.81 ng/mL]; P = .02).
These six patients ranged in age from 0 to 13 years (median age, 8.75 years); five were Afro Caribbean boys and one was a White girl.
The researchers acknowledged that, despite coming from a nationwide data set, the interpretation of this data is limited given the small size of the cohort and the lack of standardized follow-up protocol available at the time.
When asked how this data might inform follow-up guidance for children post COVID infection, Dr. Farooqi said, “although it appears from the data that we have seen in the last few months that the patients recover relatively quickly from MIS-C, I believe it is reasonable to evaluate them at 6-month intervals for the second year until we have more information regarding longer-term outcomes.”
The study authors and Dr. Farooqi disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most children who develop multisystemic inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) after infection with SARS-CoV-2 recover relatively quickly and without significant sequelae, according to a research letter published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
“The results of this research letter offer some reassurance as has been the case with other longitudinal reports, that children with MIS-C largely recover from the illness with minimal sequelae,” said Kanwal M. Farooqi, MD, a pediatric cardiologist from Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
“This is despite the severity of the initial clinical presentation, which can be quite significant with signs of systemic inflammation, hypotension, and need for ICU-level care,” continued Dr. Farooqi, who was not involved in the study.
Given that little is known about the medium- and long-term effects of MIS-C following infection with COVID-19, Patrick Davies, MRCPCH, Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust, and colleagues reviewed data from one of the earliest multicenter national cohorts of children in the United Kingdom. The cohort included children admitted to the hospital prior to May 10, 2020, and the analysis was based on data from 68 of 76 (89%) patients of the initial surviving cohort. Information regarding critical care readmissions and outpatient follow-up visits up to April 1, 2021 (1-year post admission), was included in the analysis.
Overall laboratory results appeared normal for most children at 50 days post admission, including neutrophils, platelets, ferritin, creatinine, and alanine transaminase. Just 3% (2/65 test results) of children showed elevated levels of C-reactive protein, 3% (2/59 test results) for D-dimer, and 2% (1/60 test results) for troponin.
Based on echocardiographic data, 14 of the 19 patients who presented with aneurysms had resolution. Nine of 10 patients who presented with “bright” coronary arteries had resolution and only one progressed to having unresolved coronary artery aneurysms with the latest follow-up at 86 days post admission. All of the 38 patients who presented with impaired function without aneurysm had recovered by day 74.
Of the six patients with ongoing echocardiographic abnormalities, all had aneurysmal changes noted on echocardiograms performed between 86 and 336 days post admission. The authors were surprised to find that troponin levels in this group were lower when compared with others in the cohort (0.06 ng/mL [interquartile range, 0.02-0.418 ng/mL] vs. 0.157 ng/mL [0.033-0.81 ng/mL]; P = .02).
These six patients ranged in age from 0 to 13 years (median age, 8.75 years); five were Afro Caribbean boys and one was a White girl.
The researchers acknowledged that, despite coming from a nationwide data set, the interpretation of this data is limited given the small size of the cohort and the lack of standardized follow-up protocol available at the time.
When asked how this data might inform follow-up guidance for children post COVID infection, Dr. Farooqi said, “although it appears from the data that we have seen in the last few months that the patients recover relatively quickly from MIS-C, I believe it is reasonable to evaluate them at 6-month intervals for the second year until we have more information regarding longer-term outcomes.”
The study authors and Dr. Farooqi disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long COVID symptoms can persist for more than 1 year, study shows
Nearly half of people who are hospitalized with COVID-19 suffer at least one lingering symptom 1 year after discharge, according to the largest study yet to assess the dynamic recovery of a group of COVID-19 survivors 12 months after the illness.
The most common lingering symptoms are fatigue and muscle weakness. One-third continue to have shortness of breath.
Overall, at 12 months, COVID-19 survivors had more problems with mobility, pain or discomfort, and anxiety or depression, and had lower self-assessment scores of quality of life than matched COVID-free peers, the investigators report.
The study was published online Aug. 28 in The Lancet.
“While most had made a good recovery, health problems persisted in some patients, especially those who had been critically ill during their hospital stay,” Bin Cao, MD, from the National Center for Respiratory Medicine at the China-Japan Friendship Hospital and Capital Medical University, both in Beijing, said in a Lancet news release.
“Our findings suggest that recovery for some patients will take longer than 1 year, and this should be taken into account when planning delivery of health care services post pandemic,” Dr. Cao said.
“As the COVID-19 pandemic continues, the need to understand and respond to long COVID is increasingly pressing,” says a Lancet editorial.
“Symptoms such as persistent fatigue, breathlessness, brain fog, and depression could debilitate many millions of people globally. Long COVID is a modern medical challenge of the first order,” it reads.
Study details
Dr. Cao and colleagues studied 1,276 COVID-19 patients (median age 59; 53% men) discharged from a hospital in Wuhan, China, between Jan. 7 and May 29, 2020. The patients were assessed at 6 and 12 months from the date they first experienced COVID-19 symptoms.
Many symptoms resolved over time, regardless of the severity of illness. Yet 49% of patients still had at least one symptom 12 months after their acute illness, down from 68% at the 6-month mark, the authors report.
Fatigue and muscle weakness were the most commonly reported symptoms seen in 52% of patients at 6 months and 20% at 12 months. Compared with men, women were 1.4 times more likely to report fatigue or muscle weakness.
Patients treated with corticosteroids during the acute phase of COVID-19 were 1.5 times as likely to experience fatigue or muscle weakness after 12 months, compared with those who had not received corticosteroids.
Thirty percent of patients reported dyspnea at 12 months, slightly more than at 6 months (26%). Dyspnea was more common in the most severely ill patients needing a ventilator during their hospital stay (39%), compared with those who did not need oxygen treatment (25%).
At the 6-month check, 349 study participants underwent pulmonary function tests and 244 of those patients completed the same test at 12 months.
Spirometric and lung volume parameters of most of these patients were within normal limits at 12 months. But lung diffusion impairment was observed in about 20%-30% of patients who had been moderately ill with COVID-19 and as high as 54% in critically ill patients.
Compared with men, women were almost three times as likely to have lung diffusion impairment after 12 months.
Of 186 patients with abnormal lung CT scan at 6 months, 118 patients had a repeat CT scan at 12 months. The lung imaging abnormality gradually recovered during follow-up, yet 76% of the most critically ill patients still had ground glass opacity at 12 months.
Mental health hit
Among those patients who had been employed full- or part-time before catching COVID, the majority had returned to their original job (88%) and most had returned to their pre-COVID-19 level of work (76%) within 12 months.
Among those who did not return to their original work, 32% cited decreased physical function, 25% were unwilling to do their previous job, and 18% were unemployed.
As shown in multiple other studies, COVID-19 can take a toll on mental health. In this cohort, slightly more patients reported anxiety or depression at 12 months than at 6 months (23% vs. 26%), and the proportion was much greater than in matched community-dwelling adults without COVID-19 (5%).
Compared with men, women were twice as likely to report anxiety or depression.
“We do not yet fully understand why psychiatric symptoms are slightly more common at 1 year than at 6 months in COVID-19 survivors,” study author Xiaoying Gu, PhD, from the Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, said in the news release.
“These could be caused by a biological process linked to the virus infection itself, or the body’s immune response to it. Or they could be linked to reduced social contact, loneliness, incomplete recovery of physical health, or loss of employment associated with illness. Large, long-term studies of COVID-19 survivors are needed so that we can better understand the long-term physical and mental health consequences of COVID-19,” Dr. Gu said.
The authors caution that the findings represent a group of patients from a single hospital in China and the cohort included only a small number of patients who had been admitted to intensive care (94 of 1,276; 7.4%).
The Lancet editorial urges the scientific and medical community to “collaborate to explore the mechanism and pathogenesis of long COVID, estimate the global and regional disease burdens, better delineate who is most at risk, understand how vaccines might affect the condition, and find effective treatments via randomized controlled trials.”
“At the same time, health care providers must acknowledge and validate the toll of the persistent symptoms of long COVID on patients, and health systems need to be prepared to meet individualized, patient-oriented goals, with an appropriately trained workforce involving physical, cognitive, social, and occupational elements,” the editorial states.
“Answering these research questions while providing compassionate and multidisciplinary care will require the full breadth of scientific and medical ingenuity. It is a challenge to which the whole health community must rise,” the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program of China, Major Projects of National Science and Technology on New Drug Creation and Development of Pulmonary Tuberculosis, the China Evergrande Group, the Jack Ma Foundation, Sino Biopharmaceutical, the Ping An Insurance (Group), and the New Sunshine Charity Foundation. The full list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nearly half of people who are hospitalized with COVID-19 suffer at least one lingering symptom 1 year after discharge, according to the largest study yet to assess the dynamic recovery of a group of COVID-19 survivors 12 months after the illness.
The most common lingering symptoms are fatigue and muscle weakness. One-third continue to have shortness of breath.
Overall, at 12 months, COVID-19 survivors had more problems with mobility, pain or discomfort, and anxiety or depression, and had lower self-assessment scores of quality of life than matched COVID-free peers, the investigators report.
The study was published online Aug. 28 in The Lancet.
“While most had made a good recovery, health problems persisted in some patients, especially those who had been critically ill during their hospital stay,” Bin Cao, MD, from the National Center for Respiratory Medicine at the China-Japan Friendship Hospital and Capital Medical University, both in Beijing, said in a Lancet news release.
“Our findings suggest that recovery for some patients will take longer than 1 year, and this should be taken into account when planning delivery of health care services post pandemic,” Dr. Cao said.
“As the COVID-19 pandemic continues, the need to understand and respond to long COVID is increasingly pressing,” says a Lancet editorial.
“Symptoms such as persistent fatigue, breathlessness, brain fog, and depression could debilitate many millions of people globally. Long COVID is a modern medical challenge of the first order,” it reads.
Study details
Dr. Cao and colleagues studied 1,276 COVID-19 patients (median age 59; 53% men) discharged from a hospital in Wuhan, China, between Jan. 7 and May 29, 2020. The patients were assessed at 6 and 12 months from the date they first experienced COVID-19 symptoms.
Many symptoms resolved over time, regardless of the severity of illness. Yet 49% of patients still had at least one symptom 12 months after their acute illness, down from 68% at the 6-month mark, the authors report.
Fatigue and muscle weakness were the most commonly reported symptoms seen in 52% of patients at 6 months and 20% at 12 months. Compared with men, women were 1.4 times more likely to report fatigue or muscle weakness.
Patients treated with corticosteroids during the acute phase of COVID-19 were 1.5 times as likely to experience fatigue or muscle weakness after 12 months, compared with those who had not received corticosteroids.
Thirty percent of patients reported dyspnea at 12 months, slightly more than at 6 months (26%). Dyspnea was more common in the most severely ill patients needing a ventilator during their hospital stay (39%), compared with those who did not need oxygen treatment (25%).
At the 6-month check, 349 study participants underwent pulmonary function tests and 244 of those patients completed the same test at 12 months.
Spirometric and lung volume parameters of most of these patients were within normal limits at 12 months. But lung diffusion impairment was observed in about 20%-30% of patients who had been moderately ill with COVID-19 and as high as 54% in critically ill patients.
Compared with men, women were almost three times as likely to have lung diffusion impairment after 12 months.
Of 186 patients with abnormal lung CT scan at 6 months, 118 patients had a repeat CT scan at 12 months. The lung imaging abnormality gradually recovered during follow-up, yet 76% of the most critically ill patients still had ground glass opacity at 12 months.
Mental health hit
Among those patients who had been employed full- or part-time before catching COVID, the majority had returned to their original job (88%) and most had returned to their pre-COVID-19 level of work (76%) within 12 months.
Among those who did not return to their original work, 32% cited decreased physical function, 25% were unwilling to do their previous job, and 18% were unemployed.
As shown in multiple other studies, COVID-19 can take a toll on mental health. In this cohort, slightly more patients reported anxiety or depression at 12 months than at 6 months (23% vs. 26%), and the proportion was much greater than in matched community-dwelling adults without COVID-19 (5%).
Compared with men, women were twice as likely to report anxiety or depression.
“We do not yet fully understand why psychiatric symptoms are slightly more common at 1 year than at 6 months in COVID-19 survivors,” study author Xiaoying Gu, PhD, from the Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, said in the news release.
“These could be caused by a biological process linked to the virus infection itself, or the body’s immune response to it. Or they could be linked to reduced social contact, loneliness, incomplete recovery of physical health, or loss of employment associated with illness. Large, long-term studies of COVID-19 survivors are needed so that we can better understand the long-term physical and mental health consequences of COVID-19,” Dr. Gu said.
The authors caution that the findings represent a group of patients from a single hospital in China and the cohort included only a small number of patients who had been admitted to intensive care (94 of 1,276; 7.4%).
The Lancet editorial urges the scientific and medical community to “collaborate to explore the mechanism and pathogenesis of long COVID, estimate the global and regional disease burdens, better delineate who is most at risk, understand how vaccines might affect the condition, and find effective treatments via randomized controlled trials.”
“At the same time, health care providers must acknowledge and validate the toll of the persistent symptoms of long COVID on patients, and health systems need to be prepared to meet individualized, patient-oriented goals, with an appropriately trained workforce involving physical, cognitive, social, and occupational elements,” the editorial states.
“Answering these research questions while providing compassionate and multidisciplinary care will require the full breadth of scientific and medical ingenuity. It is a challenge to which the whole health community must rise,” the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program of China, Major Projects of National Science and Technology on New Drug Creation and Development of Pulmonary Tuberculosis, the China Evergrande Group, the Jack Ma Foundation, Sino Biopharmaceutical, the Ping An Insurance (Group), and the New Sunshine Charity Foundation. The full list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nearly half of people who are hospitalized with COVID-19 suffer at least one lingering symptom 1 year after discharge, according to the largest study yet to assess the dynamic recovery of a group of COVID-19 survivors 12 months after the illness.
The most common lingering symptoms are fatigue and muscle weakness. One-third continue to have shortness of breath.
Overall, at 12 months, COVID-19 survivors had more problems with mobility, pain or discomfort, and anxiety or depression, and had lower self-assessment scores of quality of life than matched COVID-free peers, the investigators report.
The study was published online Aug. 28 in The Lancet.
“While most had made a good recovery, health problems persisted in some patients, especially those who had been critically ill during their hospital stay,” Bin Cao, MD, from the National Center for Respiratory Medicine at the China-Japan Friendship Hospital and Capital Medical University, both in Beijing, said in a Lancet news release.
“Our findings suggest that recovery for some patients will take longer than 1 year, and this should be taken into account when planning delivery of health care services post pandemic,” Dr. Cao said.
“As the COVID-19 pandemic continues, the need to understand and respond to long COVID is increasingly pressing,” says a Lancet editorial.
“Symptoms such as persistent fatigue, breathlessness, brain fog, and depression could debilitate many millions of people globally. Long COVID is a modern medical challenge of the first order,” it reads.
Study details
Dr. Cao and colleagues studied 1,276 COVID-19 patients (median age 59; 53% men) discharged from a hospital in Wuhan, China, between Jan. 7 and May 29, 2020. The patients were assessed at 6 and 12 months from the date they first experienced COVID-19 symptoms.
Many symptoms resolved over time, regardless of the severity of illness. Yet 49% of patients still had at least one symptom 12 months after their acute illness, down from 68% at the 6-month mark, the authors report.
Fatigue and muscle weakness were the most commonly reported symptoms seen in 52% of patients at 6 months and 20% at 12 months. Compared with men, women were 1.4 times more likely to report fatigue or muscle weakness.
Patients treated with corticosteroids during the acute phase of COVID-19 were 1.5 times as likely to experience fatigue or muscle weakness after 12 months, compared with those who had not received corticosteroids.
Thirty percent of patients reported dyspnea at 12 months, slightly more than at 6 months (26%). Dyspnea was more common in the most severely ill patients needing a ventilator during their hospital stay (39%), compared with those who did not need oxygen treatment (25%).
At the 6-month check, 349 study participants underwent pulmonary function tests and 244 of those patients completed the same test at 12 months.
Spirometric and lung volume parameters of most of these patients were within normal limits at 12 months. But lung diffusion impairment was observed in about 20%-30% of patients who had been moderately ill with COVID-19 and as high as 54% in critically ill patients.
Compared with men, women were almost three times as likely to have lung diffusion impairment after 12 months.
Of 186 patients with abnormal lung CT scan at 6 months, 118 patients had a repeat CT scan at 12 months. The lung imaging abnormality gradually recovered during follow-up, yet 76% of the most critically ill patients still had ground glass opacity at 12 months.
Mental health hit
Among those patients who had been employed full- or part-time before catching COVID, the majority had returned to their original job (88%) and most had returned to their pre-COVID-19 level of work (76%) within 12 months.
Among those who did not return to their original work, 32% cited decreased physical function, 25% were unwilling to do their previous job, and 18% were unemployed.
As shown in multiple other studies, COVID-19 can take a toll on mental health. In this cohort, slightly more patients reported anxiety or depression at 12 months than at 6 months (23% vs. 26%), and the proportion was much greater than in matched community-dwelling adults without COVID-19 (5%).
Compared with men, women were twice as likely to report anxiety or depression.
“We do not yet fully understand why psychiatric symptoms are slightly more common at 1 year than at 6 months in COVID-19 survivors,” study author Xiaoying Gu, PhD, from the Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, said in the news release.
“These could be caused by a biological process linked to the virus infection itself, or the body’s immune response to it. Or they could be linked to reduced social contact, loneliness, incomplete recovery of physical health, or loss of employment associated with illness. Large, long-term studies of COVID-19 survivors are needed so that we can better understand the long-term physical and mental health consequences of COVID-19,” Dr. Gu said.
The authors caution that the findings represent a group of patients from a single hospital in China and the cohort included only a small number of patients who had been admitted to intensive care (94 of 1,276; 7.4%).
The Lancet editorial urges the scientific and medical community to “collaborate to explore the mechanism and pathogenesis of long COVID, estimate the global and regional disease burdens, better delineate who is most at risk, understand how vaccines might affect the condition, and find effective treatments via randomized controlled trials.”
“At the same time, health care providers must acknowledge and validate the toll of the persistent symptoms of long COVID on patients, and health systems need to be prepared to meet individualized, patient-oriented goals, with an appropriately trained workforce involving physical, cognitive, social, and occupational elements,” the editorial states.
“Answering these research questions while providing compassionate and multidisciplinary care will require the full breadth of scientific and medical ingenuity. It is a challenge to which the whole health community must rise,” the editorialists conclude.
The study was funded by the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program of China, Major Projects of National Science and Technology on New Drug Creation and Development of Pulmonary Tuberculosis, the China Evergrande Group, the Jack Ma Foundation, Sino Biopharmaceutical, the Ping An Insurance (Group), and the New Sunshine Charity Foundation. The full list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
EMPEROR-Preserved spouts torrent of reports on empagliflozin treatment of HFpEF
The featured report from the 6,000-patient EMPEROR-Preserved trial at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology drew lots of attention for its headline finding: the first unequivocal demonstration that a medication, empagliflozin, can significantly reduce the rate of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF, a left ventricular ejection fraction of more than 40%), with the details simultaneously published online.
But at the same time, the EMPEROR-Preserved investigators released four additional reports with a lot more outcome analyses that also deserve some attention.
The puzzling neutral effect on renal events
Perhaps the most surprising and complicated set of findings among the main EMPEROR-Preserved outcomes involved renal outcomes.
The trial’s primary outcome was the combined rate of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure (HHF), and the results showed that treatment with empagliflozin (Jardiance) for a median of 26 months on top of standard treatment for patients with HFpEF led to a significant 21% relative risk reduction, compared with placebo-treated patients.
The trial had two prespecified secondary outcomes. One was the total number of HHF, which dropped by a significant 27%, compared with placebo. The second was the mean change in slope of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) on an annualized basis, and the empagliflozin regimen reduced the cumulative annual deficit, compared with placebo by an average of 1.36 mL/min per 1.73 m2, a significant difference.
This preservation of renal function was consistent with results from many prior studies of empagliflozin and all of the other U.S.-approved agents from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor class. Preservation of renal function and a reduction in renal events has become a hallmark property of all agents in the SGLT2 inhibitor class both in patients with type 2 diabetes, as well as in those without diabetes but with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) or with chronic kidney disease.
EMPEROR-Preserved threw a wrench into what had been an unbroken history of renal protection by SGLT2 inhibitors. That happened when a prespecified endpoint of the study – a composite renal outcome defined as time to first occurrence of chronic dialysis, renal transplantation, a sustained reduction of at least 40% in eGFR, or a sustained drop in eGFR of more than 10 or 15 mL/min per 1.73 m2 from baseline – yielded an unexpected neutral finding.
For this composite renal outcome, EMPEROR-Preserved showed a nonsignificant 5% reduction, compared with placebo, a result that both differed from what had been seen in essentially all the other SGLT2 inhibitor trials that had looked at this, but which also seemed at odds with the observed significant preservation of renal function that seemed substantial enough to produce a clinically meaningful benefit.
Renal effects blunted in HFpEF
The immediate upshot was a letter published by several EMPEROR-Preserved investigators that spelled out this discrepancy and came to the jolting conclusion that “eGFR slope analysis has limitations as a surrogate for predicting the effect of drugs on renal outcomes in patients with heart failure.”
The same authors, along with some additional associates, also published a second letter that noted a further unexpected twist with the renal outcome: “In prior large-scale clinical trials, the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on heart failure and renal outcomes had consistently tracked together,” they noted, but in this case it didn’t, a discordance they said was “extraordinarily puzzling”.
This led the study’s leaders to reanalyze the renal outcomes using a different definition, one that Milton Packer, MD, who helped design the trial and oversaw several of its analyses, called “a more conventional definition of renal events,” during his presentation of these findings at the congress. The researchers swapped out a 40% drop from baseline eGFR as an event and replaced it with a 50% decline, a change designed to screen out less severe, and often transient, reductions in kidney function that have less lasting impact on health. They also added an additional component to the composite endpoint, renal death. A revised analysis using this new renal composite outcome appeared in the European Journal of Heart Failure letter.
This change cut the total number of renal events tallied in the trial nearly in half, down to 112, and showed a more robust decline in renal events with empagliflozin treatment compared with the initial analysis, although the drop remained nonsignificant. The revised analysis also showed that the overall, nonsignificant 22% relative reduction in renal events in patients on empagliflozin, compared with placebo, dwindled down to completely nonexistent in the tertile of patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of 60% or greater. In this tertile the hazard ratio actually showed a nonsignificant point estimate of a 24% increased rate of renal events on empagliflozin, with the caveat that this subgroup now included a total of just 40 total events between the two treatment arms. (Each of the two other tertiles also had roughly the same number of total events.)
The biggest effect on renal-event reduction was in the tertile of patients with an ejection fraction of 41%-49%, in which empagliflozin treatment was linked with a significant 59% cut in renal events, compared with placebo. The analysis also showed significant heterogeneity in thus outcome between this subgroup and the other two tertiles that had higher ejection fractions and showed reduced rates of protection by empagliflozin against renal events.
This apparent blunting of a renal effect despite preservation of renal function seemed to mimic the blunting of the primary cardiovascular outcome effect that also appeared in patients with ejection fractions in the 60%-65% range or above.
“If we knew what blunted the effect of empagliflozin on heart failure outcomes at higher ejection fraction levels, we think the same explanation may also apply to the blunting of effect on renal outcomes, but right now we do not know the answer to either question,” Dr. Packer said in an interview. He’s suggested that one possibility is that many of the enrolled patients identified as having HFpEF, but with these high ejection fractions may have not actually had HFpEF, and their signs and symptoms may have instead resulted from atrial fibrillation.
“Many patients with an ejection fraction of 60%-65% and above had atrial fibrillation,” he noted, with a prevalence at enrollment in this subgroup of about 50%. Atrial fibrillation can cause dyspnea, a hallmark symptom leading to diagnosis of heart failure, and it also increases levels of N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide, a metric that served as a gatekeeper for entry into the trial. “Essentially, we are saying that many of the criteria that we specified to ensure that patients had heart failure probably did not work very well in patients with an ejection fraction of 65% or greater,” said Dr. Packer, a cardiologist at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas. “We need to figure out who these patients are.”
Some experts not involved with the study voiced skepticism that the renal findings reflected a real issue.
“I’m quite optimistic that in the long-term the effect on eGFR will translate into renal protection,” said Rudolf A. de Boer, MD, PhD, a professor of translational cardiology at University Medical Center Groningen (the Netherlands), and designated discussant at the congress for the presentation by Dr. Packer.
John J.V. McMurray, MD, a professor of cardiology and a heart failure specialist at Glasgow University, speculated that the unexpected renal outcomes data may relate to the initial decline in renal function produced by treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors despite their longer-term enhancement of renal protection.
“If you use a treatment that protects the kidneys in the long-term but causes an initial dip in eGFR, more patients receiving that treatment will have an early ‘event,’ ” he noted in an interview. He also cautioned about the dangers of subgroup analyses that dice the study population into small cohorts.
“Trials are powered to look at the effect of treatment in the overall population. Everything else is exploratory, underpowered, and subject to the play of chance,” Dr. McMurray stressed.
Counting additional cardiovascular disease events allows more analyses
A third auxiliary report from the EMPEROR-Preserved investigators performed several prespecified analyses that depended on adding additional cardiovascular disease endpoints to the core tallies of cardiovascular death or HHF – such as emergent, urgent, and outpatient events that reflected worsening heart failure – and also included information on diuretic and vasopressor use because of worsening heart failure. The increased event numbers allowed the researchers to perform 30 additional analyses included in this report, according to the count kept by Dr. Packer who was the lead author.
He highlighted several of the additional results in this paper that documented benefits from empagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo:
- A significant 29% reduction in the need for admission to a cardiac care unit or intensive care unit during an HHF.
- A nonsignificant 33% reduction in the need for intravenous vasopressors or positive inotropic drugs during HHF.
- A significantly increased rate of patients achieving a higher New York Heart Association functional class. For example, after the first year of treatment patients who received empagliflozin had a 37% higher rate of functional class improvement, compared with patients who received placebo.
Dr. McMurray had his own list of key takeaways from this paper, including:
- Among patients who needed hospitalization, “those treated with empagliflozin were less sick than those in the placebo group.”
- In addition to reducing HHF empagliflozin treatment also reduced episodes of outpatient worsening as reflected by their receipt of intensified diuretic treatment, which occurred a significant 27% less often, compared with patients on placebo.
- Treatment with empagliflozin also linked with a significant 39% relative reduction in emergency or urgent-care visits that required intravenous therapy.
Empagliflozin’s performance relative to sacubitril/valsartan
The fourth additional report focused on a post hoc, cross-trial comparison of the results from EMPEROR-Preserved and from another recent trial that, like EMPEROR-Preserved, assessed in patients with HFpEF a drug previously proven to work quite well in patients with HFrEF. The comparator drug was sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto), which underwent testing in patients with HFpEF in the PARAGON-HF trial.
The primary outcome of PARAGON-HF, which randomized 4,822 patients, was reduction in cardiovascular death and in total HHF. This dropped by a relative 13%, compared with placebo, during a median of 35 months, a between-group difference that came close to but did not achieve significance (P = .06). Despite this limitation, the Food and Drug Administration in February 2021 loosened the indication for using sacubitril/valsartan in patients with heart failure and a “below normal” ejection fraction, a category that can include many patients considered to have HFpEF.
Although the researchers who ran this analysis, including Dr. Packer, who was the first author, admitted that “comparison of effect sizes across trials is fraught with difficulties,” they nonetheless concluded from their analysis that “for all outcomes that included HHF the effect size was larger for empagliflozin than for sacubitril/valsartan.”
Dr. McMurray, a lead instigator for PARAGON-HF, said there was little to take away from this analysis.
“The patient populations were different, and sacubitril/valsartan was compared against an active therapy, valsartan,” while in EMPEROR-Preserved empagliflozin compared against placebo. “Most of us believe that sacubitril/valsartan and SGLT2 inhibitors work in different but complementary ways, and their benefits are additive. You would want patients with HFpEF or HFrEF to take both,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Packer agreed with that approach and added that he would probably also prescribe a third agent, spironolactone, to many patients with HFpEF.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly, which jointly market empagliflozin (Jardiance). PARAGON-HF was sponsored by Novartis, which markets sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto). Dr. Packer has received consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and from numerous other companies. Dr. de Boer has research contracts with Boehringer Ingelheim as well as from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Cardior, Ionis, Novo Nordisk, and Roche, and he has been a consultant to Novartis as well as to Abbott, AstraZeneca, Gayer, and Roche. Dr. McMurray led trials of sacubitril/valsartan sponsored by Novartis, and his institution has received compensation for his participation in studies sponsored by Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Cardurion, DalCor, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, and Theracos.
The featured report from the 6,000-patient EMPEROR-Preserved trial at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology drew lots of attention for its headline finding: the first unequivocal demonstration that a medication, empagliflozin, can significantly reduce the rate of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF, a left ventricular ejection fraction of more than 40%), with the details simultaneously published online.
But at the same time, the EMPEROR-Preserved investigators released four additional reports with a lot more outcome analyses that also deserve some attention.
The puzzling neutral effect on renal events
Perhaps the most surprising and complicated set of findings among the main EMPEROR-Preserved outcomes involved renal outcomes.
The trial’s primary outcome was the combined rate of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure (HHF), and the results showed that treatment with empagliflozin (Jardiance) for a median of 26 months on top of standard treatment for patients with HFpEF led to a significant 21% relative risk reduction, compared with placebo-treated patients.
The trial had two prespecified secondary outcomes. One was the total number of HHF, which dropped by a significant 27%, compared with placebo. The second was the mean change in slope of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) on an annualized basis, and the empagliflozin regimen reduced the cumulative annual deficit, compared with placebo by an average of 1.36 mL/min per 1.73 m2, a significant difference.
This preservation of renal function was consistent with results from many prior studies of empagliflozin and all of the other U.S.-approved agents from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor class. Preservation of renal function and a reduction in renal events has become a hallmark property of all agents in the SGLT2 inhibitor class both in patients with type 2 diabetes, as well as in those without diabetes but with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) or with chronic kidney disease.
EMPEROR-Preserved threw a wrench into what had been an unbroken history of renal protection by SGLT2 inhibitors. That happened when a prespecified endpoint of the study – a composite renal outcome defined as time to first occurrence of chronic dialysis, renal transplantation, a sustained reduction of at least 40% in eGFR, or a sustained drop in eGFR of more than 10 or 15 mL/min per 1.73 m2 from baseline – yielded an unexpected neutral finding.
For this composite renal outcome, EMPEROR-Preserved showed a nonsignificant 5% reduction, compared with placebo, a result that both differed from what had been seen in essentially all the other SGLT2 inhibitor trials that had looked at this, but which also seemed at odds with the observed significant preservation of renal function that seemed substantial enough to produce a clinically meaningful benefit.
Renal effects blunted in HFpEF
The immediate upshot was a letter published by several EMPEROR-Preserved investigators that spelled out this discrepancy and came to the jolting conclusion that “eGFR slope analysis has limitations as a surrogate for predicting the effect of drugs on renal outcomes in patients with heart failure.”
The same authors, along with some additional associates, also published a second letter that noted a further unexpected twist with the renal outcome: “In prior large-scale clinical trials, the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on heart failure and renal outcomes had consistently tracked together,” they noted, but in this case it didn’t, a discordance they said was “extraordinarily puzzling”.
This led the study’s leaders to reanalyze the renal outcomes using a different definition, one that Milton Packer, MD, who helped design the trial and oversaw several of its analyses, called “a more conventional definition of renal events,” during his presentation of these findings at the congress. The researchers swapped out a 40% drop from baseline eGFR as an event and replaced it with a 50% decline, a change designed to screen out less severe, and often transient, reductions in kidney function that have less lasting impact on health. They also added an additional component to the composite endpoint, renal death. A revised analysis using this new renal composite outcome appeared in the European Journal of Heart Failure letter.
This change cut the total number of renal events tallied in the trial nearly in half, down to 112, and showed a more robust decline in renal events with empagliflozin treatment compared with the initial analysis, although the drop remained nonsignificant. The revised analysis also showed that the overall, nonsignificant 22% relative reduction in renal events in patients on empagliflozin, compared with placebo, dwindled down to completely nonexistent in the tertile of patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of 60% or greater. In this tertile the hazard ratio actually showed a nonsignificant point estimate of a 24% increased rate of renal events on empagliflozin, with the caveat that this subgroup now included a total of just 40 total events between the two treatment arms. (Each of the two other tertiles also had roughly the same number of total events.)
The biggest effect on renal-event reduction was in the tertile of patients with an ejection fraction of 41%-49%, in which empagliflozin treatment was linked with a significant 59% cut in renal events, compared with placebo. The analysis also showed significant heterogeneity in thus outcome between this subgroup and the other two tertiles that had higher ejection fractions and showed reduced rates of protection by empagliflozin against renal events.
This apparent blunting of a renal effect despite preservation of renal function seemed to mimic the blunting of the primary cardiovascular outcome effect that also appeared in patients with ejection fractions in the 60%-65% range or above.
“If we knew what blunted the effect of empagliflozin on heart failure outcomes at higher ejection fraction levels, we think the same explanation may also apply to the blunting of effect on renal outcomes, but right now we do not know the answer to either question,” Dr. Packer said in an interview. He’s suggested that one possibility is that many of the enrolled patients identified as having HFpEF, but with these high ejection fractions may have not actually had HFpEF, and their signs and symptoms may have instead resulted from atrial fibrillation.
“Many patients with an ejection fraction of 60%-65% and above had atrial fibrillation,” he noted, with a prevalence at enrollment in this subgroup of about 50%. Atrial fibrillation can cause dyspnea, a hallmark symptom leading to diagnosis of heart failure, and it also increases levels of N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide, a metric that served as a gatekeeper for entry into the trial. “Essentially, we are saying that many of the criteria that we specified to ensure that patients had heart failure probably did not work very well in patients with an ejection fraction of 65% or greater,” said Dr. Packer, a cardiologist at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas. “We need to figure out who these patients are.”
Some experts not involved with the study voiced skepticism that the renal findings reflected a real issue.
“I’m quite optimistic that in the long-term the effect on eGFR will translate into renal protection,” said Rudolf A. de Boer, MD, PhD, a professor of translational cardiology at University Medical Center Groningen (the Netherlands), and designated discussant at the congress for the presentation by Dr. Packer.
John J.V. McMurray, MD, a professor of cardiology and a heart failure specialist at Glasgow University, speculated that the unexpected renal outcomes data may relate to the initial decline in renal function produced by treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors despite their longer-term enhancement of renal protection.
“If you use a treatment that protects the kidneys in the long-term but causes an initial dip in eGFR, more patients receiving that treatment will have an early ‘event,’ ” he noted in an interview. He also cautioned about the dangers of subgroup analyses that dice the study population into small cohorts.
“Trials are powered to look at the effect of treatment in the overall population. Everything else is exploratory, underpowered, and subject to the play of chance,” Dr. McMurray stressed.
Counting additional cardiovascular disease events allows more analyses
A third auxiliary report from the EMPEROR-Preserved investigators performed several prespecified analyses that depended on adding additional cardiovascular disease endpoints to the core tallies of cardiovascular death or HHF – such as emergent, urgent, and outpatient events that reflected worsening heart failure – and also included information on diuretic and vasopressor use because of worsening heart failure. The increased event numbers allowed the researchers to perform 30 additional analyses included in this report, according to the count kept by Dr. Packer who was the lead author.
He highlighted several of the additional results in this paper that documented benefits from empagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo:
- A significant 29% reduction in the need for admission to a cardiac care unit or intensive care unit during an HHF.
- A nonsignificant 33% reduction in the need for intravenous vasopressors or positive inotropic drugs during HHF.
- A significantly increased rate of patients achieving a higher New York Heart Association functional class. For example, after the first year of treatment patients who received empagliflozin had a 37% higher rate of functional class improvement, compared with patients who received placebo.
Dr. McMurray had his own list of key takeaways from this paper, including:
- Among patients who needed hospitalization, “those treated with empagliflozin were less sick than those in the placebo group.”
- In addition to reducing HHF empagliflozin treatment also reduced episodes of outpatient worsening as reflected by their receipt of intensified diuretic treatment, which occurred a significant 27% less often, compared with patients on placebo.
- Treatment with empagliflozin also linked with a significant 39% relative reduction in emergency or urgent-care visits that required intravenous therapy.
Empagliflozin’s performance relative to sacubitril/valsartan
The fourth additional report focused on a post hoc, cross-trial comparison of the results from EMPEROR-Preserved and from another recent trial that, like EMPEROR-Preserved, assessed in patients with HFpEF a drug previously proven to work quite well in patients with HFrEF. The comparator drug was sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto), which underwent testing in patients with HFpEF in the PARAGON-HF trial.
The primary outcome of PARAGON-HF, which randomized 4,822 patients, was reduction in cardiovascular death and in total HHF. This dropped by a relative 13%, compared with placebo, during a median of 35 months, a between-group difference that came close to but did not achieve significance (P = .06). Despite this limitation, the Food and Drug Administration in February 2021 loosened the indication for using sacubitril/valsartan in patients with heart failure and a “below normal” ejection fraction, a category that can include many patients considered to have HFpEF.
Although the researchers who ran this analysis, including Dr. Packer, who was the first author, admitted that “comparison of effect sizes across trials is fraught with difficulties,” they nonetheless concluded from their analysis that “for all outcomes that included HHF the effect size was larger for empagliflozin than for sacubitril/valsartan.”
Dr. McMurray, a lead instigator for PARAGON-HF, said there was little to take away from this analysis.
“The patient populations were different, and sacubitril/valsartan was compared against an active therapy, valsartan,” while in EMPEROR-Preserved empagliflozin compared against placebo. “Most of us believe that sacubitril/valsartan and SGLT2 inhibitors work in different but complementary ways, and their benefits are additive. You would want patients with HFpEF or HFrEF to take both,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Packer agreed with that approach and added that he would probably also prescribe a third agent, spironolactone, to many patients with HFpEF.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly, which jointly market empagliflozin (Jardiance). PARAGON-HF was sponsored by Novartis, which markets sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto). Dr. Packer has received consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and from numerous other companies. Dr. de Boer has research contracts with Boehringer Ingelheim as well as from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Cardior, Ionis, Novo Nordisk, and Roche, and he has been a consultant to Novartis as well as to Abbott, AstraZeneca, Gayer, and Roche. Dr. McMurray led trials of sacubitril/valsartan sponsored by Novartis, and his institution has received compensation for his participation in studies sponsored by Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Cardurion, DalCor, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, and Theracos.
The featured report from the 6,000-patient EMPEROR-Preserved trial at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology drew lots of attention for its headline finding: the first unequivocal demonstration that a medication, empagliflozin, can significantly reduce the rate of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF, a left ventricular ejection fraction of more than 40%), with the details simultaneously published online.
But at the same time, the EMPEROR-Preserved investigators released four additional reports with a lot more outcome analyses that also deserve some attention.
The puzzling neutral effect on renal events
Perhaps the most surprising and complicated set of findings among the main EMPEROR-Preserved outcomes involved renal outcomes.
The trial’s primary outcome was the combined rate of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure (HHF), and the results showed that treatment with empagliflozin (Jardiance) for a median of 26 months on top of standard treatment for patients with HFpEF led to a significant 21% relative risk reduction, compared with placebo-treated patients.
The trial had two prespecified secondary outcomes. One was the total number of HHF, which dropped by a significant 27%, compared with placebo. The second was the mean change in slope of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) on an annualized basis, and the empagliflozin regimen reduced the cumulative annual deficit, compared with placebo by an average of 1.36 mL/min per 1.73 m2, a significant difference.
This preservation of renal function was consistent with results from many prior studies of empagliflozin and all of the other U.S.-approved agents from the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor class. Preservation of renal function and a reduction in renal events has become a hallmark property of all agents in the SGLT2 inhibitor class both in patients with type 2 diabetes, as well as in those without diabetes but with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) or with chronic kidney disease.
EMPEROR-Preserved threw a wrench into what had been an unbroken history of renal protection by SGLT2 inhibitors. That happened when a prespecified endpoint of the study – a composite renal outcome defined as time to first occurrence of chronic dialysis, renal transplantation, a sustained reduction of at least 40% in eGFR, or a sustained drop in eGFR of more than 10 or 15 mL/min per 1.73 m2 from baseline – yielded an unexpected neutral finding.
For this composite renal outcome, EMPEROR-Preserved showed a nonsignificant 5% reduction, compared with placebo, a result that both differed from what had been seen in essentially all the other SGLT2 inhibitor trials that had looked at this, but which also seemed at odds with the observed significant preservation of renal function that seemed substantial enough to produce a clinically meaningful benefit.
Renal effects blunted in HFpEF
The immediate upshot was a letter published by several EMPEROR-Preserved investigators that spelled out this discrepancy and came to the jolting conclusion that “eGFR slope analysis has limitations as a surrogate for predicting the effect of drugs on renal outcomes in patients with heart failure.”
The same authors, along with some additional associates, also published a second letter that noted a further unexpected twist with the renal outcome: “In prior large-scale clinical trials, the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on heart failure and renal outcomes had consistently tracked together,” they noted, but in this case it didn’t, a discordance they said was “extraordinarily puzzling”.
This led the study’s leaders to reanalyze the renal outcomes using a different definition, one that Milton Packer, MD, who helped design the trial and oversaw several of its analyses, called “a more conventional definition of renal events,” during his presentation of these findings at the congress. The researchers swapped out a 40% drop from baseline eGFR as an event and replaced it with a 50% decline, a change designed to screen out less severe, and often transient, reductions in kidney function that have less lasting impact on health. They also added an additional component to the composite endpoint, renal death. A revised analysis using this new renal composite outcome appeared in the European Journal of Heart Failure letter.
This change cut the total number of renal events tallied in the trial nearly in half, down to 112, and showed a more robust decline in renal events with empagliflozin treatment compared with the initial analysis, although the drop remained nonsignificant. The revised analysis also showed that the overall, nonsignificant 22% relative reduction in renal events in patients on empagliflozin, compared with placebo, dwindled down to completely nonexistent in the tertile of patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of 60% or greater. In this tertile the hazard ratio actually showed a nonsignificant point estimate of a 24% increased rate of renal events on empagliflozin, with the caveat that this subgroup now included a total of just 40 total events between the two treatment arms. (Each of the two other tertiles also had roughly the same number of total events.)
The biggest effect on renal-event reduction was in the tertile of patients with an ejection fraction of 41%-49%, in which empagliflozin treatment was linked with a significant 59% cut in renal events, compared with placebo. The analysis also showed significant heterogeneity in thus outcome between this subgroup and the other two tertiles that had higher ejection fractions and showed reduced rates of protection by empagliflozin against renal events.
This apparent blunting of a renal effect despite preservation of renal function seemed to mimic the blunting of the primary cardiovascular outcome effect that also appeared in patients with ejection fractions in the 60%-65% range or above.
“If we knew what blunted the effect of empagliflozin on heart failure outcomes at higher ejection fraction levels, we think the same explanation may also apply to the blunting of effect on renal outcomes, but right now we do not know the answer to either question,” Dr. Packer said in an interview. He’s suggested that one possibility is that many of the enrolled patients identified as having HFpEF, but with these high ejection fractions may have not actually had HFpEF, and their signs and symptoms may have instead resulted from atrial fibrillation.
“Many patients with an ejection fraction of 60%-65% and above had atrial fibrillation,” he noted, with a prevalence at enrollment in this subgroup of about 50%. Atrial fibrillation can cause dyspnea, a hallmark symptom leading to diagnosis of heart failure, and it also increases levels of N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide, a metric that served as a gatekeeper for entry into the trial. “Essentially, we are saying that many of the criteria that we specified to ensure that patients had heart failure probably did not work very well in patients with an ejection fraction of 65% or greater,” said Dr. Packer, a cardiologist at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas. “We need to figure out who these patients are.”
Some experts not involved with the study voiced skepticism that the renal findings reflected a real issue.
“I’m quite optimistic that in the long-term the effect on eGFR will translate into renal protection,” said Rudolf A. de Boer, MD, PhD, a professor of translational cardiology at University Medical Center Groningen (the Netherlands), and designated discussant at the congress for the presentation by Dr. Packer.
John J.V. McMurray, MD, a professor of cardiology and a heart failure specialist at Glasgow University, speculated that the unexpected renal outcomes data may relate to the initial decline in renal function produced by treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors despite their longer-term enhancement of renal protection.
“If you use a treatment that protects the kidneys in the long-term but causes an initial dip in eGFR, more patients receiving that treatment will have an early ‘event,’ ” he noted in an interview. He also cautioned about the dangers of subgroup analyses that dice the study population into small cohorts.
“Trials are powered to look at the effect of treatment in the overall population. Everything else is exploratory, underpowered, and subject to the play of chance,” Dr. McMurray stressed.
Counting additional cardiovascular disease events allows more analyses
A third auxiliary report from the EMPEROR-Preserved investigators performed several prespecified analyses that depended on adding additional cardiovascular disease endpoints to the core tallies of cardiovascular death or HHF – such as emergent, urgent, and outpatient events that reflected worsening heart failure – and also included information on diuretic and vasopressor use because of worsening heart failure. The increased event numbers allowed the researchers to perform 30 additional analyses included in this report, according to the count kept by Dr. Packer who was the lead author.
He highlighted several of the additional results in this paper that documented benefits from empagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo:
- A significant 29% reduction in the need for admission to a cardiac care unit or intensive care unit during an HHF.
- A nonsignificant 33% reduction in the need for intravenous vasopressors or positive inotropic drugs during HHF.
- A significantly increased rate of patients achieving a higher New York Heart Association functional class. For example, after the first year of treatment patients who received empagliflozin had a 37% higher rate of functional class improvement, compared with patients who received placebo.
Dr. McMurray had his own list of key takeaways from this paper, including:
- Among patients who needed hospitalization, “those treated with empagliflozin were less sick than those in the placebo group.”
- In addition to reducing HHF empagliflozin treatment also reduced episodes of outpatient worsening as reflected by their receipt of intensified diuretic treatment, which occurred a significant 27% less often, compared with patients on placebo.
- Treatment with empagliflozin also linked with a significant 39% relative reduction in emergency or urgent-care visits that required intravenous therapy.
Empagliflozin’s performance relative to sacubitril/valsartan
The fourth additional report focused on a post hoc, cross-trial comparison of the results from EMPEROR-Preserved and from another recent trial that, like EMPEROR-Preserved, assessed in patients with HFpEF a drug previously proven to work quite well in patients with HFrEF. The comparator drug was sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto), which underwent testing in patients with HFpEF in the PARAGON-HF trial.
The primary outcome of PARAGON-HF, which randomized 4,822 patients, was reduction in cardiovascular death and in total HHF. This dropped by a relative 13%, compared with placebo, during a median of 35 months, a between-group difference that came close to but did not achieve significance (P = .06). Despite this limitation, the Food and Drug Administration in February 2021 loosened the indication for using sacubitril/valsartan in patients with heart failure and a “below normal” ejection fraction, a category that can include many patients considered to have HFpEF.
Although the researchers who ran this analysis, including Dr. Packer, who was the first author, admitted that “comparison of effect sizes across trials is fraught with difficulties,” they nonetheless concluded from their analysis that “for all outcomes that included HHF the effect size was larger for empagliflozin than for sacubitril/valsartan.”
Dr. McMurray, a lead instigator for PARAGON-HF, said there was little to take away from this analysis.
“The patient populations were different, and sacubitril/valsartan was compared against an active therapy, valsartan,” while in EMPEROR-Preserved empagliflozin compared against placebo. “Most of us believe that sacubitril/valsartan and SGLT2 inhibitors work in different but complementary ways, and their benefits are additive. You would want patients with HFpEF or HFrEF to take both,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Packer agreed with that approach and added that he would probably also prescribe a third agent, spironolactone, to many patients with HFpEF.
EMPEROR-Preserved was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly, which jointly market empagliflozin (Jardiance). PARAGON-HF was sponsored by Novartis, which markets sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto). Dr. Packer has received consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and from numerous other companies. Dr. de Boer has research contracts with Boehringer Ingelheim as well as from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Cardior, Ionis, Novo Nordisk, and Roche, and he has been a consultant to Novartis as well as to Abbott, AstraZeneca, Gayer, and Roche. Dr. McMurray led trials of sacubitril/valsartan sponsored by Novartis, and his institution has received compensation for his participation in studies sponsored by Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Cardurion, DalCor, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, and Theracos.
FROM ESC 2021
Early end for trial of experimental oxygenation strategies in ARDS
Background: Both observational studies and clinical trials have found that a liberal oxygenation strategy in multiple inpatient settings may be harmful. Furthermore, a conservative strategy is what has been recommended in guidelines. Conversely, the relevance of this recent concept has been challenged in a large trial of a critically ill population (ICU-ROX).
Study design: Randomized clinical trial, unblinded.
Setting: Thirteen sites in France.
Synopsis: In a multicenter randomized clinical trial, investigators enrolled patients with ARDS to either a liberal oxygenation group (PaO2 target 90-105 mm Hg or SpO2 of 96% or greater) or a conservative oxygenation group (PaO2 target 55-70 mm Hg or SpO2 88%-92%). The trial was planned for inclusion of 850 patients, but the data and safety monitoring board decided to stop the trial after inclusion of 205 patients. Although the primary outcome (28-day all-cause mortality) was not significantly different between groups (34.3% vs 26.5%; absolute difference, 7.8%; 95% confidence interval, –4.8 to 20.6), the direction was signaling possible harm and there were five episodes of mesenteric ischemia in the conservative oxygenation group (none in the liberal oxygenation group).
Bottom line: A conservative oxygenation strategy cannot be currently recommended to patients with ARDS in the ICU. A minimum SpO2 of 90% was suggested in an accompanying editorial.
Editorial commentary: Interestingly, the supplemental results of the article show that prone positioning was used much less frequently in the conservative oxygenation group (34.3 vs 51.0%). If the impressive results of Guerin (2013) would be repeated in this population, this difference could help explain the higher observed mortality in the conservative oxygenation group. It is possible that, by aiming to be less aggressive in improving the PaO2, clinicians inadvertently withheld effective treatments for ARDS. The results of this trial bring up several interesting questions, but provide the bedside clinician with few answers. The complex interplay of treatment factors needs to be dissected in future trials.
Citation: Barrot L et al. Liberal or conservative oxygen therapy for acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Eng J Med. 2020;382:999-1008.
Dr. Saraiva is a hospitalist and assistant professor of medicine at UK HealthCare, Lexington, Ky.
Background: Both observational studies and clinical trials have found that a liberal oxygenation strategy in multiple inpatient settings may be harmful. Furthermore, a conservative strategy is what has been recommended in guidelines. Conversely, the relevance of this recent concept has been challenged in a large trial of a critically ill population (ICU-ROX).
Study design: Randomized clinical trial, unblinded.
Setting: Thirteen sites in France.
Synopsis: In a multicenter randomized clinical trial, investigators enrolled patients with ARDS to either a liberal oxygenation group (PaO2 target 90-105 mm Hg or SpO2 of 96% or greater) or a conservative oxygenation group (PaO2 target 55-70 mm Hg or SpO2 88%-92%). The trial was planned for inclusion of 850 patients, but the data and safety monitoring board decided to stop the trial after inclusion of 205 patients. Although the primary outcome (28-day all-cause mortality) was not significantly different between groups (34.3% vs 26.5%; absolute difference, 7.8%; 95% confidence interval, –4.8 to 20.6), the direction was signaling possible harm and there were five episodes of mesenteric ischemia in the conservative oxygenation group (none in the liberal oxygenation group).
Bottom line: A conservative oxygenation strategy cannot be currently recommended to patients with ARDS in the ICU. A minimum SpO2 of 90% was suggested in an accompanying editorial.
Editorial commentary: Interestingly, the supplemental results of the article show that prone positioning was used much less frequently in the conservative oxygenation group (34.3 vs 51.0%). If the impressive results of Guerin (2013) would be repeated in this population, this difference could help explain the higher observed mortality in the conservative oxygenation group. It is possible that, by aiming to be less aggressive in improving the PaO2, clinicians inadvertently withheld effective treatments for ARDS. The results of this trial bring up several interesting questions, but provide the bedside clinician with few answers. The complex interplay of treatment factors needs to be dissected in future trials.
Citation: Barrot L et al. Liberal or conservative oxygen therapy for acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Eng J Med. 2020;382:999-1008.
Dr. Saraiva is a hospitalist and assistant professor of medicine at UK HealthCare, Lexington, Ky.
Background: Both observational studies and clinical trials have found that a liberal oxygenation strategy in multiple inpatient settings may be harmful. Furthermore, a conservative strategy is what has been recommended in guidelines. Conversely, the relevance of this recent concept has been challenged in a large trial of a critically ill population (ICU-ROX).
Study design: Randomized clinical trial, unblinded.
Setting: Thirteen sites in France.
Synopsis: In a multicenter randomized clinical trial, investigators enrolled patients with ARDS to either a liberal oxygenation group (PaO2 target 90-105 mm Hg or SpO2 of 96% or greater) or a conservative oxygenation group (PaO2 target 55-70 mm Hg or SpO2 88%-92%). The trial was planned for inclusion of 850 patients, but the data and safety monitoring board decided to stop the trial after inclusion of 205 patients. Although the primary outcome (28-day all-cause mortality) was not significantly different between groups (34.3% vs 26.5%; absolute difference, 7.8%; 95% confidence interval, –4.8 to 20.6), the direction was signaling possible harm and there were five episodes of mesenteric ischemia in the conservative oxygenation group (none in the liberal oxygenation group).
Bottom line: A conservative oxygenation strategy cannot be currently recommended to patients with ARDS in the ICU. A minimum SpO2 of 90% was suggested in an accompanying editorial.
Editorial commentary: Interestingly, the supplemental results of the article show that prone positioning was used much less frequently in the conservative oxygenation group (34.3 vs 51.0%). If the impressive results of Guerin (2013) would be repeated in this population, this difference could help explain the higher observed mortality in the conservative oxygenation group. It is possible that, by aiming to be less aggressive in improving the PaO2, clinicians inadvertently withheld effective treatments for ARDS. The results of this trial bring up several interesting questions, but provide the bedside clinician with few answers. The complex interplay of treatment factors needs to be dissected in future trials.
Citation: Barrot L et al. Liberal or conservative oxygen therapy for acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Eng J Med. 2020;382:999-1008.
Dr. Saraiva is a hospitalist and assistant professor of medicine at UK HealthCare, Lexington, Ky.
Number of global deaths by suicide increased over 30 years
The overall global number of deaths by suicide increased by almost 20,000 during the past 30 years, new research shows.
The increase occurred despite a significant decrease in age-specific suicide rates from 1990 through 2019, according to data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.
Population growth, population aging, and changes in population age structure may explain the increase in number of suicide deaths, the investigators note.
“As suicide rates are highest among the elderly (70 years or above) for both genders in almost all regions of the world, the rapidly aging population globally will pose huge challenges for the reduction in the number of suicide deaths in the future,” write the researchers, led by Paul Siu Fai Yip, PhD, of the HKJC Center for Suicide Research and Prevention, University of Hong Kong, China.
The findings were published online Aug. 16 in Injury Prevention.
Global public health concern
Around the world, approximately 800,000 individuals die by suicide each year, while many others attempt suicide. Yet suicide has not received the same level of attention as other global public health concerns, such as HIV/AIDS and cancer, the investigators write.
They examined data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 to assess how demographic and epidemiologic factors contributed to the number of suicide deaths during the past 30 years.
The researchers also analyzed relationships between population growth, population age structure, income level, and gender- and age-specific suicide rates.
The Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 includes information from 204 countries about 369 diseases and injuries by age and gender. The dataset also includes population estimates for each year by location, age group, and gender.
In their analysis, the investigators looked at changes in suicide rates and the number of suicide deaths from 1990 to 2019 by gender and age group in the four income level regions defined by the World Bank. These categories include low-income, lower-middle–income, upper-middle–income, and high-income regions.
Number of deaths versus suicide rates
The number of deaths was 738,799 in 1990 and 758,696 in 2019.
The largest increase in deaths occurred in the lower-middle–income region, where the number of suicide deaths increased by 72,550 (from 232,340 to 304,890).
Population growth (300,942; 1,512.5%) was the major contributor to the overall increase in total number of suicide deaths. The second largest contributor was population age structure (189,512; 952.4%).
However, the effects of these factors were offset to a large extent by the effect of reduction in overall suicide rates (−470,556; −2,364.9%).
Interestingly, the overall suicide rate per 100,000 population decreased from 13.8 in 1990 to 9.8 in 2019.
The upper-middle–income region had the largest decline (−6.25 per 100,000), and the high-income region had the smallest decline (−1.77 per 100,000). Suicide rates also decreased in lower-middle–income (−2.51 per 100,000) and low-income regions (−1.96 per 100,000).
Reasons for the declines across all regions “have yet to be determined,” write the investigators. International efforts coordinated by the United Nations and World Health Organization likely contributed to these declines, they add.
‘Imbalance of resources’
The overall reduction in suicide rate of −4.01 per 100,000 “was mainly due” to reduction in age-specific suicide rates (−6.09; 152%), the researchers report.
This effect was partly offset, however, by the effect of the changing population age structure (2.08; −52%). In the high-income–level region, for example, the reduction in age-specific suicide rate (−3.83; 216.3%) was greater than the increase resulting from the change in population age structure (2.06; −116.3%).
“The overall contribution of population age structure mainly came from the 45-64 (565.2%) and 65+ (528.7%) age groups,” the investigators write. “This effect was observed in middle-income– as well as high-income–level regions, reflecting the global effect of population aging.”
They add that world populations will “experience pronounced and historically unprecedented aging in the coming decades” because of increasing life expectancy and declining fertility.
Men, but not women, had a notable increase in total number of suicide deaths. The significant effect of male population growth (177,128; 890.2% vs. 123,814; 622.3% for women) and male population age structure (120,186; 604.0% vs. 69,325; 348.4%) were the main factors that explained this increase, the investigators note.
However, from 1990 to 2019, the overall suicide rate per 100,000 men decreased from 16.6 to 13.5 (–3.09). The decline in overall suicide rate was even greater for women, from 11.0 to 6.1 (–4.91).
This finding was particularly notable in the upper-middle–income region (–8.12 women vs. –4.37 men per 100,000).
“This study highlighted the considerable imbalance of the resources in carrying out suicide prevention work, especially in low-income and middle-income countries,” the investigators write.
“It is time to revisit this situation to ensure that sufficient resources can be redeployed globally to meet the future challenges,” they add.
The study was funded by a Humanities and Social Sciences Prestigious Fellowship, which Dr. Yip received. He declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The overall global number of deaths by suicide increased by almost 20,000 during the past 30 years, new research shows.
The increase occurred despite a significant decrease in age-specific suicide rates from 1990 through 2019, according to data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.
Population growth, population aging, and changes in population age structure may explain the increase in number of suicide deaths, the investigators note.
“As suicide rates are highest among the elderly (70 years or above) for both genders in almost all regions of the world, the rapidly aging population globally will pose huge challenges for the reduction in the number of suicide deaths in the future,” write the researchers, led by Paul Siu Fai Yip, PhD, of the HKJC Center for Suicide Research and Prevention, University of Hong Kong, China.
The findings were published online Aug. 16 in Injury Prevention.
Global public health concern
Around the world, approximately 800,000 individuals die by suicide each year, while many others attempt suicide. Yet suicide has not received the same level of attention as other global public health concerns, such as HIV/AIDS and cancer, the investigators write.
They examined data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 to assess how demographic and epidemiologic factors contributed to the number of suicide deaths during the past 30 years.
The researchers also analyzed relationships between population growth, population age structure, income level, and gender- and age-specific suicide rates.
The Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 includes information from 204 countries about 369 diseases and injuries by age and gender. The dataset also includes population estimates for each year by location, age group, and gender.
In their analysis, the investigators looked at changes in suicide rates and the number of suicide deaths from 1990 to 2019 by gender and age group in the four income level regions defined by the World Bank. These categories include low-income, lower-middle–income, upper-middle–income, and high-income regions.
Number of deaths versus suicide rates
The number of deaths was 738,799 in 1990 and 758,696 in 2019.
The largest increase in deaths occurred in the lower-middle–income region, where the number of suicide deaths increased by 72,550 (from 232,340 to 304,890).
Population growth (300,942; 1,512.5%) was the major contributor to the overall increase in total number of suicide deaths. The second largest contributor was population age structure (189,512; 952.4%).
However, the effects of these factors were offset to a large extent by the effect of reduction in overall suicide rates (−470,556; −2,364.9%).
Interestingly, the overall suicide rate per 100,000 population decreased from 13.8 in 1990 to 9.8 in 2019.
The upper-middle–income region had the largest decline (−6.25 per 100,000), and the high-income region had the smallest decline (−1.77 per 100,000). Suicide rates also decreased in lower-middle–income (−2.51 per 100,000) and low-income regions (−1.96 per 100,000).
Reasons for the declines across all regions “have yet to be determined,” write the investigators. International efforts coordinated by the United Nations and World Health Organization likely contributed to these declines, they add.
‘Imbalance of resources’
The overall reduction in suicide rate of −4.01 per 100,000 “was mainly due” to reduction in age-specific suicide rates (−6.09; 152%), the researchers report.
This effect was partly offset, however, by the effect of the changing population age structure (2.08; −52%). In the high-income–level region, for example, the reduction in age-specific suicide rate (−3.83; 216.3%) was greater than the increase resulting from the change in population age structure (2.06; −116.3%).
“The overall contribution of population age structure mainly came from the 45-64 (565.2%) and 65+ (528.7%) age groups,” the investigators write. “This effect was observed in middle-income– as well as high-income–level regions, reflecting the global effect of population aging.”
They add that world populations will “experience pronounced and historically unprecedented aging in the coming decades” because of increasing life expectancy and declining fertility.
Men, but not women, had a notable increase in total number of suicide deaths. The significant effect of male population growth (177,128; 890.2% vs. 123,814; 622.3% for women) and male population age structure (120,186; 604.0% vs. 69,325; 348.4%) were the main factors that explained this increase, the investigators note.
However, from 1990 to 2019, the overall suicide rate per 100,000 men decreased from 16.6 to 13.5 (–3.09). The decline in overall suicide rate was even greater for women, from 11.0 to 6.1 (–4.91).
This finding was particularly notable in the upper-middle–income region (–8.12 women vs. –4.37 men per 100,000).
“This study highlighted the considerable imbalance of the resources in carrying out suicide prevention work, especially in low-income and middle-income countries,” the investigators write.
“It is time to revisit this situation to ensure that sufficient resources can be redeployed globally to meet the future challenges,” they add.
The study was funded by a Humanities and Social Sciences Prestigious Fellowship, which Dr. Yip received. He declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The overall global number of deaths by suicide increased by almost 20,000 during the past 30 years, new research shows.
The increase occurred despite a significant decrease in age-specific suicide rates from 1990 through 2019, according to data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.
Population growth, population aging, and changes in population age structure may explain the increase in number of suicide deaths, the investigators note.
“As suicide rates are highest among the elderly (70 years or above) for both genders in almost all regions of the world, the rapidly aging population globally will pose huge challenges for the reduction in the number of suicide deaths in the future,” write the researchers, led by Paul Siu Fai Yip, PhD, of the HKJC Center for Suicide Research and Prevention, University of Hong Kong, China.
The findings were published online Aug. 16 in Injury Prevention.
Global public health concern
Around the world, approximately 800,000 individuals die by suicide each year, while many others attempt suicide. Yet suicide has not received the same level of attention as other global public health concerns, such as HIV/AIDS and cancer, the investigators write.
They examined data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 to assess how demographic and epidemiologic factors contributed to the number of suicide deaths during the past 30 years.
The researchers also analyzed relationships between population growth, population age structure, income level, and gender- and age-specific suicide rates.
The Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 includes information from 204 countries about 369 diseases and injuries by age and gender. The dataset also includes population estimates for each year by location, age group, and gender.
In their analysis, the investigators looked at changes in suicide rates and the number of suicide deaths from 1990 to 2019 by gender and age group in the four income level regions defined by the World Bank. These categories include low-income, lower-middle–income, upper-middle–income, and high-income regions.
Number of deaths versus suicide rates
The number of deaths was 738,799 in 1990 and 758,696 in 2019.
The largest increase in deaths occurred in the lower-middle–income region, where the number of suicide deaths increased by 72,550 (from 232,340 to 304,890).
Population growth (300,942; 1,512.5%) was the major contributor to the overall increase in total number of suicide deaths. The second largest contributor was population age structure (189,512; 952.4%).
However, the effects of these factors were offset to a large extent by the effect of reduction in overall suicide rates (−470,556; −2,364.9%).
Interestingly, the overall suicide rate per 100,000 population decreased from 13.8 in 1990 to 9.8 in 2019.
The upper-middle–income region had the largest decline (−6.25 per 100,000), and the high-income region had the smallest decline (−1.77 per 100,000). Suicide rates also decreased in lower-middle–income (−2.51 per 100,000) and low-income regions (−1.96 per 100,000).
Reasons for the declines across all regions “have yet to be determined,” write the investigators. International efforts coordinated by the United Nations and World Health Organization likely contributed to these declines, they add.
‘Imbalance of resources’
The overall reduction in suicide rate of −4.01 per 100,000 “was mainly due” to reduction in age-specific suicide rates (−6.09; 152%), the researchers report.
This effect was partly offset, however, by the effect of the changing population age structure (2.08; −52%). In the high-income–level region, for example, the reduction in age-specific suicide rate (−3.83; 216.3%) was greater than the increase resulting from the change in population age structure (2.06; −116.3%).
“The overall contribution of population age structure mainly came from the 45-64 (565.2%) and 65+ (528.7%) age groups,” the investigators write. “This effect was observed in middle-income– as well as high-income–level regions, reflecting the global effect of population aging.”
They add that world populations will “experience pronounced and historically unprecedented aging in the coming decades” because of increasing life expectancy and declining fertility.
Men, but not women, had a notable increase in total number of suicide deaths. The significant effect of male population growth (177,128; 890.2% vs. 123,814; 622.3% for women) and male population age structure (120,186; 604.0% vs. 69,325; 348.4%) were the main factors that explained this increase, the investigators note.
However, from 1990 to 2019, the overall suicide rate per 100,000 men decreased from 16.6 to 13.5 (–3.09). The decline in overall suicide rate was even greater for women, from 11.0 to 6.1 (–4.91).
This finding was particularly notable in the upper-middle–income region (–8.12 women vs. –4.37 men per 100,000).
“This study highlighted the considerable imbalance of the resources in carrying out suicide prevention work, especially in low-income and middle-income countries,” the investigators write.
“It is time to revisit this situation to ensure that sufficient resources can be redeployed globally to meet the future challenges,” they add.
The study was funded by a Humanities and Social Sciences Prestigious Fellowship, which Dr. Yip received. He declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: Psoriasis September 2021
Several recent studies have evaluated that association between psoriasis and known comorbidities including cardiovascular disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and malignancy. Several recent studies have added to our understanding of the relationship between these conditions.
Using the largest database of hospitalized patients in the United States, Edgen et al found that hospitalization rates for patients with psoriasis are increasing. While the proportion of patients with psoriasis hospitalized with psoriasis as a primary diagnosis decreased about four-fold over a 20-year period (1999-2018), incidence of hospitalizations with any diagnosis of psoriasis has increased. Hospitalized psoriasis patients are increasingly more likely to have other comorbid conditions as during the study period the proportion of hospitalized psoriasis patients with a Charlson Comorbidity Index score of 3 or higher increased from 13.9% to 30.9%. Psoriasis severity, medication use, and reasons for hospitalization were not reported. The authors suggest that screening and management of comorbidities in the outpatient setting may help reduce preventable psoriasis hospitalizations.
Both NAFLD and cardiovascular disease are well-known psoriasis comorbidities, Gonzalez-Cantaro et al studied two cohorts of patients to better define the relationship between these two conditions. In a European cohort of 76 psoriasis patients and 76 control patients, psoriasis patients with NAFLD had a higher prevalence of subclinical atherosclerosis than both psoriasis patients without NAFLD (61% vs 23%) and age, sex, and BMI-matched controls with NAFLD (61% vs 32%). Psoriasis patients were also more likely that control patients to have insulin resistance, higher weight circumference, and dysplipidemia. Among 162 psoriasis patients who underwent PET and coronary CT angiography, higher hepatic FDG uptake (indicating NAFLD) was associated higher atherosclerotic disease burden. Importantly, both the NAFLD and CAD were subclinical in these patients. While the cross-sectional study design precludes any conclusions about causality, physicians should be aware that these two comorbidities are related. Lower waist circumference and greater physical activity were both associated with lower rates of NAFLD among patients with psoriasis, providing some guidance for counseling patients.
Several recent studies have found that cancer rates among patients with psoriasis are higher than what is observed in the general population. The association of psoriasis with lymphohematologic malignancies (LHM) has been controversial. A systematic review and meta-analysis of 25 observational studies including over 2.5 million subjects (Bellinato et al.) found a 1.55-fold increased risk of LHM in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. Strikingly, the risk of cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) was increased 6.22-fold, with more severe psoriasis being associated with the highest risk of CTCL. A causal relationship cannot be established from this type of studies, but the authors hypothesize that drugs used to treat psoriasis or the chronic T cell activation caused by active disease may contribute to the risk of LMH. Additionally, psoriasis and CTCL can share clinical features and some cases may be due to misdiagnosis. Interestingly, two psoriasis comorbities, diabetes and obesity, are also associated with an increased risk of LHM.
Early identification and management of comorbidities can help in reducing morbidity and mortality. With so many psoriasis treatments available, understanding how different therapies may impact comorbid conditions is important in helping dermatologists to choose the best therapy for each individual patient.
Several recent studies have evaluated that association between psoriasis and known comorbidities including cardiovascular disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and malignancy. Several recent studies have added to our understanding of the relationship between these conditions.
Using the largest database of hospitalized patients in the United States, Edgen et al found that hospitalization rates for patients with psoriasis are increasing. While the proportion of patients with psoriasis hospitalized with psoriasis as a primary diagnosis decreased about four-fold over a 20-year period (1999-2018), incidence of hospitalizations with any diagnosis of psoriasis has increased. Hospitalized psoriasis patients are increasingly more likely to have other comorbid conditions as during the study period the proportion of hospitalized psoriasis patients with a Charlson Comorbidity Index score of 3 or higher increased from 13.9% to 30.9%. Psoriasis severity, medication use, and reasons for hospitalization were not reported. The authors suggest that screening and management of comorbidities in the outpatient setting may help reduce preventable psoriasis hospitalizations.
Both NAFLD and cardiovascular disease are well-known psoriasis comorbidities, Gonzalez-Cantaro et al studied two cohorts of patients to better define the relationship between these two conditions. In a European cohort of 76 psoriasis patients and 76 control patients, psoriasis patients with NAFLD had a higher prevalence of subclinical atherosclerosis than both psoriasis patients without NAFLD (61% vs 23%) and age, sex, and BMI-matched controls with NAFLD (61% vs 32%). Psoriasis patients were also more likely that control patients to have insulin resistance, higher weight circumference, and dysplipidemia. Among 162 psoriasis patients who underwent PET and coronary CT angiography, higher hepatic FDG uptake (indicating NAFLD) was associated higher atherosclerotic disease burden. Importantly, both the NAFLD and CAD were subclinical in these patients. While the cross-sectional study design precludes any conclusions about causality, physicians should be aware that these two comorbidities are related. Lower waist circumference and greater physical activity were both associated with lower rates of NAFLD among patients with psoriasis, providing some guidance for counseling patients.
Several recent studies have found that cancer rates among patients with psoriasis are higher than what is observed in the general population. The association of psoriasis with lymphohematologic malignancies (LHM) has been controversial. A systematic review and meta-analysis of 25 observational studies including over 2.5 million subjects (Bellinato et al.) found a 1.55-fold increased risk of LHM in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. Strikingly, the risk of cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) was increased 6.22-fold, with more severe psoriasis being associated with the highest risk of CTCL. A causal relationship cannot be established from this type of studies, but the authors hypothesize that drugs used to treat psoriasis or the chronic T cell activation caused by active disease may contribute to the risk of LMH. Additionally, psoriasis and CTCL can share clinical features and some cases may be due to misdiagnosis. Interestingly, two psoriasis comorbities, diabetes and obesity, are also associated with an increased risk of LHM.
Early identification and management of comorbidities can help in reducing morbidity and mortality. With so many psoriasis treatments available, understanding how different therapies may impact comorbid conditions is important in helping dermatologists to choose the best therapy for each individual patient.
Several recent studies have evaluated that association between psoriasis and known comorbidities including cardiovascular disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and malignancy. Several recent studies have added to our understanding of the relationship between these conditions.
Using the largest database of hospitalized patients in the United States, Edgen et al found that hospitalization rates for patients with psoriasis are increasing. While the proportion of patients with psoriasis hospitalized with psoriasis as a primary diagnosis decreased about four-fold over a 20-year period (1999-2018), incidence of hospitalizations with any diagnosis of psoriasis has increased. Hospitalized psoriasis patients are increasingly more likely to have other comorbid conditions as during the study period the proportion of hospitalized psoriasis patients with a Charlson Comorbidity Index score of 3 or higher increased from 13.9% to 30.9%. Psoriasis severity, medication use, and reasons for hospitalization were not reported. The authors suggest that screening and management of comorbidities in the outpatient setting may help reduce preventable psoriasis hospitalizations.
Both NAFLD and cardiovascular disease are well-known psoriasis comorbidities, Gonzalez-Cantaro et al studied two cohorts of patients to better define the relationship between these two conditions. In a European cohort of 76 psoriasis patients and 76 control patients, psoriasis patients with NAFLD had a higher prevalence of subclinical atherosclerosis than both psoriasis patients without NAFLD (61% vs 23%) and age, sex, and BMI-matched controls with NAFLD (61% vs 32%). Psoriasis patients were also more likely that control patients to have insulin resistance, higher weight circumference, and dysplipidemia. Among 162 psoriasis patients who underwent PET and coronary CT angiography, higher hepatic FDG uptake (indicating NAFLD) was associated higher atherosclerotic disease burden. Importantly, both the NAFLD and CAD were subclinical in these patients. While the cross-sectional study design precludes any conclusions about causality, physicians should be aware that these two comorbidities are related. Lower waist circumference and greater physical activity were both associated with lower rates of NAFLD among patients with psoriasis, providing some guidance for counseling patients.
Several recent studies have found that cancer rates among patients with psoriasis are higher than what is observed in the general population. The association of psoriasis with lymphohematologic malignancies (LHM) has been controversial. A systematic review and meta-analysis of 25 observational studies including over 2.5 million subjects (Bellinato et al.) found a 1.55-fold increased risk of LHM in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. Strikingly, the risk of cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) was increased 6.22-fold, with more severe psoriasis being associated with the highest risk of CTCL. A causal relationship cannot be established from this type of studies, but the authors hypothesize that drugs used to treat psoriasis or the chronic T cell activation caused by active disease may contribute to the risk of LMH. Additionally, psoriasis and CTCL can share clinical features and some cases may be due to misdiagnosis. Interestingly, two psoriasis comorbities, diabetes and obesity, are also associated with an increased risk of LHM.
Early identification and management of comorbidities can help in reducing morbidity and mortality. With so many psoriasis treatments available, understanding how different therapies may impact comorbid conditions is important in helping dermatologists to choose the best therapy for each individual patient.







