User login
Prebiotic in development shows promise for reducing GERD symptoms
A prebiotic therapy in development significantly reduced the number of days per month that people with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) experienced heartburn.
The prebiotic treatment, maltosyl-isomalto-oligosaccharides (MIMO, ISOT-101), under development by ISOThrive, was also associated with reduced symptom severity and improved quality of life, John Selling, MD, chief medical officer at ISOThrive, said during the presentation of his study at the virtual Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2021.
ISOT-101 is a nondigestible, nonabsorbable prebiotic carbohydrate produced by bacterial fermentation of sucrose and maltose. It was “possibly a staple of the bacterial diet that was present in the human diet during the past 10,000 years,” Dr. Selling said. He is a clinical associate professor of medicine and gastroenterology at Stanford (Calif.) University.
The prebiotic, however, “has been absent in our diet for about 50 to 100 years, driven by changes in agriculture, food production, food preservation, and dietary preferences,” he added.
Acid suppression treatments, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), have long been a staple of treating GERD. However, about 40% of people taking PPIs still have symptoms, Dr. Selling said. He noted that there are concerns about the health risks associated with long-term PPI use.
A prebiotic could work because the distal esophageal microbiome in people with GERD “differs greatly” from that of healthy persons, Dr. Selling said. The prebiotic could help reduce an abnormal increase in gram-negative bacteria in these patients, for example. These bacterial strains express lipopolysaccharides on their outer cell membranes, which, in turn, alter cytokine signaling. This mechanism could lead to the hyperinflammatory state associated with GERD.
Dr. Selling and colleagues hypothesized that this treatment could help resolve GERD symptoms in two ways. The prebiotic could selectively feed the beneficial gram-positive bacteria in the distal esophagus, thereby helping to restore a healthy balance of bacteria. ISOT-101 could also produce bacteriocins that help kill the harmful gram-negative bacteria and control inflammation.
To assess the efficacy and tolerability of ISOT-101, Dr. Selling and colleagues plan to evaluate use of the agent in 110 people with GERD. The data presented at this year’s DDW are based on the first 44 participants to complete the study protocol.
Participants had to have active symptoms four or more days a week. They verbally reported symptoms to investigators and completed a daily ReQuest validated GERD symptom questionnaire.
After a week of baseline screening, participants consumed about a quarter teaspoon of ISOT-101 as the last substance swallowed before bed every night. The investigators asked participants to rate their GI symptoms, general well-being including any sleep disturbances, and quality of life on the Short Form 36 (SF-36) health survey. Participants also recorded use of any other medications during the 4-week study.
“I thought this was a very interesting study, as it proposes an alternative approach to manage patients with GERD,” Richa Shukla, MD, who was not affiliated with the research, said in an interview when asked to comment. “We see many patients with typical GERD symptoms who do not respond to PPI therapy, and perhaps considering an alternative cause and treatment may help with these patients.”
Dr. Shukla shared a couple of caveats. “This is a relatively small study, and it has not yet completed its enrollment target, so it will be helpful to see what the results are with the full study.” Also, it would be useful to know how many participants also took a PPI during the study, she said.
“Essentially, a lot remains unknown, but the study holds promise for patients,” added Dr. Shukla, assistant professor in the section of gastroenterology and hepatology at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston. “I think there is a lot of interest in the microbiome and how modulating it can impact inflammatory conditions.”
Key findings
The increase in heartburn-free days translated to more than eight additional days a month in which patients had no complaints of acid or heartburn. The difference from baseline was statistically significant (P < .001).
About two-thirds (66%) of participants were classified as “strong responders” to treatment, meaning they experienced an improvement of >50% in their ReQuest symptom scores over the 4 weeks. Again, the difference compared to baseline was statistically significant (P < .001).
The researchers also reported statistically significant improvements in quality-of-life indicators, such as well-being and sleep (P < .001).
The primary endpoint of the study was tolerability. The prebiotic was defined as tolerable if the ReQuest symptom scores and SF-36 scores remained constant or improved by the fourth week. ReQuest symptom scores improved for 89% of participants.
Two participants experienced nausea. No other adverse events related to ISOT-101 were reported. For five participants, ReQuest GI subscores worsened over time. For four participants, ReQuest total symptom scores worsened over time; that score represents a sum of GI and general well-being scores.
Unanswered questions
Inflammation in GERD is likely due to bacterial dysbiosis and acid-induced injury, Dr. Selling said.
If development of the prebiotic continues successfully, it could represent a paradigm shift in this clinical area, he said. “It suggests moving from acid reduction to also reducing dysbiosis as a treatment modality.”
But it remains unclear whether ISOT-101 would be indicated as monotherapy or for use in combination with other therapies for GERD.
Another unanswered question is whether the agent could be used to treat progressive disease. “This type of bacterial dysbiosis remains throughout the disease progression, from GERD to Barrett’s esophagus to esophageal adenocarcinoma,” Dr. Selling said.
The investigators reported that further controlled studies are forthcoming.
Dr. Selling is a co-founder and chief medical officer at ISOThrive. Dr. Shukla has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. David Johnson, MD, one of the authors of the abstract, is an advisor and contributor to Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A prebiotic therapy in development significantly reduced the number of days per month that people with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) experienced heartburn.
The prebiotic treatment, maltosyl-isomalto-oligosaccharides (MIMO, ISOT-101), under development by ISOThrive, was also associated with reduced symptom severity and improved quality of life, John Selling, MD, chief medical officer at ISOThrive, said during the presentation of his study at the virtual Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2021.
ISOT-101 is a nondigestible, nonabsorbable prebiotic carbohydrate produced by bacterial fermentation of sucrose and maltose. It was “possibly a staple of the bacterial diet that was present in the human diet during the past 10,000 years,” Dr. Selling said. He is a clinical associate professor of medicine and gastroenterology at Stanford (Calif.) University.
The prebiotic, however, “has been absent in our diet for about 50 to 100 years, driven by changes in agriculture, food production, food preservation, and dietary preferences,” he added.
Acid suppression treatments, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), have long been a staple of treating GERD. However, about 40% of people taking PPIs still have symptoms, Dr. Selling said. He noted that there are concerns about the health risks associated with long-term PPI use.
A prebiotic could work because the distal esophageal microbiome in people with GERD “differs greatly” from that of healthy persons, Dr. Selling said. The prebiotic could help reduce an abnormal increase in gram-negative bacteria in these patients, for example. These bacterial strains express lipopolysaccharides on their outer cell membranes, which, in turn, alter cytokine signaling. This mechanism could lead to the hyperinflammatory state associated with GERD.
Dr. Selling and colleagues hypothesized that this treatment could help resolve GERD symptoms in two ways. The prebiotic could selectively feed the beneficial gram-positive bacteria in the distal esophagus, thereby helping to restore a healthy balance of bacteria. ISOT-101 could also produce bacteriocins that help kill the harmful gram-negative bacteria and control inflammation.
To assess the efficacy and tolerability of ISOT-101, Dr. Selling and colleagues plan to evaluate use of the agent in 110 people with GERD. The data presented at this year’s DDW are based on the first 44 participants to complete the study protocol.
Participants had to have active symptoms four or more days a week. They verbally reported symptoms to investigators and completed a daily ReQuest validated GERD symptom questionnaire.
After a week of baseline screening, participants consumed about a quarter teaspoon of ISOT-101 as the last substance swallowed before bed every night. The investigators asked participants to rate their GI symptoms, general well-being including any sleep disturbances, and quality of life on the Short Form 36 (SF-36) health survey. Participants also recorded use of any other medications during the 4-week study.
“I thought this was a very interesting study, as it proposes an alternative approach to manage patients with GERD,” Richa Shukla, MD, who was not affiliated with the research, said in an interview when asked to comment. “We see many patients with typical GERD symptoms who do not respond to PPI therapy, and perhaps considering an alternative cause and treatment may help with these patients.”
Dr. Shukla shared a couple of caveats. “This is a relatively small study, and it has not yet completed its enrollment target, so it will be helpful to see what the results are with the full study.” Also, it would be useful to know how many participants also took a PPI during the study, she said.
“Essentially, a lot remains unknown, but the study holds promise for patients,” added Dr. Shukla, assistant professor in the section of gastroenterology and hepatology at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston. “I think there is a lot of interest in the microbiome and how modulating it can impact inflammatory conditions.”
Key findings
The increase in heartburn-free days translated to more than eight additional days a month in which patients had no complaints of acid or heartburn. The difference from baseline was statistically significant (P < .001).
About two-thirds (66%) of participants were classified as “strong responders” to treatment, meaning they experienced an improvement of >50% in their ReQuest symptom scores over the 4 weeks. Again, the difference compared to baseline was statistically significant (P < .001).
The researchers also reported statistically significant improvements in quality-of-life indicators, such as well-being and sleep (P < .001).
The primary endpoint of the study was tolerability. The prebiotic was defined as tolerable if the ReQuest symptom scores and SF-36 scores remained constant or improved by the fourth week. ReQuest symptom scores improved for 89% of participants.
Two participants experienced nausea. No other adverse events related to ISOT-101 were reported. For five participants, ReQuest GI subscores worsened over time. For four participants, ReQuest total symptom scores worsened over time; that score represents a sum of GI and general well-being scores.
Unanswered questions
Inflammation in GERD is likely due to bacterial dysbiosis and acid-induced injury, Dr. Selling said.
If development of the prebiotic continues successfully, it could represent a paradigm shift in this clinical area, he said. “It suggests moving from acid reduction to also reducing dysbiosis as a treatment modality.”
But it remains unclear whether ISOT-101 would be indicated as monotherapy or for use in combination with other therapies for GERD.
Another unanswered question is whether the agent could be used to treat progressive disease. “This type of bacterial dysbiosis remains throughout the disease progression, from GERD to Barrett’s esophagus to esophageal adenocarcinoma,” Dr. Selling said.
The investigators reported that further controlled studies are forthcoming.
Dr. Selling is a co-founder and chief medical officer at ISOThrive. Dr. Shukla has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. David Johnson, MD, one of the authors of the abstract, is an advisor and contributor to Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A prebiotic therapy in development significantly reduced the number of days per month that people with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) experienced heartburn.
The prebiotic treatment, maltosyl-isomalto-oligosaccharides (MIMO, ISOT-101), under development by ISOThrive, was also associated with reduced symptom severity and improved quality of life, John Selling, MD, chief medical officer at ISOThrive, said during the presentation of his study at the virtual Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2021.
ISOT-101 is a nondigestible, nonabsorbable prebiotic carbohydrate produced by bacterial fermentation of sucrose and maltose. It was “possibly a staple of the bacterial diet that was present in the human diet during the past 10,000 years,” Dr. Selling said. He is a clinical associate professor of medicine and gastroenterology at Stanford (Calif.) University.
The prebiotic, however, “has been absent in our diet for about 50 to 100 years, driven by changes in agriculture, food production, food preservation, and dietary preferences,” he added.
Acid suppression treatments, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), have long been a staple of treating GERD. However, about 40% of people taking PPIs still have symptoms, Dr. Selling said. He noted that there are concerns about the health risks associated with long-term PPI use.
A prebiotic could work because the distal esophageal microbiome in people with GERD “differs greatly” from that of healthy persons, Dr. Selling said. The prebiotic could help reduce an abnormal increase in gram-negative bacteria in these patients, for example. These bacterial strains express lipopolysaccharides on their outer cell membranes, which, in turn, alter cytokine signaling. This mechanism could lead to the hyperinflammatory state associated with GERD.
Dr. Selling and colleagues hypothesized that this treatment could help resolve GERD symptoms in two ways. The prebiotic could selectively feed the beneficial gram-positive bacteria in the distal esophagus, thereby helping to restore a healthy balance of bacteria. ISOT-101 could also produce bacteriocins that help kill the harmful gram-negative bacteria and control inflammation.
To assess the efficacy and tolerability of ISOT-101, Dr. Selling and colleagues plan to evaluate use of the agent in 110 people with GERD. The data presented at this year’s DDW are based on the first 44 participants to complete the study protocol.
Participants had to have active symptoms four or more days a week. They verbally reported symptoms to investigators and completed a daily ReQuest validated GERD symptom questionnaire.
After a week of baseline screening, participants consumed about a quarter teaspoon of ISOT-101 as the last substance swallowed before bed every night. The investigators asked participants to rate their GI symptoms, general well-being including any sleep disturbances, and quality of life on the Short Form 36 (SF-36) health survey. Participants also recorded use of any other medications during the 4-week study.
“I thought this was a very interesting study, as it proposes an alternative approach to manage patients with GERD,” Richa Shukla, MD, who was not affiliated with the research, said in an interview when asked to comment. “We see many patients with typical GERD symptoms who do not respond to PPI therapy, and perhaps considering an alternative cause and treatment may help with these patients.”
Dr. Shukla shared a couple of caveats. “This is a relatively small study, and it has not yet completed its enrollment target, so it will be helpful to see what the results are with the full study.” Also, it would be useful to know how many participants also took a PPI during the study, she said.
“Essentially, a lot remains unknown, but the study holds promise for patients,” added Dr. Shukla, assistant professor in the section of gastroenterology and hepatology at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston. “I think there is a lot of interest in the microbiome and how modulating it can impact inflammatory conditions.”
Key findings
The increase in heartburn-free days translated to more than eight additional days a month in which patients had no complaints of acid or heartburn. The difference from baseline was statistically significant (P < .001).
About two-thirds (66%) of participants were classified as “strong responders” to treatment, meaning they experienced an improvement of >50% in their ReQuest symptom scores over the 4 weeks. Again, the difference compared to baseline was statistically significant (P < .001).
The researchers also reported statistically significant improvements in quality-of-life indicators, such as well-being and sleep (P < .001).
The primary endpoint of the study was tolerability. The prebiotic was defined as tolerable if the ReQuest symptom scores and SF-36 scores remained constant or improved by the fourth week. ReQuest symptom scores improved for 89% of participants.
Two participants experienced nausea. No other adverse events related to ISOT-101 were reported. For five participants, ReQuest GI subscores worsened over time. For four participants, ReQuest total symptom scores worsened over time; that score represents a sum of GI and general well-being scores.
Unanswered questions
Inflammation in GERD is likely due to bacterial dysbiosis and acid-induced injury, Dr. Selling said.
If development of the prebiotic continues successfully, it could represent a paradigm shift in this clinical area, he said. “It suggests moving from acid reduction to also reducing dysbiosis as a treatment modality.”
But it remains unclear whether ISOT-101 would be indicated as monotherapy or for use in combination with other therapies for GERD.
Another unanswered question is whether the agent could be used to treat progressive disease. “This type of bacterial dysbiosis remains throughout the disease progression, from GERD to Barrett’s esophagus to esophageal adenocarcinoma,” Dr. Selling said.
The investigators reported that further controlled studies are forthcoming.
Dr. Selling is a co-founder and chief medical officer at ISOThrive. Dr. Shukla has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. David Johnson, MD, one of the authors of the abstract, is an advisor and contributor to Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Texas hospital workers sue over vaccine mandates
objecting to its policy of requiring employees and contractors to be vaccinated against COVID-19 or risk losing their jobs.
Plaintiffs include Jennifer Bridges, RN, a medical-surgical nurse at the hospital who has become the public face and voice of health care workers who object to mandatory vaccination, as well as Bob Nevens, the hospital’s director of corporate risk.
Mr. Nevens said the hospital was requiring him to be vaccinated even though he doesn’t treat patients and has been working from home for most of the past year.
“My civil rights and liberties have been trampled on,” he said in comments posted on an online petition. “My right to protect myself from unknown side effects of these vaccines has been placed below the optics of ‘leading medicine,’ “ he said.
Mr. Nevens says in his comments that he was fired on April 15, although the lawsuit says he is currently employed by the hospital’s corporate office.
The Texas attorney who filed the lawsuit, Jared Woodfill, is known to champion conservative causes. In March 2020, he challenged Harris County’s stay-at-home order, charging that it violated religious liberty. He was chairman of the Harris County Republican Party for more than a decade. His website says he is a frequent guest on the local Fox News affiliate.
The lawsuit hinges on a section of the federal law that authorizes emergency use of medical products – US Code 360bbb-3.
That law says that individuals to whom the product is administered should be informed “of the option to accept or refuse administration of the product, of the consequence, if any, of refusing administration of the product, and of the alternatives to the product that are available and of their benefits and risks.”
Legal experts are split as to what the provision means for vaccination mandates. Courts have not yet weighed in with their interpretations of the law.
The petition also repeats a popular antivaccination argument that likens requiring a vaccine approved for emergency use to the kind of medical experimentation performed by Nazi doctors on Jewish prisoners in concentration camps. It says forcing people to choose between an experimental vaccine and a job is a violation of the Nuremberg Code, which says that people must voluntarily and knowingly consent to participating in research.
The vaccines have already been tested in clinical trials. People who are getting them now are not part of those studies, though vaccine manufacturers, regulators, and safety experts are still watching closely for any sign of problems tied to the new shots.
It is true, however, that the emergency use authorization granted by the U.S. Food and Drug Administraiton sped up the process of getting the vaccines onto market. Vaccine manufacturers are currently completing the process of submitting documentation required for a full biologics license application, the mechanism the FDA uses for full approval.
Houston Methodist sent an email to employees in April notifying them that they had until June 7 to start the vaccination process or apply for a medical or religious exemption. Those who decide not to will be terminated.
Marc Boom, MD, the health care system’s president and CEO, has explained that the policy is in place to protect patients and that it was the first hospital in the United States to require it. Since then, other hospitals, including the University of Pennsylvania Health System, have required COVID vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
objecting to its policy of requiring employees and contractors to be vaccinated against COVID-19 or risk losing their jobs.
Plaintiffs include Jennifer Bridges, RN, a medical-surgical nurse at the hospital who has become the public face and voice of health care workers who object to mandatory vaccination, as well as Bob Nevens, the hospital’s director of corporate risk.
Mr. Nevens said the hospital was requiring him to be vaccinated even though he doesn’t treat patients and has been working from home for most of the past year.
“My civil rights and liberties have been trampled on,” he said in comments posted on an online petition. “My right to protect myself from unknown side effects of these vaccines has been placed below the optics of ‘leading medicine,’ “ he said.
Mr. Nevens says in his comments that he was fired on April 15, although the lawsuit says he is currently employed by the hospital’s corporate office.
The Texas attorney who filed the lawsuit, Jared Woodfill, is known to champion conservative causes. In March 2020, he challenged Harris County’s stay-at-home order, charging that it violated religious liberty. He was chairman of the Harris County Republican Party for more than a decade. His website says he is a frequent guest on the local Fox News affiliate.
The lawsuit hinges on a section of the federal law that authorizes emergency use of medical products – US Code 360bbb-3.
That law says that individuals to whom the product is administered should be informed “of the option to accept or refuse administration of the product, of the consequence, if any, of refusing administration of the product, and of the alternatives to the product that are available and of their benefits and risks.”
Legal experts are split as to what the provision means for vaccination mandates. Courts have not yet weighed in with their interpretations of the law.
The petition also repeats a popular antivaccination argument that likens requiring a vaccine approved for emergency use to the kind of medical experimentation performed by Nazi doctors on Jewish prisoners in concentration camps. It says forcing people to choose between an experimental vaccine and a job is a violation of the Nuremberg Code, which says that people must voluntarily and knowingly consent to participating in research.
The vaccines have already been tested in clinical trials. People who are getting them now are not part of those studies, though vaccine manufacturers, regulators, and safety experts are still watching closely for any sign of problems tied to the new shots.
It is true, however, that the emergency use authorization granted by the U.S. Food and Drug Administraiton sped up the process of getting the vaccines onto market. Vaccine manufacturers are currently completing the process of submitting documentation required for a full biologics license application, the mechanism the FDA uses for full approval.
Houston Methodist sent an email to employees in April notifying them that they had until June 7 to start the vaccination process or apply for a medical or religious exemption. Those who decide not to will be terminated.
Marc Boom, MD, the health care system’s president and CEO, has explained that the policy is in place to protect patients and that it was the first hospital in the United States to require it. Since then, other hospitals, including the University of Pennsylvania Health System, have required COVID vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
objecting to its policy of requiring employees and contractors to be vaccinated against COVID-19 or risk losing their jobs.
Plaintiffs include Jennifer Bridges, RN, a medical-surgical nurse at the hospital who has become the public face and voice of health care workers who object to mandatory vaccination, as well as Bob Nevens, the hospital’s director of corporate risk.
Mr. Nevens said the hospital was requiring him to be vaccinated even though he doesn’t treat patients and has been working from home for most of the past year.
“My civil rights and liberties have been trampled on,” he said in comments posted on an online petition. “My right to protect myself from unknown side effects of these vaccines has been placed below the optics of ‘leading medicine,’ “ he said.
Mr. Nevens says in his comments that he was fired on April 15, although the lawsuit says he is currently employed by the hospital’s corporate office.
The Texas attorney who filed the lawsuit, Jared Woodfill, is known to champion conservative causes. In March 2020, he challenged Harris County’s stay-at-home order, charging that it violated religious liberty. He was chairman of the Harris County Republican Party for more than a decade. His website says he is a frequent guest on the local Fox News affiliate.
The lawsuit hinges on a section of the federal law that authorizes emergency use of medical products – US Code 360bbb-3.
That law says that individuals to whom the product is administered should be informed “of the option to accept or refuse administration of the product, of the consequence, if any, of refusing administration of the product, and of the alternatives to the product that are available and of their benefits and risks.”
Legal experts are split as to what the provision means for vaccination mandates. Courts have not yet weighed in with their interpretations of the law.
The petition also repeats a popular antivaccination argument that likens requiring a vaccine approved for emergency use to the kind of medical experimentation performed by Nazi doctors on Jewish prisoners in concentration camps. It says forcing people to choose between an experimental vaccine and a job is a violation of the Nuremberg Code, which says that people must voluntarily and knowingly consent to participating in research.
The vaccines have already been tested in clinical trials. People who are getting them now are not part of those studies, though vaccine manufacturers, regulators, and safety experts are still watching closely for any sign of problems tied to the new shots.
It is true, however, that the emergency use authorization granted by the U.S. Food and Drug Administraiton sped up the process of getting the vaccines onto market. Vaccine manufacturers are currently completing the process of submitting documentation required for a full biologics license application, the mechanism the FDA uses for full approval.
Houston Methodist sent an email to employees in April notifying them that they had until June 7 to start the vaccination process or apply for a medical or religious exemption. Those who decide not to will be terminated.
Marc Boom, MD, the health care system’s president and CEO, has explained that the policy is in place to protect patients and that it was the first hospital in the United States to require it. Since then, other hospitals, including the University of Pennsylvania Health System, have required COVID vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
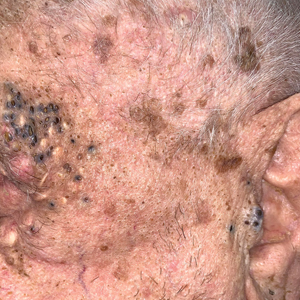
Periorbital and Tragal Cutaneous Lesions
The Diagnosis: Favre-Racouchot Syndrome
Favre-Racouchot syndrome, also known as nodular elastosis with cysts and comedones, is seen in approximately 6% of adults aged 40 to 60 years and predominantly is observed in White males.1 Typically, patients have a history of prolonged recreational or occupational UV exposure and tobacco use. The diagnosis can be made clinically; no biopsy is necessary. If a biopsy is performed, histologic findings typically consist of notable actinic elastosis, epidermal atrophy, and comedones. The differential diagnosis includes acne comedones, colloid milium, milia, chloracne, and trichoepithelioma.2 Associated conditions that have been found concurrently include cutis rhomboidalis nuchae, actinic keratosis, erosive pustular dermatosis, actinic granuloma, and basal and squamous cell carcinomas.2
The pathogenesis, while not fully understood, seems to involve a combination of chronic UV radiation exposure and heavy cigarette smoking that eventually leads to cutaneous atrophy and keratinization of the pilosebaceous follicles as well as the formation of comedones.2 Radiation therapy also has been implicated as a possible causative agent of Favre-Racouchot syndrome.1 Clinically, symmetric distribution of large black comedones over the temporal and periorbital areas is seen surrounded by distinct signs of UV-damaged skin, including wrinkles and atrophic skin.3 Although there seems to be a synergistic effect between cigarette smoking and chronic UV exposure, evidence favors smoking as the major cause of this condition,4,5 which causes striking visual changes but is a benign process. UV protection and smoking cessation are the most important factors for prevention and limiting progression.
Treatment consists of typical comedonal therapies such as tretinoin or comedone extraction. Procedural options in conjunction with medical therapy include dermabrasion or laser therapy. Newer studies have shown promising results for both CO2 laser treatment and plasma exeresis.6 Plasma exeresis is a noninvasive technique that causes ionization of atmospheric gas between the device and tissue, ultimately causing sublimation of the target tissue.7 It is important to carefully evaluate and follow up with these patients due to their history of extensive UV exposure. Both short-term and long-term follow-up is recommended due to high rates of reoccurrence within 10 to 12 months and the dangers of chronic UV exposure– related malignancies.6
- Lewis KG, Bercovitch L, Dill SW, et al. Acquired disorders of elastic tissue: part i. increased elastic tissue and solar elastotic syndromes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:1-21; quiz 22-24. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.03.013
- Patterson WM, Fox MD, Schwartz RA. Favre-Racouchot disease. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:167-169. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.01546.x
- Sonthalia S, Arora R, Chhabra N, et al. Favre-Racouchot syndrome. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5(suppl 2):S128-S129. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.146192
- Keough GC, Laws RA, Elston DM. Favre-Racouchot syndrome: a case for smokers’ comedones. Arch Dermatol. 1997;133:796-797. doi:10.1001/archderm.133.6.796
- Muto H, Takizawa Y. Dioxins in cigarette smoke. Arch Environ Health. 1989;44:171-174. doi:10.1080/00039896.1989.9935882
- Paganelli A, Mandel VD, Kaleci S, et al. Favre-Racouchot disease: systematic review and possible therapeutic strategies. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;33:32-41. doi:10.1111/jdv.15184
- Rossi E, Paganelli A, Mandel VD, et al. Plasma exeresis treatment for epidermoid cysts: a minimal scarring technique. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:1509-1515. doi:10.1097/dss.0000000000001604
The Diagnosis: Favre-Racouchot Syndrome
Favre-Racouchot syndrome, also known as nodular elastosis with cysts and comedones, is seen in approximately 6% of adults aged 40 to 60 years and predominantly is observed in White males.1 Typically, patients have a history of prolonged recreational or occupational UV exposure and tobacco use. The diagnosis can be made clinically; no biopsy is necessary. If a biopsy is performed, histologic findings typically consist of notable actinic elastosis, epidermal atrophy, and comedones. The differential diagnosis includes acne comedones, colloid milium, milia, chloracne, and trichoepithelioma.2 Associated conditions that have been found concurrently include cutis rhomboidalis nuchae, actinic keratosis, erosive pustular dermatosis, actinic granuloma, and basal and squamous cell carcinomas.2
The pathogenesis, while not fully understood, seems to involve a combination of chronic UV radiation exposure and heavy cigarette smoking that eventually leads to cutaneous atrophy and keratinization of the pilosebaceous follicles as well as the formation of comedones.2 Radiation therapy also has been implicated as a possible causative agent of Favre-Racouchot syndrome.1 Clinically, symmetric distribution of large black comedones over the temporal and periorbital areas is seen surrounded by distinct signs of UV-damaged skin, including wrinkles and atrophic skin.3 Although there seems to be a synergistic effect between cigarette smoking and chronic UV exposure, evidence favors smoking as the major cause of this condition,4,5 which causes striking visual changes but is a benign process. UV protection and smoking cessation are the most important factors for prevention and limiting progression.
Treatment consists of typical comedonal therapies such as tretinoin or comedone extraction. Procedural options in conjunction with medical therapy include dermabrasion or laser therapy. Newer studies have shown promising results for both CO2 laser treatment and plasma exeresis.6 Plasma exeresis is a noninvasive technique that causes ionization of atmospheric gas between the device and tissue, ultimately causing sublimation of the target tissue.7 It is important to carefully evaluate and follow up with these patients due to their history of extensive UV exposure. Both short-term and long-term follow-up is recommended due to high rates of reoccurrence within 10 to 12 months and the dangers of chronic UV exposure– related malignancies.6
The Diagnosis: Favre-Racouchot Syndrome
Favre-Racouchot syndrome, also known as nodular elastosis with cysts and comedones, is seen in approximately 6% of adults aged 40 to 60 years and predominantly is observed in White males.1 Typically, patients have a history of prolonged recreational or occupational UV exposure and tobacco use. The diagnosis can be made clinically; no biopsy is necessary. If a biopsy is performed, histologic findings typically consist of notable actinic elastosis, epidermal atrophy, and comedones. The differential diagnosis includes acne comedones, colloid milium, milia, chloracne, and trichoepithelioma.2 Associated conditions that have been found concurrently include cutis rhomboidalis nuchae, actinic keratosis, erosive pustular dermatosis, actinic granuloma, and basal and squamous cell carcinomas.2
The pathogenesis, while not fully understood, seems to involve a combination of chronic UV radiation exposure and heavy cigarette smoking that eventually leads to cutaneous atrophy and keratinization of the pilosebaceous follicles as well as the formation of comedones.2 Radiation therapy also has been implicated as a possible causative agent of Favre-Racouchot syndrome.1 Clinically, symmetric distribution of large black comedones over the temporal and periorbital areas is seen surrounded by distinct signs of UV-damaged skin, including wrinkles and atrophic skin.3 Although there seems to be a synergistic effect between cigarette smoking and chronic UV exposure, evidence favors smoking as the major cause of this condition,4,5 which causes striking visual changes but is a benign process. UV protection and smoking cessation are the most important factors for prevention and limiting progression.
Treatment consists of typical comedonal therapies such as tretinoin or comedone extraction. Procedural options in conjunction with medical therapy include dermabrasion or laser therapy. Newer studies have shown promising results for both CO2 laser treatment and plasma exeresis.6 Plasma exeresis is a noninvasive technique that causes ionization of atmospheric gas between the device and tissue, ultimately causing sublimation of the target tissue.7 It is important to carefully evaluate and follow up with these patients due to their history of extensive UV exposure. Both short-term and long-term follow-up is recommended due to high rates of reoccurrence within 10 to 12 months and the dangers of chronic UV exposure– related malignancies.6
- Lewis KG, Bercovitch L, Dill SW, et al. Acquired disorders of elastic tissue: part i. increased elastic tissue and solar elastotic syndromes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:1-21; quiz 22-24. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.03.013
- Patterson WM, Fox MD, Schwartz RA. Favre-Racouchot disease. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:167-169. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.01546.x
- Sonthalia S, Arora R, Chhabra N, et al. Favre-Racouchot syndrome. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5(suppl 2):S128-S129. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.146192
- Keough GC, Laws RA, Elston DM. Favre-Racouchot syndrome: a case for smokers’ comedones. Arch Dermatol. 1997;133:796-797. doi:10.1001/archderm.133.6.796
- Muto H, Takizawa Y. Dioxins in cigarette smoke. Arch Environ Health. 1989;44:171-174. doi:10.1080/00039896.1989.9935882
- Paganelli A, Mandel VD, Kaleci S, et al. Favre-Racouchot disease: systematic review and possible therapeutic strategies. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;33:32-41. doi:10.1111/jdv.15184
- Rossi E, Paganelli A, Mandel VD, et al. Plasma exeresis treatment for epidermoid cysts: a minimal scarring technique. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:1509-1515. doi:10.1097/dss.0000000000001604
- Lewis KG, Bercovitch L, Dill SW, et al. Acquired disorders of elastic tissue: part i. increased elastic tissue and solar elastotic syndromes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:1-21; quiz 22-24. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.03.013
- Patterson WM, Fox MD, Schwartz RA. Favre-Racouchot disease. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:167-169. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.01546.x
- Sonthalia S, Arora R, Chhabra N, et al. Favre-Racouchot syndrome. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5(suppl 2):S128-S129. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.146192
- Keough GC, Laws RA, Elston DM. Favre-Racouchot syndrome: a case for smokers’ comedones. Arch Dermatol. 1997;133:796-797. doi:10.1001/archderm.133.6.796
- Muto H, Takizawa Y. Dioxins in cigarette smoke. Arch Environ Health. 1989;44:171-174. doi:10.1080/00039896.1989.9935882
- Paganelli A, Mandel VD, Kaleci S, et al. Favre-Racouchot disease: systematic review and possible therapeutic strategies. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;33:32-41. doi:10.1111/jdv.15184
- Rossi E, Paganelli A, Mandel VD, et al. Plasma exeresis treatment for epidermoid cysts: a minimal scarring technique. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:1509-1515. doi:10.1097/dss.0000000000001604
A 91-year-old White man with no personal or family history of skin cancer presented to the dermatology clinic for a total-body skin examination. A 6×5-cm grouped cluster of open comedones in the periorbital region and on the left tragus as well as surrounding actinic damaged skin with coarse rhytides, dyschromia, and lentigines were seen. He had a history of excessive UV exposure and noted that the lesions had been present for approximately 10 years. They were asymptomatic and remained unchanged since their onset.
Concerts may be safe to attend with proper safety precautions: Study
Researchers in Spain have shared heartening results from the first randomized controlled trial to assess risk for COVID-19 transmission at an indoor live music concert.
The study, published May 27 in The Lancet Infectious Diseases, led by virologist Boris Revollo, MD, from the Germans Trias i Pujol University Hospital in Barcelona, included comprehensive safety measures.
It was conducted on Dec. 12, 2020, at a time when local travel restrictions were in place, indoor meetings were limited to six people, and vaccines were not yet available.
All 465 event attendees got same-day SARS-CoV-2 screening with antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic tests before they entered, wore masks throughout, and followed crowd-control measures in the well-ventilated venue, which can hold up to 900 people.
The control group consisted of 495 participants randomly assigned to go home instead of attending the concert after the screening.
None of the attendees tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test 8 days after the 5-hour event, but two in the control group did.
In fact, the study showed that the risk for infection was no higher among those at the concert than it was for those who lived in the same community and did not attend.
The Bayesian estimate for the incidence between the test and control groups was –0.15% (95% confidence Interval, –0.72 to 0.44).
“Our findings pave the way to reactivate cultural activities halted during COVID-19, which could have important sociocultural and economic implications,” the authors wrote.
All wore masks throughout
Among the comprehensive safety measures were that, in addition to testing, all attendees had their temperature checked before gaining access and were given an N95 face mask, which had to be worn at all times inside.
Hand sanitizer was provided in multiple locations, access doors remained open to allow fresh air to circulate, and the coat room was closed to prevent clustering.
There was no mandated distancing, people could sing and dance, and alcohol was available in a bar located in a separate room – and drinks were allowed only in that space.
Rosanna W Peeling, PhD, professor and chair of diagnostic research at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine in the United Kingdom, and David L. Heymann, MD, of the department of infectious disease epidemiology there, said in an accompanying commentary that there is a great need for studies like this one to help build evidence for a return to normal gatherings.
“So many countries don’t have any policy or any way of doing this because they don’t have the evidence,” Dr. Peeling said in an interview.
The study was well done and a strength was the testing 8 days later, which can be hard to do for similar events when people disperse to locations outside the community where the event or gathering was held, she said.
Study prompts additional questions
Dr. Peeling and Dr. Heymann wrote that the work raises questions such as whether triple-layered masks would have been sufficient. Or how does rapid antigen testing at the entrance compare with molecular screening within 72 hours of entering?
They noted that there are questions around whether existing rapid diagnostic tests are able to detect COVID-19 variants.
Dr. Peeling said that these kinds of results need to be shared and shared more quickly, “if we’re ever going to get out of this pandemic.”
Studies like this are also difficult, she noted, because they may involve non–health sector entities such as city governments and concert organizers working together with researchers.
In addition, the safety measures come at considerable expense and it’s unclear whether those could be employed routinely at such events.
“It’s not really sustainable at sports events with 20,000 people,” Dr. Peeling said.
Infectious disease expert William Schaffner, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., told this news organization that the study results “come a little late to the party.”
If this study had been done in today’s era with authorized vaccines, “it would have been a moot issue,” he said. “The mask is a barrier to transmission, but we now have a much more solid barrier we could put in place, which is vaccination.
“That said, it does reinforce the fact that classical mask wearing does really offer protection even in a crowded venue,” Dr. Schaffner said.
He added that the study was relatively small and he’d like to see it replicated in larger concerts or group gatherings.
Dr. Peeling and Dr. Heymann report no relevant financial relationships. A coauthor is an employee and stockholder of Primavera Sound, sponsor of the study. All other authors declare no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers in Spain have shared heartening results from the first randomized controlled trial to assess risk for COVID-19 transmission at an indoor live music concert.
The study, published May 27 in The Lancet Infectious Diseases, led by virologist Boris Revollo, MD, from the Germans Trias i Pujol University Hospital in Barcelona, included comprehensive safety measures.
It was conducted on Dec. 12, 2020, at a time when local travel restrictions were in place, indoor meetings were limited to six people, and vaccines were not yet available.
All 465 event attendees got same-day SARS-CoV-2 screening with antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic tests before they entered, wore masks throughout, and followed crowd-control measures in the well-ventilated venue, which can hold up to 900 people.
The control group consisted of 495 participants randomly assigned to go home instead of attending the concert after the screening.
None of the attendees tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test 8 days after the 5-hour event, but two in the control group did.
In fact, the study showed that the risk for infection was no higher among those at the concert than it was for those who lived in the same community and did not attend.
The Bayesian estimate for the incidence between the test and control groups was –0.15% (95% confidence Interval, –0.72 to 0.44).
“Our findings pave the way to reactivate cultural activities halted during COVID-19, which could have important sociocultural and economic implications,” the authors wrote.
All wore masks throughout
Among the comprehensive safety measures were that, in addition to testing, all attendees had their temperature checked before gaining access and were given an N95 face mask, which had to be worn at all times inside.
Hand sanitizer was provided in multiple locations, access doors remained open to allow fresh air to circulate, and the coat room was closed to prevent clustering.
There was no mandated distancing, people could sing and dance, and alcohol was available in a bar located in a separate room – and drinks were allowed only in that space.
Rosanna W Peeling, PhD, professor and chair of diagnostic research at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine in the United Kingdom, and David L. Heymann, MD, of the department of infectious disease epidemiology there, said in an accompanying commentary that there is a great need for studies like this one to help build evidence for a return to normal gatherings.
“So many countries don’t have any policy or any way of doing this because they don’t have the evidence,” Dr. Peeling said in an interview.
The study was well done and a strength was the testing 8 days later, which can be hard to do for similar events when people disperse to locations outside the community where the event or gathering was held, she said.
Study prompts additional questions
Dr. Peeling and Dr. Heymann wrote that the work raises questions such as whether triple-layered masks would have been sufficient. Or how does rapid antigen testing at the entrance compare with molecular screening within 72 hours of entering?
They noted that there are questions around whether existing rapid diagnostic tests are able to detect COVID-19 variants.
Dr. Peeling said that these kinds of results need to be shared and shared more quickly, “if we’re ever going to get out of this pandemic.”
Studies like this are also difficult, she noted, because they may involve non–health sector entities such as city governments and concert organizers working together with researchers.
In addition, the safety measures come at considerable expense and it’s unclear whether those could be employed routinely at such events.
“It’s not really sustainable at sports events with 20,000 people,” Dr. Peeling said.
Infectious disease expert William Schaffner, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., told this news organization that the study results “come a little late to the party.”
If this study had been done in today’s era with authorized vaccines, “it would have been a moot issue,” he said. “The mask is a barrier to transmission, but we now have a much more solid barrier we could put in place, which is vaccination.
“That said, it does reinforce the fact that classical mask wearing does really offer protection even in a crowded venue,” Dr. Schaffner said.
He added that the study was relatively small and he’d like to see it replicated in larger concerts or group gatherings.
Dr. Peeling and Dr. Heymann report no relevant financial relationships. A coauthor is an employee and stockholder of Primavera Sound, sponsor of the study. All other authors declare no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers in Spain have shared heartening results from the first randomized controlled trial to assess risk for COVID-19 transmission at an indoor live music concert.
The study, published May 27 in The Lancet Infectious Diseases, led by virologist Boris Revollo, MD, from the Germans Trias i Pujol University Hospital in Barcelona, included comprehensive safety measures.
It was conducted on Dec. 12, 2020, at a time when local travel restrictions were in place, indoor meetings were limited to six people, and vaccines were not yet available.
All 465 event attendees got same-day SARS-CoV-2 screening with antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic tests before they entered, wore masks throughout, and followed crowd-control measures in the well-ventilated venue, which can hold up to 900 people.
The control group consisted of 495 participants randomly assigned to go home instead of attending the concert after the screening.
None of the attendees tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test 8 days after the 5-hour event, but two in the control group did.
In fact, the study showed that the risk for infection was no higher among those at the concert than it was for those who lived in the same community and did not attend.
The Bayesian estimate for the incidence between the test and control groups was –0.15% (95% confidence Interval, –0.72 to 0.44).
“Our findings pave the way to reactivate cultural activities halted during COVID-19, which could have important sociocultural and economic implications,” the authors wrote.
All wore masks throughout
Among the comprehensive safety measures were that, in addition to testing, all attendees had their temperature checked before gaining access and were given an N95 face mask, which had to be worn at all times inside.
Hand sanitizer was provided in multiple locations, access doors remained open to allow fresh air to circulate, and the coat room was closed to prevent clustering.
There was no mandated distancing, people could sing and dance, and alcohol was available in a bar located in a separate room – and drinks were allowed only in that space.
Rosanna W Peeling, PhD, professor and chair of diagnostic research at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine in the United Kingdom, and David L. Heymann, MD, of the department of infectious disease epidemiology there, said in an accompanying commentary that there is a great need for studies like this one to help build evidence for a return to normal gatherings.
“So many countries don’t have any policy or any way of doing this because they don’t have the evidence,” Dr. Peeling said in an interview.
The study was well done and a strength was the testing 8 days later, which can be hard to do for similar events when people disperse to locations outside the community where the event or gathering was held, she said.
Study prompts additional questions
Dr. Peeling and Dr. Heymann wrote that the work raises questions such as whether triple-layered masks would have been sufficient. Or how does rapid antigen testing at the entrance compare with molecular screening within 72 hours of entering?
They noted that there are questions around whether existing rapid diagnostic tests are able to detect COVID-19 variants.
Dr. Peeling said that these kinds of results need to be shared and shared more quickly, “if we’re ever going to get out of this pandemic.”
Studies like this are also difficult, she noted, because they may involve non–health sector entities such as city governments and concert organizers working together with researchers.
In addition, the safety measures come at considerable expense and it’s unclear whether those could be employed routinely at such events.
“It’s not really sustainable at sports events with 20,000 people,” Dr. Peeling said.
Infectious disease expert William Schaffner, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., told this news organization that the study results “come a little late to the party.”
If this study had been done in today’s era with authorized vaccines, “it would have been a moot issue,” he said. “The mask is a barrier to transmission, but we now have a much more solid barrier we could put in place, which is vaccination.
“That said, it does reinforce the fact that classical mask wearing does really offer protection even in a crowded venue,” Dr. Schaffner said.
He added that the study was relatively small and he’d like to see it replicated in larger concerts or group gatherings.
Dr. Peeling and Dr. Heymann report no relevant financial relationships. A coauthor is an employee and stockholder of Primavera Sound, sponsor of the study. All other authors declare no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
GRAPPA refines recommendations on psoriatic disease treatment
The Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA) has included more drugs and data and is moving toward a slightly more stepped approach to treating some forms of psoriatic disease in the latest iteration of their recommendations.
“There’s been an explosion over the last few years in terms of the number of medications,” available to treat psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, Laura C. Coates, MBChB, PhD, said in an interview ahead of presenting the draft recommendations at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
“The good thing about having more drugs is you’ve got more choice, but actually it makes these recommendations even more important because it becomes more complicated to choose optimal treatment for individuals,” added Dr. Coates, a senior clinical research fellow at the University of Oxford (England).
“We’ve been waiting for a while now for the new GRAPPA recommendations,” Laure Gossec, MD, PhD, of Sorbonne University and Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital in Paris, said in a separate interview.
The last version of the guidelines was developed in 2015 and published in 2016, and since then there have been new data on Janus kinase inhibitors and interleukin-23 inhibitors, for example, which have now been incorporated into the updated recommendations alongside the old stalwarts of conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
“I think that we can see some similarities but also differences compared to the previous version of the recommendations,” Dr. Gossec said.
One similarity is that the recommendations retain their modular or domain-oriented approach, keeping the core way that clinicians can use the recommendations based on their patients’ presentations. So, they still cover the management of peripheral arthritis, axial disease, enthesitis, dactylitis, and skin and nail disease individually.
What’s different, however, is that the domain on comorbidities has been split into two to cover general comorbidities and to give more specific guidance on managing inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and uveitis, “both of which may not ‘strictly speaking’ be treated by rheumatologists or dermatologists, but are manifestations which can appear in psoriatic disease,” Dr. Gossec noted.
IBD and uveitis “are part of the whole spondyloarthritis syndrome and are genetically related,” Dr. Coates said in her interview. “A lot of the drugs have licenses in those particular areas. The evidence is much stronger for which medication you should choose if somebody has psoriatic arthritis and Crohn’s disease or psoriatic arthritis and uveitis,” she noted.
When it comes to the rest of the comorbidities, think “cardiovascular disease, liver disease, infections – all the ‘normal’ comorbidities,” she added, noting “that’s usually where there’s a lot less data” on which drug to use.
New overarching principle and position statements
The goal of the recommendations hasn’t really changed since the first iteration of the guidelines in 2009, Dr. Coates noted in her presentation. They are intended to provide clinicians with recommendations “based on the best available evidence” for the management of patients with psoriatic disease.
To that end, a through process was followed, starting with the setting of PICO (Patient/population/problem; intervention; comparison; outcome) questions followed by systematic literature searches, data extraction, and review that assess the quality of evidence and then grade it accordingly before using it to inform the recommendation statements.
There is a new overarching principle that says: “These recommendations, which include the most current data concerning the optimal assessment of and therapeutic approached to psoriatic arthritis, present contextual considerations to empower shared decision making.”
The other overarching principles remain the same as in the 2015 version, with “minor wording changes particularly around the comorbidities overarching principle,” Dr. Coates said.
Also new are two position statements. “One of them is specifically around biosimilars, because that’s been a big shift since 2015,” Dr. Coates said. “It has basic rules about what evidence there should be, what we should consider when we’re using them, and patient involvement and decision making.”
The second statement covers “similar advice on tapering or discontinuing therapy – what we do when people are doing really well, how we should stop or taper, and which drugs we should choose to stop along with shared decision making with patients.”
GRAPPA intentionally gives clinicians more freedom
While there may be data to show differences in efficacy and side effects between the various drugs cited in the recommendations, “GRAPPA makes the choice to not prioritize one drug over another,” Dr. Gossec said. This decision gives “a lot of freedom then to the physician to make the decision.”
One important change according to Dr. Gossec is that oral “NSAIDs have clearly been put back as first-line treatment, before going on to disease-modifying drugs for most of the musculoskeletal manifestations. She added that for skin manifestations, topical NSAIDs were recommended, but that NSAIDs were more recommended for IBD and uveitis of course.
“I feel that’s a big step towards more of a step-up approach,” Dr. Gossec said. “The old recommendations were not clear that you would precede an NSAID before moving on to a disease-modifying drug. So, I think that makes it a little bit more similar to the 2019 EULAR recommendations.” The use of csDMARDs such as methotrexate has also been “pushed up a notch” in peripheral arthritis, she said.
What’s next?
There are a few fine tunings still to be made before the final recommendations are published. They also have to be discussed at the meeting of the GRAPPA task force, which consists of rheumatologists, dermatologists, and patient representatives.
Besides the recommendations manuscript, there will be individual papers detailing the evidence underpinning the recommendations in each of the eight domains, Dr. Coates noted. Those “will look at relative efficacy in detail,” she said. “There will be a lot more discussion/evidence summary included” to help with drug selection.
“We also plan to have some case studies to illustrate how the recommendations can be used, similar to that included in the 2015 recommendations,” she added.
Paul Studenic, MD, PhD, of the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm and Medical University of Vienna, tweeted that the GRAPPA recommendations showed treatment “needs to be tailored to the patient” taking “comorbidities as well as the heterogeneity of features of the clinical presentation into account.”
He said in an interview: “The third edition of the GRAPPA is a huge collaborative effort.” The new overarching principle put the recommendations in the context of shared decision making and, he added, they emphasize an “integrated management plan taking not only ‘classical’-related manifestations like uveitis into account but [also] a spectrum of comorbidities and reproductive health.”
GRAPPA is a not-for-profit organization and receives funding from multiple pharmaceutical companies. Currently this includes AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, and Sun Pharma with Galapagos and Nordic Bioscience as Innovation Partners. Dr. Coates acknowledged receiving research funding, honoraria, speaker fees or all of these from most of the aforementioned companies.
Dr. Gossec has received research funding or other support from numerous pharmaceutical companies and is a member of GRAPPA and the task force that developed the EULAR guidelines on the pharmacological management of psoriatic arthritis.
Dr. Studenic had nothing to disclose.
The Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA) has included more drugs and data and is moving toward a slightly more stepped approach to treating some forms of psoriatic disease in the latest iteration of their recommendations.
“There’s been an explosion over the last few years in terms of the number of medications,” available to treat psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, Laura C. Coates, MBChB, PhD, said in an interview ahead of presenting the draft recommendations at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
“The good thing about having more drugs is you’ve got more choice, but actually it makes these recommendations even more important because it becomes more complicated to choose optimal treatment for individuals,” added Dr. Coates, a senior clinical research fellow at the University of Oxford (England).
“We’ve been waiting for a while now for the new GRAPPA recommendations,” Laure Gossec, MD, PhD, of Sorbonne University and Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital in Paris, said in a separate interview.
The last version of the guidelines was developed in 2015 and published in 2016, and since then there have been new data on Janus kinase inhibitors and interleukin-23 inhibitors, for example, which have now been incorporated into the updated recommendations alongside the old stalwarts of conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
“I think that we can see some similarities but also differences compared to the previous version of the recommendations,” Dr. Gossec said.
One similarity is that the recommendations retain their modular or domain-oriented approach, keeping the core way that clinicians can use the recommendations based on their patients’ presentations. So, they still cover the management of peripheral arthritis, axial disease, enthesitis, dactylitis, and skin and nail disease individually.
What’s different, however, is that the domain on comorbidities has been split into two to cover general comorbidities and to give more specific guidance on managing inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and uveitis, “both of which may not ‘strictly speaking’ be treated by rheumatologists or dermatologists, but are manifestations which can appear in psoriatic disease,” Dr. Gossec noted.
IBD and uveitis “are part of the whole spondyloarthritis syndrome and are genetically related,” Dr. Coates said in her interview. “A lot of the drugs have licenses in those particular areas. The evidence is much stronger for which medication you should choose if somebody has psoriatic arthritis and Crohn’s disease or psoriatic arthritis and uveitis,” she noted.
When it comes to the rest of the comorbidities, think “cardiovascular disease, liver disease, infections – all the ‘normal’ comorbidities,” she added, noting “that’s usually where there’s a lot less data” on which drug to use.
New overarching principle and position statements
The goal of the recommendations hasn’t really changed since the first iteration of the guidelines in 2009, Dr. Coates noted in her presentation. They are intended to provide clinicians with recommendations “based on the best available evidence” for the management of patients with psoriatic disease.
To that end, a through process was followed, starting with the setting of PICO (Patient/population/problem; intervention; comparison; outcome) questions followed by systematic literature searches, data extraction, and review that assess the quality of evidence and then grade it accordingly before using it to inform the recommendation statements.
There is a new overarching principle that says: “These recommendations, which include the most current data concerning the optimal assessment of and therapeutic approached to psoriatic arthritis, present contextual considerations to empower shared decision making.”
The other overarching principles remain the same as in the 2015 version, with “minor wording changes particularly around the comorbidities overarching principle,” Dr. Coates said.
Also new are two position statements. “One of them is specifically around biosimilars, because that’s been a big shift since 2015,” Dr. Coates said. “It has basic rules about what evidence there should be, what we should consider when we’re using them, and patient involvement and decision making.”
The second statement covers “similar advice on tapering or discontinuing therapy – what we do when people are doing really well, how we should stop or taper, and which drugs we should choose to stop along with shared decision making with patients.”
GRAPPA intentionally gives clinicians more freedom
While there may be data to show differences in efficacy and side effects between the various drugs cited in the recommendations, “GRAPPA makes the choice to not prioritize one drug over another,” Dr. Gossec said. This decision gives “a lot of freedom then to the physician to make the decision.”
One important change according to Dr. Gossec is that oral “NSAIDs have clearly been put back as first-line treatment, before going on to disease-modifying drugs for most of the musculoskeletal manifestations. She added that for skin manifestations, topical NSAIDs were recommended, but that NSAIDs were more recommended for IBD and uveitis of course.
“I feel that’s a big step towards more of a step-up approach,” Dr. Gossec said. “The old recommendations were not clear that you would precede an NSAID before moving on to a disease-modifying drug. So, I think that makes it a little bit more similar to the 2019 EULAR recommendations.” The use of csDMARDs such as methotrexate has also been “pushed up a notch” in peripheral arthritis, she said.
What’s next?
There are a few fine tunings still to be made before the final recommendations are published. They also have to be discussed at the meeting of the GRAPPA task force, which consists of rheumatologists, dermatologists, and patient representatives.
Besides the recommendations manuscript, there will be individual papers detailing the evidence underpinning the recommendations in each of the eight domains, Dr. Coates noted. Those “will look at relative efficacy in detail,” she said. “There will be a lot more discussion/evidence summary included” to help with drug selection.
“We also plan to have some case studies to illustrate how the recommendations can be used, similar to that included in the 2015 recommendations,” she added.
Paul Studenic, MD, PhD, of the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm and Medical University of Vienna, tweeted that the GRAPPA recommendations showed treatment “needs to be tailored to the patient” taking “comorbidities as well as the heterogeneity of features of the clinical presentation into account.”
He said in an interview: “The third edition of the GRAPPA is a huge collaborative effort.” The new overarching principle put the recommendations in the context of shared decision making and, he added, they emphasize an “integrated management plan taking not only ‘classical’-related manifestations like uveitis into account but [also] a spectrum of comorbidities and reproductive health.”
GRAPPA is a not-for-profit organization and receives funding from multiple pharmaceutical companies. Currently this includes AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, and Sun Pharma with Galapagos and Nordic Bioscience as Innovation Partners. Dr. Coates acknowledged receiving research funding, honoraria, speaker fees or all of these from most of the aforementioned companies.
Dr. Gossec has received research funding or other support from numerous pharmaceutical companies and is a member of GRAPPA and the task force that developed the EULAR guidelines on the pharmacological management of psoriatic arthritis.
Dr. Studenic had nothing to disclose.
The Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA) has included more drugs and data and is moving toward a slightly more stepped approach to treating some forms of psoriatic disease in the latest iteration of their recommendations.
“There’s been an explosion over the last few years in terms of the number of medications,” available to treat psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, Laura C. Coates, MBChB, PhD, said in an interview ahead of presenting the draft recommendations at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
“The good thing about having more drugs is you’ve got more choice, but actually it makes these recommendations even more important because it becomes more complicated to choose optimal treatment for individuals,” added Dr. Coates, a senior clinical research fellow at the University of Oxford (England).
“We’ve been waiting for a while now for the new GRAPPA recommendations,” Laure Gossec, MD, PhD, of Sorbonne University and Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital in Paris, said in a separate interview.
The last version of the guidelines was developed in 2015 and published in 2016, and since then there have been new data on Janus kinase inhibitors and interleukin-23 inhibitors, for example, which have now been incorporated into the updated recommendations alongside the old stalwarts of conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
“I think that we can see some similarities but also differences compared to the previous version of the recommendations,” Dr. Gossec said.
One similarity is that the recommendations retain their modular or domain-oriented approach, keeping the core way that clinicians can use the recommendations based on their patients’ presentations. So, they still cover the management of peripheral arthritis, axial disease, enthesitis, dactylitis, and skin and nail disease individually.
What’s different, however, is that the domain on comorbidities has been split into two to cover general comorbidities and to give more specific guidance on managing inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and uveitis, “both of which may not ‘strictly speaking’ be treated by rheumatologists or dermatologists, but are manifestations which can appear in psoriatic disease,” Dr. Gossec noted.
IBD and uveitis “are part of the whole spondyloarthritis syndrome and are genetically related,” Dr. Coates said in her interview. “A lot of the drugs have licenses in those particular areas. The evidence is much stronger for which medication you should choose if somebody has psoriatic arthritis and Crohn’s disease or psoriatic arthritis and uveitis,” she noted.
When it comes to the rest of the comorbidities, think “cardiovascular disease, liver disease, infections – all the ‘normal’ comorbidities,” she added, noting “that’s usually where there’s a lot less data” on which drug to use.
New overarching principle and position statements
The goal of the recommendations hasn’t really changed since the first iteration of the guidelines in 2009, Dr. Coates noted in her presentation. They are intended to provide clinicians with recommendations “based on the best available evidence” for the management of patients with psoriatic disease.
To that end, a through process was followed, starting with the setting of PICO (Patient/population/problem; intervention; comparison; outcome) questions followed by systematic literature searches, data extraction, and review that assess the quality of evidence and then grade it accordingly before using it to inform the recommendation statements.
There is a new overarching principle that says: “These recommendations, which include the most current data concerning the optimal assessment of and therapeutic approached to psoriatic arthritis, present contextual considerations to empower shared decision making.”
The other overarching principles remain the same as in the 2015 version, with “minor wording changes particularly around the comorbidities overarching principle,” Dr. Coates said.
Also new are two position statements. “One of them is specifically around biosimilars, because that’s been a big shift since 2015,” Dr. Coates said. “It has basic rules about what evidence there should be, what we should consider when we’re using them, and patient involvement and decision making.”
The second statement covers “similar advice on tapering or discontinuing therapy – what we do when people are doing really well, how we should stop or taper, and which drugs we should choose to stop along with shared decision making with patients.”
GRAPPA intentionally gives clinicians more freedom
While there may be data to show differences in efficacy and side effects between the various drugs cited in the recommendations, “GRAPPA makes the choice to not prioritize one drug over another,” Dr. Gossec said. This decision gives “a lot of freedom then to the physician to make the decision.”
One important change according to Dr. Gossec is that oral “NSAIDs have clearly been put back as first-line treatment, before going on to disease-modifying drugs for most of the musculoskeletal manifestations. She added that for skin manifestations, topical NSAIDs were recommended, but that NSAIDs were more recommended for IBD and uveitis of course.
“I feel that’s a big step towards more of a step-up approach,” Dr. Gossec said. “The old recommendations were not clear that you would precede an NSAID before moving on to a disease-modifying drug. So, I think that makes it a little bit more similar to the 2019 EULAR recommendations.” The use of csDMARDs such as methotrexate has also been “pushed up a notch” in peripheral arthritis, she said.
What’s next?
There are a few fine tunings still to be made before the final recommendations are published. They also have to be discussed at the meeting of the GRAPPA task force, which consists of rheumatologists, dermatologists, and patient representatives.
Besides the recommendations manuscript, there will be individual papers detailing the evidence underpinning the recommendations in each of the eight domains, Dr. Coates noted. Those “will look at relative efficacy in detail,” she said. “There will be a lot more discussion/evidence summary included” to help with drug selection.
“We also plan to have some case studies to illustrate how the recommendations can be used, similar to that included in the 2015 recommendations,” she added.
Paul Studenic, MD, PhD, of the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm and Medical University of Vienna, tweeted that the GRAPPA recommendations showed treatment “needs to be tailored to the patient” taking “comorbidities as well as the heterogeneity of features of the clinical presentation into account.”
He said in an interview: “The third edition of the GRAPPA is a huge collaborative effort.” The new overarching principle put the recommendations in the context of shared decision making and, he added, they emphasize an “integrated management plan taking not only ‘classical’-related manifestations like uveitis into account but [also] a spectrum of comorbidities and reproductive health.”
GRAPPA is a not-for-profit organization and receives funding from multiple pharmaceutical companies. Currently this includes AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, and Sun Pharma with Galapagos and Nordic Bioscience as Innovation Partners. Dr. Coates acknowledged receiving research funding, honoraria, speaker fees or all of these from most of the aforementioned companies.
Dr. Gossec has received research funding or other support from numerous pharmaceutical companies and is a member of GRAPPA and the task force that developed the EULAR guidelines on the pharmacological management of psoriatic arthritis.
Dr. Studenic had nothing to disclose.
FROM THE EULAR 2021 CONGRESS
Almost half of patients with migraine are reluctant to seek care
, new research shows. A survey of nearly 18,000 participants with migraine showed that 46% were reluctant to consult a physician about their condition. Among those who hesitated, 58% ultimately consulted a physician, but 42% did not.
Common reasons for failure to seek treatment included believing that migraine was not severe enough to warrant a consultation, worries about cost and health insurance, and concern that the health care professional would not take the disorder seriously.
This is the first study to query patients with migraine regarding whether and why they have hesitated to seek care, said coinvestigator Robert E. Shapiro, MD, PhD, professor of neurologic sciences and director of the division of headache medicine at the University of Vermont, Burlington. “Previous studies have noted differences in care seeking by demographic or other distinguishing characteristics but have not asked people with migraine whether they actually intended to seek or not seek such care,” he said.
Dr. Shapiro presented the findings at the American Headache Society’s 2021 annual meeting.
Delays prevent diagnosis and care
For patients with migraine, hesitating to consult a physician causes delays in, and sometimes prevents, receiving a diagnosis and appropriate care.
To assess the proportion of patients who hesitate to seek a consultation for migraine care, as well as reasons for doing so, the investigators examined data from the Observational Survey of the Epidemiology, Treatment, and Care of Migraine (OVERCOME) study. OVERCOME incorporated a prospective web-based survey that was administered to a representative sample of 41,925 individuals in the United States.
Eligible participants who completed the study’s baseline assessment had had at least one migraine attack in the previous year and either met criteria for migraine on the basis of a validated diagnostic screen or provided a self-report of a migraine diagnosis by a health care practitioner. In all, 39,494 participants reported whether they had hesitated to seek a consultation from a physician for migraine care. Of these, 17,951 were included in the analysis.
Among the 46% who hesitated to seek care, 58% ultimately sought migraine care, and 42% did not.
The investigators also examined sociodemographic characteristics and migraine-related data, including the number of monthly headache days and information regarding nausea, photophobia, and phonophobia.
Patient-reported outcomes included days with migraine-related disability during the past 3 months, treatment optimization, and the degree to which migraine limited regular activities. Investigators also examined participants’ health care use in the previous 12 months and reasons for hesitating to seek migraine care.
Reasons for hesitancy
A total of 17,920 participants provided reasons for hesitating to seek a migraine consultation. These included a desire to take care of migraine attacks on one’s own (45%), the belief that migraine would not be taken seriously (35%), the belief that the migraine attacks were not serious or painful enough (29%), inability to afford or unwillingness to spend money on care (29%), lack of or inadequate health insurance (21%), and fear of receiving a serious diagnosis (19%).
Reasons for hesitation differed between participants who ultimately sought a consultation with a physician and those who did not. Those who did not receive a consultation (n = 7,495) were more likely to want to take care of the migraine attacks on their own (48% vs. 43%) and to believe the attacks were not serious or painful enough (36% vs. 25%).
Participants who hesitated but later sought a consultation were more likely to report concerns that migraine would not be taken seriously (38% vs. 31%) and fear of receiving a serious diagnosis (22% vs. 15%).
Among those who did not seek a consultation versus those who did, a significantly higher proportion were women (76% vs. 73%; P < .001).
“This is an interesting finding, since prior studies have indicated that, overall, women with migraine are more likely to have consulted a doctor for it – and also more likely to have been diagnosed with it,” Dr. Shapiro said.
On the other hand, women were 30% more likely to visit emergency departments or urgent care clinics for migraine care than men, he noted.
“These findings suggest some women may be experiencing particular barriers to receiving successful consultation care and that they may persistently hesitate to seek it,” said Dr. Shapiro. He noted that these barriers might be financial or attitudinal.
“Women are reported to be less likely to receive treatment for pain conditions, and furthermore, stigma toward migraine in particular may limit its perceived seriousness,” he said.
‘Equitable access’ needed
Those with full-time employment were significantly more likely to seek a migraine consultation than were those who were not employed full time (46% vs. 42%; P < .001). Patients who sought care were more likely to have health insurance (87% vs. 78%; P < .001).
Having health insurance (odds ratio [OR], 1.99), having previously received a migraine diagnosis (OR, 2.71), and degree of disability (severe vs. none: OR, 2.76; moderate vs. none: OR, 2.04) were associated with increased likelihood of seeking a migraine consultation among those who initially hesitated. Other factors included being male (OR, 1.49), having nausea (OR, 1.15), or being employed full time (OR, 1.24).
“Taken together, our findings suggest consultation rates may be limited by financial barriers and pervasive attitudes that migraine is either not serious or is untreatable,” said Dr. Shapiro. Consistent with this hypothesis is the finding that individuals with migraine who had received an appropriate diagnosis and were therefore better informed about the condition were more likely to continue to seek care for it, he noted.
Because most outpatient medical encounters for migraine are with primary care practitioners, it may make sense to ensure that such clinicians are “well trained in diagnosing and treating common presentations of migraine,” Dr. Shapiro said. It is equally important to ensure “equitable access to health insurance to pay for these consultations,” he added.
‘Take migraine more seriously’
Commenting on the findings, Alan M. Rapoport, MD, clinical professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said the study was well designed.
Potential weaknesses include the fact that patients were required only to have one migraine attack per year and that not all were diagnosed by a headache specialist using ICHD-3 criteria.
Still, “online, validated, patient-reported data is quite acceptable,” said Dr. Rapoport, who was not involved in the research.
He noted that there is a clear message from the findings for all physicians who see patients with headache disorders: “You will increase the chance of patients consulting and continuing to consult when you make an accurate migraine diagnosis, take migraine more seriously, and understand the stigmas attached to it – and when there are reduced institutional barriers and costs of health care.”
The findings suggest that neurologists should strive to provide patients with ongoing care and medication, he added. In addition, there is a need for further education about the stigma associated with migraine and about how others view this disabling disease, Dr. Rapoport concluded.
The study was funded by Eli Lilly. Dr. Shapiro has consulted for Eli Lilly and Lundbeck. Dr. Rapoport has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows. A survey of nearly 18,000 participants with migraine showed that 46% were reluctant to consult a physician about their condition. Among those who hesitated, 58% ultimately consulted a physician, but 42% did not.
Common reasons for failure to seek treatment included believing that migraine was not severe enough to warrant a consultation, worries about cost and health insurance, and concern that the health care professional would not take the disorder seriously.
This is the first study to query patients with migraine regarding whether and why they have hesitated to seek care, said coinvestigator Robert E. Shapiro, MD, PhD, professor of neurologic sciences and director of the division of headache medicine at the University of Vermont, Burlington. “Previous studies have noted differences in care seeking by demographic or other distinguishing characteristics but have not asked people with migraine whether they actually intended to seek or not seek such care,” he said.
Dr. Shapiro presented the findings at the American Headache Society’s 2021 annual meeting.
Delays prevent diagnosis and care
For patients with migraine, hesitating to consult a physician causes delays in, and sometimes prevents, receiving a diagnosis and appropriate care.
To assess the proportion of patients who hesitate to seek a consultation for migraine care, as well as reasons for doing so, the investigators examined data from the Observational Survey of the Epidemiology, Treatment, and Care of Migraine (OVERCOME) study. OVERCOME incorporated a prospective web-based survey that was administered to a representative sample of 41,925 individuals in the United States.
Eligible participants who completed the study’s baseline assessment had had at least one migraine attack in the previous year and either met criteria for migraine on the basis of a validated diagnostic screen or provided a self-report of a migraine diagnosis by a health care practitioner. In all, 39,494 participants reported whether they had hesitated to seek a consultation from a physician for migraine care. Of these, 17,951 were included in the analysis.
Among the 46% who hesitated to seek care, 58% ultimately sought migraine care, and 42% did not.
The investigators also examined sociodemographic characteristics and migraine-related data, including the number of monthly headache days and information regarding nausea, photophobia, and phonophobia.
Patient-reported outcomes included days with migraine-related disability during the past 3 months, treatment optimization, and the degree to which migraine limited regular activities. Investigators also examined participants’ health care use in the previous 12 months and reasons for hesitating to seek migraine care.
Reasons for hesitancy
A total of 17,920 participants provided reasons for hesitating to seek a migraine consultation. These included a desire to take care of migraine attacks on one’s own (45%), the belief that migraine would not be taken seriously (35%), the belief that the migraine attacks were not serious or painful enough (29%), inability to afford or unwillingness to spend money on care (29%), lack of or inadequate health insurance (21%), and fear of receiving a serious diagnosis (19%).
Reasons for hesitation differed between participants who ultimately sought a consultation with a physician and those who did not. Those who did not receive a consultation (n = 7,495) were more likely to want to take care of the migraine attacks on their own (48% vs. 43%) and to believe the attacks were not serious or painful enough (36% vs. 25%).
Participants who hesitated but later sought a consultation were more likely to report concerns that migraine would not be taken seriously (38% vs. 31%) and fear of receiving a serious diagnosis (22% vs. 15%).
Among those who did not seek a consultation versus those who did, a significantly higher proportion were women (76% vs. 73%; P < .001).
“This is an interesting finding, since prior studies have indicated that, overall, women with migraine are more likely to have consulted a doctor for it – and also more likely to have been diagnosed with it,” Dr. Shapiro said.
On the other hand, women were 30% more likely to visit emergency departments or urgent care clinics for migraine care than men, he noted.
“These findings suggest some women may be experiencing particular barriers to receiving successful consultation care and that they may persistently hesitate to seek it,” said Dr. Shapiro. He noted that these barriers might be financial or attitudinal.
“Women are reported to be less likely to receive treatment for pain conditions, and furthermore, stigma toward migraine in particular may limit its perceived seriousness,” he said.
‘Equitable access’ needed
Those with full-time employment were significantly more likely to seek a migraine consultation than were those who were not employed full time (46% vs. 42%; P < .001). Patients who sought care were more likely to have health insurance (87% vs. 78%; P < .001).
Having health insurance (odds ratio [OR], 1.99), having previously received a migraine diagnosis (OR, 2.71), and degree of disability (severe vs. none: OR, 2.76; moderate vs. none: OR, 2.04) were associated with increased likelihood of seeking a migraine consultation among those who initially hesitated. Other factors included being male (OR, 1.49), having nausea (OR, 1.15), or being employed full time (OR, 1.24).
“Taken together, our findings suggest consultation rates may be limited by financial barriers and pervasive attitudes that migraine is either not serious or is untreatable,” said Dr. Shapiro. Consistent with this hypothesis is the finding that individuals with migraine who had received an appropriate diagnosis and were therefore better informed about the condition were more likely to continue to seek care for it, he noted.
Because most outpatient medical encounters for migraine are with primary care practitioners, it may make sense to ensure that such clinicians are “well trained in diagnosing and treating common presentations of migraine,” Dr. Shapiro said. It is equally important to ensure “equitable access to health insurance to pay for these consultations,” he added.
‘Take migraine more seriously’
Commenting on the findings, Alan M. Rapoport, MD, clinical professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said the study was well designed.
Potential weaknesses include the fact that patients were required only to have one migraine attack per year and that not all were diagnosed by a headache specialist using ICHD-3 criteria.
Still, “online, validated, patient-reported data is quite acceptable,” said Dr. Rapoport, who was not involved in the research.
He noted that there is a clear message from the findings for all physicians who see patients with headache disorders: “You will increase the chance of patients consulting and continuing to consult when you make an accurate migraine diagnosis, take migraine more seriously, and understand the stigmas attached to it – and when there are reduced institutional barriers and costs of health care.”
The findings suggest that neurologists should strive to provide patients with ongoing care and medication, he added. In addition, there is a need for further education about the stigma associated with migraine and about how others view this disabling disease, Dr. Rapoport concluded.
The study was funded by Eli Lilly. Dr. Shapiro has consulted for Eli Lilly and Lundbeck. Dr. Rapoport has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows. A survey of nearly 18,000 participants with migraine showed that 46% were reluctant to consult a physician about their condition. Among those who hesitated, 58% ultimately consulted a physician, but 42% did not.
Common reasons for failure to seek treatment included believing that migraine was not severe enough to warrant a consultation, worries about cost and health insurance, and concern that the health care professional would not take the disorder seriously.
This is the first study to query patients with migraine regarding whether and why they have hesitated to seek care, said coinvestigator Robert E. Shapiro, MD, PhD, professor of neurologic sciences and director of the division of headache medicine at the University of Vermont, Burlington. “Previous studies have noted differences in care seeking by demographic or other distinguishing characteristics but have not asked people with migraine whether they actually intended to seek or not seek such care,” he said.
Dr. Shapiro presented the findings at the American Headache Society’s 2021 annual meeting.
Delays prevent diagnosis and care
For patients with migraine, hesitating to consult a physician causes delays in, and sometimes prevents, receiving a diagnosis and appropriate care.
To assess the proportion of patients who hesitate to seek a consultation for migraine care, as well as reasons for doing so, the investigators examined data from the Observational Survey of the Epidemiology, Treatment, and Care of Migraine (OVERCOME) study. OVERCOME incorporated a prospective web-based survey that was administered to a representative sample of 41,925 individuals in the United States.
Eligible participants who completed the study’s baseline assessment had had at least one migraine attack in the previous year and either met criteria for migraine on the basis of a validated diagnostic screen or provided a self-report of a migraine diagnosis by a health care practitioner. In all, 39,494 participants reported whether they had hesitated to seek a consultation from a physician for migraine care. Of these, 17,951 were included in the analysis.
Among the 46% who hesitated to seek care, 58% ultimately sought migraine care, and 42% did not.
The investigators also examined sociodemographic characteristics and migraine-related data, including the number of monthly headache days and information regarding nausea, photophobia, and phonophobia.
Patient-reported outcomes included days with migraine-related disability during the past 3 months, treatment optimization, and the degree to which migraine limited regular activities. Investigators also examined participants’ health care use in the previous 12 months and reasons for hesitating to seek migraine care.
Reasons for hesitancy
A total of 17,920 participants provided reasons for hesitating to seek a migraine consultation. These included a desire to take care of migraine attacks on one’s own (45%), the belief that migraine would not be taken seriously (35%), the belief that the migraine attacks were not serious or painful enough (29%), inability to afford or unwillingness to spend money on care (29%), lack of or inadequate health insurance (21%), and fear of receiving a serious diagnosis (19%).
Reasons for hesitation differed between participants who ultimately sought a consultation with a physician and those who did not. Those who did not receive a consultation (n = 7,495) were more likely to want to take care of the migraine attacks on their own (48% vs. 43%) and to believe the attacks were not serious or painful enough (36% vs. 25%).
Participants who hesitated but later sought a consultation were more likely to report concerns that migraine would not be taken seriously (38% vs. 31%) and fear of receiving a serious diagnosis (22% vs. 15%).
Among those who did not seek a consultation versus those who did, a significantly higher proportion were women (76% vs. 73%; P < .001).
“This is an interesting finding, since prior studies have indicated that, overall, women with migraine are more likely to have consulted a doctor for it – and also more likely to have been diagnosed with it,” Dr. Shapiro said.
On the other hand, women were 30% more likely to visit emergency departments or urgent care clinics for migraine care than men, he noted.
“These findings suggest some women may be experiencing particular barriers to receiving successful consultation care and that they may persistently hesitate to seek it,” said Dr. Shapiro. He noted that these barriers might be financial or attitudinal.
“Women are reported to be less likely to receive treatment for pain conditions, and furthermore, stigma toward migraine in particular may limit its perceived seriousness,” he said.
‘Equitable access’ needed
Those with full-time employment were significantly more likely to seek a migraine consultation than were those who were not employed full time (46% vs. 42%; P < .001). Patients who sought care were more likely to have health insurance (87% vs. 78%; P < .001).
Having health insurance (odds ratio [OR], 1.99), having previously received a migraine diagnosis (OR, 2.71), and degree of disability (severe vs. none: OR, 2.76; moderate vs. none: OR, 2.04) were associated with increased likelihood of seeking a migraine consultation among those who initially hesitated. Other factors included being male (OR, 1.49), having nausea (OR, 1.15), or being employed full time (OR, 1.24).
“Taken together, our findings suggest consultation rates may be limited by financial barriers and pervasive attitudes that migraine is either not serious or is untreatable,” said Dr. Shapiro. Consistent with this hypothesis is the finding that individuals with migraine who had received an appropriate diagnosis and were therefore better informed about the condition were more likely to continue to seek care for it, he noted.
Because most outpatient medical encounters for migraine are with primary care practitioners, it may make sense to ensure that such clinicians are “well trained in diagnosing and treating common presentations of migraine,” Dr. Shapiro said. It is equally important to ensure “equitable access to health insurance to pay for these consultations,” he added.
‘Take migraine more seriously’
Commenting on the findings, Alan M. Rapoport, MD, clinical professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said the study was well designed.
Potential weaknesses include the fact that patients were required only to have one migraine attack per year and that not all were diagnosed by a headache specialist using ICHD-3 criteria.
Still, “online, validated, patient-reported data is quite acceptable,” said Dr. Rapoport, who was not involved in the research.
He noted that there is a clear message from the findings for all physicians who see patients with headache disorders: “You will increase the chance of patients consulting and continuing to consult when you make an accurate migraine diagnosis, take migraine more seriously, and understand the stigmas attached to it – and when there are reduced institutional barriers and costs of health care.”
The findings suggest that neurologists should strive to provide patients with ongoing care and medication, he added. In addition, there is a need for further education about the stigma associated with migraine and about how others view this disabling disease, Dr. Rapoport concluded.
The study was funded by Eli Lilly. Dr. Shapiro has consulted for Eli Lilly and Lundbeck. Dr. Rapoport has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHS 2021
CONCERT: Better QoL but not survival with cabazitaxel in metastatic HER2– breast cancer
For patients with HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer, first line chemotherapy with cabazitaxel (Jevtana) every 3 weeks offers efficacy comparable to that of once-weekly paclitaxel, but with lower risk for peripheral neuropathy and better patient-reported quality of life, investigators in the multicenter CONCERT trial found.
In an open-label clinical trial of 158 patients from 14 hospitals in the United Kingdom, there was no difference in the primary endpoint of progression-free survival (PFS) or a secondary overall survival endpoint between patients randomly assigned to initial chemotherapy with cabazitaxel every 3 weeks or weekly paclitaxel, reported Amit Bahl, MD, of University Hospital Bristol, England, and colleagues.
“Cabazitaxel is safe and well tolerated for metastatic breast cancer and requires fewer hospital visits than weekly paclitaxel, which is very important for patients and health care providers, but more so in the current situation,” he said in an oral abstract session at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting (Abstract 1008).
Cabazitaxel is currently approved in the United States and Europe in combination with prednisone for treatment of patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer previously treated with a docetaxel-containing treatment regimen. It is not currently approved for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer, but has been explored for this indication in clinical trials.
“In the metastatic setting, where patients continue on treatment pretty much indefinitely until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, the use of an every-3-week regimen could be attractive, because it means less visits for the patients, and it appears that this drug has lower toxicity in terms of peripheral neuropathy,” said breast cancer specialist Aditya Bardia, MD, MPH, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Bardia, of Mass General Cancer Center in Boston, commented on the study in an interview.
Although paclitaxel is commonly used as first-line chemotherapy for HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer, it is associated with only modest response rates, ranging from 21.5% to 53.7% and carries significant risk of peripheral neuropathy, Dr. Bahl and colleagues noted.
“There is an unmet need for an alternative first-line cytotoxic chemotherapy agent, and cabazitaxel is a taxoid agent which has showed promising results in phase 2 trial of metastatic breast cancer patients in the second-line setting, even those with taxane resistance,” he said.
Open-label trial
To see whether cabazitaxel could meet those requirements, the investigators conducted a phase 2 randomized trial in which patients with HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer not previously treated with cytotoxic chemotherapy were assigned, 79 in each arm, to receive cabazitaxel 25 mg/m2 every 3 weeks, or paclitaxel 80 mg/m2 weekly.
The median patient age was 56 years in the cabazitaxel group and 61 years in the paclitaxel group. Roughly two-thirds of patients in each arm had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 0, and the remainder had ECOG performance status 1.
In each arm, the median time on treatment was 15 weeks, but treatment delays and dose reductions were more common among patients on paclitaxel than cabazitaxel (61% vs. 39%, and 37% vs. 24%, respectively).
There were 149 PFS events at the time of the analysis. The median PFS with cabazitaxel was 6.7 months vs. 5.8 months with paclitaxel. This difference was not statistically significant. Median overall survival was 20.6 months in the cabazitaxel arm, vs. 18.2 months 20.0 months, respectively.
Similarly, there were no significant differences in either the overall response rates (42% vs. 37%), or time to response.
There were no complete responses with cabazitaxel vs. two (2.5%) with paclitaxel. The respective partial response rates were 41.8% vs. 34.2%.
In a subgroup analysis of PFS, there were no significant between-arm differences, except for an improved PFS in patients 65 and older with cabazitaxel (hazard ratio 0.45, 95% confidence interval, 0.25-0.80).
Quality of life favors cabazitaxel
Grade 3 or greater adverse events occurred in 42% of patients on cabazitaxel vs. 51% on paclitaxel. Diarrhea, febrile neutropenia, and nausea were the most common grade 3 or greater events in the cabazitaxel arm, whereas grade 3 or greater lung infection and peripheral neuropathy were more common with paclitaxel.
Sensory peripheral neuropathy of any grade occurred in 16% of patients assigned to cabazitaxel, compared with 54% assigned to paclitaxel. The respective rates of alopecia were 27% and 42%.
Over the course of treatment, the mean EuroQuol EQ-5D-5L single index utility score and visual analogue scale score were higher with cabazitaxel arm compared to paclitaxel, suggesting better patient quality of life with cabazitaxel.
In addition, throughout treatment patients in the cabazitaxel arm reported significantly better scores on The Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – Breast (FACT-B) breast cancer subscale, Dr. Bahl said.
Second-line may be better
ASCO invited discussant Marleen Kok, MD, PhD, from the Netherlands Cancer Institute in Amsterdam, pointed out that in the phase 2 GENEVIEVE trial comparing the efficacy and safety of cabazitaxel versus weekly paclitaxel as neoadjuvant treatment in patients with triple negative or luminal B/HER2 normal breast cancer the pathologic complete response rate with cabazitaxel was 1.2%, compared with 11% with paclitaxel.
“This GENEVIEVE trial, together with the CONCERT trial, suggests that there is not a big role for cabazitaxel to be used upfront before other taxanes,” she said.
However, in a phase 2 study of cabazitaxel as second-line therapy in patients with HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer who had previously been treated with taxanes, the overall response rate was 23%, “which is still of interest and importance for our patients,” she added.
Dr. Kok did not address quality of life differences between the regimens, however.
In a side note, Dr. Bardia said that “if there were an oral form of paclitaxel, that would certainly be very welcome, in that an oral drug is more convenient for patients, and would require fewer visits to the hospital.”
The CONCERT trial was funded by an investigator-sponsored study grant from Sanofi. Dr. Bahl disclosed honoraria and institutional research funding from Sanofi/Aventis and others, and travel expenses from Bayer and Roche. Dr. Kok disclosed a consulting or advisory role for Bristol Myers Squibb/Medarex, and institutional research funding from that company and others. Dr. Bardia disclosed a consulting or advisory role and research funding to his institution from multiple companies.
For patients with HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer, first line chemotherapy with cabazitaxel (Jevtana) every 3 weeks offers efficacy comparable to that of once-weekly paclitaxel, but with lower risk for peripheral neuropathy and better patient-reported quality of life, investigators in the multicenter CONCERT trial found.
In an open-label clinical trial of 158 patients from 14 hospitals in the United Kingdom, there was no difference in the primary endpoint of progression-free survival (PFS) or a secondary overall survival endpoint between patients randomly assigned to initial chemotherapy with cabazitaxel every 3 weeks or weekly paclitaxel, reported Amit Bahl, MD, of University Hospital Bristol, England, and colleagues.
“Cabazitaxel is safe and well tolerated for metastatic breast cancer and requires fewer hospital visits than weekly paclitaxel, which is very important for patients and health care providers, but more so in the current situation,” he said in an oral abstract session at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting (Abstract 1008).
Cabazitaxel is currently approved in the United States and Europe in combination with prednisone for treatment of patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer previously treated with a docetaxel-containing treatment regimen. It is not currently approved for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer, but has been explored for this indication in clinical trials.
“In the metastatic setting, where patients continue on treatment pretty much indefinitely until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, the use of an every-3-week regimen could be attractive, because it means less visits for the patients, and it appears that this drug has lower toxicity in terms of peripheral neuropathy,” said breast cancer specialist Aditya Bardia, MD, MPH, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Bardia, of Mass General Cancer Center in Boston, commented on the study in an interview.
Although paclitaxel is commonly used as first-line chemotherapy for HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer, it is associated with only modest response rates, ranging from 21.5% to 53.7% and carries significant risk of peripheral neuropathy, Dr. Bahl and colleagues noted.
“There is an unmet need for an alternative first-line cytotoxic chemotherapy agent, and cabazitaxel is a taxoid agent which has showed promising results in phase 2 trial of metastatic breast cancer patients in the second-line setting, even those with taxane resistance,” he said.
Open-label trial
To see whether cabazitaxel could meet those requirements, the investigators conducted a phase 2 randomized trial in which patients with HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer not previously treated with cytotoxic chemotherapy were assigned, 79 in each arm, to receive cabazitaxel 25 mg/m2 every 3 weeks, or paclitaxel 80 mg/m2 weekly.
The median patient age was 56 years in the cabazitaxel group and 61 years in the paclitaxel group. Roughly two-thirds of patients in each arm had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 0, and the remainder had ECOG performance status 1.
In each arm, the median time on treatment was 15 weeks, but treatment delays and dose reductions were more common among patients on paclitaxel than cabazitaxel (61% vs. 39%, and 37% vs. 24%, respectively).
There were 149 PFS events at the time of the analysis. The median PFS with cabazitaxel was 6.7 months vs. 5.8 months with paclitaxel. This difference was not statistically significant. Median overall survival was 20.6 months in the cabazitaxel arm, vs. 18.2 months 20.0 months, respectively.
Similarly, there were no significant differences in either the overall response rates (42% vs. 37%), or time to response.
There were no complete responses with cabazitaxel vs. two (2.5%) with paclitaxel. The respective partial response rates were 41.8% vs. 34.2%.
In a subgroup analysis of PFS, there were no significant between-arm differences, except for an improved PFS in patients 65 and older with cabazitaxel (hazard ratio 0.45, 95% confidence interval, 0.25-0.80).
Quality of life favors cabazitaxel
Grade 3 or greater adverse events occurred in 42% of patients on cabazitaxel vs. 51% on paclitaxel. Diarrhea, febrile neutropenia, and nausea were the most common grade 3 or greater events in the cabazitaxel arm, whereas grade 3 or greater lung infection and peripheral neuropathy were more common with paclitaxel.
Sensory peripheral neuropathy of any grade occurred in 16% of patients assigned to cabazitaxel, compared with 54% assigned to paclitaxel. The respective rates of alopecia were 27% and 42%.
Over the course of treatment, the mean EuroQuol EQ-5D-5L single index utility score and visual analogue scale score were higher with cabazitaxel arm compared to paclitaxel, suggesting better patient quality of life with cabazitaxel.
In addition, throughout treatment patients in the cabazitaxel arm reported significantly better scores on The Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – Breast (FACT-B) breast cancer subscale, Dr. Bahl said.
Second-line may be better
ASCO invited discussant Marleen Kok, MD, PhD, from the Netherlands Cancer Institute in Amsterdam, pointed out that in the phase 2 GENEVIEVE trial comparing the efficacy and safety of cabazitaxel versus weekly paclitaxel as neoadjuvant treatment in patients with triple negative or luminal B/HER2 normal breast cancer the pathologic complete response rate with cabazitaxel was 1.2%, compared with 11% with paclitaxel.
“This GENEVIEVE trial, together with the CONCERT trial, suggests that there is not a big role for cabazitaxel to be used upfront before other taxanes,” she said.
However, in a phase 2 study of cabazitaxel as second-line therapy in patients with HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer who had previously been treated with taxanes, the overall response rate was 23%, “which is still of interest and importance for our patients,” she added.
Dr. Kok did not address quality of life differences between the regimens, however.
In a side note, Dr. Bardia said that “if there were an oral form of paclitaxel, that would certainly be very welcome, in that an oral drug is more convenient for patients, and would require fewer visits to the hospital.”
The CONCERT trial was funded by an investigator-sponsored study grant from Sanofi. Dr. Bahl disclosed honoraria and institutional research funding from Sanofi/Aventis and others, and travel expenses from Bayer and Roche. Dr. Kok disclosed a consulting or advisory role for Bristol Myers Squibb/Medarex, and institutional research funding from that company and others. Dr. Bardia disclosed a consulting or advisory role and research funding to his institution from multiple companies.
For patients with HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer, first line chemotherapy with cabazitaxel (Jevtana) every 3 weeks offers efficacy comparable to that of once-weekly paclitaxel, but with lower risk for peripheral neuropathy and better patient-reported quality of life, investigators in the multicenter CONCERT trial found.
In an open-label clinical trial of 158 patients from 14 hospitals in the United Kingdom, there was no difference in the primary endpoint of progression-free survival (PFS) or a secondary overall survival endpoint between patients randomly assigned to initial chemotherapy with cabazitaxel every 3 weeks or weekly paclitaxel, reported Amit Bahl, MD, of University Hospital Bristol, England, and colleagues.
“Cabazitaxel is safe and well tolerated for metastatic breast cancer and requires fewer hospital visits than weekly paclitaxel, which is very important for patients and health care providers, but more so in the current situation,” he said in an oral abstract session at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting (Abstract 1008).
Cabazitaxel is currently approved in the United States and Europe in combination with prednisone for treatment of patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer previously treated with a docetaxel-containing treatment regimen. It is not currently approved for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer, but has been explored for this indication in clinical trials.
“In the metastatic setting, where patients continue on treatment pretty much indefinitely until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, the use of an every-3-week regimen could be attractive, because it means less visits for the patients, and it appears that this drug has lower toxicity in terms of peripheral neuropathy,” said breast cancer specialist Aditya Bardia, MD, MPH, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Bardia, of Mass General Cancer Center in Boston, commented on the study in an interview.
Although paclitaxel is commonly used as first-line chemotherapy for HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer, it is associated with only modest response rates, ranging from 21.5% to 53.7% and carries significant risk of peripheral neuropathy, Dr. Bahl and colleagues noted.
“There is an unmet need for an alternative first-line cytotoxic chemotherapy agent, and cabazitaxel is a taxoid agent which has showed promising results in phase 2 trial of metastatic breast cancer patients in the second-line setting, even those with taxane resistance,” he said.
Open-label trial
To see whether cabazitaxel could meet those requirements, the investigators conducted a phase 2 randomized trial in which patients with HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer not previously treated with cytotoxic chemotherapy were assigned, 79 in each arm, to receive cabazitaxel 25 mg/m2 every 3 weeks, or paclitaxel 80 mg/m2 weekly.
The median patient age was 56 years in the cabazitaxel group and 61 years in the paclitaxel group. Roughly two-thirds of patients in each arm had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 0, and the remainder had ECOG performance status 1.
In each arm, the median time on treatment was 15 weeks, but treatment delays and dose reductions were more common among patients on paclitaxel than cabazitaxel (61% vs. 39%, and 37% vs. 24%, respectively).
There were 149 PFS events at the time of the analysis. The median PFS with cabazitaxel was 6.7 months vs. 5.8 months with paclitaxel. This difference was not statistically significant. Median overall survival was 20.6 months in the cabazitaxel arm, vs. 18.2 months 20.0 months, respectively.
Similarly, there were no significant differences in either the overall response rates (42% vs. 37%), or time to response.
There were no complete responses with cabazitaxel vs. two (2.5%) with paclitaxel. The respective partial response rates were 41.8% vs. 34.2%.
In a subgroup analysis of PFS, there were no significant between-arm differences, except for an improved PFS in patients 65 and older with cabazitaxel (hazard ratio 0.45, 95% confidence interval, 0.25-0.80).
Quality of life favors cabazitaxel
Grade 3 or greater adverse events occurred in 42% of patients on cabazitaxel vs. 51% on paclitaxel. Diarrhea, febrile neutropenia, and nausea were the most common grade 3 or greater events in the cabazitaxel arm, whereas grade 3 or greater lung infection and peripheral neuropathy were more common with paclitaxel.
Sensory peripheral neuropathy of any grade occurred in 16% of patients assigned to cabazitaxel, compared with 54% assigned to paclitaxel. The respective rates of alopecia were 27% and 42%.
Over the course of treatment, the mean EuroQuol EQ-5D-5L single index utility score and visual analogue scale score were higher with cabazitaxel arm compared to paclitaxel, suggesting better patient quality of life with cabazitaxel.
In addition, throughout treatment patients in the cabazitaxel arm reported significantly better scores on The Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – Breast (FACT-B) breast cancer subscale, Dr. Bahl said.
Second-line may be better
ASCO invited discussant Marleen Kok, MD, PhD, from the Netherlands Cancer Institute in Amsterdam, pointed out that in the phase 2 GENEVIEVE trial comparing the efficacy and safety of cabazitaxel versus weekly paclitaxel as neoadjuvant treatment in patients with triple negative or luminal B/HER2 normal breast cancer the pathologic complete response rate with cabazitaxel was 1.2%, compared with 11% with paclitaxel.
“This GENEVIEVE trial, together with the CONCERT trial, suggests that there is not a big role for cabazitaxel to be used upfront before other taxanes,” she said.
However, in a phase 2 study of cabazitaxel as second-line therapy in patients with HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer who had previously been treated with taxanes, the overall response rate was 23%, “which is still of interest and importance for our patients,” she added.
Dr. Kok did not address quality of life differences between the regimens, however.
In a side note, Dr. Bardia said that “if there were an oral form of paclitaxel, that would certainly be very welcome, in that an oral drug is more convenient for patients, and would require fewer visits to the hospital.”
The CONCERT trial was funded by an investigator-sponsored study grant from Sanofi. Dr. Bahl disclosed honoraria and institutional research funding from Sanofi/Aventis and others, and travel expenses from Bayer and Roche. Dr. Kok disclosed a consulting or advisory role for Bristol Myers Squibb/Medarex, and institutional research funding from that company and others. Dr. Bardia disclosed a consulting or advisory role and research funding to his institution from multiple companies.
FROM ASCO 2021
The doctor house: What to know in 2021
The concept of home ownership has changed for this generation, not only in the logistics of the best way to do it, but also in the desire and demand for owning versus renting. According to the Penn Institute for Urban Research, the U.S. homeownership rate is now at 63.7%, the lowest in 48 years. “Homeownership rates have declined for all demographic age groups. Since 2006, the number of households who own their home in the United States has decreased by 674,000 while the number of renters has increased by over 8 million.”1
But isn’t owning your own home the American dream? Isn’t it a great investment? If we’re looking strictly at the monthly payment numbers, traditionally paying a mortgage is cheaper than paying rent for the same-size home. That became even more true as home prices dropped in 2007-2008 and as interest rates also dropped over the last several years. Then there’s the age-old concept of “building equity” or “throwing away money on rent.” As a financial planner, I get asked all the time about a home as an investment. It certainly can be, like any investment, if you buy and sell at the right time. But something is only an investment if it grows, and you can’t predict if you’re going to buy and sell your house at the right time. The median price of an existing home sold in March 2021 was $329,100. That’s a 17.2% increase from March 2020. Times are certainly crazy right now in the real estate market.
What many people don’t think about are the other costs, and not just financial costs. Today’s generation is more aware of the added stress and burden of maintaining a home and the money you can sink into it for maintenance, let alone remodeling. Then of course there’s the mortgage interest, property taxes, and insurance that you won’t have with a rental. Lastly, the biggest reason today’s generation is choosing to rent more and more is the flexibility. They want to be more mobile, able to get up and move without having to worry about listing, selling, and possibly owing more than the house is worth, and being stuck. We saw this with many residents that bought a home during residency and then tried to sell when they landed their first job, only to find out they owed more than it was worth because of the real estate market collapse of 2008. Approximately 50% of physicians will leave their first job within 1-3 years, so it’s a gamble that you’ll be able to sell your house when you want to for the price you need.
But what are the benefits of buying? First, there is the age-old argument of building equity. If you stay in your house long enough, and plan to sell it when you retire and downsize, it can definitely be an investment. If you keep a mortgage long enough, eventually you’ll pay it off, and have no payment. Mortgage interest is also tax-deductible. Lastly, there are the intangibles – like being able to put down roots, build a community, and have the ability to remodel and customize your home, a feature not usually available when renting.
Now that I’ve effectively talked you out and back in again, what’s the best way to go about buying a house in today’s crazy market? We’ve seen houses list and sell within a day and get multiple offers well over asking price. It’s a very difficult time to buy, but there are ways to make it easier. First, be clear on what you want in a house, especially location. There’s nothing worse than buyer’s remorse in your primary residence, and that happens more these days when people have to quickly make a decision. Find a good, fee-based financial planner to help you decide how much house fits in your budget and your long-term goals. You’d be surprised how easily we can talk ourselves into paying much more than we had originally decided. Use your financial planner to help avoid emotions getting involved and creeping up your price (especially when multiple offers are involved). A good rule of thumb is for a housing payment to be no more than 33% of your take-home income. This includes principal, interest, and taxes. Or, many planners will use the “2x income” rule of thumb. So if you make $300,000, don’t go over $600,000. Although with today’s low interest rates, there is some more wiggle room on that. Next, get a good referral from someone you trust in looking for a realtor. Real estate is a commission-based job and can have some potential conflicts of interest, so getting a recommendation can help. Or, there are realtors who will work for a flat fee, regardless of how much you pay for a house. That can help reduce the conflict.
You made the offer, you beat out the other bids, and you’re getting a house! How are you paying for it? Hopefully, you already got preapproved. This means finding a good, reputable mortgage professional. Get referrals, shop around, and take your time. Get multiple quotes before you start the underwriting process. They shouldn’t have to pull your credit to give you a fairly accurate estimate of what interest rate you’ll qualify for. Usually, they will give you fixed and variable interest quotes. I normally recommend fixed interest. Because interest rates are so low right now, they’re only going to go up in the future, and if you have a variable rate loan, your payment will go up as interest rates rise.
Is a physician loan a good idea? Depending on your circumstance, it can often be a good deal. Most new attendings don’t have cash saved up for a down payment, and these often don’t require one. And the other big benefit is that they won’t consider your student loan payments when calculating your debt-to-income ratio. Mortgage lenders will look at how much other debt you have when determining an approval. And a conventional mortgage will take your student loan payments into consideration, which means you’ll qualify for a much lower payment and purchase price. In my experience, you want a credit score of around 700 or higher to qualify for these types of loans. The only downside of a physician mortgage is the rates are slightly higher. I encourage you to start the application process early; they’re taking upward of 90 days lately.
As the mortgage is being processed, you’ll have an inspection and appraisal, and as long as those are all favorable, you’re in! Now, should you take any surplus income each month and pay extra on your mortgage to pay it down sooner, or invest it? Everyone’s situation is different, but a good rule of thumb is to look at interest rates on the debt you want to pay off versus expected rate of return on the potential investment. For example, if you have extra money, should you invest it in an SP500 index fund that historically gets 8%-12% per year, or put it on the principal of your mortgage that has an interest rate of 3%? Assuming no other factors or goals, and you just want the best bang for your buck, my money would go toward the investment getting 8%-12% over saving 3% on my mortgage.
Take your time, do your research, and find good professionals. There’s no right answer for everyone, but there are certainly some good practices when walking through the first home decision. Here at FinancialMD, we only work with physicians, and we’re happy to chat if you want some guidance on this. Send me an email and subscribe to our weekly Didactic Minute videos on YouTube for more financial tips for young physicians. Good luck!
Mr. Solitro is a financial planner and CEO of FinancialMD. He has no other conflicts of interest.
Investment advisory services offered through FinancialMD, a registered investment adviser. Registration as an investment adviser does not imply a certain level of skill or training. This article is provided for informational purposes only and nothing contained herein should be construed as a solicitation to buy or sell any products. Advisory services are offered only to clients and prospective clients in places where FinancialMD and its investment adviser representatives are registered or exempt from registration. Investing involves the risk of loss of principal. Past performance is no guarantee of future performance and no investment strategy can guarantee a profit or protect against loss.
This article was updated June 8, 2021.
Reference
1. Wachter S and Acolin A. Owning or Renting in the US: Shifting Dynamics of the Housing Market. Penn Institute for Urban Research. 2016 May.
The concept of home ownership has changed for this generation, not only in the logistics of the best way to do it, but also in the desire and demand for owning versus renting. According to the Penn Institute for Urban Research, the U.S. homeownership rate is now at 63.7%, the lowest in 48 years. “Homeownership rates have declined for all demographic age groups. Since 2006, the number of households who own their home in the United States has decreased by 674,000 while the number of renters has increased by over 8 million.”1
But isn’t owning your own home the American dream? Isn’t it a great investment? If we’re looking strictly at the monthly payment numbers, traditionally paying a mortgage is cheaper than paying rent for the same-size home. That became even more true as home prices dropped in 2007-2008 and as interest rates also dropped over the last several years. Then there’s the age-old concept of “building equity” or “throwing away money on rent.” As a financial planner, I get asked all the time about a home as an investment. It certainly can be, like any investment, if you buy and sell at the right time. But something is only an investment if it grows, and you can’t predict if you’re going to buy and sell your house at the right time. The median price of an existing home sold in March 2021 was $329,100. That’s a 17.2% increase from March 2020. Times are certainly crazy right now in the real estate market.
What many people don’t think about are the other costs, and not just financial costs. Today’s generation is more aware of the added stress and burden of maintaining a home and the money you can sink into it for maintenance, let alone remodeling. Then of course there’s the mortgage interest, property taxes, and insurance that you won’t have with a rental. Lastly, the biggest reason today’s generation is choosing to rent more and more is the flexibility. They want to be more mobile, able to get up and move without having to worry about listing, selling, and possibly owing more than the house is worth, and being stuck. We saw this with many residents that bought a home during residency and then tried to sell when they landed their first job, only to find out they owed more than it was worth because of the real estate market collapse of 2008. Approximately 50% of physicians will leave their first job within 1-3 years, so it’s a gamble that you’ll be able to sell your house when you want to for the price you need.
But what are the benefits of buying? First, there is the age-old argument of building equity. If you stay in your house long enough, and plan to sell it when you retire and downsize, it can definitely be an investment. If you keep a mortgage long enough, eventually you’ll pay it off, and have no payment. Mortgage interest is also tax-deductible. Lastly, there are the intangibles – like being able to put down roots, build a community, and have the ability to remodel and customize your home, a feature not usually available when renting.
Now that I’ve effectively talked you out and back in again, what’s the best way to go about buying a house in today’s crazy market? We’ve seen houses list and sell within a day and get multiple offers well over asking price. It’s a very difficult time to buy, but there are ways to make it easier. First, be clear on what you want in a house, especially location. There’s nothing worse than buyer’s remorse in your primary residence, and that happens more these days when people have to quickly make a decision. Find a good, fee-based financial planner to help you decide how much house fits in your budget and your long-term goals. You’d be surprised how easily we can talk ourselves into paying much more than we had originally decided. Use your financial planner to help avoid emotions getting involved and creeping up your price (especially when multiple offers are involved). A good rule of thumb is for a housing payment to be no more than 33% of your take-home income. This includes principal, interest, and taxes. Or, many planners will use the “2x income” rule of thumb. So if you make $300,000, don’t go over $600,000. Although with today’s low interest rates, there is some more wiggle room on that. Next, get a good referral from someone you trust in looking for a realtor. Real estate is a commission-based job and can have some potential conflicts of interest, so getting a recommendation can help. Or, there are realtors who will work for a flat fee, regardless of how much you pay for a house. That can help reduce the conflict.
You made the offer, you beat out the other bids, and you’re getting a house! How are you paying for it? Hopefully, you already got preapproved. This means finding a good, reputable mortgage professional. Get referrals, shop around, and take your time. Get multiple quotes before you start the underwriting process. They shouldn’t have to pull your credit to give you a fairly accurate estimate of what interest rate you’ll qualify for. Usually, they will give you fixed and variable interest quotes. I normally recommend fixed interest. Because interest rates are so low right now, they’re only going to go up in the future, and if you have a variable rate loan, your payment will go up as interest rates rise.
Is a physician loan a good idea? Depending on your circumstance, it can often be a good deal. Most new attendings don’t have cash saved up for a down payment, and these often don’t require one. And the other big benefit is that they won’t consider your student loan payments when calculating your debt-to-income ratio. Mortgage lenders will look at how much other debt you have when determining an approval. And a conventional mortgage will take your student loan payments into consideration, which means you’ll qualify for a much lower payment and purchase price. In my experience, you want a credit score of around 700 or higher to qualify for these types of loans. The only downside of a physician mortgage is the rates are slightly higher. I encourage you to start the application process early; they’re taking upward of 90 days lately.
As the mortgage is being processed, you’ll have an inspection and appraisal, and as long as those are all favorable, you’re in! Now, should you take any surplus income each month and pay extra on your mortgage to pay it down sooner, or invest it? Everyone’s situation is different, but a good rule of thumb is to look at interest rates on the debt you want to pay off versus expected rate of return on the potential investment. For example, if you have extra money, should you invest it in an SP500 index fund that historically gets 8%-12% per year, or put it on the principal of your mortgage that has an interest rate of 3%? Assuming no other factors or goals, and you just want the best bang for your buck, my money would go toward the investment getting 8%-12% over saving 3% on my mortgage.
Take your time, do your research, and find good professionals. There’s no right answer for everyone, but there are certainly some good practices when walking through the first home decision. Here at FinancialMD, we only work with physicians, and we’re happy to chat if you want some guidance on this. Send me an email and subscribe to our weekly Didactic Minute videos on YouTube for more financial tips for young physicians. Good luck!
Mr. Solitro is a financial planner and CEO of FinancialMD. He has no other conflicts of interest.
Investment advisory services offered through FinancialMD, a registered investment adviser. Registration as an investment adviser does not imply a certain level of skill or training. This article is provided for informational purposes only and nothing contained herein should be construed as a solicitation to buy or sell any products. Advisory services are offered only to clients and prospective clients in places where FinancialMD and its investment adviser representatives are registered or exempt from registration. Investing involves the risk of loss of principal. Past performance is no guarantee of future performance and no investment strategy can guarantee a profit or protect against loss.
This article was updated June 8, 2021.
Reference
1. Wachter S and Acolin A. Owning or Renting in the US: Shifting Dynamics of the Housing Market. Penn Institute for Urban Research. 2016 May.
The concept of home ownership has changed for this generation, not only in the logistics of the best way to do it, but also in the desire and demand for owning versus renting. According to the Penn Institute for Urban Research, the U.S. homeownership rate is now at 63.7%, the lowest in 48 years. “Homeownership rates have declined for all demographic age groups. Since 2006, the number of households who own their home in the United States has decreased by 674,000 while the number of renters has increased by over 8 million.”1
But isn’t owning your own home the American dream? Isn’t it a great investment? If we’re looking strictly at the monthly payment numbers, traditionally paying a mortgage is cheaper than paying rent for the same-size home. That became even more true as home prices dropped in 2007-2008 and as interest rates also dropped over the last several years. Then there’s the age-old concept of “building equity” or “throwing away money on rent.” As a financial planner, I get asked all the time about a home as an investment. It certainly can be, like any investment, if you buy and sell at the right time. But something is only an investment if it grows, and you can’t predict if you’re going to buy and sell your house at the right time. The median price of an existing home sold in March 2021 was $329,100. That’s a 17.2% increase from March 2020. Times are certainly crazy right now in the real estate market.
What many people don’t think about are the other costs, and not just financial costs. Today’s generation is more aware of the added stress and burden of maintaining a home and the money you can sink into it for maintenance, let alone remodeling. Then of course there’s the mortgage interest, property taxes, and insurance that you won’t have with a rental. Lastly, the biggest reason today’s generation is choosing to rent more and more is the flexibility. They want to be more mobile, able to get up and move without having to worry about listing, selling, and possibly owing more than the house is worth, and being stuck. We saw this with many residents that bought a home during residency and then tried to sell when they landed their first job, only to find out they owed more than it was worth because of the real estate market collapse of 2008. Approximately 50% of physicians will leave their first job within 1-3 years, so it’s a gamble that you’ll be able to sell your house when you want to for the price you need.
But what are the benefits of buying? First, there is the age-old argument of building equity. If you stay in your house long enough, and plan to sell it when you retire and downsize, it can definitely be an investment. If you keep a mortgage long enough, eventually you’ll pay it off, and have no payment. Mortgage interest is also tax-deductible. Lastly, there are the intangibles – like being able to put down roots, build a community, and have the ability to remodel and customize your home, a feature not usually available when renting.
Now that I’ve effectively talked you out and back in again, what’s the best way to go about buying a house in today’s crazy market? We’ve seen houses list and sell within a day and get multiple offers well over asking price. It’s a very difficult time to buy, but there are ways to make it easier. First, be clear on what you want in a house, especially location. There’s nothing worse than buyer’s remorse in your primary residence, and that happens more these days when people have to quickly make a decision. Find a good, fee-based financial planner to help you decide how much house fits in your budget and your long-term goals. You’d be surprised how easily we can talk ourselves into paying much more than we had originally decided. Use your financial planner to help avoid emotions getting involved and creeping up your price (especially when multiple offers are involved). A good rule of thumb is for a housing payment to be no more than 33% of your take-home income. This includes principal, interest, and taxes. Or, many planners will use the “2x income” rule of thumb. So if you make $300,000, don’t go over $600,000. Although with today’s low interest rates, there is some more wiggle room on that. Next, get a good referral from someone you trust in looking for a realtor. Real estate is a commission-based job and can have some potential conflicts of interest, so getting a recommendation can help. Or, there are realtors who will work for a flat fee, regardless of how much you pay for a house. That can help reduce the conflict.
You made the offer, you beat out the other bids, and you’re getting a house! How are you paying for it? Hopefully, you already got preapproved. This means finding a good, reputable mortgage professional. Get referrals, shop around, and take your time. Get multiple quotes before you start the underwriting process. They shouldn’t have to pull your credit to give you a fairly accurate estimate of what interest rate you’ll qualify for. Usually, they will give you fixed and variable interest quotes. I normally recommend fixed interest. Because interest rates are so low right now, they’re only going to go up in the future, and if you have a variable rate loan, your payment will go up as interest rates rise.
Is a physician loan a good idea? Depending on your circumstance, it can often be a good deal. Most new attendings don’t have cash saved up for a down payment, and these often don’t require one. And the other big benefit is that they won’t consider your student loan payments when calculating your debt-to-income ratio. Mortgage lenders will look at how much other debt you have when determining an approval. And a conventional mortgage will take your student loan payments into consideration, which means you’ll qualify for a much lower payment and purchase price. In my experience, you want a credit score of around 700 or higher to qualify for these types of loans. The only downside of a physician mortgage is the rates are slightly higher. I encourage you to start the application process early; they’re taking upward of 90 days lately.
As the mortgage is being processed, you’ll have an inspection and appraisal, and as long as those are all favorable, you’re in! Now, should you take any surplus income each month and pay extra on your mortgage to pay it down sooner, or invest it? Everyone’s situation is different, but a good rule of thumb is to look at interest rates on the debt you want to pay off versus expected rate of return on the potential investment. For example, if you have extra money, should you invest it in an SP500 index fund that historically gets 8%-12% per year, or put it on the principal of your mortgage that has an interest rate of 3%? Assuming no other factors or goals, and you just want the best bang for your buck, my money would go toward the investment getting 8%-12% over saving 3% on my mortgage.
Take your time, do your research, and find good professionals. There’s no right answer for everyone, but there are certainly some good practices when walking through the first home decision. Here at FinancialMD, we only work with physicians, and we’re happy to chat if you want some guidance on this. Send me an email and subscribe to our weekly Didactic Minute videos on YouTube for more financial tips for young physicians. Good luck!
Mr. Solitro is a financial planner and CEO of FinancialMD. He has no other conflicts of interest.
Investment advisory services offered through FinancialMD, a registered investment adviser. Registration as an investment adviser does not imply a certain level of skill or training. This article is provided for informational purposes only and nothing contained herein should be construed as a solicitation to buy or sell any products. Advisory services are offered only to clients and prospective clients in places where FinancialMD and its investment adviser representatives are registered or exempt from registration. Investing involves the risk of loss of principal. Past performance is no guarantee of future performance and no investment strategy can guarantee a profit or protect against loss.
This article was updated June 8, 2021.
Reference
1. Wachter S and Acolin A. Owning or Renting in the US: Shifting Dynamics of the Housing Market. Penn Institute for Urban Research. 2016 May.
Telemedicine for headache visits had high patient satisfaction
according to a study presented at the American Headache Society’s 2021 annual meeting. Most patients who used telemedicine said they would like to continue using it after the pandemic, though the study also revealed barriers to care for a small percentage of respondents.
“Telemedicine minimizes the physical and geographic barriers to health care, preserves personal protective equipment, and prevents the spread of COVID-19 by allowing encounters to happen in a socially distanced way,” said Chia-Chun Chiang, MD, assistant professor of neurology at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. “Telemedicine provides patients with opportunities to gain better control of their headache disorders while not having to commit to the time to travel and risk of exposure to COVID-19.” If insurance coverage for virtual care were rolled back, “patients and multiple levels of health care providers would be significantly affected,” she said.
The research relied on findings from a 15-question survey distributed by the nonprofit American Migraine Foundation through email and social media to more than 100,000 people. Among the 1,172 patients who responded to the survey, 1,098 had complete responses, and 86.6% were female.
The vast majority of these patients (93.8%) had had a previous diagnosis of a headache. Just over half (57.5%) said they used telemedicine during the study period, with most of those visits (85.5%) being follow-up care and 14.5% involving a new patient visit.
Among those who did not use telemedicine, most (56.1%) said they didn’t need a visit. However, a quarter of these respondents (25.2%) said they didn’t know telemedicine was an option, and 12.9% said they would have preferred telemedicine but it wasn’t offered by their doctors. A smaller proportion (3.5%) said they wanted to use virtual care but that their insurance did not cover it, and nearly as many (2.2%) said they wanted telemedicine but didn’t have the technology needed to use it.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted that reliable Internet service has contributed to disparities in access in many ways, including health care via telemedicine,” Dr. Chiang said. “Those who are not able to afford Internet, lack proficiency in the use of technology, or have cognitive impairment might not be able to utilize telemedicine.”
Among those who did receive telemedicine care for headache, about a third (34.4%) received care from a general neurologist while 43.7% saw a headache specialist and nearly a third (30.7%) saw a primary care provider. The remaining visits included 11.3% who saw headache nurse practitioners and 3.2% who saw headache nurses.
Most patients did not have a new or changed diagnosis at their visit; only 7.4% received a new headache diagnosis during their telemedicine appointment. Though 43.7% had no change to their therapy, a little more than half of patients (52.4%) received a new treatment, a finding that caught the interest of Alan M. Rapoport, MD, clinical professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, and past president of the International Headache Society.
“The techniques used [in virtual visits] were good enough for the caregiver to make critical decisions about how the patient was doing and what new treatment might be better for them,” said Dr. Rapoport, who was not involved in the research. “I believe that most headache specialists will gradually resume in office visits,” he said, but “this study shows it would be okay for some or most of the revisits to continue to be done virtually.”
The vast majority of patients rated their care as “very good” (62.1%) or “good” (20.7%). Less satisfied responses included 10.5% who felt their experience was “fair,” 3.6% who said it was “poor,” and 3.1% who gave other responses.
These results fit with the experience of Dr. Rapoport and of Paul B. Rizzoli, MD, associate professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School and clinical director of the John R. Graham Headache Center at Brigham and Women’s Faulkner Hospital, both in Boston.
“Telemedicine worked better than we anticipated,” said Dr. Rizzoli when asked for comment. “I was especially surprised how comfortable I became with its use for many, but not all, new patients. While I don’t expect it to replace in-person visits, I do expect that it will and should be a permanent part of our care going forward, especially for follow-up visits.”
The findings supported that expectation as well: An overwhelming majority of those who responded to the survey (89.8%) also said they would like to keep receiving telemedicine care for their headache care and treatment. This percentage was split evenly between those who said they would like to always receive care virtually and those who would only want to use it for some appointments. A smaller proportion said they did not want to keep using virtual care (7.1%) or weren’t sure (3.1%).
“Telemedicine has become an essential tool for patients and a wide variety of clinicians,” Dr. Chiang reported during her presentation. “Telemedicine facilitated headache care for many patients during the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in high patient satisfaction rates and a desire to continue to utilize telemedicine for future headache care for those who responded to the online survey.”
Dr. Rapoport noted that a particular benefit of telemedicine in his practice is avoiding transportation issues.
“In Santa Monica and Los Angeles, my patients coming from 10 or more miles away usually have to contend with difficult traffic, which created stress and often made them late and upset the office schedule,” Dr. Rapoport said. “I found that virtual visits were almost always shorter, on time, and were as effective for the patient as an in-person visit.”
Dr. Chiang drew attention, however, to the barriers to care found in the study, including not having or knowing of telemedicine as an option, and not having access to the technology or insurance coverage needed to take advantage of it. She listed three ways to address those challenges and increase health care accessibility to patients:
- Expand insurance coverage to reimburse telemedicine even after the pandemic.
- Widely promote and broadcast the use of virtual care.
- Make Internet access a priority as a necessity in society and expand access.
Dr. Rizzoli also noted some ways to improve telemedicine. “We could easily develop improved means of delivering vital signs and other bio-information over telemedicine to improve decision-making,” he said. “A difficult task going forward will be to fix legal questions associated with virtual visits across state lines which, especially in the small New England states, come up frequently and are currently illegal.”
Dr. Rapoport noted ways that patients can facilitate effective telemedicine visits. “Doctors should insist that patients keep careful records of their headaches, triggers, medicines, etc., either on paper or preferably via an app on their smartphones, which is usually always accessible,” Dr. Rapoport said. “With good data and a good electronic connection, the visit should go well.”
Among the study’s limitations were a comparatively small response rate (1.11% of those invited to participate) and ascertainment bias.
“The take-home message from the experience is that this turns out to be an effective, efficient and accepted means of delivering care that should be developed further,” Dr. Rizzoli said.
No external funding was noted. Dr. Chiang and Dr. Rizzoli had no disclosures. Dr. Rapoport has advised AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Cala Health, Satsuma, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Theranica, Xoc and Zosano, and is on the speakers bureau of AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Lundbeck and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries.
according to a study presented at the American Headache Society’s 2021 annual meeting. Most patients who used telemedicine said they would like to continue using it after the pandemic, though the study also revealed barriers to care for a small percentage of respondents.
“Telemedicine minimizes the physical and geographic barriers to health care, preserves personal protective equipment, and prevents the spread of COVID-19 by allowing encounters to happen in a socially distanced way,” said Chia-Chun Chiang, MD, assistant professor of neurology at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. “Telemedicine provides patients with opportunities to gain better control of their headache disorders while not having to commit to the time to travel and risk of exposure to COVID-19.” If insurance coverage for virtual care were rolled back, “patients and multiple levels of health care providers would be significantly affected,” she said.
The research relied on findings from a 15-question survey distributed by the nonprofit American Migraine Foundation through email and social media to more than 100,000 people. Among the 1,172 patients who responded to the survey, 1,098 had complete responses, and 86.6% were female.
The vast majority of these patients (93.8%) had had a previous diagnosis of a headache. Just over half (57.5%) said they used telemedicine during the study period, with most of those visits (85.5%) being follow-up care and 14.5% involving a new patient visit.
Among those who did not use telemedicine, most (56.1%) said they didn’t need a visit. However, a quarter of these respondents (25.2%) said they didn’t know telemedicine was an option, and 12.9% said they would have preferred telemedicine but it wasn’t offered by their doctors. A smaller proportion (3.5%) said they wanted to use virtual care but that their insurance did not cover it, and nearly as many (2.2%) said they wanted telemedicine but didn’t have the technology needed to use it.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted that reliable Internet service has contributed to disparities in access in many ways, including health care via telemedicine,” Dr. Chiang said. “Those who are not able to afford Internet, lack proficiency in the use of technology, or have cognitive impairment might not be able to utilize telemedicine.”
Among those who did receive telemedicine care for headache, about a third (34.4%) received care from a general neurologist while 43.7% saw a headache specialist and nearly a third (30.7%) saw a primary care provider. The remaining visits included 11.3% who saw headache nurse practitioners and 3.2% who saw headache nurses.
Most patients did not have a new or changed diagnosis at their visit; only 7.4% received a new headache diagnosis during their telemedicine appointment. Though 43.7% had no change to their therapy, a little more than half of patients (52.4%) received a new treatment, a finding that caught the interest of Alan M. Rapoport, MD, clinical professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, and past president of the International Headache Society.
“The techniques used [in virtual visits] were good enough for the caregiver to make critical decisions about how the patient was doing and what new treatment might be better for them,” said Dr. Rapoport, who was not involved in the research. “I believe that most headache specialists will gradually resume in office visits,” he said, but “this study shows it would be okay for some or most of the revisits to continue to be done virtually.”
The vast majority of patients rated their care as “very good” (62.1%) or “good” (20.7%). Less satisfied responses included 10.5% who felt their experience was “fair,” 3.6% who said it was “poor,” and 3.1% who gave other responses.
These results fit with the experience of Dr. Rapoport and of Paul B. Rizzoli, MD, associate professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School and clinical director of the John R. Graham Headache Center at Brigham and Women’s Faulkner Hospital, both in Boston.
“Telemedicine worked better than we anticipated,” said Dr. Rizzoli when asked for comment. “I was especially surprised how comfortable I became with its use for many, but not all, new patients. While I don’t expect it to replace in-person visits, I do expect that it will and should be a permanent part of our care going forward, especially for follow-up visits.”
The findings supported that expectation as well: An overwhelming majority of those who responded to the survey (89.8%) also said they would like to keep receiving telemedicine care for their headache care and treatment. This percentage was split evenly between those who said they would like to always receive care virtually and those who would only want to use it for some appointments. A smaller proportion said they did not want to keep using virtual care (7.1%) or weren’t sure (3.1%).
“Telemedicine has become an essential tool for patients and a wide variety of clinicians,” Dr. Chiang reported during her presentation. “Telemedicine facilitated headache care for many patients during the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in high patient satisfaction rates and a desire to continue to utilize telemedicine for future headache care for those who responded to the online survey.”
Dr. Rapoport noted that a particular benefit of telemedicine in his practice is avoiding transportation issues.
“In Santa Monica and Los Angeles, my patients coming from 10 or more miles away usually have to contend with difficult traffic, which created stress and often made them late and upset the office schedule,” Dr. Rapoport said. “I found that virtual visits were almost always shorter, on time, and were as effective for the patient as an in-person visit.”
Dr. Chiang drew attention, however, to the barriers to care found in the study, including not having or knowing of telemedicine as an option, and not having access to the technology or insurance coverage needed to take advantage of it. She listed three ways to address those challenges and increase health care accessibility to patients:
- Expand insurance coverage to reimburse telemedicine even after the pandemic.
- Widely promote and broadcast the use of virtual care.
- Make Internet access a priority as a necessity in society and expand access.
Dr. Rizzoli also noted some ways to improve telemedicine. “We could easily develop improved means of delivering vital signs and other bio-information over telemedicine to improve decision-making,” he said. “A difficult task going forward will be to fix legal questions associated with virtual visits across state lines which, especially in the small New England states, come up frequently and are currently illegal.”
Dr. Rapoport noted ways that patients can facilitate effective telemedicine visits. “Doctors should insist that patients keep careful records of their headaches, triggers, medicines, etc., either on paper or preferably via an app on their smartphones, which is usually always accessible,” Dr. Rapoport said. “With good data and a good electronic connection, the visit should go well.”
Among the study’s limitations were a comparatively small response rate (1.11% of those invited to participate) and ascertainment bias.
“The take-home message from the experience is that this turns out to be an effective, efficient and accepted means of delivering care that should be developed further,” Dr. Rizzoli said.
No external funding was noted. Dr. Chiang and Dr. Rizzoli had no disclosures. Dr. Rapoport has advised AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Cala Health, Satsuma, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Theranica, Xoc and Zosano, and is on the speakers bureau of AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Lundbeck and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries.
according to a study presented at the American Headache Society’s 2021 annual meeting. Most patients who used telemedicine said they would like to continue using it after the pandemic, though the study also revealed barriers to care for a small percentage of respondents.
“Telemedicine minimizes the physical and geographic barriers to health care, preserves personal protective equipment, and prevents the spread of COVID-19 by allowing encounters to happen in a socially distanced way,” said Chia-Chun Chiang, MD, assistant professor of neurology at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. “Telemedicine provides patients with opportunities to gain better control of their headache disorders while not having to commit to the time to travel and risk of exposure to COVID-19.” If insurance coverage for virtual care were rolled back, “patients and multiple levels of health care providers would be significantly affected,” she said.
The research relied on findings from a 15-question survey distributed by the nonprofit American Migraine Foundation through email and social media to more than 100,000 people. Among the 1,172 patients who responded to the survey, 1,098 had complete responses, and 86.6% were female.
The vast majority of these patients (93.8%) had had a previous diagnosis of a headache. Just over half (57.5%) said they used telemedicine during the study period, with most of those visits (85.5%) being follow-up care and 14.5% involving a new patient visit.
Among those who did not use telemedicine, most (56.1%) said they didn’t need a visit. However, a quarter of these respondents (25.2%) said they didn’t know telemedicine was an option, and 12.9% said they would have preferred telemedicine but it wasn’t offered by their doctors. A smaller proportion (3.5%) said they wanted to use virtual care but that their insurance did not cover it, and nearly as many (2.2%) said they wanted telemedicine but didn’t have the technology needed to use it.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted that reliable Internet service has contributed to disparities in access in many ways, including health care via telemedicine,” Dr. Chiang said. “Those who are not able to afford Internet, lack proficiency in the use of technology, or have cognitive impairment might not be able to utilize telemedicine.”
Among those who did receive telemedicine care for headache, about a third (34.4%) received care from a general neurologist while 43.7% saw a headache specialist and nearly a third (30.7%) saw a primary care provider. The remaining visits included 11.3% who saw headache nurse practitioners and 3.2% who saw headache nurses.
Most patients did not have a new or changed diagnosis at their visit; only 7.4% received a new headache diagnosis during their telemedicine appointment. Though 43.7% had no change to their therapy, a little more than half of patients (52.4%) received a new treatment, a finding that caught the interest of Alan M. Rapoport, MD, clinical professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, and past president of the International Headache Society.
“The techniques used [in virtual visits] were good enough for the caregiver to make critical decisions about how the patient was doing and what new treatment might be better for them,” said Dr. Rapoport, who was not involved in the research. “I believe that most headache specialists will gradually resume in office visits,” he said, but “this study shows it would be okay for some or most of the revisits to continue to be done virtually.”
The vast majority of patients rated their care as “very good” (62.1%) or “good” (20.7%). Less satisfied responses included 10.5% who felt their experience was “fair,” 3.6% who said it was “poor,” and 3.1% who gave other responses.
These results fit with the experience of Dr. Rapoport and of Paul B. Rizzoli, MD, associate professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School and clinical director of the John R. Graham Headache Center at Brigham and Women’s Faulkner Hospital, both in Boston.
“Telemedicine worked better than we anticipated,” said Dr. Rizzoli when asked for comment. “I was especially surprised how comfortable I became with its use for many, but not all, new patients. While I don’t expect it to replace in-person visits, I do expect that it will and should be a permanent part of our care going forward, especially for follow-up visits.”
The findings supported that expectation as well: An overwhelming majority of those who responded to the survey (89.8%) also said they would like to keep receiving telemedicine care for their headache care and treatment. This percentage was split evenly between those who said they would like to always receive care virtually and those who would only want to use it for some appointments. A smaller proportion said they did not want to keep using virtual care (7.1%) or weren’t sure (3.1%).
“Telemedicine has become an essential tool for patients and a wide variety of clinicians,” Dr. Chiang reported during her presentation. “Telemedicine facilitated headache care for many patients during the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in high patient satisfaction rates and a desire to continue to utilize telemedicine for future headache care for those who responded to the online survey.”
Dr. Rapoport noted that a particular benefit of telemedicine in his practice is avoiding transportation issues.
“In Santa Monica and Los Angeles, my patients coming from 10 or more miles away usually have to contend with difficult traffic, which created stress and often made them late and upset the office schedule,” Dr. Rapoport said. “I found that virtual visits were almost always shorter, on time, and were as effective for the patient as an in-person visit.”
Dr. Chiang drew attention, however, to the barriers to care found in the study, including not having or knowing of telemedicine as an option, and not having access to the technology or insurance coverage needed to take advantage of it. She listed three ways to address those challenges and increase health care accessibility to patients:
- Expand insurance coverage to reimburse telemedicine even after the pandemic.
- Widely promote and broadcast the use of virtual care.
- Make Internet access a priority as a necessity in society and expand access.
Dr. Rizzoli also noted some ways to improve telemedicine. “We could easily develop improved means of delivering vital signs and other bio-information over telemedicine to improve decision-making,” he said. “A difficult task going forward will be to fix legal questions associated with virtual visits across state lines which, especially in the small New England states, come up frequently and are currently illegal.”
Dr. Rapoport noted ways that patients can facilitate effective telemedicine visits. “Doctors should insist that patients keep careful records of their headaches, triggers, medicines, etc., either on paper or preferably via an app on their smartphones, which is usually always accessible,” Dr. Rapoport said. “With good data and a good electronic connection, the visit should go well.”
Among the study’s limitations were a comparatively small response rate (1.11% of those invited to participate) and ascertainment bias.
“The take-home message from the experience is that this turns out to be an effective, efficient and accepted means of delivering care that should be developed further,” Dr. Rizzoli said.
No external funding was noted. Dr. Chiang and Dr. Rizzoli had no disclosures. Dr. Rapoport has advised AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Cala Health, Satsuma, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Theranica, Xoc and Zosano, and is on the speakers bureau of AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Lundbeck and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries.
FROM AHS 2021
FDA approves controversial Alzheimer’s drug aducanumab (Aduhelm)
In November, the Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs Advisory Committee voted eight to one against approving the drug because, based on clinical trial results, evidence of efficacy was not strong enough. Two other members said they were uncertain on the issue of efficacy.
In a company release Michel Vounatsos, Biogen’s Chief Executive Officer, said, “this historic moment is the culmination of more than a decade of groundbreaking research in the complex field of Alzheimer’s disease. We believe this first-in-class medicine will transform the treatment of people living with Alzheimer’s disease and spark continuous innovation in the years to come.
Rocky road
The road to approval has been extremely rocky for aducanumab, an anti-amyloid-beta human monoclonal antibody, previously known as BIIB037.
As reported by this news organization, two phase 3 trials evaluating the drug were initially scrapped in March 2019 because of interim futility analysis. At the time, Biogen released a statement saying that aducanumab was unlikely to meet primary endpoints in the ENGAGE and EMERGE randomized controlled trials.
However, in an about-face 7 months later, Biogen and Eisai announced that a new analysis showed the drug met its primary endpoint of reduction in clinical decline, including cognition and function, in the EMERGE trial.
Although ENGAGE still didn’t meet its primary endpoint, data from its new analysis “supported” the EMERGE findings, the drug companies said at the time.
However, 1 year later, a majority of the members of the FDA’s advisory panel were against the drug’s approval. Details of that decision were published online March 30 in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
As reported by this news organization, a Viewpoint written by three of the committee members notes that results from the drug’s only large positive clinical trial fell short.
“There is no persuasive evidence to support approval of aducanumab at this time,” they write.
Groups such as Public Citizen’s Health Research Group not only agree with the Viewpoint’s authors, they also criticized the FDA for its collaboration with the drug’s manufacturers on briefing documents and more.
On April 1, Health Research Group members sent a letter to the U.S. Secretary of Health and Human Services requesting the temporary suspension of the FDA’s neuroscience chief, Bill Dunn, MD, because of his role in supervising the collaboration.
Alzheimer association weighs in
The Alzheimer’s Association has been a proponent of the drug throughout its development.
Ahead of today’s news, the organization noted in a statement that a decision to approve “would be historic” because it would make aducanumab “the first drug to slow Alzheimer’s disease” and would mark the beginning of a new future for AD treatments.
“The Alzheimer’s Association urgently supports FDA approval of the treatment based on clinical trial results that showed a 22% reduction in cognitive and function decline — something that could make a meaningful difference” for patients with AD, it said.
Kristen Clifford, chief program officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, said in an interview at the time that approval would be considered a “victory” for patients with AD and for the field overall.
“For individuals who would potentially be eligible for the treatment, this drug could mean more quality time. Slowing decline, particularly in early diagnosis, could add weeks or months or maybe even years of active life,” Clifford said.
“If approved, this would really be a landmark moment. And it could provide hope for those living with Alzheimer’s and their families,” she added.
Clifford noted that approval of this type of drug would also underscore the importance of early detection for AD. “This treatment would encourage earlier diagnosis of the disease,” she said.
In a new statement released just after approval for aducanumab was announced, the organization said that today’s news is a win-win for all patients with AD and their families.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In November, the Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs Advisory Committee voted eight to one against approving the drug because, based on clinical trial results, evidence of efficacy was not strong enough. Two other members said they were uncertain on the issue of efficacy.
In a company release Michel Vounatsos, Biogen’s Chief Executive Officer, said, “this historic moment is the culmination of more than a decade of groundbreaking research in the complex field of Alzheimer’s disease. We believe this first-in-class medicine will transform the treatment of people living with Alzheimer’s disease and spark continuous innovation in the years to come.
Rocky road
The road to approval has been extremely rocky for aducanumab, an anti-amyloid-beta human monoclonal antibody, previously known as BIIB037.
As reported by this news organization, two phase 3 trials evaluating the drug were initially scrapped in March 2019 because of interim futility analysis. At the time, Biogen released a statement saying that aducanumab was unlikely to meet primary endpoints in the ENGAGE and EMERGE randomized controlled trials.
However, in an about-face 7 months later, Biogen and Eisai announced that a new analysis showed the drug met its primary endpoint of reduction in clinical decline, including cognition and function, in the EMERGE trial.
Although ENGAGE still didn’t meet its primary endpoint, data from its new analysis “supported” the EMERGE findings, the drug companies said at the time.
However, 1 year later, a majority of the members of the FDA’s advisory panel were against the drug’s approval. Details of that decision were published online March 30 in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
As reported by this news organization, a Viewpoint written by three of the committee members notes that results from the drug’s only large positive clinical trial fell short.
“There is no persuasive evidence to support approval of aducanumab at this time,” they write.
Groups such as Public Citizen’s Health Research Group not only agree with the Viewpoint’s authors, they also criticized the FDA for its collaboration with the drug’s manufacturers on briefing documents and more.
On April 1, Health Research Group members sent a letter to the U.S. Secretary of Health and Human Services requesting the temporary suspension of the FDA’s neuroscience chief, Bill Dunn, MD, because of his role in supervising the collaboration.
Alzheimer association weighs in
The Alzheimer’s Association has been a proponent of the drug throughout its development.
Ahead of today’s news, the organization noted in a statement that a decision to approve “would be historic” because it would make aducanumab “the first drug to slow Alzheimer’s disease” and would mark the beginning of a new future for AD treatments.
“The Alzheimer’s Association urgently supports FDA approval of the treatment based on clinical trial results that showed a 22% reduction in cognitive and function decline — something that could make a meaningful difference” for patients with AD, it said.
Kristen Clifford, chief program officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, said in an interview at the time that approval would be considered a “victory” for patients with AD and for the field overall.
“For individuals who would potentially be eligible for the treatment, this drug could mean more quality time. Slowing decline, particularly in early diagnosis, could add weeks or months or maybe even years of active life,” Clifford said.
“If approved, this would really be a landmark moment. And it could provide hope for those living with Alzheimer’s and their families,” she added.
Clifford noted that approval of this type of drug would also underscore the importance of early detection for AD. “This treatment would encourage earlier diagnosis of the disease,” she said.
In a new statement released just after approval for aducanumab was announced, the organization said that today’s news is a win-win for all patients with AD and their families.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In November, the Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs Advisory Committee voted eight to one against approving the drug because, based on clinical trial results, evidence of efficacy was not strong enough. Two other members said they were uncertain on the issue of efficacy.
In a company release Michel Vounatsos, Biogen’s Chief Executive Officer, said, “this historic moment is the culmination of more than a decade of groundbreaking research in the complex field of Alzheimer’s disease. We believe this first-in-class medicine will transform the treatment of people living with Alzheimer’s disease and spark continuous innovation in the years to come.
Rocky road
The road to approval has been extremely rocky for aducanumab, an anti-amyloid-beta human monoclonal antibody, previously known as BIIB037.
As reported by this news organization, two phase 3 trials evaluating the drug were initially scrapped in March 2019 because of interim futility analysis. At the time, Biogen released a statement saying that aducanumab was unlikely to meet primary endpoints in the ENGAGE and EMERGE randomized controlled trials.
However, in an about-face 7 months later, Biogen and Eisai announced that a new analysis showed the drug met its primary endpoint of reduction in clinical decline, including cognition and function, in the EMERGE trial.
Although ENGAGE still didn’t meet its primary endpoint, data from its new analysis “supported” the EMERGE findings, the drug companies said at the time.
However, 1 year later, a majority of the members of the FDA’s advisory panel were against the drug’s approval. Details of that decision were published online March 30 in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
As reported by this news organization, a Viewpoint written by three of the committee members notes that results from the drug’s only large positive clinical trial fell short.
“There is no persuasive evidence to support approval of aducanumab at this time,” they write.
Groups such as Public Citizen’s Health Research Group not only agree with the Viewpoint’s authors, they also criticized the FDA for its collaboration with the drug’s manufacturers on briefing documents and more.
On April 1, Health Research Group members sent a letter to the U.S. Secretary of Health and Human Services requesting the temporary suspension of the FDA’s neuroscience chief, Bill Dunn, MD, because of his role in supervising the collaboration.
Alzheimer association weighs in
The Alzheimer’s Association has been a proponent of the drug throughout its development.
Ahead of today’s news, the organization noted in a statement that a decision to approve “would be historic” because it would make aducanumab “the first drug to slow Alzheimer’s disease” and would mark the beginning of a new future for AD treatments.
“The Alzheimer’s Association urgently supports FDA approval of the treatment based on clinical trial results that showed a 22% reduction in cognitive and function decline — something that could make a meaningful difference” for patients with AD, it said.
Kristen Clifford, chief program officer for the Alzheimer’s Association, said in an interview at the time that approval would be considered a “victory” for patients with AD and for the field overall.
“For individuals who would potentially be eligible for the treatment, this drug could mean more quality time. Slowing decline, particularly in early diagnosis, could add weeks or months or maybe even years of active life,” Clifford said.
“If approved, this would really be a landmark moment. And it could provide hope for those living with Alzheimer’s and their families,” she added.
Clifford noted that approval of this type of drug would also underscore the importance of early detection for AD. “This treatment would encourage earlier diagnosis of the disease,” she said.
In a new statement released just after approval for aducanumab was announced, the organization said that today’s news is a win-win for all patients with AD and their families.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.